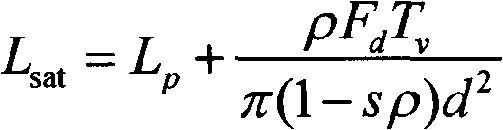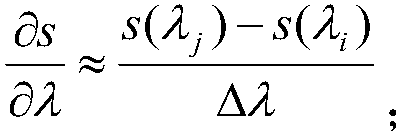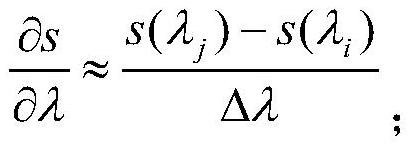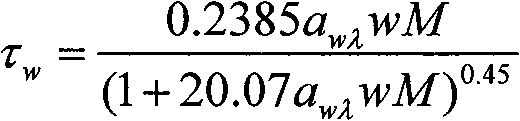Patents
Literature
36 results about "Band ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
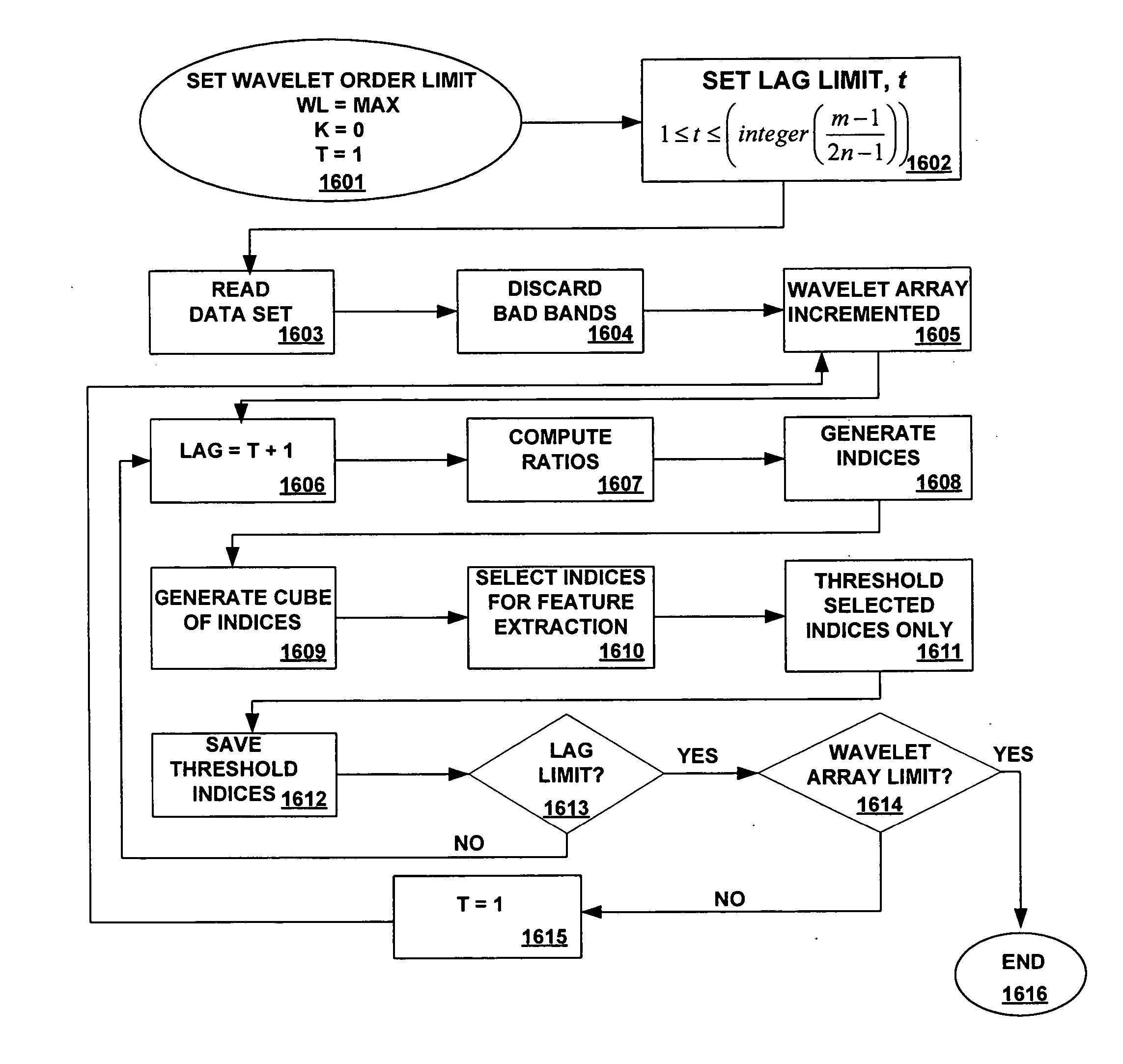
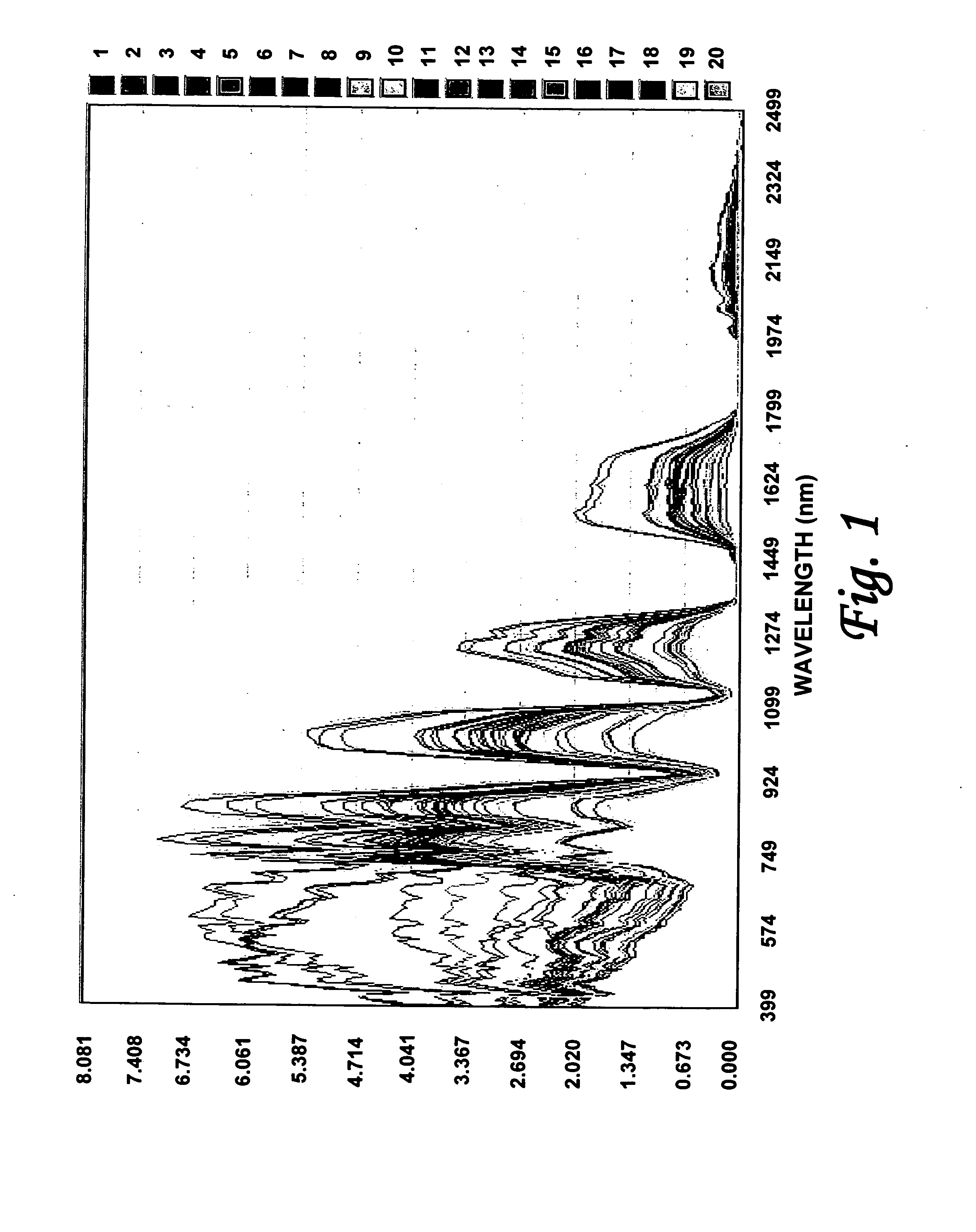
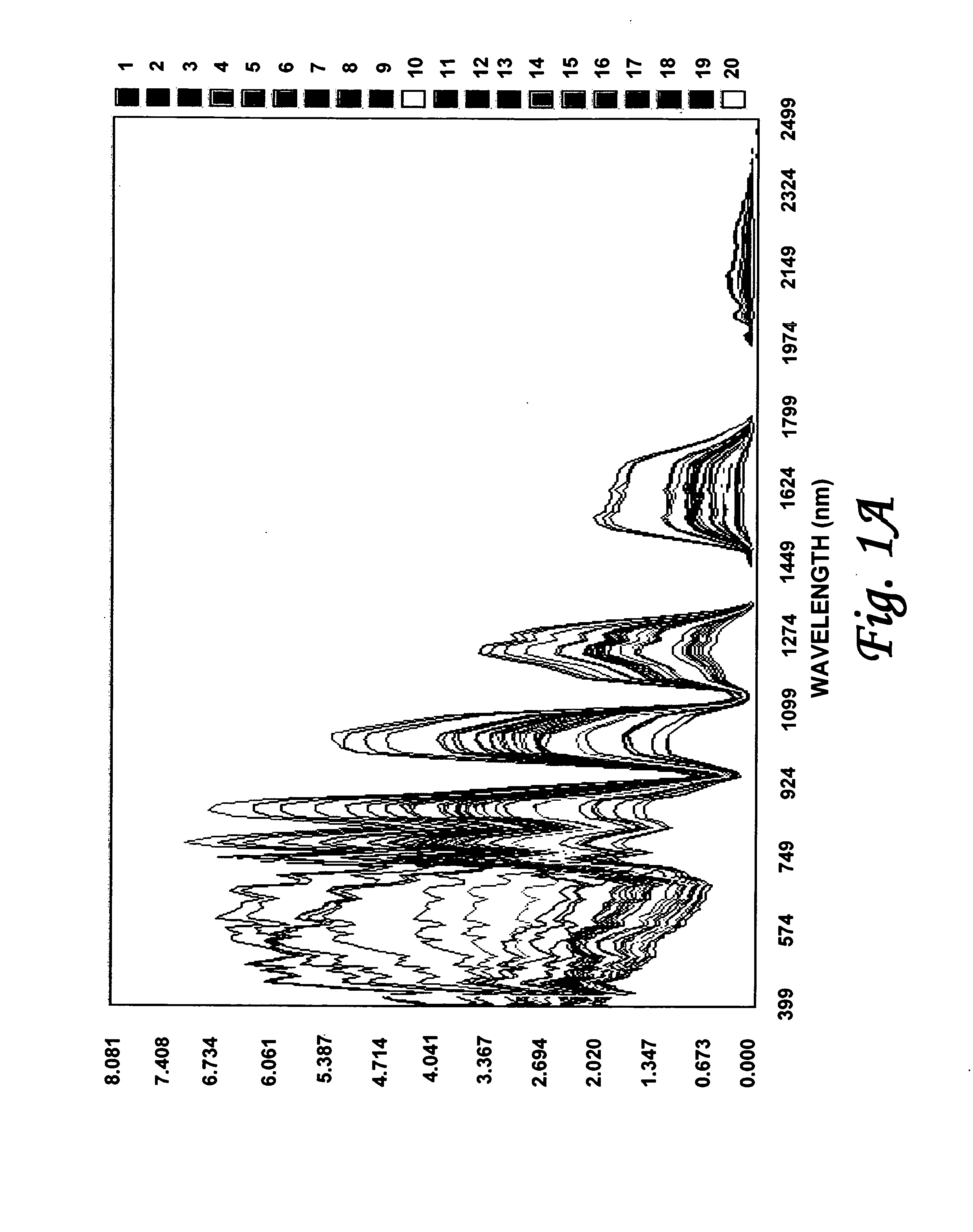
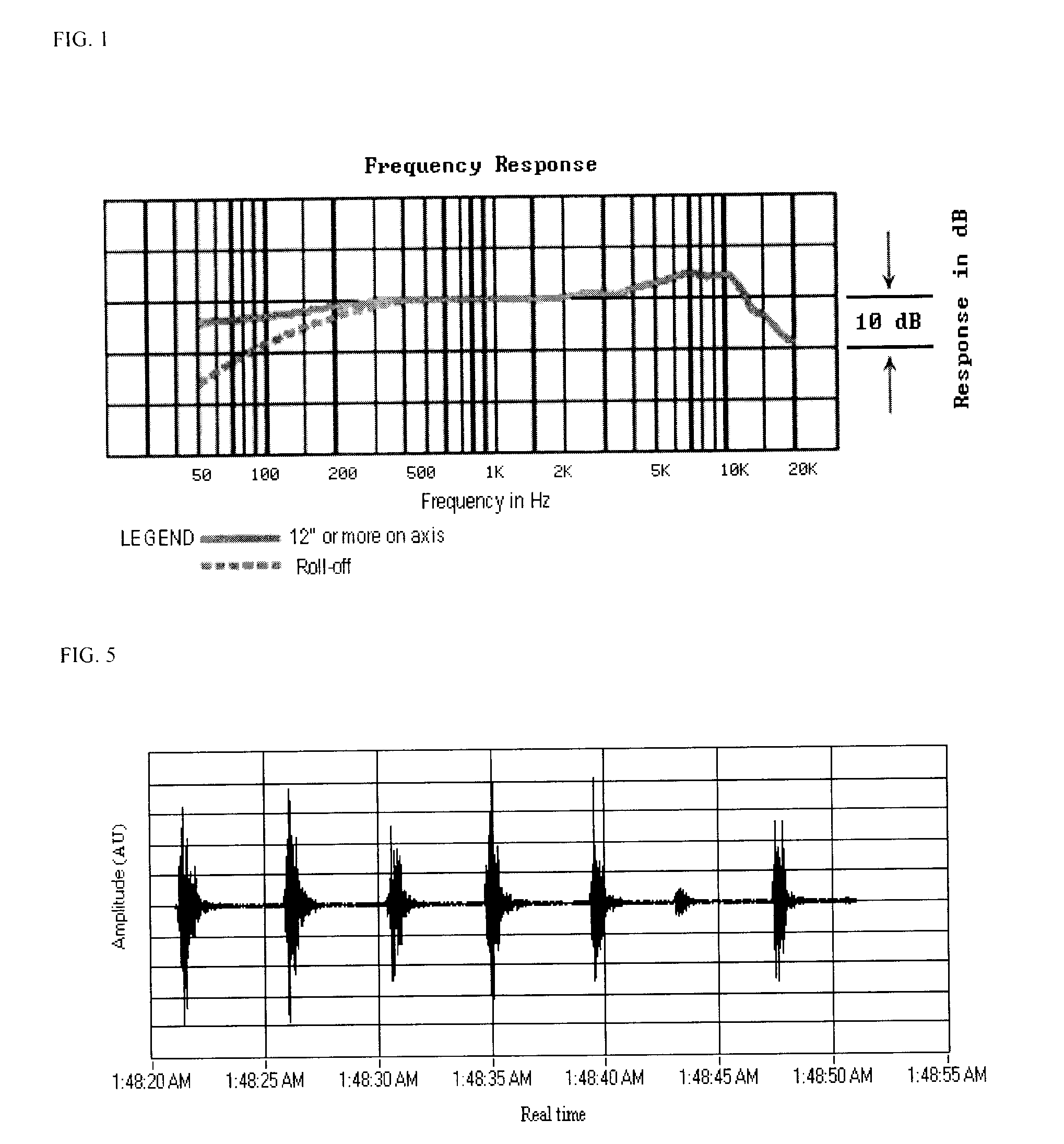
Efficient imagery exploitation employing wavelet-based feature indices
A wavelet-based band difference-sum ratio method reduces the computation cost of classification and feature extraction (identification) tasks. A Generalized Difference Feature Index (GDFI), computed using wavelets such as Daubechies wavelets, is employed in a method to automatically generate a large sequence of generalized band ratio images. In select embodiments of the present invention, judicious data mining of the large set of GDFI bands produces a small subset of GDFI bands suitable to identify specific Terrain Category / Classification (TERCAT) features. Other wavelets, such as Vaidyanathan, Coiflet, Beylkin, and Symmlet and the like may be employed in select embodiments. The classification and feature extraction (identification) performance of the band ratio method of the present invention is comparable to that obtained with the same or similar data sets using much more sophisticated methods such as discriminants, neural net classification, endmember Gibbs-based partitioning, and genetic algorithms.
