Patents
Literature
4301results about "Fluid steering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
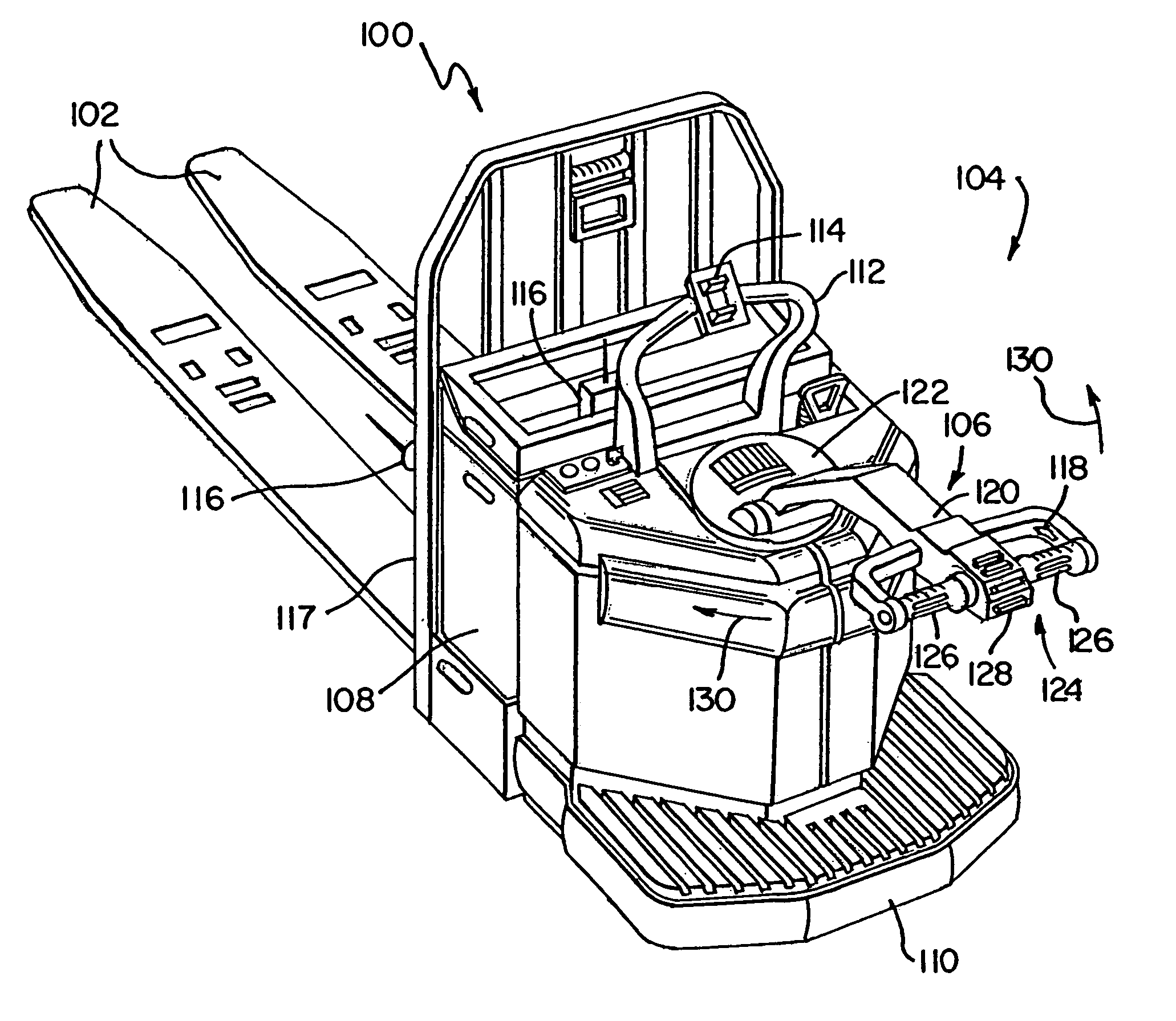
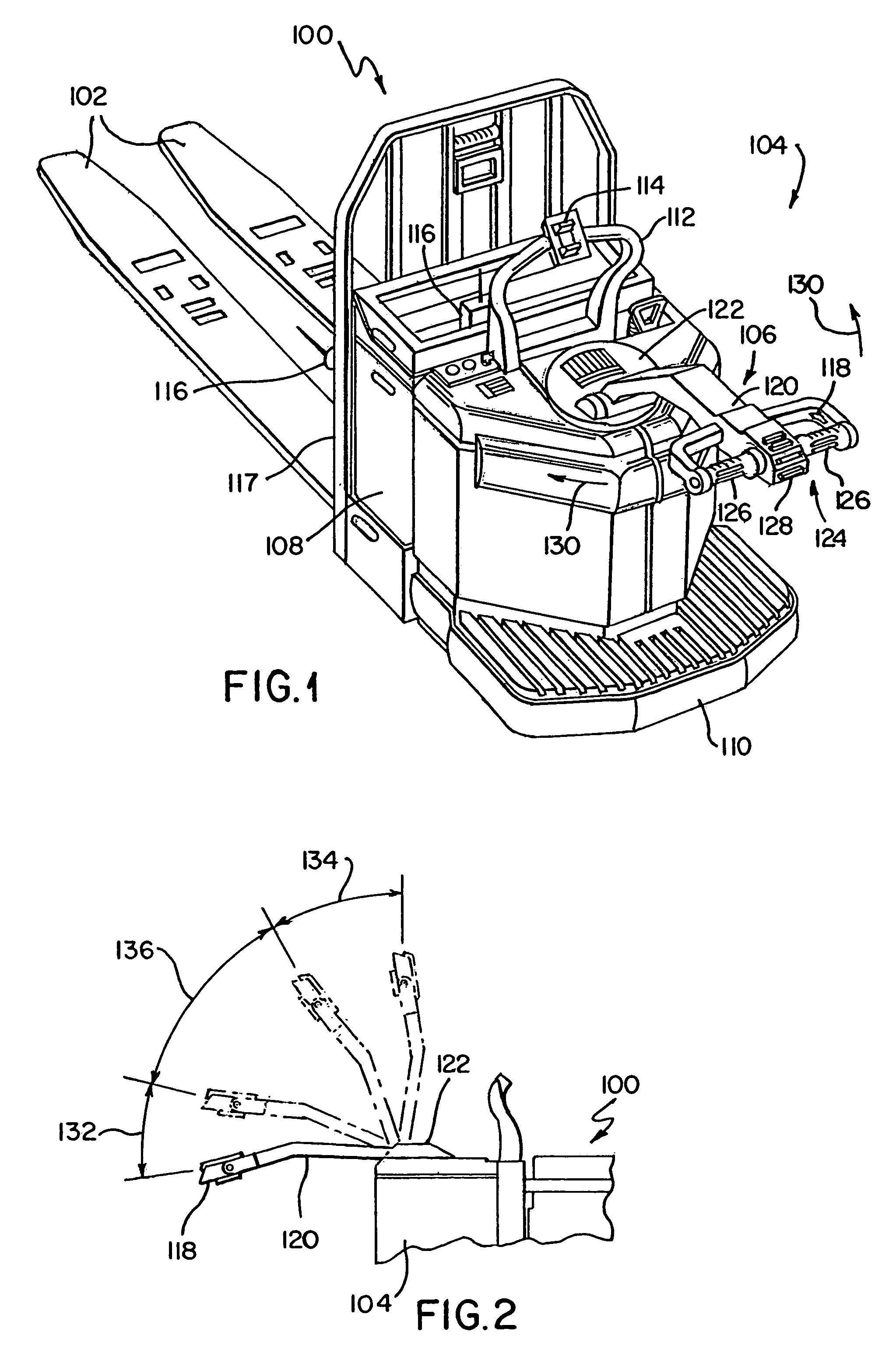
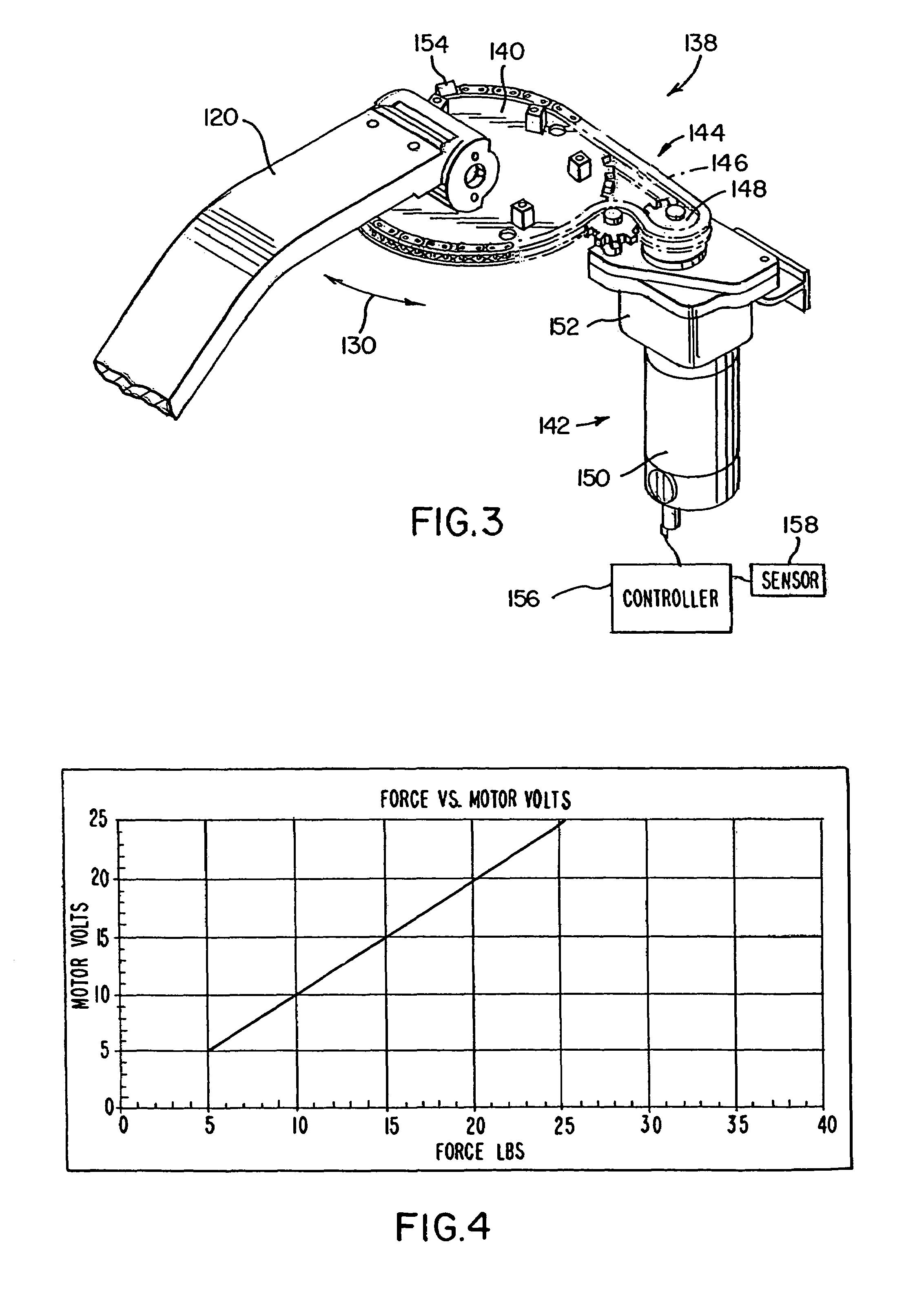
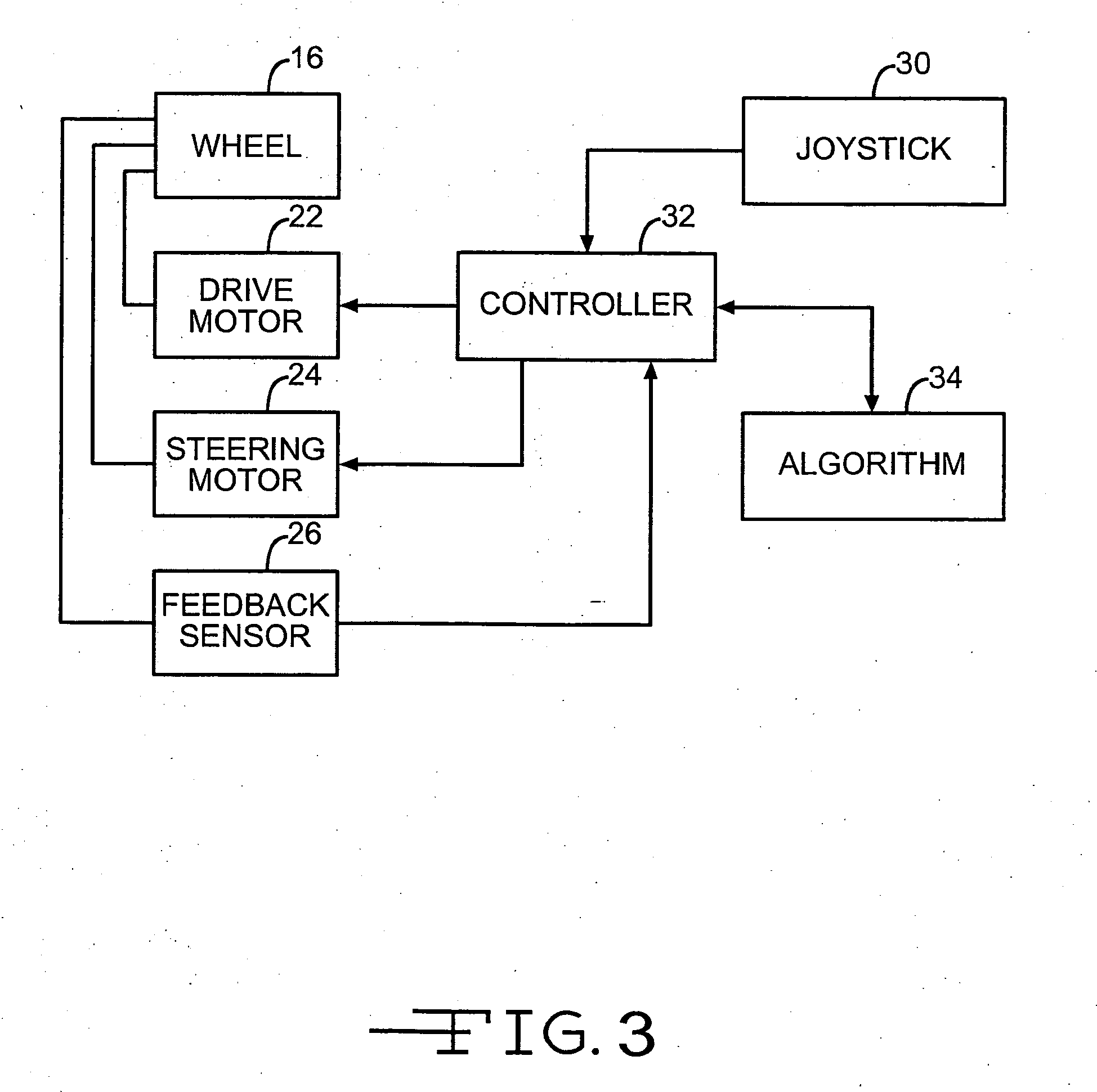
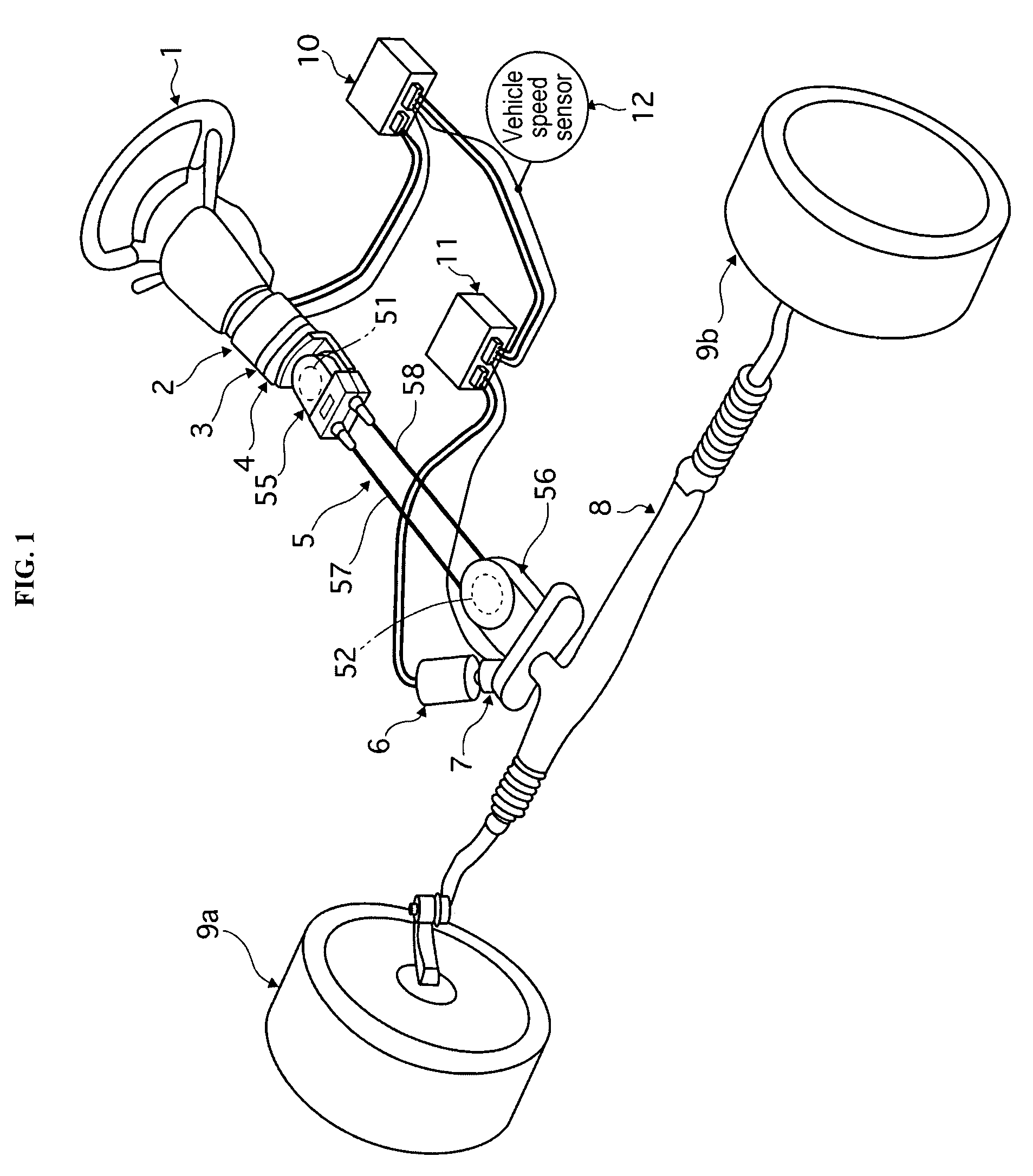
Electrical steering assist for material handling vehicles
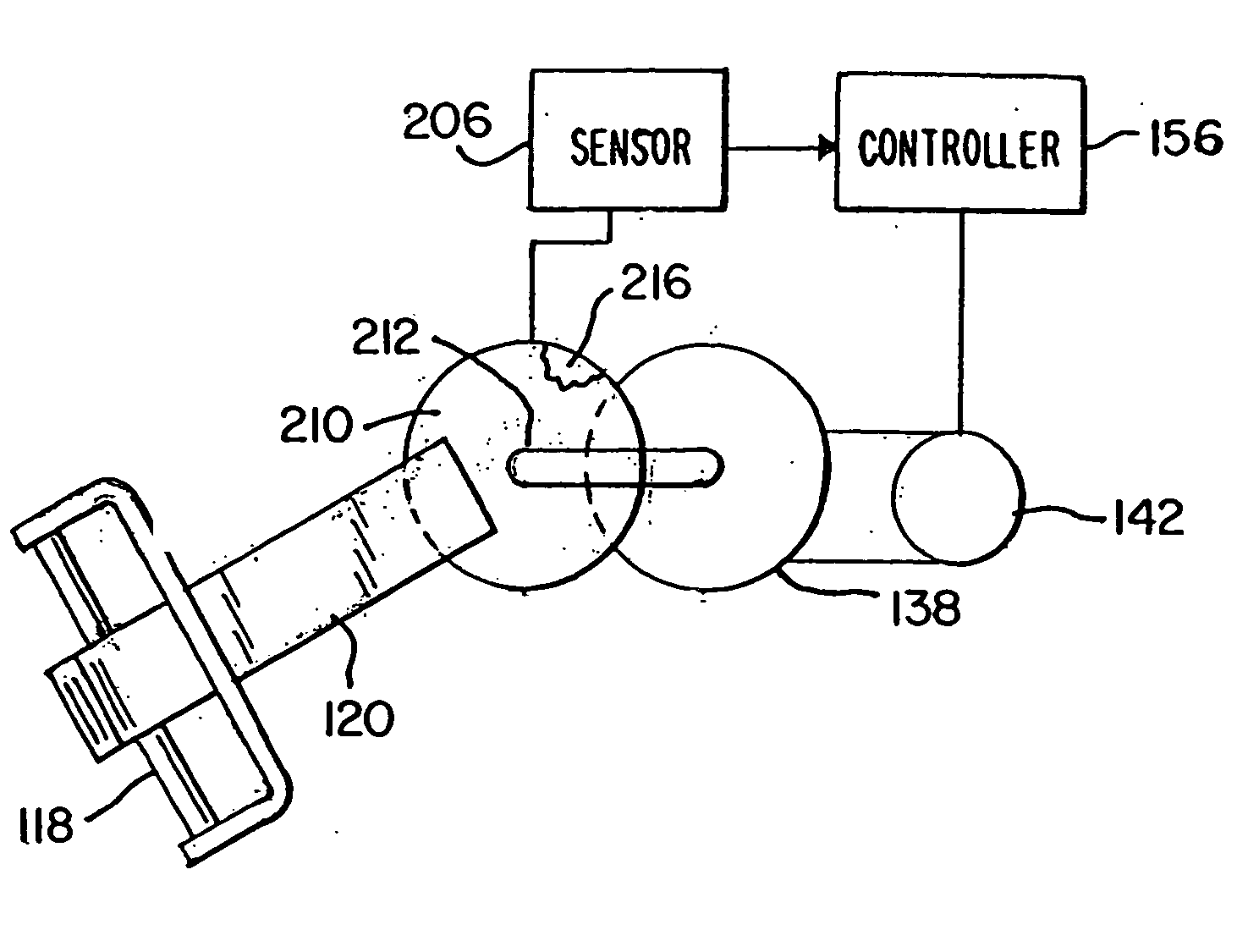
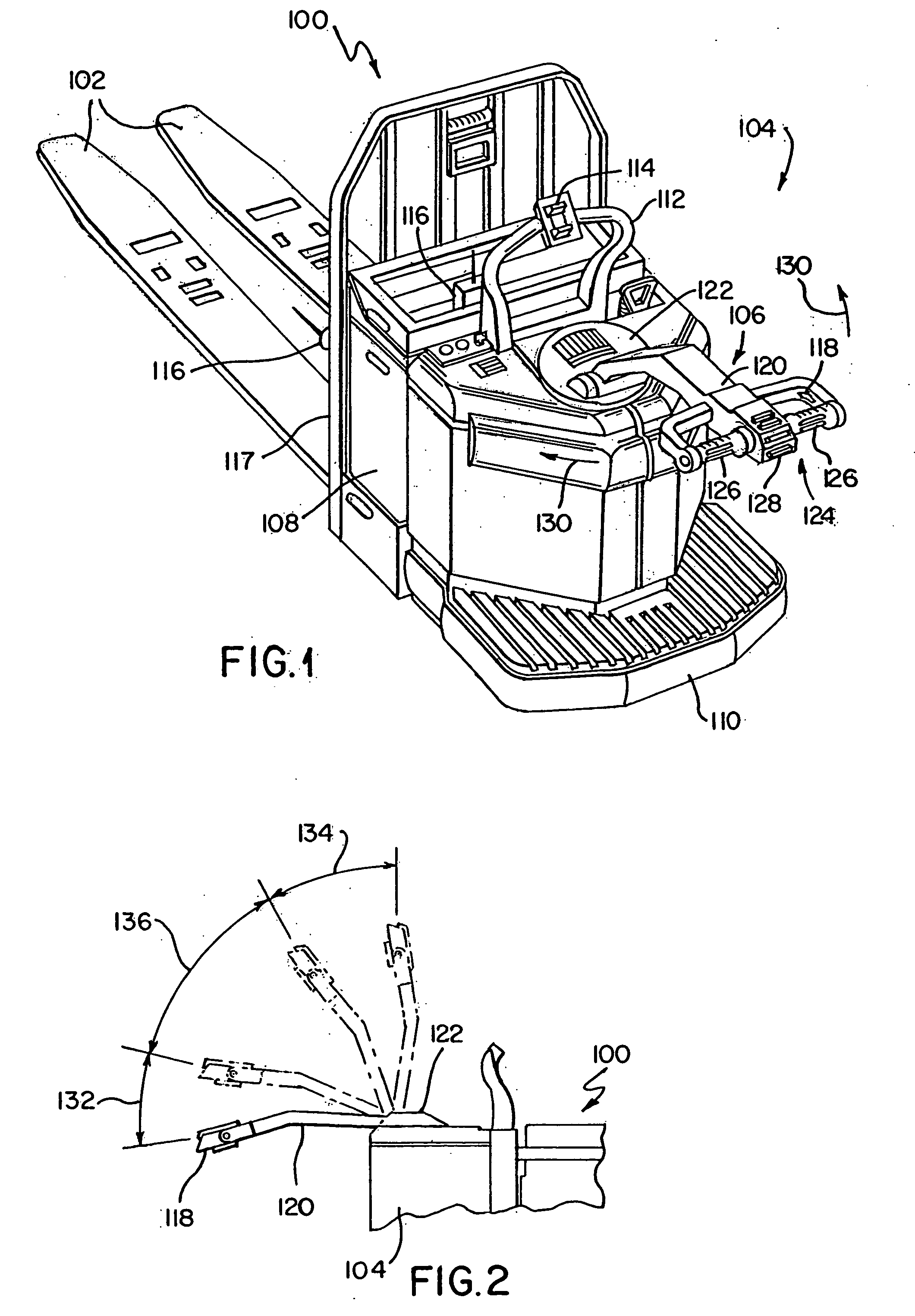
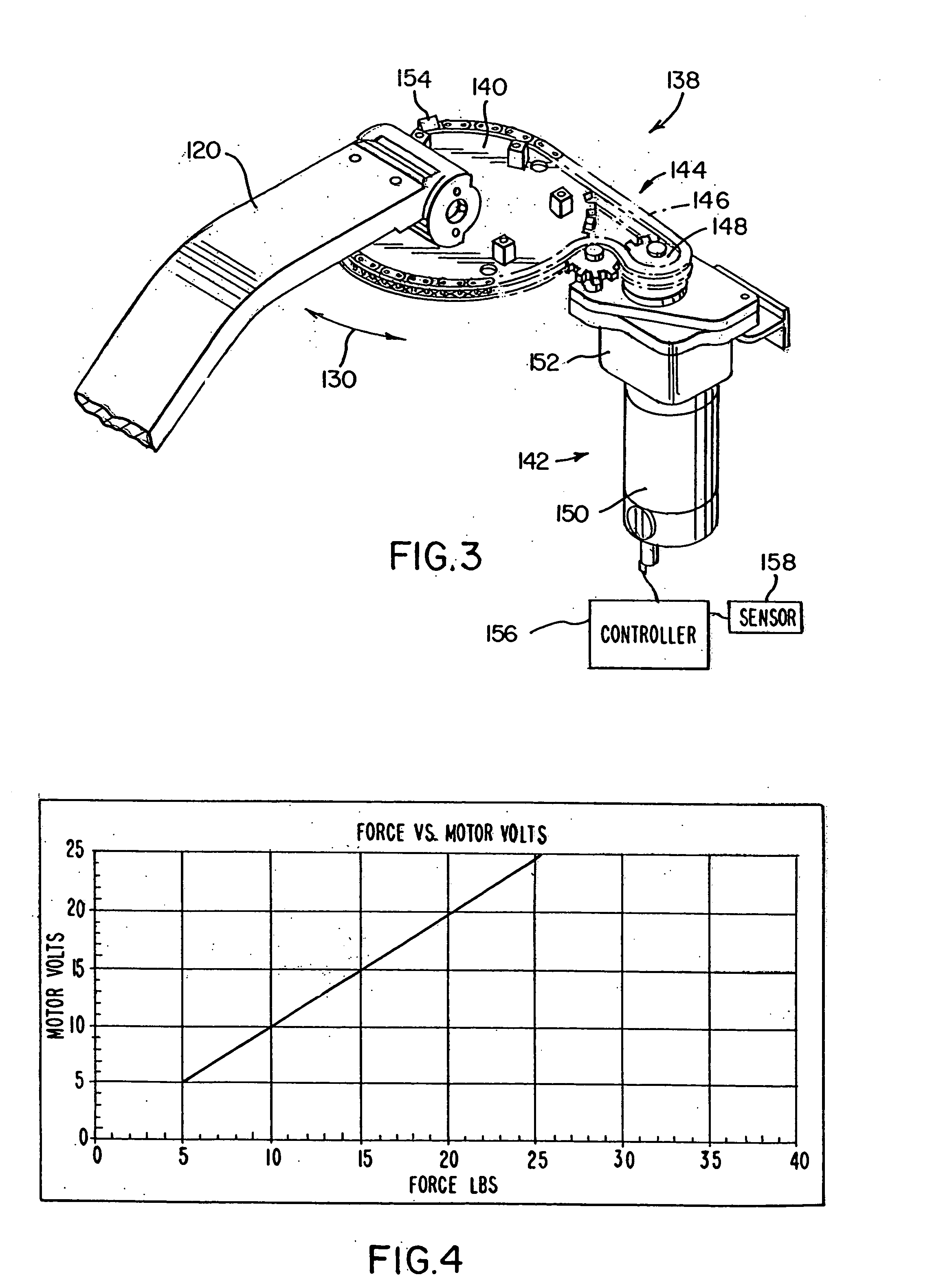
Electrical steering assist systems reduce the operator applied steering effort necessary to operate material handling vehicles. A steer drive unit including a motor is coupled to a steerable wheel for providing steering assist. The amount of steering assist provided by the steer drive unit is determined by a controller that receives input from one or more input sensing devices. The input sensing device(s) may include force sensors that detect an operator applied turning force. The input sensing device(s) may also detect the movement of one steering component relative to another. Further, the input sensing device(s) may include operator activated controls such as a joystick, potentiometer, switches and voice initiated commands. Input sensing device(s) may additionally be provided to detect operational parameters such as the load on the material handling vehicle, vehicle speed, or environmental conditions such as travel path obstruction detection, homing and proximity sensing.
