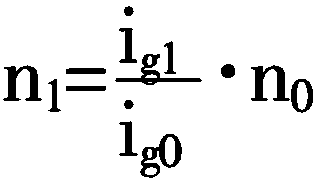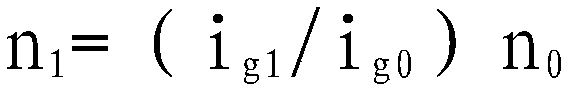Patents
Literature
69 results about "Ramp function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The ramp function is a unary real function, whose graph is shaped like a ramp. It can be expressed by numerous definitions, for example "0 for negative inputs, output equals input for non-negative inputs". The term "ramp" can also be used for other functions obtained by scaling and shifting, and the function in this article is the unit ramp function (slope 1, starting at 0).
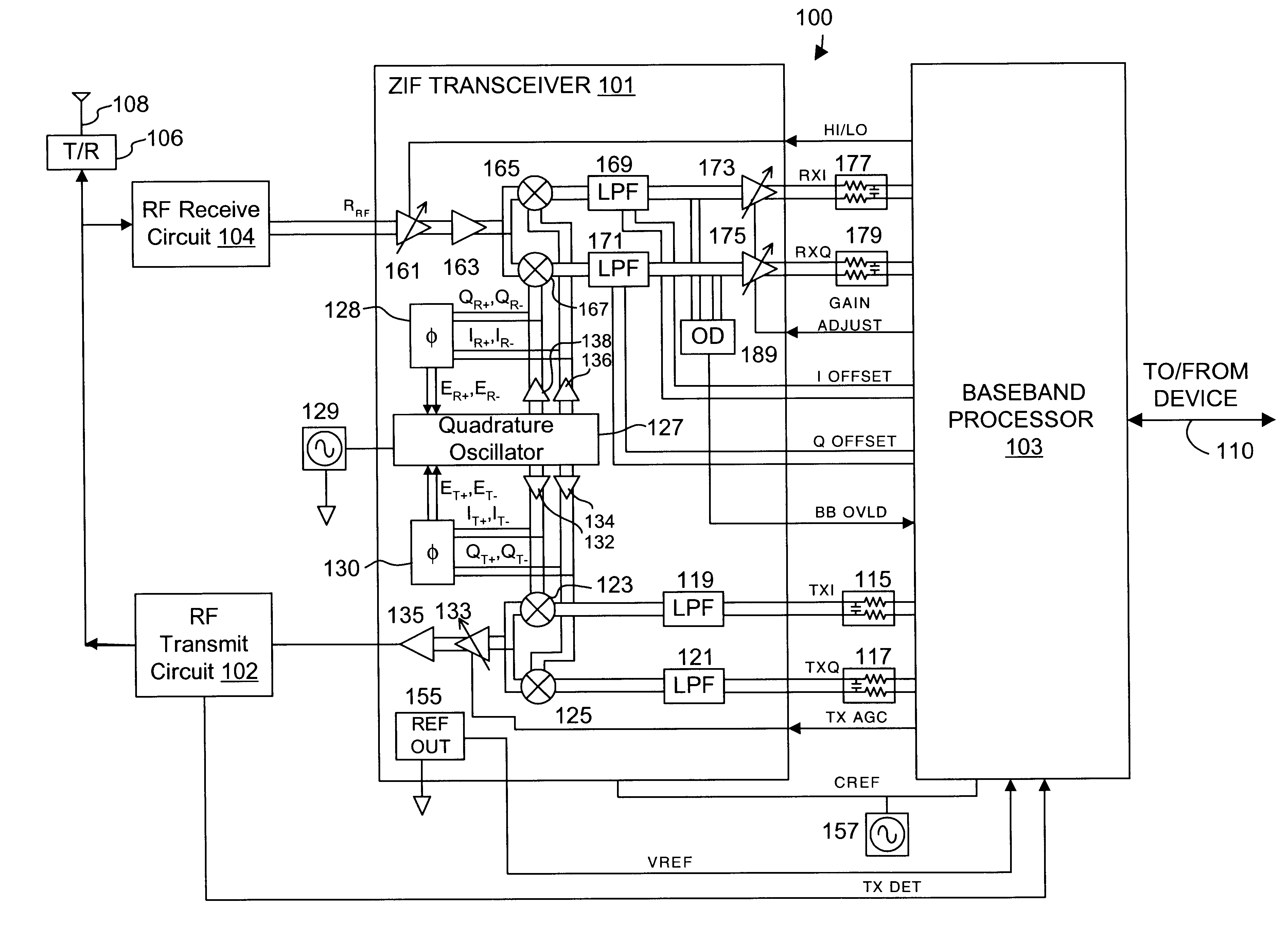
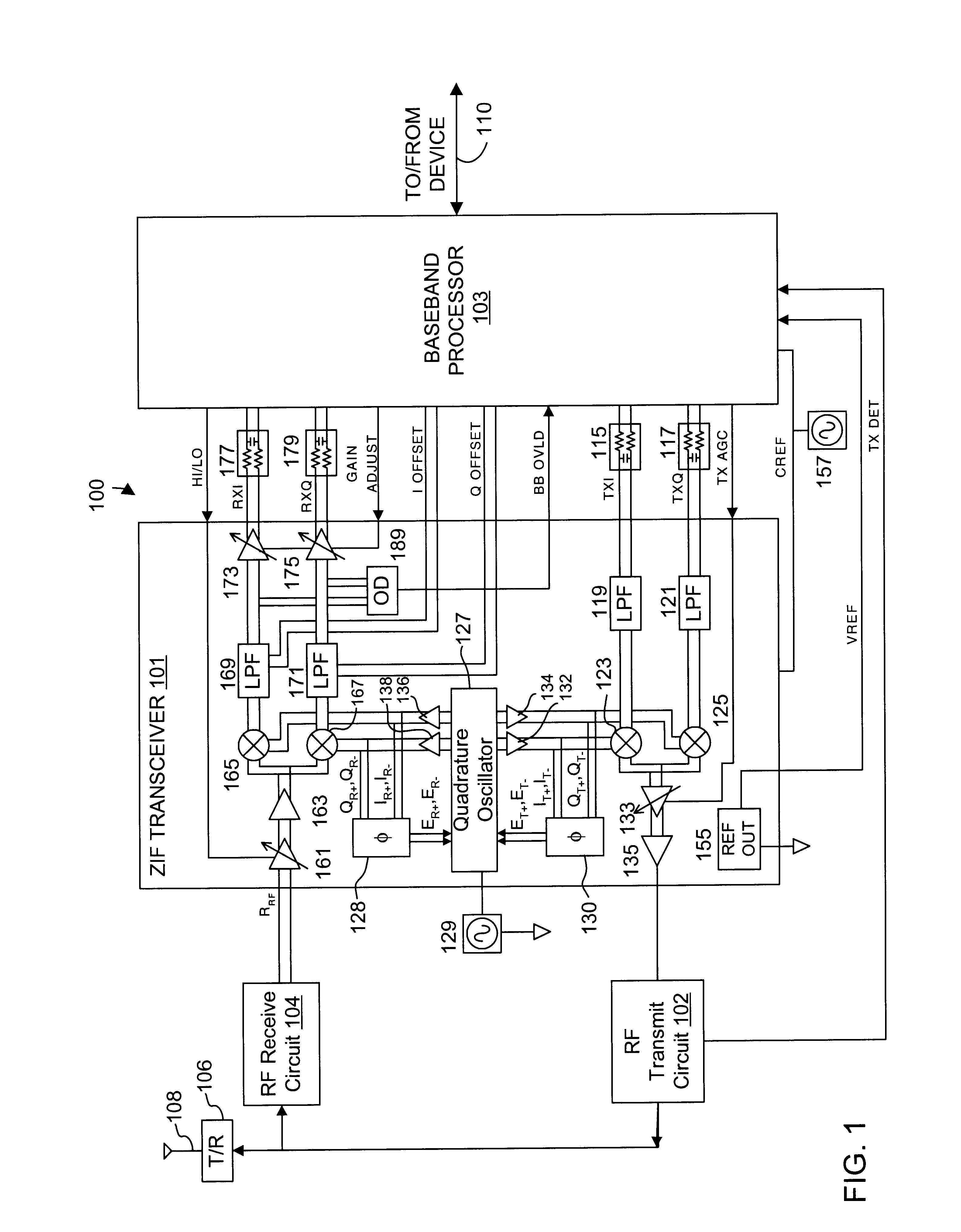
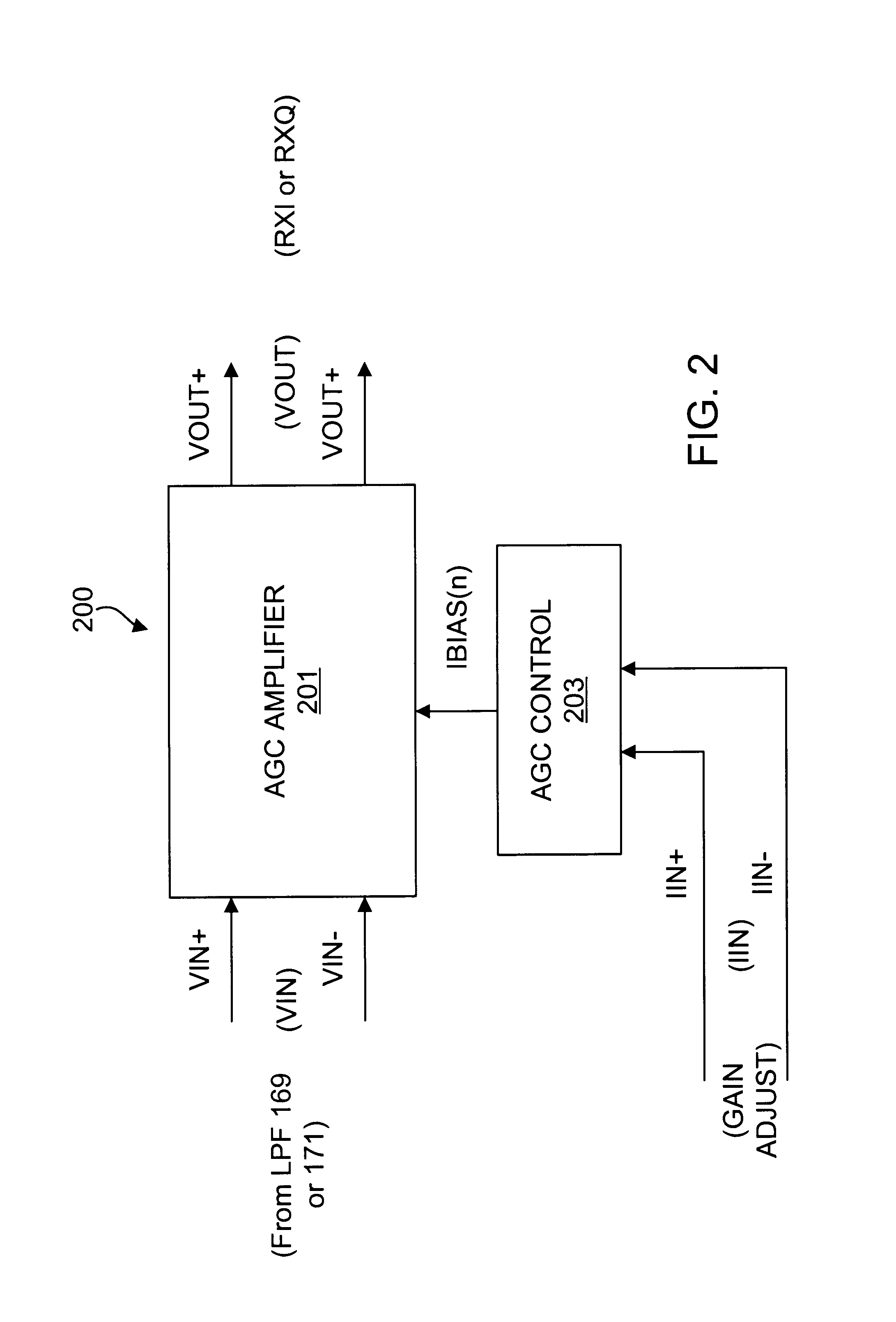
Precision automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS6763228B2Low absolute gain toleranceImprove matchResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierClosed loop
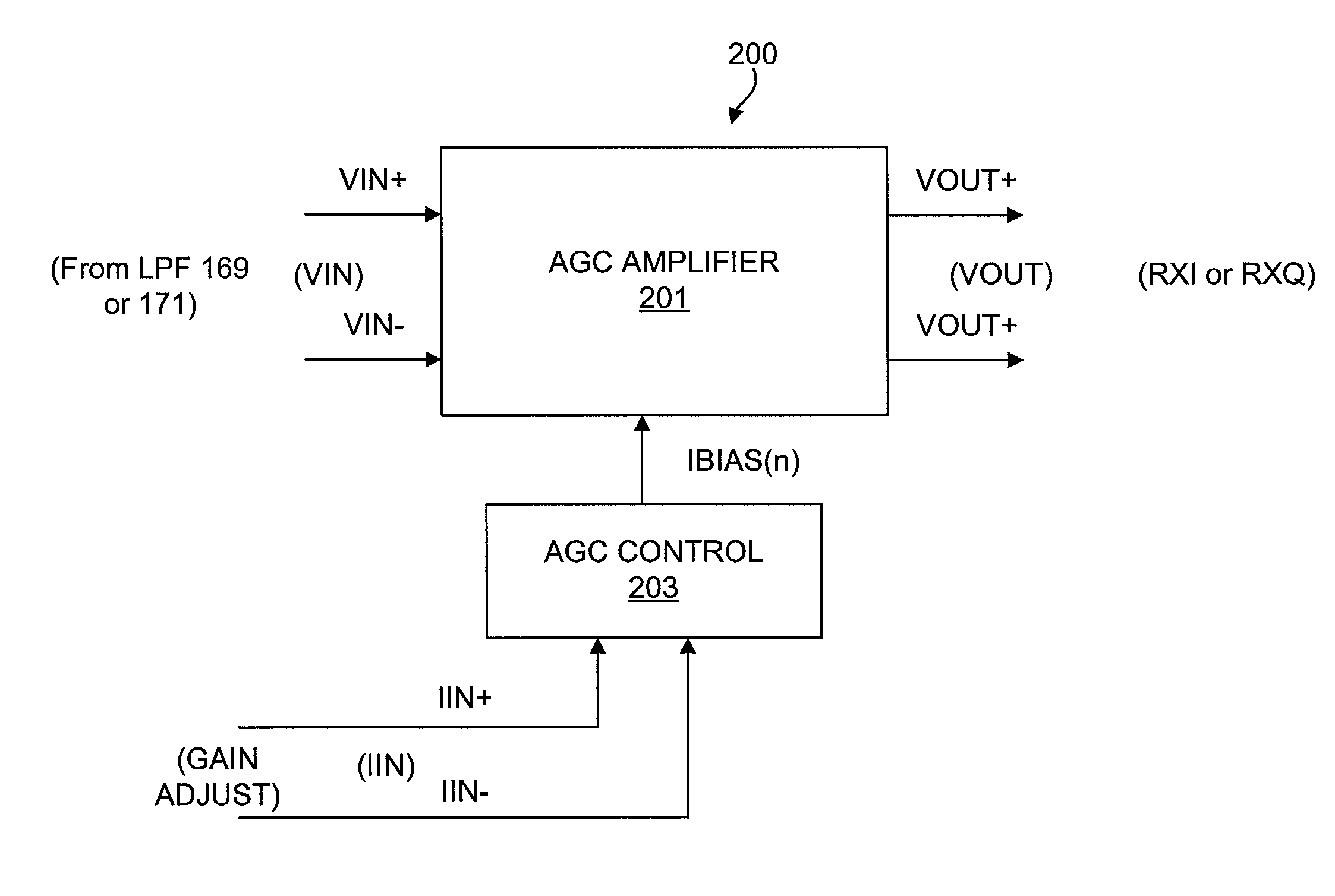
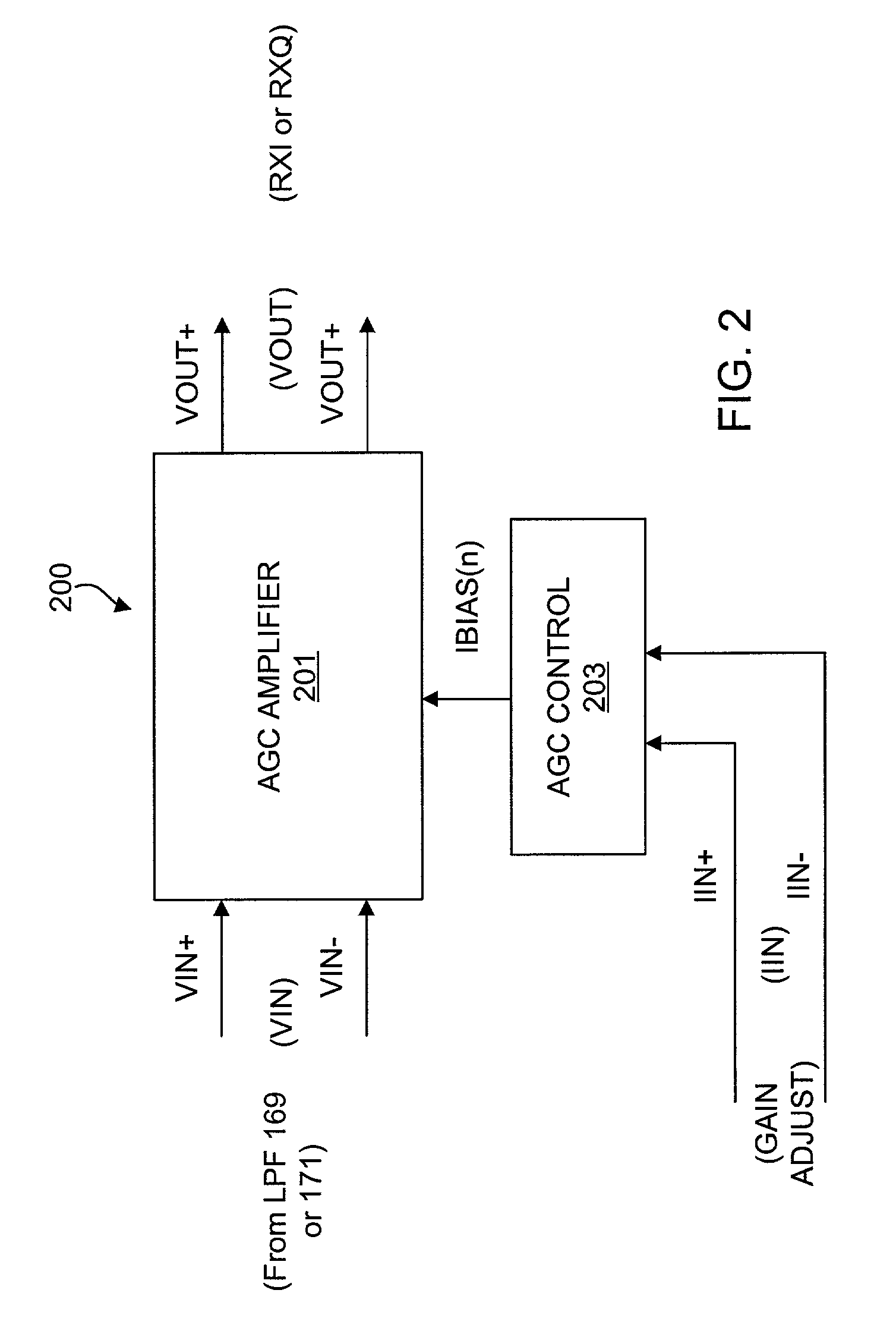
An automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier including a high gain transimpedance amplifier, a resistive feedback network and multiple transconductance stages coupled in the feedback path of the AGC amplifier. The feedback network receives an input signal and is coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and has multiple intermediate nodes. Each transconductance stage has an input coupled to an intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. Each transconductance stage is independently controllable to position a virtual ground within the feedback network to control closed loop gain. Each transconductance stage may have a bias current input coupled to a bias current control circuit. The control circuit controls each bias current to vary the gain of the AGC amplifier. The bias currents may be linearly controlled employing a ramp function to achieve a linear in dB gain response.
