Patents
Literature
52 results about "Spin density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
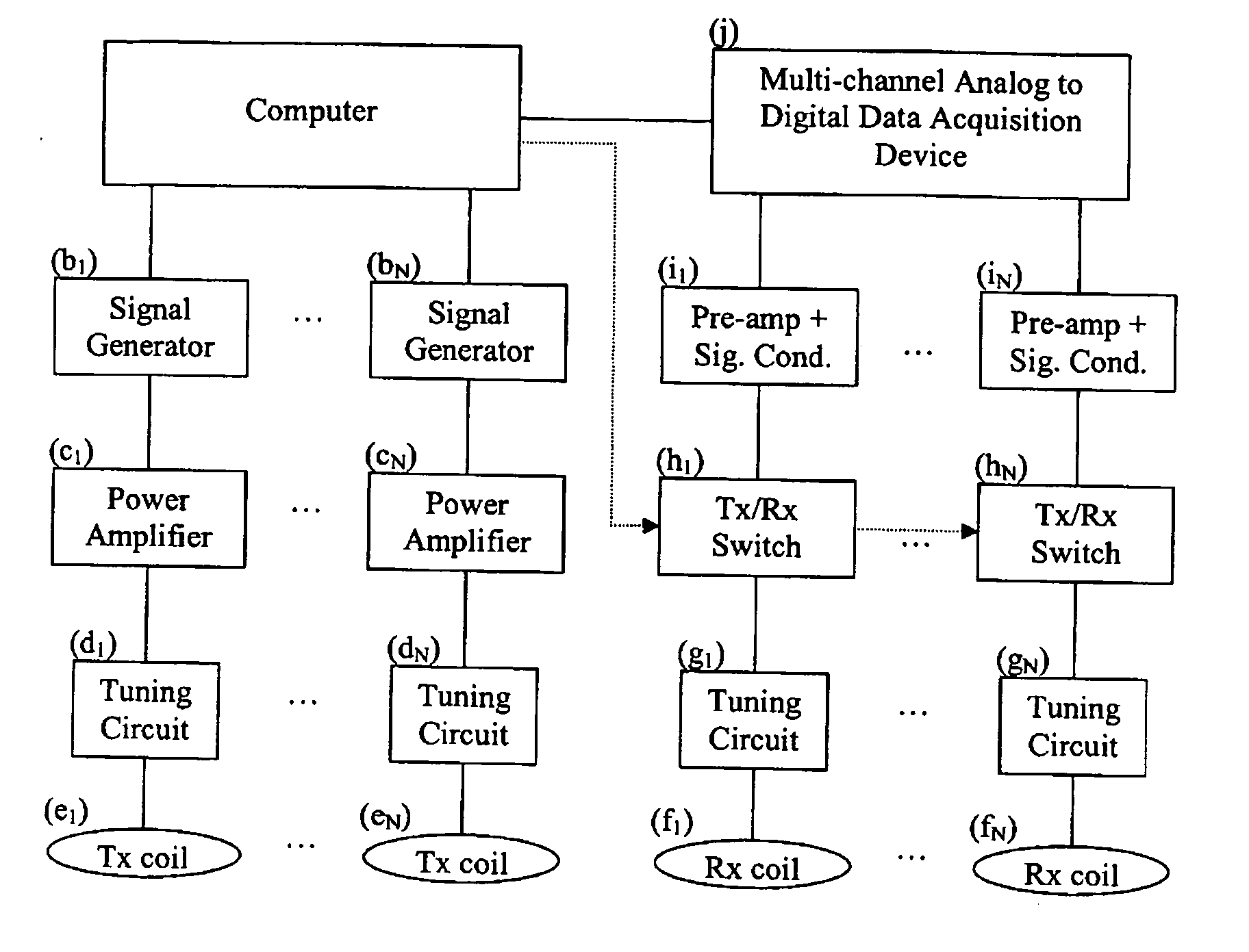
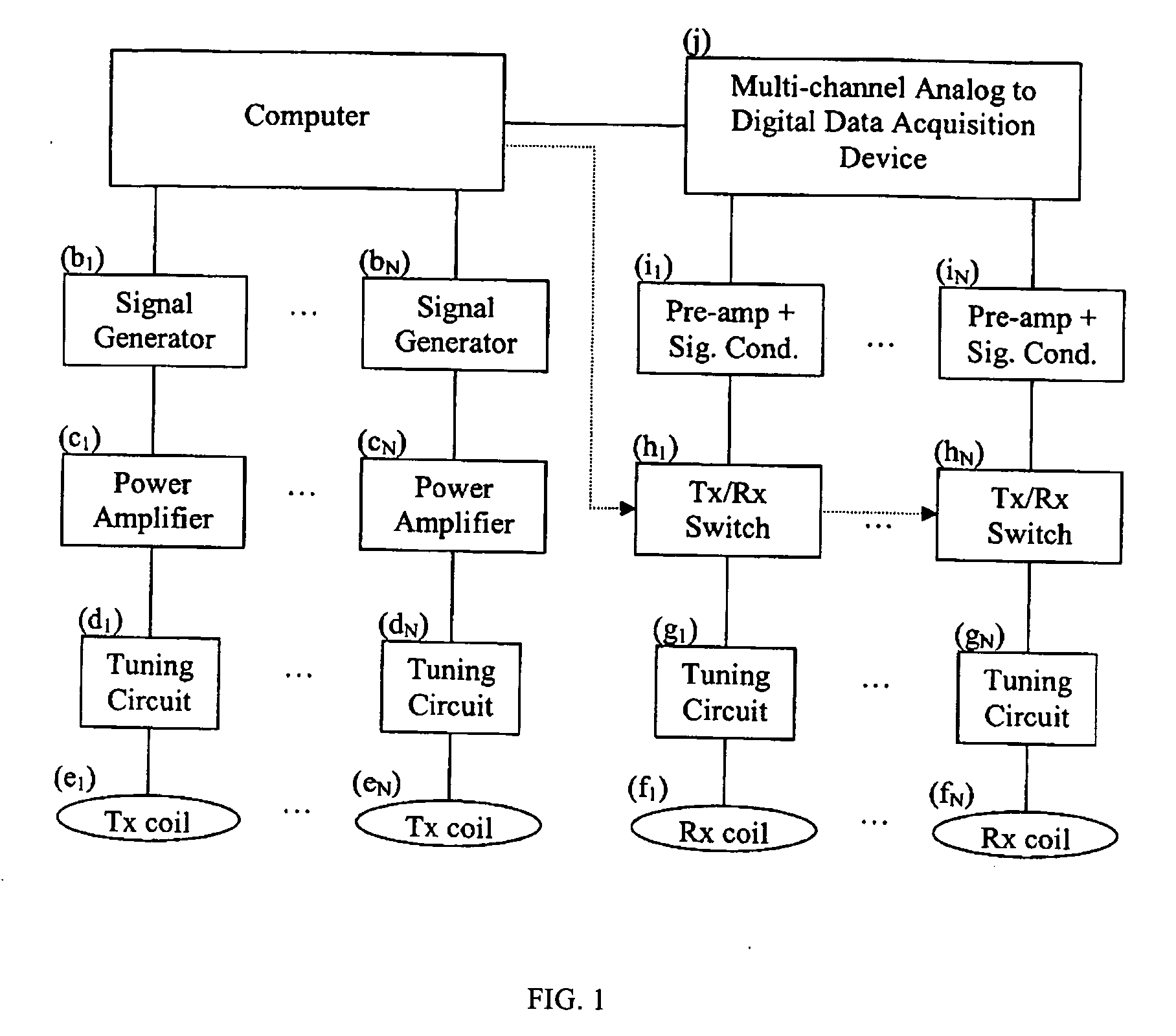
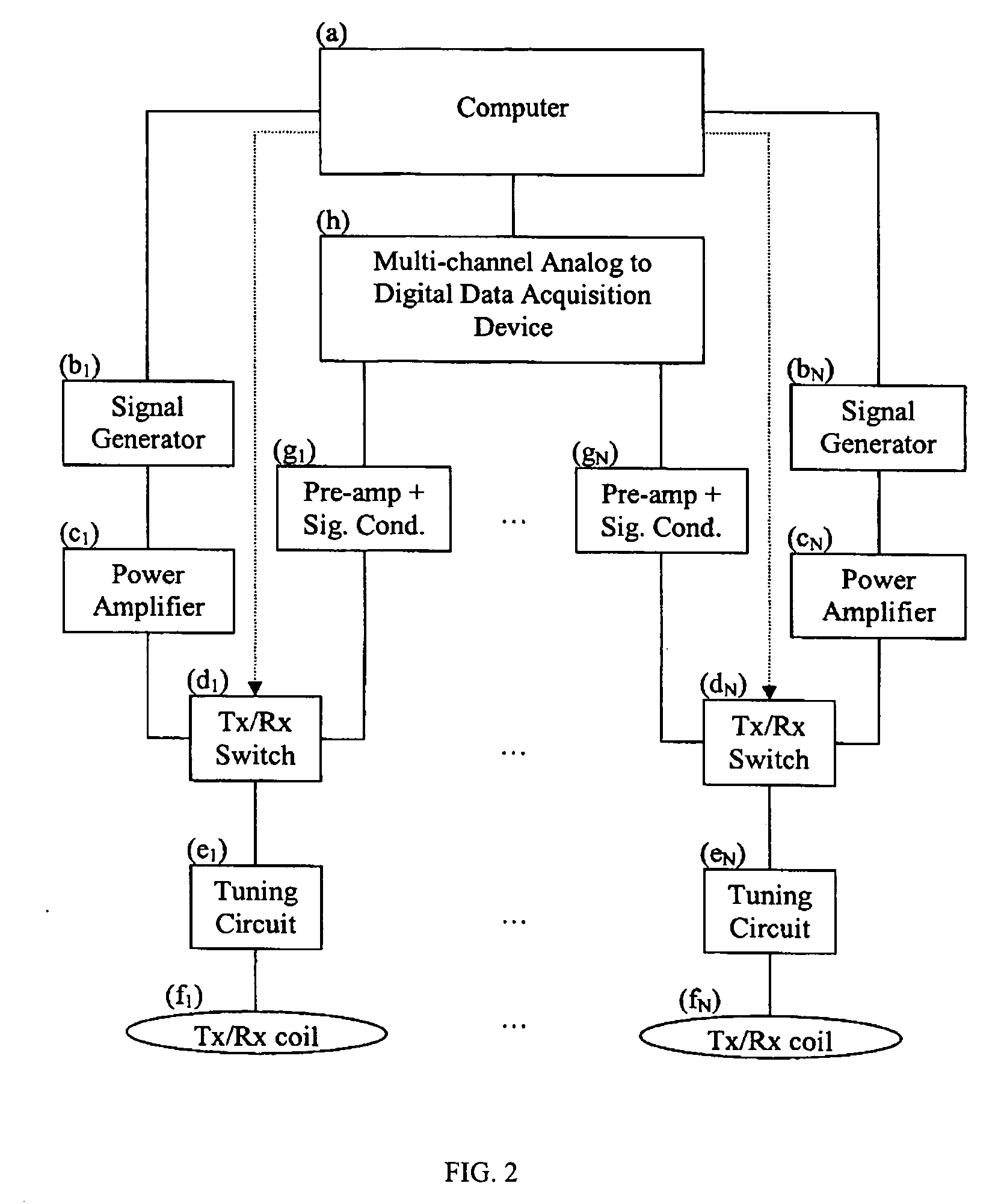
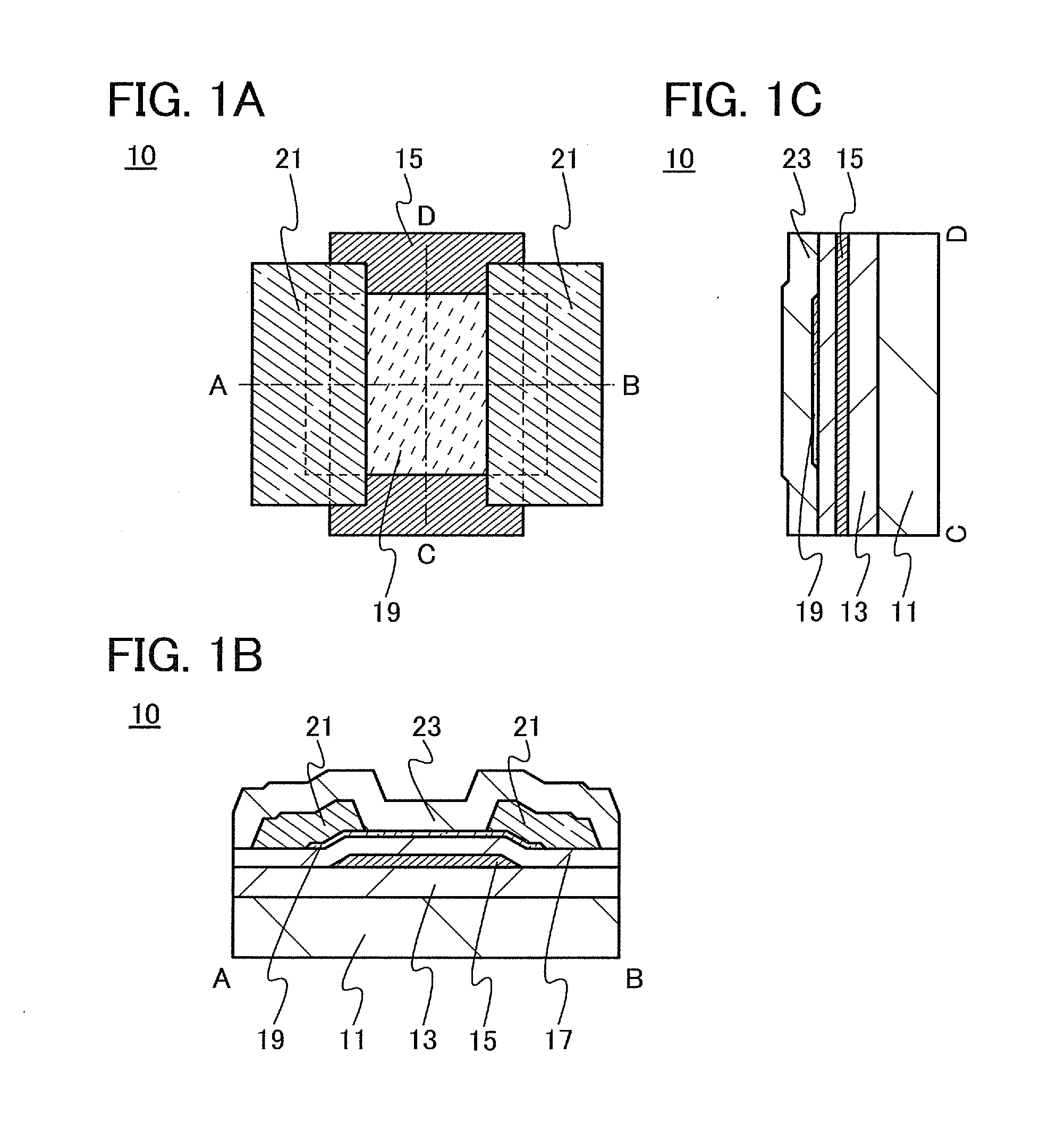
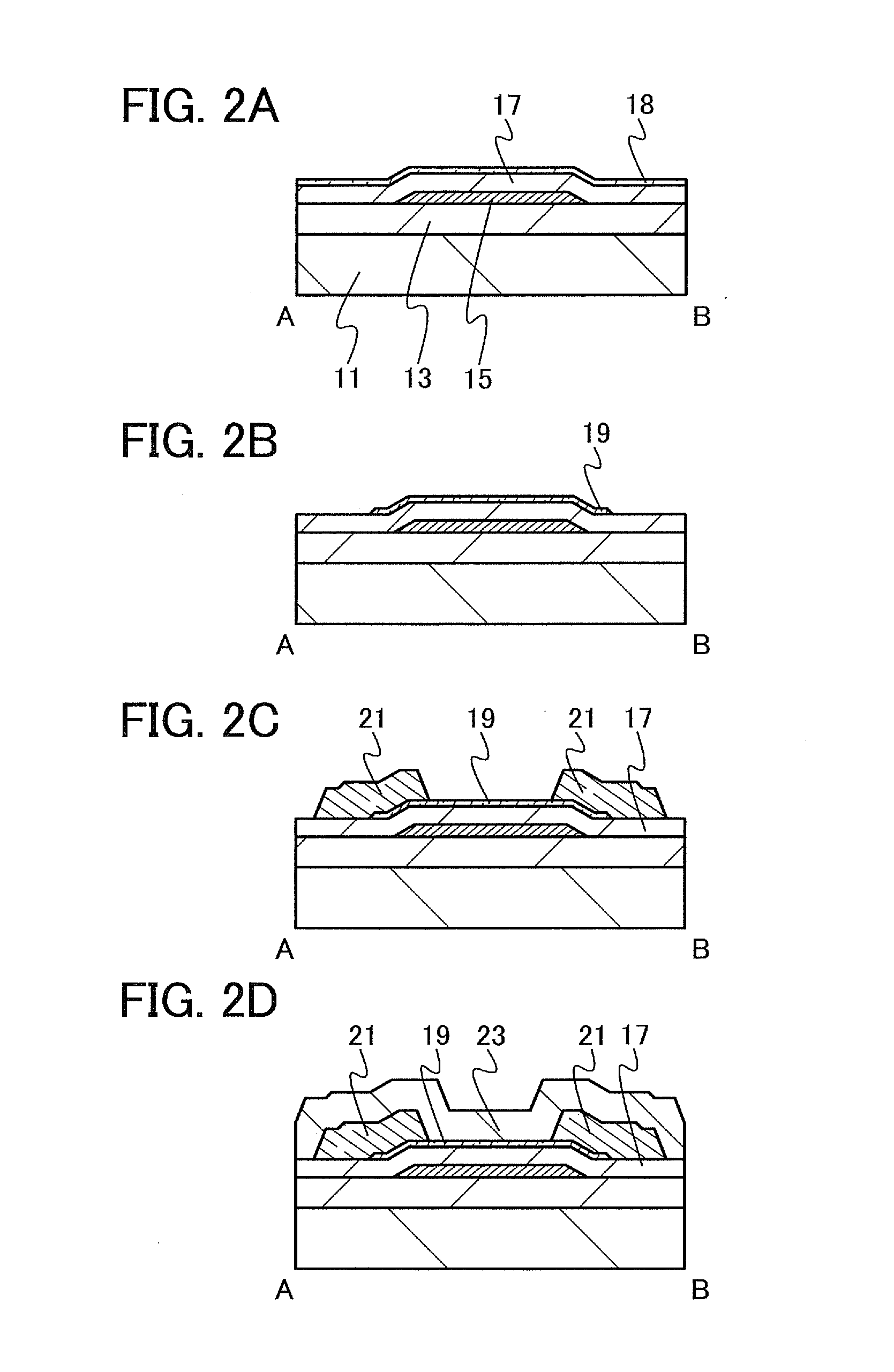
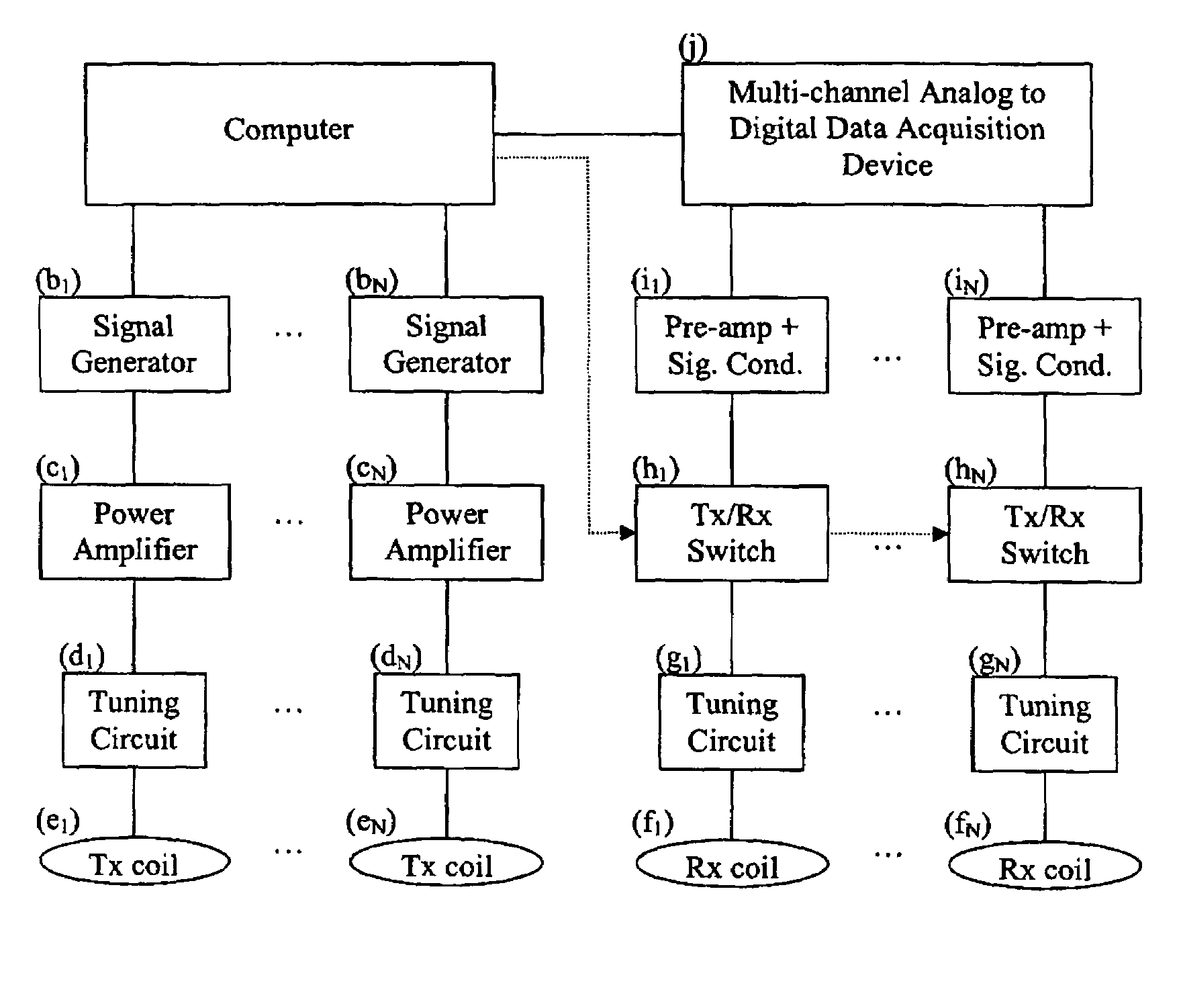
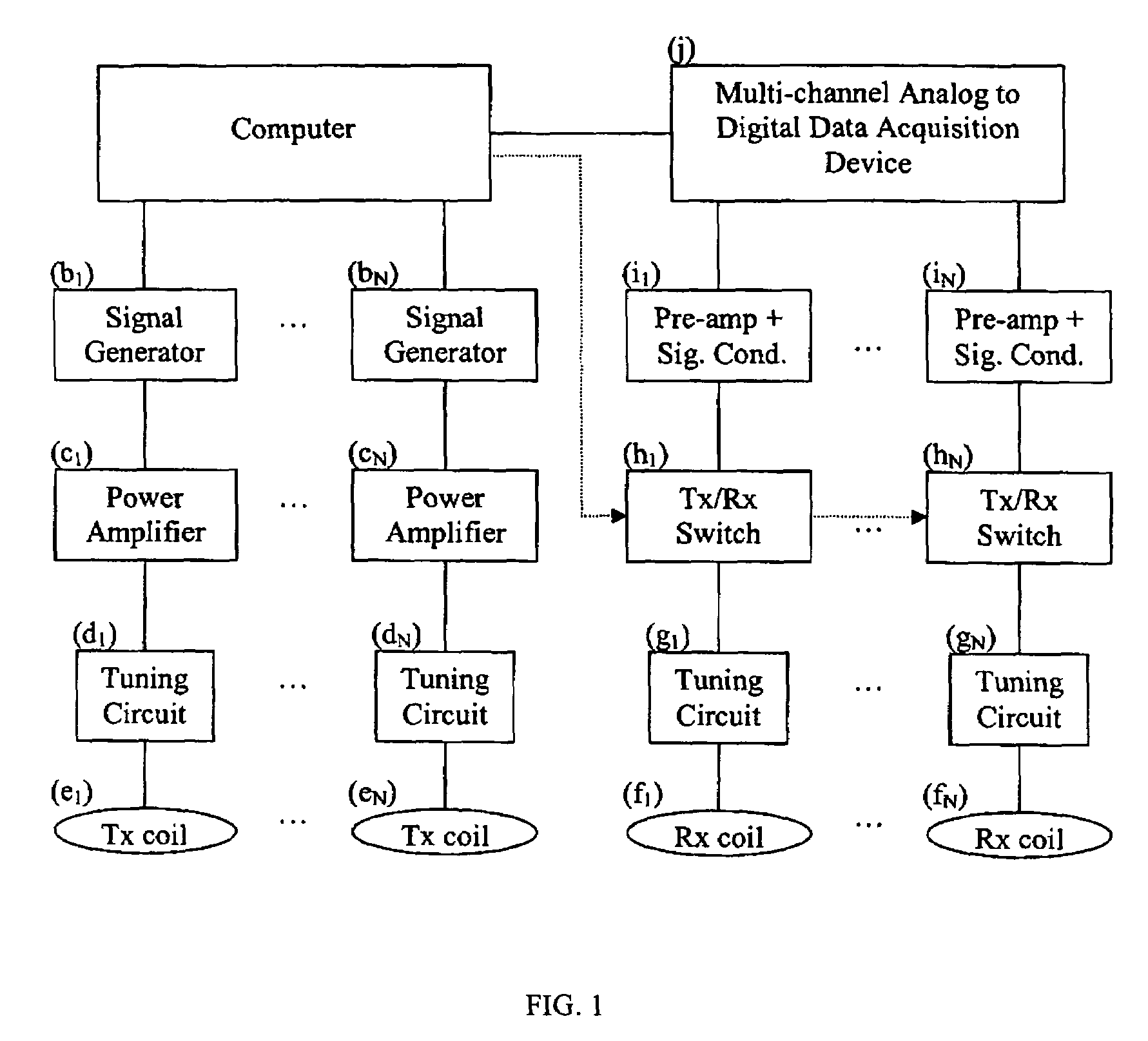
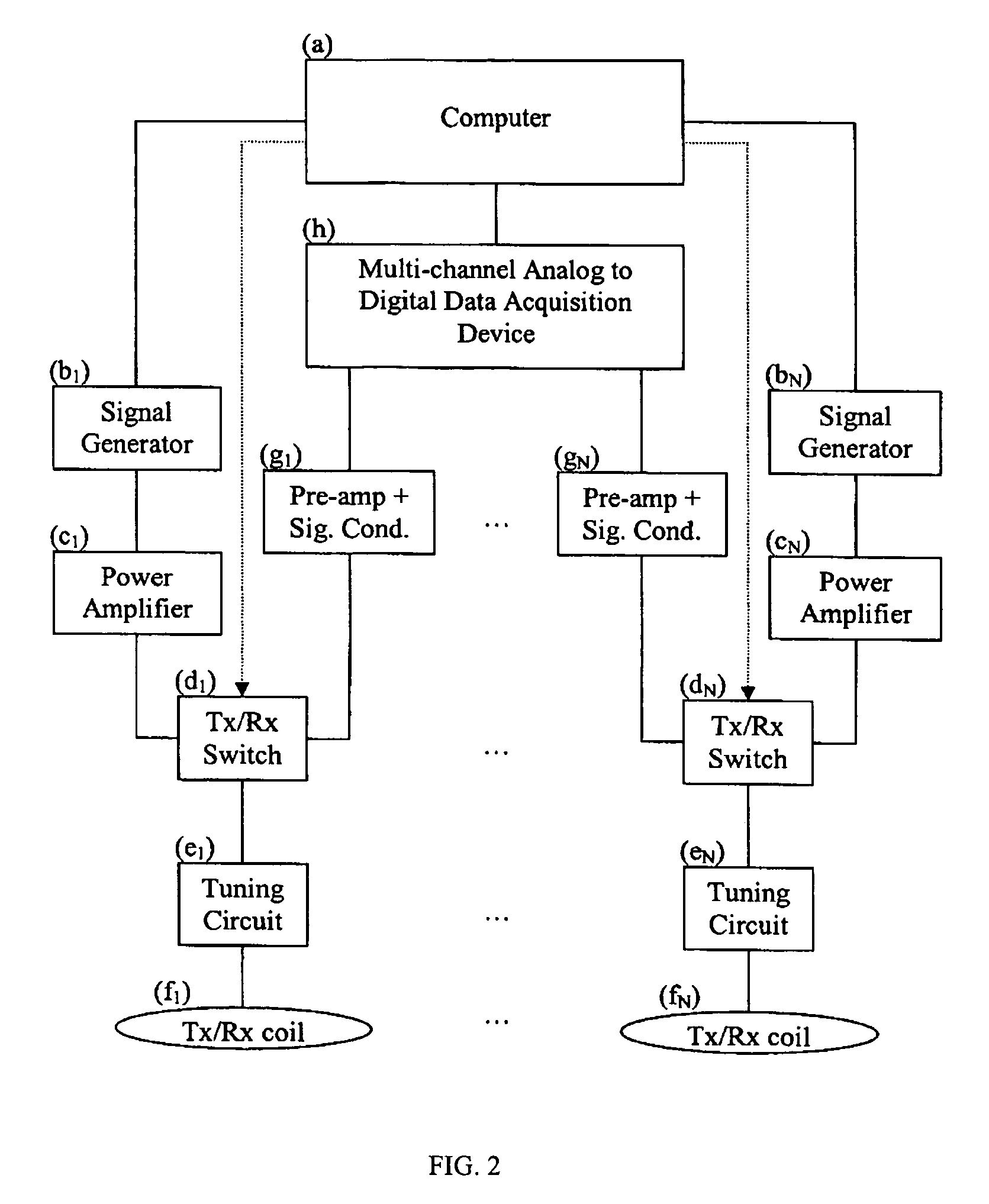
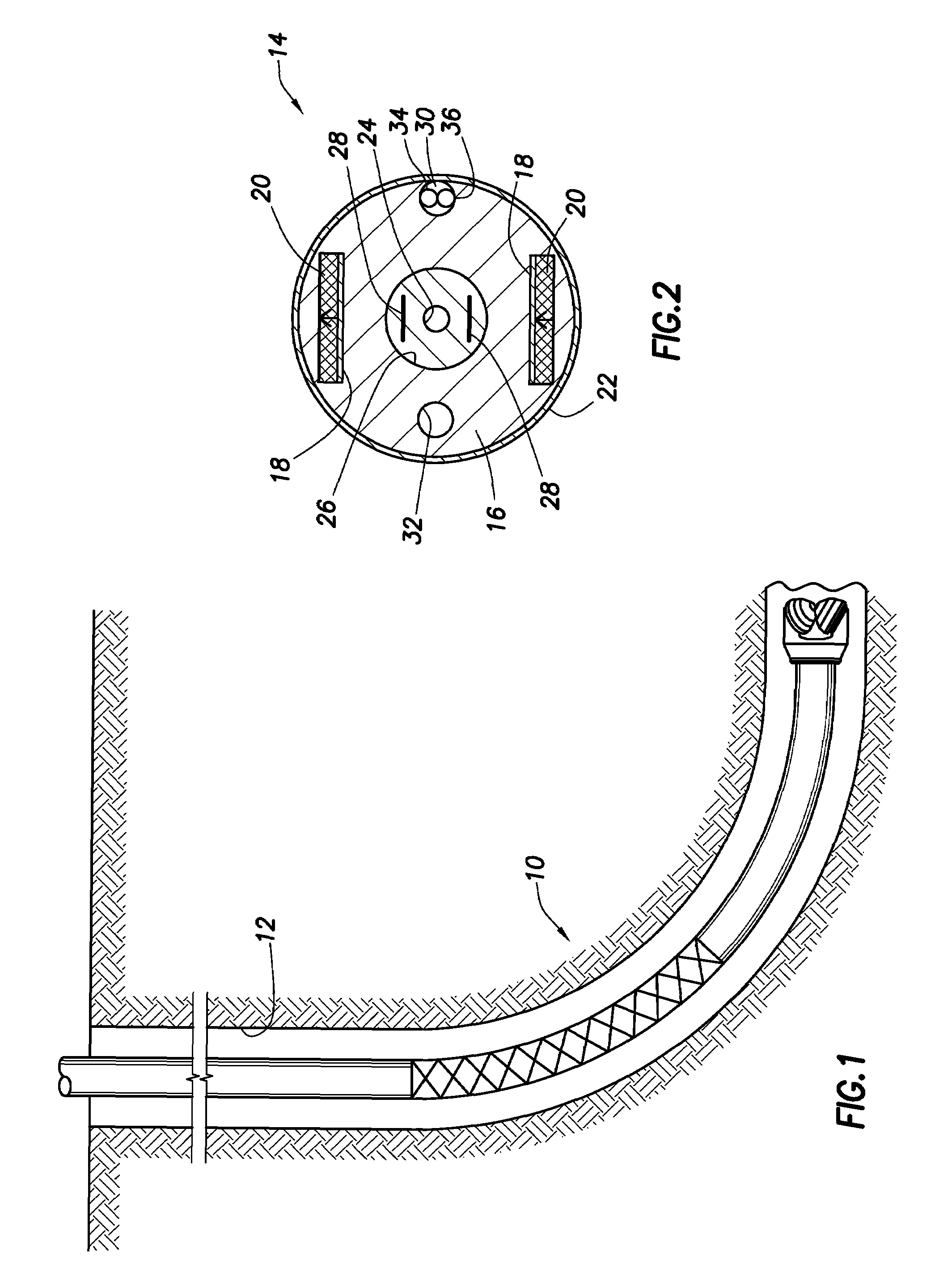
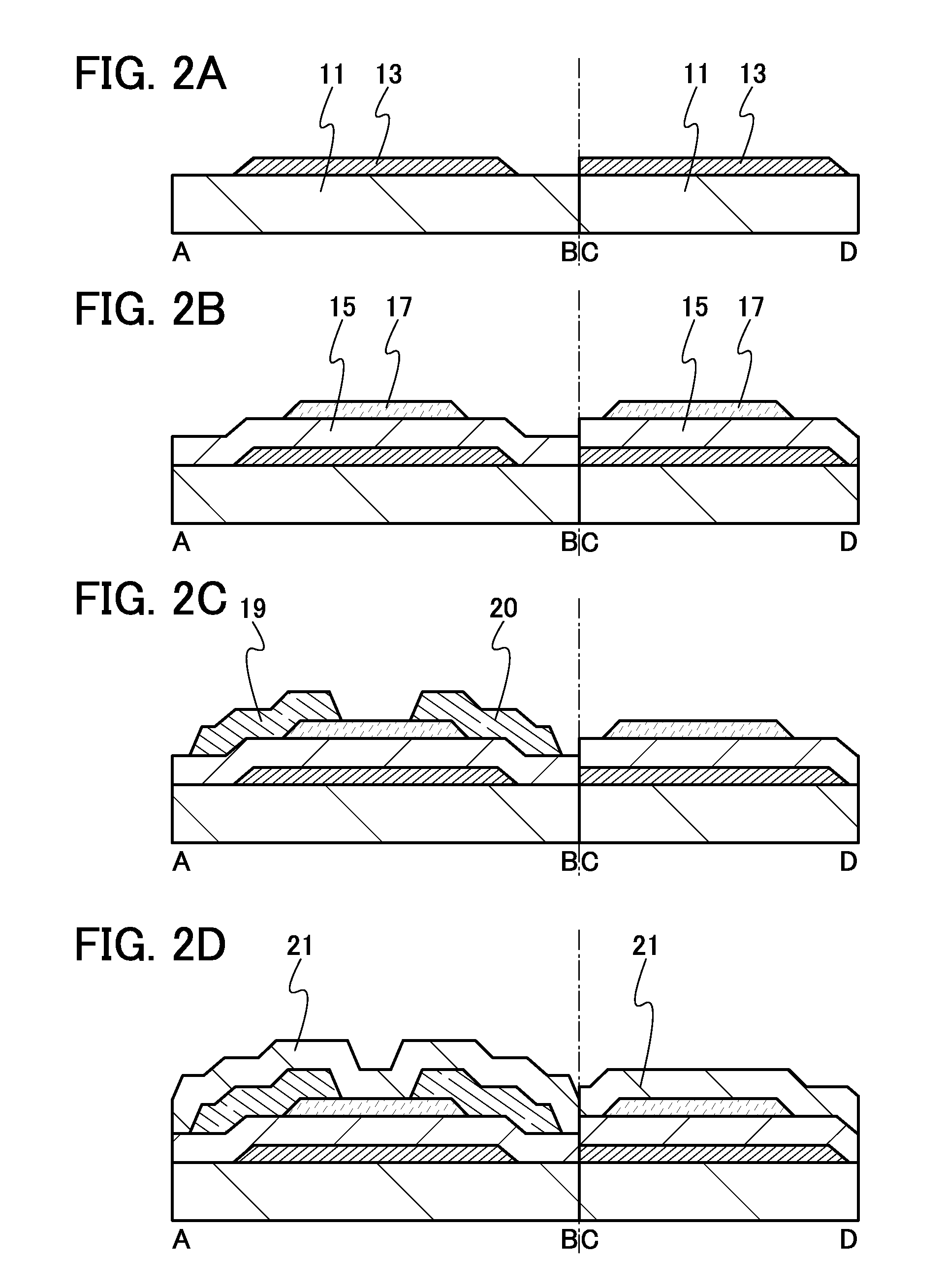
Multicoil NMR data acquisition and processing methods
ActiveUS20060186882A1Reduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientAcquisition apparatus
A multicoil NMR data acquisition apparatus and processing method for performing three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging in a static magnetic field without the application of controlled static magnetic field gradients. A preferred application relates specifically to the detection and localization of groundwater using the Earth's magnetic field. Multicoil arrays are used in both transmit and receive modes, and coherent data processing algorithms applied to the data to generate three-dimensional NMR spin density estimates. Disclosed