Owner:US ARMY CORPS OF ENGINEERS
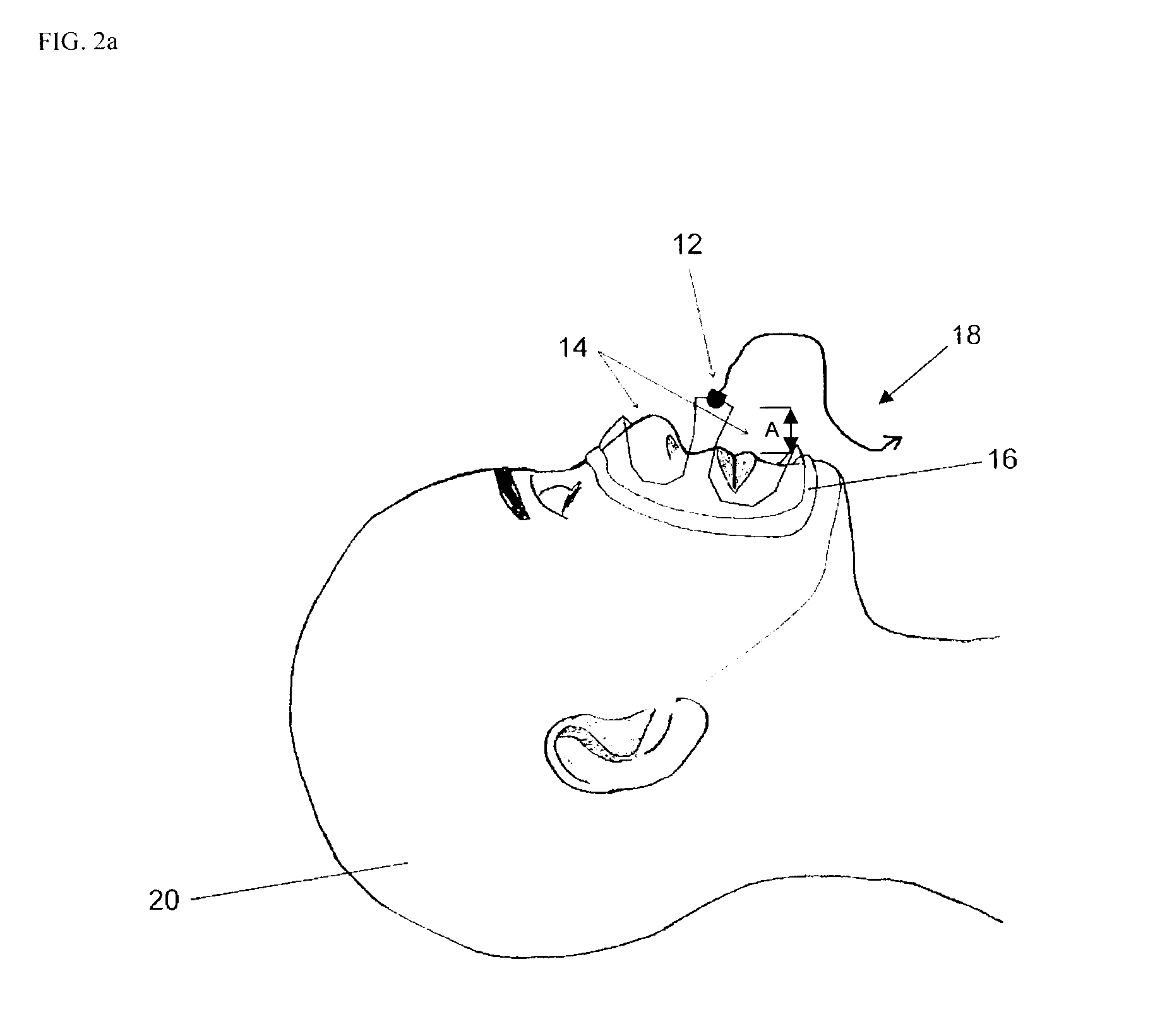
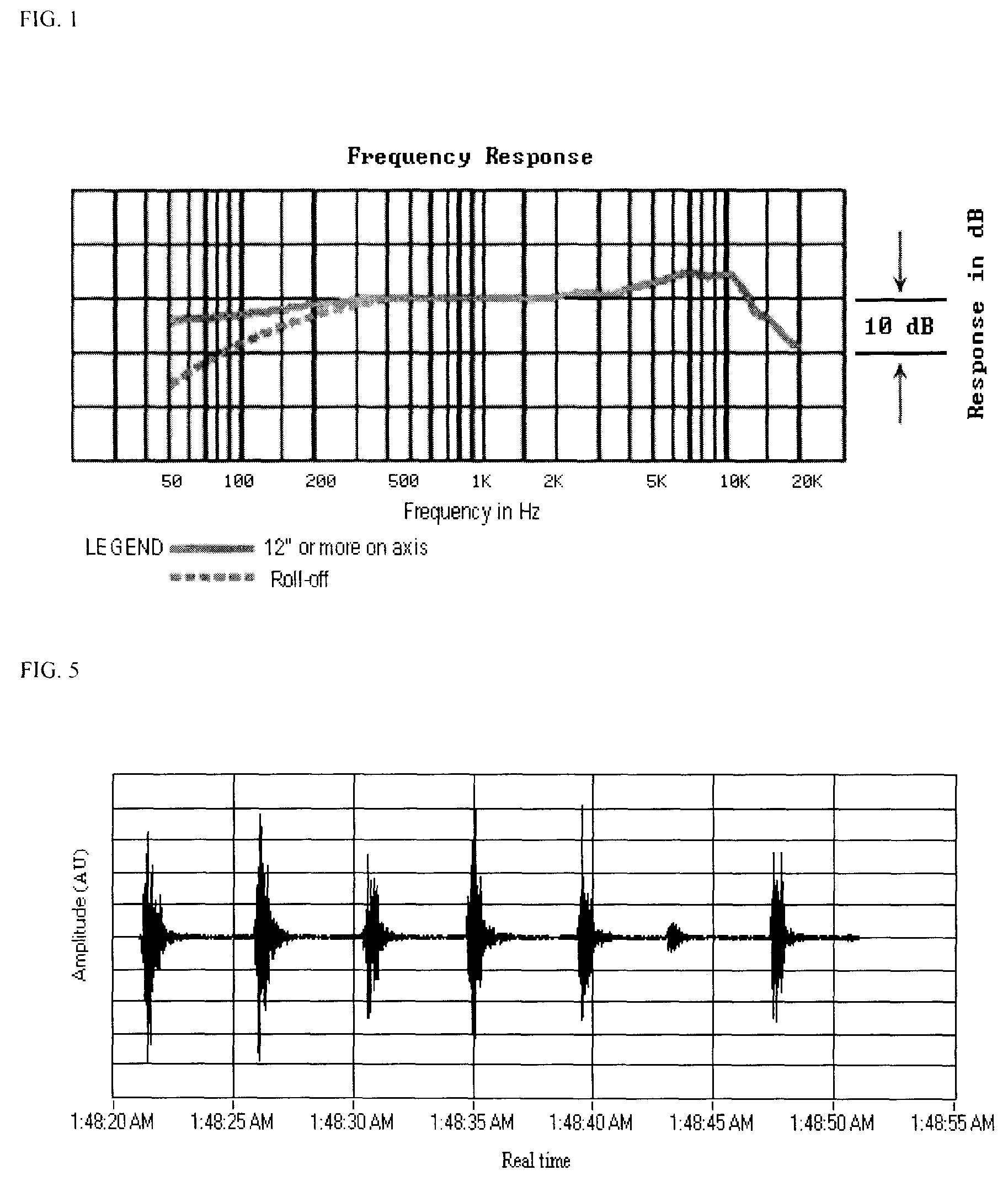
Method and apparatus for monitoring breathing cycle by frequency analysis of an acoustic data stream
Disclosed herein is a method and apparatus for monitoring, identifying and determining the breathing cycle of an individual from processed acoustic signal waveform data. The breathing sounds of an individual are recorded using a microphone and digitized such that the breathing sounds may be plotted. The data is segmented and transformed to form a plurality of segments representative of a frequency spectrum. The frequency spectrum data is transformed so as to produce magnitude bins and the sum of lower magnitude bins and the sum of higher magnitude bins are determined in a sampling of segments. A Bands Ratio is determined from the sum of lower magnitude bins and the sum of higher magnitude bins in the sampling of segments. A first bands ratio is then determined within a given segment and compared to the mean bands ratio. If the first bands ratio of the given segment is greater than the mean bands ratio by at least a predetermined multiplier, the given segment is labeled as inspiration. If the first bands ratio of the given segment is less than the mean bands ratio by at least a predetermined multiplier, the given segment is labeled as expiration.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
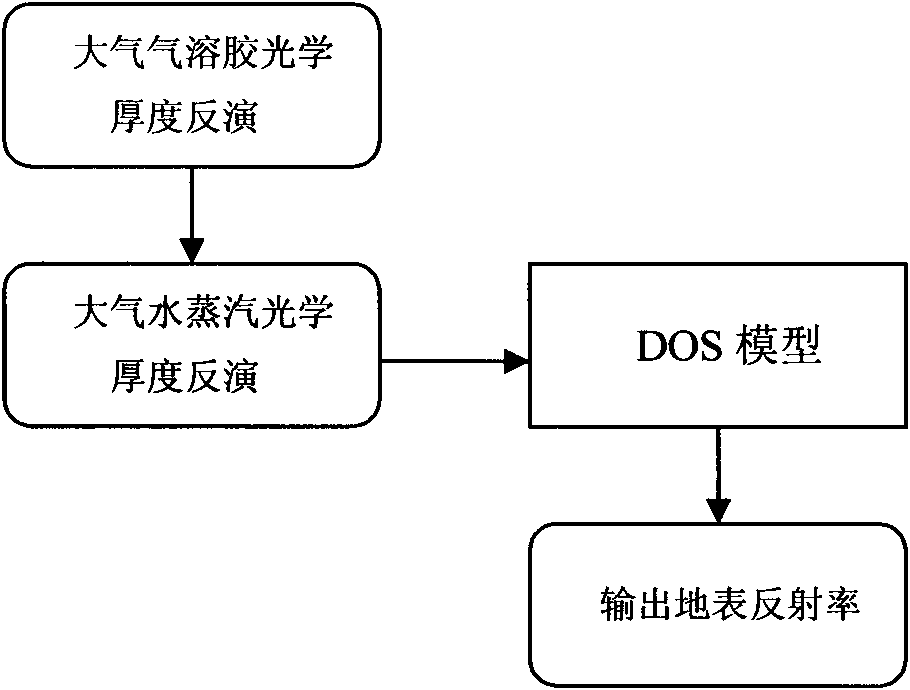
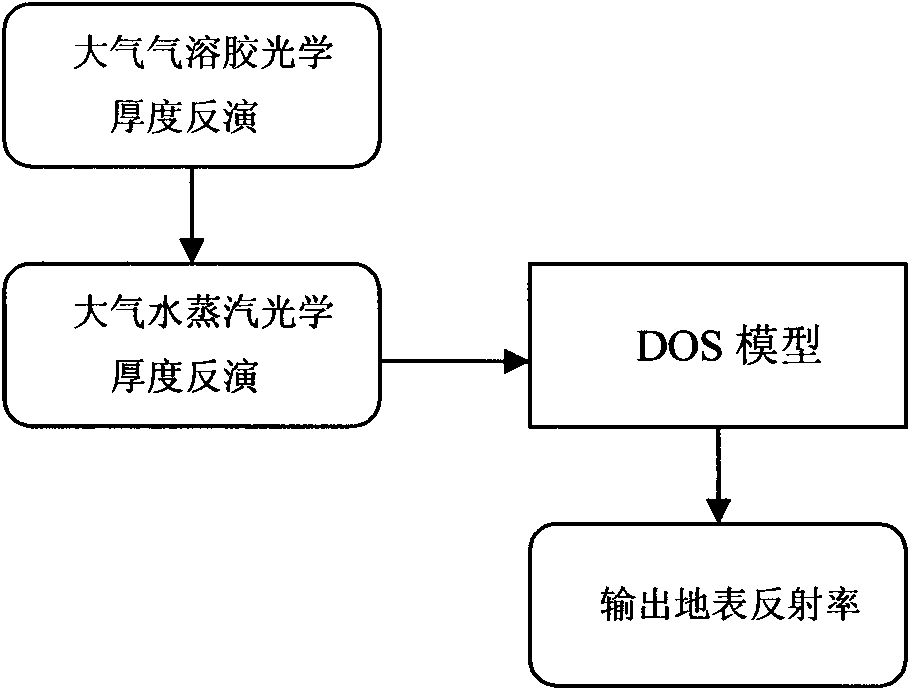
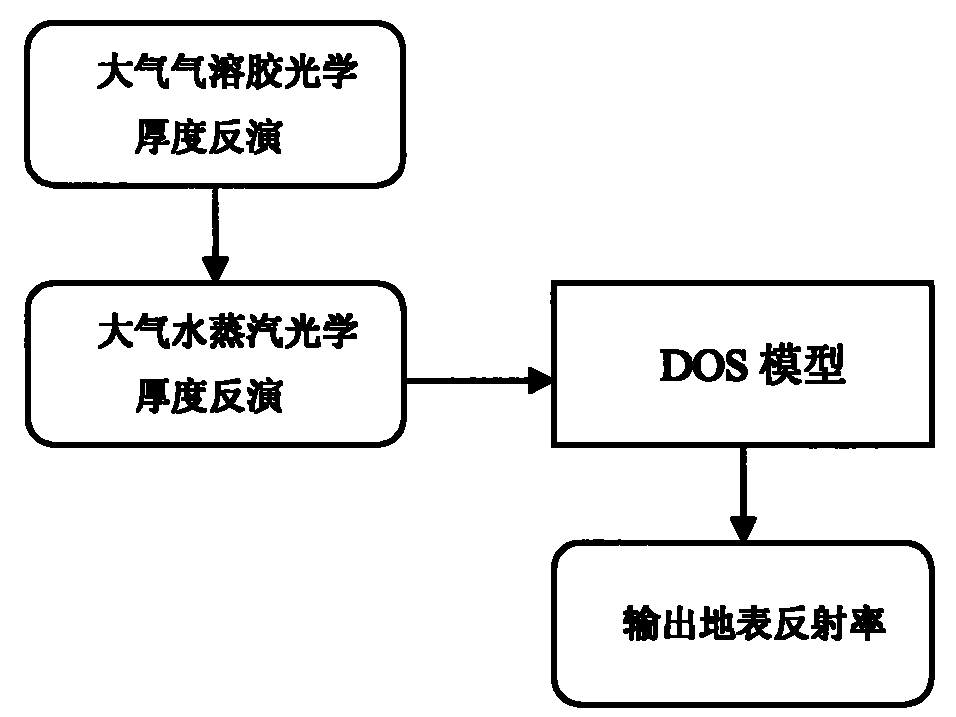
Practical atmospheric correction method for remote sensing images
InactiveCN101598543AAvoid disadvantagesHigh precisionElectromagnetic wave reradiationVegetationEarth surface
The invention discloses a practical atmospheric correction method for remote sensing images, which comprises three steps: a first step, inverting the optical thickness of atmospheric aerosol from MODIS data by means of a 6S model lookup table based on a dense vegetation algorithm; a second step, calculating total content of atmospheric vapor by using an MODIS data band ratio method, and then calculating the optical thickness of the atmospheric vapor; and a third step, combining the inverted optical thickness of the atmospheric aerosol, the optical thickness of the atmospheric vapor and a DOS model to invert the earth surface reflectance. The calculated earth surface reflectance has high precision; the method has strong practicability, and is applicable to various land satellite images; and the MODIS data can be acquired freely every day; therefore, the method can be used as a service atmospheric correction method for the remote sensing images.
Owner:CENT FOR EARTH OBSERVATION & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Compact type plane dual-band omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna
InactiveCN102931479AGood omnidirectional radiation performanceSimple structureSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a compact type plane dual-band omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna. The compact type plane dual-band omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna is characterized by comprising a plane radiating antenna, a center shorting pin, an input connector and a feed probe; the plane radiating antenna sequentially comprises a capacitor chip, a medium substrate I, a radiating chip, a medium substrate II and a floor from top to bottom, and an air layer is arranged between the radiating chip and the medium substrate II; the capacitor chip is connected with an inner conductor of the input connector through the feed probe, protection holes are arranged at corresponding positions on the radiating chip and the floor, the feed probe penetrates through the positions on the radiating chip and the floor, and inner diameters of the protection holes are larger than the diameter of the feed probe; and the radiating chip is composed of a primary round radiation chip and three groups of radiating units which are of same structures, the three groups of radiating units are loaded on the periphery of the primary round radiation chip and composed of six arc vibrators, and each group of radiating units is composed of two arc vibrators with different length. The antenna has the advantages of being good in omnidirectional radiation, good in circular polarization in the ranges of 360 degrees on a plane and flexible in dual-band ratio.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
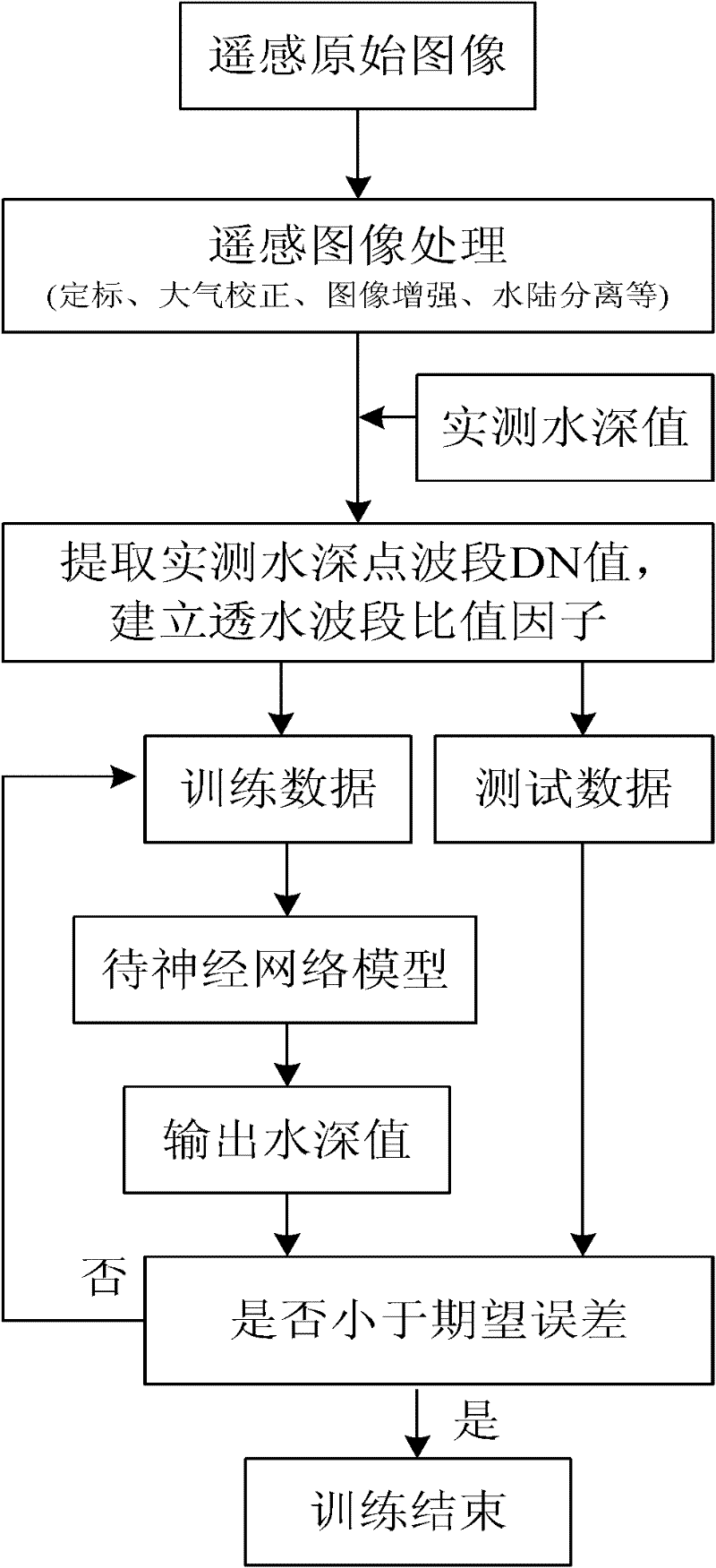
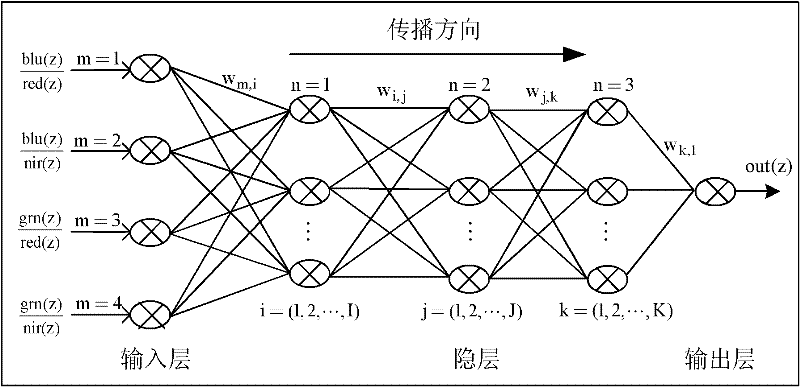
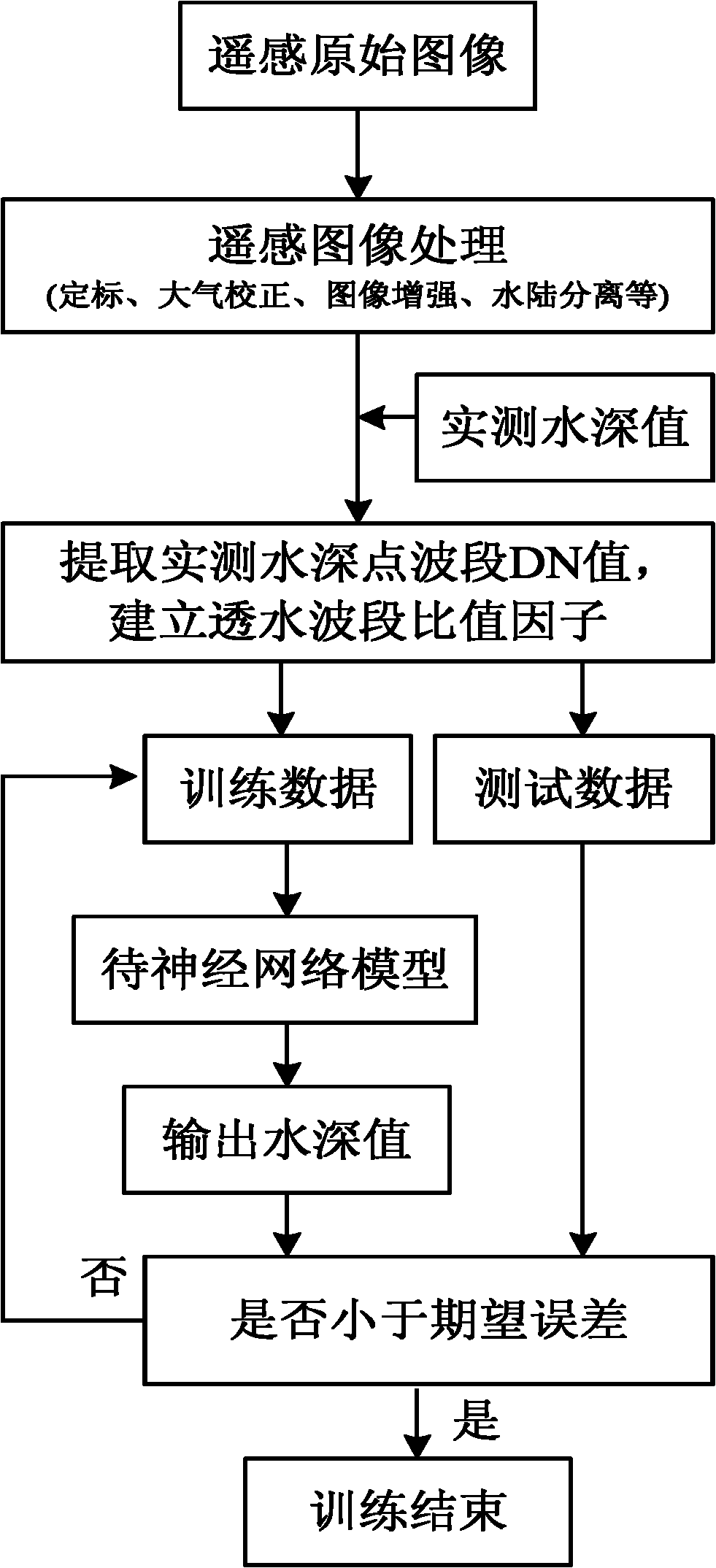
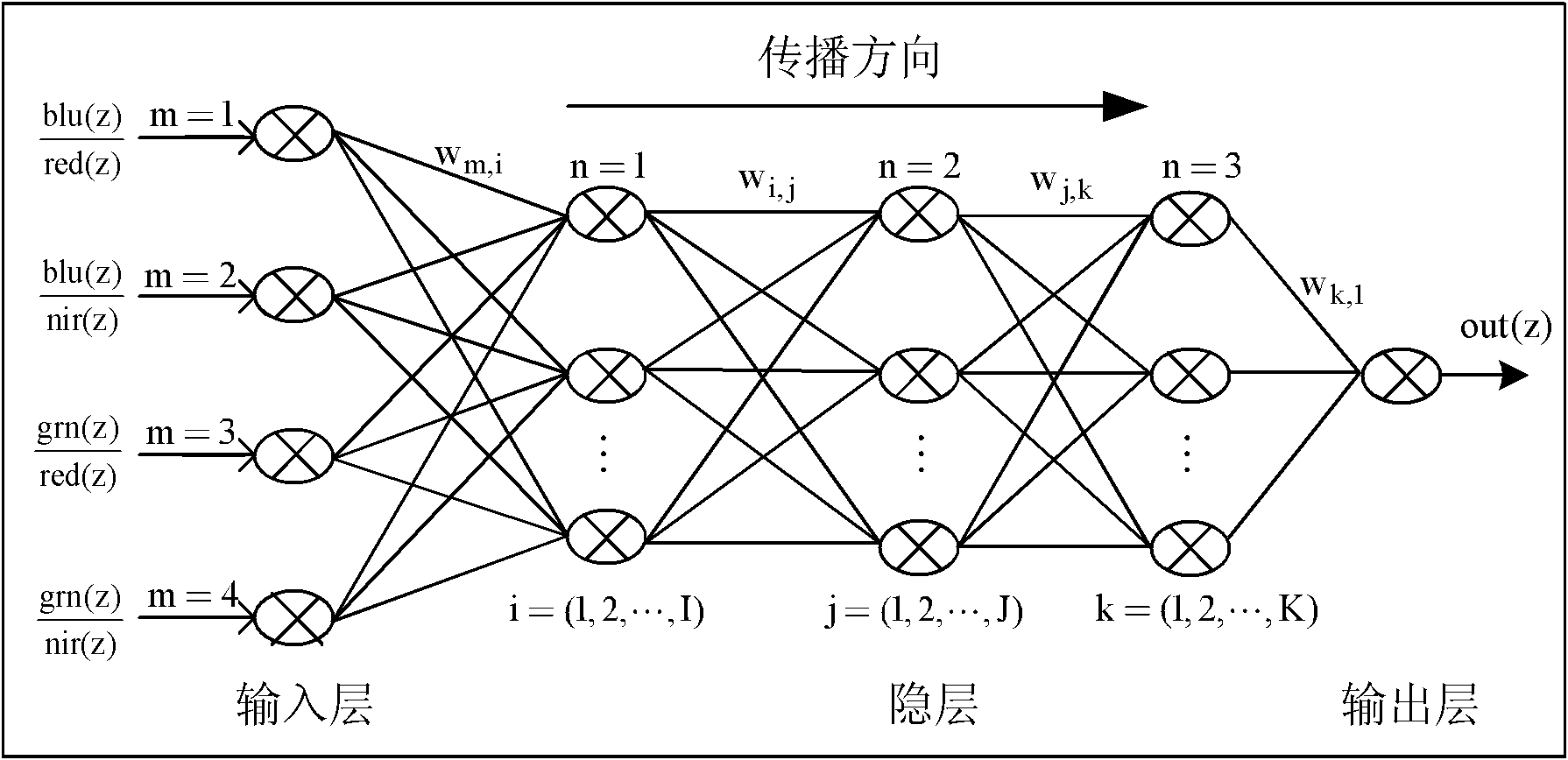
Permeable band ratio factor-based water depth inversion method
ActiveCN102176001AMake up for the defect of reduced calculation accuracySmall standard deviationImage enhancementImage analysisNetwork modelAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses a permeable band ratio factor-based water depth inversion method, which comprises the following steps of: 1, performing radiant calibration on a remote sensing image; 2, performing atmospheric correction on the remote sensing image subjected to the radiant calibration; 3, performing image enhancement on the remote sensing image subjected to the atmospheric correction; 4, performing amphibious separation on the remote sensing image subjected to the image enhancement; 5, performing geometric correction and data processing on the remote sensing image subjected to the amphibious separation; and 6, establishing a neural network water depth inversion model. Compared with a neural network model using single permeable band as input, the permeable band ratio factor-based neural network inversion model has low standard deviation and large related coefficients. The model is not affected by the seawater type and the undersea sediment, and simultaneously has the function ofsolving nonlinear mapping and good promotion capability.
