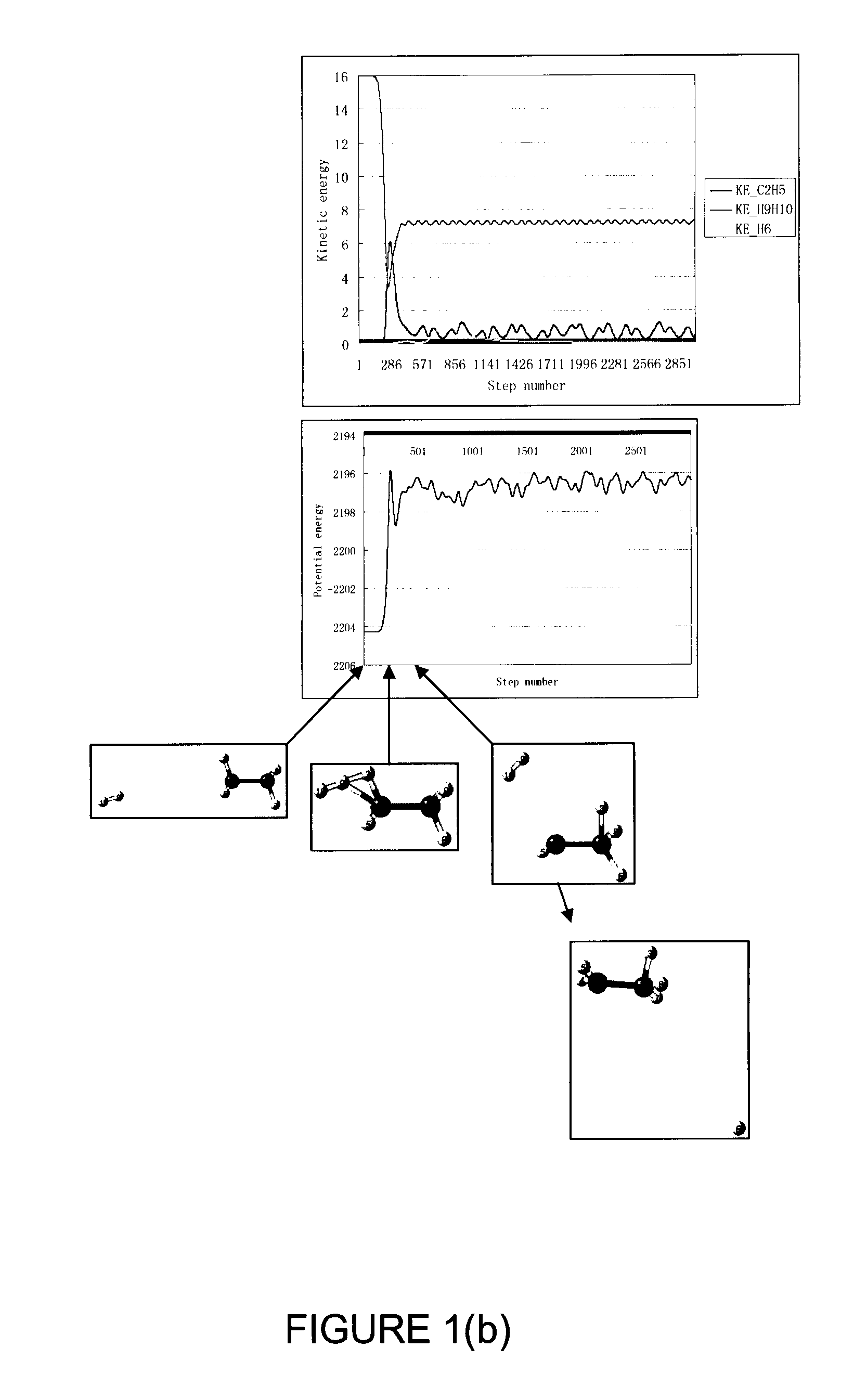
Patents
Literature
303 results about "Hydrogen molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
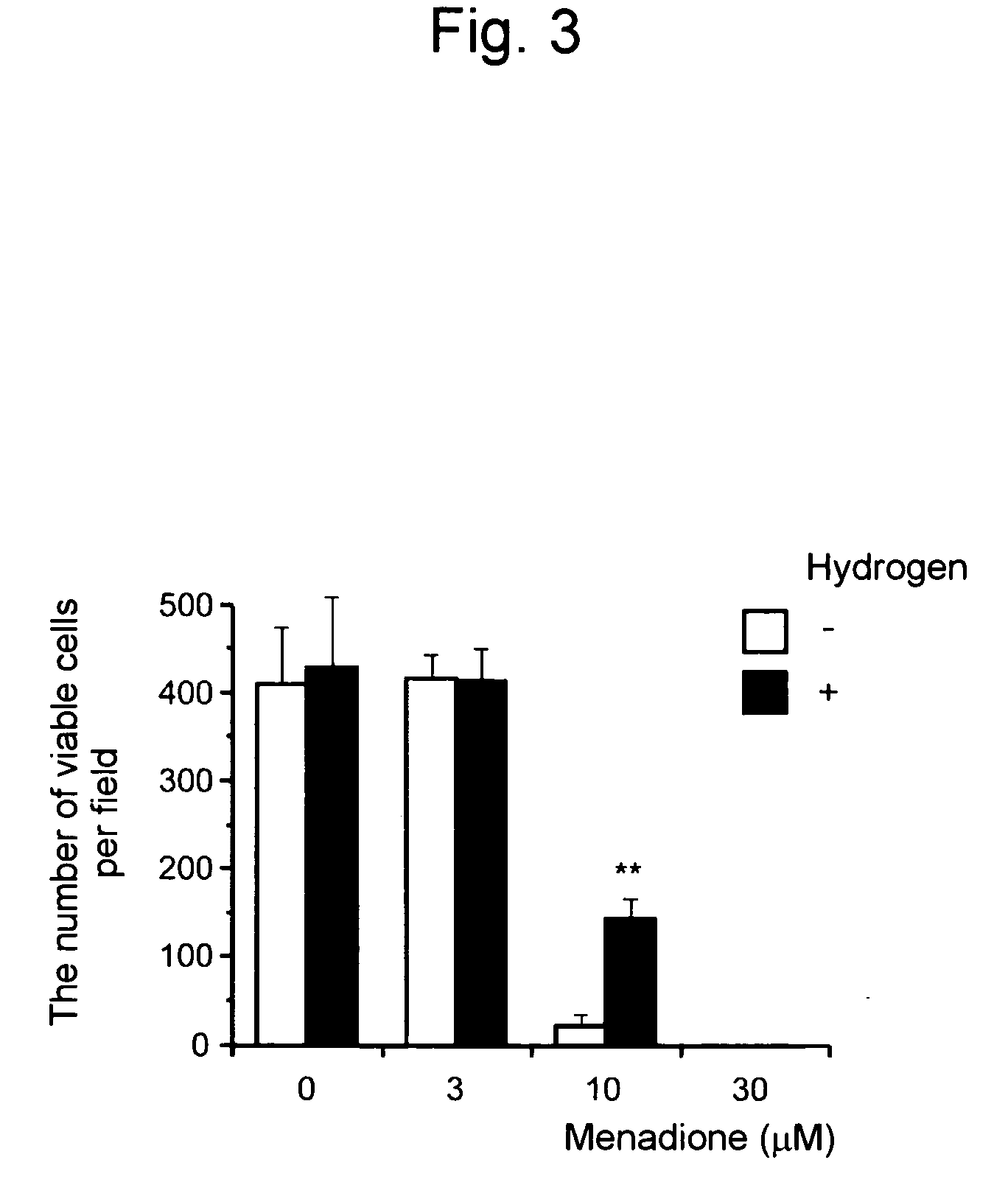
Molecular hydrogen is 2 hydrogen atoms combined into 1 molecule (H2). When infused into water, hydrogen acts as an incredible antioxidant and energizer. It does this by neutralizing free radicals which serves to protect all of our cells.
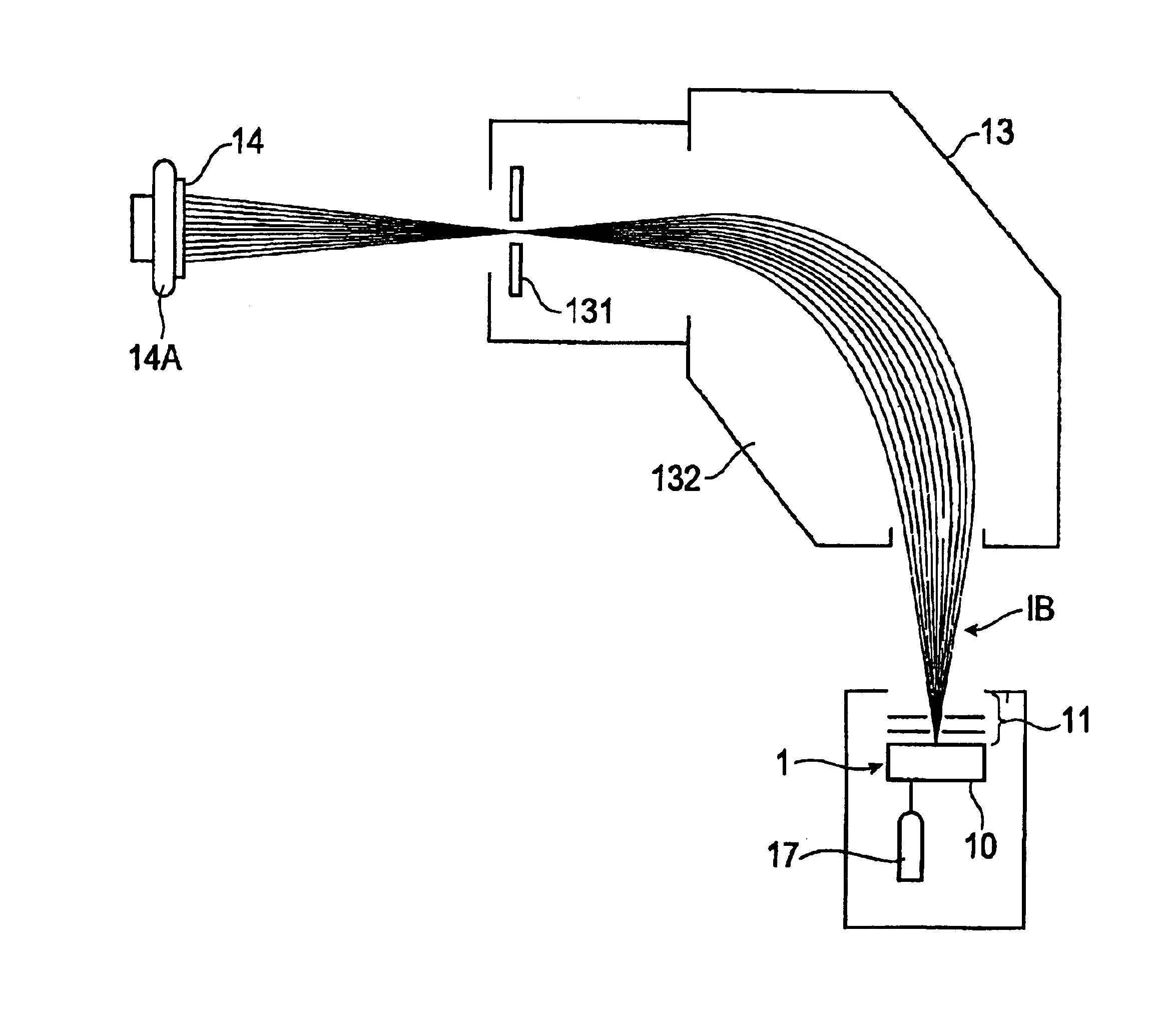
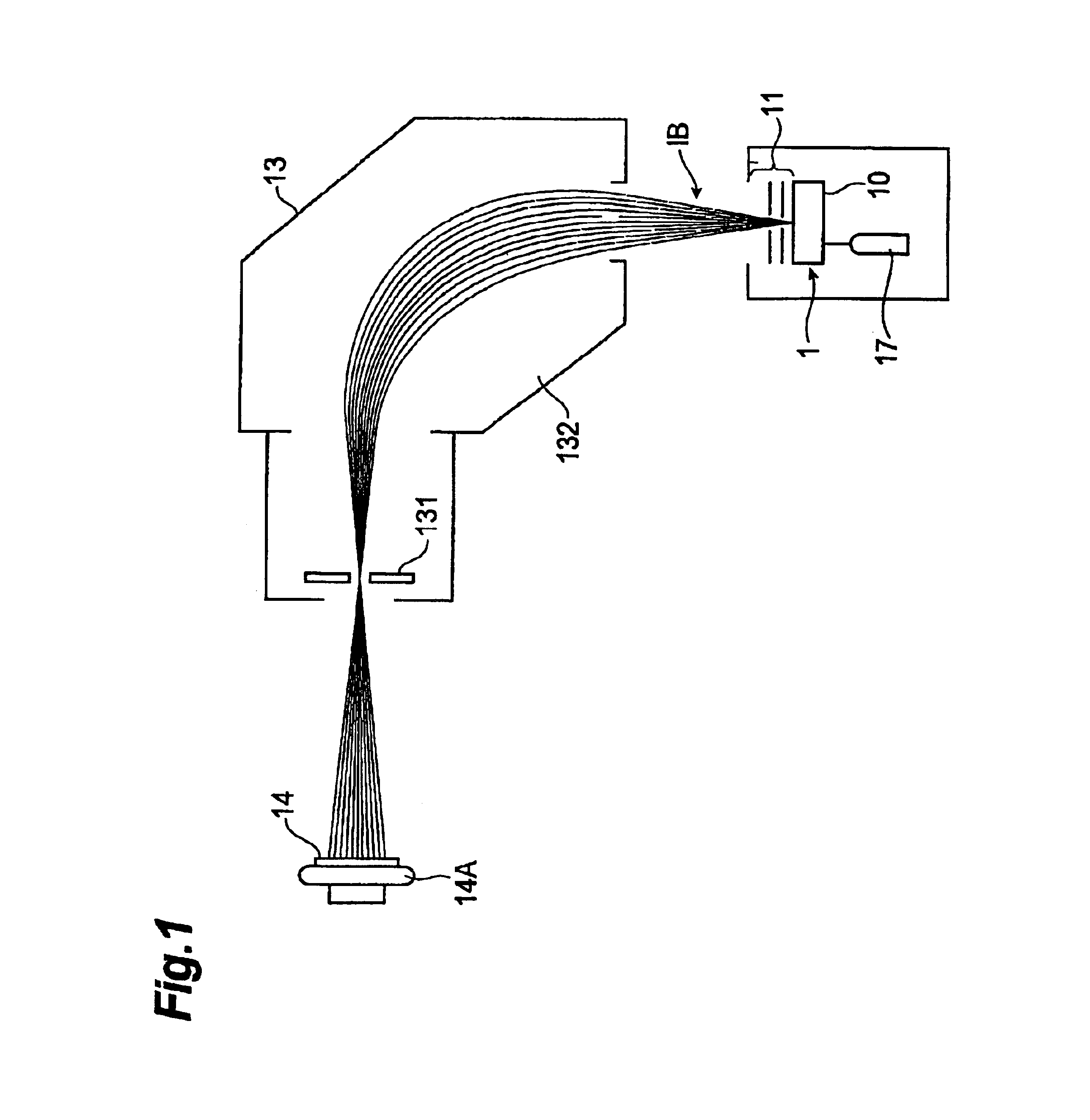
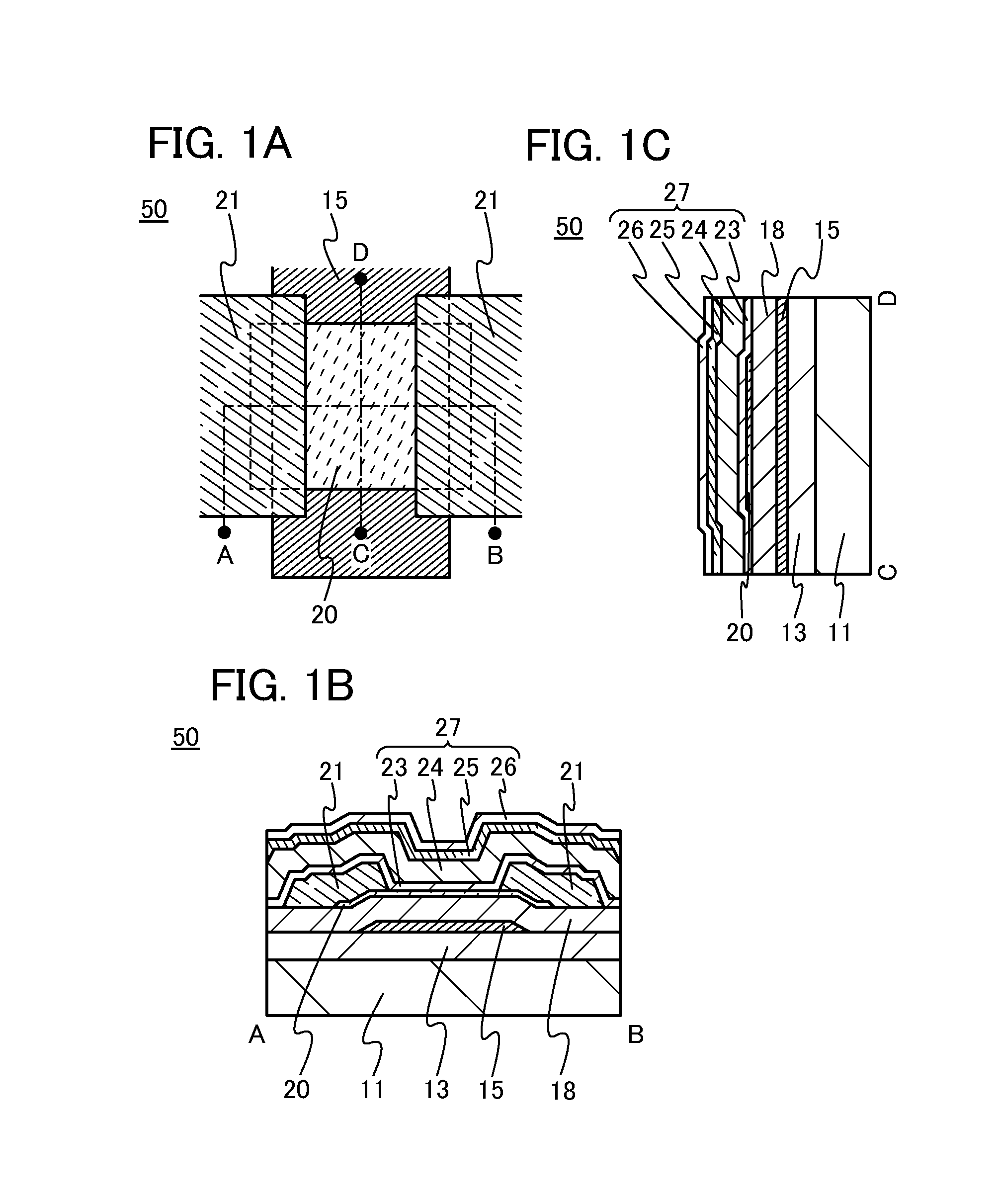
Ion implantation method and method for manufacturing SOI wafer
ActiveUS6927148B2Increase generationIncrease plasma densitySolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingInternal pressureMicrowave
Disclosed are an ion implantation method capable of dramatically increasing an implantation rate of hydrogen ions into a semiconductor substrate and a method for manufacturing an SOI wafer, in which manufacturing efficiency of the SOI wafer is sufficiently high. When the hydrogen ions are implanted to a predetermined depth of the semiconductor substrate, hydrogen gas is introduced into a chamber where an inner pressure is reduced and a predetermined magnetic field is formed, plasma is generated by introducing a microwave into the magnetic field, hydrogen ion beams containing hydrogen molecule ions is extracted from the plasma, and the hydrogen molecule ions are irradiated and implanted onto the semiconductor substrate. Thus, a throughput in the hydrogen ion implantation is improved, thus making it possible to enhance the manufacturing efficiency of the SOI wafer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Radiation-curable composition and method for manufacturing cured-product patterns therefrom
InactiveUS6096483AHighly radiation curabilityHigh sensitivityImpression capsOrganic chemistrySilicon oxygenUltraviolet lights
The present invention provides a curable composition which comprises (A) a base-generating substance which generates a base when exposed to the action of ultraviolet light, (B) a siloxane polymer which has silicon-hydrogen bonds (Si-H) capable of reacting with hydroxy groups under the effect of the base to form silicon-oxygen bonds (Si-O) and hydrogen molecules (H2), and (C) an acid substance. This composition is cured by irradiation with ultraviolet light. During this ultraviolet irradiation, a mask is placed between a coating film of the composition and the radiation source, and the uncured portions of the composition are dissolved and removed so that a pattern is formed. The residual portions are then heated to produce a pattern-cured product.
