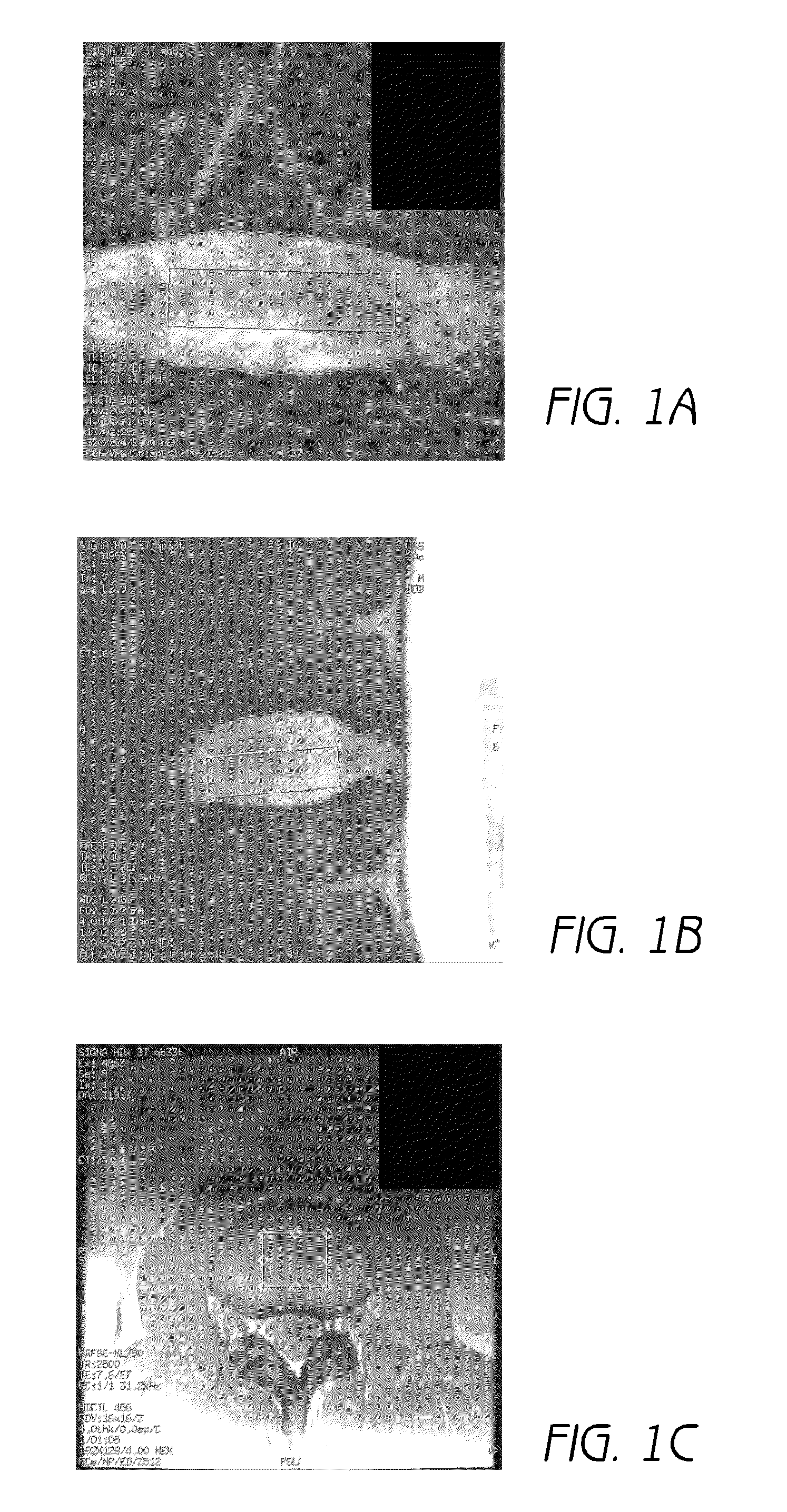
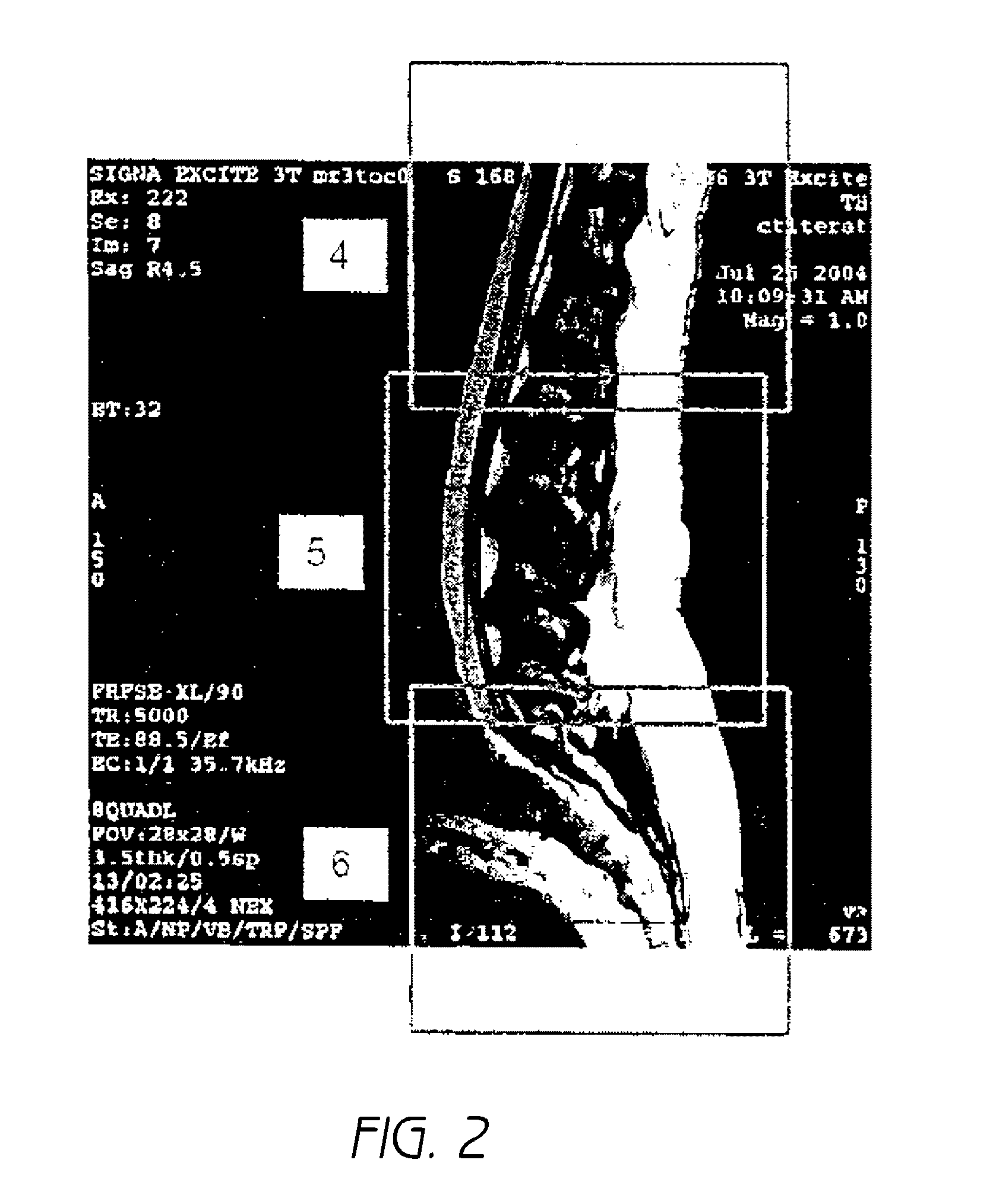
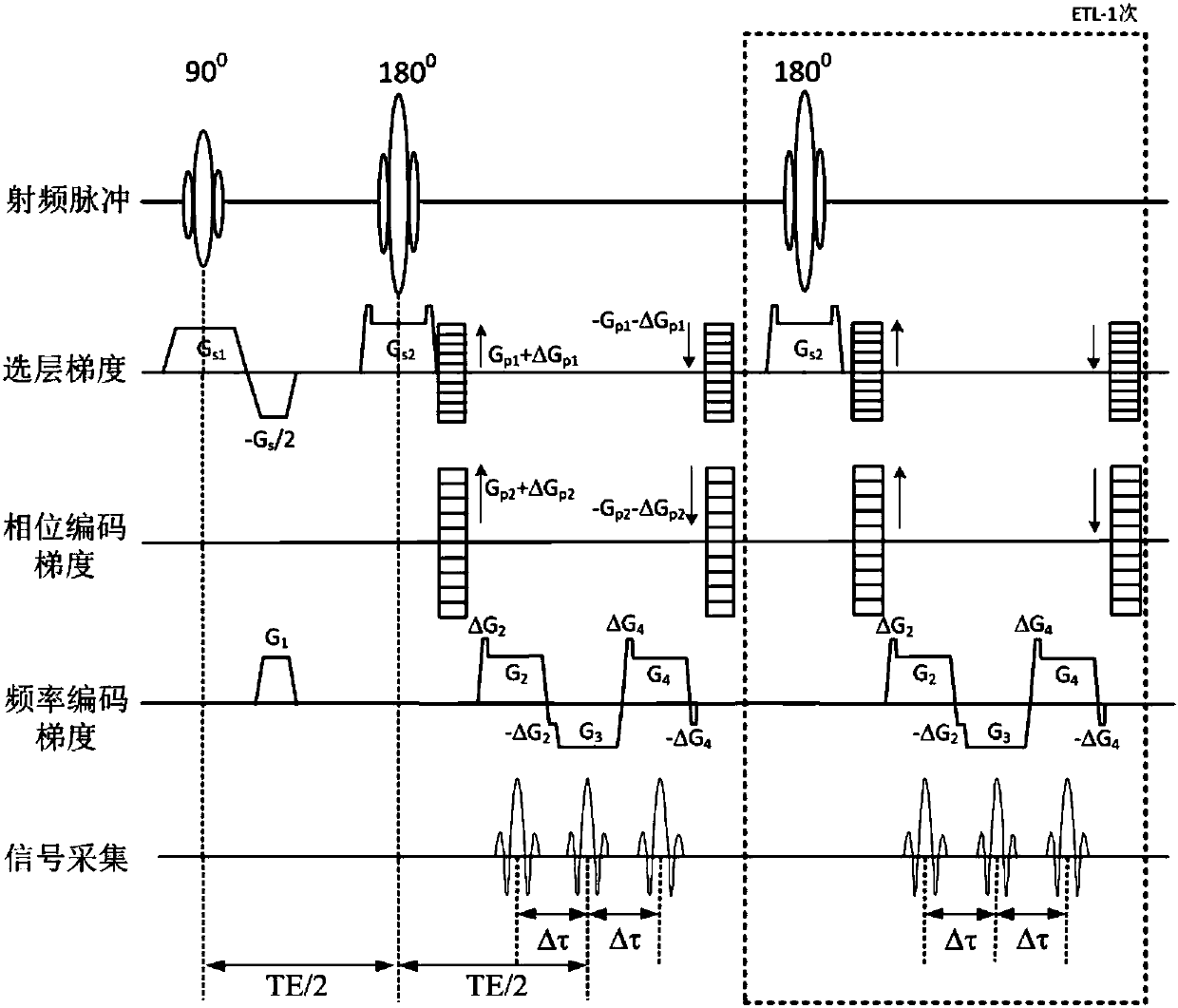
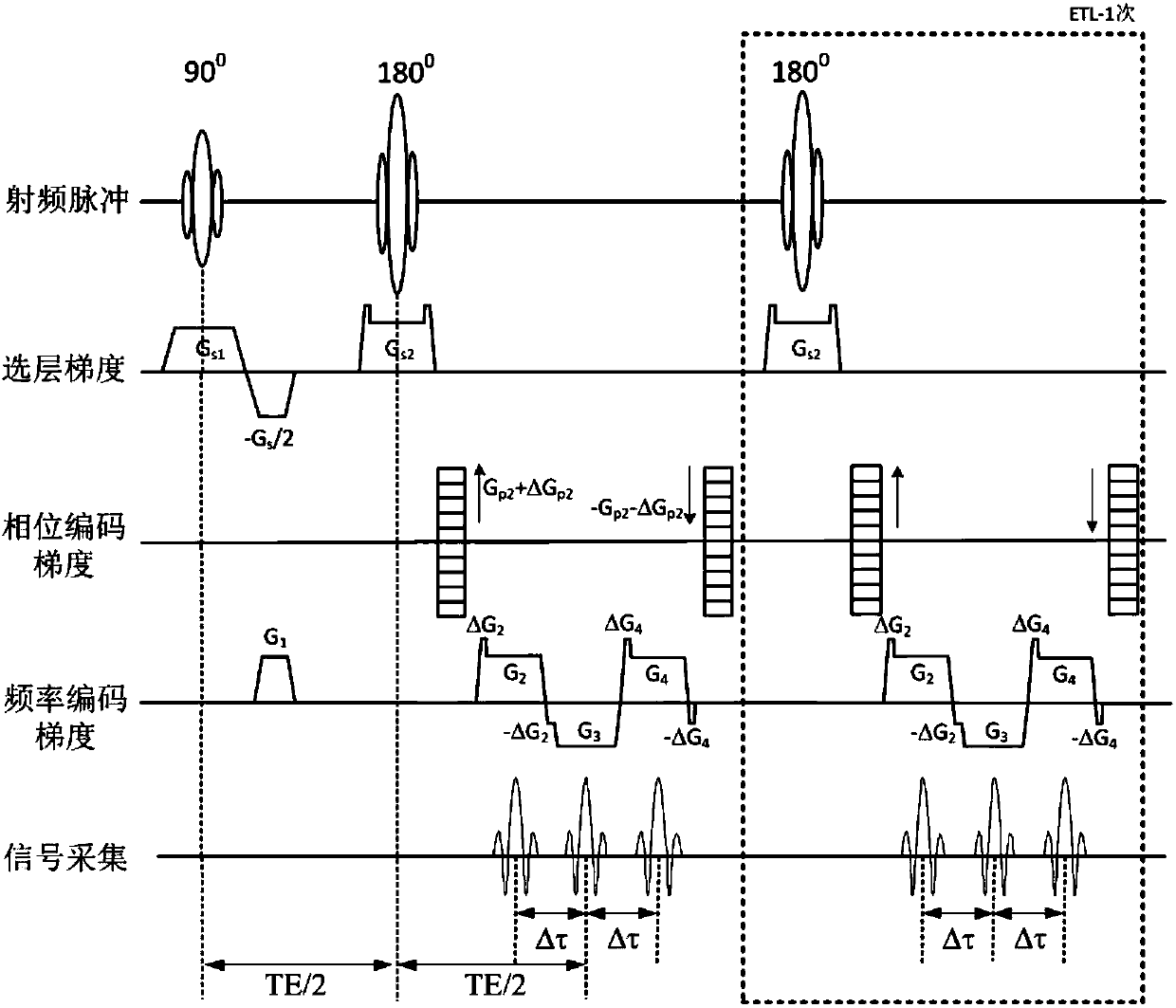
Patents
Literature
96 results about "T2 weighted" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
T2 weighted image (T2WI) is one of the basic pulse sequences in MRI. The sequence weighting highlights differences in the T2 relaxation time of tissues.
Multi-parameter magnetic resonance image based prostate cancer computer auxiliary identification system
InactiveCN104424386AImprove accuracyIncreased sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsReceiver operating characteristicImage pre processing
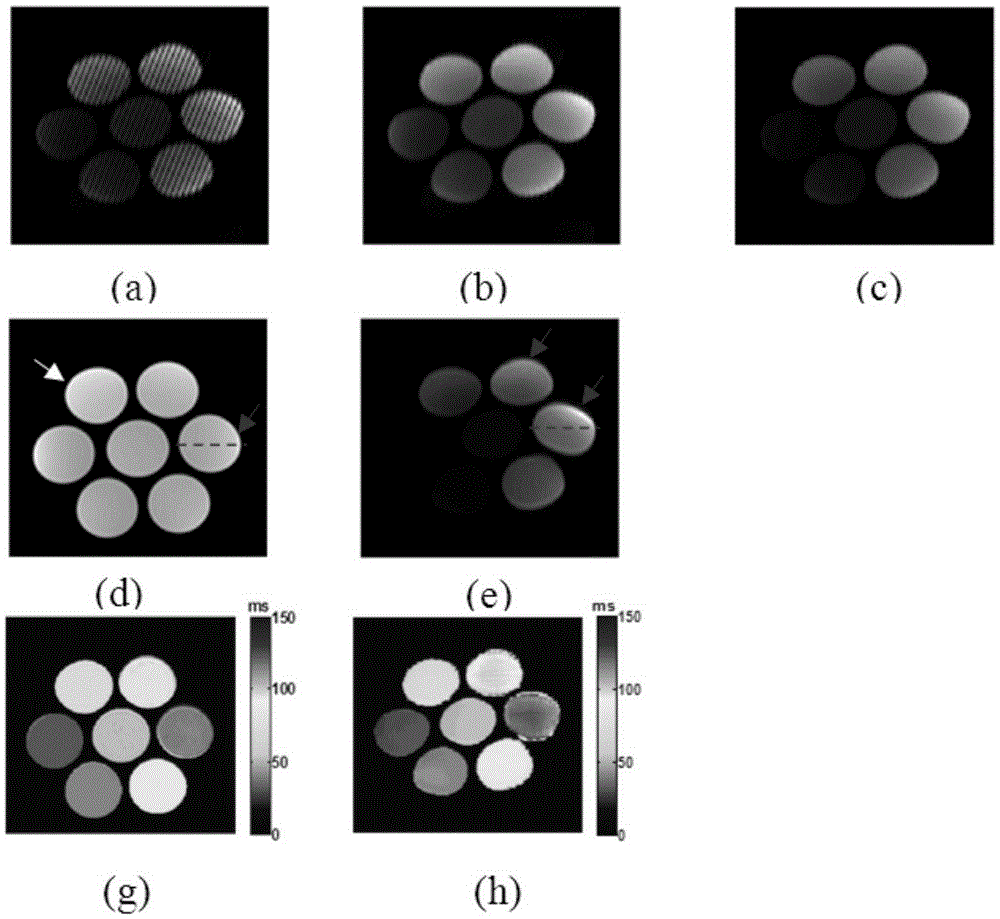
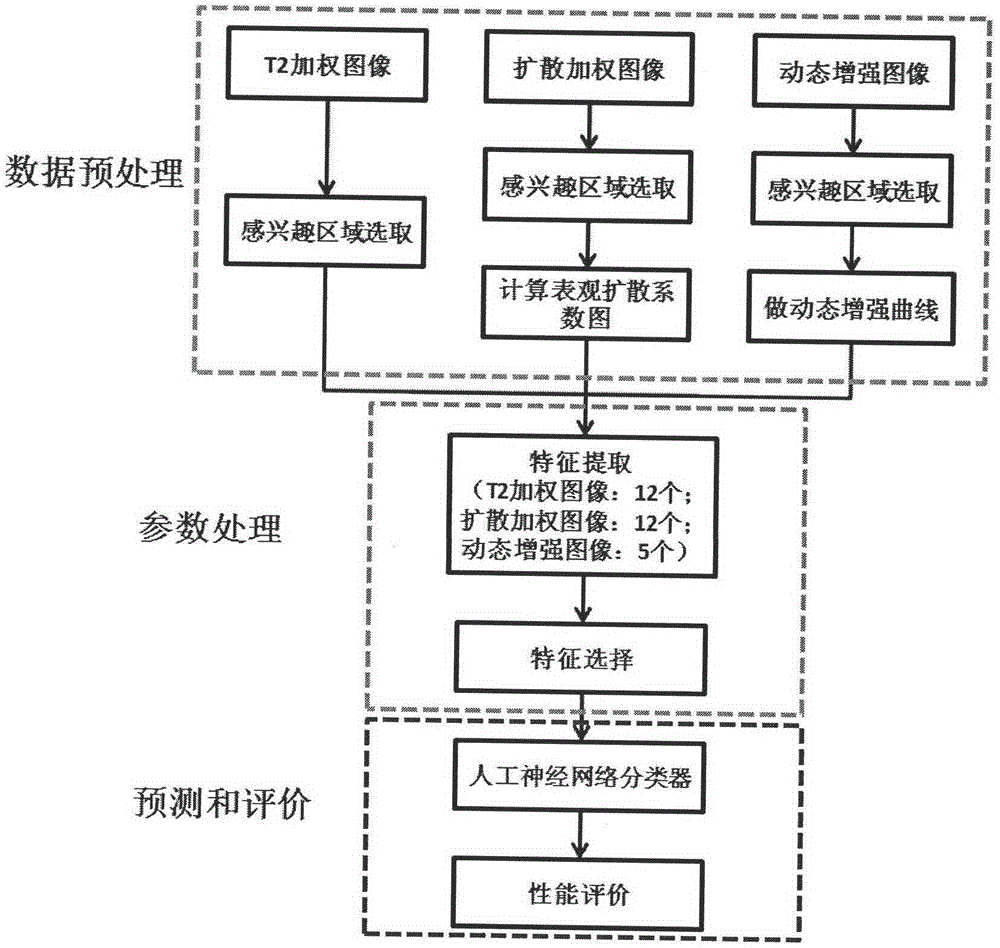
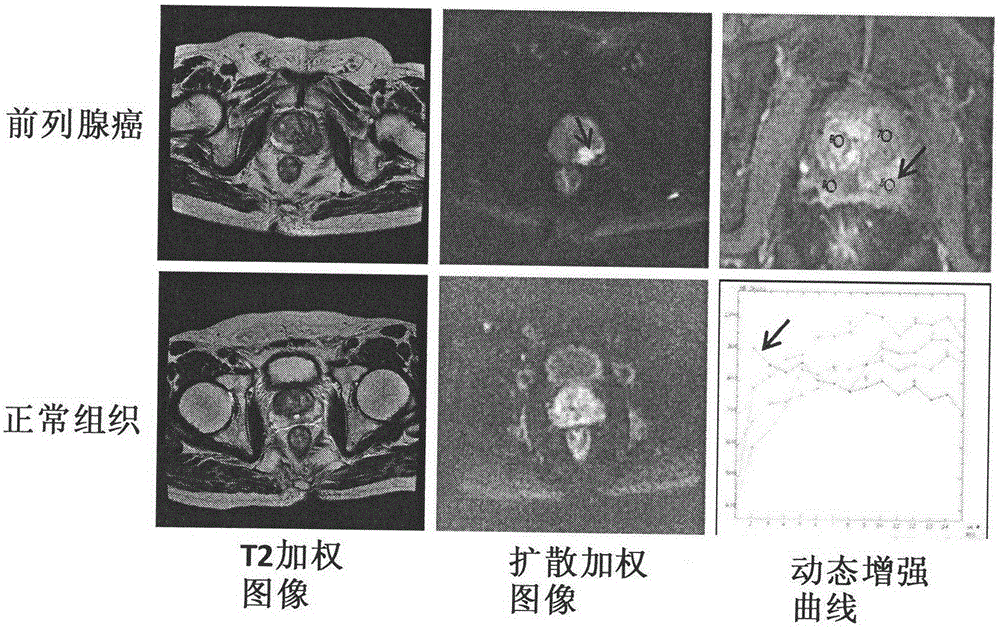
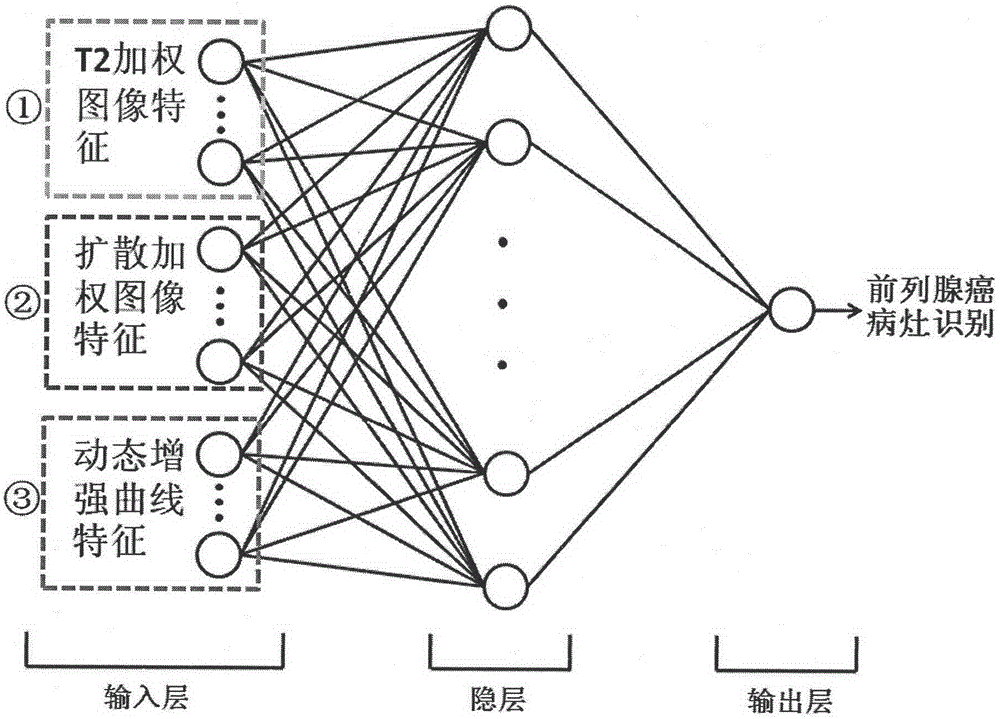
The invention discloses a multi-parameter magnetic resonance image based prostate cancer computer auxiliary identification system and method. The multi-parameter magnetic resonance image based prostate cancer computer auxiliary identification system comprises three portions of an image preprocessing module, a parameter processing module and a prediction and evaluation module. According to the multi-parameter magnetic resonance image based prostate cancer computer auxiliary identification system, the characteristics of a T2 weighted image, a diffusion weighted image and a dynamic enhanced image are comprehensively utilized and the purpose of the identification of the prostate cancer focus is achieved through an artificial neural network structure; the ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic) area under curve of the peripheral zone of prostate of the system is 0.931 and the identification accuracy is 0.887 and the ROC area under curve in the central gland is 0.909 and the identification accuracy is 0.915 through a test; the image information obtained through the conventional magnetic resonance imaging scanning sequence scanning sequence can be well integrated, quantitative parameters in the images are utilized in a maximum mode, and the identification result of the prostate cancer is objectively provided; the operation is simple and convenient, the reference can be intuitively provided for doctors, and the important basis is provided for the subsequent diagnosis scheme.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Mr spectroscopy system and method for diagnosing painful and non-painful intervertebral discs
ActiveUS20110087087A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumDisplay device
An MR Spectroscopy (MRS) system and approach is provided for diagnosing painful and non-painful discs in chronic, severe low back pain patients (DDD-MRS). A DDD-MRS pulse sequence generates and acquires DDD-MRS spectra within intervertebral disc nuclei for later signal processing & diagnostic analysis. An interfacing DDD-MRS signal processor receives output signals of the DDD-MRS spectra acquired and is configured to optimize signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) by an automated system that selectively conducts optimal channel selection, phase and frequency correction, and frame editing as appropriate for a given acquisition series. A diagnostic processor calculates a diagnostic value for the disc based upon a weighted factor set of criteria that uses MRS data extracted from the acquired and processed MRS spectra along regions associated with multiple chemicals that have been correlated to painful vs. non-painful discs. A diagnostic display provides a scaled, color coded legend and indication of results for each disc analyzed as an overlay onto a mid-sagittal T2-weighted MRI image of the lumbar spine for the patient being diagnosed. Clinical application of the embodiments provides a non-invasive, objective, pain-free, reliable approach for diagnosing painful vs. non-painful discs by simply extending and enhancing the utility of otherwise standard MRI exams of the lumbar spine.