are methods for acquiring NMR data using an array of at least two transmit and receive coils, and for processing such multicoil data to estimate the three-dimensional NMR spin density distributions.
Owner:VISTA CLARA
Fluorescent substance and production method thereof, and light emitting device
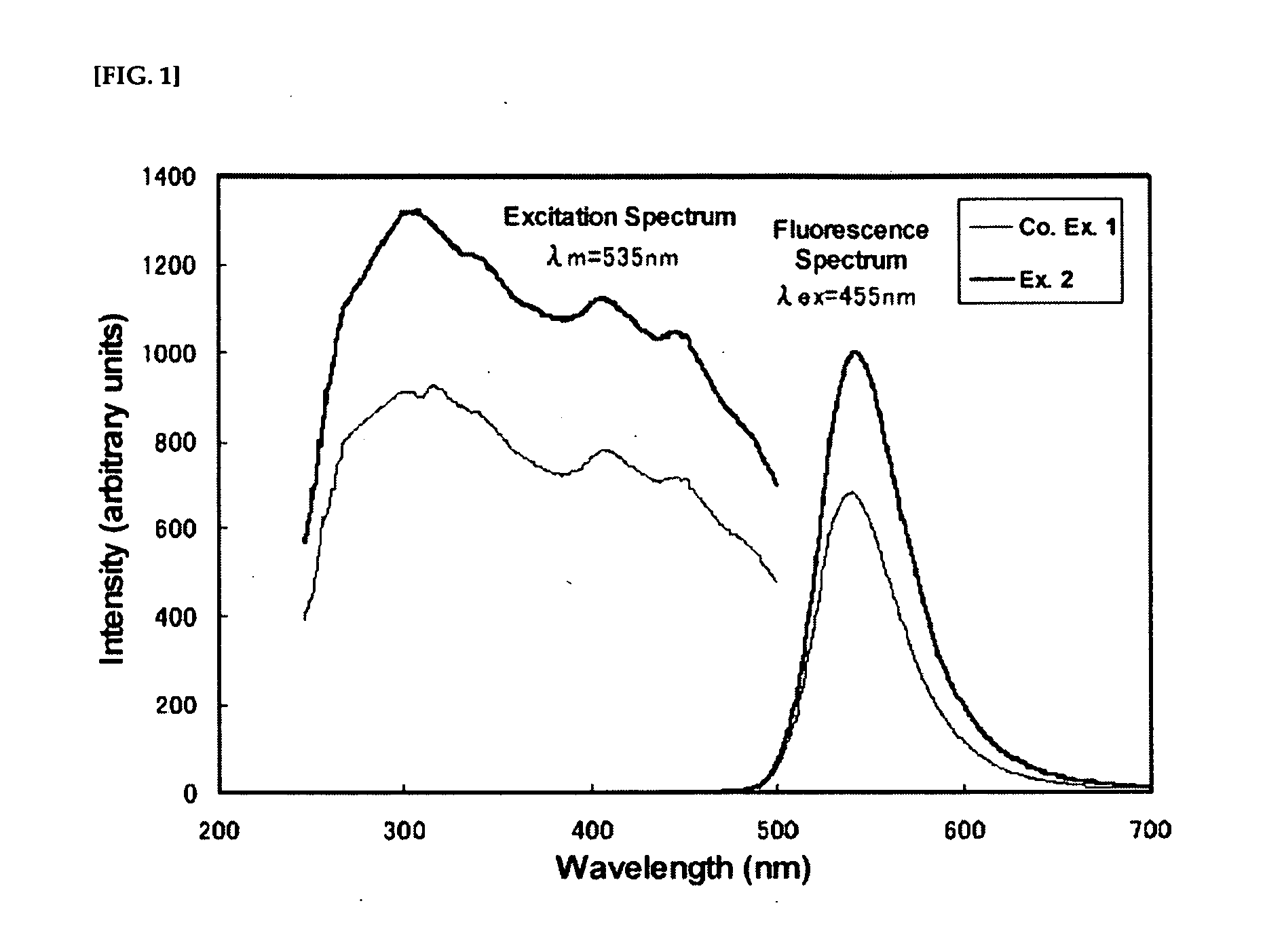
ActiveUS20100053932A1Excels substanceImprove efficiencyDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescenceUltraviolet lights
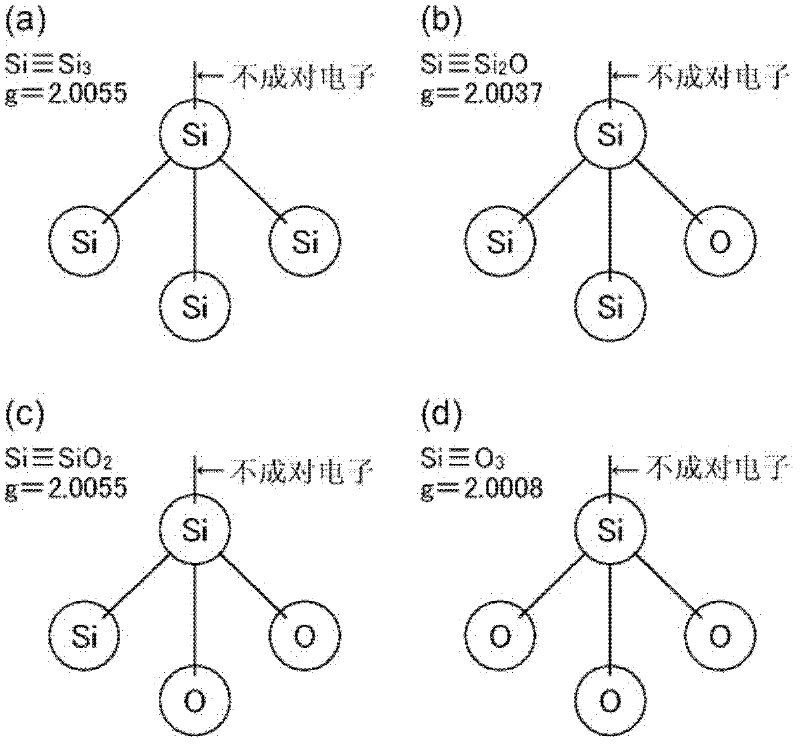
Offered is a fluorescent substance consisting of Eu-activated β-sialon and capable of enhancing the brightness of a light emitting device such as a white LED using blue or ultraviolet light as a light source. The fluorescent substance has as its main constituent a β-sialon represented by the general formula Si6-zAlzOzN8-z and containing Eu, wherein the spin density is 2.0×1017 / g or less as measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy corresponding to an absorption of g=2.00±0.02 at 25° C. In the above fluorescent substance, it is preferable that lattice constant a of the β-sialon be 0.7608-0.7620 nm, the lattice constant c be 0.2908-0.2920 nm, and the Eu content be 0.1-3 mass %.
