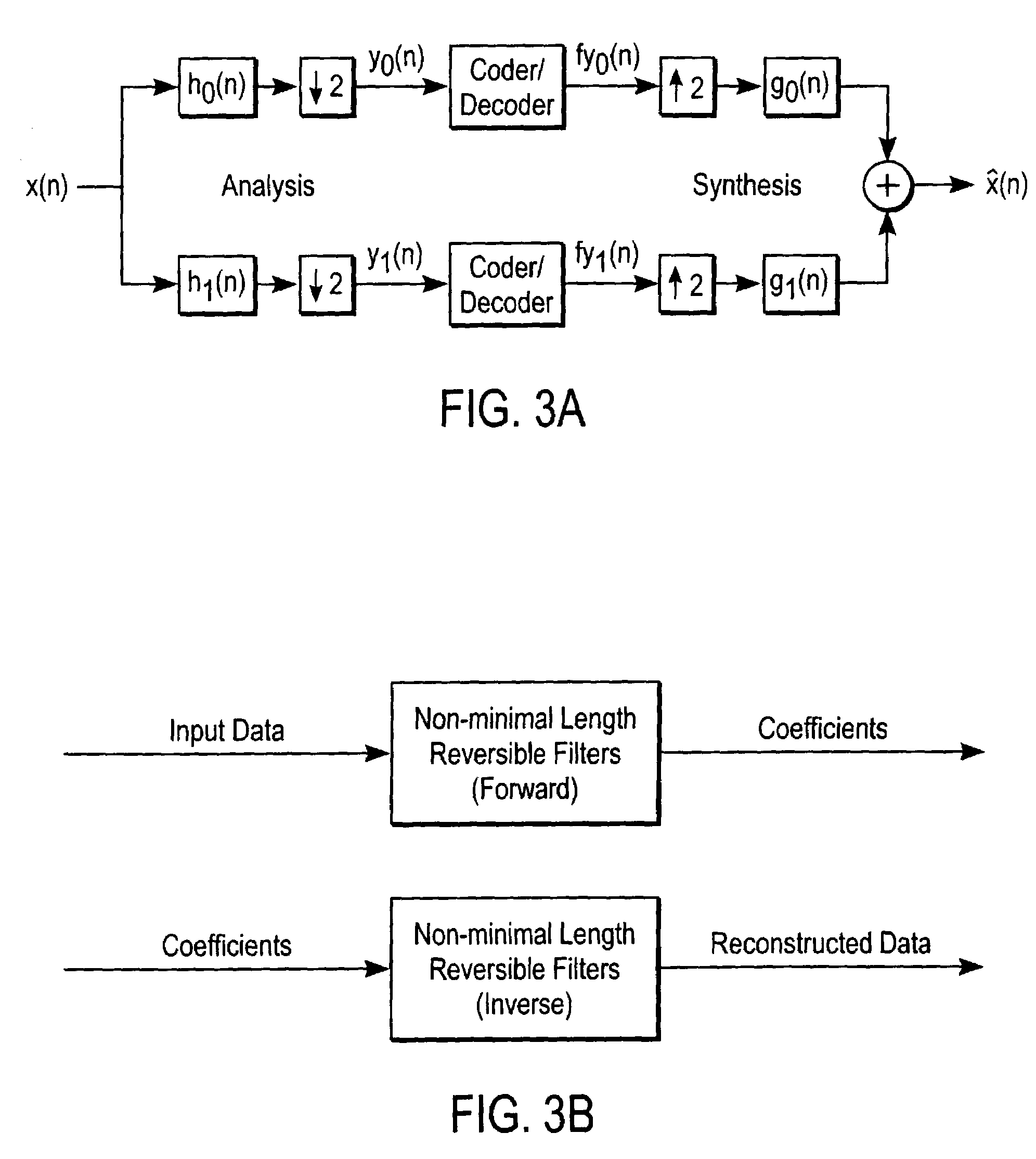
Patents
Literature
249 results about "Wavelet filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
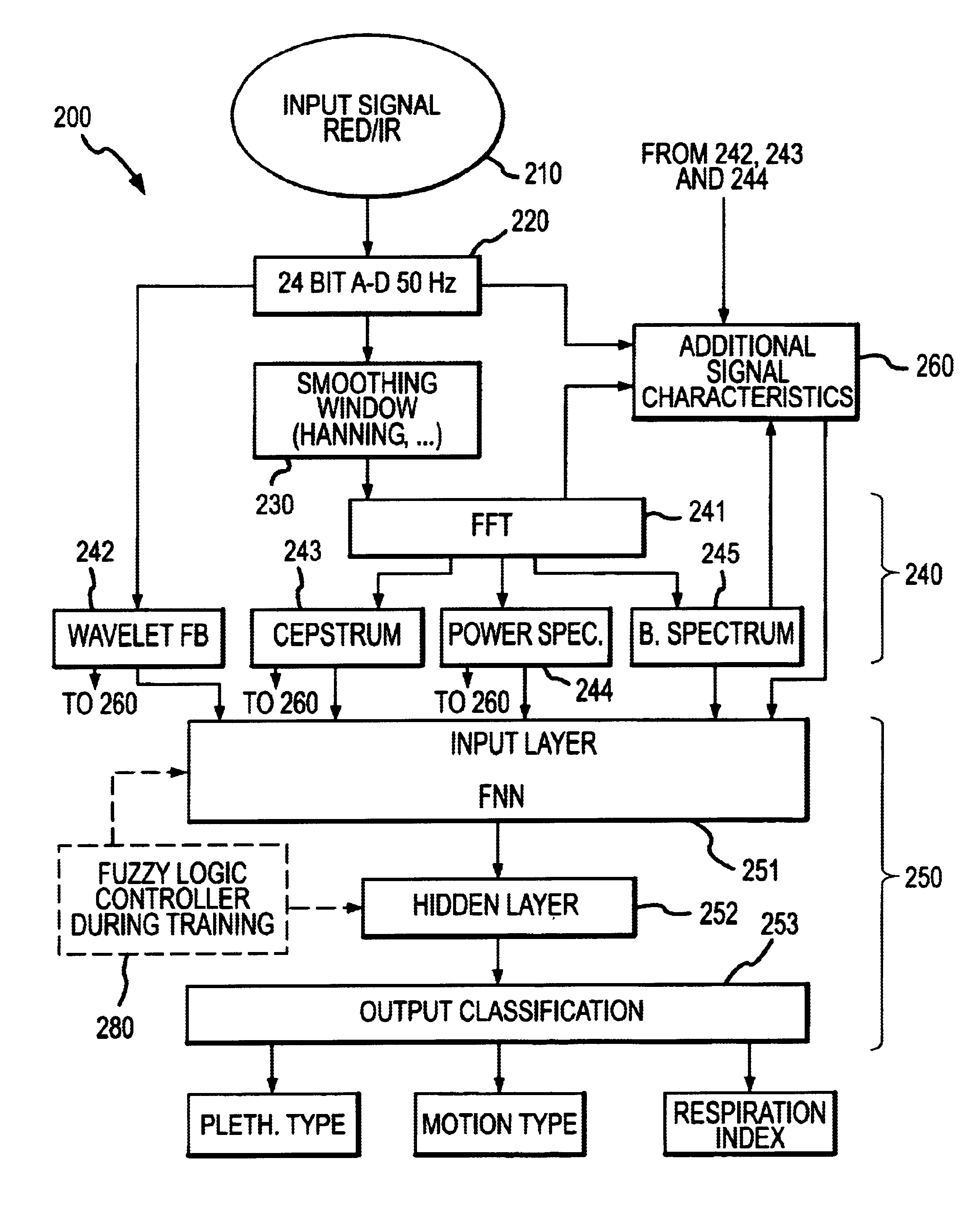
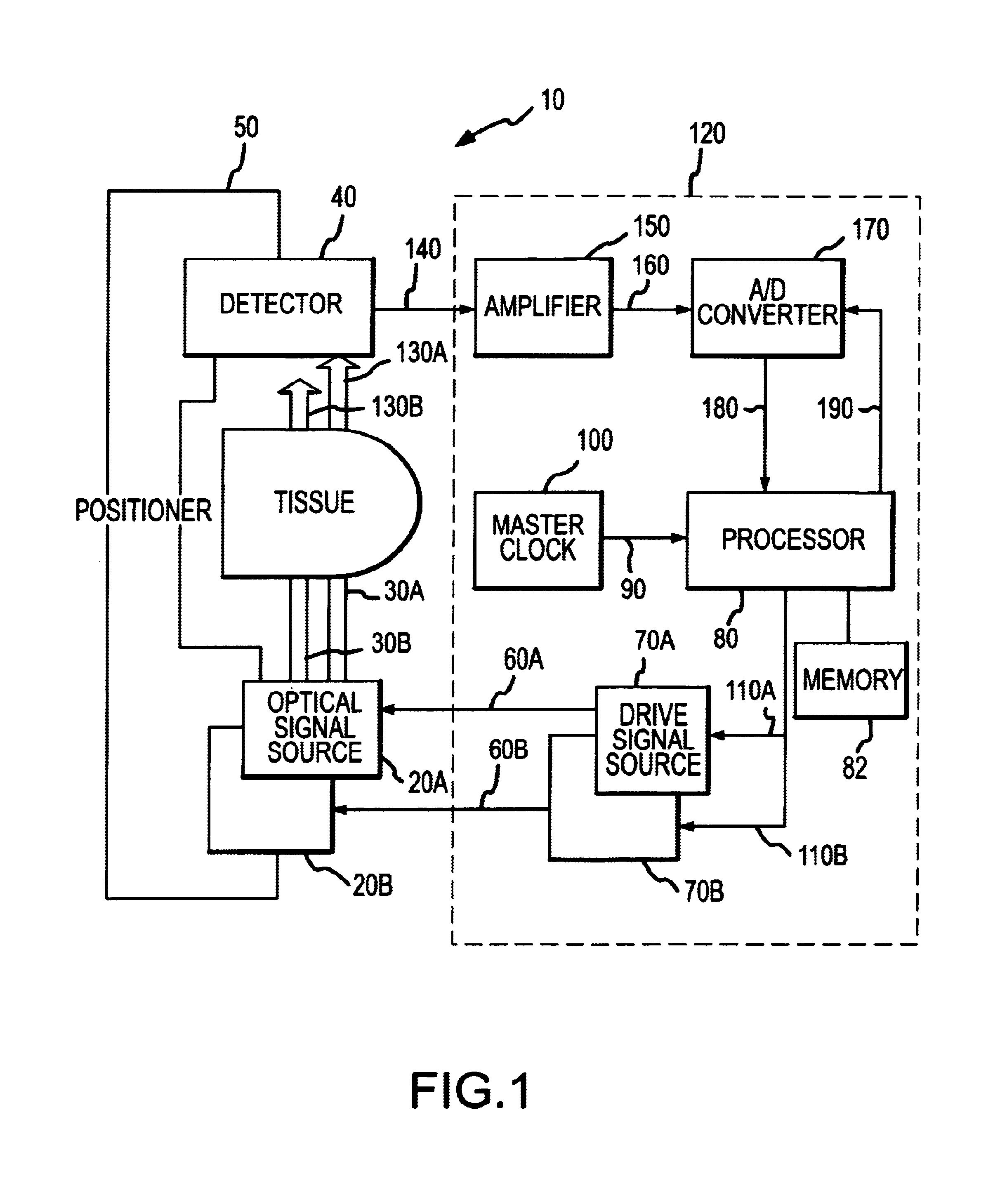
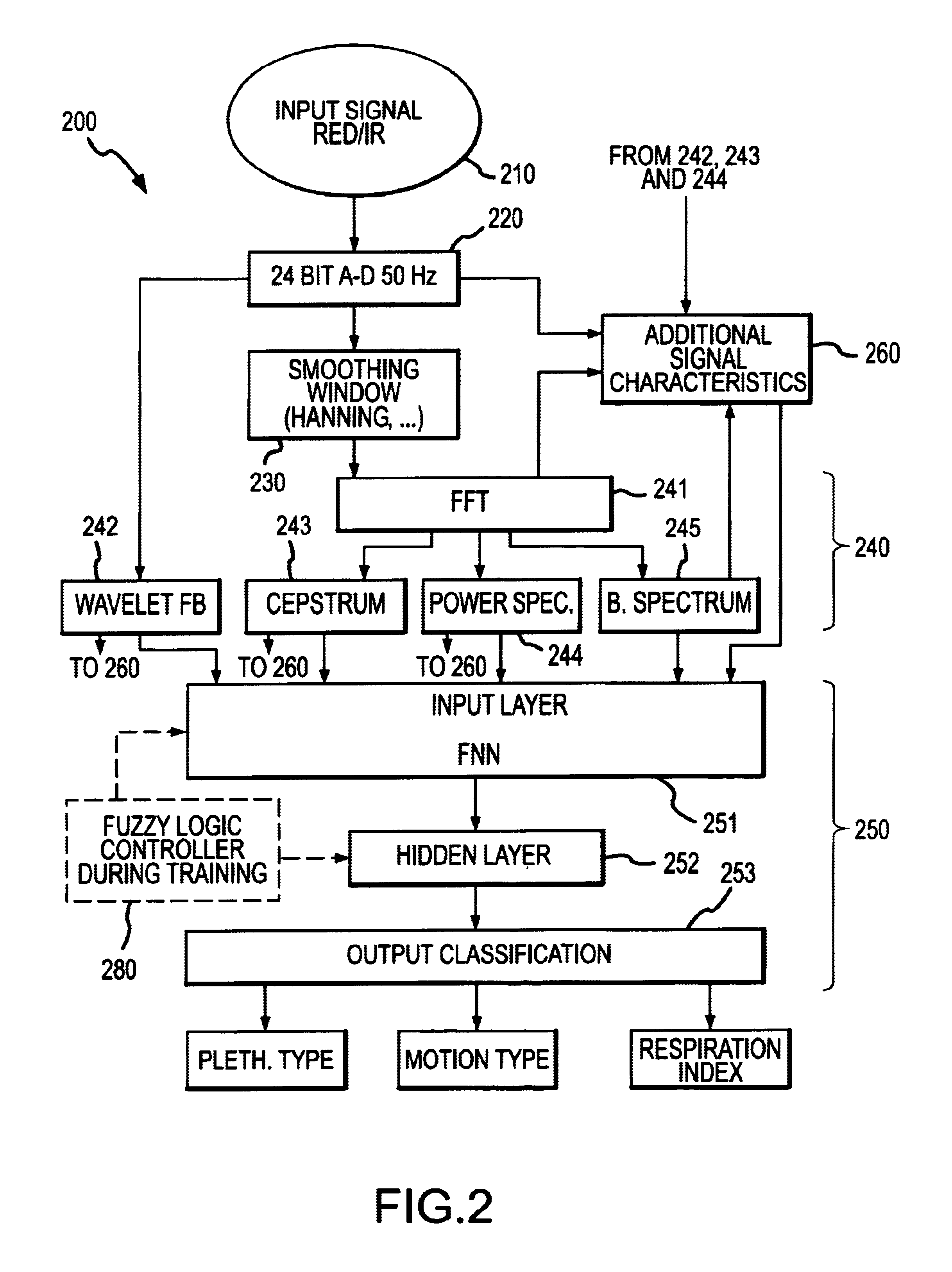
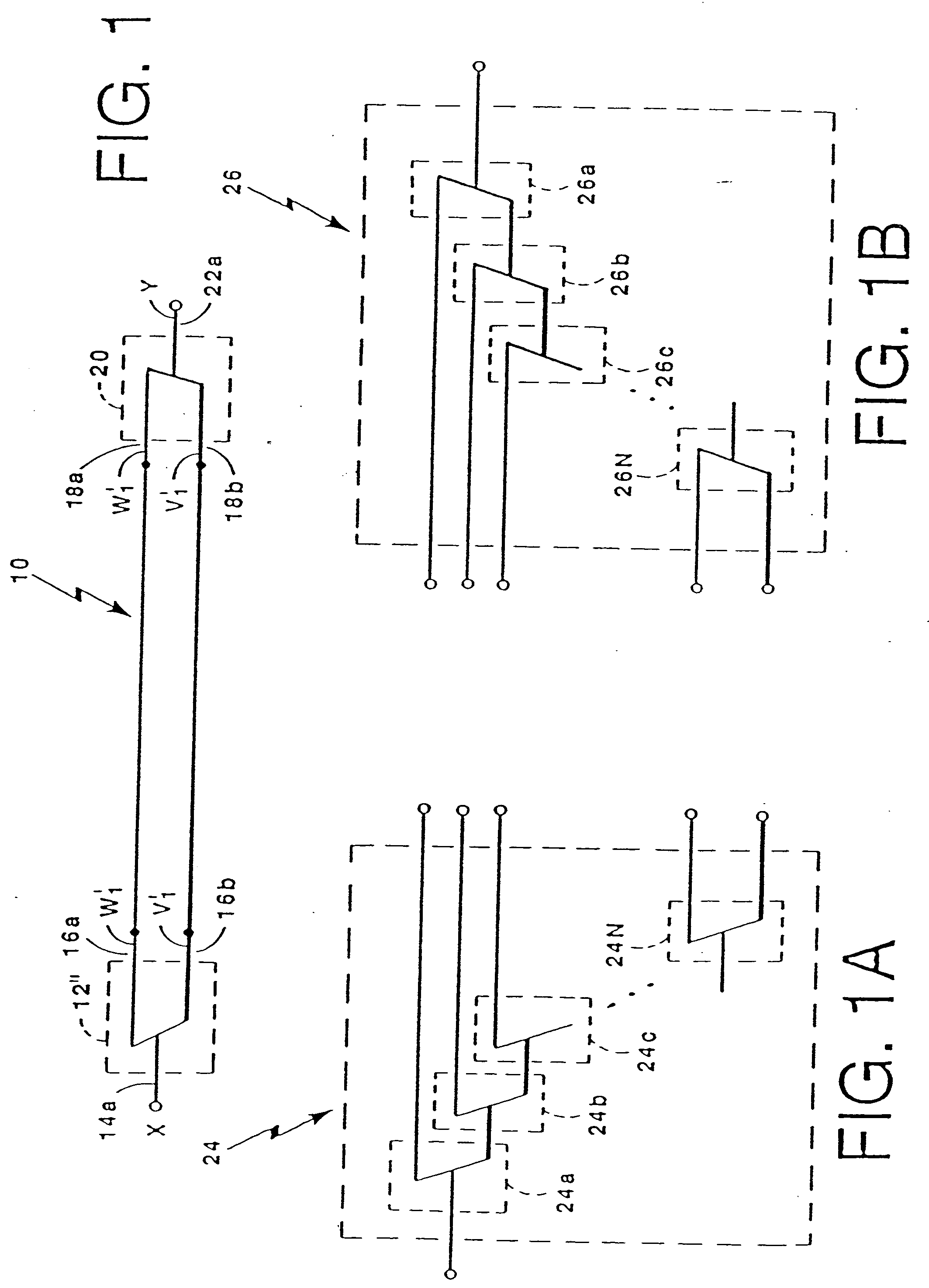
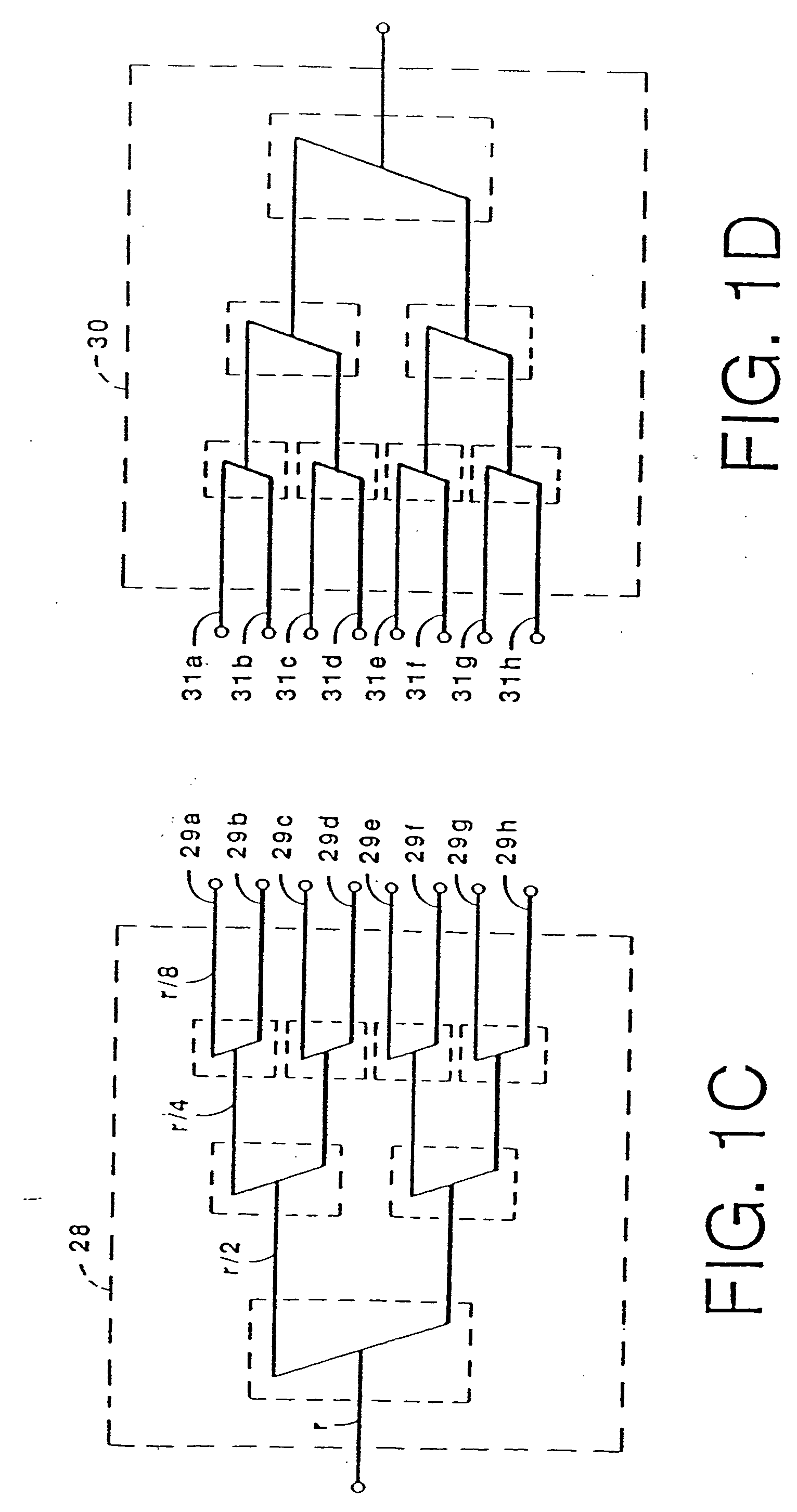
Multi-domain motion estimation and plethysmographic recognition using fuzzy neural-nets
ActiveUS6931269B2Enhanced signalImprove filtering effectSurgeryCatheterPattern recognitionHidden layer
Pulse oximetry is improved through classification of plethysmographic signals by processing the plethysmographic signals using a neural network that receives input coefficients from multiple signal domains including, for example, spectral, bispectral, cepstral and Wavelet filtered signal domains. In one embodiment, a plethysmographic signal obtained from a patient is transformed (240) from a first domain to a plurality of different signal domains (242, 243, 244, 245) to obtain a corresponding plurality of transformed plethysmographic signals. A plurality of sets of coefficients derived from the transformed plethysmographic signals are selected and directed to an input layer (251) of a neural network (250). The plethysmographic signal is classified by an output layer (253) of the neural network (250) that is connected to the input layer (251) by one or more hidden layers (252).
