Patents
Literature
54 results about "Artifact suppression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
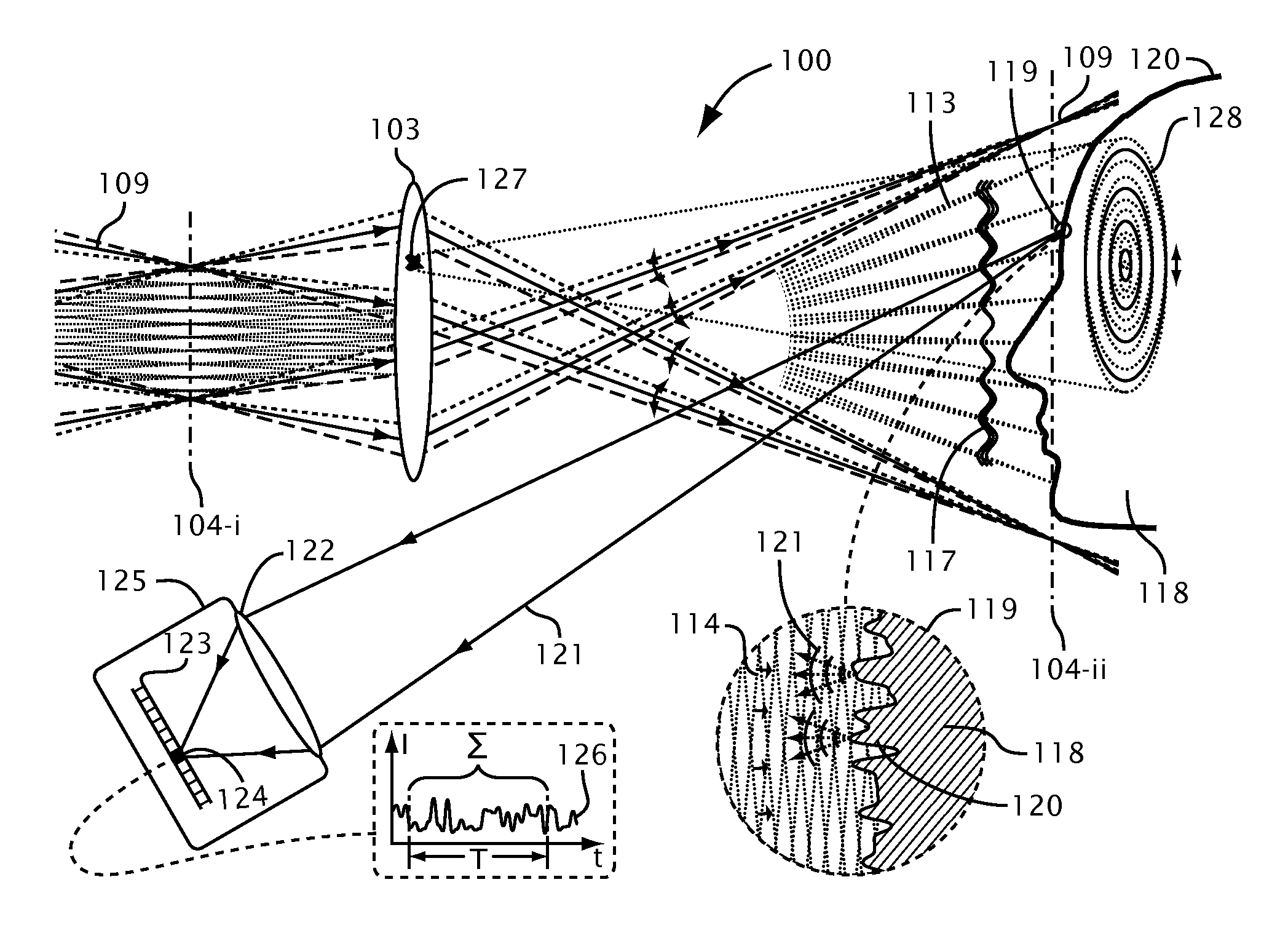
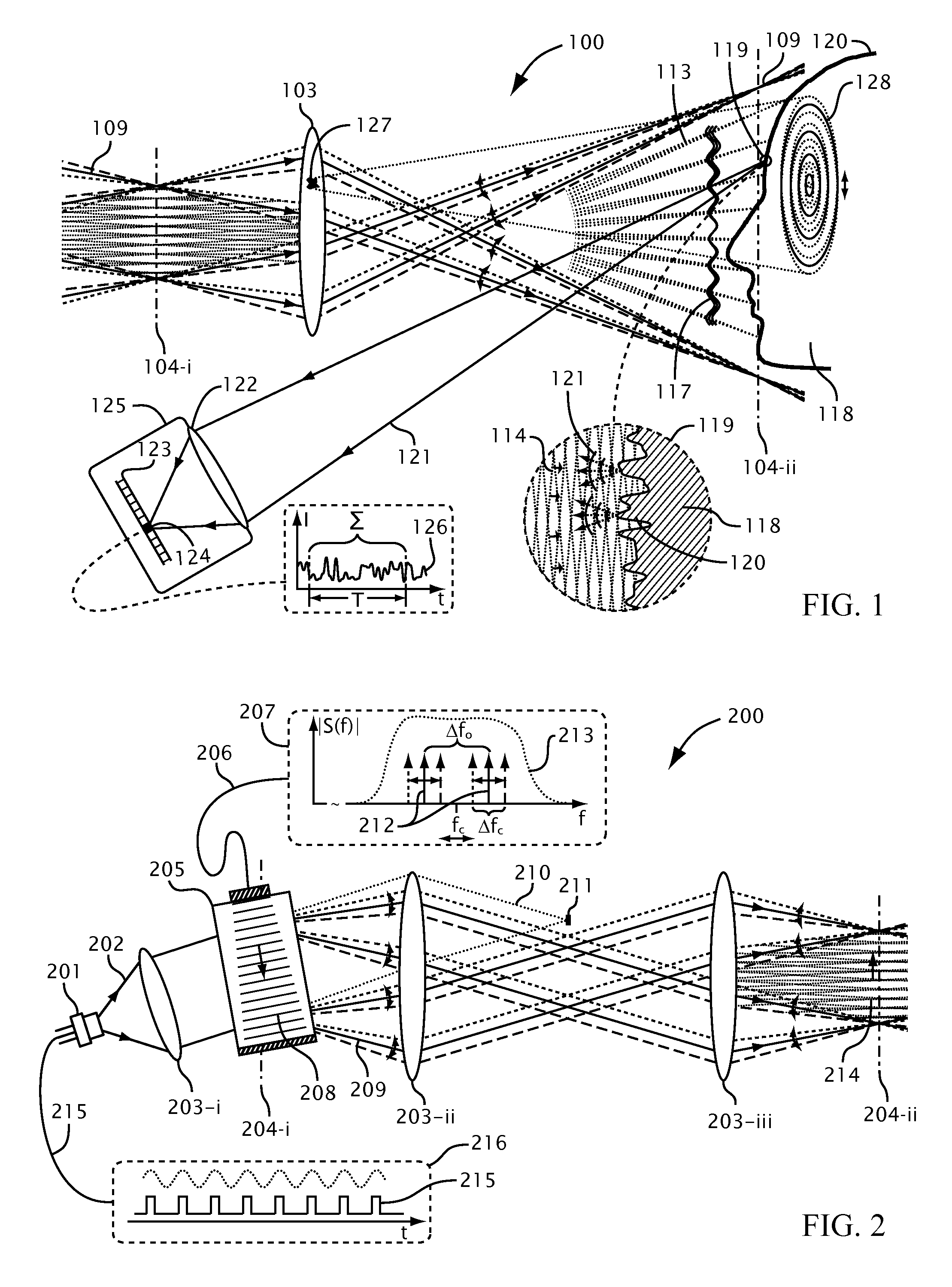
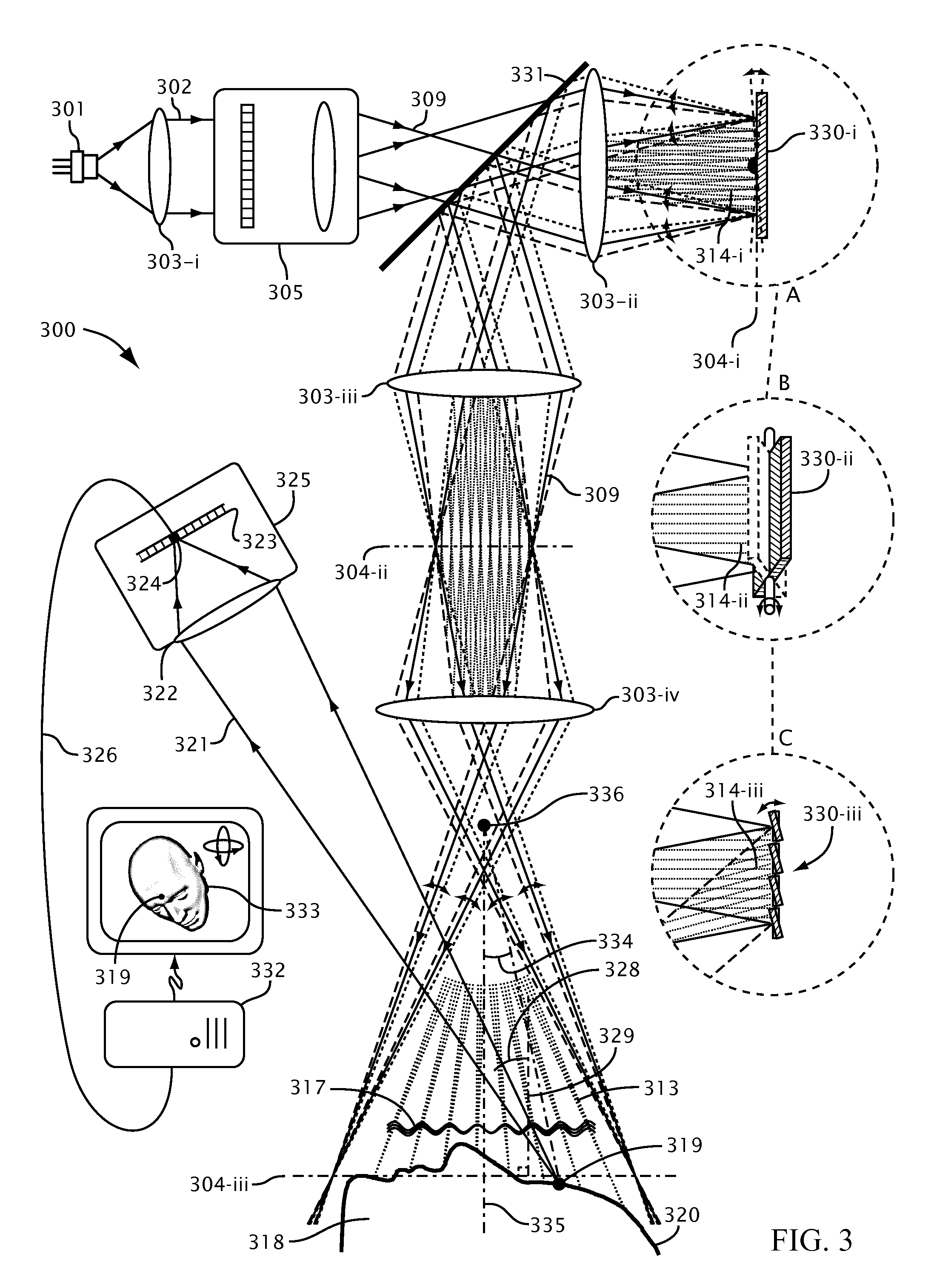
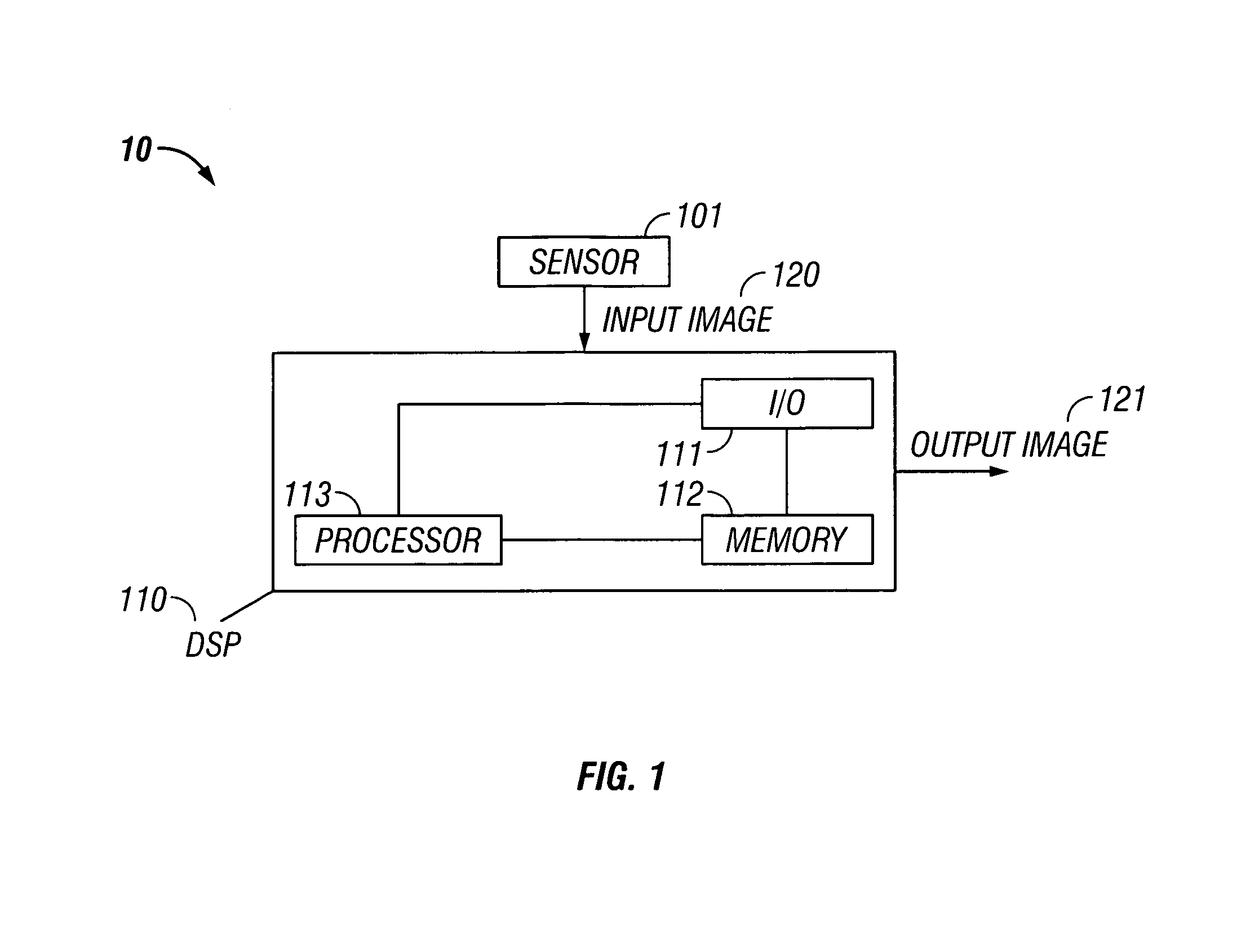
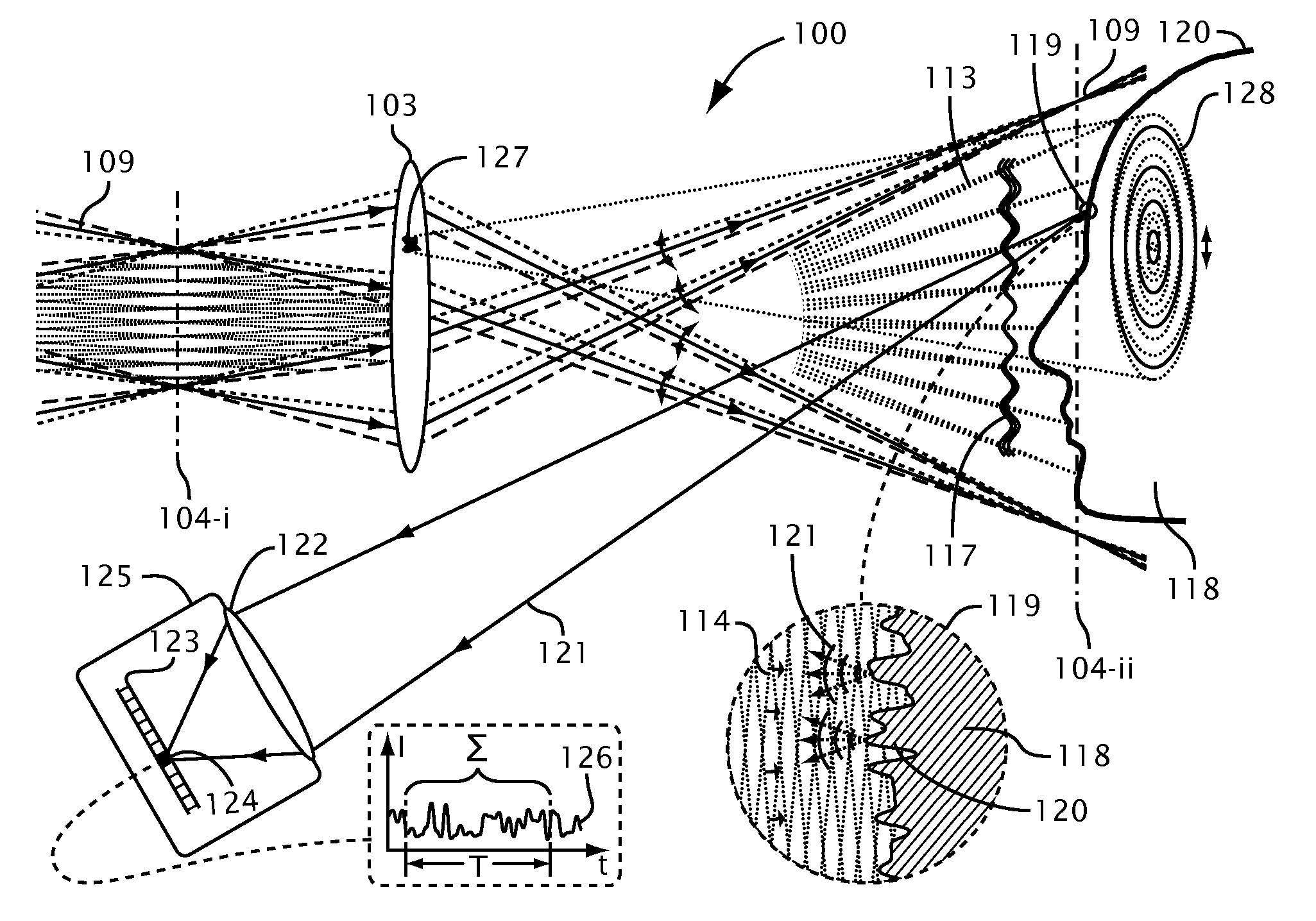
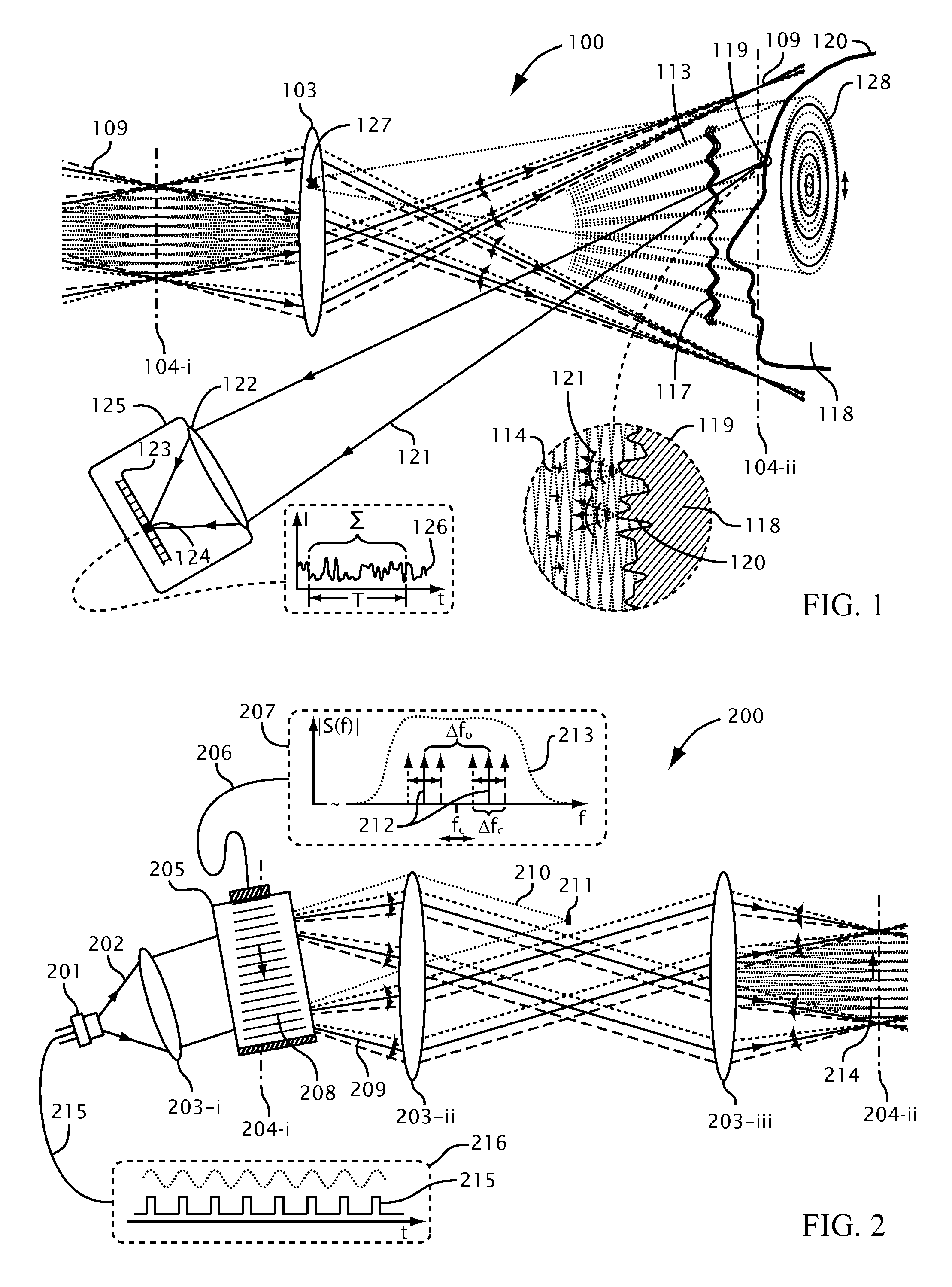
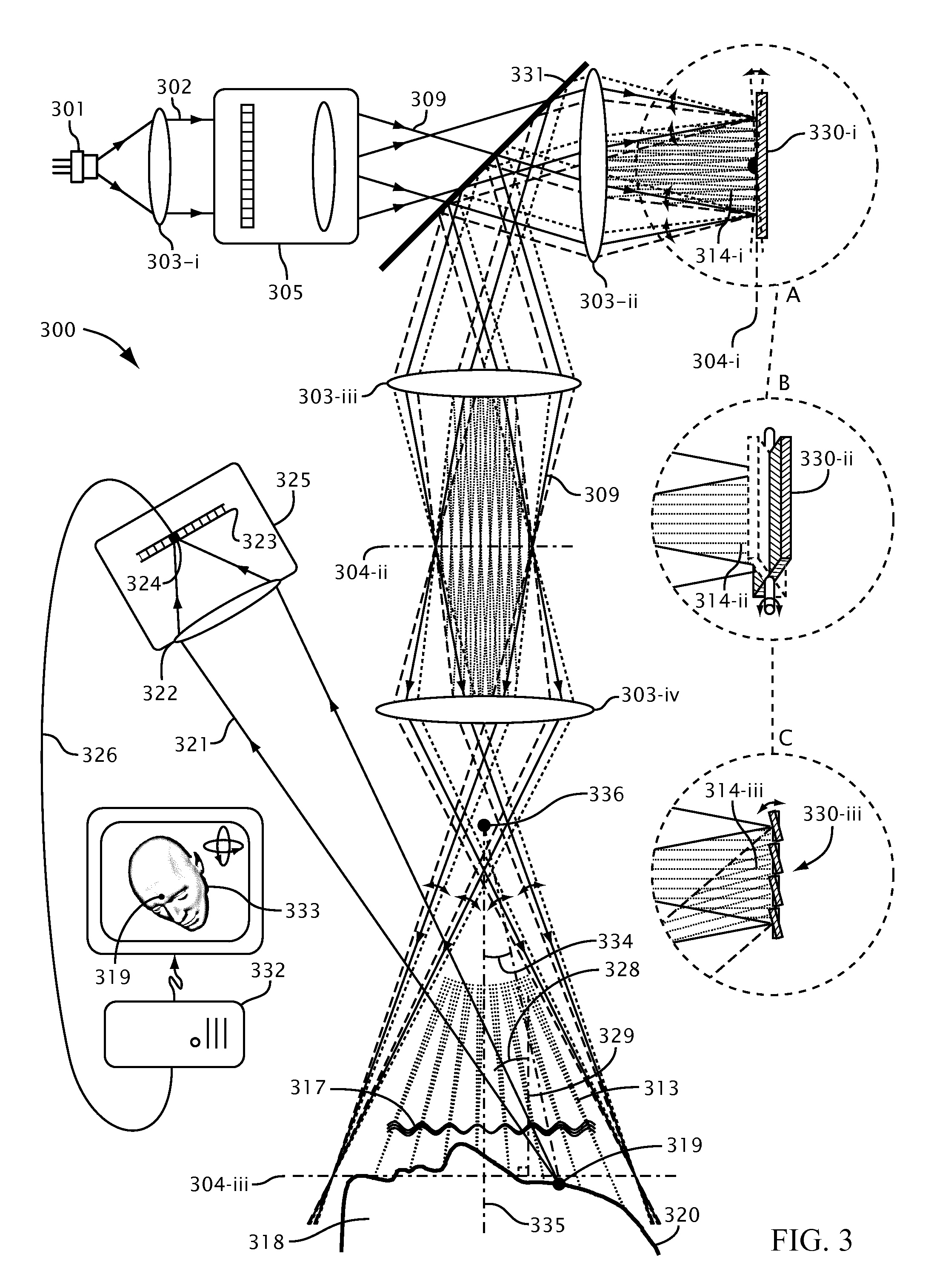
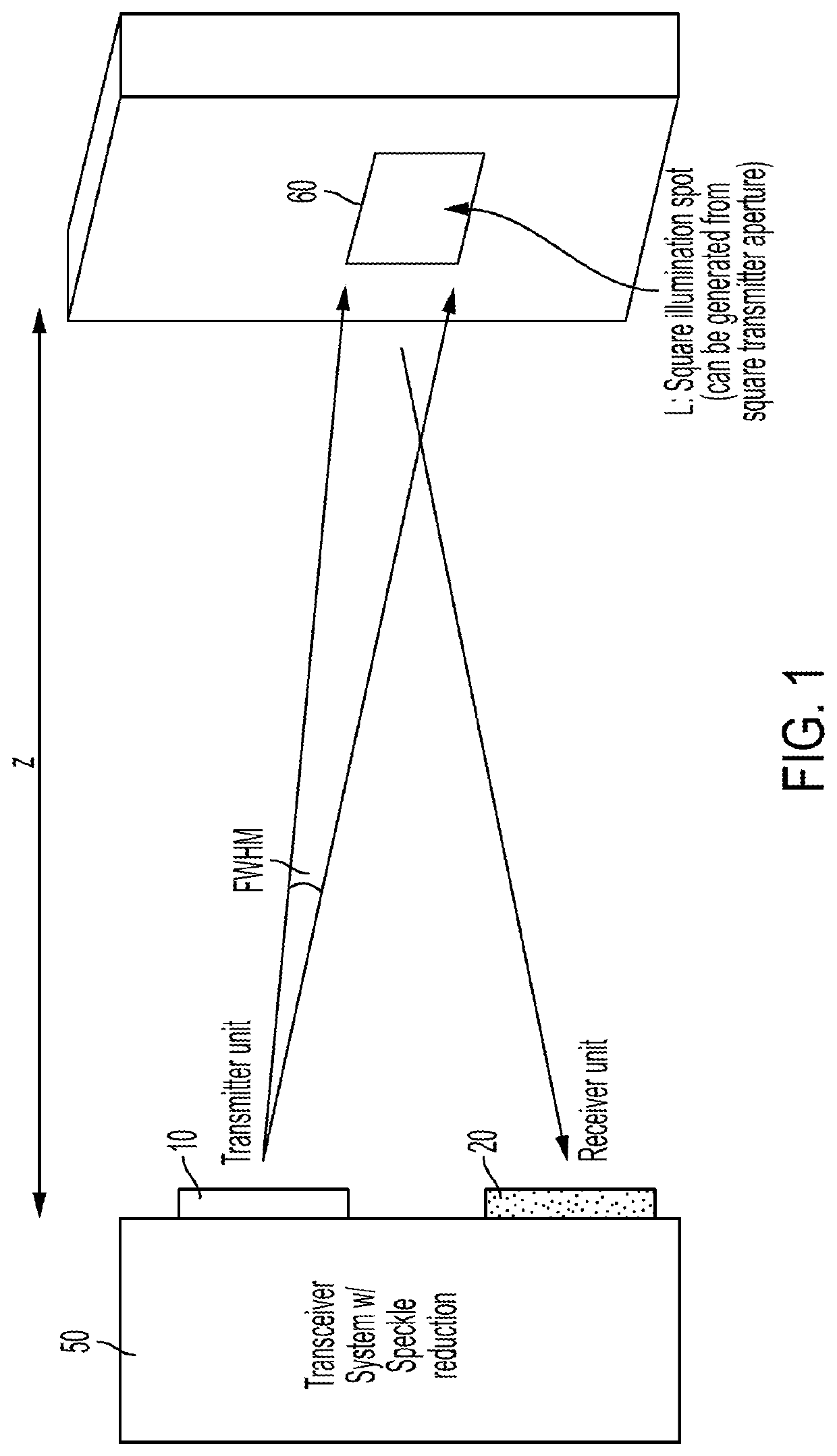
Systems and methods for suppressing coherent structured illumination artifacts
InactiveUS20130088723A1Reduce errorsNeed can be addressedMicroscopesUsing optical meansArtifact suppressionAcousto-optics
Methods and systems are provided for suppressing speckle and / or diffraction artifacts in coherent structured illumination sensing systems. A coherent radiation pattern forms an interference pattern at an illumination image plane and illuminates an object. Radiation scattered or otherwise emitted by the object is detected to produce a signal, which is integrated in time. Coherent artifact suppression is attained by using a spatial modulator, such as an acousto-optic device, to vary a phase gradient at the illumination image plane during the signal integration time. Various embodiments are provided for purposes including without limitation: preserving the depth of field of the coherent illumination; using the same acousto-optic device for pattern generation and coherent artifact suppression; electronically controlling the effective spatial coherence of the illumination system; and reducing errors due to coherent artifacts in a laser-based three dimensional imaging system.