Owner:哈尔滨哈船导航技术有限公司
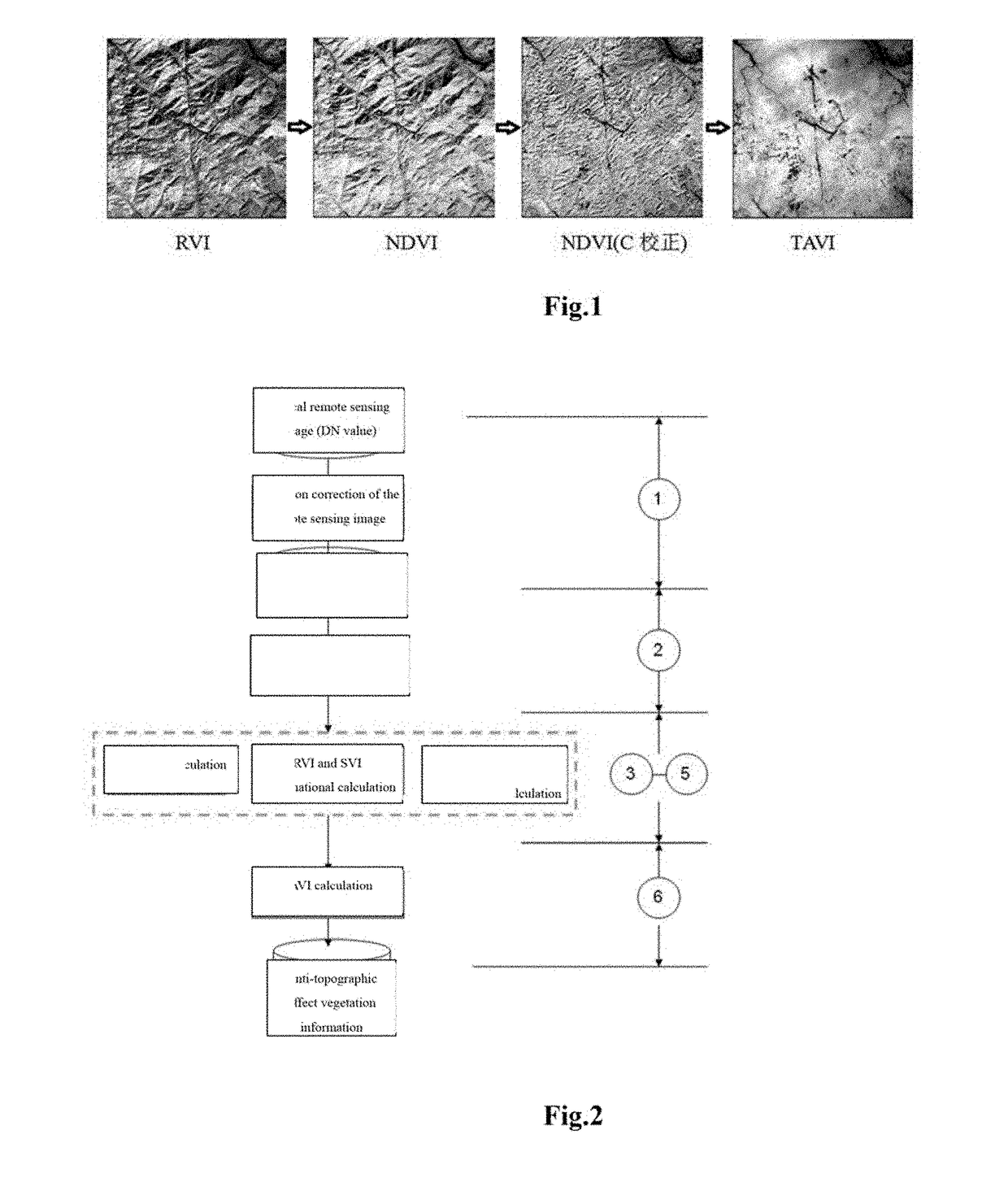
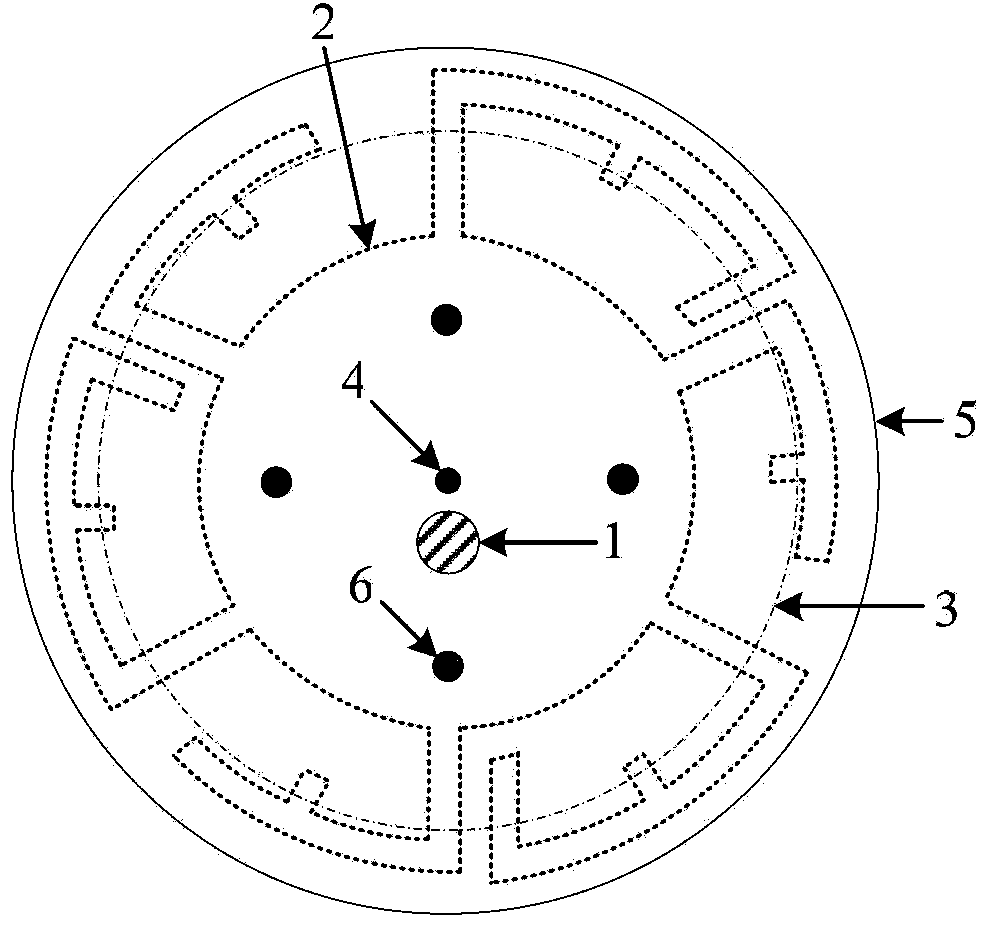
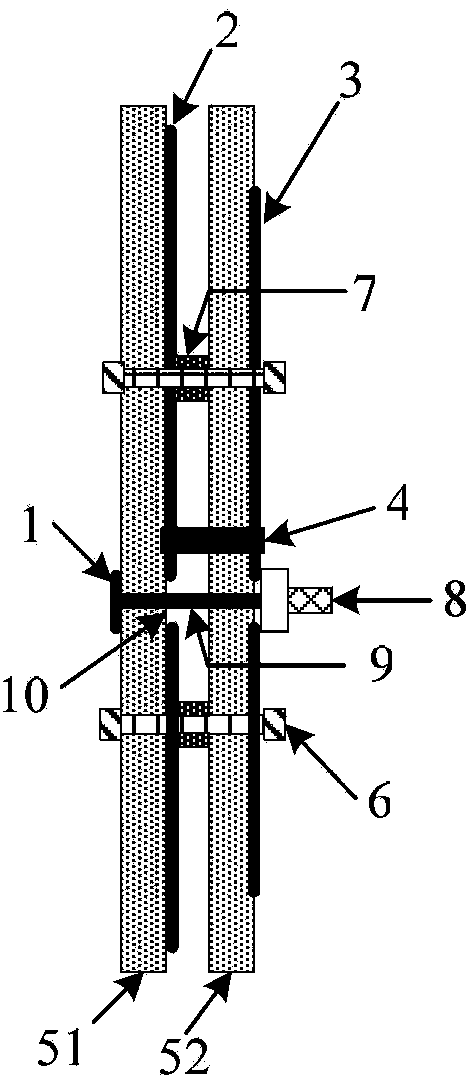
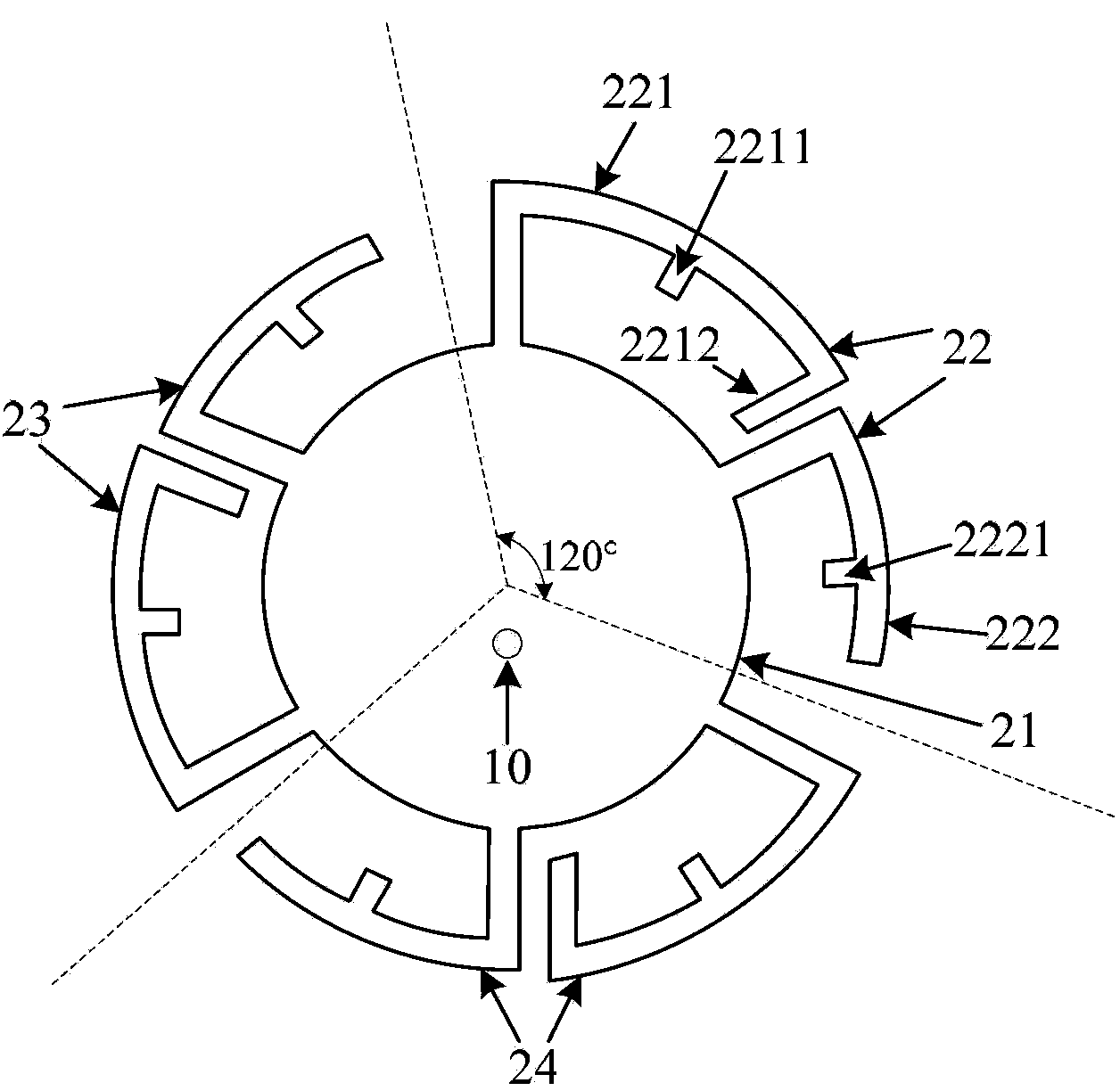
Method of calculating tavi based on a band ratio model and solar altitude angle
ActiveUS20180356339A1Broaden applicationEconomic valueMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionVegetation IndexLandform
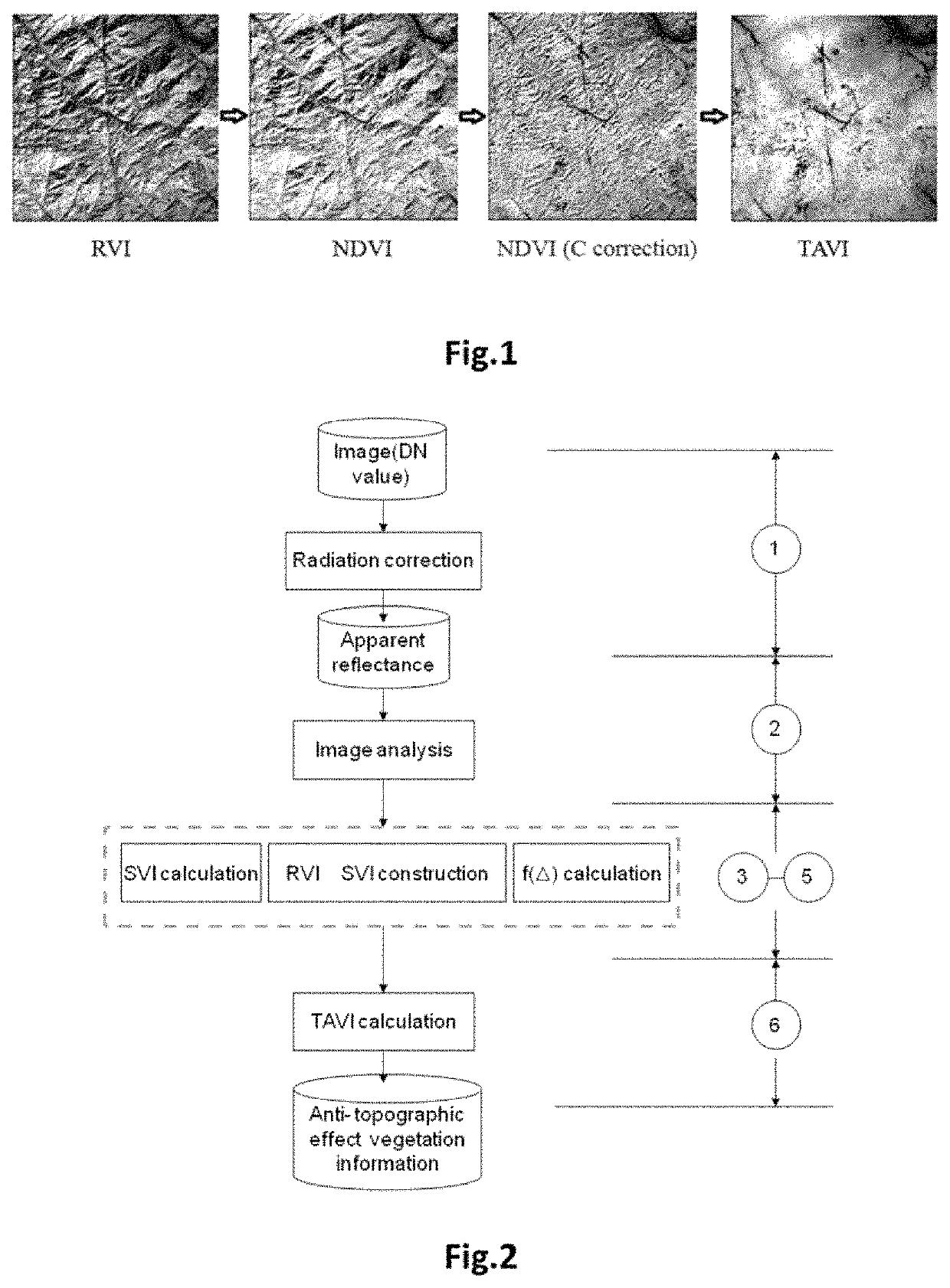
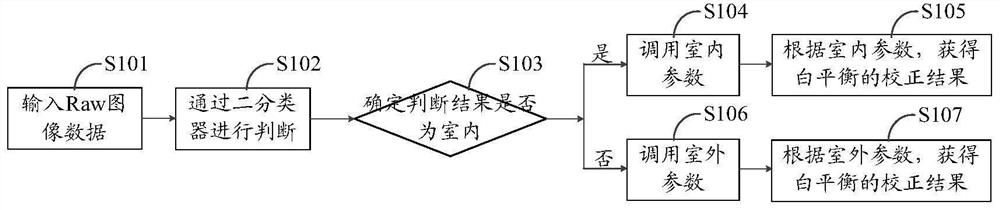
The present invention relates to a method of calculating a Topography Adjusted Vegetation Index (TAVI) based on a band ratio model and a solar altitude angle. The method includes the folio wing steps: obtaining the apparent reflectance data of a remote sensing image through image preprocessing, analyzing the quality of the image and numerical distribution, calculating a Shadow Vegetation Index (SVI), and constructing a TAVI combinational algorithm:TAVI=BirBr+f(Δ)·1Br,calculating an adjustment factor f (Δ) with the solar altitude angle, and finally obtaining anti-topographic effect TAVI vegetation information. The TAVI in the present invention is composed of two band ratio submodels RVI and SVI, the denominators of both of which are red band data of a remote sensing image, and the adjustment factor f(Δ), which is calculated by a solar altitude angle as a parameter with a sensor factor applied, has great physical significance. The TAVI calculation method does not need digital elevation model (DEM) data and remote sensing image classification when not depending on ground survey data,, and ensures that the interference of the topographic effects with the vegetation information can be effectively eliminated by the TAVI, thereby avoiding the problem of reduced inversion accuracy of ground vegetation information due to different registration accuracy of a remote sensing image and DEM data.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method and apparatus for monitoring breathing cycle by frequency analysis of an acoustic data stream
Disclosed herein is a method and apparatus for monitoring, identifying and determining the breathing cycle of an individual from processed acoustic signal waveform data. The breathing sounds of an individual are recorded using a microphone and digitized such that the breathing sounds may be plotted. The data is segmented and transformed to form a plurality of segments representative of a frequency spectrum. The frequency spectrum data is transformed so as to produce magnitude bins and the sum of lower magnitude bins and the sum of higher magnitude bins are determined in a sampling of segments. A Bands Ratio is determined from the sum of lower magnitude bins and the sum of higher magnitude bins in the sampling of segments. A first bands ratio is then determined within a given segment and compared to the mean bands ratio. If the first bands ratio of the given segment is greater than the mean bands ratio by at least a predetermined multiplier, the given segment is labeled as inspiration. If the first bands ratio of the given segment is less than the mean bands ratio by at least a predetermined multiplier, the given segment is labeled as expiration.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