Owner:DATEX OHMEDA
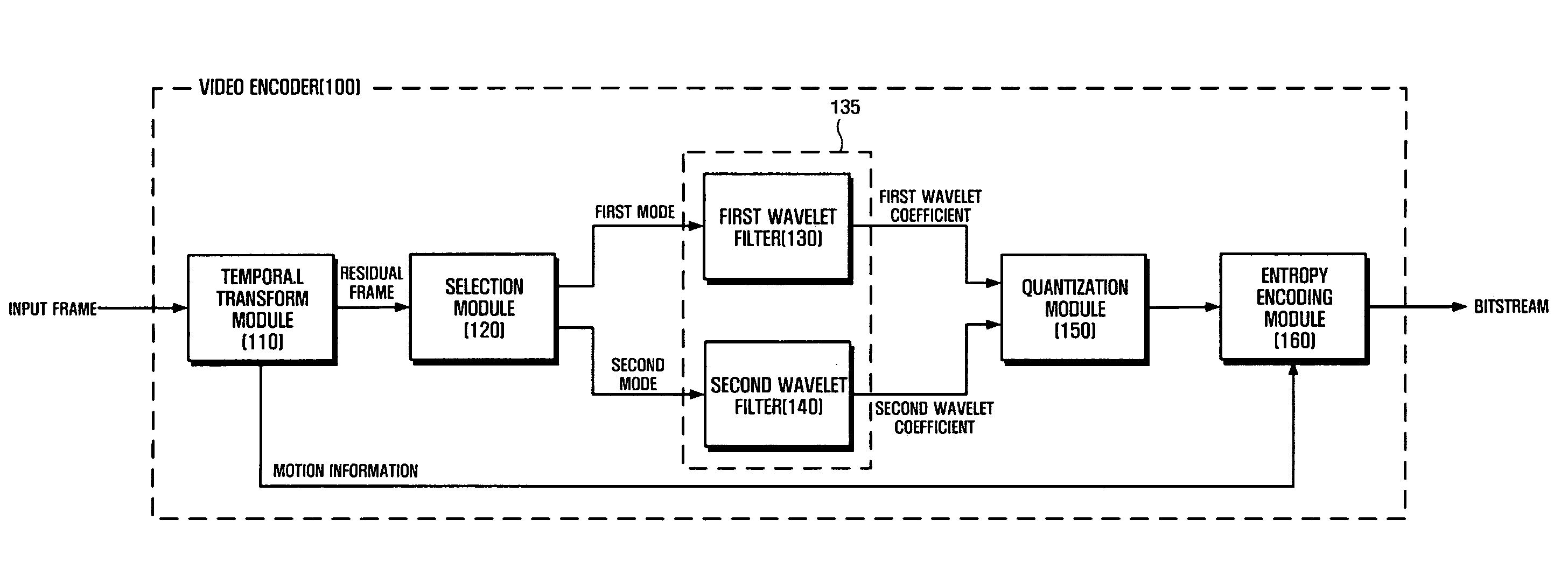
Video coding method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060088096A1Quality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSpatial correlationVideo encoding
A method and apparatus are provided for improving compression efficiency or picture quality by selecting a wavelet transform technique suitable to input video / image scene characteristics in video / image compression. The video encoder includes a temporal transform module that removes temporal redundancy of an input frame and generates a residual frame, a selection module that selects an appropriate wavelet filter among a plurality of wavelet filters having different taps according to a spatial correlation of the residual frame, a wavelet transform module that generates wavelet coefficients by performing wavelet transform on the residual frame using the selected wavelet filter, and a quantization module that quantizes the wavelet coefficients.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
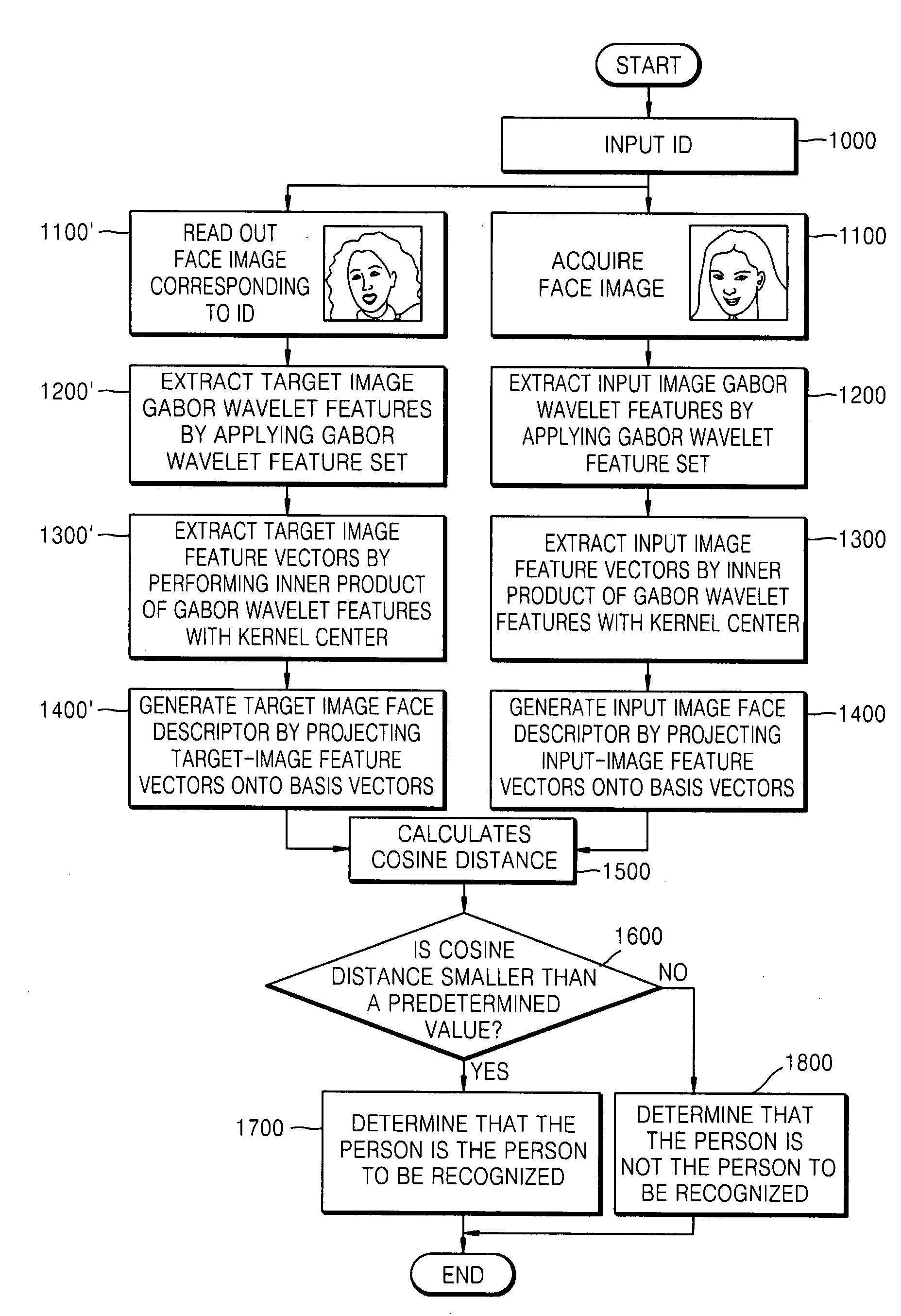
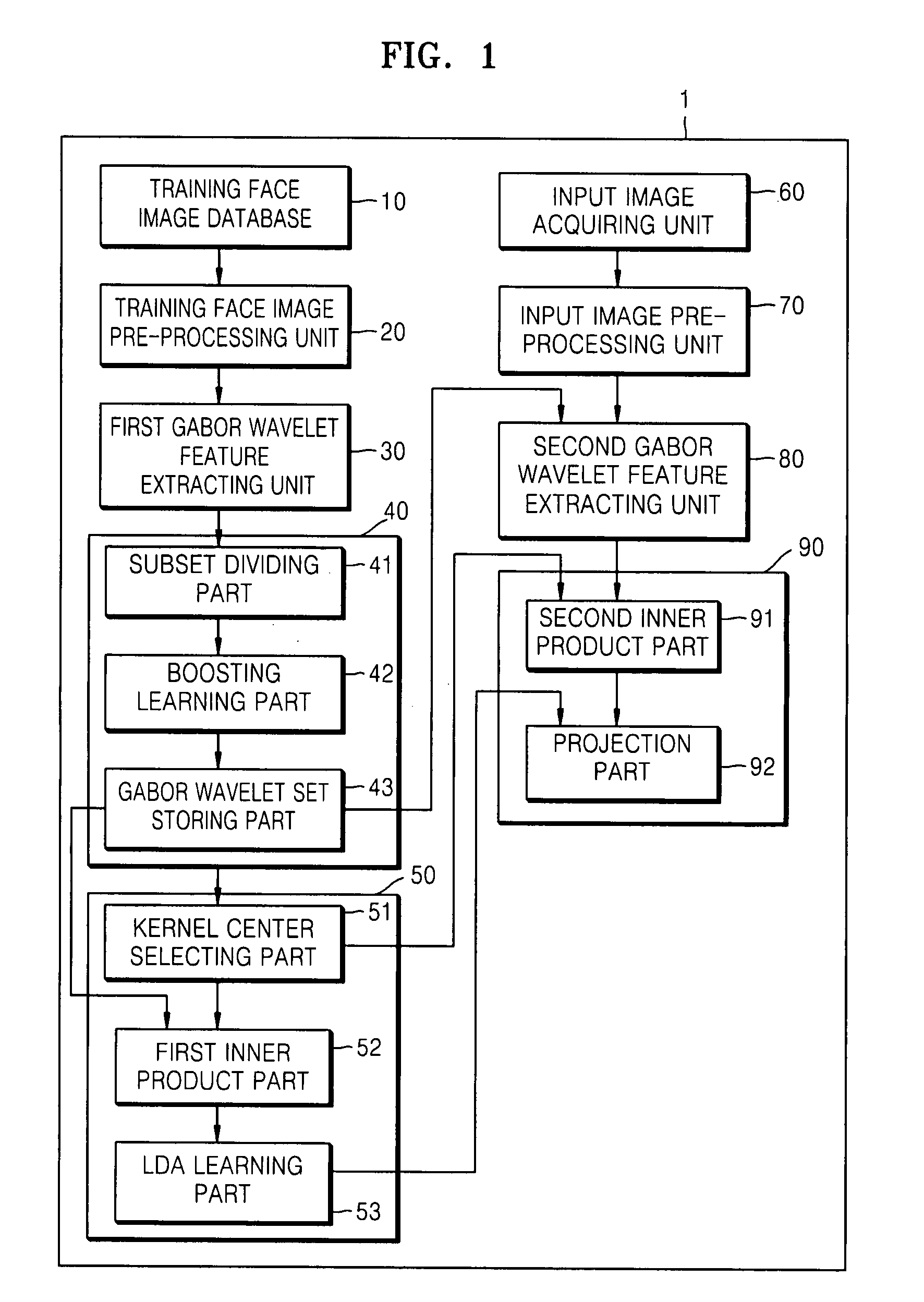
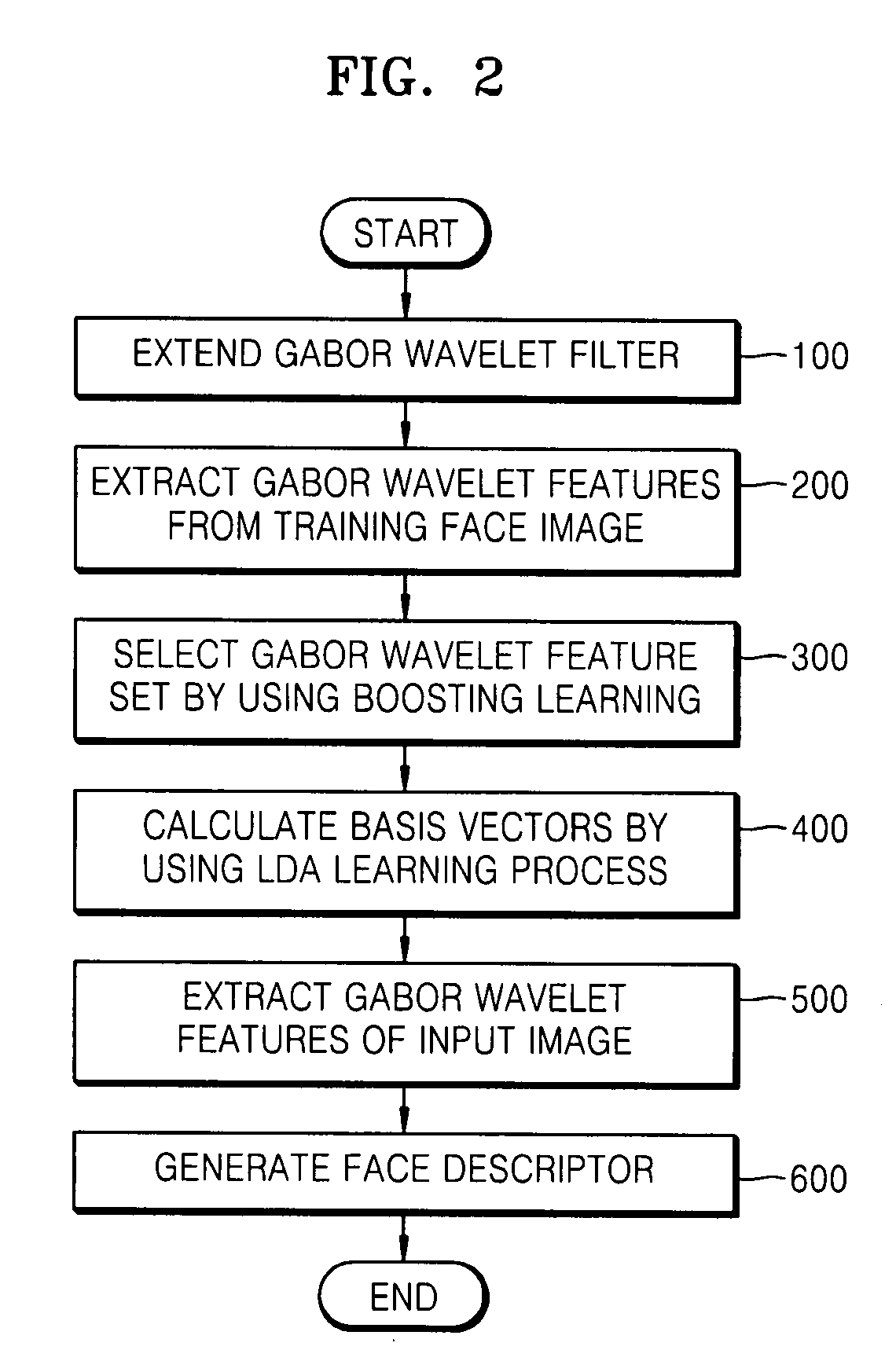
Method and apparatus for face recognition using extended gabor wavelet features
InactiveUS20080107311A1High error rateRecognition efficiency is lowImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature setComputation complexity
A face recognition method and apparatus using extended Gabor wavelet features are provided. In the face recognition method, extended Gabor wavelet features are extracted from a face image by applying an extended Gabor wavelet filter, a Gabor wavelet feature set is selected by performing a supervised learning process on the extended Gabor wavelet features, and the selected Gabor wavelet feature set is used for face recognition. Accordingly, it is possible to solve problems of a high error rate of face recognition and low face recognition efficiency caused from a limitation of parameters of the Gabor wavelet filter. In addition, it is possible to solve the problem of increased calculation complexity caused from using an extended Gabor wavelet filter and to implement robust face recognition which is excellent in dealing with a change in expression and illumination.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
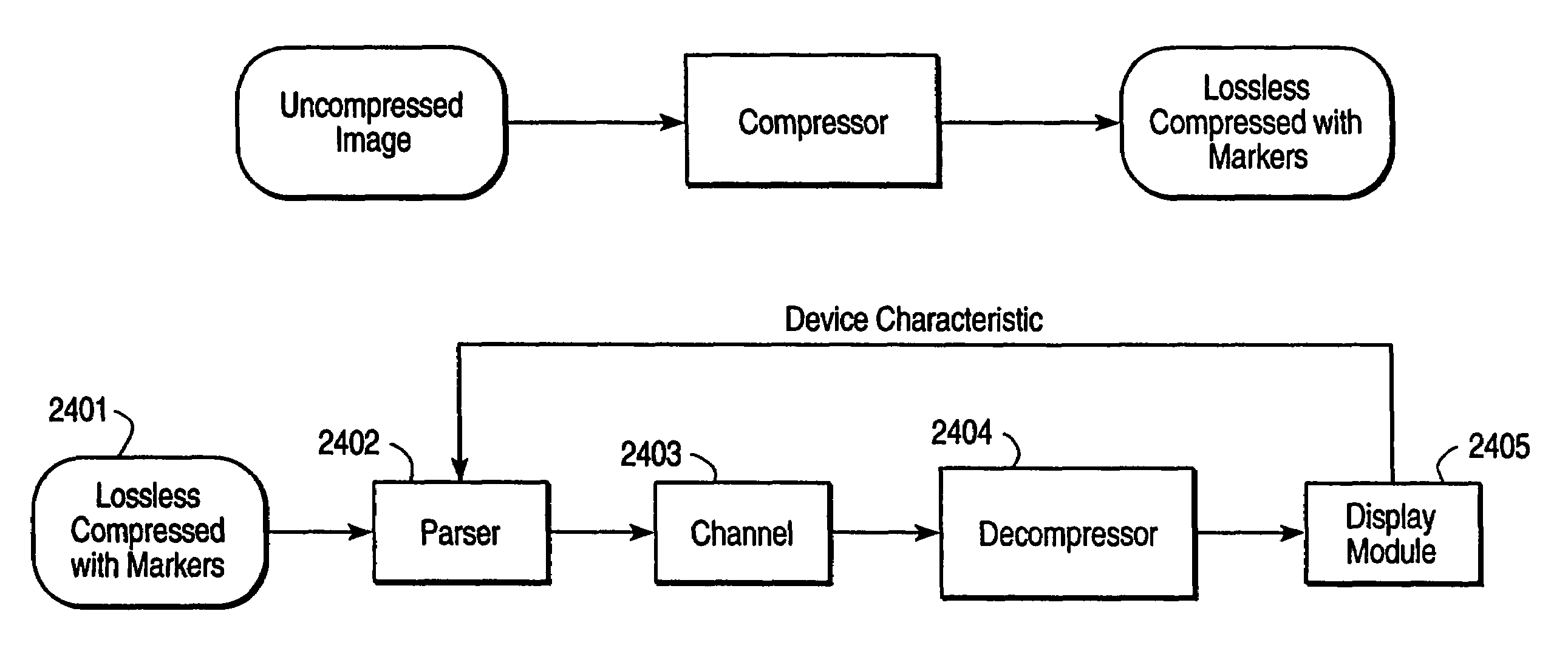
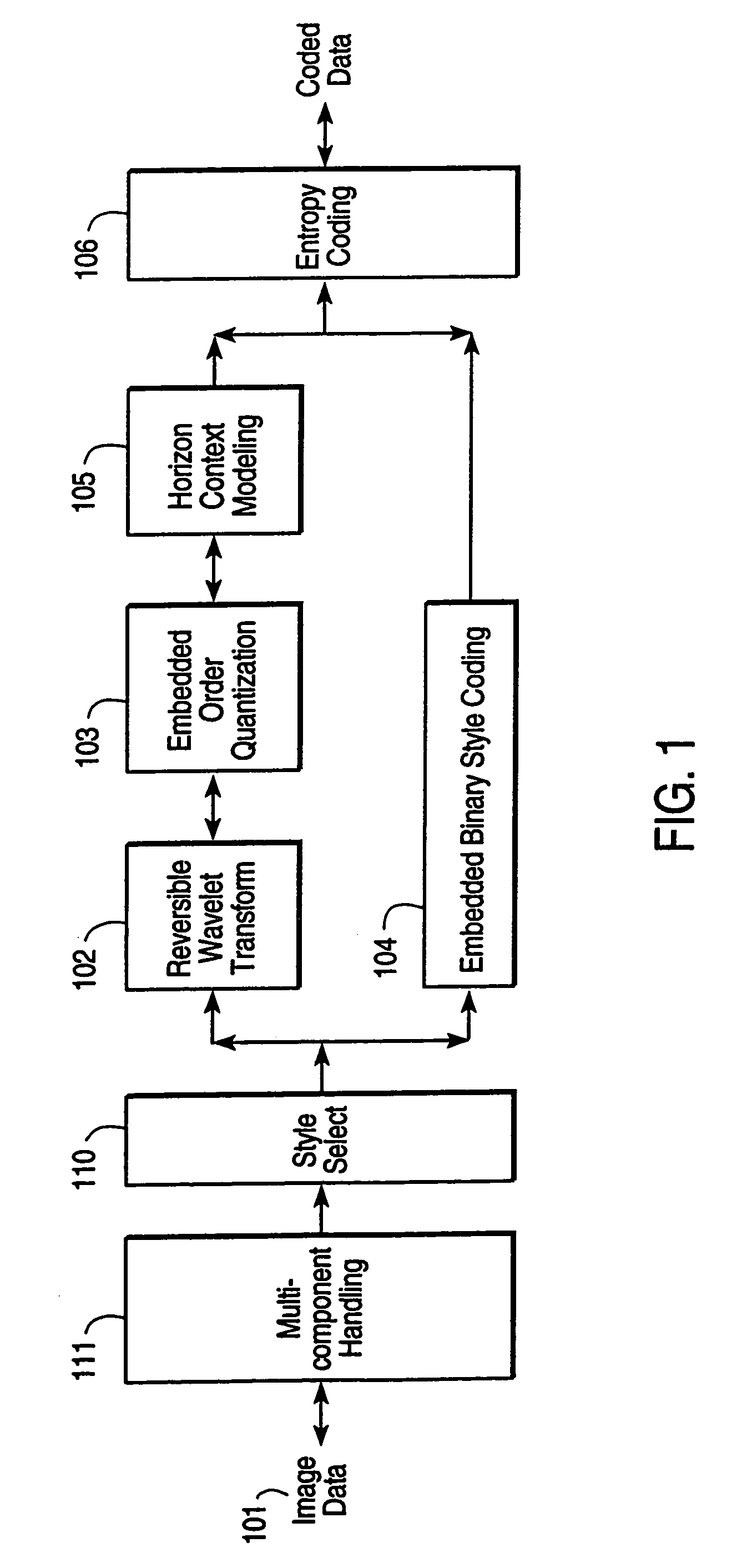
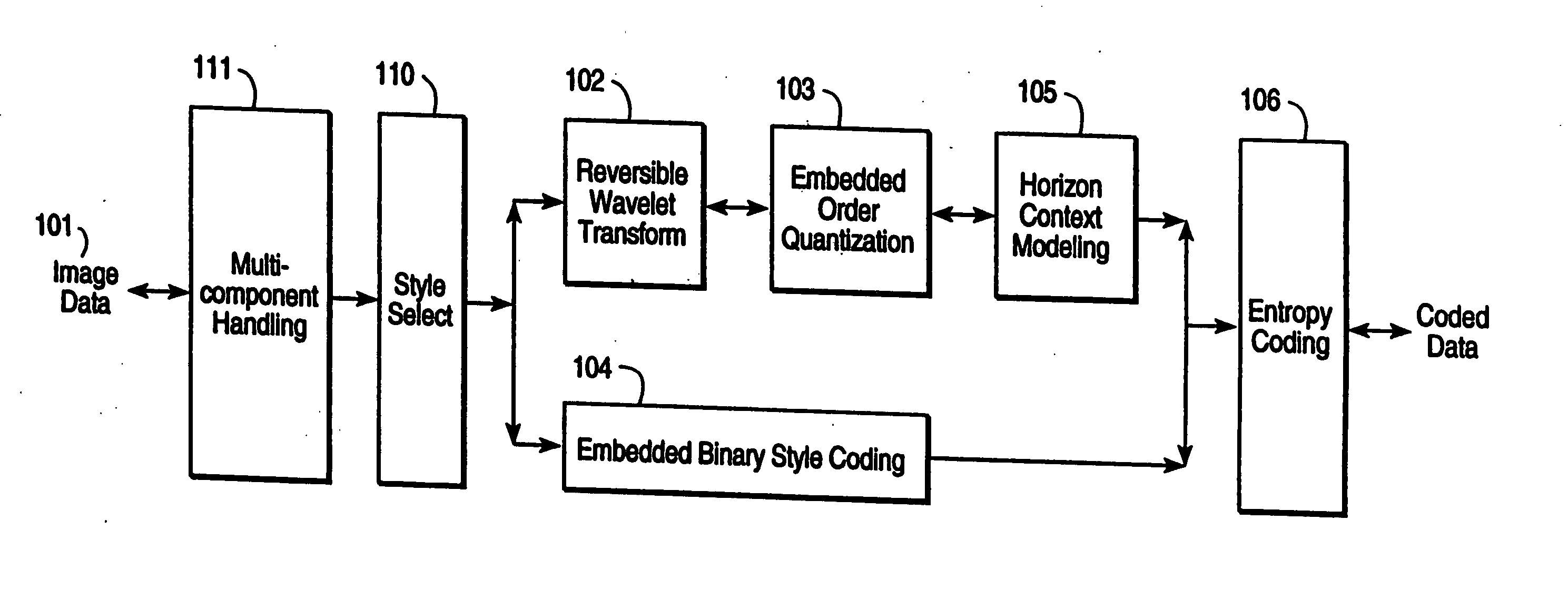
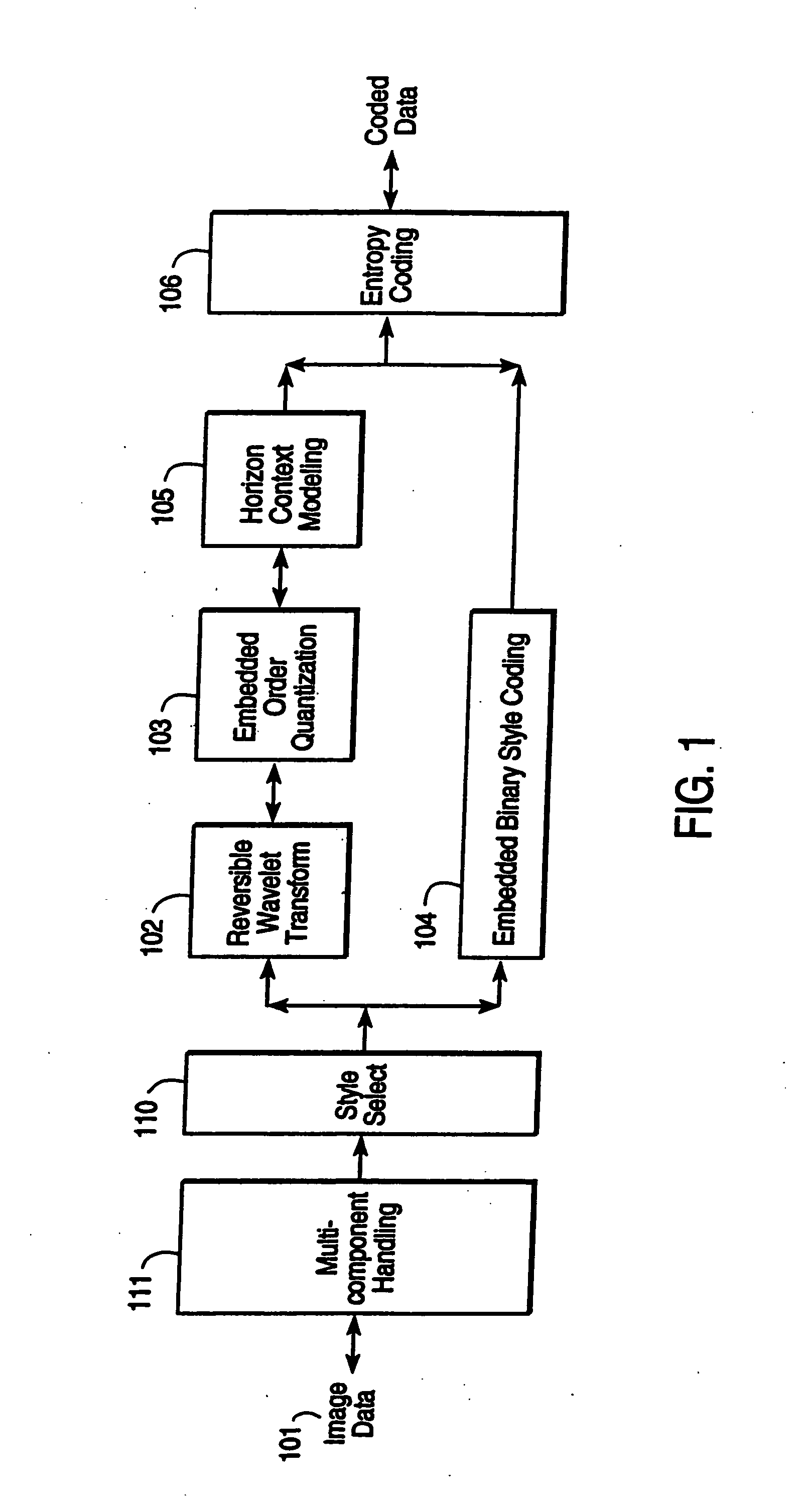
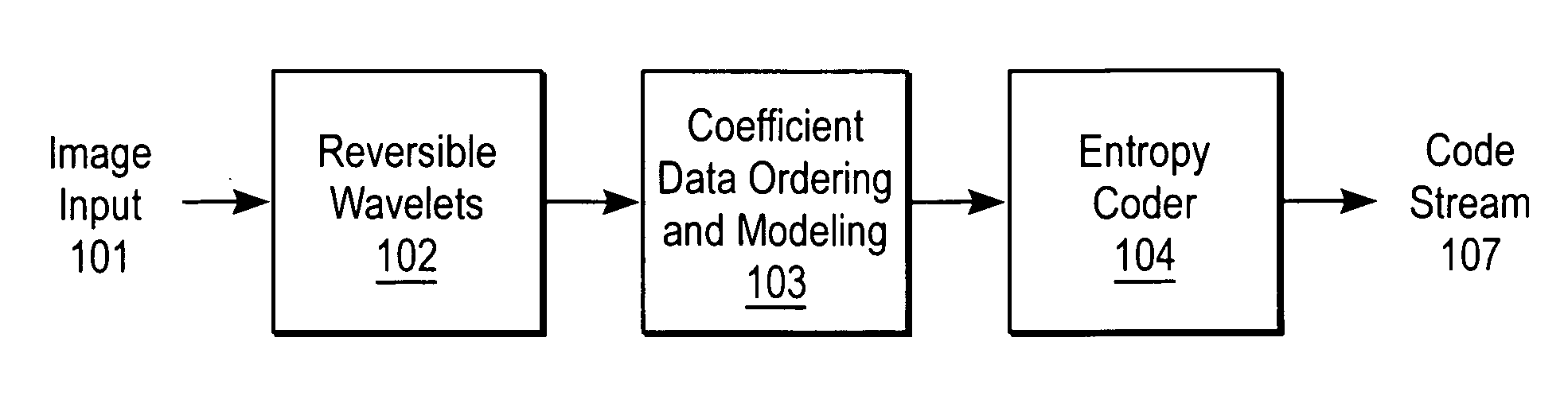
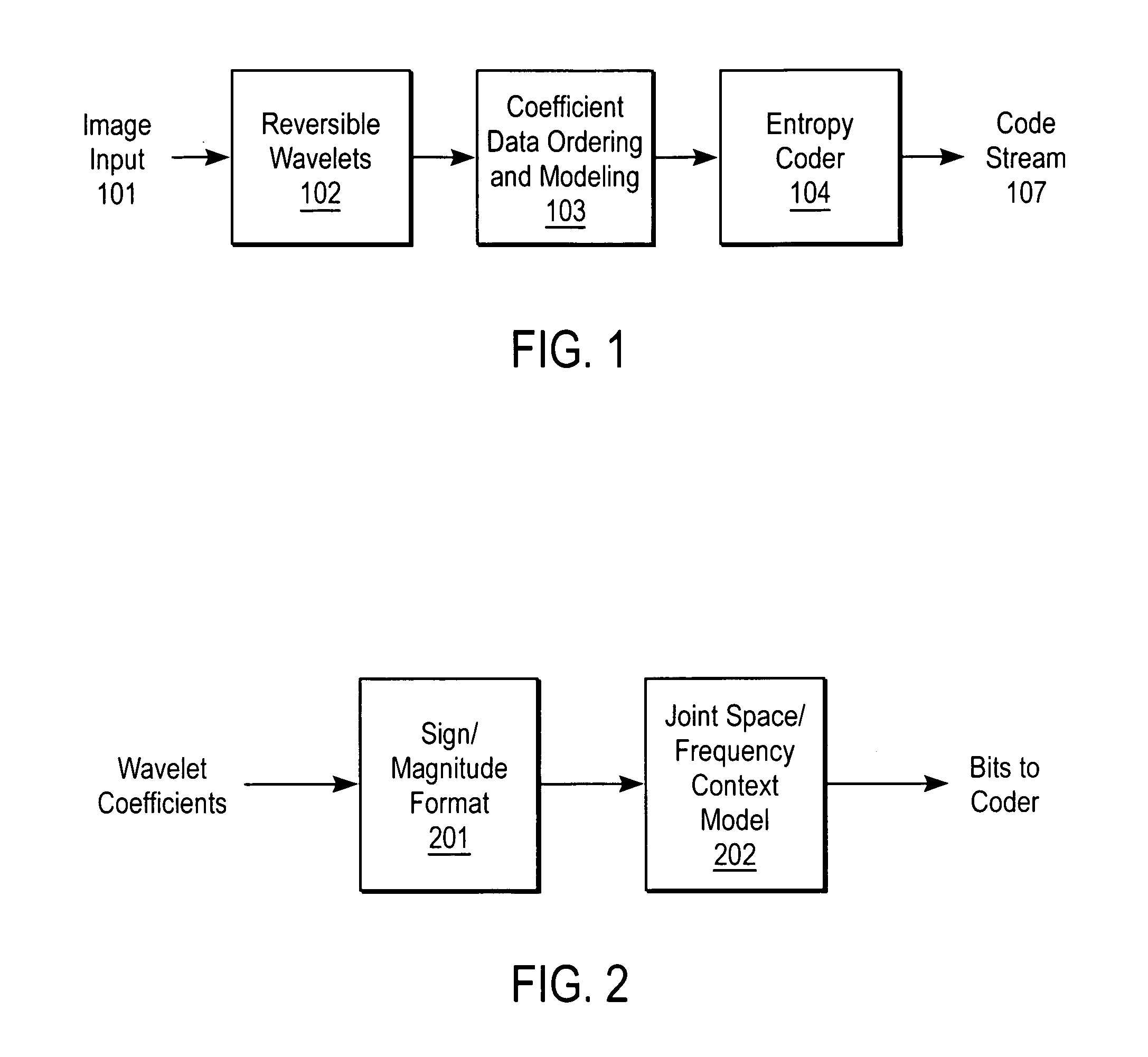
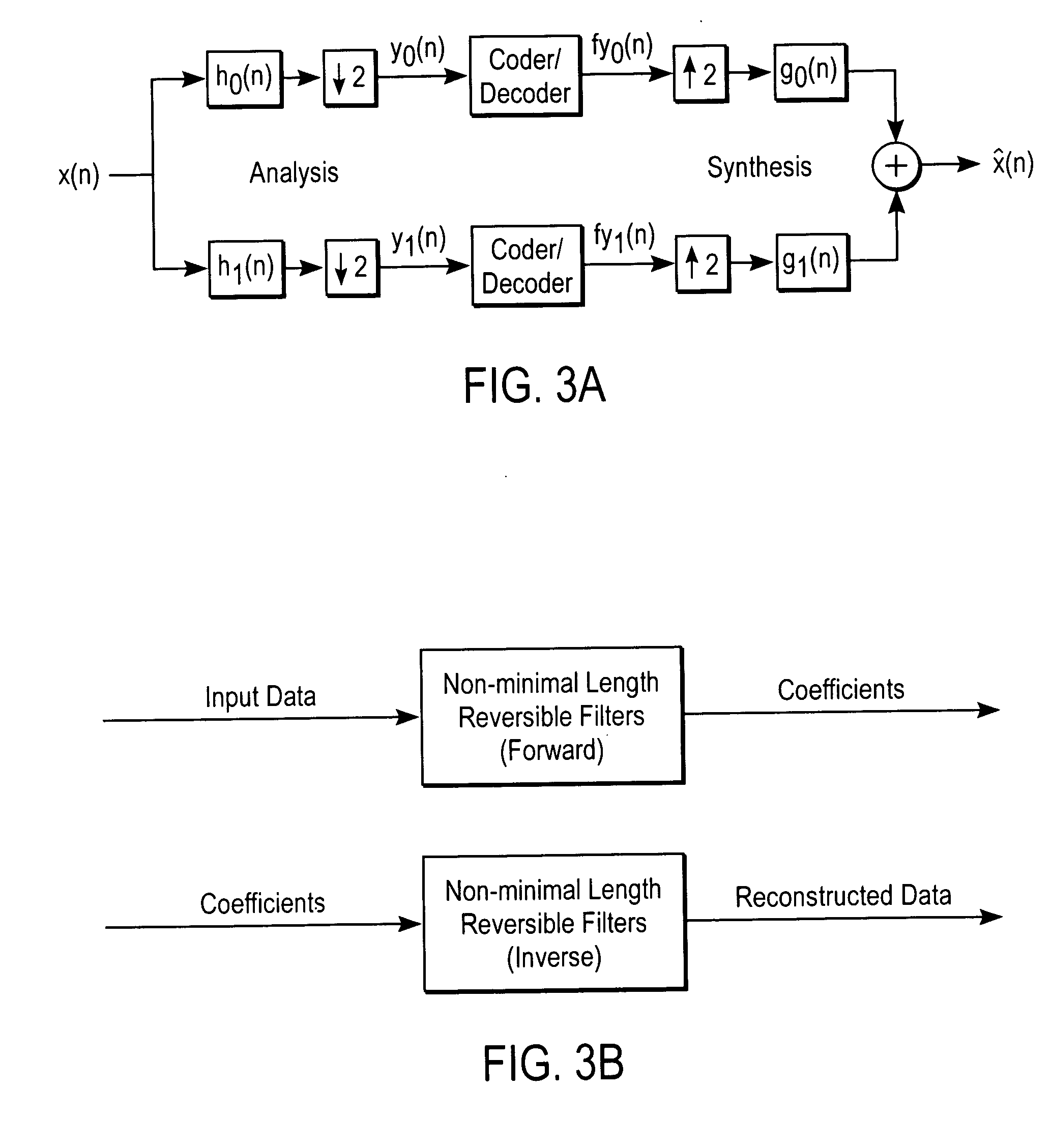
Compression and decompression with wavelet style and binary style including quantization by device-dependent parser
InactiveUS7076104B1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionCode conversionData streamComputer science
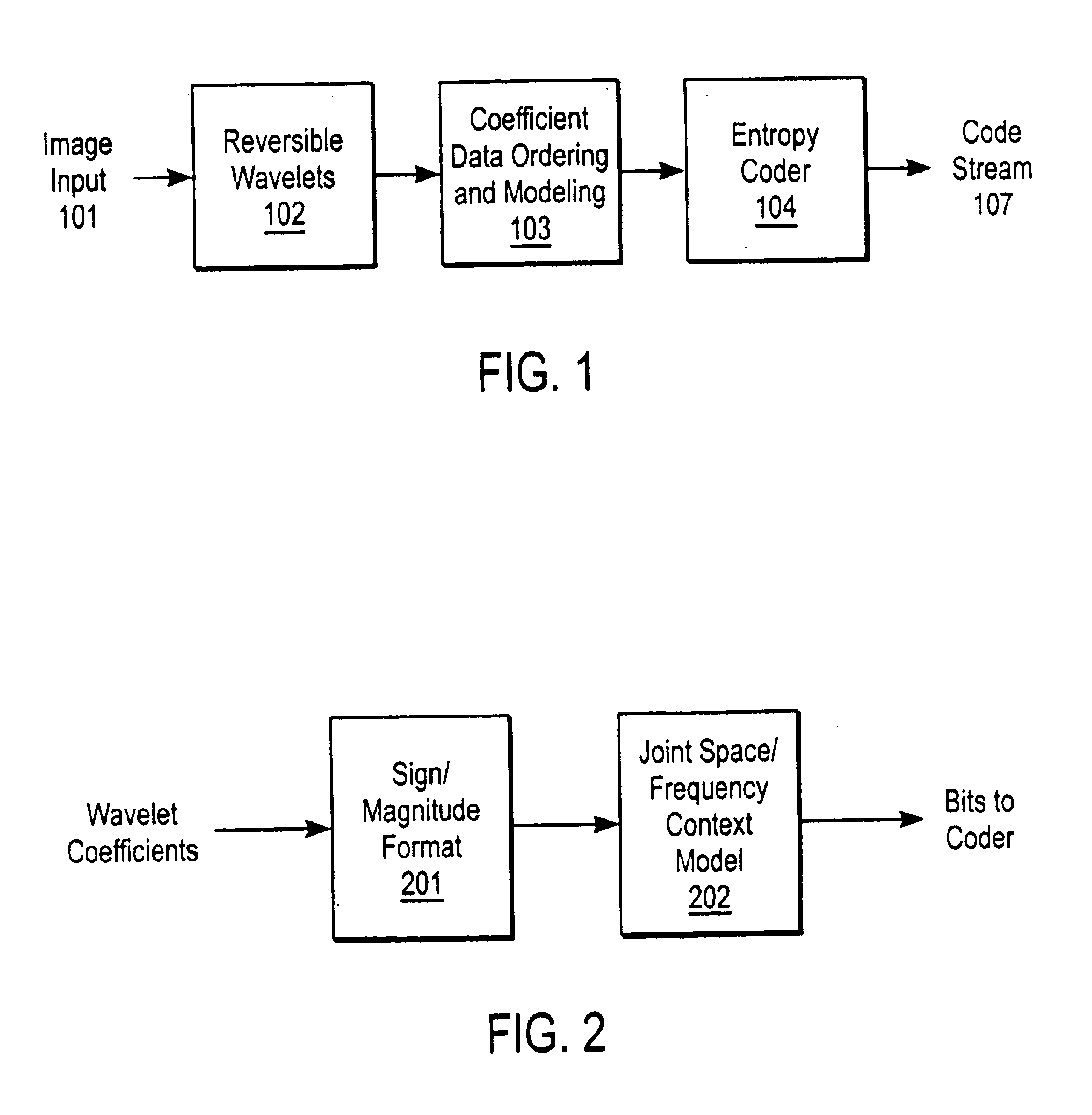
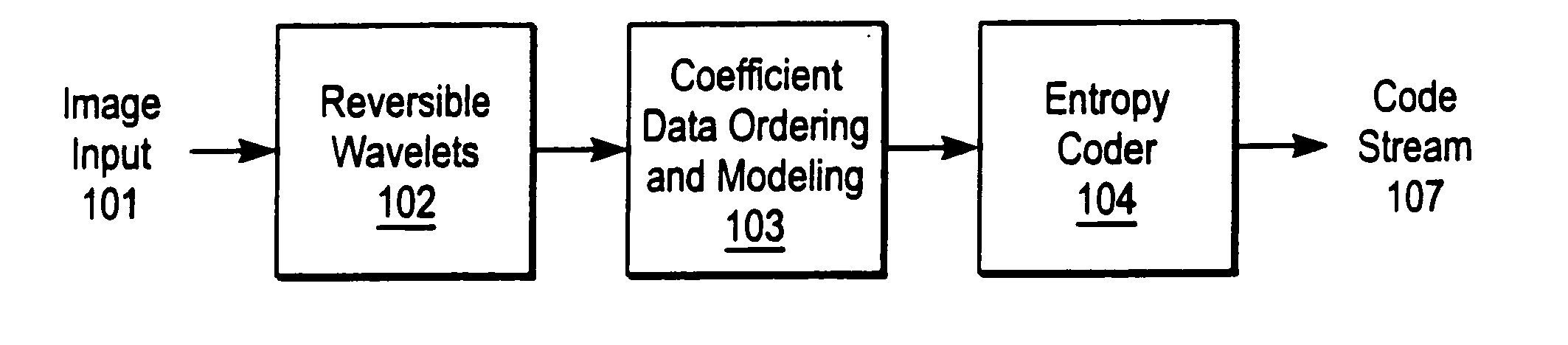
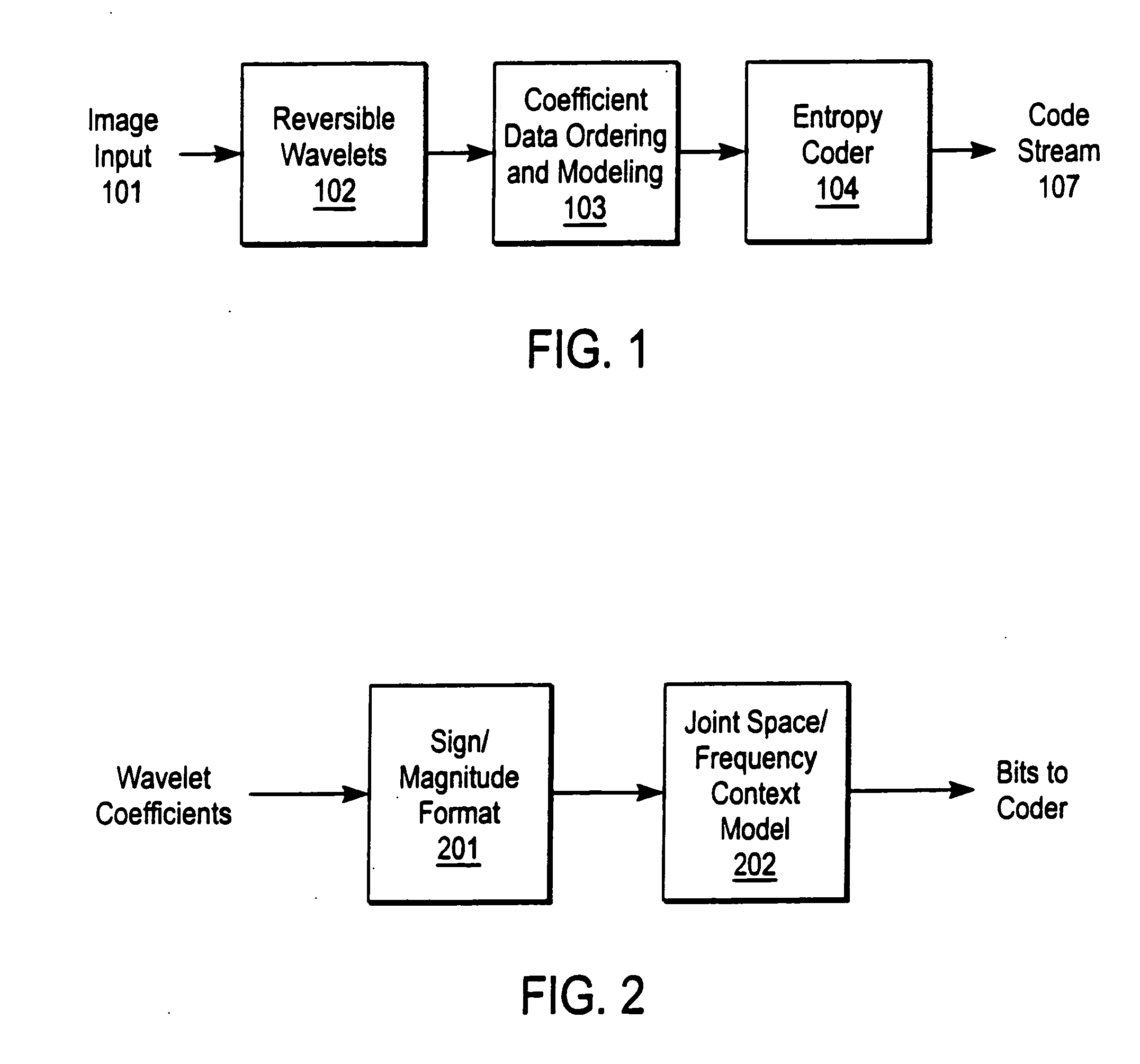
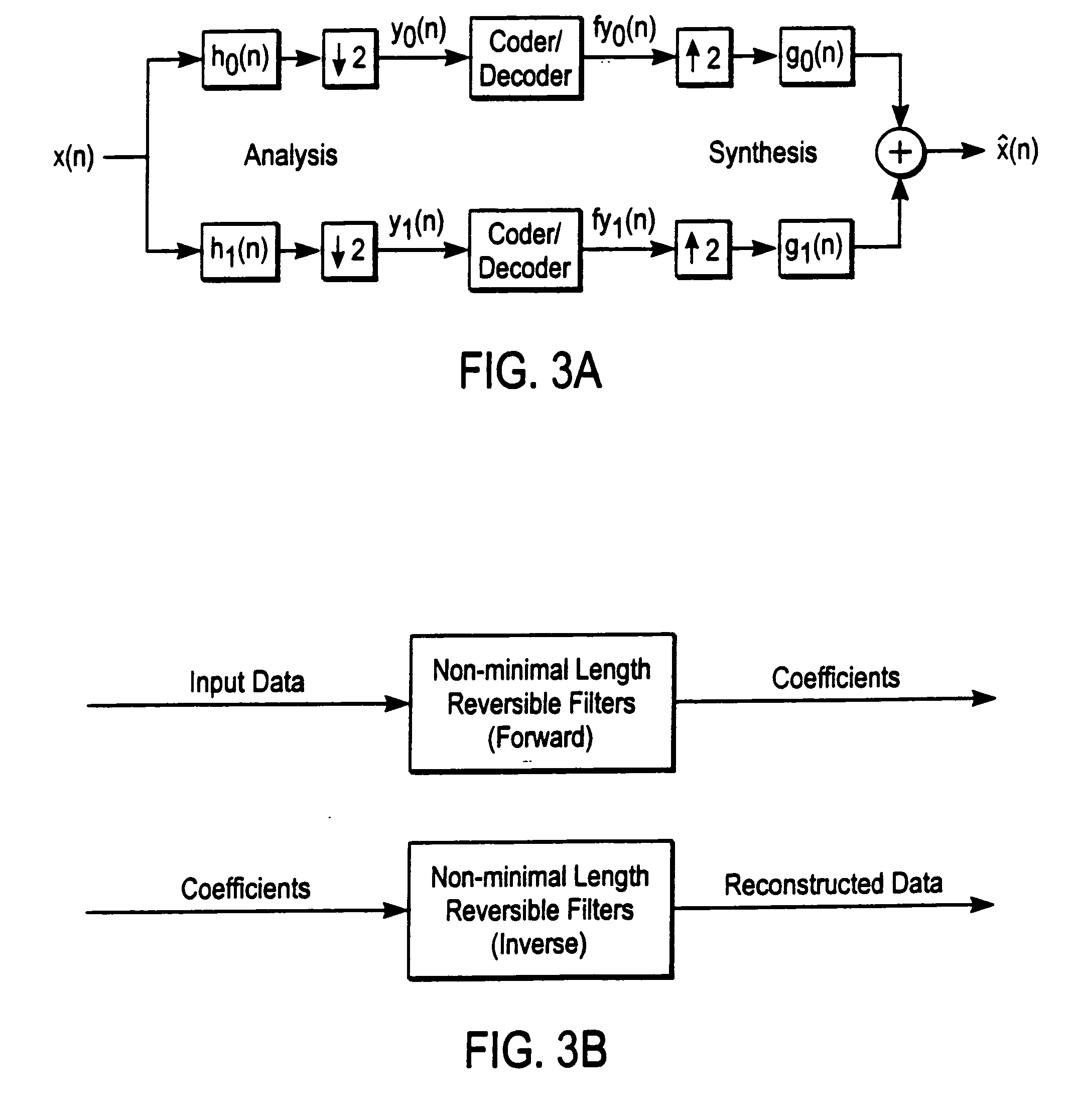
A compression and decompression system in which a reversible wavelet filter are used to generates coefficients from input data, such as image data. The reversible wavelet filter is an efficient transform implemented with integer arithmetic that has exact reconstruction. The present invention uses the reversible wavelet filter in a lossless system (or lossy system) in which an embedded codestream is generated from the coefficients produced by the filter. An entropy coder performs entropy coding on the embedded codestream to produce the compressed data stream.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
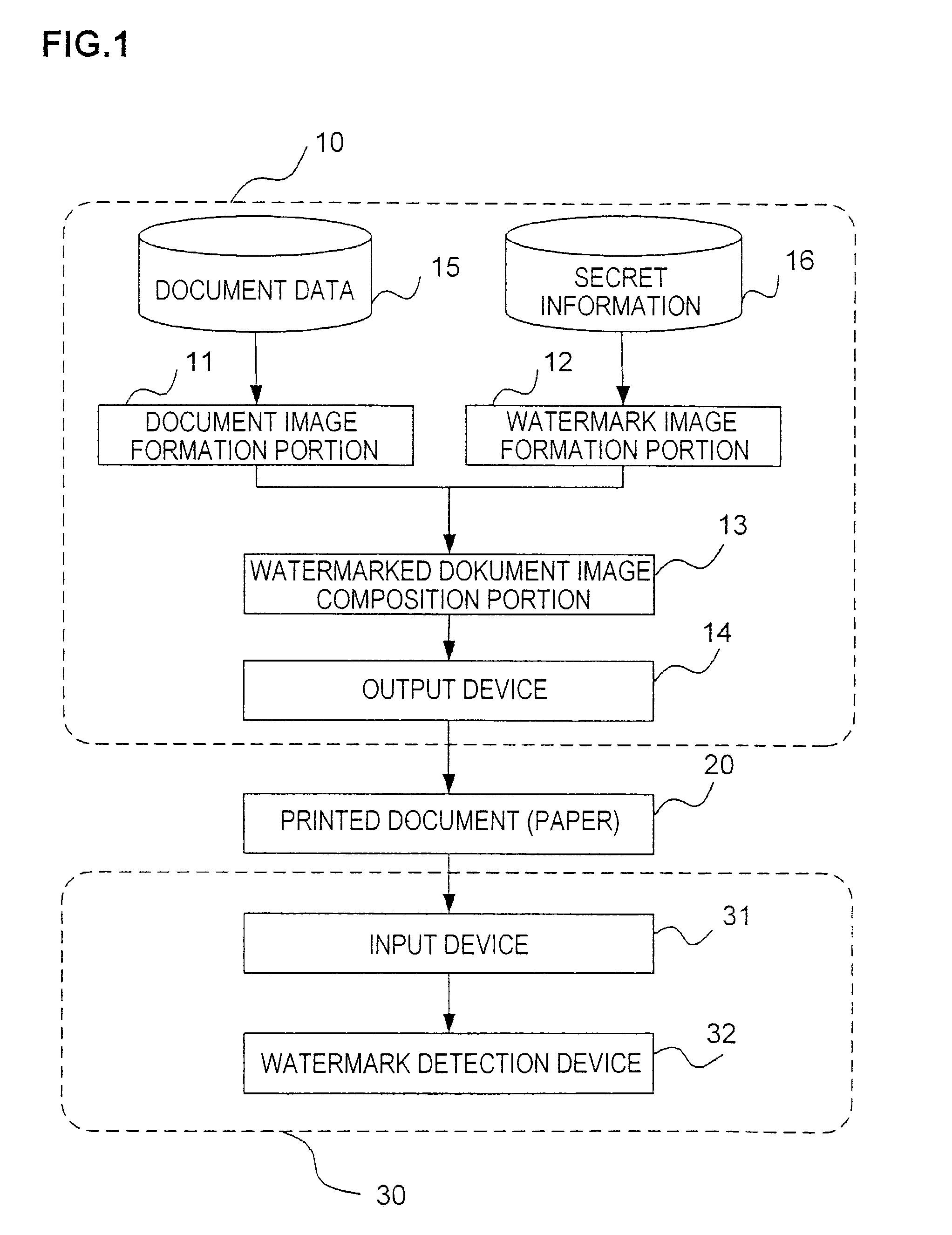
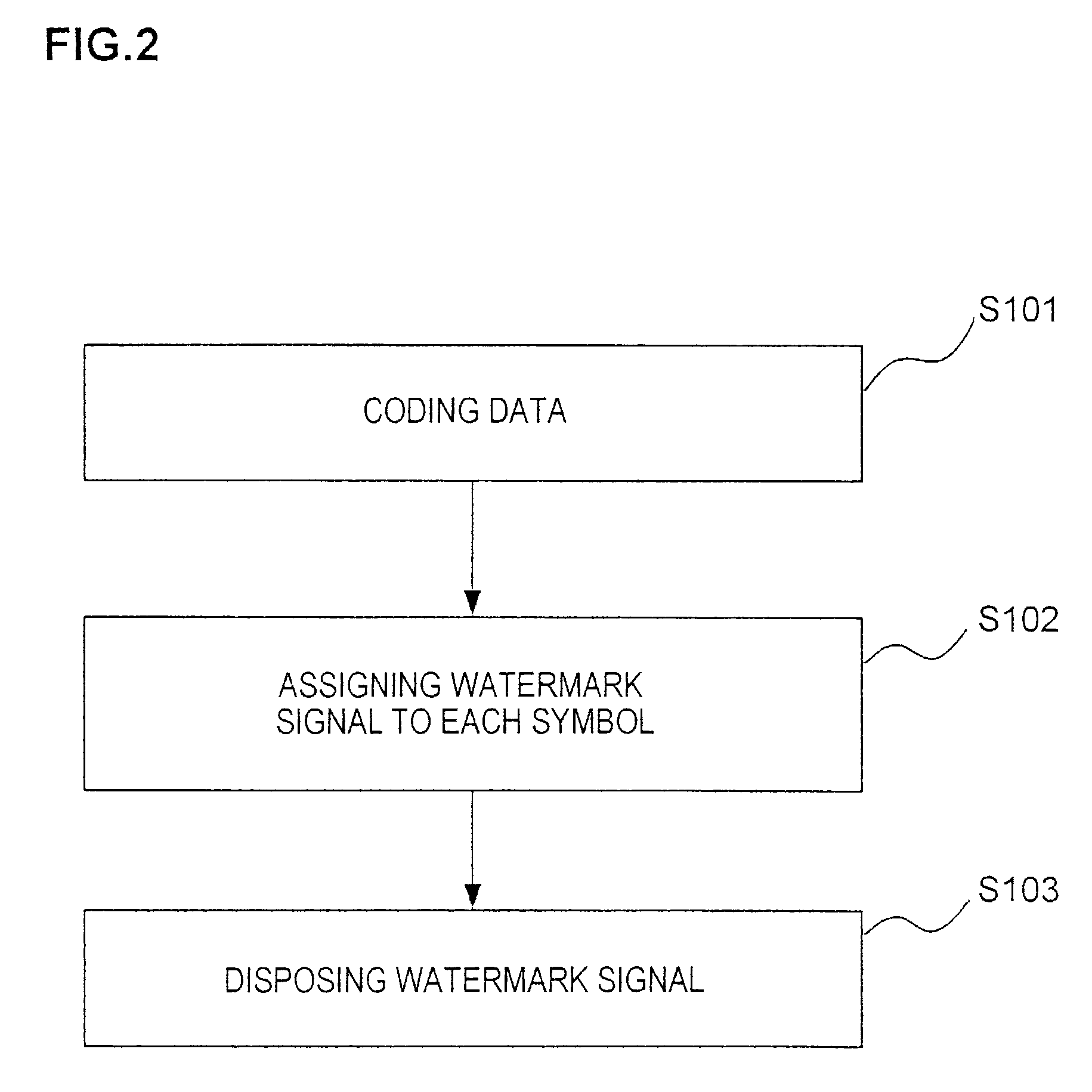
Watermark information embedding device and watermark information detection device
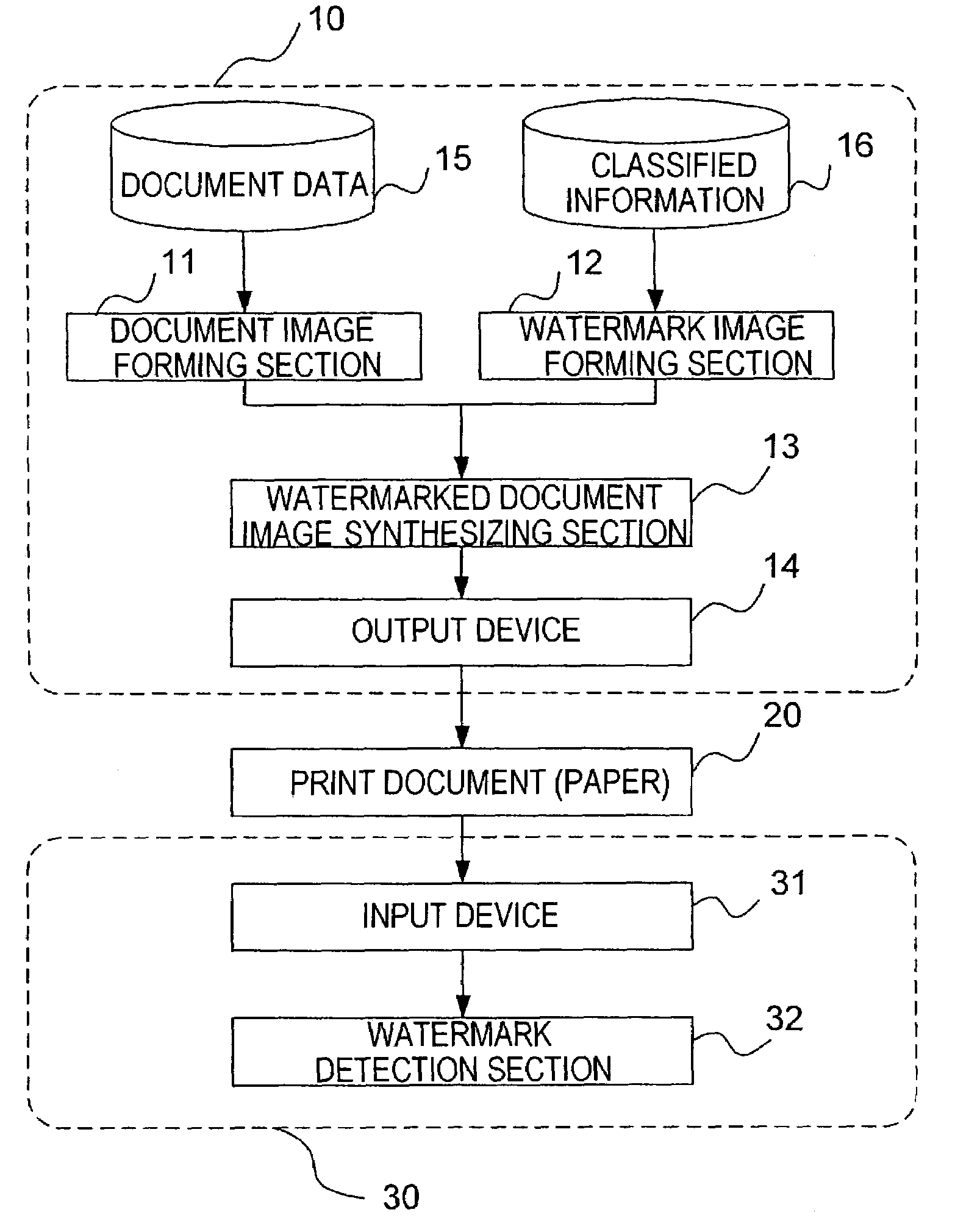
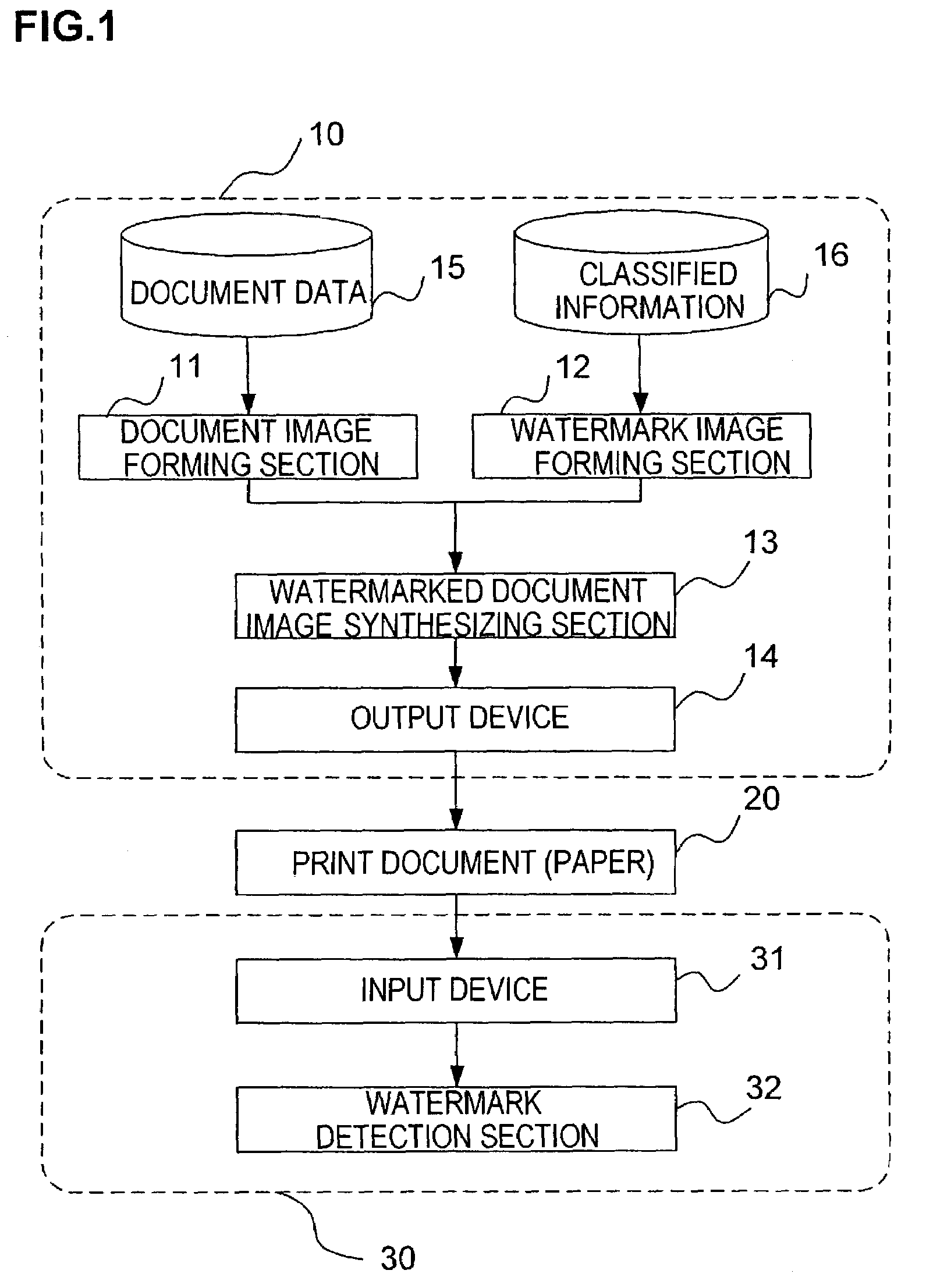
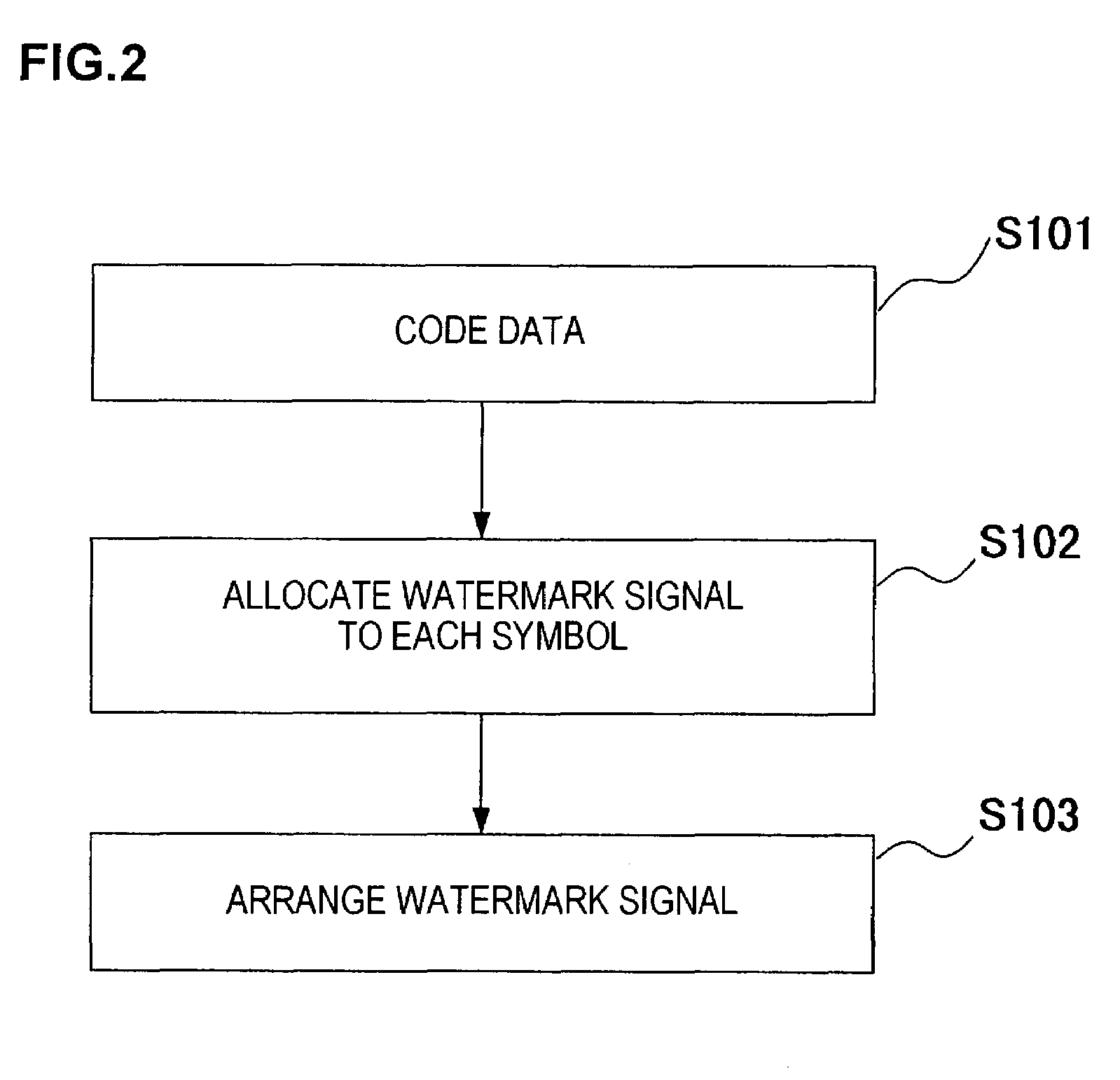
ActiveUS7085399B2Accurate extractionImprove detection efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual presentationClassified informationInformation embedding
