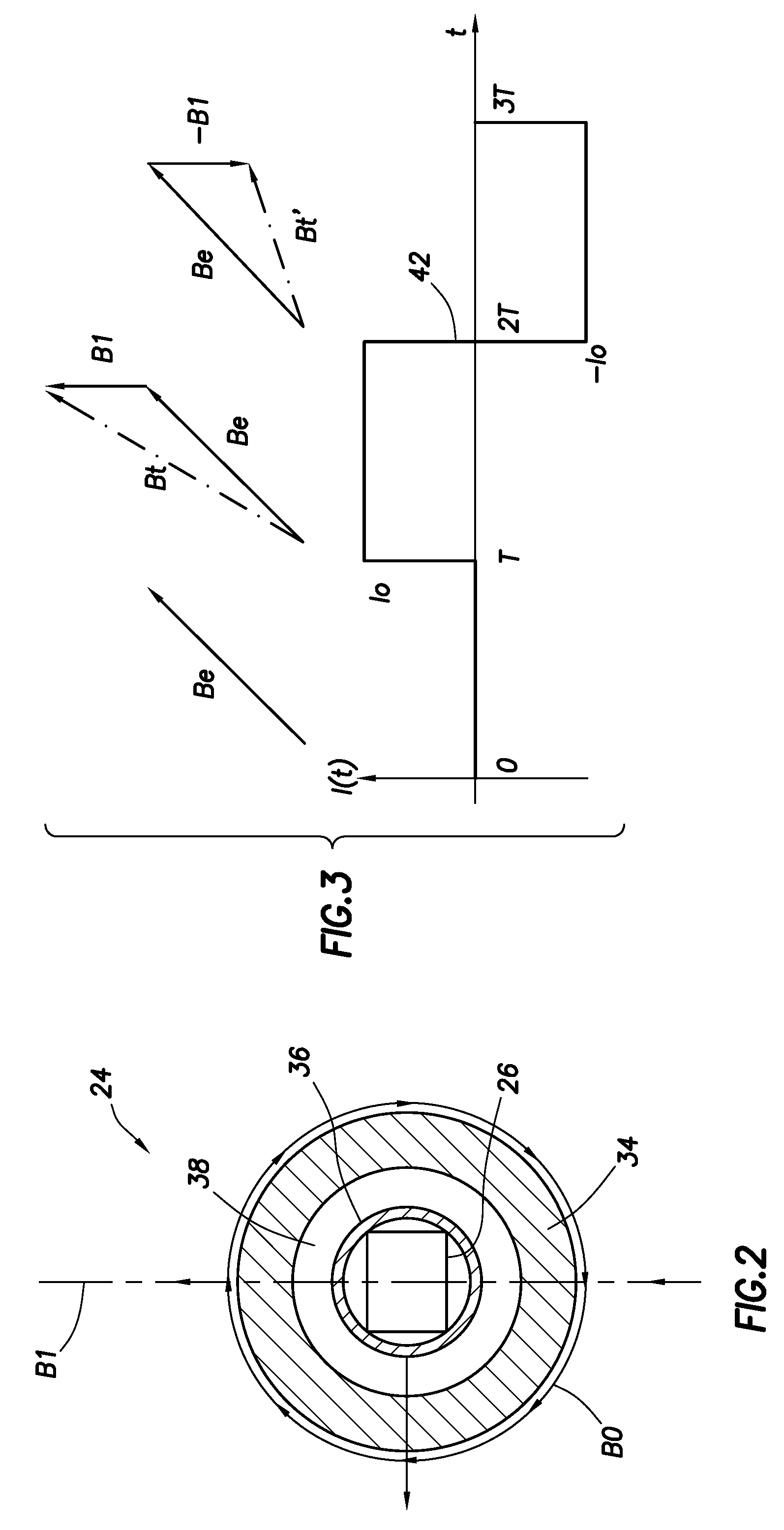
Patents
Literature
673 results about "Earth's magnetic field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of molten iron in the Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of the Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. The North geomagnetic pole, currently located near Greenland in the northern hemisphere, is actually the south pole of the Earth's magnetic field, and conversely.
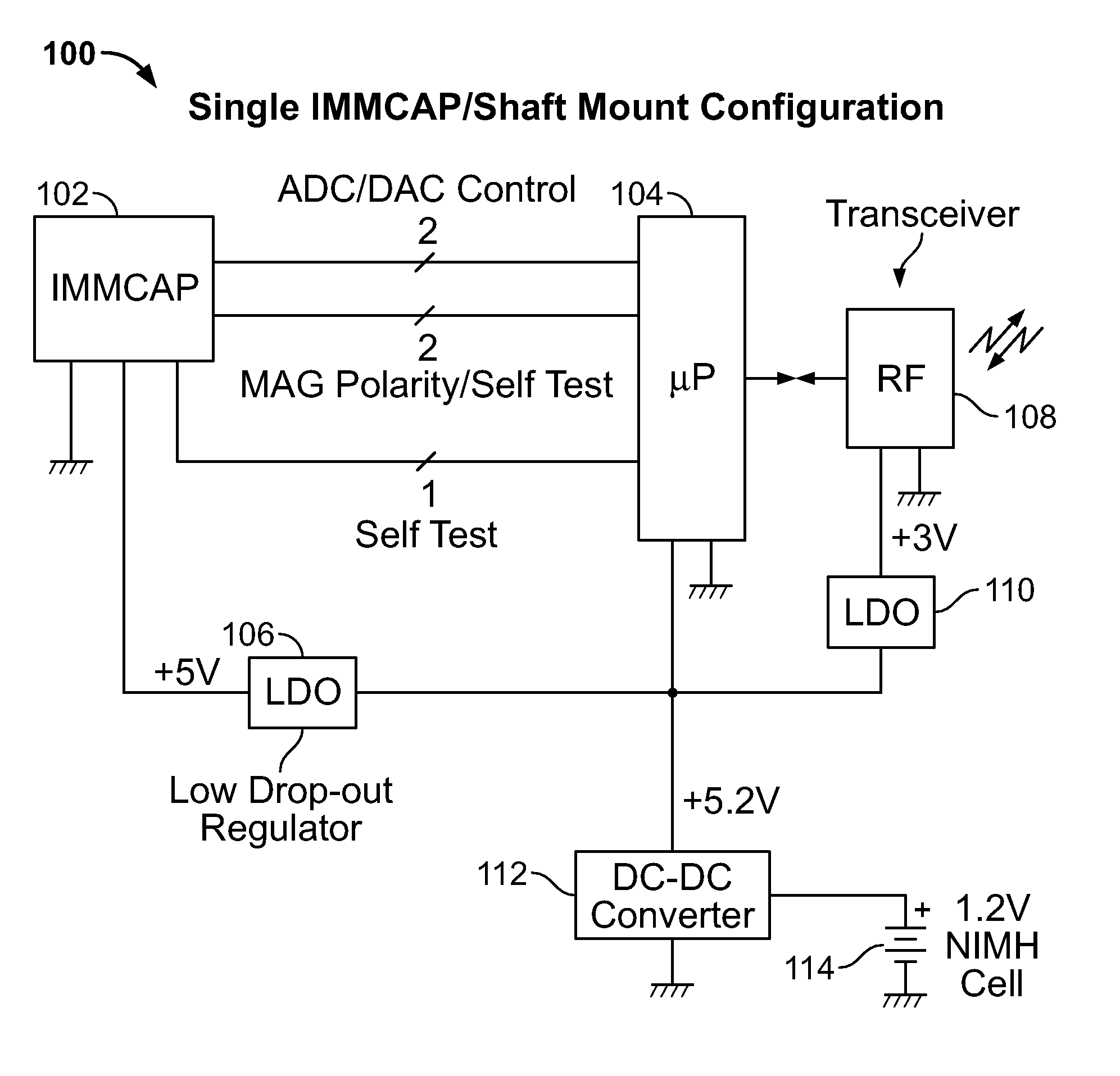
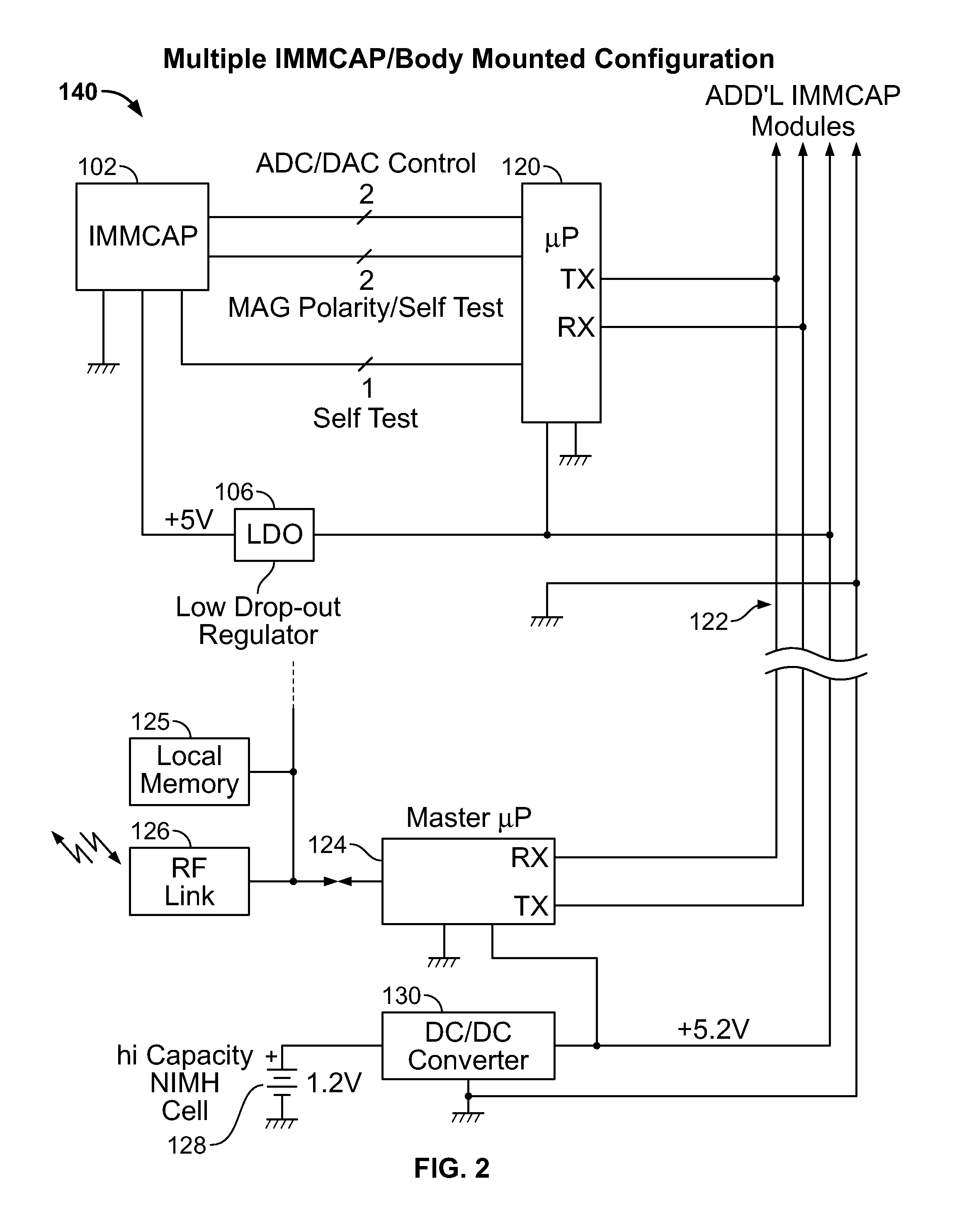
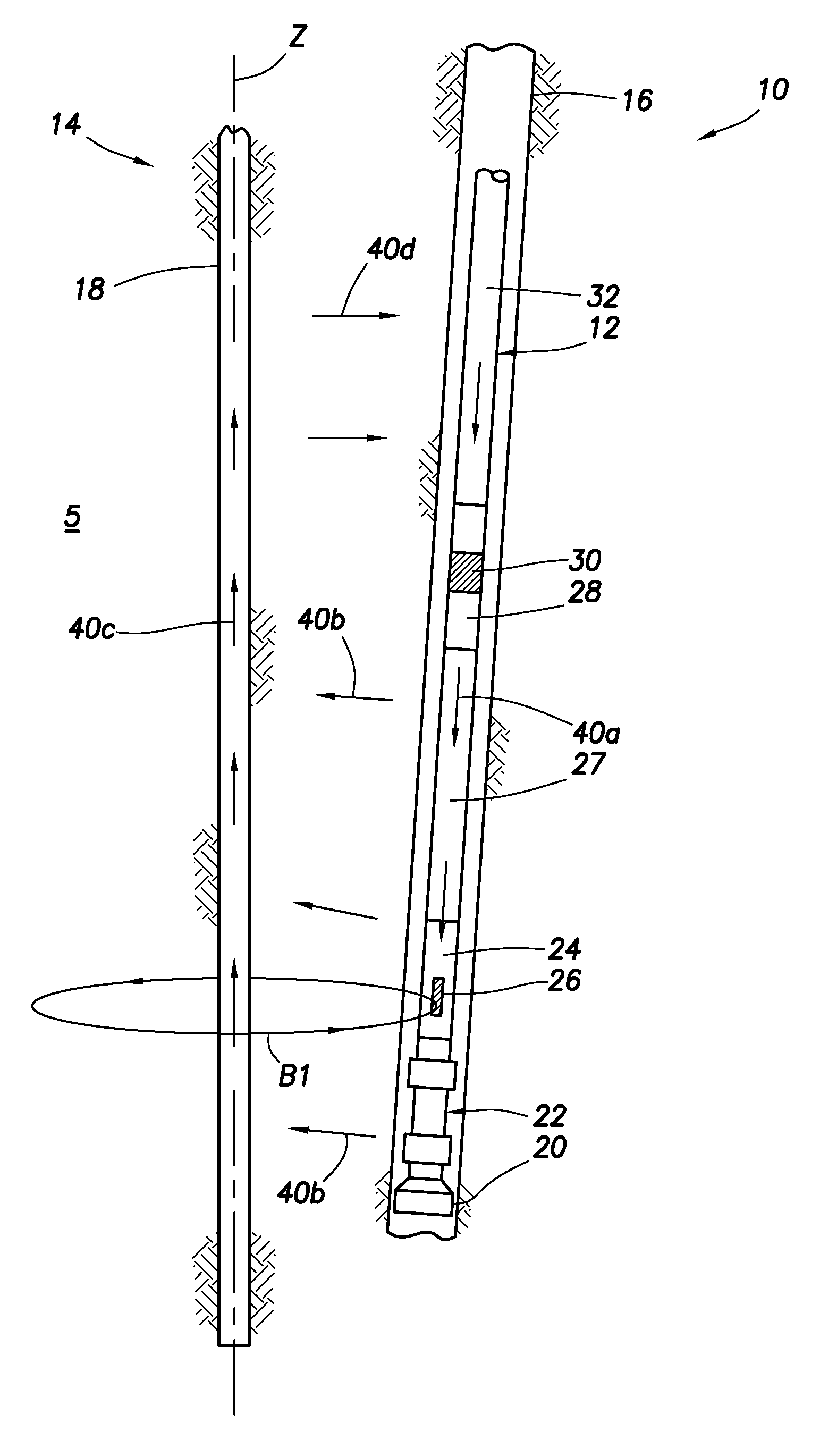
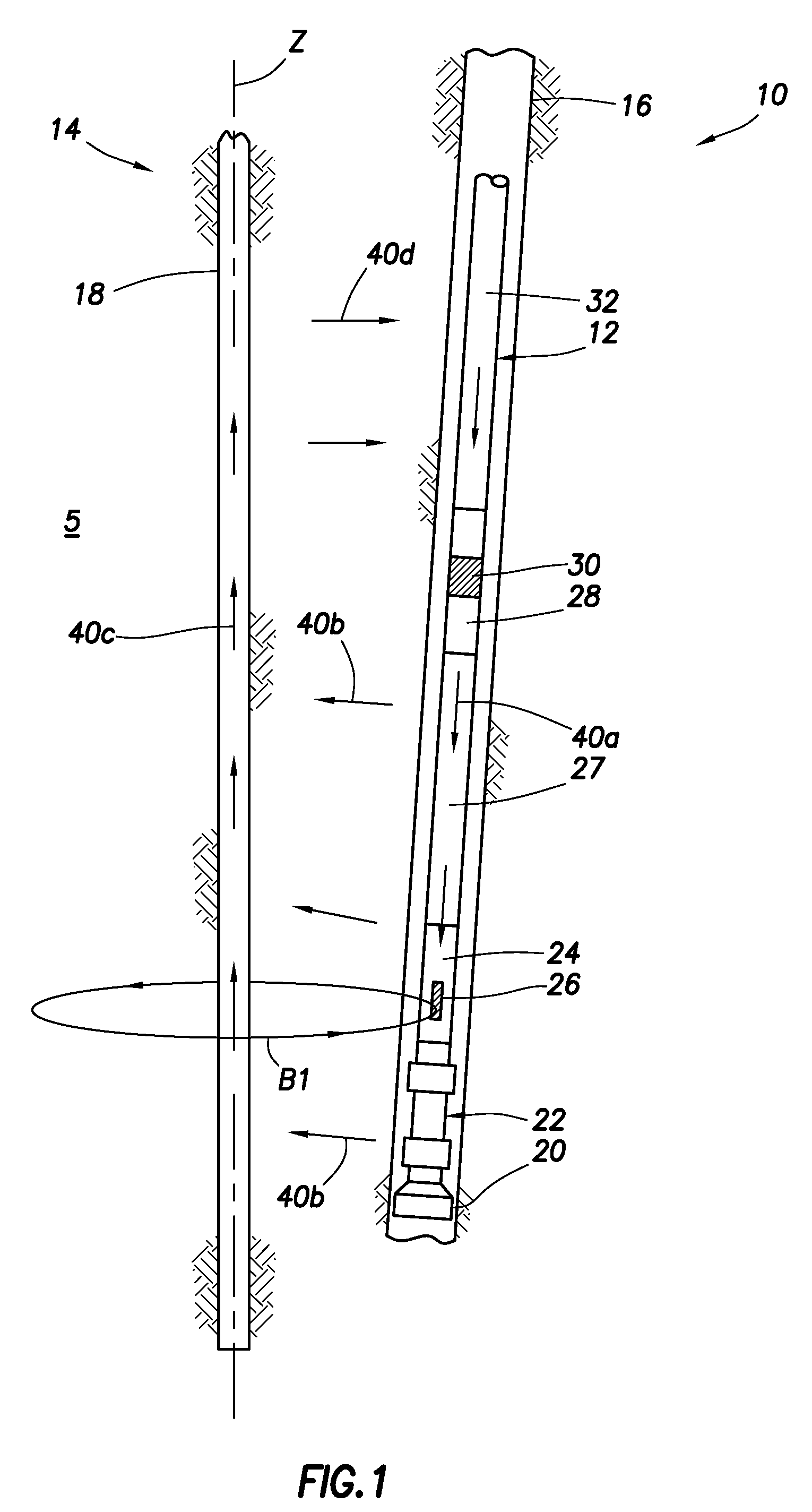
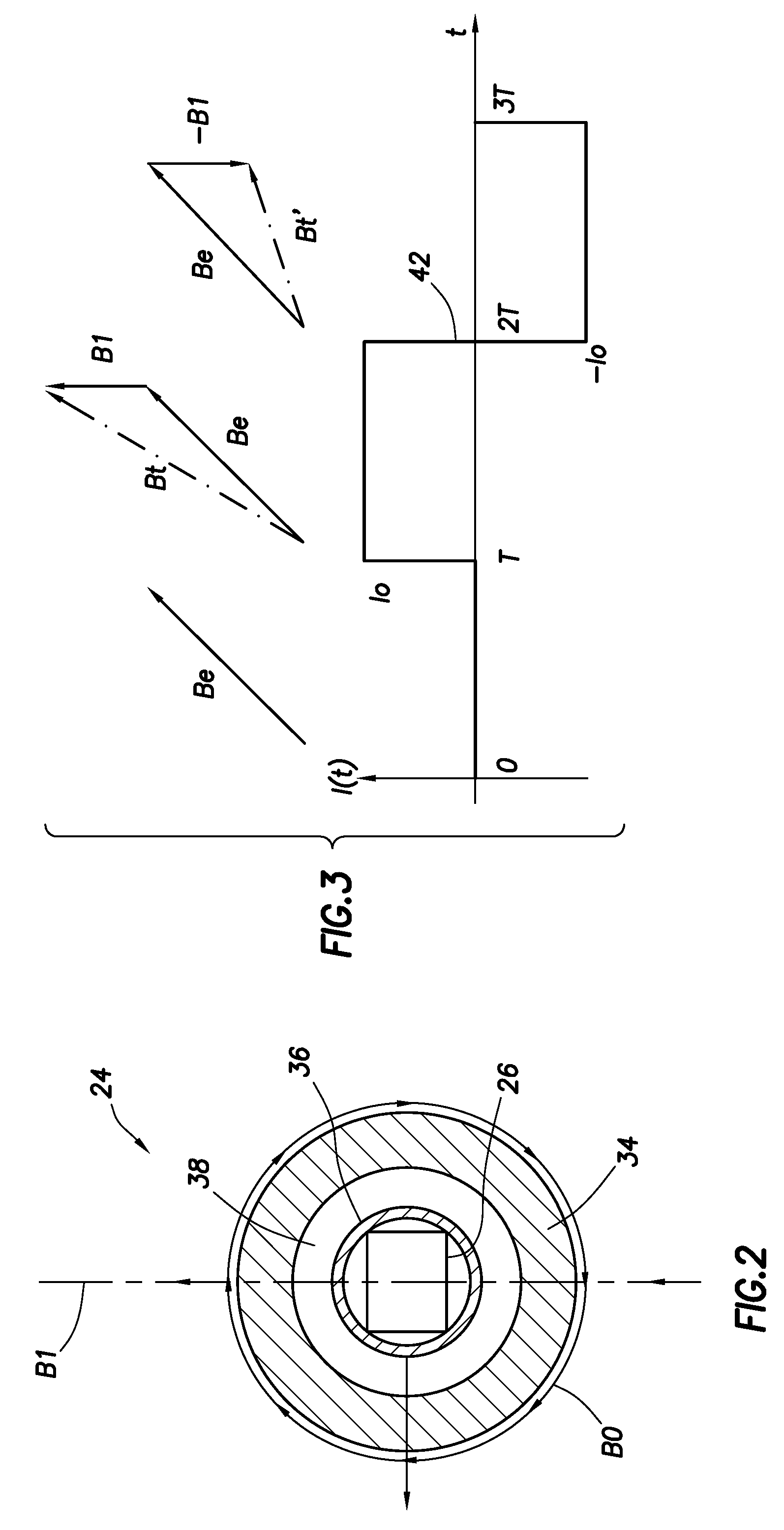
Single/multiple axes six degrees of freedom (6 DOF) inertial motion capture system with initial orientation determination capability
A highly miniaturized electronic data acquisition system includes MEMS sensors that can be embedded onto moving device without affecting the static / dynamic motion characteristics of the device. The basic inertial magnetic motion capture (IMMCAP) module consists of a 3D printed circuit board having MEMS sensors configured to provide a tri-axial accelerometer; a tri-axial gyroscope, and a tri-axial magnetometer all in communication with analog to digital converters to convert the analog motion data to digital data for determining classic inertial measurement and change in spatial orientation (rho, theta, phi) and linear translation (x, y, z) relative to a fixed external coordinate system as well as the initial spatial orientation relative to the know relationship of the earth magnetic and gravitational fields. The data stream from the IMMCAP modules will allow the reconstruction of the time series of the 6 degrees of freedom for each rigid axis associated with each independent IMMCAP module.
