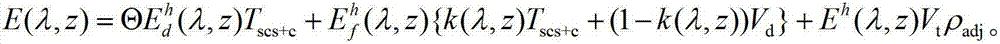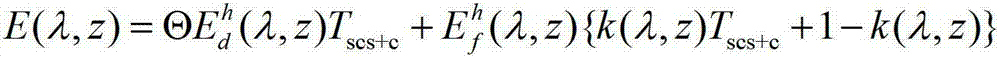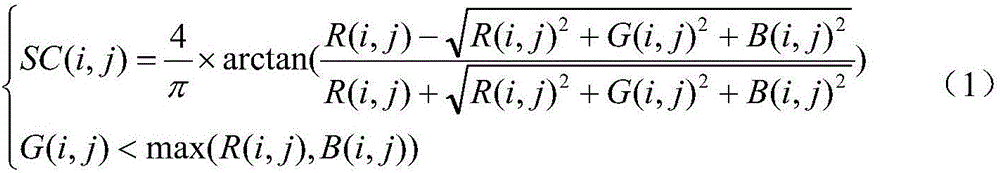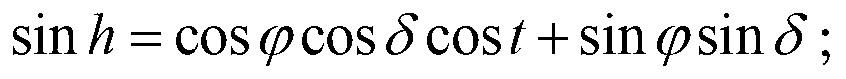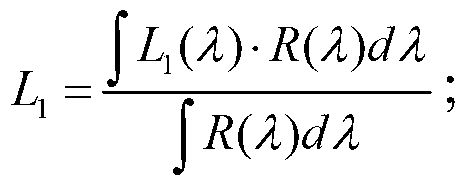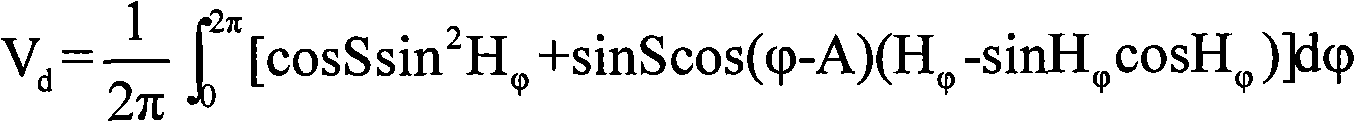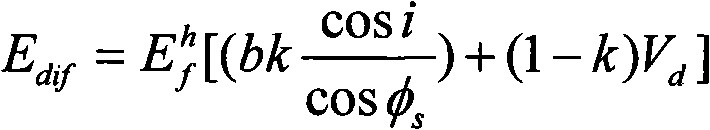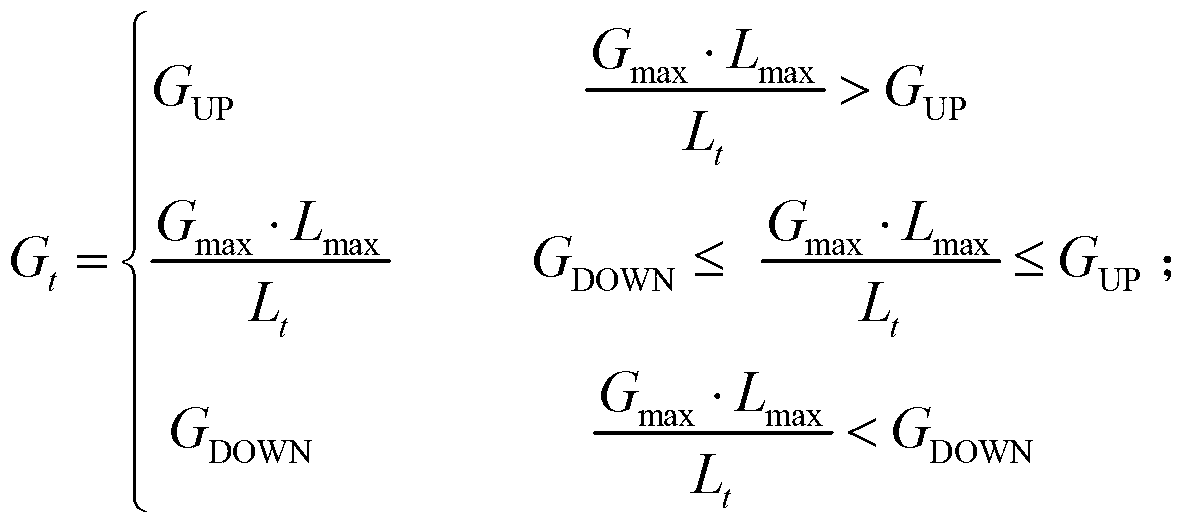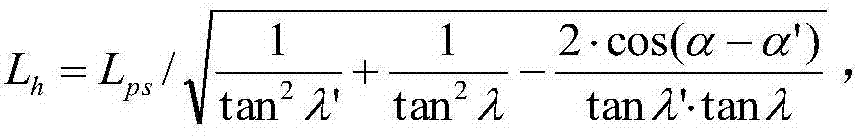Patents
Literature
470 results about "Solar zenith angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
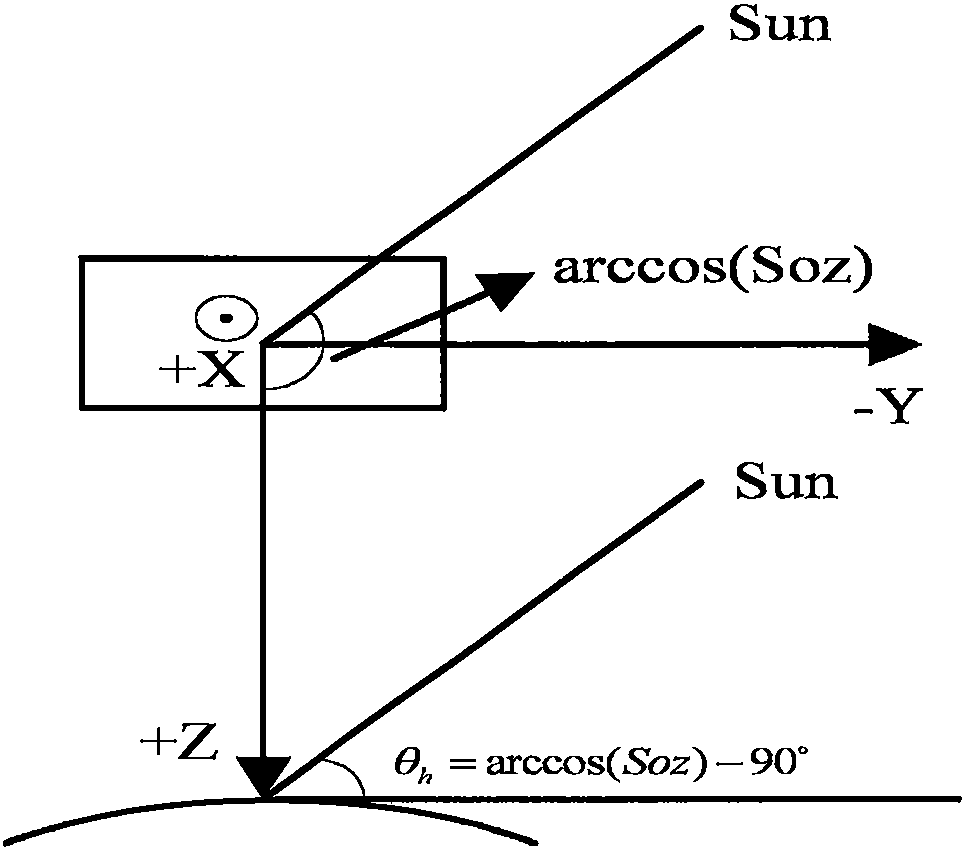
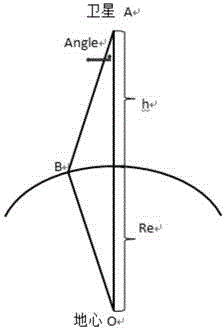
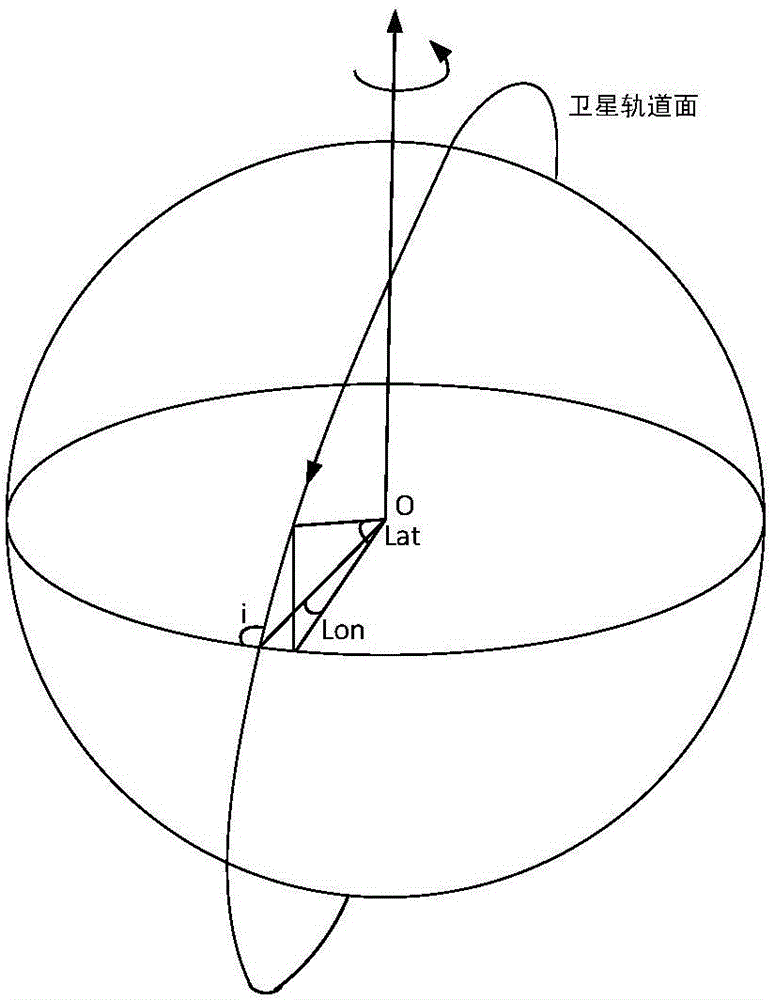
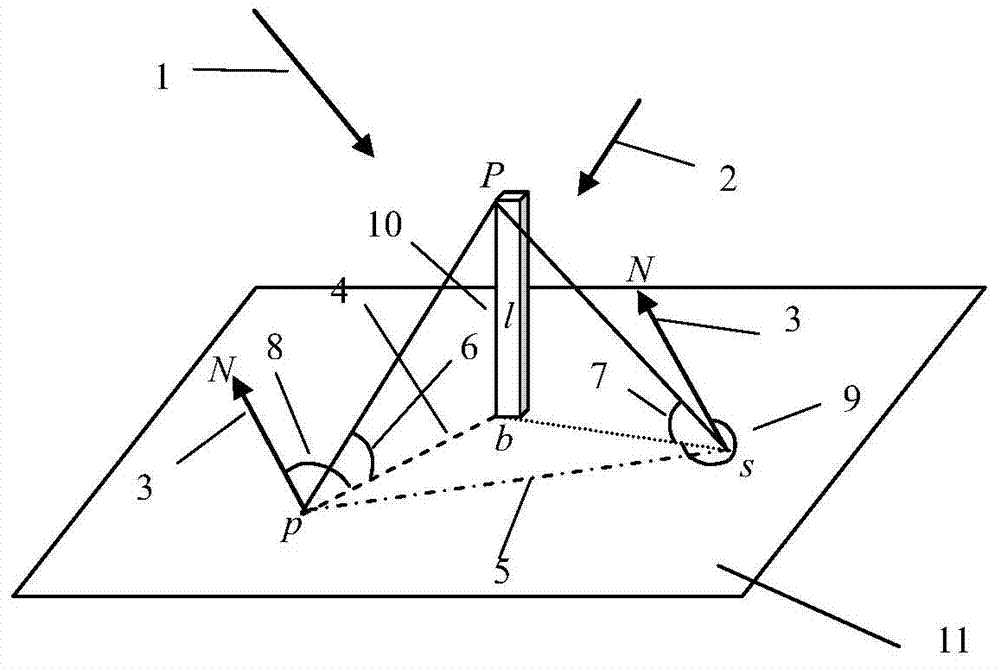
The solar zenith angle is the angle between the zenith and the centre of the Sun's disc. The solar elevation angle is the altitude of the Sun, the angle between the horizon and the centre of the Sun's disc. Since these two angles are complementary, the cosine of either one of them equals the sine of the other. They can both be calculated with the same formula, using results from spherical trigonometry.
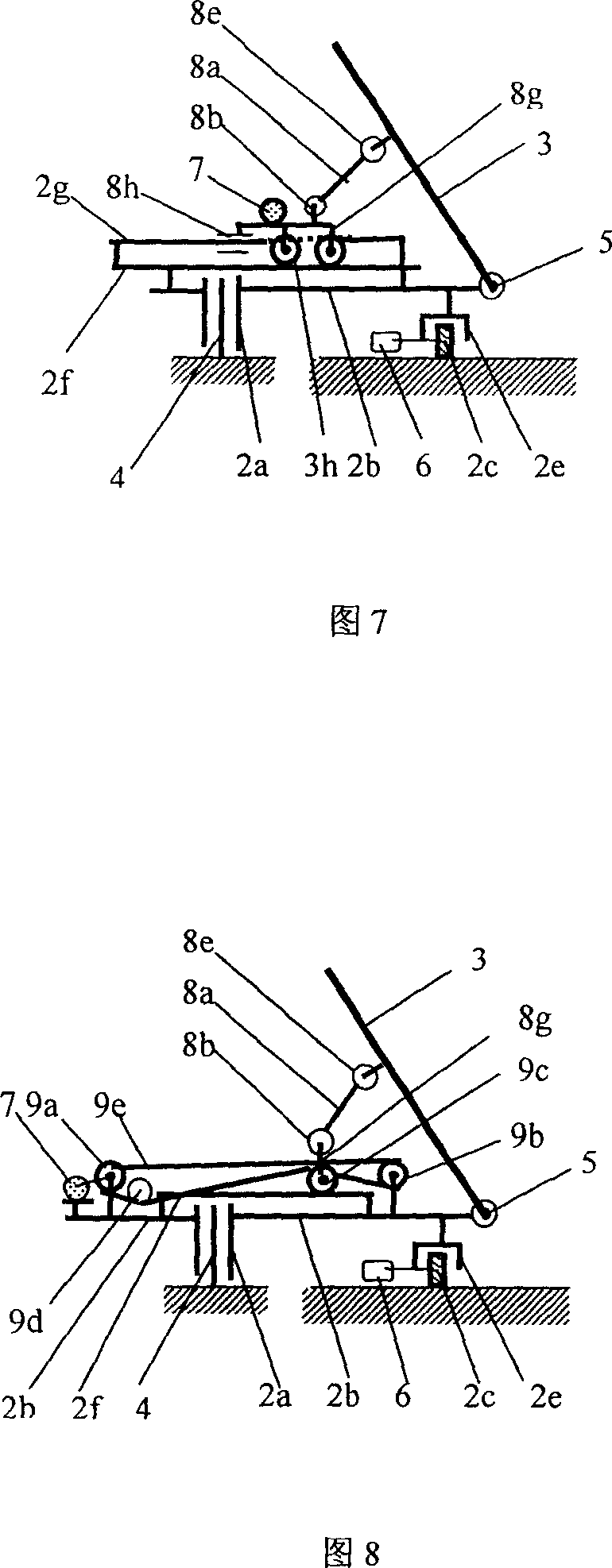
Multi-piece combined lifting type louver blade
ActiveCN101818616AOvercoming conflicting needsAdaptableLight protection screensSpecial door/window arrangementsMarine engineeringLight guide
The invention relates to a multi-piece combined lifting type louver blade characterized by comprising a main blade and two lifting blades, wherein the cross sections of the lifting blades in the width direction have the same shape as that of the cross section of the main blade in the width direction, the lifting blades are attached on the upper surface of the lower surface of the main blade, and the lifting blades can be driven to lift together with the main blade and also make lifting motion relative to the main blade by a lifting mechanism. The two lifting blades are sequentially attached on the upper surface or the lower surface of the main blade. The invention has the benefits that various louver sun shading and light guiding systems formed by the multi-piece combined lifting type louver blade with the cross section in any shapes can achieve the purposes of controlling the repeated reflection of direct sunlight and optimizing defected guiding amount according to season changes andthe specific needs of people so that the demand conflicts on the sunlight in summer and winter are overcome, and meanwhile, no matter high solar altitude or low solar altitude, the systems can keep high transmittance, thereby satisfying the demand of vision exchange between people and scenes outside windows.