Owner:ACLARION INC +1
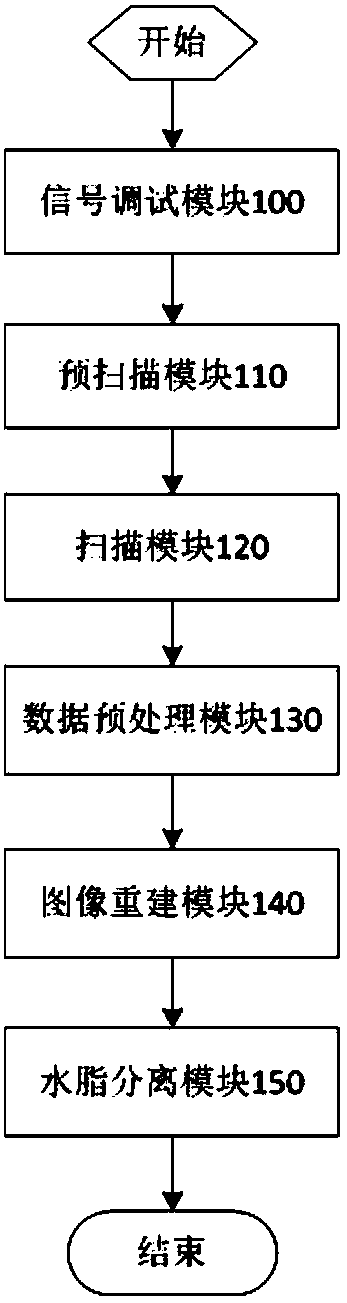
Synchronous acquisition and calibration method for three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN107271937AIncrease optionalityReduce dependenceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsReconstruction methodT2 weighted
The invention discloses a synchronous acquisition and calibration method for three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted magnetic resonance imaging. A three-dimensional / two-dimensional fast multi-echo water-fat separation sequence and a signal debugging method, a pre-scanning method, a scanning method, a data preprocessing method and an image reconstruction method thereof can obtain a water-fat separation image and T2 weighted (T1 weighted or PD weighted) image by one-time scanning. The three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted synchronous scanning and calibration method can maximize the number of images obtained in a single scan, including, an in-phase image, a reverse-phase image, a fat image, a fat-pressed image water, a conventional T2 weighted (or T1 weighted / PD weighted ) image, and a T2weighted images, significantly shortens clinical scanning time and increases the selectivity of clinical scanning schemes, and has less reliance on the hardware performance of an MRI system.
Owner:南京拓谱医疗科技有限公司
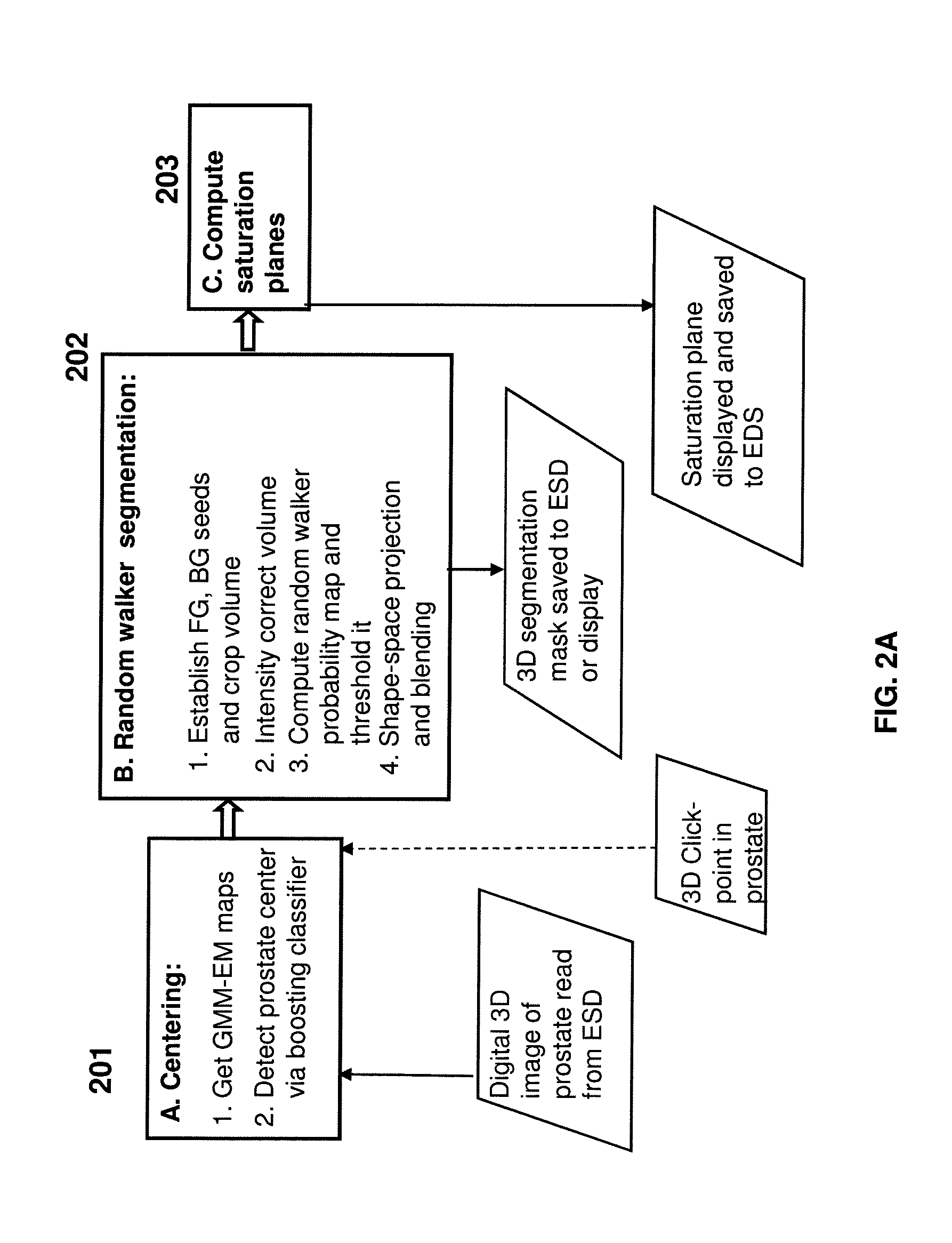
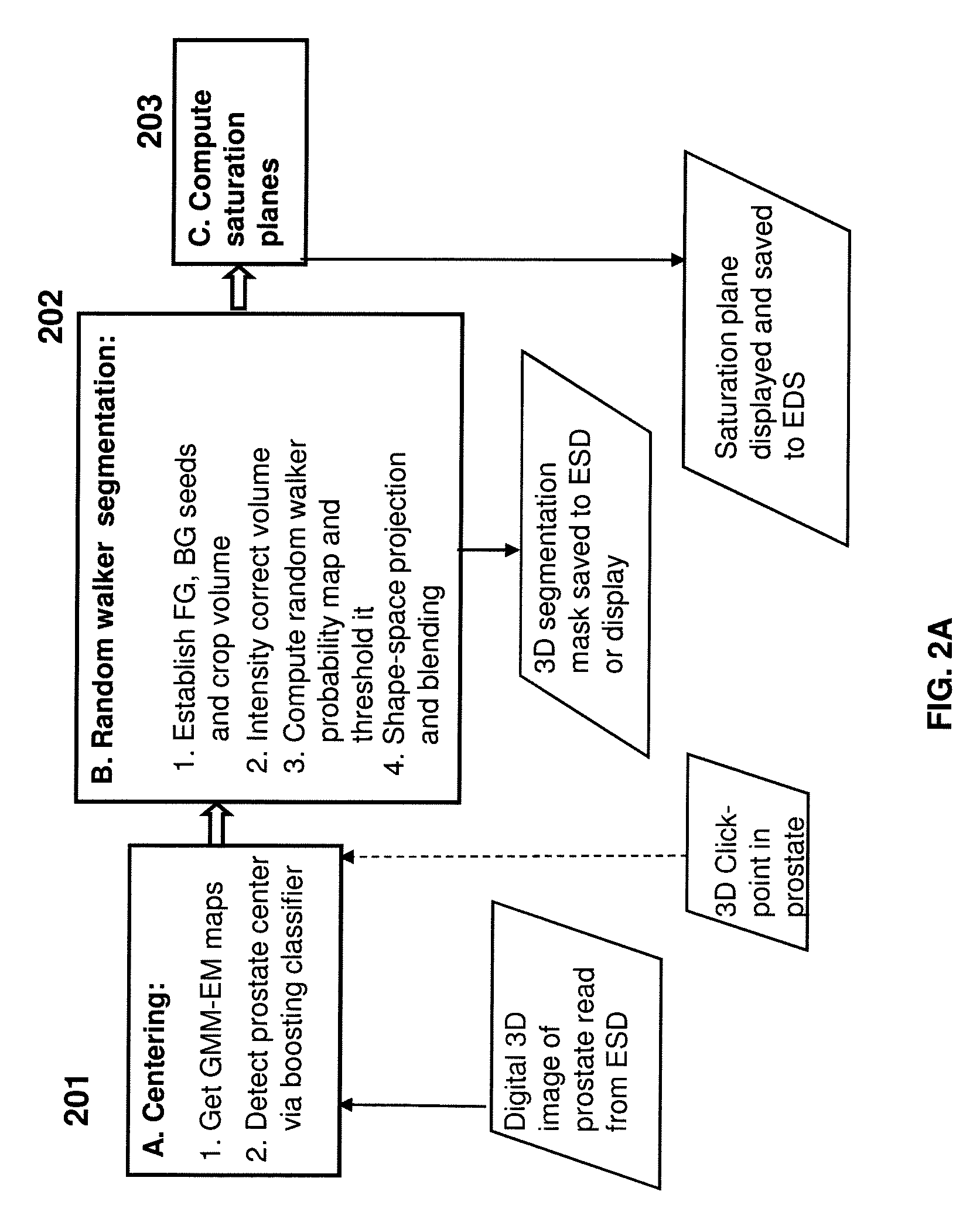
Systems and Method for Automatic Prostate Localization in MR Images Using Random Walker Segmentation Initialized Via Boosted Classifiers
Automatic prostate localization in T2-weighted MR images facilitate labor-intensive cancer imaging techniques. Methods and systems to accurately segment the prostate gland in MR images are provided and address large variations in prostate anatomy and disease, intensity inhomogeneities, and artifacts induced by endorectal coils. A center of the prostate is automatically detected with a boosted classifier trained on intensity based multi-level Gaussian Mixture Model Expectation Maximization (GMM-EM) segmentations of the raw MR images. A shape model is used in conjunction with Multi-Label Random Walker (MLRW) to constrain the seeding process within MLRW.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
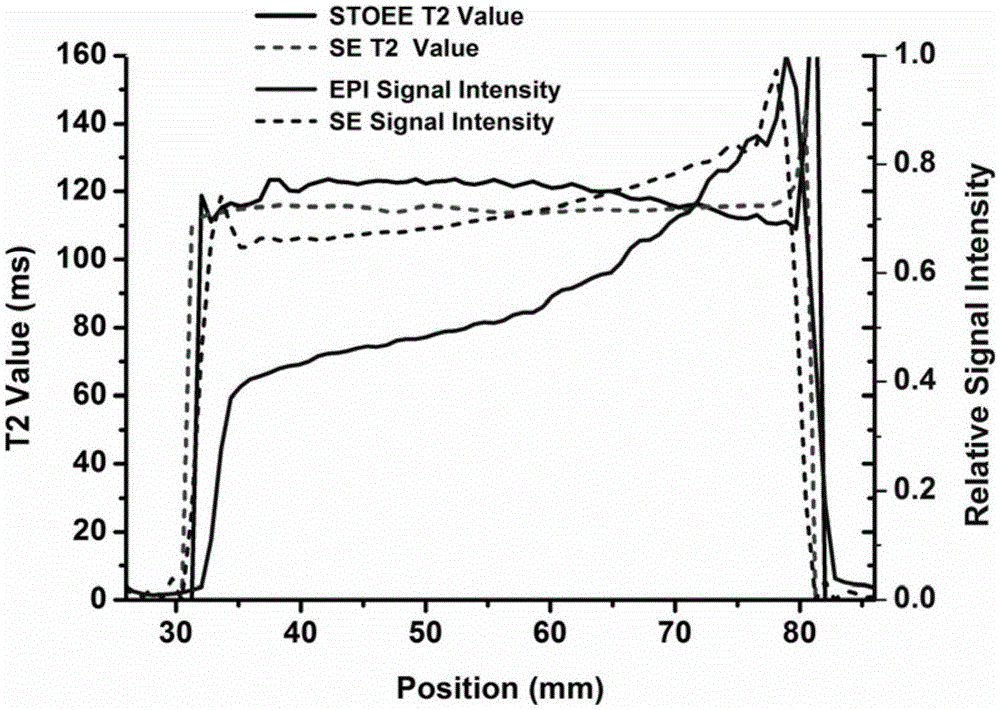
Method for single sweep quantitative magnetic resonance T2 imaging based on overlapping echoes
The invention provides a method for single sweep quantitative magnetic resonance T2 imaging based on overlapping echoes and relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method. Echo signals of two different evolution time are generated by adding two excitation pulses with the same deflection angle in single sweep. Though the evolution time of the two echo signals is different, the T2 weighing of the two echo signals is caused to be different, the two echo signals come from the same imaging slice, the two echo signals can be separated through prior knowledge between the two echo signals, namely the structural similarity in combination with edge sparsity, and the two echo signals are separated by utilizing a separation algorithm corresponding to sparse conversion matching; and finally the two signals obtained through separation undergo T2 calcualtion to obtain a quantitative T2 image. The quantitative T2 imaging in single sweep is acquired, the time of quantitative T2 imaging is reduced from the second grade and even minute grade to the ms grade, and the quality of the acquired T2 image can be equivalent to the quality of an image obtained in an EPI sequence in conventional single sweep.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
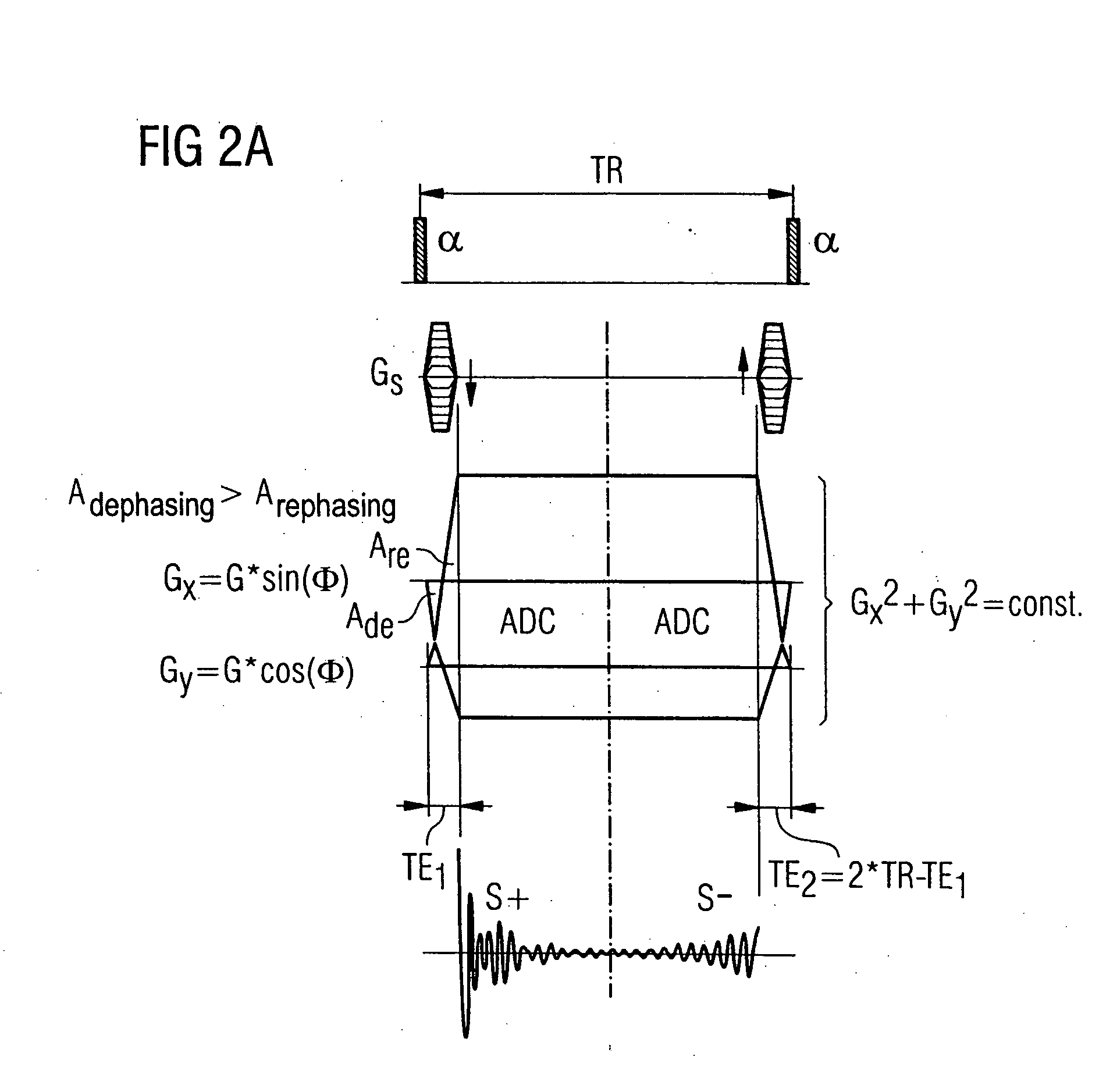
Magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method for representation of tissue with very short T2 relaxation time
InactiveUS20060036154A1Short T relaxation timeIncrease contrastMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceT2 weighted
In a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method for determination of T2-weighted images of tissue with short T2 time, in the framework of a steady-state free precession sequence with non-slice-selective RF excitation pulses and projection-reconstruction methods, in each sequence repetition a first steady-state is read out in the form of a half echo and a second steady-state signal is read out in the form of a further half echo with very short echo times TE1 and TE2=2TR−TE1, and are combined by weighted addition such that an MRT image of tissue with very short T2 time is obtained with the sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
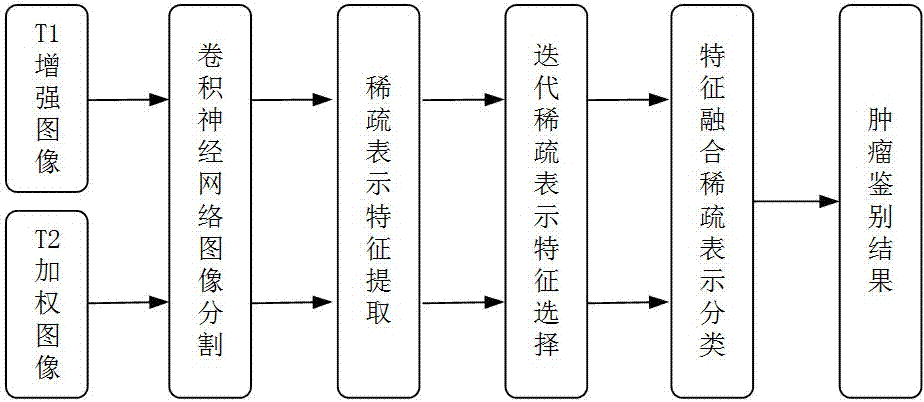
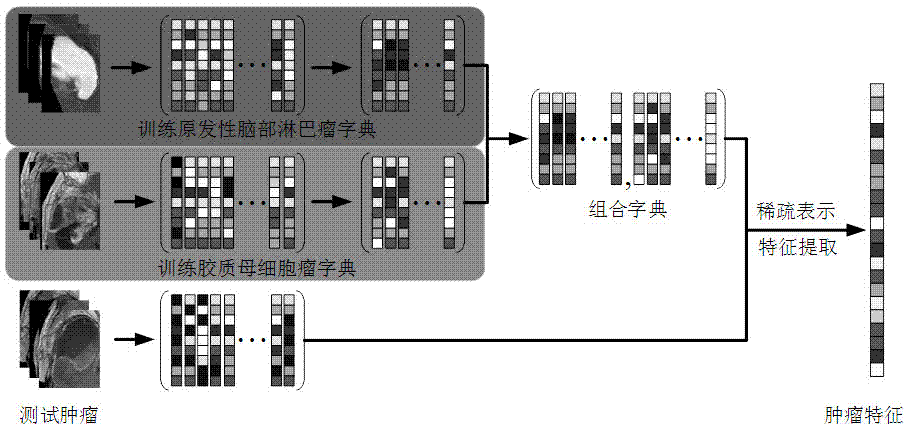