Owner:FELDKHUN DANIEL
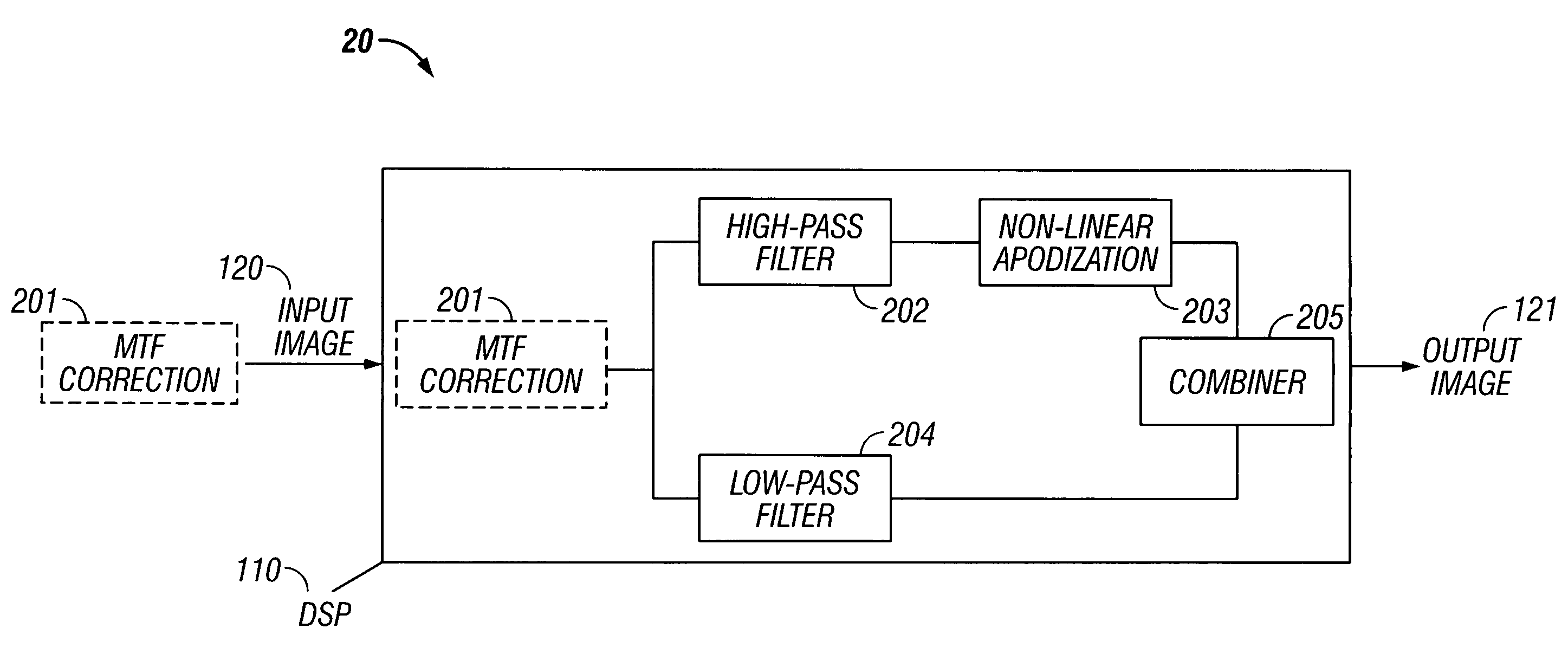
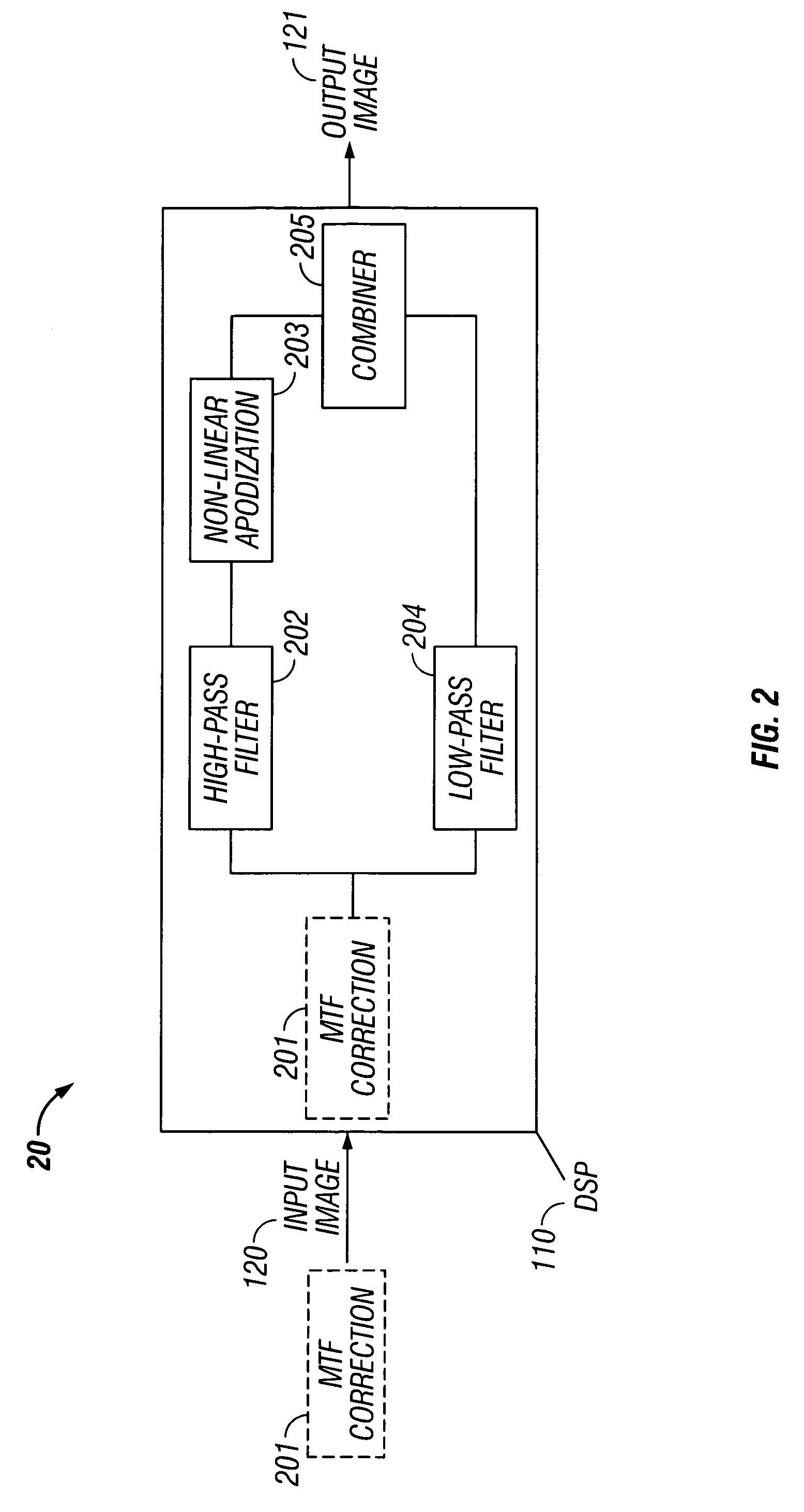
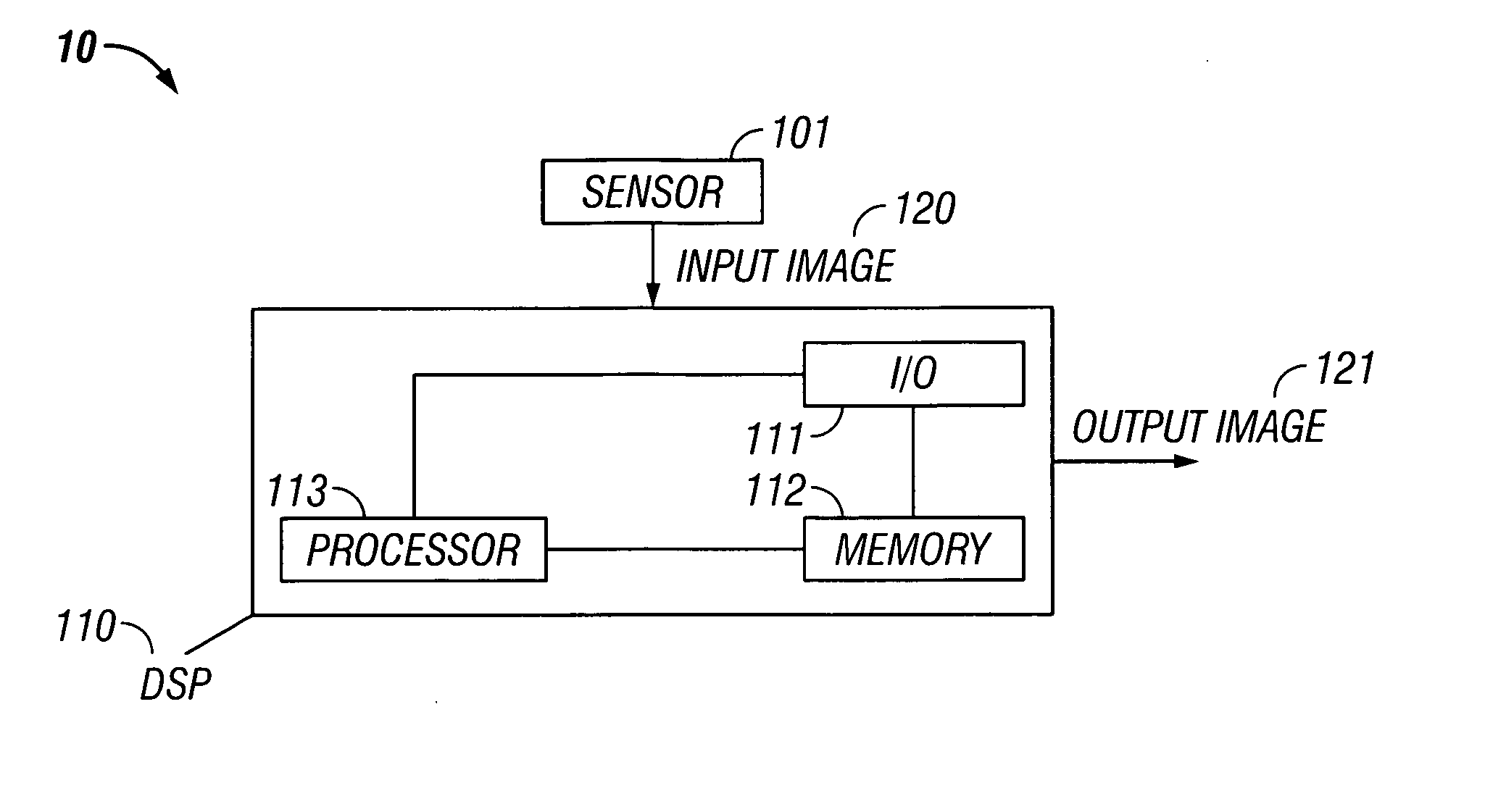
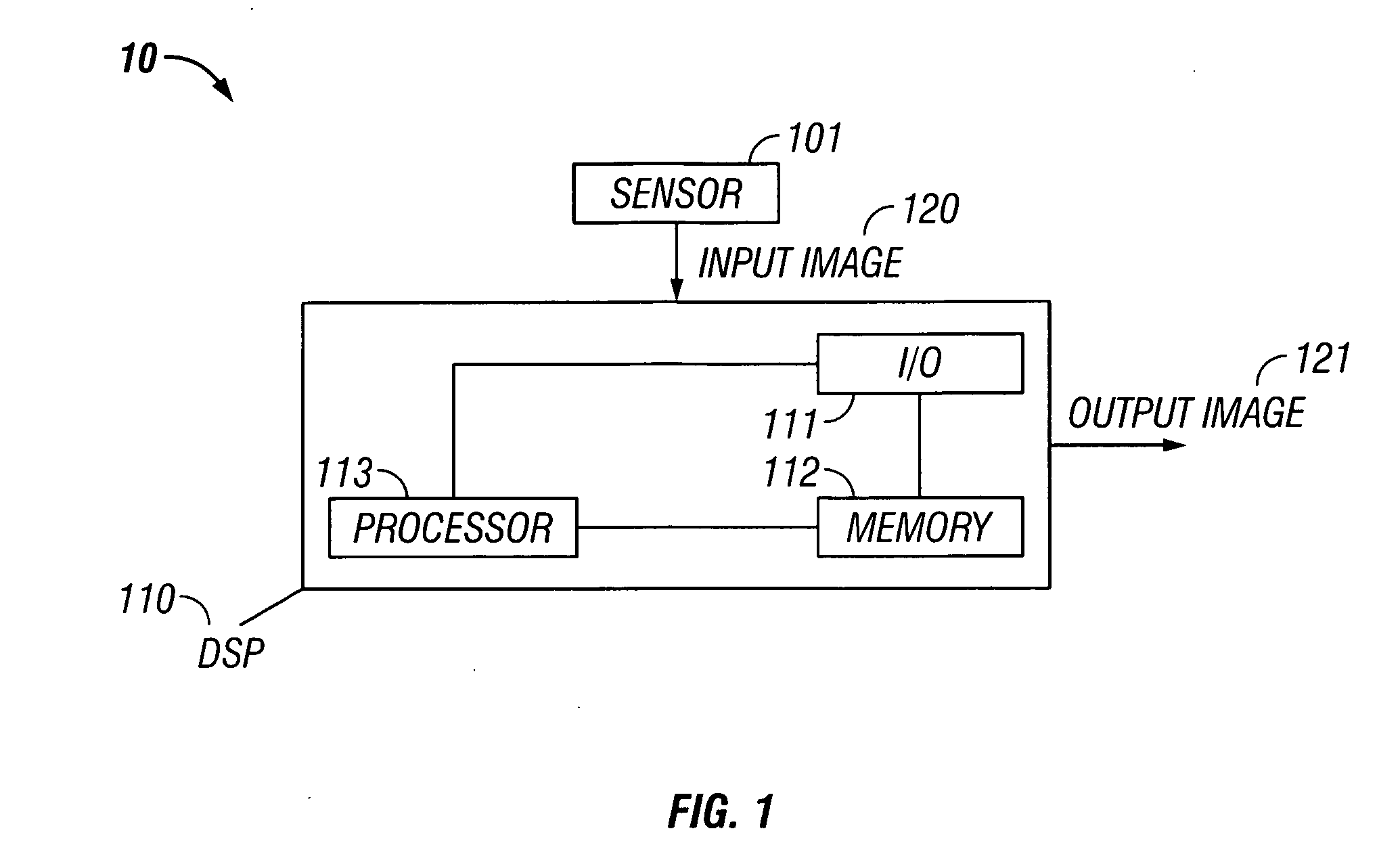
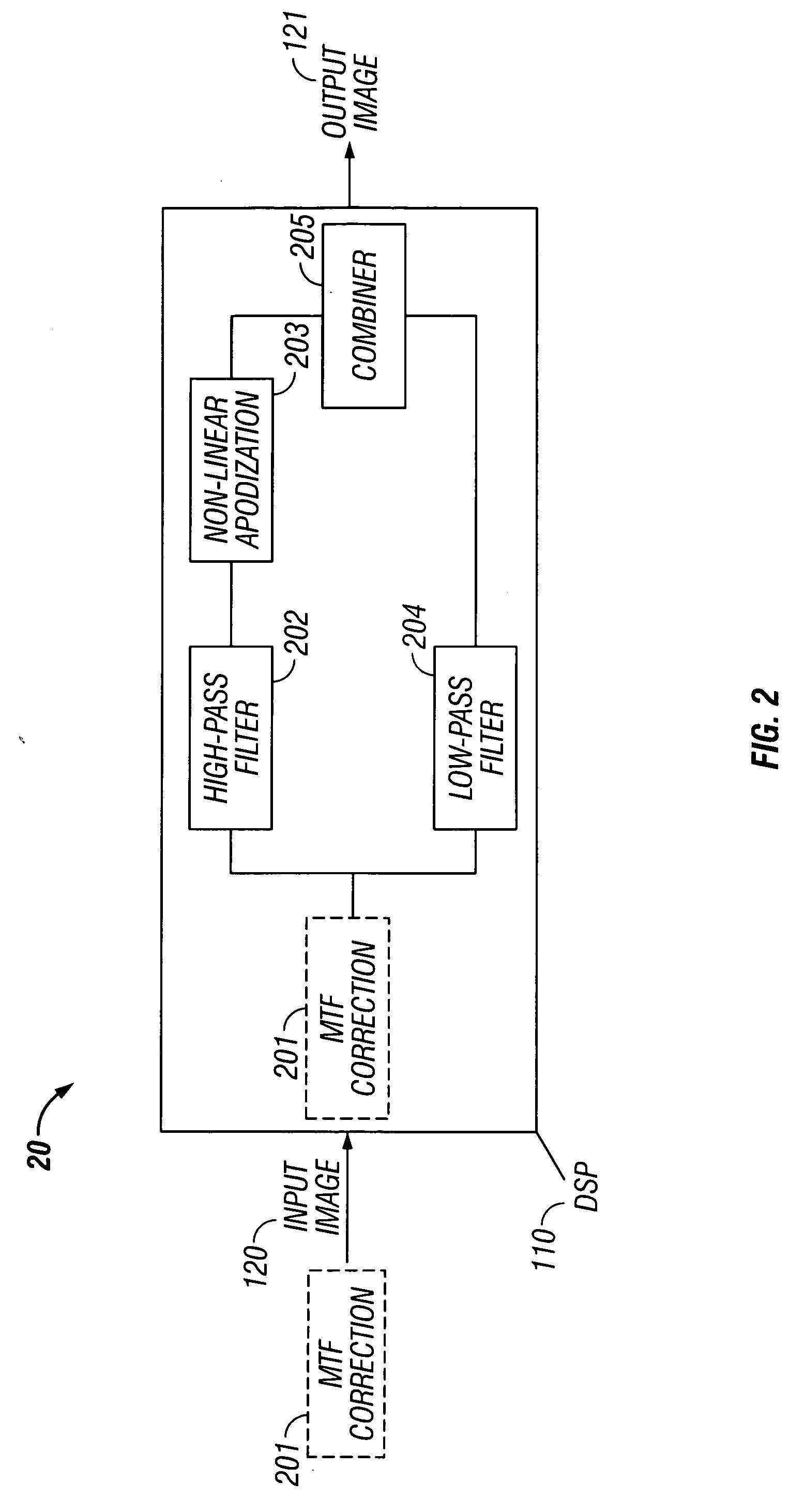
Edge ringing artifact suppression methods and apparatuses
In some embodiments, the present invention relates to methods or suppressing edge ringing in images. For example, in some embodiments a method of processing an image to suppress ringing and broadened edges induced by image correction processing, includes high-pass filtering a first image to obtain a second image, processing said second image including applying non-linear apodization to said second image to obtain a third image, low-pass filtering said first image to obtain a fourth image, and combining the third image and the fourth image to obtain an output image, wherein the output image is characterized by having reduced edge-response sidelobes as compared to the first images. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to devices comprising means and / or modules to suppress edge ringing in images.
Owner:KBR WYLE SERVICES LLC
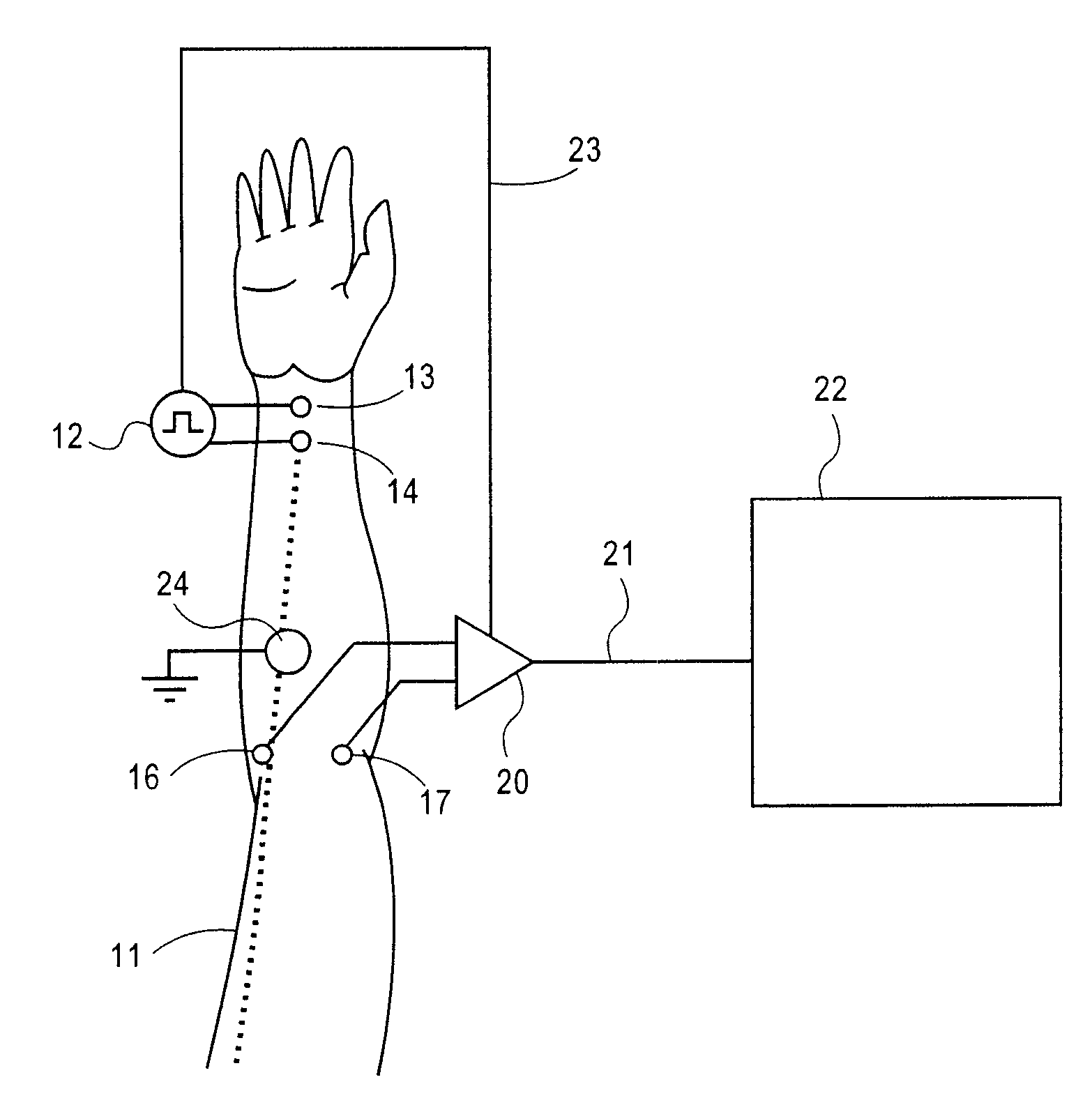
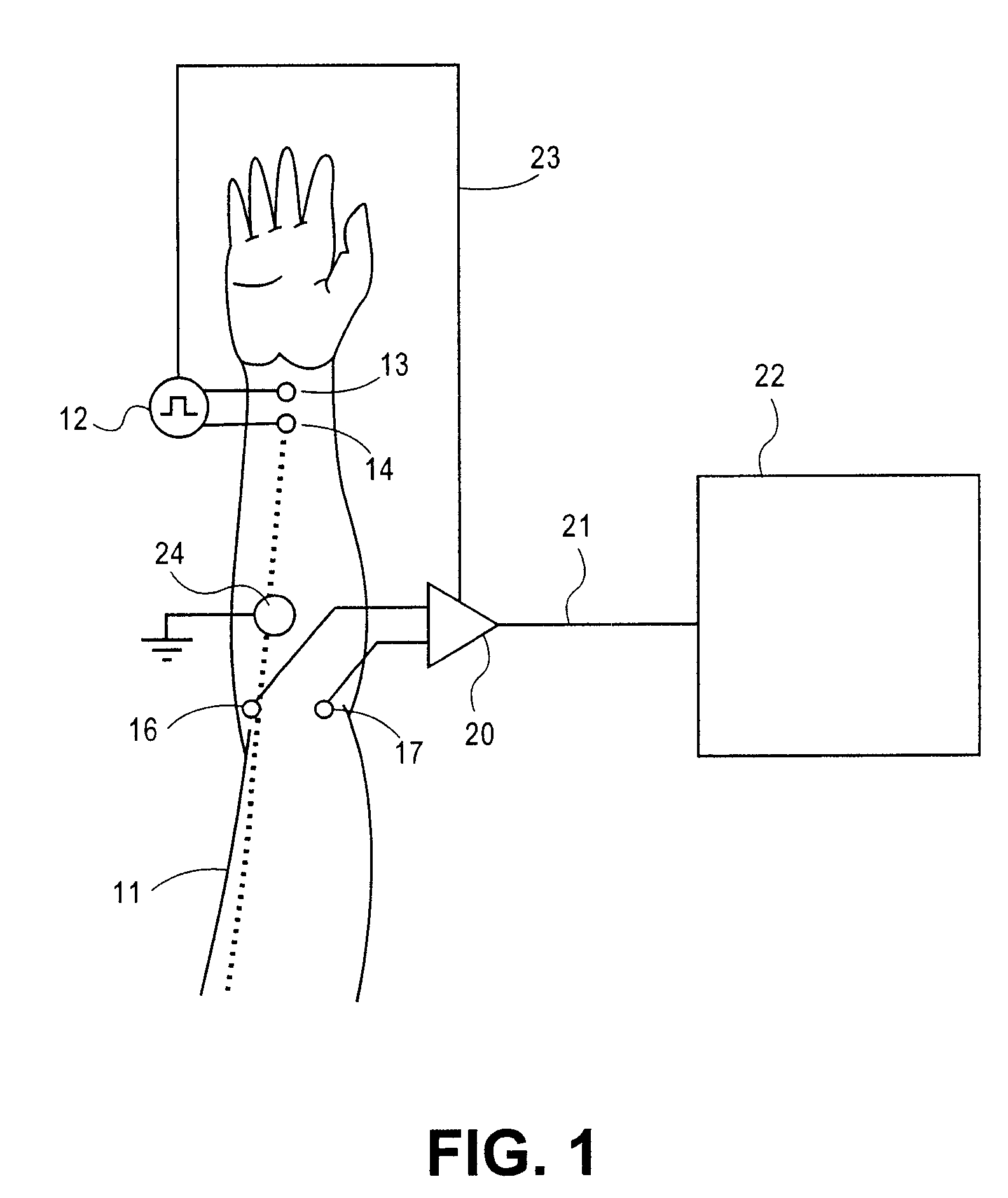
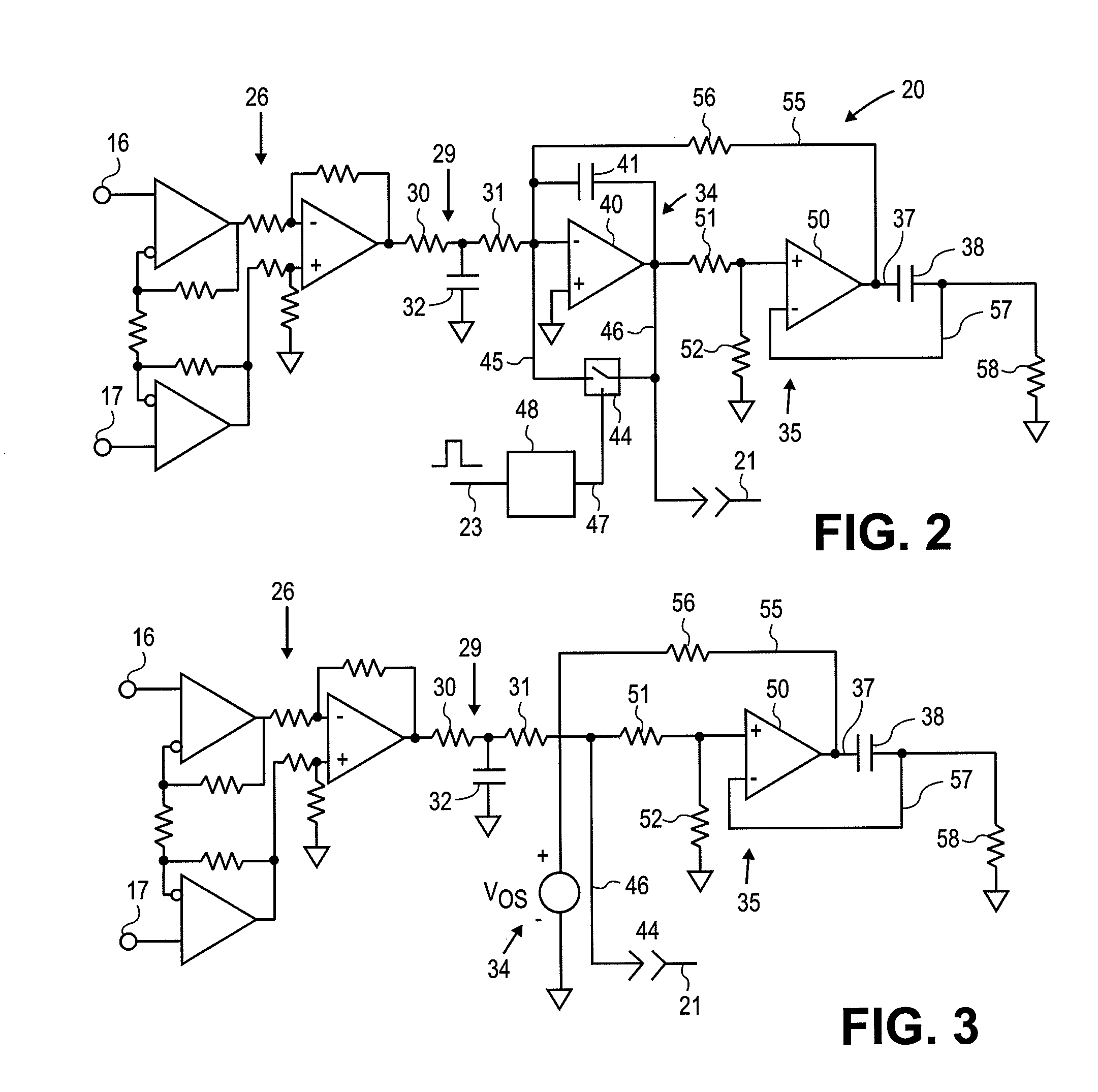
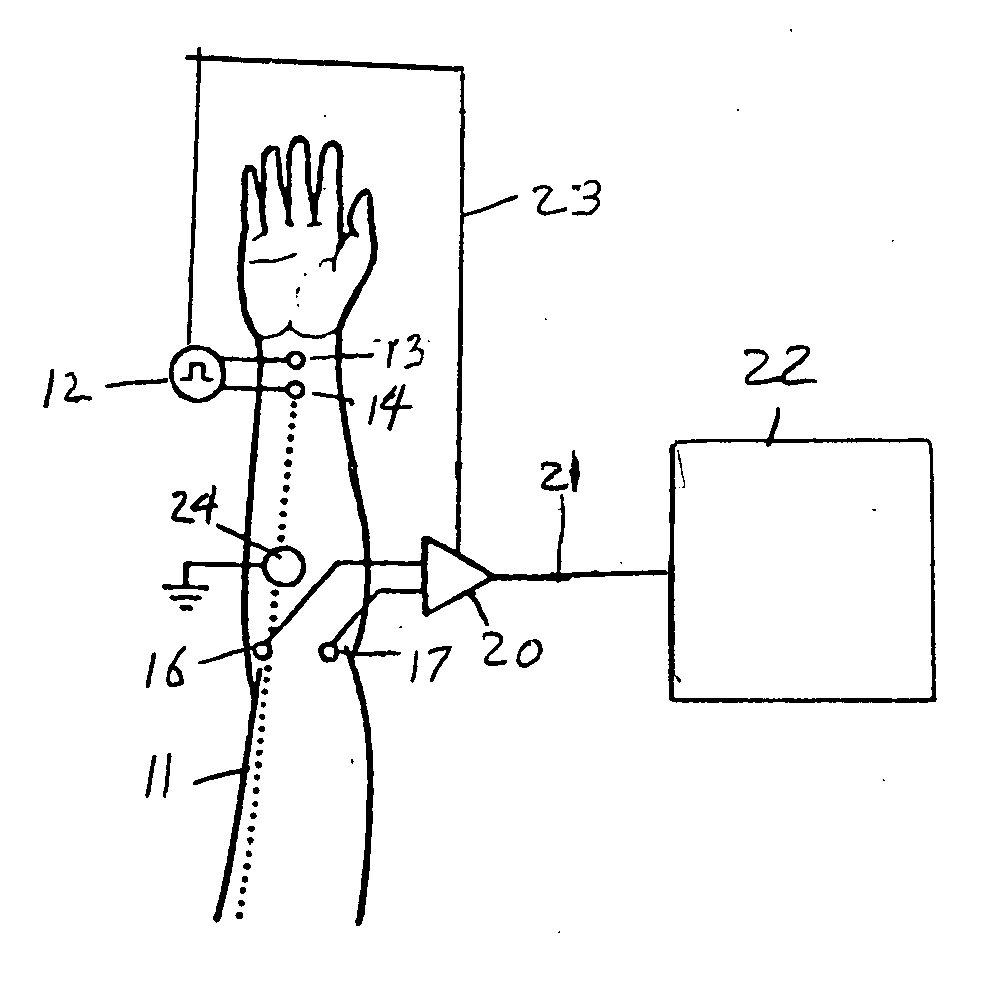
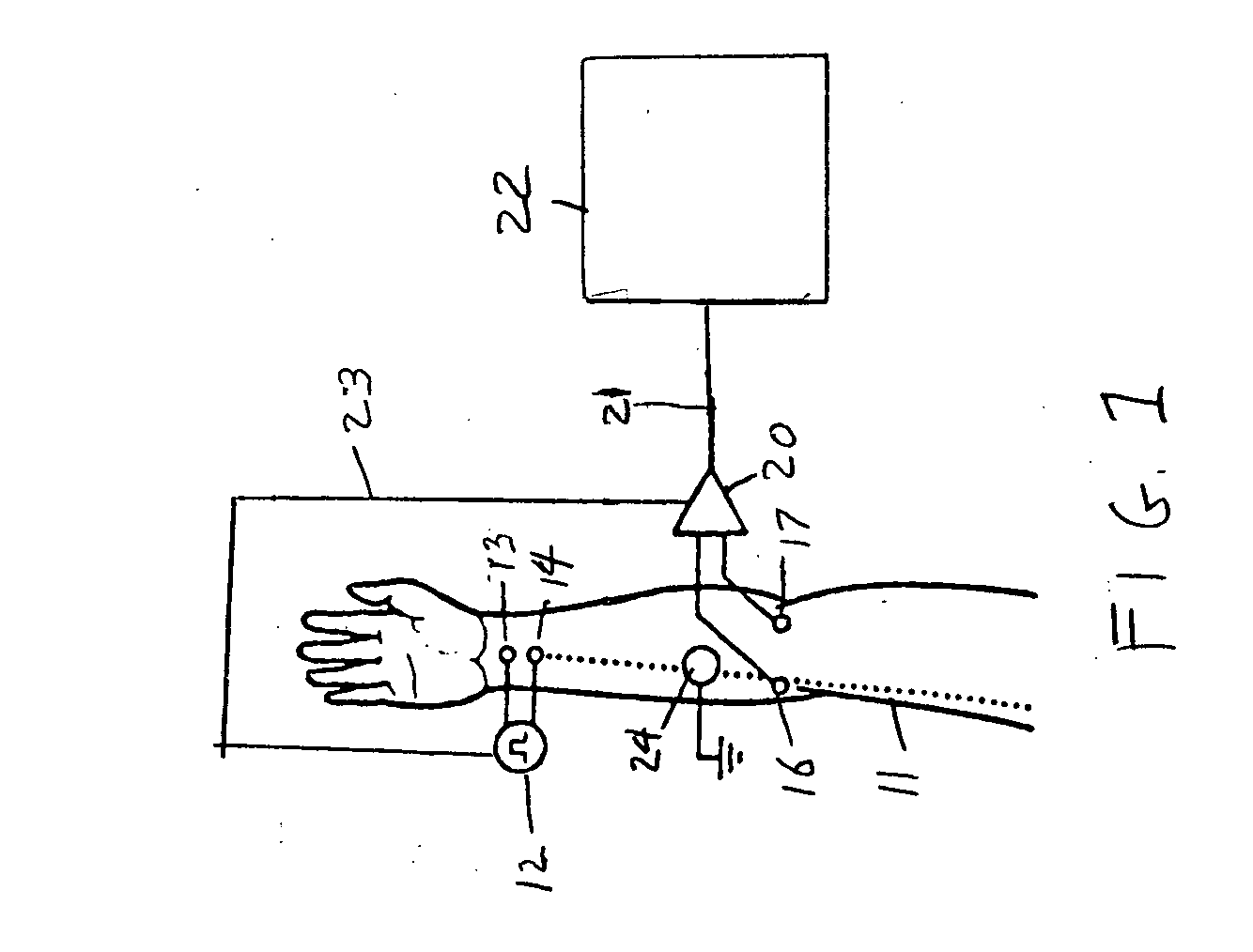
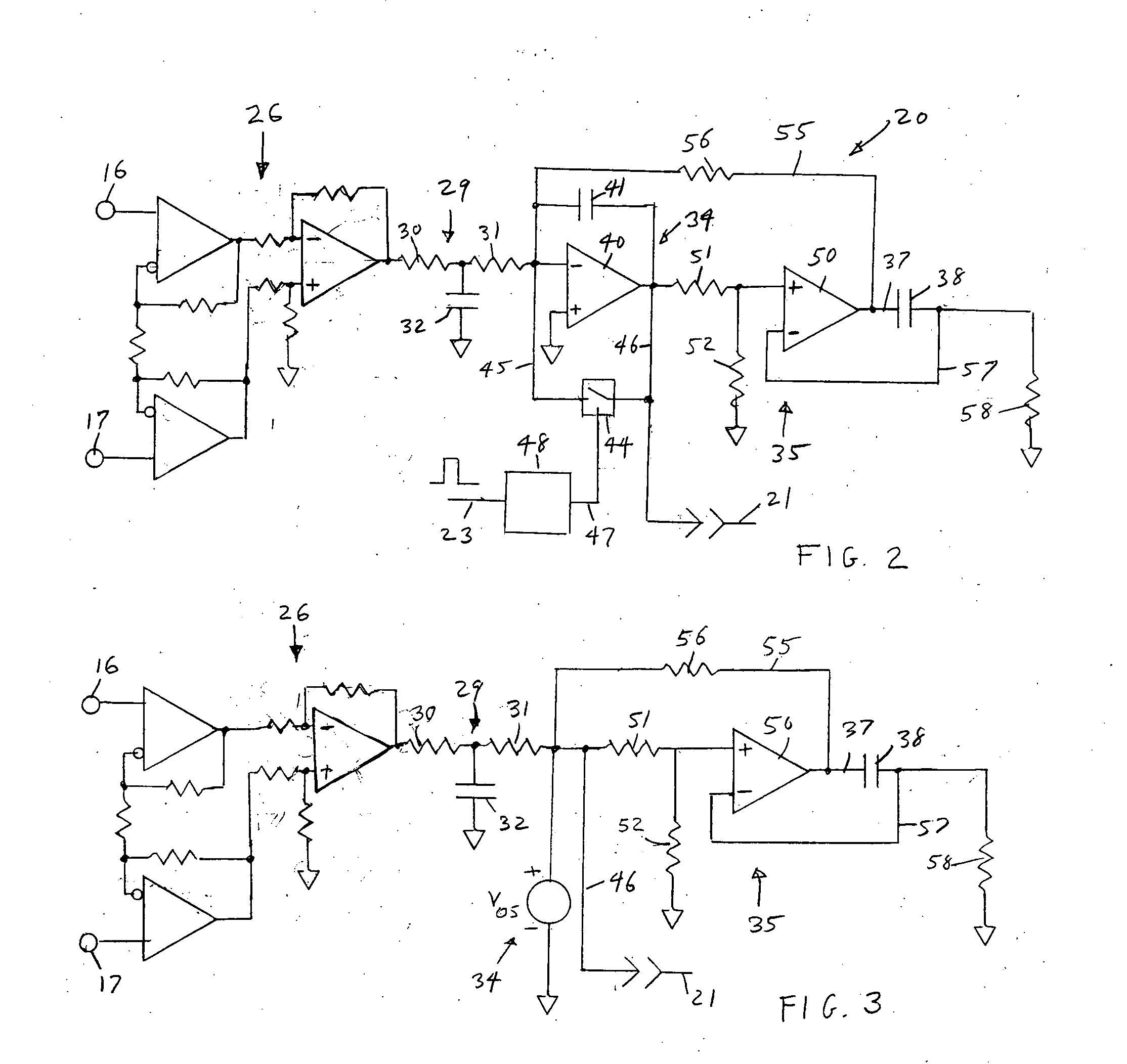
Method and apparatus for stimulus artifact suppression
Amplification of an evoked potential signal is carried out utilizing a high pass filter implemented as an integrator in a feedback loop which drives the DC offset voltage to zero. As a result, the feed-forward amplifier circuit has almost zero volts at its output since the only voltage remaining is the offset voltage of the operational amplifier, which is selected so as to maintain this parameter as low as possible. Because the voltage impressed across the feed-forward amplifier section is close to zero, the gain of this section can be set to zero during the time that the electrical stimulus pulse is present without introducing any additional artifacts and subsequent amplifier stages are not driven into saturation. When the electrical stimulus potential is no longer present or is significantly reduced in amplitude and before the time of receipt of the response signal, the feed-forward amplifier is brought back into the circuit to provide the high gain required to amplify the response signal, which can be measured without interference from saturation of any of the amplifier stages as they recover to baseline.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
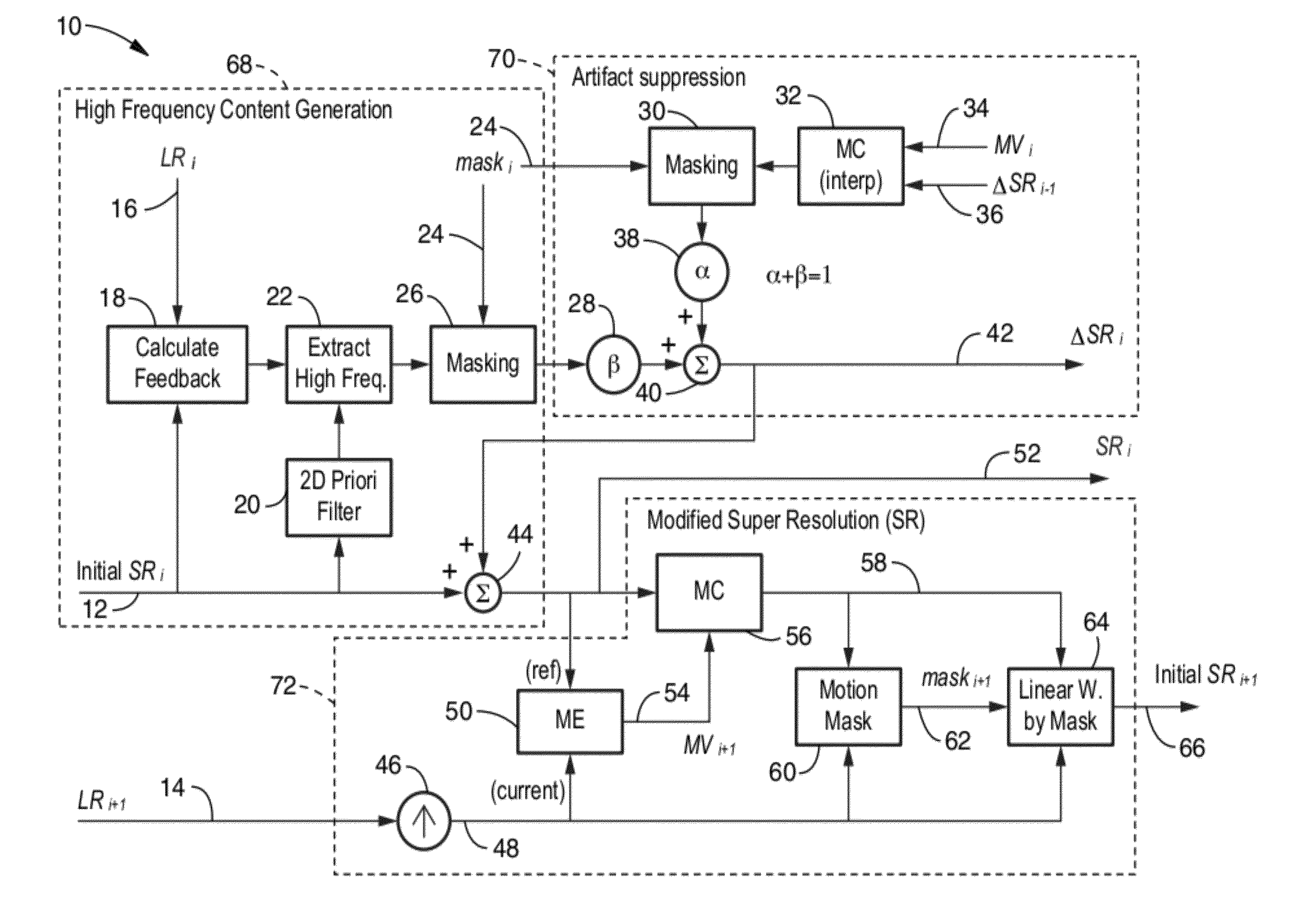