There are provided a watermark information embedding device and a watermark information detection device which can correctly extract classified information. In the watermark information embedding device, a plurality of dot patterns the wave directions and / or wavelengths of which are changed depending on dot arrangements are prepared, one symbol is given to one of the dot patterns, and the dot patterns are combined and arranged, so that the classified information is given. The watermark information detection device includes two-dimensional wavelet filters the number of which is equal to the number of dot patterns and which have the same wave directions and the same wavelengths as those of the dot patterns. Convolutions between an arbitrary region in a watermarked image and the plurality of two-dimensional wavelet filters are calculated, and it is determined that the dot pattern corresponding to the two-dimensional wavelet filter having the maximum convolution is embedded in the region.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Watermark information embedment device and watermark information detection device
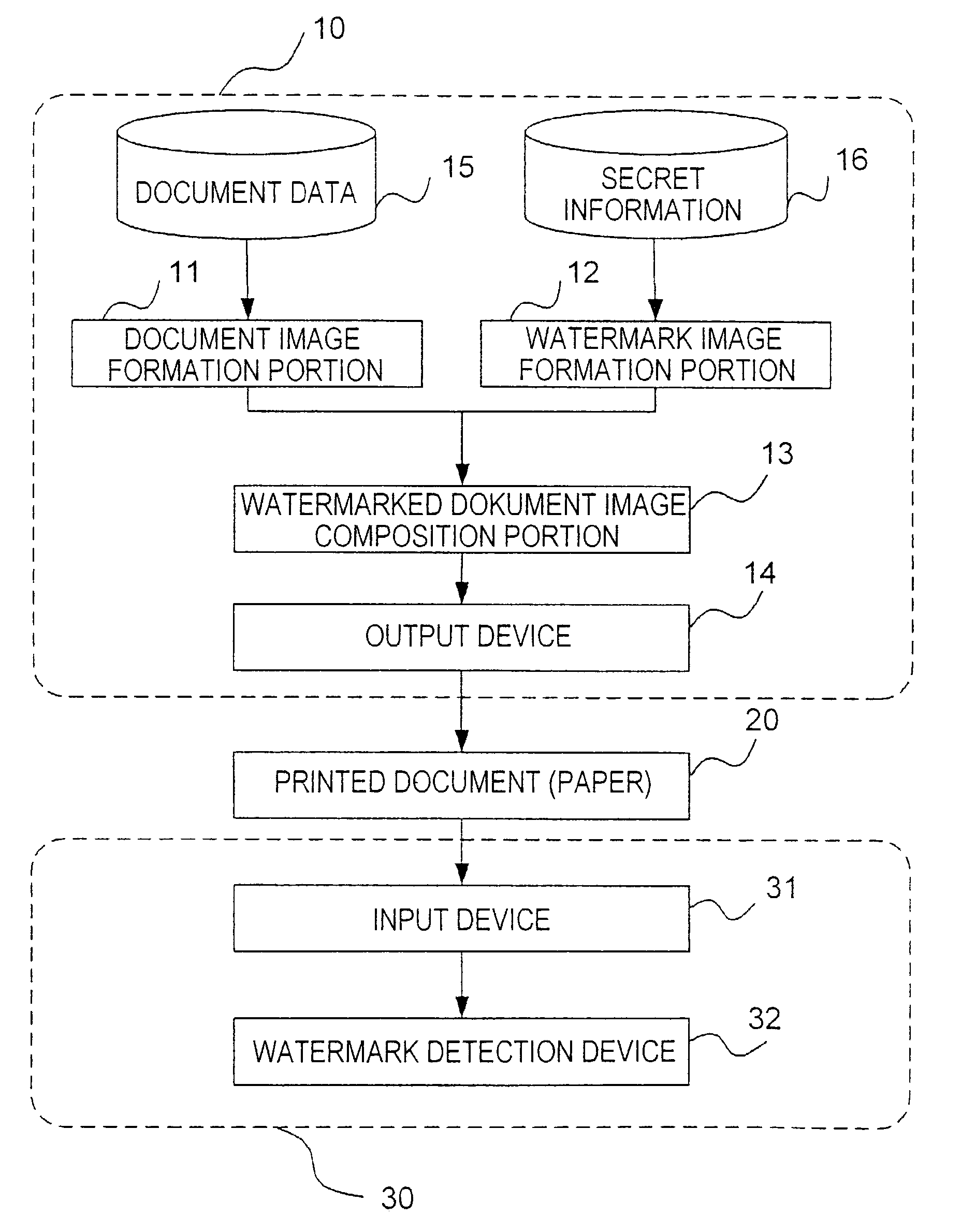
There are disclosed a watermark information embedment device capable of accurately embedding secret information, and a watermark information detection device. In the watermark information embedment device, there are prepared a plurality of different sorts of dot patterns in which the wave propagation direction and the wave length are changed depending on the dot arrangement. Each dot pattern of the same sort is given the same symbol, and the secret information is represented by combining these dot patterns. In the watermark information detection device, there are provided 2-dimensional wavelet filters having the same wave propagation direction and the wave length as the different sorts of dot patterns. There is computed convolution between an arbitrary region in the watermarked image and plural 2-dimensional wavelet filters, and it is judged that the dot pattern corresponding to a particular one of the 2-dimensional wavelet filters is embedded in the region where the computed convolution indicates a maximum value.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Compression and decompression with wavelet style and binary style including quantization by device-dependent parser
InactiveUS20060233257A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData streamComputer science
A compression and decompression system in which a reversible wavelet filter are used to generates coefficients from input data, such as image data. The reversible wavelet filter is an efficient transform implemented with integer arithmetic that has exact reconstruction. The present invention uses the reversible wavelet filter in a lossless system (or lossy system) in which an embedded codestream is generated from the coefficients produced by the filter. An entropy coder performs entropy coding on the embedded codestream to produce the compressed data stream.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
Fault diagnosis method for rolling bearing
InactiveCN103424258AReduce mistakesAccurate diagnosisSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementMachine bearings testingApplicability domainDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis method for a rolling bearing, and belongs to the technical field of fault diagnosis and signal processing analysis. High-frequency sampling and preprocessing of vibration signals are firstly performed on the rolling bearing with faults, the preprocessed signals are sequentially filtered by the aid of a Morlet wavelet filter, spectral kurtosis and unit spectral kurtosis of the filtered signals are calculated, and a filter parameter corresponding to the maximum value of the unit spectral kurtosis is selected by comparison, namely, a global optimization filter parameter is selected. According to the fault diagnosis and detection method, an operator can extract the optimal filter parameter in the diagnosis process without a lot of detection experience and numerous historical data, the method is wider in application range, errors caused by human errors are greatly decreased, the extracted optimal filter parameter can be more accurate, a diagnosis result is more correct, fault diagnosis and detection automation is more facilitated, more time is saved, and efficiency is higher.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tomographic reconstruction based on deep learning
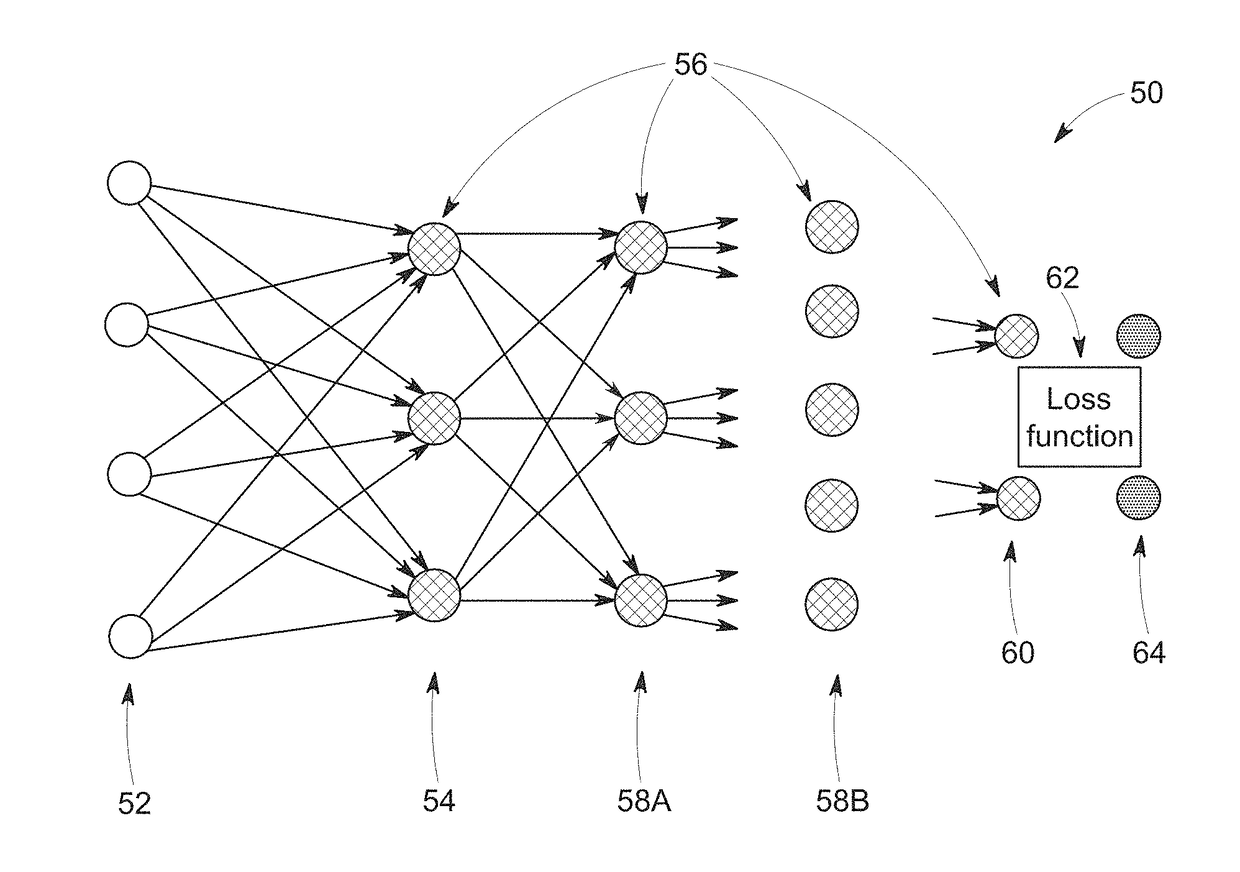
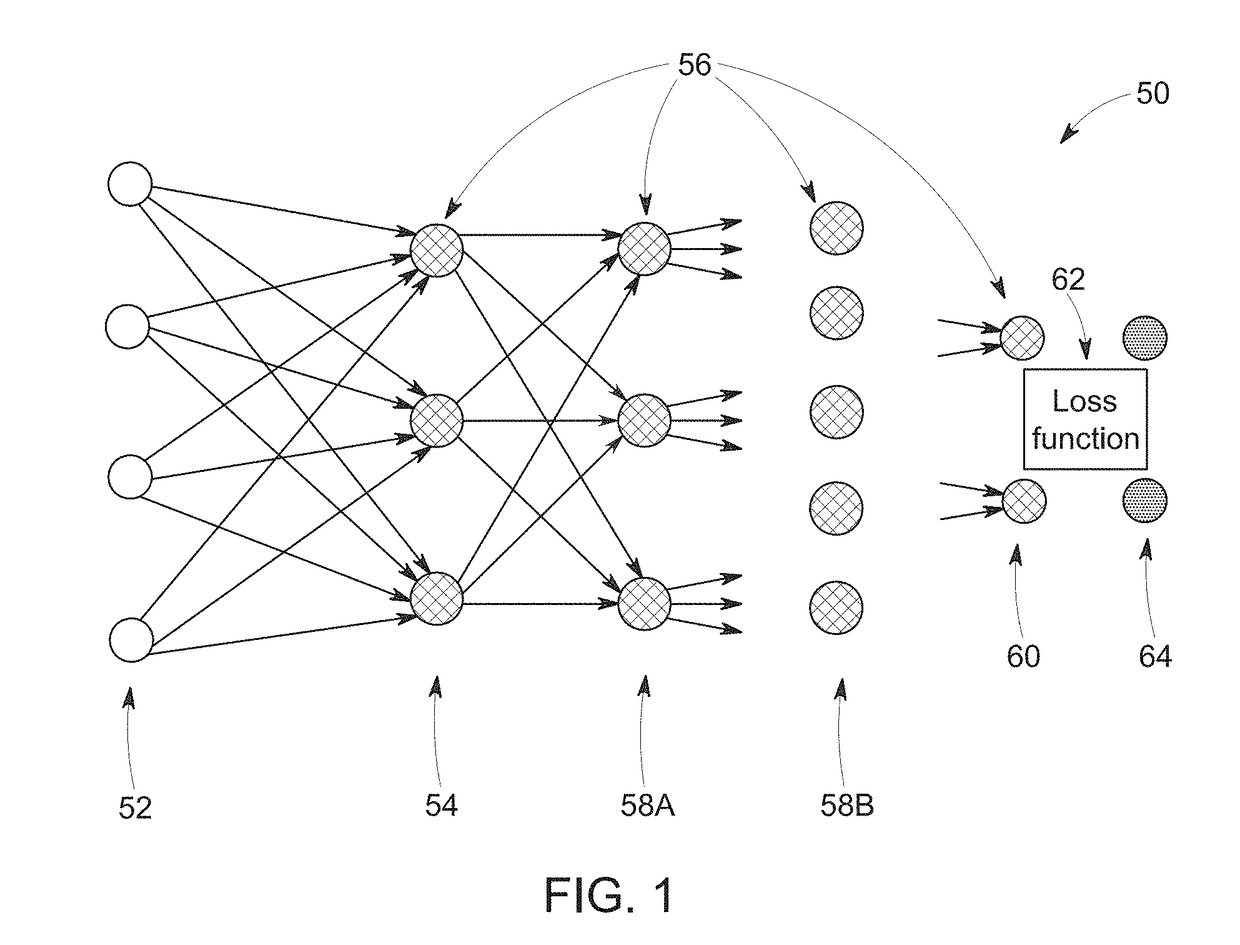
ActiveUS20180293762A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionNerve networkTomographic reconstruction