Owner:CROWN EQUIP CORP
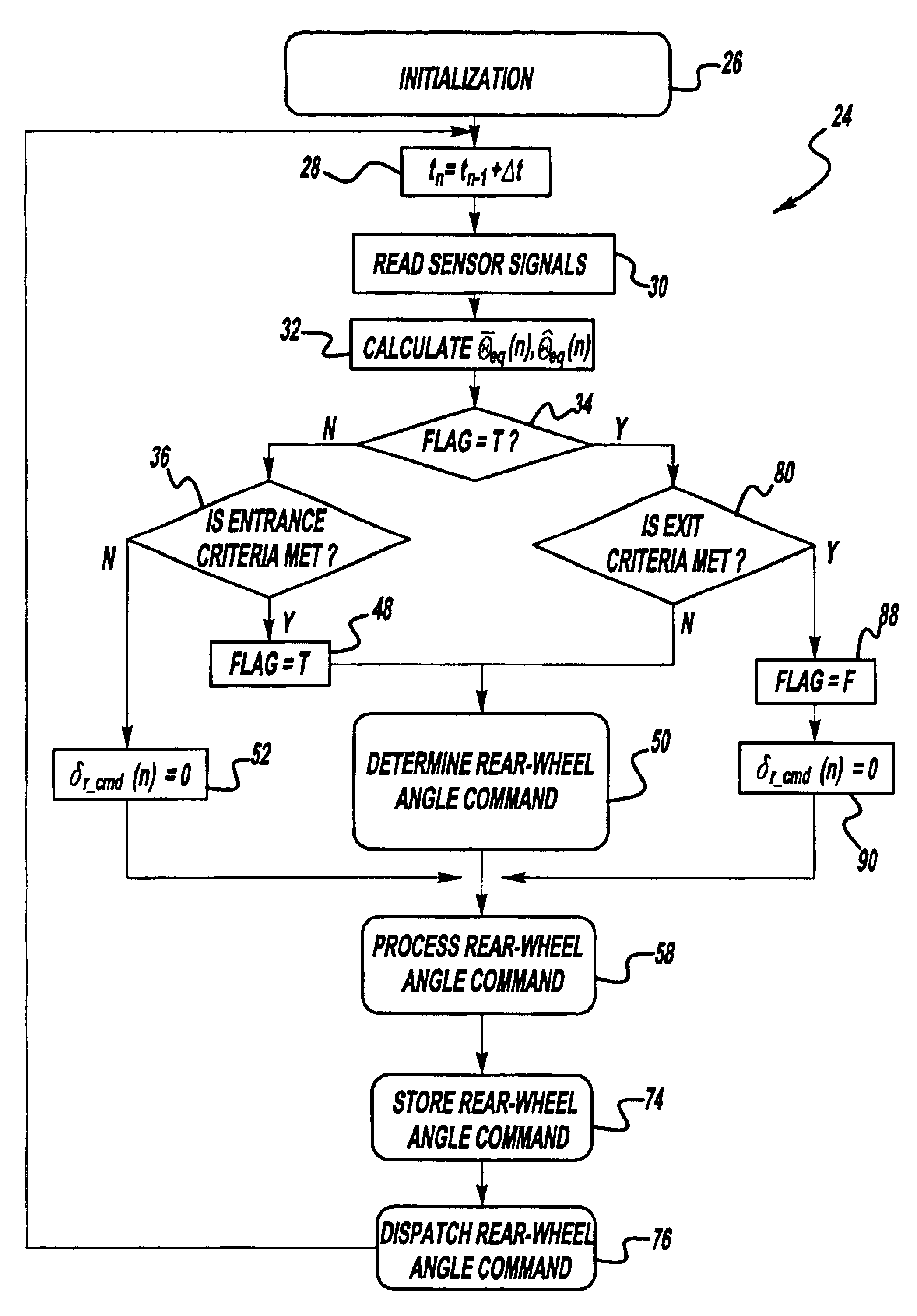
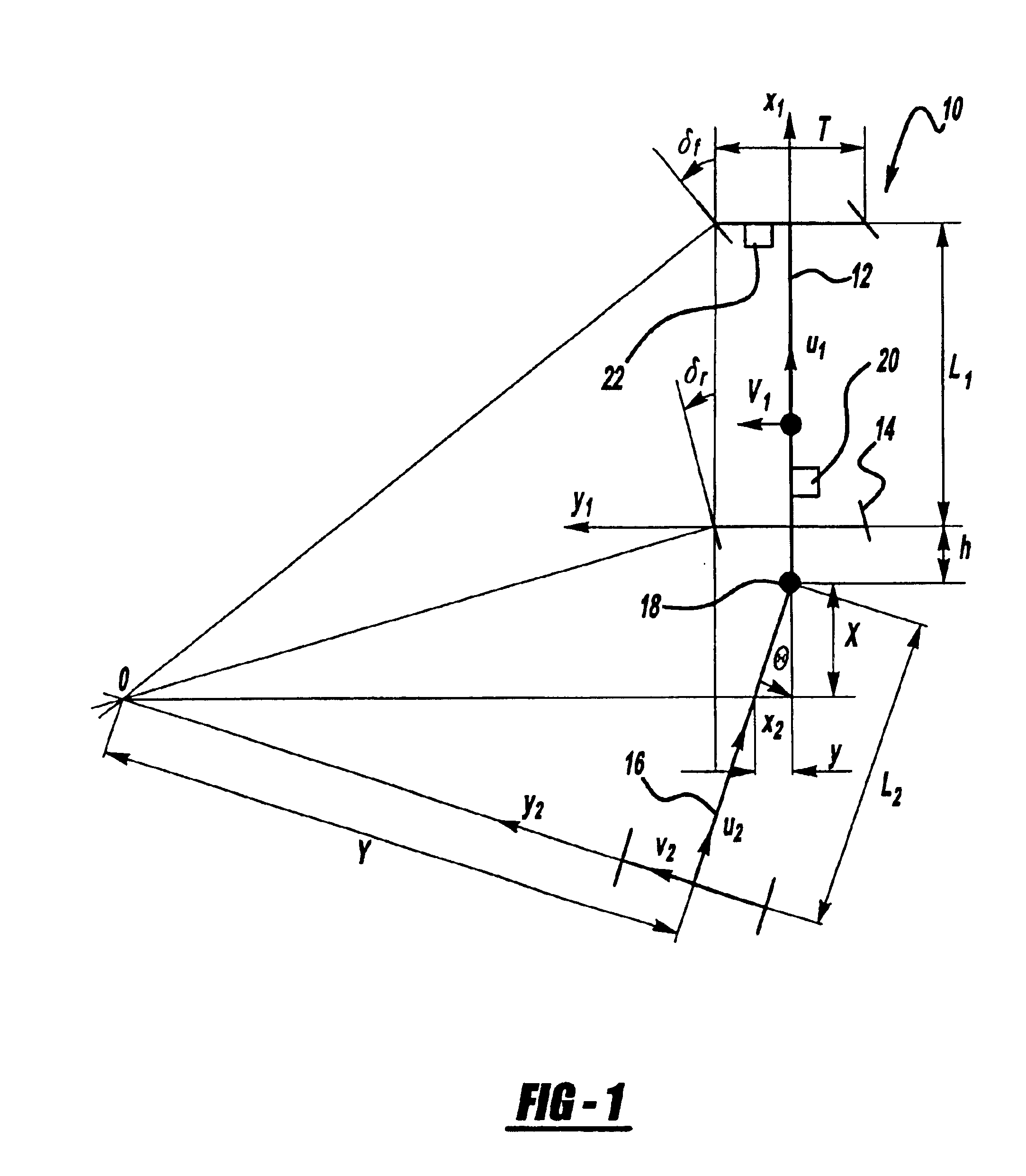
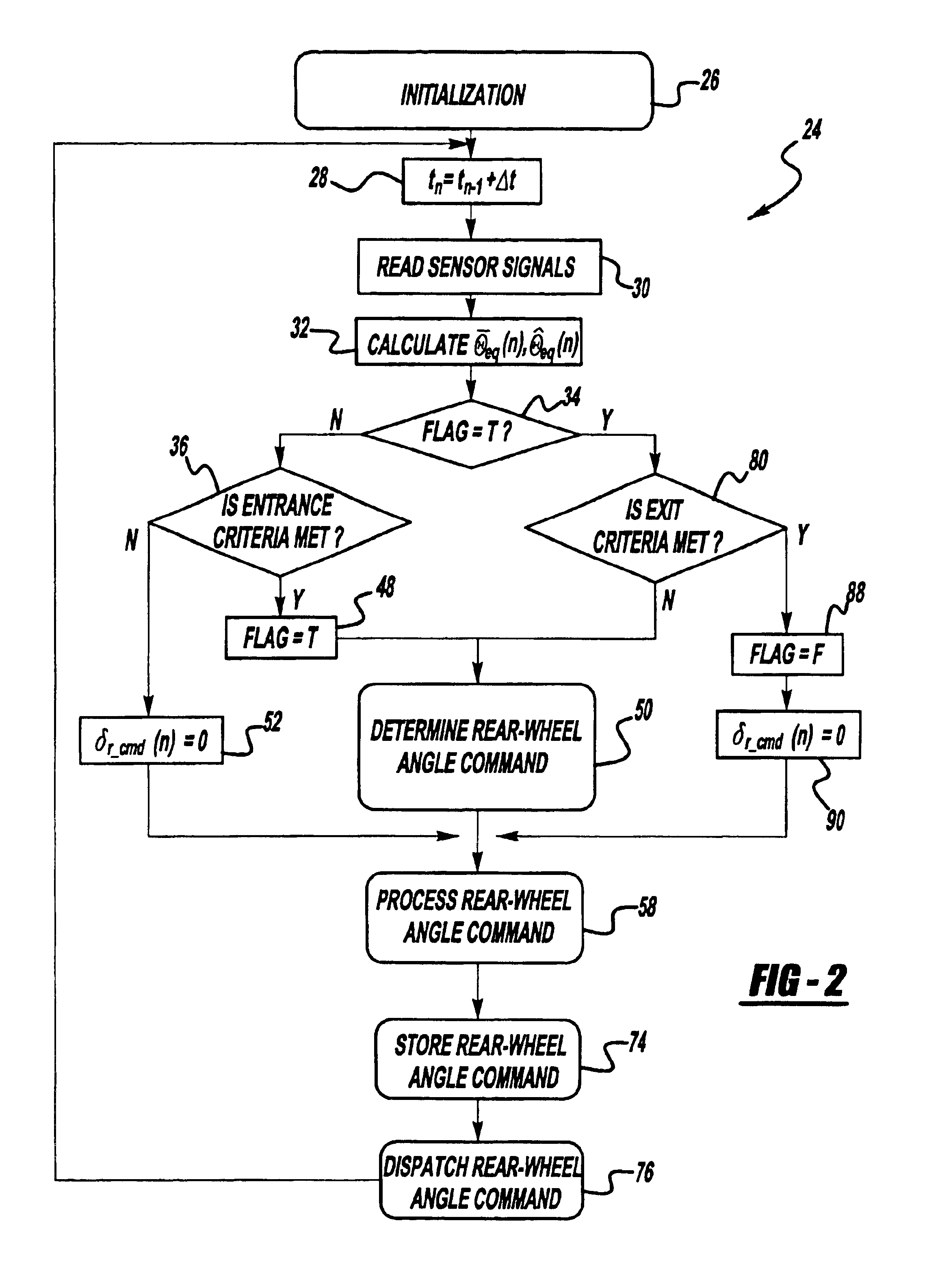
Anti-jackknife control for vehicle-trailer backing up using rear-wheel steer control
A vehicle control system that selectively provides rear-wheel steering to prevent a vehicle-trailer from jackknifing during a back-up maneuver. The system senses a steering angle of the vehicle, a speed of the vehicle and a hitch angle between the vehicle and the trailer. The system calculates an equilibrium hitch angle that is a steady-state hitch angle position based on the steering angle and the vehicle speed, and a pseudo-equilibrium hitch angle that is a steady-state hitch angle at a maximum rear-wheel steering input based on the steering angle and the vehicle speed. The system then determines whether the rear-wheel steering should be provided based on a predetermined relationship between the sensed hitch angle, the equilibrium hitch angle and the pseudo-equilibrium hitch angle.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
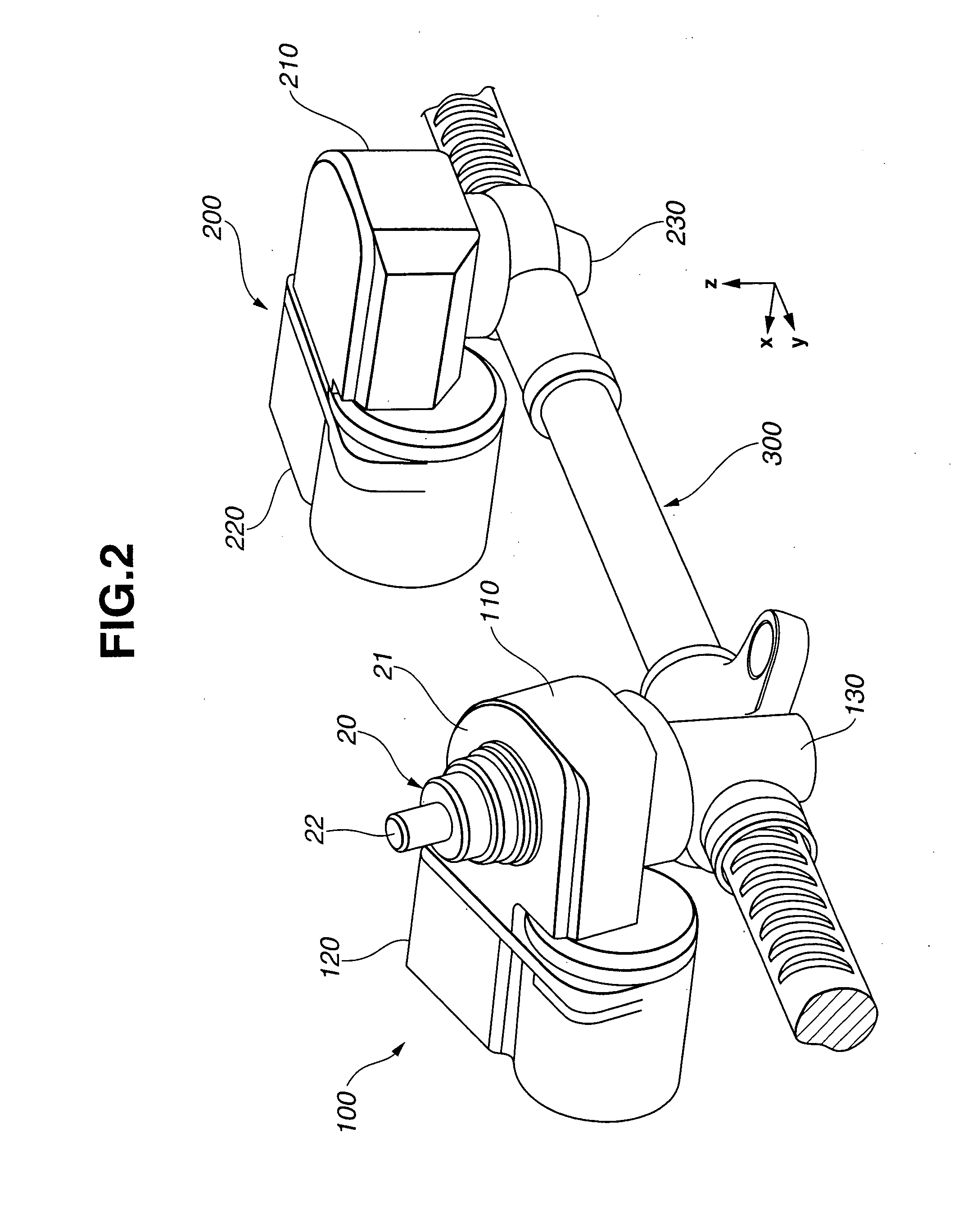
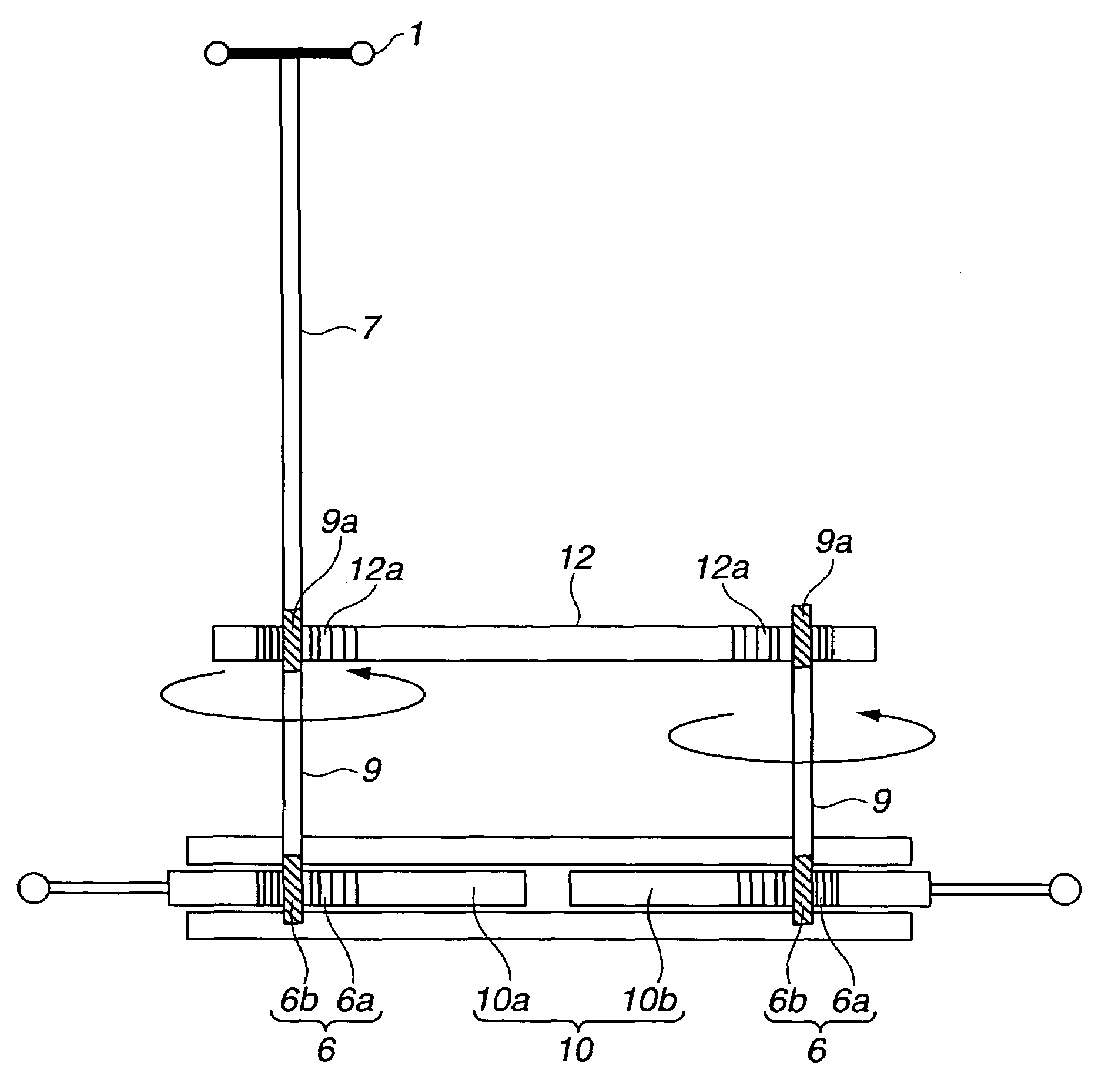
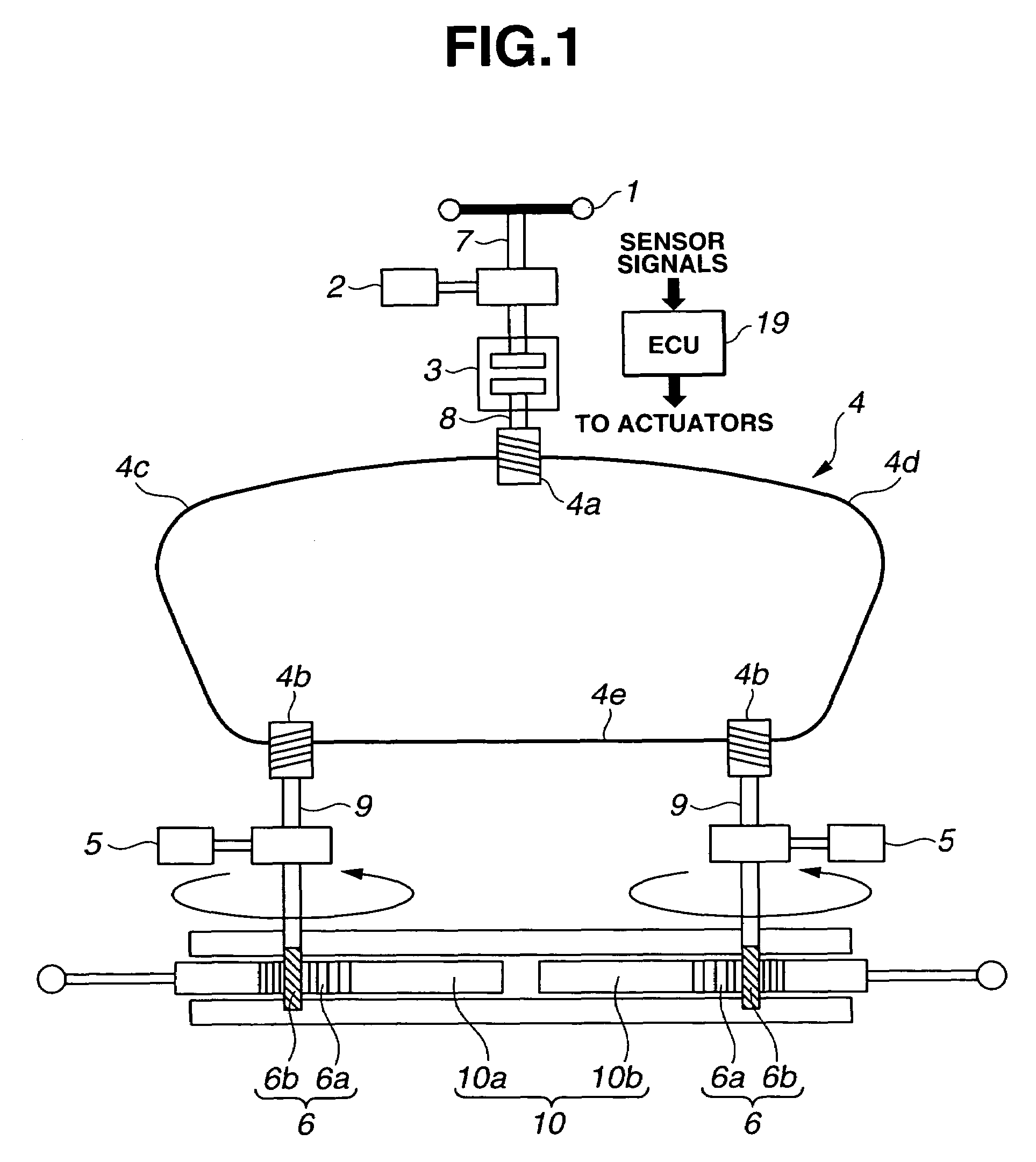
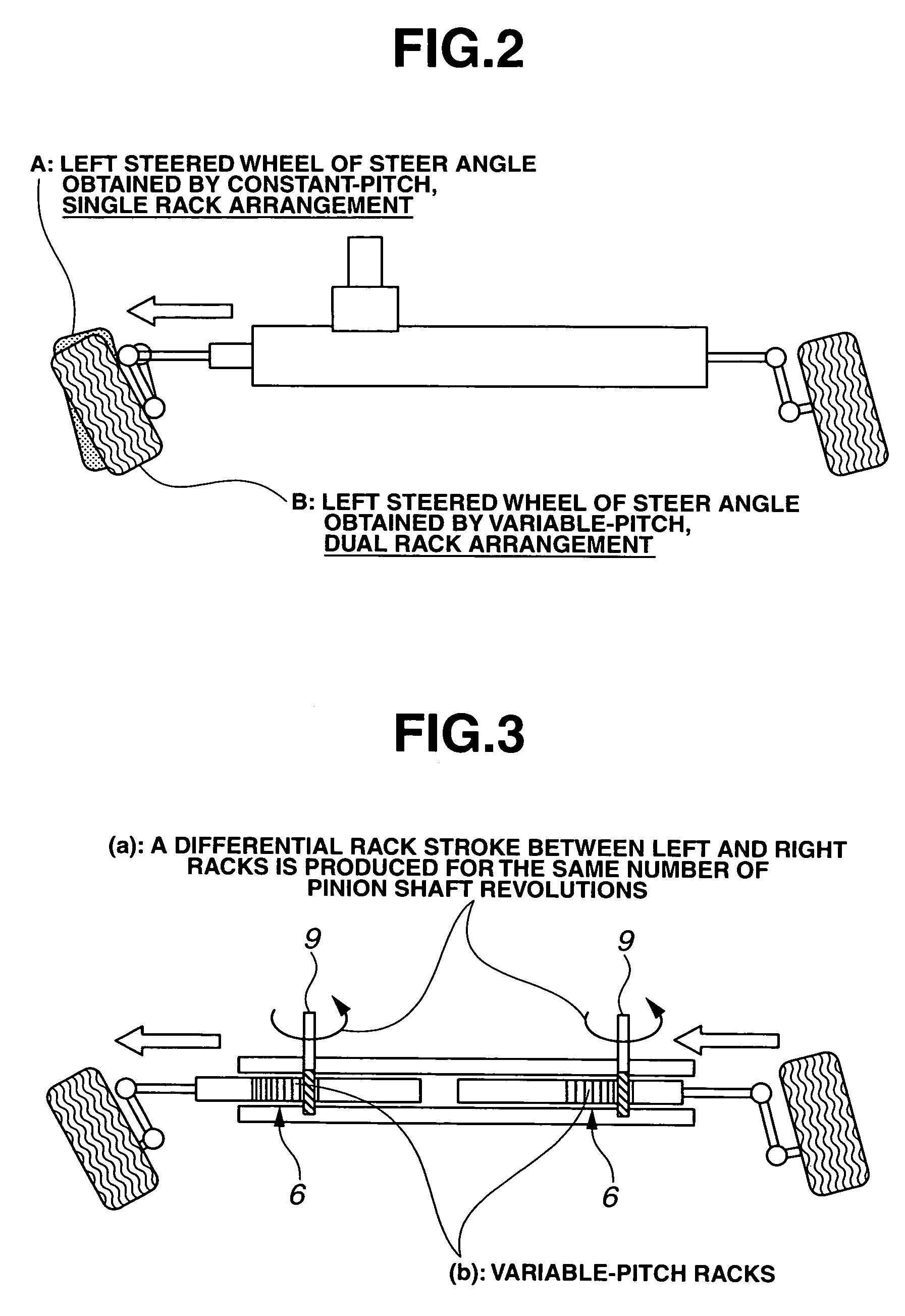
Vehicle steering apparatus
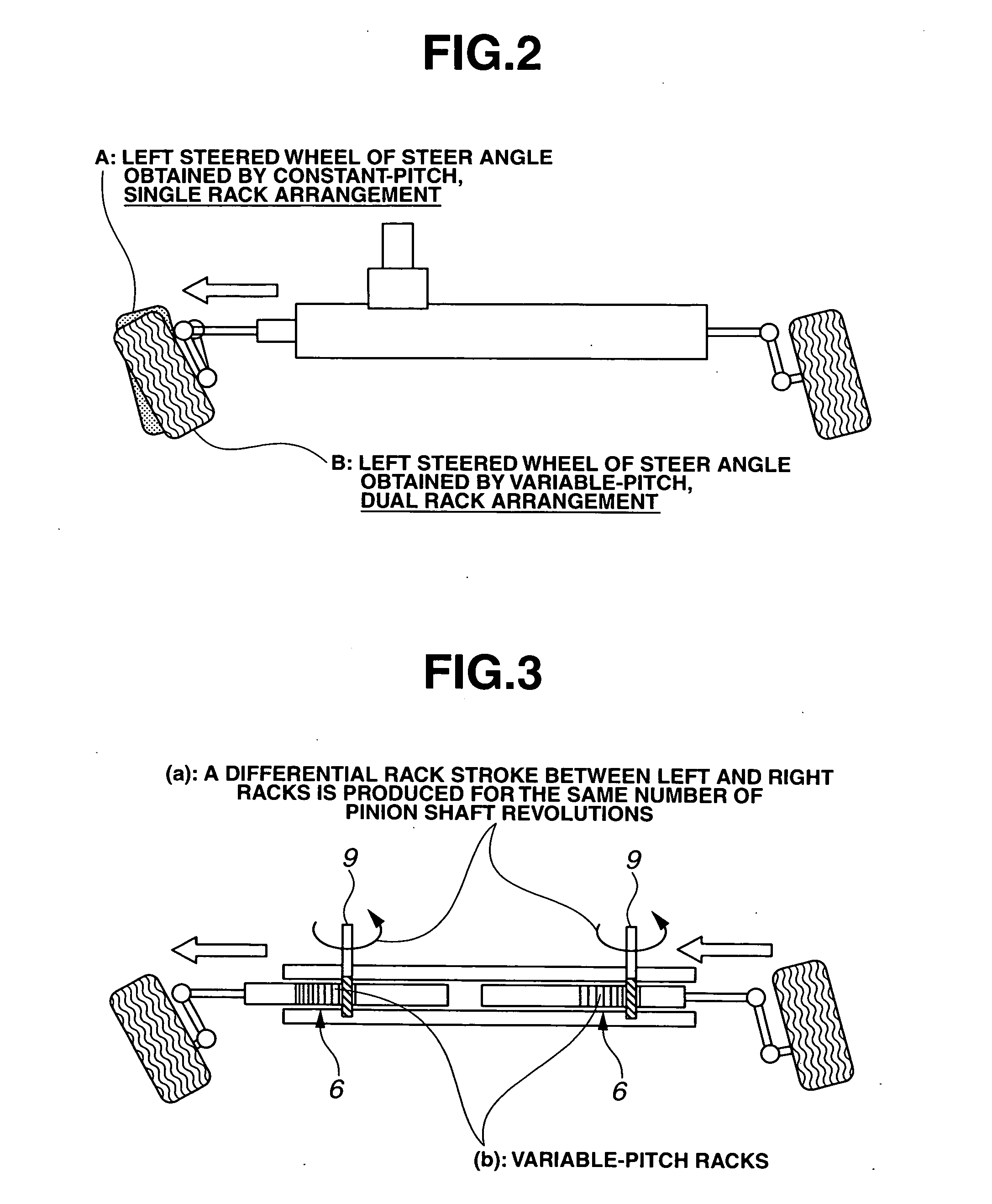
InactiveUS20050072621A1Enhanced steering link efficiencyCompensation deviationSteering linkagesMechanical steeringSteering wheelSteering angle
A vehicle steering apparatus includes a steering input section having at least a steering wheel to which steering input is applied, and a steering output section having at least a steering rack shaft and operatively associated with left and right steered wheels for steering the steered wheels by steering-rack-shaft movement produced by a steering force determined based on the steering input and transmitted directly or indirectly to the steering rack shaft. The steering rack shaft is split into left and right movable rack shaft portions. Also provided is a steer angle converter enabling a differential rack stroke between left and right rack strokes of the left and right movable rack shaft portions. The steer angle converter is constructed by at least one of a variable-pitch dual rack arrangement and a dual taper-pulley arrangement of a cable back-up mechanism.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Vehicle steering system having a rear steering control mechanism
The vehicle steering system includes front vehicle motive members, rear vehicle motive members, a steering input device, a front steering subsystem, a rear steering subsystem and a rear steering control mechanism. The front steering subsystem is operably coupled to the steering input device and coupled to the front motive members to steer the front motive members. The rear steering subsystem is coupled to the rear motive members to steer the rear motive members. The rear steering control mechanism includes a movable input member coupled to the steering input device so as to move in response to input from the device and a movable output member coupled to the rear steering subsystem. The rear steering subsystem adjusts steering of the rear motive members in response to movement of the output member. The control mechanism operates in a rear steering state in which force is transmitted from the input member to the output member to move the output member and a dwell state in which the output member does not move in response to movement of the input member.
Owner:OSHKOSH CORPORATION
Drive mechanism for vehicle
InactiveUS20050134014A1Simple structureImprove stabilitySteering linkagesFluid steeringSteering wheelDrive wheel
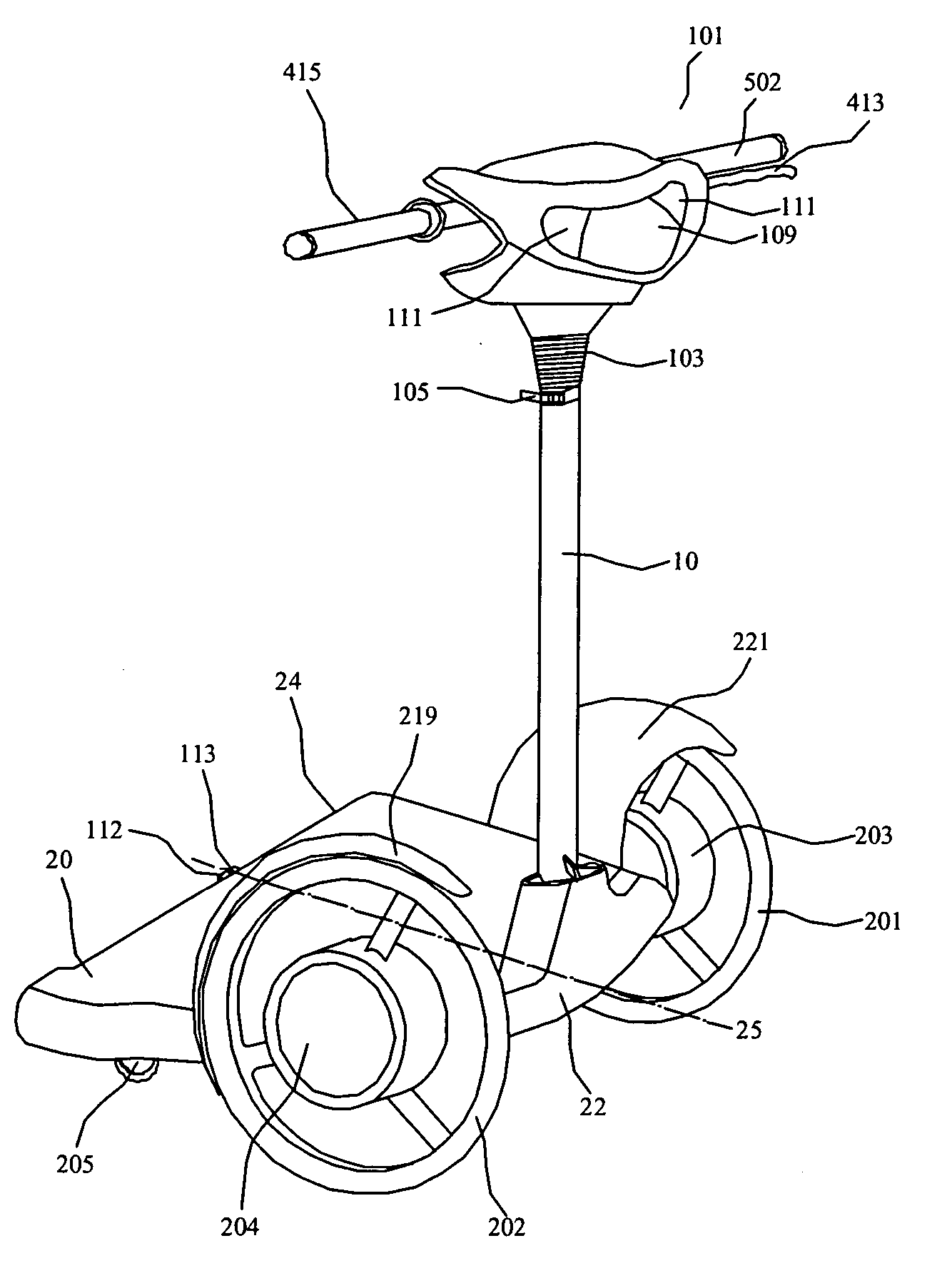
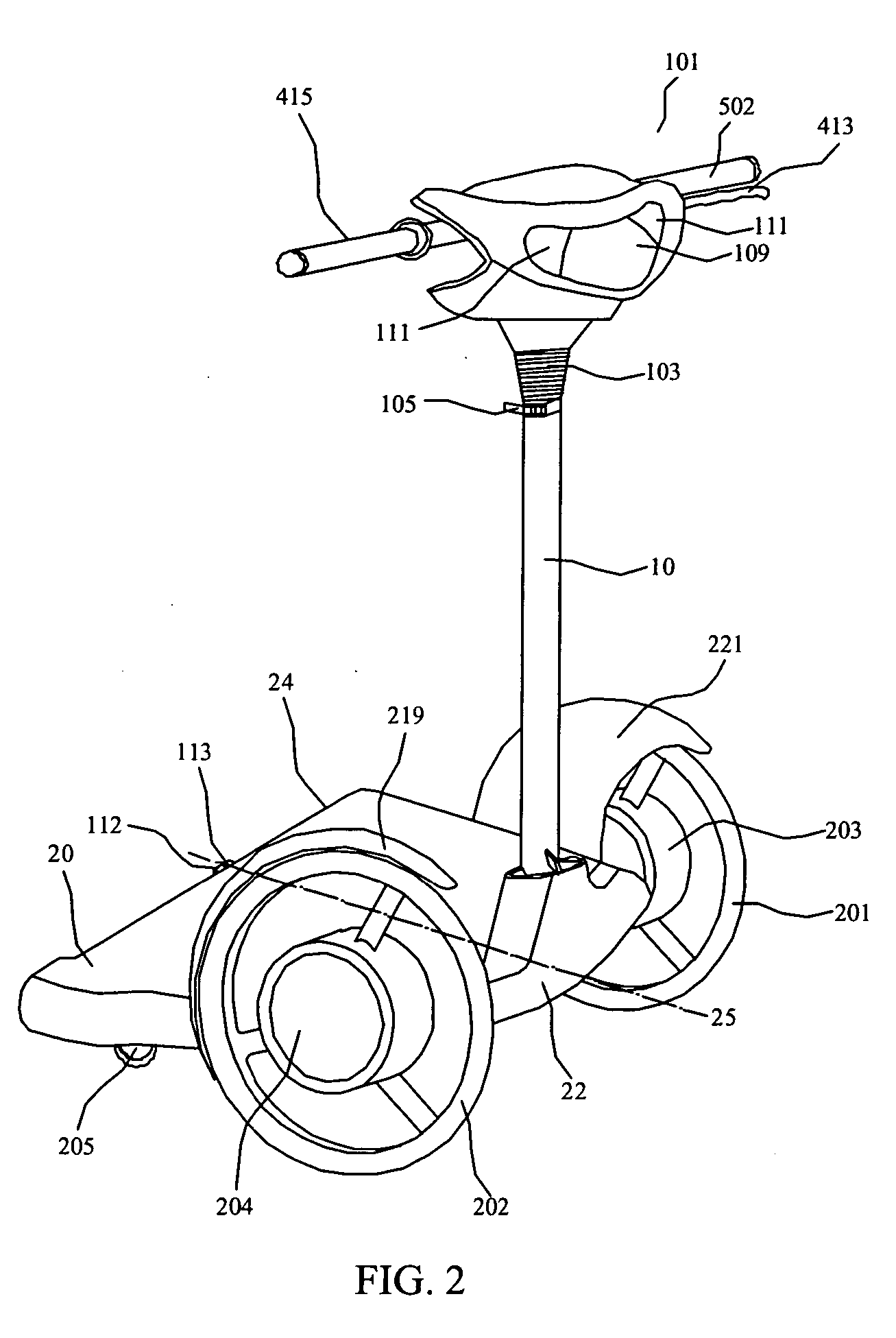
The present invention provides an electric-driven vehicle, which comprises a supporting platform and an upright tube, wherein the supporting platform has first and second ends and a longitudinal axis perpendicular to the first and second ends, the upright tube is fitted at the first end of the supporting platform and operatively connected with the supporting platform, a handle frame is provided on a top end of the upright tube. The electric-driven vehicle further includes two driving wheels operatively mounted at opposite sides of the first end of the supporting platform, at least one steering wheel operatively mounted on a bottom of the second end of the supporting platform, a driving means for the driving wheels, and a power supply means mounted on the bottom of the supporting platform and electrically connected with the driving means. The present invention also provides a support platform structure for an electric-driven vehicle, which comprises a first portion and a second portion, wherein the first portion having sleeves for operatively mounting the driving wheels, and a first side; the second portion having a steering knuckle for operatively mounting the steering wheels, and a second side corresponding to the first side; the first side and the second side are connected via a connecting member, and at least one of the first side and the second side can rotate about the bond-linkage element.