Owner:HANGZHOU WOKASOLAR TECH
Method and device for calculating reflectivity of earth surface
InactiveCN102338871AImprove accuracyEliminate AbsorbencyWave based measurement systemsMiddle infraredExtensible markup
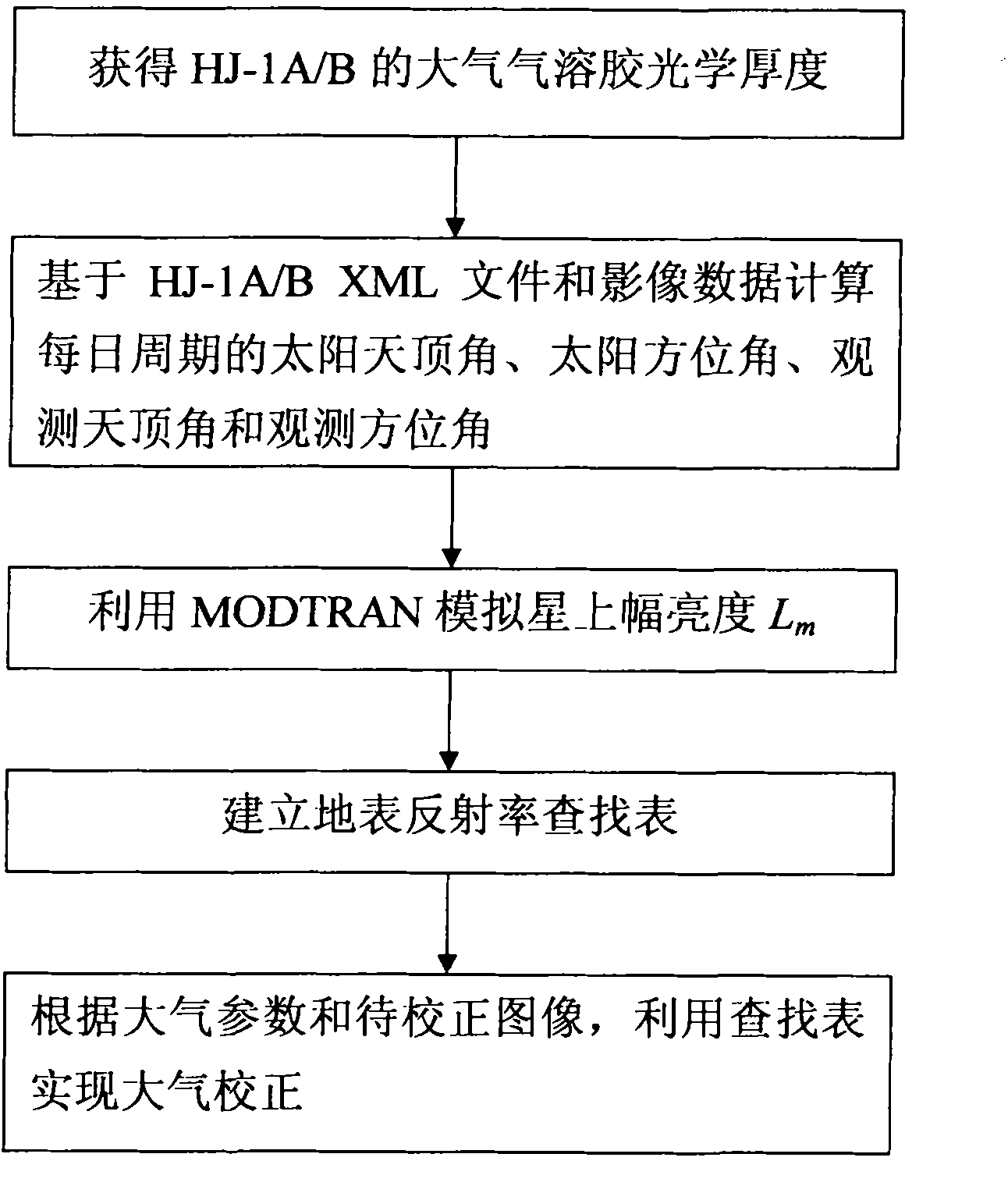
The invention relates to a method and a device for calculating the reflectivity of an earth surface, which are used for HJ-1A / B satellites. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) acquiring the optical thickness of atmospheric aerosol by using middle-infrared bands of an HJ-1B charge coupled device (CCD) and an infrared camera on the basis of a dark target method, and acquiring the optical thickness of the atmospheric aerosol by using an HJ-1A large-width quick revisit characteristic on the basis of an invariant target method; 2) calculating a solar zenith angle and a solar azimuth angle and observing the zenith angle and the azimuth angle on the basis of an HJ-1A / binary extensible markup language (BXML) file and image data; 3) simulating radiance Lm on a star through moderate resolution atmospheric transmission (MODTRAN) on the basis of parameters acquired in the steps 1) and 2); 4) establishing an earth surface reflectivity lookup table through the step 3); and 5) calibrating the atmosphere by using the lookup table according to an atmospheric parameter and an image to be calibrated. By the method and the device, the absorbing and scattering performance of the atmosphere on a remote sensing image can be effectively eliminated, the reflectivity of an earth surface target can be recovered, the bottleneck of industry application is eliminated, and the application range of environment disaster reduction moonlet data is further expanded.
Owner:曹春香 +2
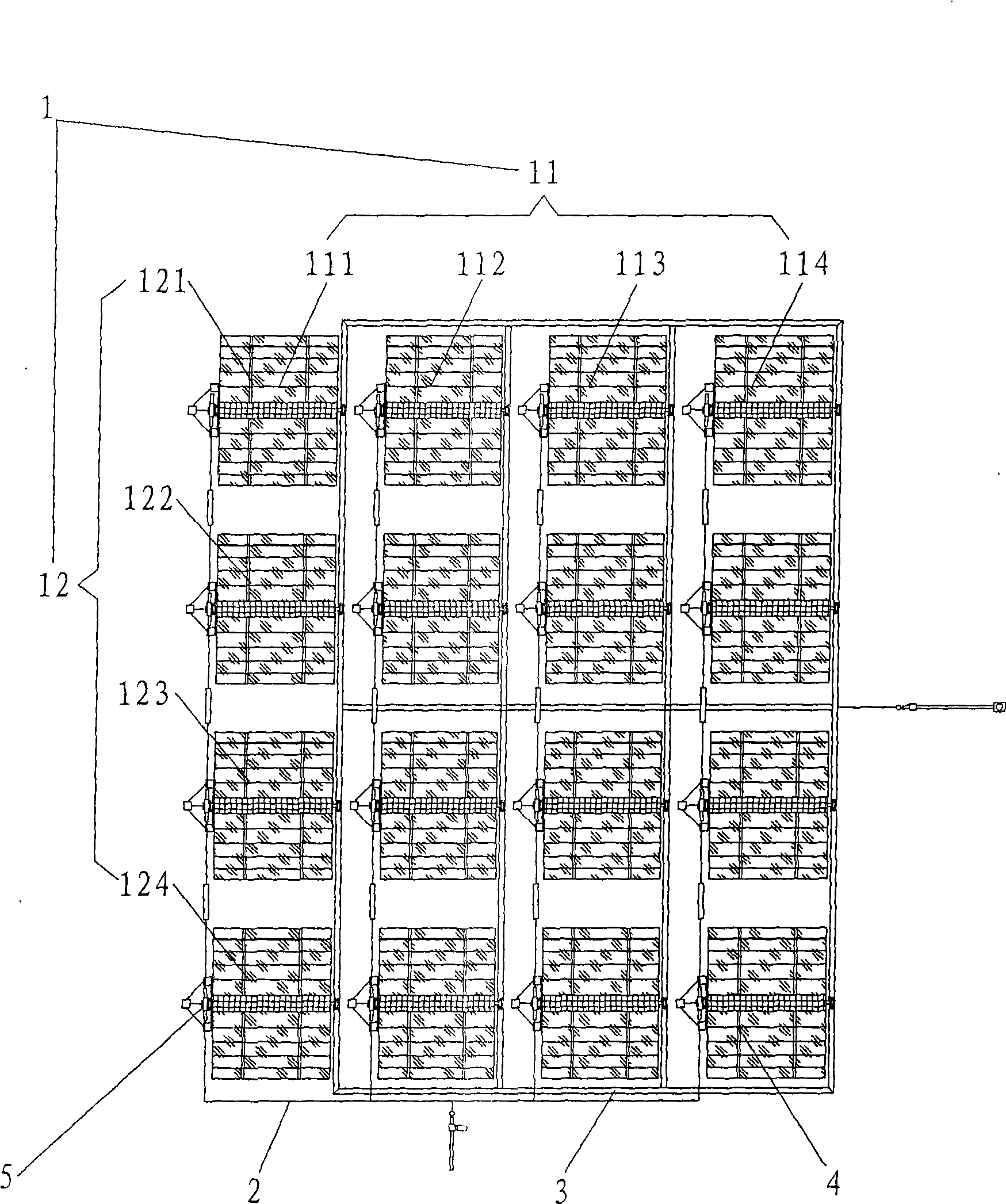
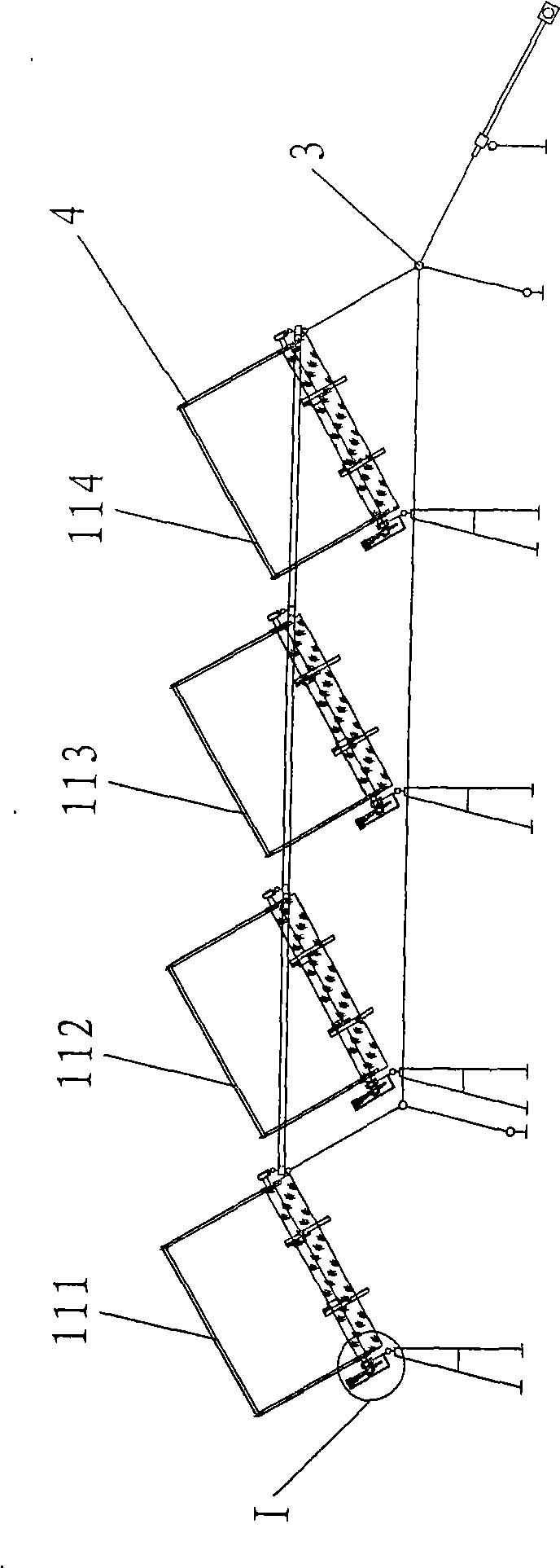
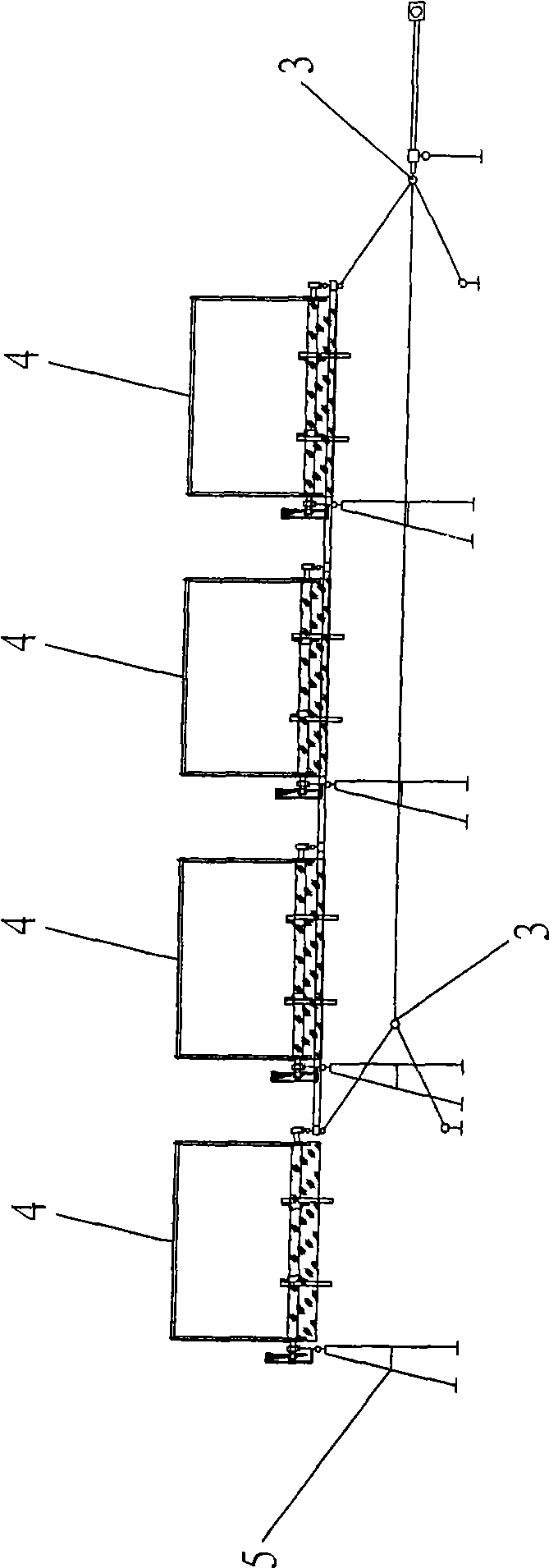
Plane grid two-dimensional sun-tracing photovoltaic generator
InactiveCN101098113AImprove the utilization rate of photovoltaic cellsReduce power generation costsPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyPhotovoltaic generatorEngineering
The invention provides a photovoltaic generator of plane network support two-dimension sun track, belonging to the technical field of solar-energy photovoltaic generation. The invention comprises a solar-energy photovoltaic generator and a sun tracker, wherein the sun tracker is a two-dimension track device, which comprises a horizontal rotary support, an inclined swing support, a vertical fixed shaft, a horizontal shaft, a sun direction track driver, and a sun altitude angle track driver. The solar-energy photovoltaic generator can be provided with a condenser and a self heat radiation in disc or groove shape while a plurality of photovoltaic generators are mounted on a plane network support of the inclined swing support. The horizontal rotary support rotates around the vertical fixed shaft. The inclined swing support rotates around the horizontal shaft. Therefore, the normal line of the photoelectric battery plate of the solar-energy photovoltaic generator is toward sun all the time. The invention has stable structure, small drive force, multiple load of elements, saved track cost, improved condense ratio caused by the utilization of condenser and self heat radiator, and improved generating efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
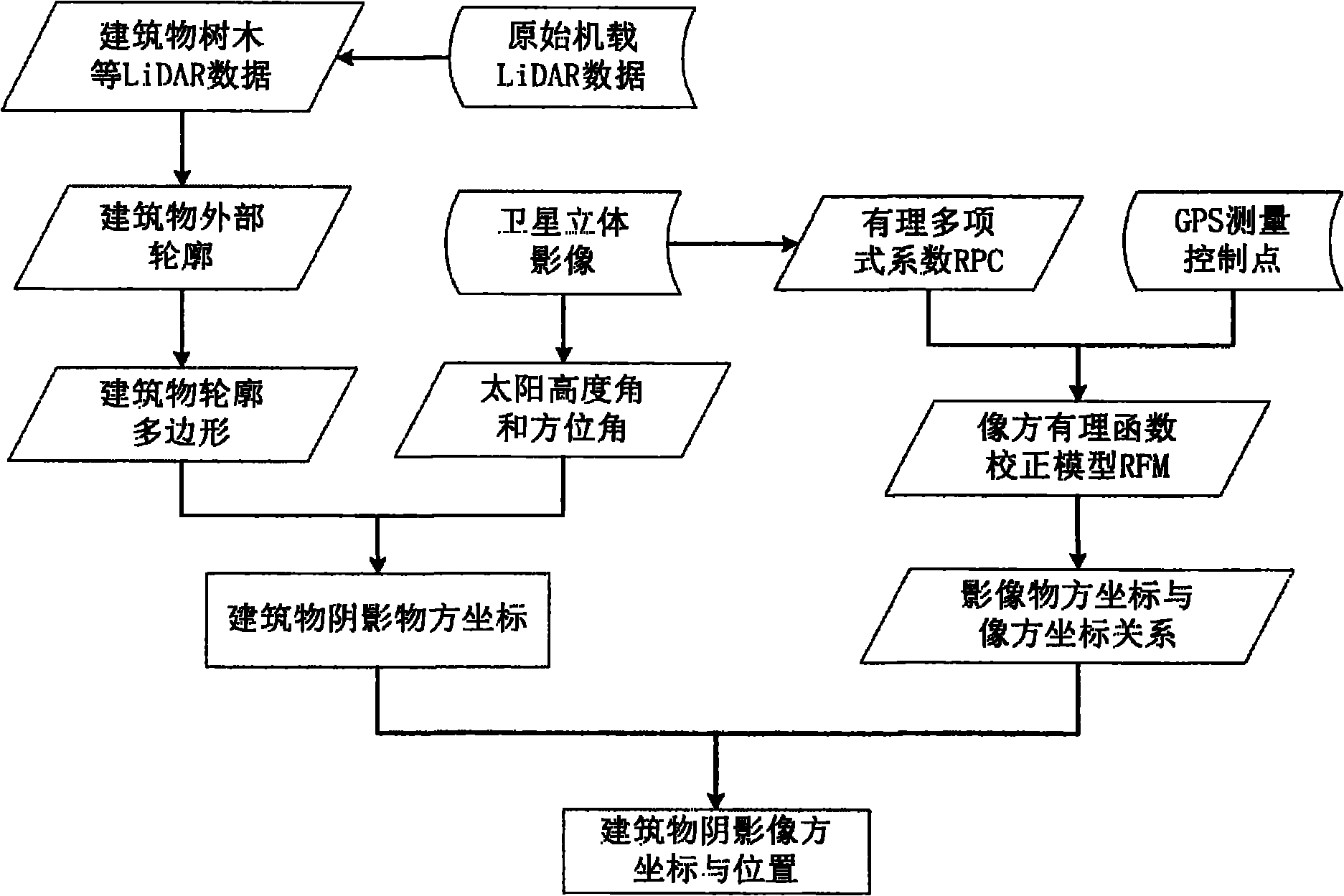
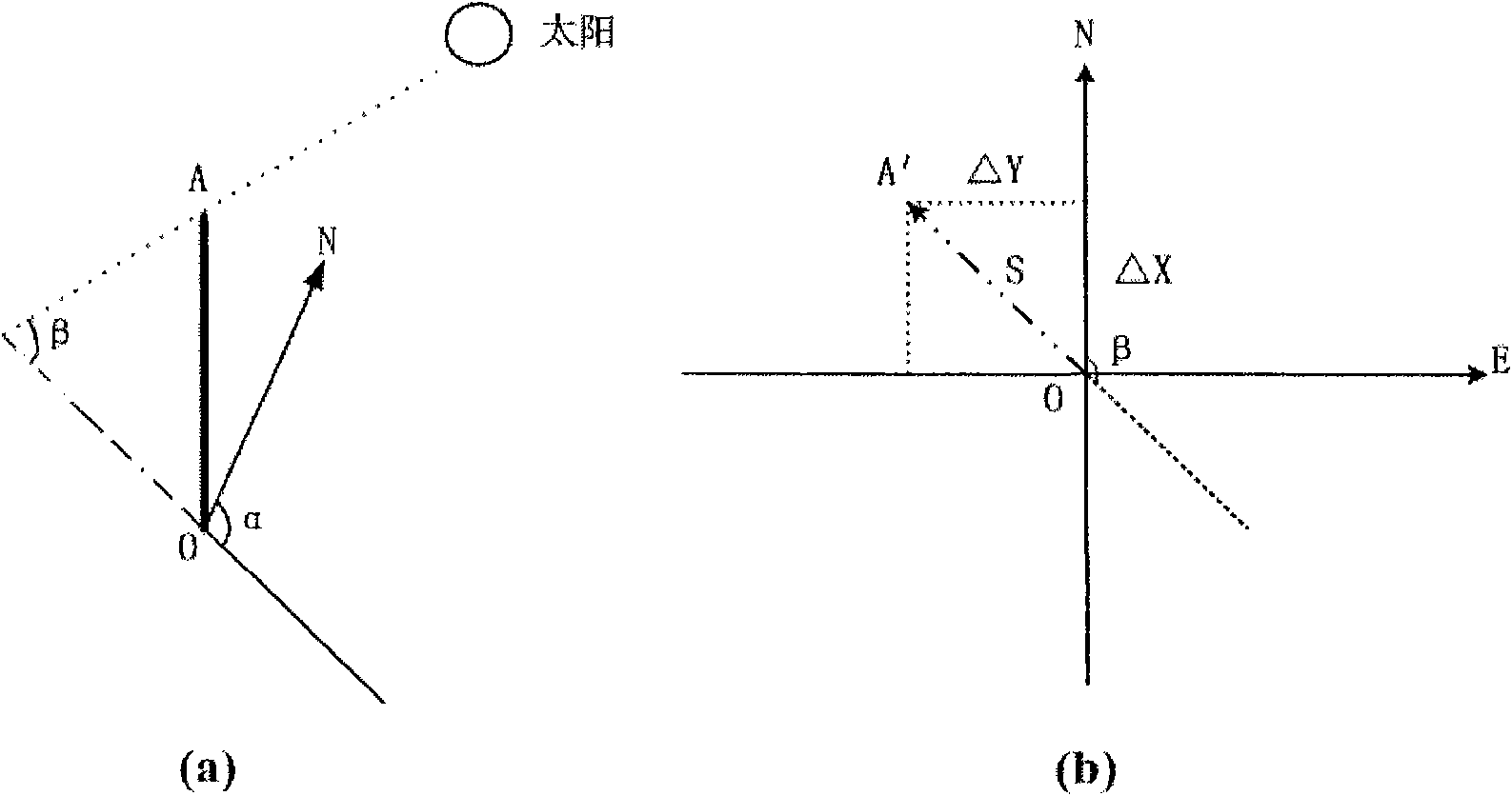
Satellite stereo image shadow calculating method integrated with light detection and ranging (LiDAR) point clouds
InactiveCN101894382ACreate precise conversion relationshipsHigh precisionImage analysisPicture interpretationTerrainPoint cloud