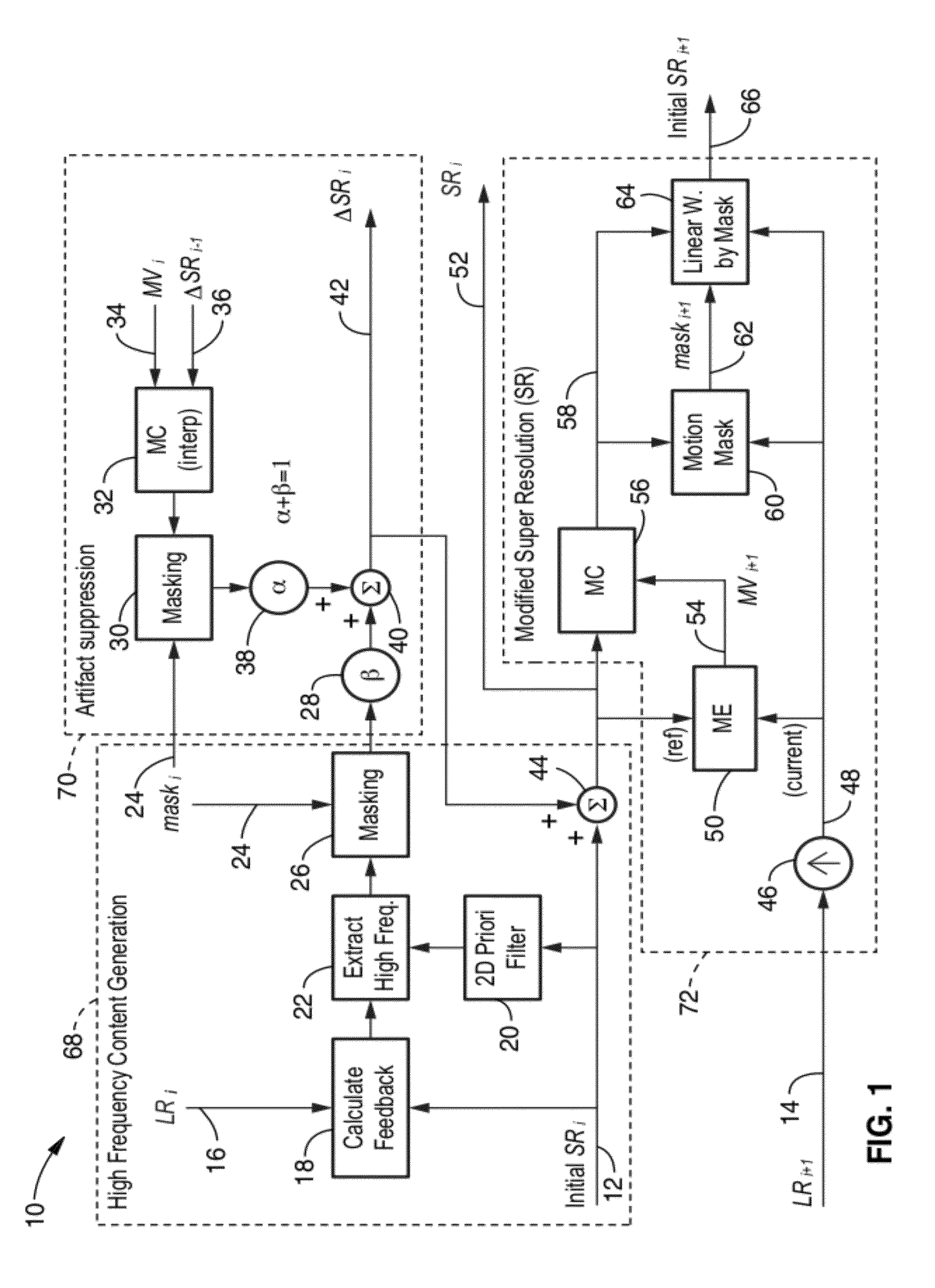
Recursive image quality enhancement on super resolution video
ActiveUS20090245375A1Quality improvementSmoothing imageTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImaging qualityArtifact suppression
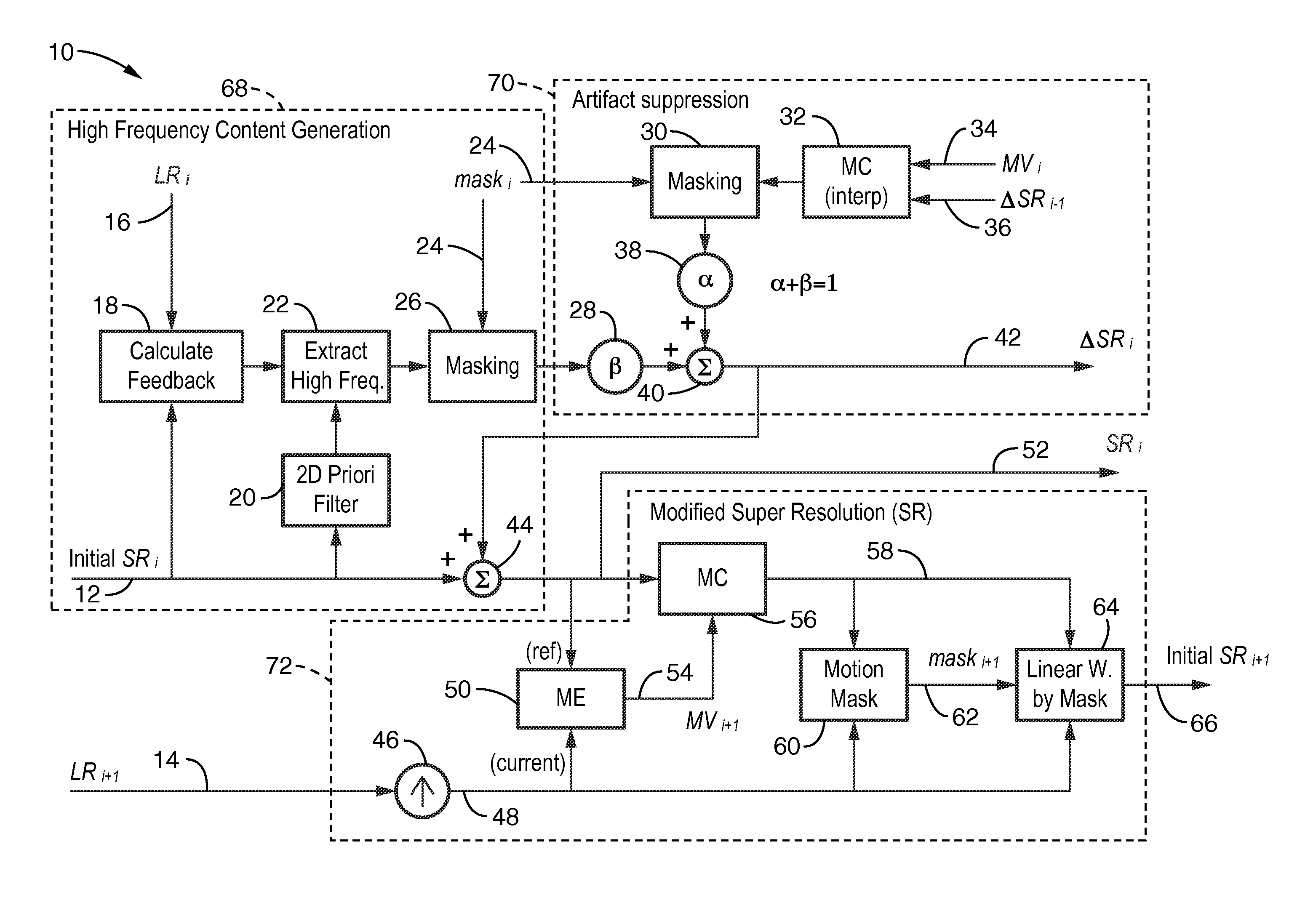
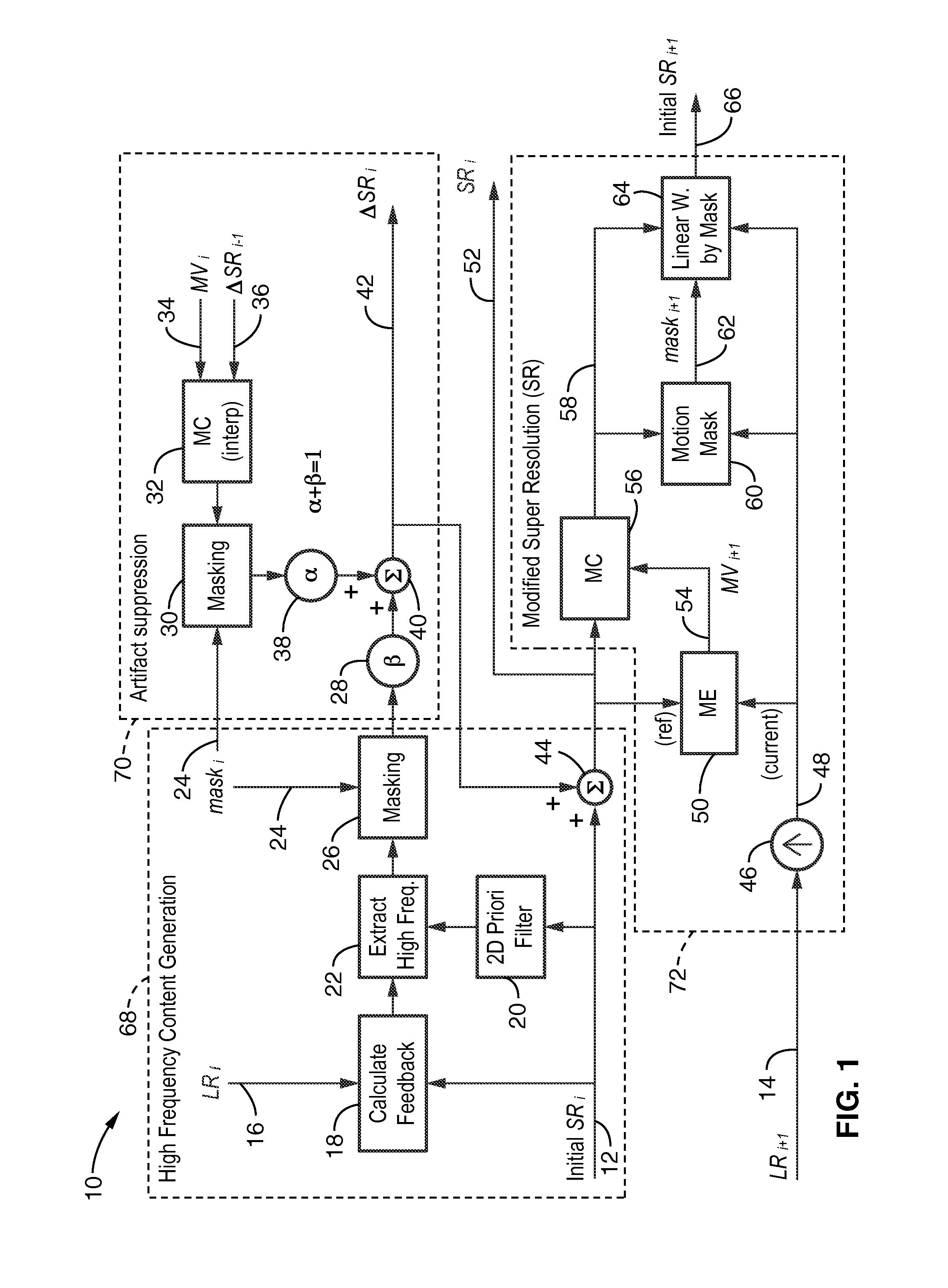
Method and apparatus for improving the quality of super-resolution video imaging by suppressing ringing artifacts, reducing high-frequency noise, reducing blocking artifacts, and smoothing out jagged edges of the image to generate pictures that appear cleaner with less edge degradation. The method operates in a recursive manner within a sequence of low resolution images. Conventional SR processing is primarily enhanced within the invention by adding an artifact suppression section which creates a high frequency component signal ΔSRi having significantly reduced artifacts therein achieving higher quality super-resolution image output. The method can be applied to images and image sequences (video) in monochrome or color and in any desired pixel format. The method can be implemented within image processing devices, in particular those containing programming for executing the described method steps.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
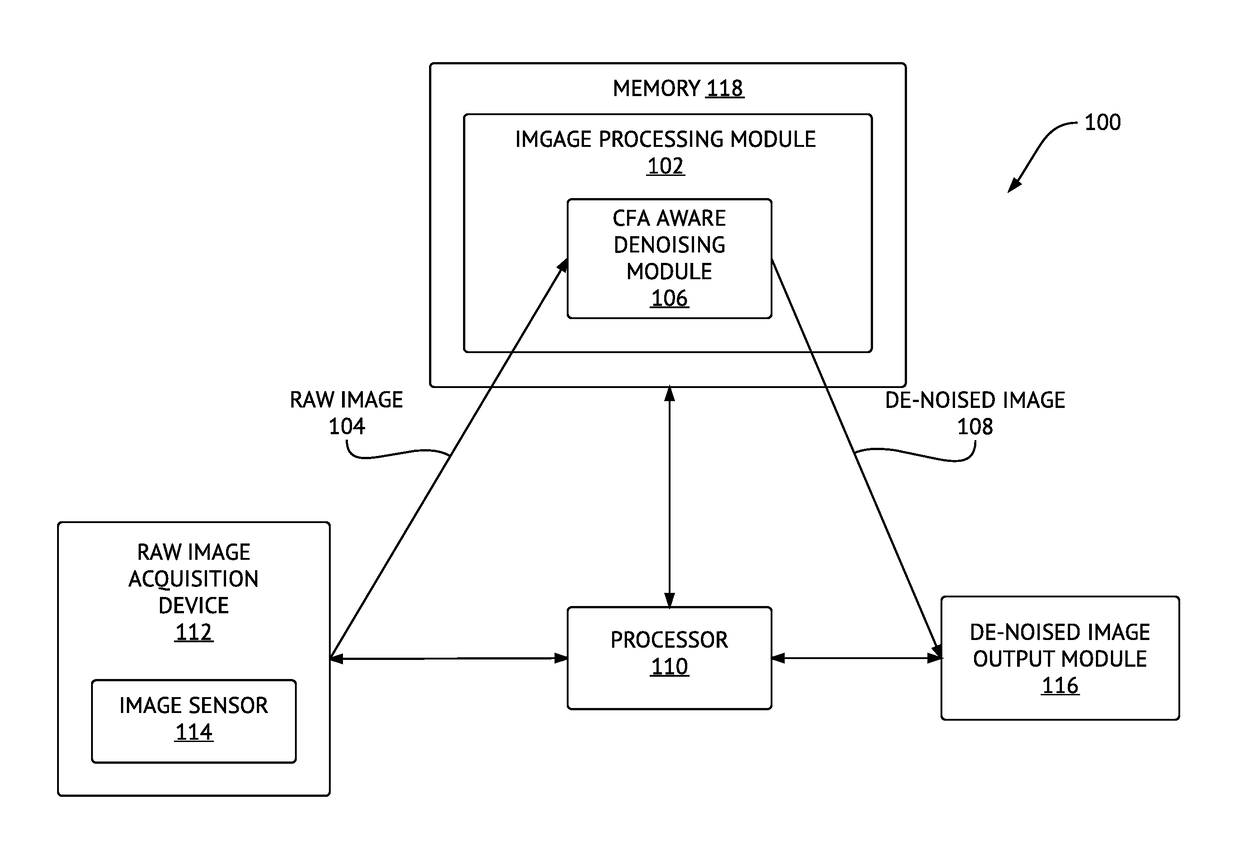
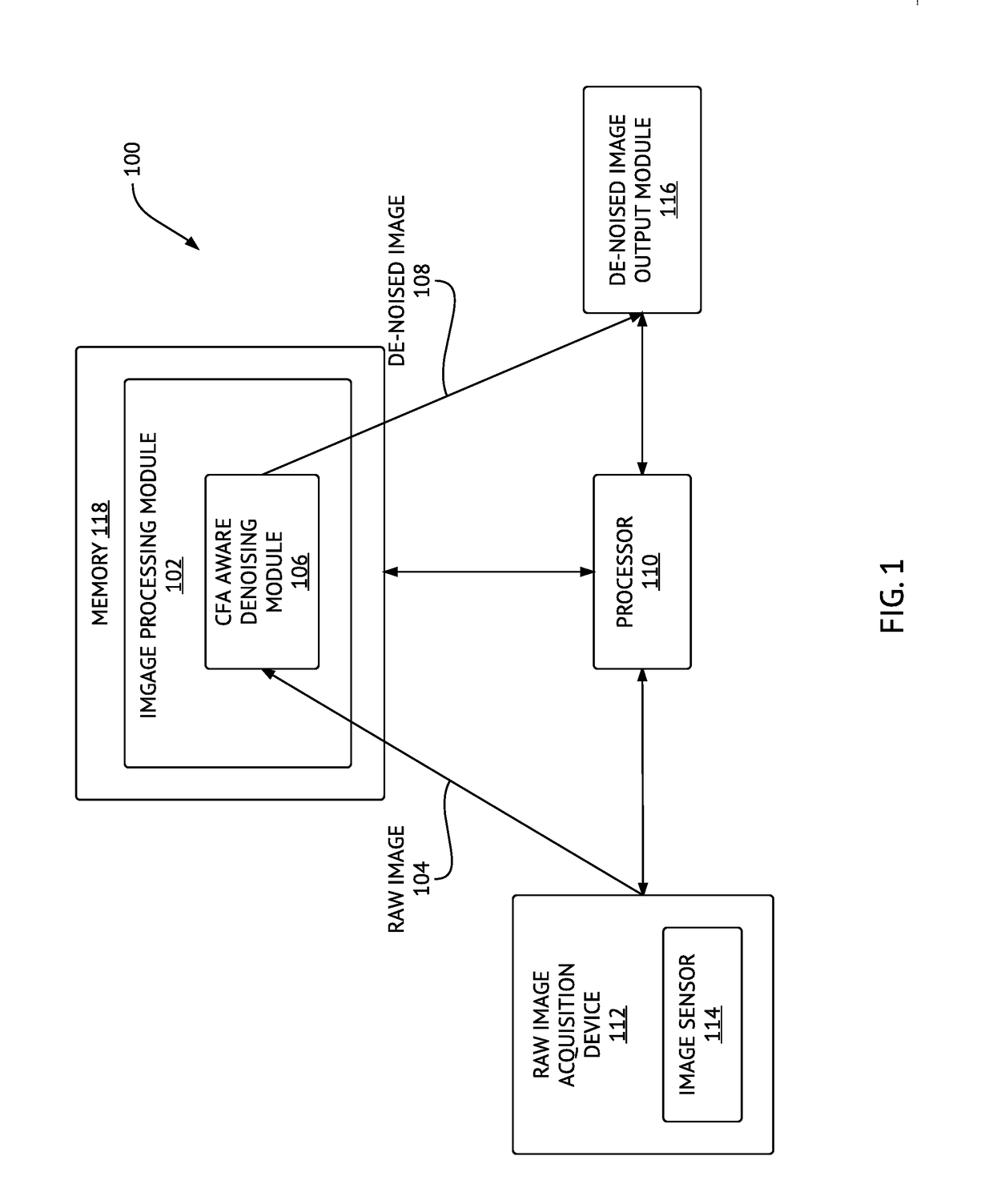
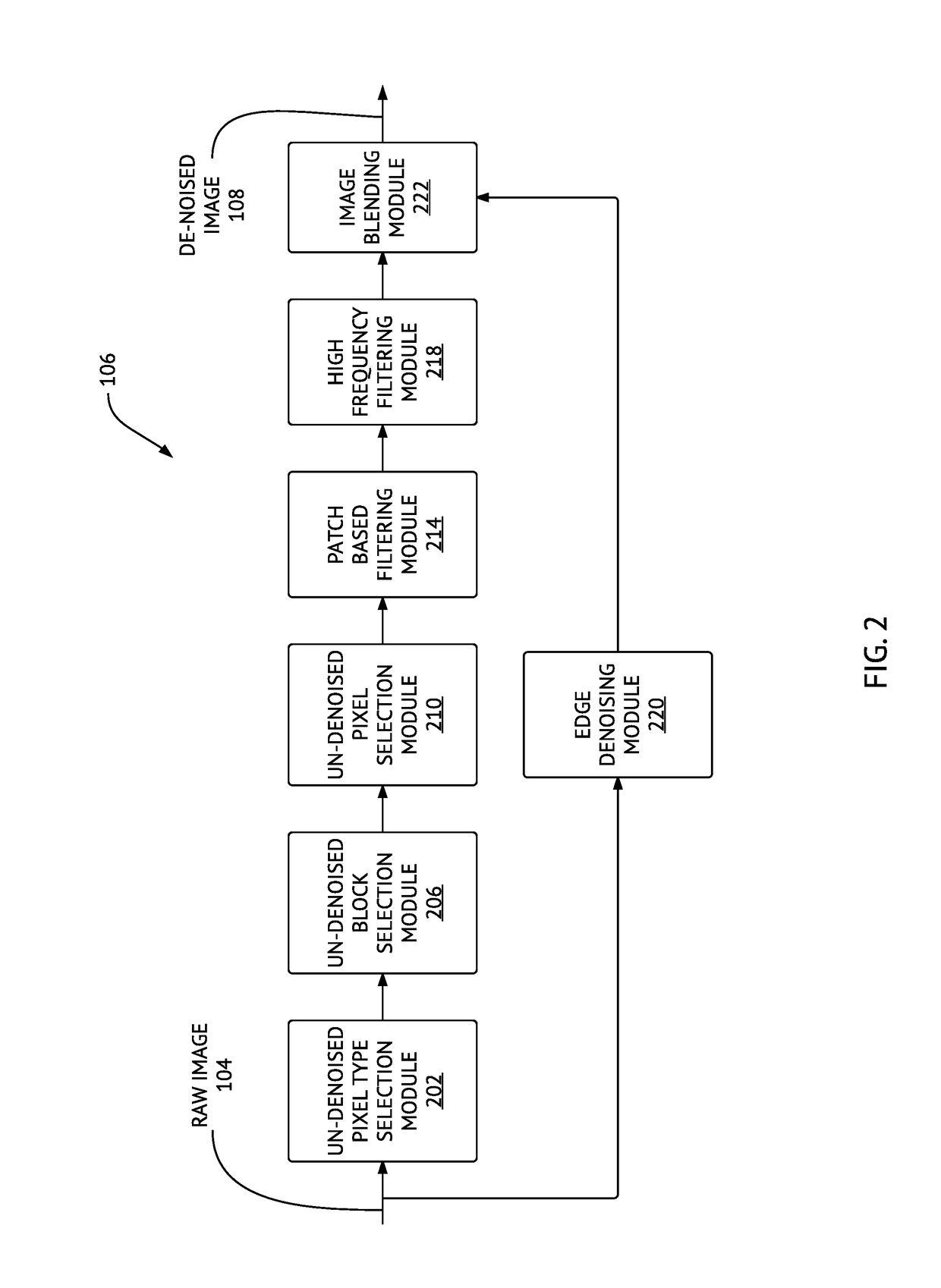
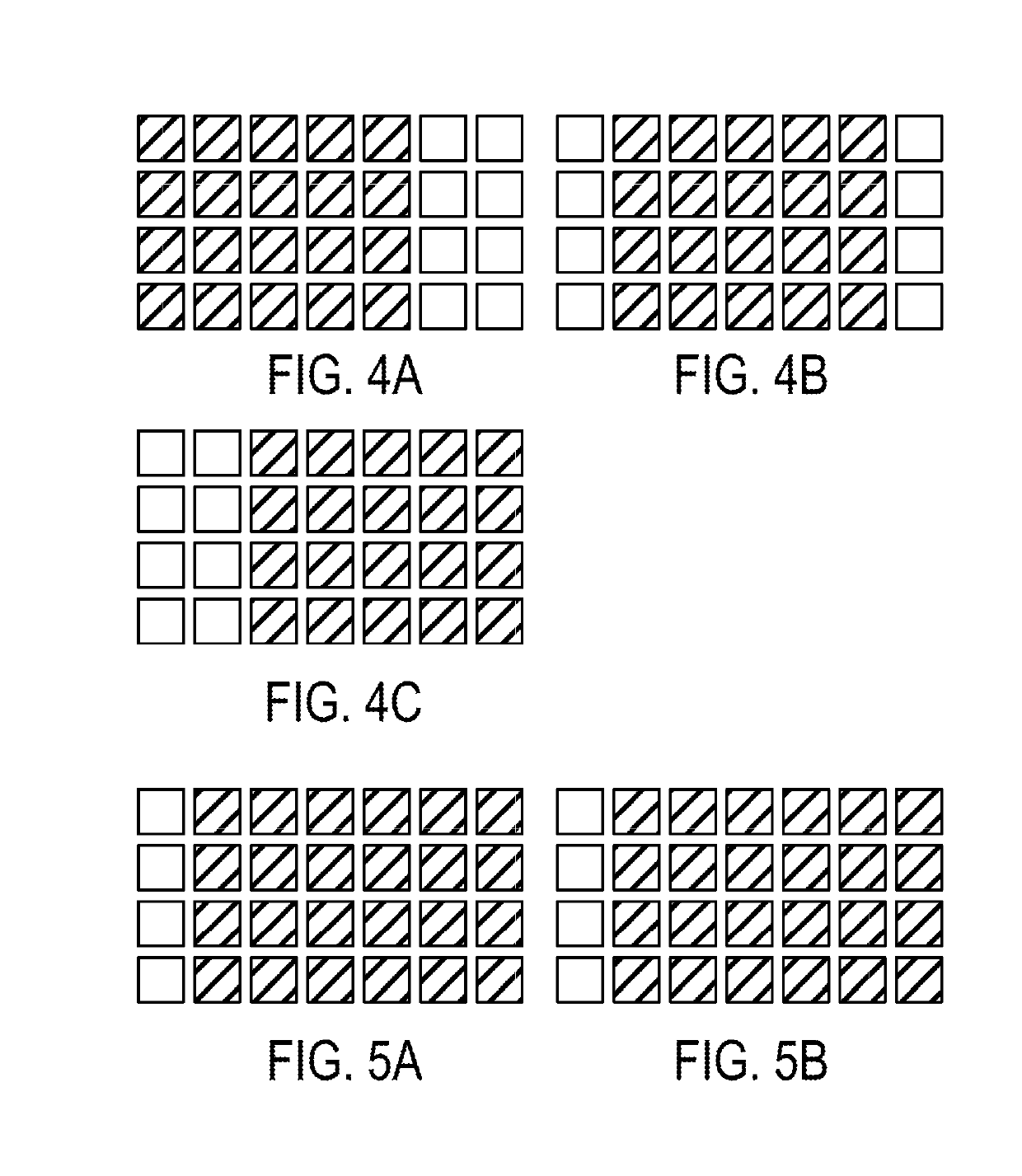
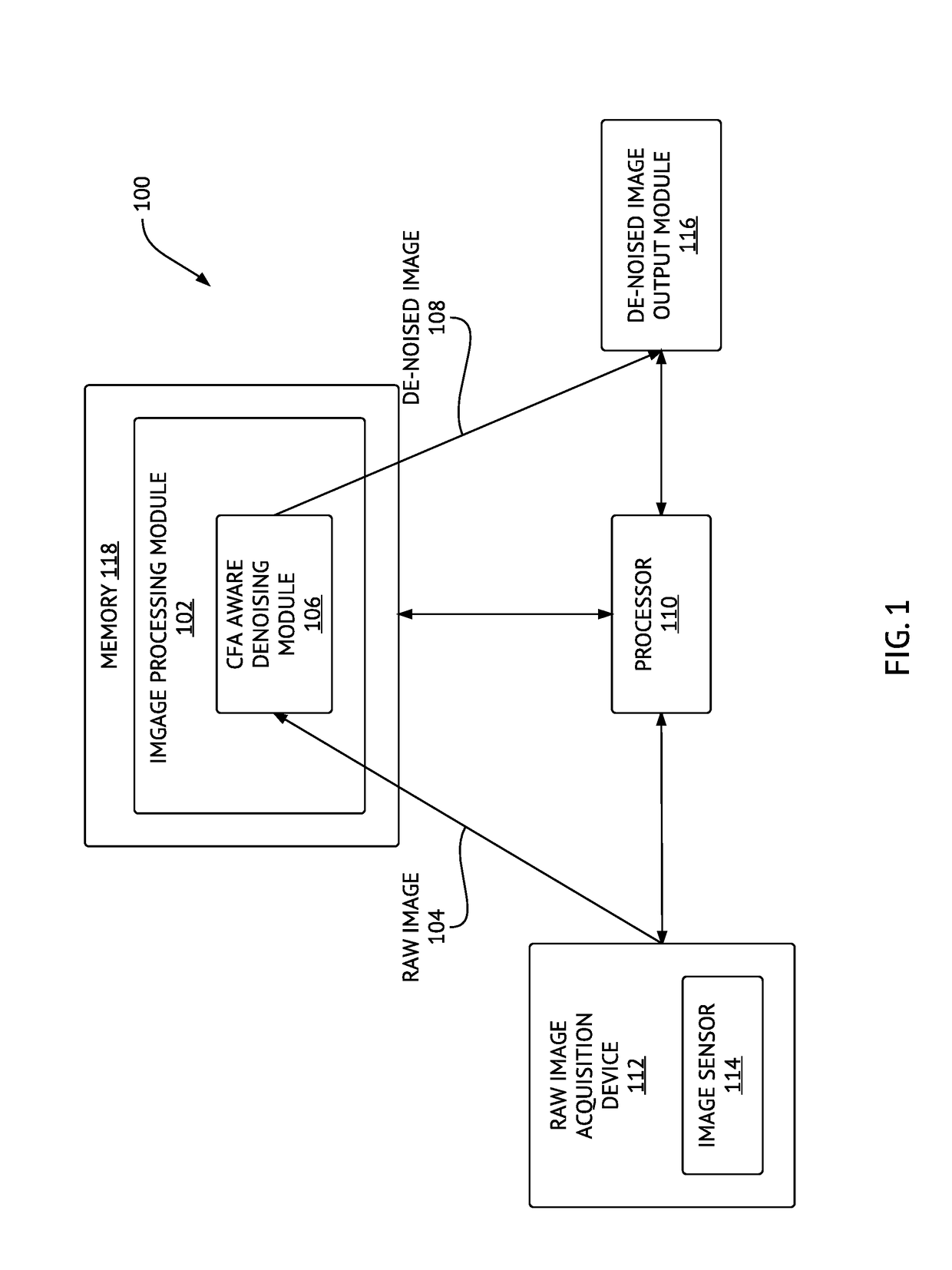
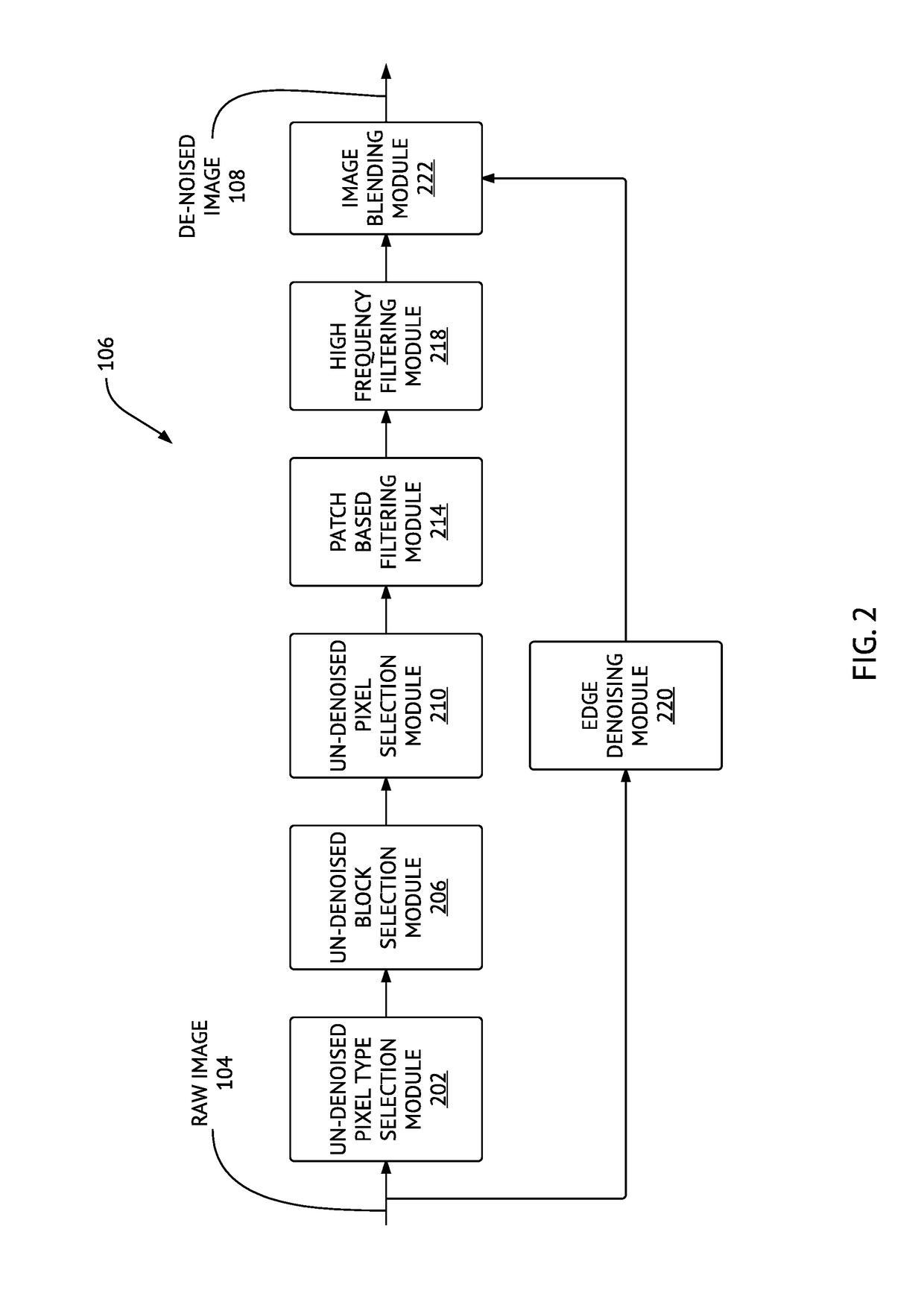
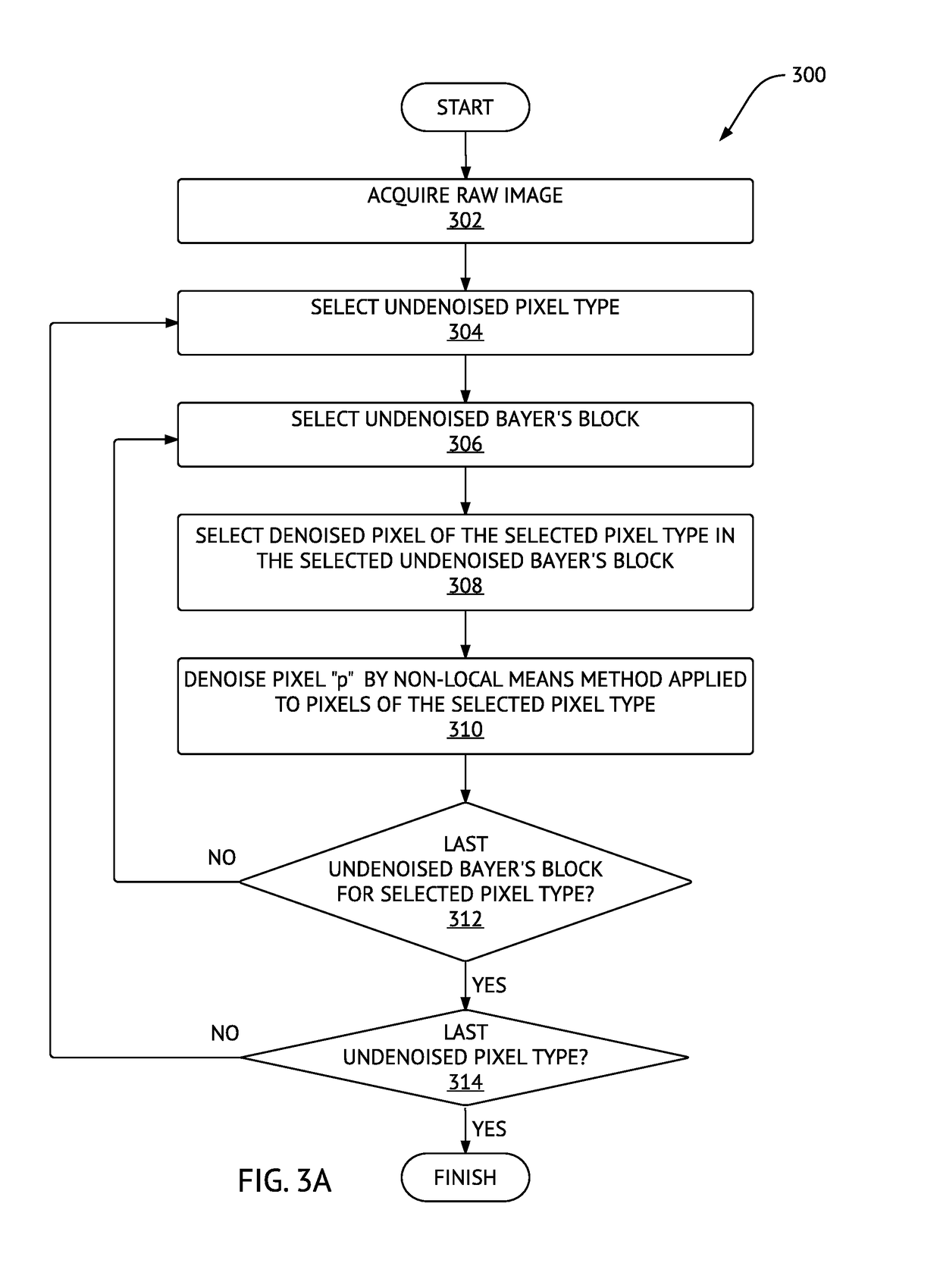
Method and system for denoising and demosaicing artifact suppression in digital images
ActiveUS20170278224A1Mitigate and avoid disadvantageAvoid leastImage enhancementImage analysisArtifact suppressionNoise reduction
Methods and systems for denoising a digital image are provided. The method includes determining first and second plurality of pixel patches including respective first (p) and second (q) pixels, determining a patch distance between each pair of corresponding pixel patches in the first plurality and the second plurality of pixel patches, determining an effective distance between the first pixel (p) and the second pixel (q), repeating the above steps for the same first pixel (p) and another second pixel (q) until a predetermined number of pixels (q) in the raw digital image is processed, and then denoising the first pixel (p), including determining respective contributions of the pixels (q) into a noise reduction of the pixel (p), using respective effective distances of the pixels (q). A corresponding system is also provided. Embodiments of the invention provide computational advantages for denoising digital images.
