Patents
Literature
408results about How to "Automatic control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
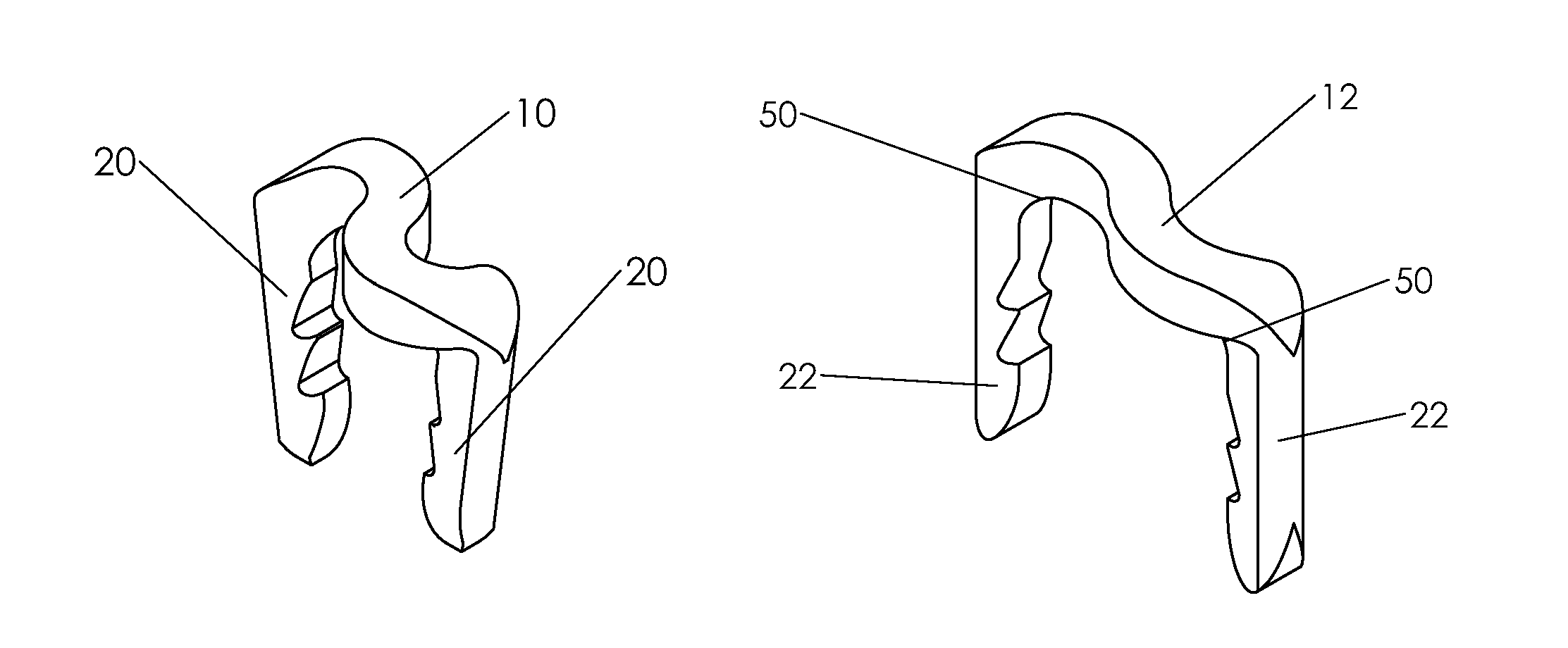
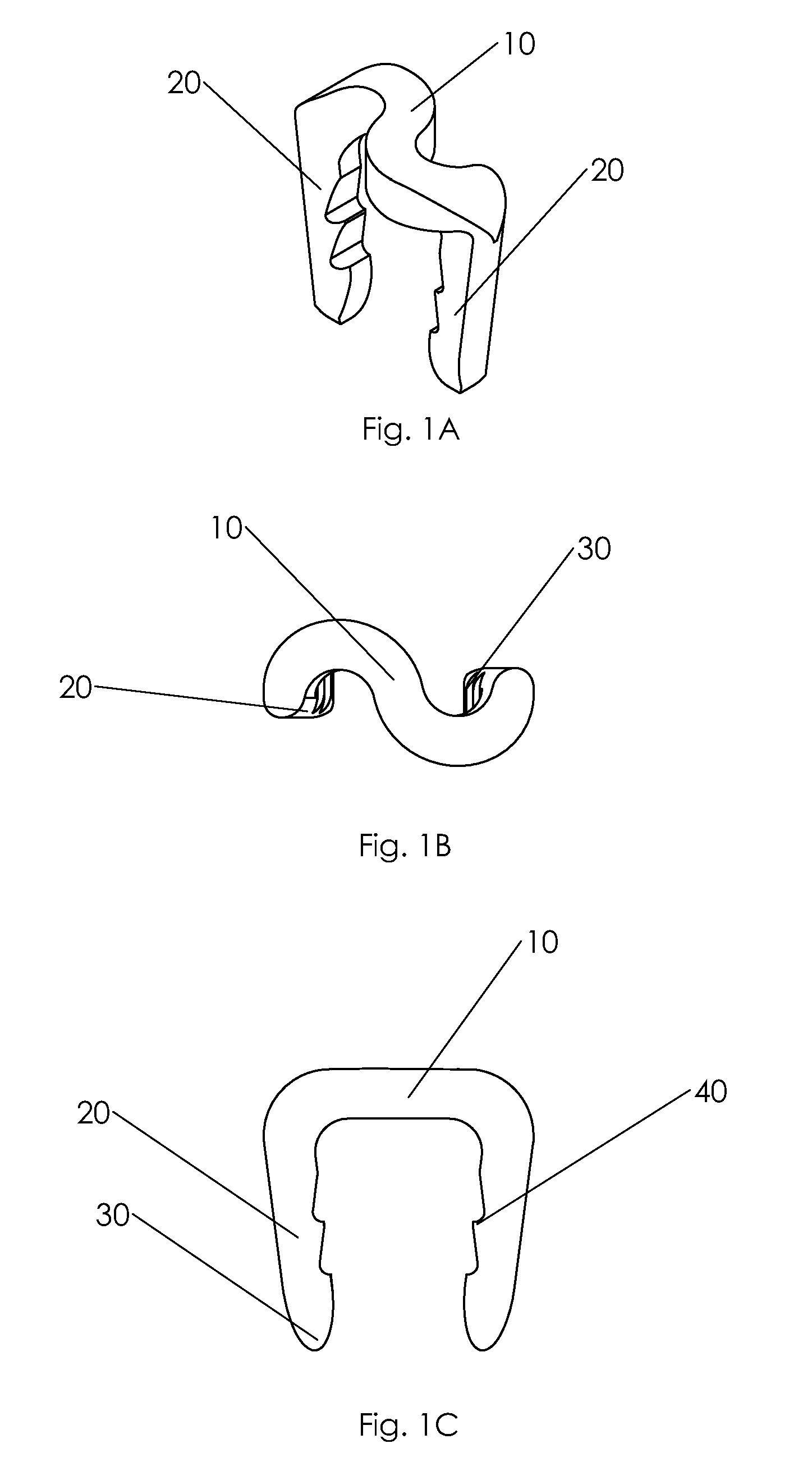
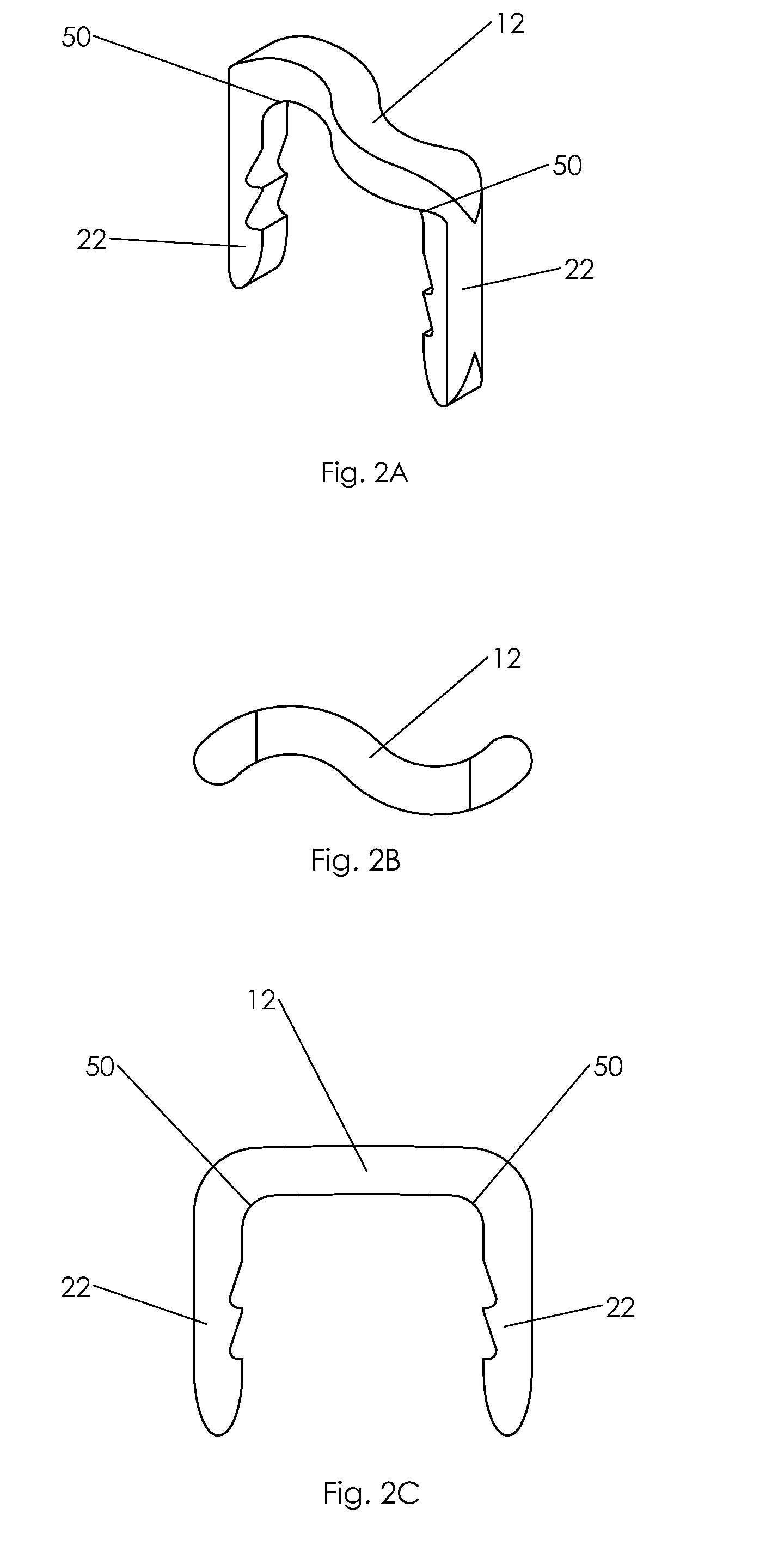
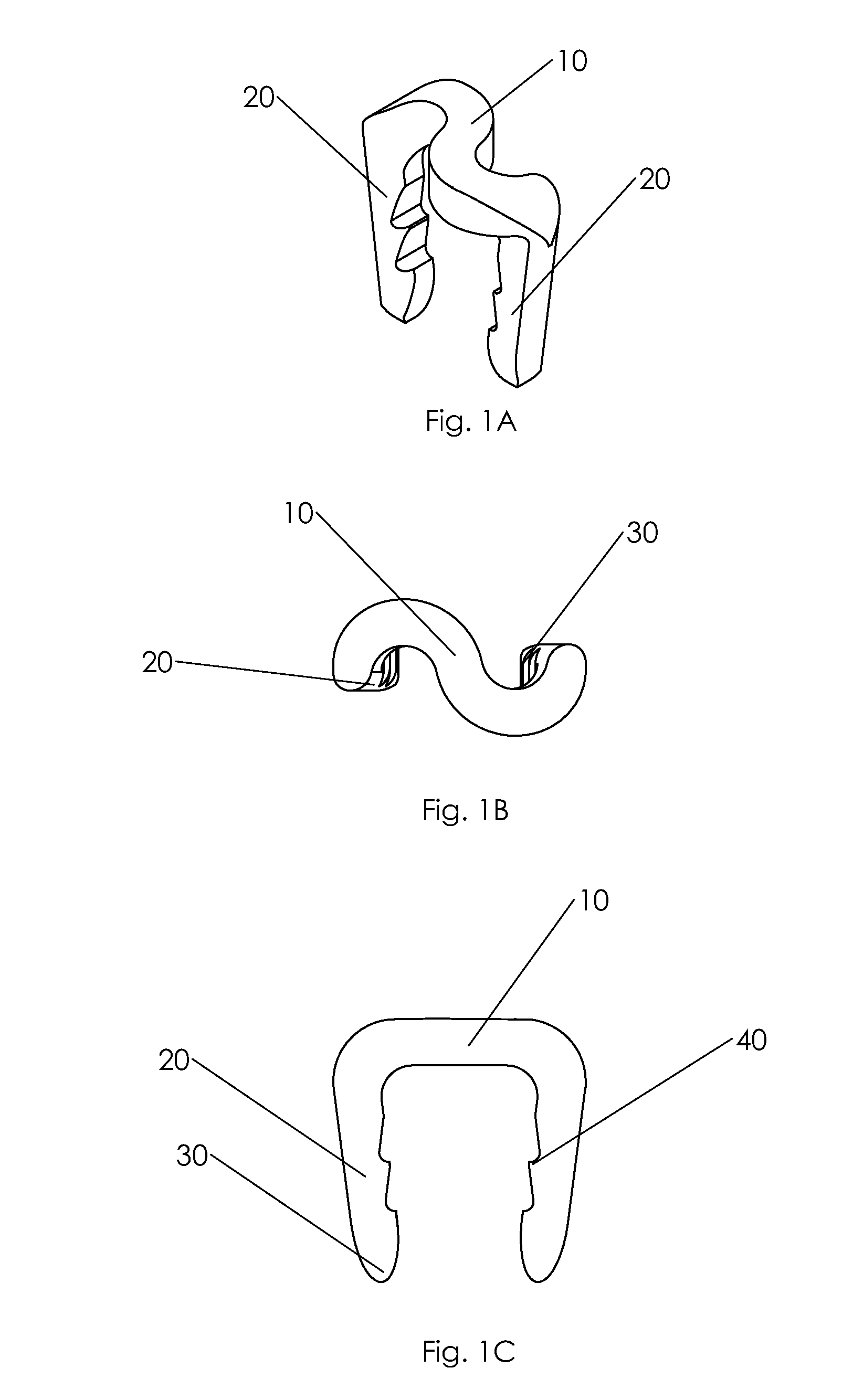
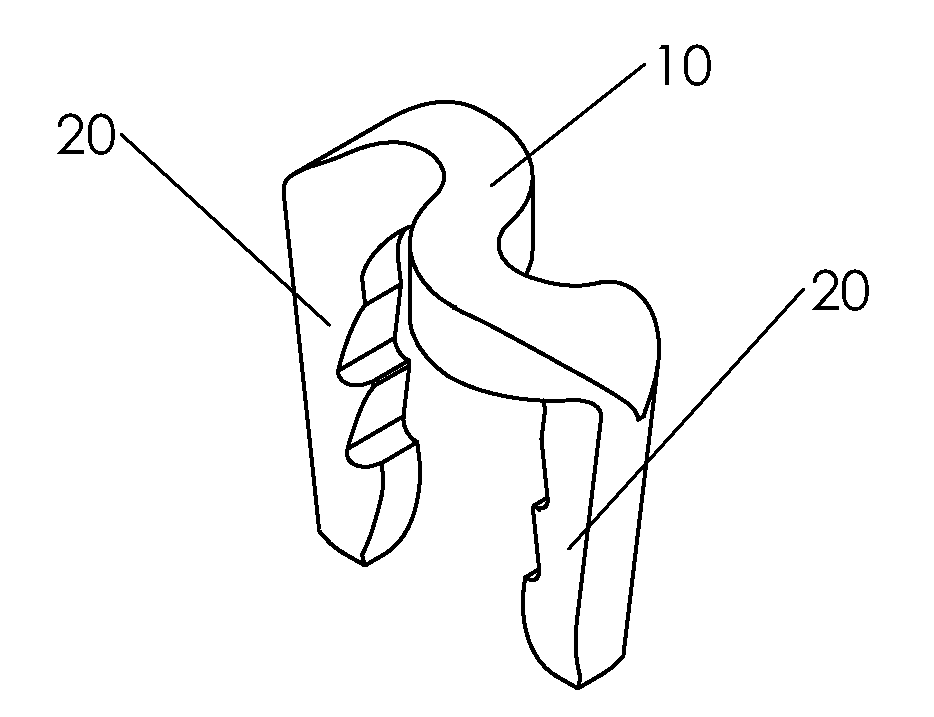
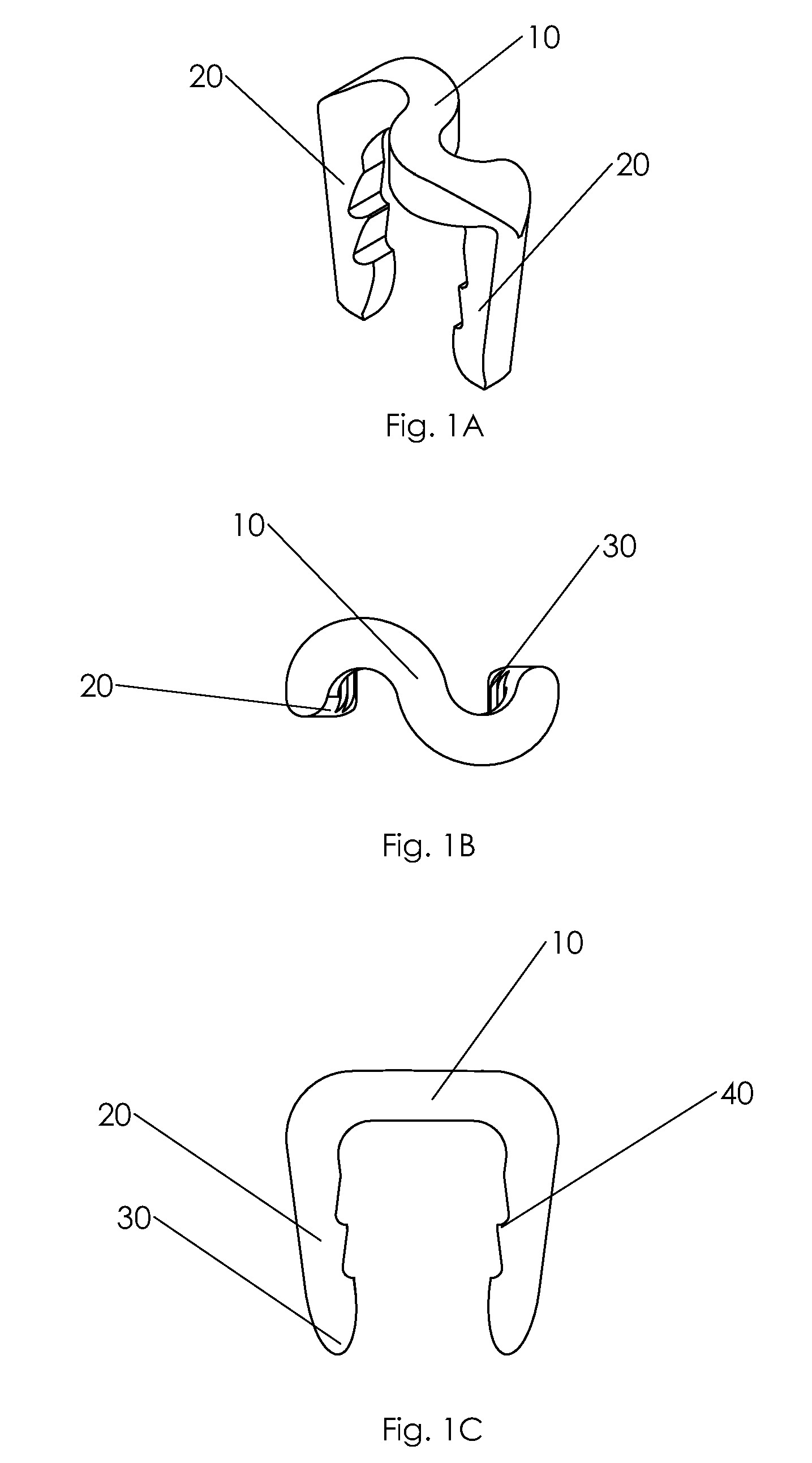
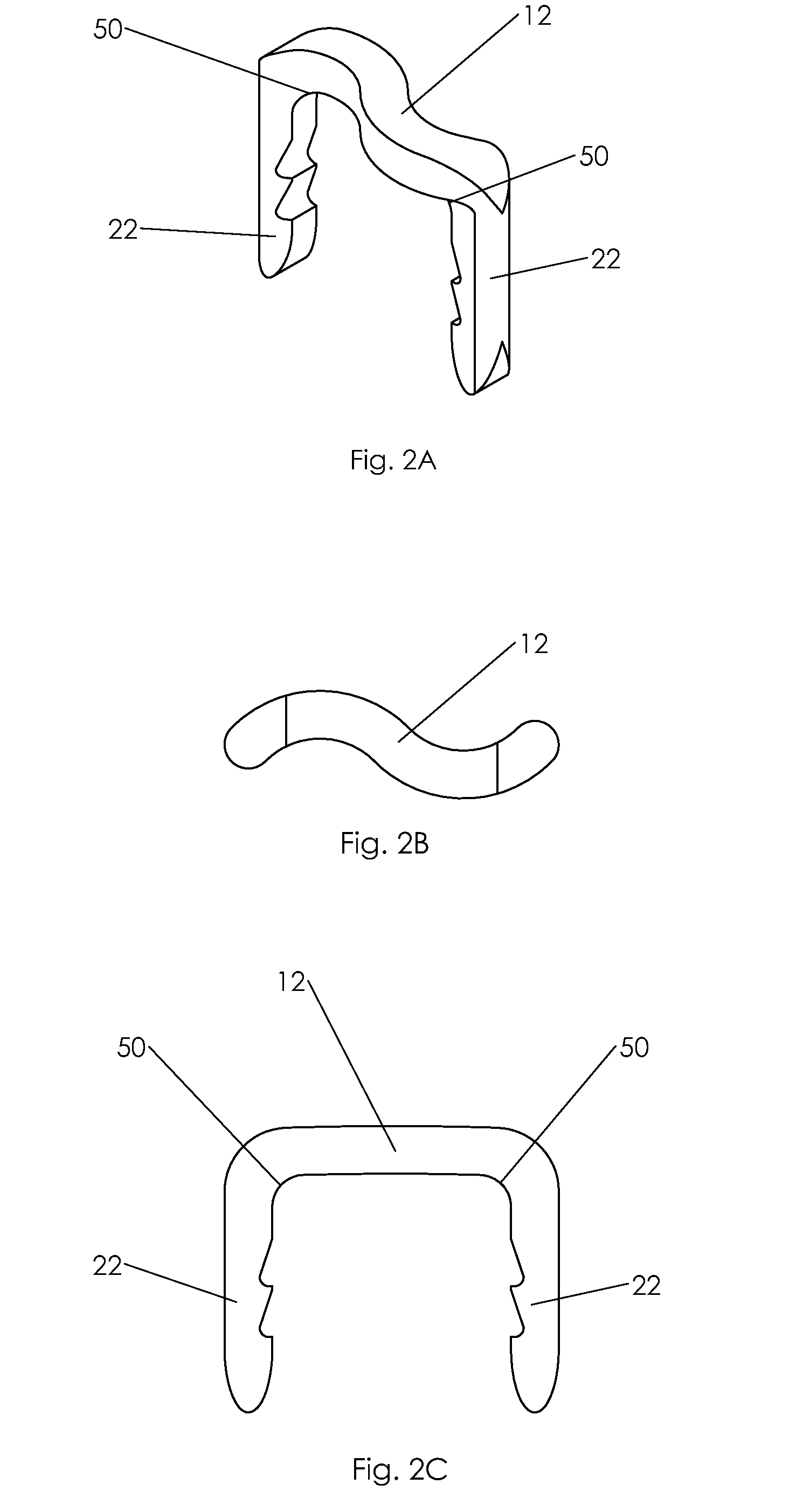
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS9017331B2Stores recoverable mechanical energyEasy to implantPinsInternal osteosythesisShape changeMechanical energy
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
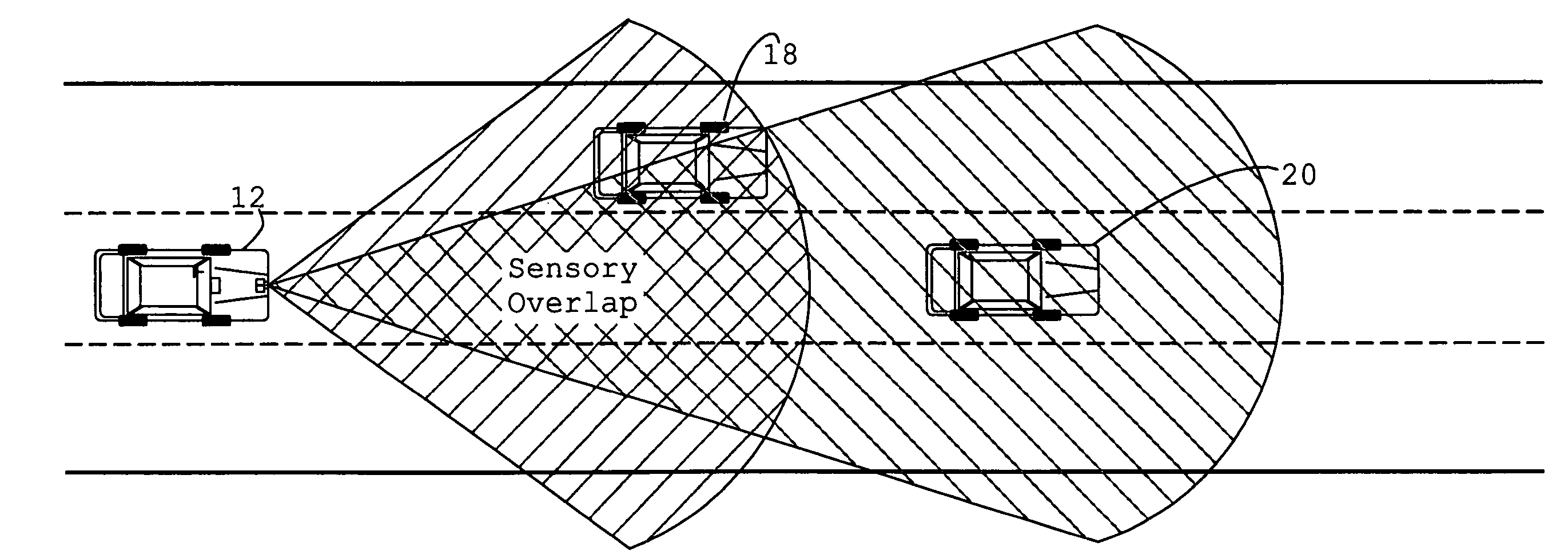
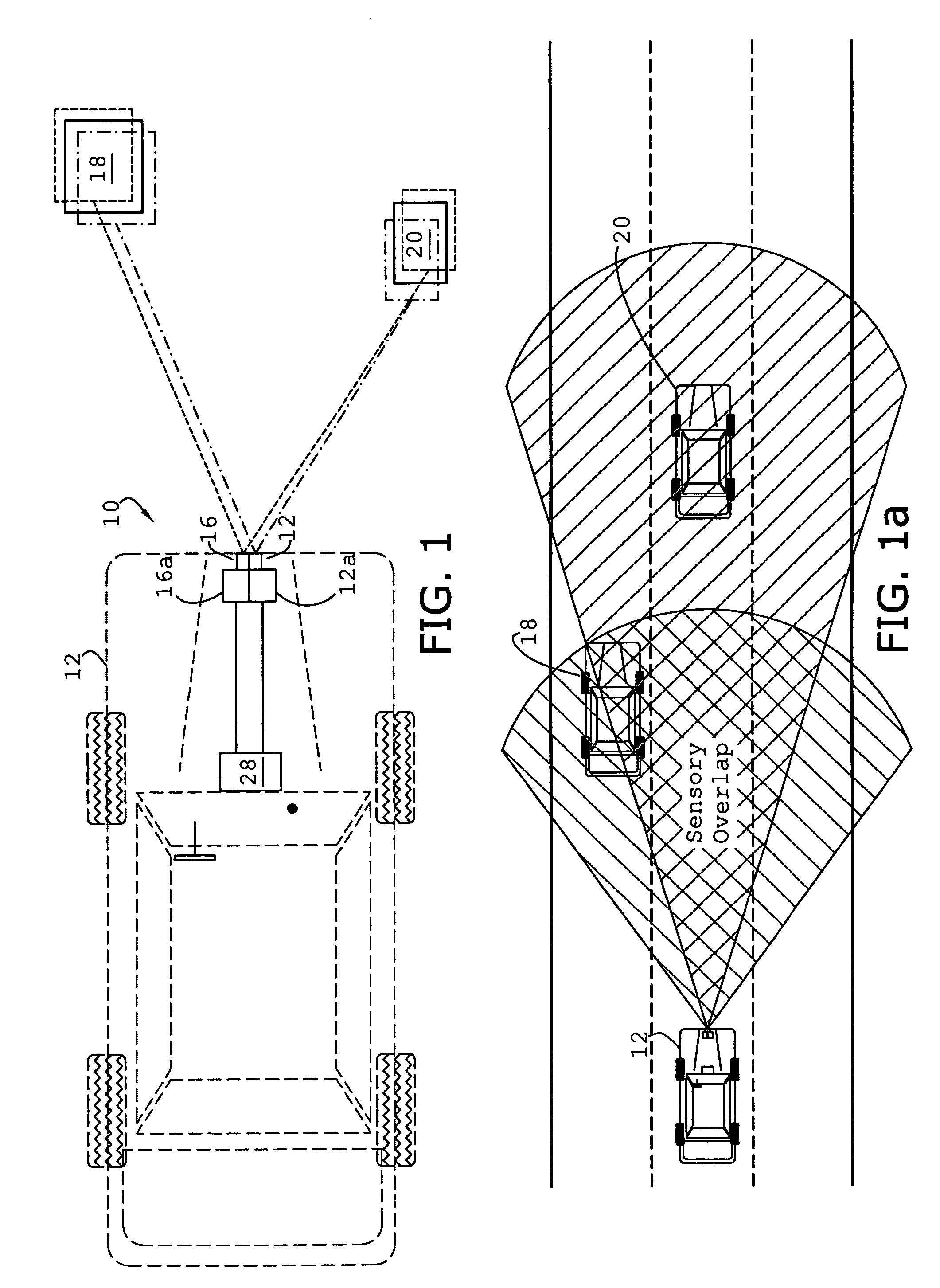
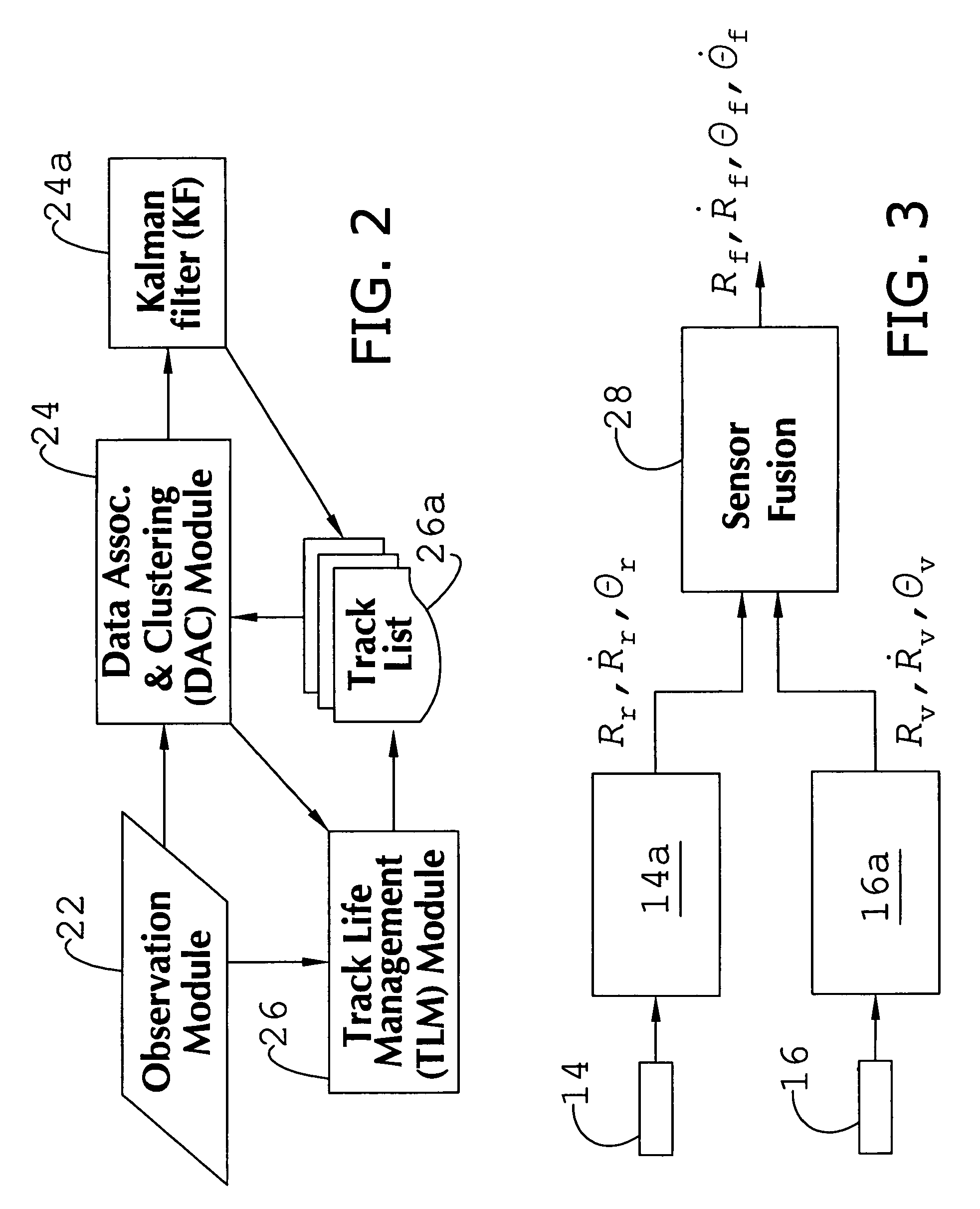
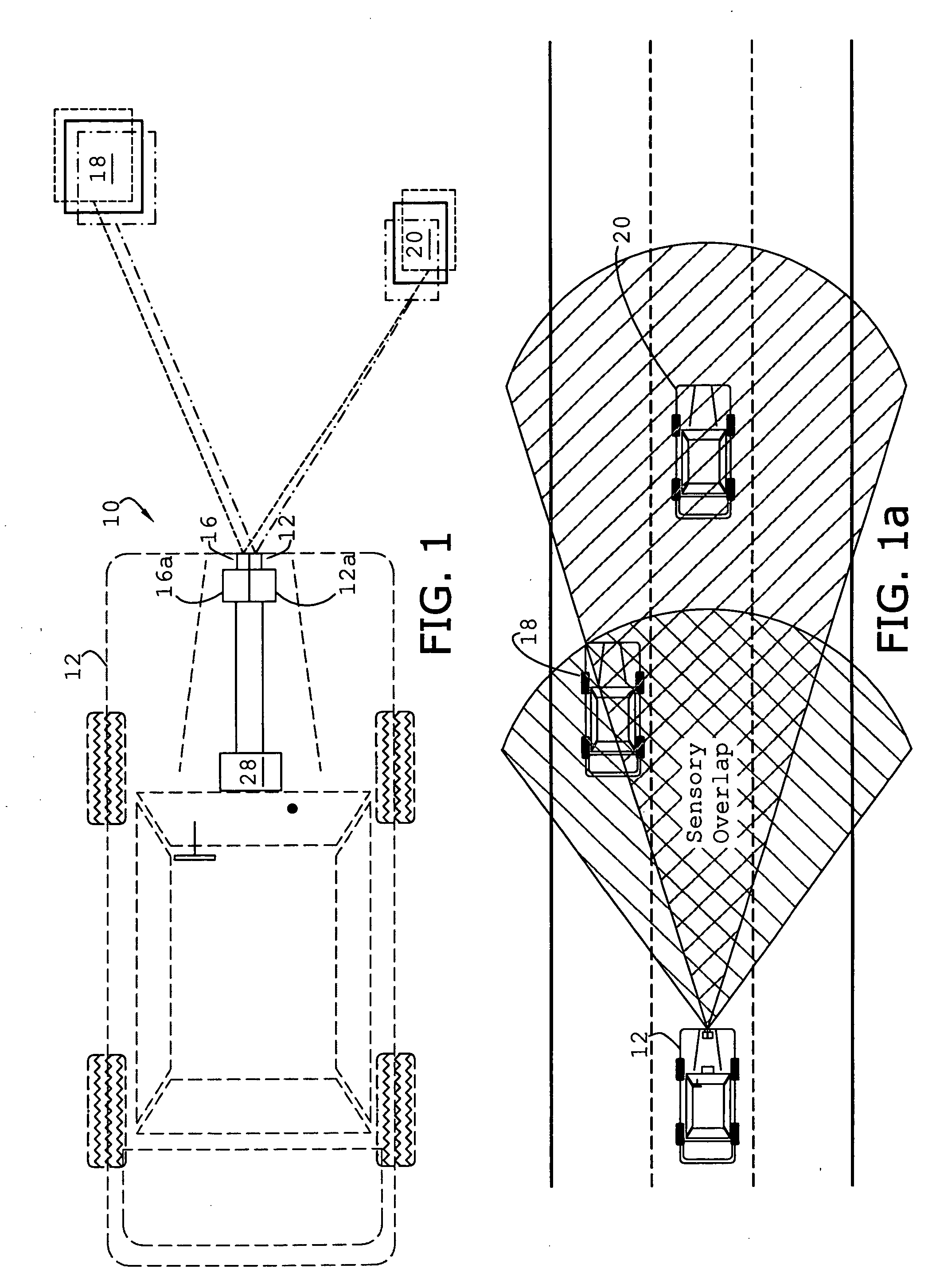
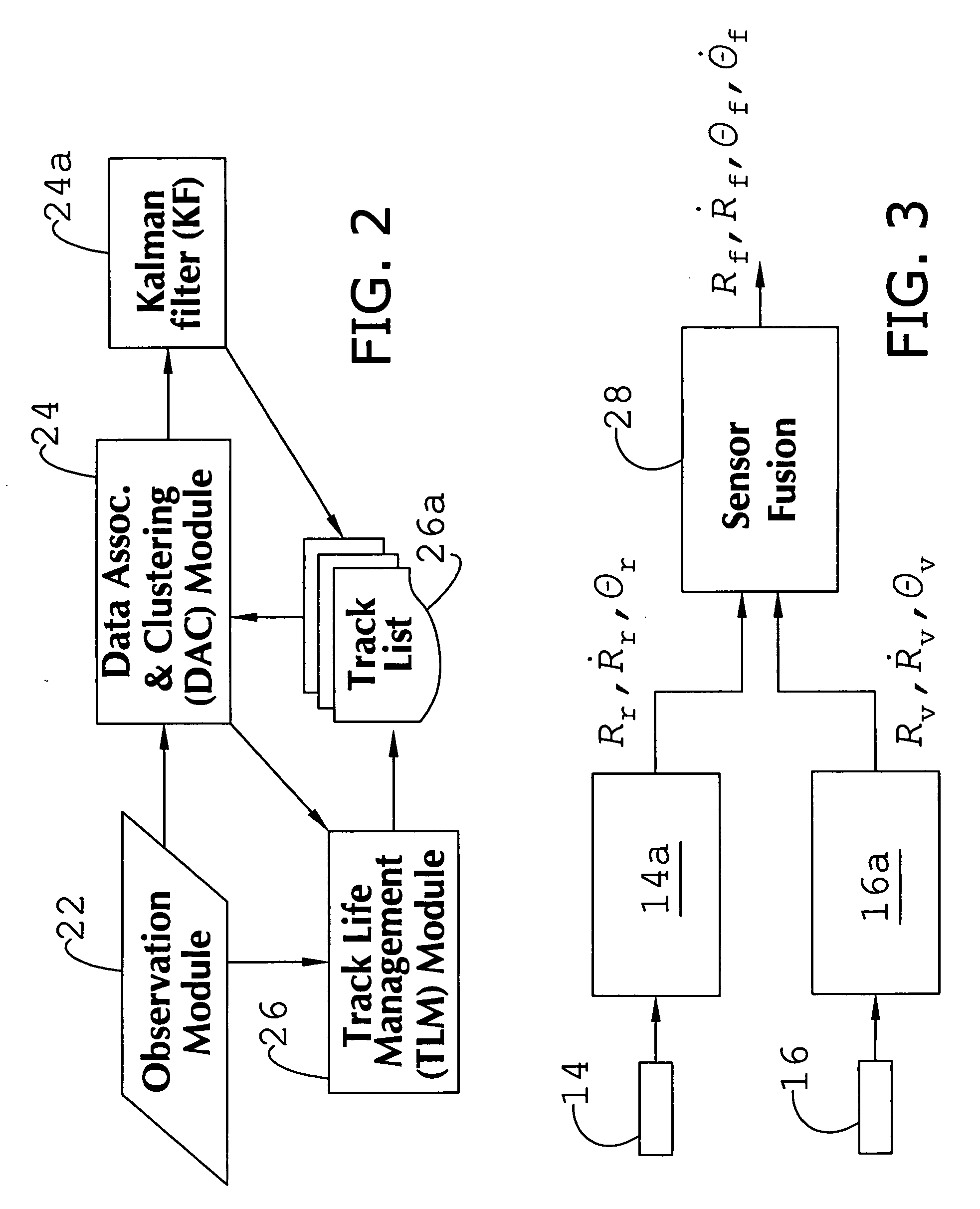
System and method of target tracking using sensor fusion
ActiveUS7460951B2Increasing precision and certaintyShorten the timeInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsSensor fusionEngineering
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
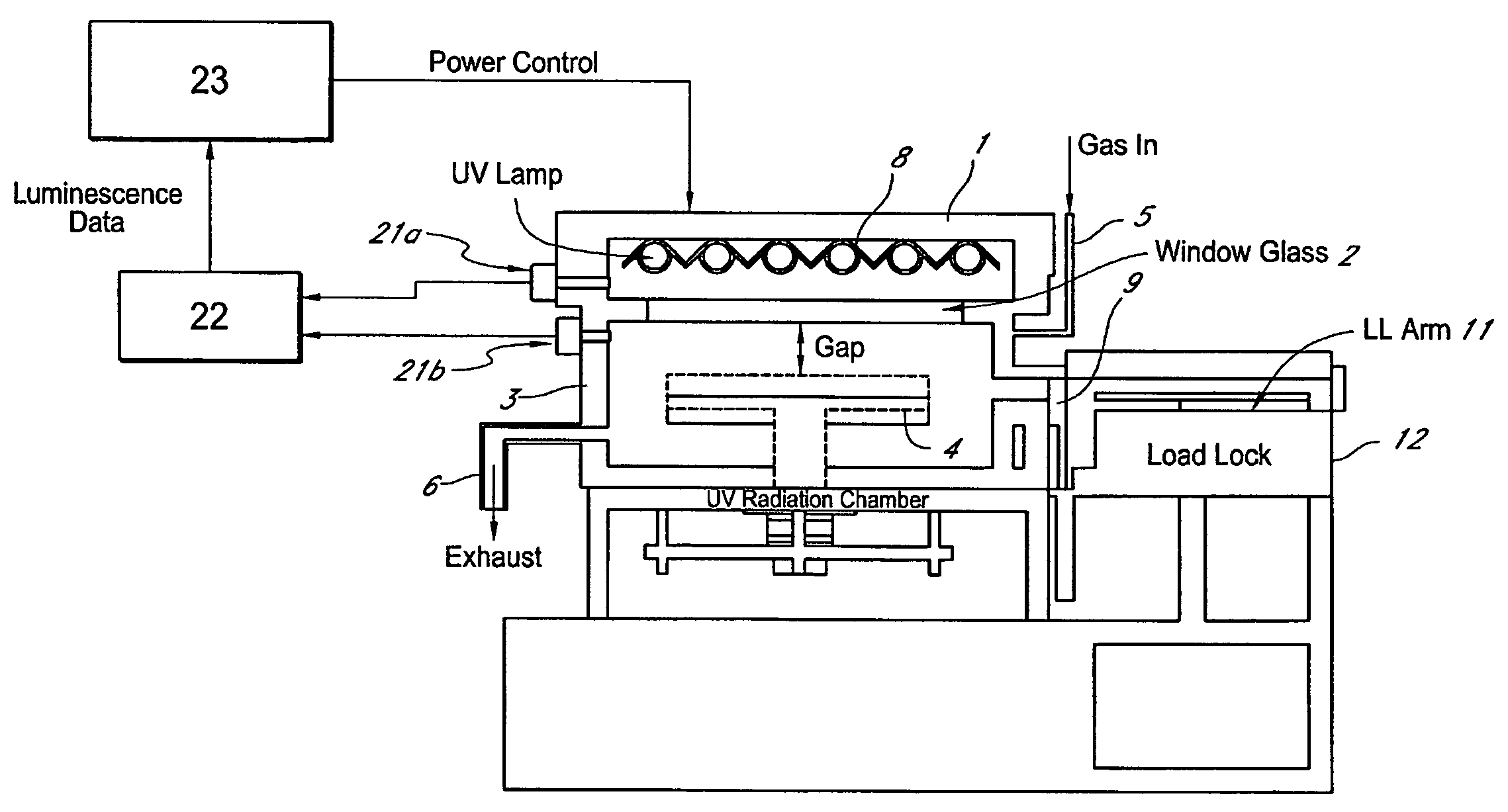
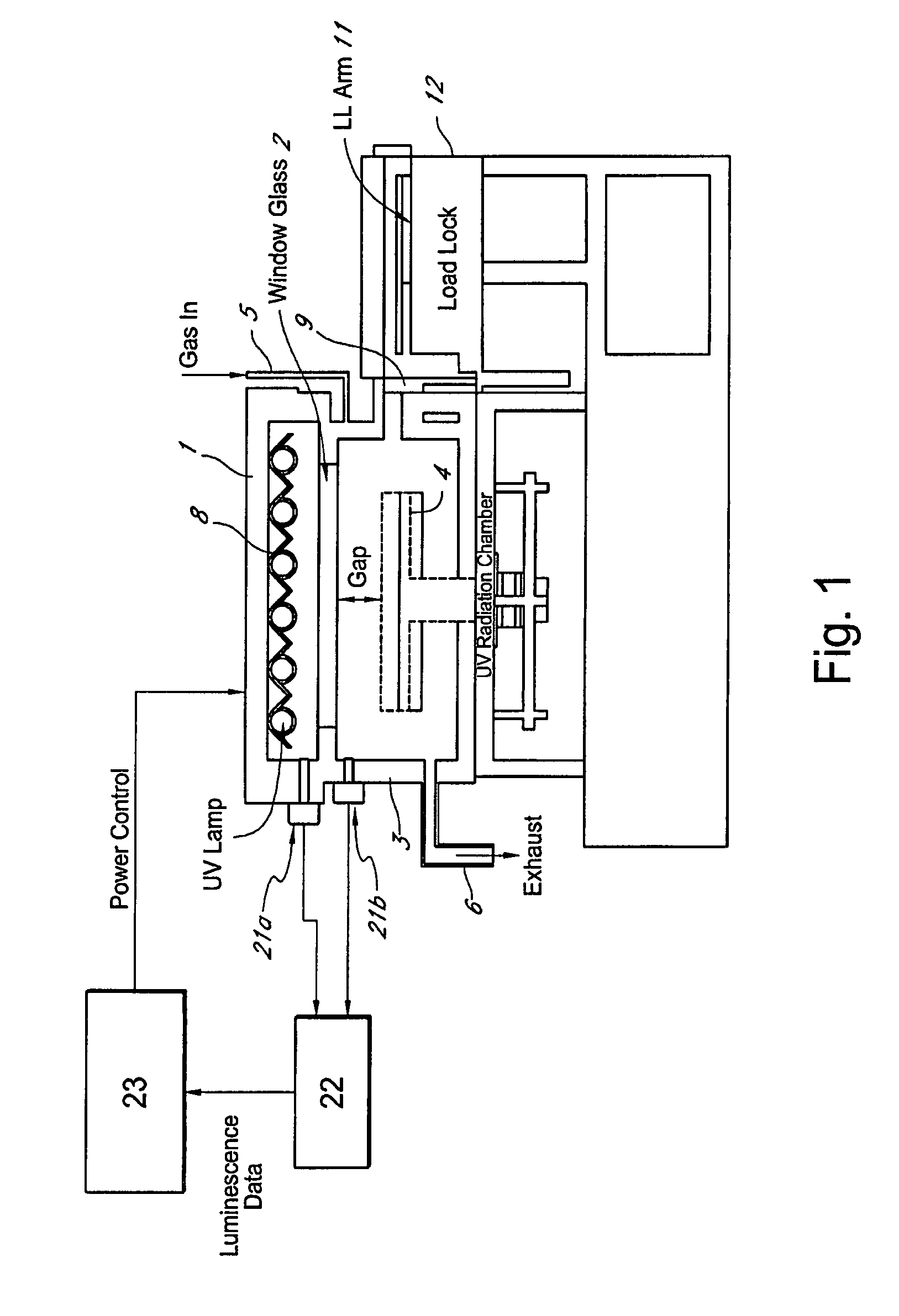
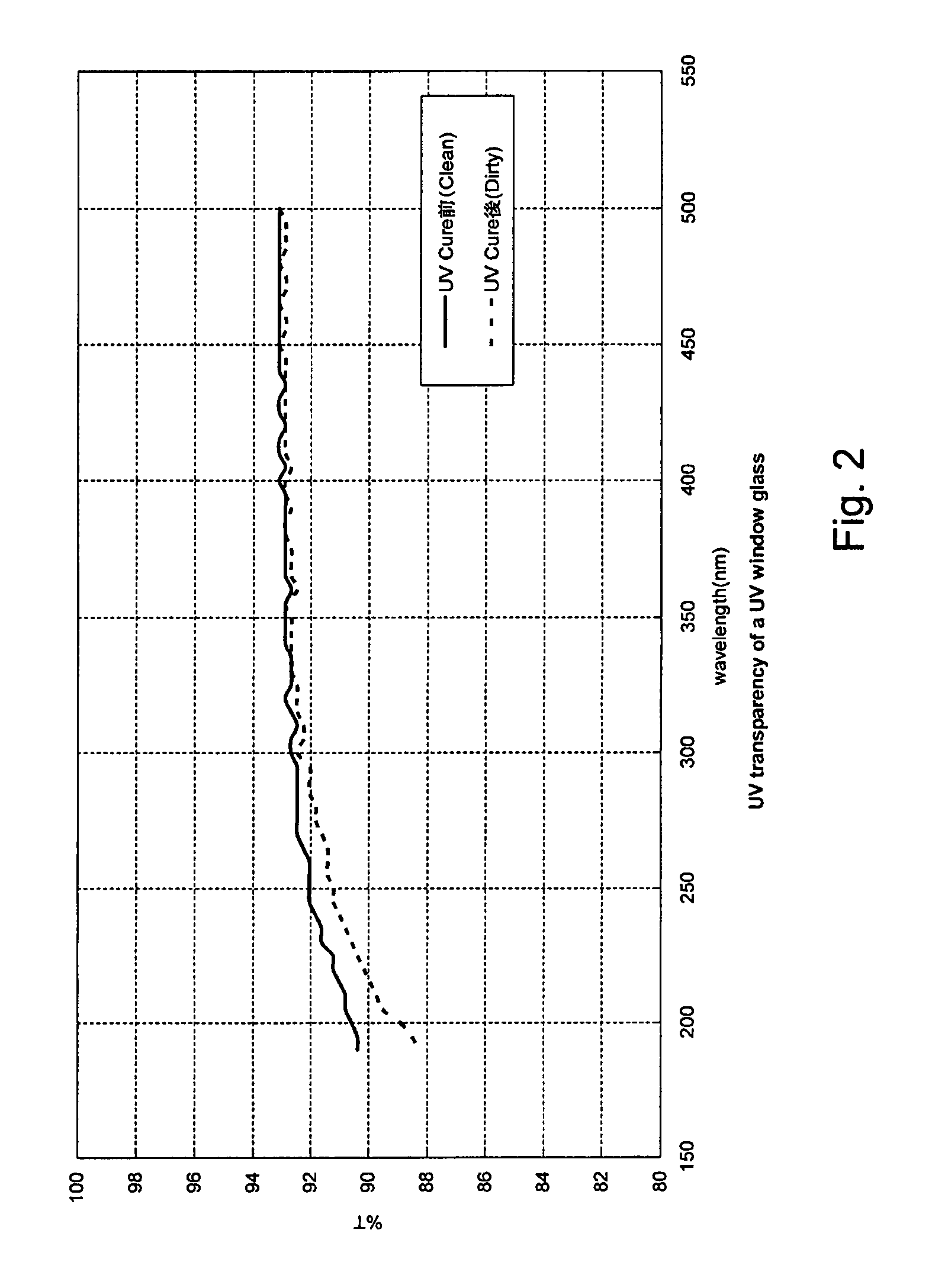
Method for managing UV irradiation for curing semiconductor substrate
ActiveUS7501292B2Maintain levelAutomatic controlSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIlluminanceEngineering
