Translation parallel mechanism with two degrees of freedom and hooke joints as passive joints
A degree of freedom, Hooke technology, applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of less freedom of movement, more degrees of freedom of constraints, complex structure, etc., to achieve simple and reliable structure, and improve lateral stiffness. , the effect of high lateral stiffness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
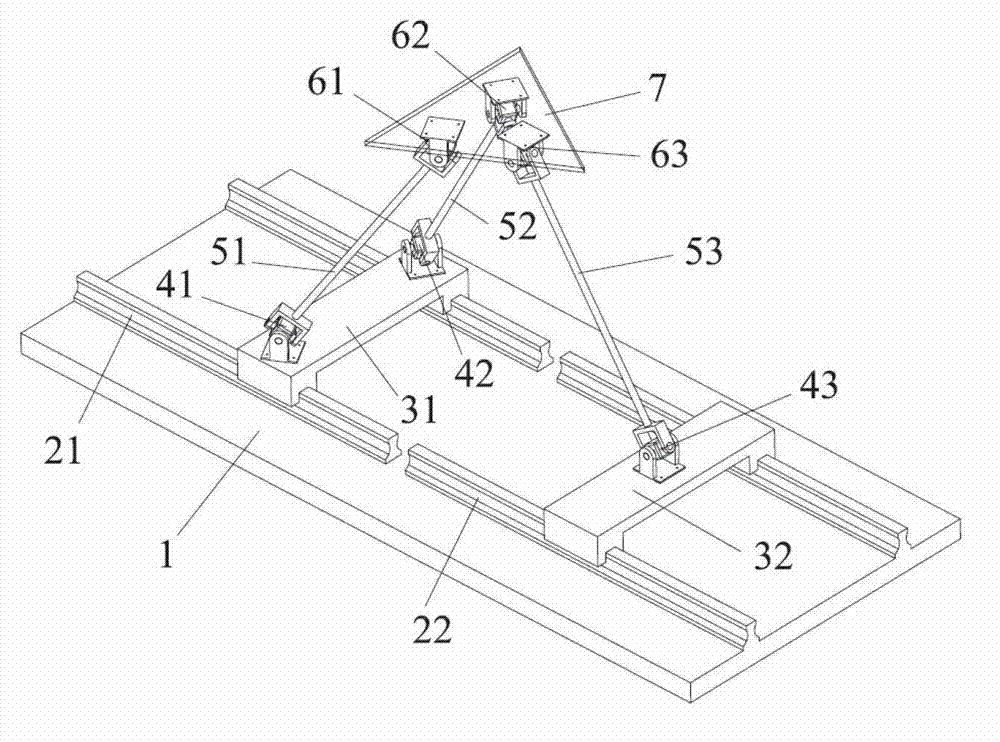
[0016] The general structure of the two-degree-of-freedom translational parallel mechanism of the present invention is as follows: figure 1 As shown, in addition to the above-mentioned structural features, the composite branch chain of the first motion branch chain includes the first motion slider 31, the first and second sub-constraint branch chains, and the first and second sub-constraint branch chains are connected in parallel Between the first motion slider 31 and the motion platform 7, the single branch chain of the second motion branch chain includes the second motion slider 32 and the third sub-constraint branch chain, and the first motion slider 31 is arranged on the first The guide rail 21, the second moving slider 32 is arranged on the second guide rail 22; the first sub-constraint branch chain is formed by connecting the first Hooke hinge 41, the first connecting rod 51 and the fourth Hooke hinge 61 in series , the second sub-constraint branch chain is formed by con...
Embodiment 2