Owner:DOW CORNING ASIA
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20140001467A1Low reliabilityAvoid changeTransistorNon-linear opticsPower semiconductor deviceNitrogen
To provide a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor in which a change in electrical characteristics is suppressed or whose reliability is improved. In a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor film in which a channel formation region is formed, an insulating film which suppresses entry of water and contains at least nitrogen and an insulating film which suppresses entry of nitrogen released form the insulating film are provided over the oxide semiconductor film. As water entering the oxide semiconductor film, water contained in the air, water in a film provided over the insulating film which suppresses entry of water, or the like can be given. Further, as the insulating film which suppresses entry of water, a nitride insulating film can be used, and the amount of hydrogen molecules released by heating from the nitride insulating film is smaller than 5.0×1021 molecules / cm3.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Ion implantation method and method for manufacturing SOI wafer
ActiveUS20040038504A1Increase generationIncrease plasma densitySolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingInternal pressureMicrowave
Disclosed are an ion implantation method capable of dramatically increasing an implantation rate of hydrogen ions into a semiconductor substrate and a method for manufacturing an SOI wafer, in which manufacturing efficiency of the SOI wafer is sufficiently high. When the hydrogen ions are implanted to a predetermined depth of the semiconductor substrate, hydrogen gas is introduced into a chamber where an inner pressure is reduced and a predetermined magnetic field is formed, plasma is generated by introducing a microwave into the magnetic field, hydrogen ion beams containing hydrogen molecule ions is extracted from the plasma, and the hydrogen molecule ions are irradiated and implanted onto the semiconductor substrate. Thus, a throughput in the hydrogen ion implantation is improved, thus making it possible to enhance the manufacturing efficiency of the SOI wafer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
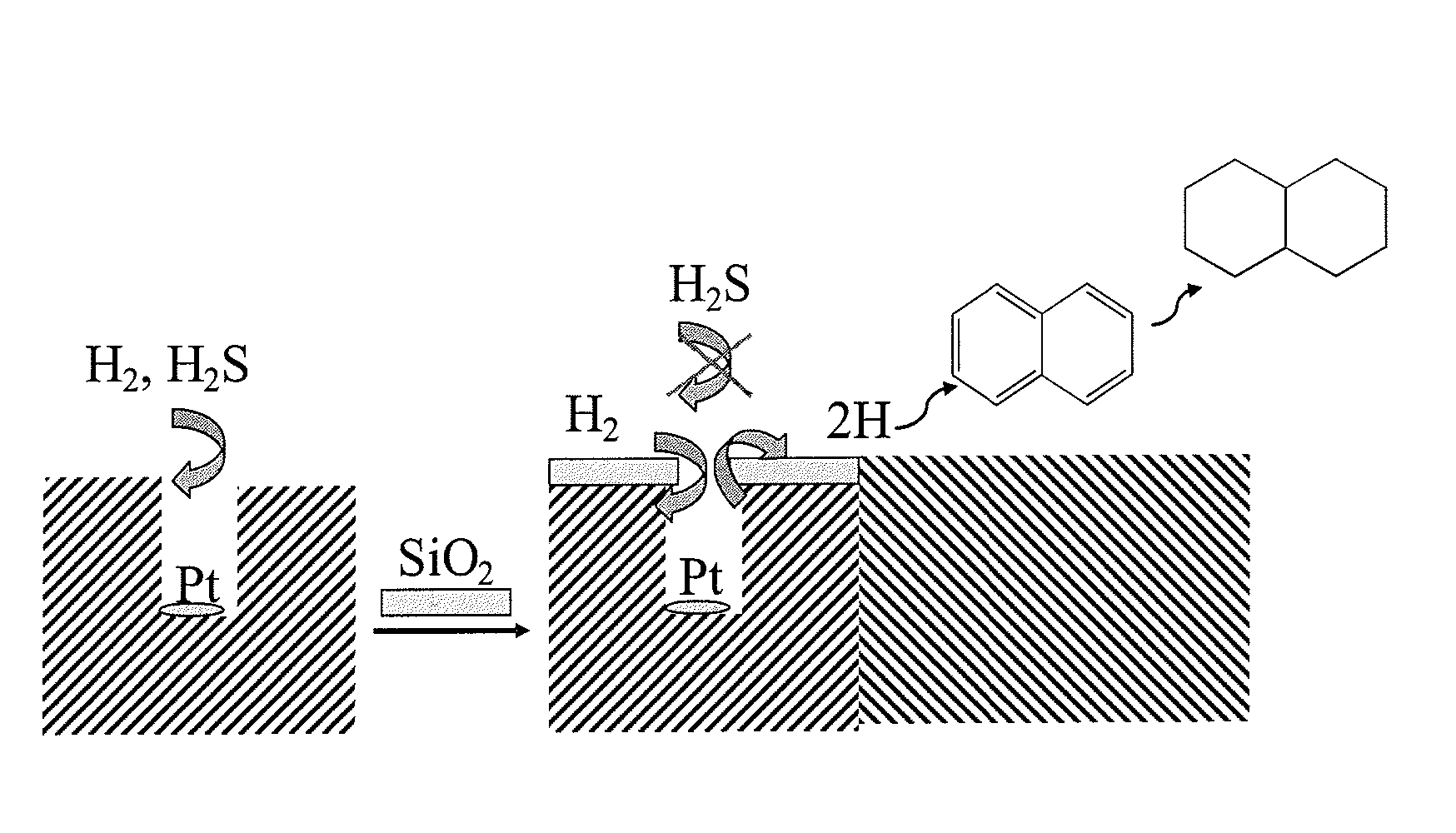
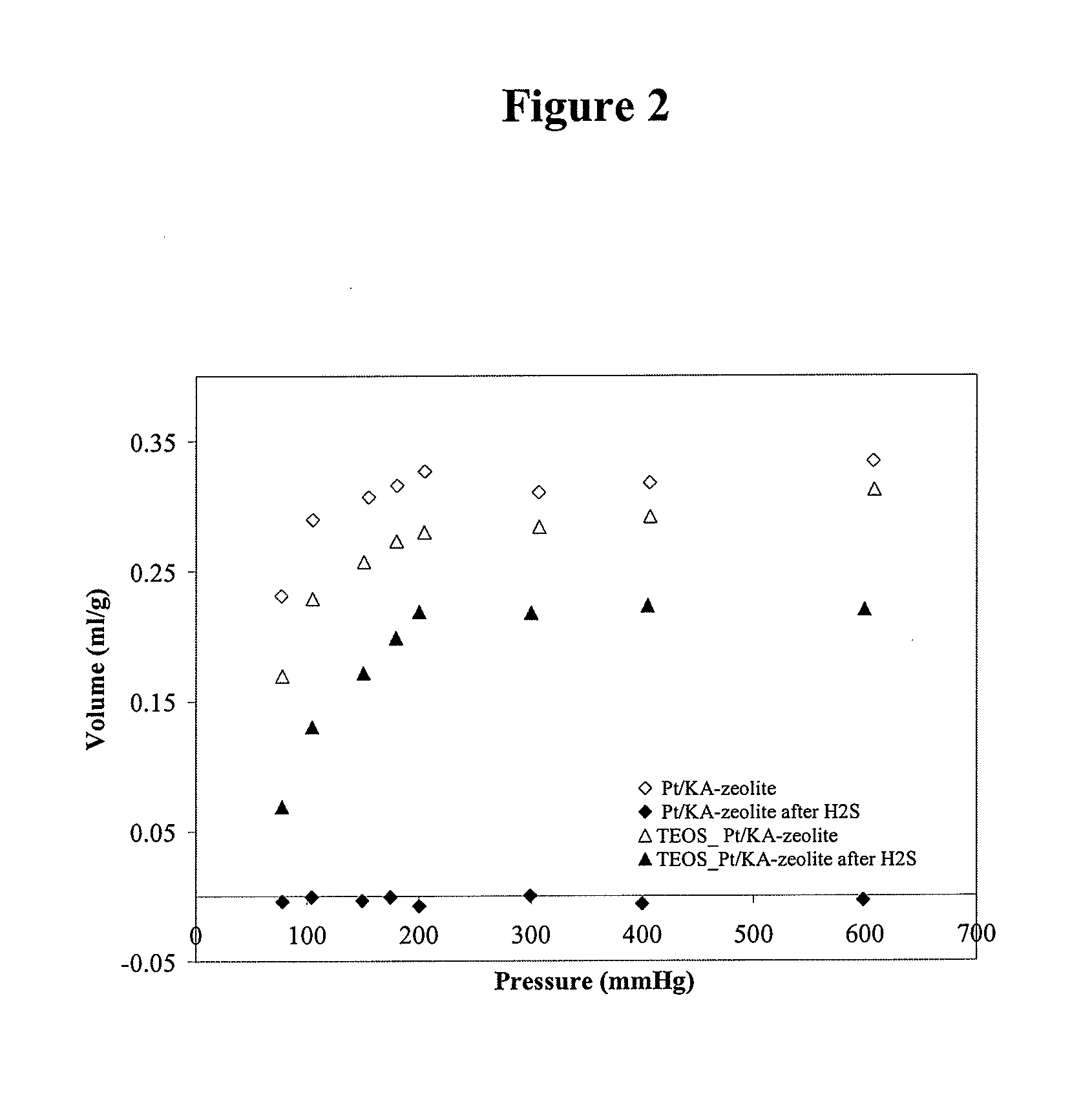
Sulfur-resistant noble metal nano-particles encapsulated in a zeolite cage as a catalyst enhancer
InactiveUS20090048094A1Small average pore sizeMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystHydrogen moleculeChemical vapor deposition
A sulfur resistant catalyst is taught having noble metal nano-particles contained in a zeolite cage having a final pore size of between about 2.9 Å and about 3.5 Å. The zeolite cage is either directly synthesized, or the final pore size of the zeolite cage is reduced by post-treatments selected from chemical vapour deposition, chemical liquid deposition, cation exchange and combinations thereof to allow passage of hydrogen molecules into the cage while excluding organic sulfur molecules. Disassociated hydrogen species from reaction with the noble metal spill over through the zeolite pores to induce hydrogenation and to regenerate neighboring catalyst supports. A method is also taught for producing a sulfur resistant catalyst having noble metal nano-particles. The method involves either synthesizing a zeolite cage having a final pore size of between about 2.9 Å and about 3.5 Å or reducing the size of pores in the zeolite cage by a post treatment selected from chemical vapour deposition, chemical liquid deposition, cation exchange and combinations thereof.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF NATURAL RESOURCES
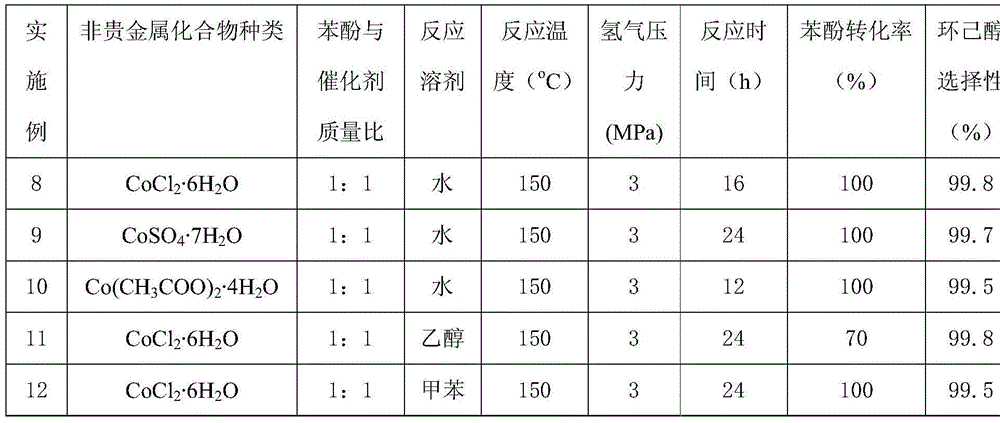
Method for preparing cyclohexanol by catalyzing by base metal catalyst
InactiveCN104447209AReduce use costLow costPreparation by hydrogenationHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsFiltrationPorous carbon
The invention discloses a method for preparing cyclohexanol by catalyzing phenol hydrogenation by taking a porous carbon material loaded base metal as a catalyst. The synthetic route of the traditional two-step method comprises phenol hydrogenation and cyclohexanol dehydrogenation, and the catalysis of phenol hydrogenation in preparing cyclohexanol is mainly completed through metals, namely nanometer noble metal Pd, Ni radical and the like which have higher activated cracked hydrogen molecules. The method is characterized in that cyclohexanol is prepared in the presence of a solvent by using the porous carbon material loaded base metal as the catalyst, taking phenol or a phenol derivative as a raw material and catalyzing hydrogenation; a general formula of the catalyst is aM@CXy, wherein a indicates the weight percentage content of the metals contained in the catalyst, M indicates the base metal, C indicates carbon, X indicates a doped mixed element, and y indicates the weight percentage content of the mixed element. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for reducing the usage cost of the catalyst by recovering the catalyst by adopting a simple filtering method, and can obtain cyclohexanol by directly concentrating filter liquor obtained through filtration.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
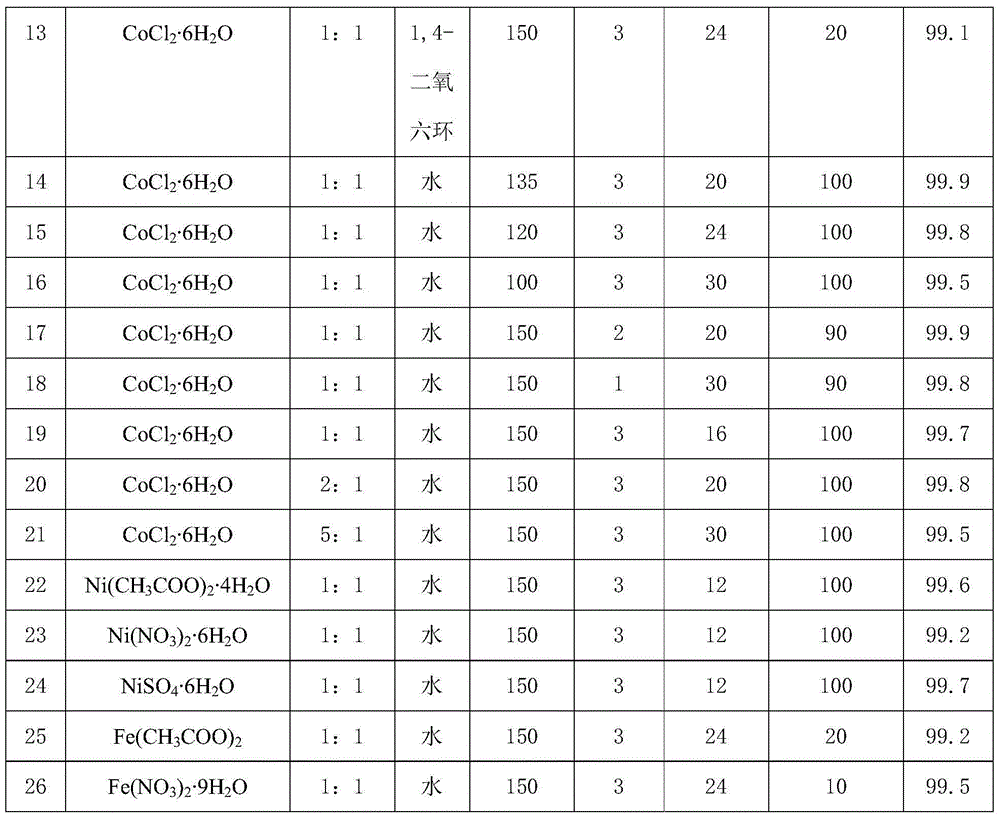
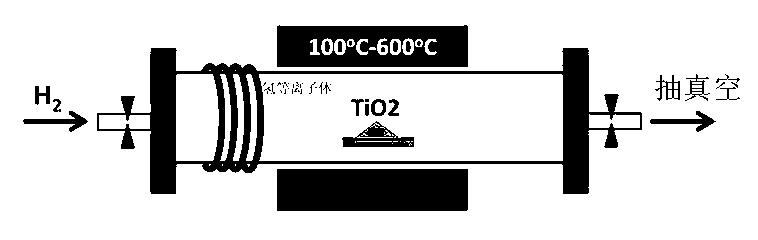
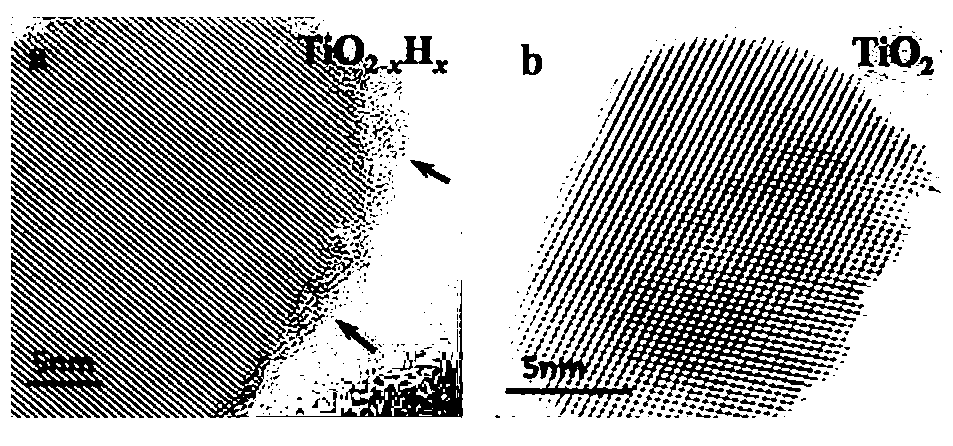
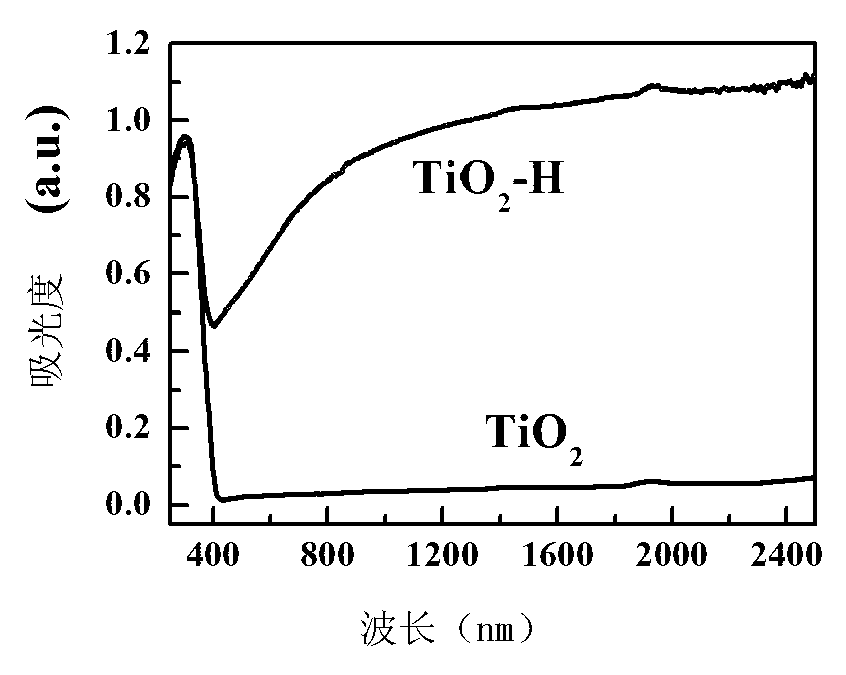
Method for preparing black titanium dioxide through auxiliary hydrogenation of hydrogen plasma
ActiveCN103214032AImprove hydrogenation efficiencyLarge particle sizeTitanium dioxideVacuum pumpingHydrogen molecule
The invention relates to a method for preparing black titanium dioxide through auxiliary hydrogenation of hydrogen plasma. The method comprises the following steps of placing the titanium dioxide into a closed system, and vacuum pumping the closed system to ensure the pressure of the closed system to be less than 30Pa; inputting a mixed atmosphere of hydrogen and argon into the closed system; heating the titanium dioxide, and adjusting the mixed atmosphere so as to ensure the pressure in the closed system to be 50 to 500Pa; and starting a radio-frequency power supply to generate the active hydrogen plasma to process the titanium dioxide within a specified time, and utilizing the hydrogen molecules ionized by the radio-frequency power supply to generate the active hydrogen plasma which is used for reducing the titanium dioxide to the black titanium dioxide.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
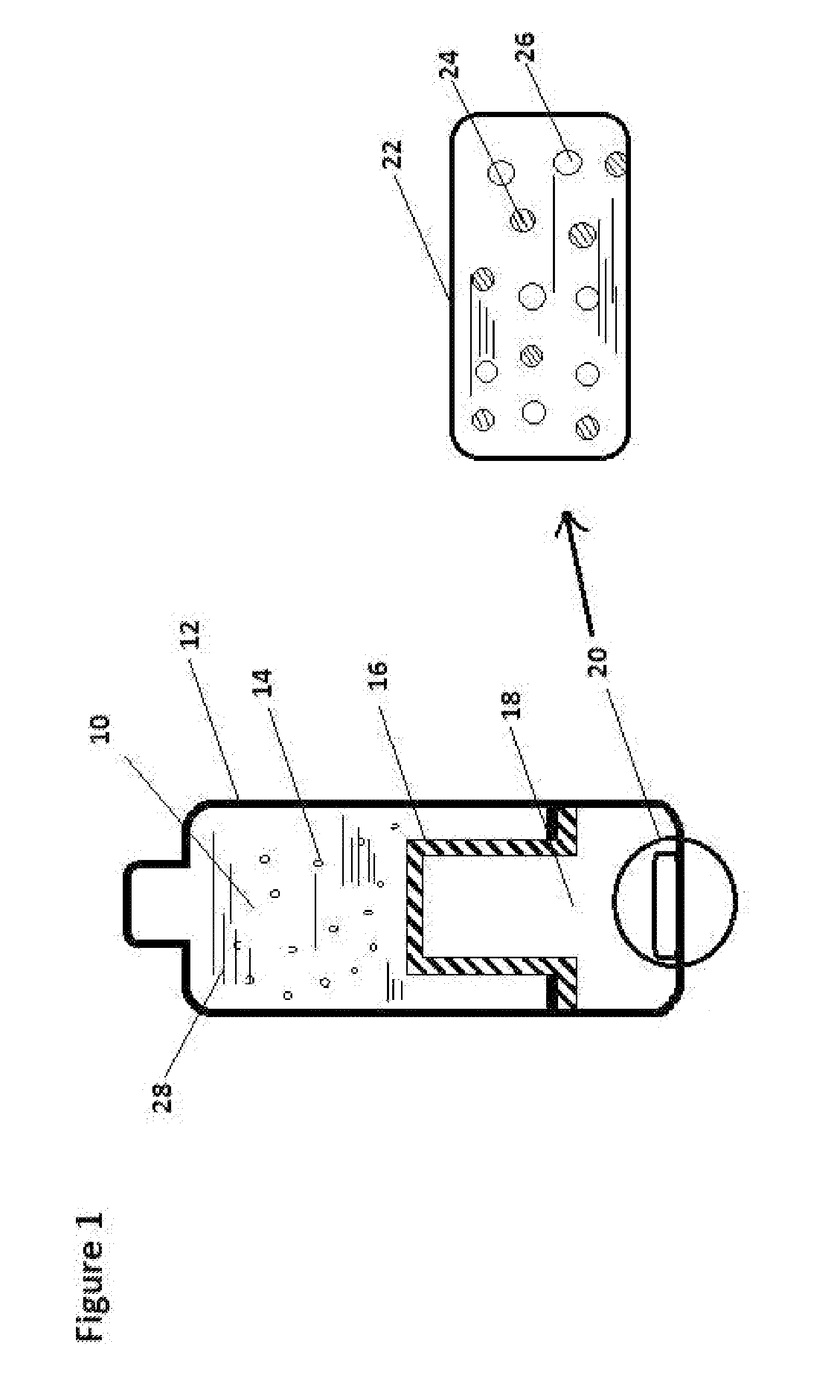
Method and Apparatus to Produce Hydrogen-Rich Materials
InactiveUS20140247689A1Increase the concentration of hydrogenImprove hydrogen permeabilityLighting and heating apparatusUsing liquid separation agentHydrogen concentrationCompound (substance)
Hydrogen molecule (H2) has been indicated as a novel anti-oxidant reagent specifically targeting OH free radicals. This invention discloses the methods and apparatus that can be used to increase the hydrogen concentration in water, in beverages, and in other hydrogen absorbing materials through a sealed hydrogen gas producing chamber made of materials that have good hydrogen permeability and can withhold gas pressure. The disclosed method and apparatus can increase the hydrogen concentration quickly without leaking other chemical by-products of the gas producing system into the treated materials.