A method for managing UV irradiation for curing a semiconductor substrate, includes: passing UV light through a transmission glass window provided in a chamber for curing a semiconductor substrate placed in the chamber; monitoring an illuminance upstream of the transmission glass window and an illuminance downstream of the transmission glass window; determining a timing and / or duration of cleaning of the transmission glass window, a timing of replacing the transmission glass window, a timing of replacing a UV lamp, and / or an output of the UV light based on the monitored illuminances.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
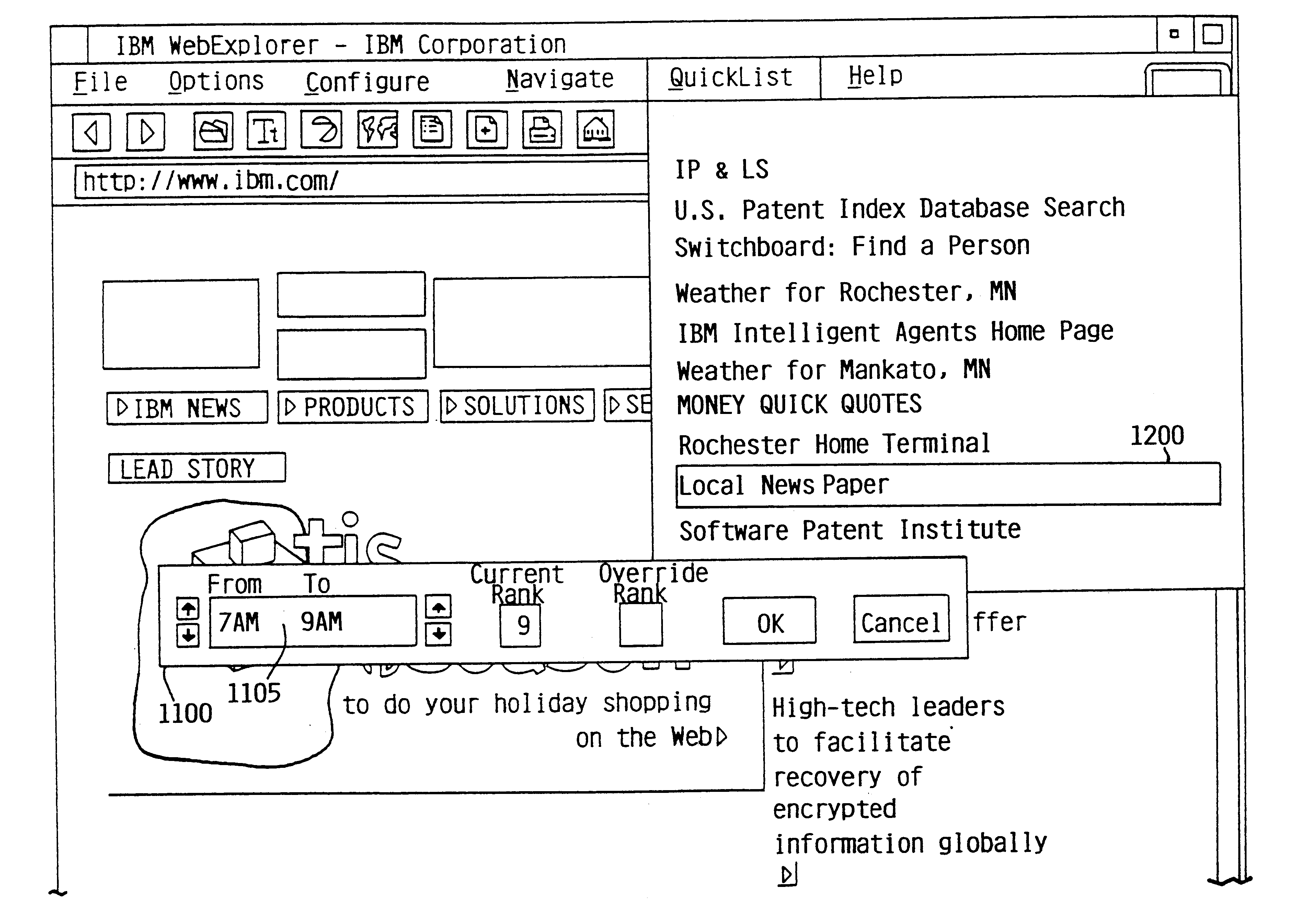
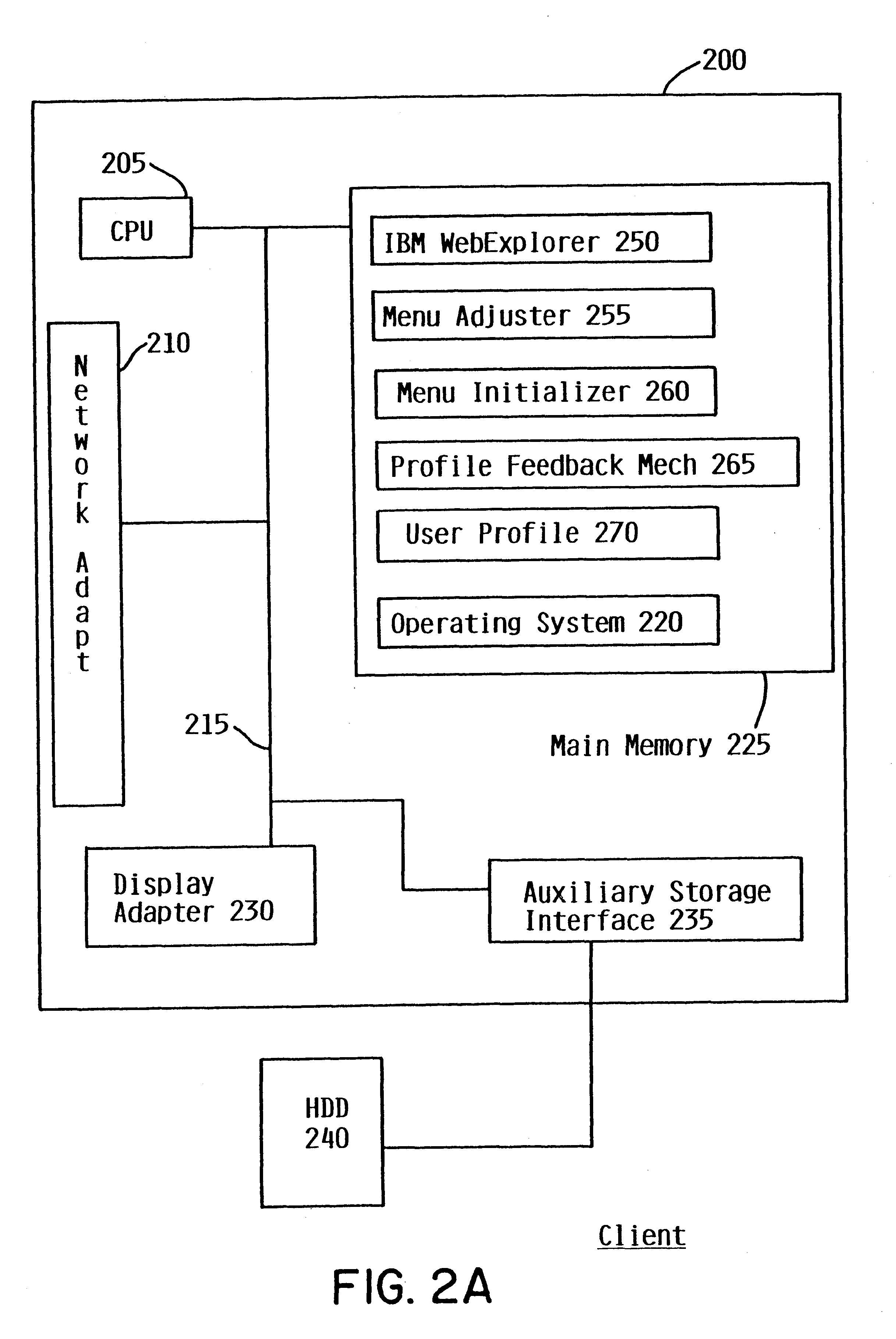
Menu management mechanism that displays menu items based on multiple heuristic factors
InactiveUS6847387B2Automatic controlAdapt quicklyDigital output to display deviceComputer scienceTime of day
The mechanisms of the present invention provide comprehensive heuristic menu arrangement control by providing several discrete, yet complementary, features. One feature is automatic menu arrangement for both fixed and variable content menus based on a combination of frequency of selection and recency of selection. Another feature is the consideration of time of day for menu arrangement. Time of day is used in two different ways. First, time of day is used as a heuristic factor (i.e., in the same way as recency and frequency) to affect the automatic arrangement of menu items. The second time of day feature allows the user to affect the order that certain menu items are presented during a user specified time period.
