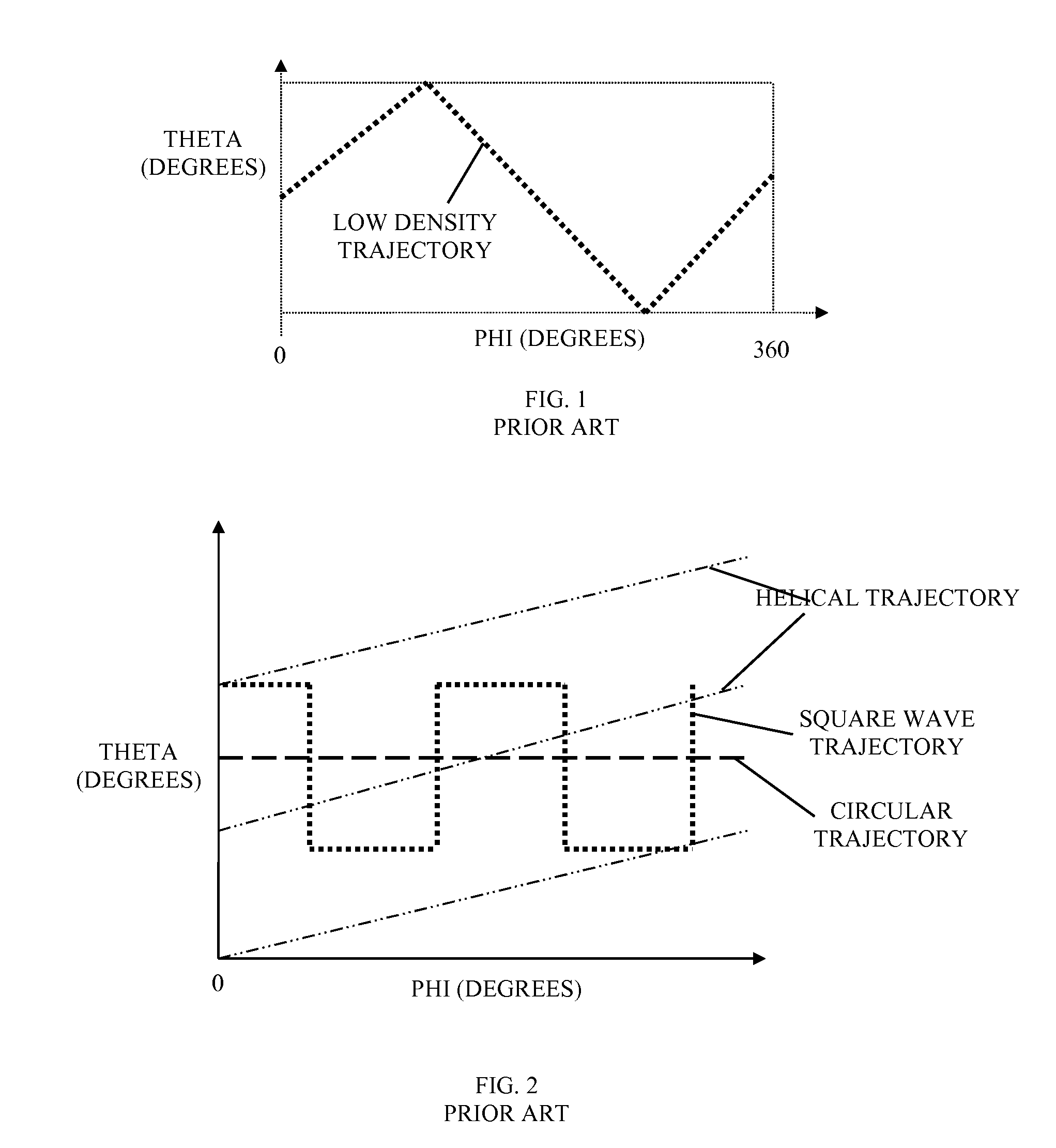
Patents
Literature
382 results about "Cone beam ct" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
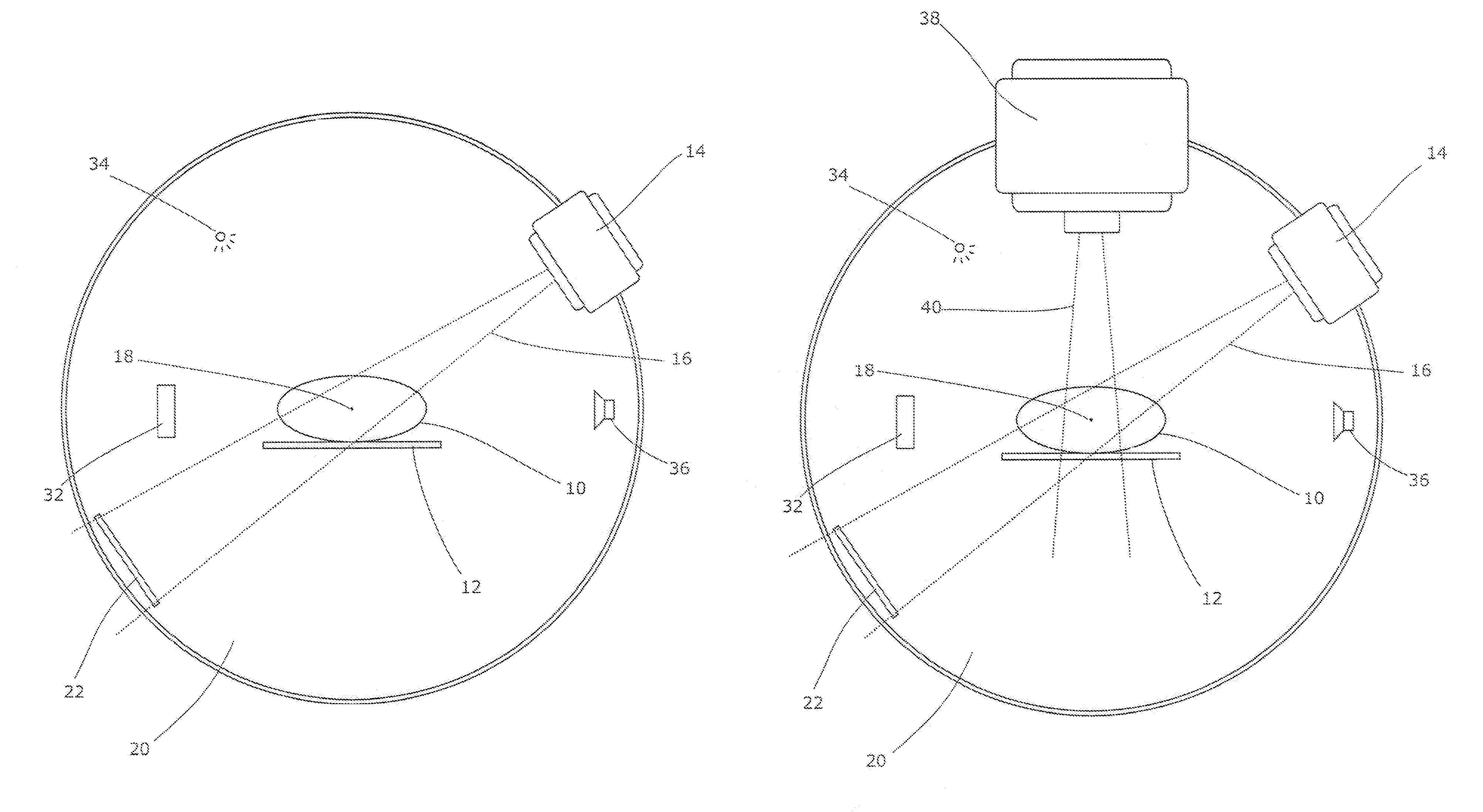
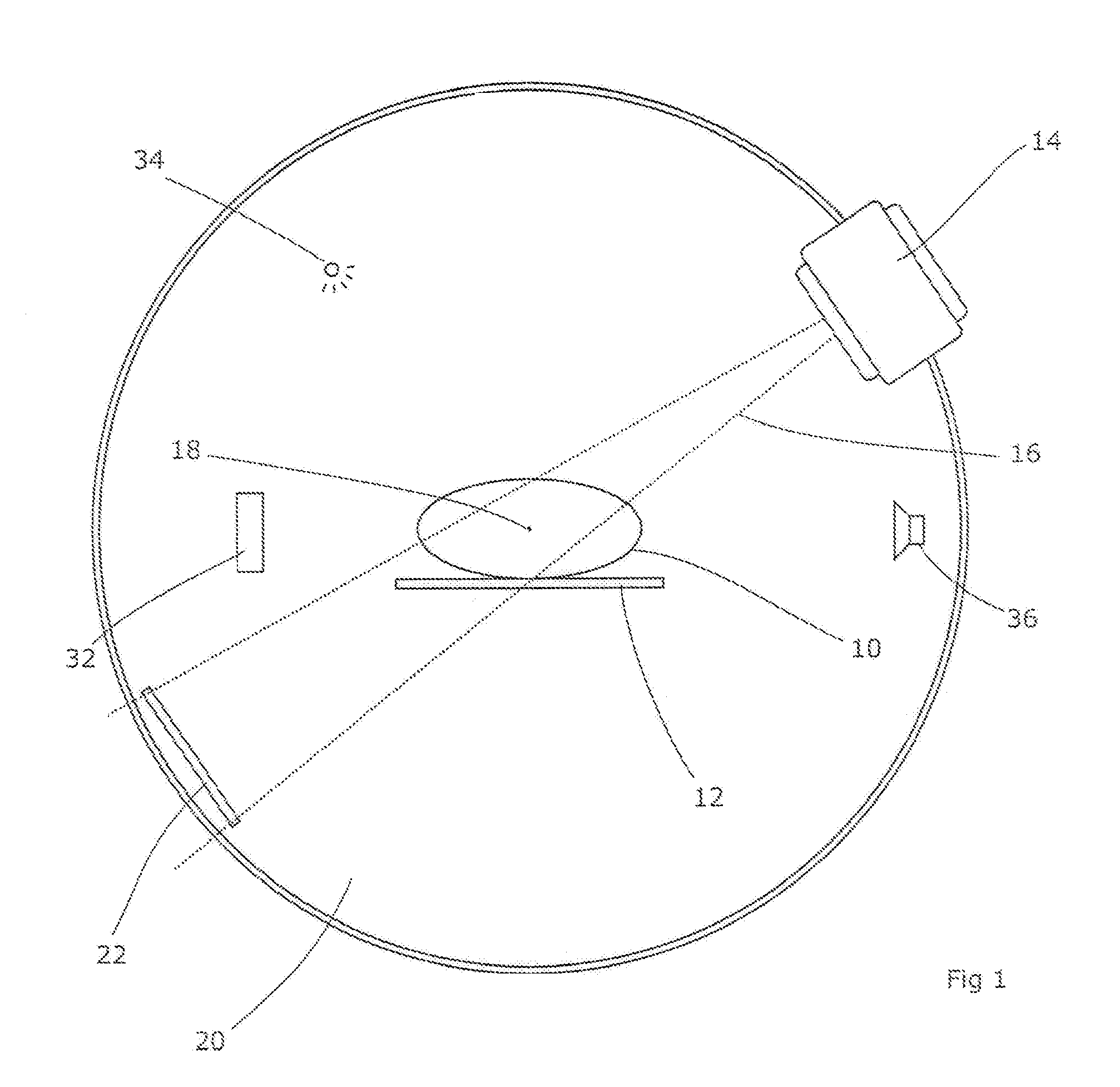
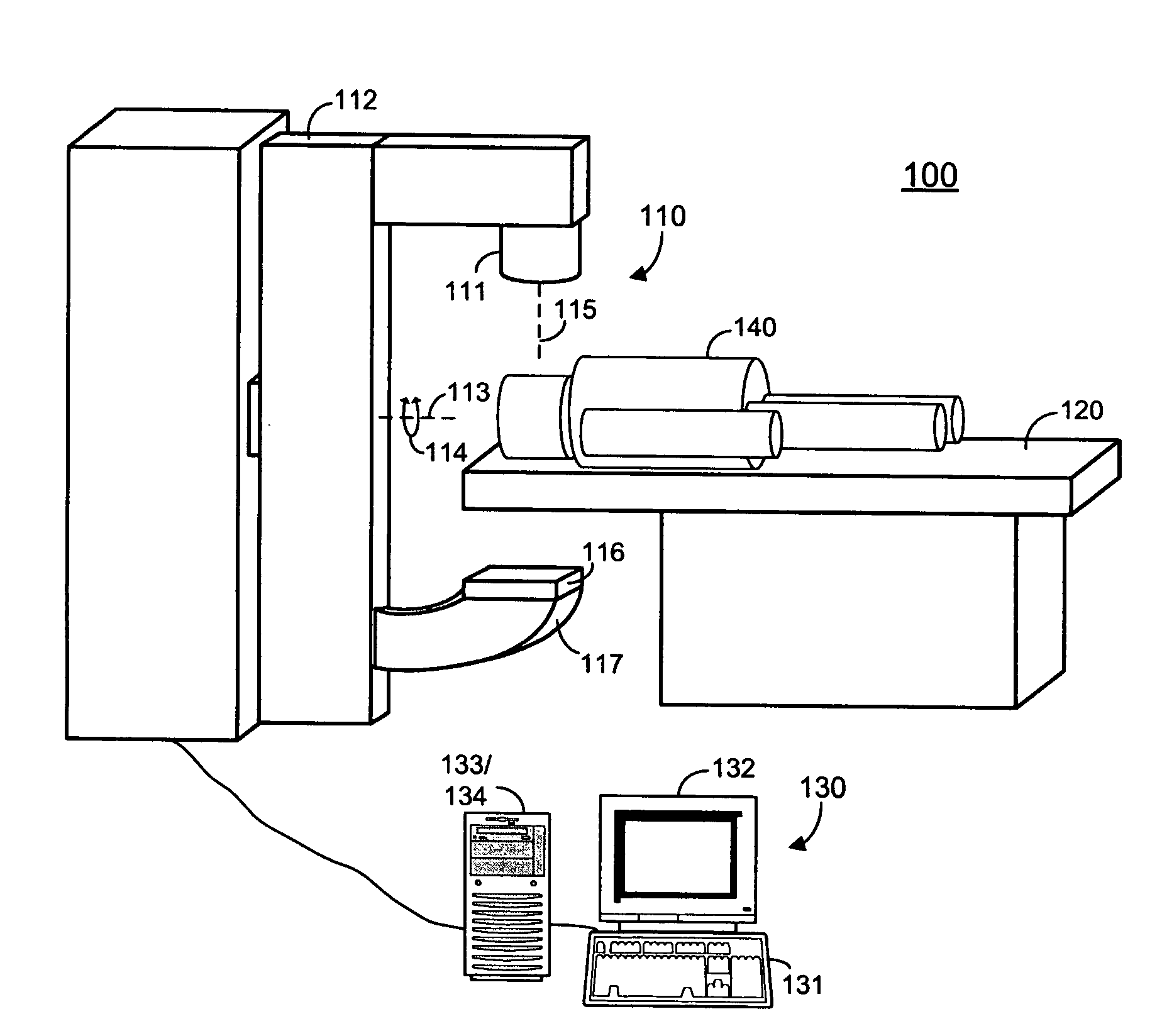
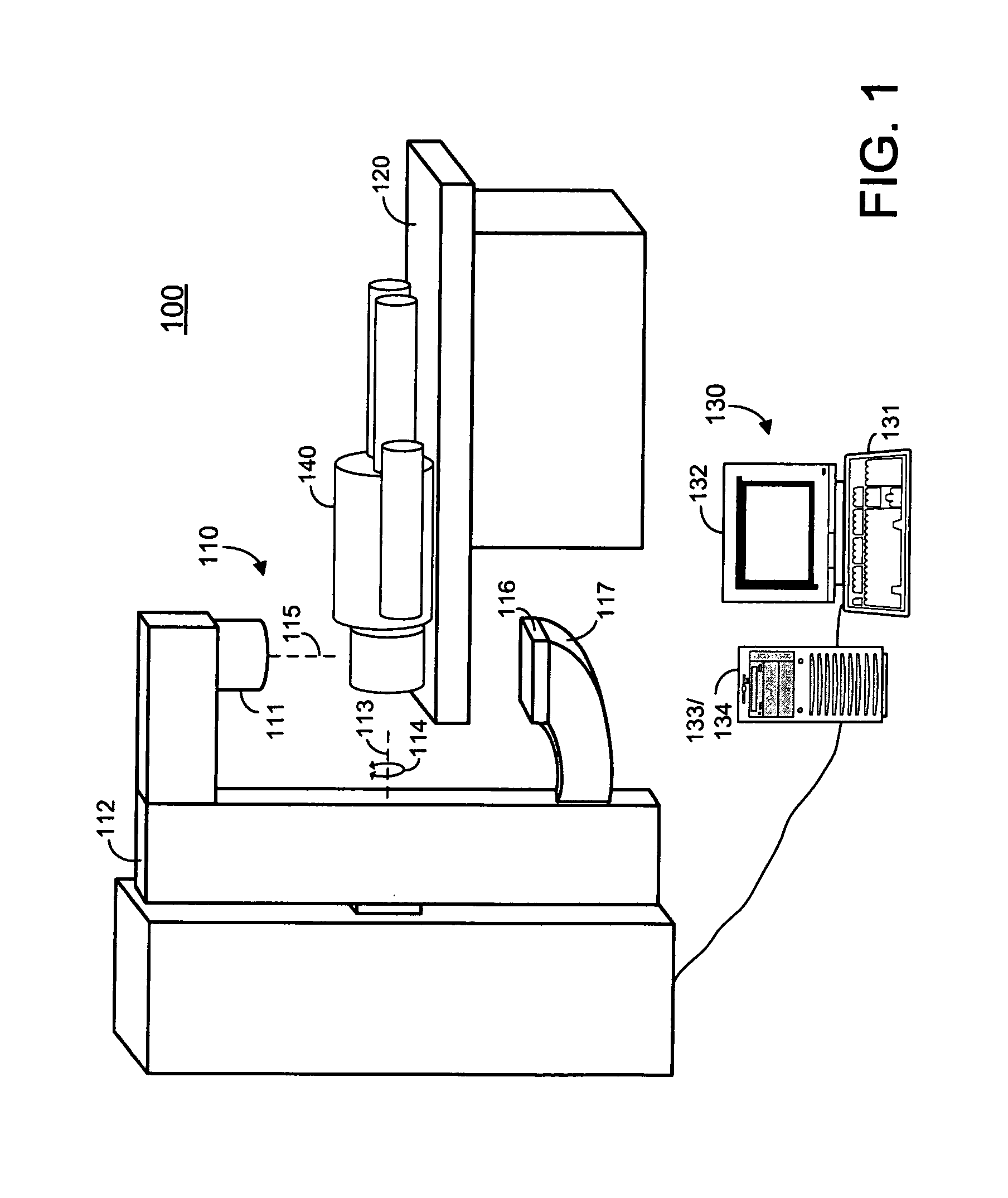
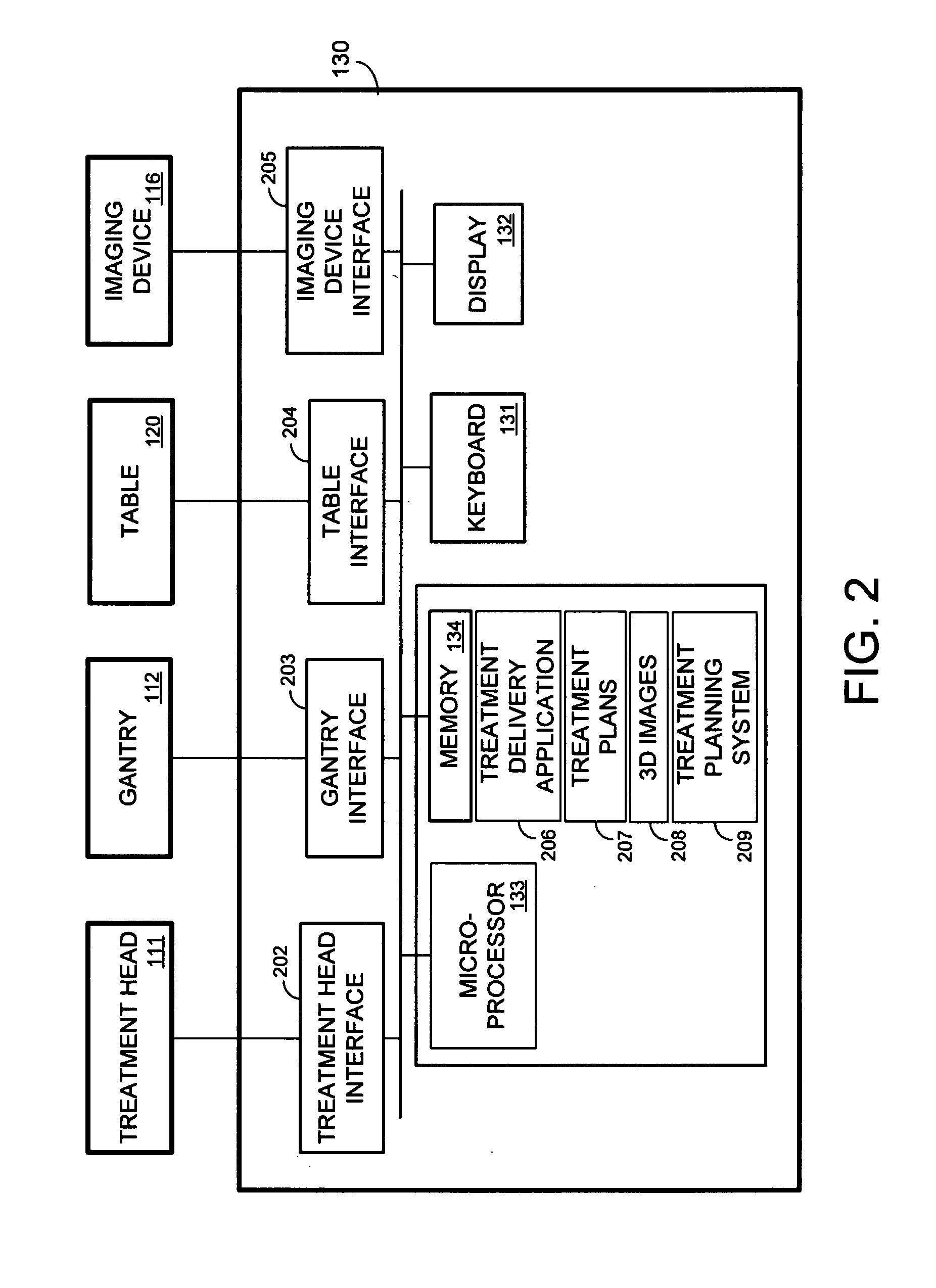
A cone beam CT is a special type of x-ray equipment used when regular facial x-rays are not sufficient. This technology is able to produce 3D images of your teeth, nerves and bones all in a single scan. This type of scan is often used for dental implants, oral surgery, oral pathology and orthodontics.