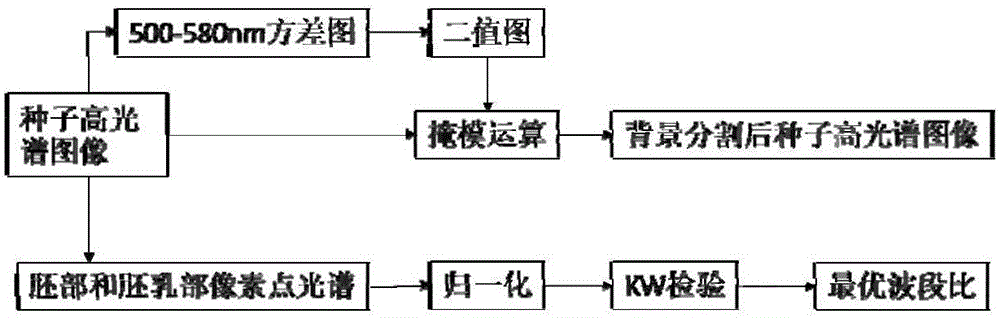
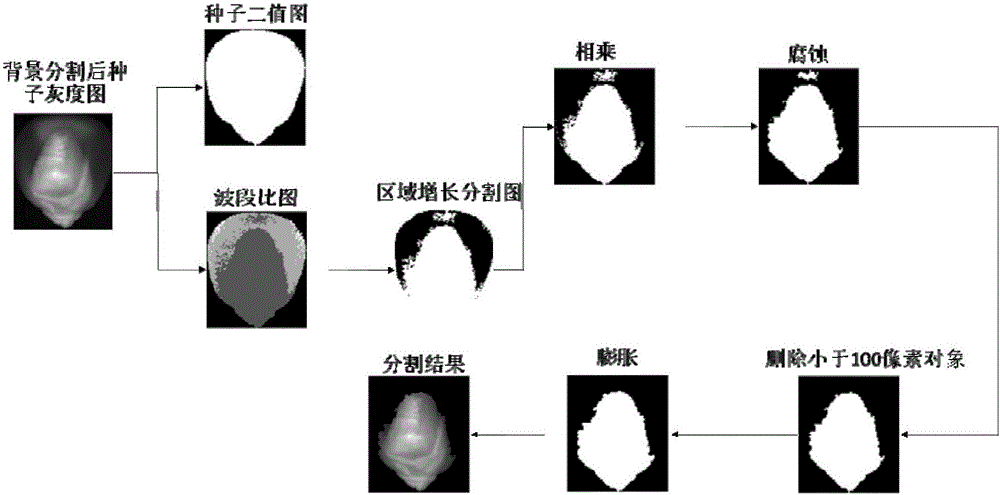
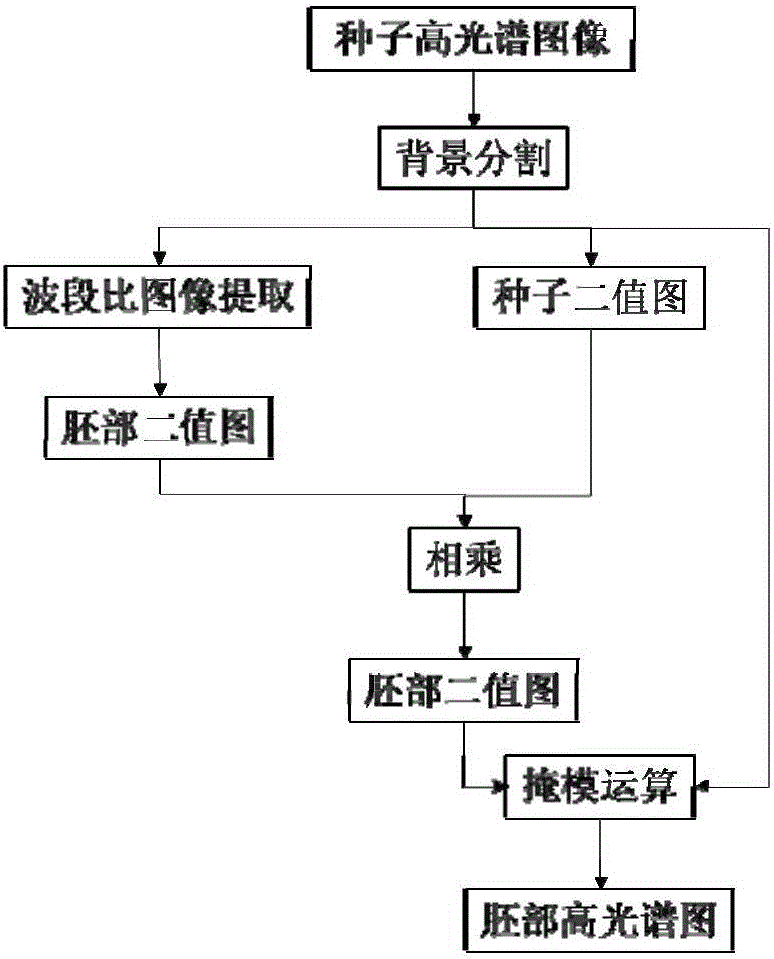
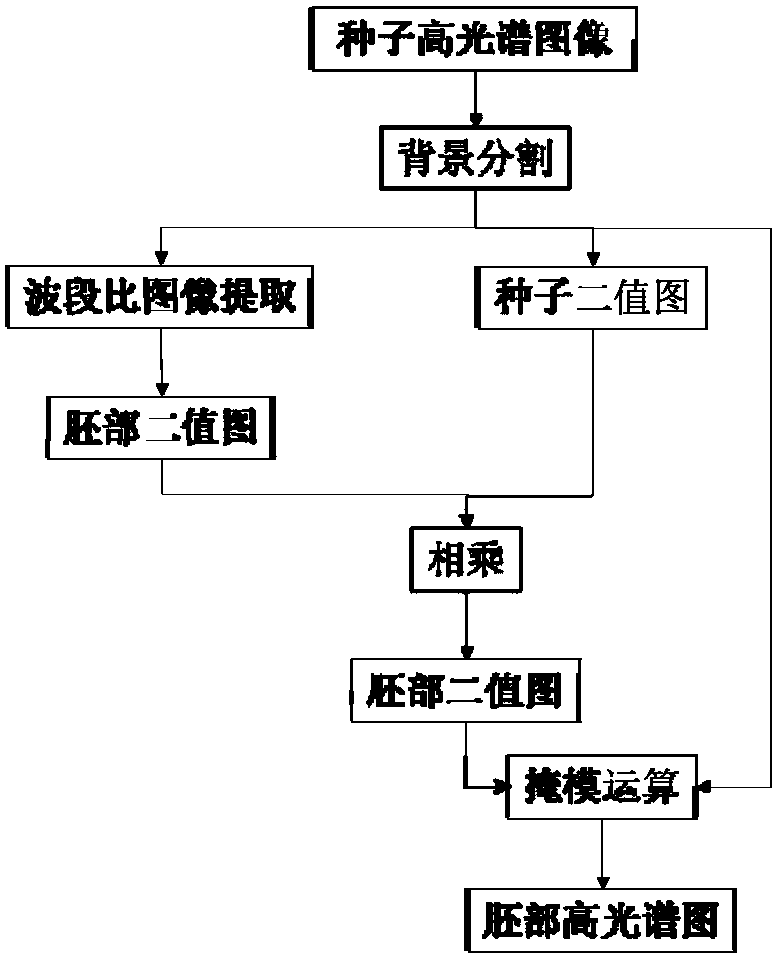
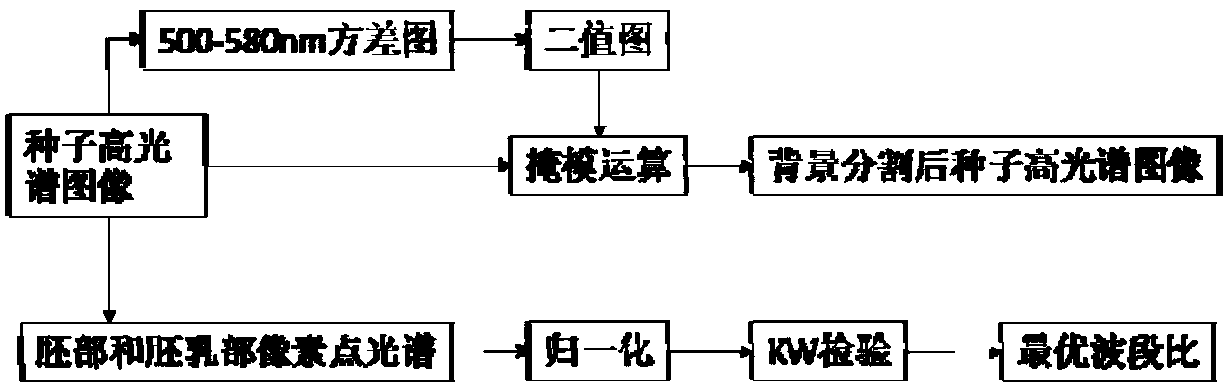
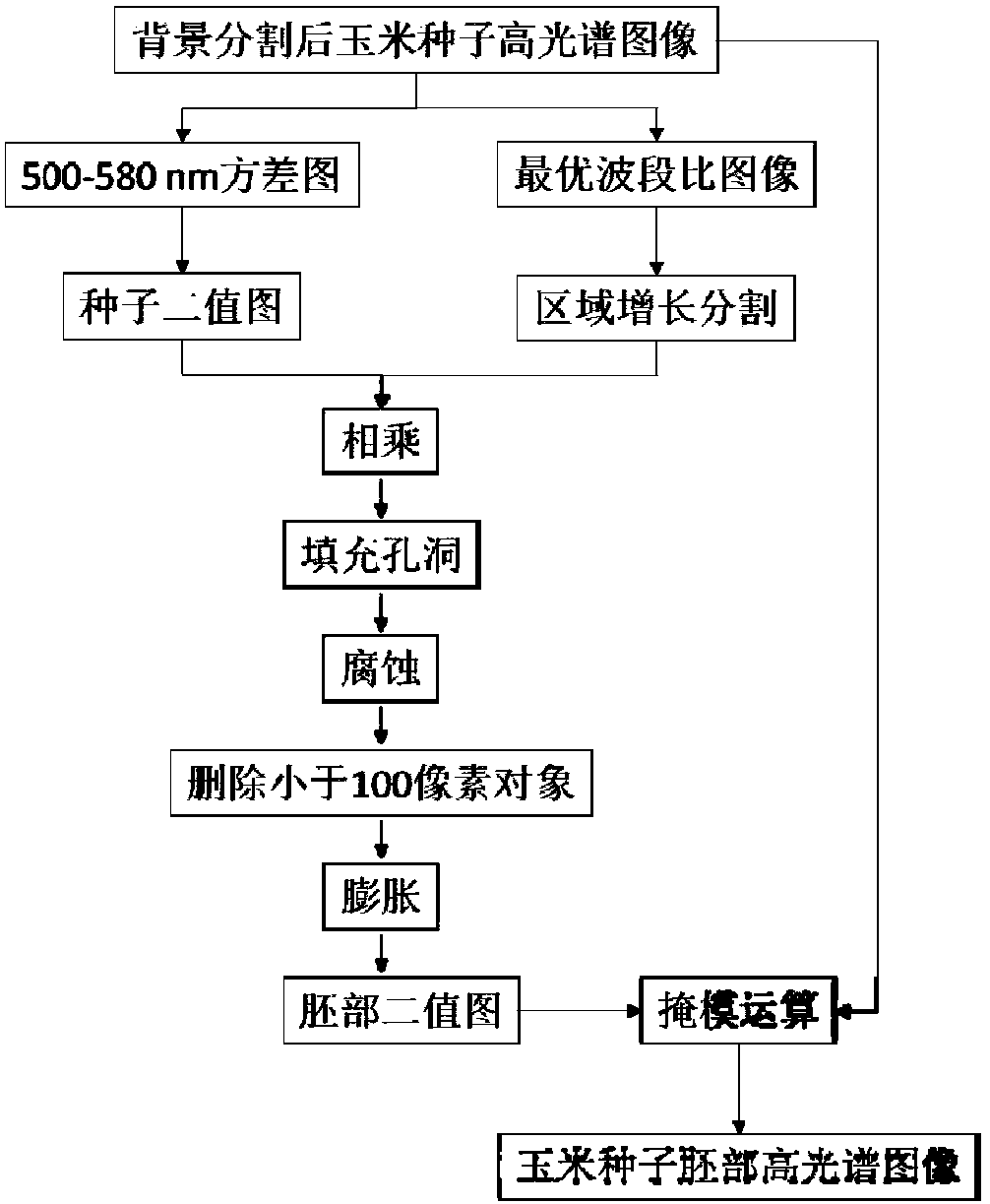
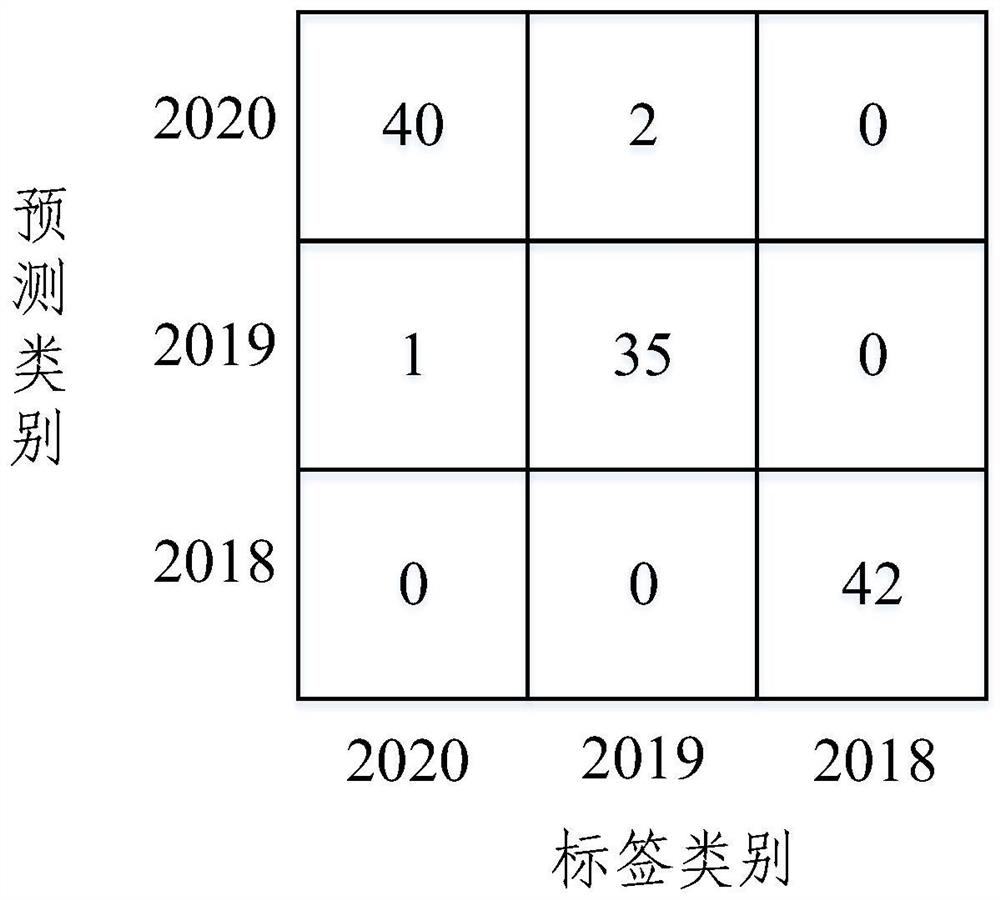
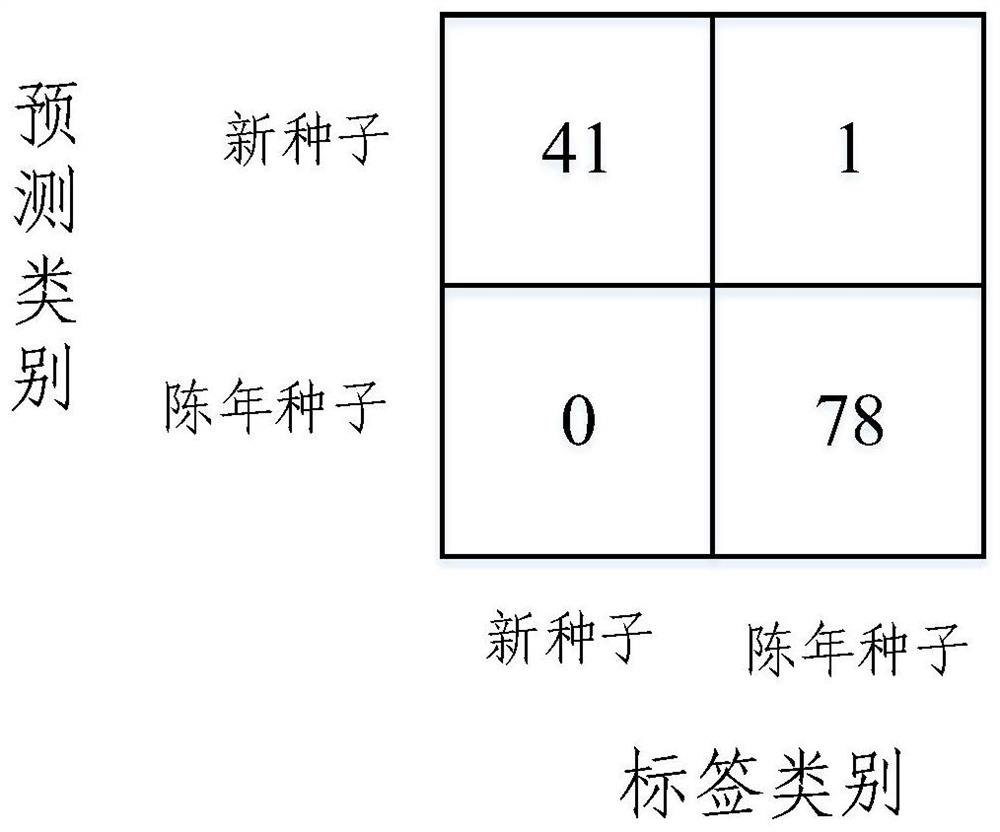
Band ratio method based maize embryo segmentation method in high-spectral reflection image
ActiveCN105931223AHigh degree of automationGood segmentation effectImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSpectral ratio
The invention discloses a band ratio method based maize embryo segmentation method in a high-spectral reflection image. The high-spectral image of a maize seed is collected with the embryo surface of the seed upwards; multiple pixels and spectrums thereof are extracted from the endosperm and embryo and normalized; the spectral ratio of two random wave bands is calculated and serves as the band ratio, and the optimal band ratio is selected; a band subset is selected, variance of all pixels in the band subset is calculated, a seed binary image is obtained via threshold segmentation, and a background removed high-spectral image of the maize seed is obtained via mask operation; and a gray scale image of the background removed high-spectral image of the maize seed under the optimal band ratio is calculated via the high-spectral image, the gray scale image is segmented in a region growing method to obtain an embryo binary image, the embryo binary image is processed to obtain a seed embryo binary image, and the high-spectral image of the maize seed embryo is obtained via mask operation. The method can be used to segment the maize seed embryo in the visible near-infrared high-spectral image effectively, the segmentation effect is good, and the practicality is higher.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
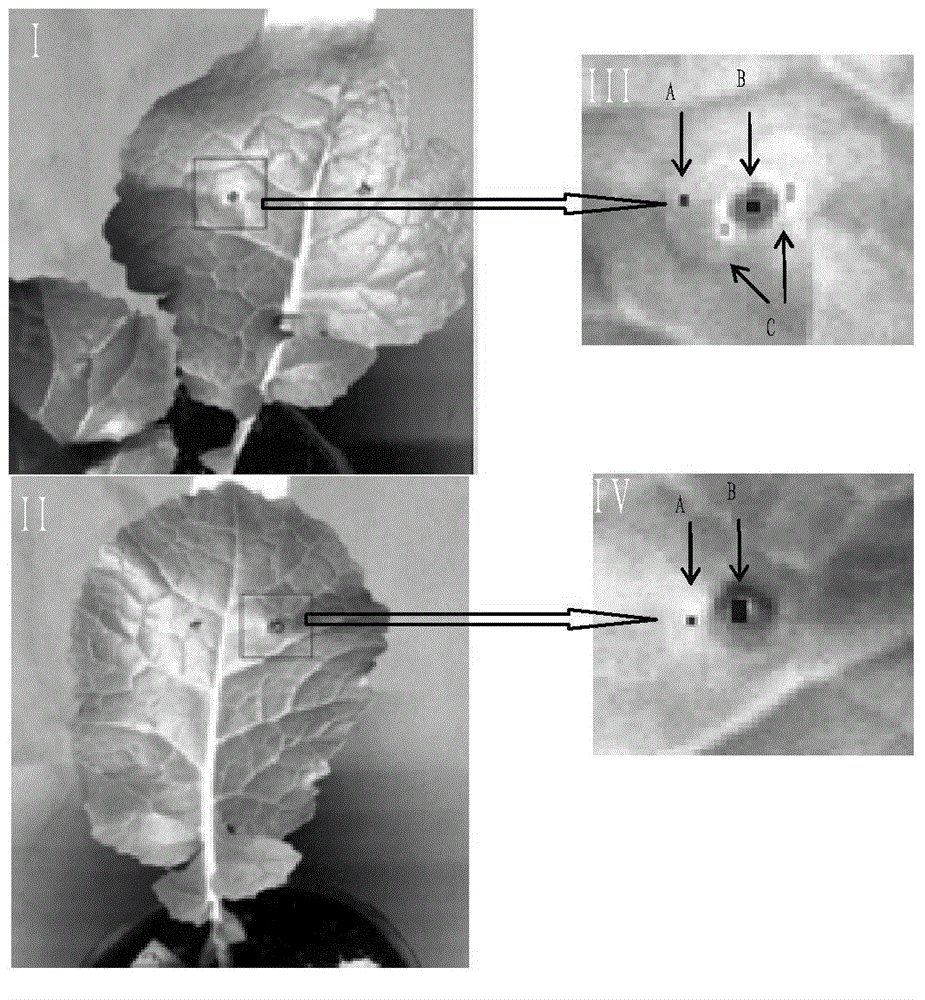
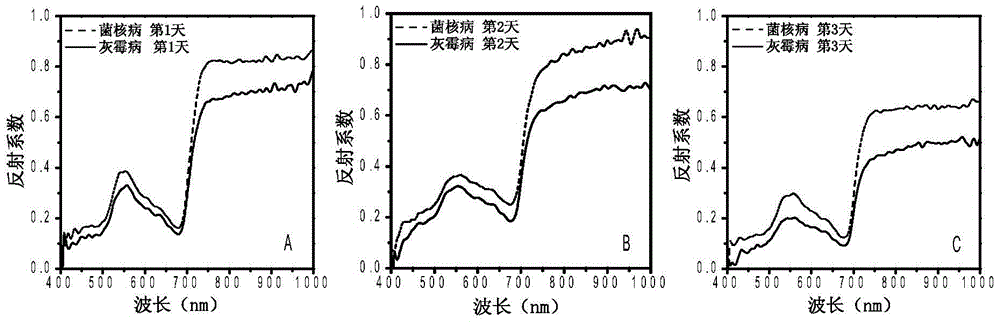
Method for identifying early-stage disease spots of sclerotinia sclerotiorum and botrytis of rape
ActiveCN105067532AAccurate identificationImprove identification accuracyColor/spectral properties measurementsFeature vectorSclerotinia