Owner:IBM CORP
Vehicle power supply system
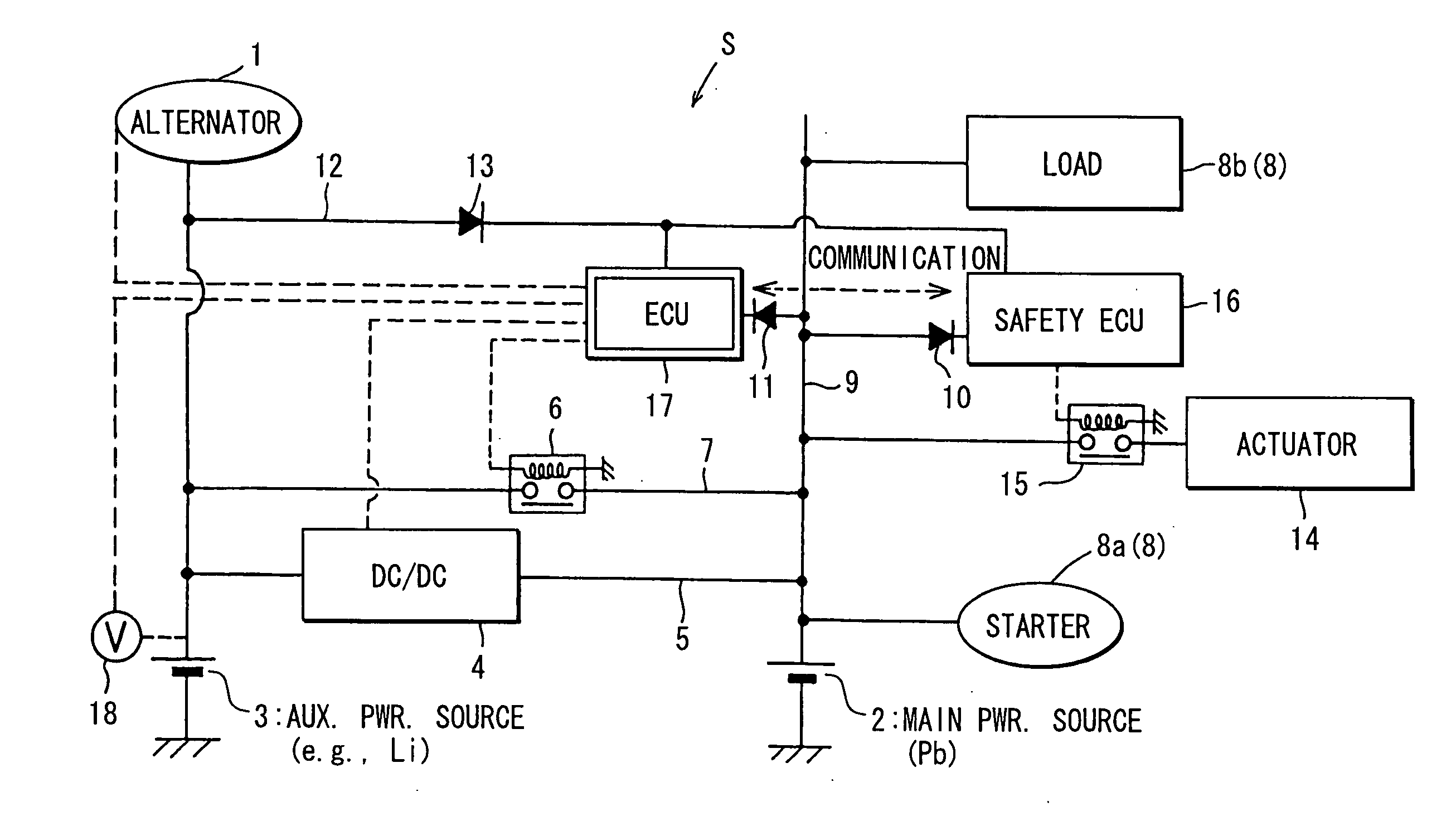
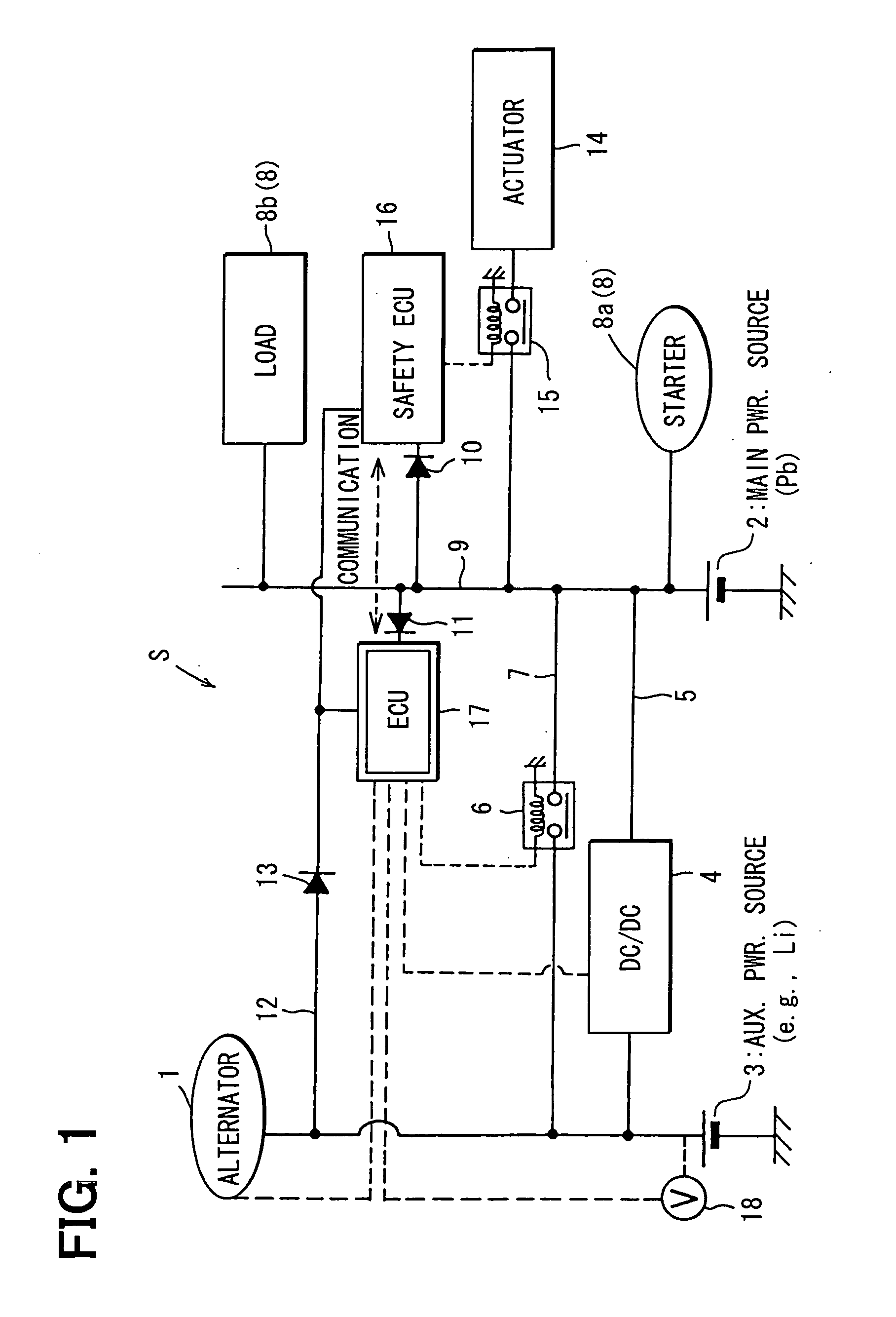
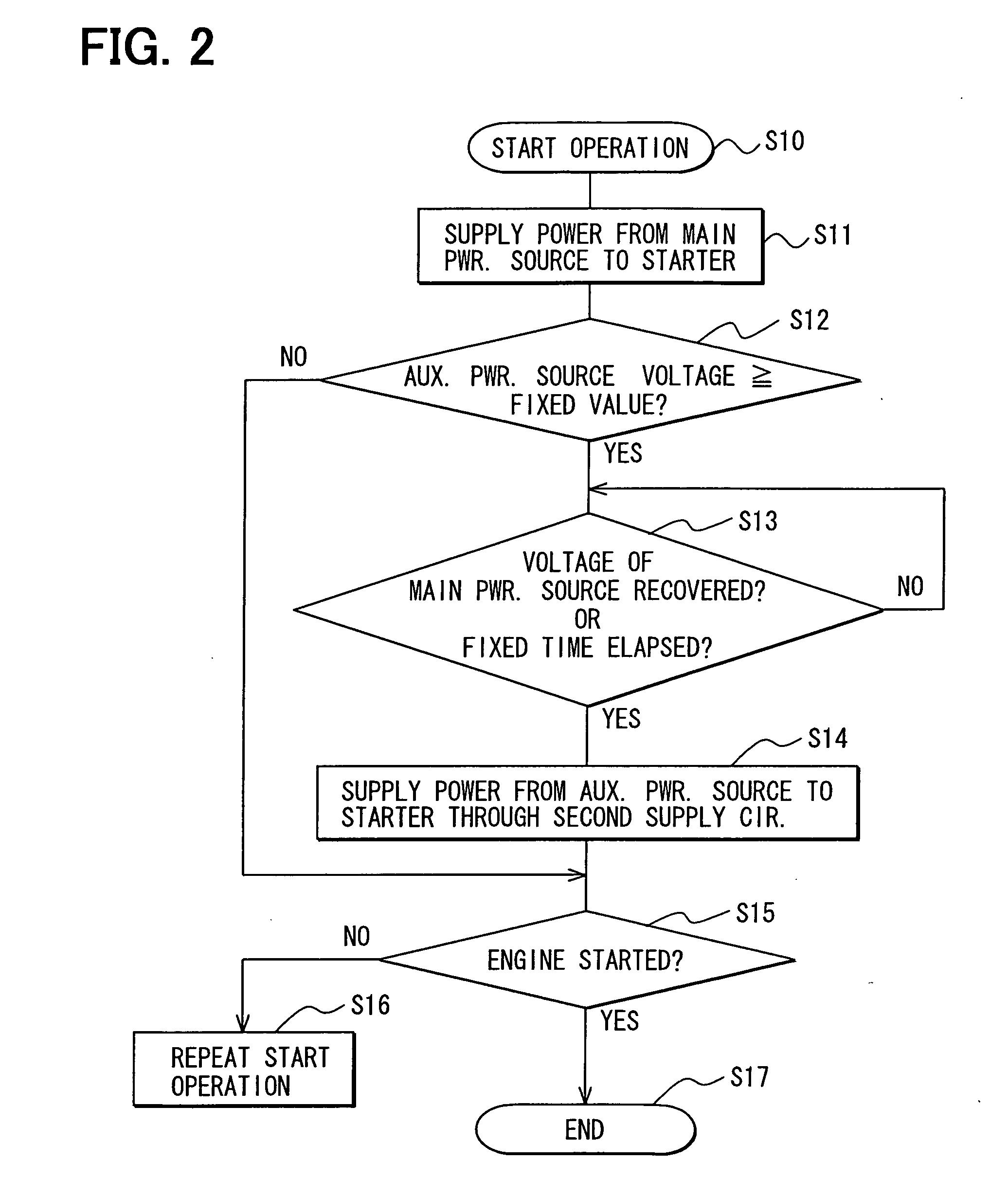
ActiveUS20060097577A1Efficient executionPower supplyBatteries circuit arrangementsDigital data processing detailsInternal resistanceEngineering
A main power source (2) is, for example, an ordinary Pb battery and generates a voltage of 12-13 V. At the time of starting an engine, the main power source (2) supplies power to a starter (8a). The main power source (2) is given a higher priority than an auxiliary power source (3) to supply power to ordinary loads (8b). The auxiliary power source (3) is a high performance battery (e.g., Li ion battery), which has superior charge acceptance capability and better state detectability over the main power source (2). Furthermore, the auxiliary power source (3) has an internal resistance per unit capacity, which is smaller than that of the main power source (2), and generates a voltage of 9-12 V. A generator (1) is directly connected to the auxiliary power source (3). The auxiliary power source (3) stores regenerative power, which is generated by the generator (1) at the time of deceleration of a vehicle, and is used as a redundant power source for the main power source (2). The main power source (2) and the auxiliary power source (3) are connected to each other through a supply circuit (5), which has a DC / DC converter (4), and a second supply circuit 7, which has a switch (6).
Owner:DENSO CORP
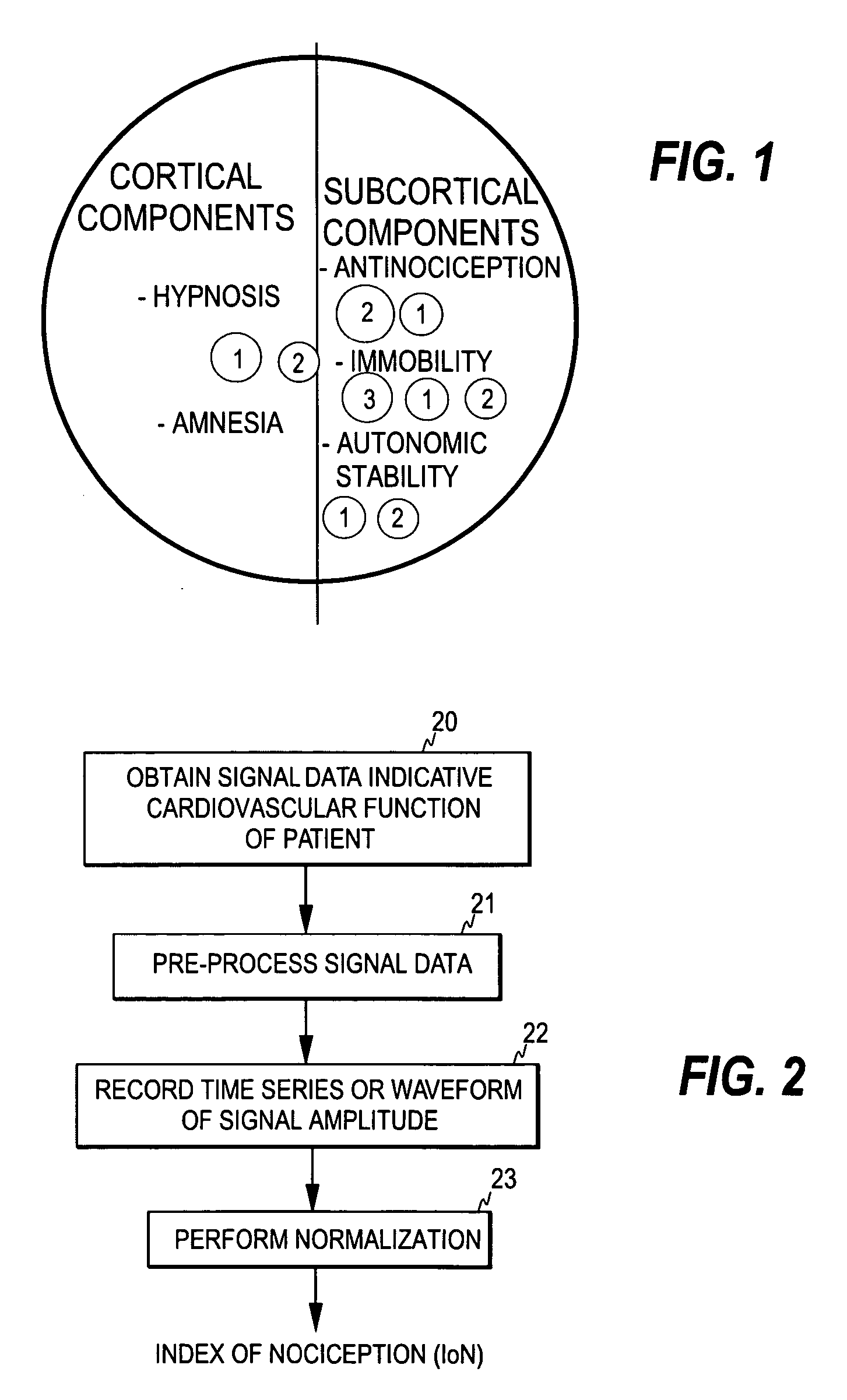
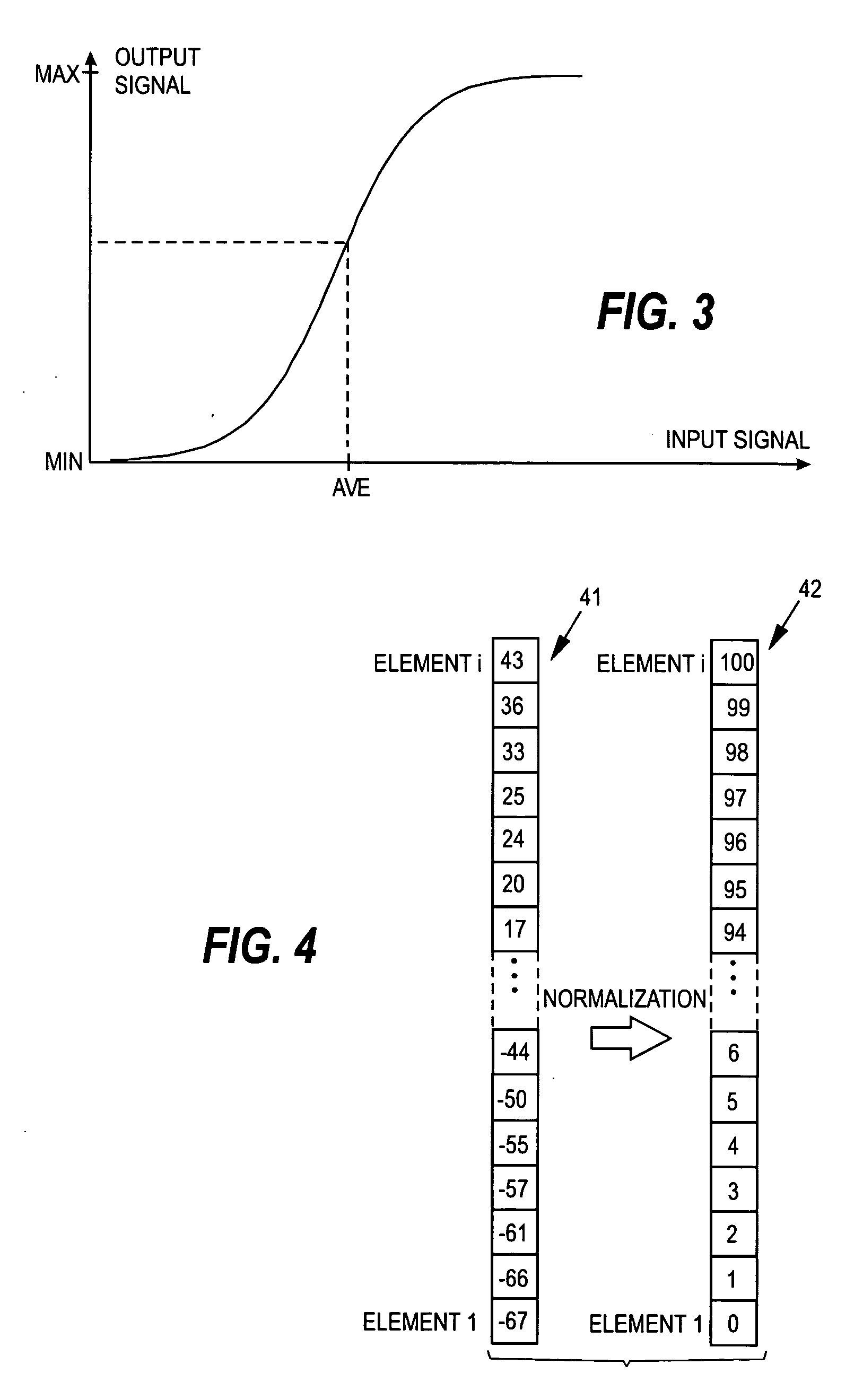
Determination of the clinical state of a subject
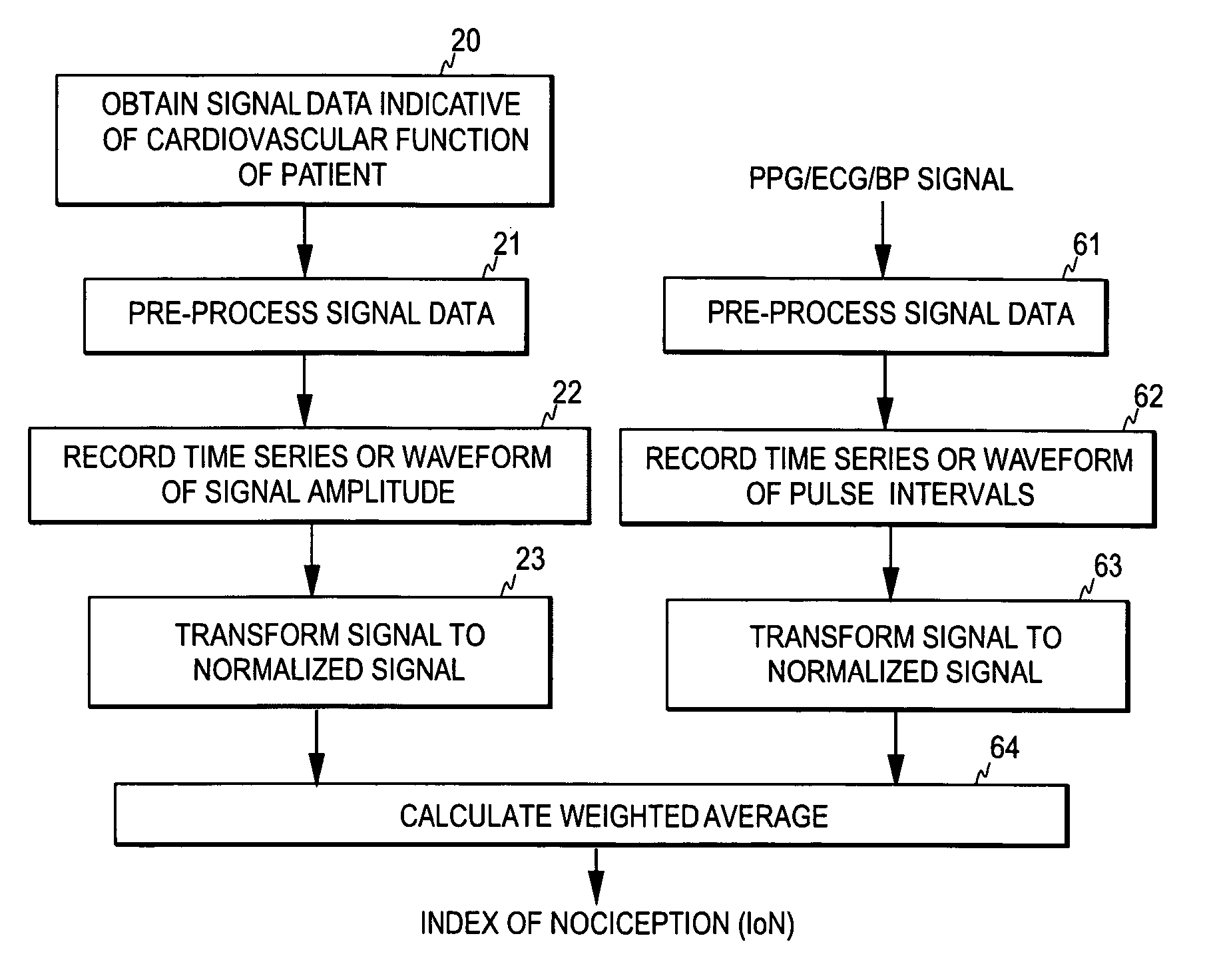
ActiveUS20060217614A1Strong specificityAutomatic controlElectrocardiographyEvaluation of blood vesselsMedicineIndex score
The invention relates to the determination of the clinical state of a subject. In order to bring about an uncomplicated method for monitoring the clinical state of a subject and for accomplishing a diagnostic scale, such as a nociception scale, on which a certain reading corresponds to the same level for all patients, a normalization transform is applied to a measurement signal containing physiological data obtained from a patient, whereby a normalized measurement signal having a predetermined value range is obtained. The normalization transform is dependent on predetermined history data, such as previous signal data of said measurement signal. A diagnostic index dependent on the normalized measurement signal is then formed, the diagnostic index serving as a measure of the clinical state of the patient. The diagnostic index may be formed based on one or more normalized measurement signals.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS20130030438A1Simple and reliable processLow costInternal osteosythesisPinsShape changeBone tissue
A new shape changing staple and instrument for the fixation of structures to include bone tissue and industrial materials. This new staple stores elastic mechanical energy to exert force on fixated structures to enhance their security and in bone affect its healing response. This staple once placed changes shape in response to geometric changes in the materials structure, including healing bone tissue. The staple is advanced over prior staples due to its: 1) method of operation, 2) high strength, 3) method of insertion, 4) compressive force temperature independence, 5) energy storing staple retention and delivery system, 6) compatibility with reusable or single use product configuration, 7) efficient and cost effective manufacturing methods, and 8) reduction in the steps required to place the device. In addition to the staple's industrial application an embodiment for use in the fixation of the musculoskeletal system is shown with staple, cartridge, and extrusion handle.