Computed tomography scanning
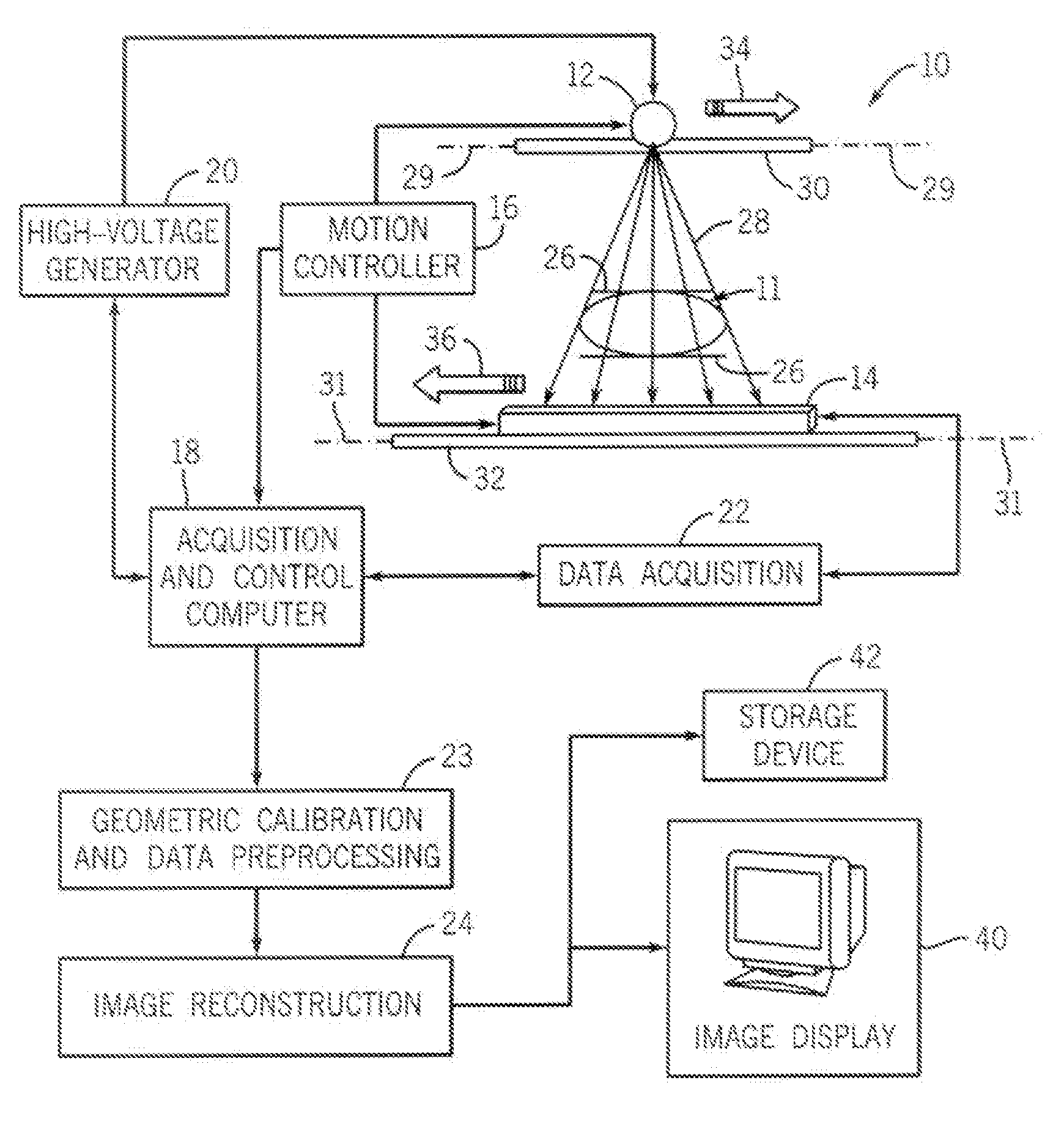
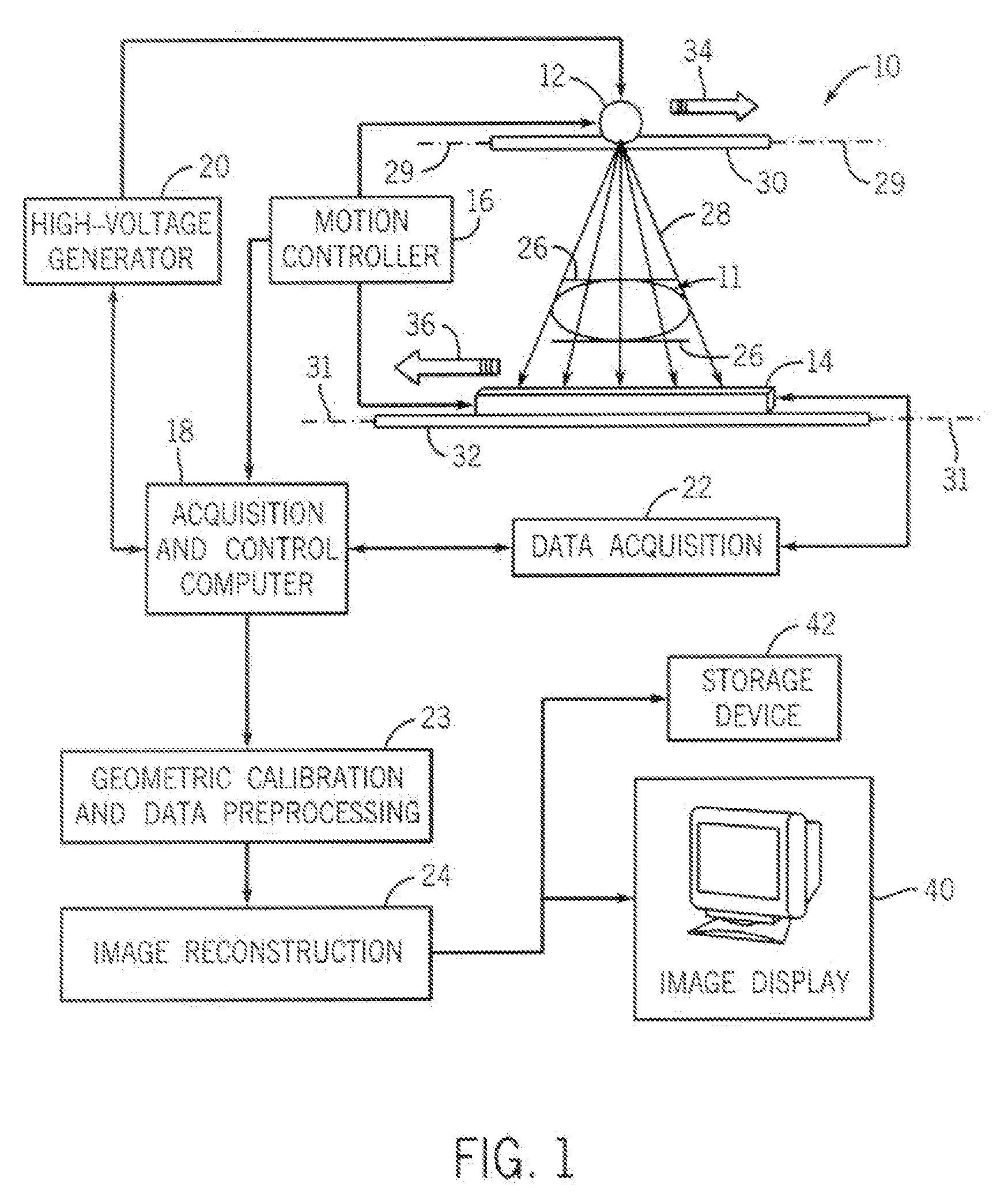
InactiveUS7356112B2Effect can be studiedContinuous acquisitionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionProjection imageTherapeutic radiation
Artifacts in the reconstructed volume data of cone beam CT systems can be removed by the application of respiration correlation techniques to the acquired projection images. To achieve this, the phase of the patients breathing is monitored while acquiring projection images continuously. On completion of the acquisition, projection images that have comparable breathing phases can be selected from the complete set, and these are used to reconstruct the volume data using similar techniques to those of conventional CT. Any phase can be selected and therefore the effect of breathing can be studied. It is also possible to use a feature in the projection images such as the patient's diaphragm to determine the breathing phase. This feature in the projection images can be used to control delivery of therapeutic radiation dependent on the patient's breathing cycle, to ensure that the tumor is in the correct position when the radiation is delivered.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Cone beam CT scanning
A CBCT system is described that includes a radiation source for emitting a cone beam of radiation in a beam direction towards an object, a detector for detecting the cone beam of radiation, and a positioner for moving the radiation source and the object according to a scanning trajectory. The system is operated according to a sampling pattern that includes intersections of the scanning trajectory and a reconstruction trajectory, wherein motion of the radiation source is substantially confined to a spherical shell. The positioner moves the radiation source at a speed higher than a highest speed of the object by a factor of at least 10. The largest angular discrepancy between any vector in a range of the scanning trajectory and the nearest sample of the scanning trajectory does not exceed 10°, preferably 6° and more preferably 3°.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
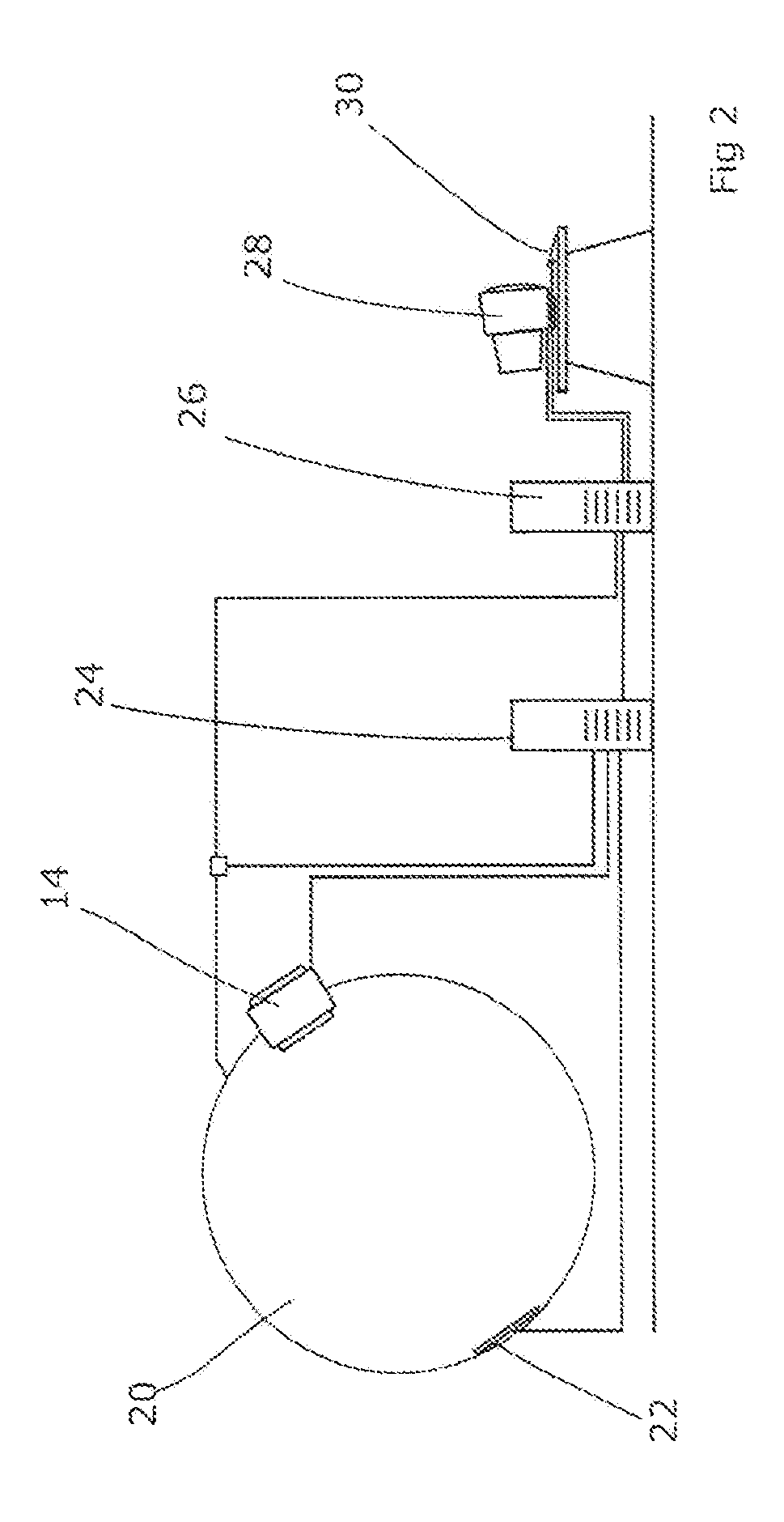
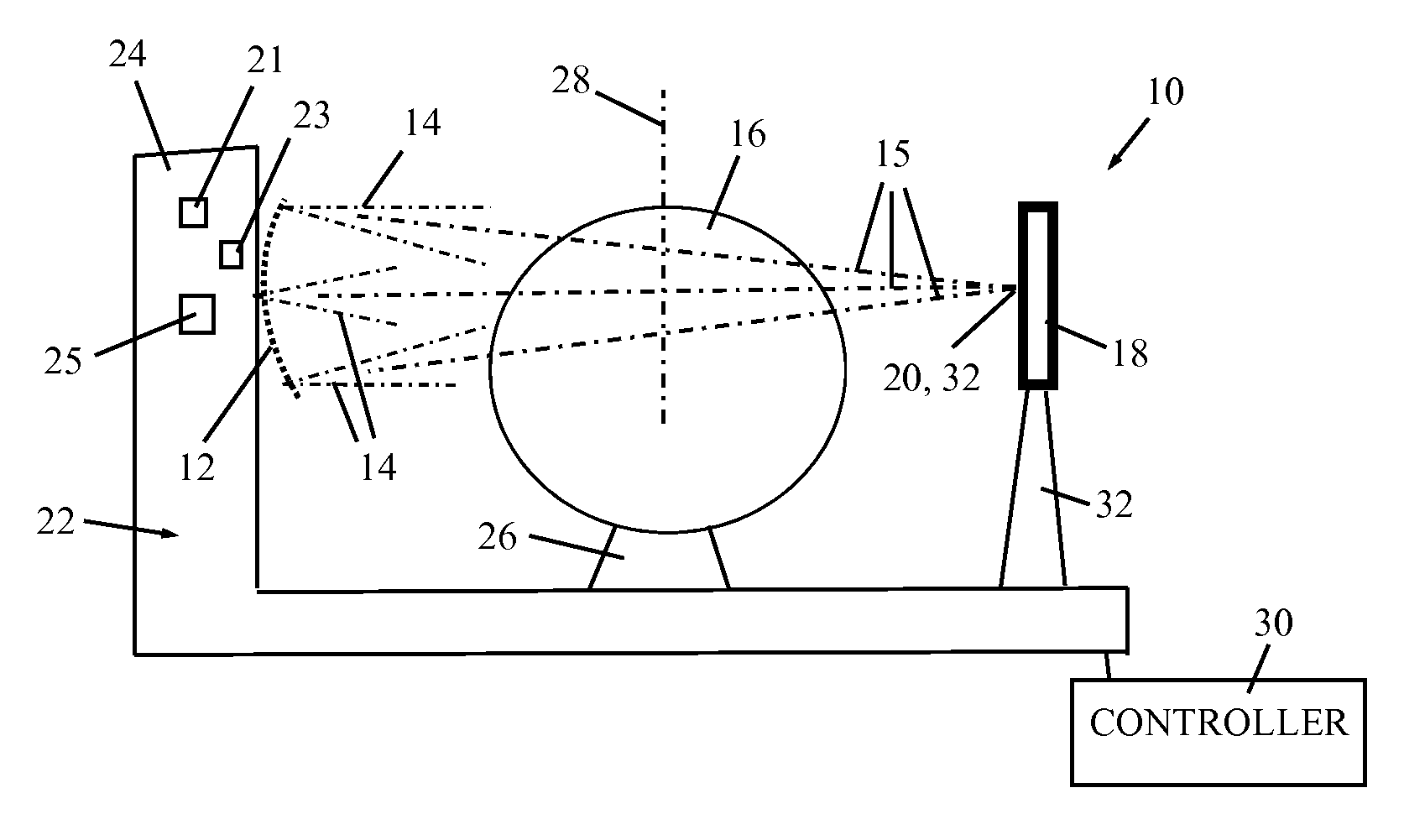
Dynamic computed tomography imaging using positional state modeling
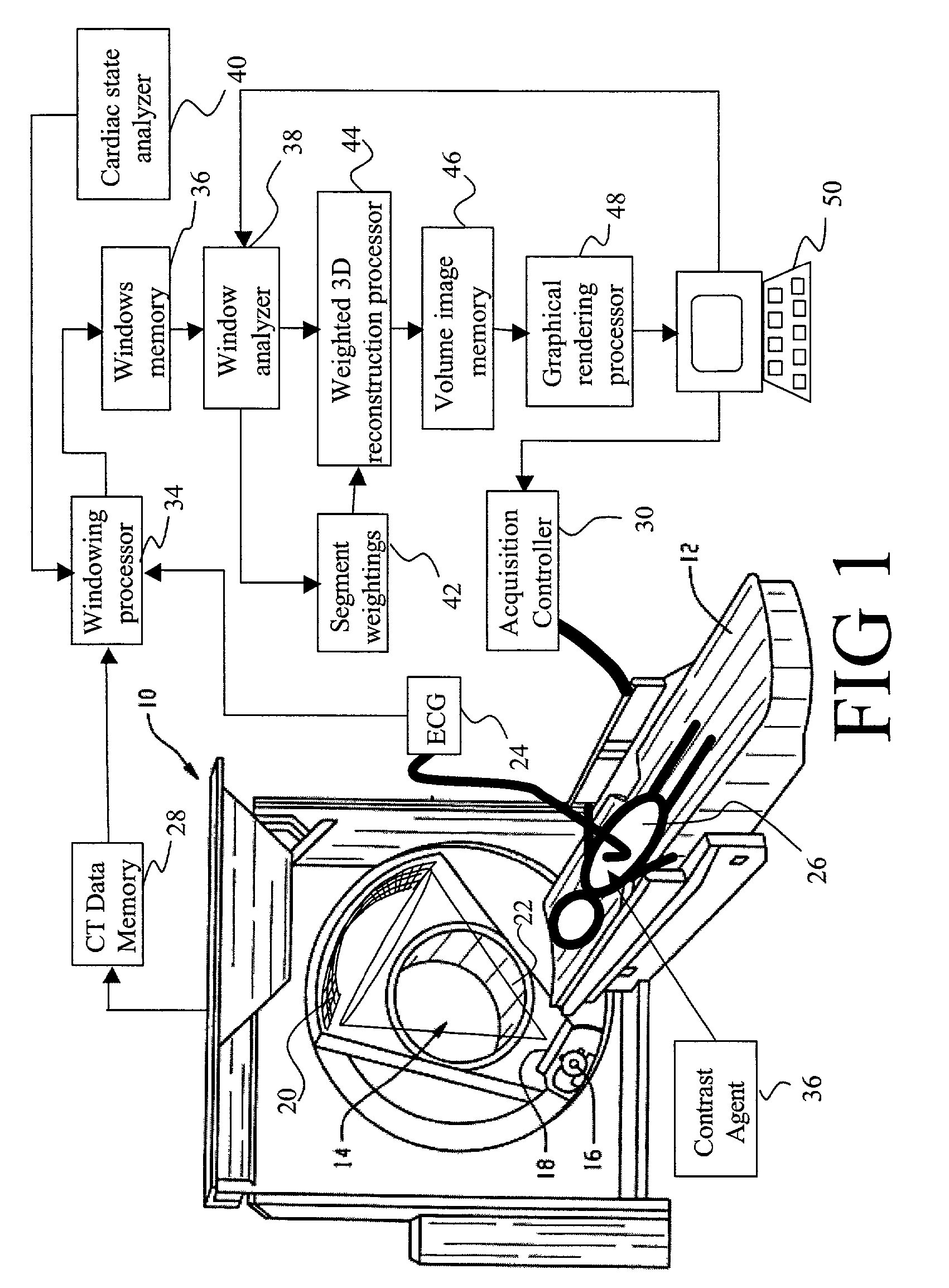
