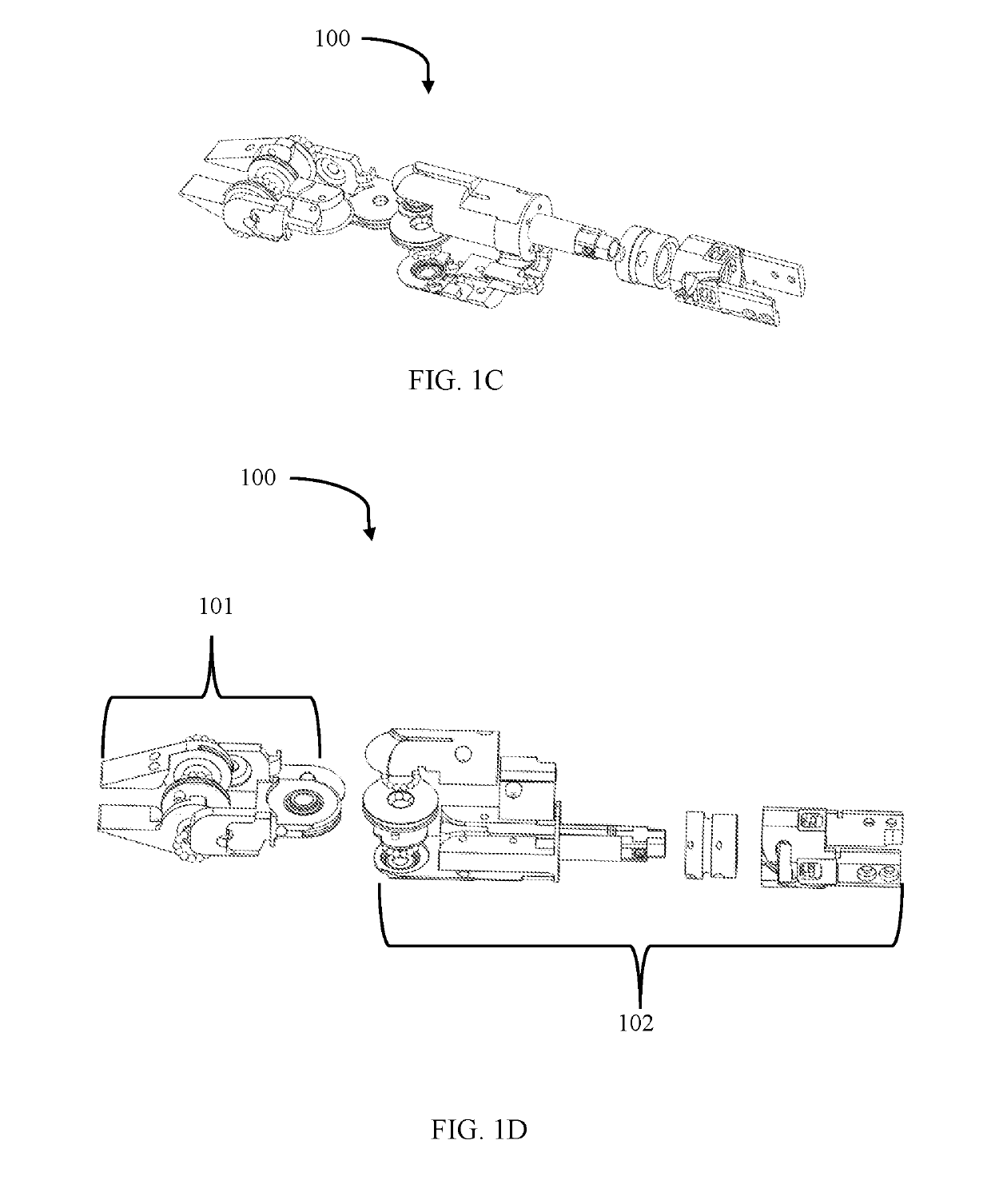
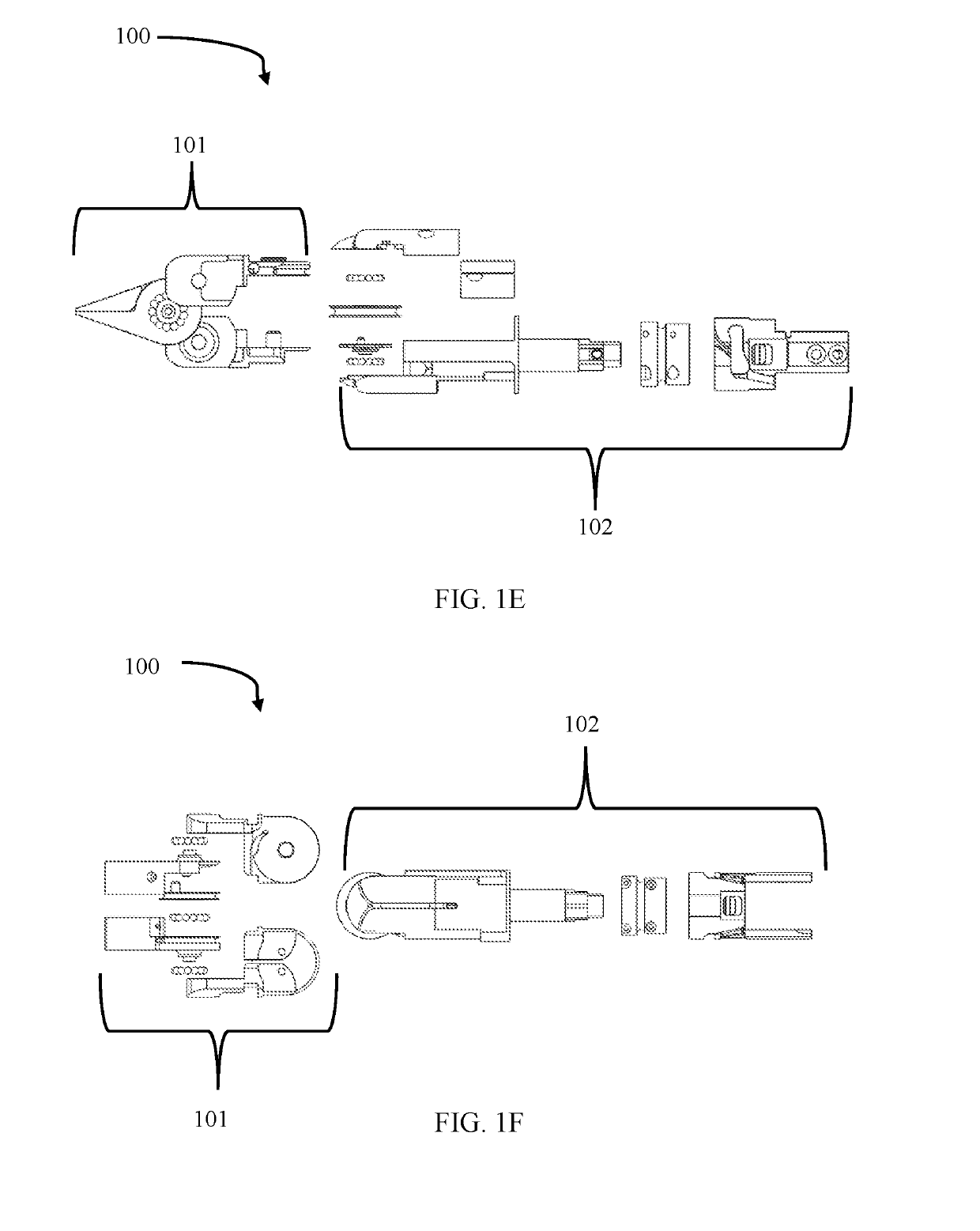
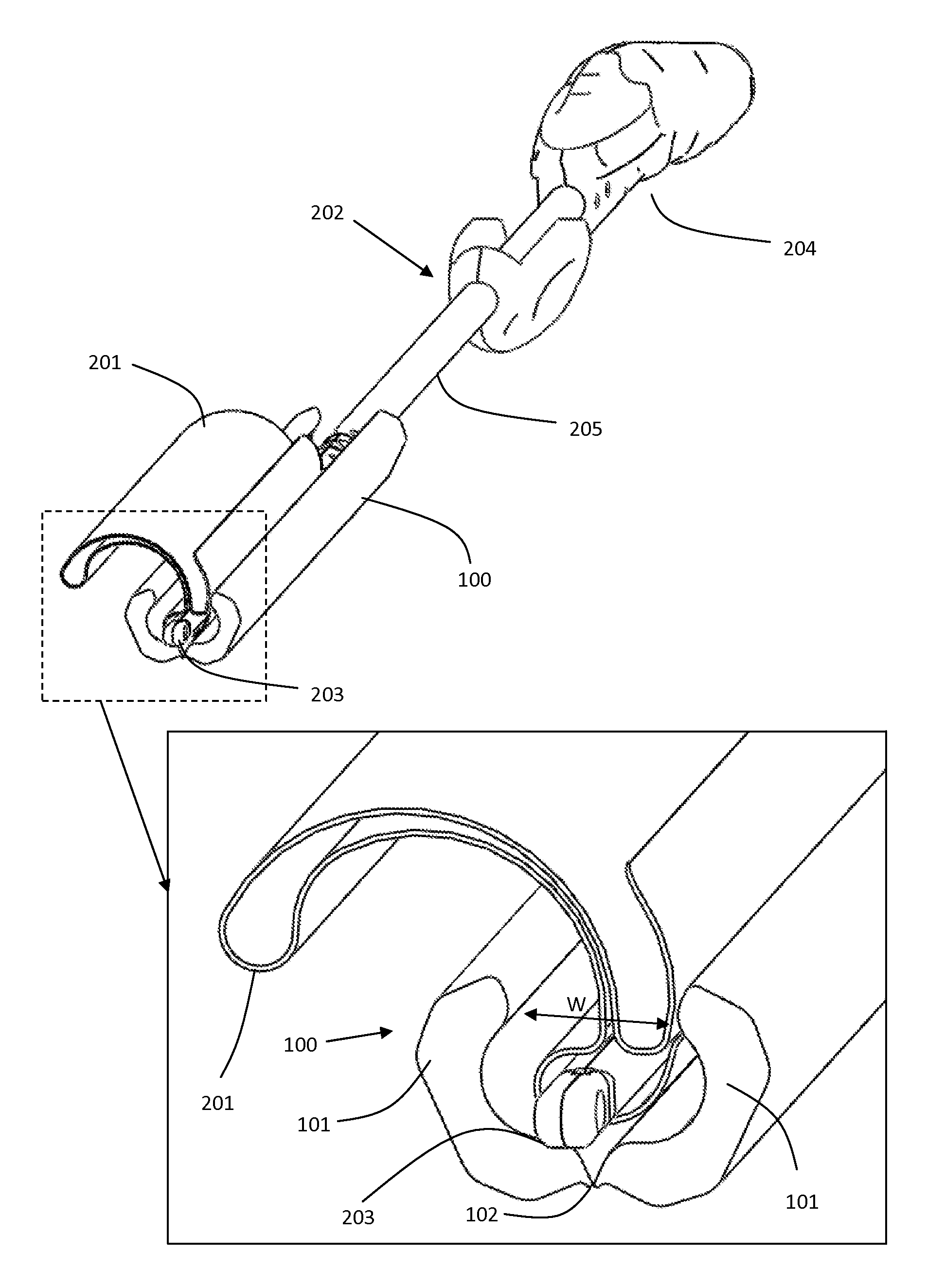
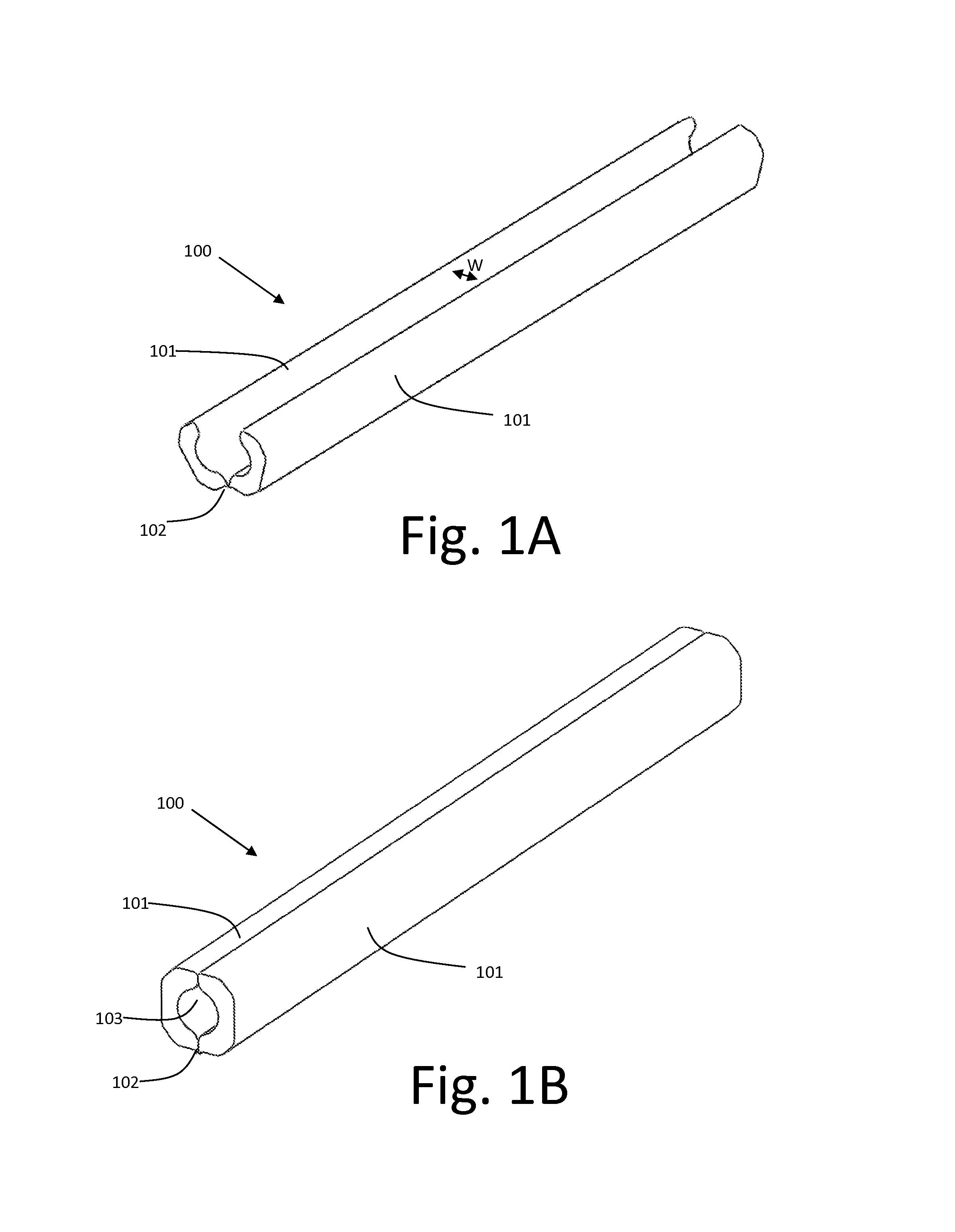
Patents
Literature
485 results about "Minimal invasive surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
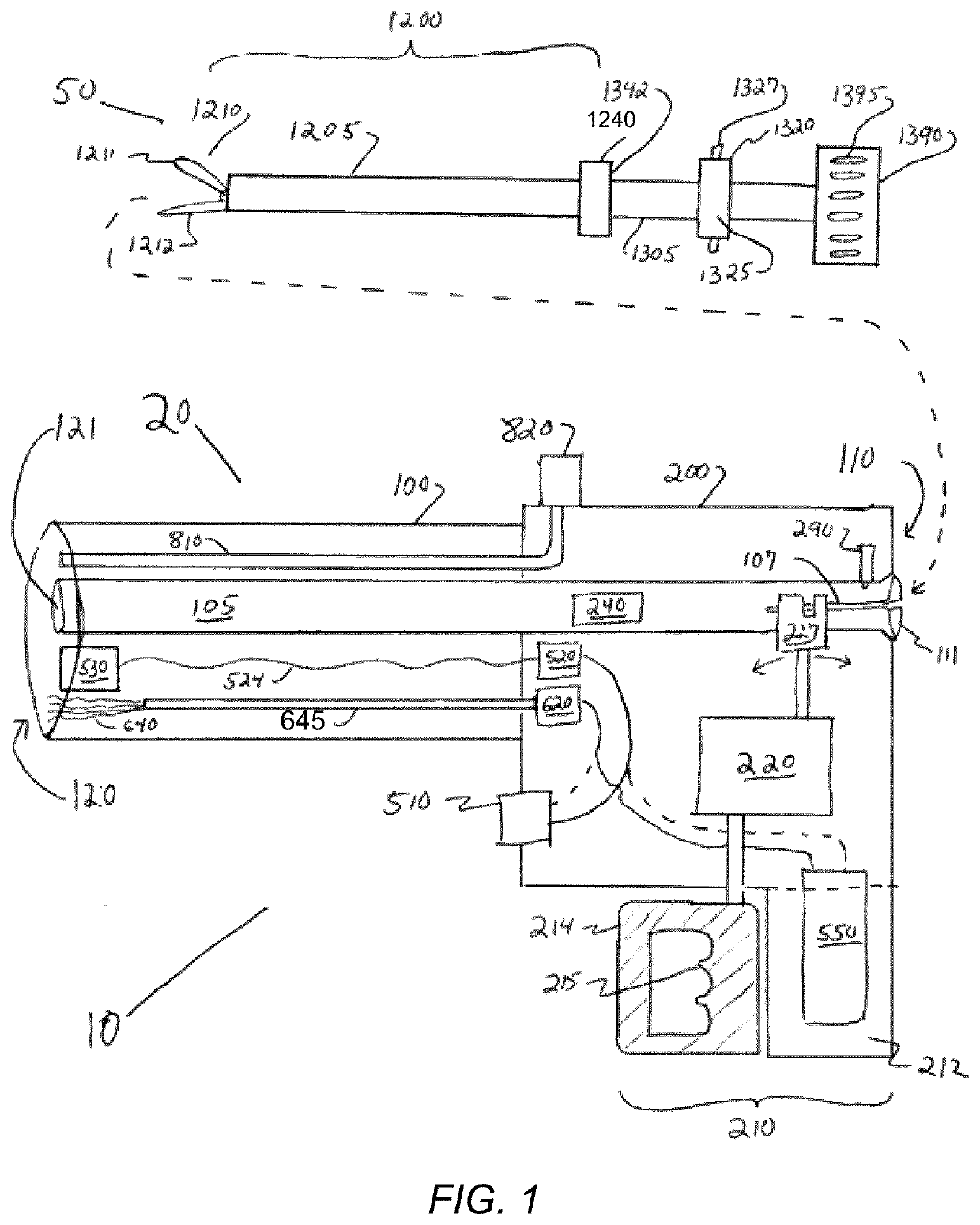
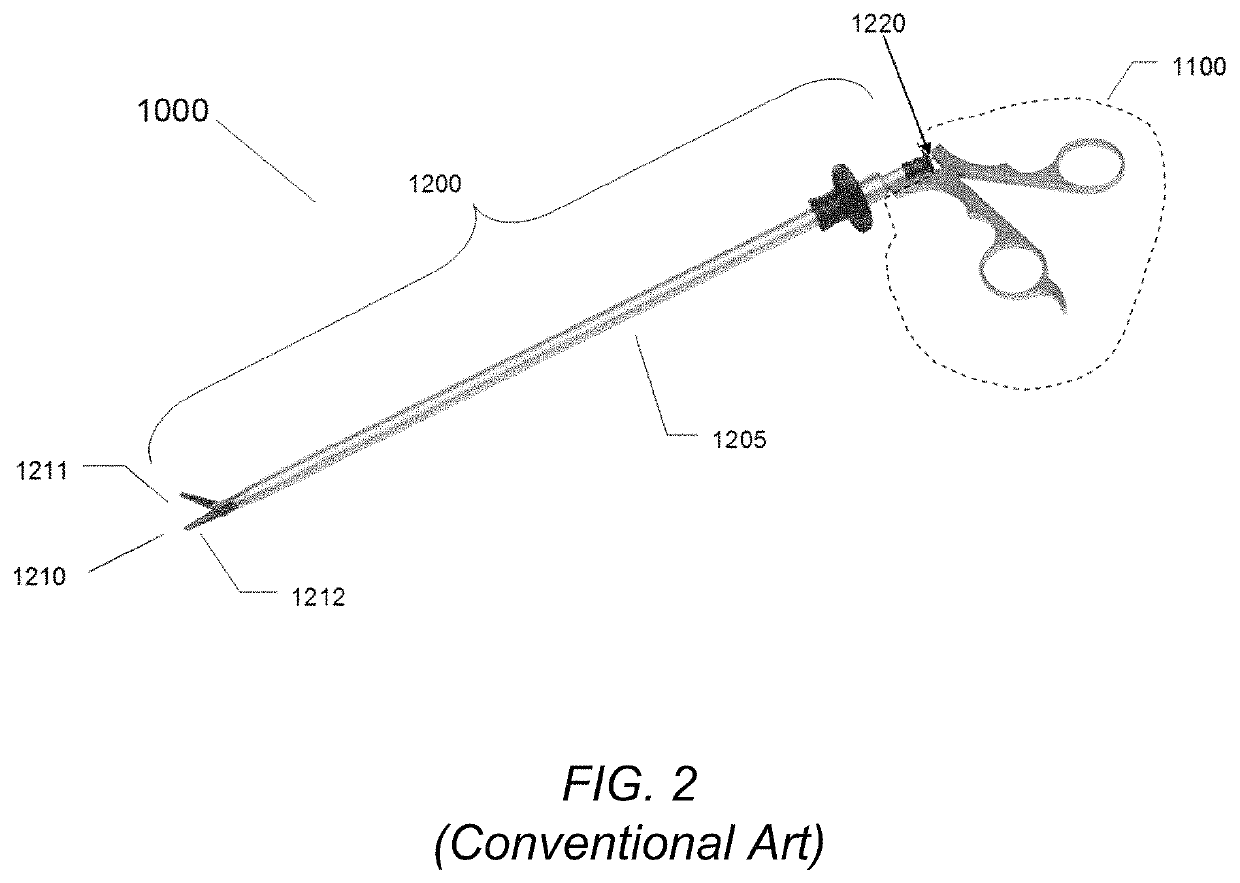
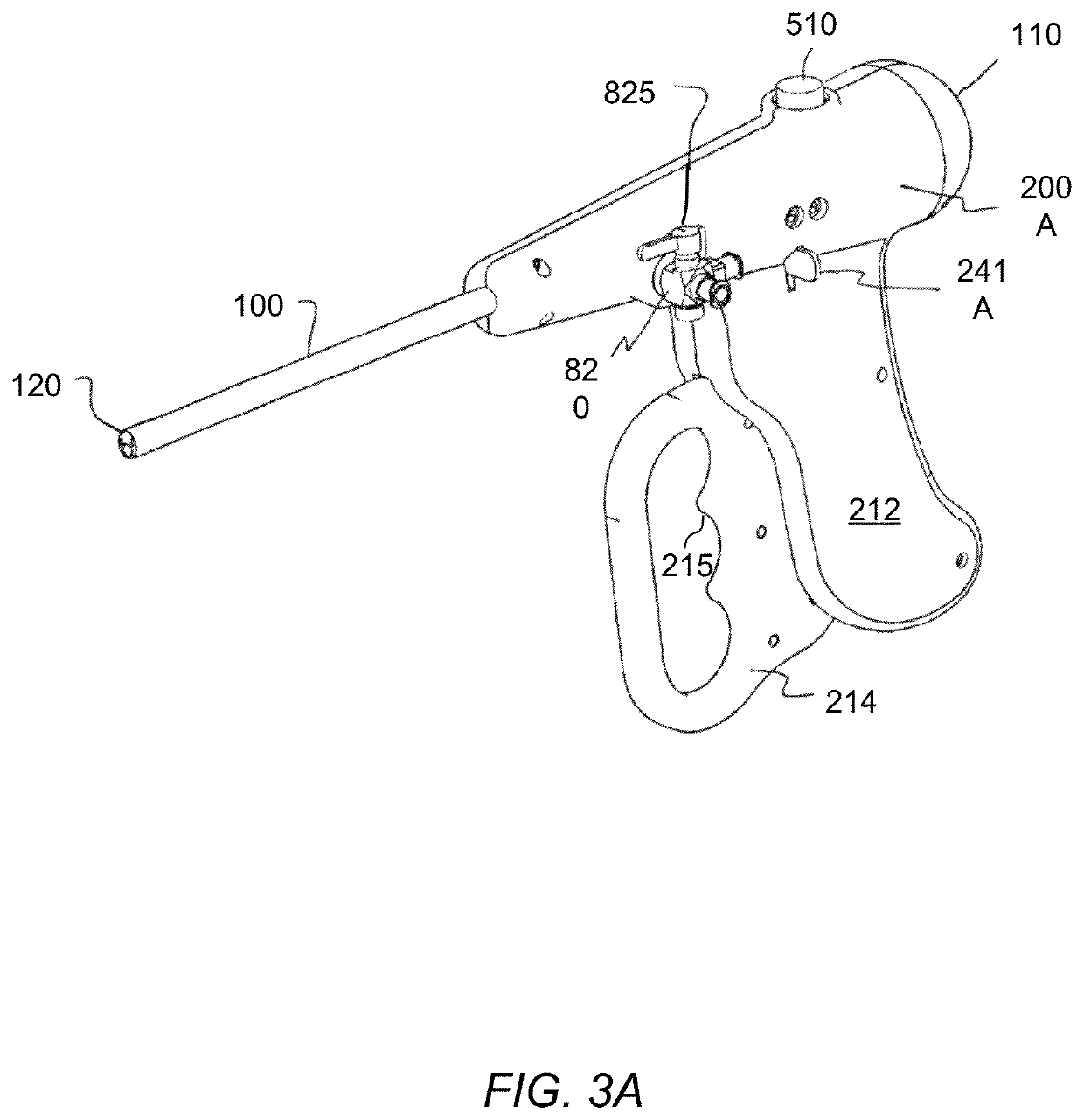
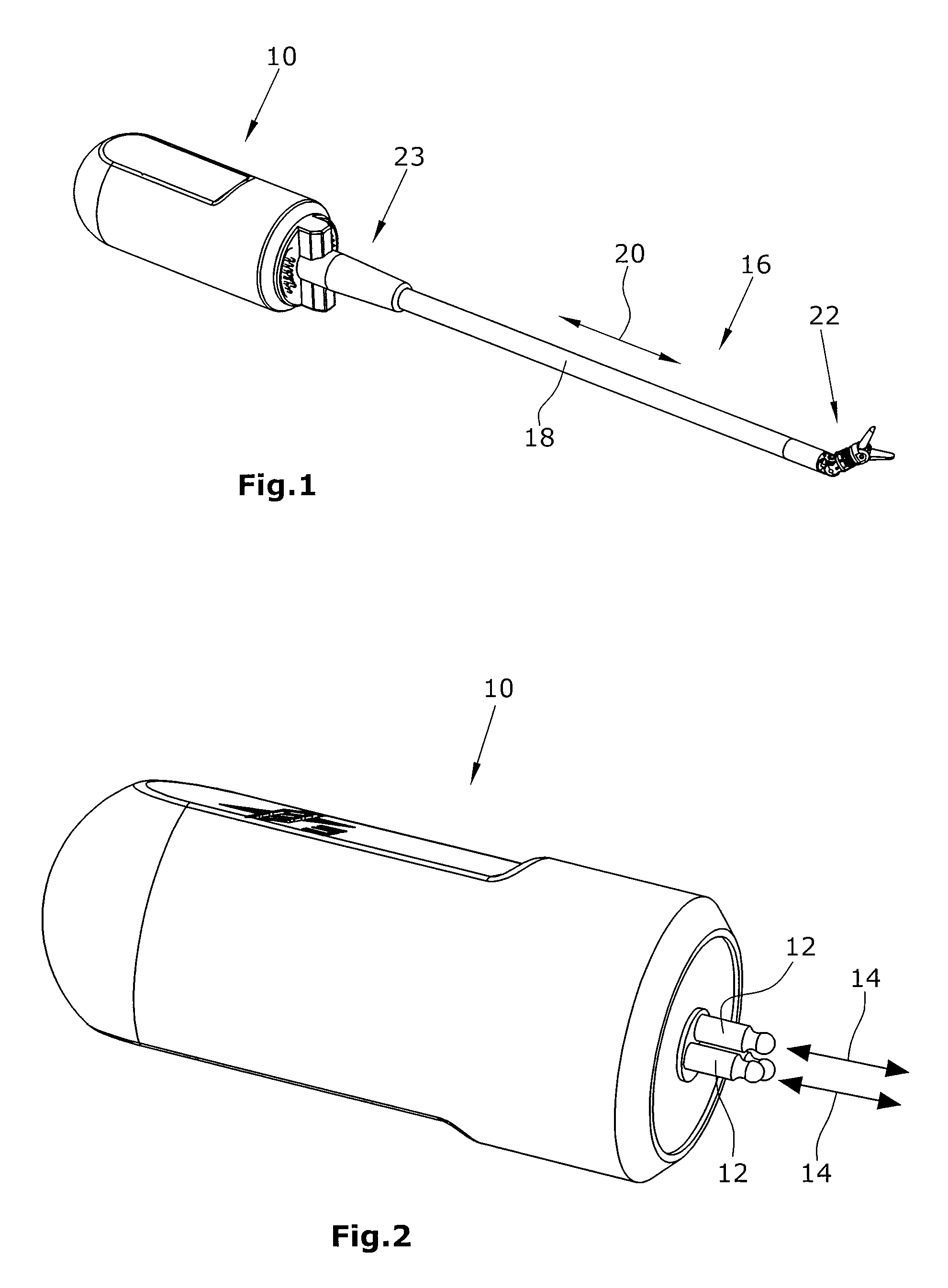
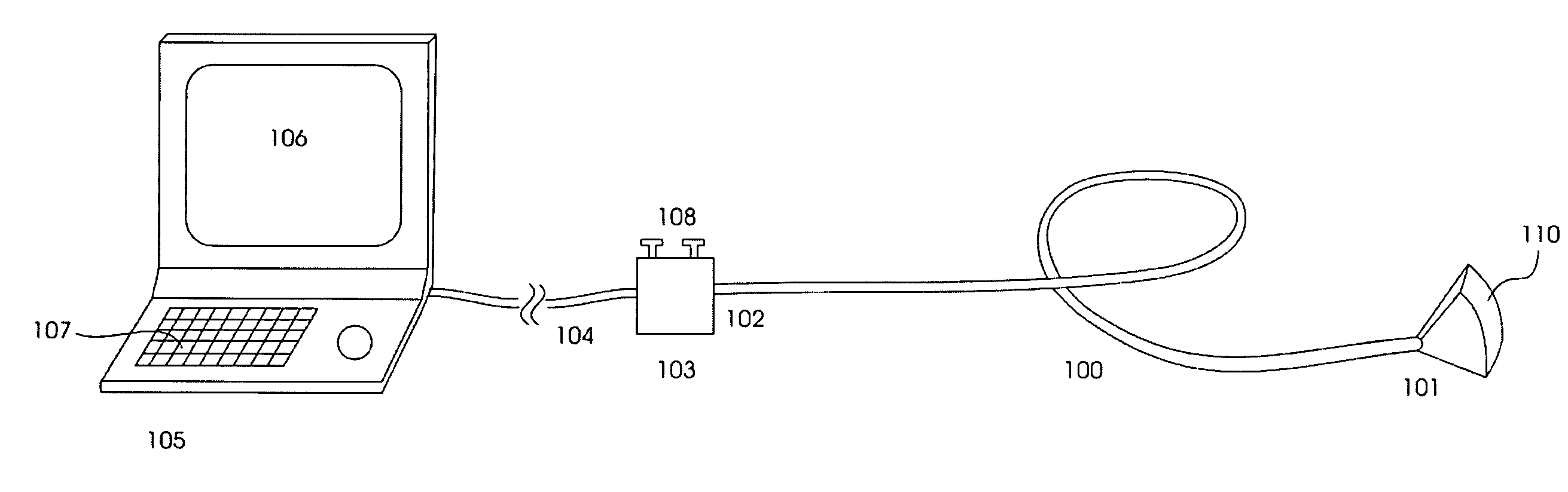
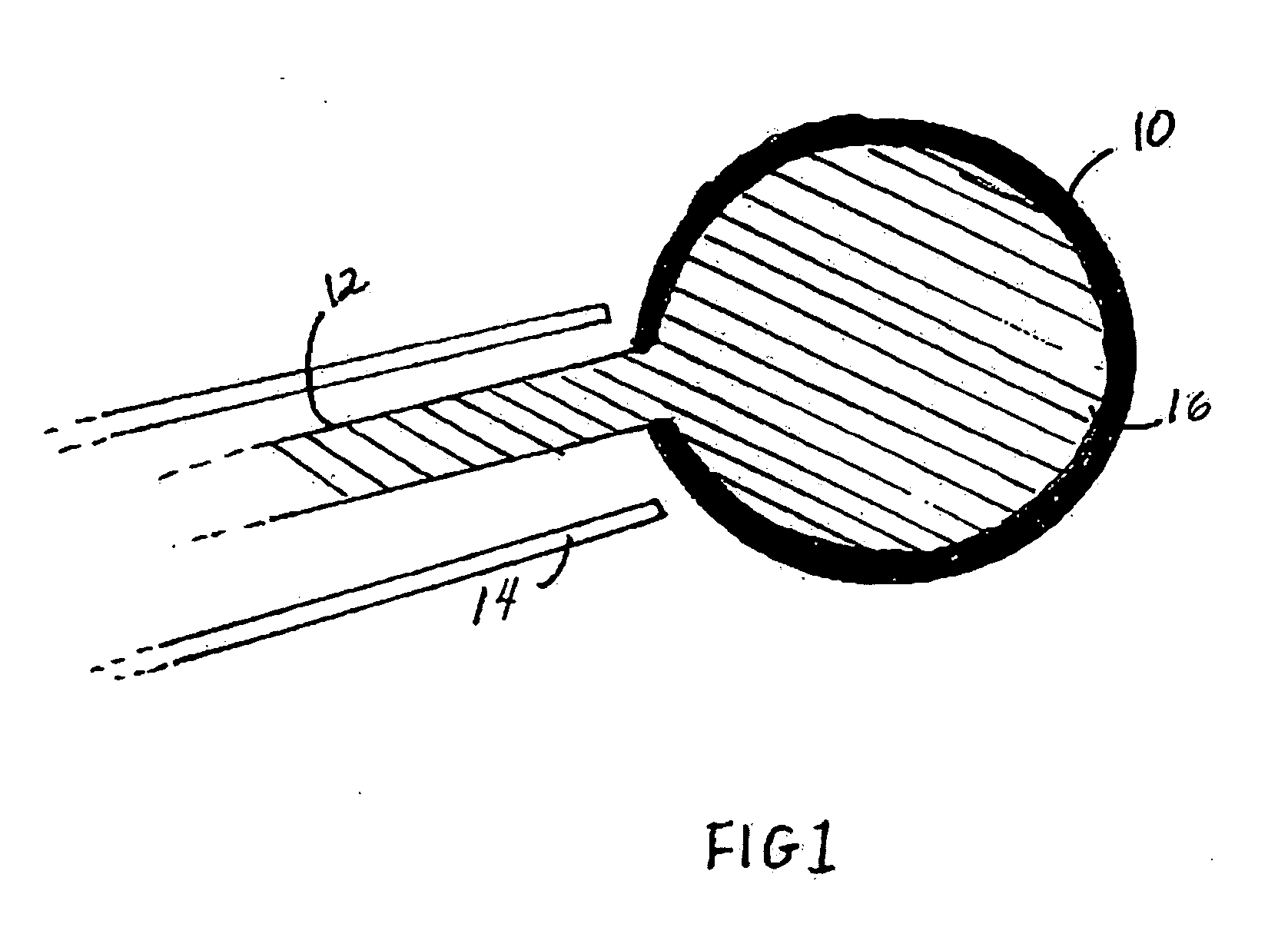
Endoscopic surgical system
The present invention is an apparatus, device or tool for performing endoscopic (that is, minimally invasive) surgery. An exemplary embodiment of the invention includes a video endoscope whilst in another embodiment of the invention includes an endoscopic surgical tool which, when equipped with one of a suite of endoscopic surgical instruments, can be used by a surgeon to perform surgical procedures inside a body. Another embodiment of the present invention includes a suite of endoscopic surgical instruments designed to work co-operatively with the endoscopic surgical tool. In another embodiment of the present invention, a video-assisted endoscopic surgical tool system is provided. In one embodiment, the system includes the video-assisted endoscopic surgical tool and a suite of at least one endoscopic surgical instrument.
