Patents
Literature
448 results about "Current strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Current intensity. noun. variants: or current strength. : the magnitude of an electric current as measured by the quantity of electricity crossing a specified area of equipotential surface per unit time.
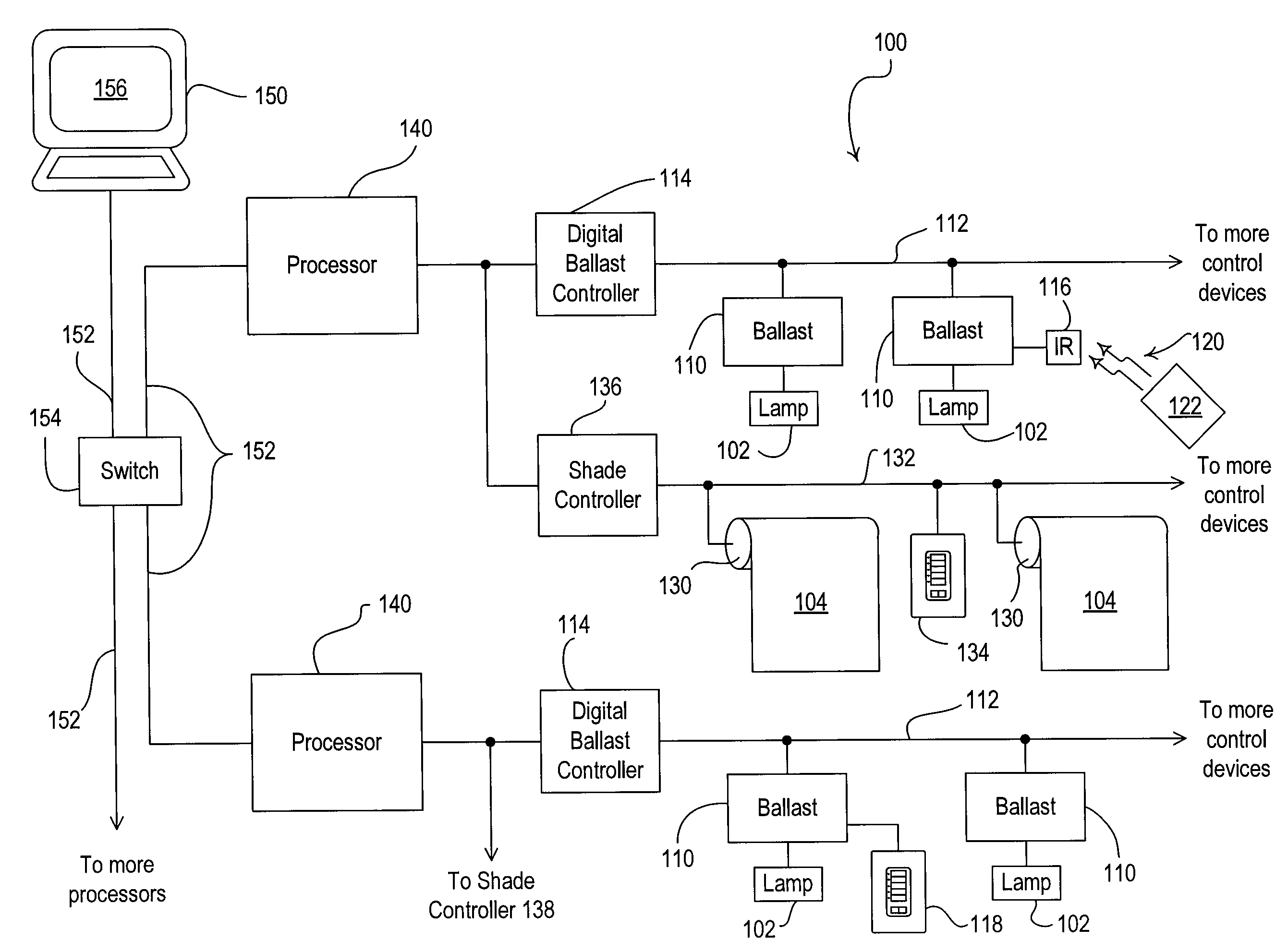
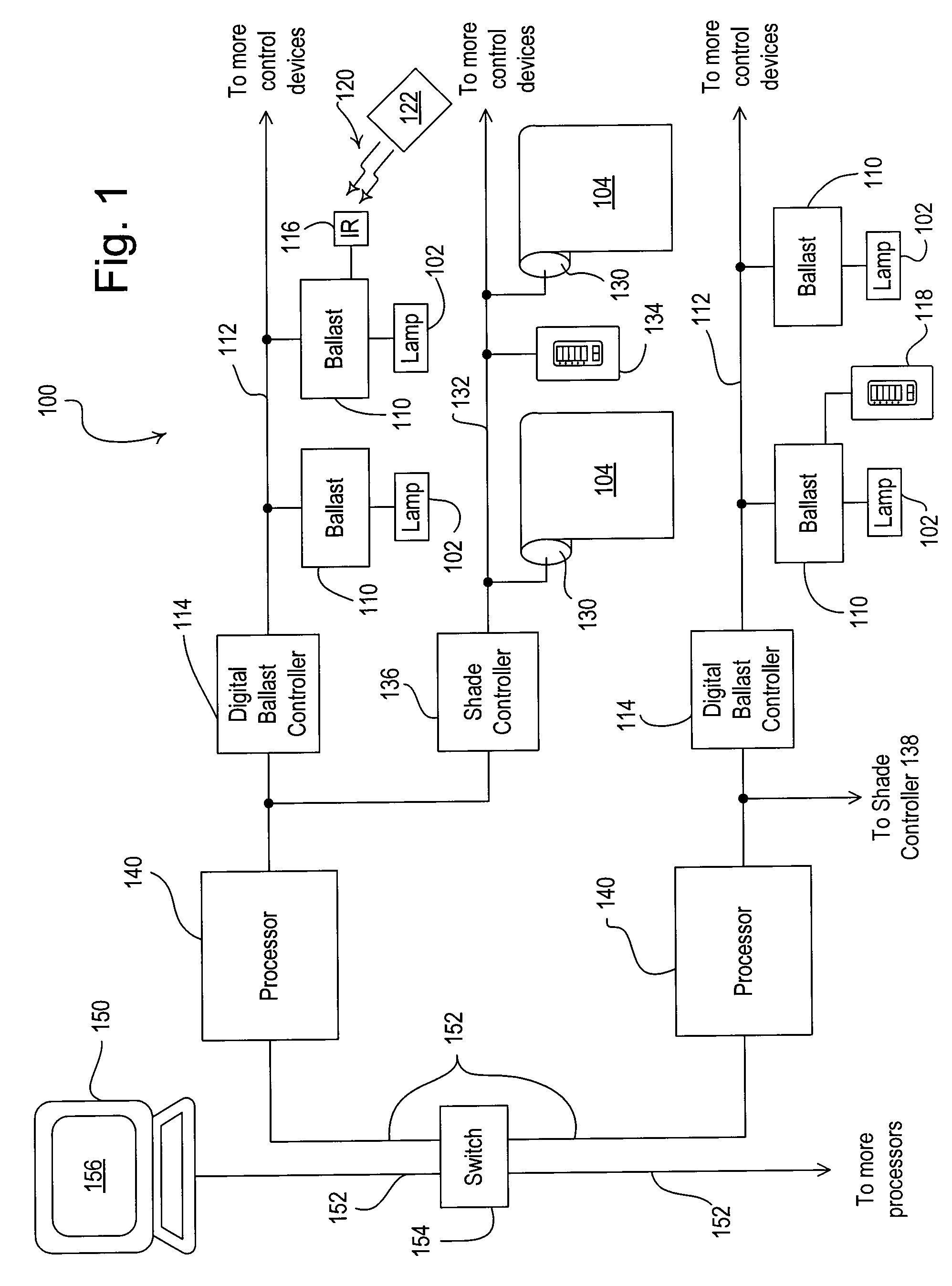
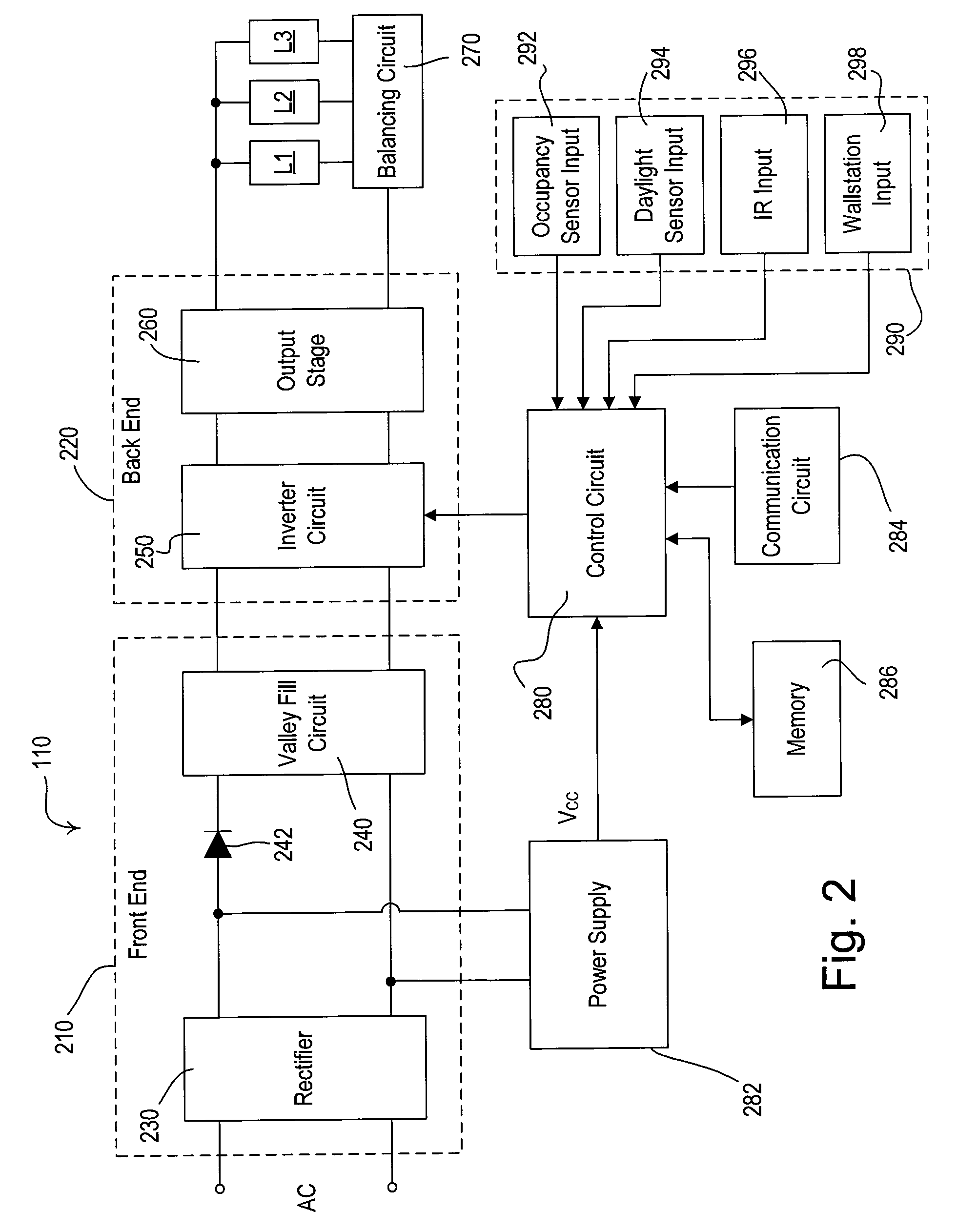
Method of load shedding to reduce the total power consumption of a load control system
InactiveUS20080088180A1Reducing value of setpointReduce the amount of powerDc network circuit arrangementsPower network operation systems integrationEngineeringWattmeter
A lighting control system is operable to control the amount of power delivered to a plurality of electrical loads. The lighting control system includes load control devices (such as digital electronic dimming ballasts), motorized window treatments, controllers, processors, and personal computers. The personal computer is preferably executing a graphical user interface (GUI) software, which allows a user to configure and monitor the operation of the lighting control system. The lighting control system offers a load shedding functionality without using power meters. Each load control device transmits its current intensity level to the personal computer, which is operable to determine a total power consumption of the lighting control system. If the total power consumption exceeds a predetermined power threshold, the personal computer causes the load control devices to shed loads.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
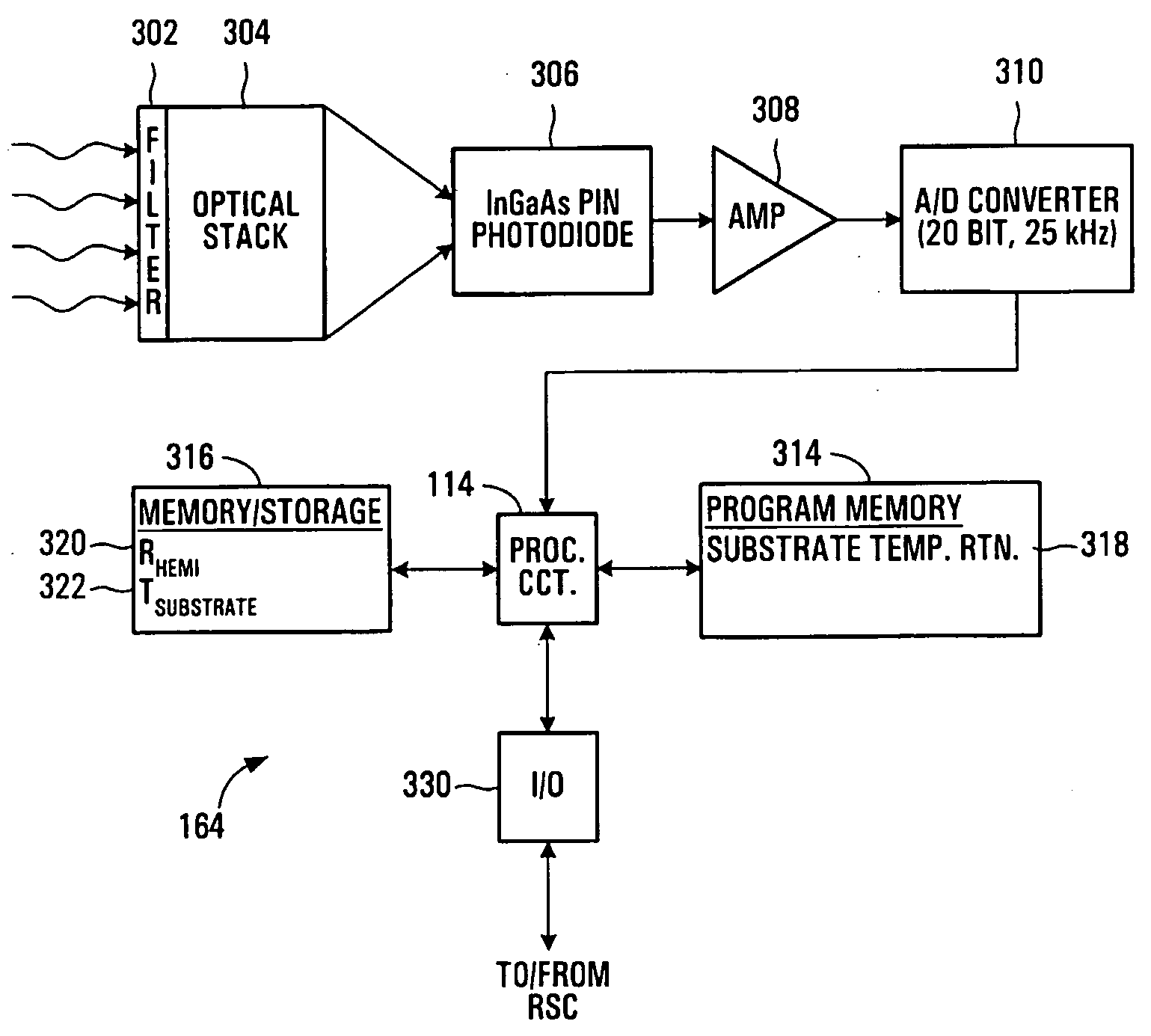
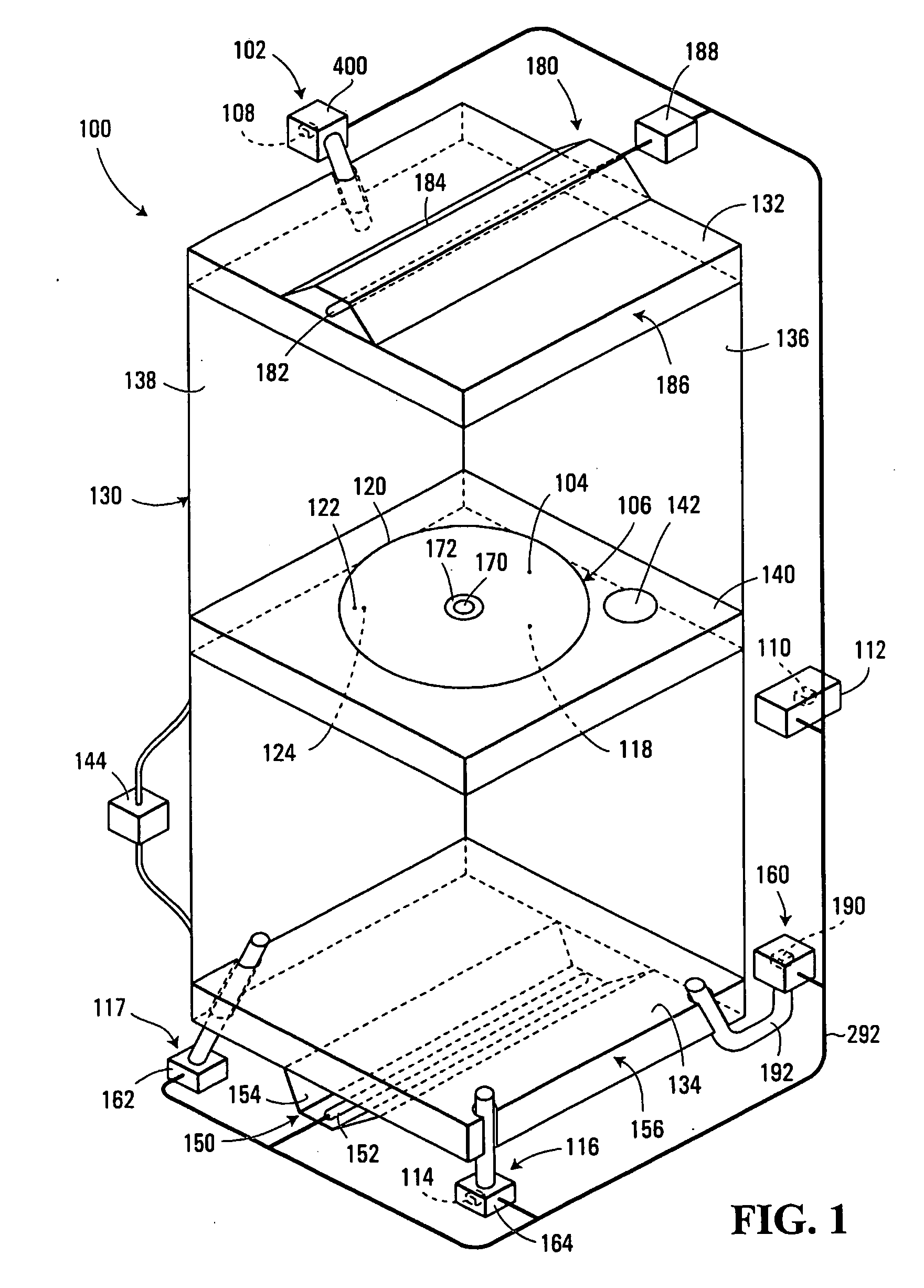
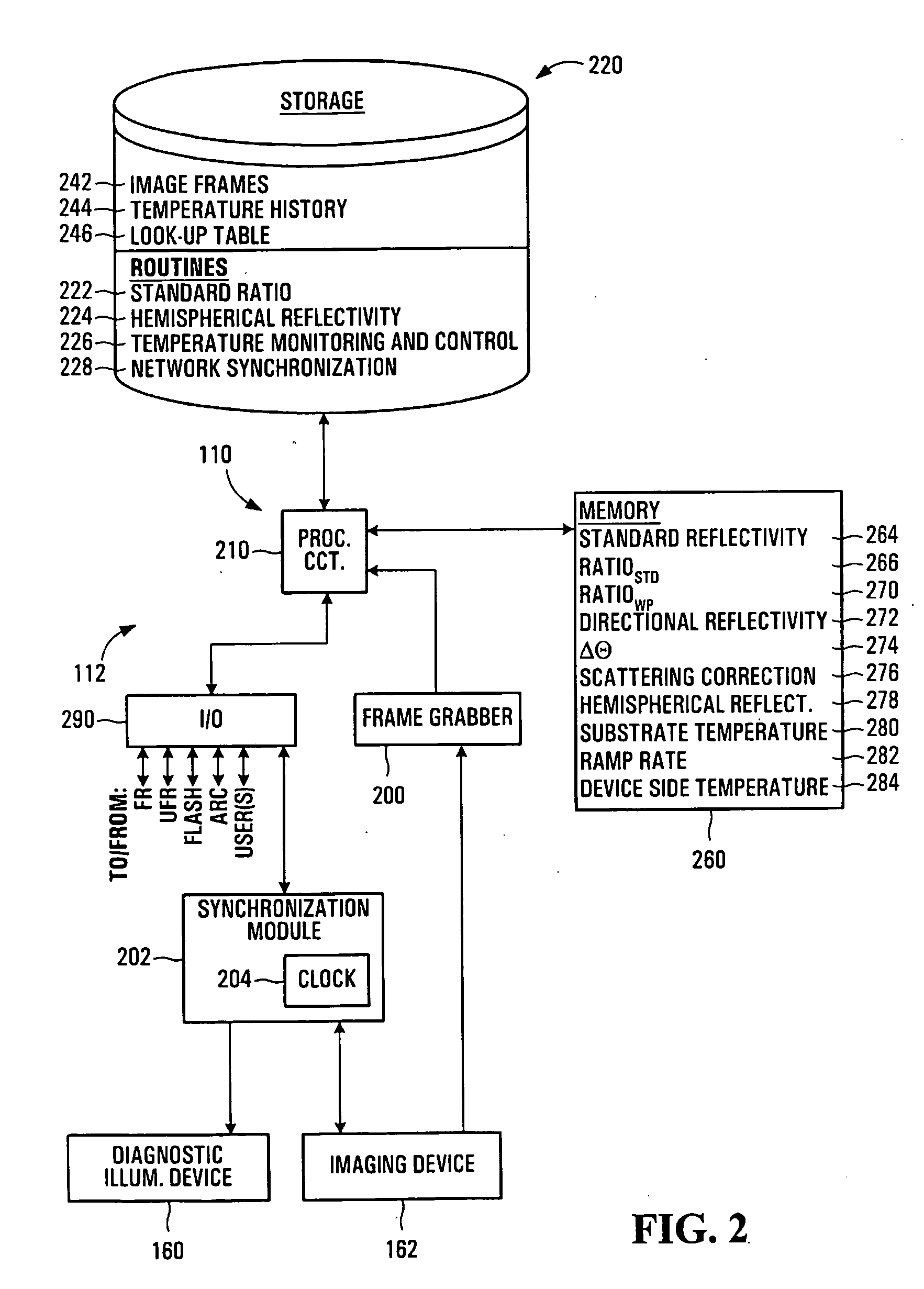
Temperature measurement and heat-treating metods and system
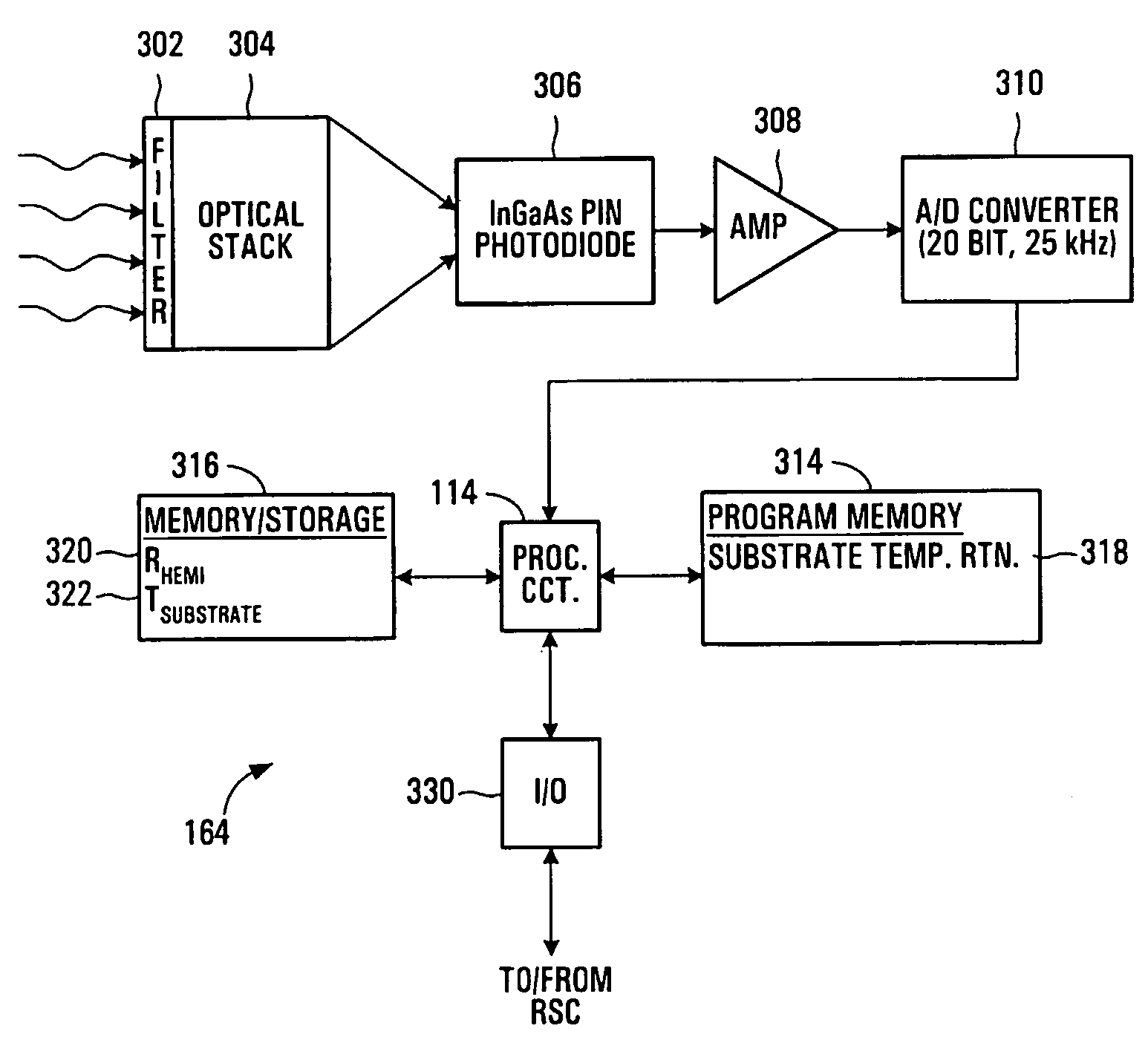
InactiveUS20050063453A1Accurate temperature measurementEnsure consistencyThermometer detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsCurrent strength
Temperature measurement and heat-treating methods and systems. One method includes measuring a present intensity of radiation thermally emitted from a first surface of a workpiece, and identifying a present temperature of the first surface in response to the present intensity and at least one previous thermal property of the first surface. Preferably, the workpiece includes a semiconductor wafer, and the first and second surfaces respectively include device and substrate sides thereof. The present temperature of the device side is preferably identified while the device side is being irradiated, e.g. by an irradiance flash having a duration less than a thermal conduction time of the wafer. The device side temperature may be identified in response to a previous device side temperature, which may be identified in response to a previous temperature of the substrate side unequal to the previous device side temperature, and a temperature history of the wafer.