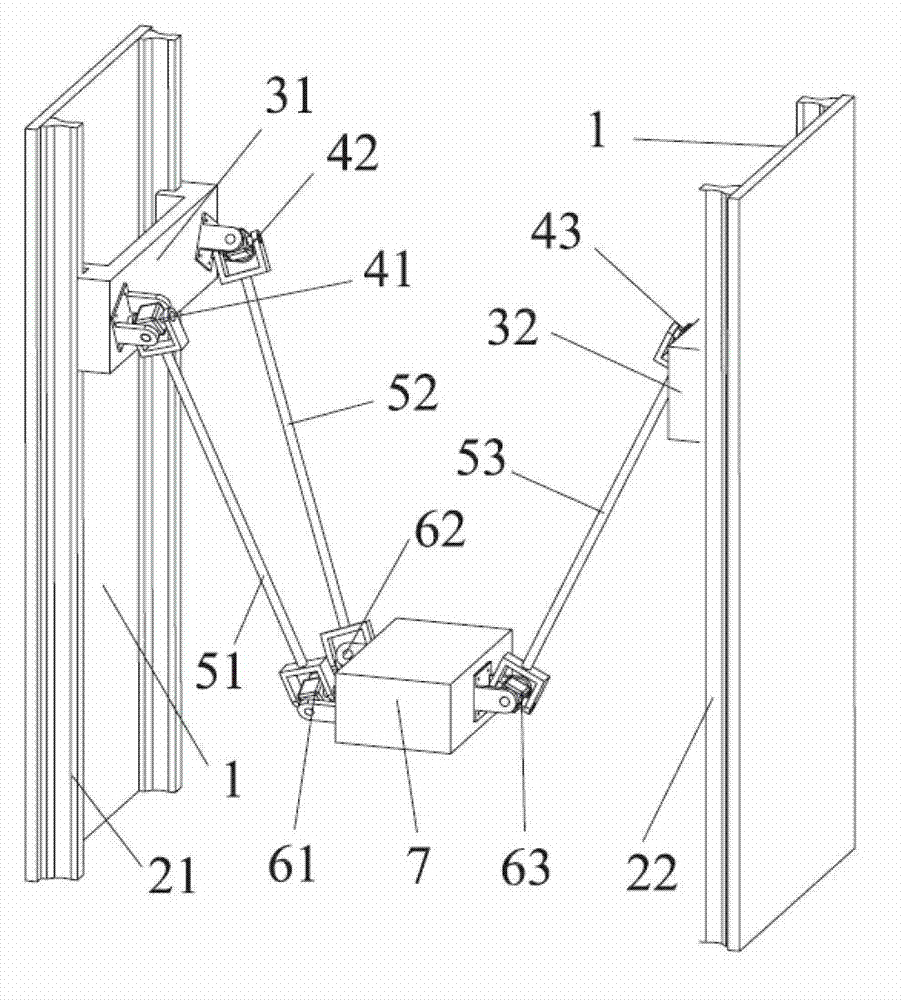
[0019] The general structure of the two-degree-of-freedom translational parallel mechanism of the present invention is as follows: figure 2 As shown, in addition to the characteristics of Embodiment 1, the axes of the first and second pairs of guide rails 21 and 22 arranged on the fixed platform 1 are arranged in parallel, so the moving directions of the first and second moving sliders 31 and 32 are parallel to each other.
Embodiment 3
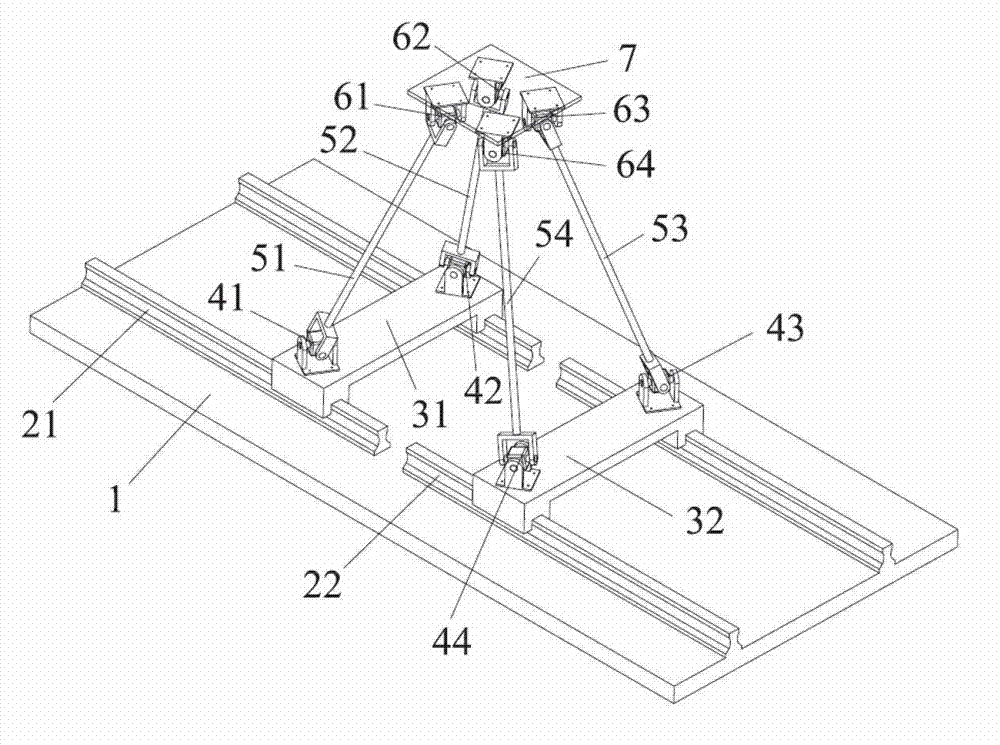
[0021] The general structure of the two-degree-of-freedom translational parallel mechanism of the present invention is as follows: image 3 As shown, the difference between this mechanism and the mechanism of Embodiment 1 is that the two moving branch chains connecting the fixed platform 1 and the moving platform 7 in parallel are both compound branch chains, and the structural arrangement of the two compound branch chains is the same as that of Embodiment 1. The branch chains are identical, wherein the sub-branches connected in series by the third Hookee hinge 43, the third connecting rod 53 and the sixth Hookee hinge 63 are equivalent to the second sub-constrained branch chain of the composite branch chain in Embodiment 1, by The sub-branch connected in series by the fourth Hookee hinge 44 , the fourth connecting rod 54 and the seventh Hookee hinge 64 is equivalent to the first sub-constraint branch of the composite branch in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com