Owner:MOSKOWITZ FAMILY LLC
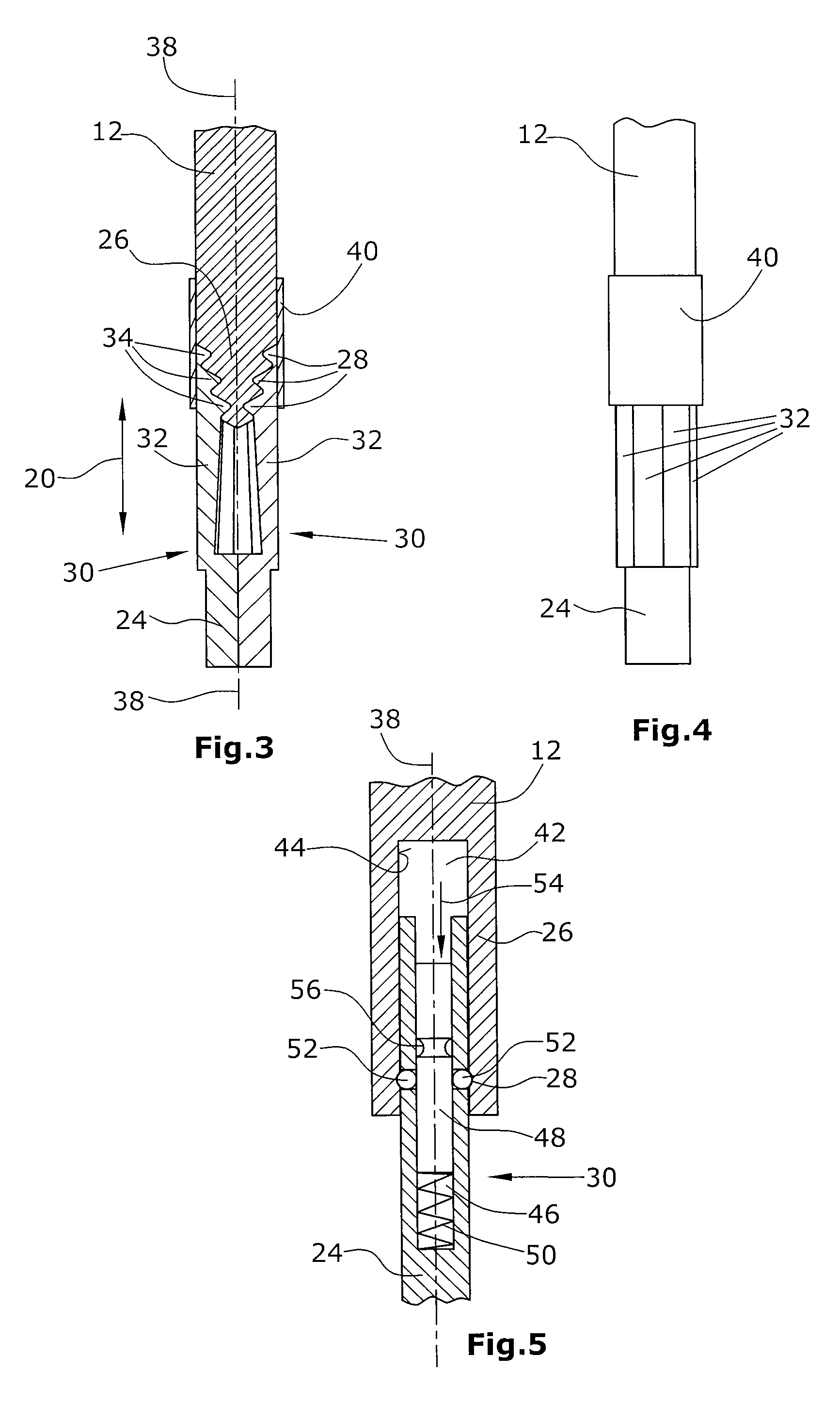
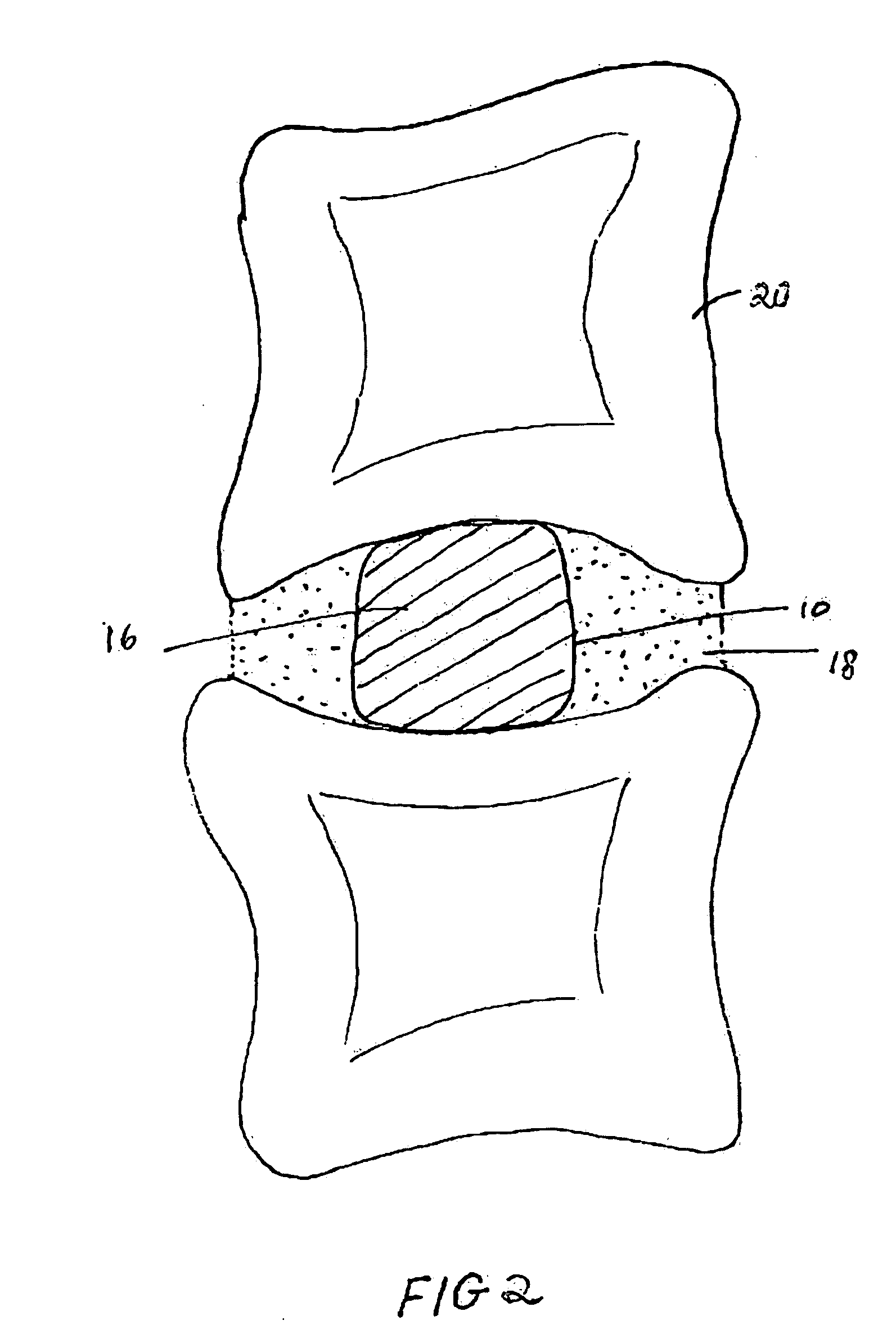
Surgical manipulation instrument
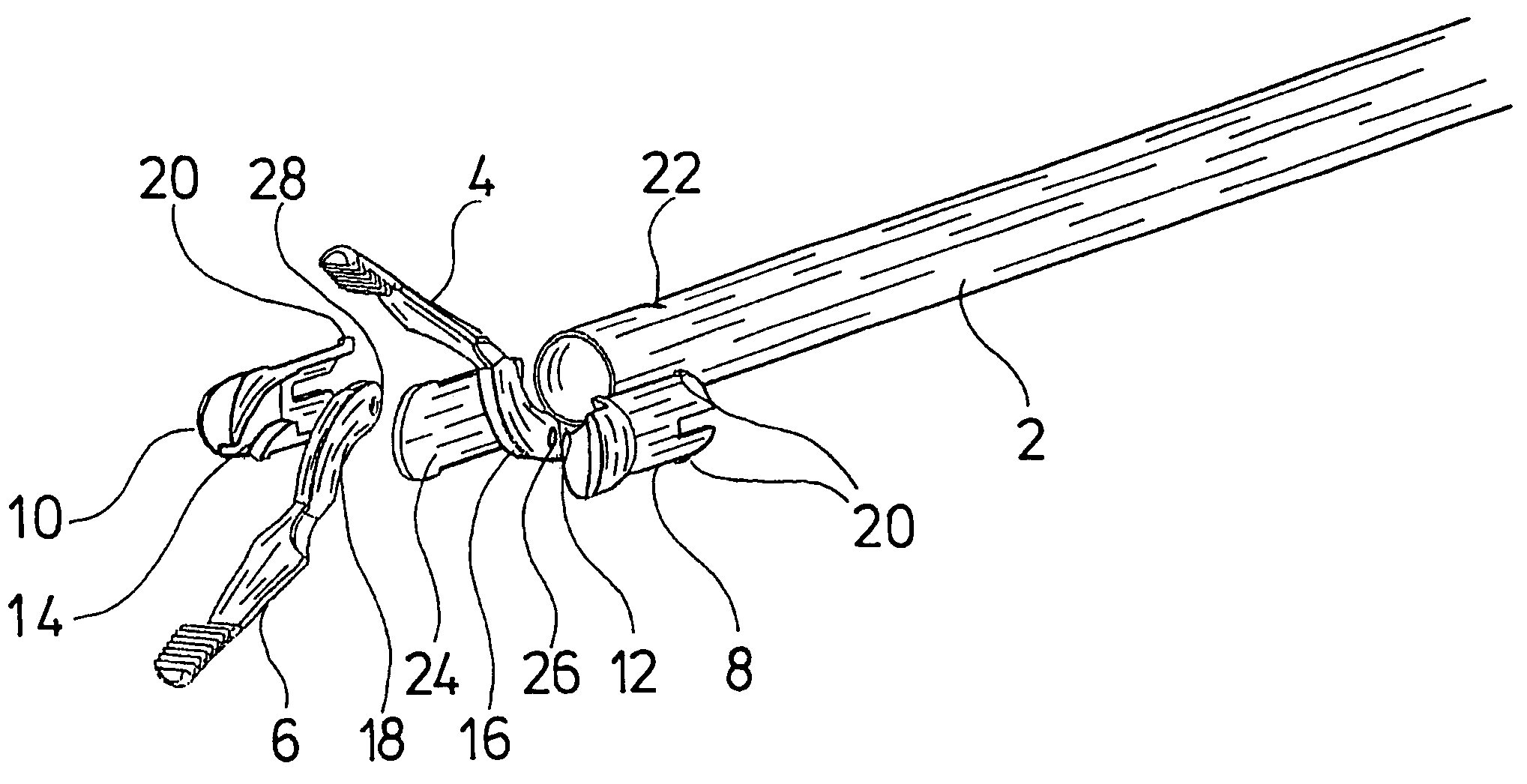
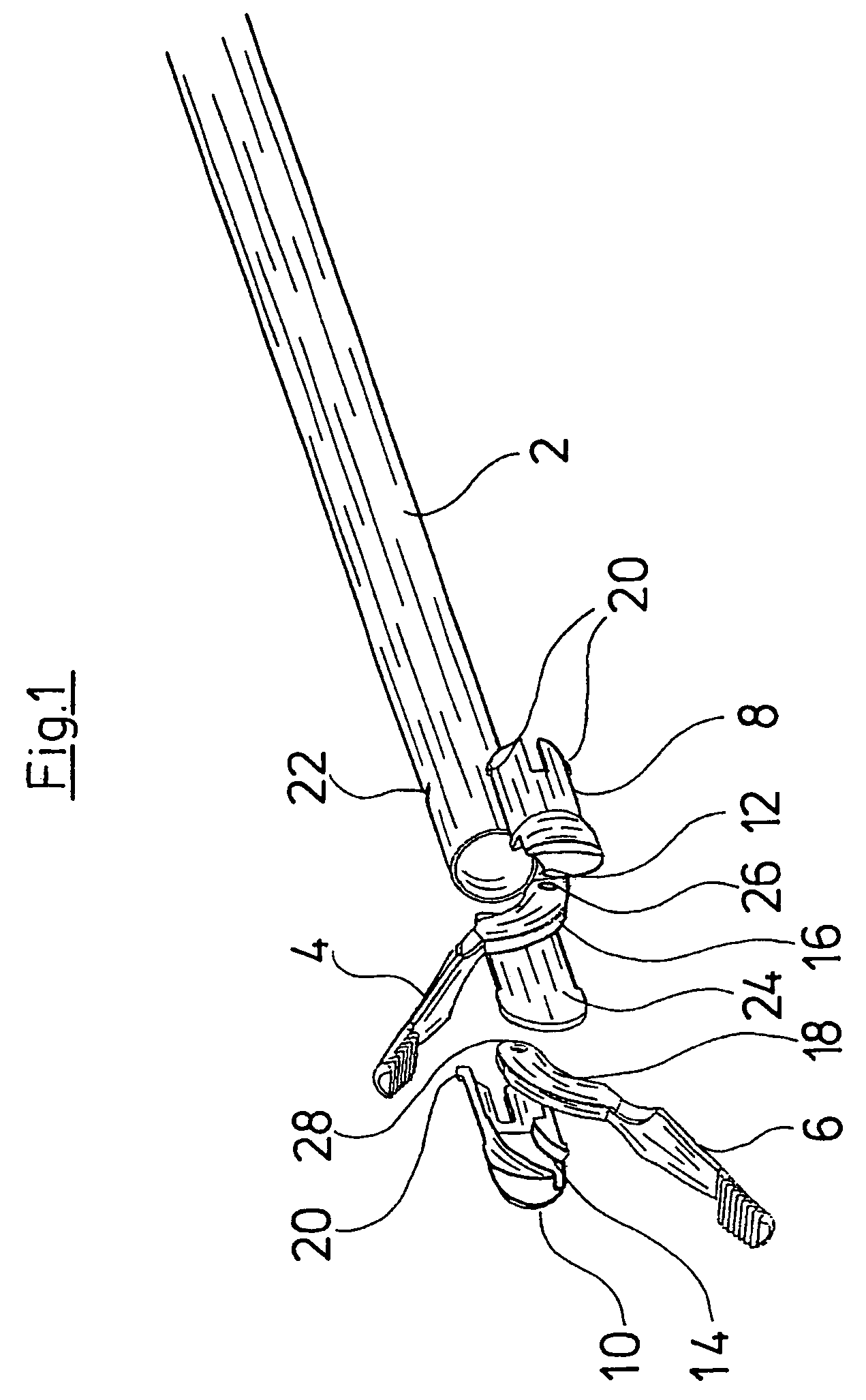
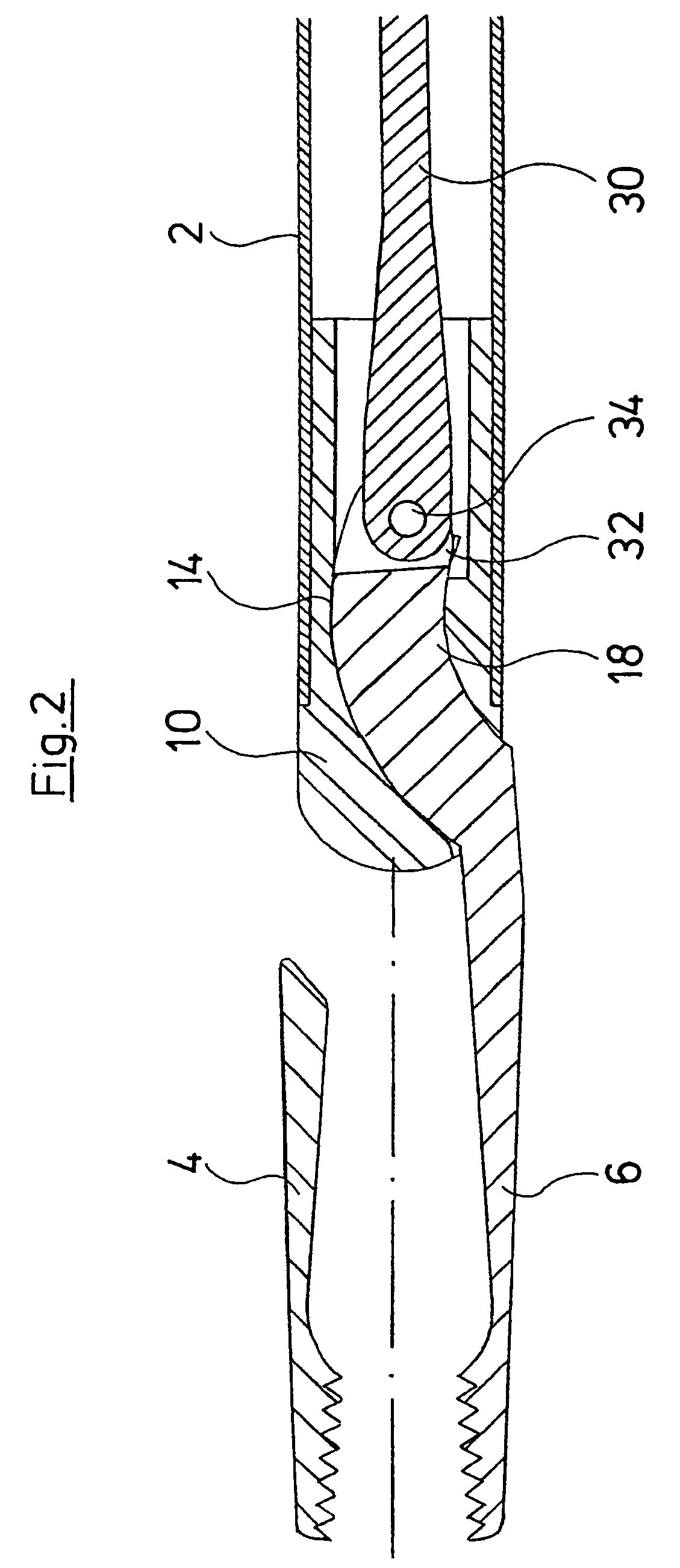
ActiveUS8945098B2High strengthSmall structure sizeDiagnosticsSurgical forcepsSurgical ManipulationMinimal invasive surgery
A surgical manipulation instrument which is particularly suitable for minimal invasive surgery, comprising an extra-corporeal drive device and a partial intra-corporeal manipulator part. The drive device comprises several axially displaceable first actuation elements. The first actuation elements are detachably connected to axially displaceable second actuation elements, by a coupling device, the second actuation elements being used to actuate an end effector. The coupling device comprises two coupling elements, one of the coupling elements having undercut recesses in which the second coupling element engages.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Telerobotic surgery system using minimally invasive surgical tool with variable force scaling and feedback and relayed communications between remote surgeon and surgery station
ActiveUS10813710B2Surgical systems user interfaceEducational modelsMinimal invasive surgeryPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A telerobotic surgery system includes a robotic surgery station having a first pair of robot arms, each carrying a laparoscopic tool and each having a robot arm drive. A first controller is connected to each robot arm drive. Harvested animal tissue is at the robotic surgery station. A remote surgeon station includes a second pair of robot arms, each carrying a laparoscopic tool and each having a robot arm drive. A second controller receives data regarding movement of the second pair of robot arms and respective laparoscopic tool based on user manipulation of each laparoscopic tool at the remote surgeon station. A communications network couples the first and second controllers with the second controller operative as a master and the first controller configured to control each robot arm drive and effect one-to-one movement of the first pair of robot arms and carried laparoscopic tools as a slave.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
