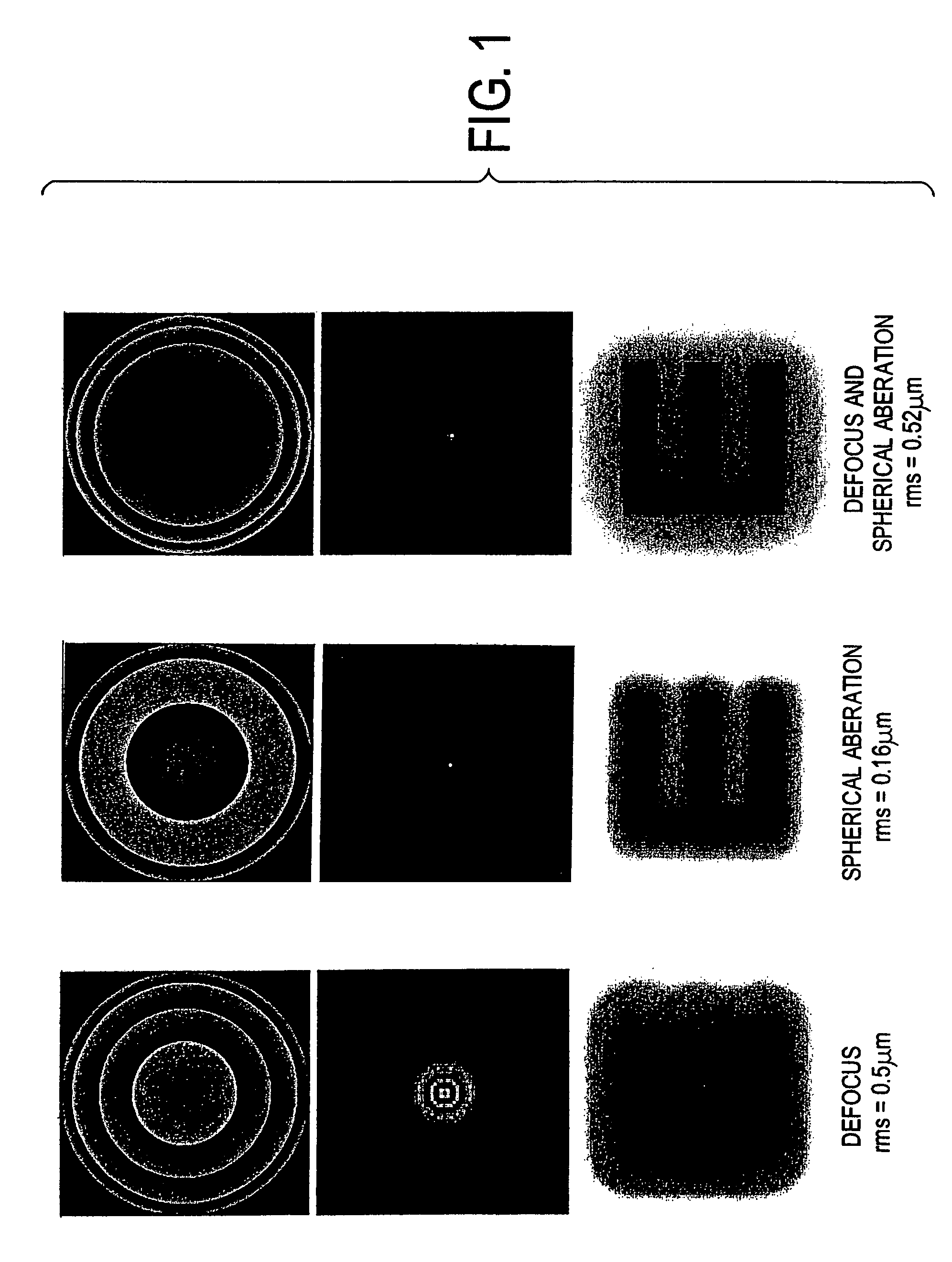
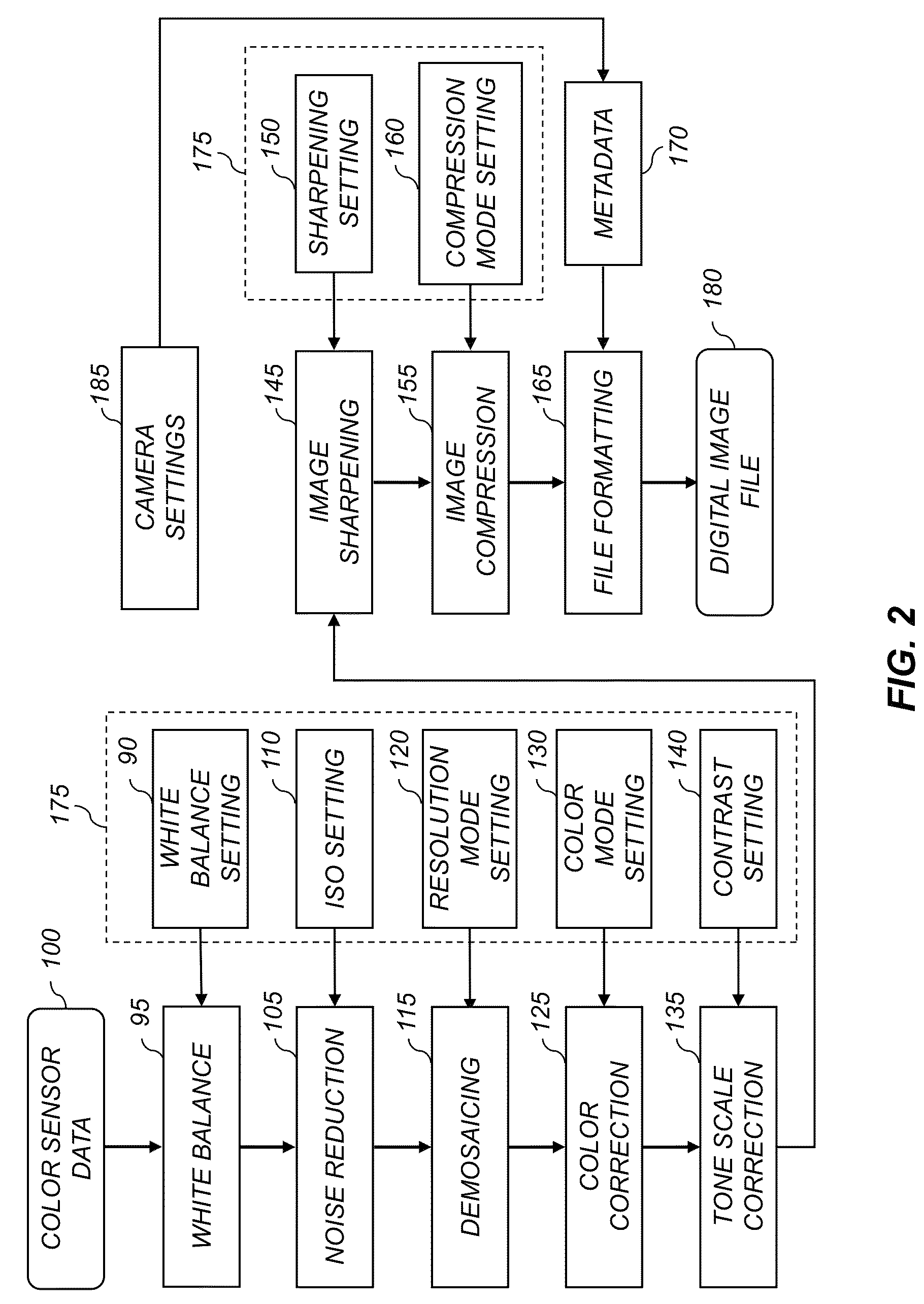
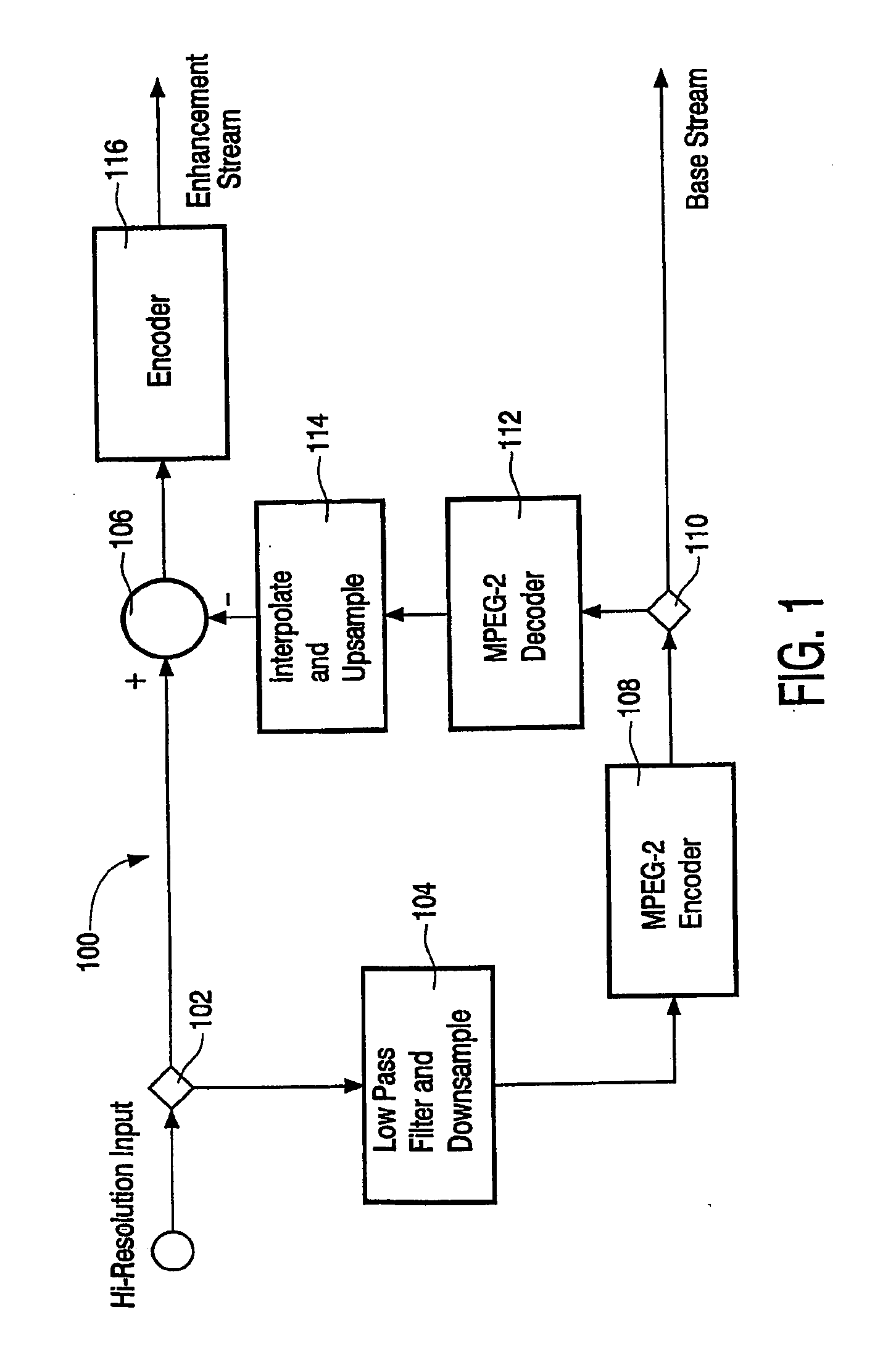
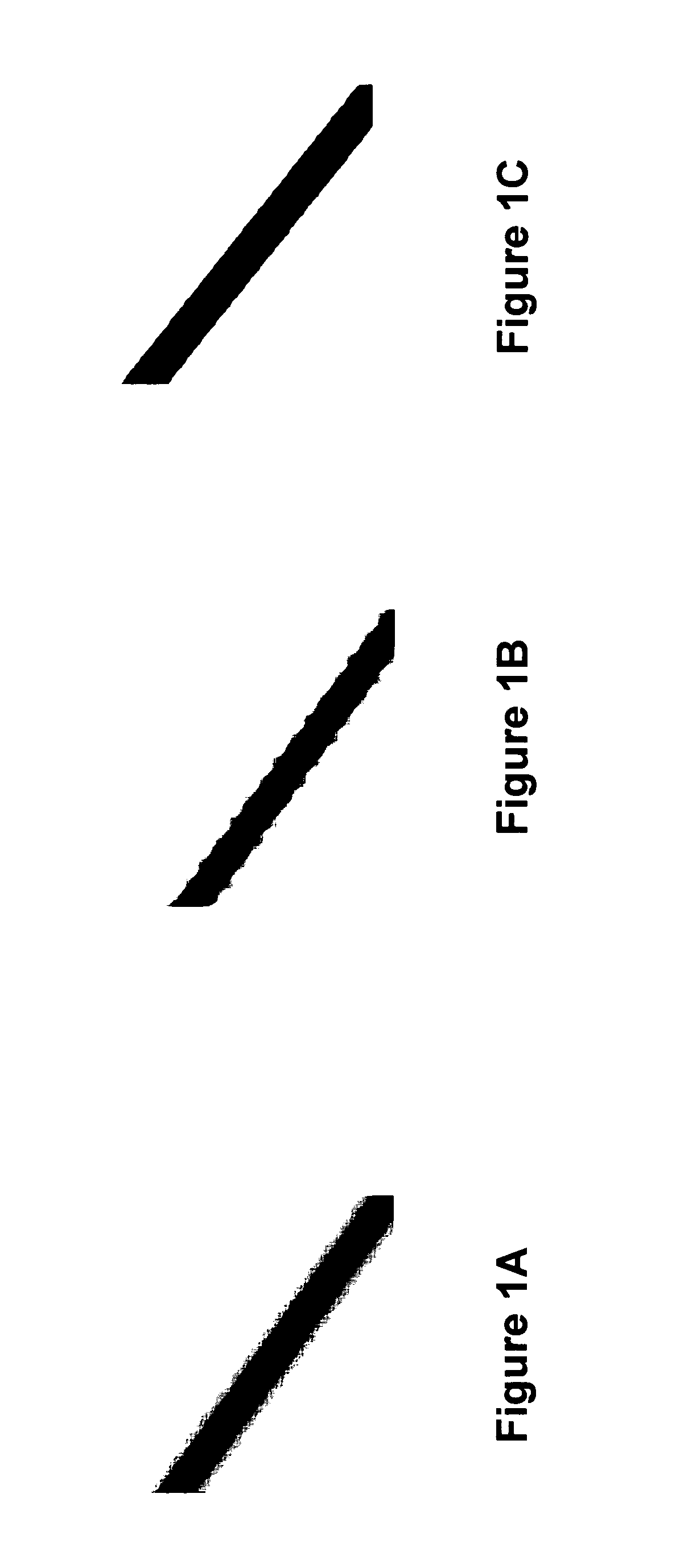Patents
Literature
315 results about "Acutance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
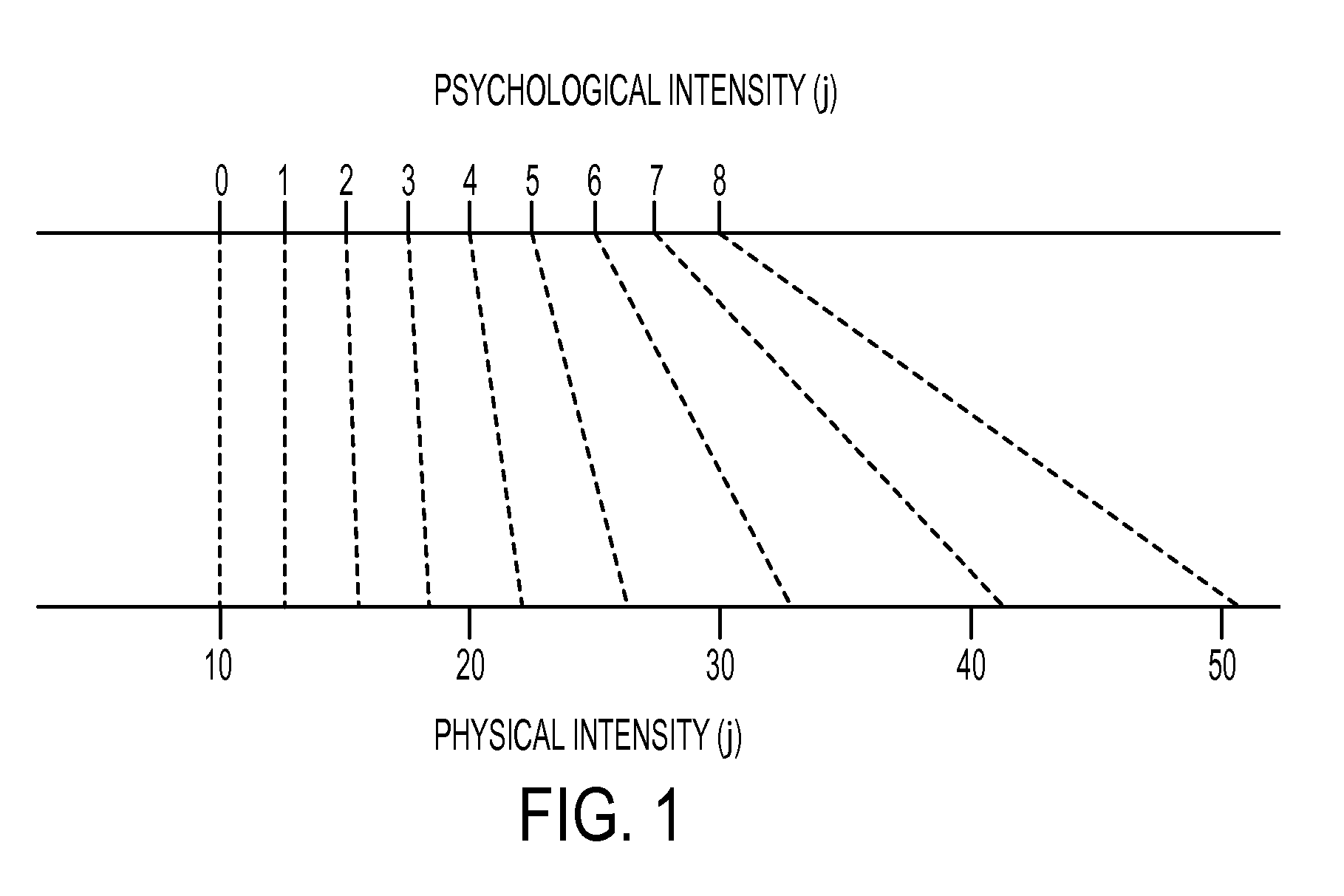
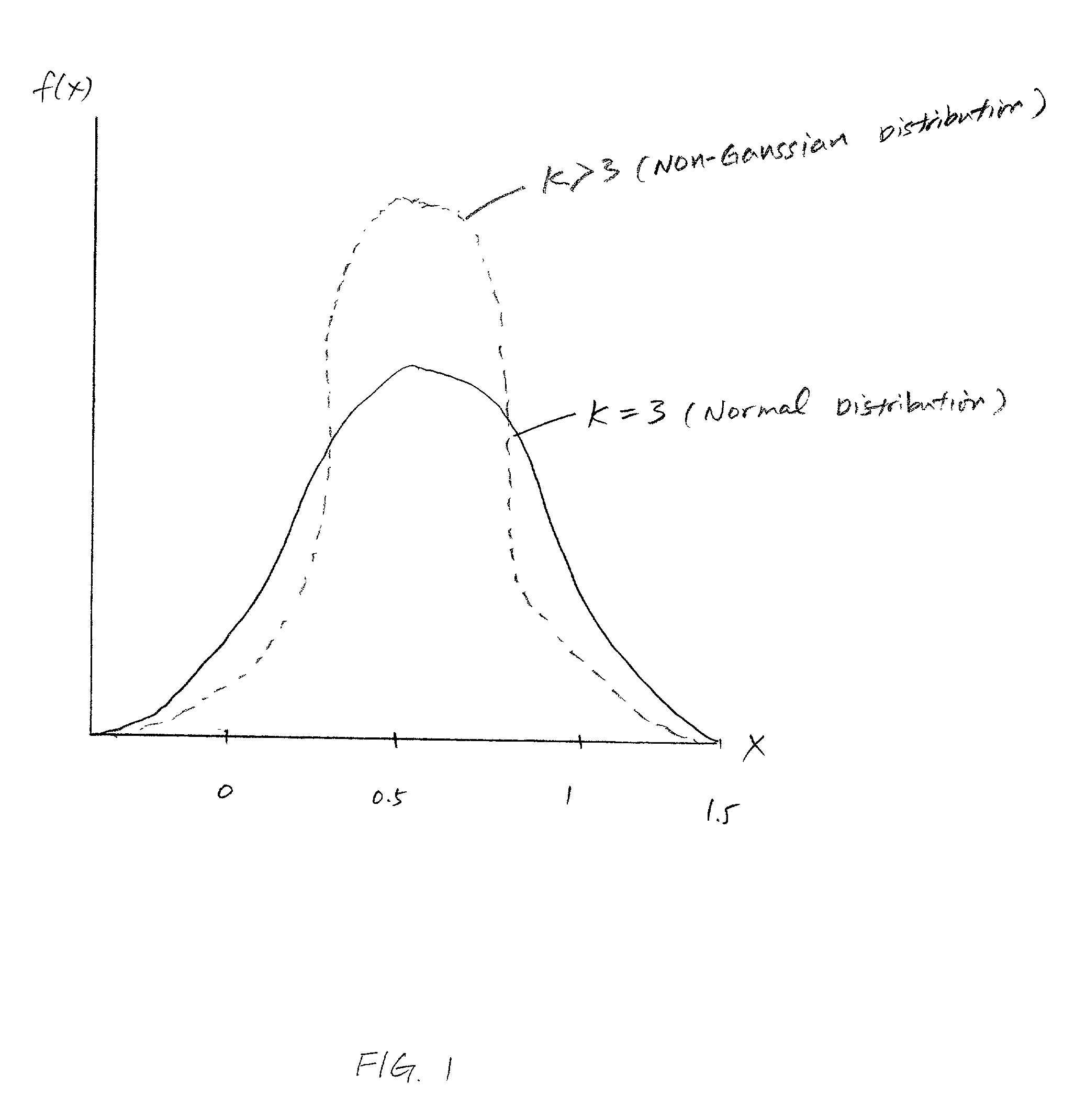
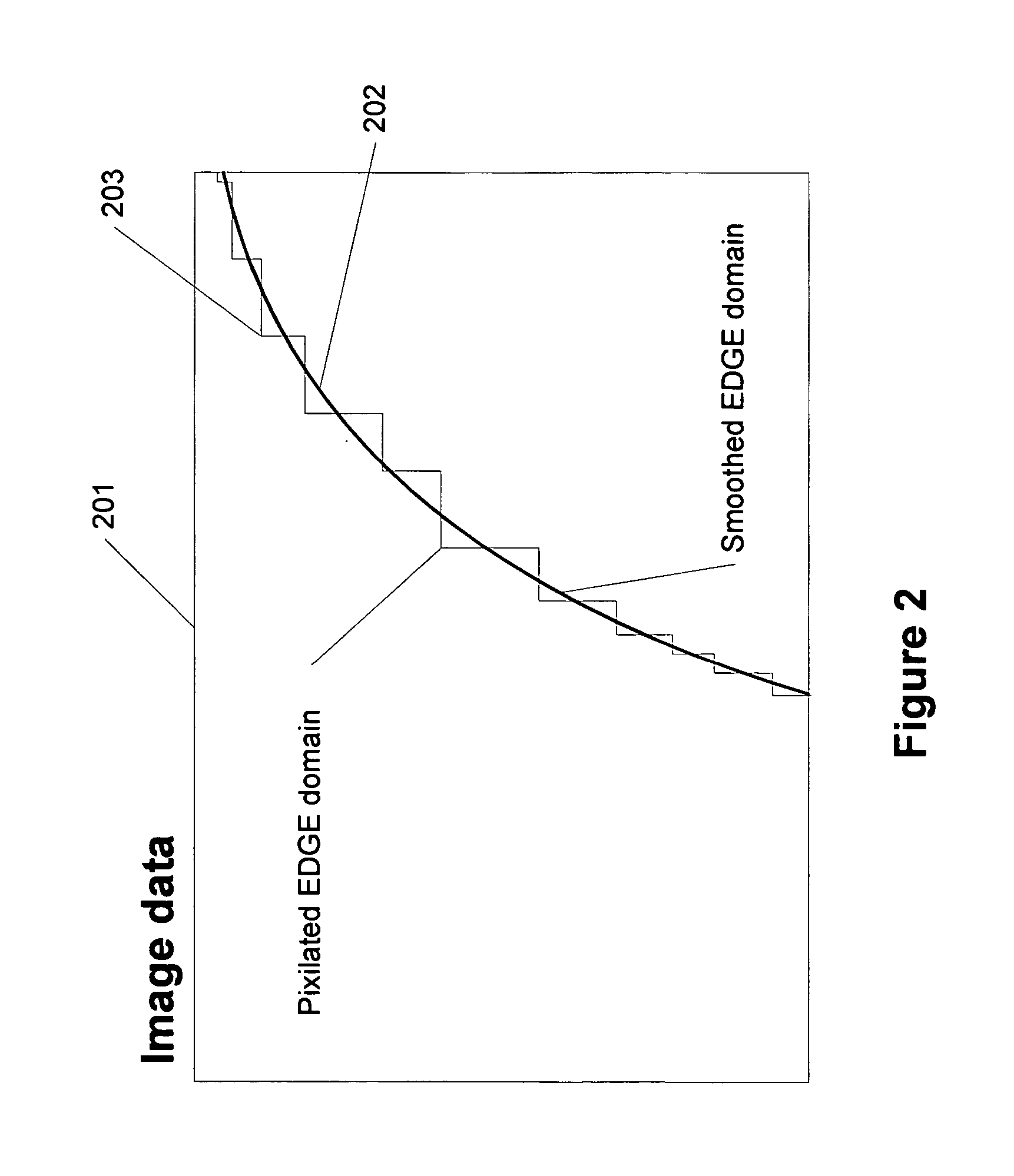
In photography, the term "acutance" describes a subjective perception of sharpness that is related to the edge contrast of an image. Acutance is related to the amplitude of the derivative of brightness with respect to space. Due to the nature of the human visual system, an image with higher acutance appears sharper even though an increase in acutance does not increase real resolution.