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
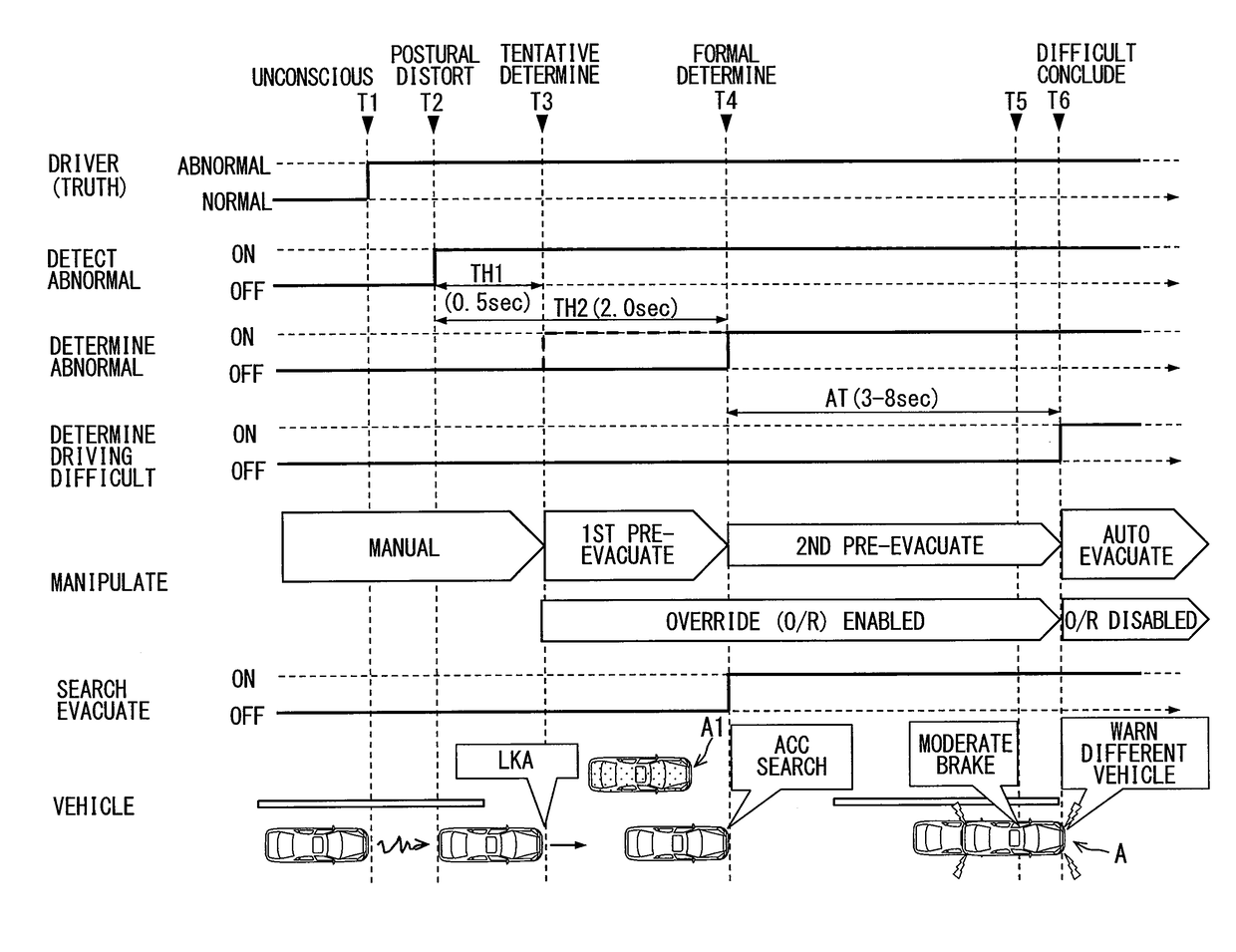
Travel control apparatus and travel control method
ActiveUS20180111628A1Prevent deviationAutomatic controlRoad vehicles traffic controlAutomatic initiationsDriver/operatorInformation acquisition
A travel control apparatus includes: an abnormality information acquisition section that acquires information indicating that an abnormality of a driver of a vehicle is detected; a status determination section that makes a determination that the driver is in a driving difficulty state, when the abnormality of the driver is detected continuously; and an evacuation control section that initiates an automatic evacuation control stopping automatically the vehicle when the status determination section makes a determination that the driver is in the driving difficulty state. The travel control apparatus further includes an assistance control section that initiates a driving assistance control during an interval from when the abnormality is detected to when the driving difficulty state is determined; the driving assistance control includes at least activating a lane departure prevention function of the vehicle.
Owner:DENSO CORP
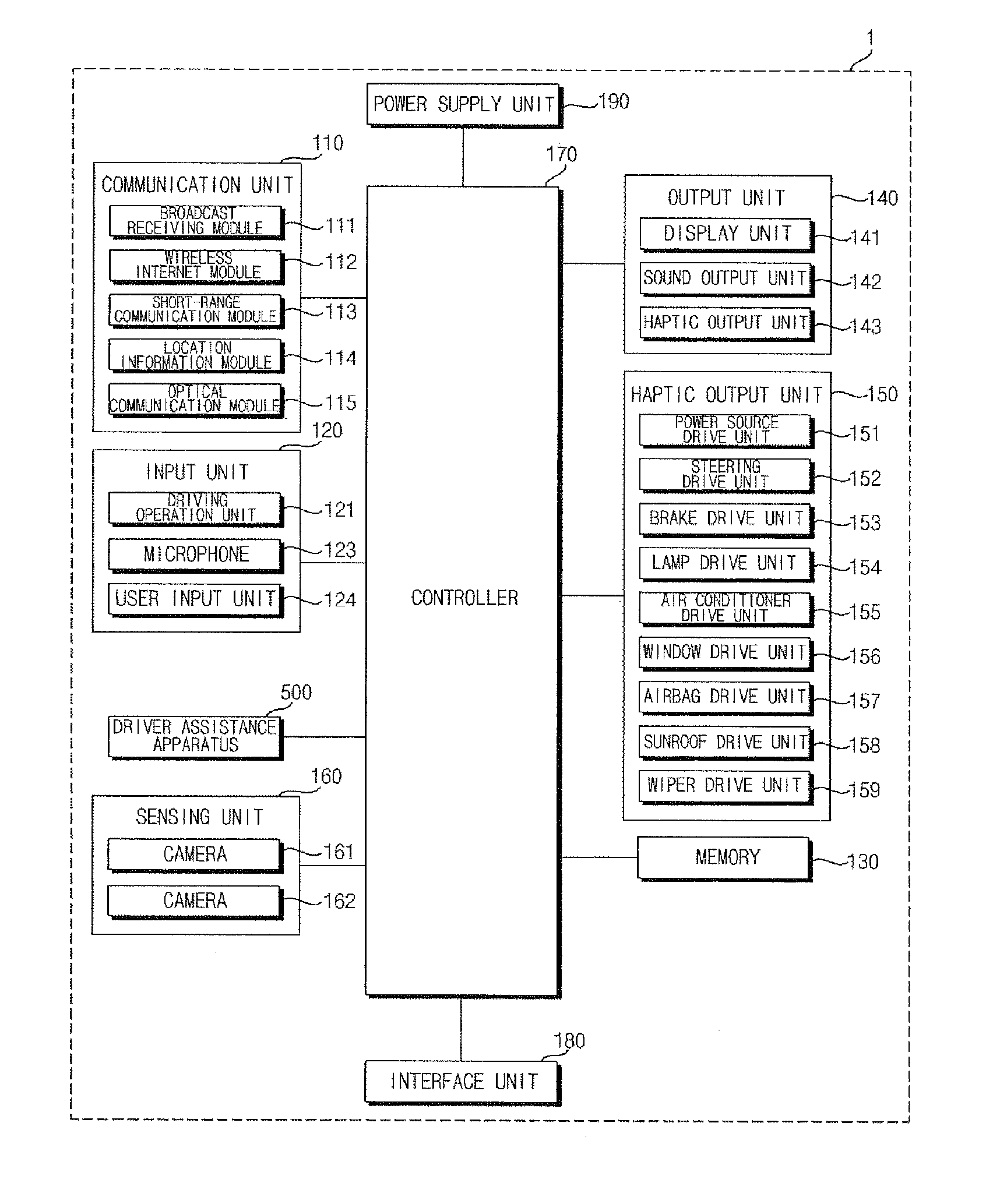
Driver assistance apparatus and control method for the same
ActiveUS20170036673A1Automatic controlInput/output for user-computer interactionAnti-collision systemsDriver/operatorUser input
Disclosed are driver assistance apparatus and a control method for the same. The driver assistance apparatus includes a sensing unit configured to acquire information regarding an object outside a vehicle, the object including a first other vehicle being driven in the vicinity of the vehicle, and a processor configured to judge whether the first other vehicle is a dangerous vehicle based on at least one of the information regarding the object, user input provided from a driver of the vehicle, information regarding the state of the driver, and information regarding the first other vehicle provided from a second other vehicle being driven in the vicinity of the vehicle, and to execute at least one predetermined operation upon judging that the first other vehicle is a dangerous vehicle.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
System and method of target tracking using sensor fusion
ActiveUS20070073473A1Improve precisionImprove certaintyInstruments for road network navigationAnti-collision systemsSensor fusionEngineering
A target tracking and sensory fusion system is adapted for use with a vehicle, and configured to observe a condition of at least one object during a cycle. The system includes a plurality of sensors, and a novel controller communicatively coupled to the sensors and configured to more accurately estimate the condition based on sensory fusion. In a preferred embodiment, Kalman filtering is utilized to produce a fused estimate of the object location. The preferred controller is further configured to match each new sensory observation with a track in a track list, and remove the track from the track list, when a matching observation is not determined, during a subsequent cycle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Access control method for medical facilities and retirement facilities
InactiveUS20070222554A1Avoid enteringAutomatic controlElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageEngineeringResidence
A method for controlling access to a building selected from a hospital, a medical clinic or the like, or a nursing home, a retirement residence or the like or a portion of the building, comprises (a) positioning an apparatus comprising an input member and an output dispenser proximate to a barrier to entry of the building or the portion thereof; (b) requiring a person to use the input member to provide the apparatus with at least one of (i) their destination in the building or the portion thereof, and (ii) the duration of their attendance at the building or the portion thereof; and (c) using a dispenser apparatus to automatically provide a pass to the person wherein the pass incorporates at least one of the following items of information: (I) the portions of the building which the person may enter, and (ii) the time during which the person may be in the building or the portion thereof.
Owner:HART ENTERPRISES
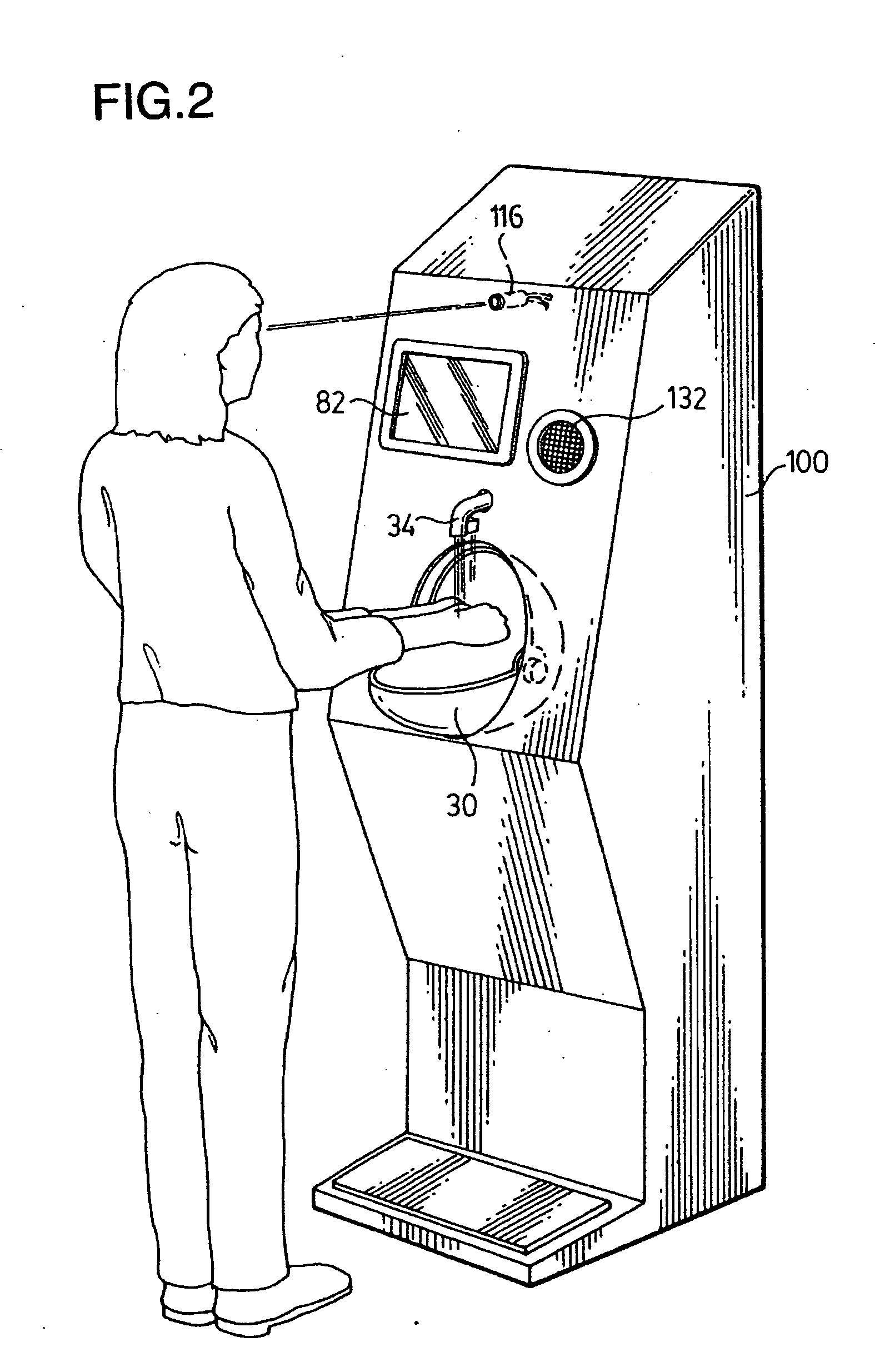
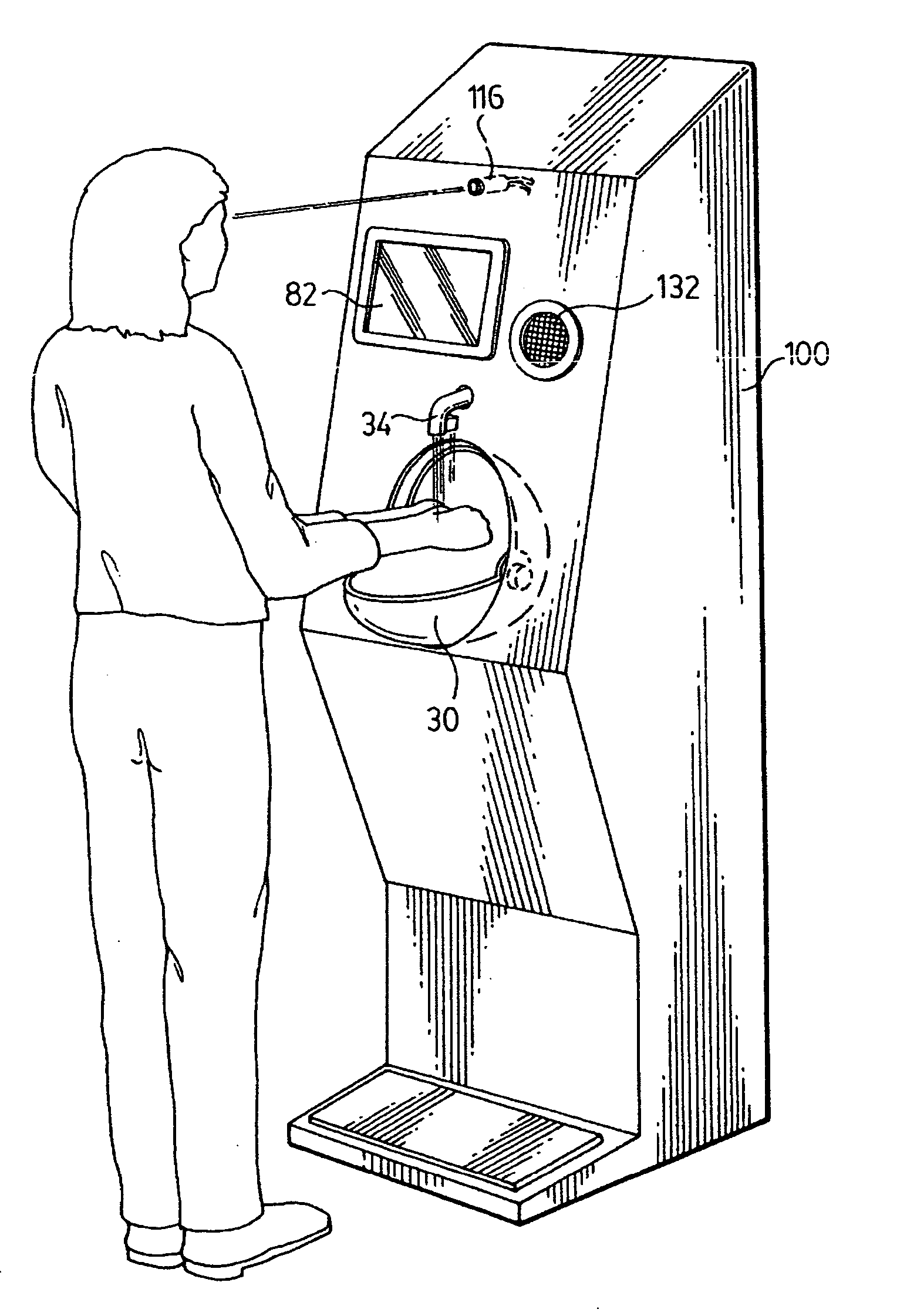
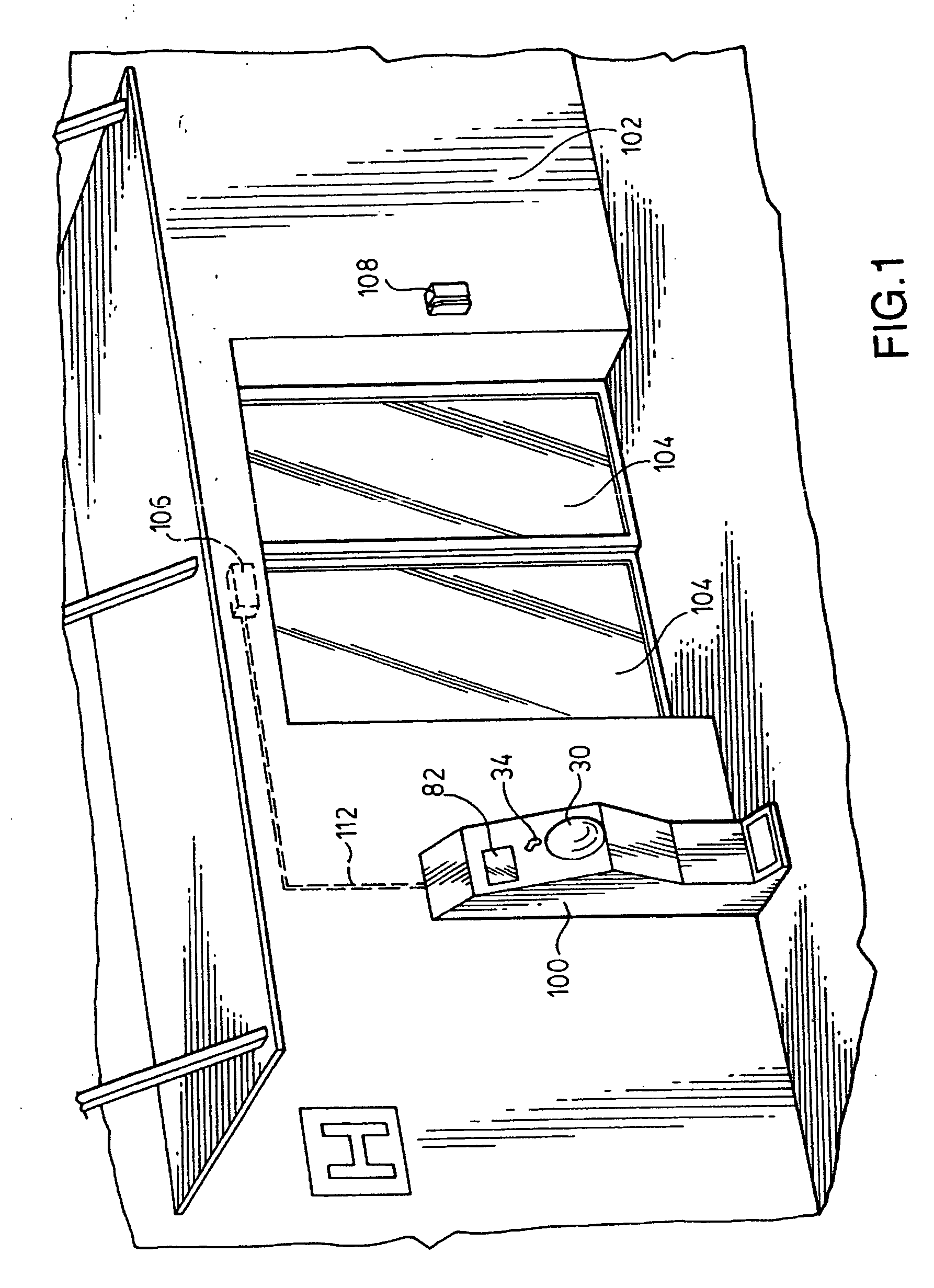
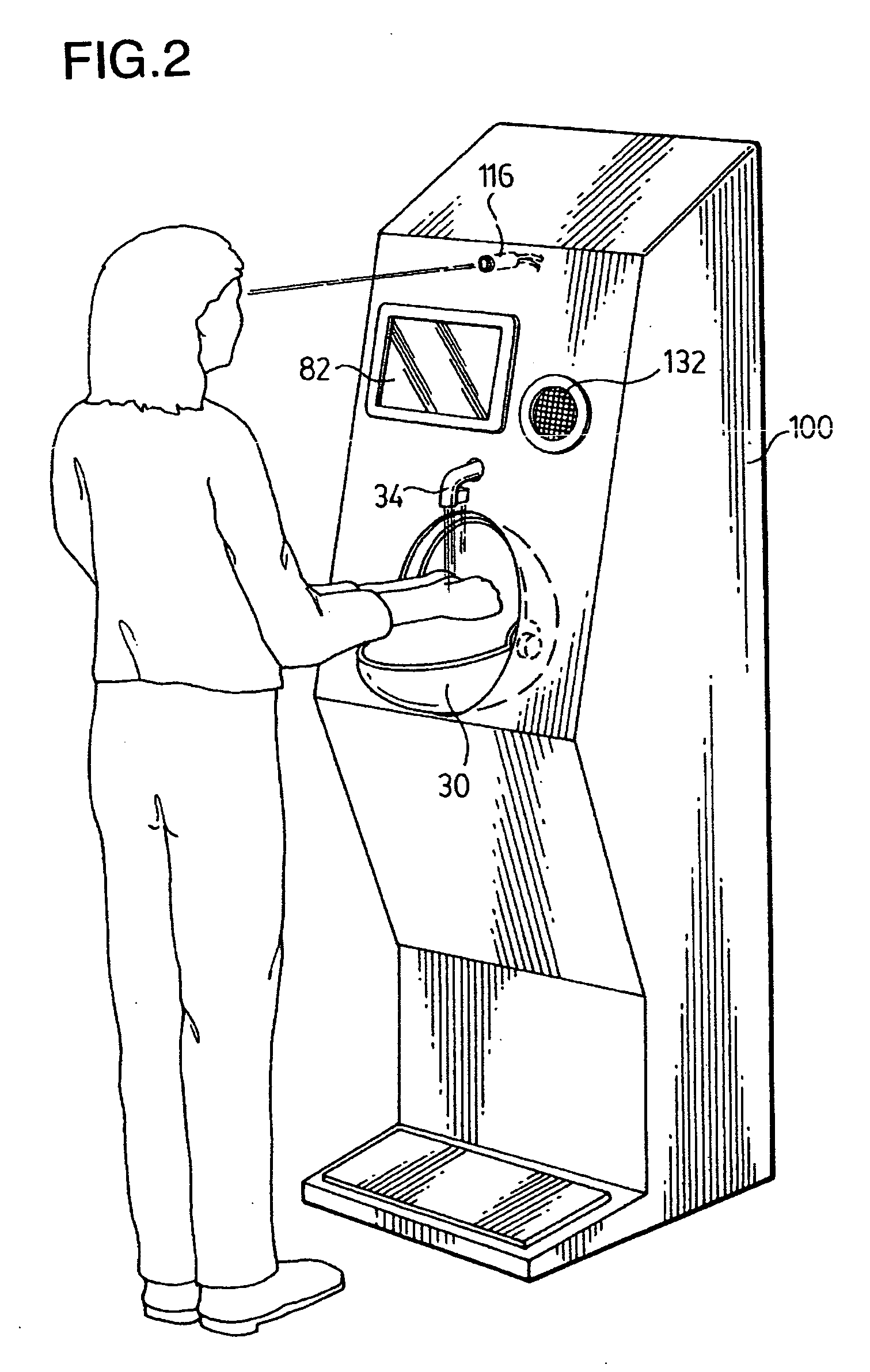
Hand cleaning apparatus and method of use of same
InactiveUS20070213877A1Prevent buildupAutomatic controlBathroom accessoriesPower-operated mechanismEngineeringAuthorization
An apparatus for providing control for the access to a building or a portion of a building based upon a user washing or disinfecting their hands comprises a hand cleaning apparatus and an output module wherein the output module controls the operation of automatic doors or provides an access card or an authorization badge, or any combination thereof, to permit entry to a building. A method of using the hand cleaning apparatus as part of a system to control entrance to a building is also provided. A method of using the hand cleaning apparatus as part of a system to control entrance to certain parts of a building only is also provided. A hand cleaning apparatus, and a method of use thereof, to check the health of a person or to dispense a mask and / or gloves is also provided.