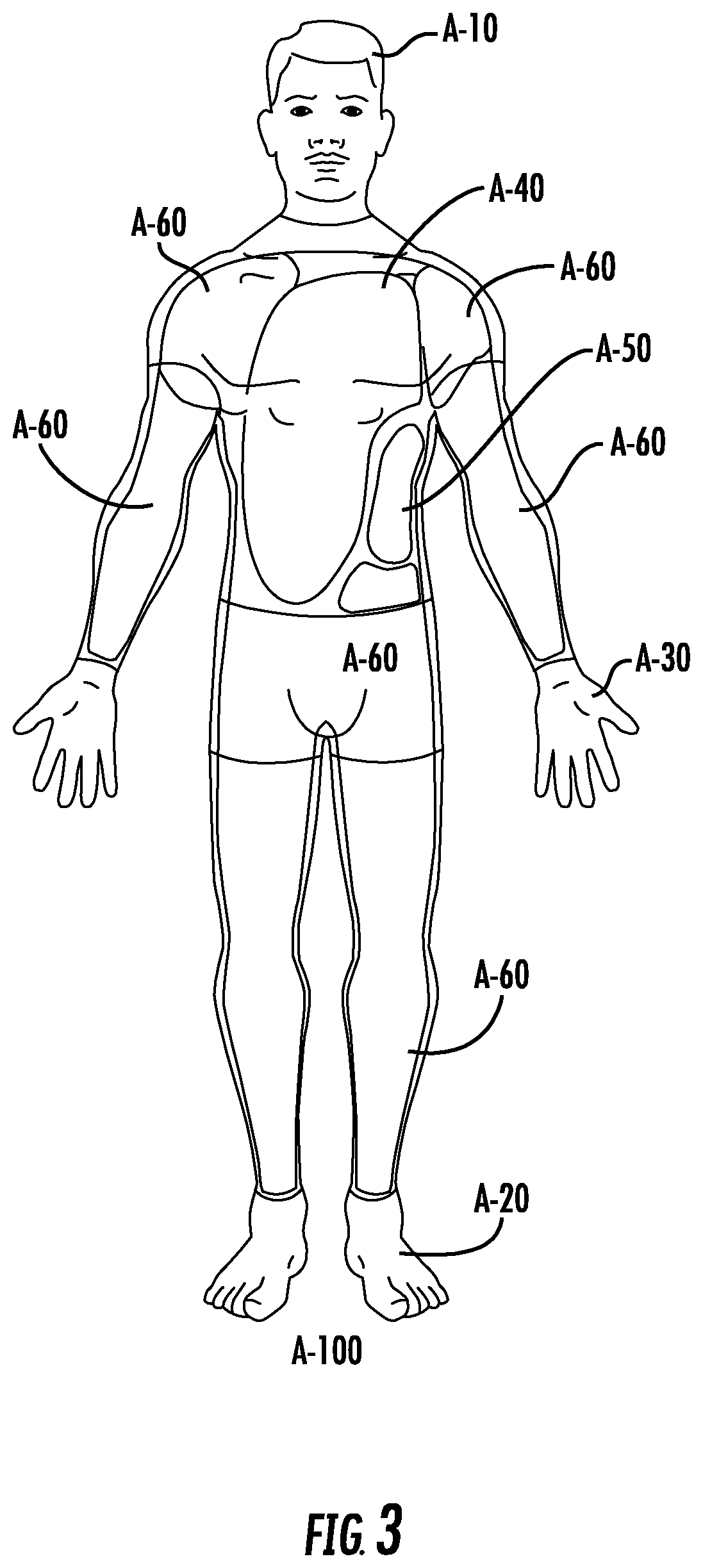
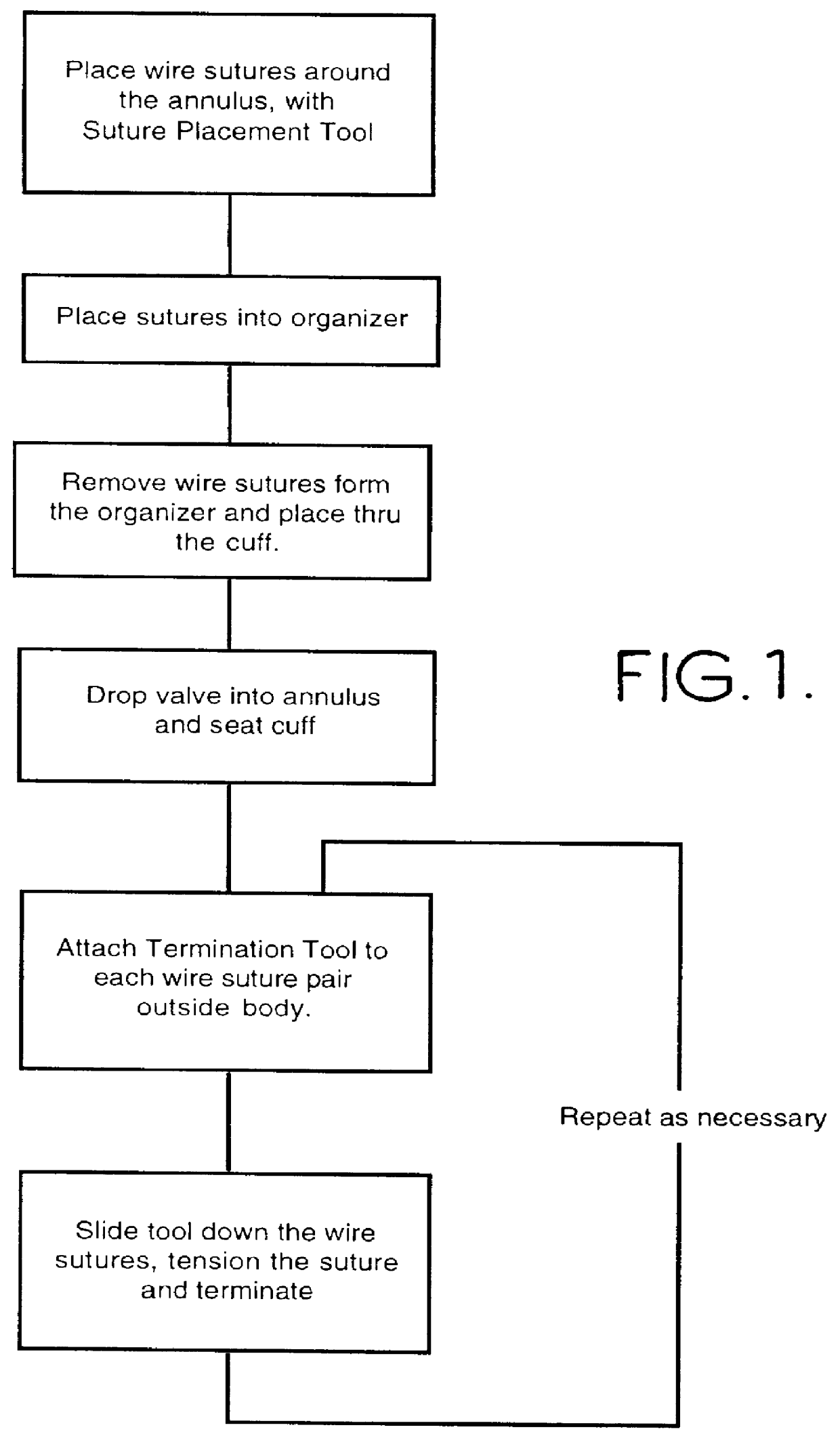
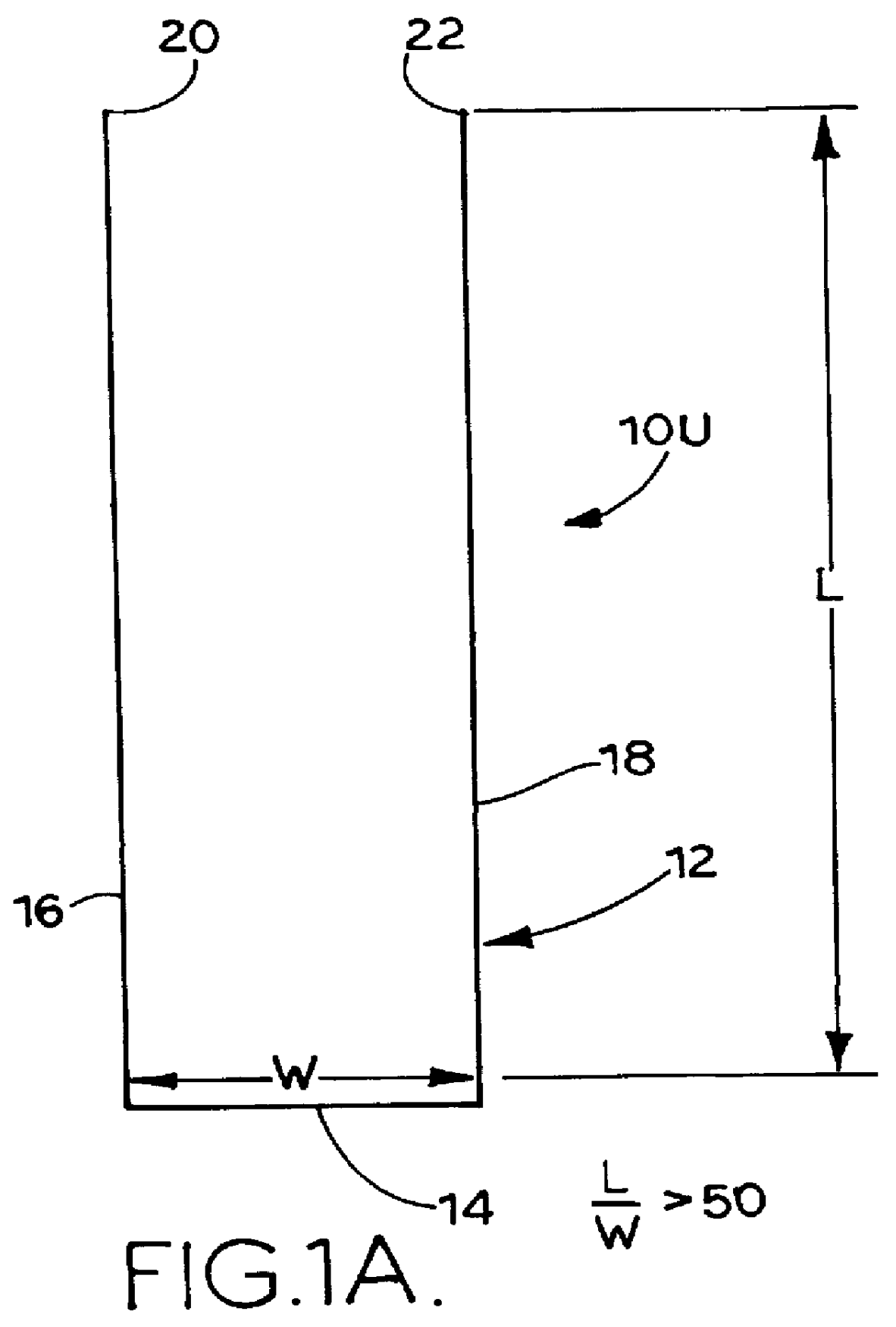
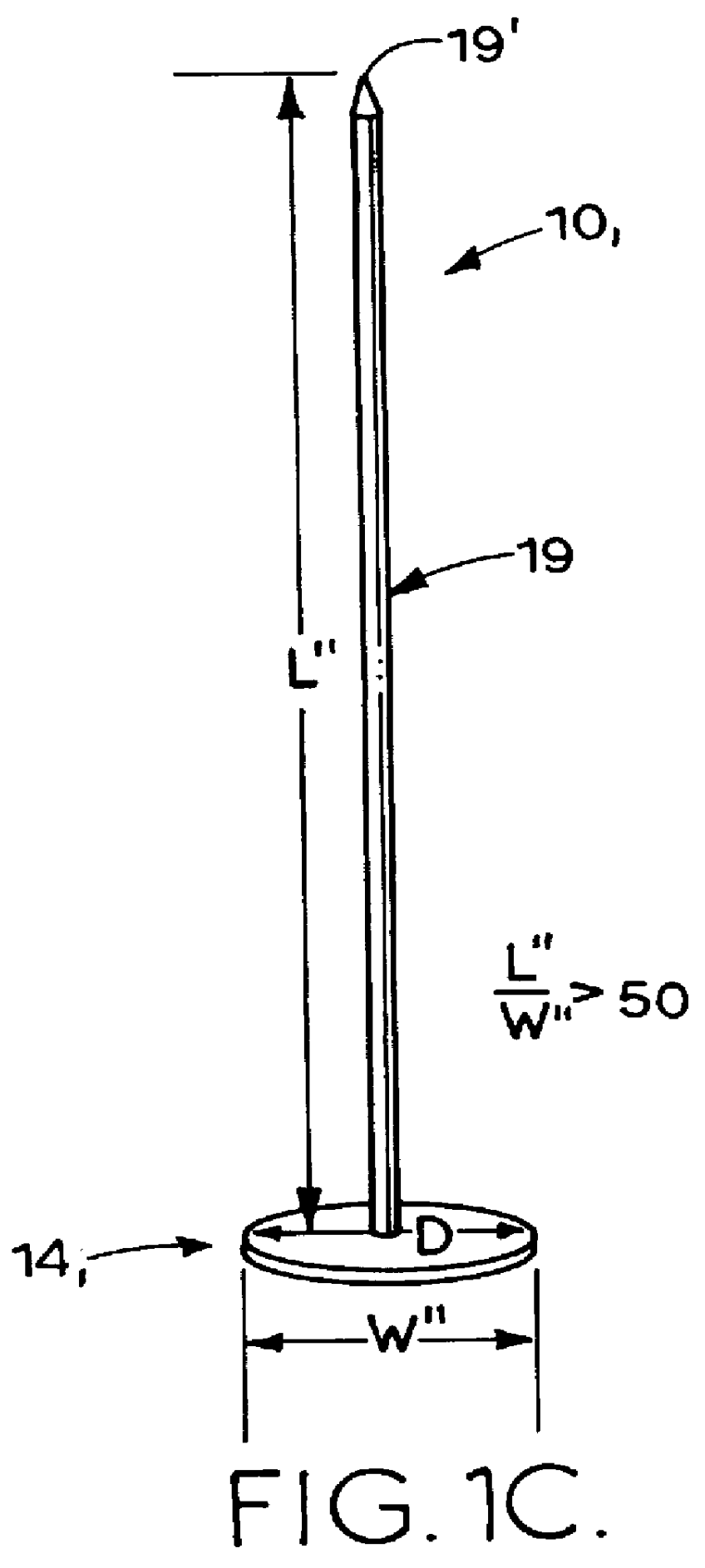
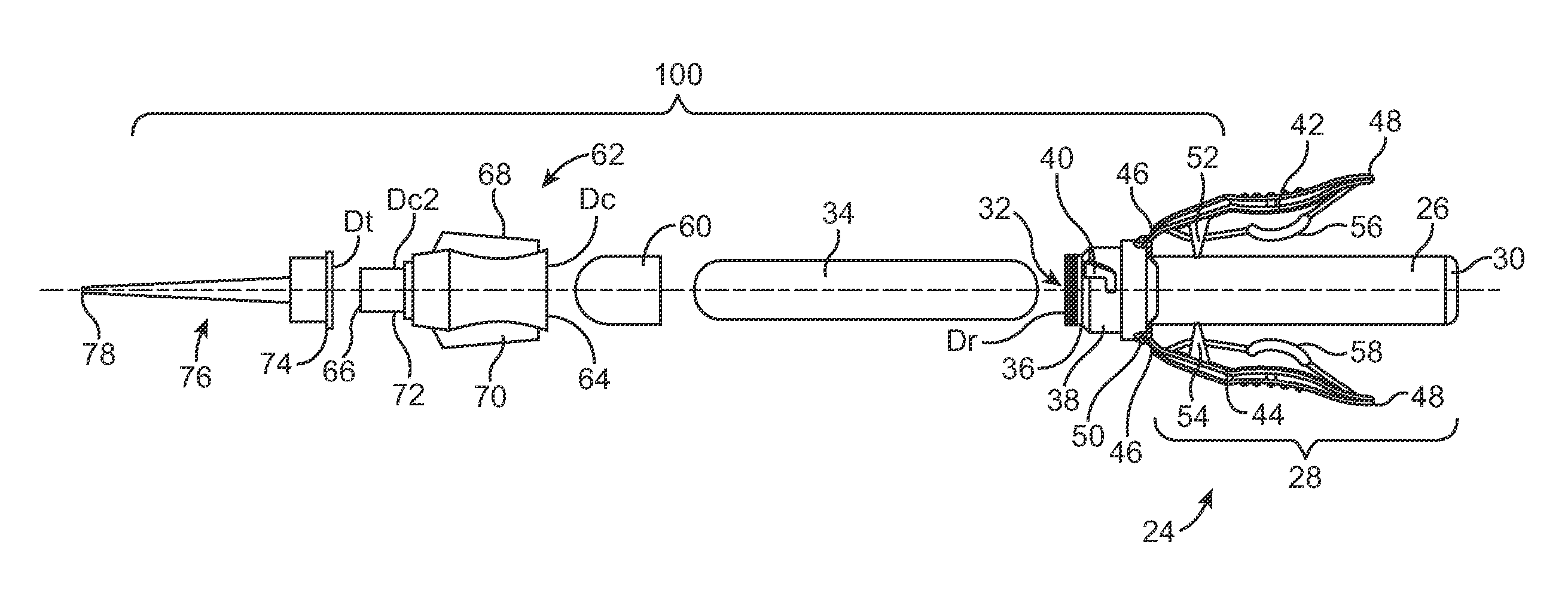
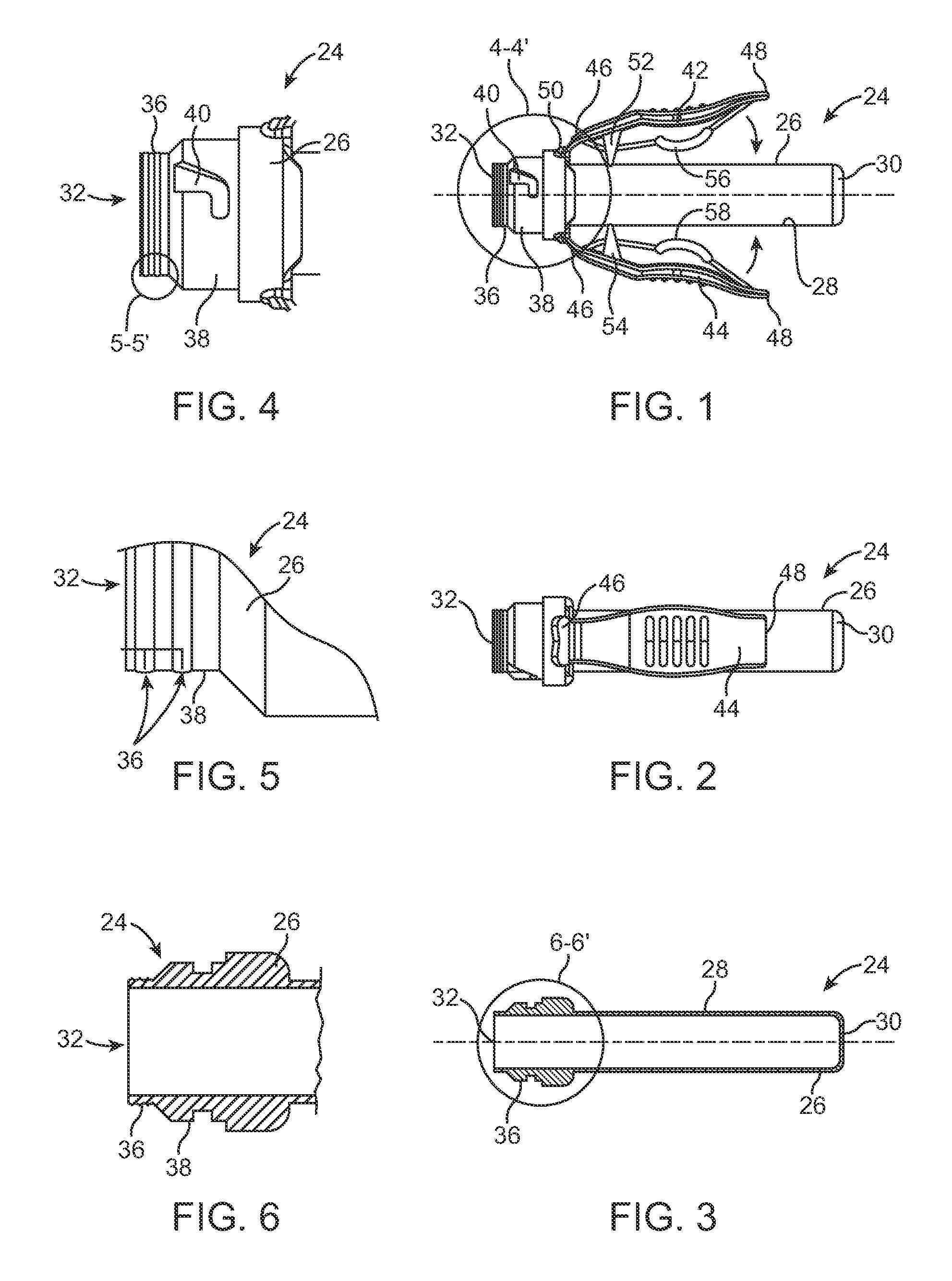
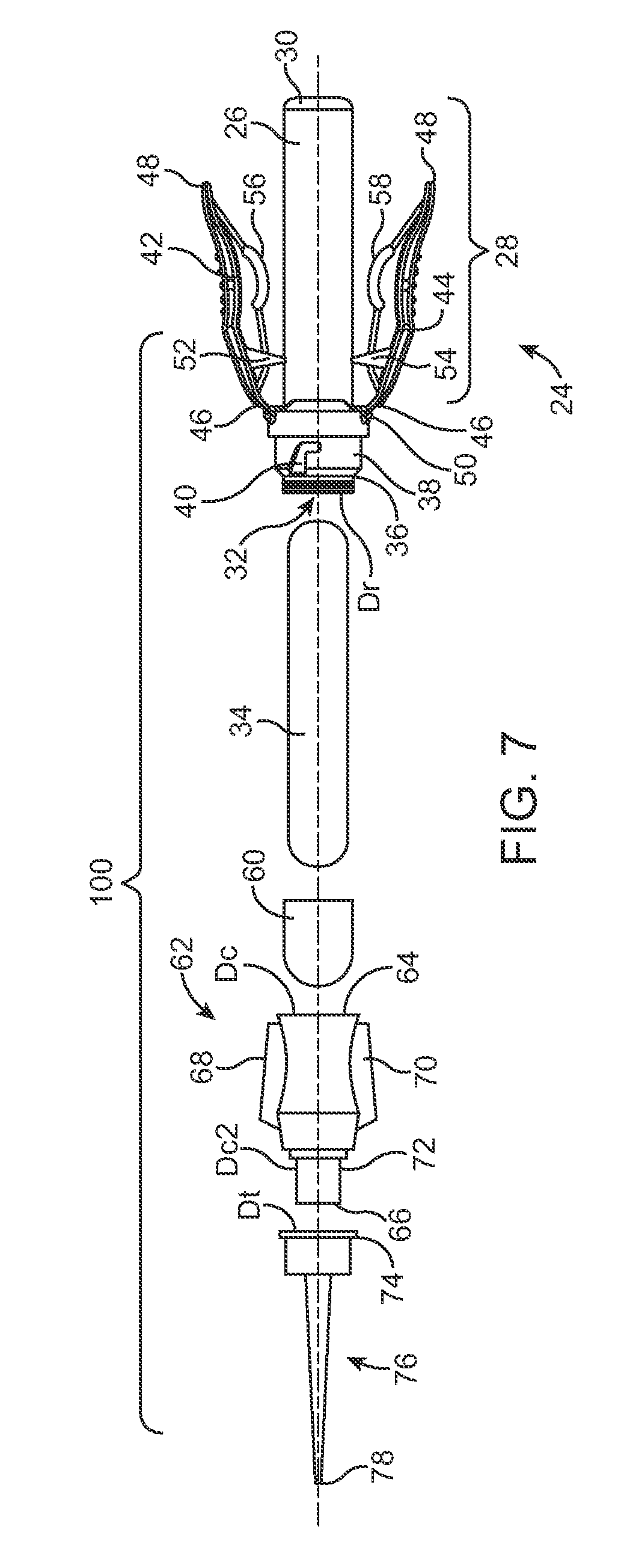
Wire fasteners for use in minimally invasive surgery and means and methods for handling those fasteners
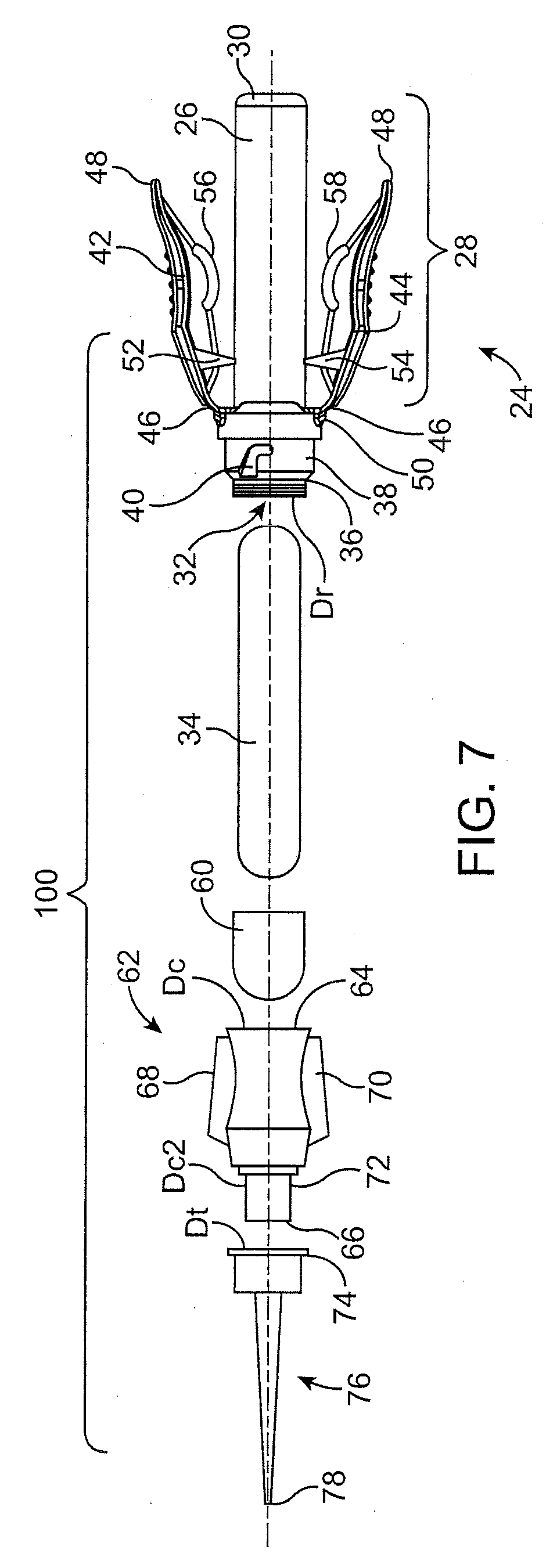
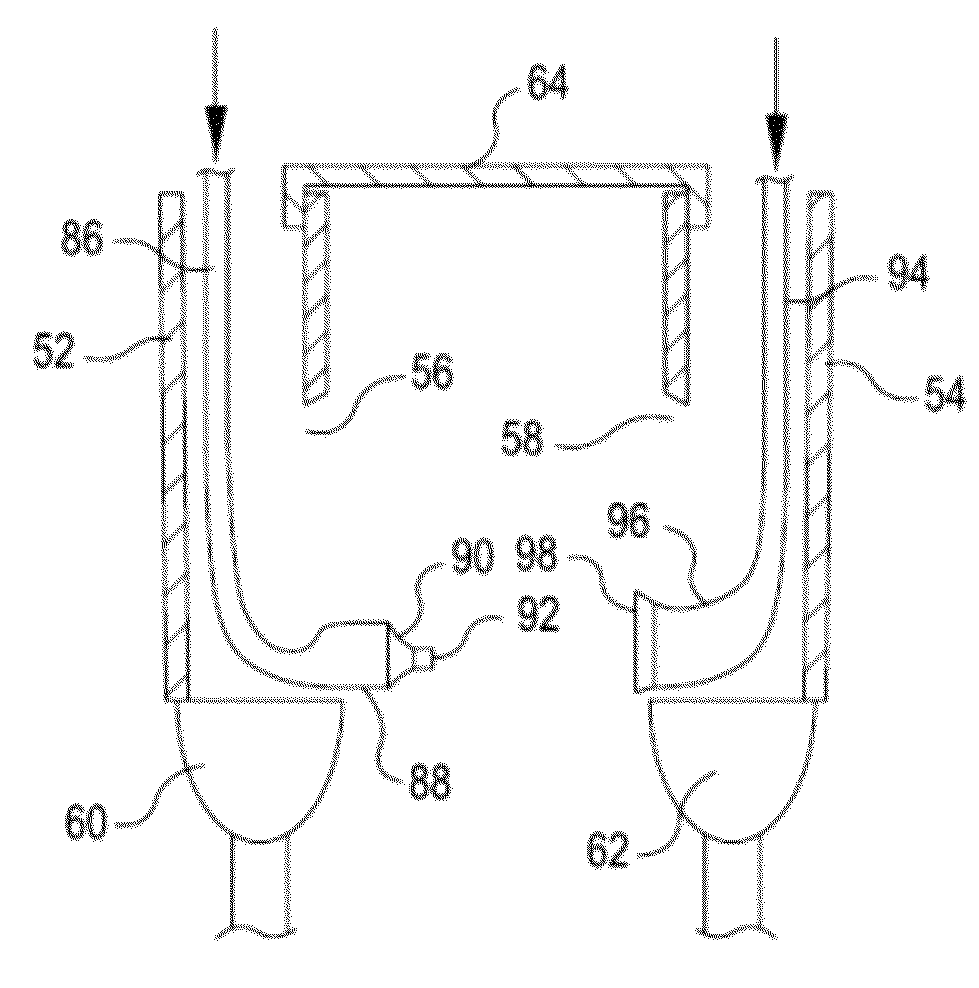
Wire fasteners having legs with lengths that can be one hundred times the width of the fastener are used to secure items, such as prosthesis valves to a patient during minimally invasive surgery. The fasteners are manipulated into position and then are immobilized by the legs thereof for tensioning, cutting and forming in situ. The fasteners are manipulated, tensioned and formed from the leg end of the fasteners. Tools for initially placing the fasteners and for immobilizing, tensioning, cutting and bending the fastener legs are disclosed. Once the fasteners are initially placed, the prosthesis is placed on the long legs of the placed fasteners and is guided into position on the legs. Once the prosthesis is in position, the legs of the fasteners are immobilized, tensioned, cut and bent into staple-like shapes to secure the prosthesis to the patient. A method for carrying out the procedure using the long fastener is also disclosed. Using the teaching of the present disclosure, a surgeon can customize a fastener to the particular surgery or even to the particular portion of surgery being performed during the surgery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Surgical access device
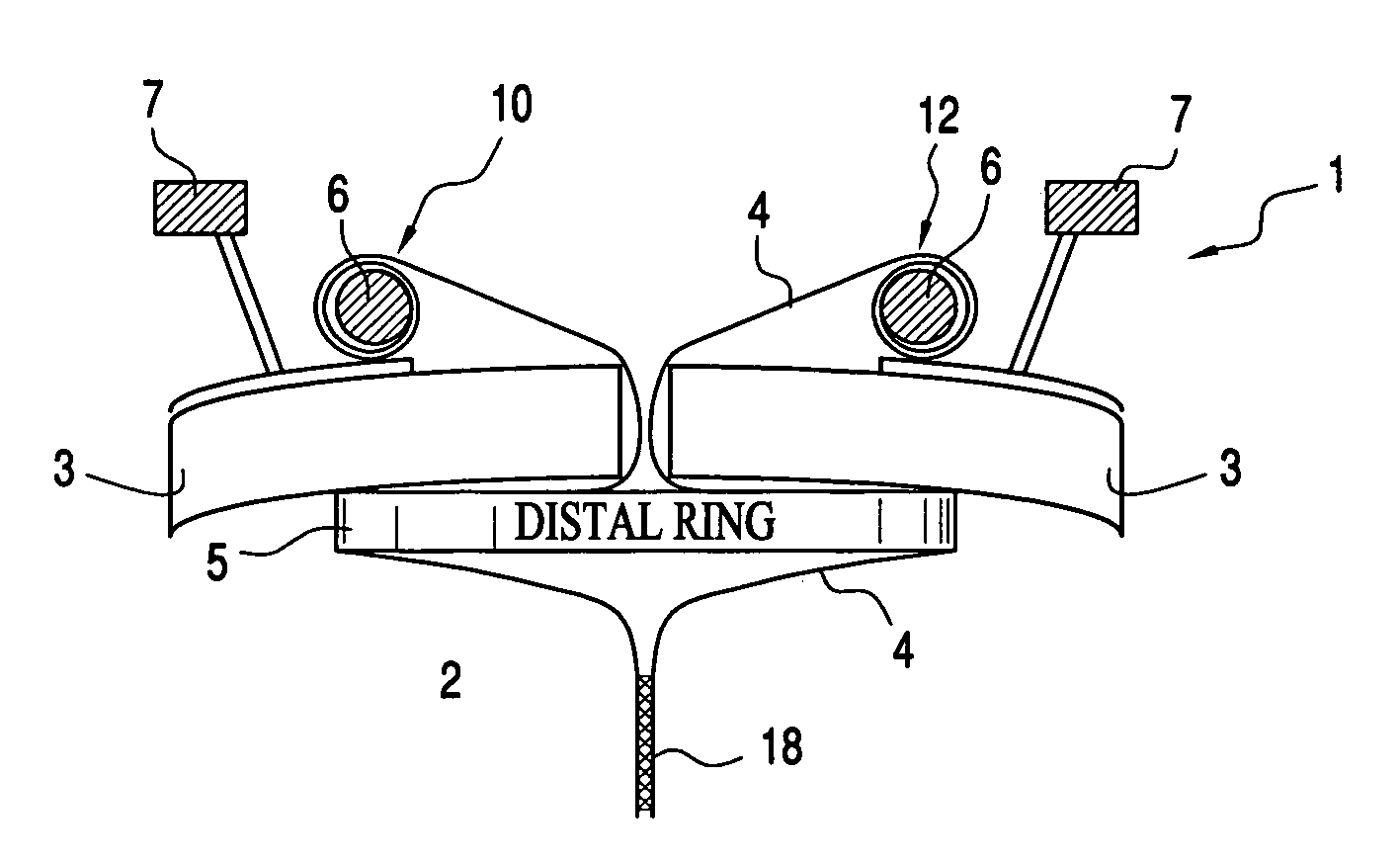
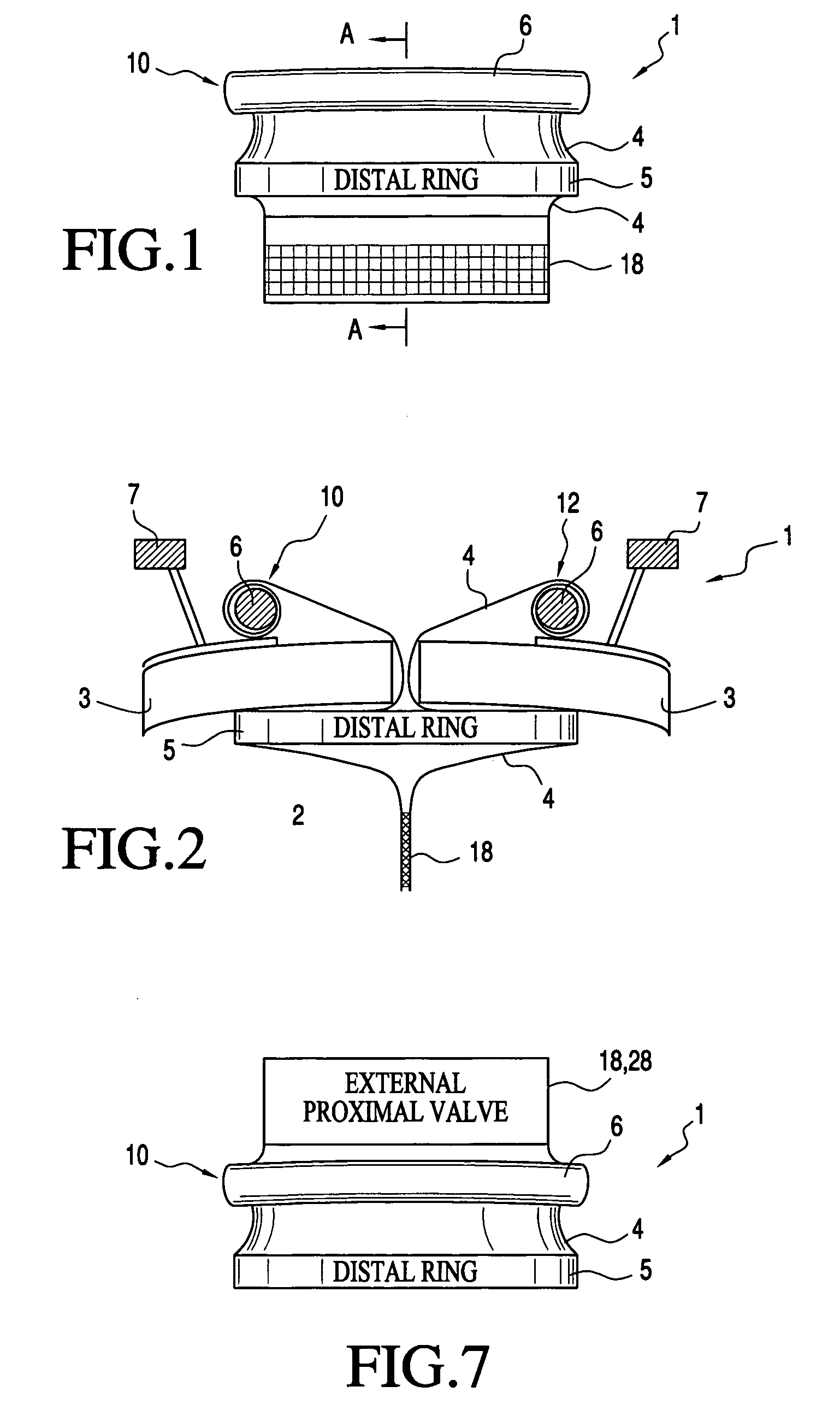
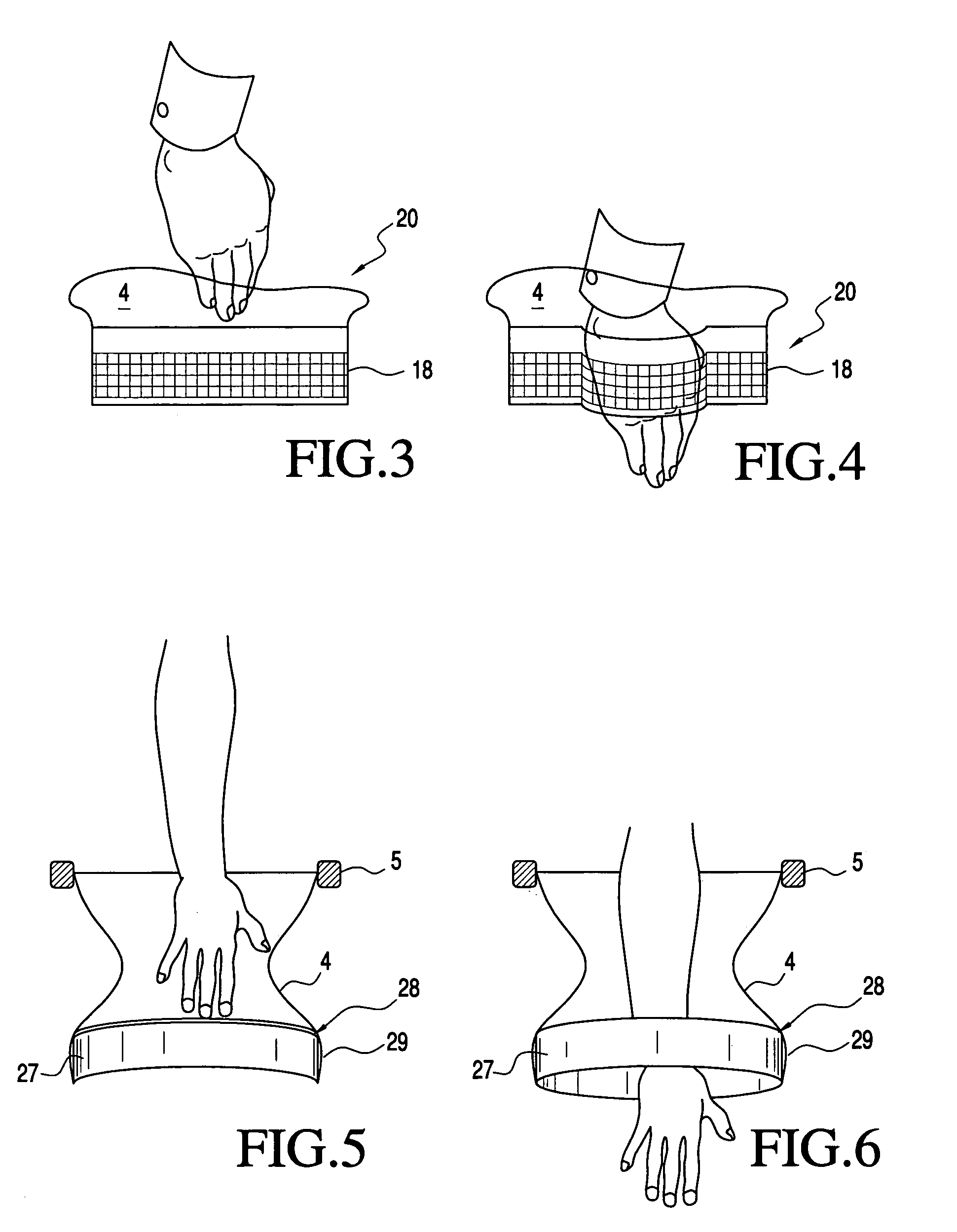
Surgical device (1) is for use in minimally invasive surgery using an inflated body cavity (2) accessible to a surgeon through an access port defined by a sleeve (4) passing through an incision in a patient's abdominal wall (3). The device is held in position by a distal ring (5) and a proximal ring (6). The device (1) is sealed by cuff valve (8), self sealing valve (18), spring valve (28) or snap open / snap shut valve (38).