Owner:MAGNETO INERTIAL SENSING TECH
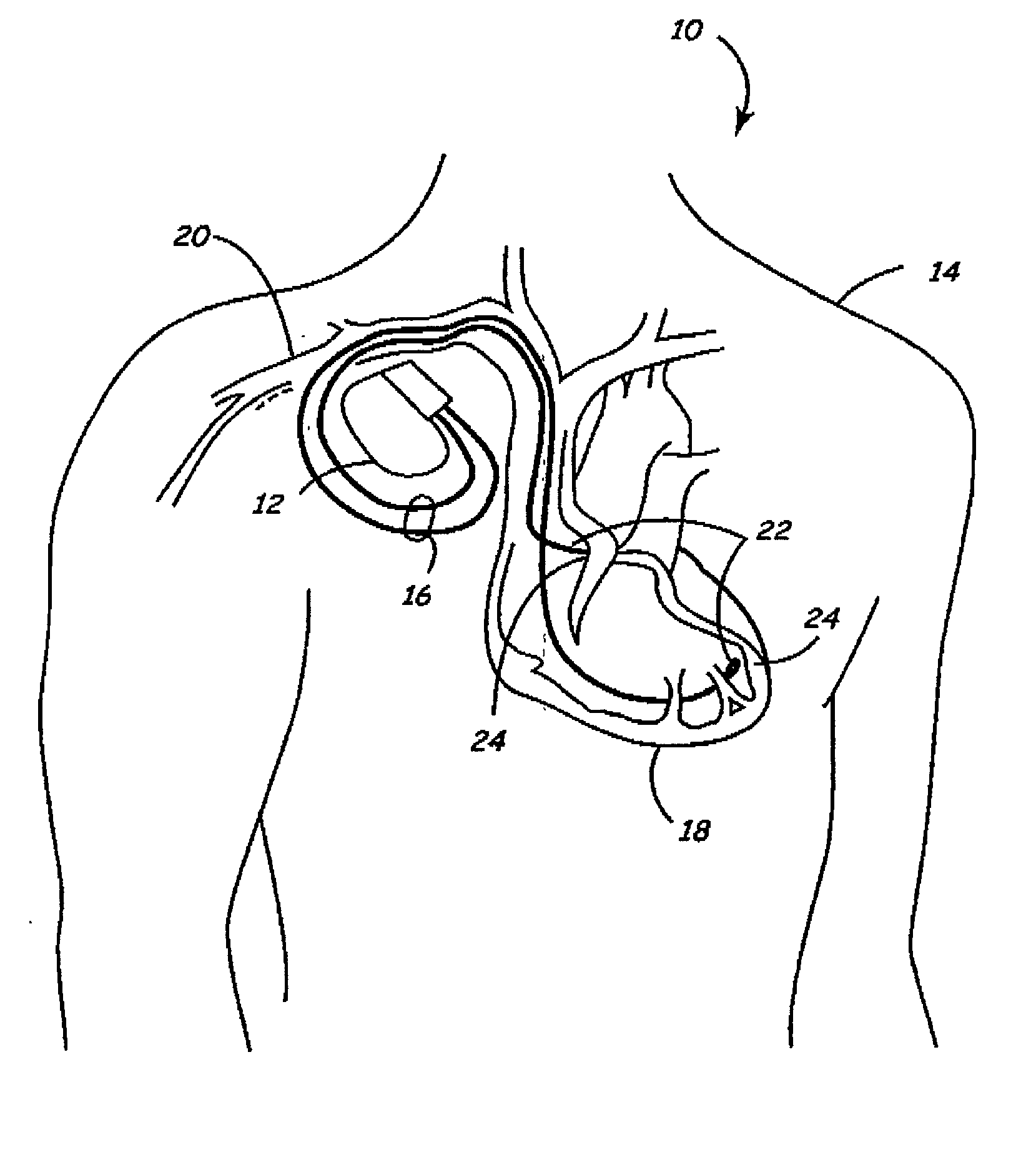
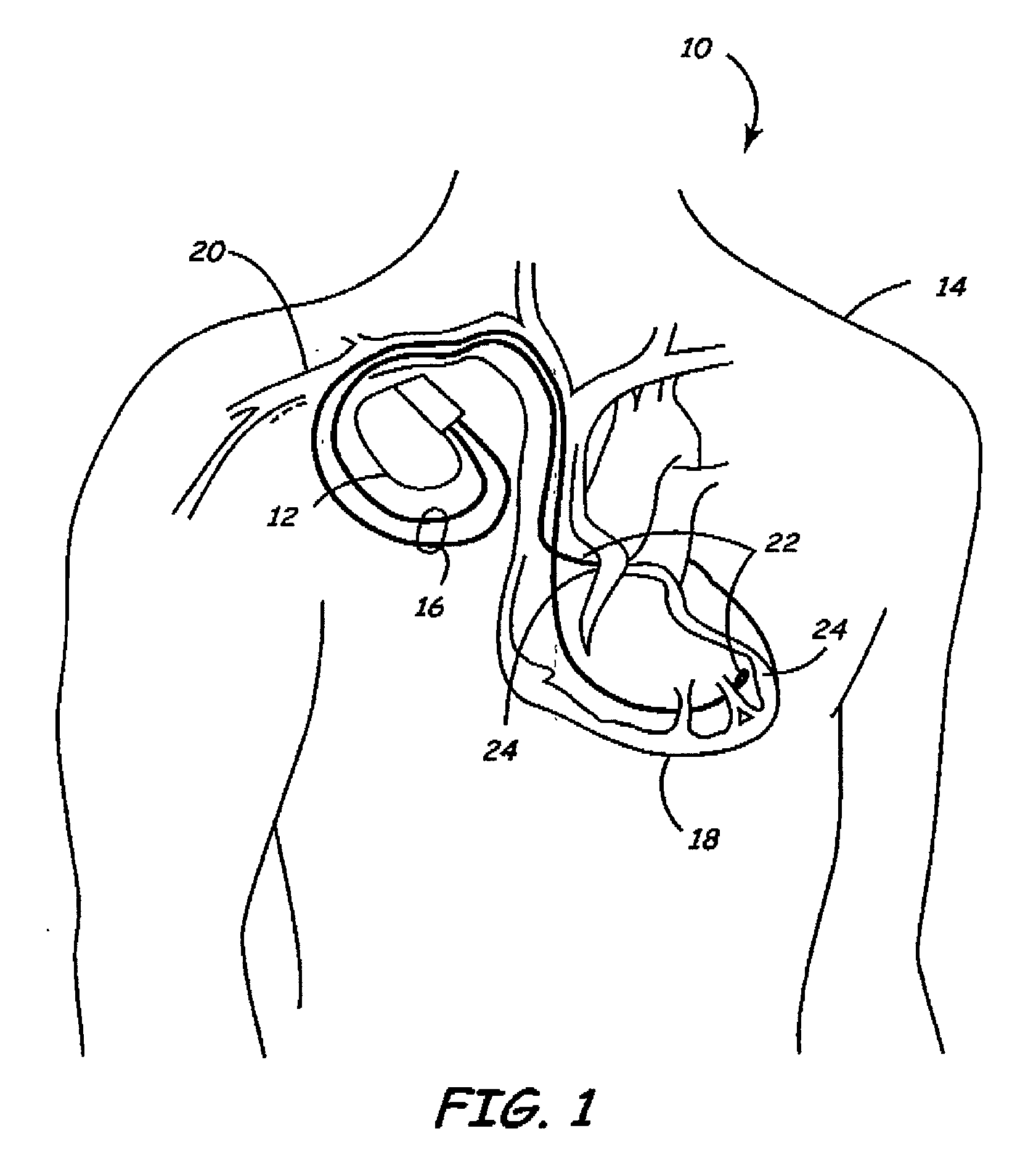
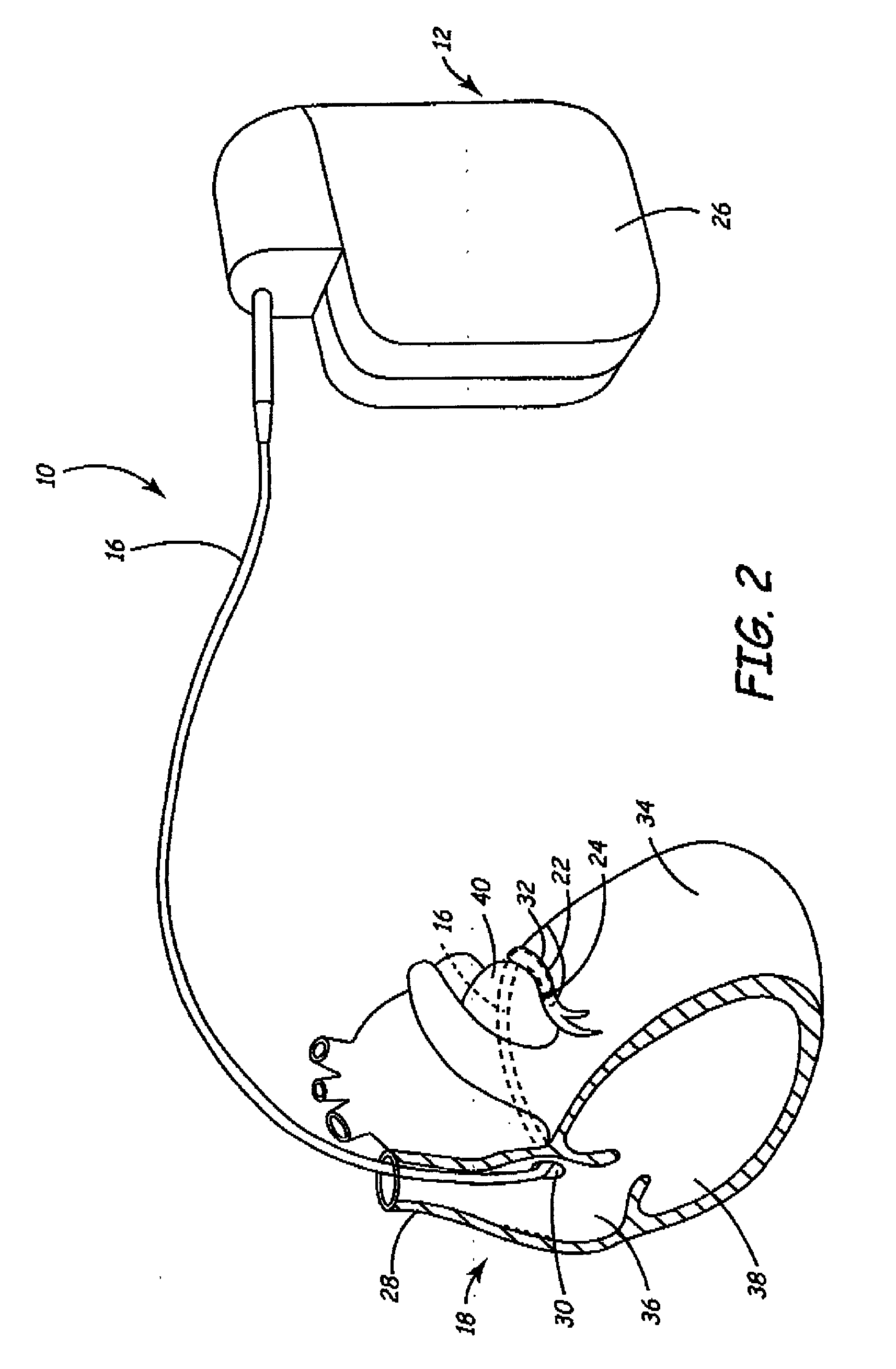
Medical implantable system for reducing magnetic resonance effects
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for reducing the potentially harmful effects of electromagnetic waves on an implantable medical device. In one embodiment of the present invention, an implantable medical system comprising a dual threshold magnetic sensor capable of detecting an elevated magnetic field is disclosed. The sensor can comprise a solid-state sensor capable of detecting a static magnetic field in excess of about 1500 Gauss. The magnetic sensor can be operatively coupled to electronics that are capable of altering the operation of the system upon detection of an elevated magnetic field by the magnetic sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
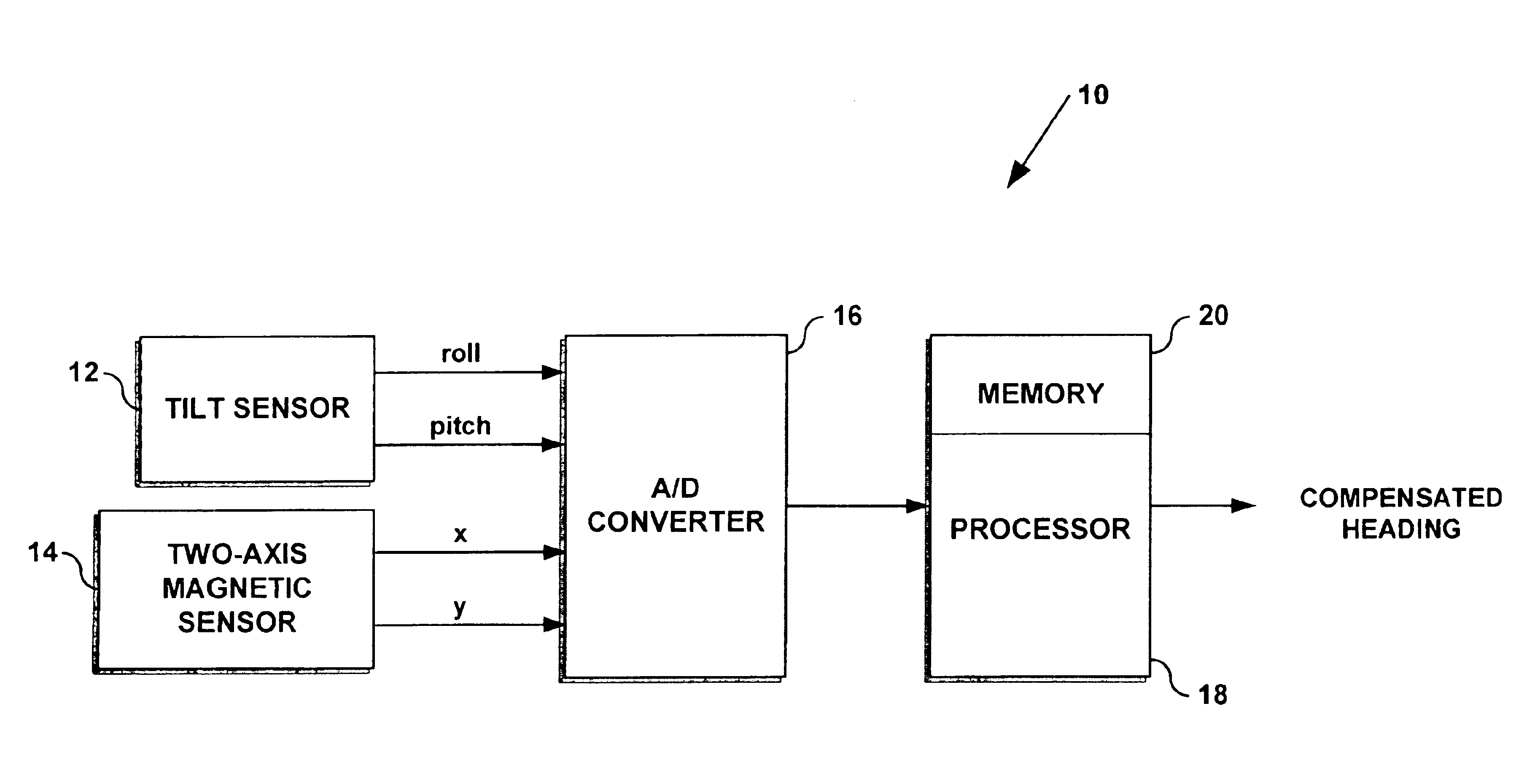
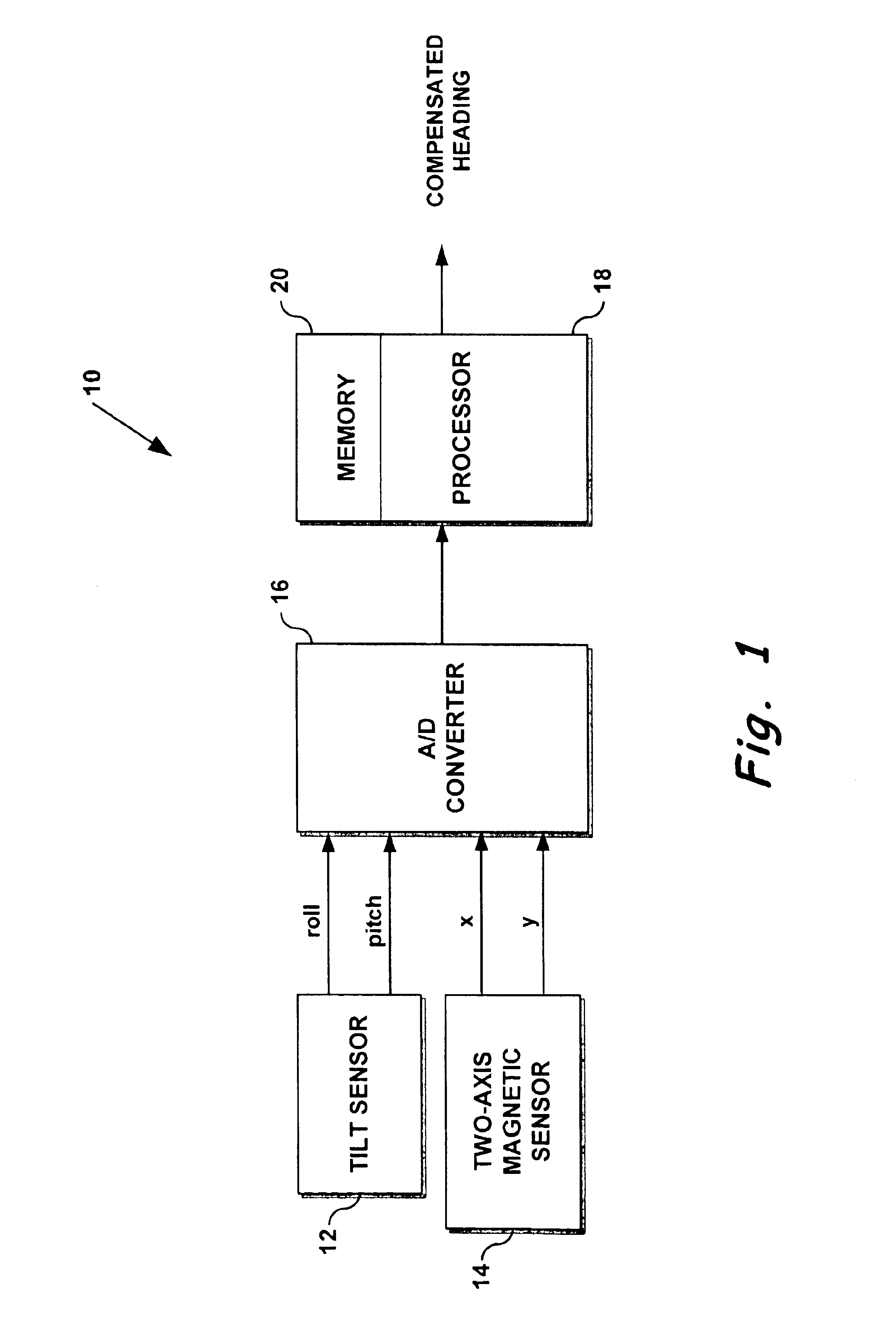
System for using a 2-axis magnetic sensor for a 3-axis compass solution
A tilt-compensated electronic compass can be realized by calculating rather than measuring Earth's magnetic field component Z in a direction orthogonal to the two measurement axes of a 2-axis magnetic sensor. The orthogonal component Z can be calculated using a stored value for the Earth's magnetic field strength applicable over a wide geographic region. The calculation also requires using measured field values from the 2-axis sensor. Once Z is known, and using input from a 2-axis tilt sensor, compensated orthogonal components X and Y can be calculated by mathematically rotating the measured field strength values from a tilted 2-axis sensor back to the local horizontal plane. Thus, a very flat and compact tilt-compensated electronic compass is possible.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
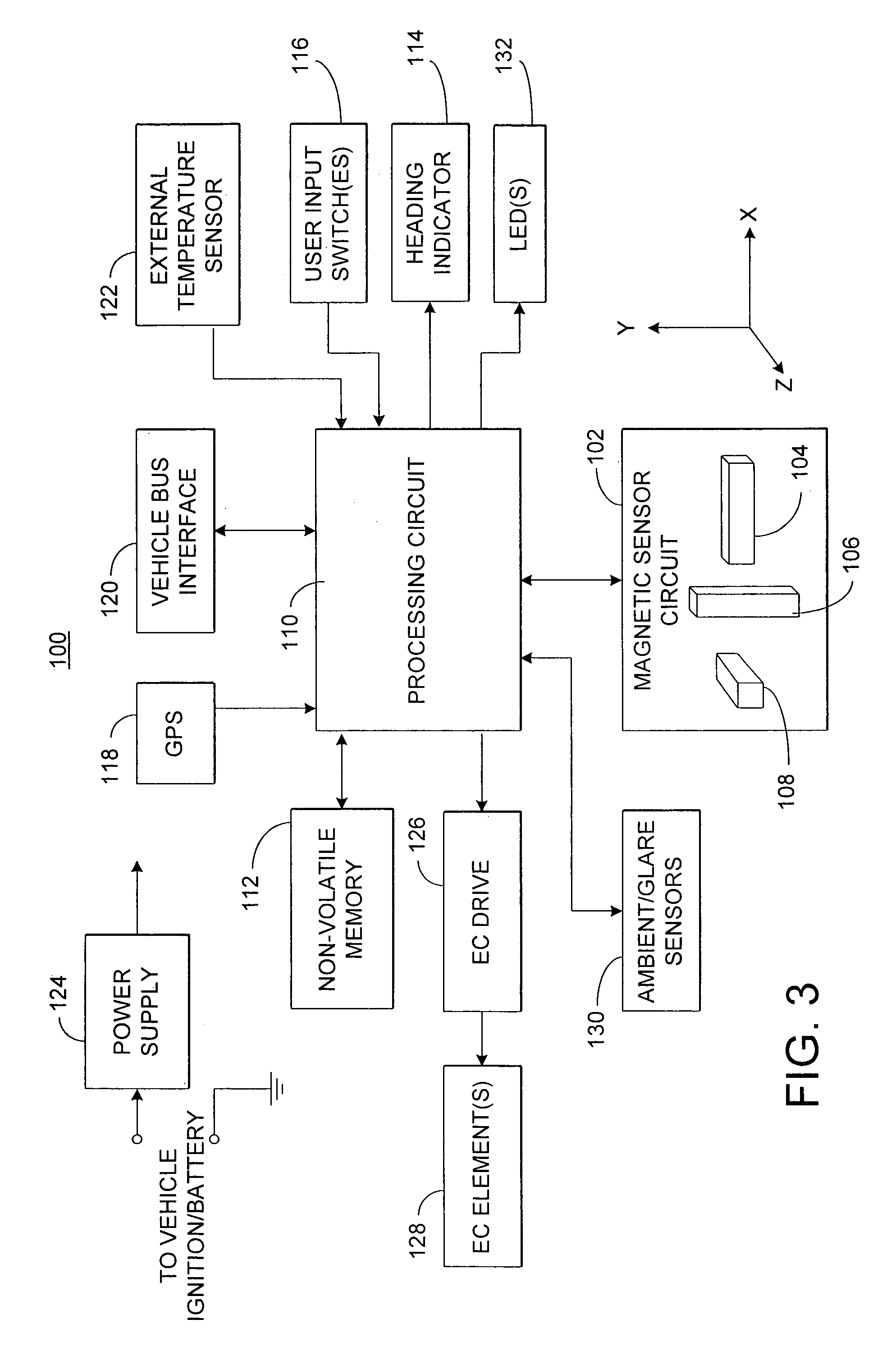
Electronic compass system
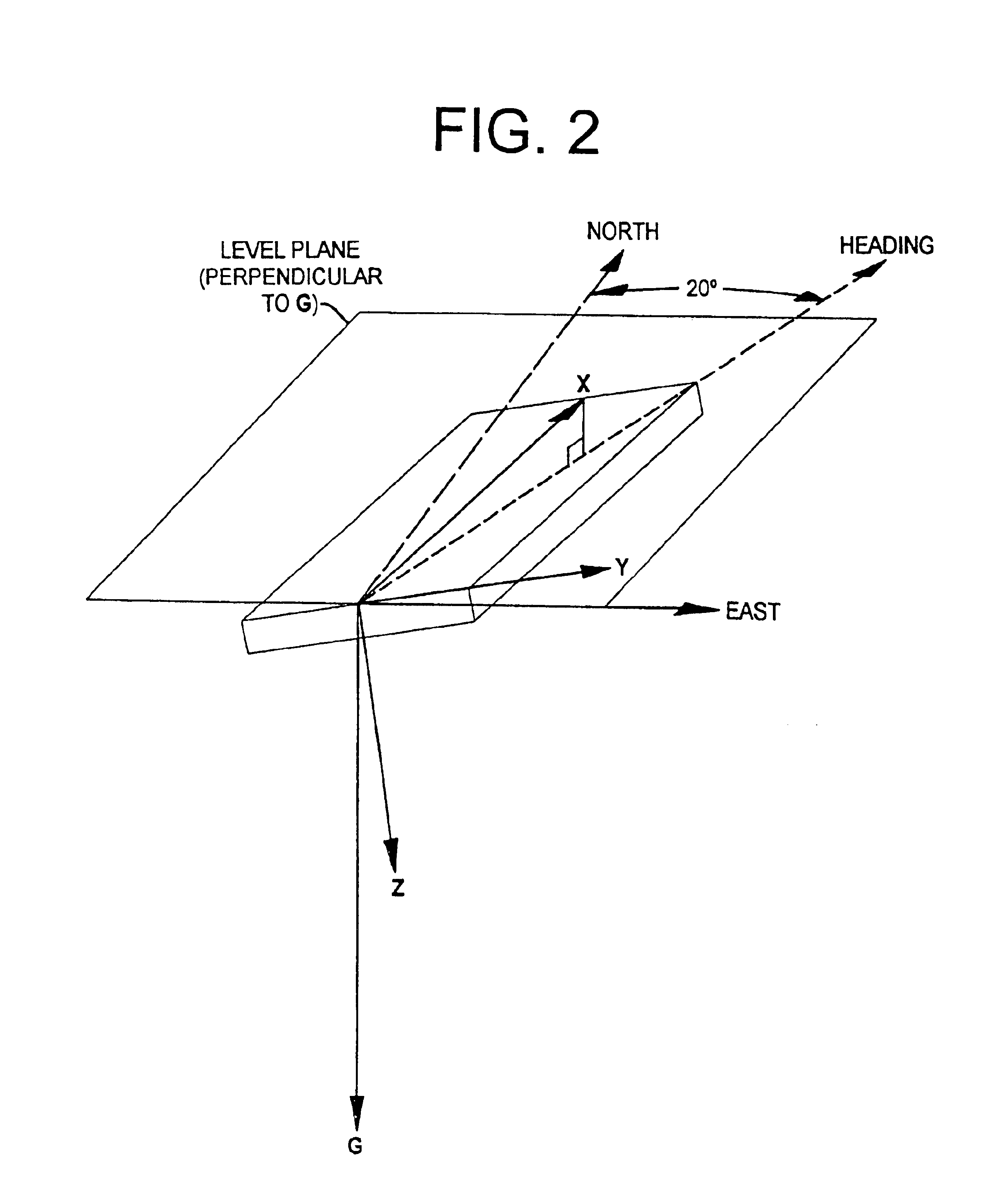
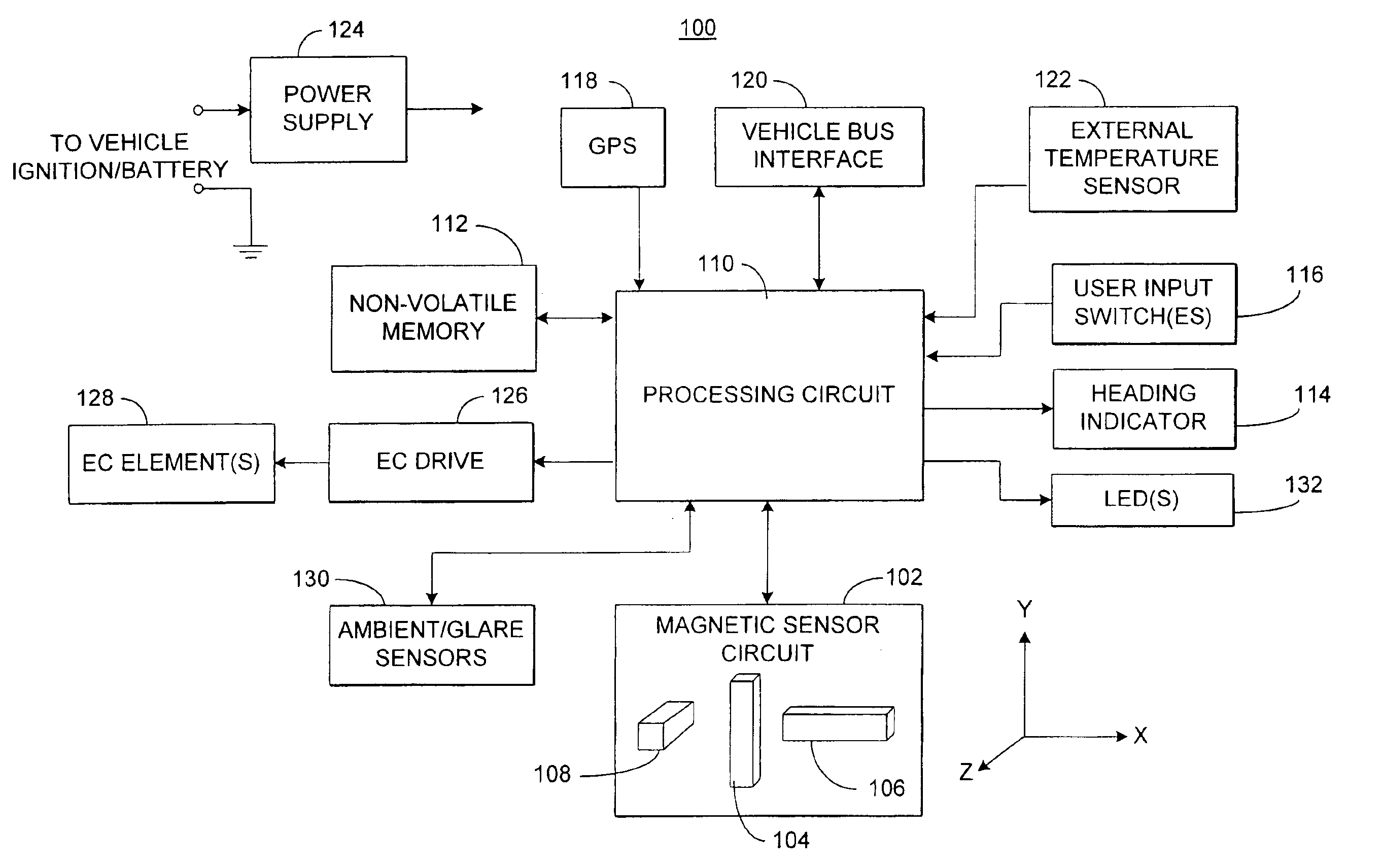
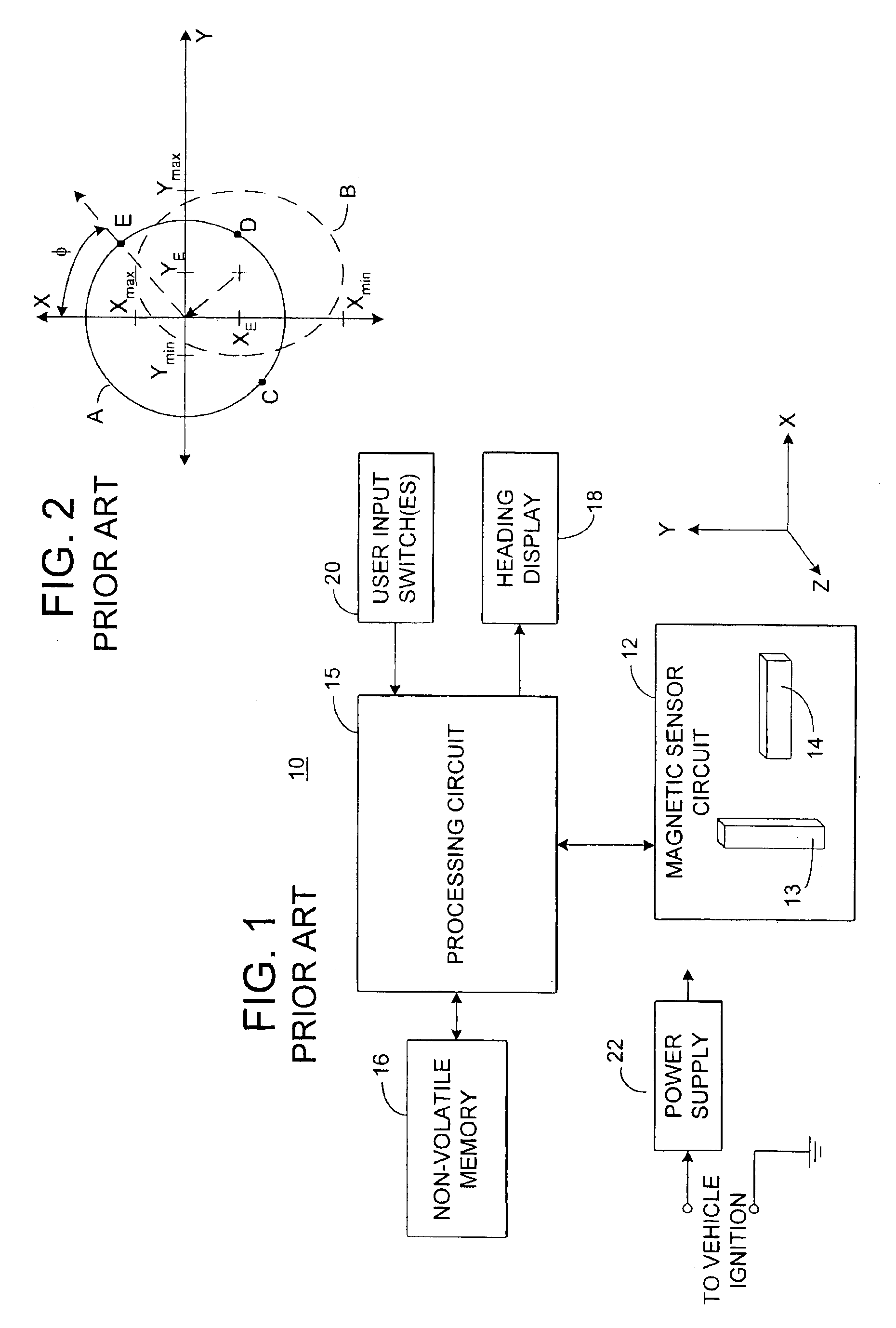
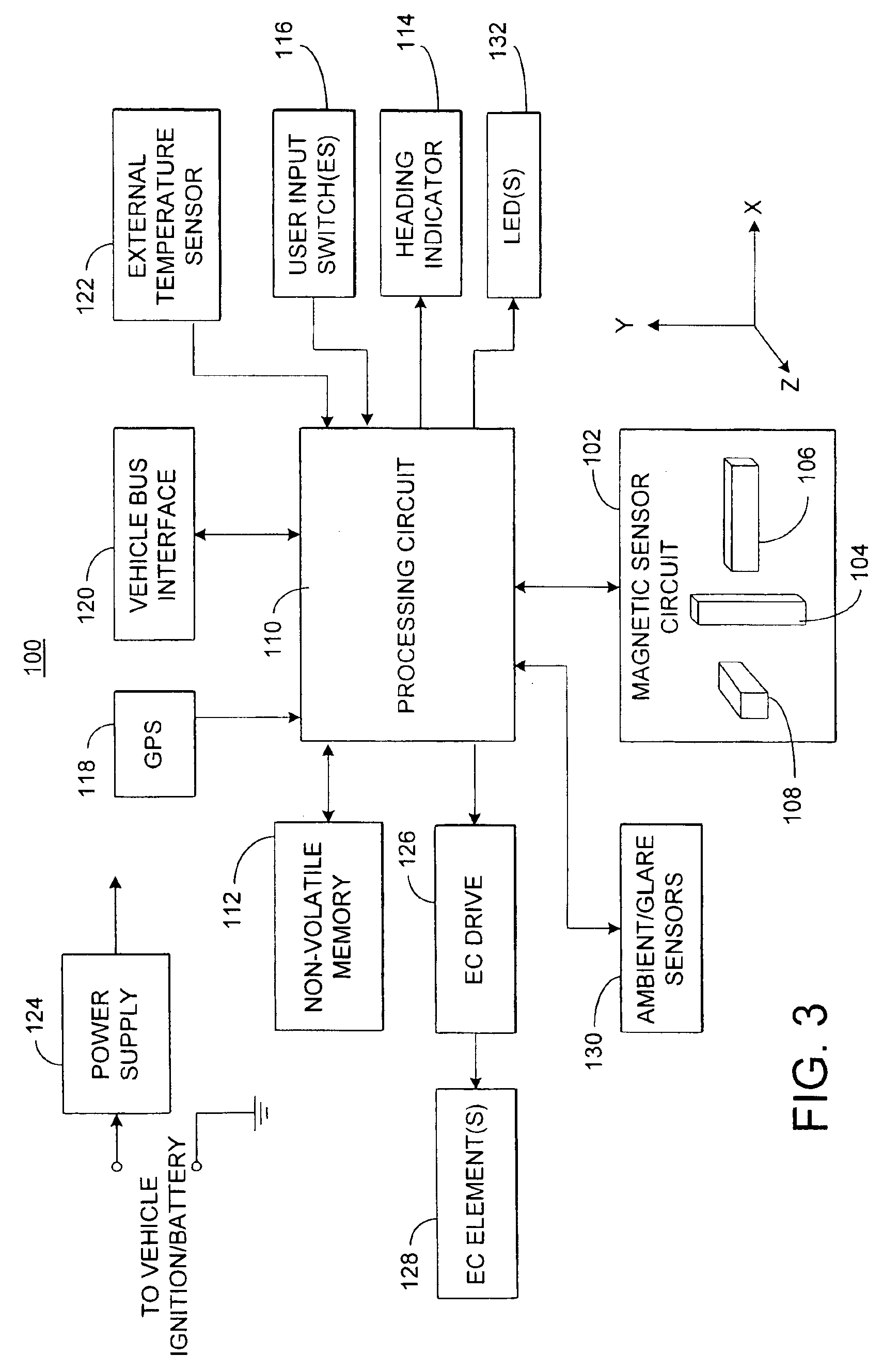
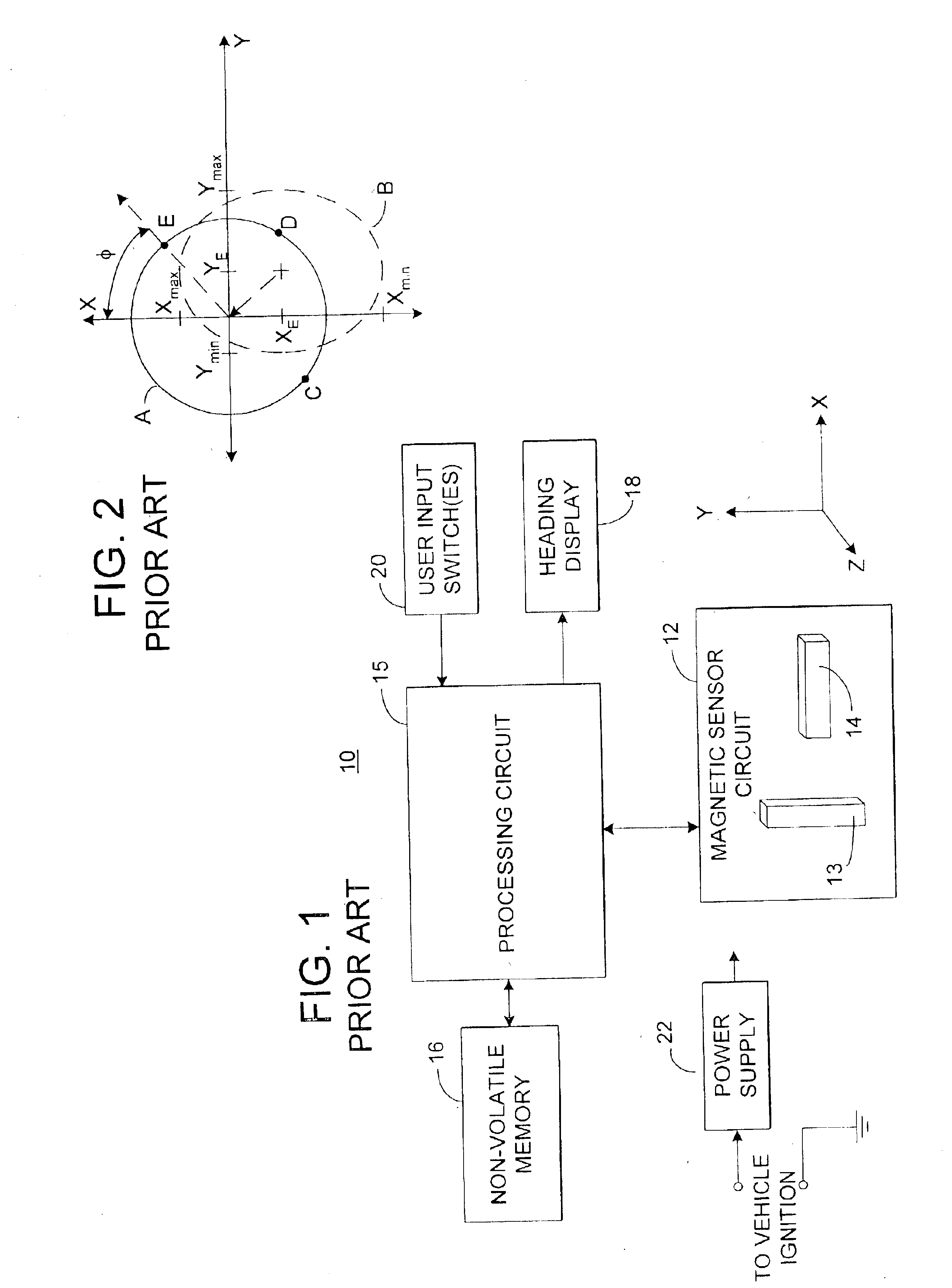
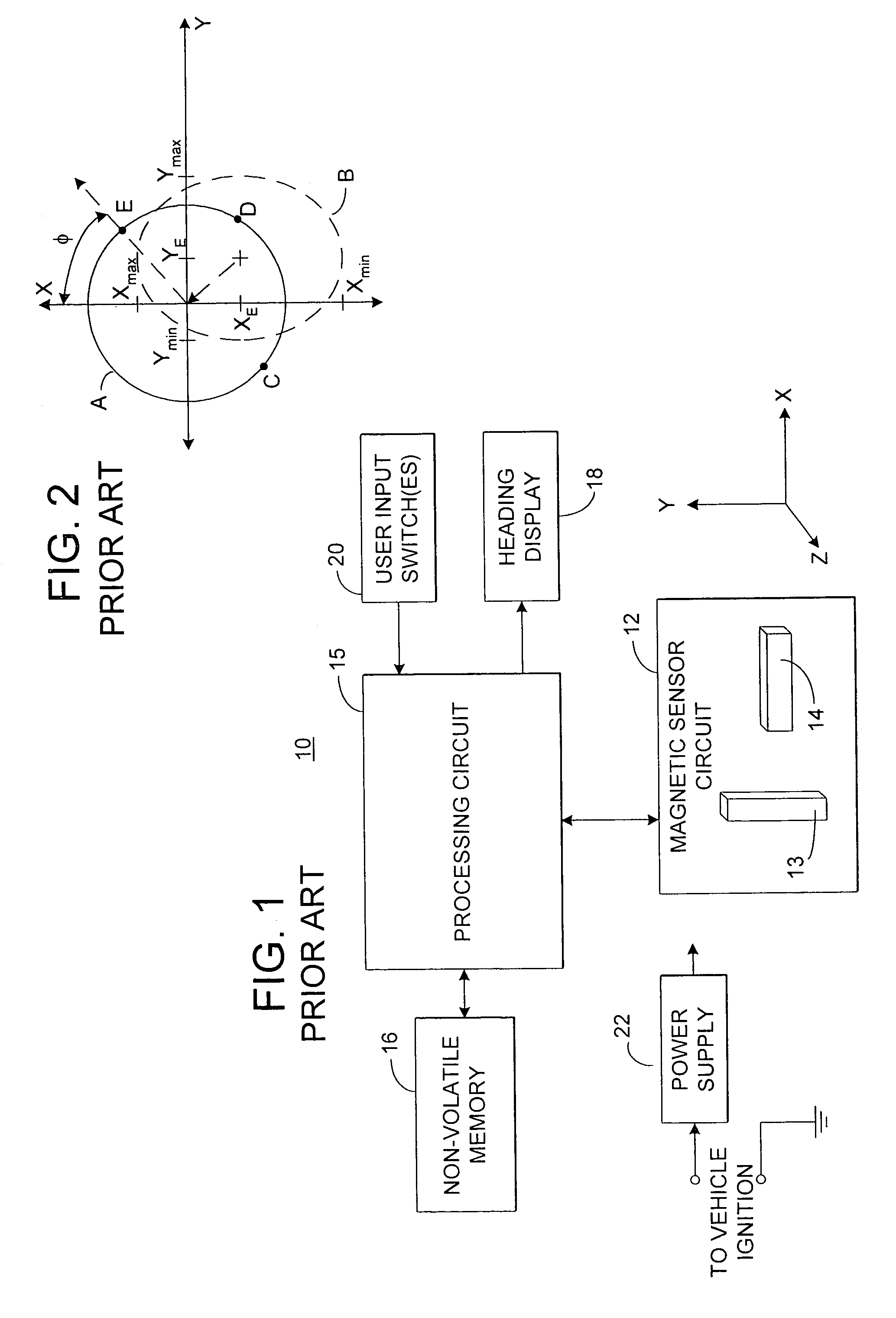
An electronic compass system includes a magnetic sensor circuit having at least two sensing elements for sensing perpendicular components of the Earth's magnetic field vector. A processing circuit is coupled to the sensor circuit to filter, process, and compute a heading. The processing circuit further selects an approximating geometric pattern, such as a sphere, ellipsoid, ellipse, or circle, determines an error metric of the data points relative to the approximating pattern, adjusts the pattern to minimize the error, thereby obtaining a best fit pattern. The best fit pattern is then used to calculate the heading for each successive sensor reading provided that the noise level is not noisy and until a new best fit pattern is identified. The electronic compass system is particularly well suited for implementation in a vehicle rearview mirror assembly.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Micro integrated global positioning system/inertial measurement unit system
InactiveUS20020008661A1Precise positioningInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationCarrier signalClosed loop