Owner:ALGOLUX INC
Structured illumination microscopy optical arrangement including projection artifact supression element
ActiveUS20150136949A1Well formedReduce variationSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSpatial light modulatorHarmonic
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
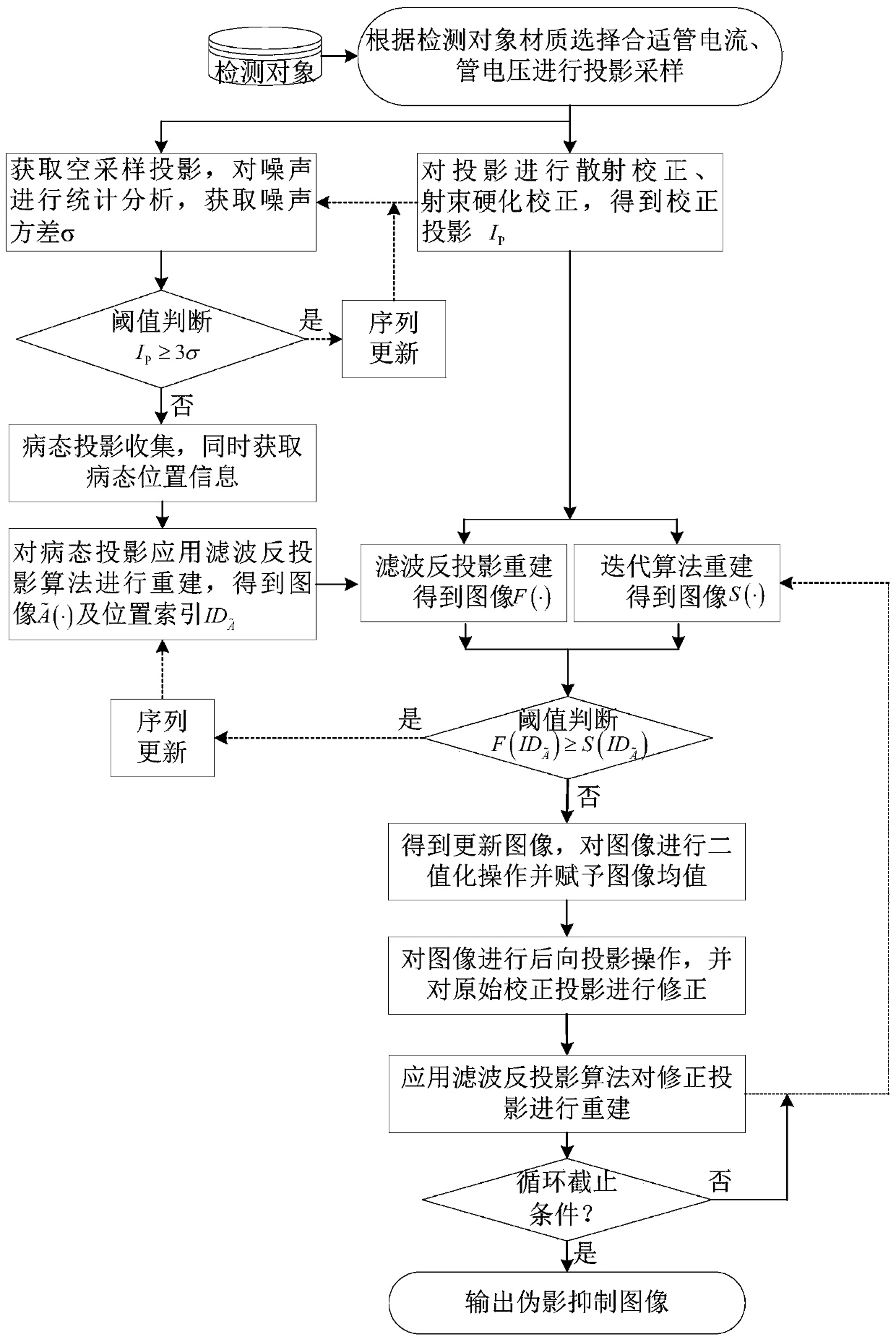
A cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact inhibition method
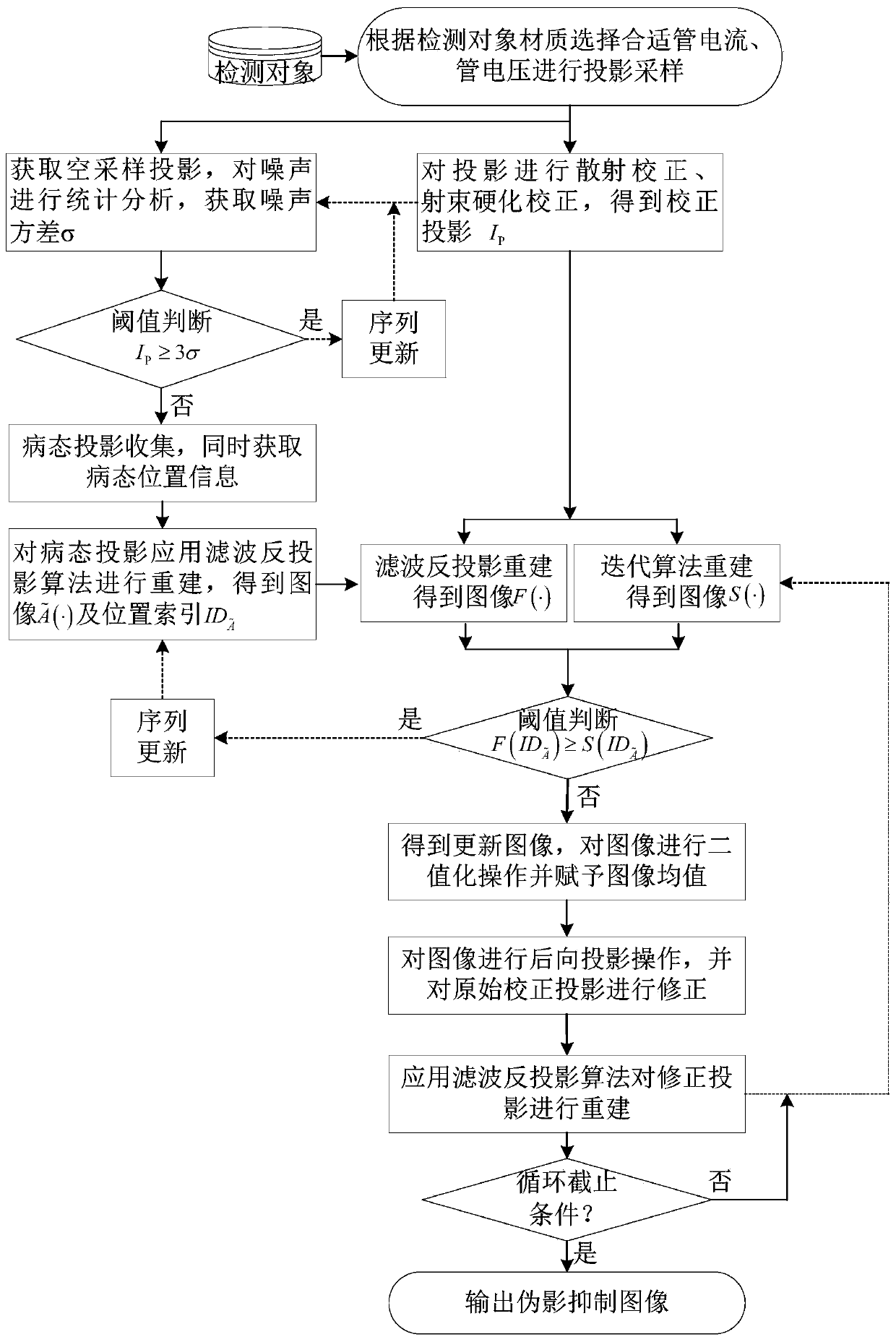
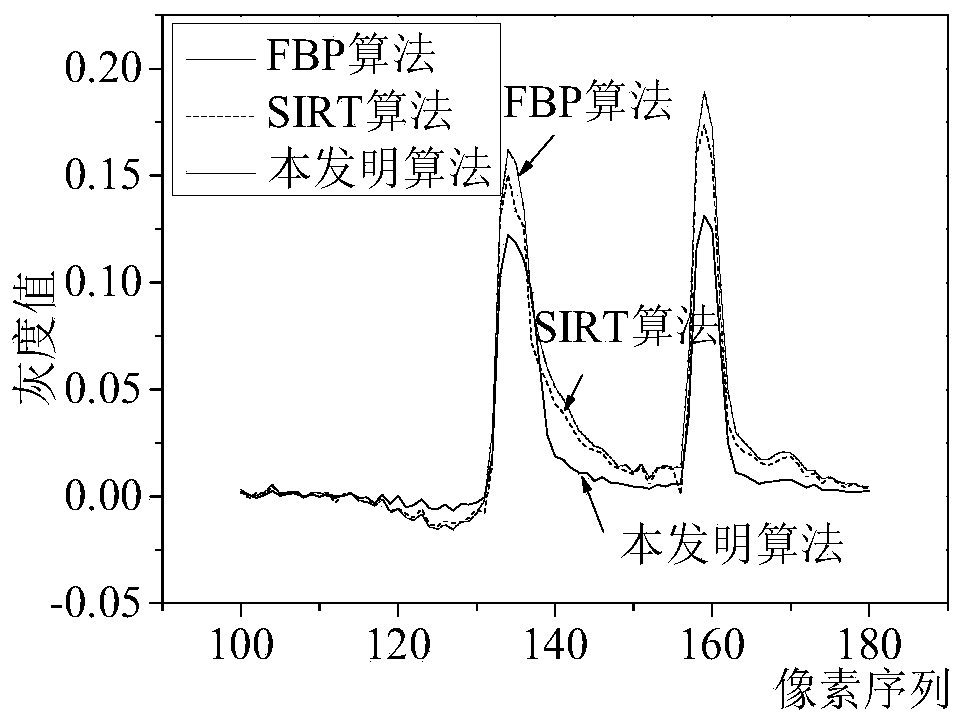
ActiveCN109920020AReduce distractionsReduce the impactImage enhancementImage analysisArtifact suppressionBack projection
The invention discloses a cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact inhibition method. By utilizing the accuracy of a filtering back projection algorithm and the noise suppressionadvantage of an iterative algorithm, reconstruction image fusion of an analytical algorithm and an iterative algorithm and an iterative updating method, ill-conditioned projection reconstruction artifact suppression is realized, the signal-to-noise ratio of the image is improved, and artifact interference caused by ill-conditioned projection reconstruction is prevented. The cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact inhibition method is suitable for the projection reconstruction artifact inhibition under the conditions of normal projection and less ill-condition projection angles, is good in reliability, stability and noise resistance, can reduce the interference and influence of the cone beam CT ill-condition projection reconstruction artifact on the image to a great extent, and obviously improves the quality of the cone beam CT image.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Edge ringing artifact suppression methods and apparatuses
In some embodiments, the present invention relates to methods or suppressing edge ringing in images. For example, in some embodiments a method of processing an image to suppress ringing and broadened edges induced by image correction processing, includes high-pass filtering a first image to obtain a second image, processing said second image including applying non-linear apodization to said second image to obtain a third image, low-pass filtering said first image to obtain a fourth image, and combining the second image and the fourth image to obtain an output image, wherein the output image is characterized by having reduced edge-response sidelobes as compared to the first images. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to devices comprising means and / or modules to suppress edge ringing in images.