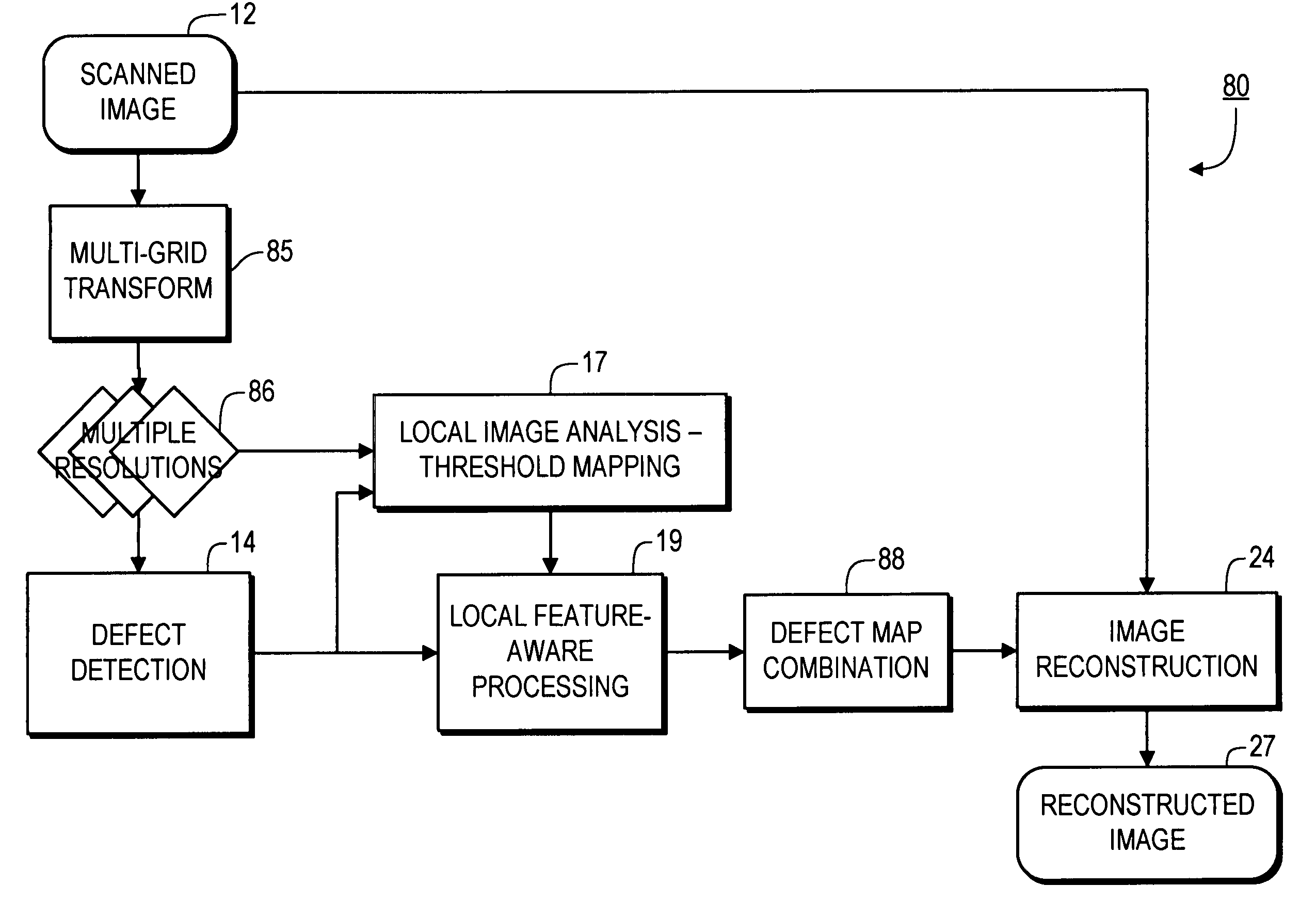
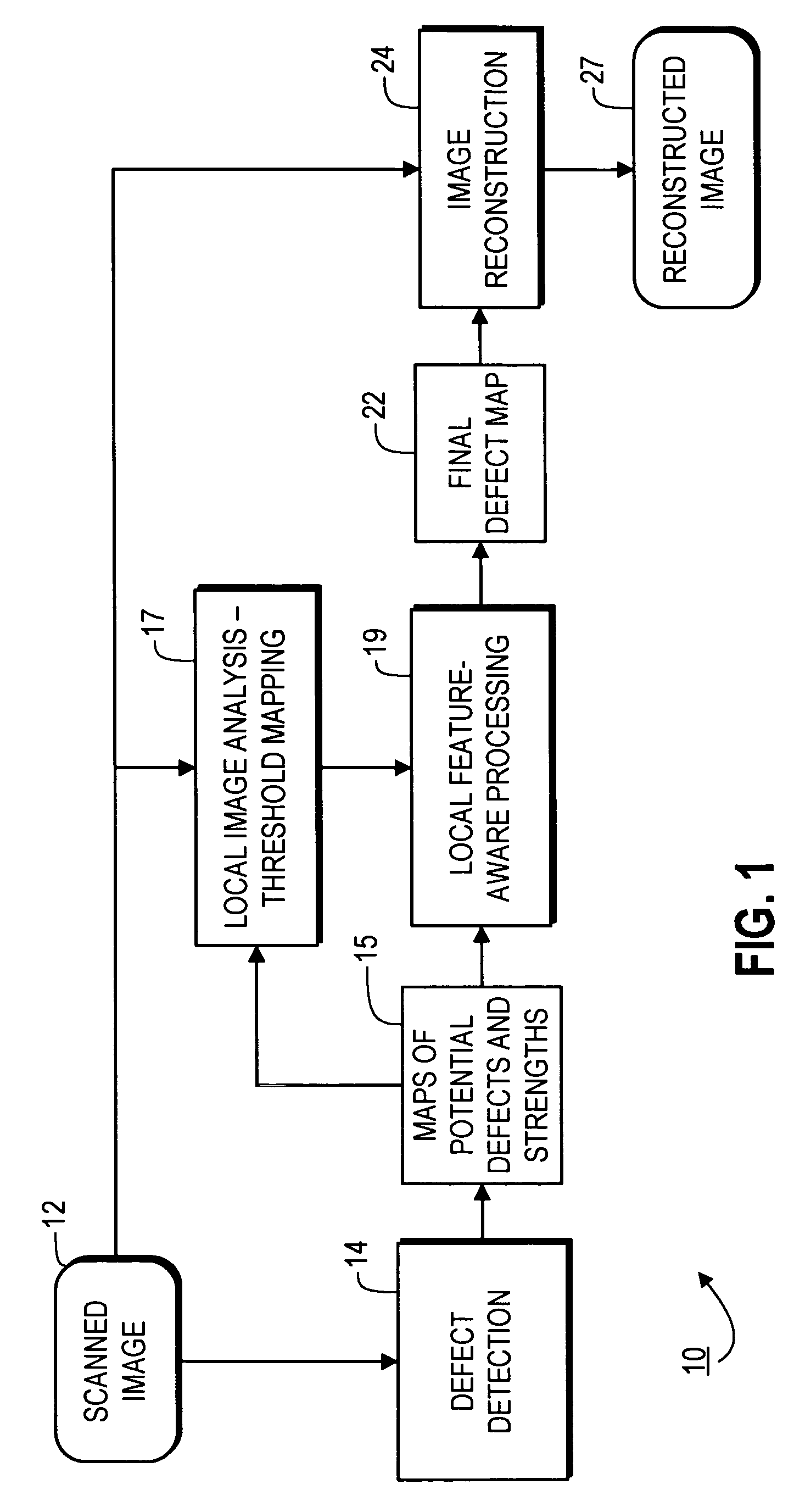
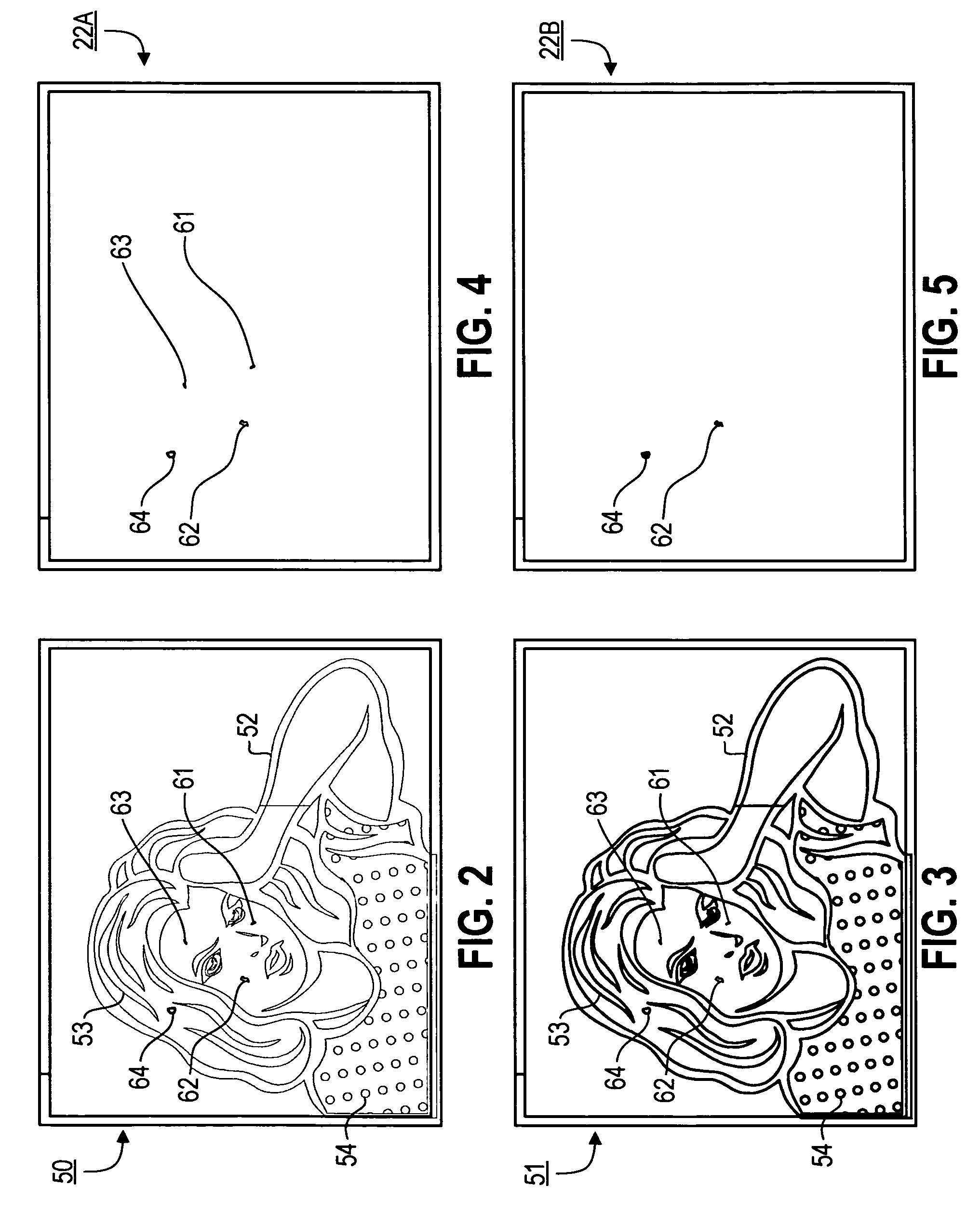
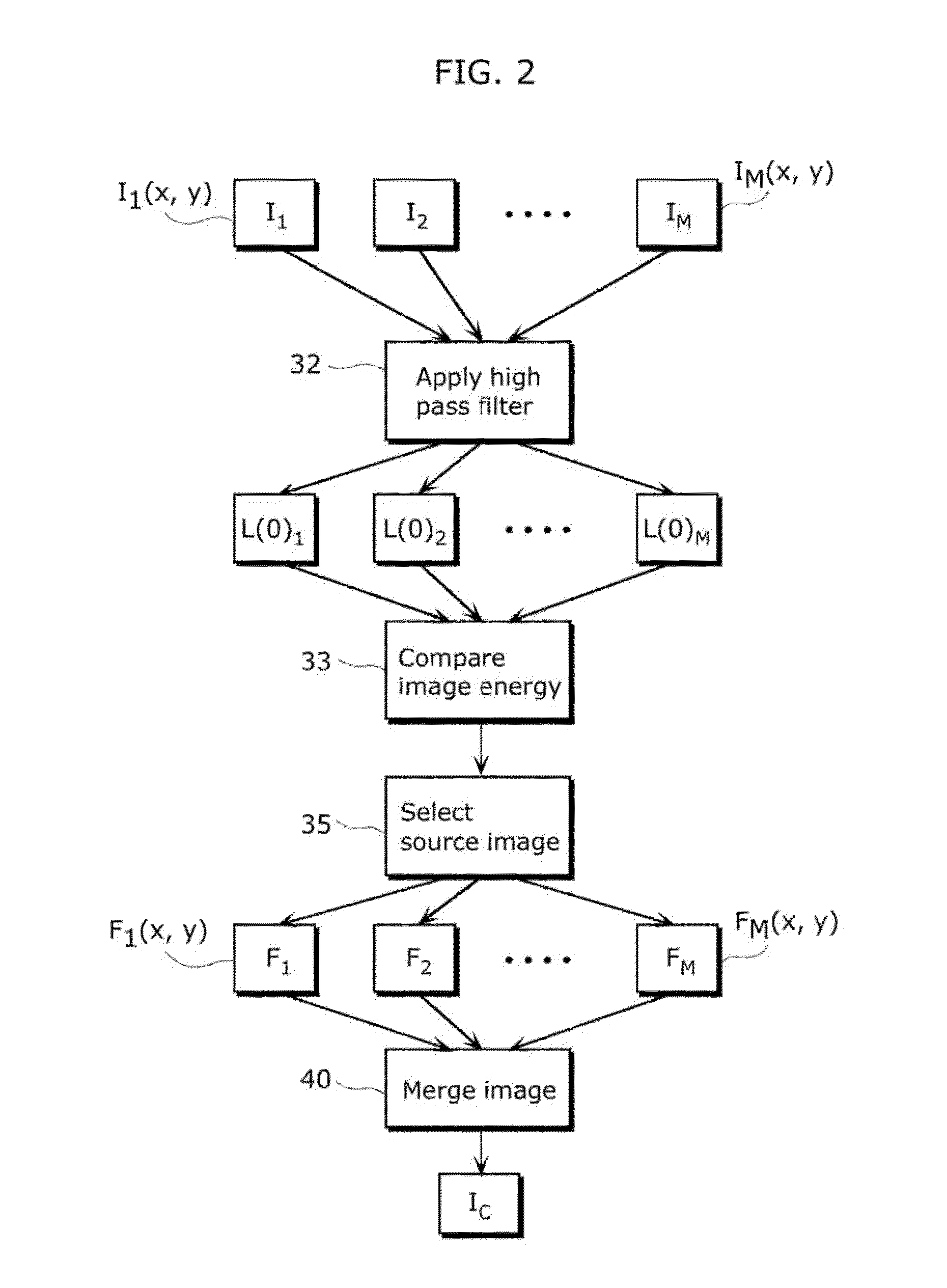
Feature-aware image defect removal
Provided are systems, methods and techniques which use local image properties to determine which potential defects in an image should be corrected. In one representative embodiment, potential defects in an image are identified based on edge sharpness, and measures of strength for the different potential defects are calculated. The measures of strength for the potential defects are then evaluated in view of certain local properties of the image, in an immediate vicinity of such potential defects, in order to identify the image defects to be corrected.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
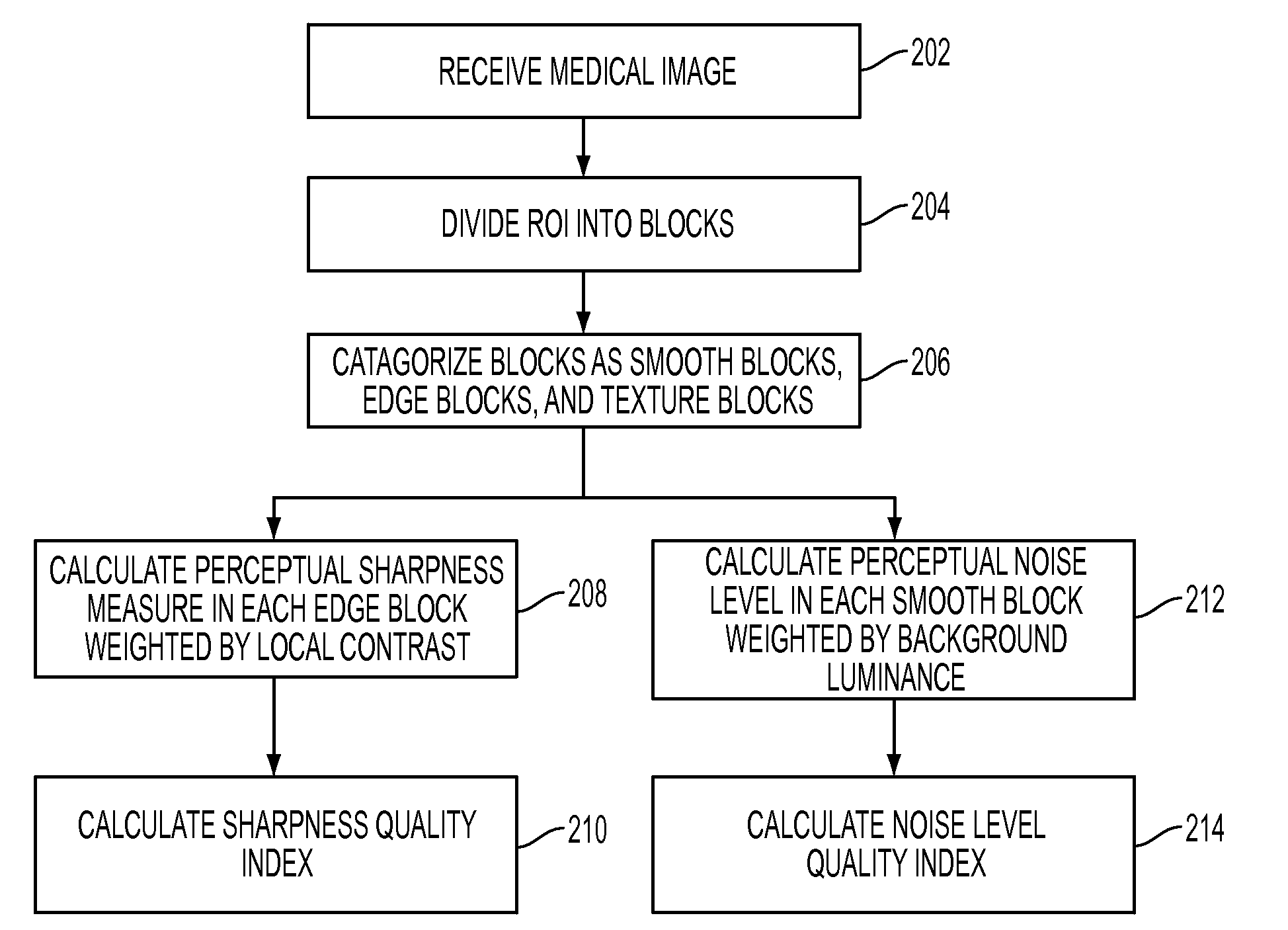
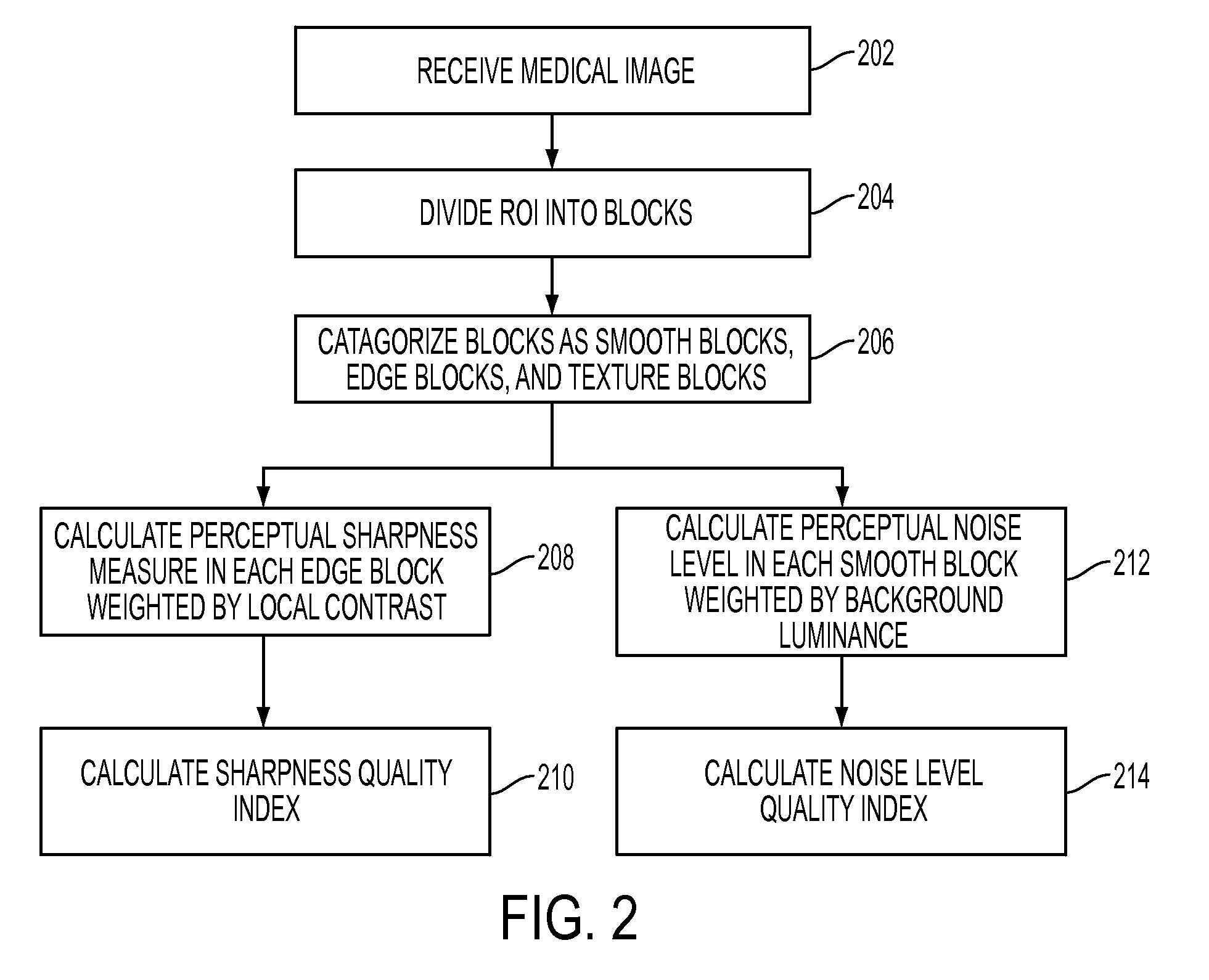
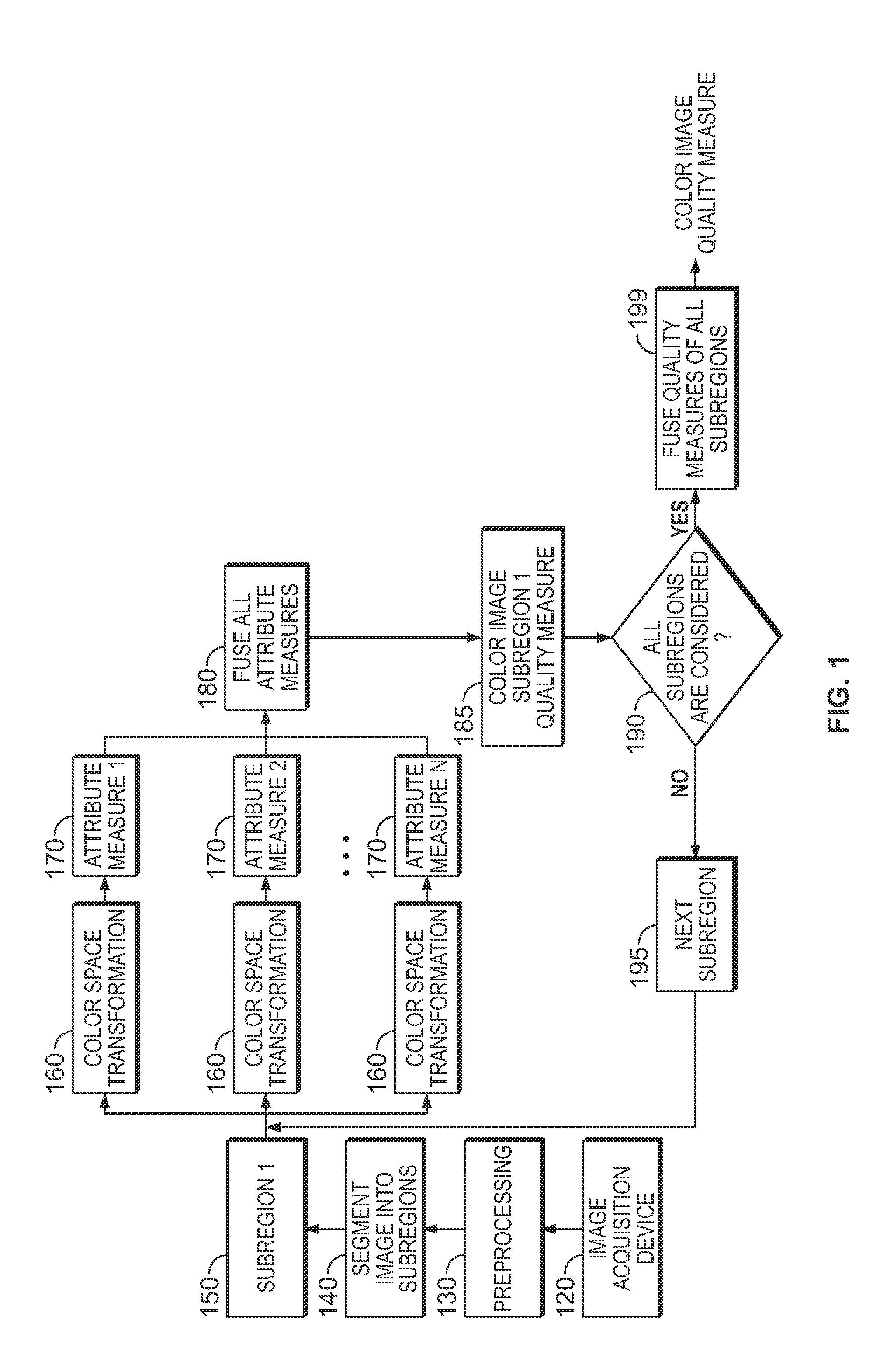
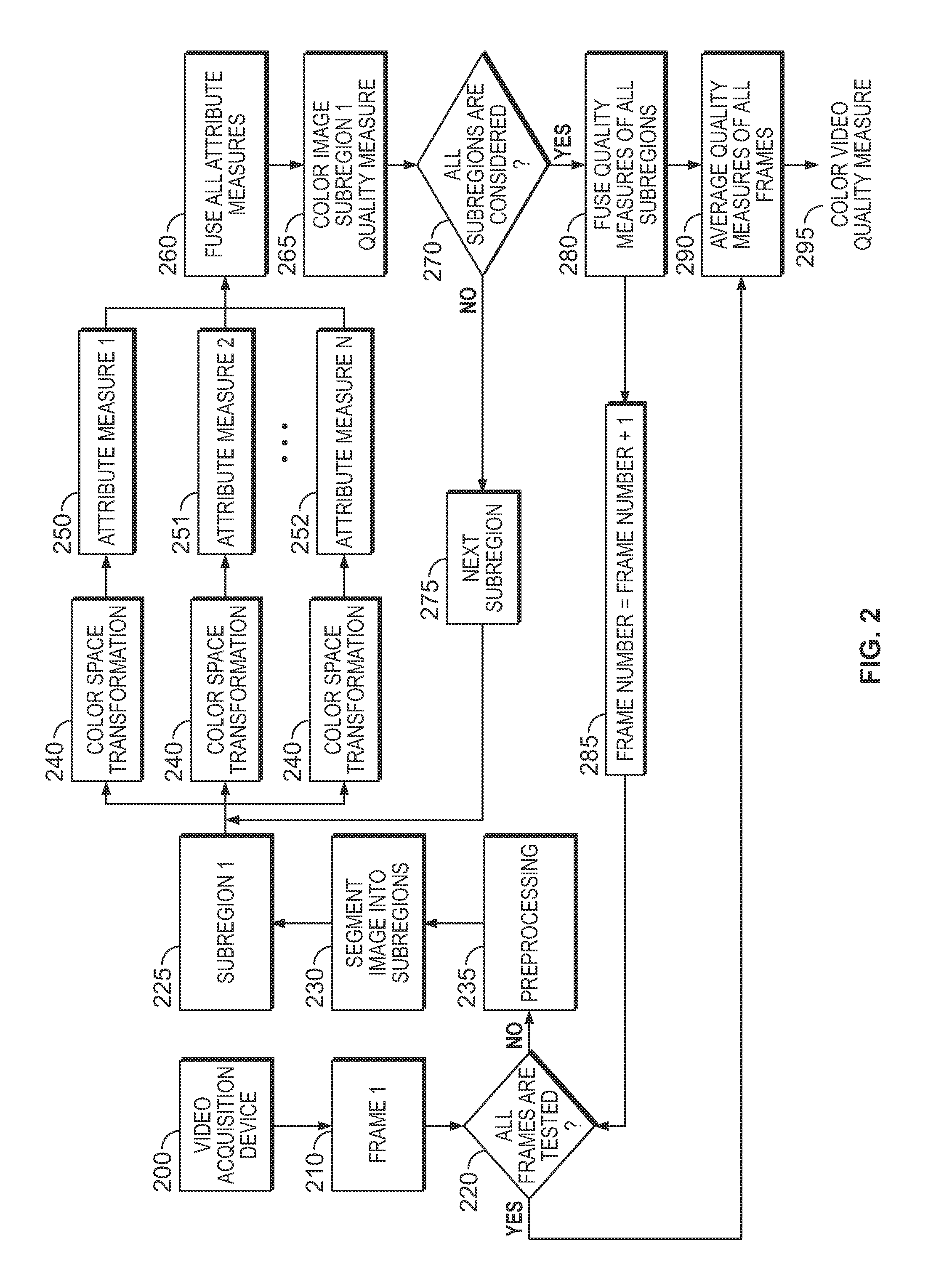
Method and system for human vision model guided medical image quality assessment
InactiveUS20090116713A1Image analysisRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsPattern recognitionNoise level
A method and system for image quality assessment is disclosed. The image quality assessment method is a no-reference method for objectively assessing the quality of medical images. This method is guided by the human vision model in order to accurately reflect human perception. A region of interest (ROI) of medical image is divided into non-overlapping blocks of equal size. Each of the blocks is categorized as a smooth block, a texture block, or an edge block. A perceptual sharpness measure, which is weighted by local contrast, is calculated for each of the edge blocks. A perceptual noise level measure, which is weighted by background luminance, is calculated for each of the smooth blocks. A sharpness quality index is determined based on the perceptual sharpness measures of all of the edge blocks, and a noise level quality index is determined based on the perceptual noise level measures of all of the smooth blocks. An overall image quality index can be determined by using task specific machine learning of samples of annotated images. The image quality assessment method can be used in applications, such as video / image compression and storage in healthcare and homeland security, and band-width limited wireless communication.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
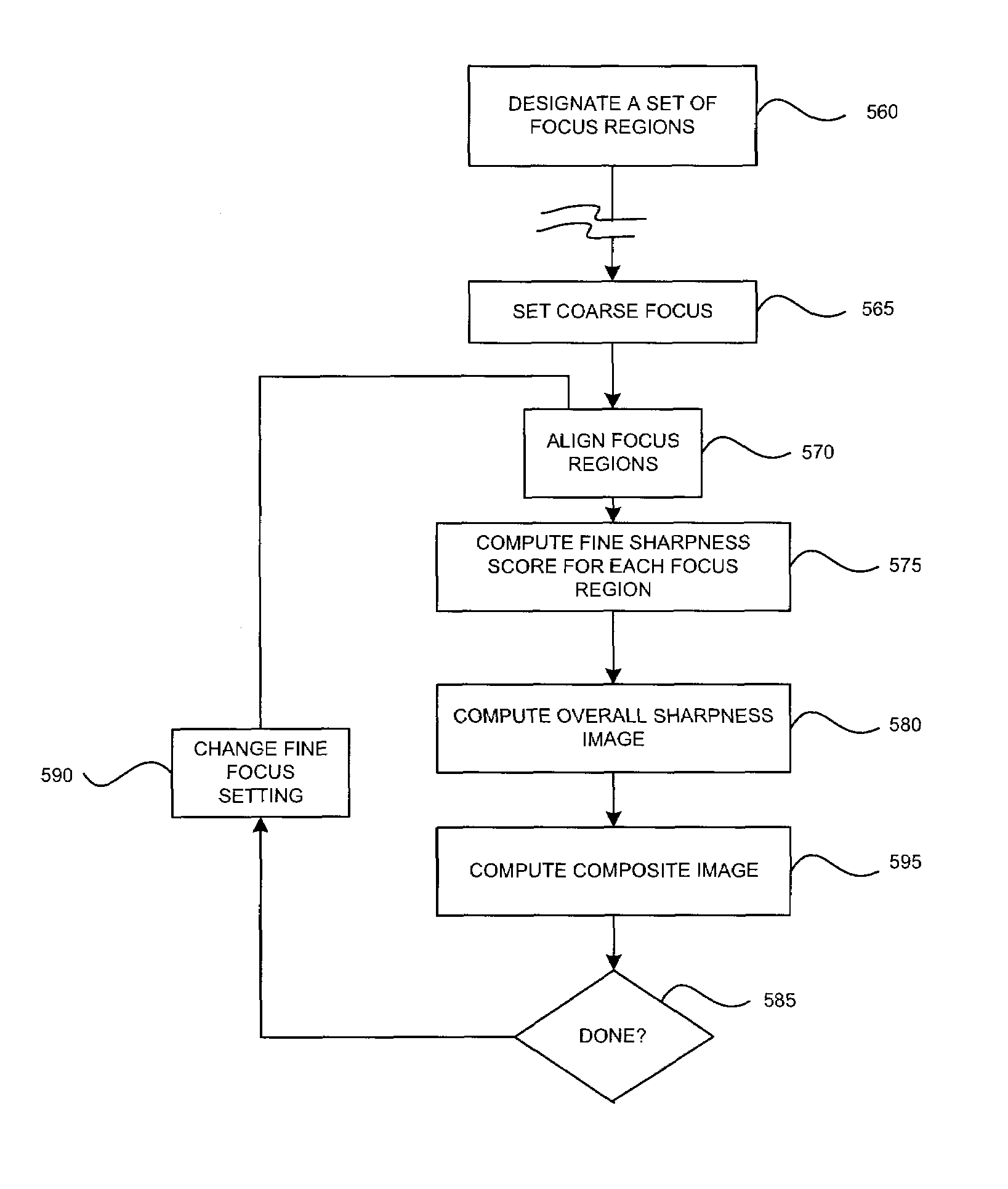
Method for generating a focused image of an object
InactiveUS7221805B1Reduce measurementTaking imageTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine visionAcutance
A method is provided for computing a composite image representing a focused image of an object in an application of machine vision in an optical inspection system. An image tessellated into focus regions is evaluated by region for fine feature sharpness. A sharpness image is computed for each focused region using a fine feature sharpness measurement. A focused composite image is computed by combining as a weighted average, the images at several focus settings, using the sharpness image at each focus setting as the weight. The focused composite image can be further analyzed, inspected, or otherwise processed.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
Noise reduction apparatus for electronic edge enhancement
InactiveUS6097848ATelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionNoise reduction
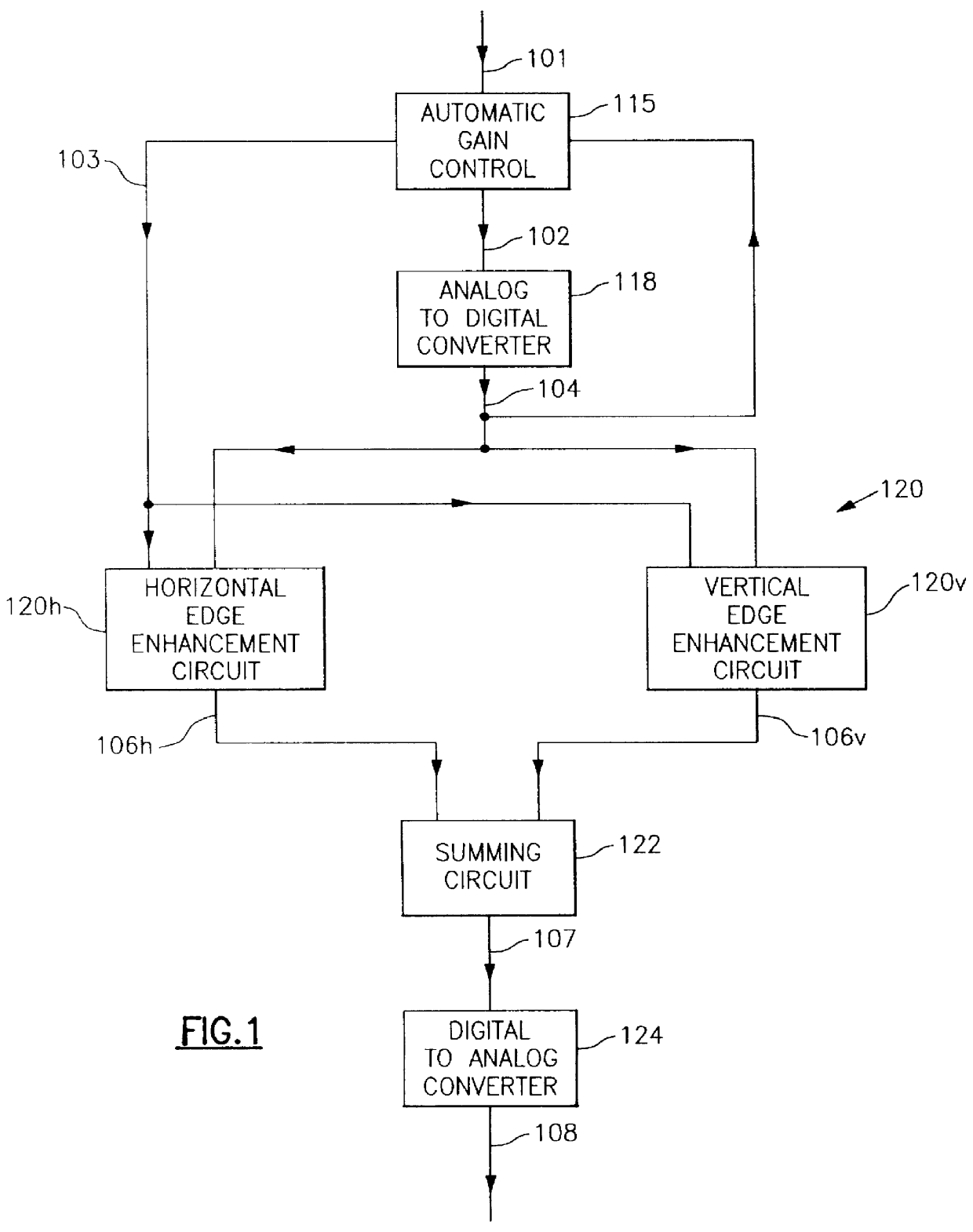
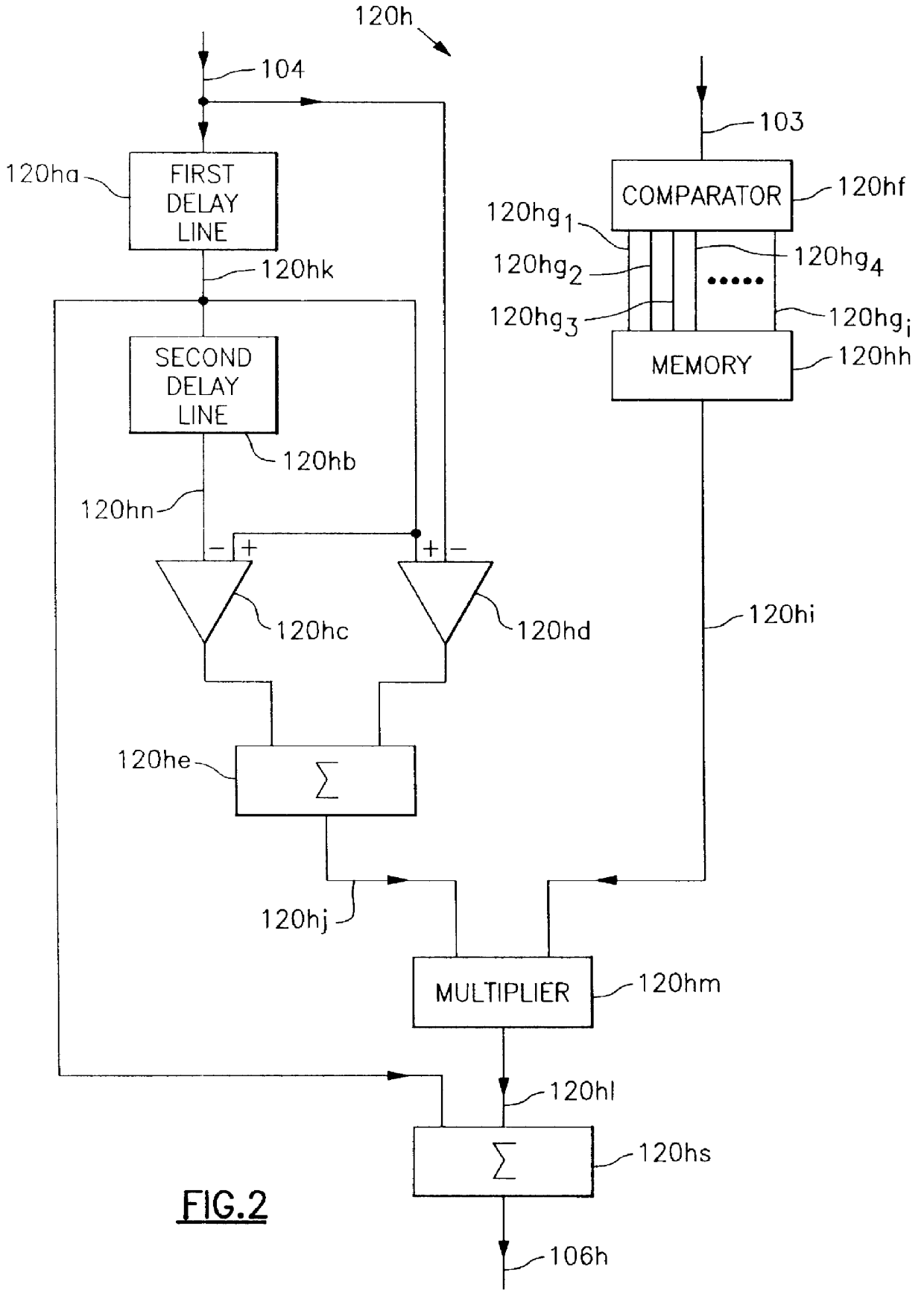
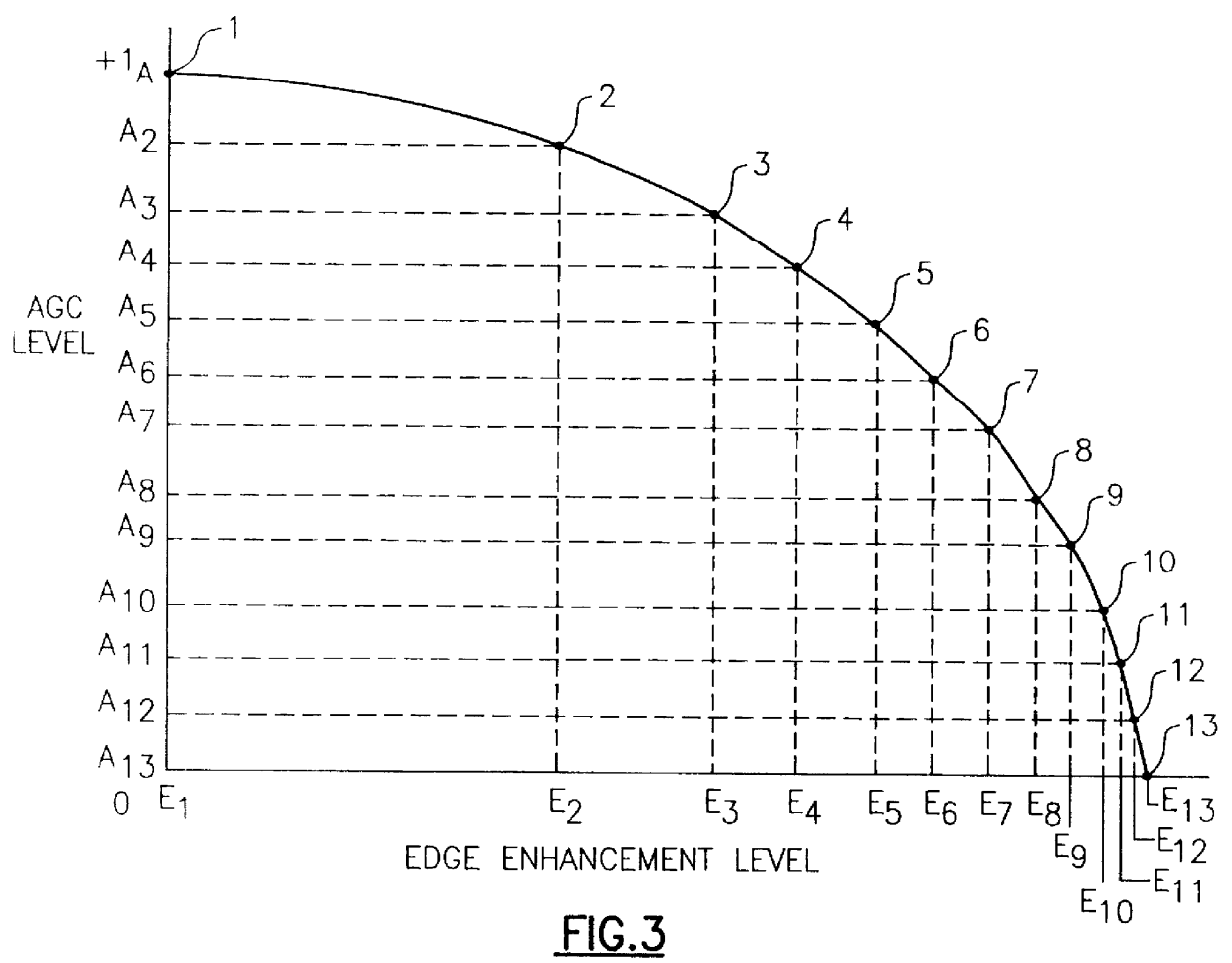
A video signal processor includes an edge enhancement determining circuit that senses the amount of some characteristic of that signal which provides a measure of noise inherent in the signal, precisely determines a preferred amount of edge enhancement to be applied to a video signal as a function of that characteristic, and applies that amount of edge enhancement to the video signal. The video signal characteristic, used to determine the noise content of the video signal includes the amount of automatic gain control amplification and the brightness of the viewed scene. Thus, the amount of edge enhancement added to the video signal is adaptively controlled according to the brightness level of the viewed scene and the amplification level of the video signal by the automatic gain control circuit, and provides the proper amount of edge sharpness to the viewed video scene as a function of its noise content. This provides an increase in perceived sharpness of the viewed image, without an increase in background noise that occurs in conventional non-adaptive systems.