The invention discloses a satellite stereo image shadow calculating method integrated with light detection and ranging (LiDAR) point clouds. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, filtering original LiDAR point cloud data to obtain the LiDAR point clouds of non-ground points such as buildings, trees and the like; secondly, obtaining an enclosing polygon of a terrain point set, a terrain contour polygon and an outline polygon of a building by using a point wrapping algorithm with distance control, judging the position relation between a point and a polygon and filtering and simplifying the shape of the terrain contour polygon respectively; and finally, resolving an object space coordinate of the shadow of the building by taking an image of the altitude angle and azimuth angle of the sun instantaneously and determining the conversion relationship between the object space coordinate and an image space coordinate according to a satellite stereo image space RFM geometry correction result to obtain the coordinate and position of the shadow of the building in the image space. The method has the advantages of capability of obtaining a shadow area and a coordinate range of a high-resolution satellite image efficiently and fast and obtaining a precise shadow position coordinate and stability.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
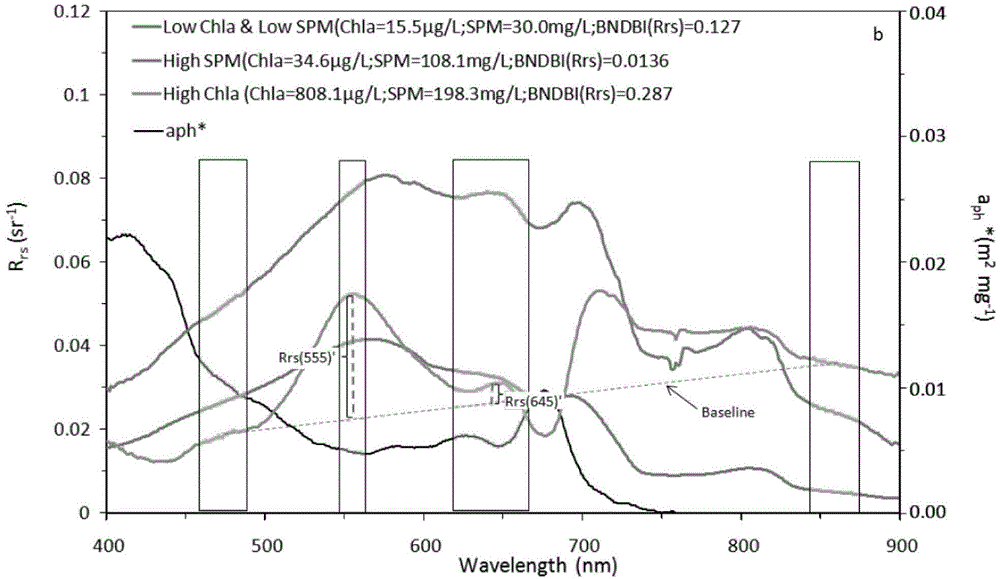
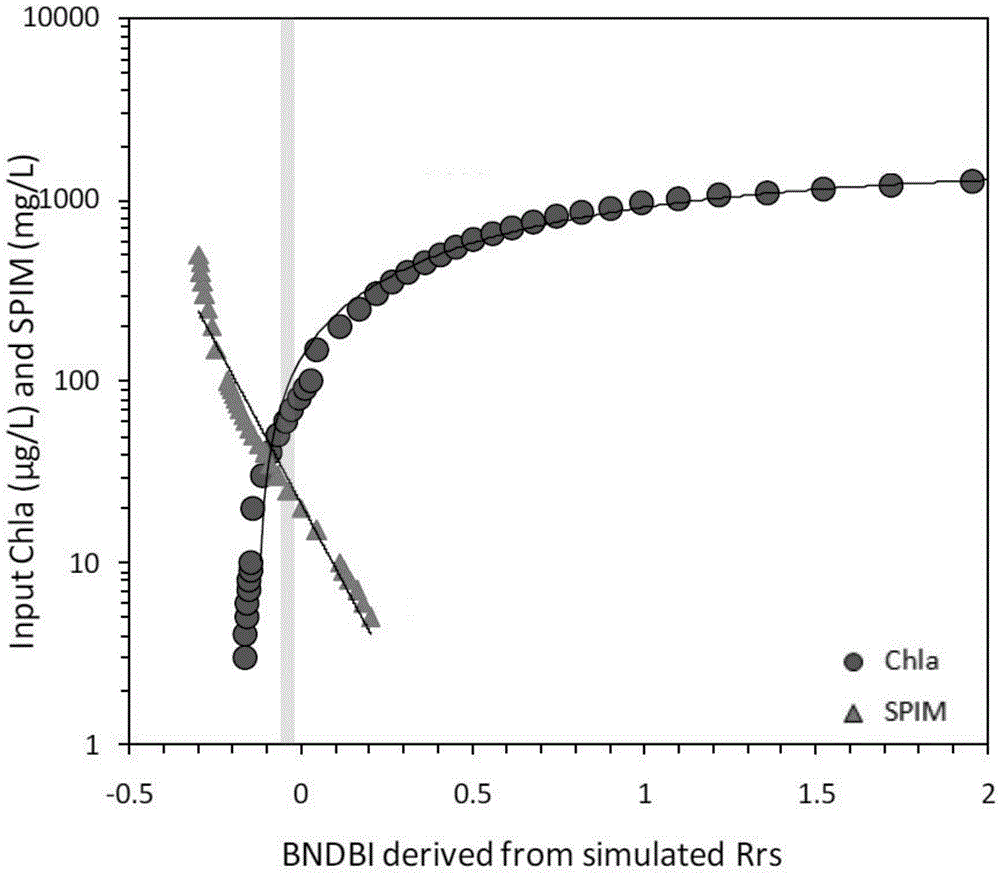
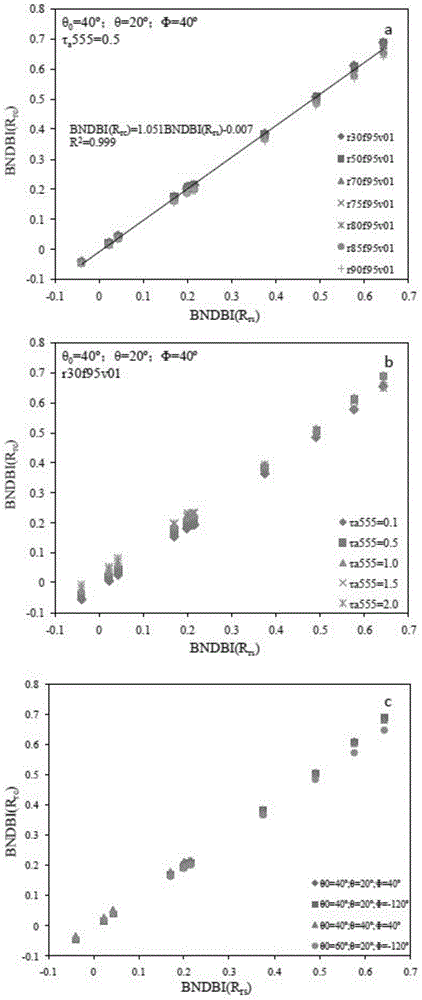
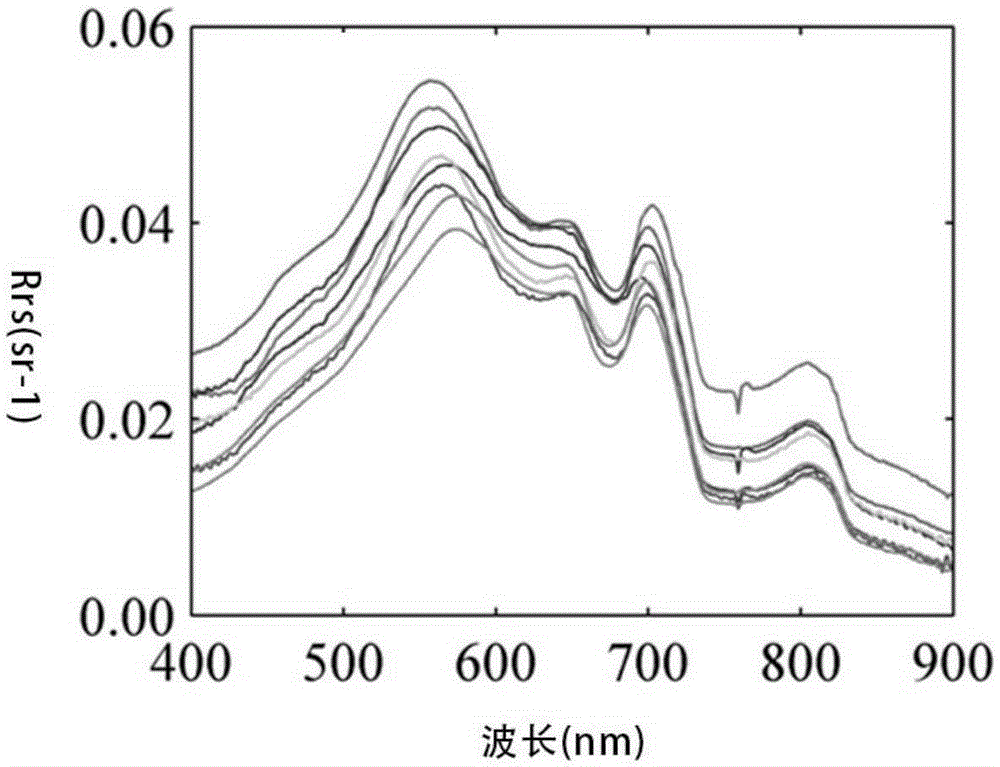
MODIS satellite high-precision monitoring method for chlorophyll-a in eutrophic lake water body
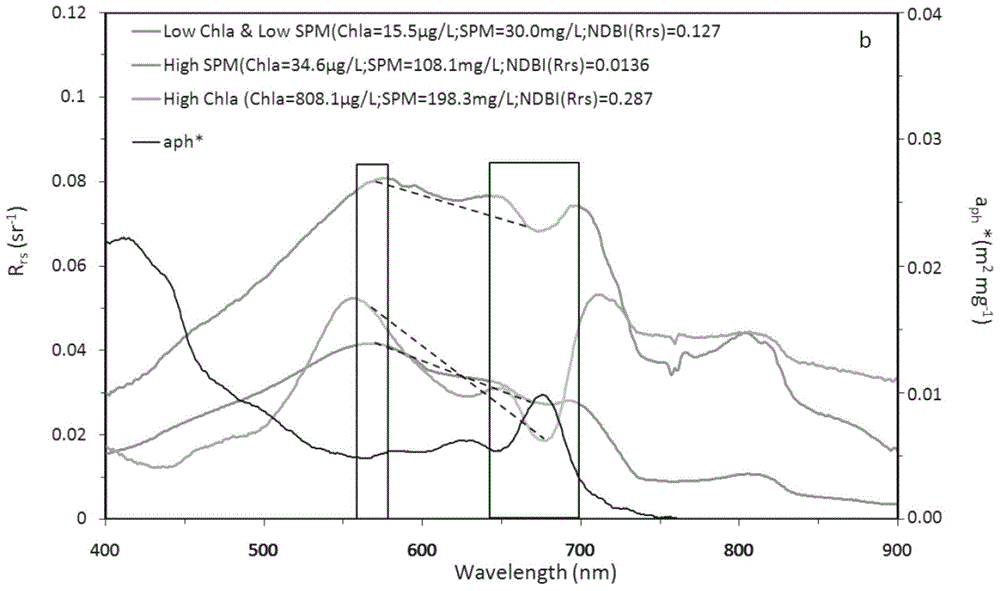
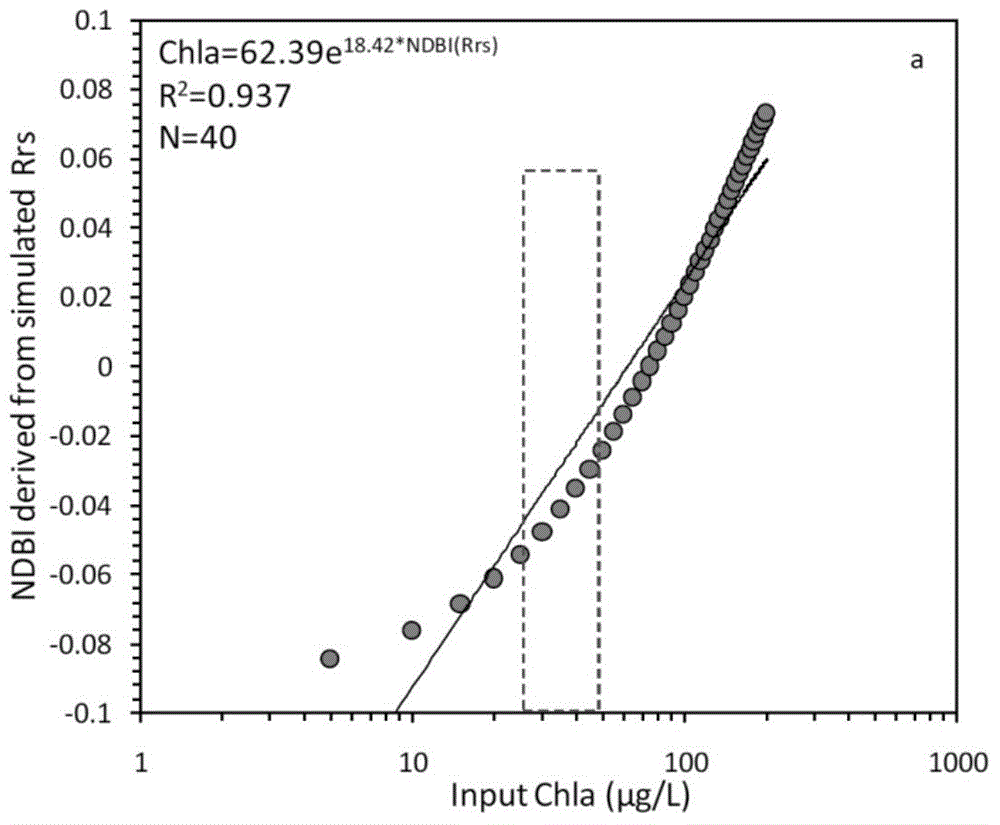
ActiveCN104820224AAchieving High-Precision EstimationReflect the space-time distributionElectromagnetic wave reradiationRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
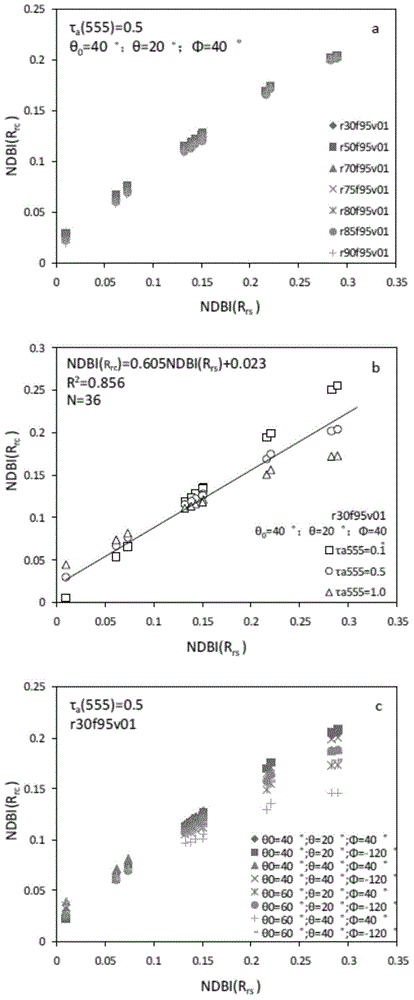
The invention provides an MODIS satellite high-precision monitoring method for chlorophyll-a in a eutrophic lake water body. The method comprises the following steps: screening a chlorophyll-a evaluation index (BNDBI) which is sensitive to the concentration change of chlorophyll-a and not affected by highly suspended matters, thin cloud and solar flares; acquiring the quantitative relationship between BNDBI and the concentration of chlorophyll-a on the basis of biological optical model simulation; acquiring a chlorophyll-a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectrum (Rrs) and BNDBI by referring to water body spectral information and corresponding water body chlorophyll-a concentration of 2013-2014 lake field monitoring; acquiring the quantitative relationship between the ground monitoring and remote sensing reflectance ratio (Rrs) and Rrc after simulated Rayleigh scattering correction by simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses and different solar elevation angles, satellite observation angles and azimuth angles; and extending the chlorophyll-a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectrum data to satellite image data after Rayleigh scattering correction. Based on the method, inter-annual and inter-monthly change rules and spatial distribution of chlorophyll-a in a eutrophic lake can be acquired accurately.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Two-dimensional photovoltaic generator bracket for tracing sun
InactiveCN101098111AImprove structural stabilitySmall driving forcePhotovoltaic supportsPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotovoltaic generatorEngineering
The invention provides a photovoltaic generator support for tracking sun at two-dimension, belonging to the technical field of solar-energy photovoltaic generation. The invention is characterized in that the two-dimension track support comprises a horizontal rotary support and a vertical fixed shaft, an incline swing support, a horizontal shaft, a sun azimuth photoelectric detector, a track driver, a sun altitude angle photoelectric detector, and a track driver. A plurality of photovoltaic generators are mounted on a plane network support of the incline swing support, the horizontal rotary support rotates around the vertical fixed shaft, the inclined swing support rotates around the horizontal shaft, therefore, the normal line of the photoelectric battery plate of the solar-energy photovoltaic generator is toward sun all the time. The invention has stable structure, small drive force, multiple load of elements, saved track cost, avoided lighting cosine loss, improved utilization and generating efficiency of battery plate, and the support for photovoltaic generation with two-dimension focus.