Owner:XIE SHOUCHUN
Robot system
InactiveUS7082350B2Good flexibilityEasy to operateVehicle fittingsSpeed/accelaration controlRobotic systemsCommunications system
An autonomous wheeled mobile robot (1) comprising at least one wheel-driving motor, an on-board computer, means for navigation, orientation, and maneuvering in an environment with moving obstacles; a sensor system; and a wireless communication system for receiving and sending.
Owner:UNIBAP AB
Automatic fluid exchanger
InactiveUS20050166993A1Preventing air infusionEffective blockingLiquid fillingPackaging by pressurising/gasifyingFluid controlPositive pressure
A fluid exchanger for servicing the fluid circuits of vehicular power steering systems and other fluid circulating or hydraulic circuits. The fluid exchanger uses a float operated fluid control valve to harness fluid pressure provided by a pump of an accessed hydraulic circuit. The fluid control valve uses both negative and positive pressure of the circuit's pump to control fluid flow patterns. The float and fluid control valve are matched to be either mechanical / hydraulic or electrical / hydraulic in design. If the exchanger is provided with a mechanically operated fluid control valve, a mechanical float is provided in the exchanger's fresh fluid reservoir and is directly connected to the valve slide of the fluid control valve. If the exchanger is provided with an electric solenoid operated fluid control valve, a float operated electrical switch is provided in the exchanger's fresh fluid reservoir and is wired to control the solenoid of the valve.
Owner:VIKEN JAMES P +1
Steering triangle
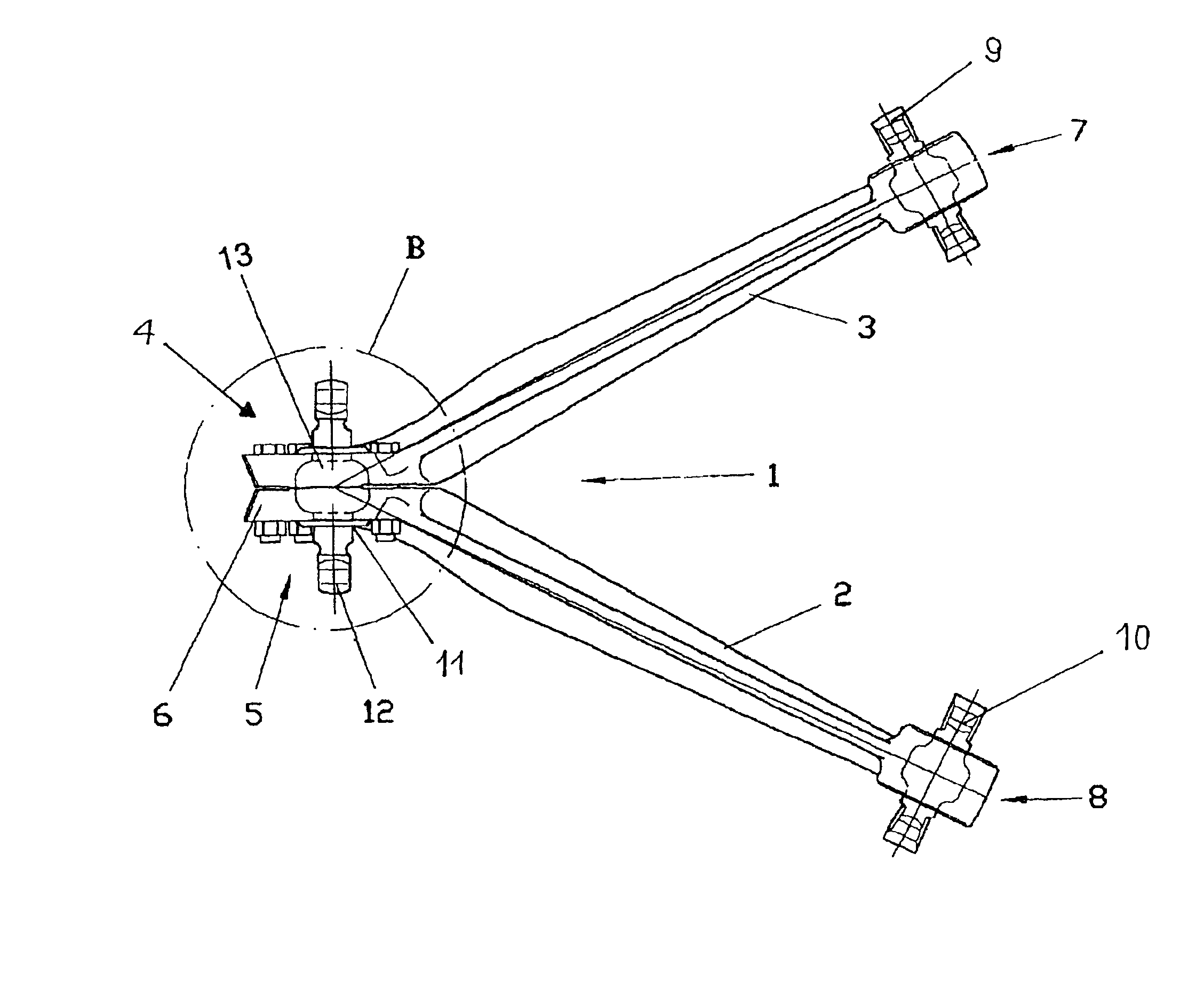
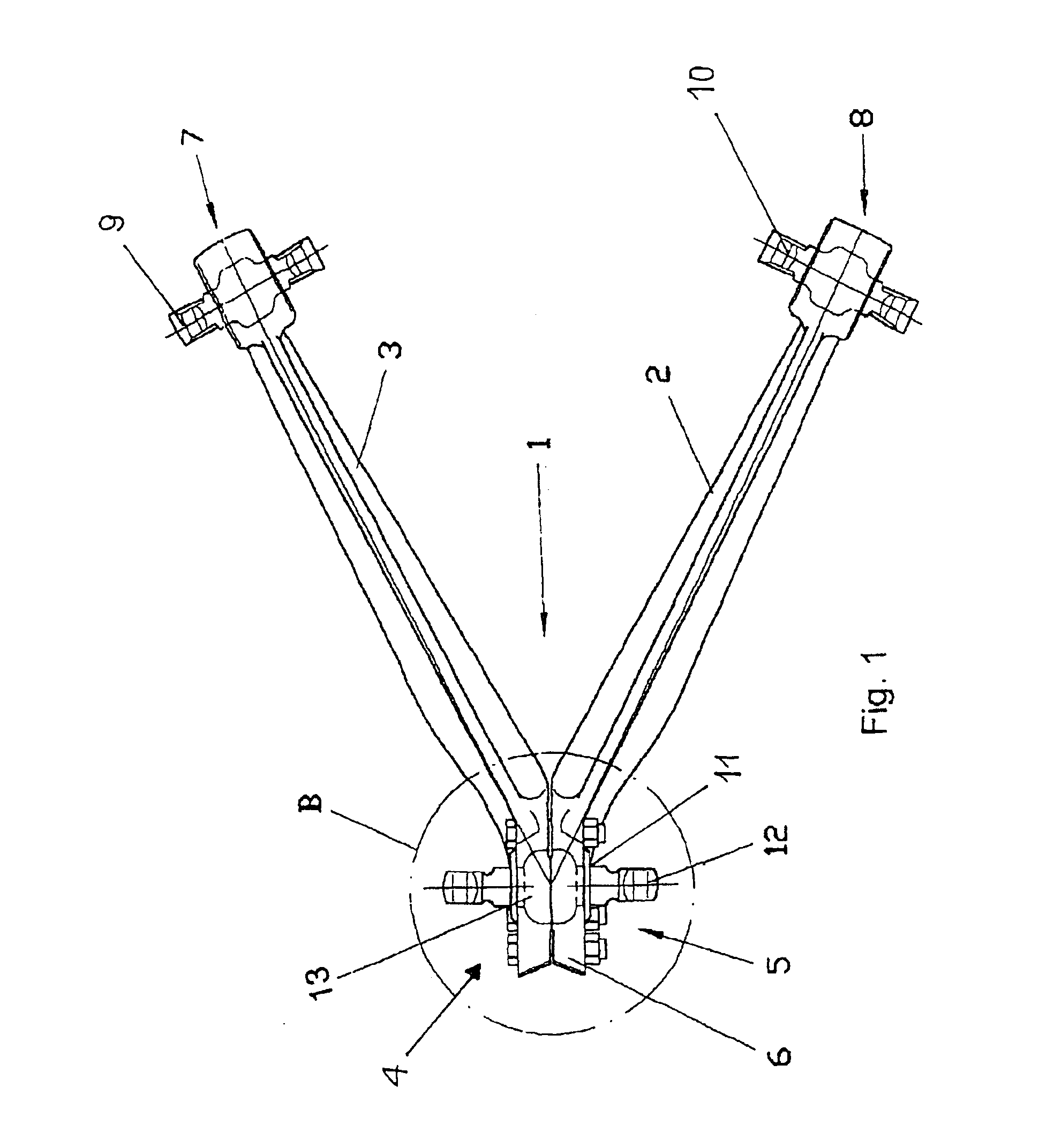
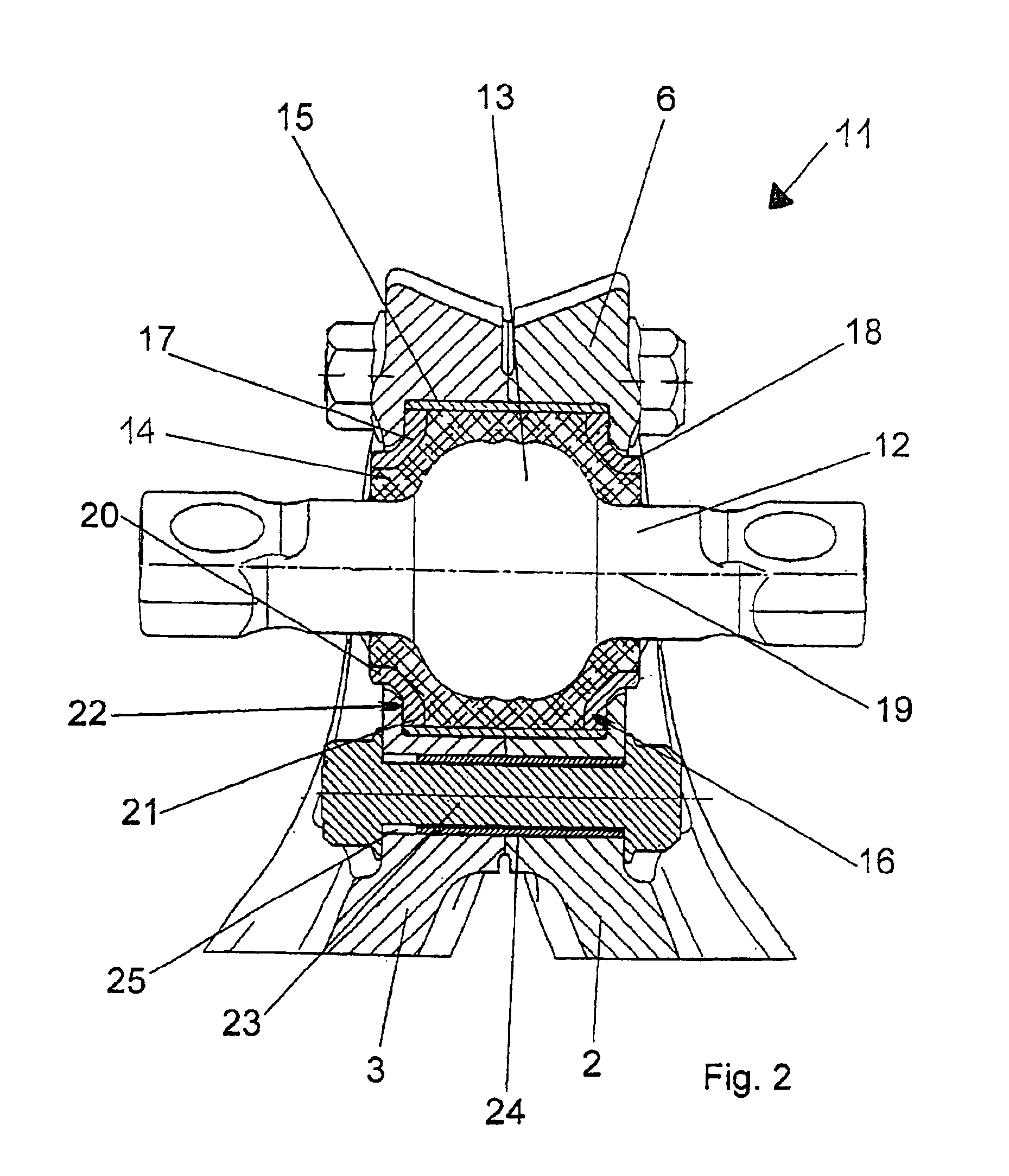
InactiveUS6959935B2Simple designReduce shear forceNon-rotating vibration suppressionRigid suspensionsElastomerControl arm
A steering triangle (1) is provided for the axle suspension of motor vehicles for the articulated connection of a vehicle axle with a vehicle chassis with two control arms (2, 3). The control arms are connected to each other in a joint housing (6) formed by the control arms (2, 3) together for a rubber-metal bearing (11) for fixing the steering triangle (1) on the vehicle axle. The rubber-metal bearing (11) has a pivot axis (12) provided with a spherical surface and an elastomer body (14), which extends around the pivot axis (12) at least in the area of the spherical surface and which is accommodated in a recess (16) located within the joint housing (6), in which steering triangle two pressing rings (17, 18) are arranged within the recess (16) of the joint housing (6) on the axial outer sides of the elastomer body (14). The pressing rings can be moved toward each other by a tensioning device via the intermediary of stop faces (22) of the joint housing (6). The stop faces are in contact with the outer sides of the pressing rings (17, 18), which outer sides face away from each other. The rubber-metal bearing can be pretensioned both in the axial direction and in the radial direction, so that stronger forces can be absorbed due to the higher rigidity achieved as a result.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Electrical steering assist for material handling vehicles
ActiveUS20050247508A1Reduce effortOvercome disadvantagesLifting devicesHand leversJoystickElectric machinery
Electrical steering assist systems reduce the operator applied steering effort necessary to operate material handling vehicles. A steer drive unit including a motor is coupled to a steerable wheel for providing steering assist. The amount of steering assist provided by the steer drive unit is determined by a controller that receives input from one or more input sensing devices. The input sensing device(s) may include force sensors that detect an operator applied turning force. The input sensing device(s) may also detect the movement of one steering component relative to another. Further, the input sensing device(s) may include operator activated controls such as a joystick, potentiometer, switches and voice initiated commands. Input sensing device(s) may additionally be provided to detect operational parameters such as the load on the material handling vehicle, vehicle speed, or environmental conditions such as travel path obstruction detection, homing and proximity sensing.
Owner:CROWN EQUIP CORP
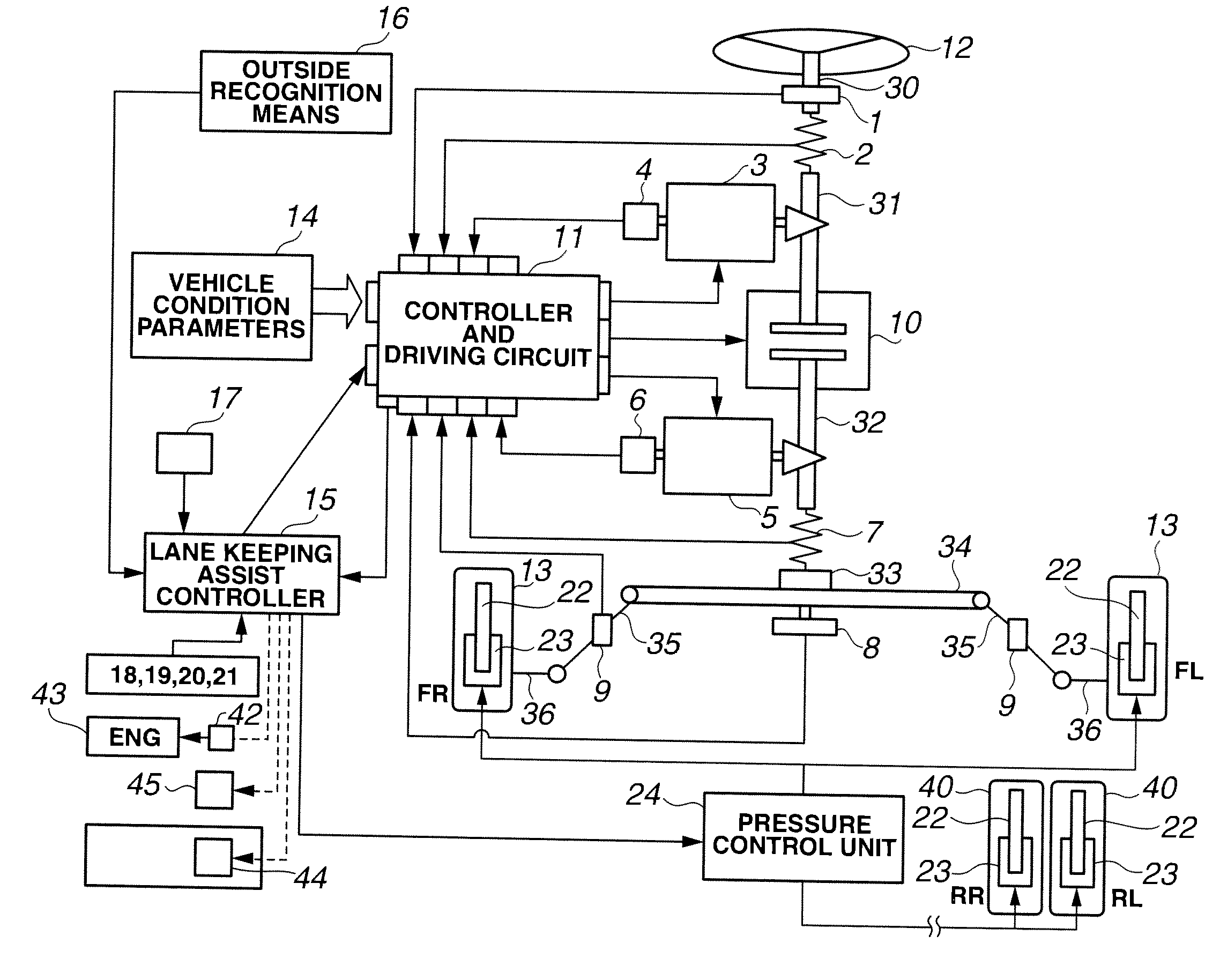
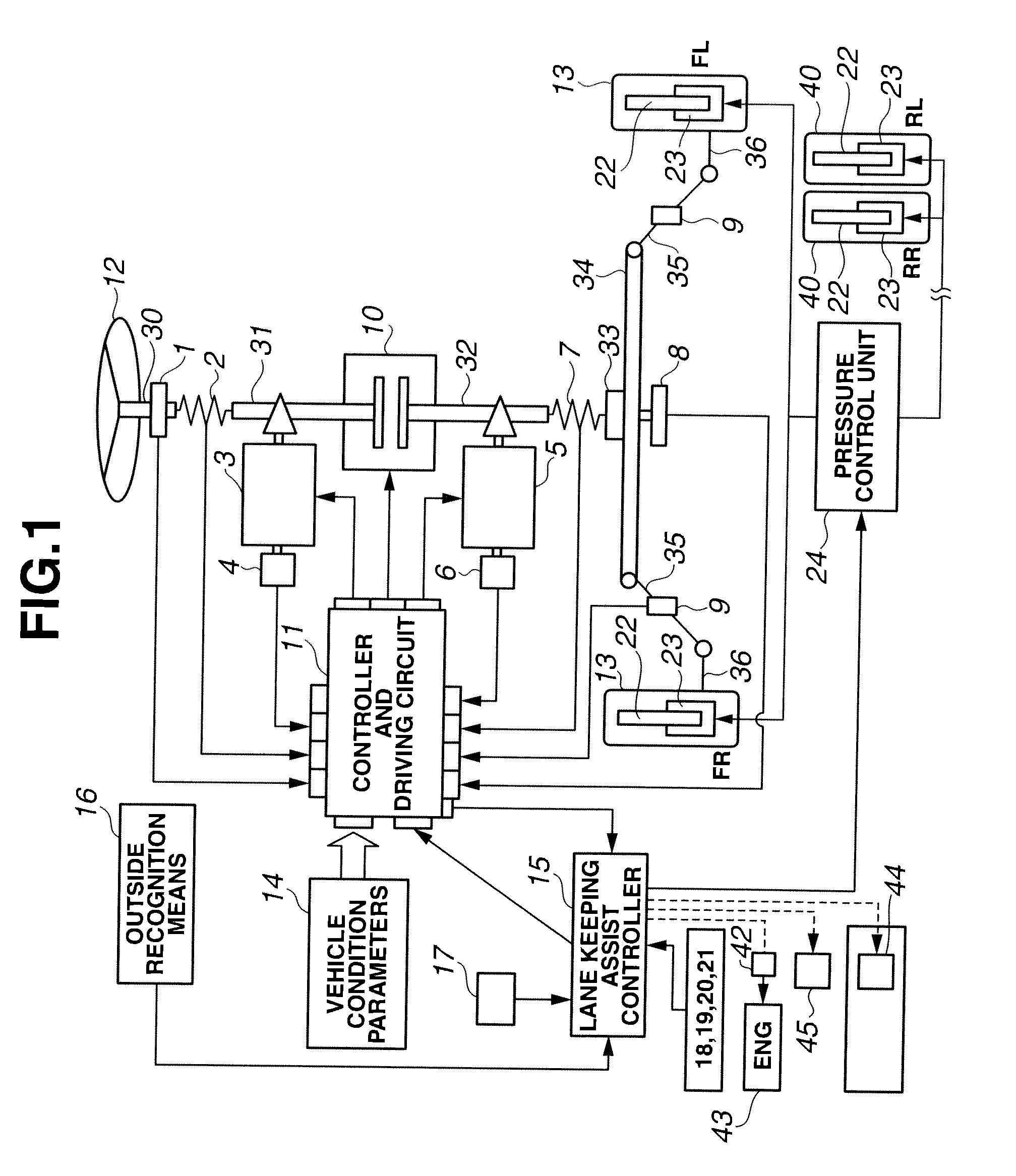
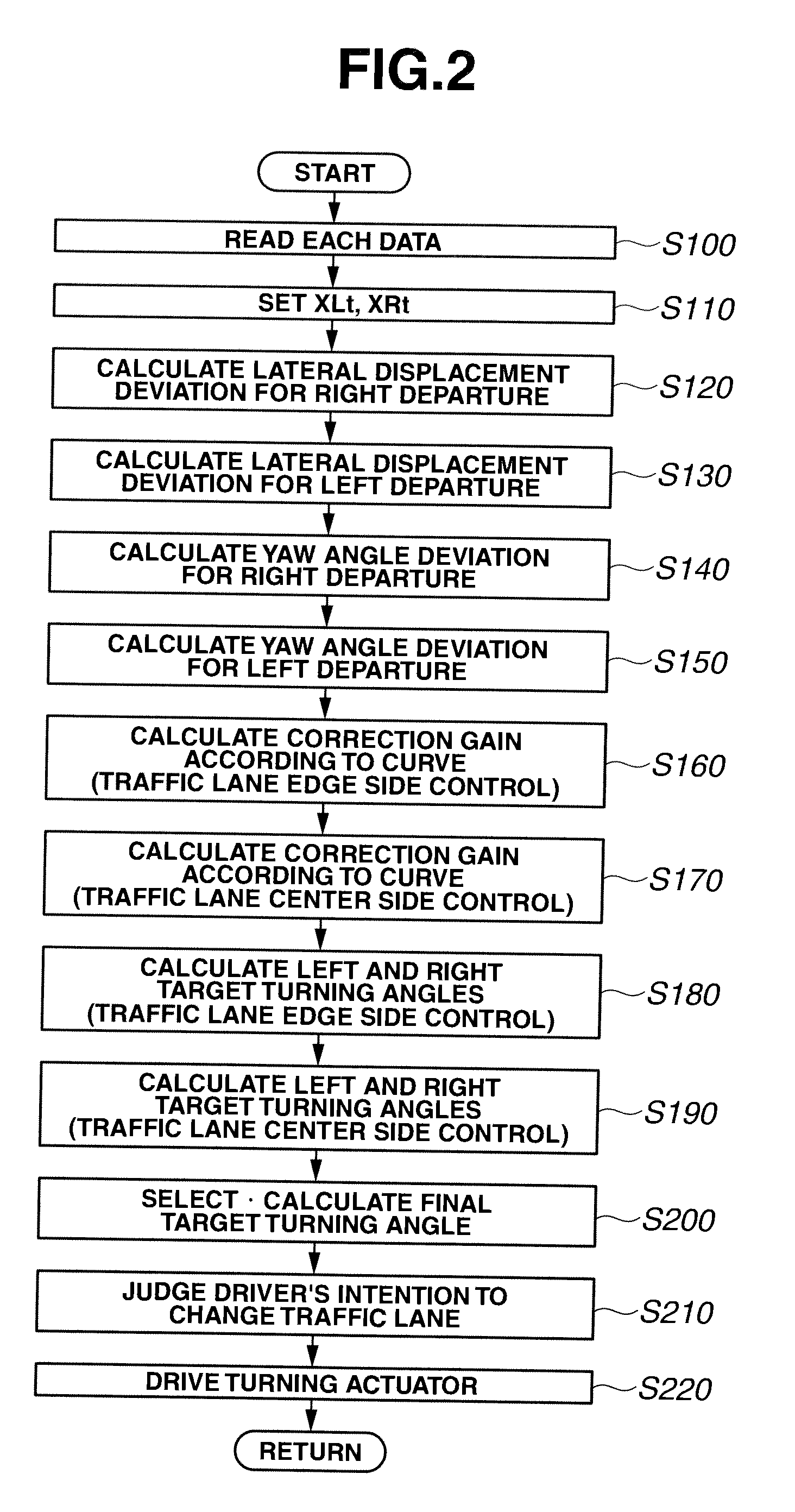
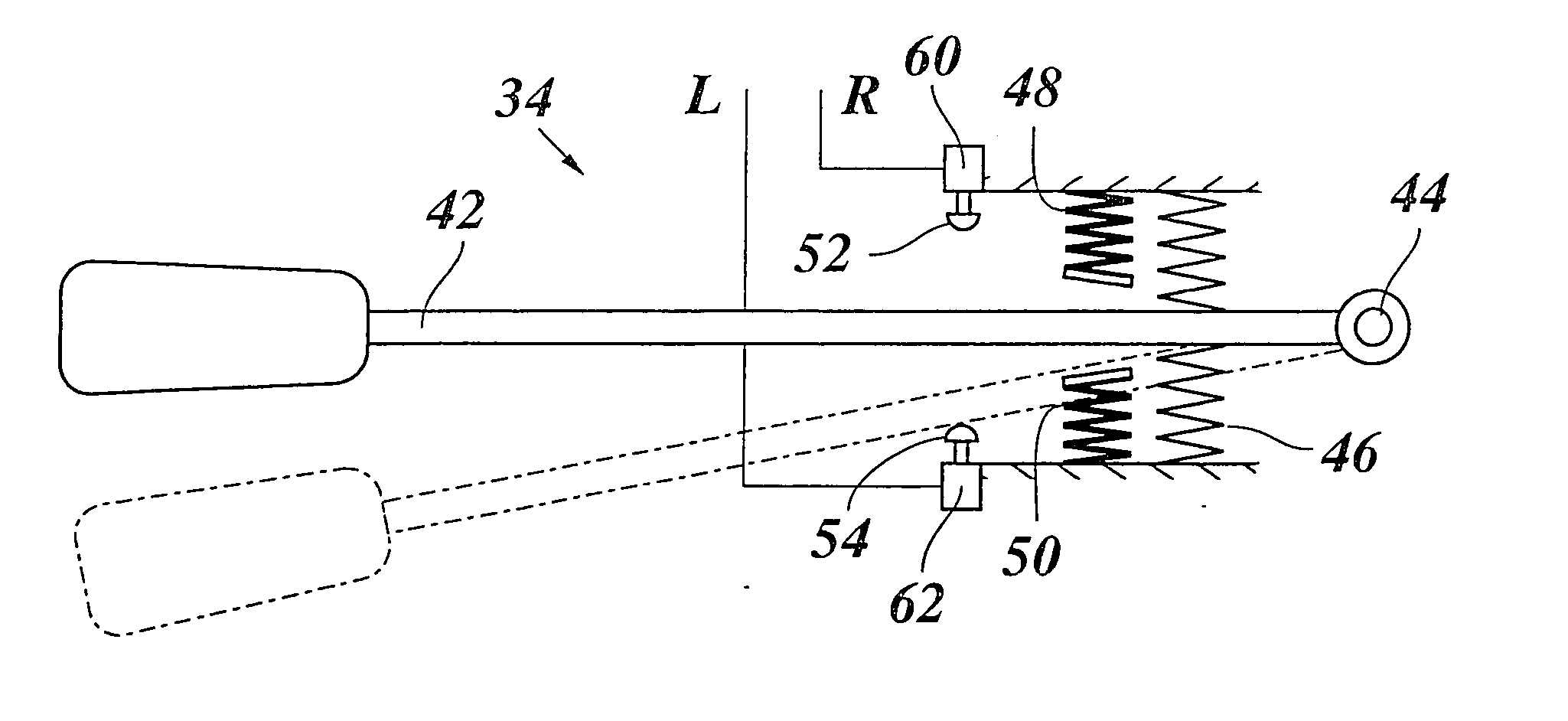
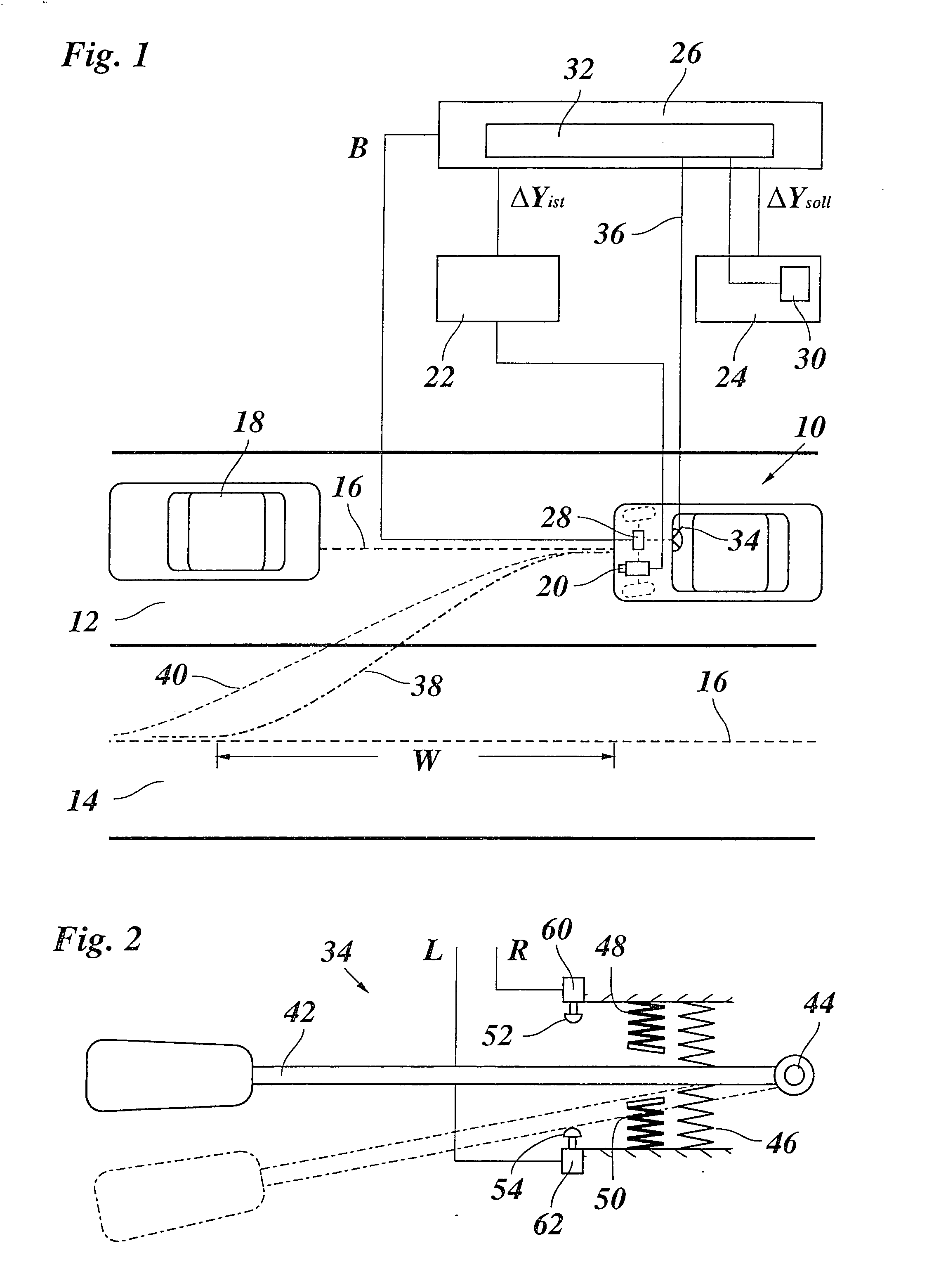
Lane keeping assist device and lane keeping assist method
ActiveUS20110015850A1Lessen awkward feelingAvoid performance degradationDigital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlFeedback controlLateral displacement
Lateral displacement reference positions LXL, LXR are set on left and right from a center in a width direction of a traffic lane L where a vehicle travels. Then, at least in a case where the vehicle is positioned on an inner side of the left and right lateral displacement reference position LXL, LXR, the vehicle is feedback-controlled so as to decrease a yaw angle deviation. Further, in a case where the vehicle is positioned at an outer side of the left and right lateral displacement reference position LXL, LXR with respect to the traffic lane center, the feedback control is performed so as to decrease the angle deviation and a lateral displacement deviation.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