Owner:CENTAQUA
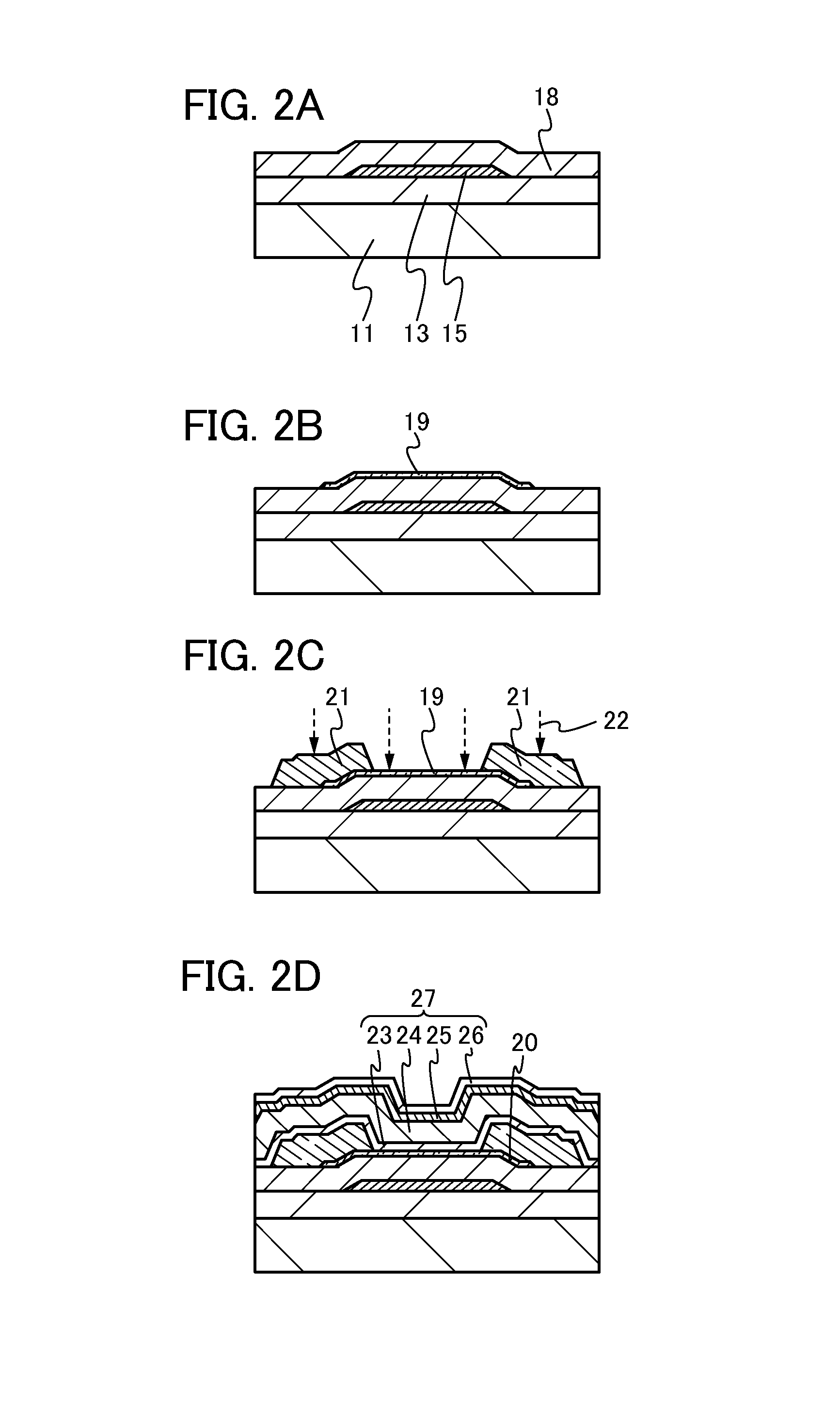
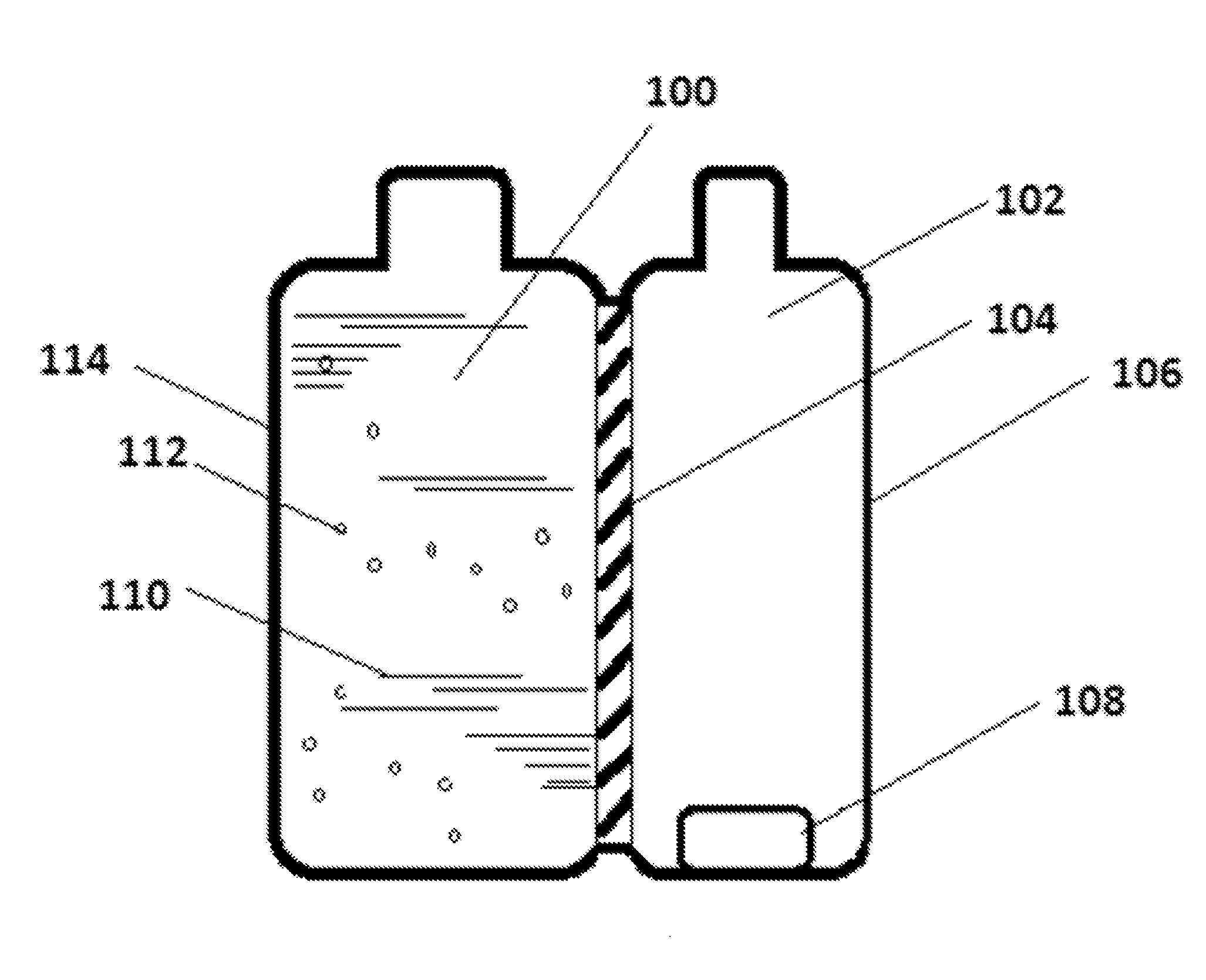
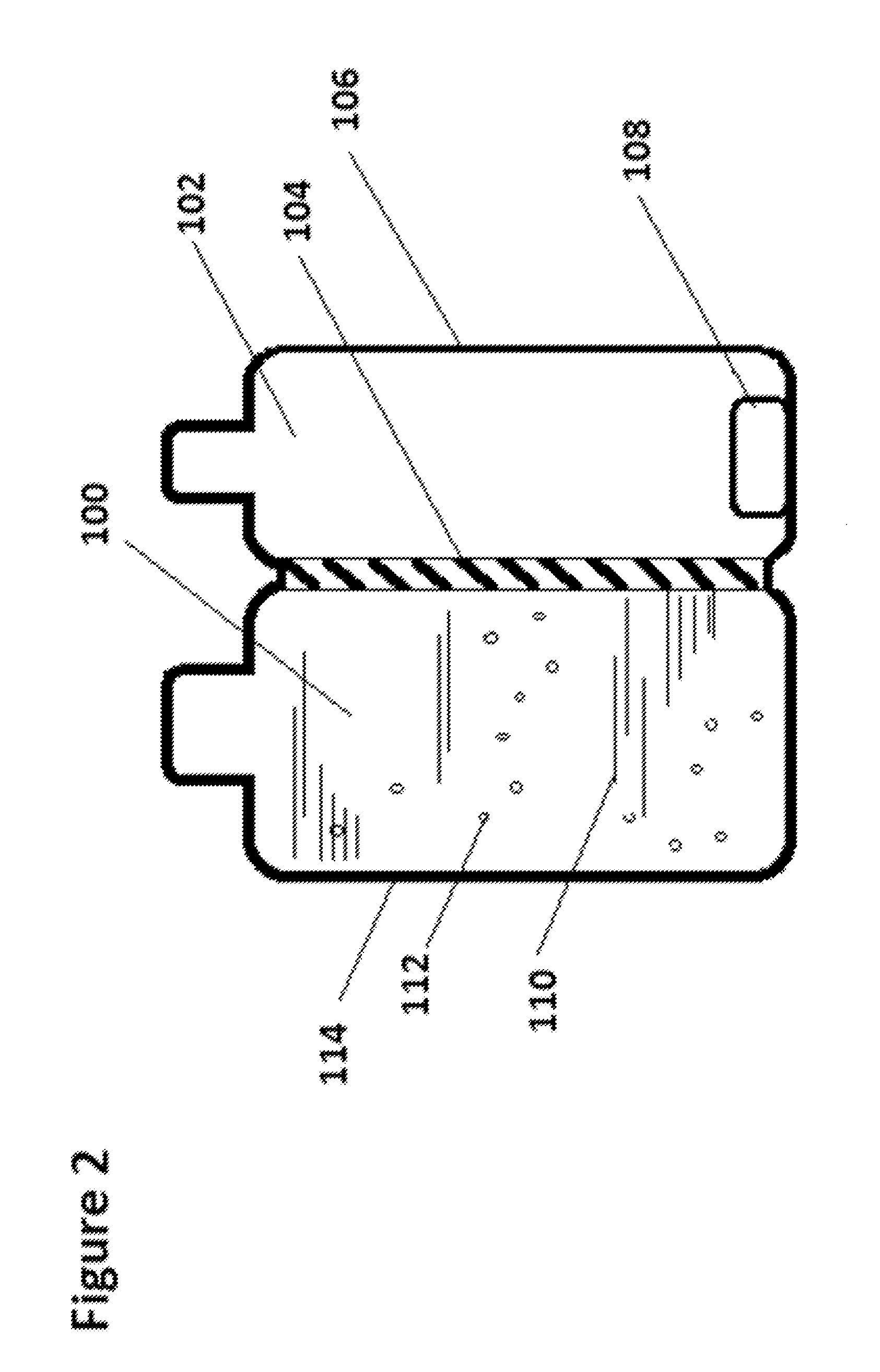
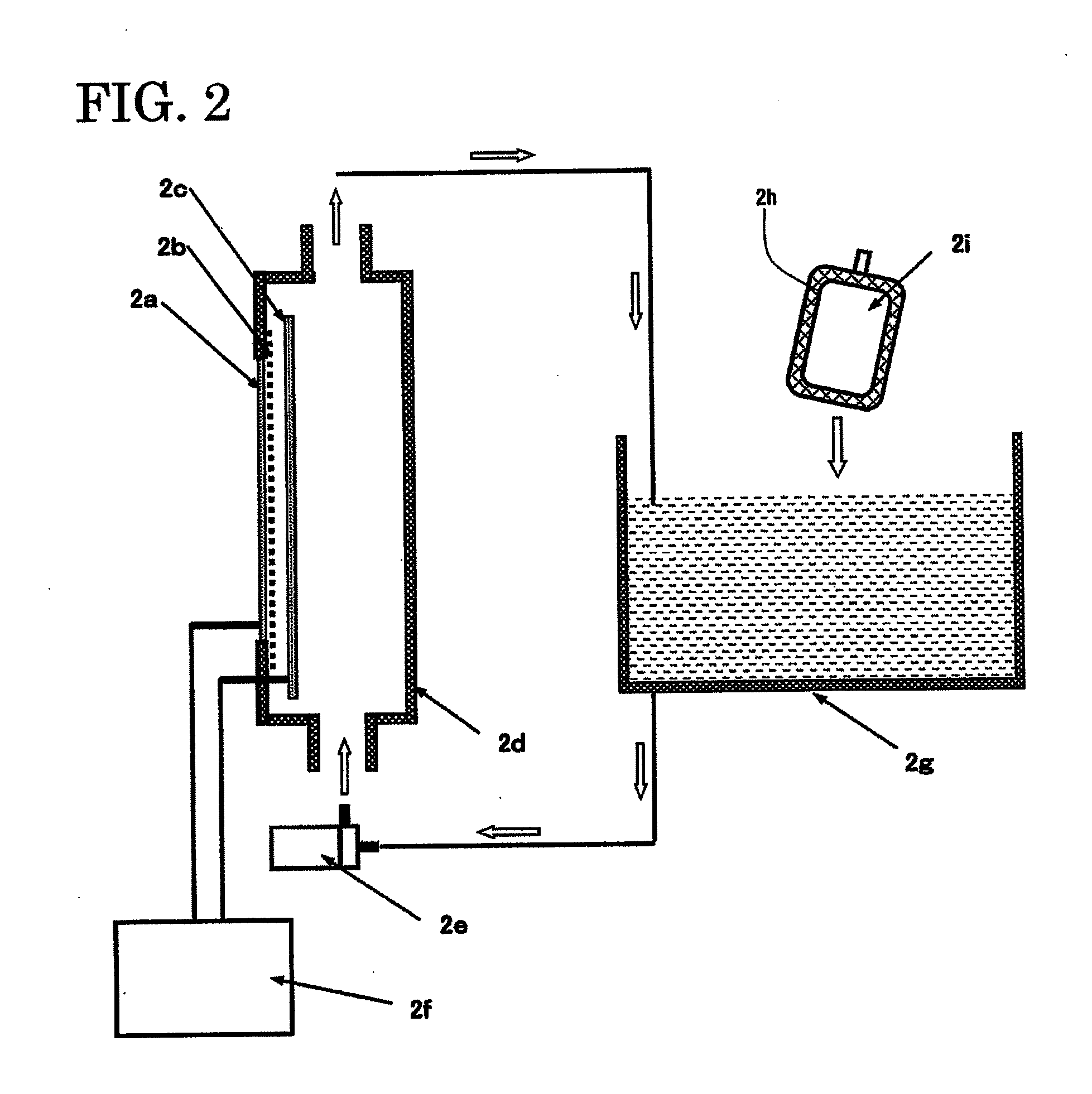
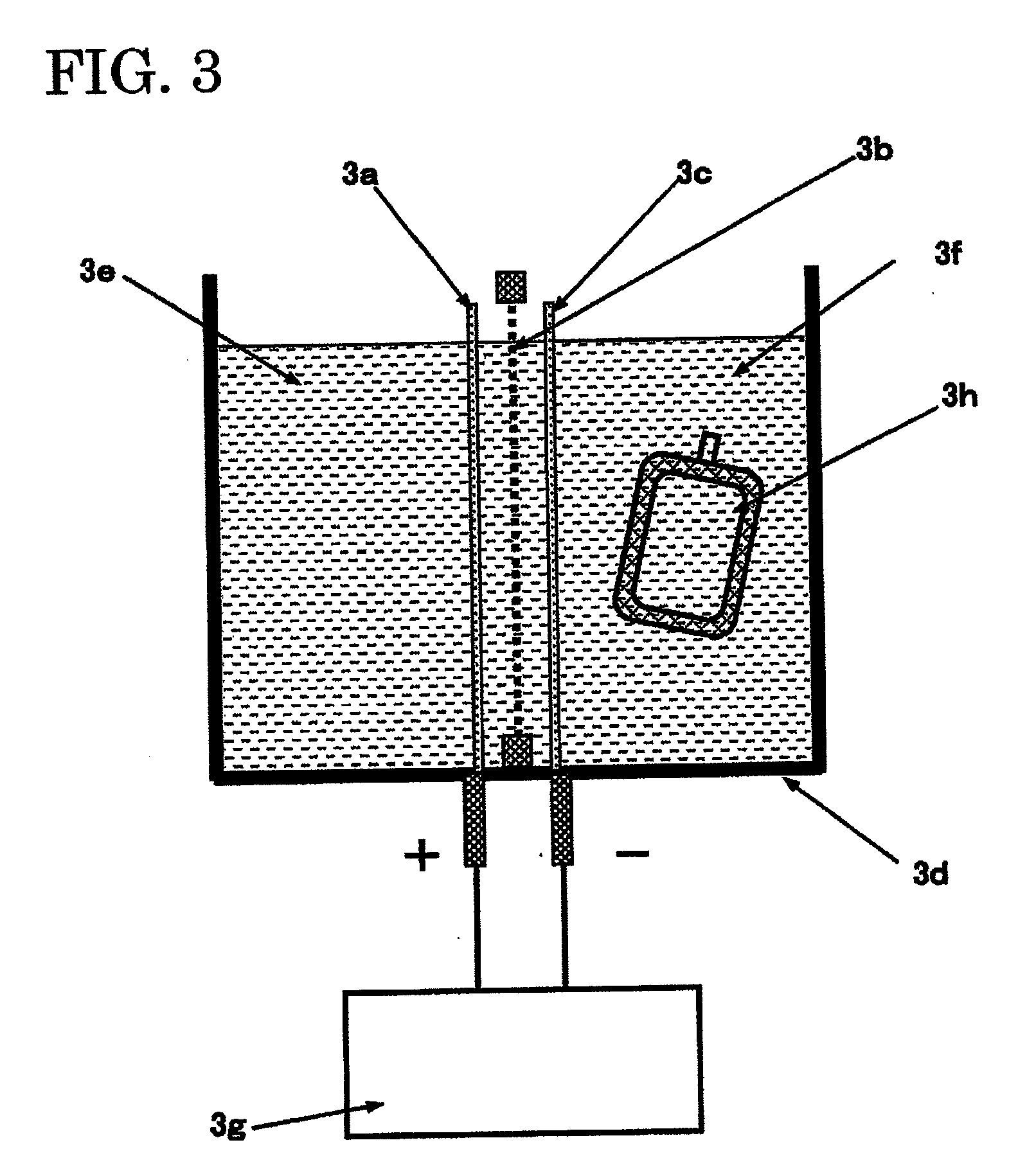
Producing method for living organism-applicable hydrogen-contained fluid and producing apparatus for the same
InactiveUS20110111048A1Without any changeEasily includedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSenses disorderBiological bodySaline water
A producing method for a living organism-applicable hydrogen-contained fluid, which includes hydrogen molecules in living organism-applicable fluid enclosed in a container (2i) with hydrogen molecule permeability, is provided. This method includes a hydrogen exposing step of exposing hydrogen molecules to the container (2i) in which the living organism-applicable fluid is enclosed from the outside of the container without opening the container. The container with hydrogen molecule permeability is one that allows a dissolved hydrogen concentration of a normal saline solution to be 1 ppb or greater when the container filled with the normal saline solution is immersed for 5 hours in a volume of hydrogen water, which stably maintains an approximately saturated state (1.6 ppm at 20 C degrees under 1 barometric pressure) and is 20 times the content volume of the container.
Owner:MIZ CO LTD
Container superior in air-tightness and a method of keeping gas molecules or volatile components in the container
InactiveUS20150069056A1Excellent gas barrier performanceMultiple wrapper applicationPackaging under vacuum/special atmospherePolyethylene terephthalate glycolVacuum pack
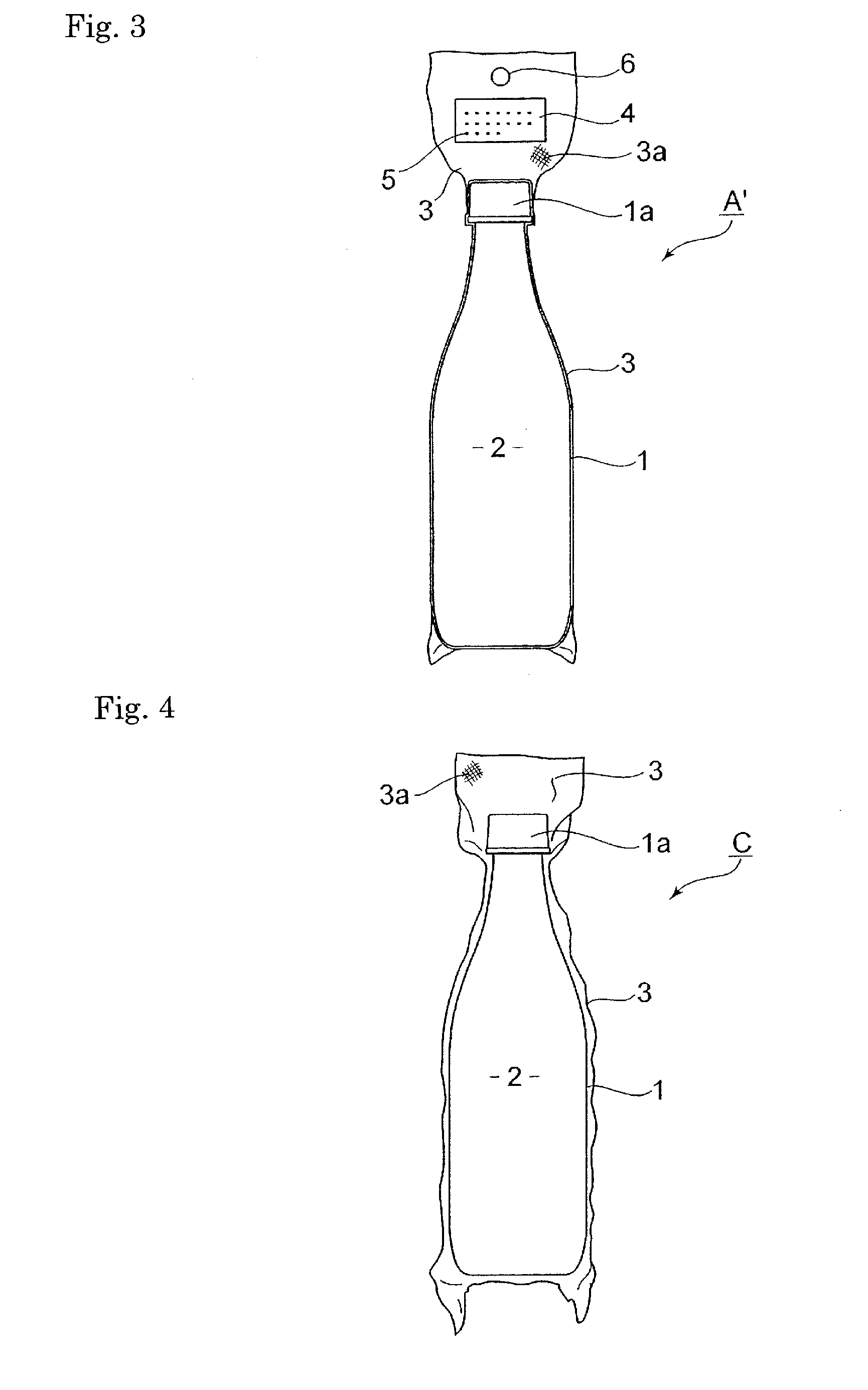
A bottle made of polyethylene terephthalate does likely undergo that a gas having a small molecular weight or volatile component escapes from the bottle in a short time in comparison with a glass bottle, steel can, and aluminum can. For a countermeasure, a simple operation prevents hydrogen molecules, helium gas, and volatile component from scattering and being lost. A container filled with gas, or liquid or viscous fluid in which gas is dissolved, or metal granules adsorbing gas is given a cap, and then, the whole of the container including the cap is packed with a metal foil laminated film superior in gas-barrier properties to be vacuum packaged.