Owner:DENKA CO LTD
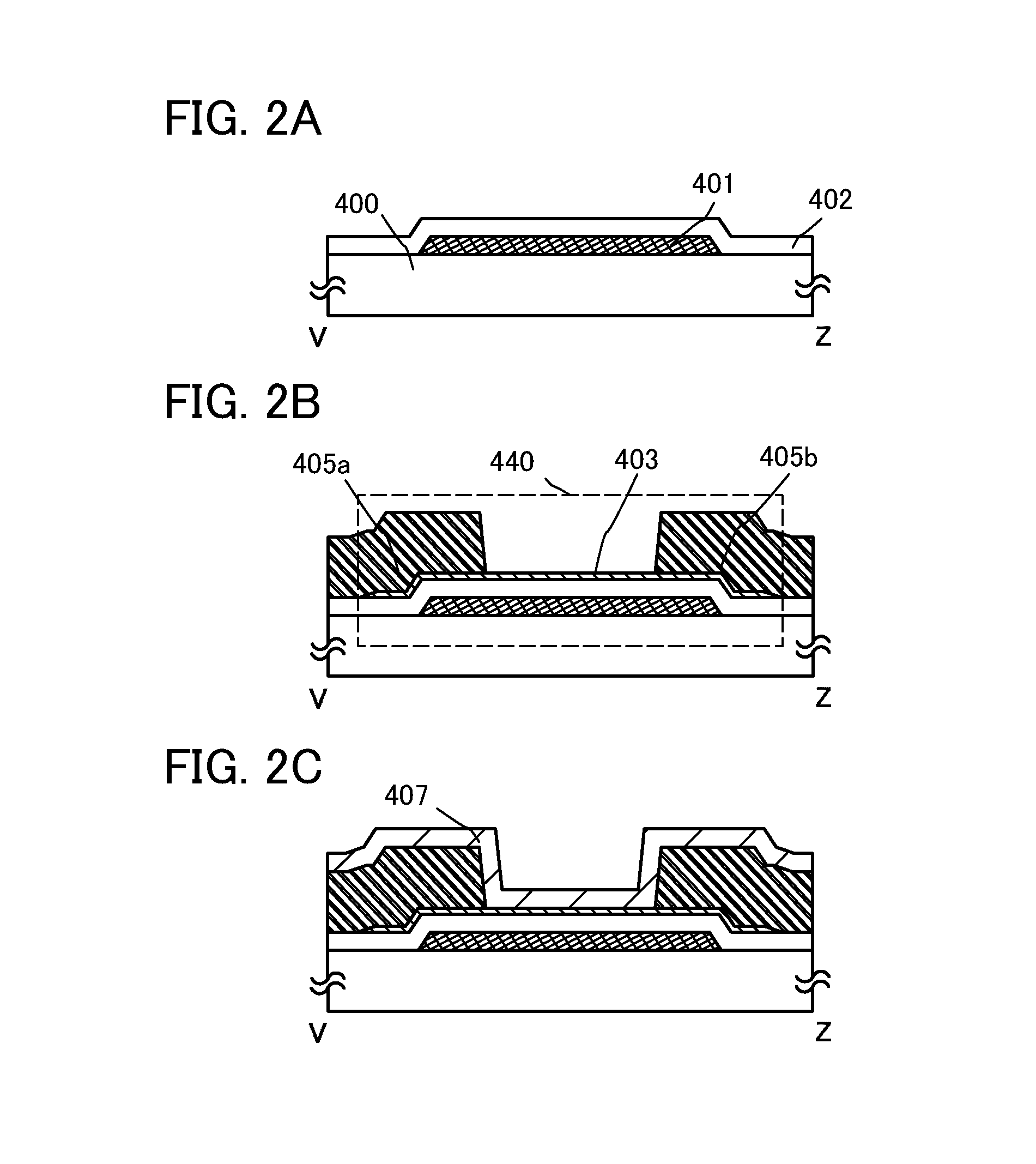
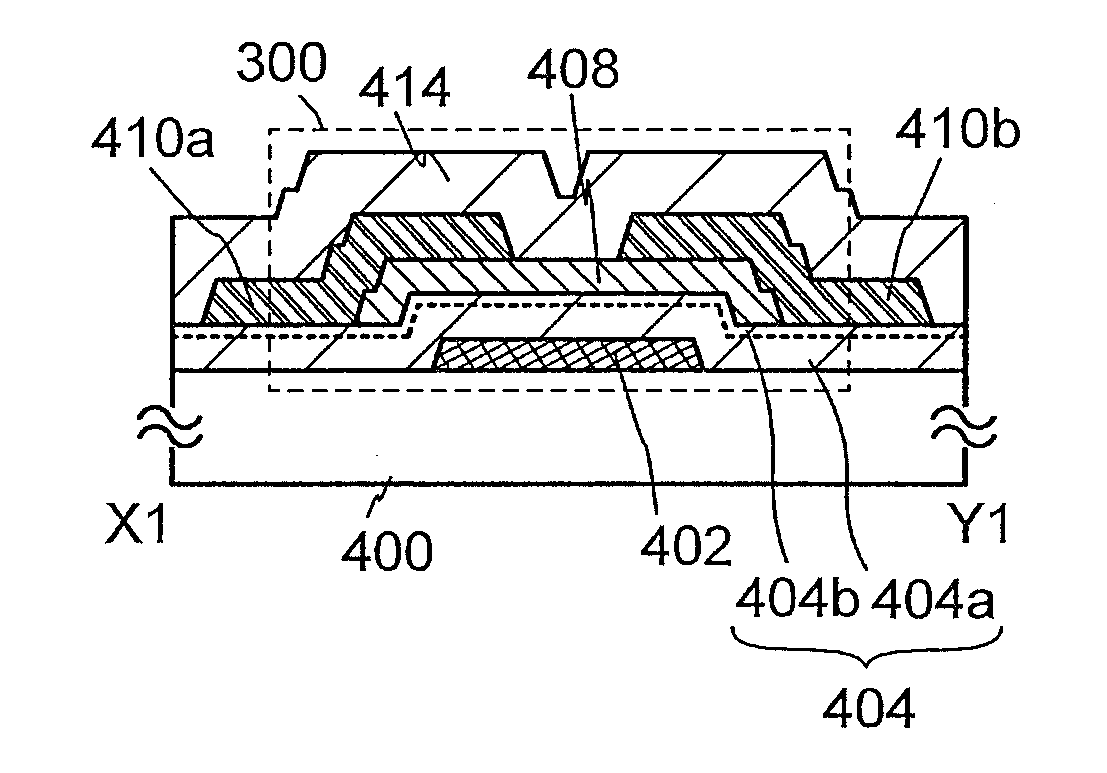
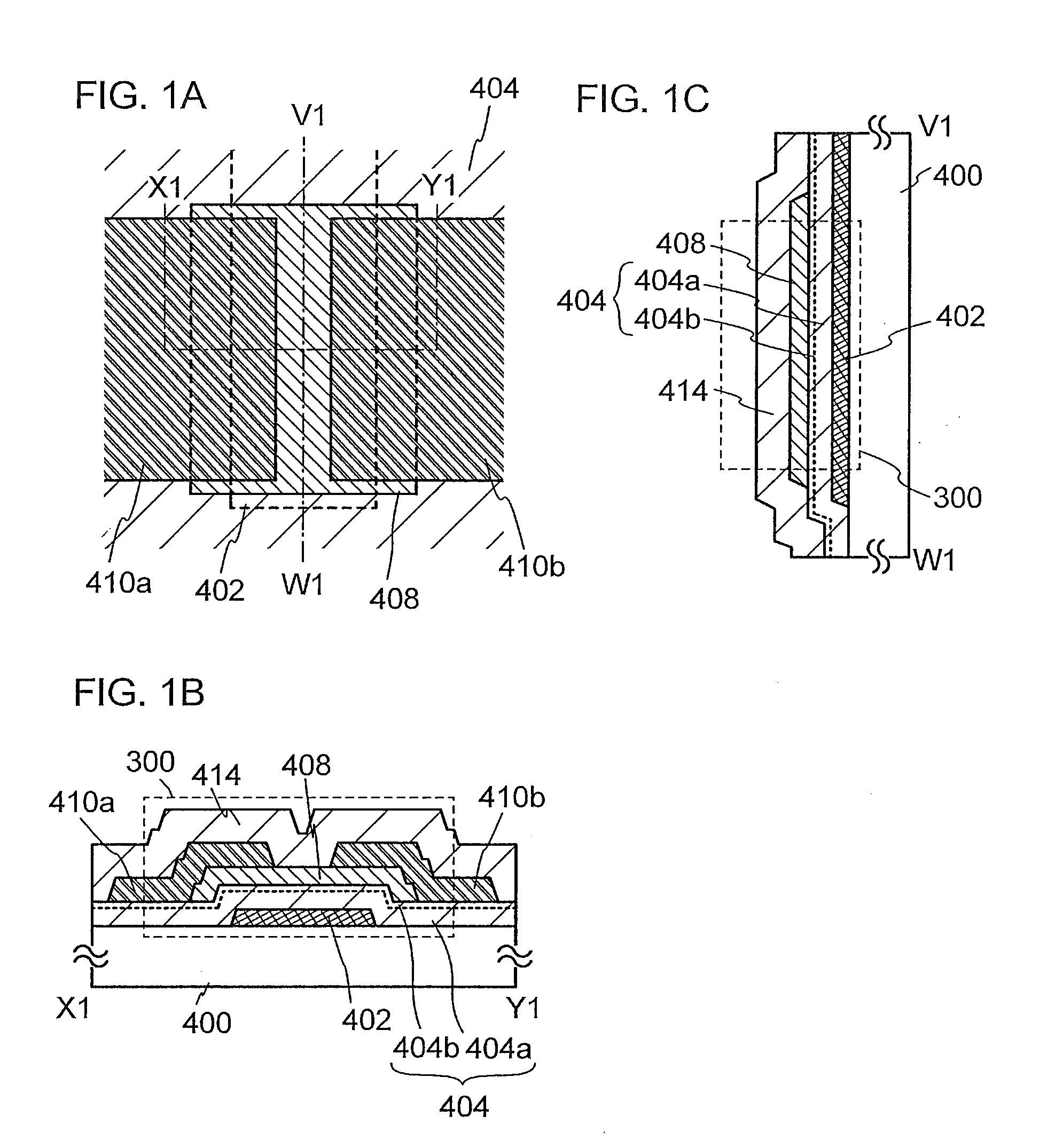
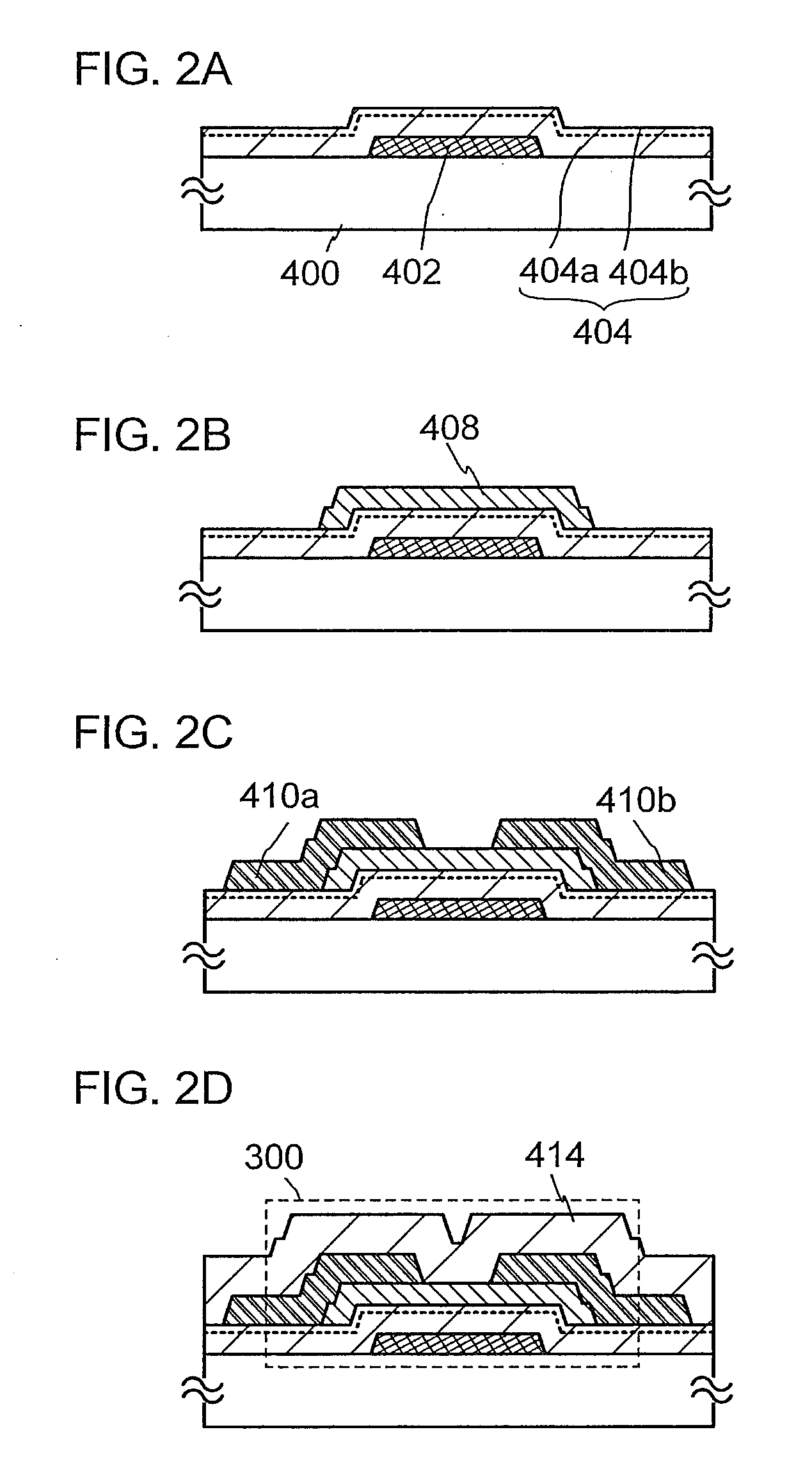
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130270550A1Excellent electrical propertiesIncrease film densityTransistorSolid-state devicesElectronPhysics
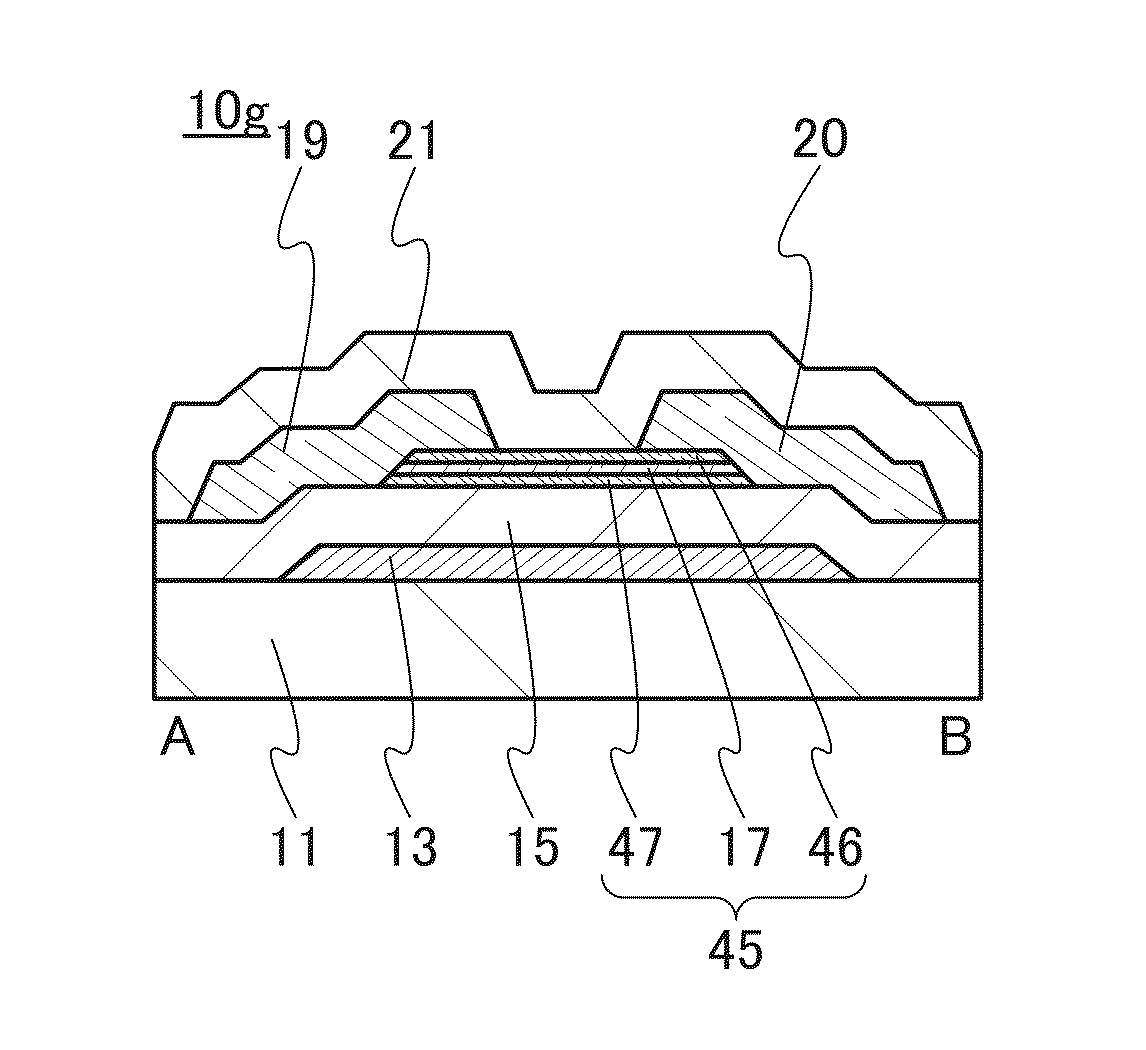
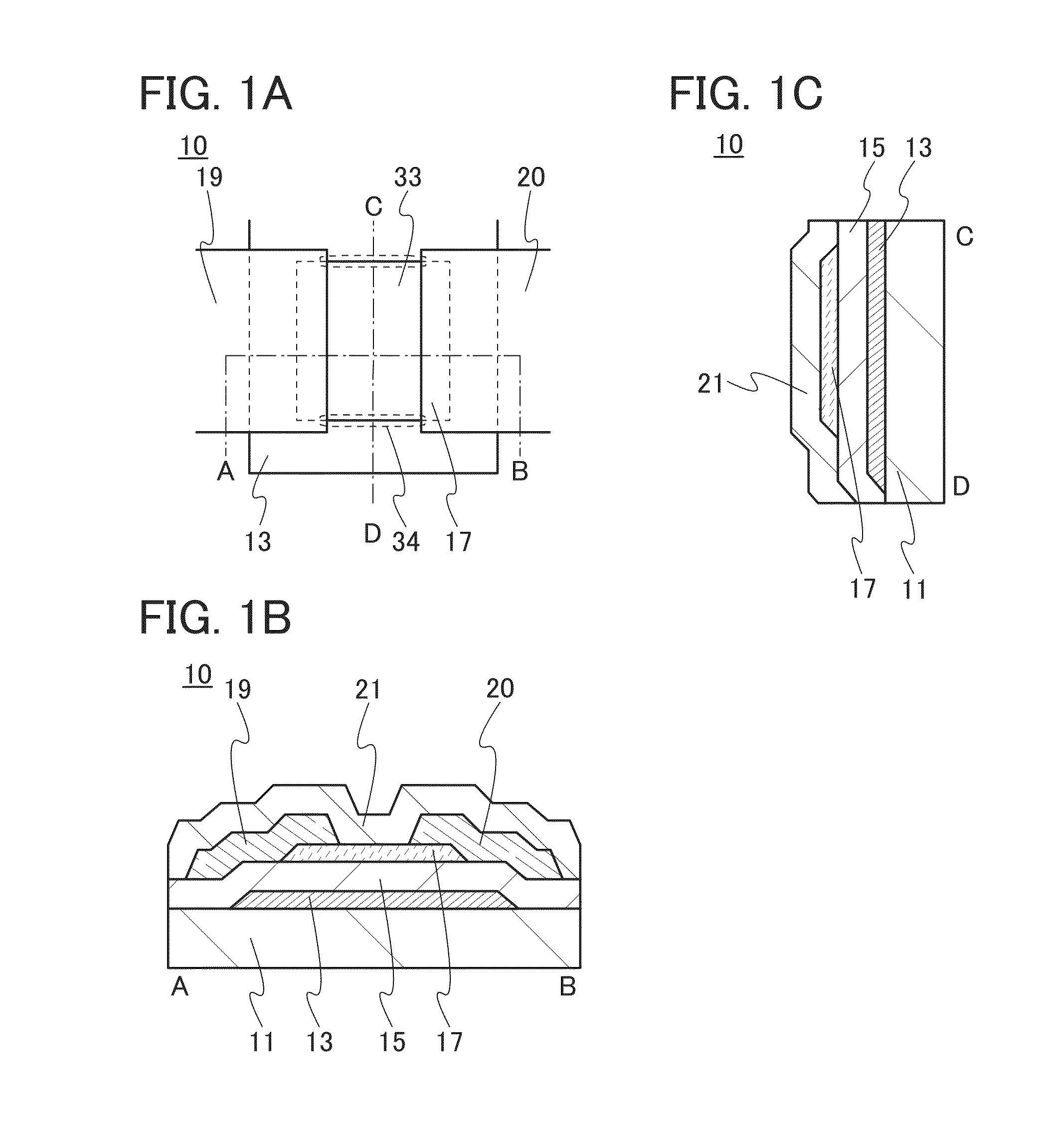
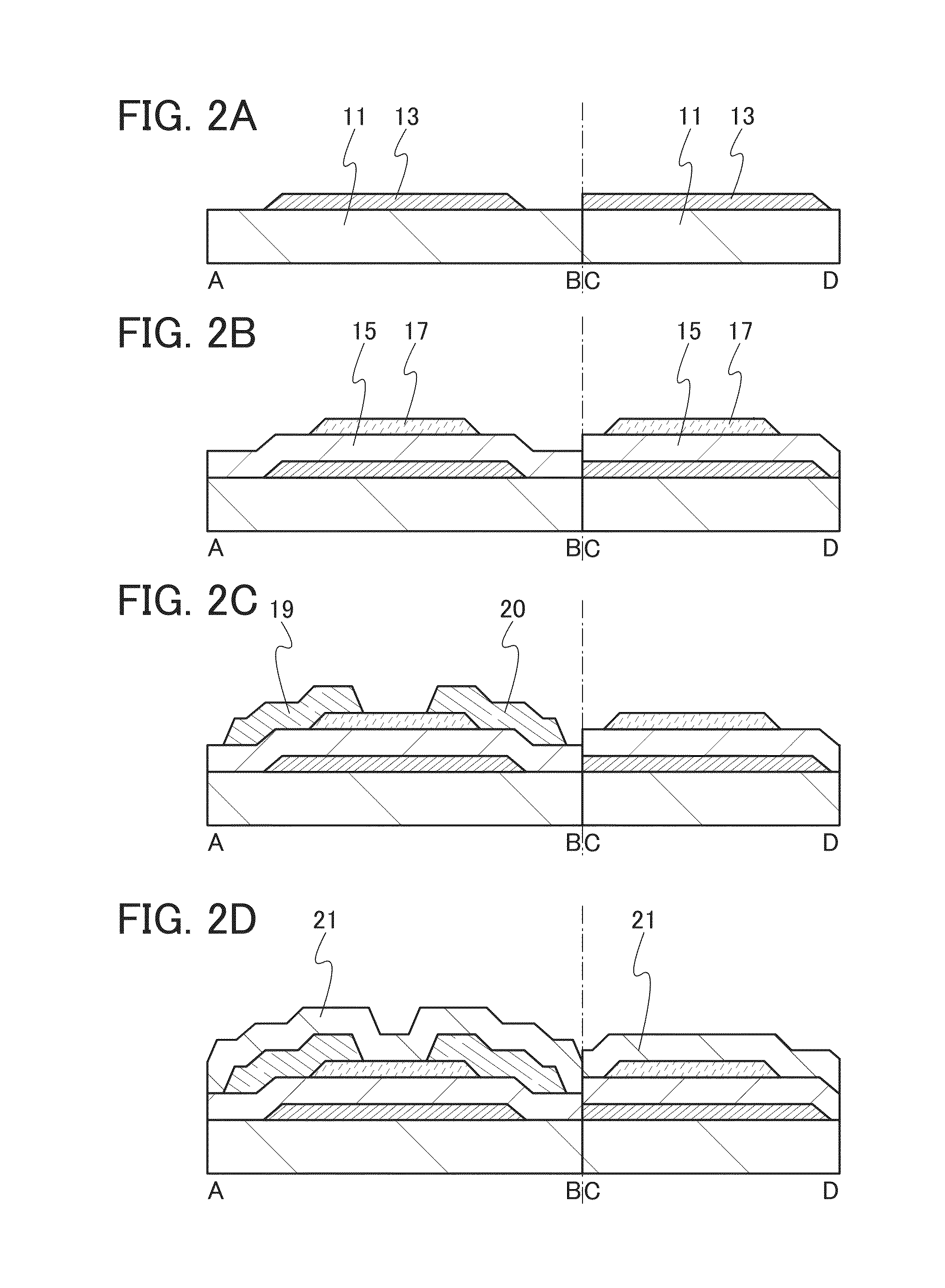
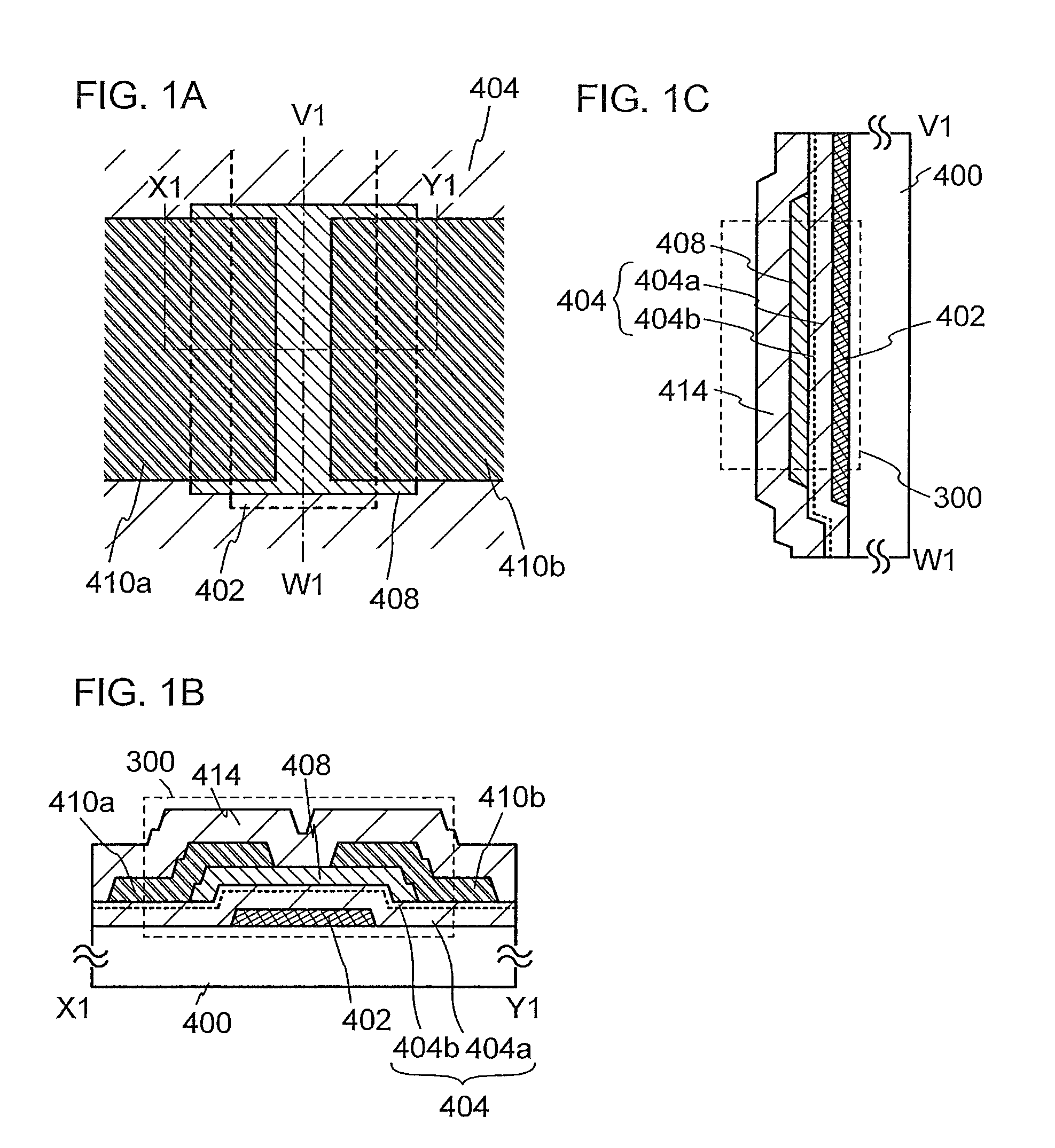
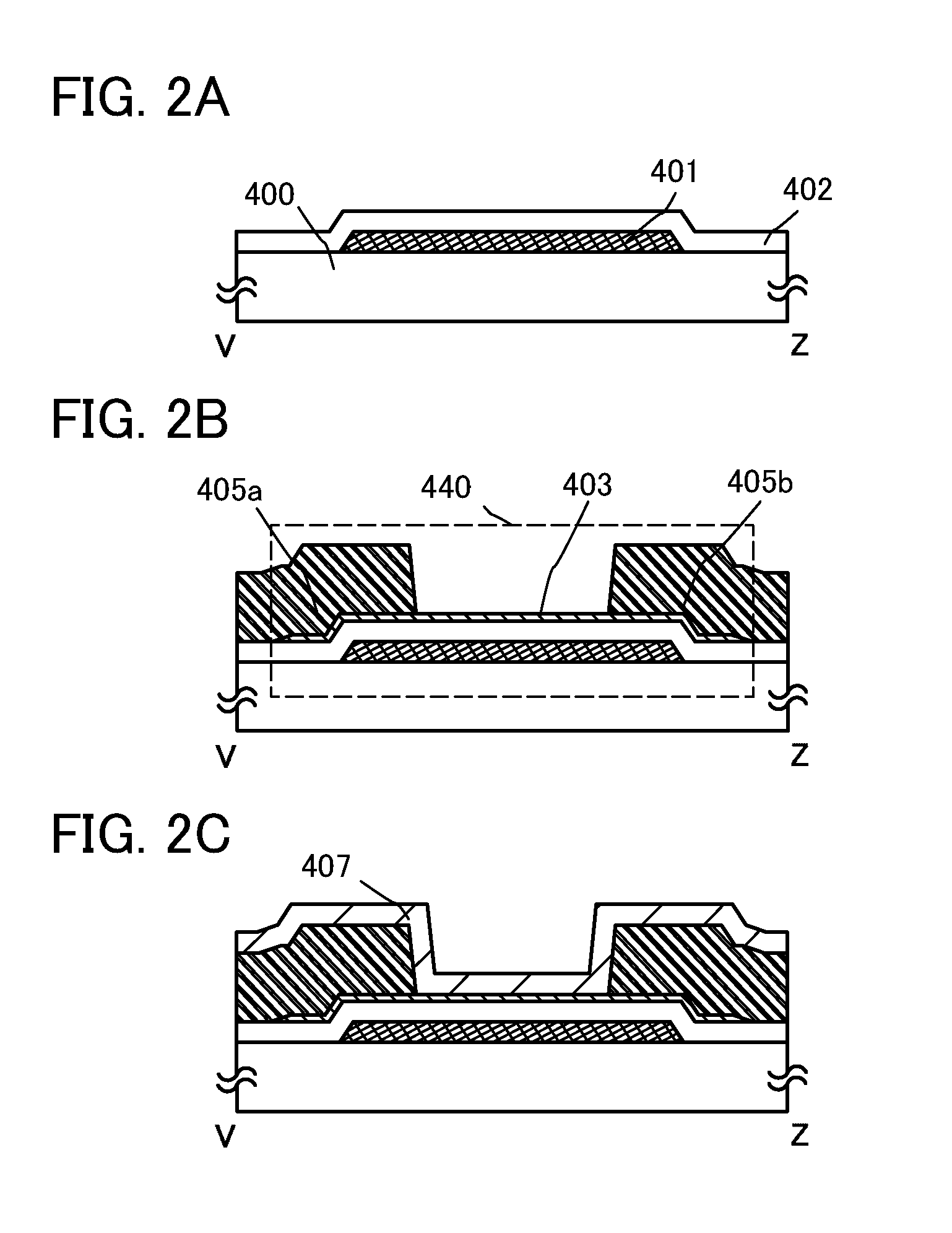
Electric characteristics of a semiconductor device using an oxide semiconductor are improved. Further, a highly reliable semiconductor device in which a variation in electric characteristics with time or a variation in electric characteristics due to a gate BT stress test with light irradiation is small is manufactured. A transistor includes a gate electrode, an oxide semiconductor film overlapping with part of the gate electrode with a gate insulating film therebetween, and a pair of electrodes in contact with the oxide semiconductor film. The gate insulating film is an insulating film whose film density is higher than or equal to 2.26 g / cm3 and lower than or equal to 2.63 g / cm3 and whose spin density of a signal with a g value of 2.001 is 2×1015 spins / cm3 or less in electron spin resonance.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Multicoil NMR data acquisition and processing methods
ActiveUS7466128B2Reduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientAcquisition apparatus
Owner:VISTA CLARA
High pressure/high temperature magnetic resonance tool
InactiveUS7683613B2Easy to useMeasurements using electron paramagnetic resonanceMaterial analysis by using resonanceResonance measurementHigh pressure
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
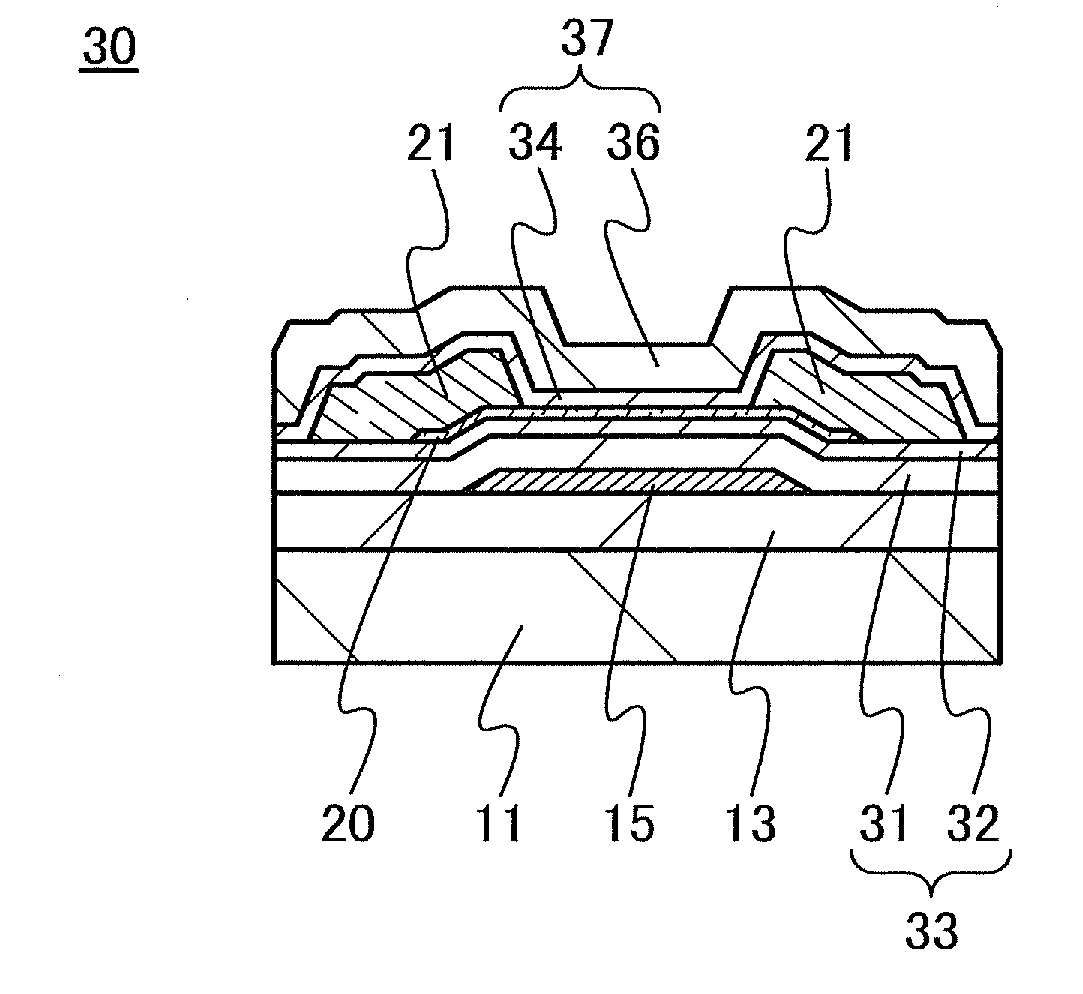
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20130153892A1Improve reliabilityLow reliabilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialBottom gate
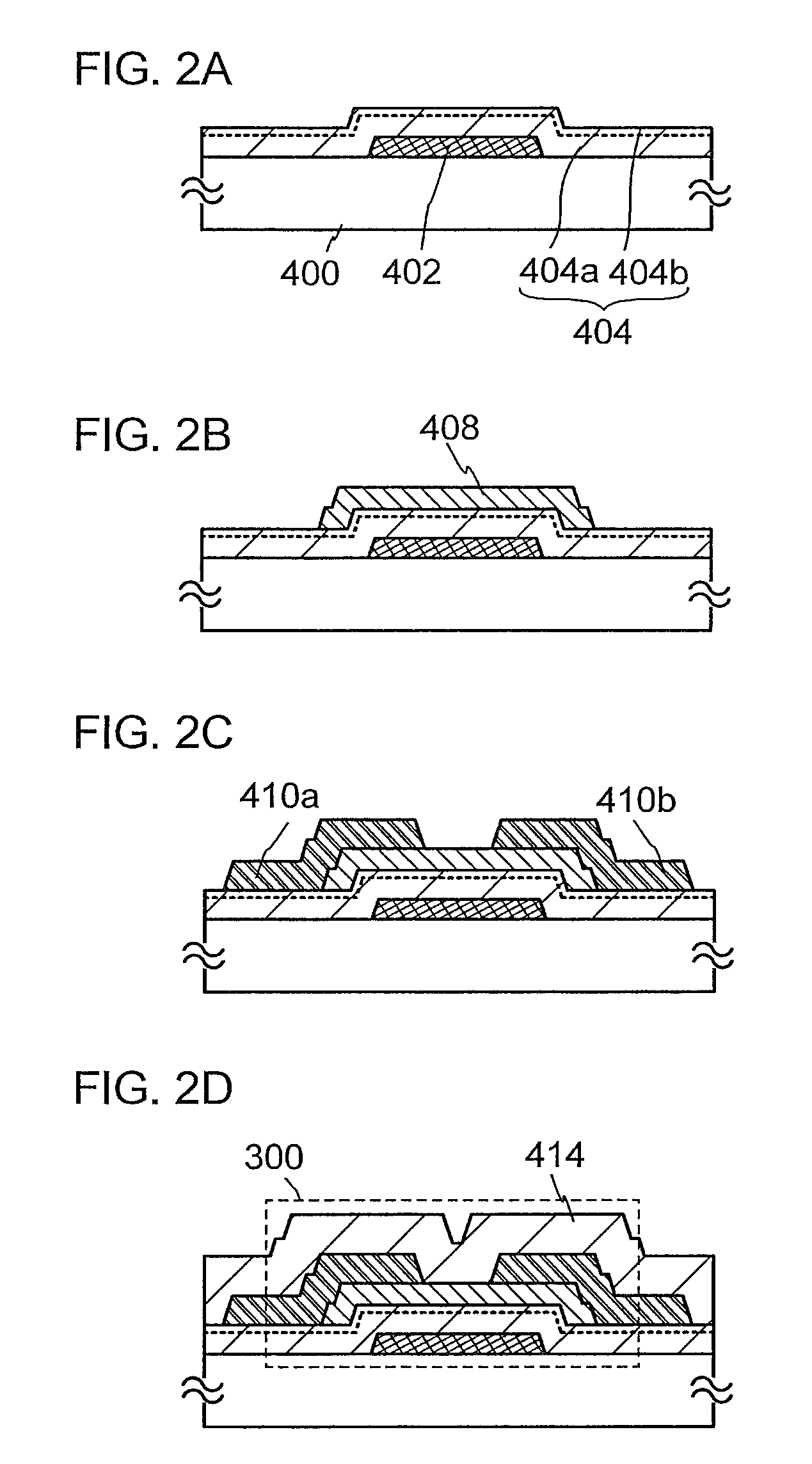
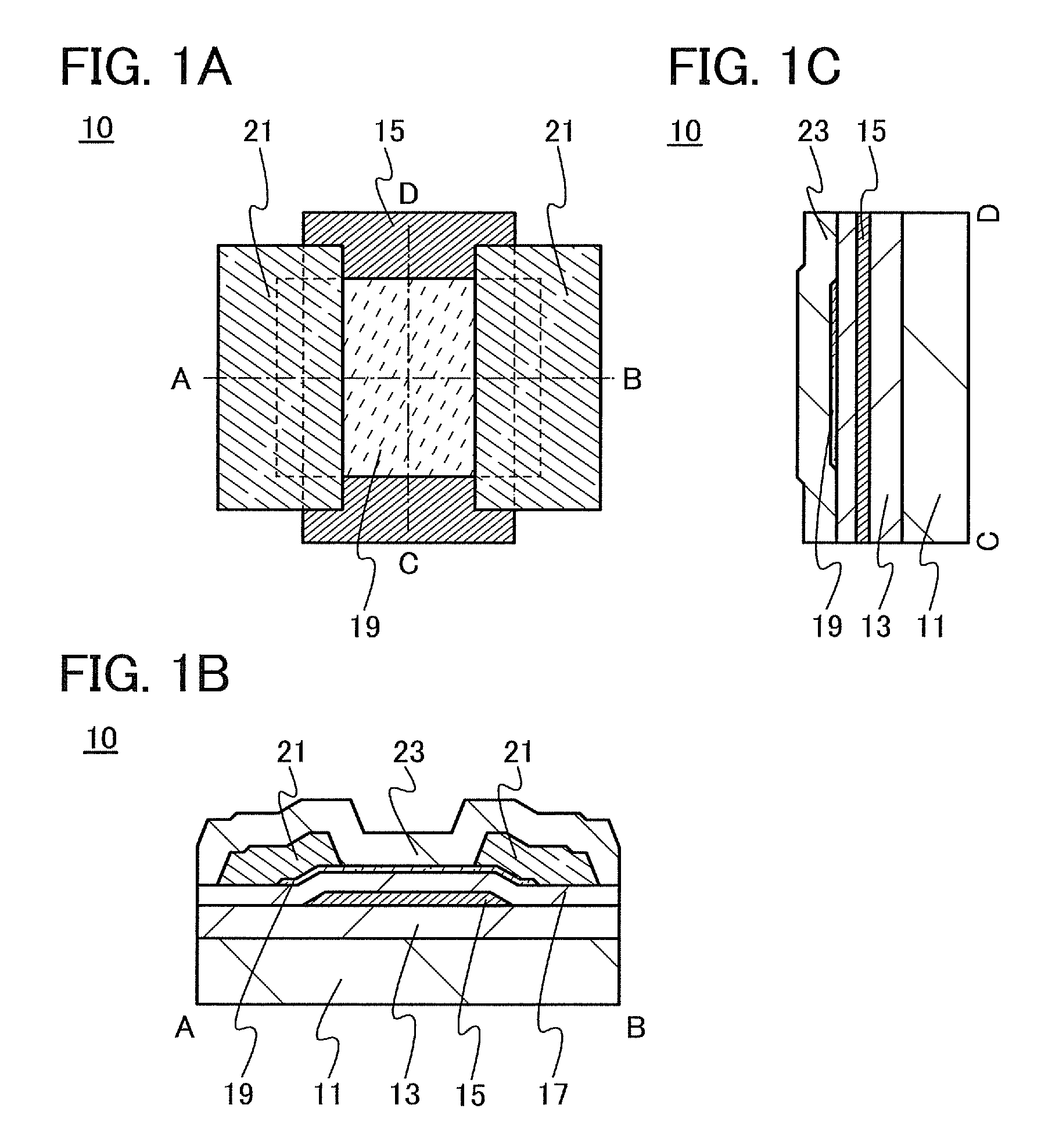
A highly reliable semiconductor device that includes a transistor including an oxide semiconductor is provided. In a semiconductor device which includes a bottom-gate transistor including an oxide semiconductor film, the spin density of the oxide semiconductor film is lower than or equal to 1×1018 spins / cm3, preferably lower than or equal to 1×1017 spins / cm3, further preferably lower than or equal to 1×1016 spins / cm3. The conductivity of the oxide semiconductor film is lower than or equal to 1×103 S / cm, preferably lower than or equal to 1×102 S / cm, further preferably lower than or equal to 1×101 S / cm.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