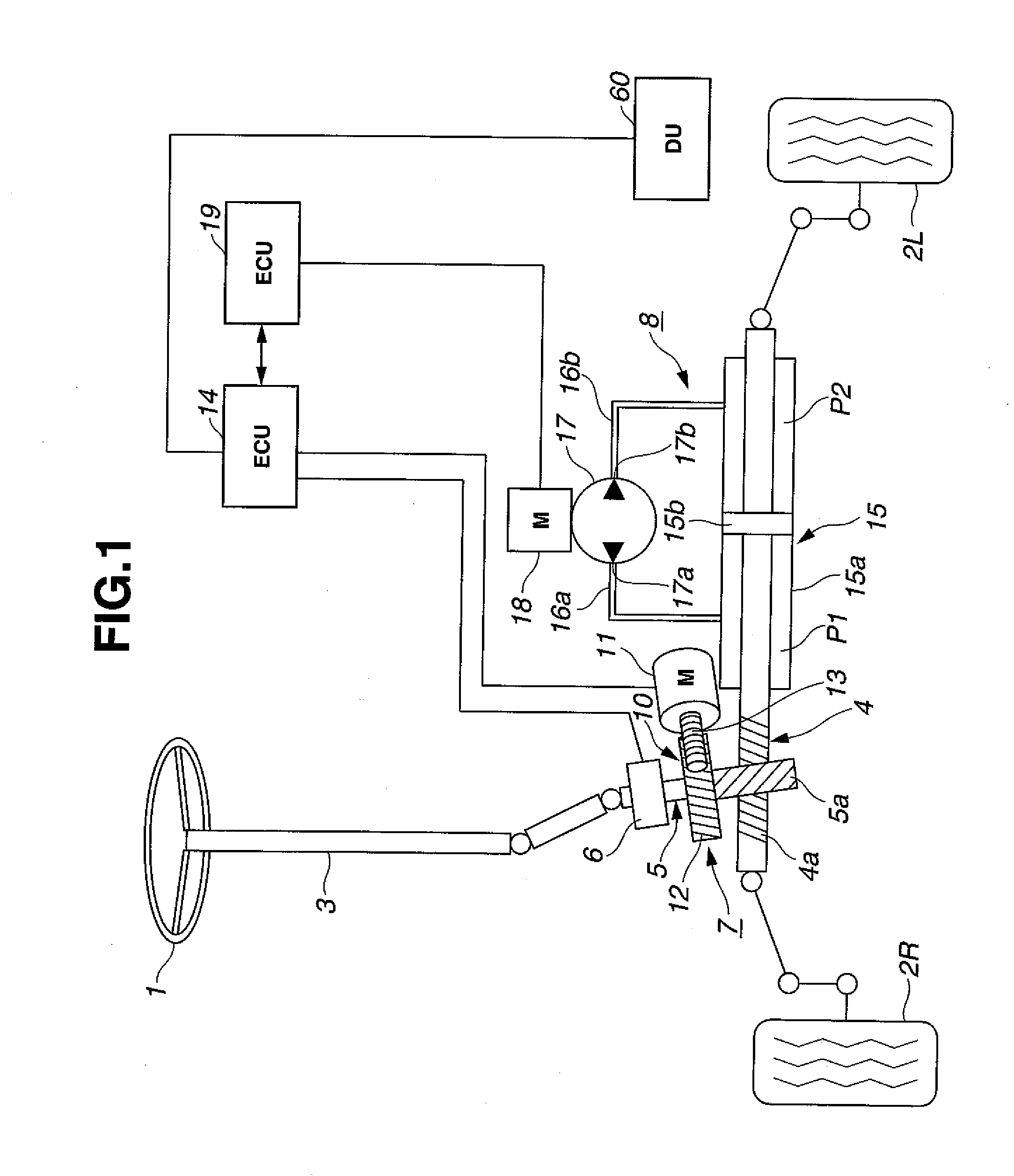
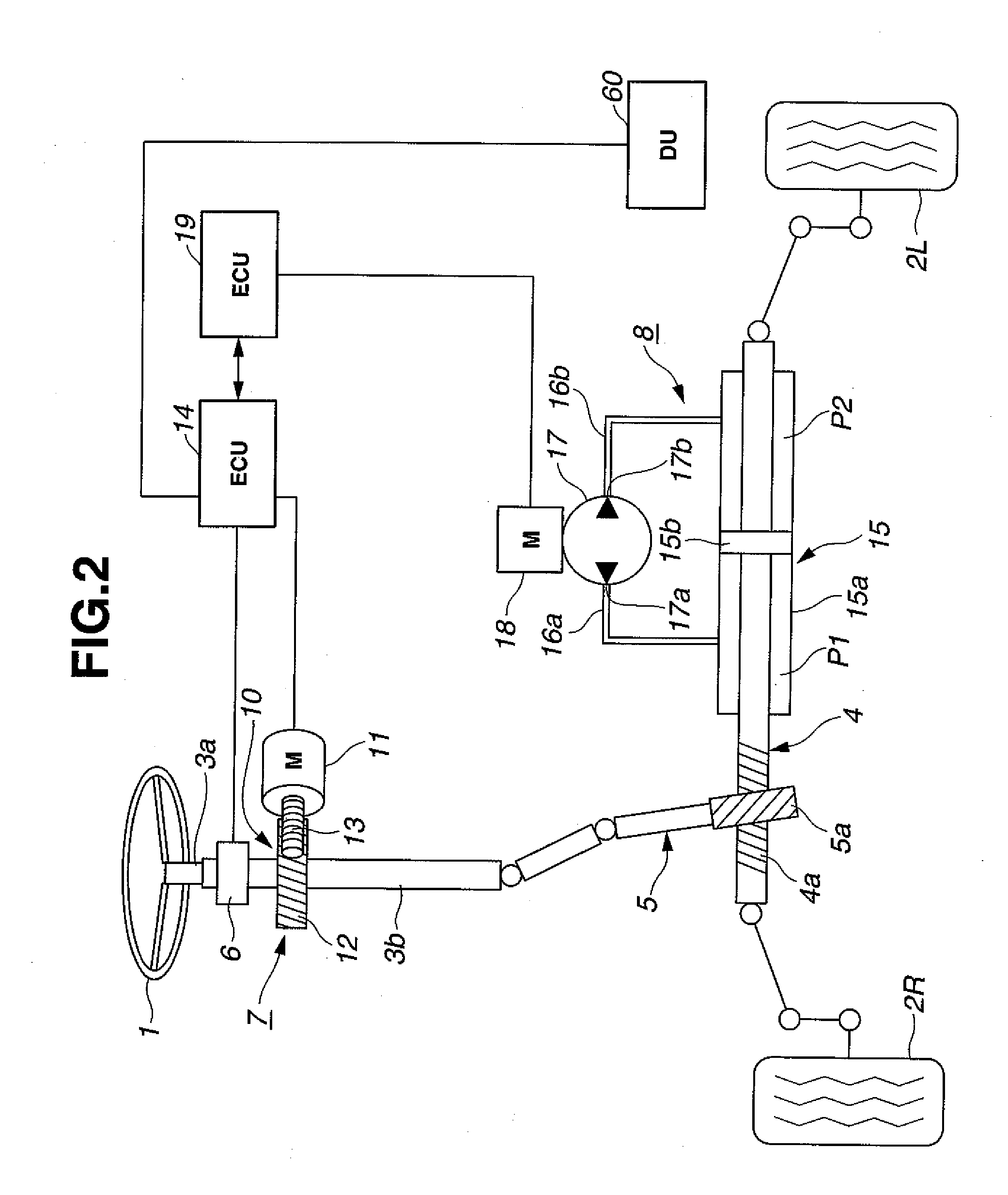
Electric power steering system
InactiveUS20050257992A1Sufficient steering assist torqueEffectively overcome drawbacksSteering linkagesFluid steeringElectric power steeringElectric machine
An electric power steering system for an automotive vehicle, includes a torque sensor disposed to a steering shaft to detect a steering torque. A first pinion is disposed to the steering shaft. A rack shaft is in mesh with the first pinion and connected with the steering shaft to change a rotational motion of the steering shaft to an axial motion of the rack shaft and provided to be operated in relation to the steering shaft. A first motor is connected with the first pinion to generate a steering assist torque in accordance with the steering torque detected by the torque sensor. A second pinion is disposed to be separate from the first pinion and in mesh with the rack shaft. A second motor is connected with the second pinion to generate a steering assist torque in accordance with the steering torque.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Vehicle steering apparatus
InactiveUS7308964B2Durability is deterioratedImprovement effortsSteering linkagesMechanical steeringSteering angleSteering wheel
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Rotary position sensing apparatus
InactiveUS20100163333A1Avoid rotational movementDeflectable wheel steeringIncline measurementLinear motionSignal processing circuits
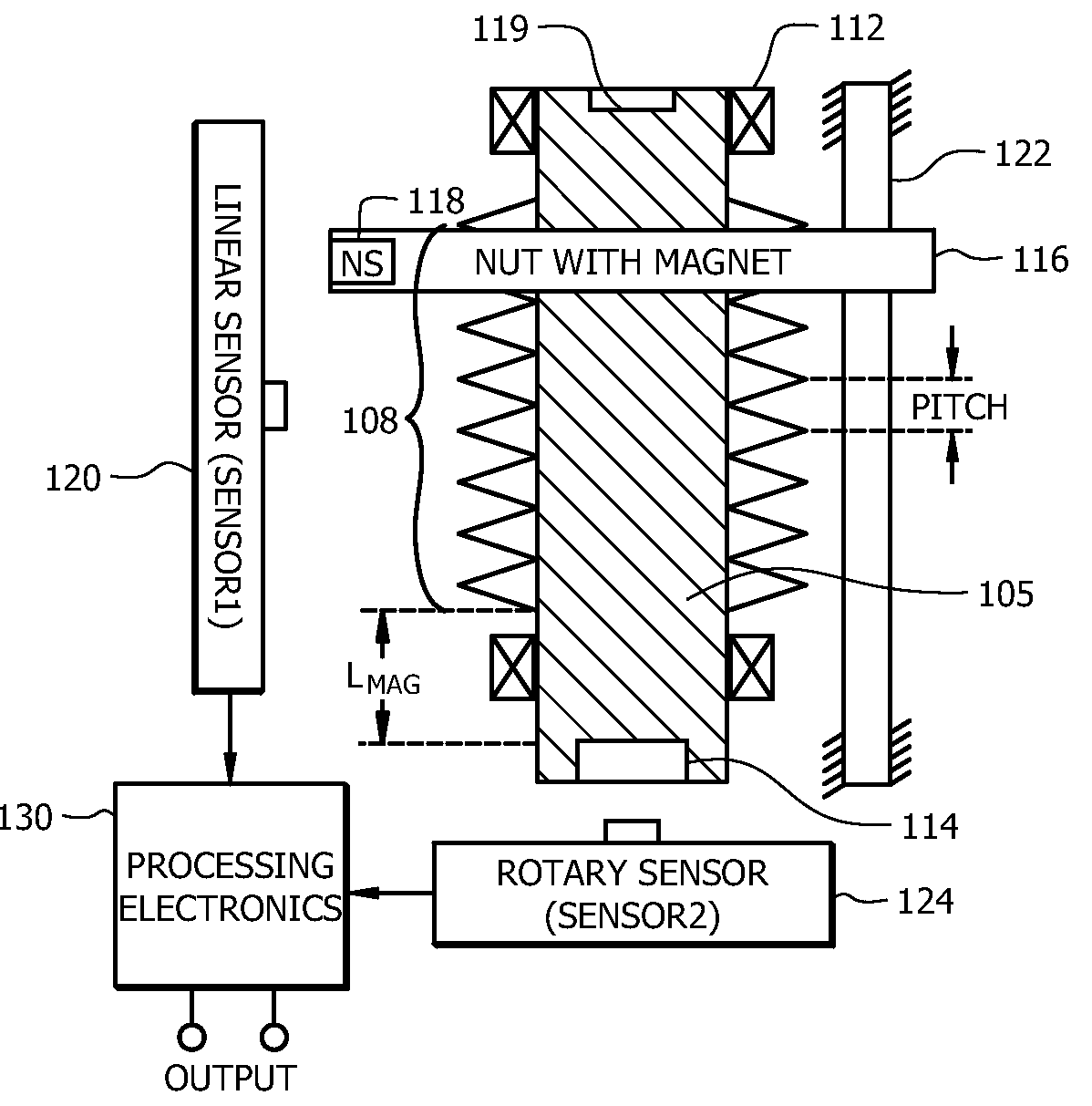
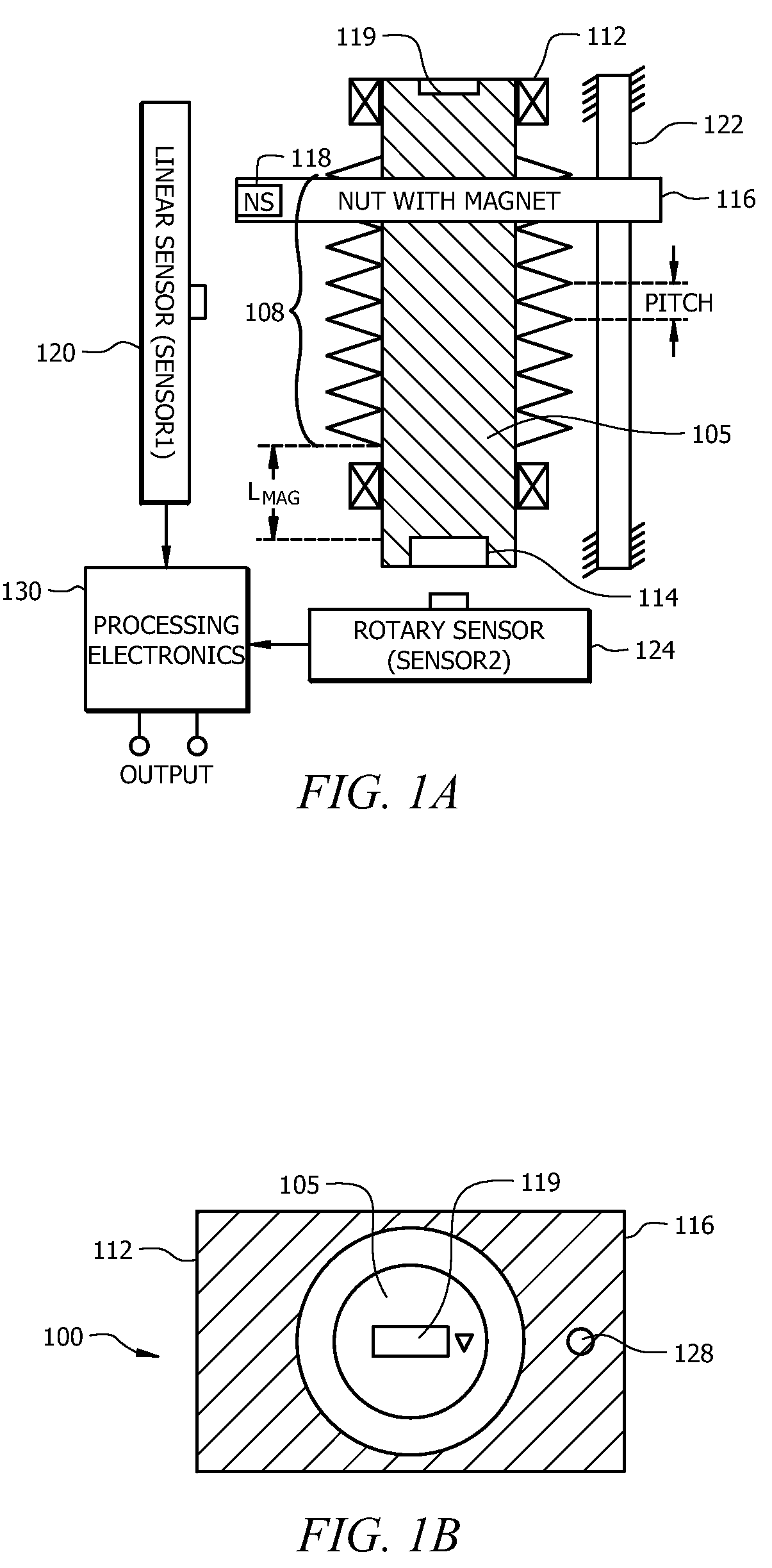
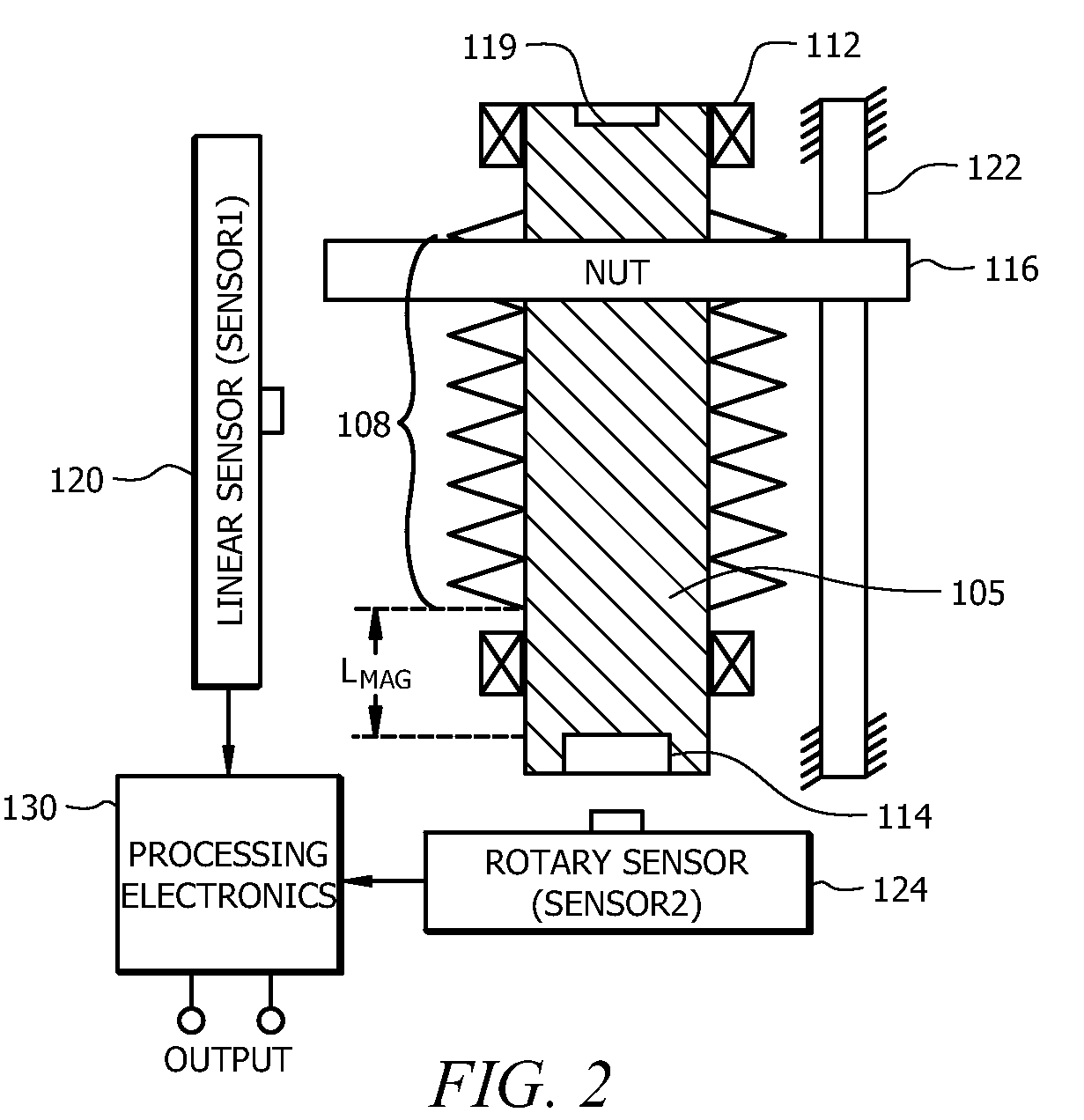
An angular position sensor (100) for determining angular position includes a shaft (105) having a threaded portion (108), and a structure for engaging an external application (119). The shaft (105) includes a first permanent magnet (114). A nut (116) is threaded on the threaded portion (108). The nut (116) is formed from a first magnetic permeable material or includes a second permanent magnet (118). At least one constraint (122) is coupled to the nut (116) for preventing rotational movement of the nut (116) while allowing linear motion of the nut (116). A first magnetic sensor (120) is positioned along a length of the threaded portion (108) of the nut (116) for measuring a linear position of the nut (116). A second magnetic sensor (124) is provided for measuring an angular position of the shaft (105). Signal processing circuitry (130) is coupled to receive outputs from both the first magnetic sensor (120) and second magnetic sensor (124) for calculating a parameter relating to an angular position of the rotatable member.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
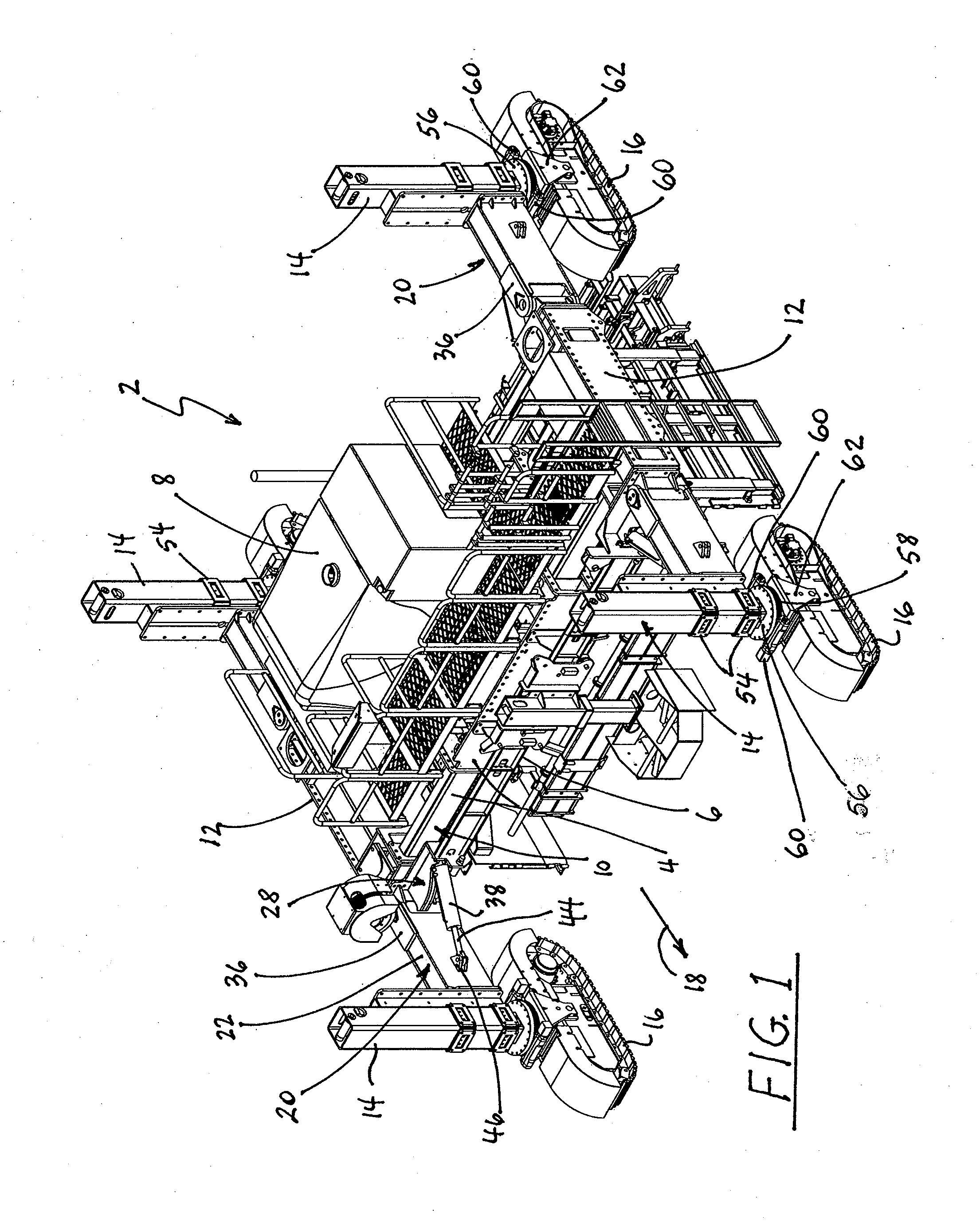
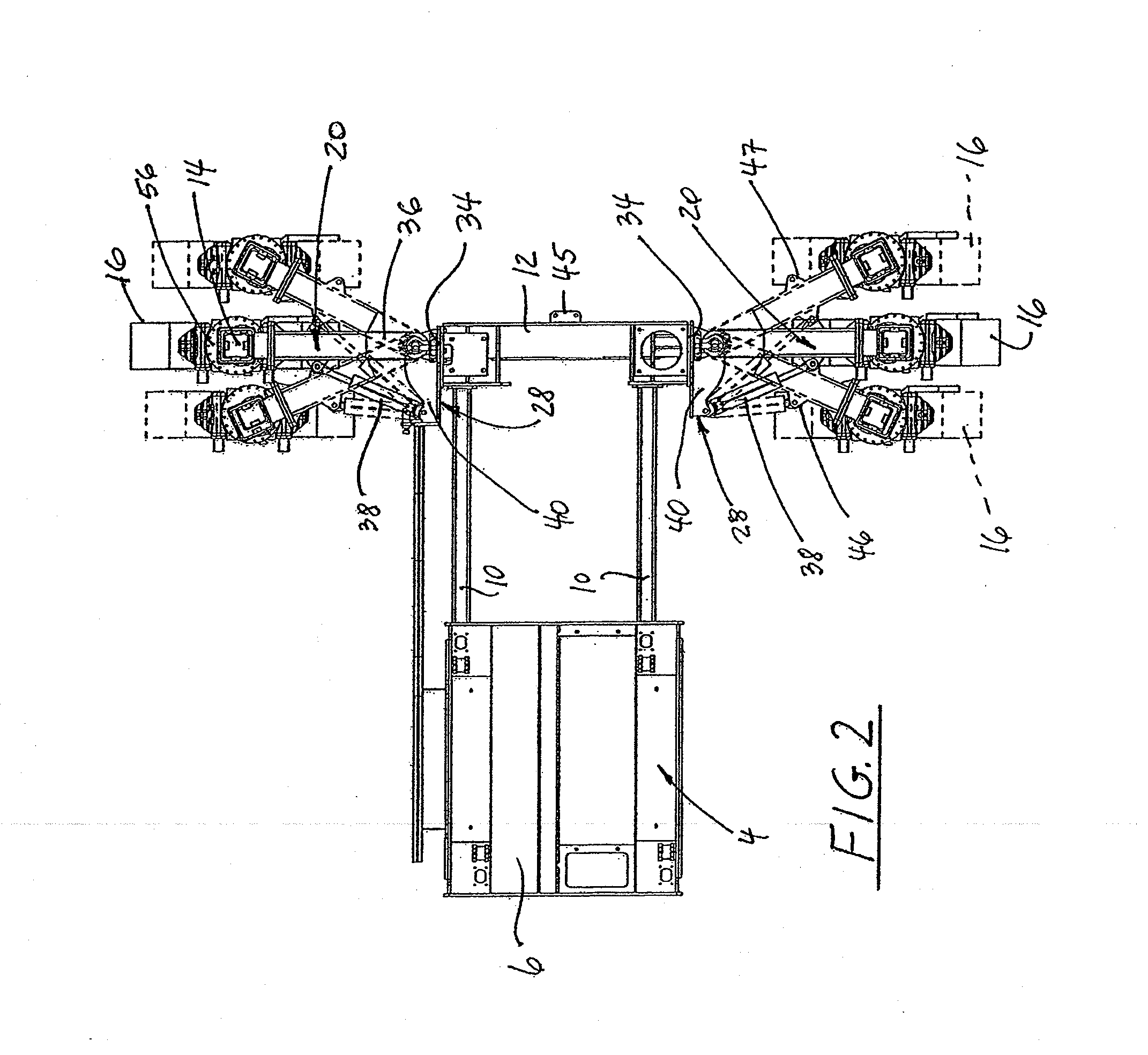
Adjustable Bolster Swing Legs for Mounting and Aligning and Reorienting Crawlers for Slipform Paving Machines
ActiveUS20110236129A1Improve mobilityShorten the timeSteering linkagesPaving detailsGear driveLeg moving
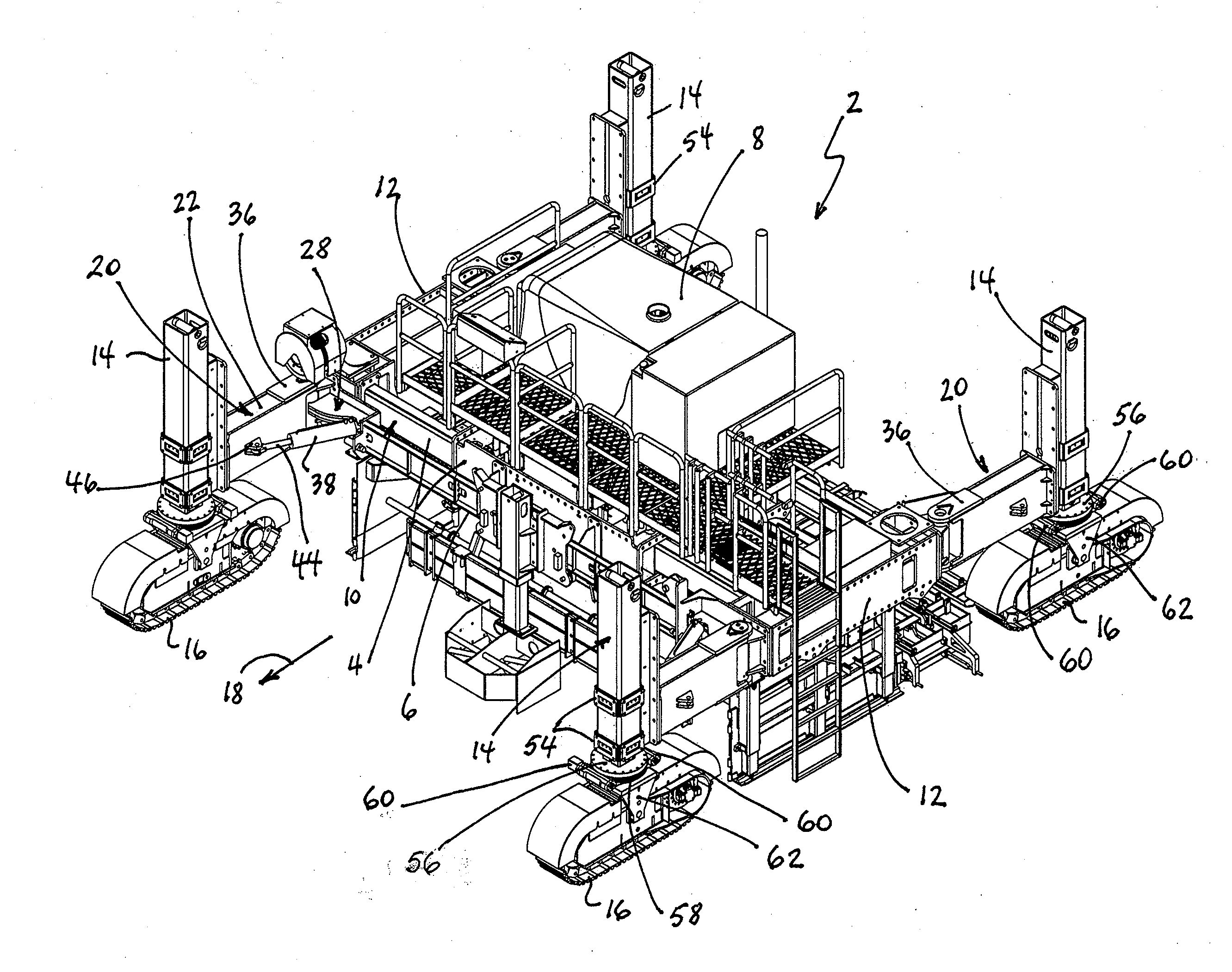
A paving machine which is configured to move in a paving direction for spreading, leveling and finishing concrete into a form having a generally upwardly exposed, finished concrete surface and terminating in lateral concrete sides. The paving machine has a main frame, including a center module, bolsters laterally movably connected to respective lateral sides of the center module for changing a spacing between the bolsters, and a crawler track associated with respective aft and forward ends of the bolsters. A bolster swing leg for each crawler track supports an upright jacking column secured to the swing leg proximate a free end thereof. A worm gear drive between the jacking column and the crawler track permits rotational movements of the crawler track and the jacking column about an upright axis. A hinge bracket is interposed between each swing leg and an associated surface of the bolsters and includes a fixed, upright pivot shaft that pivotally engages the swing leg to enable pivotal movements of the swing leg about an upright axis in a substantially horizontal plane. The hinge bracket further includes a pivot pin that is laterally spaced from and fixed in relation to the pivot shaft. A length-adjustable holder capable of being held at a fixed length has a first end pivotally engaging the pivot pin on the hinge bracket and a second end that pivotally engages the swing leg. The holder permits pivotal motions of the swing leg about the hinge pin when it is in its length-adjustable configuration and prevents substantially any motion of the swing leg when the holder is in its fixed-length configuration. A feedback loop cooperates with angular position transducers and automatically keeps the crawler tracks oriented in the paving direction of the machine when the swing legs move in a horizontal plane relative to a remainder of the paving machine. The paving machine can be reconfigured between its paving orientation and a road transport orientation by activating the crawlers to move the swing legs and the crawlers into a narrowed transport configuration.