Owner:NANO JET JAPAN +1
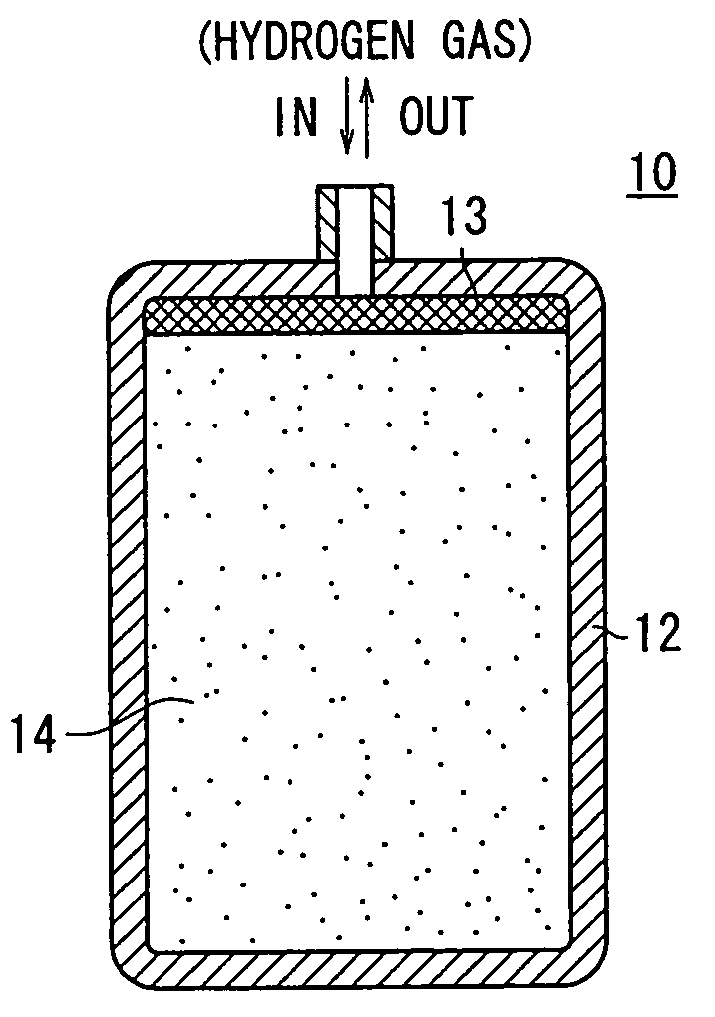
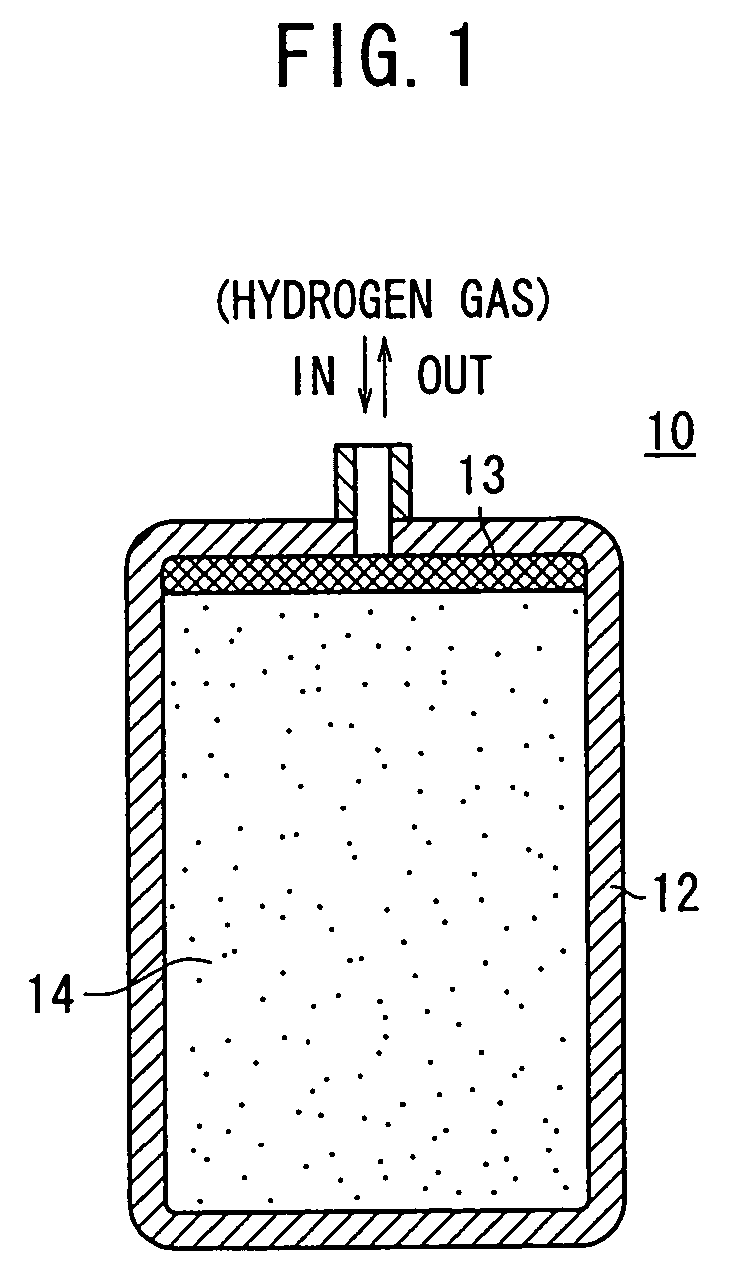
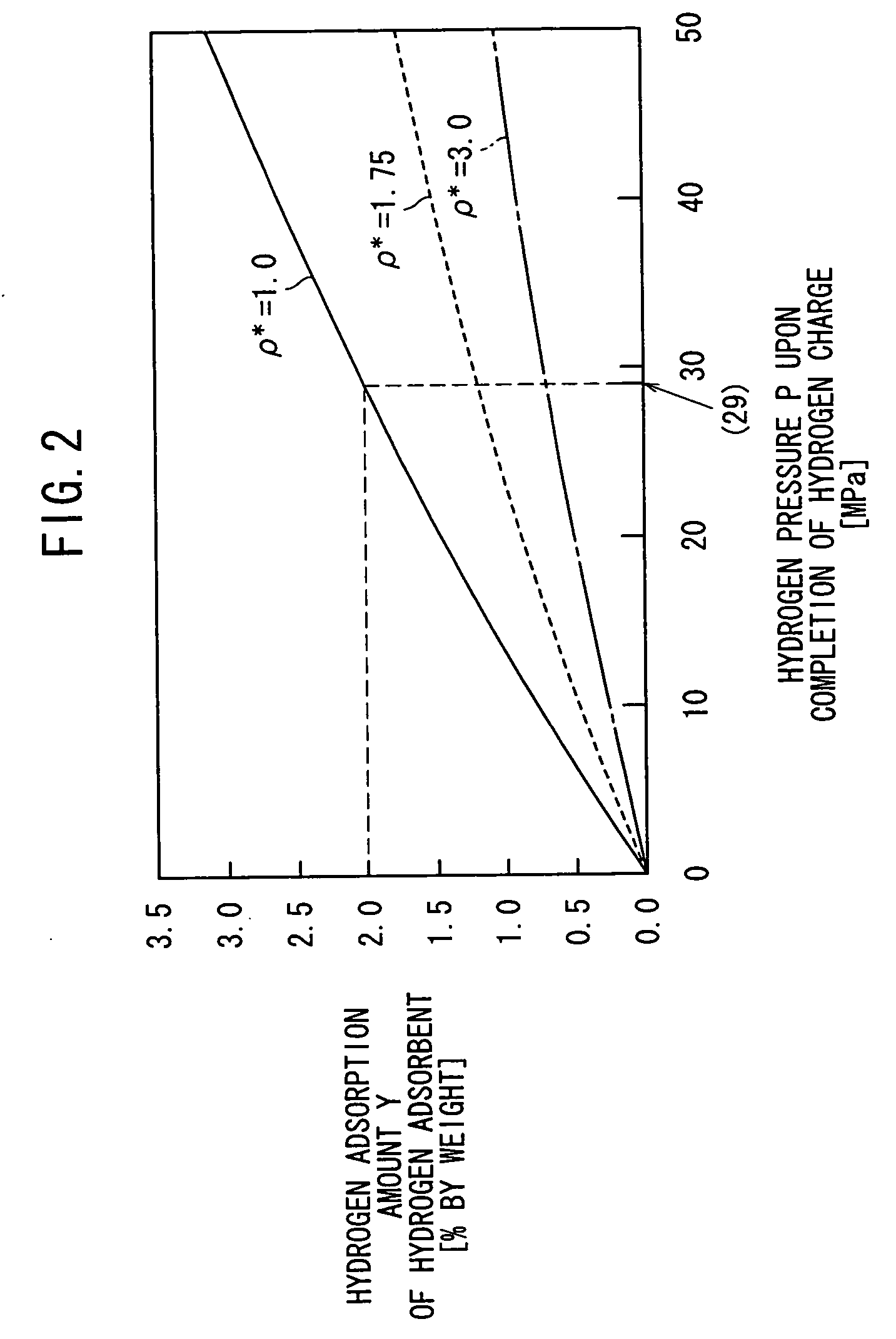
Hydrogen storage tank
InactiveUS20060054022A1Small amountAmount of endothermic is smallMaterial nanotechnologyInorganic chemistryHydrogen moleculeChemistry
A hydrogen storage tank comprises a hydrogen adsorbent accommodated in a pressure-resistant container. The hydrogen adsorbent is capable of adsorbing and retaining hydrogen gas of a volume exceeding an occupation volume occupied by the hydrogen adsorbent itself. As for the hydrogen adsorbent, the amount of endothermic heat, which is generated when the adsorbed hydrogen gas is released, is not more than 16 kJ per mol of hydrogen molecules. The hydrogen adsorbent is prevented from leaking outside of the pressure-resistant container by a filter.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
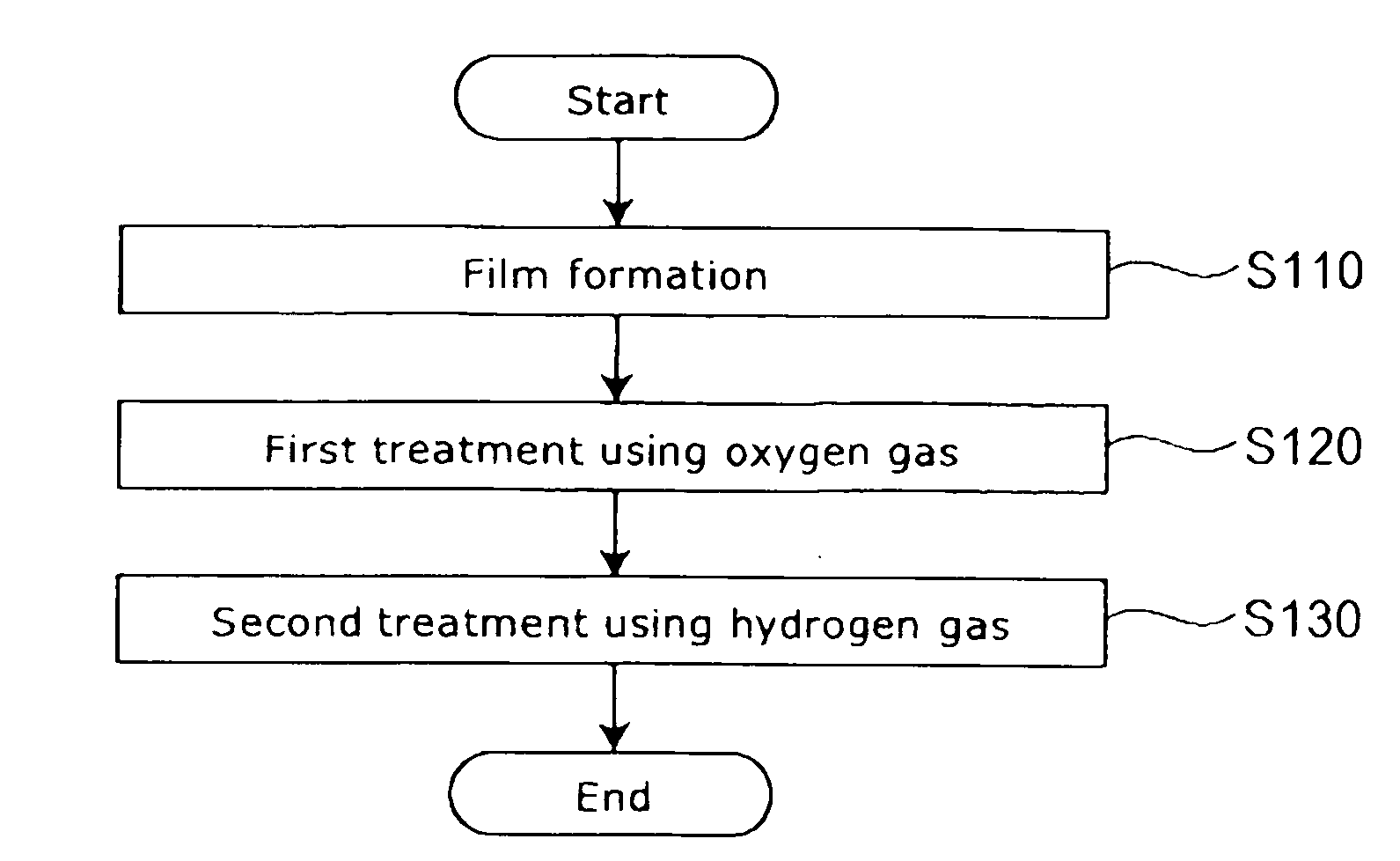
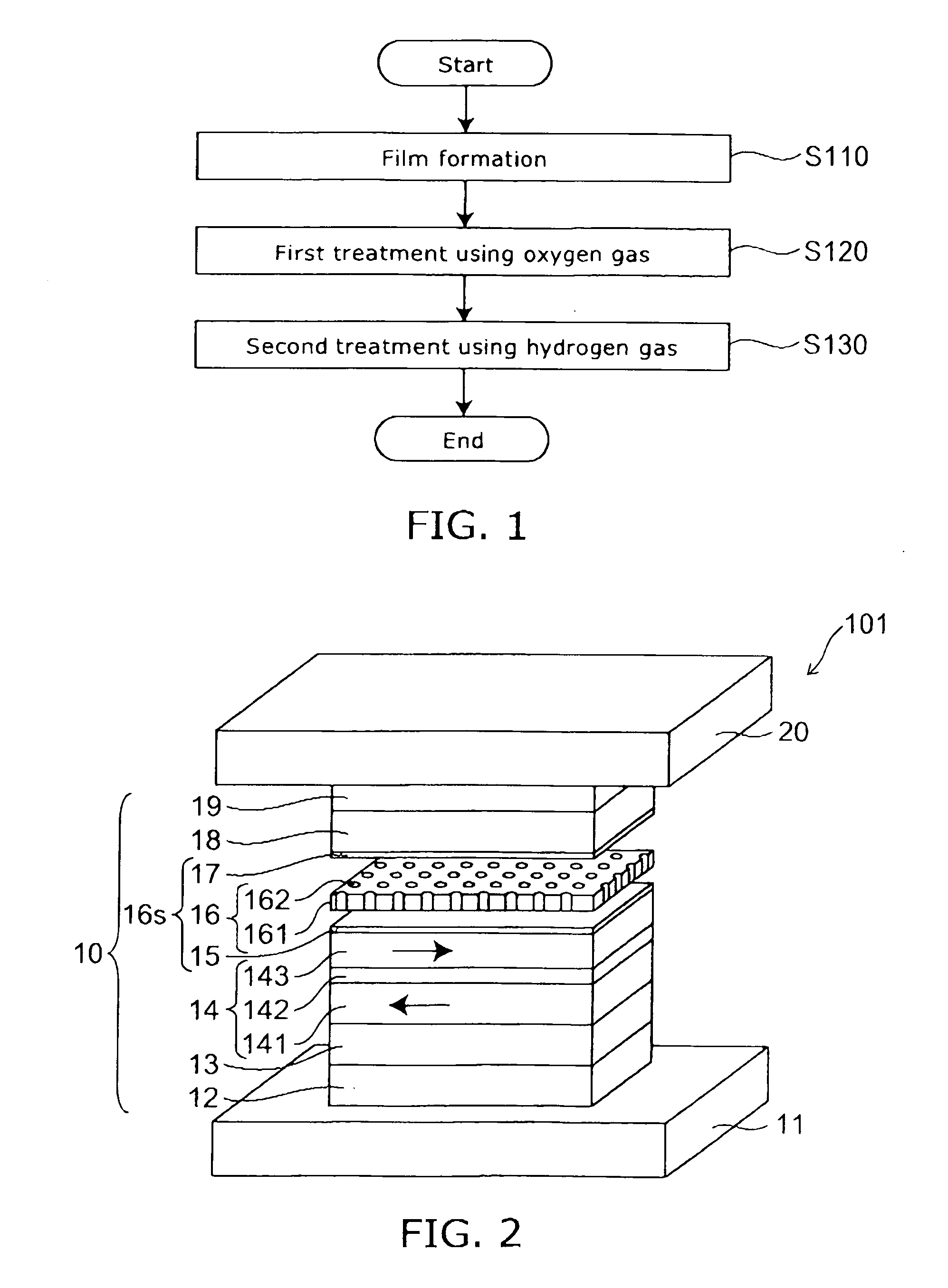
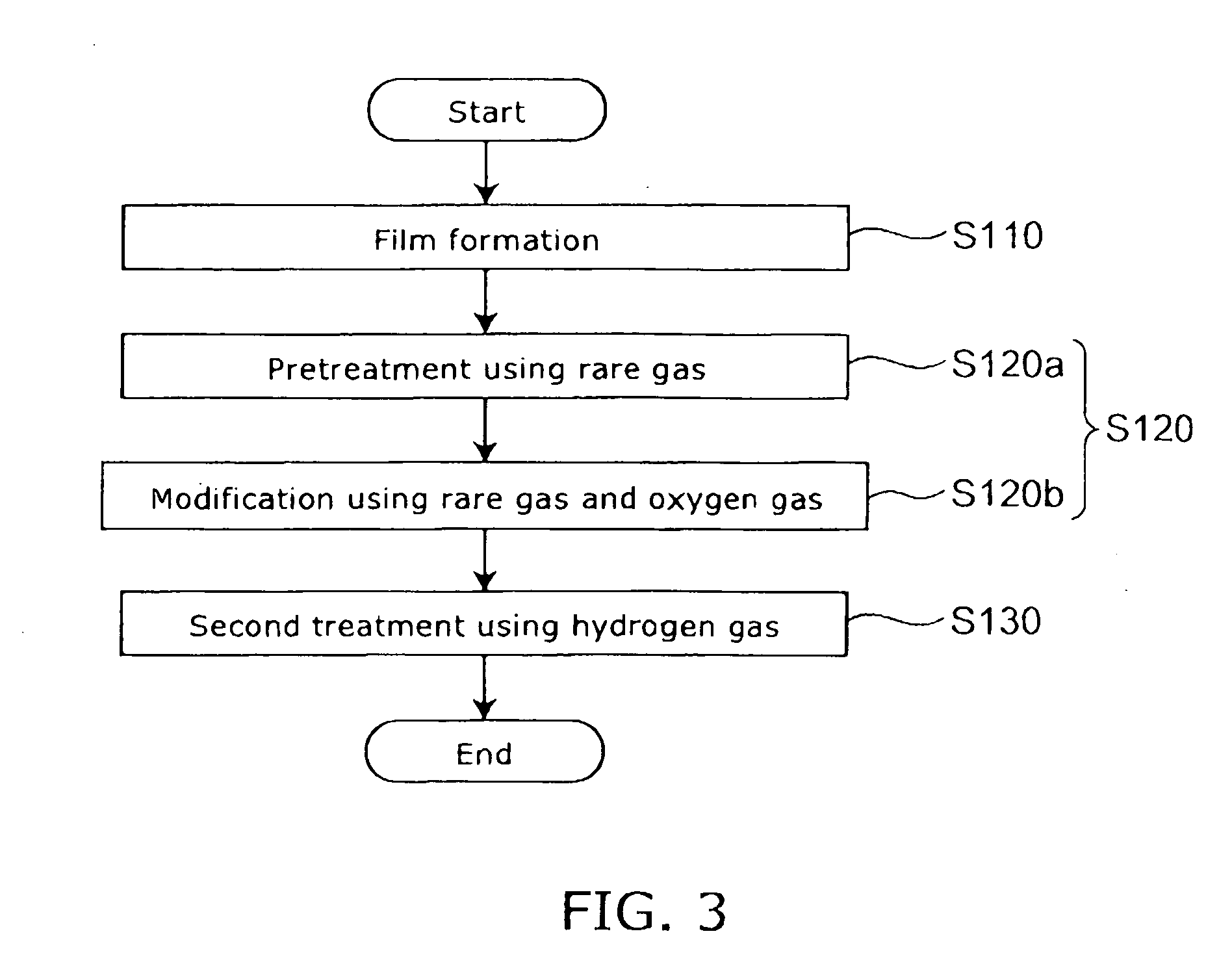
Method for manufacturing a magneto-resistance effect element and magnetic recording and reproducing apparatus
A method for manufacturing a magneto-resistance effect element is provided. The magneto-resistance effect element includes a first magnetic layer including a ferromagnetic material, a second magnetic layer including a ferromagnetic material and a spacer layer provided between the first magnetic layer and the second magnetic layer, the spacer layer having an insulating layer and a conductive portion penetrating through the insulating layer. The method includes: forming a film to be a base material of the spacer layer; performing a first treatment using a gas including at least one of oxygen molecules, oxygen atoms, oxygen ions, oxygen plasma and oxygen radicals on the film; and performing a second treatment using a gas including at least one of hydrogen molecules, hydrogen atoms, hydrogen ions, hydrogen plasma, hydrogen radicals, deuterium molecules, deuterium atoms, deuterium ions, deuterium plasma and deuterium radicals on the film submitted to the first treatment.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
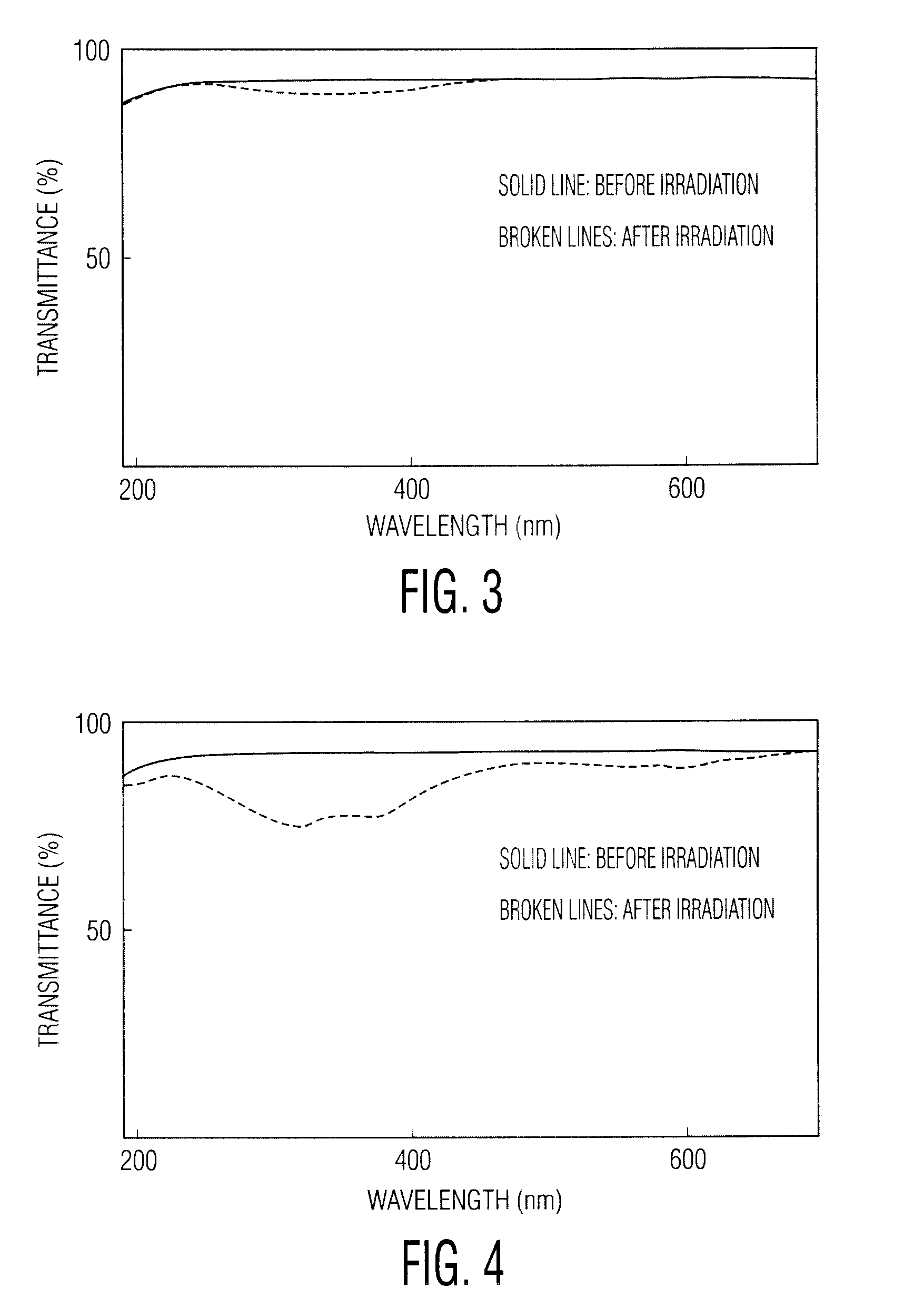
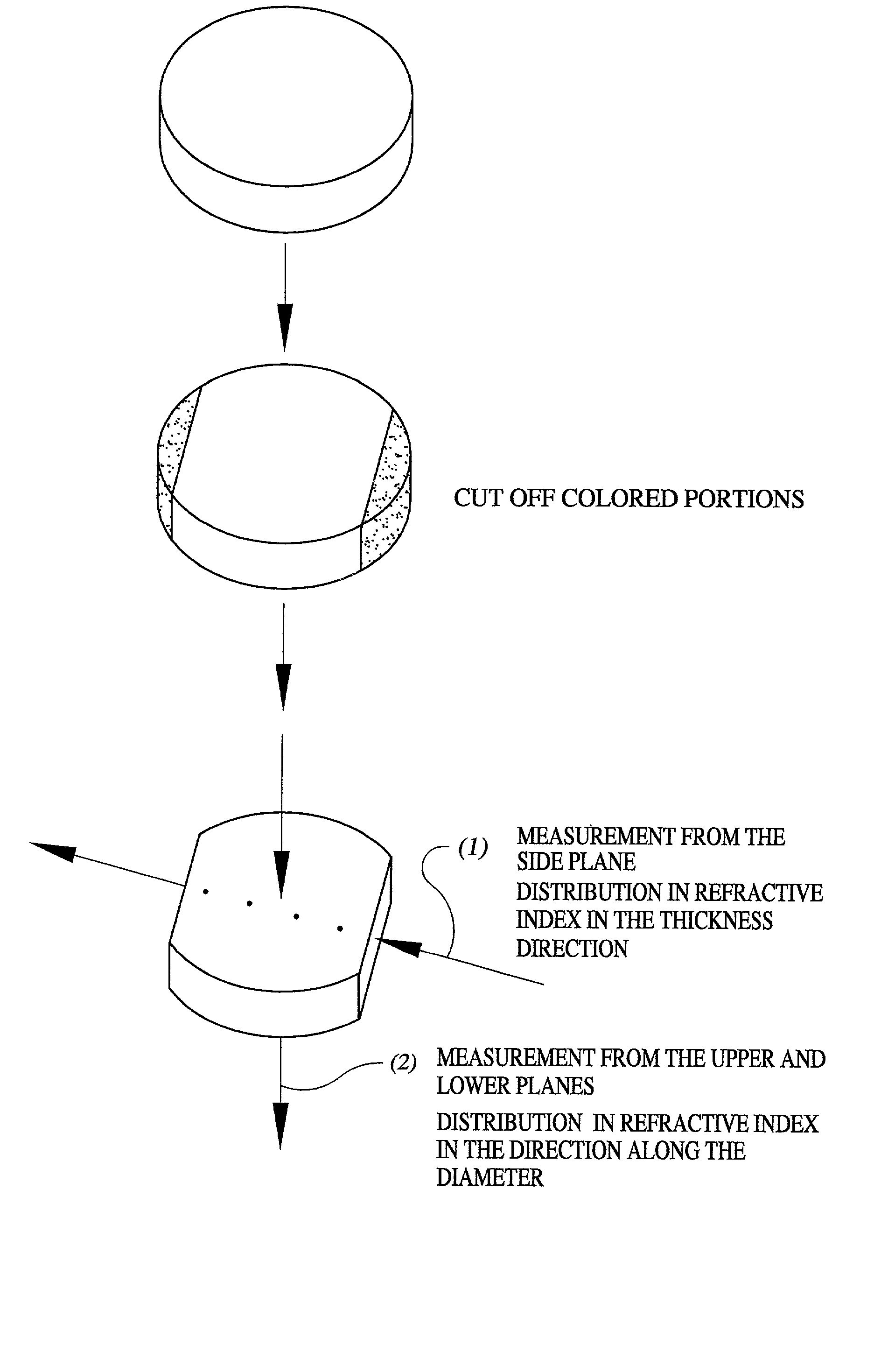