The invention discloses a method for identifying early-stage disease spots of sclerotinia sclerotiorum and botrytis of rape. The method comprises steps as follows: (1), a high-spectrum image of a to-be-detected leaf of the rape is taken, and the pixel of a local disease spot of the high-spectrum image is picked; (2), a band ratio operation value and a band differential operation value of the pixel at the band of 681.95 nm-748.23 nm are calculated and obtained; (3), a feature vector composed of a spectrum value of the pixel at the band of 555.29 nm, the band ratio operation value and the band differential operation value is input into a trained least square support vector machine model, and the type of the disease spot is judged according to an output result. A band with a characteristic difference is obtained from the high-spectrum image information with the early-stage disease spots of sclerotinia sclerotiorum and botrytis through analysis, the early-stage disease spots of sclerotinia sclerotiorum and botrytis are accurately classified by combination of a characteristic wavelength, the band ratio operation value, the band differential operation value and a least square support vector machine, and the identification accuracy is higher.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
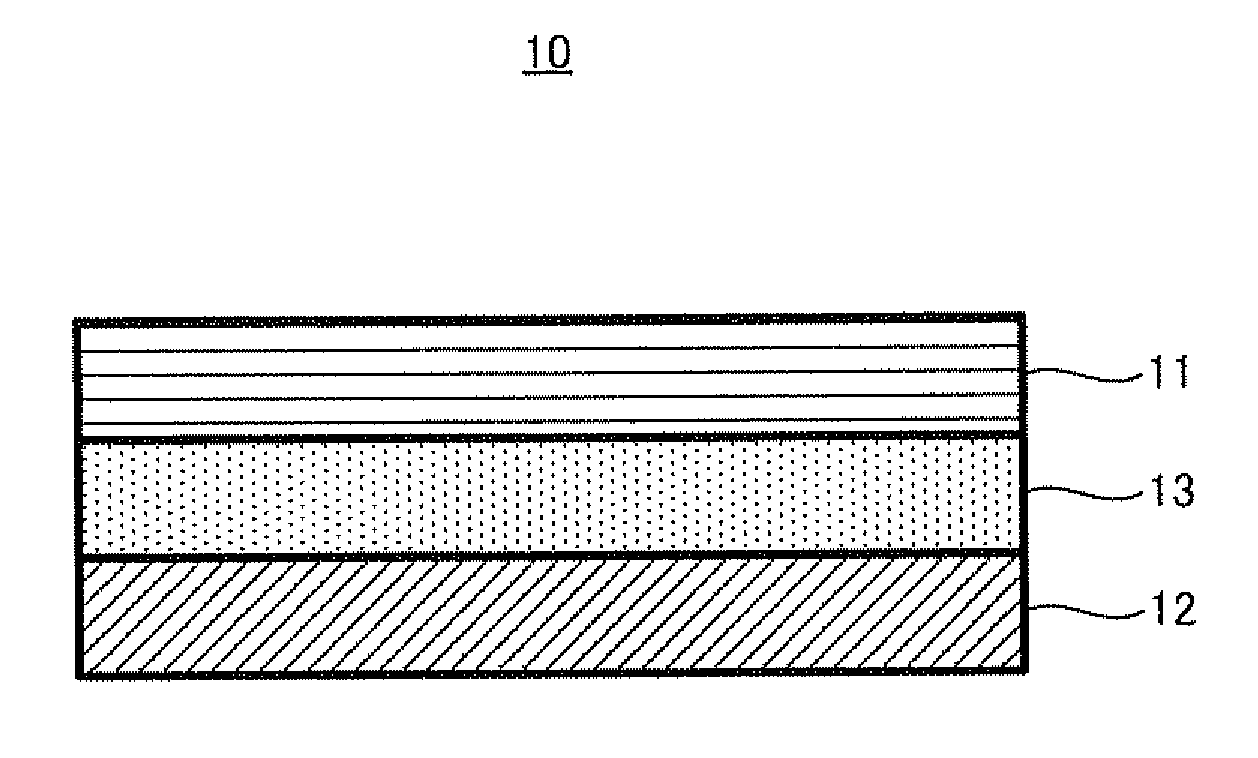
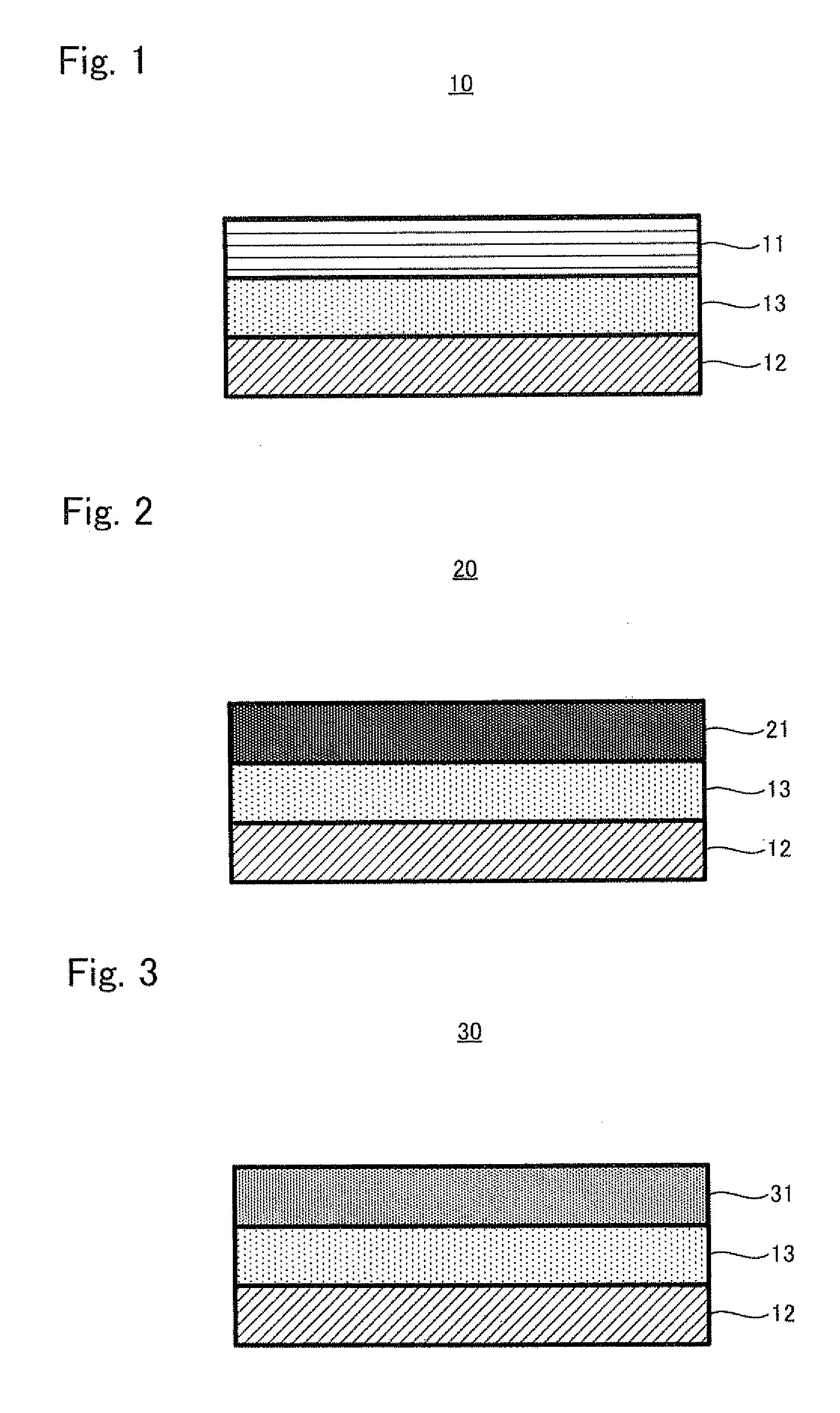
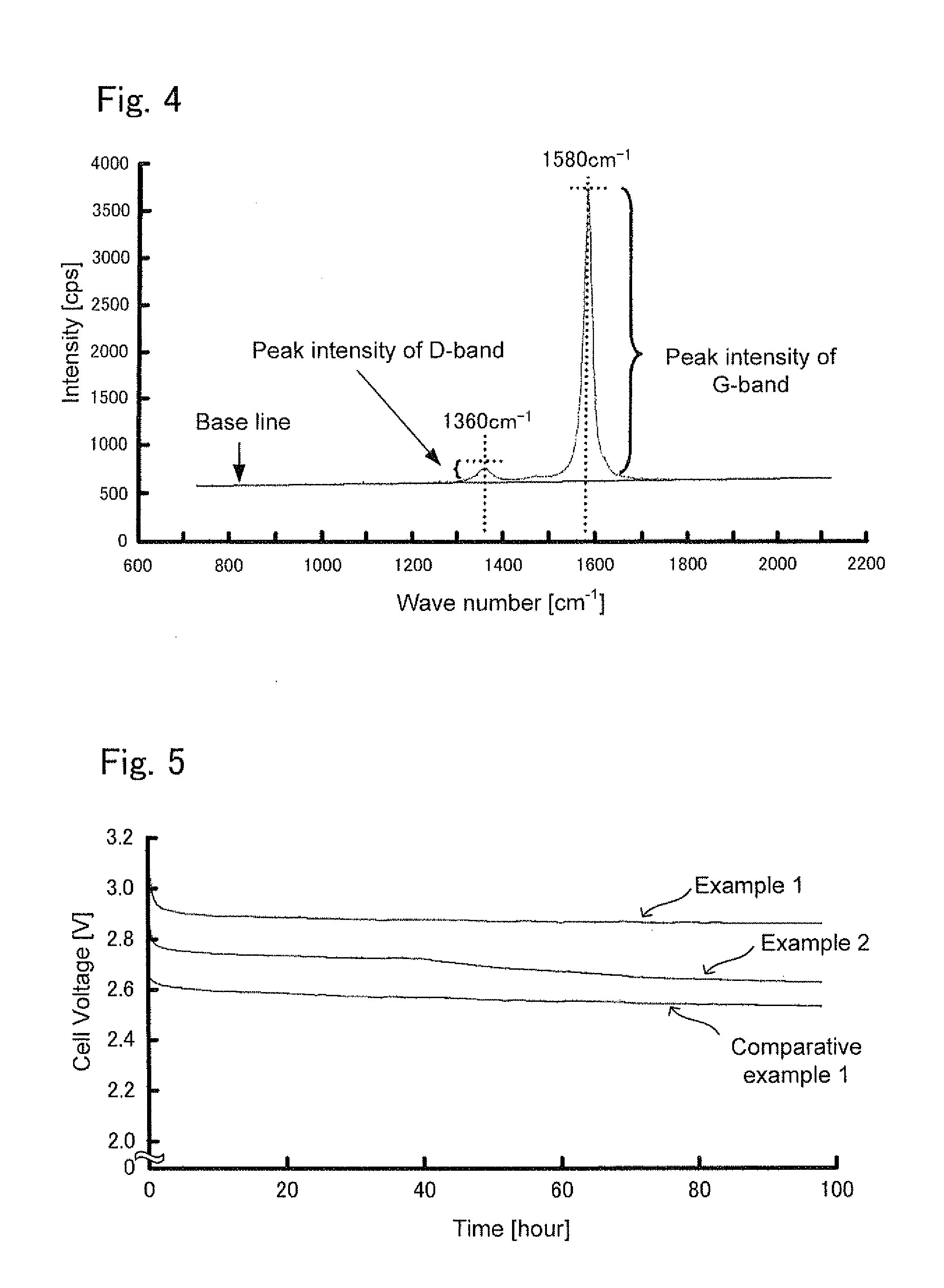
Air battery
An air battery which is capable of improving operating voltage. The air battery includes: an air electrode containing a carbonaceous matter; an anode; and an electrolyte layer containing an electrolyte which conducts ions between the air electrode and the anode, the DIG band ratio X of the carbonaceous matter being 0.058≦X≦0.18.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
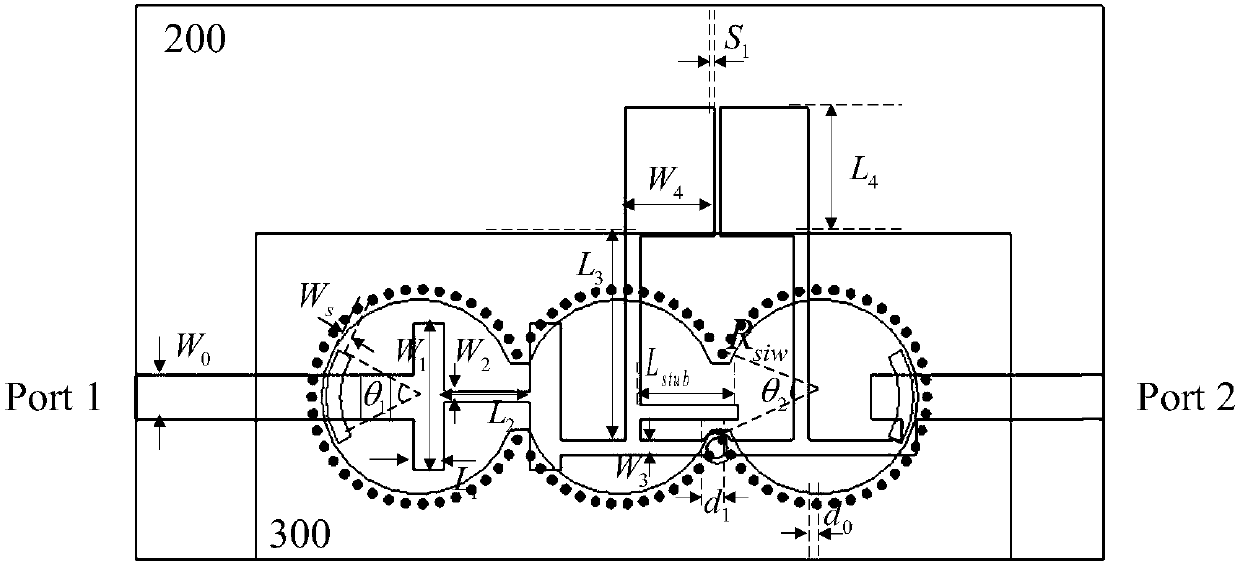
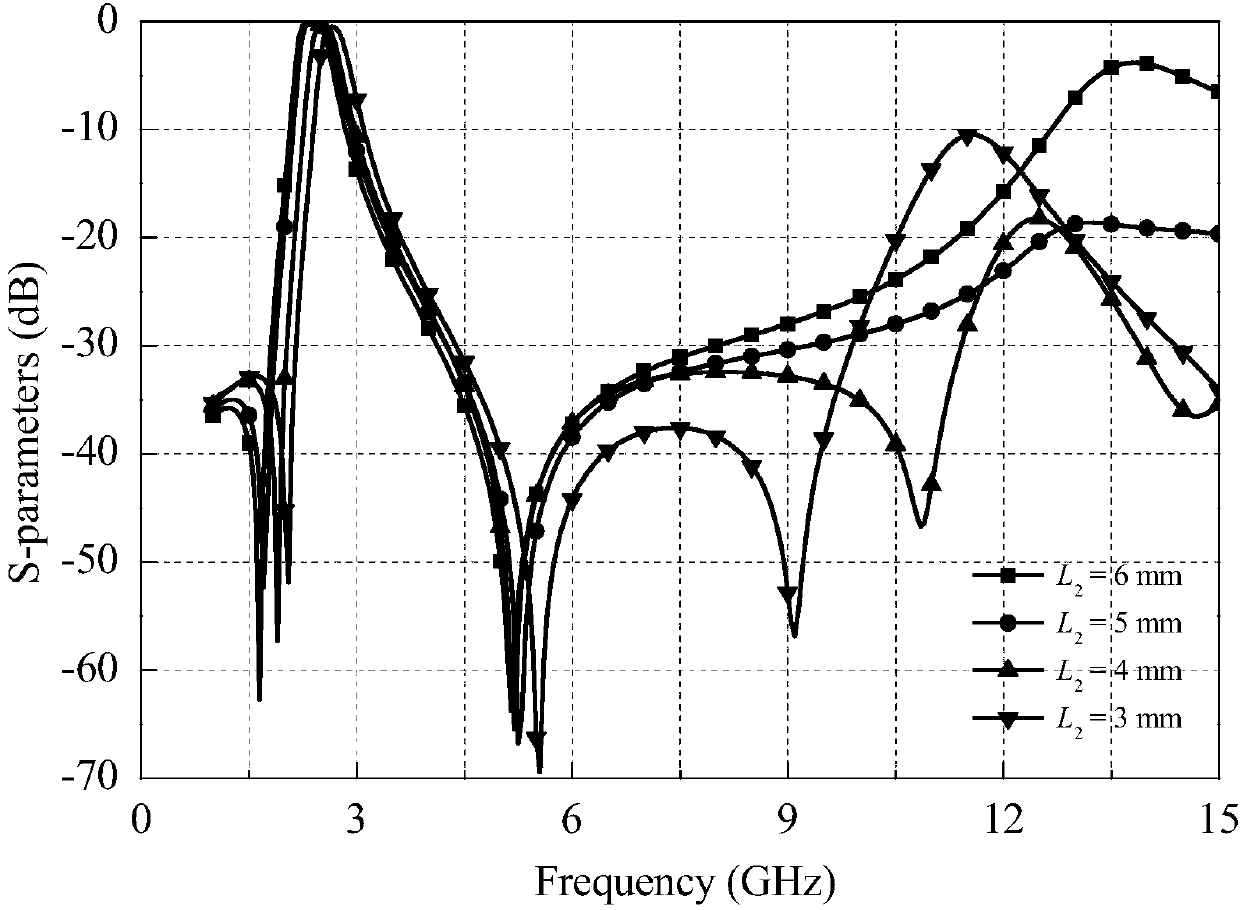
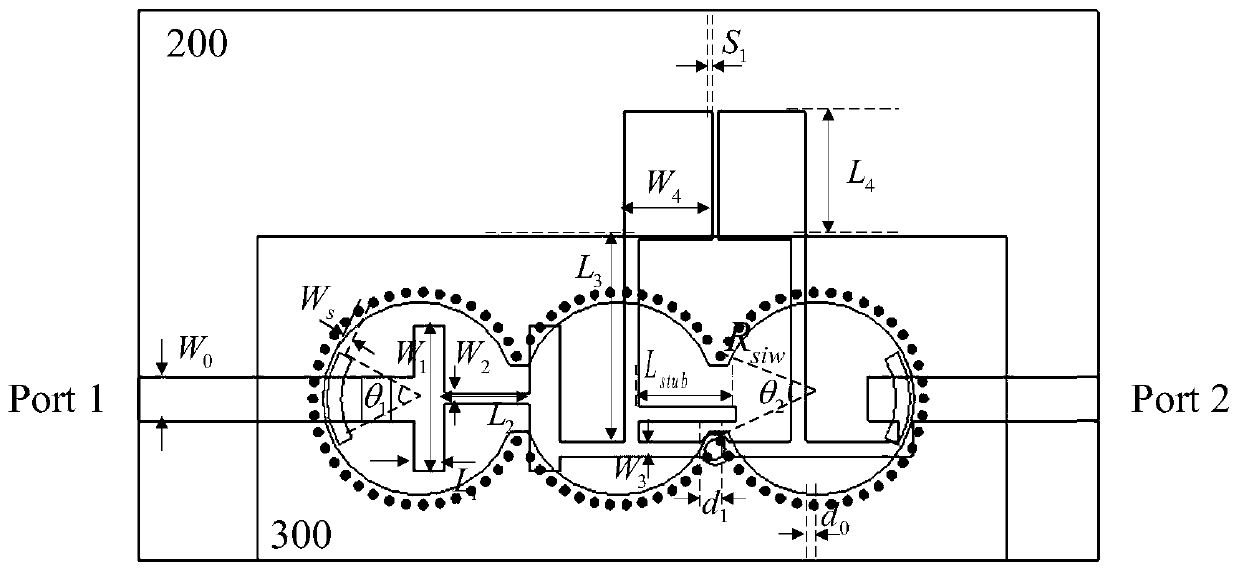
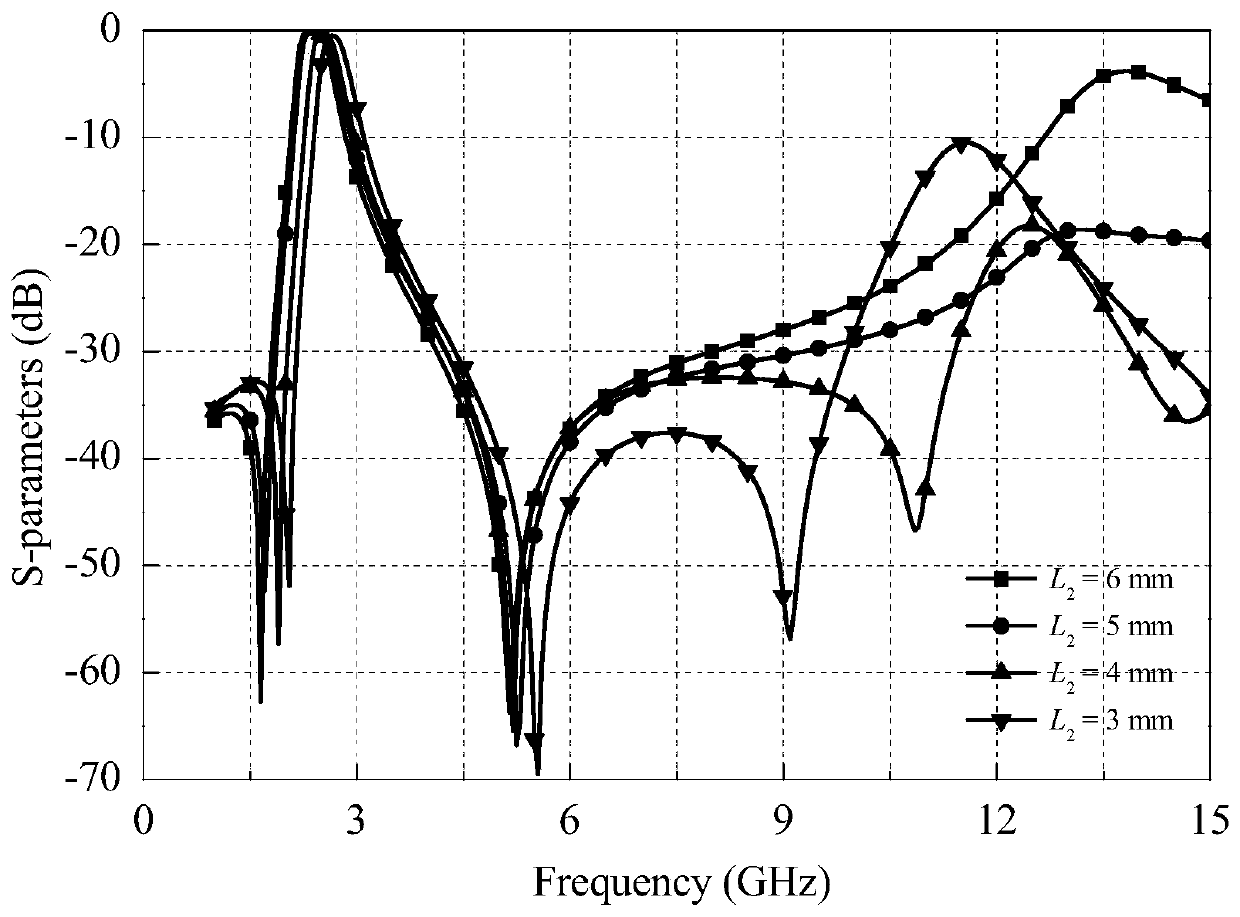
Microstrip and substrate integrated waveguide-based dual-frequency band-pass filter and design method thereof
ActiveCN107946706AChange working frequencyLow costWaveguide type devicesBand-pass filterDielectric substrate
The invention provides a microstrip and substrate integrated waveguide-based dual-frequency band-pass filter and a design method thereof. The filter comprises two coupled gaps positioned in a signal input end and a signal output end respectively, a phase step impedance resonator-based three-order low-pass filter, a 1 / 4 wavelength phase step impedance resonator-based two-order band-pass filter, a section of embedded open circuit stub, three air filled and connected circular cavities, a plurality of metalized via holes distributed in the edges of the circular cavities, a three-layer dielectric substrate, a layer of shared metal ground and a layer of bottom surface metal cover plate. The low-pass filter can realize the frequency response characteristic complementary with the band-pass filterby adjusting lengths of high and low impedances, thereby realizing the microwave band-pass filter based on an ultra-wide stop band; and then by combination with a substrate integrated waveguide circular cavity-based millimeter wave band-pass filter with low-frequency cut-off characteristics, the dual-frequency band-pass filter with ultra-high transmission band ratio is further realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