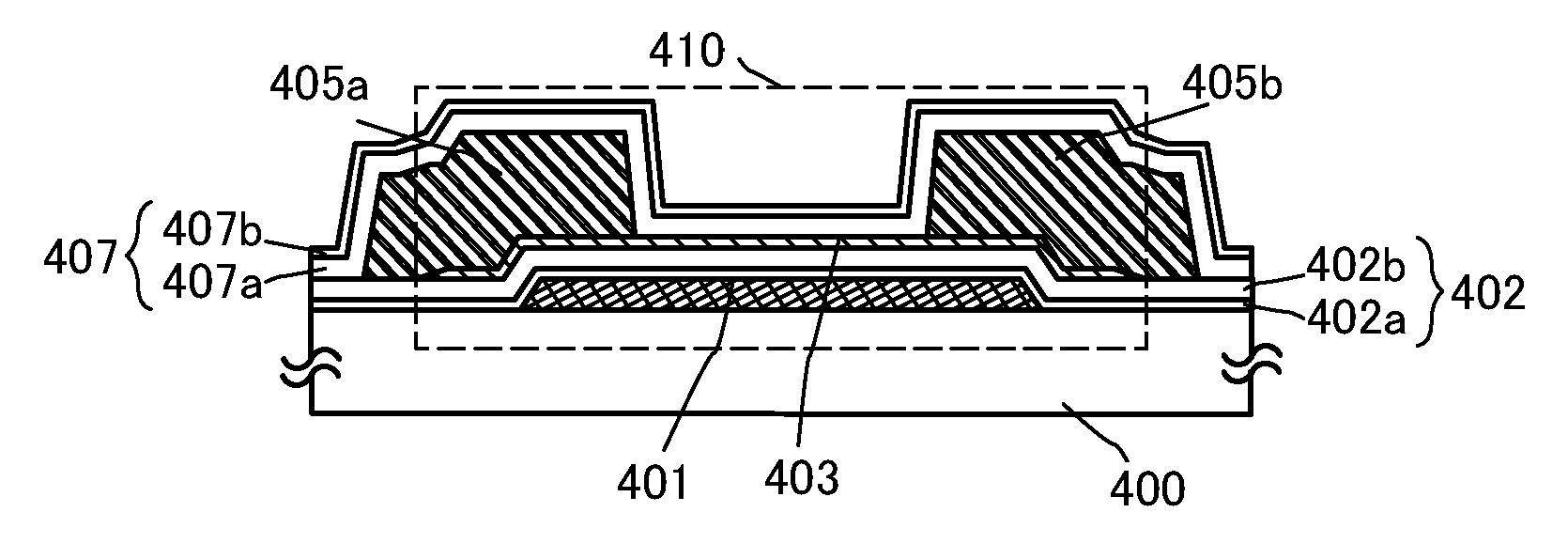
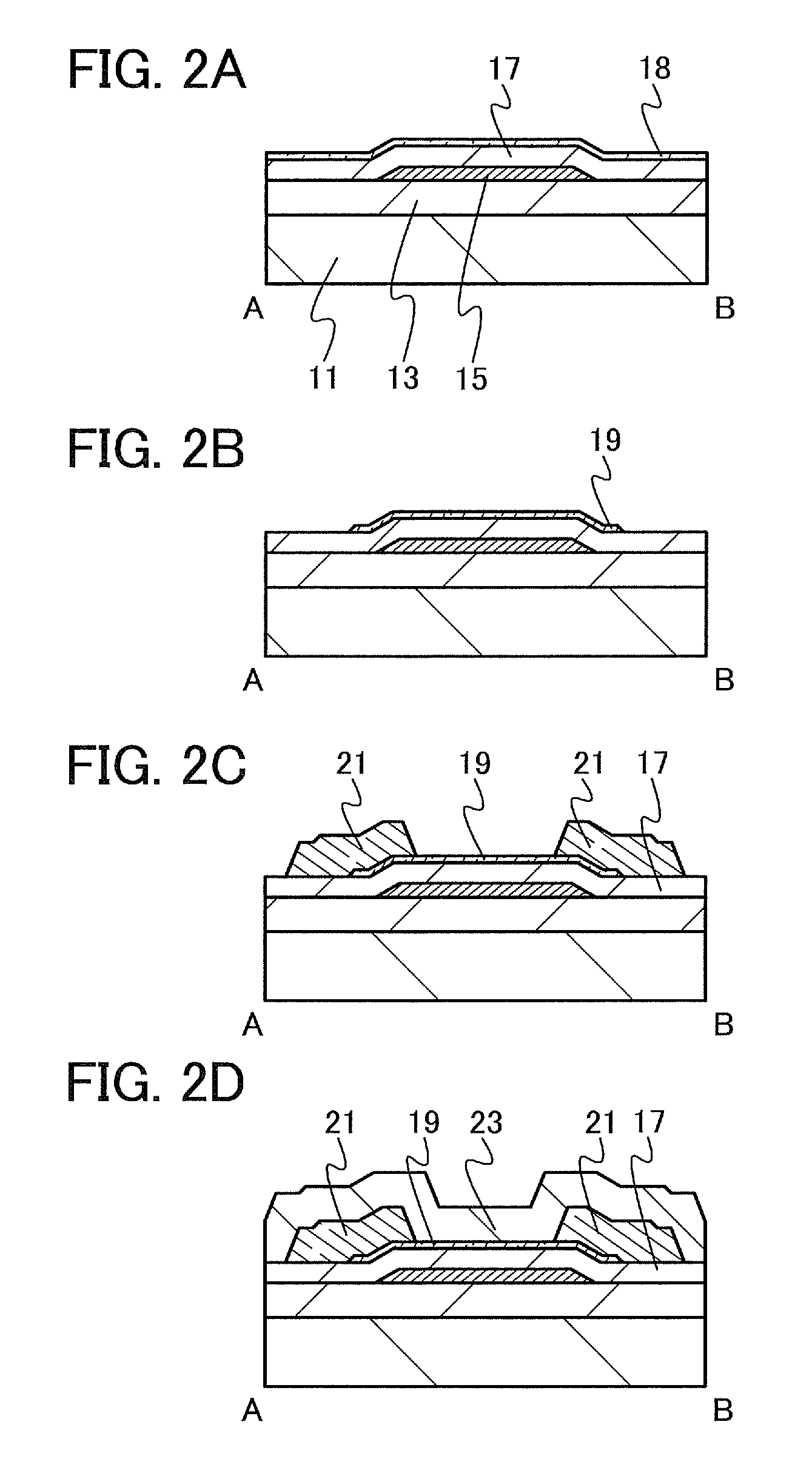
A highly reliable semiconductor device the yield of which can be prevented from decreasing due to electrostatic discharge damage is provided. A semiconductor device is provided which includes a gate electrode layer, a first gate insulating layer over the gate electrode layer, a second gate insulating layer being over the first gate insulating layer and having a smaller thickness than the first gate insulating layer, an oxide semiconductor layer over the second gate insulating layer, and a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor layer. The first gate insulating layer contains nitrogen and has a spin density of 1×1017 spins / cm3 or less corresponding to a signal that appears at a g-factor of 2.003 in electron spin resonance spectroscopy. The second gate insulating layer contains nitrogen and has a lower hydrogen concentration than the first gate insulating layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Catalyst and process for producing the same, catalytic electrode and process for producing the same, membrane/electrode union, and electrochemical device
InactiveUS20060263674A1Easy to moveEffective displayCarbon compoundsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsConductive polymerCoal
In producing an oxygen reduction catalyst including a nitrogen-containing active carbide by converting either a mixture of a carbonaceous solid raw material (coal-derived binder pitch) and a nitrogen-containing organic compound (melamine or the like) or a nitrogen-containing organic polymer compound (polyacrylonitrile, melamine resin or the like) into a powdery material, baking the powdery material, and subjecting the baked product to steam activation, the presence ratio of nitrogen and the presence ratio of carbon relating to a shake-up process in the surface and the spin density of unpaired electrons showing Curie paramagnetism are controlled to be high, by selection of the baking temperature, the mixing ratio between the carbonaceous solid raw material and the nitrogen-containing organic compound, or the nitrogen-containing organic polymer compound material. In incorporating the catalyst into an electrochemical device, the catalyst and an ion conductive polymer are mixed and a catalyst layer is formed from the mixture so as to make smooth the movement of ions and electrons, and, in applying the catalyst to a polymer electrolyte type fuel cell, an MEA is produced. This makes it possible to provide a catalyst comprised of a nitrogen-containing active carbide and a production method thereof, and an electrochemical device using the catalyst.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical fiber, evaluation and fabrication method thereof