Owner:ANDREW J HART ENTERPRISES
Test system and method for portable electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20050222690A1Easy and fast processingSave powerElectric controllersElectrical measurementsLight sourceComputer hardware
A test system for testing a portable electronic apparatus is described. The test system has at least a display, a platform, and a controller. The controller controls the display to display test images in sequence. The controller commands the portable electronic apparatus, via a test interface, to capture the test images on the display to generate image data. The controller determines whether the image data meet a predetermined test requirement. The test system can further include at least a light source and a reflector. The reflector reflects the light on the display, so that the display reaches a predetermined uniformity of light.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
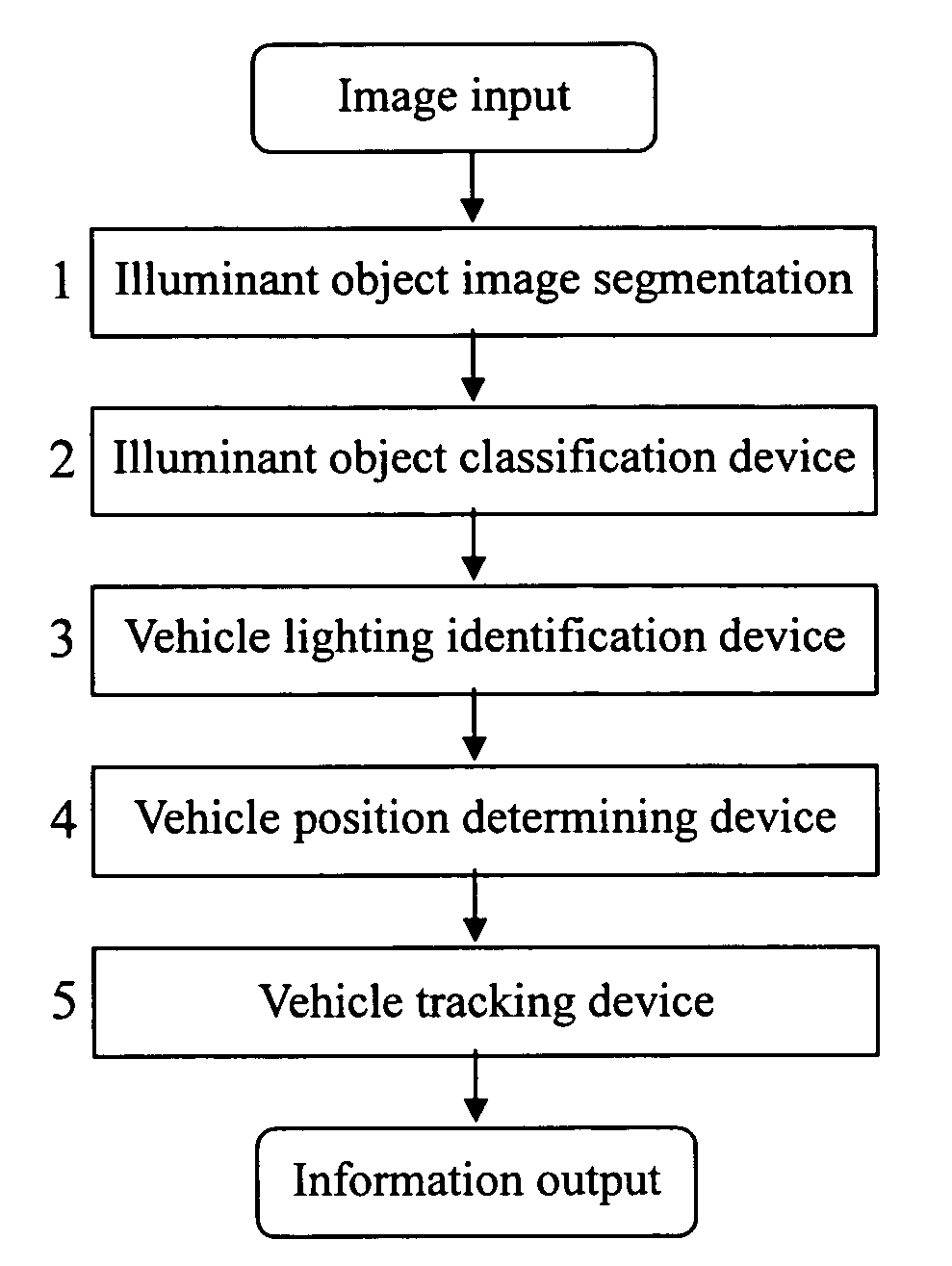
Real-time nighttime vehicle detection and recognition system based on computer vision
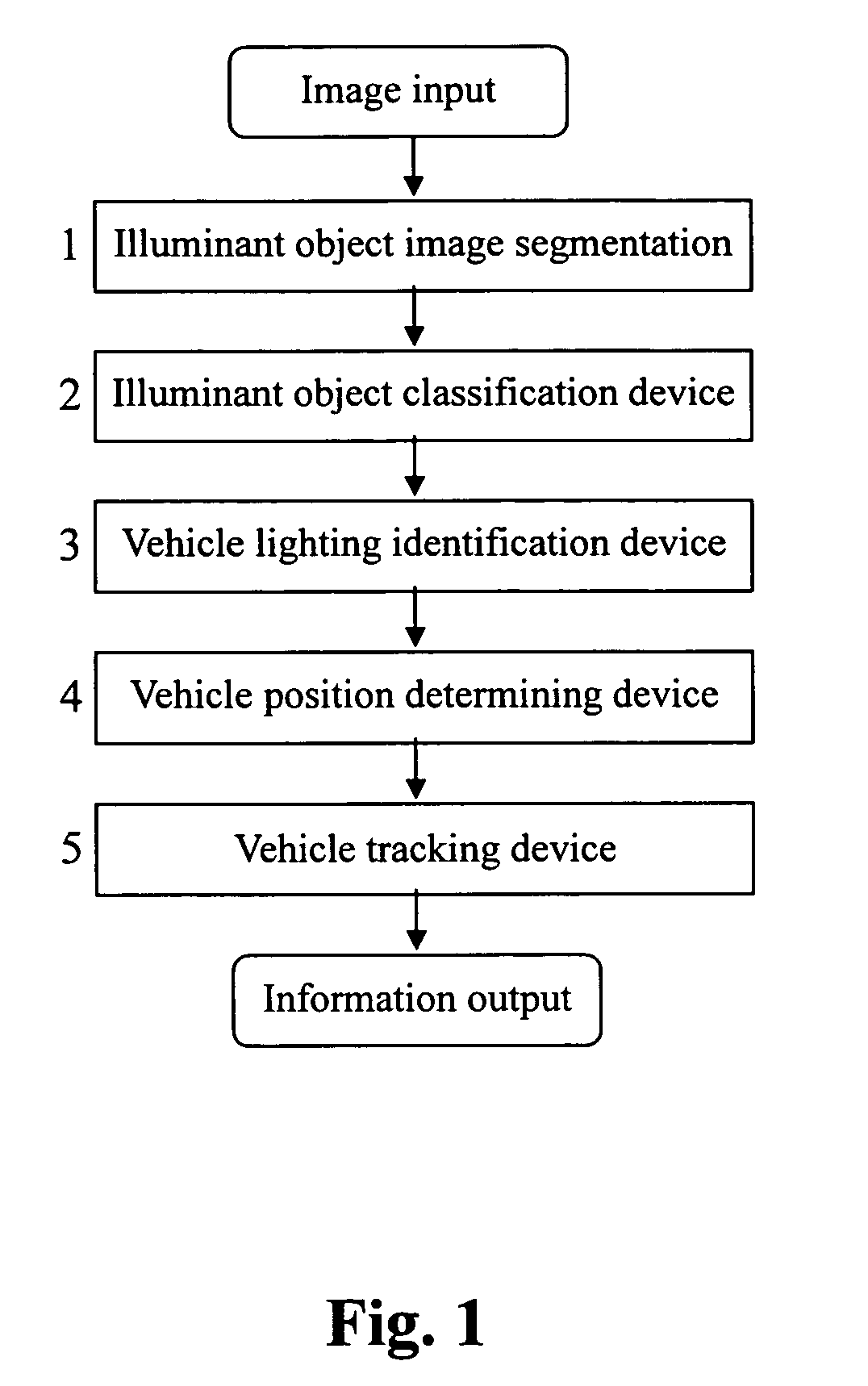
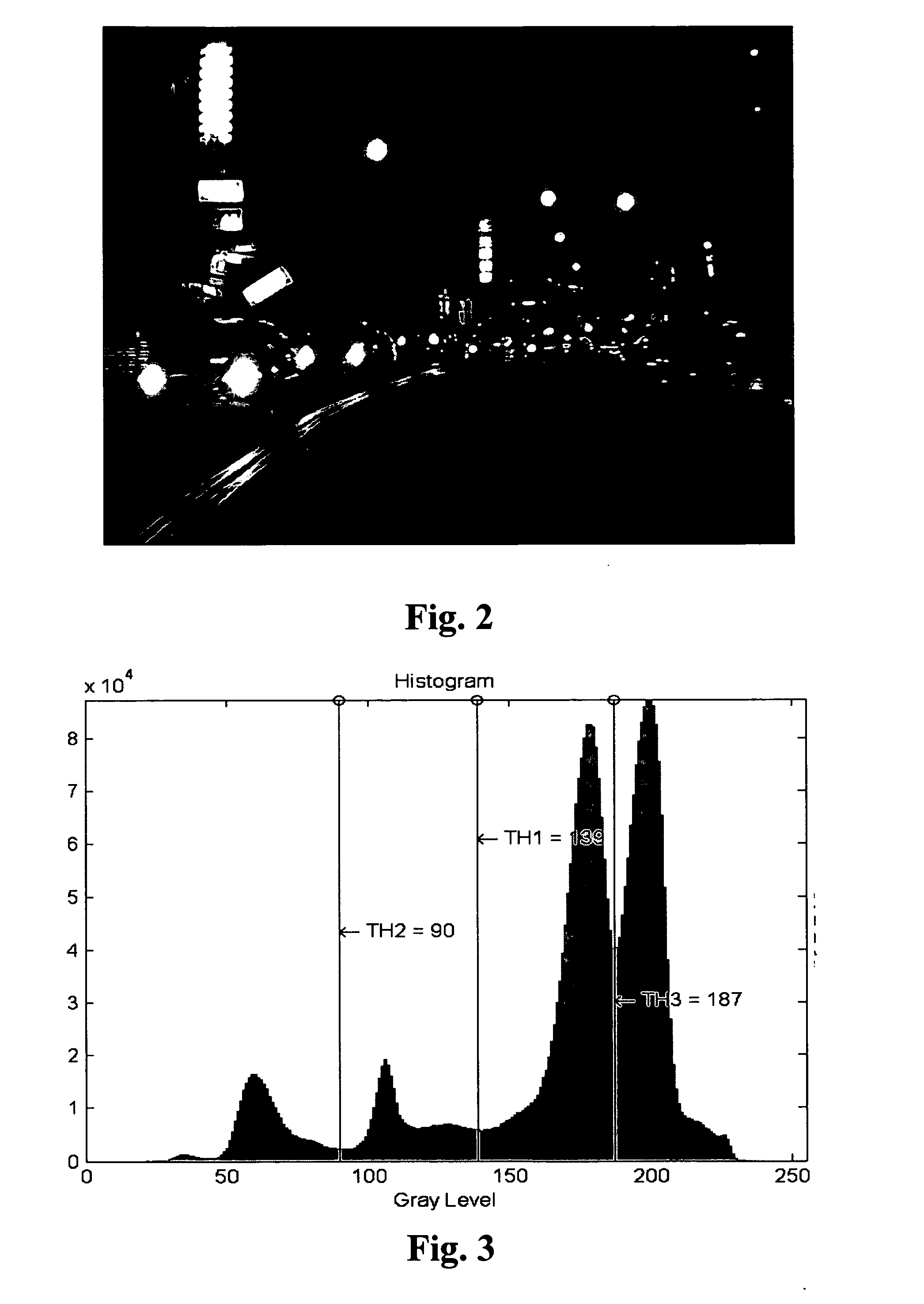
The present invention relates to a real time night time vehicle detection and identification system comprising of an illuminant object image segmentation device 1, an illuminant object classifying device 2, a vehicle lighting object identification device 3, a vehicle position determining device 4 and a vehicle tracking device 5. Under various circumstances of road lighting during nighttime, the system can efficiently and accurately demarcate and identify the lamps of incoming and preceding vehicles and accurately provides the driver with auxiliary information needed to analyze the traffic conditions in front of the vehicle during the conditions met on the road at that time.
Owner:CSSP
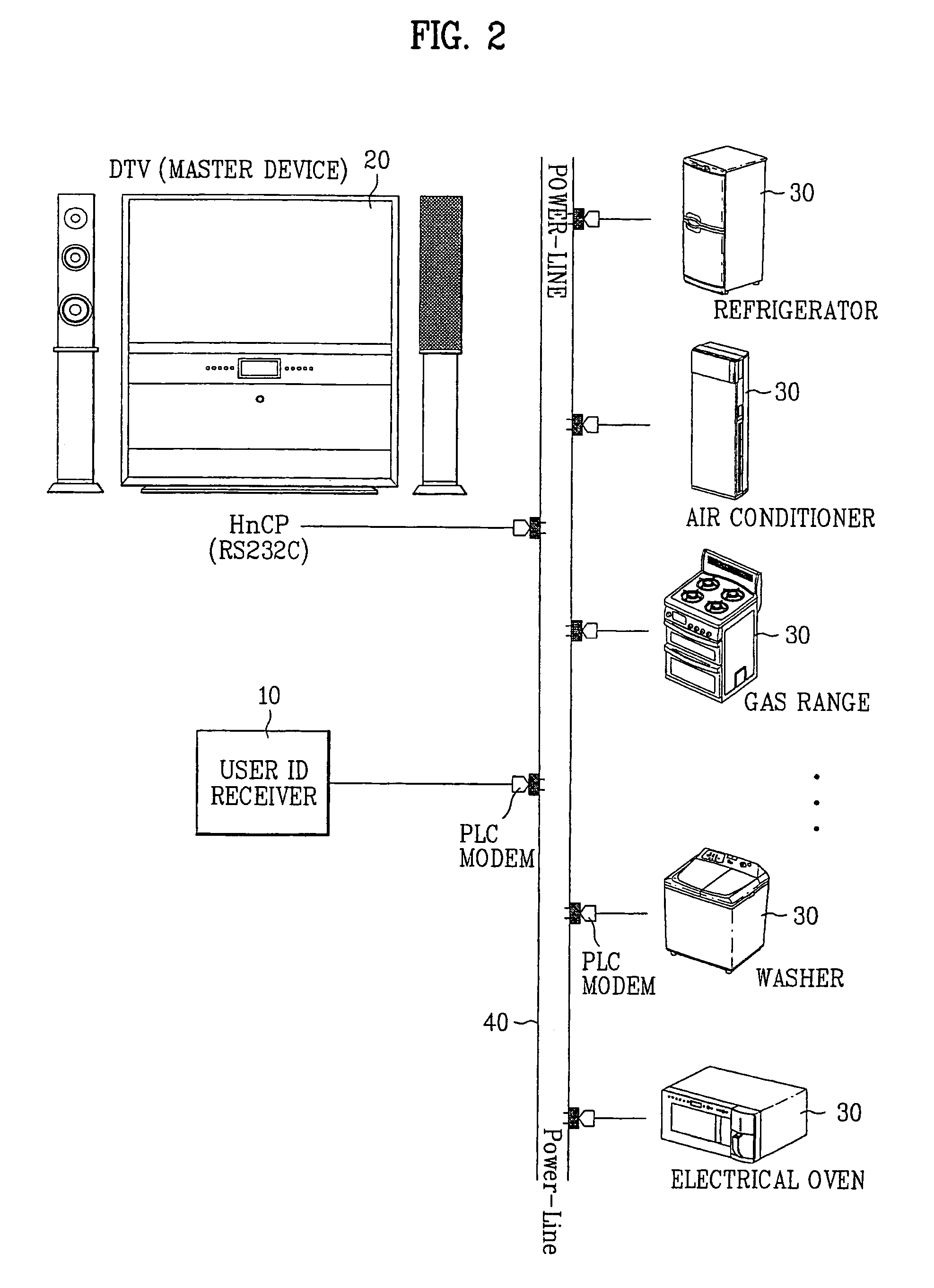
Control system and method for home network system
ActiveUS7366498B2Automatic controlInterconnection arrangementsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionControl systemMulti user environment
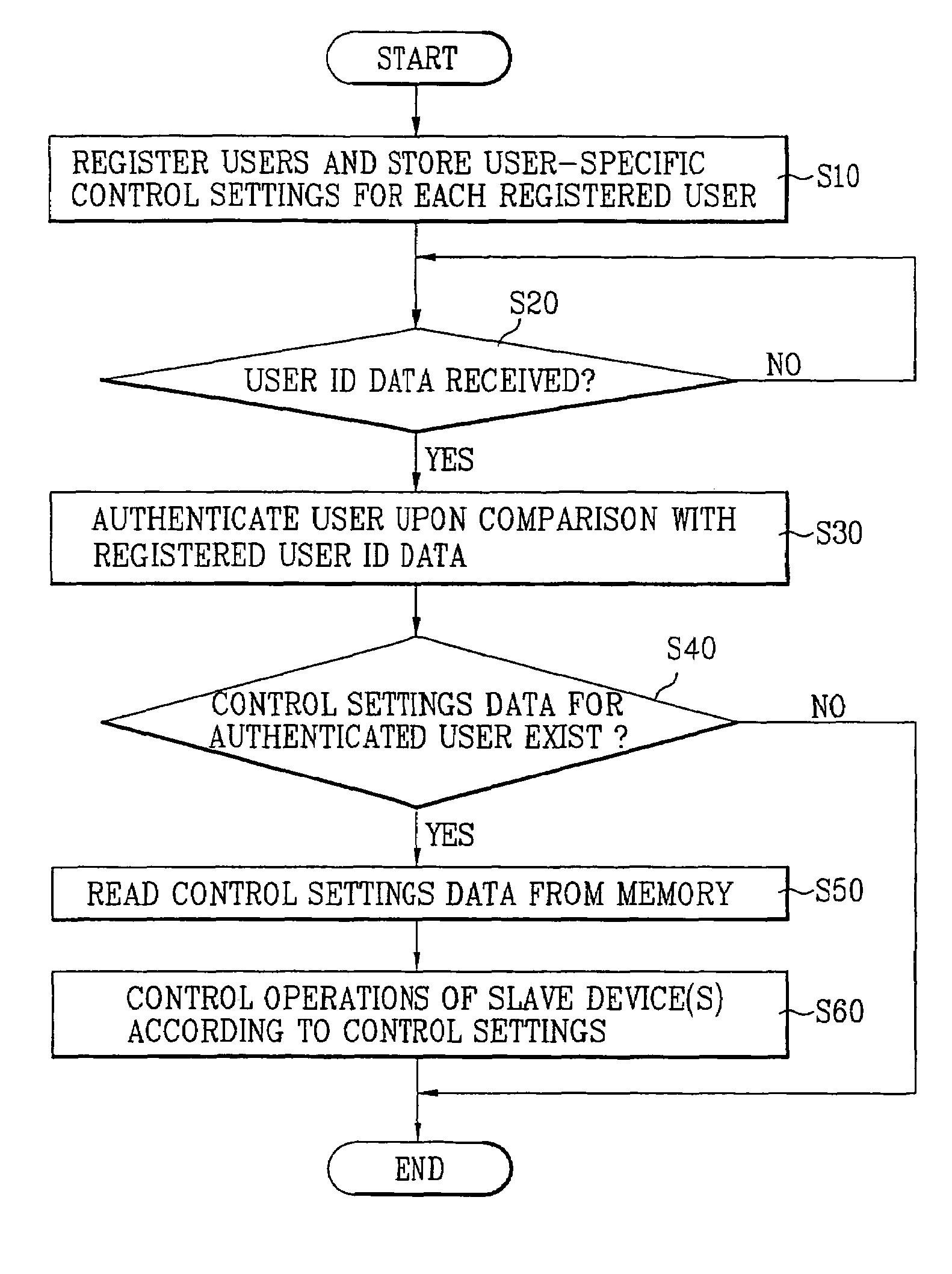
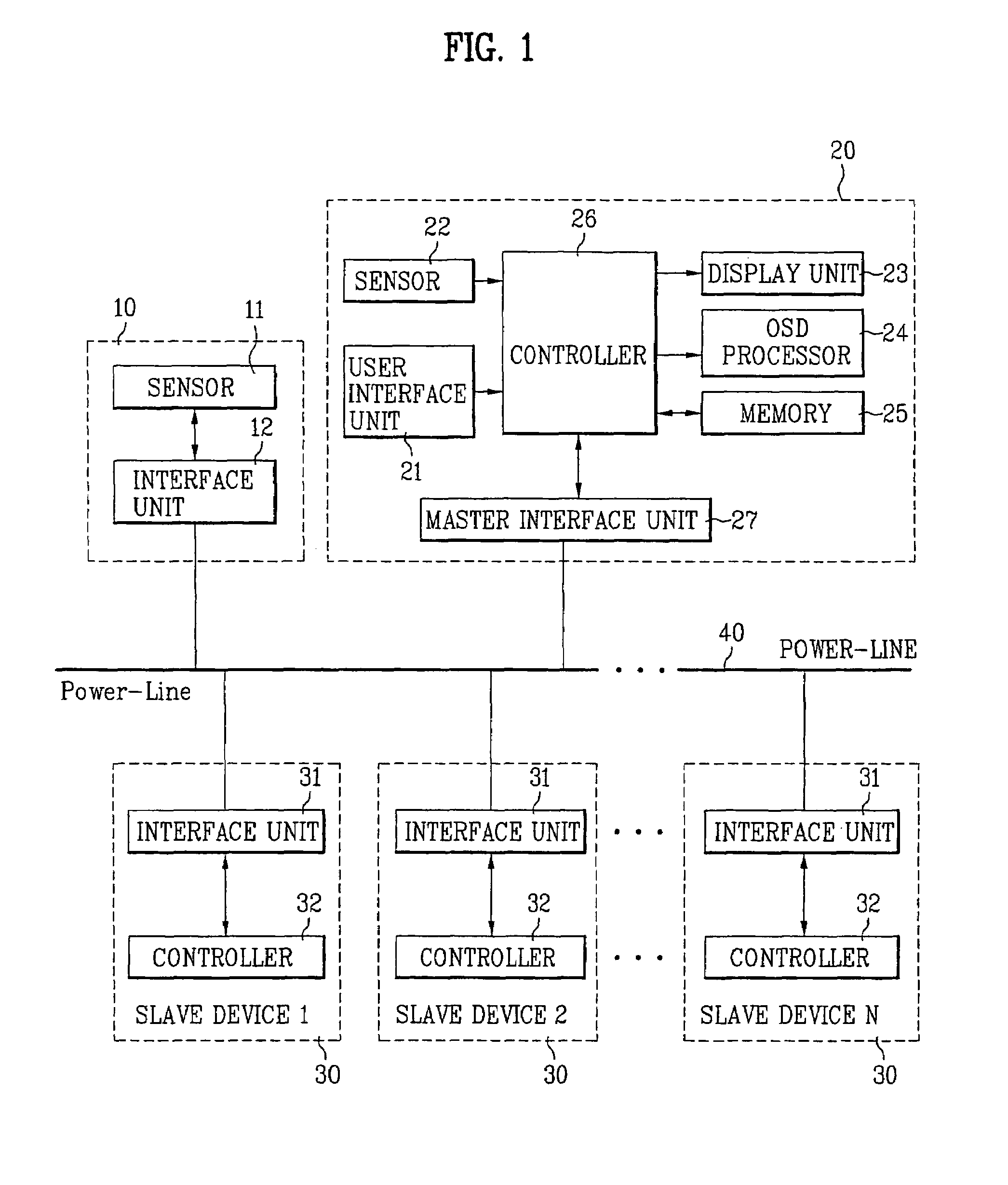
A control method and a control system for a home network system in a multi-user environment are disclosed. The control system includes a plurality of slave devices, a user ID receiver receiving user ID data from a user, and a master device coupled to the slave devices for operation control. The master device includes a memory and a controller coupled to the memory and the user ID receiver. The memory initially prestores user-specific control settings preset by a plurality of preregistered users and user ID data of the preregistered users. Then, the controller authenticates the user upon receiving the user ID data from the user ID receiver, and it automatically controls operational functions of the slave devices according to the user-specific control settings of the authenticated user, which is extracted from the memory.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
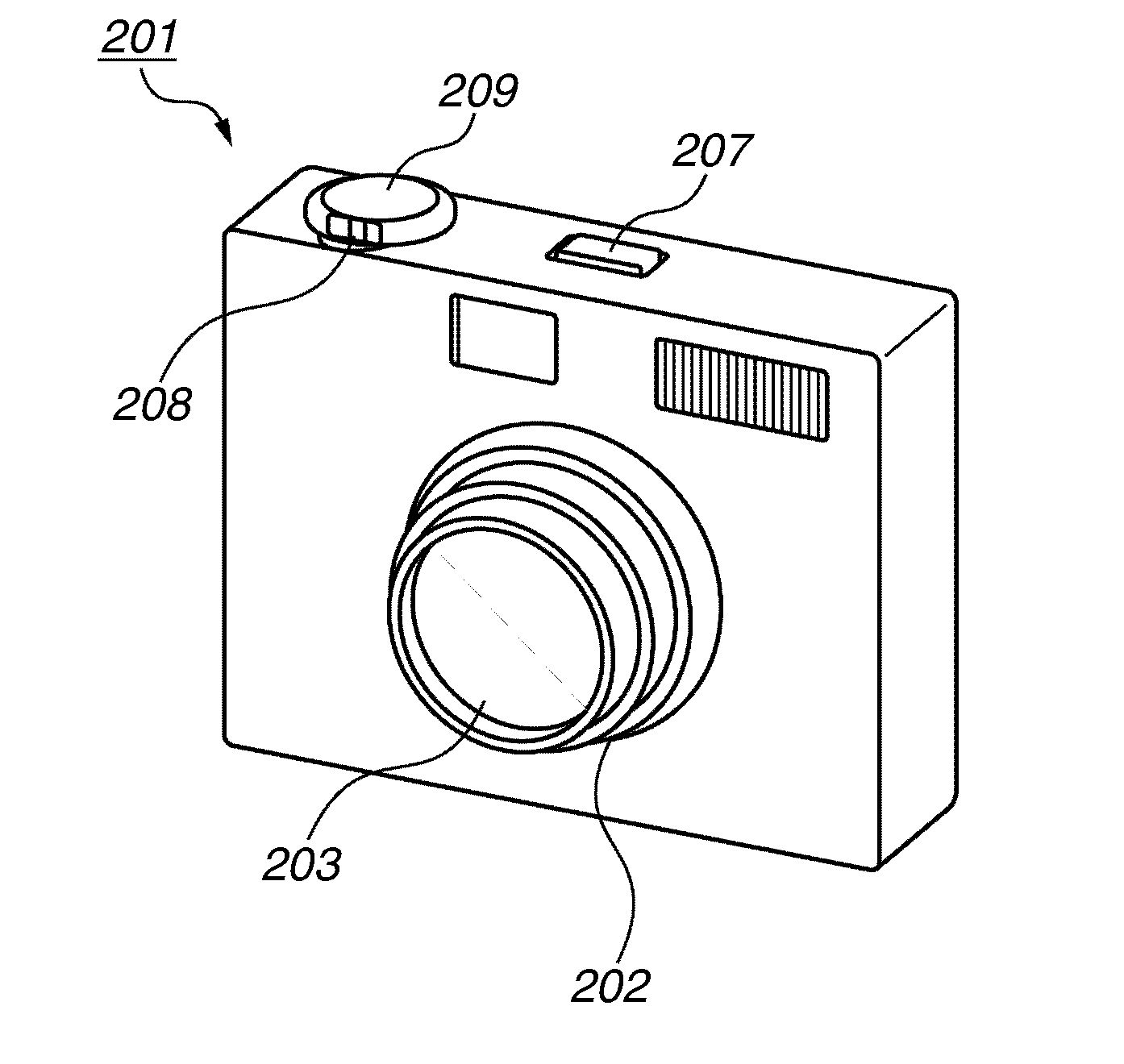
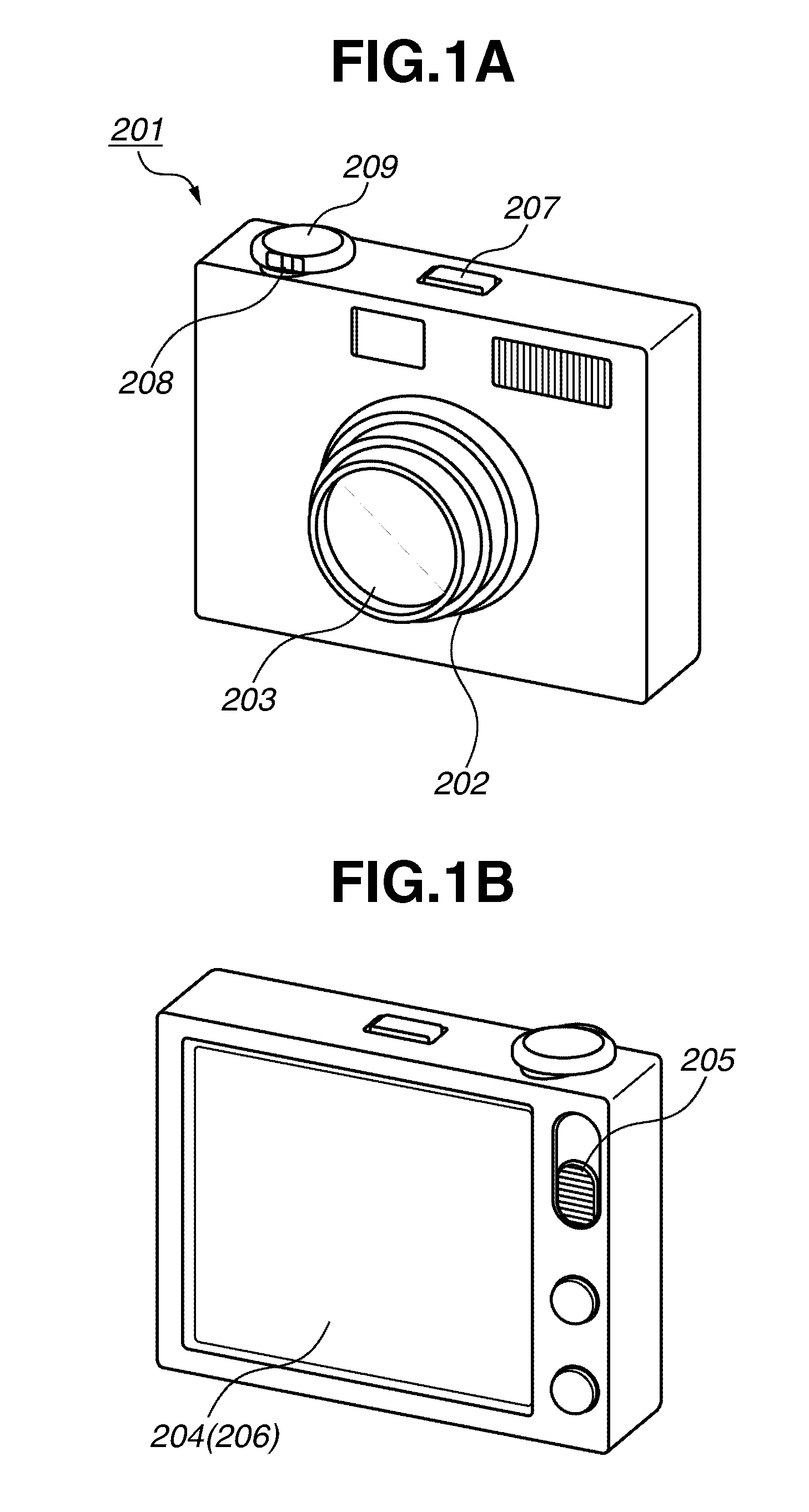
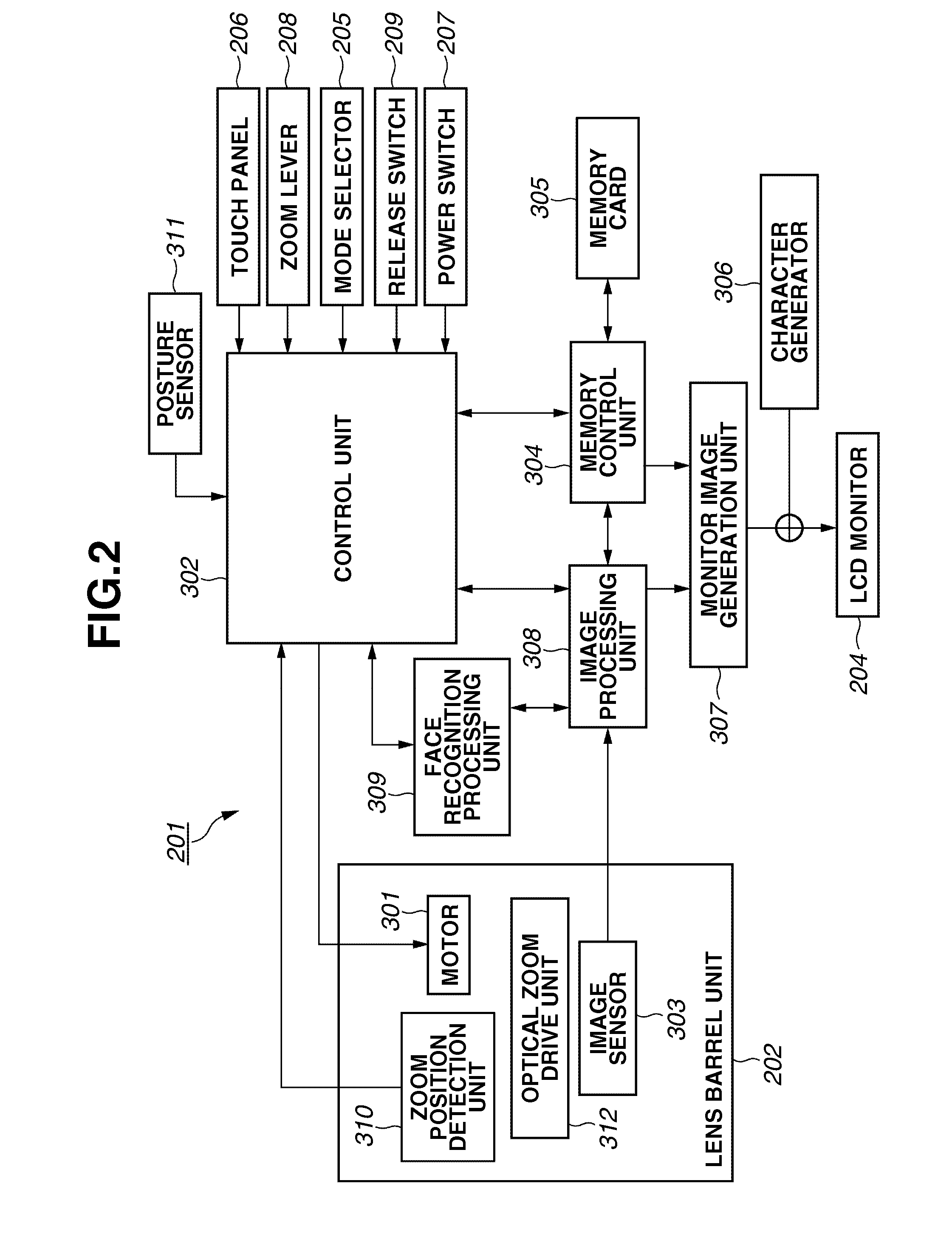
Imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20120098992A1Automatic controlTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionFace sizeAngle of view
A controller controls a photographing angle of view based on the face size detected by the face size calculation unit and the face inclination detected by the face inclination detection unit, wherein the controller controls the photographing angle of view so that a size with respect to the photographing angle of view of the subject image recognized by the face recognition unit becomes a predetermined size.