Owner:GUNTERT & ZIMMERMAN CONSTR DIV
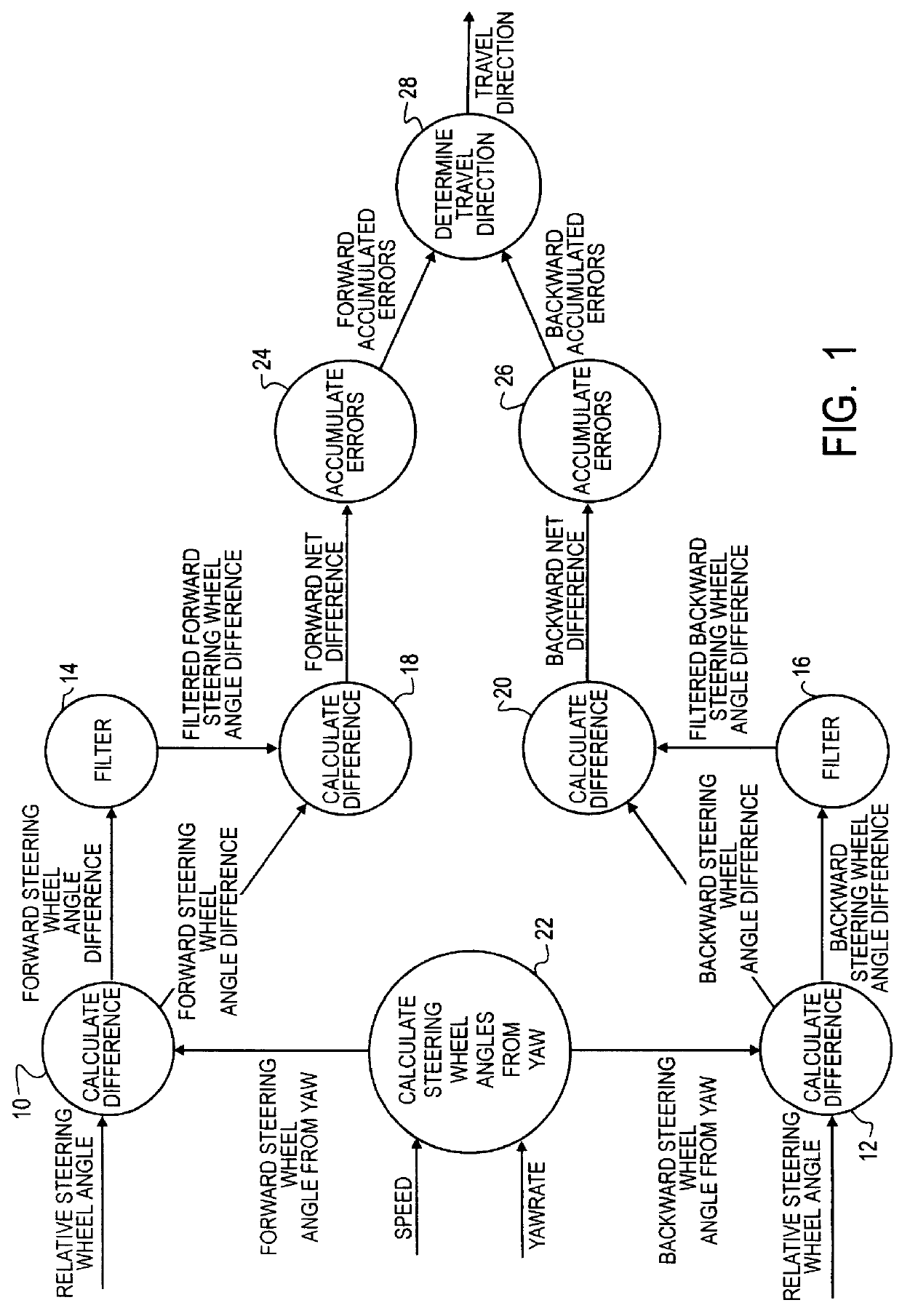
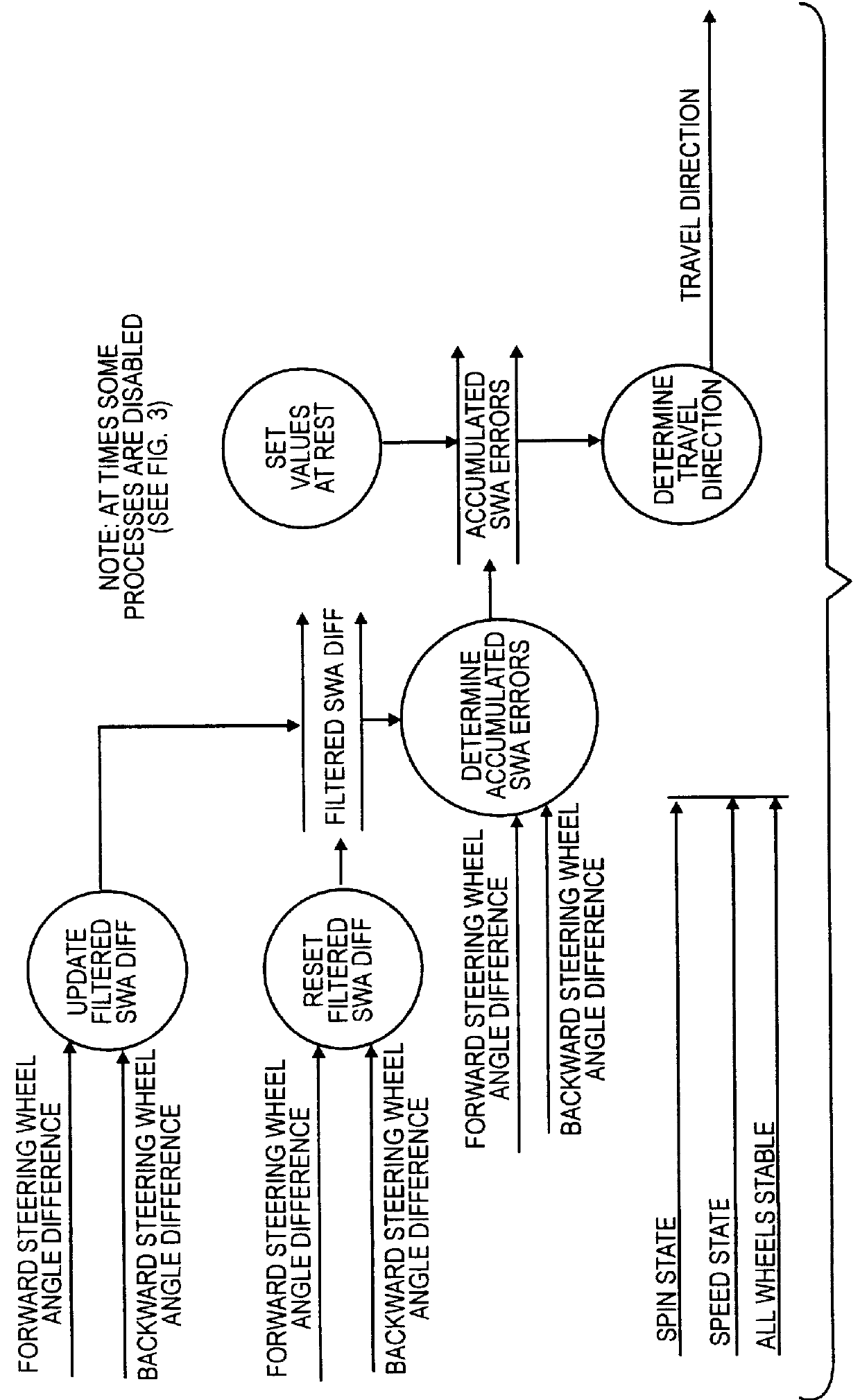
Determining the direction of travel of an automotive vehicle from yaw rate and relative steering wheel angle
A method of using relative steering wheel angle of an automotive vehicle, vehicle yaw rate, and vehicle speed to determine whether the vehicle is traveling forward or backward. Forward and backward steering wheel angles are calculated from vehicle speed and yaw rate (22). A difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle (10), and a difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle (12) are calculated. The difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle is filtered (14), and a difference between the filtered and the unfiltered difference between relative steering wheel angle and forward steering wheel angle is calculated to obtain a forward net difference (18). The difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle is filtered (16), and a difference between the filtered and the unfiltered difference between relative steering wheel angle and backward steering wheel angle is calculated to obtain a backward net difference (20). While repeatedly performing the foregoing steps, forward net difference values derived from the forward net differences are accumulated (24), and backward net difference values derived from the backward net differences are accumulated (26). The travel direction is determined by comparing the accumulation of forward net difference values and the accumulation of backward net difference values (28). Absolute steering wheel angle and road bank angle can also be calculated.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Route guidance assistance by moment support at the steering wheel
ActiveUS20100280713A1Easy to followCosmonautic condition simulationsInstruments for road network navigationSteering wheelControl signal
A device and a method for route guidance assistance in a vehicle that is connected to a navigation system. In order to make it easier for the driver to follow a route calculated by a navigation system, an assisting device is provided for route guidance. The assisting device includes a control unit for generating a control signal for haptic feedback to the driver of the vehicle. As haptic feedback, the control unit can output an additional moment on the steering system of the vehicle, for example, the additional moment being negative when the vehicle departs from the travel route while being positive when the vehicle follows the calculated direction of the navigation route.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
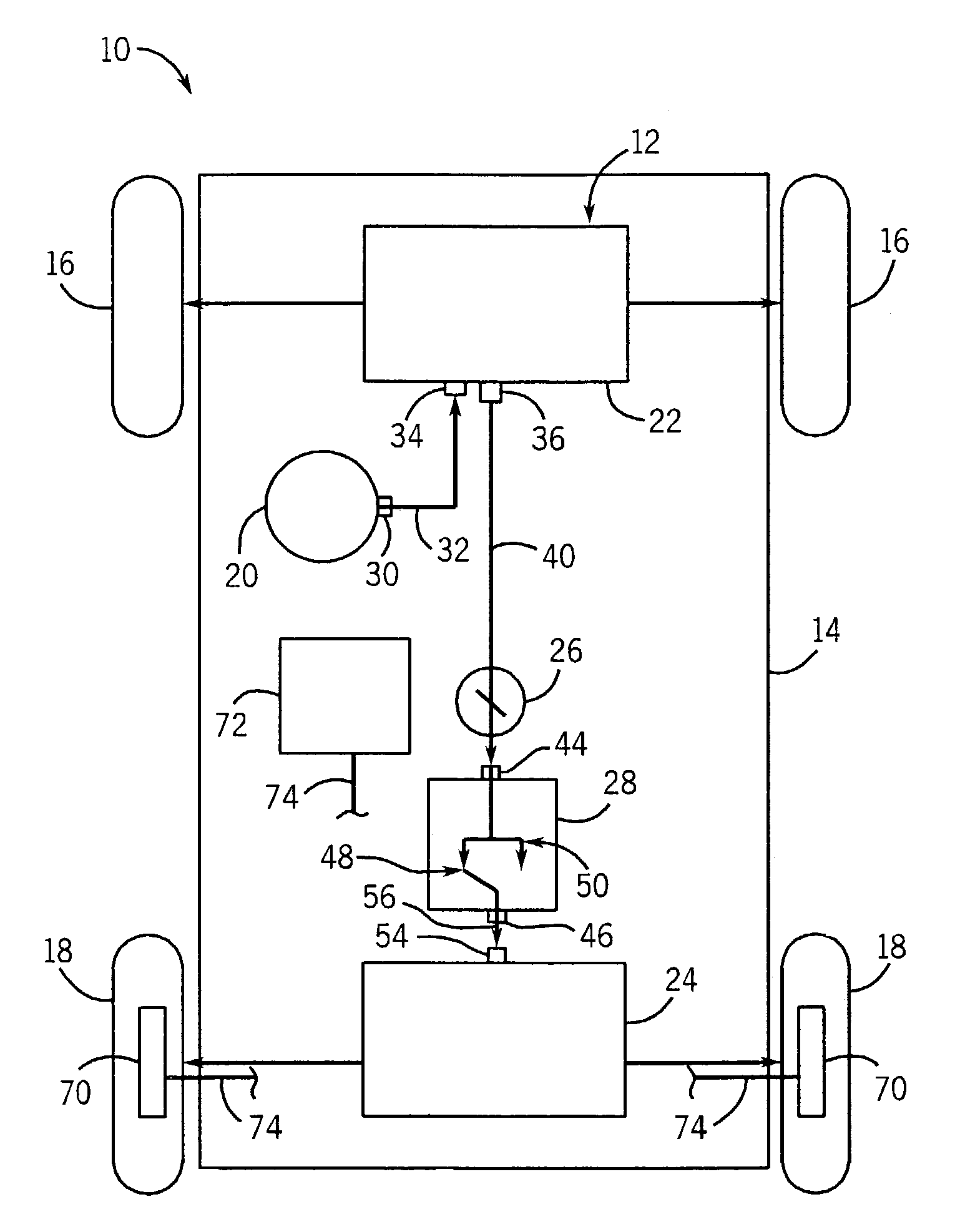
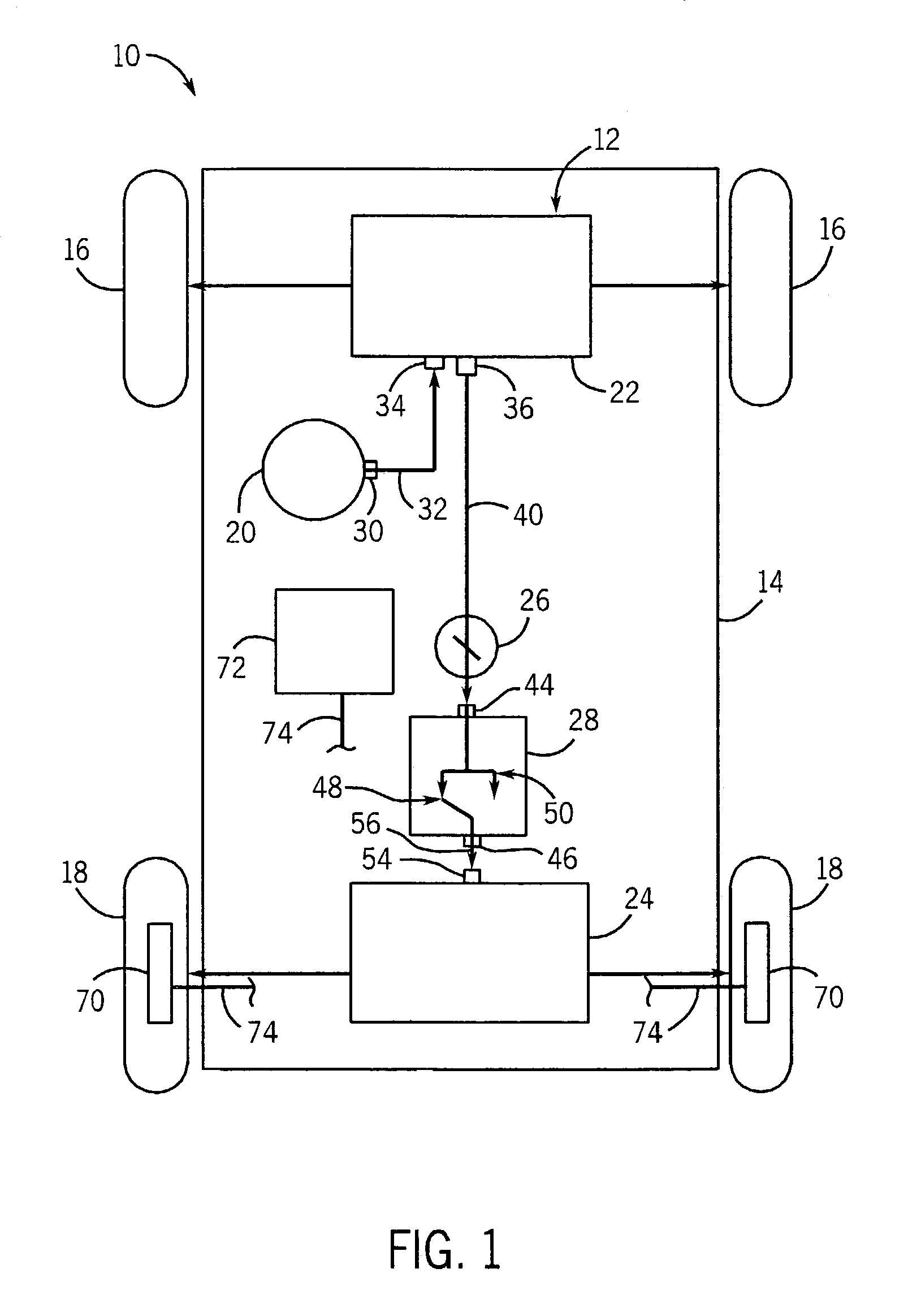
Steering control apparatus
InactiveUS20100152971A1Digital data processing detailsSteering initiationsEngineeringSteering control
A steering control apparatus includes a rack shaft connected to steerable wheels and having rack teeth in a given axial range, a first steering mechanism having a reduction gear and a first electric motor to apply a drive force to the rack shaft through the reduction gear, a second steering mechanism having a second electric motor, a power cylinder equipped with hydraulic pressure chambers, an oil pump driven by the second electric motor to provide a supply of hydraulic oil to the hydraulic pressure chambers such that the power cylinder applies a driving force to the rack shaft in accordance with a pressure difference between the hydraulic pressure chambers and a switching unit capable of selectively switching the supply of hydraulic oil from the oil pump to the hydraulic pressure chambers, and a control device that controls the first and second electric motors in response to a driver's steering operation.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Lane-change assistant for motor vehicles
InactiveUS20050155808A1Increase dynamicsIncrease driving speedDigital data processing detailsSteering linkagesEngineeringMotorized vehicle
Lane changing assistant for motor vehicles, controlling an automatic changing of the vehicle to a neighboring lane in response to a command by the driver as part of a lane keeping system of the motor vehicle and having an operating element that is movable in opposite directions out of a neutral position, wherein a sensor is assigned to the operating element for each adjustment direction and the sensor supplies a multi-valued output signal which corresponds to the operation of the operating element and determines the dynamics of the lane changing procedure.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
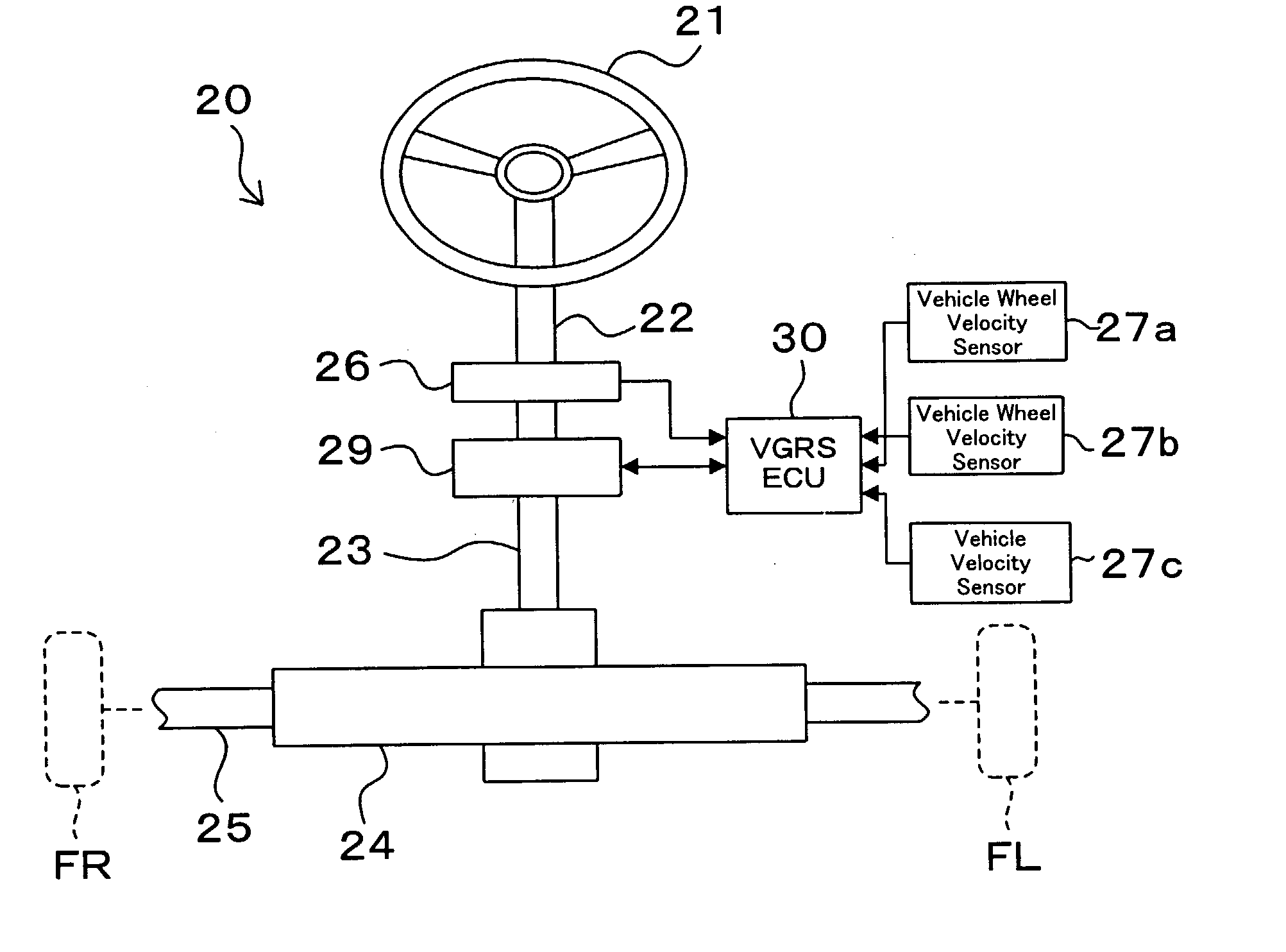
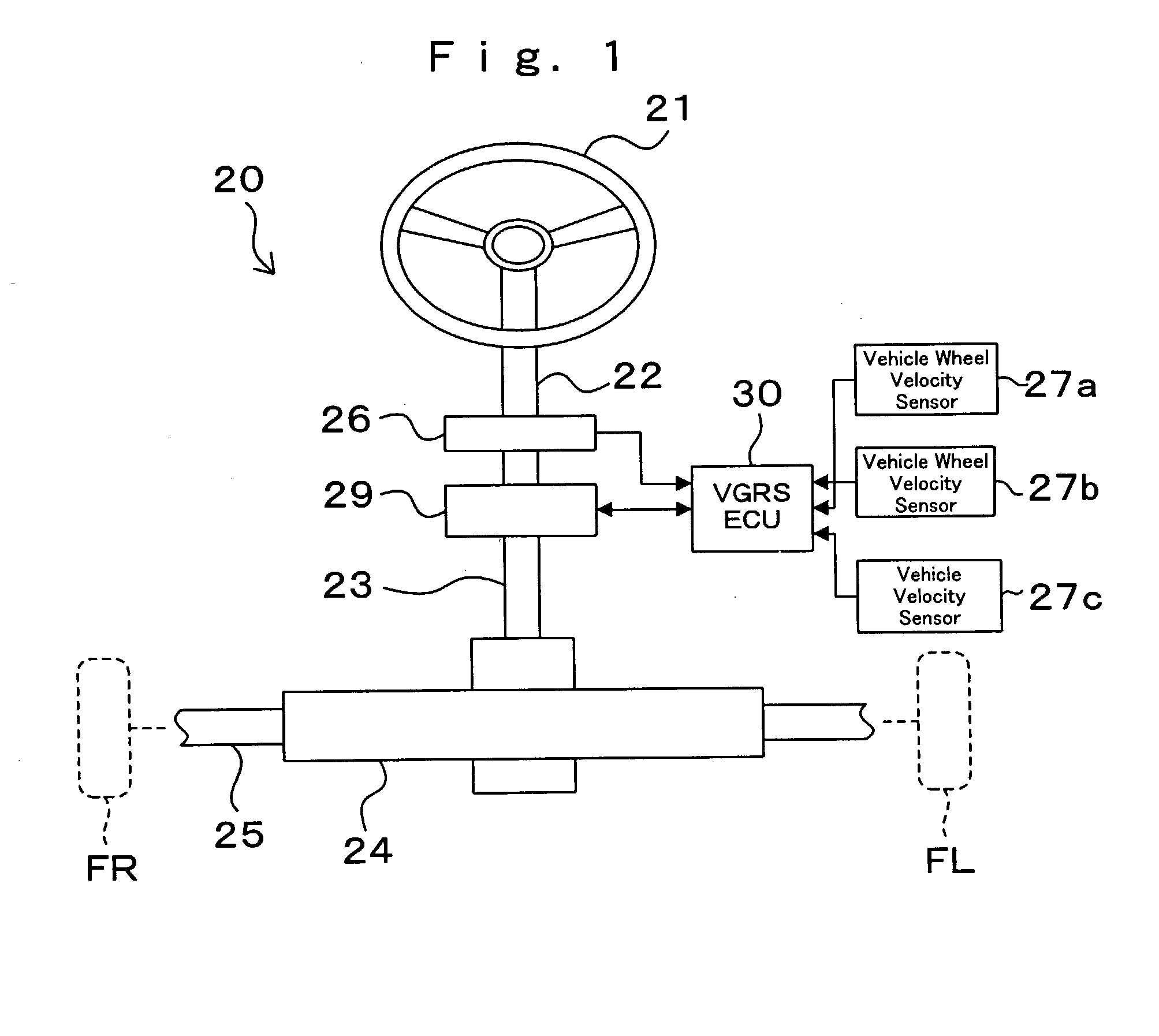
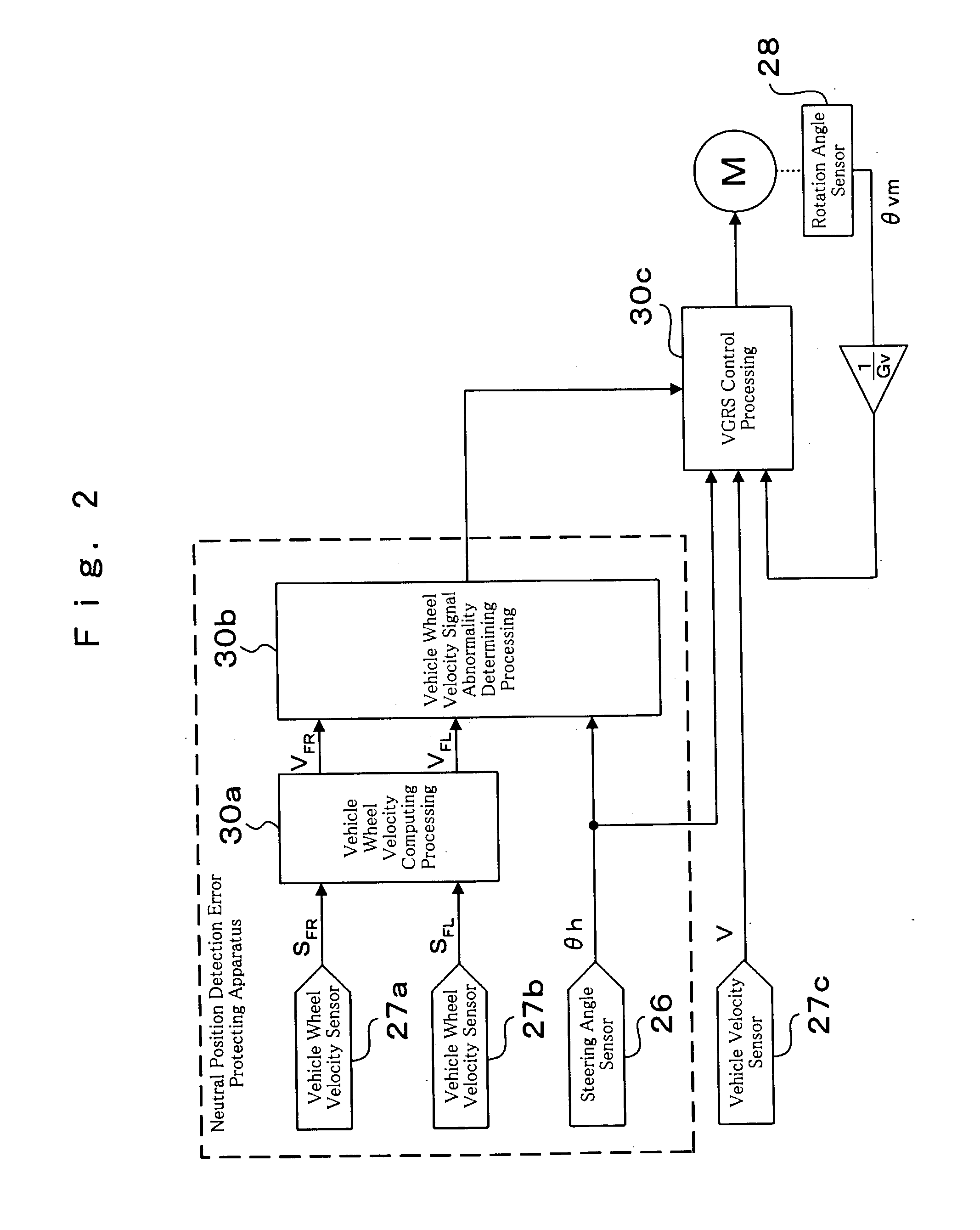
Steering angle neutral position detection error protecting method and detection error protecting apparatus
InactiveUS20040046346A1Detection errorAvoid detectionVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesLocation detectionDrive wheel
In a neutral position detection error protecting apparatus, vehicle wheel velocities SFR, SFL of right / left driven wheels FR, FL are detected by vehicle wheel sensors 27a, 27b and a right / left wheel velocity difference VFD is obtained from vehicle wheel velocities VFR, VFL of the driven wheels FR, FL through vehicle wheel velocity signal abnormality determining processing 30b so as to detect steering angle information thetah from the steering wheel 21. Then, when a condition that a right / left wheel velocity difference VFD is less than a predetermined velocity V1, a condition that a rotation angle of steering angle information thetah is more than a predetermined value thetak and a condition that a vehicle wheel velocity is more than a predetermined velocity V2 according to vehicle wheel velocities VFR, VFL of the driven wheels FR, FL are all satisfied in a predetermined period T, it is determined that there is any abnormality in the vehicle wheel velocities SFR, SFL (VFR, VFL) of the driven wheels FR, FL through vehicle wheel velocity signal abnormality determining processing 30b.