InactiveUS7058440B2Improves temporalImprove spatial resolutionElectrocardiographyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData segmentData set
An apparatus for computed tomography (CT) imaging of a cyclically moving organ includes a positional state monitor (24, 40) that monitors a positional state of the cyclically moving organ such as the heart. A cone-beam CT scanner (10) acquires image data at least within a plurality of time windows. Each time window is centered about an occurrence of a selected positional state of the organ. A window analyzer (38) selects a data segment within each time window such that the data segments combine to form a complete data set covering a selected angular range. A reconstruction processor (44) reconstructs the selected data segments into an image representation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
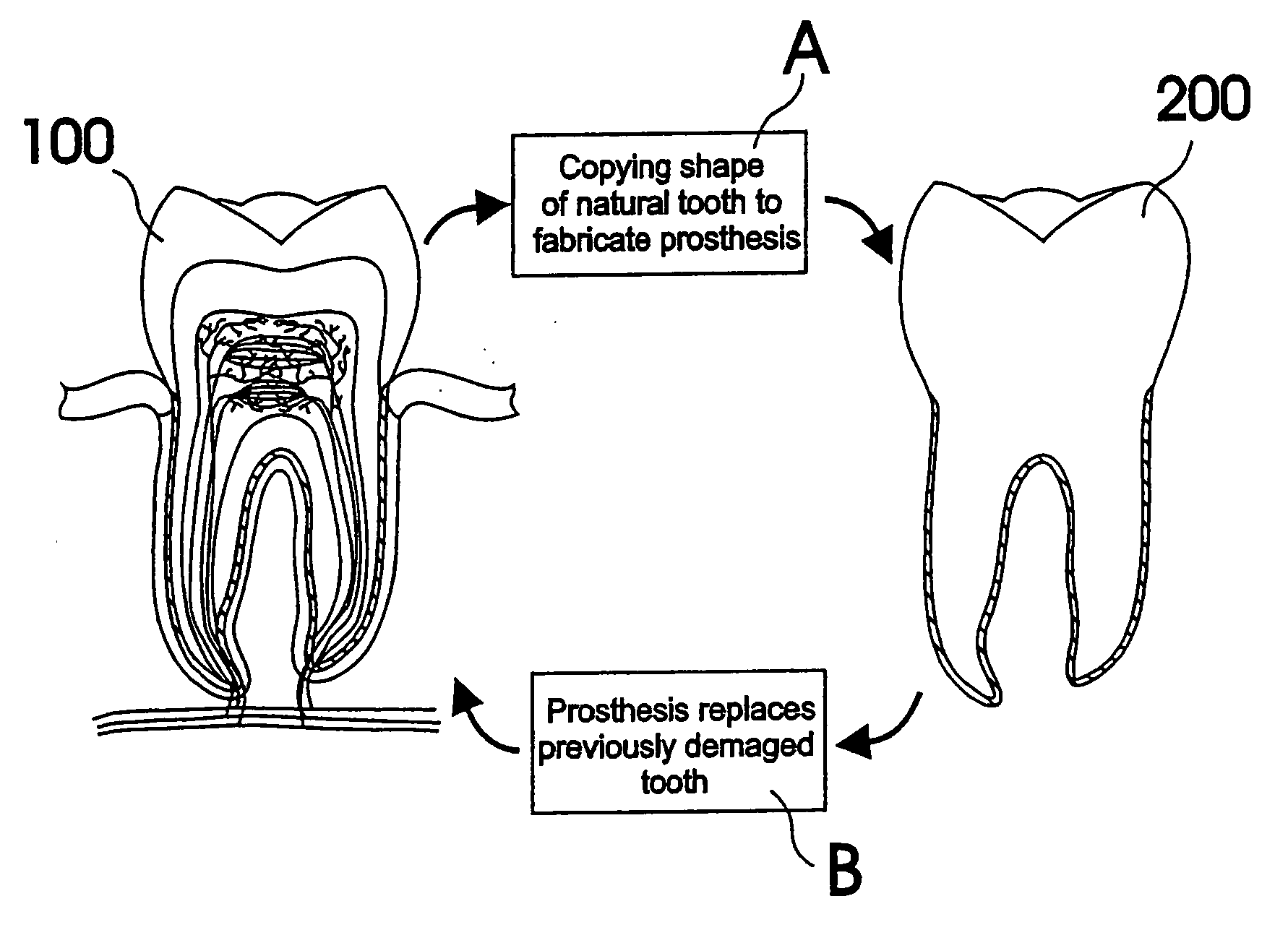
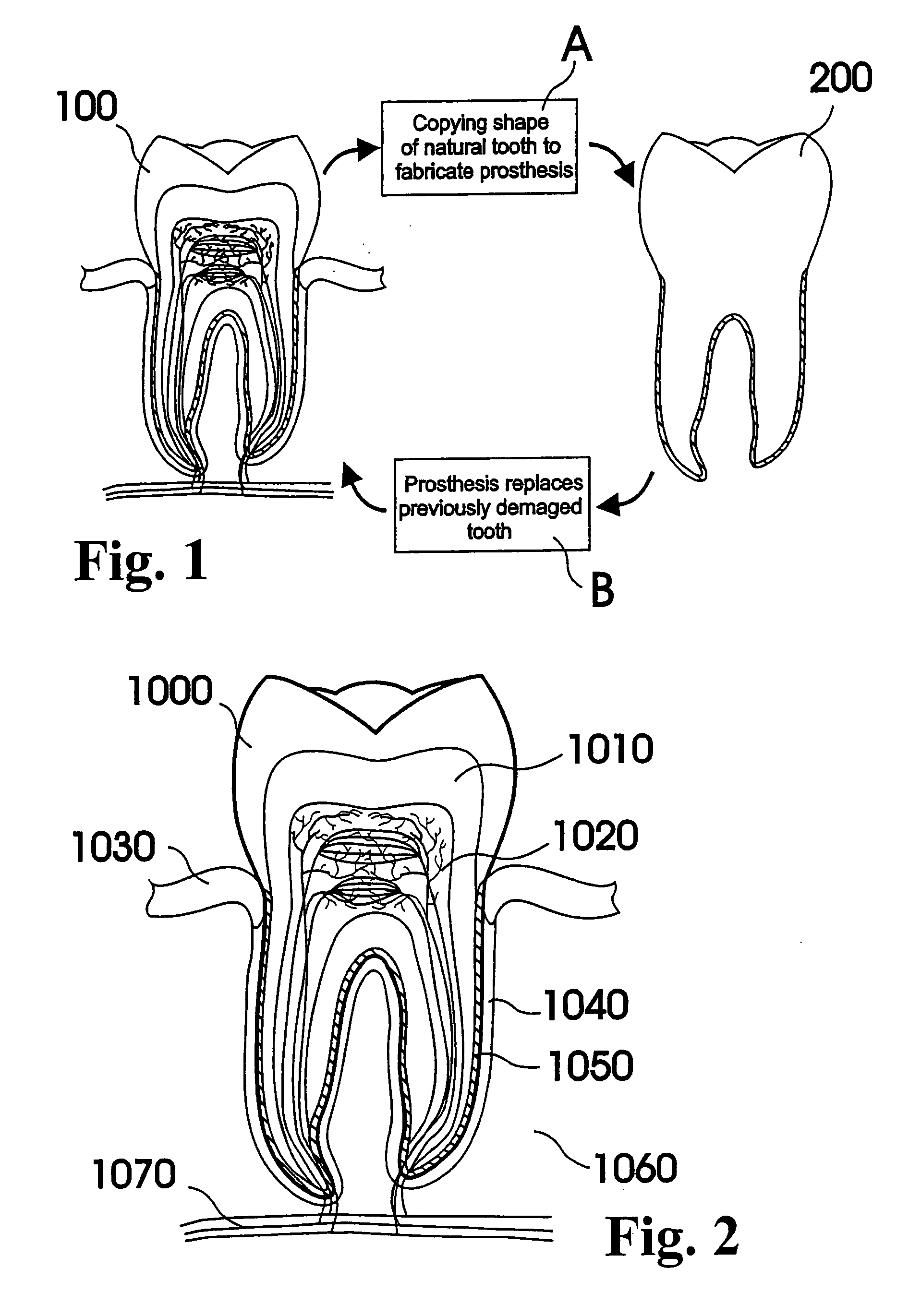
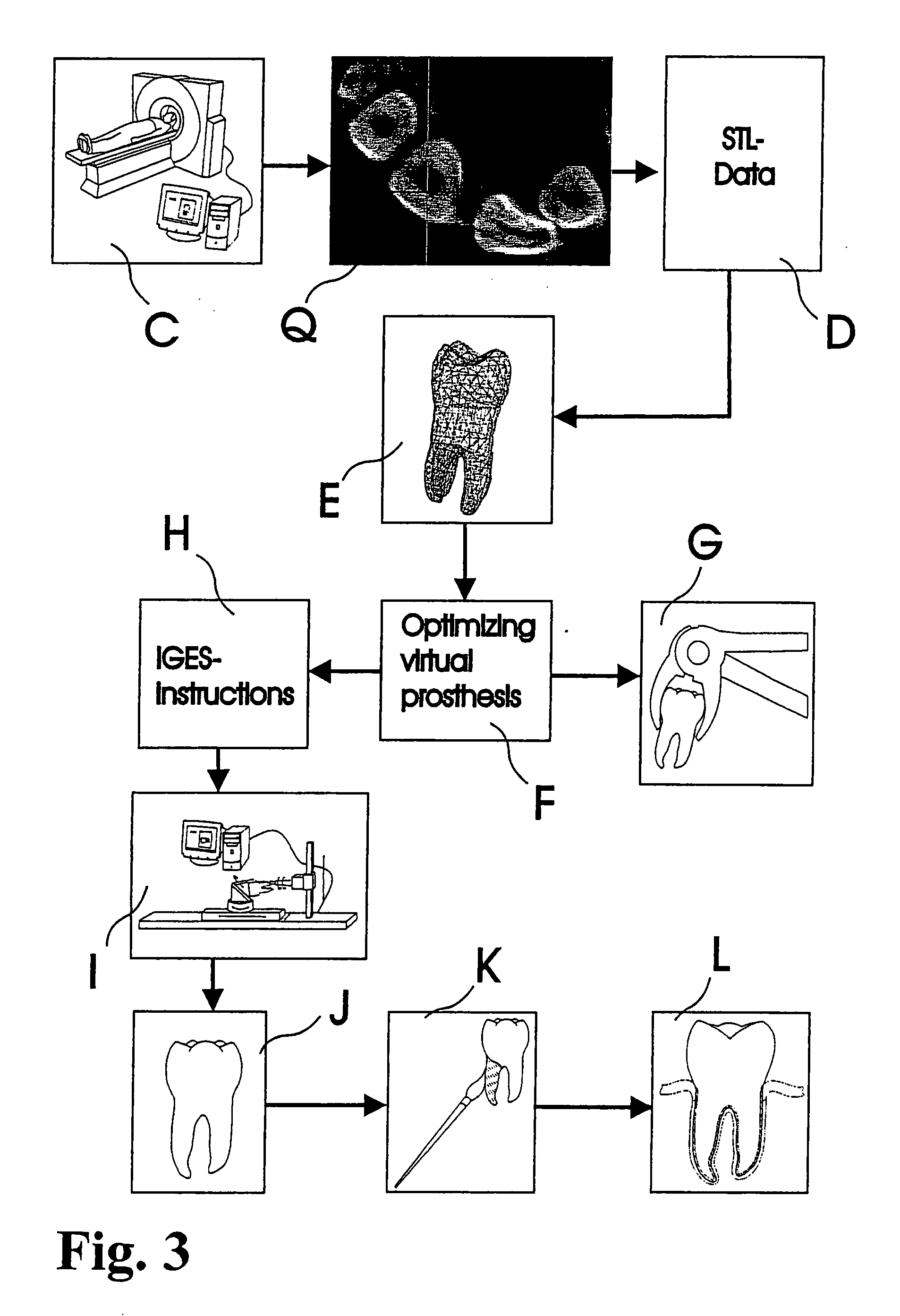
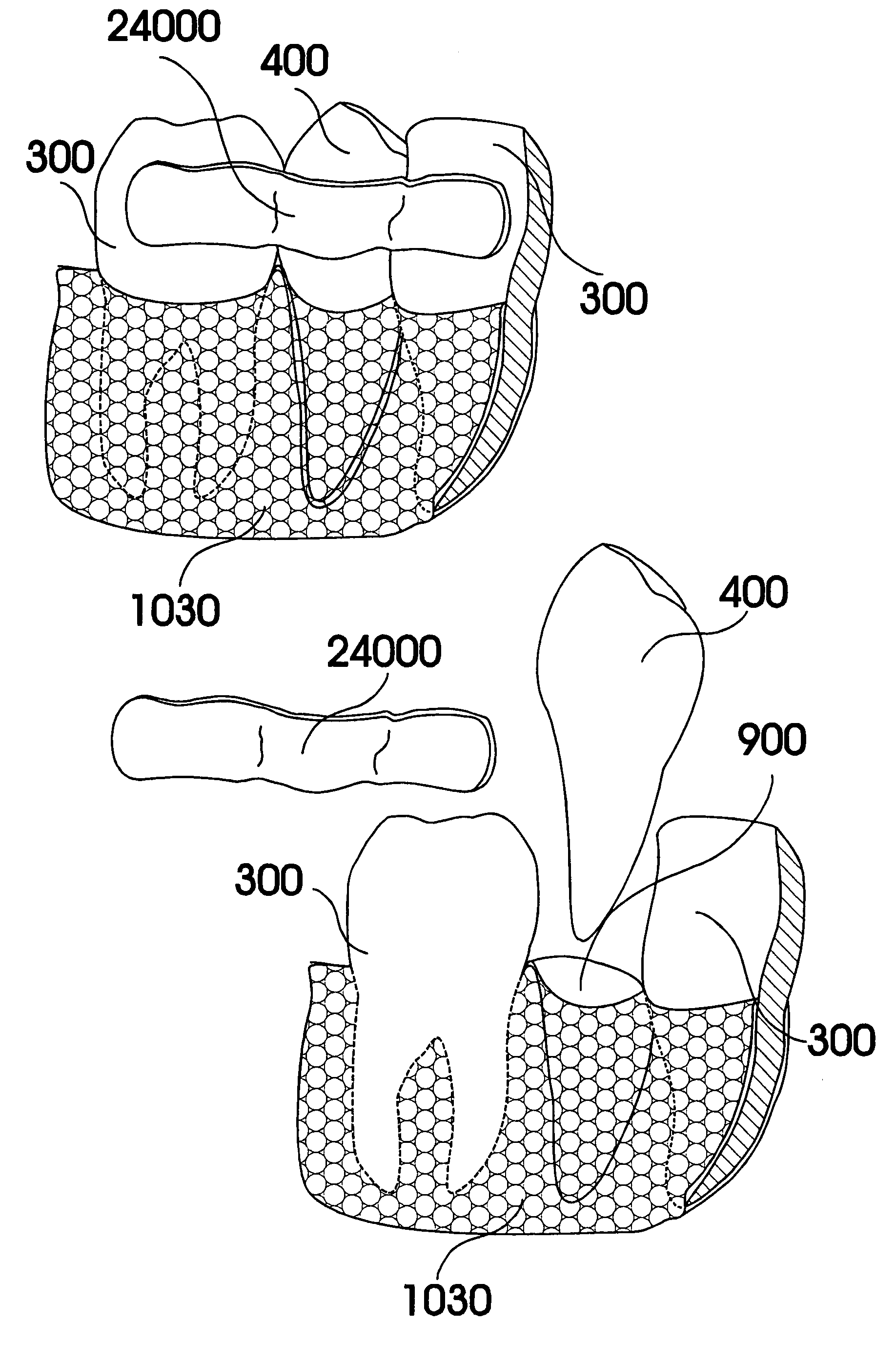
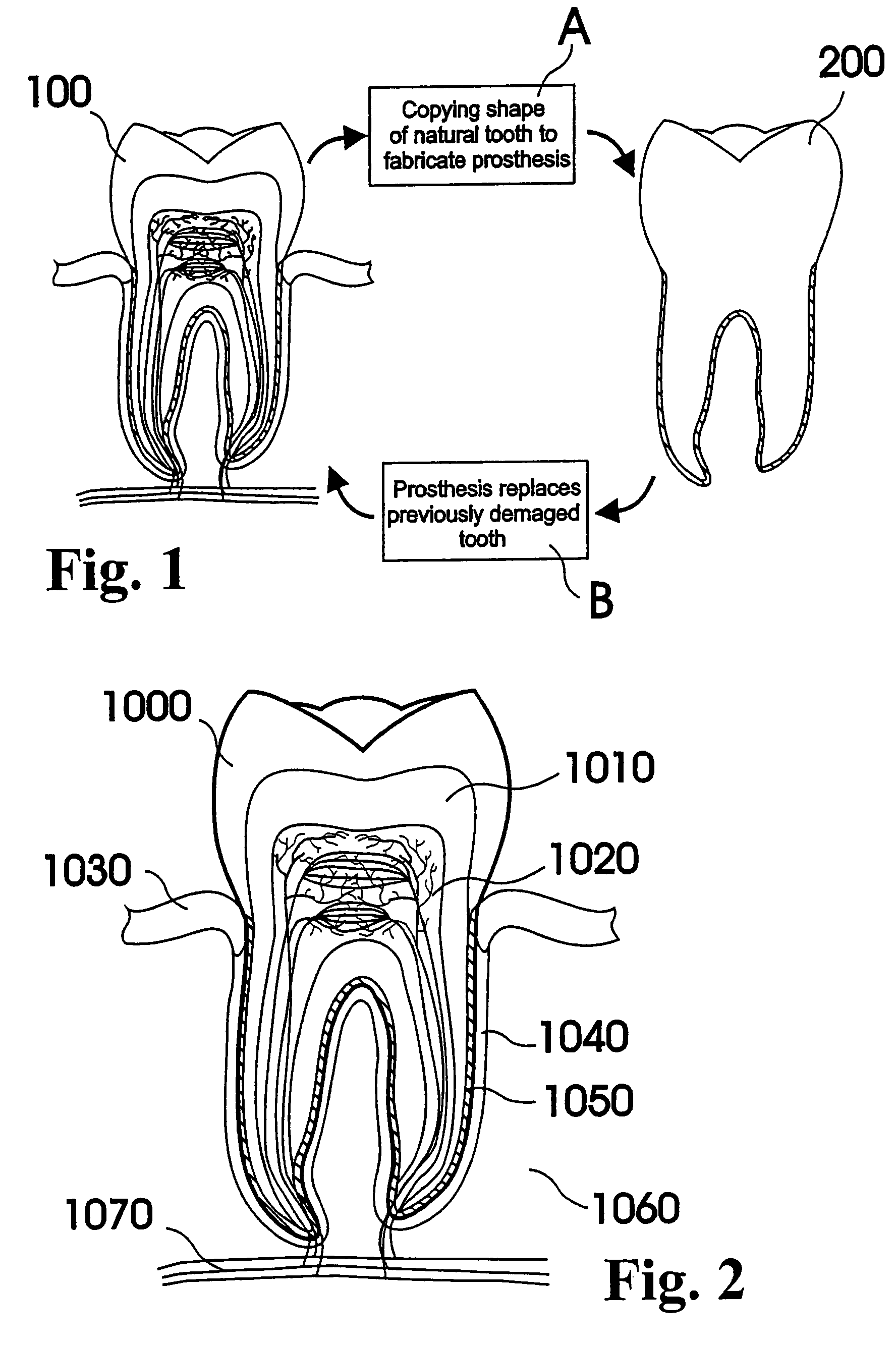
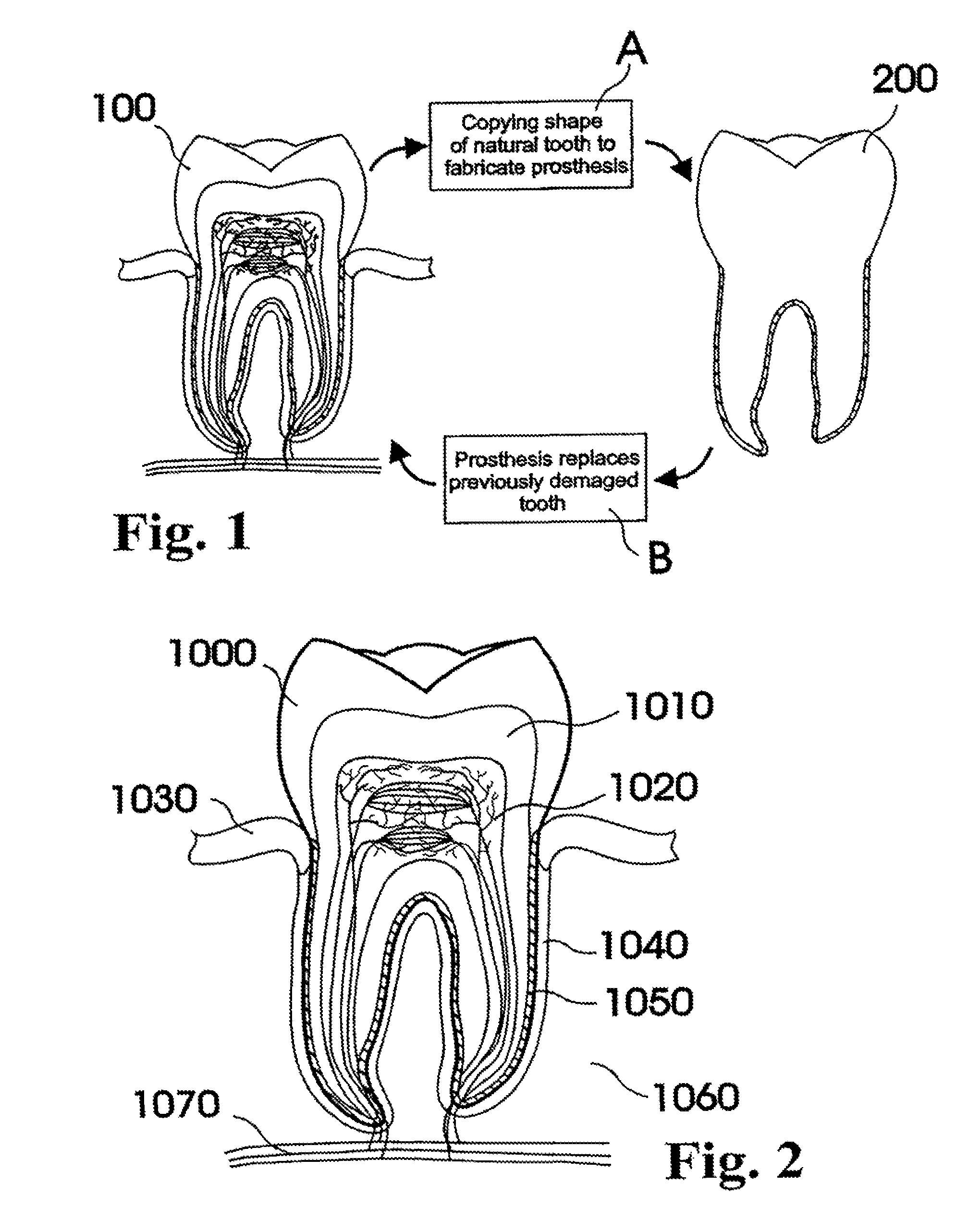
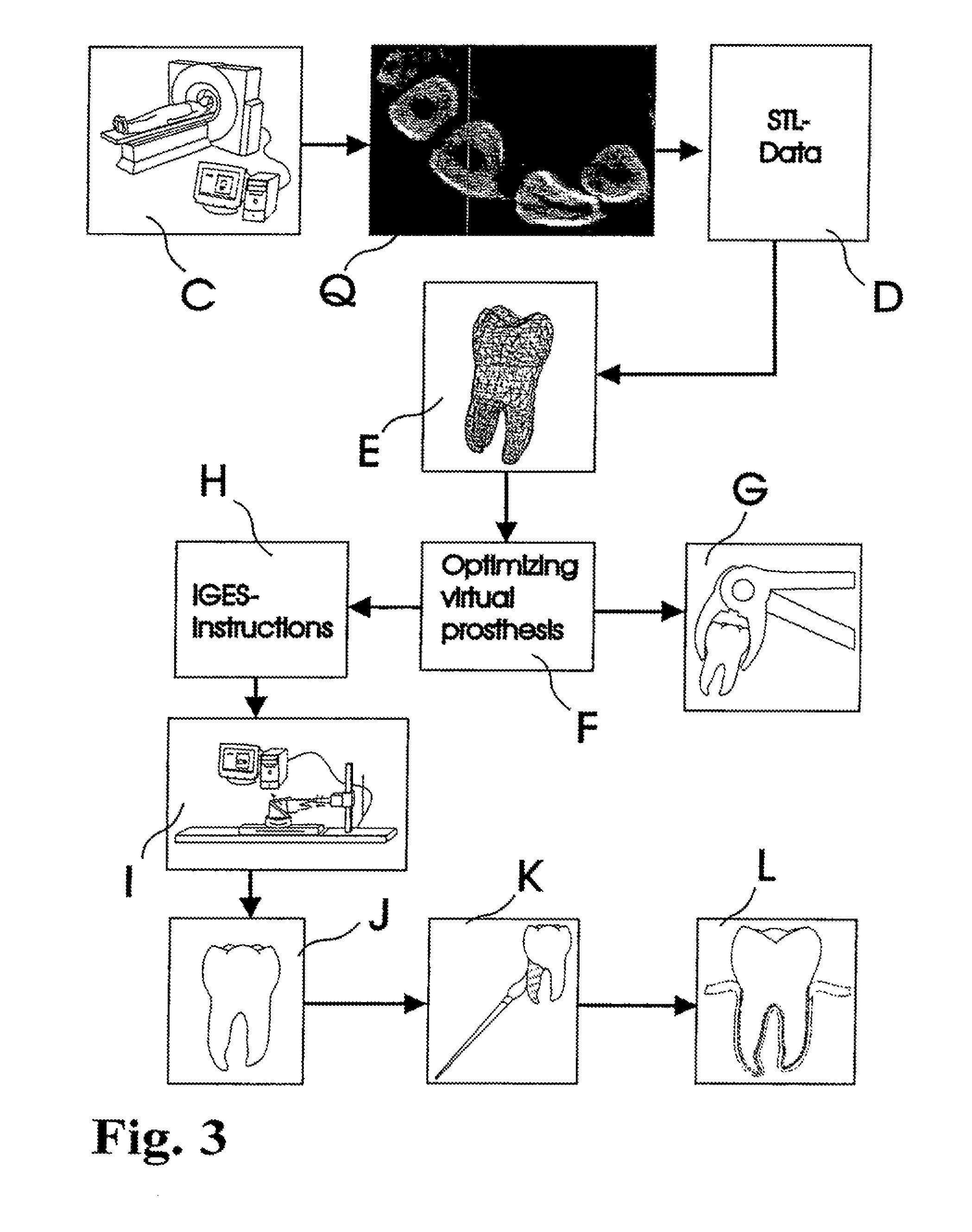
Customized dental prosthesis for periodontal- or osseointegration, and related systems and methods
ActiveUS20080090207A1None have achieved superiorQuality improvementDental implantsImpression capsOsseointegrationExtracted tooth
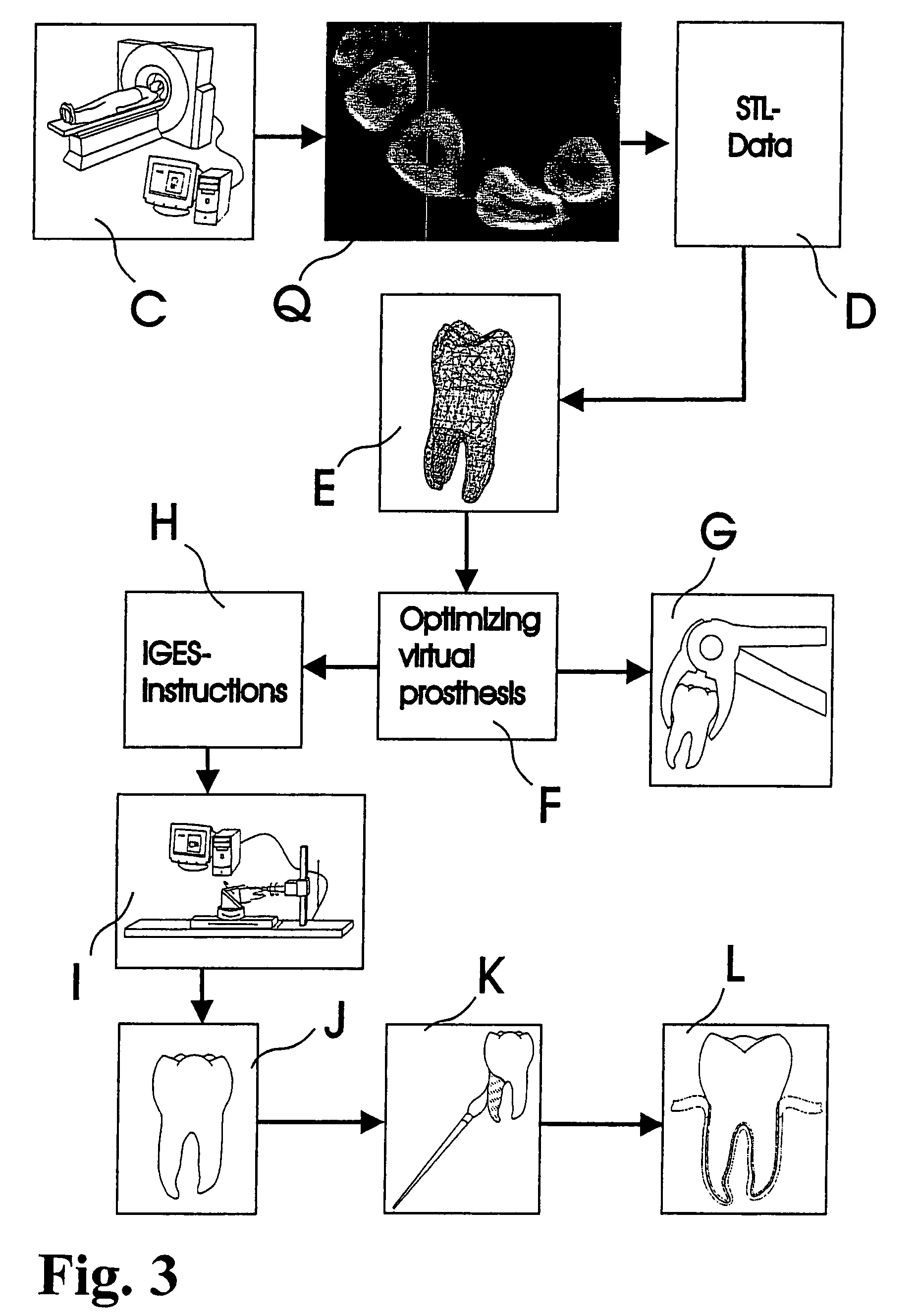
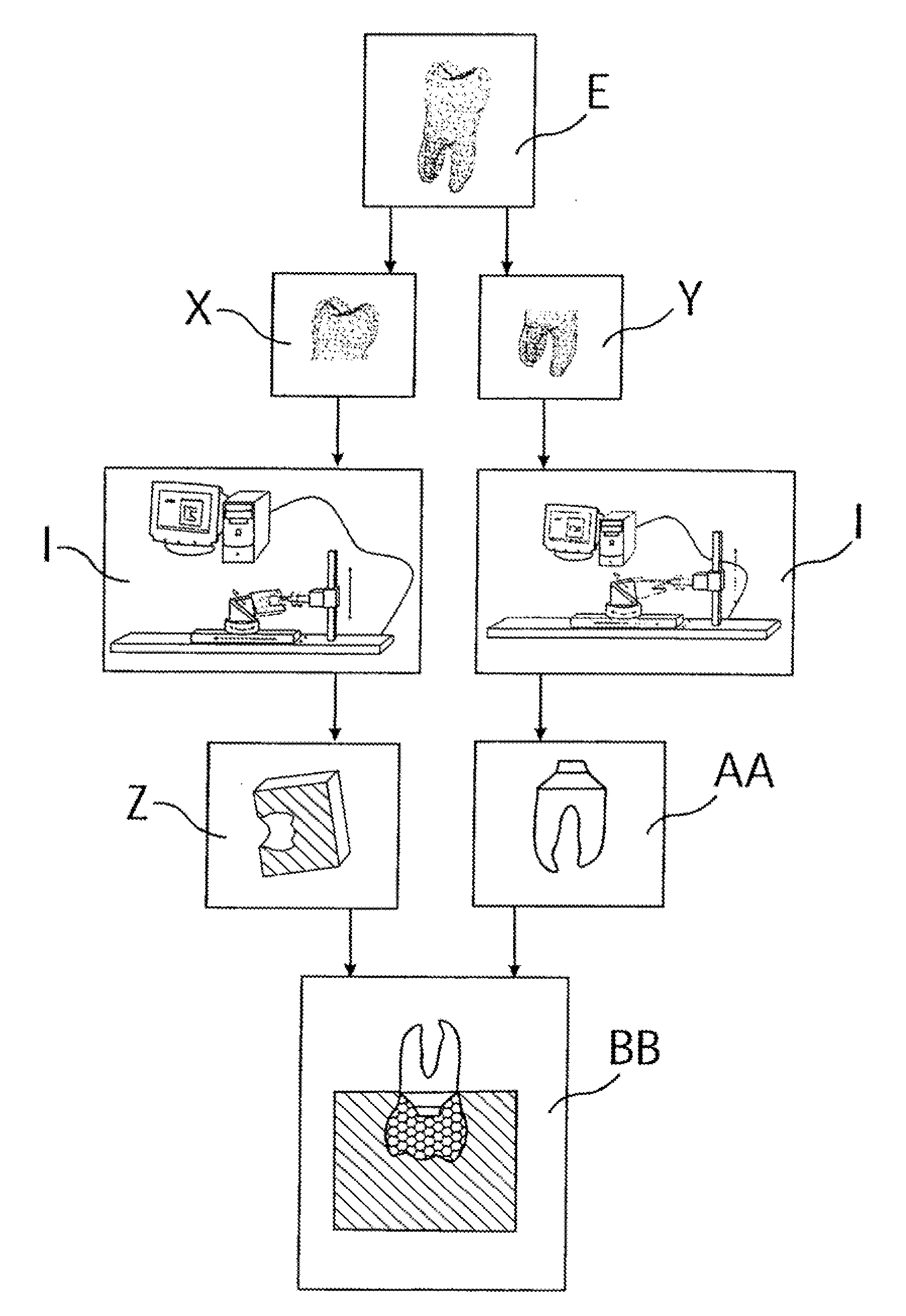
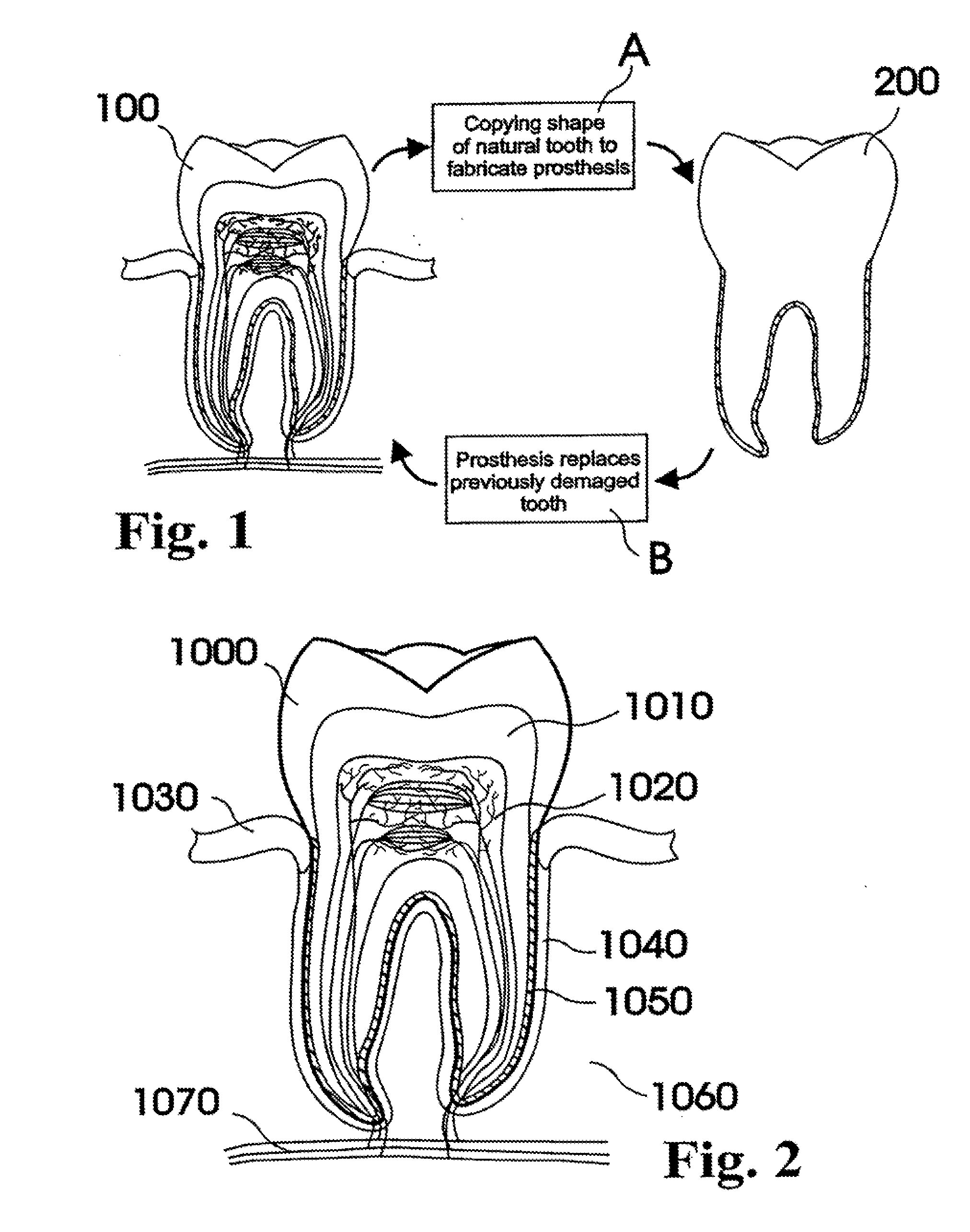
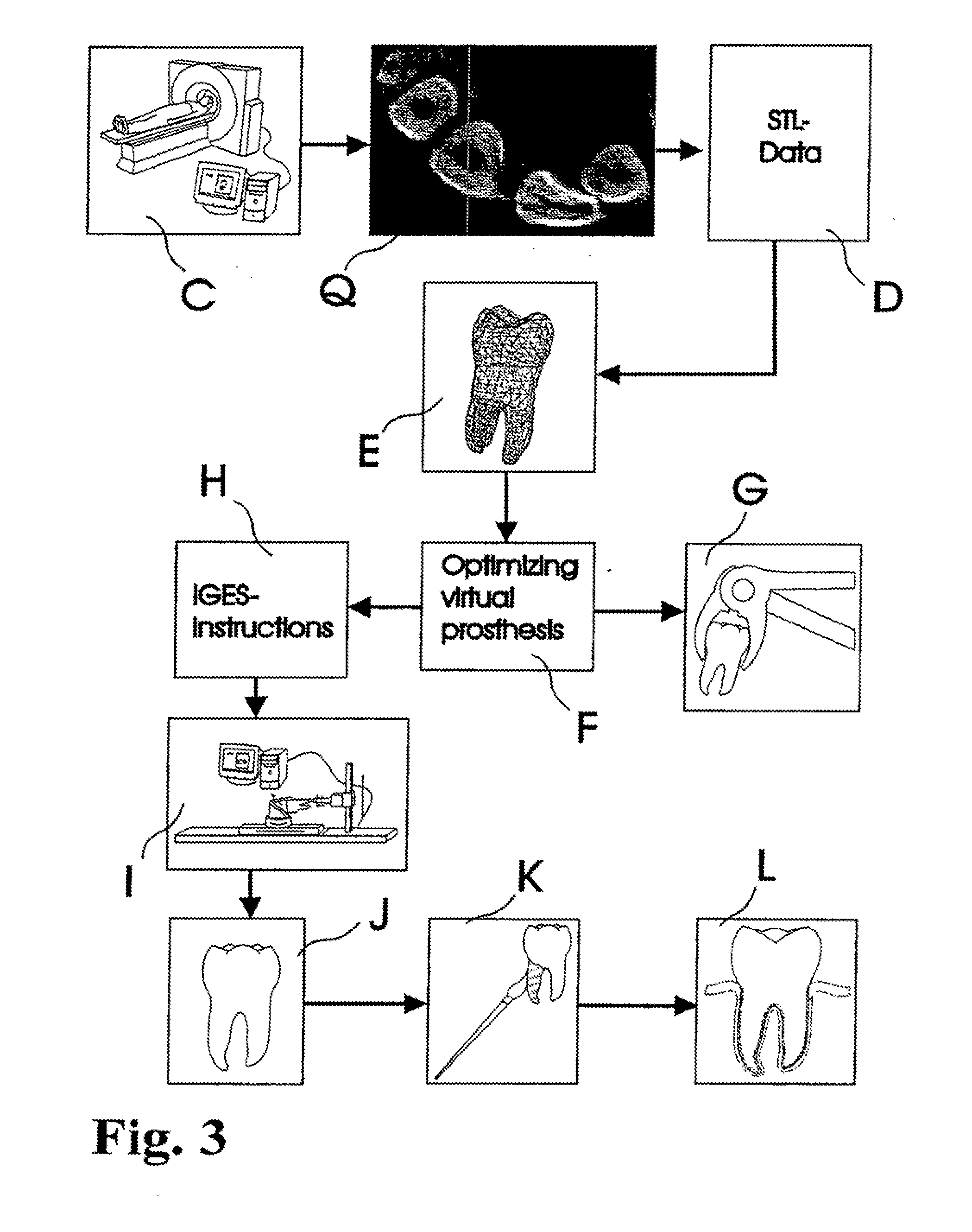
A dental prosthesis for periodontal integration is disclosed. Furthermore a customized dental prosthesis for osseointegration is disclosed having a first manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a root of a tooth to be replaced and a second manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a crown of a tooth to be replaced. Furthermore a customized manufactured splint is disclosed to position and fixate a tooth-shaped prosthesis. Furthermore a CAD / CAM based method of and a system for manufacturing a customized dental prosthesis replacing an extracted tooth is disclosed, where the extracted tooth is scanned regarding its three-dimensional shape and substantially copied using (a) an imaging system in-vitro like a 3D scanner or in-vivo like a cone beam CT system, (b) CNC machinery and (c) biocompatible material that is suitable to be integrated into the extraction socket and at least partially adopted by the existing tissue forming the socket.