Owner:陈则韶
Autotracking link gear of solar concentrating photovoltaic power generation array
InactiveCN101504202AImprove tracking accuracyReduce tracking costsPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heat devicesDrive shaftEngineering
The invention discloses an automatic tracking linkage mechanism of a solar energy concentration photovoltaic power generating array, which comprises a solar concentrator array, an altitude linkage mechanism, and an azimuth linkage mechanism. The solar energy concentration photovoltaic power generating array drives the whole array of all concentrators to obliquely track a solar altitude through a set of altitude driving mechanism, and drives the whole array of all concentrators rotate around a transmission shaft to track a solar azimuth through a set of azimuth driving mechanism. The whole solar energy concentration photovoltaic power generating array only adopts the set of the altitude driving mechanism and the set of the azimuth driving mechanism, so that the whole array of all concentrators realize tracking the running of the sun by two-dimensional linkage, and the tracking cost is low; moreover, the altitude driving mechanism and the azimuth driving mechanism are formed by simple mechanisms completely, so that the whole solar energy concentration photovoltaic power generating array is manufactured easily, and has high tracking accuracy and strong capability of strong wind resistance.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV +1
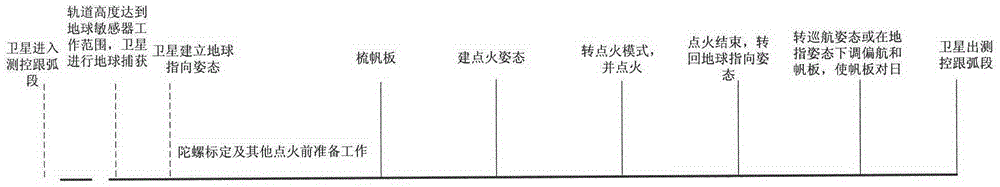
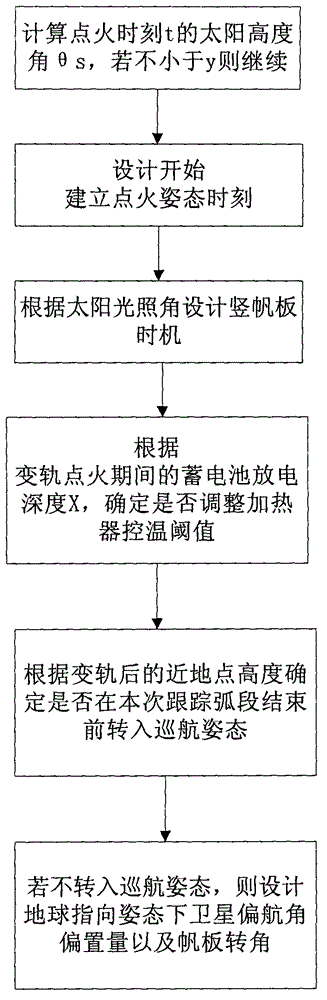
Method for improving orbit-transferring safety of inclined orbit satellite
The invention relates to a method for improving the orbit-transferring safety of an inclined orbit satellite, wherein the problem of energy-source shortage of the inclined orbit satellite in the period of orbit-transferring motorization under the condition of high solar angles is solved through the reasonable adjustment of flight events by considering the condition of solar altitude angles in the designing process of a flight program, and meanwhile, flight-control operation can be simplified. The discharging time of a storage battery in the period of orbit-transferring ignition can be shortened by designing the flight program according to the method, so that the load power in the power-supplying period of the storage battery is reduced, therefore the discharging depth of the storage battery is reduced, the energy-source safety of the satellite is ensured, and a launch window is not limited by solar illumination angles.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
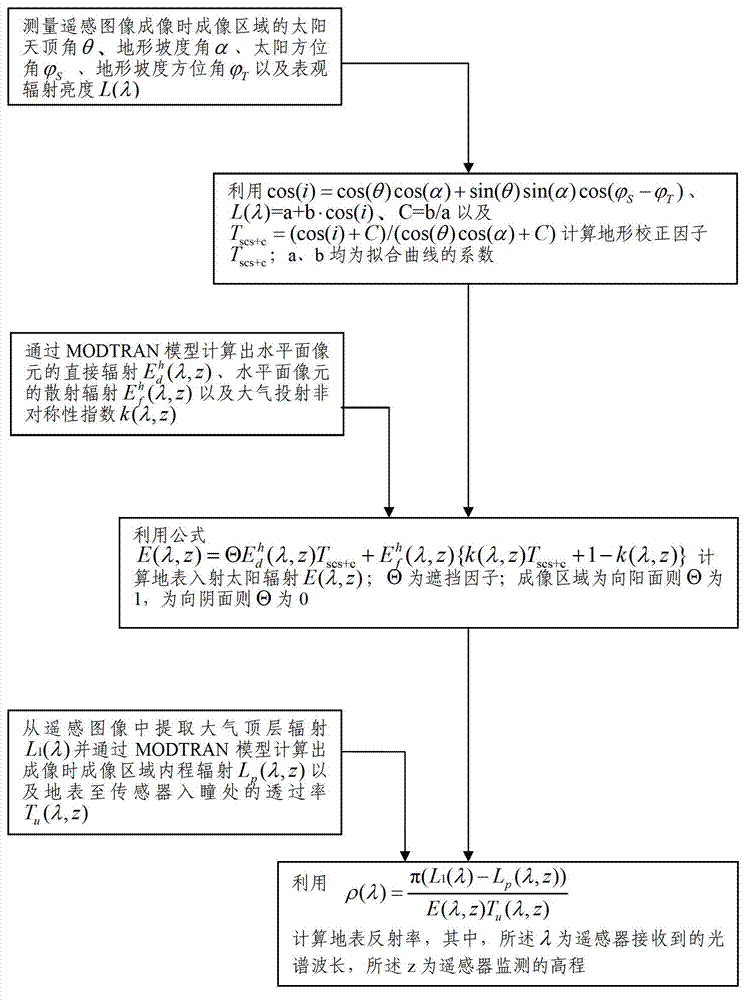
Remote sensing image radiation correction method
ActiveCN103198314AHigh precisionEasy to optimize applicationCharacter and pattern recognitionAsymmetry IndexPupil
The invention discloses a remote sensing image radiation correction method which includes the steps of measuring a solar zenith angle theta, a topographic slope angle alpha, a solar azimuth, a topographic slope azimuth and earth surface radiance L (lambada) of an imaging area when a remote sensing image is imaged, calculating a topographical correction factor Tscs+c, calculating direct radiation, scattered radiation of a horizontal plane pixel and an atmospheric projection asymmetry index k (lambada, z) through a MODTRAN model, calculating earth surface incidence solar radiation E (lambada, z), extracting atmospheric top layer radiation L1 (lambada) from the remote sensing image, working out path radiation Lp (lambada, z) of the imaging area and transmittance Tu (lambada, z) from the earth surface to a pupil-inlet position of a sensor through the MODTRAN model, and obtaining earth surface reflectance rho (lambada), wherein the lambada is a spectral wavelength received by a remote sensor and the z is an elevation monitored by the remote sensor.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Method of calculating tavi based on a band ratio model and solar altitude angle
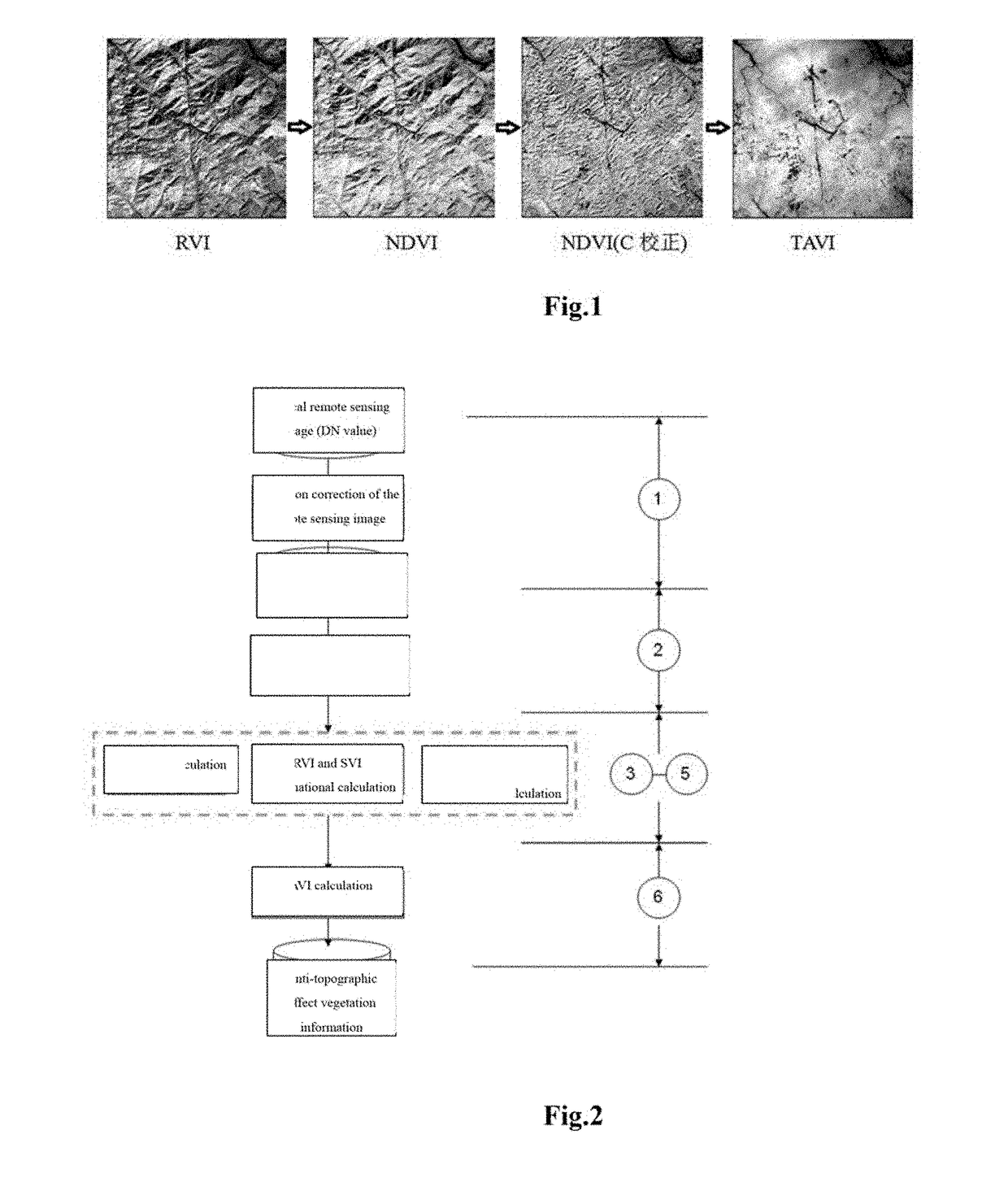
ActiveUS20180356339A1Broaden applicationEconomic valueMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionVegetation IndexLandform
The present invention relates to a method of calculating a Topography Adjusted Vegetation Index (TAVI) based on a band ratio model and a solar altitude angle. The method includes the folio wing steps: obtaining the apparent reflectance data of a remote sensing image through image preprocessing, analyzing the quality of the image and numerical distribution, calculating a Shadow Vegetation Index (SVI), and constructing a TAVI combinational algorithm:TAVI=BirBr+f(Δ)·1Br,calculating an adjustment factor f (Δ) with the solar altitude angle, and finally obtaining anti-topographic effect TAVI vegetation information. The TAVI in the present invention is composed of two band ratio submodels RVI and SVI, the denominators of both of which are red band data of a remote sensing image, and the adjustment factor f(Δ), which is calculated by a solar altitude angle as a parameter with a sensor factor applied, has great physical significance. The TAVI calculation method does not need digital elevation model (DEM) data and remote sensing image classification when not depending on ground survey data,, and ensures that the interference of the topographic effects with the vegetation information can be effectively eliminated by the TAVI, thereby avoiding the problem of reduced inversion accuracy of ground vegetation information due to different registration accuracy of a remote sensing image and DEM data.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
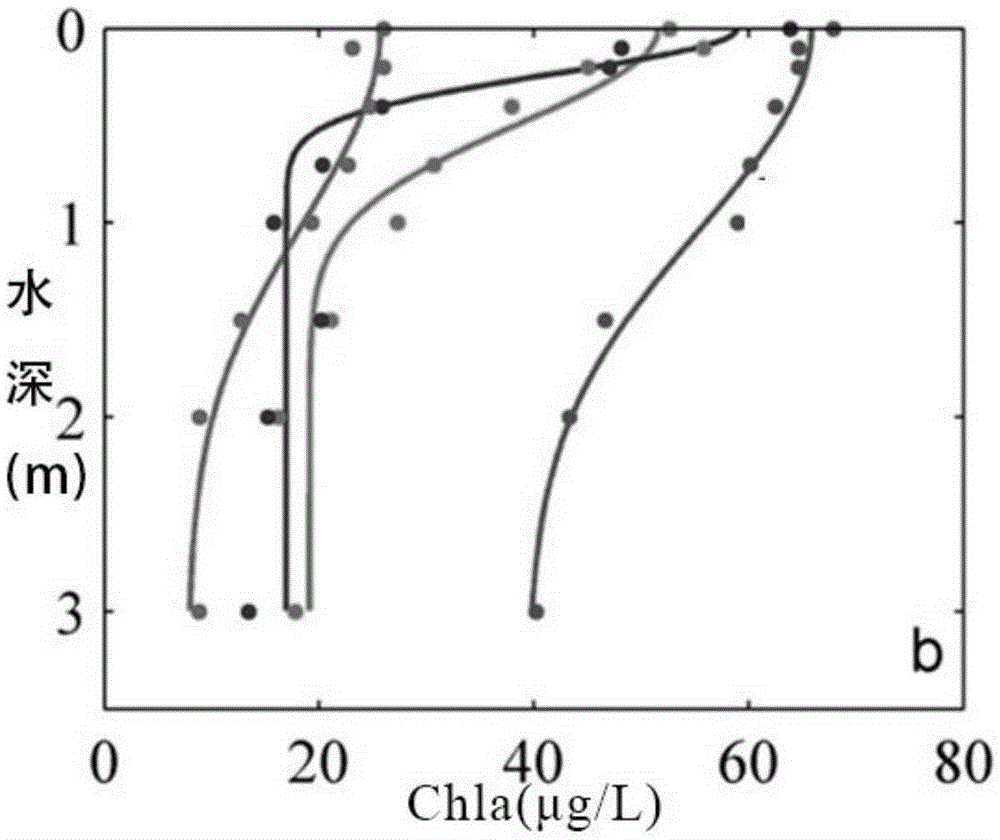
MODIS remote sensing monitoring method for vertical distribution pattern of eutrophic lake water algae
ActiveCN104374713AImprove practicalityInterannualColor/spectral properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringRemote sensing reflectance
The invention provides an MODIS remote sensing monitoring method for the vertical distribution pattern of eutrophic lake water algae. The method includes: acquiring the vertical distribution pattern of the algae by means of field monitoring; on the basis of field measured water surface spectral information and environmental information, creating a ground measured spectral data (Rrs) based remote sensing monitoring method for vertical algae distribution; acquiring the quantitative relationship between ground monitoring and remote sensing reflectance Rrs and simulated Rrc after Rayleigh scattering correction by simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses and different solar altitudes, satellite observation angles and azimuthal angles; further promoting the ground measured spectral data based monitoring method for vertical algae distribution to MODIS satellite image data subjected to Rayleigh scattering correction. On the basis of the method, interannual and inter-monthly change rules and spatial distribution of the vertical distribution pattern of the eutrophic lake water algae can be acquired accurately, and scientific support is provided for scientific decision-making on water resource management and water environment protection water conservancy and environmental protection departments.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