The present approach relates to the use of machine learning and deep learning systems suitable for solving large-scale, space-variant tomographic reconstruction and / or correction problems. In certain embodiments, a tomographic transform of measured data obtained from a tomography scanner is used as an input to a neural network. In accordance with certain aspects of the present approach, the tomographic transform operation(s) is performed separate from or outside the neural network such that the result of the tomographic transform operation is instead provided as an input to the neural network. In addition, in certain embodiments, one or more layers of the neural network may be provided as wavelet filter banks.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Bearing fault diagnosis method and system device based on improved empirical wavelet transform
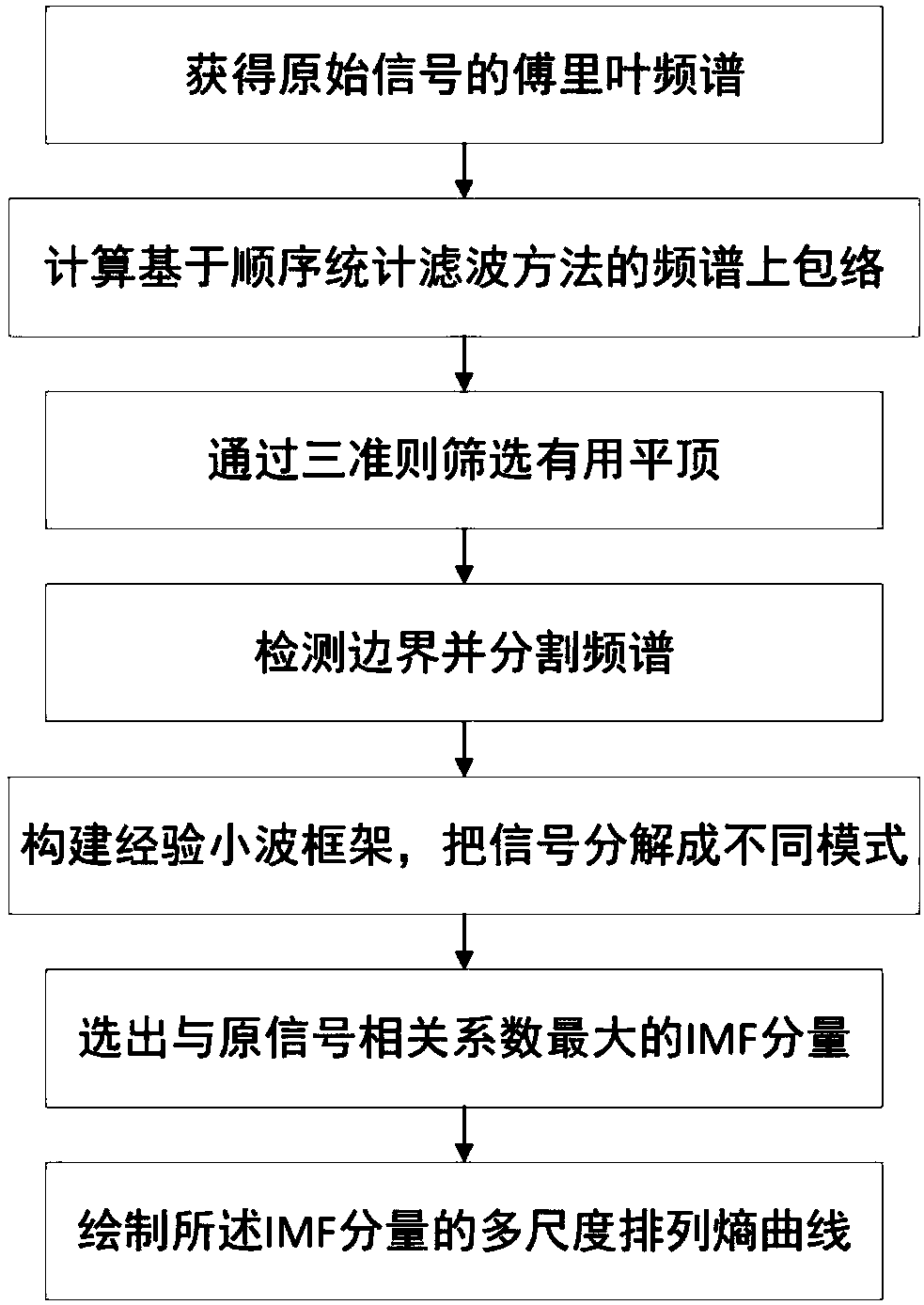
InactiveCN108375472AImprove the shortcomings of unreasonable segmentationAvoid mode aliasingMachine bearings testingCharacter and pattern recognitionCorrelation coefficientFrequency spectrum
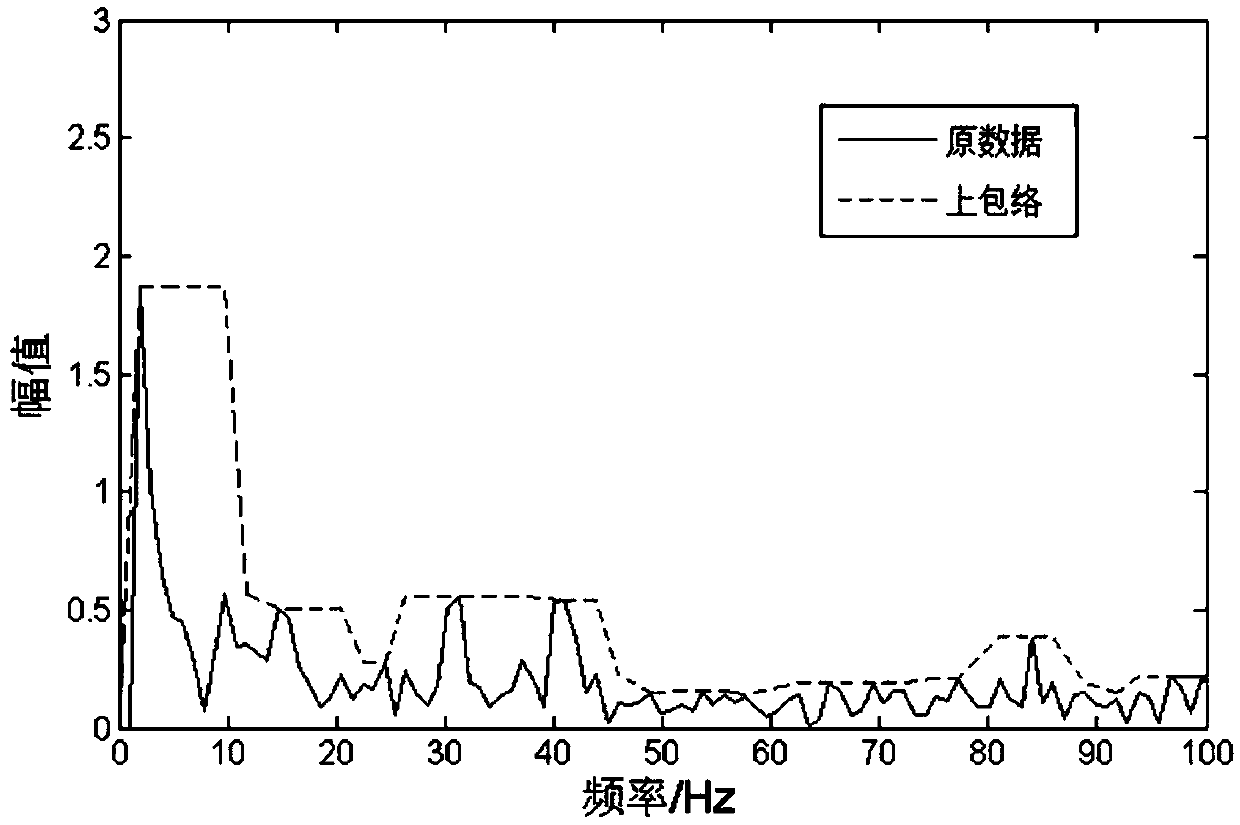
The invention provides a bearing fault diagnosis method and system device based on improved empirical wavelet transform. The method comprises: step one, collecting different fault bearing signals as analysis signals and converting a time domain waveform into a frequency domain waveform; step two, drawing an upper envelope of a frequency spectrum and transforming a frequency peak with a tight support into a flat top; step three, screening flat tops in the frequency domain based on criteria, removing meaningless flat tops, and keeping a main frequency; step four, using a minimum value between adjacent flat tops as the boundary of spectrum segmentation; step five, establishing wavelet filters respectively for segmented frequency spectrums and decomposing the signals into N mode components; step six, calculating similarity values between mode components and the original signals by using a cross-correlation coefficient and selecting a component with the highest similarity value; and step seven, taking a fault sample, calculating an IMF component with the largest correlation coefficient of the sample, calculating a multi-scale entropy of the IMF component, and drawing the multi-scale entropy curve of the sample to realize fault classification.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
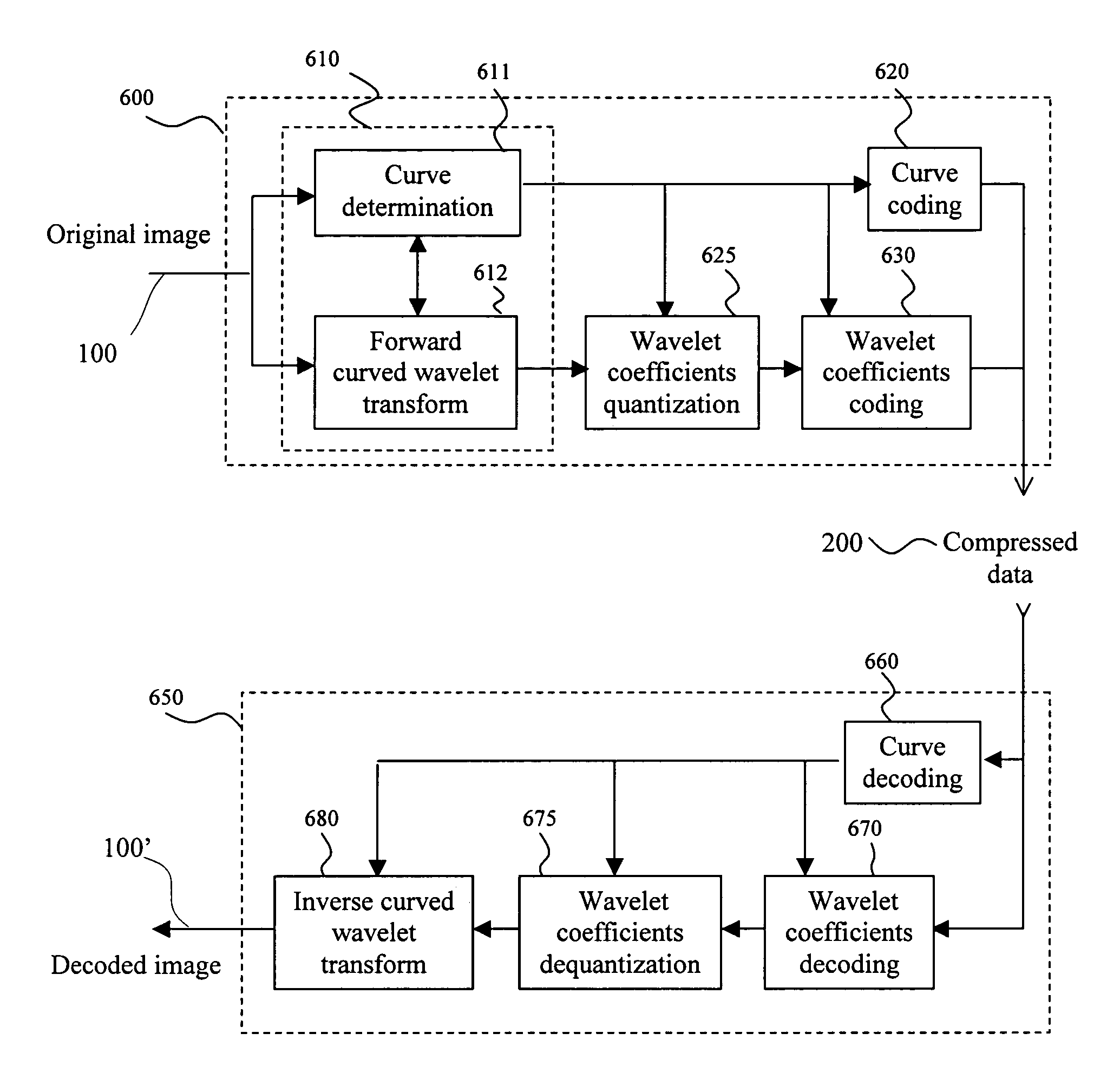
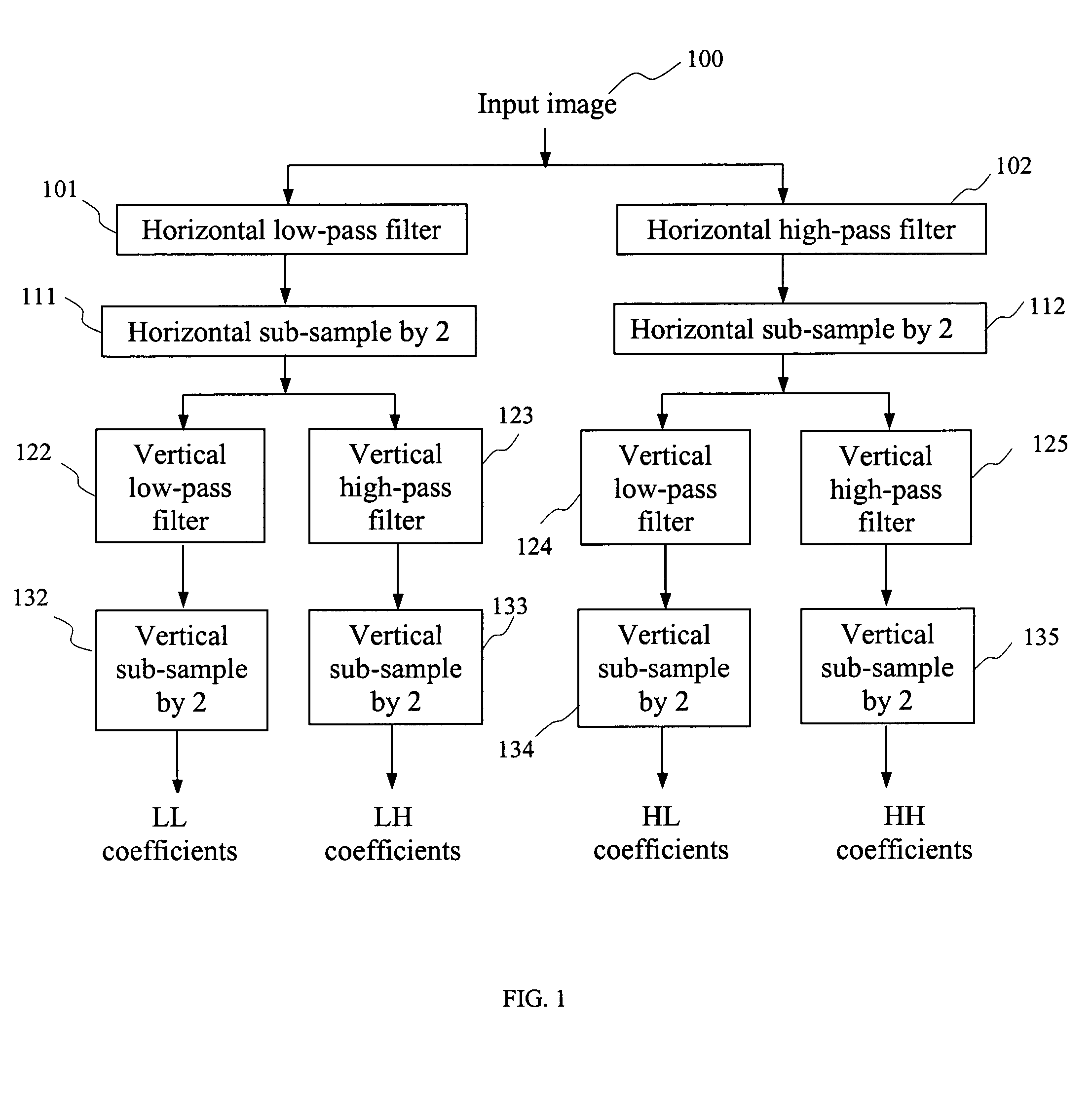
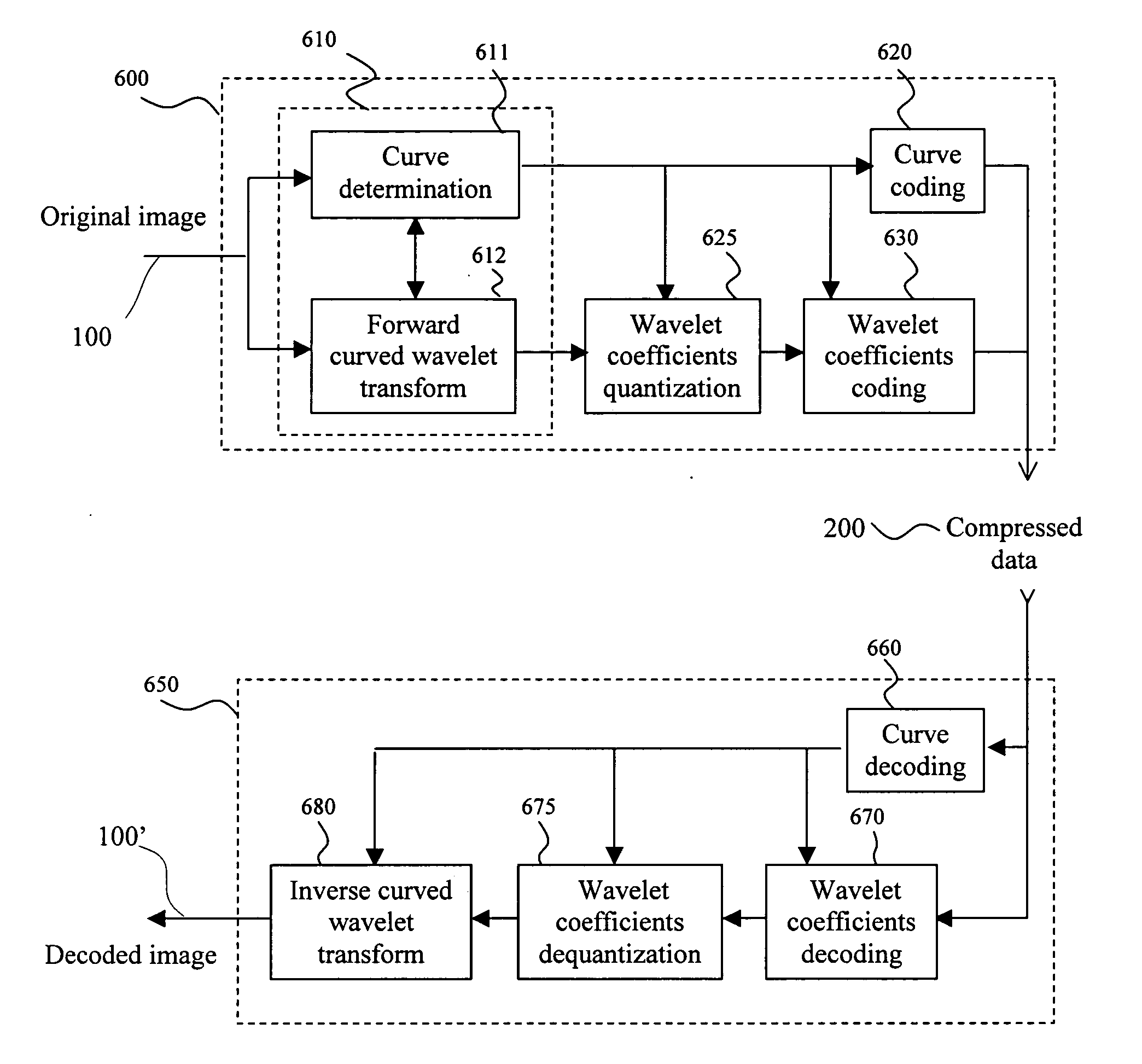
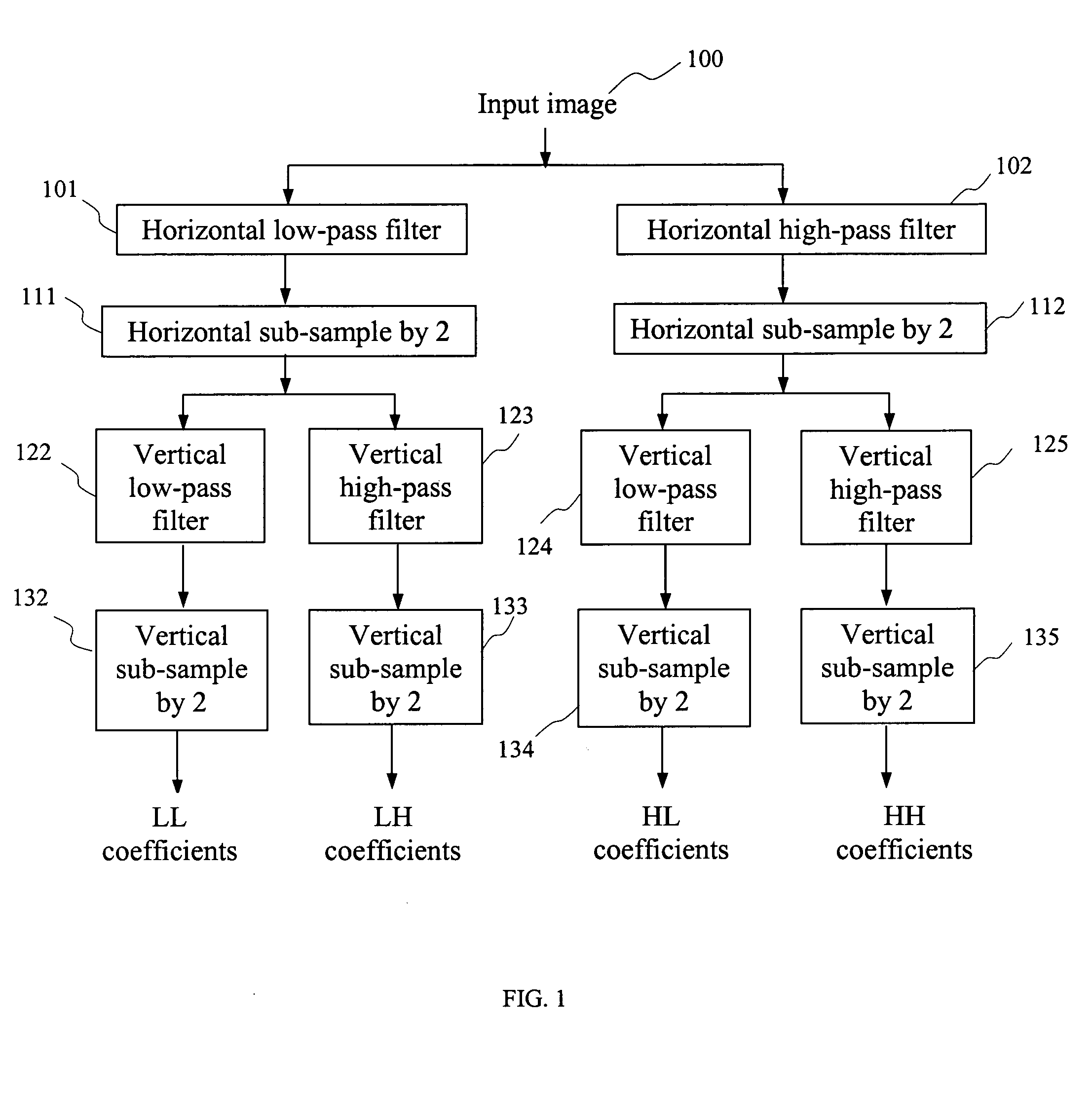
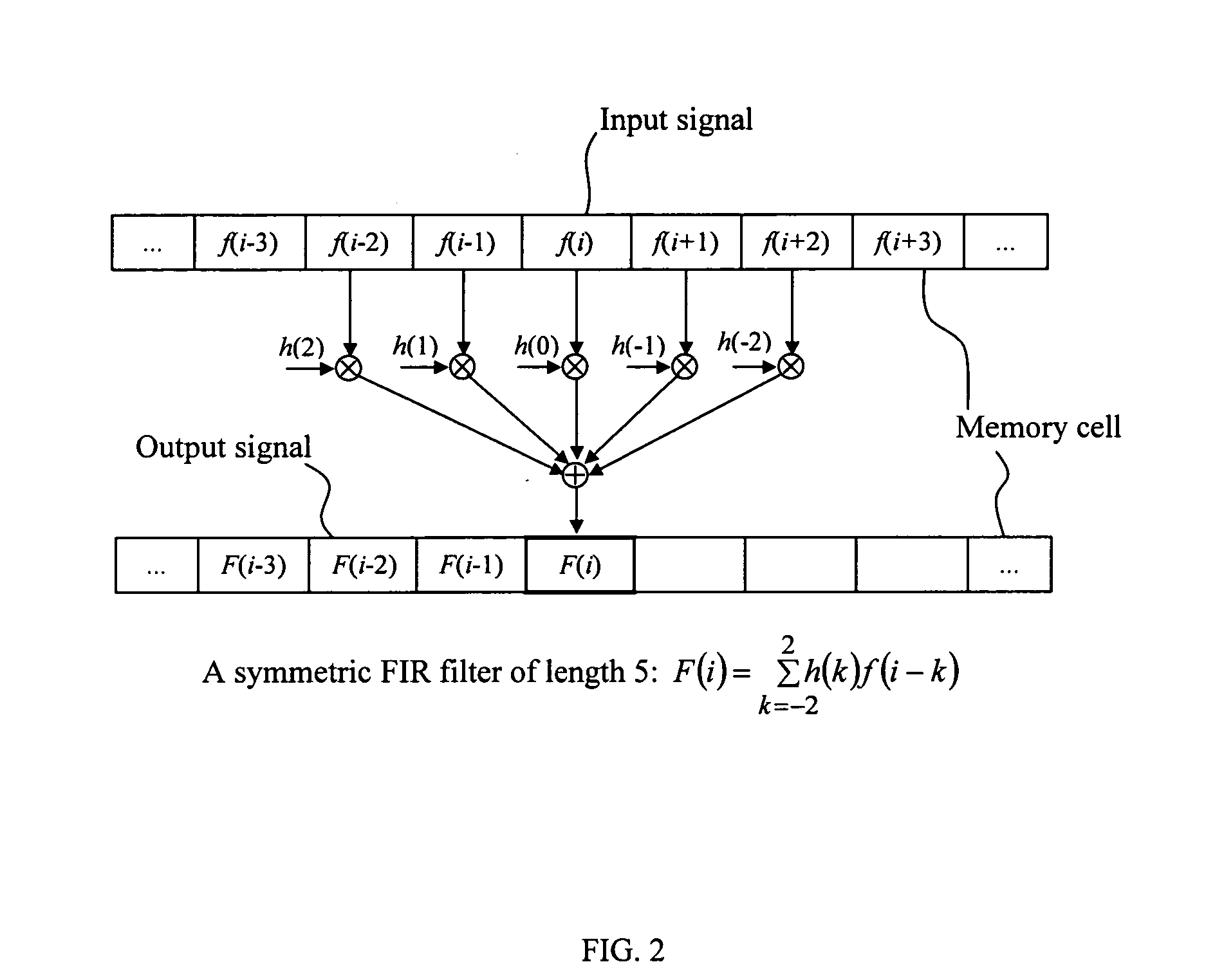
Curved wavelet transform for image and video compression
InactiveUS7418144B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionWavelet decompositionImage compression
A curved wavelet transform and a related image / video compression system are disclosed. The curved wavelet transform (CWT) is carried out by applying one-dimensional (1-D) wavelet filters along curves, rather than along only horizontal and vertical directions. The image / video compression system includes a curve determination unit, a curved wavelet transform unit, a wavelet coefficient quantization unit, a wavelet coefficient coding unit, and a curve coding unit. The quantization and coding of the wavelet coefficients are related to the curves. In one embodiment, recursive wavelet filters are used for inverse wavelet decomposition. The system provides higher compression capability than conventional wavelet-based image compression systems.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
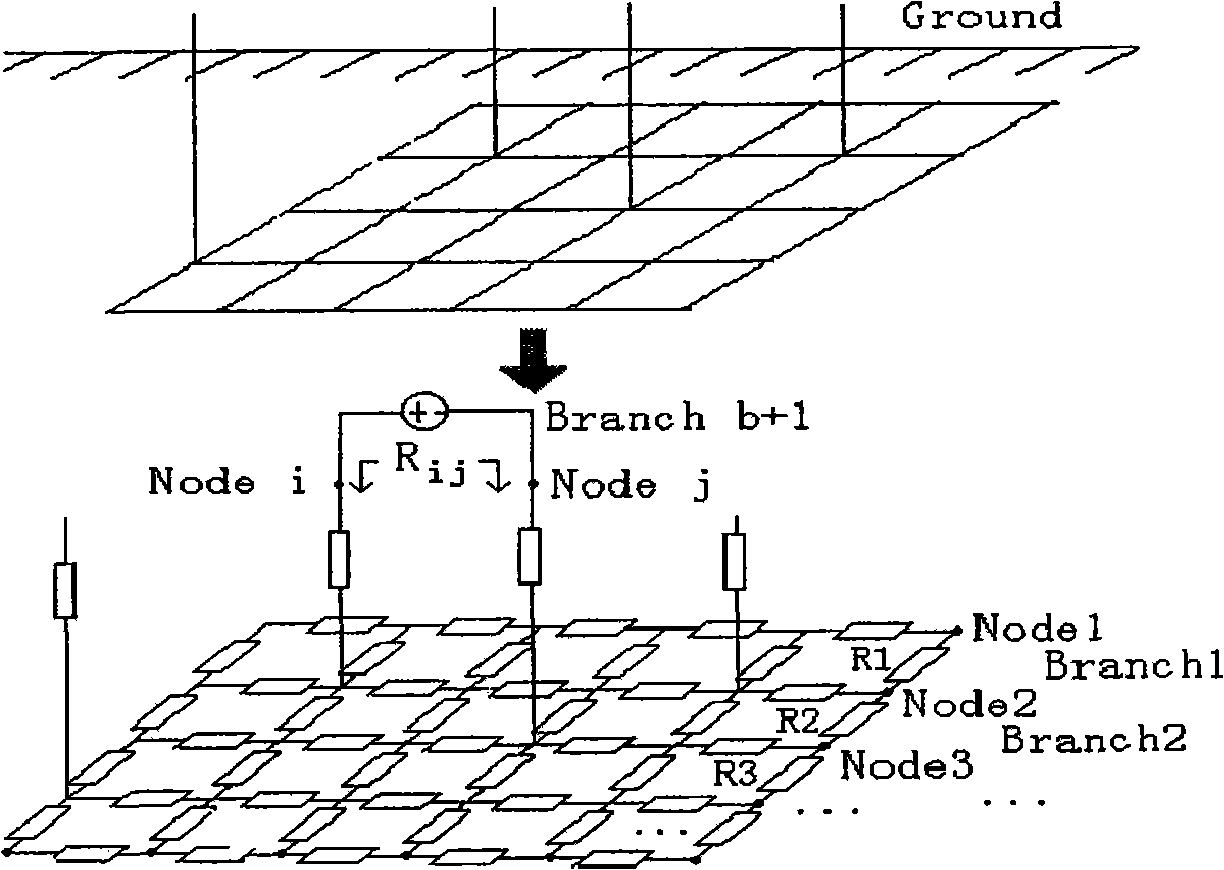
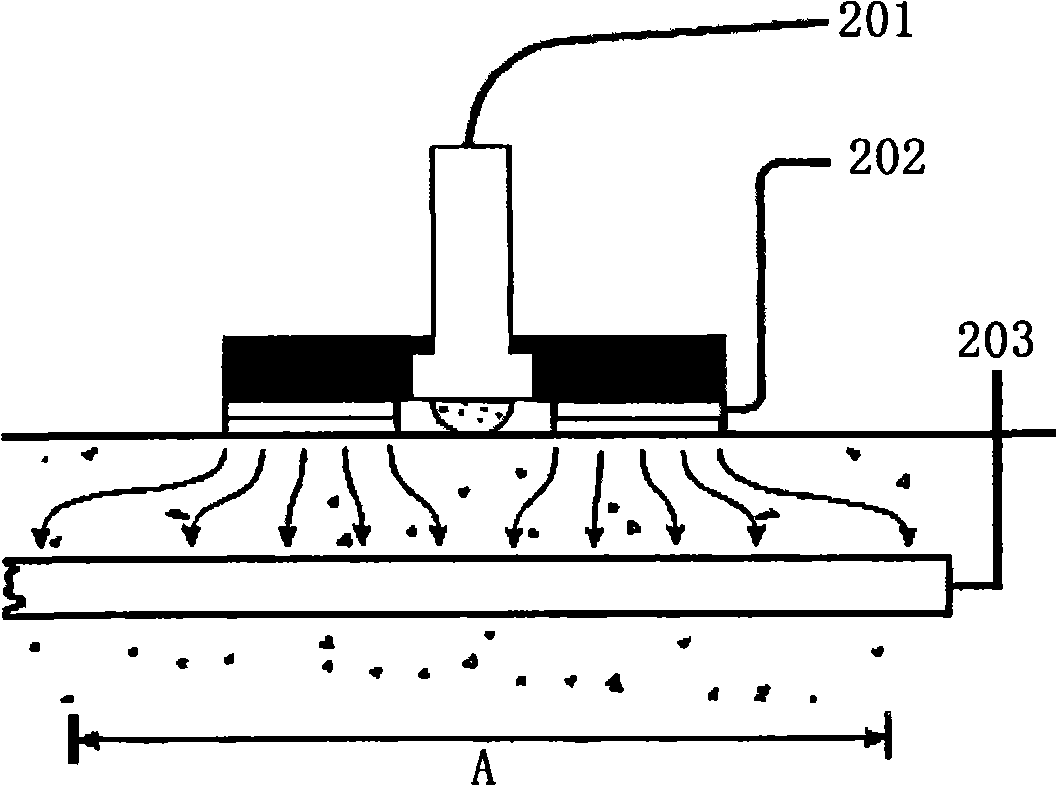
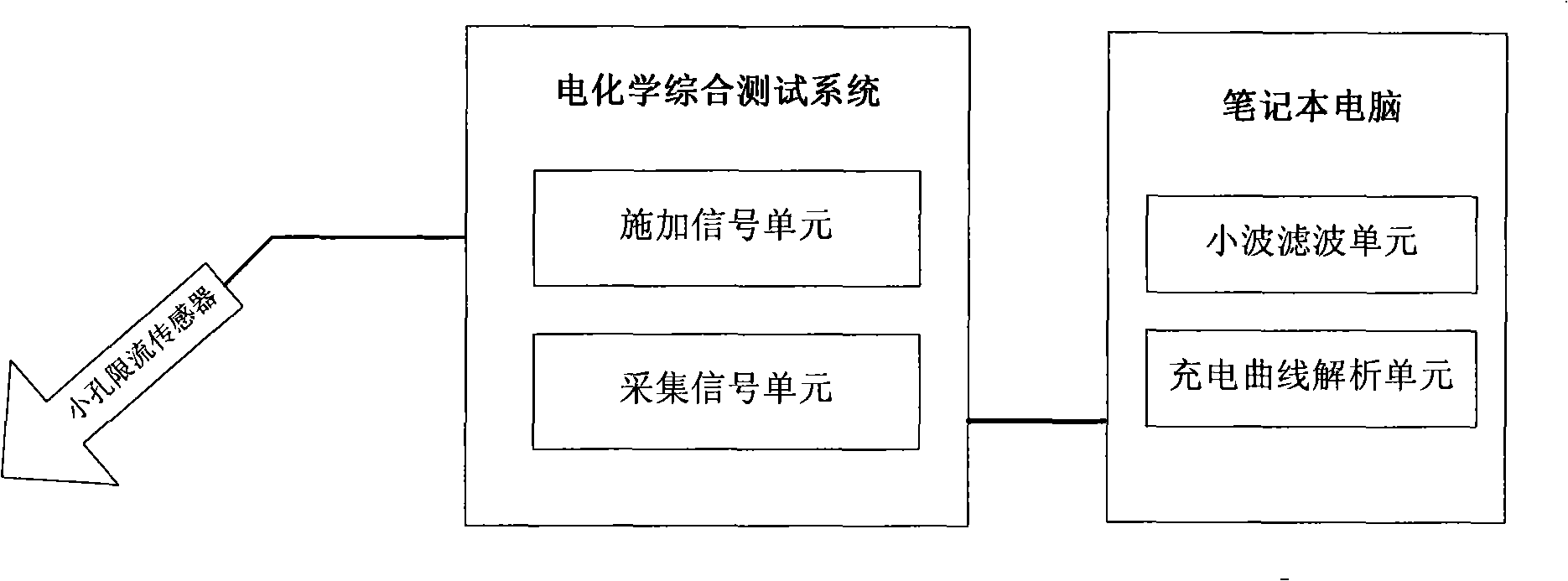
Ground net corrosion detection method and system
ActiveCN101315403AEasy to measureQuick testWeather/light/corrosion resistanceFault locationStep responseMetal
The invention provides a corrosion detection method for a grounding net, as well as a system. The method comprises the steps as follows: the corrosion potential of detected grounding net metal is measured, constant current step signals are applied to the detected grounding net metal, and the constant current step response signals are collected; the wavelet filter treatment is performed to the collected grounding net soil corrosion electrochemical detection data; and the corrosion electrochemical parameter analysis processing is performed to the grounding net soil corrosion electrochemical detection data after the wavelet filter treatment, thereby generating the grounding net soil corrosion detection result. The grounding net corrosion status is detected accurately and conveniently by the electrochemical detection method.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRICAL POWER RES INST +1
Adaptive non-uniformity compensation using feedforward shunting and wavelet filter