Owner:M RED INC
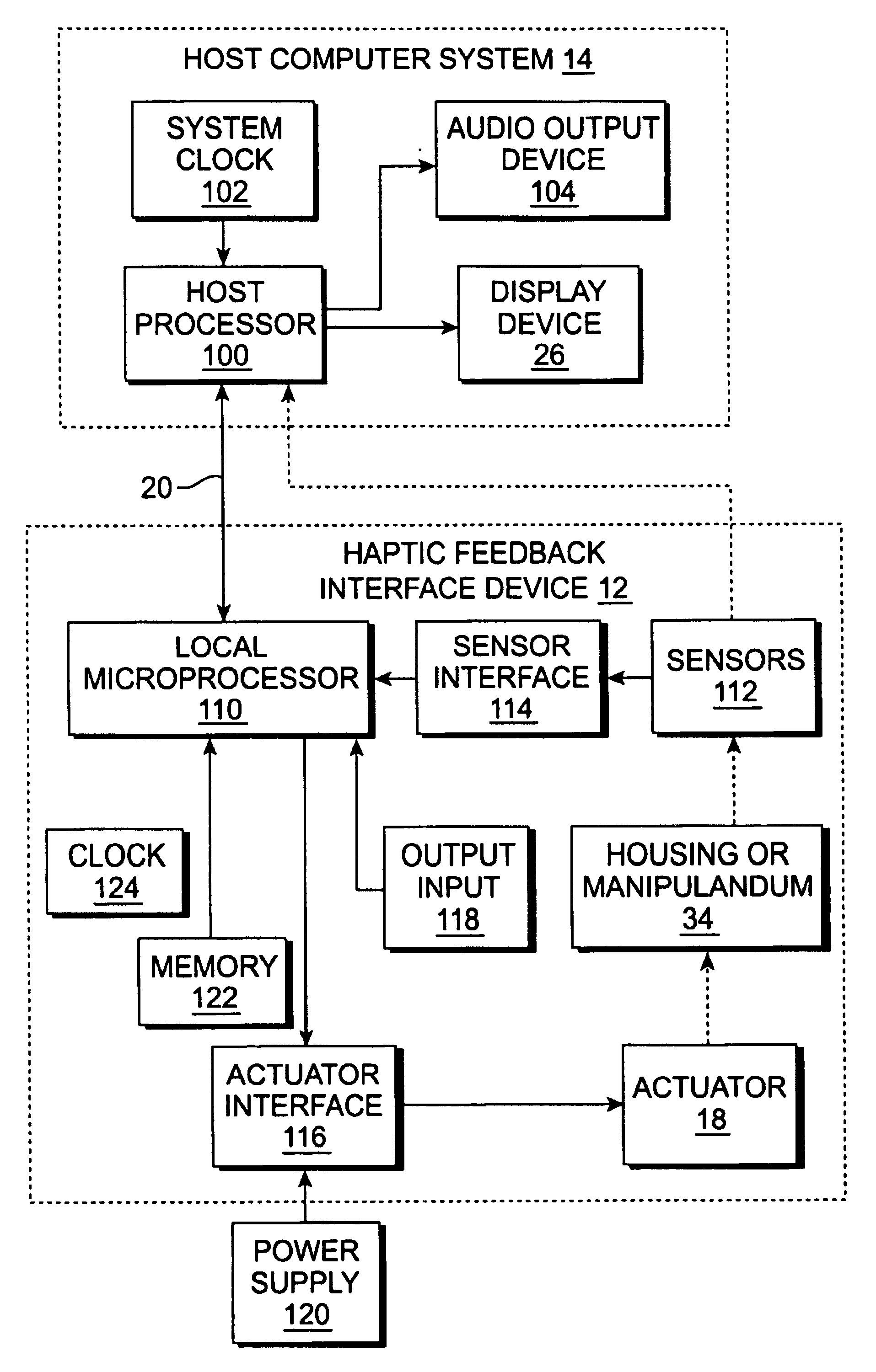
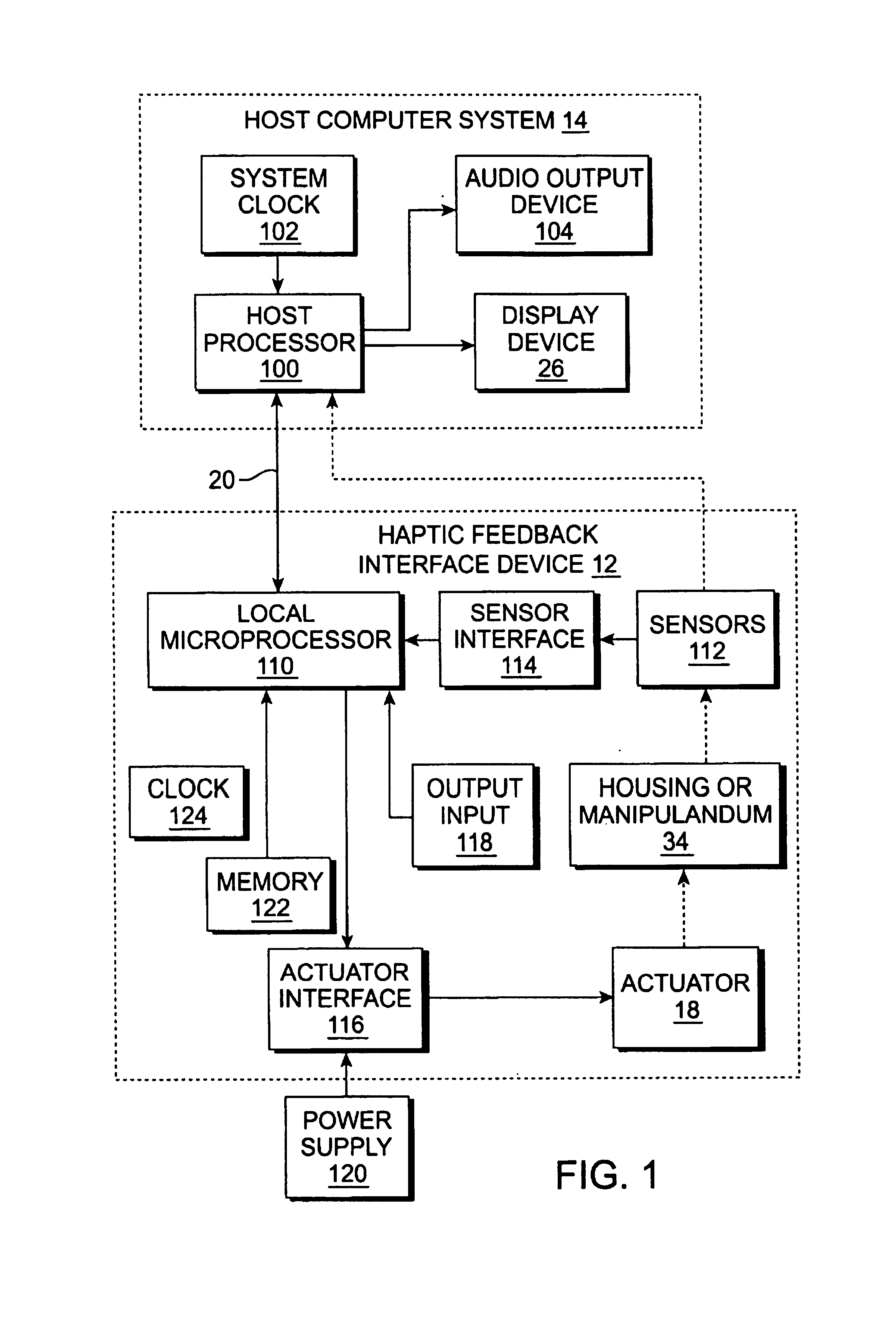
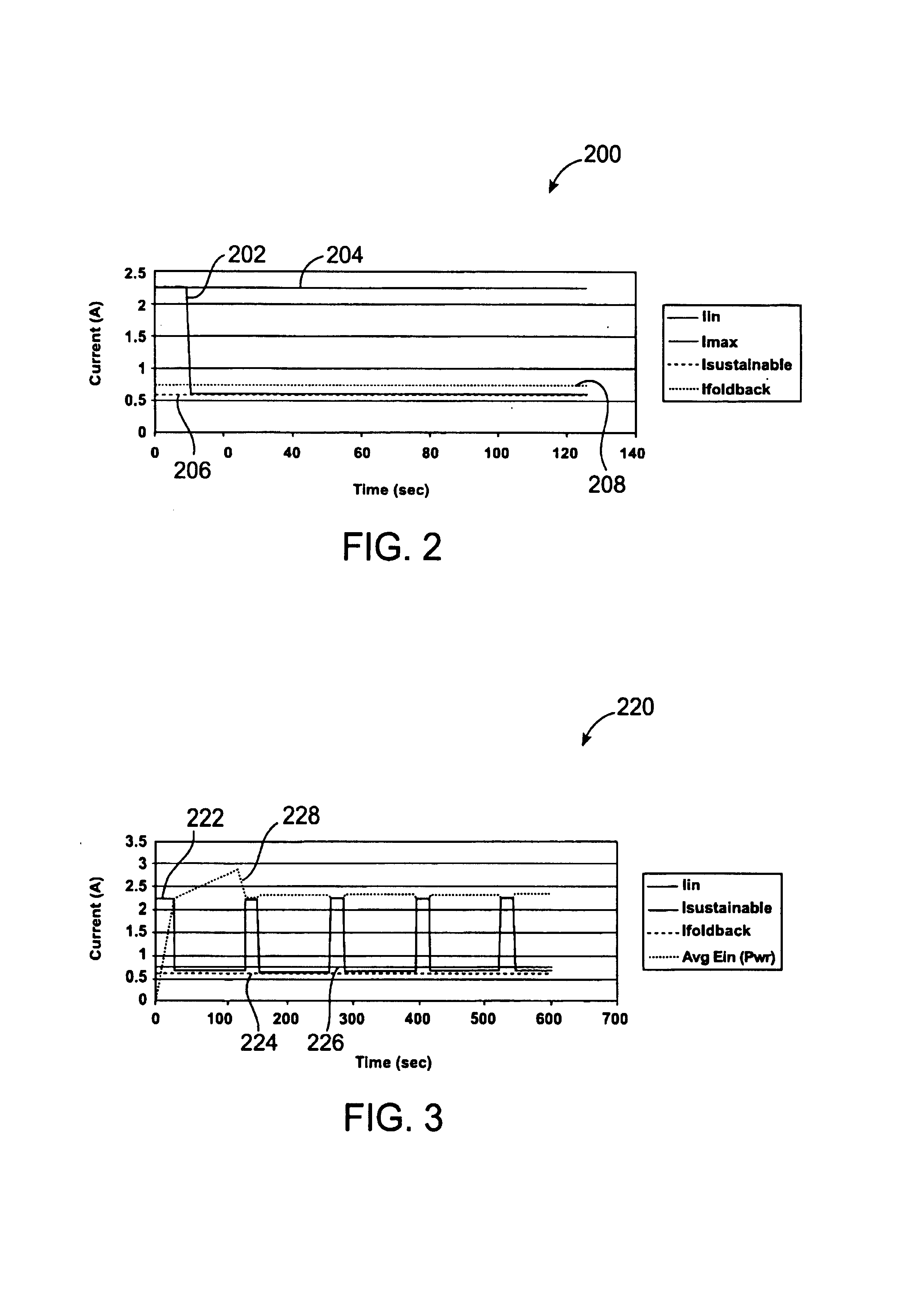
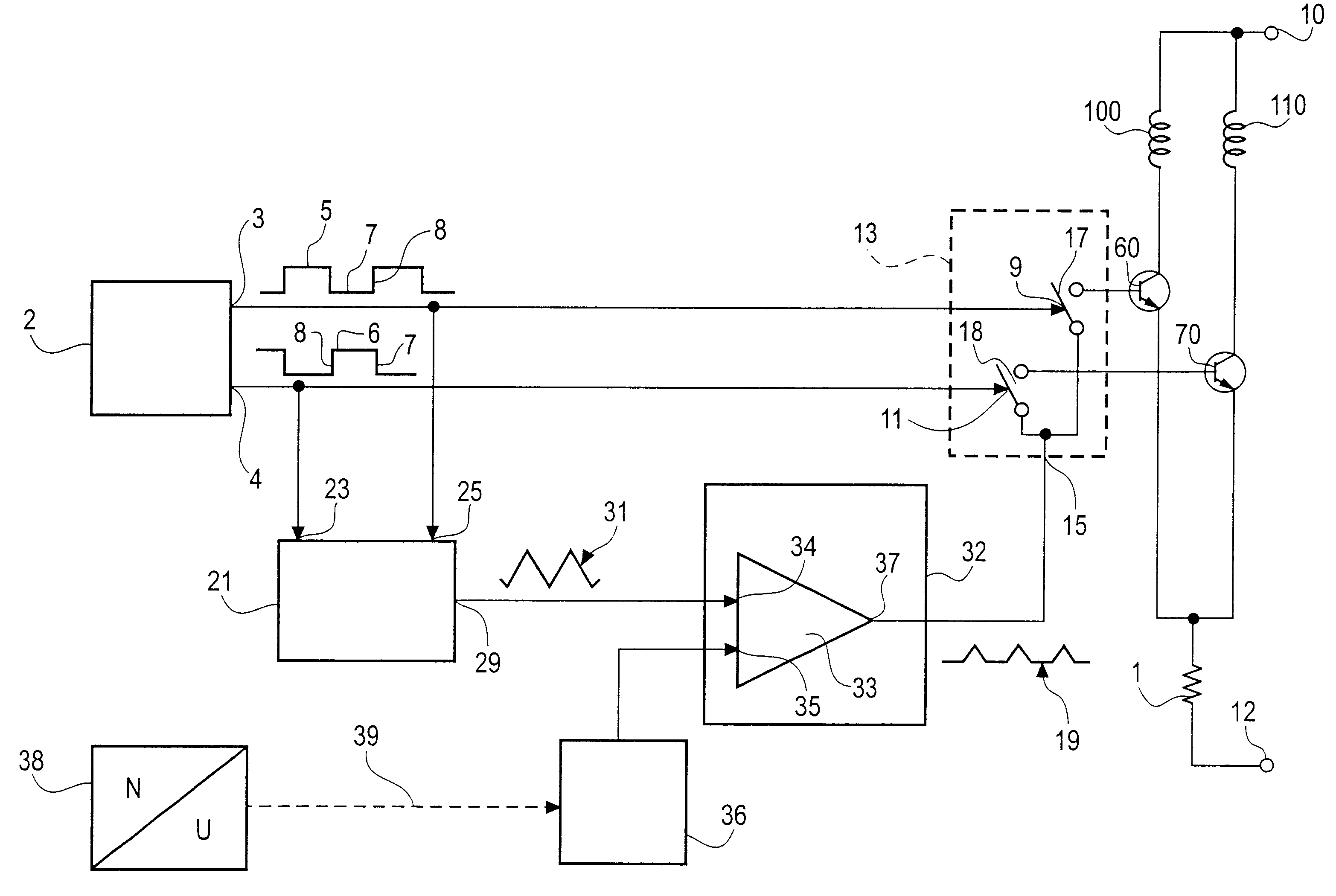
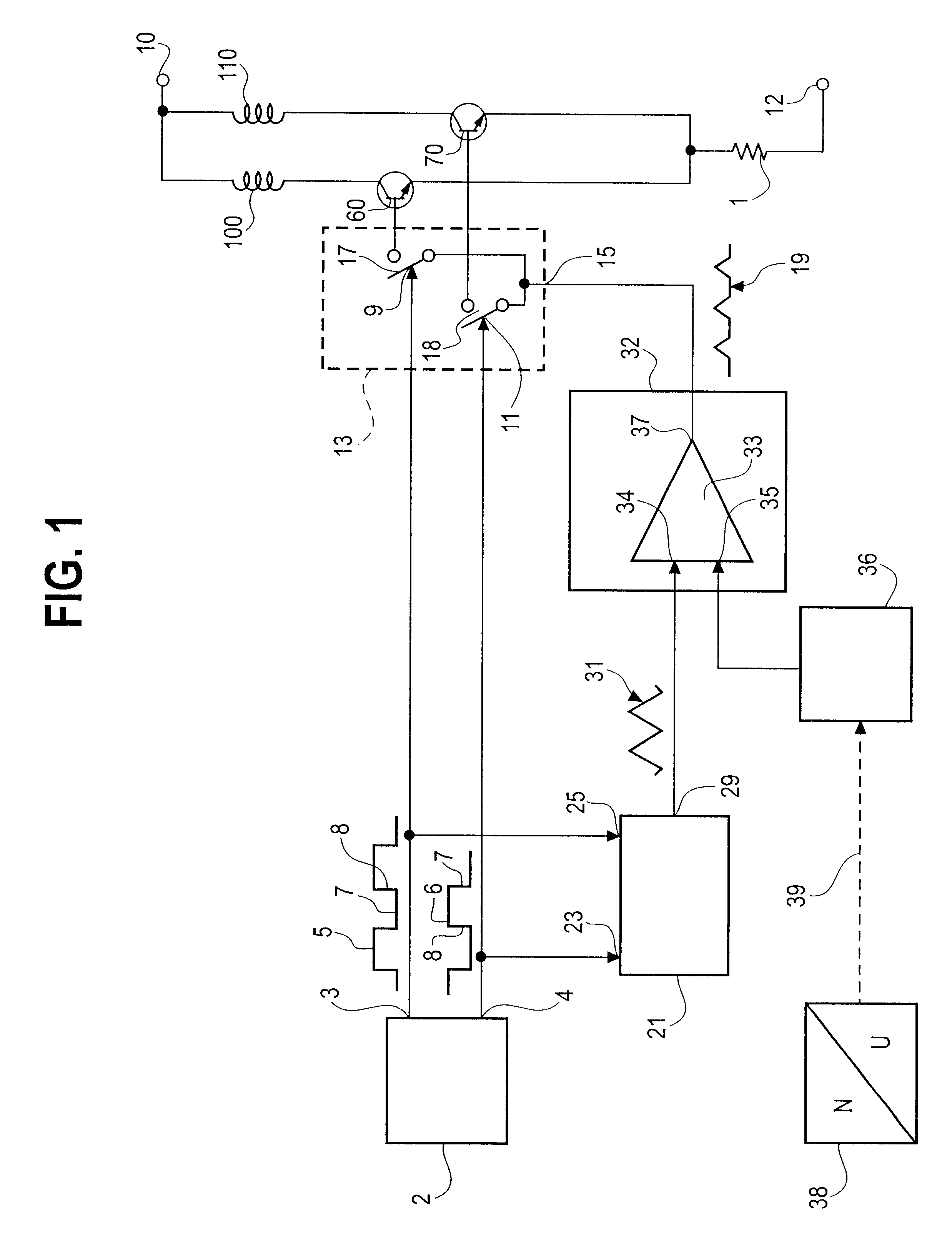
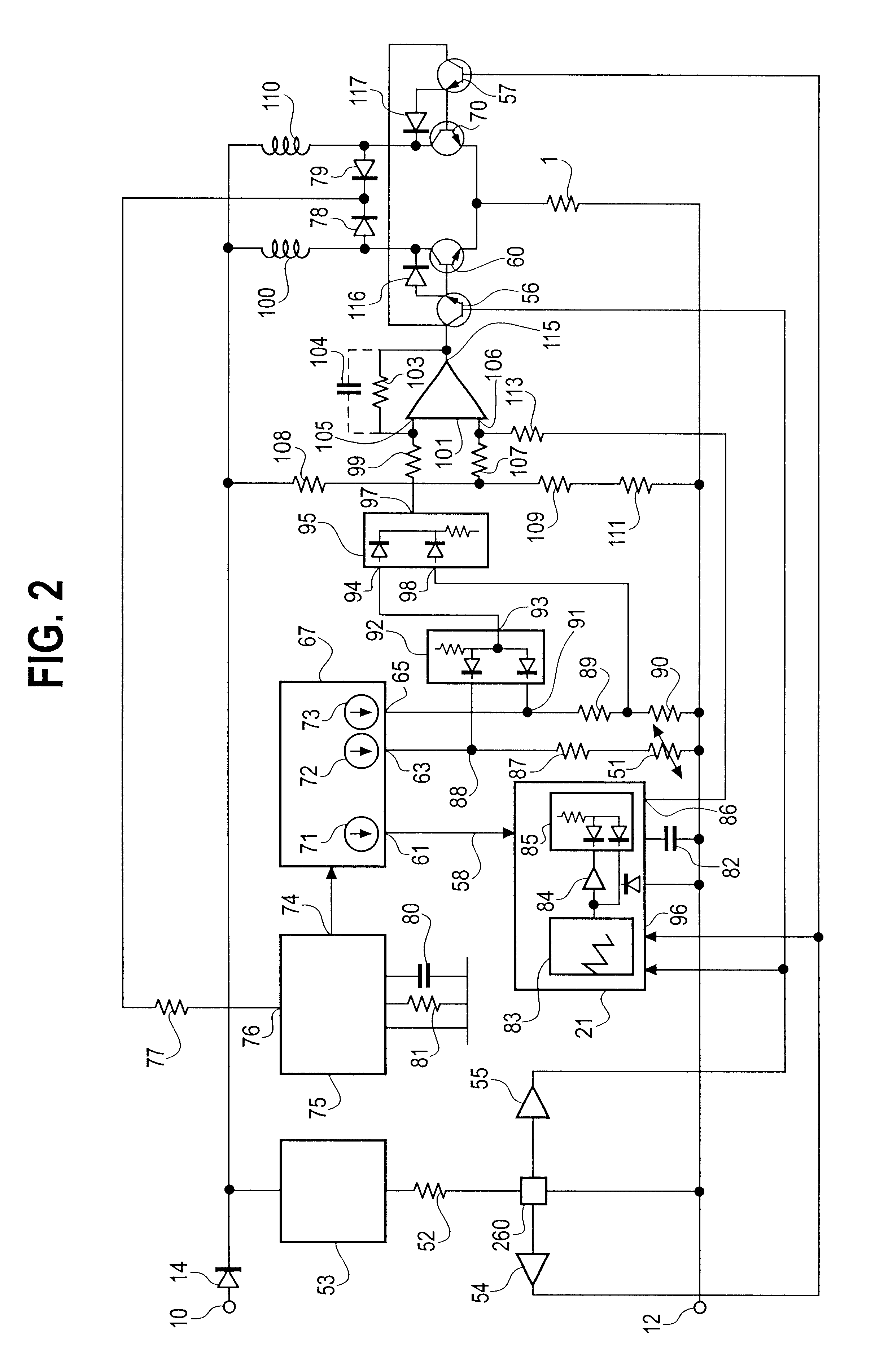
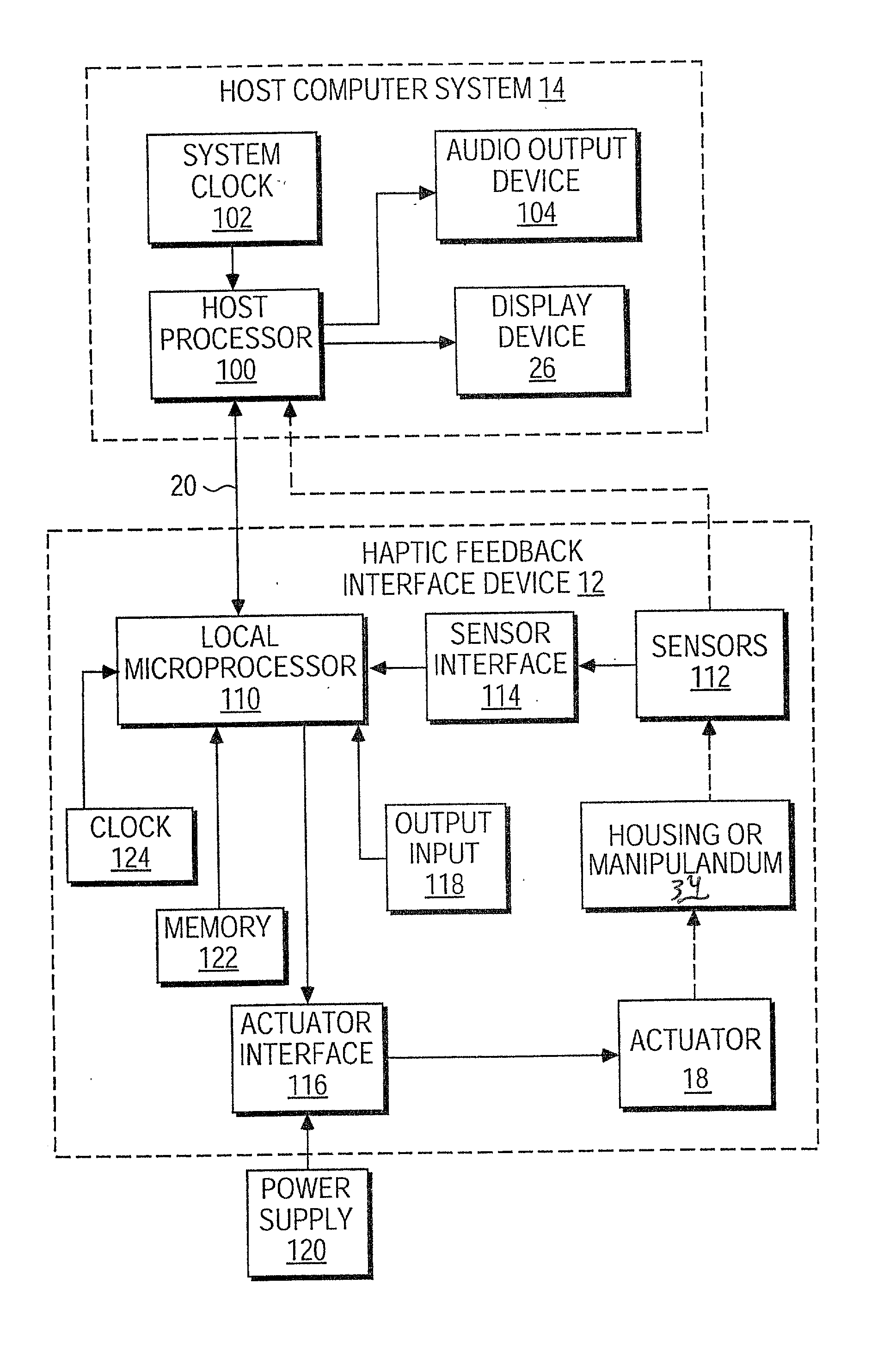
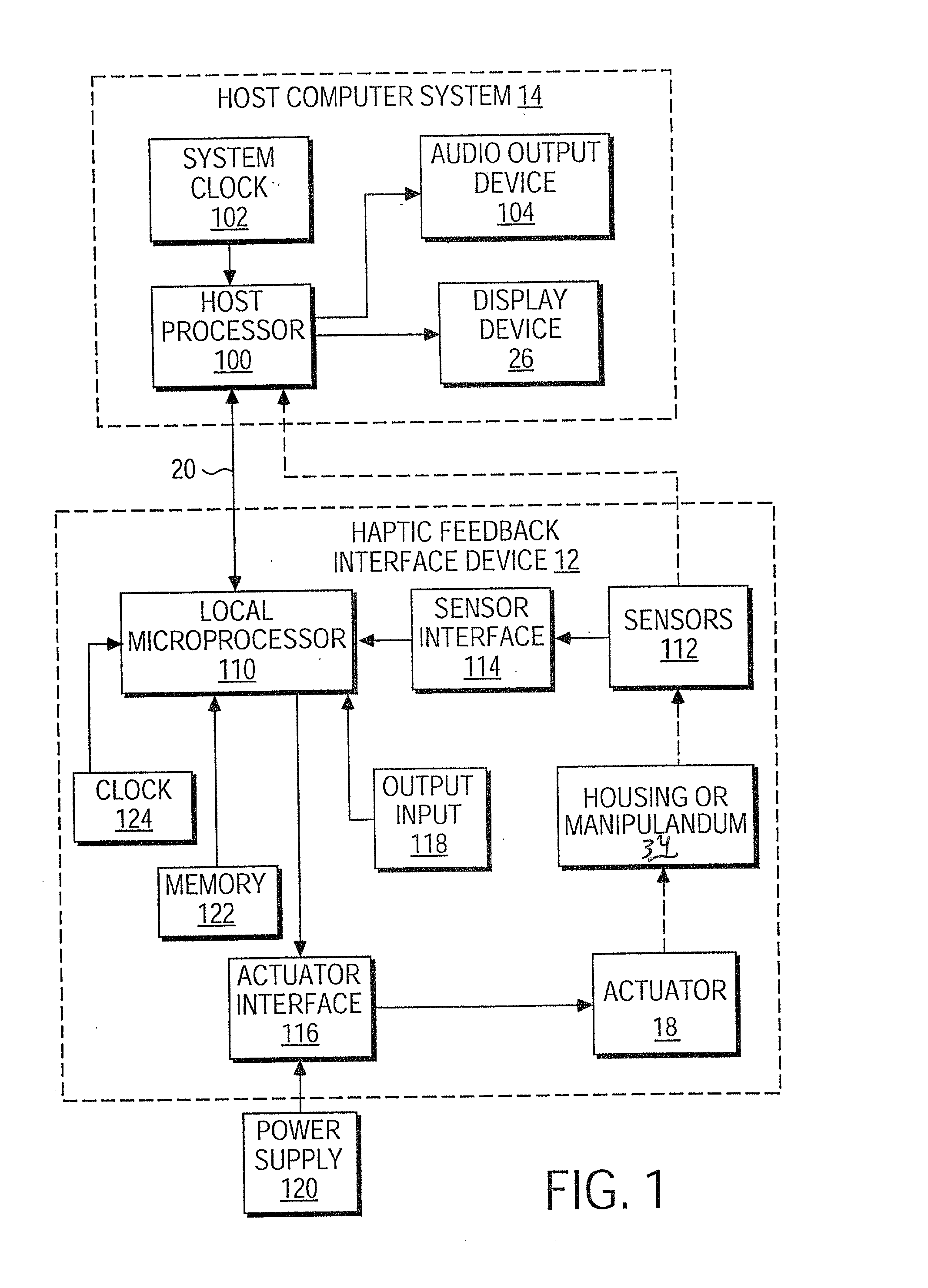
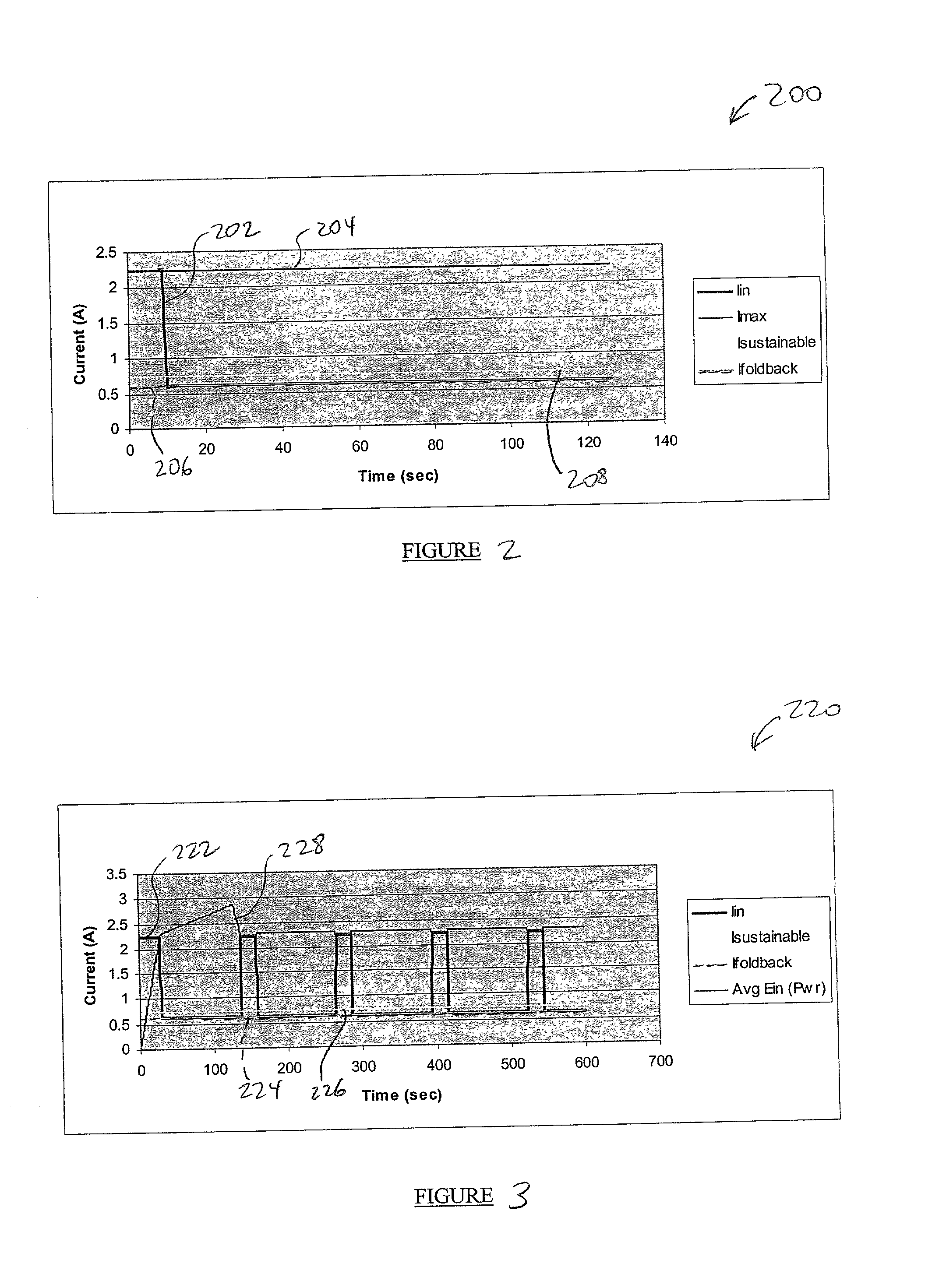
Actuator thermal protection in haptic feedback devices
InactiveUS7233476B2Reducing maximum allowable current levelReduces maximum allowable current levelInput/output for user-computer interactionEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionActuatorPersistent current
Method and apparatus for providing thermal protection for actuators used in haptic feedback interface devices. An average energy in the actuator over a predetermined period of time is determined, and the maximum allowable current level in the actuator is reduced if the average energy is determined to exceed a predetermined warning energy level. The maximum allowable current level can be reduced to a sustainable current level if the average energy reaches a maximum energy level allowed, and the maximum allowable current level in the actuator can be raised if the average energy is determined to be below the predetermined warning energy level. Preferably, the maximum allowable current level is reduced smoothly as a ramp function.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
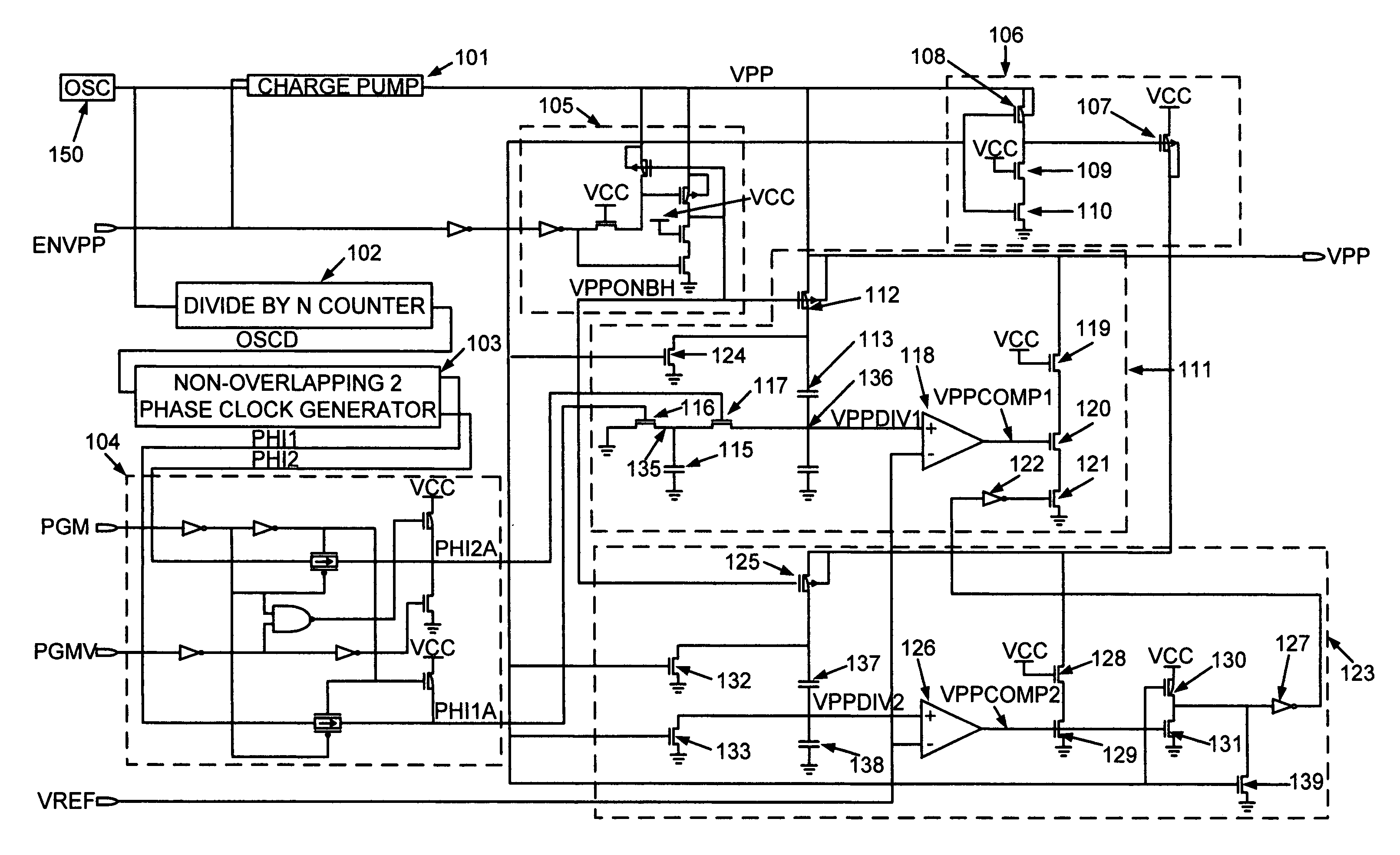
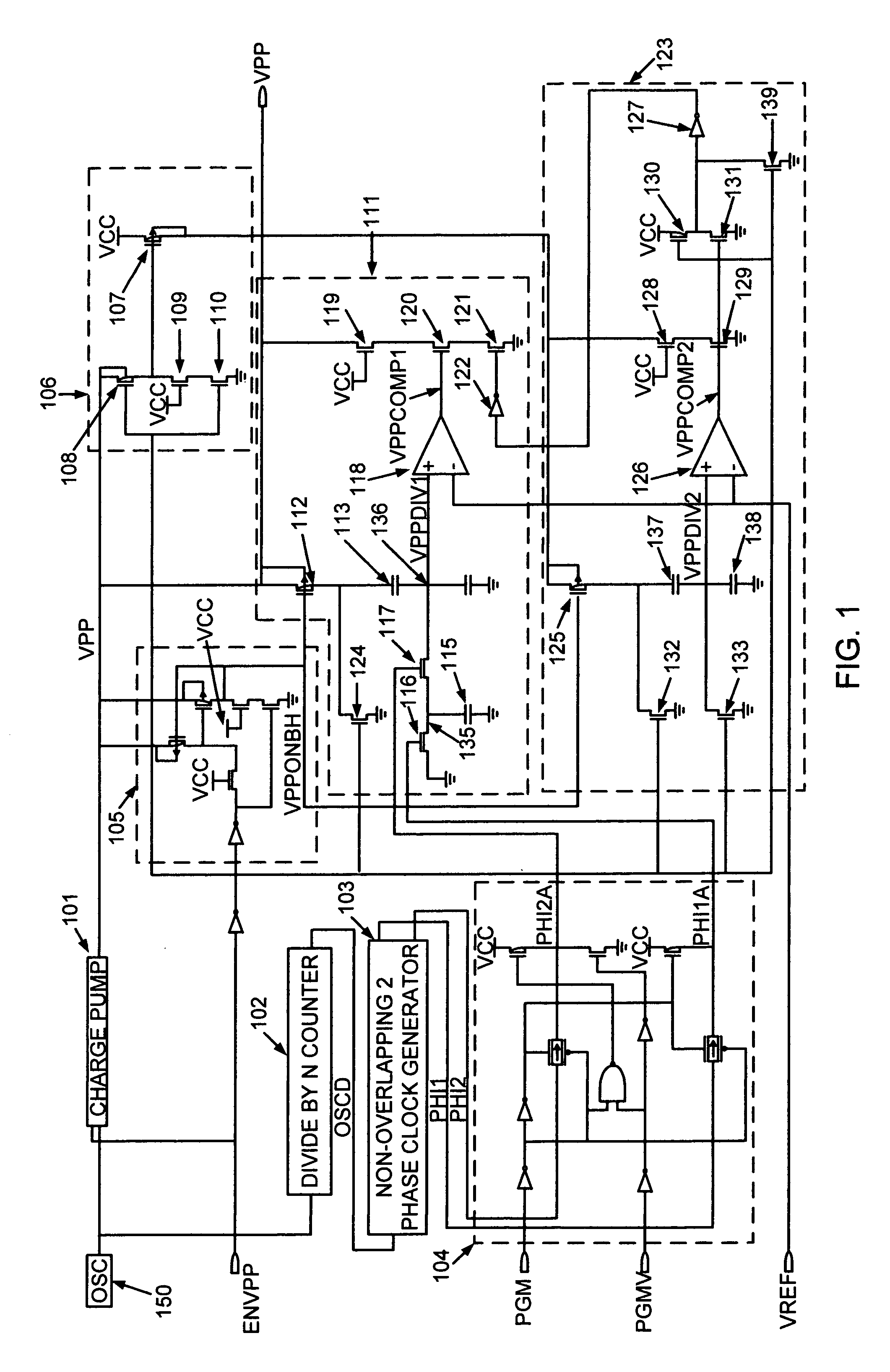
Switched-capacitor controller to control the rise times of on-chip generated high voltages
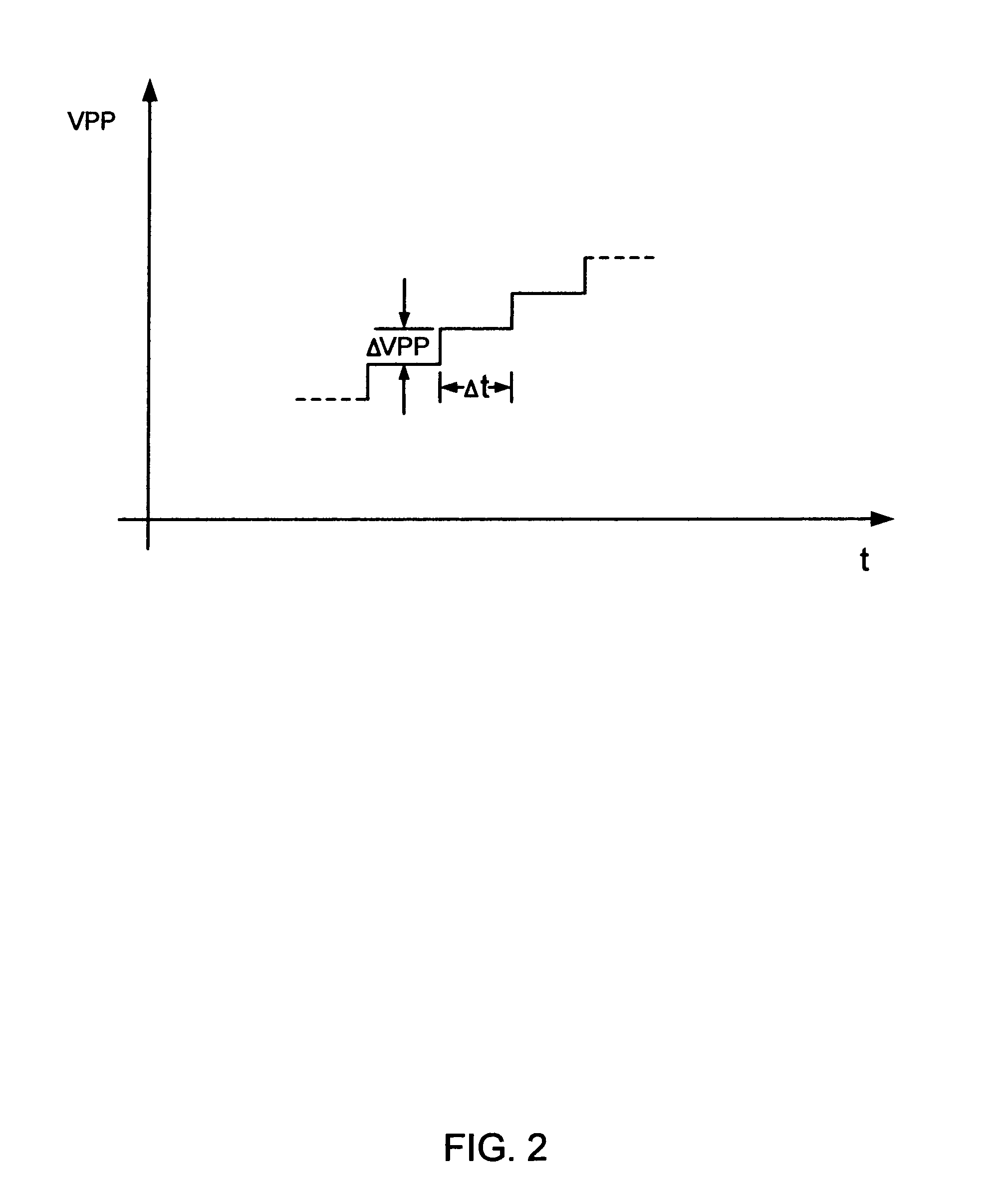
A switched capacitor controller accurately controls the rise time of an on-chip generated high voltage. An on-chip charge pump is used to generate a high voltage (VPP) from an external power supply voltage (VCC). This high voltage signal (VPP) can be used to program Flash memory cells. A capacitor of a switched capacitor circuit is selectively switched between ground and a given node voltage. This generates a stair-stepped ramp function. The period of the steps is controlled according to a clock signal. This clock signal may be altered to produce the desired period. The voltage increases of the steps is regulated by a reference voltage multiplied by a ratio between two capacitor values. Thereby, the rise-time of the ramp function is accurately controlled as a function of the frequency of the clock signal and the ratio of the two capacitor values.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Precision automatic gain control circuit
InactiveUS20020086651A1Low absolute gain toleranceImprove matchResonant long antennasVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesAudio power amplifierClosed loop
An automatic gain control (AGC) amplifier including a high gain transimpedance amplifier, a resistive feedback network and multiple transconductance stages coupled in the feedback path of the AGC amplifier. The feedback network receives an input signal and is coupled to the output of the high gain amplifier and has multiple intermediate nodes. Each transconductance stage has an input coupled to an intermediate node of the feedback network and an output coupled to the input of the high gain amplifier. Each transconductance stage is independently controllable to position a virtual ground within the feedback network to control closed loop gain. Each transconductance stage may have a bias current input coupled to a bias current control circuit. The control circuit controls each bias current to vary the gain of the AGC amplifier. The bias currents may be linearly controlled employing a ramp function to achieve a linear in dB gain response.
Owner:M RED INC
Heavy duty cargo bed extender with ramp for pickup trucks
The present invention provides an assembly for extending the bed of a pickup truck, having a hitch receiver and a down folded tailgate past the end of tailgate and providing a ramp function. By supporting the assembly by both an attachment to the hitch receiver and supporting the assembly on the down folded tailgate the assembly can support more weight and at greater distances and angles the previous bed extenders and ramp combinations.
Owner:WEBB TERRY K
Depth map compression technique
InactiveUS7245768B1Simple technologyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingRamp functionDepth map
A method of compressing depth maps including the steps of determining the boundary of at least one object within a depth map, applying a curve to the boundary of each object, and converting the continuous depth data within an area bounded by the curve into at least one ramp function.
Owner:DYNAMIC DIGITAL DEPTH RES
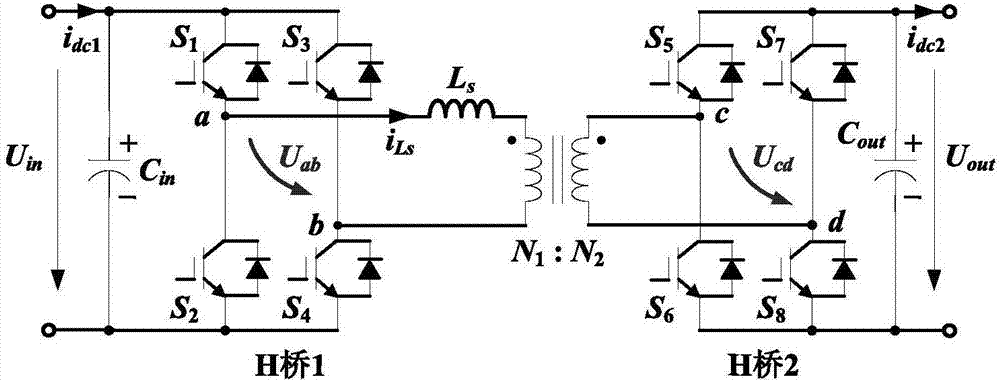
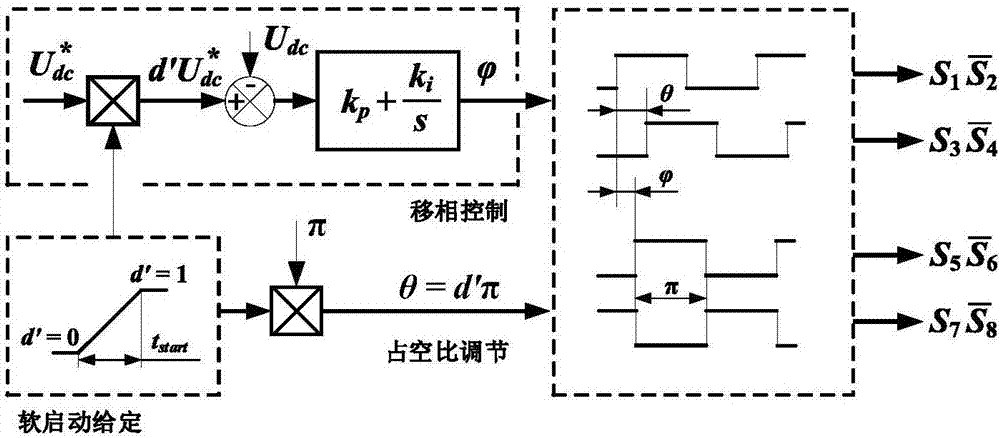
System and method for soft starting of isolation direct-current converter applied to direct current distribution network
ActiveCN107104588ANo impactNo oscillationEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionStart timeEngineering
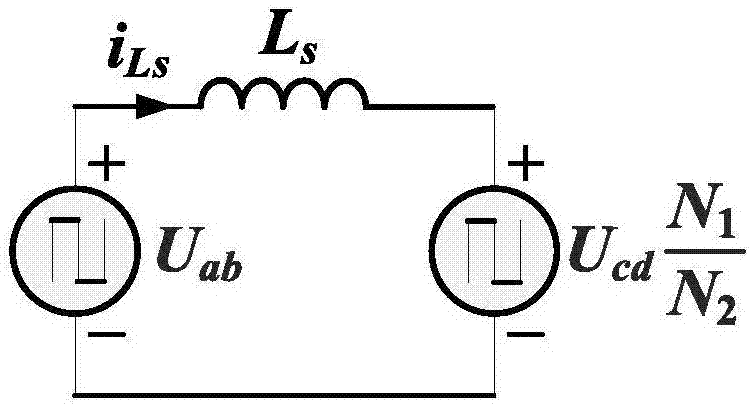