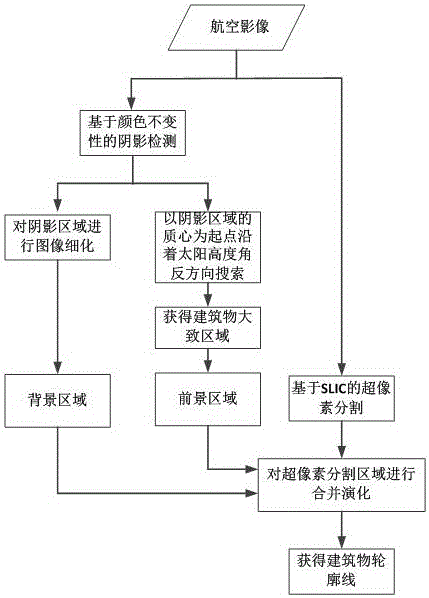
Building contour extraction method of aviation remote sensing image
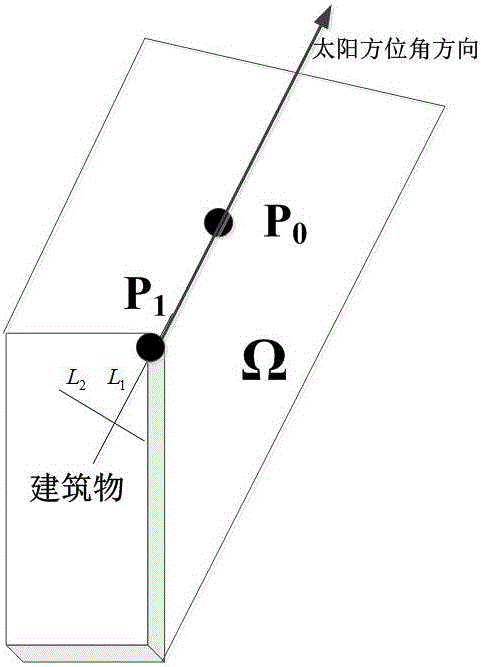
ActiveCN106127791AHigh precisionReduce the amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisElevation angleAviation
The invention provides a building contour extraction method of an aviation remote sensing image. A color invariant algorithm is used to detect the shadow area in the building in the aviation remote sensing image, the shadow area is subjected to image refinement, and a refinement result is used as the background area of the building. With the center of mass of the shadow area as a start point, the negative direction search to a sun elevation angle is carried out, the area of a building part is obtained, and the area is used as the target area of the building. A linear iteration cluster method is used to carry out super pixel segmentation on the aviation image. Based on the obtained background area and target area, a maximum similarity is used to carry out the combination of super pixel division blocks, and the contour of the building is extrated. According to the method, an object-faced segmentation idea and the context information of the target in the image are subjected to the extraction of the building contour, the precision of the building contour extraction is improved substantially, and the complexity of the method is reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
High-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of eutrophic lake water body
ActiveCN104390917AAchieving High-Precision EstimationReflect the space-time distributionColor/spectral properties measurementsRayleigh scatteringEutrophication
The invention provides a high-precision satellite MODIS (Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) monitoring method for chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake water body. The method comprises the following steps: screening a chlorophyll a evaluation index (NDBI) which is sensitive to the concentration change of the chlorophyll a and is not influenced by high suspended solids; obtaining a quantitative relation between the NDBI and the concentration of the chlorophyll a on the basis of biological optical model simulation; combining spectral information of the water body and the corresponding concentration of the chlorophyll a of the water body monitored in the field in Chaohu Lake in year 2013-2014, so as to obtain a chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on a ground measured spectrum (Rrs) and the NDBI; simulating different aerosol types and thicknesses, different solar altitudes, satellite observation angles and azimuth angles, so as to obtain a quantitative relation between the ground monitored remote sensing reflectance (Rrs) and simulated Rrc subjected to Rayleigh scattering correction; and further extending the chlorophyll a inversion algorithm based on ground measured spectral data to satellite image data subjected to the Rayleigh scattering correction. According to the method, the inter-annual and inter-monthly change rules and space distribution of the rules of the concentration of the chlorophyll a of a eutrophic lake can be accurately obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
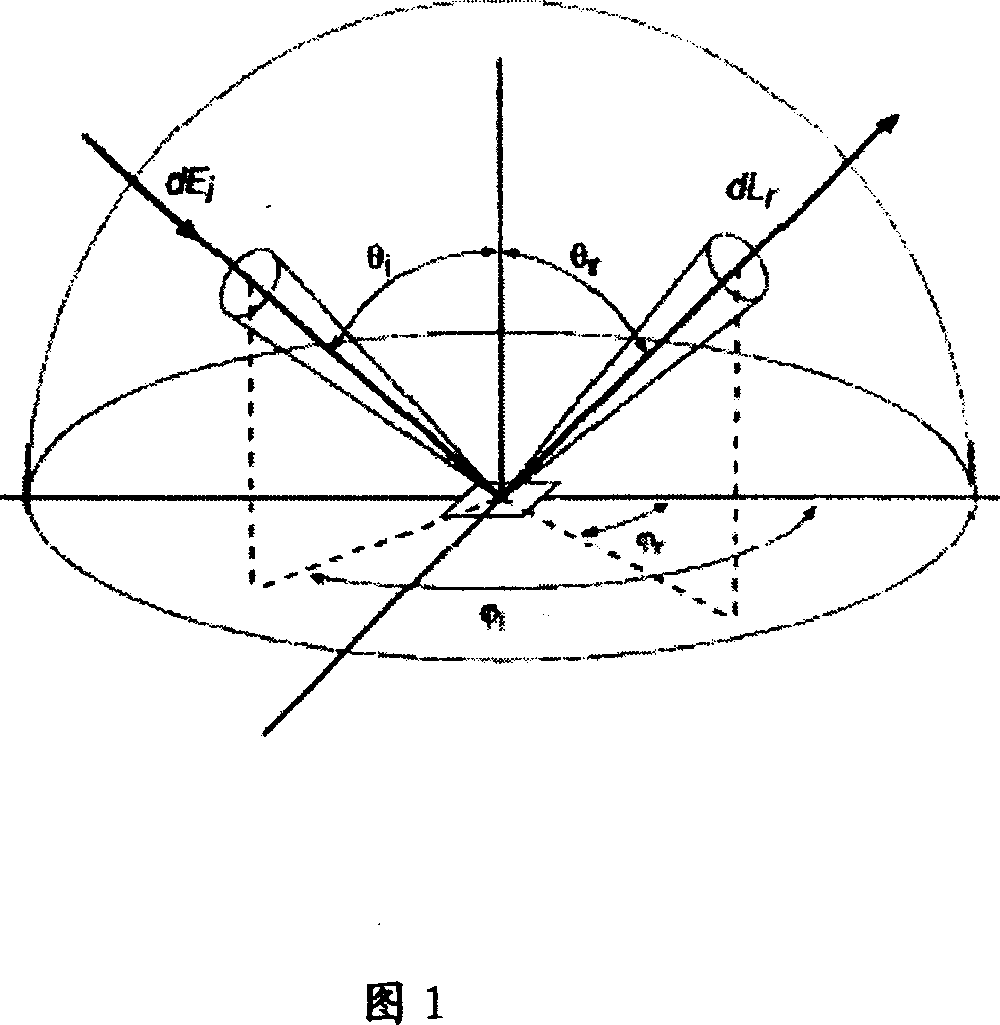
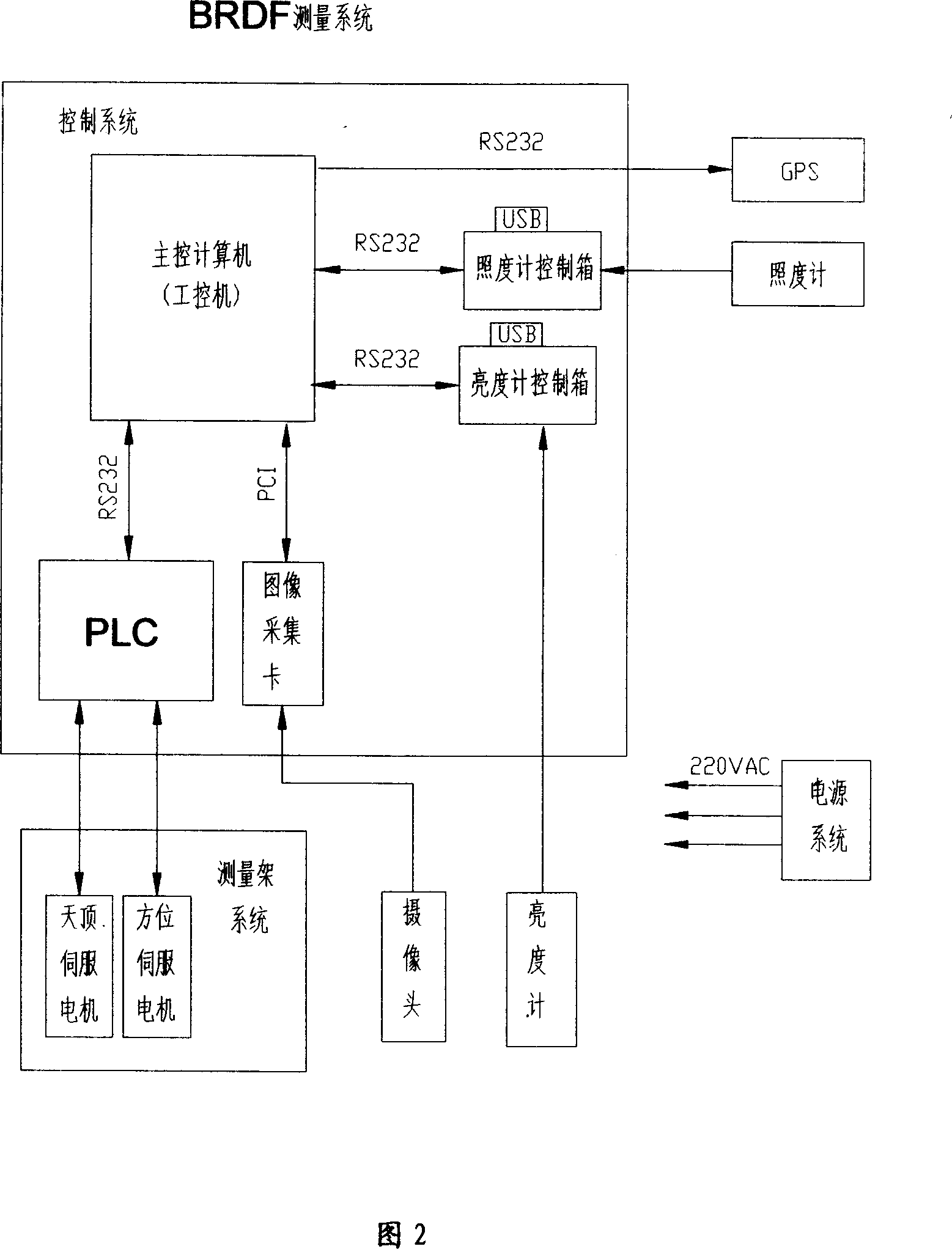
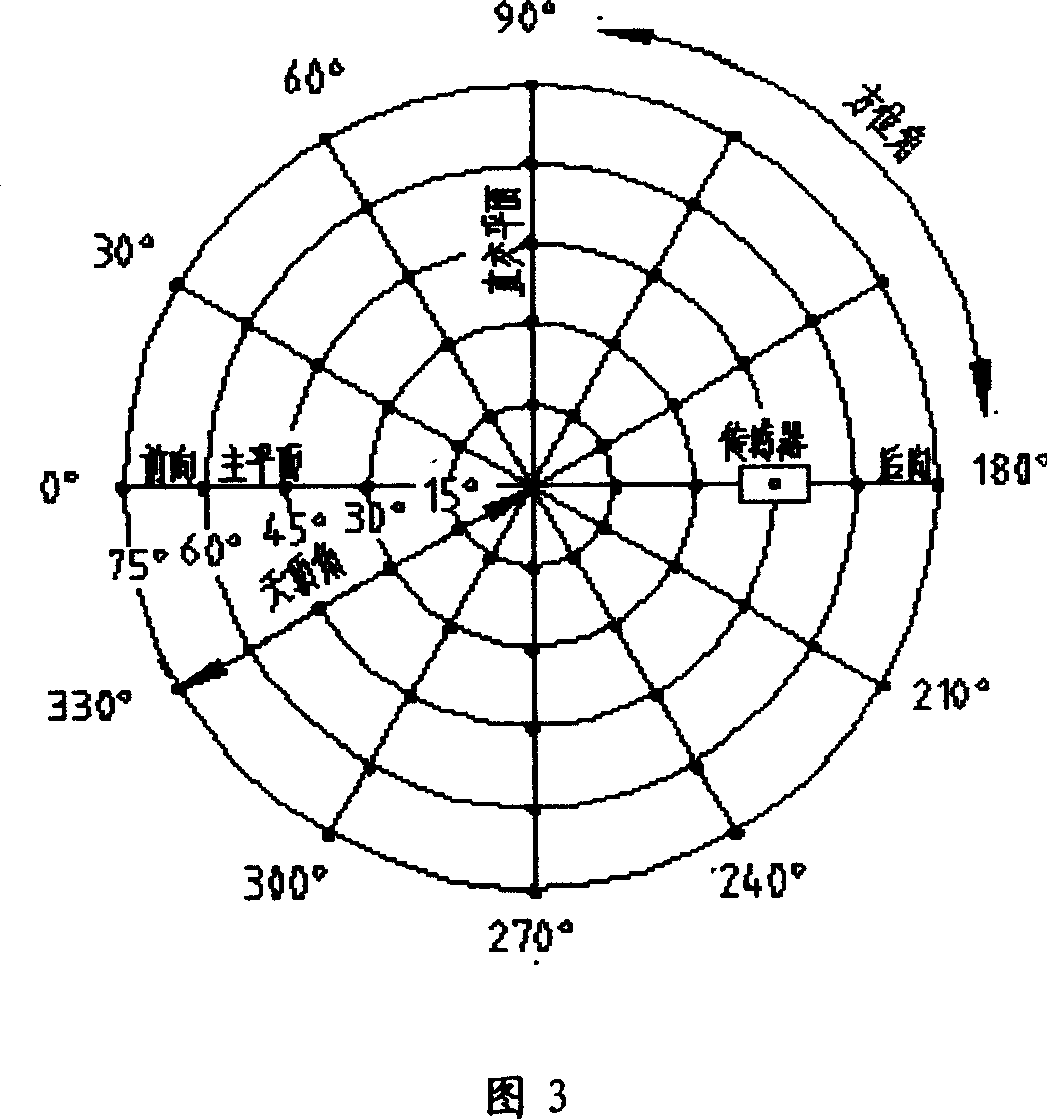
Outdoor high optical spectrum BRDF automatic detection method
InactiveCN1928533AHigh resolutionReduce the impactScattering properties measurementsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopySpatial directionMeasurement precision
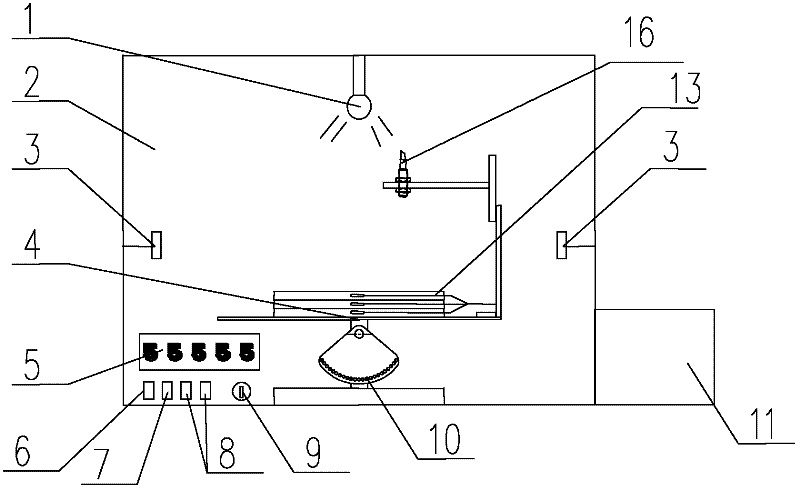
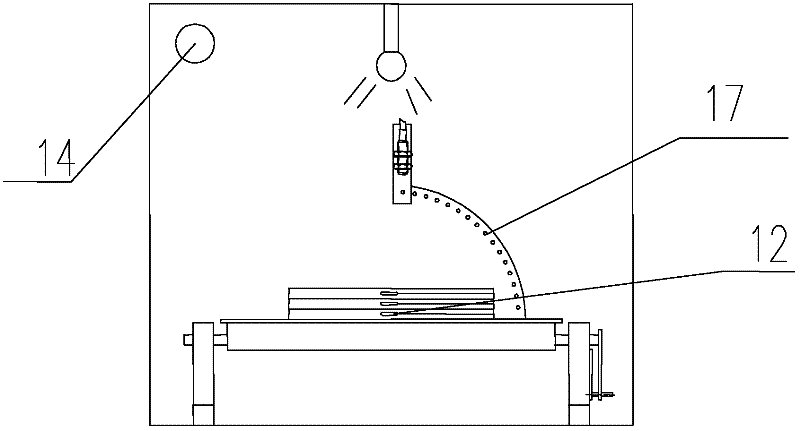
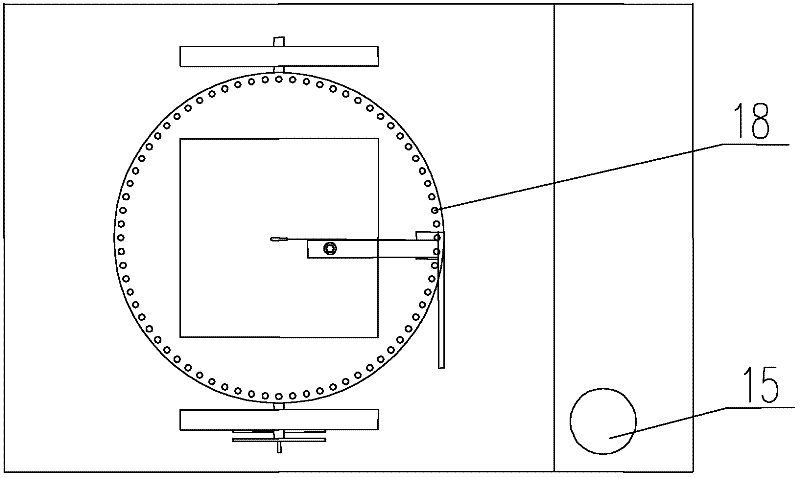
The disclosed BRDF measurement method comprises: setting an azimuth circle orbit with support feet and a zenith arc orbit with a movable spectrum amplitude luminance meter, arranging a spectrum irradiation meter. Wherein, when keeping the luminance meter on set position, it measures data to acquire and process to obtain target BRDF. This invention is benefit to improve measurement precision.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
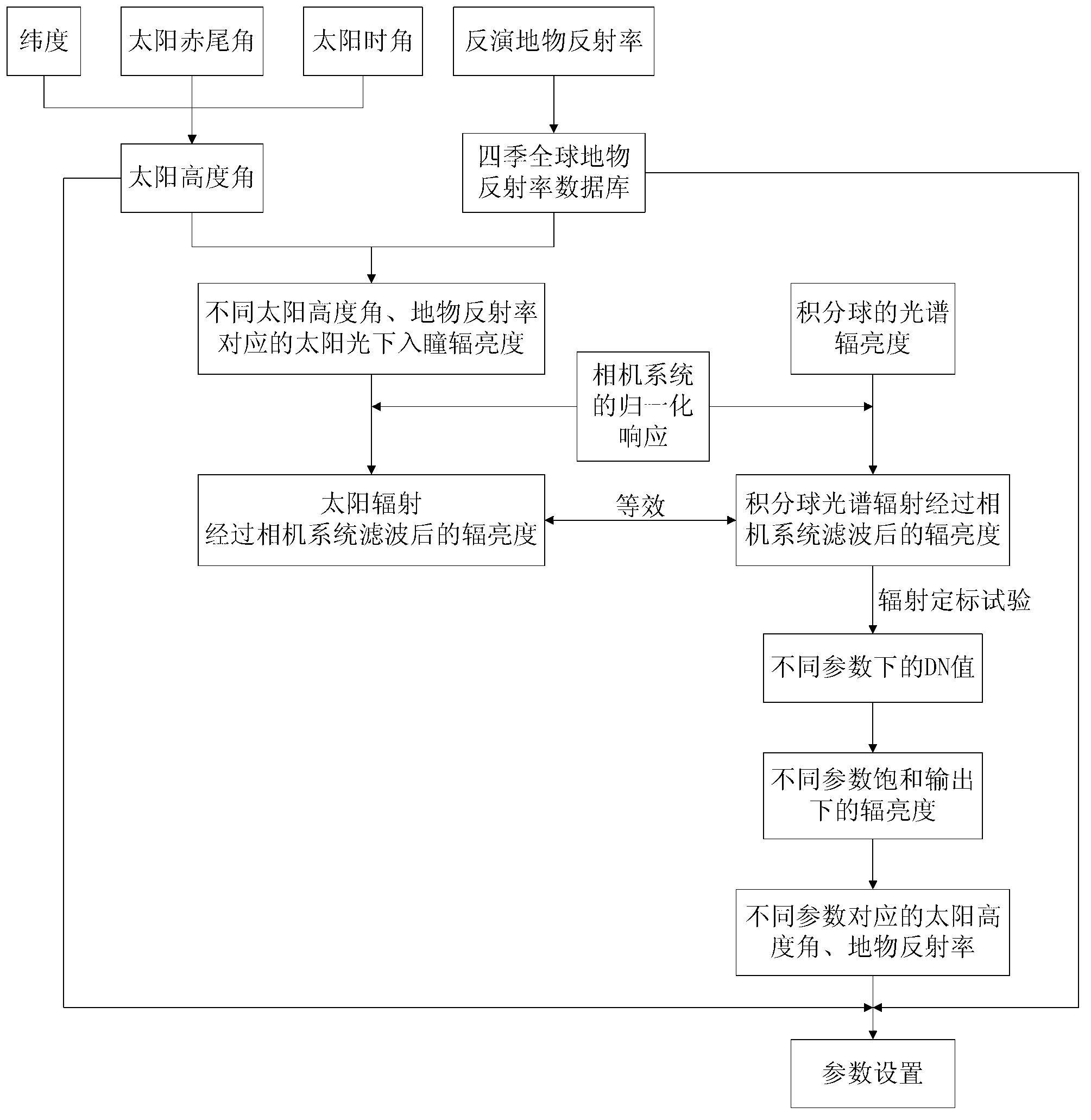
Method for on-orbit optimization of imaging parameters of TDI CCD camera
ActiveCN103322981AImprove impactImprove accuracyTelevision system detailsPicture taking arrangementsImaging conditionImaging quality
The invention discloses a method for on-orbit optimization of imaging parameters of a TDI CCD camera. The method is suitable for different imaging conditions. The method comprises the following steps of 1, aiming at a season change, building a global ground feature reflectivity database by an acquired satellite image, 2, making solar spectral radiance and integrating sphere spectral radiance equivalent by normalized responsibility of a camera system, and acquiring a relationship between a camera system output and apparent radiance according to a radiometric calibration test result, and 3, by the global ground feature reflectivity database and a solar altitude change, acquiring a camera parameter arrangement suggestion by the above computed result. Aiming at different ground feature objects and imaging conditions, the method can realize real time calculation of TDI integration class and gain and provide the calculation result for a user. The method guarantees accuracy, real-time performances and reliability of on-orbit parameter arrangement and improves on-orbit imaging performances and image quality of an optical remote sensor.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Sunshine intelligent household-entry system
InactiveCN102374477AImprove practicalityImprove tracking accuracyWith built-in powerUsing daylightElevation angleComputer module
The invention relates to a sunshine collection guiding device, and in particular discloses a sunshine intelligent household-entry system. On the basis of the existing sunlight collection guiding device, a tracking unit which consists of a GPS (global position system) module and a signal processing module and receives the time service of satellites is added; the signal processing module calculatesand acquires a sun azimuth signal and a sun elevation angle signal according to the time service signal of satellites; a mechanical driving part rotates according to the sun azimuth signal and the sun elevation angle signal to track the running track of the sun. According to the invention, the tracking pattern of the tracking unit composed of the GPS module and the signal processing module is unconcerned with the weather changes and ray of lights. So, under the insufficient illumination such as dark clouds, cloudy, the system provided by the invention can still continue to track the track of the sun according to the running track of the sun, thus the sun track performance of the system provided by the invention is improved.