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Apparatus and Method for Ocular Treatment
InactiveUS20080058704A1Reduce releaseFacilitate tissue targetingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsLaser surgeryLess invasive surgerySuprachoroidal space
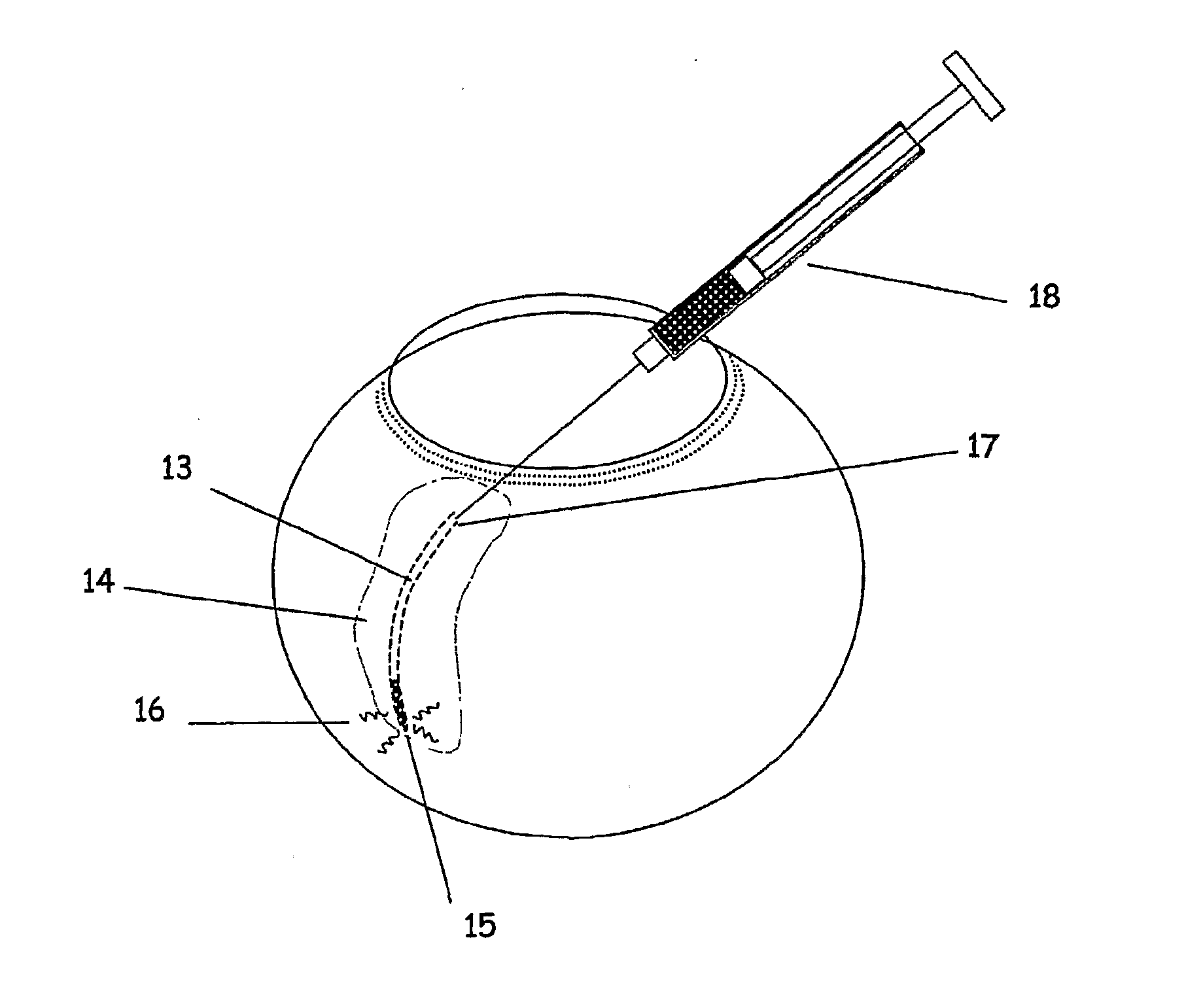
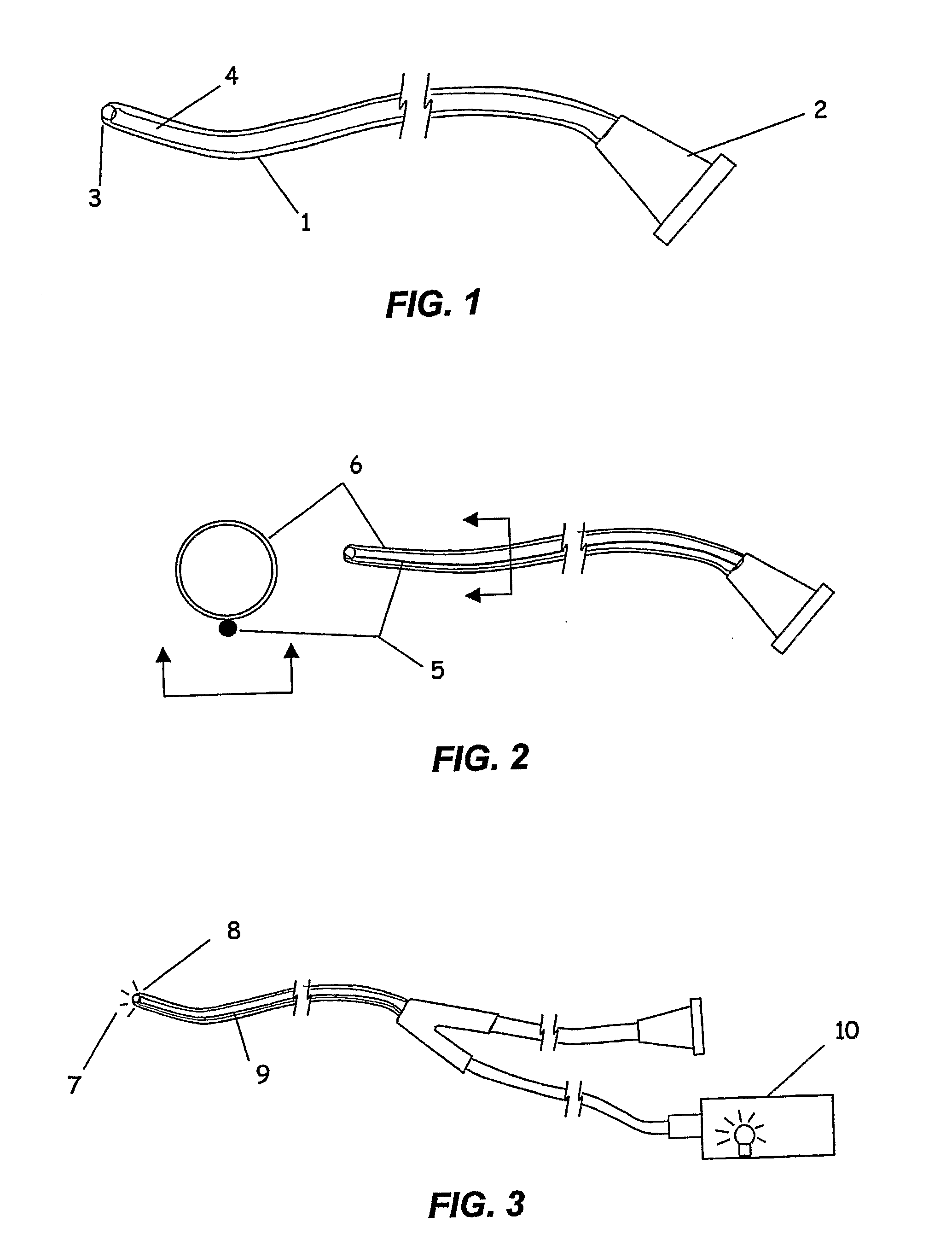
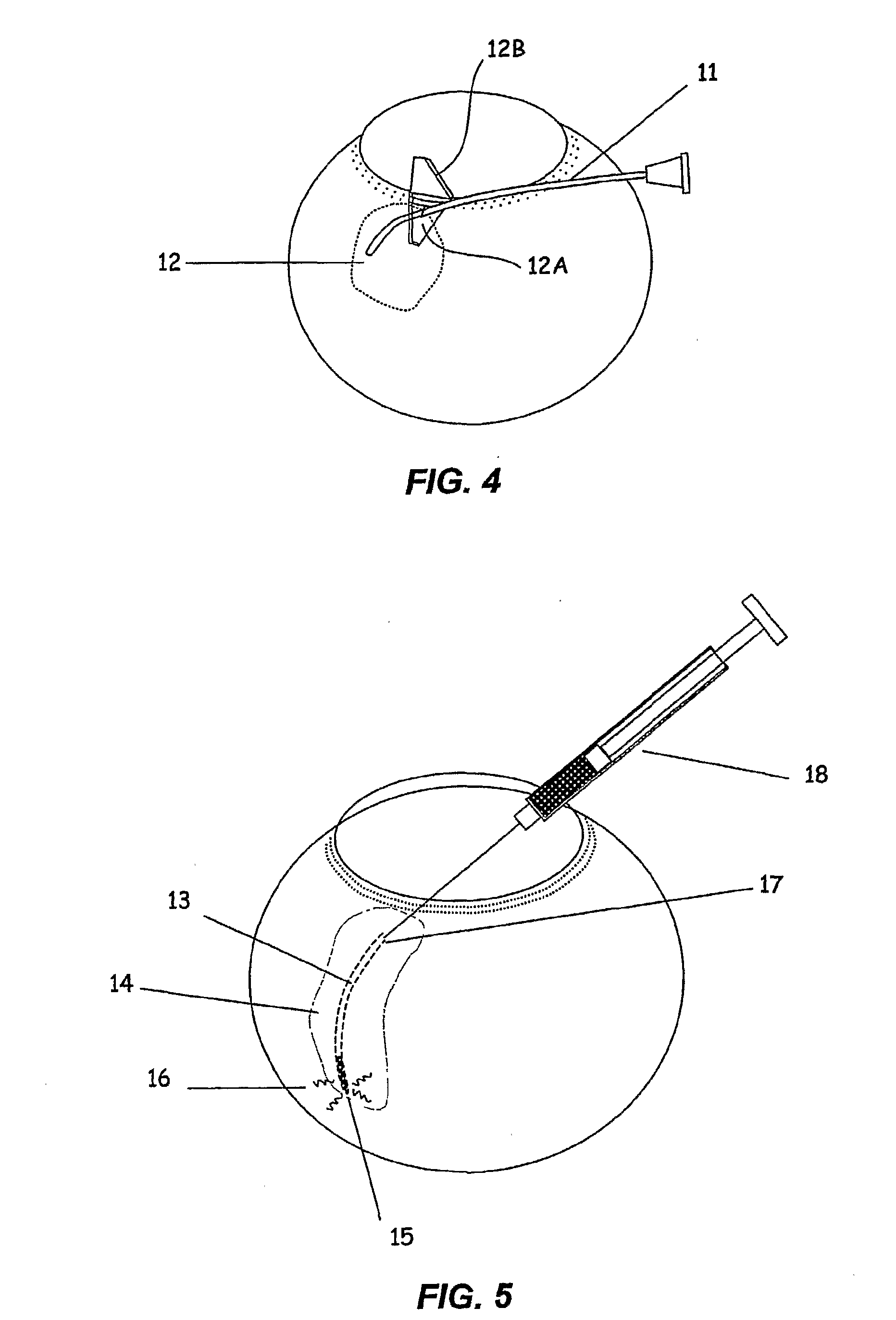
The invention provides tools, materials and related methods to surgically access the suprachoroidal space of an eye for the purpose of performing minimally invasive surgery or to deliver drugs to the eye. The invention provides a flexible microcannula device (11, 13) that may be placed into the suprachoroidal space (12, 14) through a small incision (12A) of the overlying tissues, maneuvered into the appropriate region of the space, and then activated to treat tissues adjacent to the distal tip of the device.
Owner:ISCI INTERVENTIONAL CORP
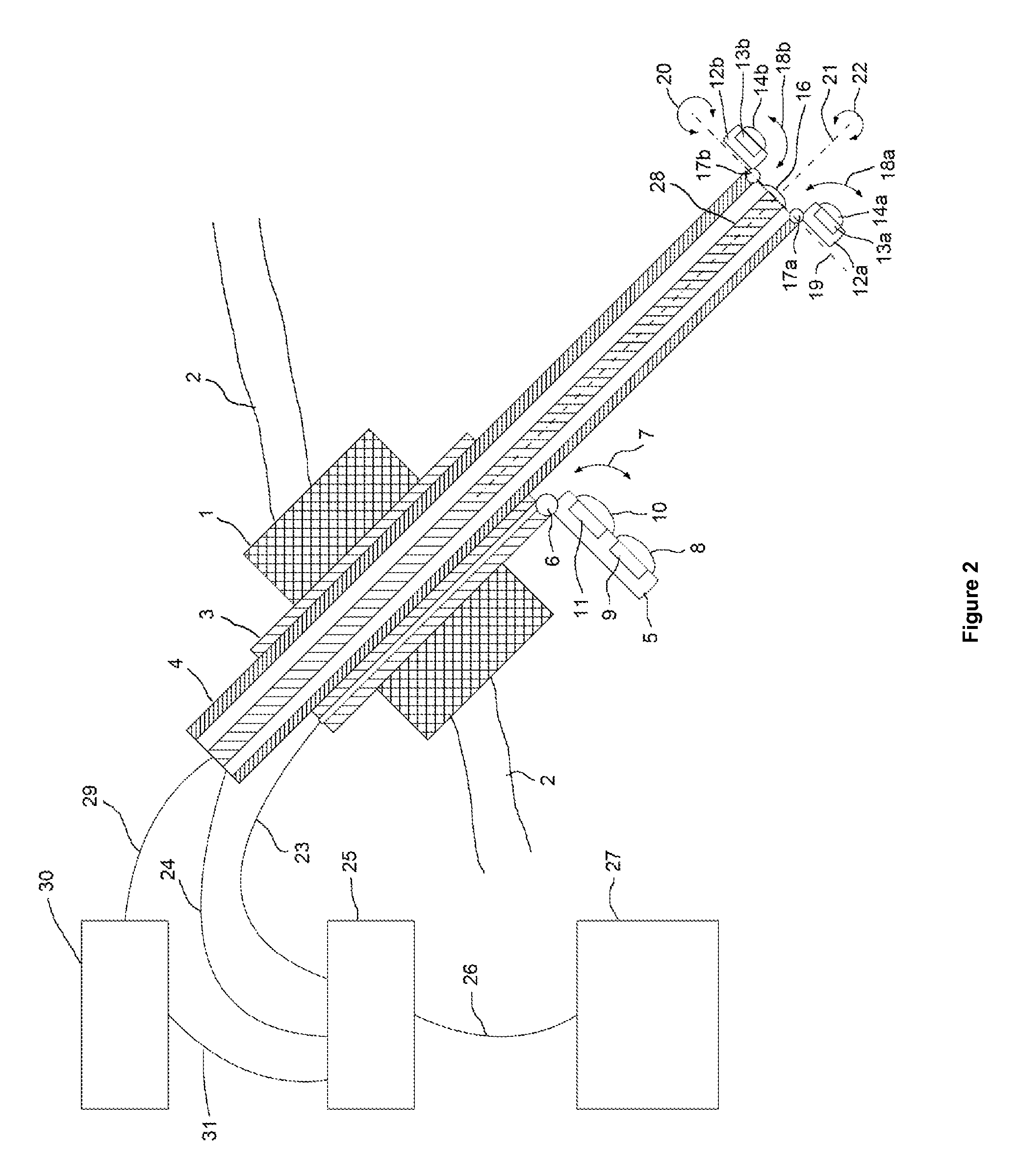
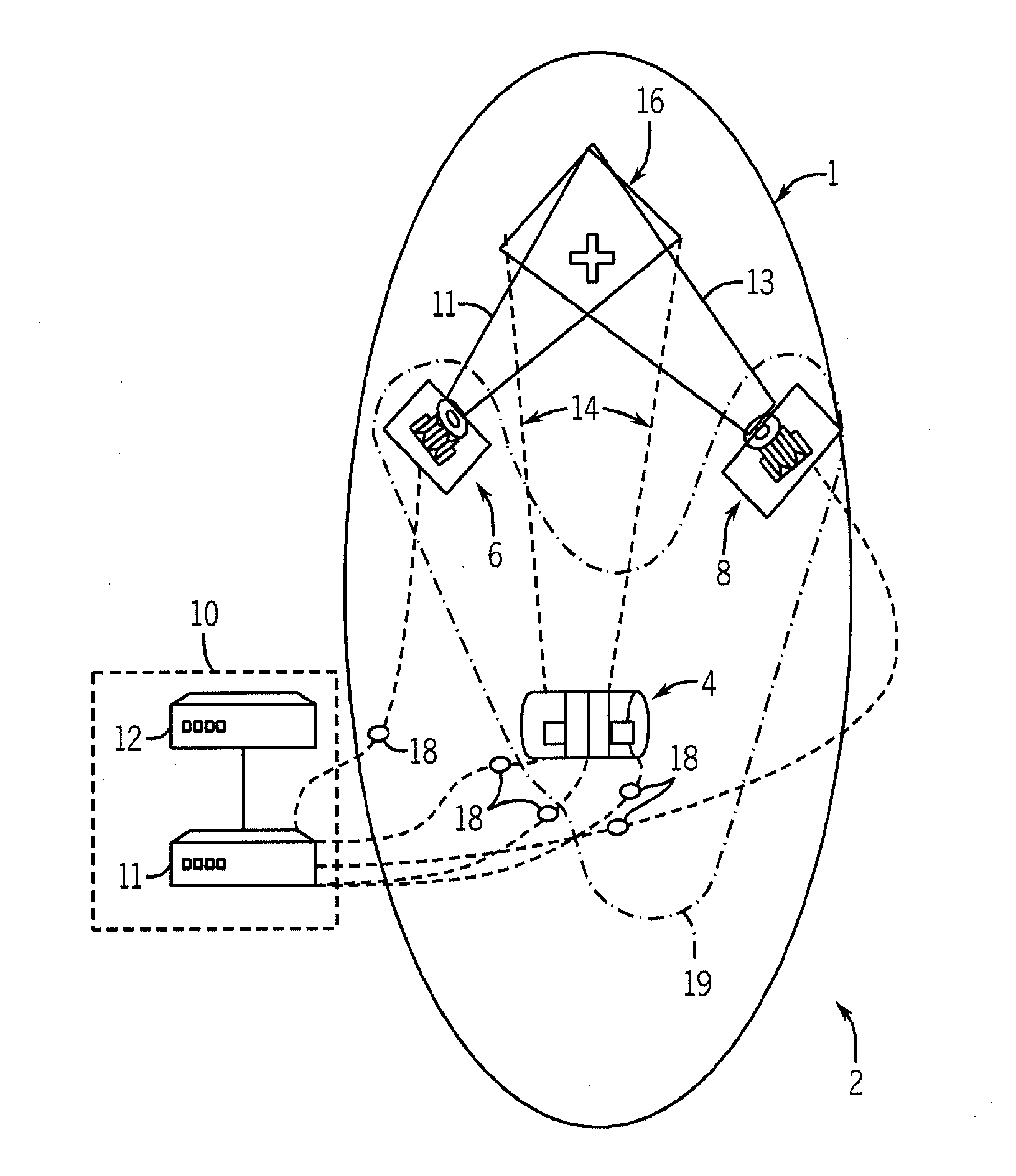
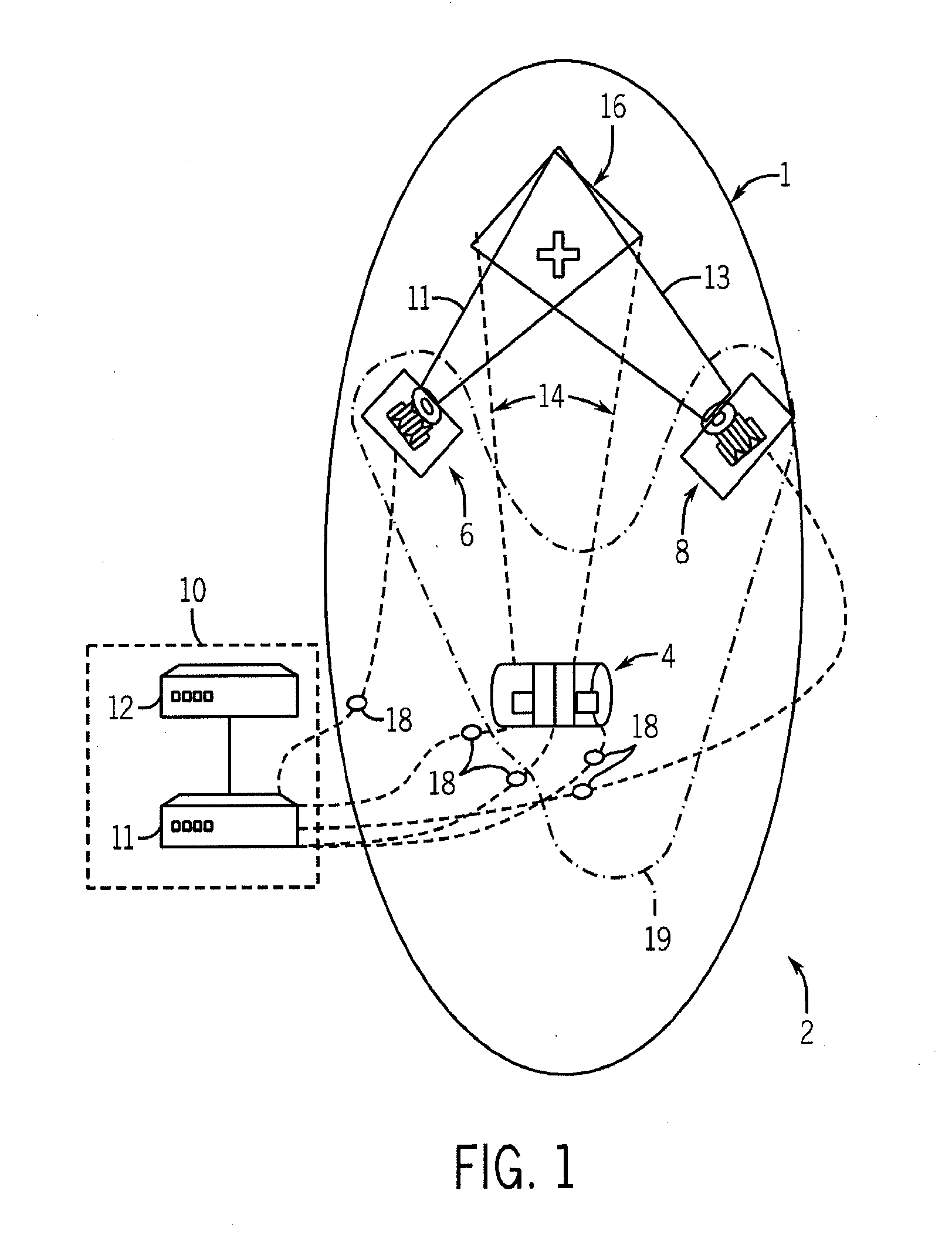
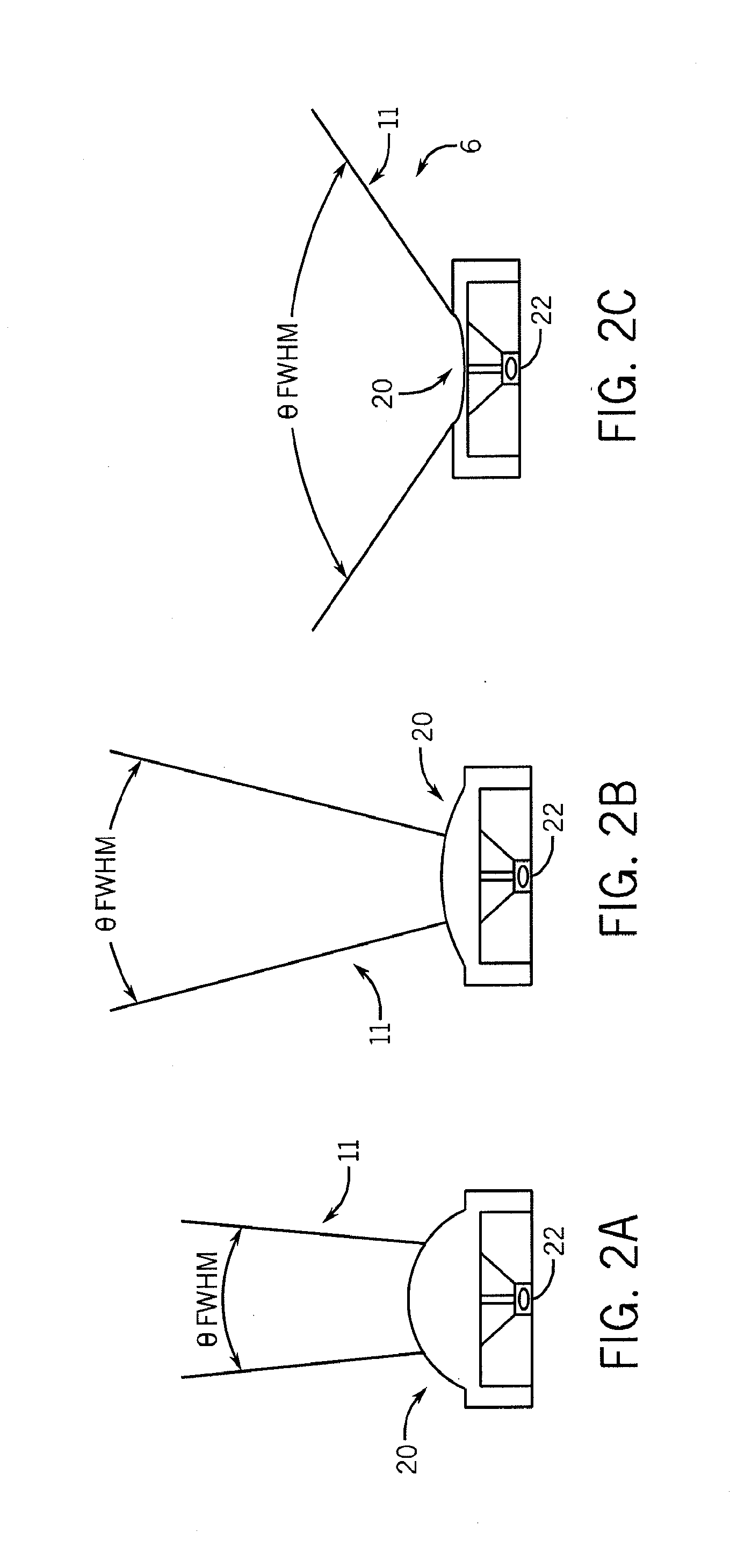
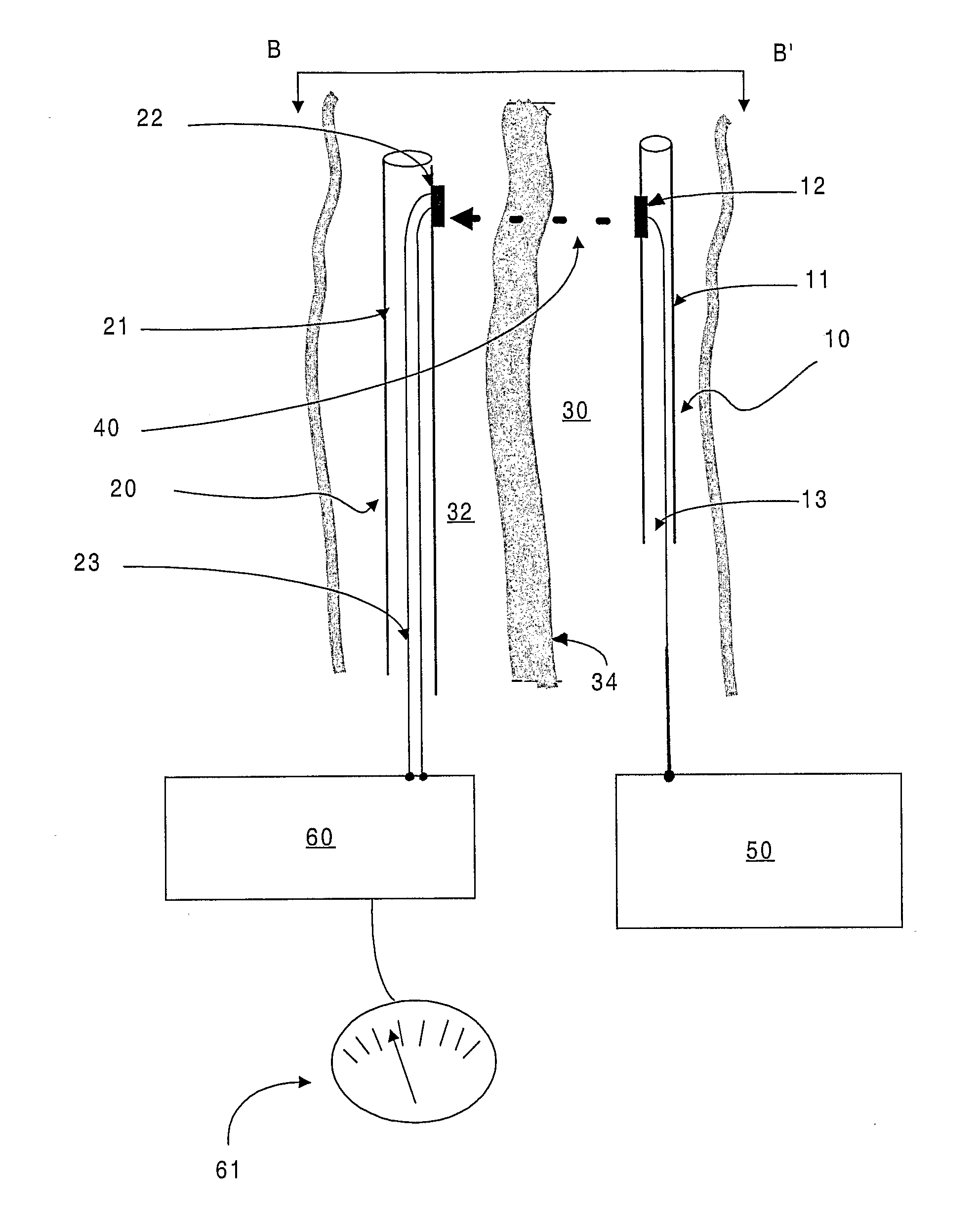
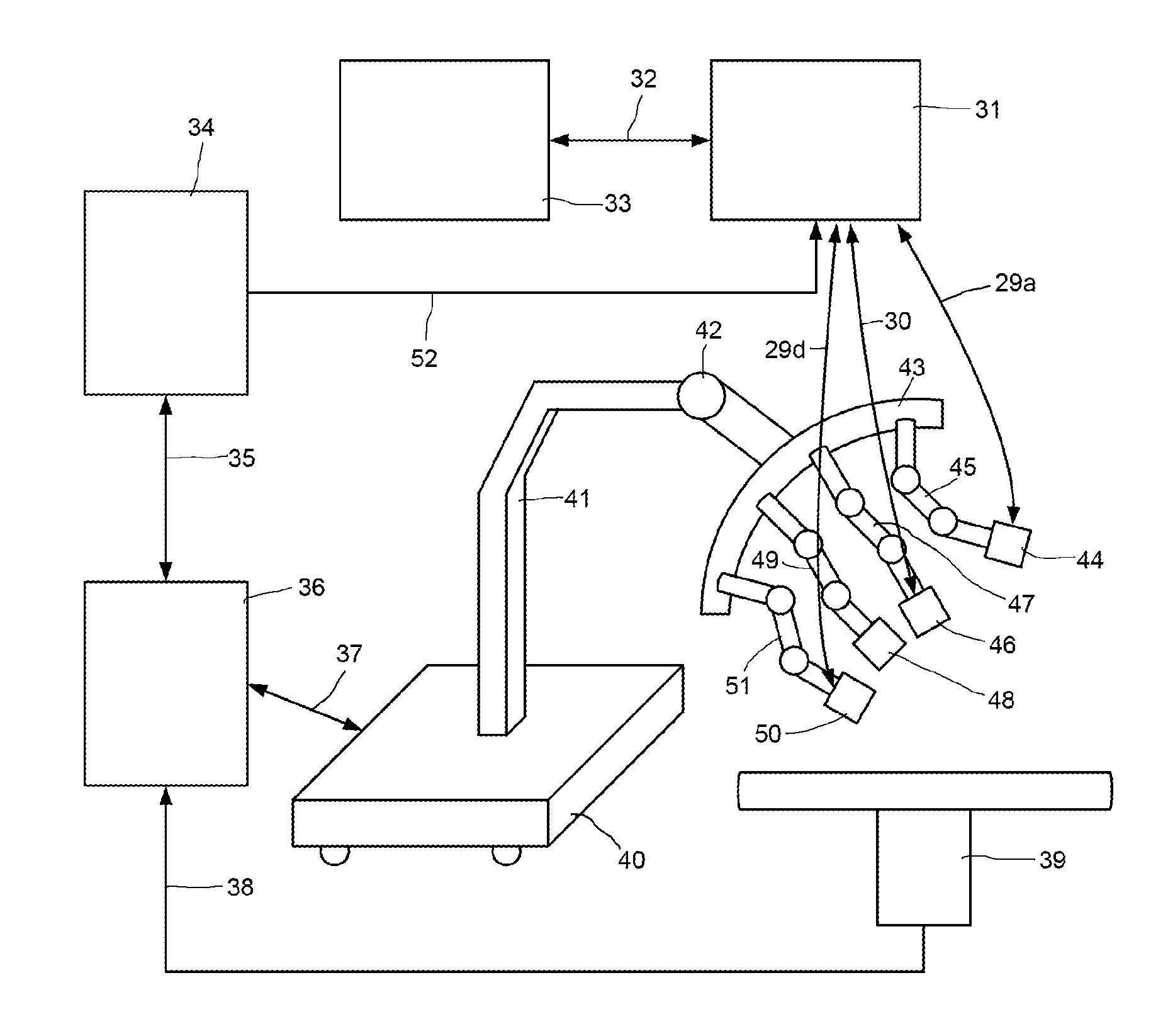
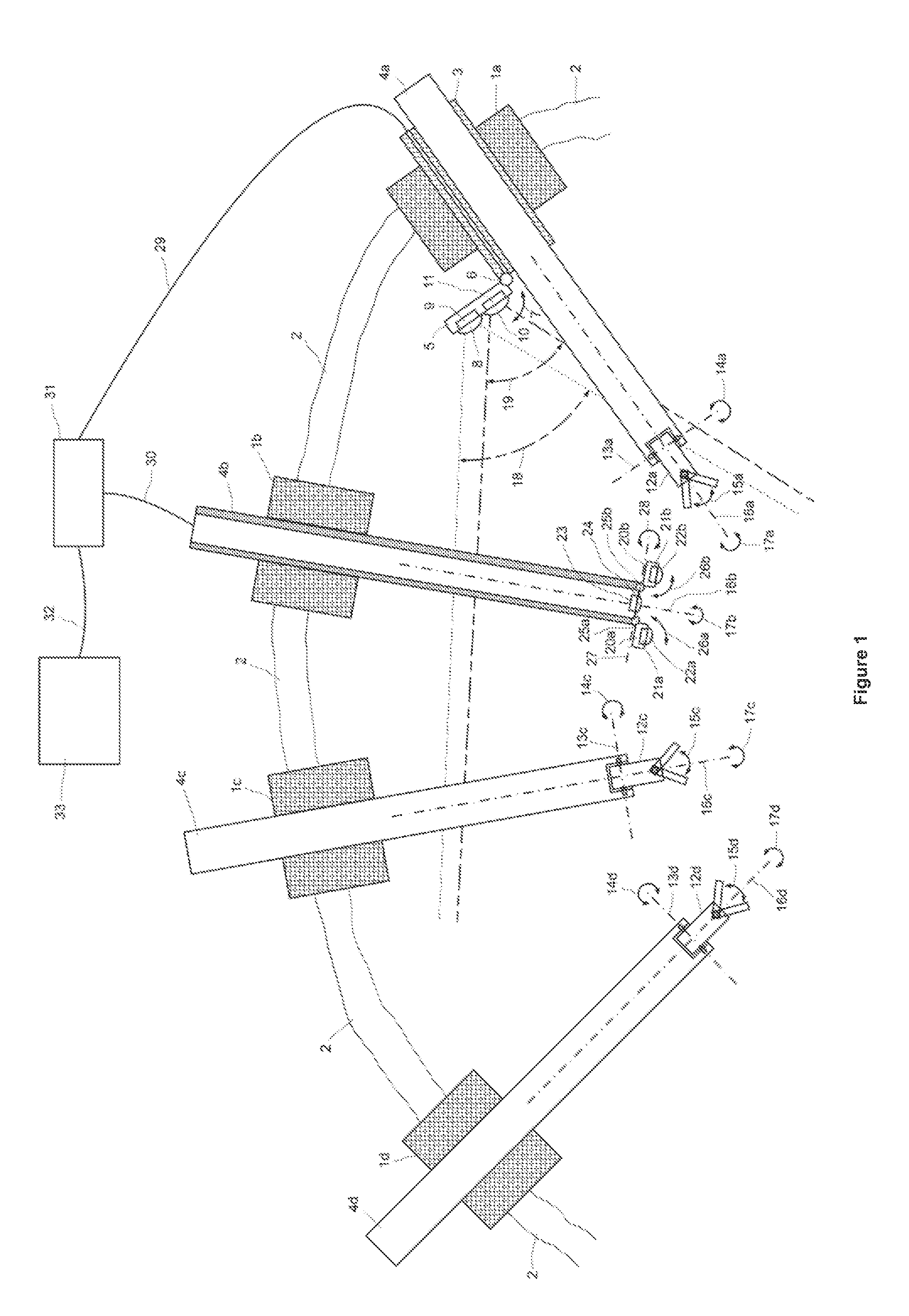
Endoscope comprising a system with multiple cameras for use in minimal-invasive surgery
ActiveUS9307894B2Improve coordinationReduce in quantityCannulasSurgical needlesMinimal invasive surgeryBiomedical engineering
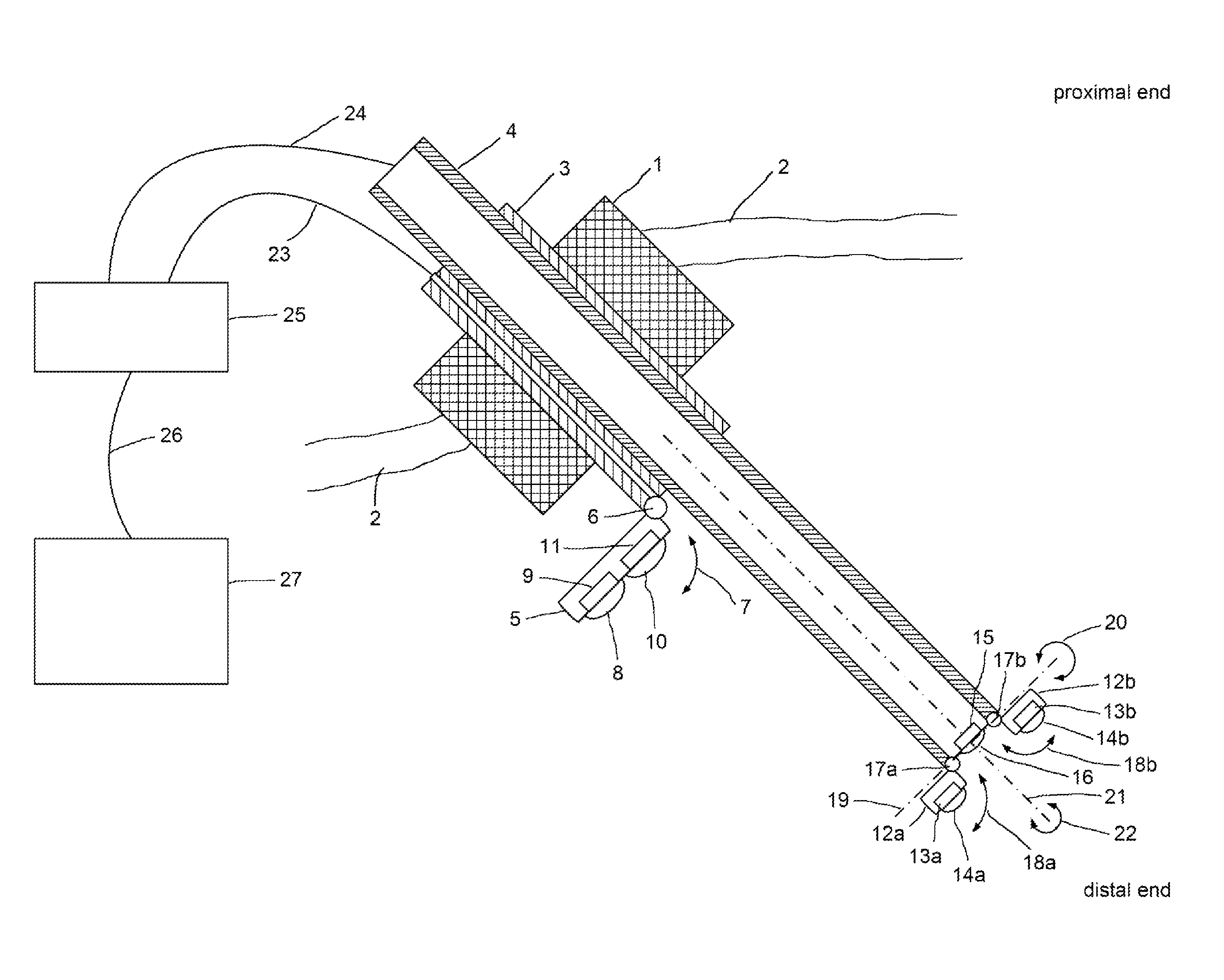
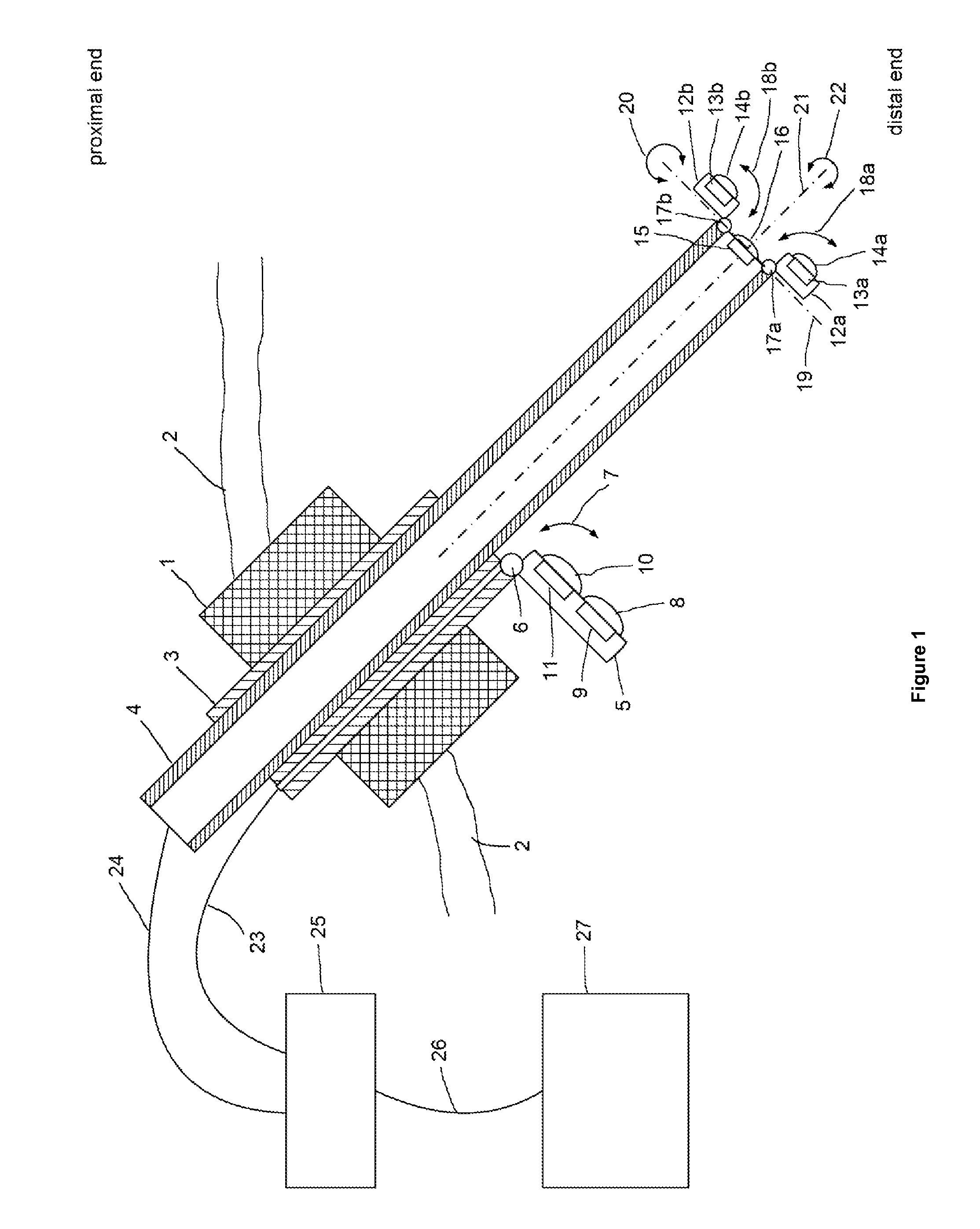
The present invention concerns an endoscope for minimally invasive surgery, especially for use within a surgical robotic system, which comprises a main support device (4), which basically extends over the entire length of the endoscope from the outside to the interior of the body, and which comprises at its distal end at least one illumination unit (15, 16) and two imaging devices (12a, 13a, 14a, 12b, 13b, 14b; 12c), wherein each of the imaging devices (12a, 13a, 14a, 12b, 13b, 14b; 12c) is basically arranged in such a way that it can be rotated to the outside on the same level as the main support device (4), a trocar (1), by means of which the endoscope can enter the body, and an additional support device (3), which is provided at the trocar (1) and / or the main support device (4), wherein the additional support device (3) comprises at its distal end an additional imaging device (8, 9, 10, 11), which can be rotated from the additional support device (3) to the outside and wherein the additional imaging device (7, 8, 9, 10) comprises an additional illumination unit (10, 11) and at least an additional image sensor (8, 9), which comprises a monitoring area, which encompasses the two monitoring areas of the imaging devices (12a, 13a, 14a, 12b, 13b, 14b; 12c) of the main support device (4).