Synthetic quartz glass optical material and optical member for f2 excimer lasers
InactiveUS20020151425A1Improve uniformityImproving the resistance against laser irradiationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlass shaping apparatusHigh resistanceRefractive index
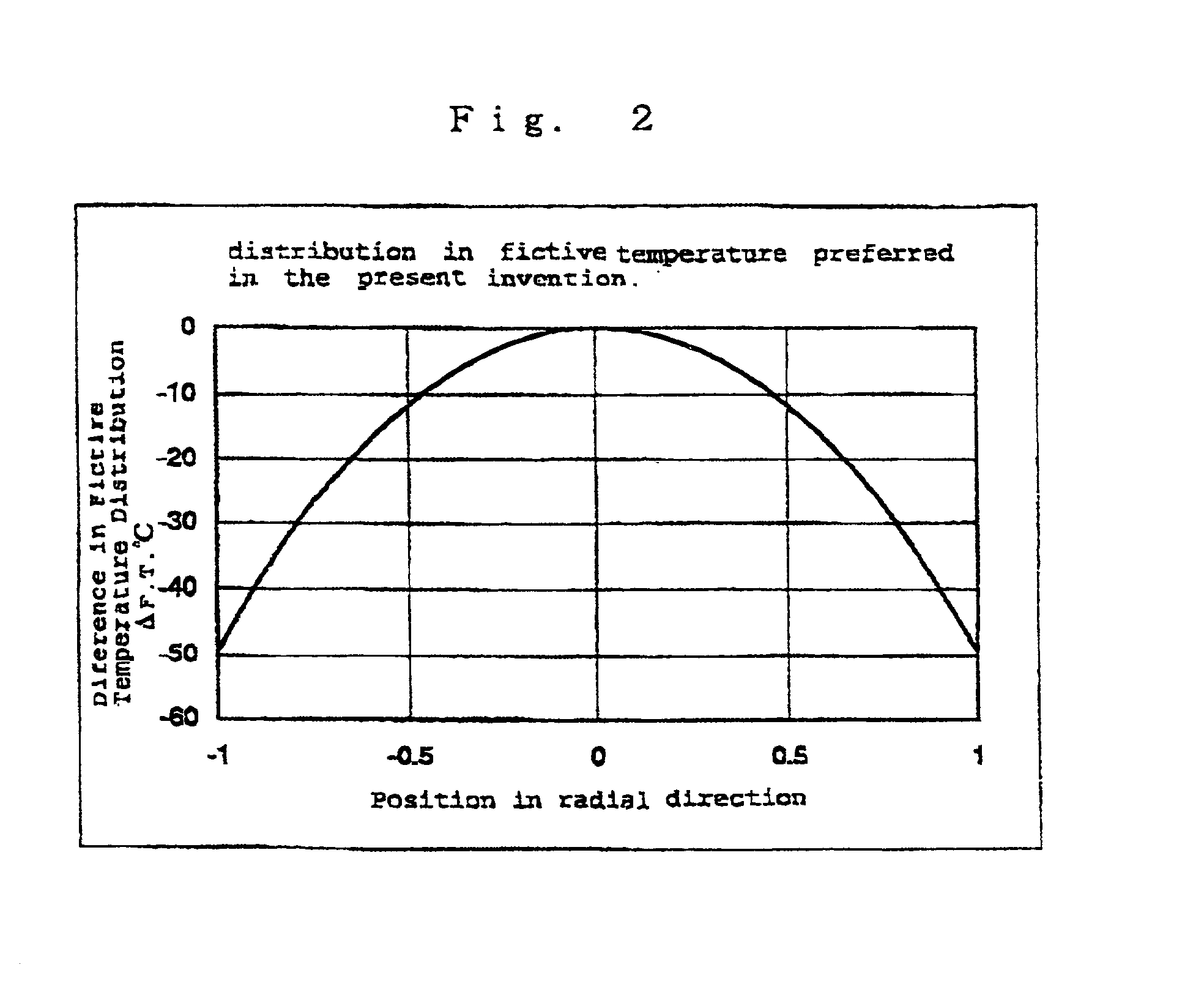
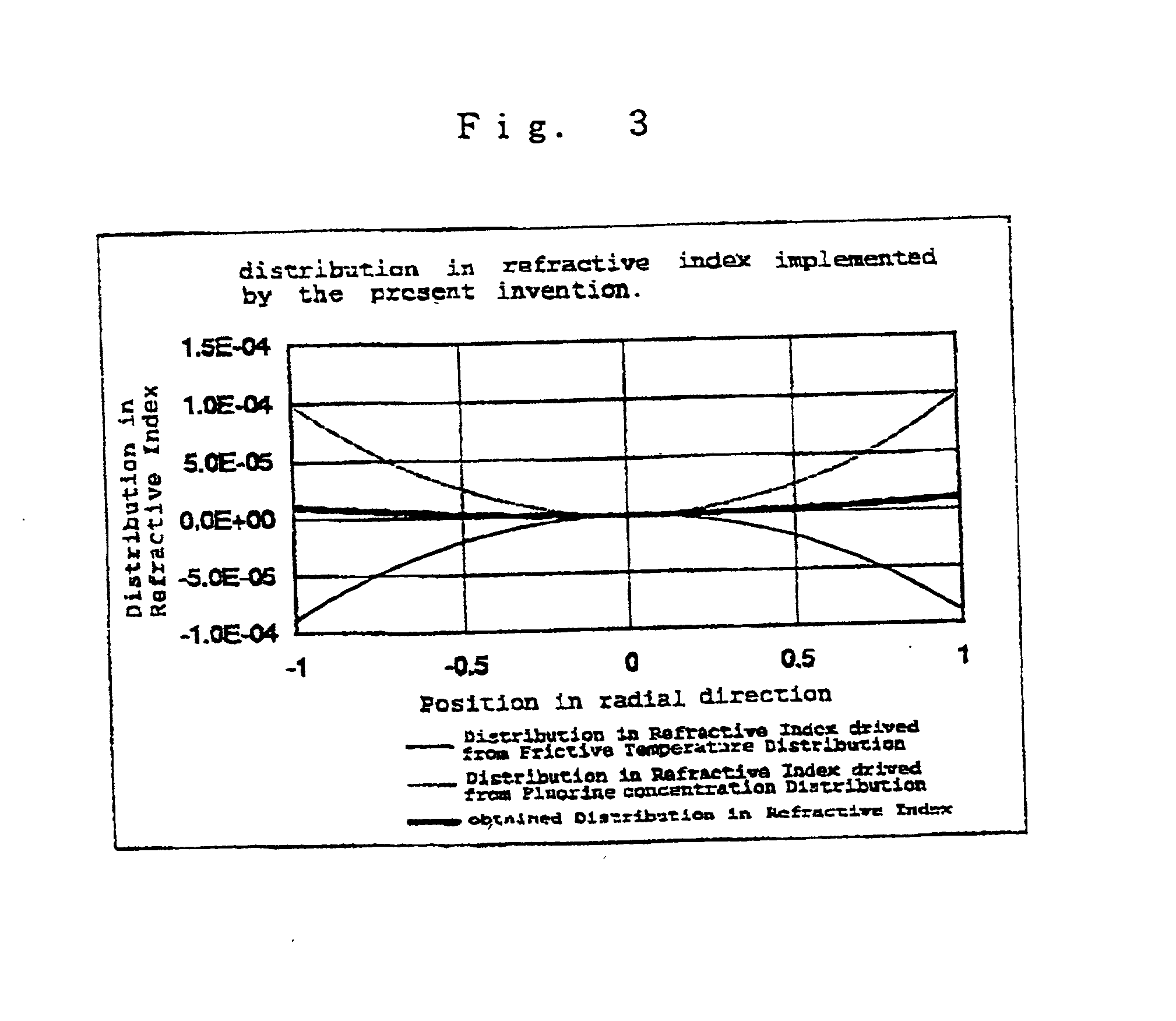
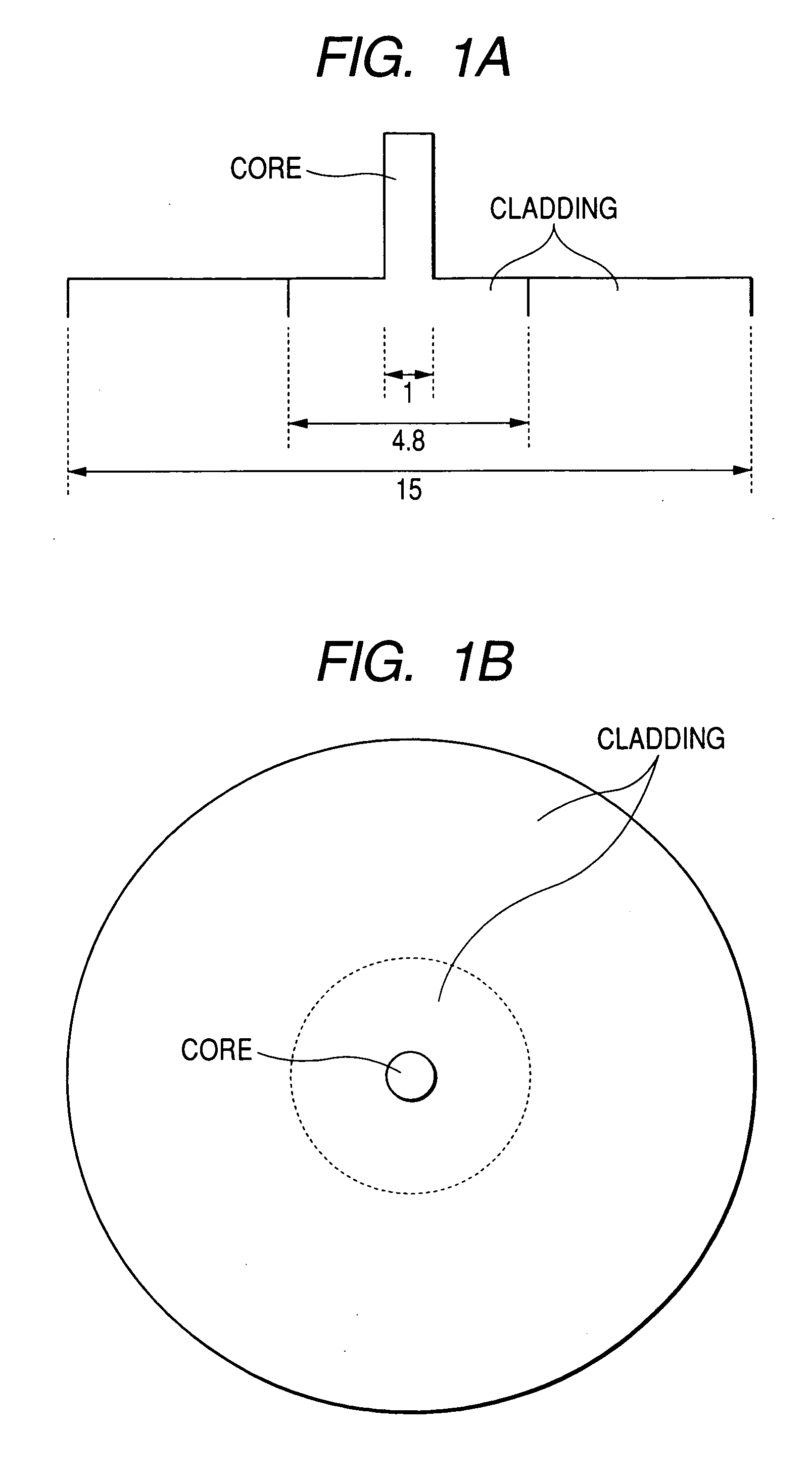
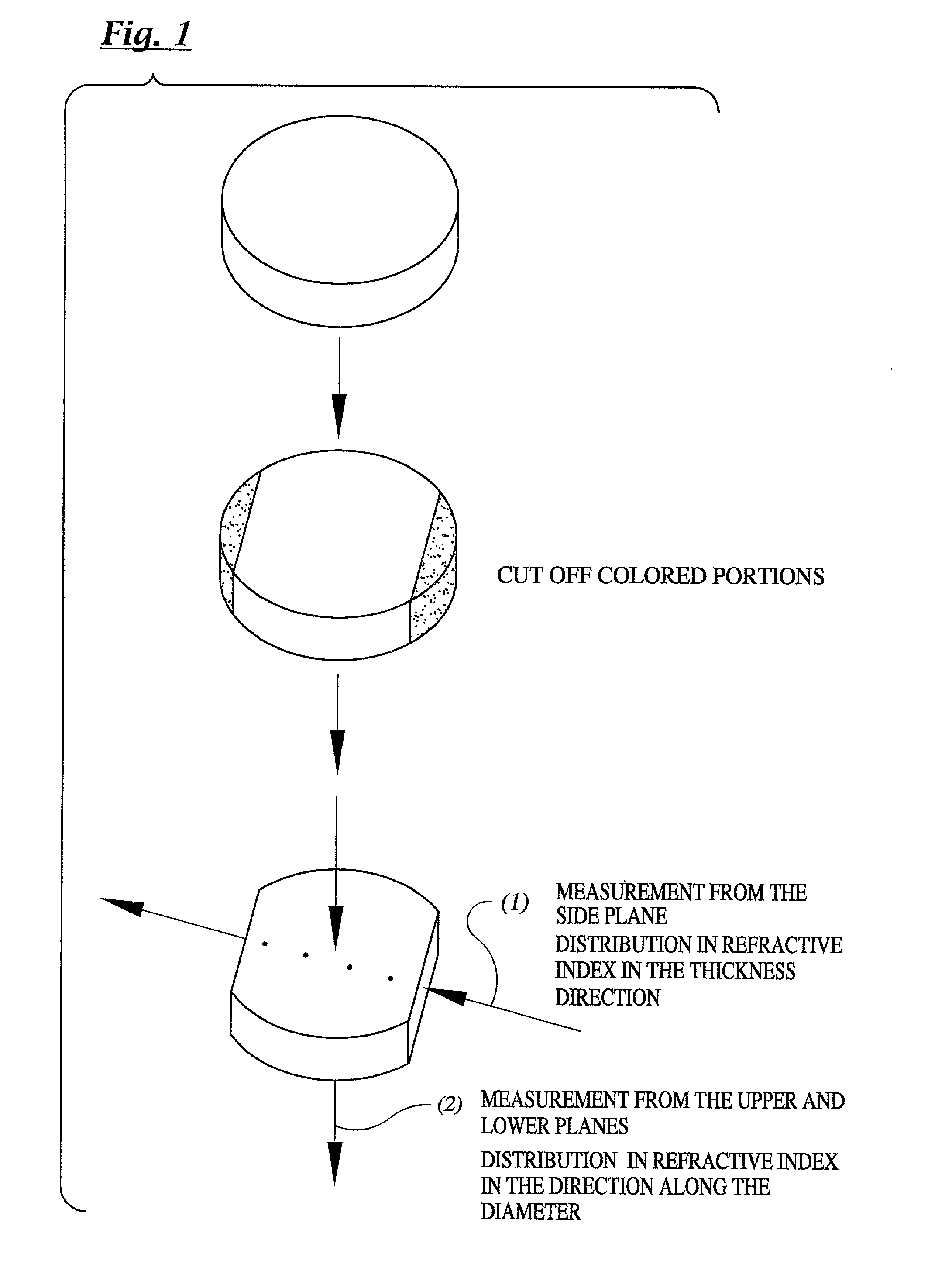
An object of the present invention is to provide a synthetic quartz glass optical material having a high optical transmittance for a radiation 157 nm in wavelength emitted from F2 excimer laser and a high resistance against irradiation of a F2 excimer laser radiation, yet having a uniformity suitable for such a fine patterning using a F2 excimer laser, and to provide an optical member using the same. The problems above are solved by a synthetic quartz glass optical material for F2 excimer lasers having an OH group concentration of 0.5 ppm or lower, a fluorine concentration of 0.1 to 2 mol %, a hydrogen molecule concentration of 5x1016 molecules / cm3 or lower, a difference between the maximum and minimum fluorine concentrations within 20 mol ppm, and a difference between the maximum and minimum refraction indices of 2x10-5 or lower.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS +1
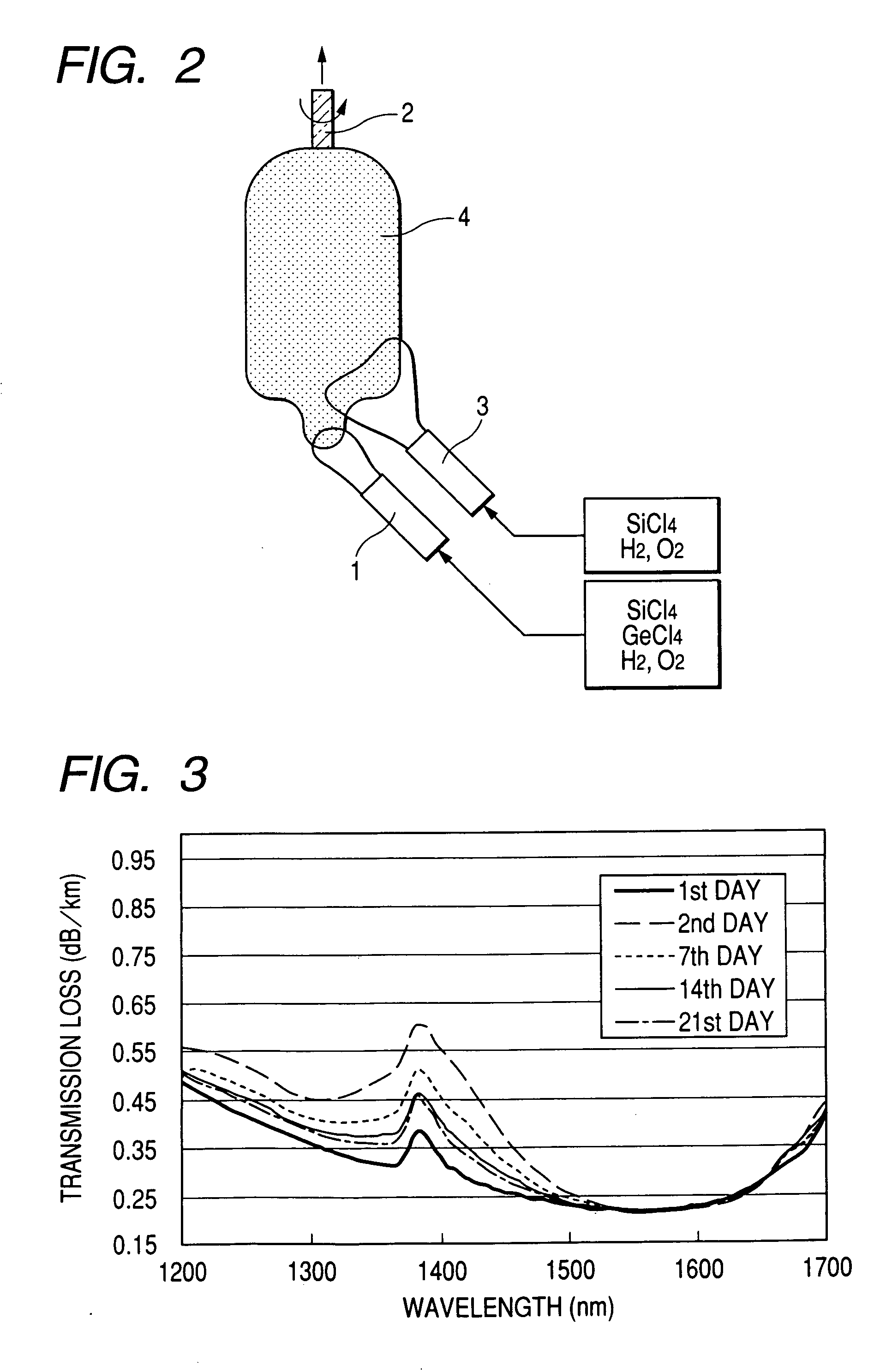
Optical fiber, evaluation and fabrication method thereof
ActiveUS20060013546A1Increase in electron spin densityGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreHydrogen moleculeVolumetric Mass Density
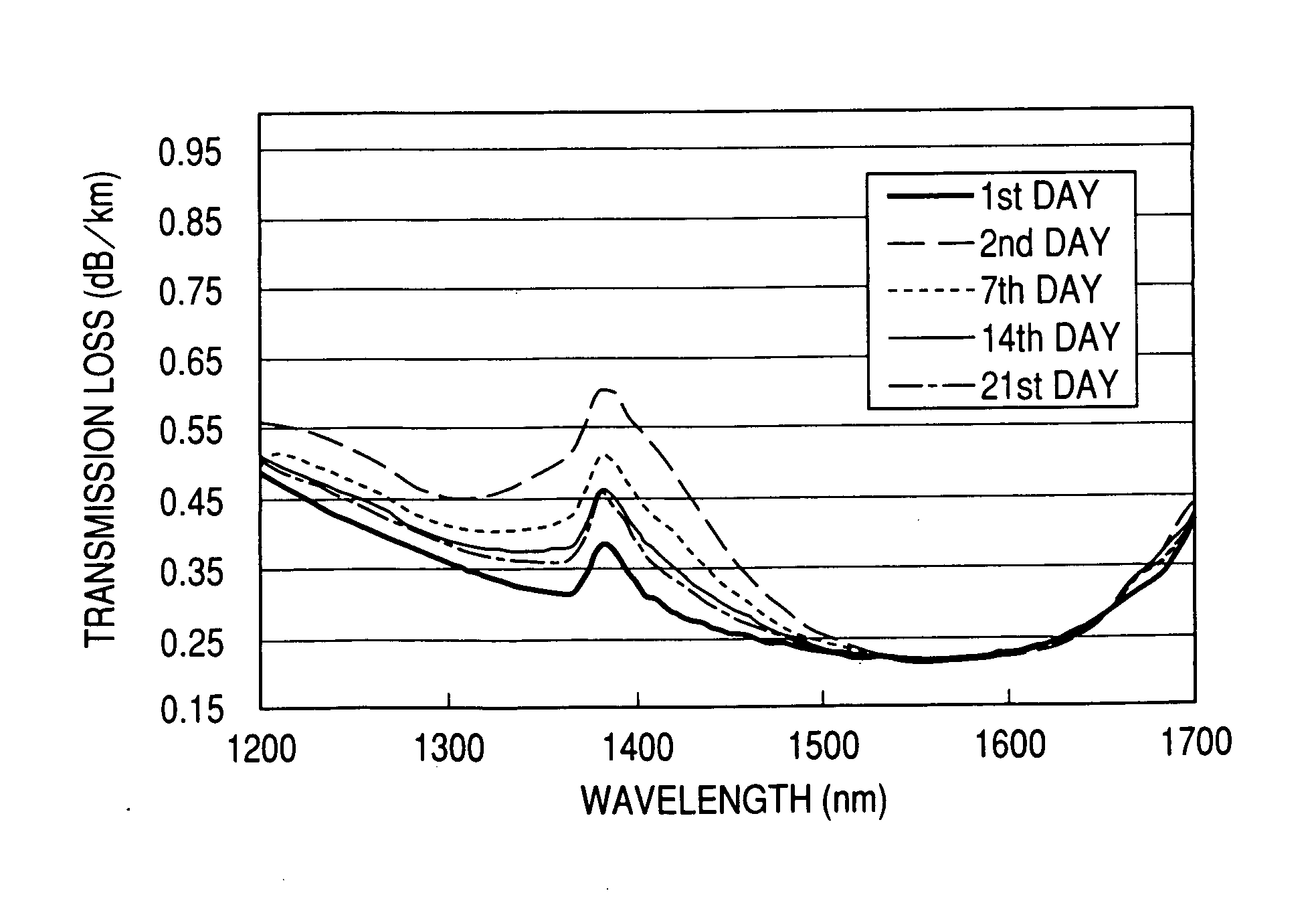
An optical fiber having a small increase in loss at a wavelength of approximately 1400 nm involved in a deuterium treatment is provided, and an evaluation method to decide whether an optical fiber is that having such a loss increase, and a fabrication method of an optical fiber having a small increase in such a loss are also provided. An optical fiber according to the present invention comprises a core composed of a silica glass doped with at least germanium and a cladding composed of a silica glass surrounding it. The optical fiber is exposed to an atmosphere containing hydrogen or deuterium to diffuse hydrogen molecules or deuterium molecules in the optical fiber, and after that, the outer periphery of the glass region of the optical fiber is etched to an outer diameter of 50 μm, and then the electron spin density of PORs is 1×1013 spins / g or less when the glass region is measured by the electron-spin resonance method.