Identification method of primary central nervous system lymphoma and glioblastoma based on sparse representation system
ActiveCN107016395AEliminate redundancyReduce computationImage enhancementImage analysisDictionary learningGlioblastoma
The invention belongs to the technical field of computer auxiliary diagnosis, and specifically relates to an identification method of primary central nervous system lymphoma and glioblastoma based on a sparse representation system. The method includes: segmenting T1 enhanced and T2 weighted MRI image tumor regions by employing an image segmentation method based on a convolutional neural network; then designing a dictionary learning and sparse representation method, and extracting texture characteristics of the tumor regions; selecting some characteristics with high stability and high resolution for tumor identification by employing an iterative sparse representation characteristic selection method in order to reduce the characteristic redundancy and improve the tumor identification efficiency; and finally establishing a combined sparse representation classification model containing two modals of T1 enhanced or T2 weighted based on the thought of eigenstate fusion in order to improve the tumor identification precision. According to the method, high tumor identification precision can be obtained, manual operation for extraction of identification parameters is avoided, the robustness is high, and the method can be applied to clinic identification of primary central nervous system lymphoma and glioblastoma.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
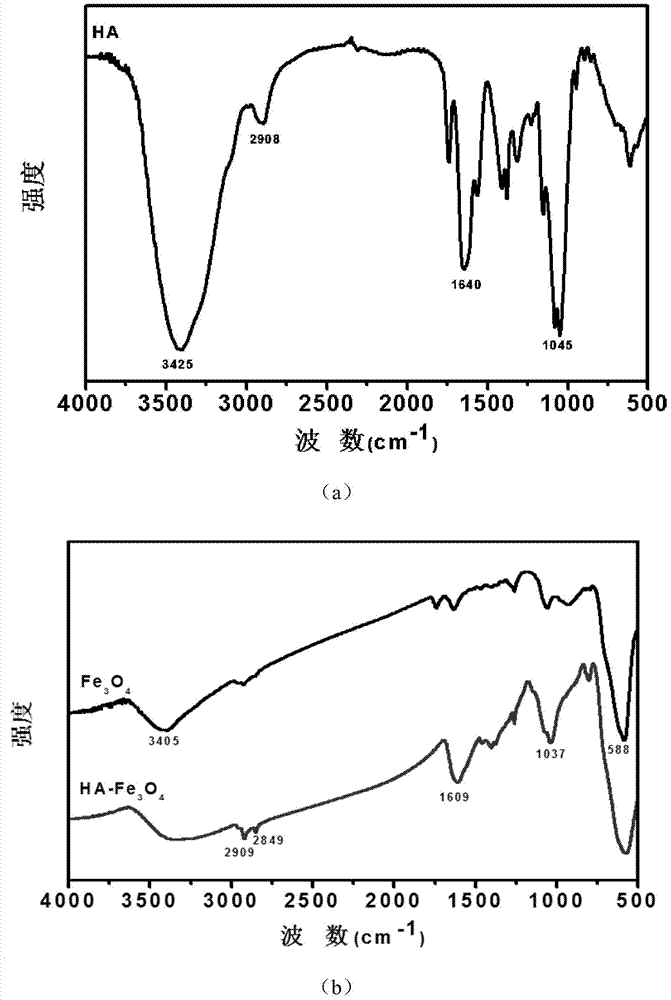
Tumor-targeted T1-T2 double nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104758956ASuperparamagneticHas a relaxation-enhancing effectEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsTumor targetFerrous salts
The invention relates to a tumor-targeted T1-T2 double nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent and a preparation method and an application thereof. The contrast agent comprises hyaluronic acid-coated ferroferric oxide composite magnetic nanoparticles, wherein the molecular formula of hyaluronic acid is as shown in the specification; n is an integer of 17-290. The preparation method of the contrast agent comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving hyaluronic acid into deionized water, introducing a gas, and heating to obtain a reaction system A; (2) dissolving ferric salt and ferrous salt into a strong acid to obtain a solution B; (3) injecting the solution B into the reaction system A, adjusting the pH to be alkaline, and then refluxing at a high temperature to obtain a reaction system C; and (4) cooling a reaction system C to a room temperature, and dialyzing to obtain the contrast agent. The invention further provides an application of the contrast agent in T1 and T2 weighted imaging in in-vivo and in-vitro nuclear magnetic resonance. The contrast agent provided by the invention has superparamagnetism and outstanding T1 and T2 relaxation enhancement effects, and is suitable for being used as a T1-T2 double nuclear magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
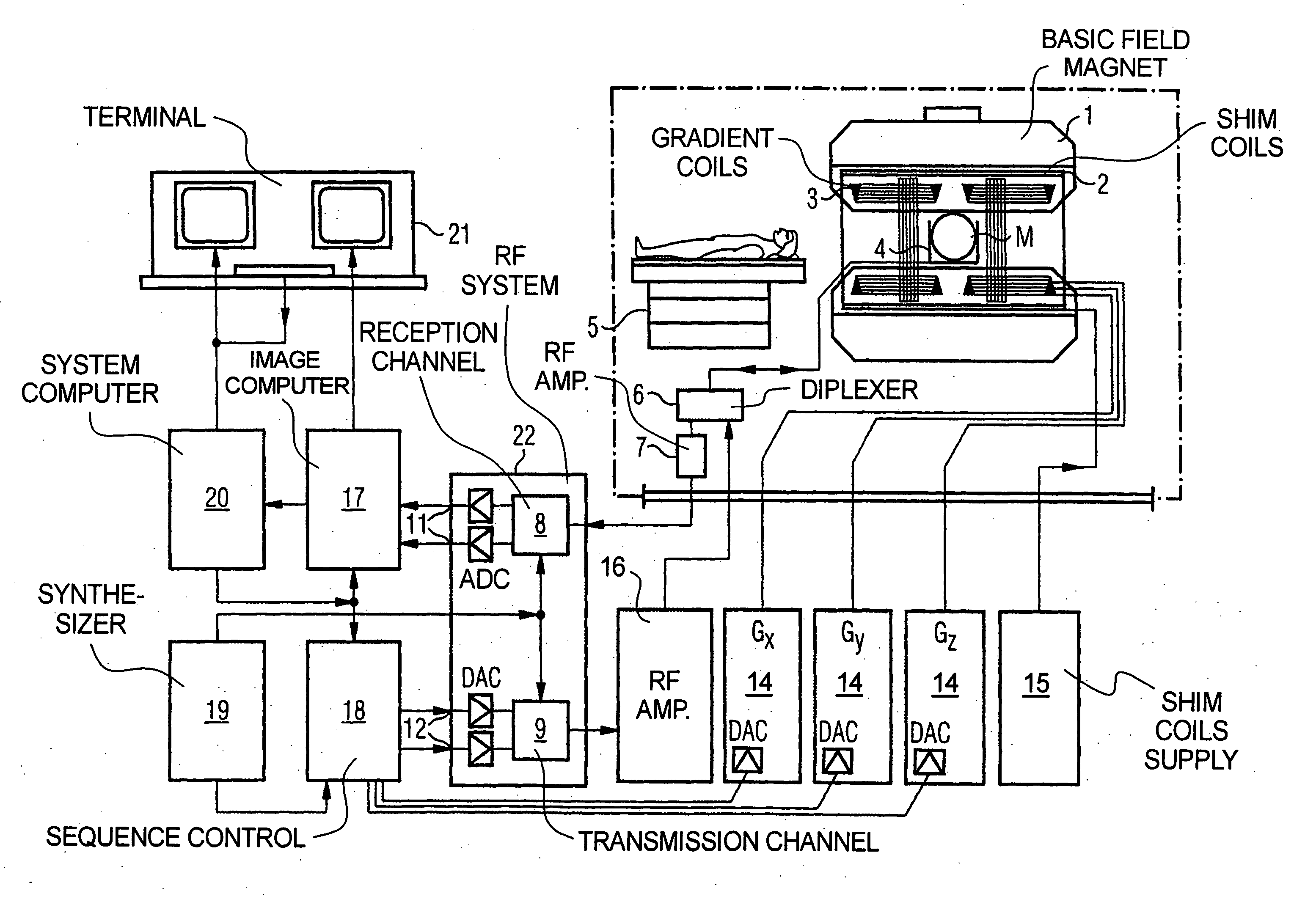
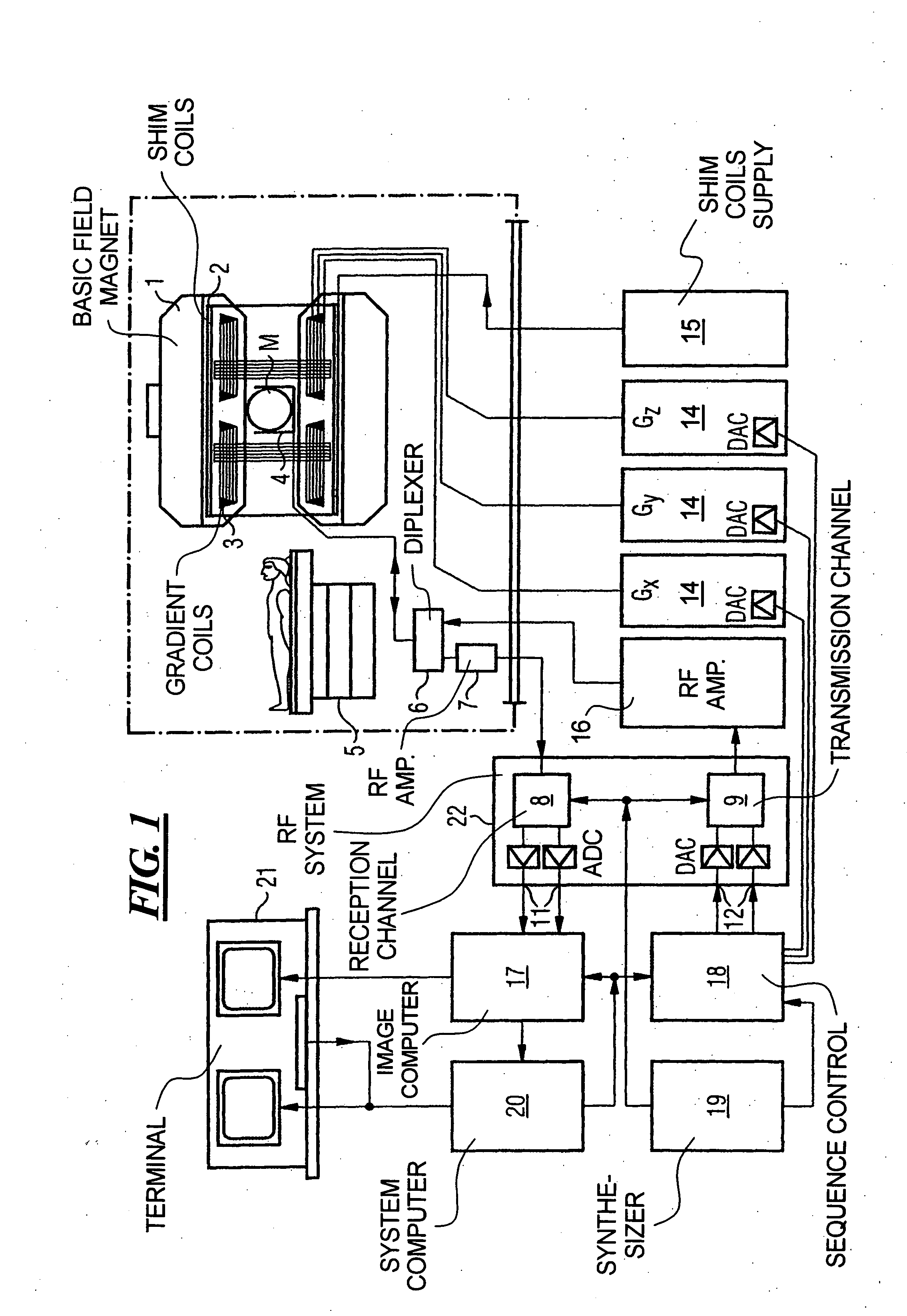
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS7015696B2Accurate calculationAccurate imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsProton magnetic resonanceT2 weighted
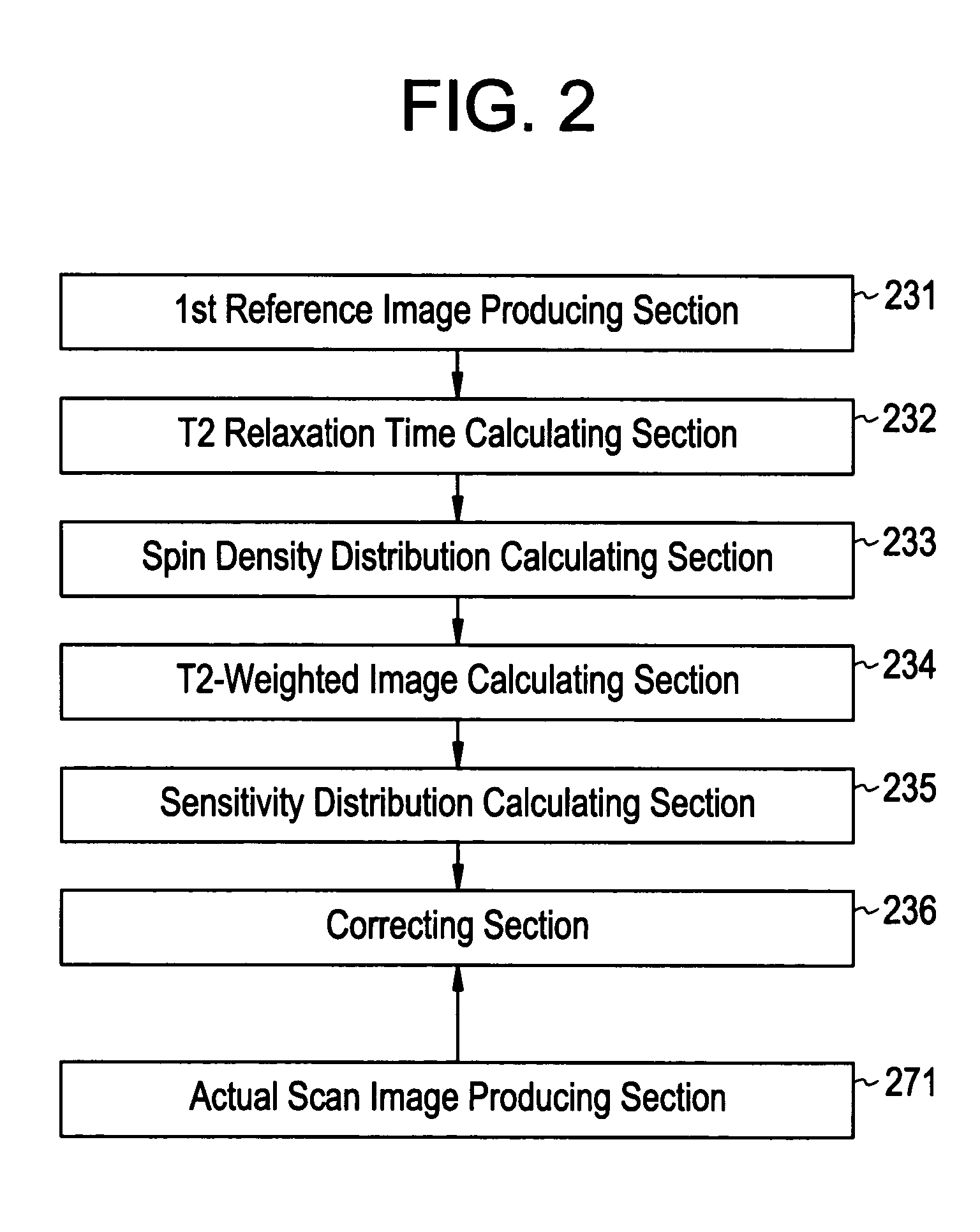
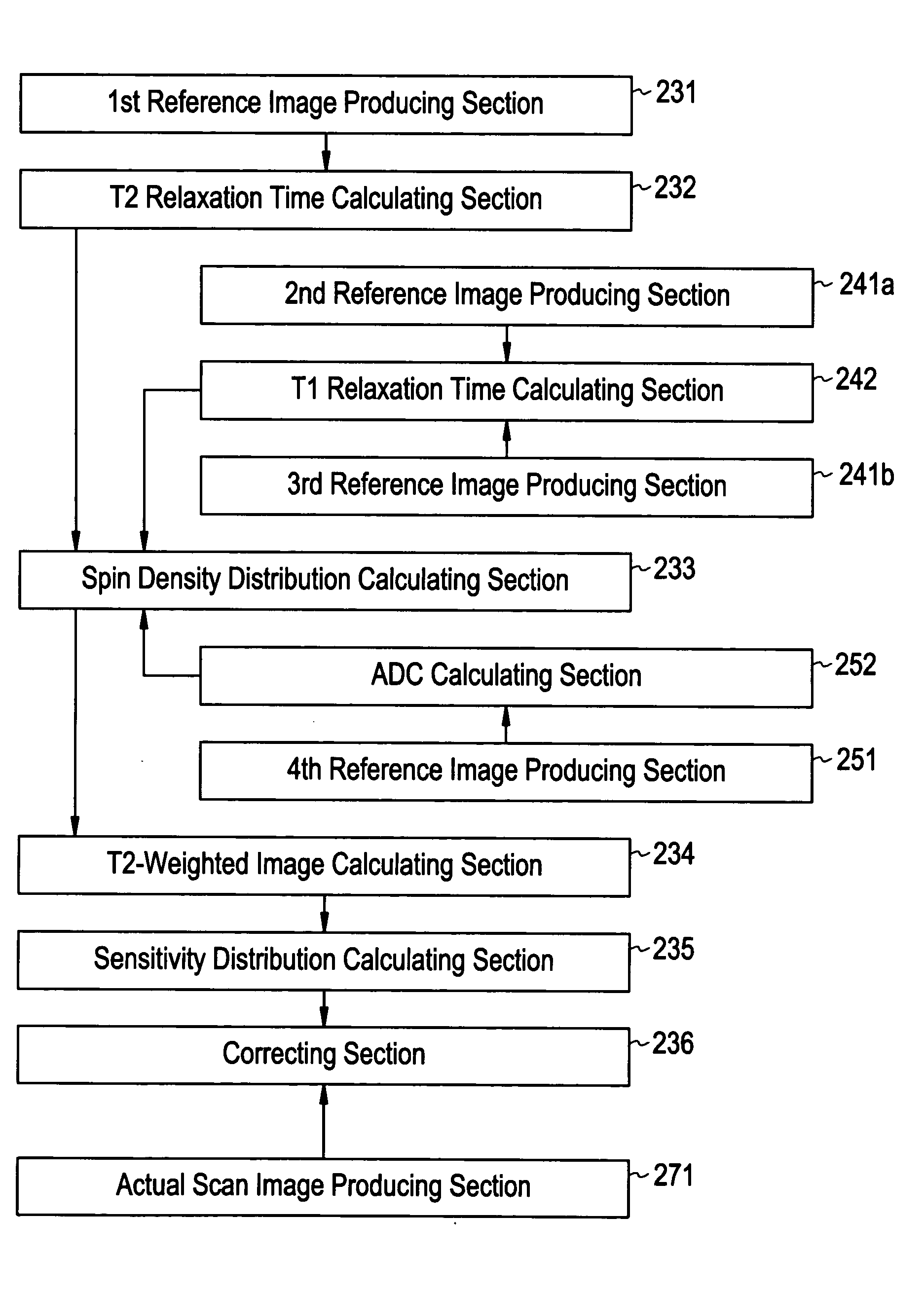
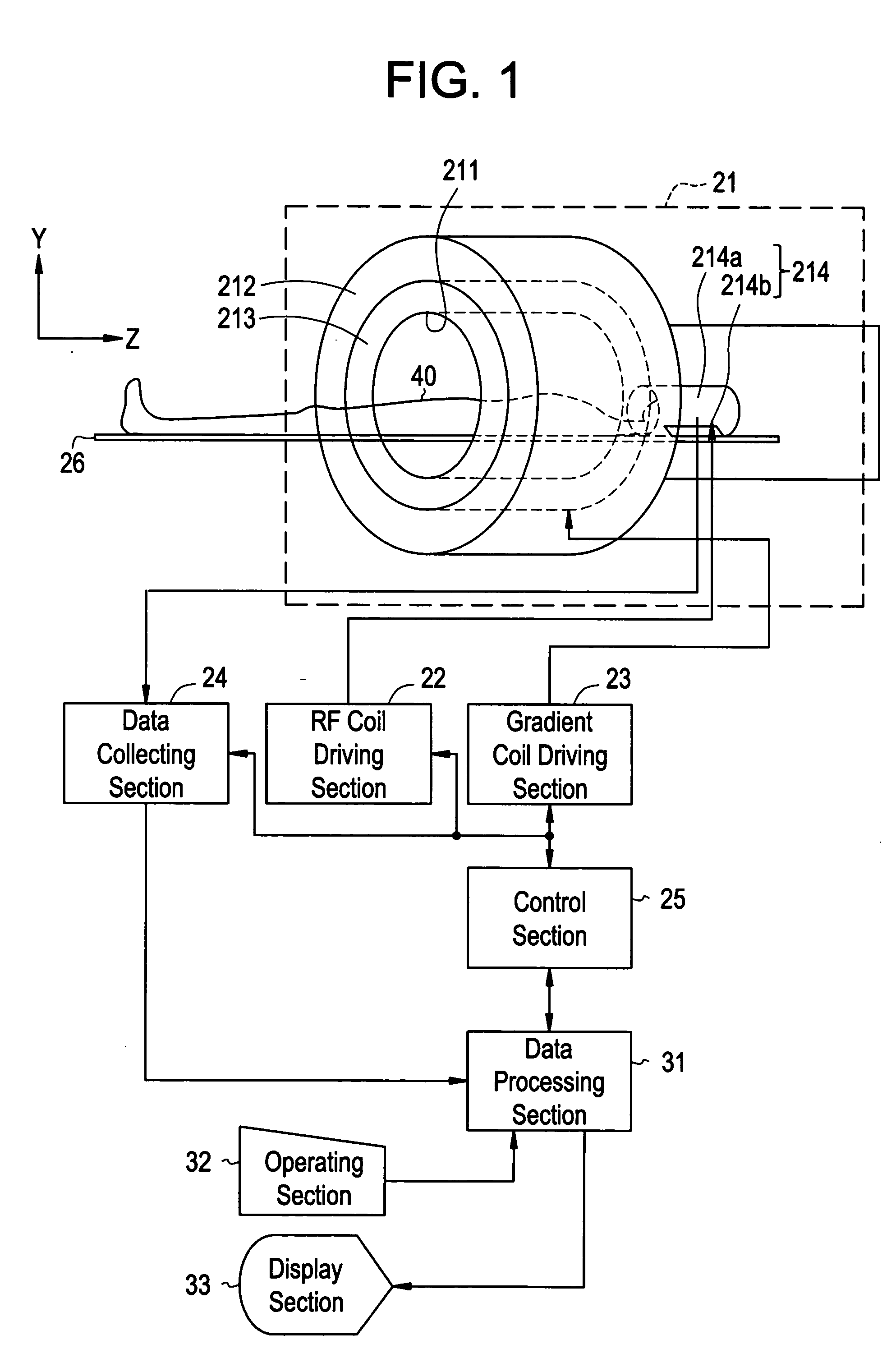
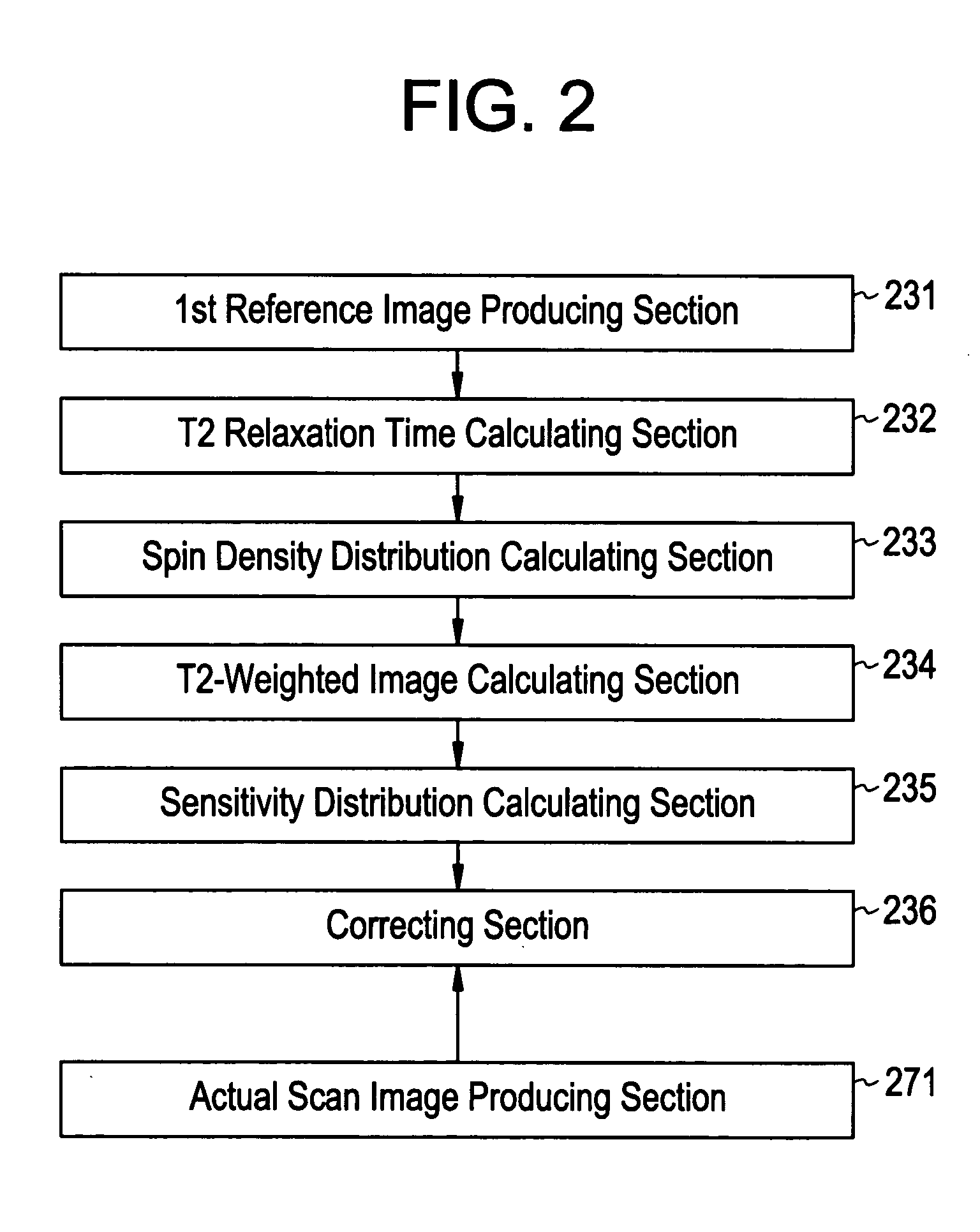
A method for calculating a sensitivity distribution of a receive coil and taking a tomographic image of a subject, based on magnetic resonance signals received by a surface coil in an imaging sequence with a plurality of different echo times TE1 and TE2 in a reference scan, a plurality of reference images are produced by a first reference image producing section; and based on the plurality of reference images, a T2 relaxation time is calculated by a T2 relaxation time calculating section. Then, based on the calculated T2 relaxation time, a T2-weighted image at the echo time TE2 is calculated by a T2-weighted image calculating section, and thereafter, based on the reference image and T2-weighted image at the echo time TE2, a sensitivity distribution is calculated by a sensitivity distribution calculating section. Based on the sensitivity distribution, a tomographic image by an actual scan is corrected by a correcting section.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
MRI method and MRI apparatus