Owner:MATTSON TECHNOLOGY +1
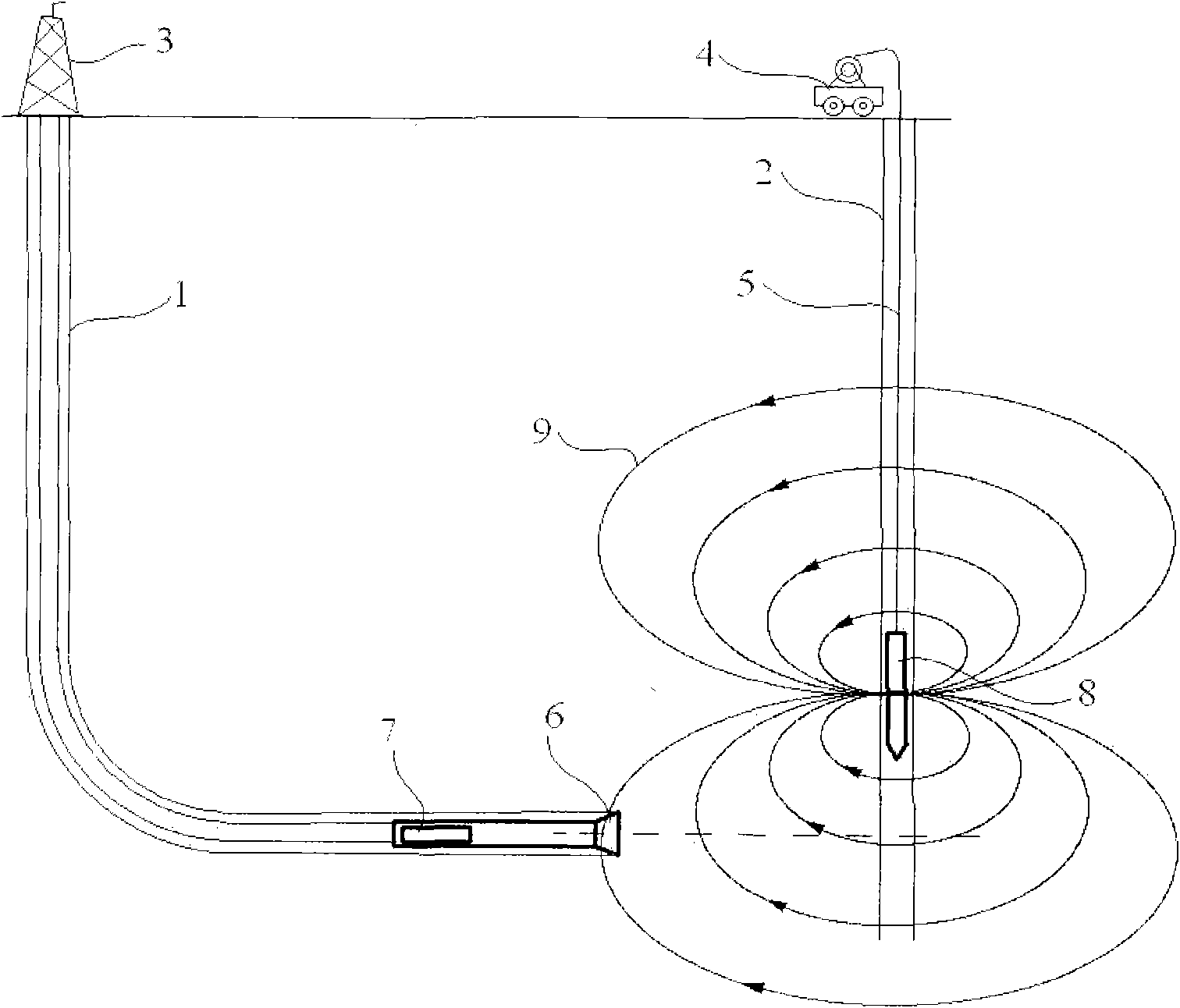
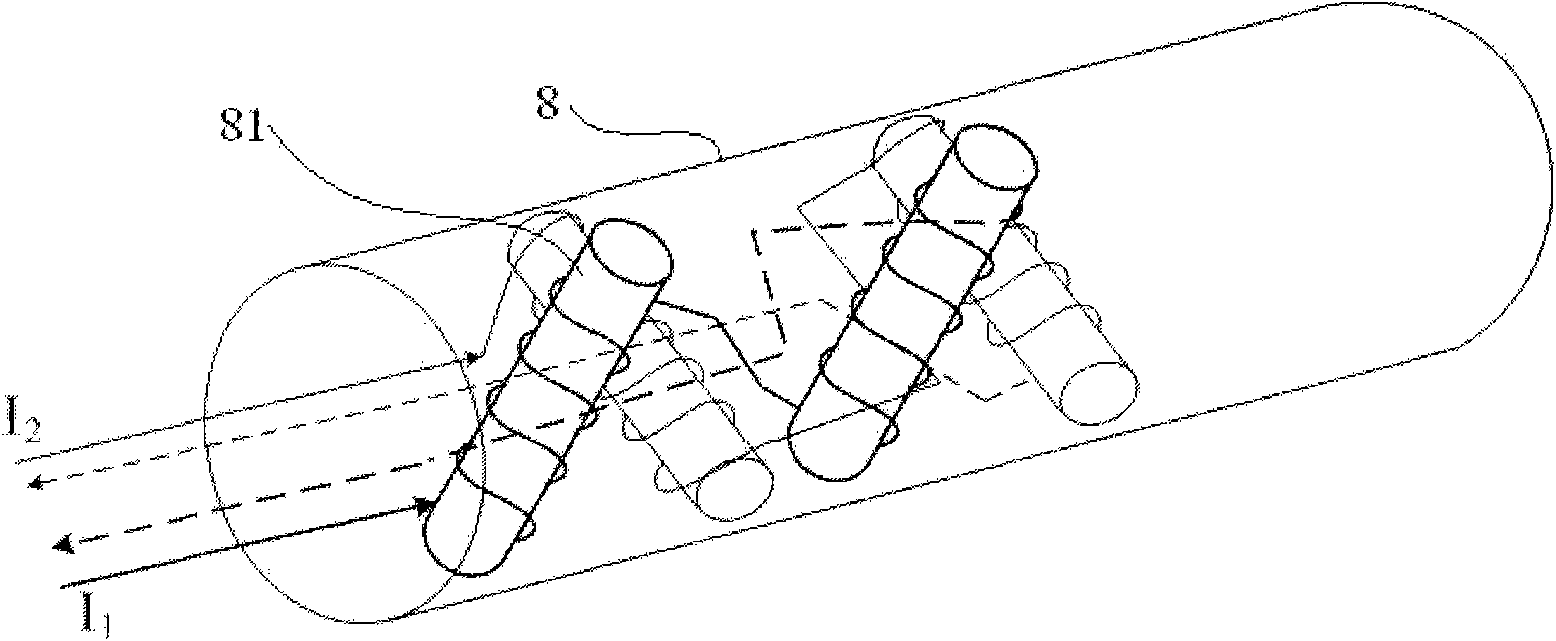
System using solenoid groups to achieve electromagnetic guiding distance measurement while drilling
ActiveCN101806210AEasy to change intensityEasy to control ranging rangeSurveyConstructionsHorizontal wellsEngineering
The invention provides a system using solenoid groups to achieve the electromagnetic guiding distance measurement while drilling (MWD) and providing precise guiding measurement and calculation for the directional drilling control of dual horizontal wells, communicated wells, infill wells, relief wells and other complex wells. The system mainly comprises a nipple joint of the solenoid group, a converted MWD device, an adjacent well distance calculation system and surface equipment. By arranging two orthogonal solenoid groups as a magnetic signal emission source in a drilled well, the system of the invention can generate a rotating magnetic field just as that generated by the rotating magnetic nipple joint of an RMRS (rotating magnet ranging system), thus ensuring the measurement precision equivalent to that of the RMRS; meanwhile, by using the method for increasing the current intensity of the solenoid coil, the system of the invention can increase the intensity of the magnetic signal emission source and help extend the distance measurement range; and the invention has the advantages of high guiding accuracy, wide distance measurement range and simple structure, thus providing an effective hi-tech way for the detection and control while drilling the adjacent well distance.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Implantable medical devices evaluating thorax impedance
InactiveUS20080300504A1Inter-pulse delays can be alteredReduce the amount requiredElectrotherapyCatheterVoltage sourceElectrical impedance
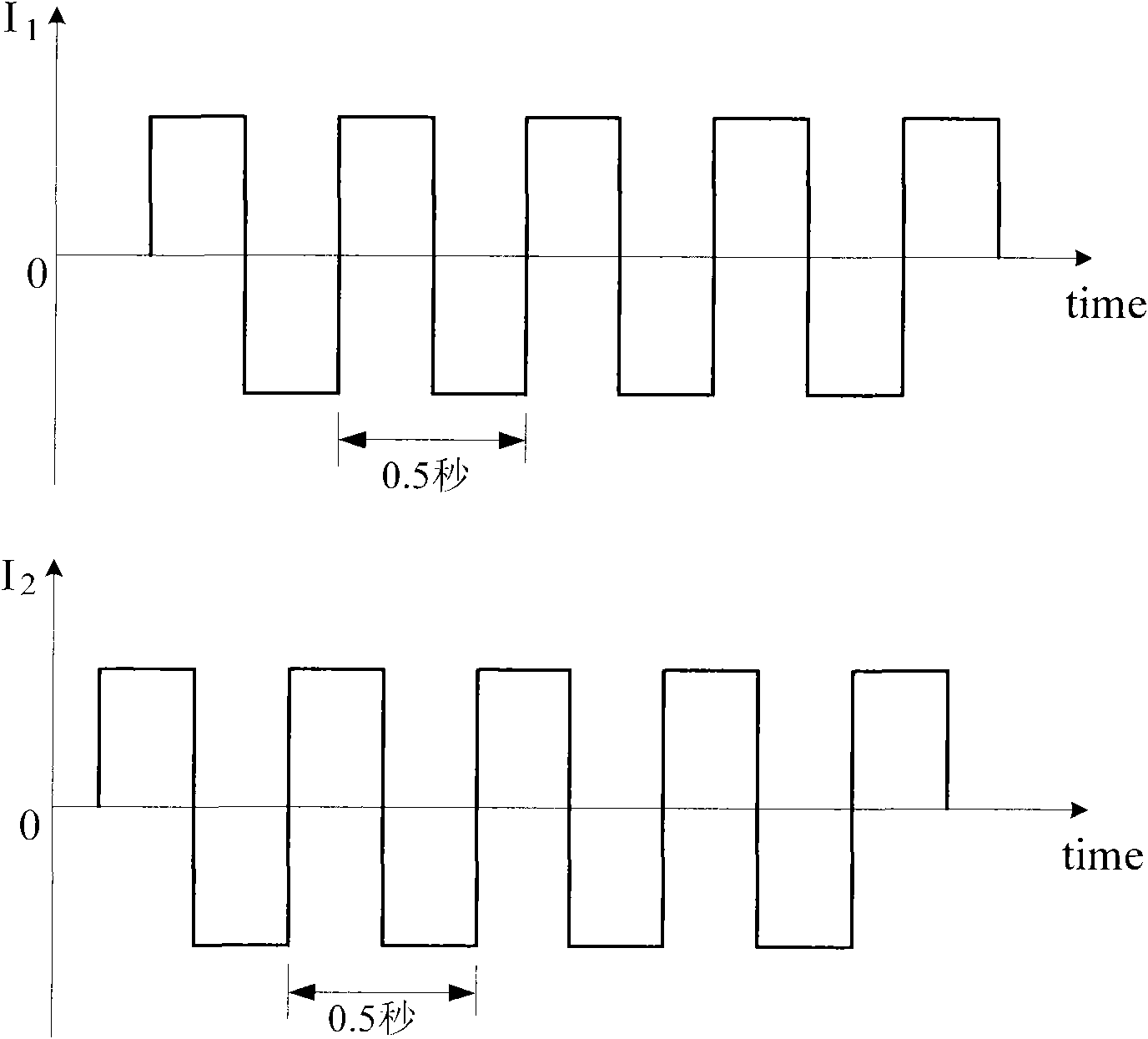
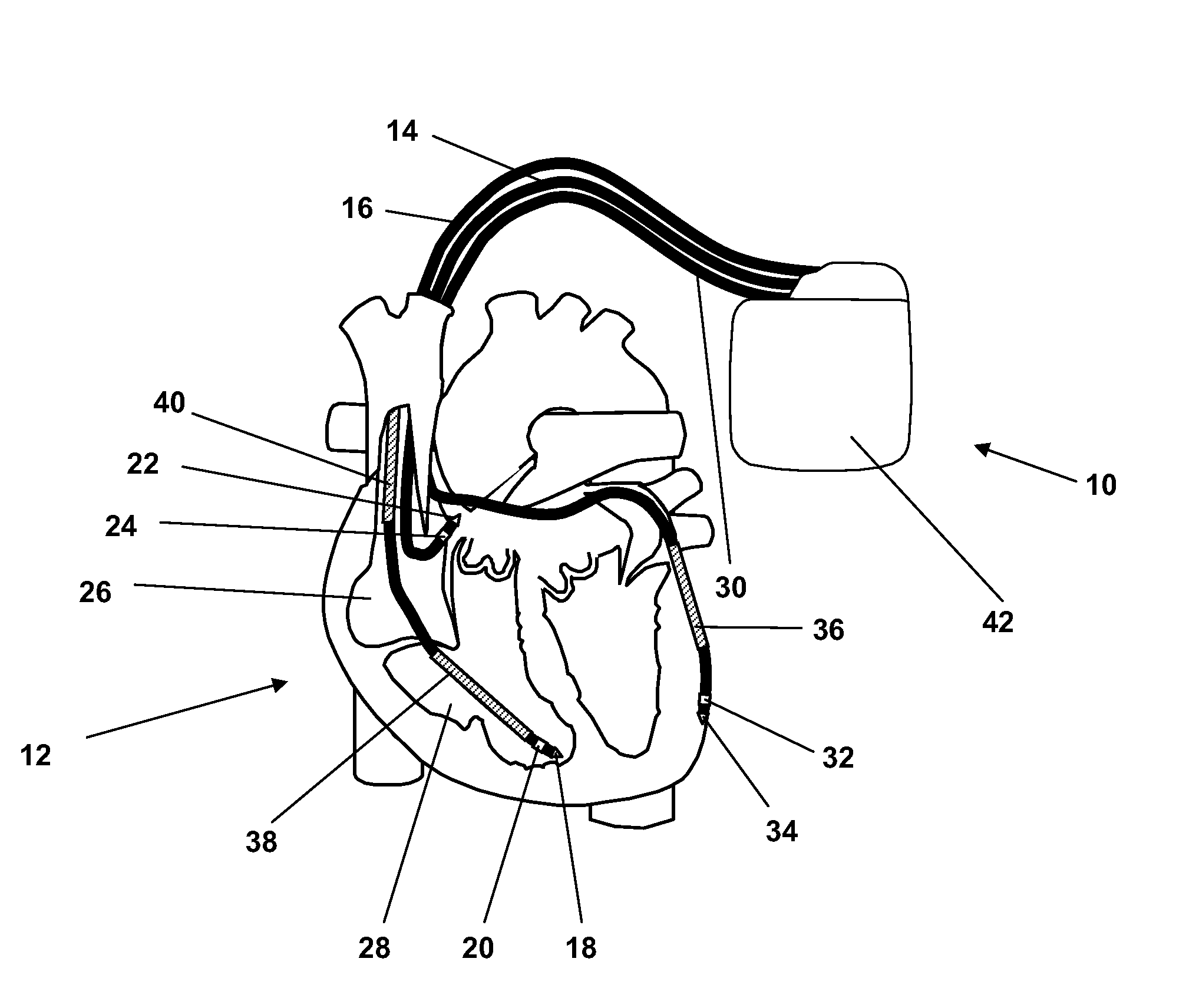
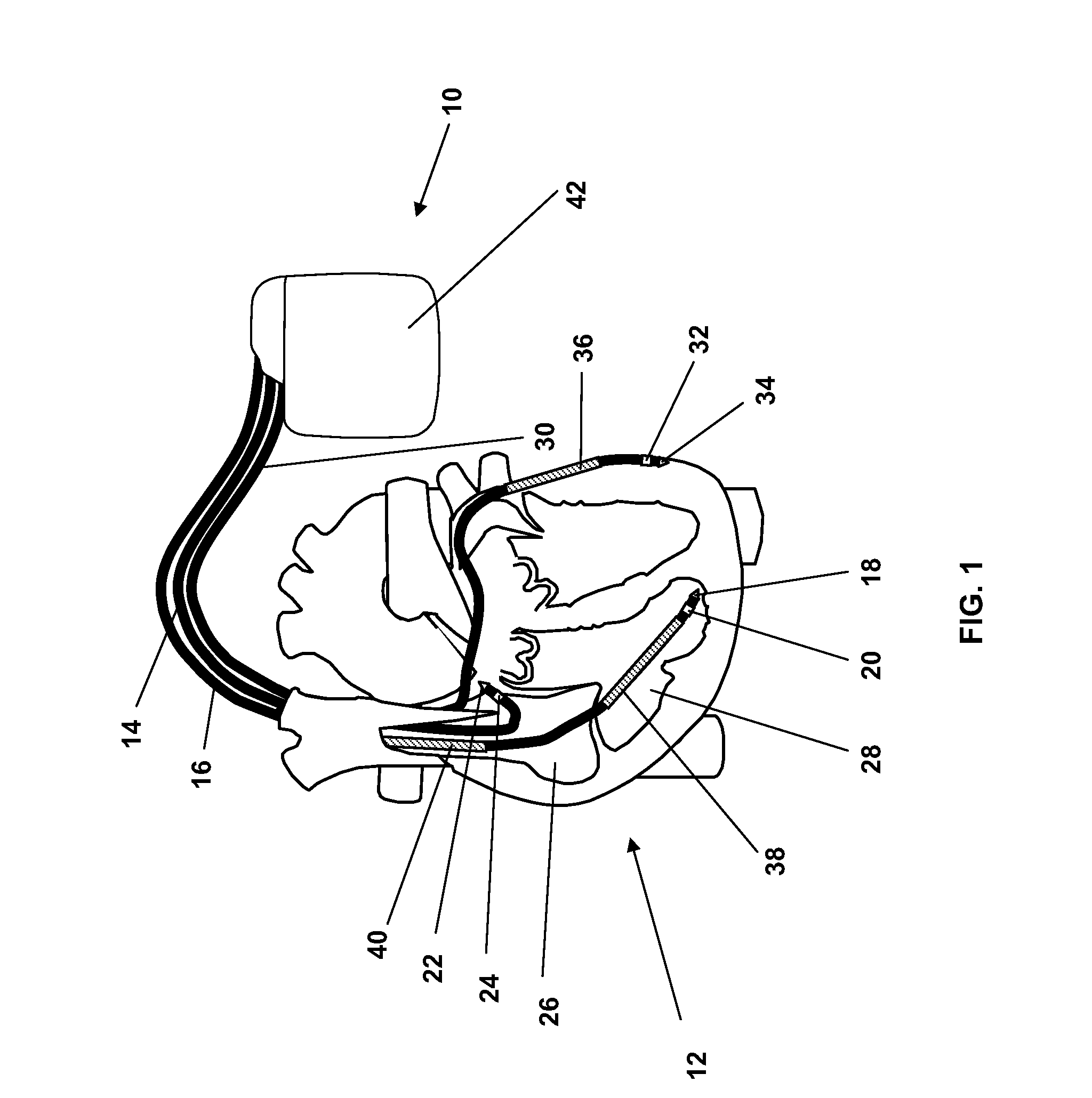
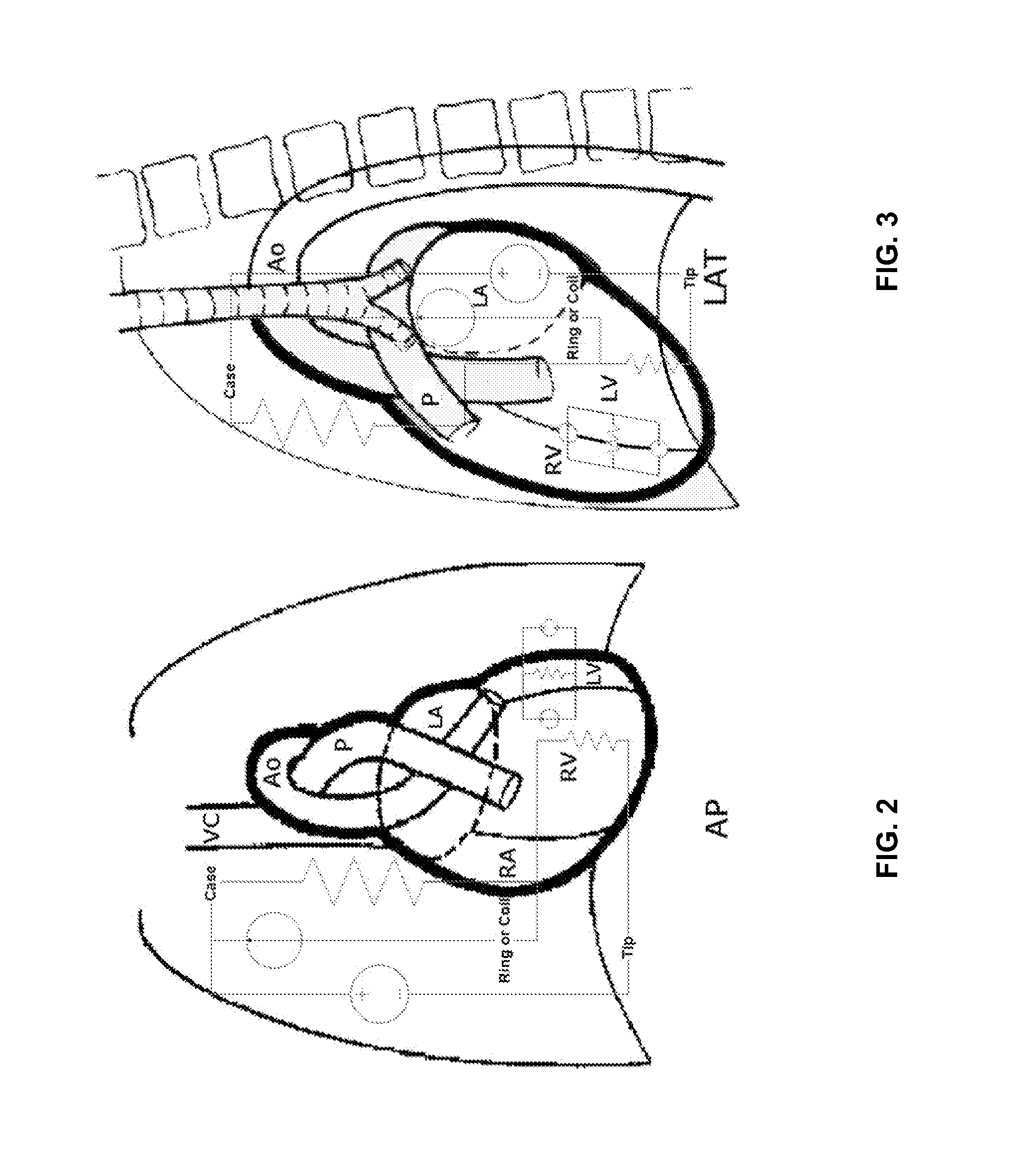
Implantable medical device with an impedance determination unit with constant current / voltage source having current feed terminals connected to electrodes for intracorporal placement which generates measuring current pulses having constant current / voltage, for causing a current through a body via intracorporally placed electrodes, a measuring unit for measuring voltage / current strength of voltage / current fed through body, an impedance value determination unit connected to the current / voltage source and adapted to determine an impedance value for each measuring current pulse, and an impedance measuring control and evaluation unit connected to the impedance determination unit which controls the unit and evaluates a sequence of consecutive impedance values, the impedance determination unit further adapted to determine at least intrathoracic and intracardiac impedance values for same period of time, the intrathoracic values sampled with a lower sampling rate than the intracardiac values.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Small neutron source adopting windowless gas target