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Optical system for integrated circuit fabrication
InactiveUS6483639B2Reduce resistanceReduce contentOptical filtersPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLight energyLaser light
An optical system for integrated circuit fabrication comprises optical members made of synthetic quartz glass and fluorite, wherein: an optical member disposed in a position through which laser light is transmitted at a high light energy density, is made of single crystal fluorite; and an optical member in a position through which laser light is transmitted at a low light energy density, is made of synthetic quartz glass containing approximately such a hydrogen molecule concentration as can be doped under atmospheric pressure.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS +1
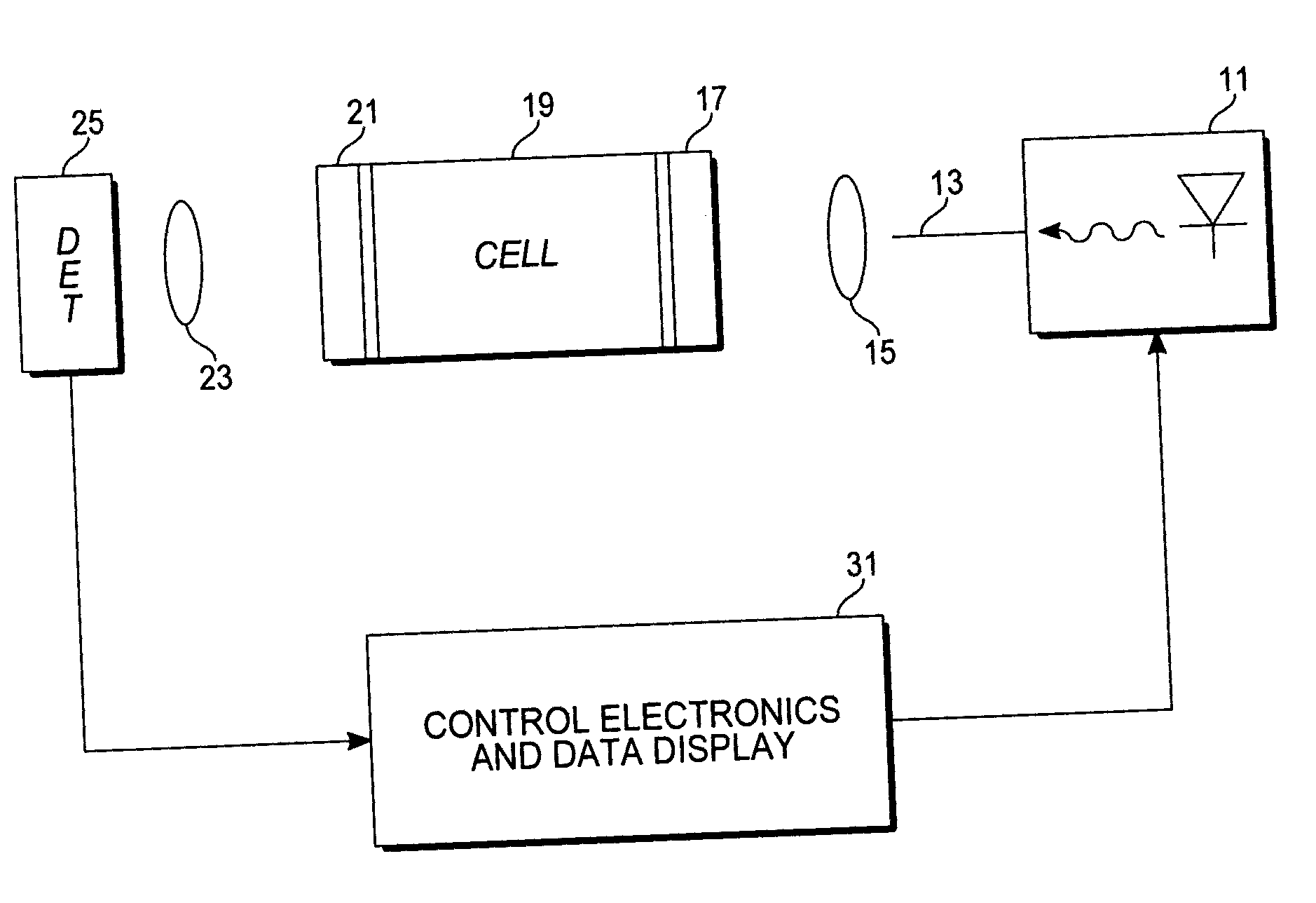
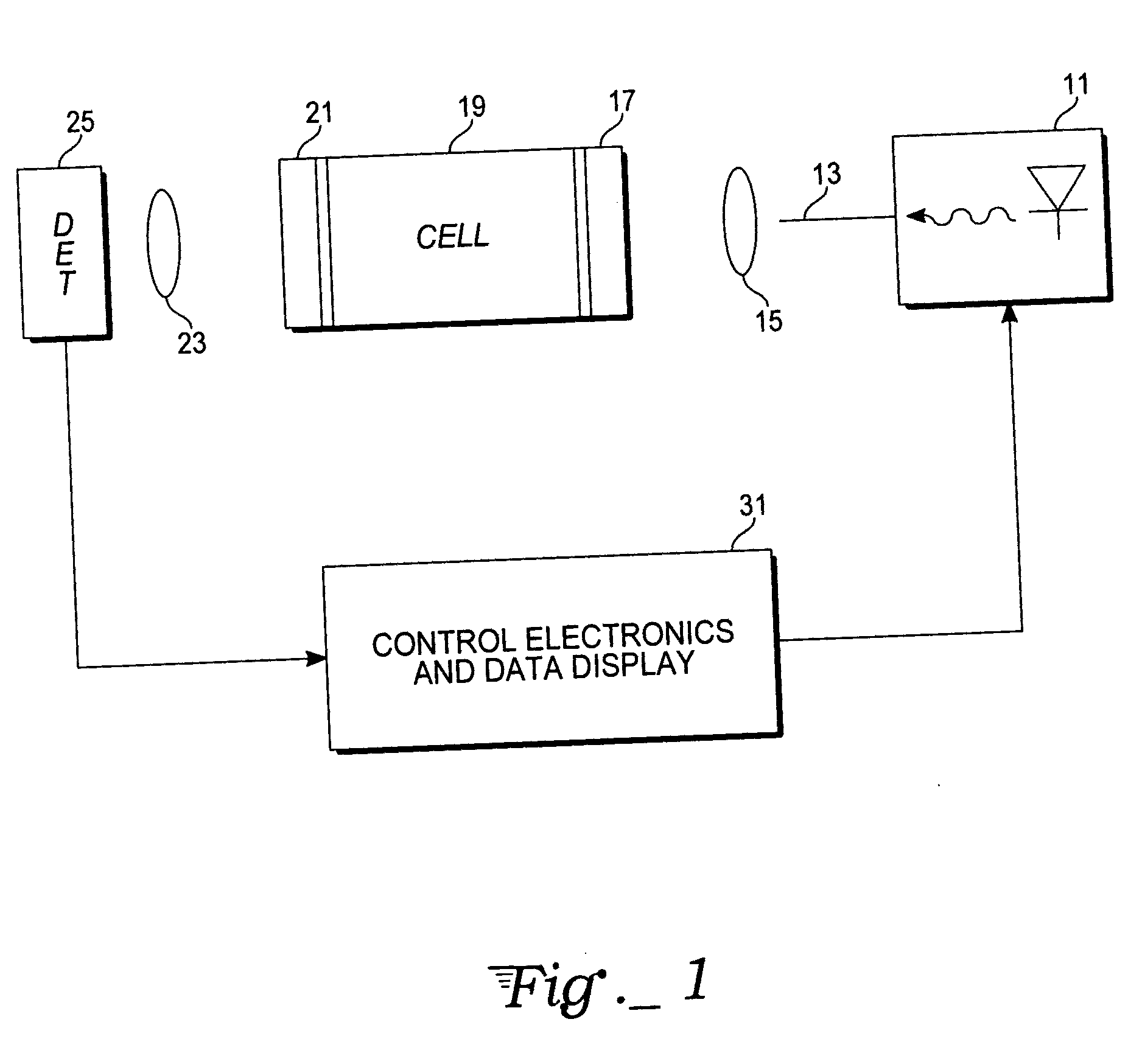
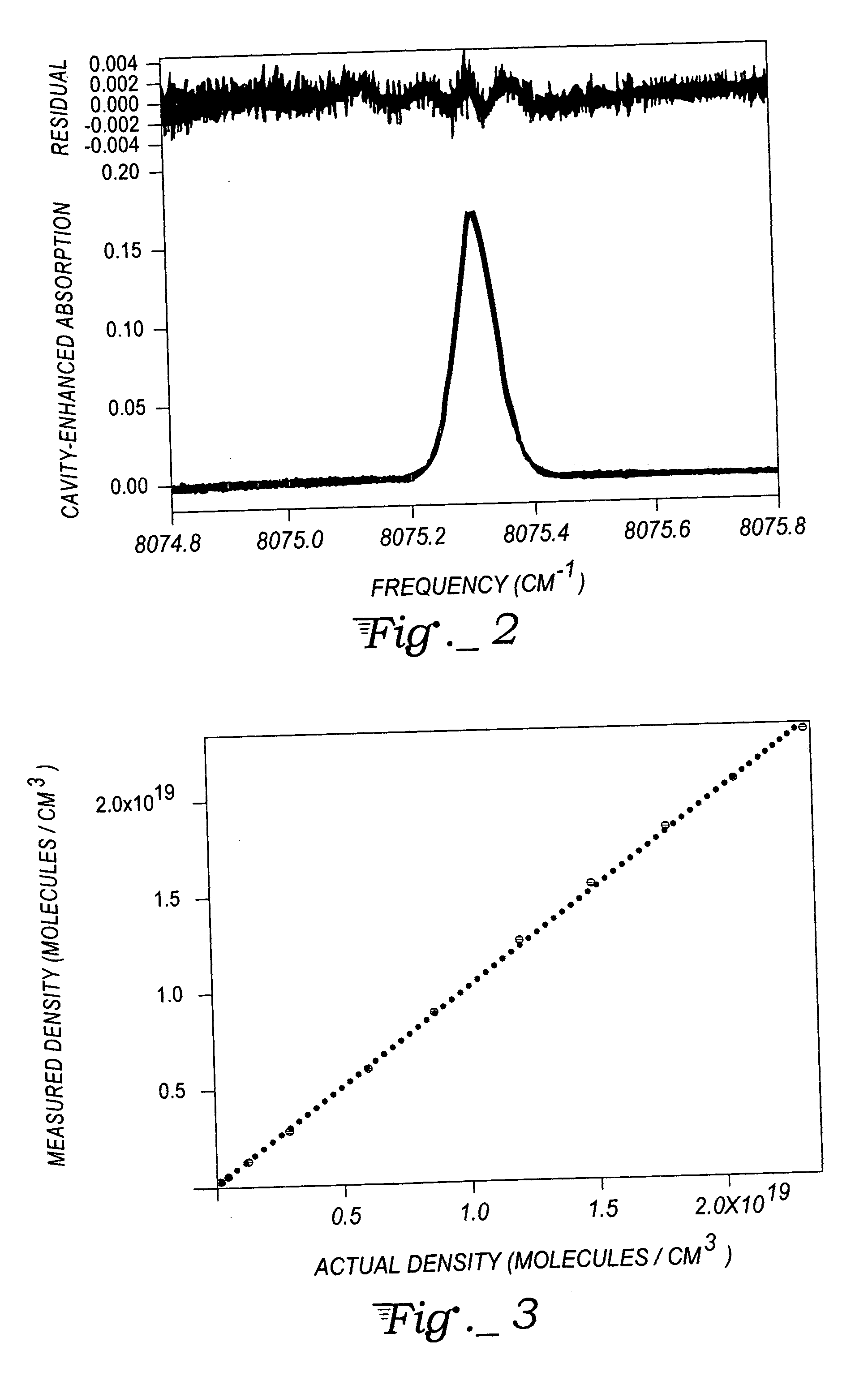
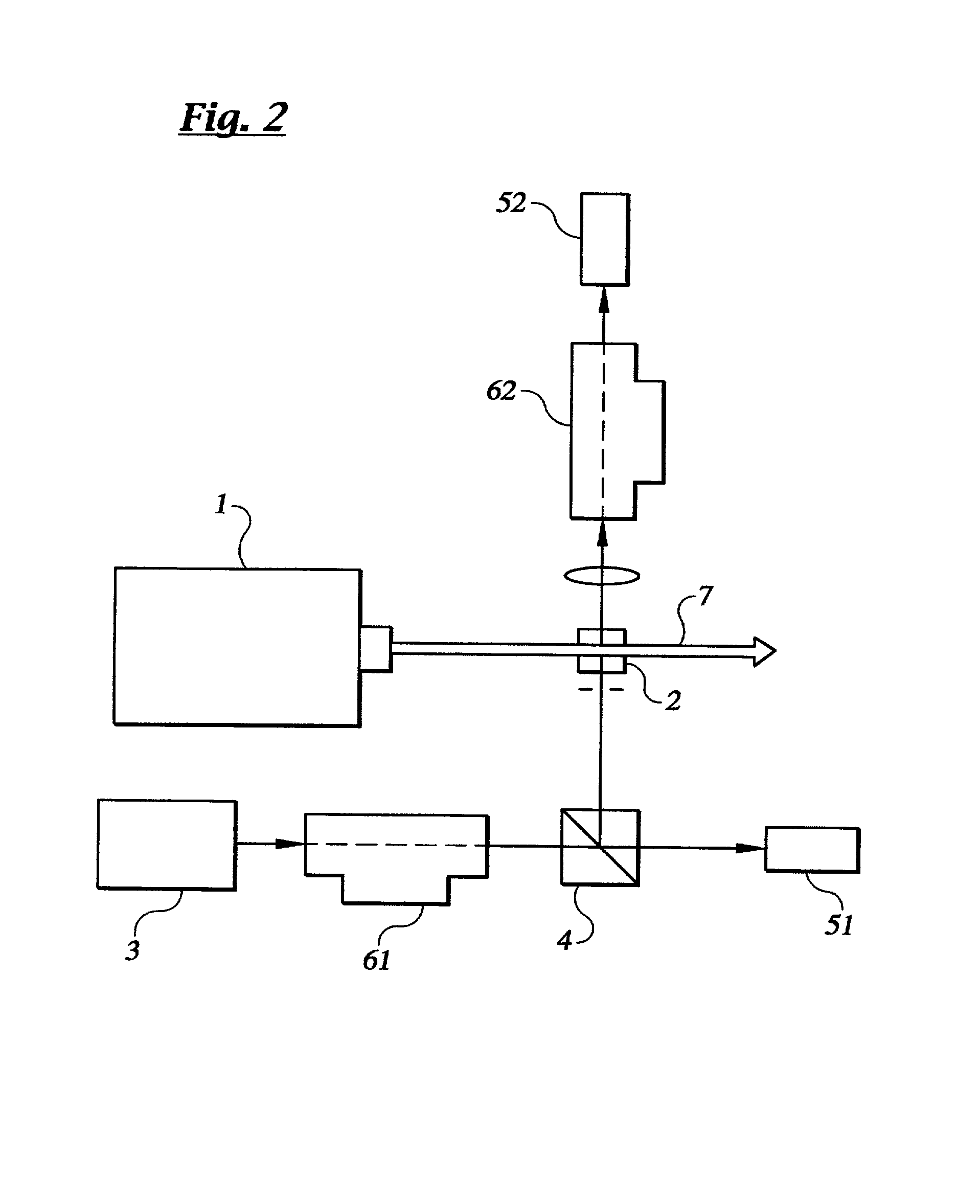
Hydrogen sensor based upon quadrupole absorption spectroscopy
ActiveUS20070076209A1Increasing effective path lengthIncrease the lengthRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryCavity resonanceHydrogen molecule
The disclosure describes an absorption spectroscopy method for sensing hydrogen gas in a sample atmosphere and an associated hydrogen sensor. A light beam, having a wavelength corresponding to a vibrational transition of hydrogen molecules from a ground vibration state to any excited rotational vibration state via a quadrupole interaction, is introduced into an optical cavity adapted to receive a sample atmosphere to be tested for the presence of hydrogen gas. The light is introduced into the cavity in an off-axis alignment to systematically eliminate cavity resonances, while preserving the absorption signal amplifying properties of such cavities. Hydrogen absorption is measured is terms of cavity output, as in the ICOS technique.