Owner:CANON KK
Dynamic dispatching and schedule management methods for an intelligent transit system with electronic guided buses
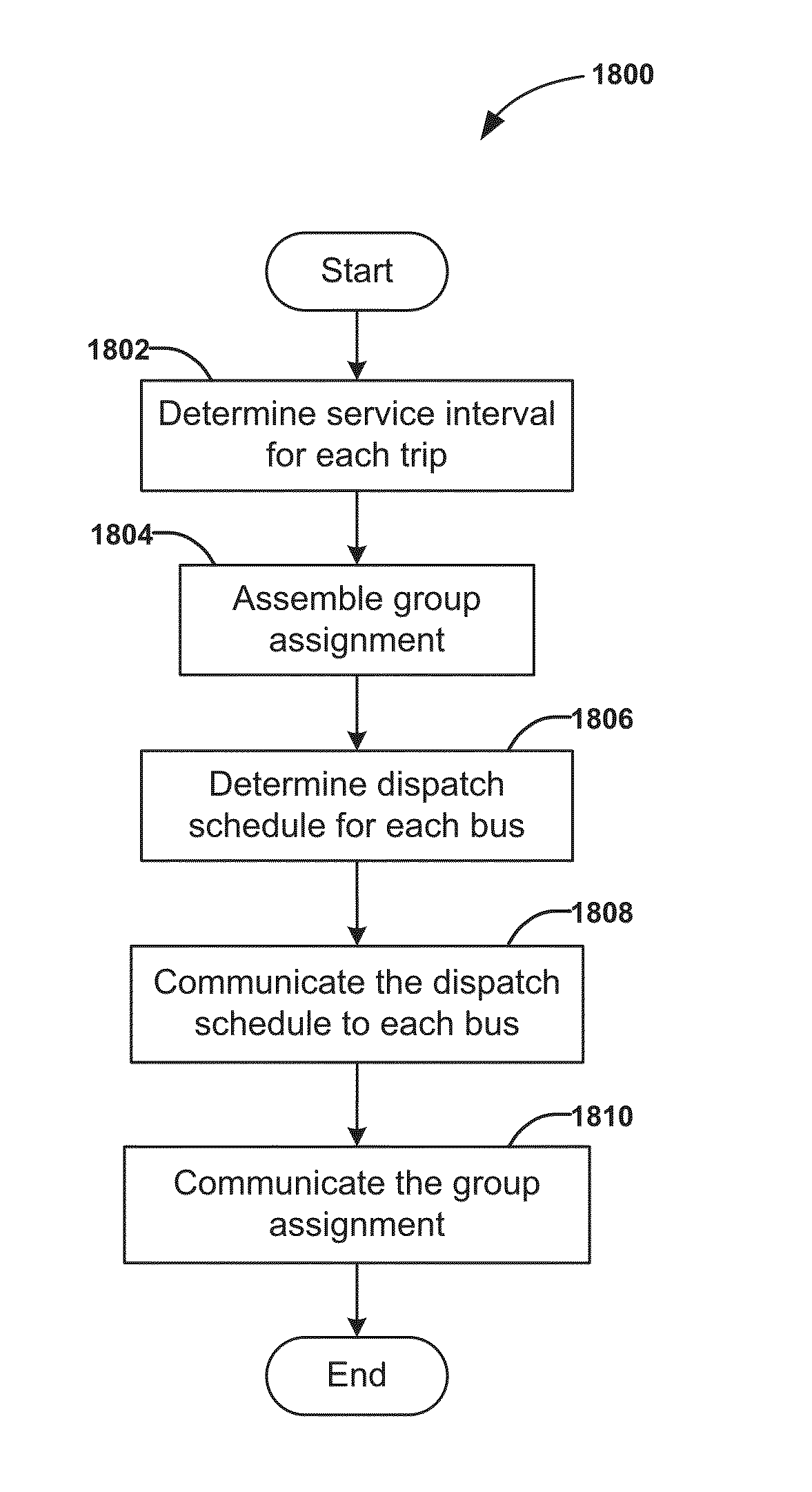
InactiveUS20150294430A1Increasing driver workloadIncreasing transit operational costDigital data processing detailsExternal condition input parametersGuided busTransit system
A method for dispatching buses in groups for a bus transit system comprising determining a service interval for each trip of the bus transit system, assembling group assignments based on the service interval for each trip, determining a dispatch schedule for each bus based on the service interval and the group assignment, communicating the dispatch schedule to each bus, and communicating group assignment information to each of a plurality of the buses in a group. The group assignment assigns a plurality of the buses into a group on a segment of the trip shared by the plurality of buses such that multiple buses for different trips can dock at a station at the same time like a train to facilitate transferring passengers.
Owner:TOMORROWS TRANSPORTATION TODAY
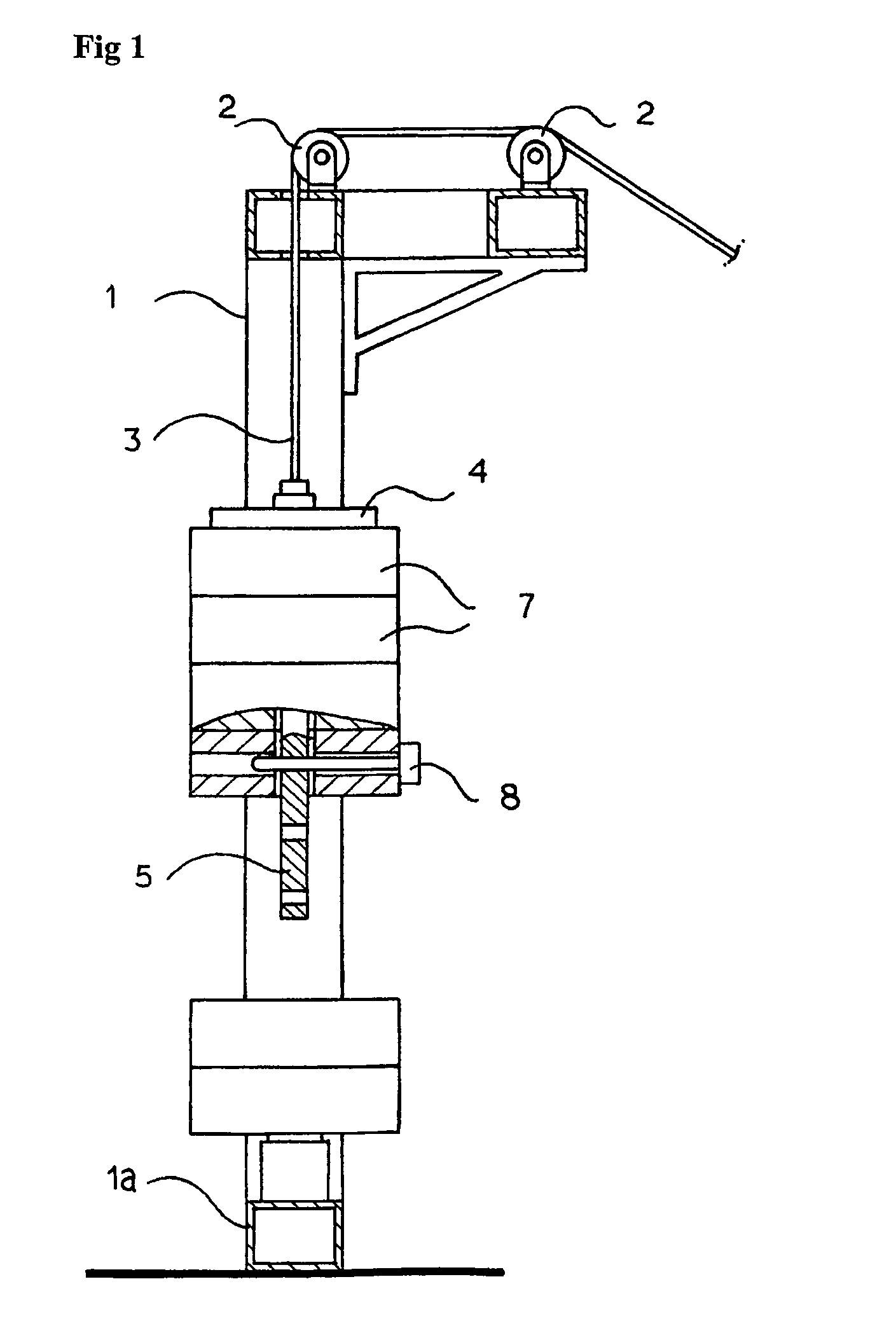
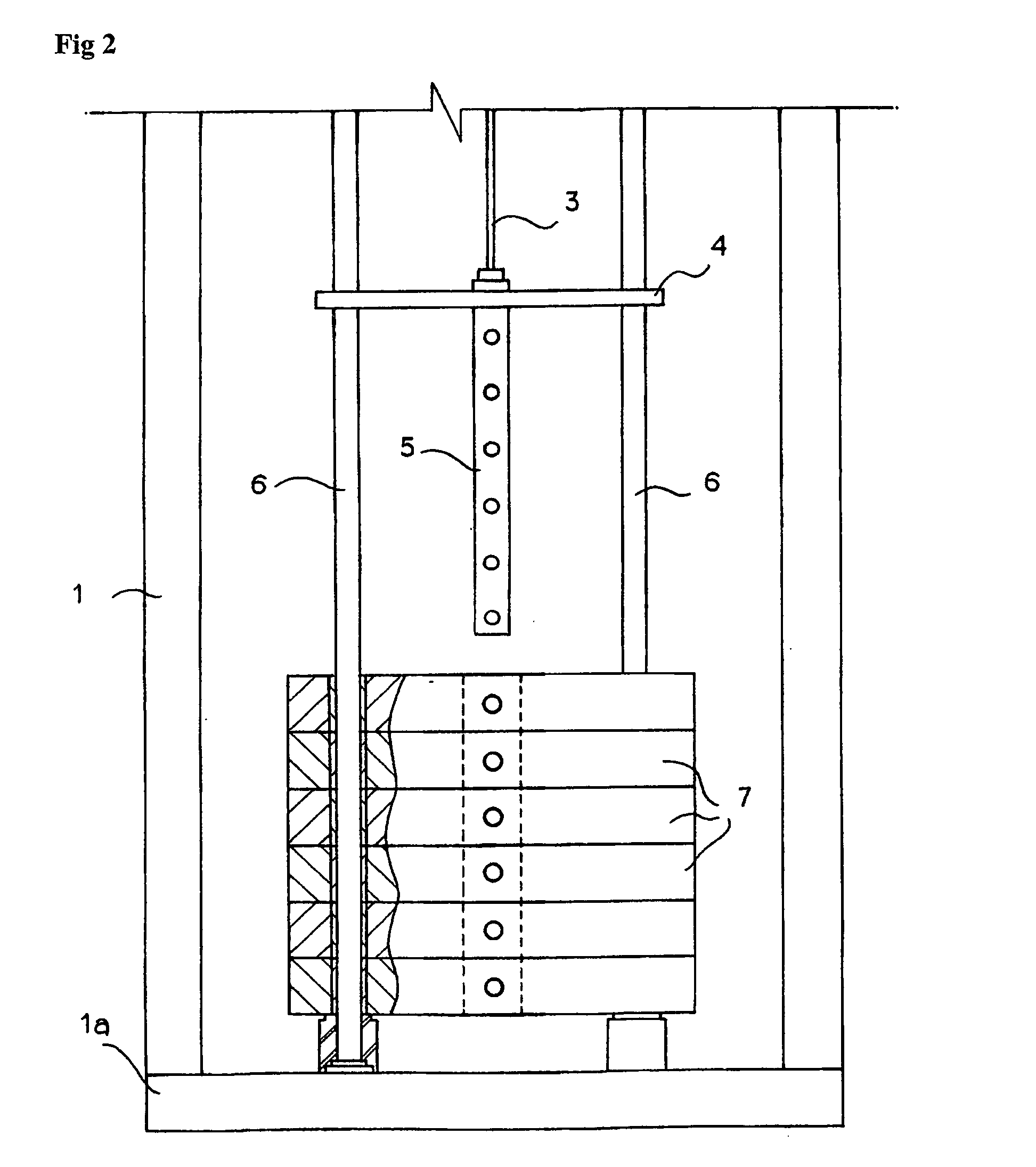
Device for controlling weight of a weight training machine and its method
The present invention relates to a device for controlling the weight of a weight training machine and its method which is capable of allowing a user of the weight training machine to control weight of a stack more conveniently, eliminating any inconvenience caused when a fixing pin is inserted into a hole of the stack, which is a weight unit of the conventional weight training machine, preventing the fixing pin from escaping out of the stack during the weight training by the user of the weight training machine so that any safety accident can be kept previously from occurring, allowing the user to control minutely weight for the weight training, being programmable by means of remote electrical control so as to bring about a motive for exercise, and eliminating any restriction of design, which is common in the prior art because of the fixing pin.
Owner:LEE BYUNG DON
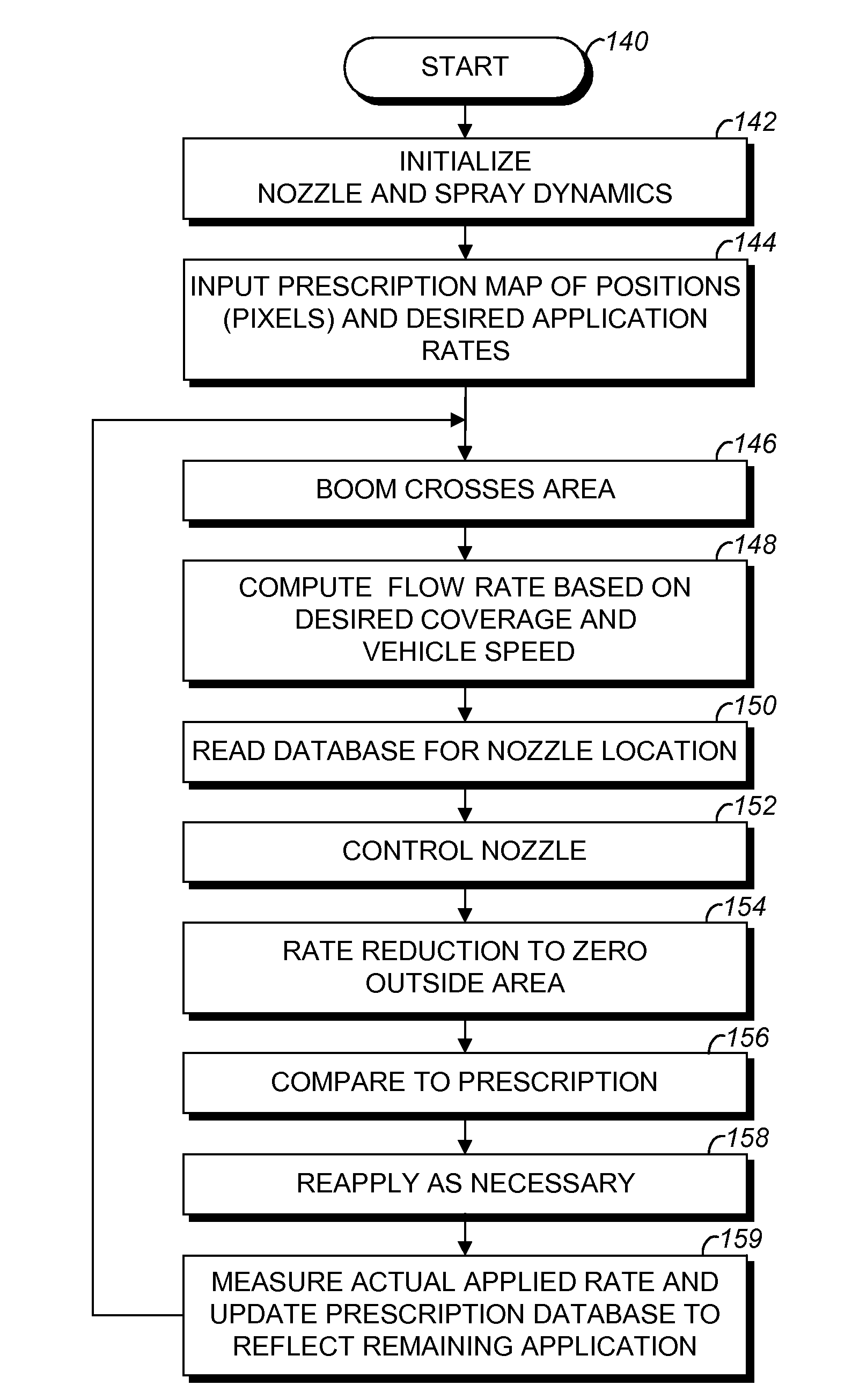
Raster-based contour swathing for guidance and variable-rate chemical application
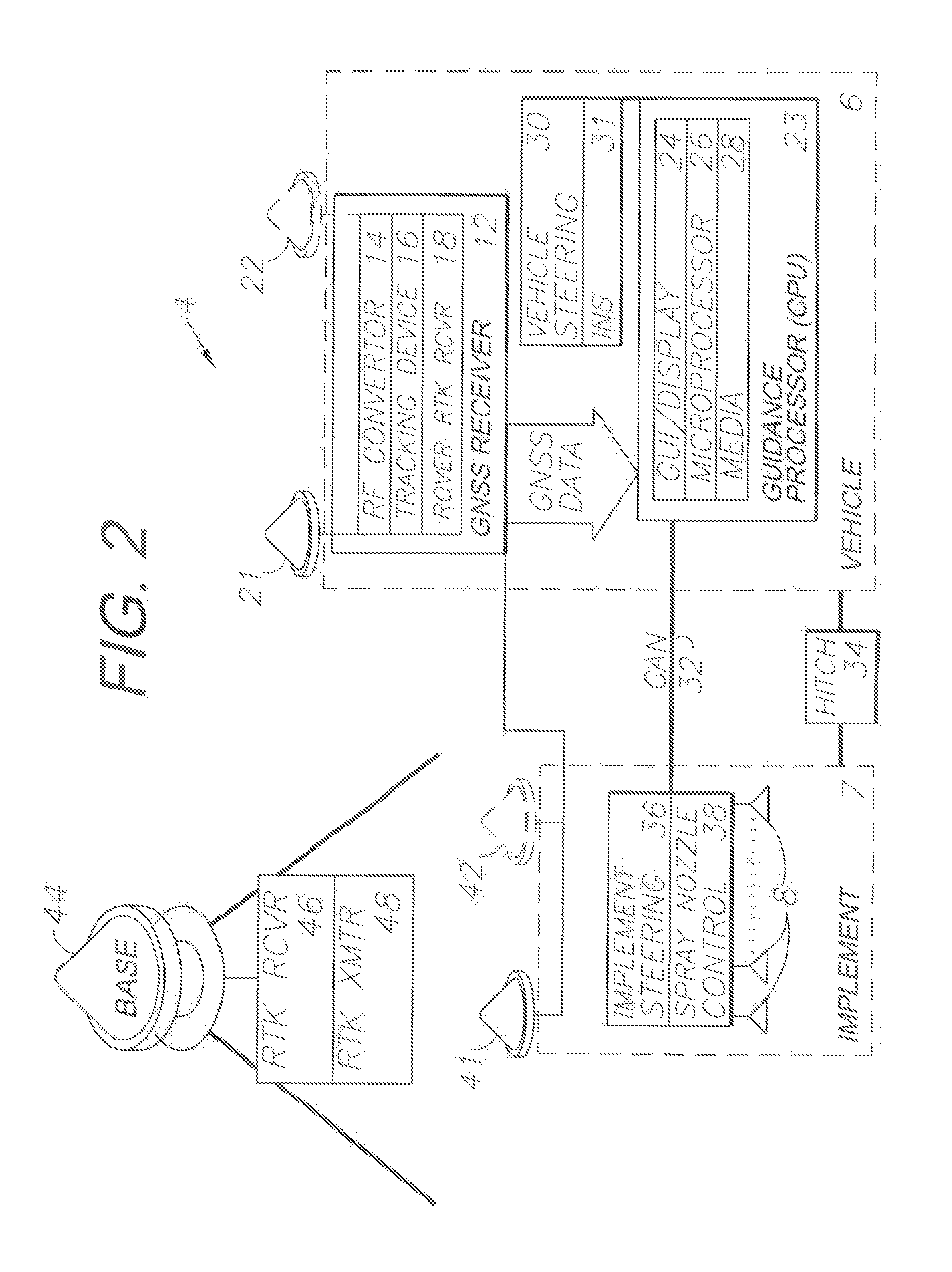
ActiveUS20100185364A1Automatic controlDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsGratingSprayer
A raster-based system for GNSS guidance includes a vehicle-mounted GNSS antenna and receiver. A processor provides guidance and / or autosteering commands based on GNSS-defined pixels forming a grid representing an area to be treated, such as a field. Specific guidance and chemical application methods are provided based on the pixel-defined treatment areas and preprogrammed chemical application prescription maps, which can include variable chemical application rates and dynamic control of the individual nozzles of a sprayer.