The present invention discloses a system and method for soft starting of an isolation direct-current converter applied to a direct current distribution network. After a direct-current converter is started, the H-bridge output square-wave voltage duty ratio of an input side is gradually increased from 0 to 0.5 according to a ramp function, and the time of setting the duty ratio from 0 to 0.5 is a starting time; after the direct-current converter is started, the H-bridge output square-wave voltage duty ratio of an output side is always 0.5, and the direct-current converter is started, in the starting time, output given voltage is gradually increased from 0 to a rated value according to the ramp function, and the changing of the output given voltage is consistent to the changing of the H-bridge output square-wave voltage duty ratio of the input side. Through cooperation control of the two methods, the current impact and direct voltage oscillation are effectively inhibited when starting, the system has a good anti-interference capacity and does not need additional circuits and starting resistors, and the starting logic is simple.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Surgical port seal
InactiveUS20100241078A1Quality improvementCannulasInfusion syringesRamp functionMechanical engineering
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Collectorless direct current motor, driver circuit for a drive and method of operating a collectorless direct current motor
InactiveUSRE37589E1Constant operation voltageReduce power consumptionTemperature control using analogue comparing deviceMotor/generator/converter stoppersDriver circuitAudio power amplifier
Owner:PAPST MOTOREN GMBH & CO KG
Actuator thermal protection in haptic feedback devices
InactiveUS20020126432A1Reducing maximum allowable current levelLarge levelInput/output for user-computer interactionArrangements responsive to excess currentActuatorPersistent current
Method and apparatus for providing thermal protection for actuators used in haptic feedback interface devices. An average energy in the actuator over a predetermined period of time is determined, and the maximum allowable current level in the actuator is reduced if the average energy is determined to exceed a predetermined warning energy level. The maximum allowable current level can be reduced to a sustainable current level if the average energy reaches a maximum energy level allowed, and the maximum allowable current level in the actuator can be raised if the average energy is determined to be below the predetermined warning energy level. Preferably, the maximum allowable current level is reduced smoothly as a ramp function.
Owner:IMMERSION CORPORATION
Surgical port seal
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
System and method for operating a dual clutch transmission during failure of an engine speed sensor or a bus connection between control modules
ActiveUS20100241325A1Improve overall utilizationGuaranteed uptimeVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMobile vehicleAutomatic transmission
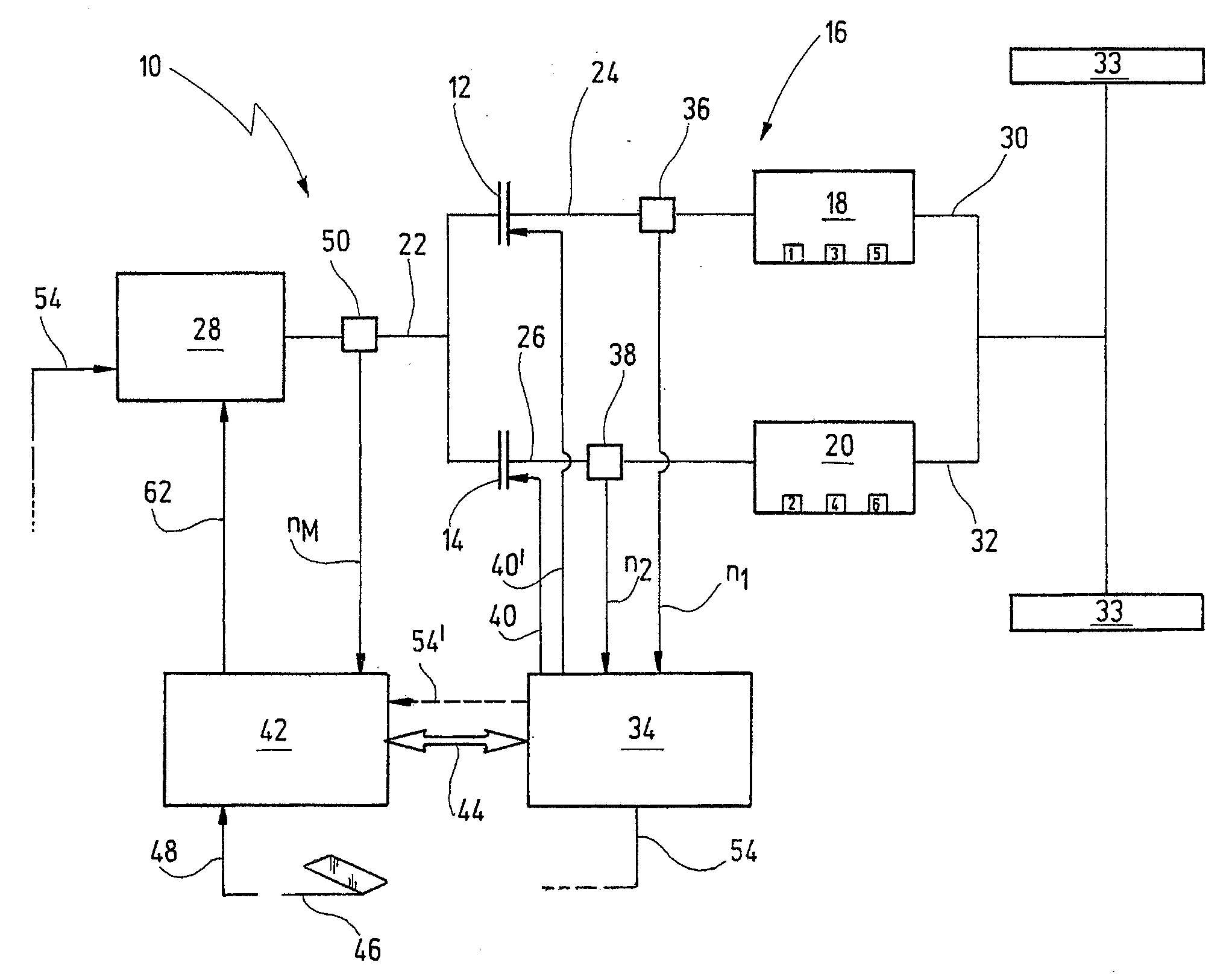
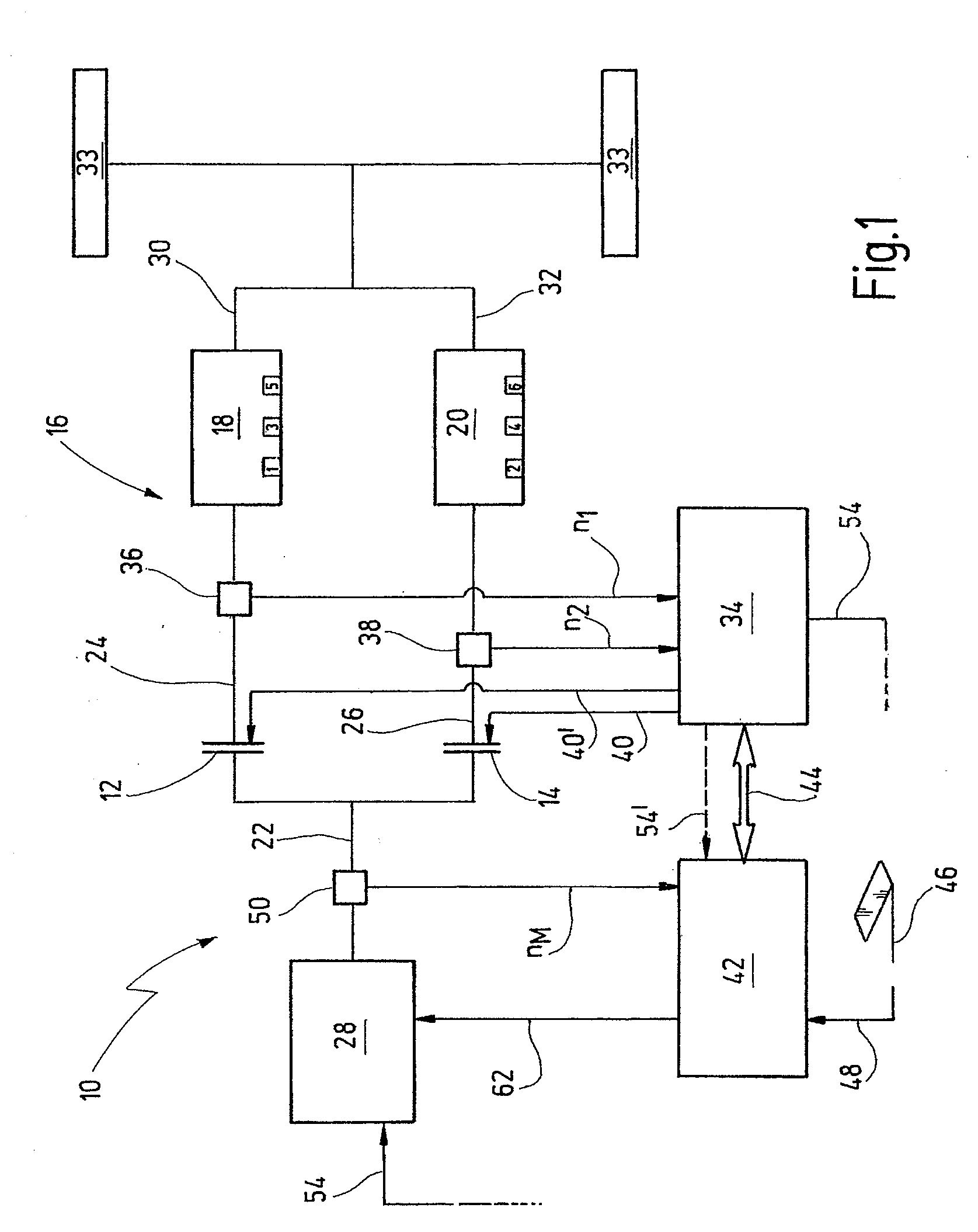
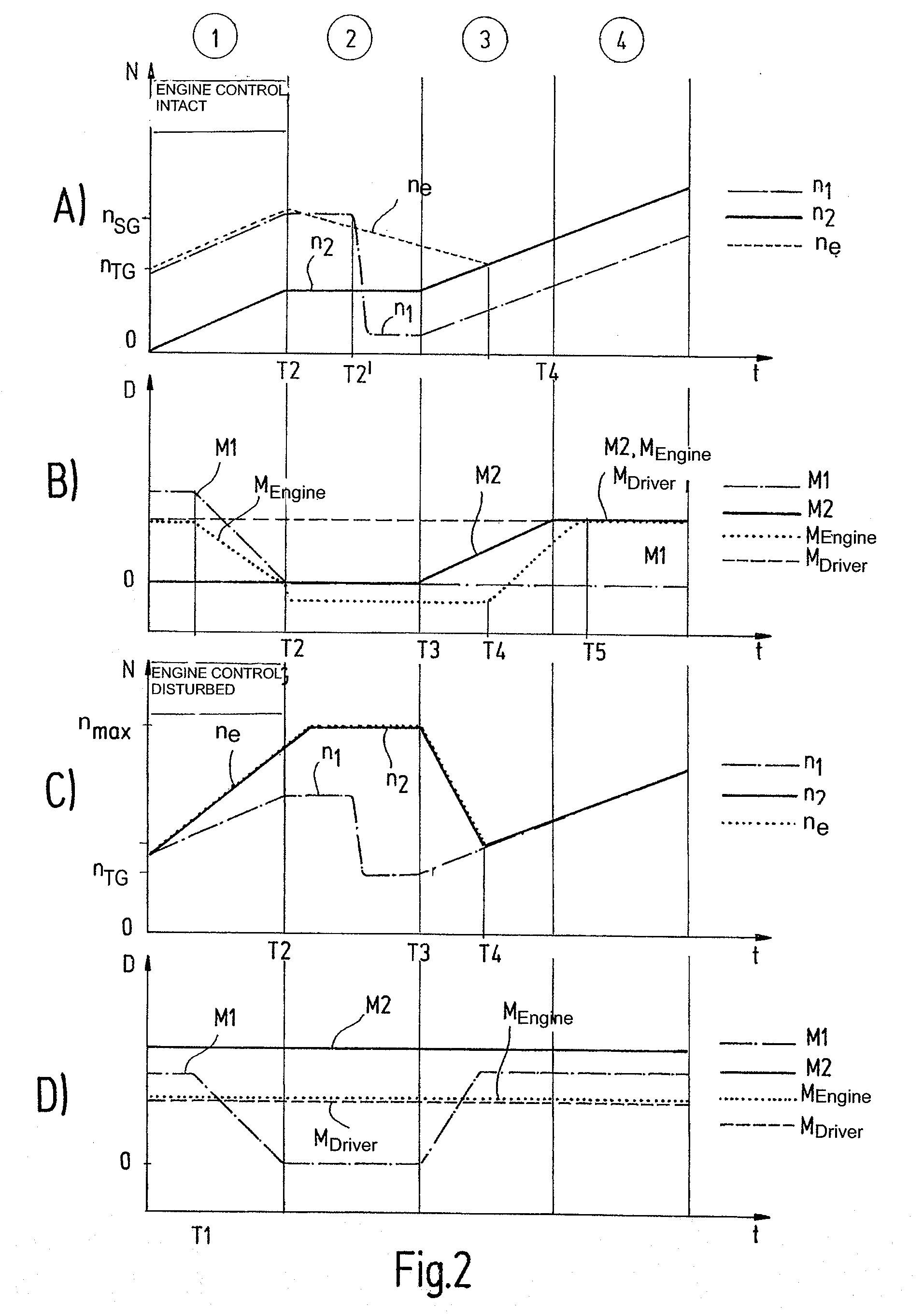
It is disclosed a system and method for maintaining the operation of an automated transmission (16), particularly a dual clutch transmission, for a motor vehicle, in case of a failure of an engine speed sensor (50) or a bus connection (44) between a first control module (42) controlling an engine (28) being connectable to the transmission (16) through at least one separation clutch (12, 149, and a second control module (34) controlling regulating units (12, 14) for connecting the engine (28) to the transmission (16) or to one or more driving wheels (34) in a force-transmitting manner, wherein gear-shift relevant data, particularly a number of revolutions (ne) of the engine, is exchanged between the control modules (34, 42) over the bus connection (44), the method comprising the following steps: checking whether a number of revolutions (ne; n1, n2) of a shaft (22; 30, 32, particularly an engine shaft (22), which is detected by a sensor (50) of one of the control modules (42) dedicated to this purpose can be transmitted from the one of the control modules (34, 42) via the bus connection (44) to the other one of the control modules (42, 34); and performing the following steps, if the number of revolutions cannot be transmitted: opening all synchronizer devices assigned to the transmission (16) or one of the partial transmissions (18, 20) so that the engine shaft (22) can no longer transmit force via a transmission shaft to the driving wheels (33) of the motor vehicle; closing the separations clutch (12, 14) assigned to the transmission (16) or the partial transmission (18, 20) by means of the opened synchronizer devices, if this separation clutch (12, 14) is not closed; detecting a number of revolutions (n1, n2; ne) of another shaft (24, 26), particularly the transmission shaft, which can be connected to the shaft (22) through the separation clutch (12, 14) by means of a sensor (36, 38) of another control module (34), wherein the sensor (36, 38) is dedicated to this purpose; and determining a gear-shift ramp function for one of the control modules (34, 42), preferably the second control module (42), based on the detected number of revolutions, particularly from a field of characteristic lines, for allowing performance of a shifting process from a source gear to a target gear (FIG. 4).