InactiveCN1618399AReduce signal strengthEasy to calculate contrastDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsT2 weightedPulse sequence
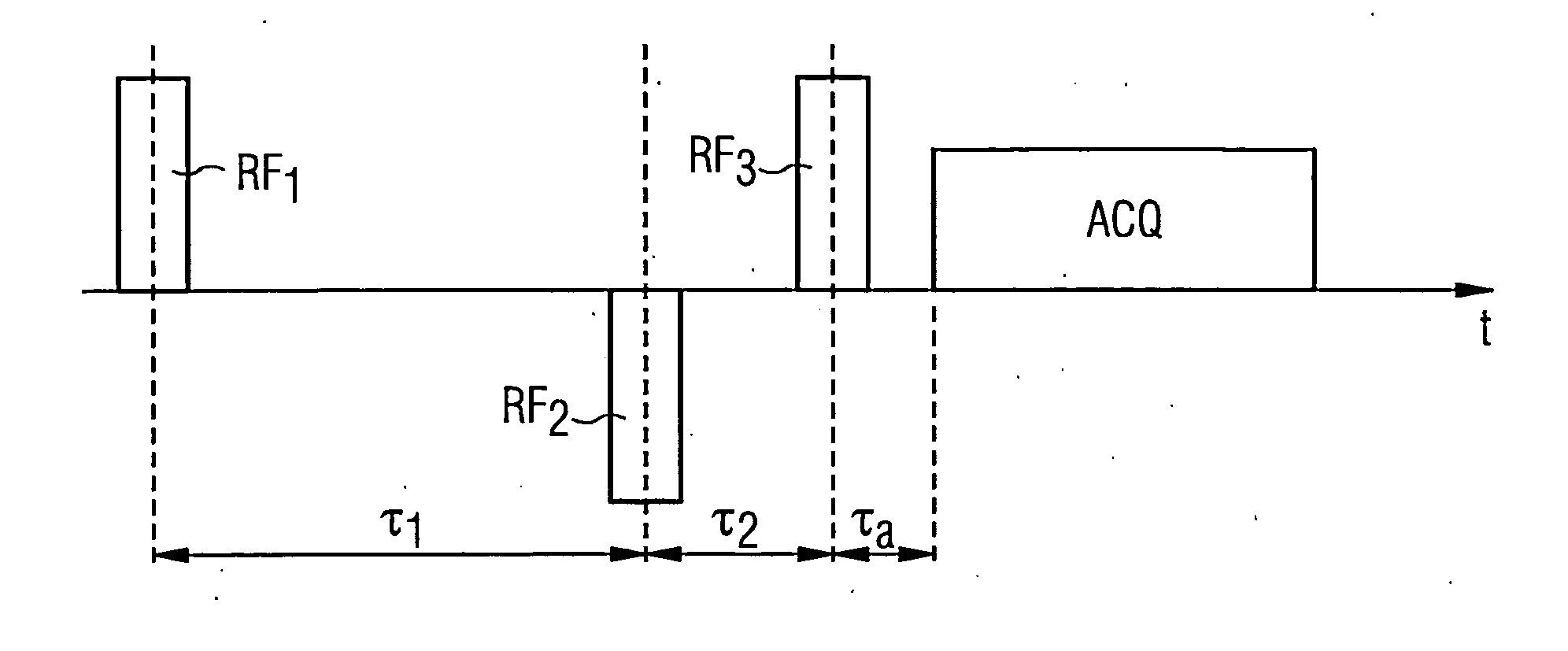
It is an object of the present invention to simultaneously provide images with a desired new contrast, eg T1 weighted and T2 weighted images. (1) Provide 4 pulse sequence databases (PSD) (step 11). The provided PSD is: the first image PSD (TE, TR) = (TE1, TR1); the second image PSD (TE, TR) = (TE1, TR2); the third image PSD (TE, TR) = ( TE2, TR1); and the fourth image PSD(TE, TR)=(TE2, TR2), where TE1<TE2 and TR1<TR2. (2) Drive the magnet system of the MRI apparatus based on the 4 PSDs, and collect MR signals (steps 12 to 15). (3) Generate 4 MR images S1 to S4 from the MR signals collected from the PSD (step 16). (4) Calculate the difference (S3-S4)-(S1-S2) between the images to obtain T1-weighted and T2-weighted images based on the images corresponding to the calculated difference.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20050134266A1Accurate calculationAccurate imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsT2 weightedSurface coil
A method for calculating a sensitivity distribution of a receive coil and taking a tomographic image of a subject, based on magnetic resonance signals received by a surface coil in an imaging sequence with a plurality of different echo times TE1 and TE2 in a reference scan, a plurality of reference images are produced by a first reference image producing section; and based on the plurality of reference images, a T2 relaxation time is calculated by a T2 relaxation time calculating section. Then, based on the calculated T2 relaxation time, a T2-weighted image at the echo time TE2 is calculated by a T2-weighted image calculating section, and thereafter, based on the reference image and T2-weighted image at the echo time TE2, a sensitivity distribution is calculated by a sensitivity distribution calculating section. Based on the sensitivity distribution, a tomographic image by an actual scan is corrected by a correcting section.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
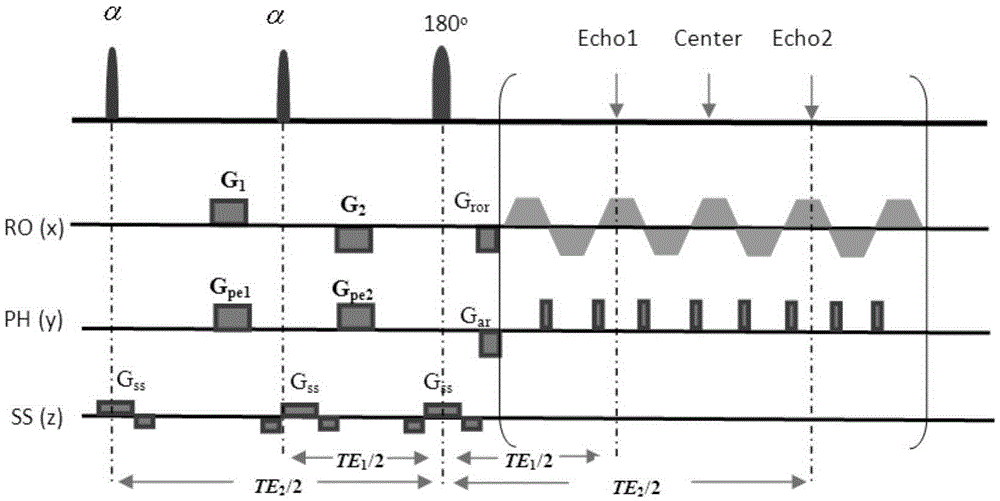
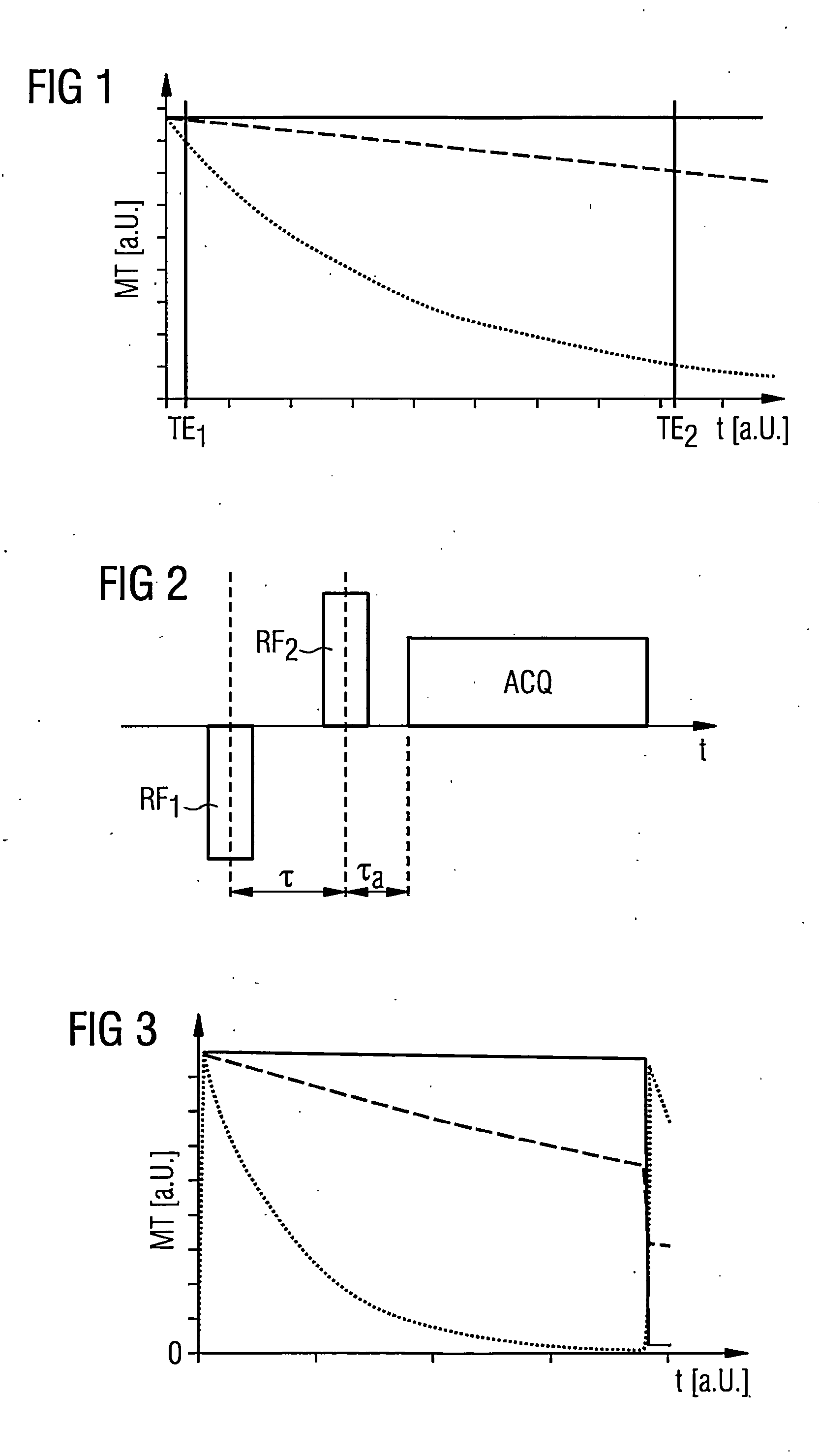
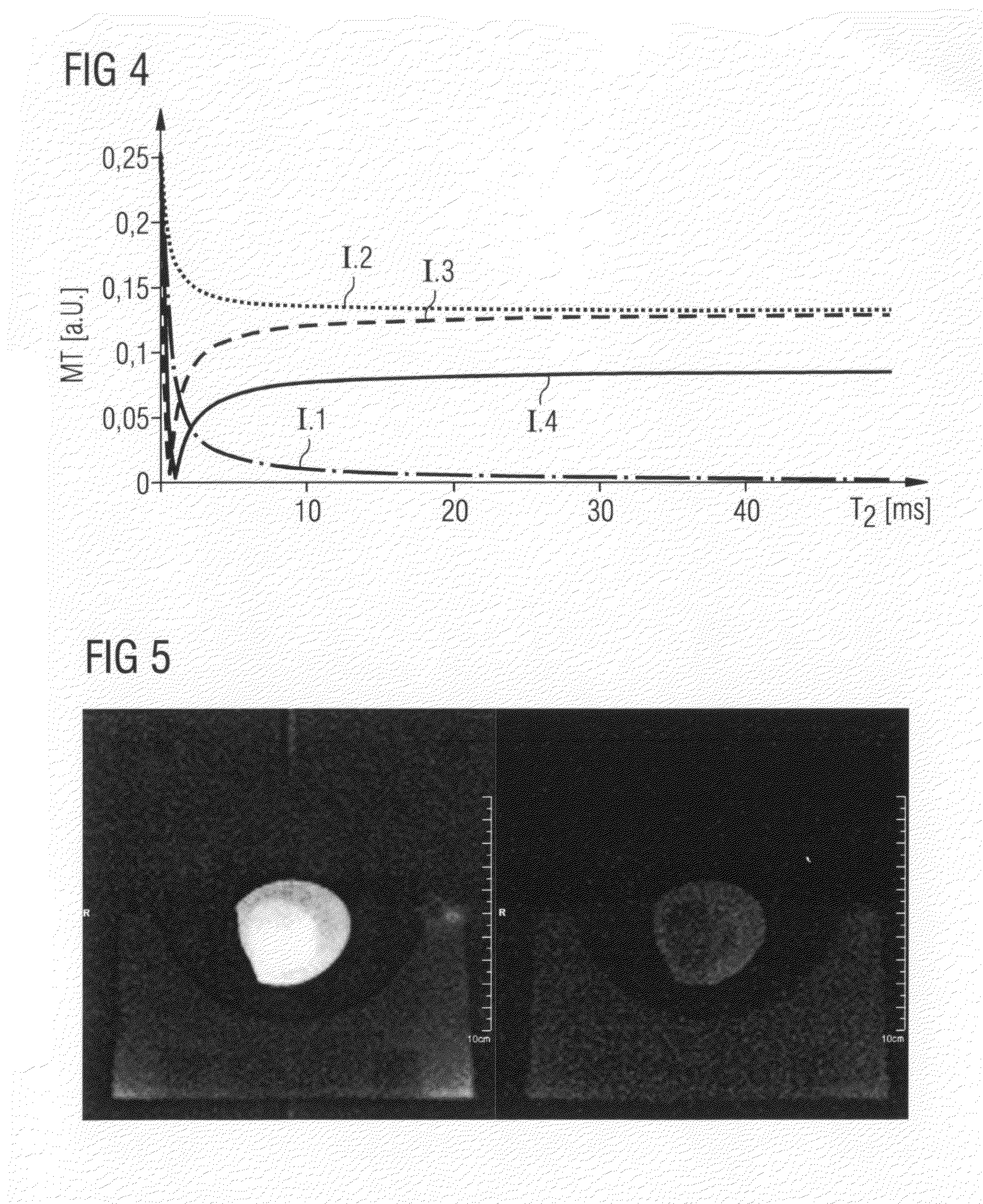
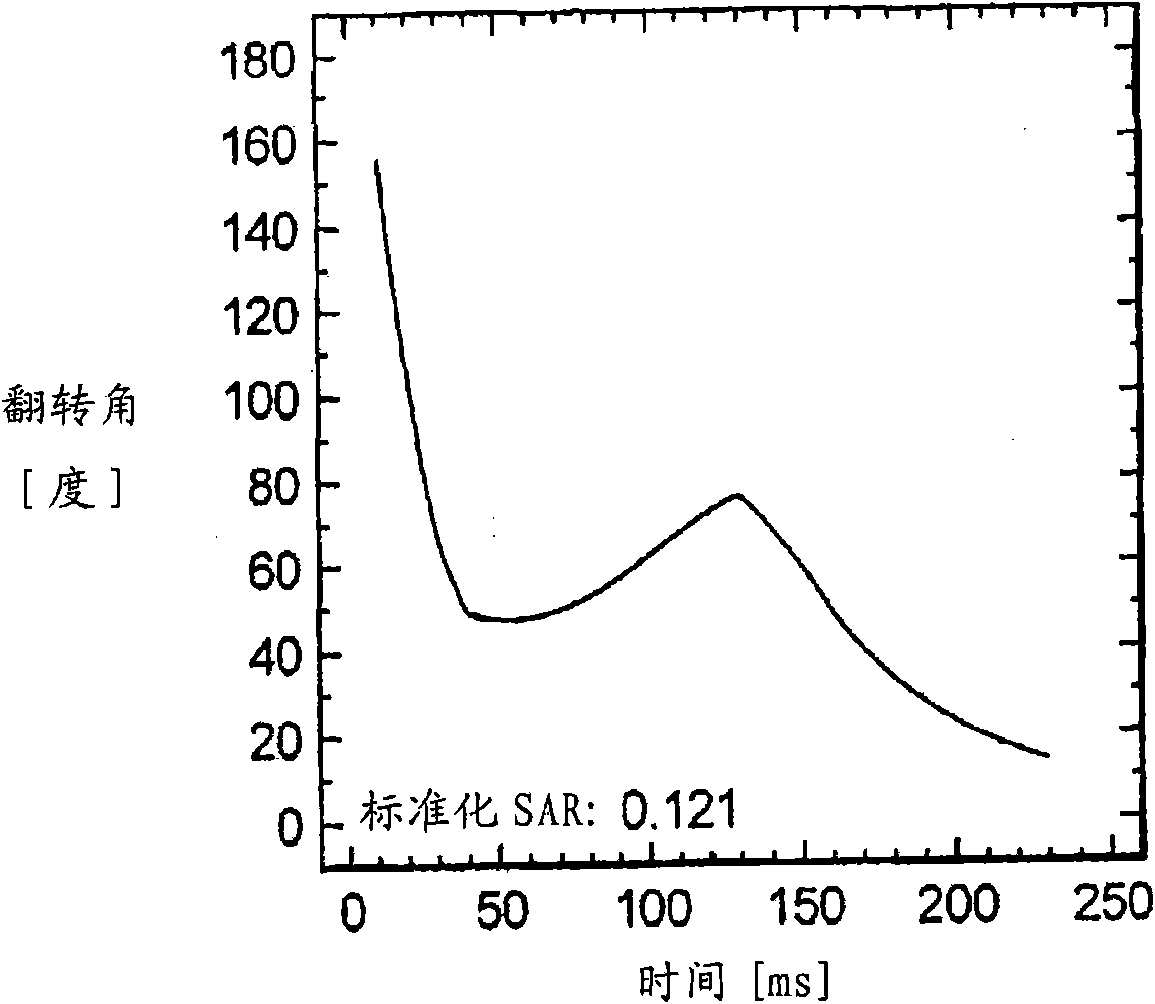
Magnetic resonance system, operating method and control device to generate t2-weighted images using a pulse sequence with very short echo times
InactiveUS20130169273A1Suppressed quickly and wellSuppressed quickly and effectivelyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsProton magnetic resonanceResonance
In a method to control a magnetic resonance system to generate magnetic resonance exposures of an examination subject, a first magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse with a pulse length of at most 50 μs is initially emitted in a volume region of the examination subject. At least one second magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse, whose phase is essentially rotated by 180° relative to the first magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse, with a pulse length of at most 50 μs, is emitted in the same volume region of the examination subject in a predetermined time interval immediately after the first magnetic resonance radio-frequency pulse. An acquisition of raw data from the volume region of the examination subject then takes place. Furthermore, a control device for operating a magnetic resonance system as well as a magnetic resonance system with such a control device to implement such a method, are described.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for generating different weighted images from the same magnetic resonance echo signal evolution
InactiveCN101653360ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPulse sequenceRadio frequency
In a method and an apparatus for acquiring magnetic resonance data, a region of a subject is exposed to a spin echo magnetic resonance pulse sequence that includes a refocusing radio-frequency pulse flip angle evolution that causes magnetic resonance signals to be emitted from the region with a signal evolution following each excitation radio-frequency pulse. The signal evolution is sampled to extract two or more sets of sampled data therefrom respectively with different contrast weightings of tissues in the region. The multiple sets of sampled data are made available as respective outputs ina form allowing multiple different images of the region to be generated therefrom, respectively with said different contrast weightings. For example, a spin density-weighted image and a T2-weighted image, or a T2-weighted image and a heavily T2-weighted image, thus can be generated by sampling from the same variable-flip-angle echo train.