Owner:E SYS MEDICAL GMBH +1
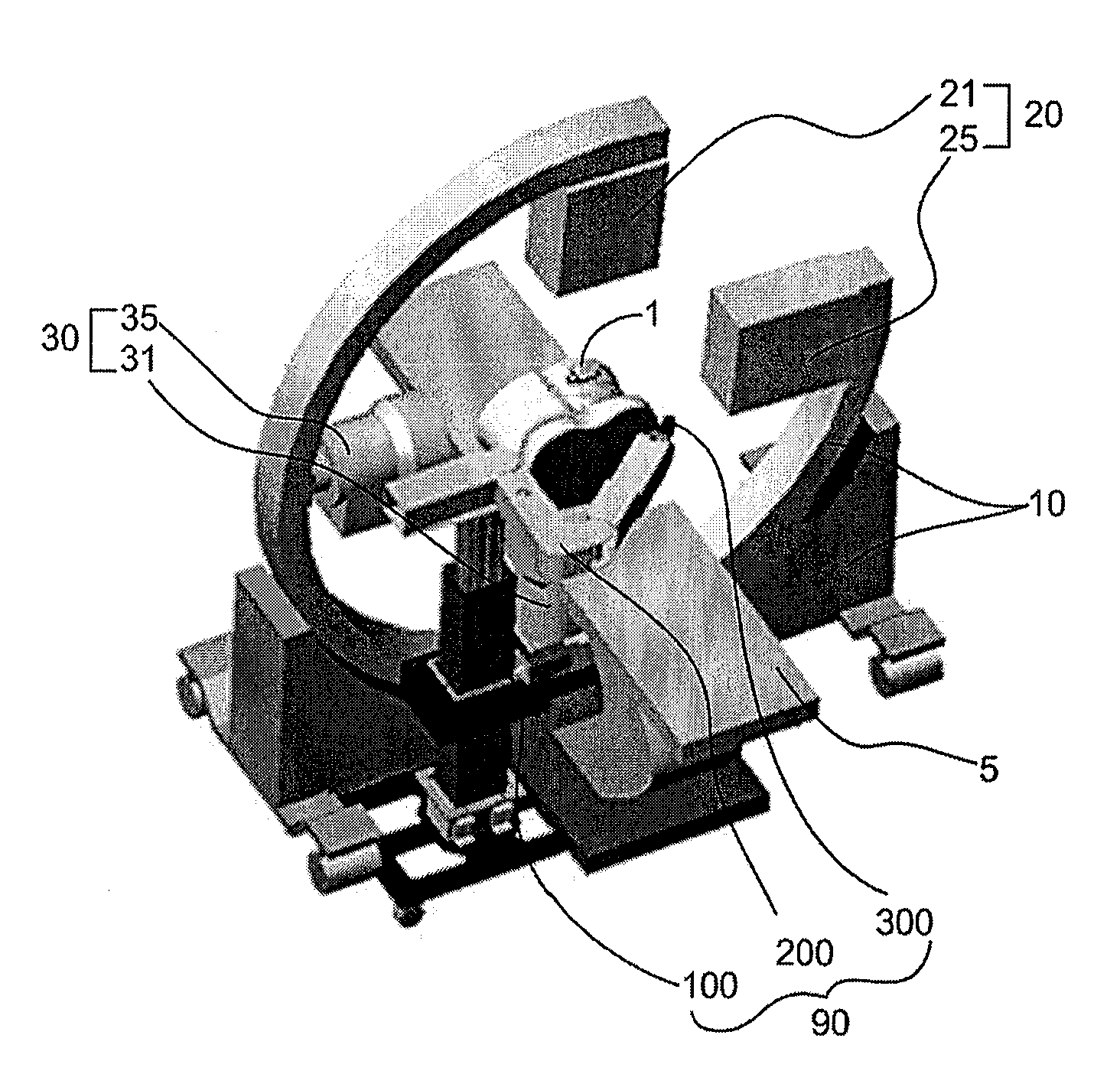
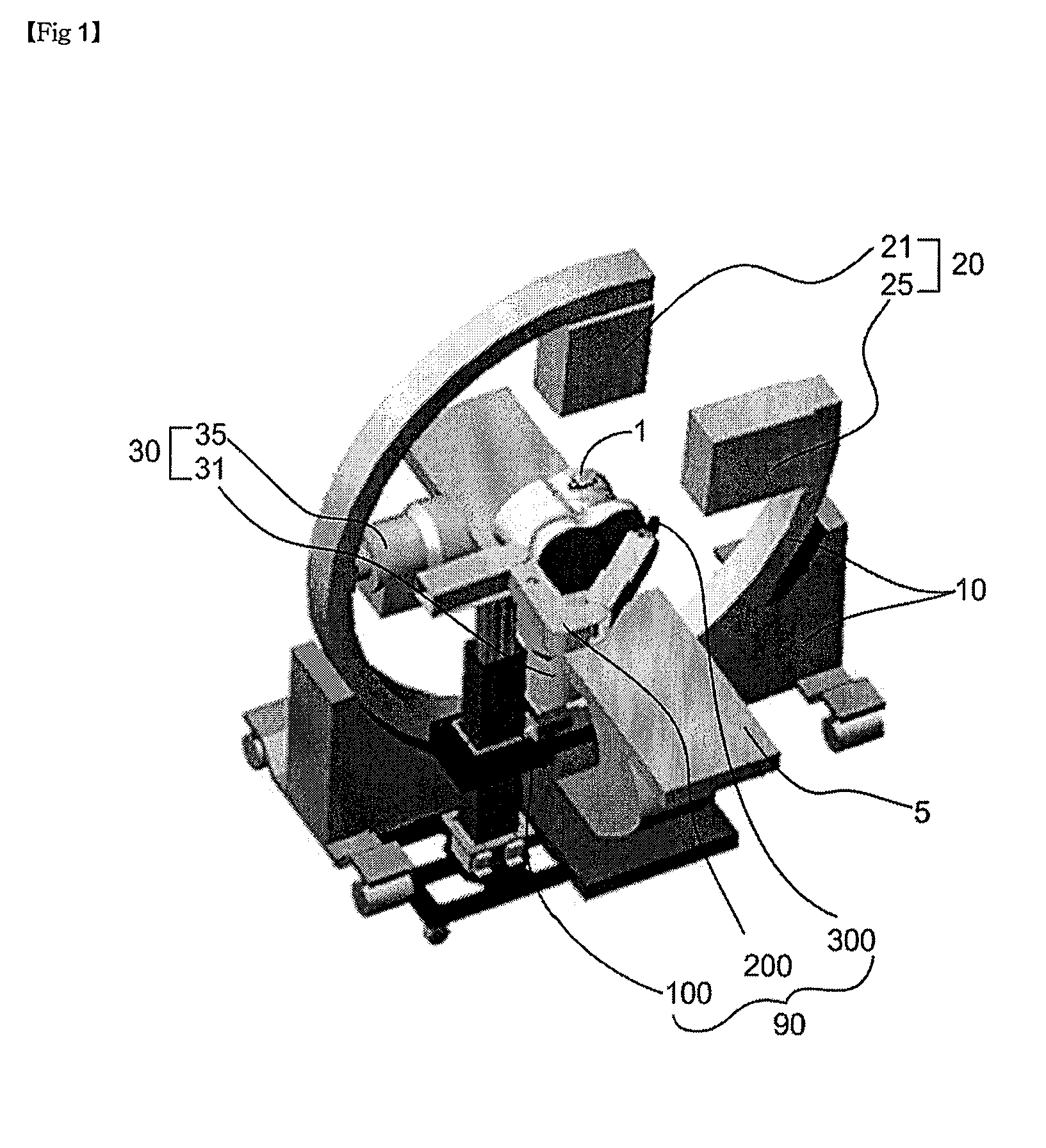
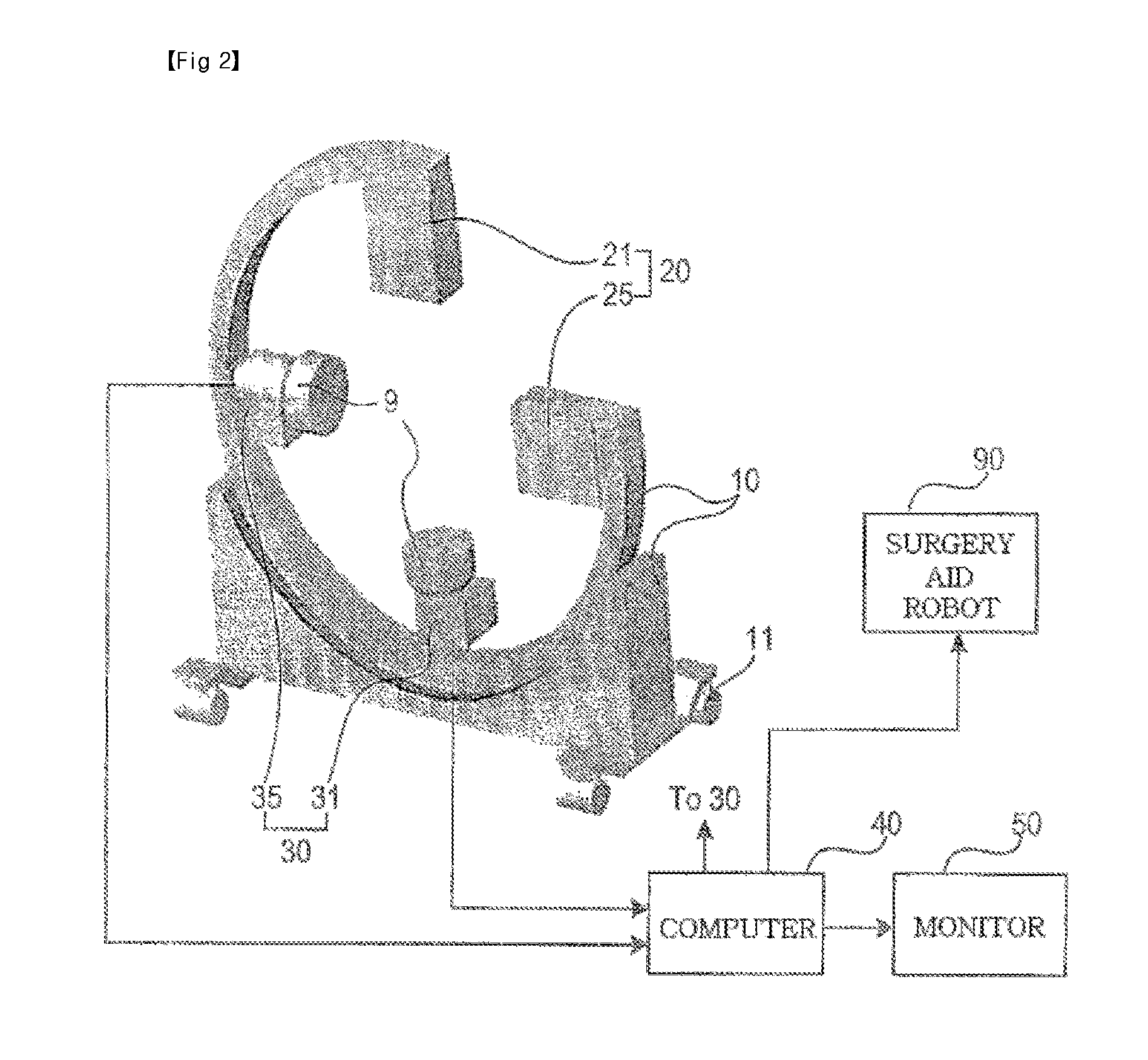
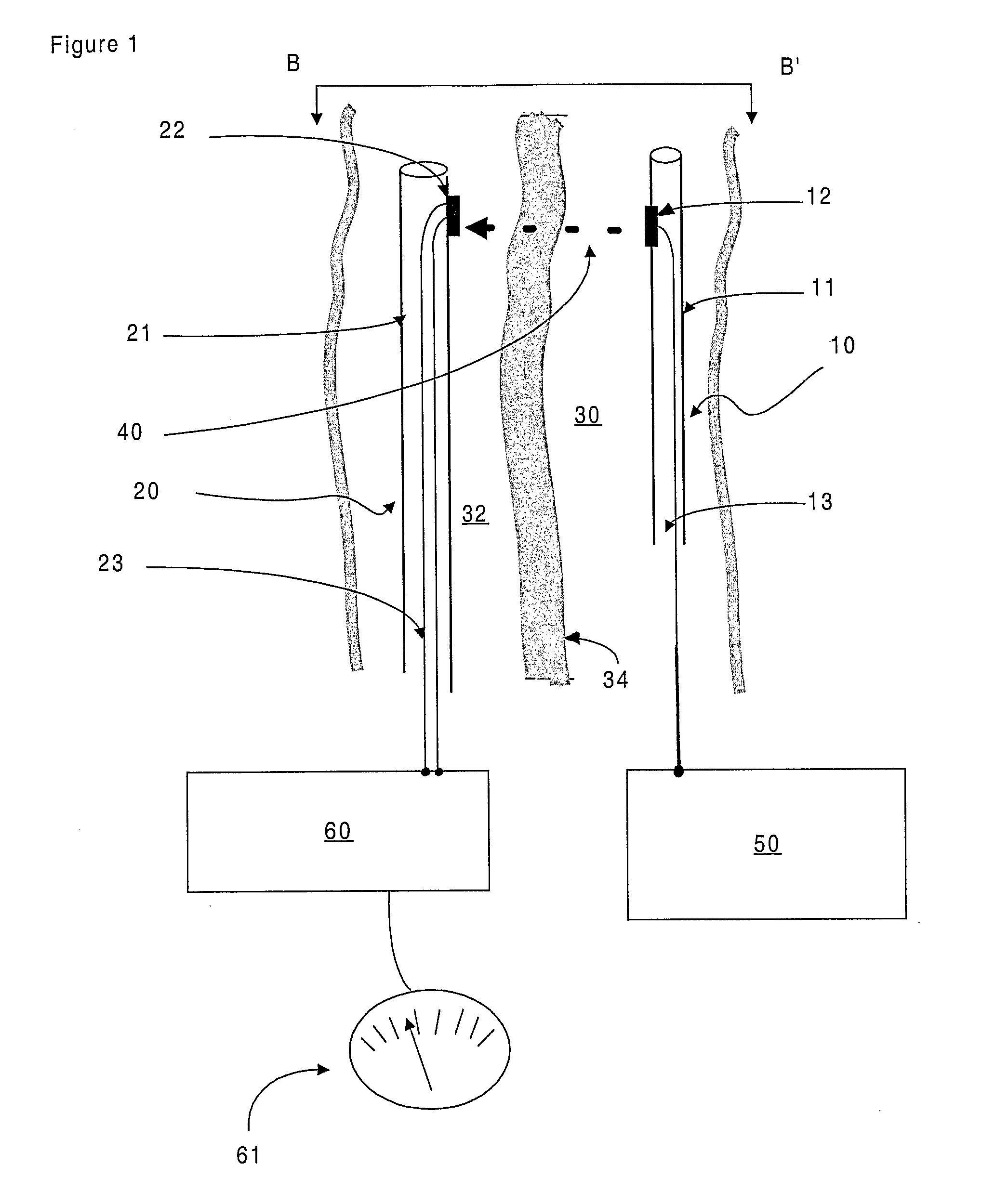
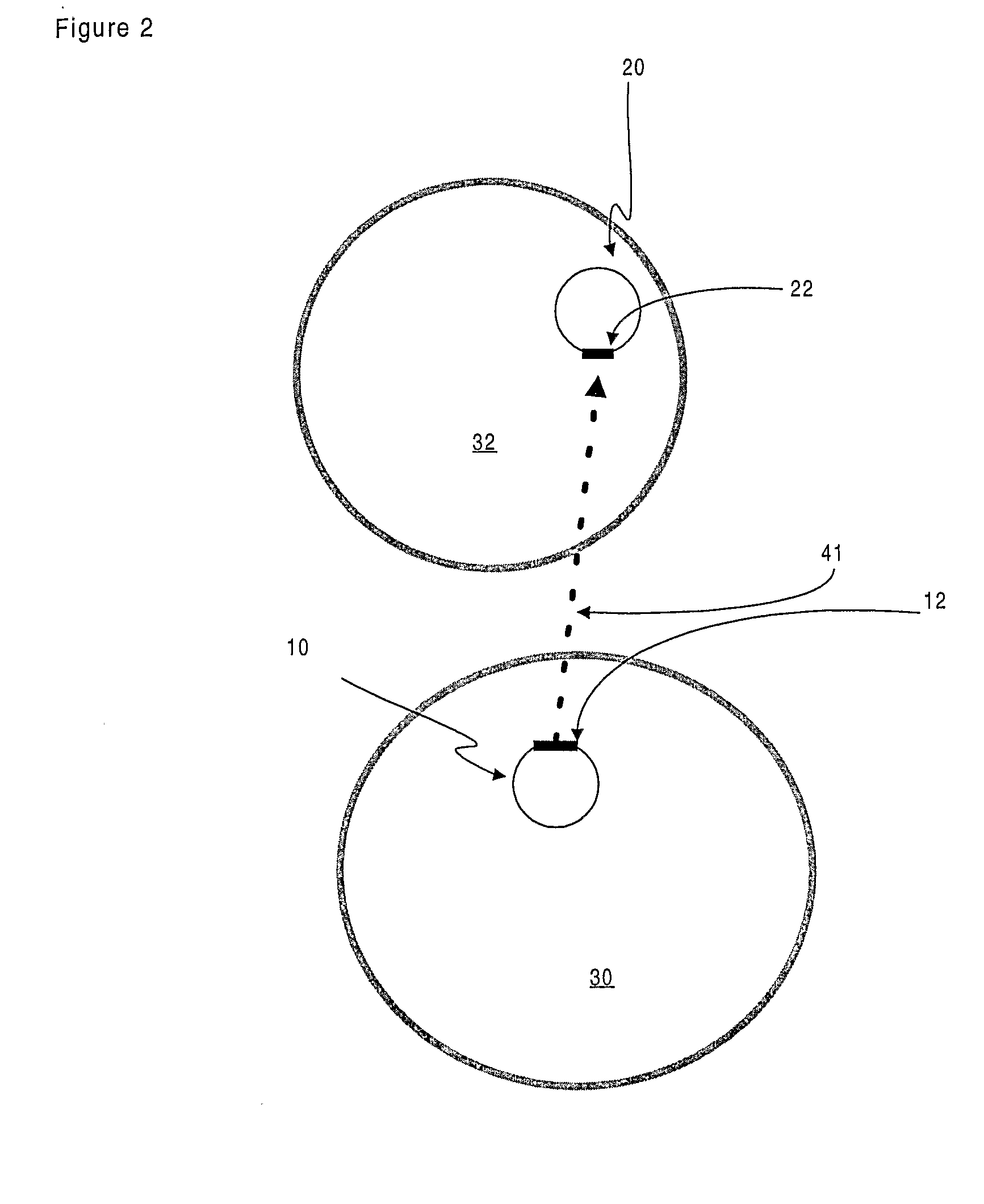
Bi-planar fluoroscopy guided robot system for minimally invasive surgery and the control method thereof
InactiveUS8046054B2Accurate three-dimensional surgery planAccurate surgery planMasksUmbrellasLess invasive surgeryProgram planning
Disclosed is a computer-integrated surgery aid system for minimally invasive surgery and a method for controlling the same. The system includes a surgery planning system for creating three-dimensional information from two-dimensional images obtained by means of biplanar fluoroscopy so that spinal surgery can be planned according to the image information and a scalar-type 6 degree-of-freedom surgery aid robot adapted to be either driven automatically or operated manually.
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Extended, ultrasound real time 3D image probe for insertion into the body
InactiveUS20050203396A1Minimize the numberReduce in quantityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasound imagingMinimal invasive surgery
An ultrasound imaging probe for real time 3D ultrasound imaging from the tip of the probe that can be inserted into the body. The ultrasound beam is electronically scanned within a 2D azimuth plane with a linear array, and scanning in the elevation direction at right angle to the azimuth plane is obtained by mechanical movement of the array. The mechanical movement is either achieved by rotation of the array through a flexible wire, or through wobbling of the array, for example through hydraulic actuation. The probe can be made both flexible and stiff, where the flexible embodiment is particularly interesting for catheter imaging in the heart and vessels, and the stiff embodiment has applications in minimal invasive surgery and other procedures. The probe design allows for low cost manufacturing which allows factory sterilized probes to be disposed after use.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
Balloon technologies for tissue repair
A medical device containing an inflatable balloon structure for use in minimally invasive surgery and minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedures are described herein. The device is delivered by a catheter and expanded using gases, liquids or liquids that solidify in situ. The inflatable balloon may be constructed from a wide variety of materials and may be reinforced by supporting structures, when necessary. The device may form an endoprosthesis in a patient. In the preferred embodiment, the device is used in spinal fusion. Optionally, the device may also be used in combination with bone graft materials and bioactive factors.
Owner:KUROS BIOSURGERY AG
Extended, ultrasound real time 3D image probe for insertion into the body
InactiveUS7699782B2Minimize the numberReduce in quantityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasound imagingMinimal invasive surgery
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +1
Device and method for rolling and inserting a prosthetic patch into a body cavity
This invention generally relates to minimal invasive surgery. More specifically the current invention relates to an apparatus especially adapted to fold prosthetic patches and to insert said patches into a body cavity through a cannula or an incision.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Camera system with autonomous miniature camera and light source assembly and method for image enhancement
InactiveUS20110261178A1Convenient lightingQuality improvementSurgeryEndoscopesRadiation angleInvasive surgery
The present Invention relates to a camera system suitable for use in minimally invasive surgery (MIS), among other applications. In at least one embodiment, the camera system includes an autonomous miniature camera, a light source assembly providing features such as steerable illumination and a variable radiation angle, and a control and processing unit for processing images acquired by the camera Io generate improved images having reduced blurring using a deblurring algorithm.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Minimally Invasive Surgical Appartus and Methods
InactiveUS20080194939A1Improved targeting and localisationTechnique is invasiveStentsInfusion syringesThree vesselsDirect Treatment
Apparutus and methods are described for performing percutancous catheter-based interventional surgery. The apparatus comprises first and second devices that are located in adjacent body cavities, such as adjacent blood vessels, the first device being capable of transmitting a directional signal that can be received by the second device. The direction of the signal is correlated with the facility to direct therapy, such that improved accuracy in therapy placement is thereby achieved. Methods for treating patients utilising the means and apparatus are also provided.
Owner:LIMFLOW
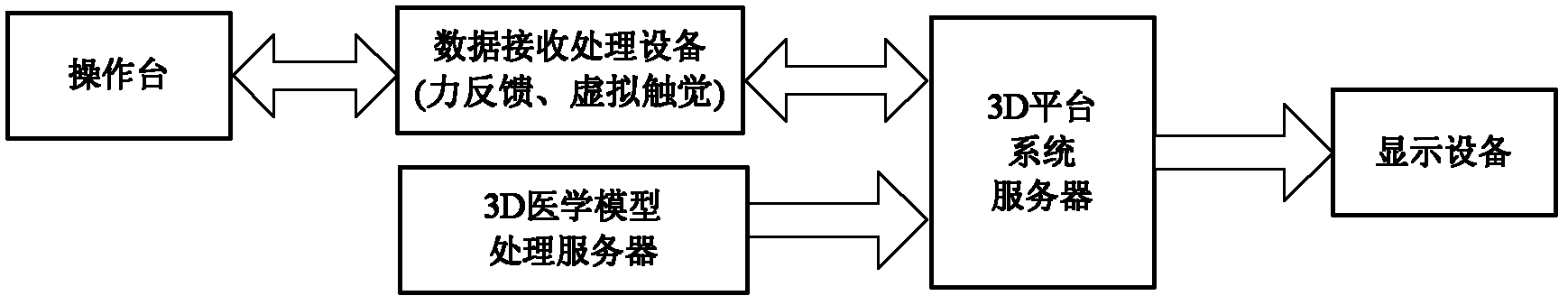
Endoscopic minimally invasive surgery simulation training method and system
ActiveCN102254476ARealize force feedbackRealize the virtual sense of touchEducational modelsSimulation trainingMedical model
The invention provides an endoscopic minimally invasive surgery simulation training method which comprises the following steps of: (1) constructing and editing an endoscopic minimally invasive surgery medical model; (2) constructing a system foundation component library by using a fundamental algorithm; (3) constructing a core algorithm by using the system foundation component library to realize the core function of a 3D platform system; (4) constructing a medical model description language; (5) calling the medical model, constructing a medical scene, and simulating various actions of an endoscopic minimally invasive surgery; and (6) simulating various operations by using endoscopic minimally invasive surgery instruments in a driving virtual environment of an operating table, and outputting a feedback force through an operating rod of a data receiving and feedback signal processing driving operating platform to realize force feedback and virtual touch, so that the simulation training is more vivid. Meanwhile, the invention provides an endoscopic minimally invasive surgery simulation training system. By using the method and the system, force feedback and virtual touch effects can be provided, and high fidelity and a good simulation training effect can be achieved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SAIBAO LIANRUI INFORMATION TECH
Surgical adhesive applicator
An adhesive applicator for applying medical adhesives, particularly cyanoacrylates, to incisions such as those made during minimally invasive surgery. The applicator employs a pipette tip or similar narrow flow restrictor tip to close the incision and a body of foam to seal the incision. Methods of using the applicator are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL SOLUTIONS PLYMOUTH
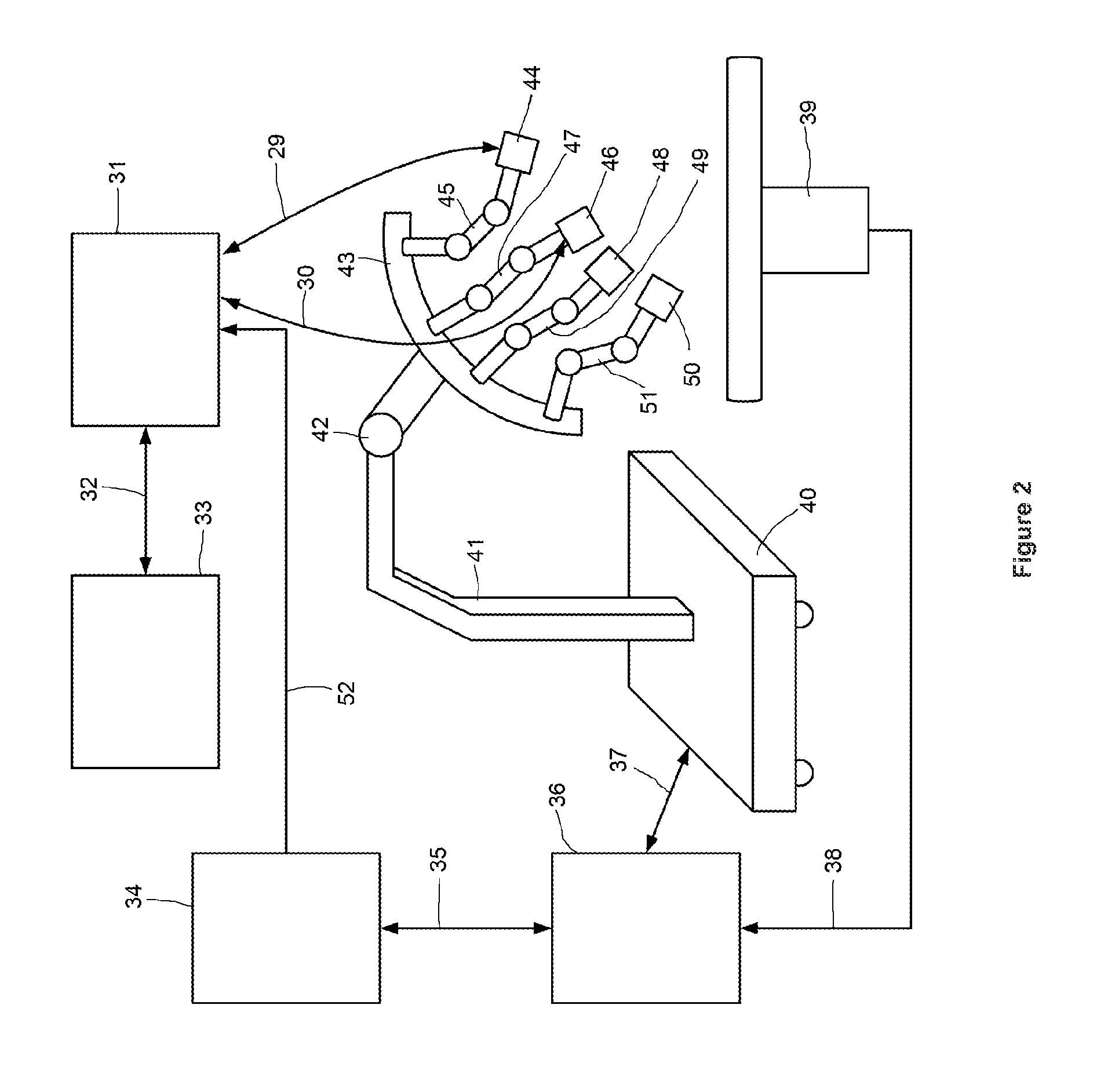
System with Decoupled Multiple Cameras for Use in Minimal-Invasive Surgery
InactiveUS20140179997A1Improve representationCannulasEndoscopesMinimal invasive surgerySurgical robot
The present invention relates to a surgical robot system with at least two robot arms (45, 47, 49, 51), on each of which is arranged at least one endoscope for a minimally invasive surgery, wherein the first endoscope on the first robot arm (47) comprises a main support means (4b) and which comprises at the distal end at least one lighting unit (23, 24) and two image-taking devices (20a, 21a, 22a, 20b, 21b, 22b), and a trocar (1b), and wherein the second endoscope on to the second robot arm (45) comprises a main support means (4a), a trocar (1a), and an auxiliary support means (3).