Owner:GETRAG GETRIEBE & ZAHNRADFABRIK HERMANN HAGENMEYER GMBH & CO KG +2
Rolling control device and rolling control method
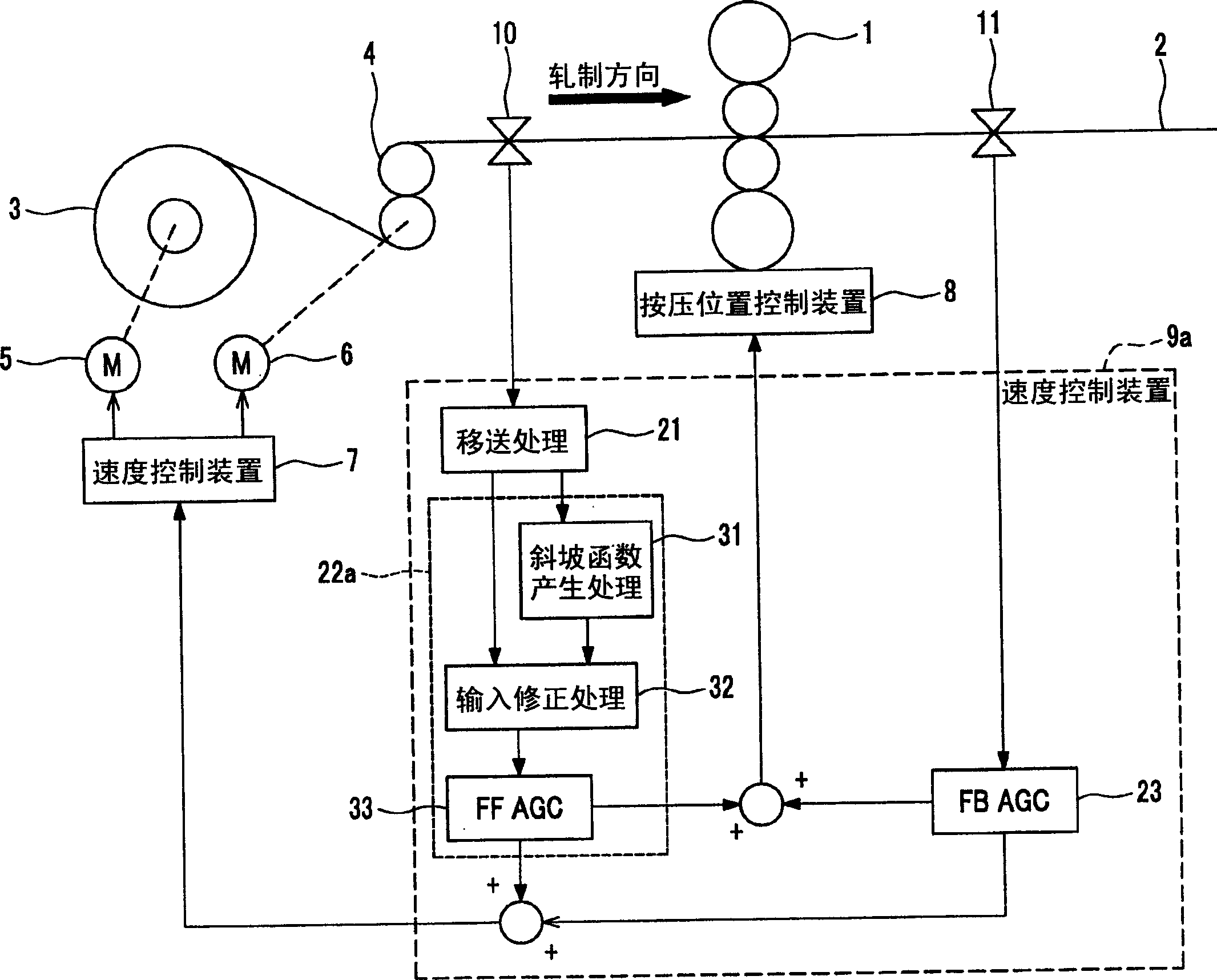
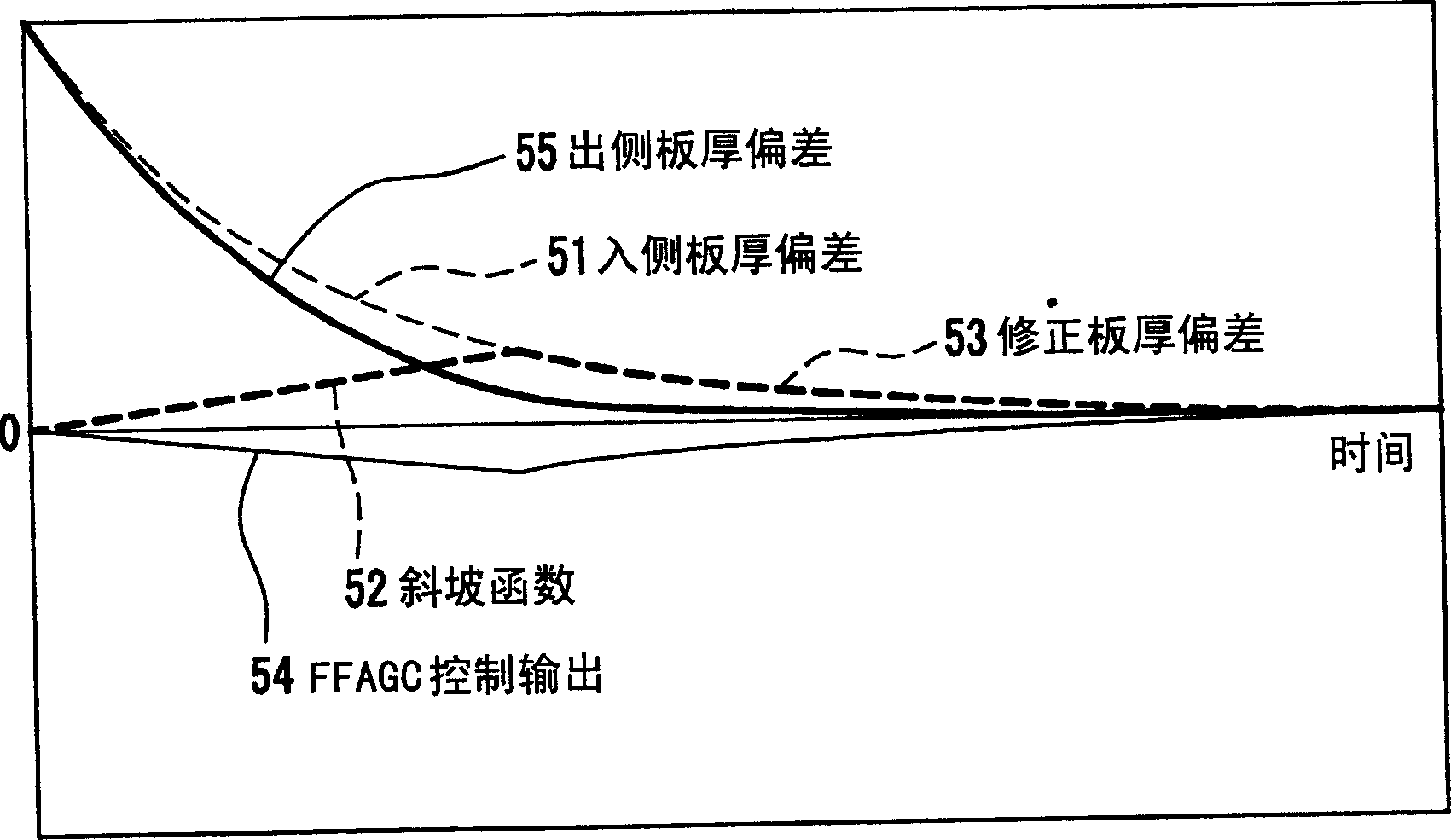
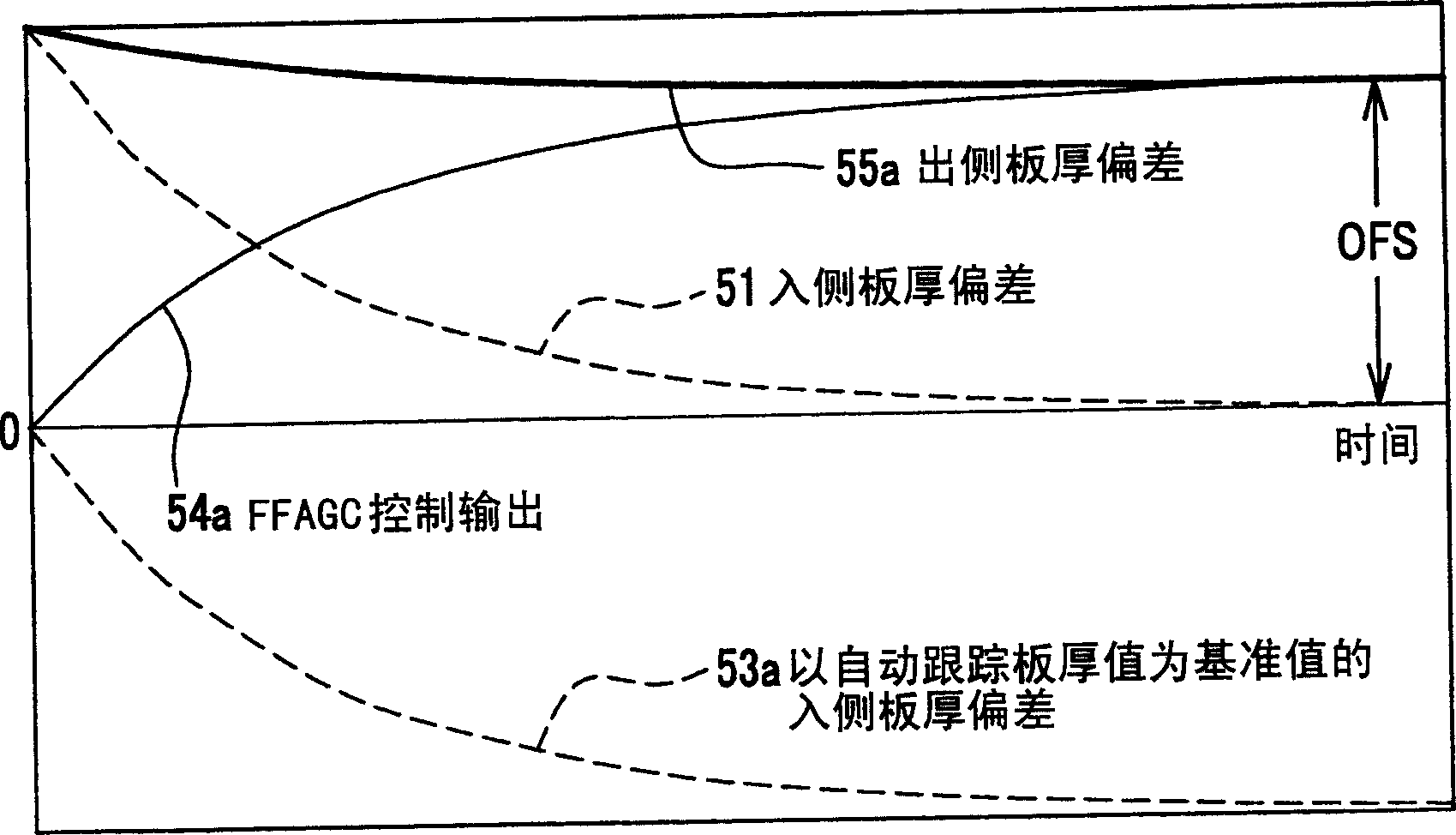
InactiveCN1607045AQuality improvementReduce the actual non-conforming lengthRoll force/gap control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsRamp functionNose parts
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a feedforward thickness controller and its control method by which offset equivalent to lock-on thickness deviation is prevented from appearing in the thickness deviation on the outlet side even in the nose part of a material to be rolled where the effect of the feedback thickness control just after starting the thickness control is not expectable. SOLUTION: This controller is provided with a ramp function generating means 31 and an input correcting means 32. The input correcting means 32 outputs the output data of the ramp function generating means 31 to the feedforward thickness controlling means 33 from the start of thickness control until the output data of the ramp function generating means 31 becomes equal to the thickness deviation on the inlet side, and the thickness deviation on the inlet side is outputted thereafter. The feedforward thickness controlling means 33 controls a speed controlling means 7 and / or a screw-down location controlling means 8 by taking the output of the input correcting means 31 as the input.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
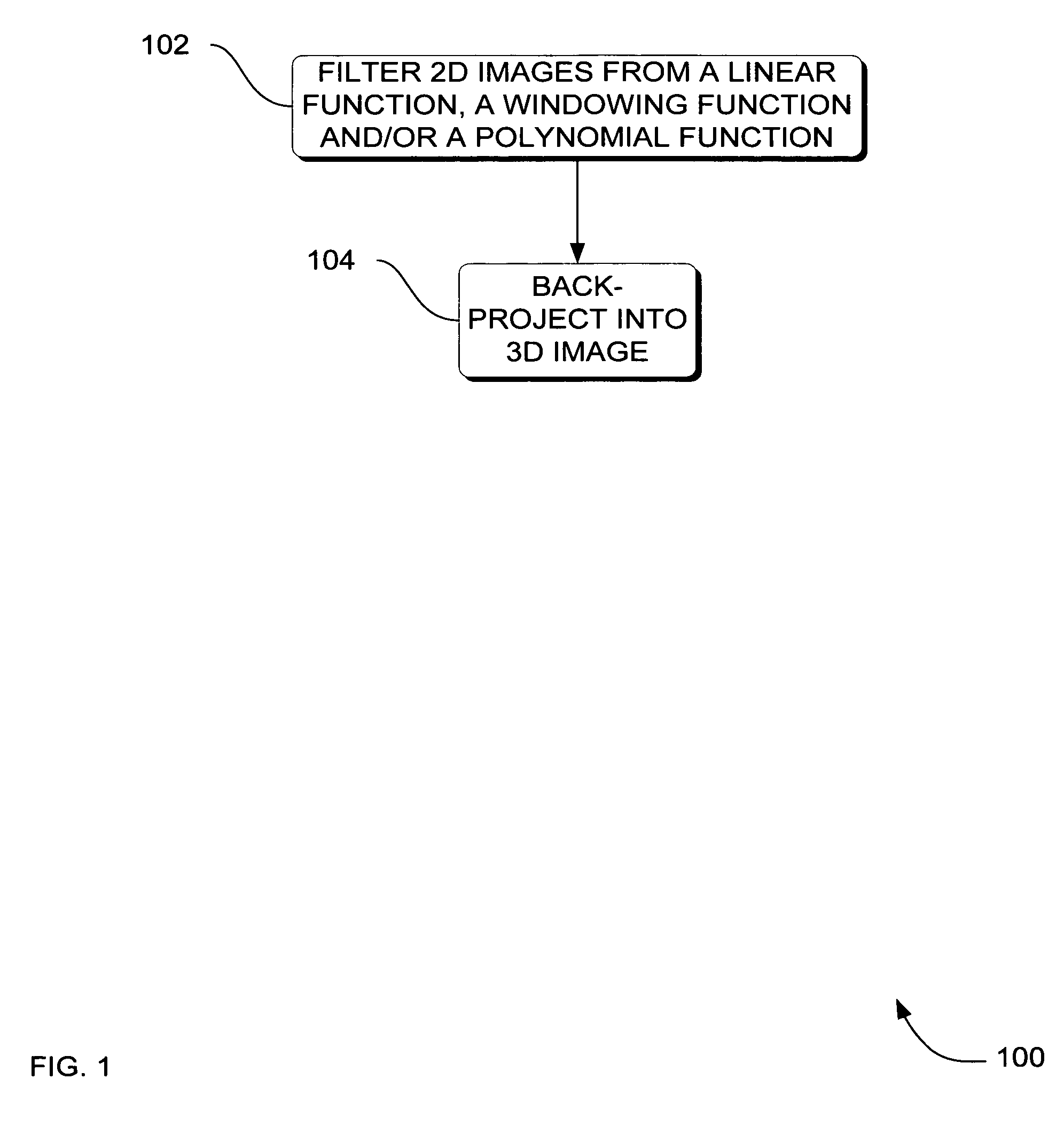
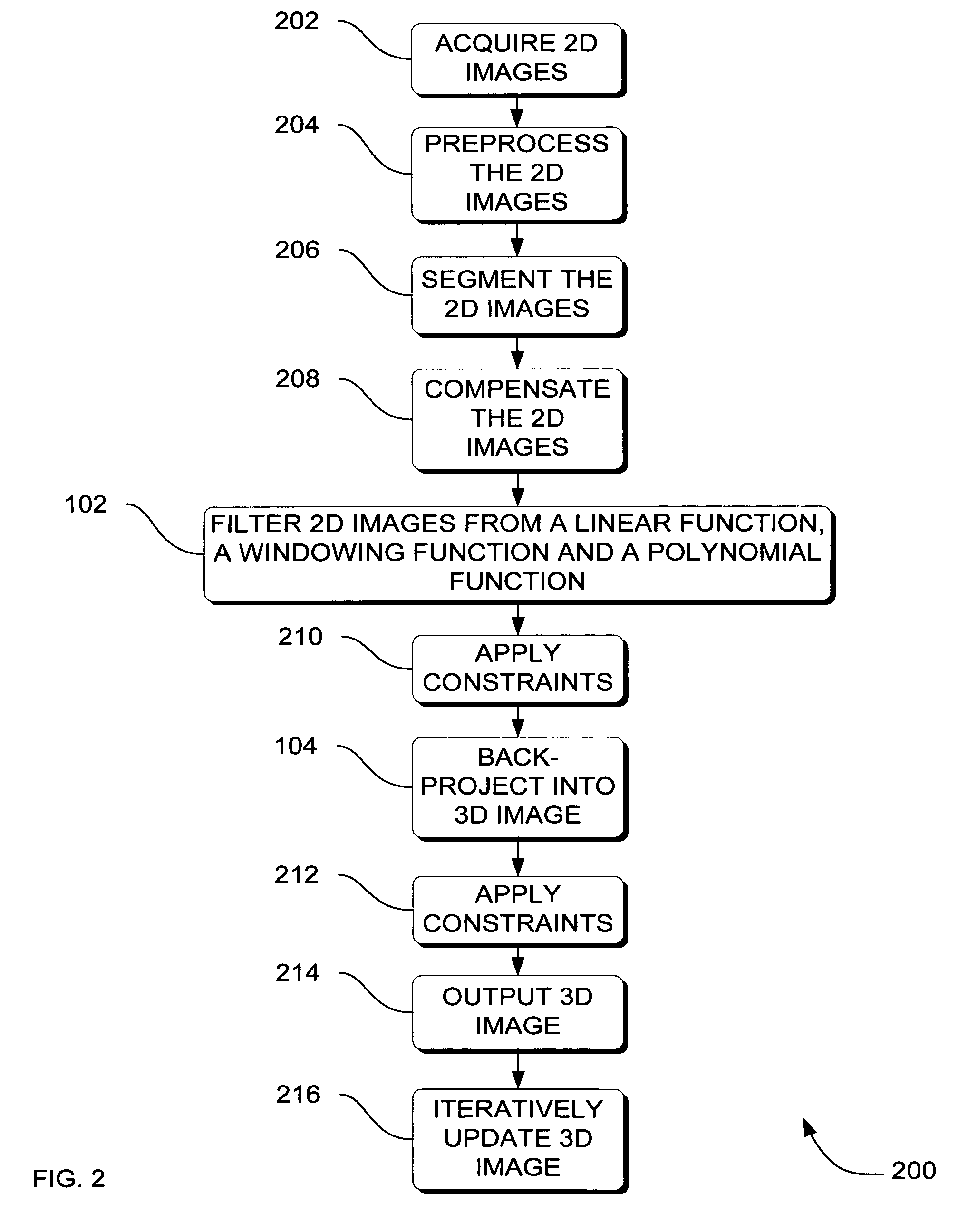
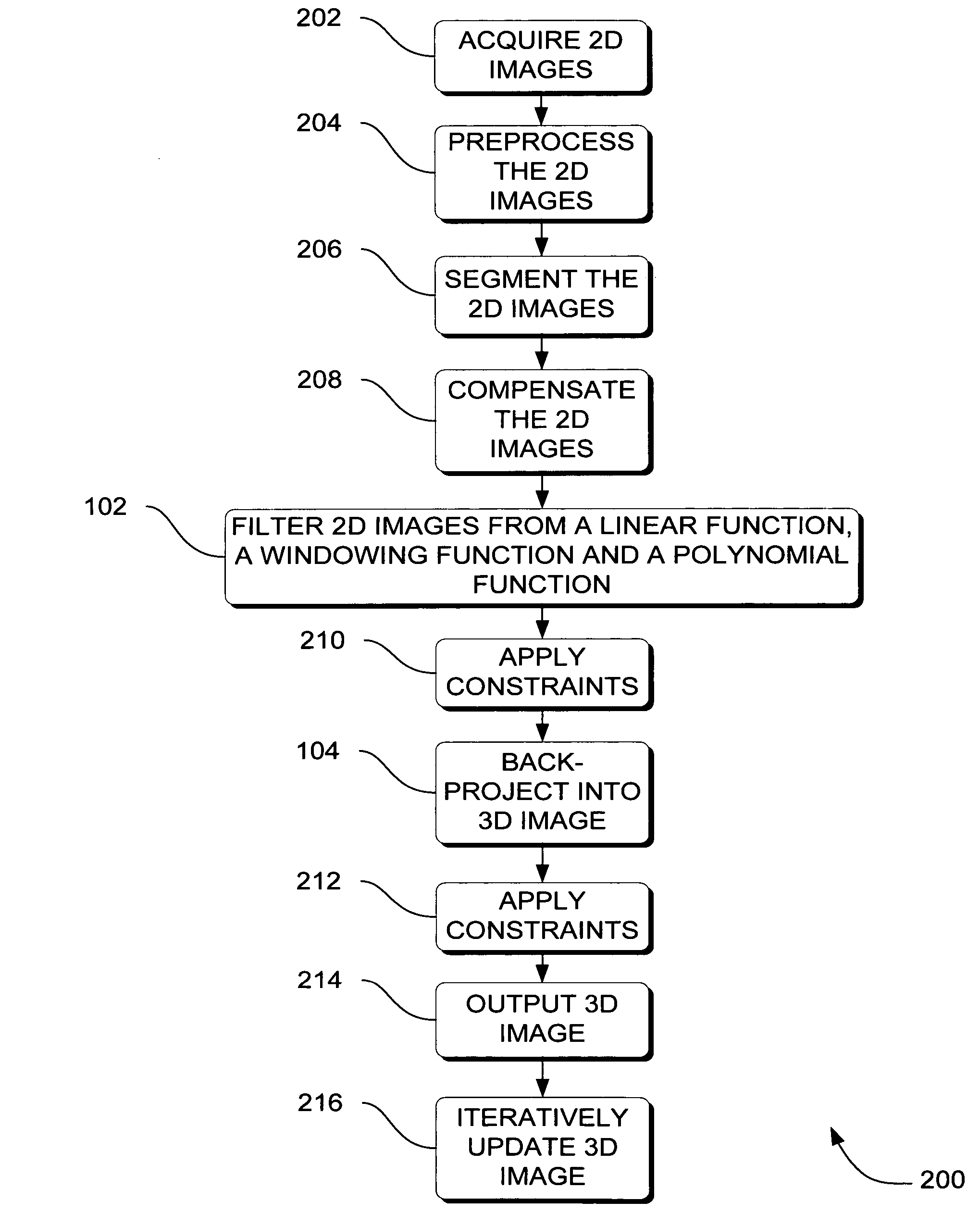
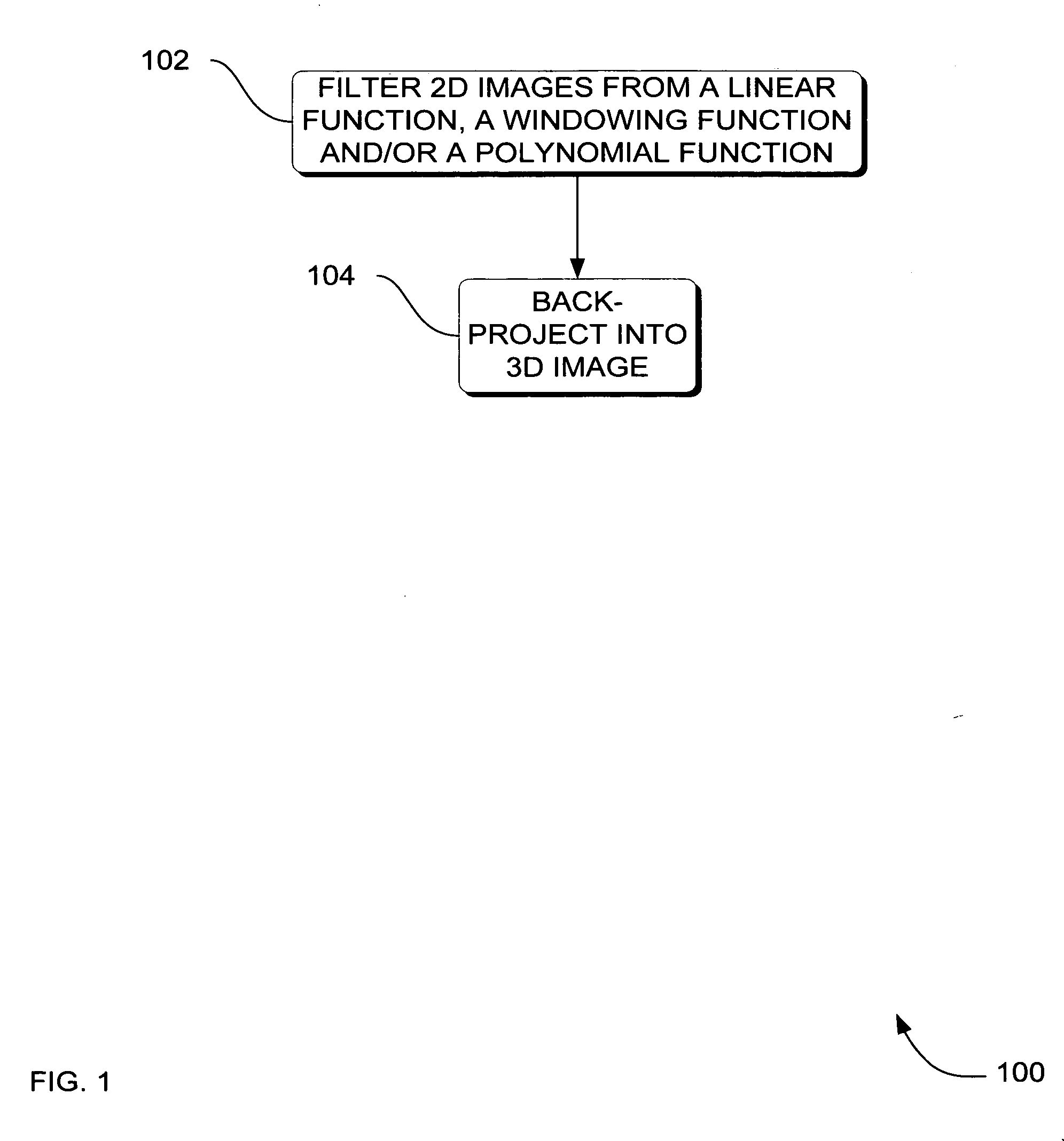
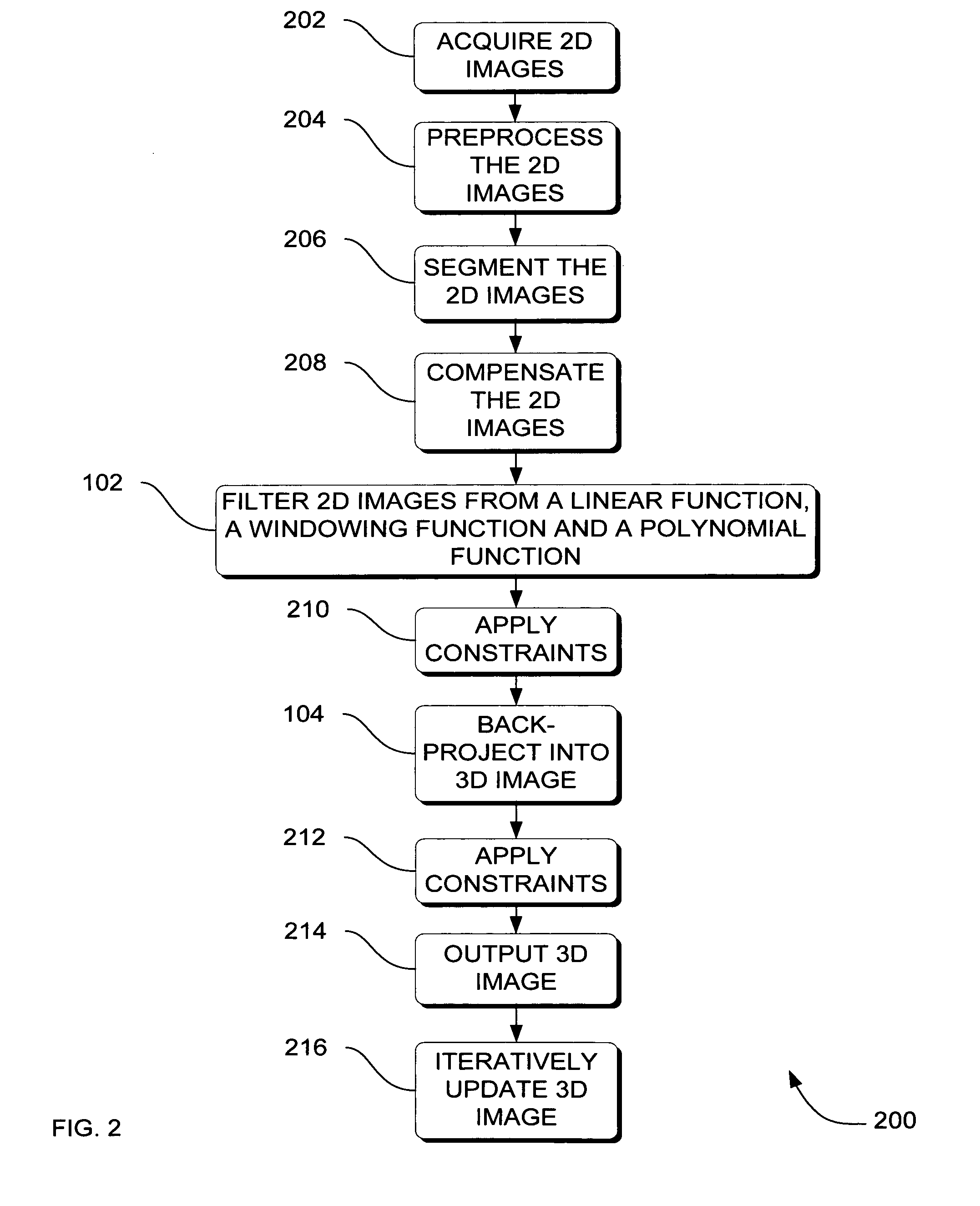
Systems, methods and apparatus for specialized filtered back-projection reconstruction for digital tomosynthesis
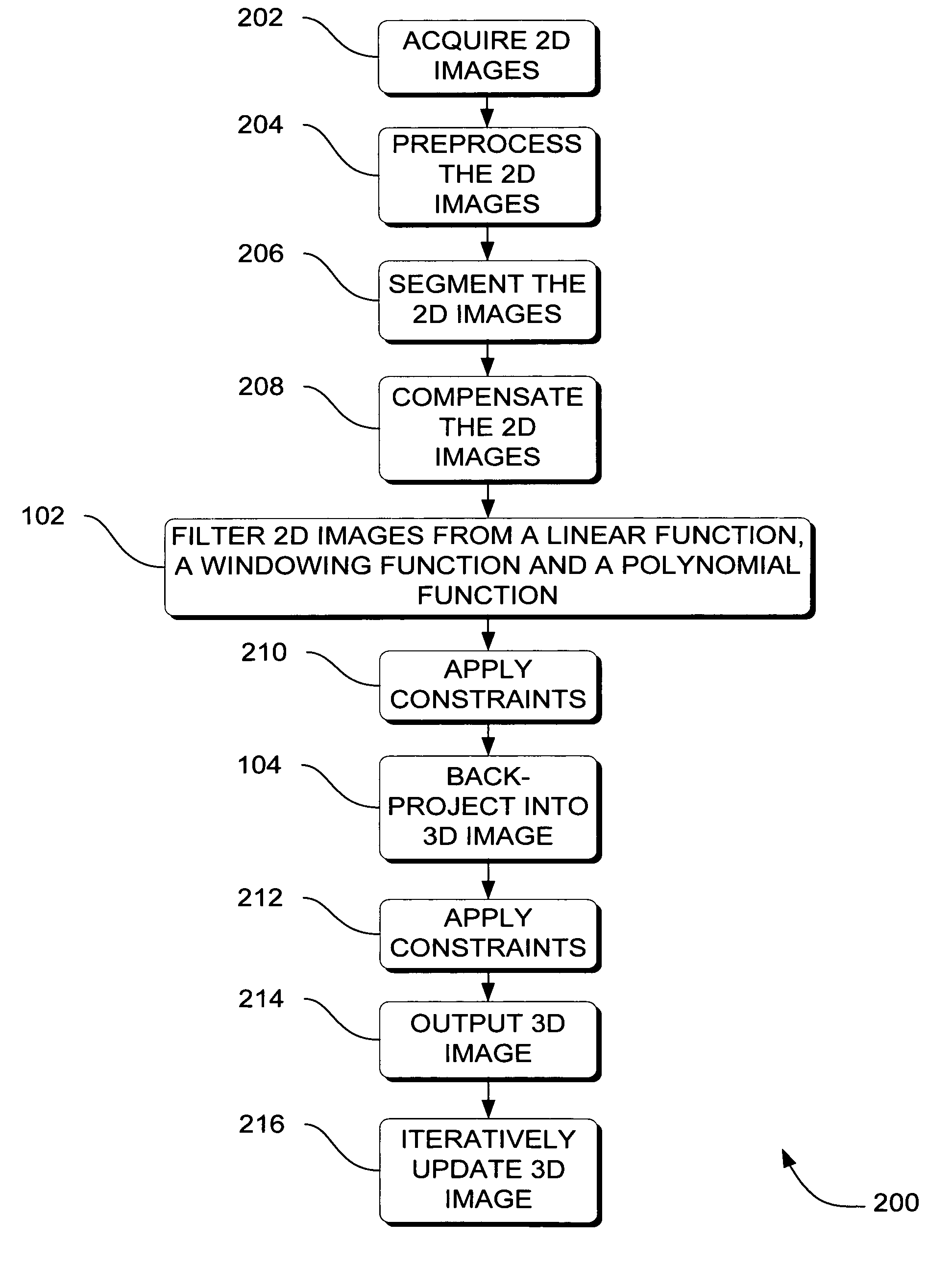
ActiveUS7310436B2Reduce blurReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesis3d image
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which in one aspect, a three-dimensional (3D) image of an object is constructed from a plurality of two-dimensional (2D) images of the object using a specialized filter. The specialized filter implements a linear ramp function, a windowing function, and / or a polynomial function. The 3D image is back-projected from the filtered two-dimensional images, yielding a 3D image that has improved visual distinction of overlapping anatomic structures and reduced blurring.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems, methods and apparatus for specialized filtered back-projection reconstruction for digital tomosynthesis
ActiveUS20050265590A1Reduce blurReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomosynthesis3d image
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which in one aspect, a three-dimensional (3D) image of an object is constructed from a plurality of two-dimensional (2D) images of the object using a specialized filter. The specialized filter implements a linear ramp function, a windowing function, and / or a polynomial function. The 3D image is back-projected from the filtered two-dimensional images, yielding a 3D image that has improved visual distinction of overlapping anatomic structures and reduced blurring.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
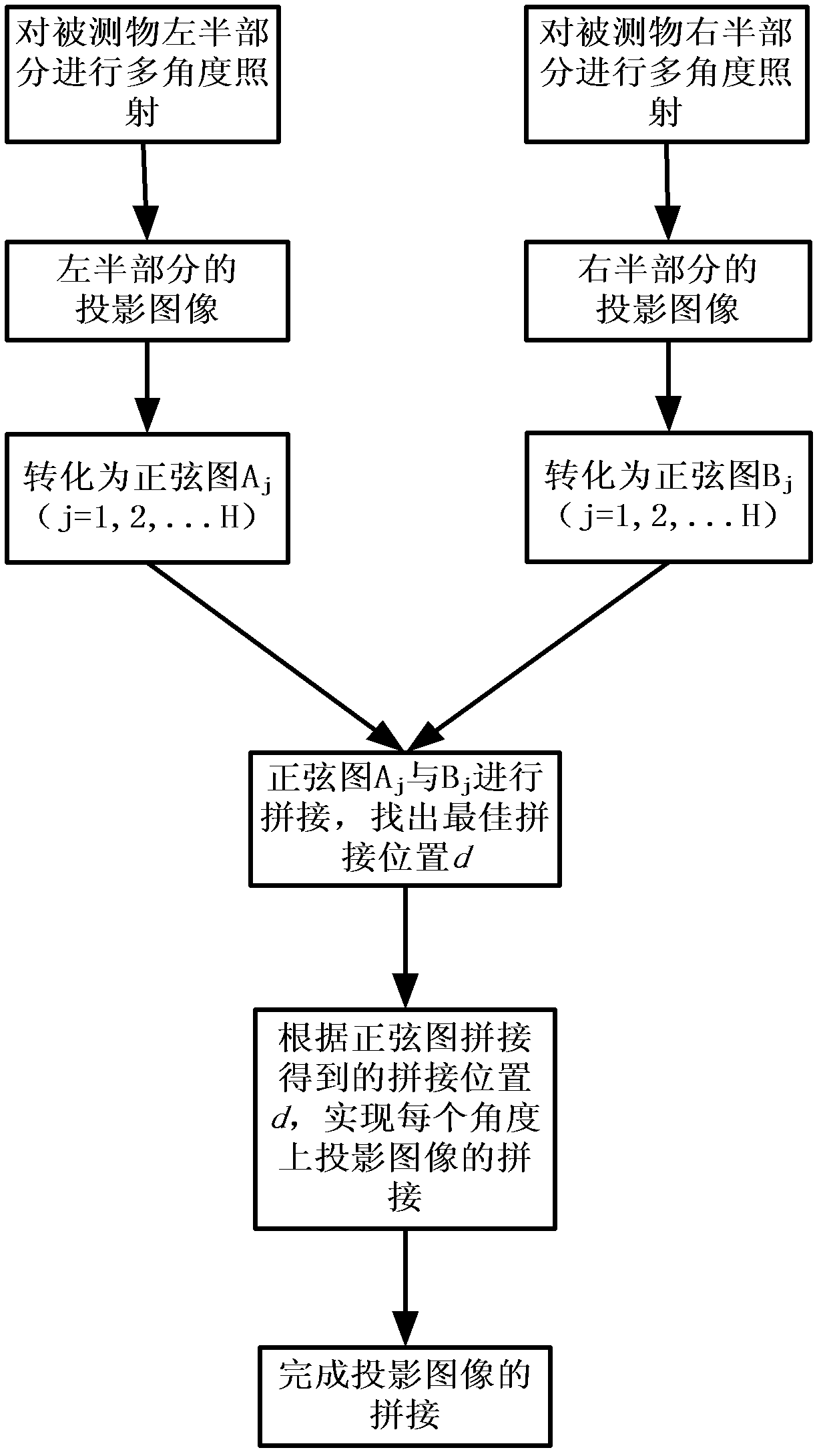
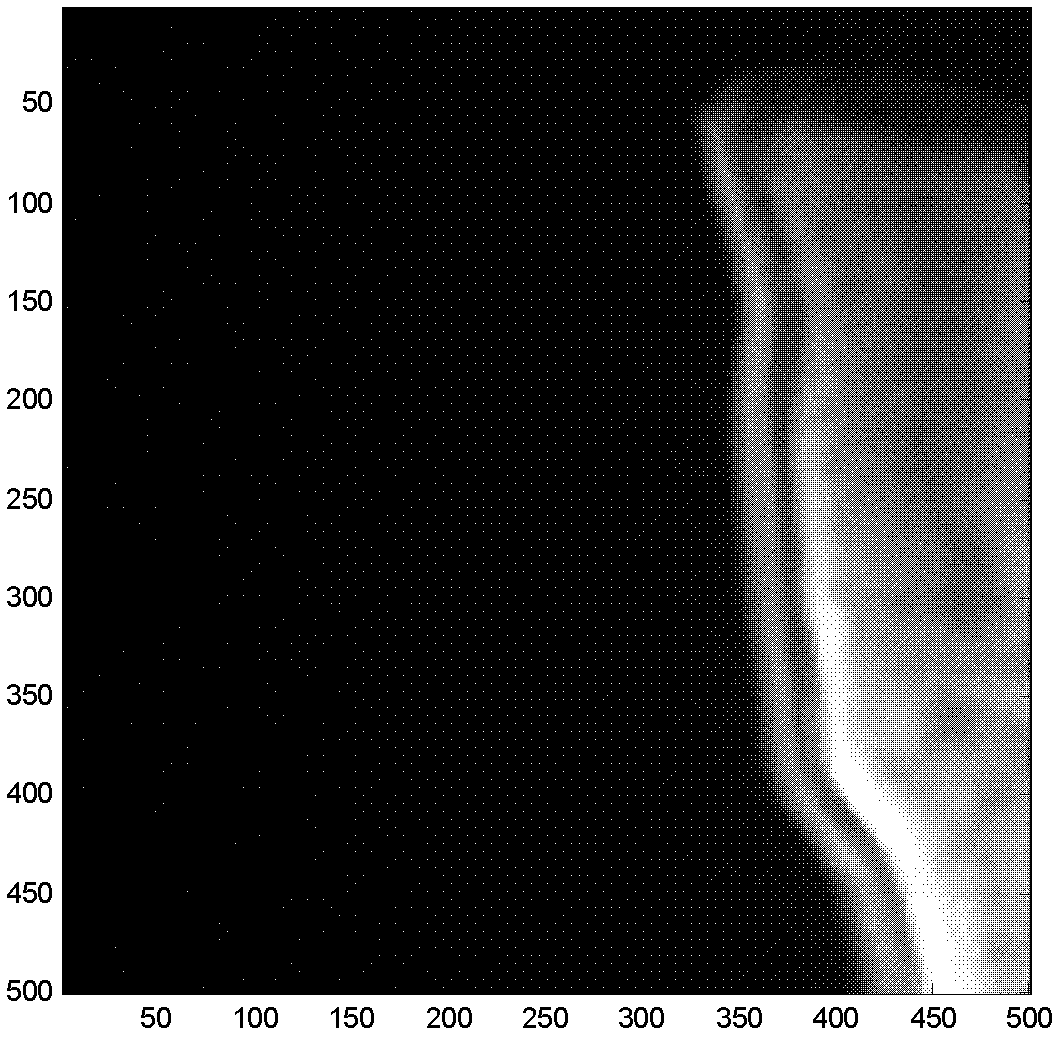
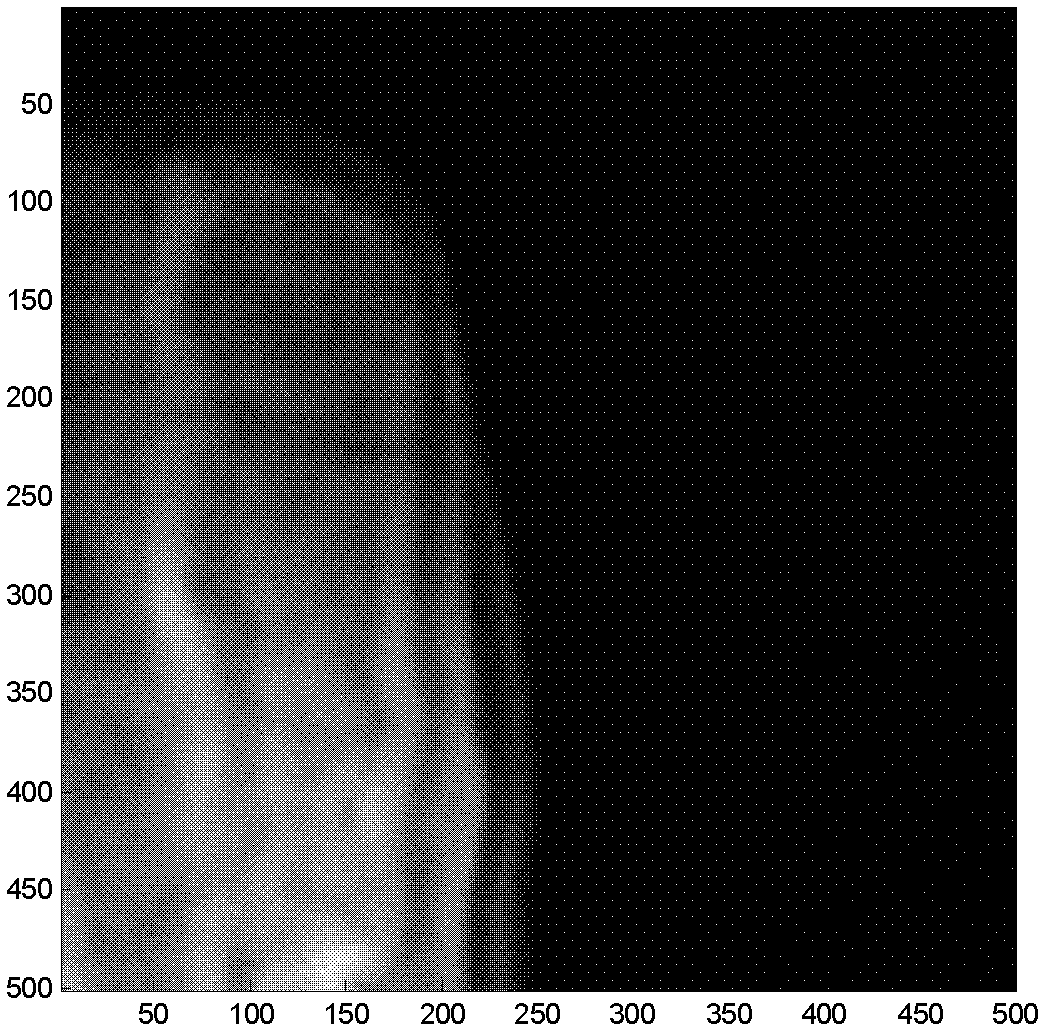
Measured object image splicing method based on optical projection tomographic imaging system
InactiveCN102324101AAvoid the obviousAvoid the disadvantage of image blurring in the stitching area2D-image generationMaterial analysis by optical meansLeft halfProjection image
The invention discloses a measured object image splicing method based on an optical projection tomographic imaging system, which mainly solves the problem of blurring spliced regional images or obvious splicing mark in splicing a measured object image based on the optical projection tomographic imaging system in the prior art is solved. The measured object image splicing method based on the optical projection tomographic imaging system is realized by the following steps of: (1) respectively irradiating the left half part and the right half part of a measured object, and collecting to obtain projection images of the left half part and the right half part of the measured object; (2) respectively converting the left half part and the right half part of the measured object into a sinogram with a clear textural feature; (3) splicing the sinograms and confirming the splicing distance between the projection images by utilizing the correlation of image overlapping regions; and (4) finishing the splicing the projection images in a ramp function weighting way. The measured object image splicing method based on the optical projection tomographic imaging system has the advantages of high definition of spliced regions, small splicing marks and small calculated amount and can be used for carrying out three-dimensional reconstruction on the measured object.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Vehicle movement control method, control device and automobile