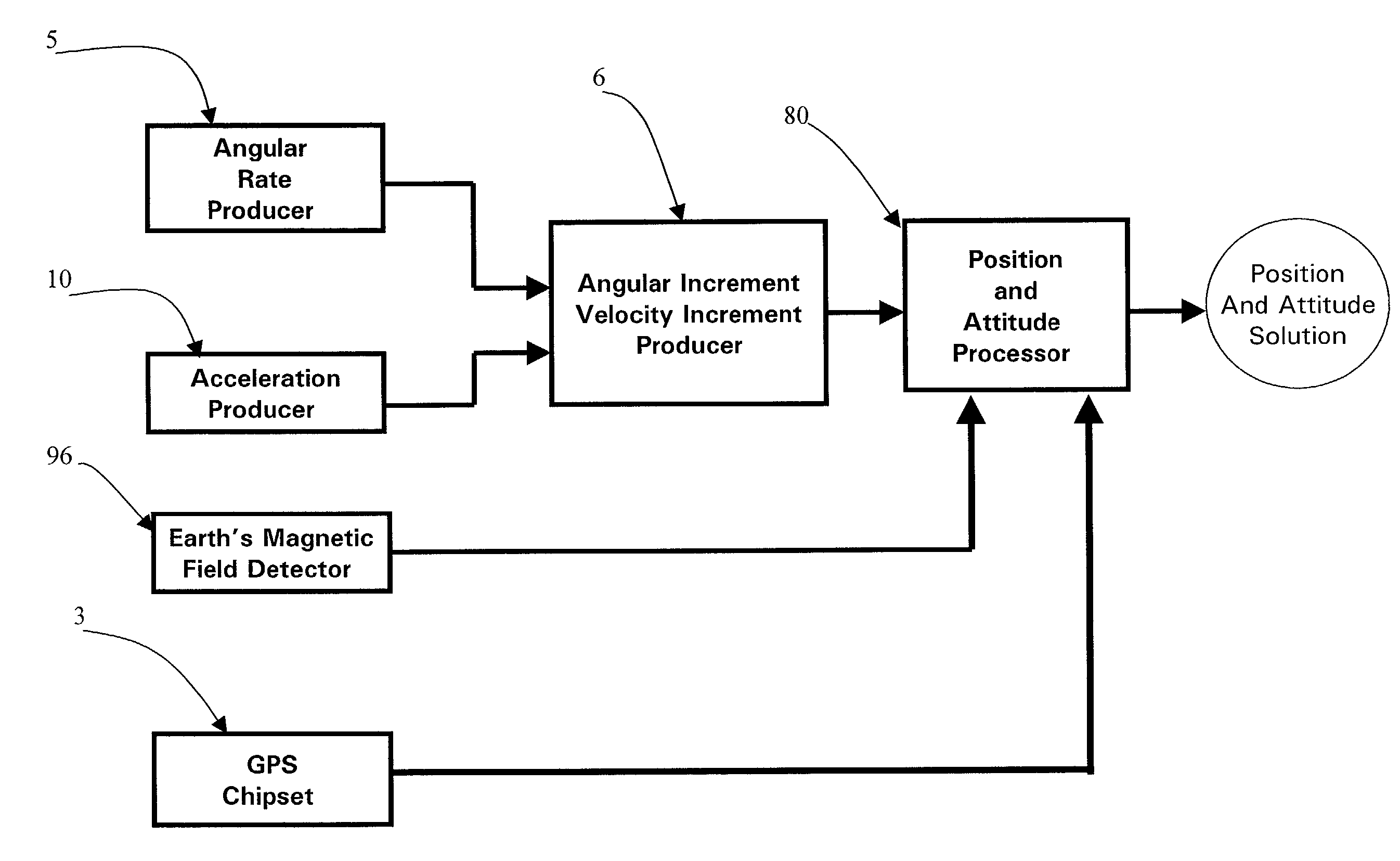
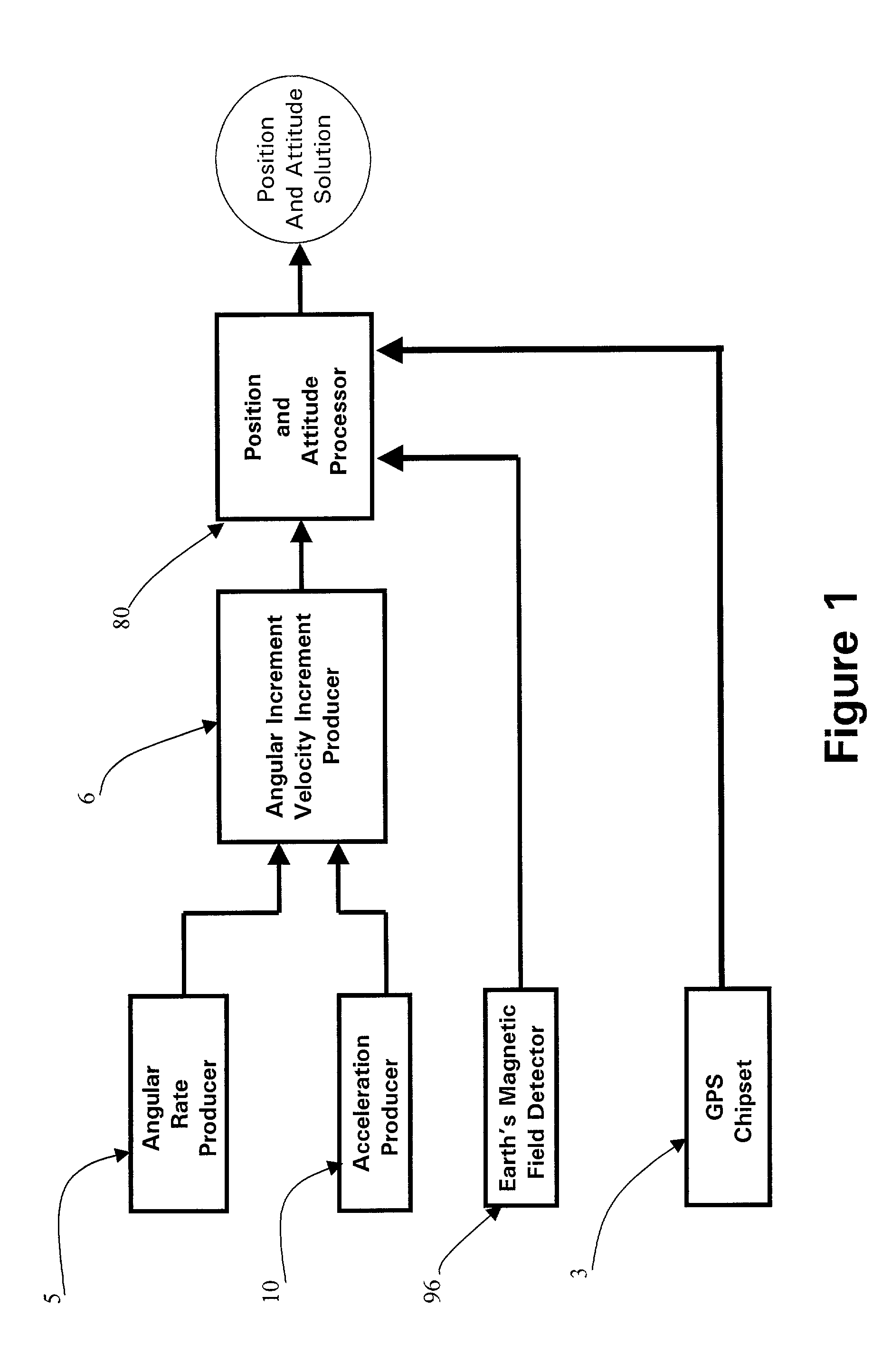
A micro integrated Global Positioning System (GPS) / Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) System, which is adapted to apply to output signals proportional to rotation and translational motion of a carrier and GPS measurements of the carrier, respectively from angular rate sensors, acceleration sensors, and GPS chipset, is employed with MEMS angular rate and acceleration sensors and GPS chipset. Compared with a conventional IMU / GPS system, the system of the present invention uses an integrated processing scheme by means of digital closed loop control of the dither driver signals for MEMS angular rate sensors, a feedforward open-loop signal processing scheme of the IMU, digital temperature control and compensation, the earth's magnetic field-based heading damping, robust error estimator, and compact sensor and circuit architecture and dramatically shrinks the size of mechanical and electronic hardware and power consumption, meanwhile, obtains highly accurate motion measurements.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
Electronic compass system
An electronic compass system includes a magnetic sensor circuit having at least two sensing elements for sensing perpendicular components of the Earth's magnetic field vector. A processing circuit is coupled to the sensor circuit to filter, process, and compute a heading. The processing circuit further selects an approximating geometric pattern, such as a sphere, ellipsoid, ellipse, or circle, determines an error metric of the data points relative to the approximating pattern, adjusts the pattern to minimize the error, thereby obtaining a best fit pattern. The best fit pattern is then used to calculate the heading for each successive sensor reading provided that the noise level is not noisy and until a new best fit pattern is identified. The electronic compass system is particularly well suited for implementation in a vehicle rearview mirror assembly.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Electronic compass system
InactiveUS7149627B2Change effectInstruments for road network navigationTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
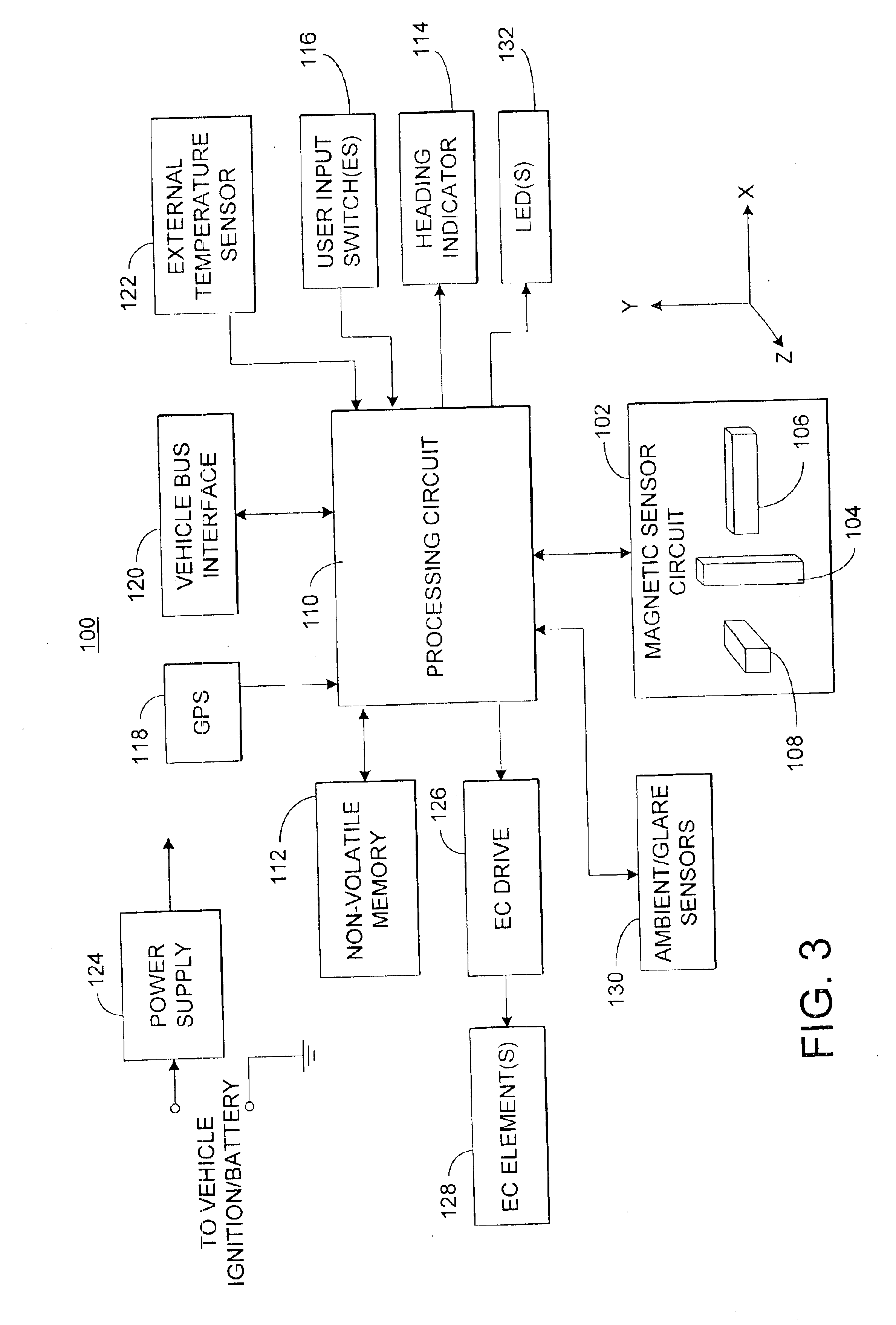
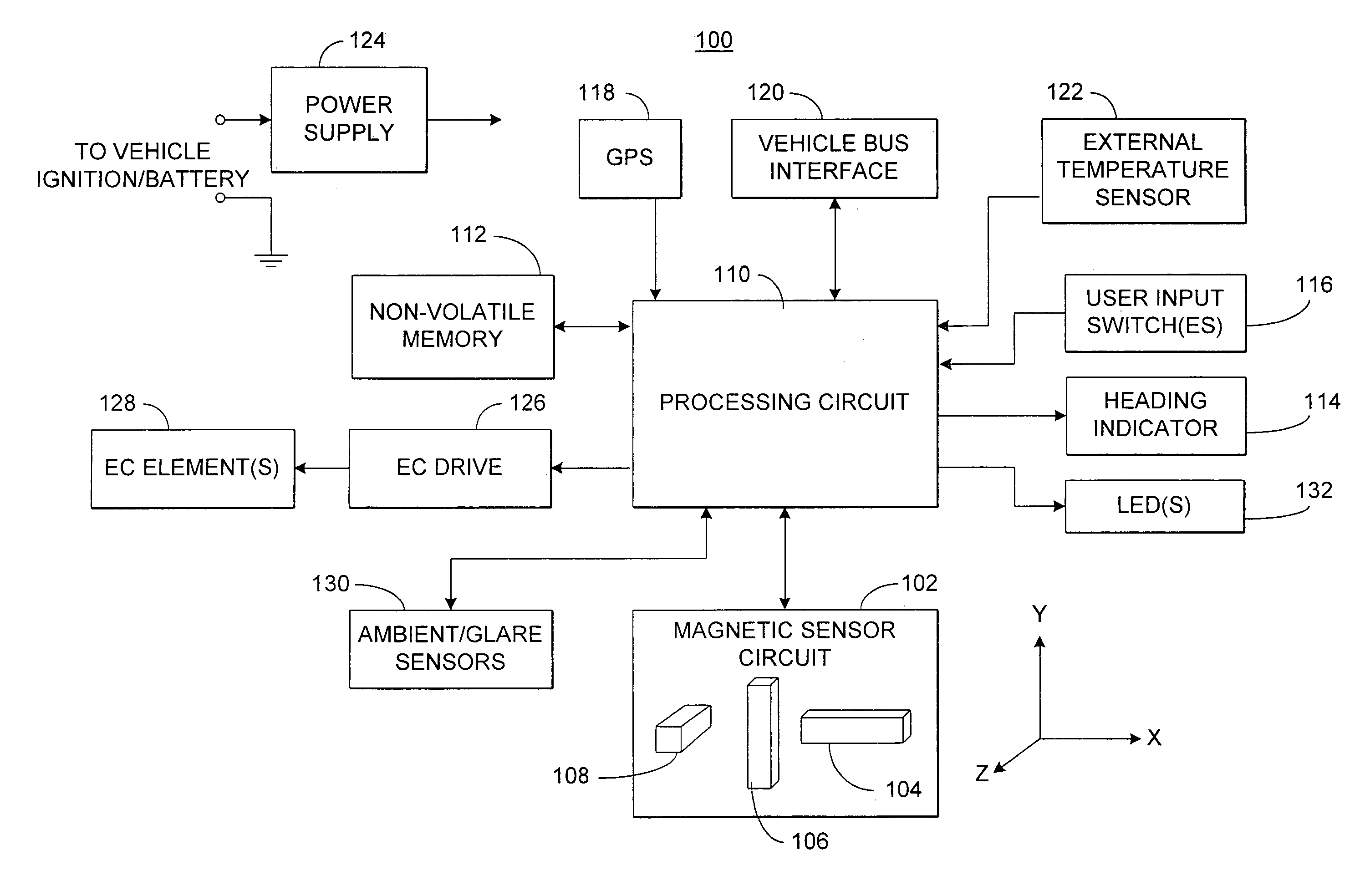
An electronic compass system includes a magnetic sensor circuit having at least two sensing elements for sensing perpendicular components of the Earth's magnetic field vector. A processing circuit is coupled to the sensor circuit to filter, process, and compute a heading. The processing circuit may determine whether too much noise is present in the output signals received from said magnetic sensor circuit as a function of the relative strength of the Earth's magnetic field vector. The magnetic sensor circuit may include three magnetic field sensing elements contained in a common integrated package having a plurality of leads extending therefrom for mounting to a circuit board. The sensing elements need not be perpendicular to each other or parallel or perpendicular with the circuit board. The electronic compass system is particularly well suited for implementation in a vehicle rearview mirror assembly.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Medical implantable system for reducing magnetic resonance effects