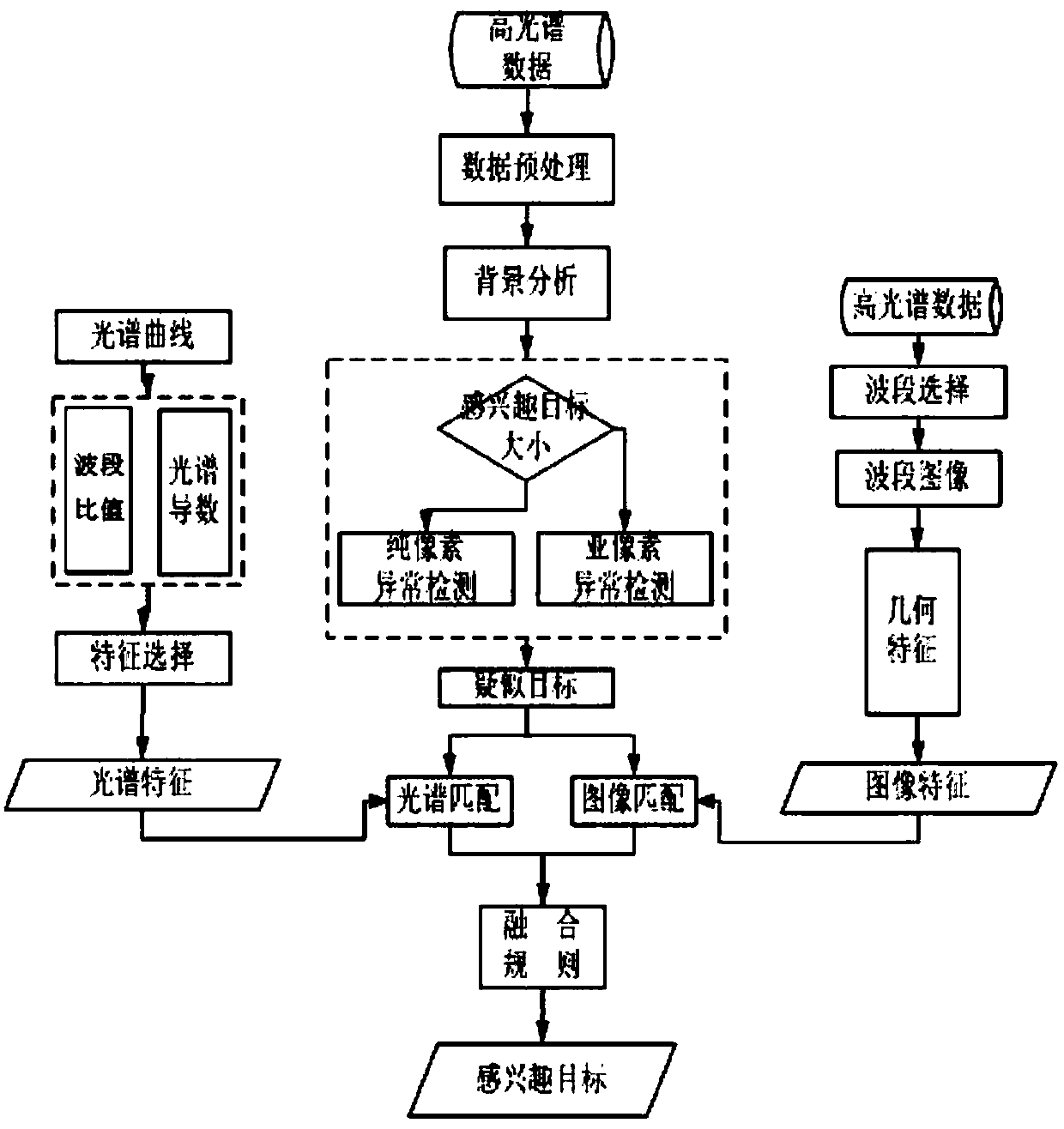
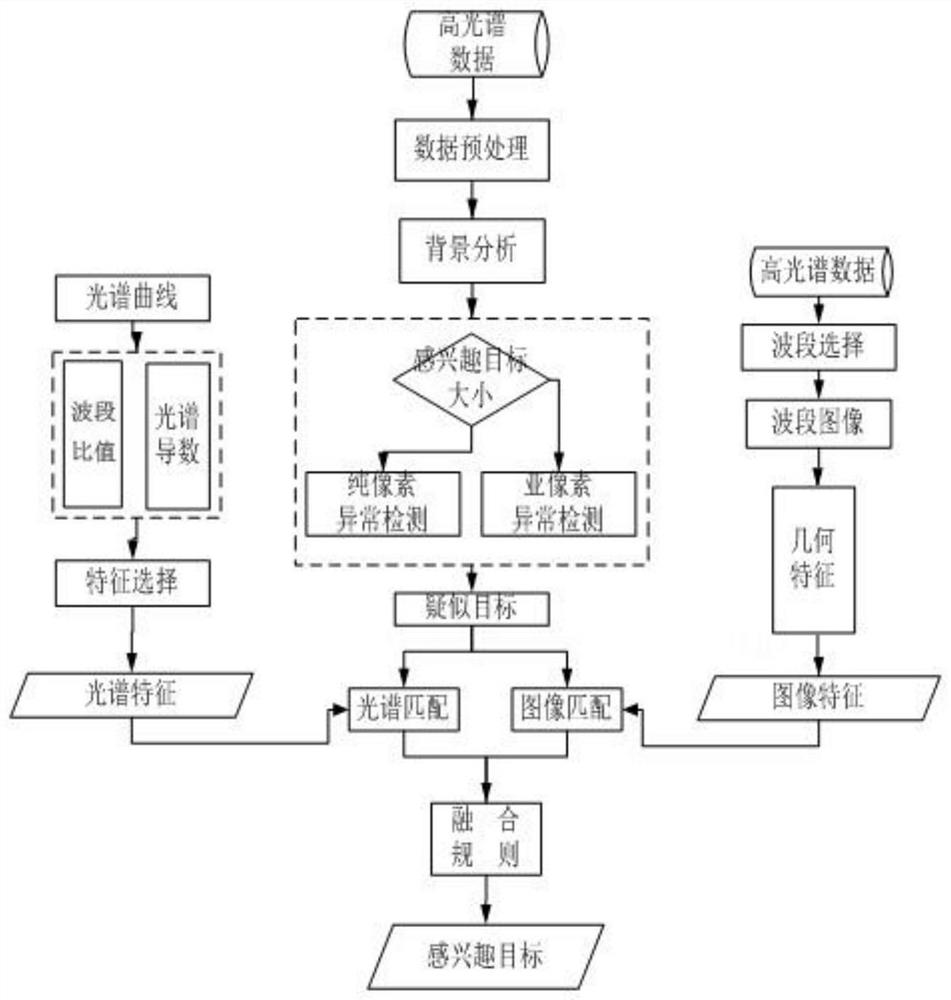
Method for identifying marine artificial facilities by using spectral remote sensing images
The present invention discloses a method of identifying marine artificial facilities using spectral remote sensing images. According to the method, hyperspectral data are preprocessed, thereafter, anomaly detection is performed, and therefore, a suspected target can be obtained; spectral features such as a band ratio and a spectral derivative are extracted in a spectral domain; the linear and circular features of target images are extracted in an image domain by using the clear geometric texture of a red band; and a target of interest is identified through fusion analysis. The method providedby the invention fills a technical blank by utilizing remote sensing images to automatically identify marine artificial facilities. The method is suitable for the detection and identification of marine artificial facilities by hyperspectral sensors, is also applicable to multi-spectral images, and has a bright application prospect.
Owner:北京市遥感信息研究所
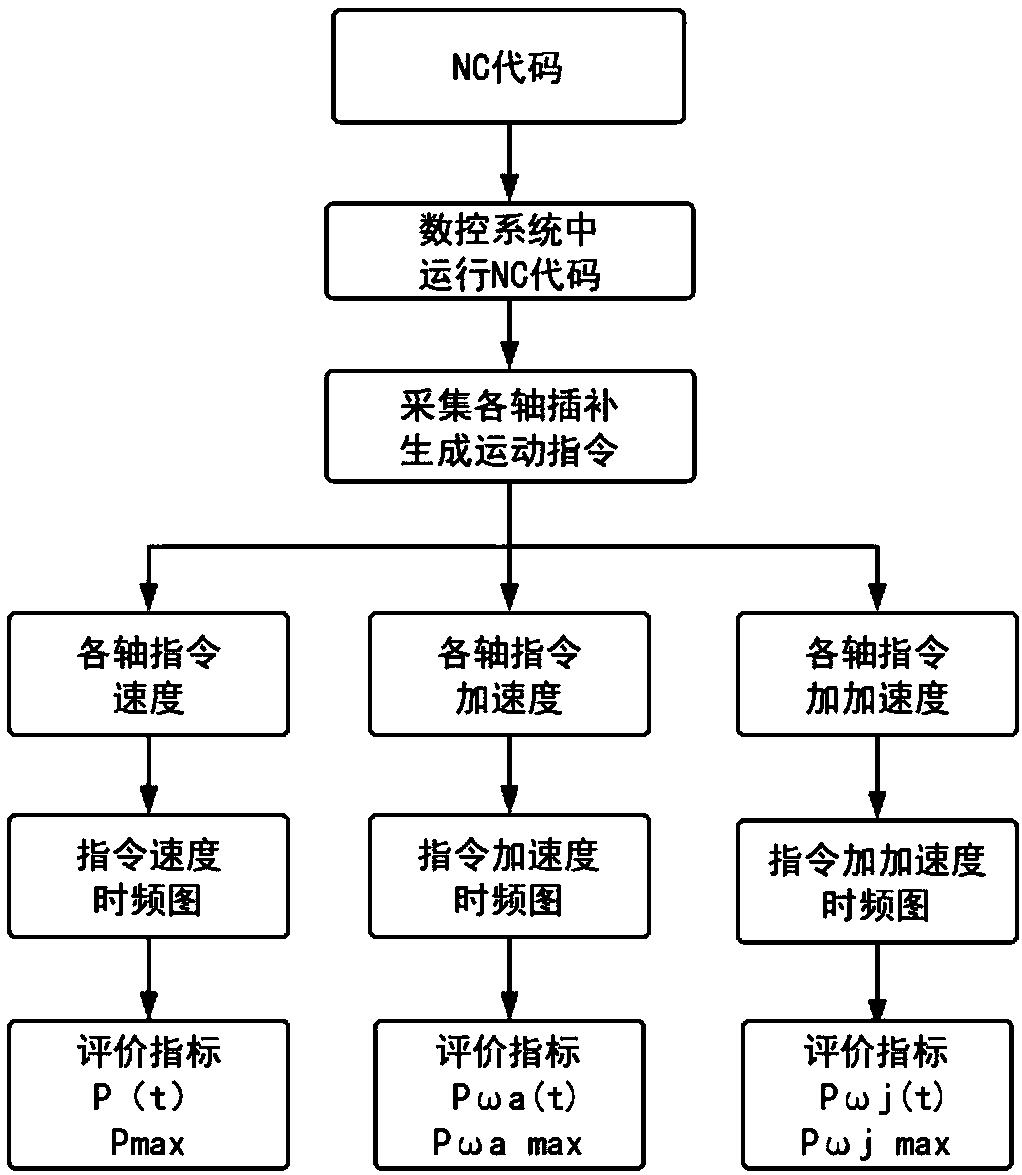
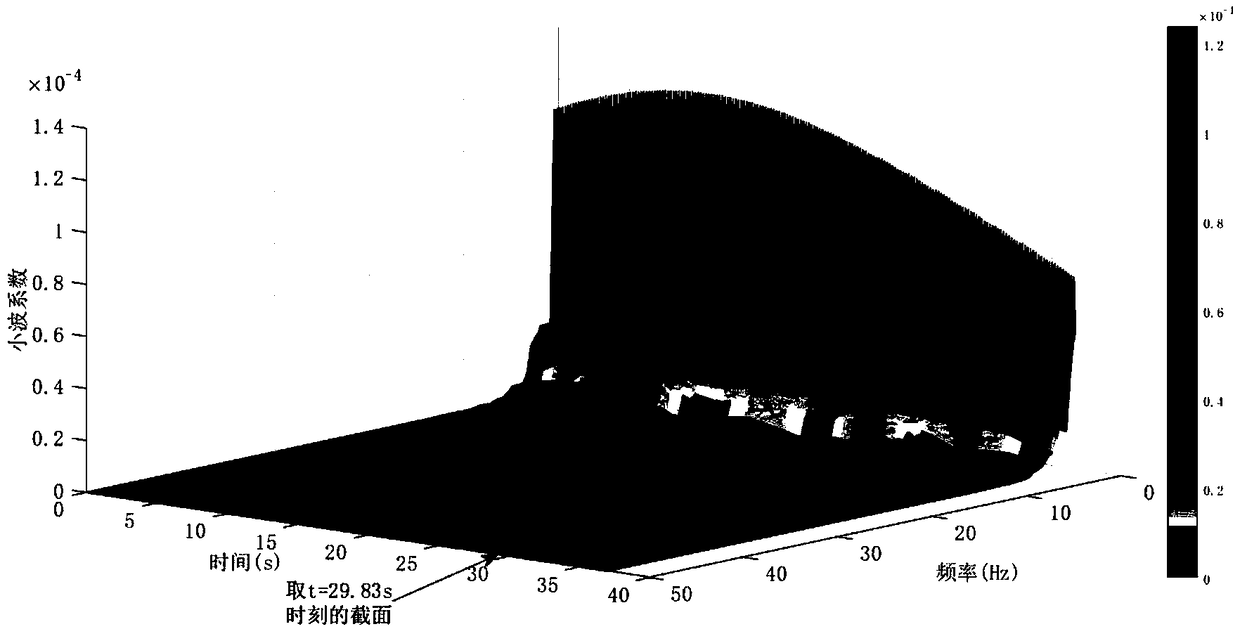
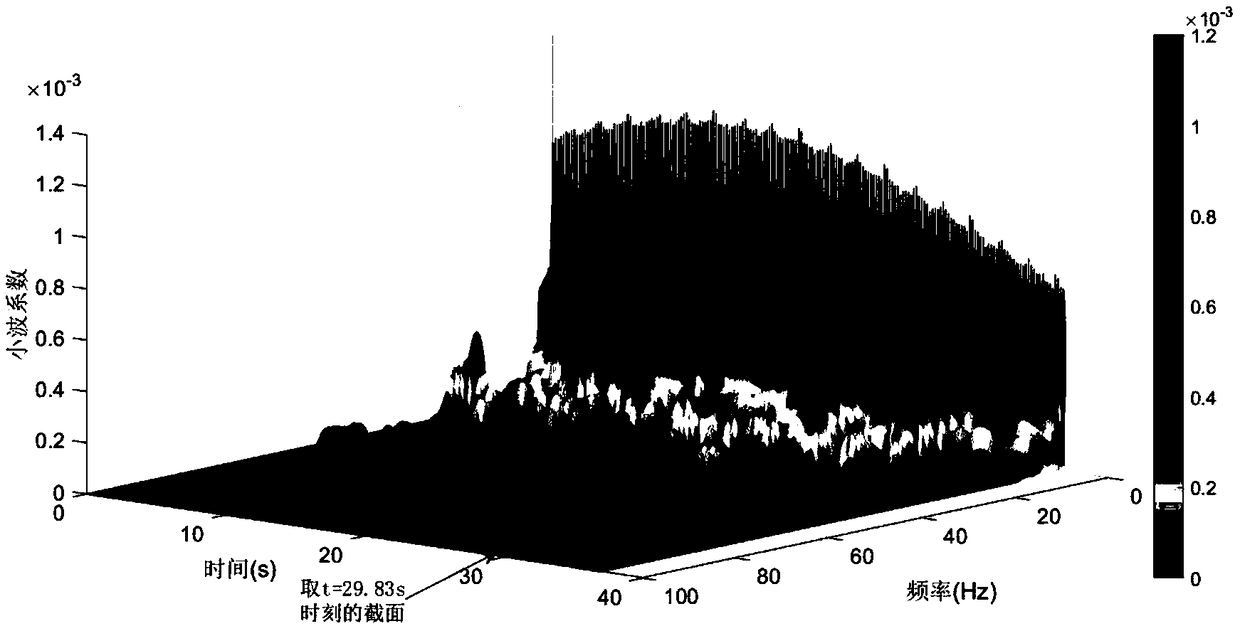
Dynamic precision oriented numerical control system interpolation generation motion instruction evaluation method
The invention provides a dynamic precision oriented numerical control system interpolation generation motion instruction evaluation method. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, collecting an instruction speed, an instruction acceleration and an instruction jerk sequence which are output to each shaft servo system after interpolation; then performing time-frequency transform to obtain a corresponding time-frequency graph; and finally, calculating a curve of an instruction speed high frequency band ratio which changes over time, namely changes with the tool path according to theinstruction speed time-frequency graph, thereby reflecting ability of the numerical control system interpolation generation motion instruction to realize position following precision; respectively calculating a curve of a frequency band ratio near a low order mechanical natural frequency of the instruction acceleration which changes over time and a curve of a frequency band ratio near a high order mechanical natural frequency of the instruction jerk which changes over time according to the instruction acceleration time-frequency graph and the instruction jerk time-frequency graph, thereby reflecting restraining ability of the numerical control system interpolation generation motion instruction for machine resonance. According to the dynamic precision oriented numerical control system interpolation generation motion instruction evaluation method, a relationship that changes over time between a frequency component and an amplitude value thereof can be obtained simultaneously.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Dual-band dual-polarized electromagnetic band gap structure