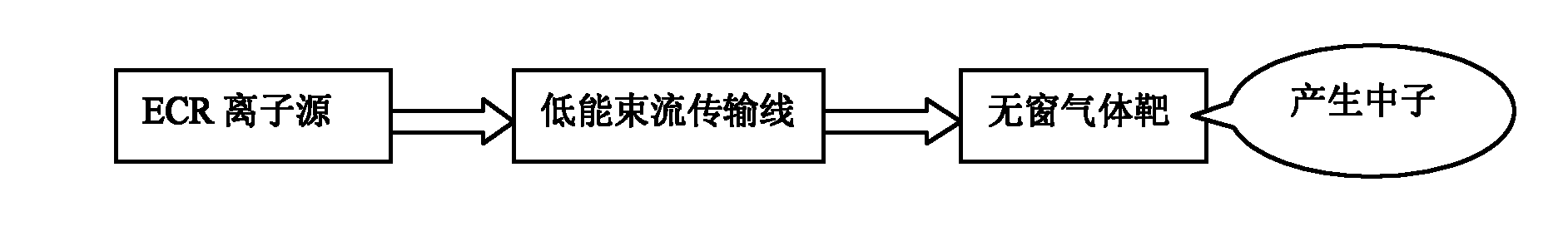
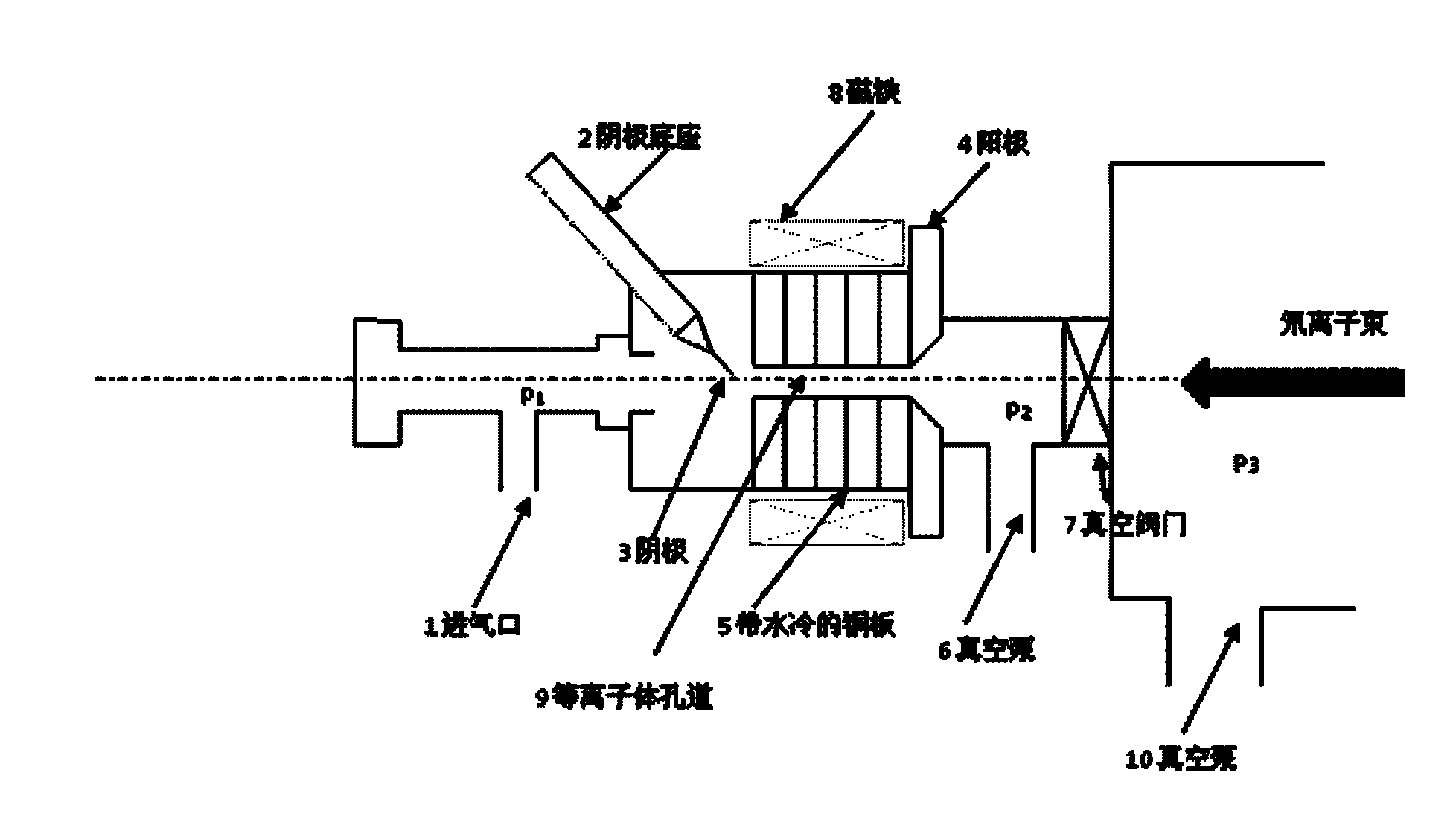
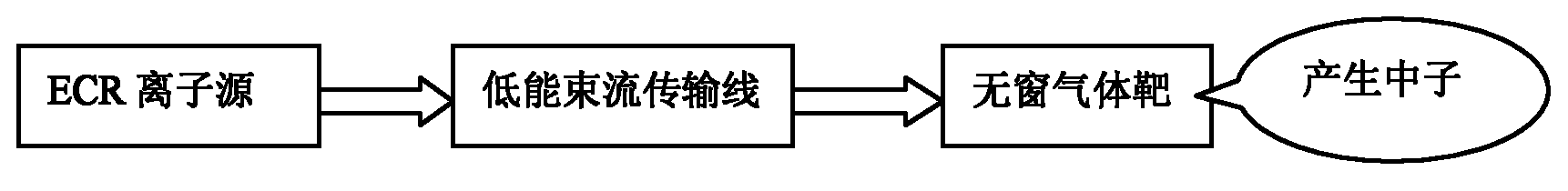
The invention discloses a small neutron source adopting a windowless gas target, which belongs to the field of nuclear technology and application. In the invention, an ECR (Electron Cyclotron Resonance) ion source is used for generating a deuterium ion and directly extracted by a high-voltage extraction electrode for bombarding a windowless gas target sealed by a plasma; because the windowless deuterium gas target is sealed by adopting the plasma, the windowless deuterium gas target is allowed to bear high-flow-strength beam current; and because the energy loss of the deuterium ion when penetrating through a plasma window is less, the neutron yield is higher. Compared with a neutron pipe, the neutron source provided by the invention has high allowed beam current strength and high neutron yield. Compared with an accelerator neutron source with large size, complex system and high cost, the neutron source provided by the invention has small size, simple system and low cost. Compared with a neutron source for directly carrying out deuterium-tritium reaction on an ion source to generate neutron, the ion source has simple system, low cost and no tritium radioactive processing and circulating problem. The invention has very wide application prospect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Low-power consumption APD bias controller, bias control method, and photoelectric receiver
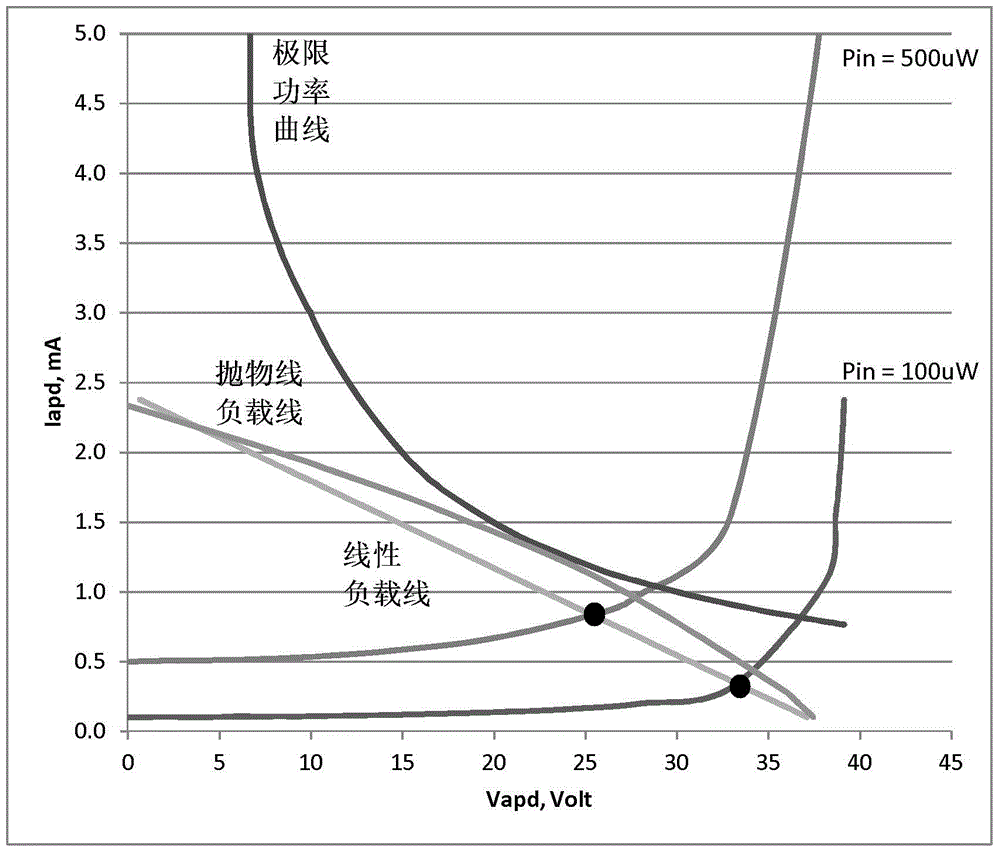
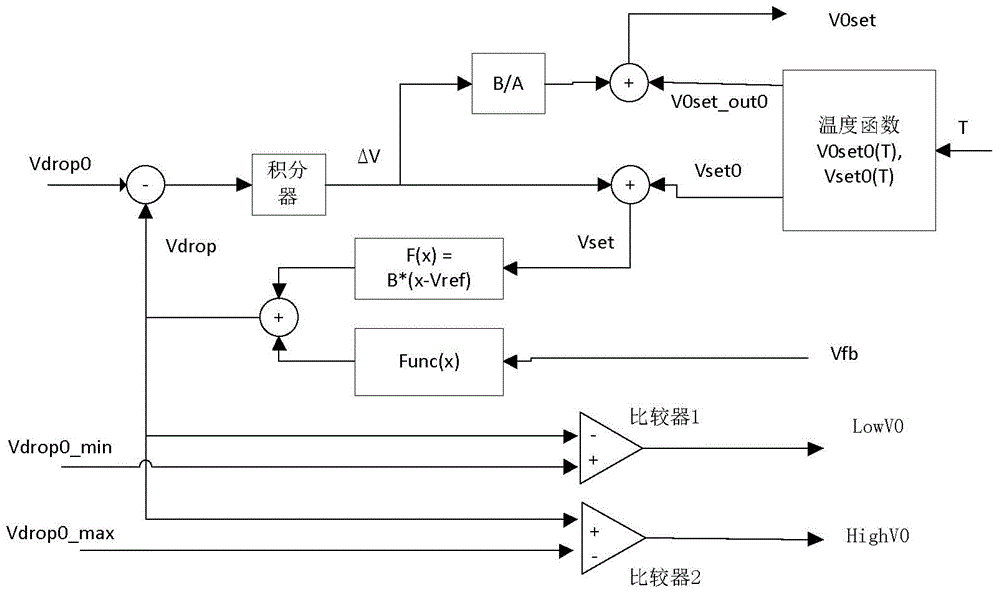
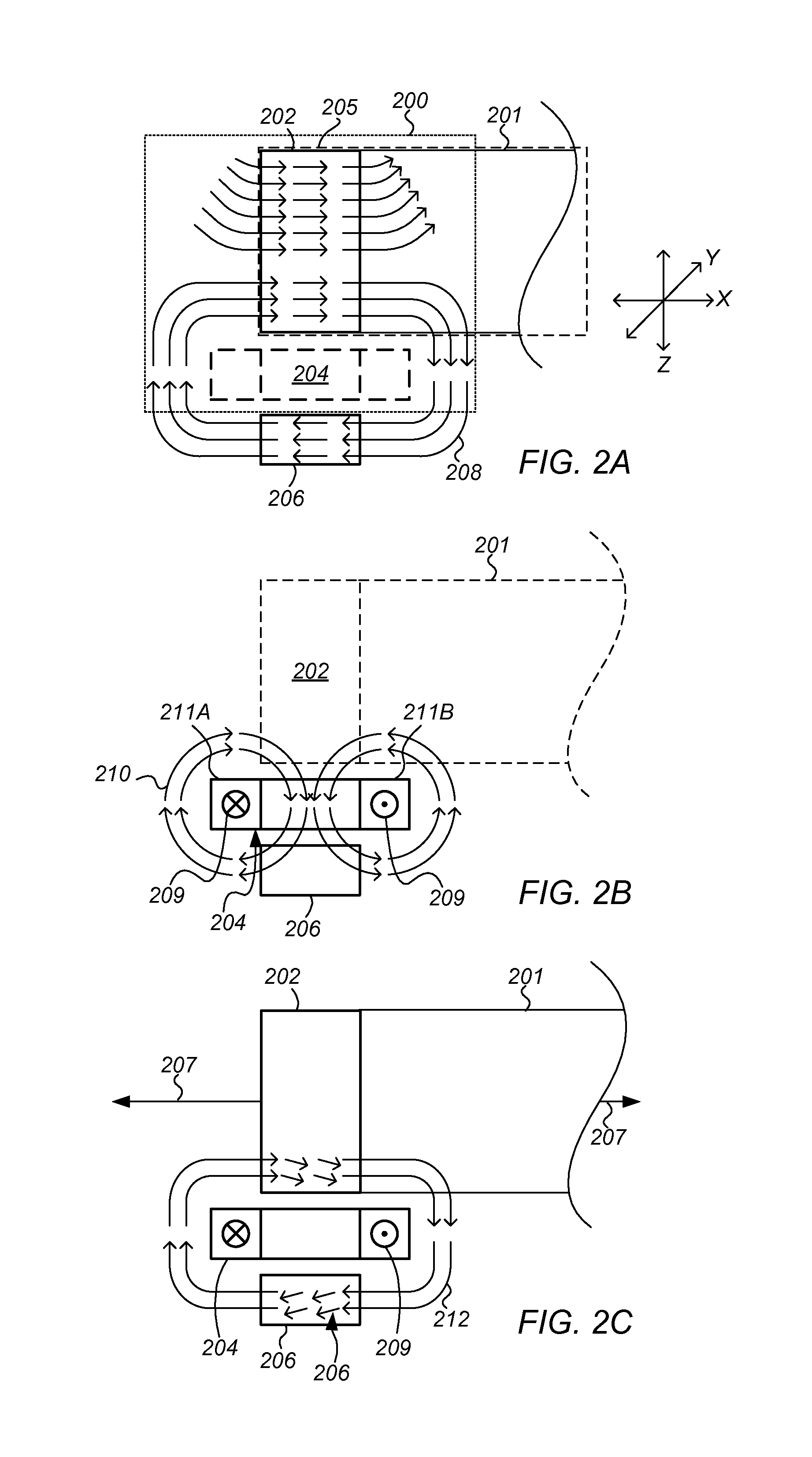
ActiveCN106033225ANo damageReduce power consumptionPhotometryElectromagnetic transmissionOvervoltageControl signal
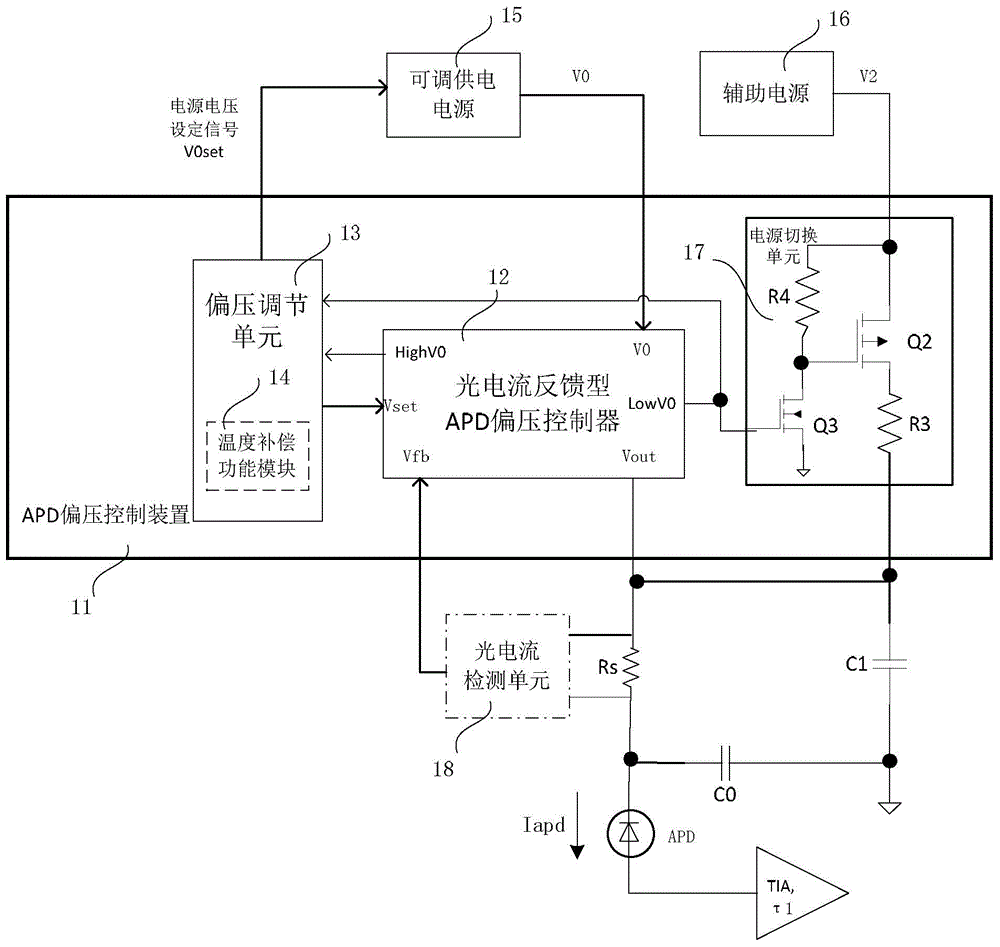
The invention provides an APD bias control method, comprising: acquiring a light current strength voltage signal corresponding to a light current signal passing through an APD; overlaying the light current strength voltage signal with a bias setting signal, to generate a control signal, used to control voltage drop between output voltage of an adjustable power supply and APD voltage; and adjusting the output voltage of the adjustable power supply and the bias setting signal at the same time, to control the voltage drop in a preset range. The invention also provides an APD bias controller, comprising a bias voltage generation unit used to generate a bias voltage signal according to a light current strength feedback signal from external, to determine APD bias voltage, wherein the bias voltage generation unit also generates a second voltage signal, and compares the second voltage signal with one or more reference voltage, to generate undervoltage or overvoltage instructions. The APD bias controller and the photoelectric receiver are advantaged by low power consumption, high dynamic, high signal to noise ratio, high sensitivity, and timely temperature compensation.