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Vehicle compass compensation
A compass compensation system is provided for automatically and continuously calibrating an electronic compass for a vehicle, without requiring an initial manual calibration or preset of the vehicle magnetic signature. The system initially adjusts a two axis sensor of the compass in response to a sampling of at least one initial data point. The system further calibrates the compass by sampling data points that are substantially opposite to one another on a plot of a magnetic field and averaging an ordinate of the data points to determine a respective zero value for the Earth magnetic field. The system also identifies a change in magnetic signature and adjusts the sensor assembly.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Solar Collection Apparatus and Methods Using Accelerometers and Magnetic Sensors
InactiveUS20080011288A1Precise positioningSolar heating energyRoof coveringIndependent motionAccelerometer
Owner:SEEKTECH
Method and apparatus for locating well casings from an adjacent wellbore
ActiveUS20070126426A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsEngineeringConductive materials
A wellbore tool for locating a target wellbore containing a conductive member from a second wellbore and directing the trajectory of the second wellbore relative to the target wellbore includes an electric current driver having an insulated gap; a three-axis magnetometer positioned within a non-magnetic housing that is disposed within a non-magnetic tubular, the three-axis magnetometer positioned below the electric current driver; a drill bit positioned below the three-axis magnetometer; a hollow tubular connected between the electric current driver and the three-axis magnetometer; and a measurement-while-drilling tool. The current driver generates an electric current across the gap to the portion of the tool below the insulated gap. In a method a current is generated across the insulated gap to the portion of the tool below the insulated gap to the conductive material in the target wellbore returning to a portion of the bottom hole assembly above the insulated gap thereby producing a target magnetic field. Measuring the target magnetic field at the bottom hole assembly and the earth's magnetic field; and determining the position of the second wellbore relative to the target wellbore. Then steering the bottom hole assembly to drill the second wellbore along a trajectory relative to the target wellbore.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Devices and methods of low frequency magnetic stimulation therapy
Described herein, in certain embodiments, are devices and methods for modulating the electrical activity of a brain in a targeted manner using a weak magnetic field, generally field with a strength of less than about 100 Gauss. The magnetic field is varied over time in a periodic manner, generally with a frequency tuned to specifically affect one of the intrinsic frequencies of the brain, optionally the alpha frequency. The “Low Field Magnetic Stimulation” devices and methods described herein modulate the electrical activity of a brain without requiring medication. Methods and devices described herein gently “tune” the brain and affect mood, focus, and cognition of human subjects.
