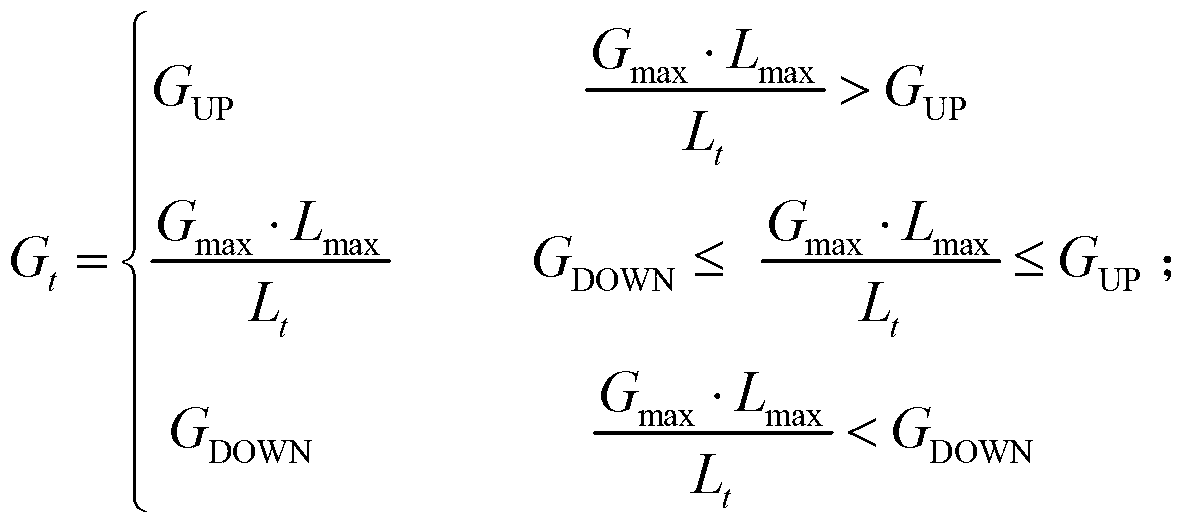On-track space camera gain regulating method
A technology of a space camera and an adjustment method, which is applied in the direction of a photographic device, etc., can solve the problems of large difference in image grayscale, insufficient image layers, and overall dark image, and achieves the effects of high accuracy, high precision, and improved processing efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
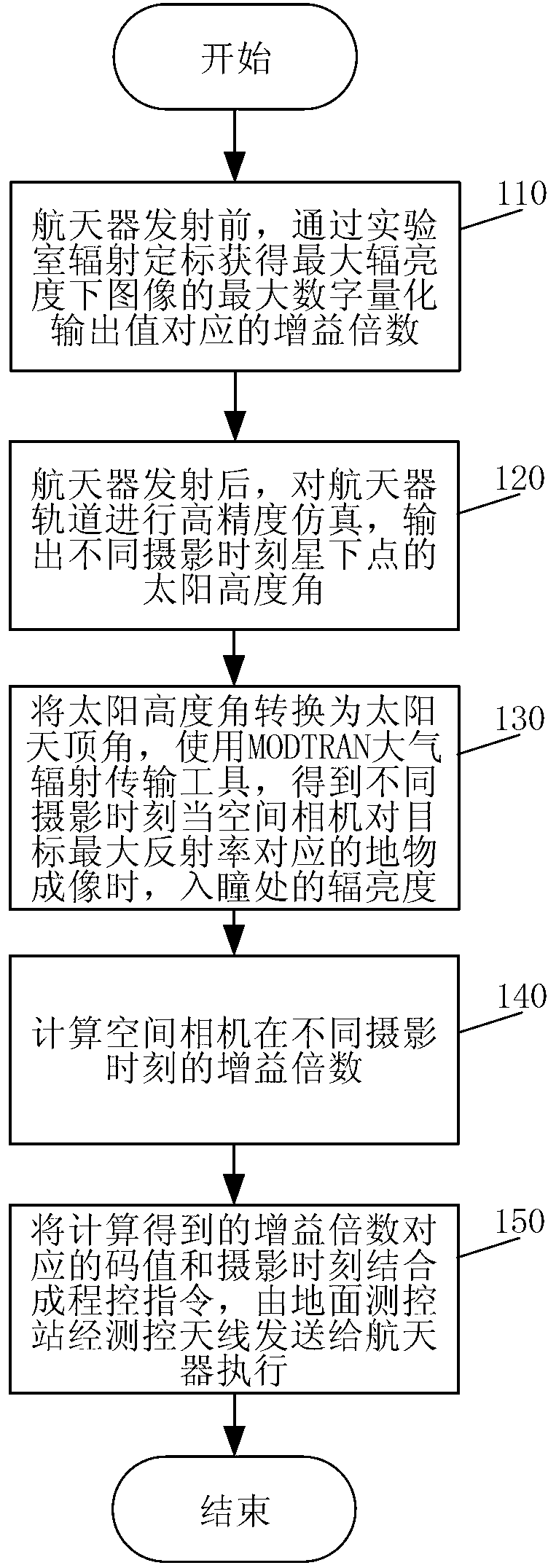
[0024] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 and figure 2 Describe this embodiment, a method for adjusting the gain of a space camera on-orbit, the method is implemented by the following steps:
[0025] Step 1. Before the launch of the spacecraft, during the radiation calibration of the space camera laboratory, the maximum radiance L required by the user max Adjust the gain of the space camera down, so that the digital quantization output value of the image increases from small to the maximum value, and the gain multiple G corresponding to the maximum digital quantization output value of the image is obtained max ;
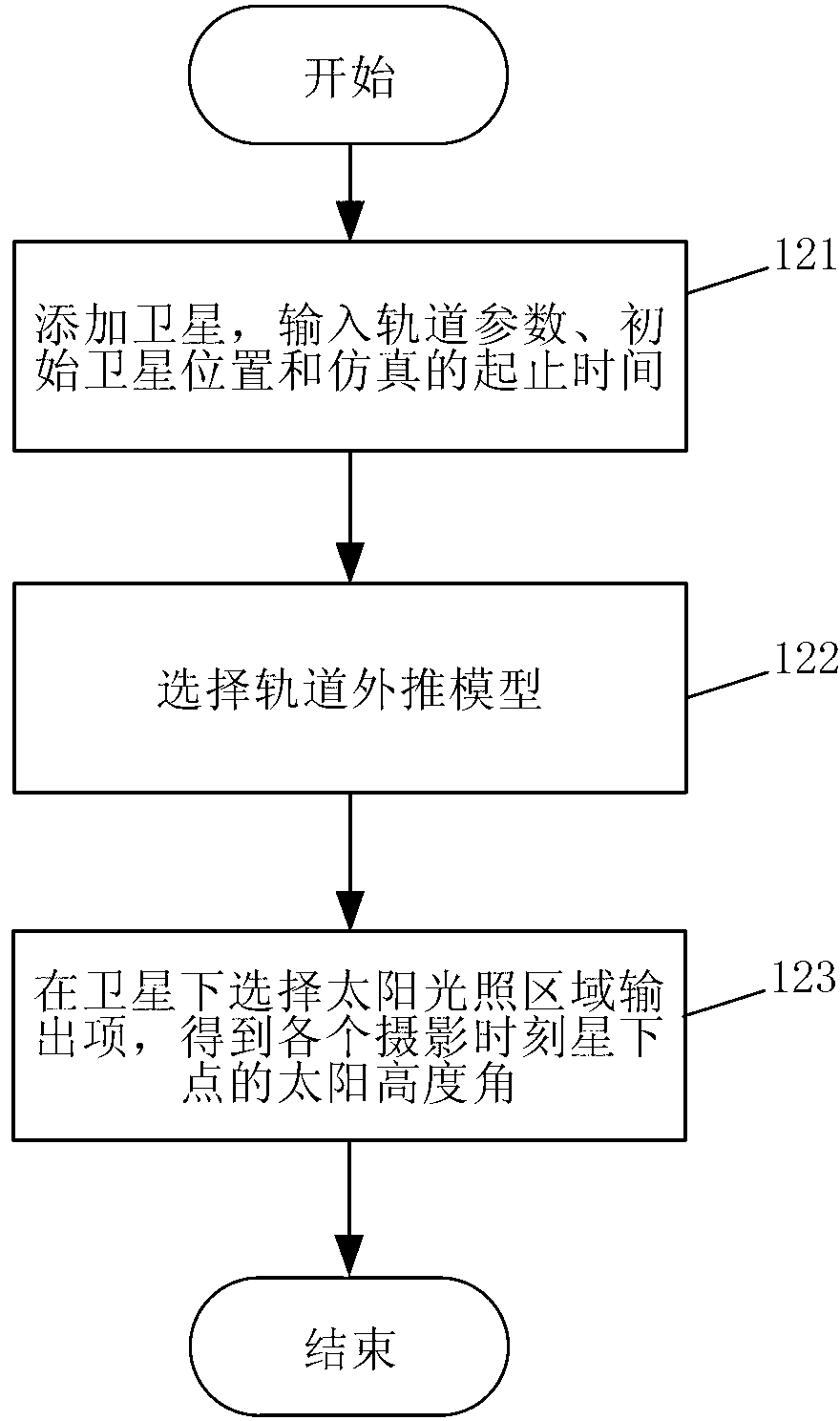
[0026] Step 2, after the spacecraft is launched, carry out high-precision simulation on the orbit of the spacecraft platform such as the satellite or the space station equipped with the space camera, and output the solar altitude angle of the sub-satellite point at different photography moments; the simulation adopts the STK simulation tool, and ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0036] Specific embodiment two, combine figure 1 and figure 2 This implementation mode is described. This implementation mode is an example of the on-orbit adjustment method for the space camera gain described in the first specific implementation mode. Through this example, the specific implementation process of the on-orbit adjustment method for the space camera gain is described in detail. In this embodiment, the wavelength range of the space camera is 510-690nm, and the maximum radiance L required by the user max 42.236W / m 2 ·sr, the target maximum reflectance required by the user is 0.5.
[0037] Step 110, before the launch of the spacecraft, set the radiance output by the integrating sphere and the maximum radiance L required by the user during the radiometric calibration of the space camera. max Same, that is 42.236W / m 2 · sr. Adjust the gain of the space camera so that the digital quantization output value of the image increases from small to the maximum value, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com