Owner:旭创科技有限公司
Method for controlling direction of rotation axis and rotation direction of space universal superposition rotating magnetic field
ActiveCN102579048AImprove cornering performanceEasy to adjustSurgeryEndoradiosondesHelmholtz coilCurrent amplitude
The invention belongs to the technical field of automation engineering and discloses a method for controlling the direction of a rotation axis and the rotation direction of a space universal superposition rotating magnetic field. Three z-axis, y-axis and x-axis square Helmholtz coil groups are orthogonally nested, so that when the three groups of coils are driven by direct currents with the same current strength, the magnetic inductions generated at the center points of the three groups of coils have the same strength; the superposition rotating magnetic field is driven by an amplitude and phase compensation voltage signal through digitization so as to eliminate the influence of current lagging and inductive reactance on the current amplitude; and a same-frequency three-phase sinusoidal signal with the amplitude and the phase related to the axis azimuthal angle of a robot is used for driving to form the space universal uniform rotating magnetic field with the corresponding azimuthal rotating axis in a superimposed mode in a certain space surrounded by the three-axis orthogonal Helmholtz coil devices. According to the invention, by implementing the random regulation of the direction of the rotation axis and the rotation direction of the space universal rotating magnetic field, various operations of turning, moving forward, moving backward and the like of the micro robot in the bent or branch cavity environment are further implemented; and the method has wide application prospect.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Container formation method of valve-regulated lead-acid battery
ActiveCN101673844AImprove methodFast wayFinal product manufactureSecondary cells charging/dischargingState of artEngineering
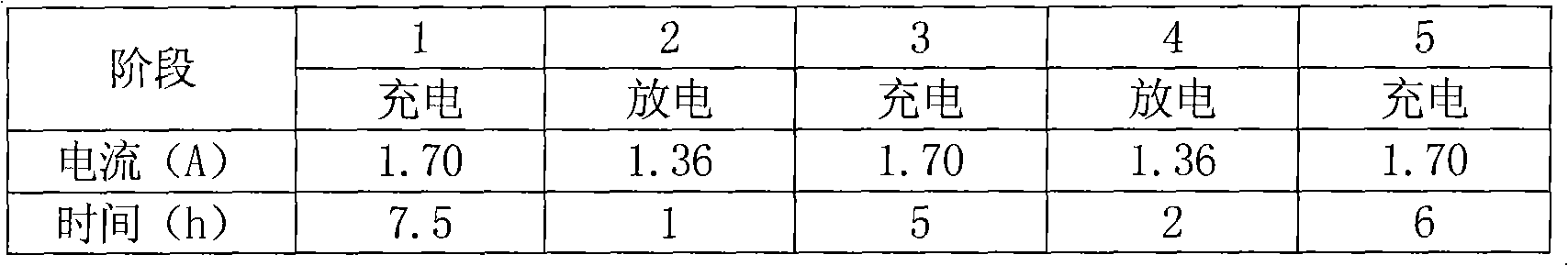
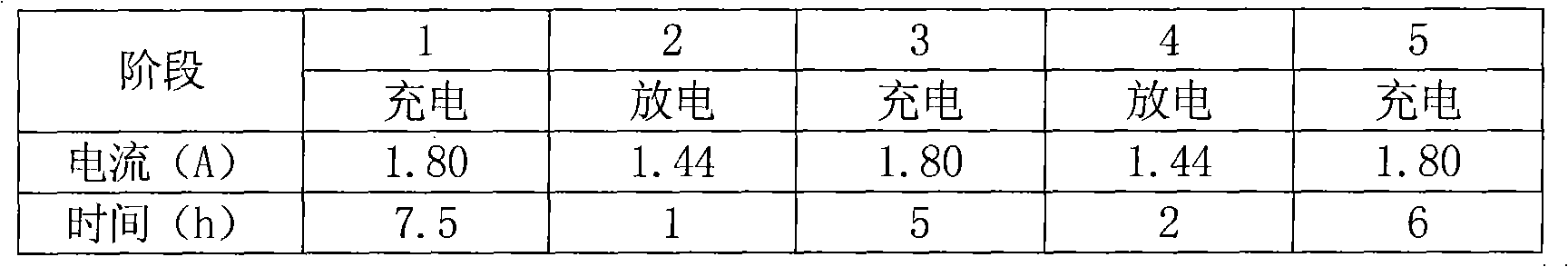
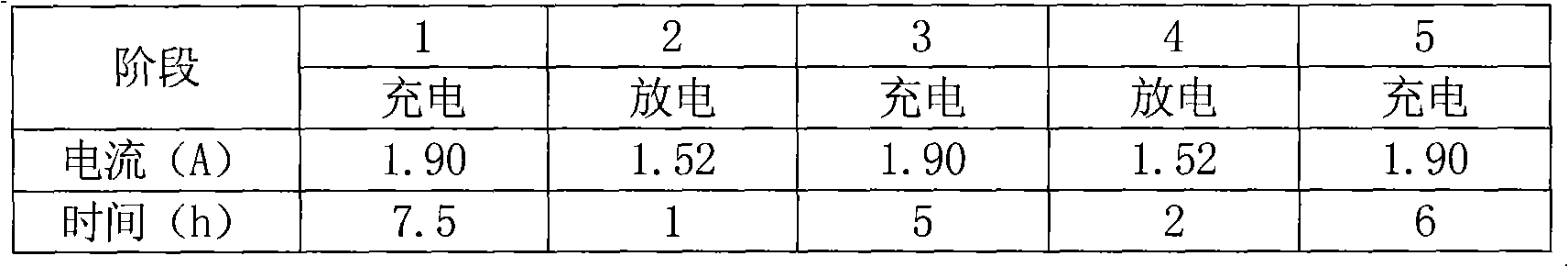
The invention relates to a container formation method of a valve-regulated lead-acid battery, which is used for solving the problems of long time consumption and long production cycle of container formation of the valve-regulated lead-acid battery. The method is carried out according to the following steps: a. first charge: the charge time is 7.5h and the current is 1.7-1.9A; b. first discharge: the discharge time is 1h and the current is 1.36-1.52A; c. second charge: the charge time is 5h and the current is 1.7-1.9A; d. second discharge: the discharge time is 2h and the current is 1.36-1.52A;and e. third charge: the charge time is 6h and the current is 1.7-1.9A. The method provides the optimal mixing ratio of current strength to formation time, controls the water temperature during the process, fully forms a plate, forms the optimized container formation technology of the 12V7Ah valve-regulated lead-acid battery, shortens the formation time of the battery to one half of that of the prior art, saves energy consumption and simultaneously, greatly improves production efficiency.
Owner:FENGFAN
System for variably configurable, adaptable electrode arrays and effectuating software
ActiveUS20170087367A1Improve cognitive abilityAccurate informationElectroencephalographyUltrasound therapyDiseasePresent method
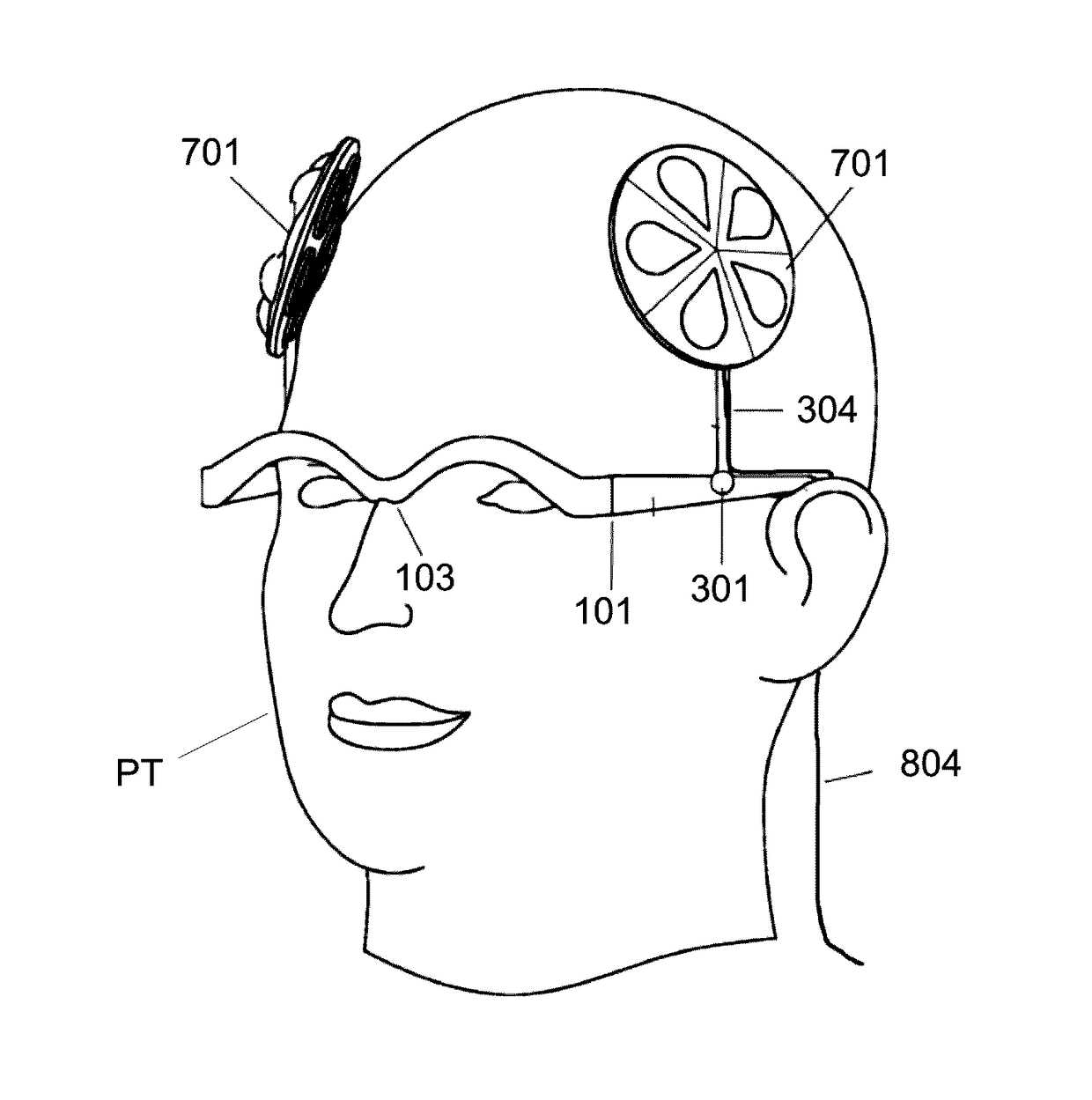
Electrical non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS) delivers weak electrical currents to the brain via electrodes that are affixed to the scalp. NIBS can excite or inhibit the brain in areas that are impacted by that electrical current during and for a short time following stimulation. Electrical NIBS can be used to change brain structure in terms of increasing white matter integrity as measured by diffusion tensor imaging. Together the electrical NIBS can induce changes in brain structure and function. The present methods and devices are adaptable to and configurable for facilitating the enhancement of brain performance, and the treatment of neurological diseases and tissues. The present methods and devices are advantageously designed to utilize modern electrodes deployed with, inter alia, various spatial arrangements, polarities, and current strengths to target brain areas or networks to thereby enhance performance or deliver therapeutic interventions.
Owner:STIMSCI INC
Method for operating and/or reviewing a magneto-inductive flow meter
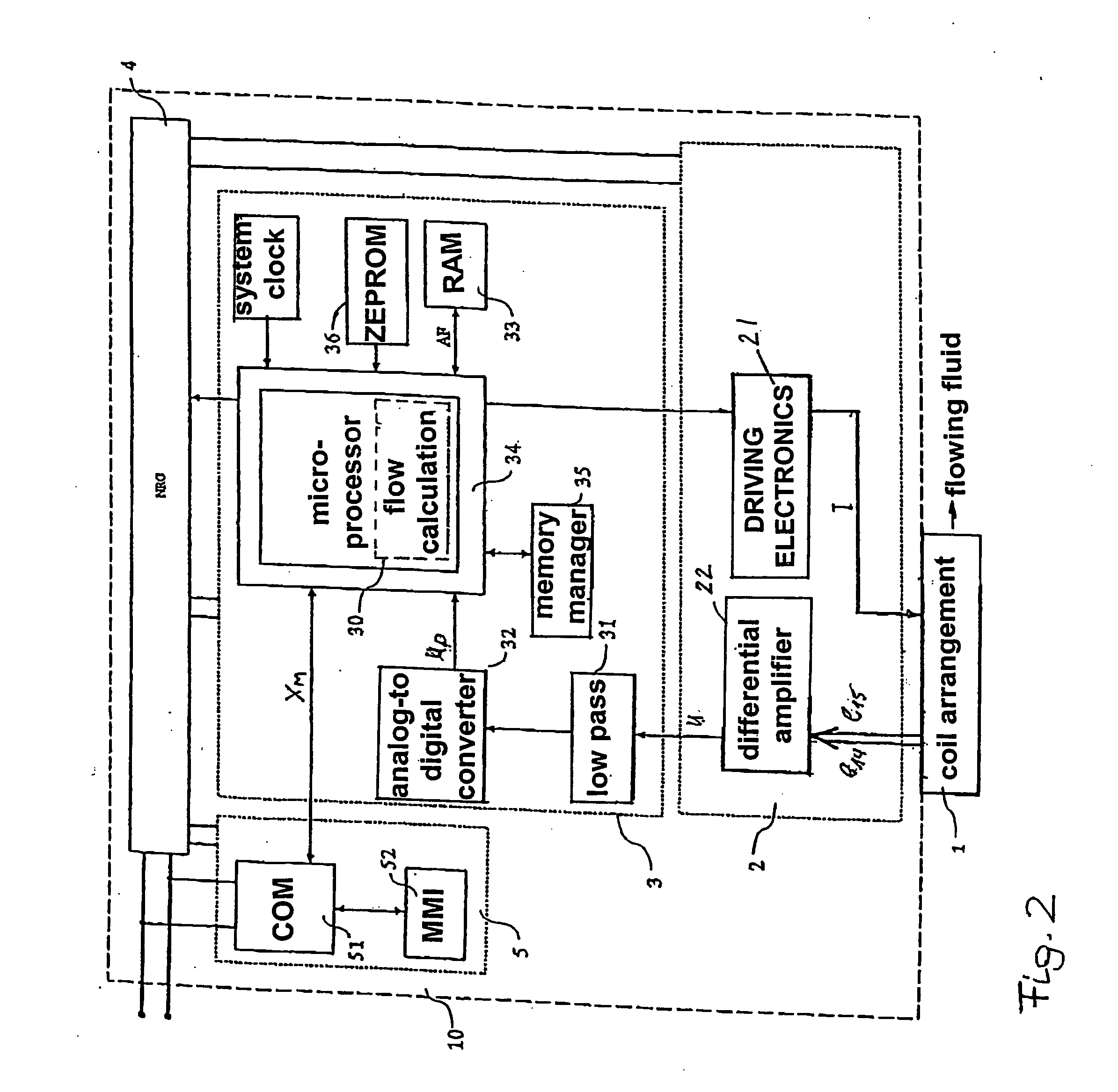
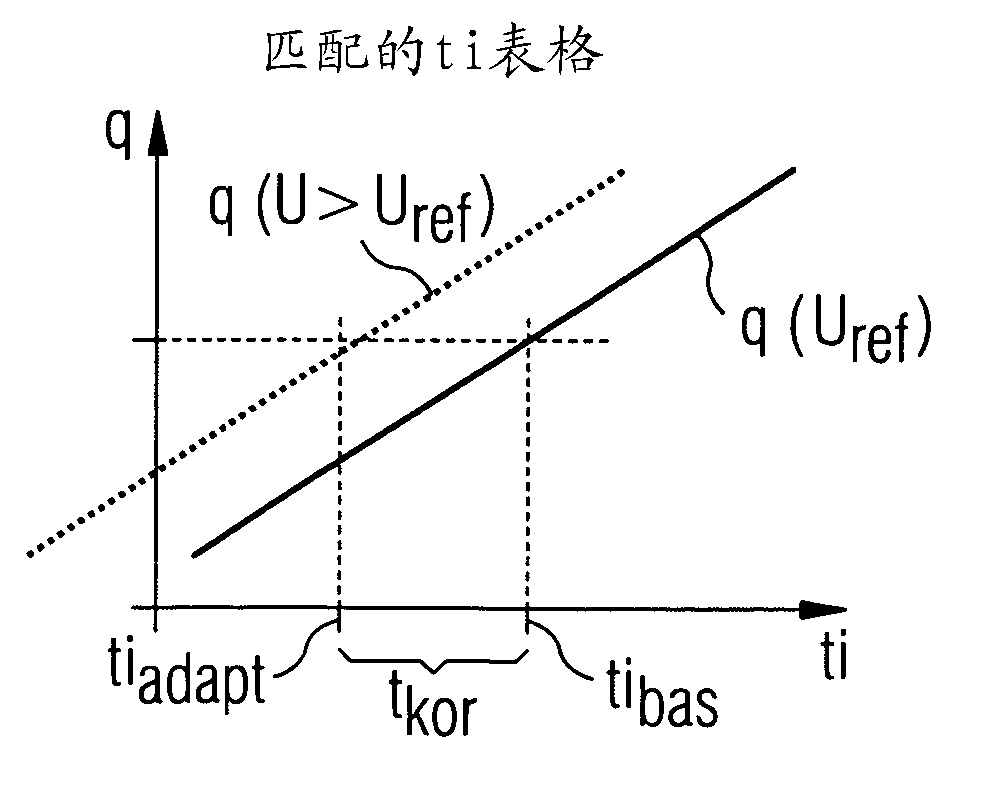
ActiveUS20060081067A1Shorten rise timeTotal current dropTesting/calibration apparatusVolume/mass flow measurementExcitation currentCurrent strength
A flow meter includes a measuring tube for conveying a fluid to be measured and a magnetic field system, which has at least one field coil, through which an exciter current (IM) flows, at least at times, for producing a magnetic field passing through the fluid at least partly perpendicularly to a stream direction. In the method, the voltage (UH) instantaneously driving the exciter current (IM) is changed at a second point in time, t2, from the second voltage level, Udrv, to a third voltage level, Ushort, especially to a third voltage level which is constant or controlled to be constant, in order to achieve a sinking of the electrical current strength of the exciter current (IM) instantaneously flowing in the at least one field coil from the maximum current value, Im, to an electrical current end value, Iczu, especially a constant end value, predetermined for the exciter current (IM) In such case, the third voltage level, Ushort, is chosen smaller than the second voltage level, Urev. For determining a third point in time, t3, which corresponds to the reaching of the electrical current end value, Ic, the exciter current IM is registered, at least at times. Based on this, a first time constant, Tshort, for the magnetic field system is determined, which corresponds to a time span, t3−t2, lying between the second point in time, t2, and the third point in time, t3, and / or a second time constant, Trev+Tshort, for the magnetic field system, which corresponds to a time span, t3−t1, lying between the first point in time, t1, and the third point in time, t3. For determining a diagnosis value representing an instantaneous operating state of the flow meter, the determined first time constant, Tshort, is then compared with a predetermined first reference value, T1ref, and / or the determined second time constant, Trev+Tshort, is compared with a predetermined second reference value, T2ref.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
Temperature measurement and heat-treating methods and system
InactiveUS7445382B2Accurate temperature measurementEnsure consistencyThermometer detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsCurrent strength
Temperature measurement and heat-treating methods and systems. One method includes measuring a present intensity of radiation thermally emitted from a first surface of a workpiece, and identifying a present temperature of the first surface in response to the present intensity and at least one previous thermal property of the first surface. Preferably, the workpiece includes a semiconductor wafer, and the first and second surfaces respectively include device and substrate sides thereof. The present temperature of the device side is preferably identified while the device side is being irradiated, e.g. by an irradiance flash having a duration less than a thermal conduction time of the wafer. The device side temperature may be identified in response to a previous device side temperature, which may be identified in response to a previous temperature of the substrate side unequal to the previous device side temperature, and a temperature history of the wafer.
