Imaging method for lunar based optical sensor
An optical sensor and imaging method technology, applied in astronomical navigation, navigation through velocity/acceleration measurement, etc., can solve the problems where there is no research on imaging methods of moon-based optical sensors, less research on the temporal and spatial characteristics of global changes, and the combination of global change research Issues such as not being clear enough to achieve the effect of a wide range of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0125] Set the sensor, set the input data: imaging time, image resolution.
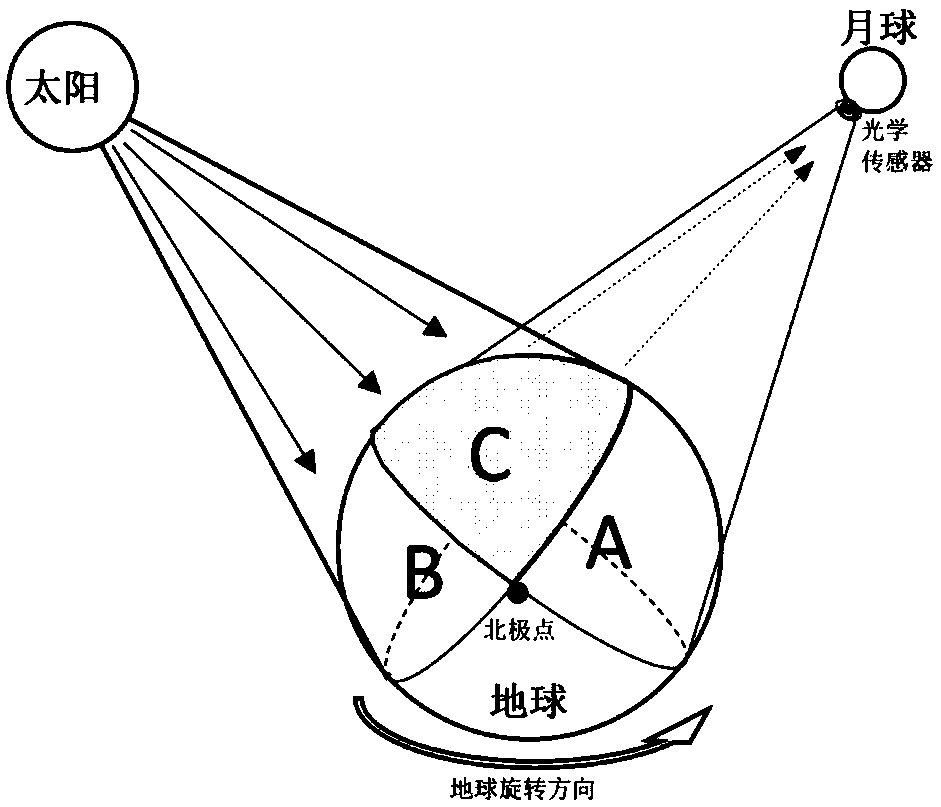
[0126] We assume that a commonly used optical sensor - a multispectral camera, is placed on the surface of the moon facing the earth. The spatial resolution of the sensor is 1° in the WGS84 coordinate system. In this way, the multispectral camera can obtain a 360*180 image Moon-based observation images in raster format, each raster takes the latitude and longitude of the center position.