Owner:NATURAL DENTAL IMPLANTS
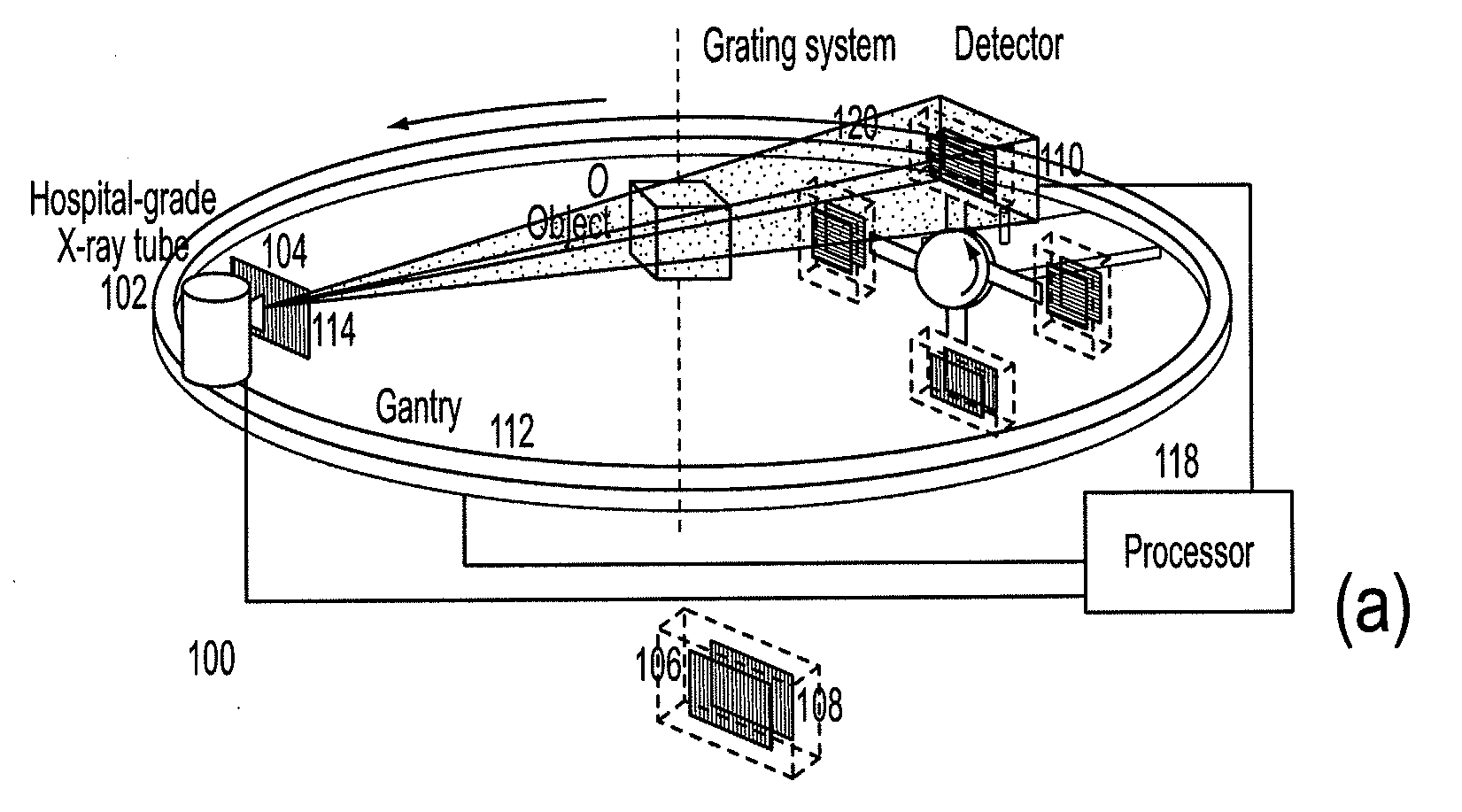
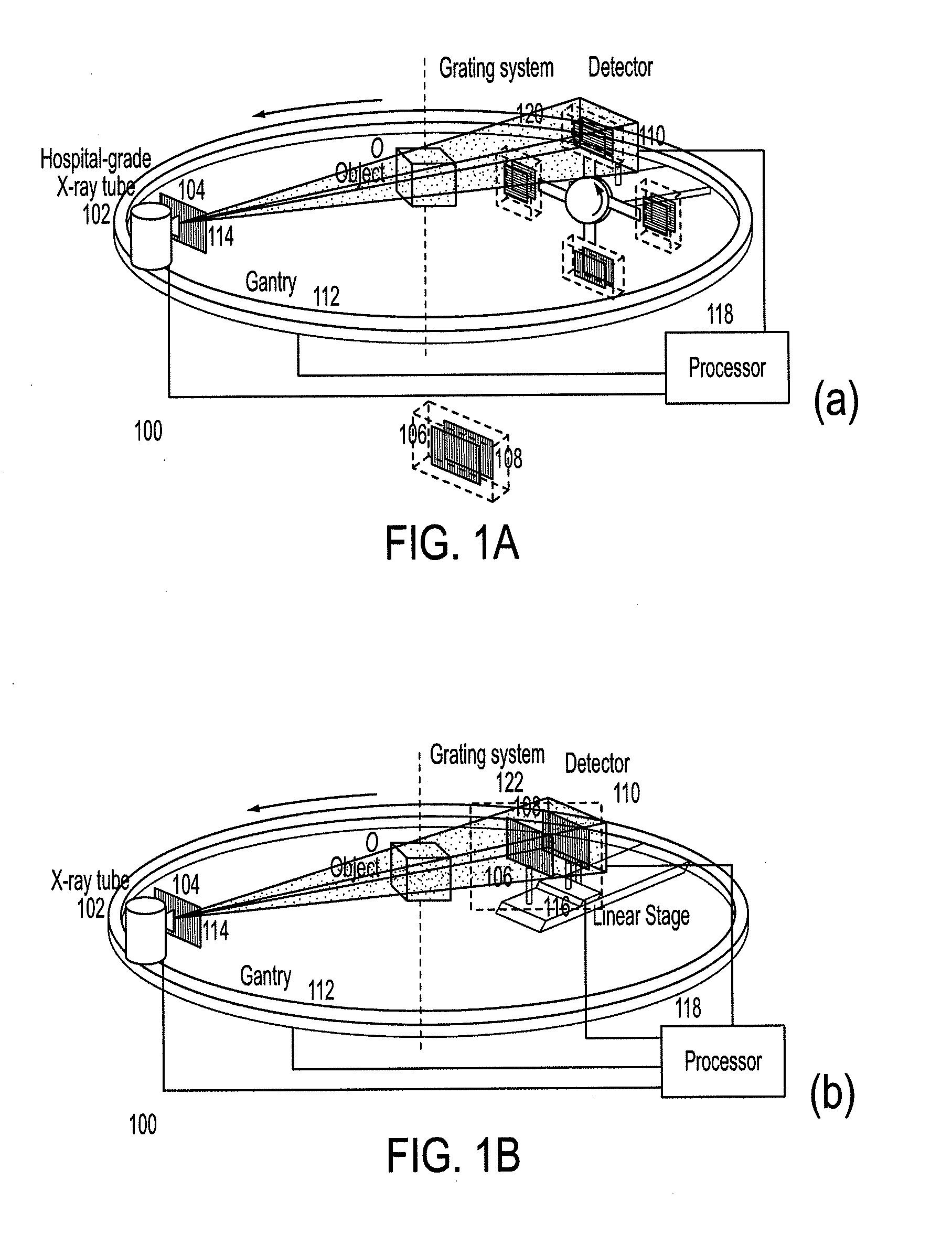
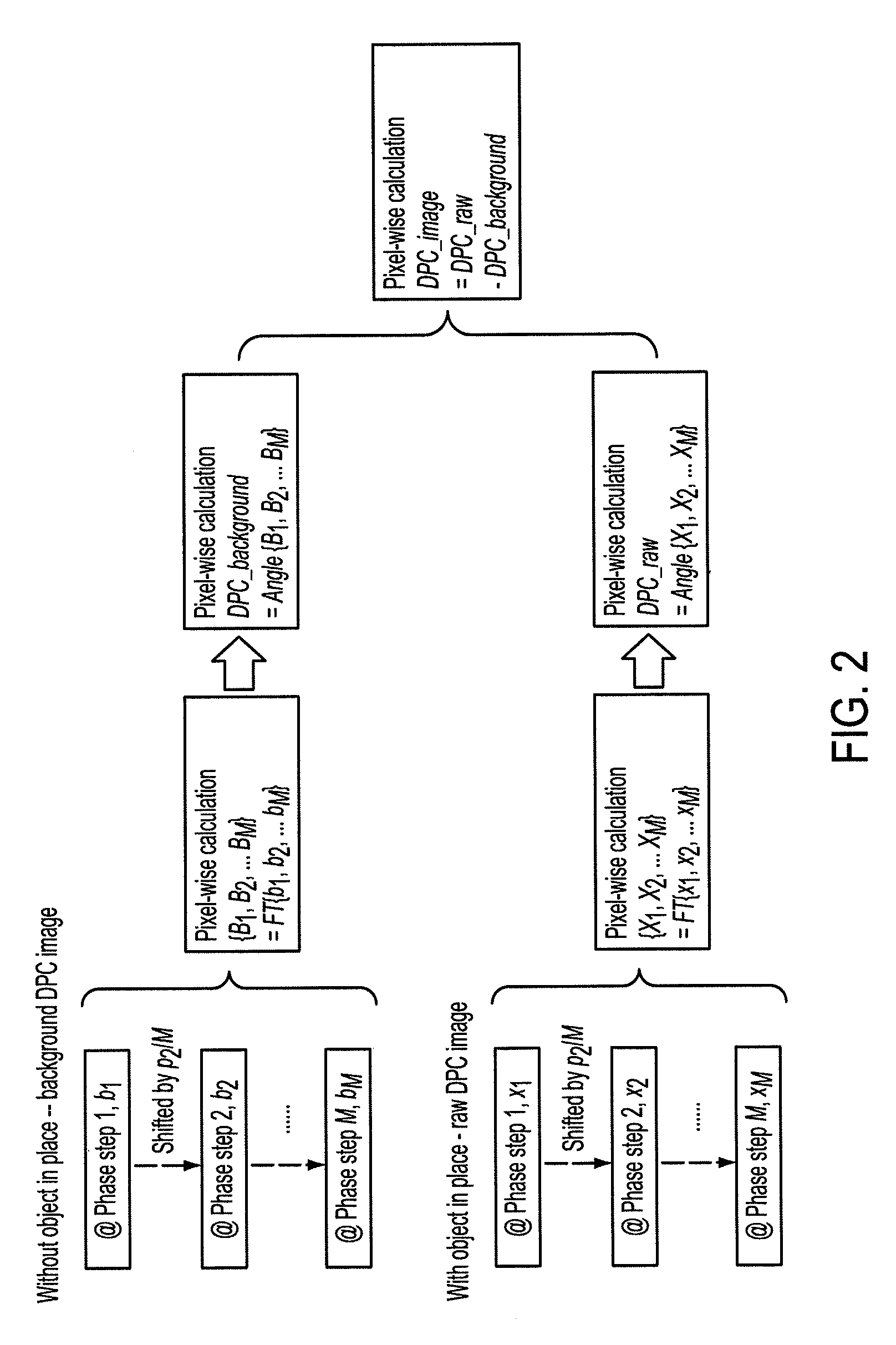
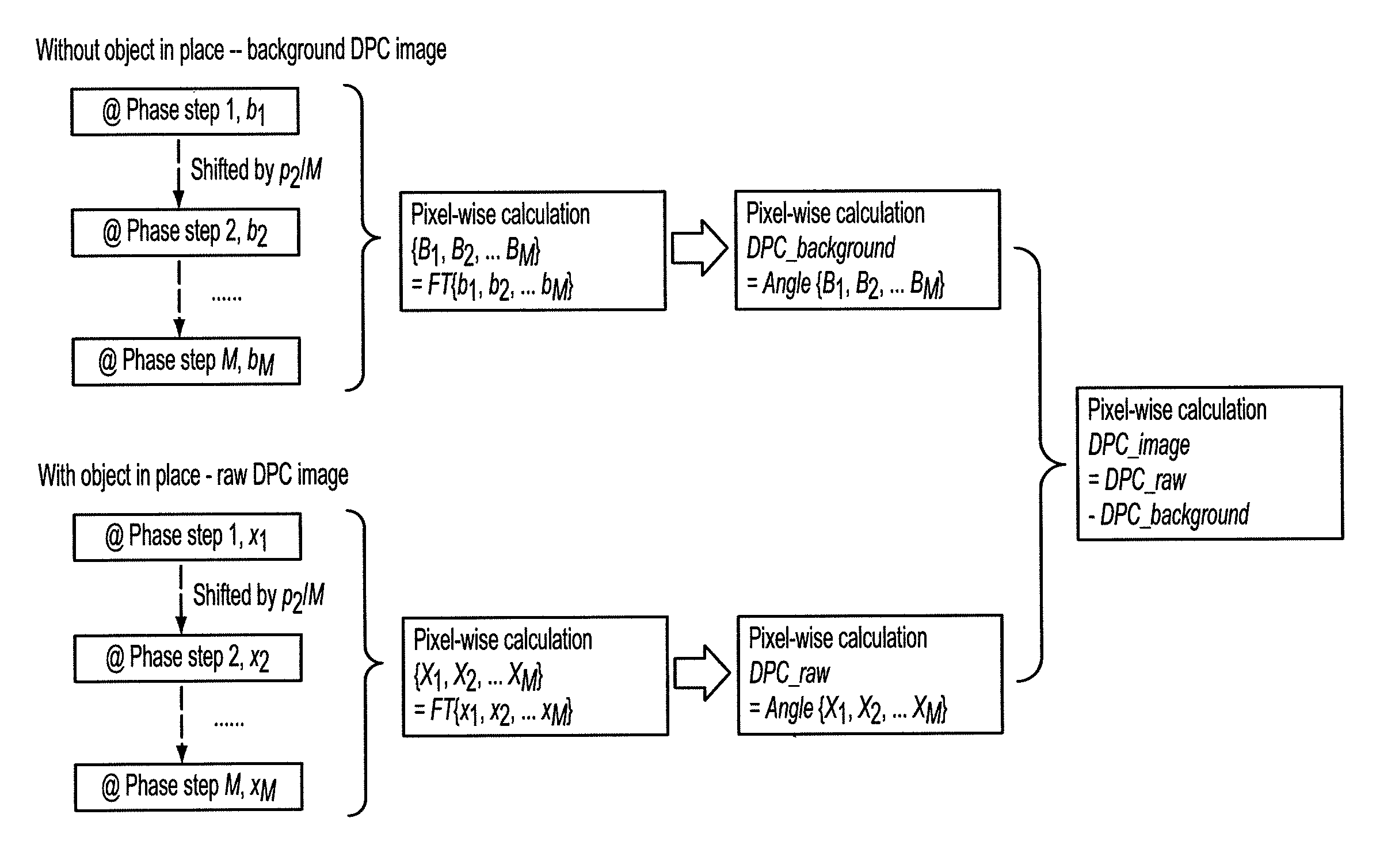
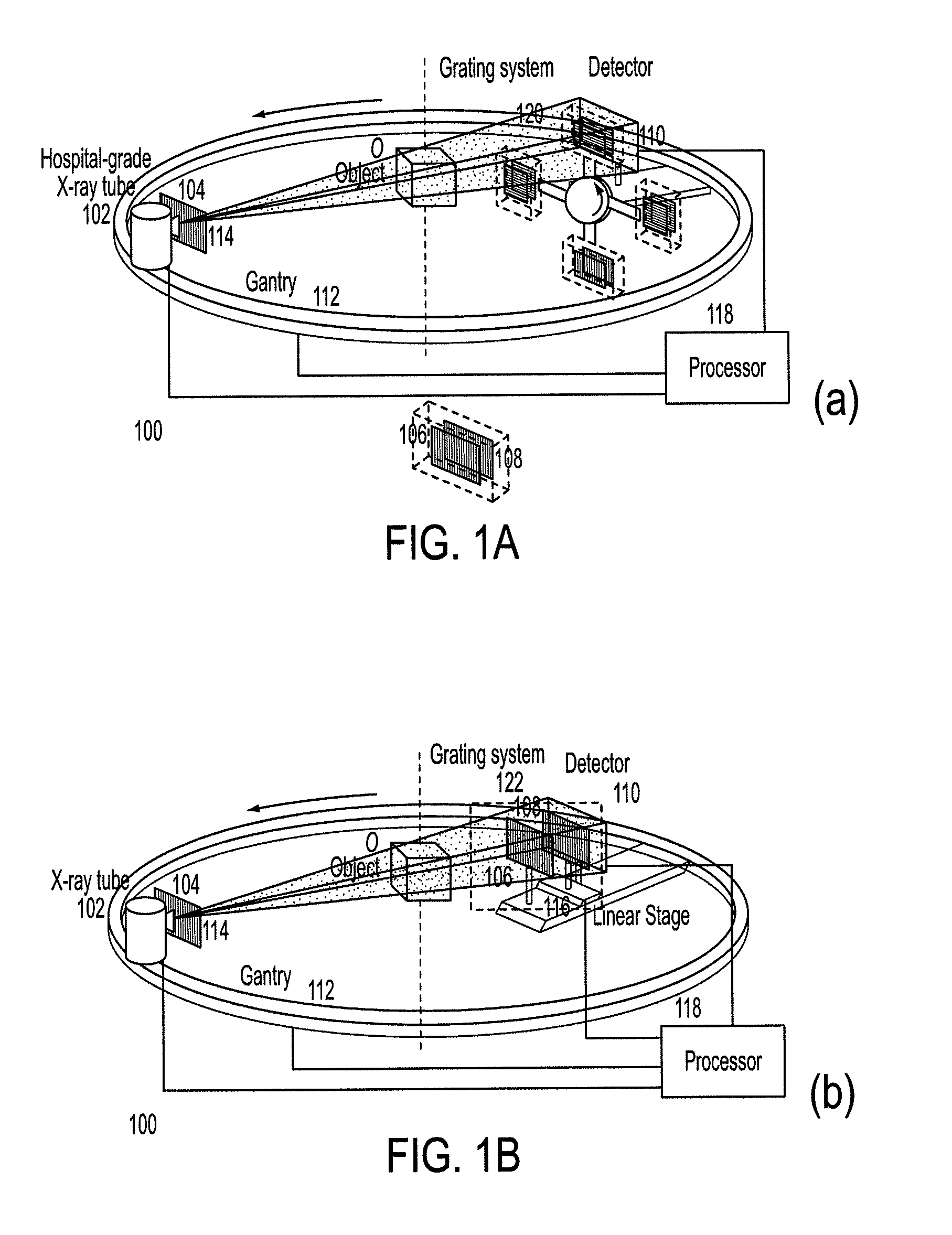
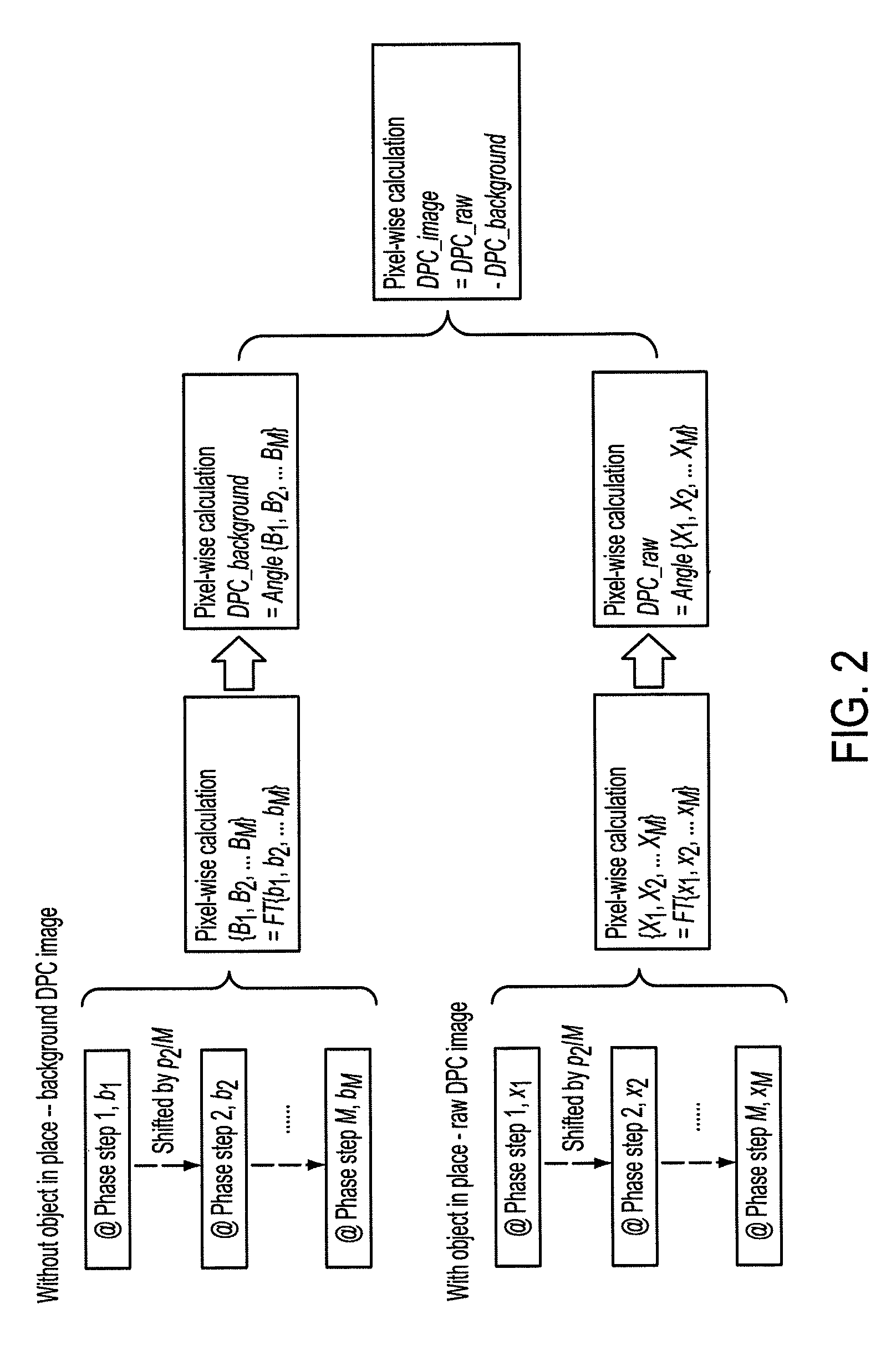
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam ct, cone-beam ct and hybrid cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20100220832A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease doseImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingHybrid systemPhase grating
A device for imaging an object, such as for breast imaging, includes a gantry frame having mounted thereon an x-ray source, a source grating, a holder or other place for the object to be imaged, a phase grating, an analyzer grating, and an x-ray detector. The device images objects by differential-phase-contrast cone-beam computed tomography. A hybrid system includes sources and detectors for both conventional and differential-phase-contrast computed tomography.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Methods and apparatus for differential phase-contrast fan beam CT, cone-beam CT and hybrid cone-beam CT
ActiveUS7949095B2Increase doseImprove spatial resolutionImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingPhase gratingHybrid system
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Customized dental prosthesis for periodontal- or osseointegration, and related systems and methods
ActiveUS7708557B2Quality improvementNone have achieved superiorDental implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatusOsseointegrationExtracted tooth
A dental prosthesis for periodontal integration is disclosed. Furthermore a customized dental prosthesis for osseointegration is disclosed having a first manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a root of a tooth to be replaced and a second manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a crown of a tooth to be replaced. Furthermore a customized manufactured splint is disclosed to position and fixate a tooth-shaped prosthesis. Furthermore a CAD / CAM based method of and a system for manufacturing a customized dental prosthesis replacing an extracted tooth is disclosed, where the extracted tooth is scanned regarding its three-dimensional shape and substantially copied using (a) an imaging system in-vitro like a 3D scanner or in-vivo like a cone beam CT system, (b) CNC machinery and (c) biocompatible material that is suitable to be integrated into the extraction socket and at least partially adopted by the existing tissue forming the socket.
Owner:NATURAL DENTAL IMPLANTS
Customized Dental Prosthesis for Periodontal or Osseointegration and Related Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20100203478A1Great primary stabilityQuality improvementDental implantsImpression capsOsseointegrationProsthesis
Dental prosthesis, systems, and methods of forming and using a dental prosthesis, are provided. An example of a dental prosthesis includes a first manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a root of a tooth to be replaced and a second manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a crown of the tooth. Furthermore, customized manufactured splints to position and fixate a tooth-shaped prosthesis, are provided. Furthermore, a CAD / CAM based methods of and a systems for manufacturing a customized dental prosthesis are provided. The tooth can be scanned to determine its three-dimensional shape and substantially copied using an imaging system in-vitro like a 3D scanner or in-vivo like a cone beam CT system and CNC machinery. Biocompatible material that is suitable to be integrated into the extraction socket and adopted by existing tissue forming the socket can be manufactured or engineered.
Owner:NATURAL DENTAL IMPLANTS
Dose-guided radiation therapy using cone beam CT
ActiveUS20090003512A1Easy to adaptMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiation therapyScattering radiation
A system includes acquisition of a three-dimensional cone beam image, and determination of a dose to be delivered based on the three-dimensional image and on parameters of a treatment beam to deliver the dose. Some systems may include modification of a three-dimensional cone beam image to correct for scatter radiation, and determination of a dose based on the modified three-dimensional cone beam image.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +2
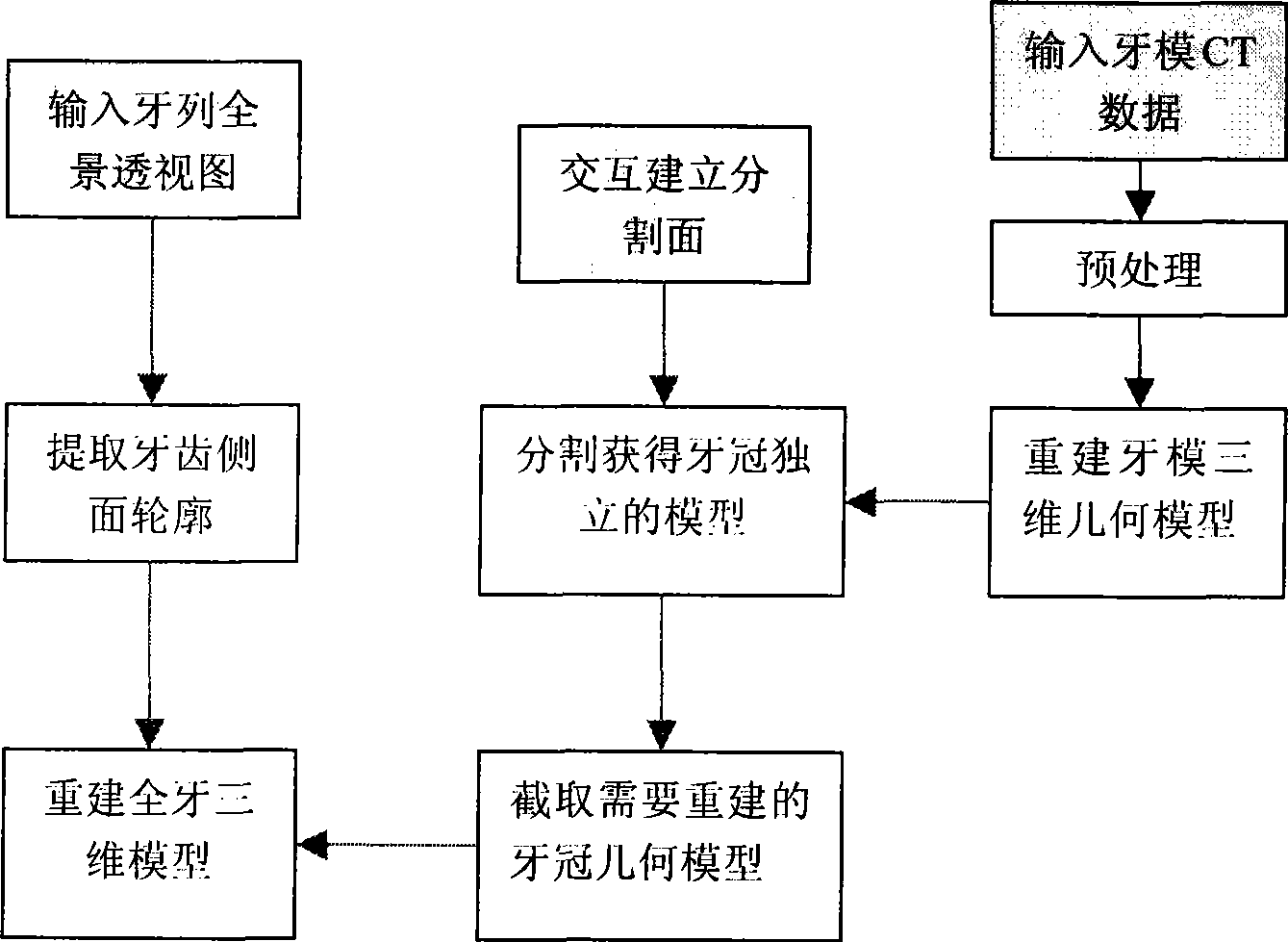
Method for reconstructing three dimensional model of complete teeth through CT data of dentognathic gypsum model and dentognathic panoramic perspective view
The invention provides a method for reconstructing a three-dimensional model of an entire tooth through the CT data of a plaster model of jaw and the panoramic drawing of the jaw. The method adopts the following steps: a cone beam CT (CBCT) specially used for the oral cavity is used for scanning the plaster model of the jaw to obtain the CT data of the plaster model of the jaw; three-dimensional reconstruction is performed to the CT data of the plaster model of the jaw to obtain the three-dimensional geometric model of the jaw; the three-dimensional geometric model of the jaw is extracted; the information on the side contour of the tooth is extracted and the three-dimensional geometric model of the radix dentis is generated in combination with the model of the corona dentis; and the three-dimensional model of the entire tooth is formed by combining the three-dimensional geometric models of the corona dentis and the radix dentis. The invention has the advantages that the three-dimensional geometric digit model of the entire tooth can be generated on the basis of the two-dimensional information of the side contour of the tooth on the panoramic drawing and according to the three-dimensional geometric information of the corona dentis part in the CT data. The method can be applied to every tooth in the panoramic drawing to generate the jaw model with accurate dentition, and can be applied to orthodontics and computer simulated tooth arrangement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
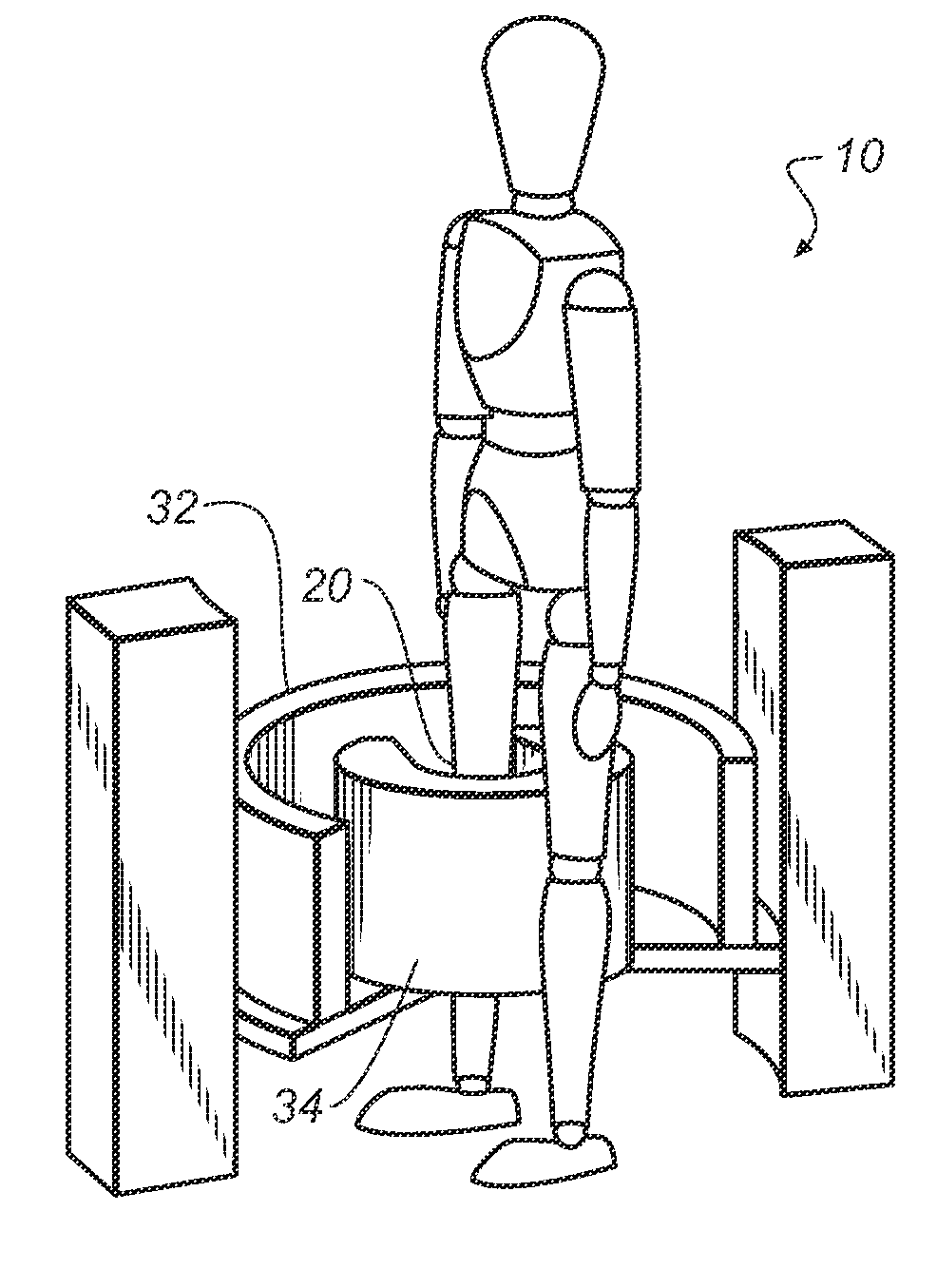
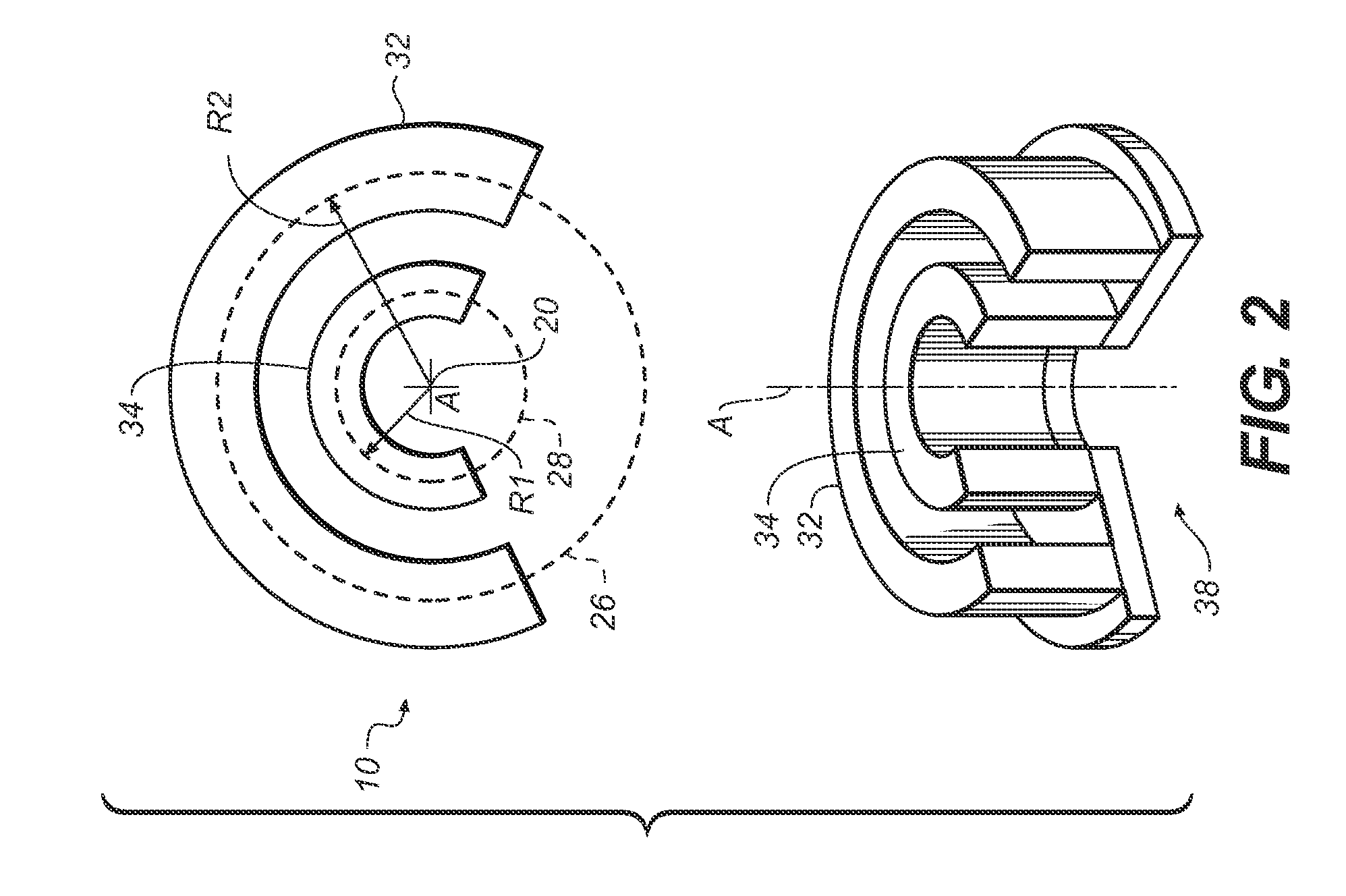