Owner:李建敏
Inclined orbit spacecraft energy obtaining method based on yaw steering
InactiveCN104090612AAchieve pointingSimultaneous control of multiple variablesElevation angleNatural satellite
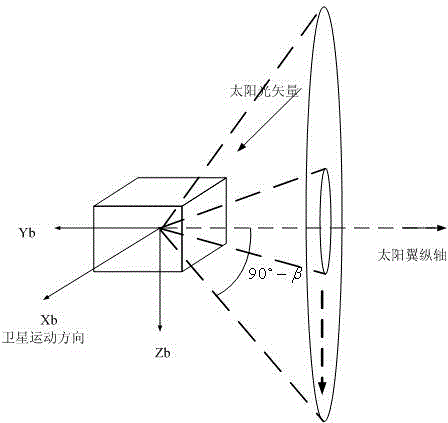
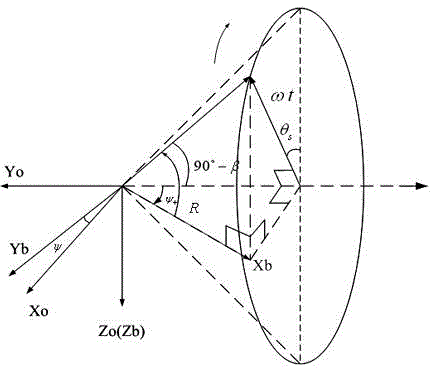
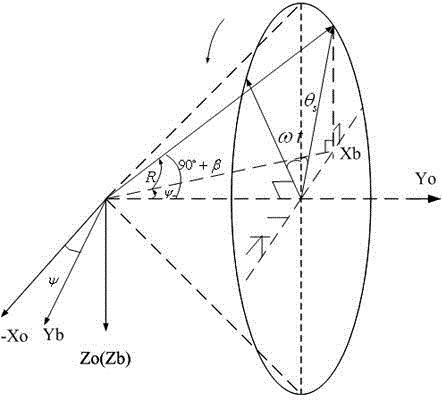
The invention relates to an inclined orbit spacecraft energy obtaining method based on yaw steering. The inclined orbit spacecraft energy obtaining method based on yaw steering includes the steps of calculating the solar unit vector of a J2000 inertial coordinate system according to Julian century numbers, calculating a solar elevation angle beta according to the solar unit vector, the satellite position and the satellite running speed, calculating a transfer matrix Aoi from the J2000 inertial coordinate system to an orbital coordinate system according to the satellite position and the satellite running speed, calculating the solar angular altitude theta s of the orbital coordinate system according to the solar unit vector and the transfer matrix Aoi from the J2000 inertial coordinate system to the orbital coordinate system, calculating the yaw steering angle psi and a sailboard drive angle R according to the solar elevation angle beta and the solar angular altitude theta s, and enabling the solar vector to be perpendicular to the plane of the solar sailboard through yaw posture control and sailboard one-dimensional driving to ensure that a spacecraft can obtain energy. The normal of the solar sailboard of the spacecraft can point to the sun under the situation of the large change range of the solar elevation angle and the complex lighting condition, so that it is ensured that the spacecraft can obtain solar energy under the situation of an inclined orbit.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINYUE METER FACTORY
Automatic removing method of vehicle-mounted laser point cloud noisy point based on angle and intensity
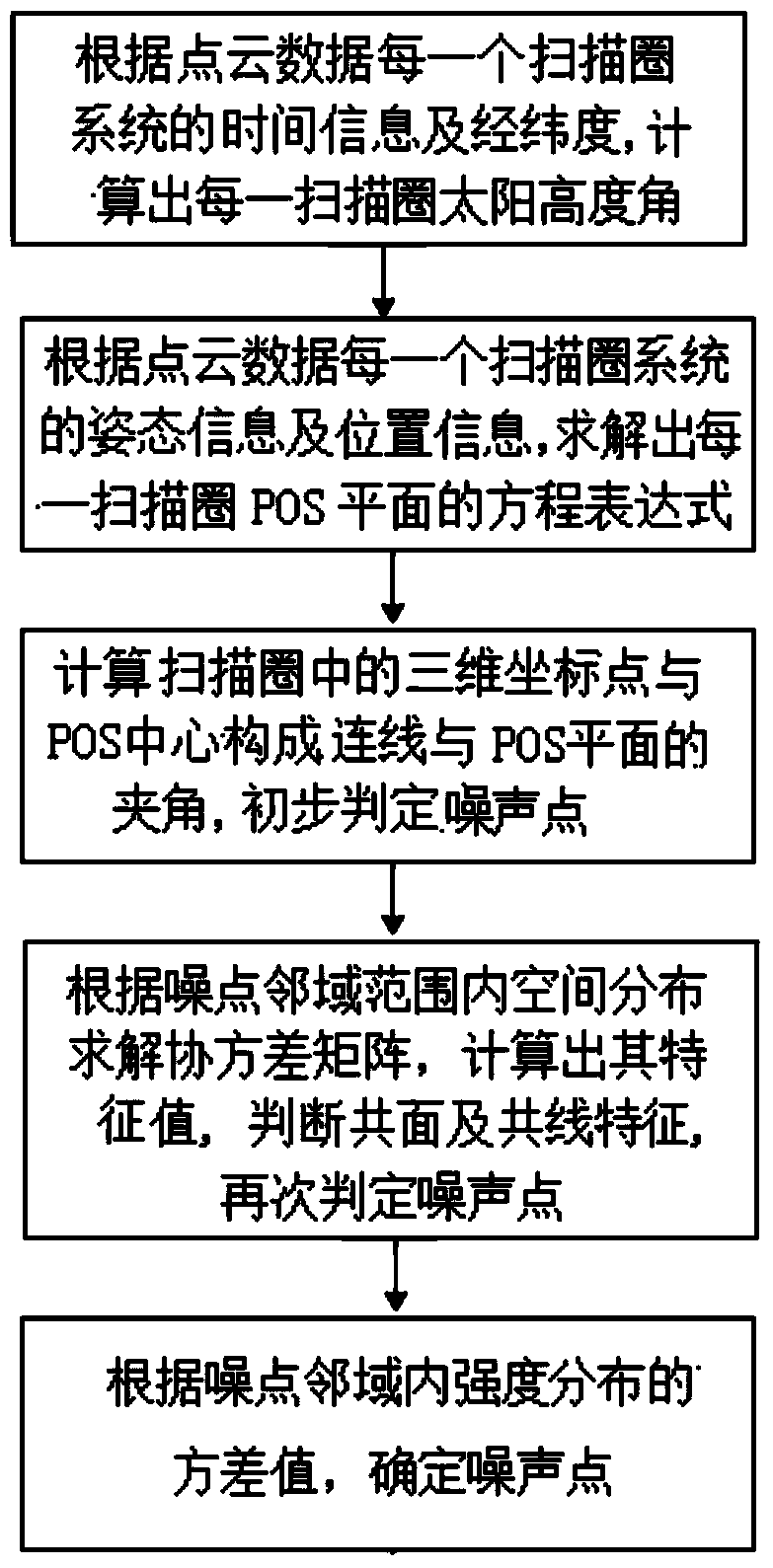
ActiveCN103542868AAutomated destinationHigh degree of automationSurveying instrumentsPicture interpretationPoint cloudLaser scanning
The invention relates to an automatic removing method of a vehicle-mounted laser point cloud noisy point based on angle and intensity. The operation steps comprise: acquiring point cloud data by utilizing a laser scanner, and calculating the solar altitude angle according to the time and longitude and latitude of each scan circle of the point cloud data; solving the equation of a POS (point of sale) plane of each scan circle time according to the posture and position information of a POS system; calculating an included angle between a connection line formed by three-dimensional coordinate points in a scan circle and the POS center and the POS plane, calculating the difference value of the included angle and the complementary angle of the solar altitude angle, comparing the difference value and the threshold value of the angle, and determining the points less than the angle threshold value to be the noisy points; calculating the covariance matrix of point coordinates in neighborhood of the noisy points, solving the property value of the matrix, determining the coplanarity and colinearity of the matrix, and determining the points less than the threshold value to be noisy points again; and calculating the variance value of intensity distribution in the neighborhood of the noisy points, and determining the points greater than the threshold value as the noisy points. The method has the advantages of high automation degree, quickness and high efficiency.
Owner:WUHAN HI TARGET DIGITAL CLOUD TECH CO LTD
Data collector of tree coronal layer analyzer
InactiveCN101413875AReduce mistakesReduce Optical Imaging ErrorsMaterial analysis by optical meansPorosityExtinction
A data acquisition device of a tree canopy analyzer comprises an optical filter, a sensing device which is connected with the optical filter in a sealing way; the sensing device is connected with an acquisition control unit and a memory device; the sensing device is an array which comprises a plurality of opto-electrical sensing units arranged in the same plane. The device measures characteristic parameterS of the tree canopy structure on the plane; when in working, the device is arranged under the canopy of trees or forest; the intensity of the sun illumination permeating the canopy and the change process of the facula structure in a period of time are measured so as to calculate leaf area indexes, extent of porosity, extinction coefficient of the canopy and anisotropic characters of the structure parameters; as the leaf space distribution, the zenith angle of the sensor and the solar altitude can be considered at the same time, the error can be reduced; in addition, as a photoelectric sensor is adopted, the optical imaging error is reduced; and the sensing unit is connected with a memory device, thus realizing data measurement in long period.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Photovoltaic system tracking and backtracking method
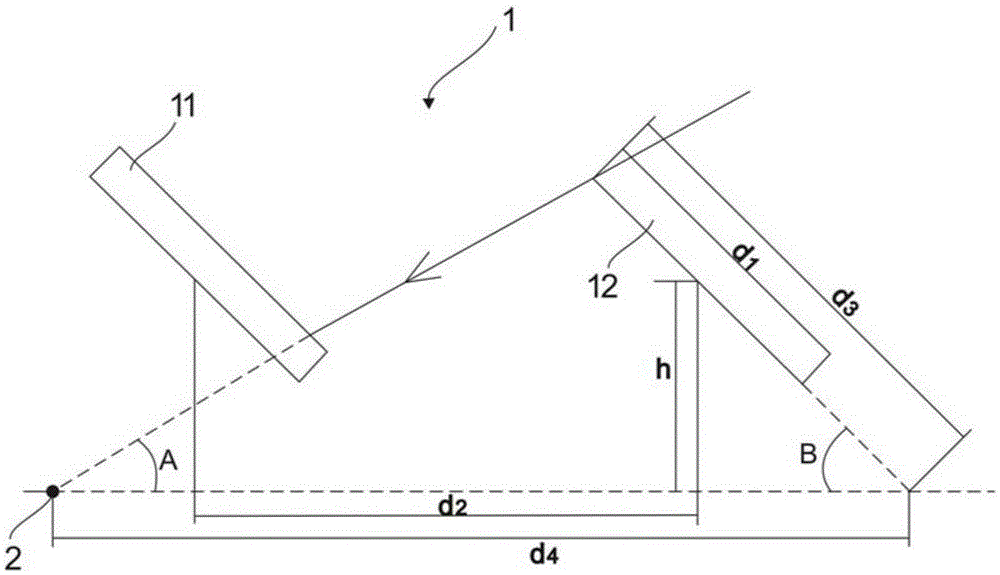
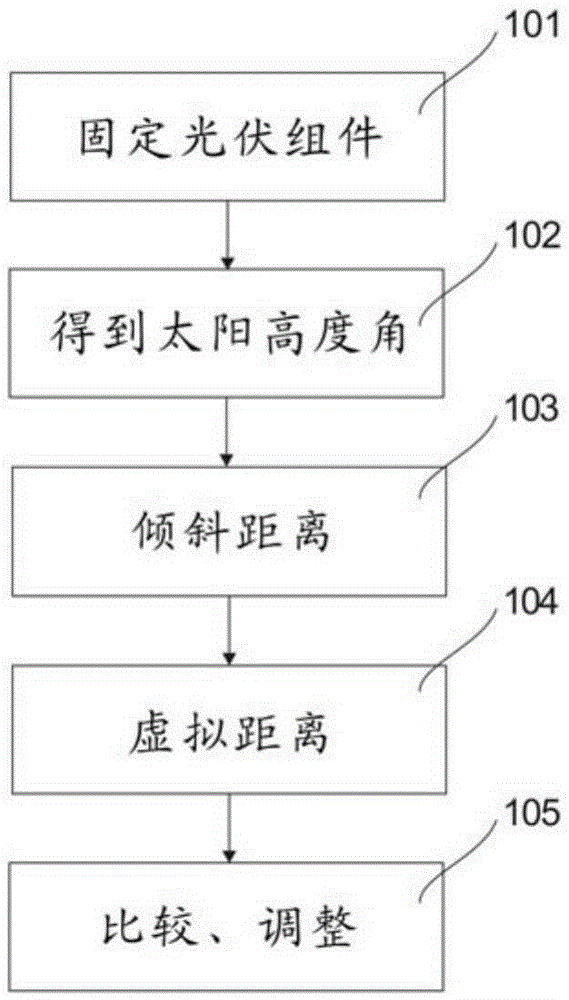
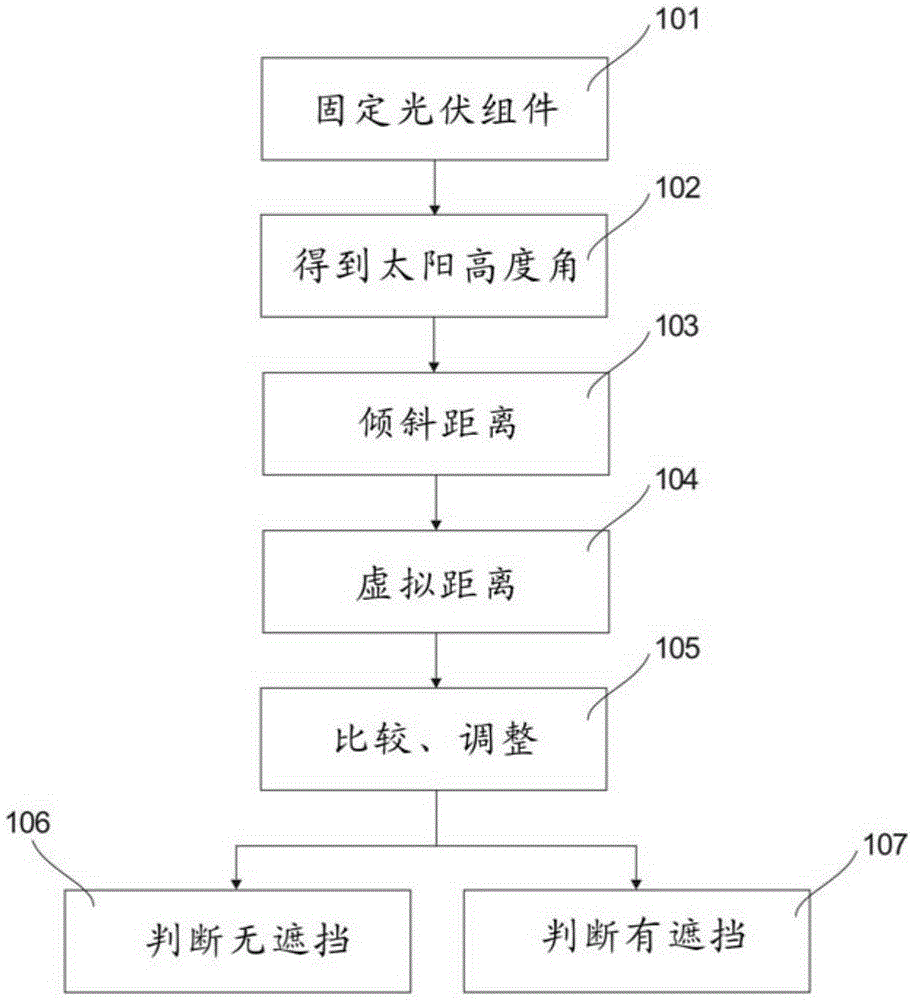
ActiveCN105242693AAccurate Angle SizeSimple structureControl using feedbackGenerating capacitySolar altitude
The invention provides a photovoltaic system tracking and backtracking method which comprises the following steps: a) fixedly arranging at least two photovoltaic assemblies; b) obtaining local time and latitude of a direct solar ray point, and obtaining the solar altitude angle; c) obtaining inclined plane length of each photovoltaic assembly, distance between the geometric center of the photovoltaic assembly and the horizontal plane and inclination angle, and obtaining an inclination distance of the photovoltaic assembly extending from the inclined plane top end to the horizontal plane along the bottom end direction; d) obtaining a virtual distance between an image point and a contact point of the inclination distance and the horizontal plane according to the solar altitude angle, the inclination angle and the inclination distance; e) comparing the distance between the geometric centers of the two adjacent photovoltaic assemblies and the virtual distance; and f) carrying out judgment according to the comparison data, and controlling the position relation between the photovoltaic assemblies and the solar rays through a tracker. Through the method, the solar altitude angle can be monitored, and the inclination angle of the photovoltaic assemblies is adjusted, thereby effectively preventing the adjacent photovoltaic assemblies from generating shadow in between, improving generating capacity and enlarging application range.