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD
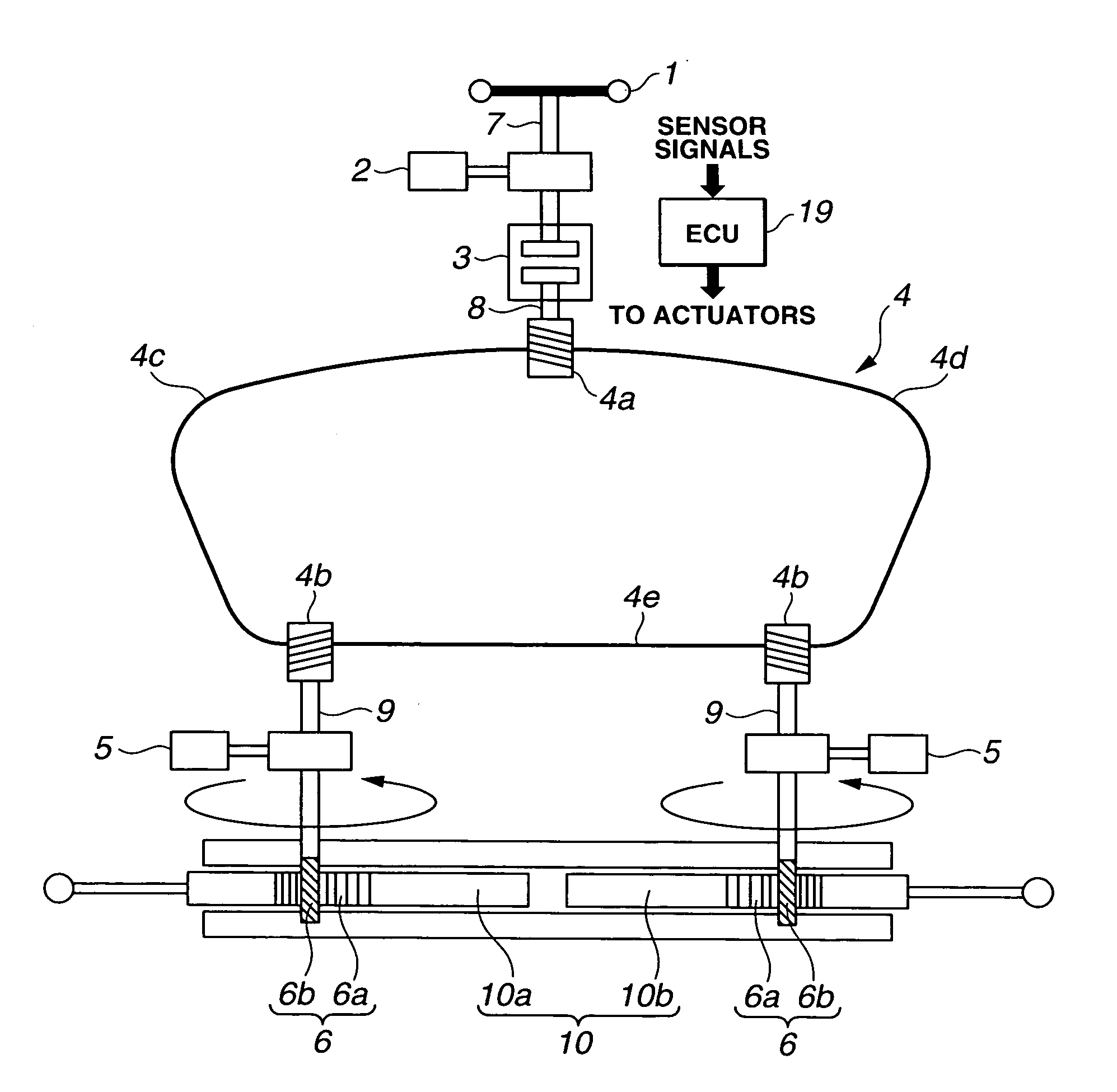
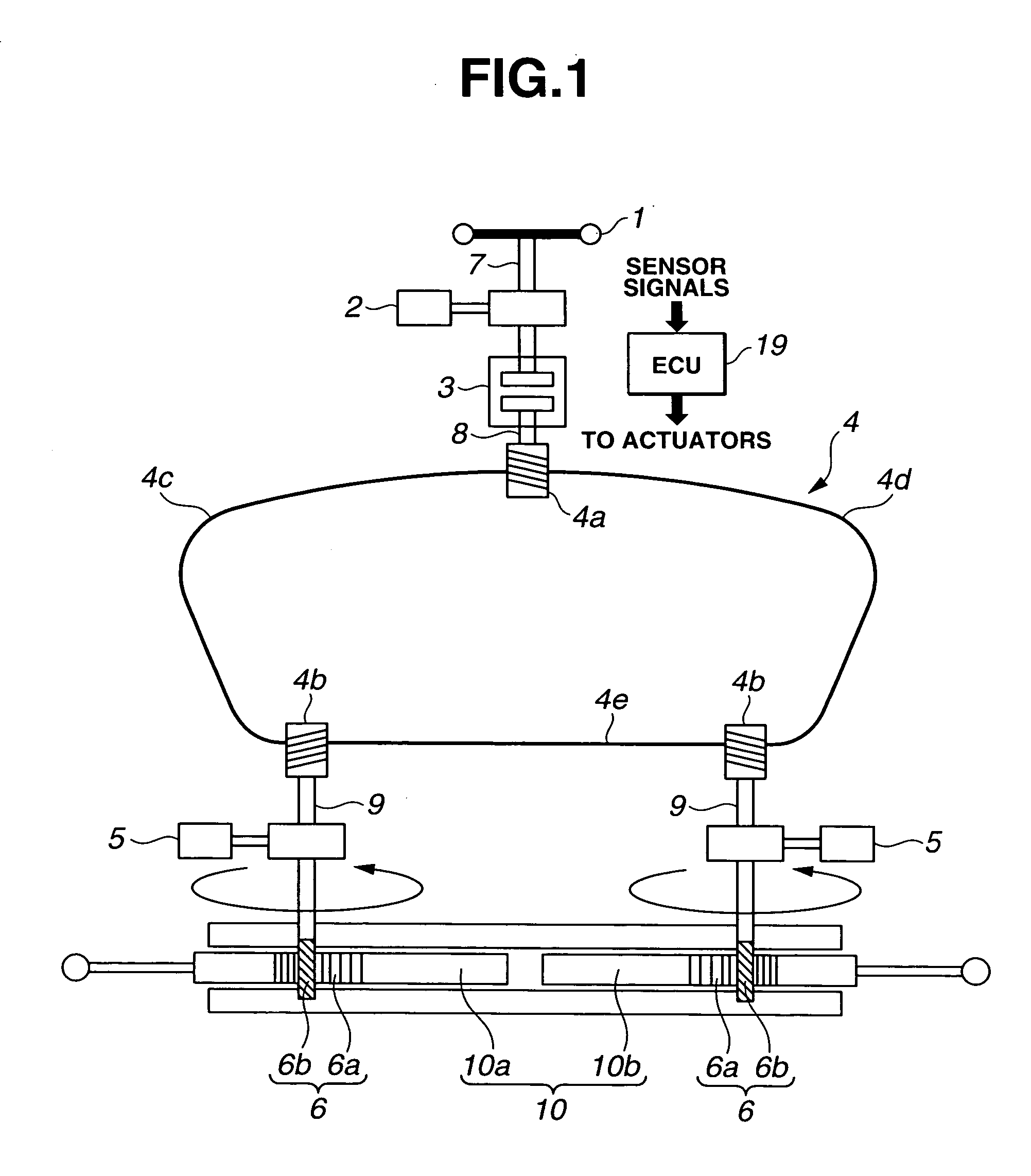
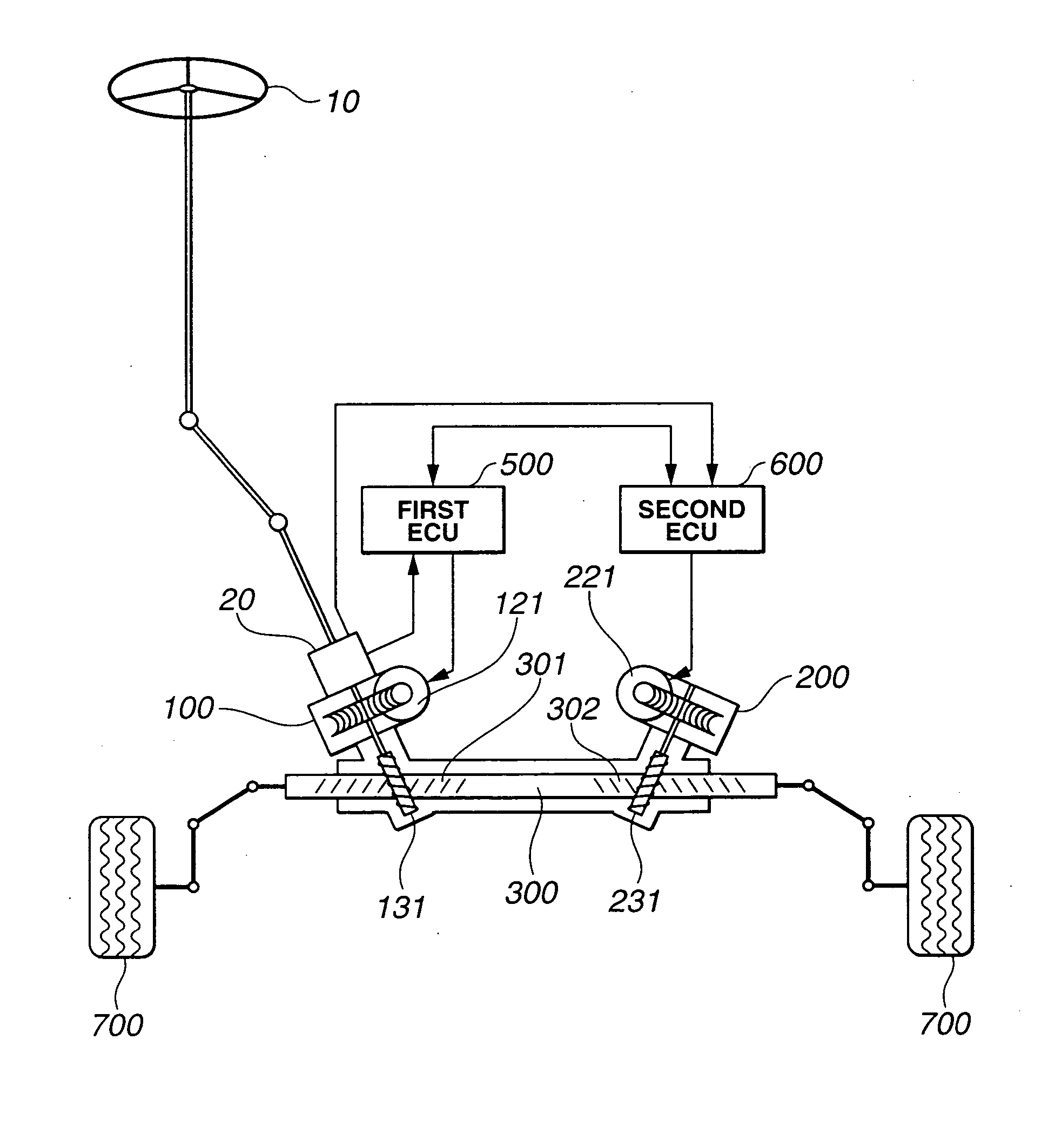
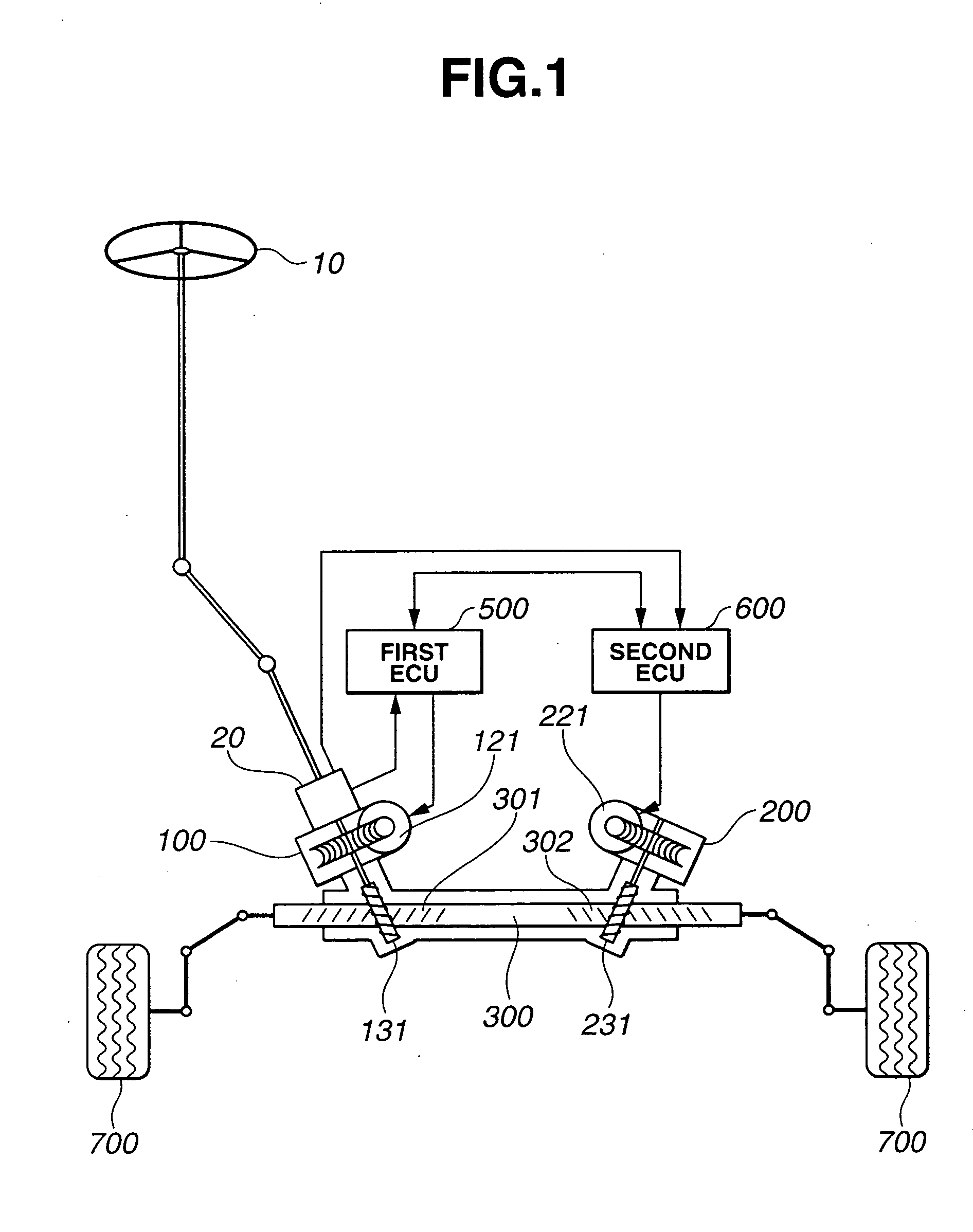
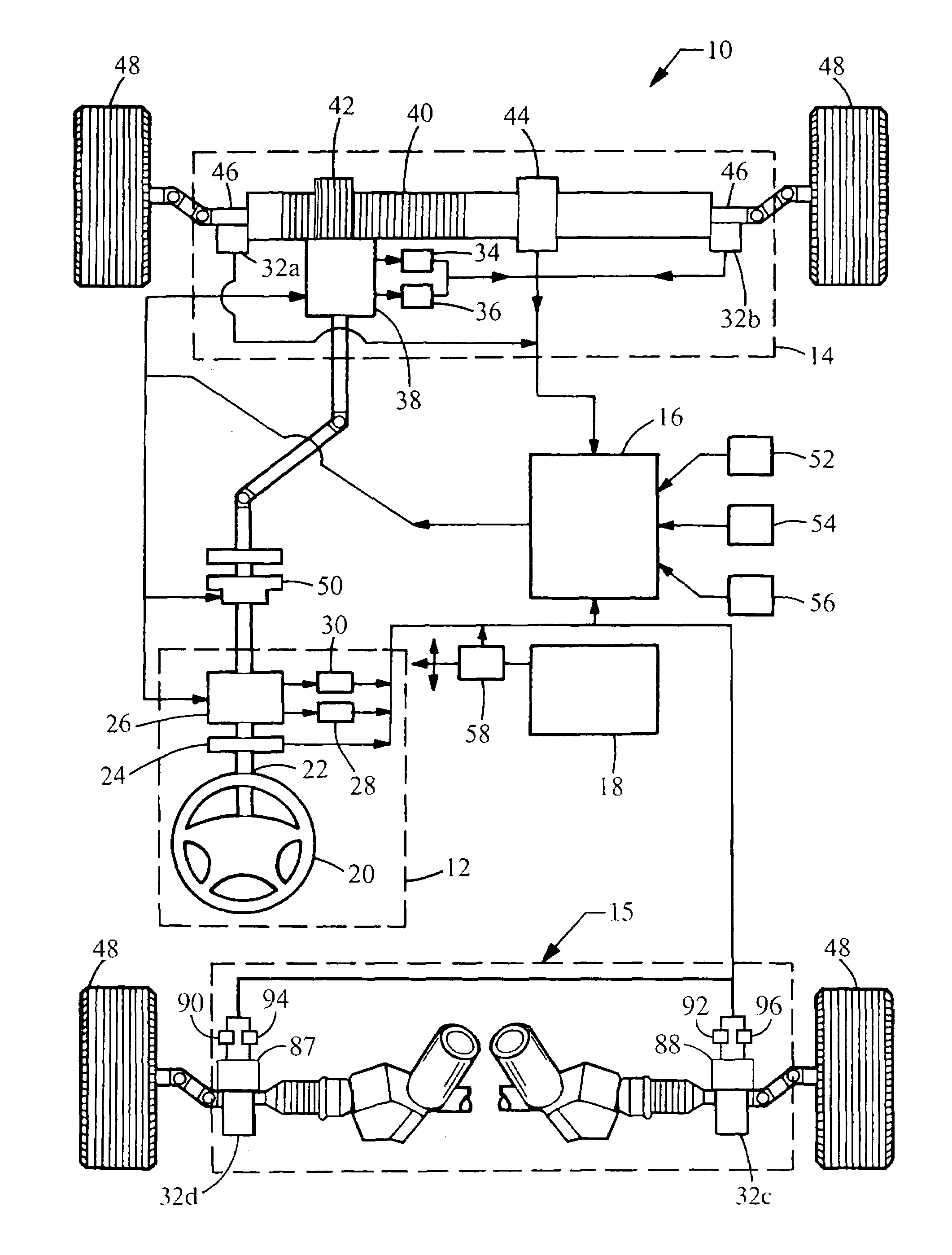
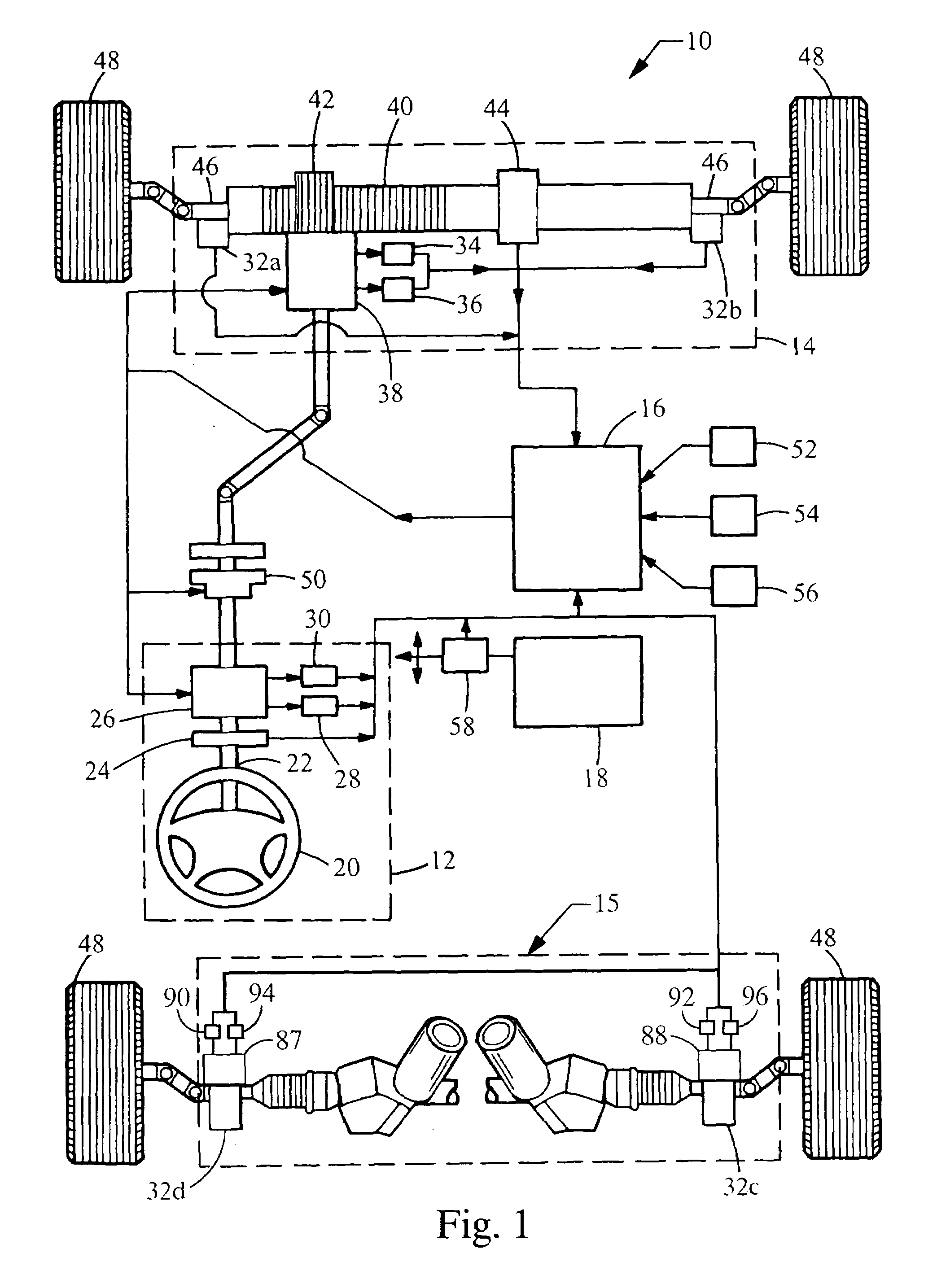
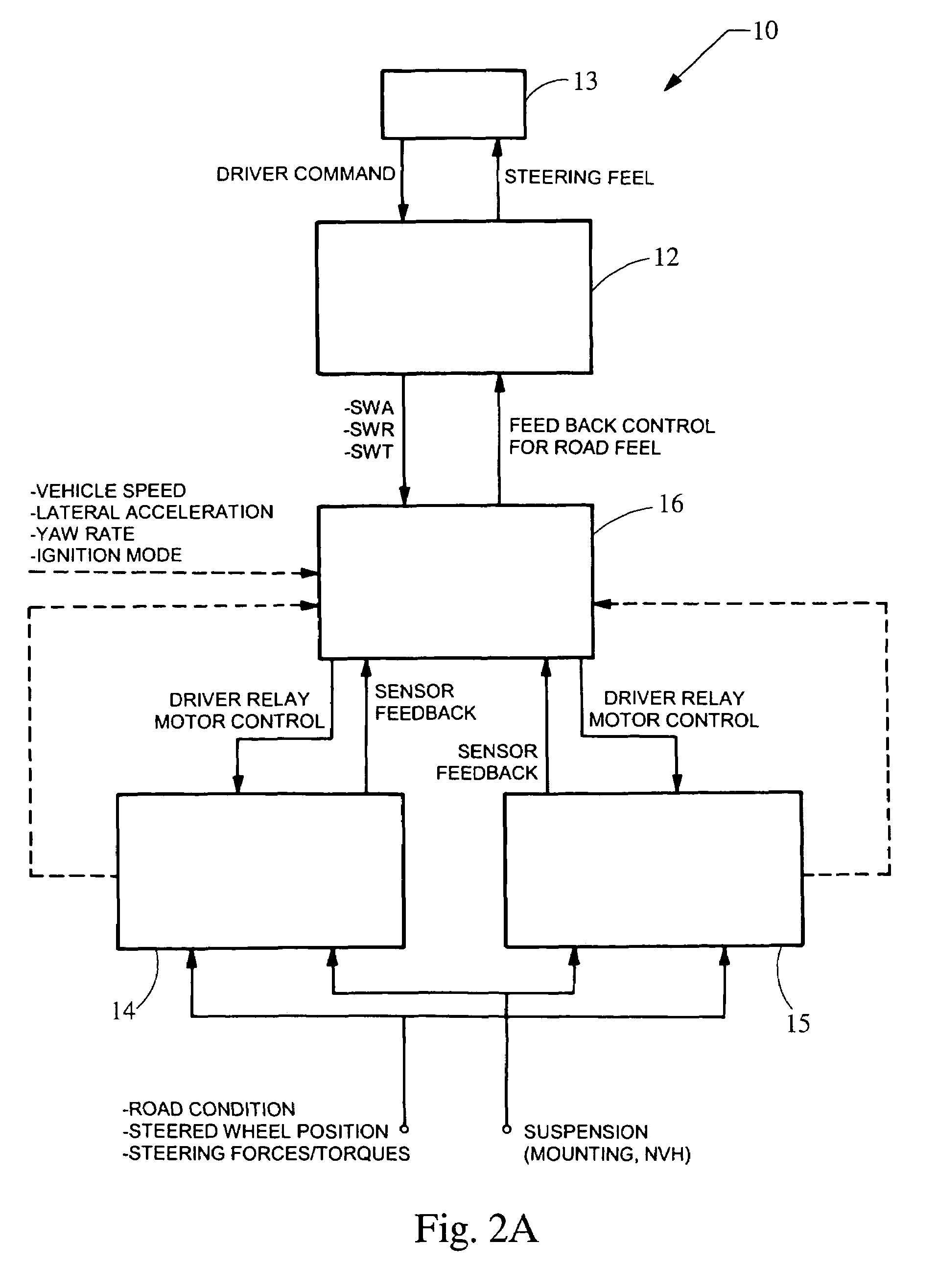
Motor vehicle steering system
A steering system selectively operable in one of six modes: steer-by-wire with rear steering, steer-by-wire without rear steering, electronic power assist steering (EPAS) with rear steering, electronic power steering (EPAS) without rear steering, mechanical backup manual steering with rear steering, and mechanical backup manual steering without rear steering. The steer-by-wire system includes a driver interface system (DIS), a front road wheel actuator system (FRWAS), a rear road wheel actuator system (RRWAS), and a controller for monitoring and implementing the preferred control strategy. The steering system operates normally in a steer-by-wire mode. In each of the EPAS mode and manual mode, the controller causes a clutch mechanism to engage, thus creating a mechanical linkage between the steerable member and the rack and pinion system while maintaining rear wheel assisted steering. In the EPAS mode, one of the front road wheel actuator or the reaction torque generator is available to assist in the steering operation along with rear wheel steering. Alternatively, in the manual mode, both the DIS and the FRWAS are deactivated and the vehicle is steerable through mechanical device along with the rear wheel assisted steering.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
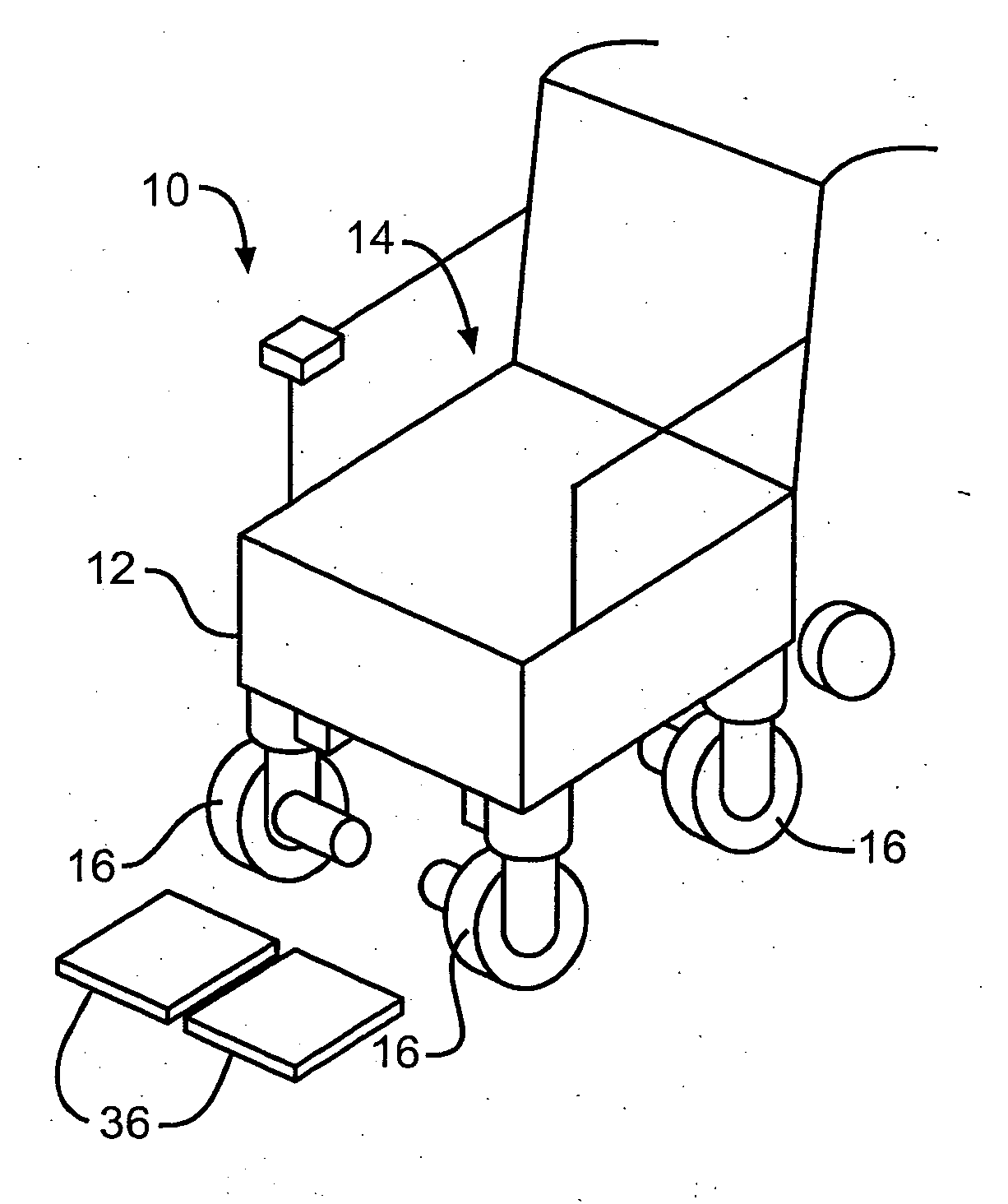
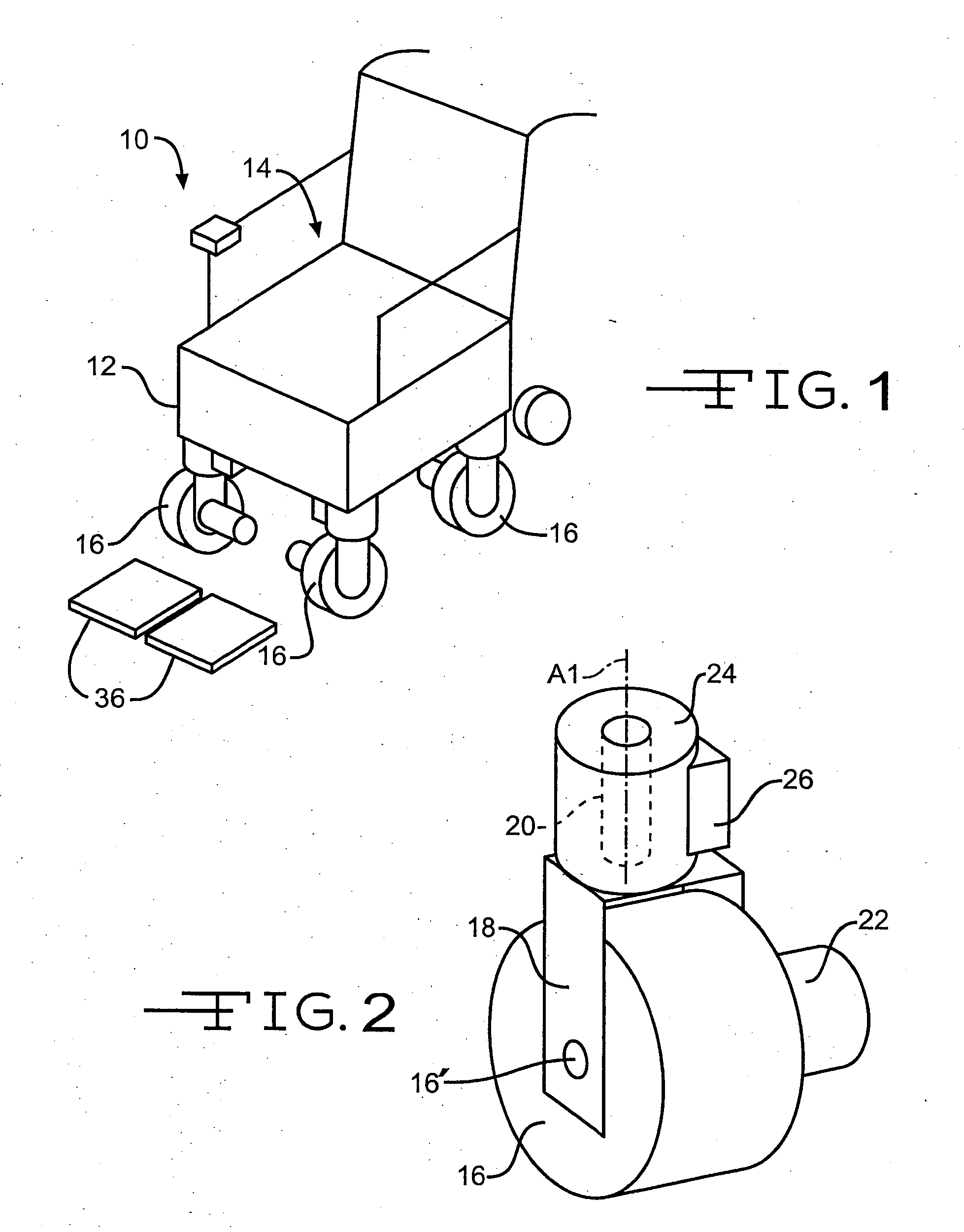
Wheelchair
A powered wheelchair comprises three or more wheels for supporting the wheelchair relative to a supporting surface. The three or more wheels are adapted to be steered independently of one another to steer the wheelchair in virtually any direction. At least one of the wheels is adapted to be driven for propelling the wheelchair on the supporting surface.