Owner:GE INSPECTION TECH LP
Focusing aid for camera
InactiveUS6937284B1More adjust focusAdjust moreTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPersonal computerVisual perception
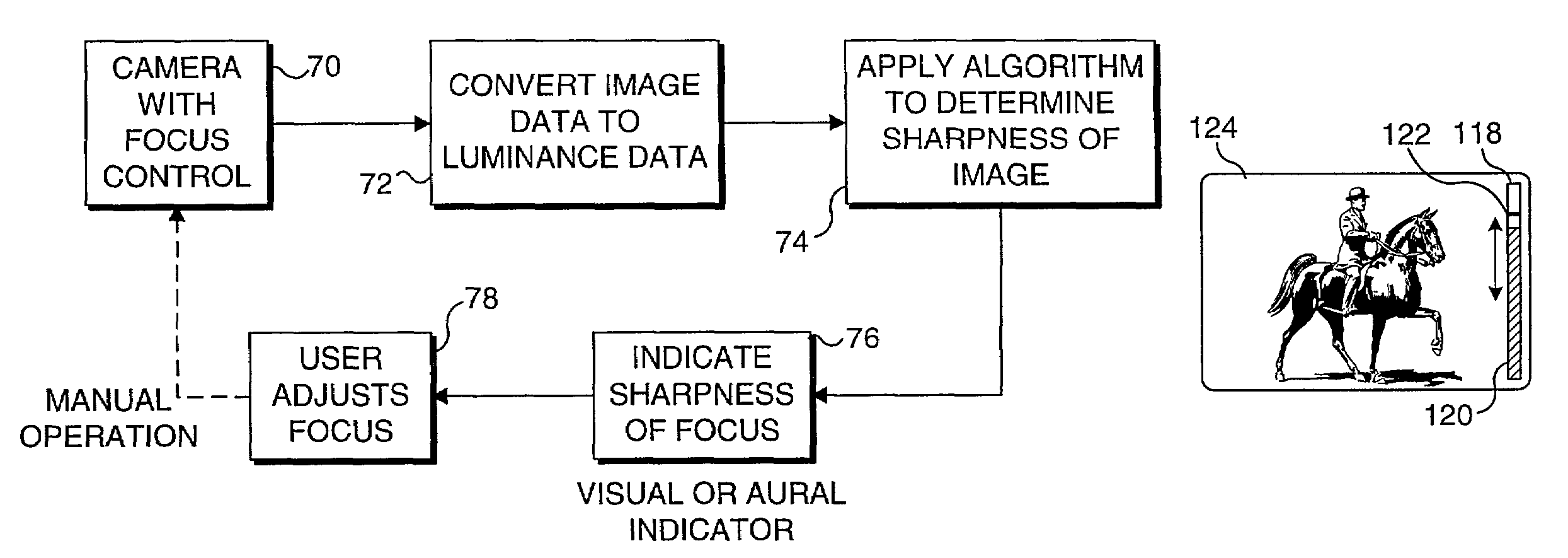
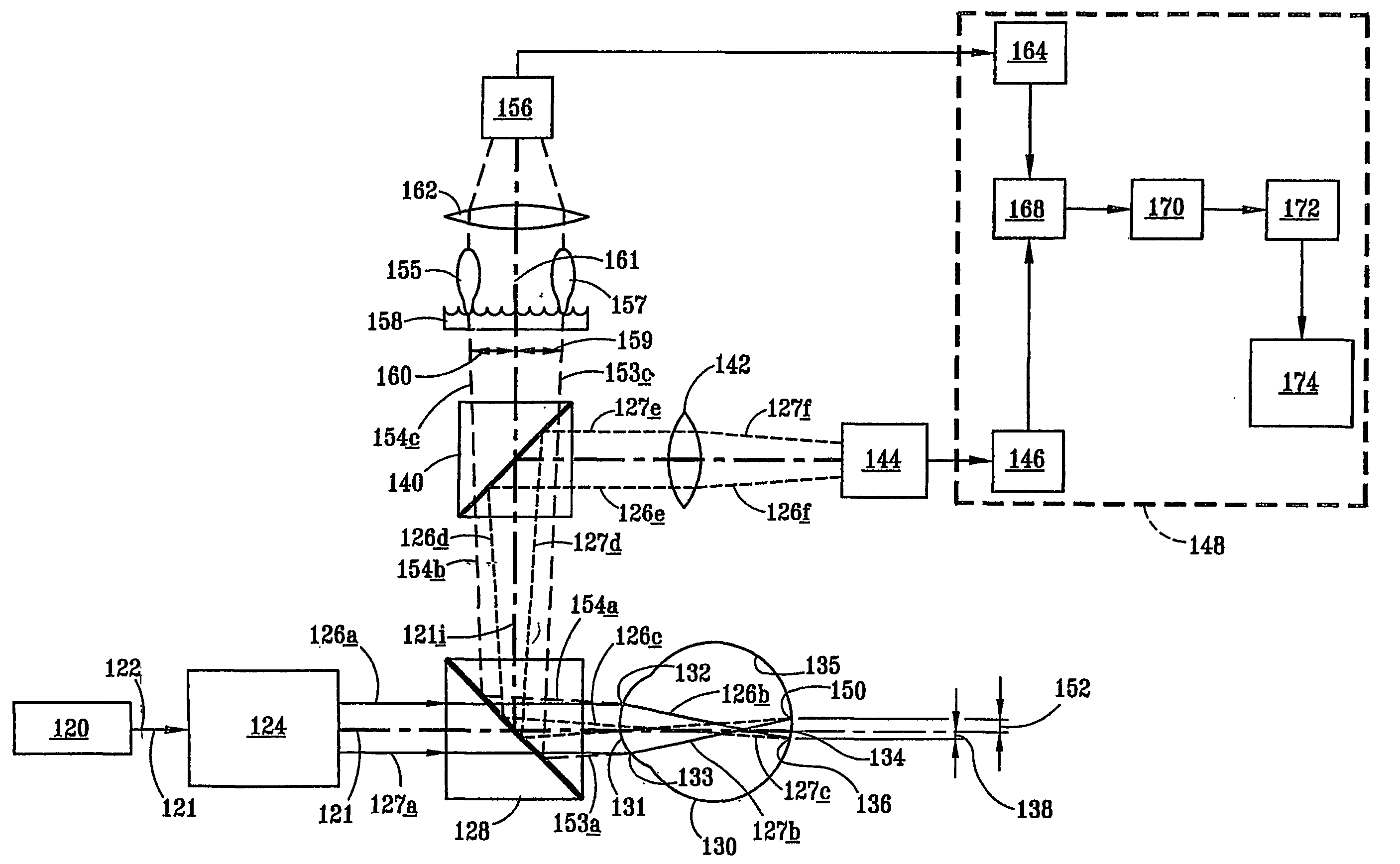
An indication of sharpness of focus is provided to a user to assist in focusing a camera. In one embodiment, the camera is coupled to a personal computer. An algorithm is implemented by the personal computer to determine a sharpness of focus based upon differences between the luminance of adjacent pixels in a selected region of an image produced by the camera. A visual or aural indication of the sharpness of focus is provided to the user to enable the user to focus the camera to the sharpest possible focus. Alternatively, the algorithm can be implemented by a processor within a camera so that a visual or aural indicator on the camera provides the indication of sharpness of focus as a user adjusts the focus of the camera.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
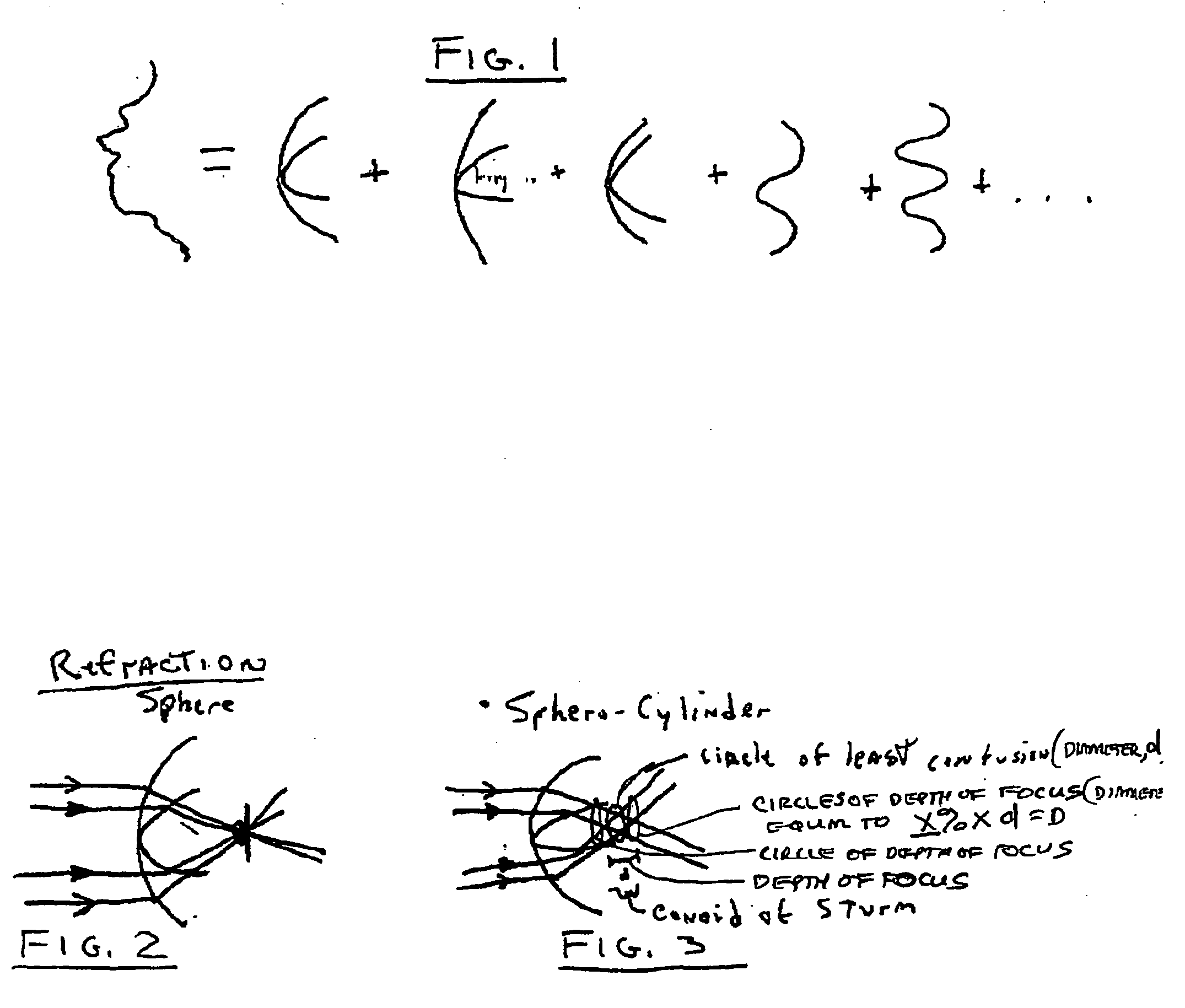
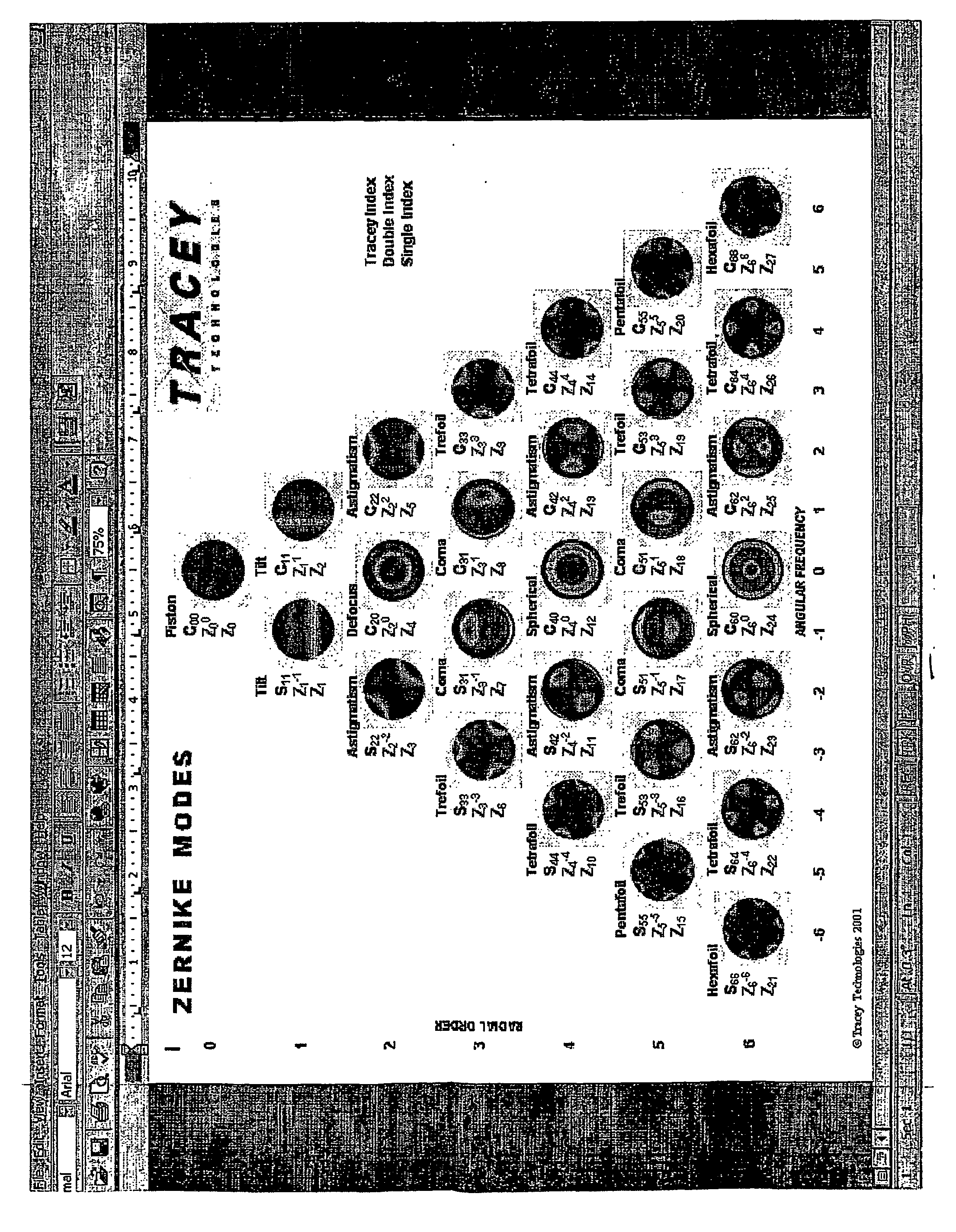
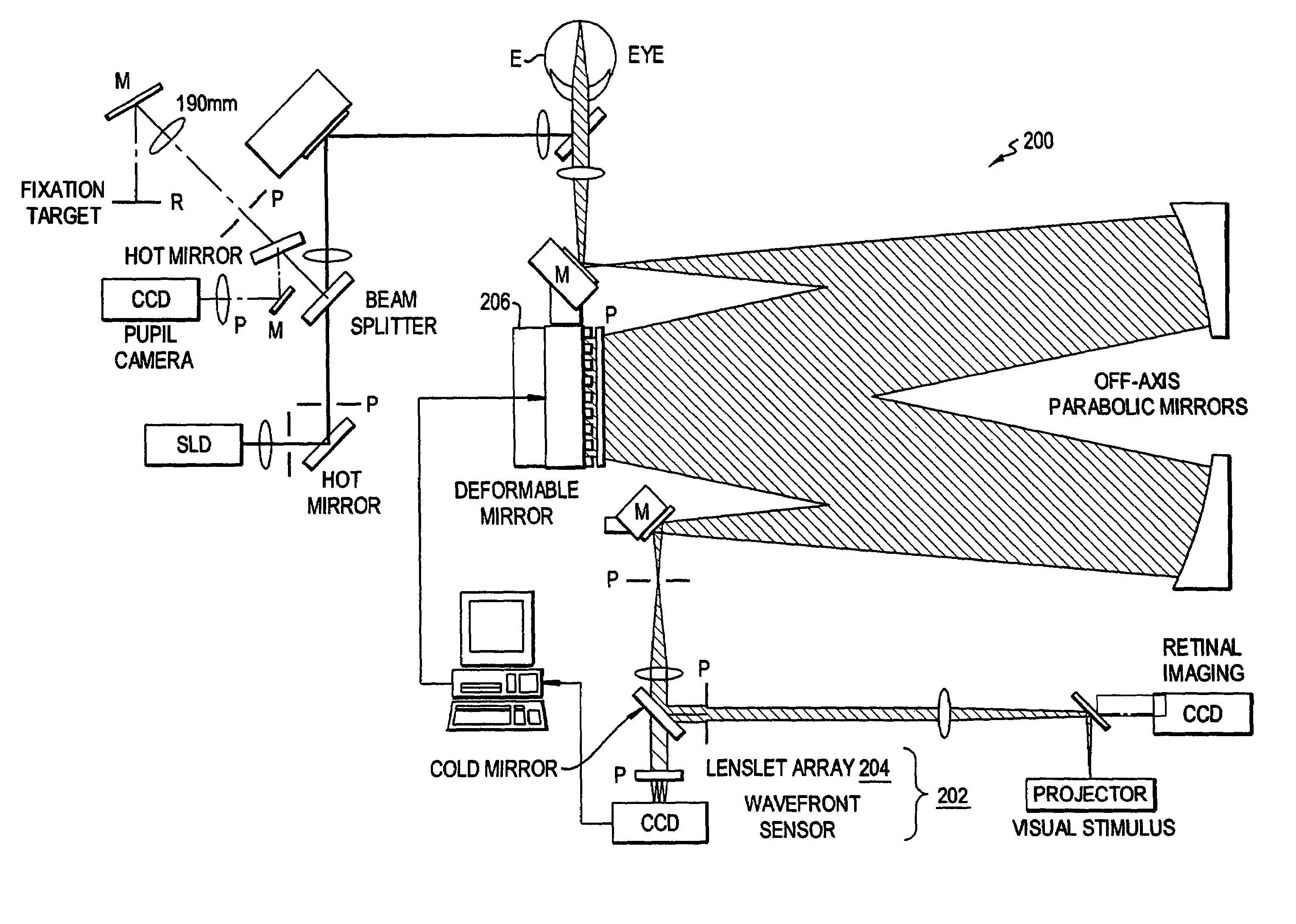
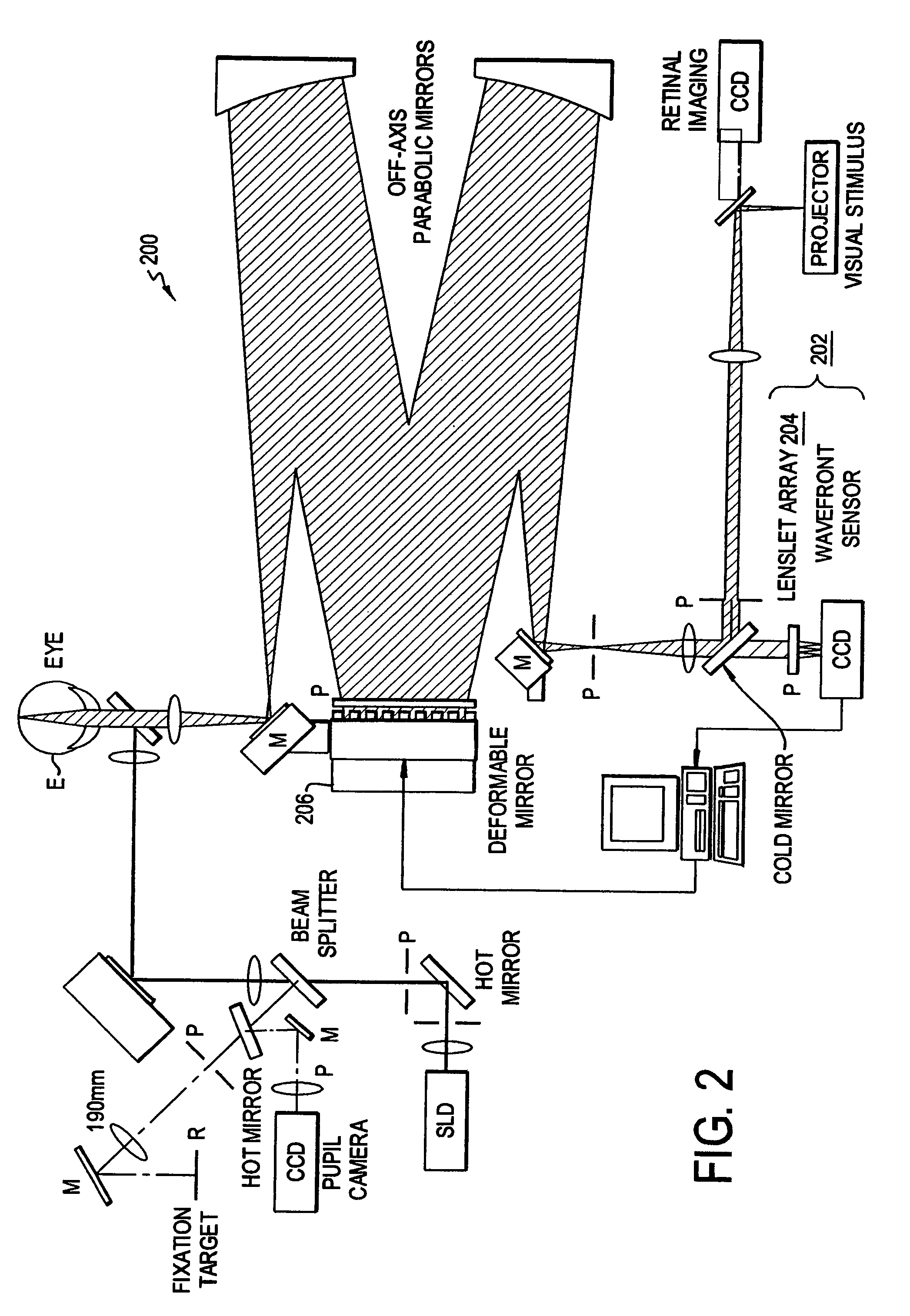
Determining clinical refraction of eye
A method of measuring eye refraction to achieve desired quality according to a selected vision characteristics comprising the steps of selecting a characteristic of vision to correlate to the desired quality of vision from a group of vision characteristics comprising acuity, Strehl ratio, contrast sensitivity, night vision, day vision, and depth of focus, dynamic refraction over a period of time during focus accommodation, and dynamic refraction over a period of time during pupil constriction and dilation; using wavefront aberration measurements to objectively measure the state of the eye refraction that defines the desired vision characteristic; and expressing the measured state of refraction with a mathematical function to enable correction of the pre-selected vision characteristic to achieve the desired quality of vision. The mathematical function of expression may be a Zernike polynomial having both second order and higher order terms or a function determined by spline mathematical calculations. The pre-selected desired vision characteristics may be determined using ray tracing technology.
