Self-adaption bit and power distribution method with low complex degree
A self-adaptive, bit-error-rate technology, applied in the direction of preventing/detecting errors through diversity reception, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc. requirements and other issues to achieve the effect of low computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The present invention will be described in detail below through the accompanying drawings and examples.
[0022] The adaptive bit and power allocation method provided by the invention is suitable for MIMO systems and also for MIMO-OFDM systems. The MIMO system is taken as an example for description below.
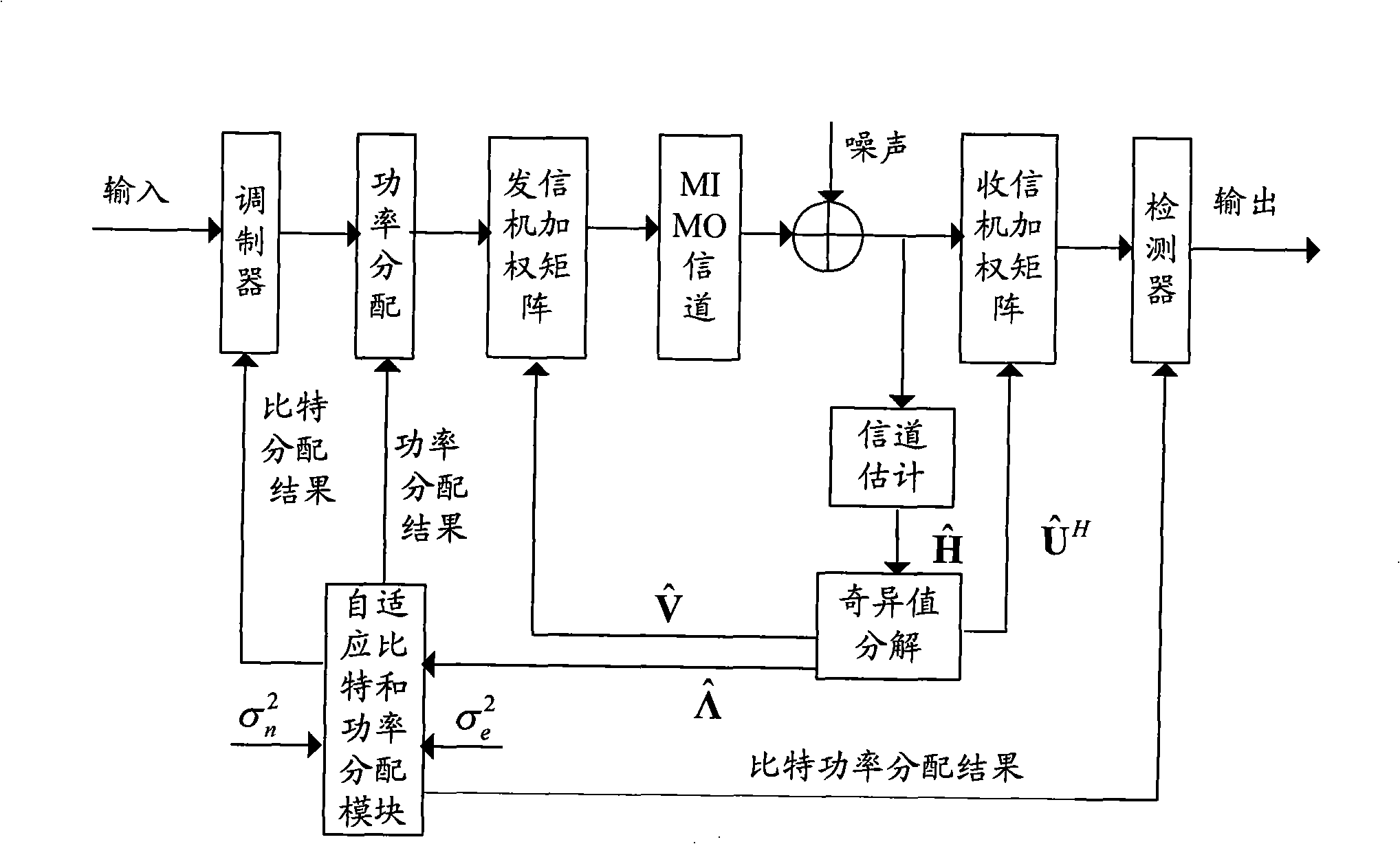
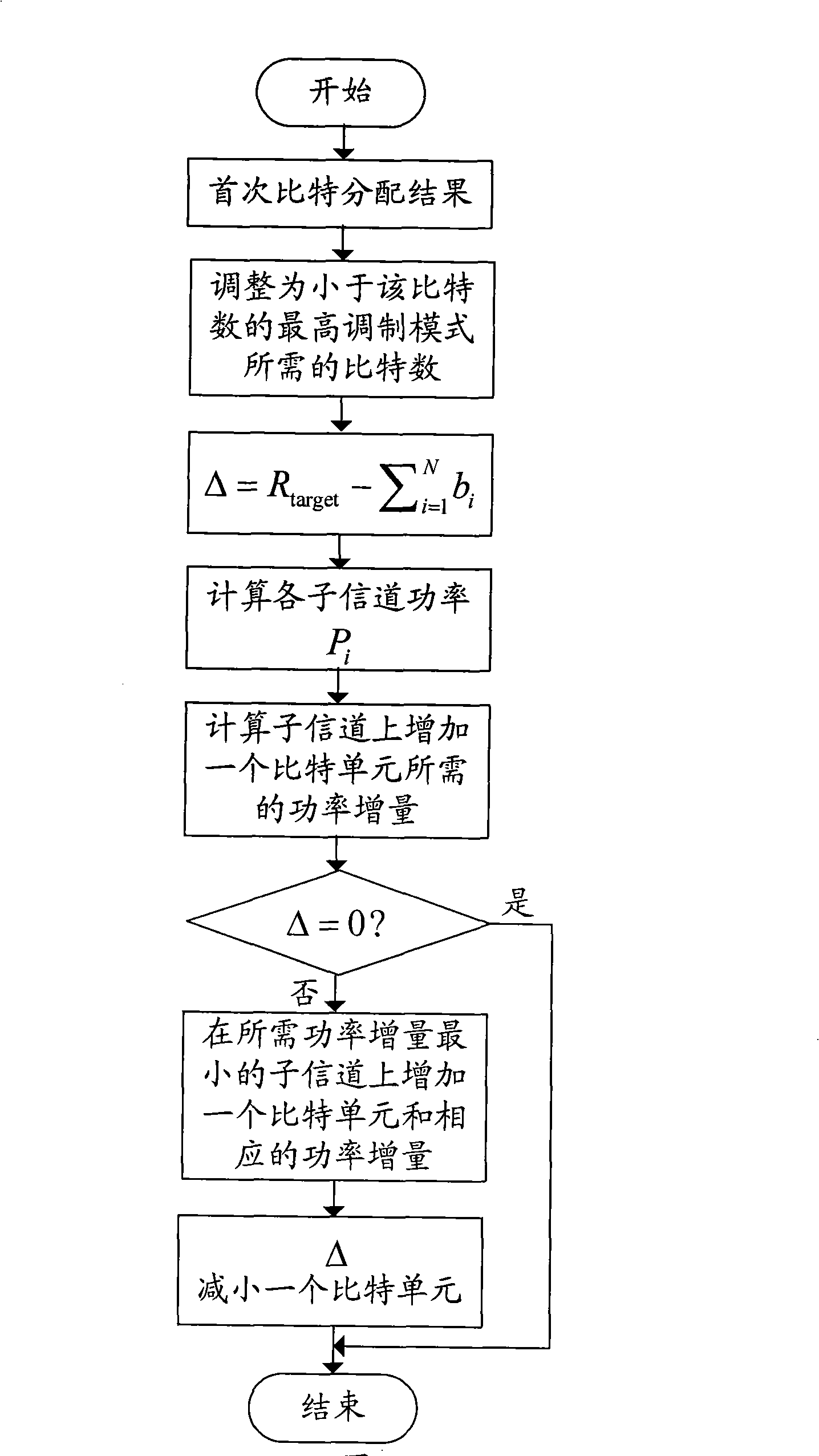
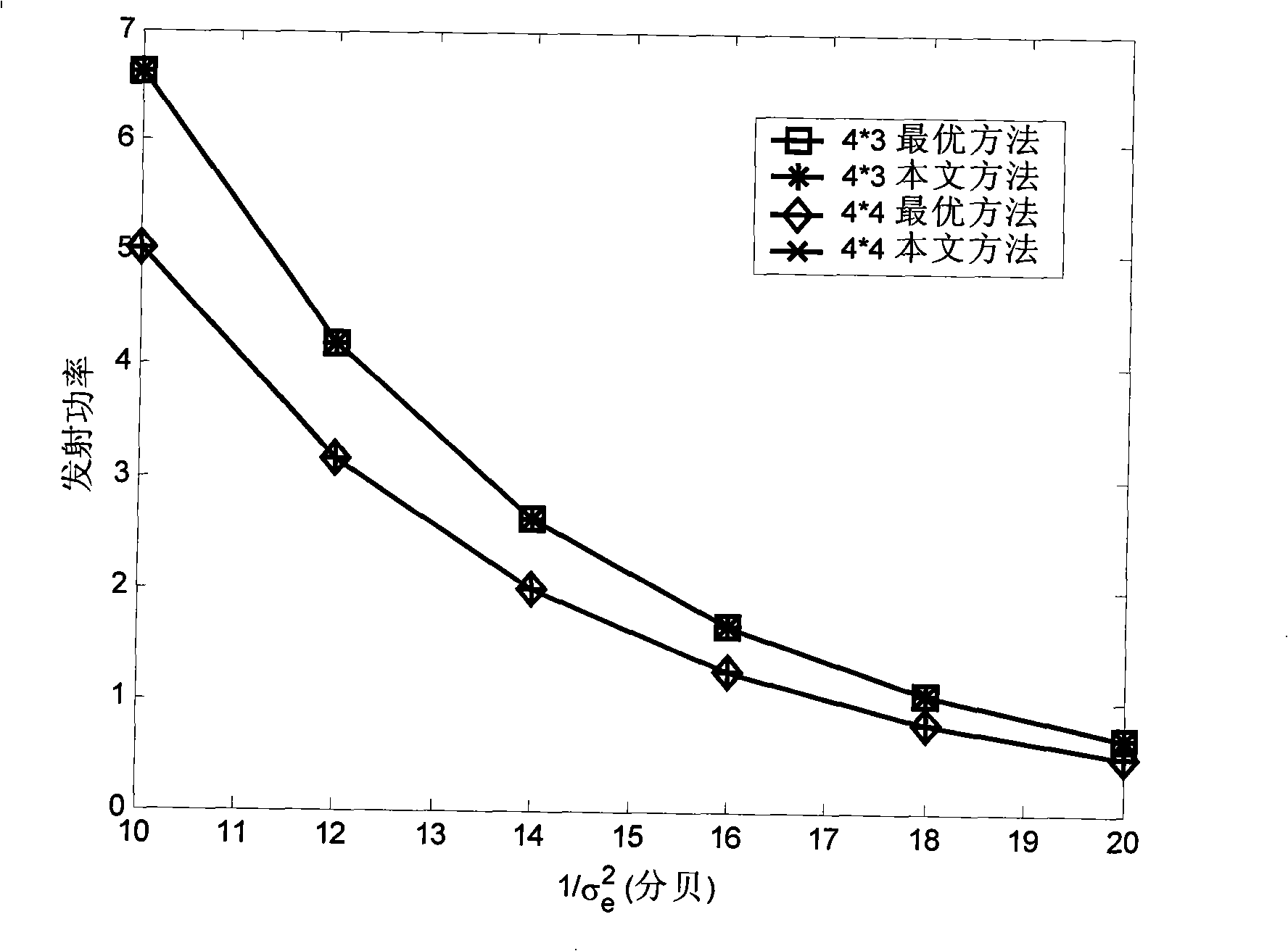
[0023] figure 1 It is a block diagram of a MIMO system adopting the adaptive bit and power allocation method provided by the invention. At the receiving end, the channel moments with errors are obtained through channel estimation or channel prediction. ,Will After performing singular value decomposition, the weighting matrix of the receiver and transmitter is obtained and and the singular value matrix (·) H Represents the matrix conjugate transpose. Feedback the receiver and transmitter weighting matrices to the sender and receiver respectively, and the singular value matrix Feedback to adaptive bit and power allocation block. The adaptive bit and pow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com