Owner:ARCTECH SOLAR HLDG CO LTD
In-orbit autonomous adjusting method of optical remote sensing satellite camera imaging parameter
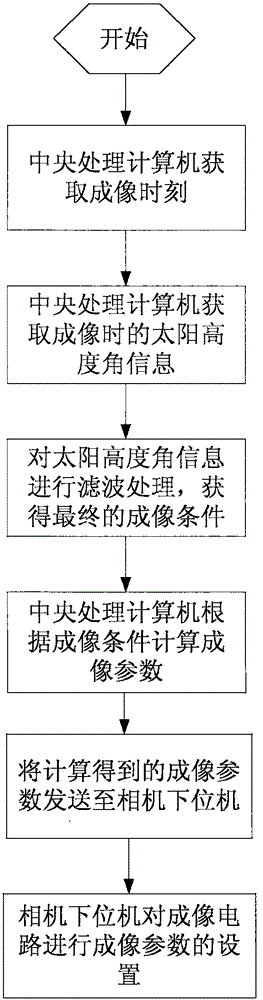
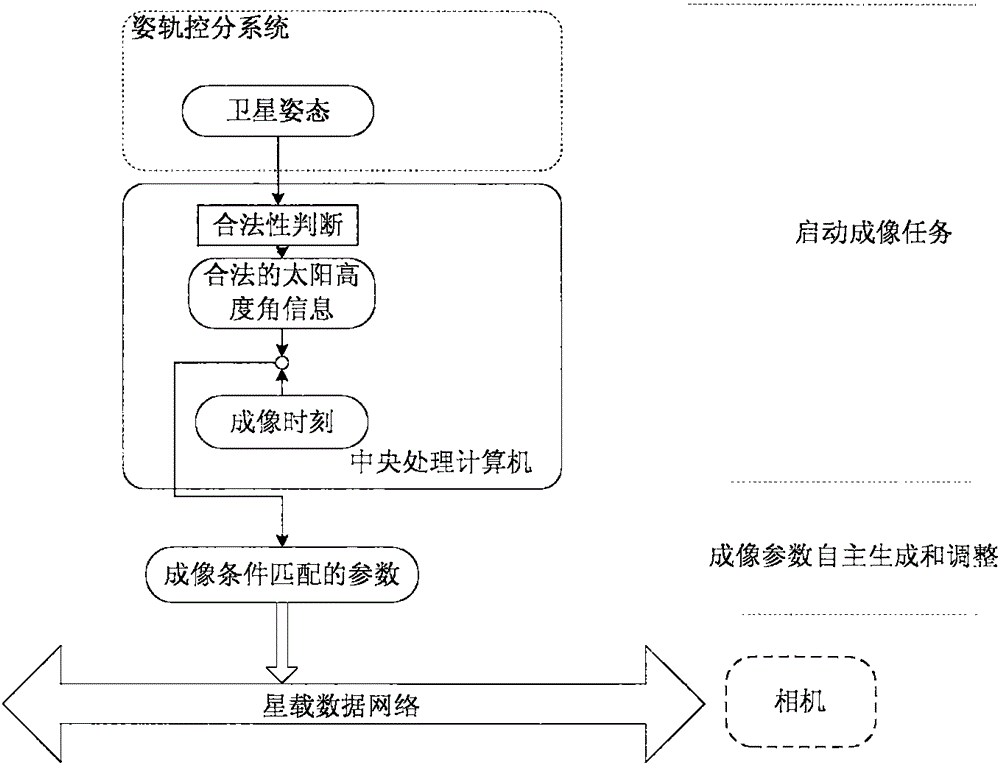
InactiveCN106441237AFlexible useAdjust imaging parametersPicture taking arrangementsElevation angleCamera control
The invention provides an in-orbit autonomous adjustment method of the imaging parameter of an optical remote sensing satellite camera. The method is used for adaptively adjusting the dynamic range of an optical remote sensing satellite camera to ensure obtaining of an image with optimum gray scale and layering quality. The method includes the following steps: acquiring the solar elevation angle when a shot subject is imaged by a spacecraft before or during imaging operation, and carrying out validity judgment to select suitable imaging parameters; periodically querying a relationship table of the solar elevation angle and a gain grade through a central processing computer in order to obtain a camera gain grade parameter value matching with the selected suitable imaging parameter; and sending the camera gain grade parameter value to a camera controller in a predetermined format in order to realize corresponding setting of an imaging circuit. The method can very well meet requirements of flexible adjustment of satellite-mounted CCD camera imaging gain and integral grade with the energy, can be widely applied to imaging parameter calculation of the optical remote sensing satellite, and has high practicality and generality.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
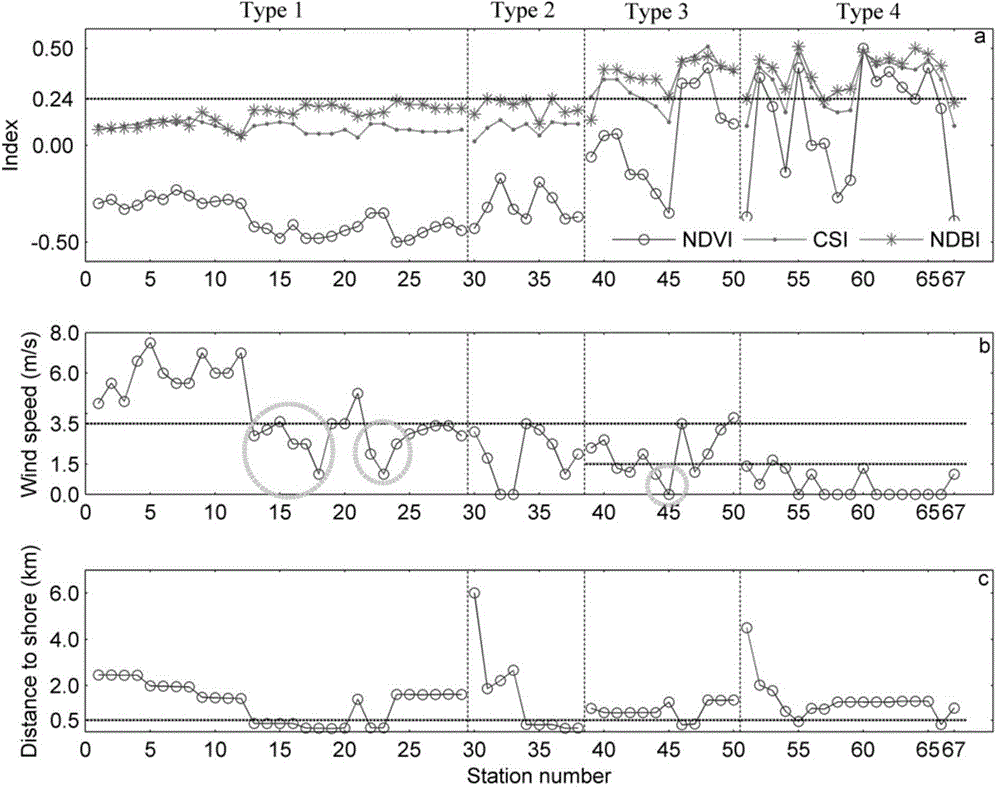
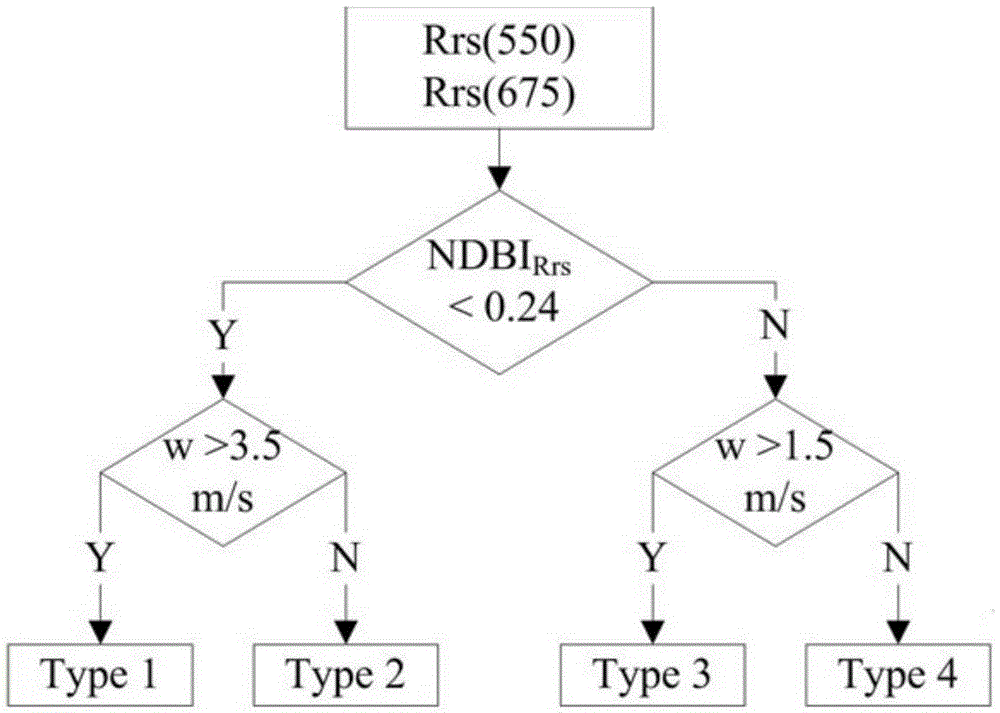
MODIS remote sensing evaluation method for eutrophication lake algae gauss vertical distribution structural parameters
The invention provides a MODIS remote sensing evaluation method for eutrophication lake algae gauss vertical distribution structural parameters. Based on field actual measurement data, a function expression and remote sensing identification method for the same for alge gauss vertical distribution are determined with a combination a alge bloom identification index NDBI and synchronous external environment factor wind speed; based on Hydrolight radiation transferring simulation, ground spectrum database of different alge gauss vertical distribution can be built; by the use of a BP neural network model, a remote sensing evaluation method for the lake algae gauss vertical distribution structural parameters based on simulation data is built; with simulation of various aerosol types, thickness, various solar altitude, satellite observation angles and azimuthal angles, a quantitative relation between ground-based simulation remote sensing reflectance ratio Rrs and a simulated Rayleigh scattering corrected Rrc is acquired; the evaluation method for the algae gauss vertical distribution structural parameters based on spectrum data simulation can be promoted to MODIS satellite image data corrected by Rayleigh scattering.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
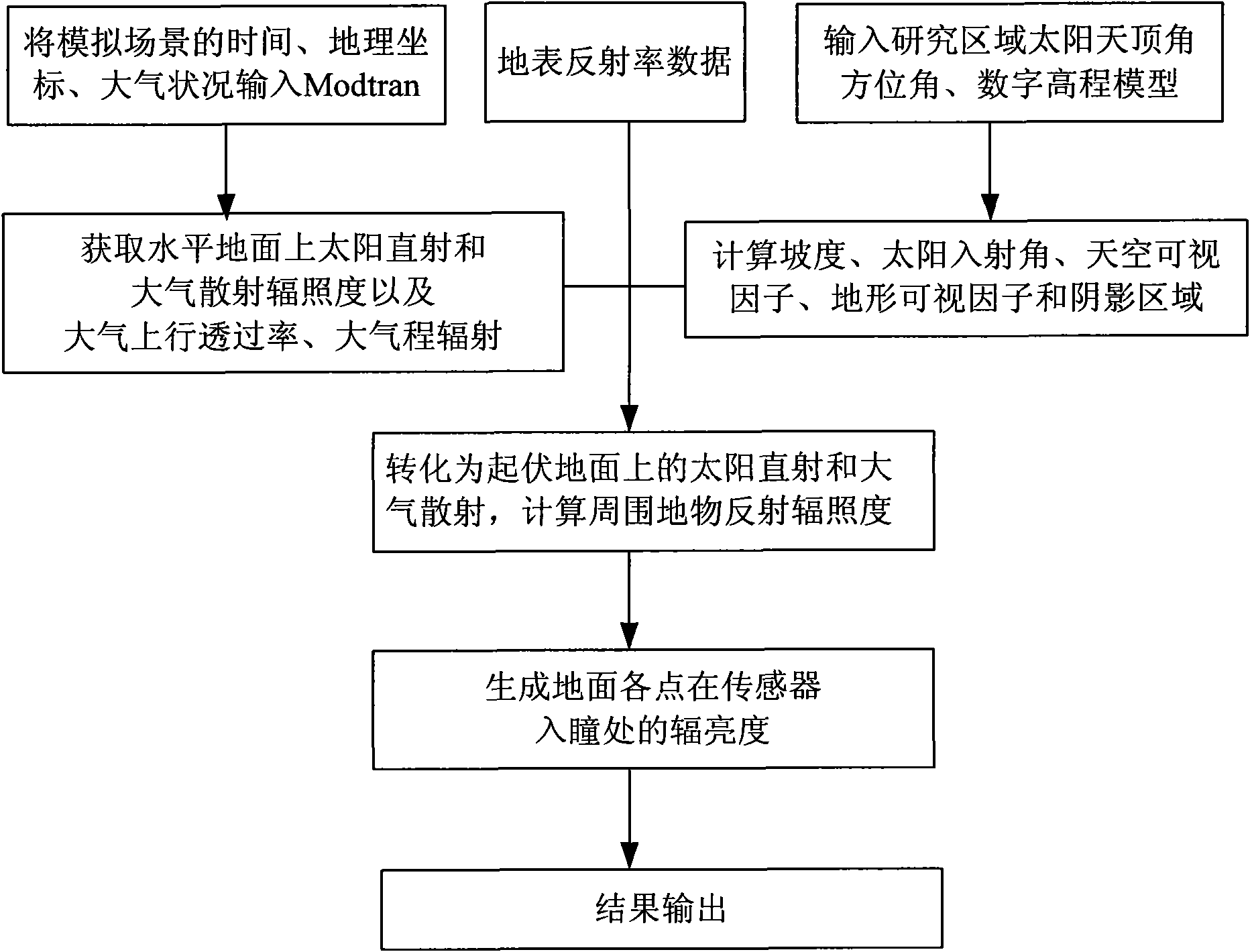
Method for realizing rugged topography remote sensing scene simulation
InactiveCN101598797ARealize high-precision simulationCorrection errorElectromagnetic wave reradiationEarth surfaceLandform
The invention relates to a method for realizing rugged topography remote sensing scene simulation, comprising: (1) inputting time, geographic coordinates, atmospheric condition and the like of the simulated scene into atmospheric transmissivity model Modtran with medium spectral resolution, and acquiring the irradiancy of direct solar radiation and atmospheric scattering on the level ground as well as atmospheric uplink transmittance and atmospheric path radiance; (2) inputting solar zenith angle, azimuth angle and digital elevation model, and calculating gradient, slope direction, solar incident angle, visible factors in the sky, topography visible factors and shadow regions; (3) according to the irradiancy of direct solar radiation and atmospheric scattering on the level ground and the data of ground surface reflectivity, calculating the irradiancy of direct solar radiation and atmospheric scattering on the rugged ground by utilizing the gradient, and calculating the solar incident angle, the visible factors in the sky, the topography visible factors and the shadow regions, the irradiancy of surrounding indirect radiation, thus forming total irradiancy received by ground surface by the irradiancy of direct solar radiation and atmospheric scattering on the level ground, the data of ground surface reflectivity and the irradiancy of direct solar radiation and atmospheric scattering on the rugged ground; (4) generating radiance data of all points on the ground at the entrance pupil of a sensor by utilizing the data of ground surface reflectivity, the atmospheric uplink transmittance and the atmospheric path radiance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Ground point target push-scanning imaging task parameter spaceborne solving method
ActiveCN105115477AAccurate imagingPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryTemporal changeInertial coordinate system
The invention provides a ground point target push-scanning imaging task parameter spaceborne solving method. The method comprises 1, building a coordinate system and defining vectors of a satellite, a ground object and the earth's core, 2, building an optical system equivalent optical path with a scanning mirror, 3, acquiring sub-satellite point solar altitude information, a satellite position and ground target information, 4, solving motion state characterization parameters of the satellite and ground target in an instantaneous inertial coordinate system, 5, calculating an expression of ground target coordinates and rate of change over time in the instantaneous inertial coordinate system, 6, calculating an expression of ground target coordinates and rate of change over time in a satellite body coordinate system and 7, building a constraint equation and calculating imaging task parameters. After acquiring ground point target coordinates, the satellite in orbit can automatically, fast and accurately adjust a scanning mirror in real time so that the scanning mirror targets an object and thus object imaging is ensured.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
Self-maintaining photovoltaic external sunshade device with adjustable length and angle and regulation and control method
ActiveCN104090587AThe effect of external shading is obviousImprove energy savingControl using feedbackSolar altitudeVertical angle
The invention discloses a self-maintaining photovoltaic external sunshade device with the adjustable length and angle and a regulation and control method. A sunshade photovoltaic power generation panel is mounted on a traditional external sunshade device, and multidirectional automatic regulation can be conducted according to the solar altitude and the azimuth angle, so it is guaranteed that the sunshade effect is optimal; meanwhile, energy for adjusting the sunshade photovoltaic power generation panel comes from photovoltaic power generation of the sunshade photovoltaic power generation panel. The adjustable external sunshade photovoltaic power generation panel is composed of three stretchable sunshade photovoltaic power generation panel sections, and the stretchable length of the sunshade photovoltaic power generation panel can be adjusted according to the solar radiation intensity and the sunshade requirements of residents; meanwhile, the sunshade photovoltaic power generation panel can be adjusted vertically or horizontally according to the direct solar radiation azimuth angle and the requirements for indoor sunshade effects. The optimal sunshade effect can be achieved through reasonable adjustment of the length, the horizontal angle and the vertical angle of the external sunshade photovoltaic power generation panel, and the sunshade photovoltaic power generation panel can absorb more solar heat.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