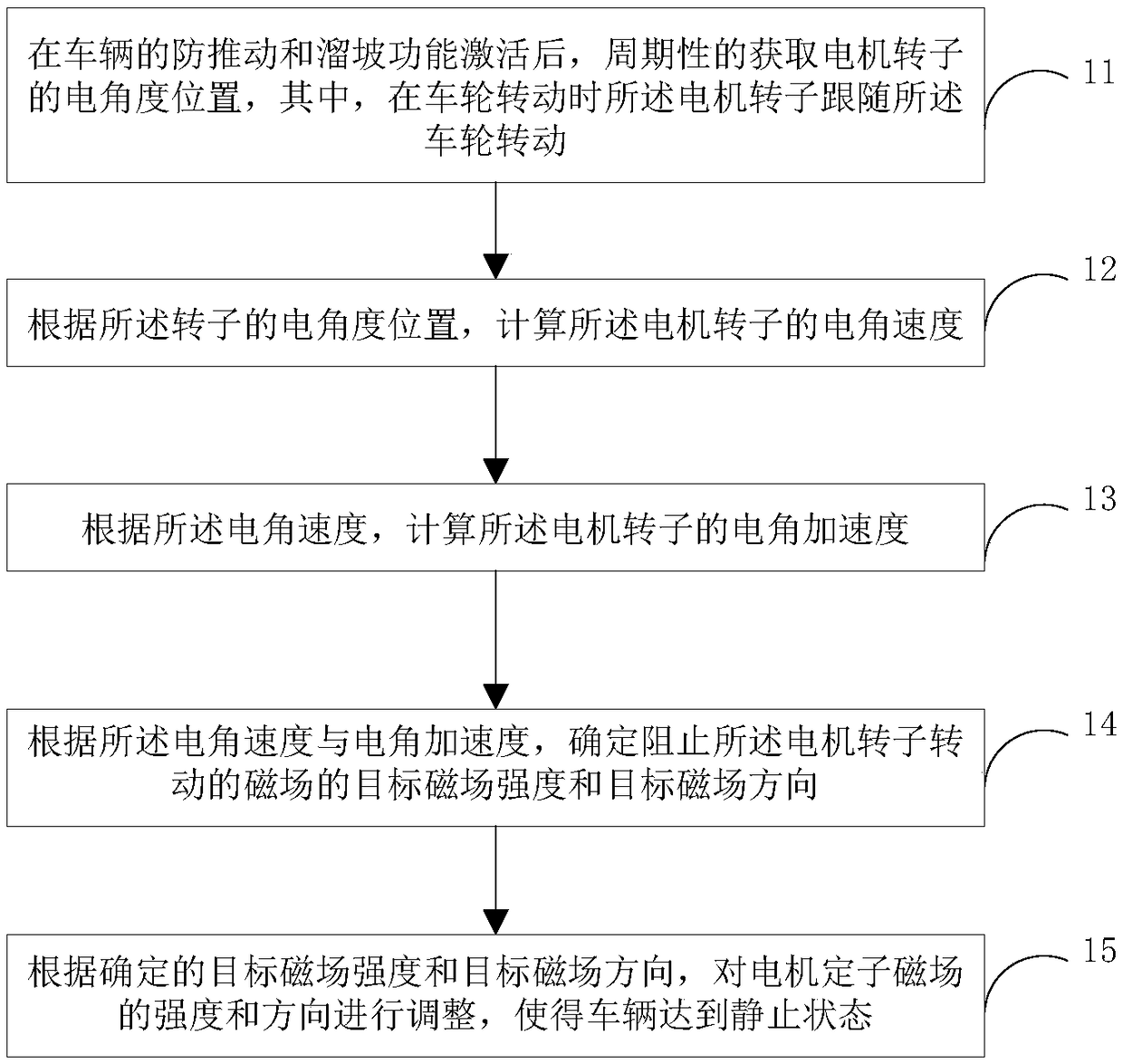
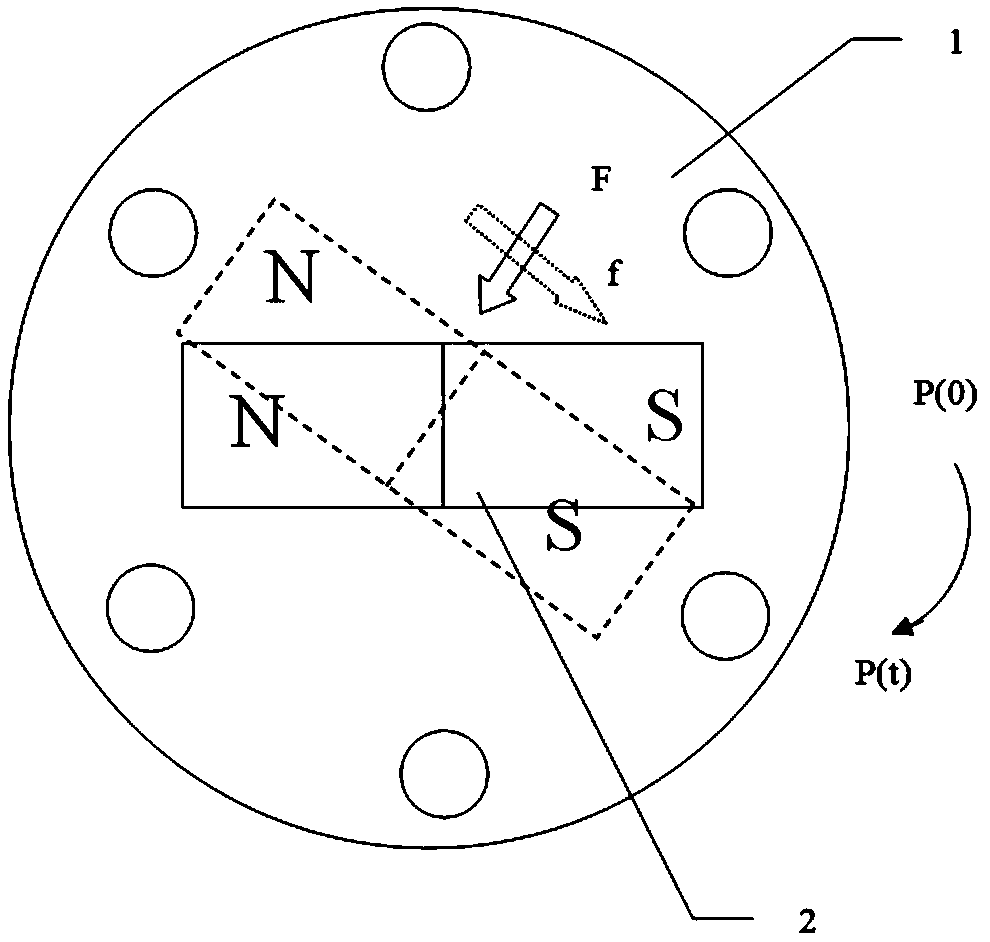
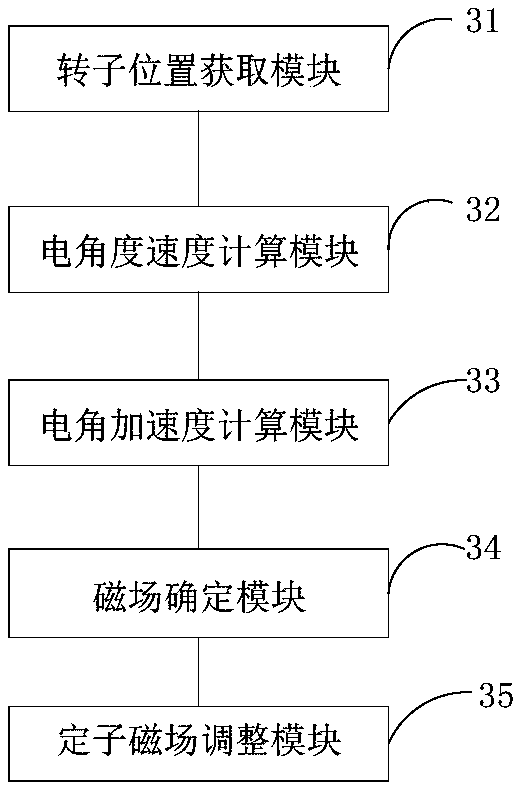
ActiveCN109017438ASolve the problem of undesired movementEasy to useSpeed controllerElectric energy managementElectric machineMovement control
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRIC VEHICLE
Three-phase voltage type PWM rectifier startup inrush current suppression method
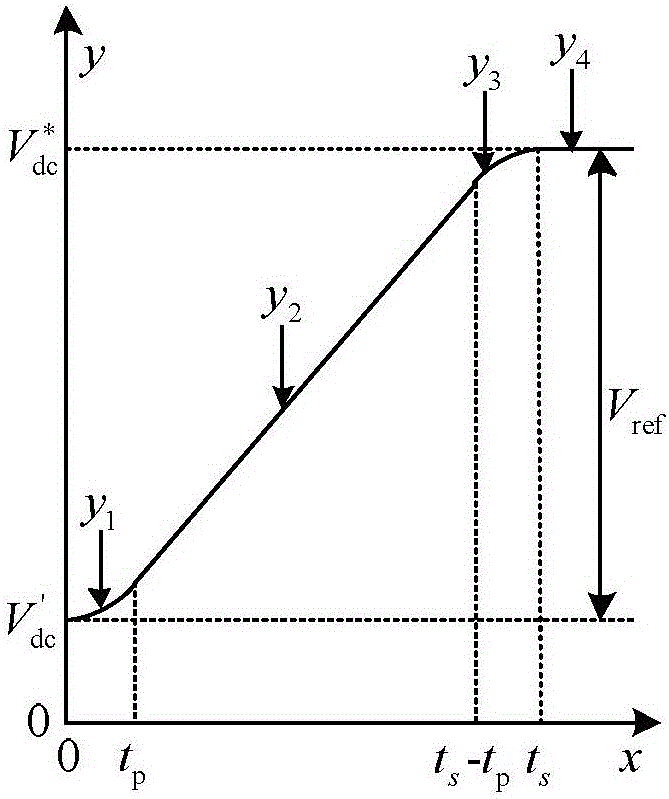
The invention provides a three-phase voltage type PWM rectifier startup inrush current suppression method, relates to the technical field of three-phase voltage type PWM rectifier startup, and solves the problems of burnout of electric inductors, burnout of the insulating layer of leads and damage to switching device caused by inrush current generated in the startup process of an existing PWM rectifier or the phenomena that control is complex and the effect is poor and damage caused by inrush current on the rectifier cannot be completely eliminated. A superposition signal of input voltage V'dc and a parabolic function y1, a superposition signal of voltage V'dc and a ramp function y2, a superposition signal of voltage V'dc and a parabolic function y3 and a superposition signal of voltage V'dc and DC stable voltage Vref are inputted to the DC bus voltage given end of a three-phase voltage type PWM rectifier in turn so that suppression of inrush current generated in the startup process of the three-phase voltage type PWM rectifier can be realized. The three-phase voltage type PWM rectifier startup inrush current suppression method is suitable for suppressing startup inrush current of the three-phase voltage type PWM rectifier.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Vacuum coating high-speed constant coiling tension apparatus and control method thereof
ActiveCN105603380AIncrease the level of automationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingManufacturing technologyEngineering
The invention discloses a vacuum coating high-speed constant coiling tension apparatus and a control method thereof, and relates to the technical field of film manufacturing technologies. A monitoring device and a control device are arranged on a traditional coating machine, and a system runs a vapor deposition drum linear speed control technology, a vapor deposition drum acceleration process ramp function curve design technology and a coating device constant coiling tension control technology, so fully-automatic process control of uncoiling, vapor deposition and rolling of a film substrate is realized, thereby the problems of large labor intensity, low coating efficiency and low product quality induced by artificial setting of the tension and speed control of film substrates in the prior art and real-time adjustment of the tension and the speed in the coating process by experience are solved, real-time control of the tension and the speed of the system is realized, the production efficiency and the quality of a coating layer are improved, the labor intensity is reduced, and the automatic level of the system is improved.
Owner:海锐星(武汉)科技有限责任公司
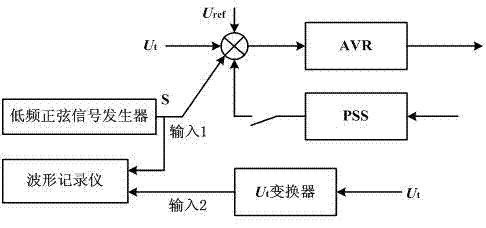
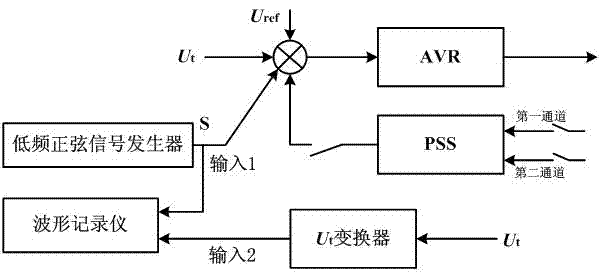
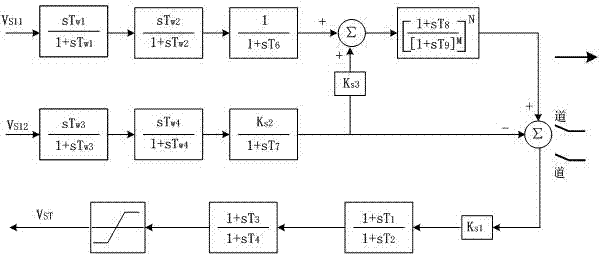
Double input PSS experiment method
ActiveCN102226826AImprove stabilitySuppress low frequency oscillationElectrical testingSignal onAngular velocity
The invention discloses a double input PSS experiment method which comprises a first channel input signal and a second channel input signal. The first channel input signal is a signal of mechanical angular velocity and the second channel input signal is an electrical power input signal. The method comprises the following steps: 1. shielding the second channel and verifying an effect of the first channel input signal on inhibiting electrical-network low-frequency oscillation through modifying ramp function passband; 2. shielding the first channel and verifying an effect of the second channel input signal on inhibiting electrical-network low-frequency oscillation through modifying the ramp function passband. In the invention, the double input PSS can be effectively verified whether the double input PSS can have effect on inhibiting low-frequency oscillation in a full frequency range with the effect of the PSS through shielding one of the channels. Stability of the electrical network canbe raised.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +2
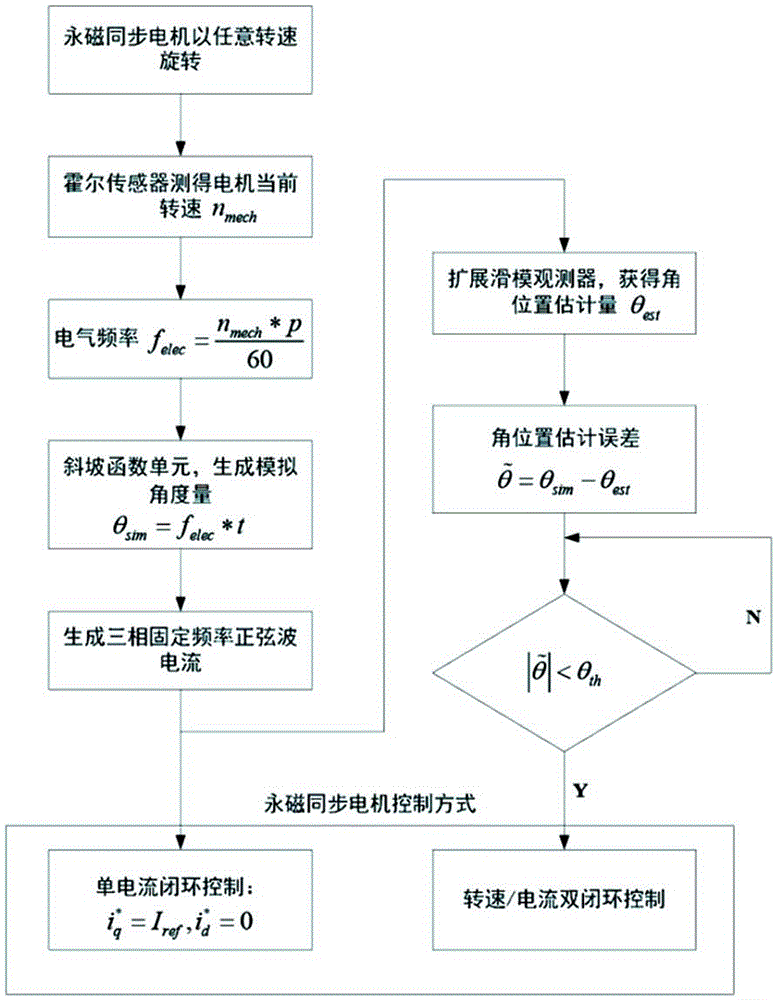
Optional rotation speed quick starting method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