Owner:KBR WYLE SERVICES LLC
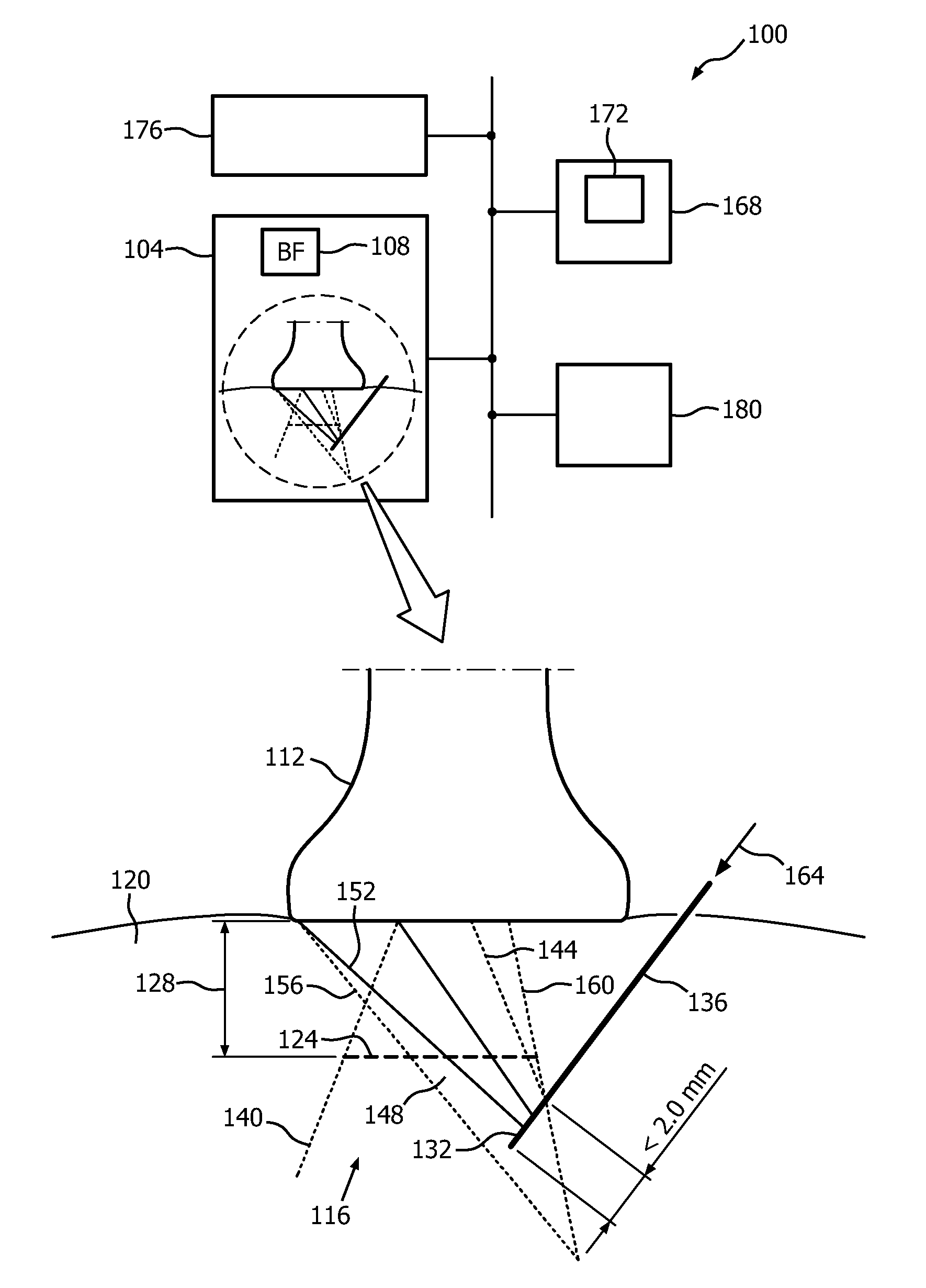
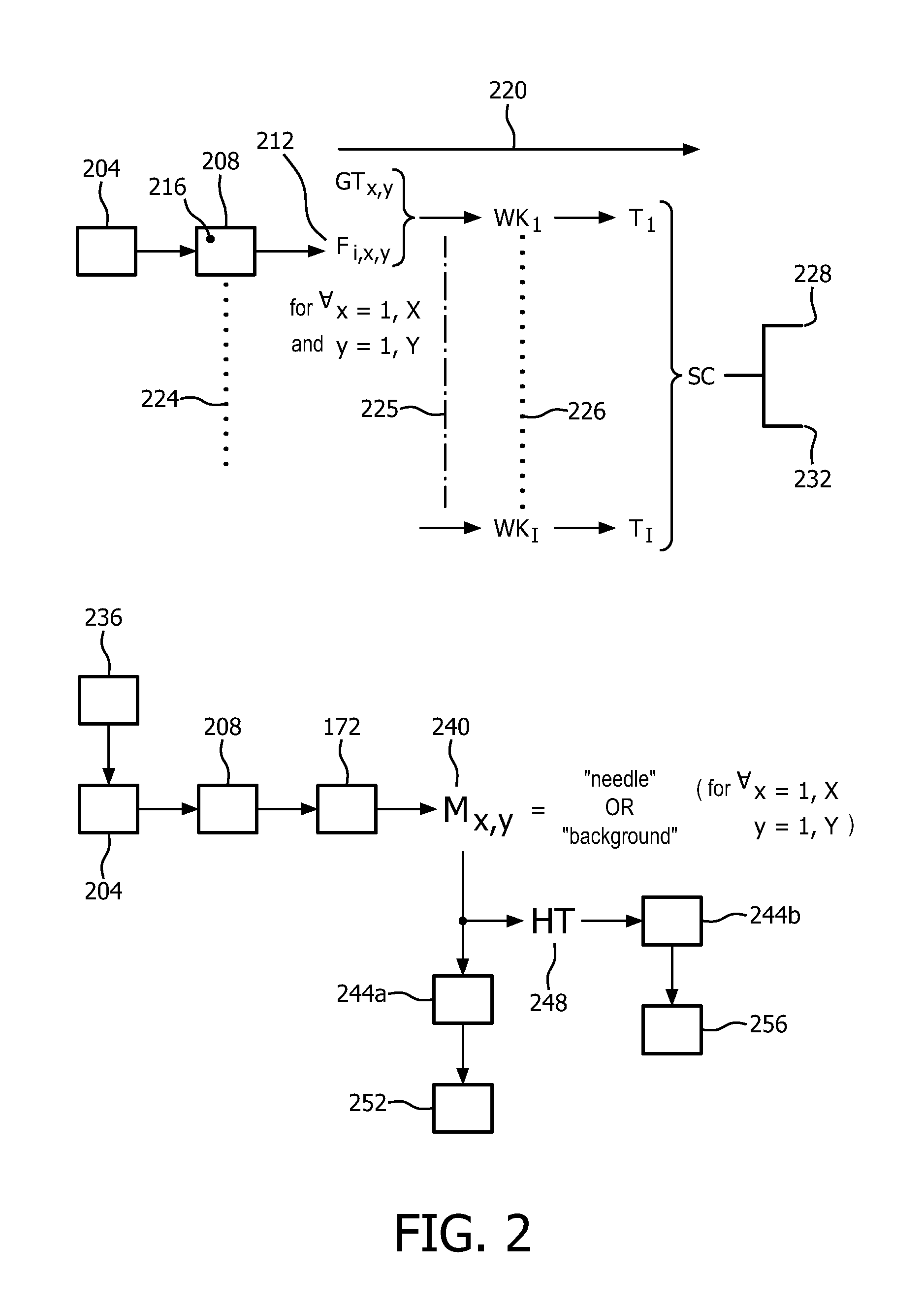
Automatic ultrasound beam steering and needle artifact suppression
InactiveUS20160317118A1Good lookingEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisLearning basedSonification
A classification-based medical image segmentation apparatus includes an ultrasound image acquisition device configured for acquiring, from ultrasound, an image depicting a medical instrument such as needle; and machine-learning-based-classification circuitry configured for using machine-learning-based-classification to, dynamically responsive to the acquiring, segment the instrument by operating on information (212) derived from the image. The segmenting can be accomplished via statistical boosting (220) of parameters of wavelet features. Each pixel (216) of the image is identified as “needle” or “background.” The whole process of acquiring an image, segmenting the needle, and displaying an image with a visually enhanced and artifact-free needle-only overlay may be performed automatically and without the need for user intervention.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
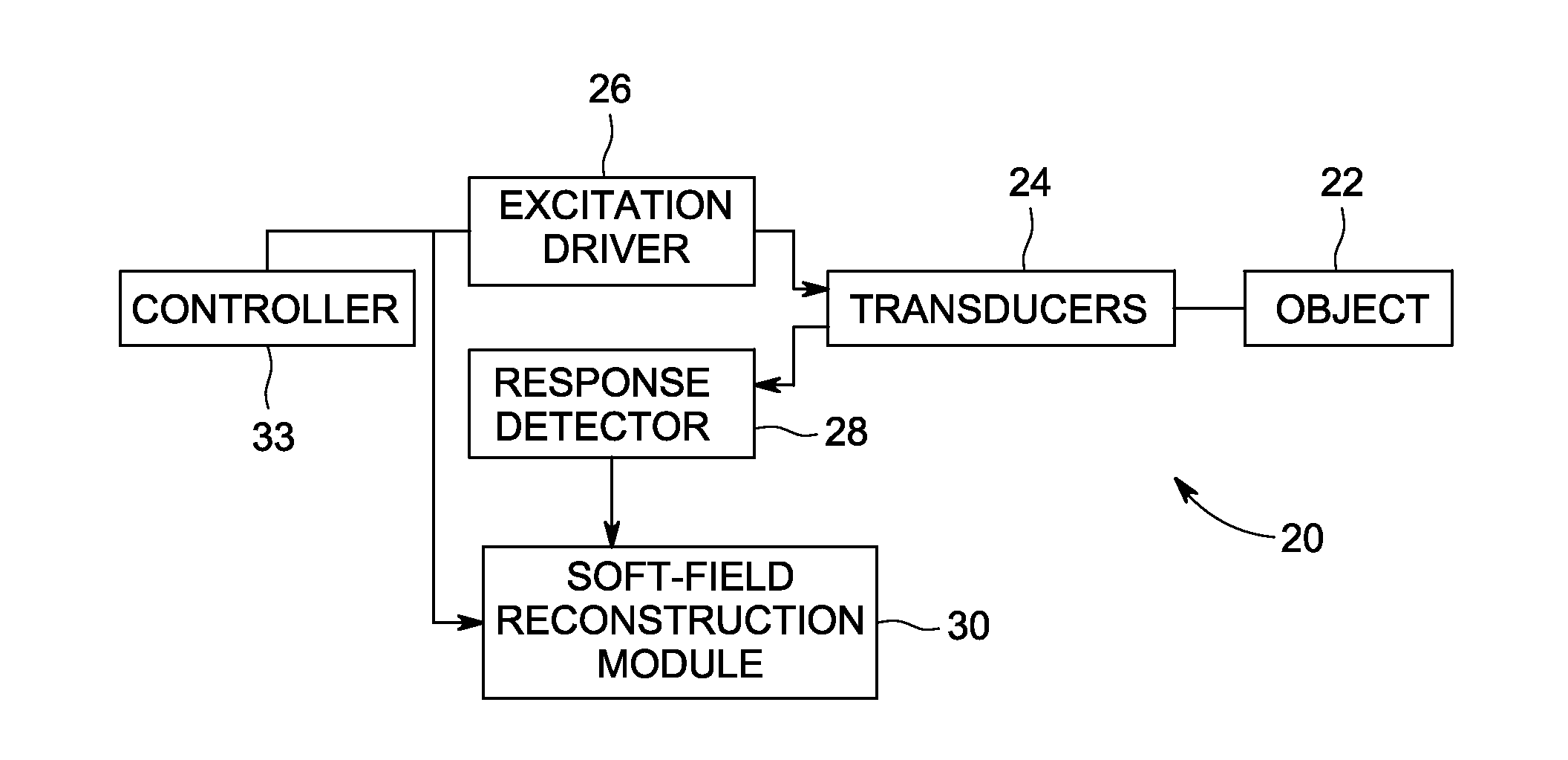
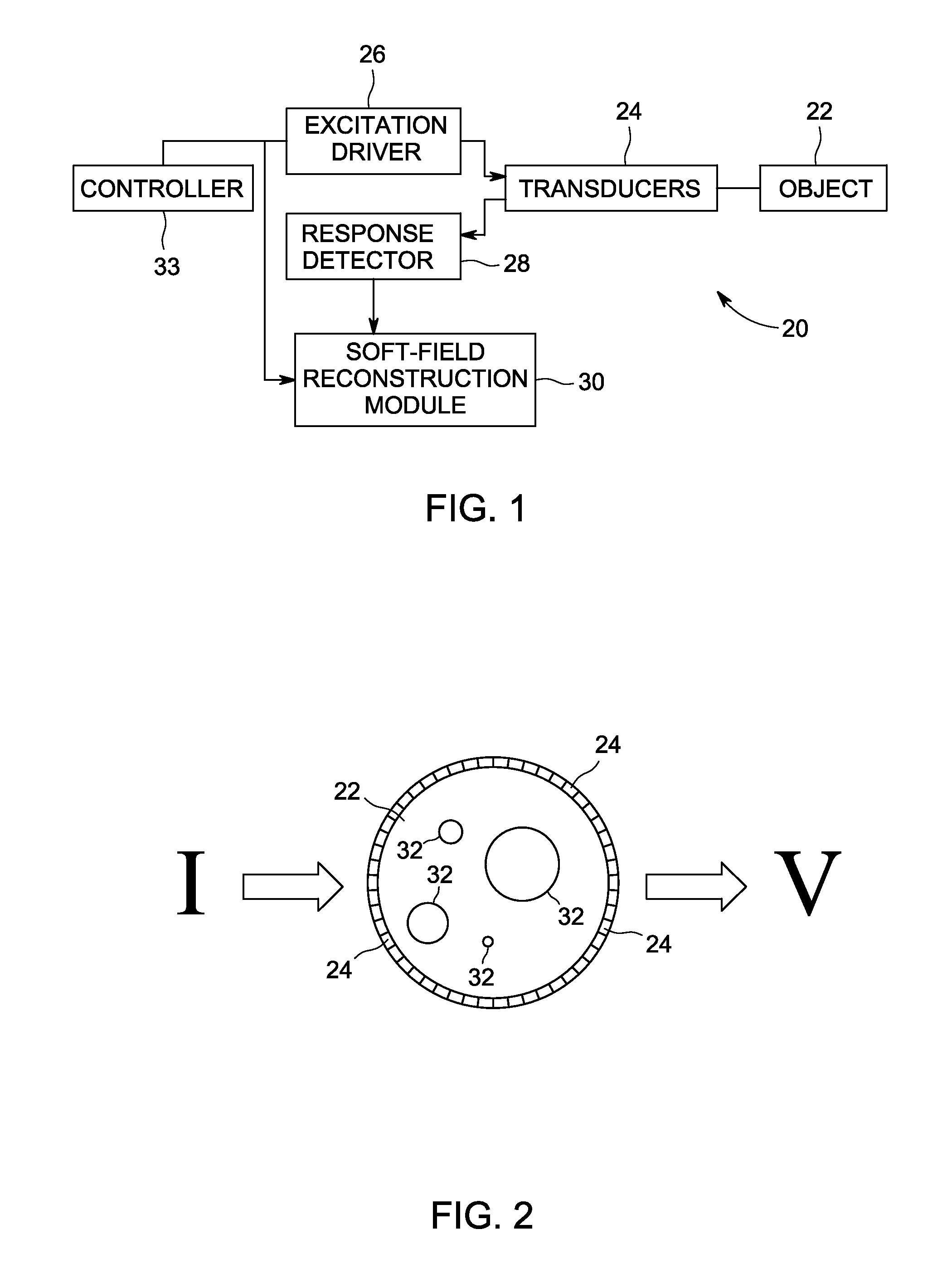
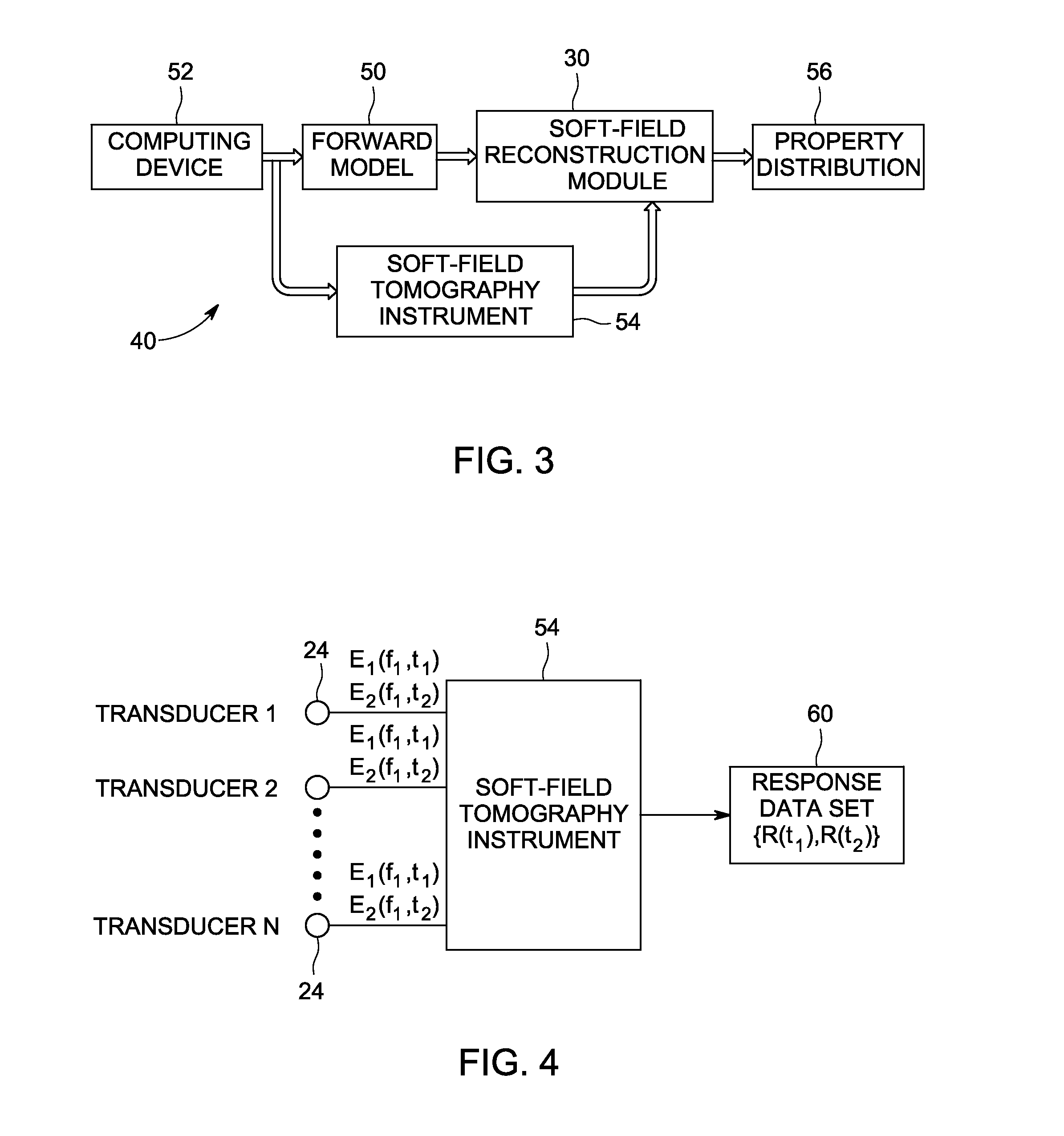
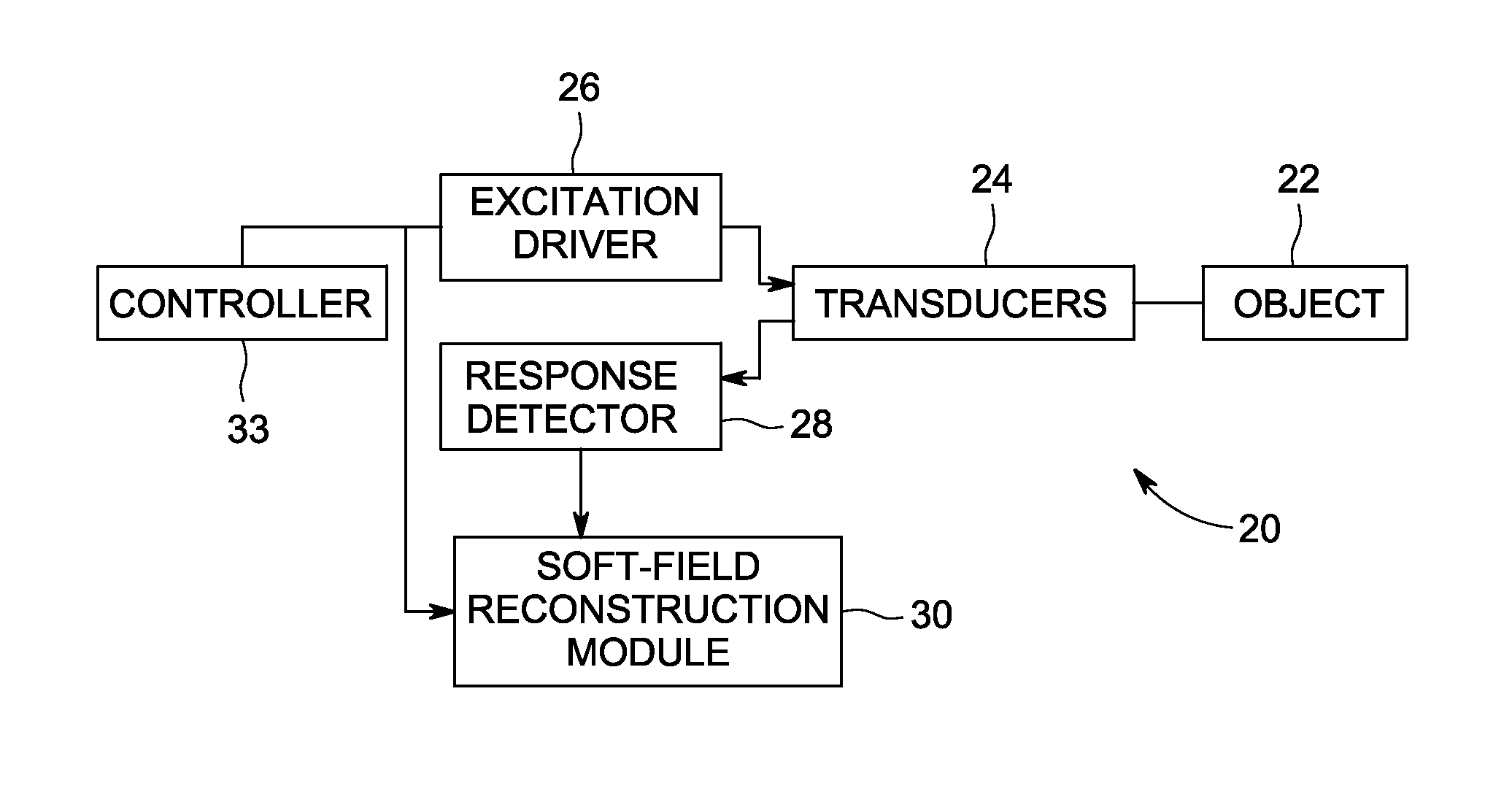
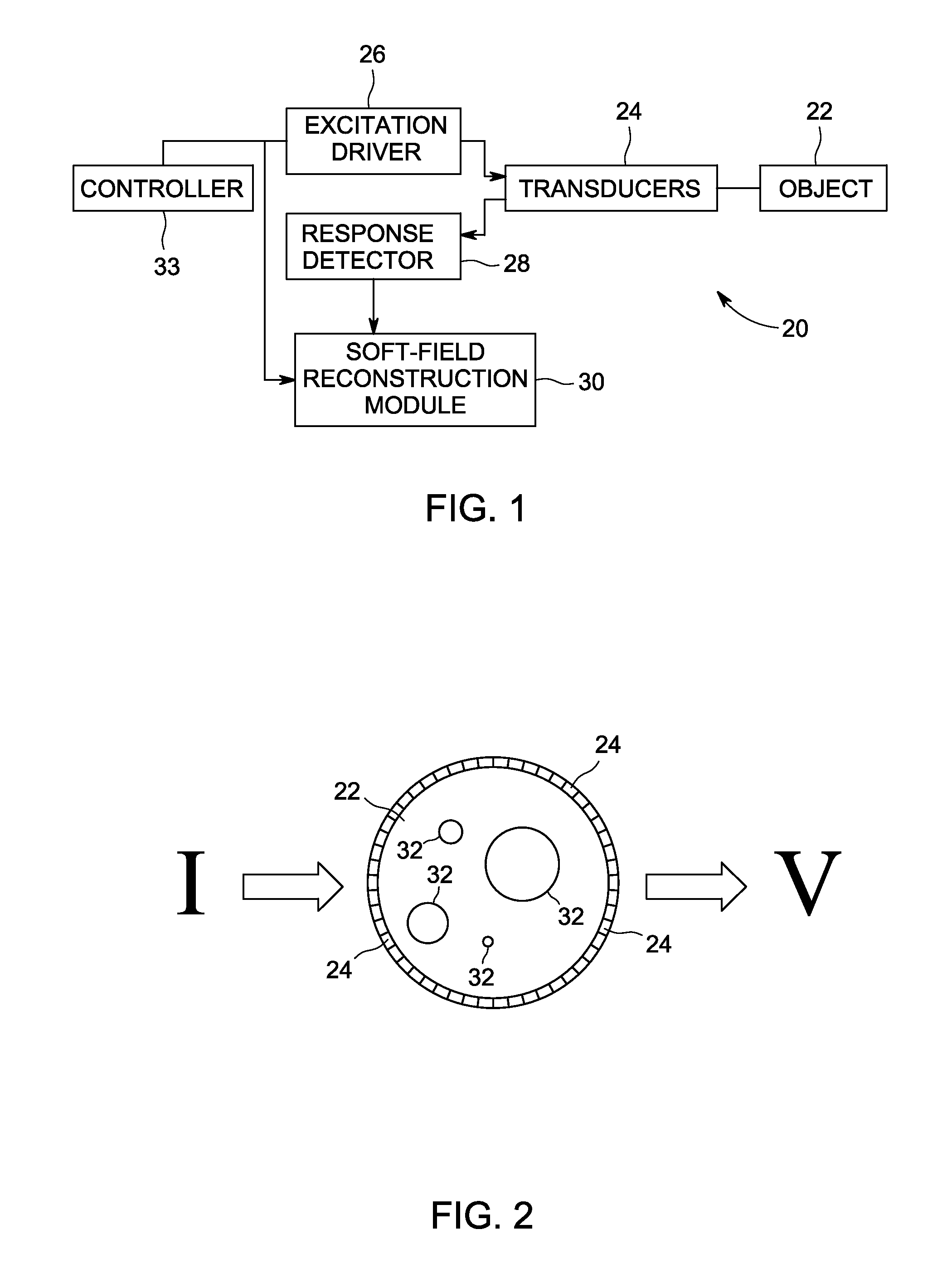
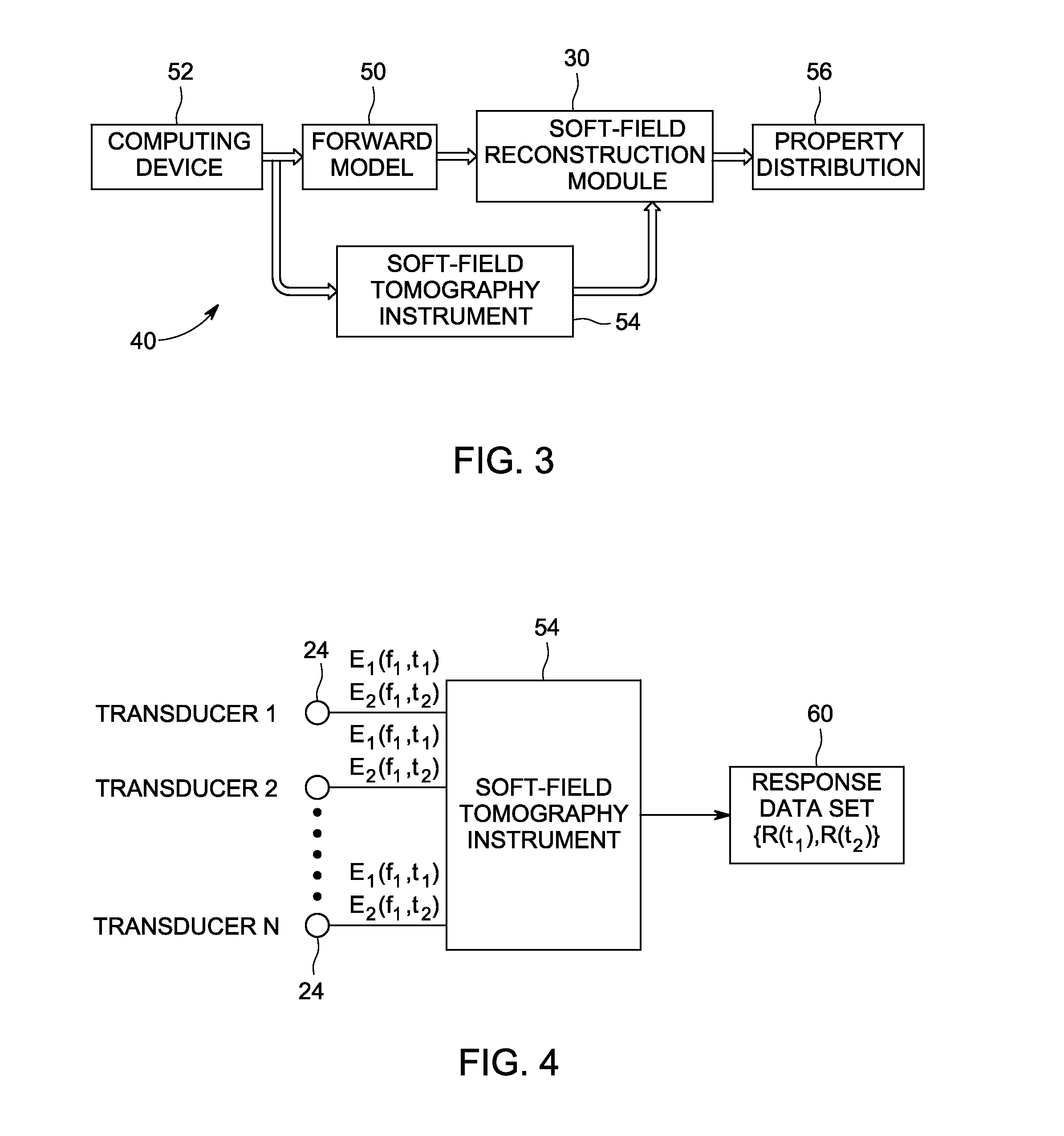
System and method for artifact suppression in soft-field tomography
ActiveUS20120161782A1Suppress and more artifactRadiation pyrometryCurrent/voltage measurementExcitation patternArtifact suppression
A system and method for artifact suppression in soft-field tomography are provided. One method includes obtaining an excitation pattern and applying the excitation pattern to an object, wherein the excitation pattern includes a plurality of frequency components. The method also includes measuring a response at one or more of a plurality of transducers coupled to the object and separating the responses among the plurality of frequency components to suppress one or more artifacts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
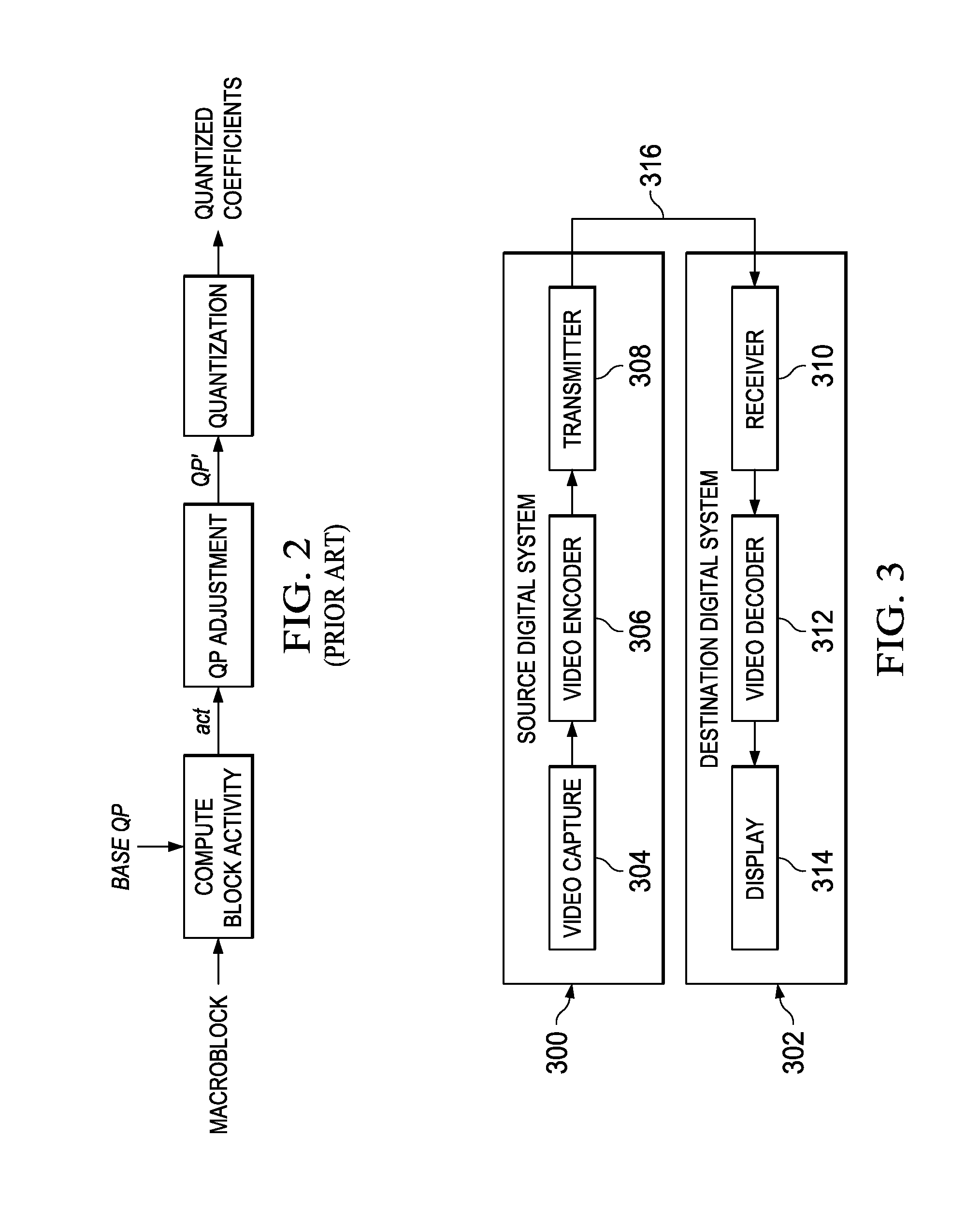
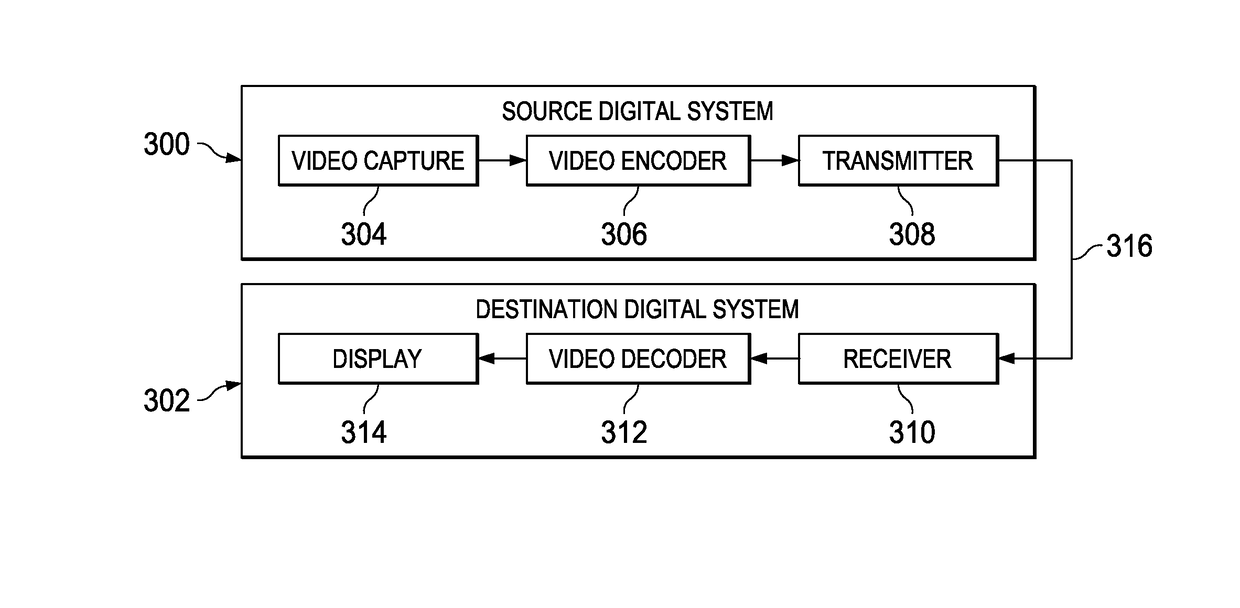
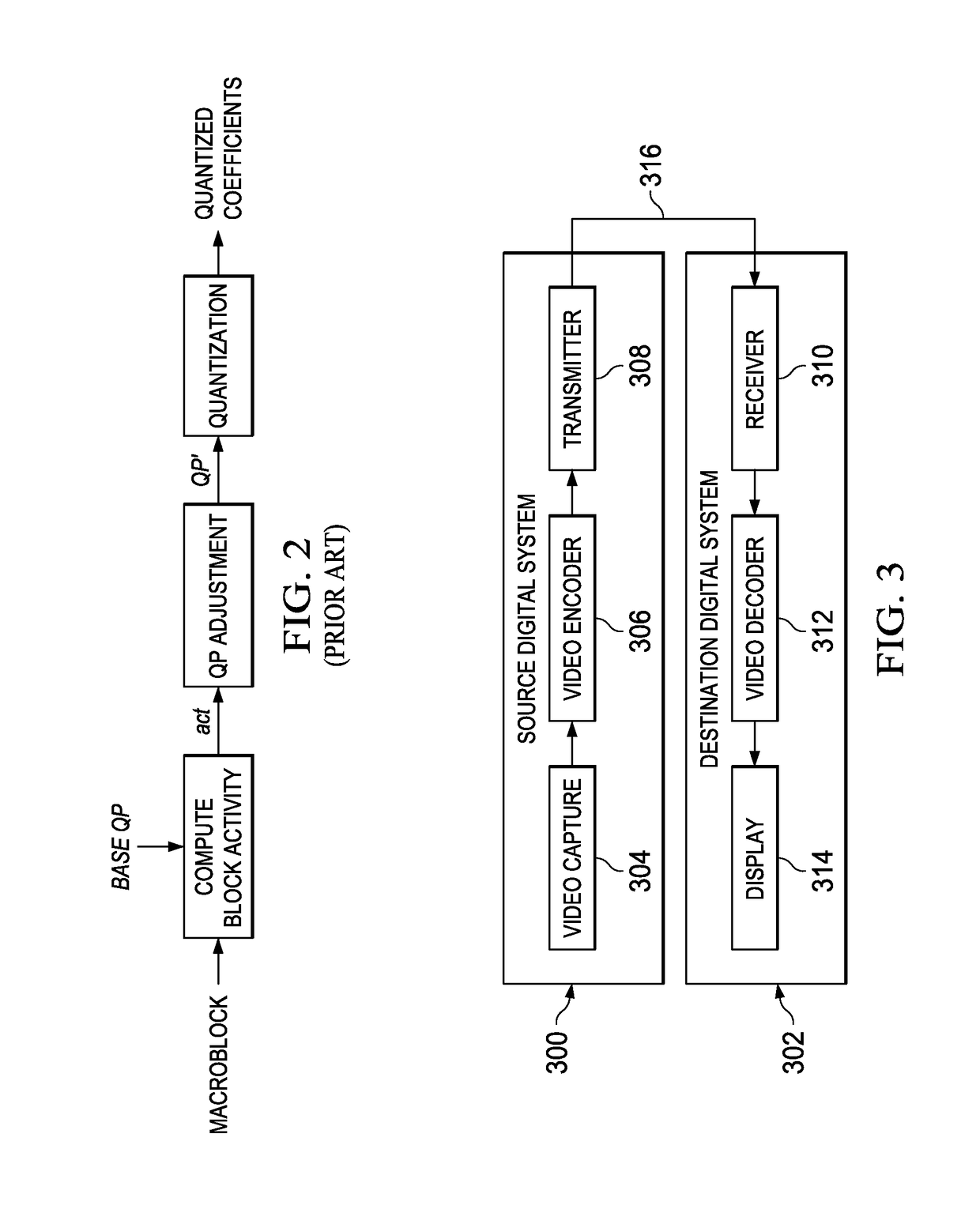
Block Artifact Suppression in Video Coding
ActiveUS20130287099A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionArtifact suppression
A method for encoding a video sequence in a video encoder is provided that includes adapting a quantization parameter of a block of pixels in a picture of the video sequence based on a transform block size of the block of pixels to determine a final quantization parameter, and quantizing transform coefficients of the block of pixels using the final quantization parameter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for artifact suppression in soft-field tomography
ActiveUS8593154B2Radiation pyrometryCurrent/voltage measurementExcitation patternArtifact suppression
A system and method for artifact suppression in soft-field tomography are provided. One method includes obtaining an excitation pattern and applying the excitation pattern to an object, wherein the excitation pattern includes a plurality of frequency components. The method also includes measuring a response at one or more of a plurality of transducers coupled to the object and separating the responses among the plurality of frequency components to suppress one or more artifacts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
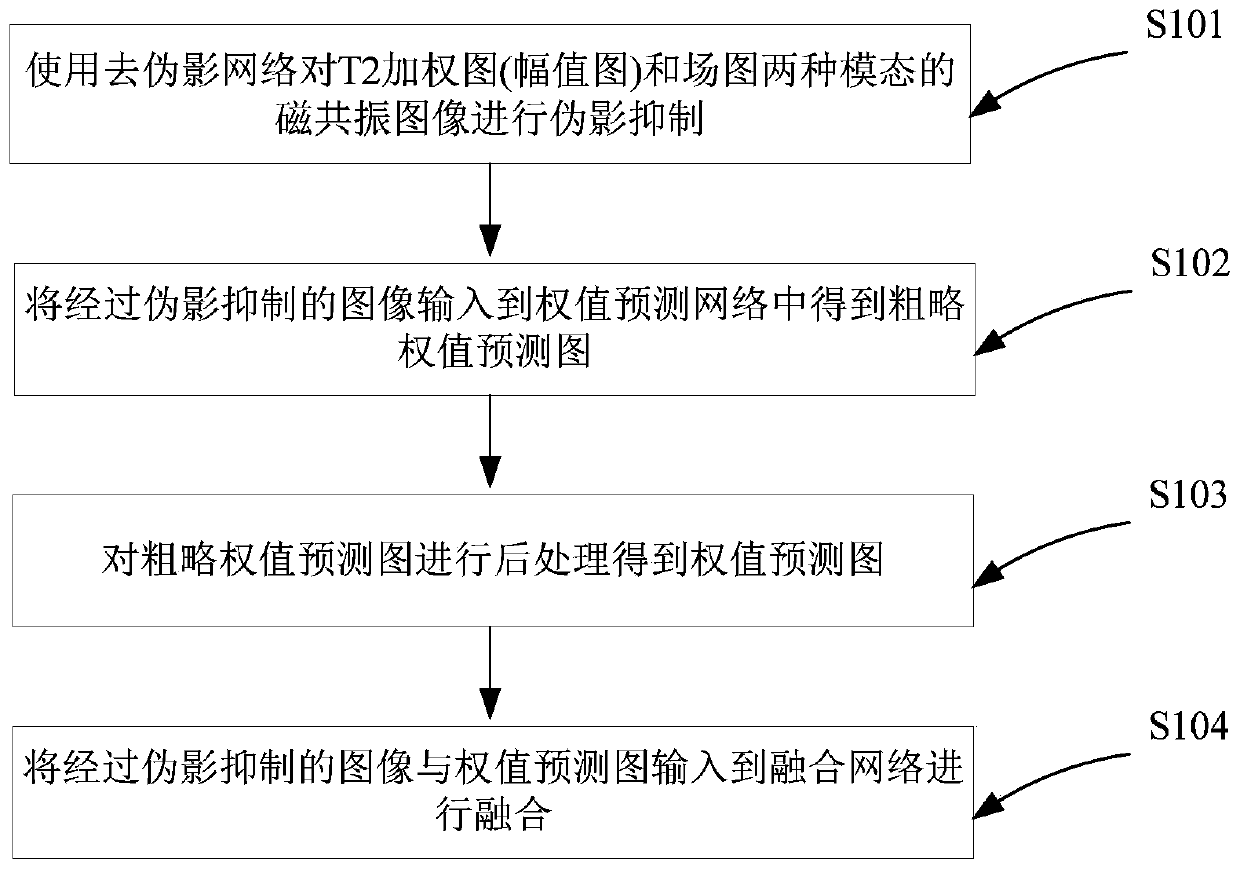
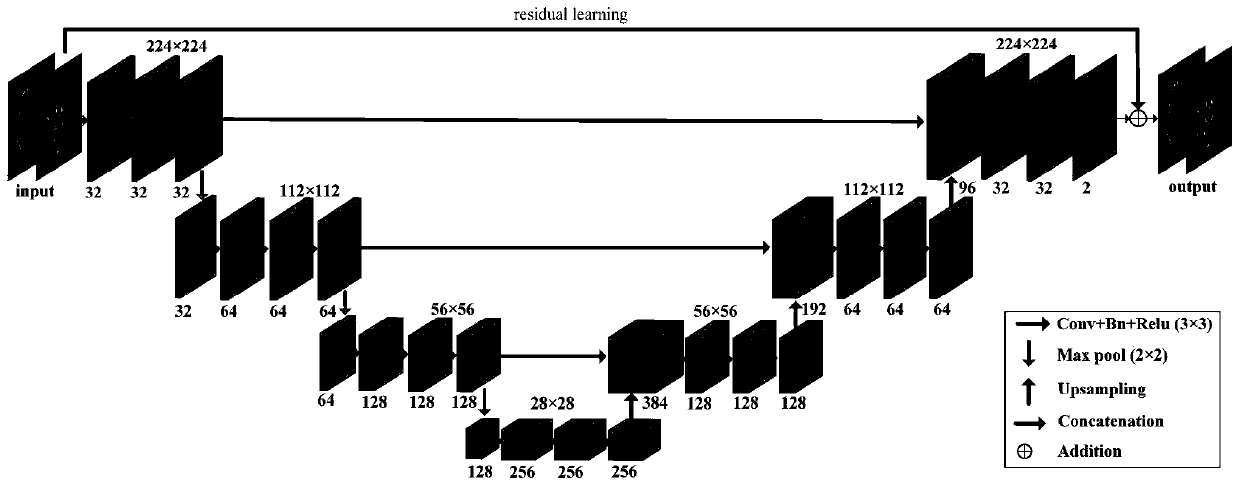
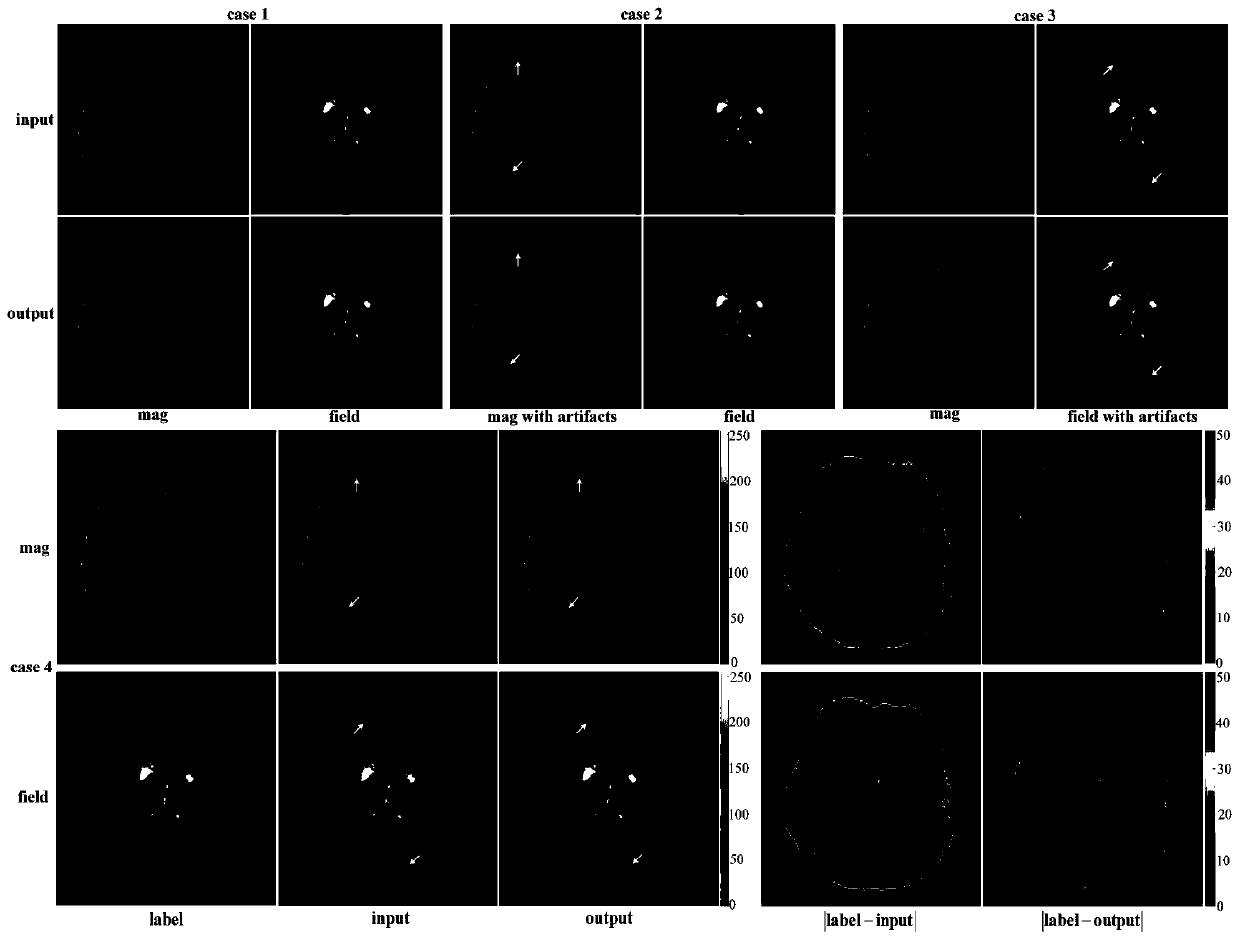
Magnetic resonance image fusion method based on weight prediction network
InactiveCN110276736ASmooth transition partImprove visual effectsImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionResonance
The invention provides a magnetic resonance image fusion method based on a weight prediction network. The magnetic resonance image fusion method comprises the steps: firstly designing an artifact removal network, and carrying out artifact recognition and suppression on an input multi-mode image; secondly, constructing a weight prediction network, generating fusion weight prediction graphs of images with different contrast ratios, and endowing regions with rich details with higher weights; and finally, establishing a fusion network, and inputting the image subjected to the artifact suppression and the corresponding weight prediction image to obtain a composite image with the advantage of each modal contrast ratio. According to the magnetic resonance image fusion method, the magnetic resonance image is subjected to artifact preprocessing, so that the image fusion applicability is effectively improved; by integrating the advantages of the images with different contrast ratios, the biological tissue structure can be described more comprehensively and accurately. Compared with a traditional method, complex feature extraction does not need to be designed, the obvious anti-artifact capability is achieved, the fusion effect is good, and medical diagnosis and treatment guided by images are facilitated.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