Owner:NEOSYNC
Process for determining the direction of the earth's magnetic field
InactiveUS6009629ATesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesElectric/magnetic detectionEarth's magnetic fieldAtomic physics
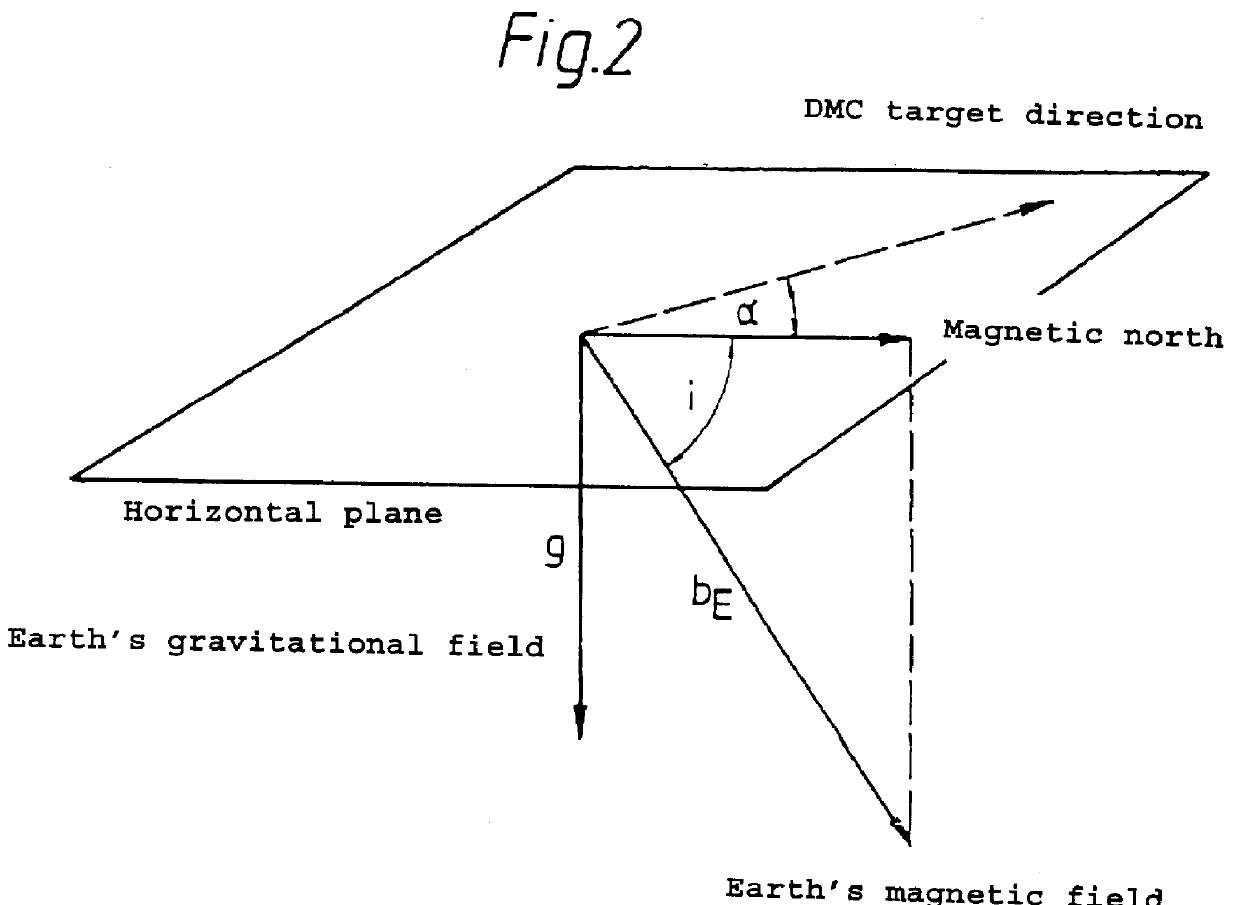
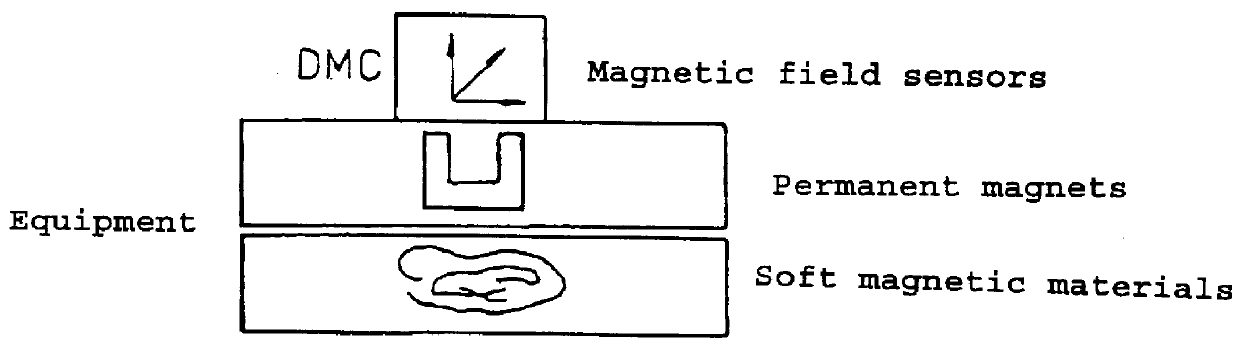
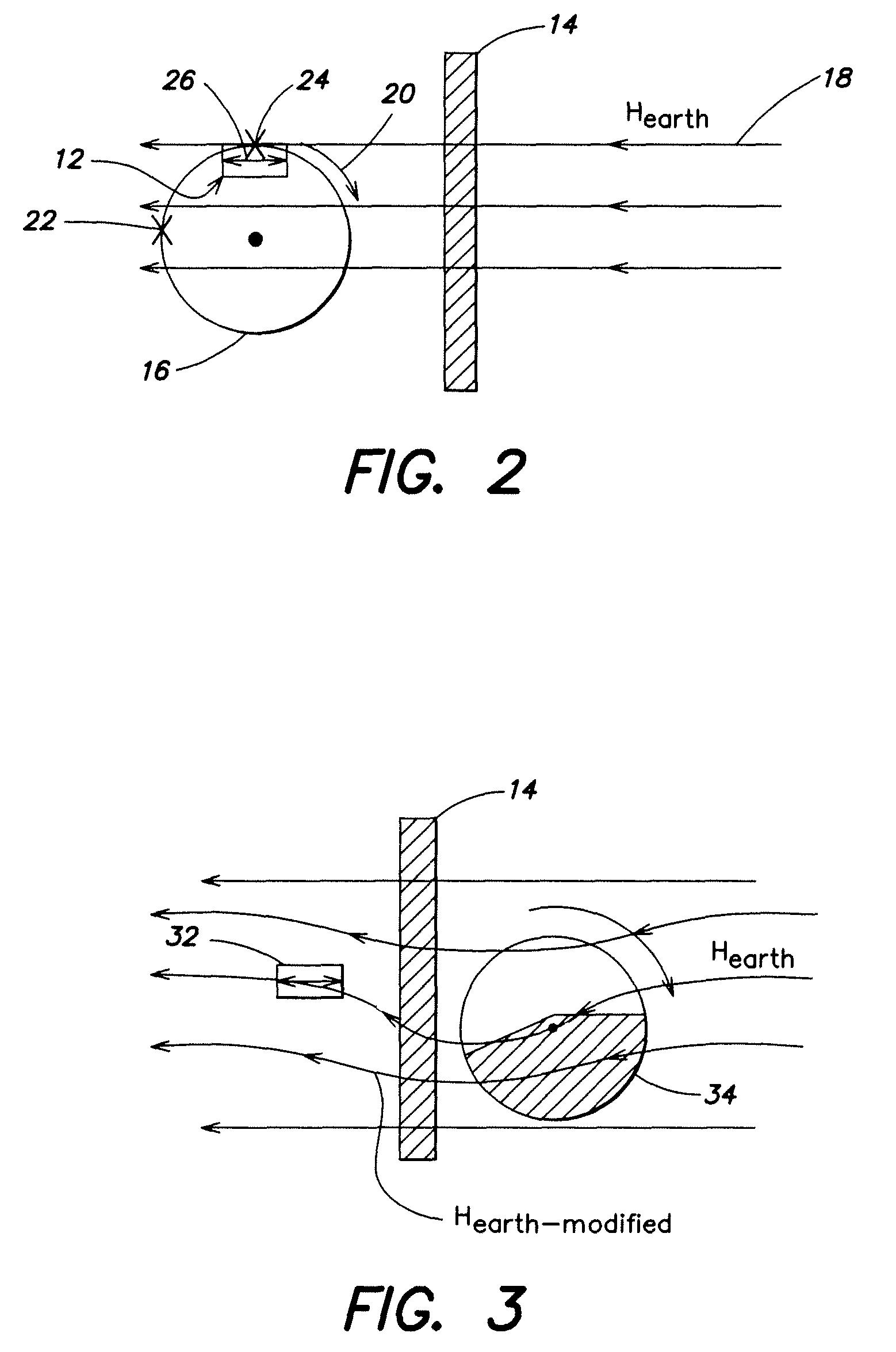
PCT No. PCT / EP97 / 00583 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 10, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 10, 1997 PCT Filed Feb. 10, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 34125 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 18, 1997A method for determining the direction of the Earth's magnetic field, which may be interfered with by magnetic materials built into equipment and by electric currents, using an electronic magnetic compass which contains three magnetic field sensors and two devices for measuring inclination is provided. The electronic magnetic compass is arranged in N different spatial positions, in each of these N positions, the inclination sensor signals and the magnetic field sensor signals being measured and inclination values and magnetic field values being determined from these signals. On the basis of these inclination values and magnetic field values, the magnitude of the Earth's magnetic field vector is determined using the vector equationconst=bg=bEsin(i)=gTL(bE)=gTm(bmes-bo)with N having to be at least equal to the number of parameters to be determined in the vector equation.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Apparatus and method utilizing magnetic field
InactiveUS7952349B2Small and lightElectrotherapyMagnetostrictive property measurementsInertial massEnergy harvester
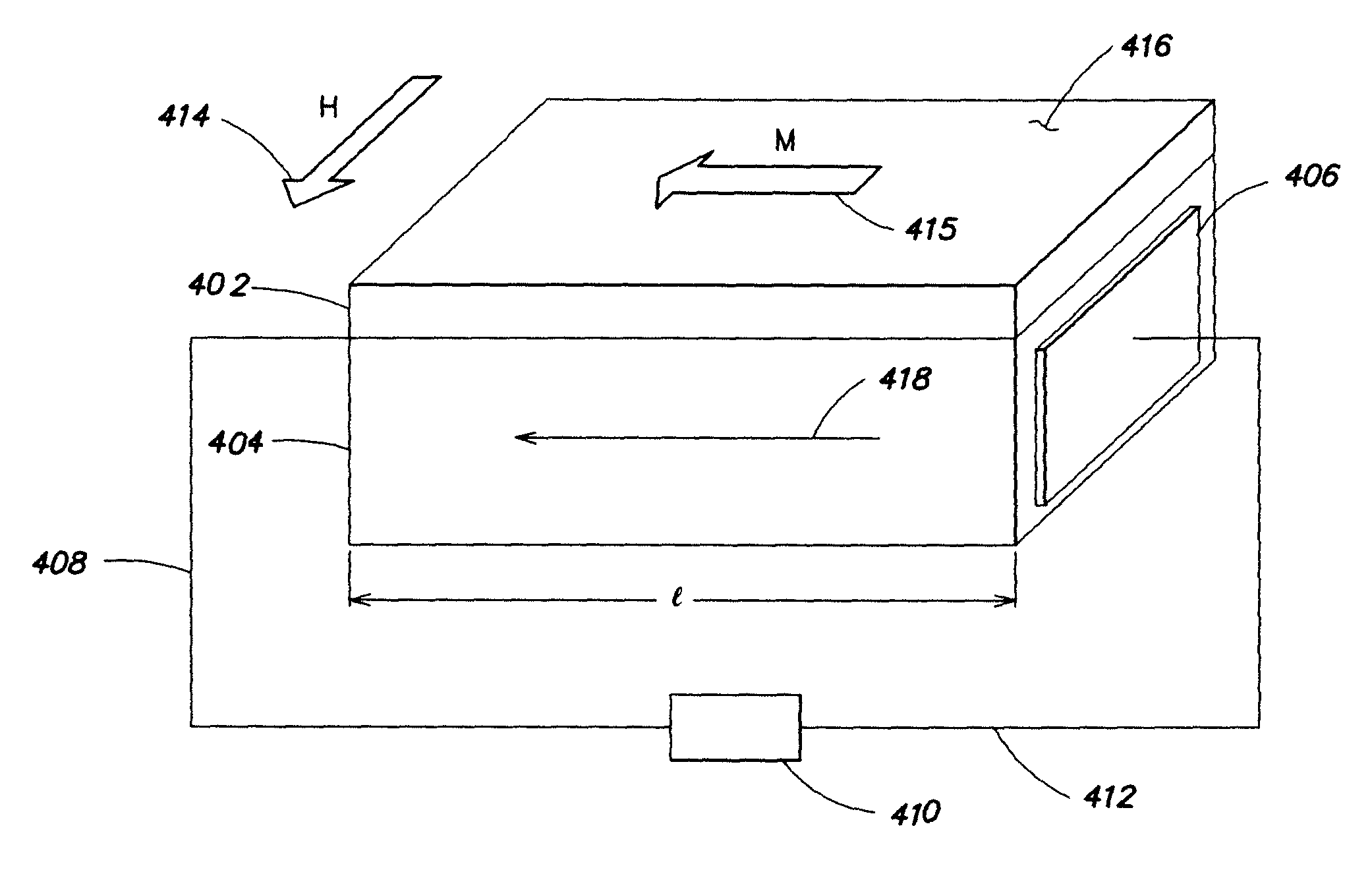
Apparatus and method for harvesting energy from the environment and / or other external sources and converting it to useful electrical energy. The harvester does not contain a permanent magnet or other local field source but instead relies on the earth's magnetic field of another source of a magnetic field that is external to the sensing device. One advantage of these new harvesters is that they can be made smaller and lighter than energy harvesters that contain a magnet and / or an inertial mass.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for measuring magnetic offset of geomagnetic sensor and portable electronic apparatus
InactiveUS7210236B2Easy to operateEasy CalibrationDevices with sensorTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesMagnetizationData storing
A method is designed for measuring a magnetic offset of a geomagnetic sensor equipped in a portable information terminal apparatus having a storage. The geomagnetic sensor has a magnetic sensitivity to a geomagnetic field and is affected by magnetization to cause the magnetic offset. In the method, an output of the geomagnetic sensor is measured to successively provide measurement data of the geomagnetic field from the output of the geomagnetic sensor. The measurement data is stored in the storage. The measurement data is read out from the storage when a number of the measurement data stored in the storage reaches a predetermined number, and an offset value of the magnetic offset is estimated based on the predetermined number of the measurement data read out from the storage.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Utilizing magnetic field based navigation
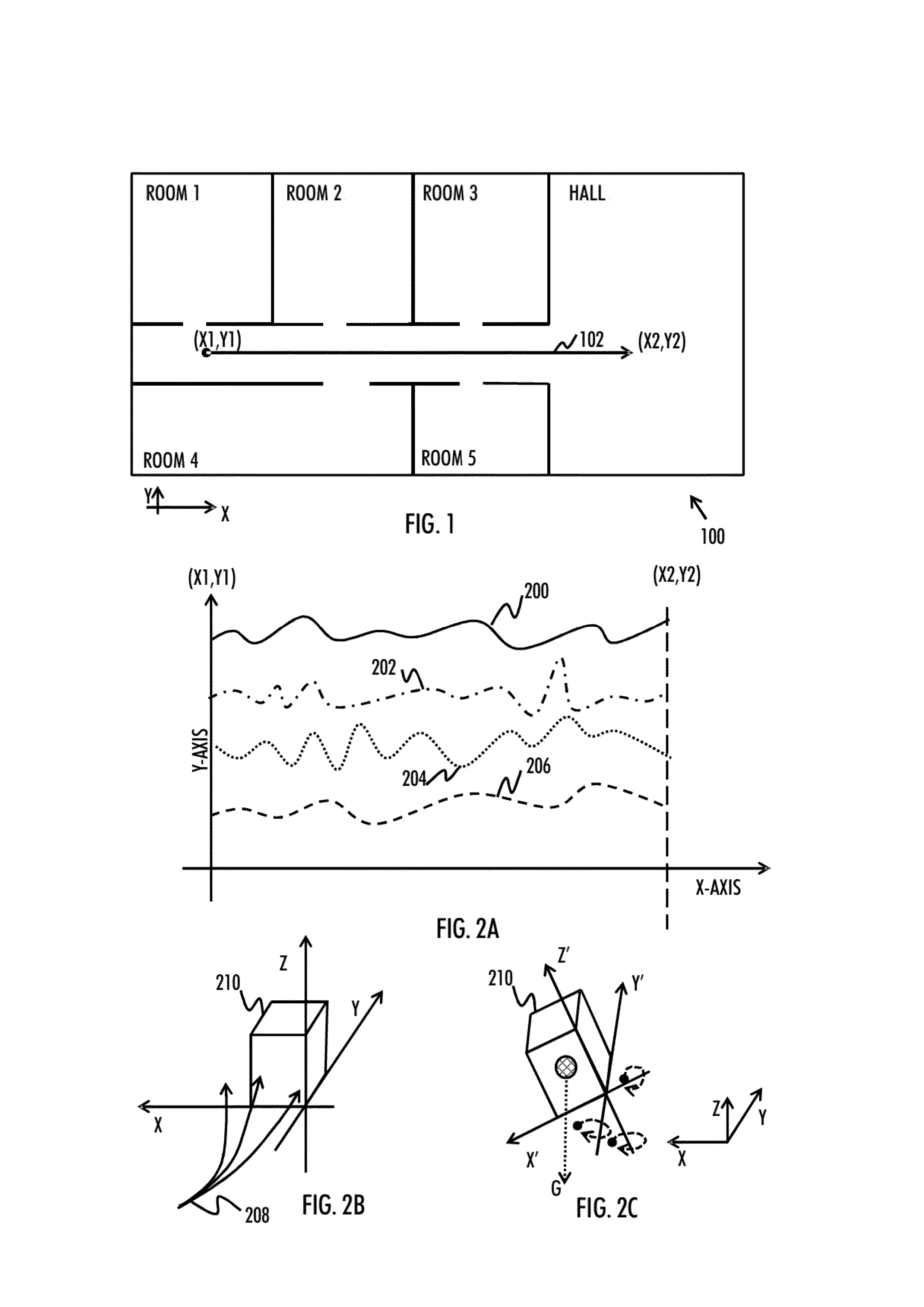
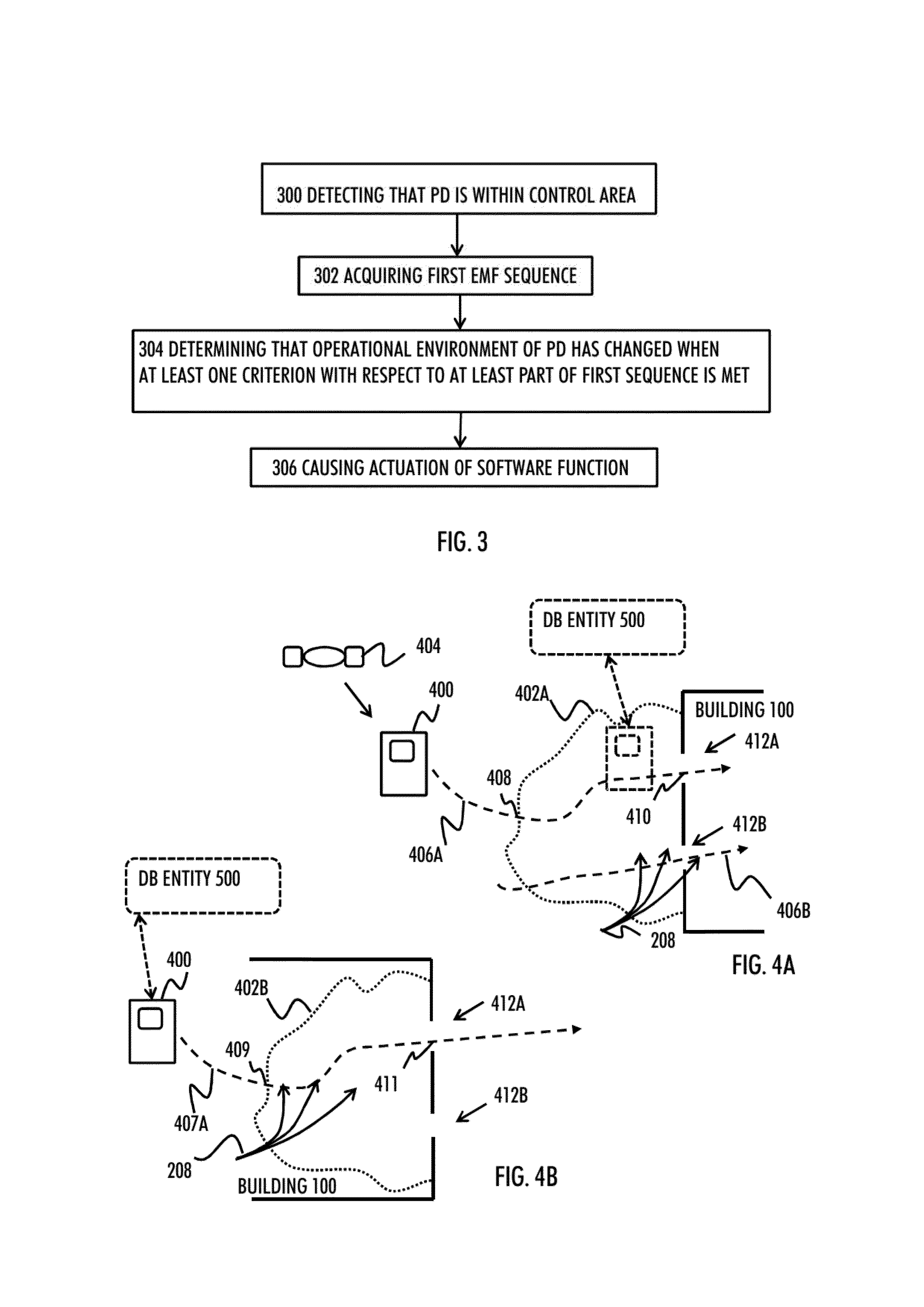
ActiveUS20130179074A1Particular environment based servicesNavigation by terrestrial meansControl areaMarine navigation
There is provided a solution comprising detecting that a positioning device is within a predetermined control area associated with a building, acquiring a first sequence of magnetic field measurements carried out by the positioning device, wherein the first sequence represents at least one of the magnitude and the direction of Earth's magnetic field; determining that an operational environment of the positioning de-vice has changed between an indoor environment and an outdoor environment when a at least one predetermined criterion with respect to the first sequence is met; and causing actuation of a predetermined software function in or with respect to the positioning device when the operational environment of the positioning device has changed.
Owner:INDOORATLAS
GMR sensor with flux concentrators
ActiveUS7112957B2Improve dynamic rangeMinimize impactMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesProximity sensorEngineering
A proximity sensor that is capable of producing a relatively larger output signal than past proximity sensors, and in some cases, an output signal that is relatively independent of the speed at which a target passes the sensor. In one illustrative embodiment, the proximity sensor includes a first magnetoresistive resistor and a second magnetoresistive resistor connected in a bridge configuration. The first magnetoresistive resistor is spaced from the second magnetoresistive resistor along the path of a moving ferrous target. A bias magnet source is positioned behind the proximity sensor, and the ferrous target passes in front of the proximity sensor. The ferrous target alters the direction of the bias magnetic field in the vicinity of the first and second magnetoresistive resistors as the ferrous target passes by the proximity sensor. Flux concentrators are positioned proximate to each of the first and second magnetoresistive resistors. The flux concentrators may help redirect or shunt the magnetic field component produced by the bias magnet source that is perpendicular to the direction of motion of the target through the first and second magnetoresistive resistors in a direction that is parallel to the direction of motion of the target.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Dynamic motion compensation for orientation instrumentation
InactiveUS7844415B1Accurate readingDigital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsMeasuring instrumentDynamic motion
Owner:P&I
Configurations for integrated MRI-linear accelerators
ActiveUS20100239066A1Electric/magnetic detectionChemical conversion by chemical reactionResonanceProton
The present invention provides a radiotherapy treatment apparatus that includes a treatment beam, a magnetic field disposed parallel collinear to the treatment beam, and a target that is disposed along the treatment beam. The treatment beam can be a charged particle beam, a proton beam, an electron beam, or a linear accelerator (Linac) beam. The magnetic field is from a magnetic resonance imager (MRI), a megavolt x-ray imager, or a kilovolt x-ray imager and is disposed to operate in coordination with operation of the treatment beam and to narrow the beam. The tumor is disposed to rotate with respect to the treatment beam and the magnetic field, or the treatment beam and the magnetic field are disposed to rotate up to 360° with respect to the target when mounted to a ring gantry. The apparatus can include a rotation angle dependent shim disposed to account for Earth's magnetic field.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Electronic compass and direction finding method
InactiveUS20060190174A1Free a driver from uneasinessNavigation instrumentsCompassesMicrocomputerDriver/operator
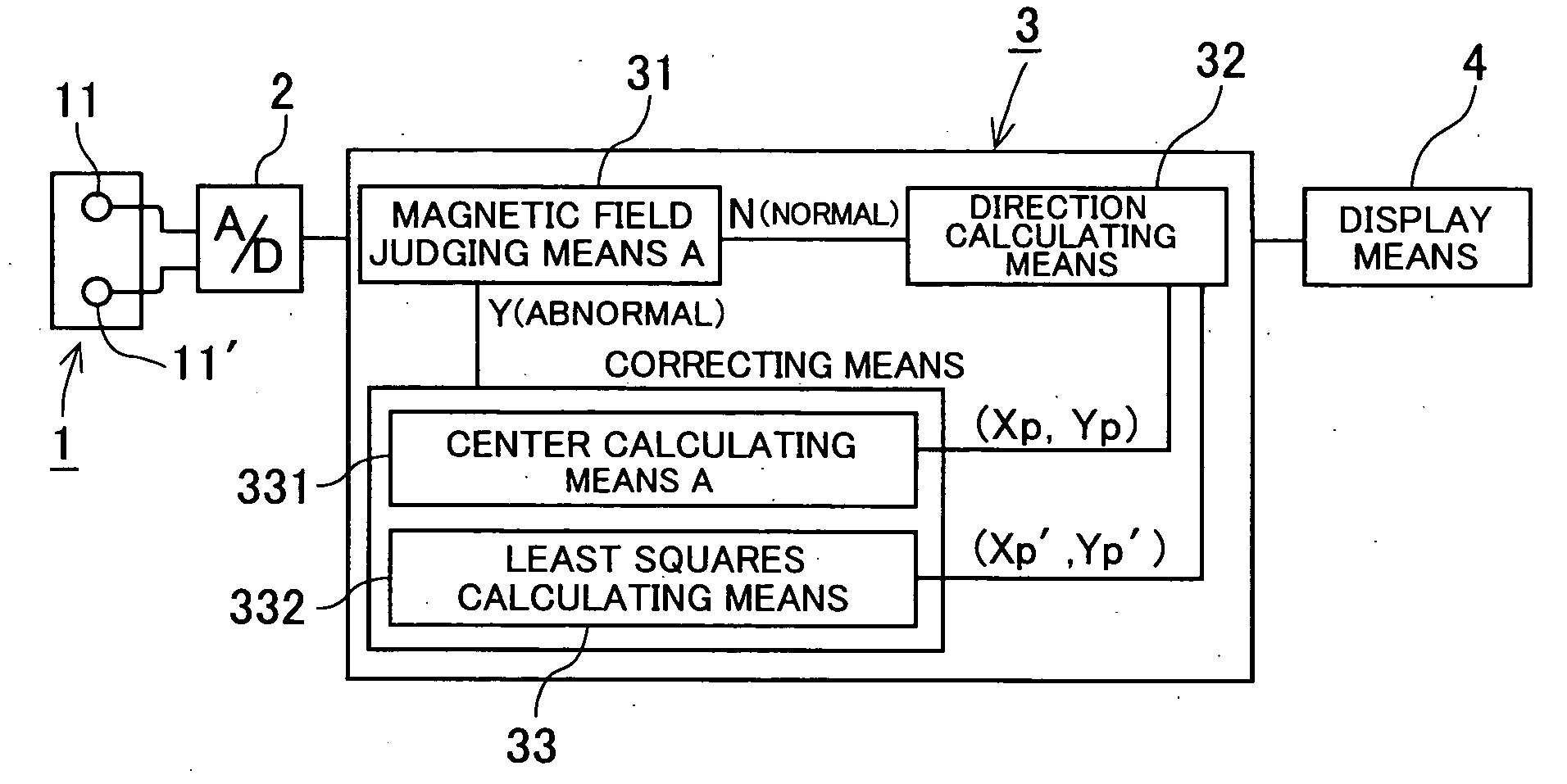
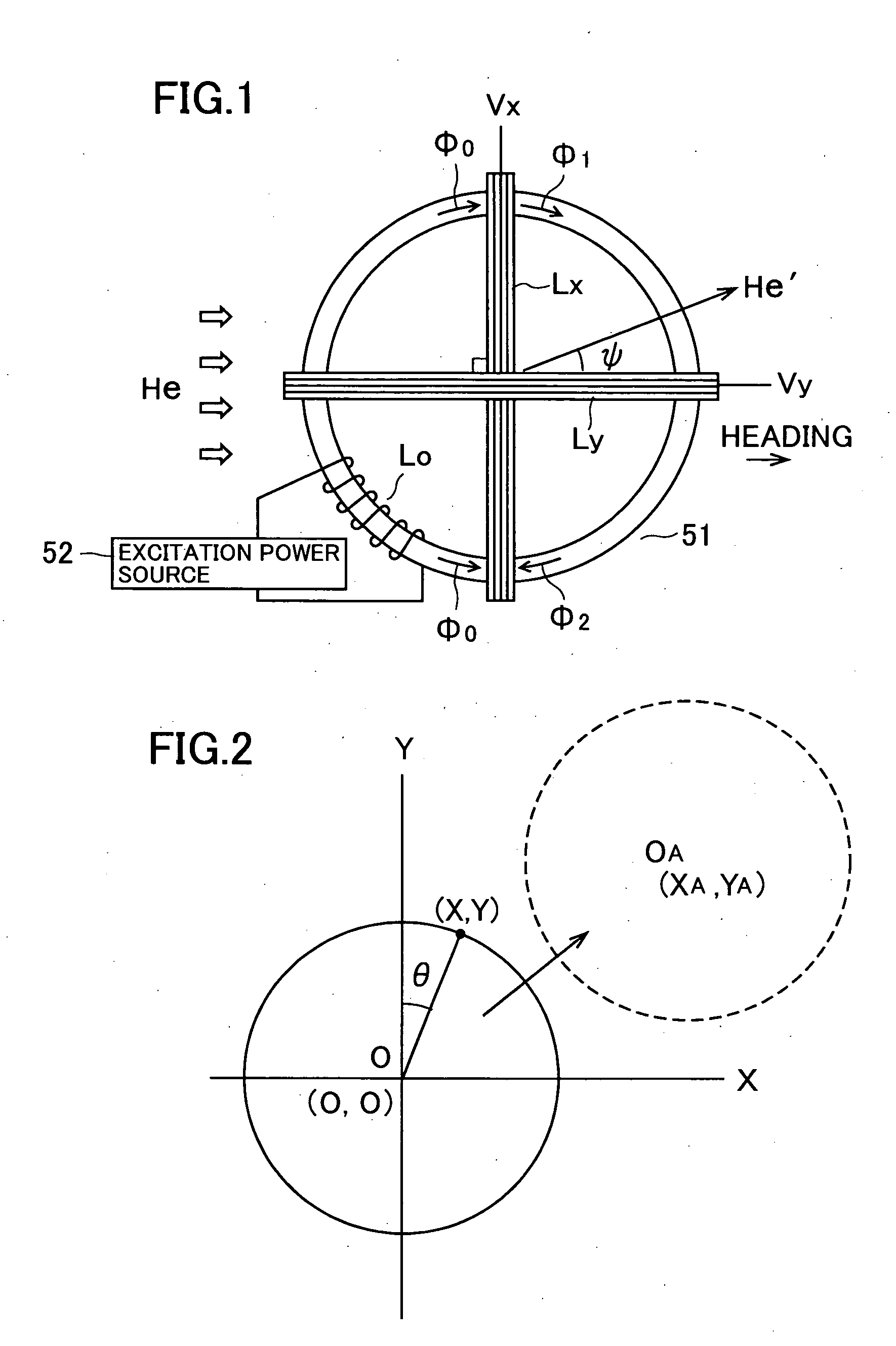
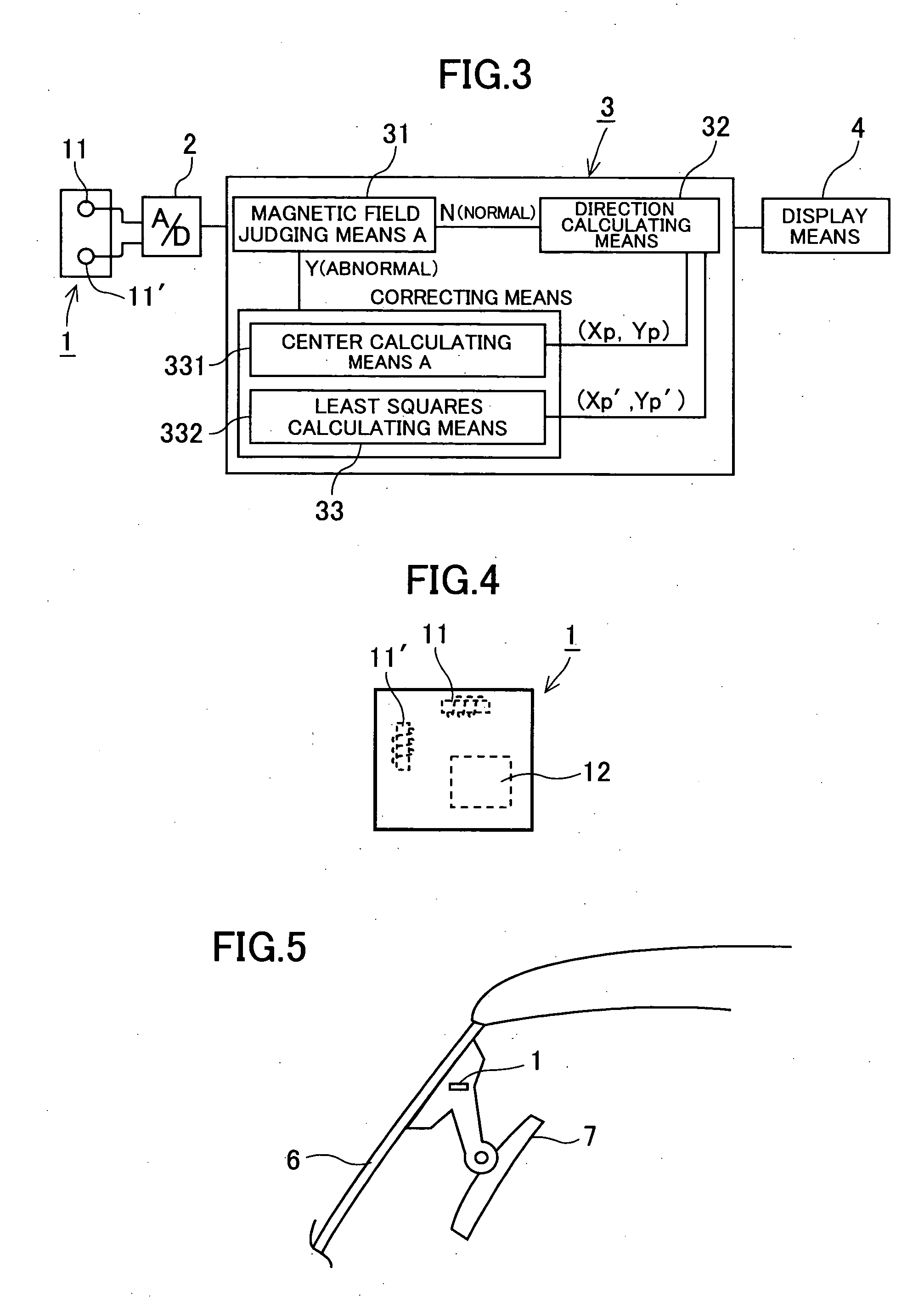
An electronic compass and direction finding method includes a geomagnetic direction sensor having two sensor elements for detecting perpendicular components of the Earth's magnetic field vector. A microcomputer is coupled to the geomagnetic direction sensor to compute a heading of a vehicle in software. Even if the electronic compass displays directional errors due to magnetization of the vehicle, a center of an azimuth circle can be immediately corrected by a center calculating means and a relatively accurate heading can be displayed. Later, the center of the azimuth circle can be corrected with a higher accuracy by a least squares calculating means. This frees a vehicle driver from uneasiness due to display of an intelligible direction.