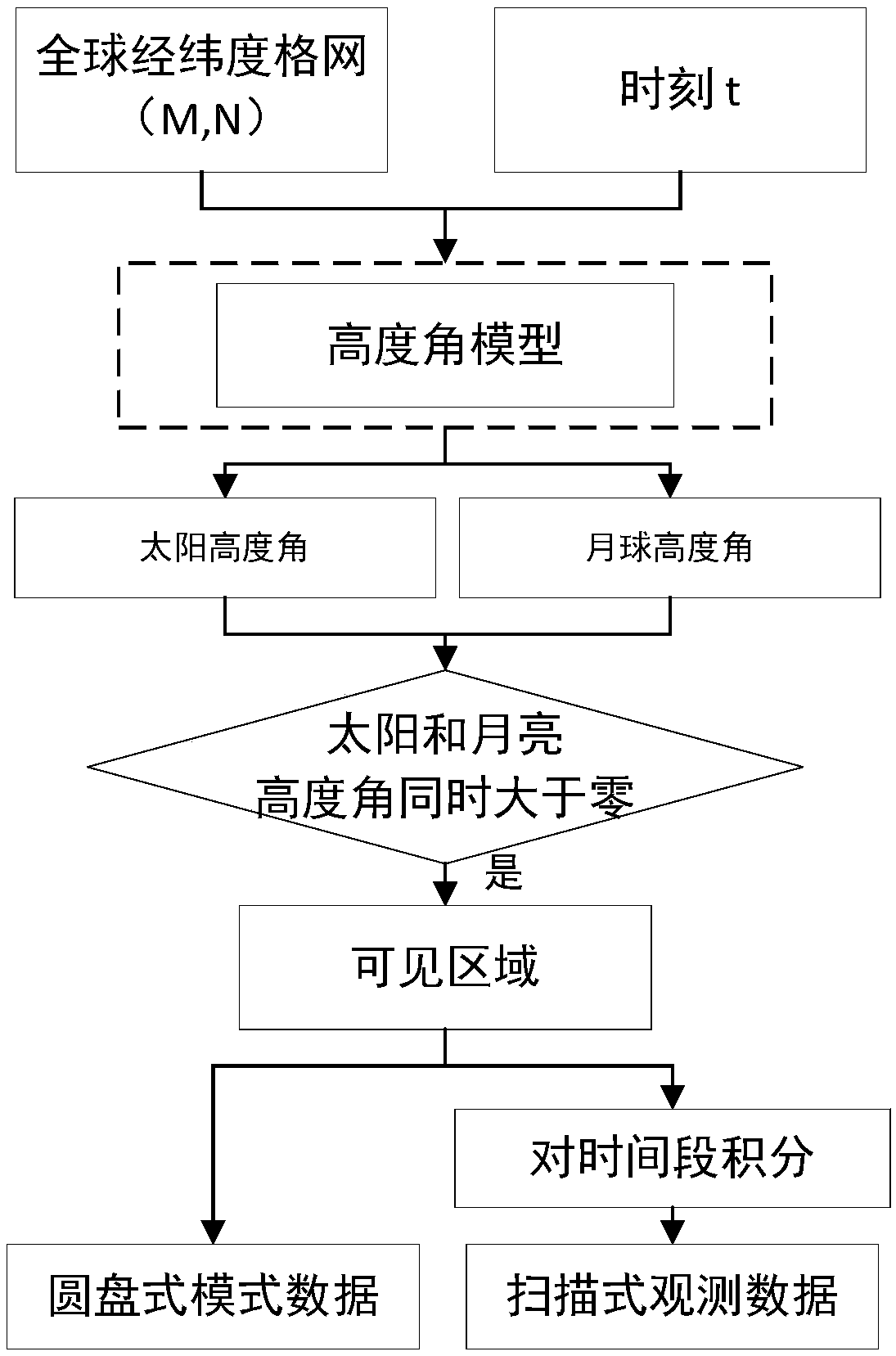
[0127] We take 01:00 (UTC) on September 08, 2016 as an example to simulate and obtain one disc-shaped observation image. Scanning simulated observation of a continuous observation image of 24 hours on September 08, 2016 (UTC). The altitude angle of the sun and the moon are obtained in each region of the world through the altitude angle model.
