Optional rotation speed quick starting method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, fast start technology, applied in the direction of control generator, motor generator control, control electromechanical brake, etc., to achieve the effect of improving estimation performance, fast switching, and suppressing influence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
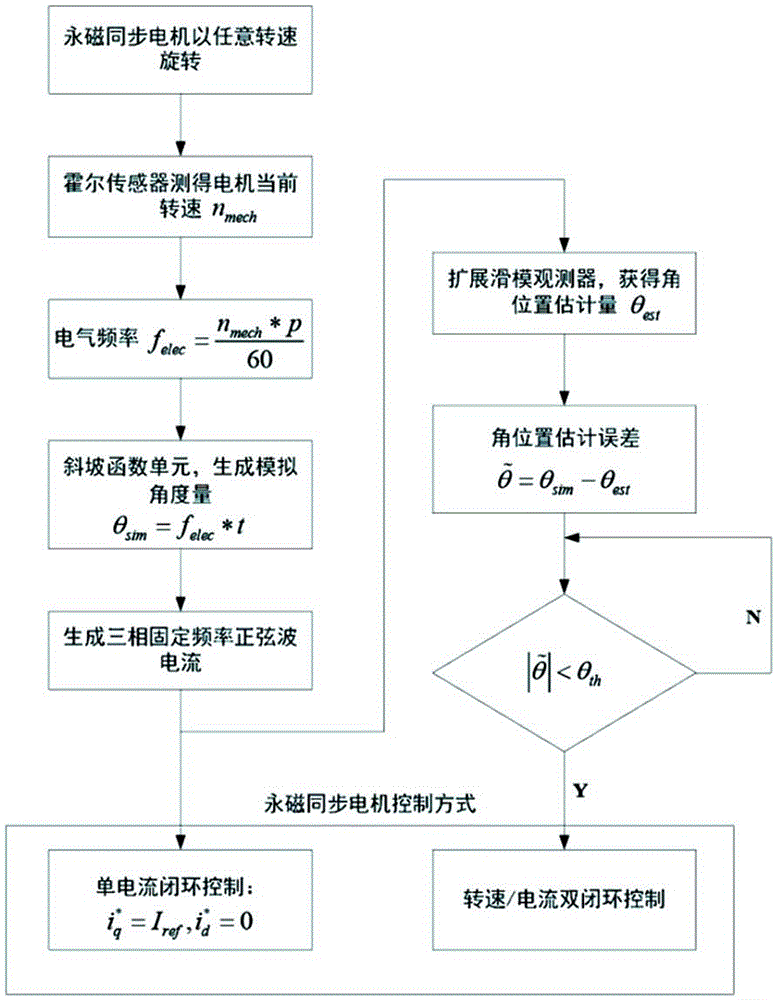
[0027] A method for quickly starting a permanent magnet synchronous motor at any speed, characterized in that: the method includes seven steps, the first step is to measure the current speed n of the mechanical angular velocity of the motor by a Hall sensor installed on the rotor side of the permanent magnet synchronous motor mech r / min; the second step is based on the speed information n in the first step mech Find the electrical frequency The unit is Hz, where p is the number of pole pairs of the motor stator;
[0028] In the third step, the electrical frequency f obtained in the second step is elec Input to the ramp function unit to generate the analog angle θ sim = f elec *t; where t is the amount of time;
[0029] The fourth step is based on the simulated angle θ in the third step sim Carry out single current closed-loop control, generating frequency f elec The three-phase sine wave current keeps the motor stable at the current speed;
[0030] The fifth step is to...