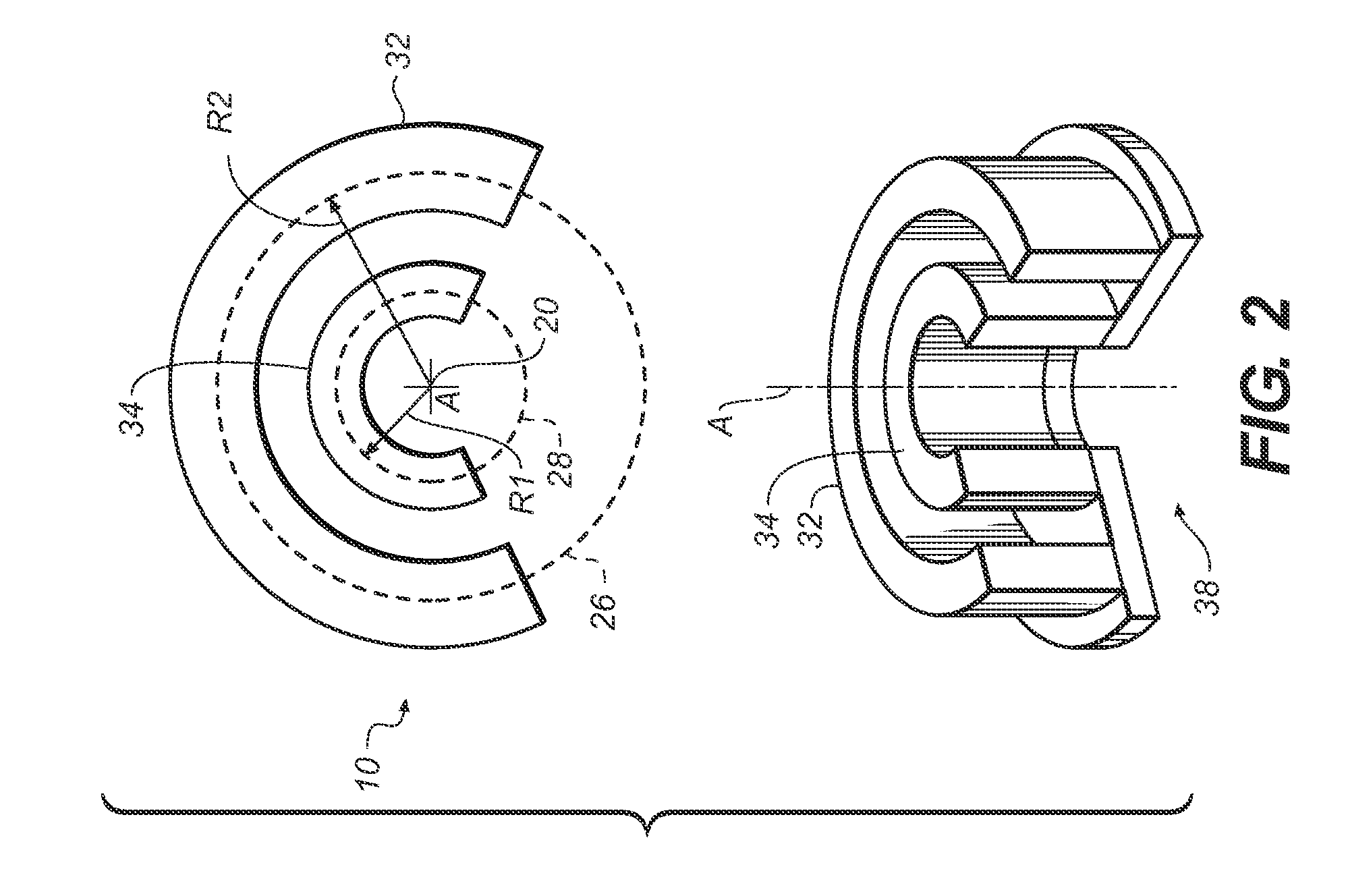
Extremity imaging apparatus for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS20100278300A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiation exposureImaging equipment
An apparatus for cone beam computed tomography of an extremity has a digital radiation detector and a first device to move the detector along a circular detector path extending so that the detector moves both at least partially around a first extremity of the patient and between the first extremity and a second, adjacent extremity. The detector path has radius R1 sufficient to position the extremity approximately centered in the detector path. There is a radiation source with a second device to move the source along a concentric circular source path having a radius R2 greater than radius R1, radius R2 sufficiently long to allow adequate radiation exposure of the first extremity for an image capture by the detector. A first circumferential gap in the source path allows the second extremity to be positioned in the first circumferential gap during image capture.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
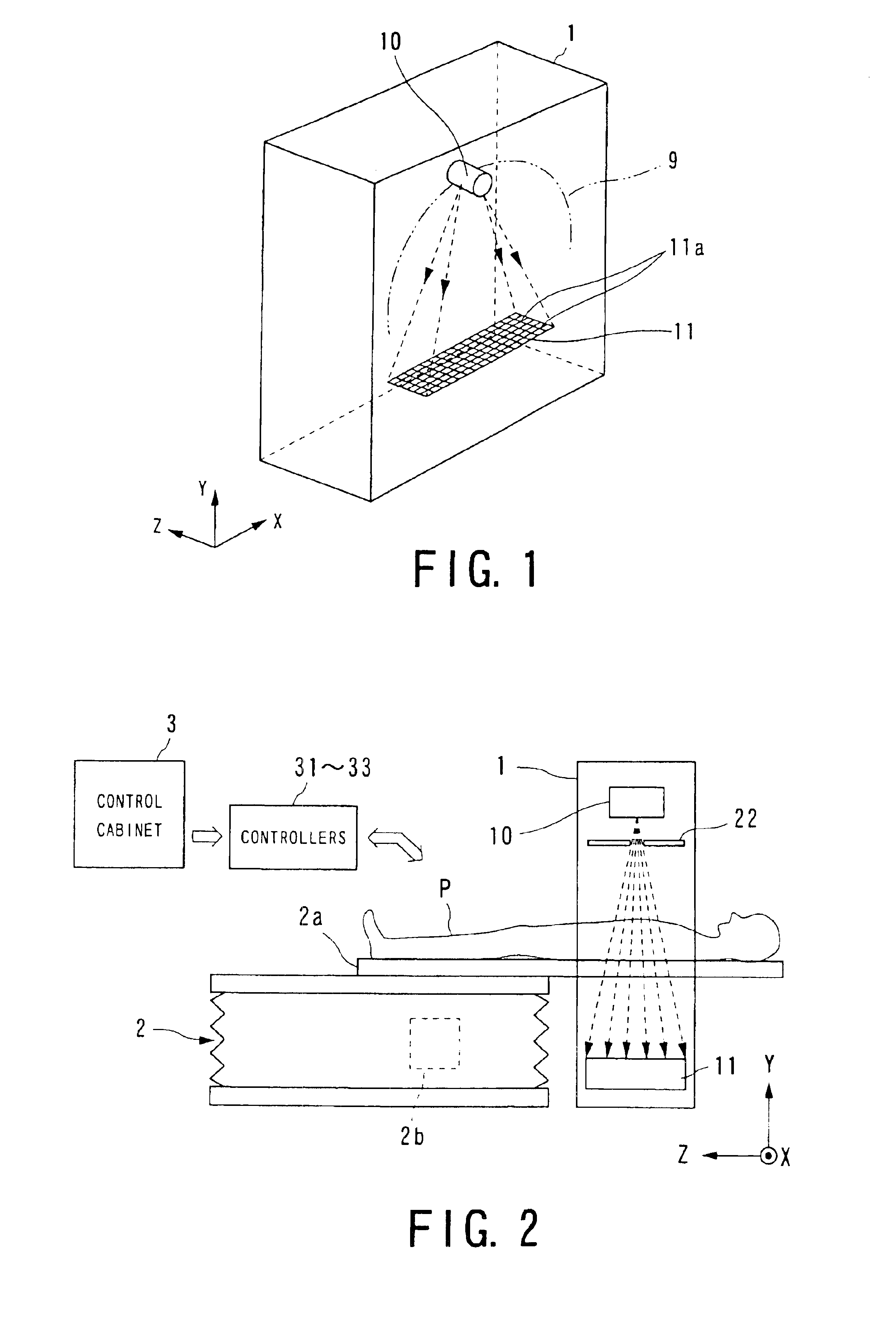
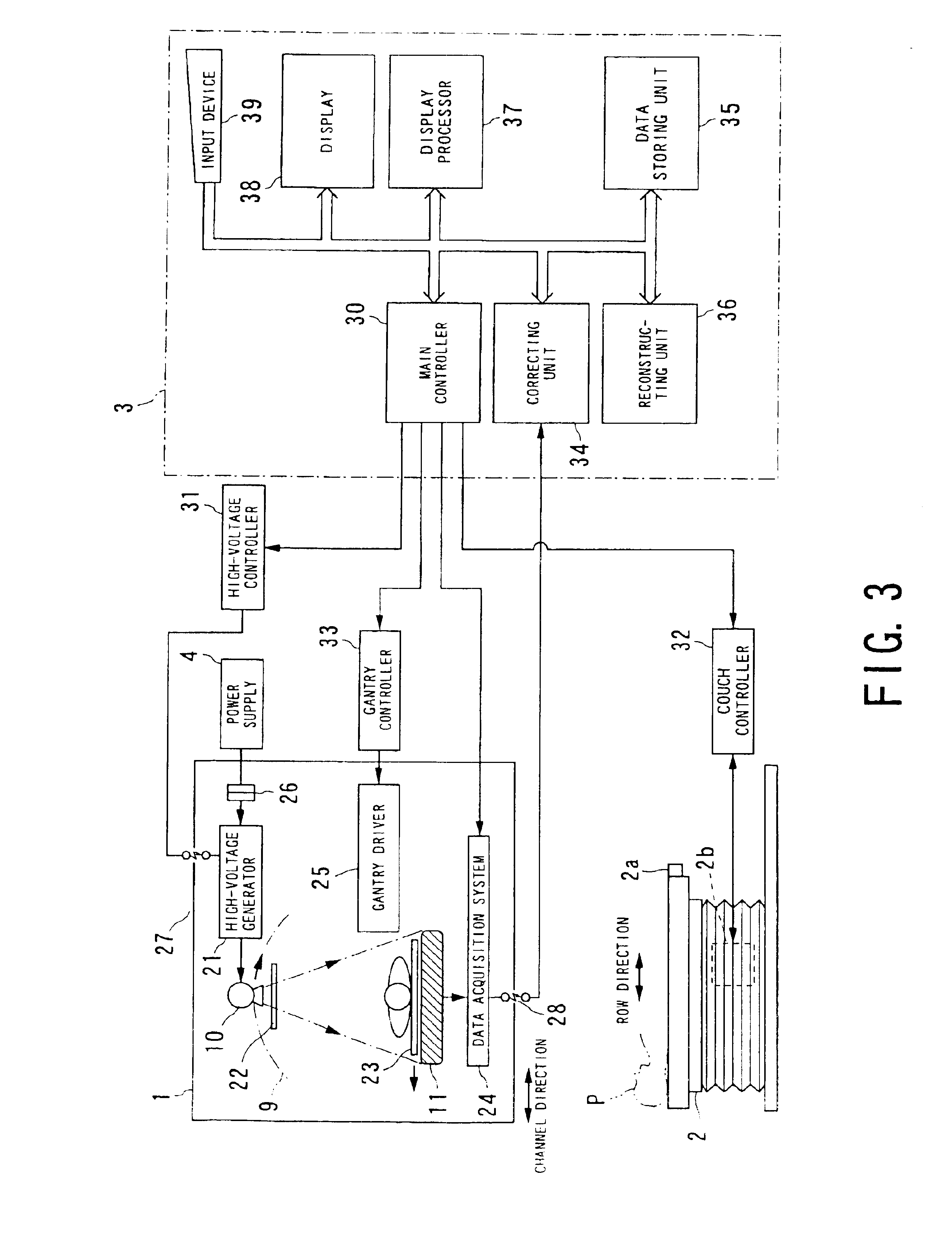
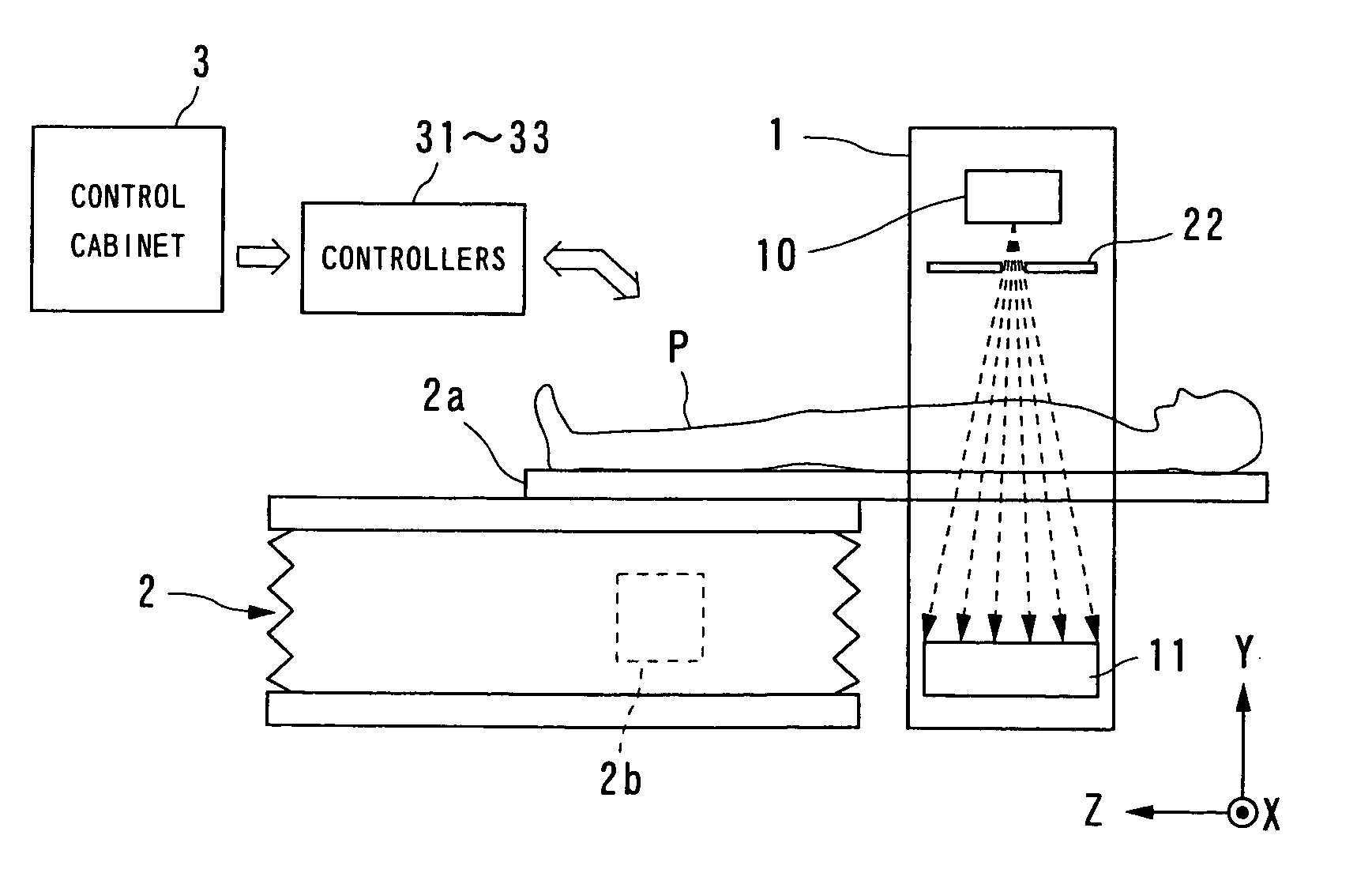
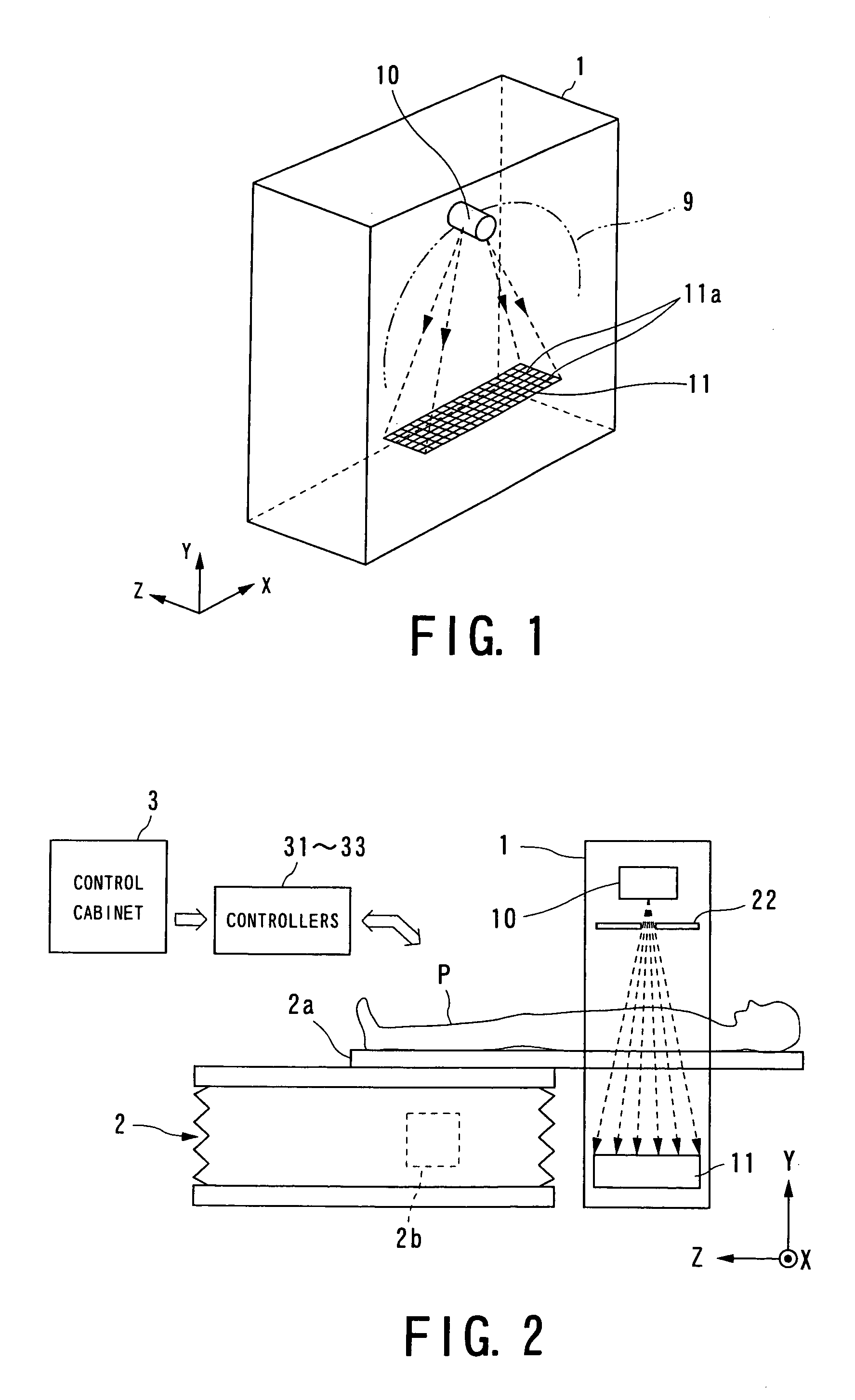
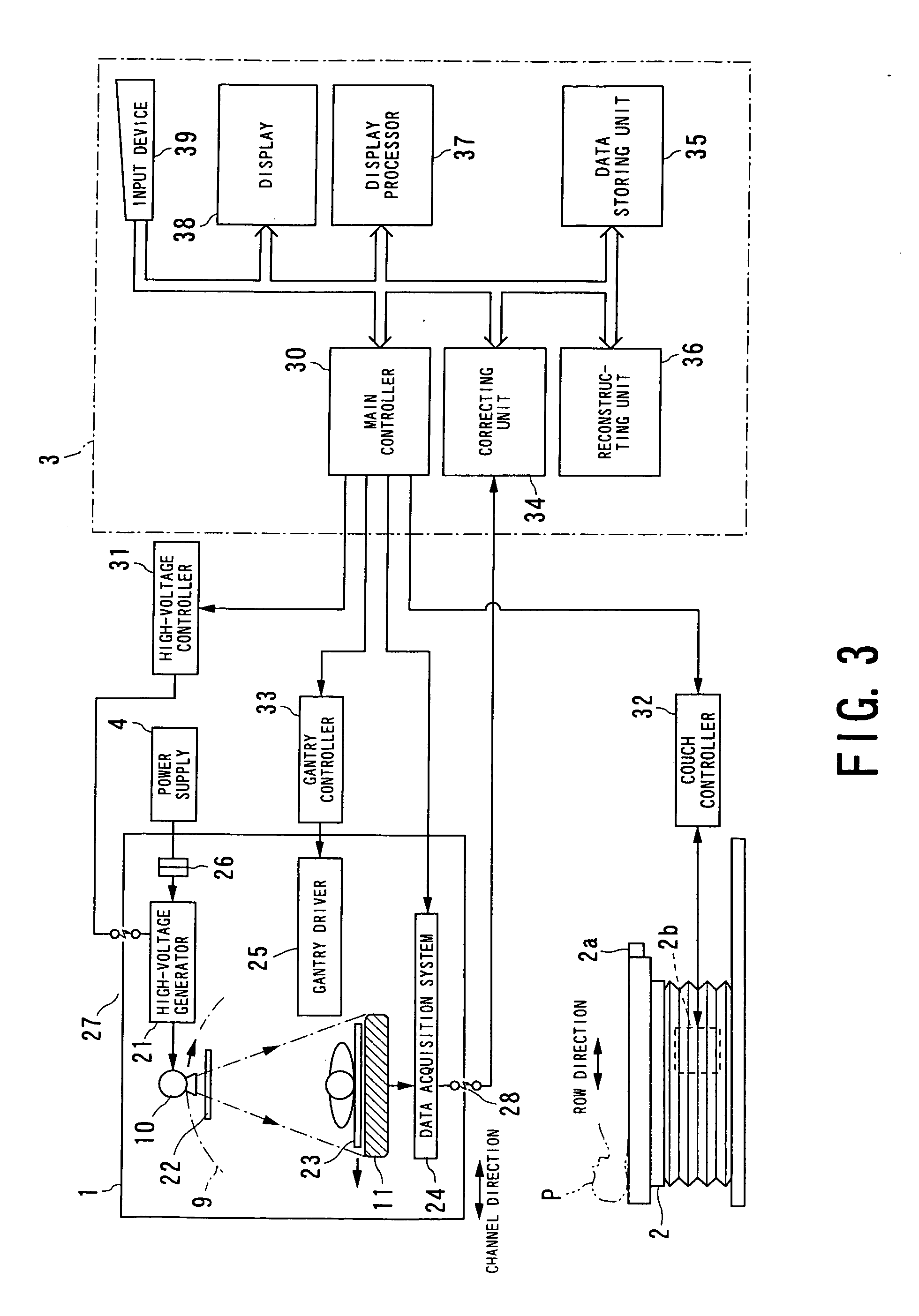
Cone beam type of X-ray CT system for three-dimensional reconstruction
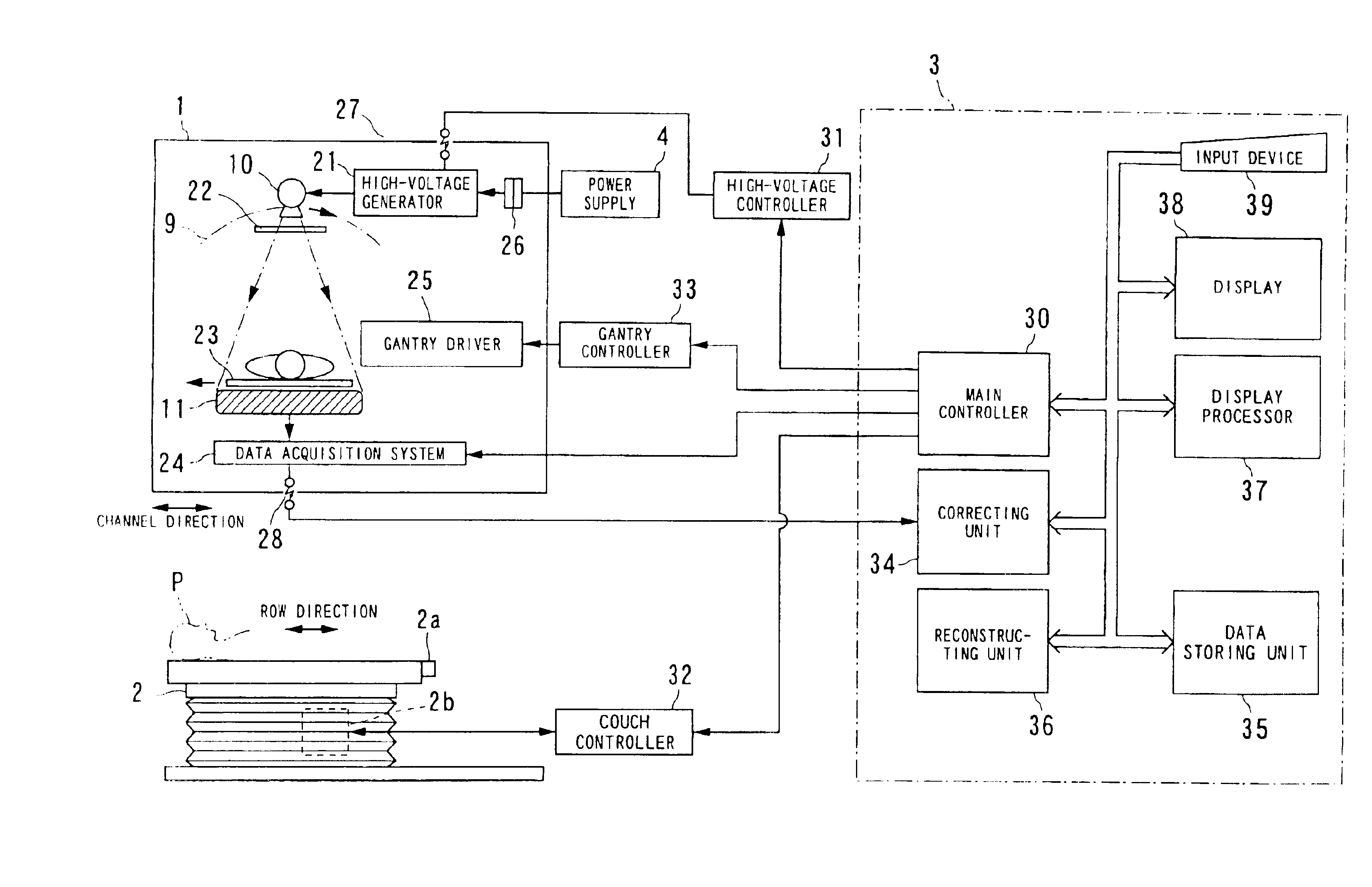
InactiveUS6907100B2Reduce resultHigh resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTemporal resolutionAcquisition time
An X-ray CT system is equipped with a gantry, couch and control cabinet and configured to scan a cone-beam X-ray toward an object along a given orbit to acquire cone-beam data in which a three-dimensional distribution of an X-ray absorption coefficient within the object is reflected. The control cabinet decides a degree of reliability for the cone-beam data according to an acquisition time of the cone-beam data, and then decides a weight for three-dimensional Radon data from the cone-beam data on the basis of the degree of reliability. Using this weight, the control cabinet reconstructs the three-dimensional Radon data based on a three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm. Thus, when the three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm for cone-beam CT is applied to medical CT, artifacts attributable to object's motion can be suppressed and temporal resolution can be improved.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
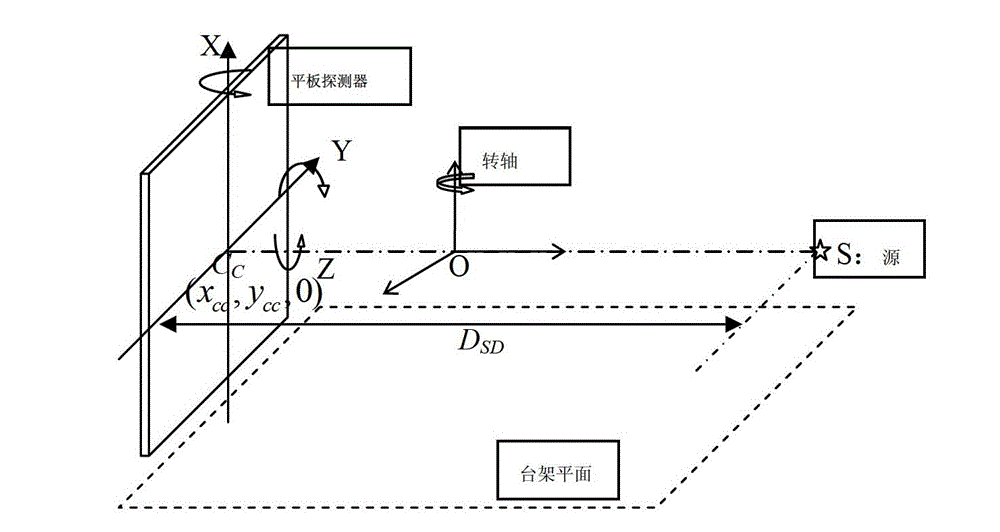
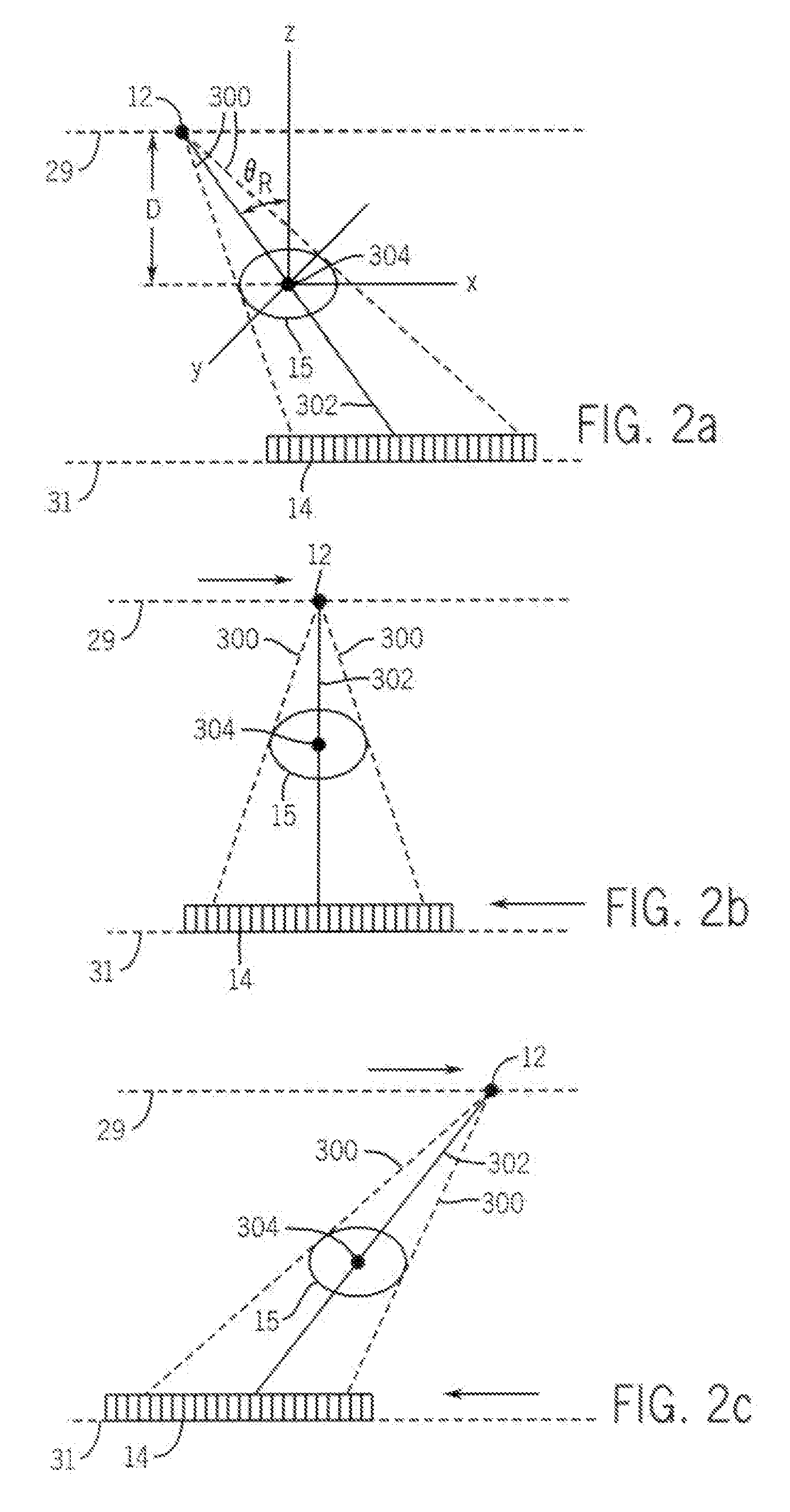
Geometrical parameter calibration method of X-ray cone beam computed tomography system
The invention discloses a geometrical parameter calibration method of an X-ray cone beam computed tomography system and belongs to the field of the X-ray cone beam computed tomography systems (a cone beam CT for short). By means of a camera calibration technique, a geometrical position relationship among an X-ray source, a panel detector and a rotary shaft in a cone beam CT system is reproduced, thereby geometrical parameters and errors of the cone beam CT can be directly solved, the geometrical parameter calibration method is a systematized measurement solving method, the cone beam CT can beabstracted to be a basic camera system model, and then a plurality of correlative geometrical parameters in the system can be simultaneously solved. Compared with prior calibration methods, the geometrical parameter calibration method has the advantages that the geometrical parameters are not required to be measured one by one, repeated adjustment for the parameters one by one is not required, thereby the complexity level of calibration measurement of the whole system is greatly simplified, and simultaneously the stability of the cone beam CT geometrical calibration is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cone beam type of x-ray CT system for three-dimensional reconstruction
InactiveUS20040086074A1High resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTemporal resolutionAcquisition time
An X-ray CT system is equipped with a gantry, couch and control cabinet and configured to scan a cone-beam X-ray toward an object along a given orbit to acquire cone-beam data in which a three-dimensional distribution of an X-ray absorption coefficient within the object is reflected. The control cabinet decides a degree of reliability for the cone-beam data according to an acquisition time of the cone-beam data, and then decides a weight for three-dimensional Radon data from the cone-beam data on the basis of the degree of reliability. Using this weight, the control cabinet reconstructs the three-dimensional Radon data based on a three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm. Thus, when the three-dimensional reconstruction algorithm for cone-beam CT is applied to medical CT, artifacts attributable to object's motion can be suppressed and temporal resolution can be improved.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Diffuse transmission measuring and correcting method of cone-beam CT system
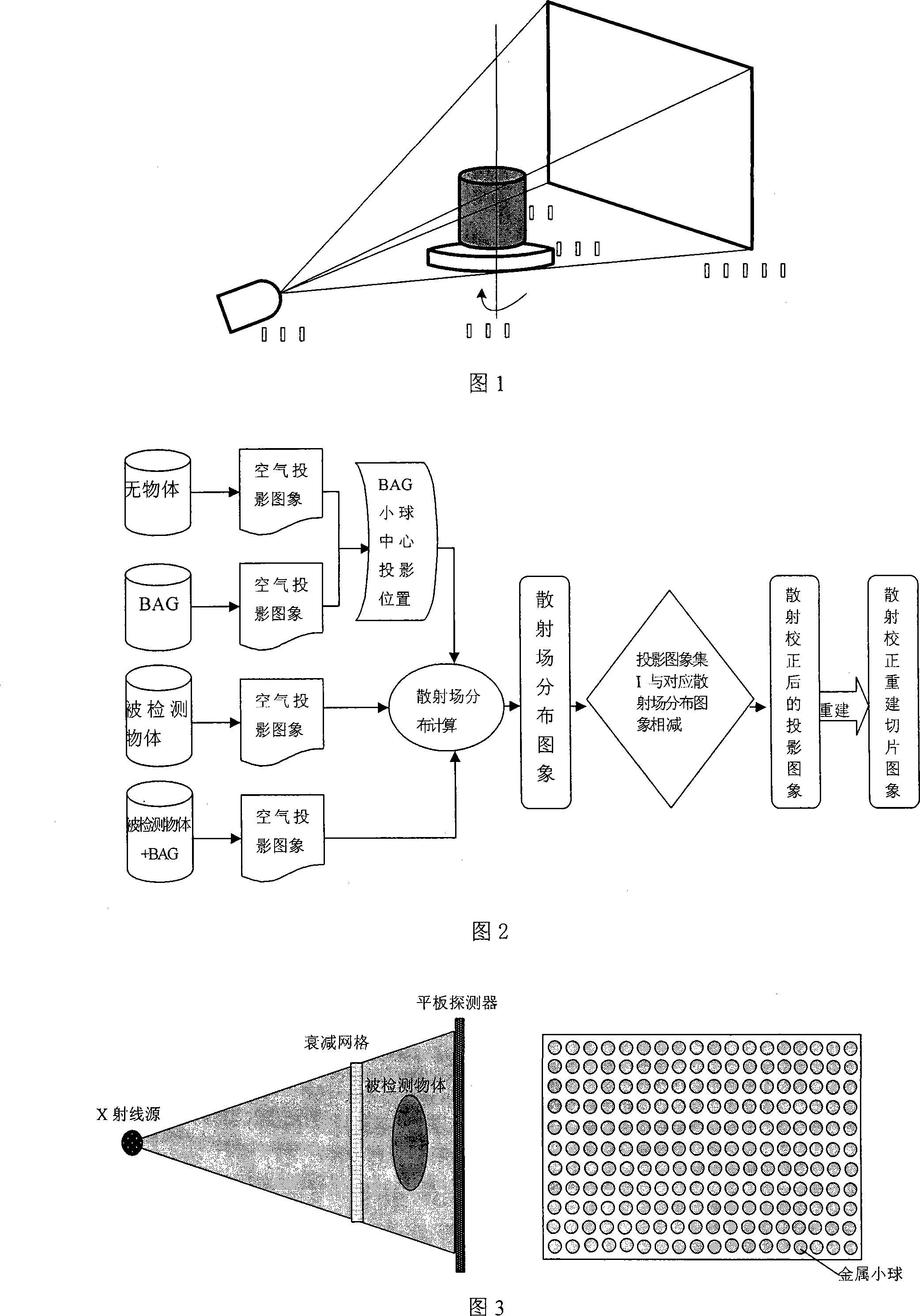
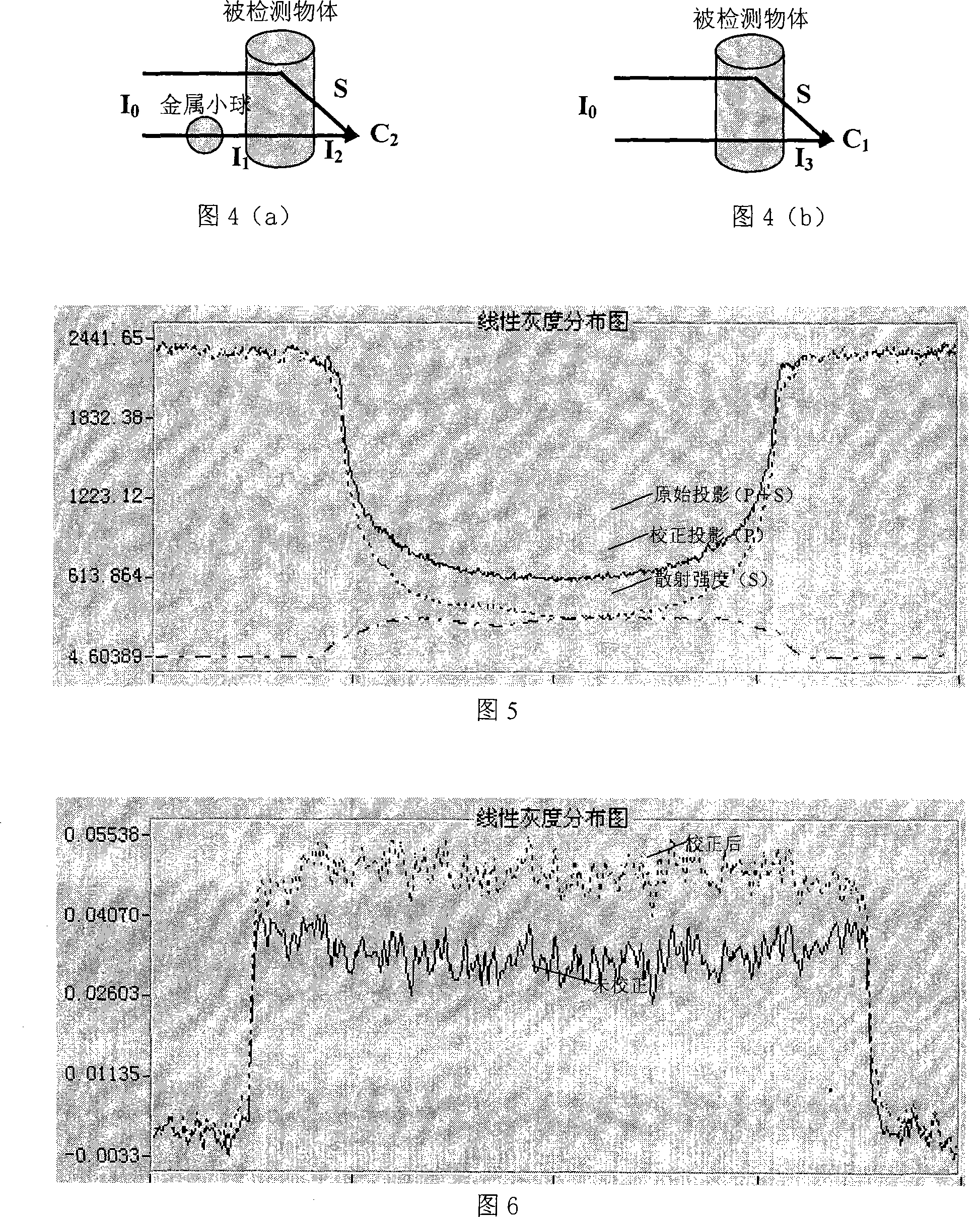
InactiveCN101158653AIncrease contrastImprove image qualityMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationRadiation intensity measurementUltrasound attenuationHigh energy
The invention discloses a scattering determination and corrector method of a taper bunch CT system. After arranging a parameter, an air projected picture and a beam attenuation grid projected picture are collected. A circular scanning is carried out on the detected object. A projected picture set I of the detected object with beam attenuation grid and a projected picture set II of the detected object are collected. The projected attitude of the center of each metal ball in the beam attenuation grid is calculated. A scattered field distributing image corresponding to the projected picture of the projected picture set I is calculated through a beam attenuation grid corrector method. A projected picture set III after scattering correction is gained through the projected picture set I subtracting the corresponding scattered field distributing image. Thereby, a sequence slice image after scattering correction is reconstructed through a filter back-projection reconstruction method. The invention can be applied to the scattering correction of the taper bunch CT system from low energy to medium or high energy. The invention is a simple and effective scattering correction method of the taper bunch CT system.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