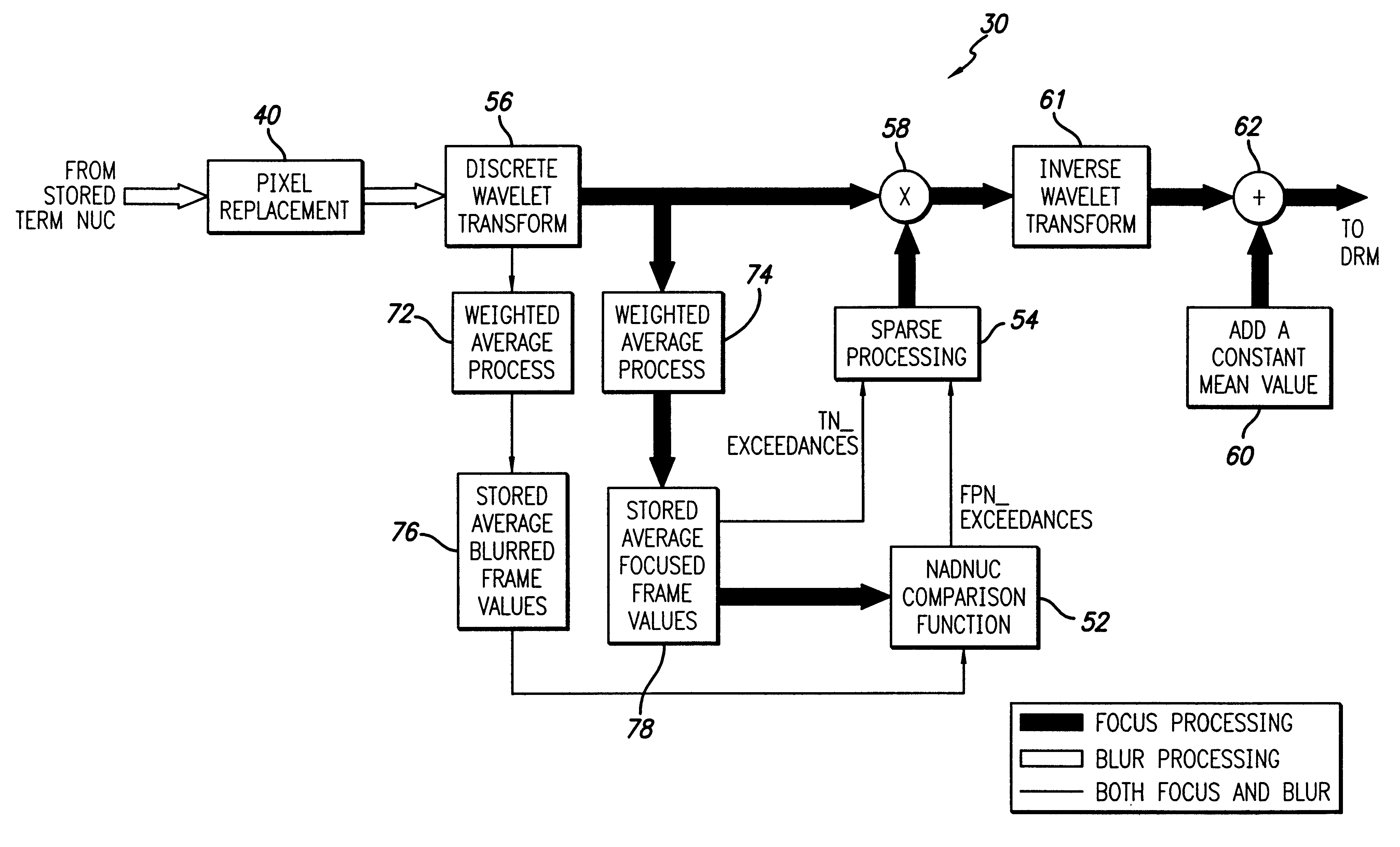
A system and method adapted for use with a focal plane array of electromagnetic energy detectors to receive first and second frames of image data from electromagnetic energy received from at least a portion of a scene. The first frame is a focused frame and the second frame is a blurred frame. In a feed-forward path the system compares the first frame to the second frame and provides an error signal in response thereto. In a main path, the system multiplies at least a portion of the second frame of image data with the error signal to provide a noise error corrected output signal. In the preferred embodiment, a wavelet filter is used to remove dome shading effects from the frames of image data. In the best mode, the wavelet filter is disposed in the main path and blurred and focused outputs therefrom are weighted, averaged and stored. Coefficients from the weighted, averaged and stored focused frames are compared to coefficients from the weighted, averaged and stored blurred frames to provide a fixed pattern noise error signal. A temporal noise error signal is identified from the weighted, averaged and stored focused frames. The fixed pattern noise error signal and the temporal noise error signals are sparse processed and shunted from a current frame. Thereafter, a constant mean value may be added to provide the output signal. Pixel replacement can be consolidated into a single circuit and positioned prior to the wavelet filter.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
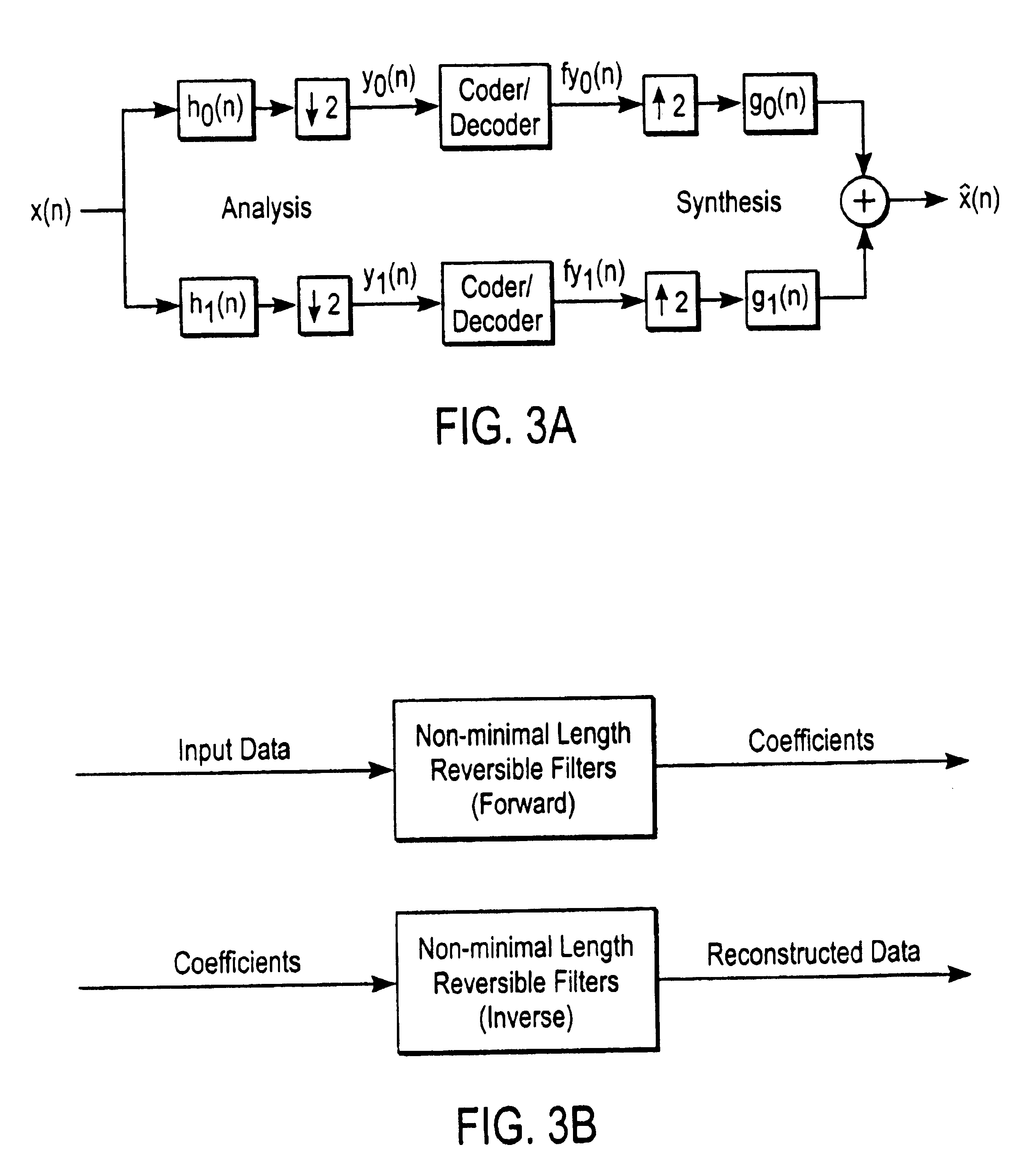
Method and apparatus for compression using reversible wavelet transforms and an embedded codestream
InactiveUS6873734B1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionCode conversionData streamComputer science
A compression and decompression system in which a reversible wavelet filter are used to generates coefficients from input data, such as image data. The reversible wavelet filter is an efficient transform implemented with integer arithmetic that has exact reconstruction. The present invention uses the reversible wavelet filter in a lossless system (or lossy system) in which an embedded codestream is generated from the coefficients produced by the filter. An entropy coder performs entropy coding on the embedded codestream to produce the compressed data stream.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
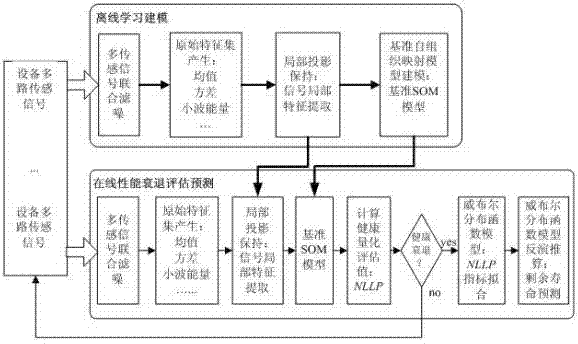
Equipment health state evaluation and recession prediction method based on multi-channel sensing signals
InactiveCN102313577AReduce dimensionalityReduce complexityMeasurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsFiltrationEngineering
The invention relates to an equipment health state evaluation and recession prediction method based on multi-channel sensing signals. The operation steps of the method are as follows: the first step: joint noise filtration of the multiple sensing signals: adopting a multi-scale wavelet filtering algorithm to perform the joint noise filtration on the multi-channel sensing signal collected from equipment so as to improve the quality of the multiple sensing signals; the second step: generation of an original characteristic set; the third step: extraction of local characteristics of the signals; the fourth step: modeling of a reference self-organizing mapping model; and the fifth step: health quantitative evaluation and residual life prediction. By adopting the method, the quantitative evaluation and the life prediction of performance recession of the equipment can be realized, the operation reliability of the equipment can be further improved and the maintenance cost can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
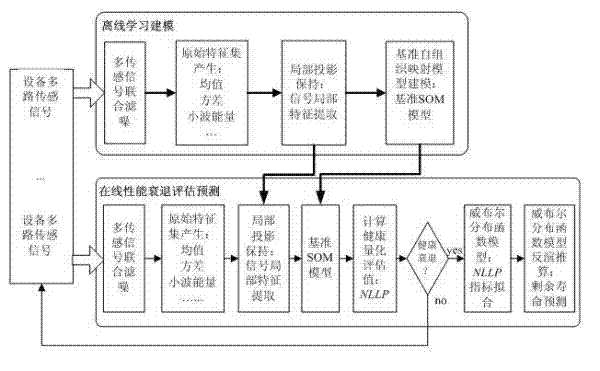
Method and apparatus for compression using reversible wavelet transforms and an embedded codestream
InactiveUS20060222254A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital technique networkData streamEntropy encoding
A compression and decompression system in which a reversible wavelet filter are used to generates coefficients from input data, such as image data. The reversible wavelet filter is an efficient transform implemented with integer arithmetic that has exact reconstruction. The present invention uses the reversible wavelet filter in a lossless system (or lossy system) in which an embedded codestream is generated from the coefficients produced by the filter. An entropy coder performs entropy coding on the embedded codestream to produce the compressed data stream.