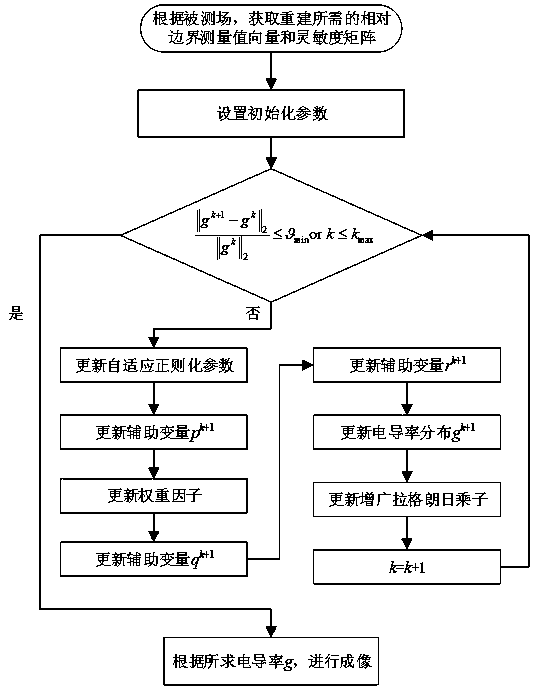
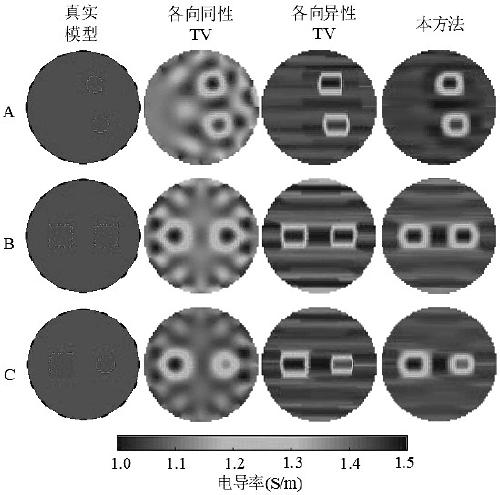
Electrical tomography artifact suppression image reconstruction method
ActiveCN111047663AImprove objectivityImprove simplicityReconstruction from projectionImage generationAlgorithmArtifact suppression
The invention discloses an electrical tomography artifact suppression image reconstruction method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining a relative boundary measurement value vectorbmeas and a sensitivity matrix A required by reconstruction according to a measured field domain; (2) setting initialization parameters; (3) updating an adaptive regularization parameter lambda k; (4)updating the auxiliary variable pk + 1; (5) updating the weight factor omega k; (6) updating the auxiliary variable qk + 1; (7) updating the auxiliary variable rk + 1; (8) updating the conductivity distribution gk + 1; (9) newly adding Gamma < 1 > T, Gamma < 2 > T and Gamma < 3 > T of the Cantonese multiplier; (10) judging whether the iteration meets an iteration termination condition or k is less than or equal to kmax, if so, terminating the iteration, and carrying out the next operation; if not, k is set to be equal to k + 1, the step (3) is executed again, and iterative solution is continued; and (11) imaging according to the gray value obtained by final solution. According to the invention, the step artifact can be effectively reduced, the noise immunity is improved, the algorithm structure is simplified, and the applicability of the algorithm is improved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
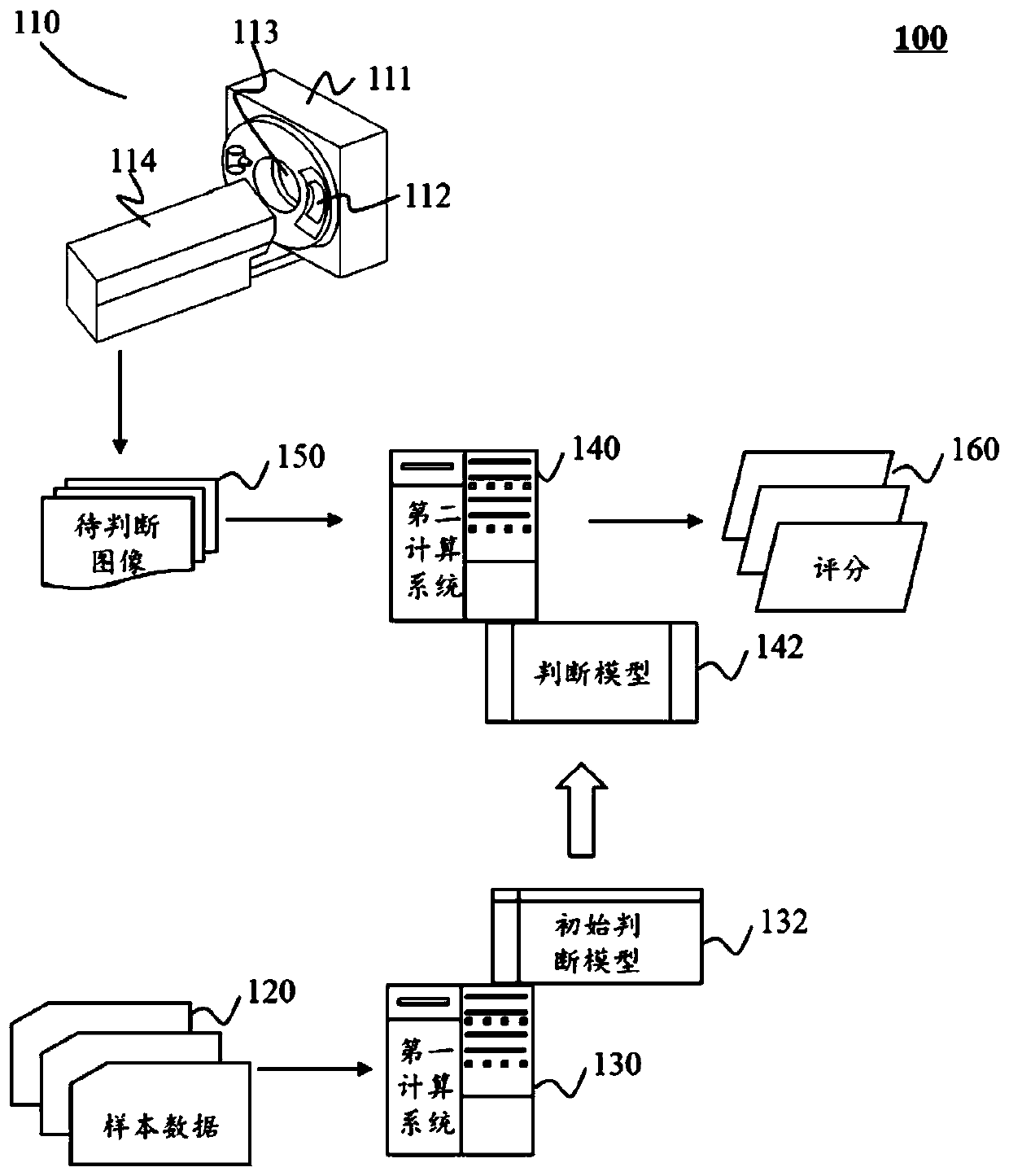
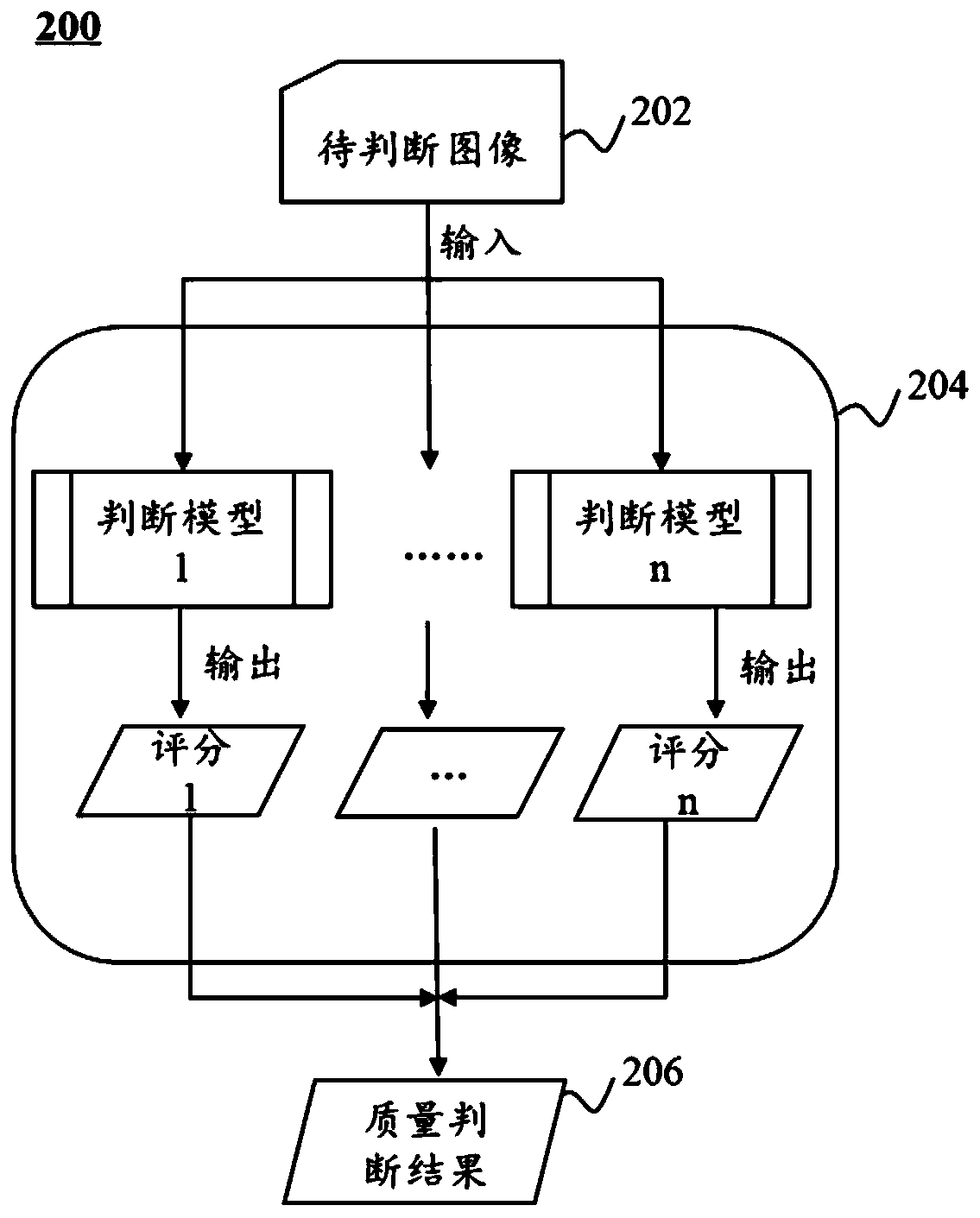
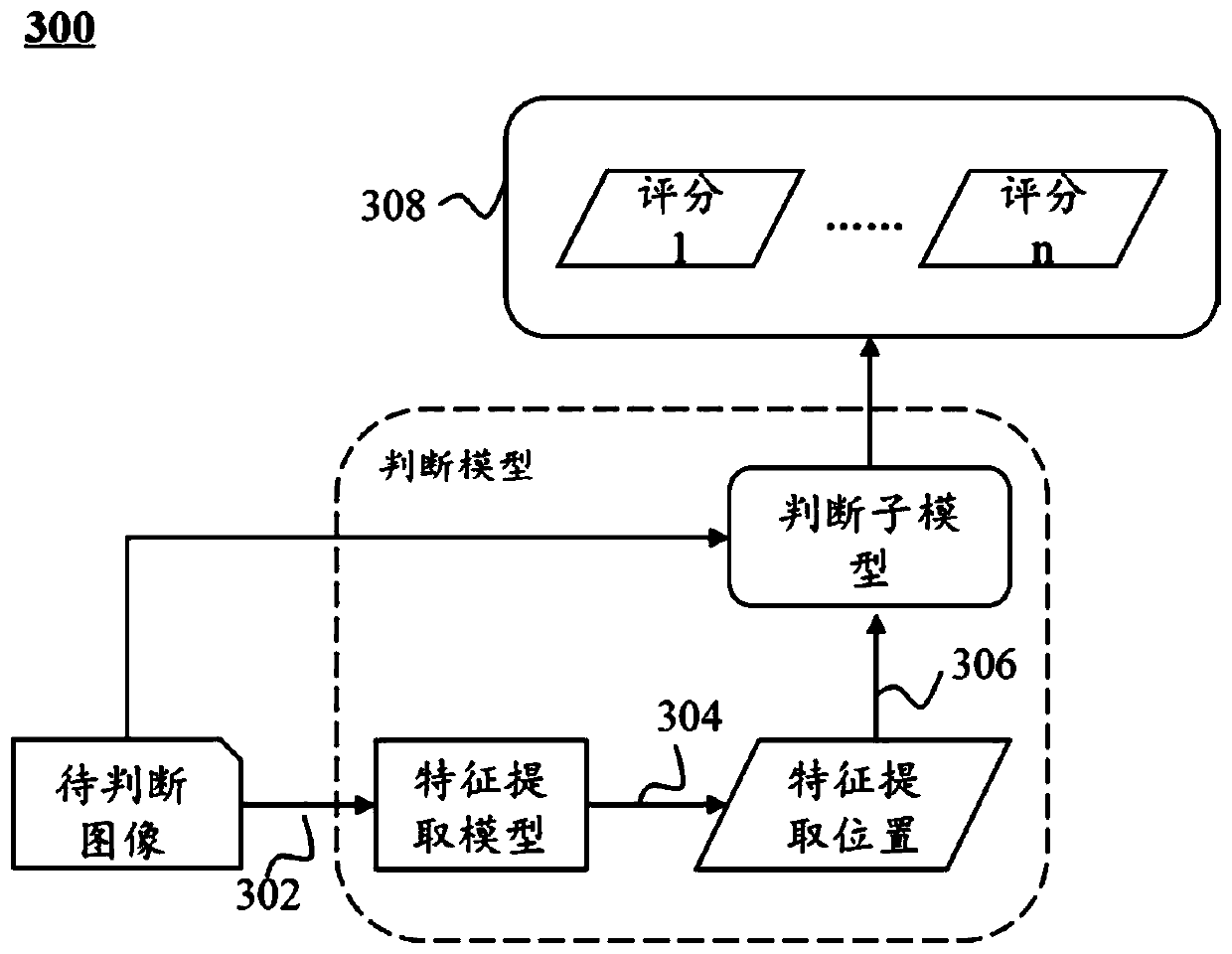
Method and system for judging image quality
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for judging image quality. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-judged image; obtaining scores, related to judgment indexes, of the to-be-judged image based on one or more judgment models, wherein the judgment indexes comprise one or more of anatomical structure definition, target part contrast, image signal uniformity, image noiselevel and artifact suppression degree, the scores related to the judgment indexes are obtained based on the different judgment models respectively; based on the scores related to the judgment indexes,obtaining a quality judgment result of the to-be-judged image. According to the method disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, manual participation of image quality judgment can be reduced, theerror rate of image judgment is effectively reduced, and the efficiency and precision of image quality judgment are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
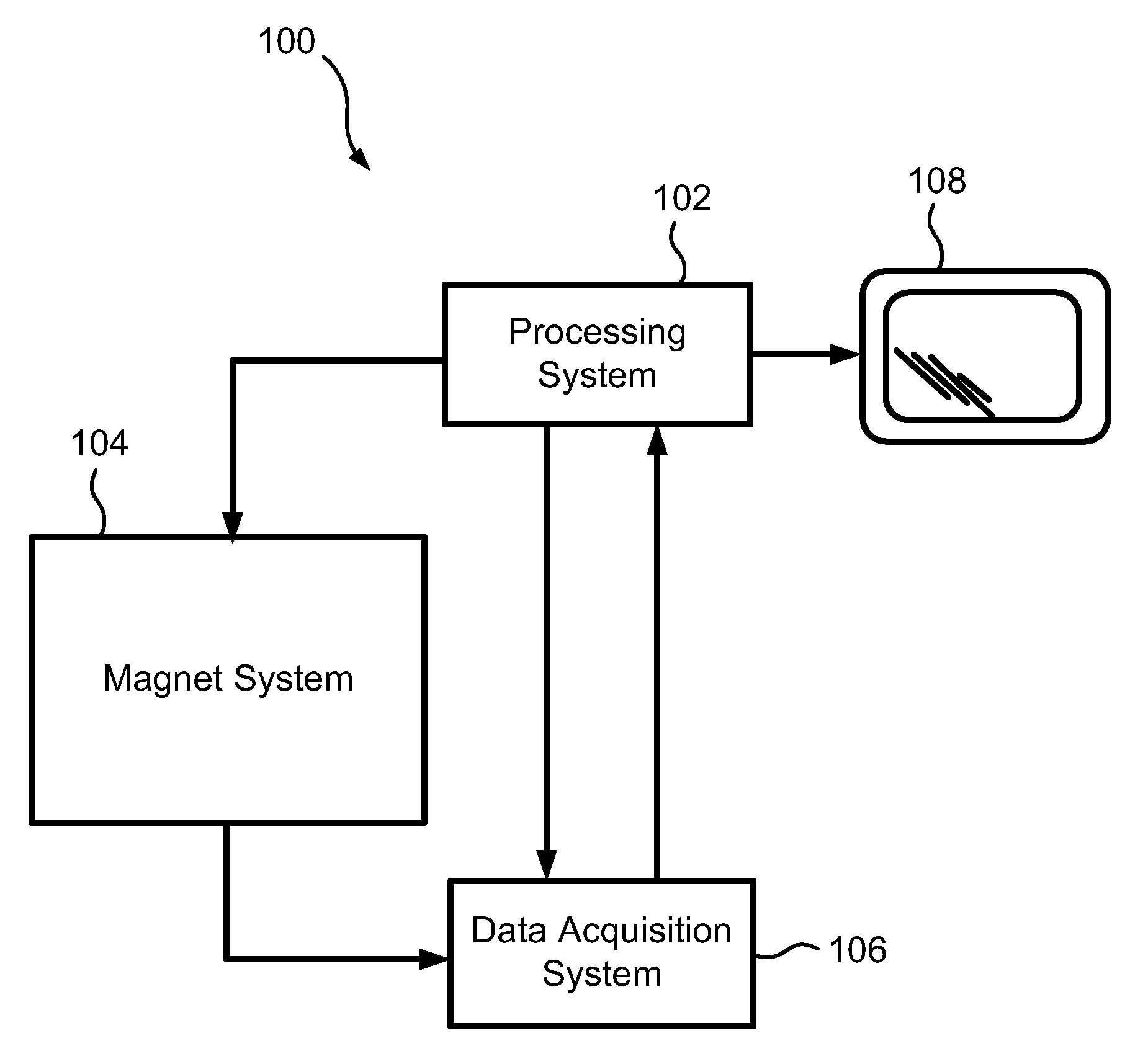
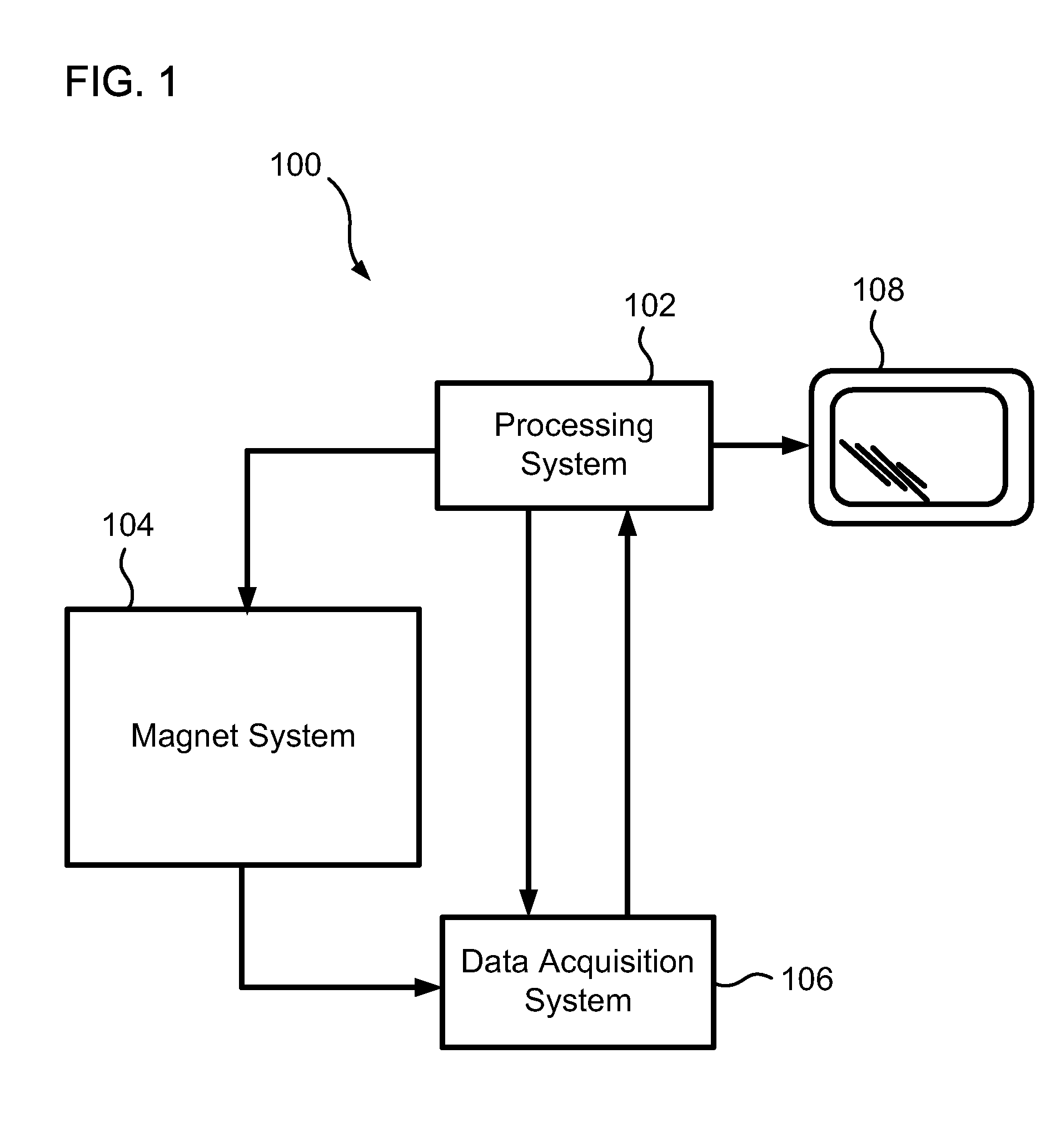
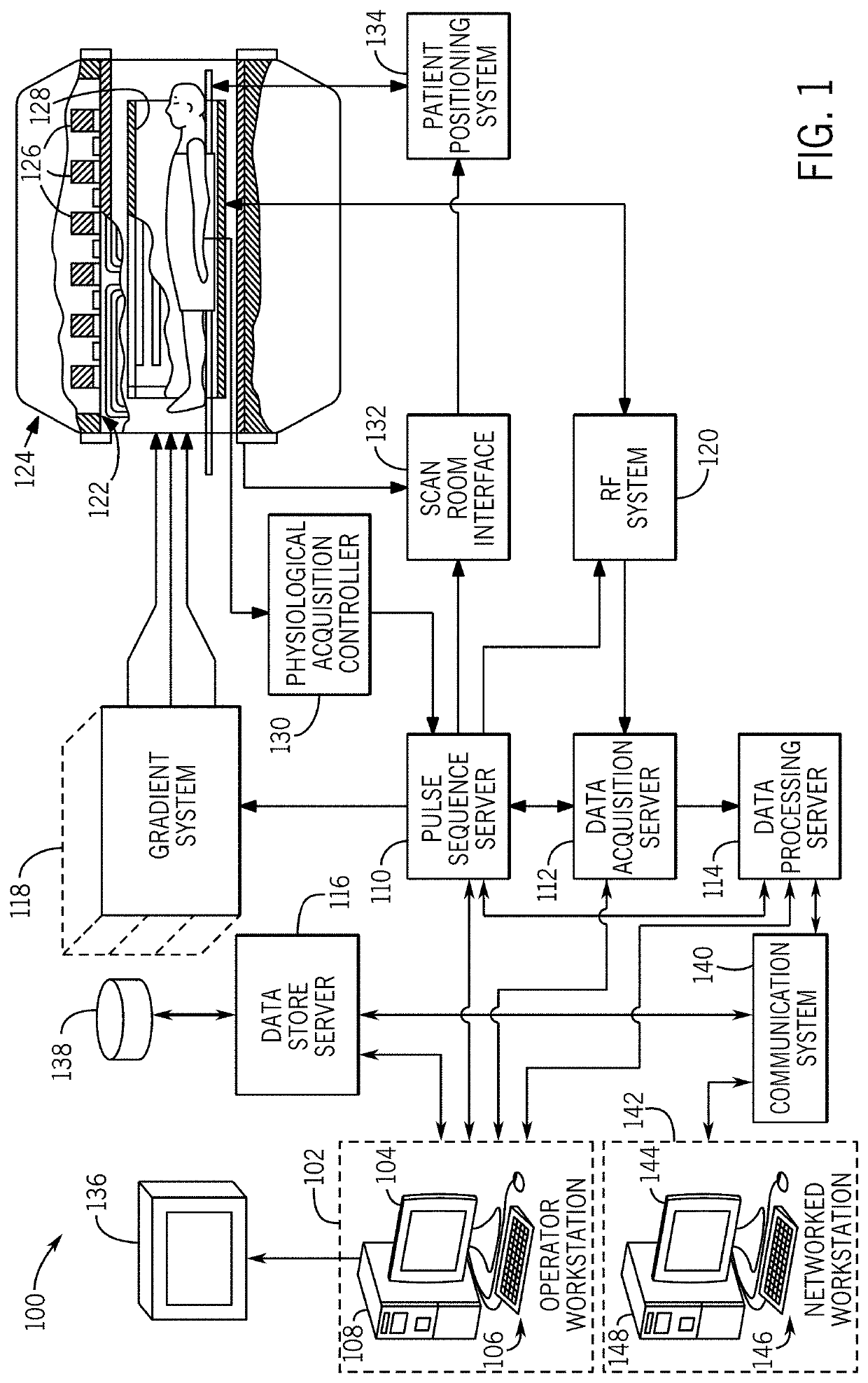
Artifact suppression in multi-coil MRI
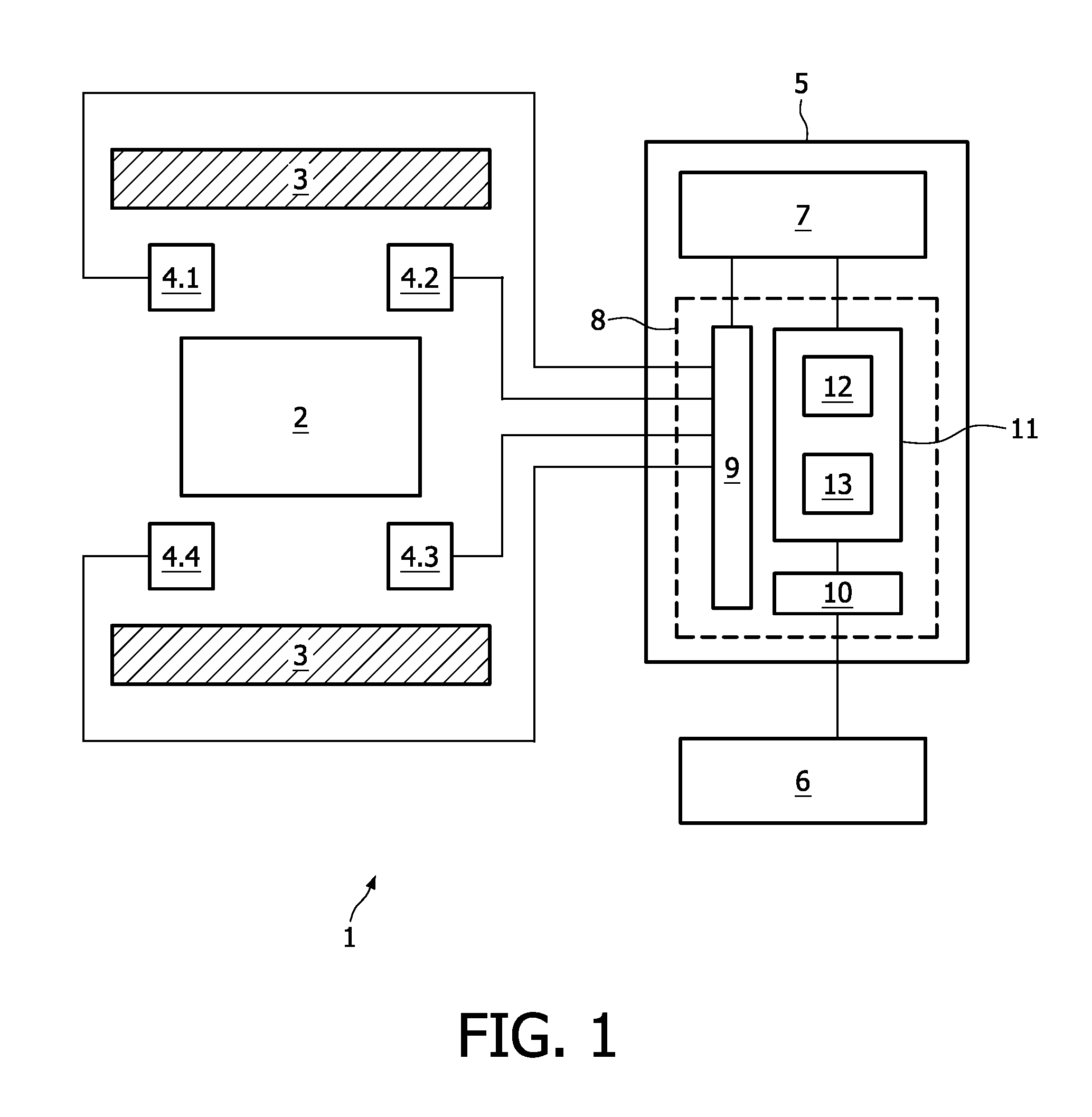
ActiveUS20090257629A1Quality improvementGuaranteed high-quality imagingMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionArtifact suppressionImage reconstruction algorithm
A magnetic resonance imaging system (1), comprising a plurality of receiving units (4.1-4.4) for receiving magnetic resonance signals from an object (2), and an image reconstruction device (8), said image reconstruction device being adapted to receive magnetic resonance signals of said object (2) from said plurality of receiving units (4.1-4.4) and to perform image reconstruction by combining magnetic resonance signals received by said plurality of receiving units using an image reconstruction algorithm (11), characterised in that said image reconstruction device (8) comprises means (12a) for combining magnetic resonance signal contributions from respective receiving units (4.1-4.4) in such a way that a combined sensitivity of the plurality of receiving units (4.1-4.4) to a predetermined spatial region of the object (2) is reduced.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Systems and methods for suppressing coherent structured illumination artifacts