Owner:MATTSON TECHNOLOGY +1
Setting method of functional electrical stimulation PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) parameter double source characteristic fusion particle swarm
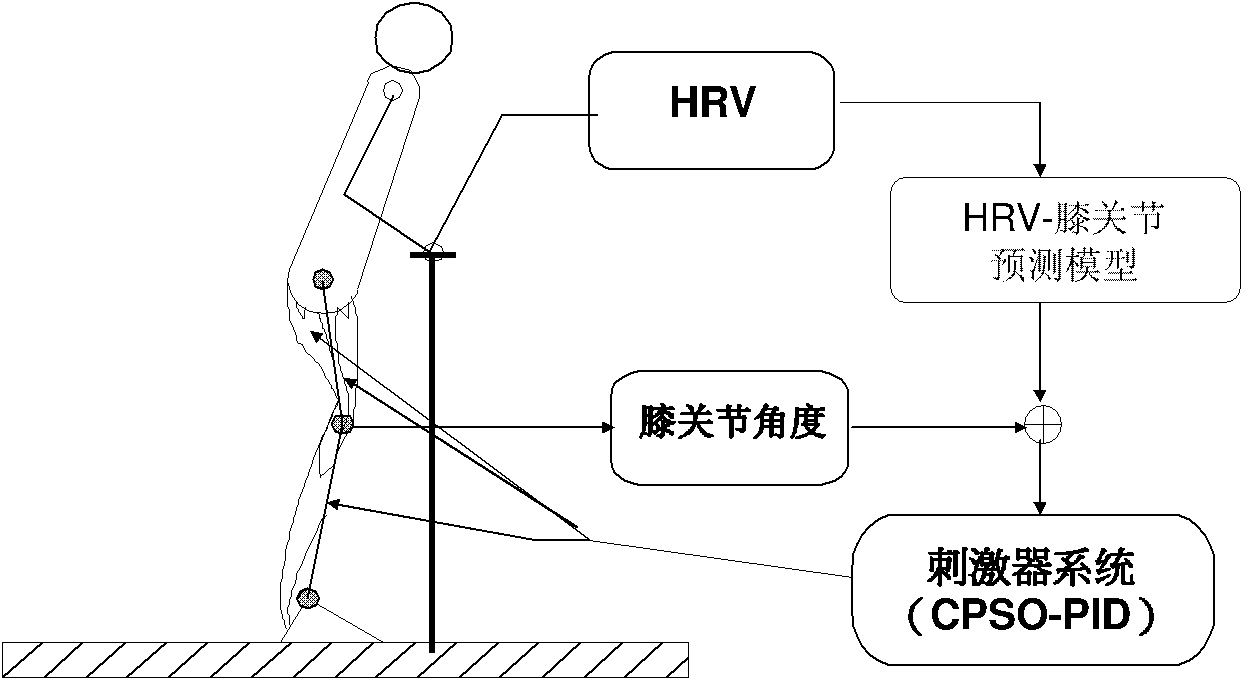
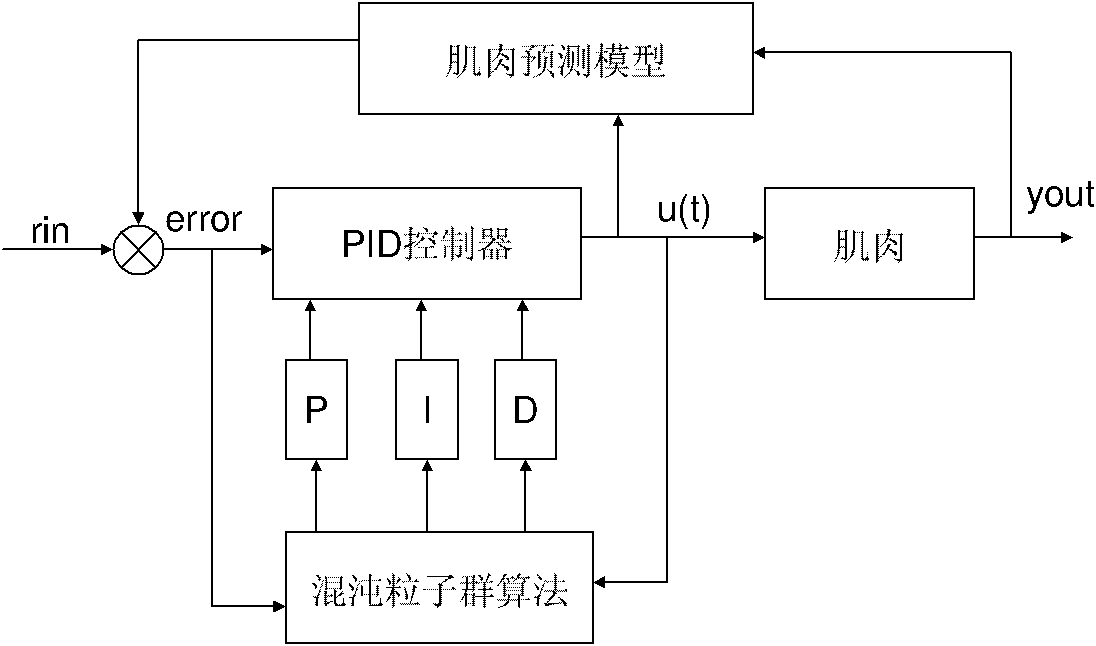
ActiveCN101816822AControl current pulse strengthImprove accuracyWalking aidsArtificial respirationKnee JointEngineering
The invention relates to the field of instruments for extremity rehabilitation by utilizing electric pulse stimulation and provides a setting method of a functional electrical stimulation PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) parameter double source characteristic fusion particle swarm. With the setting method, the current strength of an FES (Functional Electrical Stimulation) system can be accurately and stably controlled in real time and the accuracy and the stability of the FES system can be efficiently enhanced. The invention adopts the technical scheme that: firstly, a knee joint angle is predicted by utilizing a handle reaction vector (HRV) in the walk aid process; and secondly, a proportion calculus PID parameter is set by utilizing a chaos particle swarm algorithm, the FES current level strength is regulated in real time, and finally self-adaptive online setting of the proportion calculus PID parameter is realized, and the invention is also used for a functional electrical stimulation FES system. The invention is mainly applied to setting the PID parameter in functional electrical stimulation.
Owner:禹锡科技(天津)有限公司
Lorentz actuator mechanism calibration
ActiveUS20160070270A1Eliminate corruptionControl using feedbackElectric variable regulationCurrent strengthActuator
An actuator module which includes a Hall sensor, configured to generate output signals indicating a displacement of a mobile component by a Lorentz actuator mechanism, can be calibrated to remove corruption of the output signals due to magnetic fields generated by a coil assembly of the actuator mechanism. Such calibration can include tracking and manipulating one or more of current strength, output signal voltage strength, and mobile component displacement to establish a relationship between output signal voltage and current applied to the coil assembly. The relationship can be used to generate, for a given generated output signal voltage and applied current strength, an offset signal voltage which can be subtracted from the voltage strength of the output signal to determine a corrected output signal, independent of coil assembly corruption, which indicates a displacement of the mobile component.
Owner:APPLE INC
Low-power APD bias controller, bias control method, and photoelectric receiver
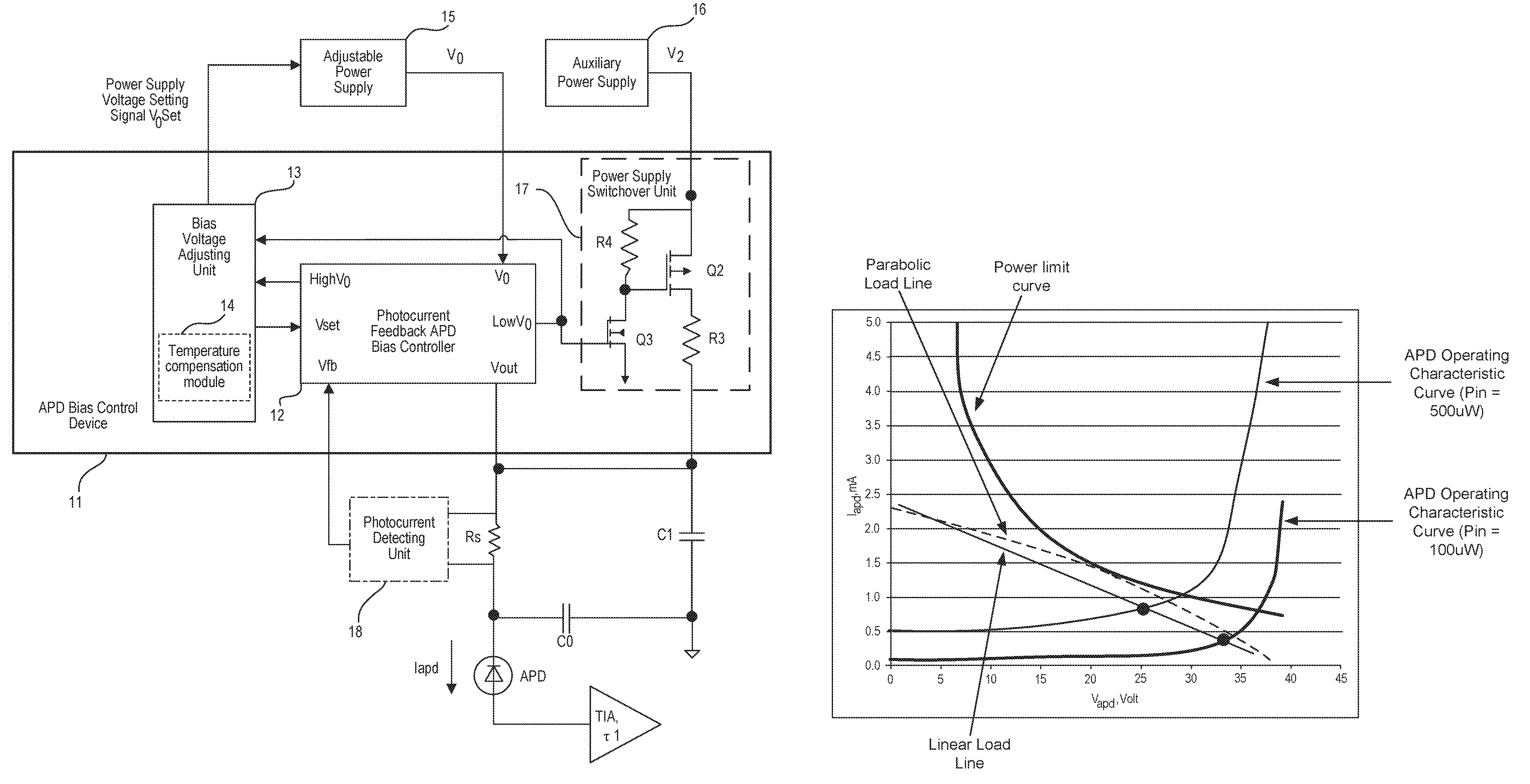
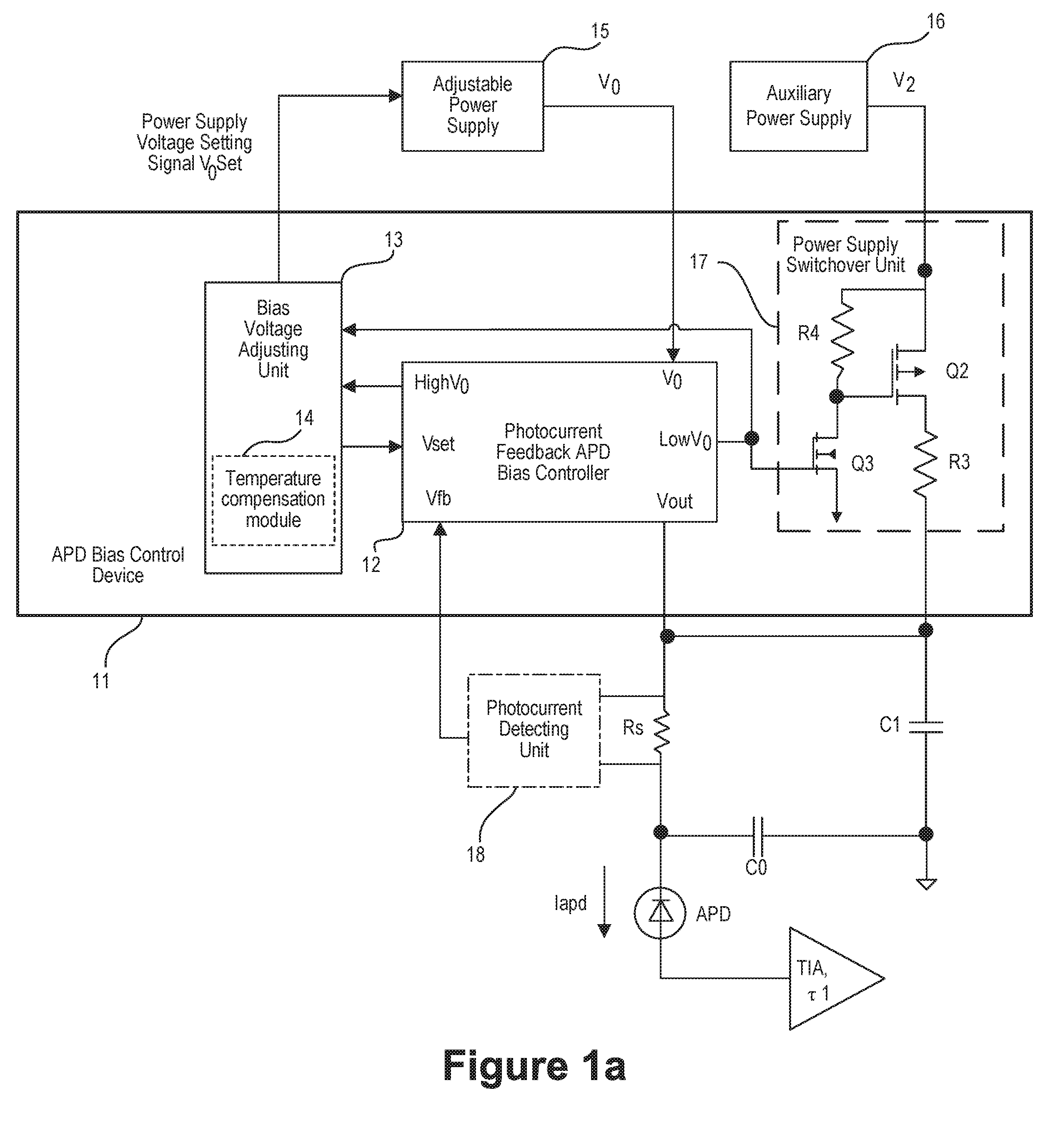
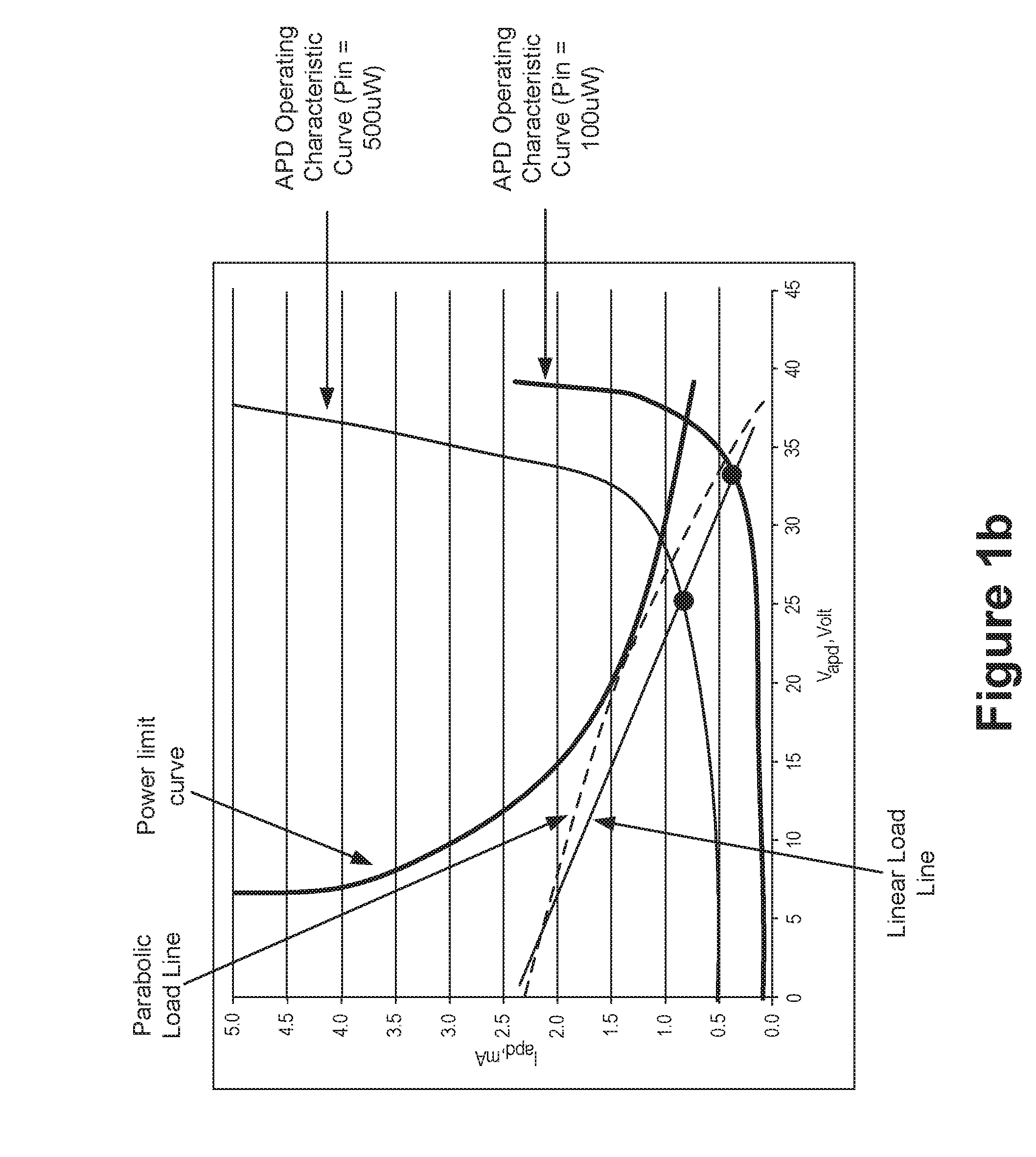
ActiveUS20160273959A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease speedElectromagnetic transmissionPhotometry electrical circuitsControl signalVoltage drop
An avalanche photodiode (APD) bias control method may include acquiring a photocurrent intensity voltage and generating a control signal by superposing the acquired photocurrent intensity voltage and a bias setting signal, wherein the control signal controls a voltage drop between an adjustable power supply output voltage and a voltage of the APD. The APB bias control method may further include adjusting the adjustable power supply output voltage and the bias setting signal simultaneously so that the voltage drop is within a target voltage drop range and the APD bias voltage approaches a bias voltage that corresponds to an APD optical input power. An avalanche photodiode (APD) bias controller and an avalanche photodiode (APD) photoelectric receiver are also provided.