Owner:AICHI MICRO INTELLIGENT
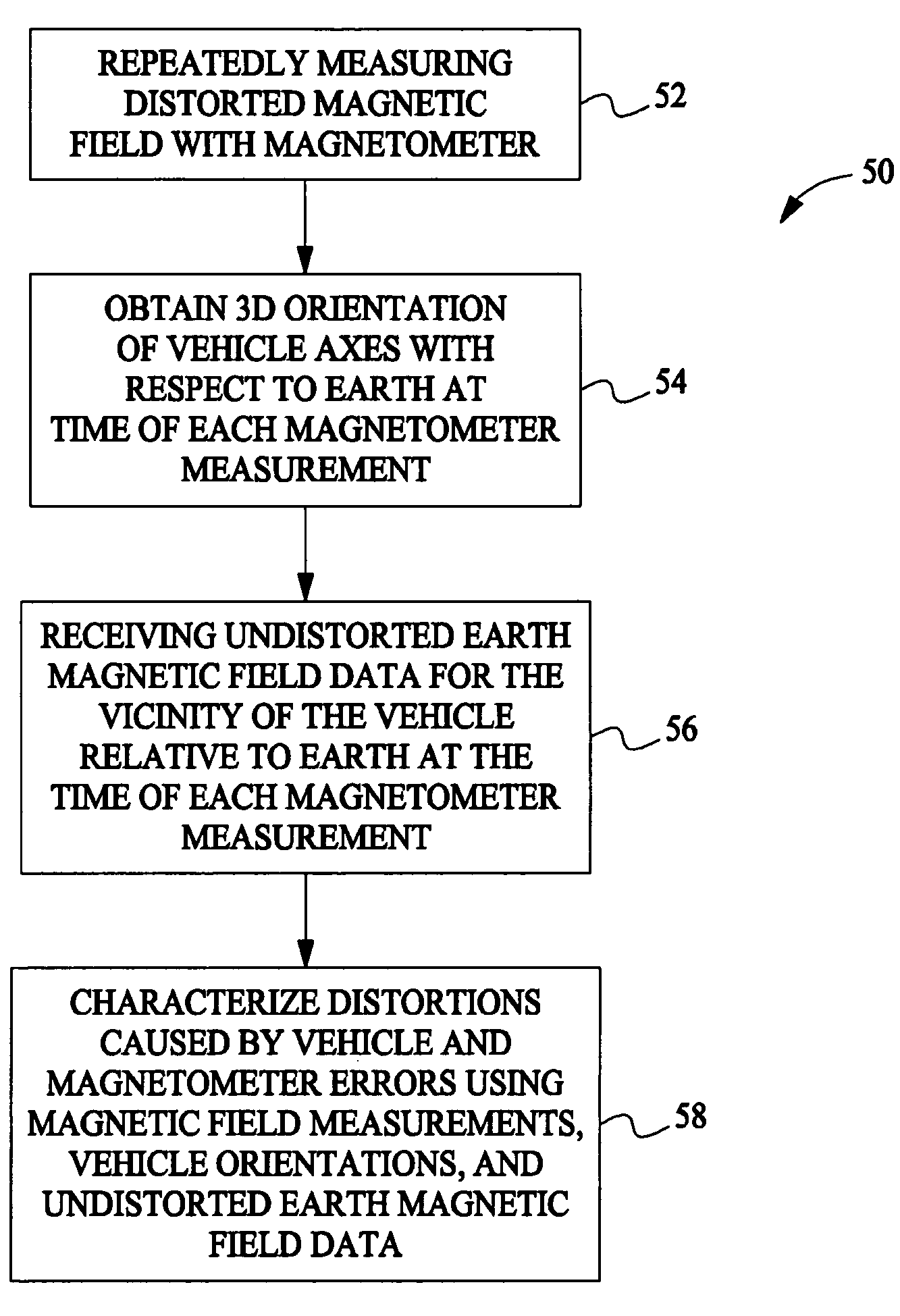
Methods and apparatus for automatic magnetic compensation
ActiveUS6860023B2Compensation DistortionRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsClassical mechanicsDistortion
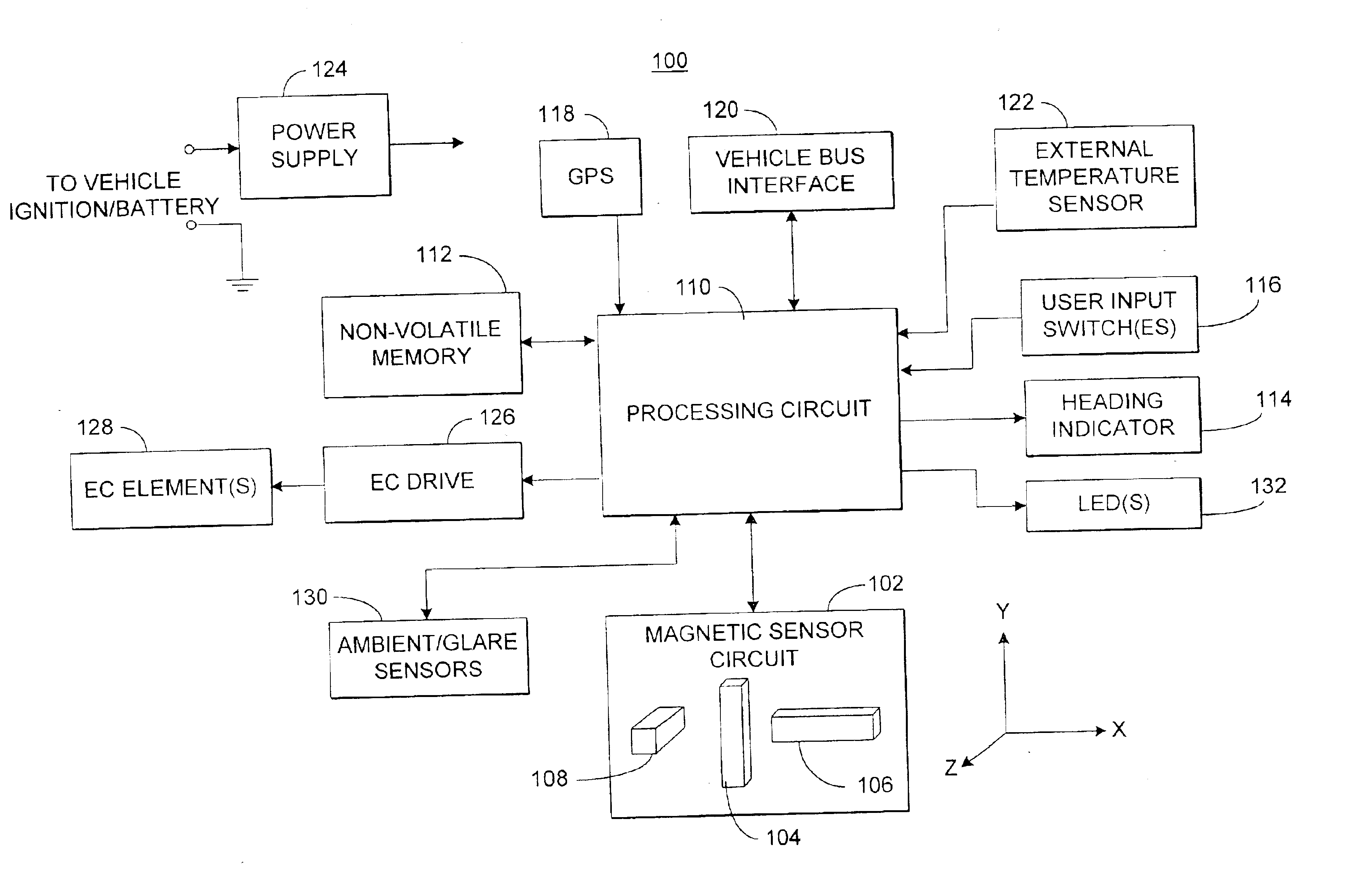
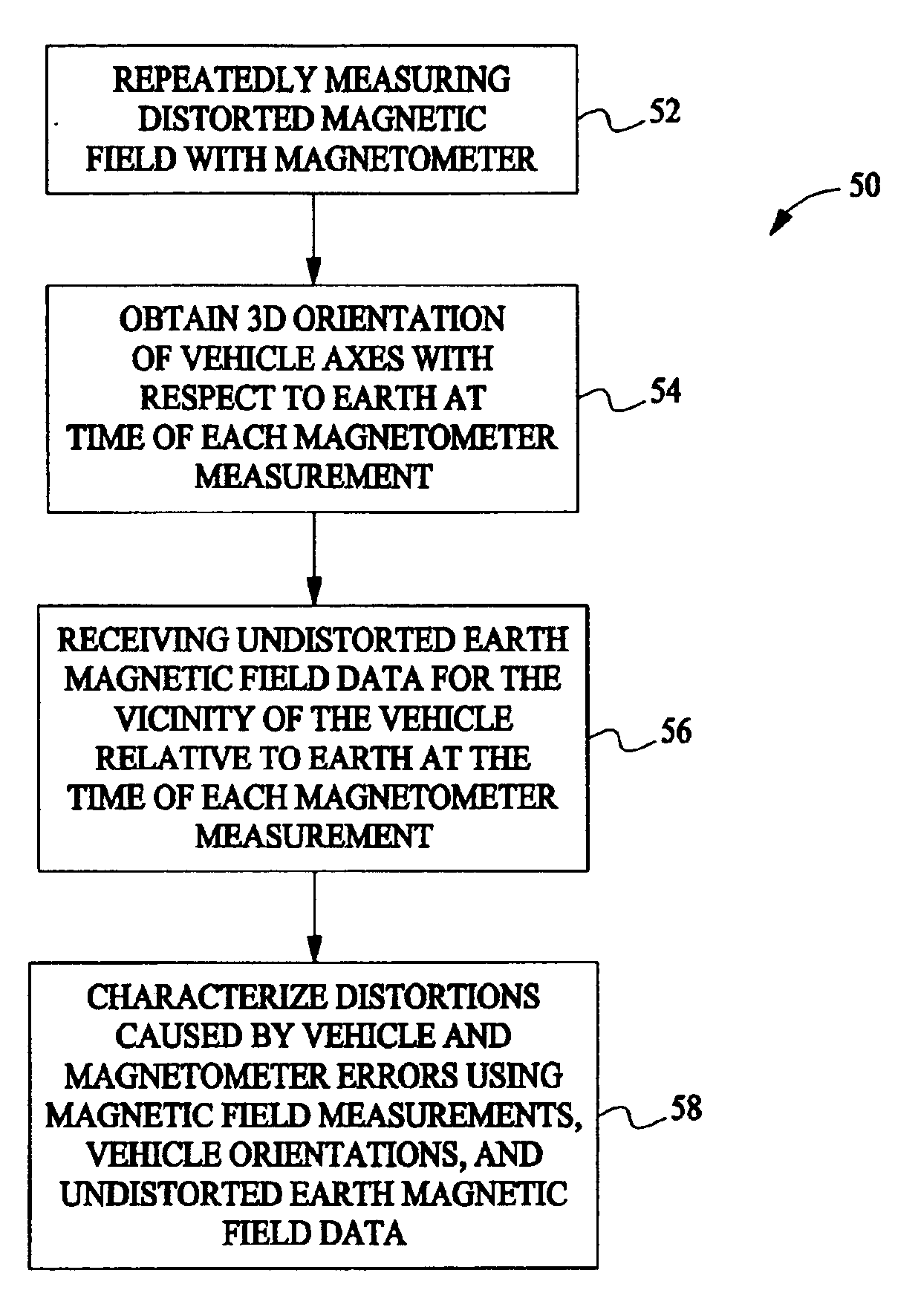
A method for characterizing distortions in the earth's magnetic field caused by a vehicle having a magnetometer affixed therein is described. The method includes repeatedly measuring the distorted magnetic field utilizing the magnetometer and obtaining a three-dimensional orientation of the vehicle axes with respect to the earth at a time of each magnetometer measurement. The method also includes receiving undistorted earth magnetic field data for the vicinity of the vehicle relative to the earth at the time of each magnetometer measurement and characterizing distortions caused by one or more of the vehicle and magnetometer errors utilizing the magnetic field measurements, the orientations of the vehicle, and the undistorted earth magnetic field data.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
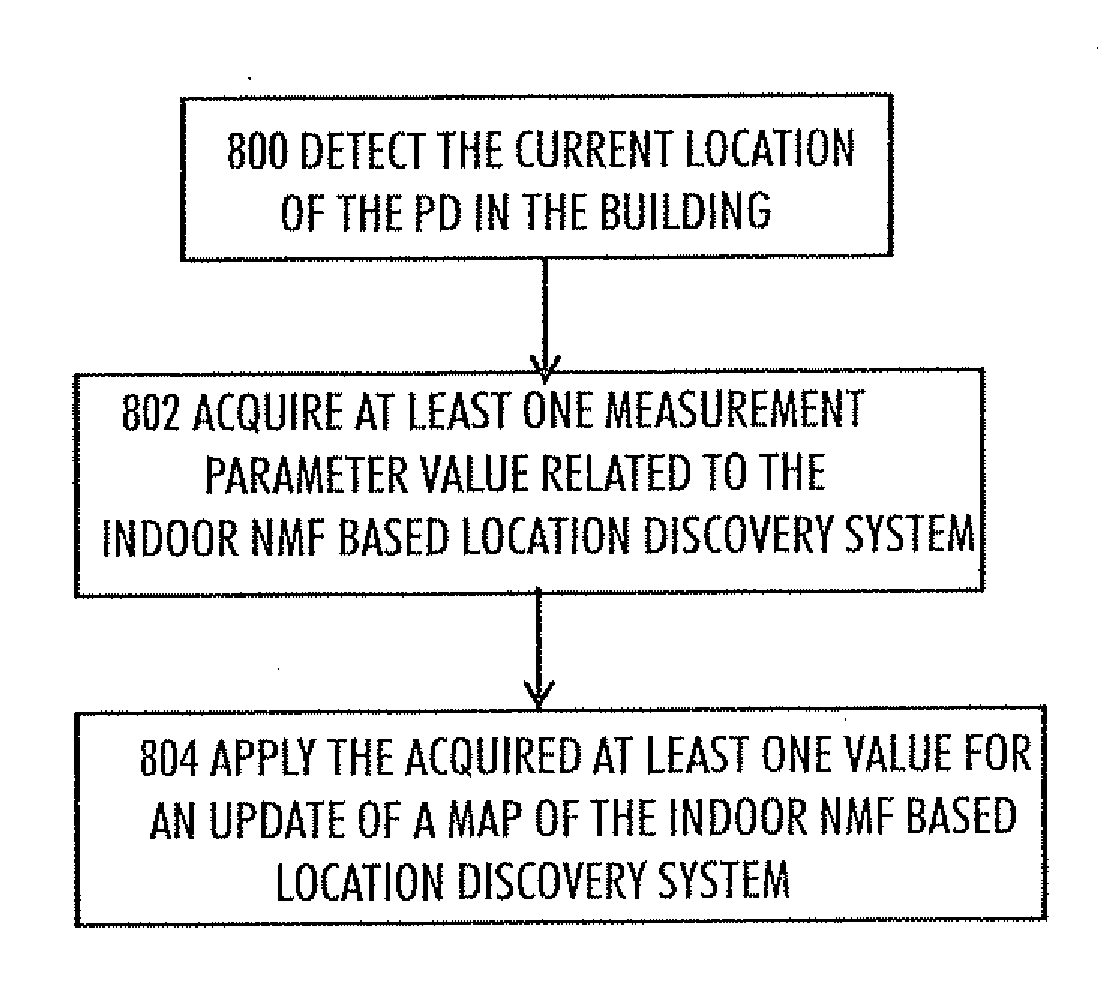
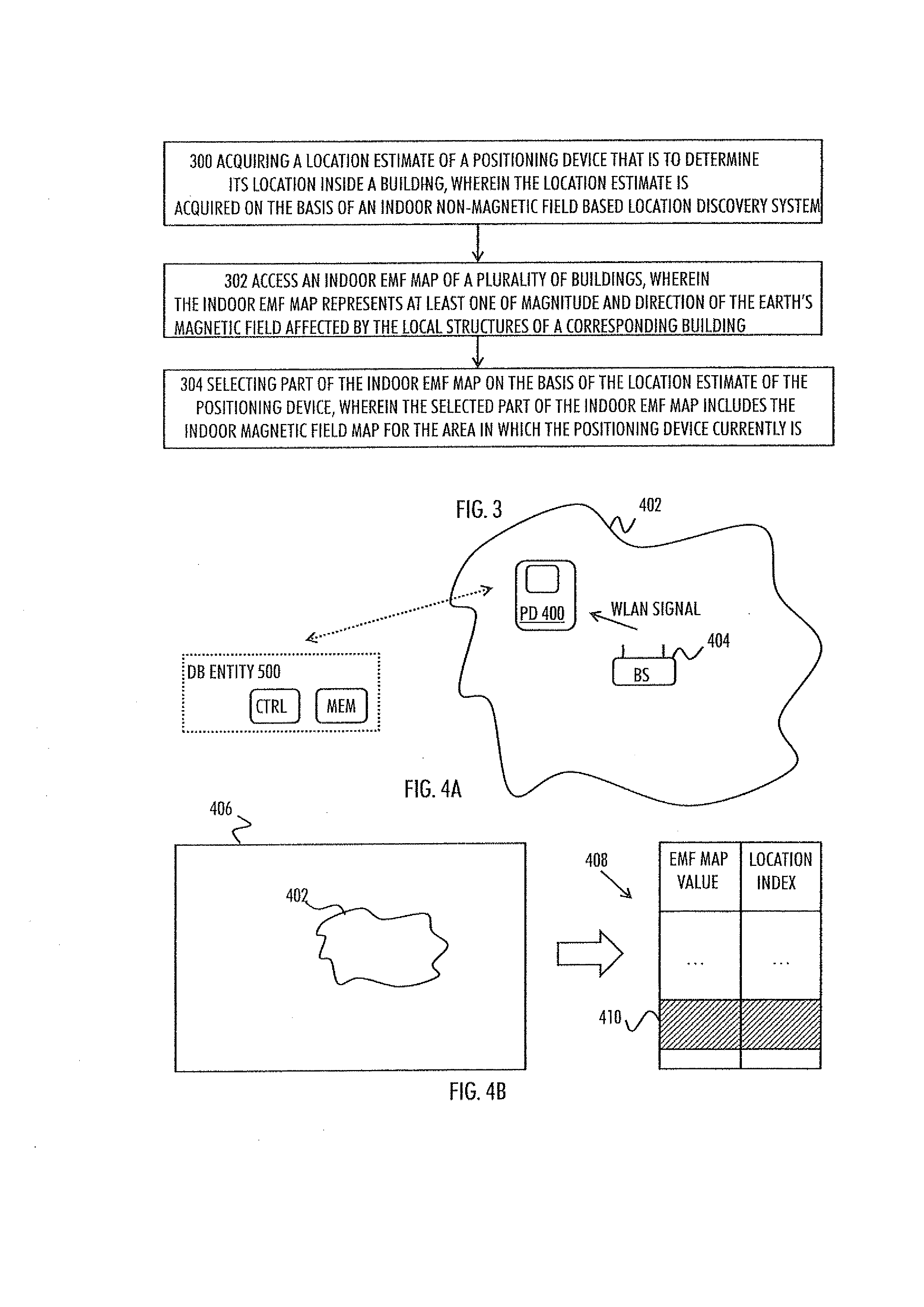
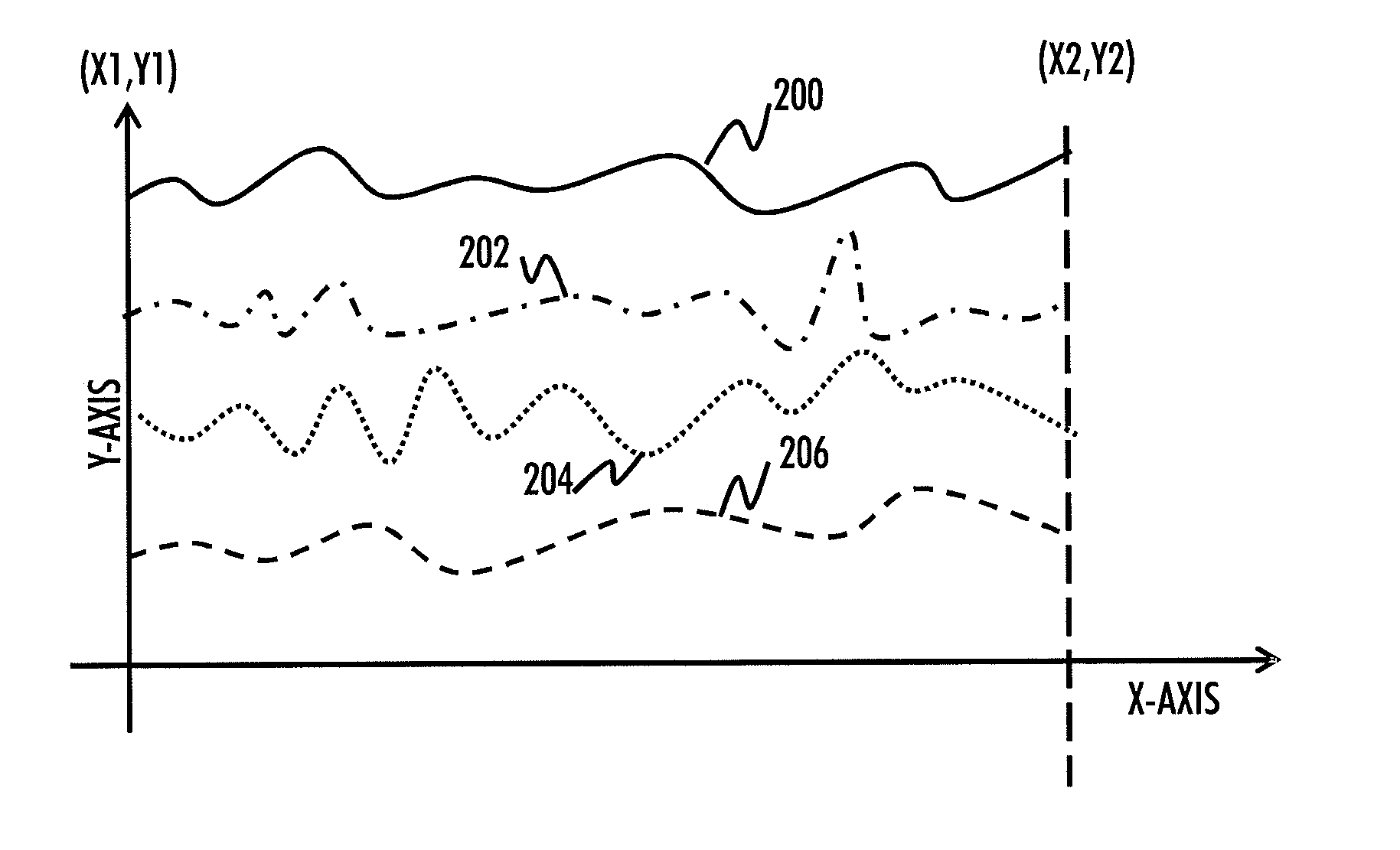
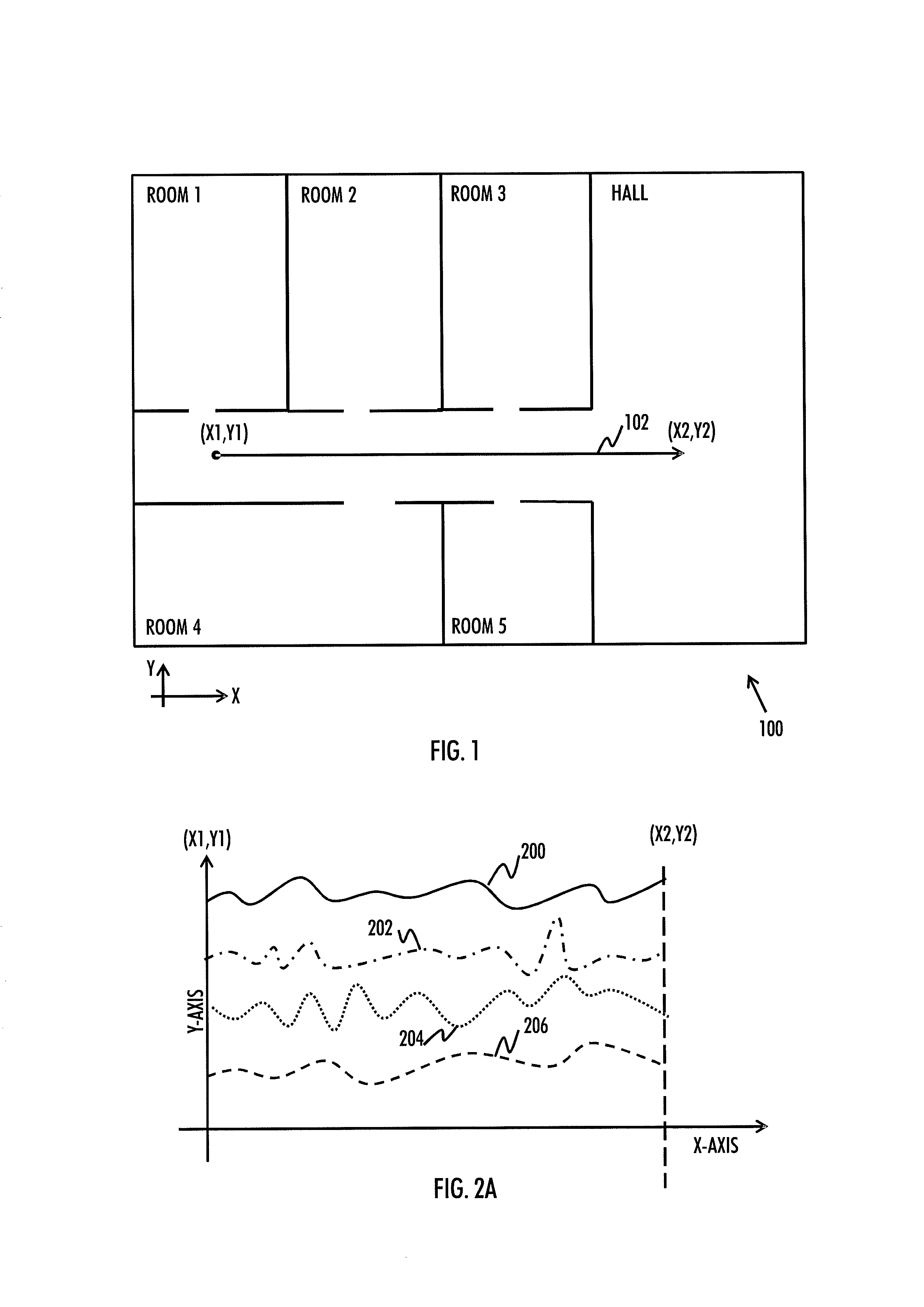
Indoor magnetic field based location discovery
There is provided an apparatus, wherein the apparatus is caused to acquire a location estimate of a positioning device that is to determine its location inside a building, wherein the location estimate is acquired on the basis of an indoor non-magnetic field based location discovery system; access an indoor Earth's magnetic field, EMF, map of plurality of buildings, wherein the indoor EMF map represents at least one of magnitude and direction of the Earth's magnetic field affected by the local structures of a corresponding building; and select a part of the indoor EMF map on the basis of the location estimate of the positioning device, wherein the selected part of the indoor magnetic field map includes the indoor EMF map for the area in which the positioning device currently is.
Owner:INDOORATLAS
Apparatus and method utilizing magnetic field
Apparatus and method for harvesting energy from the environment and / or other external sources and converting it to useful electrical energy. The harvester does not contain a permanent magnet or other local field source but instead relies on the earth's magnetic field of another source of a magnetic field that is external to the sensing device. One advantage of these new harvesters is that they can be made smaller and lighter than energy harvesters that contain a magnet and / or an inertial mass. A small implantable stimulator(s) includes at least one passive magnetostrictive / electro-active (PME) magnetic-field sensor for delivering electrical stimulation to surrounding tissue. The PME is charged utilizing a changing magnetic field from an external alternating magnetic field source at a frequency particular to the PME. The small stimulator provides means of stimulating a nerve, tissue or internal organ with direct electrical current, such as relatively low-level direct current for temporary or as needed therapy. The field source may be a hand-held device or a small antenna affixed to the wearer's skin, clothing or accessories. The stimulator may be configured to be small enough to be implanted through a surgical needle. Open- and closed-loop systems are disclosed with measurement of current flow and therapy through PME sensor function.
Owner:FERRO SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for locating well casings from an adjacent wellbore