InactiveCN105811843ASolve the defect that the traditional method cannot be used to estimate the angular position when the input current is zeroSolve the defect that traditional methods cannot be used for angular position estimationElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMathematical modelPermanent magnet synchronous motor
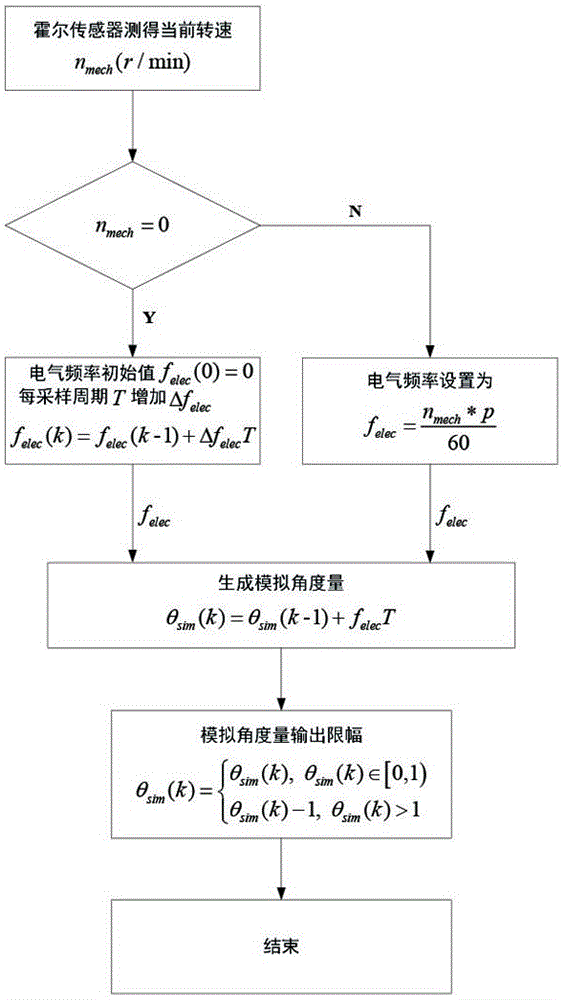
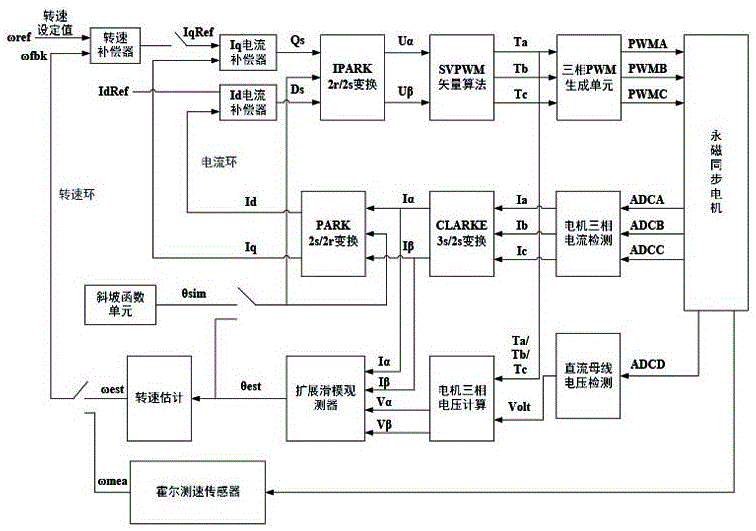
The invention provides an optional rotation speed quick starting method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following seven steps: (1) measuring a current rotating speed n<mech>r / min of a mechanical angular velocity of the motor by a hall sensor arranged at a rotor side of the permanent magnet synchronous motor; (2) determining an electric frequency as shown in the specification according to the rotating speed information n<mech> obtained in the sep (1); (3) inputting the electric frequency f<elec> obtained in the step (2) into a ramp function unit and generating an analogue angle quantity theta<sim>= f<elec>*t; (4) carrying out single-current closed-loop control on the analogue angle quantity theta<sim> in the step (3) and generating a three-phase sine wave current with the frequency f<elec>; (5) building an extended sliding mode observer on the basis of an alpha-beta mathematical model of the permanent magnet synchronous motor according to the three-phase sine wave current generated in the step (4); (6) making a difference between the analogue angle quantity theta<sim>obtained in the step (4) and an angular position estimator theta<est> obtained in the step (5) to obtain an angular position estimation error as shown in the specification; and (7) comparing the angular position estimation error as shown in the specification obtained in the step (6) with a given threshold theta. The optional rotation speed quick starting method is applied to optional rotation speed quick starting of the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:BEIJING HONGHUI INT ENERGY TECH DEV CO LTD
Tooth profile correcting method for automobile steering device rockshaft gear sector
The invention discloses a tooth profile correcting method for an automobile steering device rockshaft gear sector. The method is a modification amount changing profile correcting method. Profile correcting is achieved through slotting machining, the modification amount of profile correcting is determined by three parameters including a modification start, a terminal angle and the maximal modification amount by adopting a ramp function related to gear sector rotating angles, and in the slotting machining process with a certain transmission ratio curve, a radial feed shaft retracts or feeds according to the law of motion of the ramp function to achieve profile correcting. By means of modification correcting within the range of the modification start and the terminal angle, tooth profiles of a certain section in the middle portion of the gear sector become thick, and the purpose that the back lash of an automobile steering device gear sector and rack pair is reduced or the purpose of backlash-free engaging is achieved. For the overcutting phenomenon in the profile correcting process, theoretical tooth profiles are calculated through a tooth profile normal method, and actual tooth profiles are calculated through an envelope line method. When the actual profile correcting amount does not conform to the theoretical profile correcting mount, the three parameters are adjusted, the actual profile correcting amount is calculated again until the actual profile correcting amount conforms to the theoretical profile correcting amount, and once the three parameters are adjusted, the three parameters are fixed and put on production.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
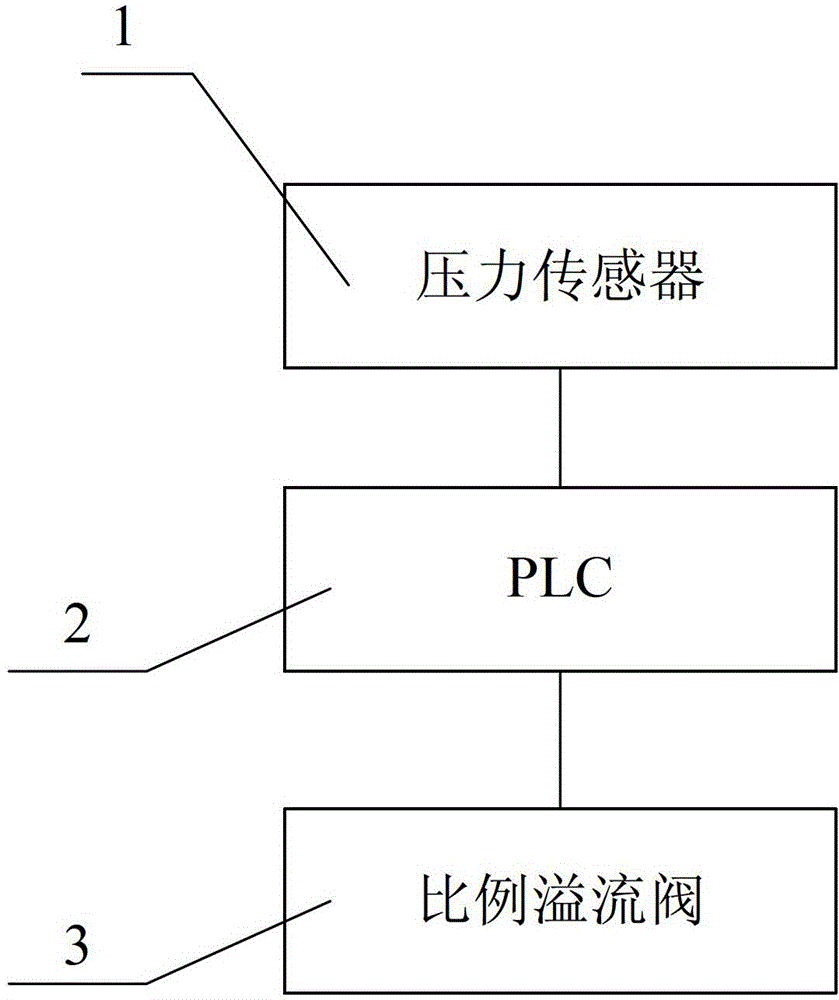
Numerical control hydraulic machine decompression system based on pressure feedback
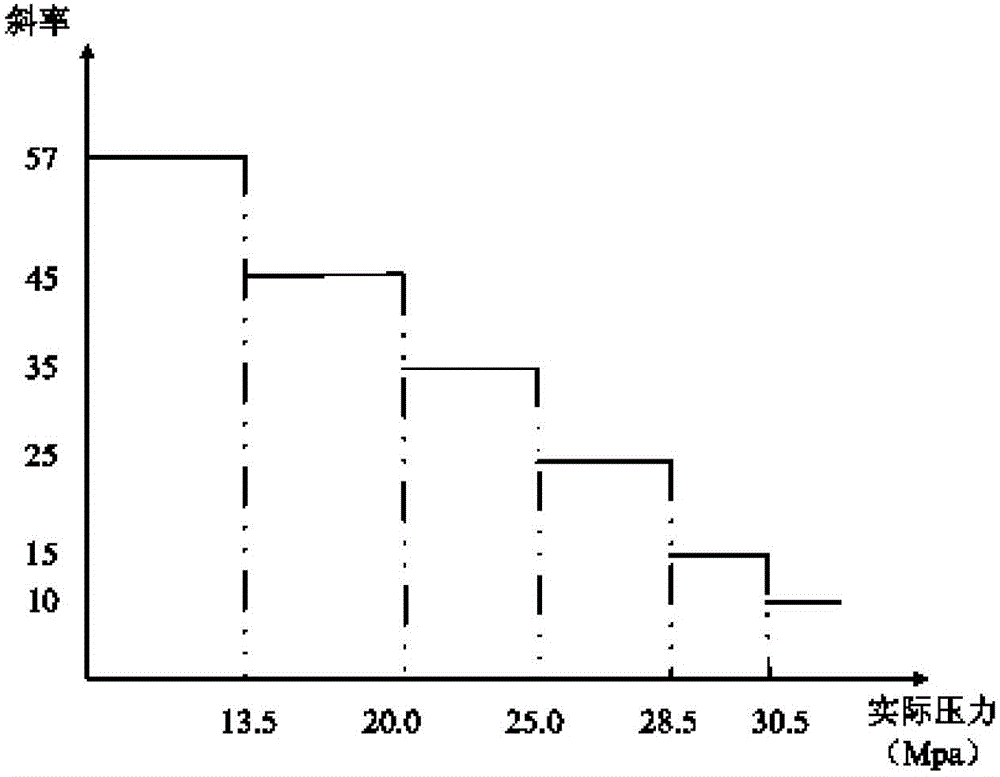
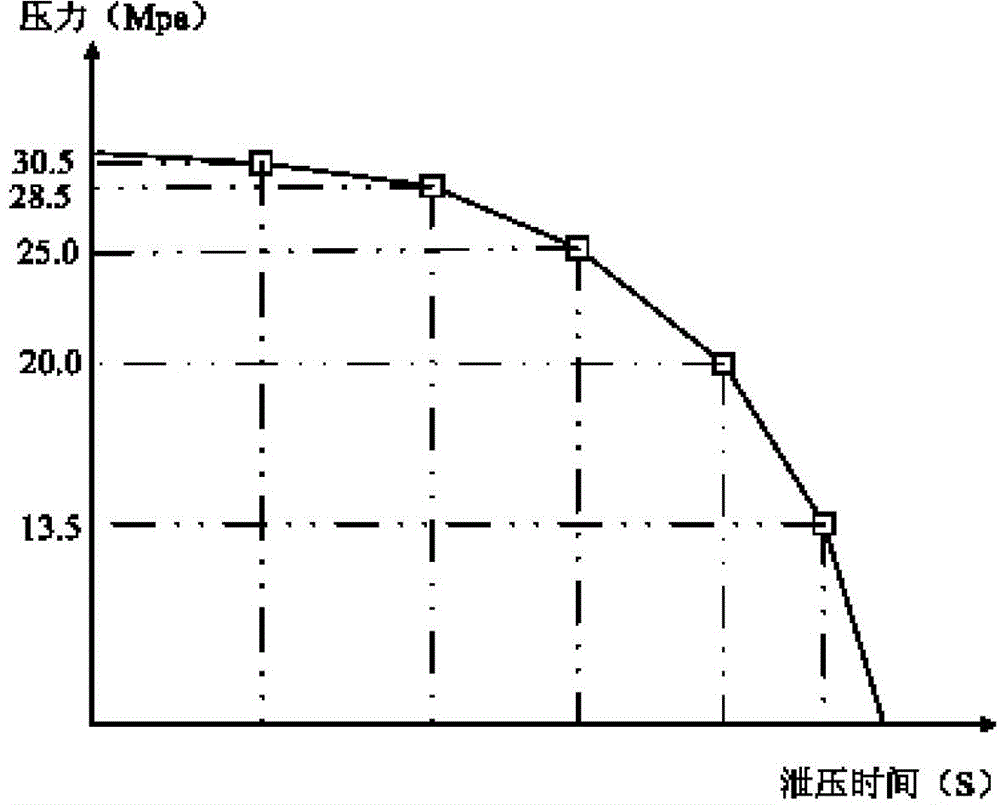
The invention discloses a numerical control hydraulic machine decompression system based on pressure feedback, and relates to the technical field of hydraulic machines. The numerical control hydraulic machine decompression system comprises a pressure sensor, a programmable logic controller and a proportional overflow valve, wherein the pressure sensor is used for collecting oil pressure data of a slide block main cylinder, the programmable logic controller is used for receiving the oil pressure data, dividing the oil pressure data into sections according to the oil pressure data, and outputting different linear control commands in the different sections, and the proportional overflow valve is used for regulating oil pressure in the slide block main cylinder according to the linear control commands. The pressure sensor is electrically connected with an analog quantity input port of the programmable logic controller. An analog quantity output port of the programmable logic controller is electrically connected with the proportional overflow valve. The decompression of a slide block is controlled continuously in a variable-rate mode by controlling the rate of continuous progressive decrease of the proportional overflow valve according to the corresponding relationship between the oil pressure data of the slide block main cylinder and the slope of the ramp function of the proportional overflow valve. Therefore, the aims of high-pressure and small-slope stable decompression and low-pressure and large-slope rapid decompression are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN TIANDUAN PRESS CO LTD