Owner:INNOLIGHT TECHNOLOGY PTE LTD
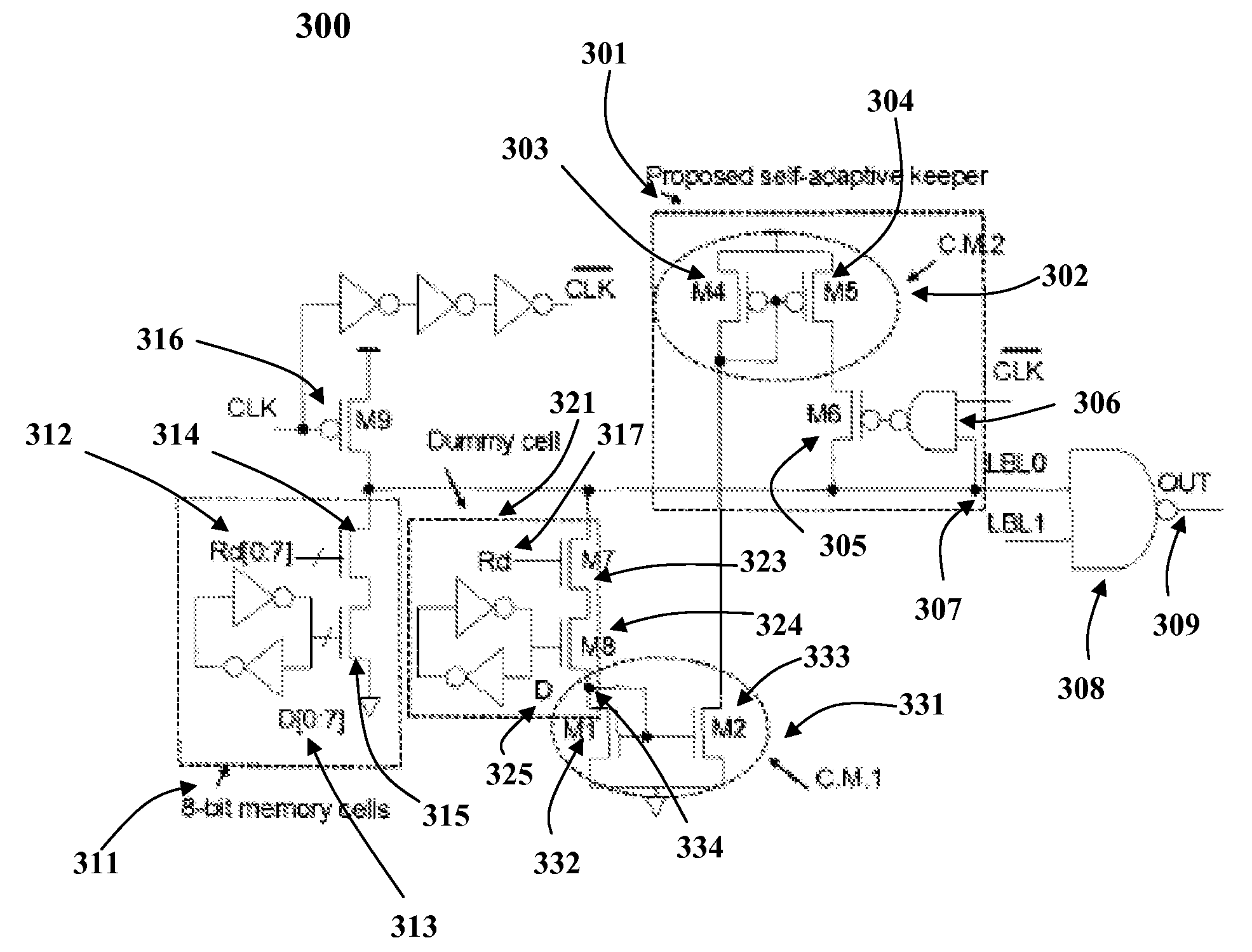
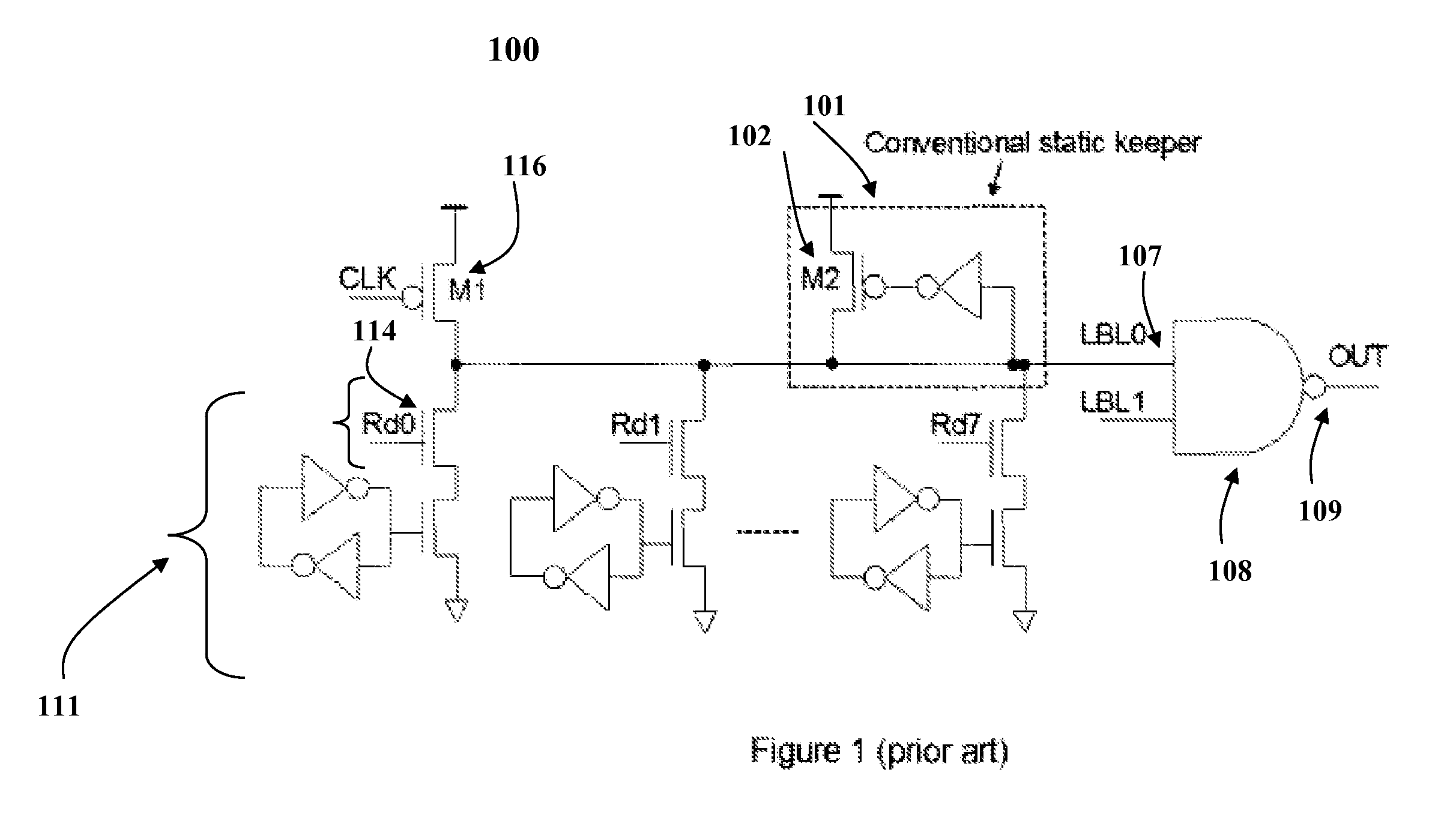
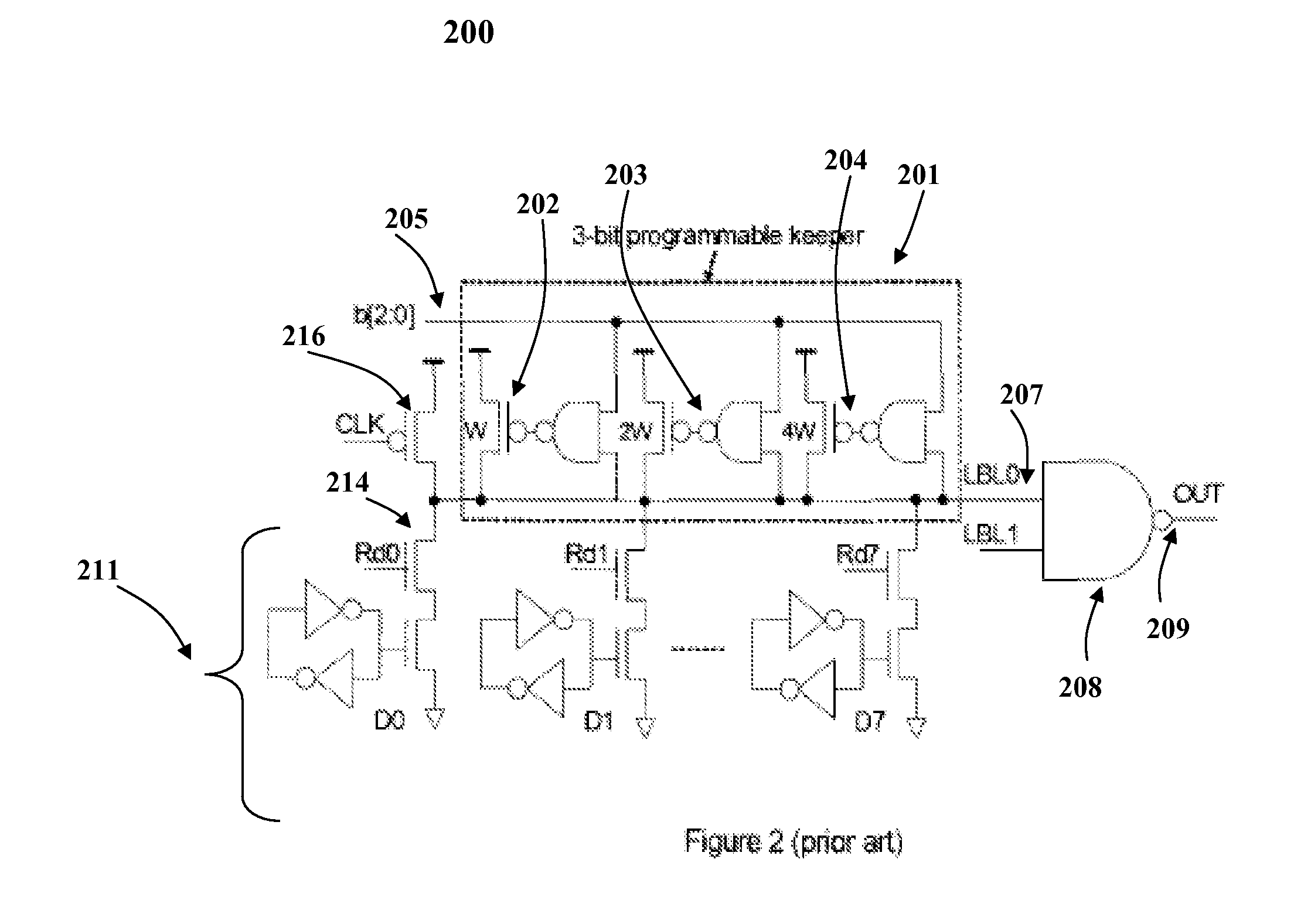
Compensation for leakage current from dynamic storage node variation by the utilization of an automatic self-adaptive keeper
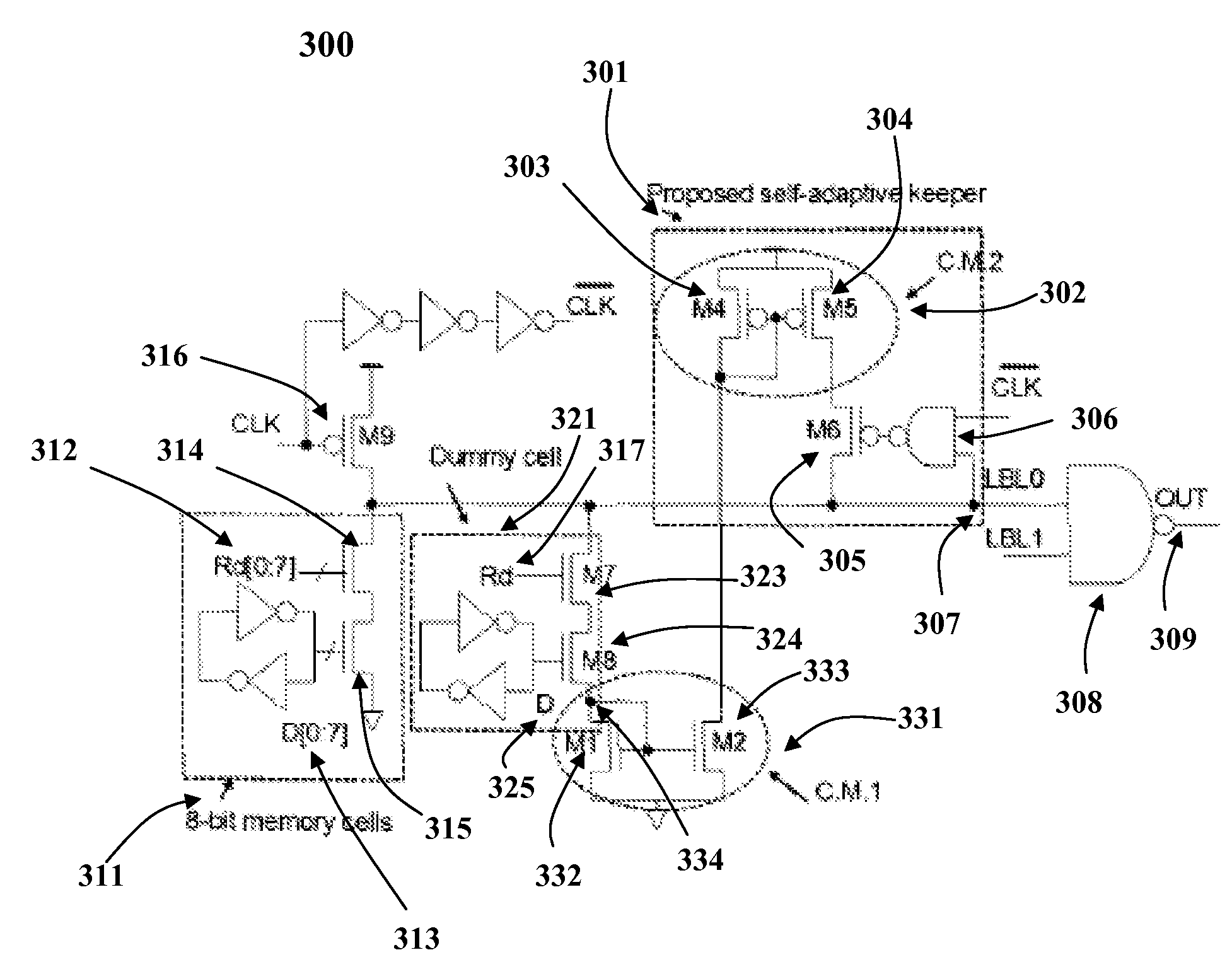
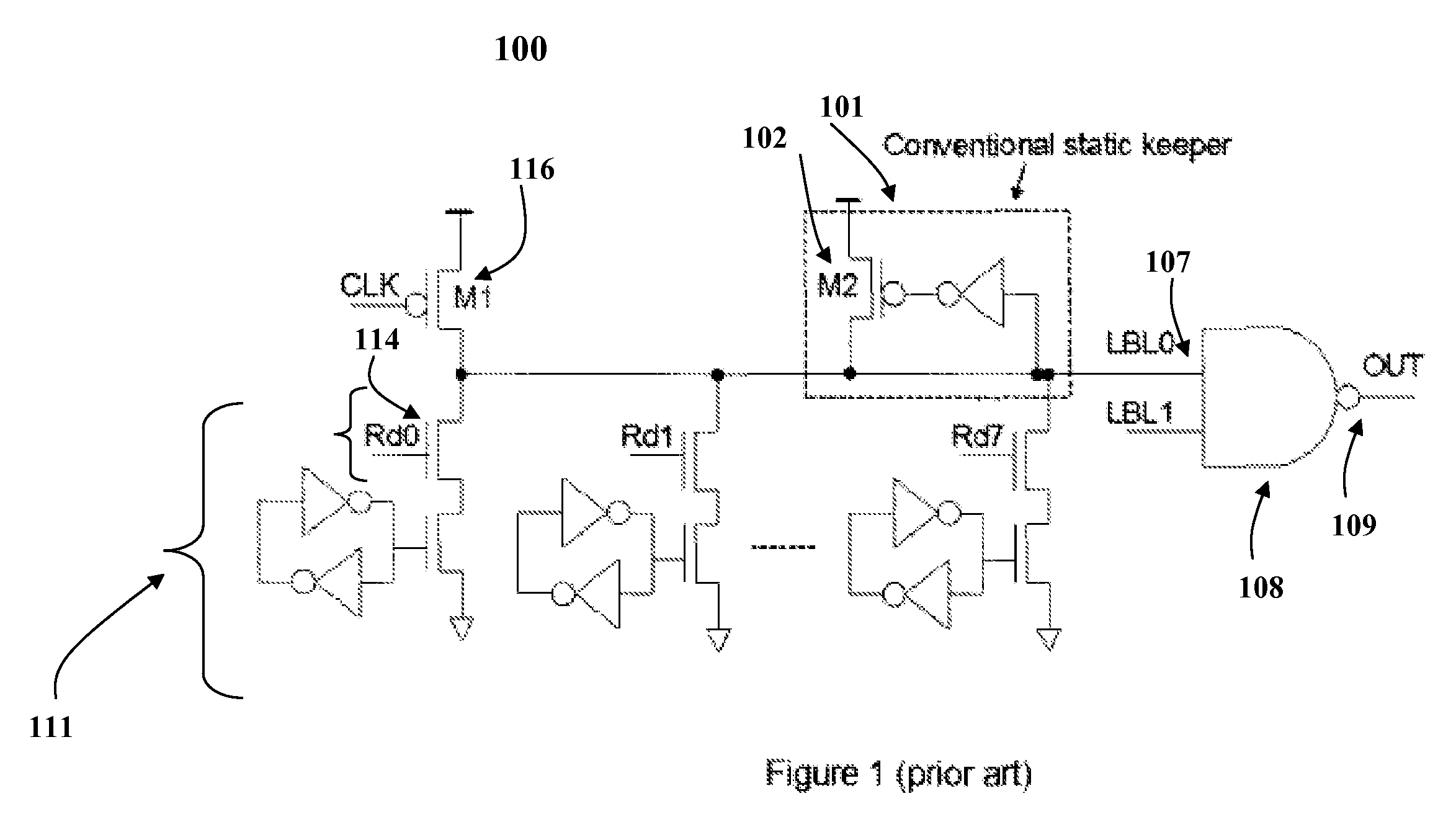
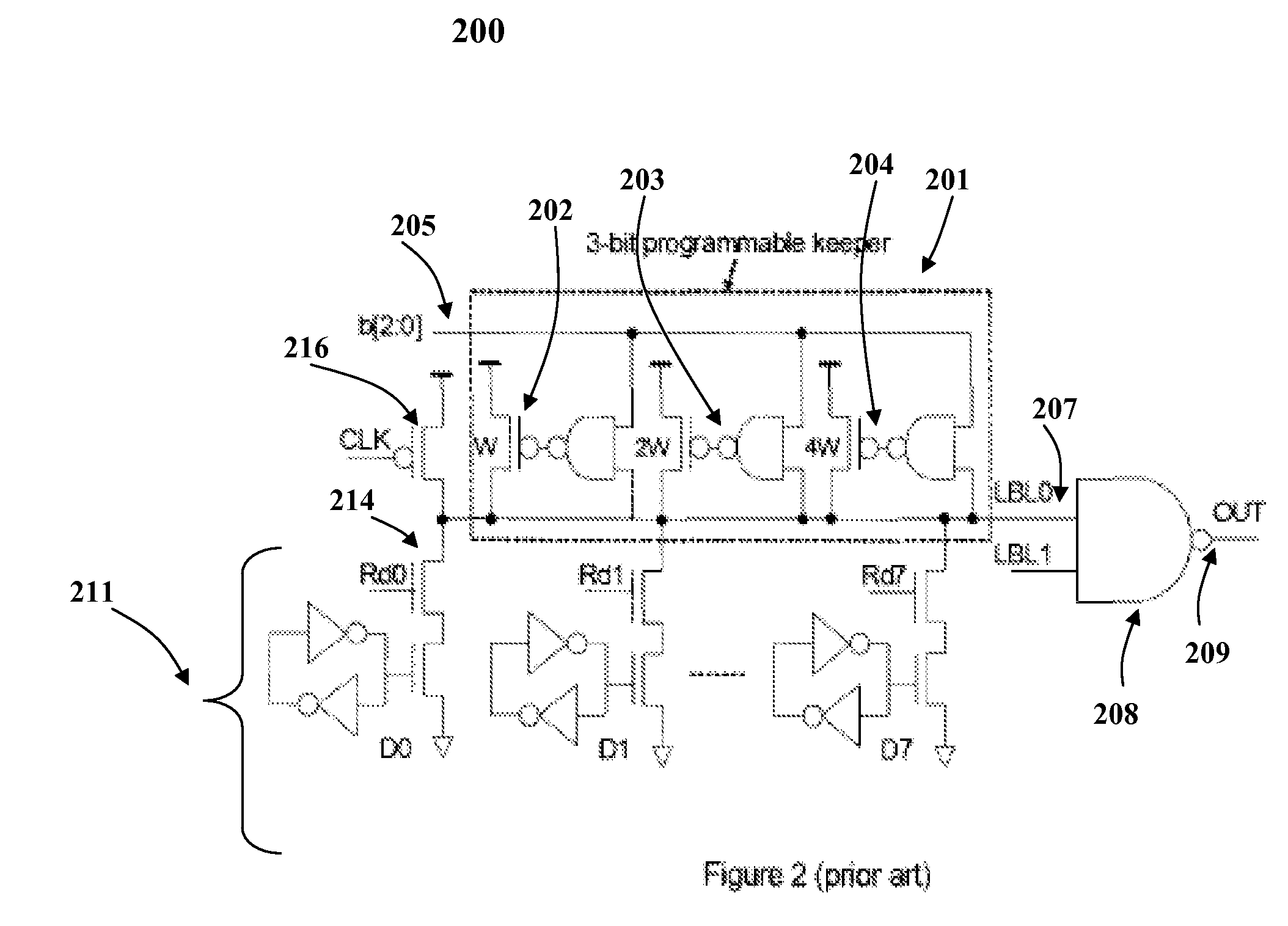
InactiveUS7417469B2Optimal current strengthEliminate the effects ofLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital storageVirtual cellVoltage drop
A method and system for automatically detecting and optimally compensating a wide range of die leakage currents in dynamic circuits is presented. A self-adaptive keeper tracks the leakage and reduces the leakage effects by optimally controlled compensation current. The self-adaptive keeper utilizes a 2-stage embedded current mirror circuit, a dummy cell and a keeper transistor to compensate leakage current. The load impact of the self-adaptive keeper on the dynamic circuit components (for example, the impact on memory cells) is minimized by a dummy cell which detects and matches the instant leakage current. Amplification in the 2-stage embedded current mirror circuit provides an optimal current strength in the keeper transistor. The optimally amplified leakage current is utilized to compensate for a leakage induced voltage drop at the circuit's output. Thus, the self-adaptive keeper ensures the robustness of the circuit in real time and does not create any negative trade-off on read latency.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Real time detecting device and method for optical glass roughness
InactiveCN1945205ATo achieve the purpose of real-time controlHigh precisionUsing optical meansOptoelectronicsOptical glass
The present invention is real-time roughness detecting device and method in optical glass polishing machine. By means of laser surface scattering principle, the incident angle of laser source beam to the measured optical glass surface is regulated to greater than or equal to the total reflection angle so as to separate scattered light from the reflected light, and the strengths of these two light beams are measured separately and converted into current strengths and the current strength ratio of these two light beams is calculated to calculate the roughness of the measured surface precisely. The present invention is non-destructive test, and has no damage to the tested workpiece and high detection precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device for measuring the intensity of an electric current and electric appliance including such device
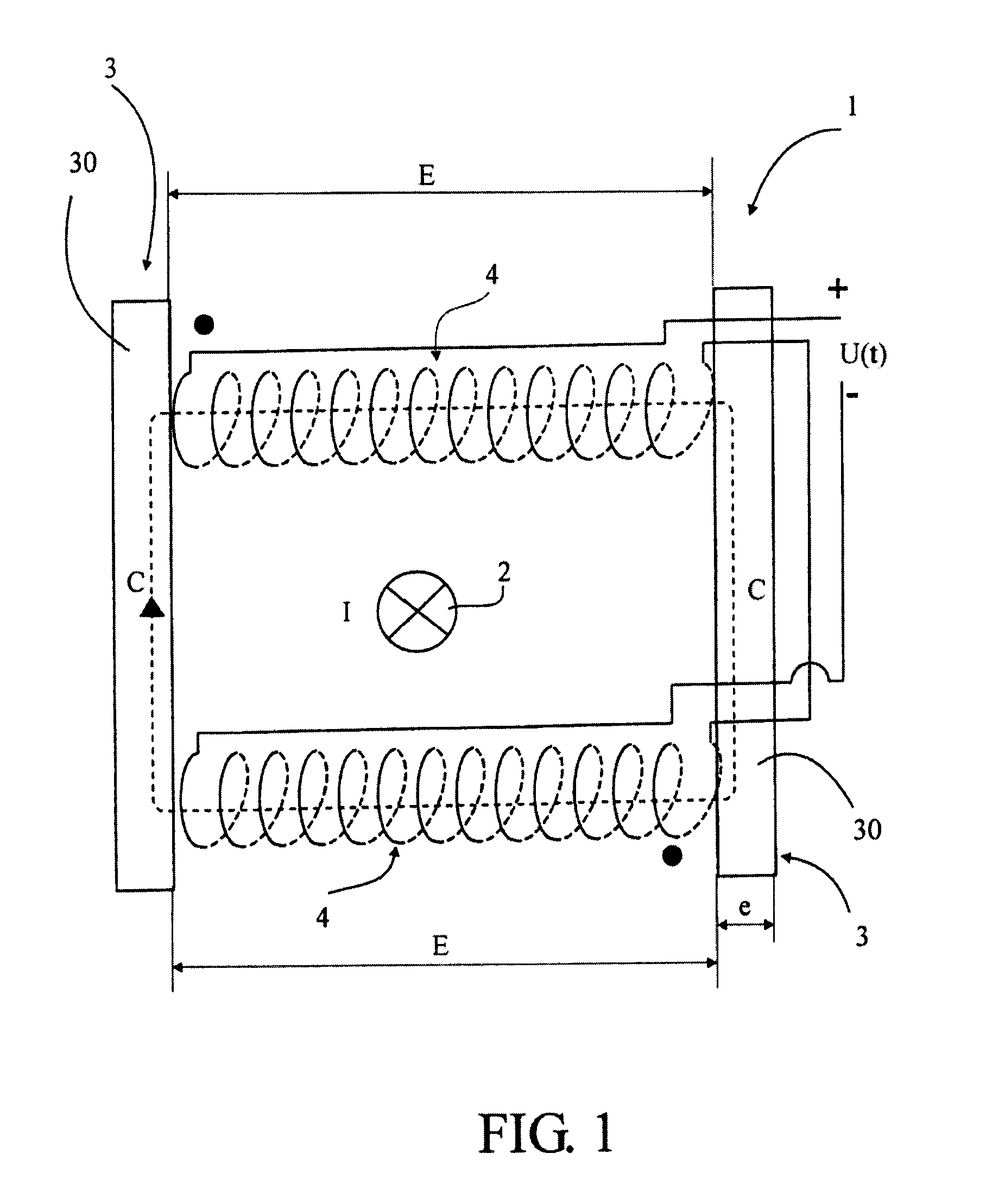
ActiveUS20100301836A1Simple and economic designEasy to integrateMeasurement using dc-ac conversionVoltage/current isolationElectrical conductorEnergy metering
A device for measuring the intensity of an electric current which has a simple and economical design and offers a high measurement dynamic compatible with combined measurement, protection and energy metering applications. The device (1) is insensitive to parasitic fields and to the position of the electric conductor to be measured, and that can be opened to facilitate placement thereof. The device (1) defines a closed path (C), about a conductor (2) for the circulation of the lines of magnetic field induced by the current to be measured, and the path is formed by two plates (30) having a high magnetic permeability separated by two air gaps (E) closed by two identical and opposed electric coils (4) for supplying a voltage proportional to the derivative of the intensity (I) of the current to be measured. The device (1) reduces the is compact so that it can be easily integrated into any type of electric appliance.