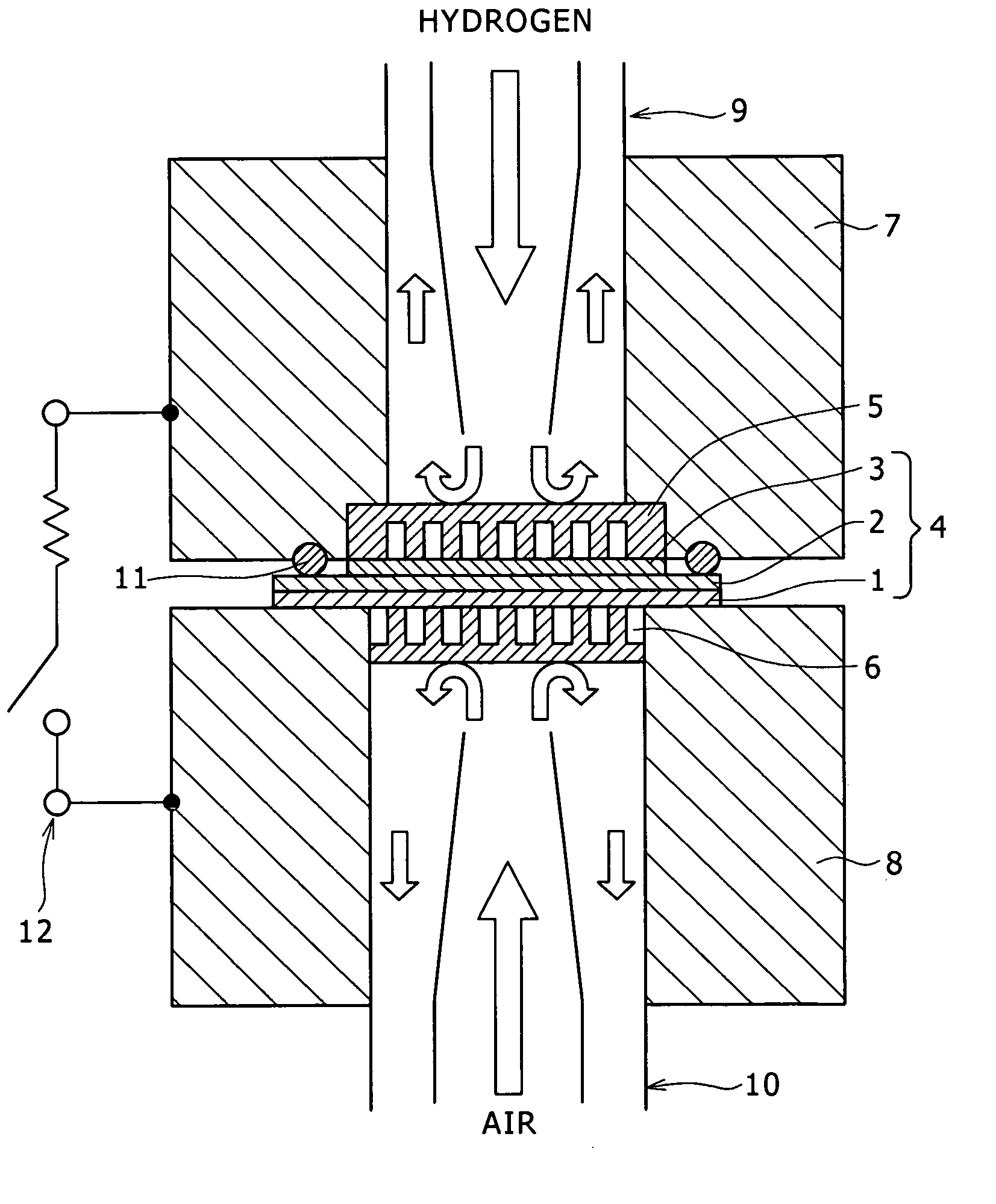
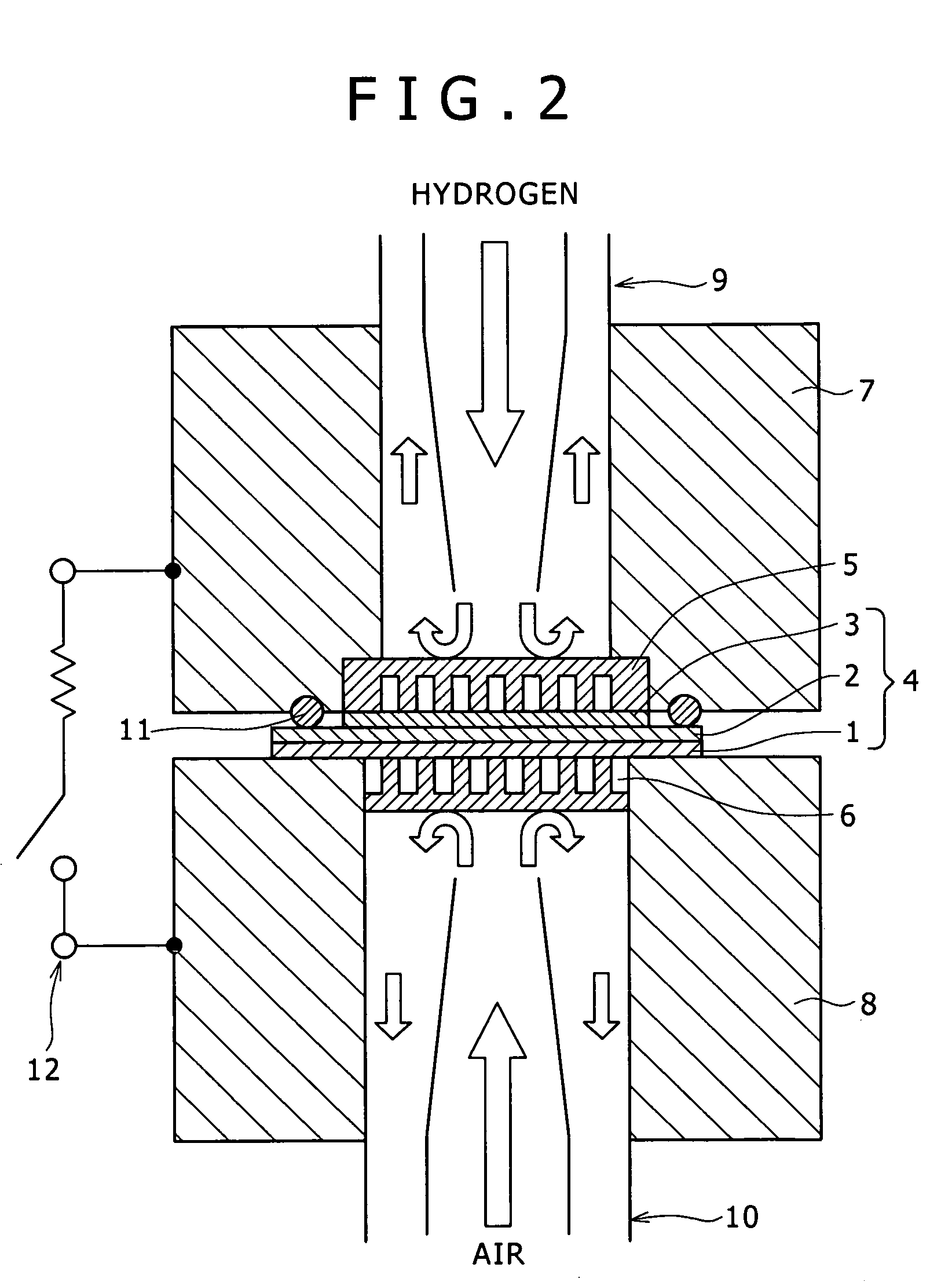
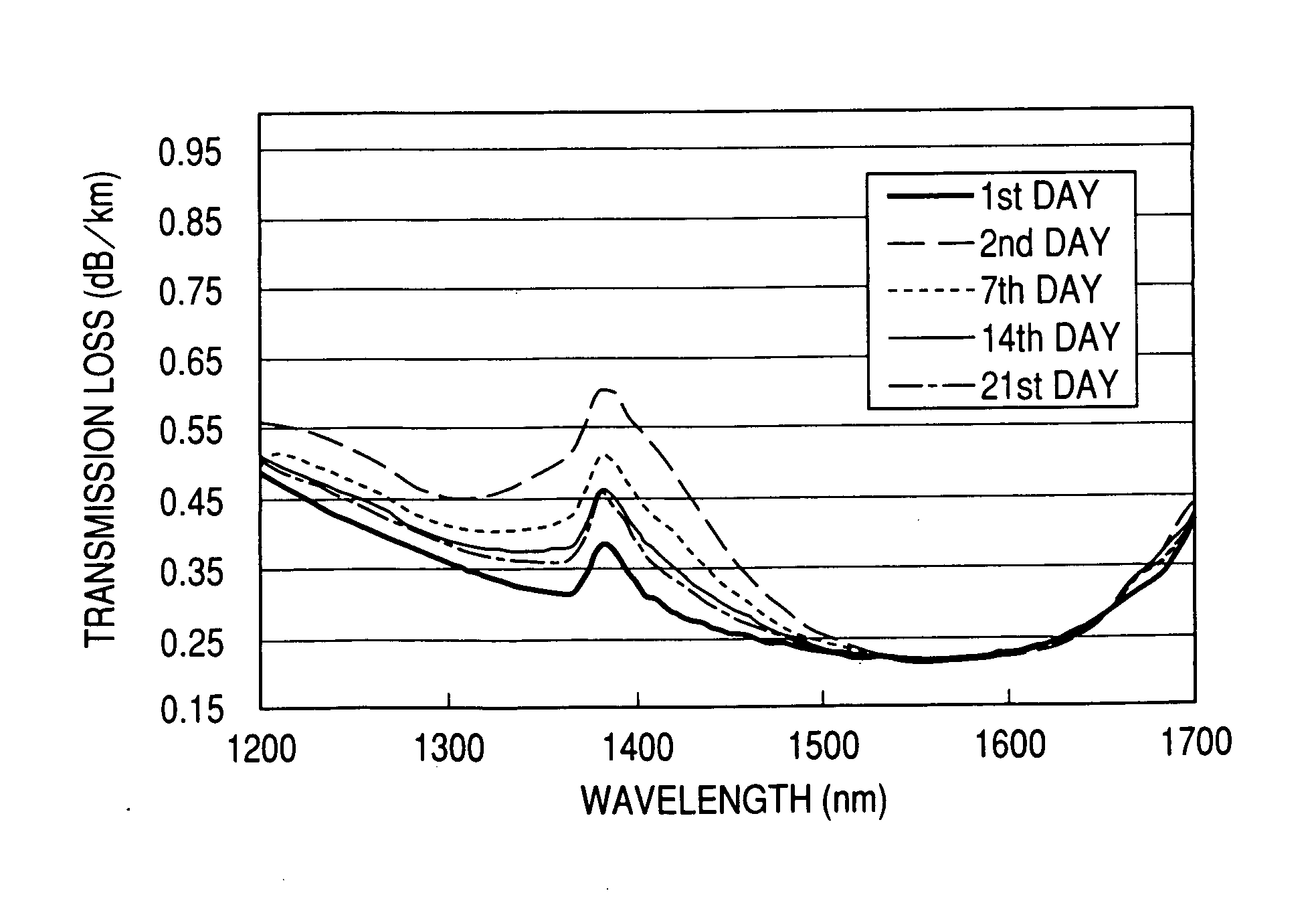
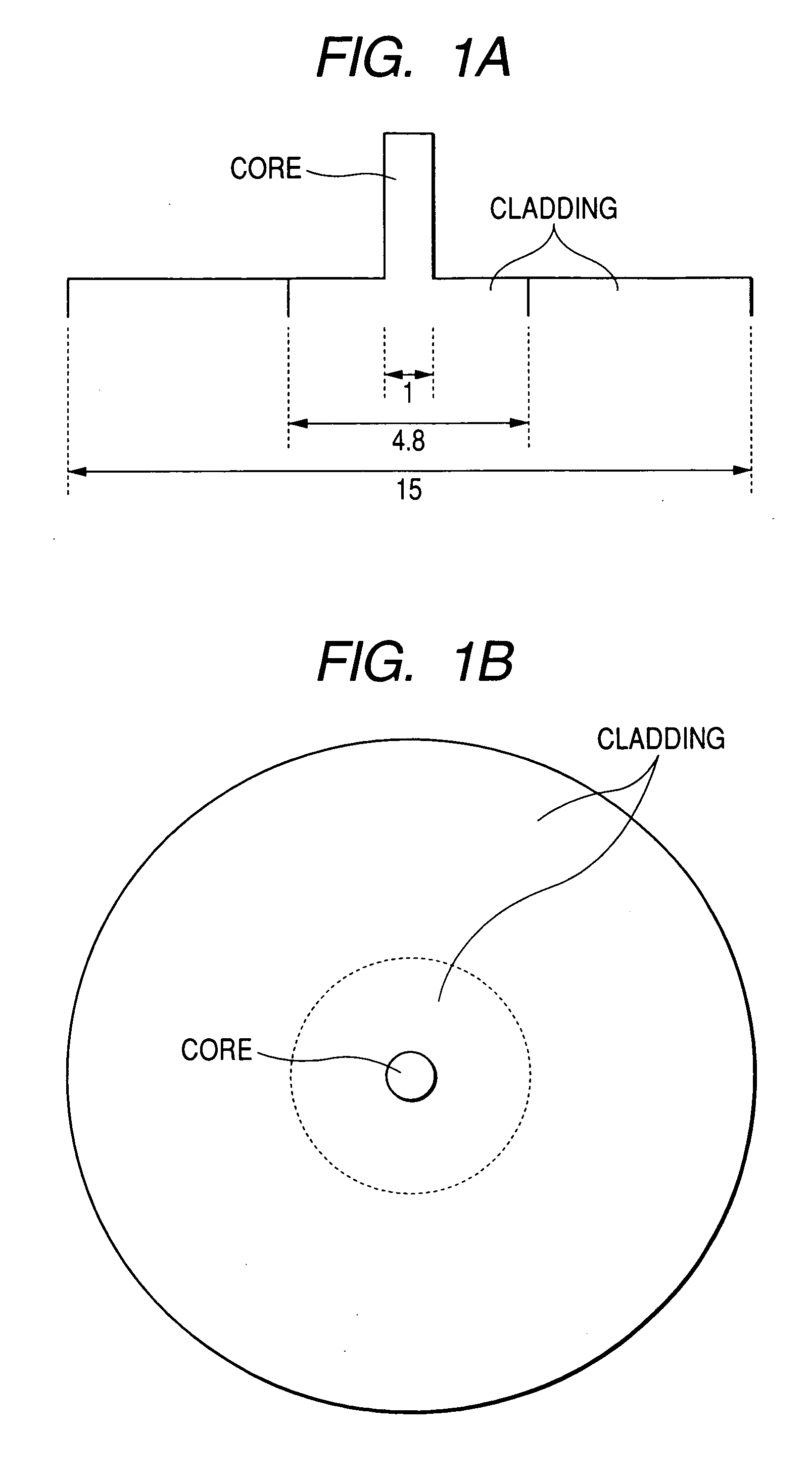
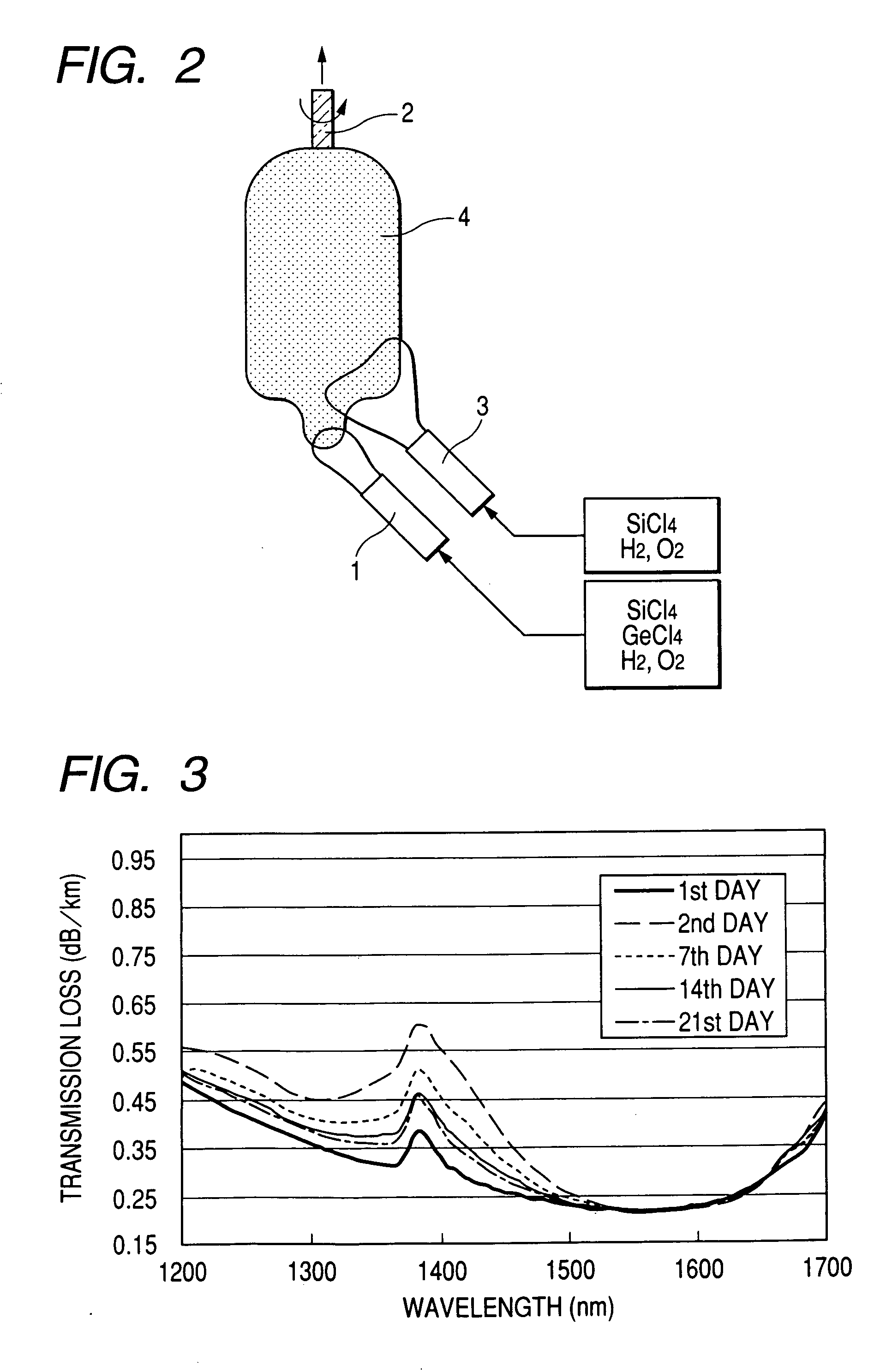
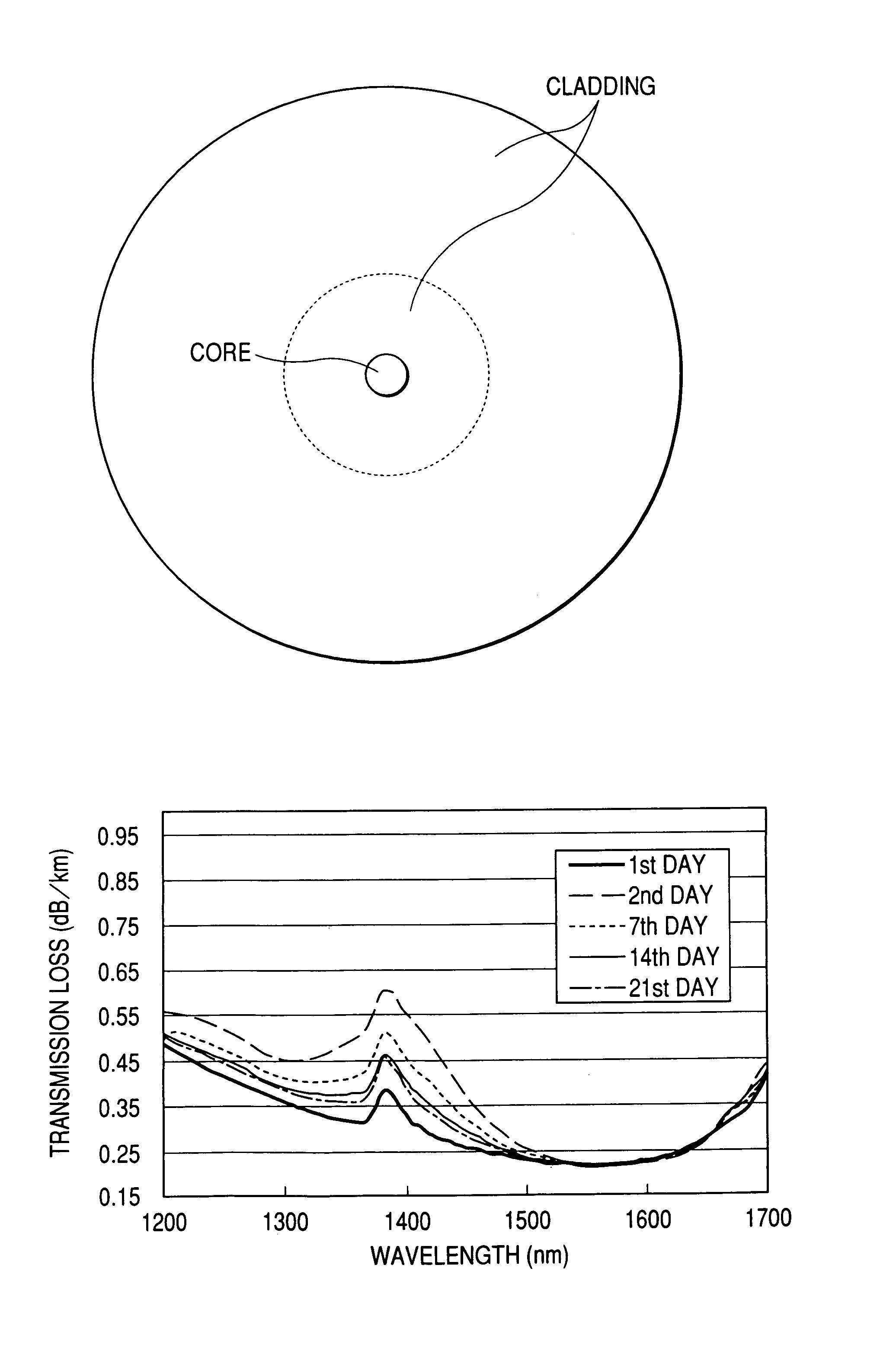
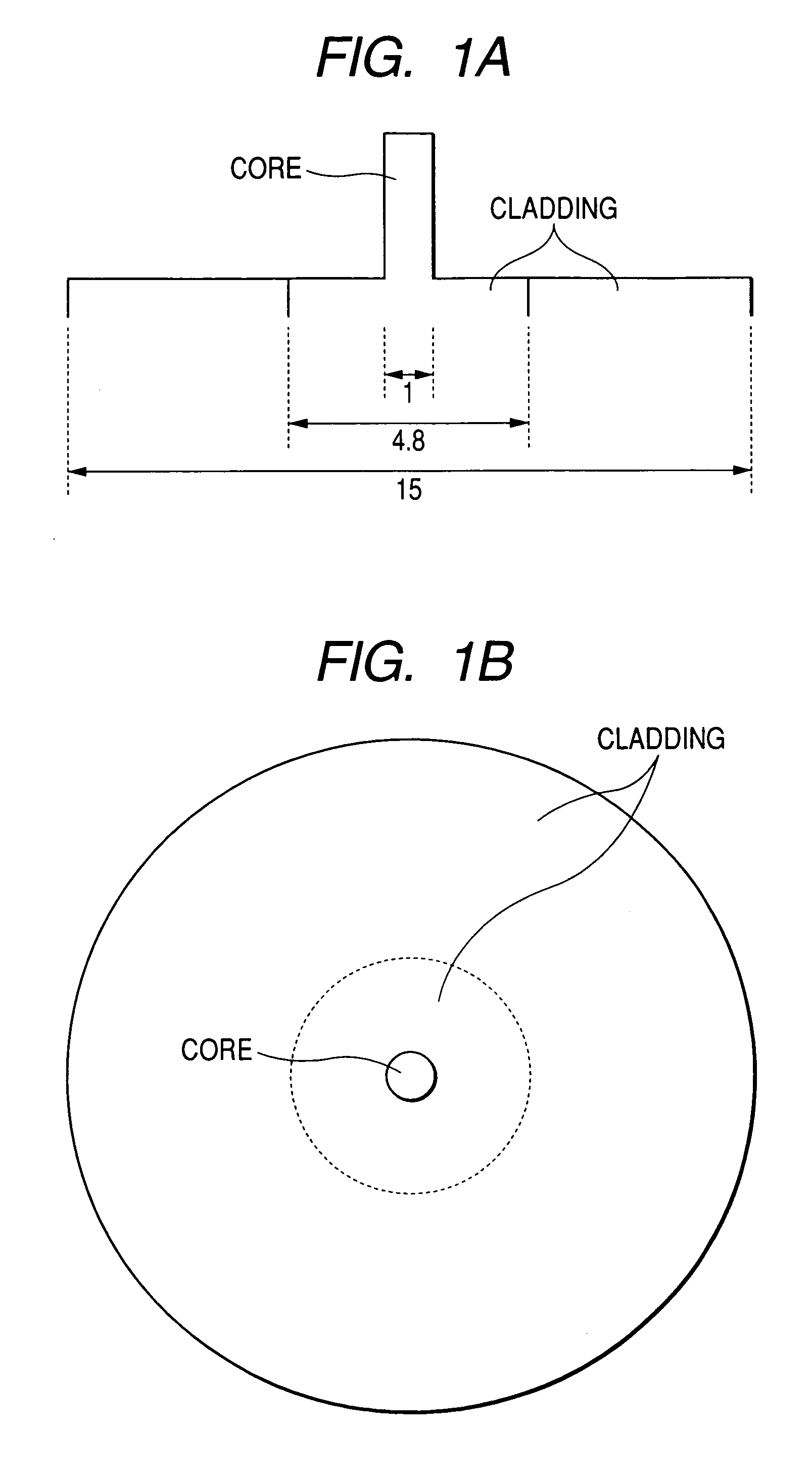
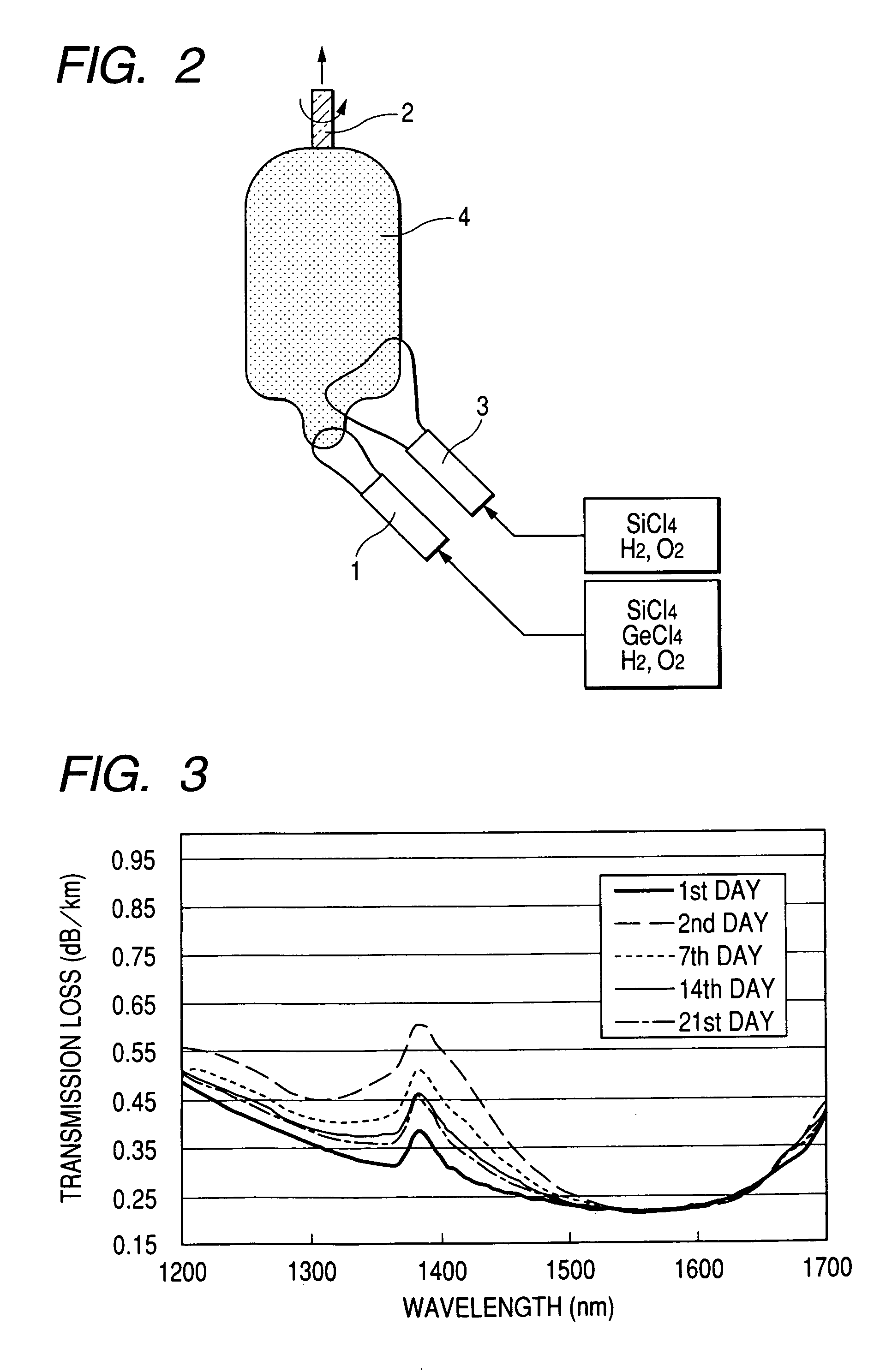
ActiveUS20060013546A1Increase in electron spin densityGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreHydrogen moleculeVolumetric Mass Density
An optical fiber having a small increase in loss at a wavelength of approximately 1400 nm involved in a deuterium treatment is provided, and an evaluation method to decide whether an optical fiber is that having such a loss increase, and a fabrication method of an optical fiber having a small increase in such a loss are also provided. An optical fiber according to the present invention comprises a core composed of a silica glass doped with at least germanium and a cladding composed of a silica glass surrounding it. The optical fiber is exposed to an atmosphere containing hydrogen or deuterium to diffuse hydrogen molecules or deuterium molecules in the optical fiber, and after that, the outer periphery of the glass region of the optical fiber is etched to an outer diameter of 50 μm, and then the electron spin density of PORs is 1×1013 spins / g or less when the glass region is measured by the electron-spin resonance method.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Method for preparing silk quilt by using plate cocoons
ActiveCN104352121AHigh strengthGood hair effectBed-coversAnimal fibresAgricultural engineeringSpin density
The invention discloses a method for preparing a silk quilt by using plate cocoons. Particularly, the method comprises the following steps: 1) breeding silkworms; 2) controlling a plate cocoon production device; 3) regulating the plate cocoon production environment; 4) controlling the spinning density; 5) producing the plate cocoons; 6) harvesting the plate cocoons; 7) puffing silk; 8) refining with a special refining agent; 9) rinsing and dehydrating; 10) drying and regaining moisture; 12) making the quilt. The special refining agent is added in the refining process, the refining effect is improved, meanwhile, the refined silk has the characteristics of high strength, soft hand feel, excellent whiteness, and low cost, and the quality of the silk quilt is ensured.