Owner:ZANDI AHMAD +3
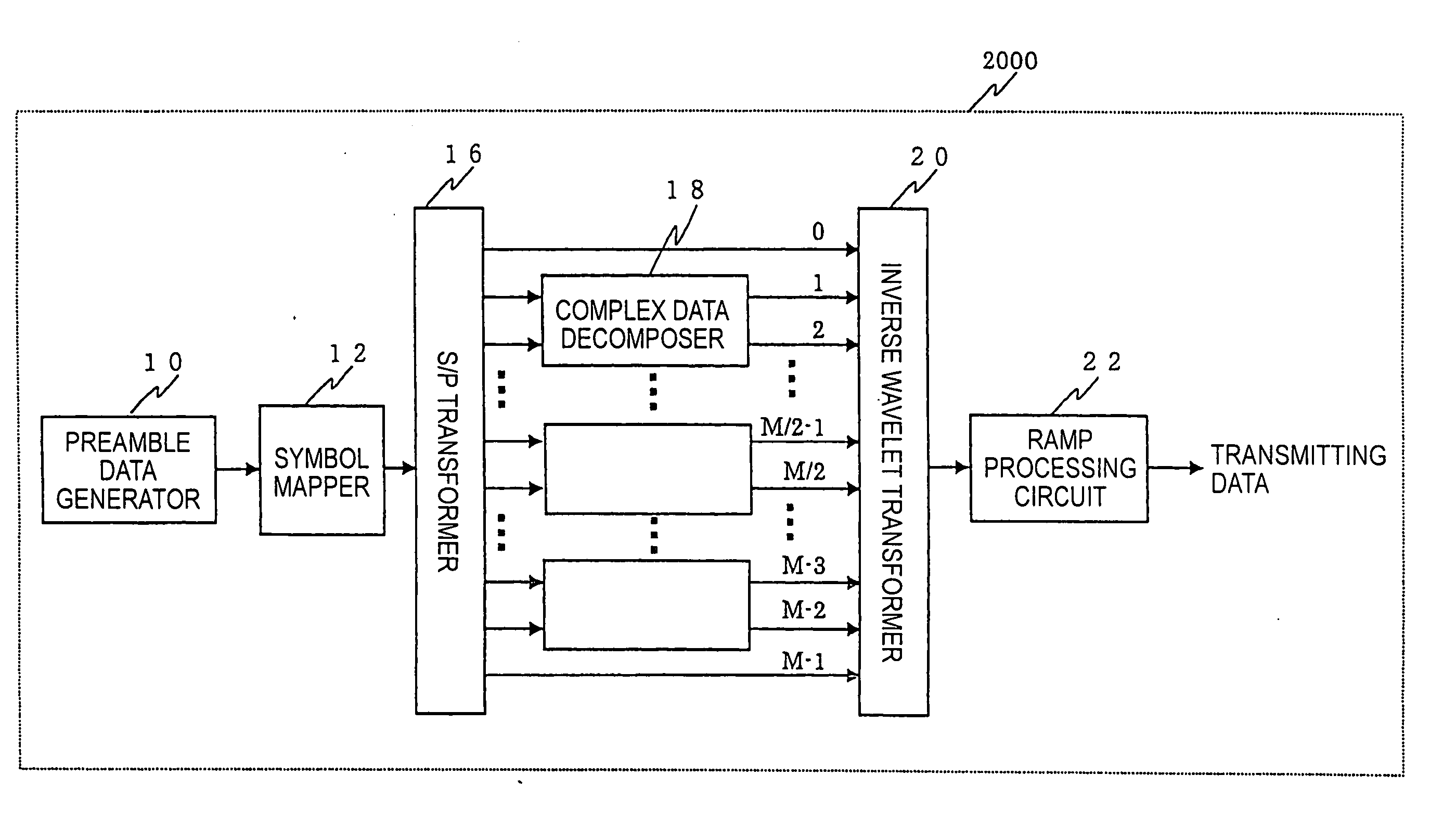
Method and apparatus for signal transmission and reception
InactiveUS20050141603A1Minimal costMinimal complexitySecret communicationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksModem deviceCarrier signal
A method and modem for communicating serial input data over a transmission link. Serial input data is partitioned into parallel data elements prior to rotation by an invertible linear mapping. Resulting frames of parallel signal elements sequentially modulate a carrier, which is then transmitted over the link. After receipt of the modulated carrier from the link, the signal is demodulated and assembled into frames of parallel signal elements which are de-rotated by an inverse linear mapping. Thresholding the result of the inverse mapping recovers the parallel data elements, which are then re-assembled into serial output data. The linear mapping employs: 1) commuting rotation matrices for convolutionally rotating data vectors into signal vectors and vice-versa; 2) filter bank polyphase rotation matrices; or 3) computationally efficient multi-rate wavelet filter banks. Transmitter pre-emphasis places most of the information in lower baseband frequencies; complimentary de-emphasis occurs in the receiver. Logarithmic amplification of the baseband signal prior to carrier modulation improves modulation gain and transmit channel noise attenuation. Coefficients of the rotation matrix of the receiver are adaptively equalized to correct for transmission path distortion. FM double-side band is employed in systems requiring minimized cost and complexity. FM single-side band is employed in systems in which bandwidth reduction is desirable. AM is also employable.
Owner:INTRATECH
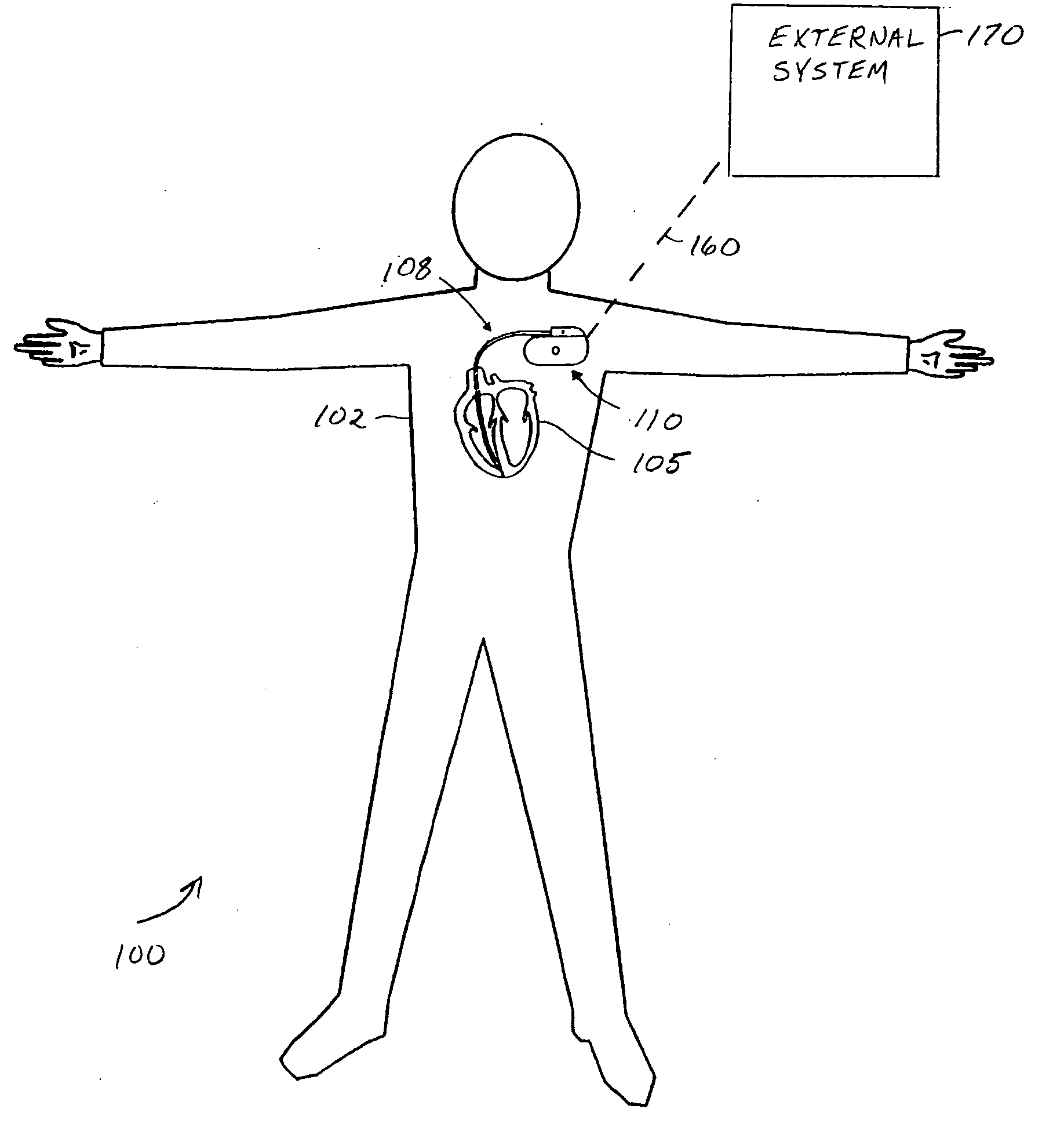
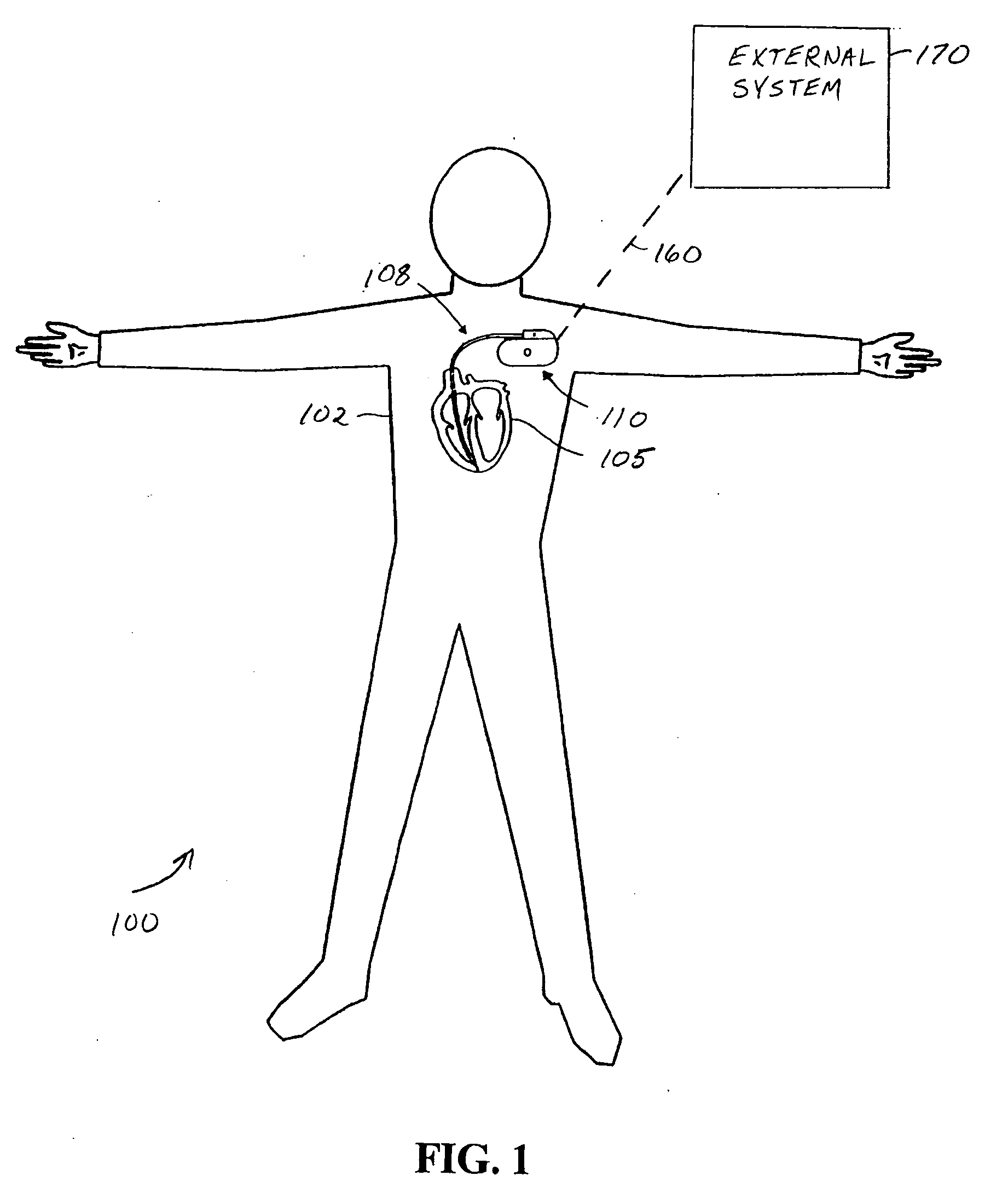
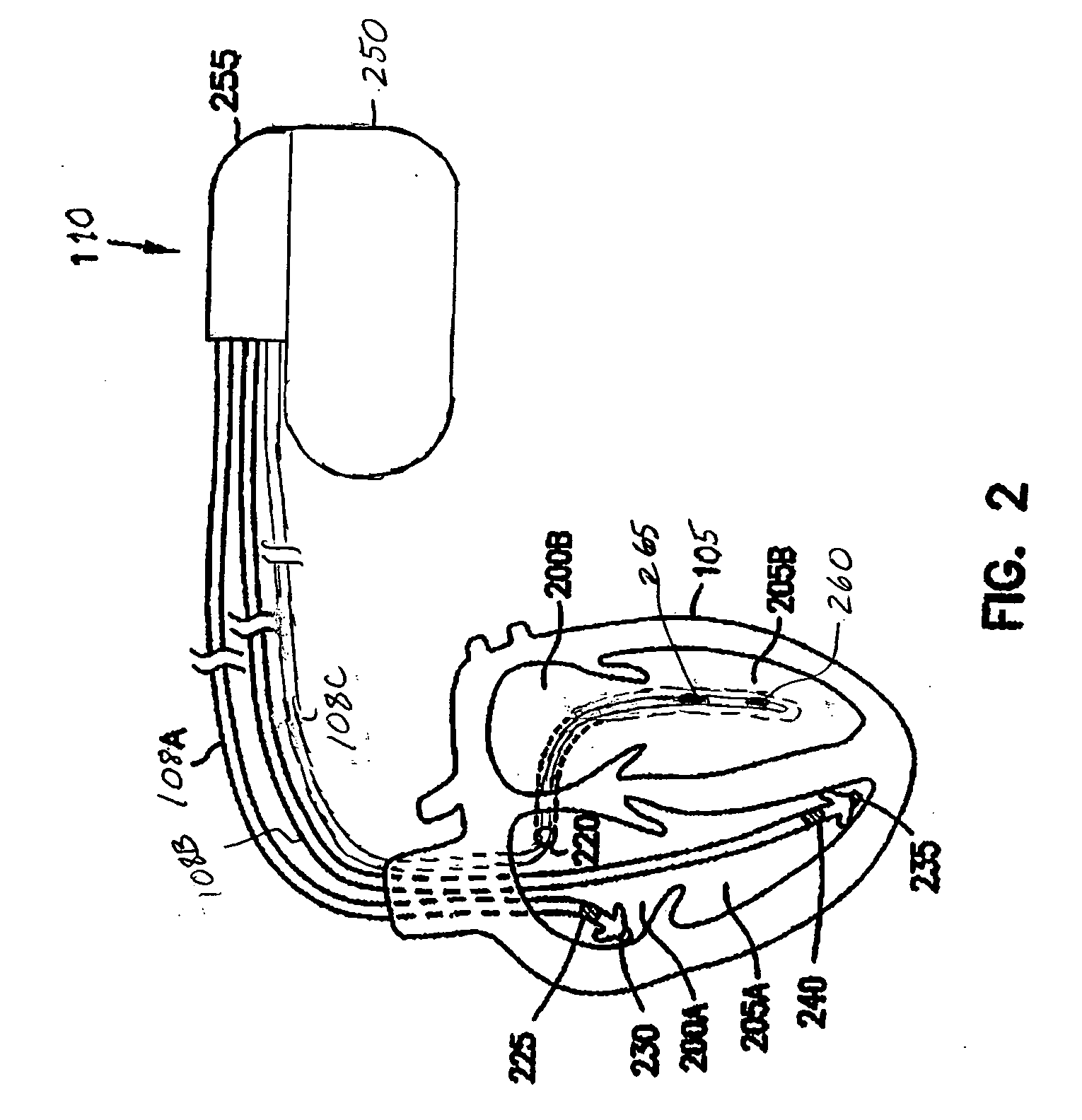
Systems and methods for valvular regurgitation detection
A system comprising an implantable medical device (IMD). The IMD includes an implantable sensor operable to produce an electrical signal representative of mechanical activity of a heart of a subject and a controller circuit coupled to the sensor. The controller circuit includes a wavelet filter module and a valvular regurgitation (VR) calculation module. The wavelet filter module is configured to extract signal energy information from the electrical signal. The energy information includes variation of signal amplitude with frequency and time. The VR calculation module is configured to calculate a measurement of VR for one or more heartbeats using the energy information.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
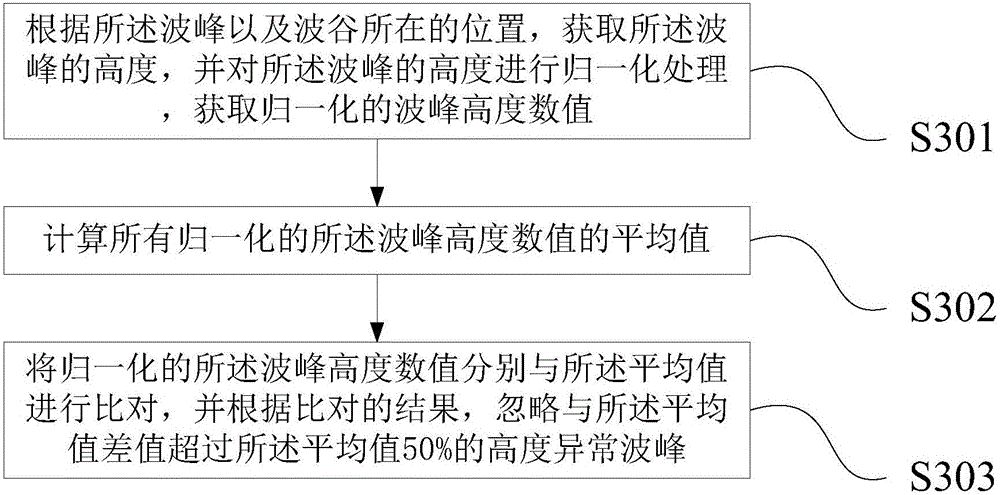
Heart sign obtaining method and device
InactiveCN106175742AEasy accessReduce mistakesCharacter and pattern recognitionSensorsInterval valuedInterval data
The invention relates to the technical field of computer application, specifically, relates to a heart sign obtaining method and a heart sign obtaining device. The heart sign obtaining method comprises the steps of: obtaining photoplethysmography (PPG) data; performing low-pass filtering processing with cut-off frequency less than or equal to 4 HZ on the PPG value and removing high-frequency noise; performing discrete wavelet filtering processing on the PPG value subjected to high-frequency noise removal and correcting baseline drift; obtaining the wave crest and wave trough positions of PPG waveform according to the PPG data subjected to baseline drift correction, and obtaining the time interval value between the wave crests according to the wave crest and wave trough positions and the sampling rate of the PPG data; obtaining RR interval data according to the time interval value between the wave crests, and calculating the heart sign according to the RR interval data. By adoption of the method and the device, a user can comprehensively obtain the heart sign value.