ActiveCN108718000AImprove performanceWide frequency ratio adjustment rangeAntenna couplingsAntenna designDouble frequency
The invention discloses a dual-band dual-polarized electromagnetic band gap structure, belonging to the field of wireless communication. The electromagnetic band gap structure comprises a medium substrate, a metal floor arranged on the back of the medium substrate, a variant 'Jerusalem' cross-type cell arranged on the front of the medium substrate, and four T-type cells. The dual-band dual-polarized electromagnetic band gap structure can be widely used in the field of wireless communication, can be used for designing dual-band dual-polarized antennas to improve the performance of the antennas.The dual-band dual-polarized electromagnetic band gap structure has both two 'in-phase reflection phase' bands and two 'surface wave suppression' bands, has a wider band ratio adjustment range and iscompact.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
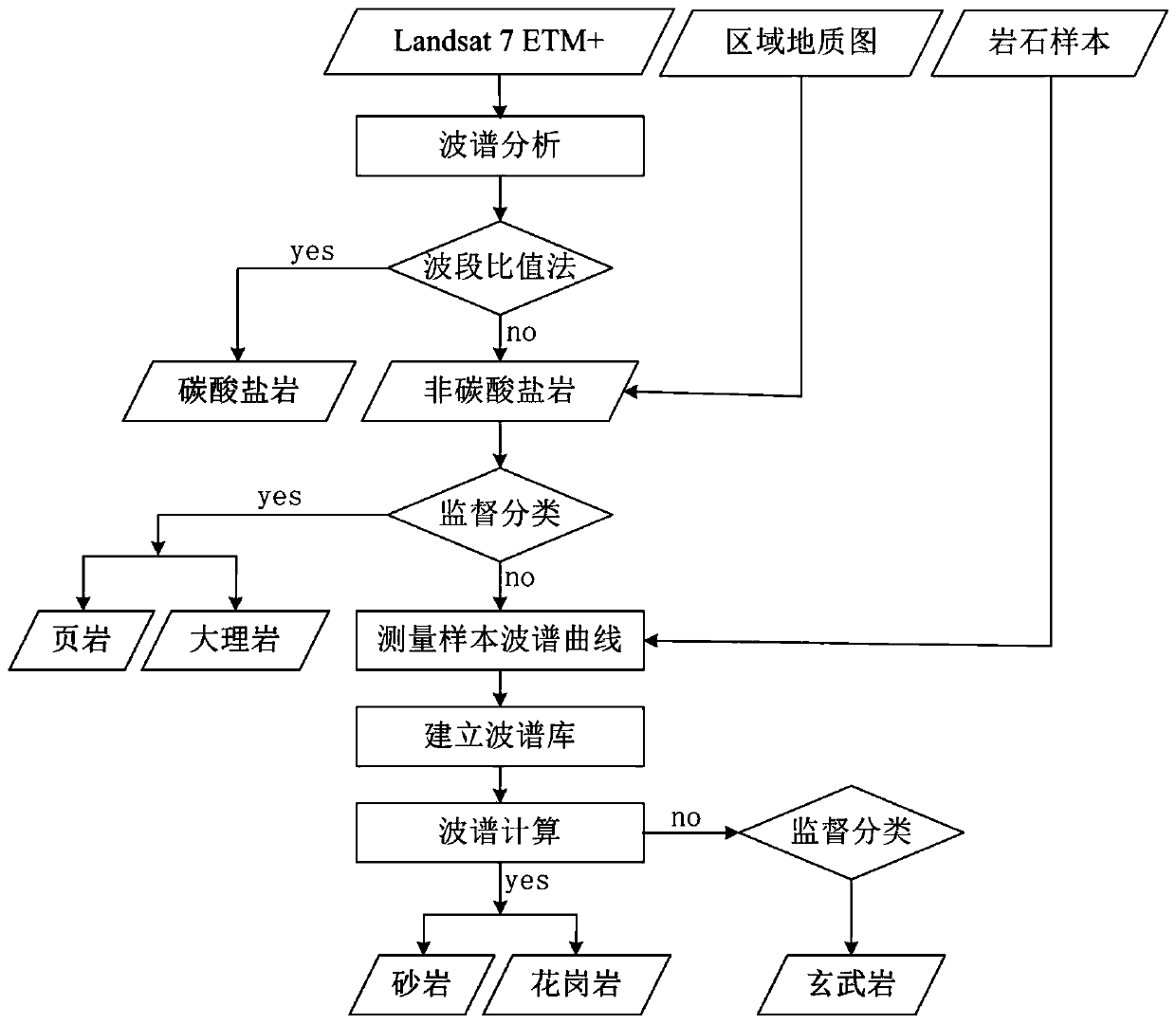
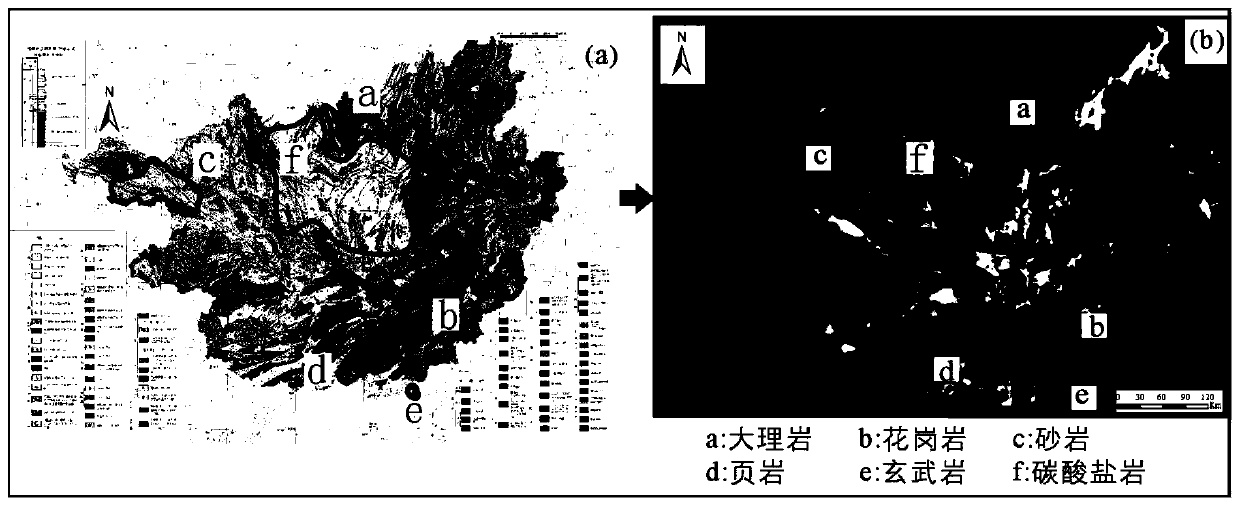
Method for performing rock classification based on spectral features
InactiveCN110261330ACharacter and pattern recognitionColor/spectral properties measurementsKarstClassification methods
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Optical Method of Multi-Band Mixing
InactiveUS20080122709A1Improve color differenceEnhancing difference chromaticness differenceSpectrum investigationOptical filtersMulti bandOpto electronic
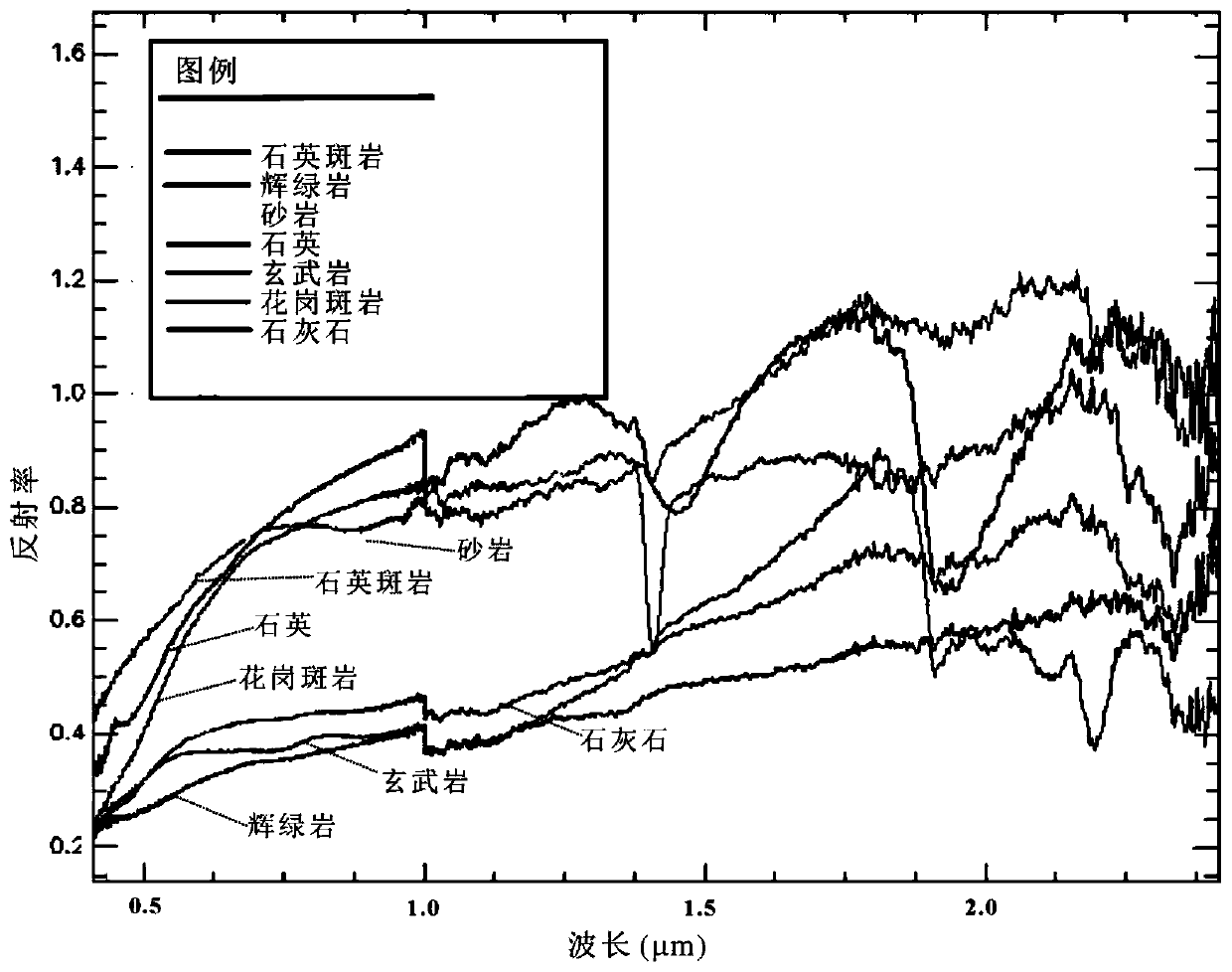
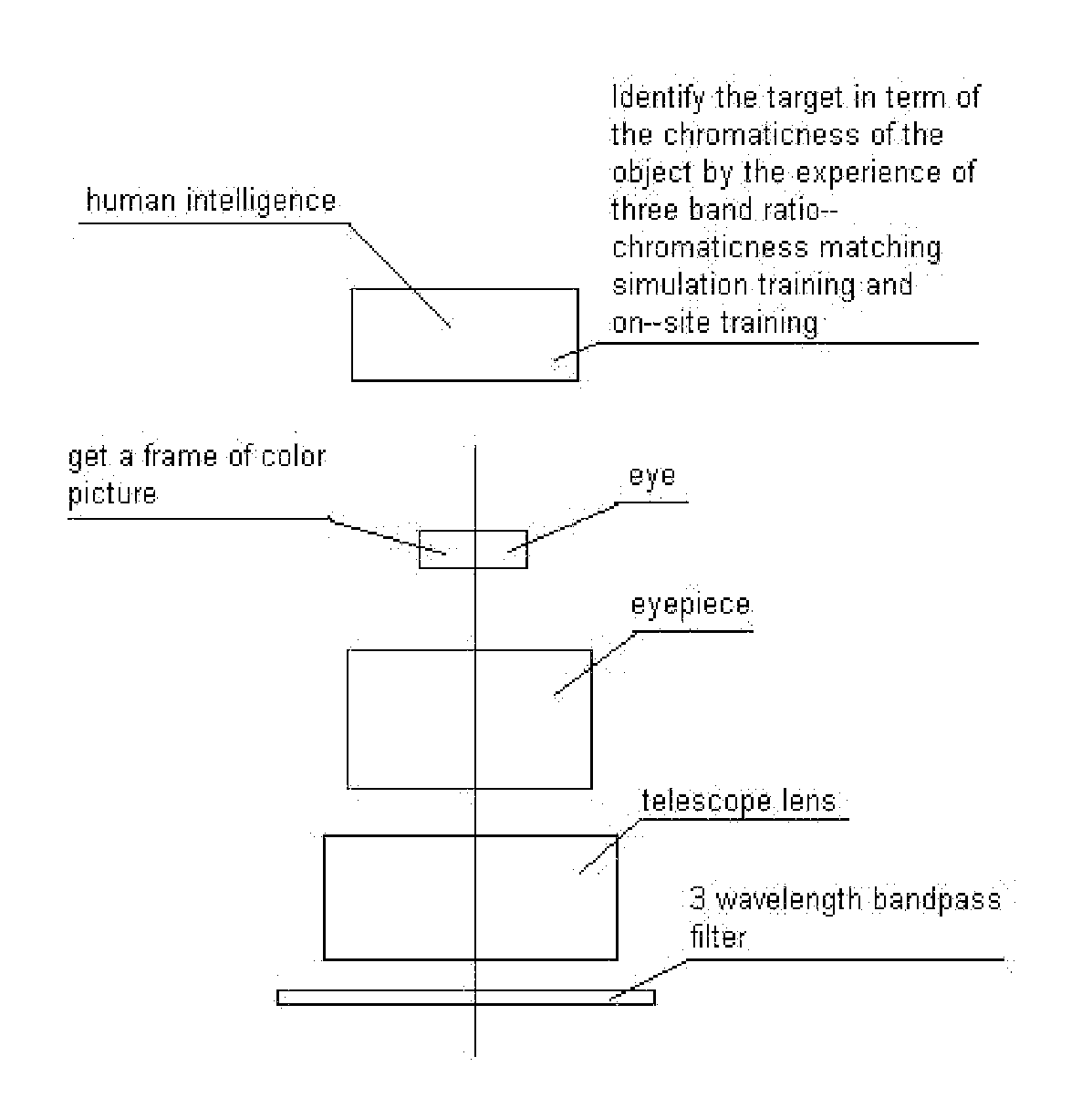
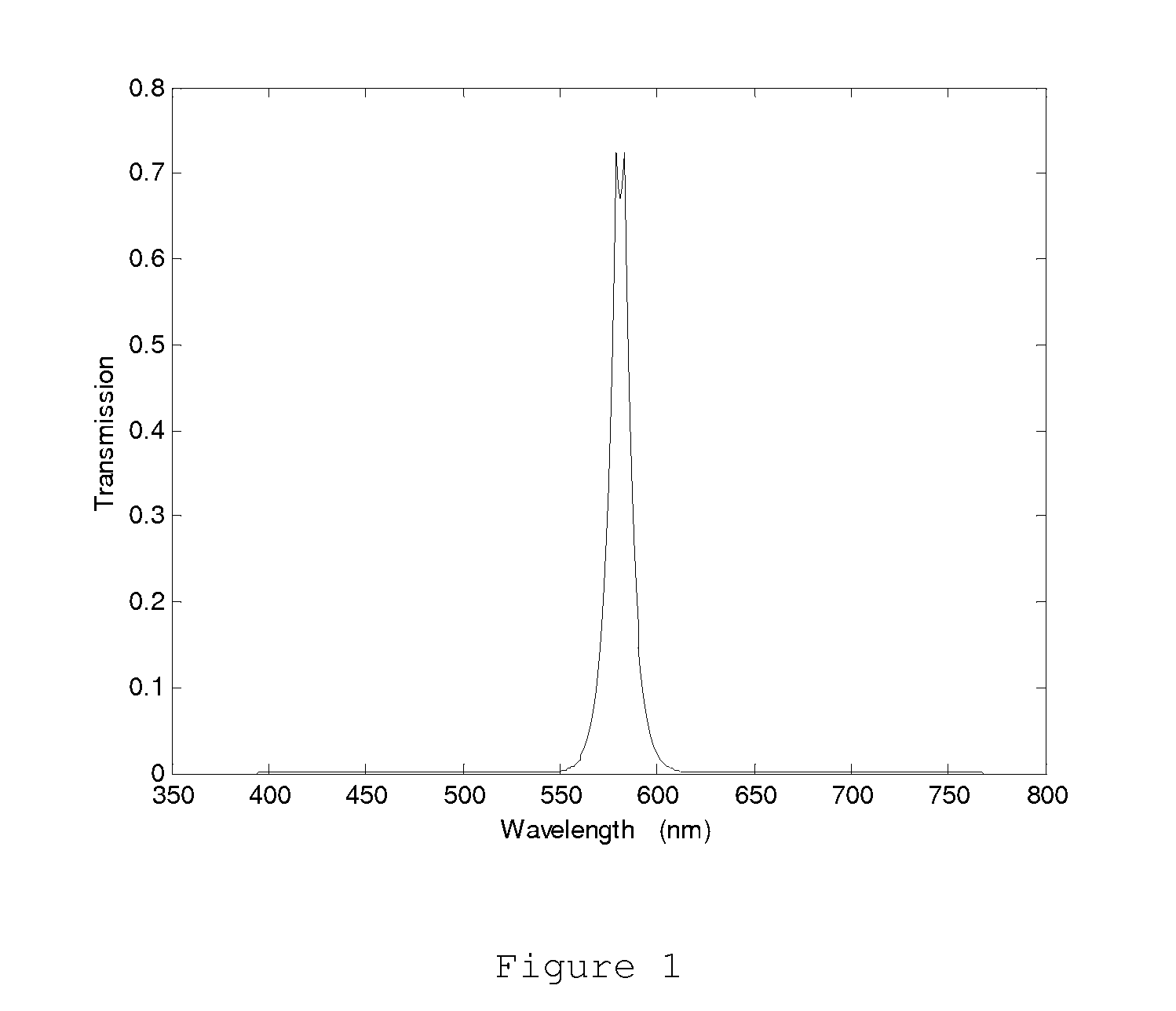
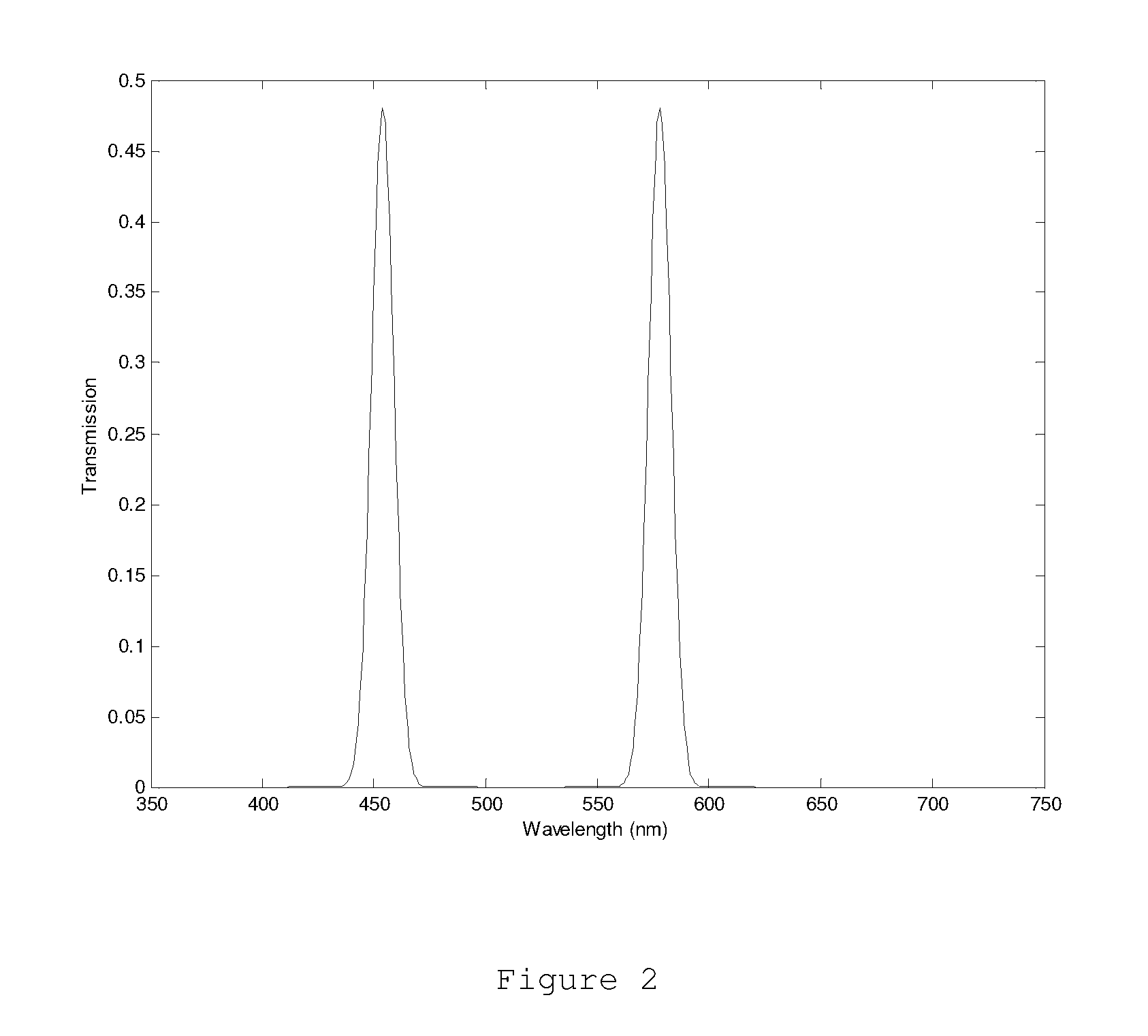
The light is filtered by a two- or three-band optical device integrated with two- and three-band mixing method so that only the light in the wavelength range of the pass bands can pass through this optical device and reach the optical sensor for the opto-electronic sensing application, or human eyes for the visual instrument application, or the surface of target object for the illumination application. The color difference and / or chromaticness difference can be enhanced by this method. And the target identification or object classification can be implemented by this method in terms of color attributes. With this method, two- and / or three-band ratio criteria widely used in remote sensing and machine vision applications can be calculated in terms of color attributes, and two- and / or three-band multi-spectral imaging can be acquired so that the complicated and expensive two and three band multi-spectral imaging system can be replaced by this kind of sensing device.