Owner:SIEMENS AG +1
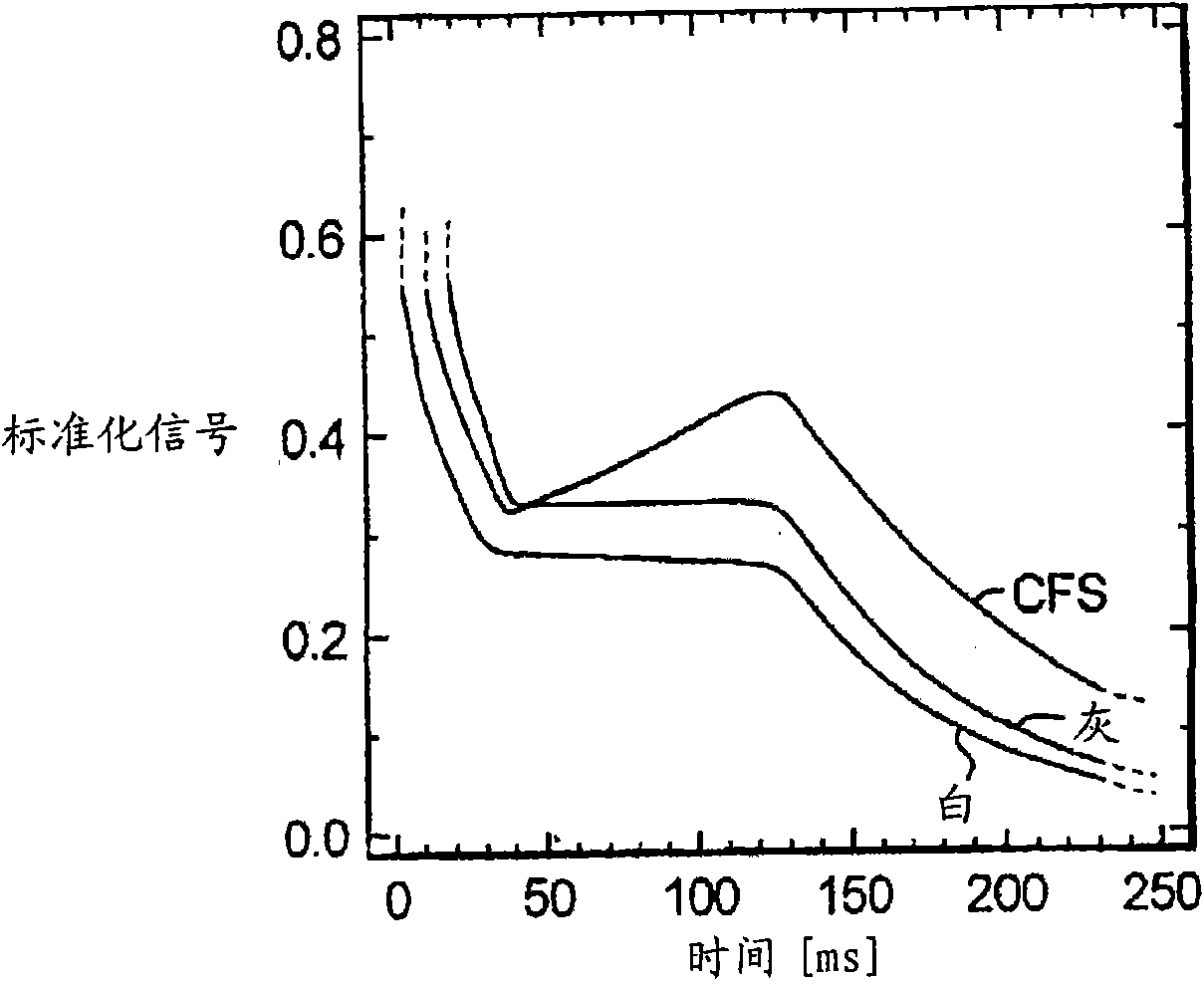
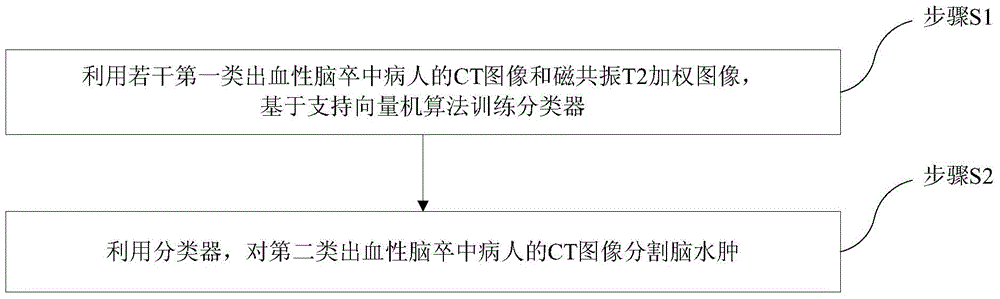
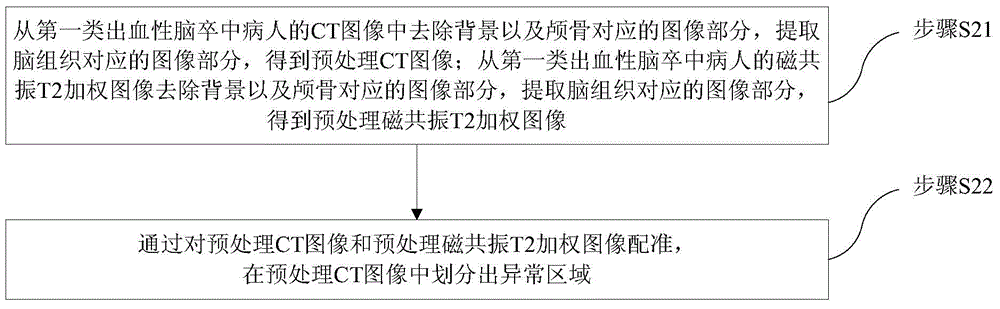
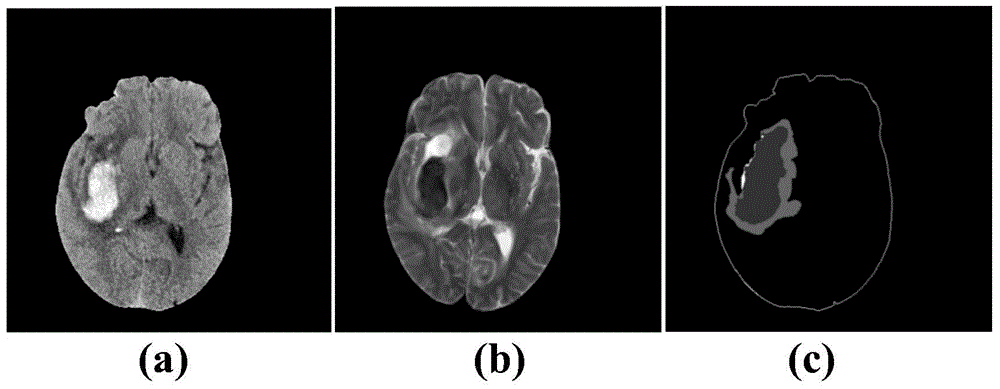
Encephaledema segmentation method and system based on support vector machine algorithm
The invention provides an encephaledema segmentation method and system based on a support vector machine algorithm, which are applied to the medical diagnosis technology field. The encephaledema segmentation method comprises steps of using a plurality of CT images and a plurality of magnetic resonance T2 weighted images of patients suffering from first type hemorrhagic cerebral apoplexy to train a classifier based on the support vector machine algorithm, using the classifier to perform encephaledema segmentation on CT images of patients suffering from the second type hemorrhagic cerebral apoplexy, wherein the patients suffering from the first type hemorrhagic cerebral apoplexy have the CT images and the magnetic resonance T2 weighted images; and the patients suffering from the second type hemorrhagic cerebral apoplexy only have the CT images and do not have the magnetic resonance T2 weighted images. The invention utilizes few patients suffering from the hemorrhagic cerebral apoplexy having the CT images and the magnetic resonance T2 images to perform combined modeling, through studying, establishes a classifier which can identify the encephaledema on the CT from the CT image characteristics, can be applied to the patients who suffer from the hemorrhagic cerebral apoplexy and have the CT images and have no magnetic resonance T2 weighted images, and obtains the higher encephaledema segmentation accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
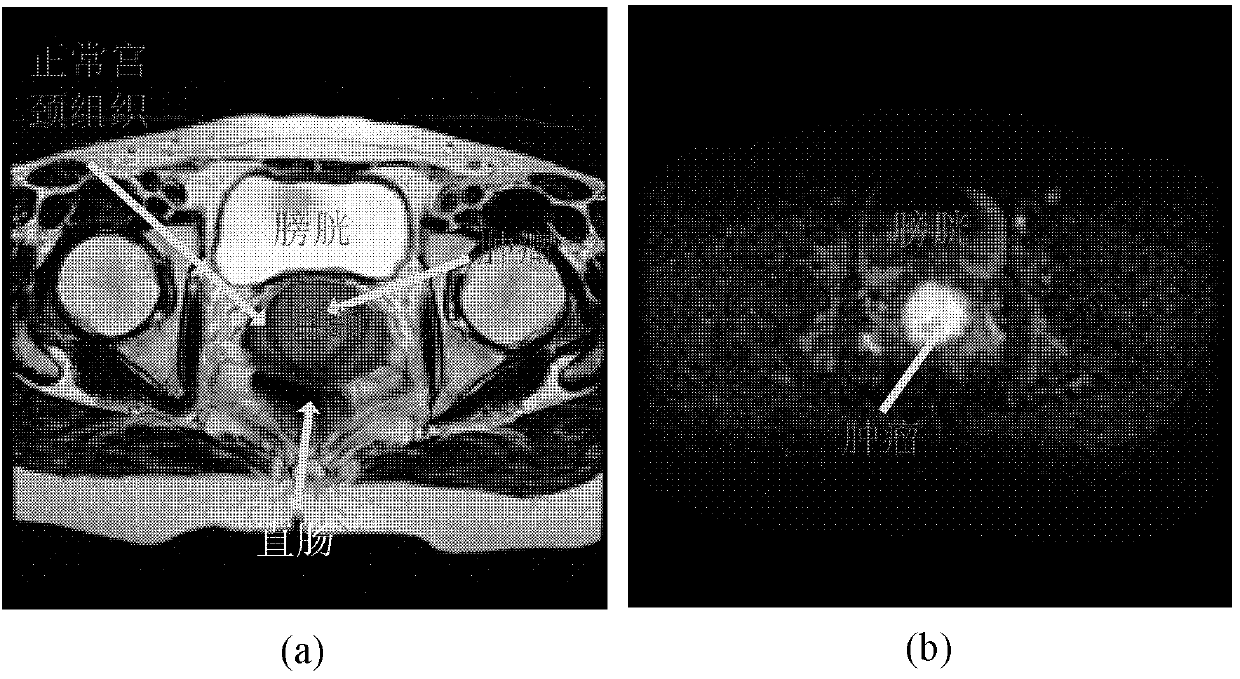
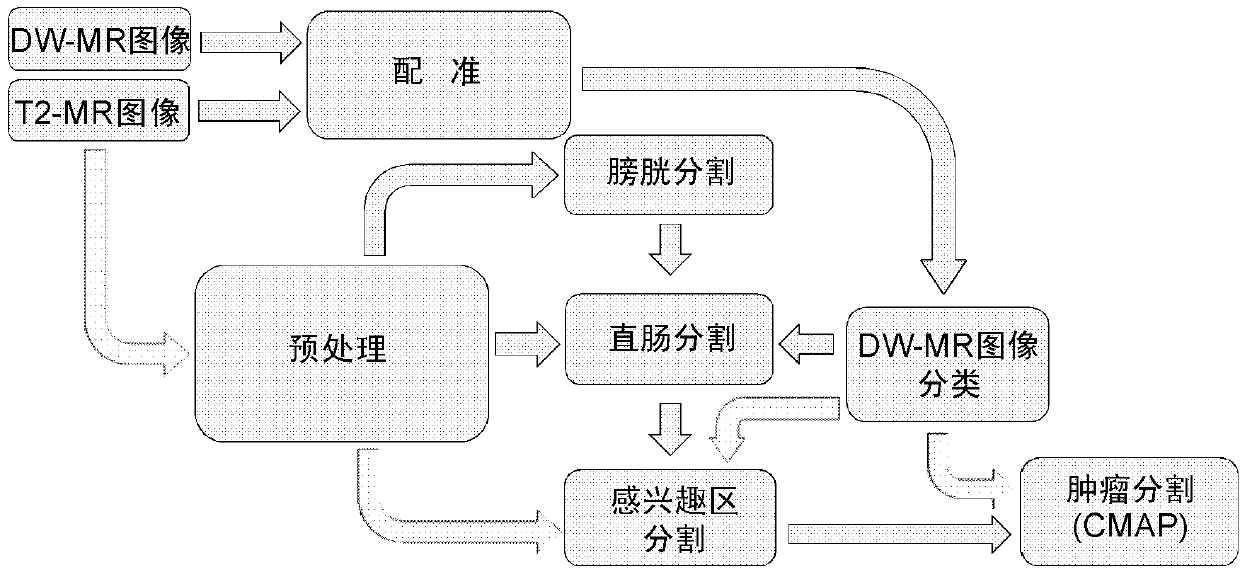
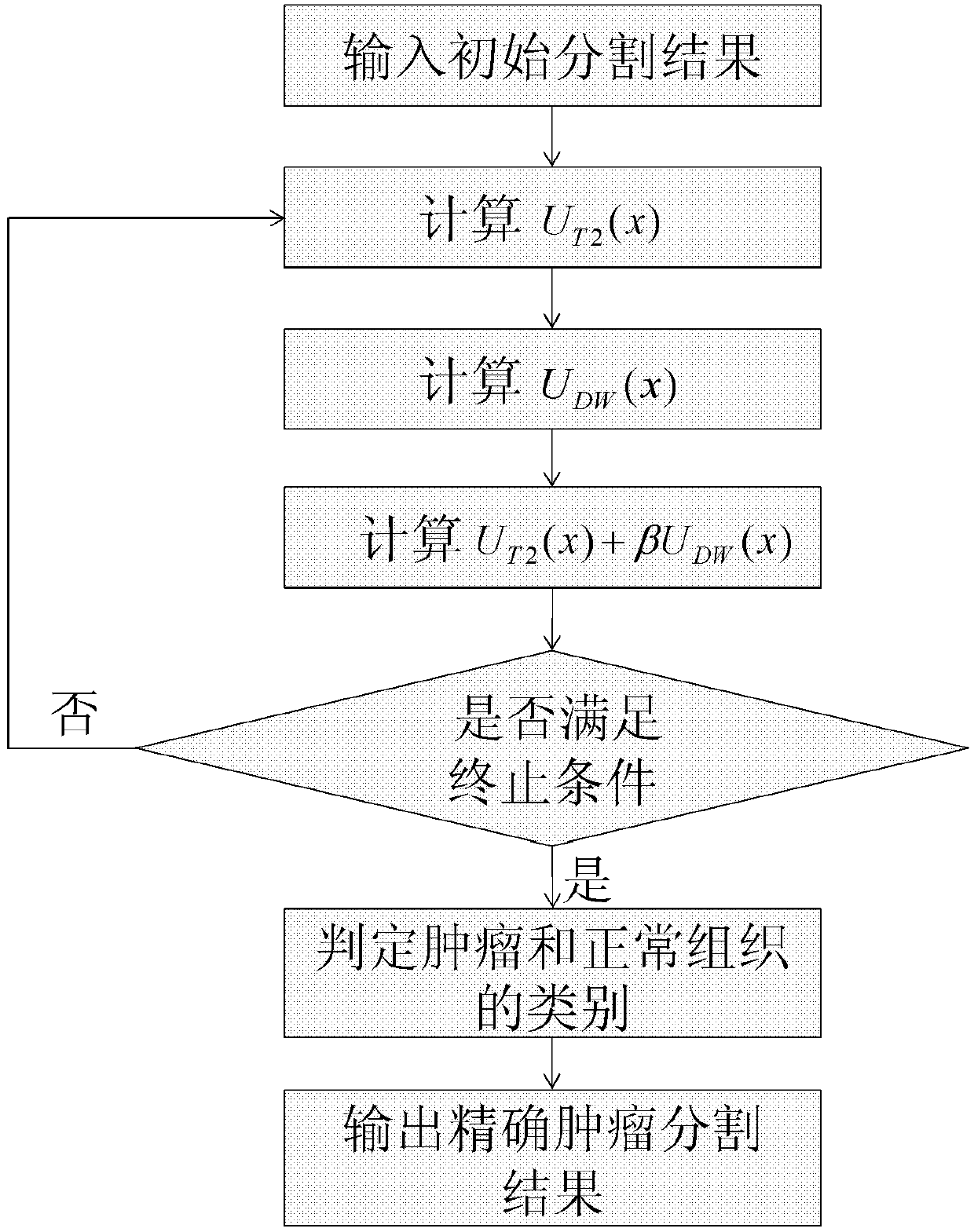
Cervical caner image automatic partition method based on T2-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and dispersion weighted (DW)-MRI
ActiveCN102999917AOvercoming noiseOvercome the local volume effectImage enhancementImage analysisT2 weightedComputer vision
A cervical caner image automatic partition method based on T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2-MRI and dispersion weighted (DW)-MRI includes that a DW-MR image is registered to a T2-MR image by using a non-linear register method, and the registered DW-MR image is sorted; the T2-MR image is filtered through non-linear anisotropic diffusion filtering technology, a bladder and a rectum are partitioned, and an interested area is partitioned through a partition result of the bladder and the rectum; and a combined maximum a posterior (CMAP) method is adopted for an interested area of the T2-MR image and the DW-MR image to conduct precise partition of a tumor. The cervical caner image automatic partition method fully uses effective information of the T2-MR image and the DW-MR image, can effectively overcome effects of noise, partial volume effect and strength overlapping in the T2-MR image, is precise and effective, and has important clinical and application value on prevention, diagnosis and treatment of the cervical cancer.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
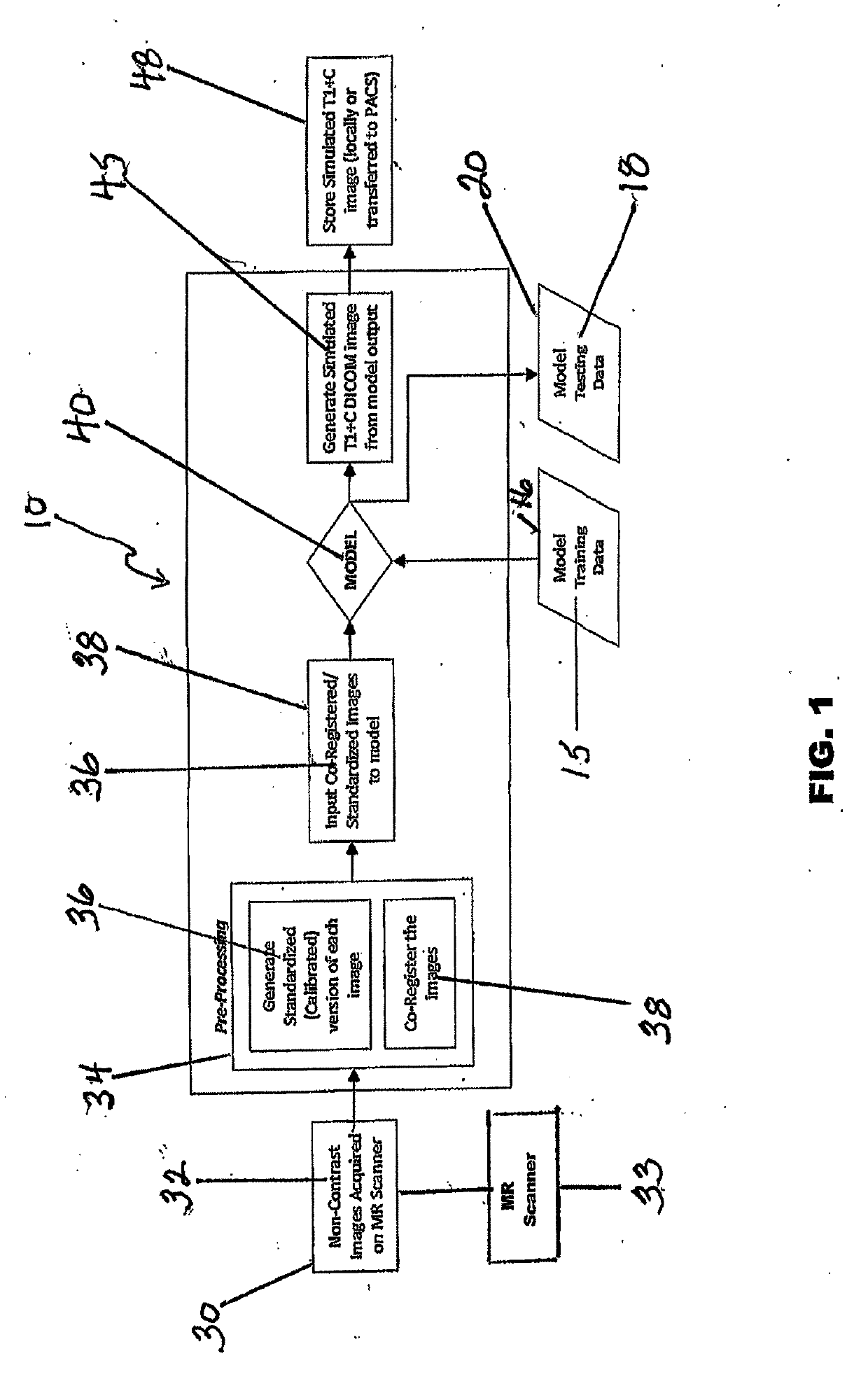
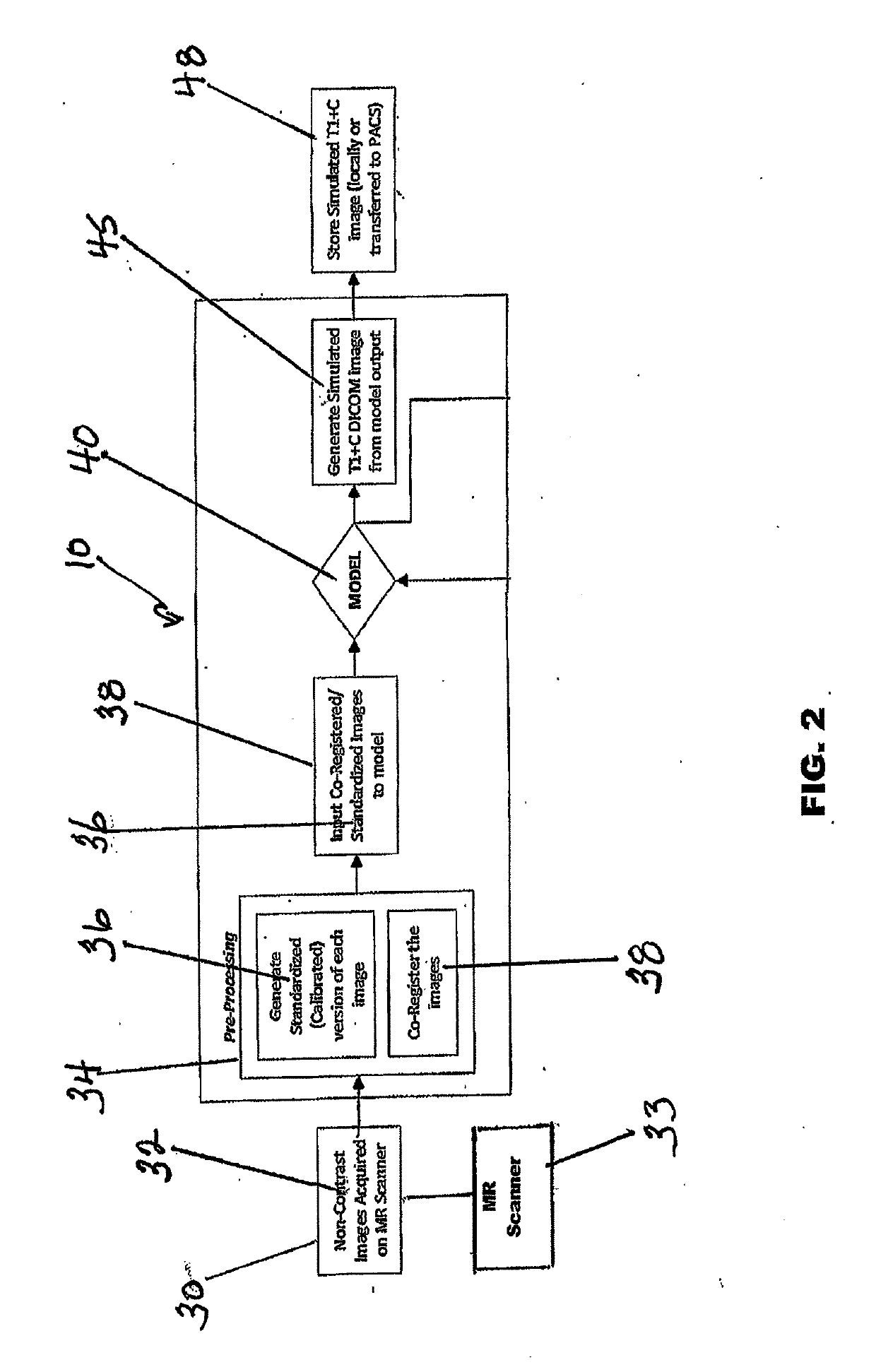
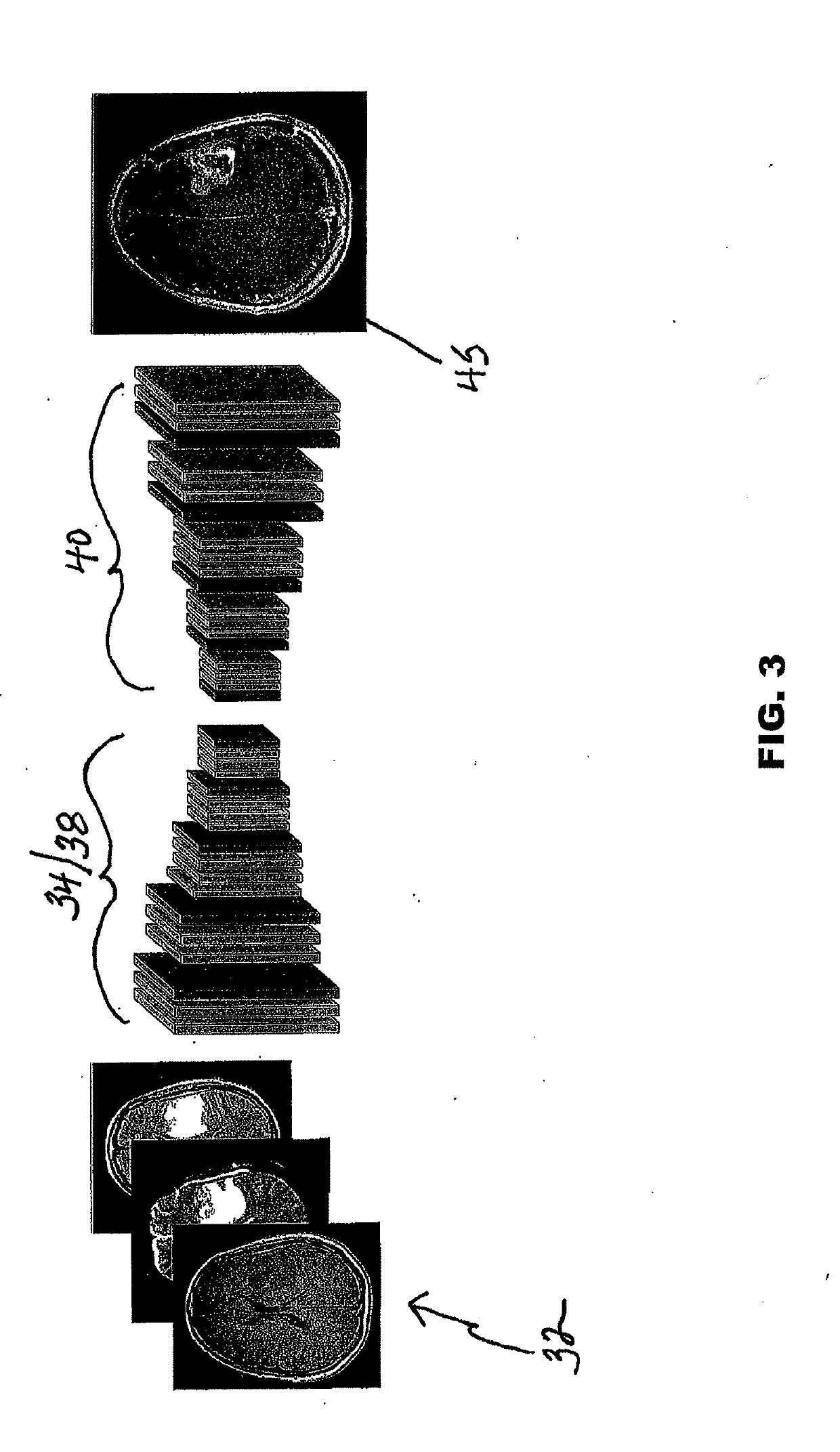
Simulated Post-Contrast T1-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
ActiveUS20190122348A1Eliminates common operationalEliminate errorsMedical simulationImage enhancementDiffusionInversion recovery
A system and method for generating simulated post-contrast T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images without the use of exogenous contrast material based upon patient-specific non-contrast MR images using machine learning / artificial intelligence techniques to train the system to generate post-contrast T1-weighted magnetic resonance images based upon retrospectively collected non-contrast MR images of various sequence types including T1-weighted, T2-weighted, FLAIR (Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery), and / or DWI (Diffusion-Weighted Imaging).