A wellbore tool for locating a target wellbore containing a conductive member from a second wellbore and directing the trajectory of the second wellbore relative to the target wellbore includes an electric current driver having an insulated gap; a three-axis magnetometer positioned within a non-magnetic housing that is disposed within a non-magnetic tubular, the three-axis magnetometer positioned below the electric current driver; a drill bit positioned below the three-axis magnetometer; a hollow tubular connected between the electric current driver and the three-axis magnetometer; and a measurement-while-drilling tool. The current driver generates an electric current across the gap to the portion of the tool below the insulated gap. In a method a current is generated across the insulated gap to the portion of the tool below the insulated gap to the conductive material in the target wellbore returning to a portion of the bottom hole assembly above the insulated gap thereby producing a target magnetic field. Measuring the target magnetic field at the bottom hole assembly and the earth's magnetic field; and determining the position of the second wellbore relative to the target wellbore. Then steering the bottom hole assembly to drill the second wellbore along a trajectory relative to the target wellbore.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
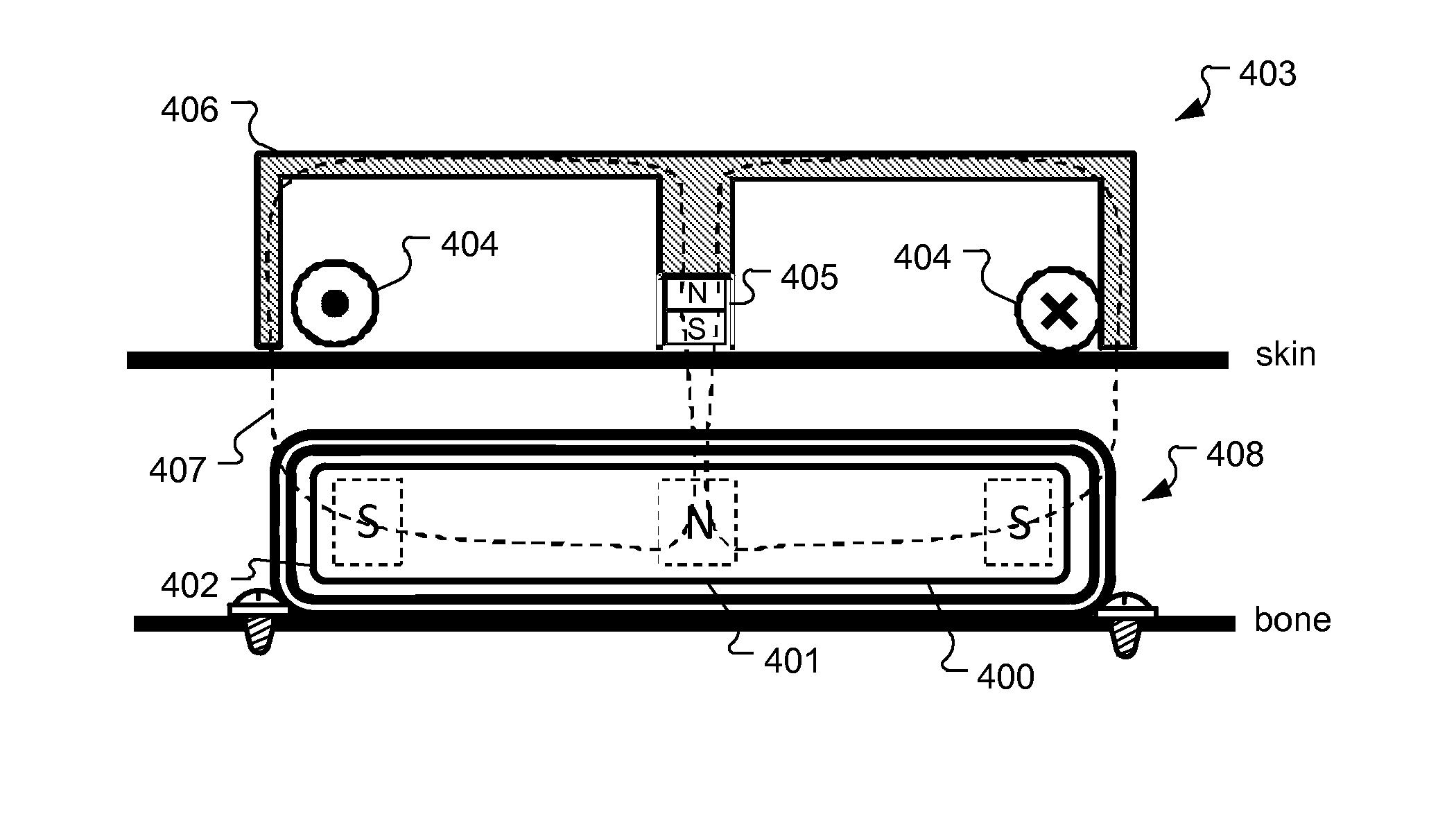
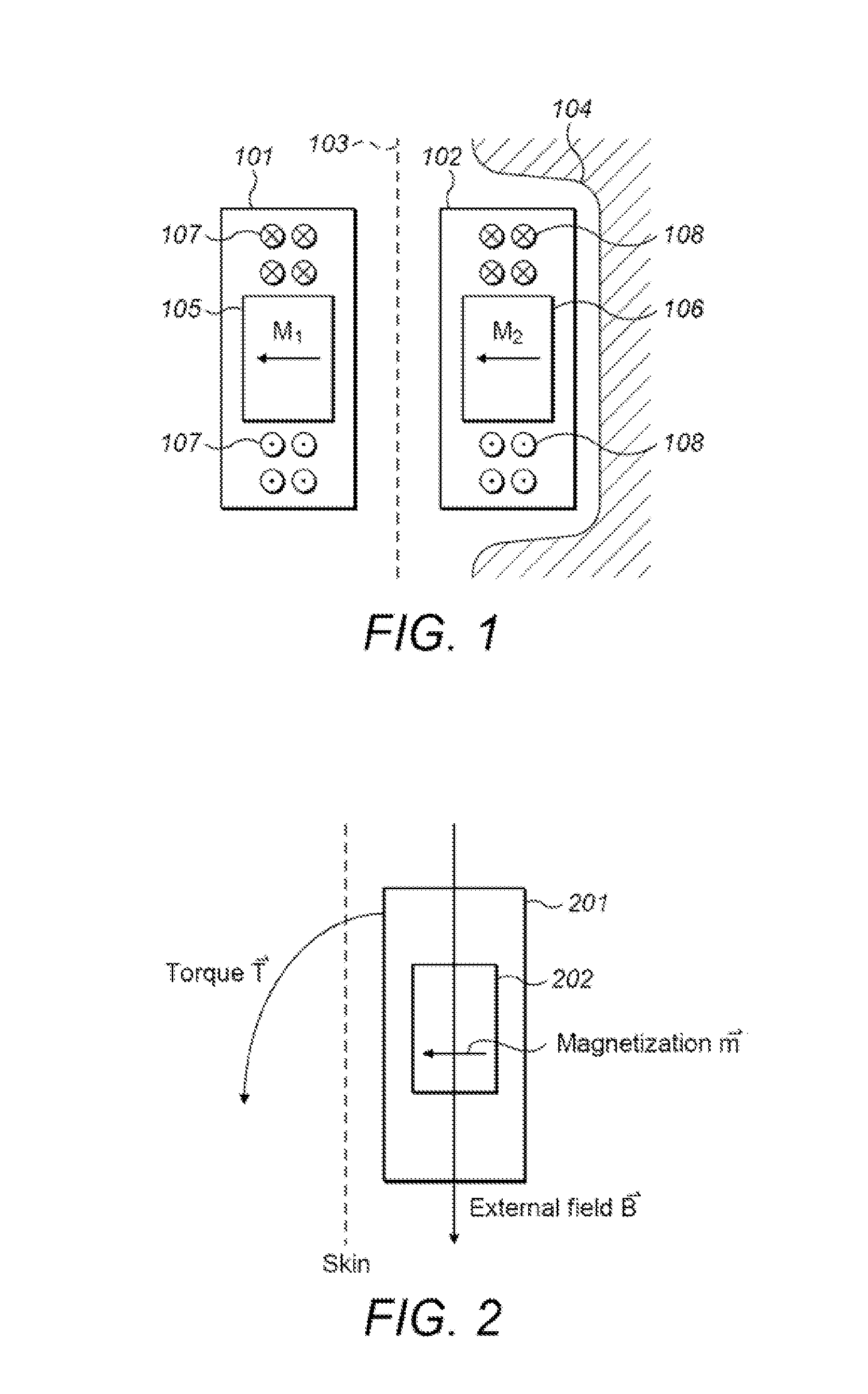
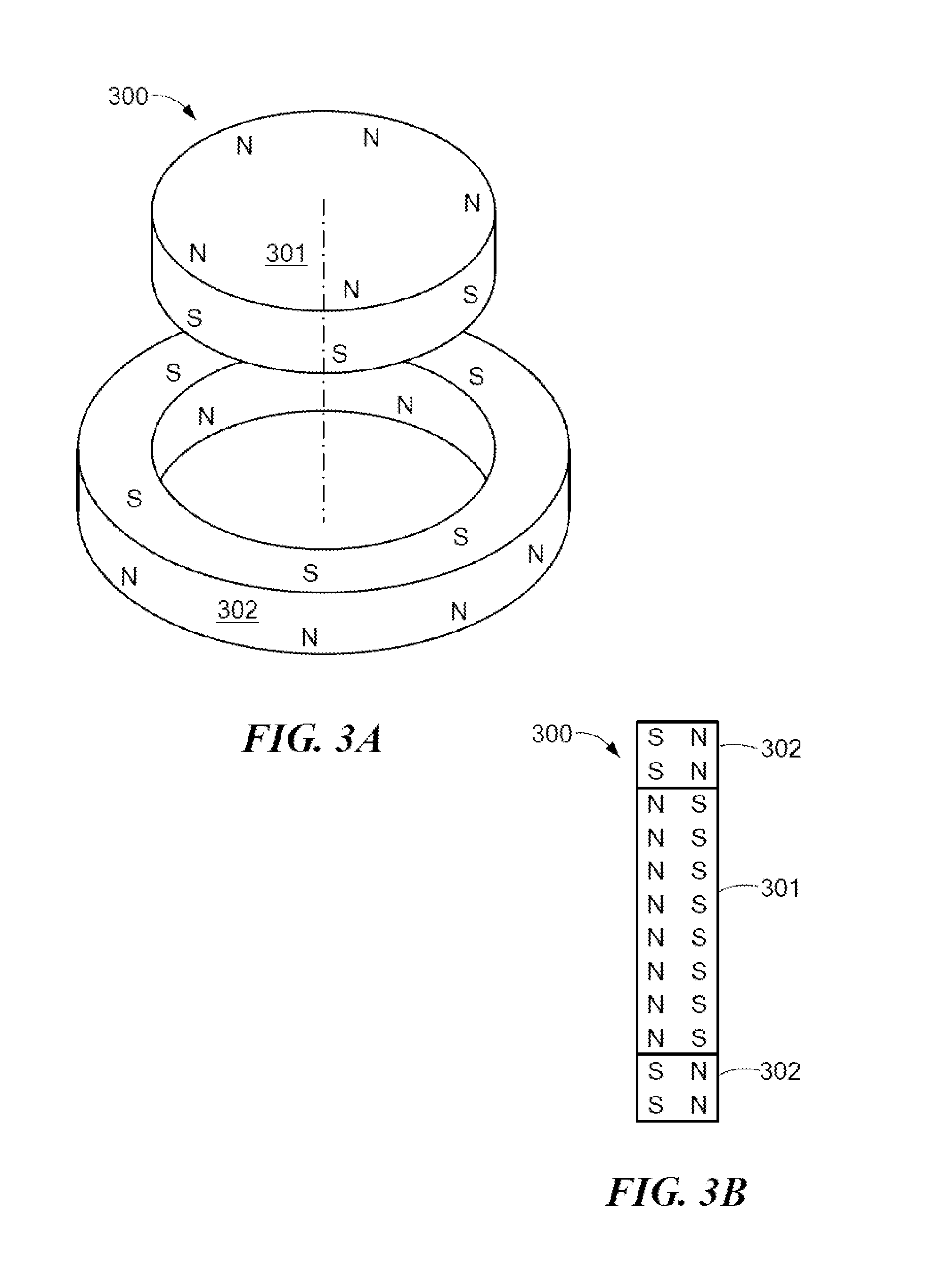
Symmetric Magnet Arrangement for Medical Implants
An arrangement is described for a hearing implant system. An implantable housing has an outer surface configured to lie under and parallel to the skin of the implanted patient. An implant magnet arrangement is located within the implantable housing and has multiple local magnetic sections with different independent local magnetic fields that are combined together to form a net magnetic field with at least two-fold symmetry and zero net magnetic dipole moment, wherein the magnetic fields are oriented parallel to the outer surface of the implant housing.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Methods and apparatus for automatic magnetic compensation
InactiveUS7146740B2Compensation DistortionRoad vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsClassical mechanicsDistortion
A method for characterizing distortions in the earth's magnetic field caused by a vehicle having a magnetometer affixed therein is described. The method includes repeatedly measuring the distorted magnetic field utilizing the magnetometer and obtaining a three-dimensional orientation of the vehicle axes with respect to the earth at a time of each magnetometer measurement. The method also includes receiving undistorted earth magnetic field data for the vicinity of the vehicle relative to the earth at the time of each magnetometer measurement and characterizing distortions caused by one or more of the vehicle and magnetometer errors utilizing the magnetic field measurements, the orientations of the vehicle, and the undistorted earth magnetic field data.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Stylus input device utilizing a permanent magnet
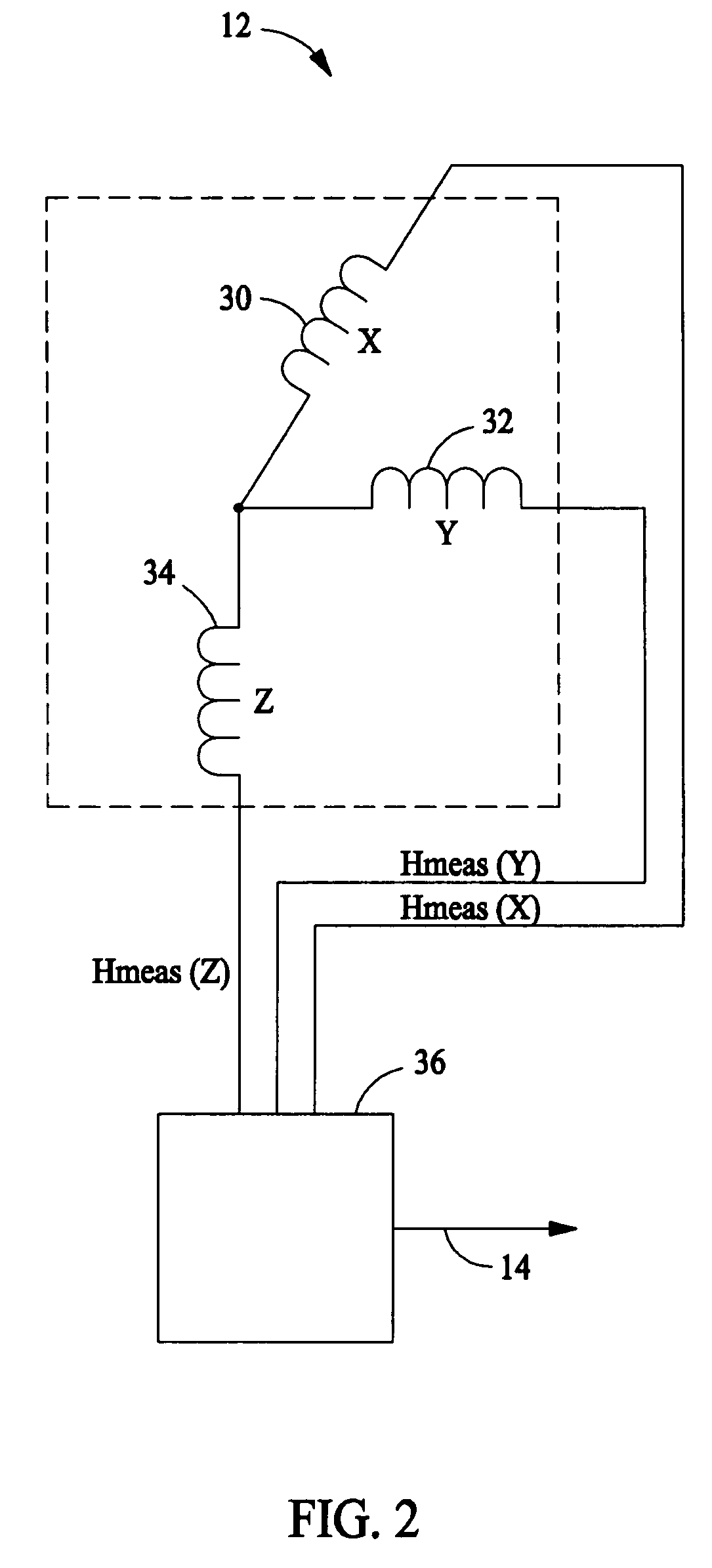
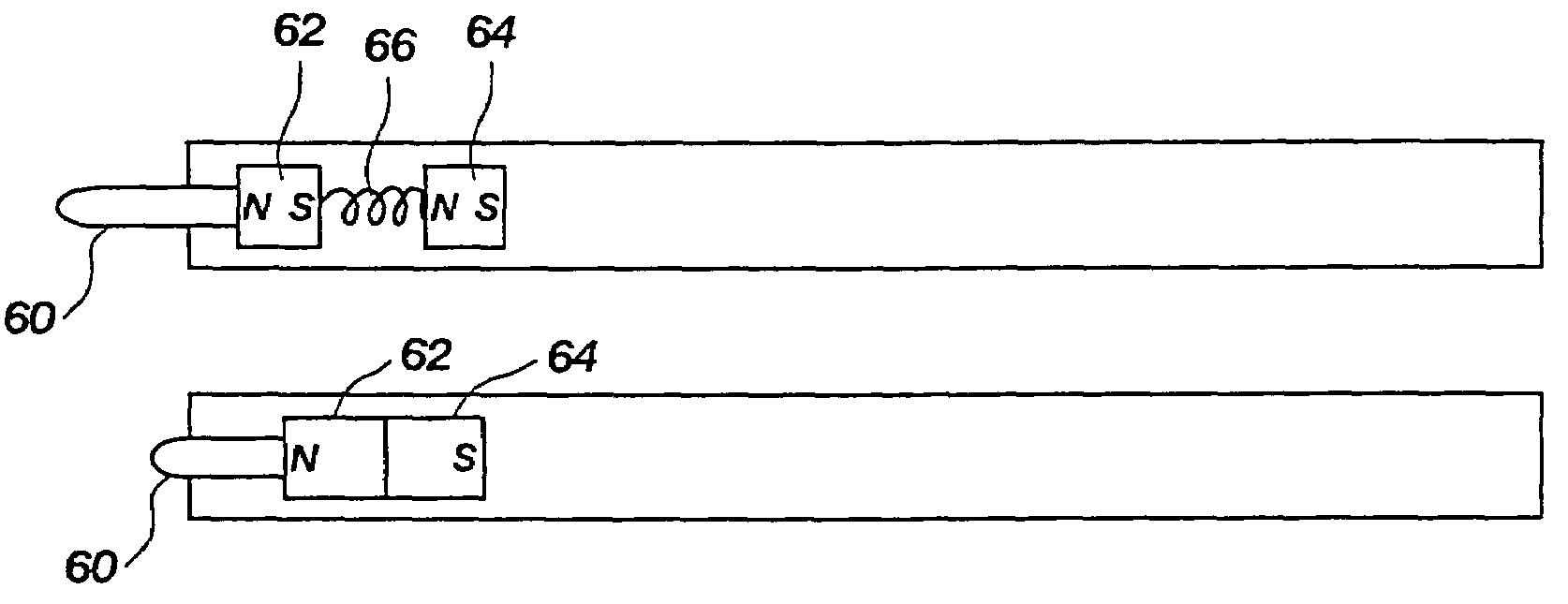
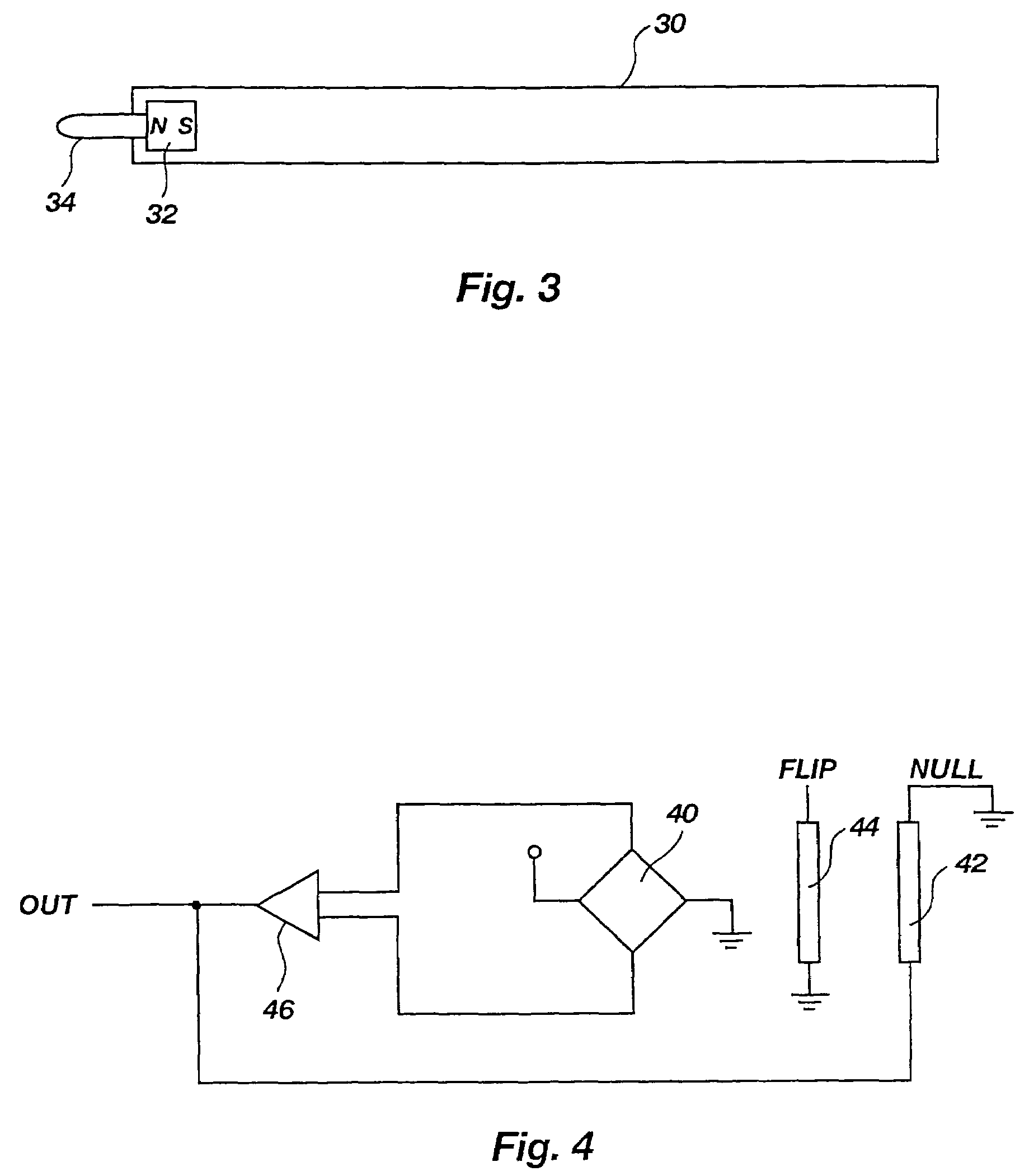
InactiveUS7145555B2Increase the magnetic field strengthInput/output for user-computer interactionTransmission systemsTriangulationCondensed matter physics
A stylus that operates utilizing magnetic fields, wherein a permanent magnet is disposed within a passive stylus that is detectable by a plurality of magnetic sensors that remove the magnetic field of the stylus from the earth's relative magnetic field to thereby obtain vectors that are used in a triangulation equation to determine the location of the stylus in two or three dimensions, depending upon the number of magnetic sensors that are used, wherein one set of magnetic sensors can be used as a reference for earth's magnetic field, and wherein each of the magnetic sensors includes a polarizing coil to change direction of sensitivity, a null coil and a flipping coil.
Owner:CIRQUE CORPORATION
Generating magnetic field map for indoor positioning