Owner:北京心量科技有限公司
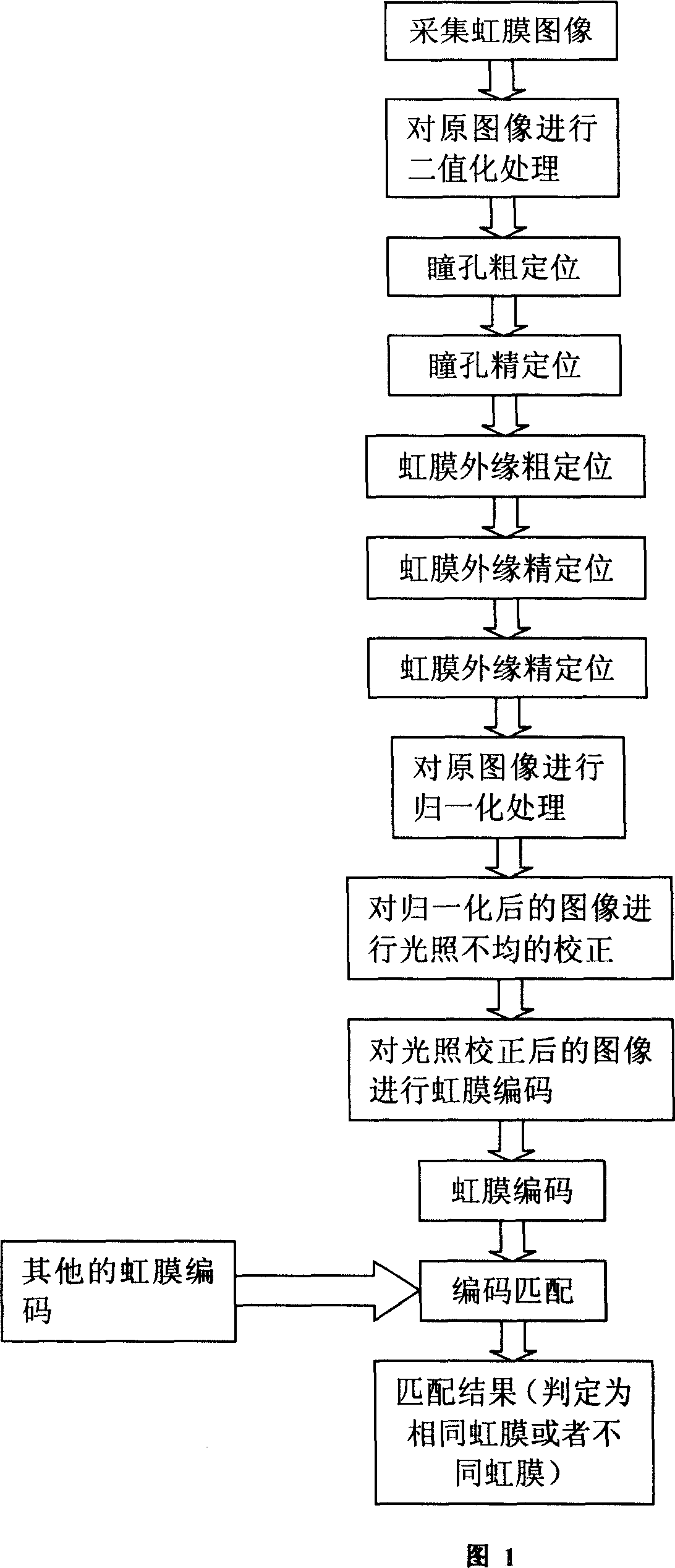
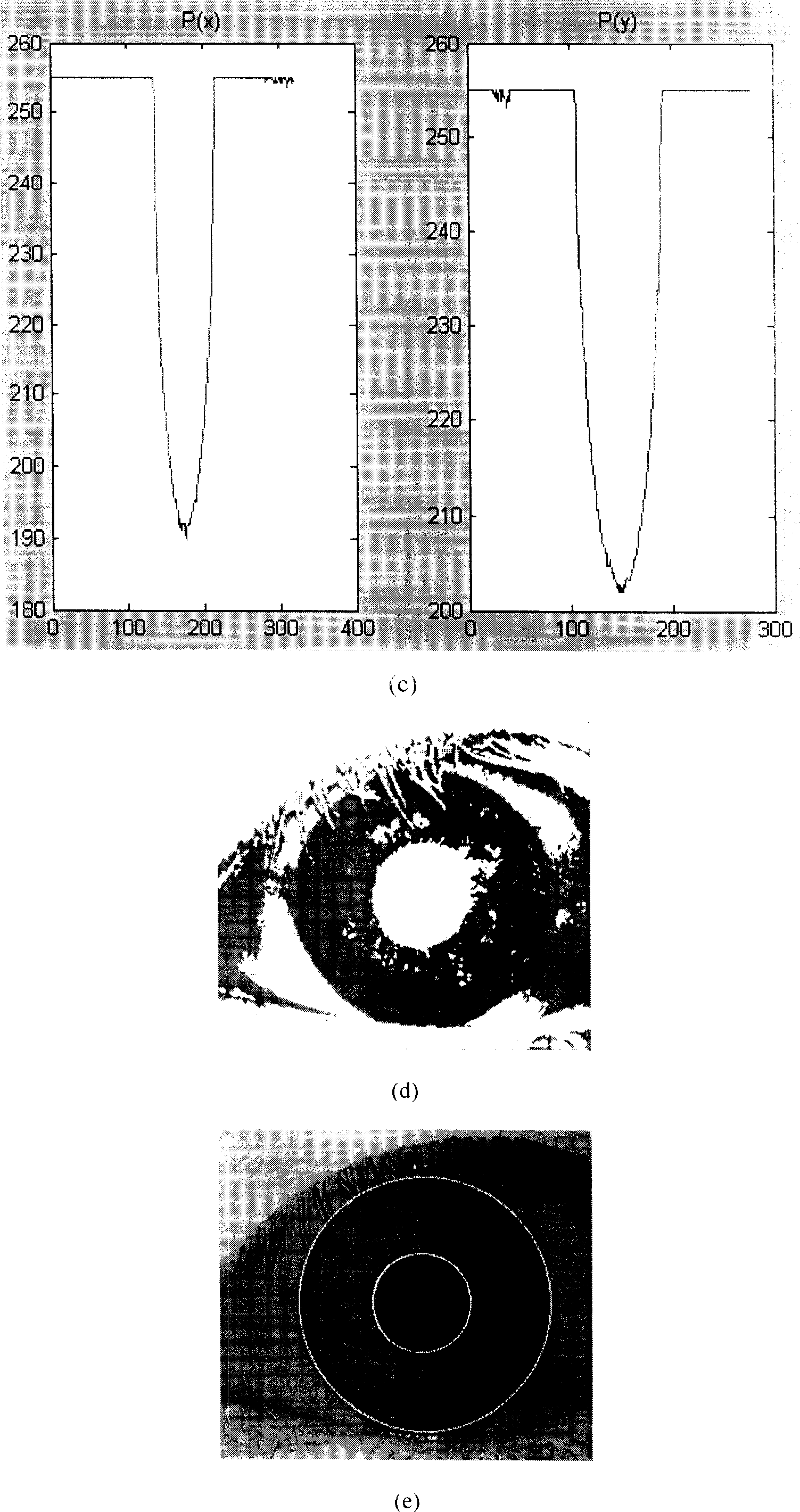
Method for identifying iris based on zero crossing indication of wavelet transforms
InactiveCN101093538ACancel noisePrecise positioningCharacter and pattern recognitionIris codeRecognition algorithm
An iris identifying-method based on wavelet transform zero cross presentation includes carrying out binary state treatment on original image based on certain threshold to raise rough positioning precision of pupil, making double-threshold treatment based on external edge rough positioning of iris and carrying out intermediate value filtering to pick up general part of iris effectively, making quick and accurate rough positioning, accurately positioning external edge of iris by utilizing rough positioning result and using wavelet filter to carry out iris coding to effectively pick up information.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for compression using reversible wavelet transforms and an embedded codestream
InactiveUS20070116369A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital technique networkData streamEntropy encoding
Owner:RICOH KK
EMAT Acoustic Signal Measurement Using Modulated Gaussian Wavelet and Hilbert Demodulation
Casing signals generated by an EMAT in a borehole are processed using at least two orthogonal band-limited filters. The band-limited filters may include Gaussian or Cauchy Wavelet filters. By using the Hilbert transform, an envelope of the filtered signals is determined and amplitudes and arrival times of individual arrivals are estimated. These can be used to estimate casing and cement properties.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
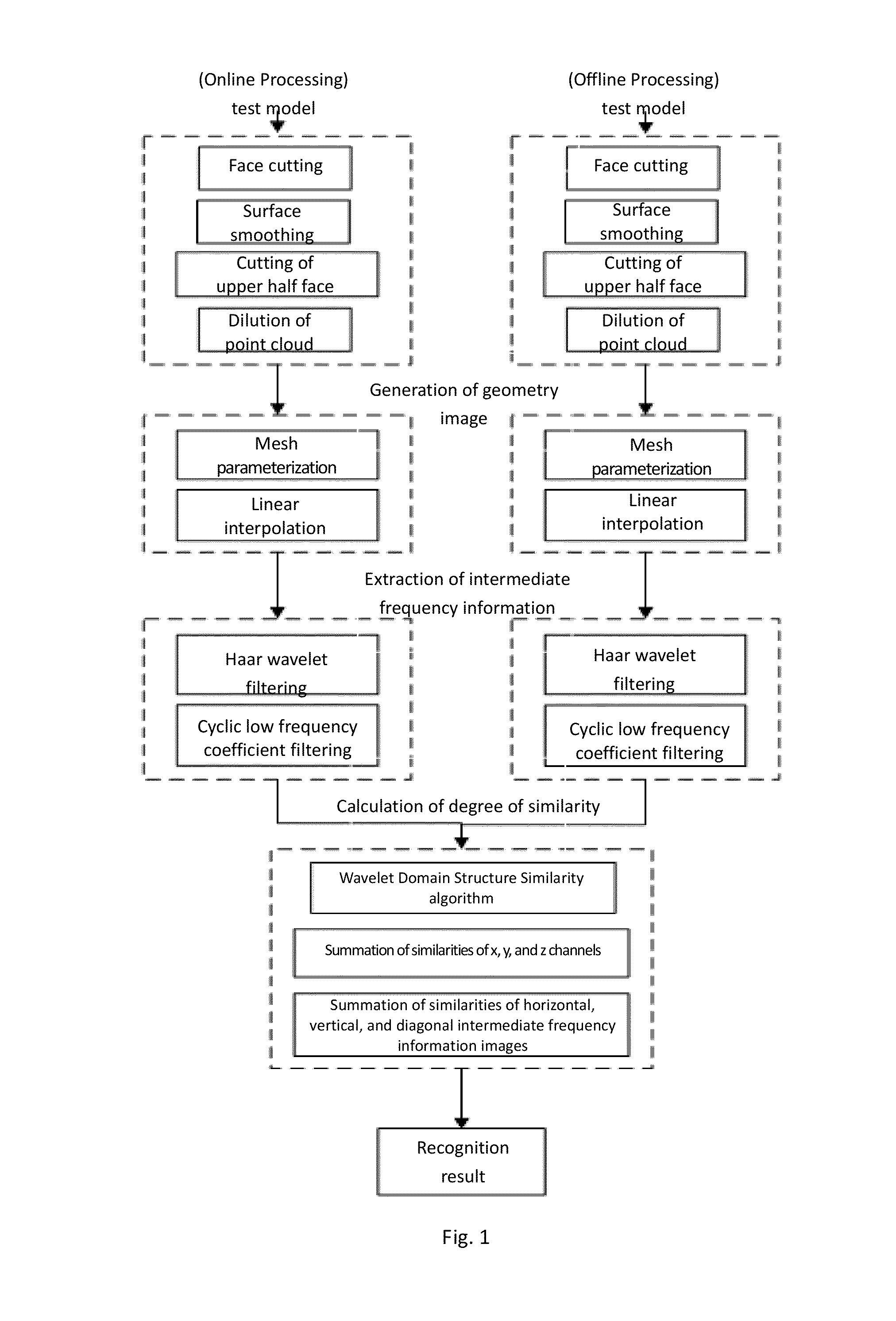
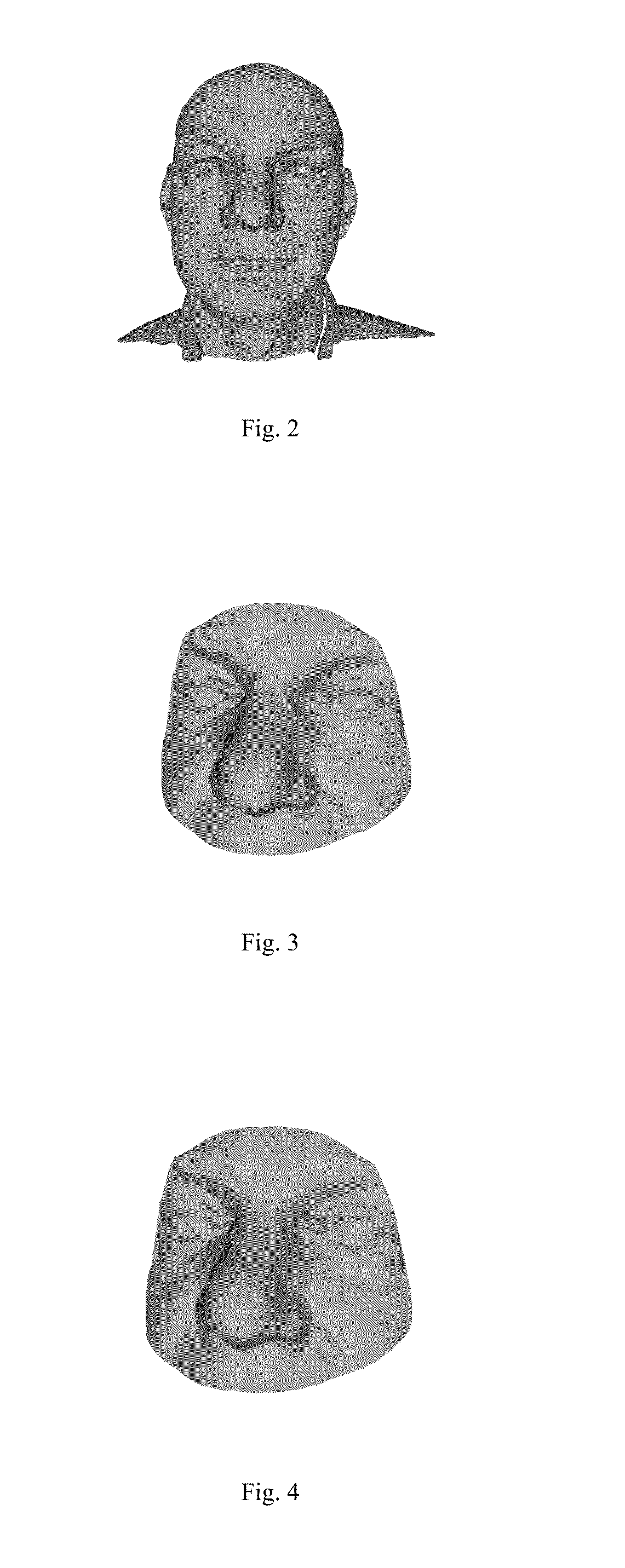
3D face recognition method based on intermediate frequency information in geometric image
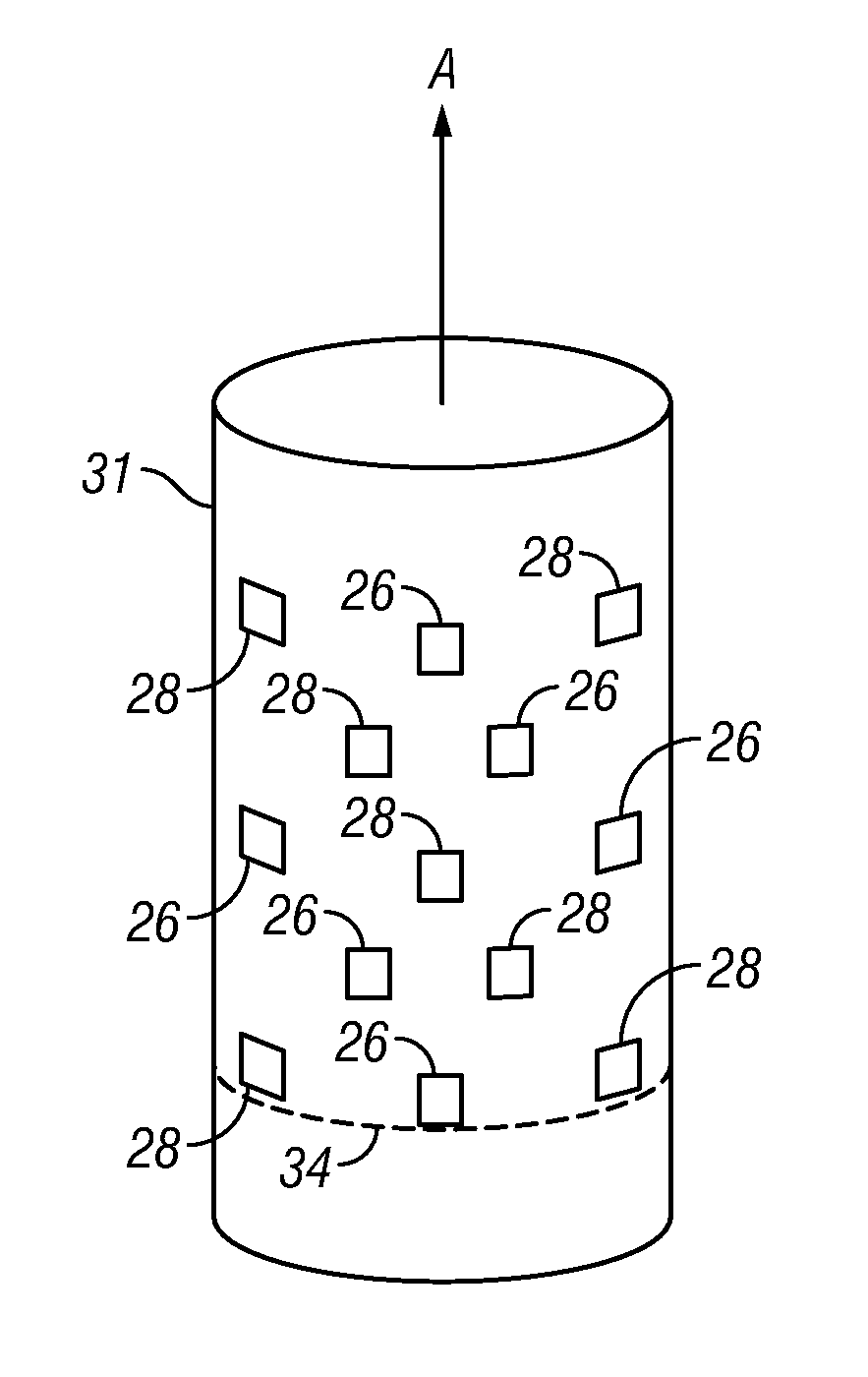
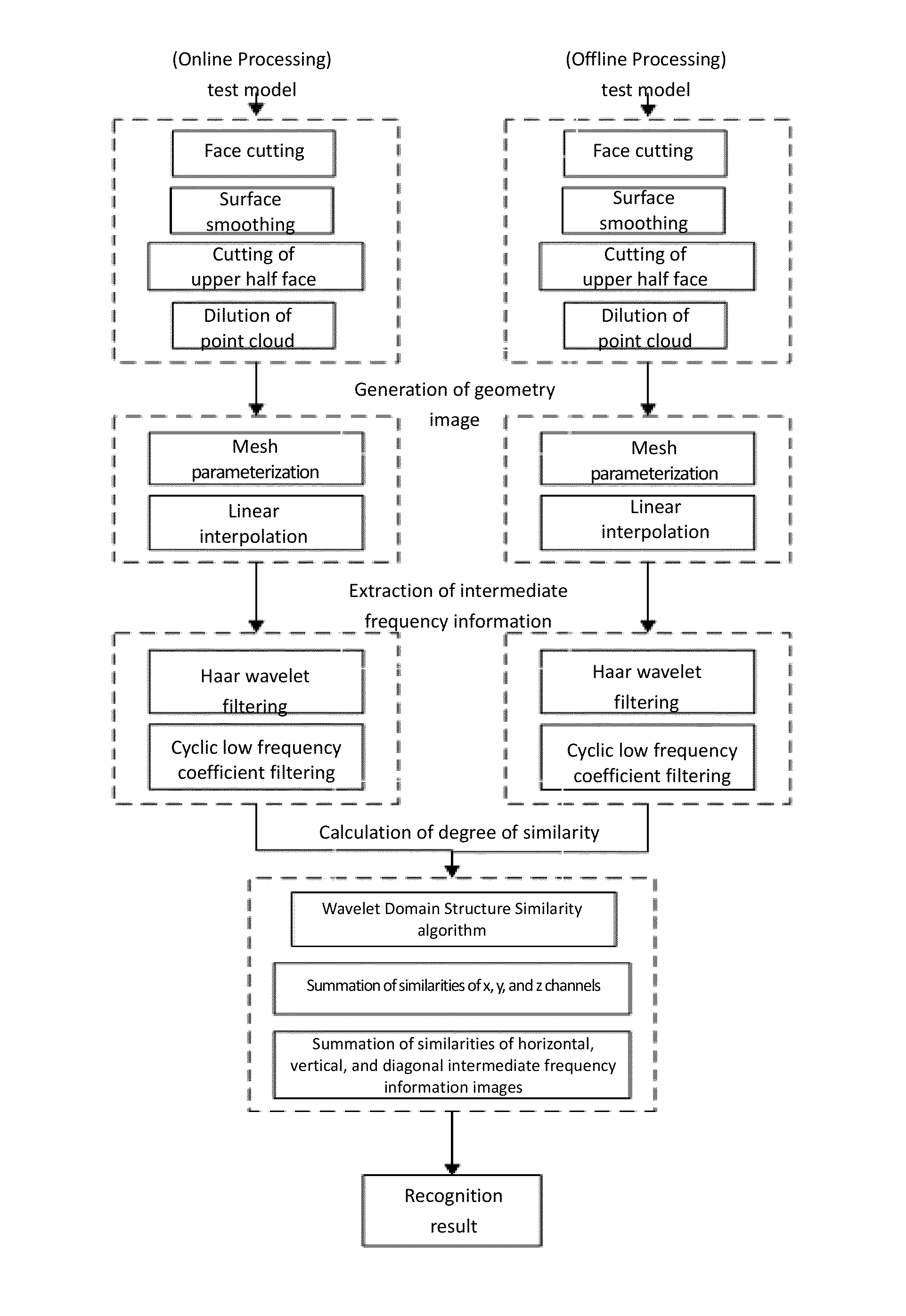
ActiveUS20140355843A1Impact efficiency performanceImpact recognition efficiencyImage analysis3D modellingPoint cloudIntermediate frequency
A 3D face recognition method based on intermediate frequency information in a geometric image as follows: (1) preprocessing a library and test models of 3D faces, including 3D face area cutting, smoothing processing and point cloud thinning, and discarding the lower portion of the face; (2) mapping the remainder of the face to a 2D grid using grid parameters, and performing linear interpolation on the 3D coordinates of the grid top to acquire the 3D coordinate attributes and generating a geometric image of a 3D face model; (3) performing multi-scale filtering with a multi-scale Haar wavelet filter to extract horizontal, vertical, and diagonal intermediate frequency information image images as invariable facial features; (4) calculating the similarity between the test model and the library set model with a wavelet domain structuring similarity algorithm; and (5) judging the test and library set model models with the maximum similarity belong to the same person.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Distribution type water information monitoring system for underground working face of coal mine
InactiveCN102587984AFocus on monitoringImprove accuracyMining devicesDrainageMonitoring systemEngineering
A distribution type water information monitoring system for an underground working face of a coal mine is disclosed, belongs to the technical field of underground automation and water disaster prevention and control of the coal mine, and is an automatic monitoring system used for monitoring dynamic water information of an underground working face area of the coal mine. The distribution type water information monitoring system is characterized in that the system can perform non-uniform distribution type multidirectional sensor arrangement and monitor multi-parameter dynamic water burst information in an excavating working face area. The system has the advantages that a non-uniform type multi-point water information monitoring network for a mining working face area is built, an area with hidden dangers is intensively monitored, a wavelet filter is adopted to extract characteristic value sample data, a water burst grade evaluation model is calculated, so that the accuracy of a calculation result is improved. According to an intrinsic safety type digital water level sensor adopting the independent patent technology, the difficult problem of water level measurement in a small water sump and a headrace channel is solved, in addition, the dynamic water information of the working face is connected with a drainage system of a main water sump so as to be beneficial for the advanced detection and early warning of the water disaster and the timely prevention and control of the water disaster.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Sliding window residual error model-based load switching action monitoring method
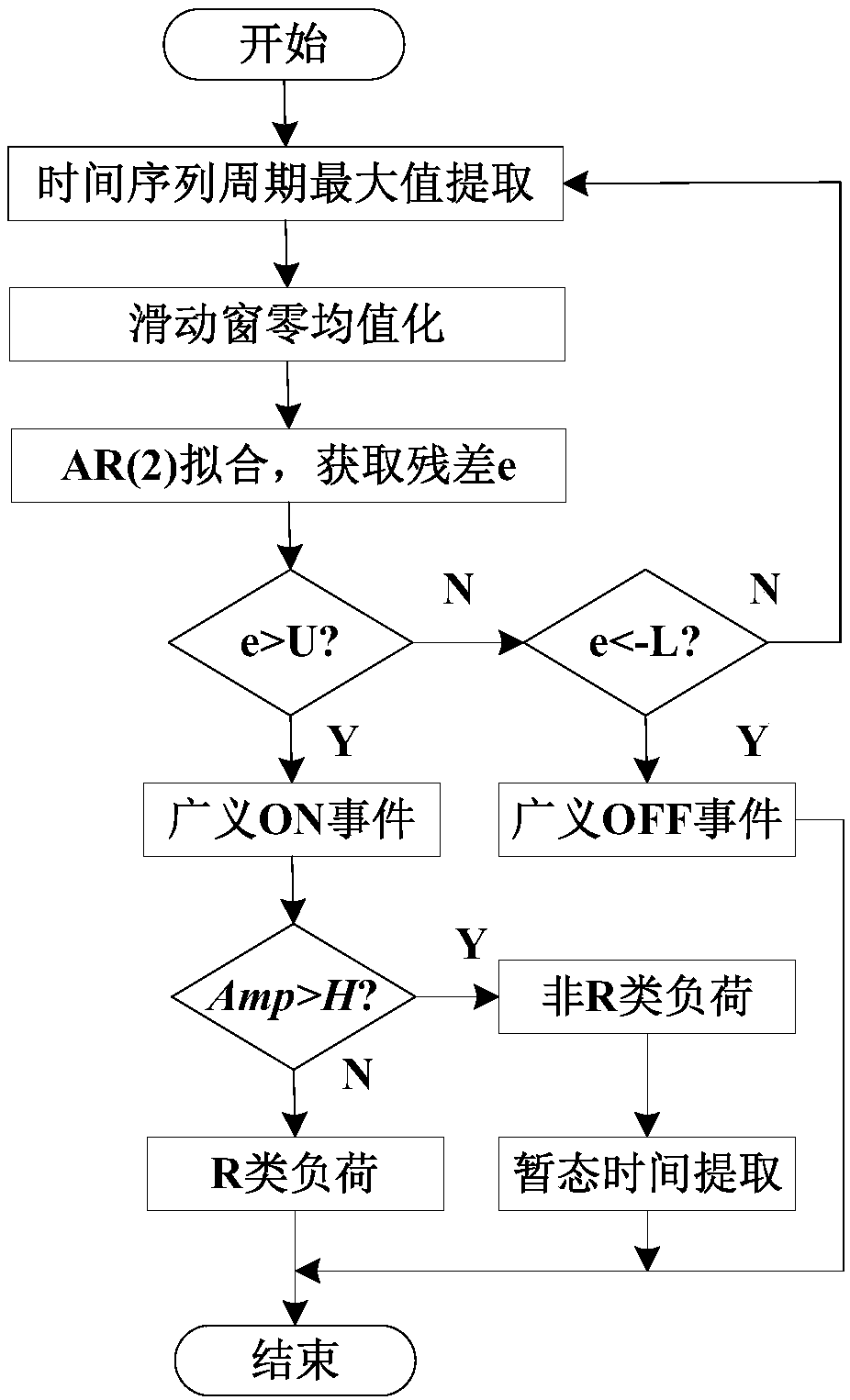
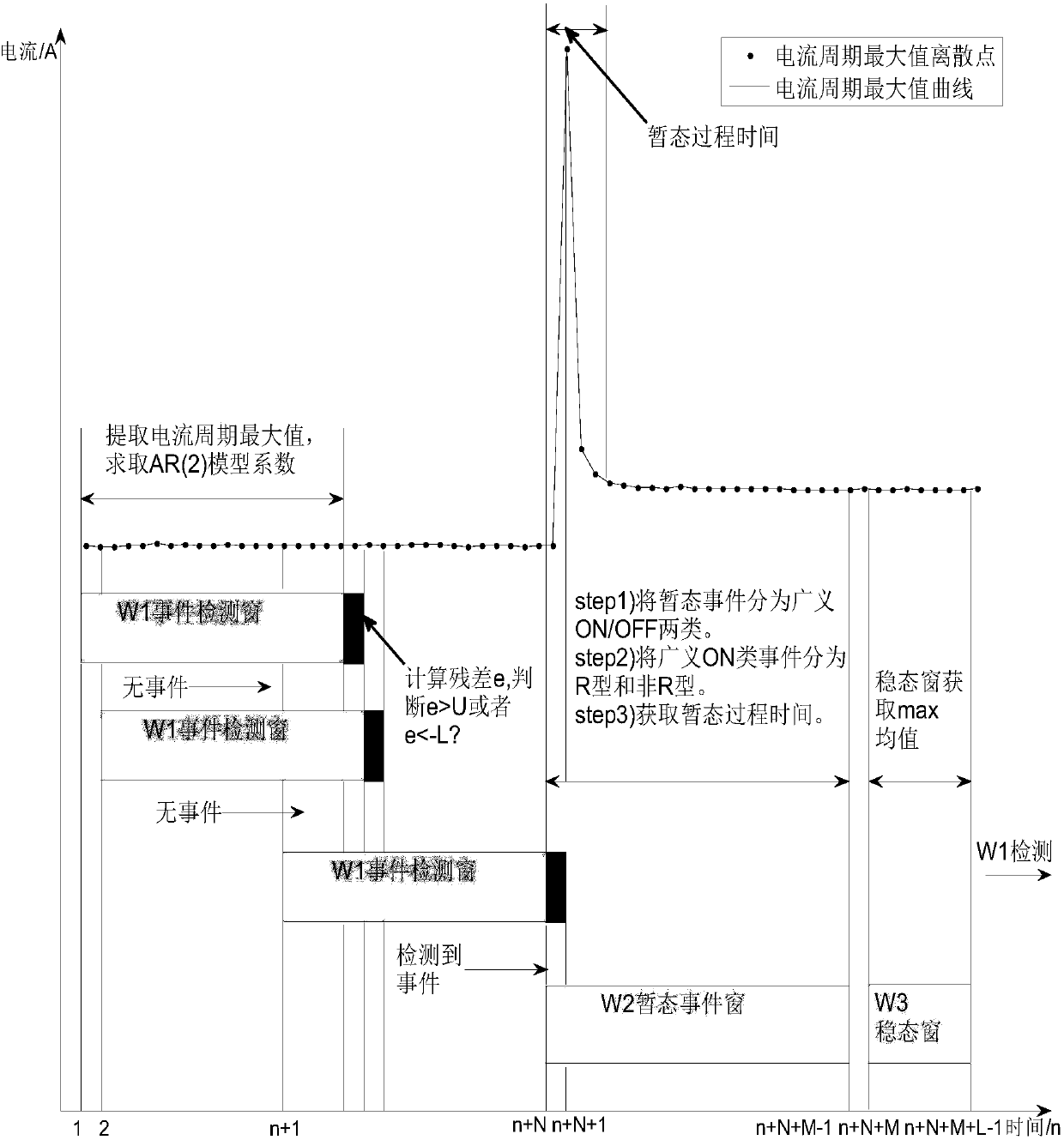
ActiveCN108021736AInnovation of switching action monitoring methodSimplify performance requirementsData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationSlide windowRecognition algorithm
The invention discloses a sliding window auto-regression residual error model-based non-intrusive load switching action monitoring method. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining current of a bus through NILM equipment such as an intelligent electric meter, and carrying out wavelet filtering and denoising on the current; and obtaining a current period maximum value sequence, obtaining a next current maximum residual error by using an AR regression model, and judging a load state according to a size relationship between the residual error and a threshold value. According to the method, double threshold values U and L are used for dividing corresponding events of load switching; the load switching action monitoring range is enlarged, and load switching actions with relativelylow power can be detected, so that missing detection, caused by power change, of load switching actions with small power is avoided; other electricity parameters of non-intrusive measurement equipmentdo not need to be obtained, and only current parameters of the bus are required, so that the requirement for non-intrusive performance is simplified; and through the category division of loads, the complexity of a whole NILM recognition algorithm can be simplified.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Curved wavelet transform for image and video compression