Owner:TRACEY TECH
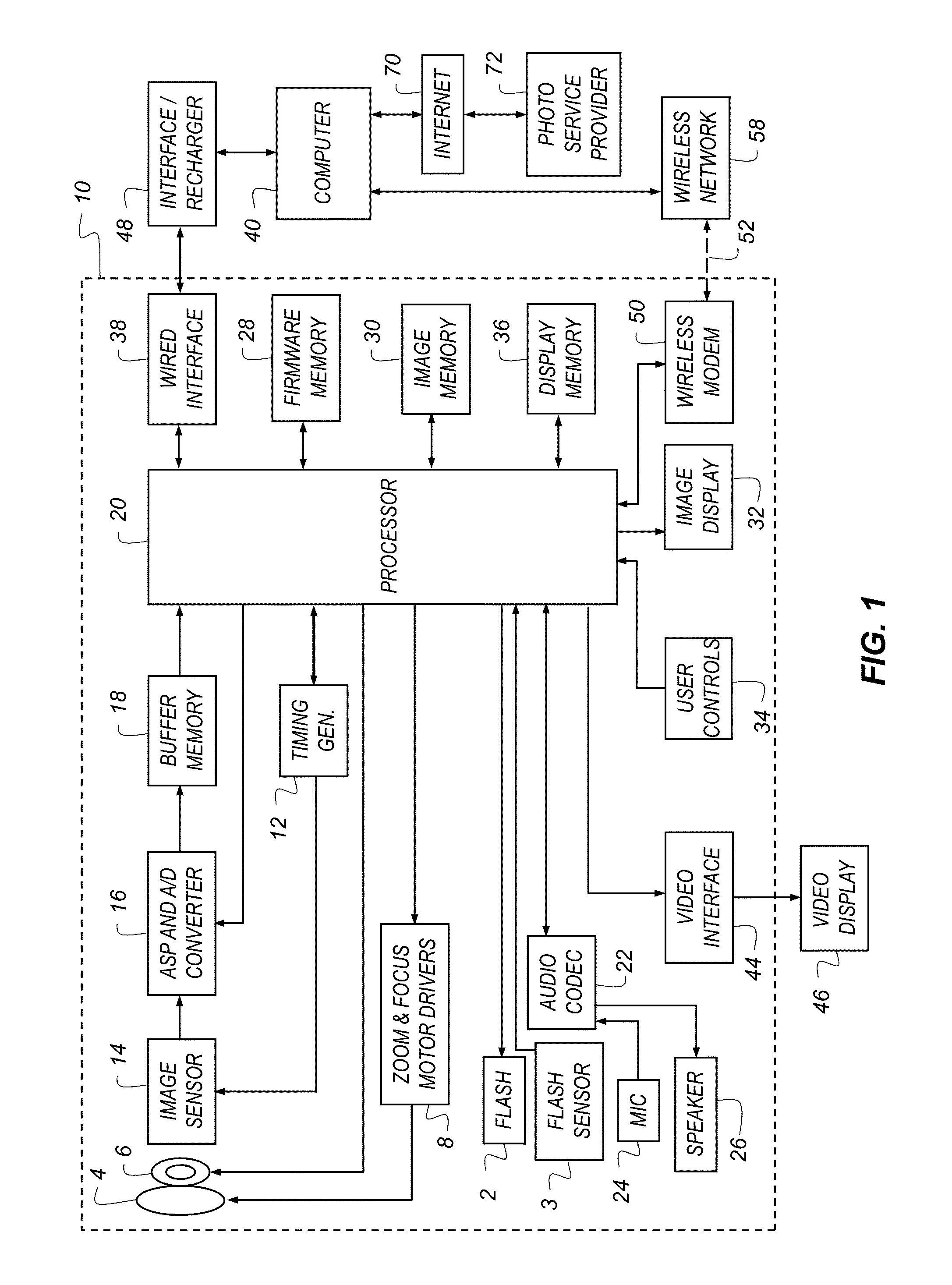
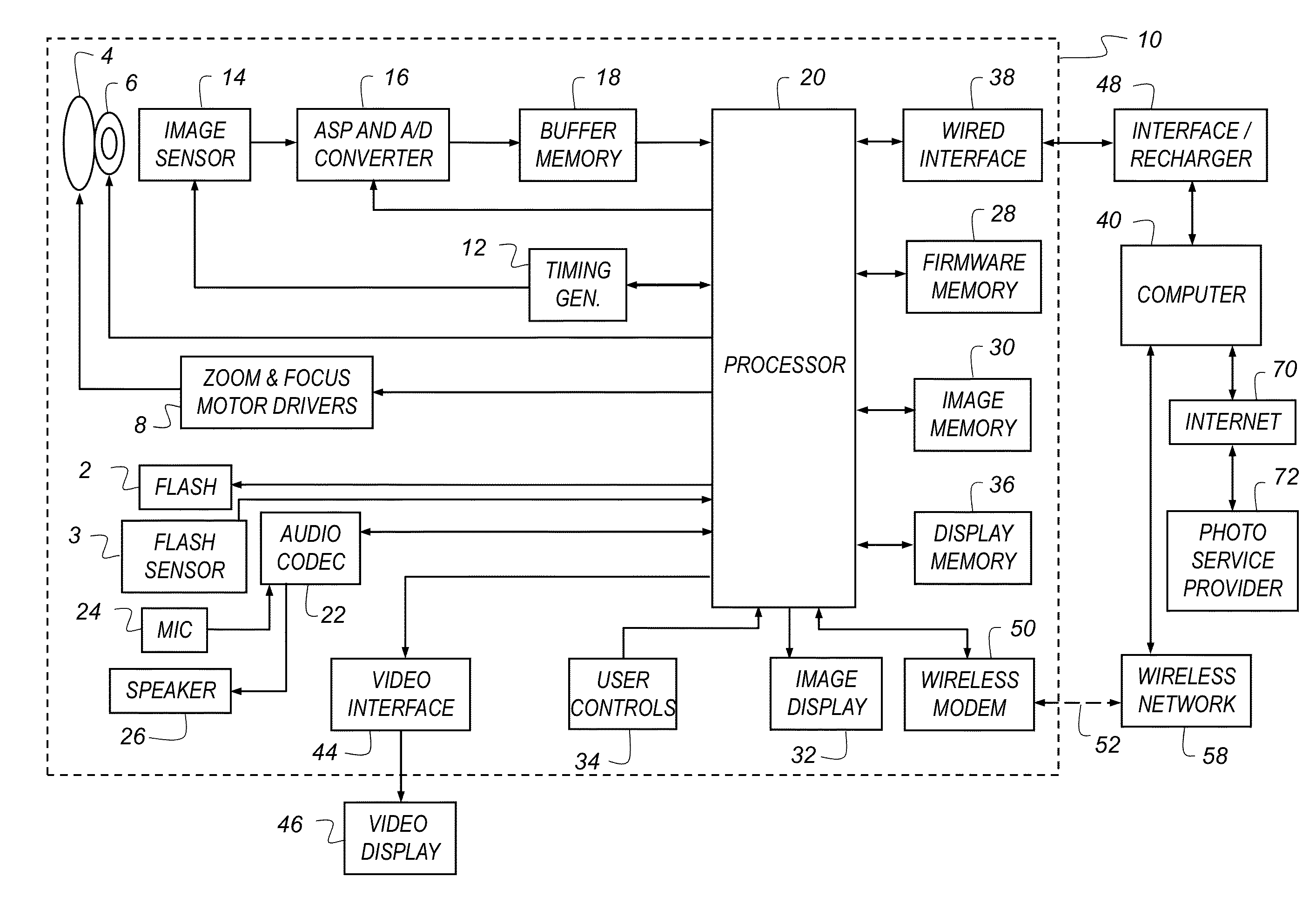
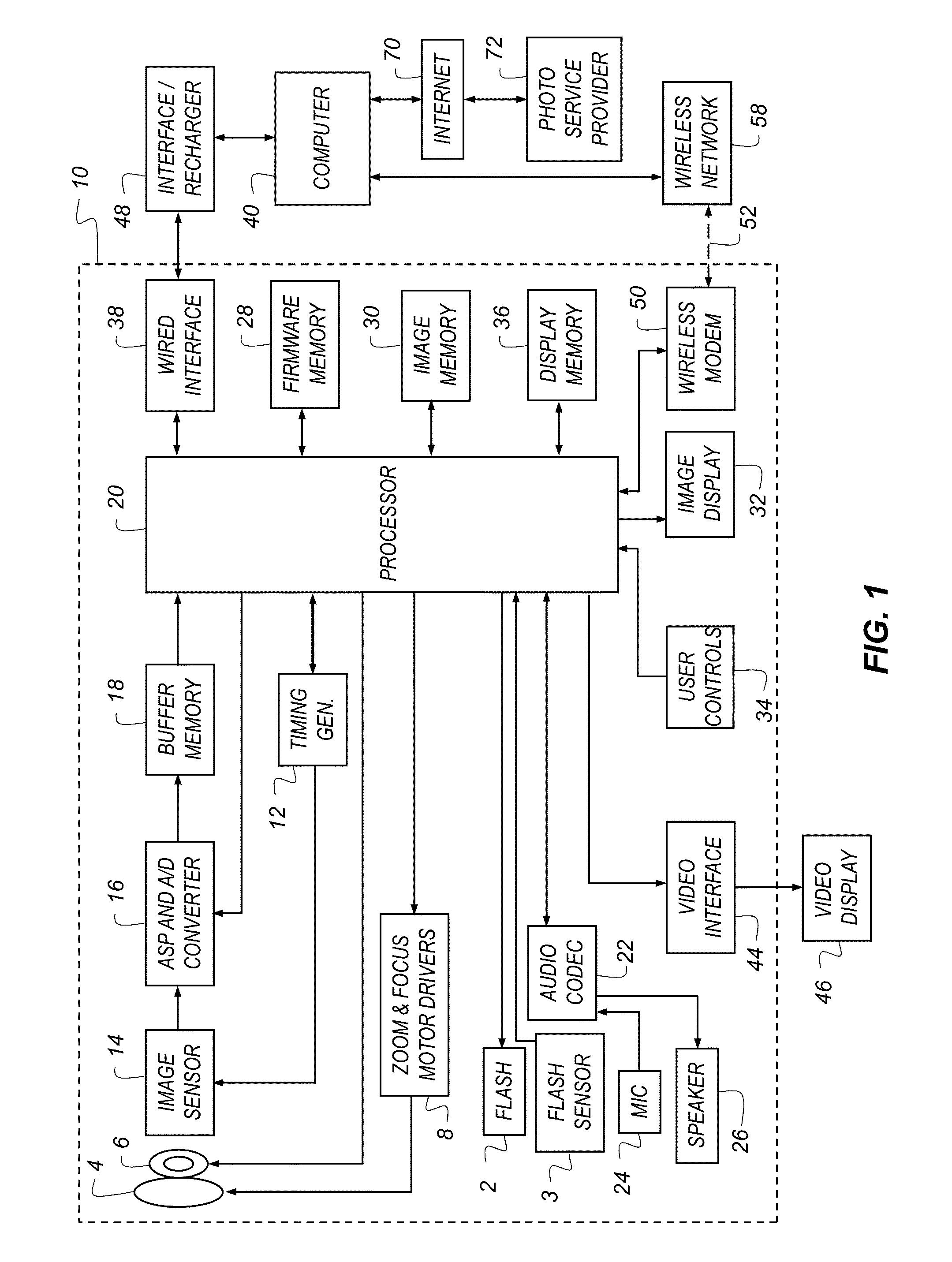
Image capturing device, image capturing method, program, and integrated circuit
InactiveUS20120281132A1Easy to operateReduce confusionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Image resolution
An image capturing device includes: a pre-capturing module which captures an imaging target at each of different focus positions in a predetermined focus range and outputs, as a capturing result, a plurality of pre-captured images lower in resolution than the output image; an object sharpness evaluating module which computes a sharpness level of each of the pre-captured images captured by the pre-capturing module; a focus varying range determining module which determines a focus position varying range within the predetermined focus range based on sharpness levels computed by the object sharpness evaluating module, such that a signal-to-noise ratio of the output image is greater than or equal to a predetermined threshold; and an image capturing module which captures the imaging target while varying the focus position according to the focus position varying range determined by the focus varying range determining module, and outputs the output image as a capturing result.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Sharpness metric for vision quality
InactiveUS7077522B2Remove wave aberrationSubjective blurRefractometersSkiascopesQuality of visionPoint spread function
A vision metric, called the sharpness metric, indicates the subjective sharpness of a patient's vision by taking into account both the wavefront aberration and the retinal response to the image. A retinal image quality function such as the point spread function is convolved by a neural quality function, and the maximum of the convolution over the retinal plane provides the sharpness metric. The sharpness metric can be used to control eye surgery or the fabrication of a lens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
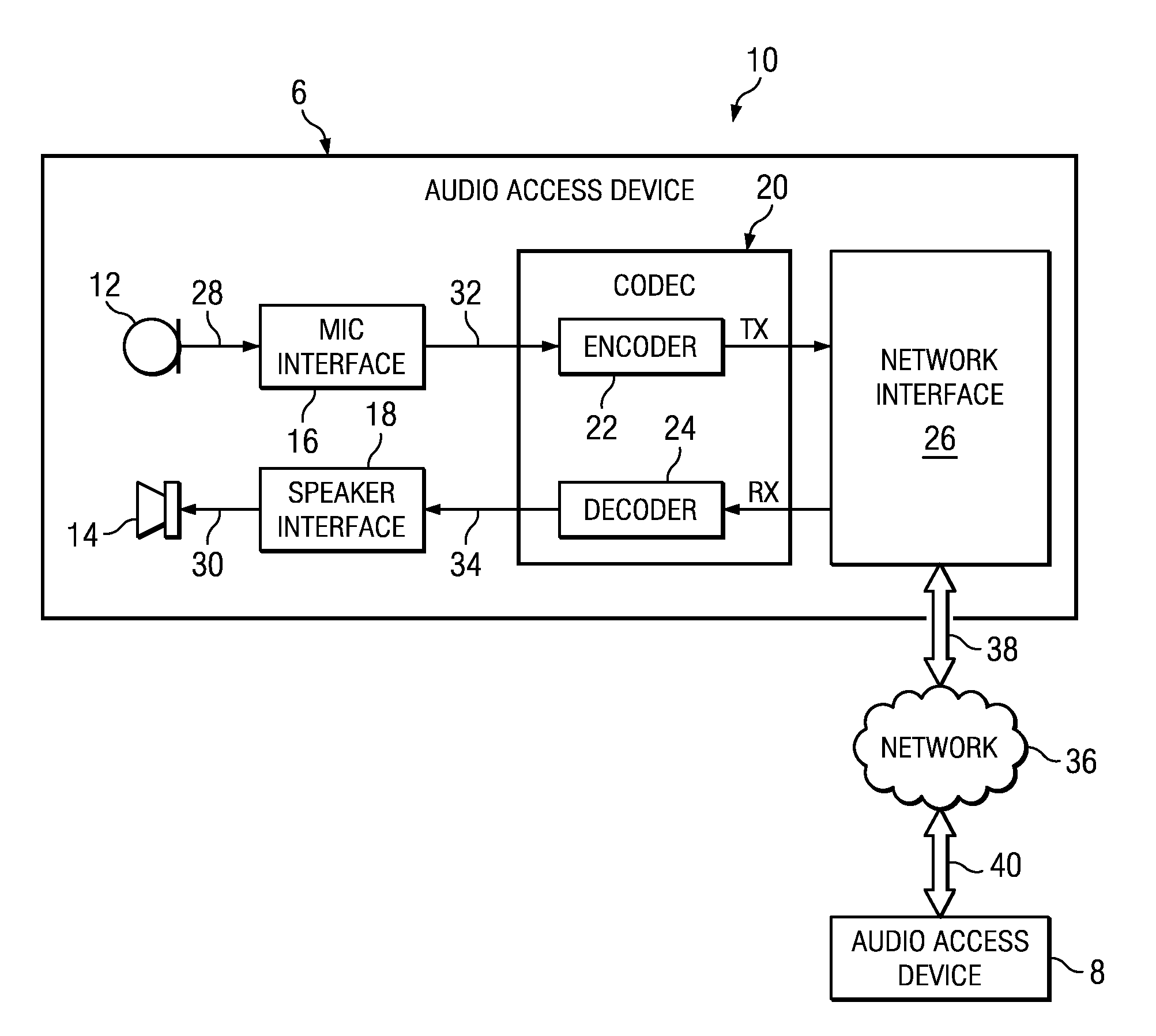
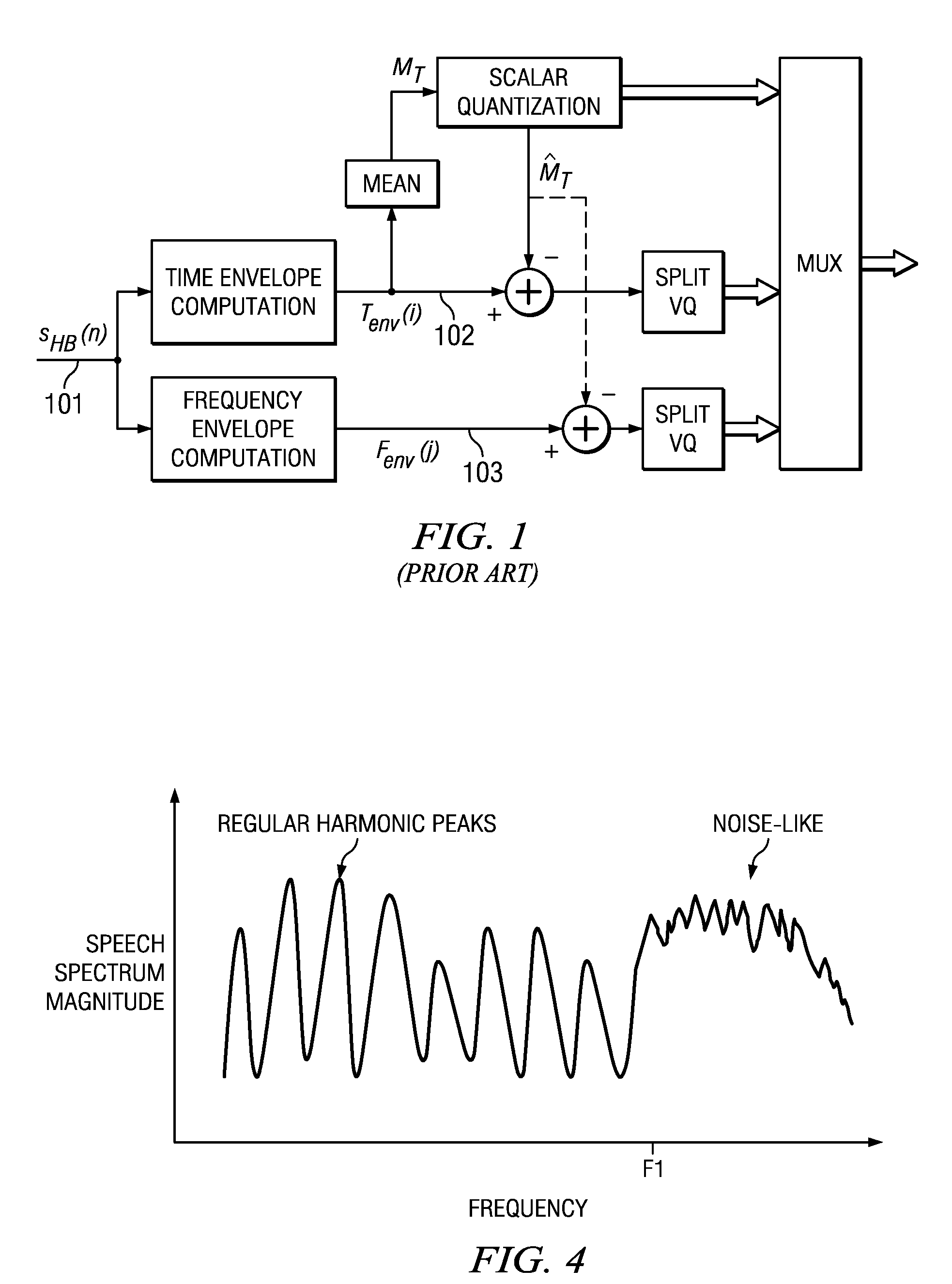
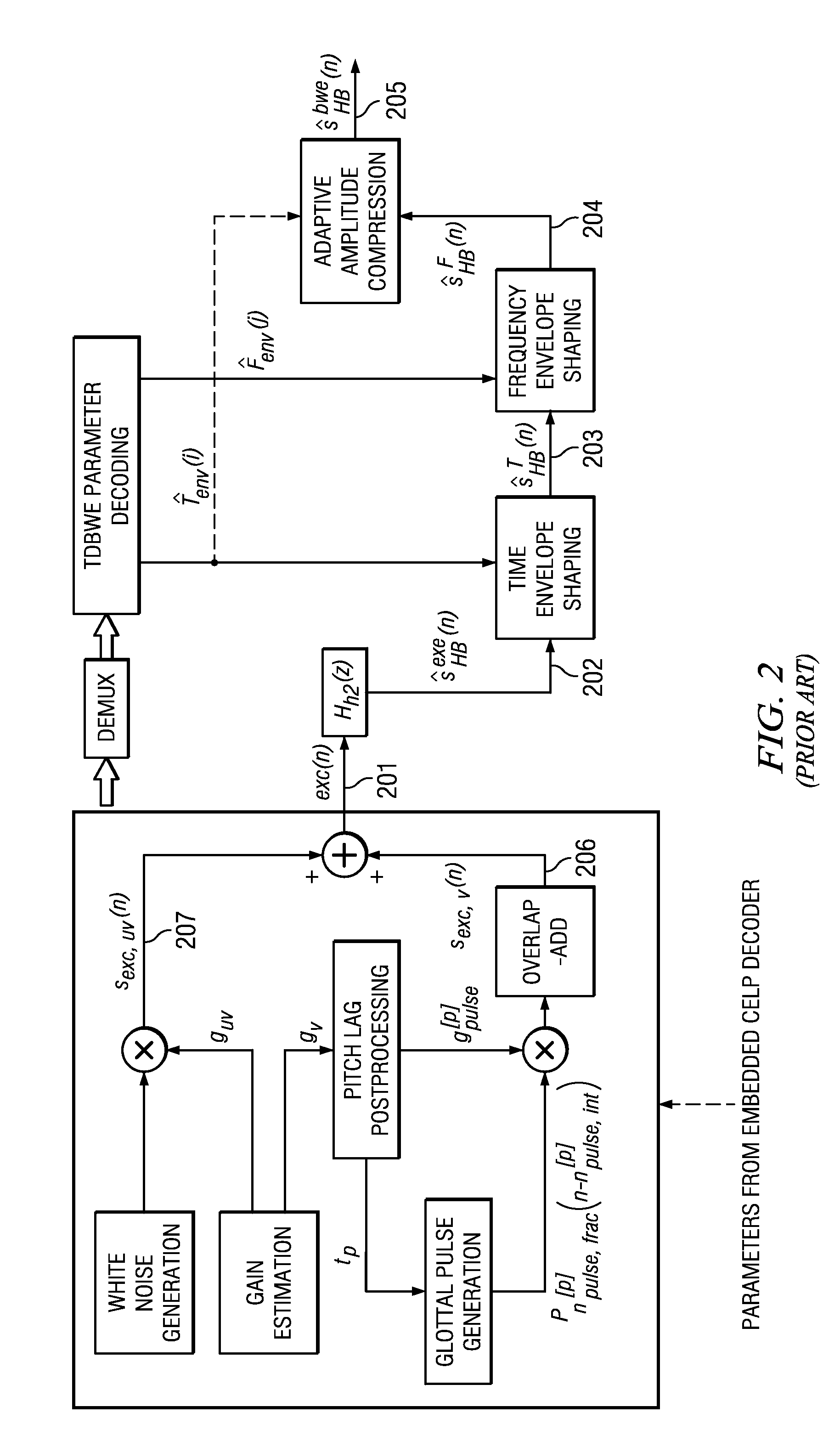
Spectrum Harmonic/Noise Sharpness Control
A transmitted data that includes audio data and a transmitted spectral sharpness parameter representing a spectral harmonic / noise sharpness of a plurality of subbands are received. A measured spectral sharpness parameter is estimated from received audio data. The transmitted spectral sharpness parameter is compared with the measured spectral sharpness parameter. A main sharpness control parameter is formed for each of the decoded subbands. The main sharpness control parameter for each of the decoded subbands is analyzed. Ones of the decoded subbands are sharpened if the corresponding main sharpness control indicates that a corresponding subband is not sharp enough, wherein sharpened subbands are formed. Likewise, ones of the decoded subbands are flattened if the corresponding main sharpness control indicates that a corresponding subband is not flat enough, wherein flattened subbands are formed. An energy level of each sharpened subband and each flattened subband is normalized to keep an energy level of each sharpened and / or flattened subband substantially unchanged.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
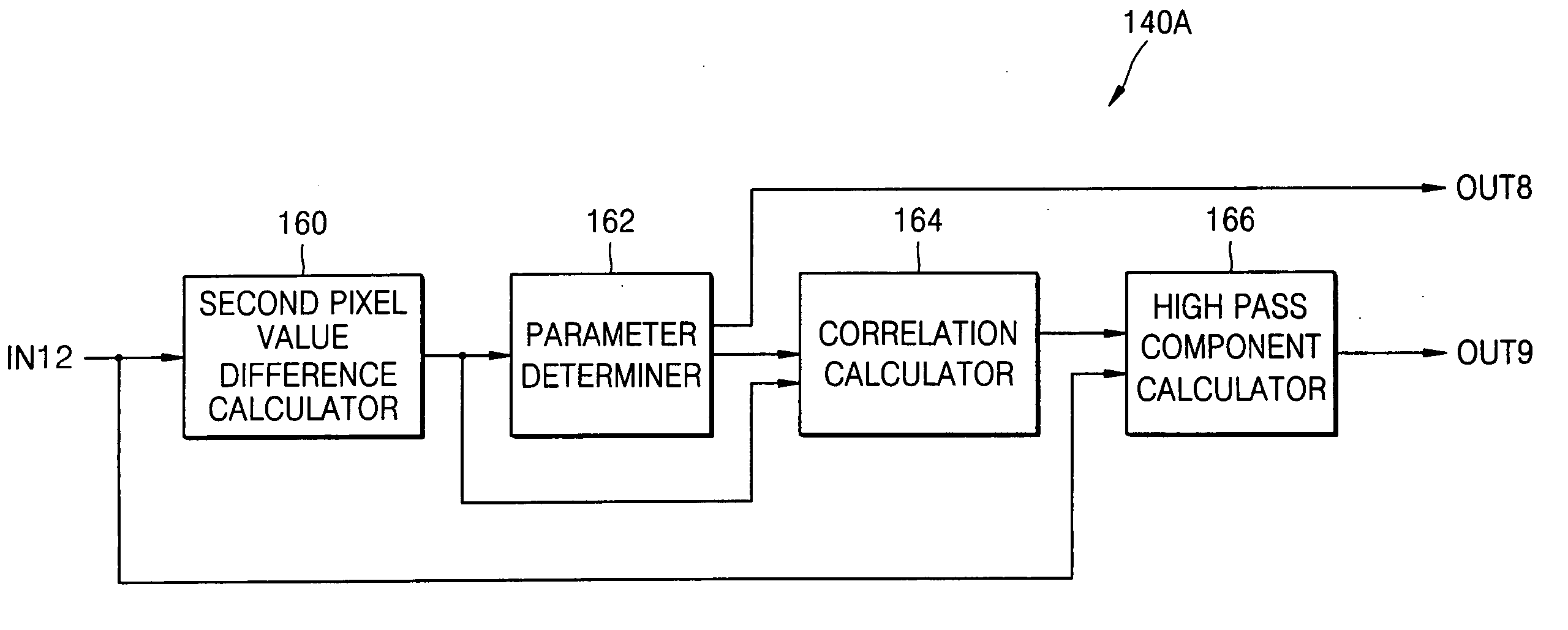
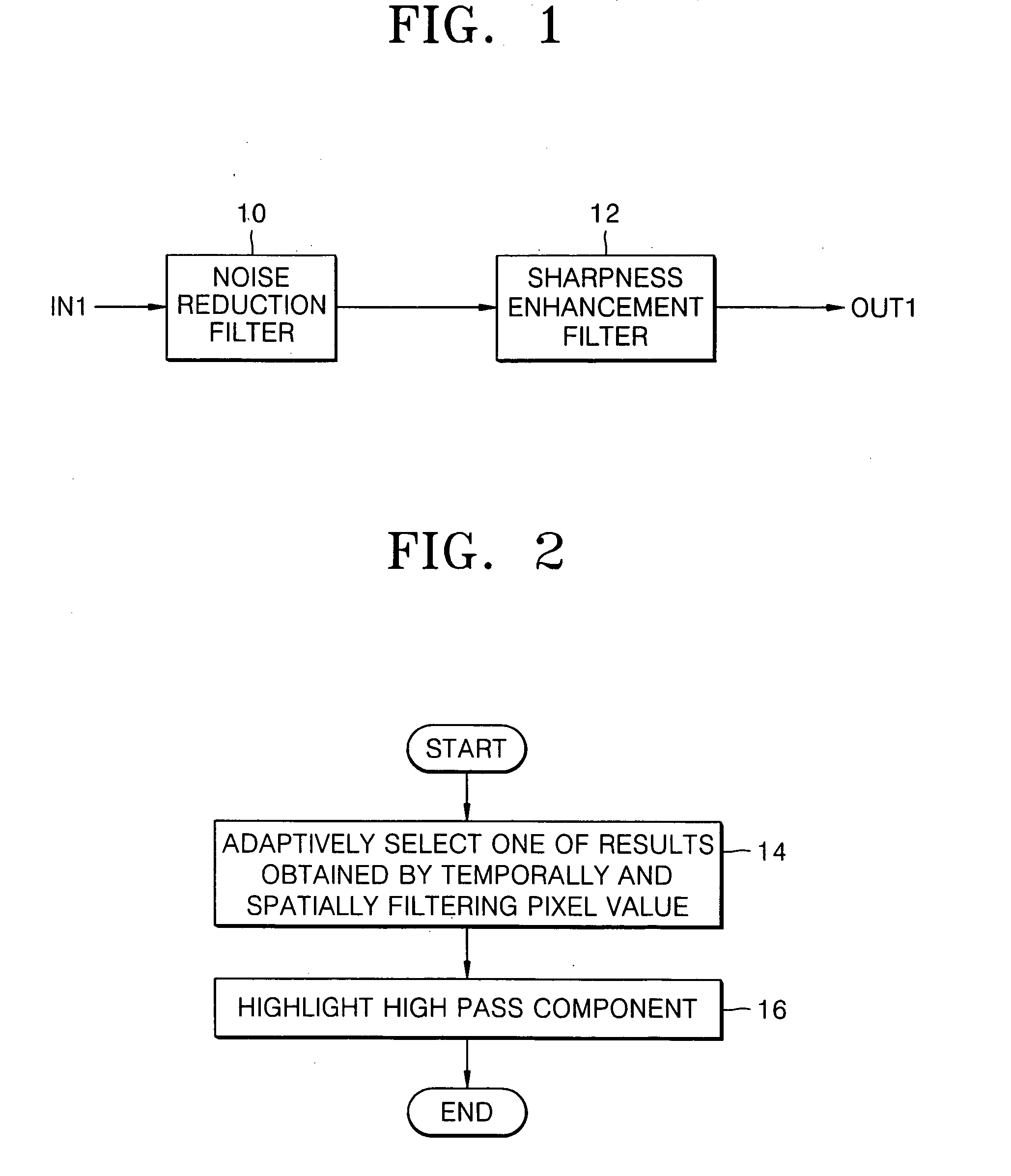
Apparatus and method for filtering digital image signal
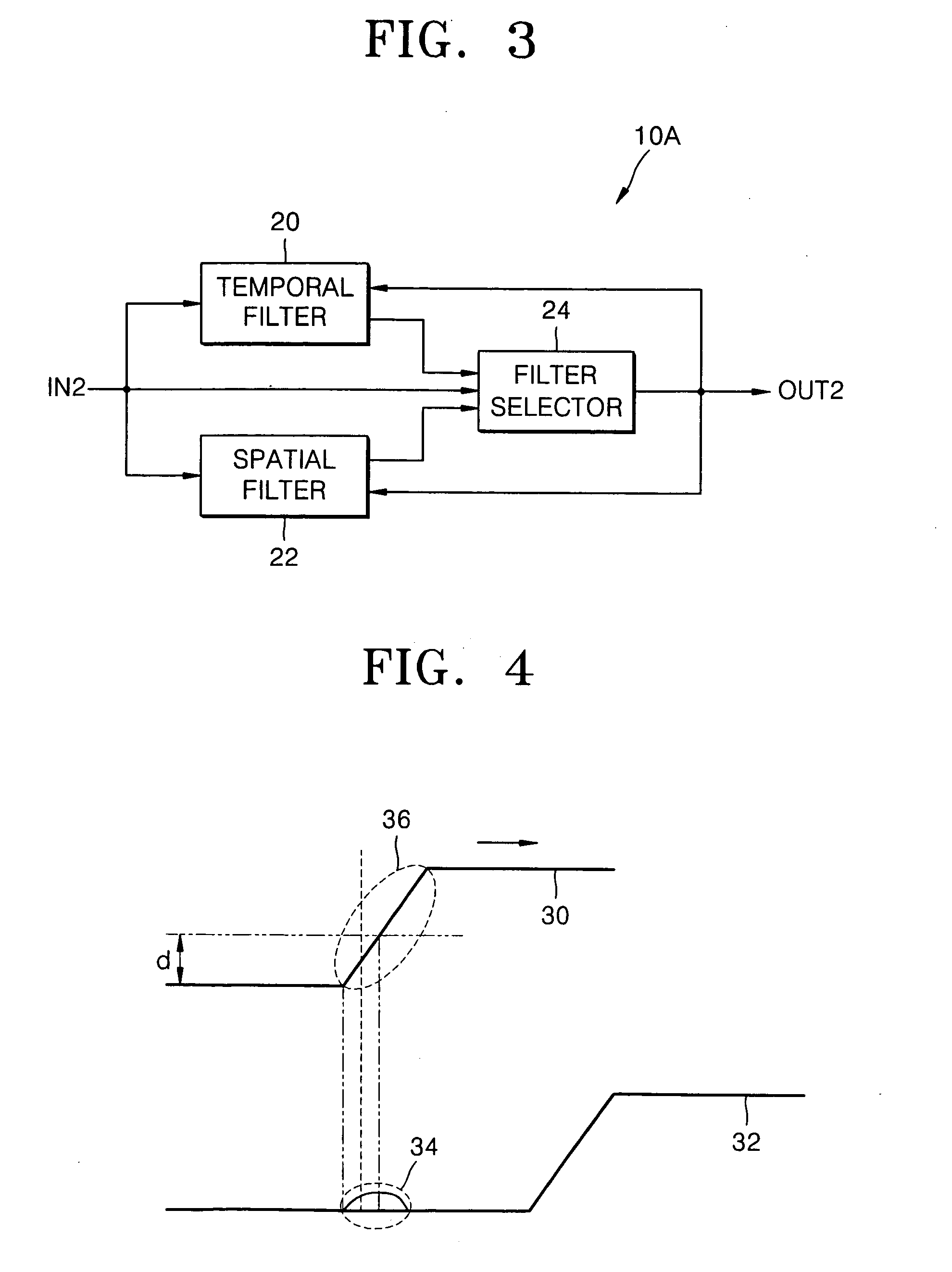
InactiveUS20050248687A1Efficiently and economically reduce noiseImprove clarityImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
An apparatus and method of filtering a digital image signal. The apparatus includes: a noise reduction filter which selectively outputs one of results obtained by temporally and spatially filtering pixel values of pixels of each of frames of an image as a temporal or spatial filtering value in response to magnitudes of the results of temporal and spatial filtering; and a sharpness enhancement filter which highlights and outputs a high pass component of the temporal or spatial filtering value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
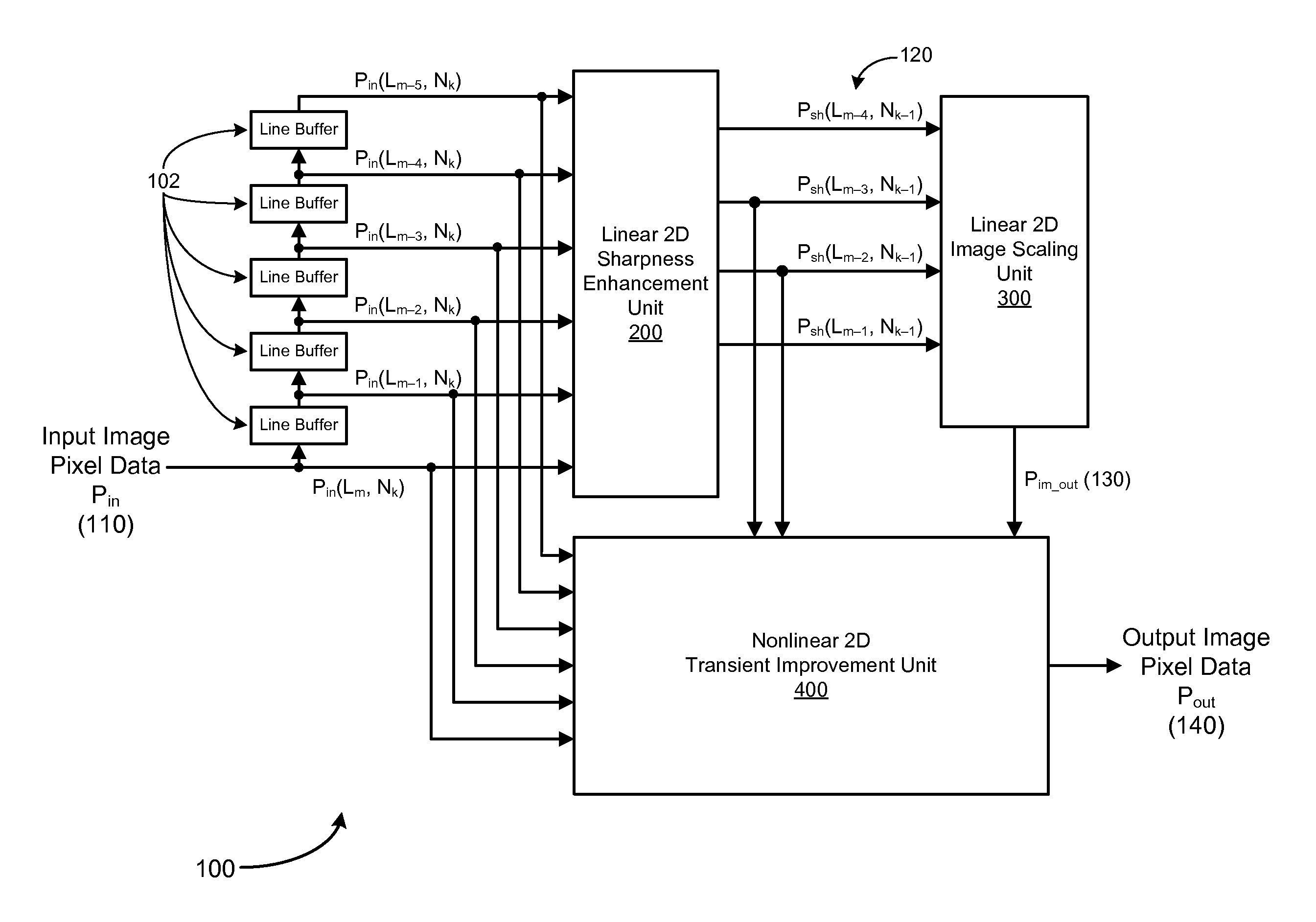
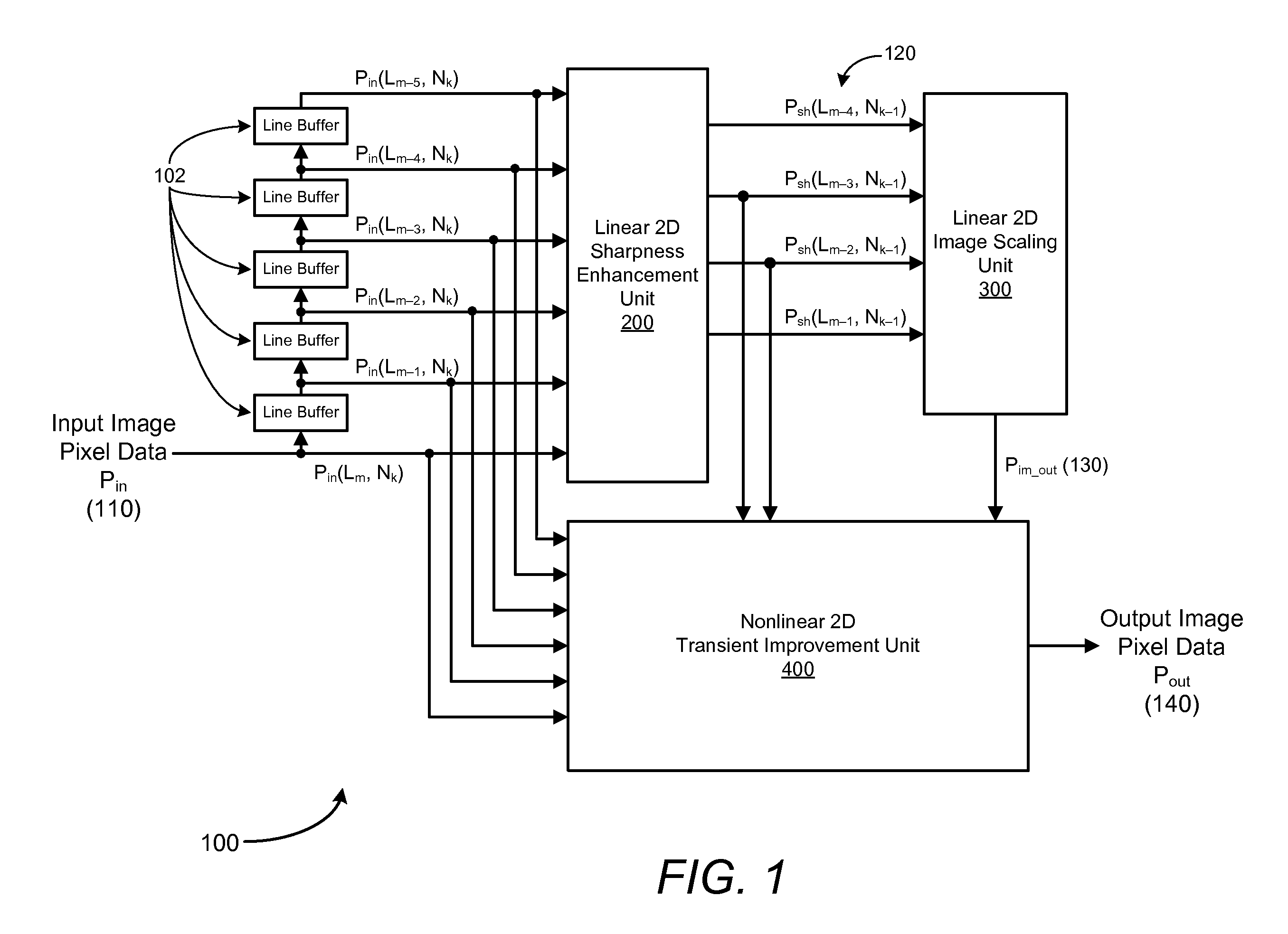
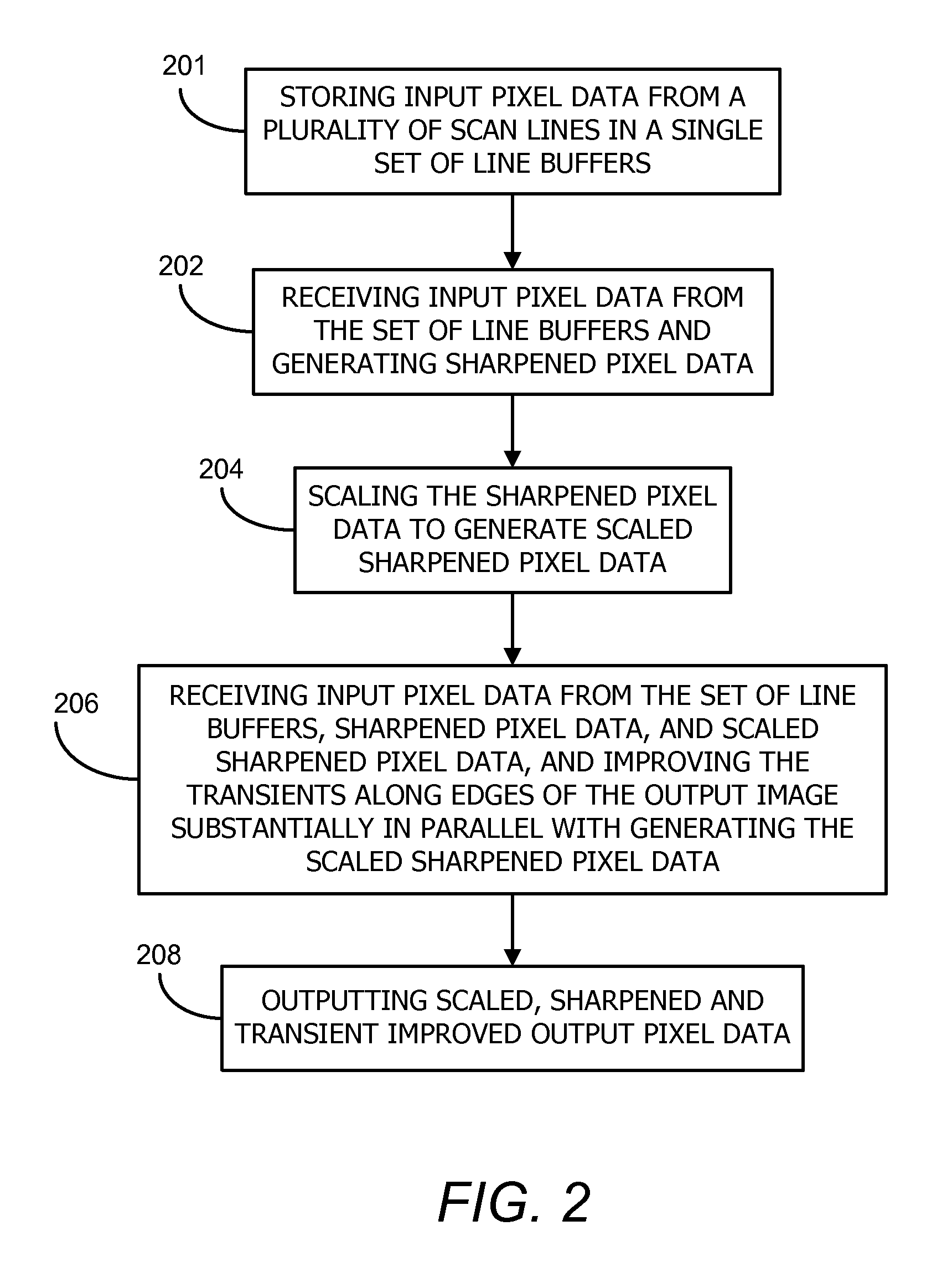
Method and system for digital image scaling with sharpness enhancement and transient improvement
InactiveUS7782401B1Low costReduce complexityTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImage resolutionImage scale
An image scaling system includes a single set of line buffers that receive and store input image pixel data in an input video frame. The scaling system also includes a linear two-dimensional sharpness enhancement unit configured to receive input pixel data from the line buffers and to generate sharpened pixel data by enhancing high frequency components of the input pixel data at an input image resolution, a linear two-dimensional image scaling unit configured to receive the sharpened pixel data and to convert the sharpened pixel data into scaled sharpened pixel data at an output image resolution, and a transient improvement unit configured to receive the input pixel data from the line buffers, sharpened pixel data and scaled sharpened pixel data to improve transient responses at edges in an output image, and to generate output image pixel data at the output image resolution.