There is provided an apparatus caused to acquire information indicating a measured magnetic field vector and information relating to an uncertainty measure of the measured magnetic field vector in at least one known location inside the building, wherein the indicated magnetic field vector represents magnitude and direction of the earth's magnetic field affected by the local structures of the building, and to generate the indoor magnetic field map for at least part of the building on the basis of at least the acquired information and the floor plan.
Owner:INDOORATLAS
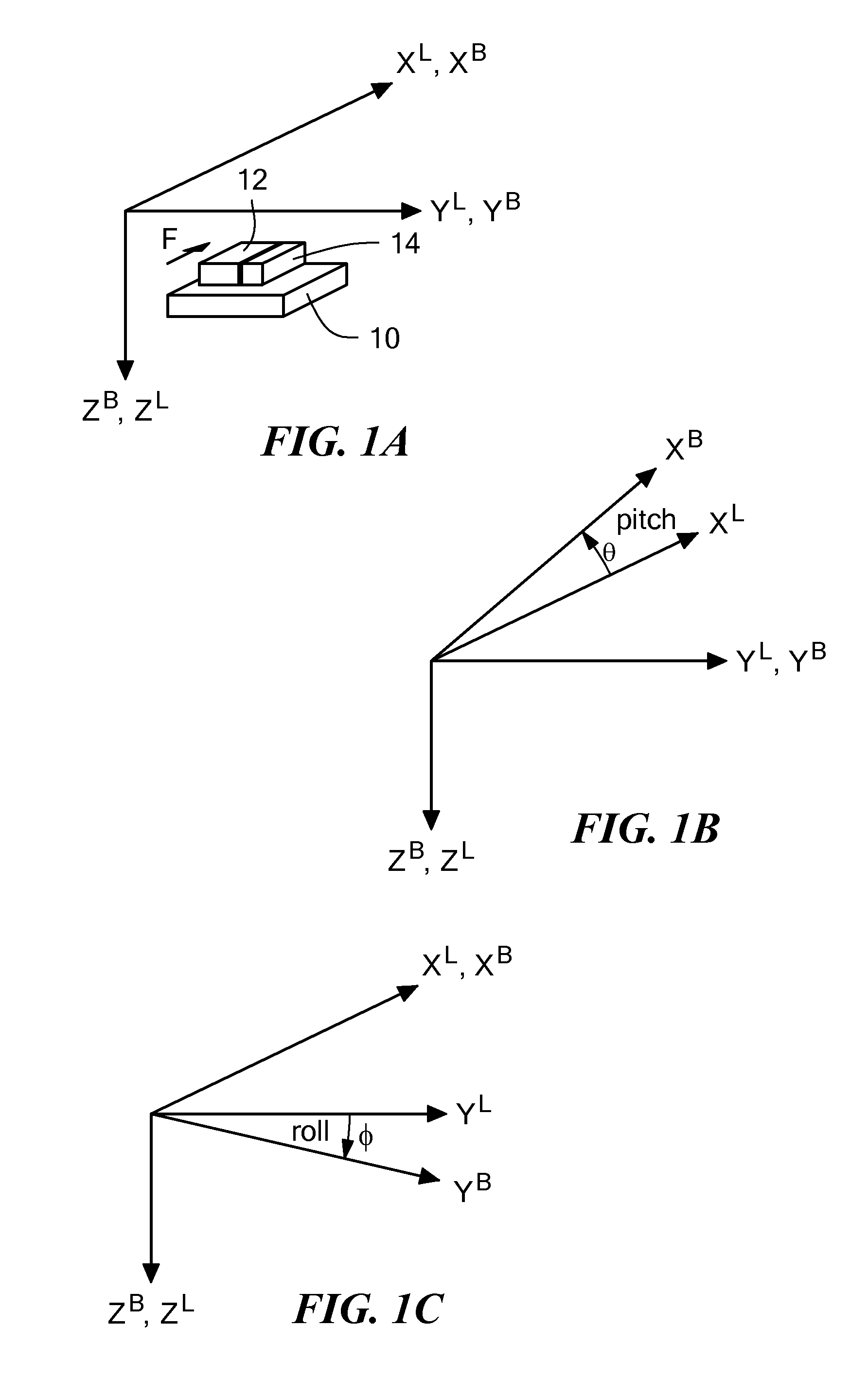
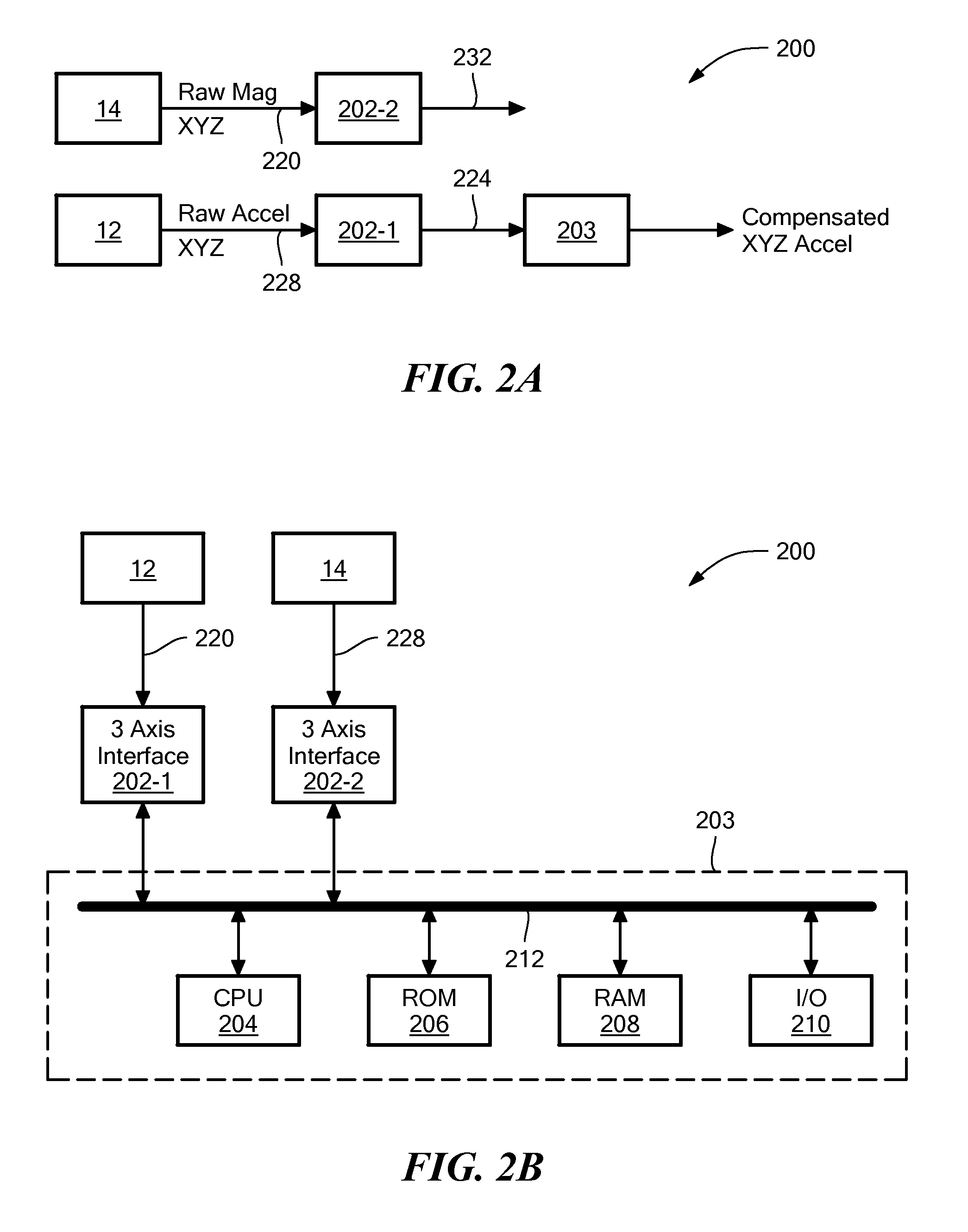
Method and apparatus for data fusion of a three-axis magnetometer and three axis accelerometer
ActiveUS20150177020A1Accurately determineSuppress noiseAcceleration measurementElectrical measurementsKaiman filterAccelerometer data
Method and apparatus of integrating a three-axis magnetometer and a three-axis accelerometer to provide attitude and heading, calibrated magnetometer and accelerometer data, and angular rate, while removing sensor error sources over time and temperature and to compensate for hard and soft iron distortions of the Earth magnetic field. Filtered accelerometer data are corrected to account for various error sources. The magnetic heading is calculated from a horizontal magnetic field vector transformed from three dimensional Earth's magnetic field vector by using quasi-static roll and pitch angles from the filtered accelerometer data. A first Kalman filter estimates the state vector, based on the principle that the magnitude of local Earth's magnetic field vector is constant, to form hard and soft iron correction matrices. A second Kalman filter estimates a correction matrix of coupled remaining soft iron and the misalignment of the magnetometer and the accelerometer, as the dot product of local Earth's magnetic field vector and a corrected gravitational acceleration vector, at a quasi-static position, is constant. The three dimensional Earth's magnetic field vector is received by removing the hard and soft irons through the soft iron and hard iron correction matrixes.
Owner:MEMSIC
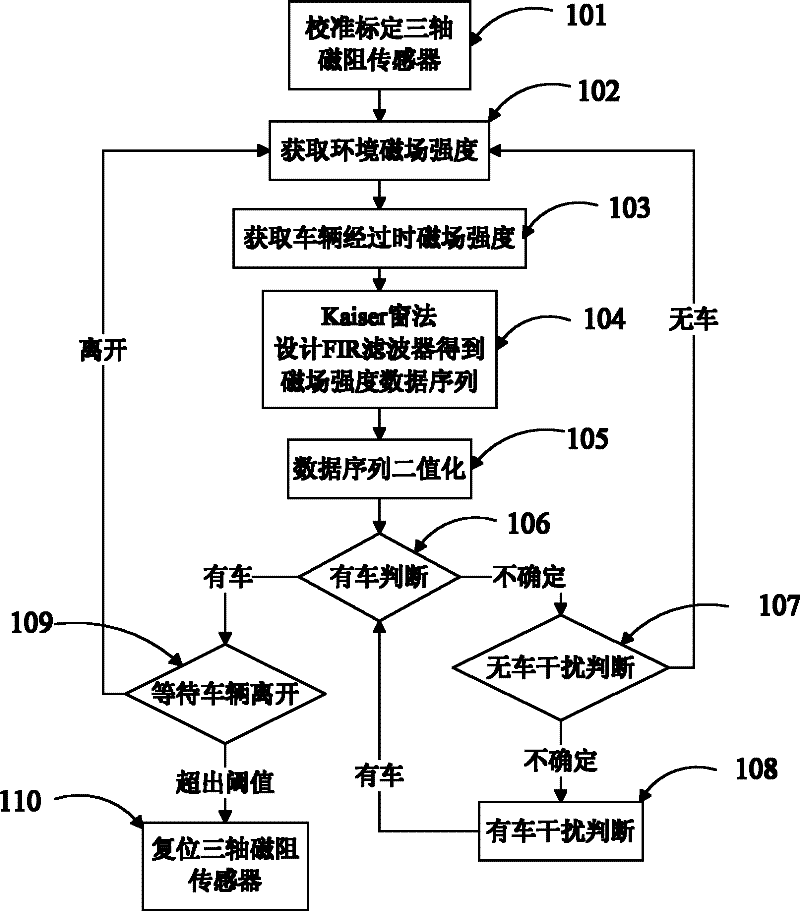
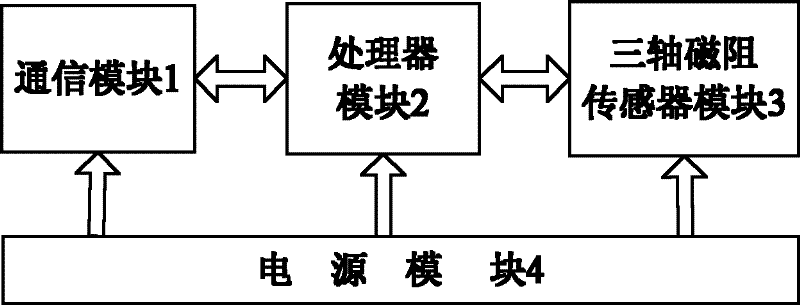
A vehicle/traffic flow detection method based on a three-axis magnetoresistive sensor
InactiveCN102289939AArbitrary placementImprove anti-interference abilityRoad vehicles traffic controlVehicle detectionIntelligent management
The invention relates to a vehicle / vehicle flow detection method based on a three-axis magnetoresistive sensor, comprising the following steps: calibrating or calibrating the three-axis magnetoresistance sensor; obtaining the environmental magnetic field strength when there is no car, and obtaining the magnetic field strength when there is a car passing by; using Kaiser The FIR filter is designed to filter the measured magnetic field strength data to obtain the data sequence; the data sequence is binarized; whether there is a car is judged; when there is no car, interference is judged; when there is a car, interference is judged; the vehicle leaves the judgment; after the vehicle is judged The software forcibly resets the three-axis magnetoresistive sensor. It is characterized in that the method integrates the three-axis magnetic field information, which can fully reflect the disturbance information of the geomagnetic field when the vehicle passes by, the sensor can be placed arbitrarily, and the software reset method can effectively overcome the signal drift of the magnetic resistance sensor generated when the vehicle passes continuously Problems, through the judgment of vehicle entry, interference, and vehicle departure, it can ensure high detection accuracy and strong anti-interference ability. This method is easy to implement and is suitable for vehicle / traffic flow detection on traffic roads, bridges, squares, tunnels, etc. It can also be used in Vehicle detection in the parking lot for intelligent management.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com