InactiveUS20050196060A1SmallEasy to implementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionWavelet decompositionImage compression
A curved wavelet transform and a related image / video compression system are disclosed. The curved wavelet transform (CWT) is carried out by applying one-dimensional (1-D) wavelet filters along curves, rather than along only horizontal and vertical directions. The image / video compression system includes a curve determination unit, a curved wavelet transform unit, a wavelet coefficient quantization unit, a wavelet coefficient coding unit, and a curve coding unit. The quantization and coding of the wavelet coefficients are related to the curves. In one embodiment, recursive wavelet filters are used for inverse wavelet decomposition. The system provides higher compression capability than conventional wavelet-based image compression systems.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Transmitter and method for digital multi-carrier transmission
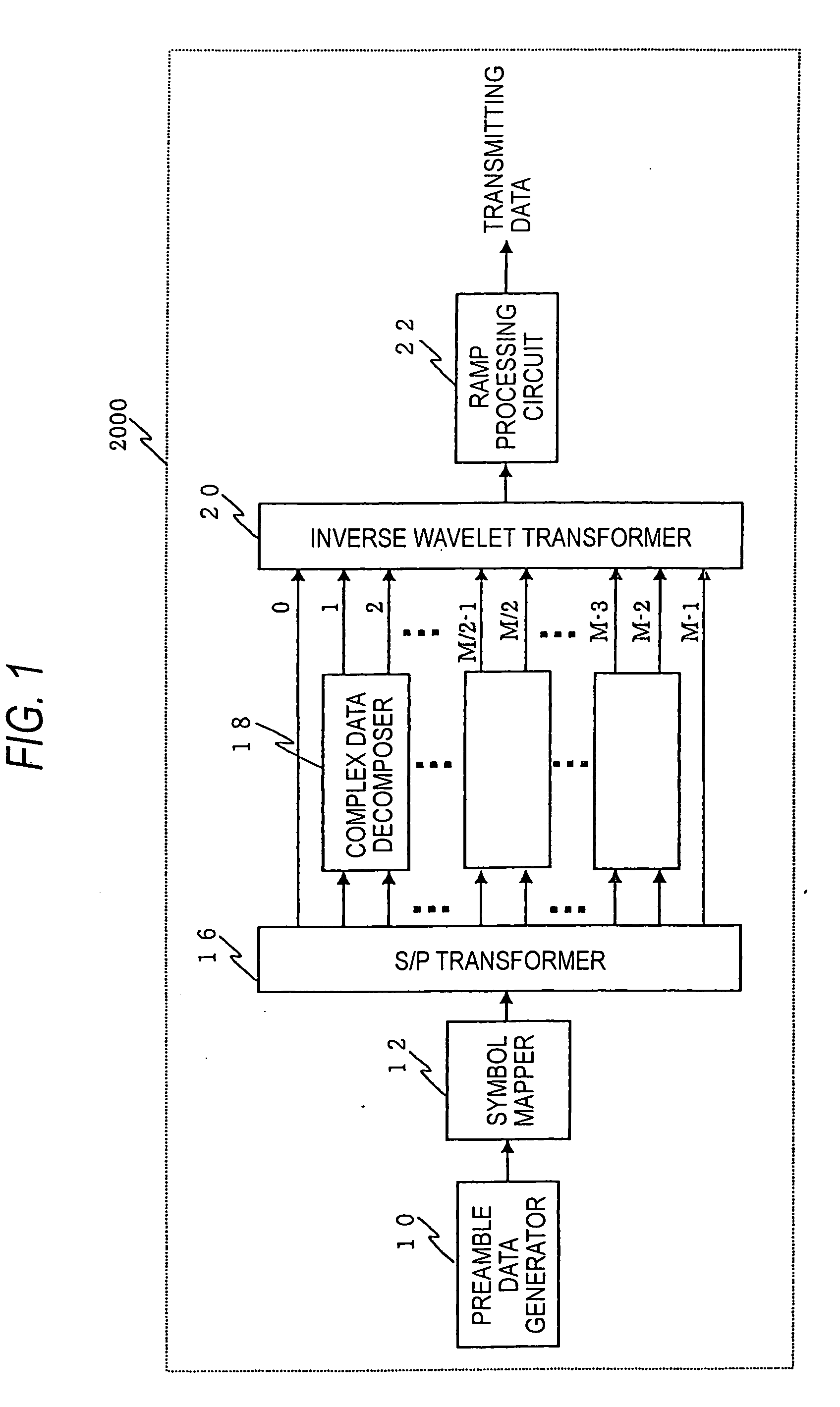
ActiveUS20050031048A1Shorten the lengthFast convergenceModulated carrier system with waveletsSecret communicationCarrier signalMulti carrier
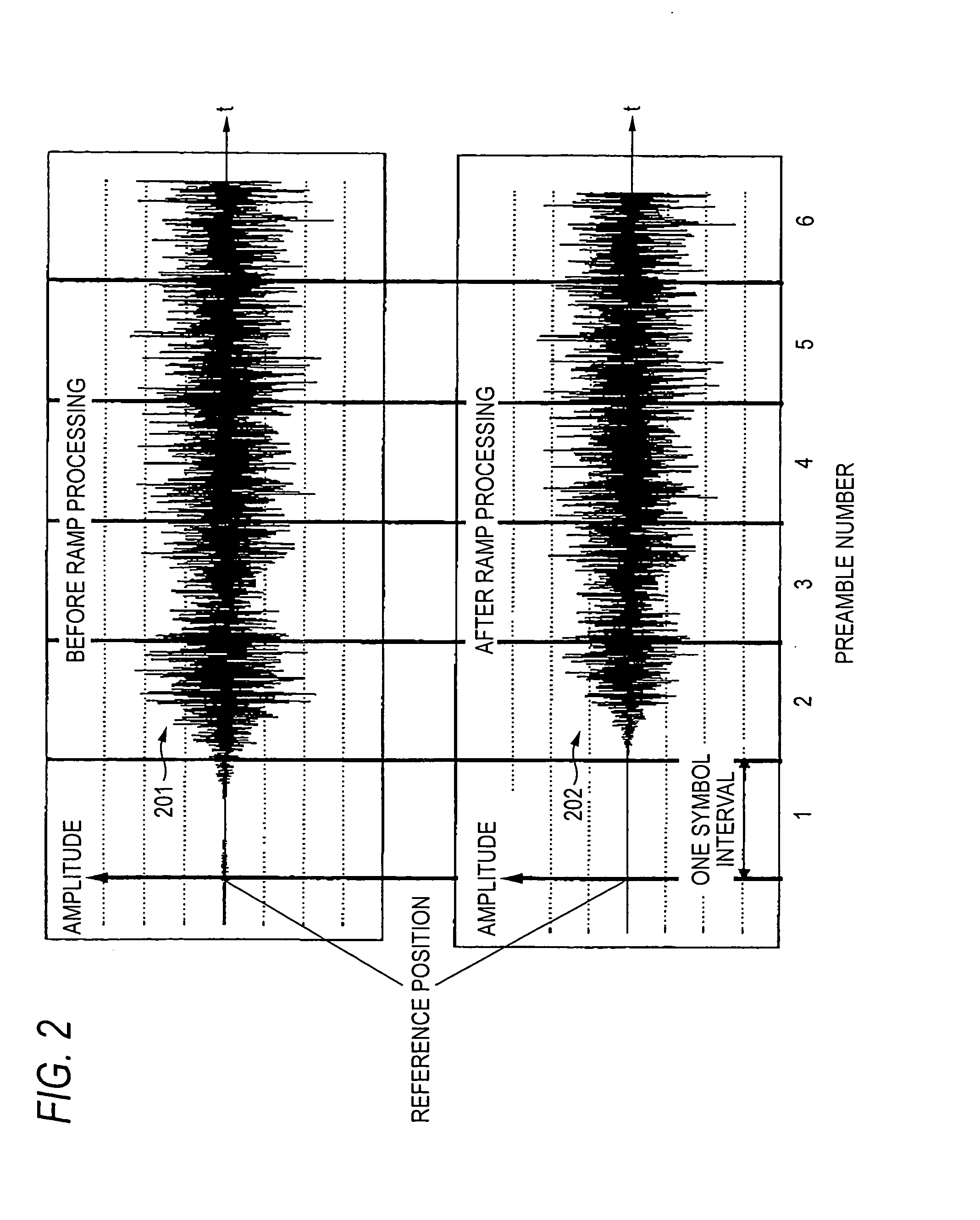
The present invention relates to a transmitter and method employing a multi-carrier transmission method, especially utilizing real coefficient wavelet filter banks. The transmitter includes a preamble data generator, a modulator, and a ramp processor. The preamble data generator generates preamble bit data, and outputs the preamble data. The modulator modulates the preamble data, generates a plurality of subcarriers, and outputs a composite wave of the time waves of the plurality of subcarriers. Subsequently, the ramp processor performs ramp processing on the composite wave with a certain delay period from a reference position of the composite wave.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for compression using reversible wavelet transforms and an embedded codestream
InactiveUS7068849B2Pulse modulation television signal transmissionCode conversionData streamEmbedded system
A compression and decompression system in which a reversible wavelet filter are used to generates coefficients from input data, such as image data. The reversible wavelet filter is an efficient transform implemented with integer arithmetic that has exact reconstruction. The present invention uses the reversible wavelet filter in a lossless system (or lossy system) in which an embedded codestream is generated from the coefficients produced by the filter. An entropy coder performs entropy coding on the embedded codestream to produce the compressed data stream.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
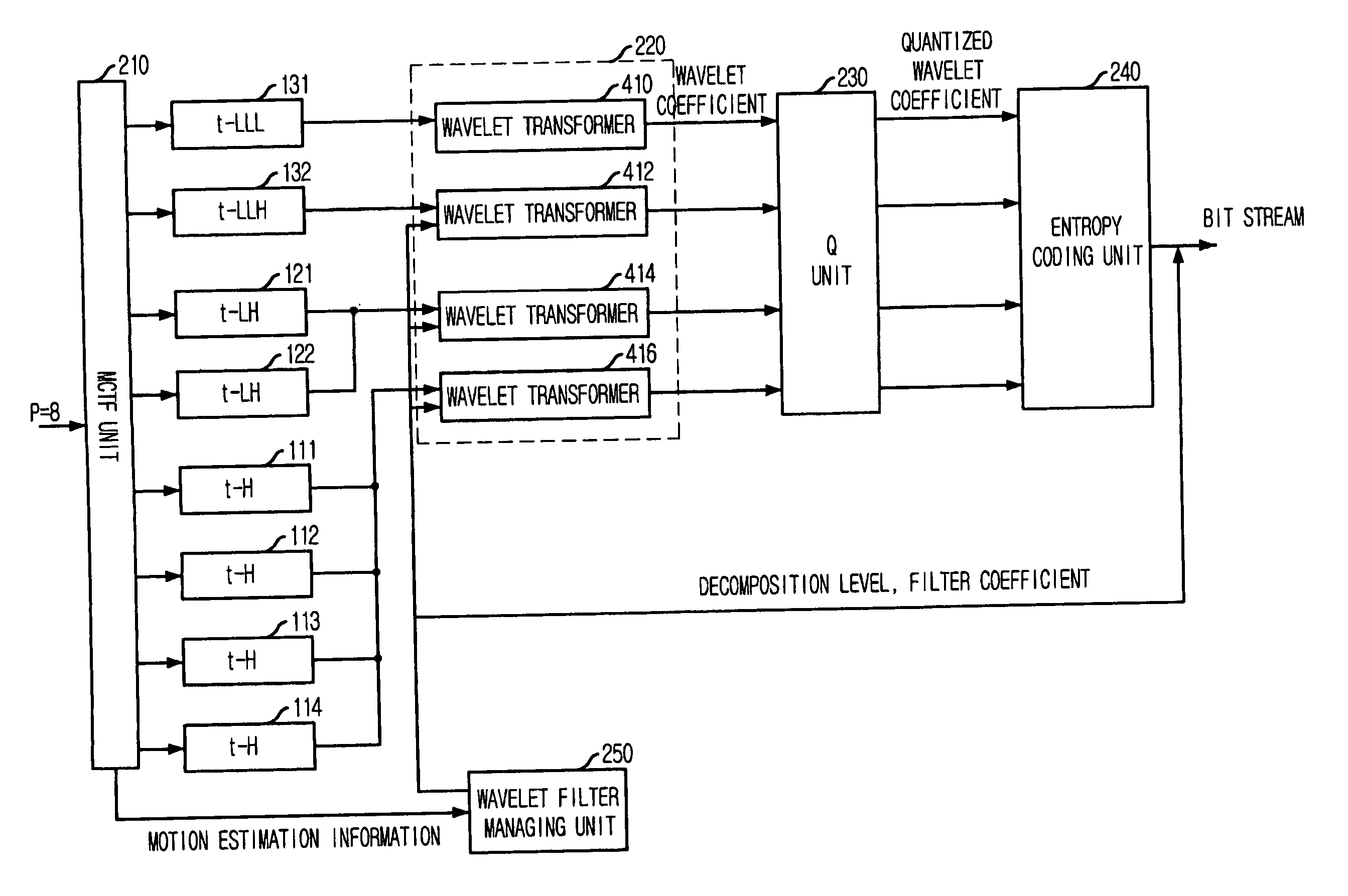
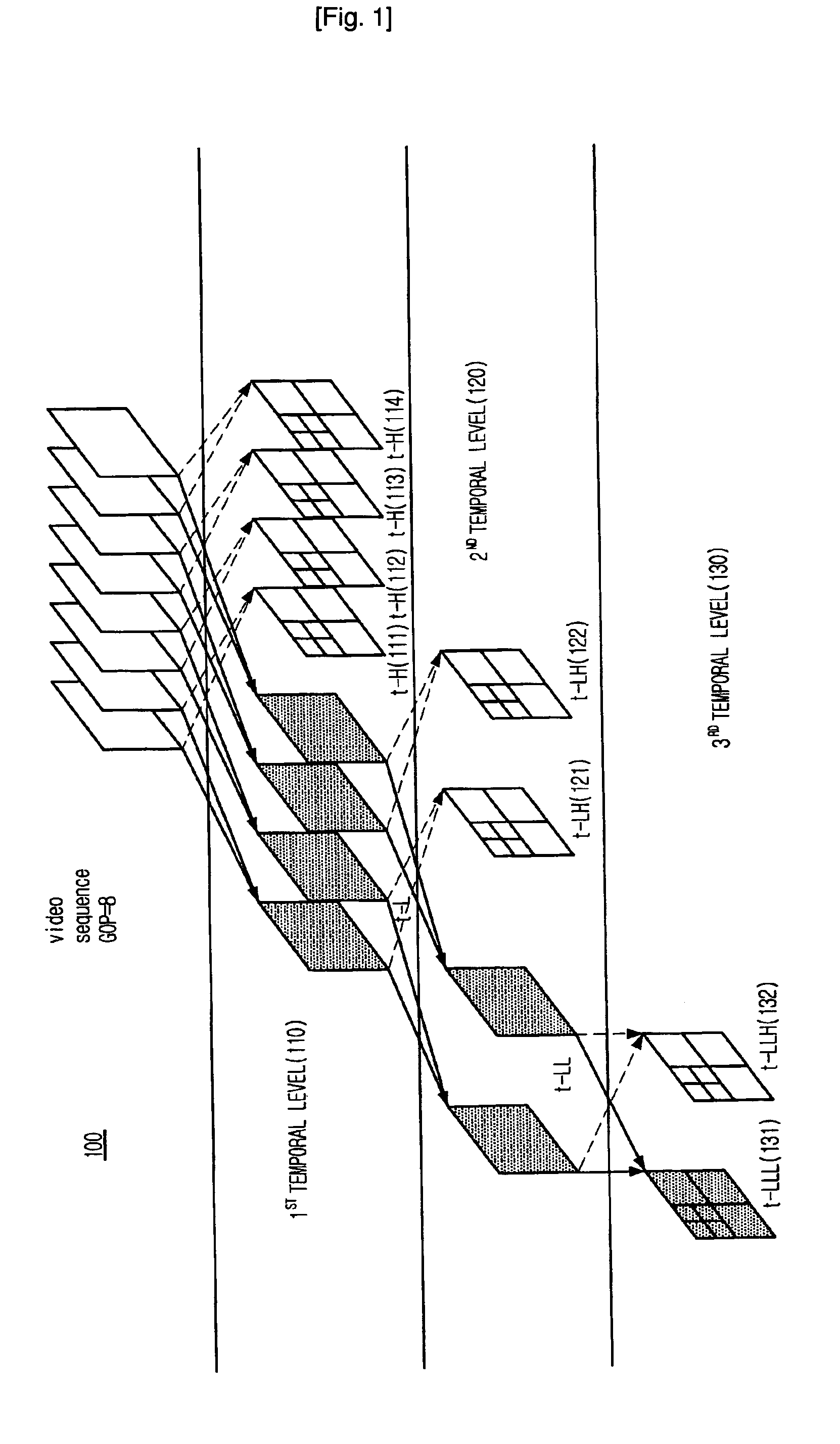
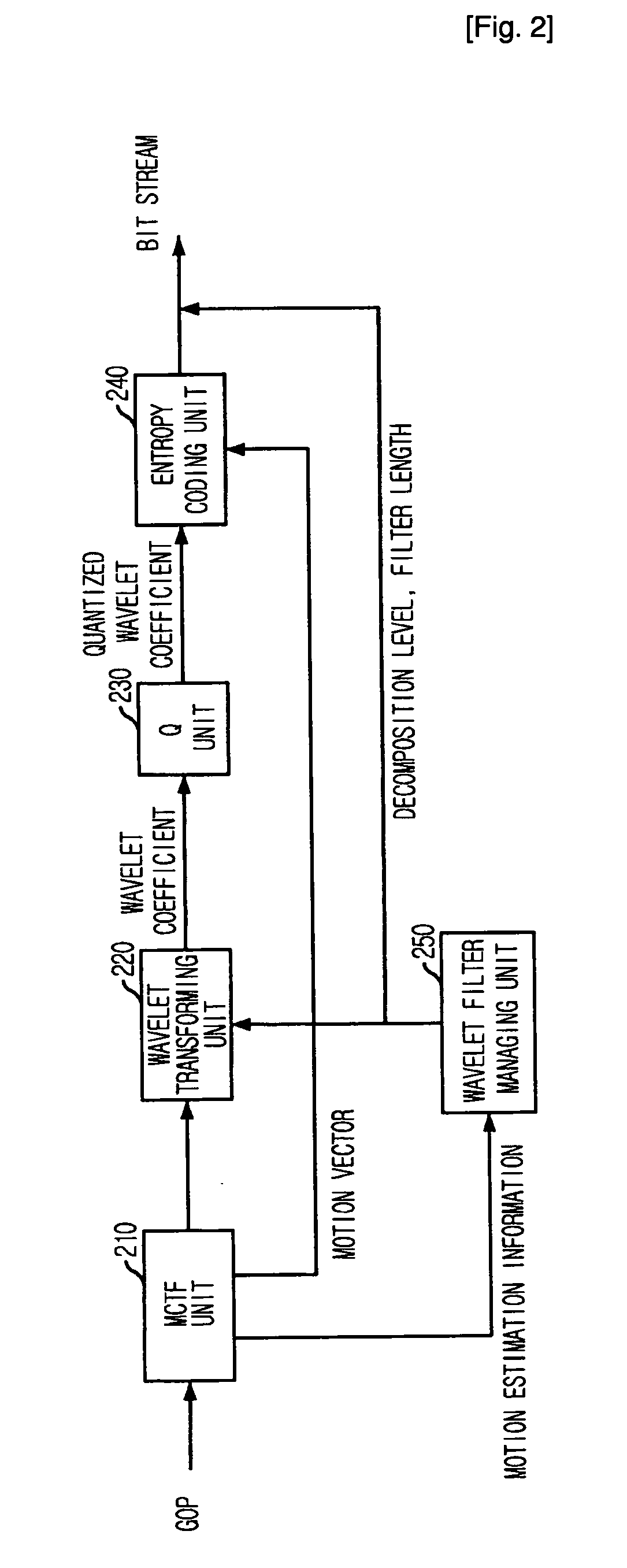
Interframe wavelet coding apparatus and method capable of adjusting computational complexity
InactiveUS20070081593A1Reduce complexityLow computing performanceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputation complexityWavelet coding
Provided is an inter-frame wavelet coding apparatus that can reduce the computation complexity of a decoder by adjusting a decomposition level and a filter length based on the information amount of a frame during wavelet transform and a method therefor. The inter-frame wavelet coding apparatus includes: a Motion Compensated Temporal Filtering (MCTF) unit for computing a motion vectors of a group of pictures (GOP) and filtering the GOP with respect to the temporal axis, to thereby obtain filtered frame; a wavelet transforming unit for performing spatial wavelet transform on the filtered frame and outputting a wavelet coefficient; a quantization unit for quantizing the wavelet coefficient; an entropy coding unit for entropy-coding the motion vector computed in the MCTF unit and the quantized wavelet coefficient, to thereby generate an entropy-coded bit stream; and a wavelet filter managing unit for selecting a decomposition level and a filter length for the wavelet transforming unit based on motion estimation information of the GOP video computed in the MCTF unit, wherein the decomposition level and the filter length are included in the entropy-coded bit stream.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Contourlet transformation-adaptive medical image fusion method based on non-sampling
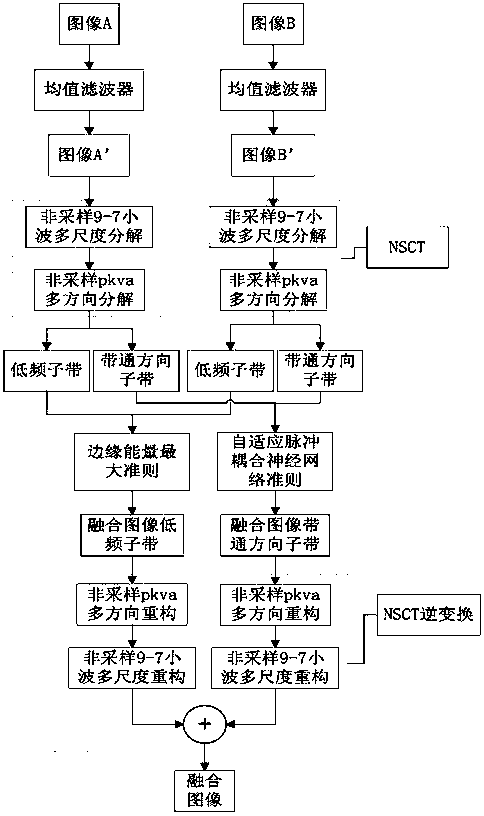
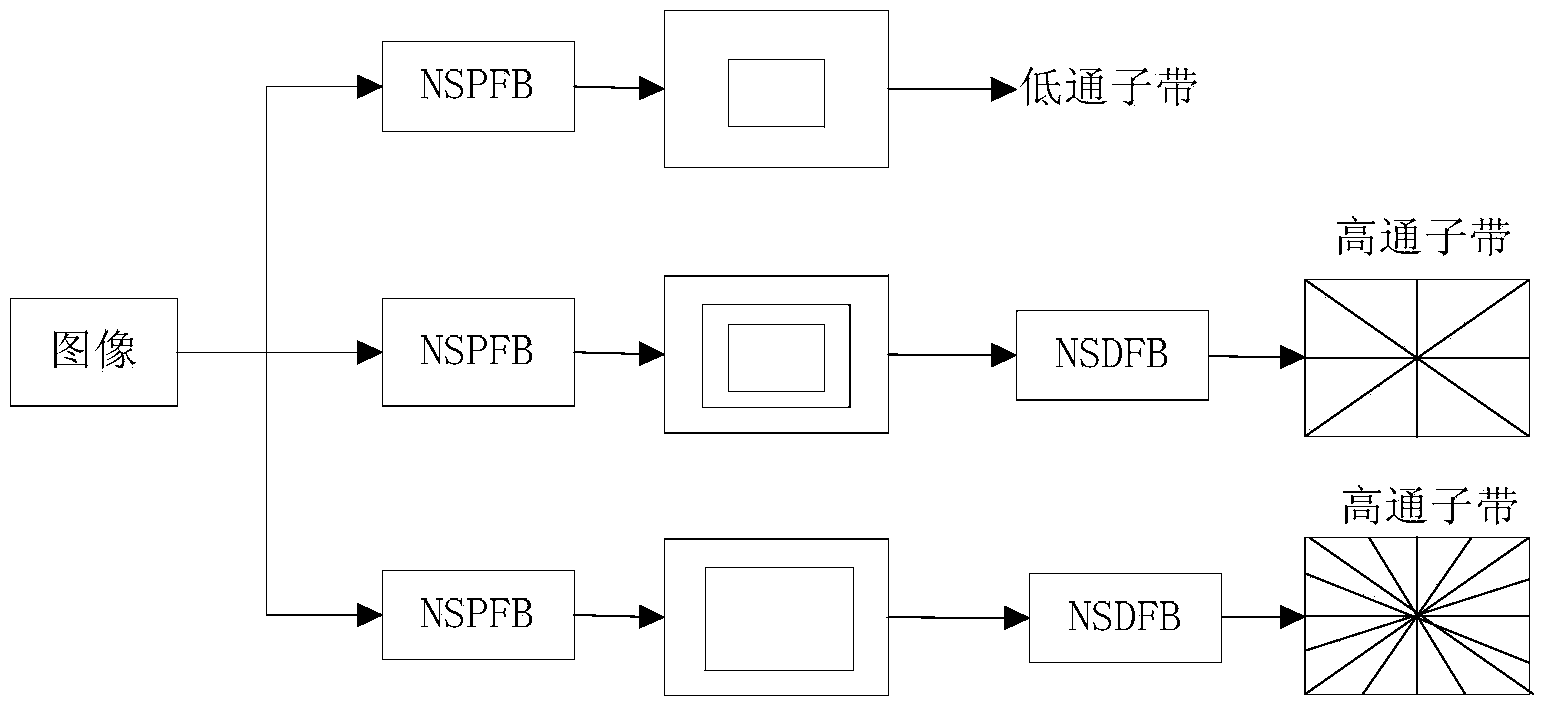
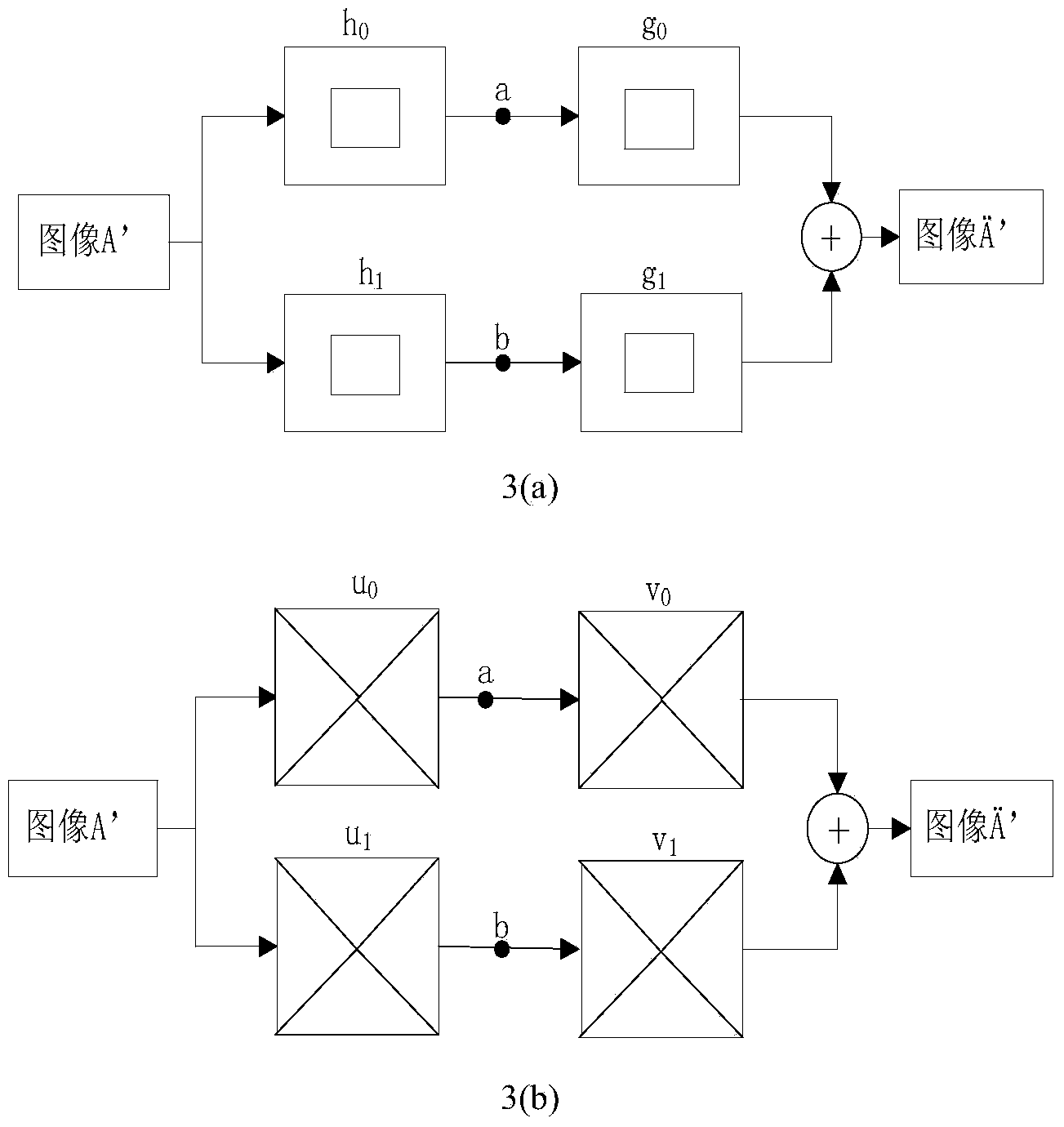
InactiveCN104282007ALimited universalityFast decompositionImage enhancementGeometric image transformationImaging processingContourlet
The invention relates to a contourlet transformation-adaptive medical image fusion method based on non-sampling and belongs to the field of image processing. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a source image is subjected to arithmetic average filtering and then is decomposed through an orthogonal 9-7 wavelet filter and a pkva filter during non-sampling to obtain low-frequency sub-band coefficients and all band-pass direction sub-band coefficients; secondly, the low-frequency sub-band coefficients are selected and fused according to the edge information maximum criterion, all the band-pass sub-band coefficients are selected and fused through an adaptive PCNN model based on a visual neuron model; lastly, a final fused image is obtained by means of inverse transformation of NSCT. According to the contourlet transformation-adaptive medical image fusion method based on non-sampling, the algorithm is very effective and correct, the edge and space texture information of the fused image is clear, color distortion is low, the false contour phenomenon does not exist, and feature information of the source image is well reserved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com