Owner:CORONA
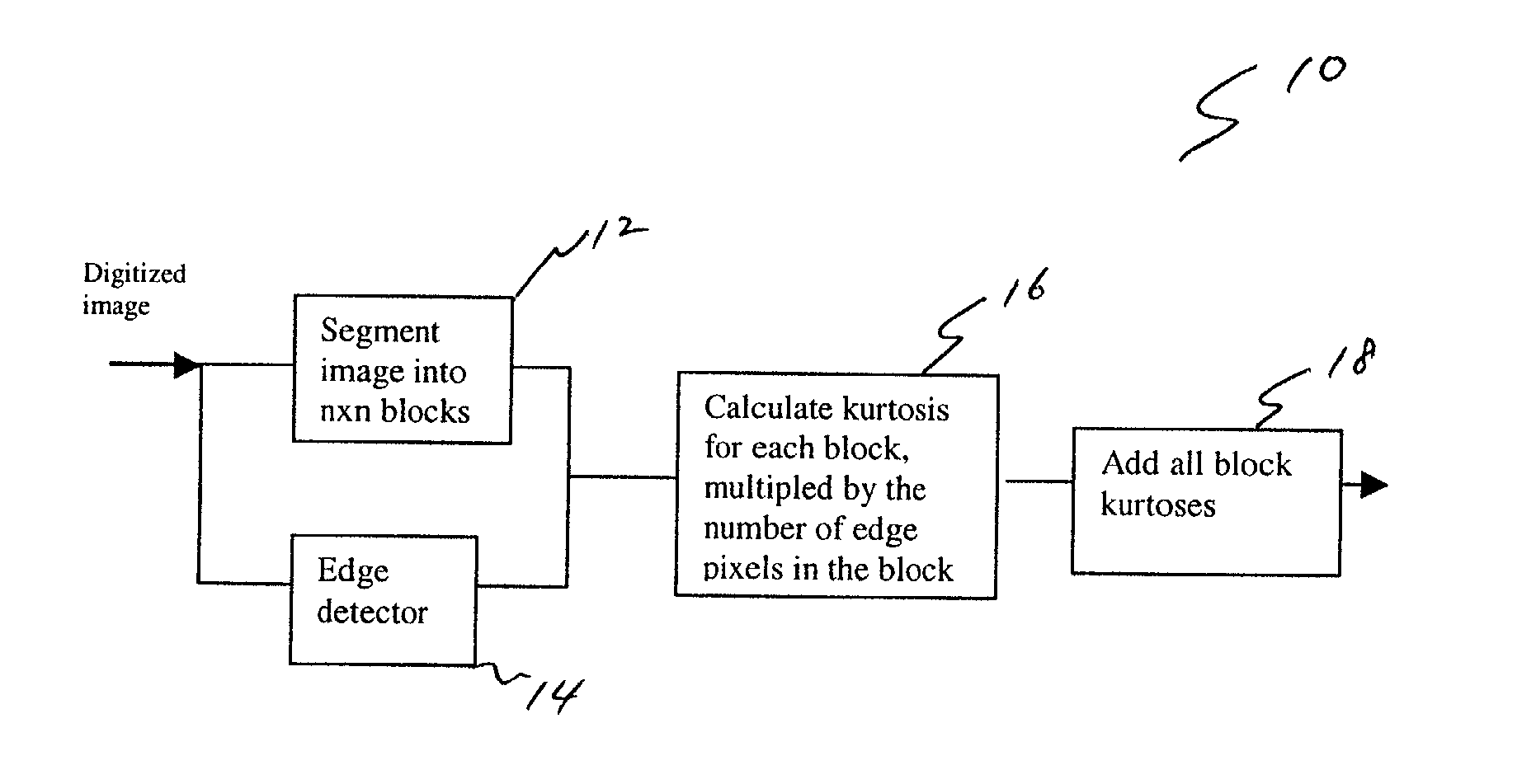
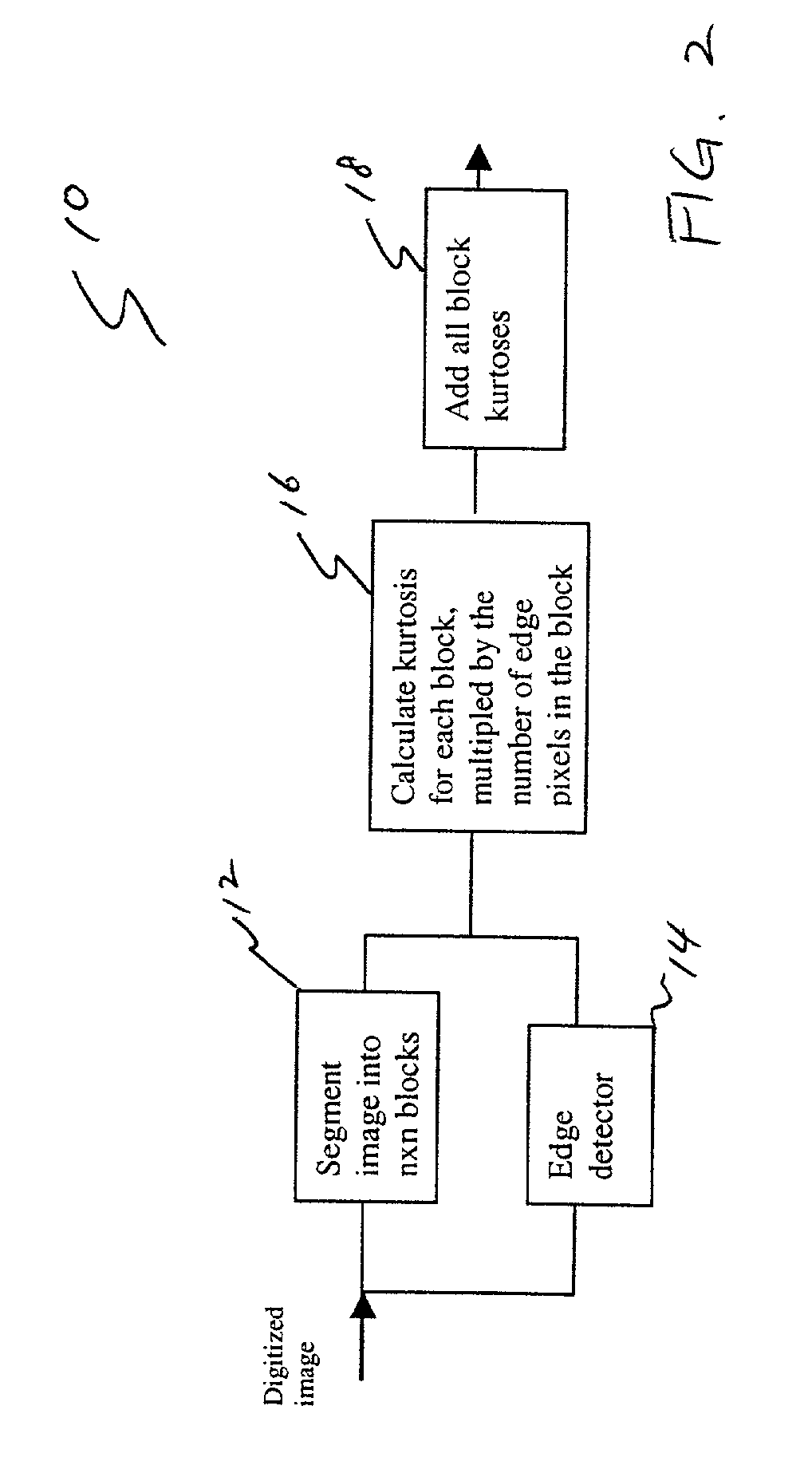
Method and system for estimating sharpness metrics based on local edge kurtosis
The present invention relates to a method and system for evaluating the quality of video data without gaining access to the source data. The system is configured to estimate sharpness metrics by detecting edge pixels and enclosing them with 8x8 pixel blocks. For each block, the sharpness according to the Kurtosis of the DCT is computed. The final metric is the average sharpness of the blocks in the edge profile and includes a robust combination of spatial and frequency domain information.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
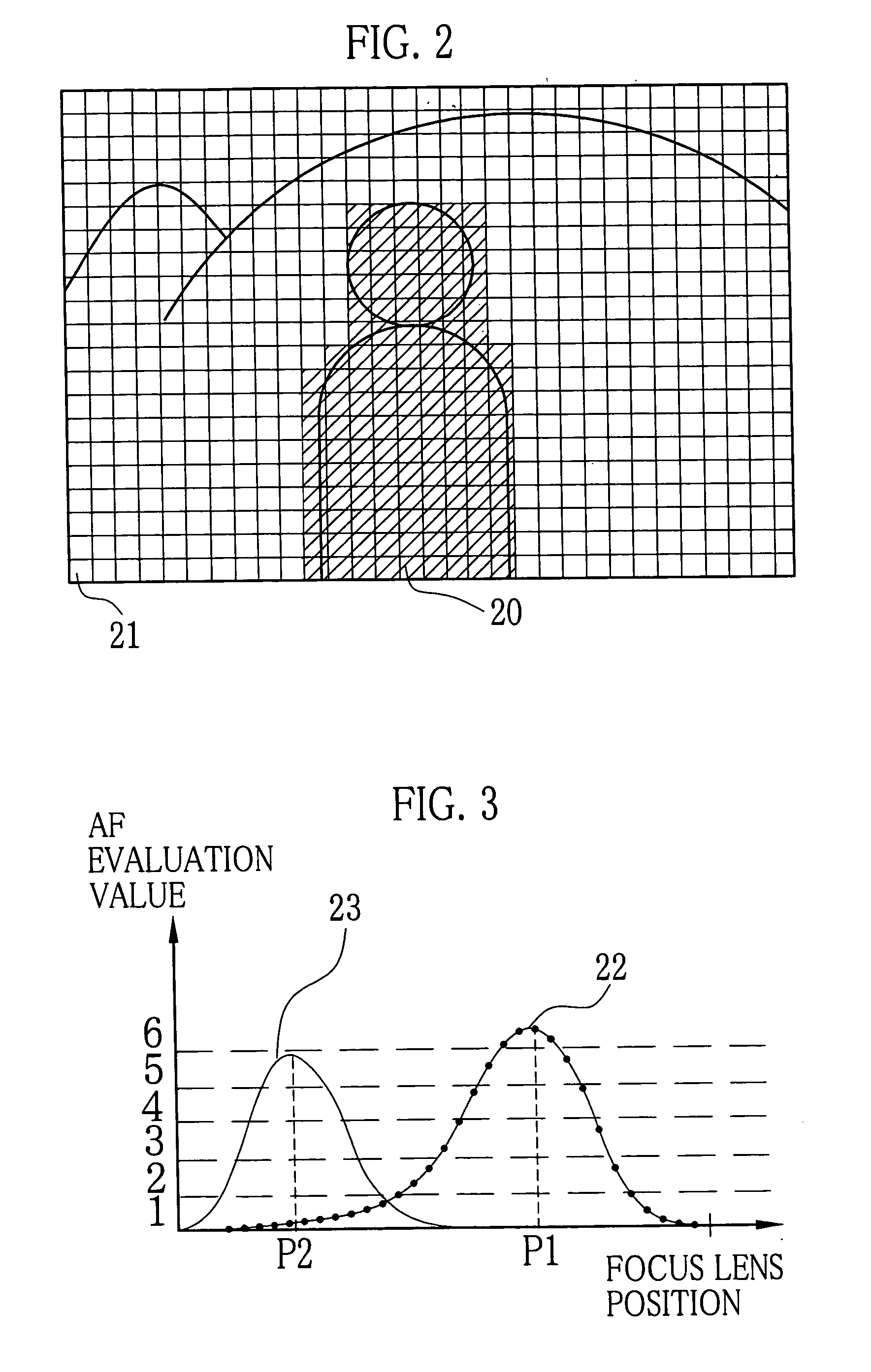
Automatic focusing and locating method
ActiveCN103945126AGet rid of distractionsAccurate focusTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAlgorithmPeak value
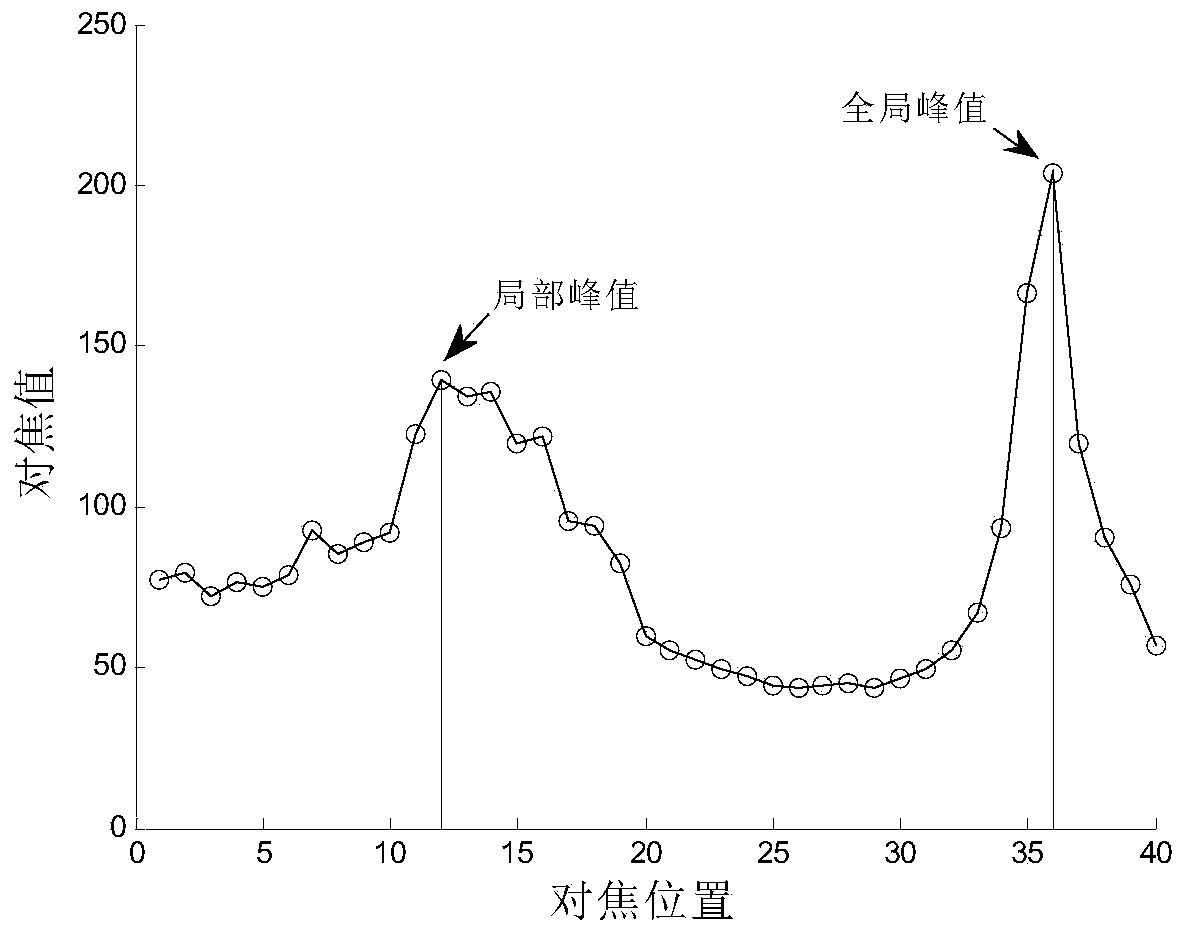
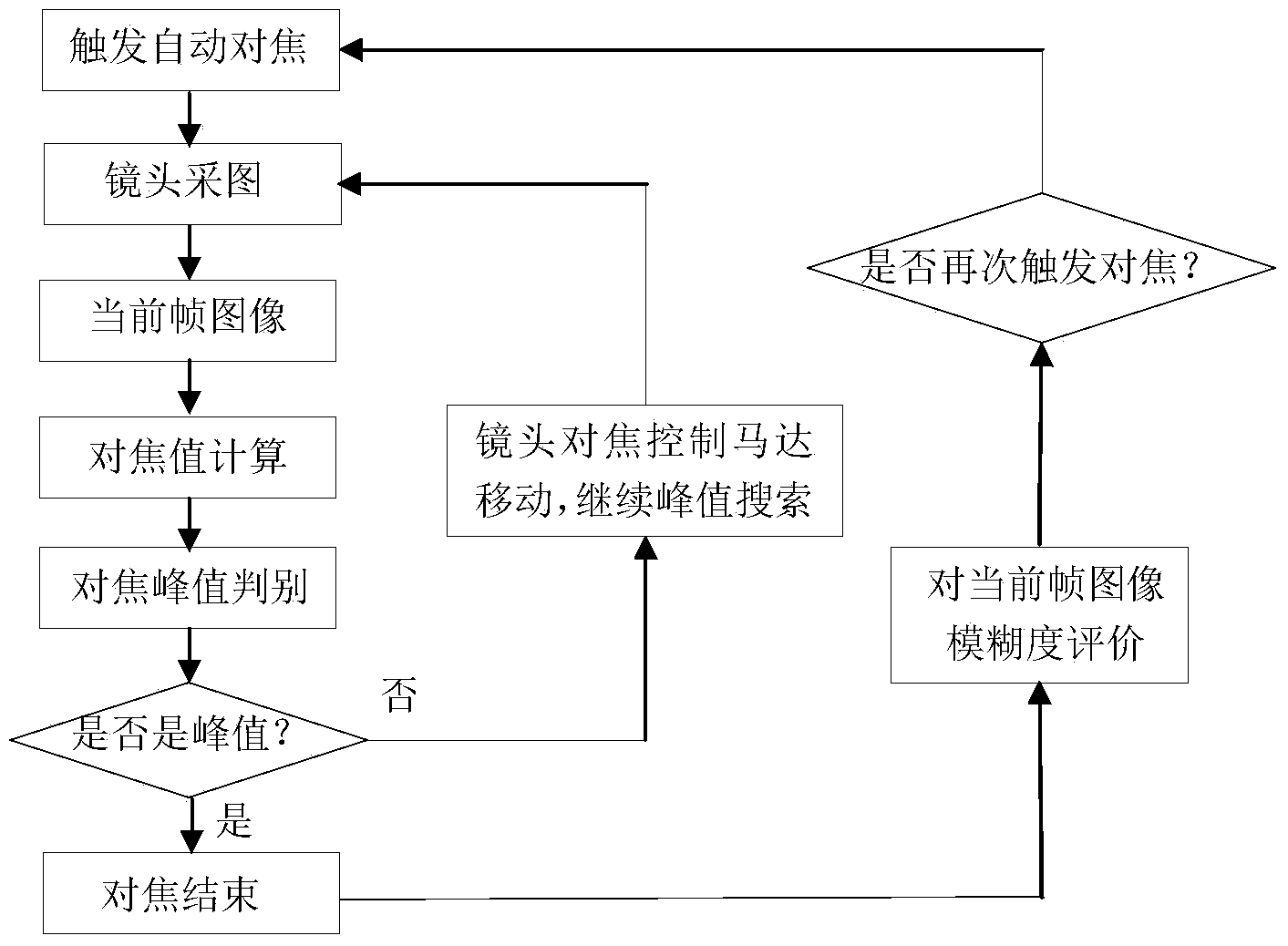
The invention discloses an automatic focusing and locating method. The search direction is judged according to an absolute ambiguity value, and the automatic focusing and locating method relates to a search direction rapid judgment rule depending on only one frame of images under the certain condition through the absolute ambiguity value and a current focusing position value and a search direction judgment rule under the common condition according to several frames of continuous changes of the absolute ambiguity value. A dual-acutance change threshold value is adopted for determining a fine search area to eliminate local peak values and guarantee the capacity of long-scale contrast scene accurate focusing. The fluctuation time number is counted to distinguish the local peak values and overall peak values, and interference of the local peak values is eliminated. A multi-window focusing mode is adopted, a focusing target area is comprehensively judged according to the acutance and the ambiguity, and the capacity of initiatively selecting the focusing target area to a certain degree is achieved. The automatic focusing and locating method is high in focusing efficiency and accurate in focusing.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method of and system for improving temporal consistency in sharpness enhancement for a video signal
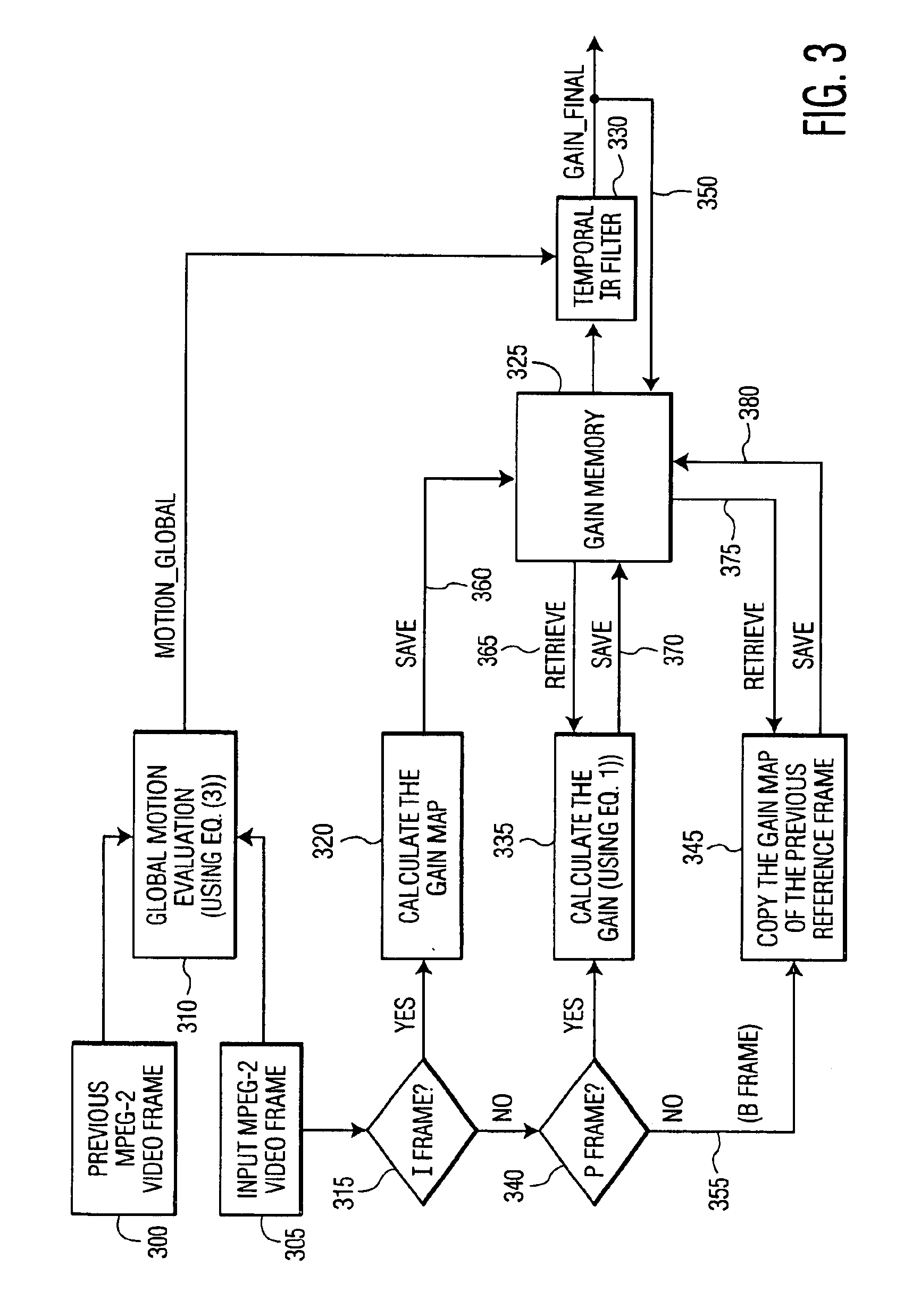
ActiveUS6873657B2Improving temporal consistencyHigh gainTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesIir filteringMotion vector
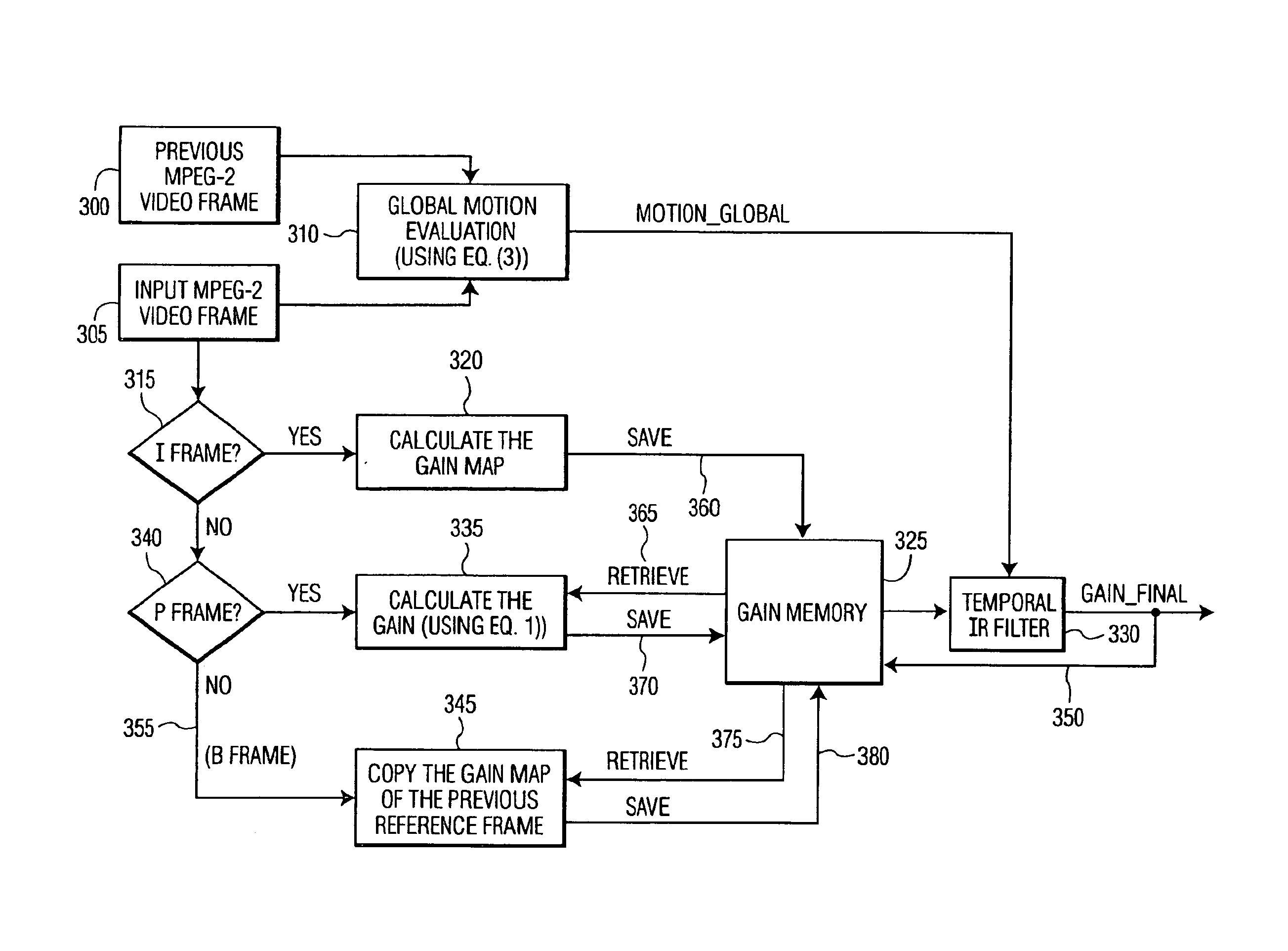
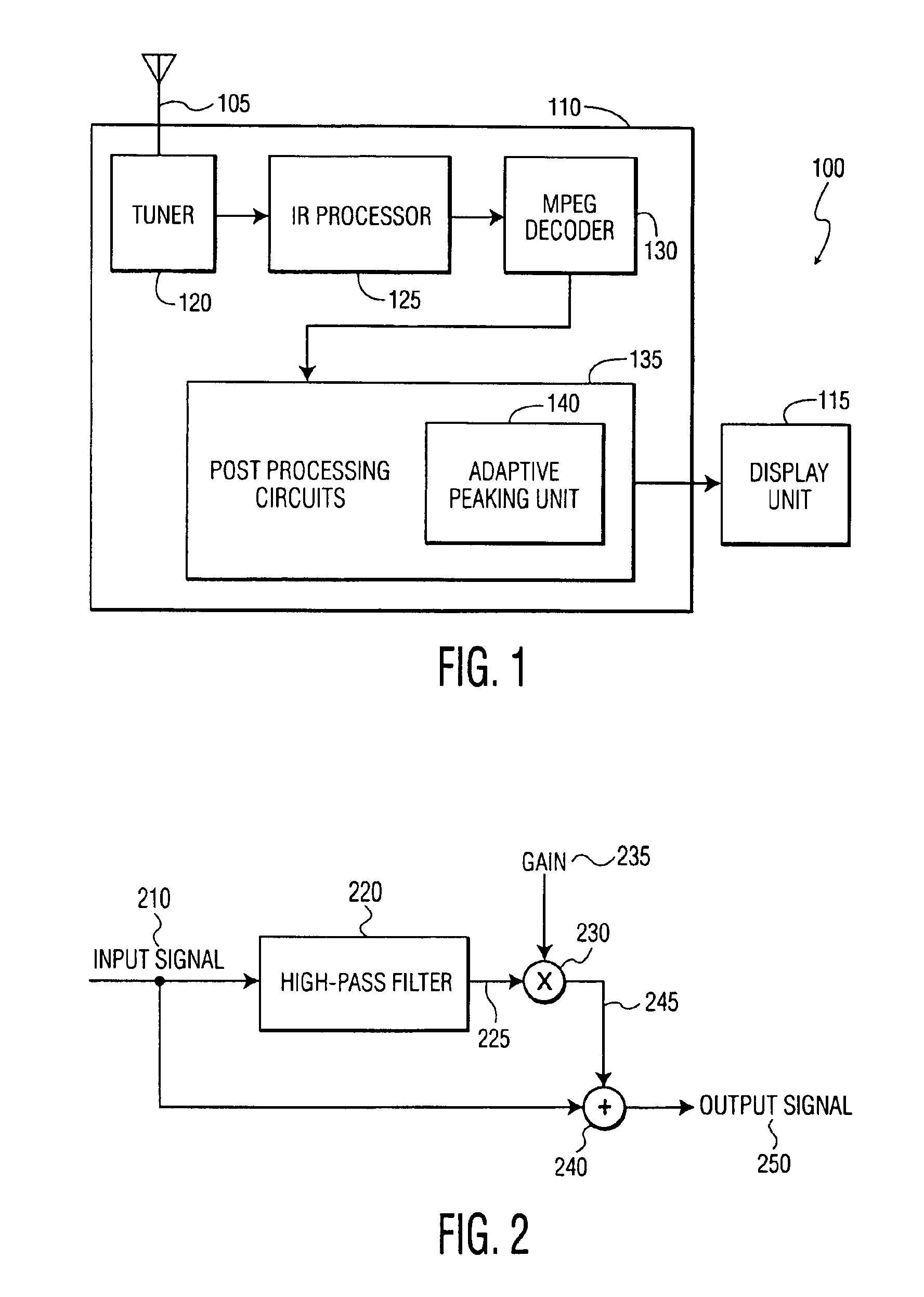
In accordance with the preferred embodiment of the present invention, a method of and system for improving temporal consistency of an enhanced signal representative of at least one frame using a sharpness enhancement algorithm with an enhancement gain are provided. The method comprises the steps of: receiving the enhanced signal comprising at least one frame, obtaining an enhancement gain for each pixel in the frame, retrieving an enhancement gain value of each pixel in a reference frame from a gain memory using motion vectors, identifying if the frame is an I, P or B frame type and determining an updated enhancement gain for an I frame type by calculating a gain map for use in the sharpness enhancement algorithm. The updated enhancement gain of each pixel is equal to enhancement gain previously determined for use in the sharpness enhancement algorithm. In addition, the method includes storing the updated enhancement gain to gain memory, and applying the updated enhancement gain to the sharpness enhancement algorithm to improve temporal consistency of the enhanced signal. The method may further comprise the step of further improving the updated enhancement gain by applying a motion adaptive temporal IIR filter on the updated enhancement gain.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Blur detection with local sharpness map
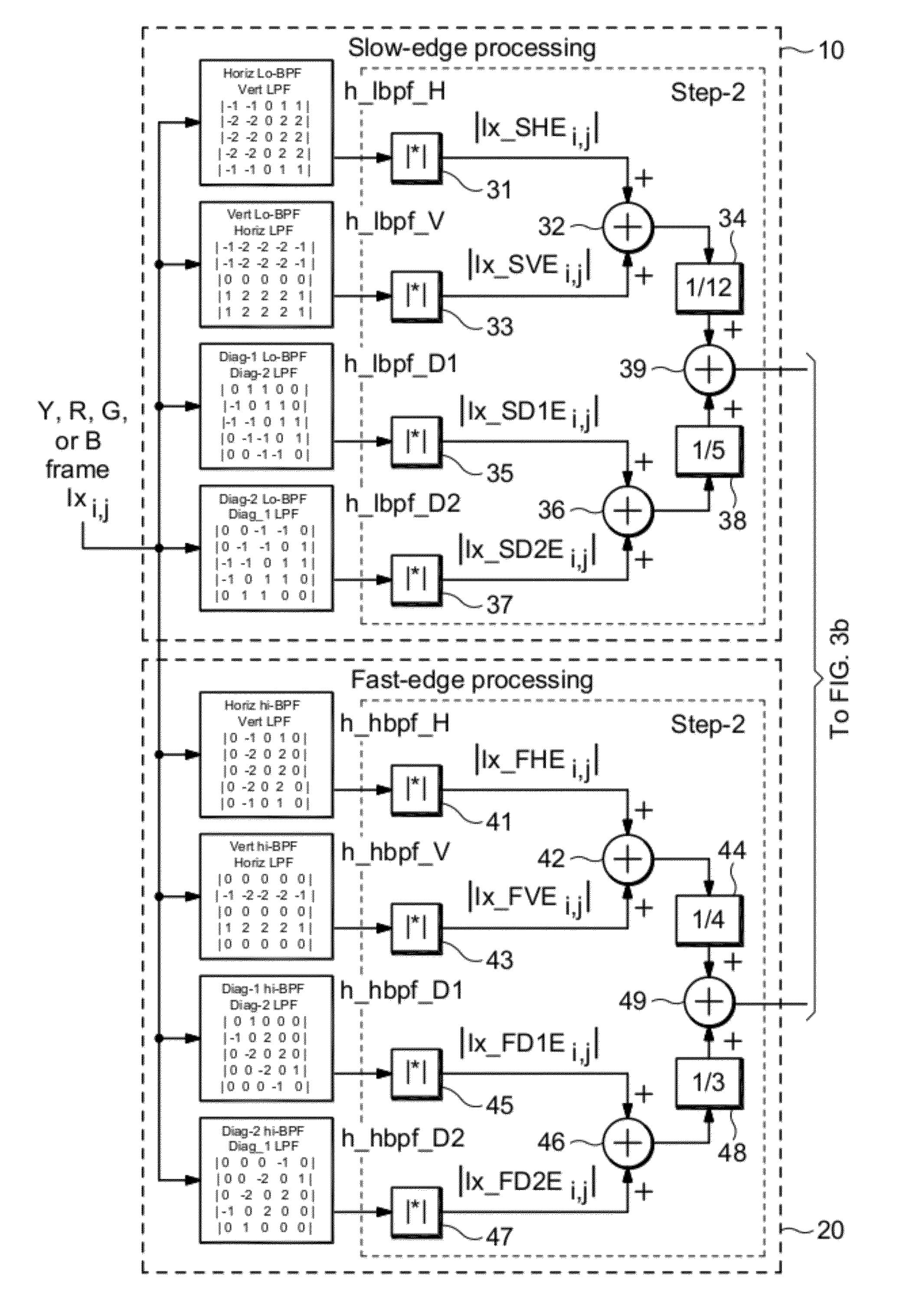
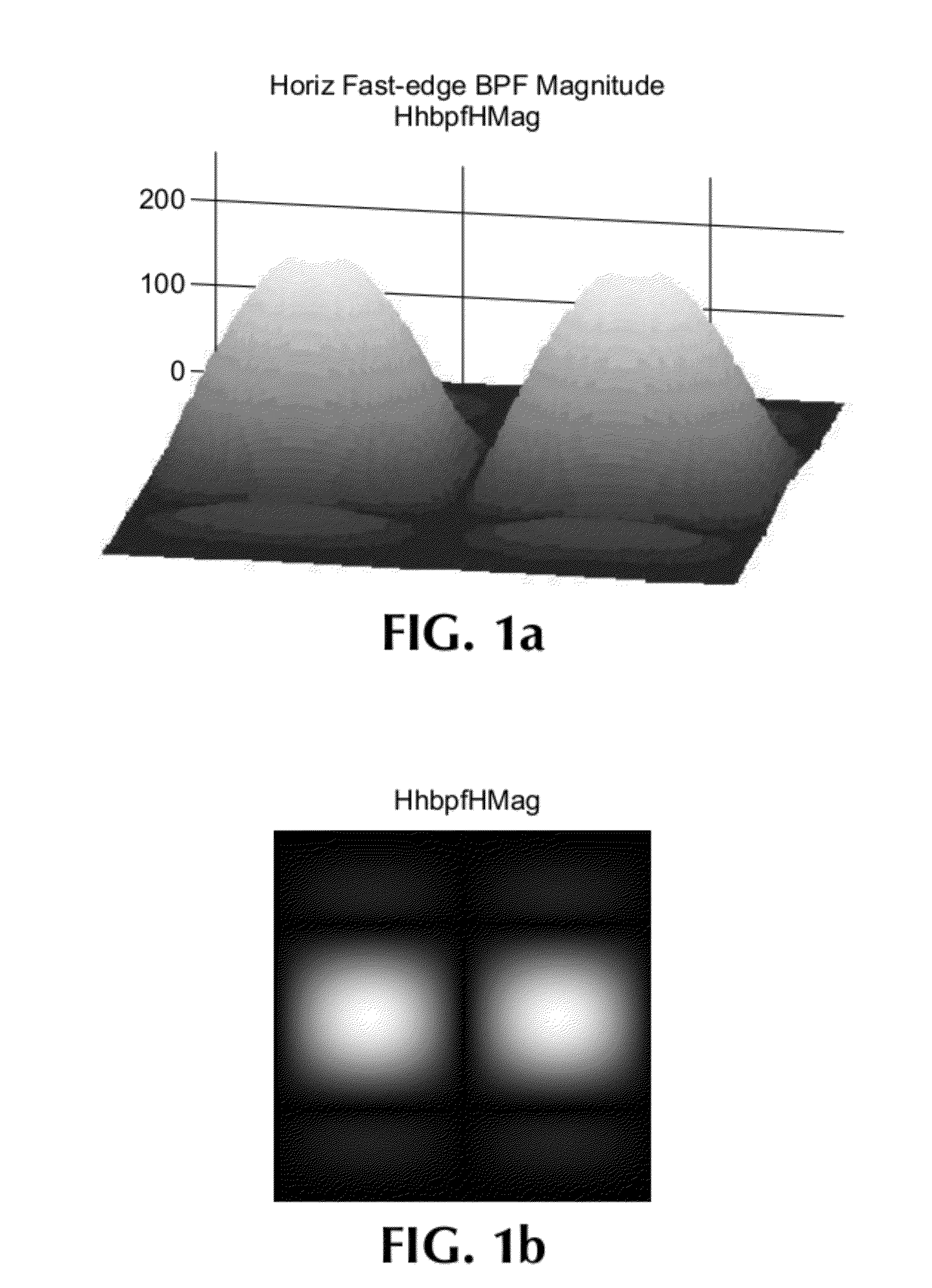
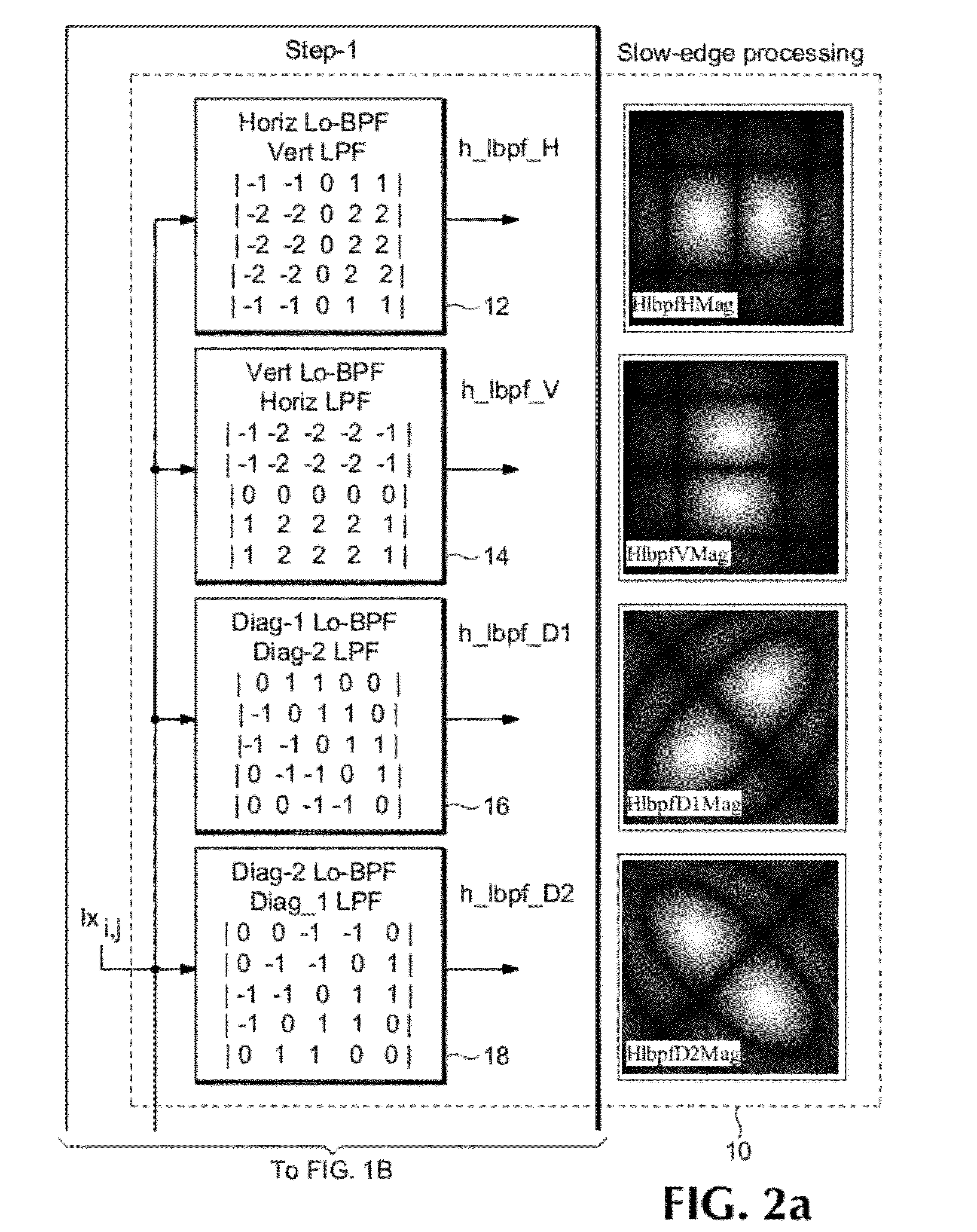
ActiveUS20120162527A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionBandpass filtering
A single-ended blur detection probe and method with a local sharpness map for analyzing a video image sequence uses two sets of edge filters, one for “fast edges” and the other for “slow edges.” Each set of edge filters includes a horizontal bandpass filter, a vertical bandpass filter and a pair of orthogonal diagonal filters where the frequency response of the fast edge filters overlap the frequency response of the slow edge filters. The video image sequence is input to each filter of each set, and the output absolute values are combined with weighting factors to produce a slow edge weighted sum array and a fast edge weighted sum arra. The respective weighted sum arrays are then decimated to produce a slow edge decimated array and a fast edge decimated array. The ratio of the maximum difference value between the decimated arrays and the maximum value from the fast edge decimated array, weighted by an appropriate factor, produces a localized maximum sharpness value, the log of which produces a dimensionless blur value.