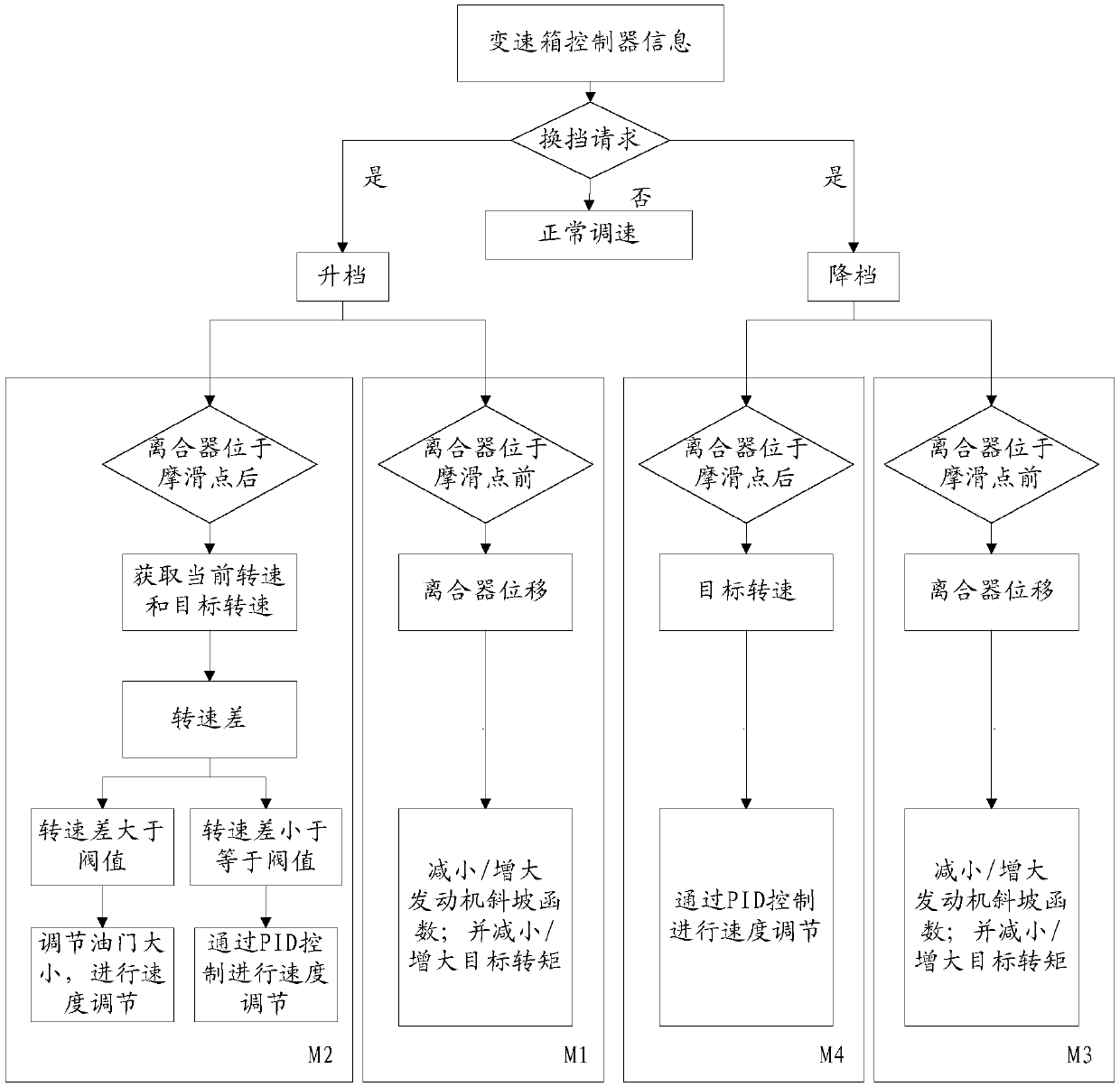
Coordinated control method of engine and transmission during gear shifting
ActiveCN109606371AMinimize sudden torque changesReduce sliding workGearing controlClosed loopRamp function
The invention discloses a control method of an engine and a transmission during gear shifting. The control method comprises the following steps: receiving information of a transmission box controller,and if so, judging as an upshifting / downshifting request, wherein an upshifting process comprises the following substeps: acquiring displacement point information of a clutch, entering an upshiftingcoordinated control mode when the clutch is in front of a frictional sliding point, and entering an upshifting rotation speed control mode when the clutch is behind the frictional sliding point; and adownshifting process comprises the following substeps: acquiring the displacement point information of the clutch, entering a downshifting coordinated control mode when the clutch is in front of thefrictional sliding point, and entering a downshifting rotation speed control mode when the clutch is behind the frictional sliding point. During the gear shifting, in the engine deloading and loadingstages, torque is interfered by a transmission box and the output torque of the engine is controlled by an engine ramp function, so that sudden change of the torque of the engine during the gear shifting is effectively reduced. Through closed-loop PID control and rotation speed control which are adopted in the no-load stage of the engine, the rotation speed of the engine can be quickly adjusted toa target rotation speed and the slipping frictional power is reduced.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
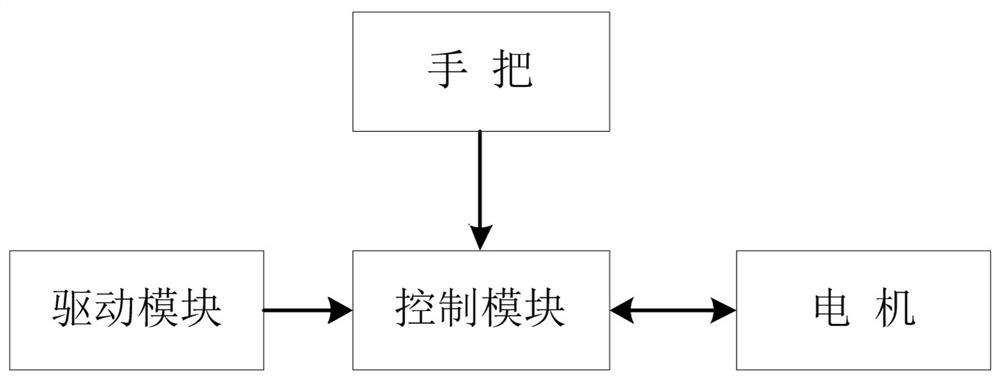
Electric vehicle starting control method
ActiveCN112549986ASolve the problem of matching a variety of motorsAchieve a smooth startSpeed controllerElectric devicesElectric machineryElectric cars
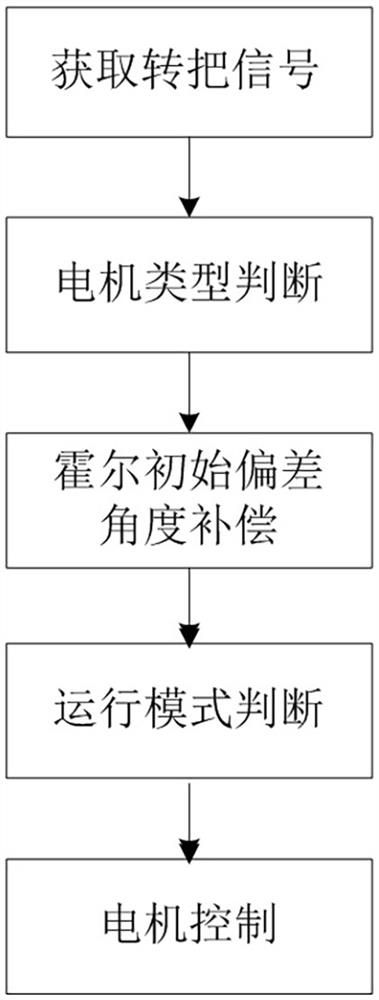
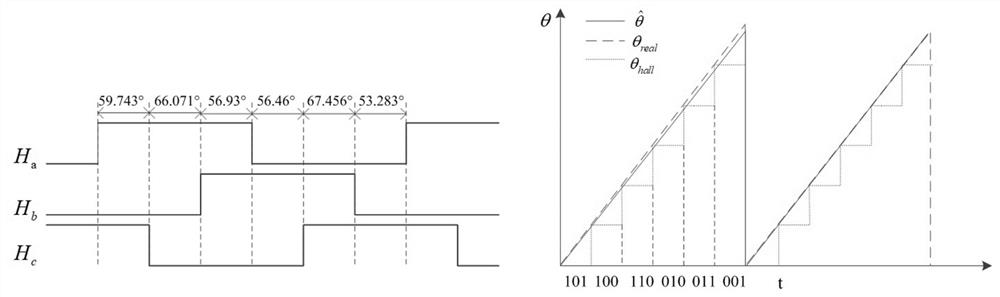
The invention discloses an electric vehicle starting control method, and relates to the technical field of electric vehicle starting control, when a rotating handle rotates to obtain a motor startingsignal, motor type judgment is firstly realized through positive and negative codes. Different motor parameters are identified by utilizing the discreteness characteristic of the motor under specificexcitation through giving a high pulse to the motor according to different inductance values of different motors and different generated currents, and the type of the connected motor is judged. And then Hall initial deviation angle compensation is realized through angle integral processing. And an operation mode is judged, soft start is realized by adopting a slope function method, and finally themotor is controlled to realize smooth start. The beneficial effects of the invention are that the method achieves the recognition of the motor parameters through the positive and negative codes, andsolves a problem that a single controller is matched with various motors; hall initial angle compensation is achieved through Hall self-learning, the problem of non-standard sectors of Hall sectors issolved, and smooth starting of the motor is achieved. Soft start is achieved through a slope function, and riding experience comfort is improved.
Owner:湖南小黄鸭科技有限公司
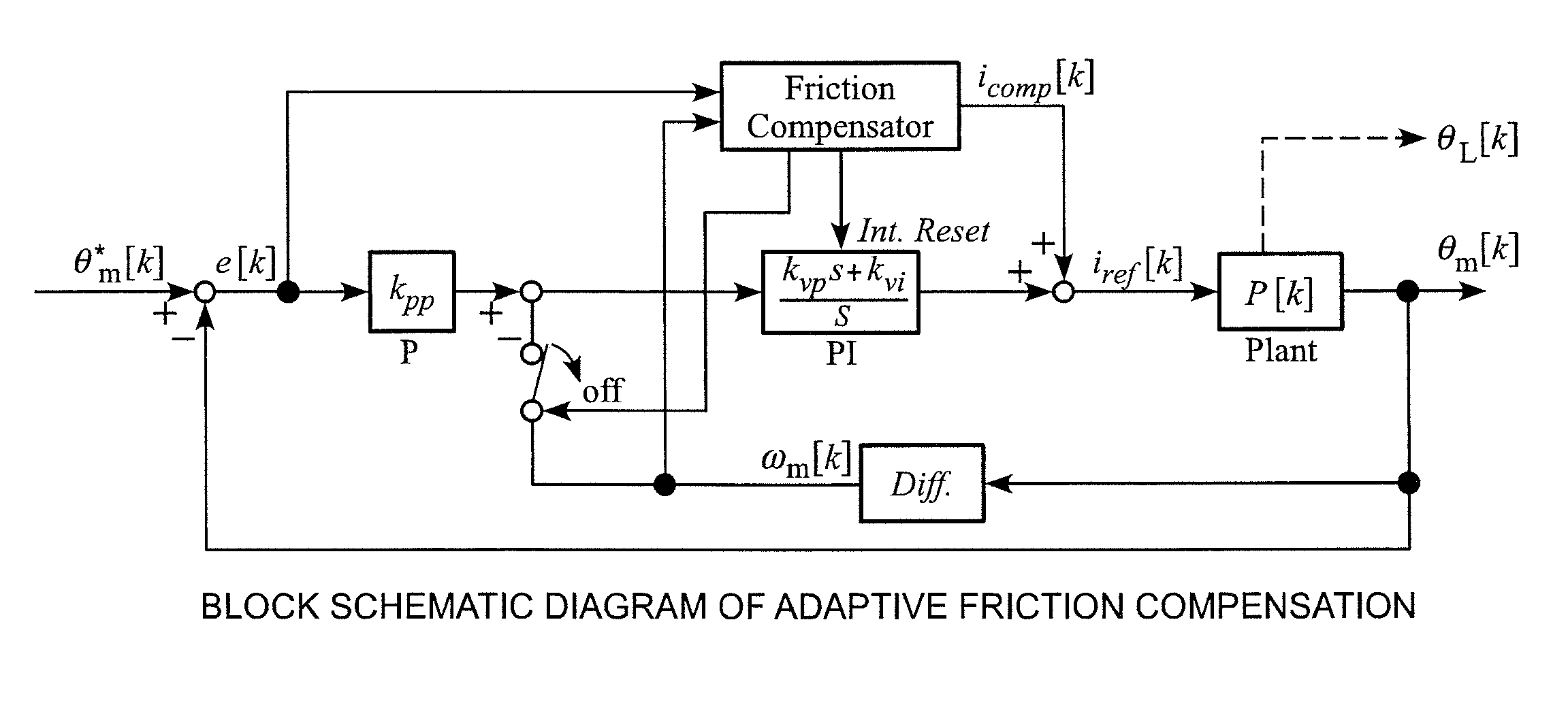
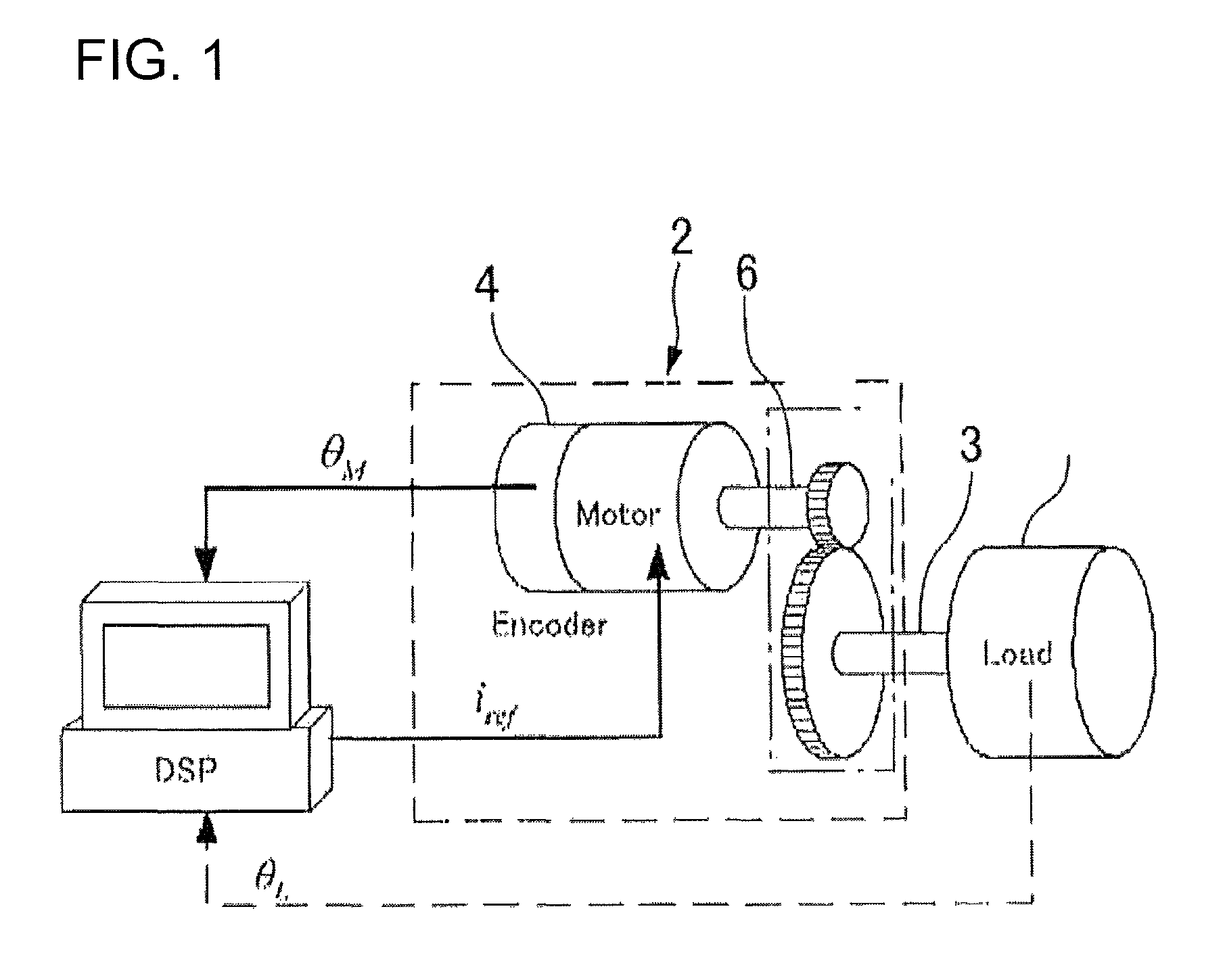
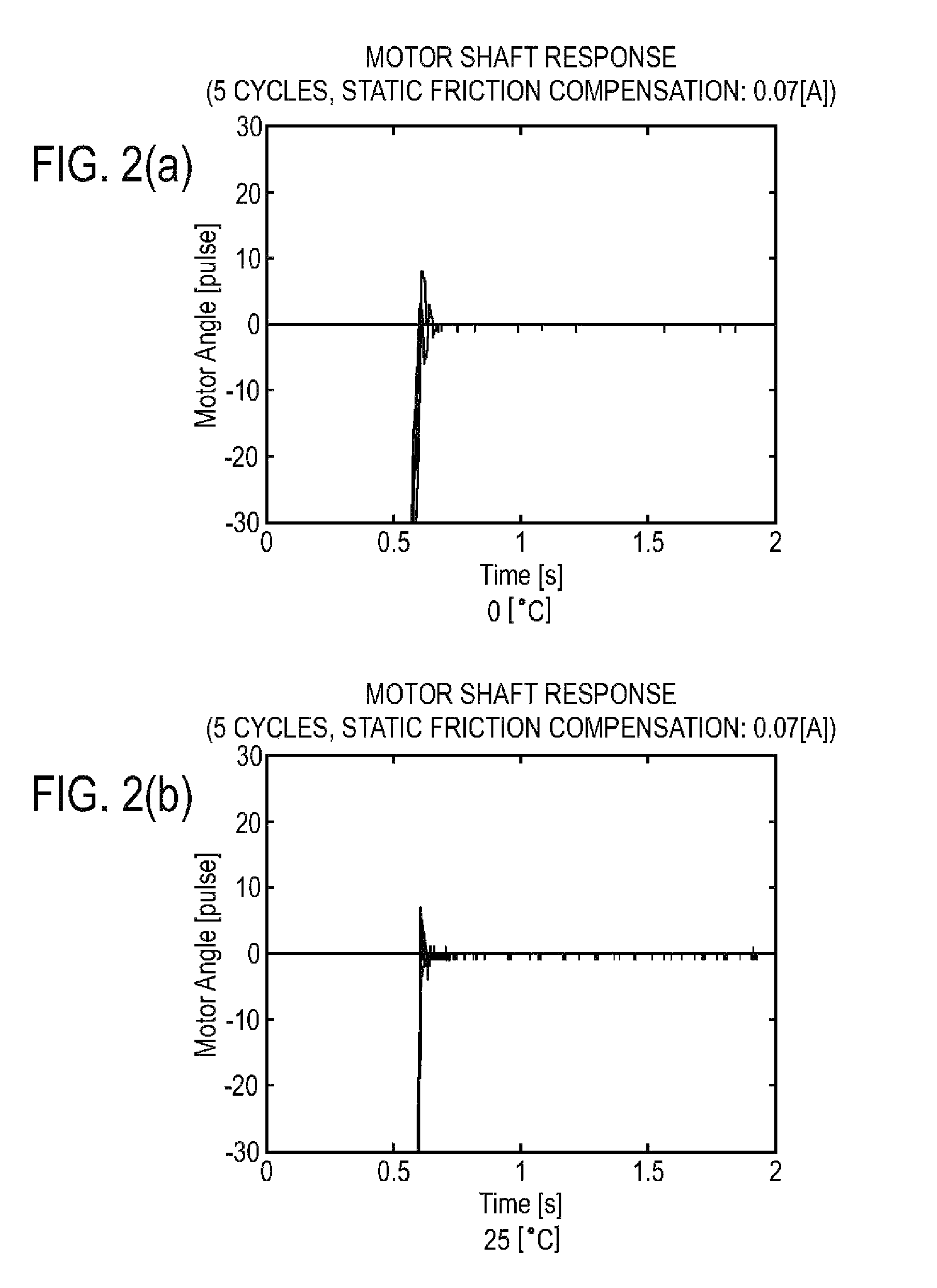
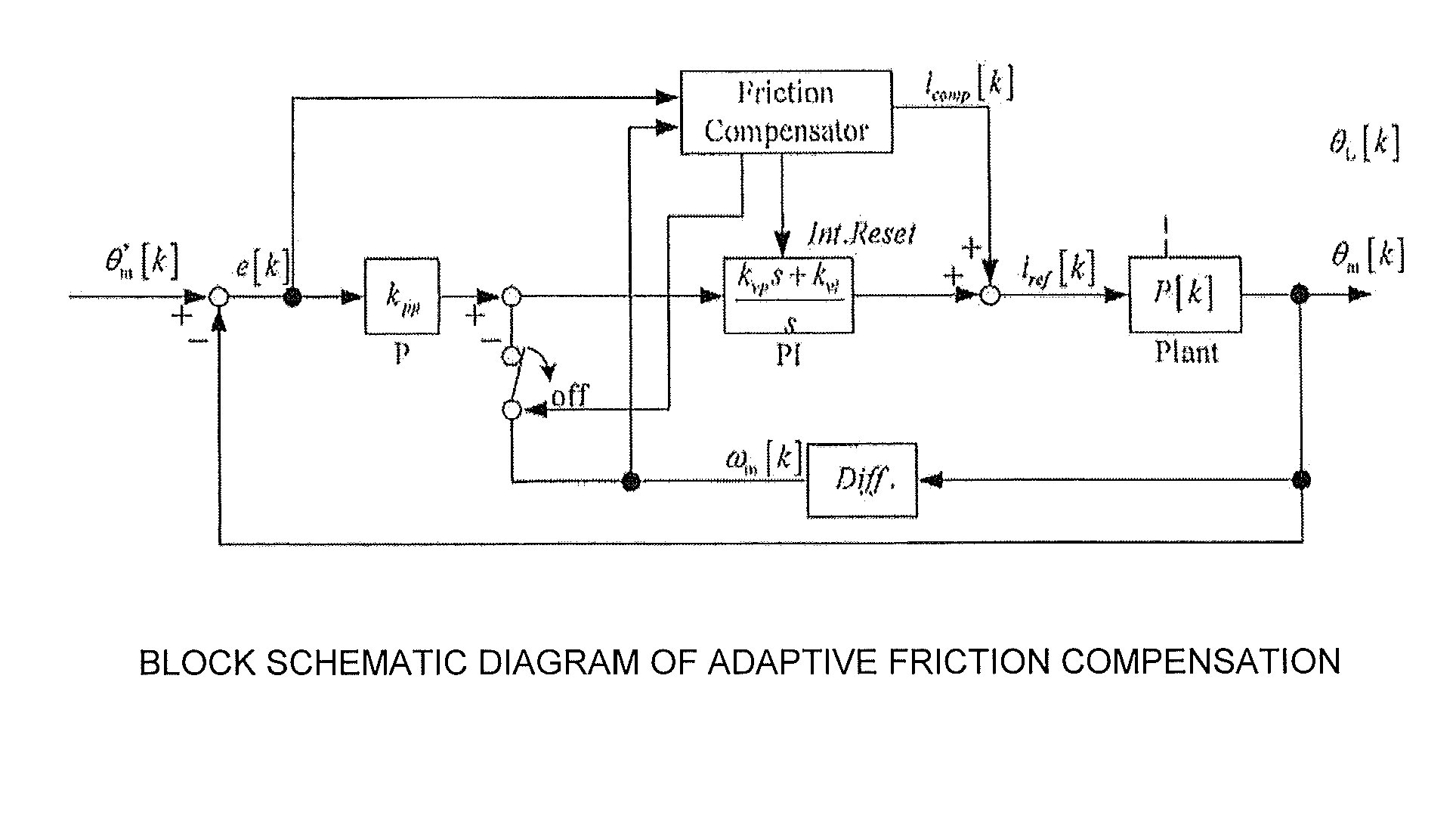
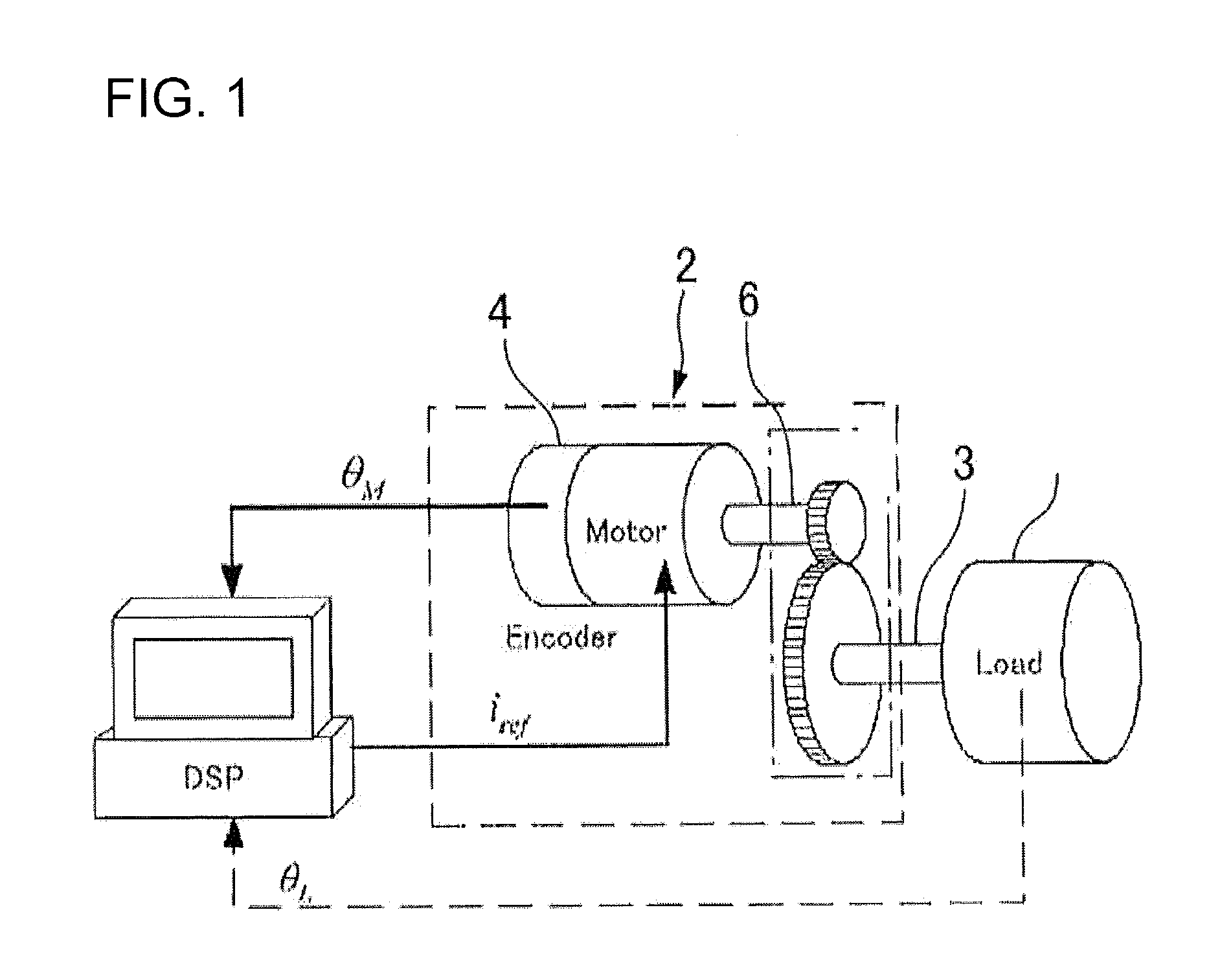
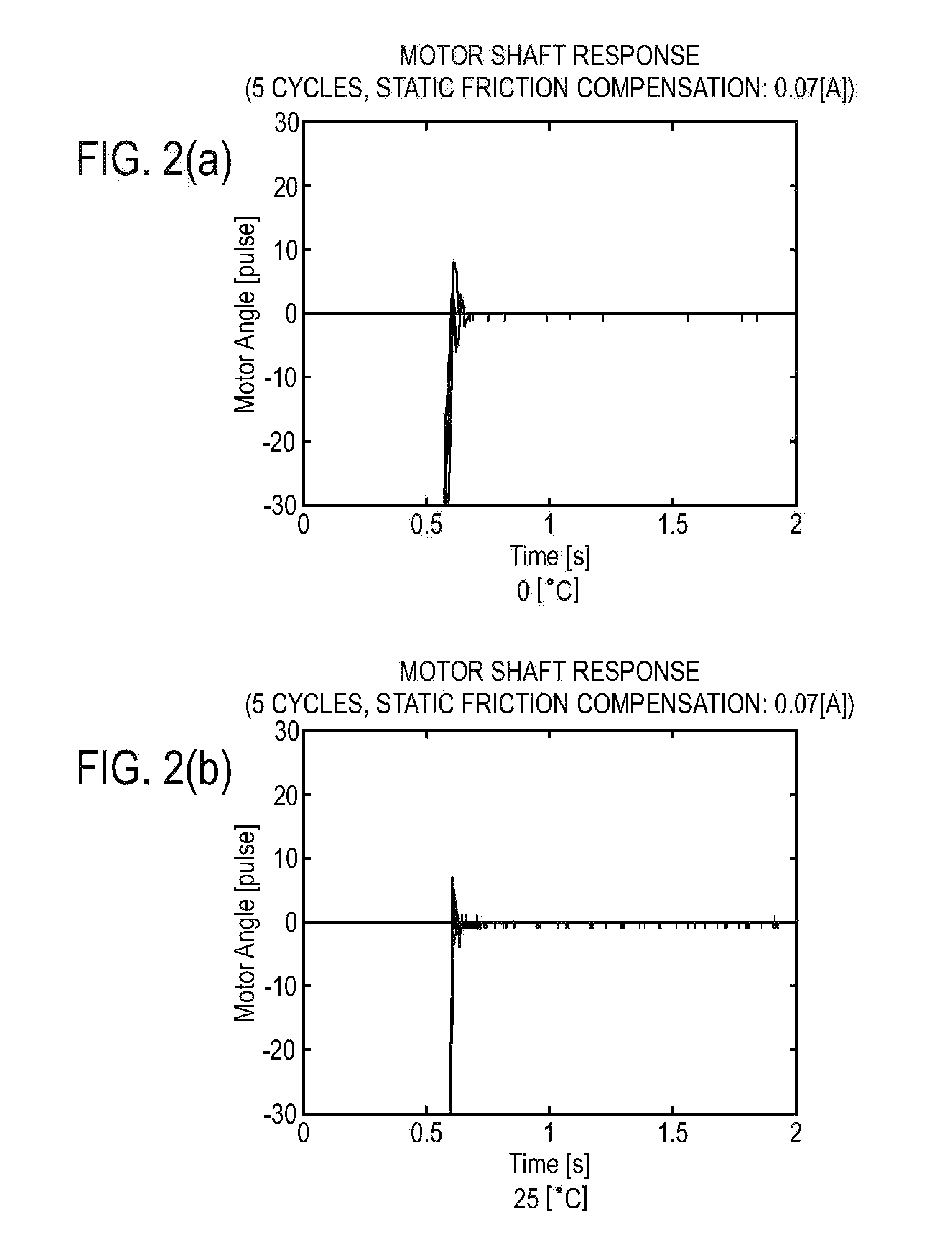
Method for performing adaptive friction compensation in an actuator accounting for variation in friction characteristics of wave gear drive accompanying change in temperature
ActiveUS8442692B2Improve controlReduction in accuracySampled-variable control systemsComputer controlStatic frictionEngineering
According to a method for performing adaptive friction compensation of an actuator including a wave gear drive, there is used as a friction compensation current applied to a motor drive current a static friction compensation current is when a motor shaft stops with a deviation, and a Coulomb friction compensation current ic in other circumstances. The static friction compensation current is is obtained by adding a compensation amount isr of a monotonically increasing ramp function to a compensation amount iss of a step function, and a step-function compensation amount ics is used as the Coulomb friction compensation current ic. Since the amount of friction compensation can be changed adaptively based on the data during positioning-control response, a motor shaft can be stabilized at a target angle without prominent accompanying vibration, even if the ambient temperature changes and the friction characteristics of the wave gear drive fluctuate.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
