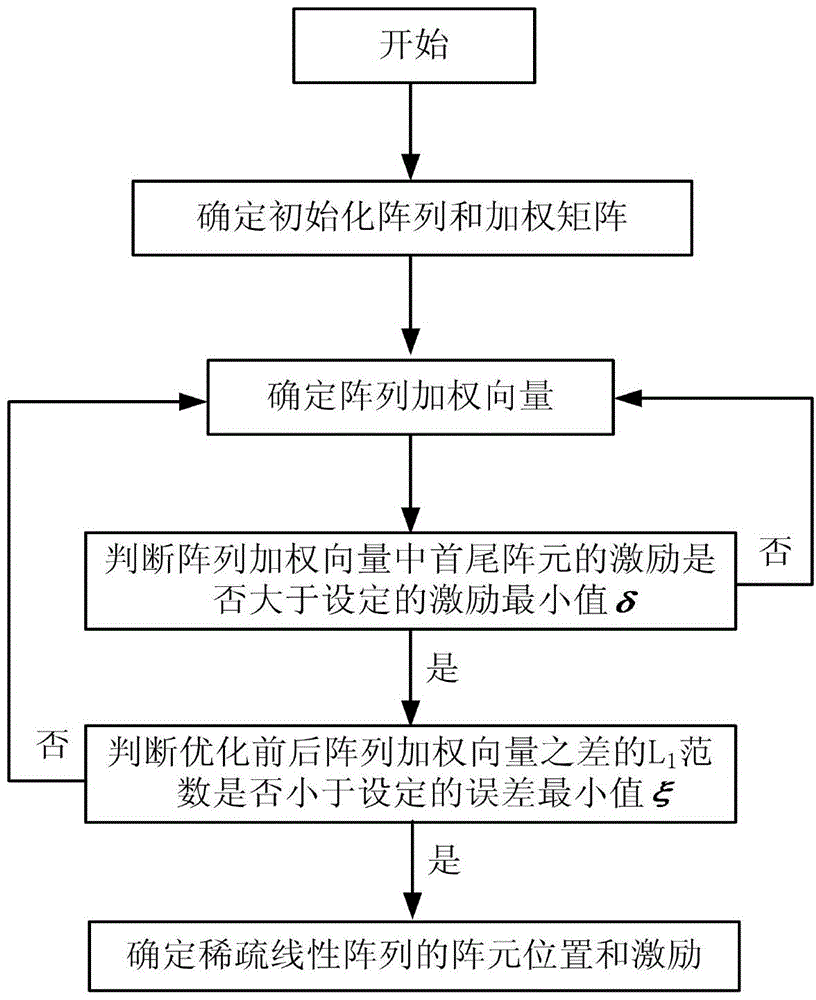
L1/2-norm-based sparse linear array optimization method
A linear array, L1 norm technology, used in electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not meeting the constraints of the array aperture, dense arrays, and large array apertures.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
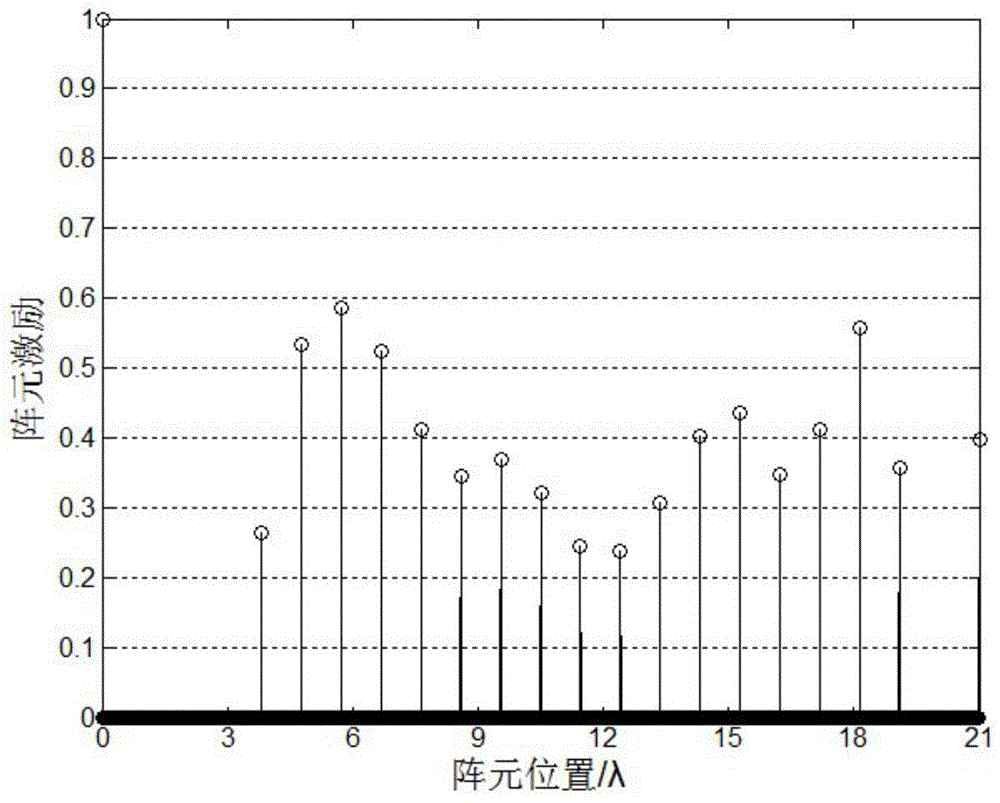
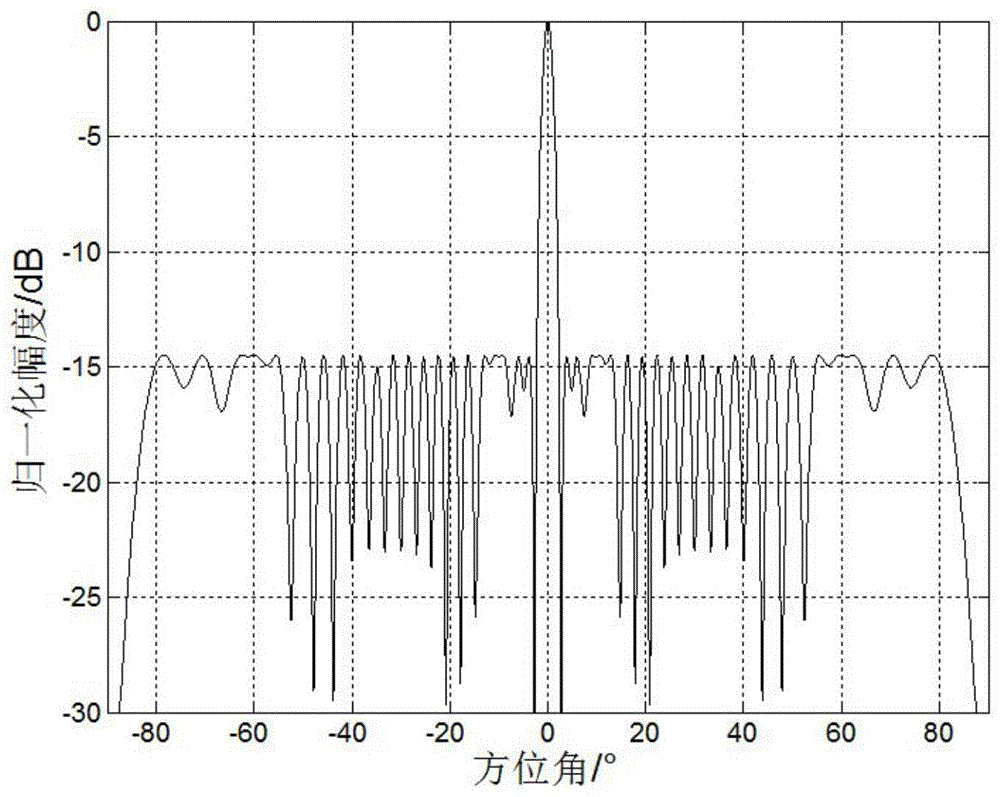
[0068] Under the condition that the main lobe width is 4.6°, the peak side lobe level is less than -14.49dB, and the array aperture is 21λ, the sparse linear array is optimized. Firstly, Giancarlo Prisco and Michele D’Urso based on iterative weighted L 1 The norm array optimization method optimizes the array, and the distance d between adjacent array elements is set to 0.01λ, so the initial number of array elements is 2101. After optimization, the array element positions and excitation value distribution of the sparse array are as follows: figure 2 as shown, image 3 Its corresponding beam pattern; then adopt the method of the present invention to optimize the array, the distance d between adjacent array elements is set to 0.1λ, and the initial array element distribution is set to be looser, so the calculation amount during optimization can be reduced; Figure 4 The array element position and excitation value distribution diagram of the sparse array optimized for the method ...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Under the condition that the main lobe width is 4°, the peak side lobe level is less than -30dB, and the array aperture is 50λ, the 192 -Based on iterative weighted L proposed in the paper on page 195 1 The array optimization method of the norm and the method of the present invention perform sparse linear array optimization respectively; under the same condition of initializing the array, that is, the distance d between adjacent array elements is set to 0.1λ, based on the iterative weighted L 1 The simulation results of array optimization using norm array optimization method are as follows: Figure 6 shown by Figure 6 It can be seen that the sparse linear array optimized by this method will have the absence of the first and last array elements, so it does not meet the given array aperture length condition; considering that any element in the array weight vector may be zero during the optimization process, in order to satisfy the given For a given array aperture lengt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com