Owner:PROJECT GIANTS LLC
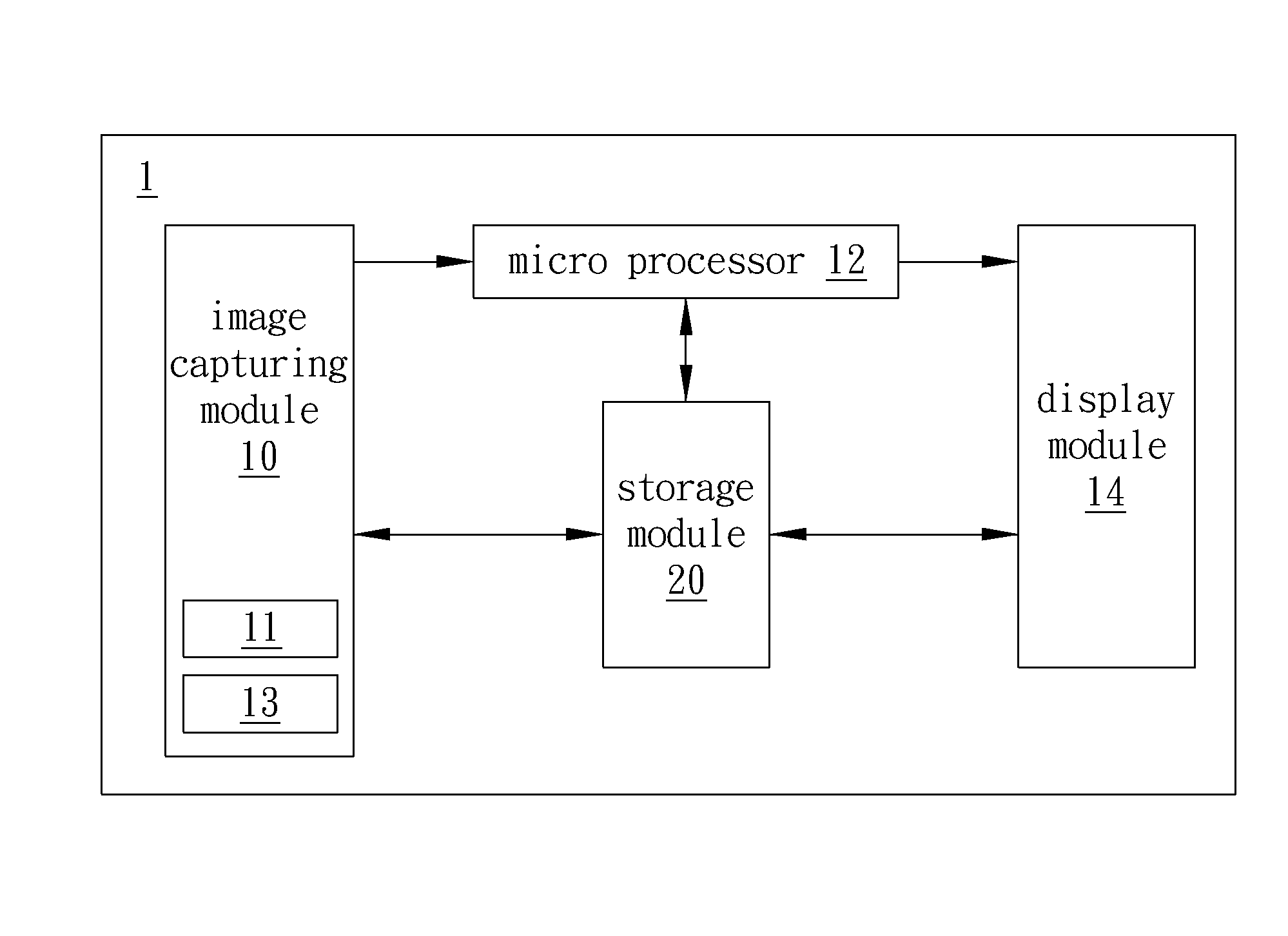
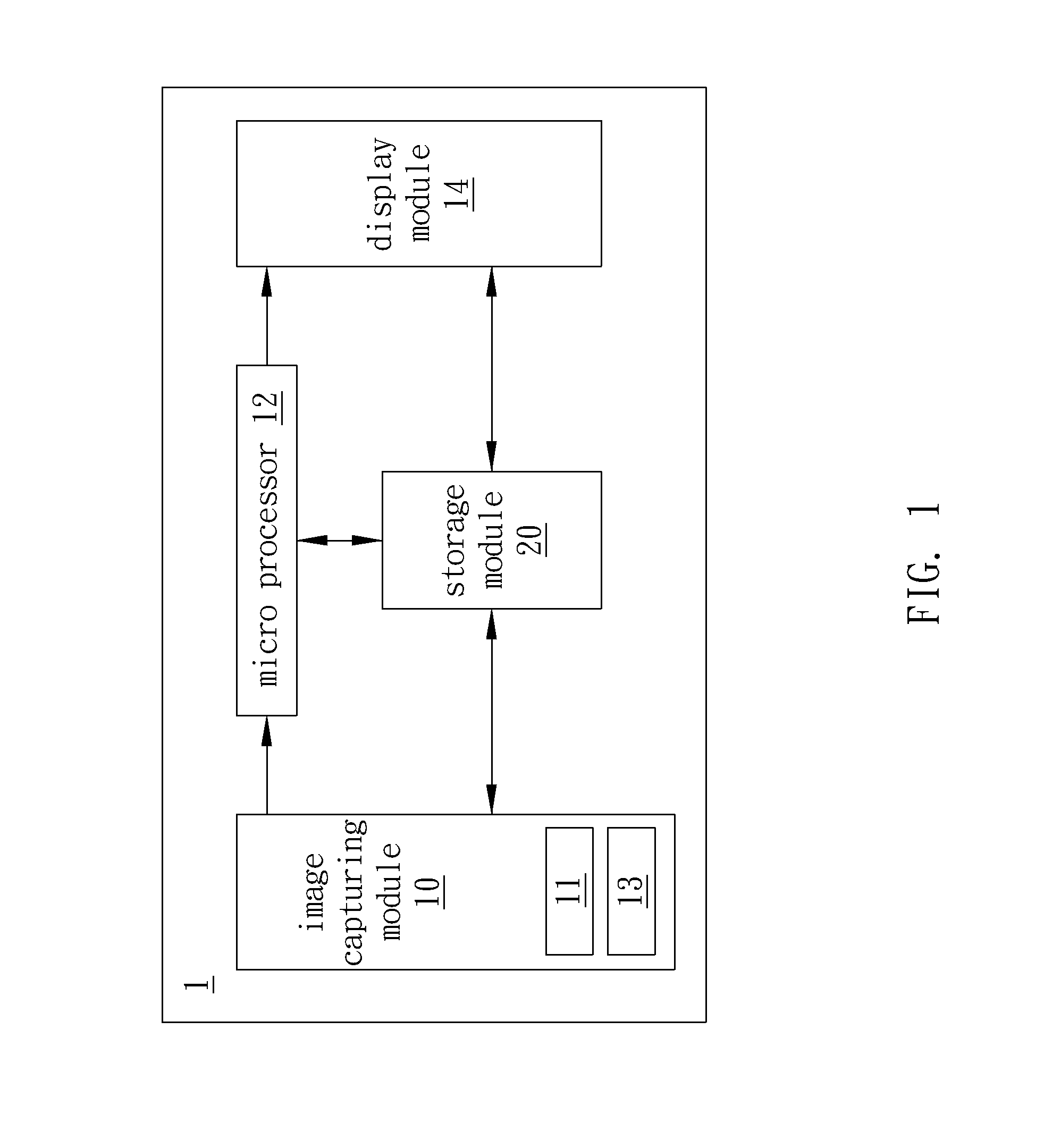
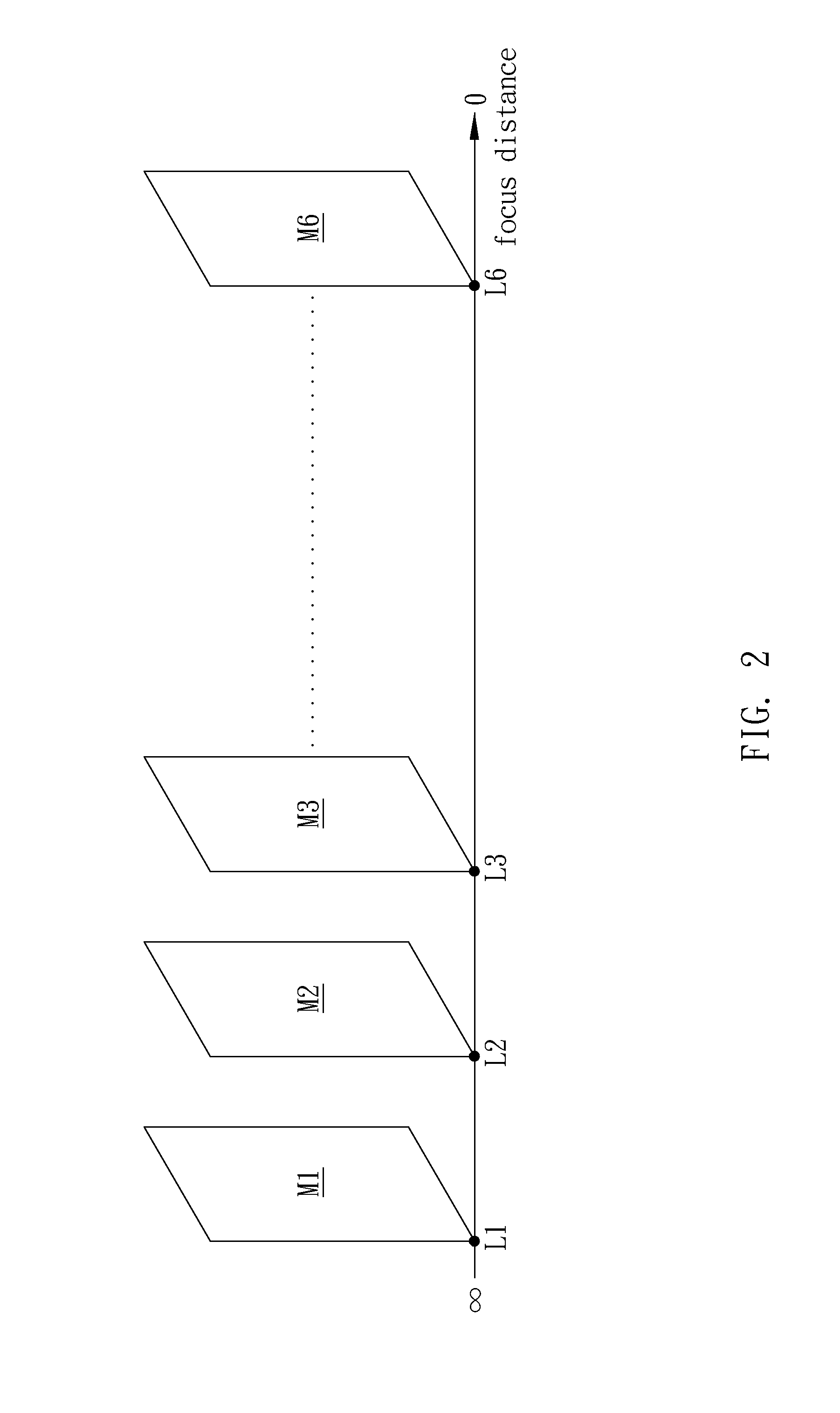
Image capturing apparatus and image processing method
InactiveUS20140198242A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingImage capture
An image capturing apparatus and an image processing method are disclosed. The image capturing apparatus includes an image capturing module, a micro processor, and a display module. The image capturing module continuously captures images corresponding to different focus distances. The display module displays an initial display image of the images. The micro processor divides the initial display image into a plurality of lattice areas and uses one of the plurality of lattice areas as a specific lattice area. The micro processor compare sharpness values of areas corresponding to the specific lattice area in the plurality of images corresponding to the different focus distances to generate a comparison result and selects a first image from the plurality of images according to the comparison result. The display module displays the first image to replace the initial display image previously displayed.
Owner:BENQ CORP
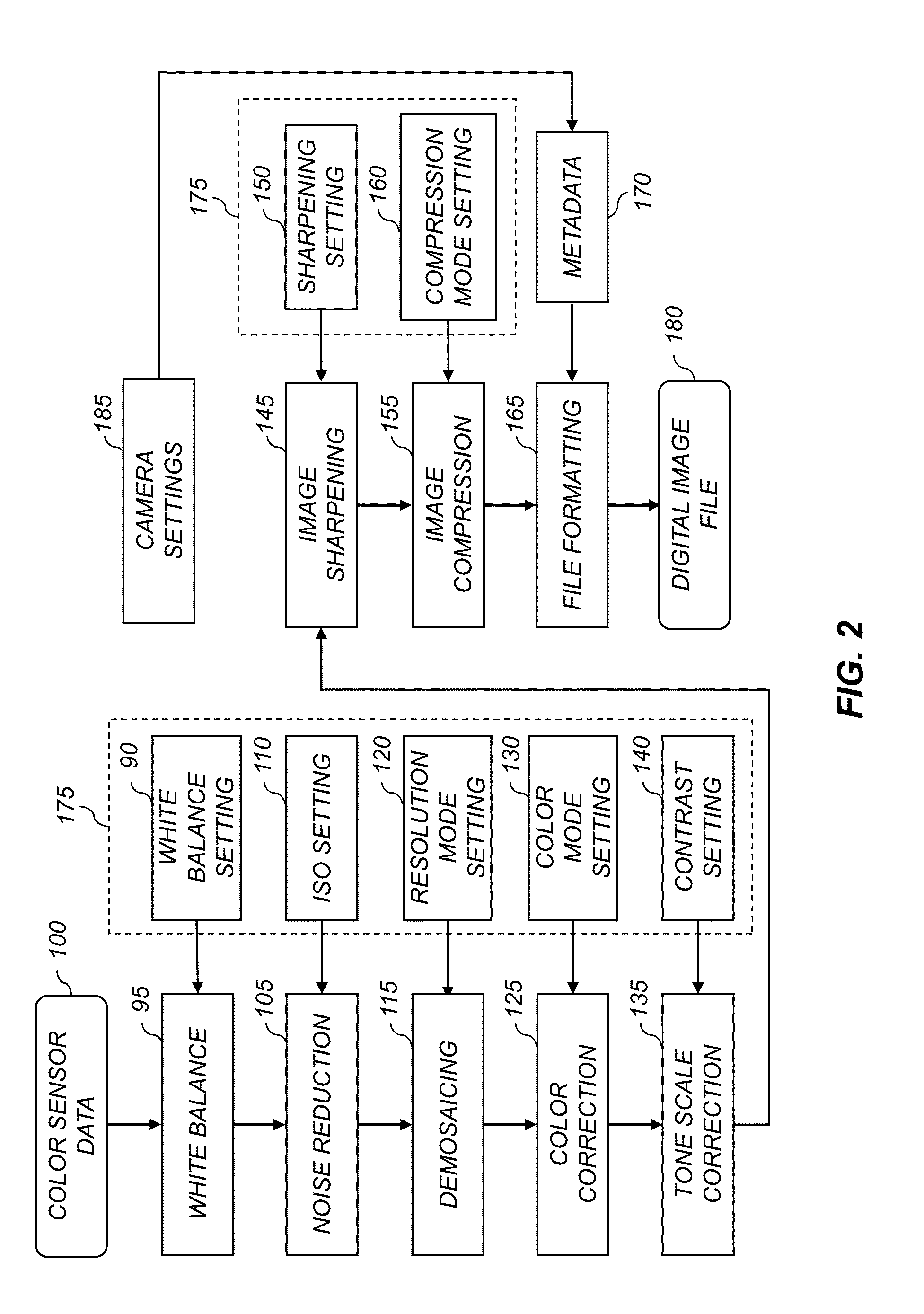
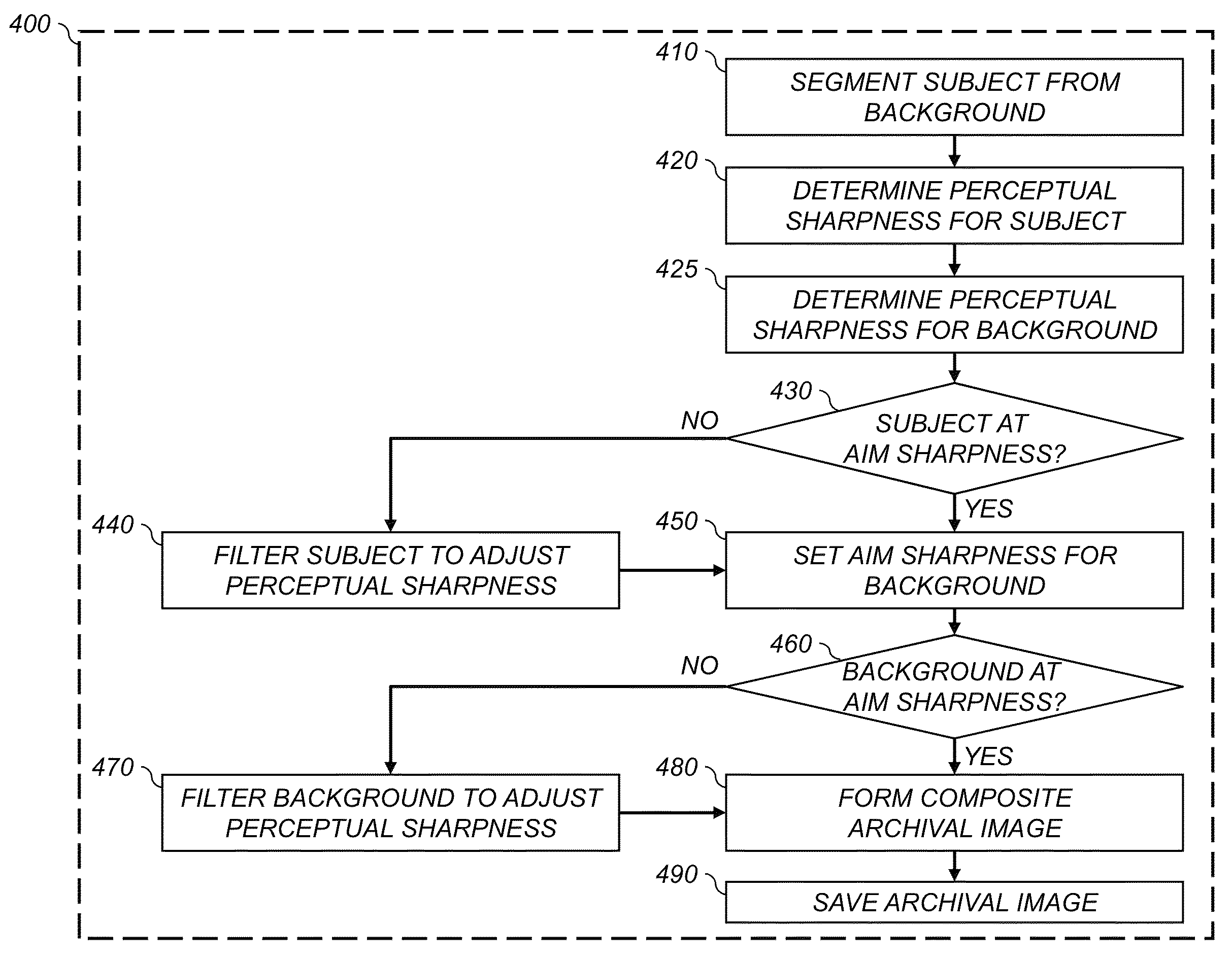
Controlling the sharpness of a digital image
InactiveUS20140085507A1Image enhancementTelevision system detailsTyping ClassificationImage segmentation
A method for selecting a digital image having controlled sharpness characteristics from a set of candidate digital images of a common scene, each digital image having different sharpness characteristics. An image segmentation process is used to segment each of the candidate digital images into a subject region and a background region. For each candidate digital image the subject and background regions are analyzed to determine an associated subject and background sharpness levels. An output digital image is selected by comparing the determined subject and background sharpness levels to respective aim subject and background sharpness levels. In some embodiments, the aim subject and background sharpness levels are defined in accordance with a scene type classification.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
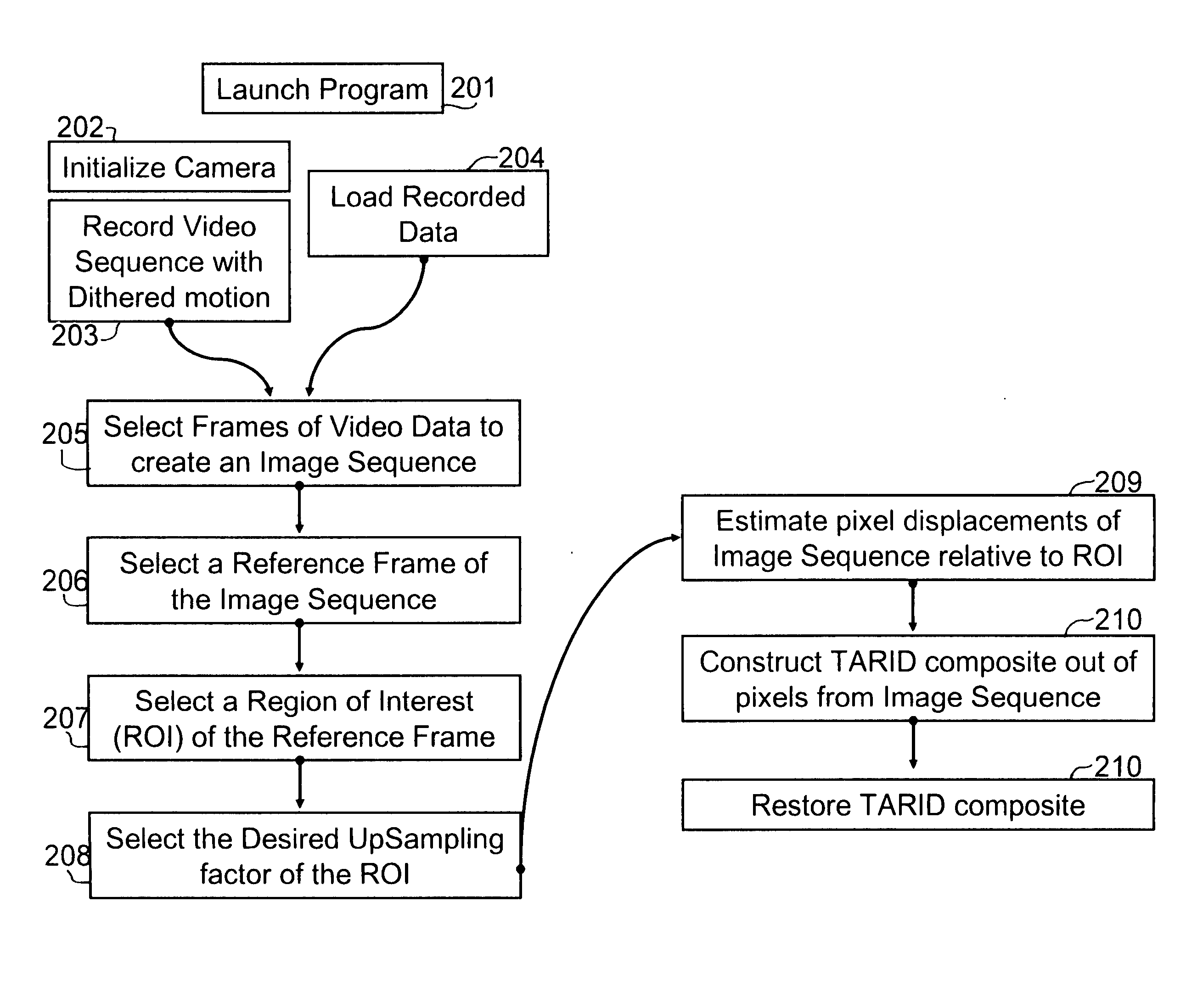
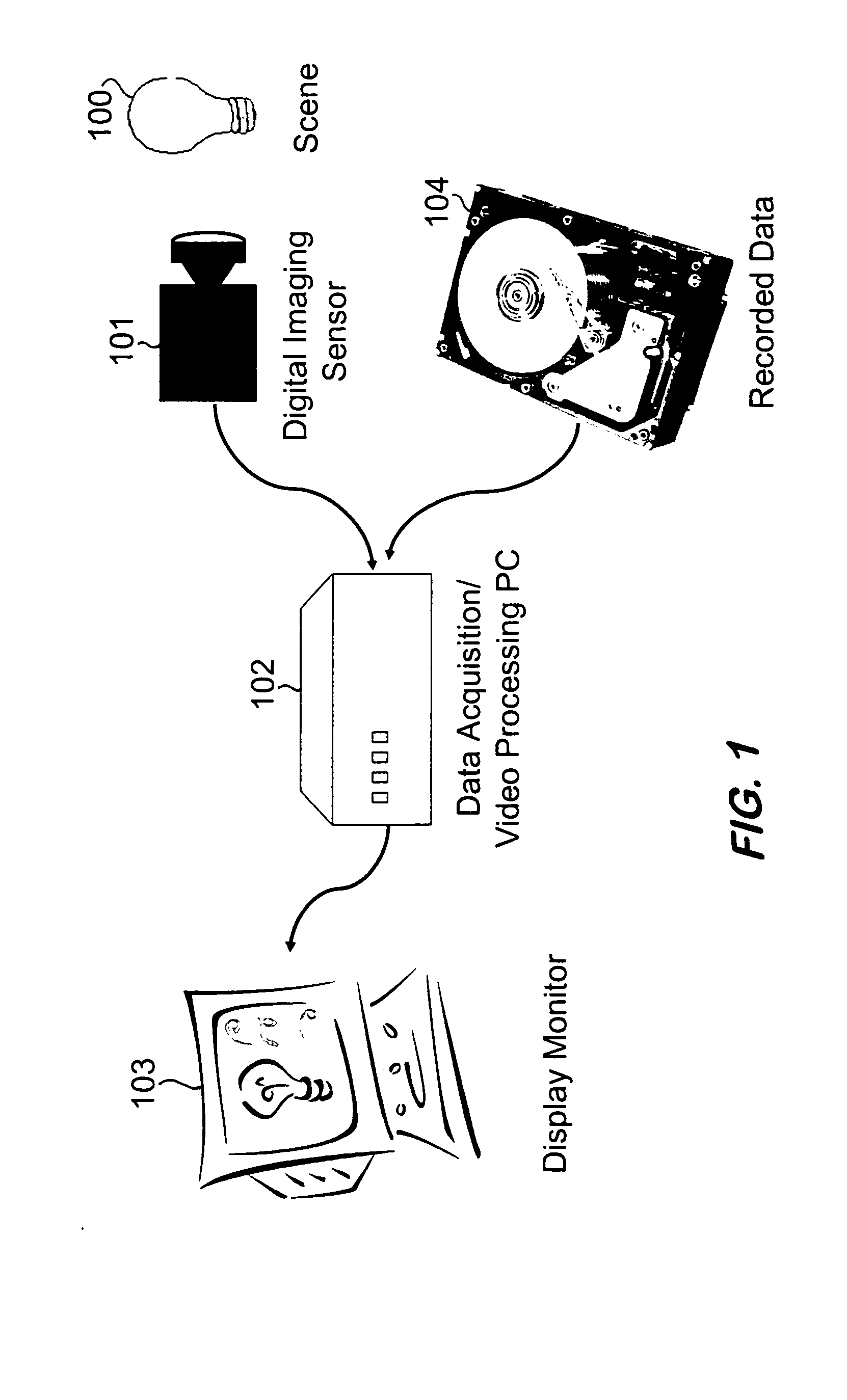
Algorithmic technique for increasing the spatial acuity of a focal plane array electro-optic imaging system
InactiveUS20050201637A1Improve spatial resolutionIncrease the physically achievable resolution of an imaging systemTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationPixel densityVideo sequence
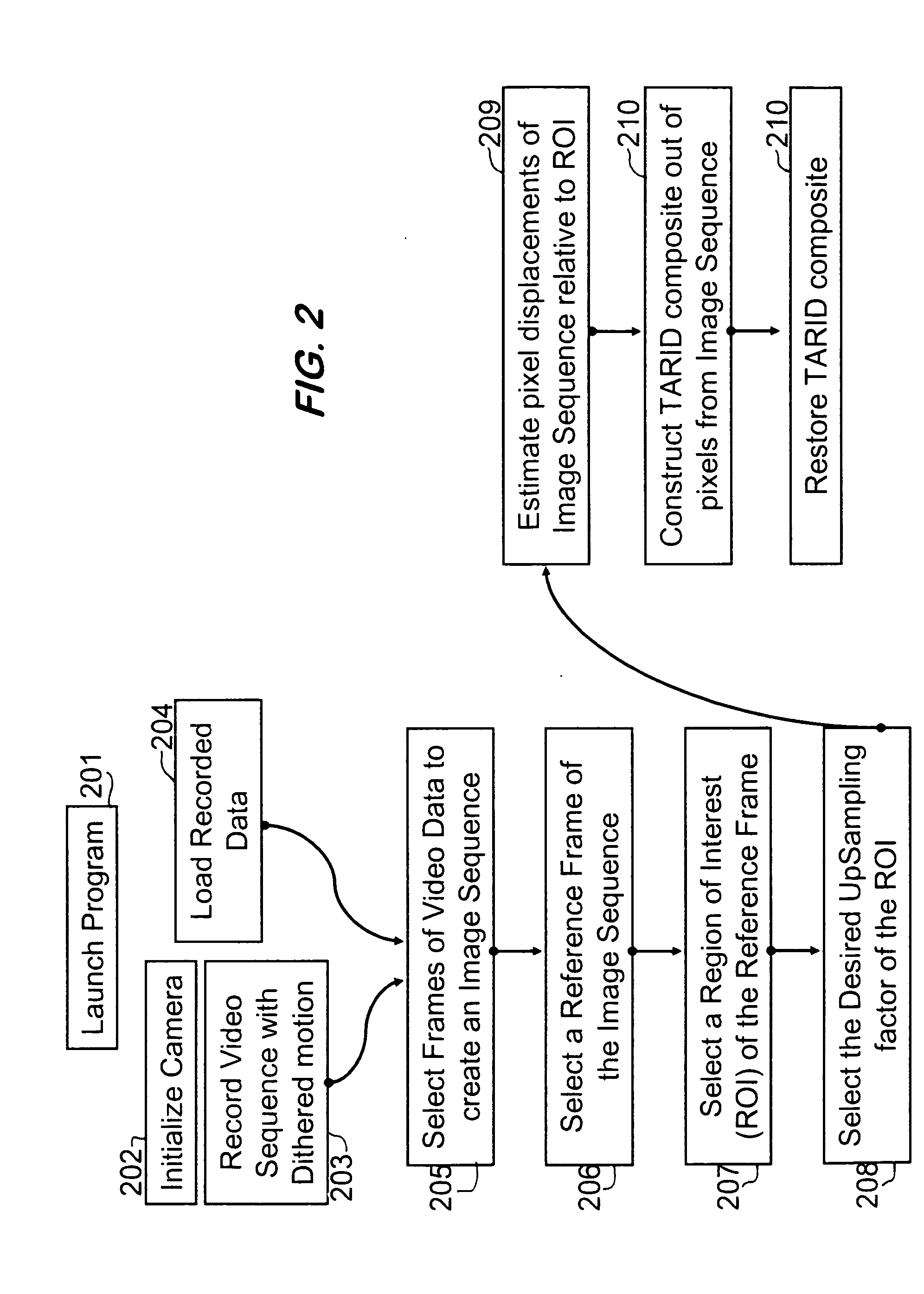
A system for enhancing images from an electro-optic imaging sensor and for reducing the necessary focal length of a sensor while preserving system acuity. This system uniquely reduces the necessary focal length and enhances images by collecting a video sequence, estimating motion associate with this sequence, assembling video frames into composite images, and applying image restoration to restore the composite image from pixel, lens blur, and alias distortion. The invention synthetically increases the pixel density of the focal plane array. Thus it reduces the necessary size of the projected blur circle or equivalently it reduces the minimum focal length requirements.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
Video signal processing apparatus and method to enhance image sharpness and remove noise
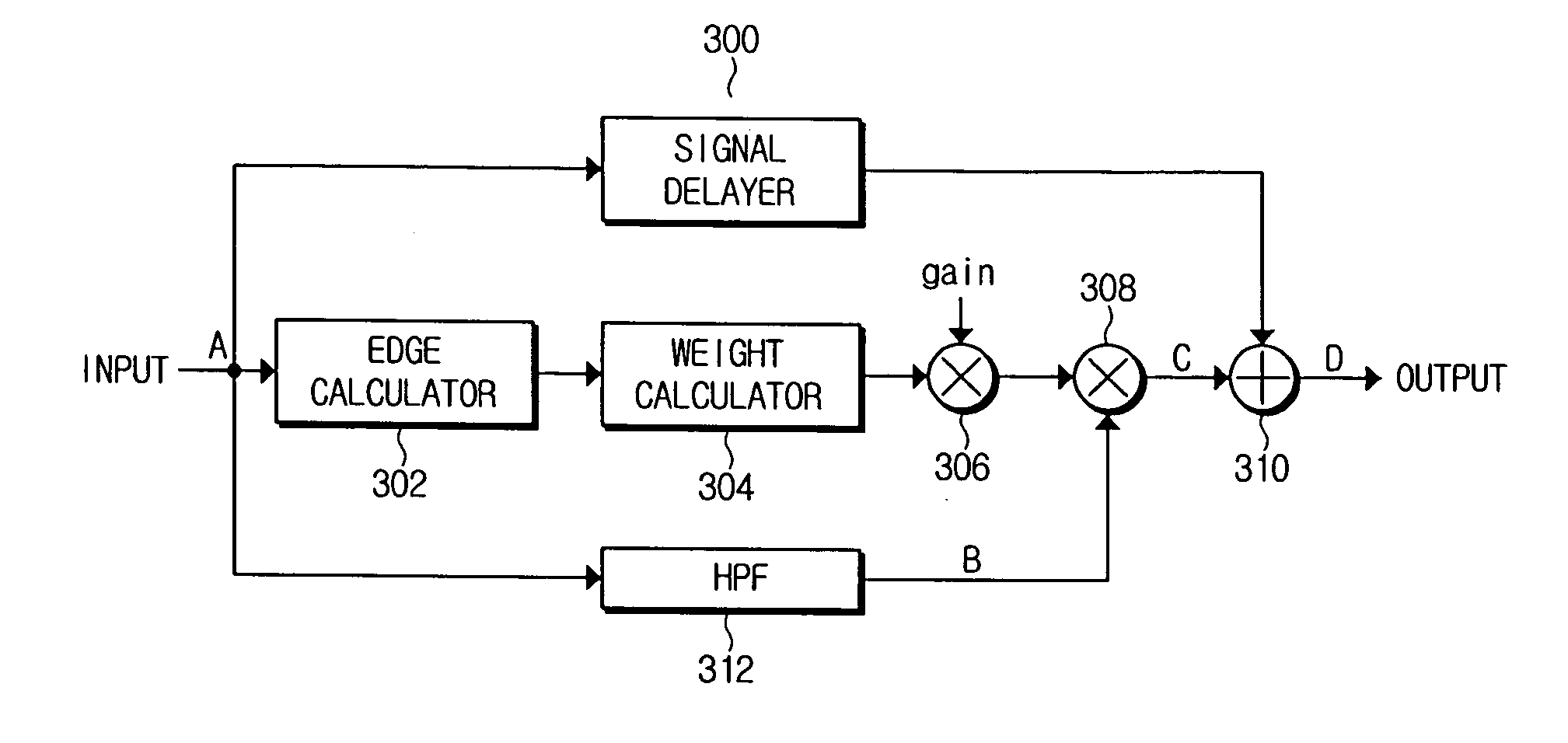
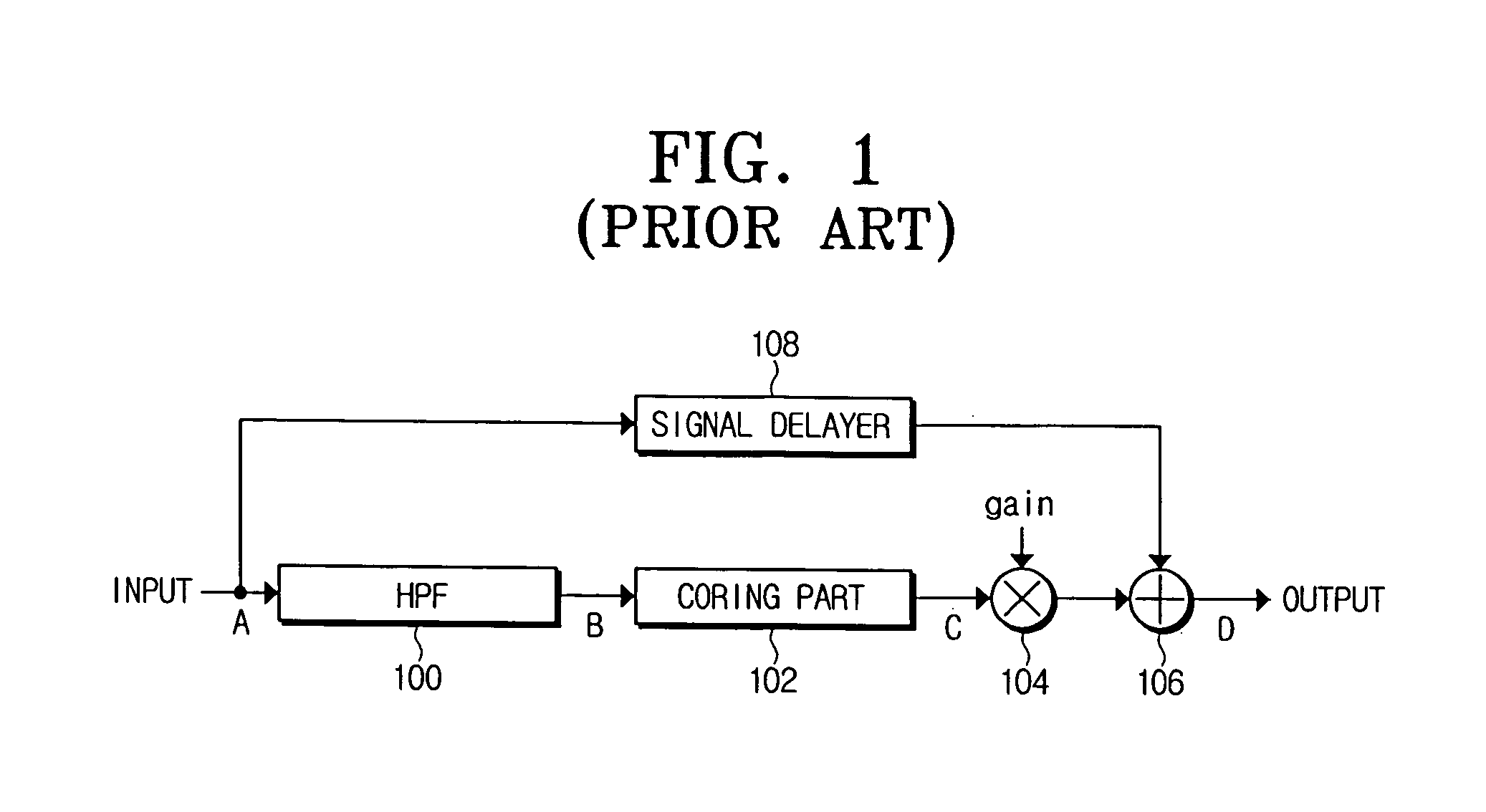
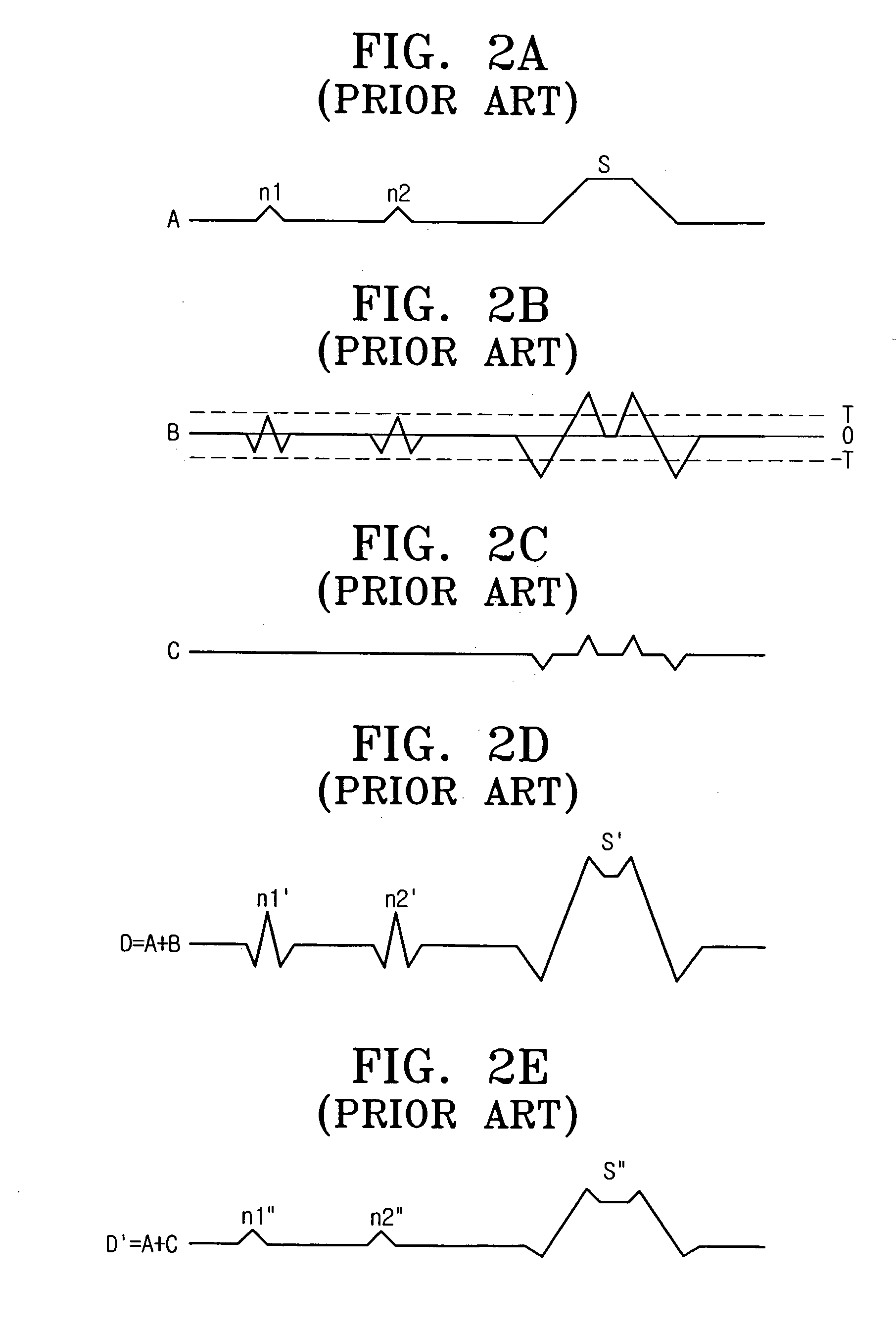
InactiveUS20050270425A1Improve edge sharpnessEnhancement in definitionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionAcutance
In a method of removing a noise signal from a video signal and enhancing edge sharpness to improve the video signal definition, a different weight is assigned depending on a characteristic of input pixels. To this end, at least two pixel blocks including the input and at least two adjacent pixels. A pixel difference between the pixels in the each of the pixel blocks is calculated and one of the calculated pixel differences is selected. The input pixel is assigned with a weight corresponding to the selected pixel difference. Accordingly, the definition of the video signal is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Infrared and visible light image signal processing method and implementation device thereof
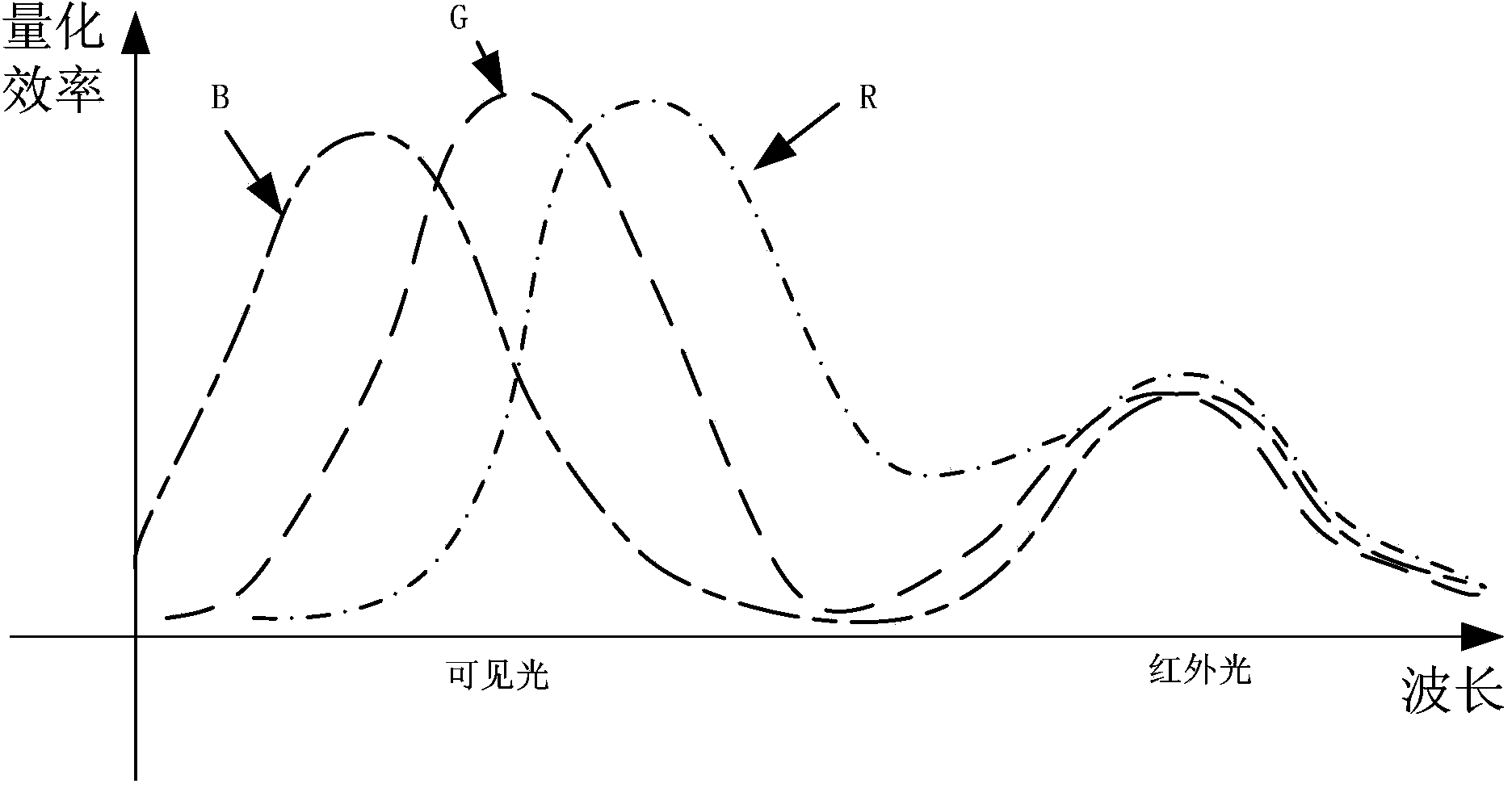
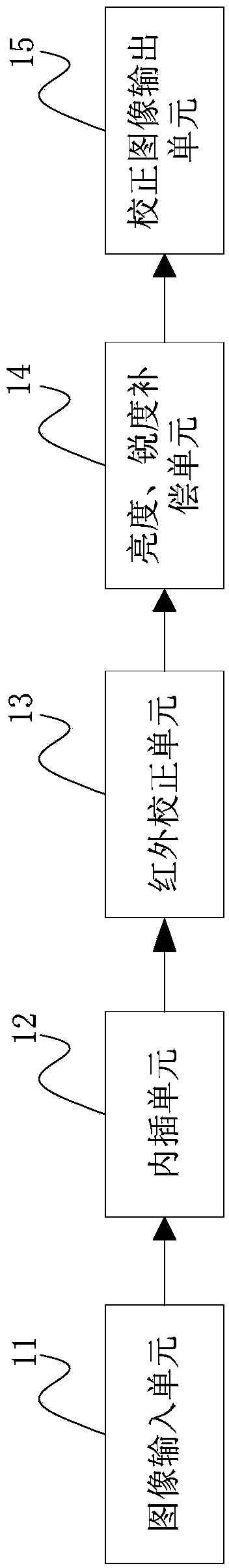
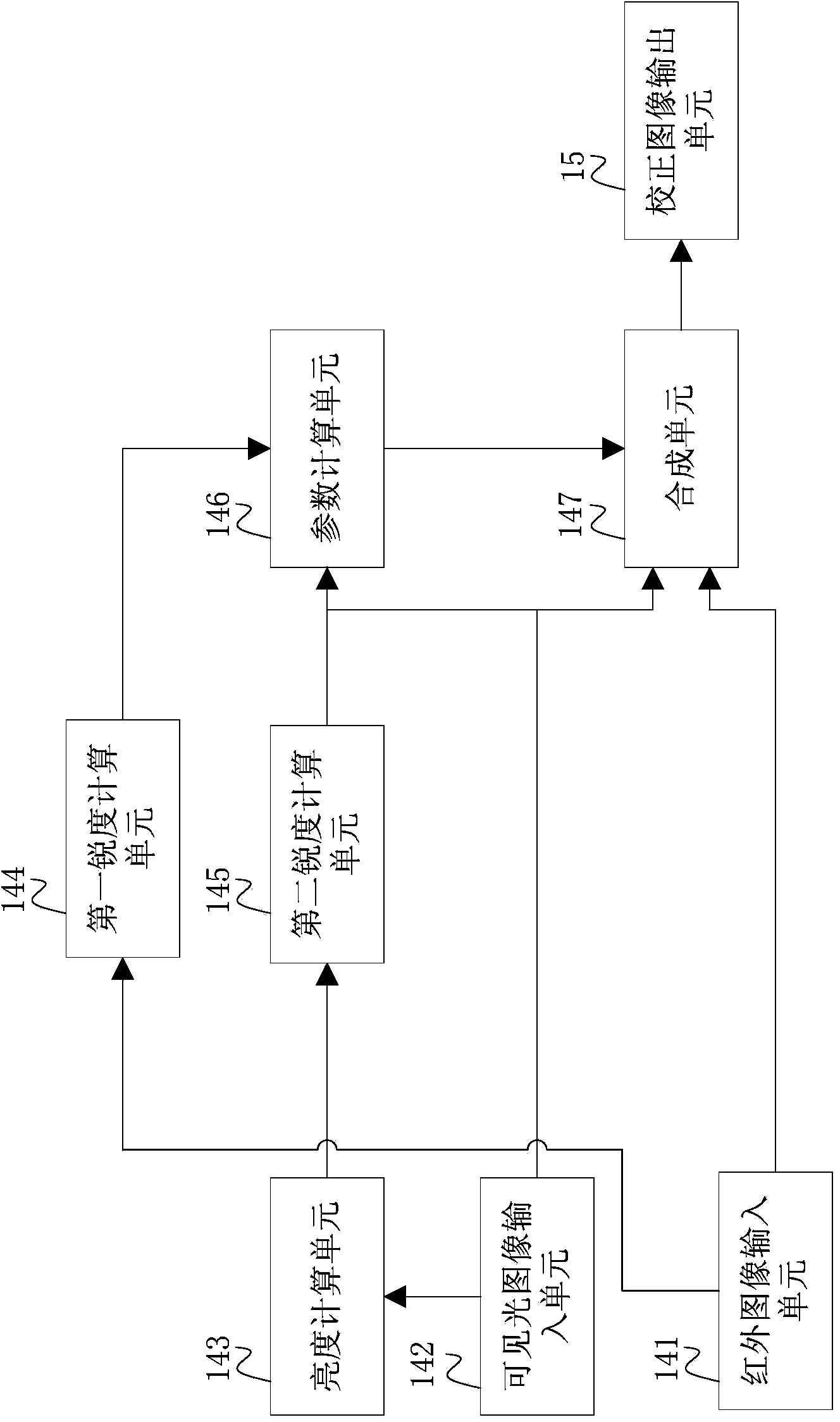
ActiveCN104079908ANo loss of sharpnessNo loss of colorTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImage signalAcutance