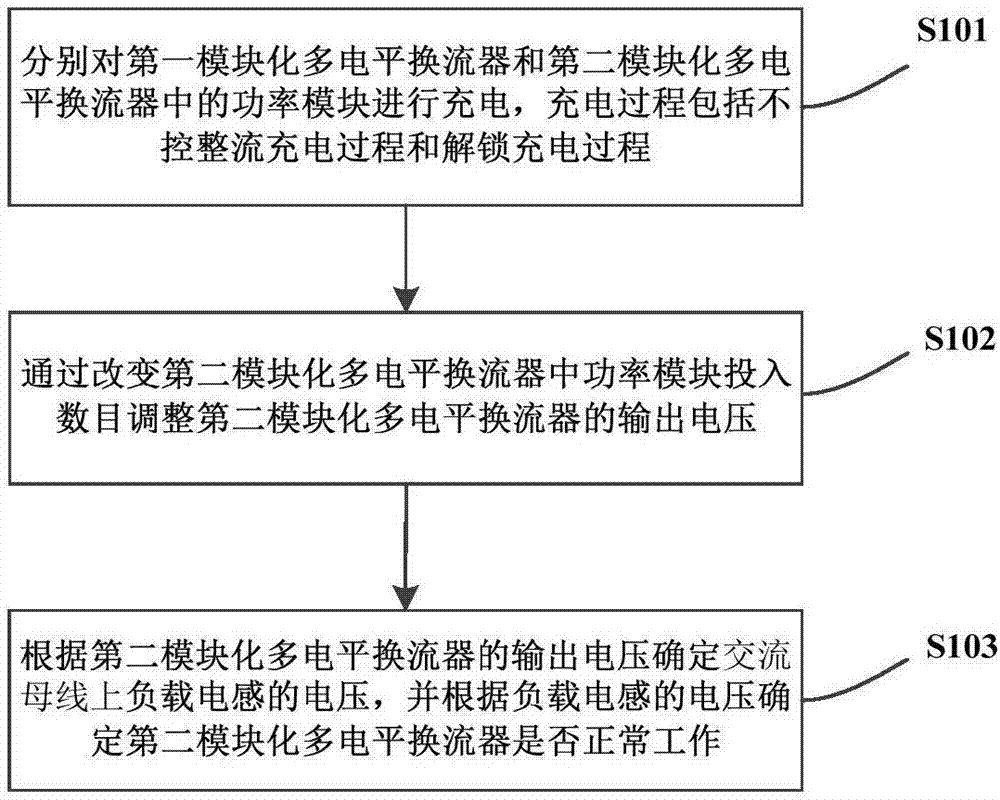
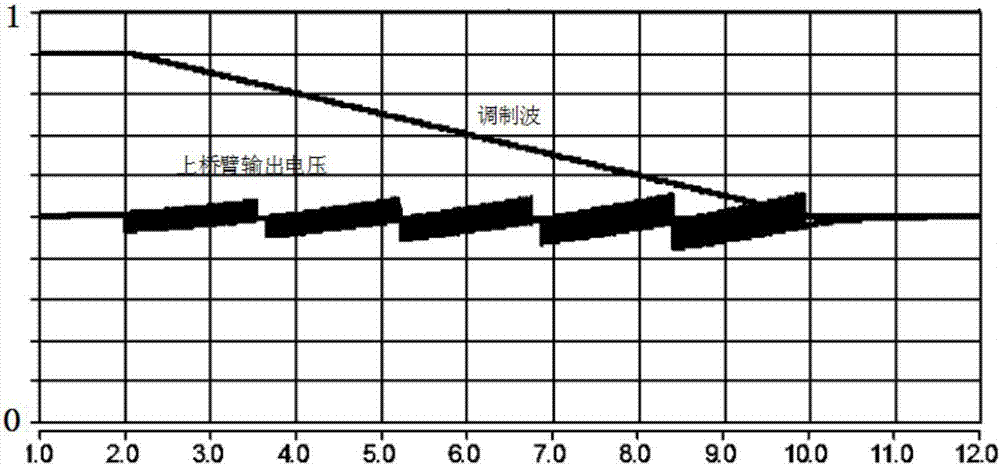
Modular multilevel converter test method, device and system
ActiveCN107966623ASmall duty cycleReduce inrush currentElectrical testingRamp functionElectrical current
The invention provides a modular multilevel converter test method, device and system. Power modules in a first modular multilevel converter and a second modular multilevel converter are firstly charged, the output voltage of the second modular multilevel converter is then adjusted, whether the second modular multilevel converter works normally is finally determined, and test on the second modularmultilevel converter is realized. The unlocking charging process adopts a soft start control strategy combining DC chopper and a ramp function, the duty cycle of the first modular multilevel converterand the second modular multilevel converter is gradually reduced through modulation waves in a ramp function form, the current of the power module rises slowly, the impact current during the chargingprocess can be effectively reduced, the process is simple and convenient, realization is easy, and the test cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD +2
Method for performing adaptive friction compensation in an actuator accounting for variation in friction characteristics of wave gear drive accompanying change in temperature
ActiveUS20110251722A1Compensation changesImprove controlSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlStatic frictionActuator
According to a method for performing adaptive friction compensation of an actuator including a wave gear drive, there is used as a friction compensation current applied to a motor drive current a static friction compensation current is when a motor shaft stops with a deviation, and a Coulomb friction compensation current ic in other circumstances. The static friction compensation current is is obtained by adding a compensation amount isr of a monotonically increasing ramp function to a compensation amount iss of a step function, and a step-function compensation amount ics is used as the Coulomb friction compensation current ic. Since the amount of friction compensation can be changed adaptively based on the data during positioning-control response, a motor shaft can be stabilized at a target angle without prominent accompanying vibration, even if the ambient temperature changes and the friction characteristics of the wave gear drive fluctuate.
Owner:NAGOYA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Draft force detection on a vehicle having a linkage
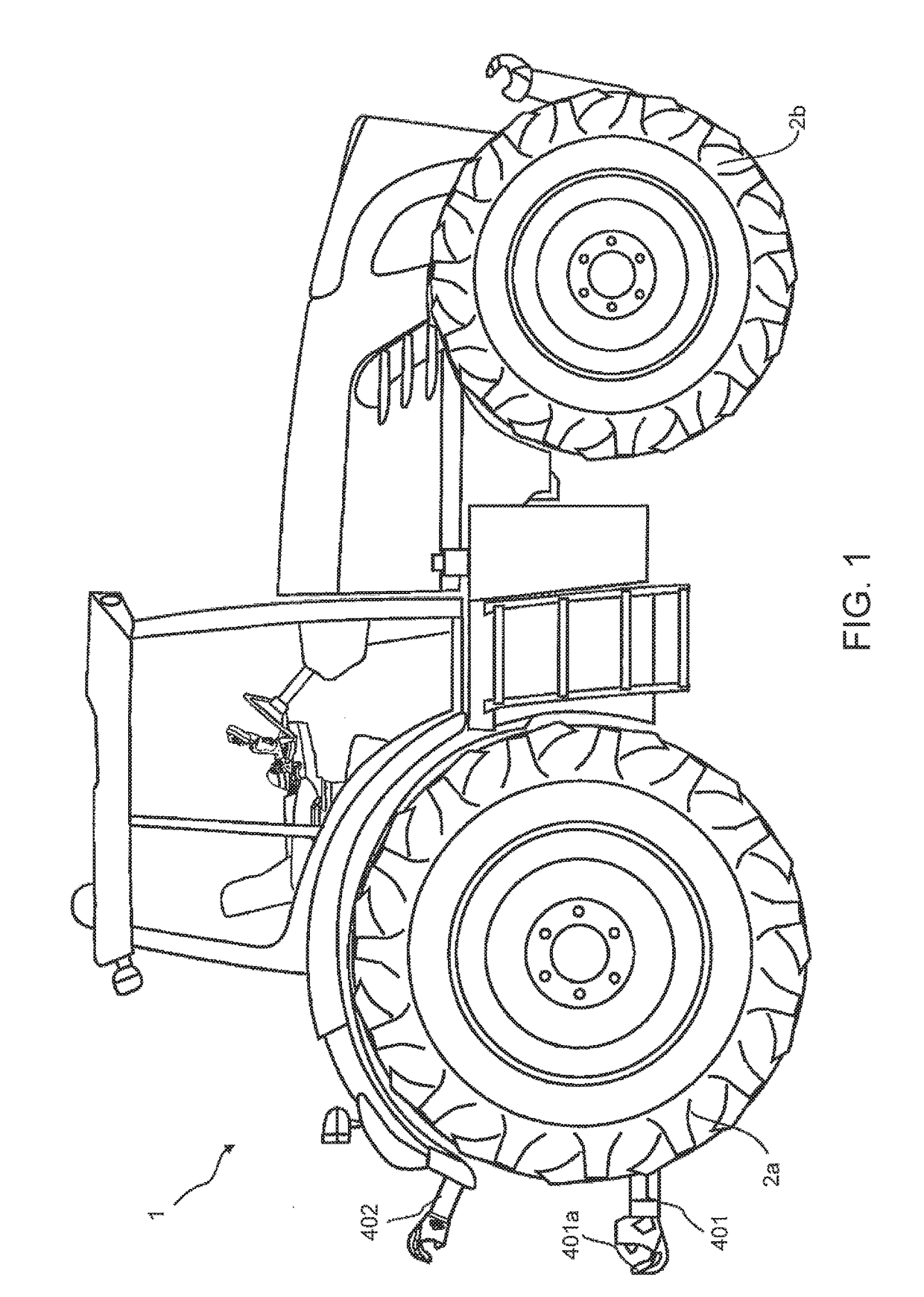
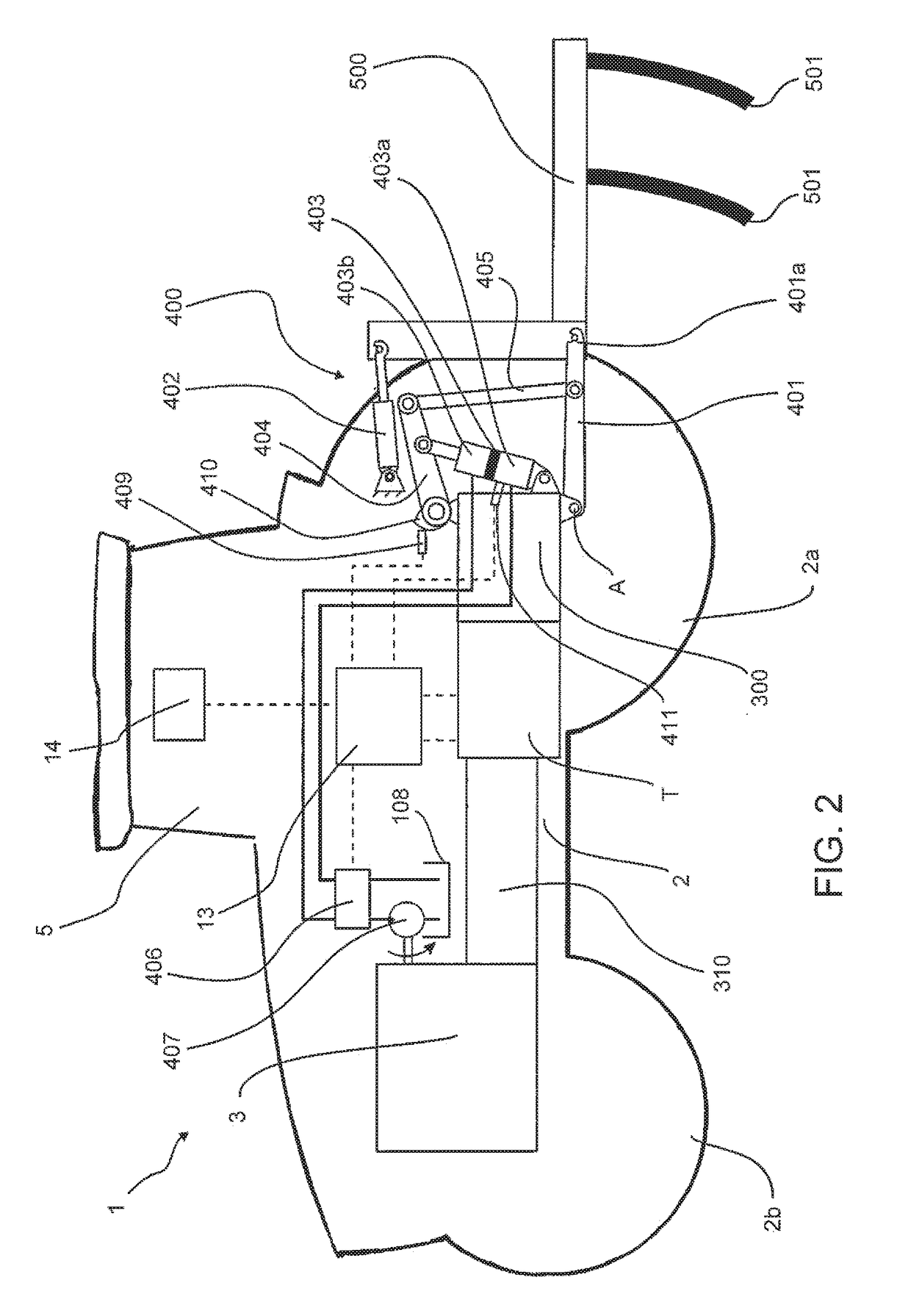
ActiveUS20170215327A1Move preciselyReduce forceAgricultural machinesAdjusting devicesControl systemVehicle detection
A vehicle control system for controlling the height of a linkage on a vehicle having a continuously variable transmission (CVT) in which the linkage is automatically raised and lowered depending on a draft force detected by the vehicle including an input draft force detected by sensors in the CVT or driveline is inputted into the control system and the system further processes said input draft force to provide an output draft force upon which movement of the linkage is based and the control system processes the input draft force by compensating the input draft force detected during acceleration or deceleration and / or compensating the input draft detected whilst travelling along a slope, and / or equalising the input draft force by applying a ramp function, and / or reducing the input draft force when the linkage is at a predetermined height.
Owner:AGCO INT GMBH
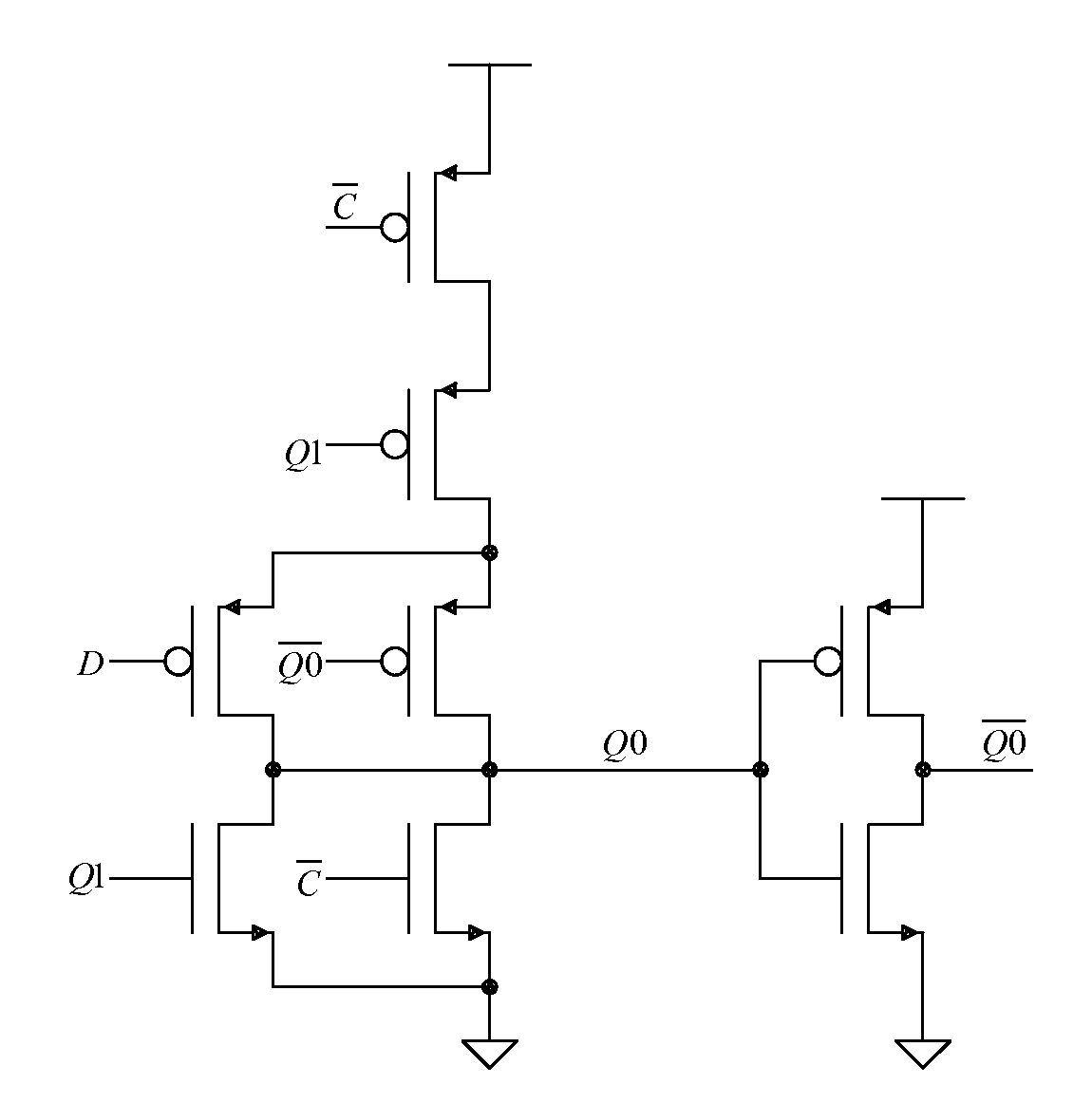
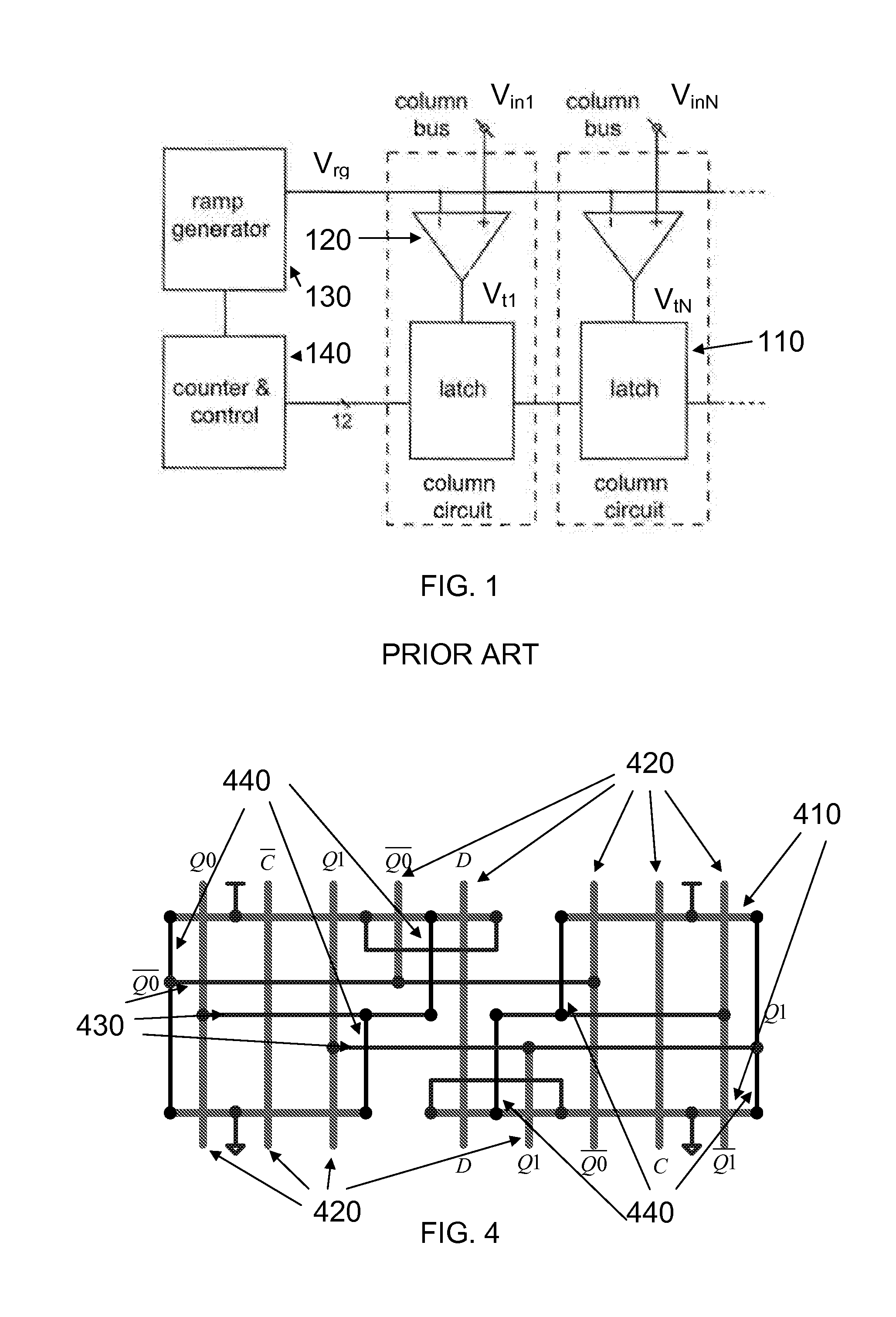
MINIMAL POWER LATCH FOR SINGLE-SLOPE ADCs
ActiveUS20130214760A1Power saving provisionsCurrent/voltage measurementEngineeringAnalog-to-digital converter
A latch circuit that uses two interoperating latches. The latch circuit has the beneficial feature that it switches only a single time during a measurement that uses a stair step or ramp function as an input signal in an analog to digital converter. This feature minimizes the amount of power that is consumed in the latch and also minimizes the amount of high frequency noise that is generated by the latch. An application using a plurality of such latch circuits in a parallel decoding ADC for use in an image sensor is given as an example.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com