Owner:AVATERAMEDICAL GMBH +1
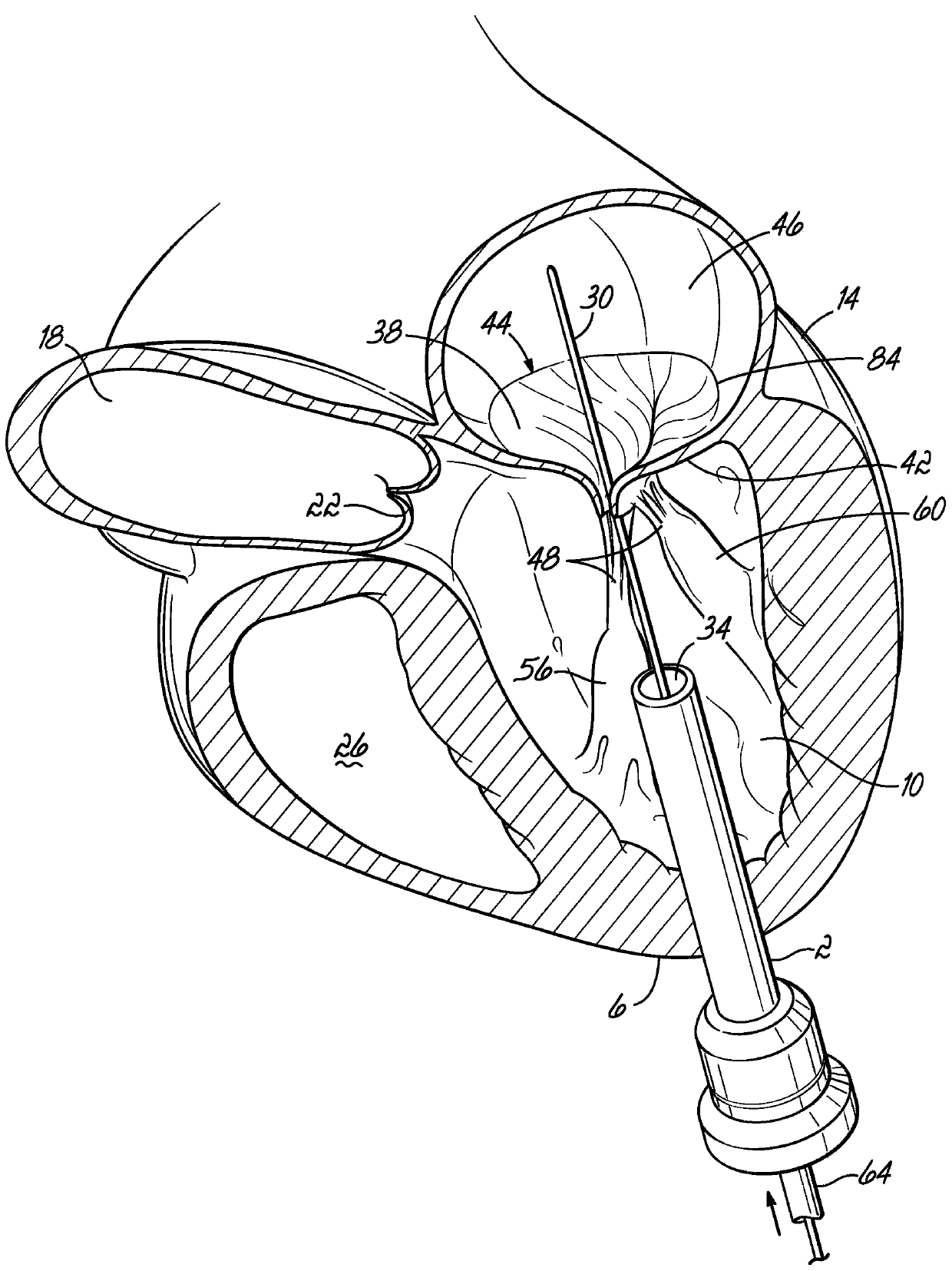
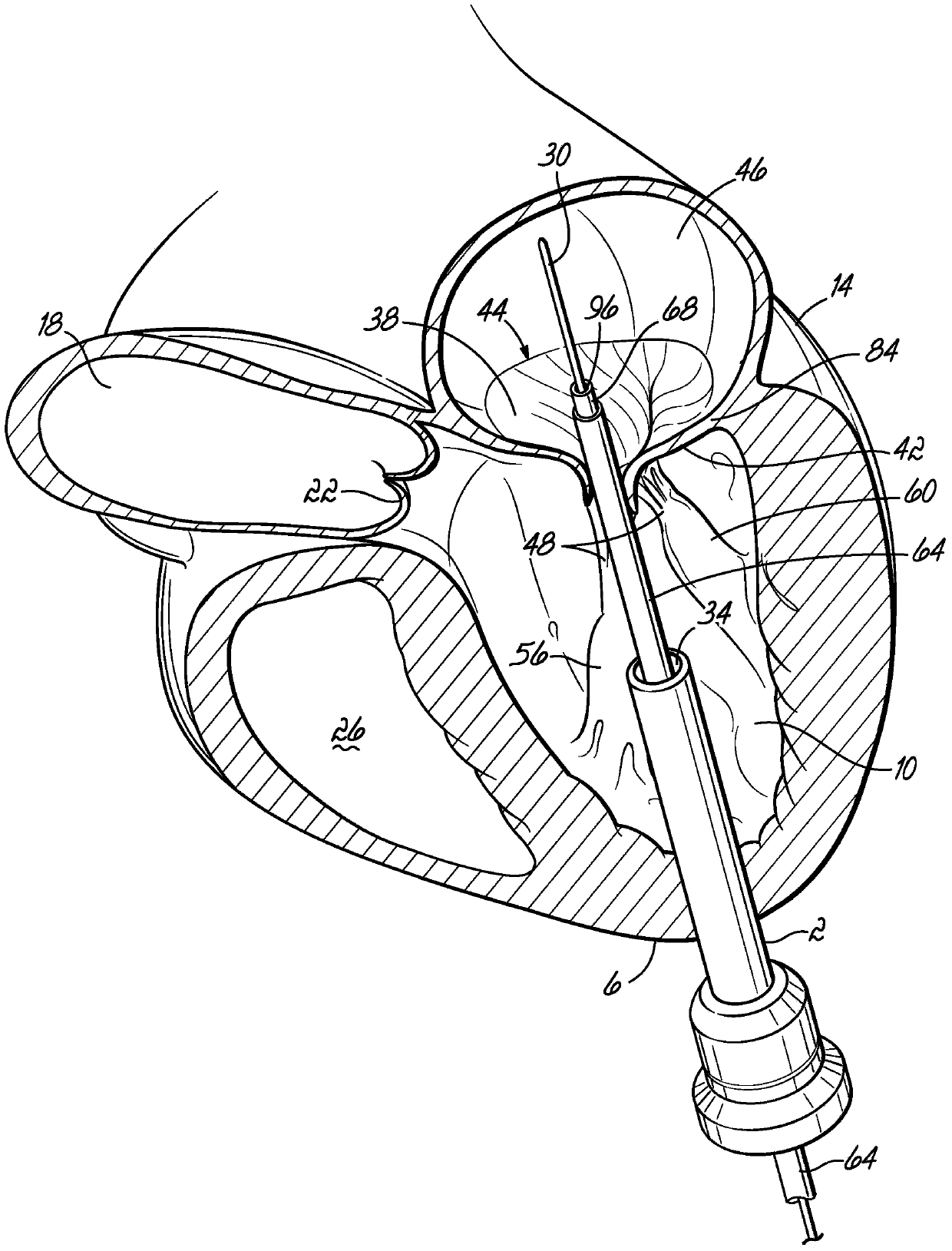
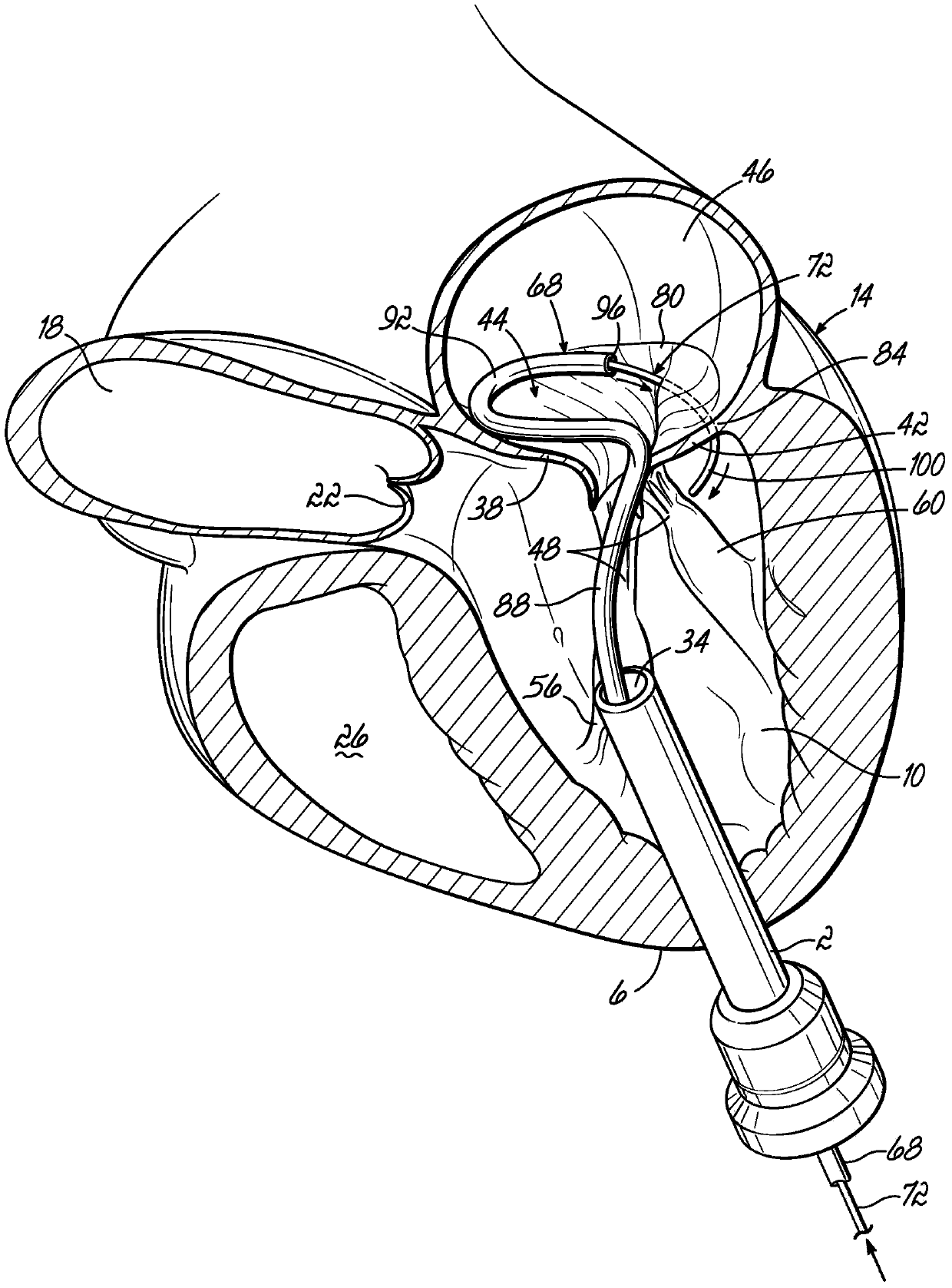
Mitral valve docking devices, systems and methods
Various systems, devices and methods associated with the placement of a dock or anchor (72) for a prosthetic mitral valve (120). The anchor (72) may take the form of a helical anchor having multiple coils (104, 108) and / or a stent-like structure. Various methods include different levels of minimal invasive procedures for delivering the prosthetic valve anchor (72) and prosthetic valve (120), as well as tissue anchors for plication or other purposes to the mitral valve position in the heart (14).
Owner:MITRAL VALVE TECHNOLOGIES SARL
Surgical adhesive applicator
An adhesive applicator for applying medical adhesives, particularly cyanoacrylates, to incisions such as those made during minimally invasive surgery. The applicator employs a pipette tip or similar narrow flow restrictor tip to close the incision and a body of foam to seal the incision. Methods of using the applicator are also disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL SOLUTIONS PLYMOUTH
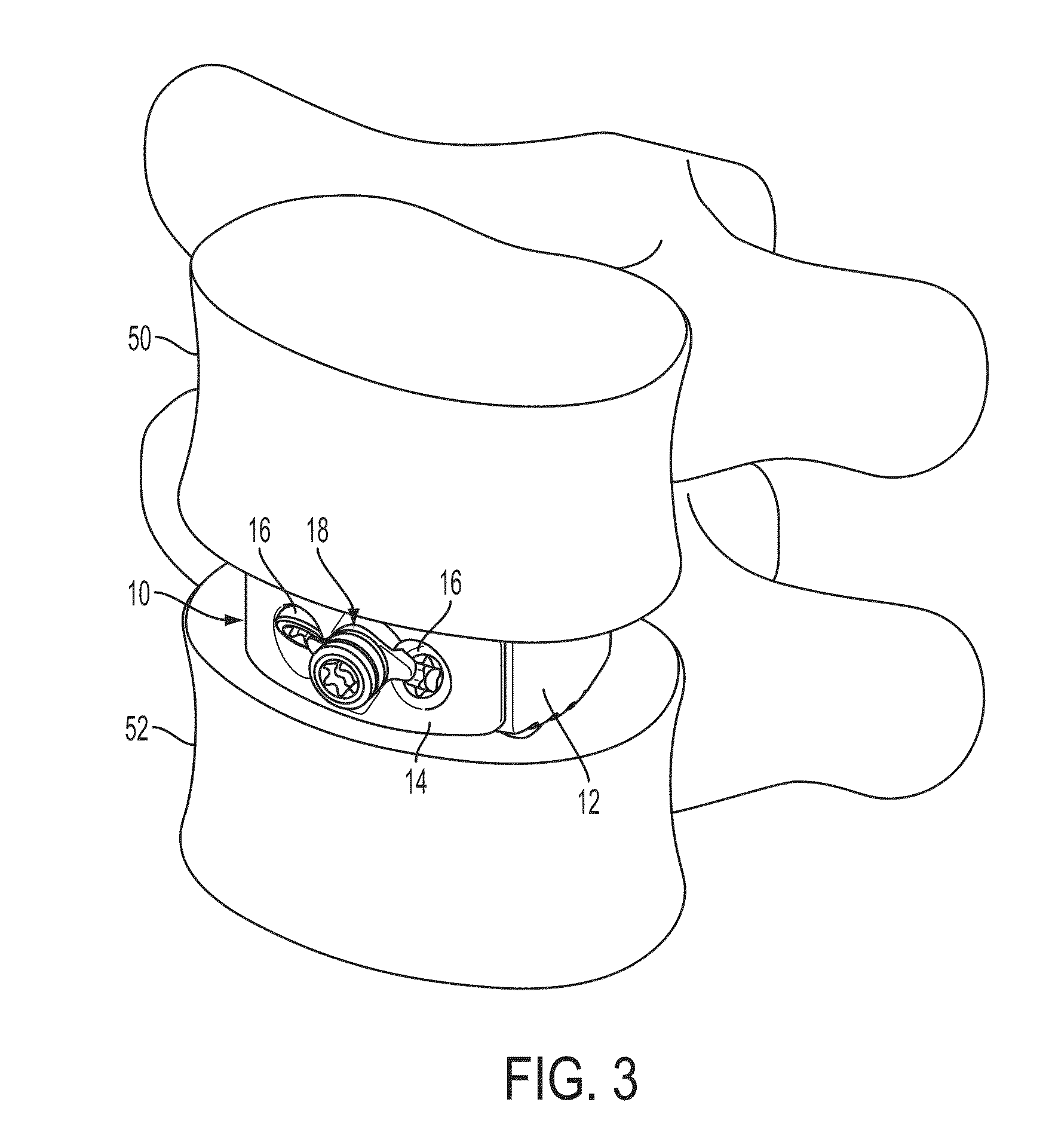
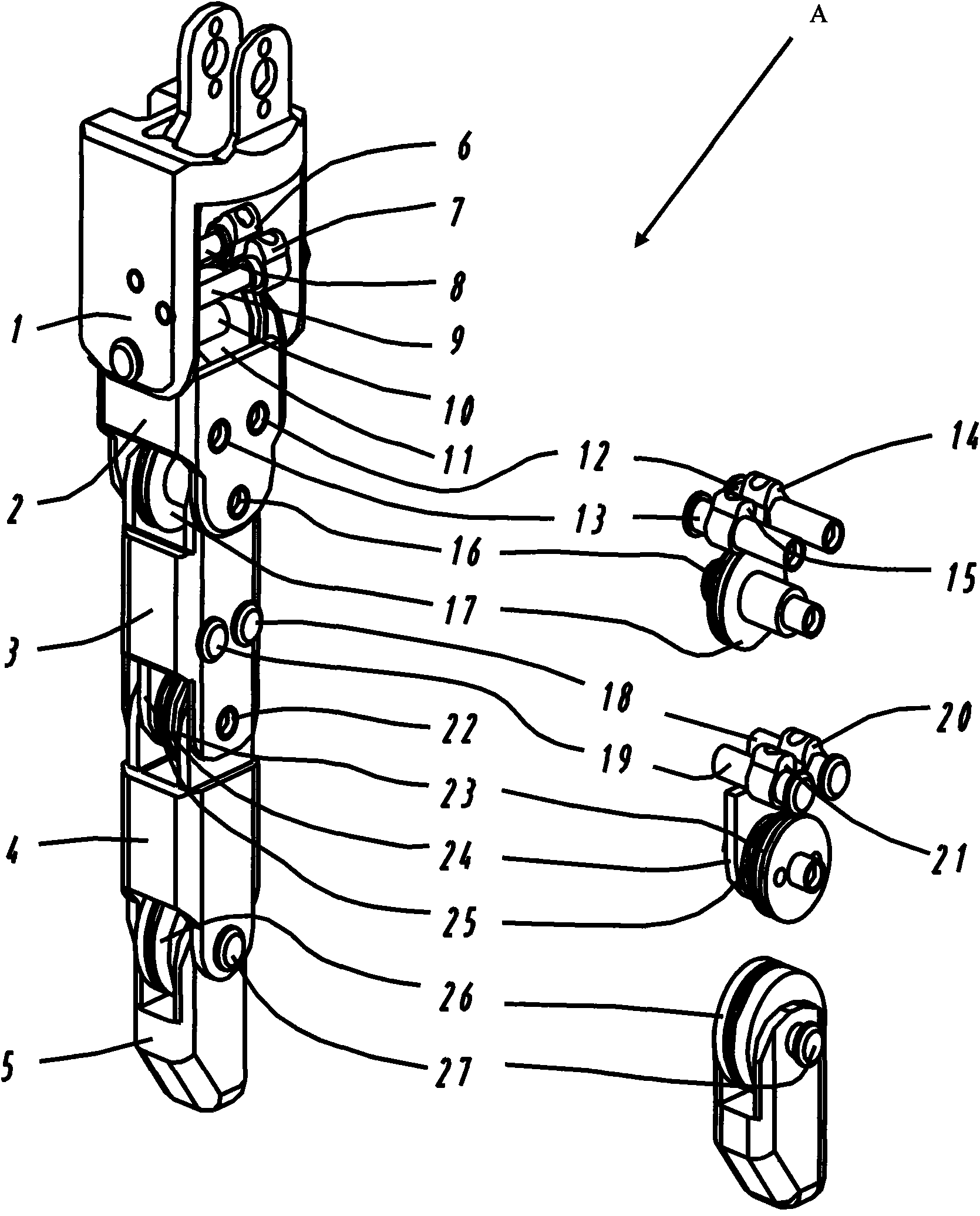
Percutaneous system for dynamic spinal stabilization
ActiveUS8267968B2Effective and stableReduce the amount requiredSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnLess invasive surgery
Bone anchoring assemblies for use with minimally invasive surgery (MIS) techniques for dynamic stabilization of the spine, together with placement systems for use in such techniques are provided.
Owner:NEUROPRO TECH
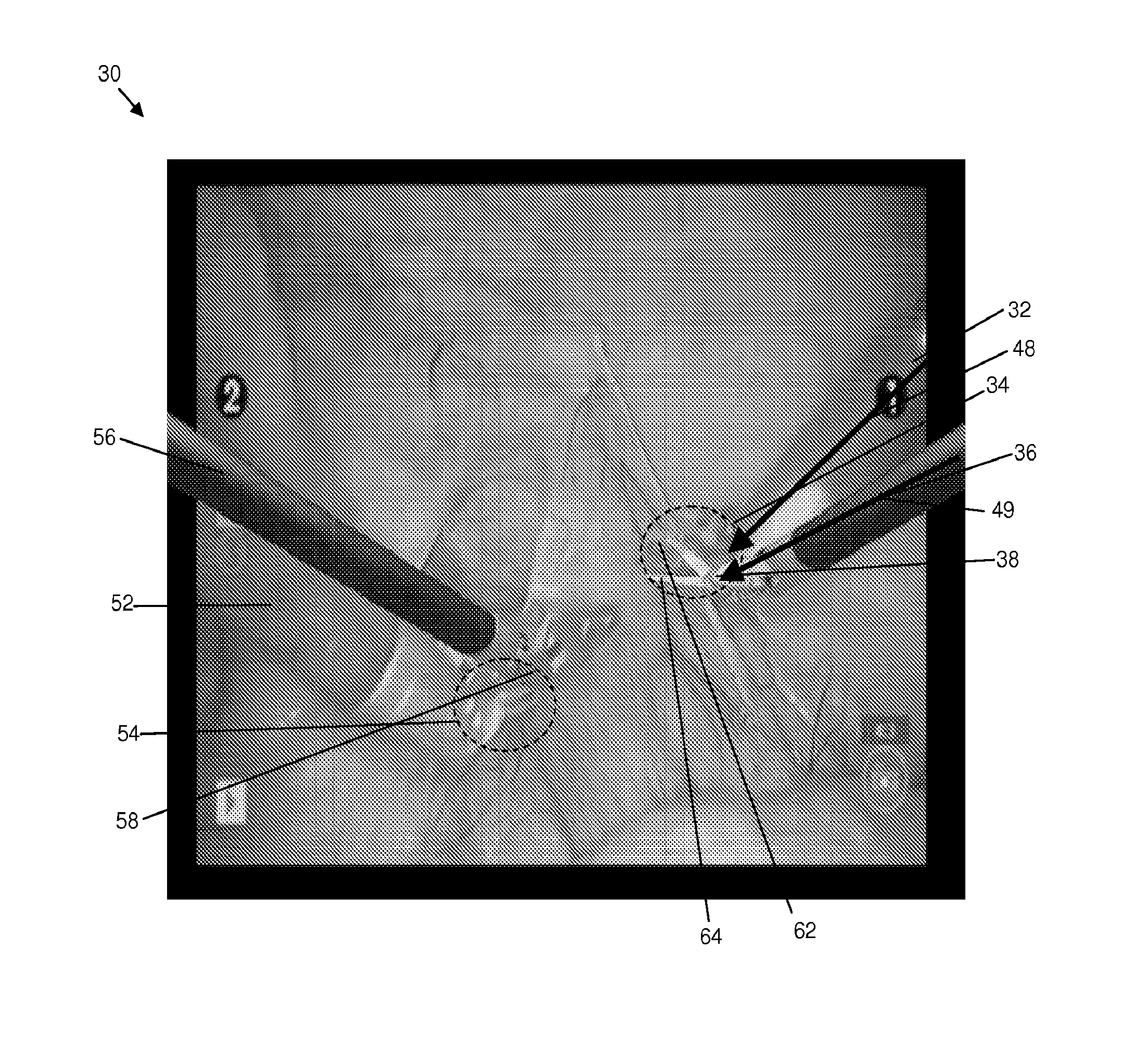
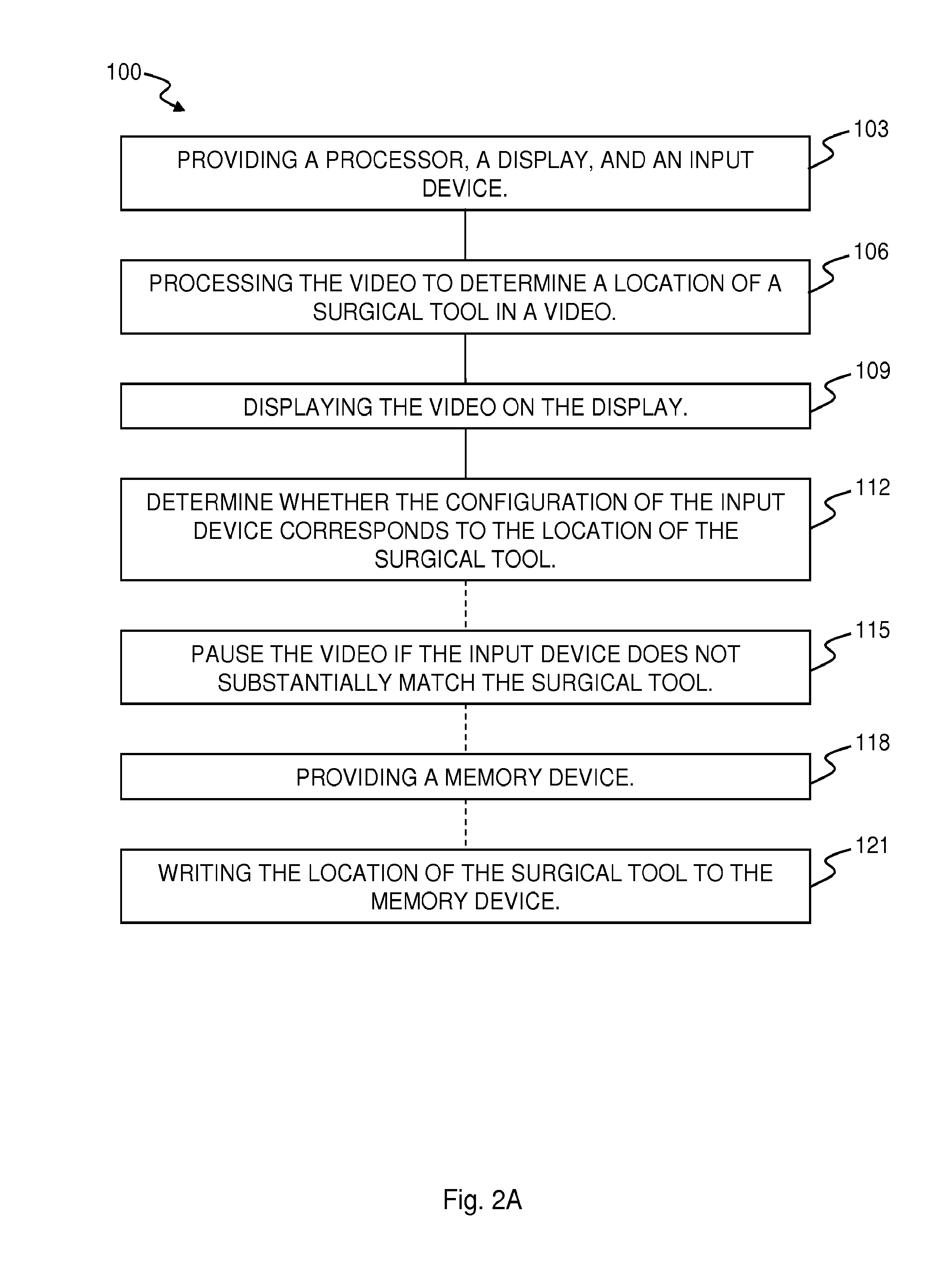
Method and System for Automatic Tool Position Determination for Minimally-Invasive Surgery Training
ActiveUS20130288214A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesEducational modelsMinimal invasive surgeryPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present invention may be embodied as a method of minimally-invasive surgery (“MIS”) training using a video of an MIS comprising the steps of providing a processor, a display, and a first input device. The method comprises the step of processing the video using the processor to determine a location of the first surgical tool in each of the frames, determining whether the configuration of the first input device substantially corresponds to the location of the first surgical tool in each frame of the video while the video is displayed. The present invention may be embodied as a system for MIS training. The system comprises a processor, a communication device, and a first input device in communication with the processor. The processor is programmed perform any or all of the described disclosed methods.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC +1
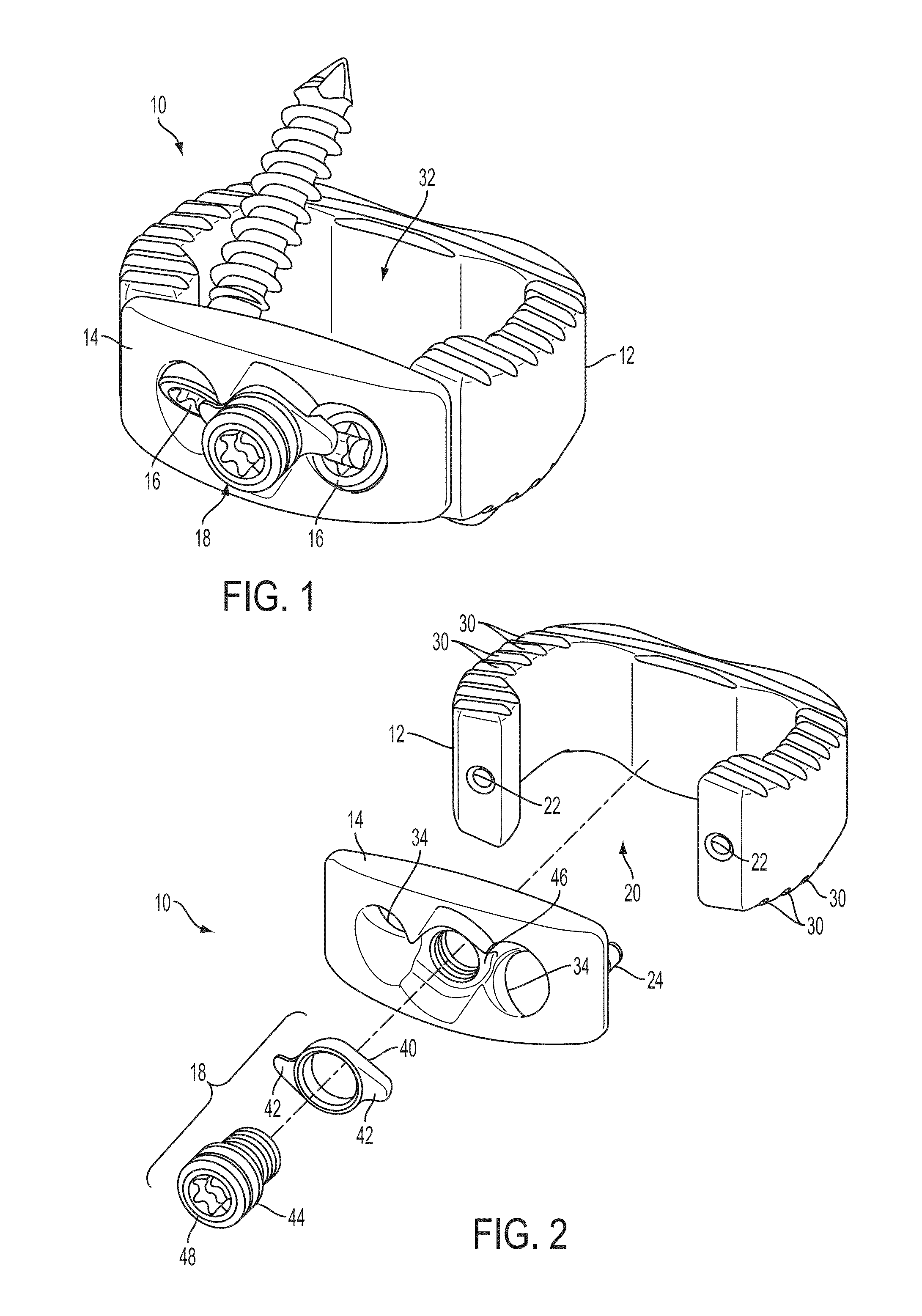
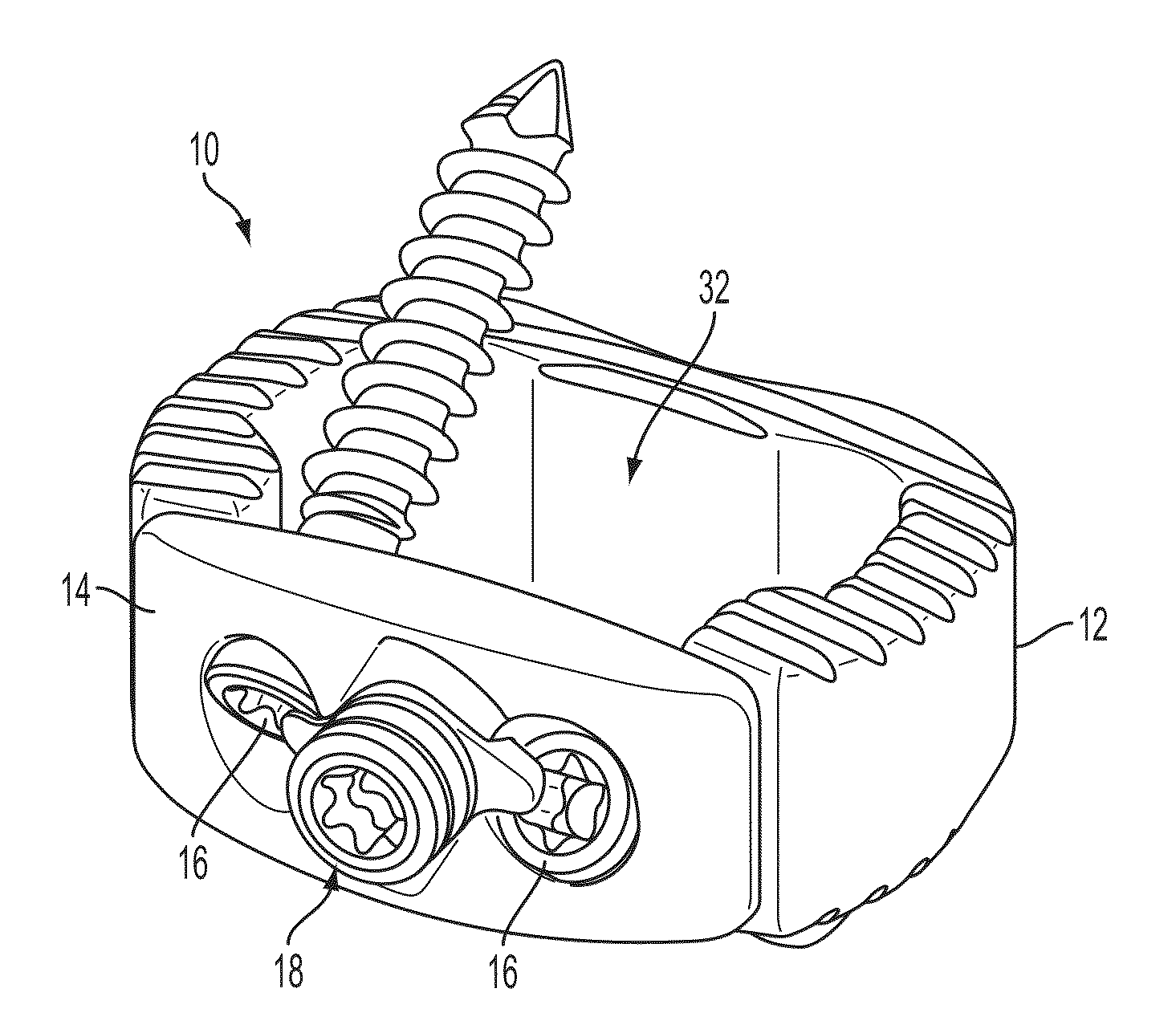
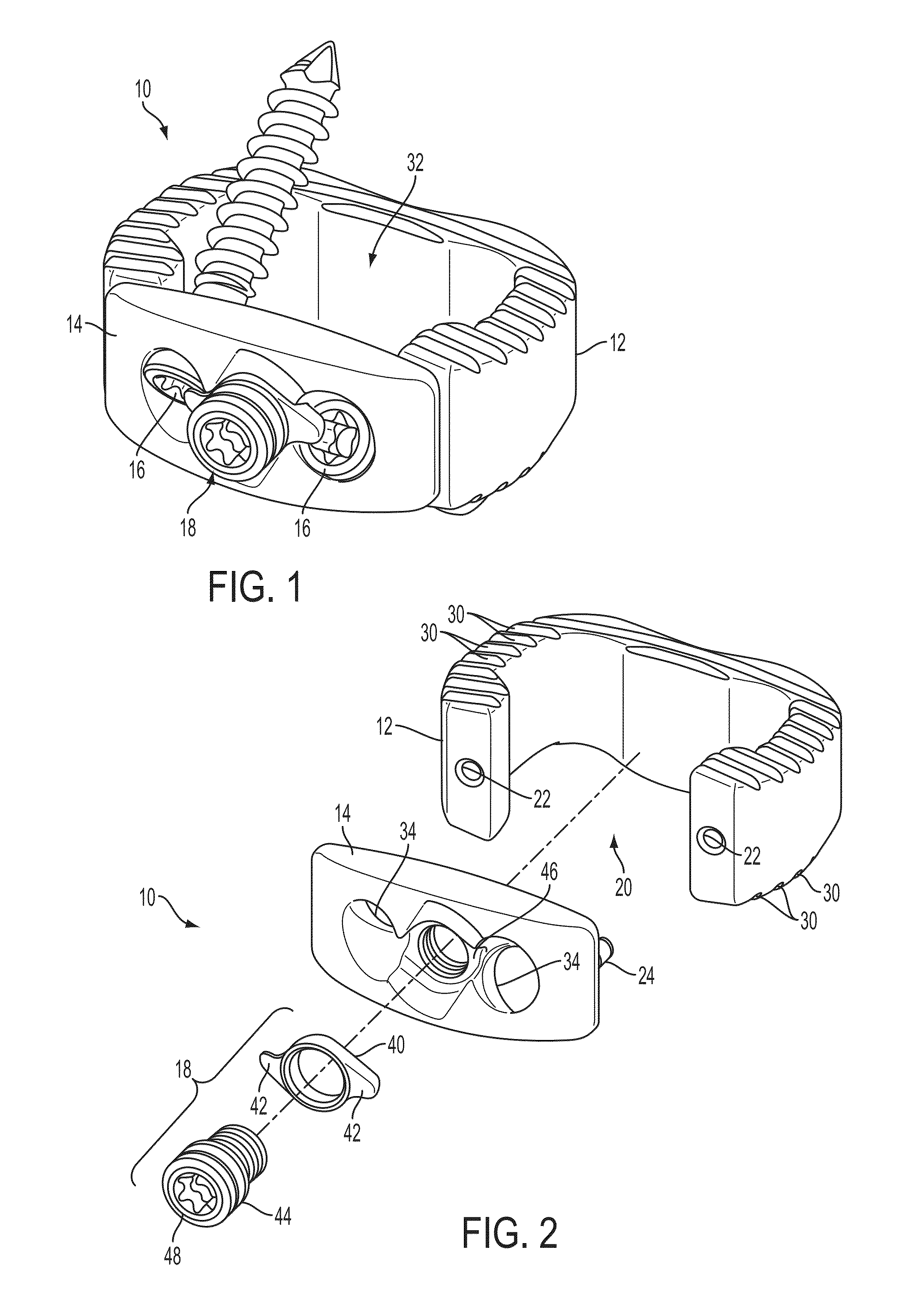
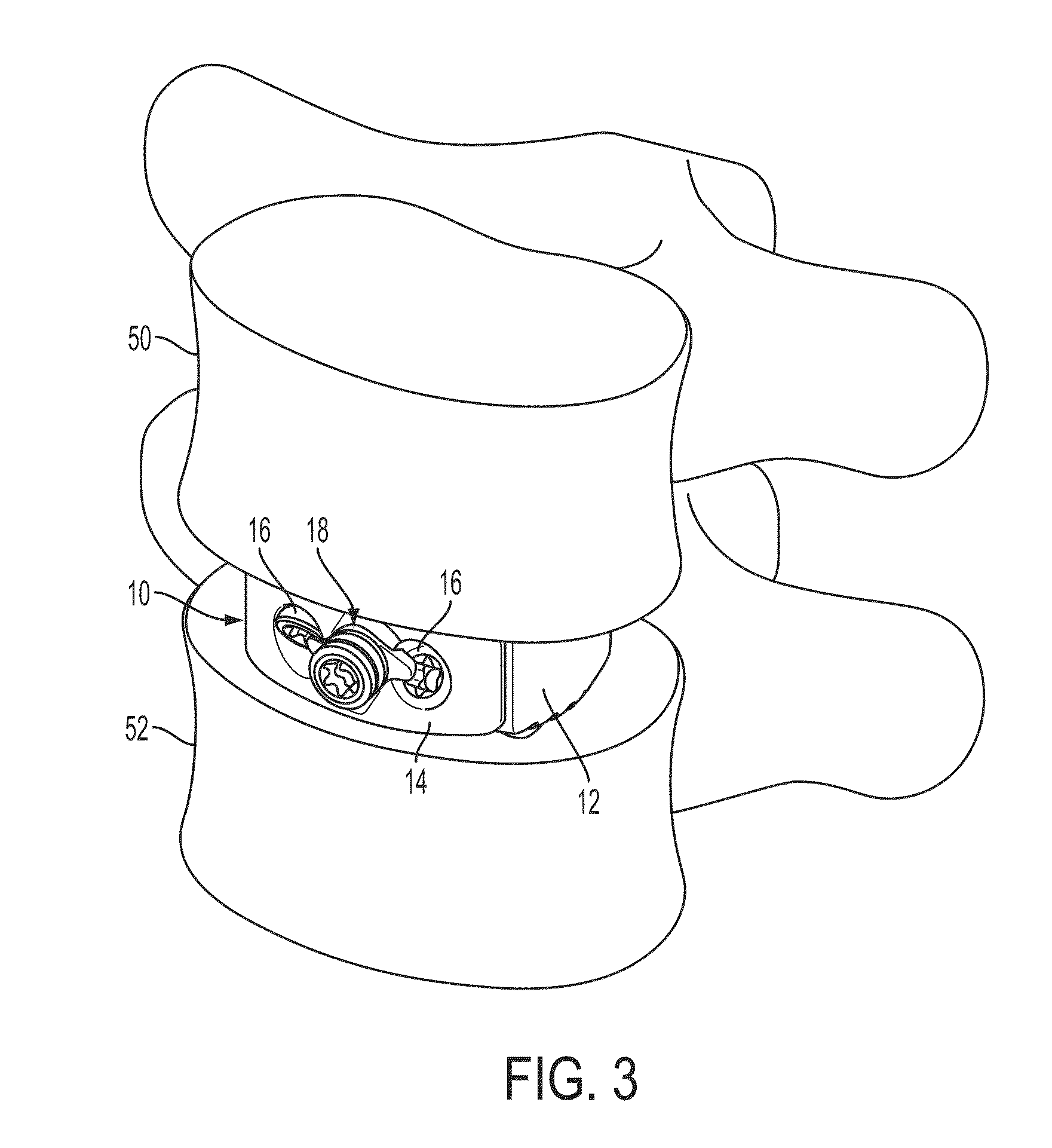
Interbody fusion device and associated methods
ActiveUS20140012384A1Reduces potential to cause discomfort and damageBone implantSpinal implantsMinimal invasive surgeryEngineering
A method and apparatus is provided for use in spinal fusion procedures. An interbody fusion device has a first piece that is a load bearing device designed to bear the axial loading from the end plates of adjacent vertebrae. A second piece of the interbody fusion device is a retention component whose primary functions are to prevent migration of the load bearing device and loss or migration of graft material from within the load bearing device. A secondary function of the retention component is to address fixation of fasteners when the surgeon is confronted with a challenging access to adequate boney structures due to excessive curvature / angulation of the vertebrae column, minimal invasive surgery techniques, danger to surrounding vascular or neurological tissues, poor bone quality, or similar surgical complications. A tertiary function of the retention component is to provide better alignment and stabilization of misaligned vertebrae when spondylolisthesis is a significant factor. One or more fasteners secure the retention component to each of the vertebrae above and below the load bearing device. The fasteners cause the end plates of the vertebrae to compress the end plates to the load bearing device to facilitate proper fusion.