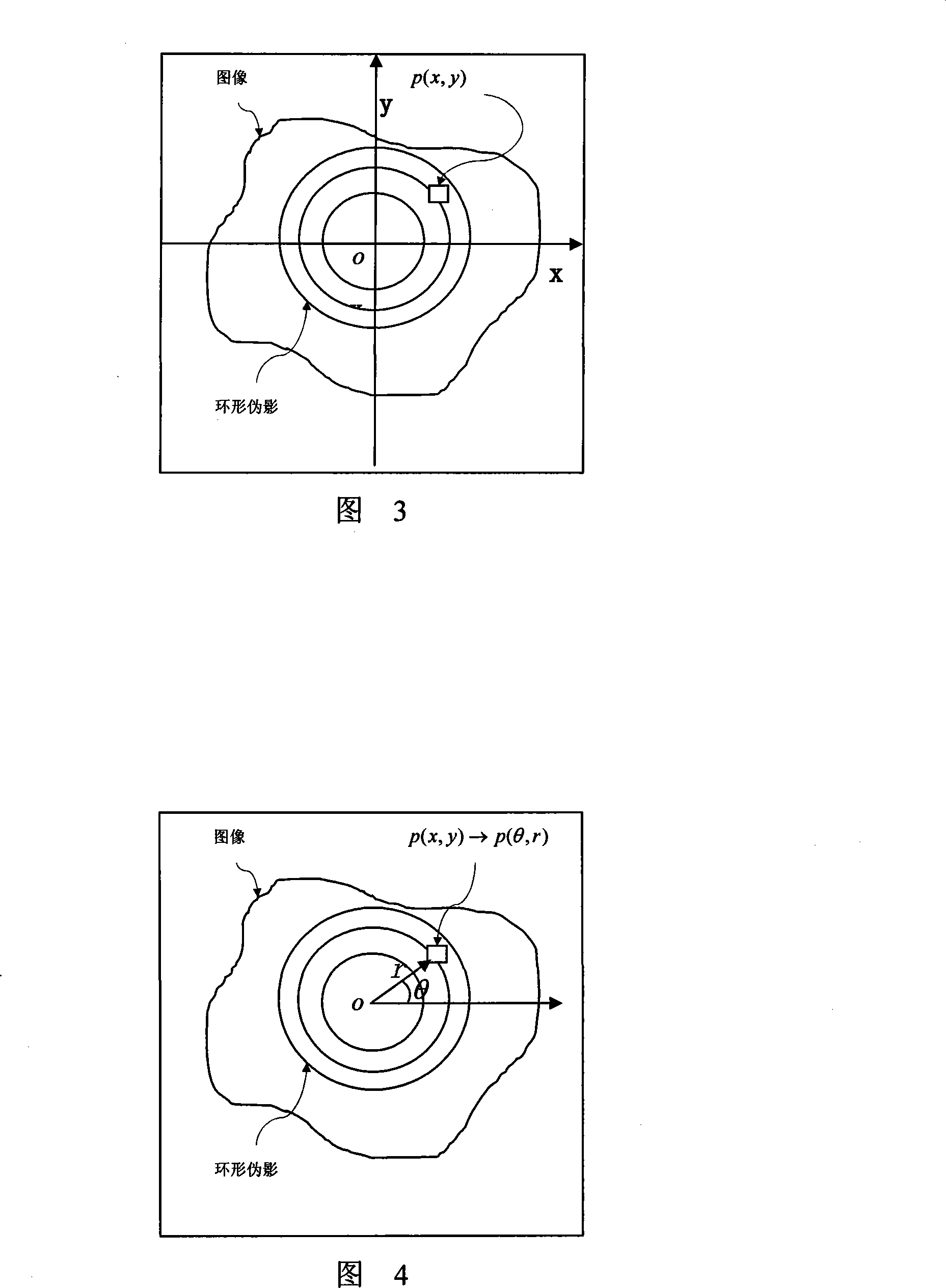
Method for removing improved conical bind CT ring shaped false shadow
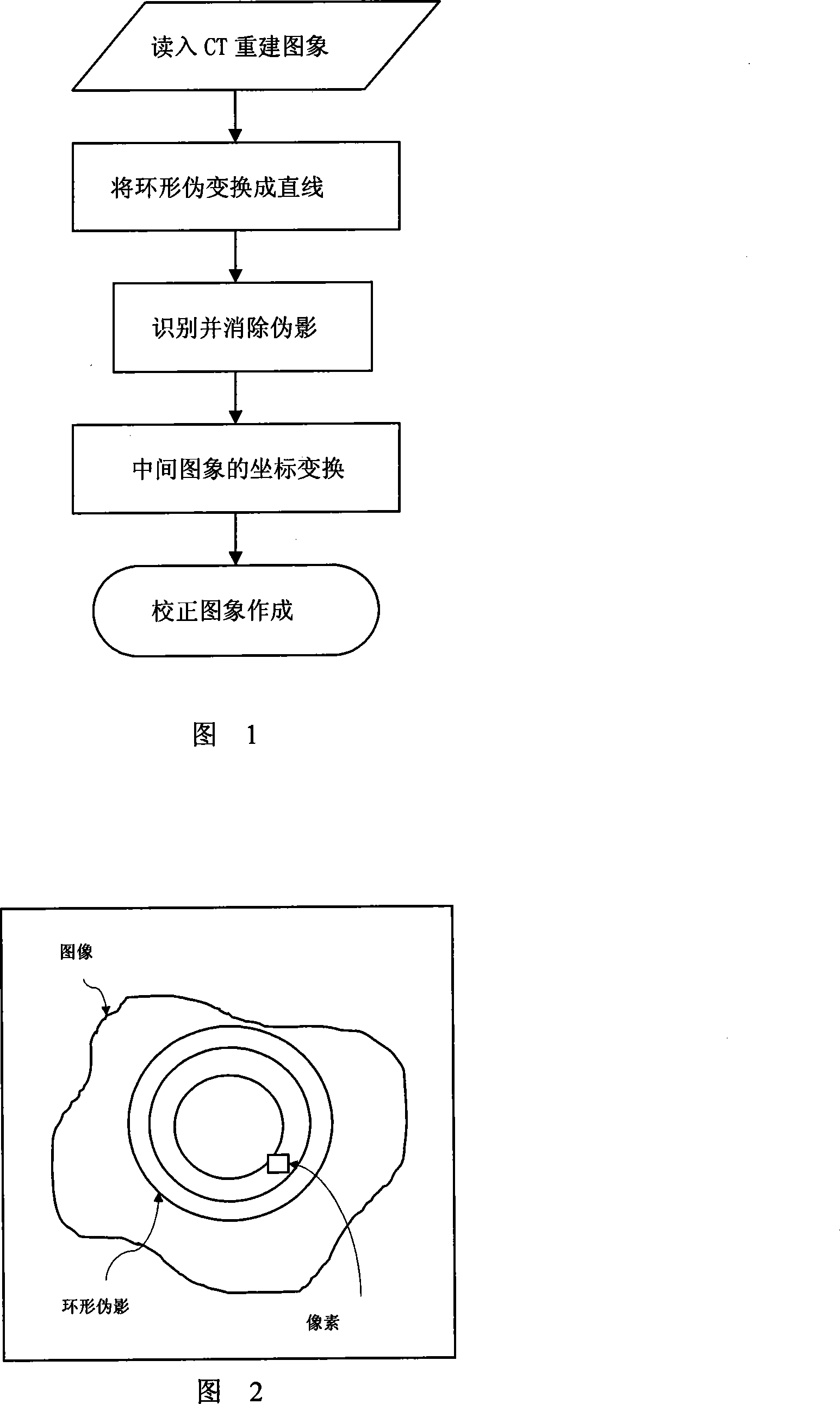
InactiveCN101178808ANot limited by artifact widthHigh resolutionImage enhancement2D-image generationPattern recognitionCoordinate change
The invention discloses an improved eliminating method of tapered beam CT reconstruction image annular false shade, comprising the steps as follows: the invention changes the annular false shade of reading CT reconstruction image into a straight line through a method of coordinate change, then takes a one-dimension filter parallel with the false shade as a mask to search a middle image regularly line by line and acquire sample space, at the same time calculates out the variance about the pixel value of each sample space, acknowledges the false shade according to whether the variance is less than the preset valve value, substitutes the pixel value of each sample space with the average pixel value between the point and two upper and lower false shades in the ordinate axis direction in order to eliminate the annular false shade, and finally changes the middle image free from the false shade to be under the original frame of axes to gain a corrected image.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Customized dental prosthesis for periodontal or osseointegration and related systems and methods
ActiveUS8602780B2Quality improvementNone have achieved superiorDental implantsImpression capsOsseointegrationProsthesis
Dental prosthesis, systems, and methods of forming and using a dental prosthesis, are provided. An example of a dental prosthesis includes a first manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a root of a tooth to be replaced and a second manufactured portion shaped to substantially conform to the three-dimensional surface of a crown of the tooth. Furthermore, customized manufactured splints to position and fixate a tooth-shaped prosthesis, are provided. Furthermore, a CAD / CAM based methods of and a systems for manufacturing a customized dental prosthesis are provided. The tooth can be scanned to determine its three-dimensional shape and substantially copied using an imaging system in-vitro like a 3D scanner or in-vivo like a cone beam CT system and CNC machinery. Biocompatible material that is suitable to be integrated into the extraction socket and adopted by existing tissue forming the socket can be manufactured or engineered.
Owner:RTRS INVESTMENT LLC
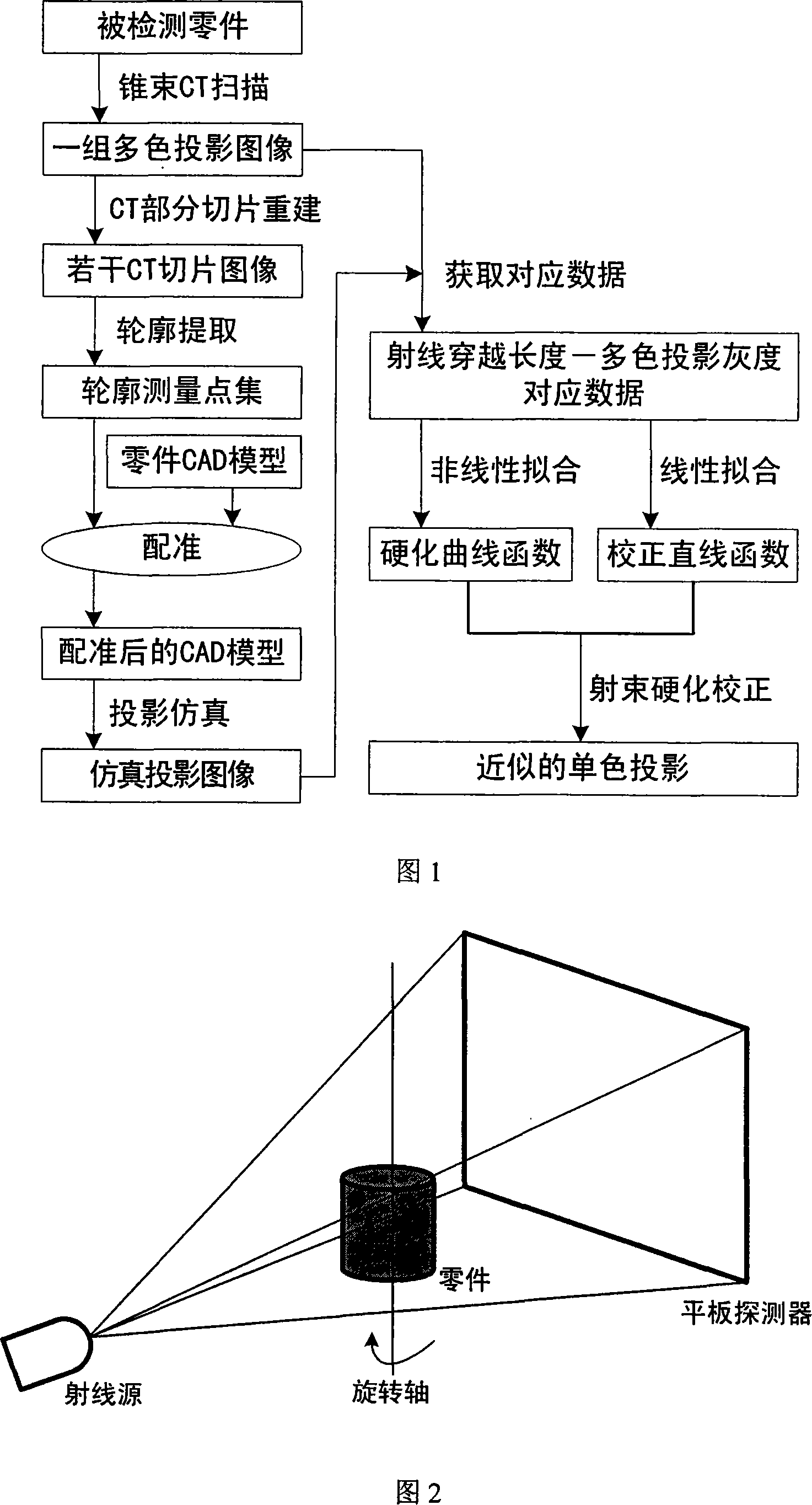
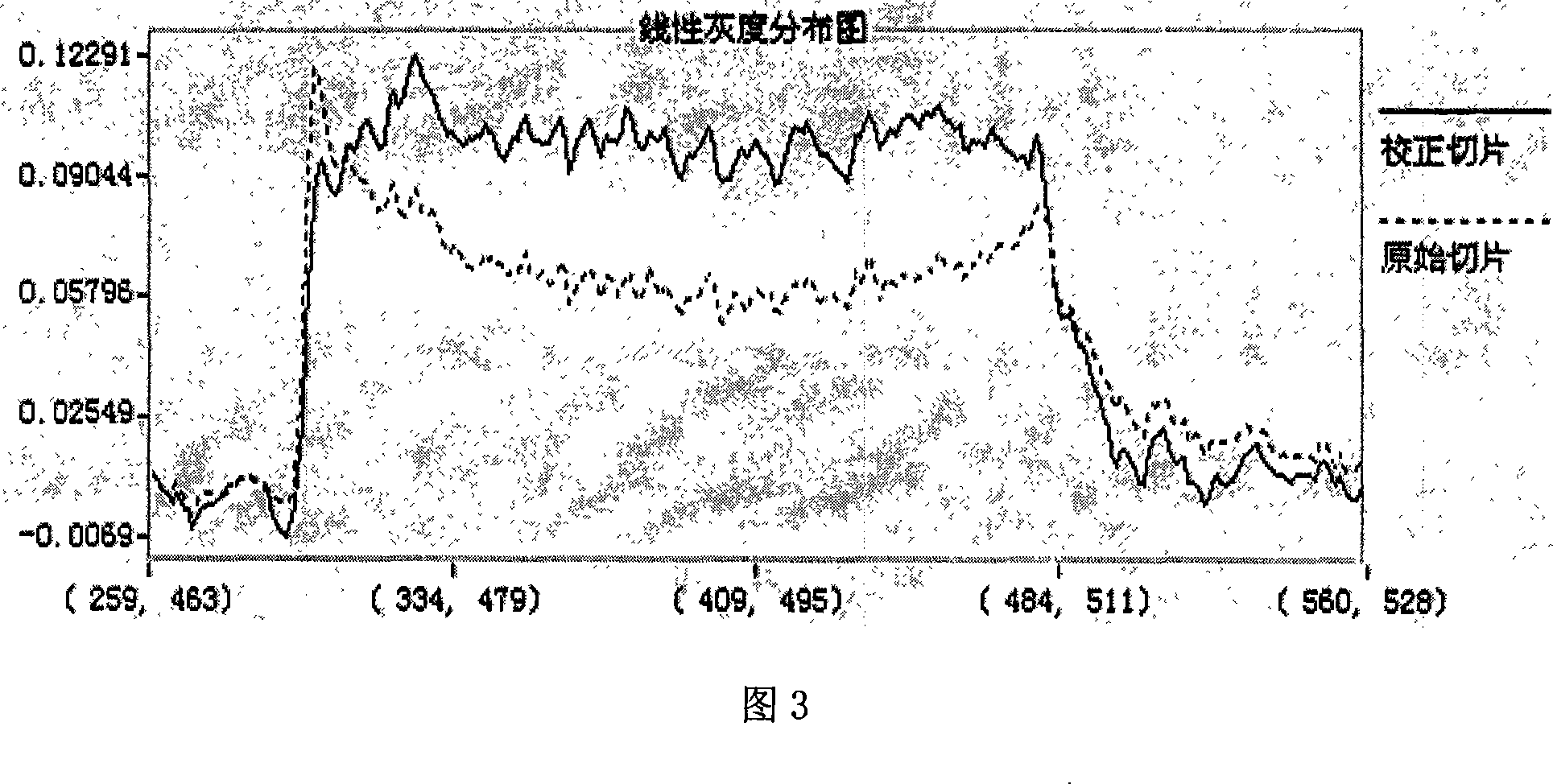
Cone-beam CT beam hardening calibration method based on registration model emulation
InactiveCN101126722AFlexibleReduced beam hardening artifactsImage enhancementImage data processing detailsMeasurement pointBeam hardening
The utility model discloses a beam hardening correction method of cone beam CT based on registration model simulation, which acquires multi-color projection data through circle locus cone beam CT scanning to a spare part. After acquiring CT images of sequence slices by cone beam CT reconstitution to the multi-color projection, the contour of certain pieces of the images are extracted so that a measurement point formed a plurality of closed contour lines is acquired. Projection simulation is processed after the registration of the measurement point and the CAD model of the part, and then the length of the part passing through the part at every imaging point is acquired. A hardening curve that passes through the original point is acquired by nonlinear fitting and a straight line that passes through the original point is acquired by linear fitting. The beam hardening constructed defect of the cone beam CT is corrected according to the hardening curve and the rectifying straight line. The utility model is flexible in application, and can approximately corrected through multi-color projection to unique color projection, and the beam hardening artifacts is reduced obviously after correction.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
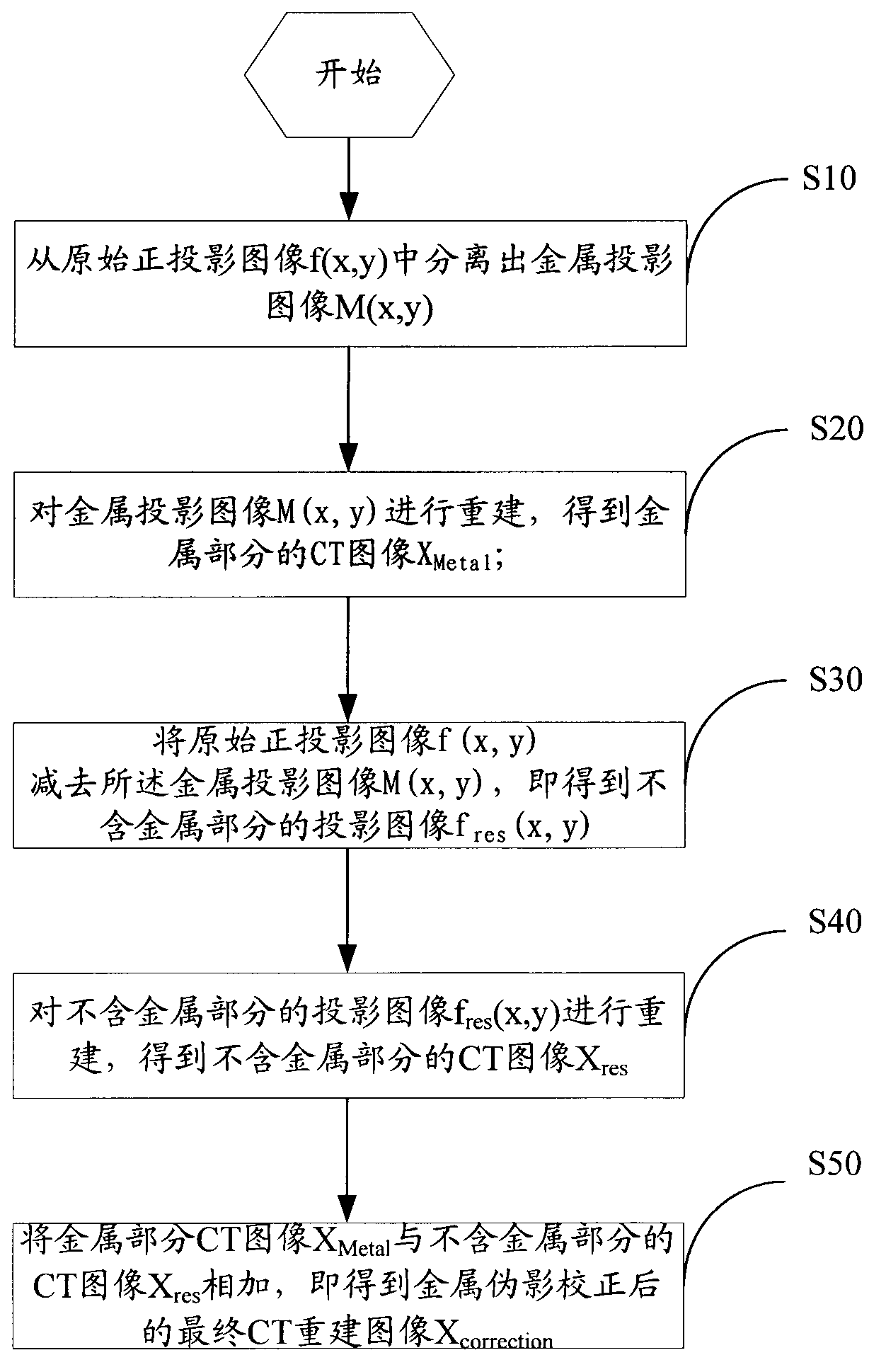
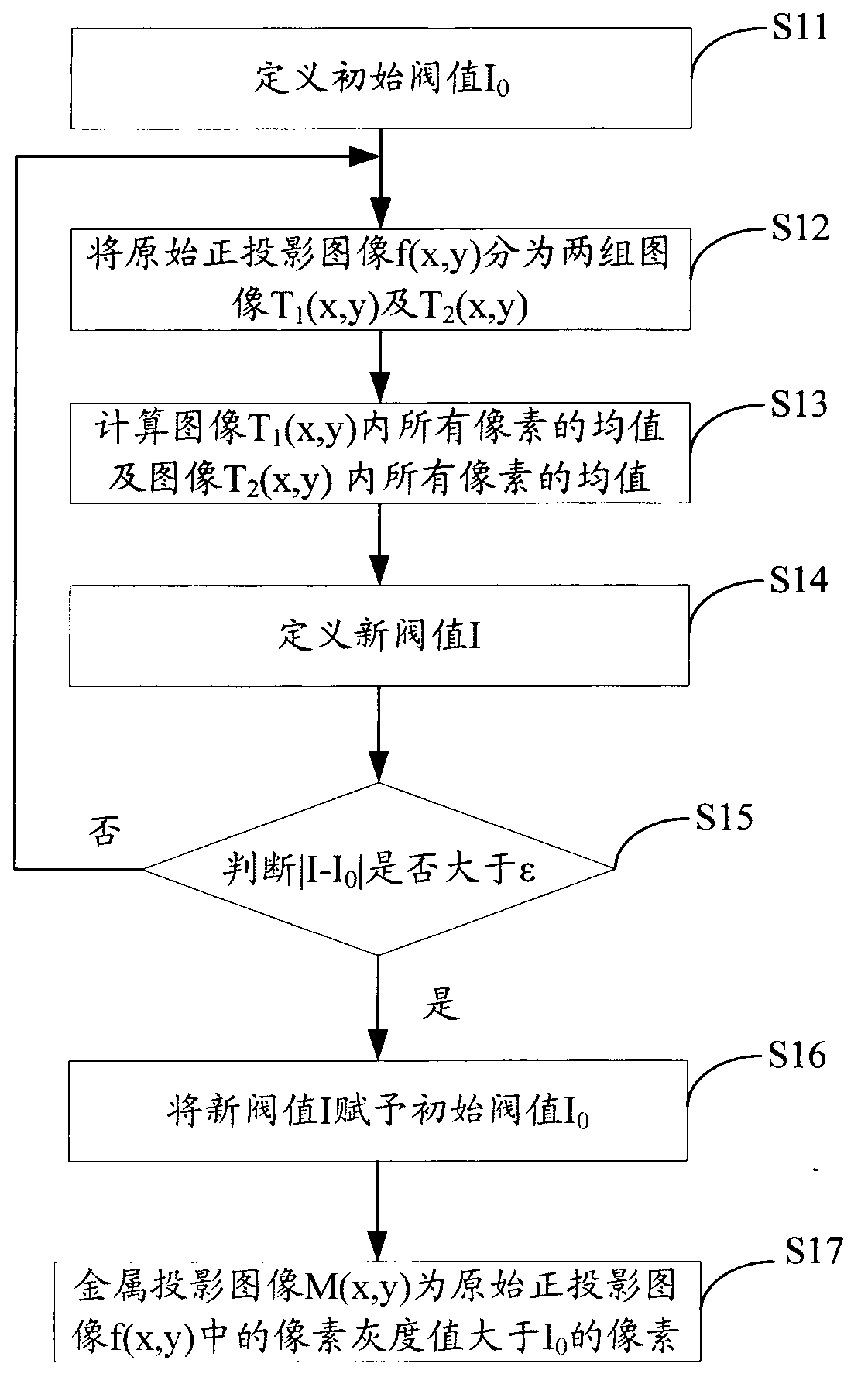
Metal artifact correcting method of cone-beam CT (computed tomography) system
The invention relates to a metal artifact correcting method of a cone-beam CT (computed tomography) system. The metal artifact correcting method of the cone-beam CT system comprises the steps of separating a metal projection image M (x, y) from an original orthographic projection image f(x, y), reconstructing the metal projection image M (x, y) to obtain a CT reconstruction image XMetal of the metal part, reducing the metal projection image M (x, y) of the original orthographic projection image f(x, y) to obtain a projection image fres(x, y) without the metal part, reconstructing the projection image fres(x, y) without the metal part to obtain a CT (computed tomography) image Xres without the metal part, and adding a CT (computed tomography) image Xmetal of the metal part with the CT (computed tomography) image Xres without the metal part to obtain a final CT (computed tomography) reconstruction image Xcorrection after the correction of a metal artifact. Coordinates are not changed in the metal artifact correcting method, so that the image space resolution is not lost, and the image quality is enhanced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Ultra Low Radiation Dose X-Ray CT Scanner
ActiveUS20080267484A1High in-plane spatial resolutionExcellent low contrast detectabilityReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisData setTotal variation minimization