Owner:SUNRISE MEDICAL HHC INC
Variable displacement pump
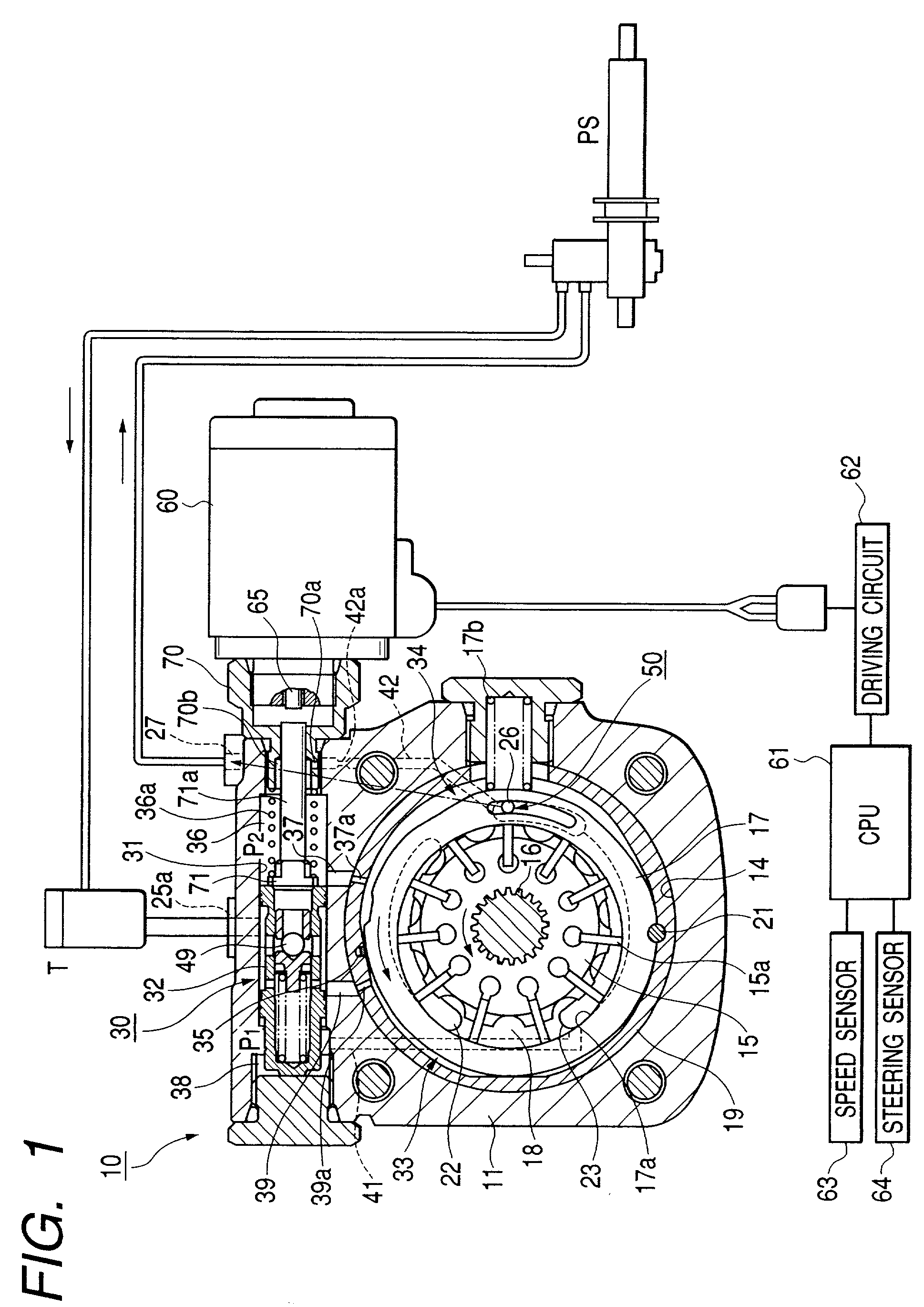
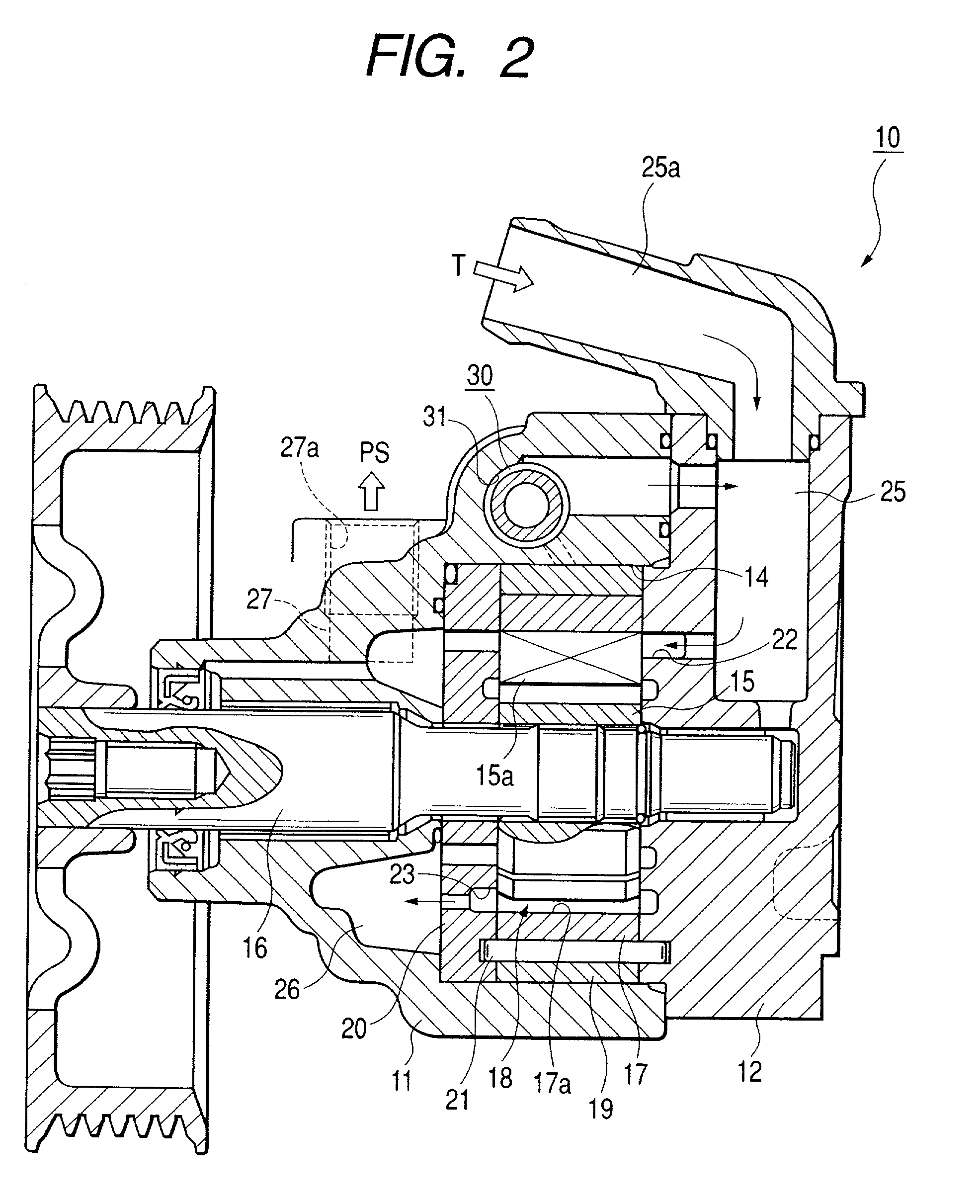
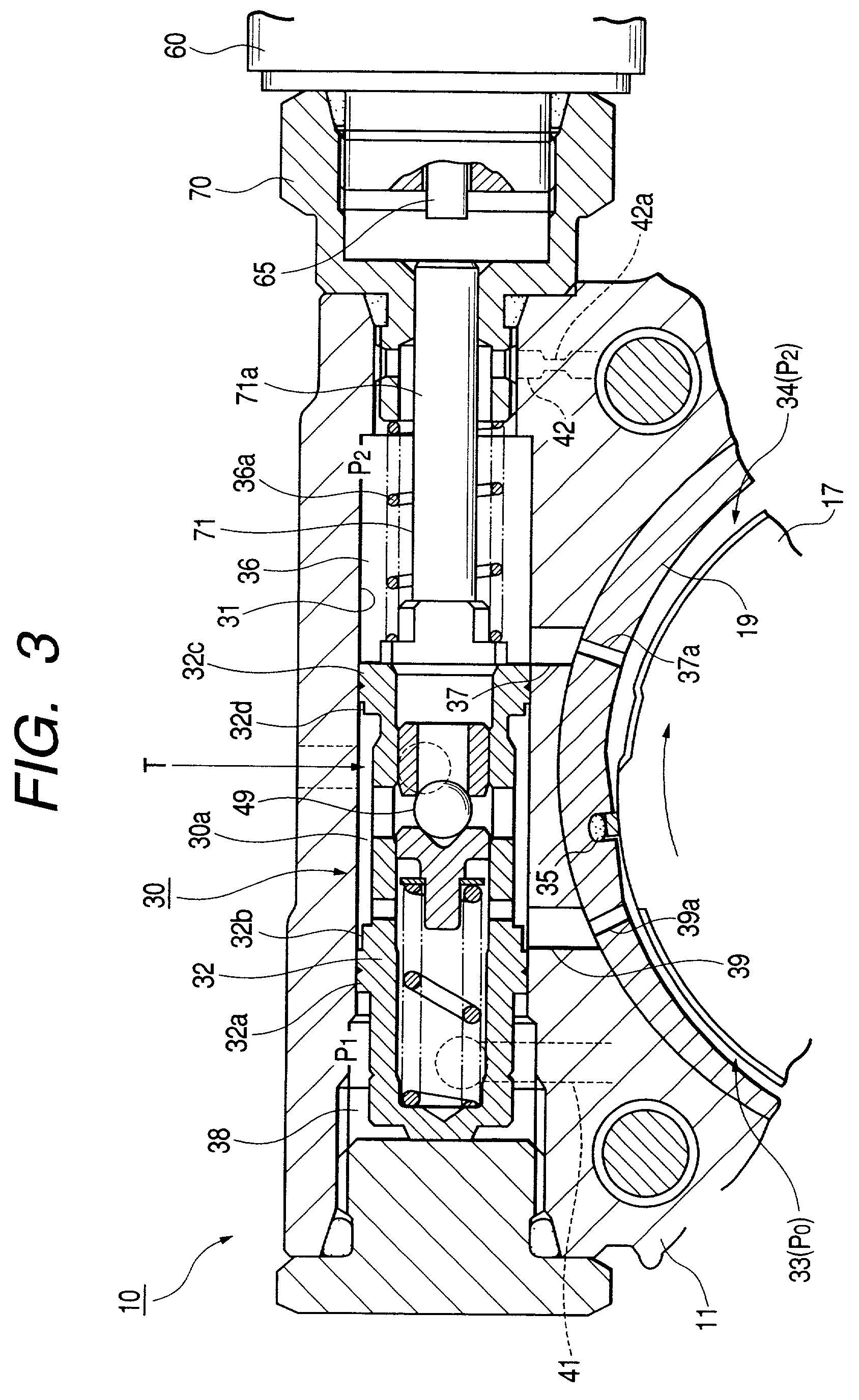
InactiveUS20010036412A1Feel comfortableEnergy saving effectSteering linkagesRotary piston pumpsPump chamberControl valves
A pump chamber 18 is formed between a cam ring 17 and a rotor 15 in a pump body 11. The cam ring is formed so as to move to direction that pump capacity of the pump chamber increases and decreases. A first and second fluid pressure chambers 33 and 34 are formed at both sides of moving direction of the cam ring 17. The pump has a spool operates to axis direction by difference in fluid pressure of upper and lower stream sides of a metering throttle 50 formed on a way of a discharge side passage 27 of the pump chamber and provides at least a control valve 30 controlling fluid pressure in the first fluid pressure chamber. An electronic driving unit applying thrust to axis direction to the spool of the control valve, for example, a solenoid 60 is provided.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST STEERING
Steer-by-wire system for automobiles
InactiveUS20090024281A1Minimize the differenceEasy to controlDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsSteering angleControl signal
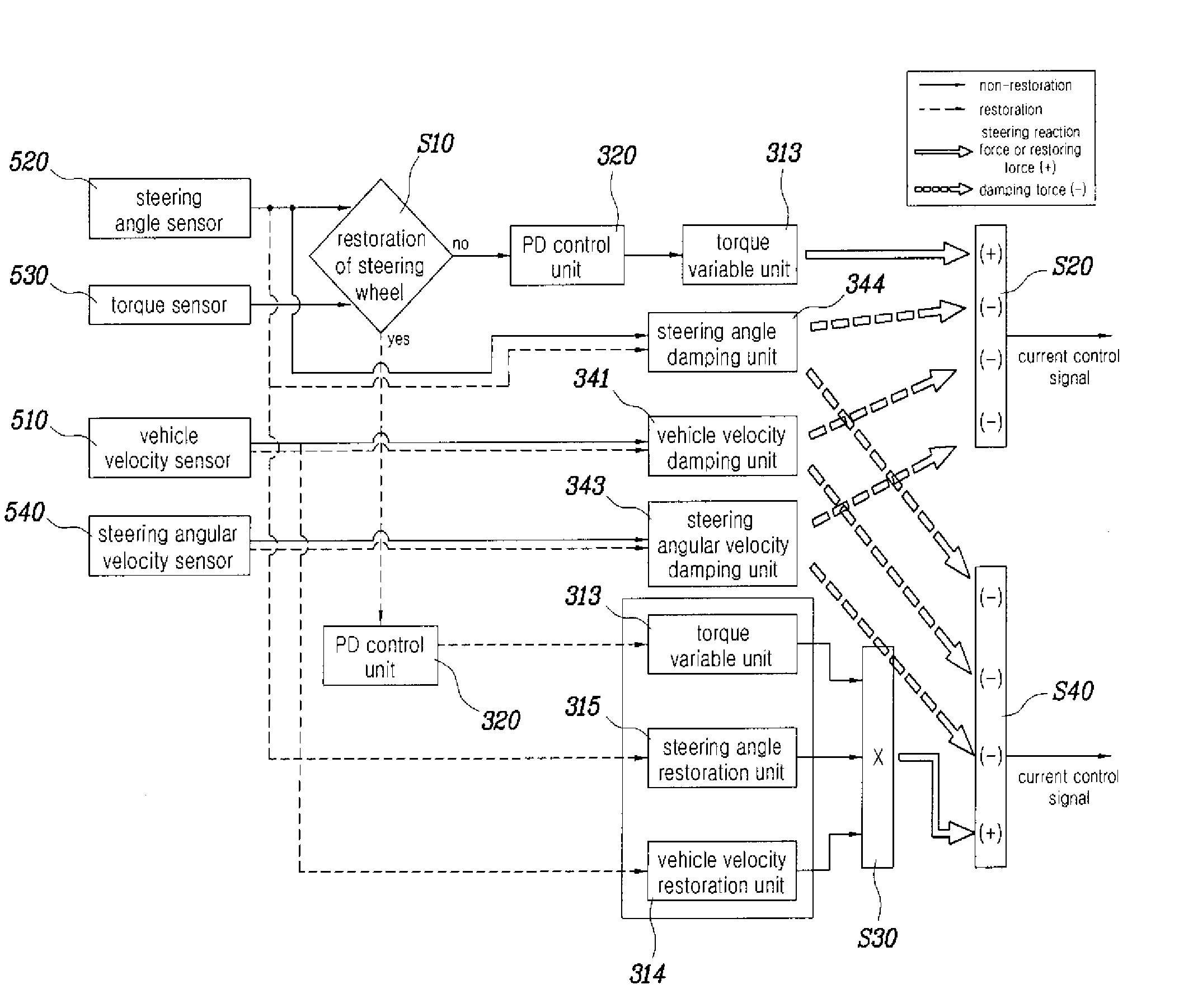
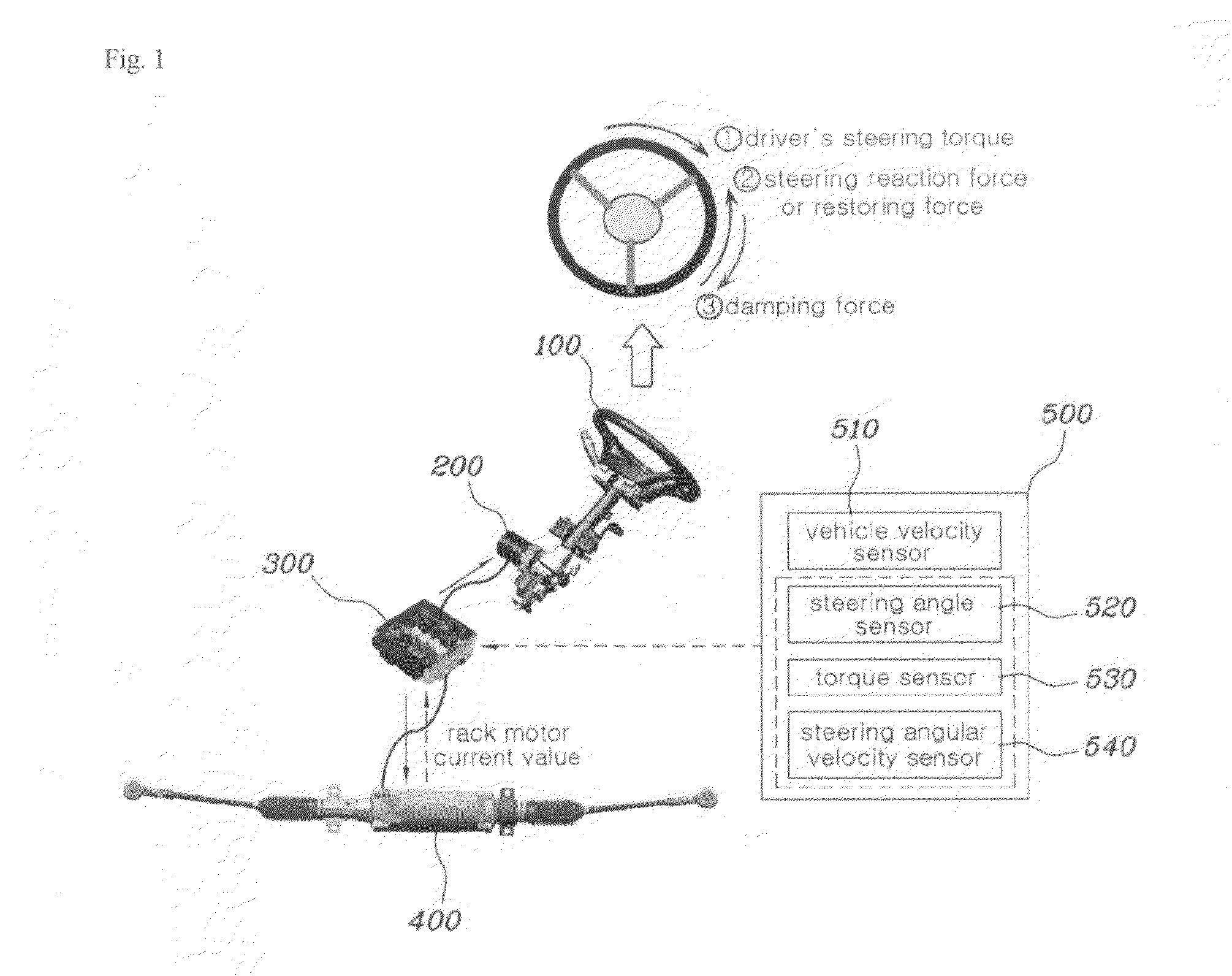
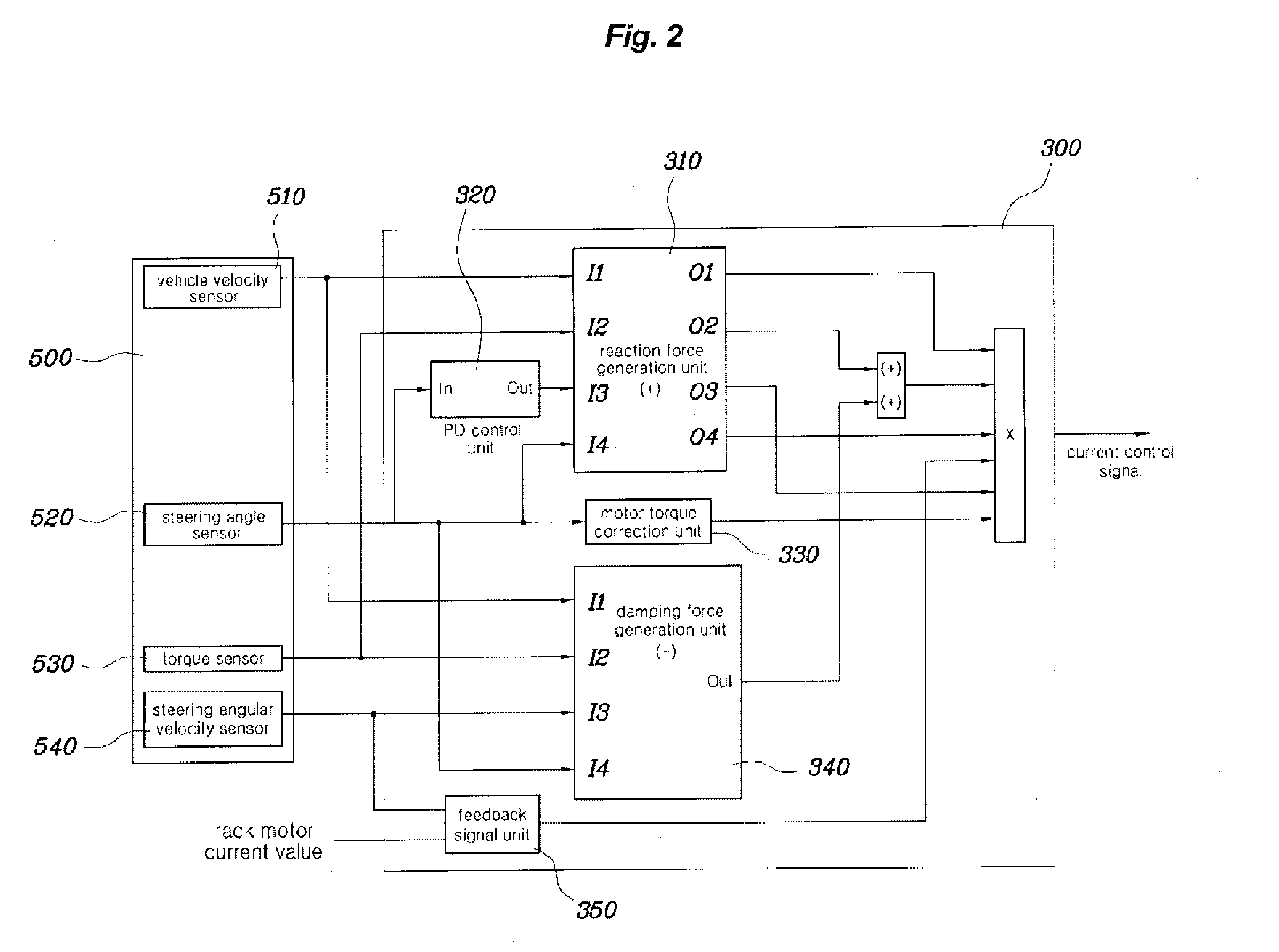
Disclosed herein is a steer-by-wire system for automobiles. The steer-by-wire system includes a steering control unit and a signal input unit. The central control unit includes a reaction force generation unit, a damping force generation unit. The reaction force generation unit generates steering reaction force or restoring force, acting in the reverse direction to that of a steering torque. The damping force generation unit generates damping force, acting in the reverse direction to the steering reaction force or the restoring force (in the same direction as the steering torque). Furthermore, the central control unit generates a current control signal, which is applied to a steering feel generation motor, by combining the resulting values determined by the reaction force generation unit and the damping force generation unit a vehicle velocity signal in response to a steering angle signal, a steering torque signal and a steering angular velocity signal.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Off road vehicle
InactiveUS20050217906A1Maximises manoeuvrabilitySteering linkagesHand leversDrive wheelDriver/operator
Owner:SPARK IAN JAMES
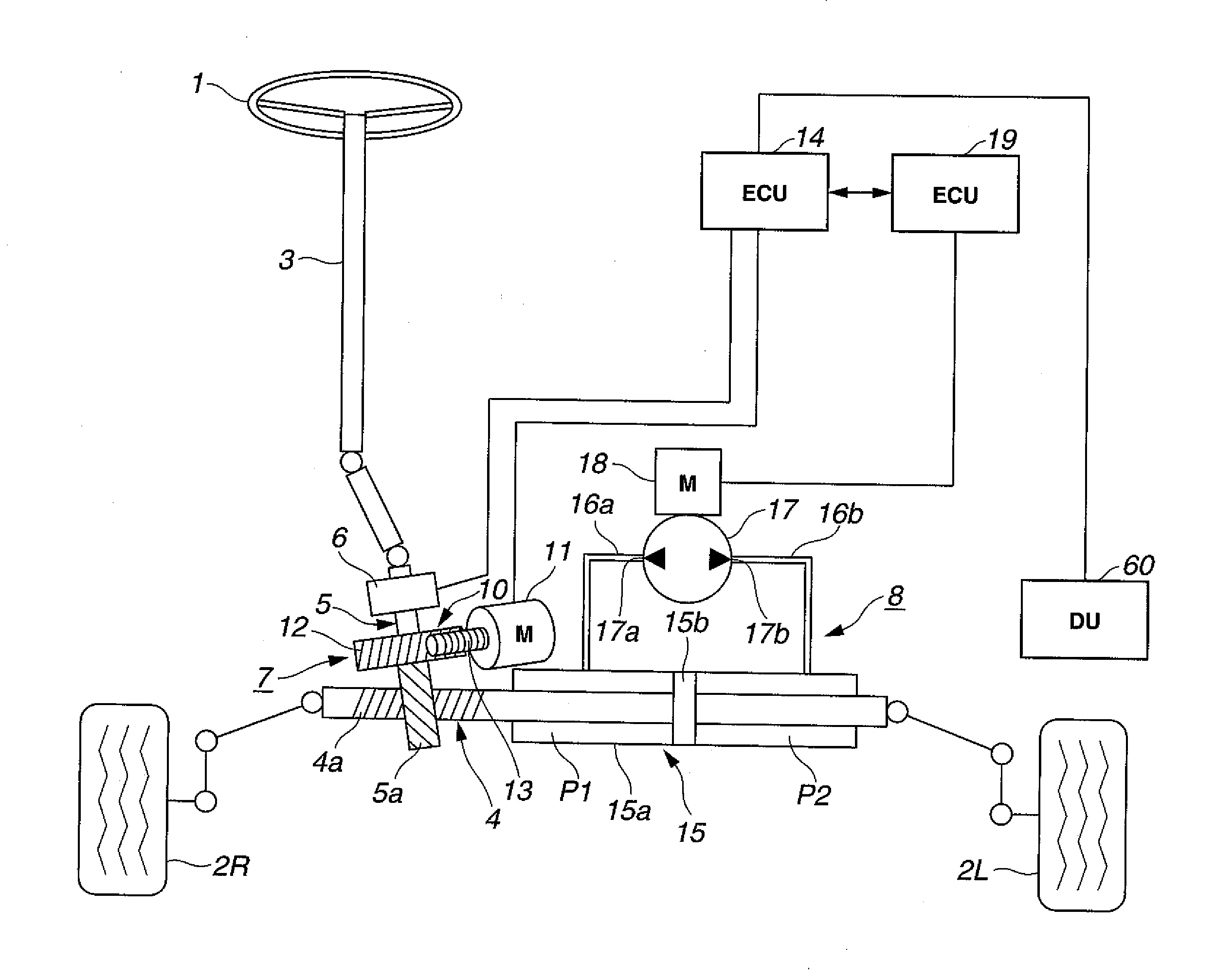
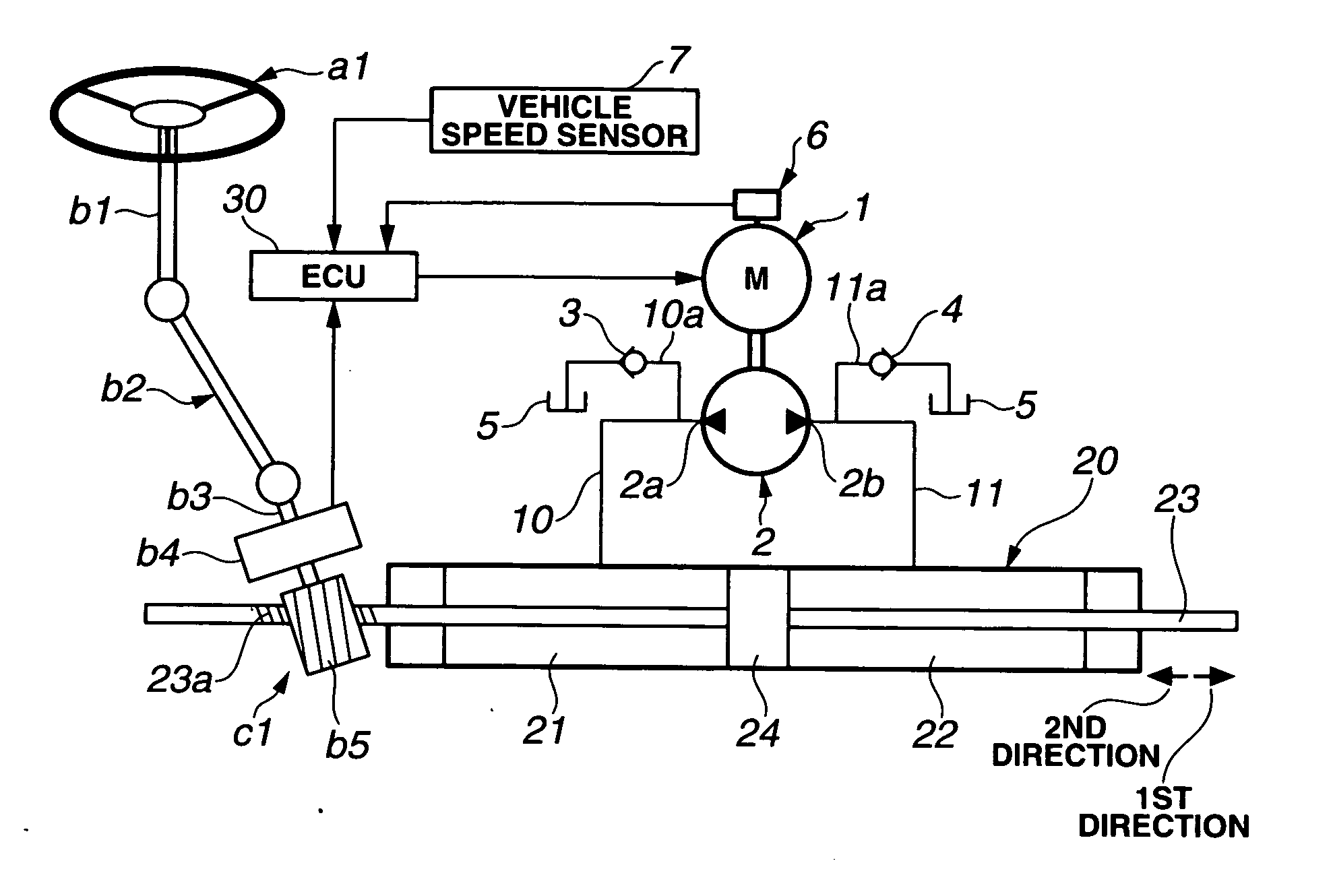
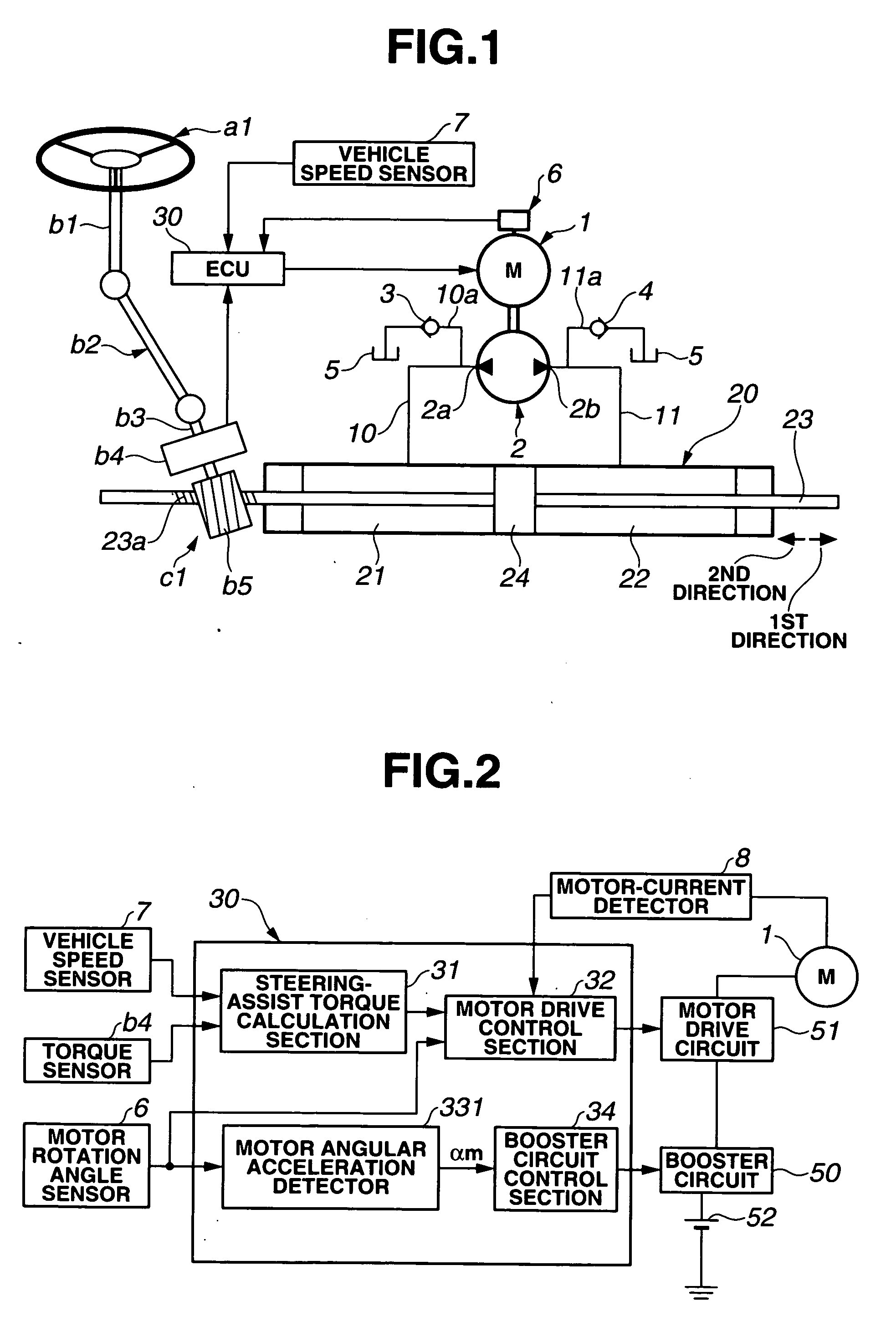
Power steering device
InactiveUS20070043490A1Increase working frequencyIncrease the burdenSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectricityMotor drive
In a power steering device employing a hydraulic power cylinder, a motor-driven pump, and a driving power source for the motor, a power steering control system is configured to electrically connected to at least the motor and the power source for controlling a driving state of the motor and a power source voltage of the power source. The power steering control system includes a motor control circuit that generates a motor driving signal, whose command signal value is determined based on a steering assist force applied through the power cylinder to steered road wheels, a booster circuit that boosts the power source voltage, a motor angular acceleration detection circuit that detects or estimates a motor angular acceleration, and a booster-circuit control circuit that controls, responsively to the motor angular acceleration, switching between operating and non-operating states of the booster circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
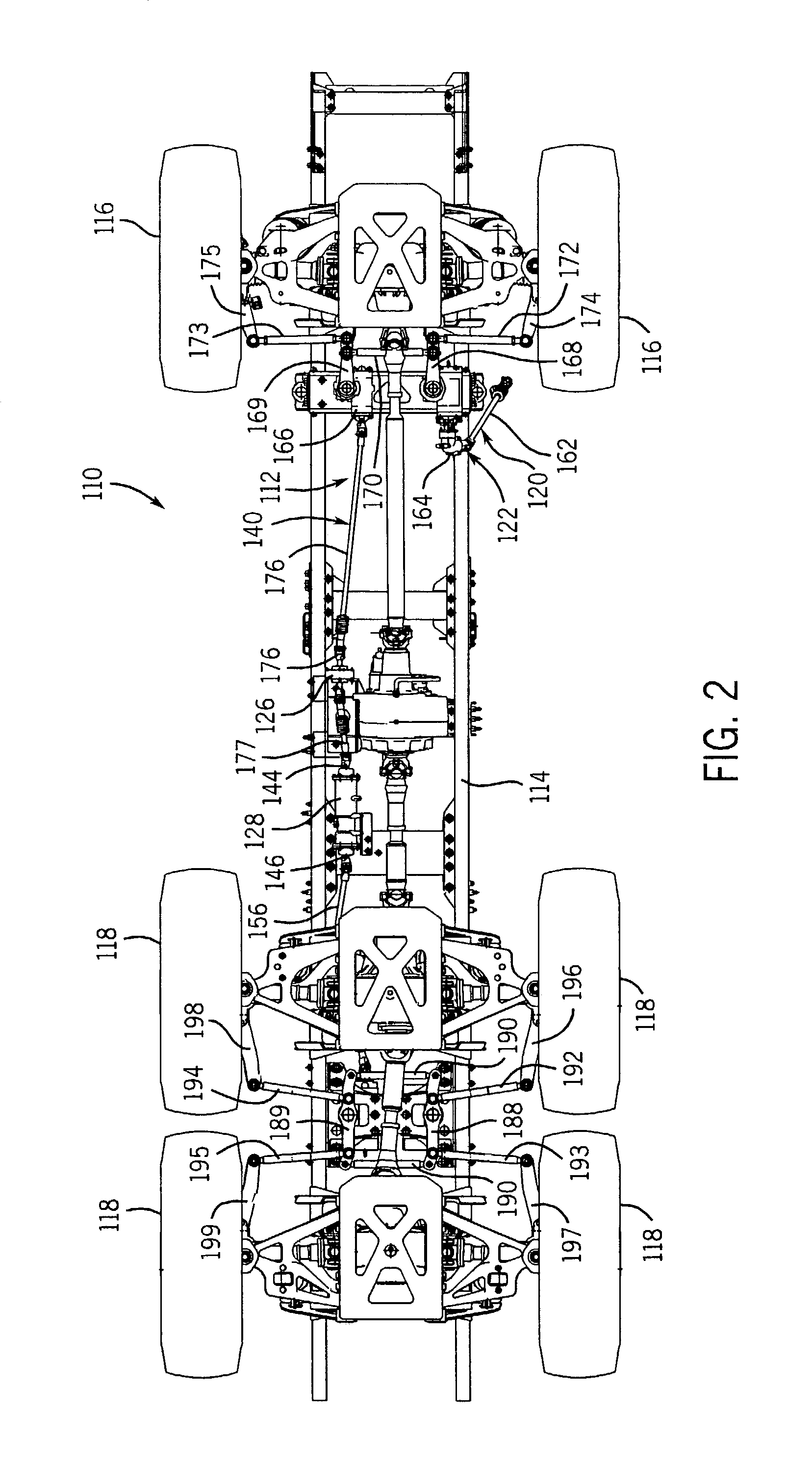
Methods and apparatus for steering an ATV
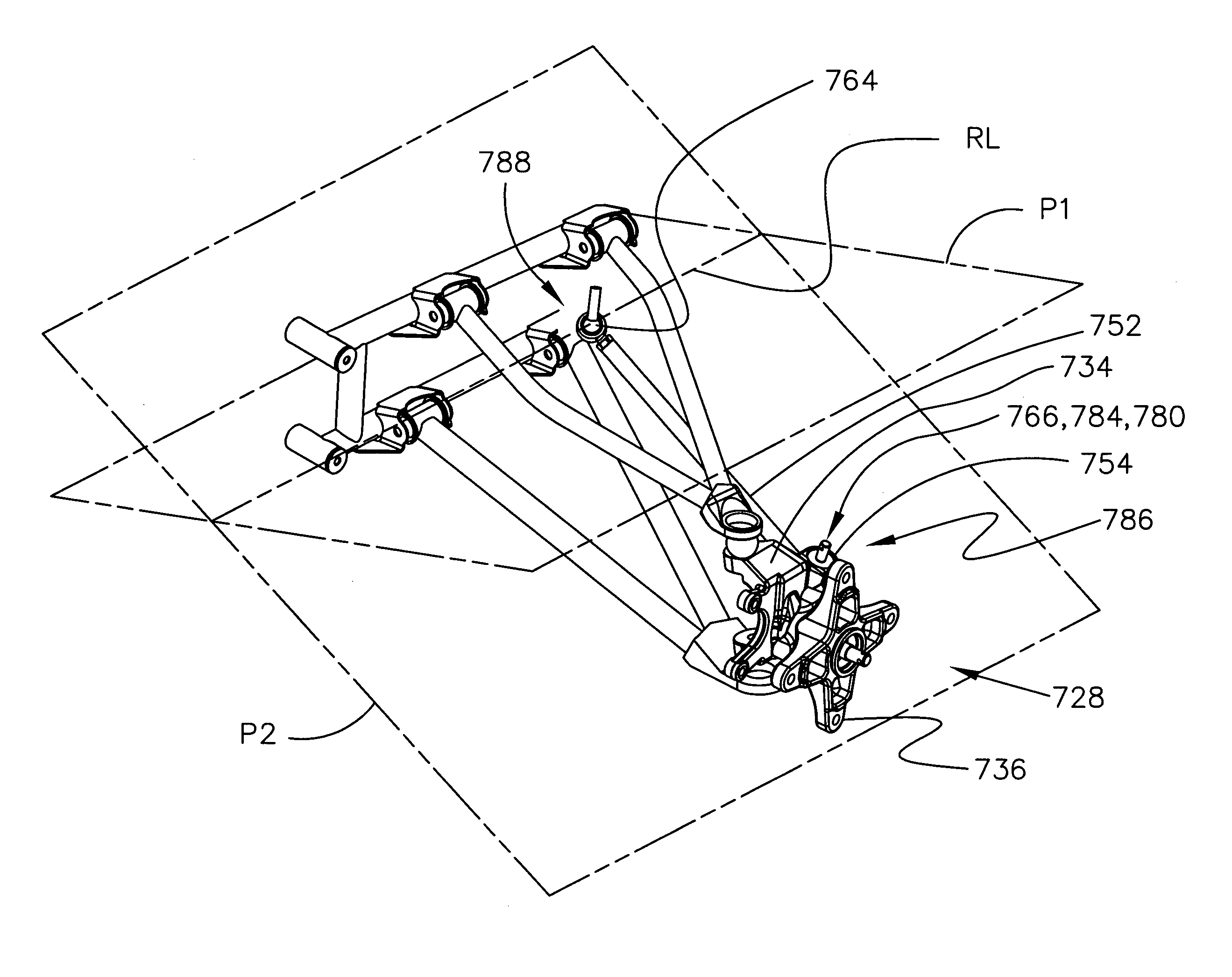
Methods and apparatus related to the suspension and steering of all terrain vehicles (ATVs) are disclosed. An ATV having a frame and a wheel carrier for rotatably supporting a wheel is provided. A tie rod is coupled to the wheel carrier at an outer joint. An inner joint of the tie rod is preferably located in a desirable location. A method for identifying the desirable location may include the steps of defining a first reference plane associated with a full compression position of the suspension, defining a second reference plane associated with a full extension position of the suspension, identifying a reference line formed by an intersection of the first reference plane and the second reference plane, and selecting a location proximate the reference line as the desirable location for the inner joint.