Owner:SPINESMITH PARTNERS
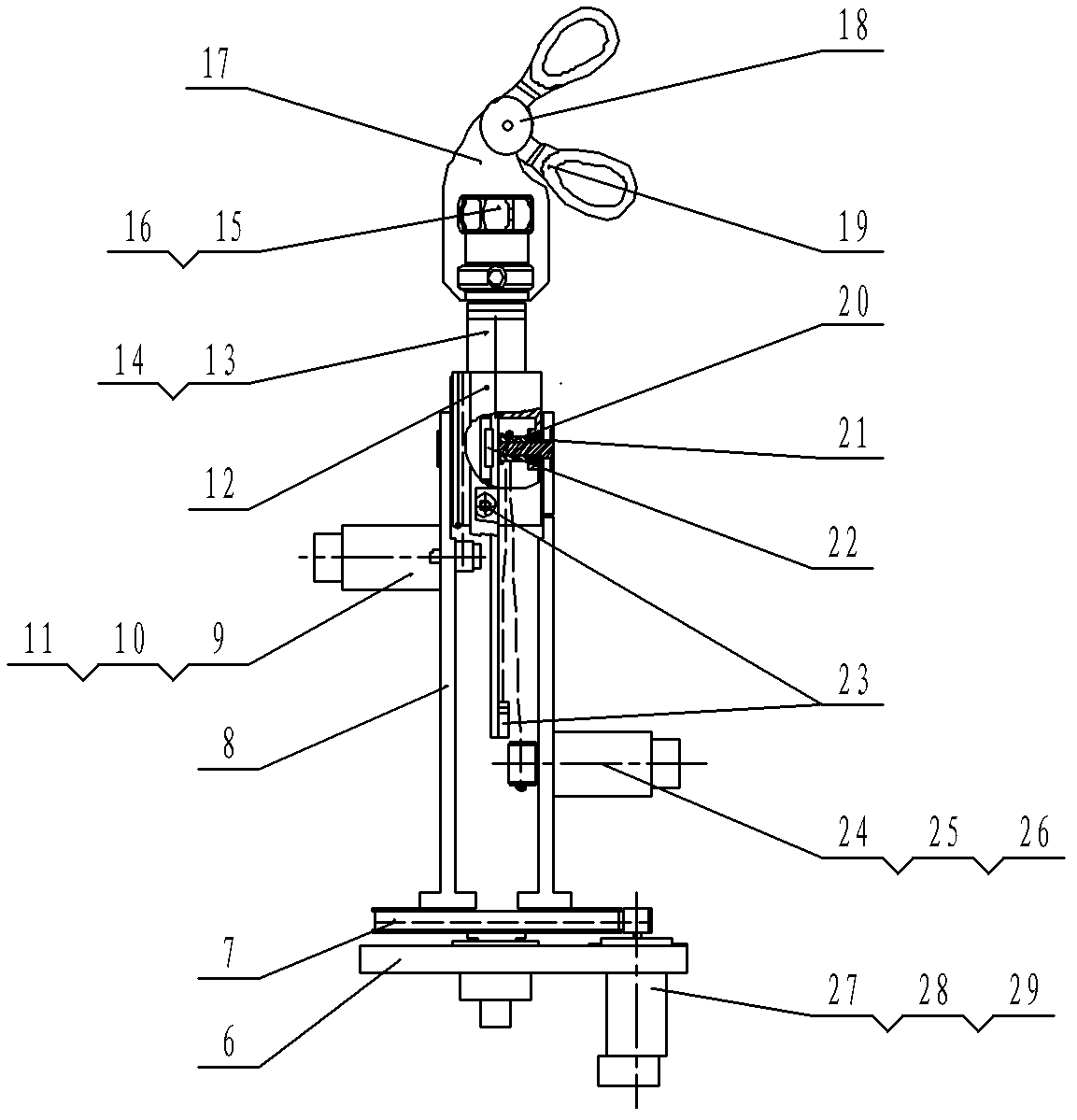
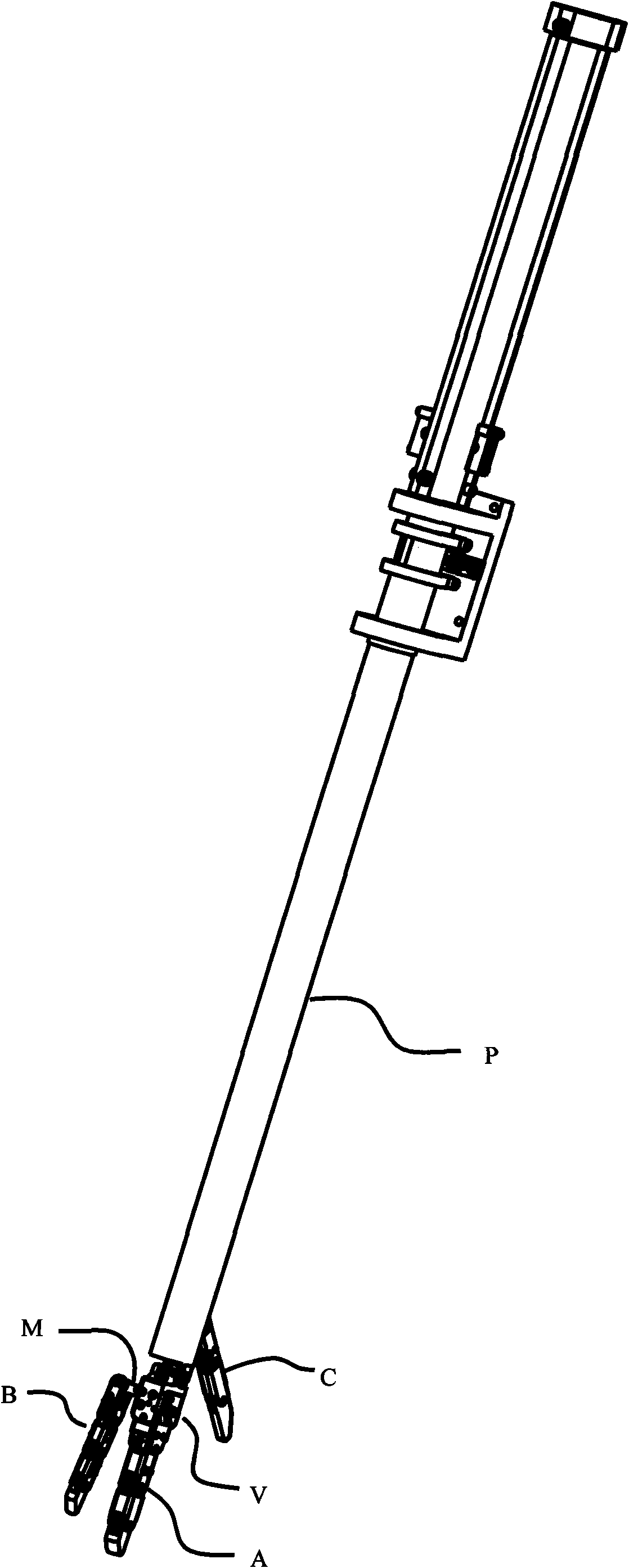
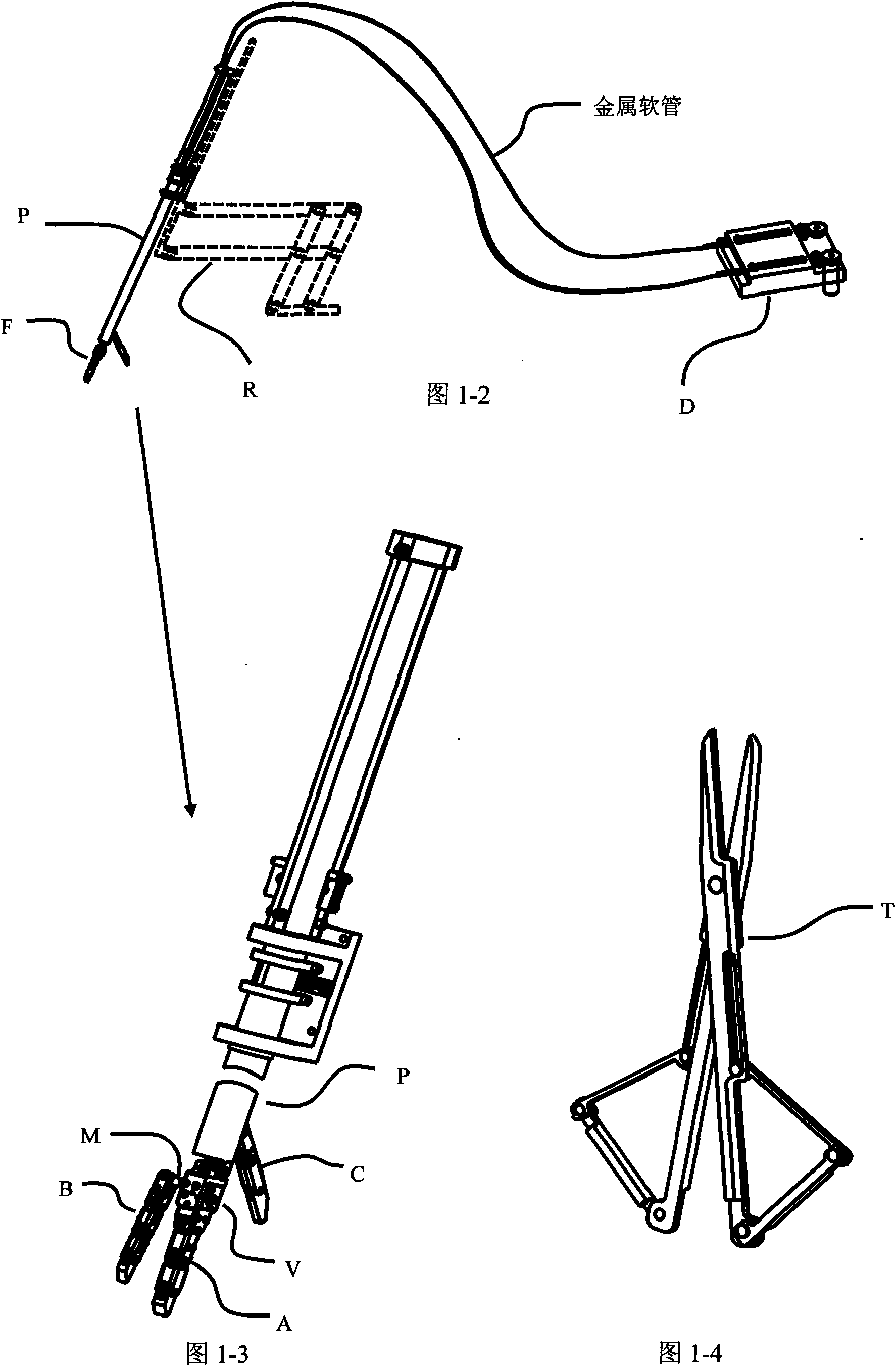
Metamorphic tool hand for abdominal cavity minimal invasive surgery robot
ActiveCN101584594AIncrease the number of degrees of freedomIncrease flexibilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisComing outWhole body
The present invention discloses a metamorphic tool hand for abdominal cavity minimal invasive surgery robot, which comprises the following components: a finger mechanism which is composed of a forefinger, a middle finger and a thumb; a palm mechanism; a metamorphic executing mechanism; a basal rod mechanism; a driving detecting mechanism and a special tool. The forefinger and the middle finger are hinged in the palm mechanism. The metamorphic executing mechanism is hinged between the palm mechanism and the basal rod mechanism. The palm mechanism and the thumb are respectively hinged with the basal rod mechanism. The basal rod mechanism is connected with the driving detecting mechanism through the soft wire provided in the metal flexible pipe. The basal rod mechanism is equipped in the robot body through screw bolts and move along with the robot body. The joint of the tool hand is driven by the soft wire in the metal flexible pipe. The middle finger and the thumb can be retreated into the basal rod. The forefinger is straight and is parallel with the basal rod. The whole body of the metamorphic tool hand can enter and come out from the scarfskin of the abdominal cavity. The metamorphic tool hand expands to the tool hand with different configuration after entering the abdominal cavity. The metamorphic tool hand not only can directly operate the organ and tissue of the abdominal cavity but also can grasp the tool for indirectly operation.
Owner:SHANDONG WEIGAO SURGICAL ROBOT CO LTD
Interbody fusion device and associated methods
ActiveUS9161841B2Reduces potential to cause discomfort and damageBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnEngineering
A method and apparatus is provided for use in spinal fusion procedures. An interbody fusion device has a first piece that is a load bearing device designed to bear the axial loading from the end plates of adjacent vertebrae. A second piece of the interbody fusion device is a retention component whose primary functions are to prevent migration of the load bearing device and loss or migration of graft material from within the load bearing device. A secondary function of the retention component is to address fixation of fasteners when the surgeon is confronted with a challenging access to adequate boney structures due to excessive curvature / angulation of the vertebrae column, minimal invasive surgery techniques, danger to surrounding vascular or neurological tissues, poor bone quality, or similar surgical complications. A tertiary function of the retention component is to provide better alignment and stabilization of misaligned vertebrae when spondylolisthesis is a significant factor. One or more fasteners secure the retention component to each of the vertebrae above and below the load bearing device. The fasteners cause the end plates of the vertebrae to compress the end plates to the load bearing device to facilitate proper fusion.
Owner:SPINESMITH PARTNERS
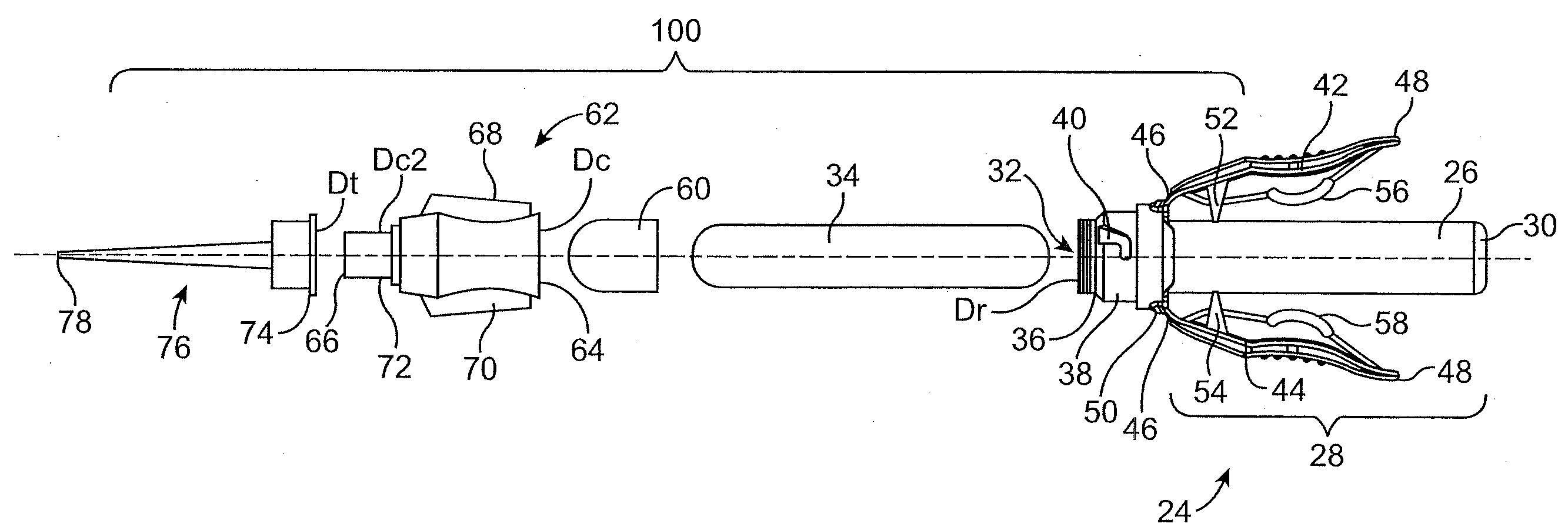
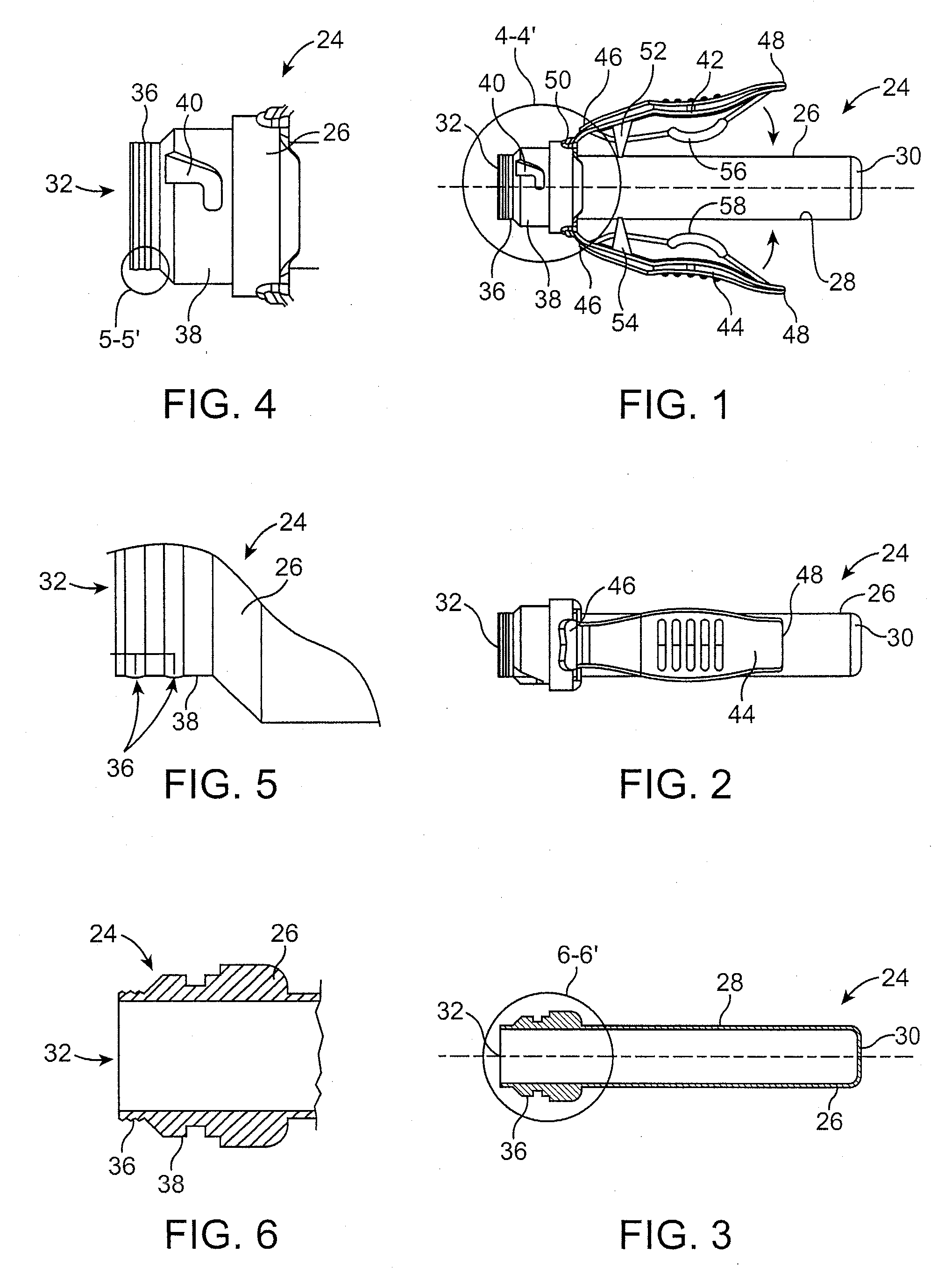
Instrument for minimal invasive surgery
ActiveUS7204836B2Reduce in quantityEffective insulationSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical forcepsMinimal invasive surgeryForceps
A medical forceps has a forceps shank and a forceps jaw which comprises at least one movable jaw part, wherein the jaw part has a curved linkage arm at its proximal end. The linkage arm is movably guided in a curved guide path of an insert which is inserted into at least one receiver at the distal end of the forceps shank.