Owner:AGJUNCTION
Communication apparatus
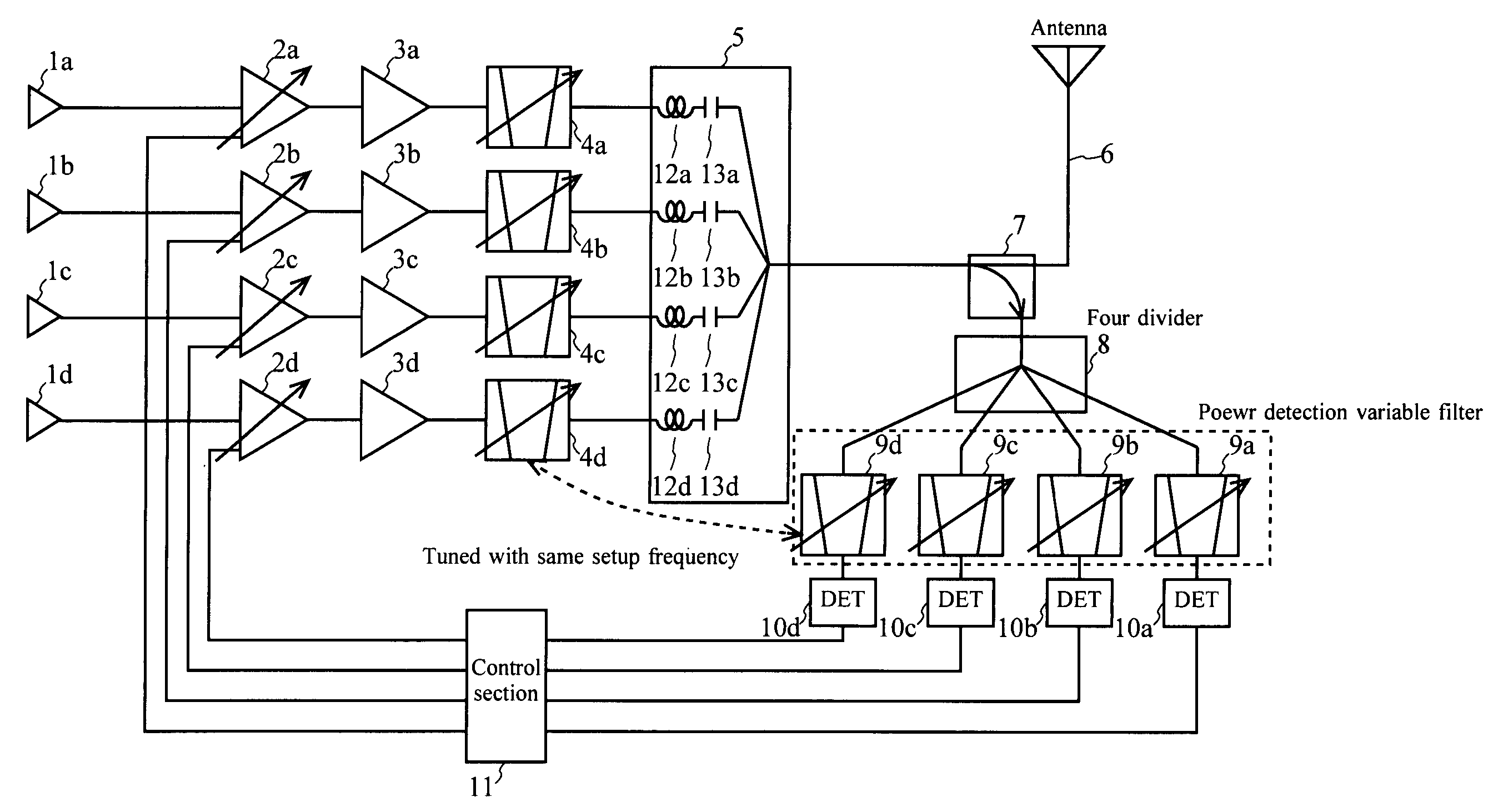
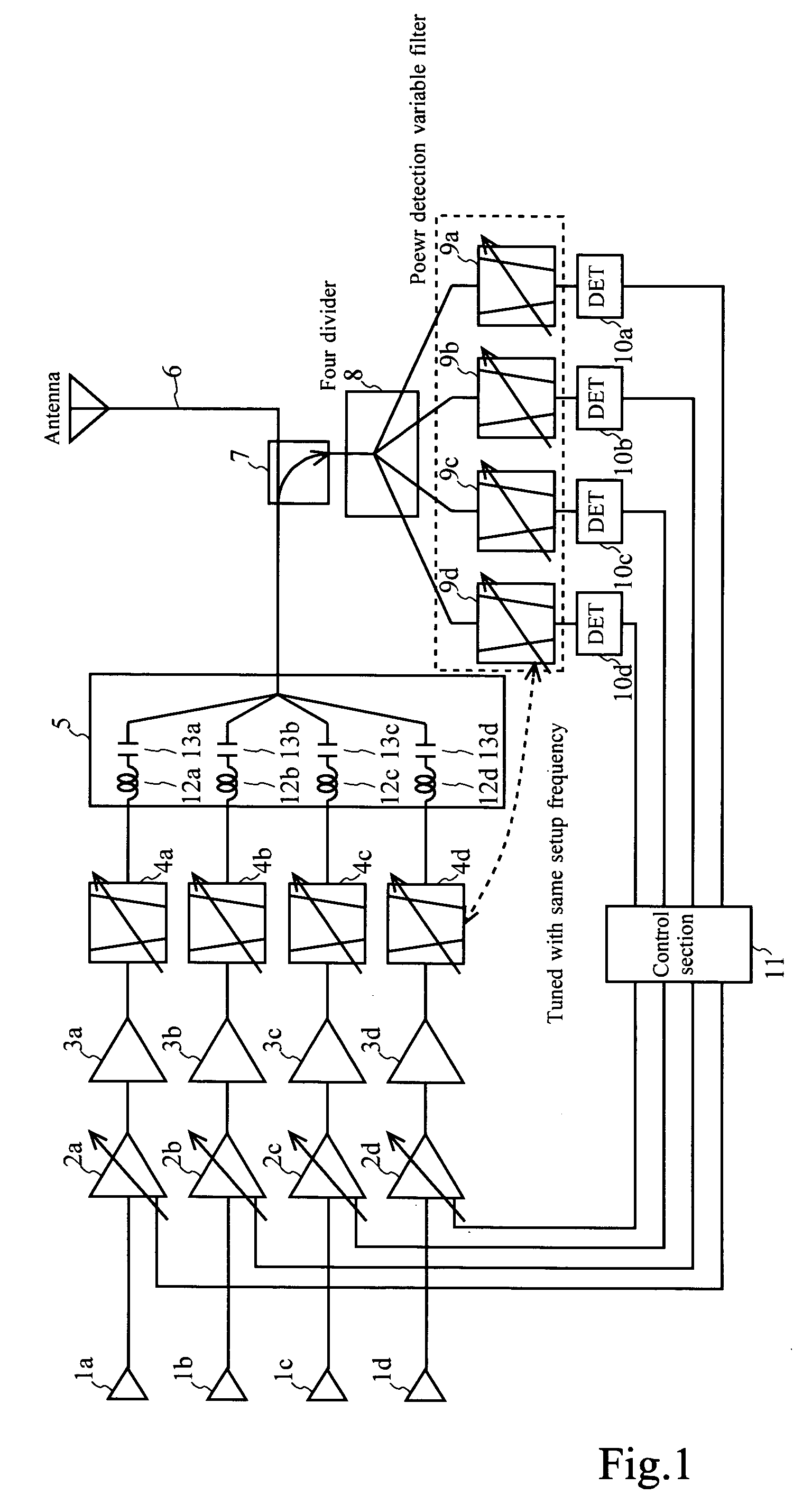
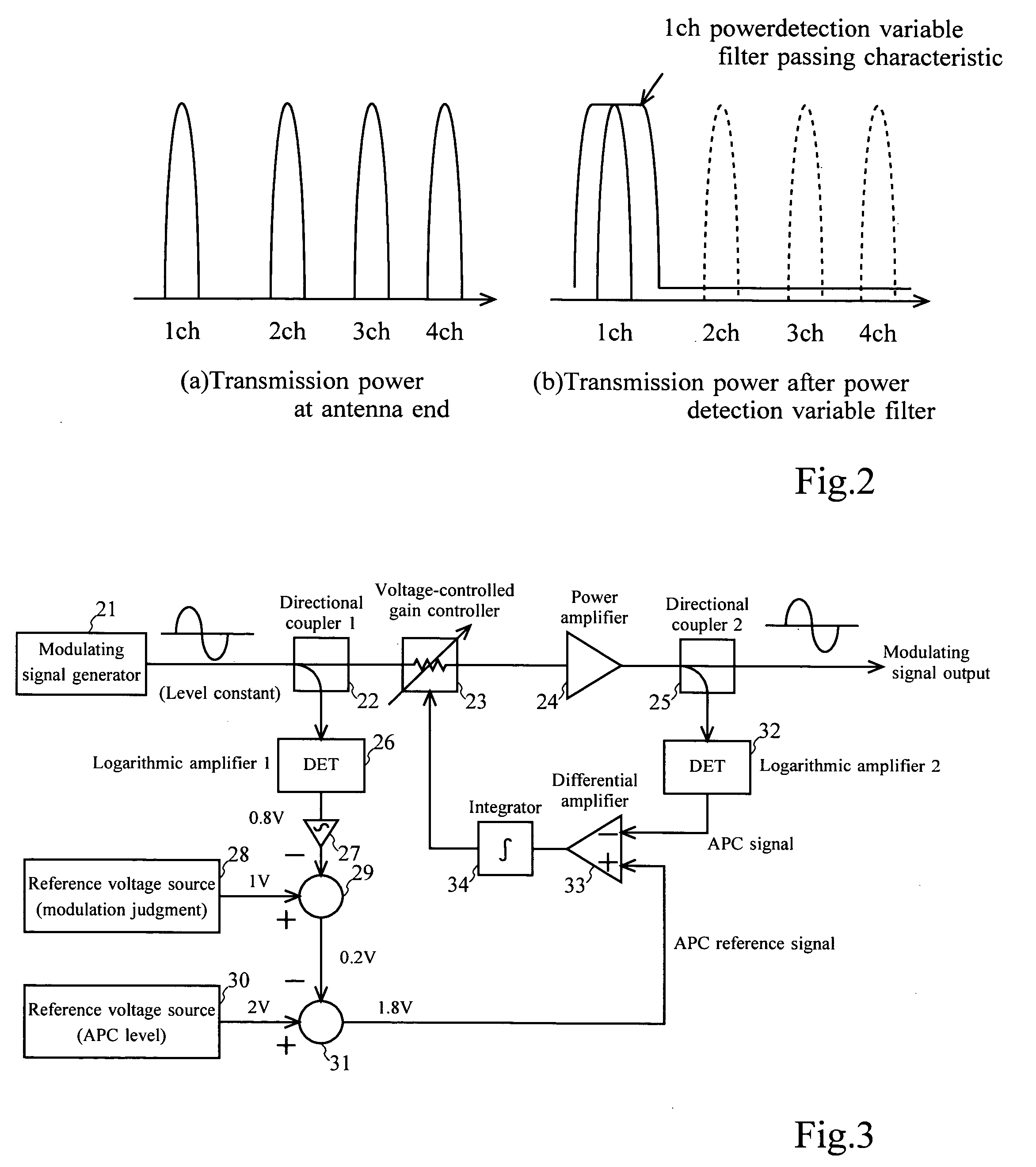
InactiveUS20050245213A1Automatic controlImprove the level ofResonant long antennasGain controlWireless transmissionMode control
In a communication apparatus, effective automatic power control (APC) is realized. Transmission object signal level changing units change a level of a transmission object signal of each channel, and transmission filter units carry out filtering for a signal of each channel after its level was changed with a characteristic for allowing a passage of a frequency component of each channel, and a transmission signal coupling unit couples signals of plural channels after the filtering was carried out, and an antenna transmits a coupled signal by wireless, and coupled signal dividing units divide a part of the coupled signal into a plurality of signals, and level detection filter units carry out filtering for each divided signal with an identical characteristic to the above-described characteristic, and signal level detecting units detect a level of a signal of each channel after the filtering was carried out, and a transmission object signal level change mode controlling unit controls a level change mode of a transmission object signal of each channel on the basis of the detection result.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
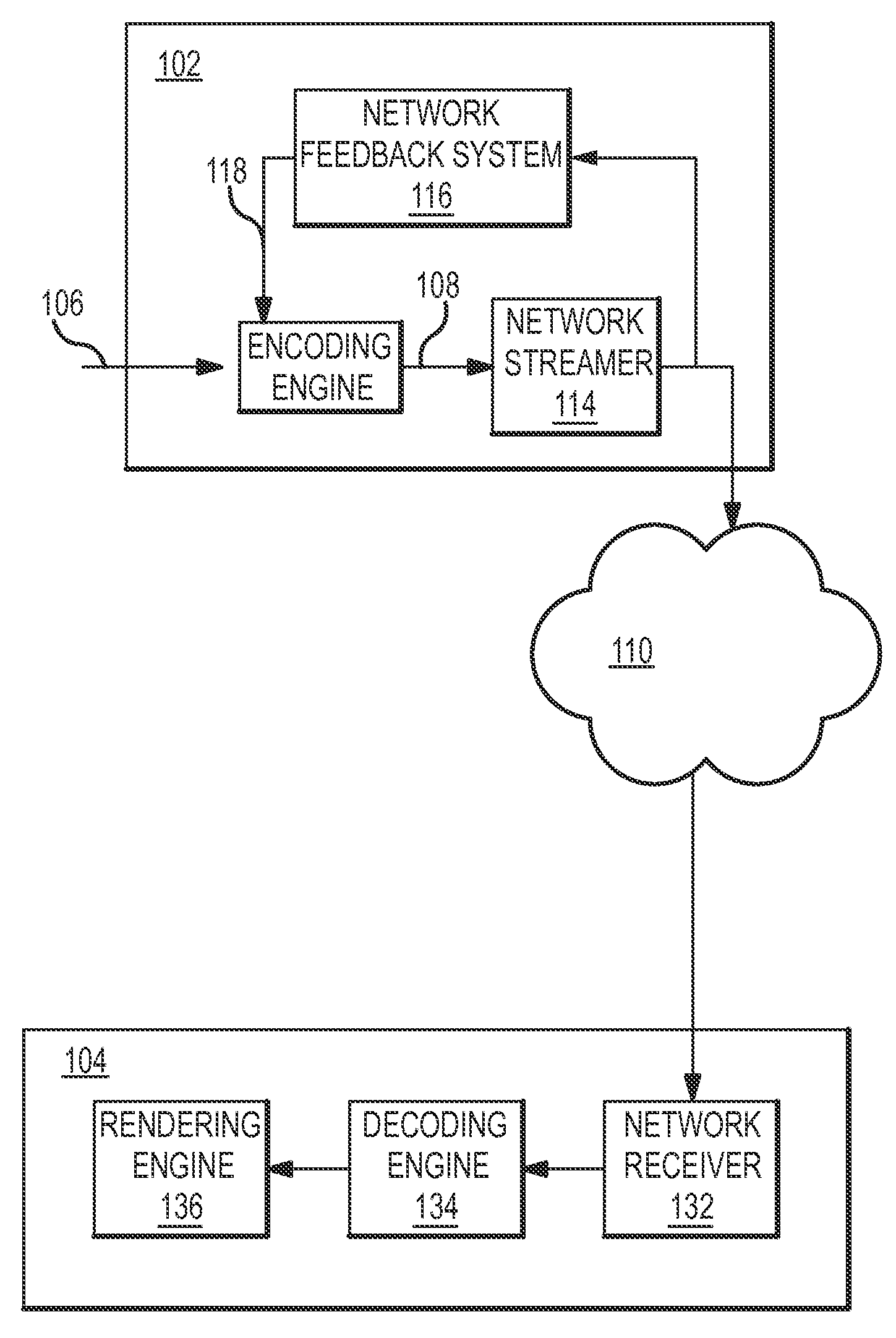
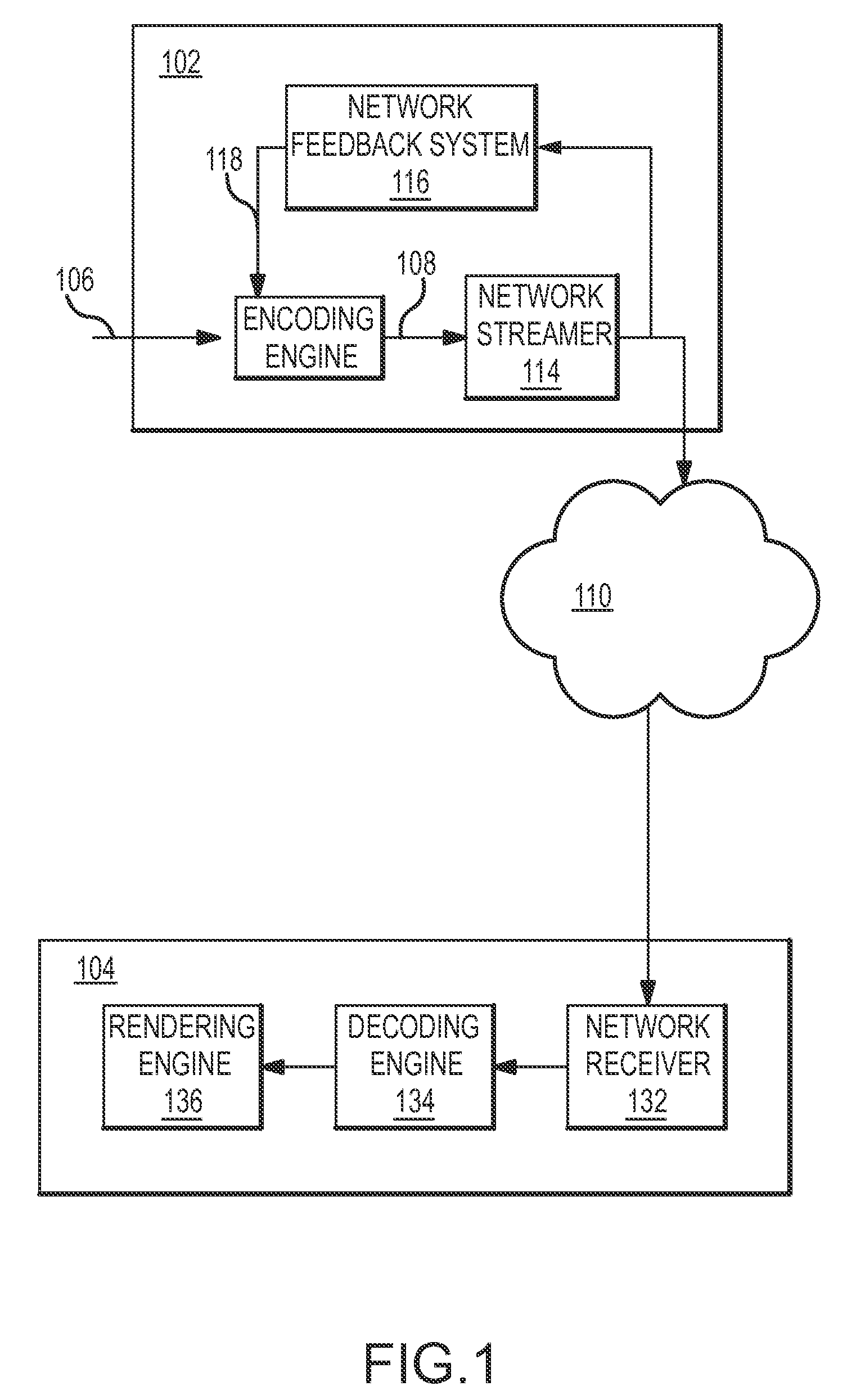
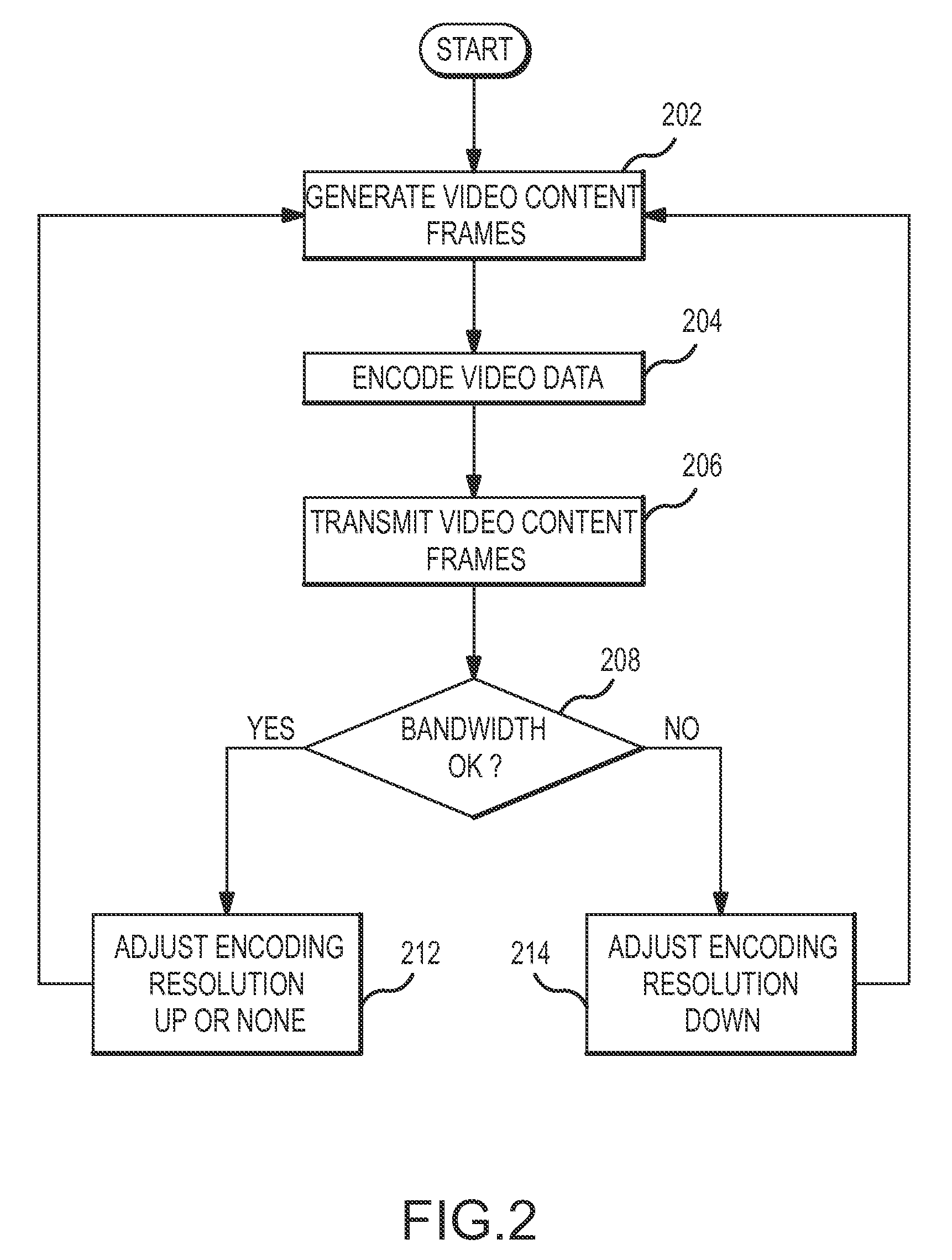
Systems and methods for automatically controlling the resolution of streaming video content
InactiveUS20110032986A1Automatic controlColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData connectionComputer graphics (images)
Systems and methods are described for automatically controlling the resolution of video content that is streaming over a data connection. Video content frames are generated that each have a predetermined frame resolution and comprise video data encoded at an encoding resolution. The video content frames are transmitted over a network, and one or more conditions of the network are sensed. The encoding resolution of the video data is selectively adjusted in each video content frame in response to the one or more sensed network conditions.
Owner:SLING MEDIA PVT LTD
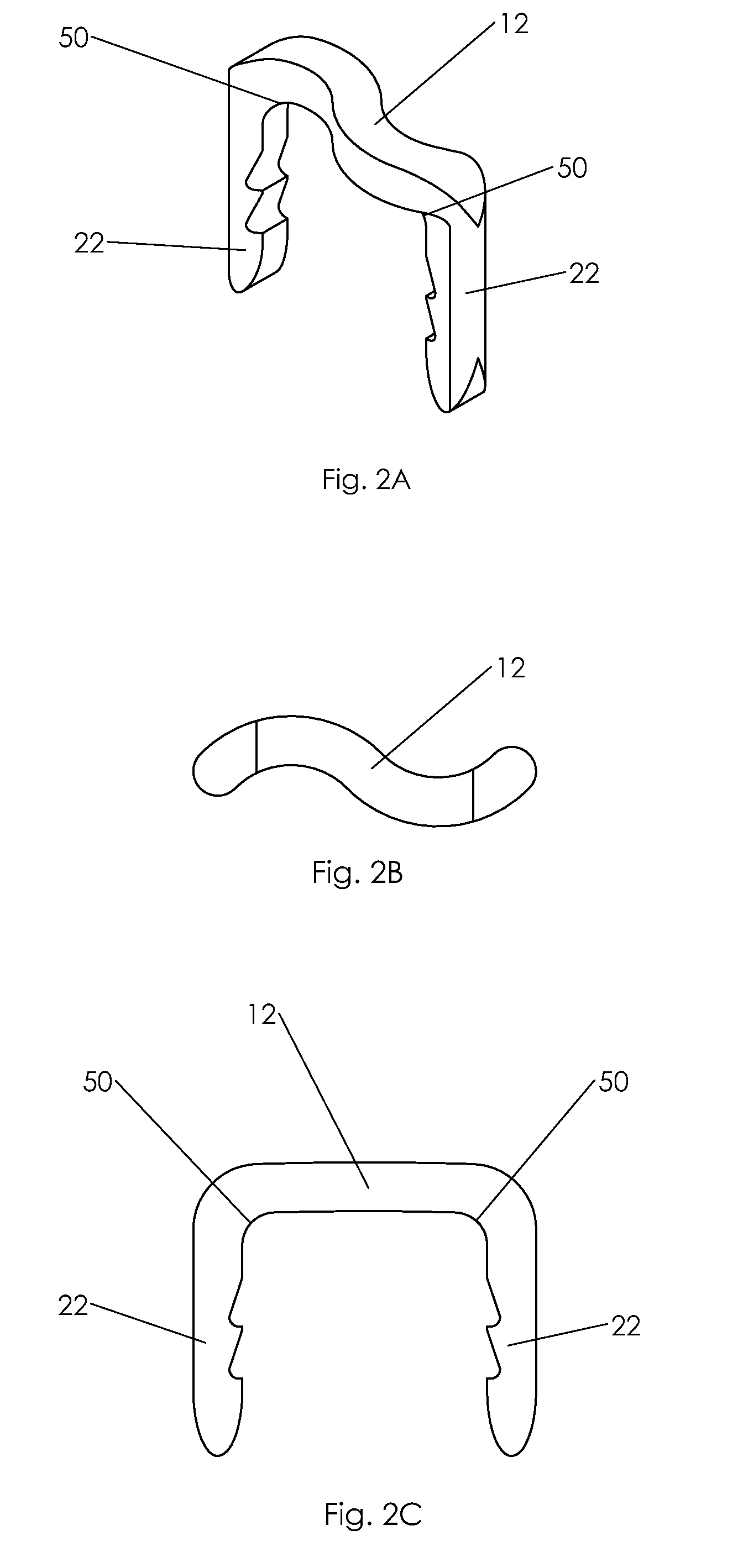
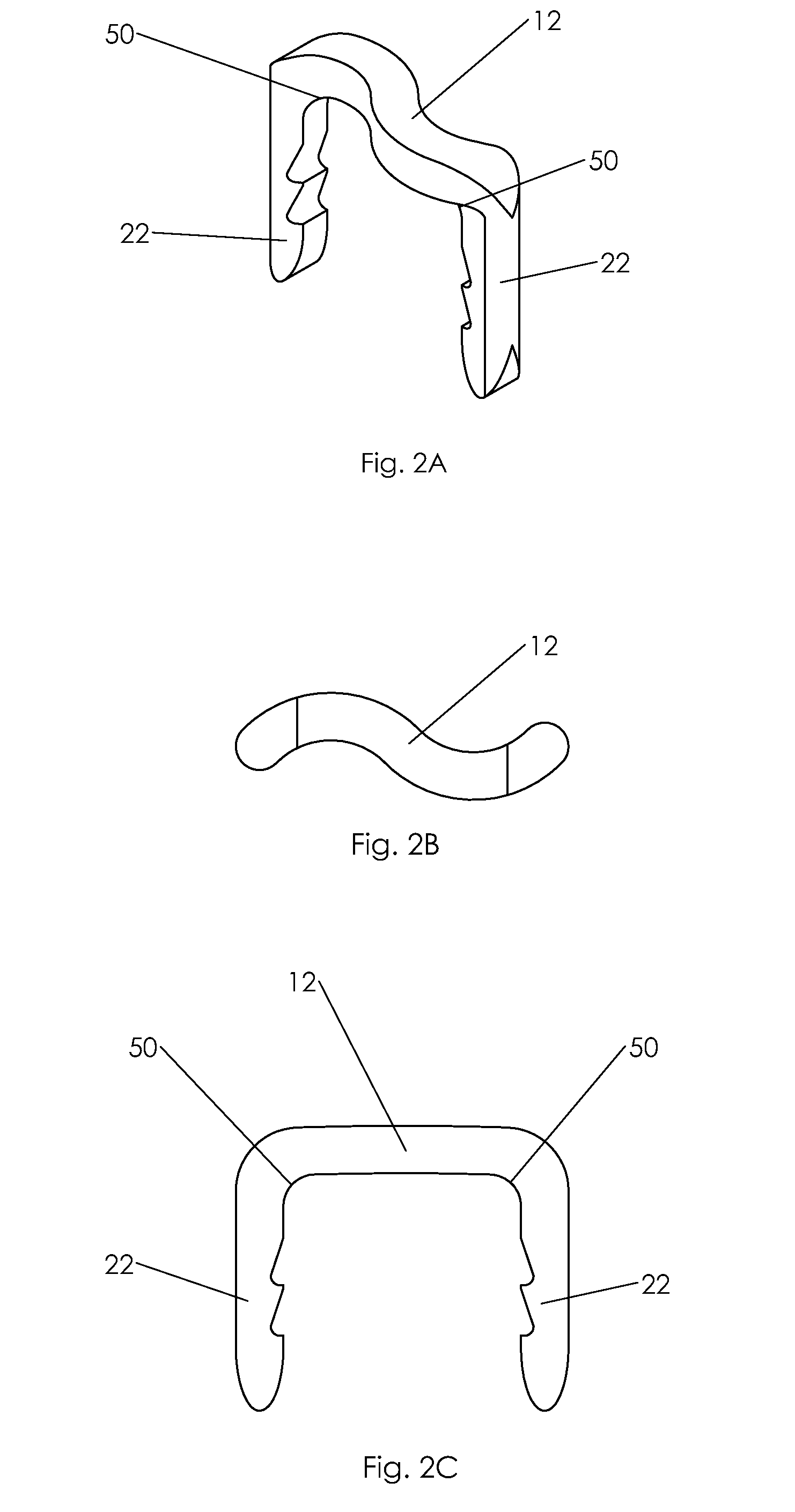
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS20130026206A1Simple and reliableLow costSuture equipmentsStapling toolsSingle useBone staple
A new shape changing staple and instrument for the fixation of structures to include bone tissue and industrial materials. This new staple stores elastic mechanical energy to exert force on fixated structures to enhance their security and in bone affect its healing response. This staple once placed changes shape in response to geometric changes in the materials structure, including healing bone tissue. The staple is advanced over prior staples due to its: 1) method of operation, 2) high strength, 3) method of insertion, 4) compressive force temperature independence, 5) energy storing staple retention and delivery system, 6) compatibility with reusable or single use product configuration, 7) efficient and cost effective manufacturing methods, and 8) reduction in the steps required to place the device. In addition to the staple's industrial application an embodiment for use in the fixation of the musculoskeletal system is shown with staple, cartridge, and extrusion handle.
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS20130030437A1Simple and reliable processLow costInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsShape changeMechanical energy
A new shape changing staple and instrument for the fixation of structures to include bone tissue and industrial materials. This new staple stores elastic mechanical energy to exert force on fixated structures to enhance their security and in bone affect its healing response. This staple once placed changes shape in response to geometric changes in the materials structure, including healing bone tissue. The staple is advanced over prior staples due to its: 1) method of operation, 2) high strength, 3) method of insertion, 4) compressive force temperature independence, 5) energy storing staple retention and delivery system, 6) compatibility with reusable or single use product configuration, 7) efficient and cost effective manufacturing methods, and 8) reduction in the steps required to place the device. In addition to the staple's industrial application an embodiment for use in the fixation of the musculoskeletal system is shown with staple, cartridge, and extrusion handle.
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
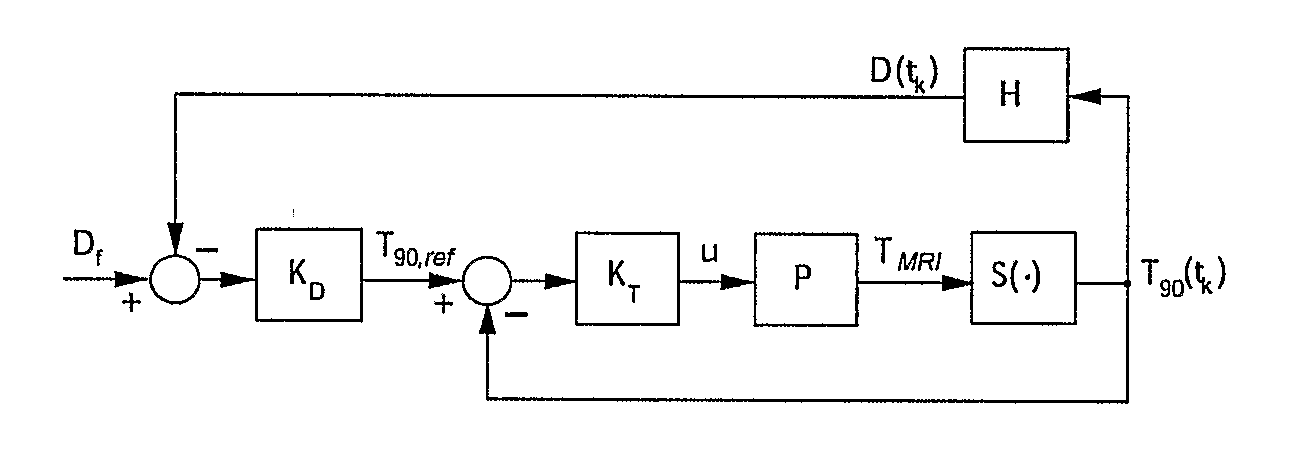
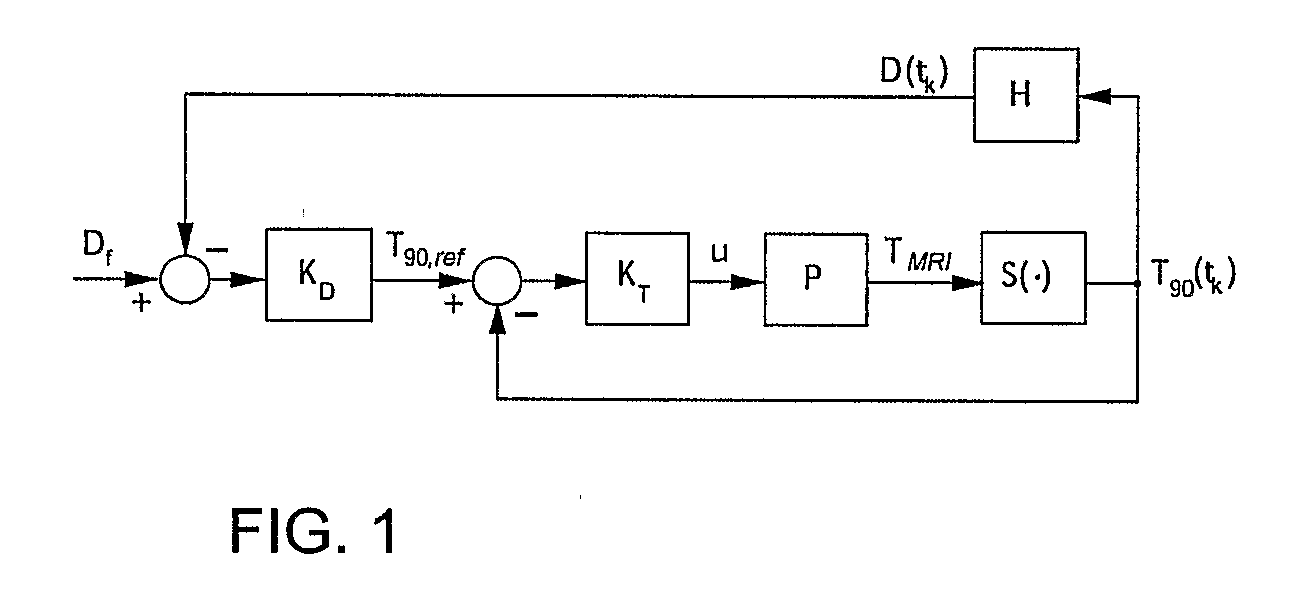
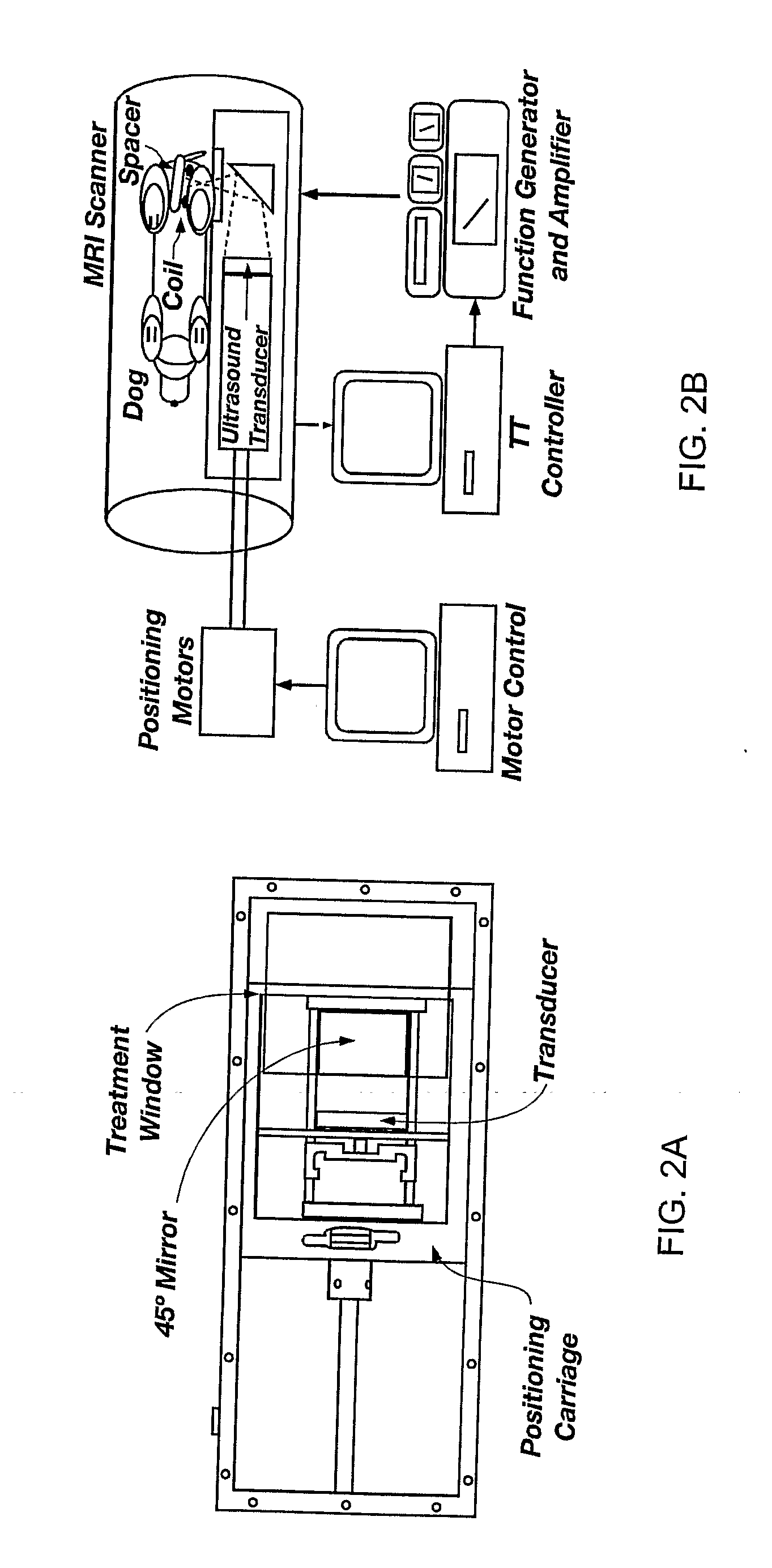
Minimum time feedback control of efficacy and safety of thermal therapies
InactiveUS20110137147A1Robustness with respectShorten treatment timeUltrasound therapySurgical instrument detailsMedicineFeedback controller
A thermal treatment control system including an imaging device for specifying the geometry and / or location of the treatment target, a thermal energy element for applying a thermal treatment for the heating or cooling of a target tissue for therapeutic purposes, a thermal energy detecting element for detecting a measured tissue response to the thermal treatment and a feedback controller for a real-time modification of the intensity and spatial distribution of the thermal dose in order to achieve therapeutic efficacy over a minimum or reduced treatment time while satisfying treatment constraints imposed to limit damage to normal tissues.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Uninterrupted ink supply system
ActiveUS20100201761A1Increase power consumptionOvercome problemsPrintingEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
An uninterrupted ink supply system is provided, including a main cartridge connected to a printer, a connection device having an automatic airflow control structure and installed on said main cartridge, and a replenishment cartridge for connecting to the connection device. The replenishment cartridge is connected to the connection device, and is able to refill the ink into the main cartridge, and automatically stop refilling when the ink level reaching a specific height and start refilling again when ink level below a specific height. When the replenishment cartridge is removed for refilling when the ink is used up, the main cartridge still contains ink so that the printing will not be suspended.