Owner:NANTONG LOVER APPL
Amorphous carbon film, process for producing the same and amorphous carbon film-coated material
InactiveUS20060246290A1High hardnessImprove adhesionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSolid carbonVolumetric Mass Density
An amorphous carbon film is provided with a density of 2.8-3.3 g / cm3. It would be preferable for the film to have: a spin density of 1×1018-1×1021 spins / cm3; a carbon concentration of at least 99.5 atomic percentage; a hydrogen concentration of no more than 0.5 atomic percentage; an inert gas element concentration of no more than 0.5 atomic percentage; and a Knoop hardness of 3000-7000. A mixed layer with a thickness of at least 0.5 nm and no more than 10 nm is formed from a parent material and at least material selected from: B, Al, Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, and W. An amorphous carbon film is disposed on the mixed layer or a metallic intermediate layer formed on the mixed layer, thereby increasing adhesion. This amorphous carbon film is formed with solid carbon using sputtering, cathode-arc ion plating, or laser abrasion.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150053971A1Less power consumptionAvoid changeTransistorSolid-state devicesResonanceSpectroscopy
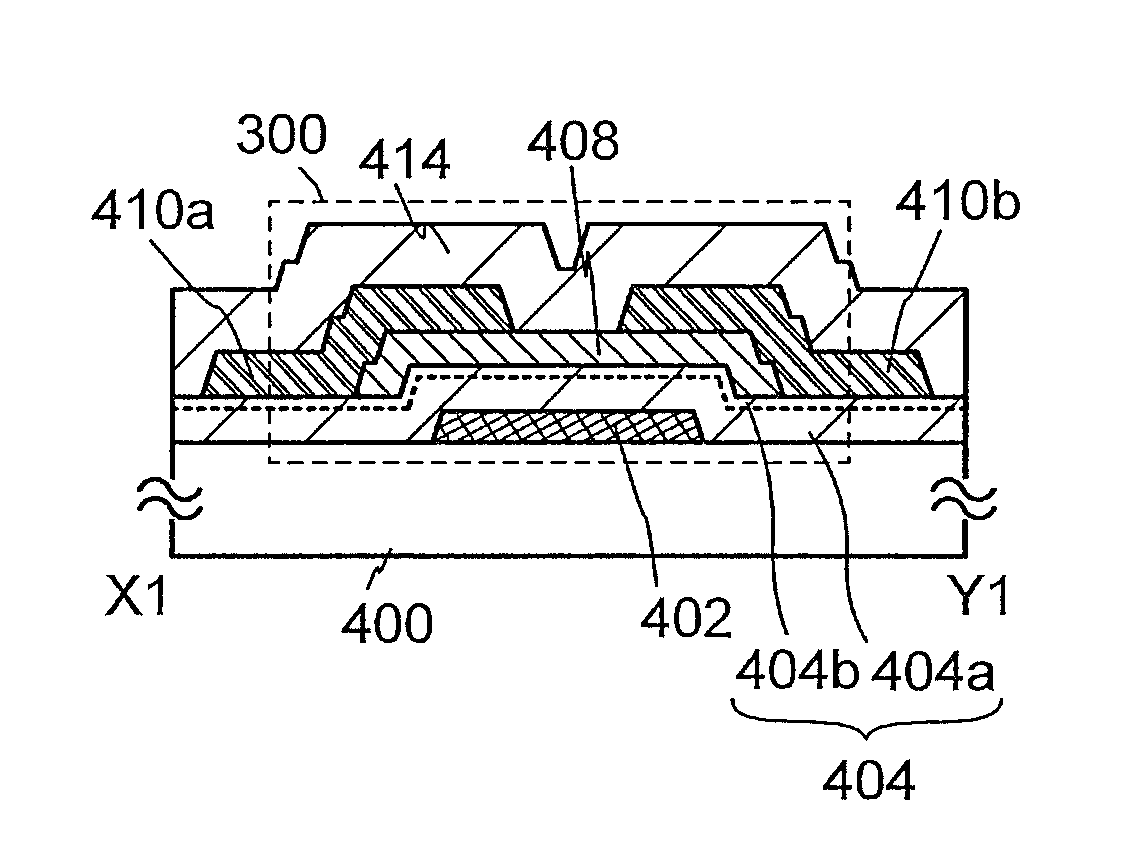
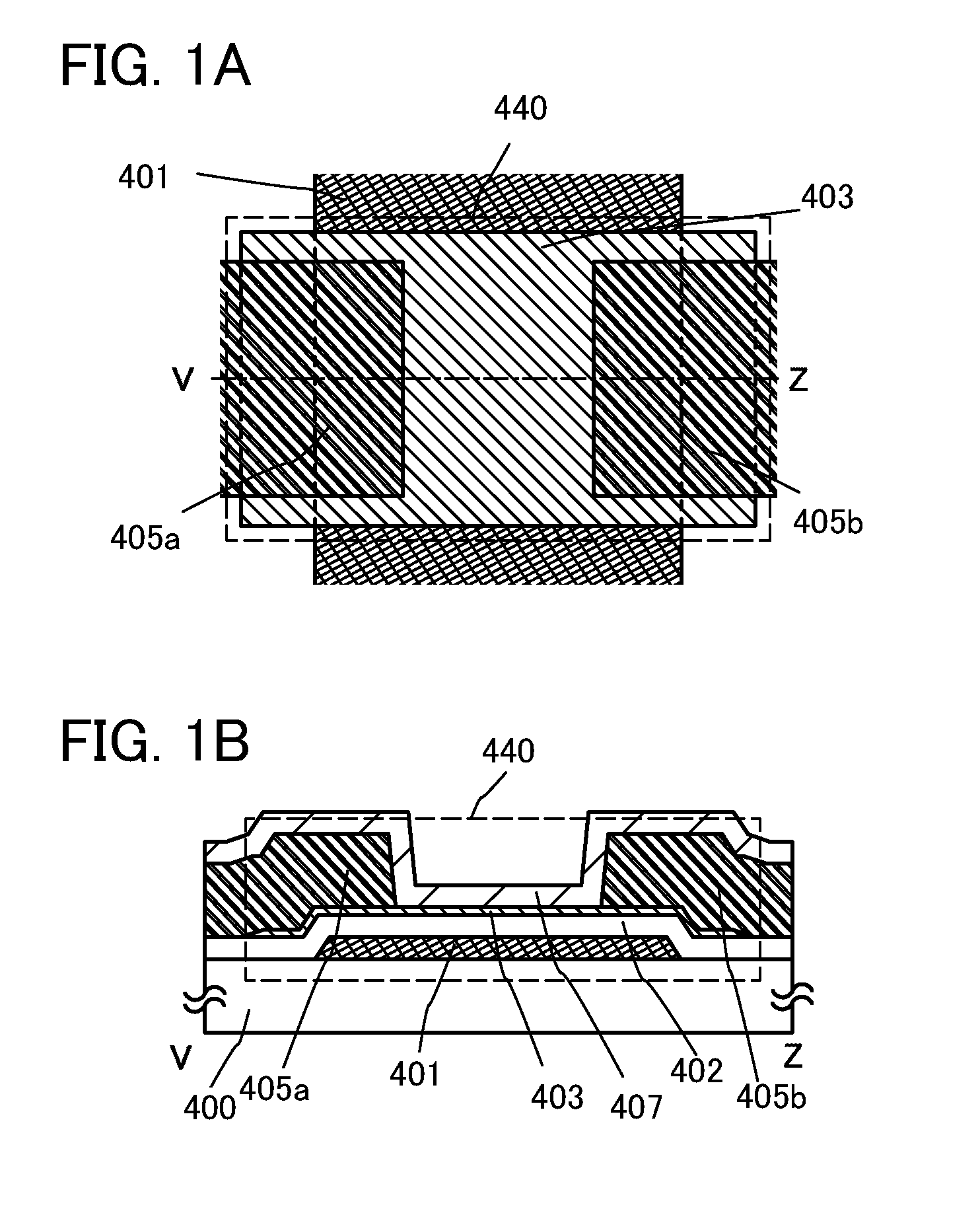
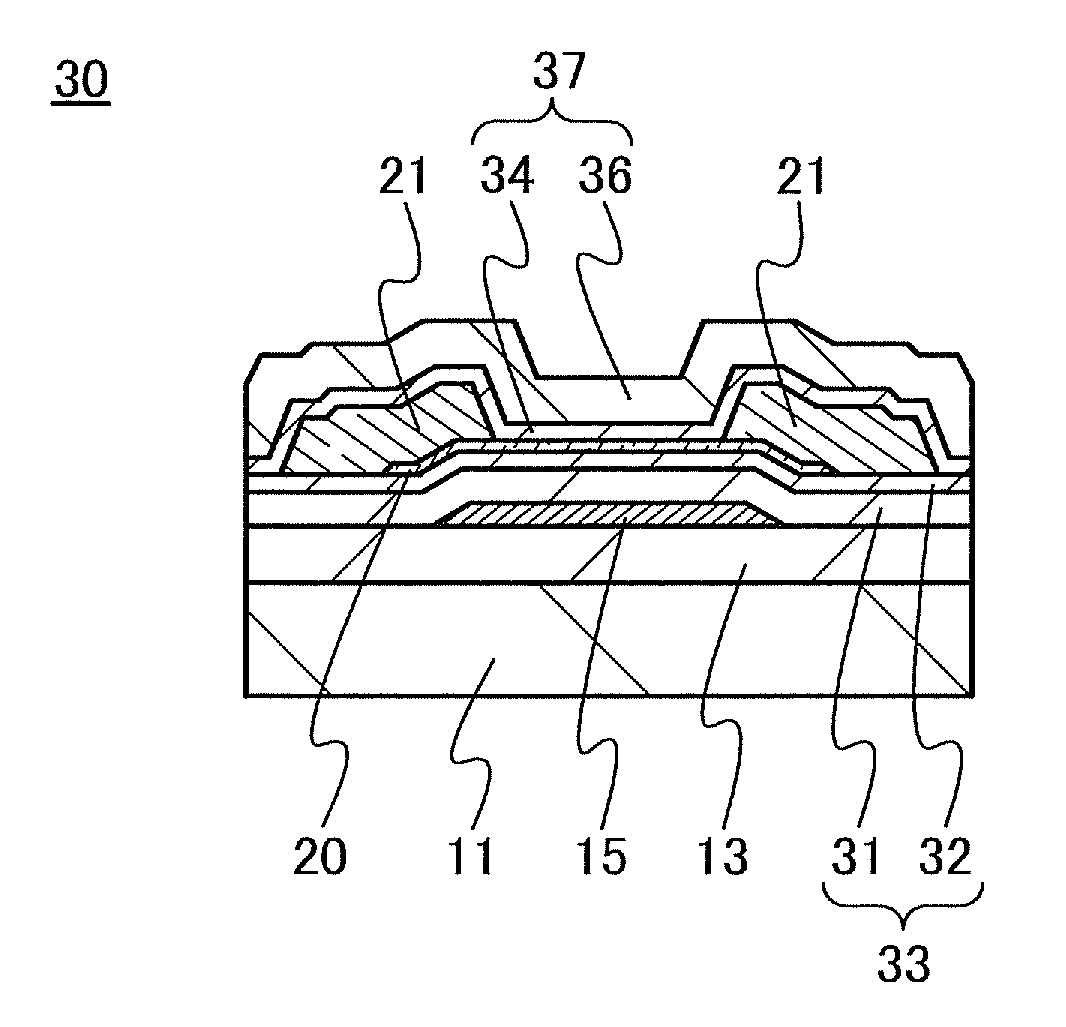
In a semiconductor device using a transistor including an oxide semiconductor, a change in electrical characteristics is suppressed and reliability is improved. The semiconductor device includes a gate electrode over an insulating surface; an oxide semiconductor film overlapping with the gate electrode; a gate insulating film that is between the gate electrode and the oxide semiconductor film and in contact with the oxide semiconductor film; a protective film in contact with a surface of the oxide semiconductor film that is an opposite side of a surface in contact with the gate insulating film; and a pair of electrodes in contact with the oxide semiconductor film. The spin density of the gate insulating film or the protective film measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy is lower than 1×1018 spins / cm3, preferably higher than or equal to 1×1017 spins / cm3 and lower than 1×1018 spins / cm3.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Amorphous carbon film, process for producing the same and amorphous carbon film-coated material
InactiveUS7416786B2High hardnessImprove adhesionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSolid carbonVolumetric Mass Density
An amorphous carbon film is provided with a density of 2.8-3.3 g / cm3. It would be preferable for the film to have: a spin density of 1×1018-1×1021 spins / cm3; a carbon concentration of at least 99.5 atomic percentage; a hydrogen concentration of no more than 0.5 atomic percentage; an inert gas element concentration of no more than 0.5 atomic percentage; and a Knoop hardness of 3000-7000. A mixed layer with a thickness of at least 0.5 nm and no more than 10 nm is formed from a parent material and at least material selected from: B, Al, Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, and W. An amorphous carbon film is disposed on the mixed layer or a metallic intermediate layer formed on the mixed layer, thereby increasing adhesion. This amorphous carbon film is formed with solid carbon using sputtering, cathode-arc ion plating, or laser abrasion.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Silicon oxide and negative electrode material for lithium-ion secondary battery
ActiveUS20120085974A1Excellent cycle characteristicsImprove initial efficiencyPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesCell electrodesLithiumSilicon oxide
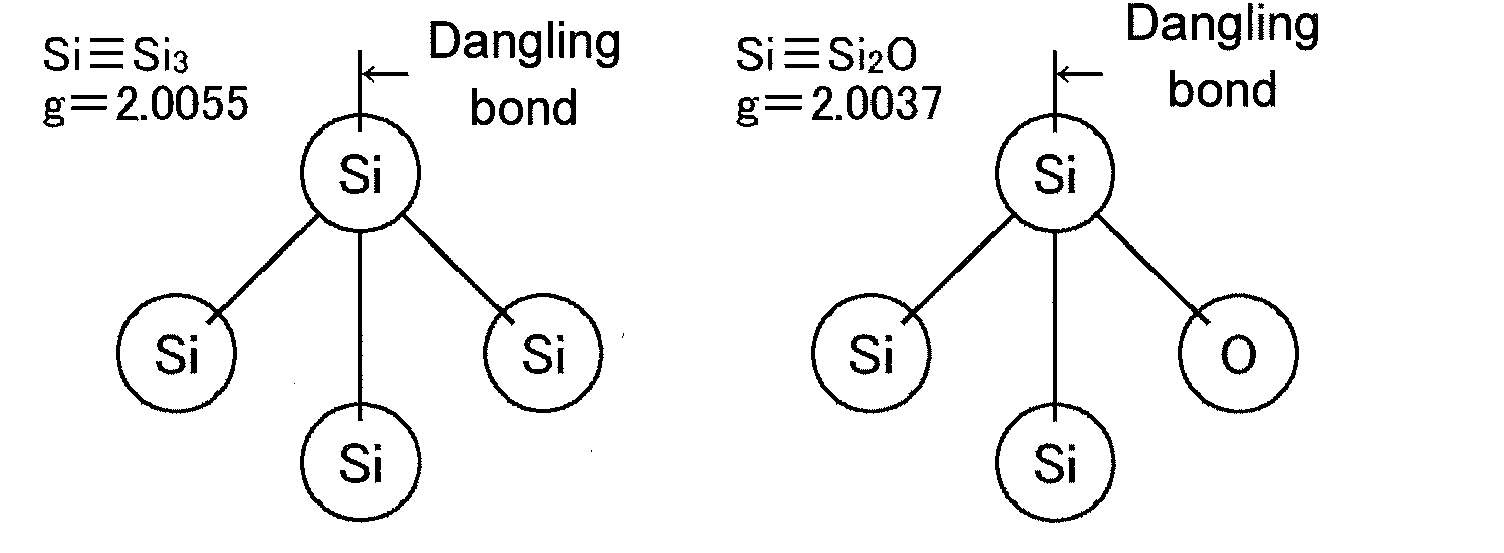
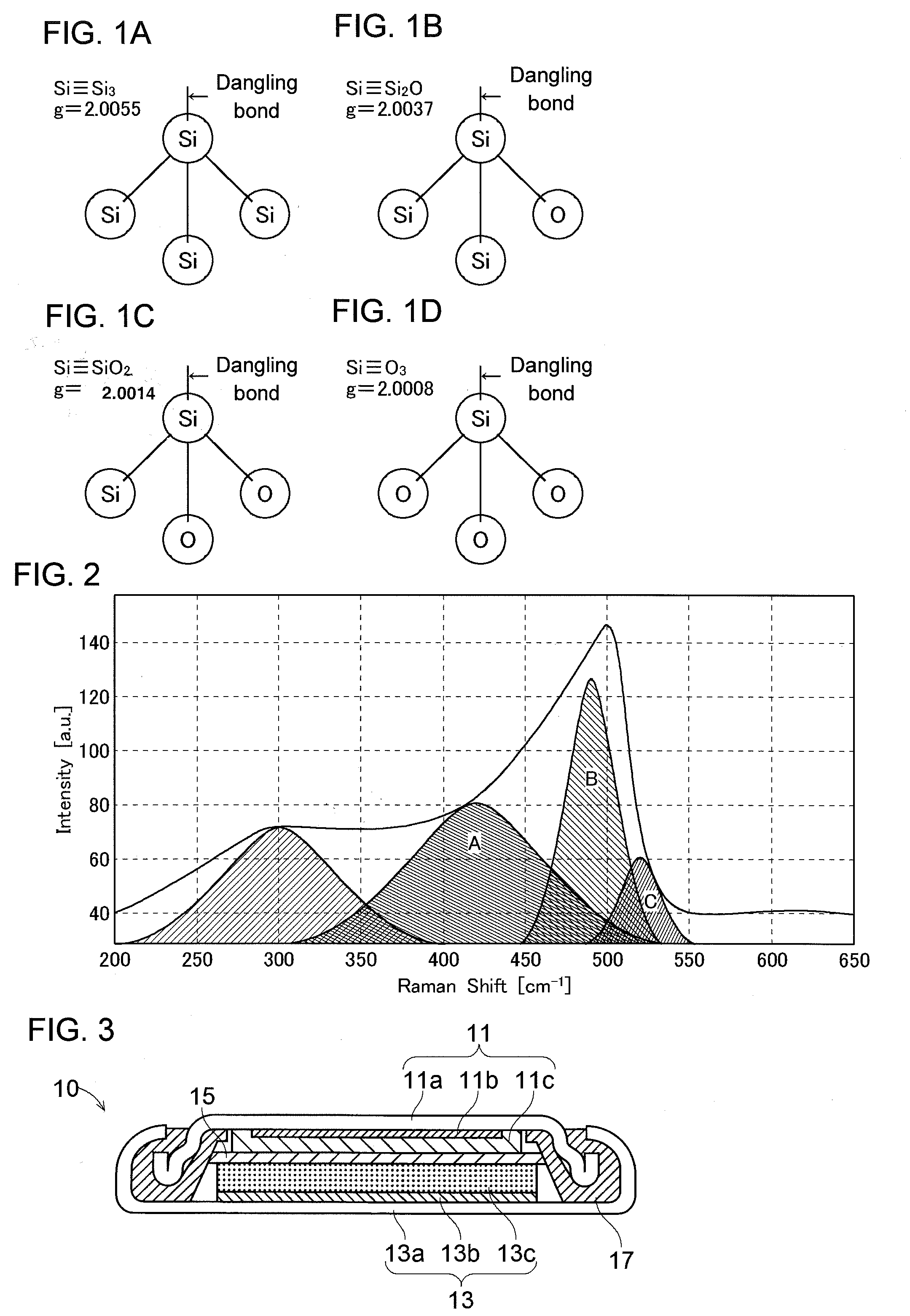
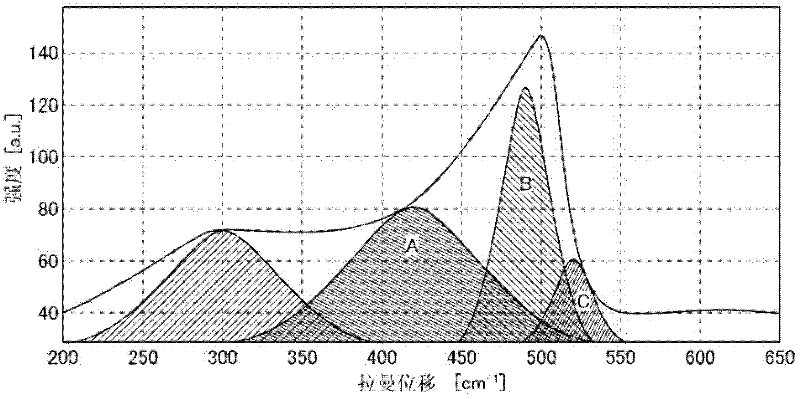
A silicon oxide for use as a negative electrode active material of a lithium-ion secondary battery is characterized by: a g-value measured by an ESR spectrometer is in the range of not less than 2.0020 to not more than 2.0050; and given that A, B, and C are the area intensities of peaks near 420 cm−1, 490 cm−1 and 520 cm−1 respectively in a Raman spectrum measured by a Raman spectroscopy, A / B is not less than 0.5 and C / B is not more than 2. The lithium-ion secondary battery has excellent cycle characteristic and initial efficiency in addition to high capacity. The silicon oxide preferably has a spin density in the range of not less than 1×1017 spins / g to not more than 5×1019 spins / g. A negative electrode material for the lithium-ion secondary battery contains not less than 20% by mass of this silicon oxide as a negative electrode active material.
Owner:OSAKA TITANIUM TECHNOLOGIES
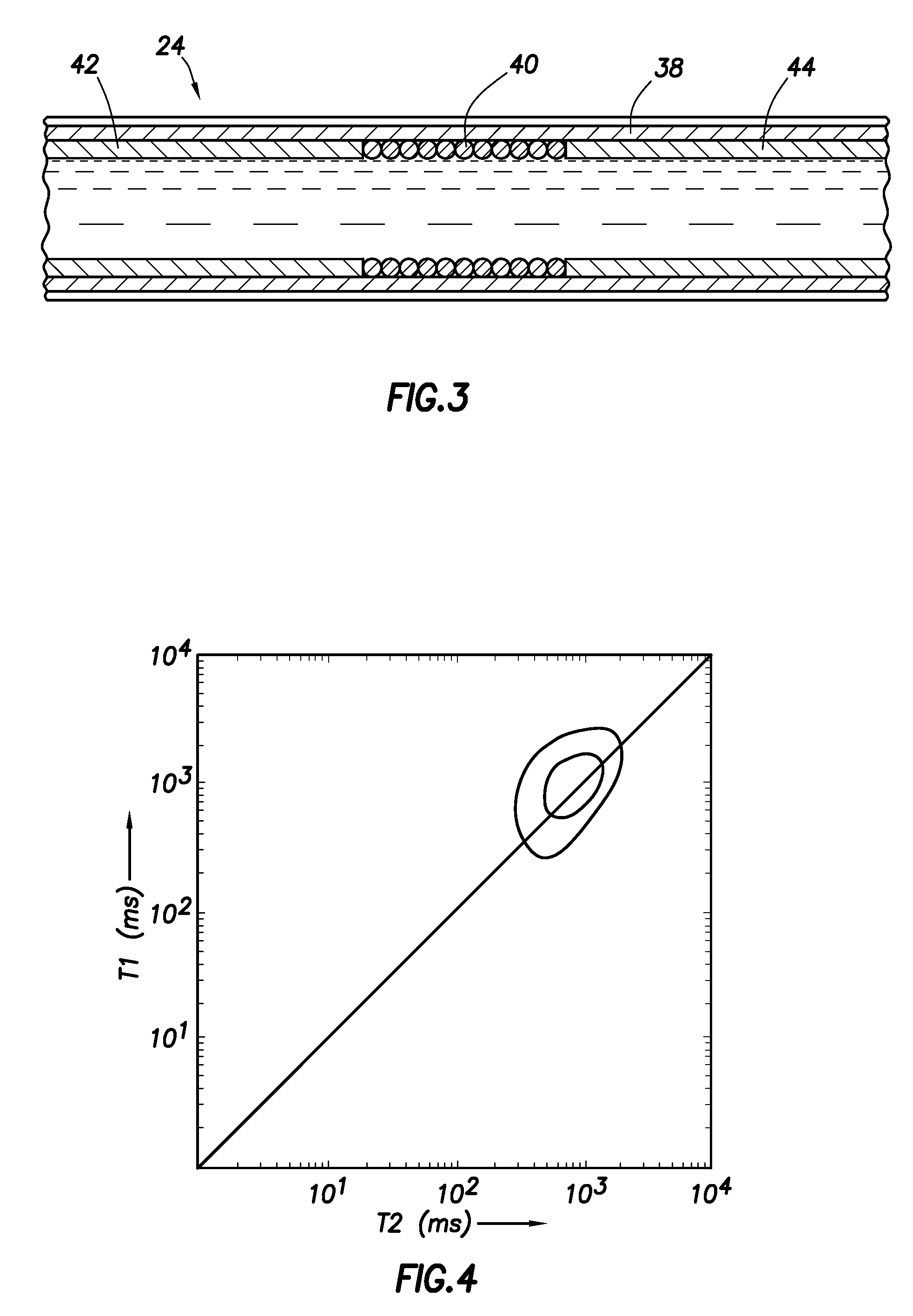
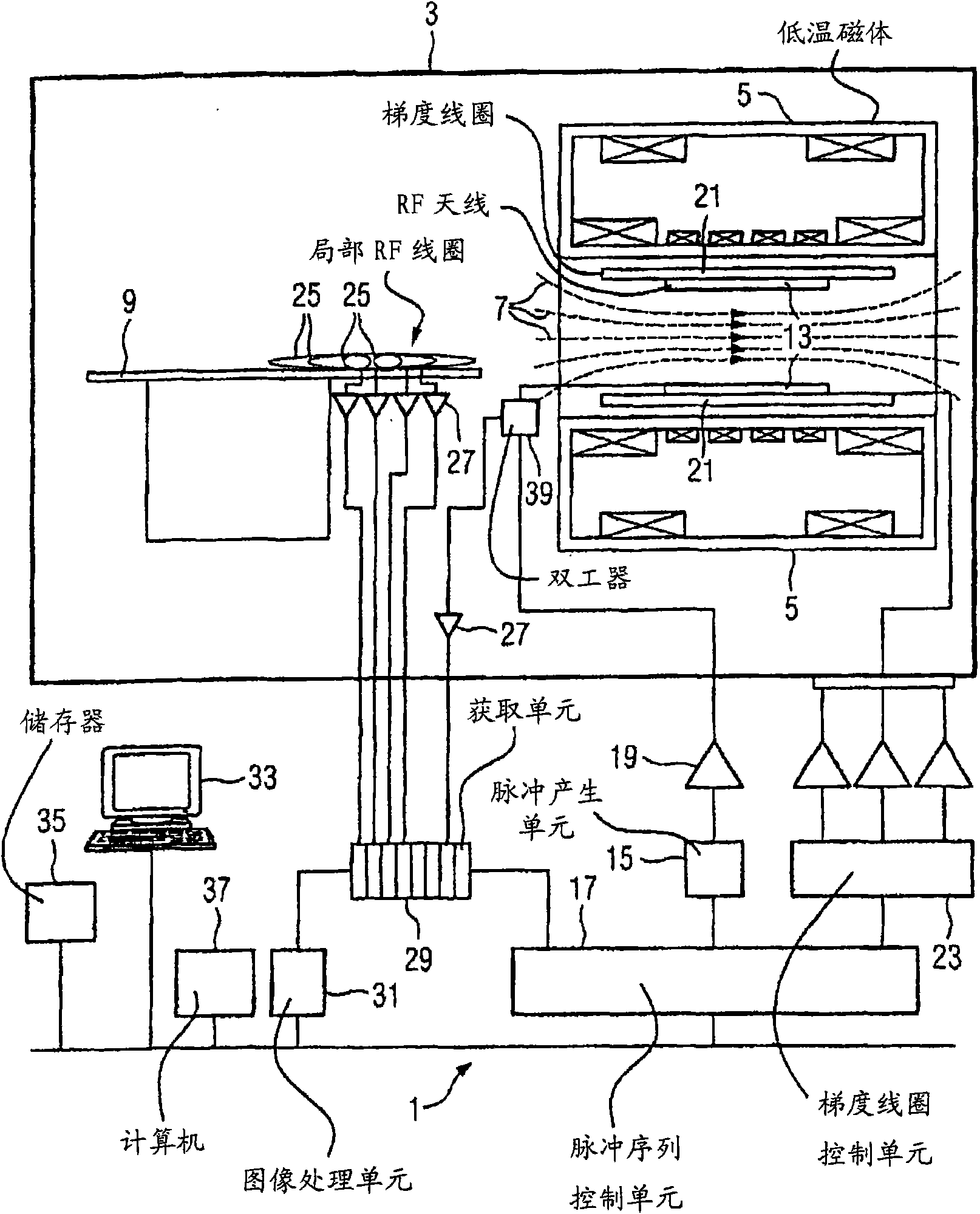
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for generating different weighted images from the same magnetic resonance echo signal evolution
InactiveCN101653360ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPulse sequenceRadio frequency
In a method and an apparatus for acquiring magnetic resonance data, a region of a subject is exposed to a spin echo magnetic resonance pulse sequence that includes a refocusing radio-frequency pulse flip angle evolution that causes magnetic resonance signals to be emitted from the region with a signal evolution following each excitation radio-frequency pulse. The signal evolution is sampled to extract two or more sets of sampled data therefrom respectively with different contrast weightings of tissues in the region. The multiple sets of sampled data are made available as respective outputs ina form allowing multiple different images of the region to be generated therefrom, respectively with said different contrast weightings. For example, a spin density-weighted image and a T2-weighted image, or a T2-weighted image and a heavily T2-weighted image, thus can be generated by sampling from the same variable-flip-angle echo train.