Owner:IMAGING BIOMETRICS
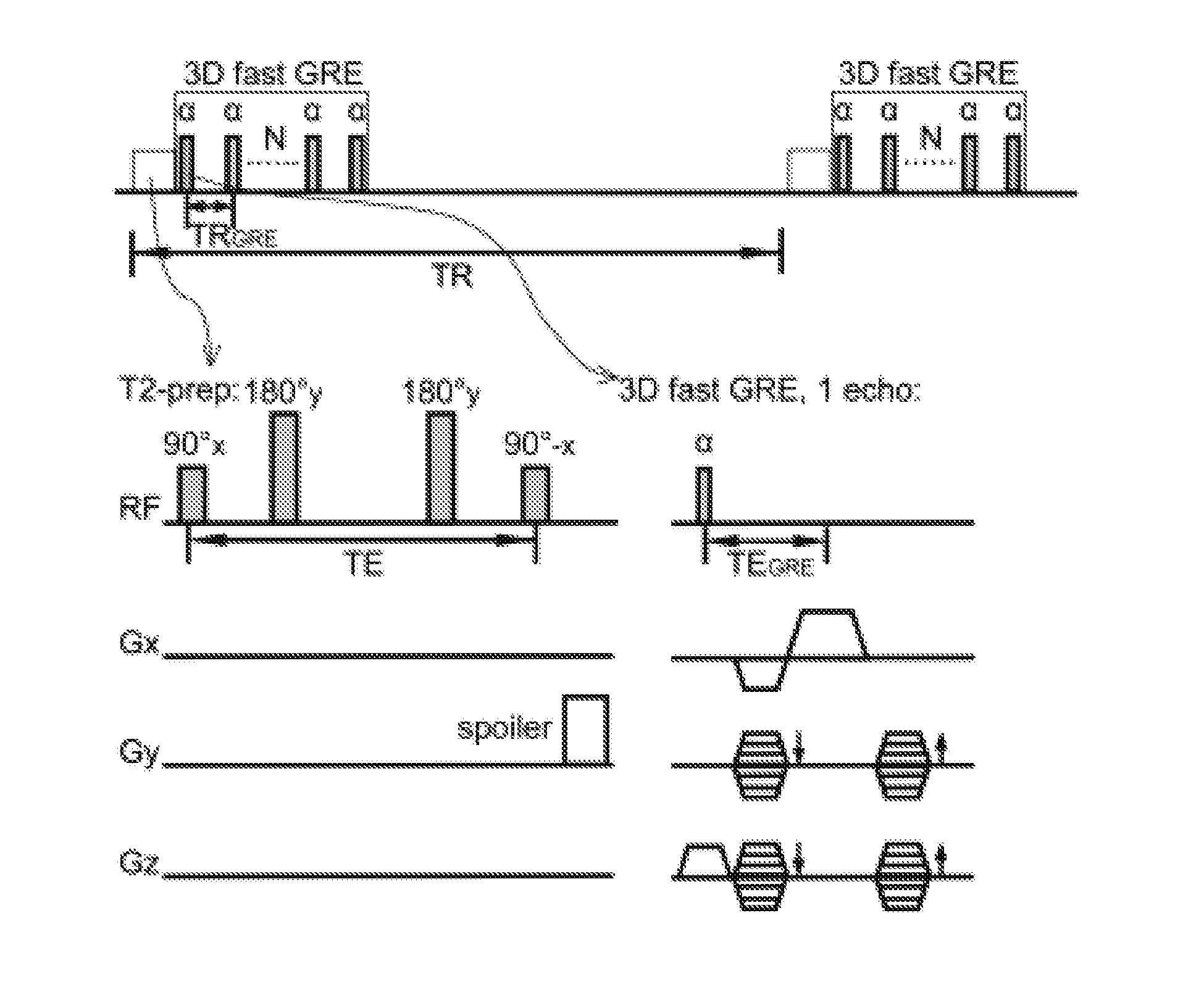
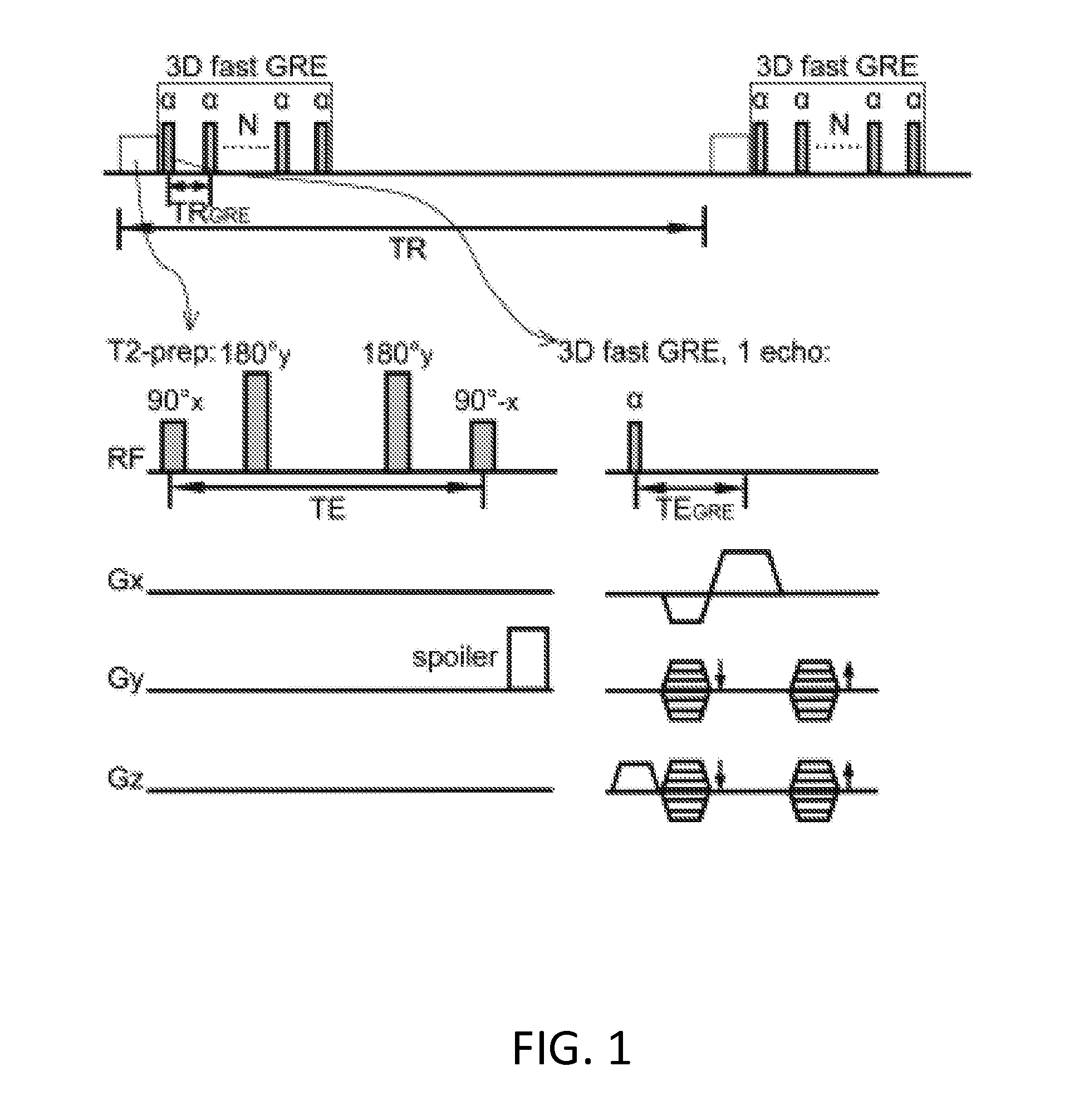
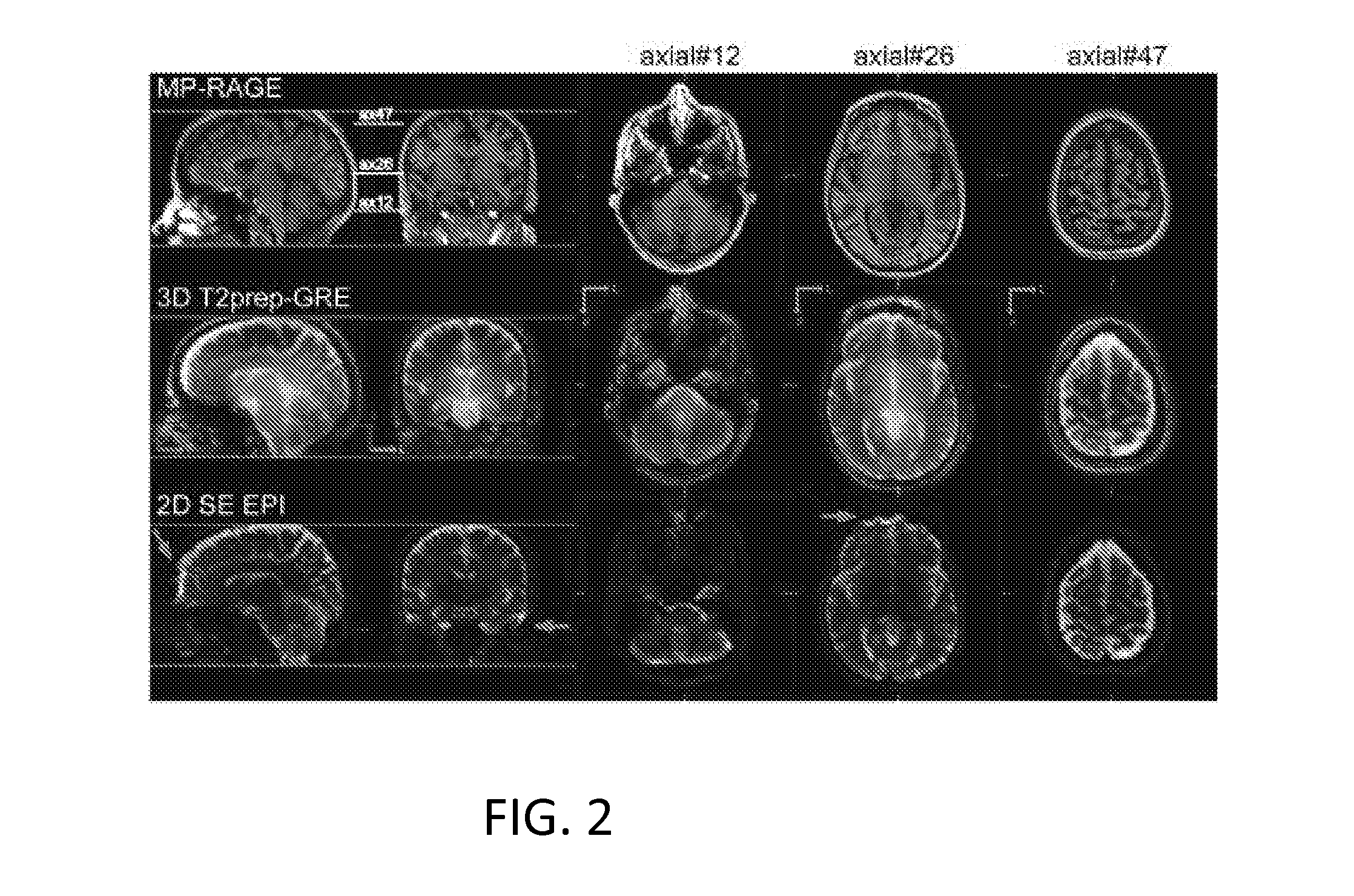
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Methodology Using Transverse Relaxation Preparation and Non-Echo-Planar Imaging (EPI) Pulse Sequences
InactiveUS20160113501A1Short timeEliminate the effects ofMedical imagingMagnetic measurementsDead timePulse sequence
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides a new acquisition scheme for T2-weighted BOLD fMRI. It employs a T2 preparation module to induce the BOLD contrast, followed by a single-shot 3D fast gradient echo (GRE) readout with short echo time (TE<2 ms). The separation of BOLD contrast generation from the readout substantially reduces the “dead time” due to long TE required in spin echo (SE) BOLD sequences. This approach termed “3D T2prep-GRE,” can be implemented with any magnetic resonance imaging machine, known to or conceivable by one of skill in the art. This approach is expected to be useful for ultra-high field fMRI studies that require whole brain coverage, or focus on regions near air cavities. The concept of using T2 preparation to generate BOLD contrast can be combined with many other fast imaging sequences at any field strength.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Systems and method for automatic prostate localization in MR images using random walker segmentation initialized via boosted classifiers
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
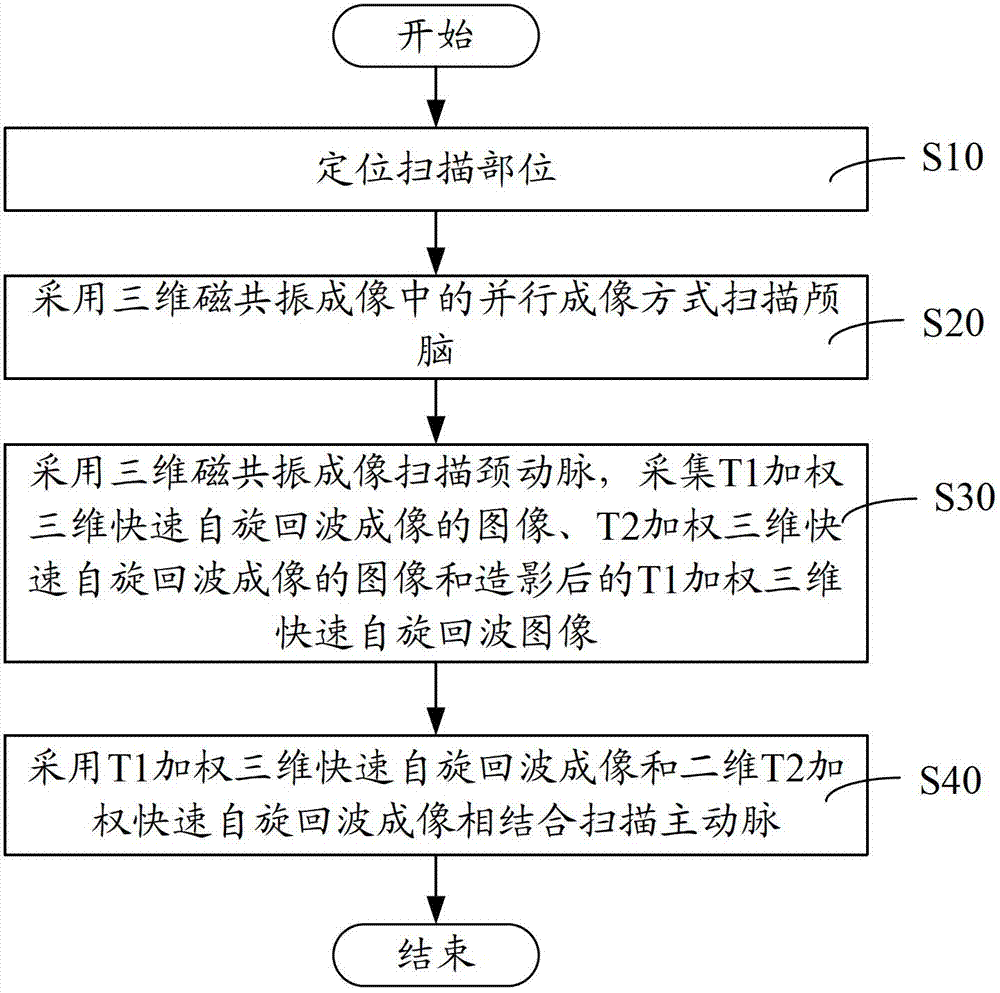
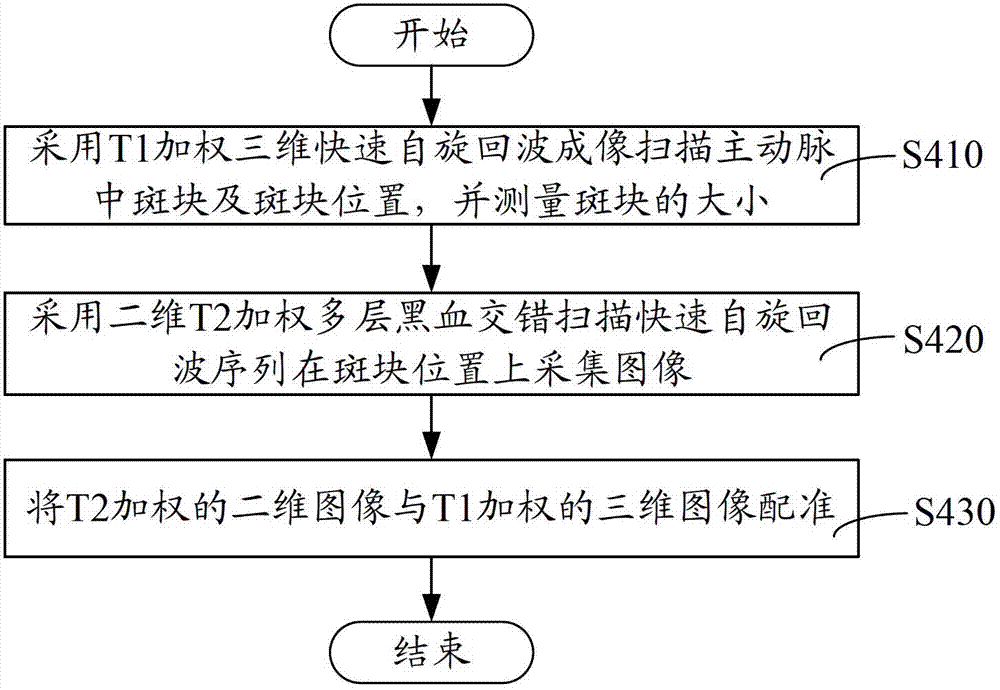
Brain, carotid artery and aorta three-in-one scanning method and scanning system
ActiveCN102727206AReduce scan timeImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringFast spin echoRapid imaging
The invention relates to a brain, carotid artery and aorta three-in-one scanning method, comprising the following steps of: positioning a scanning part; scanning a brain by utilizing parallel imaging of three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging; scanning a carotid artery by utilizing the three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging and collecting a T1 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaged image, a T2 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaged image and a radiographed T1 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo image; and scanning a carotid artery by utilizing T1 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaging and T2 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaging which are combined. The brain, carotid artery and aorta three-in-one scanning method and system disclosed by the invention firstly adopt the steps of firstly positioning the scanning part and directly scanning the brain, the carotid artery and the aorta; the positioning and the scanning do not need to be repeated so that the scanning time is shortened; the brain is scanned by using a rapid imaging method by parallel imaging so that the scanning time is reduced; and three-dimensional T1 weighted imaging and two-dimensional T2 weighted imaging are combined to scan the carotid artery so that the scanning time is further shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
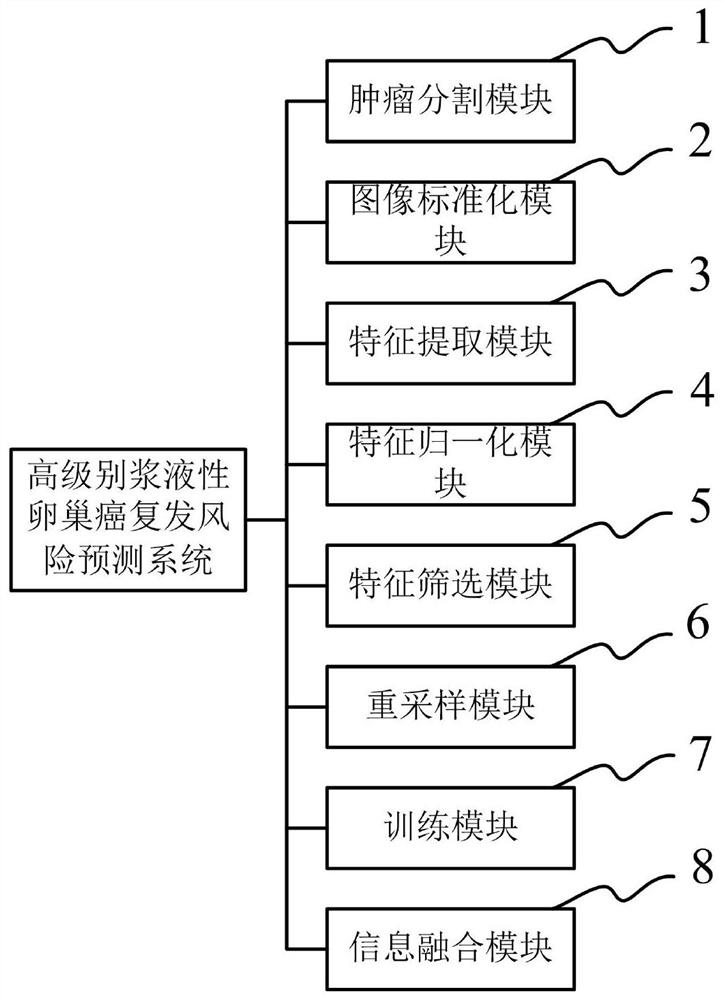
High-grade serous ovarian cancer recurrence risk prediction system based on imaging omics
ActiveCN111862079AAchieve early predictionEnable early detectionMedical simulationImage enhancementFeature extractionRadiology
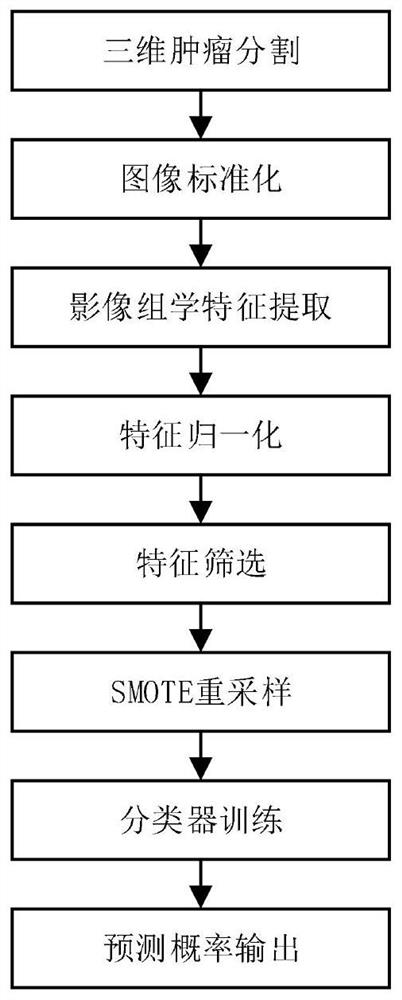
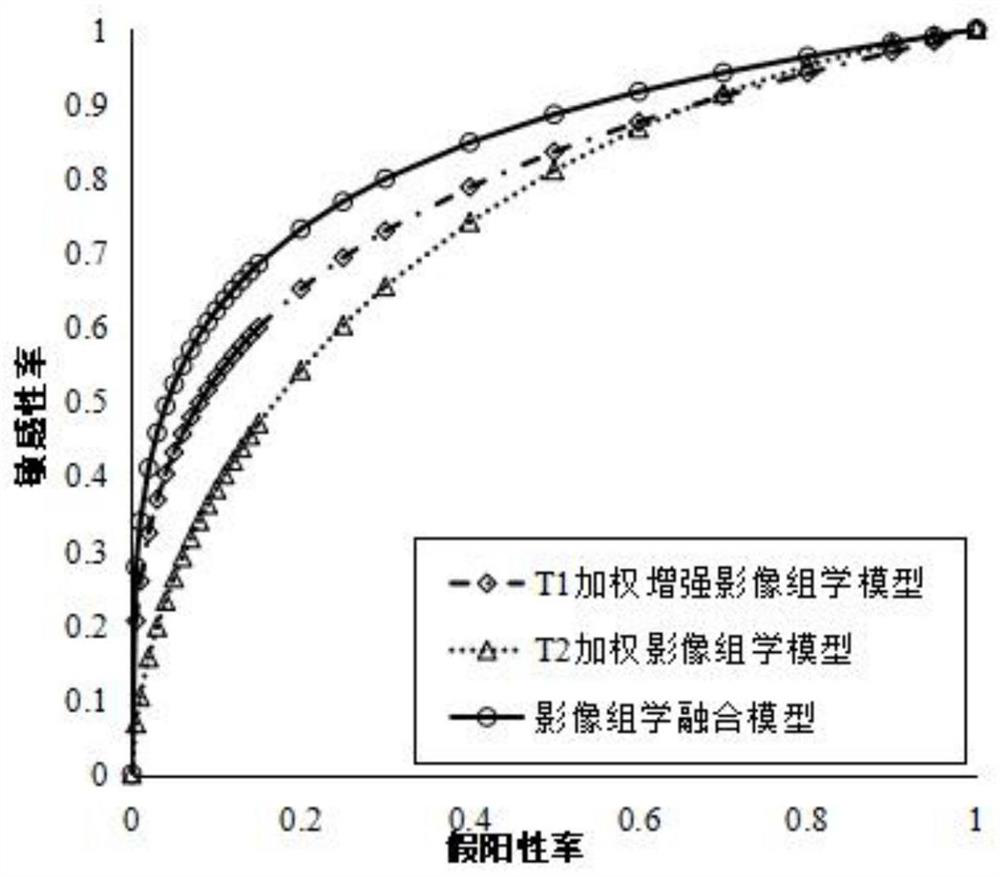
The invention discloses a high-grade serous ovarian cancer recurrence risk prediction system based on imaging omics. A method comprises the steps of T1 weighted enhanced imaging omics processing, T2 weighted imaging omics processing and information fusion. The image omics processing mainly comprises the steps of three-dimensional tumor segmentation, image standardization, image omics feature extraction, feature normalization, feature screening, SMOTE resampling and classifier training; the information fusion is mainly used for fusing recurrence risk prediction probabilities output by T1 and T2image omics processing, so the risk prediction accuracy is further improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
Aqueous contrast agents for dynamic MRI and mra
InactiveUS20170089997A1Increase MR relaxation timeExtension of timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSensorsT2 weightedPerfusion
In a first aspect this invention provides methods comprising administering an aqueous contrast agent to the vascular system of a subject, and performing a magnetic resonance scan to detect the MR signal enhancement effects of the aqueous contrast agent. In embodiments the magnetic resonance scan comprises applying at least one pulse sequence selected from a PD-weighted pulse sequence, a T1-weighted pulse sequence, a T2-weighted pulse sequence, and a D-weighted pulse sequence. In embodiments the magnetic resonance scan comprises applying a T1-weighted pulse sequence. A system for performing perfusion MRI comprising an aqueous contrast solution and an injection apparatus configured to provide a maximum injection rate of the aqueous contrast solution to a subject vascular system of at least about 5 ml / s. is also provided.