The invention discloses an infrared and visible light image signal processing method and an implementation device thereof. The method comprises the following steps that an infrared image and a visible light image corrected in an infrared mode are provided; a color feature value corresponding to each pixel in the visible light image is calculated; acutance information corresponding to each pixel in the visible light image is calculated by means of the corresponding color feature value; acutance information corresponding to each pixel in the infrared image is calculated; acutance correction parameters and brightness correction parameters of the visible light image and the infrared image are calculated; according to the acutance correction parameters and the brightness correction parameters which are obtained through calculation, one-by-one pixel weighted combination is conducted on a certain color space. Due to the fact that acutance analysis, color analysis and brightness analysis are conducted on the infrared image and the visible light image corrected in the infrared mode, the infrared image and the visible light image are dynamically fused into one image, and the brightness, colors and acutance of the output image have no loss.
Owner:SHANGHAI FULLHAN MICROELECTRONICS
Iris recognizing preprocessing method based on grey level information
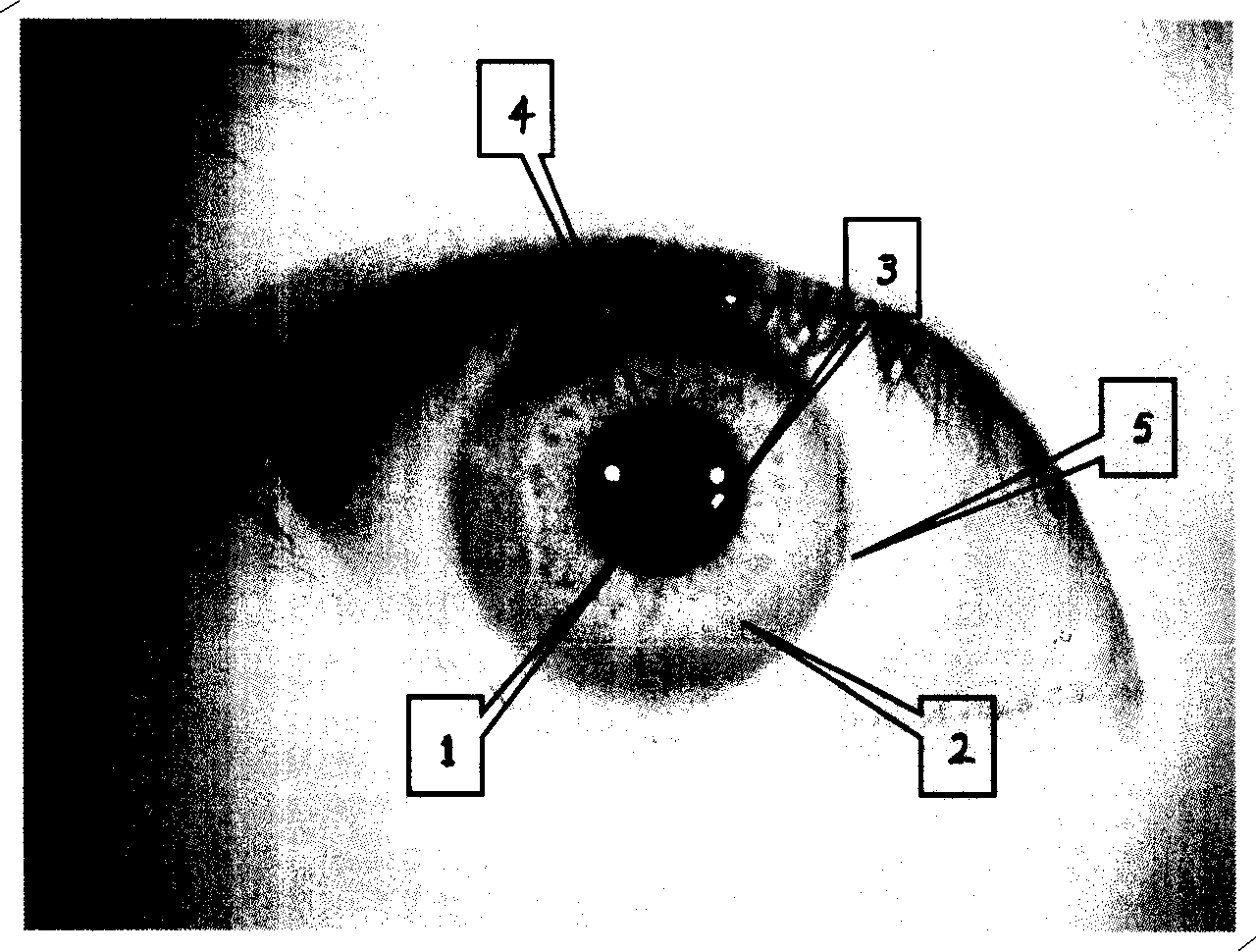
InactiveCN101201893AHigh positioning accuracyImprove versatilityCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionGray level
The invention provides a pretreatment method of iris images based on gray information. A rough circle center (xo, yo) of a pupil is located through binary, mathematical morphology, gray projection and other operations, the point, which has a gray value larger than T and the shortest distance to the (xo, yo), is searched at a plurality of lines close to the (xo, yo) from the center to the two sides as a pupil boundary point; the accurate circle center and the radius of the pupil can be located through curve fitting; the gray level first difference of the lines where the searched pixel points lie is calculated and the point with the largest value of the sum of the level first difference is searched in the range of places where iris external boundary point possibly appears and taken as the iris external boundary point; the accurate circle center and radius of the iris external boundary is obtained after curve fitting. The quality of iris image is judged through calculating point sharpness and number of effective pixel points according to the normalized image. The pretreatment method of iris images of the invention not only can decrease the time needed by repeated iteration during location, but also can judge the quality of iris image accurately and quickly according to the extracted iris image.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA ZHONGSHAN INST
Adjusting the sharpness of a digital image
InactiveUS20140086486A1Enhance the imageAutomatic controlImage enhancementImage analysisTyping ClassificationImage segmentation
The sharpness of a digital image is adjusted according to defined aim subject and background sharpness levels. An image segmentation process is used to segment an input digital image into a subject region and a background region. The subject and background regions are analyzed to determine corresponding subject and background sharpness levels. An enhanced digital image is formed wherein the sharpness of the subject region is adjusted responsive to the subject sharpness level and the aim subject sharpness level, and the sharpness of the background region is adjusted responsive to the background sharpness level and the aim background sharpness level. In some embodiments, the input digital image is analyzed to determined a scene type classification and the aim subject and background sharpness levels are defined in accordance with the determined scene type classification.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Circular preferential hyperacuity perimetry video game to monitor macular and retinal diseases
Systems and methods for providing a video game to map macular visual acuity comprising a test where a fixation point is ensured by brief simultaneous presentation of central and pericentral targets. The game may be implemented on a hardware platform including a video display, a user input device, and a video camera. The camera is used to monitor ambient light level and the distance between the device and the eyes of the test subject. The game serves as a macular acuity perimeter that produces a map of the acuity of an eye that may be compared with normative data. The type of acuity tested is preferably Vernier acuity, but resolution acuity can also be tested. The test results are transmitted to a health care professional by telecommunications means to facilitate the diagnosis or monitoring of age-related macular degeneration or other relevant eye diseases.