Owner:SIEMENS AG +1
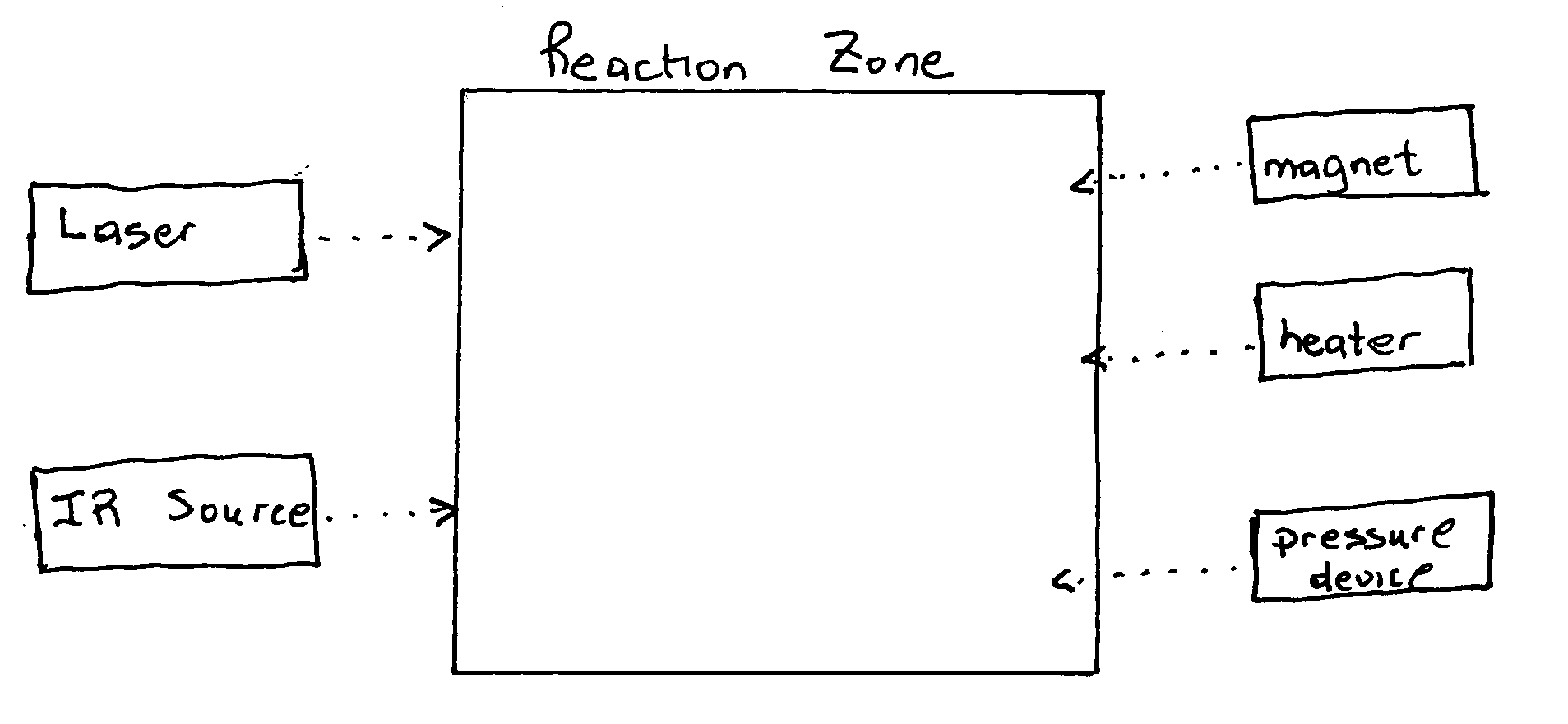
Magnetic stimulated nucleation of single crystal diamonds
InactiveUS20060018820A1High yield and purity and selectivity and efficiencyMass productionMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthGas phaseContamination
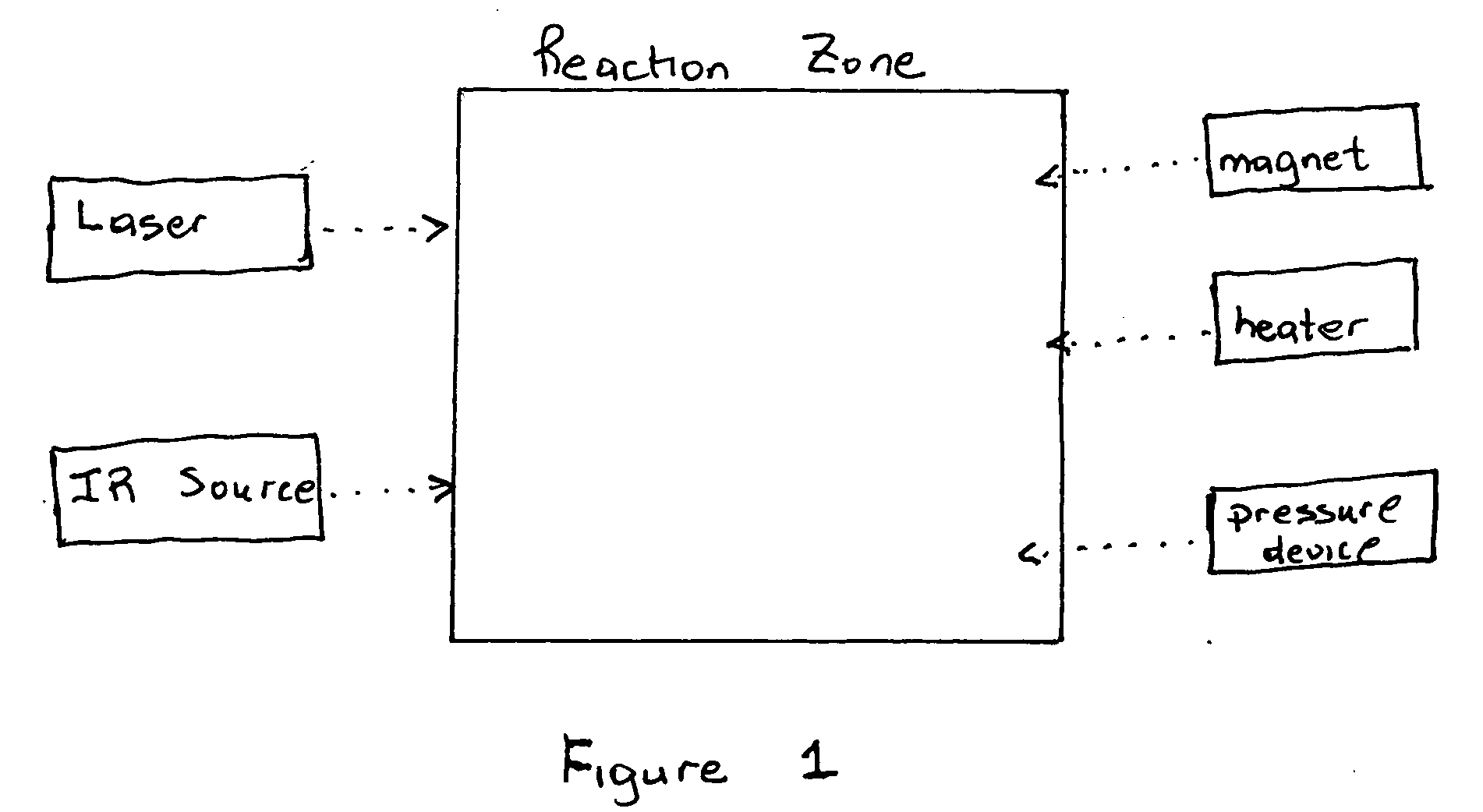
An apparatus for the crystalline, mass and selective syntheses of diamonds and carbon nanotubes (CNT) includes a chamber having at least one source of carbon and possibly a source of metal on a substrate surface (atoms, clusters and / or nanoparticles); at least one resistance heating element; at least one exciting and heating laser at least one IR source; at least one magnetic field generator; and at least one pressure device. In operation, carbon and metal atoms are supplied to the heated reaction chamber for contacting with substrate supported catalyst, a heating laser beam and an IR source, and then for contacting with an intense magnetic field sufficient amount of interaction between the excited carbon and metal atoms IR, laser, thermal energy and the magnetic field so as to excite, create, catalyze and stabilize electronic spin transitions and high electronic spin states of the excited carbon and metal atoms (for the production of high spin triplett, quartet and pentet carbon atoms) under chemical vapor deposition conditions, leading to the activated and more efficient rehybridization of these high spin carbon atoms for the massive chemical condensation of diamonds and / or CNTs. The specific photons of the laser may stimulate the nucleation of specific helical and diametric CNTs. An even greater massive chemical condensation is driven by selective, periodic and rapidly heating the metal catalyst via the IR-heating source for more efficient localization of energy for electronic, chemical and transport dynamics of high spin carbon atoms through the catalyst for lower ambient temperature selective condensation of CNT. The external magnetic field also provides conditions for creating, stabilizing, reacting and confining these high spin carbon and metal atoms. The continual supply, rehybridization and population inversion of carbon atoms overtime provides conditions conducive the massive and selective diamond and / or CNT productions. By operating the device to physically catalyze and stabilize electronic fixation of high spin states of carbon atoms by intense static arid / or dynamic magnetic fields, the chemical contamination is eliminated or may be modulated for controlled doping during the formation of diamonds and / or CNT, respectively. By operating the device to electronically fix carbon using the catalyst and magnetic fields, the electronic rehybridization rate is enhanced over the rates of currently used older arts of chemical catalytic fixation due to the reinforcing external magnetic field under CVD conditions relative to the intrinsic field of the catalyst and spin interactions with carbon atoms in the absence of the external magnetic field. The external field stabilizes high spin states of carbon and metal atoms, and enhances the intrinsic spin effects of the transition metal for chemical catalytic fixation. Moreover, an intense static external magnetic field stabilizes high spin carbon intermediates leading to stimulated diamond formation. On the other hand an intense dynamic external magnetic field intensified intrinsic spin density waves of the catalyst for enhanced CNT formation. This monumental discovery of magnetically activated rehybridization and stabilization of excited carbon contributes a watershed in the industrial massive production of diamonds and CNT when this magnetic discovery is coupled to new heating methods using IR photons. Furthermore, the stronger magnetic stabilization in this art relative to the weaker inherent fields in the catalyst of the older chemical catalytic art allow lower temperature generation of diamond and CNT. This new art provides diamond-CNT composite materials for novel diamond-CNT interfaces, new doping during the synthesis of diamond. Also in this new art, the magnetic densification of high spin carbon atoms allows more low pressure synthesis of diamond relative to older art. By switching the magnetic field on and off, this new art allows the selection of diamond or carbon nanotube growth.
Owner:LITTLE REGINALD BERNARD
Method for producing colourful plane cocoon and the produced colourful plane cocoon
InactiveCN101081017AInnovative production processEasy to industrializeAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsUltravioletEngineering
The present invention is color plate cocoon and its production process. The production process includes the following steps: 1. raising silkworm for color cocoon via feeding colorant; 2. providing color plate cocoon producing unit; 3. controlling environment conditions; 4. controlling the spinning density; 5. managing the color plate cocoon producing process; and 6. gathering natural color plate cocoon. The present invention can produce natural color plate cocoon without needing the post chemical dyeing. The color plate cocoon has the functions of resisting fungus, resisting oxidation and preventing ultraviolet ray, and is high quality material for producing cosmetics, underwear, medical dressing, functional clothing and other products.
Owner:丁志强
Methods and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging in inhomogeneous fields
ActiveUS7309986B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSelective excitationSpins
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Preparation of heteroatom-doped carbon material/Ni-MOF composite electrocatalyst
ActiveCN109174188AHigh activityIncrease exposureOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsElectrodesThioureaPorous carbon
The invention especially relates to preparation of a heteroatom-doped carbon material / Ni-MOF composite electrocatalyst, belonging to the technical field of novel energy. According to the invention, the synergistic effect of co-doping of N and S elements is mainly utilized for changing the charge density of adjacent carbon atoms, which resulting in redistribution of the spin density of a matrix material; so rich active sites are formed in a prepared composite catalyst material, which is favorable for the progress of a catalytic reaction; and thus, the catalytic performance of a MOF-based material is improved. Glucose is used as a carbon source, thiourea is used as a sulfur source and nitrogen source, and zinc chloride is used as a structure-directing agent; a carbon material is preliminarily synthesized by using a hydrothermal method and then subjected to dezincification; and the dezincified carbon material is washed, then dried at 110 DEG C, and then subjected to high-temperature carbonization in a tubular furnace so as to obtain a sulfur-and-nitrogen-doped porous carbon (SNPC) material. The composite electrocatalyst (SNPC / Ni-MOF) of the heteroatom-doped carbon material and Ni-MOFis then prepared by using the hydrothermal method. Test results show that the composite electrocatalyst is obviously improved in the performance of electrolysis of water.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Light-Emitting Element and Light-Emitting Device
ActiveUS20120286252A1Reduce power consumptionHigh visible light transmittanceOLED parametersSolid-state devicesResonanceSpins
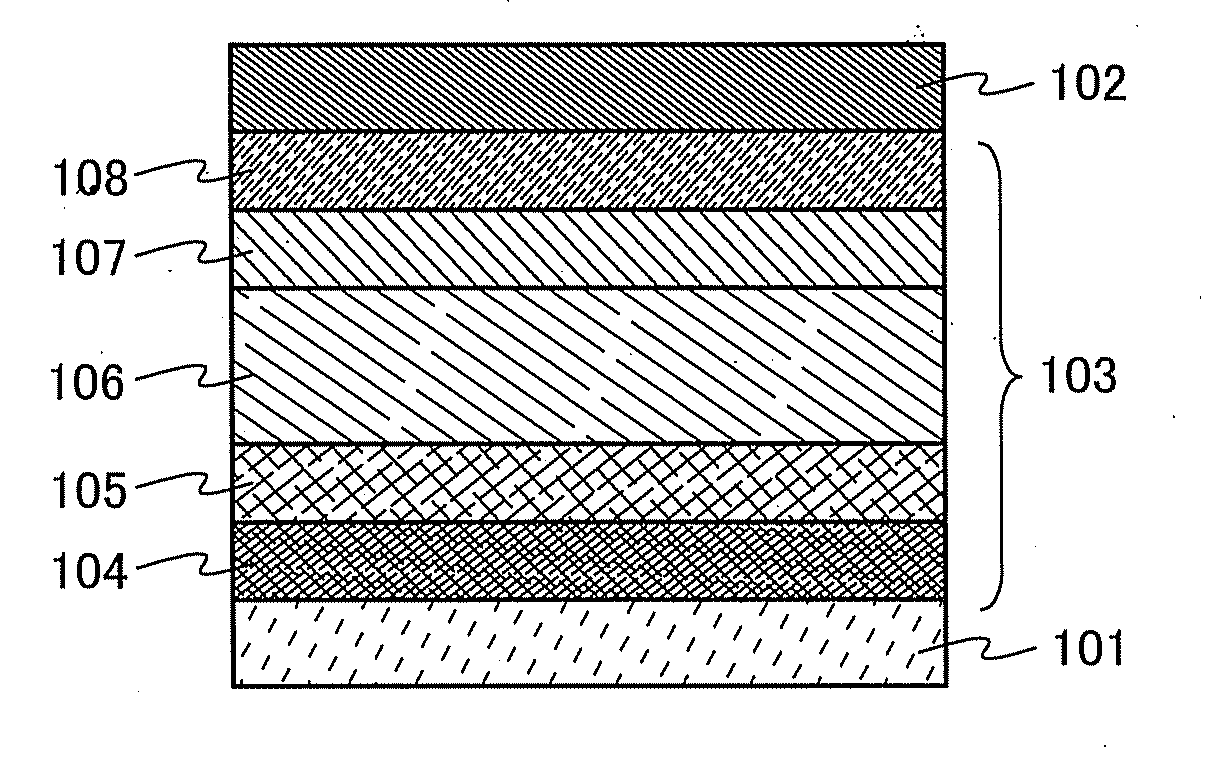
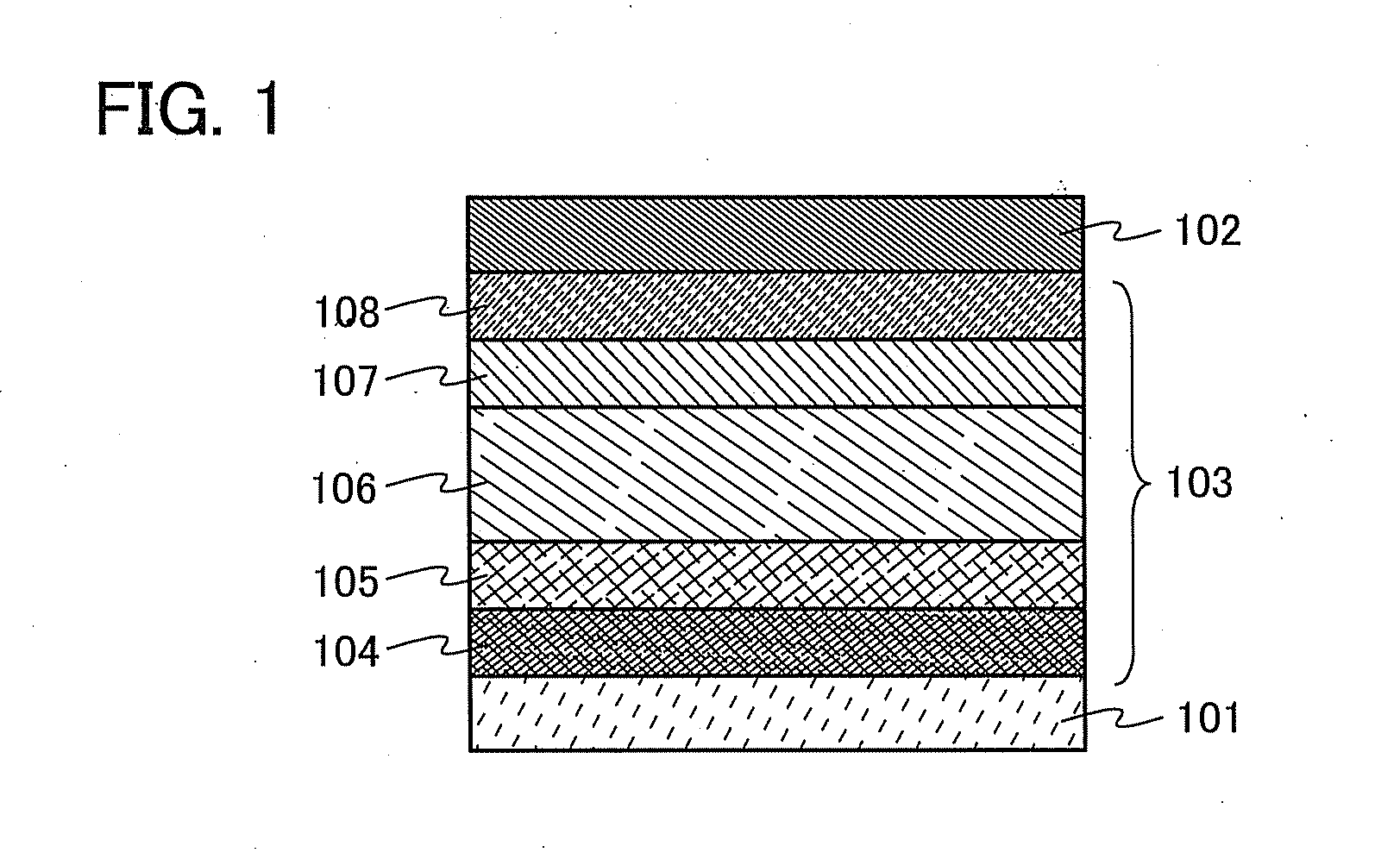
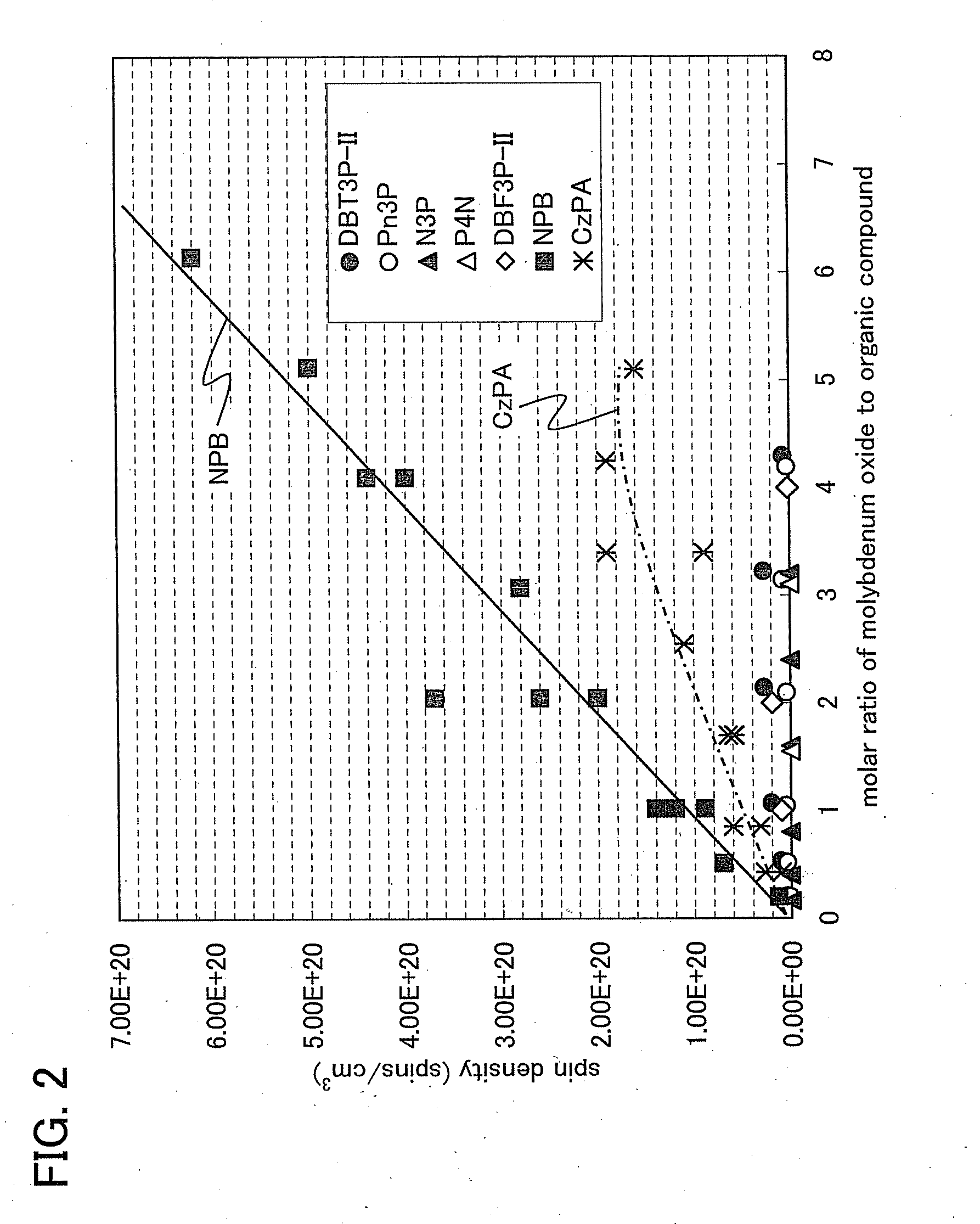
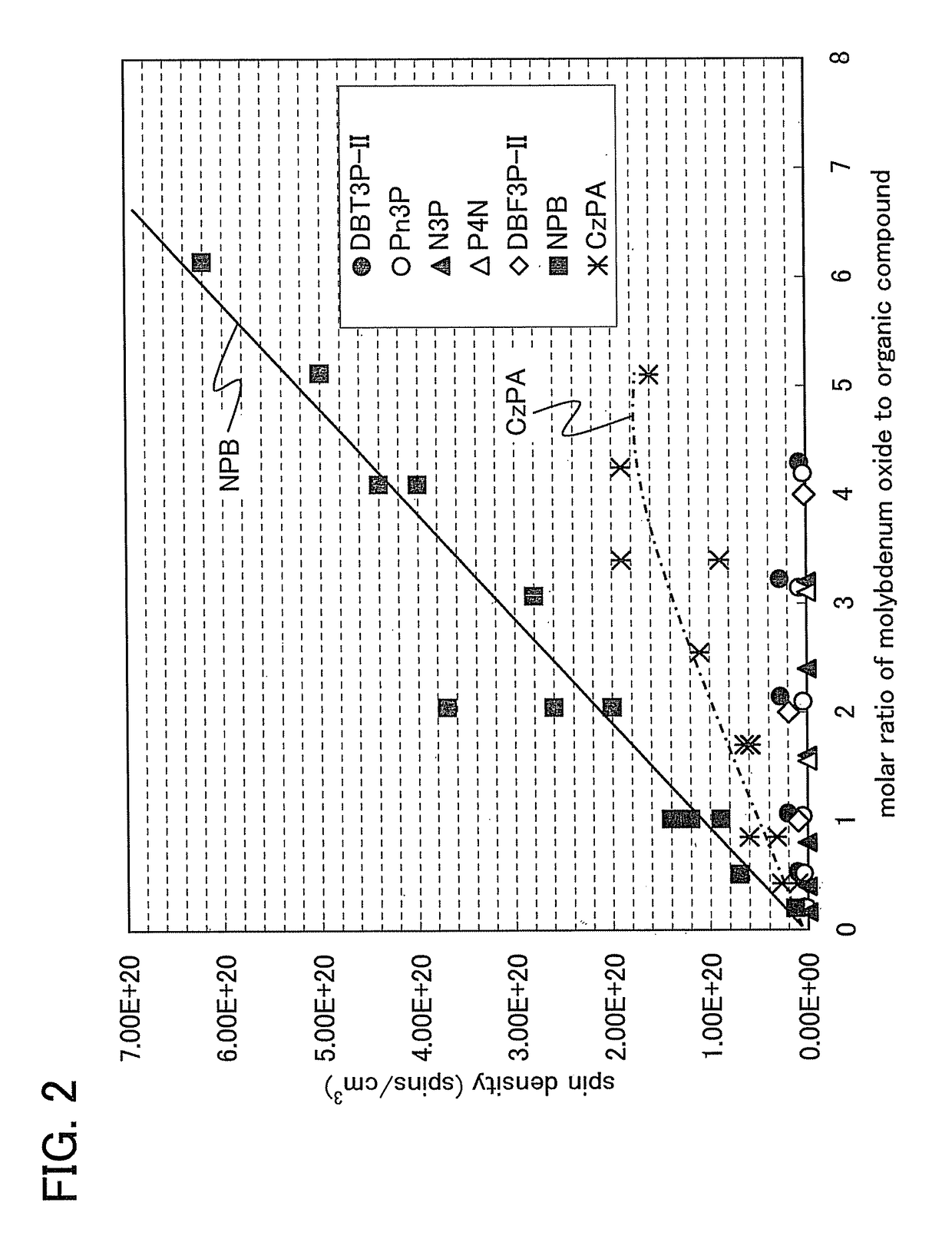
Provided are a light-emitting element capable of reducing power consumption by increasing its light extraction efficiency and a light-emitting device using the light-emitting element. A light-emitting element includes a composite material, which contains an organic compound having a high hole-transport property and an electron acceptor and in which the spin density measured by an electron spin resonance (ESR) method is less than or equal to 1×1019 spins / cm3, the spin density is less than or equal to 3×1019 spins / cm3 when the molar ratio of the electron acceptor to the organic compound is greater than or equal to 1, or the spin density is less than or equal to 5×1019 spins / cm3 when the molar ratio is greater than or equal to 2.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
In a semiconductor device using a transistor including an oxide semiconductor, a change in electrical characteristics is suppressed and reliability is improved. The semiconductor device includes a gate electrode over an insulating surface; an oxide semiconductor film overlapping with the gate electrode; a gate insulating film that is between the gate electrode and the oxide semiconductor film and in contact with the oxide semiconductor film; a protective film in contact with a surface of the oxide semiconductor film that is an opposite side of a surface in contact with the gate insulating film; and a pair of electrodes in contact with the oxide semiconductor film. The spin density of the gate insulating film or the protective film measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy is lower than 1×1018 spins / cm3, preferably higher than or equal to 1×1017 spins / cm3 and lower than 1×1018 spins / cm3.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
A highly reliable semiconductor device the yield of which can be prevented from decreasing due to electrostatic discharge damage is provided. A semiconductor device is provided which includes a gate electrode layer, a first gate insulating layer over the gate electrode layer, a second gate insulating layer being over the first gate insulating layer and having a smaller thickness than the first gate insulating layer, an oxide semiconductor layer over the second gate insulating layer, and a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer electrically connected to the oxide semiconductor layer. The first gate insulating layer contains nitrogen and has a spin density of 1×1017 spins / cm3 or less corresponding to a signal that appears at a g-factor of 2.003 in electron spin resonance spectroscopy. The second gate insulating layer contains nitrogen and has a lower hydrogen concentration than the first gate insulating layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS9070778B2Low reliabilityReduced characteristicsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialBottom gate
A highly reliable semiconductor device that includes a transistor including an oxide semiconductor is provided. In a semiconductor device which includes a bottom-gate transistor including an oxide semiconductor film, the spin density of the oxide semiconductor film is lower than or equal to 1×1018 spins / cm3, preferably lower than or equal to 1×1017 spins / cm3, further preferably lower than or equal to 1×1016 spins / cm3. The conductivity of the oxide semiconductor film is lower than or equal to 1×103 S / cm, preferably lower than or equal to 1×102 S / cm, further preferably lower than or equal to 1×101 S / cm.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS9054200B2Improve featuresImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesLight irradiationResonance
Electric characteristics of a semiconductor device using an oxide semiconductor are improved. Further, a highly reliable semiconductor device in which a variation in electric characteristics with time or a variation in electric characteristics due to a gate BT stress test with light irradiation is small is manufactured. A transistor includes a gate electrode, an oxide semiconductor film overlapping with part of the gate electrode with a gate insulating film therebetween, and a pair of electrodes in contact with the oxide semiconductor film. The gate insulating film is an insulating film whose film density is higher than or equal to 2.26 g / cm3 and lower than or equal to 2.63 g / cm3 and whose spin density of a signal with a g value of 2.001 is 2×1015 spins / cm3 or less in electron spin resonance.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Silicon oxide and negative-electrode material for a lithium-ion secondary battery
ActiveCN102460784AIncrease capacityExcellent cycle characteristicsSecondary cellsSilicon oxidesLithiumElectrical battery
Provided is a silicon oxide used in a negative-electrode active material for a lithium-ion secondary battery. Said silicon oxide is characterized by a g-value of at least 2.0020 and no more than 2.0050, measured by an ESR spectrometer, and is further characterized in that A / B is at least 0.5 and C / B is no more than 2, where A, B, and C are the integrated intensities of peaks near 420 cm-1, 490 cm-1, and 520 cm-1 respectively, in a Raman spectrum measured by a Raman spectrometer. Using this silicon oxide as a negative-electrode active material allows a high-capacity lithium-ion secondary battery having excellent cycle characteristics and initial efficiency. The silicon oxide preferably has a spin density of at least 1 1017 spins / g and no more than 5 1019 spins / g. Also provided is a negative-electrode material for a lithium-ion secondary battery, said negative-electrode material containing at least 20% by mass of the silicon oxide as a negative-electrode active material.