Owner:BOSTON MEDICAL CENTER INC
Dual-contrast mr imaging using fluid-attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR)
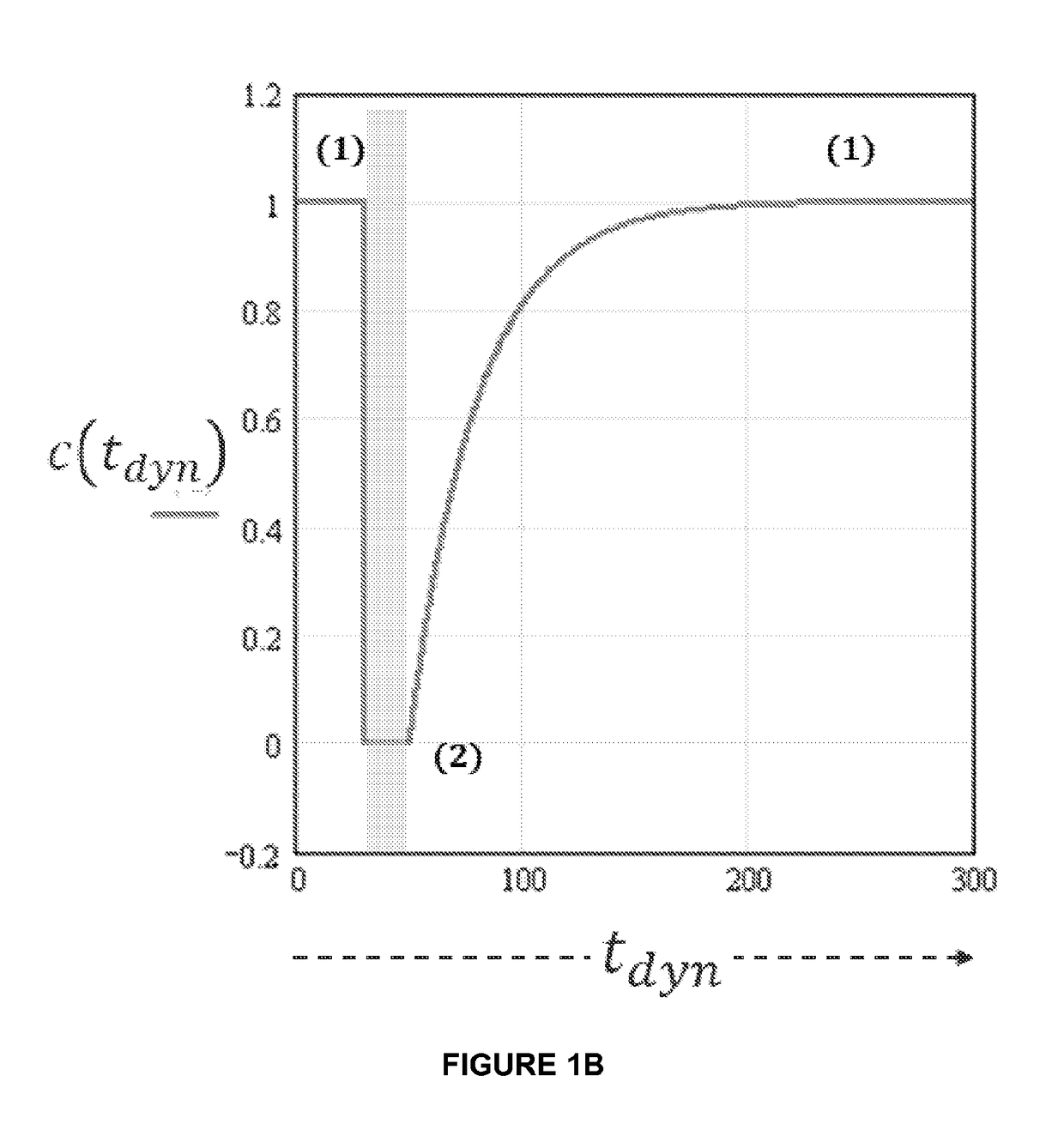
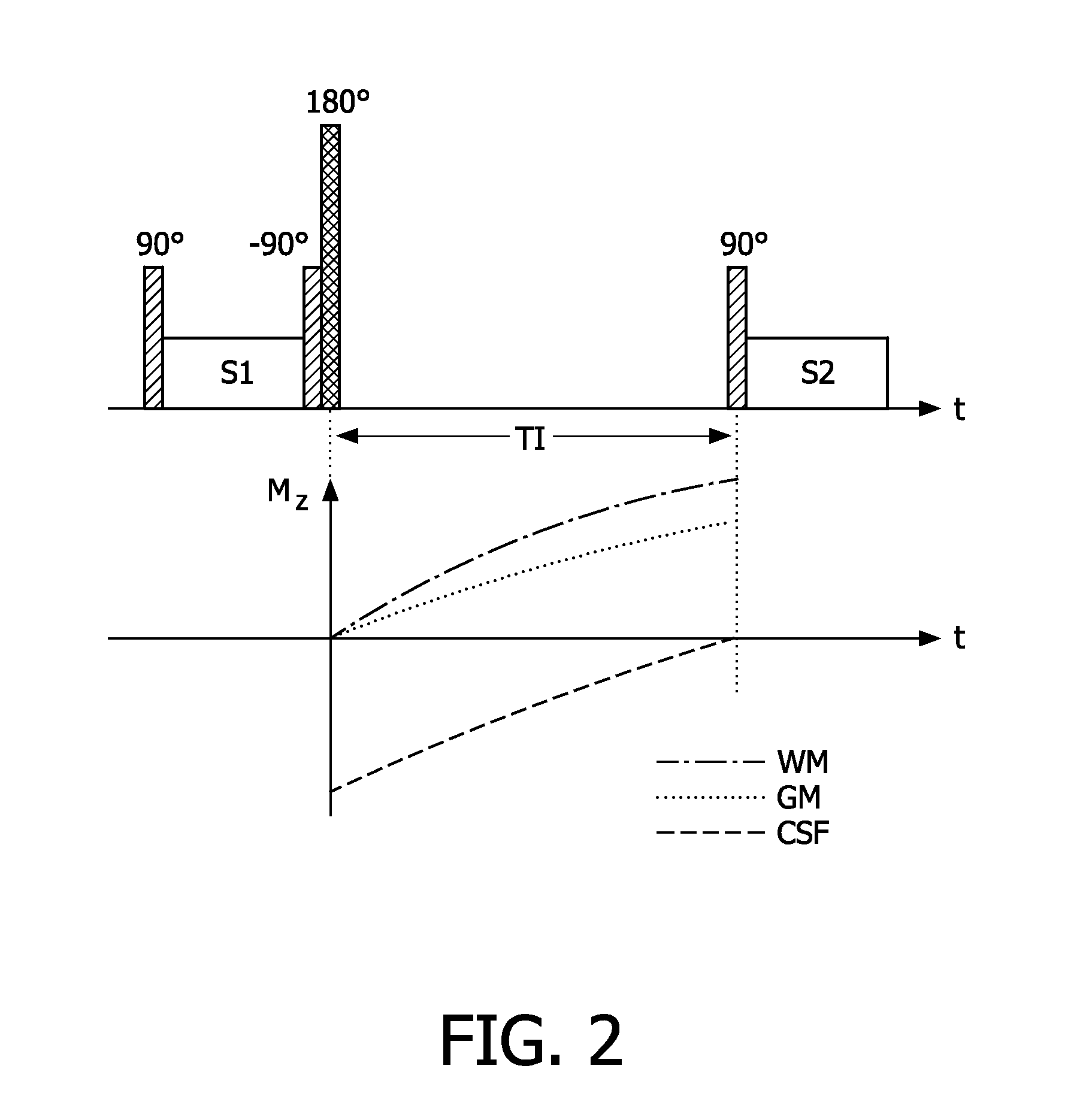
InactiveUS20120046539A1Reduce the differenceIncrease relaxation timeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDelayed periodsData set
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of at least a portion of a body (10) of a patient placed in an examination volume of an MR device (1). The acquisition of high-resolution three-dimensional FLAIR images as well as T2-weighted images at high main magnetic field strength (>3 Tesla) results in unacceptable long scan times. The present invention contemplates a new and improved MR imaging method which overcomes this problem. The method of the invention comprises the steps of subjecting the portion of the body (10) to a first imaging sequence (S1) for acquiring a first signal data set; immediately subsequent to the first imaging sequence (S1) subjecting the portion of the body (10) to an inversion RF pulse that inverses longitudinal magnetization within the portion; after an inversion delay period (TI) subjecting the portion of the body (10) to a second imaging sequence (S2) for acquiring a second signal data set; reconstructing first and second MR images from the first and second signal data sets respectively.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for positioning three axial positions of fetal brain through nuclear magnetic resonance
InactiveCN102309322AClear reconstructionAccurate reconstructionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceMedicine
The invention relates to a method for positioning three axial positions of a fetal brain through magnetic resonance. The method is used for further rapidly, accurately and normatively positioning an image of the three axial positions of the fetal brain on the basis of the traditional nuclear magnetic resonance scanning and positioning technology and providing a more accurate and normative cross-section image for clinical medicine. Because the position and the direction of a fetus in a parent are possibly changed at any time, the standard three axial positions of only a few fetuses can be directly positioned through the standard three axial positions of the parent; in many cases, the position of the fetus in the parent is changeable; the standard image of the three axial positions cannot be obtained through the traditional technology; when the standard three axial positions of the parent cannot be given or the standard three axial positions of the fetus cannot be better given, a series of images of various positions can be obtained by rotating and positioning in 360 DEG through a haste sequence, namely a heavy T2 weighted line; and the image closest to the standard fetal position is selected from the series of images and served as the standard to position the brain.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
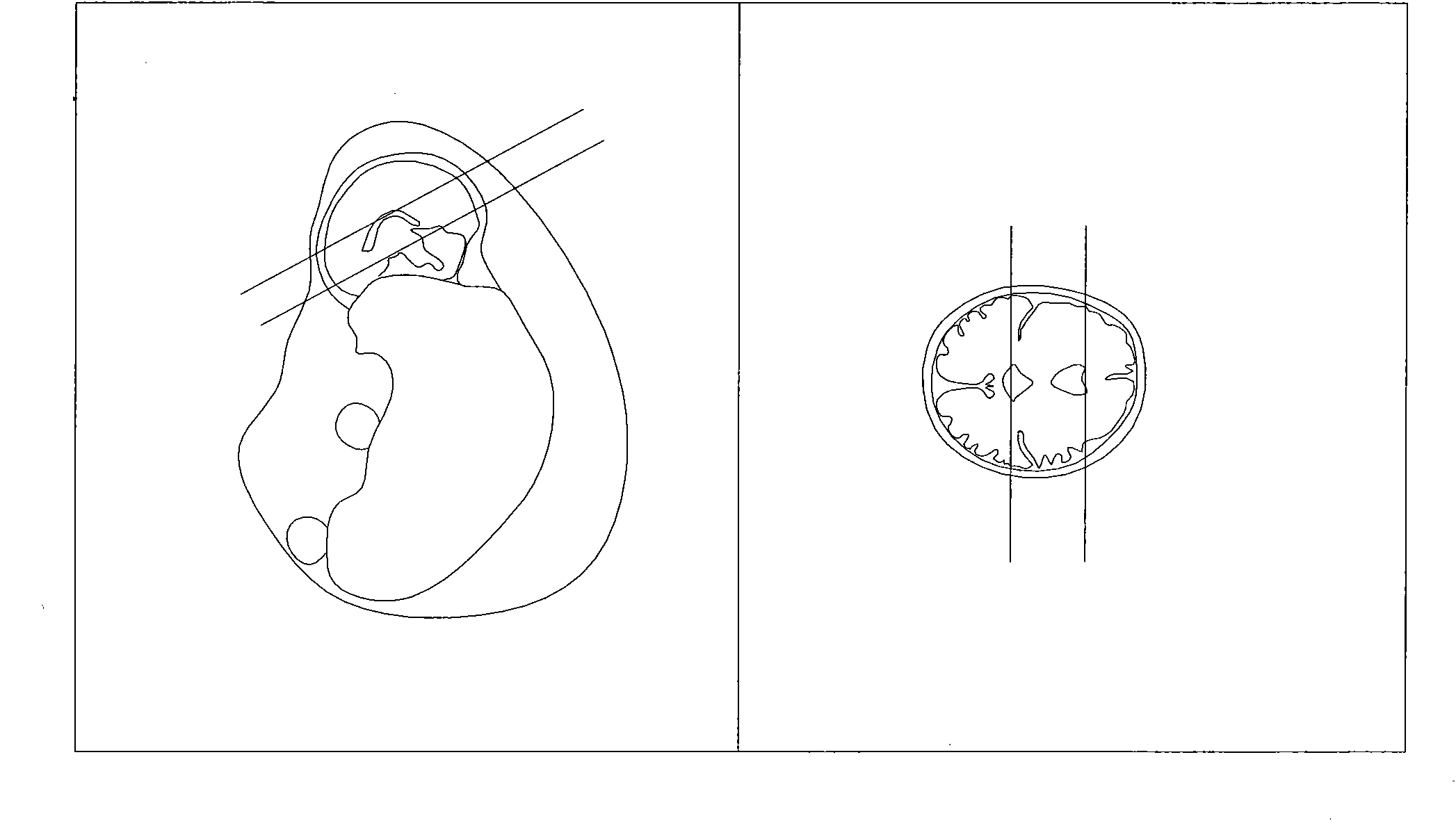
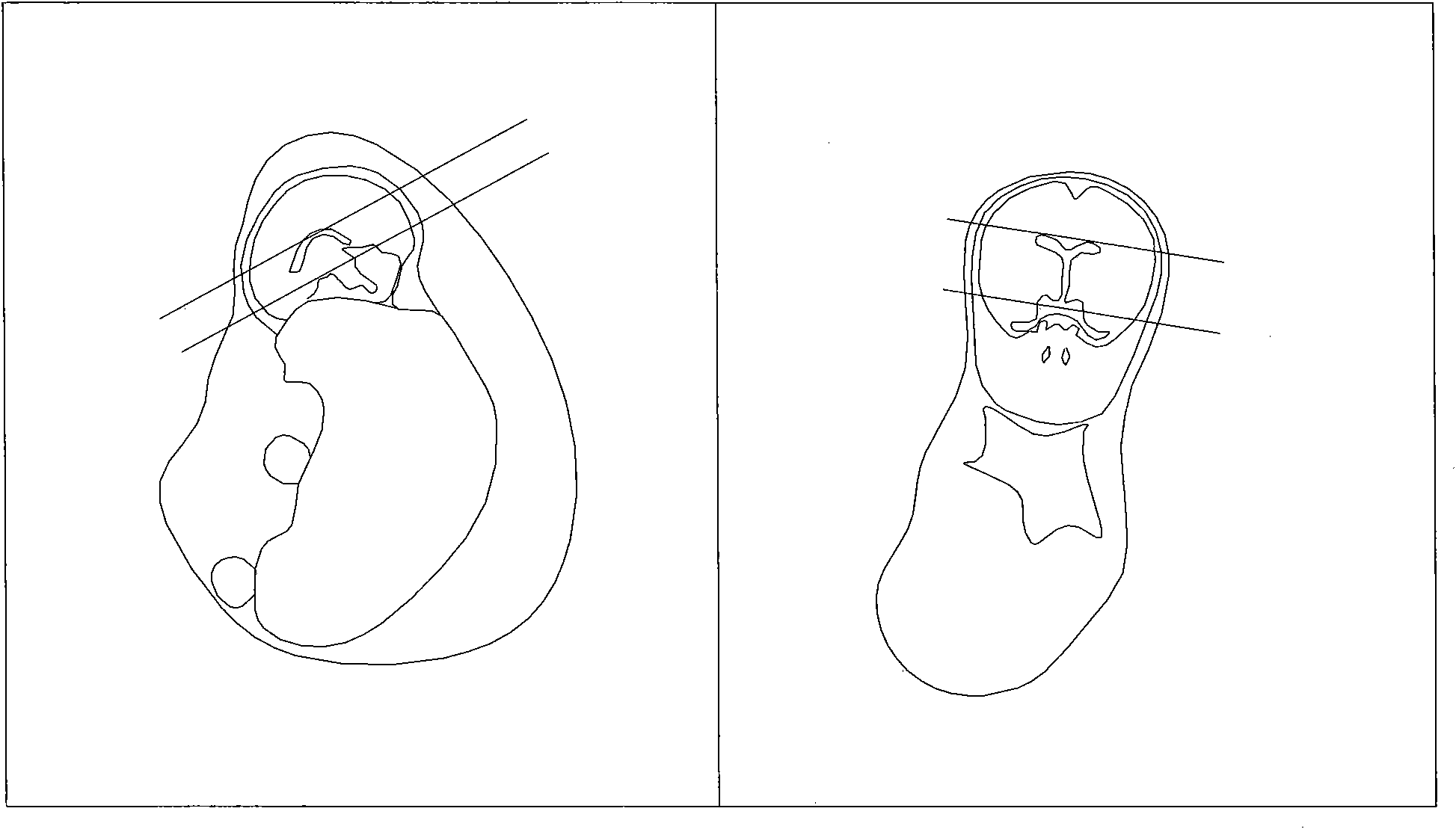
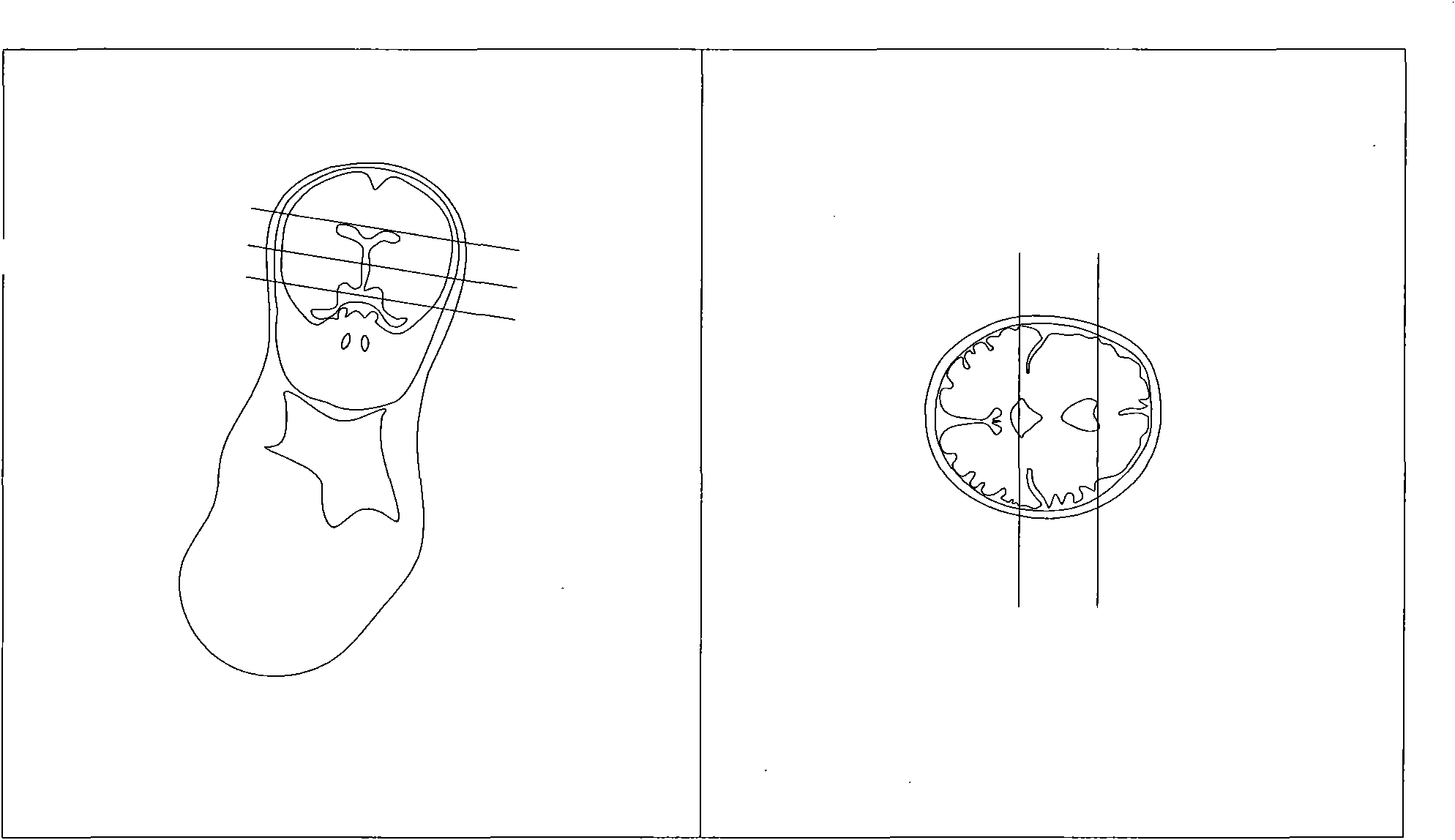
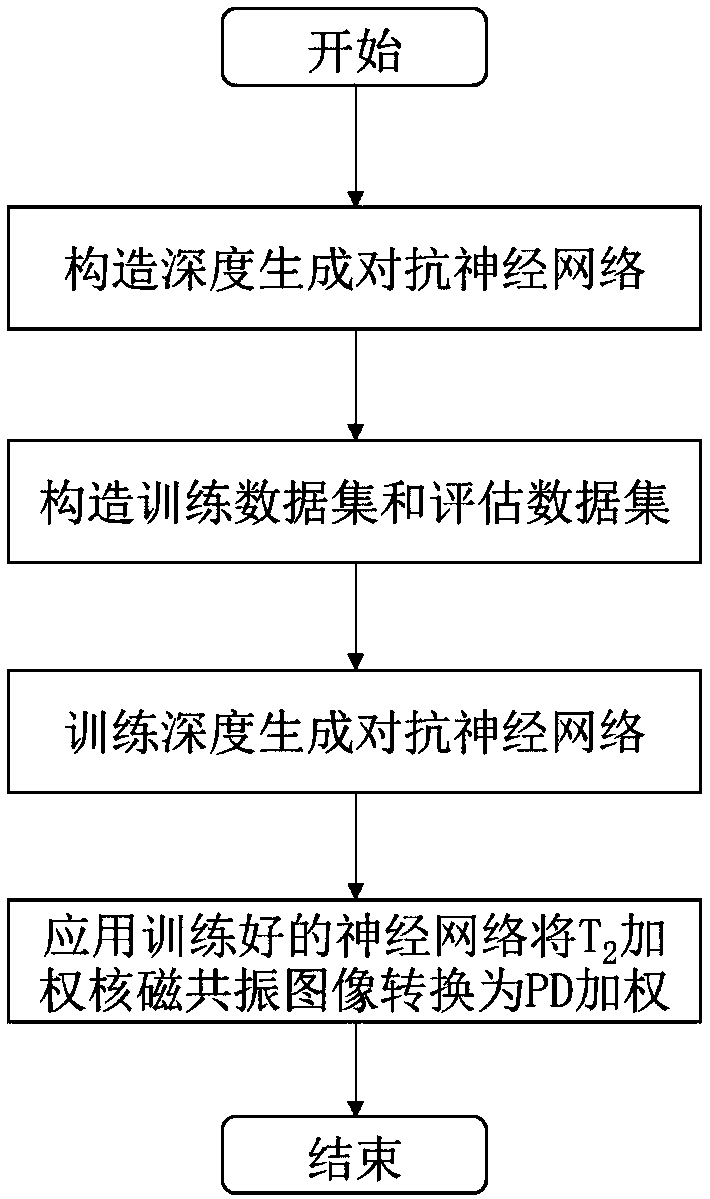
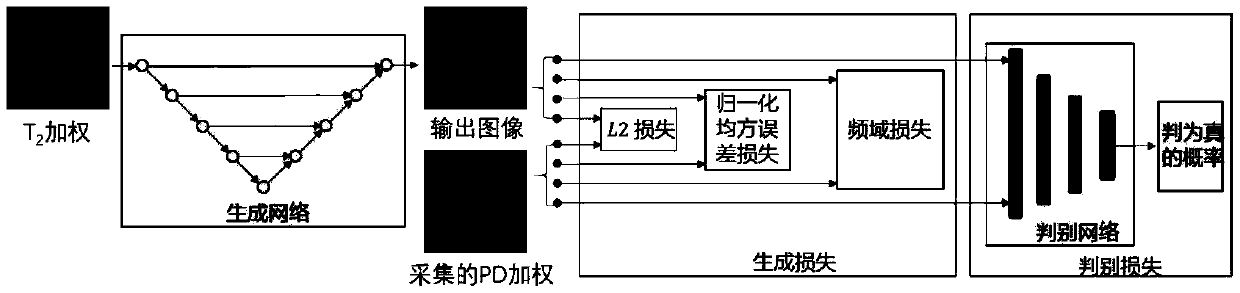
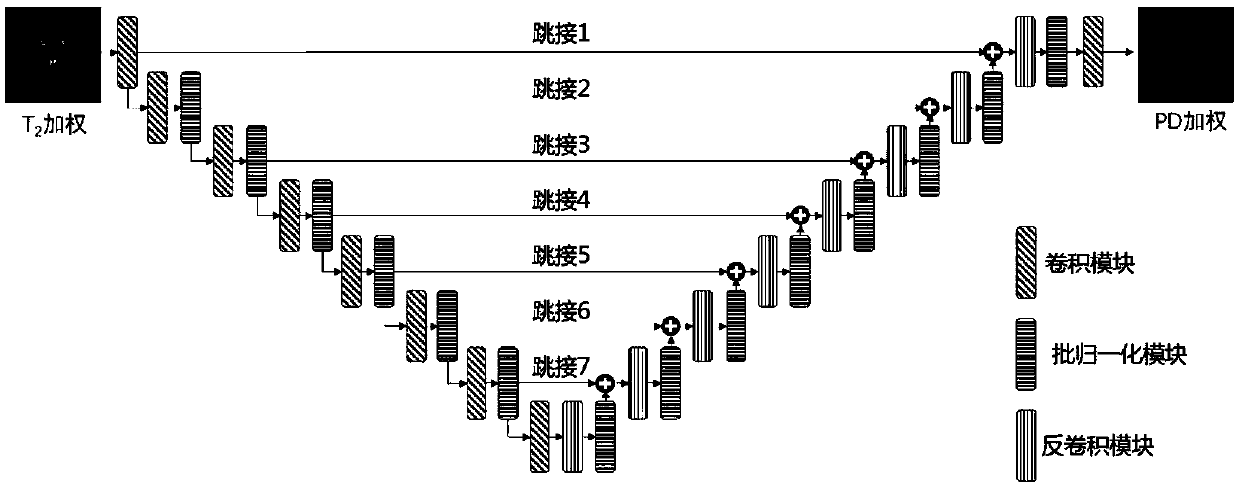
A nuclear magnetic resonance multi-weighted imaging method based on a depth generative adversarial neural network
PendingCN109544652AImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionSolid-state nuclear magnetic resonanceData set
The invention relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance multi-weighted imaging method based on a depth generative adversarial neural network, which comprises the following four steps: the constructionof the depth generative adversarial neural network, the construction of a training data set and an evaluation data set, the training of network weights and the application of the network weights to aplurality of weighted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. More than 40,000 pairs and 10,000 pairs of T2-weighted and PD-weighted NMR images collected from the same site at the same time were used as training data set and evaluation data set respectively, The model weight of the depth generative adversarial neural network is trained, and the generation network uses the T2-weighted image as the input of the network, and maps the data distribution of the generated image to the PD-weighted image data distribution obtained by acquisition maximally; The invention can convert the T2-weighted nuclearmagnetic resonance image acquired by the nuclear magnetic resonance imaging device into a high-quality PD-weighted nuclear magnetic resonance image in a very short time, thereby providing two kinds of weighted nuclear magnetic resonance images in a single imaging process.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
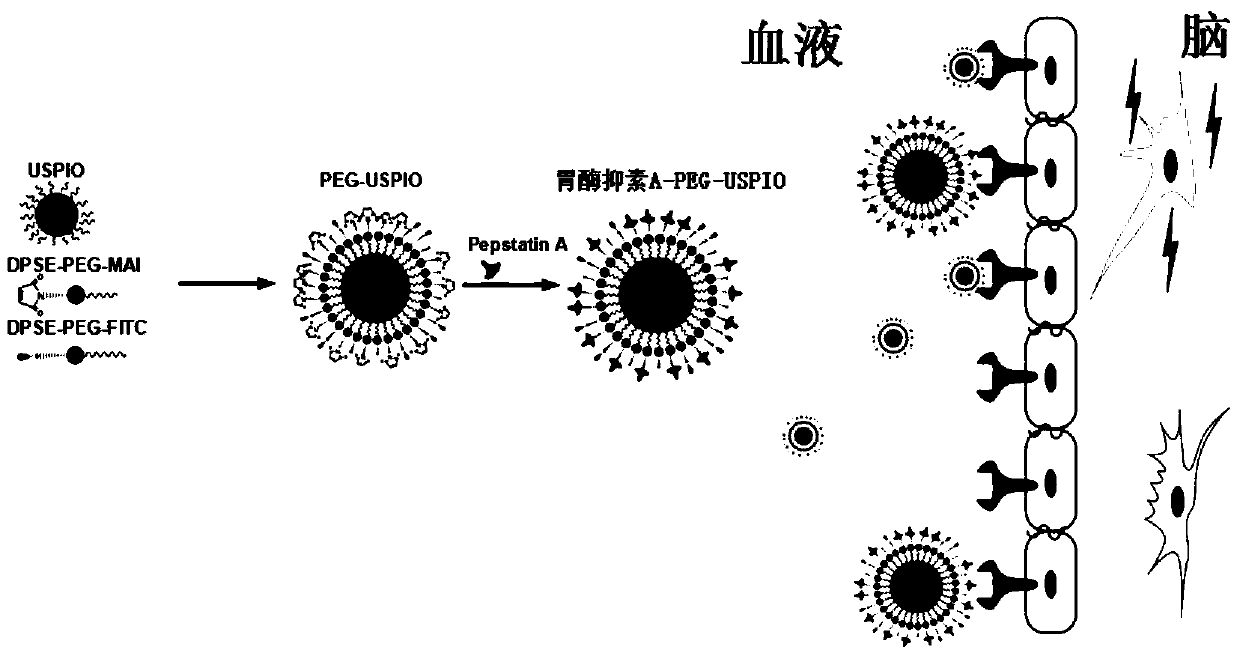
Targeted nano-magnetic resonance contrast agent for brain epileptic foci, preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN105497922AHigh precisionImprove securityNervous disorderEmulsion deliveryEpilepsy treatmentFluorescence
The invention discloses a targeted nano-magnetic resonance contrast agent for brain epileptic foci, preparation and application thereof. The magnetic resonance contrast agent comprises a target functional molecule, a fluorescent marker and a nano-carrier. The target functional molecule is short peptide that has high affinity to epileptic focus area high expression P-glycoprotein. The fluorescent marker is encapsulated in the nano-carrier by means of covalent connection, and the short peptide is in connection with polyethylene glycol on a nanoparticle surface through covalent connection. The contrast agent can combine the short peptide with the epileptic focus area high expression P-glycoprotein through intravenous injection, promotes gathering of the nano-carrier at epileptic foci, and makes MRI T2 weighted imaged focus area show significant low signal, thereby accurately and visually display idiopathic / cryptogenic epilepsy foci. The contrast agent is conducive to clinical improvement of the treatment accuracy and safety, evaluation of the efficacy of anti-epilepsy treatment means, and assessment of the prognosis of epilepsy patients.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
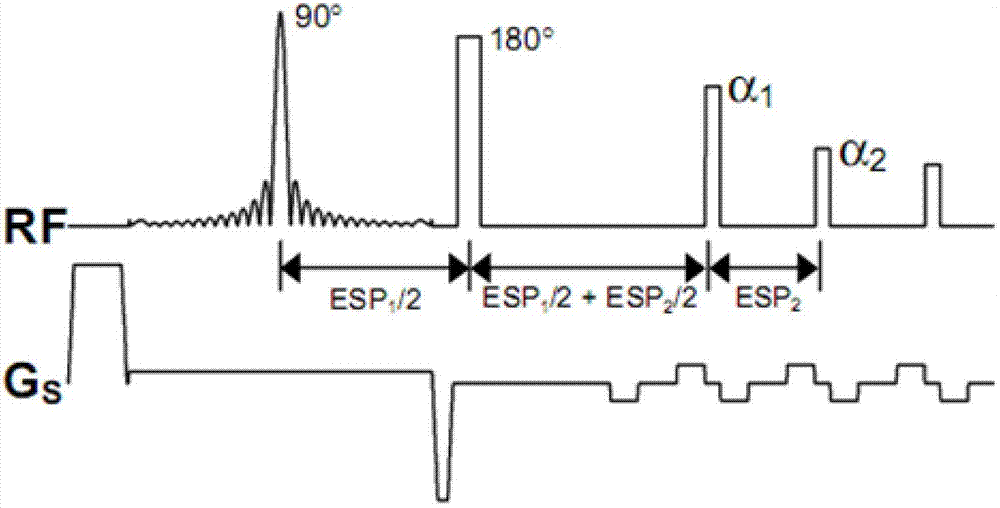
Fast three dimensional t2 weighted balanced steady-state free precession imaging
InactiveUS20160313427A1Maintaining spatial resolutionHigh imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImage resolutionT2 weighted
A fast 3D T2-weighted imaging system and method is disclosed that uses balanced steady state free precession (bSSFP), variable flip angles, and an interleaved multi-shot spiral-out phase encode ordering strategy to acquire high resolution T2-weighted images quickly while maintaining spatial resolution.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