Methods and systems are provided for suppressing speckle and / or diffraction artifacts in coherent structured illumination sensing systems. A coherent radiation pattern forms an interference pattern at an illumination image plane and illuminates an object. Radiation scattered or otherwise emitted by the object is detected to produce a signal, which is integrated in time. Coherent artifact suppression is attained by using a spatial modulator, such as an acousto-optic device, to vary a phase gradient at the illumination image plane during the signal integration time. Various embodiments are provided for purposes including without limitation: preserving the depth of field of the coherent illumination; using the same acousto-optic device for pattern generation and coherent artifact suppression; electronically controlling the effective spatial coherence of the illumination system; and reducing errors due to coherent artifacts in a laser-based three dimensional imaging system.
Owner:FELDKHUN DANIEL
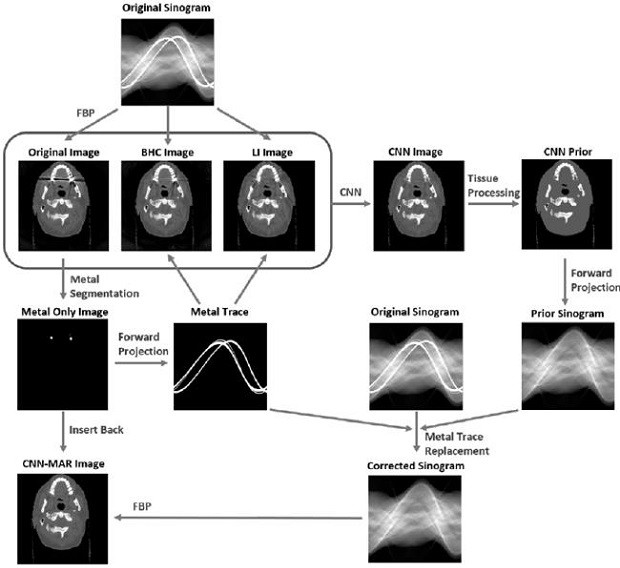
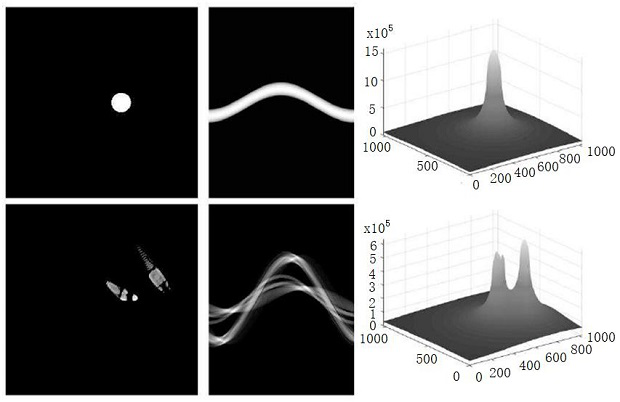
CT image metal artifact removing method and device and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN112017131AQuality improvementOvercomes the inability to incorporate data integrity information from metal scan data into image domain processingImage enhancementImage analysisMetal ArtifactData integrity
The invention discloses a CT image metal artifact removing method and device and a computer readable storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: collecting a metal artifact-containing image and a metal artifact-free image, and processing the metal artifact-containing image and the metal artifact-free image to obtain corresponding projection data; reconstructing the generated two projectiondata respectively to generate an image containing metal artifacts and an image without artifacts, and further processing to obtain an initial artifact suppression image and a data integrity map; anddesigning a neural network and a loss function, wherein the neural network outputs an image after artifact removal and the like. The CT image metal artifact removing method is characterized in that correlation between metal artifacts and a surrounding structure and the relation between metal artifacts and tissue components are utilized, the problem that data integrity information in metal scanningdata cannot be fused into the image domain processing process in the existing image domain technology is solved, and the artifact correction accuracy and the CT image quality are improved.
Owner:NANJING ANKE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
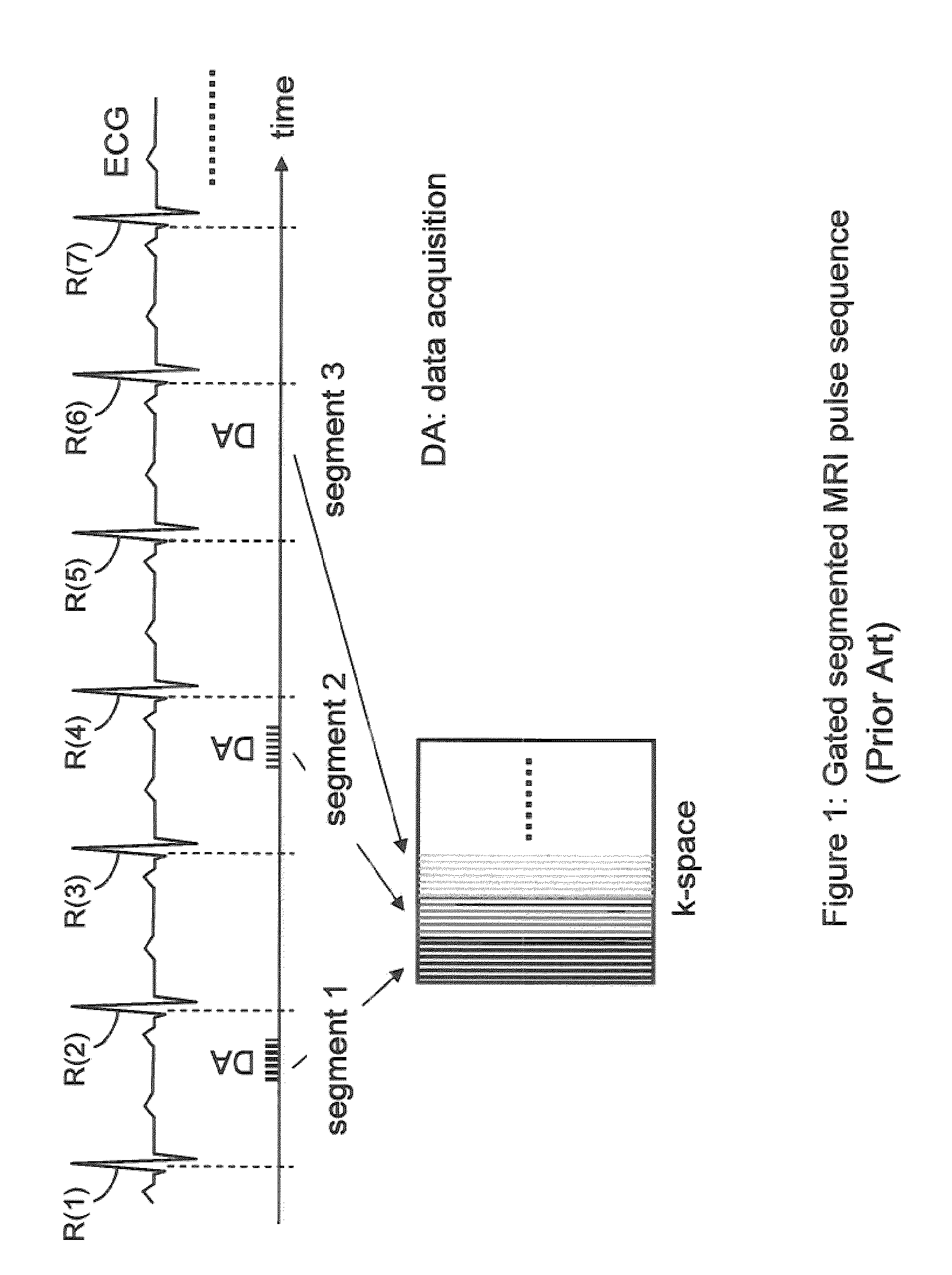
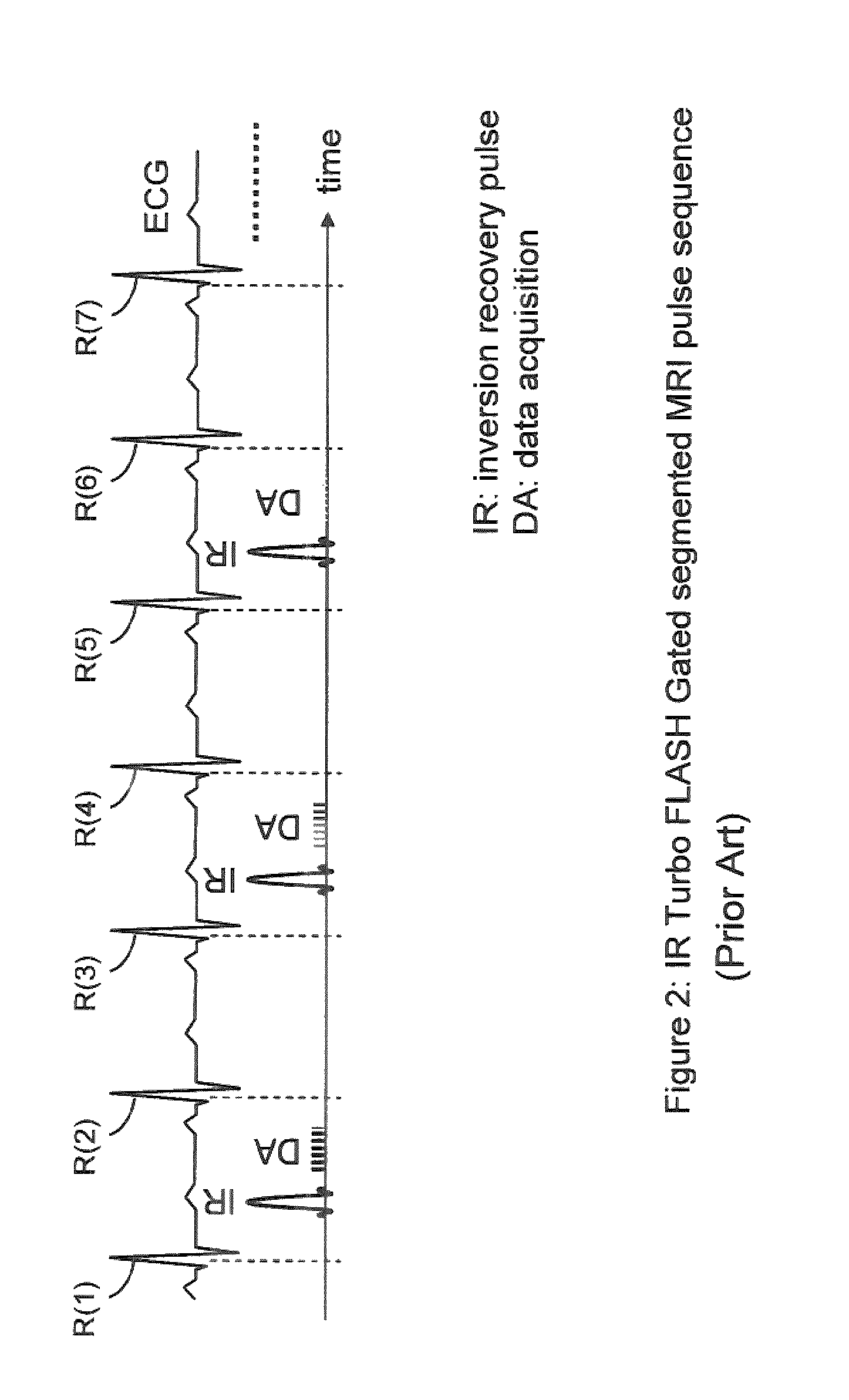
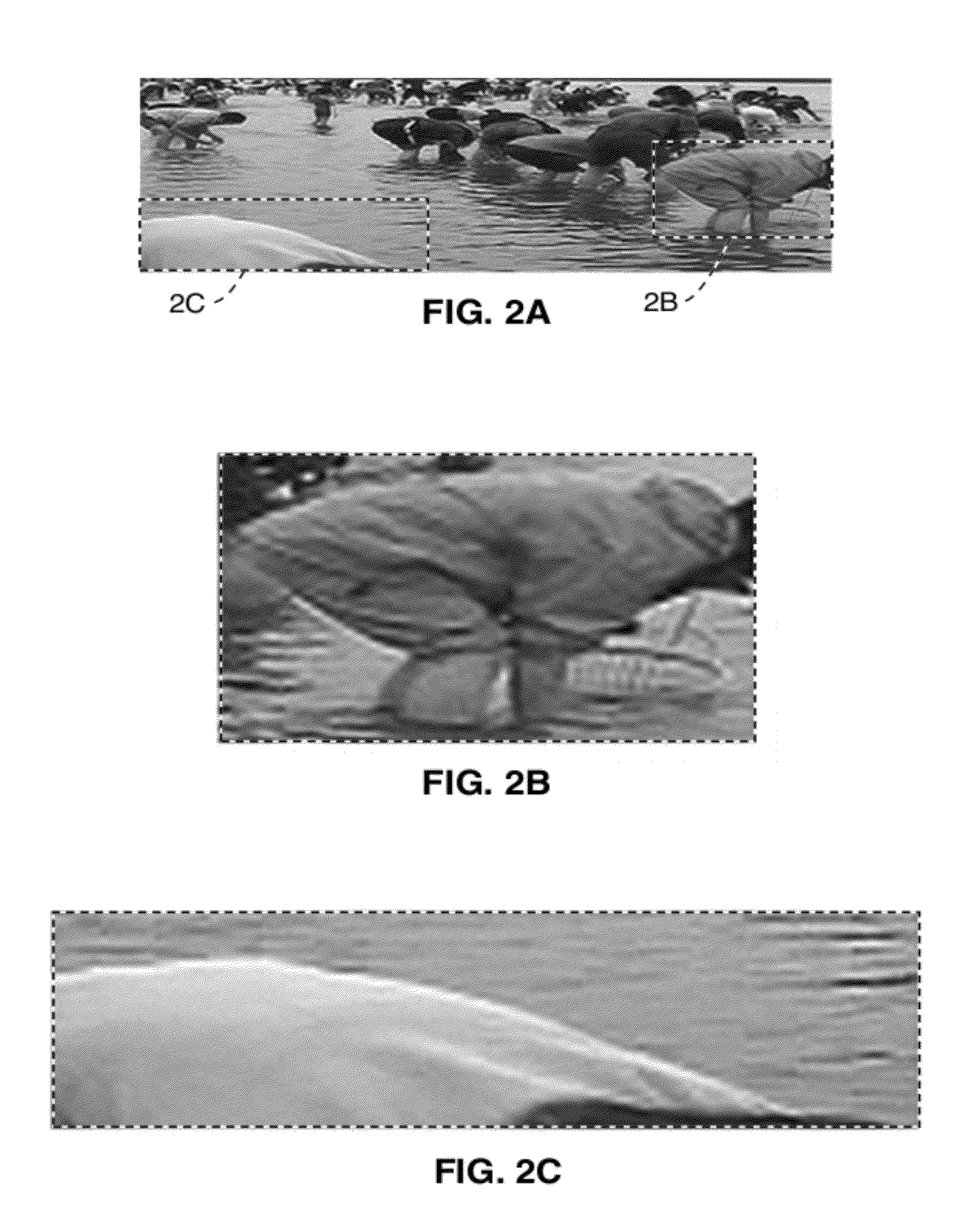
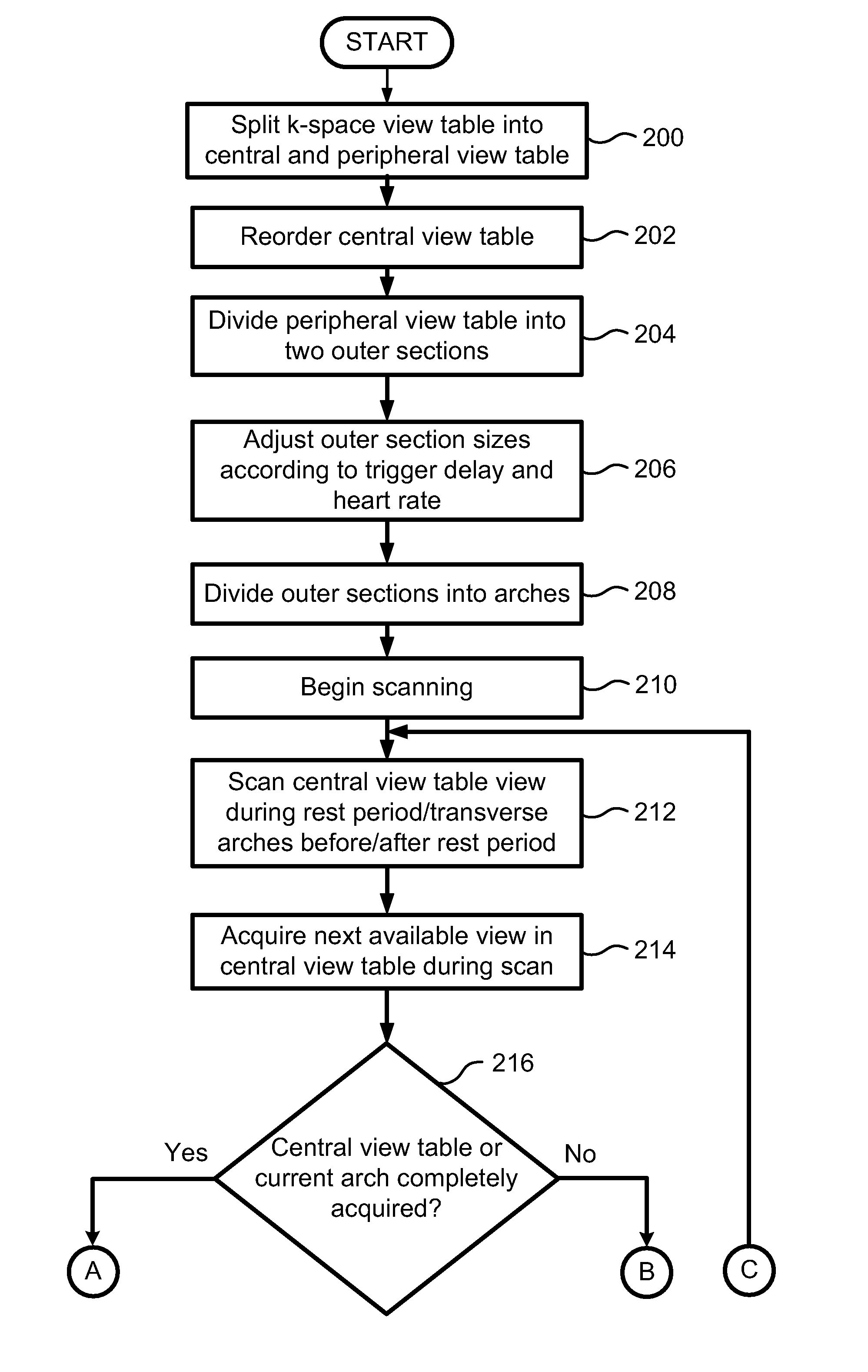
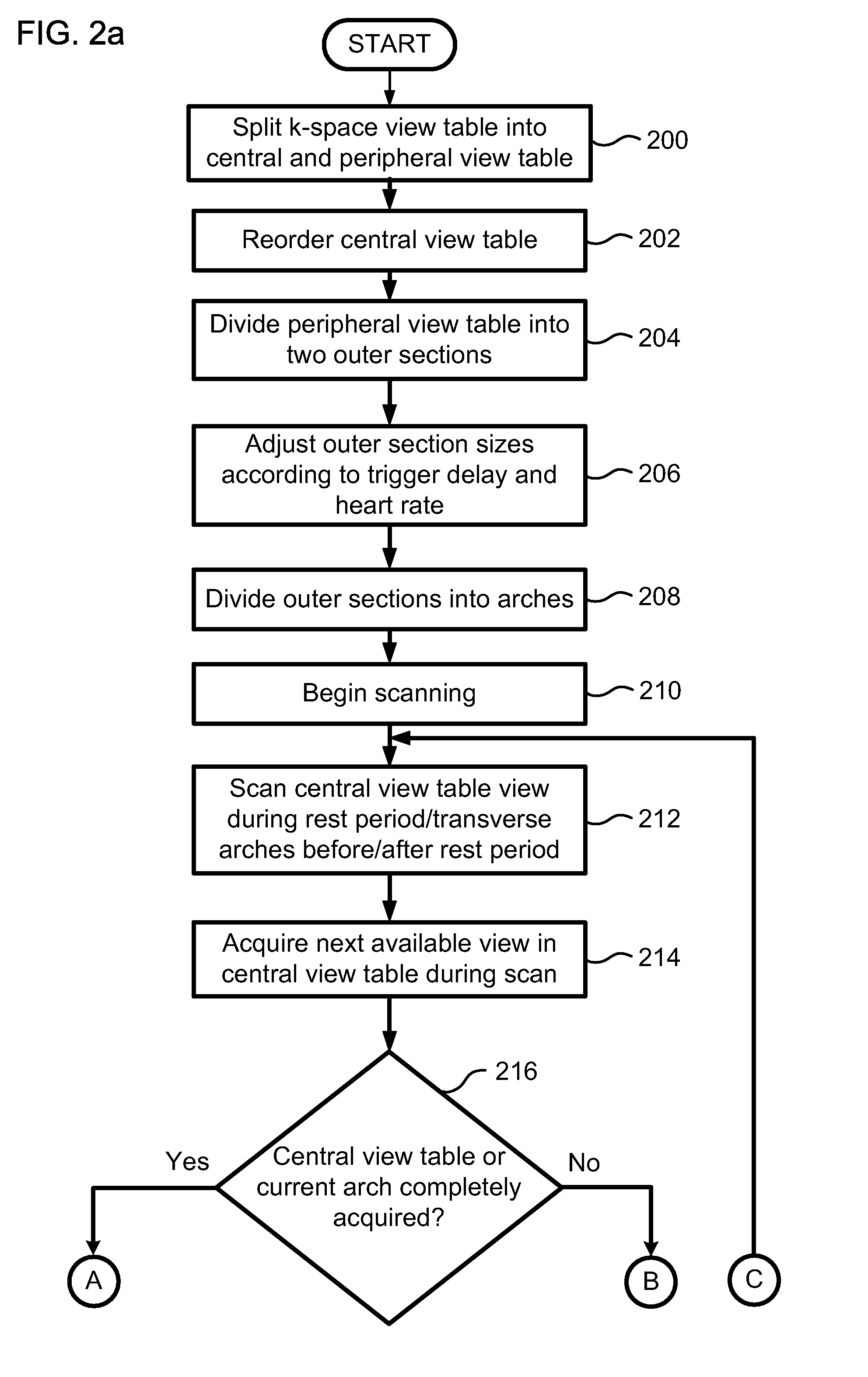
Cardiac Motion Artifact Suppression Using ECG Ordering
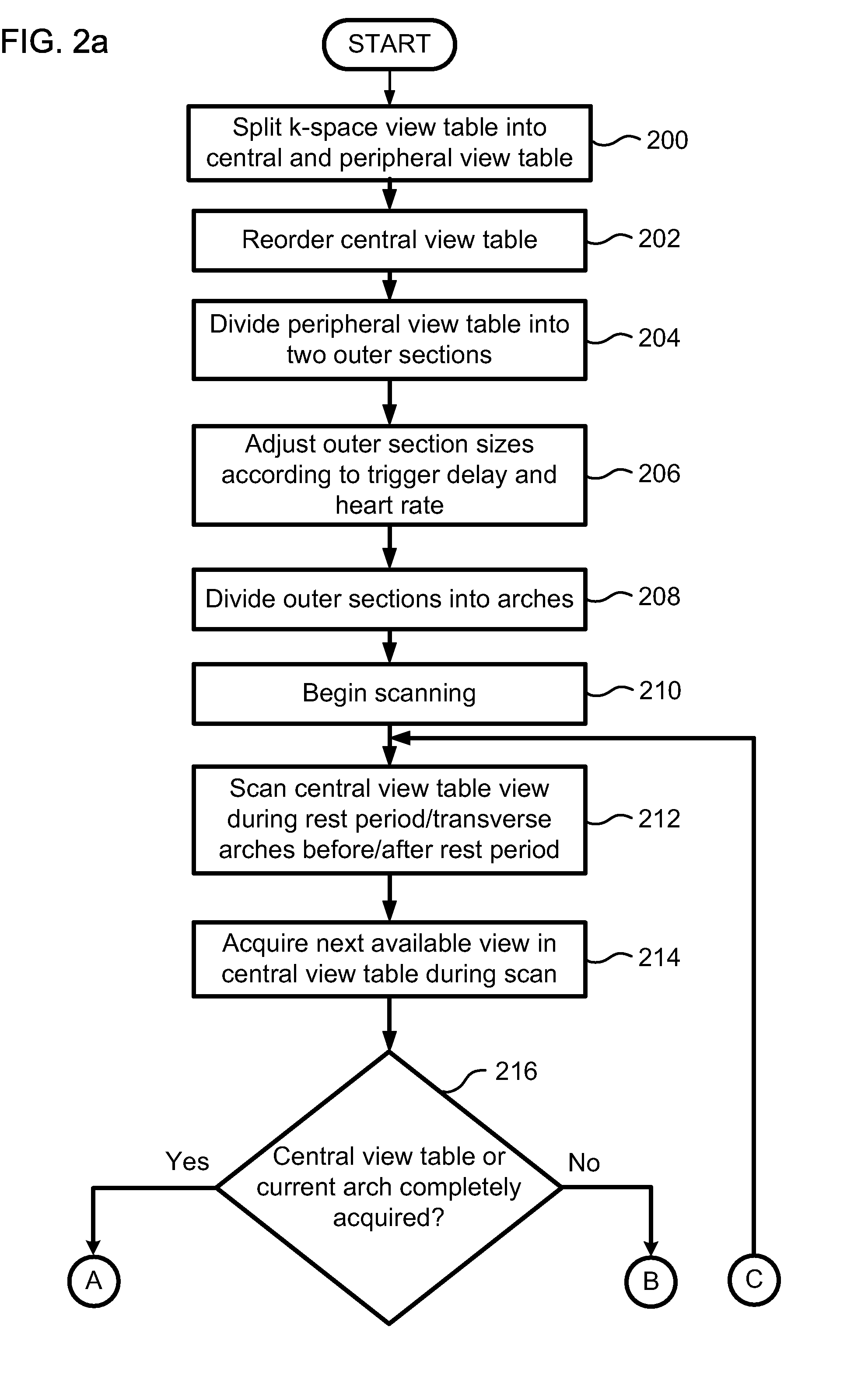
ActiveUS20070287907A1Increase scan timeElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsEcg signalArtifact suppression
Described is a robust electrocardiogram (ECG) ordering technique of k-space for breath hold contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA) that acquires the central part of k-space in a motion-free portion of diastole and fills in from the periphery of k-space at all other times. To make maximal use of the contrast enhancement, data is acquired continuously even when the ECG signal is lost. The ECG signal is monitored in real time. The ECG ordering technique allows a flexible acquisition matrix and is robust against ECG signal imperfections. The ECG ordering technique allows thoracic and pulmonary magnetic resonance angiography with a higher resolution when compared to the conventional gated sequence.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and apparatus for stimulus artifact suppression
Amplification of an evoked potential signal is carried out utilizing a high pass filter implemented as an integrator in a feedback loop which drives the DC offset voltage to zero. As a result, the feed-forward amplifier circuit has almost zero volts at its output since the only voltage remaining is the offset voltage of the operational amplifier, which is selected so as to maintain this parameter as low as possible. Because the voltage impressed across the feed-forward amplifier section is close to zero, the gain of this section can be set to zero during the time that the electrical stimulus pulse is present without introducing any additional artifacts and subsequent amplifier stages are not driven into saturation. When the electrical stimulus potential is no longer present or is significantly reduced in amplitude and before the time of receipt of the response signal, the feed-forward amplifier is brought back into the circuit to provide the high gain required to amplify the response signal, which can be measured without interference from saturation of any of the amplifier stages as they recover to baseline.