Owner:RICHARD WOLF GMBH
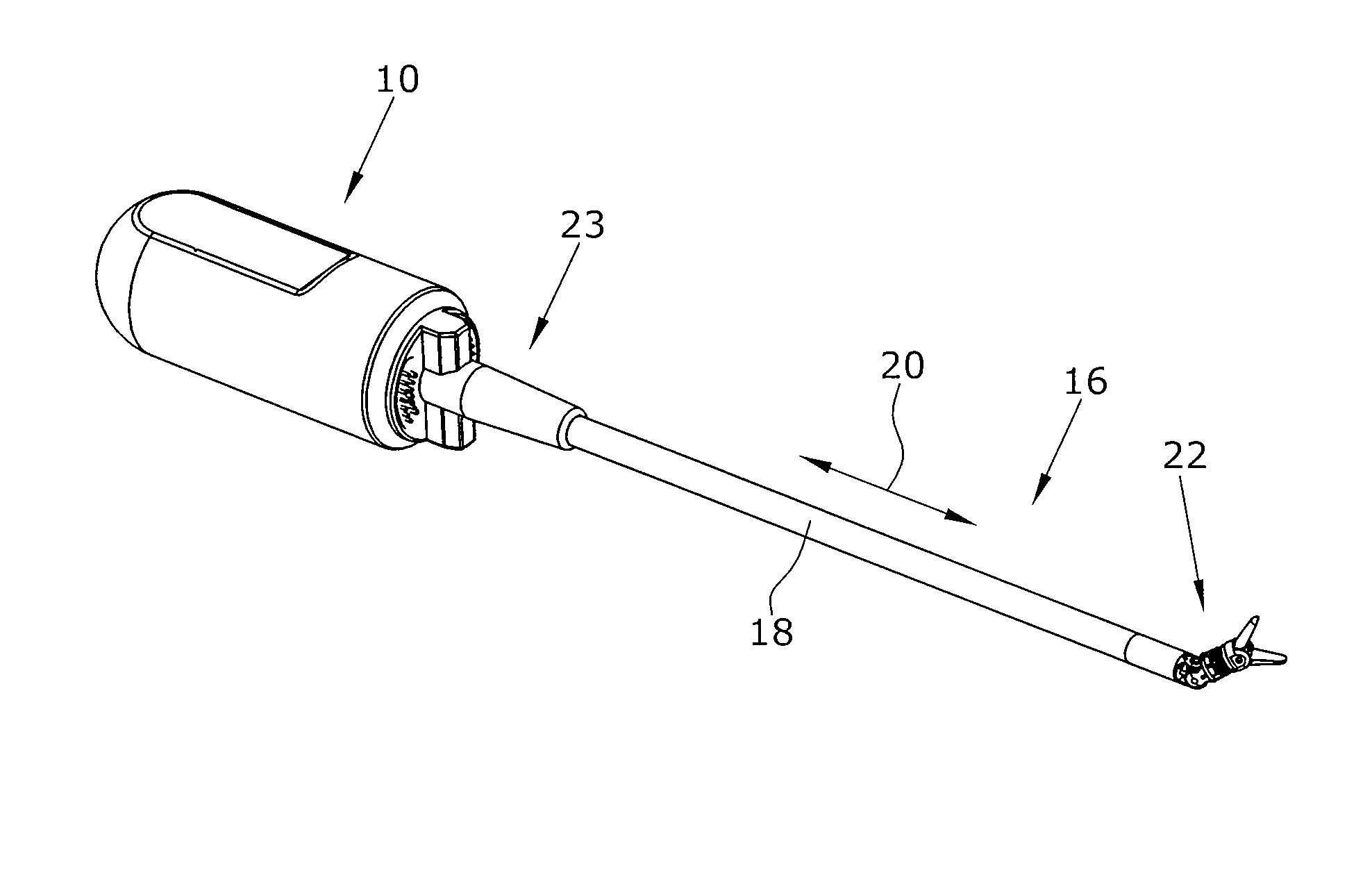
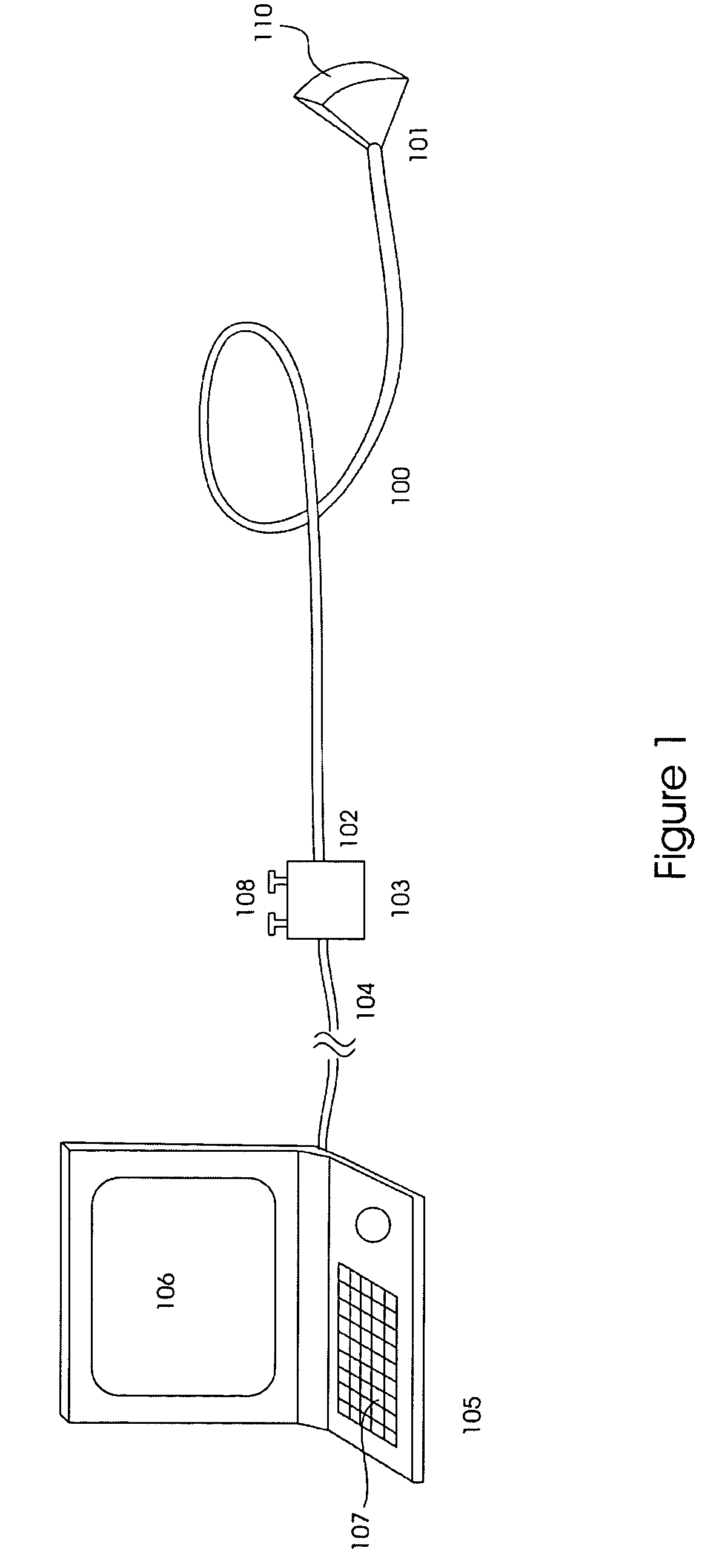
Virtual reality wrist assembly
A surgical apparatus system for minimally invasive surgery (MIS) which includes a wrist assembly. The wrist assembly includes a first jaw, a first actuation hub, and a cable redirecting hub operably coupled to the first actuation hub, a second jaw, a second actuation hub, a housing for the first and second jaws, a first cable, a second cable, a third cable, rotational position sensors, and a control system. The first and second jaws of the wrist assembly are movably opposed, and the cables are configured such that applying tensions upon them cables produces rotation about a jaw axis. The wrist assembly may further include a hinge-rotary assembly to configured to provide rotation about a pitch axis and / or a roll axis. The wrist assembly may further include a fourth cable configured such that applying tensions upon the fourth cable and the opposing cable produces rotation about a pitch axis.
Owner:VICARIOUS SURGICAL INC
Device and method for rolling and inserting a prosthetic patch into a body cavity
This invention generally relates to minimal invasive surgery. More specifically the current invention relates to an apparatus especially adapted to fold prosthetic patches and to insert said patches into a body cavity through a cannula or an incision.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
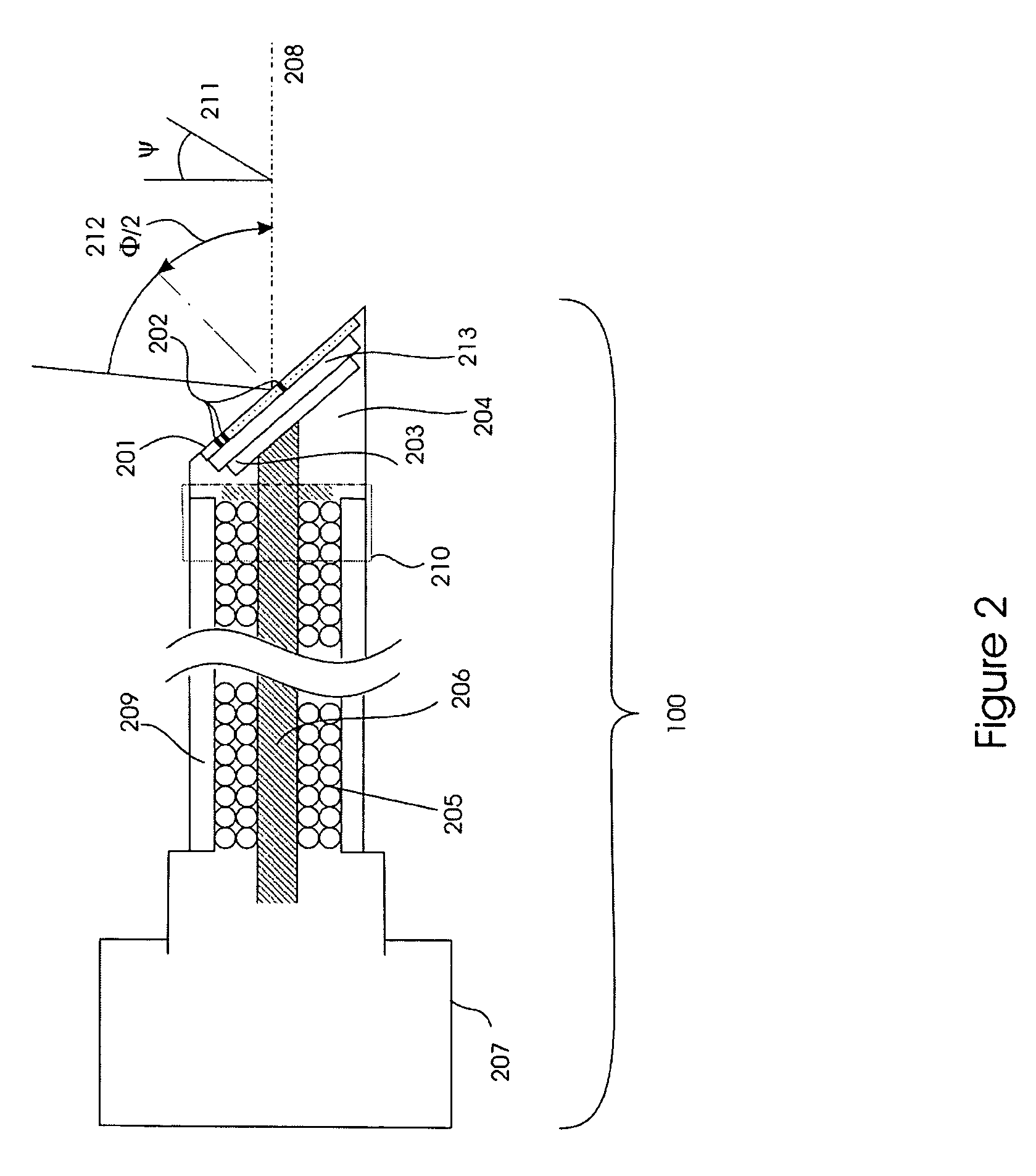
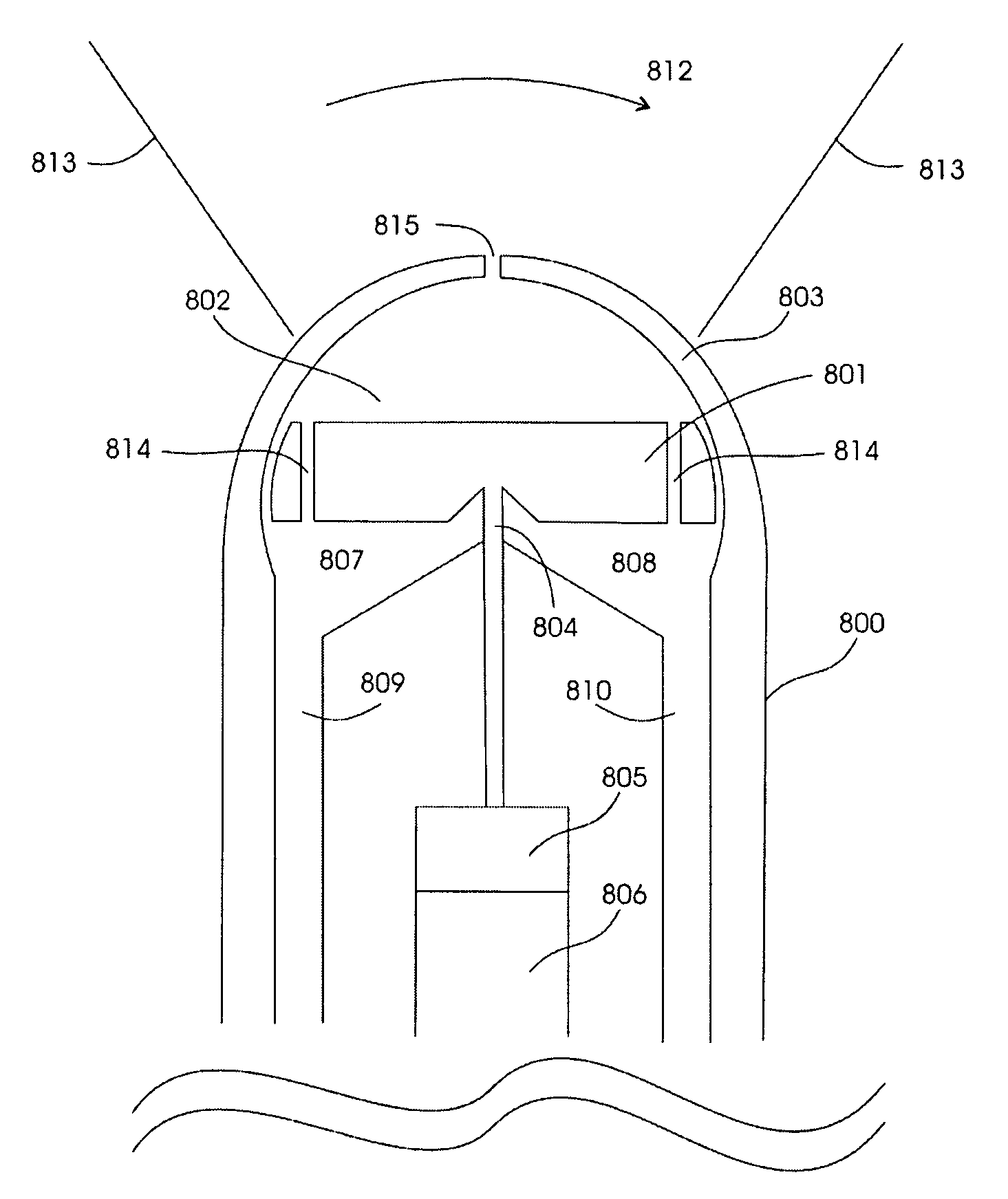
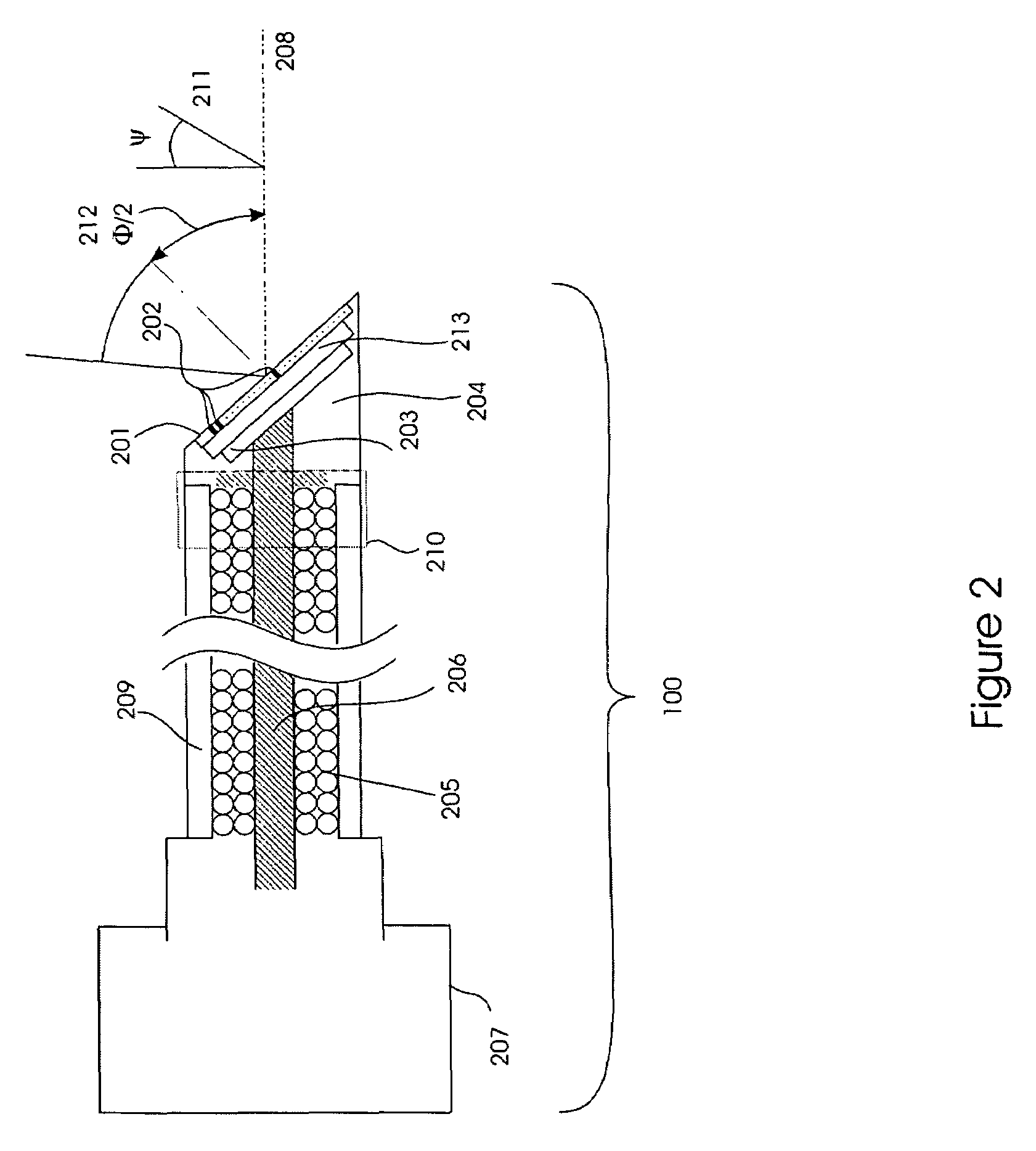
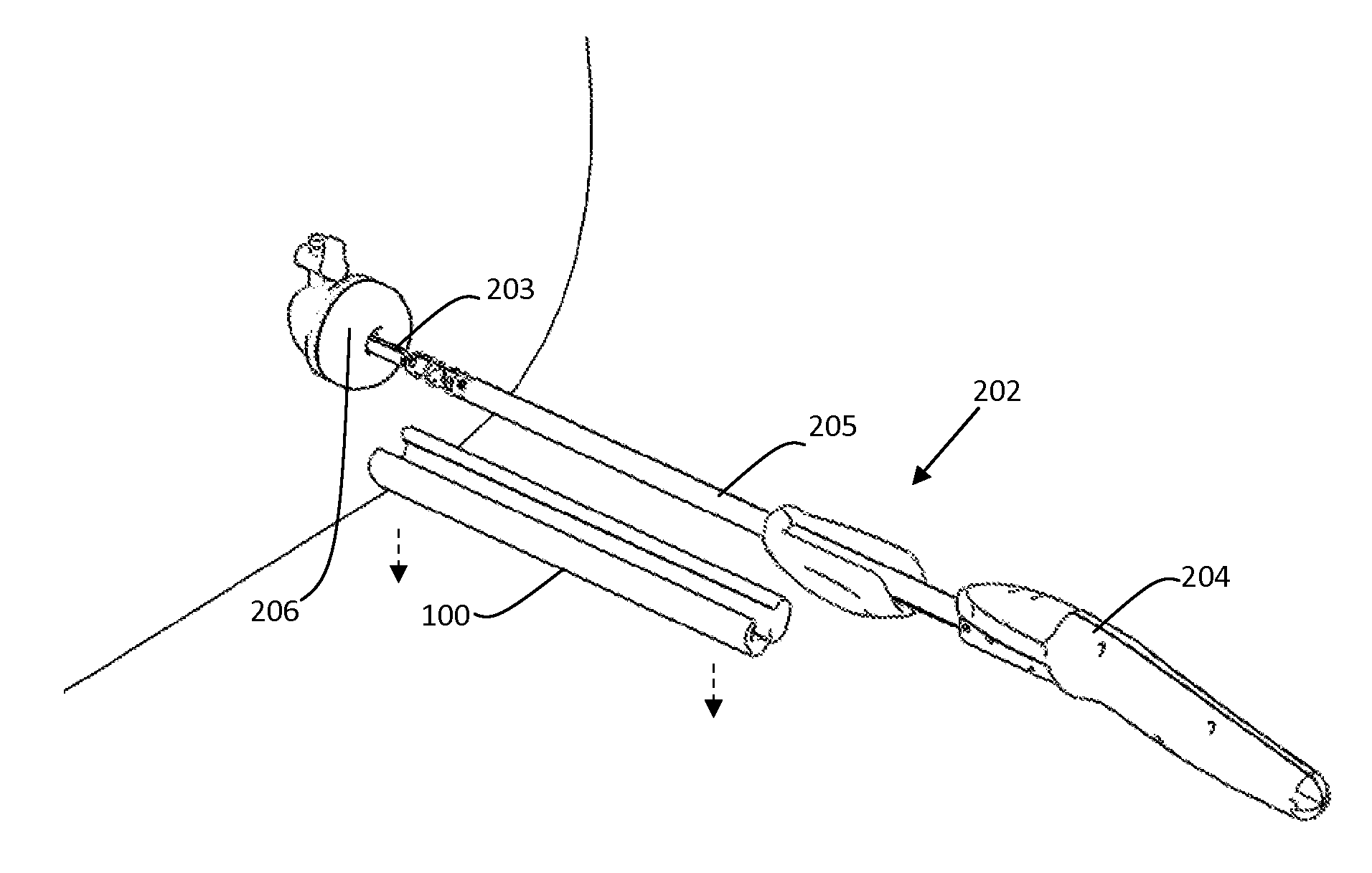
Interstitial microwave antenna with lateral effect for tissue hyperthermia in minimal invasive surgery
InactiveUS20060015161A1Reducing treatment invasivityElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyMinimal invasive surgeryElectrical conductor
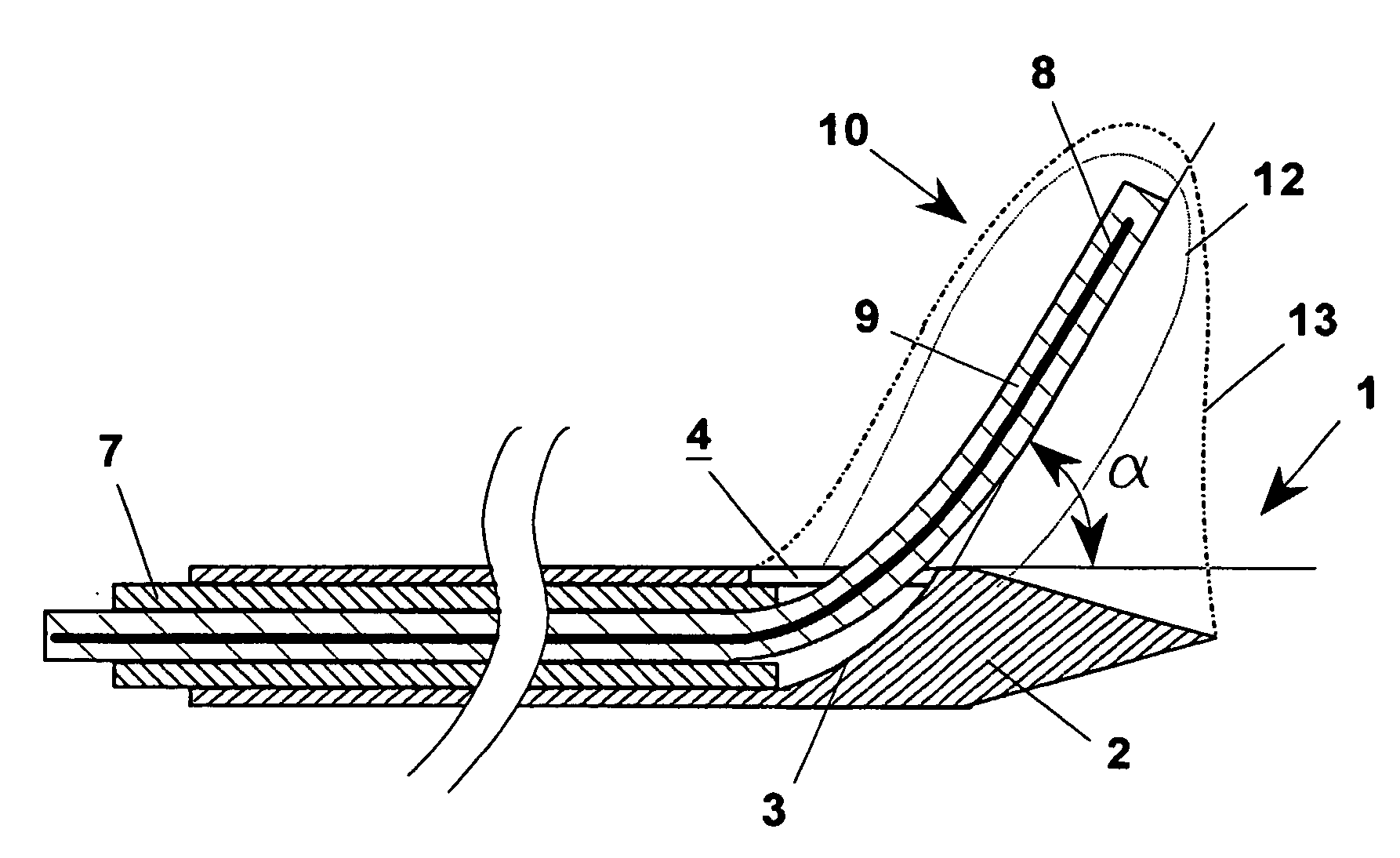
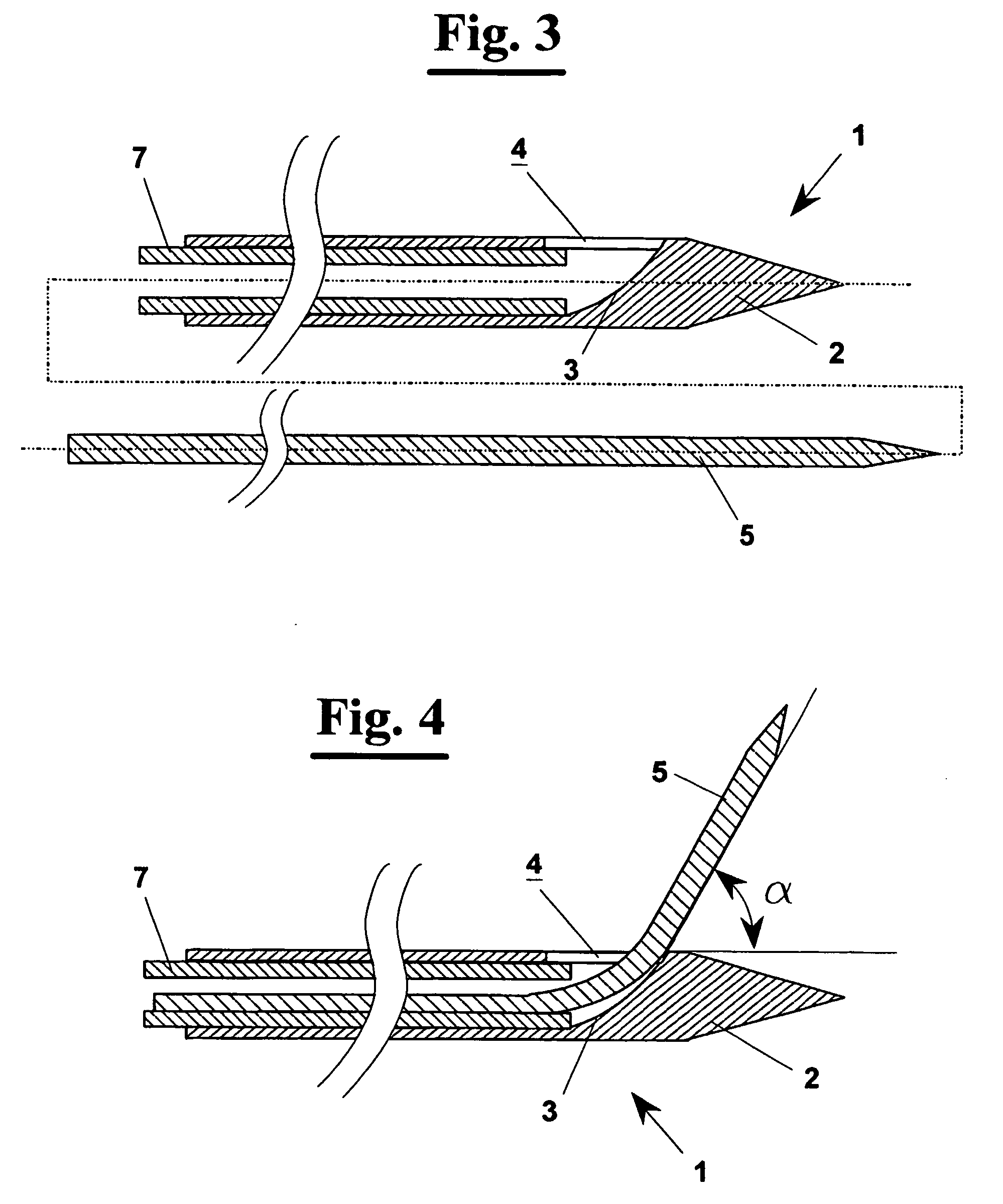
Application device (1), for example, a metal needle or a plastic catheter that has in the end portion (2) of the free end a gradually increasing thickness to form substantially a chute guide (3) which ends at a side opening (4) made on the application device (1). This way, an interstitial antenna (10) is obtained formed by a co-axial tube having an external conductor (7), by a dielectric layer (9) and by a central conductor (8) embedded in the dielectric layer (9) that insulates it from the external conductor (7). The antenna (10) can be put in a target tissue, along an actuation direction forming an angle a with the introduction direction. This way, the antenna (10) achieves an actual surface isothermal, i.e. a mass of tissue actually coagulated within a curved surface (13), since the tip of the application device (1) is connected electrically with the external conductor (7) and increases its area of action.
Owner:LONGO IGNIO +1
Device especially useful for hernia repair surgeries and methods thereof
The present invention discloses an inflatable contour-balloon useful in minimal invasive and / or open surgery. The inflatable contour-balloon positioned in the contour of a mesh and / or a patch and / or a net. The inflatable contour-balloon is adapted to spread and / or deploy the mesh and / or the patch and / or the net in the abdominal cavity and / or pre-peritoneal and / or space and / or hollow body organs and / or natural and / or artificial orifices and / or spaces and / or post operative spaces. The present invention also discloses an elongate open-bored applicator (EOBP) adapted to spread and / or deploy a mesh and / or a patch and / or a net. The EOBP is useful in minimal invasive surgery. The EOBP has a distal portion that is insertable into the abdominal cavity and / or pre-peritoneal and / or space arid / or hollow body organs and / or natural and / or artificial orifices and / or spaces and / or post operative spaces; and a proximal portion that remains outside the body. The EOBP comprises: (a) at least one inflatable contour-balloon; (b) at least one inflatable dissection balloon. The inflatable contour-balloon and the inflatable dissection balloon are adjustable and located at the distal portion; and, (c) at least one actuating means located at the proximal portion. The actuating means is in communication with the inflatable contour-balloon and the inflatable dissection balloon. The actuating means is adapted to provide the inflatable contour-balloon and the inflatable dissection balloon with independent activation and / or de-activation.
Owner:DAVOL
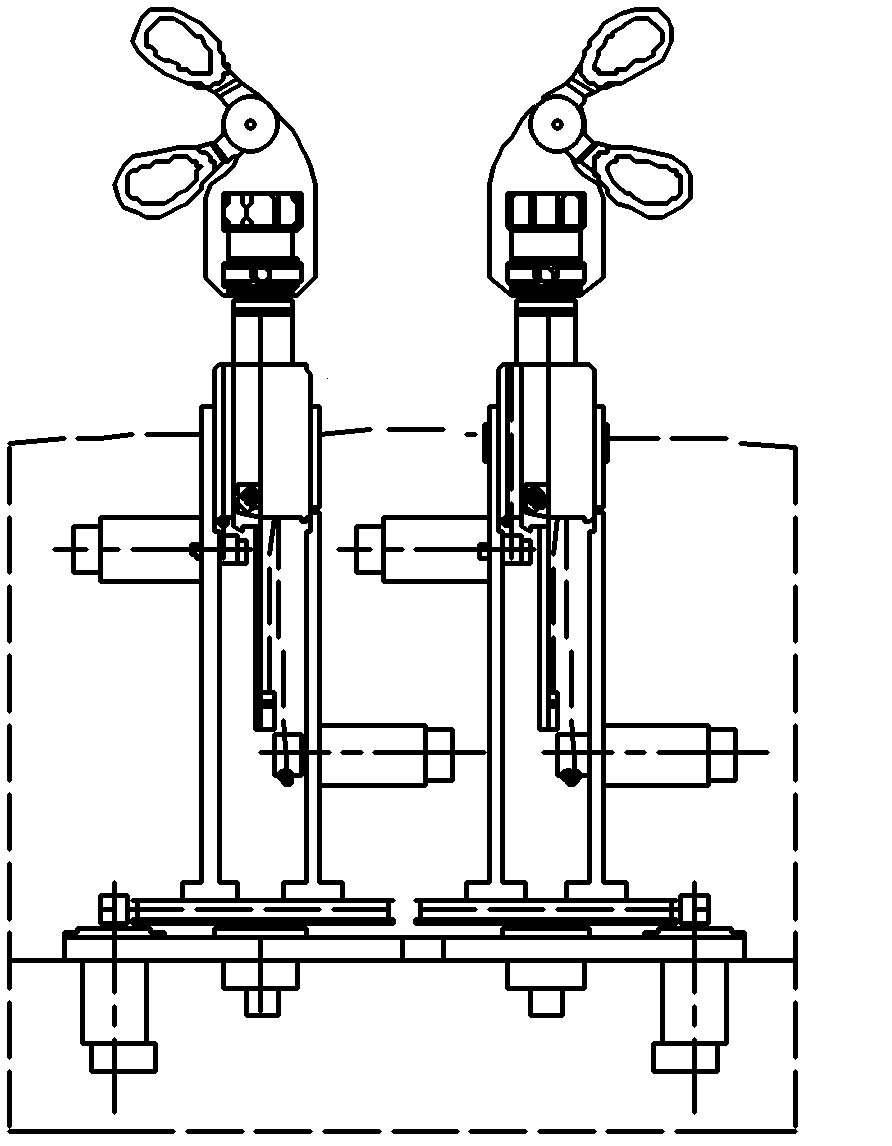
Positioning system for assisting in spine minimally invasive surgery
PendingCN107361859ARapid positioningPrecise positioningSurgical robotsInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryLess invasive surgeryDetent
The invention relates to a positioning system for assisting in spine minimally invasive surgery. The positioning system mainly comprises a degree mechanical arm and a path positioner. The path positioner comprises a flange short locking component, a lifting and sliding component and a double-ring positioning assembly. The mechanical arm can be installed on a trolley; the path positioner is fixed to the tail end of the mechanical arm through the flange short locking component. The lifting and sliding component is connected with the flange short locking component through a clamping and locking body; the double-ring positioning component is connected with a lifting and translation component through a screw. The double-ring positioning assembly is provided with a first positioning ring and a second positioning ring which are used for a guide needle to penetrate through in sequence to position the guide needle, and the first positioning ring and the second positioning ring are separated with each other and concentrically arranged; the lifting and sliding component can drive the double-ring positioning component to conduct translation motion in the axial direction of two rings. The positioning system for assisting in the spine minimally invasive surgery can assist a doctor in accurately positioning the transplanting path of the spine minimally invasive surgery under the condition that the radiation frequency is few.
Owner:苏州铸正机器人有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com