Owner:LOS GATOS RES
Method for producing synthetic quartz glass members for excimer lasers and synthetic quartz glass members for excimer laser optics produced by the same
InactiveUS20030027705A1Glass shaping apparatusPhotomechanical exposure apparatusHigh resistanceState of art
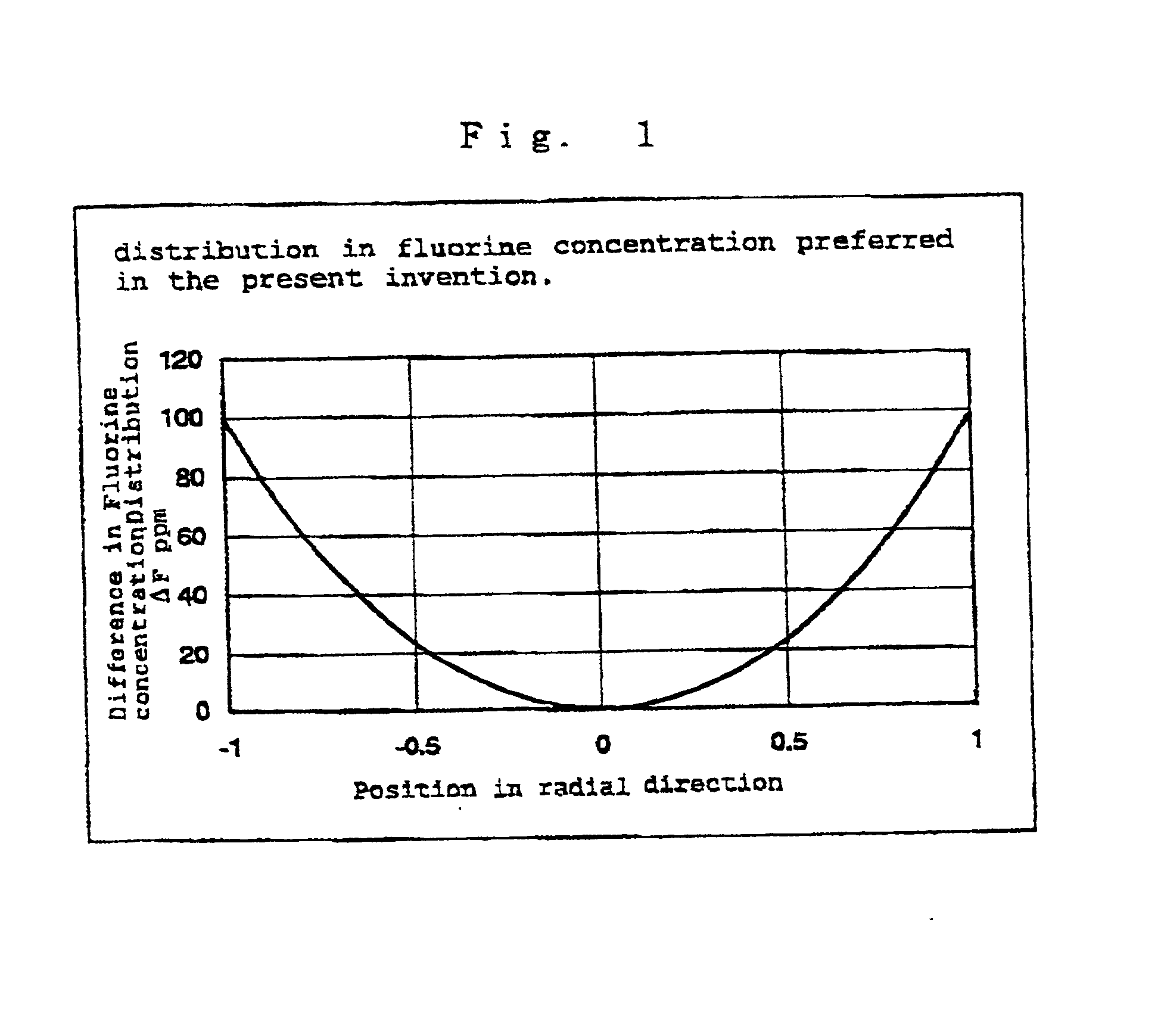
In the light of the disadvantages of the prior art technology, an object of the present invention is to provide a method for producing a synthetic quartz glass member for excimer lasers, which comprises, while suppressing the generation of reductive defects which impairs the resistance against laser radiations, incorporating a sufficient amount of hydrogen molecules capable of achieving a high resistance against laser radiation into the quartz glass, yet uniformly incorporating the hydrogen molecules to realize a flat distribution in refractive indices attributed to the distribution in the density of hydrogen molecules. It is also an object of the present invention to provide a synthetic quartz glass member for excimer lasers obtained by the production method above, which yields high resistance against laser radiations and homogeneity. The above problems have been overcome by a method for producing a synthetic quartz glass member for excimer lasers, which, in a method for producing a synthetic quartz glass member for excimer laser optics comprising a step of incorporating hydrogen molecules into a synthetic quartz glass body by heat treating the synthetic quartz glass body at a temperature of 600° C. or lower under an atmosphere in a pressure range of 1 atm or higher but lower than 150 atm and containing hydrogen, said method comprises varying the pressure of the gas containing hydrogen either continuously or stepwise in at least a part of the heat treatment.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS +1
Scavenger of in vivo harmful reactive oxygen species and/or free radicals
InactiveUS20090035383A1Reduce oxidative stressReduce harmBiocideSenses disorderScavengerOxidative stress
An object of the present invention is to provide a scavenger of in vivo harmful reactive oxygen species and / or free radicals, which is capable of effectively reducing the concentrations of in vivo reactive oxygen species and / or free radicals and exhibiting given effects such as the suppression of aging process, the prevention of geriatric or lifestyle-related disease, health promotion, and the inhibition of oxidative stress by virtue of this reduction in the concentrations of reactive oxygen species and / or free radicals. The scavenger of in vivo harmful reactive oxygen species and / or free radicals of the present invention comprises a liquid or gas comprising at least a hydrogen molecule. This medium may further comprise an oxygen molecule. Furthermore, this medium may comprise water or an aqueous solution or may be a gas. The scavenger of reactive oxygen species and / or free radicals can be used in the treatment or prevention of a disorder attributed to reactive oxygen species and / or free radicals.
Owner:OHTA SHIGEO +1
Diamond single crystal, method for producing the same, and single crystal diamond tool
ActiveUS20150176155A1High hardnessEasy to processPolycrystalline material growthLayered productsGas phaseTransmittance
A method for producing a diamond single crystal includes implanting an ion other than carbon into a surface of a diamond single crystal seed substrate and thereby decreasing the transmittance of light having a wavelength of 800 nm, the surface having an off-angle of 7 degrees or less with respect to a {100} plane, and homoepitaxially growing a diamond single crystal on the ion-implanted surface of the seed substrate using a chemical vapor synthesis under synthesis conditions where the ratio NC / NH of the number of carbon-containing molecules NC to the number of hydrogen molecules NH in a gas phase is 10% or more and 40% or less, the ratio NN / NC of the number of nitrogen molecules NN to the number of carbon-containing molecules NC in the gas phase is 0.1% or more and 10% or less, and the seed substrate temperature T is 850° C. or more and less than 1000° C.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Plasma resistant quartz glass jig
InactiveUS20020046992A1Less generationAdvantageously producedElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface roughnessHydrogen molecule
It is an object of the present invention to provide a quartz glass jig excellent in the plasma etching resistant characteristics, which does not generate an abnormal etching and particles when used for a plasma generating apparatus. The above Object is obtained by a plasma resistant quartz glass jig that is used for an apparatus of generating plasma, wherein the surface roughness Ra of the quartz glass surface is in a range of from 5 mum to 0.05 mum, the number of microcracks of the surface is not more than 500 microcracks / cm2, and the hydrogen molecule concentration in the quartz glass is at least 5x1016 molecules / cm3.
Owner:HERAEUS QUARZGLAS +1
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140001466A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove reliabilityElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor devicesThermal desorption spectroscopyNitrogen
In a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film, movement of hydrogen and nitrogen to the oxide semiconductor film is suppressed. Further, in a semiconductor device using a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film, a change in electrical characteristics is suppressed and reliability is improved. A transistor including an oxide semiconductor film and a nitride insulating film provided over the transistor are included, and an amount of hydrogen molecules released from the nitride insulating film by thermal desorption spectroscopy is less than 5×1021 molecules / cm3, preferably less than or equal to 3×1021 molecules / cm3, more preferably less than or equal to 1×1021 molecules / cm3, and an amount of ammonia molecules released from the nitride insulating film by thermal desorption spectroscopy is less than 1×1022 molecules / cm3, preferably less than or equal to 5×1021 molecules / cm3, more preferably less than or equal to 1×1021 molecules / cm3.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for improving surface wetting property of thin polymer film through surface grafting
The invention discloses a method for improving surface wetting property of a thin polymer film through surface grafting. The method comprises the following steps: (2) taking the thin polymer film, coating the surface with a layer of hydrophilic polymer material, and drying; (3) in the vacuum environment, bombarding the thin polymer film by using hydrogen molecules with kinetic energy, so as to obtain the thin polymer film with surface wetting property, wherein the polymer substrate is a hydrophilic high-molecular polymer. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: the reaction condition is mild; during the processes of polymer crosslinking and surface coating, polymer molecules are not degraded and damaged; the wetting property of the thin film can be effectively improved; the formed surface hydrophilic coating can stably exist, so that the problem of reduction of the wetting property is overcome; meanwhile, the original physical properties of the polymer film are reserved.
Owner:CHENGDU SCI & TECH DEV CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS +1
Method for manufacturing liquid tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and electrolyte preparation thereof
The invention provides a method for manufacturing liquid tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and electrolyte preparation thereof. On the basis of the prior production process, additives are added to working electrolyte in a process of manufacturing liquid tantalum electrolytic capacitors so as to reduce hydrogen atoms or hydrogen molecules produced by H+ on the inner wall of a silver shell and increase the thickness of electric double layers. The electrolyte is shake-soluble working electrolyte, and consists of high-purity silica sol aqueous solution, concentrated sulfuric acid, sulfate, and hydrated chloroplatinic acid. A preparation method for the electrolyte comprises: taking 28 to 35 portions of silica sol, 9 to 12 portions of concentrated sulfuric acid, platinum aqueous solution accounting for 0.1 to 2 percent of the total weight of the electrolyte and 0.1 to 1.5 percent of sulfate according to volume ratio; preparing platinum acid into 8 to 10 percent aqueous solution; adding the platinum acid and the sulfate to the silica sol pro rata and mixing the three well; and adding corresponding proportion of concentrated sulfuric acid, mixing well and obtaining the working electrolyte.
Owner:ZHUZHOU RIWANG ELECTRONICS TECH
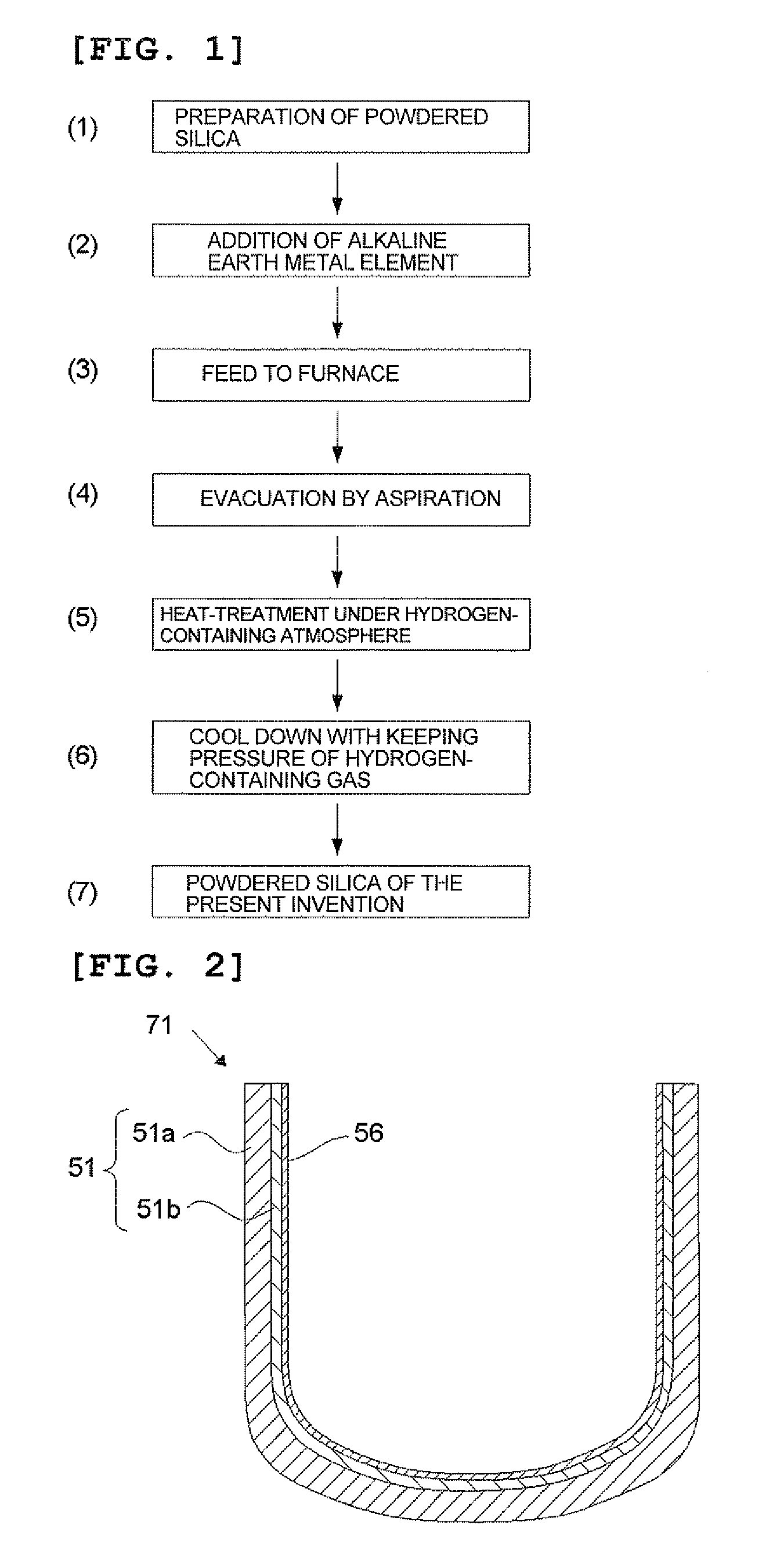
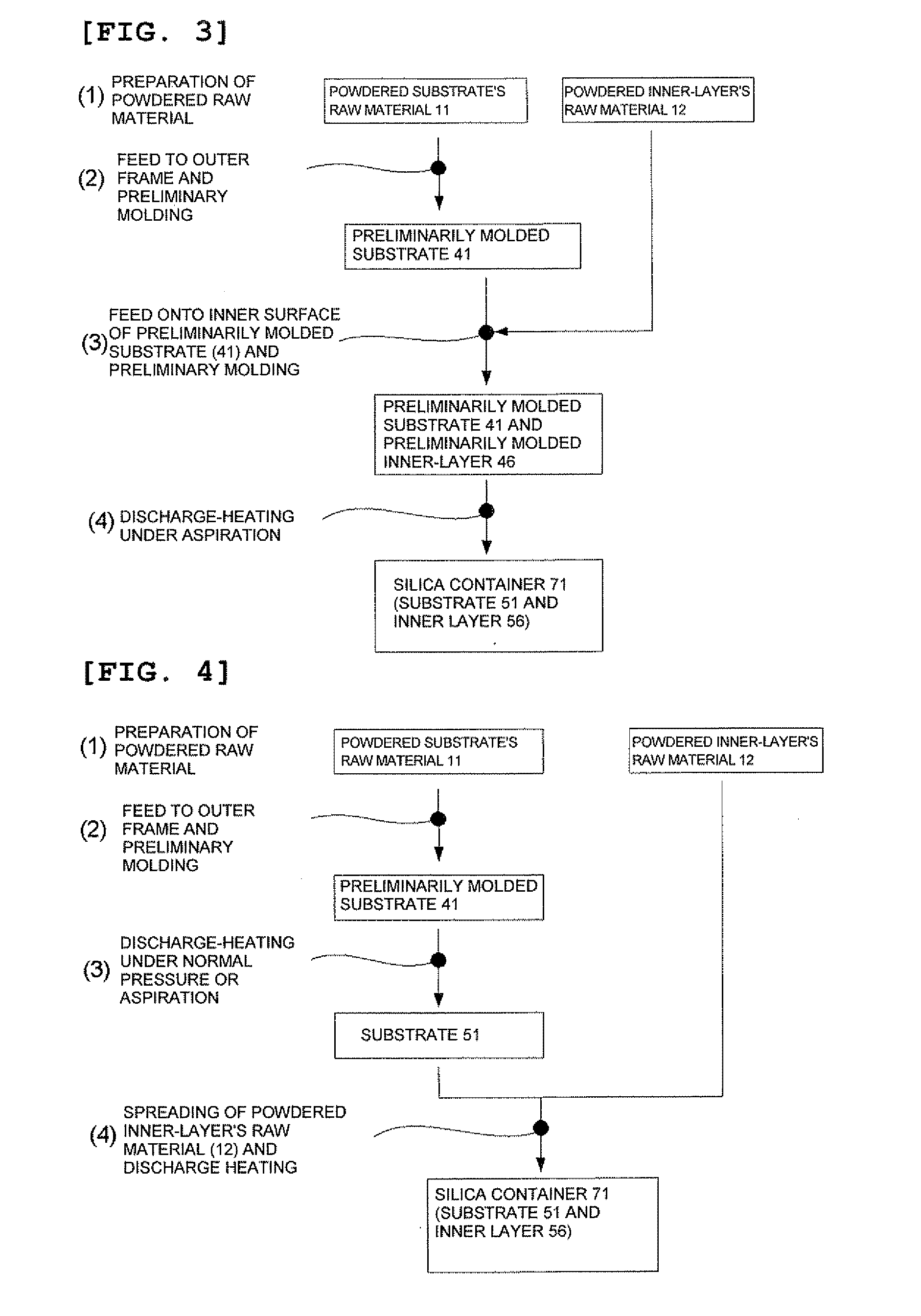
Powdered silica, silica container, and method for producing them
InactiveUS20110256330A1Increased durabilitySuppress generationSilicaBy pulling from meltHydrogen moleculeSilicon dioxide
A method is provided for producing a silica container arranged with a substrate, having a rotational symmetry, comprised of mainly a silica, and containing gaseous bubbles at least in its peripheral part, and an inner layer, formed on an inner surface of the substrate and comprised of a transparent silica glass; wherein a powdered silica, having particle diameter of 10 to 1000 μm, containing Ca, Sr, and Ba with the total concentration of 50 to 5000 ppm by weight, and releasing hydrogen molecules with the amount of 3×1016 to 3×1019 molecules / g upon heating at 1000° C. under vacuum, is prepared at least as a powdered raw material for forming the inner layer, and then the inner layer is formed from the powdered silica as the powdered raw material for forming the inner layer.