Owner:OSAKA TITANIUM TECHNOLOGIES
Fluorescent substance and production method thereof, and light emitting device
ActiveUS8404152B2High luminous efficiencyIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesFluorescenceSpectroscopy
Offered is a fluorescent substance consisting of Eu-activated β-sialon and capable of enhancing the brightness of a light emitting device such as a white LED using blue or ultraviolet light as a light source. The fluorescent substance has as its main constituent a β-sialon represented by the general formula Si6-zAlzOzN8-z and containing Eu, wherein the spin density is 2.0×1017 / g or less as measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy corresponding to an absorption of g=2.00±0.02 at 25° C. In the above fluorescent substance, it is preferable that lattice constant a of the β-sialon be 0.7608-0.7620 nm, the lattice constant c be 0.2908-0.2920 nm, and the Eu content be 0.1-3 mass %.
Owner:DENKA CO LTD
Optical fiber, evaluation and fabrication method thereof
An optical fiber having a small increase in loss at a wavelength of approximately 1400 nm involved in a deuterium treatment is provided, and an evaluation method to decide whether an optical fiber is that having such a loss increase, and a fabrication method of an optical fiber having a small increase in such a loss are also provided. An optical fiber according to the present invention comprises a core composed of a silica glass doped with at least germanium and a cladding composed of a silica glass surrounding it. The optical fiber is exposed to an atmosphere containing hydrogen or deuterium to diffuse hydrogen molecules or deuterium molecules in the optical fiber, and after that, the outer periphery of the glass region of the optical fiber is etched to an outer diameter of 50 μm, and then the electron spin density of PORs is 1×1013 spins / g or less when the glass region is measured by the electron-spin resonance method.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
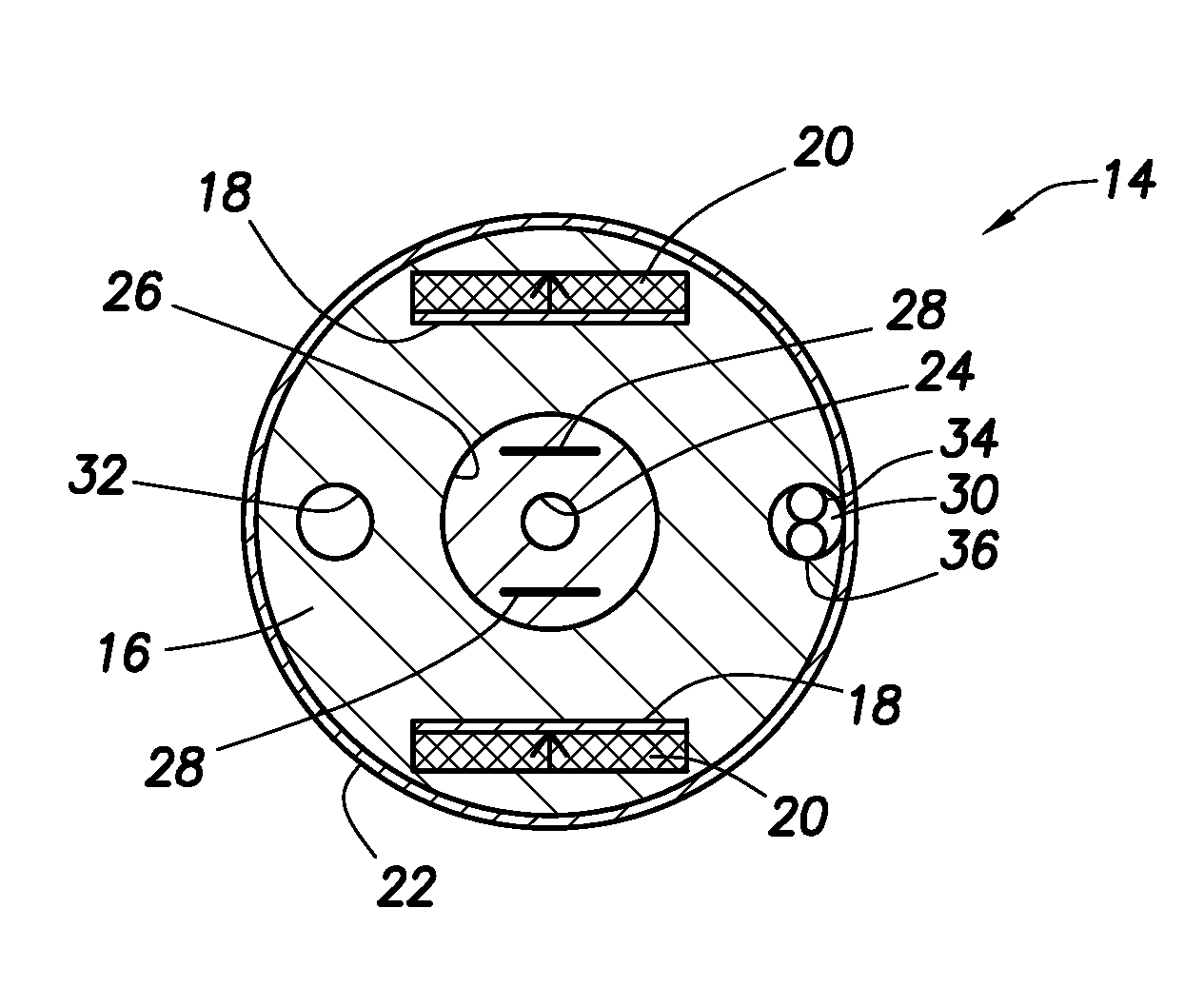
Nonaqueous electrolyte air battery and method of use of the same
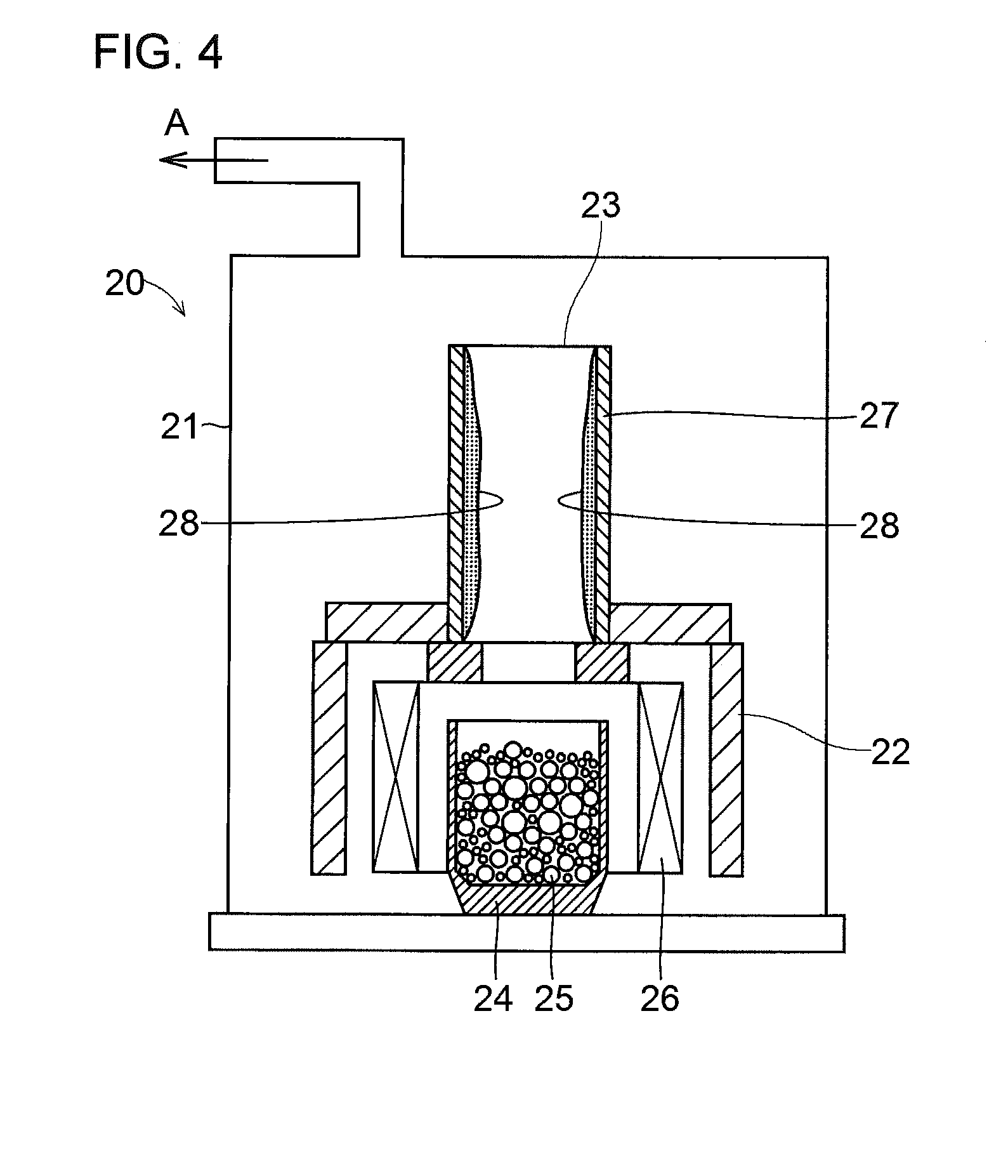
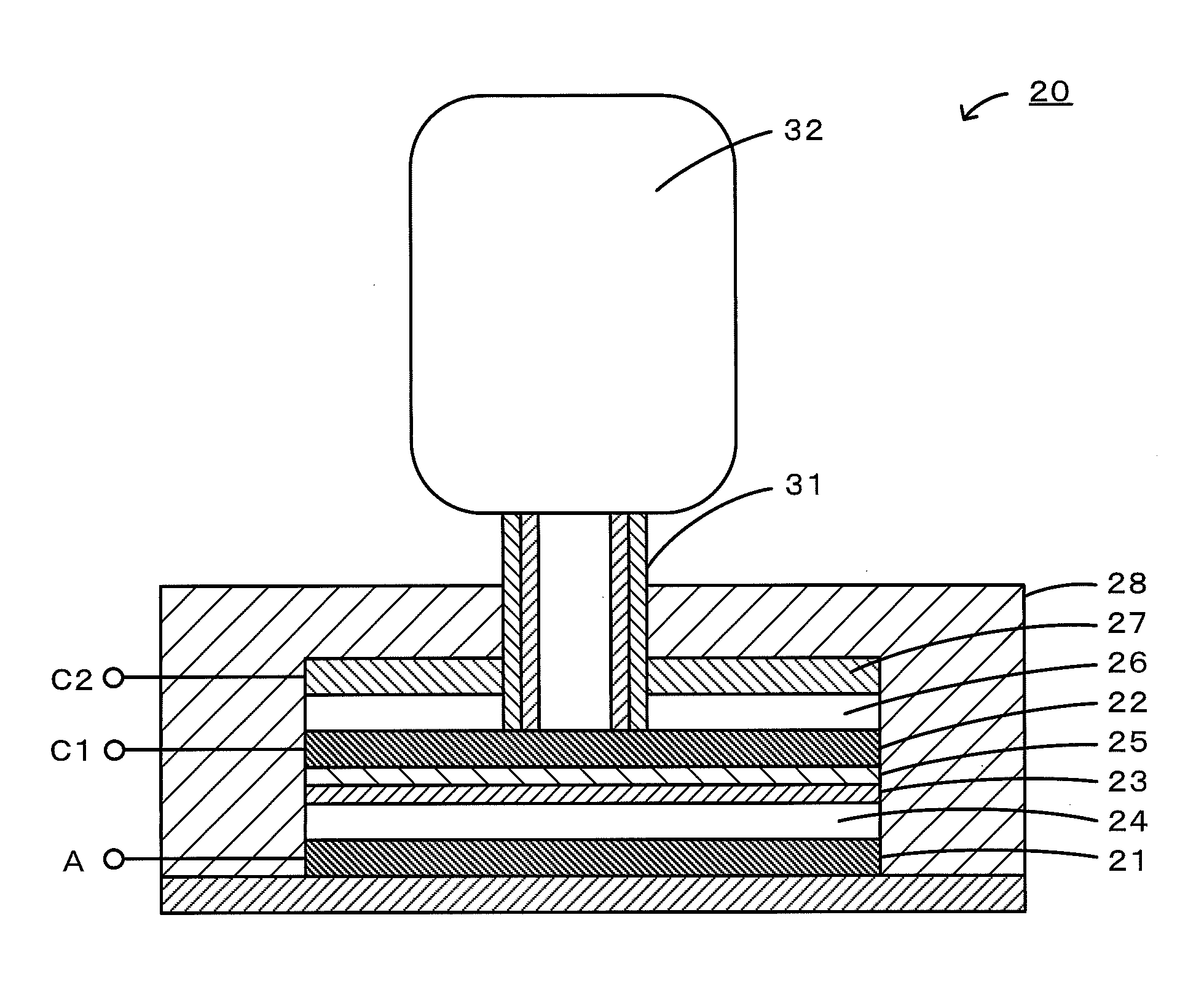
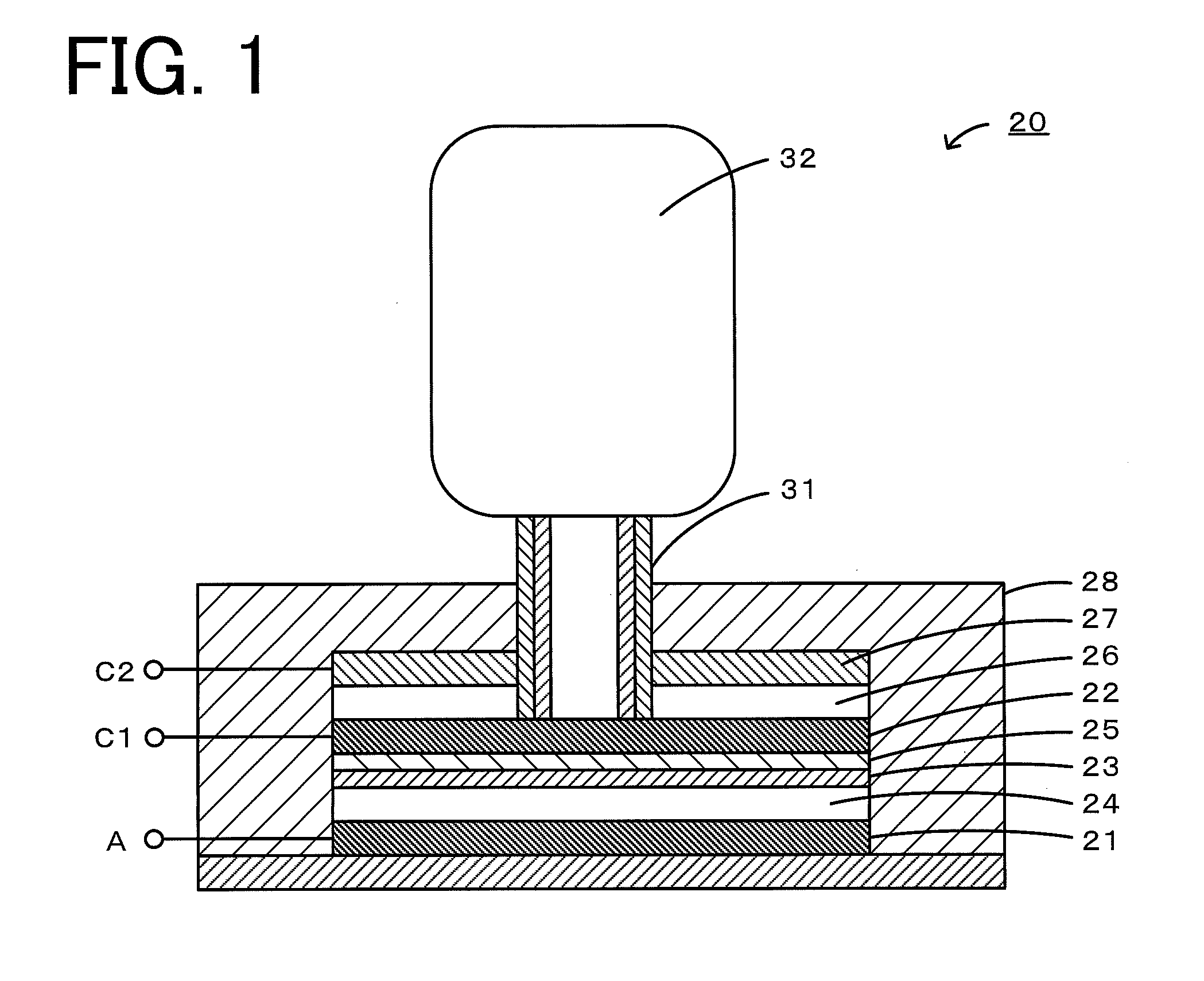
InactiveUS20160261013A1Improve charge and discharge cycle characteristicsPrevent degradationFuel and secondary cellsSecondary cellsSpin densityElectron
A nonaqueous electrolyte air battery 20 according to the present invention includes a negative electrode 21 having a negative electrode active material, a first positive electrode 22 including oxygen as a positive electrode active material, a nonaqueous electrolyte 26 which is in contact with the first positive electrode 22 and includes a compound having a structure containing a radical skeleton whose spin density measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy is 1019 spins / g or more, and a second positive electrode 27 which is in contact with the nonaqueous electrolyte 26 and oxidizes the above compound. This first positive electrode 22 is to be connected when the nonaqueous electrolyte air battery 20 is discharged, and the second positive electrode 27 is to be connected when the nonaqueous electrolyte air battery 20 is charged.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
High-sensitivity magnetic field measurement method based on electron spin magnetic resonance linewidth narrowing
ActiveCN111060855AHigh sensitivityImprove consistencyMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMeasurements using magnetic resonanceHigh densityResonance line
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity magnetic field measurement method based on electron spin magnetic resonance linewidth narrowing. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, setting adriving light frequency; step 2, performing electron spin magnetic resonance line width measurement; step 3, optimizing the power of driving light; and step 4, optimizing the electron spin density. The high-sensitivity magnetic field measurement method has the beneficial effect that the optically polarized electron spin ground state low ultrafine energy level is driven by high power; magnetic resonance linewidth narrowing is realized by improving the atomic polarizability, so that the magnetic field measurement sensitivity is improved; and the method is particularly suitable for a high-densityand small-size buffer gas chamber. On the one hand, the consistency of the buffer gas chamber is good, the yield is high, and the high-sensitivity magnetic field measurement method is suitable for engineering application; and on the other hand, the whole volume of the atom magnetometer is greatly reduced by adopting a high-density and small-volume air chamber, so that the atom magnetometer is applied to the hot spot fields of magnetoencephalogram, unmanned magnetic anomaly detection and the like; and the application range of the electron spin magnetic field measurement method is widened.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
Light-emitting element and light-emitting device
ActiveUS9647228B2Light extraction efficiencyReduce power consumptionOLED parametersSolid-state devicesSimple Organic CompoundsResonance
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com