Owner:NATUS MEDICAL
A high-precision sparse-angle CT reconstruction method combined with sparse-induced dynamic guided filtering is proposed
ActiveCN109523458AHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingArtifact suppression
The invention provides a high-precision sparse angle CT reconstruction method combined with sparse induced dynamic guiding filter, belonging to the technical field of image processing of medical images. The high-precision sparse-angle CT reconstruction method combined with sparse-induced dynamic guiding filtering comprises the following steps: S1, taking the image obtained by analyzing and reconstructing the collected projection data as an initialization image and adopting POCS (Convex Set Projection) to obtain a filtered input image; S2, the sparse-angle CT reconstruction method comprises thefollowing steps: 2, carrying out image gradient sparse regularization constraint on that filtered input image to obtain a guide image; 3, fusing that guide image and the filter input image to obtaina guide filter image; S4: performing Iterative reconstruction on the bootstrap filter image. At first, that filter input image and the guide image are respectively obtained, and then the guide filterimage and the filter input image are fused to obtain the guide filter image, and the guide filter image is taken as an initial image for iterative reconstruction, which has remarkable effects in noisereduction, edge preservation and blocky artifact suppression.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
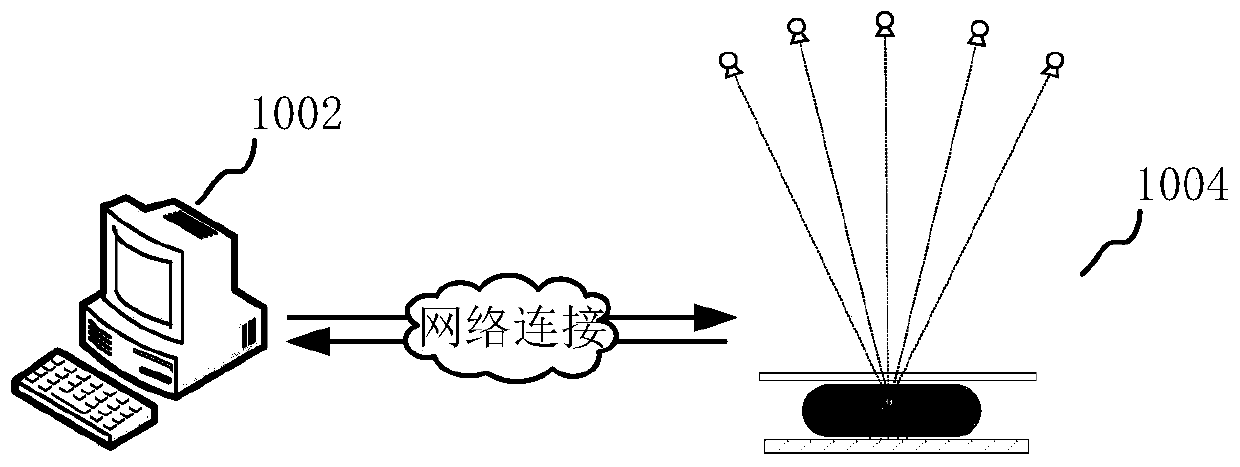
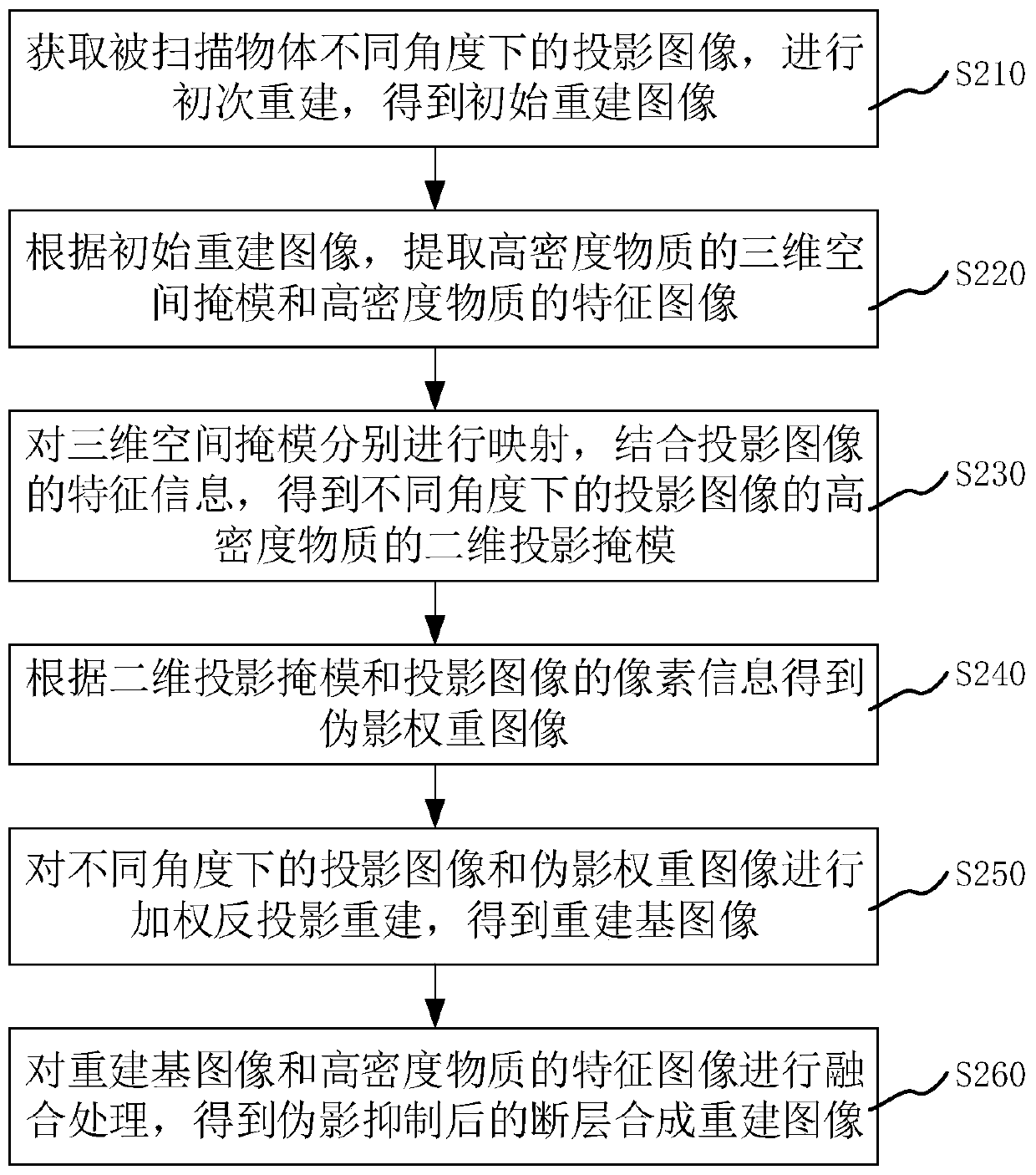
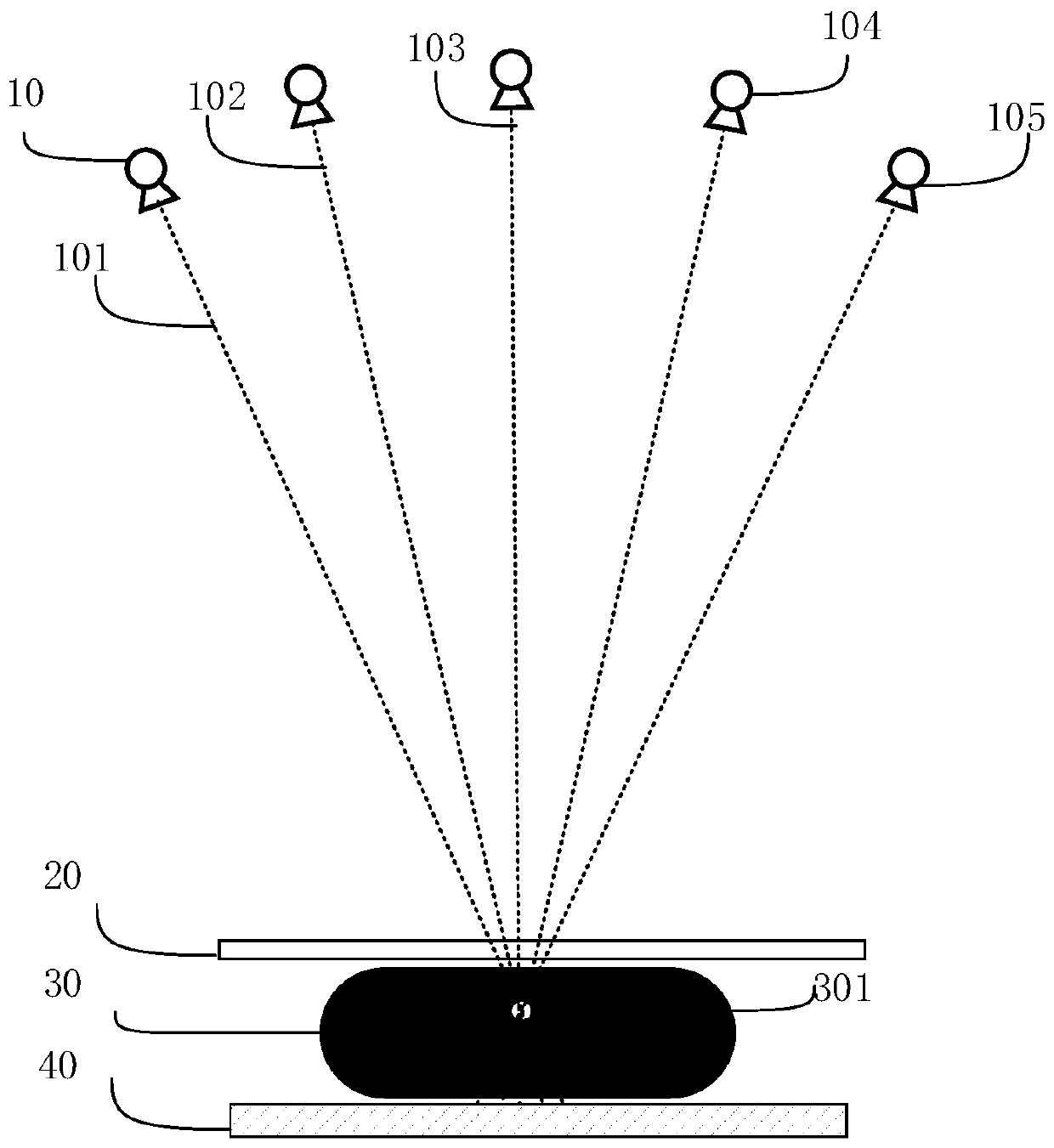
Interlayer artifact suppression method and device for mammary gland tomographic reconstruction image
ActiveCN110796620AQuality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisArtifact suppression
The invention relates to an interlayer artifact suppression method and device for a mammary gland tomographic reconstruction image, computer equipment and a storage medium. The interlayer artifact suppression method comprises the following steps: acquiring projection images of a scanned object at different angles, and performing primary reconstruction to obtain an initial reconstructed image; extracting a three-dimensional space mask of the high-density substance and a feature image of the high-density substance according to the initial reconstructed image; respectively mapping the three-dimensional space masks of the high-density substance, and combining the feature information of the projection image to obtain two-dimensional projection masks of the high-density substance of the projection image at different angles; obtaining an artifact weight image according to the two-dimensional projection mask and the pixel information of the projection image; performing weighted back projectionreconstruction on the projection image and the artifact weight image at different angles to obtain a reconstructed base image; and performing fusion processing on the reconstructed base image and thefeature image of the high-density substance to obtain a tomosynthesis reconstructed image after artifact suppression. According to the scheme, the quality of the reconstructed image can be improved.
Owner:卡乐福医疗科技集团有限公司
Long T1 artifact suppression techniques for magnetic resonance imaging
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Recursive image quality enhancement on super resolution video
ActiveUS8233541B2Quality improvementSuppress artifactsTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImaging qualityArtifact suppression
Method and apparatus for improving the quality of super-resolution video imaging by suppressing ringing artifacts, reducing high-frequency noise, reducing blocking artifacts, and smoothing out jagged edges of the image to generate pictures that appear cleaner with less edge degradation. The method operates in a recursive manner within a sequence of low resolution images. Conventional SR processing is primarily enhanced within the invention by adding an artifact suppression section which creates a high frequency component signal ΔSRi having significantly reduced artifacts therein achieving higher quality super-resolution image output. The method can be applied to images and image sequences (video) in monochrome or color and in any desired pixel format. The method can be implemented within image processing devices, in particular those containing programming for executing the described method steps.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Cardiac motion artifact suppression using ECG ordering
ActiveUS8200311B2Increase scan timeElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsEcg signalArtifact suppression
Described is a robust electrocardiogram (ECG) ordering technique of k-space for breath hold contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA) that acquires the central part of k-space in a motion-free portion of diastole and fills in from the periphery of k-space at all other times. To make maximal use of the contrast enhancement, data is acquired continuously even when the ECG signal is lost. The ECG signal is monitored in real time. The ECG ordering technique allows a flexible acquisition matrix and is robust against ECG signal imperfections. The ECG ordering technique allows thoracic and pulmonary magnetic resonance angiography with a higher resolution when compared to the conventional gated sequence.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Coherence artifacts suppression in integrated photonic systems
An optical phased array includes, in part, a multitude of receiving elements arranged along N rows and M columns, and a controller configured to activate a first subset of the receiving elements during a first time interval to capture first data representative of a first image of a target, to activate a second subset of the receiving elements during a second time interval to capture second data representative of a second image of the target, and to combine the first and second data to generate the image of the target. The first and second subsets may share common receiving elements. The controller may be further configured to compute an average of the first and second data to generate the image of the target. The first subset may represent a subset of the M columns.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
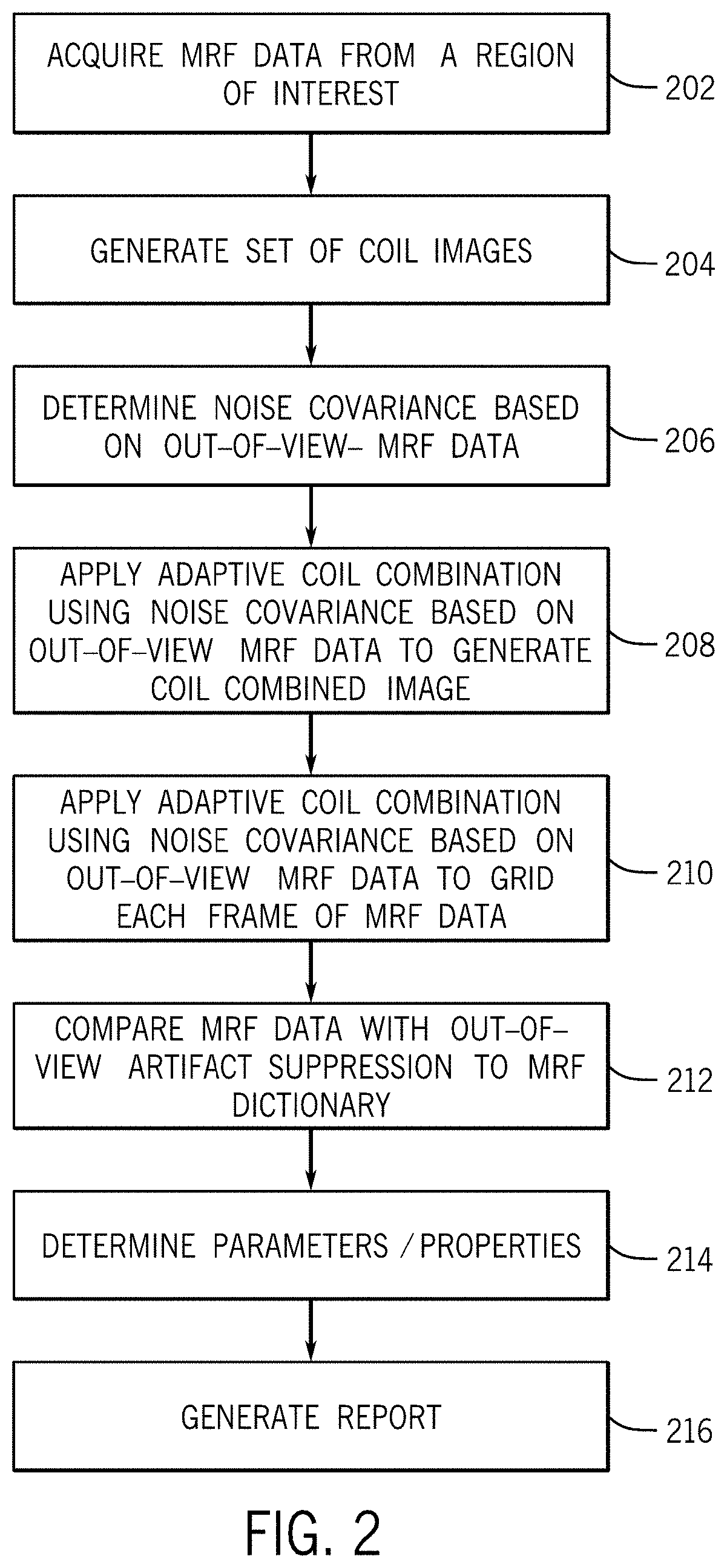
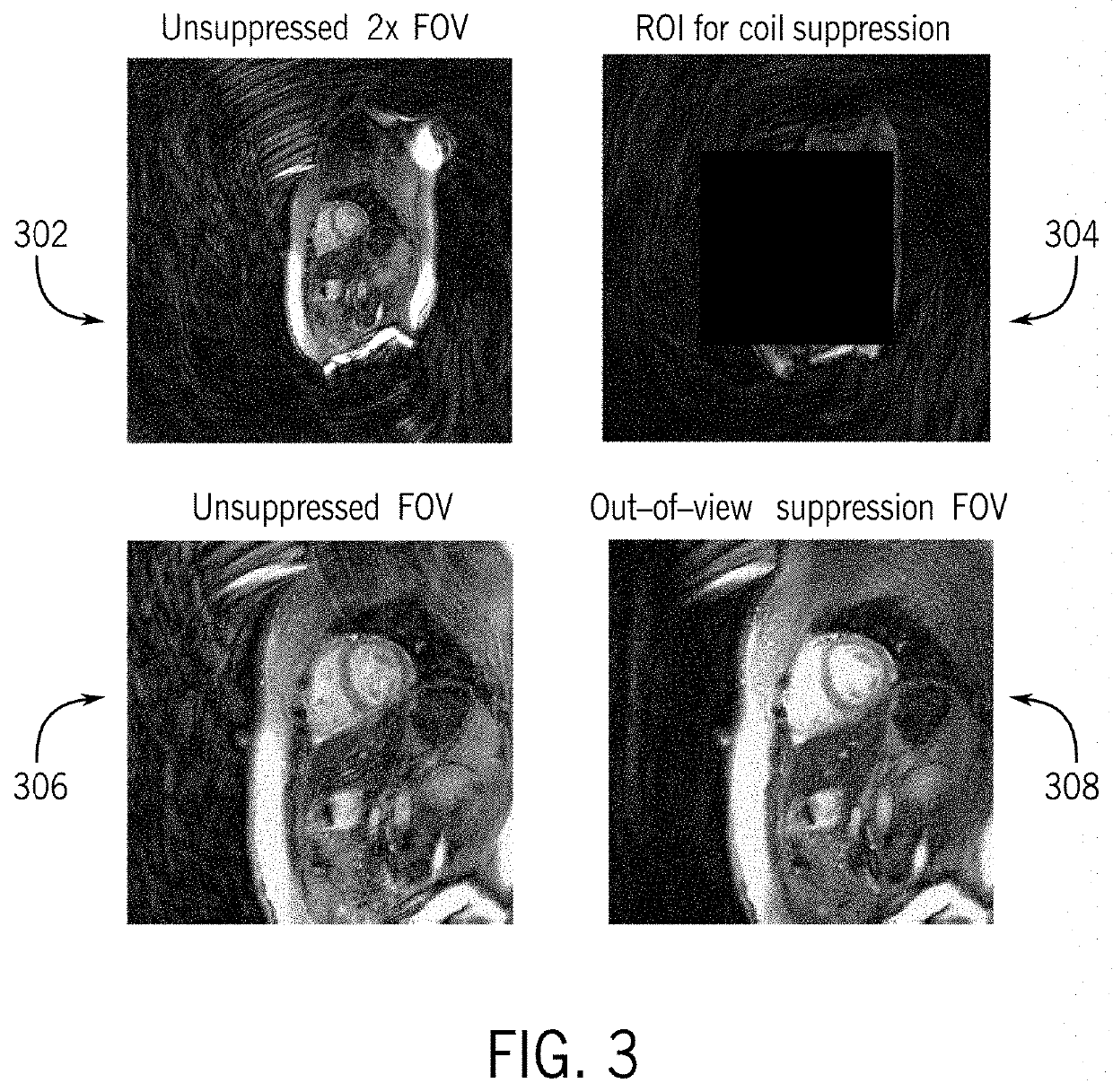
System and method for out-of-view artifact suppression for magnetic resonance fingerprinting
ActiveUS20200341102A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsArtifact suppressionComputational physics
A method for magnetic resonance fingerprinting with out-of-view artifact suppression includes acquiring MRF data from a region of interest in a subject. The MRF data is acquired using a non-Cartesian, variable density sampling trajectory. The MRF data includes data from within a desired field-of-view and data from outside the desired field-of-view. The method also includes generating a set of coil images based on the MRF data with a field-of-view larger than the desired field-of-view, determining a noise covariance based on the MRF data from outside the desired field-of-view, generating a coil combined image using an adaptive coil combination determined based on the noise covariance, applying the adaptive coil combination to the MRF data to grid each frame of the MRF data and generate MRF data with out-of-view artifact suppression. The method also includes identifying at least one property of the MRF data and generating a report.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Coherence artifacts suppression in integrated photonic systems
An optical phased array includes, in part, a multitude of receiving elements arranged along N rows and M columns, and a controller configured to activate a first subset of the receiving elements during a first time interval to capture first data representative of a first image of a target, to activate a second subset of the receiving elements during a second time interval to capture second data representative of a second image of the target, and to combine the first and second data to generate the image of the target. The first and second subsets may share common receiving elements. The controller may be further configured to compute an average of the first and second data to generate the image of the target. The first subset may represent a subset of the M columns.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and system for denoising and demosaicing artifact suppression in digital images
ActiveUS10223772B2Avoid leastMitigate leastImage enhancementImage analysisArtifact suppressionNoise reduction
Methods and systems for denoising a digital image are provided. The method includes determining first and second plurality of pixel patches including respective first (p) and second (q) pixels, determining a patch distance between each pair of corresponding pixel patches in the first plurality and the second plurality of pixel patches, determining an effective distance between the first pixel (p) and the second pixel (q), repeating the above steps for the same first pixel (p) and another second pixel (q) until a predetermined number of pixels (q) in the raw digital image is processed, and then denoising the first pixel (p), including determining respective contributions of the pixels (q) into a noise reduction of the pixel (p), using respective effective distances of the pixels (q). A corresponding system is also provided. Embodiments of the invention provide computational advantages for denoising digital images.
Owner:TORC CND ROBOTICS INC
Block Artifact Suppression in Video Coding
ActiveUS20170289540A9Television systemsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionArtifact suppression
A method for encoding a video sequence in a video encoder is provided that includes adapting a quantization parameter of a block of pixels in a picture of the video sequence based on a transform block size of the block of pixels to determine a final quantization parameter, and quantizing transform coefficients of the block of pixels using the final quantization parameter.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com