Embodiment 2
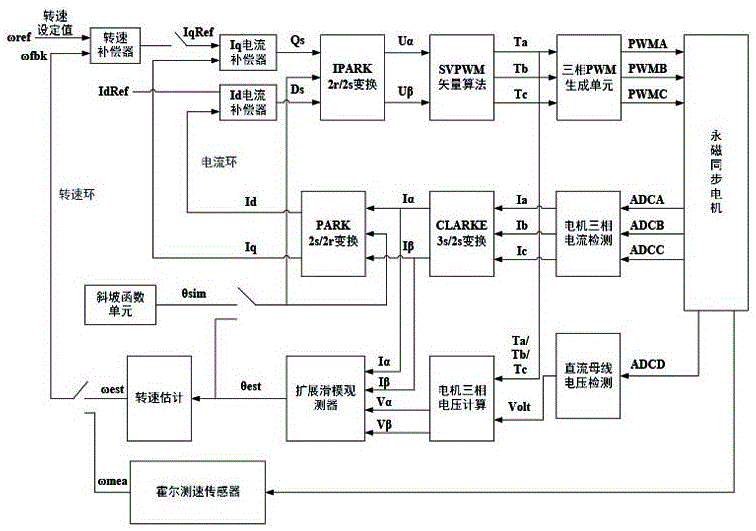
[0034] A method for quickly starting a permanent magnet synchronous motor at any speed described in Embodiment 1, the specific implementation steps of the extended sliding mode observer in the fifth step are as follows:
[0035] The first step is to establish the mathematical model of the current and back EMF under the α-β system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor: e α = -λωsin(θ), e β = λωcos(θ), where R s , L s Respectively, the motor stator phase winding resistance and inductance, u α , u β i α i β 、e α 、e β are the two-phase static voltage, current and back electromotive force under the α-β system respectively, λ is the back electromotive force coefficient, ω is the electrical angular velocity, and θ is the electrical angle;
[0036] The second step uses the Hall current sensor connected in series in the motor circuit to measure the three-phase winding current of the motor, which are respectively I a , I b and I c ;
[0037] Step 3 Based on the mathema...
Embodiment 3
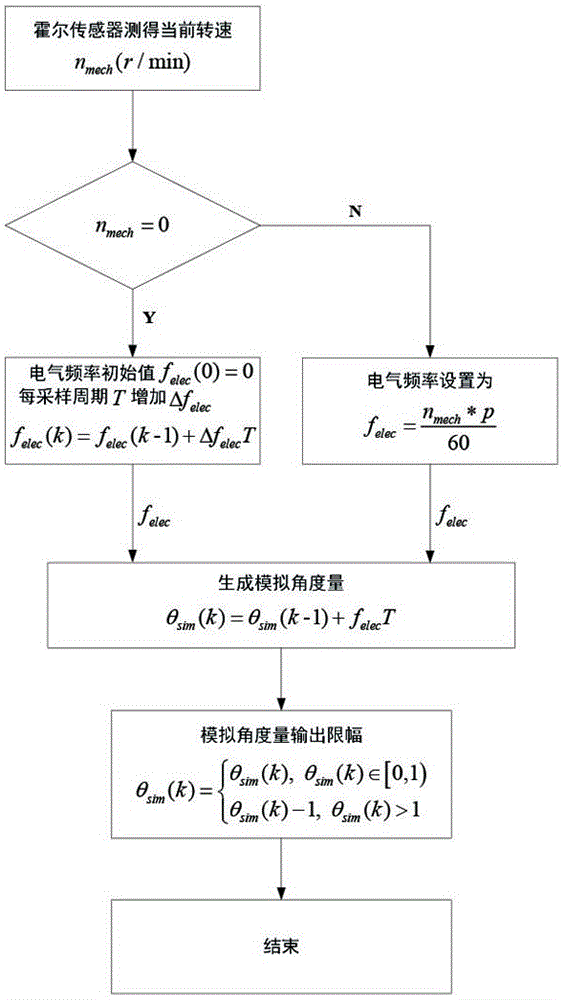
[0040] In the method for quickly starting a permanent magnet synchronous motor at any speed described in Embodiment 1, the time amount t is replaced by the sampling period T during the discretization of the third step, that is, θ sim (k) = θ sim (k-1)+f elec *T, θ sim (k)∈[0,1); where k is the sampling moment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com