Owner:SOCOMEC
Compensation for leakage current variation by the utilization of an automatic self-adaptive keeper
InactiveUS20080111616A1Optimal current strengthEliminate the effects ofLogic circuits characterised by logic functionDigital storageVoltage dropEngineering
A method and system for automatically detecting and optimally compensating a wide range of die leakage currents in dynamic circuits is presented. A self-adaptive keeper tracks the leakage and reduces the leakage effects by optimally controlled compensation current. The self-adaptive keeper utilizes a 2-stage embedded current mirror circuit, a dummy cell and a keeper transistor to compensate leakage current. The load impact of the self-adaptive keeper on the dynamic circuit components (for example, the impact on memory cells) is minimized by a dummy cell which detects and matches the instant leakage current. Amplification in the 2-stage embedded current mirror circuit provides an optimal current strength in the keeper transistor. The optimally amplified leakage current is utilized to compensate for a leakage induced voltage drop at the circuit's output. Thus, the self-adaptive keeper ensures the robustness of the circuit in real time and does not create any negative trade-off on read latency.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for measuring atmospheric optical turbulent current profile based on imaging laser radar of laser light beam
ActiveCN103267969ARealize measurementImprove time resolutionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadarDivergence angle
The invention discloses a method for measuring an atmospheric optical turbulent current profile based on an imaging laser radar of a laser light beam. Laser light is emitted vertically upward by a laser emission unit, beam expanding is carried out on the laser light through a beam expanding mirror to reduce a divergence angle of the laser light, and the light beam is formed; a pupil plate is installed at the front end of a telescope objective lens of an optical receiving unit, an optical wedge mirror is installed on the pupil plate, a CCD is installed at the rear end of a telescope, and when the telescopic mirror is aligned to the laser light beam to image the light beam, due to beam split action of a light wedge, two light beam images in the vertical direction occur on a CCD target face; light beam images formed by various image elements of the CCD correspond to light beams on different heights, the jitter amount of the CCD images in the horizontal direction on the different heights are counted through the adoption of a differential image moving method, turbulent current information in the route of an imaging receiving face of the laser light beam can be obtained, then turbulent current information on different integral paths is analyzed, and a turbulent current strength profile is obtained. The method has high time resolution and space resolution, and is easy to implement and complete in theory.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for annealing and pickling 409L stainless steel
InactiveCN102864459AEffective adjustment of specific gravityEffectively adjust PH valueHeating timeElectrolysis
The invention discloses a method for annealing and pickling 409L stainless steel through neutral salt electrolyzing and mixed acid pickling technology. The method comprises the steps as follows: a, annealing, controlling the concentration of excess oxygen to 3 to 5%, controlling the heating temperature to 950-1100 DEG C, wherein the heating time is 1 to 3 minutes per millimeter based on thickness; b, electrolyzing, and controlling the specific gravity of neutral salt to 1.2 to 1.24, pH to 3.5 to 4.5, temperature to 70 to 90 DEG C, and current strength in electrifying to 4500 to 5500A; and c, pickling, wherein pickling solution in the first stage includes 9 to 13% of HNO3 and 0.1 to 0.2% of HF, pickling solution in the second stage includes 11 to 15% of HNO3 and 0.1 to 0.2% of HF, the temperature of the pickling solutions in the two stages is at 50 to 60 DEG C, and the pickling time is 30 to 50 seconds. With the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the collinear annealing and pickling of FeCr system and FeCrNi system stainless steels can be achieved; and good 2D surface can be obtained.
Owner:YUNNAN TIANGAO NICKEL IND CO LTD
Implantable medical devices evaluating thorax impedance
InactiveUS7970462B2Inter-pulse delays can be alteredReduce the amount requiredElectrotherapyCatheterElectrical resistance and conductanceMedicine
Implantable medical device with an impedance determination unit with constant current / voltage source having current feed terminals connected to electrodes for intracorporal placement which generates measuring current pulses having constant current / voltage, for causing a current through a body via intracorporally placed electrodes, a measuring unit for measuring voltage / current strength of voltage / current fed through body, an impedance value determination unit connected to the current / voltage source and adapted to determine an impedance value for each measuring current pulse, and an impedance measuring control and evaluation unit connected to the impedance determination unit which controls the unit and evaluates a sequence of consecutive impedance values, the impedance determination unit further adapted to determine at least intrathoracic and intracardiac impedance values for same period of time, the intrathoracic values sampled with a lower sampling rate than the intracardiac values.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Method for determining the opening point in time of a fuel injector
ActiveCN103270279AElectrical controlFuel injection apparatusInternal combustion engineControl valves
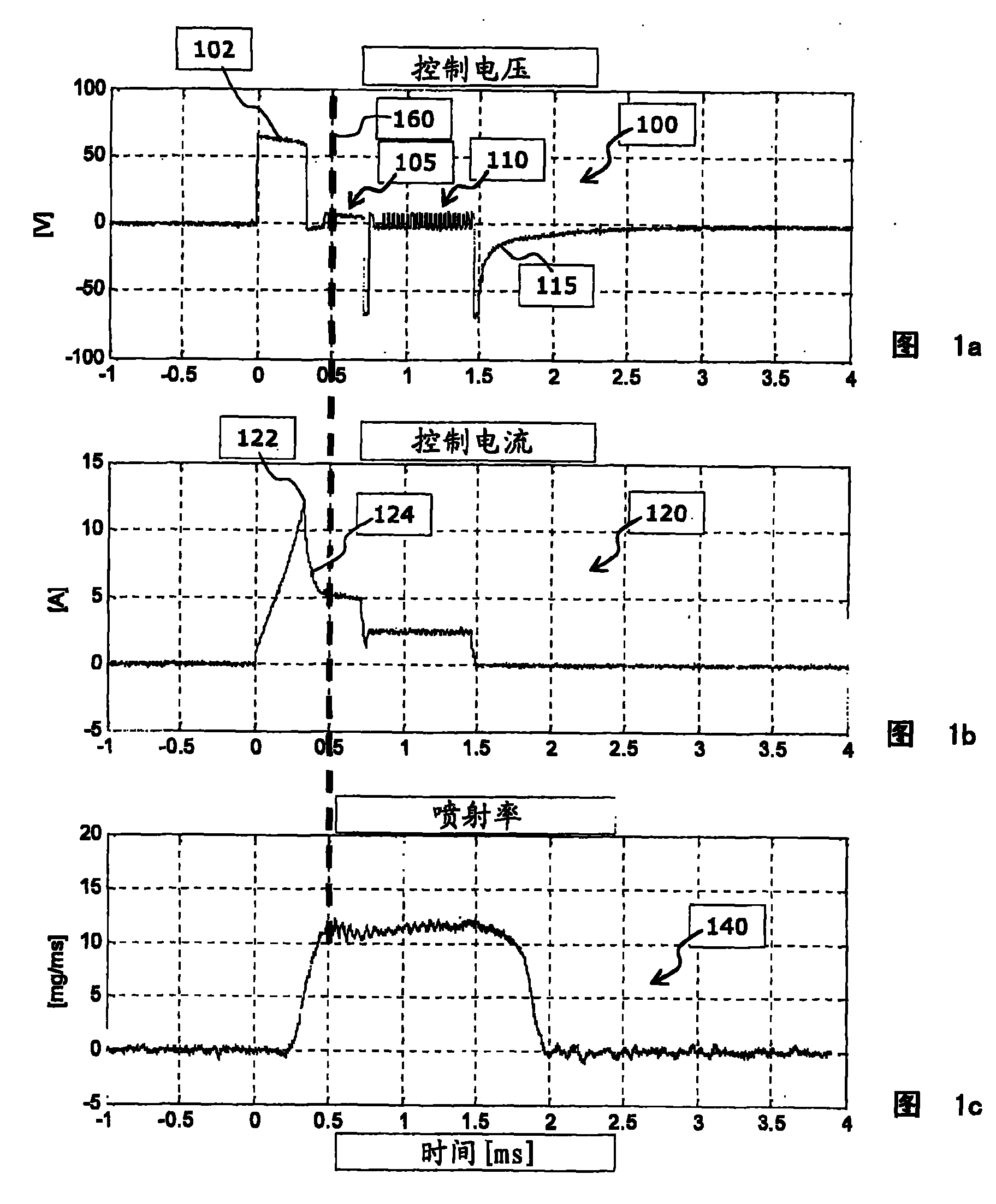
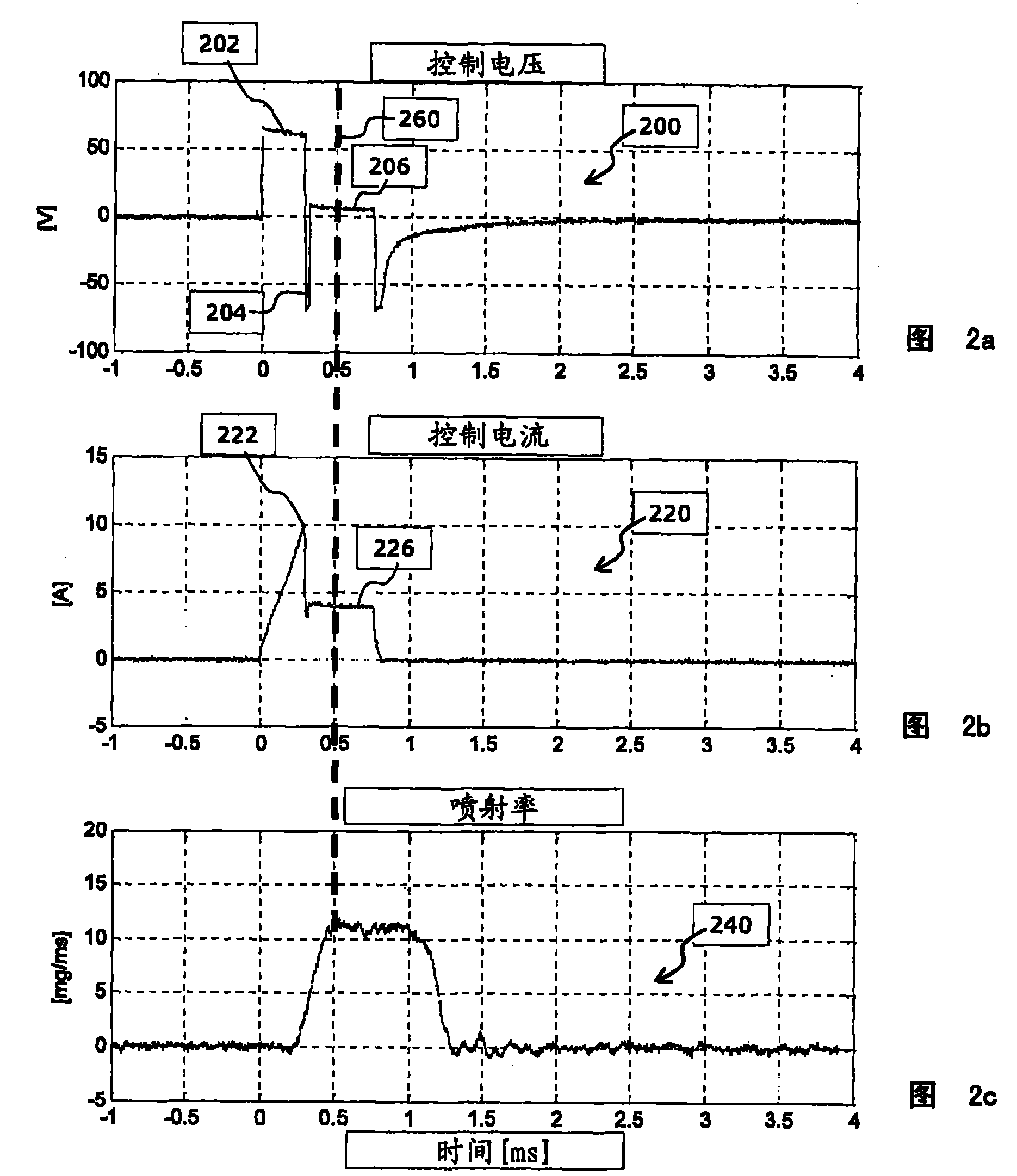
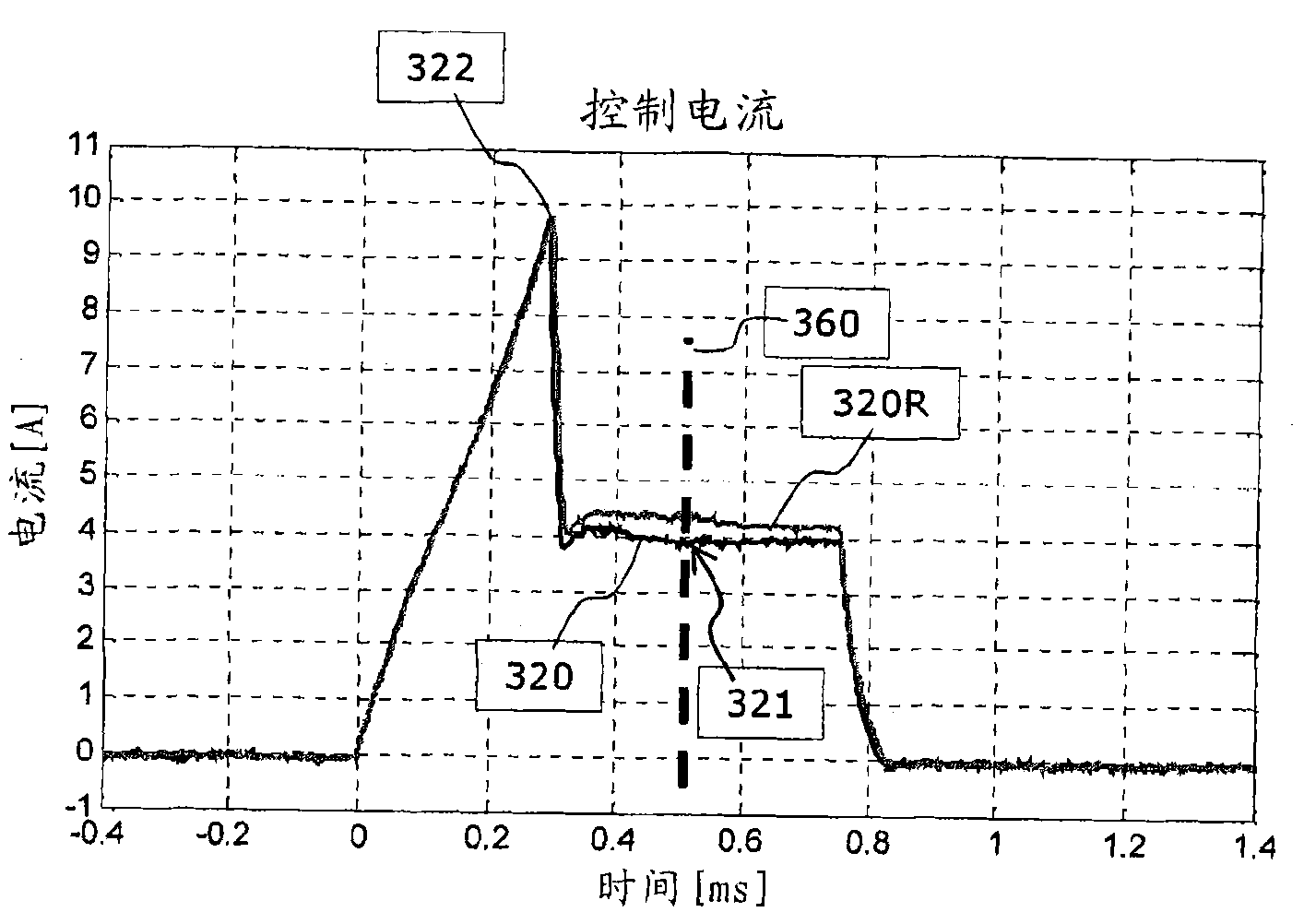
The invention relates to a method for determining the opening point in time of a control valve (520) having a coil drive of an indirectly driven fuel injector (500) for an internal combustion engine of a motor vehicle. The method comprises: (a) detecting the time curve of the current intensity of a current flowing through the coil drive, (b) determining a current integral with respect to the detected current intensity as a function of the time and starting from a defined initial time, and (c) determining a time at which the current integral reaches at least a predefined current integral reference value, wherein the determined time is the opening point in time of the control valve. The invention further relates to a corresponding device and to a computer programme for determining the opening point in time of a control valve of an indirectly driven fuel injector.
Owner:VTESCO TECH GMBH
Protector Device with Improved Capacity to Break Follow Current
InactiveUS20070223171A1Increase capacityConserving good capacitySpark gap detailsEmergency protective arrangement detailsOvervoltageCurrent strength
A device (1) to protect electrical equipment against transient overvoltages, comprising (i) a spark gap having an intrinsic follow current interrupting capacity and (ii) an element (5) for improving the follow current interrupting power, which co-operates with the spark gap (2) such that the resulting follow current interrupting capacity of the protective device (1) is essentially greater than the aforementioned intrinsic capacity. When the equipment has a suspected short-circuit current that exceeds the intrinsic interrupting capacity of the spark gap (2), element (5) comprises a means (6) for limiting the intensity of the electric current that can pass through the spark gap (2), said limiting means (6) being specifically designed and mounted in relation to the spark gap (2) in order to limit the intensity of the follow current, such that the follow current can be interrupted thanks to the intrinsic follow current interrupting capacity of the spark gap (2).
Owner:GUY LAFON +1
Modified electrical actuation of actuator for determining the time at which armature stops
ActiveCN103518241AGood sports characteristicsStable motion characteristicsElectrical controlMachines/enginesTemporal changePower flow
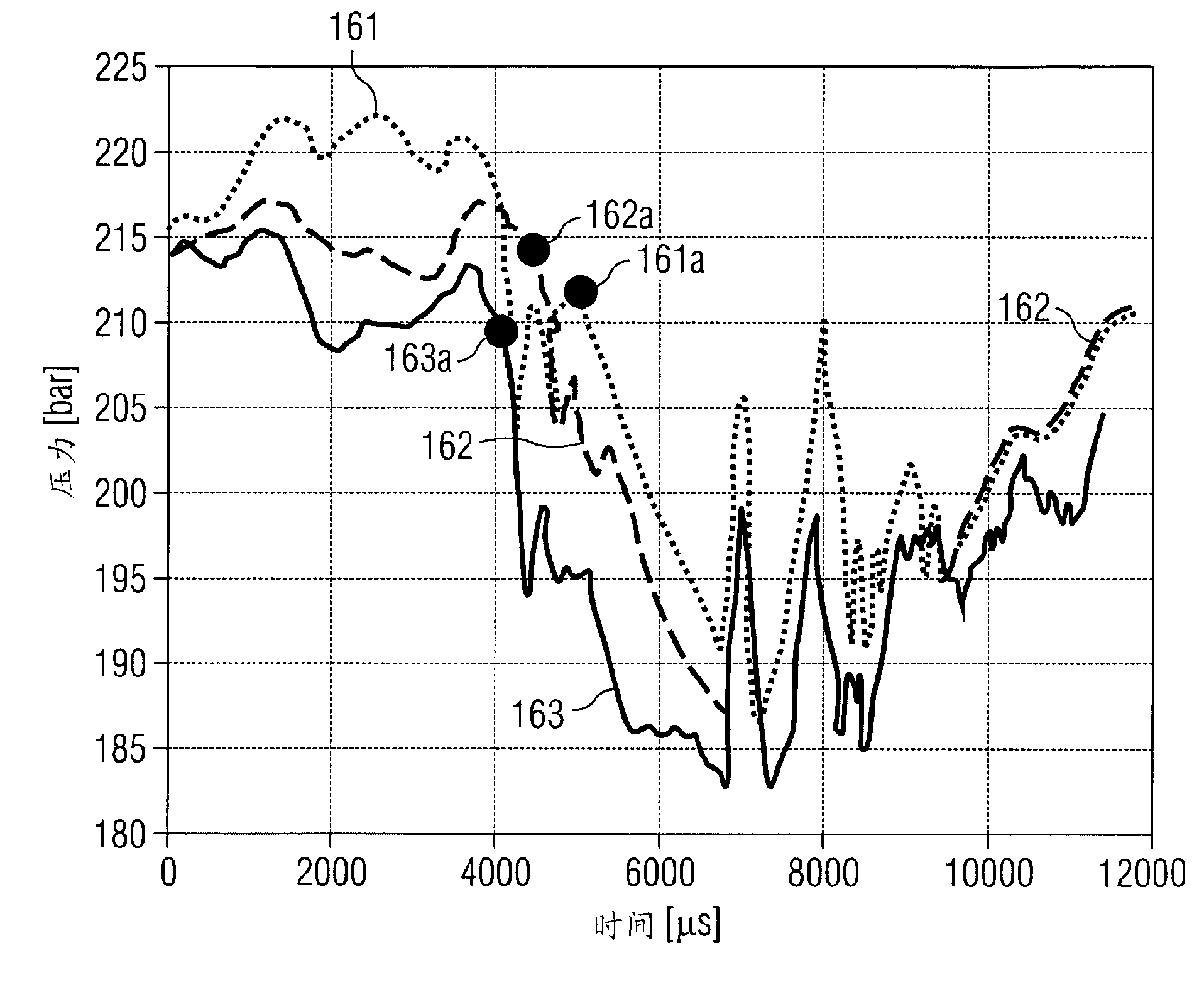
The invention describes a method for operating an actuator having a coil and a displaceably mounted armature, which is driven by a magnetic field which is generated by the coil, in a measurement operating mode for ascertaining a time (260) at which the armature reaches its stop position after activation of the actuator. The method comprises (a) applying to the coil an actuation voltage signal (200) which is dimensioned in such a way that the expected time (260) at which the armature stops falls in a time window (206) in which a temporally constant voltage is applied to the coil, (b) detecting the time profile (220) of the intensity of the current which flows through the coil within the time window (206), and (c) determining the time (260) at which the armature reaches its stop position, based on an evaluation of the detected time profile (220) of the intensity of the current. The invention also describes a method for operating an actuator of this kind, wherein information about the stop time is obtained in a measurement operating mode and this information can be used in a series operating mode for the purpose of optimized actuation of the actuator. The invention also describes an apparatus and a computer program for ascertaining a time at which a displaceably mounted armature reaches a stop position after activation of an actuator.