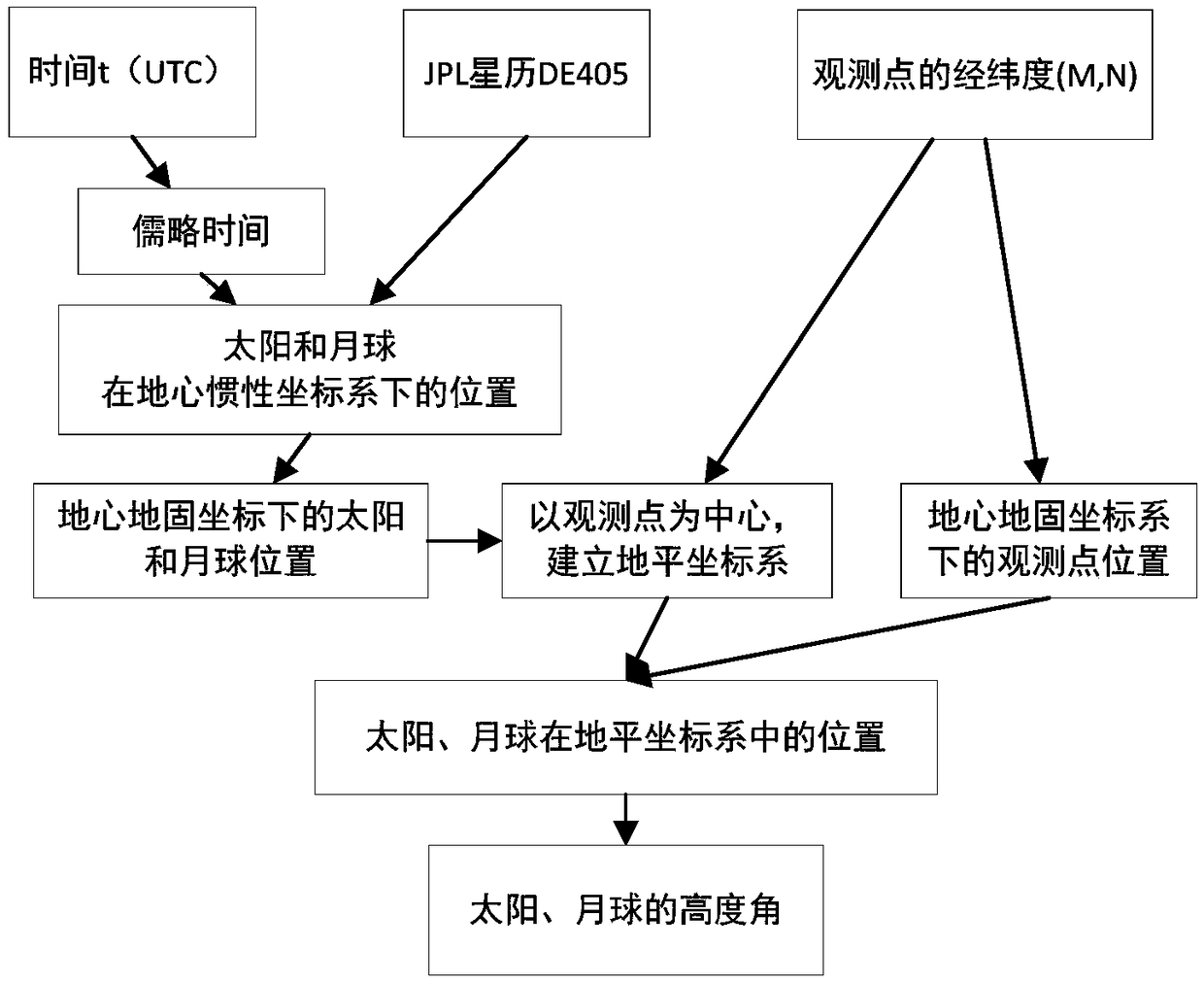
[0128] The first step is to obtain the positions of the center of mass of the sun and the center of mass of the moon in the geocentric inertial coordinate system from the e...
Embodiment 2
[0167] Set the sensor, set the input data: imaging time, image resolution.
[0168]We assume that a commonly used optical sensor - a multispectral camera, is placed on the surface of the moon facing the earth. The spatial resolution of the sensor is 0.5° in the WGS84 coordinate system. In this way, the multispectral camera can obtain a 720*360 image Moon-based observation images in raster format, each raster takes the latitude and longitude of the center position.
[0169] We take July 04, 2016 01:00 (UTC) as an example to simulate and obtain one disc observation image. Scanning simulated observation on July 04, 2016 (UTC), a total of 24 hours of continuous observation images.
[0170] Obtain the altitude angle of the sun and the altitude angle of the moon in each region of the world through the altitude angle model
[0171] The first step is to obtain the positions of the center of mass of the sun and the center of mass of the moon in the geocentric inertial coordinate syst...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com