A line scan cone beam CT imaging system irradiates an object with an x-ray cone beam for multiple views. A projection data set of the object is acquired at each view. Between views, the cone beam and detector array are translated along parallel lines in opposite directions. An image is generated by converting the cone beam projection data set of the real object into a parallel-beam projection data set corresponding to a virtual object and using a total variation minimization image reconstruction algorithm to reconstruct a virtual image of the virtual object. The reconstruction algorithm includes the constraint that the Fourier transform of the reconstructed virtual image matches the known Fourier coefficients in the set of converted parallel-beam projections of the virtual object. The constructed virtual image is then transformed into an image of the real object.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
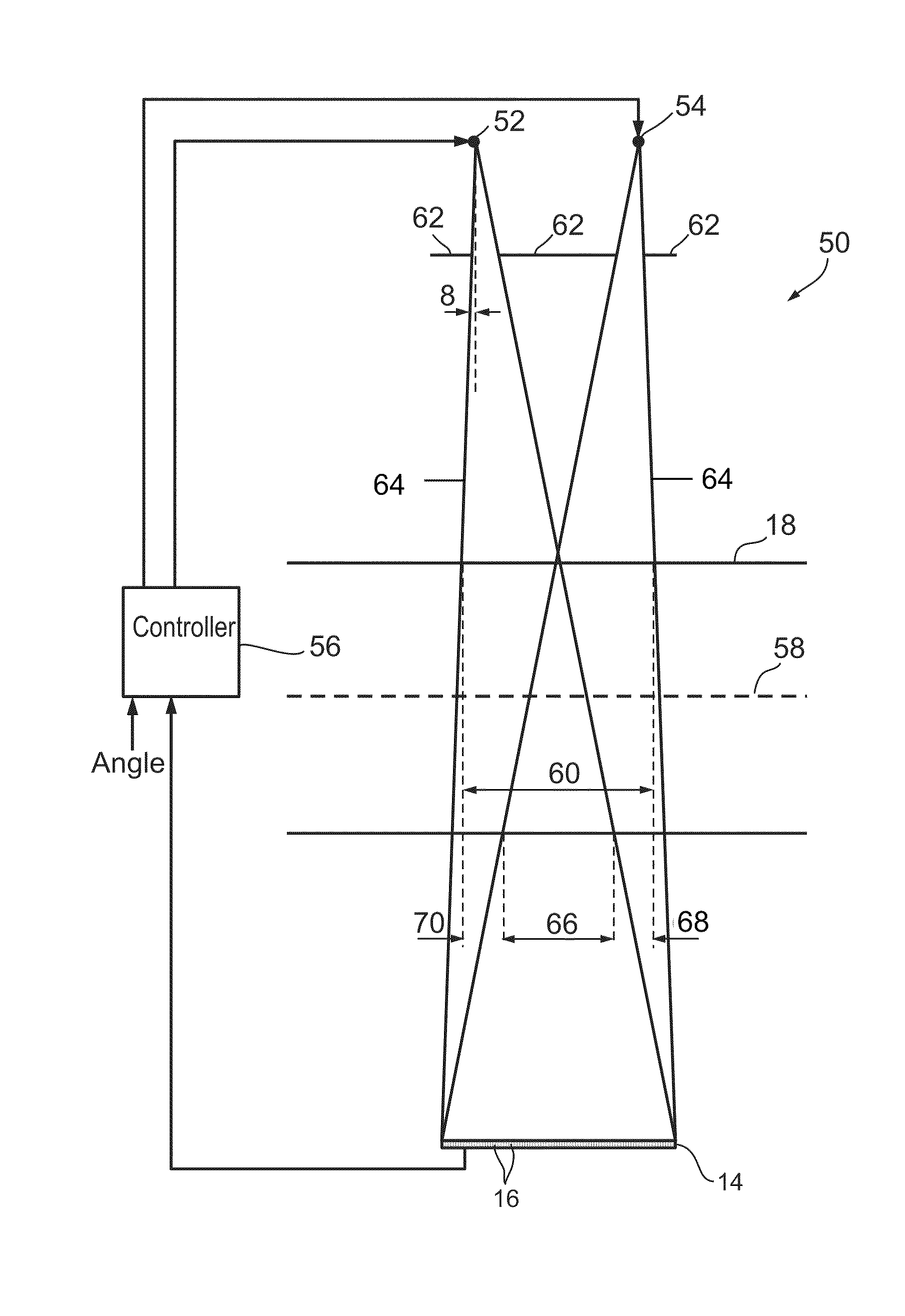
Cone-beam ct
ActiveUS20110080992A1Smaller anode angleIncrease the areaMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingCt scannersX-ray
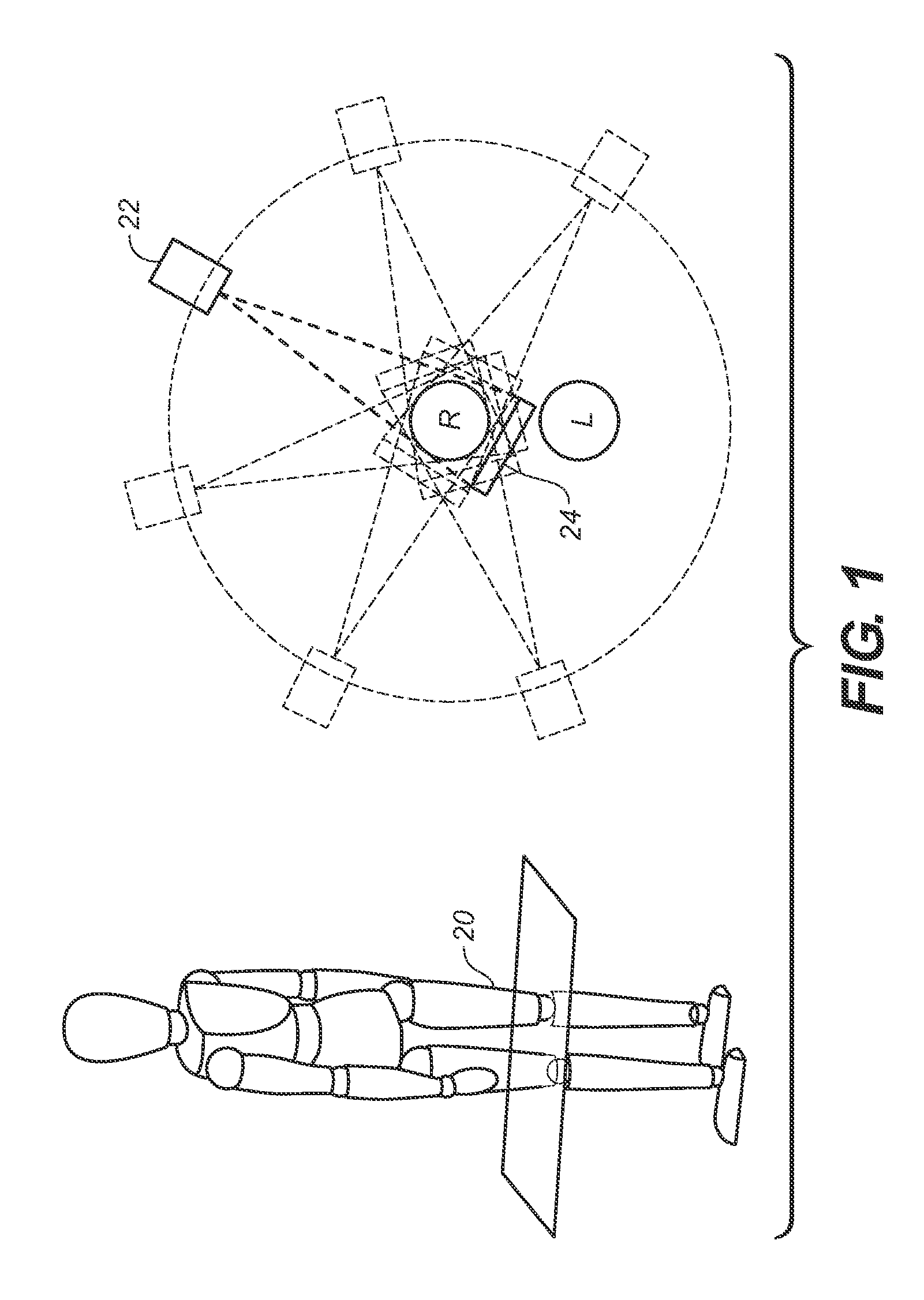
An X-ray source system for a CT scanner includes a plurality of X-ray sources, wherein each X-ray source of the plurality is provided with a cathode from which an electron beam is emitted, an anode to receive the electron beam and at least one grid electrode, wherein the grid electrodes are configured to selectably block radiation from said X-ray sources; a high voltage generator for applying voltage to the plurality of X-ray sources, wherein each of the plurality of X-ray sources are configured to present substantially the same load to the high voltage generator; a grid modulator configured to apply voltage to grid electrodes of each of the plurality of X-ray sources in turn; and a controller for controlling the grid modulator so that only one of the plurality of X-ray sources emits radiation at any one time.
Owner:ARINETA
CT (Computed Tomography) value correcting method for cone-beam CT
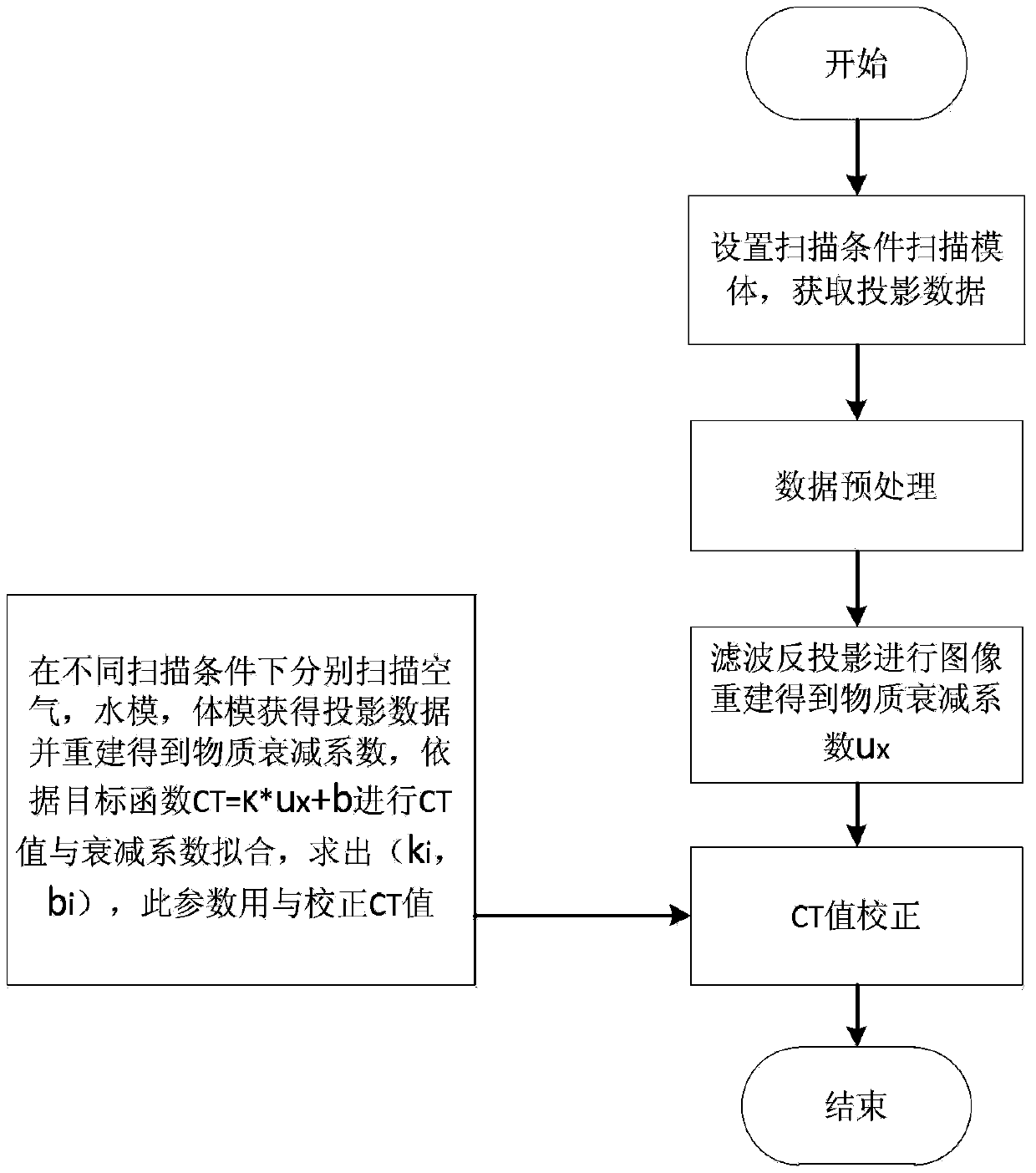
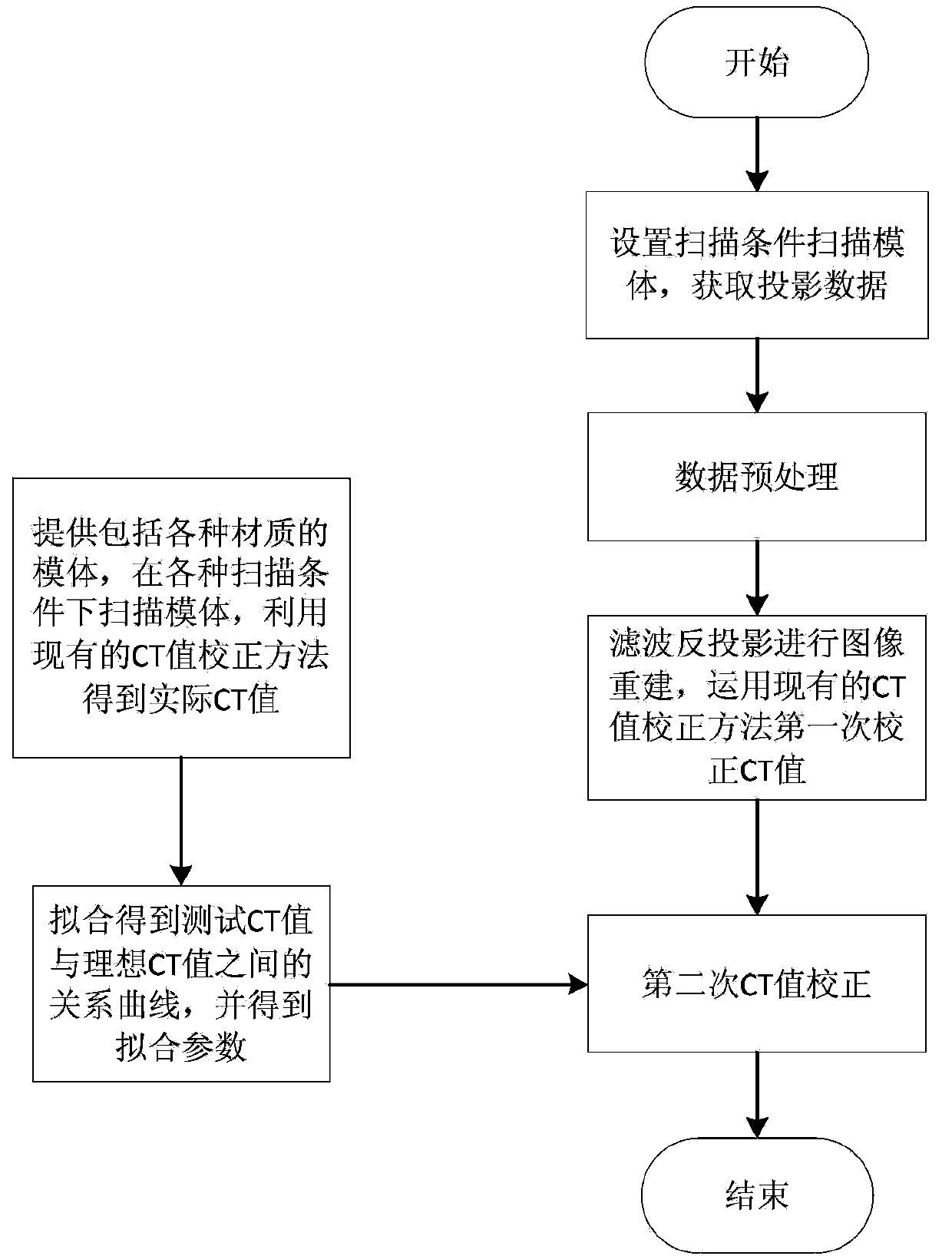
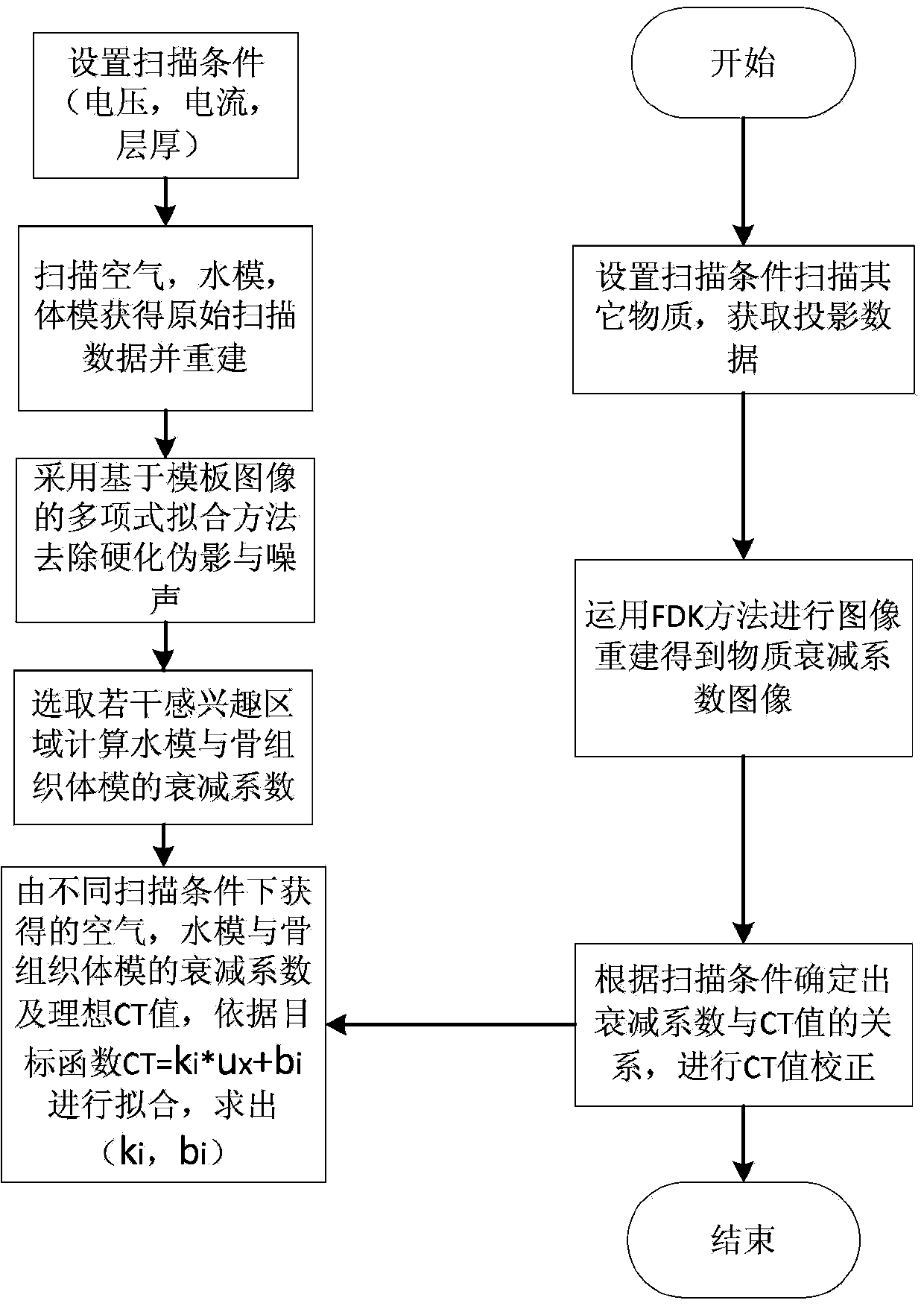
ActiveCN103961125AAccurate Attenuation CoefficientGuaranteed accuracyComputerised tomographsTomographyAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
The invention discloses a CT (Computed Tomography) value correcting method for cone-beam CT. The CT value correcting method comprises the following steps: scanning air, a water phantom and a bone tissue body phantom under different scanning conditions to respectively obtain projection data; reestablishing an image; removing noise and artifacts by adopting a polynomial fitting method based on a template image; selecting a plurality of interested regions and calculating a mean value of an attenuation coefficient and a standard deviation of the attenuation coefficient; obtaining the value range of the attenuation coefficient and taking the attenuation coefficient of maximum occurrence probability; fitting the attenuation coefficients of the air, the water phantom and the bone tissue body phantom under the different scanning conditions with corresponding ideal CT values to obtain respective fitting curves; performing CT scanning and image reestablishment on a scanned material; obtaining a CT value image according to a material attenuation coefficient image and a fitting curve and finishing the CT value correction. According to the CT value correcting method disclosed by the invention, image noise and artifact can be effectively reduced, the reestablished image of single material reaches the uniformity to the great degree, the precision of the attenuation coefficient of the material becomes higher and further high accuracy for the fitting of the curve of the CT value and the material attenuation coefficient is realized.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
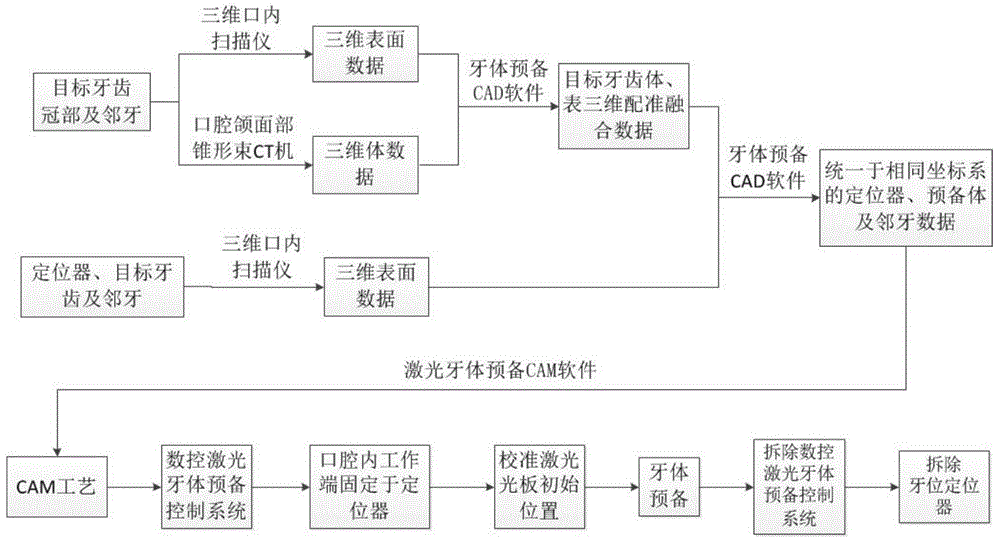
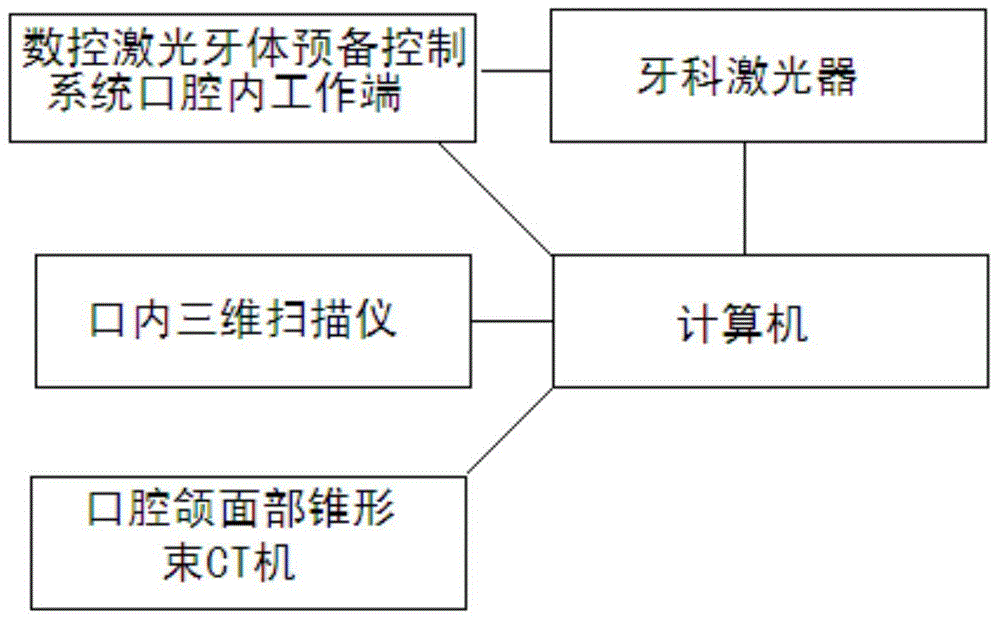
Numerical control laser automatic tooth preparation method and equipment thereof
InactiveCN104546151AImproving the technical level of clinical treatment operationImprove the efficiency of diagnosis and treatmentDental toolsNumerical controlFacial region
The invention relates to a numerical control laser automatic tooth preparation method and equipment thereof. The equipment contains an intraoral spatial digitizer, a dental laser, a numerical control laser tooth preparation control system intraoral working end, an oromaxillo-facial region cone-beam CT machine, a computer, a tooth fixator and a negative pressure aspirator. The computer is respectively connected with the intraoral spatial digitizer, the dental laser, the oromaxillo-facial region cone-beam CT machine and the negative pressure aspirator. The dental laser is connected with the numerical control laser tooth preparation control system intraoral working end which is connected with the tooth fixator. The equipment can replace part of manual operation of a doctor. A traditional mechanical grinding apparatus is replaced with laser. Clinical therapy operative level of grass-roots doctors can be effectively raised within a short period of time, and diagnosis and treatment efficiency and quality can be improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SCHOOL OF STOMATOLOGY +4
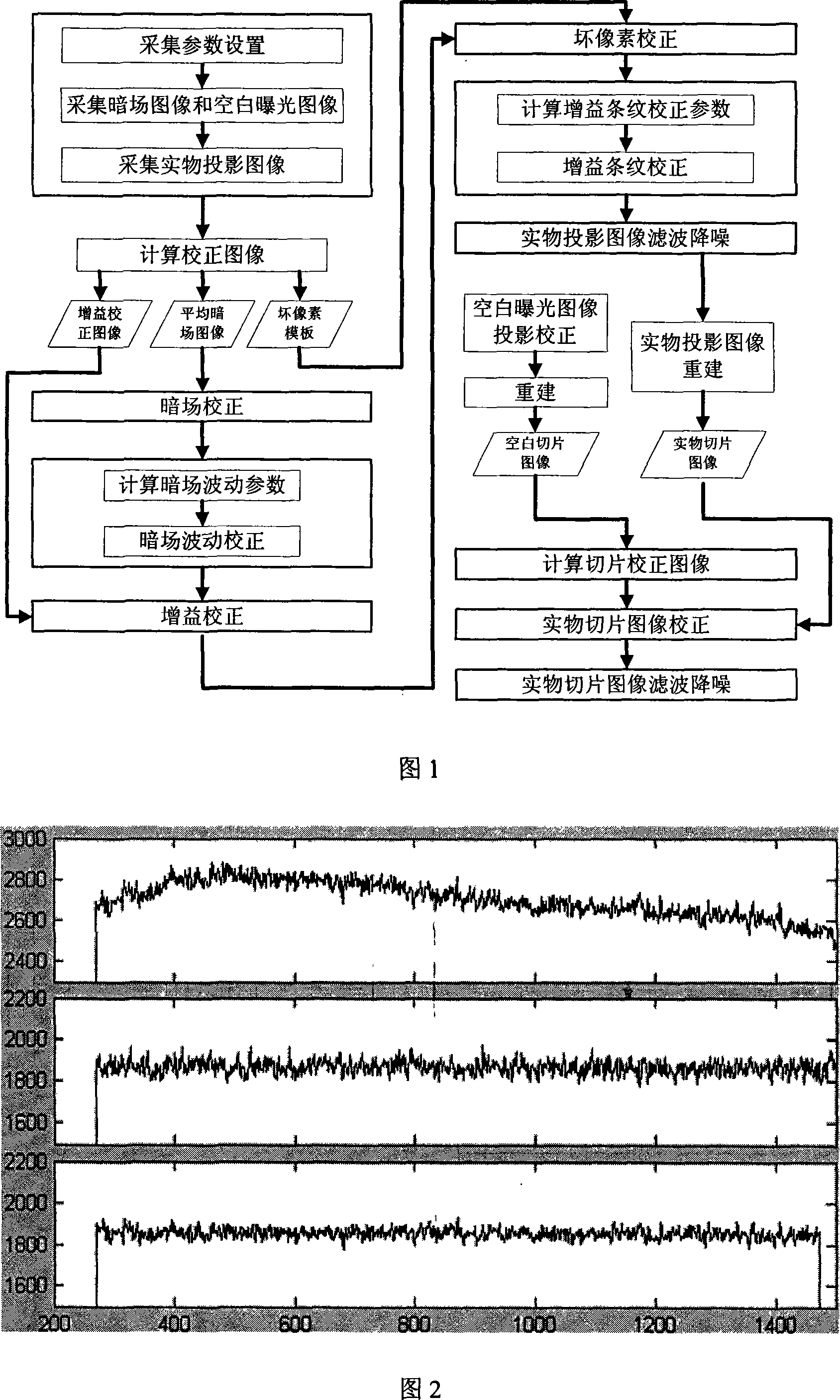
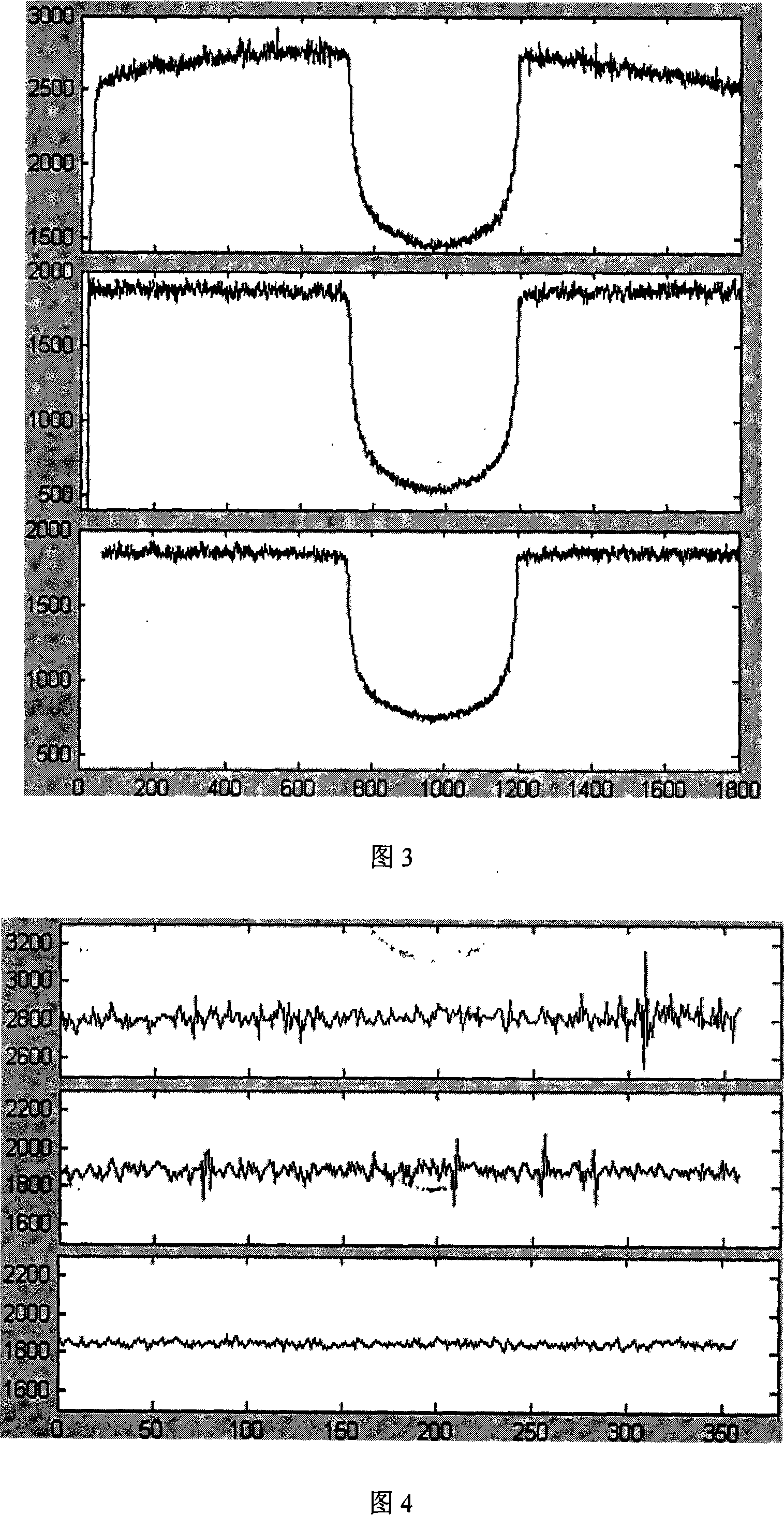
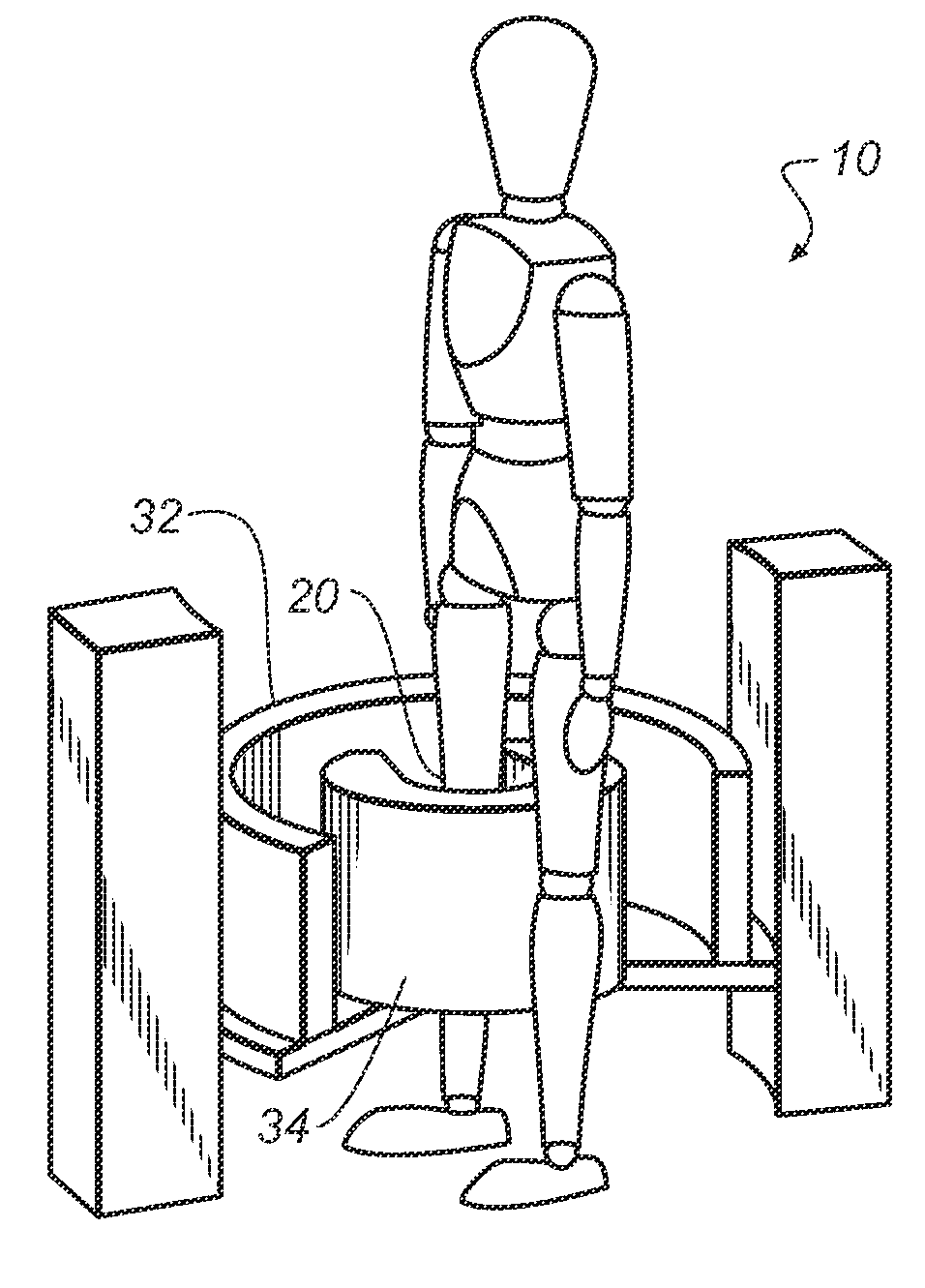
Cone-beam CT system plate detector image anti-interference calibration method
InactiveCN101126724ARemove threadRemove Ring ArtifactsImage enhancementImage data processing detailsCorrection algorithmFlat panel detector
The utility model discloses an anti-interference correction method of flat panel detector image in cone-beam CT system, which is characterized in that collection parameter is set, the plat panel detector is shielded partially, dark image, blank exposure image and object projection image are collected; average dark field image, gain correction image and bad pixel template image are calculated; dark field correction, dark field fluctuation correction, gain correction, bad pixel correction and gain strip correction are made on the object projection image; the filtering de-noising treatment is made on the object projection image, the object segmentation image is re-constructed by the object projection image. The blank exposure image is reconstructed to be a blank segmentation image, the segmentation correction image is calculated; the segmentation correction is made on the object segmentation image; the filtering de-noising treatment is made on the object segmentation image. The utility model has the advantages that the correction result is obviously better than that of the prior correction calculation method, enabling. to effectively dispose the linear and annular artifacts that can not be eliminated by the prior correction method, moreover image signal-to-noise ratio is higher or equal to the prior level.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Extremity imaging apparatus for cone beam computed tomography