Owner:GOBIQUITY INC
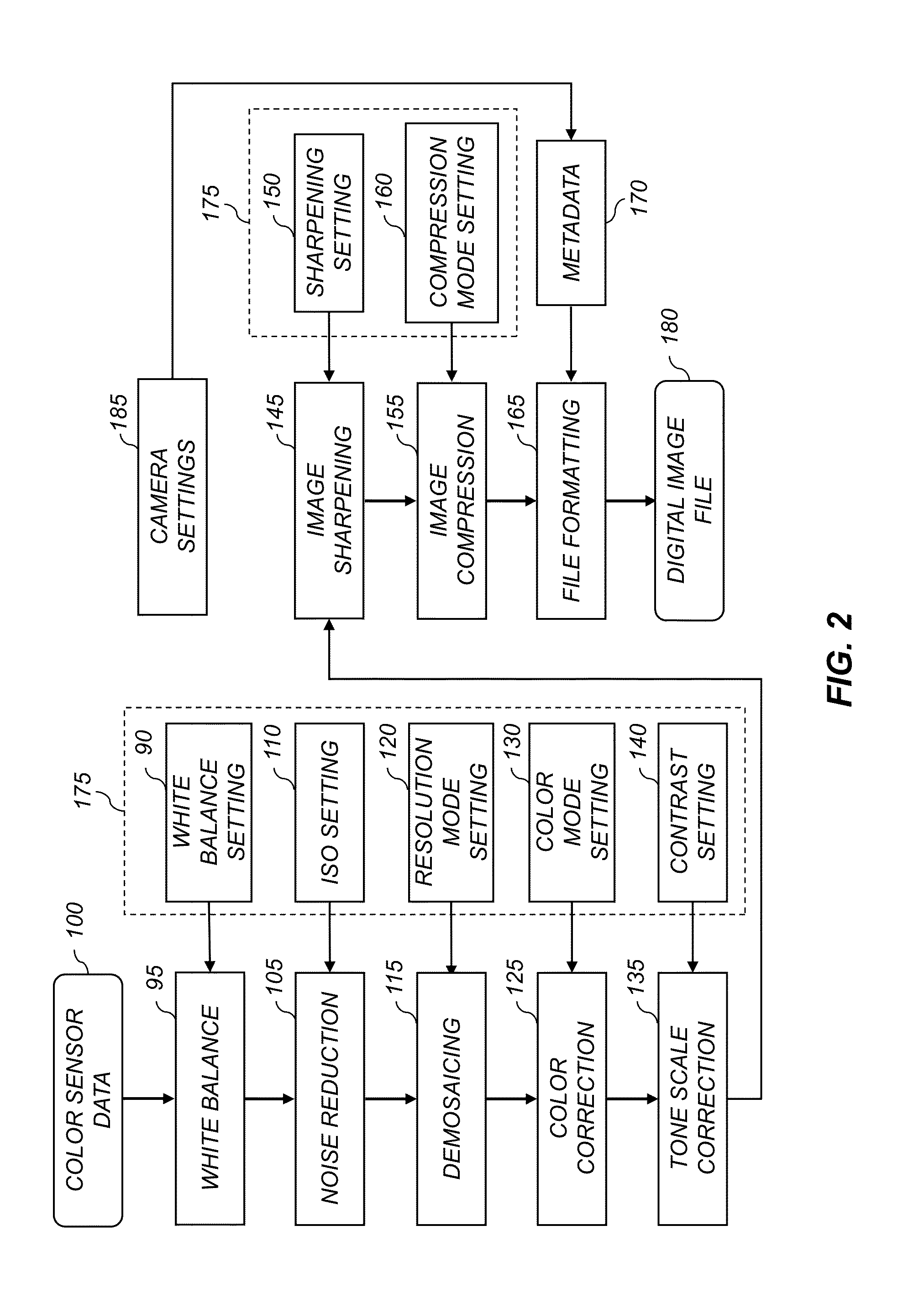
Image sharpening with region edge sharpness correction
InactiveUS20050025383A1Improved image sharpening processResultant imageImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityEdge maps
A system and process for improving image quality is described. The process uses an edge map to smooth colors based on at least one of how close a pixel is to an edge and the strength of the edge.
Owner:CELARTEM TECH
Three-dimensional photographic device
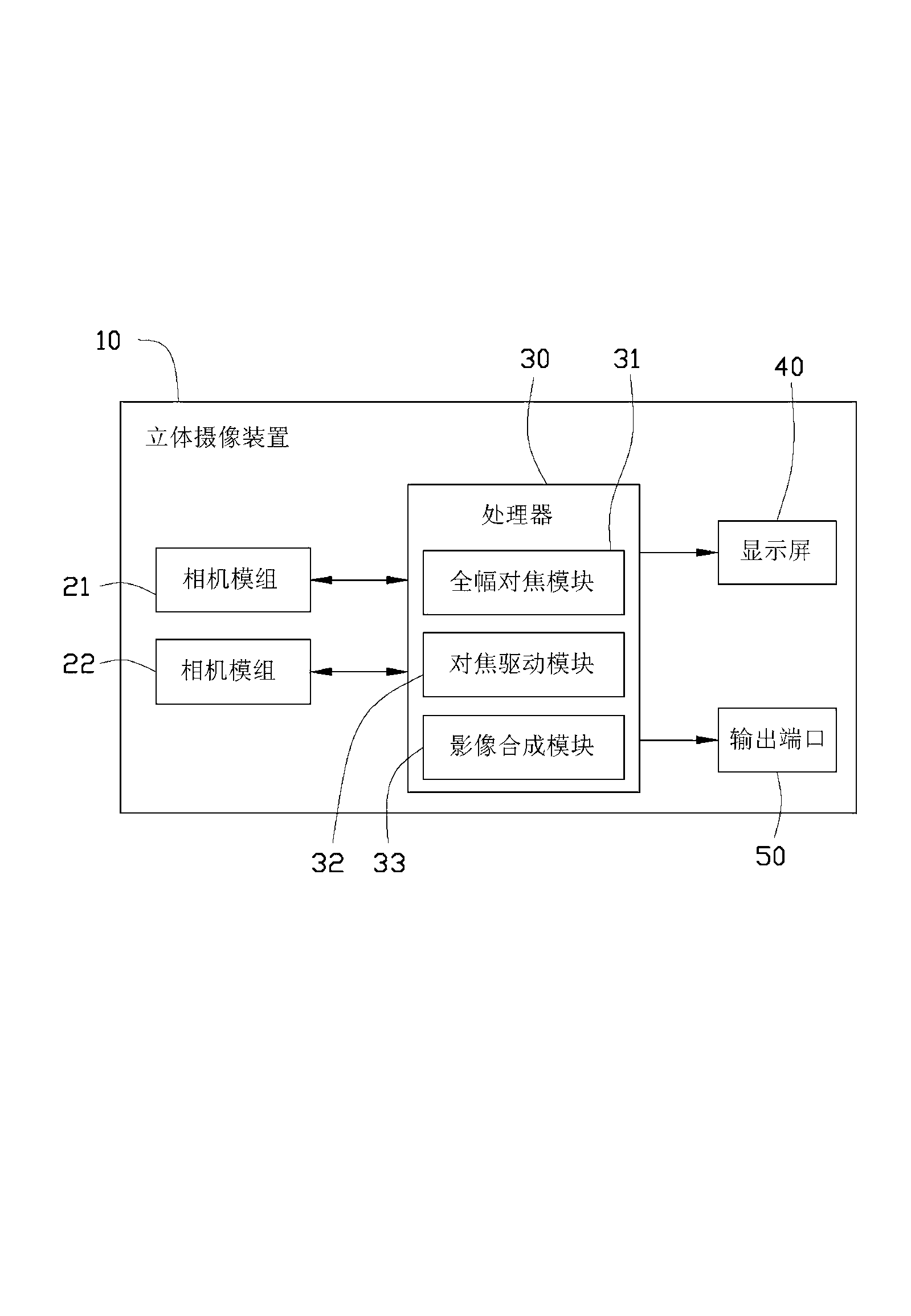
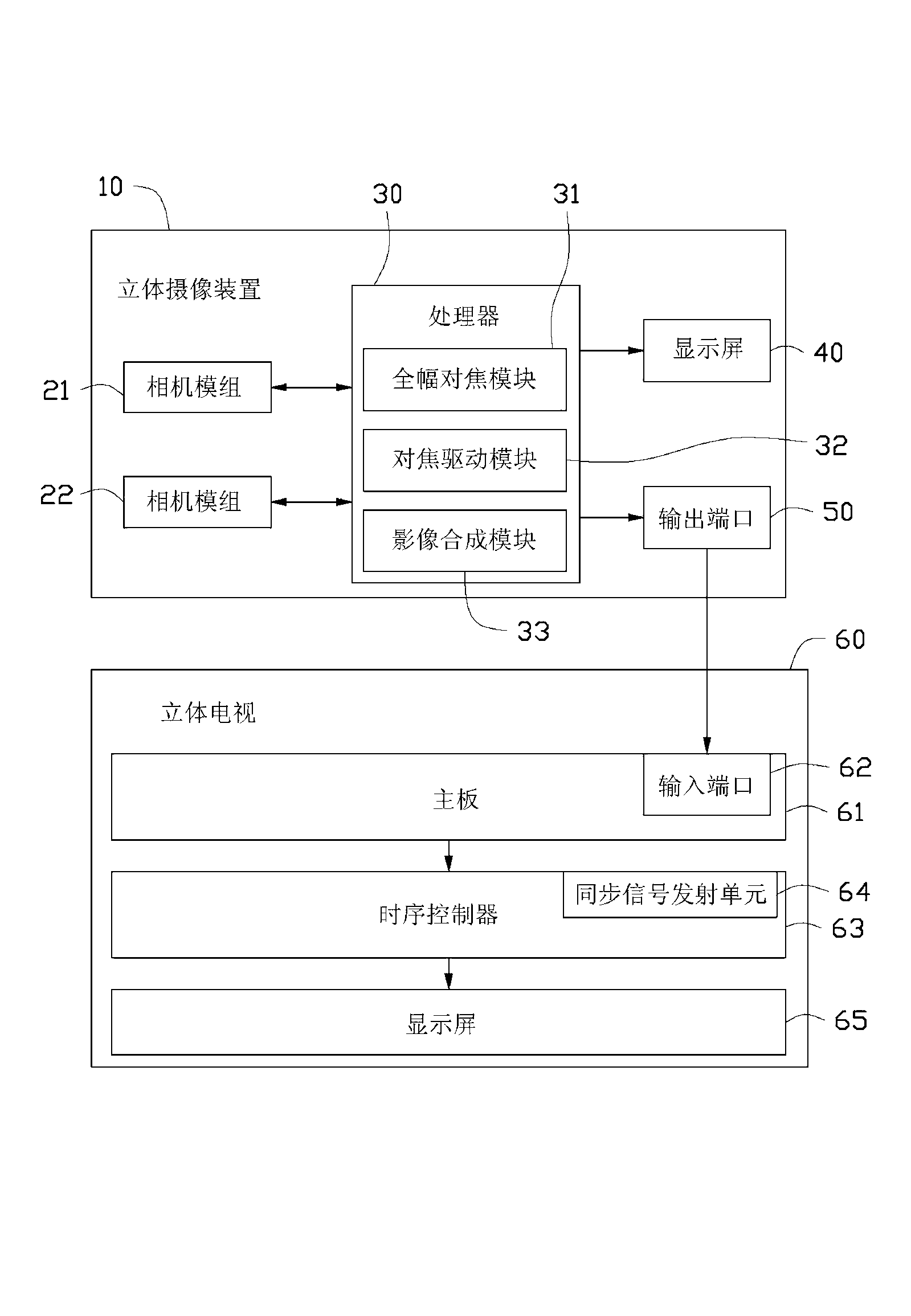
The invention provides a three-dimensional photographic device. The three-dimensional photographic device comprises two camera modules and a processor, wherein each camera module comprises a camera lens unit and an image sensor, the camera lens unit utilizes a shape memory alloy element as a variable focal length actuator, and the image sensor is used for forming images with at least two colors. The processor comprises a full width focusing module, a focusing driving module and an image synthesis module, the full width focusing module is used for judging an object distance according to acutance of colors, judging whether the object distance is larger than a certain preset distance or not, when the object distance is larger than the preset distance, the images are conducted sharpening processing and the images become distinct, otherwise a control signal is sent to the focusing driving module, the camera modules are driven to change a focal distance to directly acquire distinct images after the focusing driving module receives the control signal, and the image synthesis module is used for utilizing the distinct images to synthesize three-dimension images. The three-dimensional photographic device utilizes a full width focusing technology, and therefore the distinct images can be further acquired in a close distance.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Lens system and method with antireflective coating
ActiveUS7717557B2Low costImproves perceived clarity of transmitted imageOptical partsOptical elementsColor shiftHue
An improved method is provided for applying an antireflective high contrast coating to a lens, as well as a lens system made with said method. By coating the lenses with a mixture of an oxide and fluoride, the transmission of undesirable visible light wavelengths is reduced, as is the reflection of undesirable light. This combination not only increases perceived sharpness and detail associated with viewing objects through the lenses, but also reduces undesirable reflected glare. Utilization of increased vacuum during the coating process reduces problems of humidity associated with plastic lenses. The combination of oxide and fluoride is controlled to reduce colored tint or hue in the resulting lenses. By imparting little to no color hue to the lenses, the lenses virtually eliminate any undesired color shift associated with prior art lenses.
Owner:MAUI JIM
Electronic camera having improved focus performance
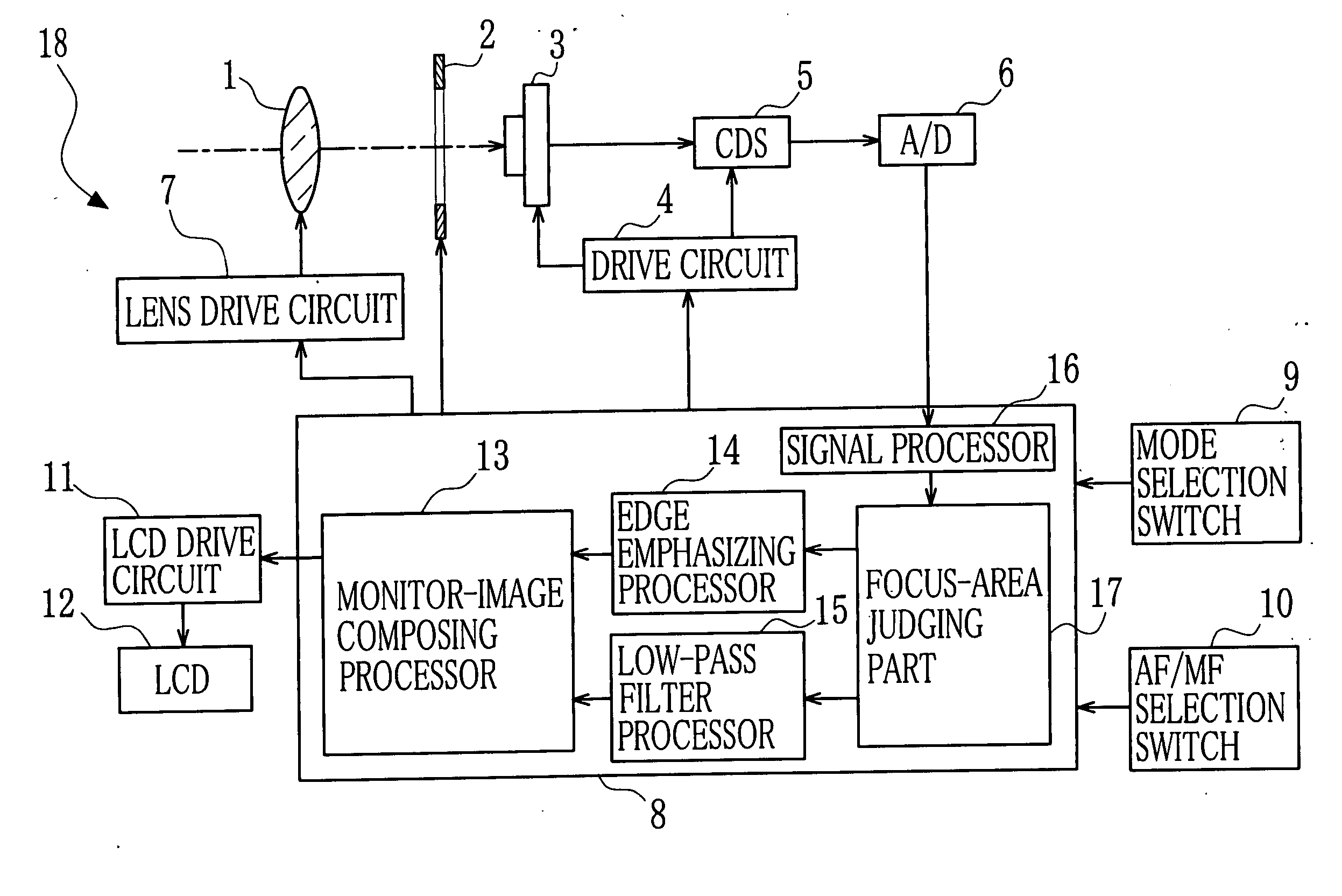
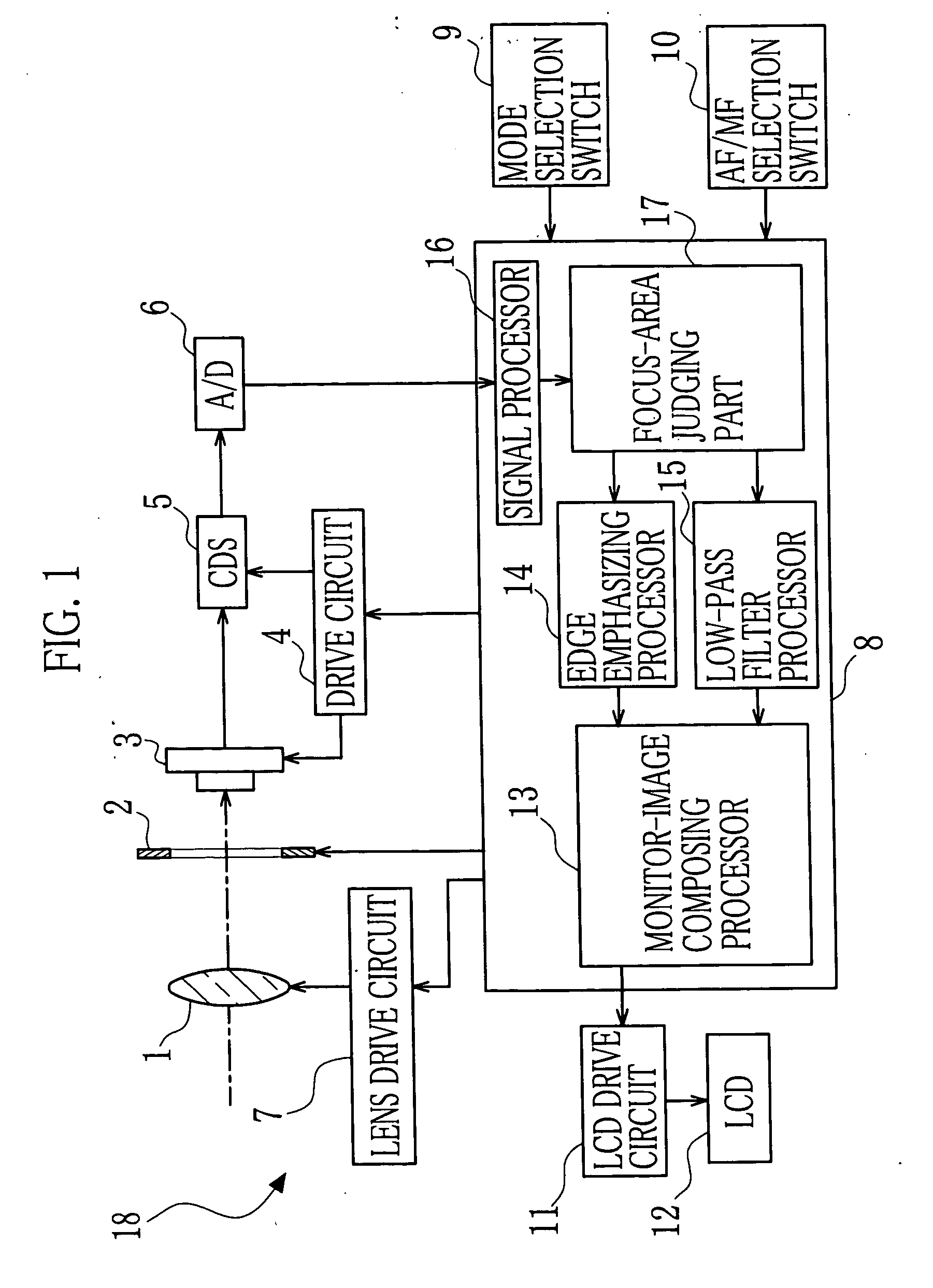
InactiveUS20070071432A1Easily focus changeEasy to adjustTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementREFLEX DECREASEAcutance
An image is divided into areas in accordance with degrees of focusing. As the divided areas, there are a focus area and a non-focus area. With respect to the non-focus area, the image thereof is processed so as to emphasize its blur. In contrast, with respect to the focus area, the image thereof is processed so as to emphasize its sharpness. The processed image is displayed on a monitor so that perspective is expressed like a single-lens reflex.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
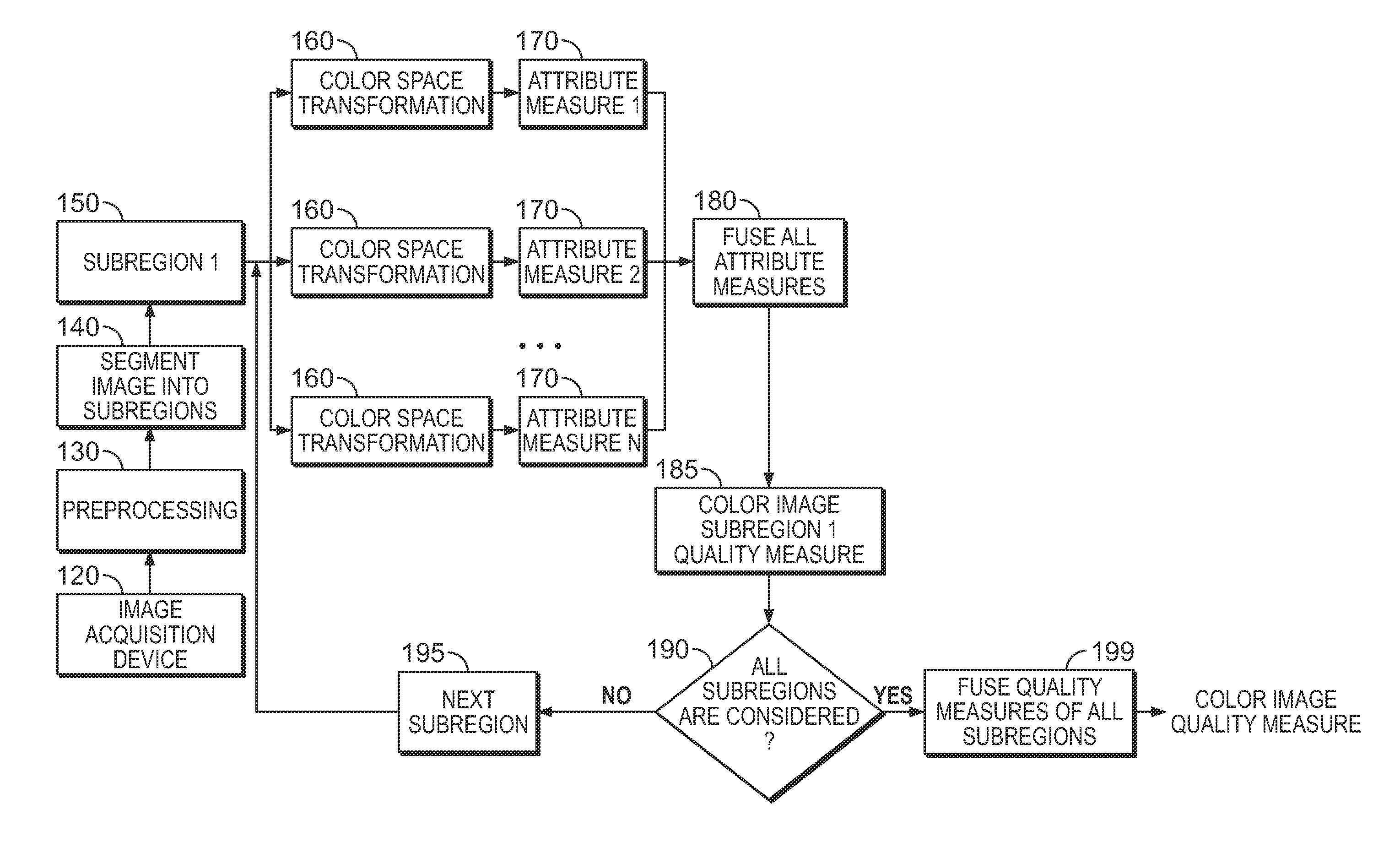
Systems and methods for image and video signal measurement
An image / video may be analyzed to determine quality of its attributes, including local, global and pixel colorfulness, sharpness, and contrast to obtain an image quality measure. Invented quality may be obtained for captured images or videos and compared to a database or reference value of quality measures to identify quality of products, component anomalies, and product matches.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV +1
Adjusting the sharpness of a digital image
InactiveUS8724919B2Enhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisTyping ClassificationImage segmentation
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
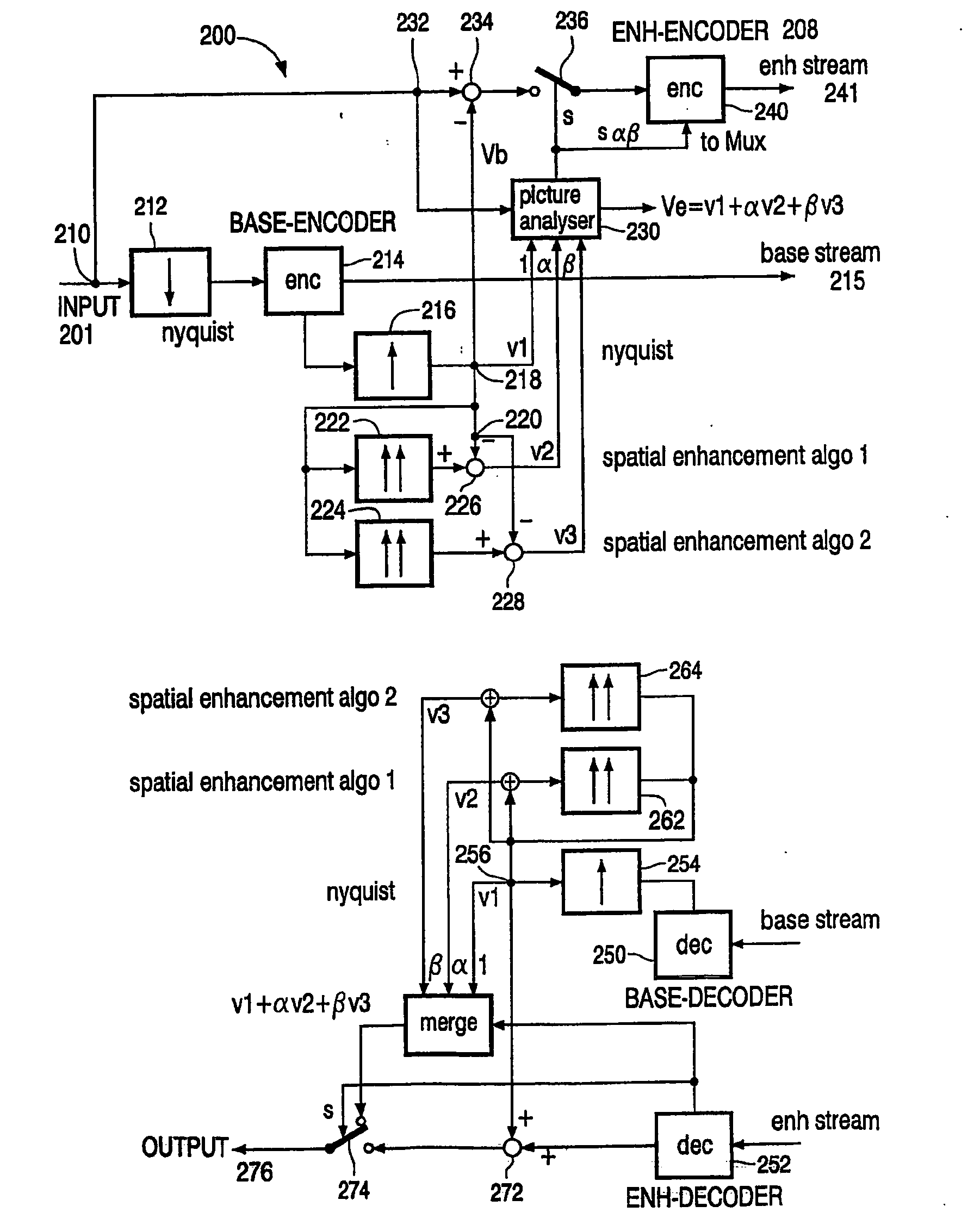
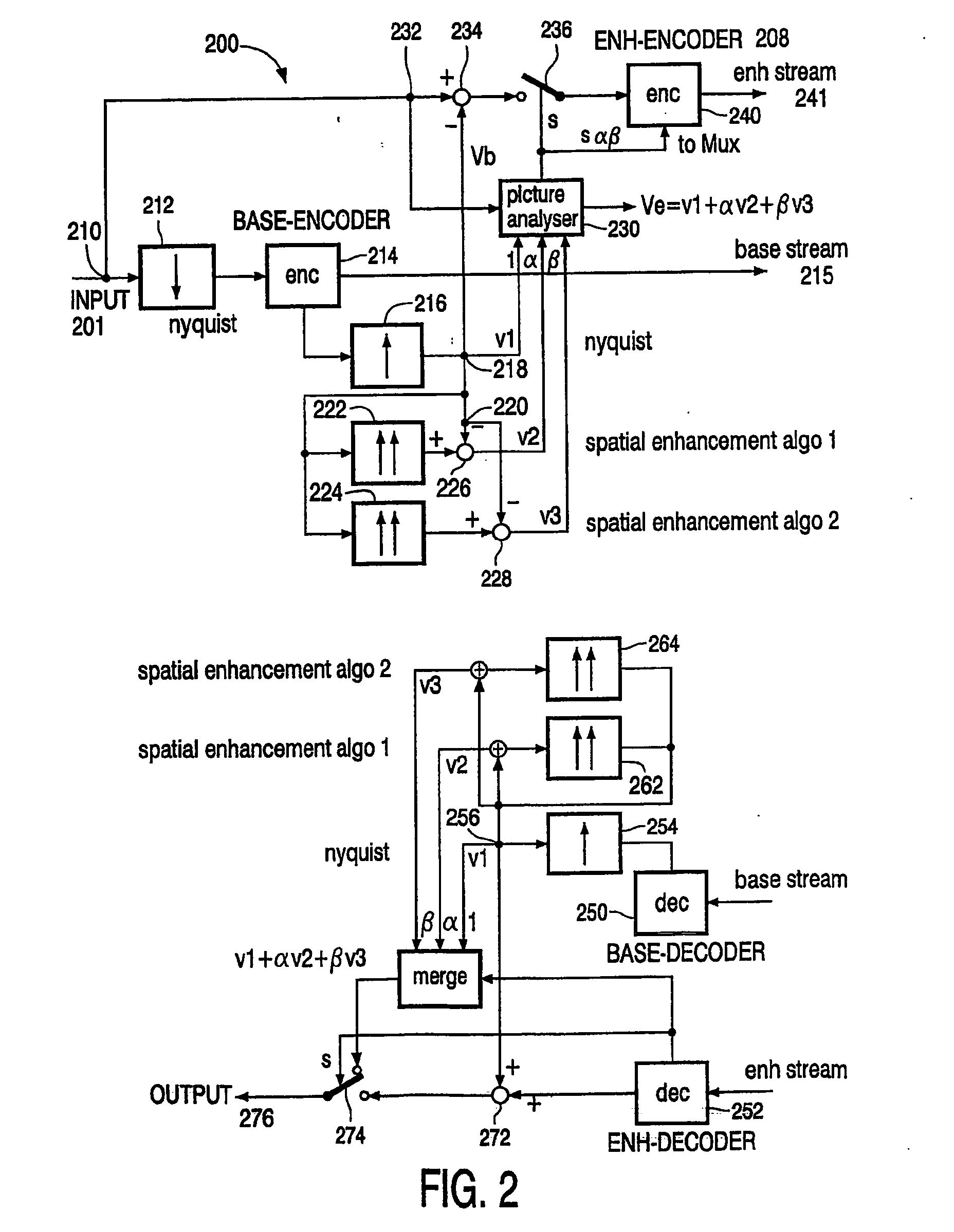
Spatial scalable compression scheme using spatial sharpness enhancement techniques
InactiveUS20050105814A1Enhanced video compressionOvercome deficienciesCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsPattern recognitionScalable compression
A video encoder / decoder with spatial scalable compression schemes using spatial sharpness enhancement techniques is disclosed. The video compression scheme introduces a number of various video enhancement techniques on the base layer. A picture analyzer is used to determine the best or the best mix of various video enhancement techniques. The picture analyzer compares the selected mix of video enhancement techniques with the original full resolution input signal to determine for which of the pixels or groups of pixels a residual enhancement layer is required. Parameters defining the selected mix of video enhancement techniques are transmitted to the decoder layer so the same mix of video enhancement techniques can be used in the decoder layer.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com