Owner:JETBEST CORP
Device for controlling weight of a weight training machine and its method
The present invention relates to a device for controlling the weight of a weight training machine and its method which is capable of allowing a user of the weight training machine to control weight of a stack more conveniently, eliminating any inconvenience caused when a fixing pin is inserted into a hole of the stack, which is a weight unit of the conventional weight training machine, preventing the fixing pin from escaping out of the stack during the weight training by the user of the weight training machine so that any safety accident can be kept previously from occurring, allowing the user to control minutely weight for the weight training, being programmable by means of remote electrical control so as to bring about a motive for exercise, and eliminating any restriction of design, which is common in the prior art because of the fixing pin.
Owner:LEE BYUNG DON
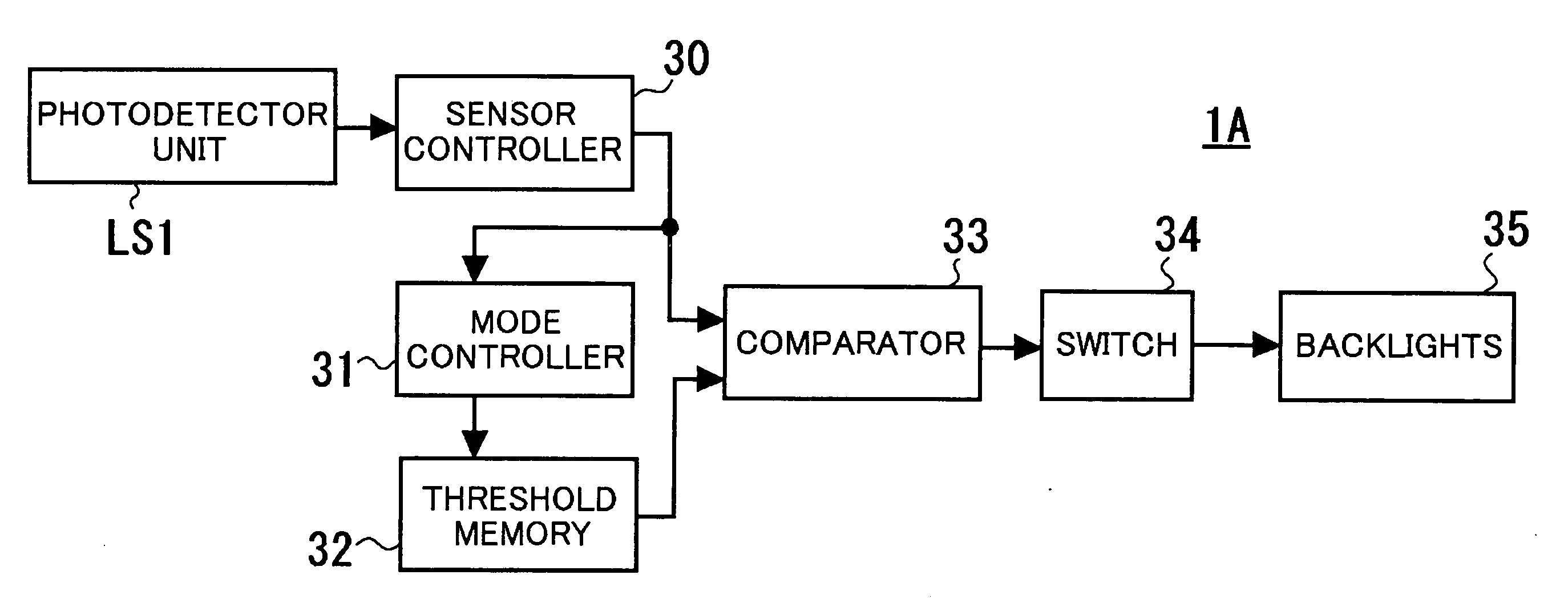
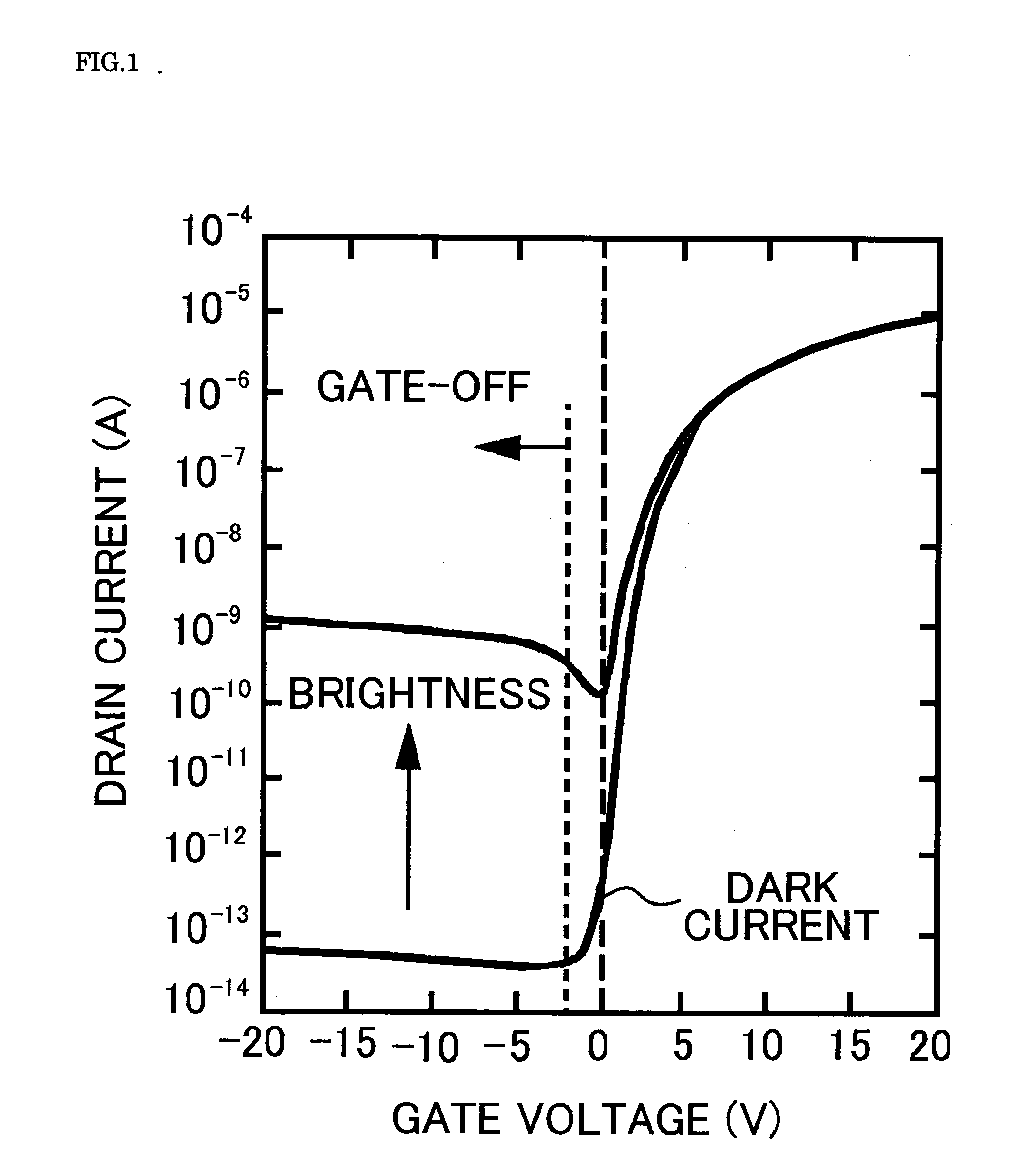
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20070229452A1Simple structureReduce sensitivityStatic indicating devicesPhotometryPhotovoltaic detectorsLiquid-crystal display
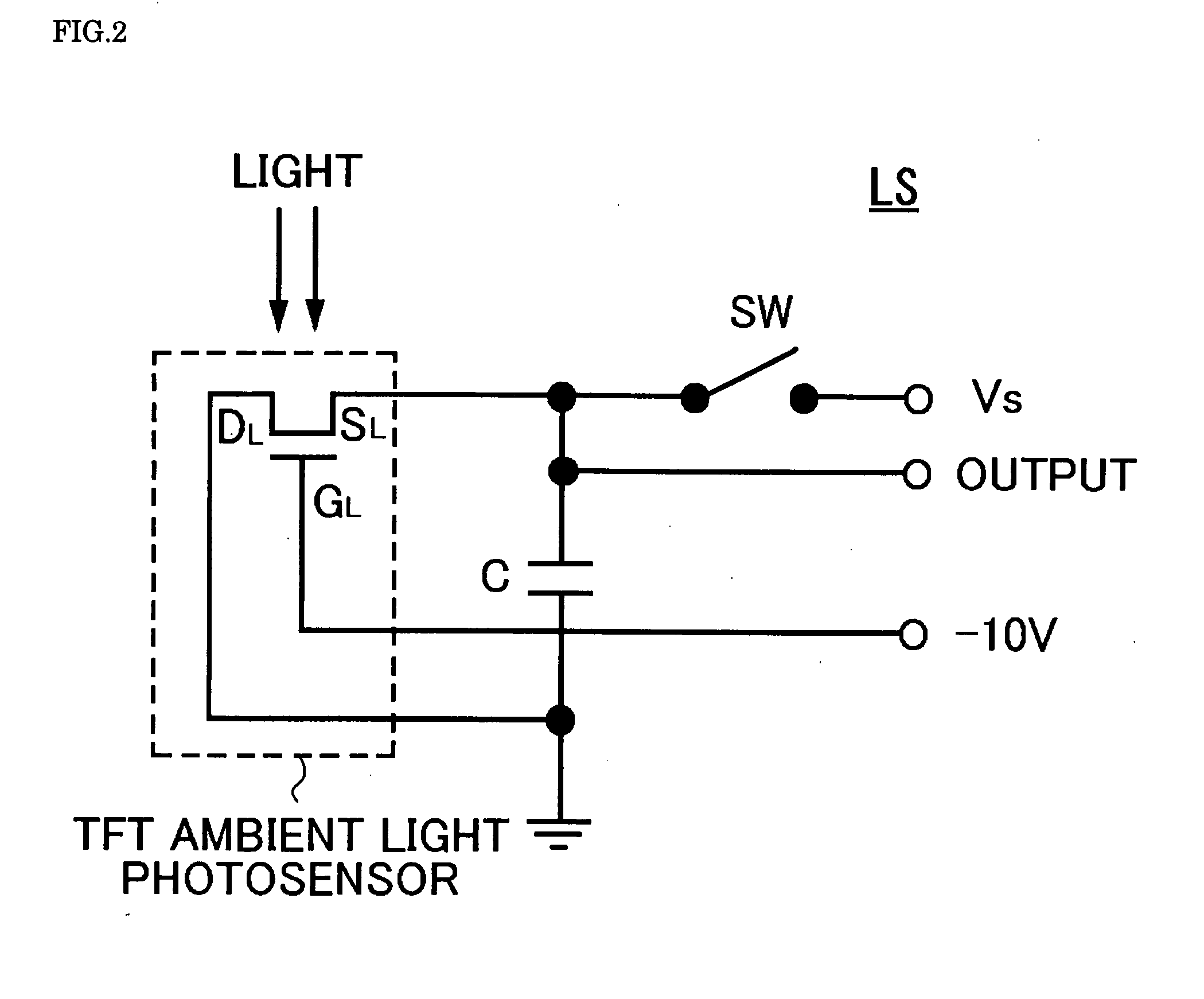
A liquid crystal display (LCD) 1 according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a liquid crystal panel having a TFT substrate 2, a CF substrate 25, and a liquid crystal layer 14 interposed between the two substrates; a TFT ambient light photosensor having a semiconductor layer 19L for detecting external light; a photodetector unit LS1 having a capacitor Cw in which a predetermined reference voltage is charged and a voltage charged by leakage current of the TFT ambient light photosensor is lowered; and an ambient light photosensor reader unit Re1 for reading a voltage charged in the capacitor for a predetermined read period. The photodetector unit is disposed on a first surface of the TFT substrate 2 that is in contact with the liquid crystal layer, and the surface of the photodetector unit except for the semiconductor layer 19L and its periphery is covered by a light-shielding layer 21. It is therefore possible to provide an LCD in which malfunction or reduced sensitivity of its ambient light photosensor due to light from its backlights is prevented with a simple structure.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Stereoscopic video magnification and navigation system
InactiveUS20050090730A1Accurate informationImprove ergonomicsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsStereoscopic videoDisplay device
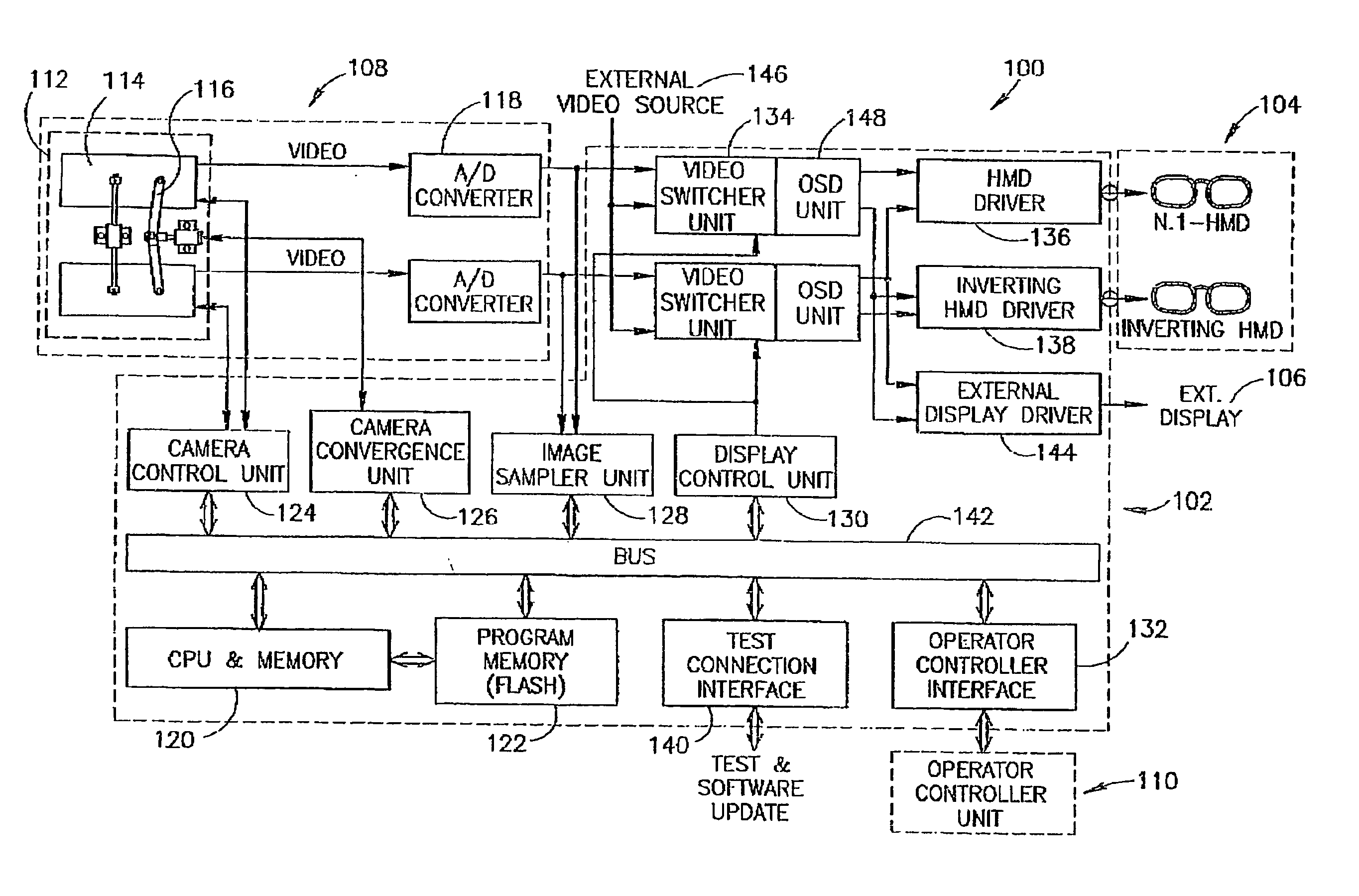
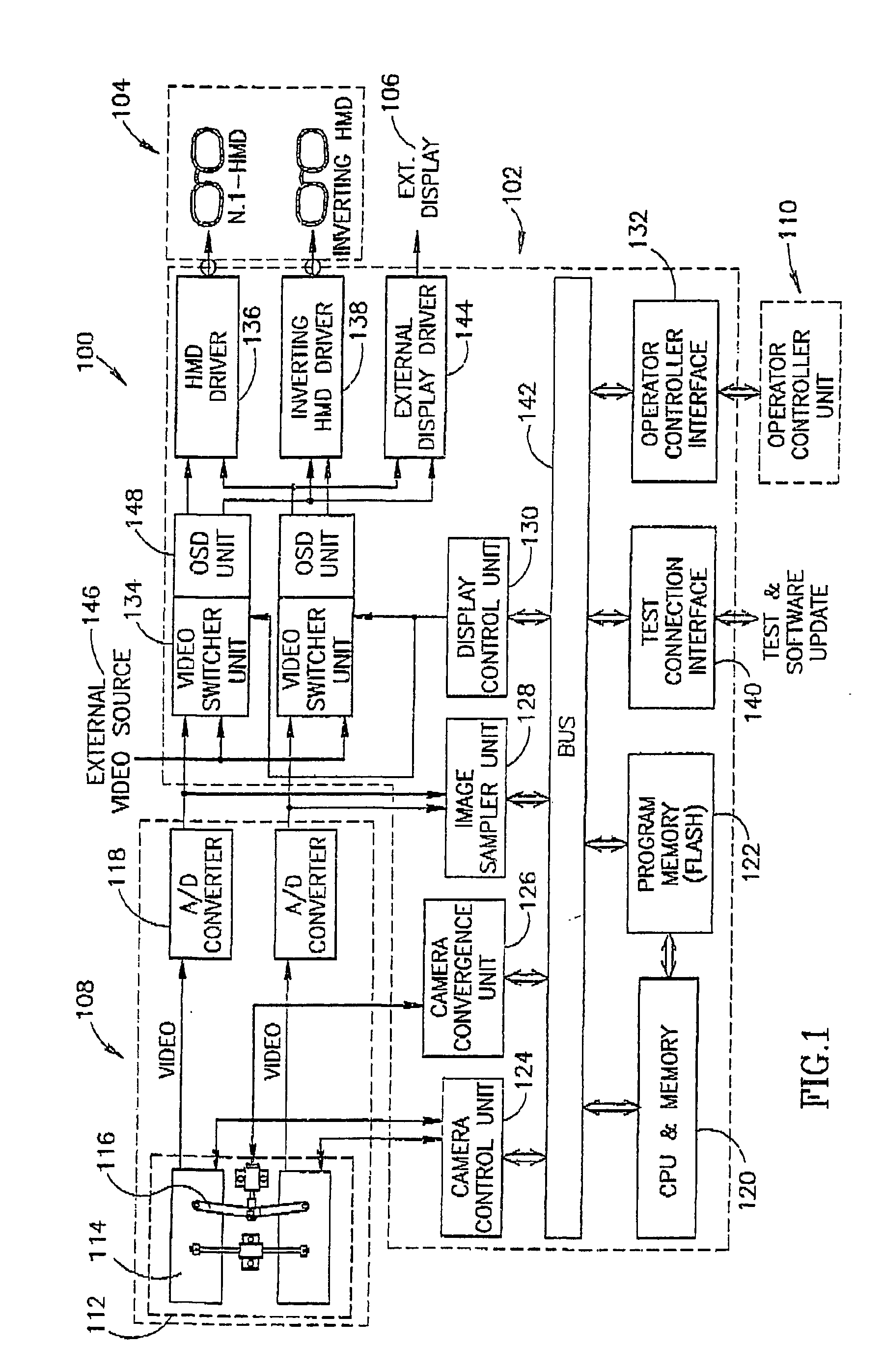
An apparatus and method for providing stereoscopic magnified observation enabling an operator to perform surgical procedures without having to remove his eyes from the operating field comprising a head mounted display for provding the operator with stereoscopic magnified images in an operating field, a camera module for providing stereoscopic magnified images, an operator controller unit for enabling an operator to control the operation of the apparatus; and an interface processing unit for processing and dynamically presenting the stereoscopic magnified images in an operating field.
Owner:FRENI BREMBO SPA
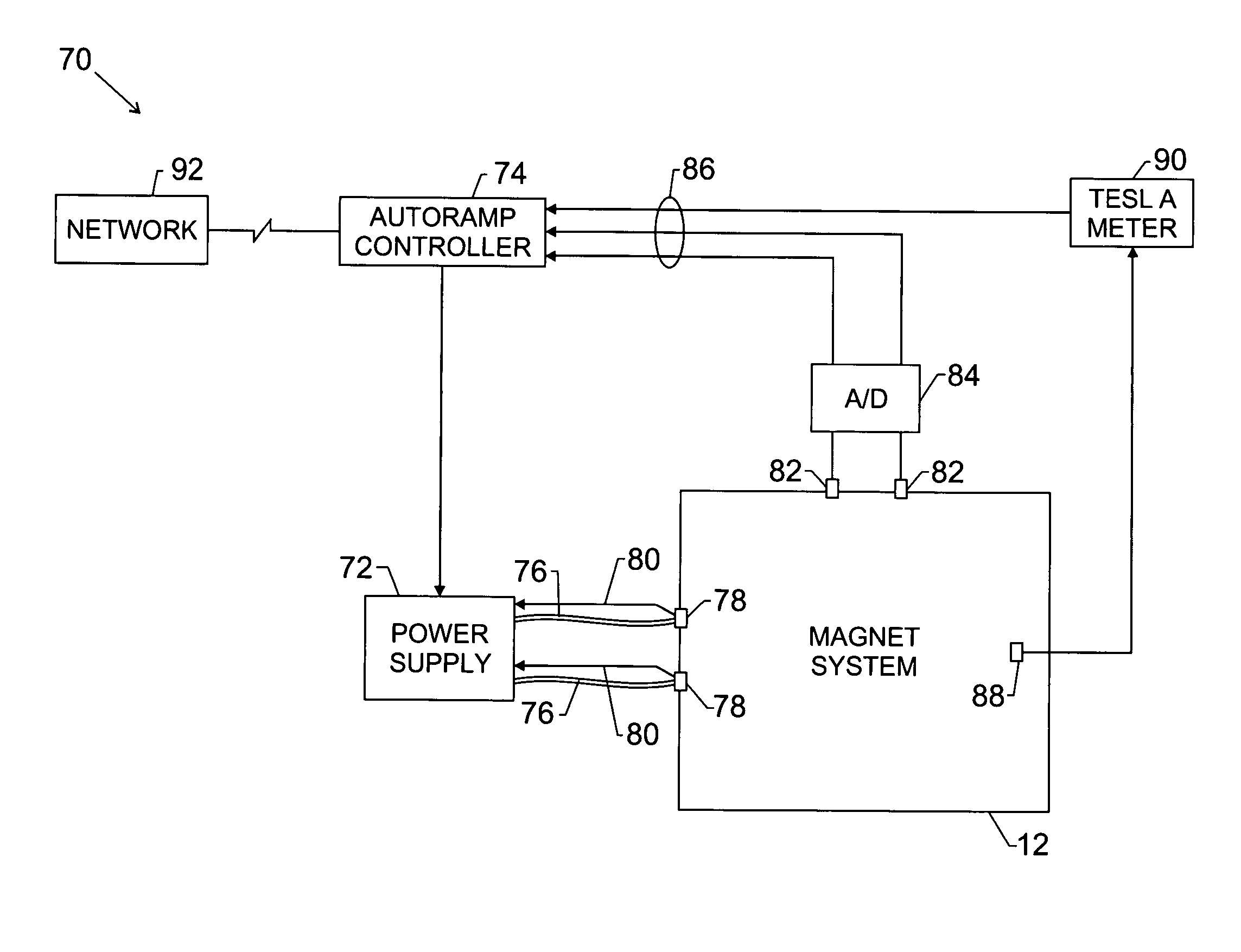
Automated superconducting magnet ramp-up system and method
InactiveUS20050111159A1Automatic controlMagnetic measurementsRelaysAutomatic controlSuperconducting Coils
The present invention provides for a novel technique for placing superconducting magnets into operation. For example, the technique provides for automatically controlling ramp-up of a superconducting magnet. In one aspect, the technique includes connecting a power supply to the magnet, determining constraining parameters of the ramp,-up automatically applying power to the magnet, automatically controlling the ramp-up based on the constraining parameters, and wherein the ramp-up is complete upon reaching a predetermined value of a target parameter.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYSTEMS INC
Multiple application purification and recycling device
InactiveUS20070170049A1Easy constructionFlexible operationDistillation regulation/controlEvaporation with vapour compressionDistillationMultiple applications
A multiple application recycling and purification device has a coaxial core that is horizontally oriented, non-rotating, cylindrical distillation chamber. The enhanced, completely coaxial configuration continuously cleans the entire distillation chamber and spreads a thin film of liquid to enhance distillation and positively aid in the removal of remaining contaminants. Through a timed and positioned valve, the device removes and purges lower-temperature contaminants. Timed valves and sensors control all phases of the distillation to provide a coaxially integrated, stand-alone, adaptable, scalable and maintenance free distillation unit that self-monitors, self-cleans and economically functions to produce the pure distilled liquid, e.g., water. This device can be modified to purify any numerous array of liquids and can be scaled to produce any amount of purified liquids for either household, commercial, or industrial applications.
Owner:MANSUR CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com