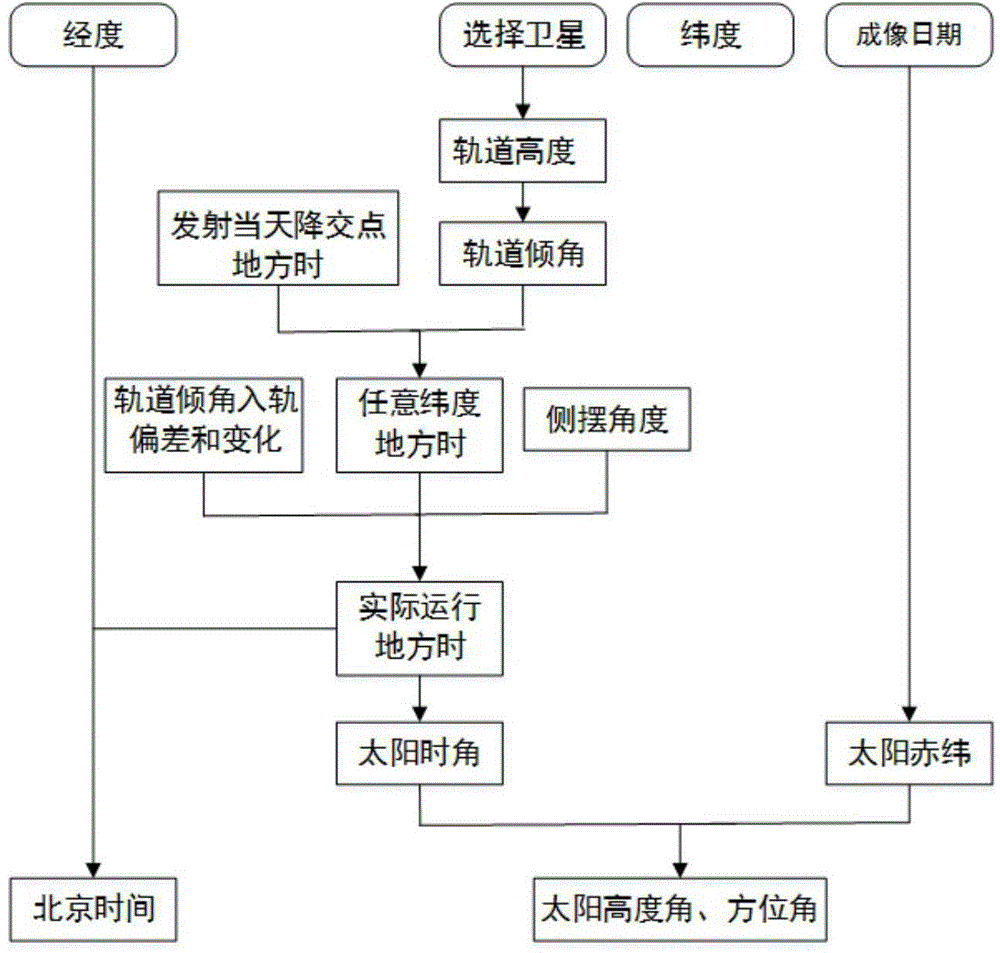
Method for obtaining satellite solar angle and time on basis of satellite orbit characteristics
ActiveCN104833335AEasy accessThe calculation result is accurateAngle measurementNatural satelliteLongitude
A method for obtaining satellite solar angle and time on the basis of satellite orbit characteristics comprises the following steps: (1) according to the satellite sun-synchronous orbit characteristics, calculating the orbit inclination angle from the height of the satellite orbit; (2) according to the number of satellite orbits, calculating the longitude and Beijing time of sub-satellite point of the position where a satellite descending orbit intersects the equator, and converting the Beijing time into the local time so as to obtain the time of the position; (3) calculating to obtain the local times of any latitude where the satellite sub-satellite point pass; (4) according to the orbit injection error of satellite orbit inclination angle and the daily change rate of satellite orbit inclination angle during the operation process, calculating to obtain the change of satellite local time and actual local times of any latitude; (5) calculating to obtain the actual local time after satellite side-sway; (6) calculating to obtain the solar altitude, solar azimuth, and the Beijing time of an observation site. The provided method can precisely obtain the solar altitude, solar azimuth, and imaging time of a satellite according to a remote sensing satellite nominal orbit and changes thereof without knowing the satellite ephemeris data and specific imaging time.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
On-track space camera gain regulating method
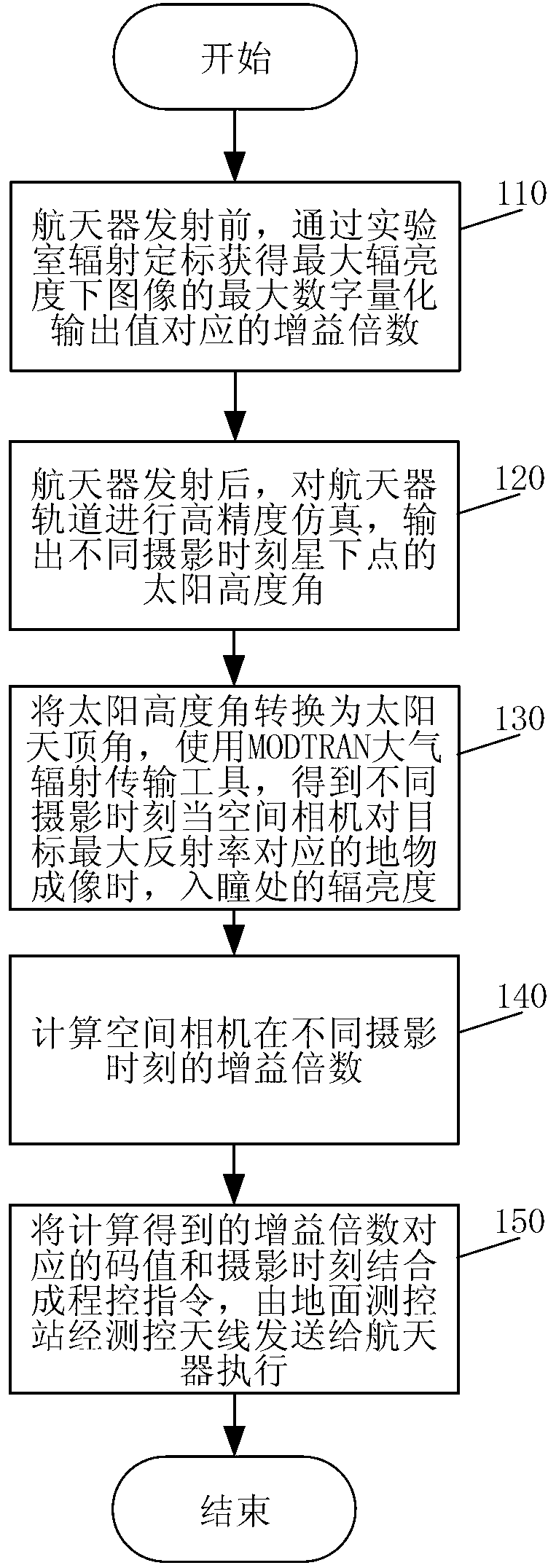
ActiveCN103322982ASolve the darkSolve the image level is not richPicture taking arrangementsEarth observationEngineering
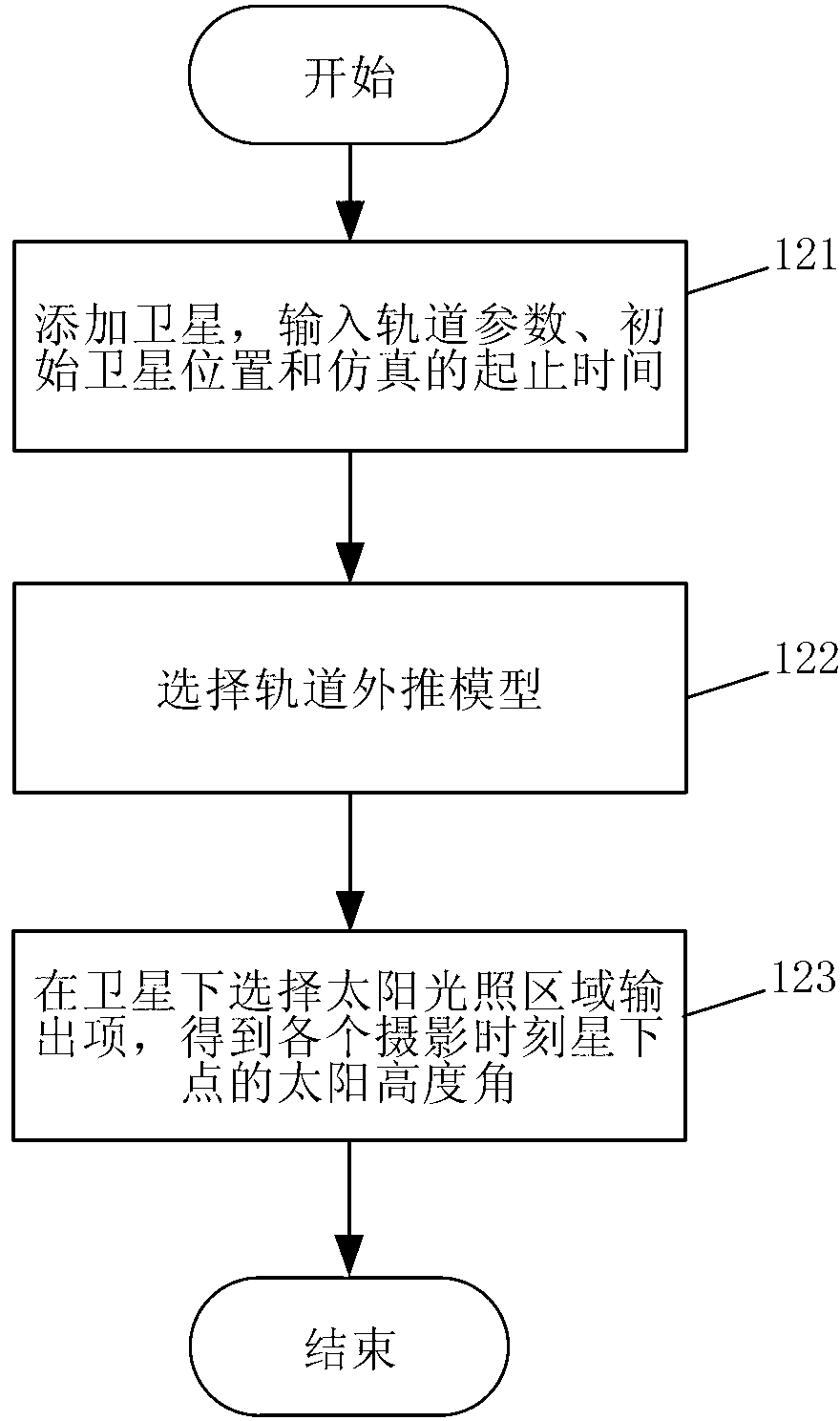
The invention discloses an on-track space camera gain regulating method, which relates to an on-track gain regulating method of a space camera for earth observation, and aims to the solve the problems that at present, a space camera adopts a fixed gain so as to lead to overall dimming of part of images, poor image gradation, low signal to noise ratio and the like. The regulating method comprises the following steps of: before a spacecraft is launched, acquiring a gain factor corresponding to the maximal digital quantification output value of images under maximal radiance through laboratory radiometric calibration; after the spacecraft is launched, simulating the track of the spacecraft with high accuracy, and outputting the solar altitude of sub-satellite points at different shooting time; converting the solar altitude into the solar zenith angle, thereby obtaining the radiance of an entrance pupil part by an MODTRAN atmospheric radiation transfer tool when the space camera forms images of a ground feature corresponding to the maximal object reflectivity at different time; calculating gain factors of the space camera at different shooting time; combining the code values corresponding to the gain factors obtained through calculation with the shooting time into a program control instruction, and sending the program control instruction from a ground measurement and control station to the spacecraft to execute through a measurement and control antenna.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Comprehensive testing device for improving thermal physical environmental performance of heat-reflecting asphalt pavement
InactiveCN102539658ASimulate the distribution of temperature fieldGood correlationMaterial testing goodsCombined testData acquisition
The invention discloses a comprehensive testing device for improving the thermal physical environmental performance of a heat-reflecting asphalt pavement. The device consists of an environmental control system, a data acquisition system, a test piece assembling system. According to the device, the acquisition of a structural layer temperature of the asphalt pavement under the action of solar thermal radiation can be realized, the temperature variation conditions of a pavement structure with a heat-reflecting coating and a pavement structure without the heat-reflecting coating are compared and the heat reflecting approach of the heat-reflecting asphalt pavement at different solar altitudes or angles can be measured so as to evaluate the influence of the heat-reflecting asphalt pavement on the surrounding environment. The device has the advantages of being simple in test and maintenance, convenient in data acquisition and the like.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
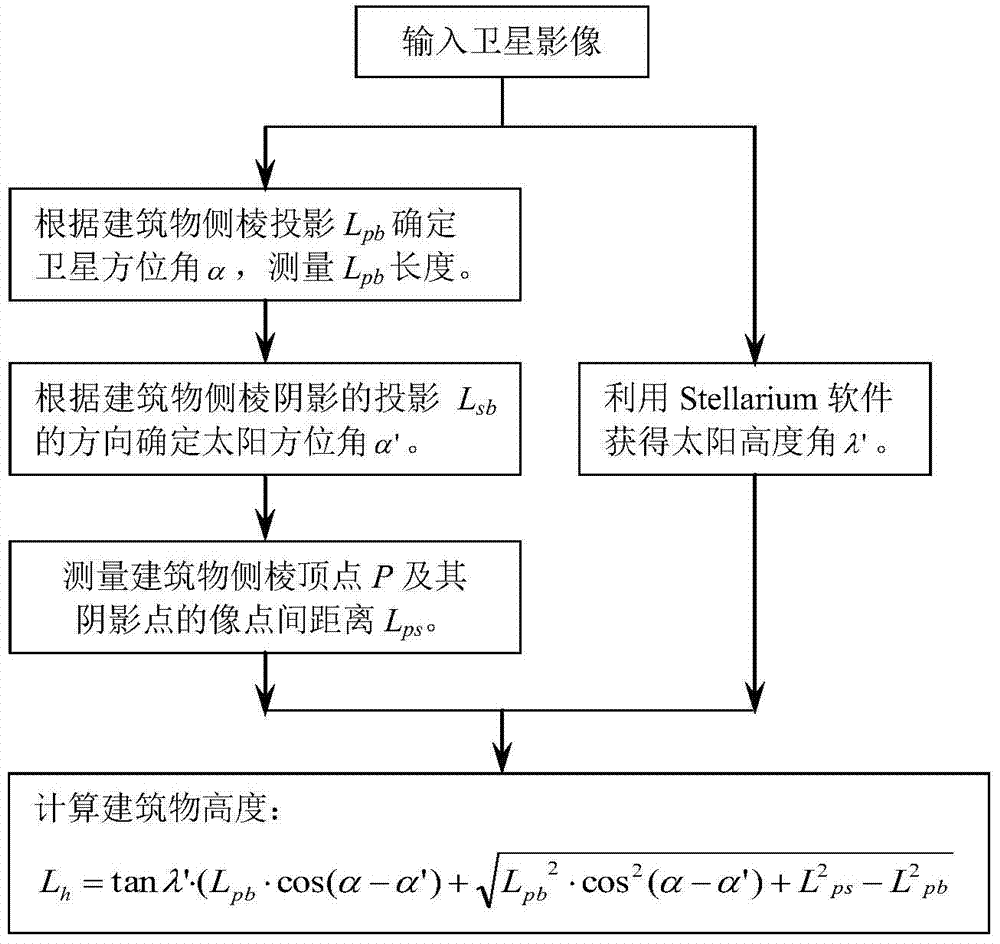
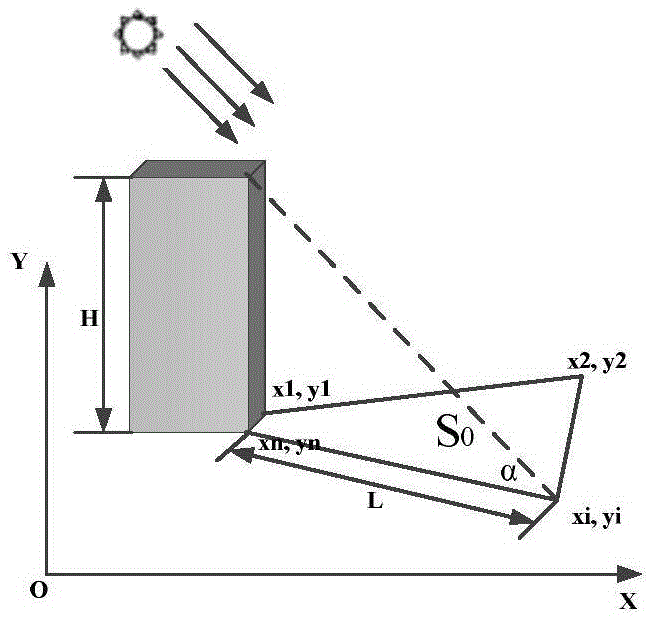
Single satellite image-oriented self-acquired triangular element height calculation method
ActiveCN103791885AThe solution is not easy to obtainAltitude calculation works wellAngle measurementHeight/levelling measurementElevation angleNatural satellite
The invention provides a single satellite image-oriented self-acquired triangular element height calculation method. The method comprises the steps of calculating three angle parameters, namely a sun elevation angle, a sun azimuth angle and a satellite azimuth angle, according to direction information in a single satellite image and a relation between the sun azimuth angle and the sun elevation angle, performing equivalent expression on a satellite elevation angle through a building height and a building projection length, and finally calculating a triangular element height which does not contain the satellite elevation angle. The effect of realizing calculation on the height of a building in the single satellite image is good.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
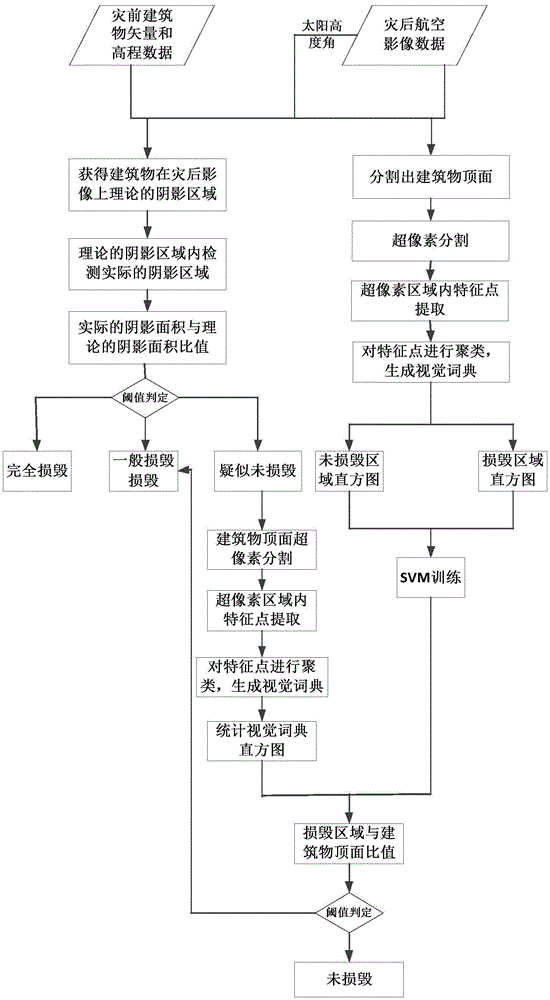
Aviation image building damage detection method based on shadow and texture characteristics
ActiveCN105631892AAchieve the effect of damageHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisAviationThree level
The invention discloses an aviation image building damage detection method based on shadow and texture characteristics, and the method comprises the steps: estimating a theoretical shadow area of a building in an image through the vector data and altitude data of the building before damages and a solar altitude angle; carrying out the detection of an actual shadow in the theoretical shadow area through employing constrained color invariance; obtaining the actual shadow area of the building; obtaining the damage level of the building according to the proportional relation of the actual shadow area and the theoretical shadow area, and dividing the damage level into three levels: complete damage, general damage, and suspected intactness; detecting the top surface of the intact building through employing a vision bag-of-word model, and further judging whether the building is damaged or not. The method integrates the shadow information (height) and top surface information (texture) of the building for detection, avoids registering difficulties in conventional data fusion, and improves the detection accuracy of the damage of the building.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com