Owner:POLARIS IND INC
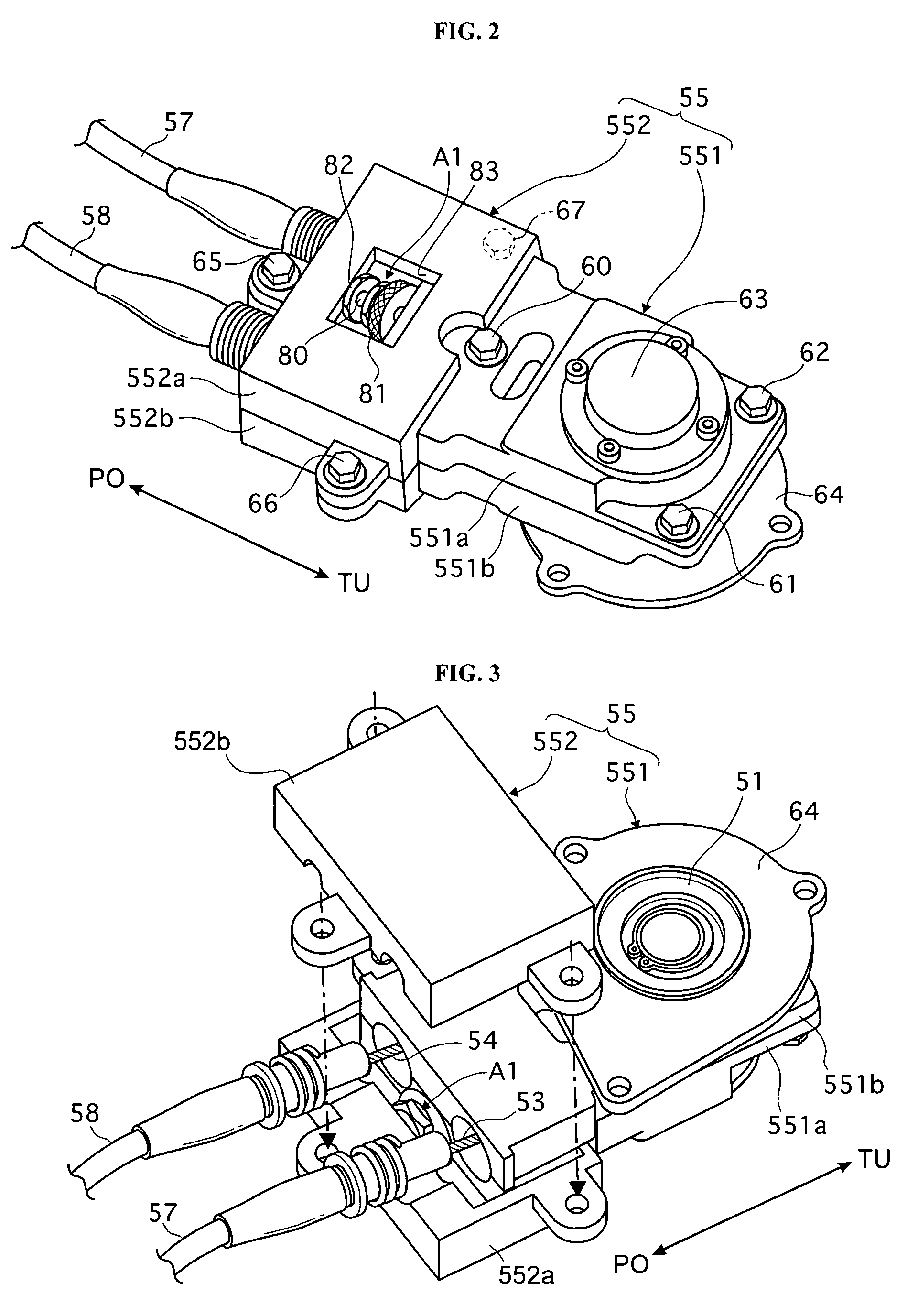
Steering device
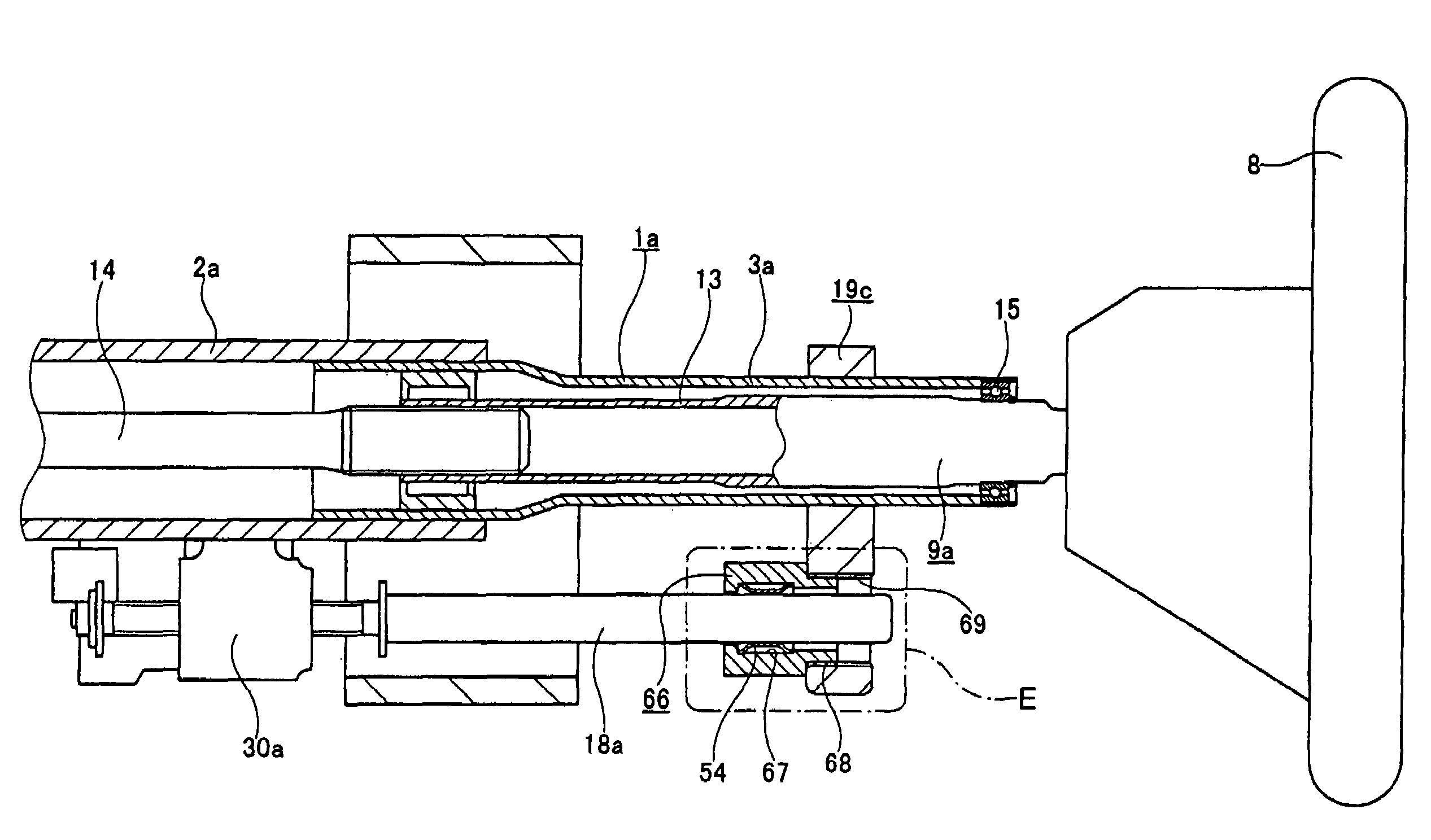
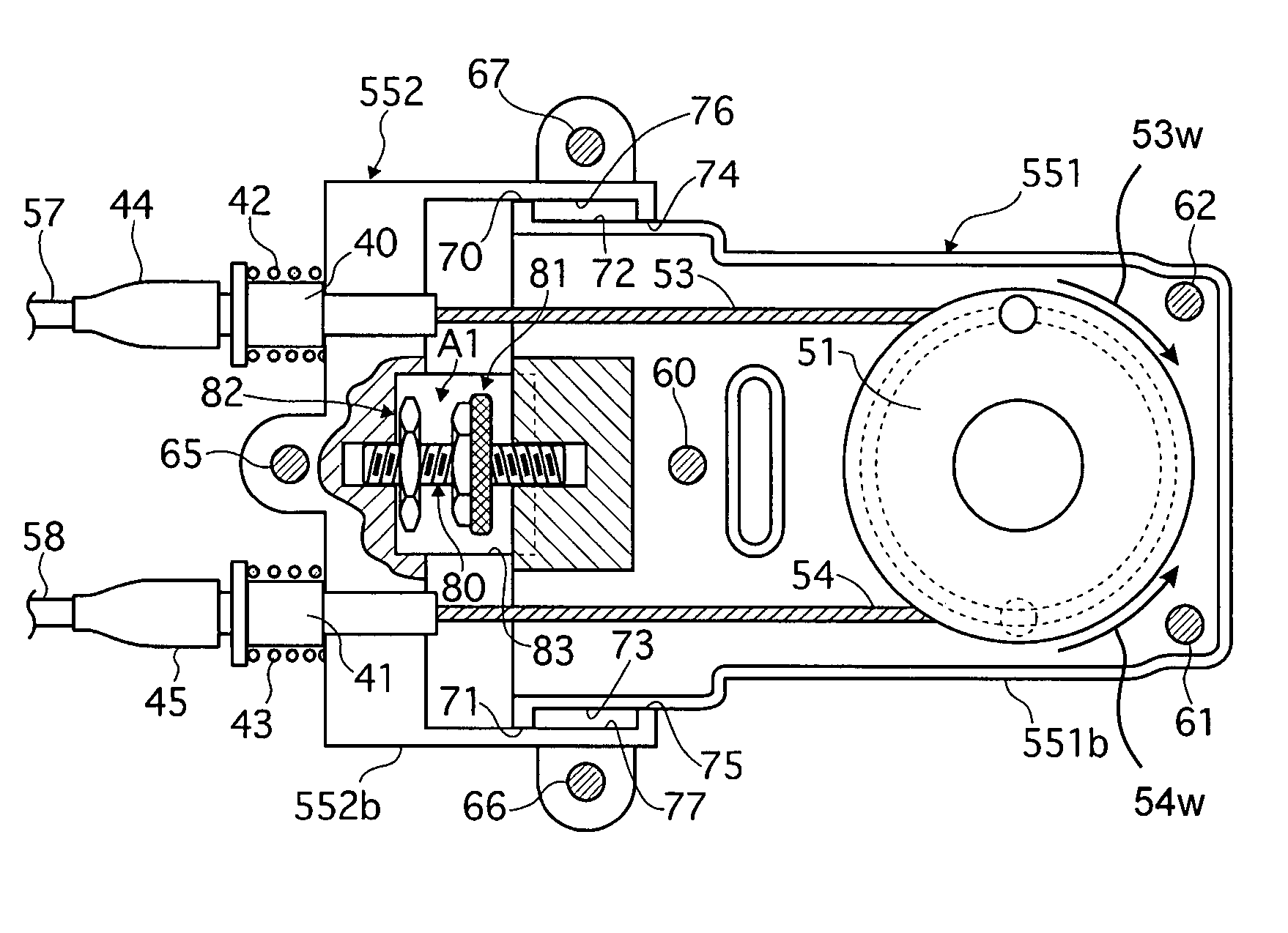
InactiveUS7628244B2Adjusting the tensions of the cablesQuickly and easily achievedFluid steeringElectrical steeringRelative displacementElectric cables
A steering device includes a first housing, first and second cables, and first and second sheaths. The first housing includes a first part that supports a rotatable first cable pulley, and a second part that is disposed for relative displacement with respect to the first part. The first cable is at least partially wound on the first cable pulley in a first direction of rotation. The second cable is at least partially wound on the first cable pulley in a second direction of rotation. The first sheath surrounds the first cable and extends between first and second ends, and the first end of the first sheath is coupled to the second part of the first housing. The second sheath surrounds the second cable and extends between first and second ends, and the first end of the second sheath is coupled to the second part of the first housing.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Steering-mode adjustable electric automobile steering system and control method
InactiveCN103754256ASimple structureIncrease control flexibilityMechanical steering gearsFluid steeringFault toleranceElectric power steering
The invention relates to a steering-mode adjustable electric automobile steering system and a control method. The steering-mode adjustable electric automobile steering system comprises two motors, a mechanical steering module, an electric assisting steering module and a steering-by-wire module, wherein the two motors are arranged on a steering column and a steering pinion respectively, the mechanical steering module, the electric assisting steering module and the steering-by-wire module are formed by three electromagnetic clutches and the like and are used for mechanical steering, electric assisting steering and steering-by-wire. The control method mainly includes the first step of carrying out system initialization, the second step of allowing an ECU to start the corresponding steering mode and carrying out control according to the steering mode selected by a driver, the third step of controlling the steering modes, and the fourth step of carrying out fault diagnosis and fault-tolerant control on the steering system. The steering-mode adjustable electric automobile steering system and the control method have the advantages that the same automobile has high control flexibility on the precondition of being simple in structure, and consequently switching of driving modes can be achieved; when one motor breaks down, an original steering mode can be switched to a steering column assisting type electric assisting steering mode or a pinion assisting type electric assisting steering mode or a mechanical steering mode, and consequently the operation stability, reliability and the fault-tolerance capacity of the automobile are improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
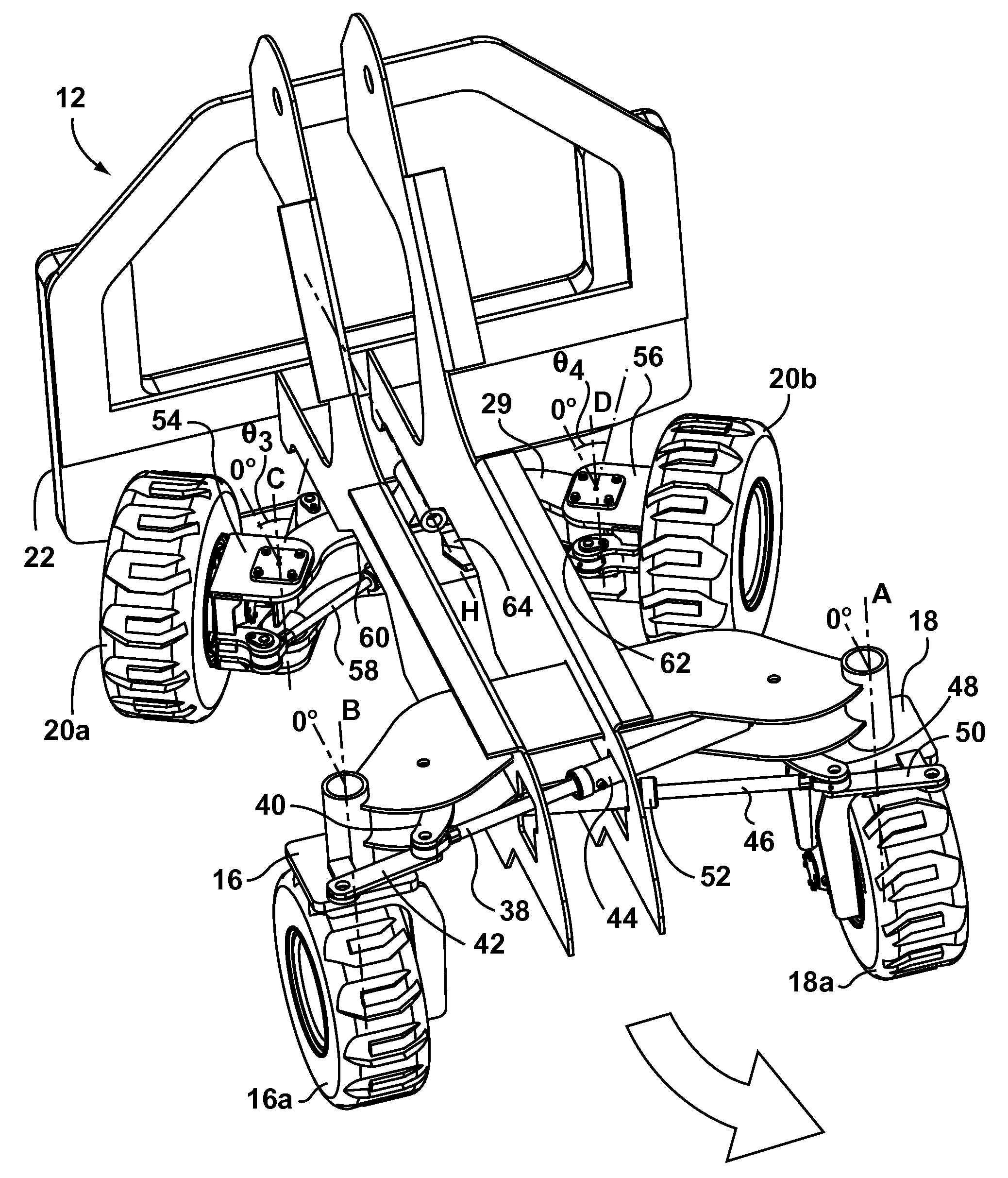
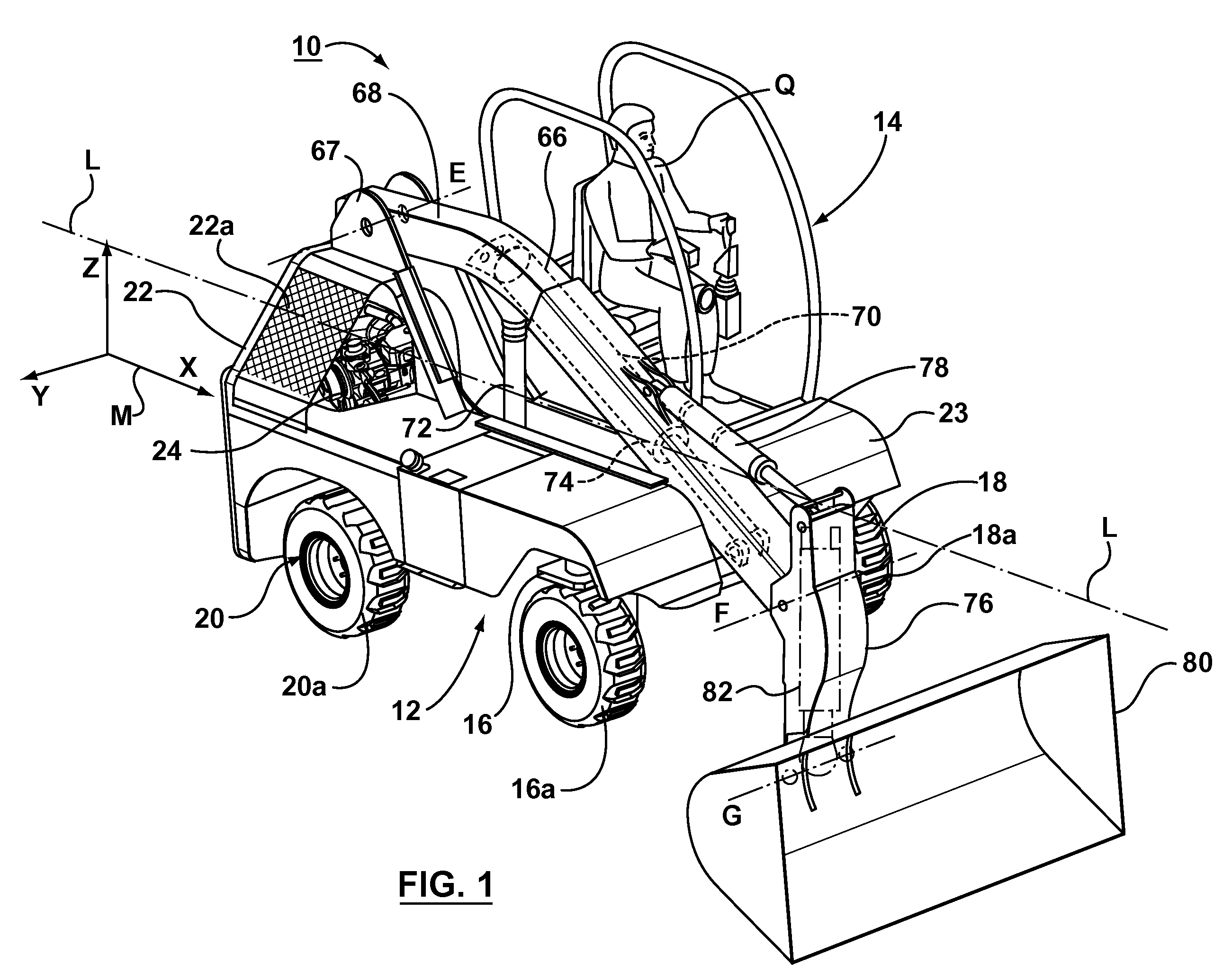
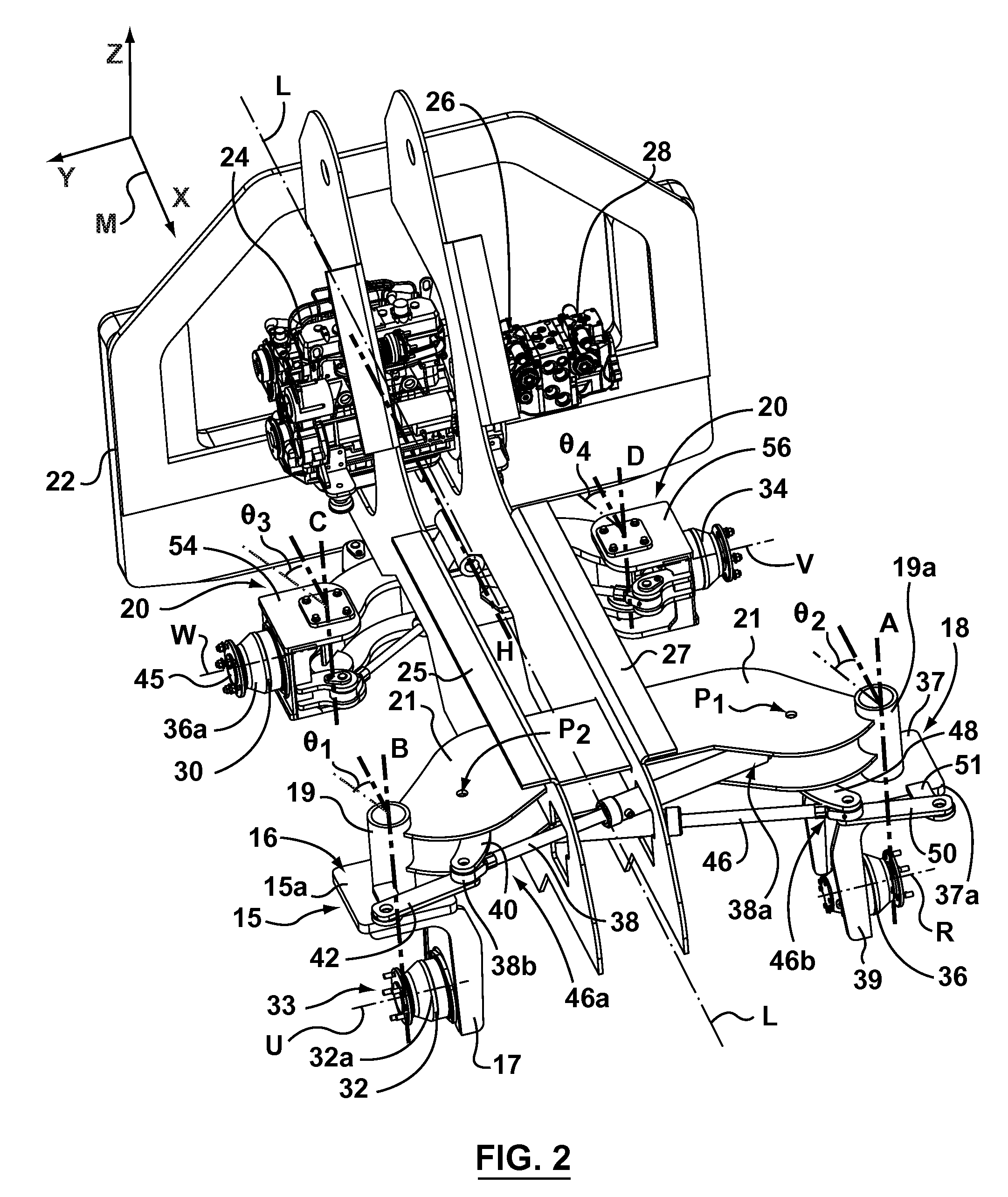
Compact construction vehicle with improved mobility
InactiveUS20070240928A1Great tractionImprove stabilitySteering linkagesSoil-shifting machines/dredgersControl systemSteering control
A loader type construction vehicle includes a chassis having a longitudinal axis, a plurality of wheeled ground-engaging structures pivotally coupled to the chassis, and a steering control system. Each of the plurality of ground-engaging structures includes a wheel pivotable about a steering axis and drivable about a drive axis, wherein each of the wheeled ground-engaging structures is shaped and configured so that the wheel of each of the ground-engaging structures can be pivoted from a first angular position in which the drive axis is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis, to a second angular position that is at least 90° degrees from the first angular position. The steering control system is operatively connected to each of the ground engaging structures for pivoting the wheel of each of the ground-engaging structures about the steering axis. The steering system may be operable to selectively configure the ground engaging structures into a plurality of different steering configurations, such as crab steering and side steering. The loader vehicle may include a telescopic loader arm.
Owner:COLTSON W CRAIG +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com