ActiveUS8348506B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingRadiation exposureCone beam computed tomography
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Metal artifacts reduction for cone beam ct
ActiveUS20130070991A1Reduce artifactsImprove processing efficiencyReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionMetal ArtifactRadiography
A method for suppressing metal artifacts in a radiographic image, the method executed at least in part on a computer, obtains at least one two-dimensional radiographic image of a subject, wherein the subject has one or more metal objects and identifies a material that forms the one or more metal objects and a radiation energy level used to generate the obtained image. The obtained radiographic image is segmented to identify boundaries of the metal object. A conditioned radiographic image is formed by replacing pixel values in the radiographic image that correspond to the one or more metal objects with compensating pixel values according to the identified material and the identified radiation energy level. The conditioned radiographic image is then displayed.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Cone-beam CT
ActiveUS7869561B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingElement spaceX-ray
Apparatus for CT cone beam scanning, comprising:a table for holding a subject;a gantry;a first detector array, having a given number of rows of detector elements spaced along an rotation axis of the gantry, mounted on the gantry;a first plurality of x-ray sources mounted on the gantry for rotation about the patient table on a rotation axis, the number of rows being at least twice the number of sources; anda controller that acquires data responsive to radiation from the sources from the detector array attenuated by at least part of the common volume of the subject irradiated by the plurality of radiation sources.
Owner:ARINETA
Cone-beam computed tomography image and X-ray image registration method
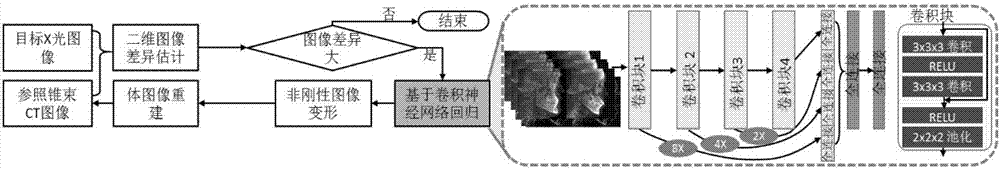
ActiveCN107507234AMeet the precision requirementsReduce mistakesImage enhancementImage analysisNerve networkX-ray
The invention discloses a cone-beam computed tomography image and X-ray image registration method; the method uses a regression model based on a mixing residual error convolution nerve network to build associations between two-dimension X-ray images and three dimensional cone-beam CT image non-rigid deformation parameters, and uses a mixing residual error convolution nerve network and deformation parameter iteration optimization method to realize reliable online two-dimension three dimensional image registration; the method comprises the following steps: extracting to obtain an image channel; training the regression model based on the mixing residual error convolution nerve network; carrying out two-dimension three dimensional non-rigid registration based on regression; iterating and optimizing deformation parameters; obtaining a final body image determined by the deformation parameters, and thus realizing two-dimension three dimensional image registration based on iteration regression. The method can realize reliable online two-dimension three dimensional image registration, can be applied to oral cavity clinics, and can evaluate treatments and analyze craniofacial growth according to two-dimension three dimensional image registrations.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Methods and apparatus of cone beam ct imaging and image-guided procedures
ActiveCN101983033AReconstruction from projectionVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsThree degrees of freedomMulti axis
Disclosed are embodiments of methods of and systems for detecting and biopsying lesions with a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) system. The system comprises, in some embodiments, a CBCT device configured to output a cone beam CT image of at least a portion of a patient's breast and a multi-axis transport module, having at least three degrees of freedom and configured to position a biopsy needle within a 3D frame of reference based on inputs received from the cone beam CT device. The transport module can be configured to place the biopsy needle adjacent to, or within, a target of interest within the breast. Also disclosed are embodiments of methods of and systems for testing CBCT systems with phantoms.
Owner:CORNING LTD
Wide view-field three-D CT imaging method
InactiveCN1865954AScan structure is simpleCompatibleComputerised tomographsTomographyDigital RayVisual field loss
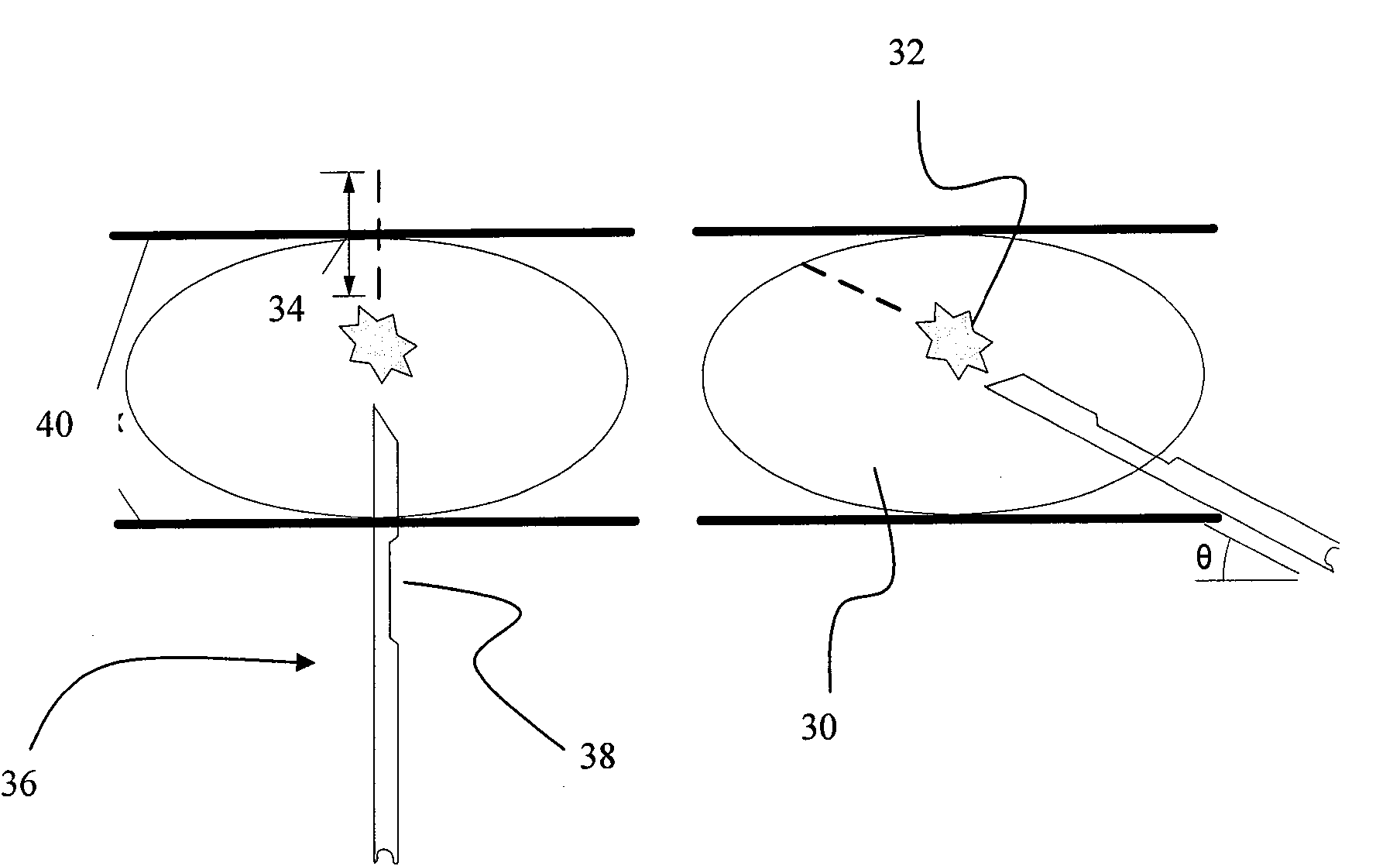
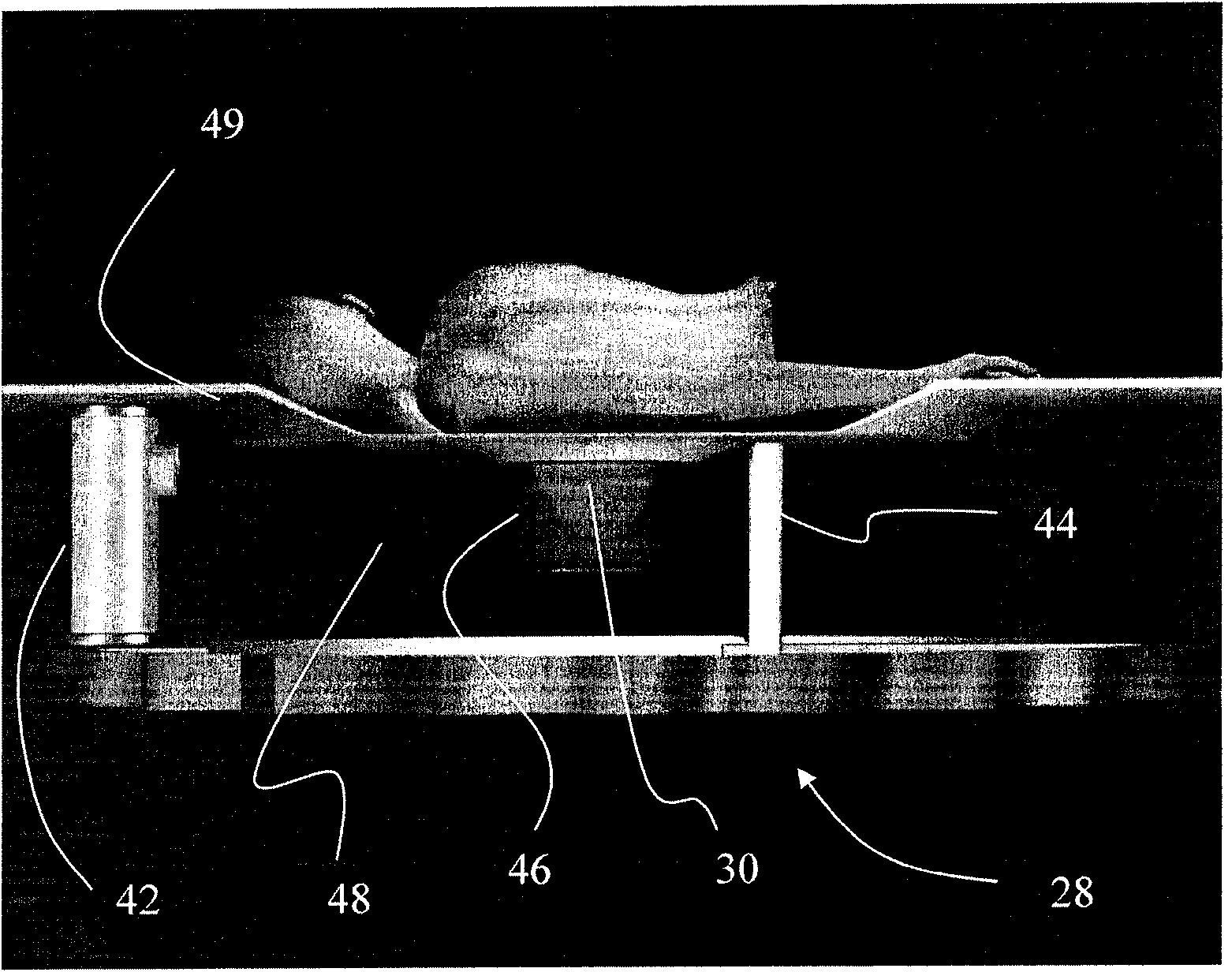
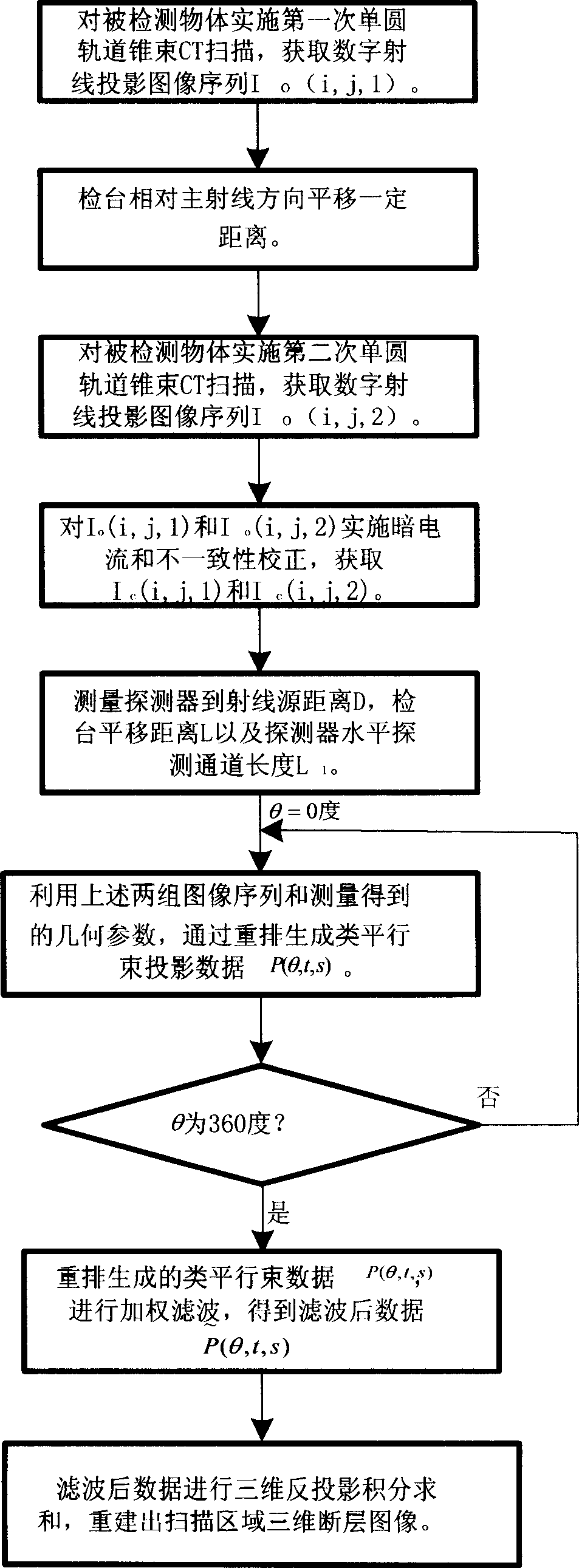
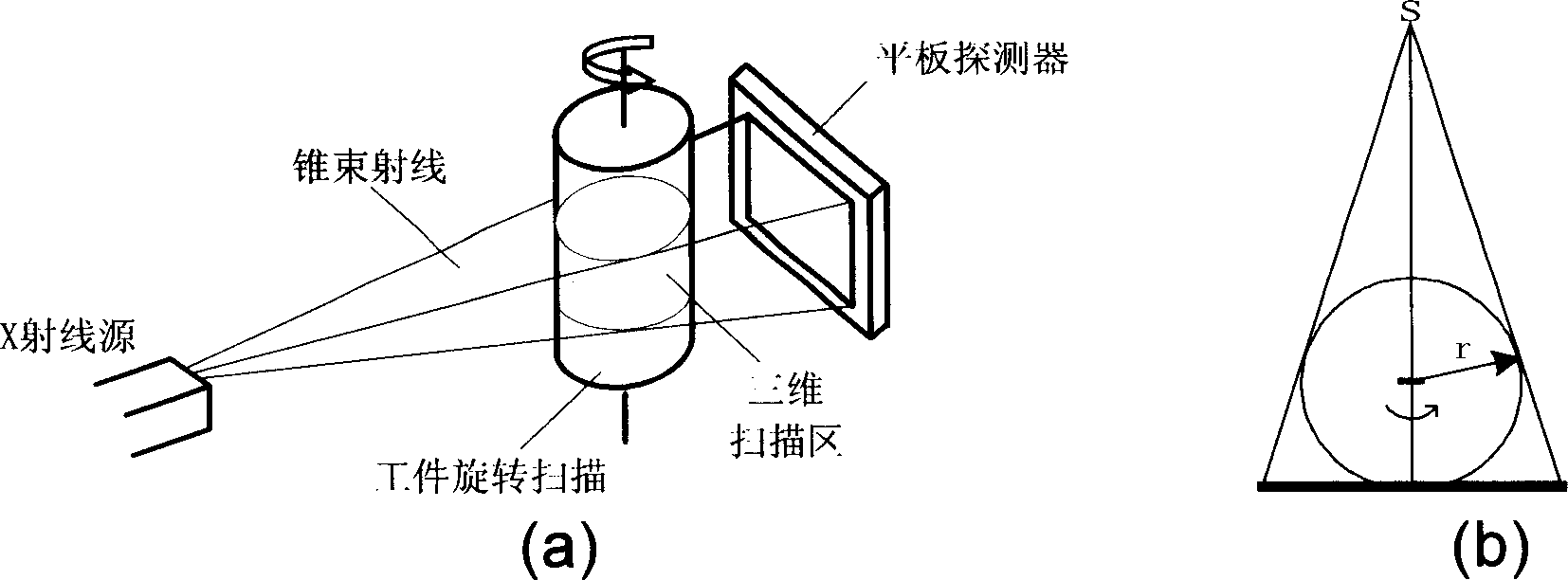
The 3D CT imaging method for large view field comprises: (1) taking first single-circular orbit cone-beam CT scanning to obtain the first digital ray projection image sequence; (2) removing the platform vertical the main ray with some distance to take the second CT scanning and obtain the second image sequence; (3) correcting former two images for dark current and inconsistency; (4) recording distance from ray source to detector, former moved distance and detector level channel number; (5) with the projection rearrangement algorithm in this invention, rearranging former two images into self-contained quasi-parallel image sequence; (6) with the quasi-parallel ray reconstructing algorithm in this invention, reconstructing the 3D CT image. This invention can enlarge the view area more than 3 times with high efficiency.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com