Owner:VTESCO TECH GMBH
Synthesis method of 1,2,4-triazolohetercyclic compound
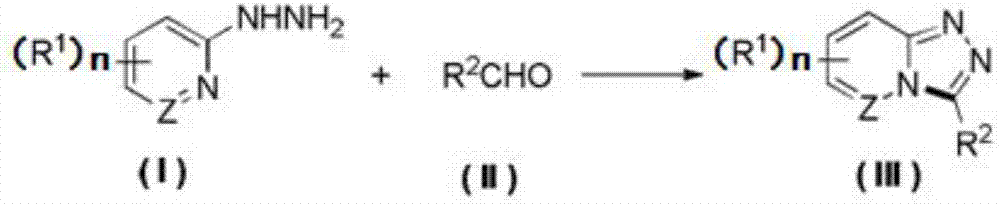
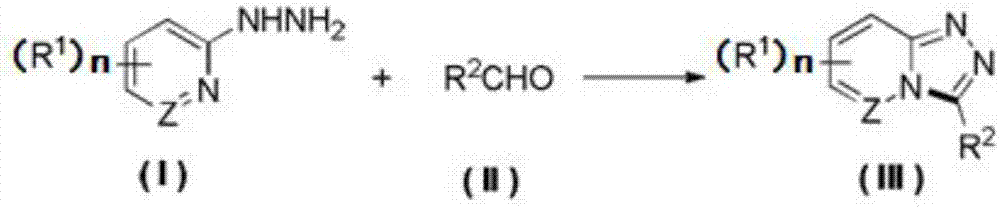
ActiveCN107474047AHigh yieldSimple reaction systemOrganic chemistryElectrolysis componentsSynthesis methodsHydrogen molecule
The invention provides a method for synthesizing a 1,2,4-triazolohetercyclic compound. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a 2-hydrazinohetercyclic compound (I) and an aldehyde compound (II) into acetonitrile A; stirring at 25 DEG C to 80 DEG C and reacting for 1h to 8h; then adding tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate, acetonitrile B and water; taking a graphite carbon rod as an anode and a platinum sheet as a cathode; switching on a power supply and electrifying for 3h to 8h, wherein the current strength is 15mA / mmol to 30mA / mmol according to the amount of substance of the aldehyde compound (II); carrying out post-treatment on a reaction solution to obtain the product 1,2,4-triazolohetercyclic ring compound (III). The method has the advantages of simple reaction system, easiness for obtaining raw materials and high total yield; the 2-hydrazinohetercyclic compound and the aldehyde compound are subjected to electrochemical catalysis to obtain the 1,2,4-triazolohetercyclic compound in one step; only one water molecule and one hydrogen molecule are removed and the atomic economy is extremely high; the formula is shown in the description.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Whole induction heating temperature control method for support rollers
ActiveCN104805276AMeet the process requirementsUniform hardnessIncreasing energy efficiencyFurnace typesTemperature controlHeating time
The invention relates to a whole induction heating temperature control method for support rollers. According to the method, an induction coil is divided into five sections, wherein the current strengths of the induction coil upper section, the induction coil sub-upper section, the induction coil sub-lower section and the induction coil lower section are 80-120% of the current strength of the induction coil middle section; and then the support roller is heated, wherein the support roller rotates through a support member along the axis line during the heating process and performs reciprocating movement through the support member along the axis line during the heating process, the whole heating process is divided into the stage using high-power heating to achieve the roller surface target temperature and the stage using heating with a plurality of small powers to carry out thermal insulation, the total heating time is controlled at 90-240 min, and the support roller surface axial temperature difference is controlled within + / =10 DEG C. With the method of the present invention, the temperature distribution of the work-piece can completely meet the process requirements, the ideal work-piece surface hardness layer can be obtained, and the method has characteristics of production cost reducing, significant energy saving effect, cleaning property, and environmental protection.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for handling organic wastewater based on Fenton reaction
InactiveCN102020384AImprove current efficiencyReduce concentration polarizationMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by oxidationFenton reactionDC - Direct current
The invention discloses a method for handling organic wastewater based on Fenton reaction, comprising the following steps of: (1) high-voltage pulse electric coagulating reaction: regulating the pH value of wastewater to be 3-4 so that wastewater performs high-voltage pulse electric coagulating reaction in a high-voltage pulse electric coagulating device at the current intensity of 1-30A, wherein the electric coagulating reaction time ranges from 30-120min, the high-voltage pulse electric coagulating device is input by the 100-400V alternating current which is then converted into direct current after rectification, the pulse voltage of 80V to 350V is formed by utilizing a pulse generator, the anode and cathode plates adopted by the high-voltage pulse electric coagulating device are iron plates with the carbon content above 0.45wt% and the space between the polar plates ranges from 10-30mm; (2) Fenton reaction; and (3) concrete precipitation reaction. Compared with the prior art, the invention reduces the handling cost, shortens the handling time and ensures better handling effect.
Owner:JIANGSU SUJING GROUP +1
Device and method for radio frequency ablation (RFA)
ActiveUS20130012937A1Foolproof connectivityAccurate connectionDiagnosticsSurgical needlesPower flowSwitch box
A device for radio frequency ablation (RFA) of diseased tissue hasa mesh or plate with a grid of holes for holding electrodes;a plurality of electrodes with adaptable active tip length;means for visualizing and probing insertion depth of each of the electrodes in the diseased tissue;a switch box, connectable to the electrodes and adapted to distribute current between the electrodes during the RFA process;a control unit for controlling the switch box; andmeans for monitoring radio RFA process.The control unit is adapted to determine groups of electrodes, an electric mode for activation of each group of electrodes, a polarity for electrodes within each group of electrodes, an activation mode for the groups, a time interval and order for activation of the groups, a power output and current strength, and a duration of the RFA process.
Owner:VESALIUS MEDICAL TECH
Electromagnetic interference prediction method and system
ActiveCN109828162AEasy to buildOvercome deficienciesElectrical testingElectromagentic field characteristicsElectromagnetic interferencePrediction system
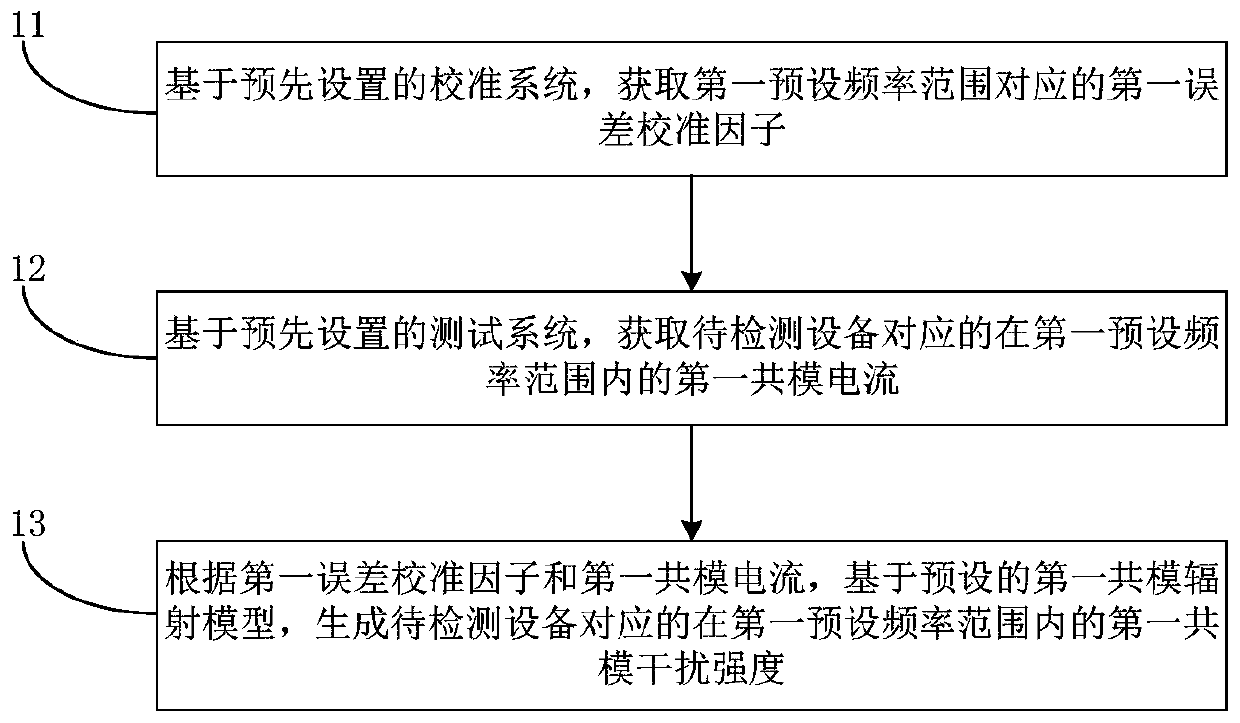
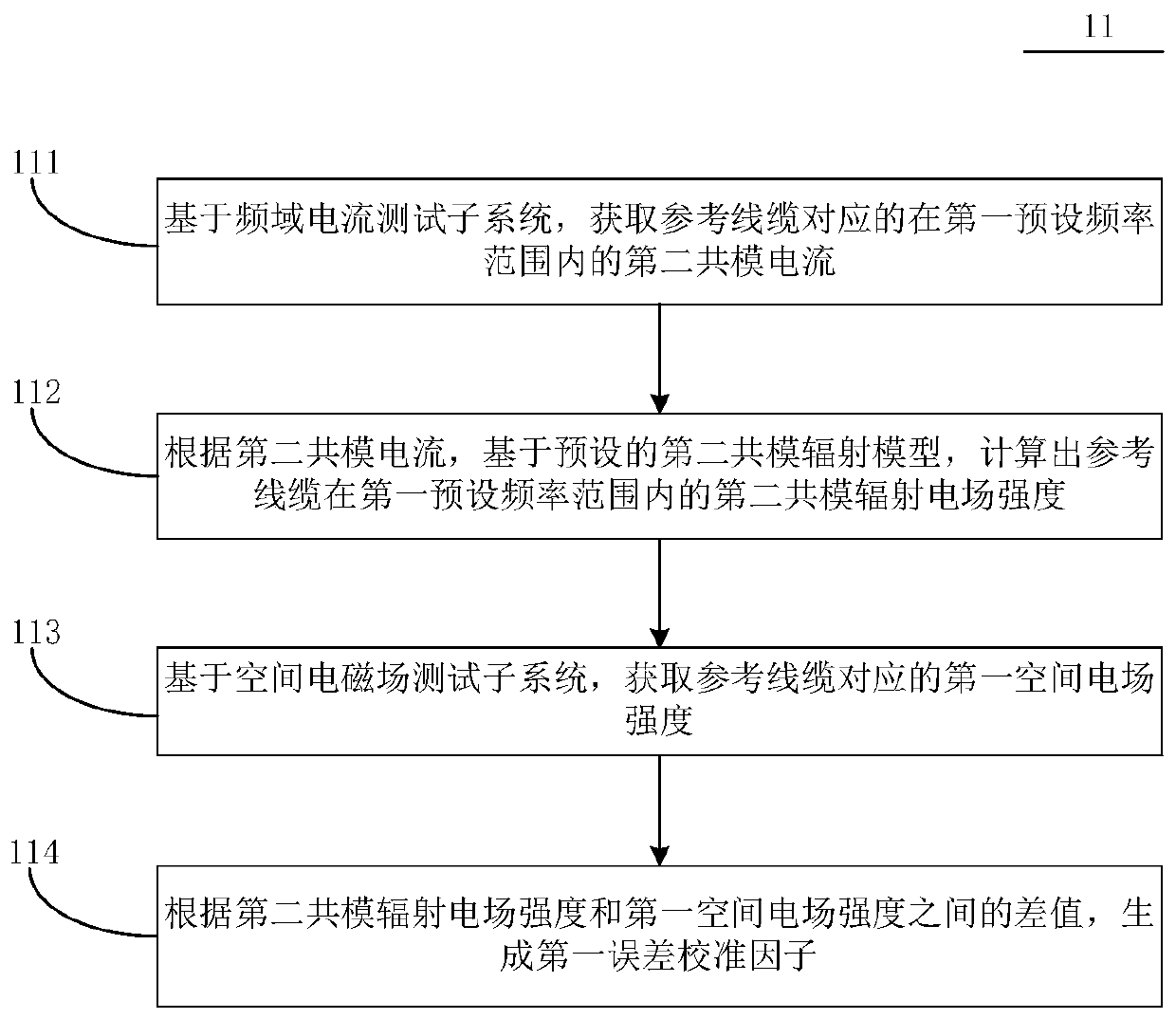
The present invention provides an electromagnetic interference prediction method. The method includes the following steps that: a first error calibration factor corresponding to a first preset frequency range is obtained based on a preset calibration system; first common-mode current within the first preset frequency range corresponding a device to be detected is obtained according to a preset test system; and first common-mode current strength within the first preset frequency range corresponding the device to be detected is generated on the basis of a preset first common-mode radiation modeland according to the first error calibration factor and the first common-mode current. The present invention also provides an electromagnetic interference prediction system.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Superconducting magnet configuration with switch
InactiveUS20070024404A1Less susceptible to quenchHigh currentMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSuperconducting CoilsEngineering
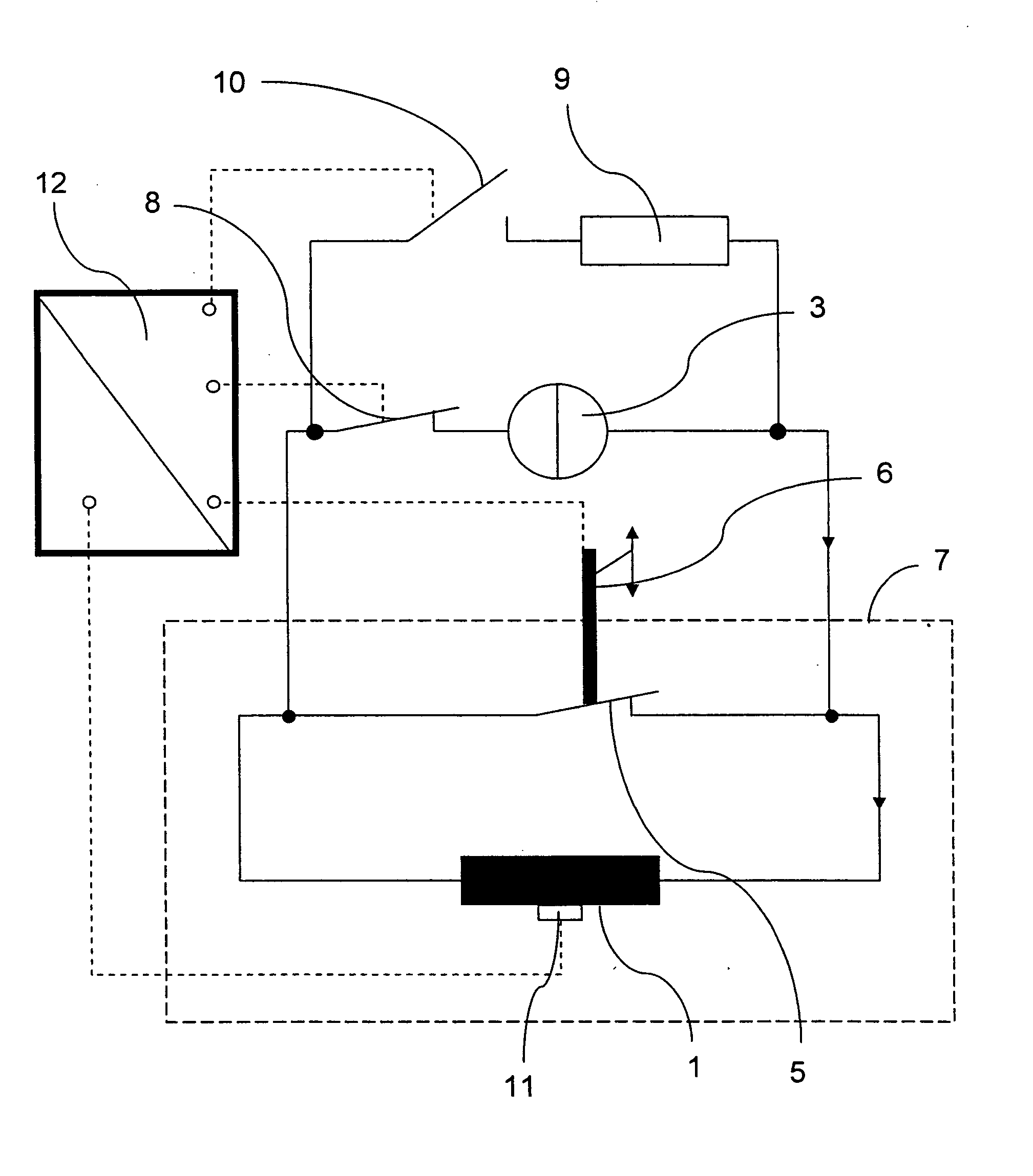
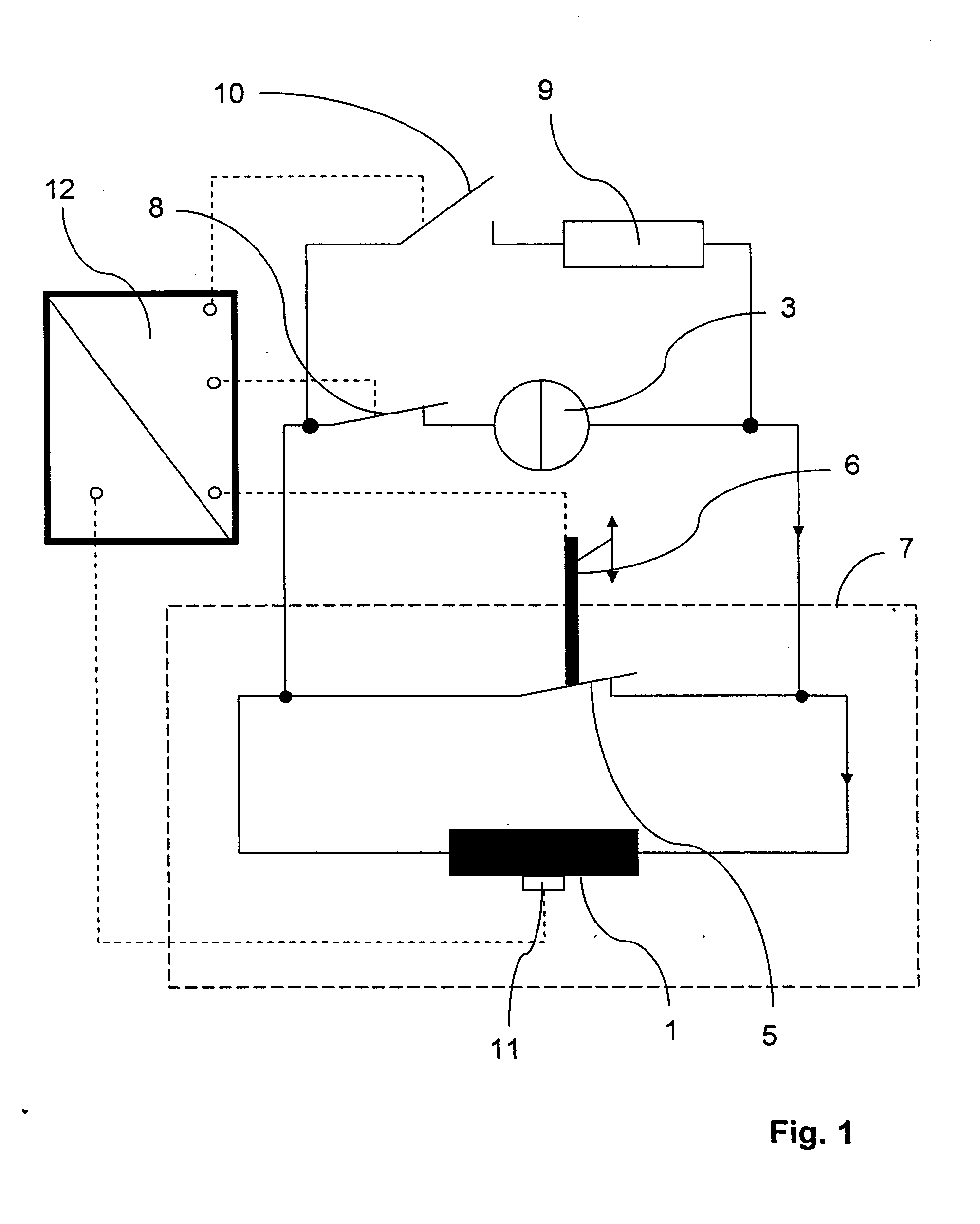
A superconducting magnet configuration with a magnet coil (1) of inductance L which is disposed in a cryostat (7) at a cryogenic temperature, for generating a temporally stable magnetic field, in a working volume, which is suitable for NMR measurements, and with current feed lines to an external current source (3) via which a current of a current strength IPS can be supplied, wherein, at a cryogenic temperature, the magnet coil (1) can be exclusively short-circuited via a switch (5), is characterized in that the switch (5) is normally conducting and comprises a mechanically operable bridge (6) with an ohmic resistance R1 which can be predetermined. The inventive magnet configuration ensures straightforward stable permanent operation via a mains supply even at high currents (>1000A) and also effective discharge of the energy released during a quench.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com