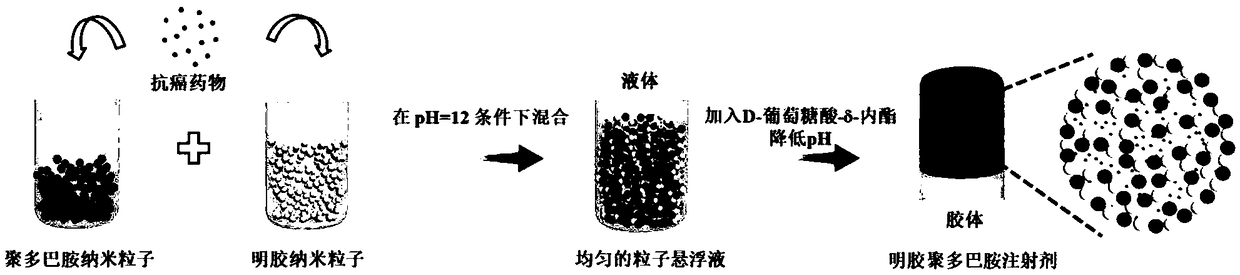
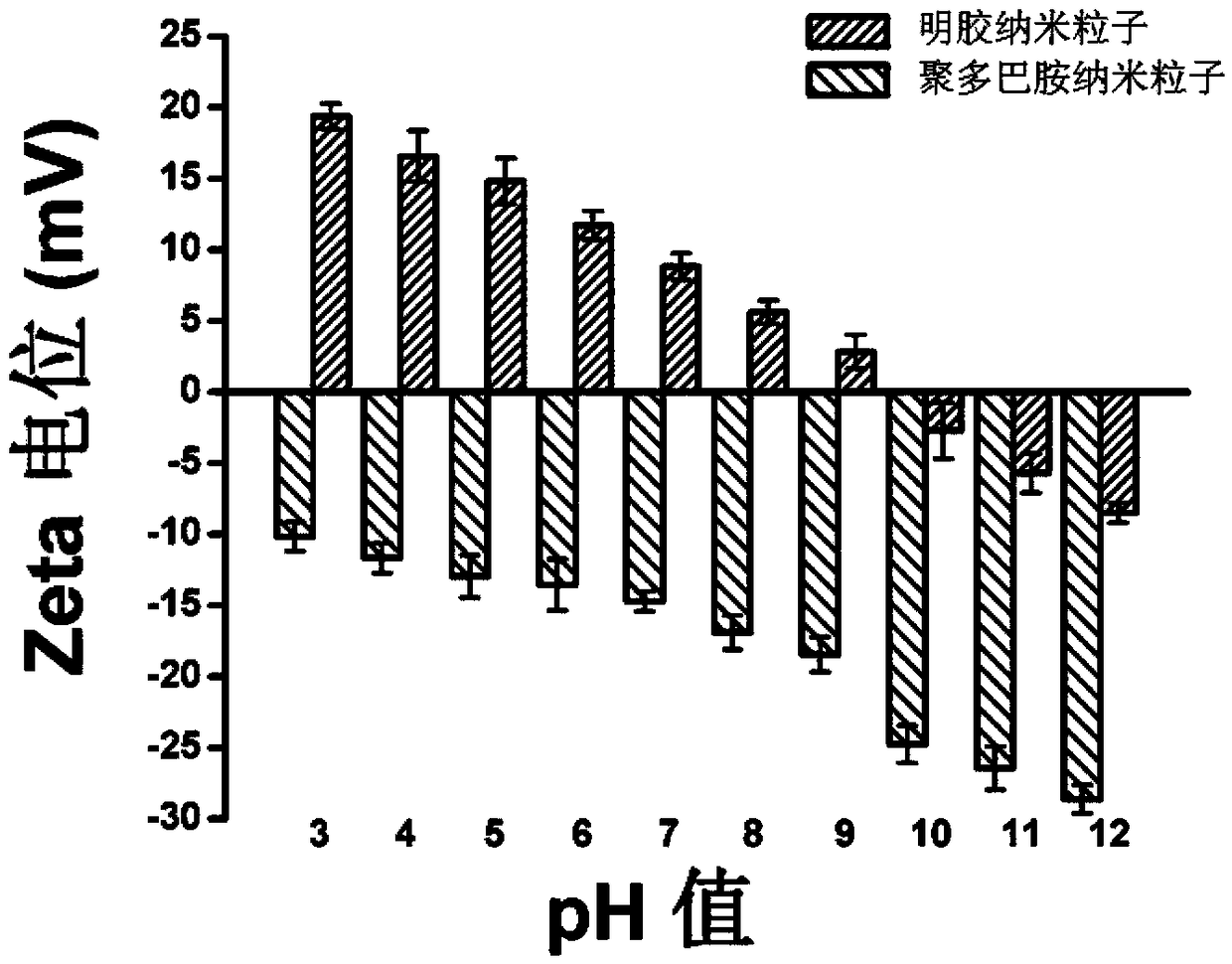
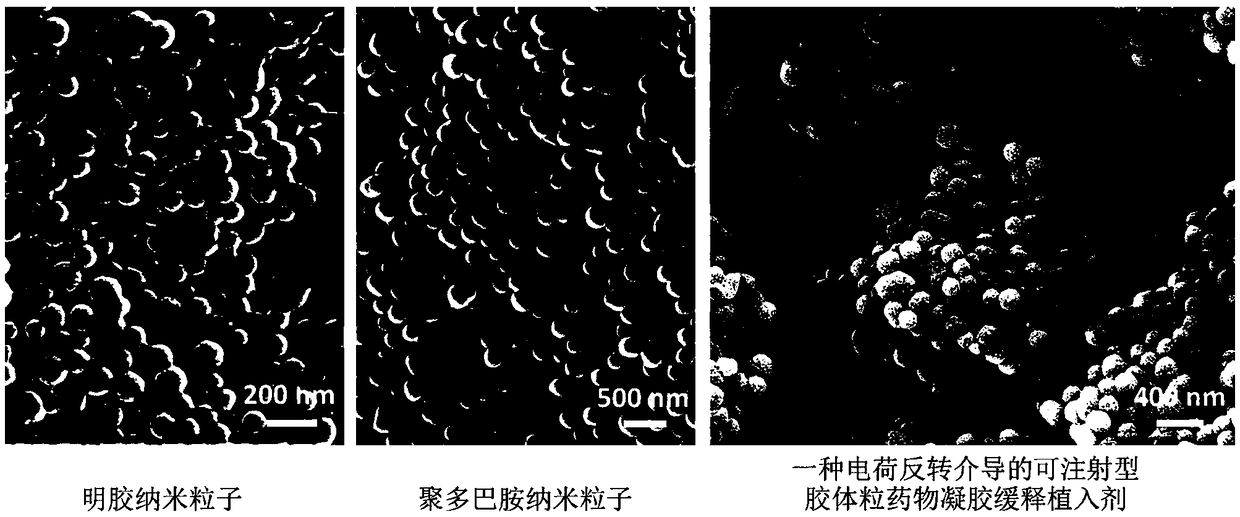
Charge reversal-mediated injectable colloid grain drug gel slow-release implant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109481393AGood biocompatibilitySimple and mild preparation conditionsDispersion deliveryAntipyreticLaser intensityDrug release
The invention discloses a charge reversal-mediated injectable colloid grain drug gel slow-release implant and a preparation method thereof. The implant contains the following components: polydopaminenanoparticles, gelatin nanoparticles, an acid former and a drug. The preparation method comprises the steps of respectively dispersing the polydopamine nanoparticles and the gelatin nanoparticles intoan alkaline solution, adding an anti-cancer drug before use, acidizing by virtue of the acid former, uniformly mixing until the mixture is acidized into gel, and carrying out intratumor injection. The implant prepared by virtue of the preparation method can be simultaneously taken as a photo-thermal treatment agent and a drug carrier, the nuclear magnetism imaging diagnosis can be realized through T2 weighting under relatively low laser intensity and relatively chemotherapy drug dosage, and the release of acid / thermal / enzyme responsive drug and the synergetic treatment of the photo-thermal treatment are realized, so that the integration of the diagnosis and treatment of cancers is realized.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Mr spectroscopy system and method for diagnosing painful and non-painful intervertebral discs
ActiveUS20150112183A1Magnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumDisplay device
An MR Spectroscopy (MRS) system and approach is provided for diagnosing painful and non-painful discs in chronic, severe low back pain patients (DDD-MRS). A DDD-MRS pulse sequence generates and acquires DDD-MRS spectra within intervertebral disc nuclei for later signal processing & diagnostic analysis. An interfacing DDD-MRS signal processor receives output signals of the DDD-MRS spectra acquired and is configured to optimize signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) by an automated system that selectively conducts optimal channel selection, phase and frequency correction, and frame editing as appropriate for a given acquisition series. A diagnostic processor calculates a diagnostic value for the disc based upon a weighted factor set of criteria that uses MRS data extracted from the acquired and processed MRS spectra along regions associated with multiple chemicals that have been correlated to painful vs. non-painful discs. A diagnostic display provides a scaled, color coded legend and indication of results for each disc analyzed as an overlay onto a mid-sagittal T2-weighted MRI image of the lumbar spine for the patient being diagnosed. Clinical application of the embodiments provides a non-invasive, objective, pain-free, reliable approach for diagnosing painful vs. non-painful discs by simply extending and enhancing the utility of otherwise standard MRI exams of the lumbar spine.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
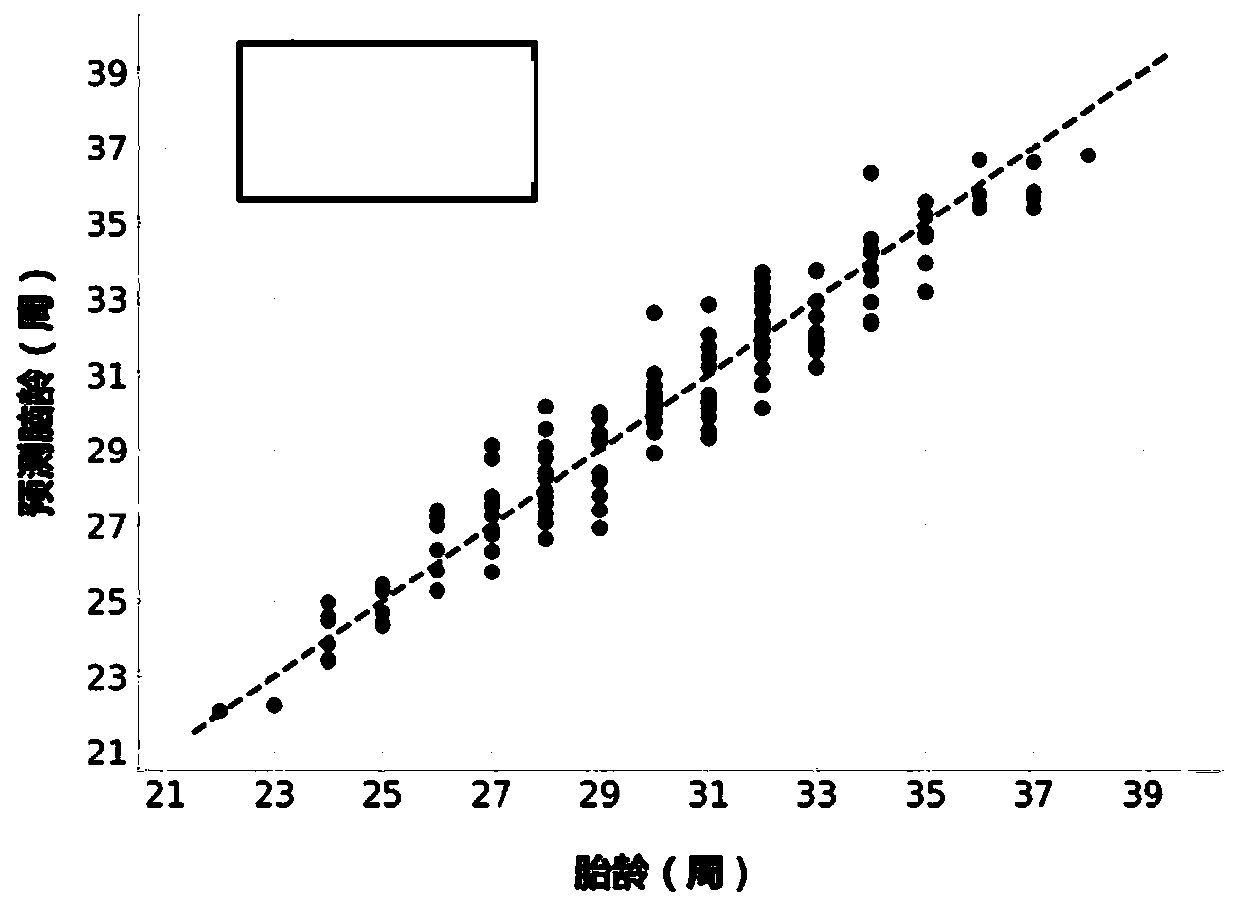
Fetal brain age estimation and anomaly detection method and device based on deep learning
ActiveCN111415361AAccurate segmentationAccurate estimateImage enhancementImage analysisBrain developmentIn utero
The invention discloses a fetal brain age estimation and anomaly detection method and device based on deep learning. The brain age estimation and anomaly detection method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a data set of T2 weighted magnetic resonance images of the brain of a normal fetus by utilizing T2 weighted images in the uterus of a pregnant woman, which are collected clinically and conventionally; secondly, segmenting the brain of the fetus from the uterus by using a U-shaped network, predicting the brain age of the fetus by using a deep residual network based on an attention mechanism, and generating the uncertainty of the brain age and the credibility of the estimation of the brain age of the fetus; and finally, constructing a classifier according to the difference, uncertainty, credibility and other indexes of the actual fetal age and the predicted brain age, and judging whether the brain development of the fetus is abnormal or not. According to the method, the brain age of the fetus can be estimated at the same time, indexes such as uncertainty and estimation credibility are generated to be used for detecting the fetus with abnormal brain development, and the method and device have high accuracy and precision and high clinical application prospect and value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
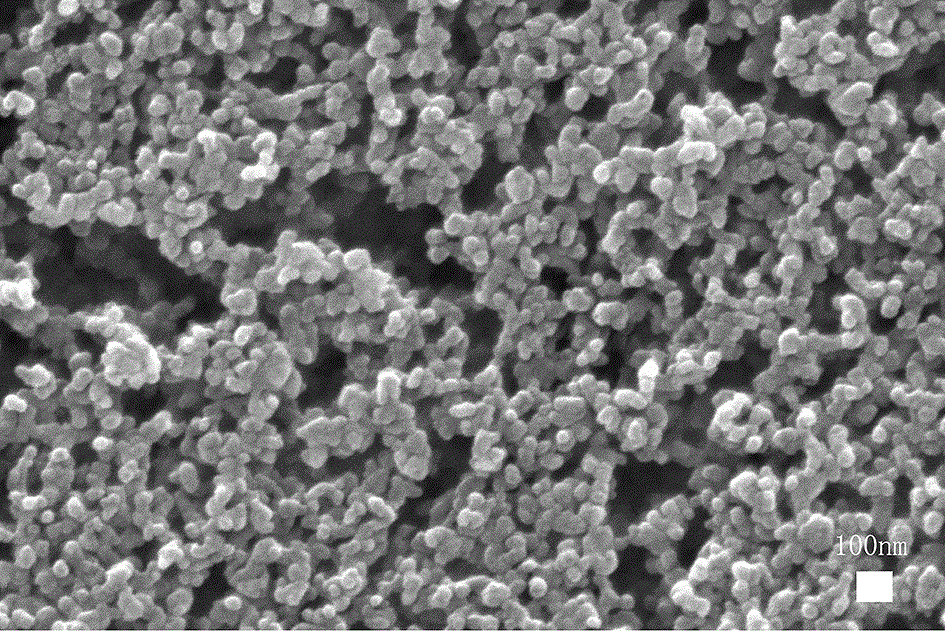
Preparation method of nano Gd-MOFs for magnetic resonance imaging
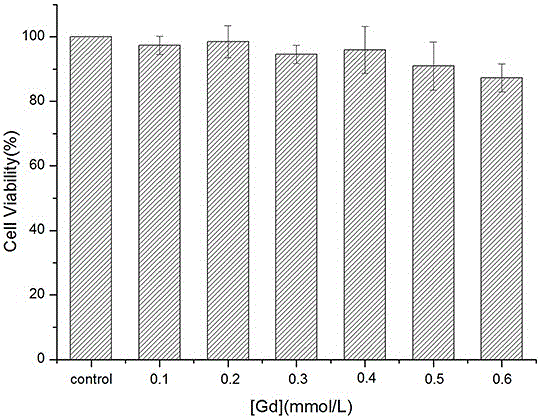
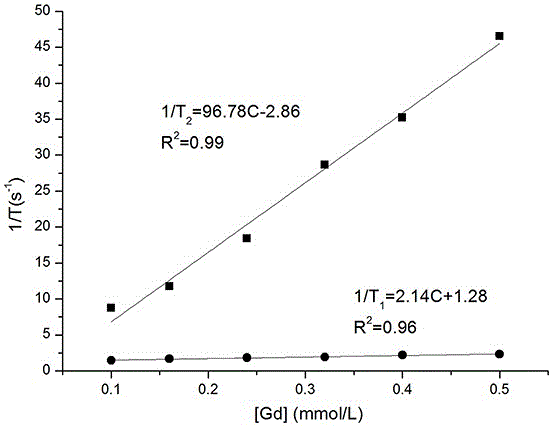
InactiveCN106822926ALow toxicitySimple preparation processNanosensorsEmulsion deliveryWater bathsCytotoxicity
The invention discloses a preparation method of nano Gd-MOFs for magnetic resonance imaging. The preparation method of the nano Gd-MOFs comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving a metal salt, a ligand and a terminating agent in a solvent, and then mixing to obtain a mixed solution; (2) stirring the obtained mixed solution at room temperature, placing in a water bath, carrying out a stirring reaction, then placing in an oven, allowing to stand, centrifuging and washing, and dispersing and preserving by a solvent, to obtain oil-phase dispersed Gd-MOFs; (3) taking a certain amount of the Gd-MOFs obtained in the step (2), centrifuging to remove the solvent, modifying by an ethanol solution containing triethylamine, and finally, dispersing in water to obtain the nano Gd-MOFs for magnetic resonance imaging. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method is simple in preparation process and mild in reaction conditions. The prepared nano Gd-MOFs have the particle size of 45-60 nm, are near spherical, have uniform particle size distribution, and are more suitable for phagocytosis; in an ultra high field intensity of 11.7 T, the transverse relaxation rate r2 is measured to be 96.8 mM<-1>*s<-1>, and the magnetic relaxation rate is high; the disadvantage of high cytotoxicity of the nano Gd-MOFs is overcome; when the concentration of Gd is 0.4 mmol / L or less, the cell close packing T2 weighted imaging effect is obvious.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com