Owner:SHIN ETABU QUARTZ PRODS
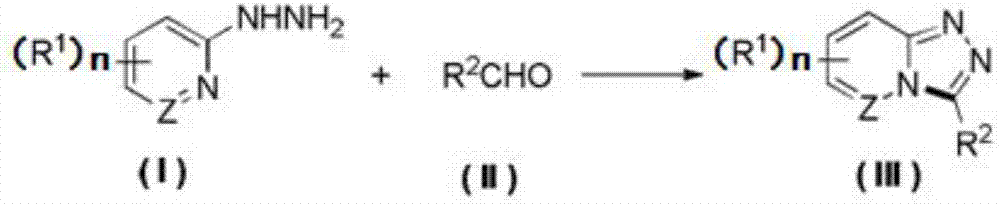
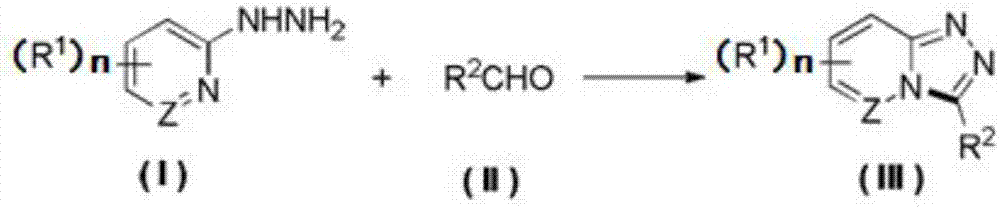
Synthesis method of 1,2,4-triazolohetercyclic compound
ActiveCN107474047AHigh yieldSimple reaction systemOrganic chemistryElectrolysis componentsSynthesis methodsHydrogen molecule
The invention provides a method for synthesizing a 1,2,4-triazolohetercyclic compound. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a 2-hydrazinohetercyclic compound (I) and an aldehyde compound (II) into acetonitrile A; stirring at 25 DEG C to 80 DEG C and reacting for 1h to 8h; then adding tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate, acetonitrile B and water; taking a graphite carbon rod as an anode and a platinum sheet as a cathode; switching on a power supply and electrifying for 3h to 8h, wherein the current strength is 15mA / mmol to 30mA / mmol according to the amount of substance of the aldehyde compound (II); carrying out post-treatment on a reaction solution to obtain the product 1,2,4-triazolohetercyclic ring compound (III). The method has the advantages of simple reaction system, easiness for obtaining raw materials and high total yield; the 2-hydrazinohetercyclic compound and the aldehyde compound are subjected to electrochemical catalysis to obtain the 1,2,4-triazolohetercyclic compound in one step; only one water molecule and one hydrogen molecule are removed and the atomic economy is extremely high; the formula is shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
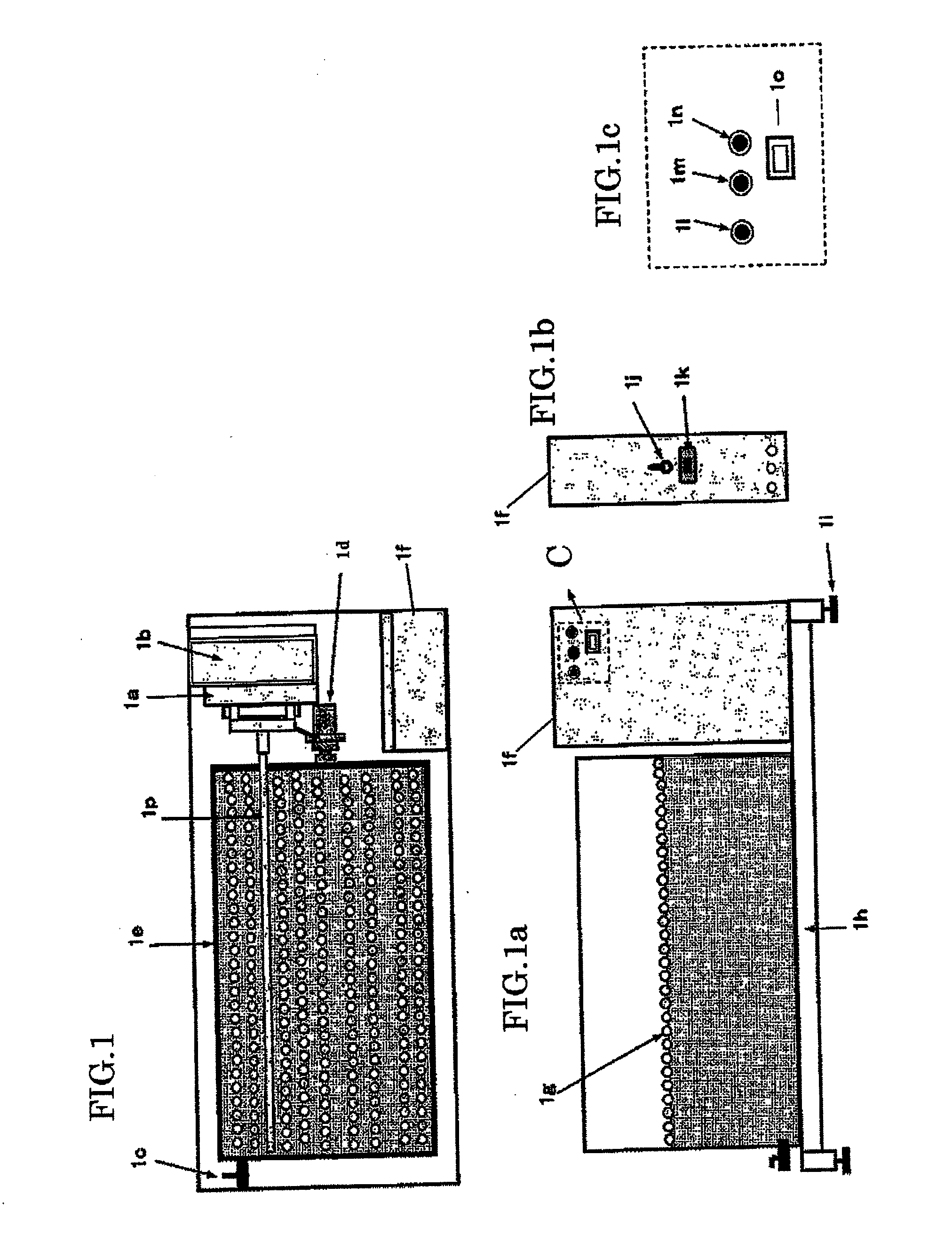
Microwave drive cesium-free negative hydrogen ion source
InactiveCN103956314AHighly innovativeSimple structureElectric discharge tubesHigh energyHydrogen molecule
The invention provides a negative hydrogen ion source, in particular to a high-current microwave drive cesium-free negative hydrogen (H-) ion source of a 2.45 GHz microwave drive and full permanent magnet structure. Plasma is generated through 2.45 GHz microwaves. Ion source magnetic fields are all generated through permanent magnets. An H- generating region is of a shoulder structure made of tantalum, and small-aperture and lateral deflection magnetic fields are adopted in the H- generating region. A large number of excited state hydrogen molecules (H2*) are generated through discharge of the 2.45 GHz microwaves, high-energy electrons cannot enter the H- generating region through the proper lateral magnetic fields, and passed low-energy electrons generate H- in the H- generating region through interaction with H2*. The probability that H- is generated on the surface of the H- generating region through the shoulder structure made of tantalum is increased. The aperture of the H- generating region is small, it is avoided that the microwaves heat the electrons in the region, the lateral magnetic fields of the region deflect to lead out the electrons in beam current, and then H- ion beam current with high current intensity and low electron proportion is finally acquired. The negative hydrogen ion source is mainly used for providing negative hydrogen ions for an accelerator.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Hydrogen-rich water generating device
PendingCN107459203AIncrease surface tensionEscape is slowWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsElectrolysisHydrogen molecule
The invention relates to the technical field of domestic water treatment and particularly relates to a hydrogen-rich water generating device. The device comprises a purifying system, a mineralizing activating system, a magnetizing system, a hydrogen water electrolysis system and a hydrogen dissolving system which are connected with each other in turn; the hydrogen dissolving system comprises an ultrasonic gas explosion hole fuser; a plurality of 35K60W transduction vibrators are arranged at the bottom of the tank body of the ultrasonic gas explosion hole fuser; an ultrasonic generator is arranged at the top; the ultrasonic frequency is 38KHz-45KHz; the hydrogen dissolving system further comprises an electric field treatment water storage device; the electric field treatment water storage device comprises a metal tank, a pole plate and a high voltage power supply. The device is capable of generating the hydrogen-rich water in the manner of purifying, mineralizing, activating, magnetizing and electrolyzing water; an acoustic hole technique is adopted for achieving the saturated dissolved hydrogen concentration in water; the speed of the hydrogen molecule for escaping to the outside air is reduced under the effect of high voltage electric field to the hydrogen-rich water; the long-term storage of the hydrogen-rich water under a natural sealing condition is realized.
Owner:临汾市康宜派饮品有限公司
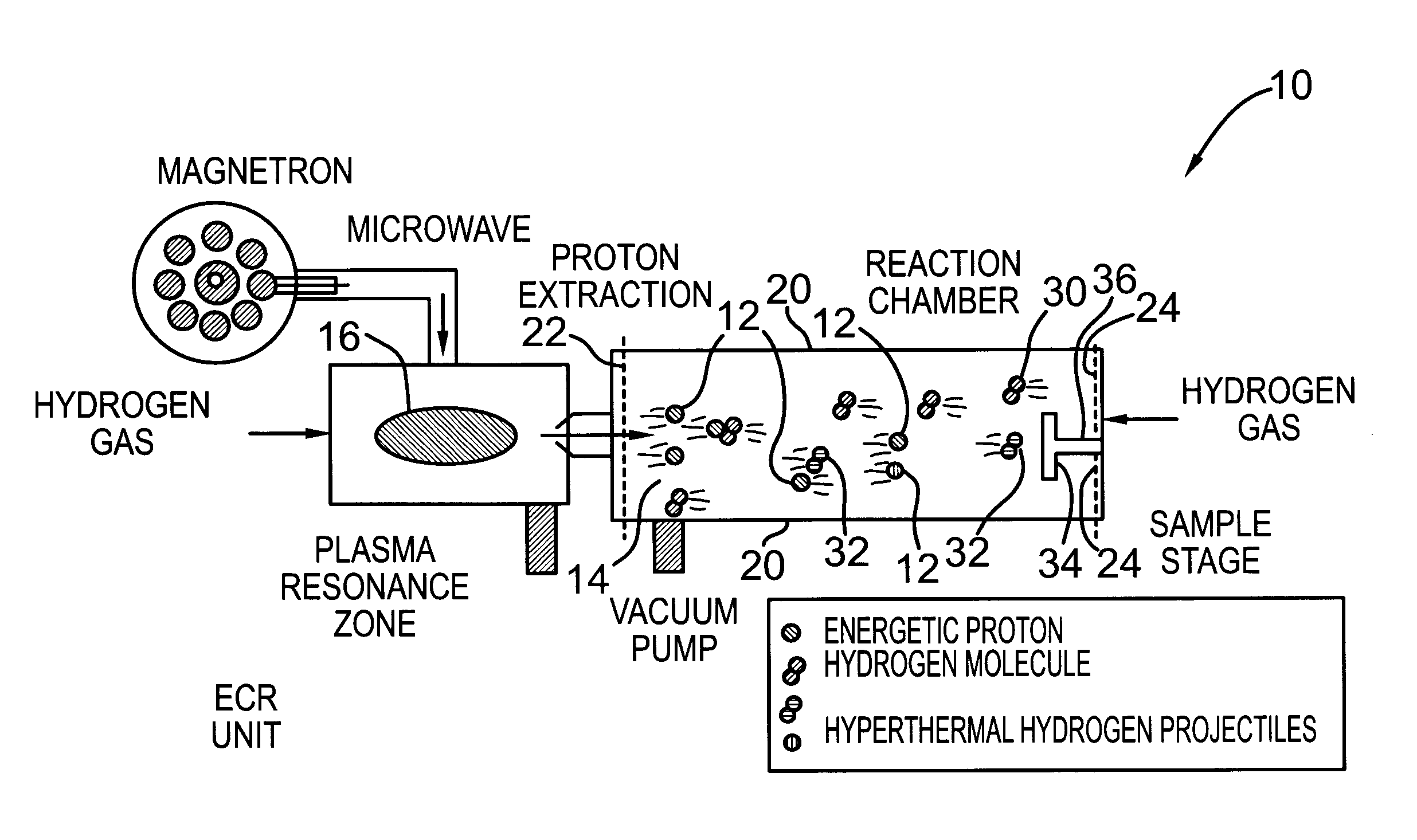
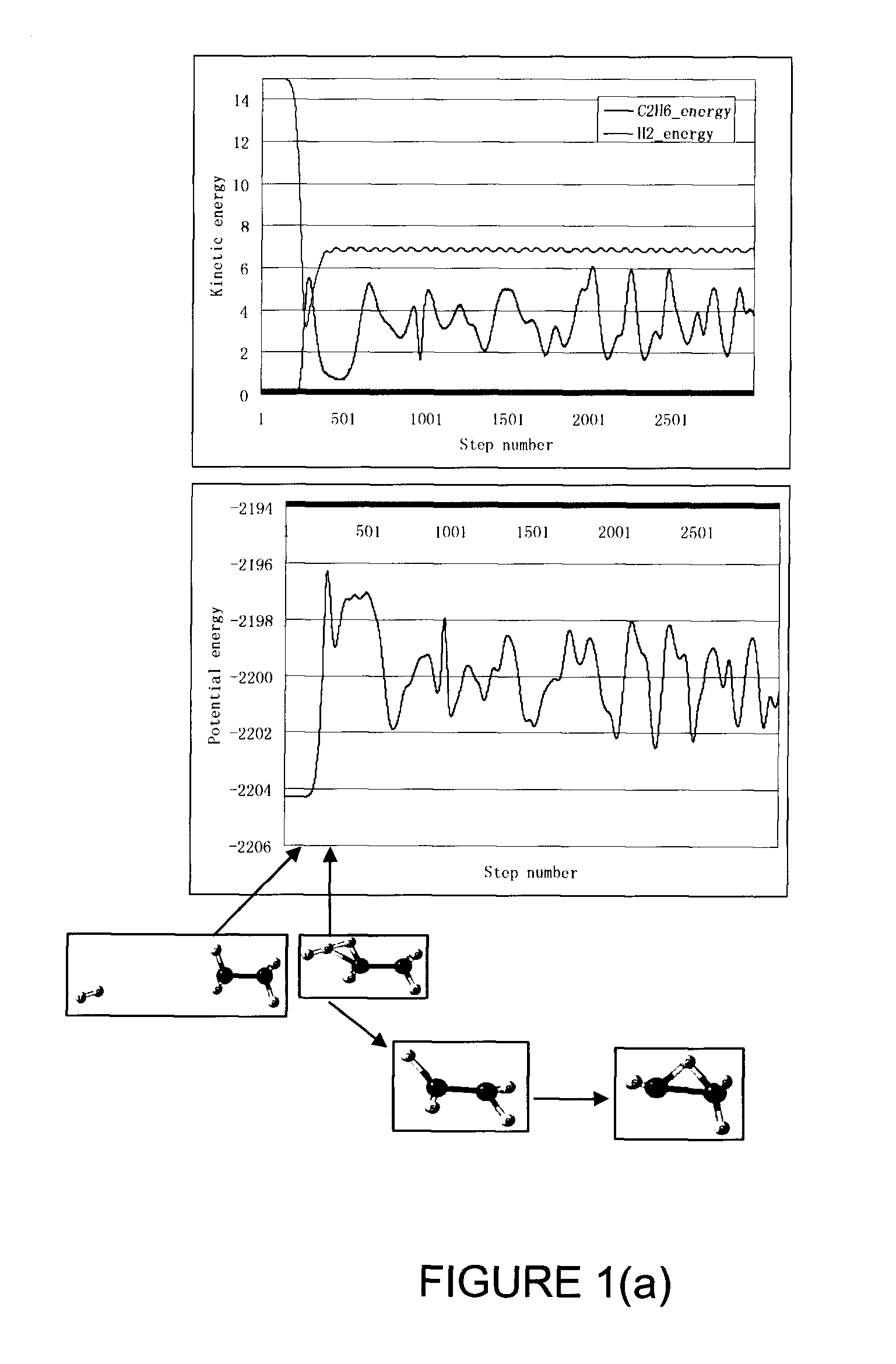
METHOD FOR PRODUCING HYPERTHERMAL HYDROGEN MOLECULES AND USING SAME FOR SELECTIVELY BREAKING C-H AND/OR Si-H BONDS OF MOLECULES AT OR ON SUBSTRATE SURFACES
ActiveUS20120061558A1Easy to controlAccurate Mechanical PropertiesLaser detailsElectrolysis componentsCross-linkGas phase
A method for producing hyperthermal molecular hydrogen is disclosed and use of same for selectively breaking C—H or Si—H bonds without breaking other bonds are disclosed. A hydrogen plasma is maintained and protons are extracted with an electric field to accelerate them to an appropriate kinetic energy. The protons enter into a drift zone to collide with molecular hydrogen in gas phase. The cascades of collisions produce a high flux of hyperthermal molecular hydrogen with a flux many times larger than the flux of protons extracted from the hydrogen plasma. The nominal flux ratio of hyperthermal molecular hydrogen to proton is controlled by the hydrogen pressure in the drift zone, and by the length of the drift zone. The extraction energy of the protons is shared by these hyperthermal molecules so that average energy of the hyperthermal molecular hydrogen is controlled by extraction energy of the protons and the nominal flux ratio. Since the hyperthermal molecular hydrogen projectiles do not carry any electrical charge, the flux of hyperthermal hydrogen can be used to engineer surface modification of both electrical insulating products and conductive products. When this method of generating a high flux of hyperthermal molecular hydrogen is applied to bombard organic precursor molecules (or silicone, or silane molecules) with desirable chemical functionality / functionalities on a substrate, the C—H or Si—H bonds are thus cleaved preferentially due to the kinematic selectivity of energy deposition from the hyperthermal hydrogen projectiles to the hydrogen atoms in the precursor molecules. The induced cross-linking reactions produce a stable molecular layer having a controllable degree of cross-linking and retaining the desirable chemical functionality / functionalities of the precursor molecules.
Owner:FOSHAN QIAOLUAN TECH CO LTD
Preparation process of hydrogen-rich water
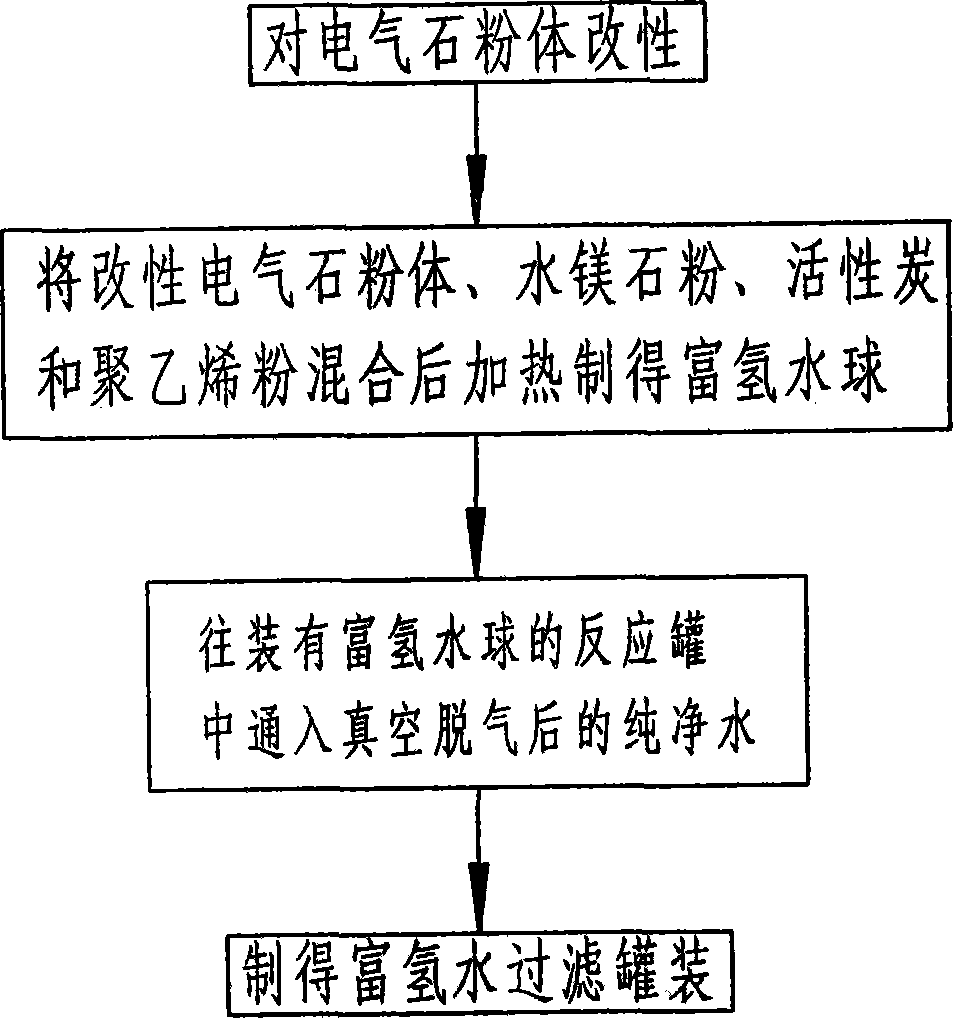
InactiveCN103910450ABalance pHStrong reductionMultistage water/sewage treatmentAlkalinityHydrogen content
The invention relates to a preparation process of hydrogen-rich water. The preparation process comprises the following steps of modifying tourmaline powder, mixing the modified tourmaline powder with brucite powder, active carbon and polyethylene powder, which are directly bought from the market to prepare a hydrogen-rich water mixture, heating the hydrogen-rich water mixture to prepare a hydrogen-rich water ball, placing the hydrogen-rich water ball into a closed reaction tank, introducing the degassed pure water into the reaction tank, stirring the degassed pure water and the hydrogen-rich water ball to prepare the hydrogen-rich water, and filtering and filling the hydrogen-rich water. The hydrogen molecule content in the processed water is 20 times that in ordinary weak alkaline ion water, the capacity for eliminating the acid substances in the human body can be improved by 20 times, the high hydrogen content, weak alkalinity, negative potential and small-molecular water are integrated, the acidity and alkalinity of the human body can be balanced, and different diseases can be effectively prevented.
Owner:张冬营 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com