Owner:DING FUJIAN
Permeable band ratio factor-based water depth inversion method
ActiveCN102176001BMake up for the defect of reduced calculation accuracySmall standard deviationImage enhancementImage analysisOcean bottomNetwork model
The invention discloses a permeable band ratio factor-based water depth inversion method, which comprises the following steps of: 1, performing radiant calibration on a remote sensing image; 2, performing atmospheric correction on the remote sensing image subjected to the radiant calibration; 3, performing image enhancement on the remote sensing image subjected to the atmospheric correction; 4, performing amphibious separation on the remote sensing image subjected to the image enhancement; 5, performing geometric correction and data processing on the remote sensing image subjected to the amphibious separation; and 6, establishing a neural network water depth inversion model. Compared with a neural network model using single permeable band as input, the permeable band ratio factor-based neural network inversion model has low standard deviation and large related coefficients. The model is not affected by the seawater type and the undersea sediment, and simultaneously has the function ofsolving nonlinear mapping and good promotion capability.
Owner:哈尔滨哈船导航技术有限公司
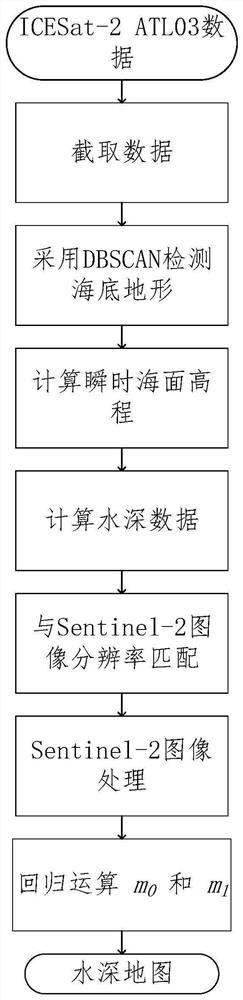
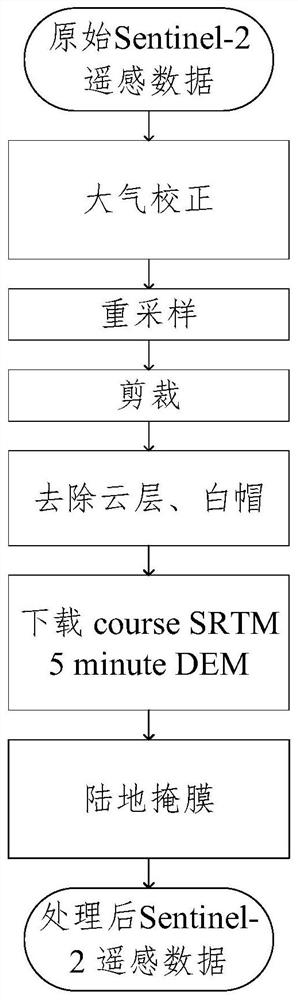
Water depth inversion method based on satellite-borne single-photon laser active and passive remote sensing fusion
PendingCN113960625AHigh measurement accuracyIncreased spatial coverageElectromagnetic wave reradiationOriginal dataAtmospheric correction
The invention discloses a water depth inversion method based on satellite-borne single-photon laser active and passive remote sensing fusion. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, reading an ICESat-2ATL03 original data set; then extracting shallow water body water depth data by adopting a DBSCAN method; then selecting a Sentinel remote sensing image with less cloud in the region, and carrying out atmospheric correction, space cutting and land cloud layer masking on the Sentinel remote sensing image; substituting the water depth data detected in the ICESat-2 data into a band ratio empirical model for regression training to obtain parameters, and finally substituting the parameters into the Sentinel remote sensing image to invert a water depth map of the region. According to the invention, no in-situ sounding data is used as a control point, water depth measurement can be carried out in a region where airborne water depth measurement is not easy, and good measurement precision is maintained.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR +1
Optical method of multi-band mixing
InactiveUS7733489B2Increase chromatic aberrationColor differenceSpectrum investigationOptical filtersMulti bandHue
The color difference and / or chromaticness difference between target objects and background objects can be enhanced. Different colors with different color attributes mean different objects. In some cases, different chromaticness, such as saturation and hue, mean different two- or three-band ratio. The light from the surface of objects is filtered by optical system integrated with two- and three-band mixing method so that only the light in the wavelength range of the pass bands can reach optical sensors for opto-electronic sensing devices. With this kind of opto-electronic sensing devices, two- and / or three-band ratio criteria widely used in remote sensing and machine vision applications can be calculated in terms of color attributes. Multi-spectral imaging system can be replaced by this kind of sensing devices. This kind of two- or three-band mixing illumination can be used to identify, classify, and detect objects for human visual application, remote sensing, and machine vision application.
Owner:DING FUJIAN
Segmentation method of corn germ in hyperspectral reflectance image based on band ratio method
ActiveCN105931223BHigh degree of automationGood segmentation effectImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral ratioVisible near infrared
The invention discloses a band ratio method based maize embryo segmentation method in a high-spectral reflection image. The high-spectral image of a maize seed is collected with the embryo surface of the seed upwards; multiple pixels and spectrums thereof are extracted from the endosperm and embryo and normalized; the spectral ratio of two random wave bands is calculated and serves as the band ratio, and the optimal band ratio is selected; a band subset is selected, variance of all pixels in the band subset is calculated, a seed binary image is obtained via threshold segmentation, and a background removed high-spectral image of the maize seed is obtained via mask operation; and a gray scale image of the background removed high-spectral image of the maize seed under the optimal band ratio is calculated via the high-spectral image, the gray scale image is segmented in a region growing method to obtain an embryo binary image, the embryo binary image is processed to obtain a seed embryo binary image, and the high-spectral image of the maize seed embryo is obtained via mask operation. The method can be used to segment the maize seed embryo in the visible near-infrared high-spectral image effectively, the segmentation effect is good, and the practicality is higher.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
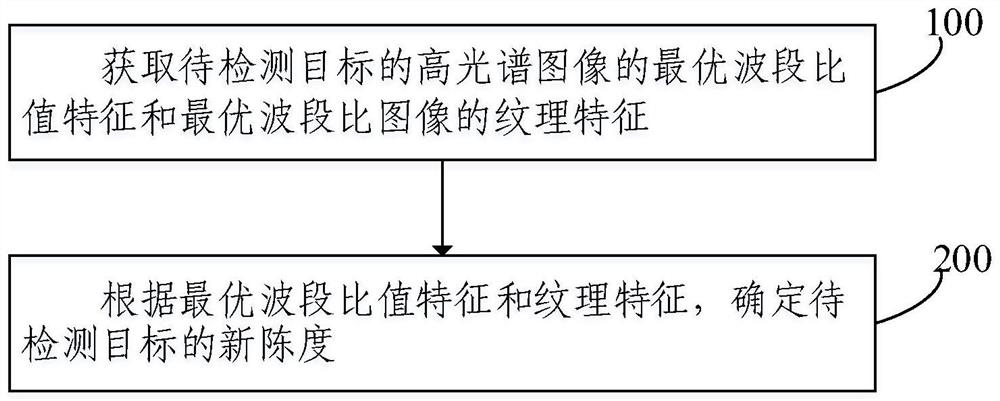
Target freshness detection method and system
PendingCN114693608AReduce development difficultyReduce development costsImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer vision
Owner:北京市农林科学院智能装备技术研究中心
A Method for Identifying Maritime Artificial Facilities Using Spectral Remote Sensing Images
Owner:北京市遥感信息研究所
Dual-band bandpass filter based on microstrip and substrate integrated waveguide and its design method
ActiveCN107946706BChange working frequencyLow costWaveguide type devicesBand-pass filterDielectric substrate
The invention provides a microstrip and substrate integrated waveguide-based dual-frequency band-pass filter and a design method thereof. The filter comprises two coupled gaps positioned in a signal input end and a signal output end respectively, a phase step impedance resonator-based three-order low-pass filter, a 1 / 4 wavelength phase step impedance resonator-based two-order band-pass filter, a section of embedded open circuit stub, three air filled and connected circular cavities, a plurality of metalized via holes distributed in the edges of the circular cavities, a three-layer dielectric substrate, a layer of shared metal ground and a layer of bottom surface metal cover plate. The low-pass filter can realize the frequency response characteristic complementary with the band-pass filterby adjusting lengths of high and low impedances, thereby realizing the microwave band-pass filter based on an ultra-wide stop band; and then by combination with a substrate integrated waveguide circular cavity-based millimeter wave band-pass filter with low-frequency cut-off characteristics, the dual-frequency band-pass filter with ultra-high transmission band ratio is further realized.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Sampling mixer and receiver
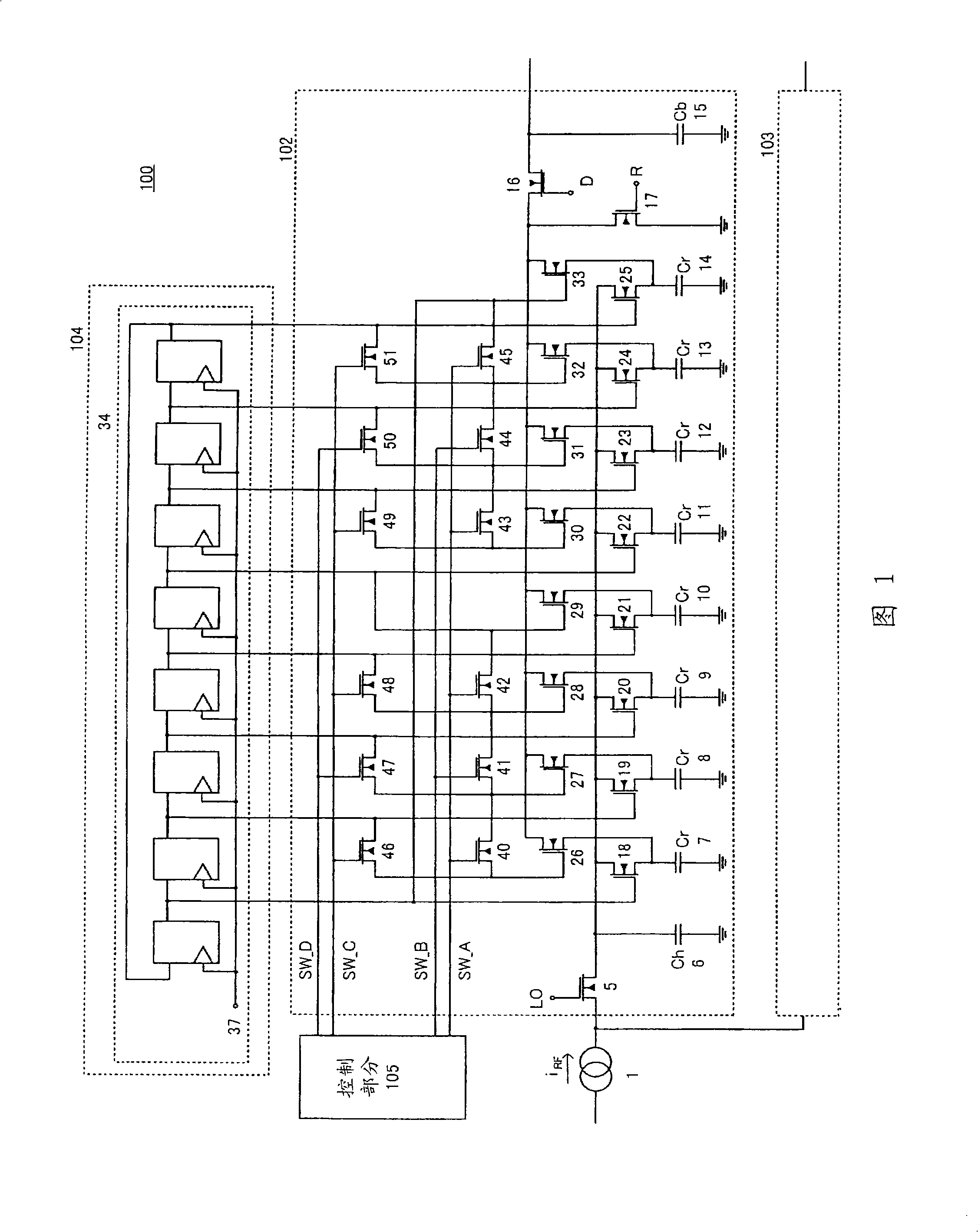
InactiveCN101313464AReduce consumptionReduce quantization noiseModulation transferenceTransmissionSnubber capacitorEngineering
A receiver and a sampling mixer capable of optimizing the sampling rate of an output signal in accordance with the band ratio of a modulation band to the RF frequency of a received signal. A sampling mixer comprises a history capacitor (6) that integrates input signals current-converted for a continuous time interval; rotation capacitors (7-14) that repeat the integration and discharging of the input signals; a digital control (104) that controls the integration intervals of the rotation capacitors (7-14); and a control part (105) that controls the discharging of the rotation capacitors (7-14). In the sampling mixer, the number of ones of the rotation capacitors (7-14) that are simultaneously connected to a buffer capacitor (15) is changed in accordance with the band ratio of the modulation band to the RF frequency. In this way, the decimation ratio is made variable, whereby the quantized noise during the A / D conversion can be reduced.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
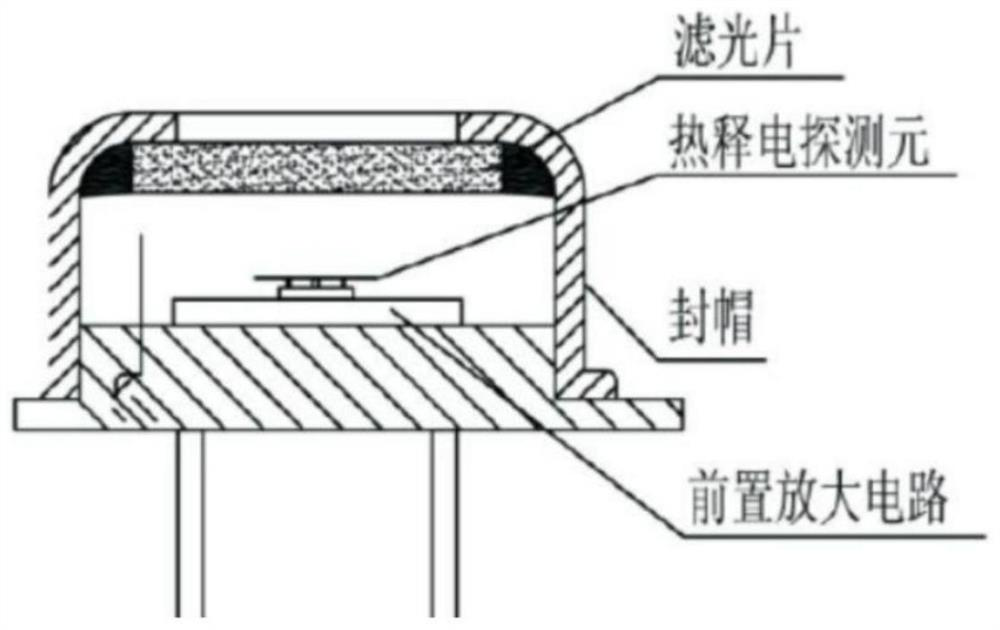
Temperature identification and classification method based on dual-band pyroelectric device
ActiveCN114239654ALow universalityGood temperature recognition and classification effectEnsemble learningCharacter and pattern recognitionTime domainAlgorithm
The invention relates to the field of temperature identification and classification of pyroelectric detection, in particular to a temperature identification and classification method based on a dual-band pyroelectric device. According to the dual-band characteristic output by a dual-band pyroelectric device, the characteristic that different temperatures of a target black body can map different dual-band ratios is utilized, the dual-band ratios serve as the main characteristic of a signal, and part of characteristics of a time domain and a frequency domain are additionally added to serve as a characteristic set of the signal, so that extraction of the main characteristic of the signal is completed; and the method is combined with machine learning, so that a good temperature identification and classification effect is achieved. The method is easy to implement, can achieve a good classification effect, effectively solves the problem that an existing temperature recognition and classification method is limited by respective categories and is low in universality, can be applied to other fields, and provides a new thought for development of other fields.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Compact type plane dual-band omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna
InactiveCN102931479BGood omnidirectional radiation performanceSimple structureSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a compact type plane dual-band omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna. The compact type plane dual-band omnidirectional circularly polarized antenna is characterized by comprising a plane radiating antenna, a center shorting pin, an input connector and a feed probe; the plane radiating antenna sequentially comprises a capacitor chip, a medium substrate I, a radiating chip, a medium substrate II and a floor from top to bottom, and an air layer is arranged between the radiating chip and the medium substrate II; the capacitor chip is connected with an inner conductor of the input connector through the feed probe, protection holes are arranged at corresponding positions on the radiating chip and the floor, the feed probe penetrates through the positions on the radiating chip and the floor, and inner diameters of the protection holes are larger than the diameter of the feed probe; and the radiating chip is composed of a primary round radiation chip and three groups of radiating units which are of same structures, the three groups of radiating units are loaded on the periphery of the primary round radiation chip and composed of six arc vibrators, and each group of radiating units is composed of two arc vibrators with different length. The antenna has the advantages of being good in omnidirectional radiation, good in circular polarization in the ranges of 360 degrees on a plane and flexible in dual-band ratio.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
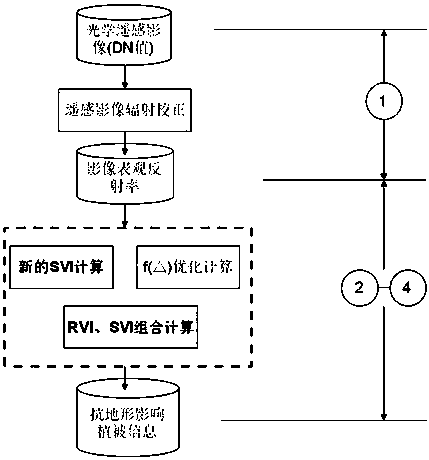
A new tavi combination algorithm
ActiveCN106324614BThe form is concise and similarStrong Band Ratio Physical Significance BasisElectromagnetic wave reradiationTerrainVegetation Index
The invention relates to a new TAVI combination algorithm, and the algorithm is characterized in that the algorithm comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out the radiation correction: carrying out the radiation correction of a remote sensing image at first, and then obtaining the apparent reflectance data of the remote sensing image; S2, calculating a new SVIn; S3, building a new TAVI combination algorithm which is specifically shown in the description; S4, carrying out the optimization: calculating the new TAVI. The new TAVI combination algorithm consists of an RVI sub-model and an SVI sub-model. The RVI sub-model and the SVI sub-model can meet the requirement of a band ratio module, and the forms are concise and similar. Moreover, the denominators are the infrared band data of the remote sensing image, and have the stronger band ratio physical significance basis. The new TAVI combination algorithm provided by the invention guarantees that a terrain adjustment vegetation index can effectively eliminate impact on the vegetation information from the terrain. The new TAVI combination algorithm achieves an effect of terrain correction and atmospheric correction, and solves a problem that the inversion accuracy of surface vegetation information decreases because of the difference of the registration precisions of the remote sensing images and DEM data.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method of calculating TAVI based on a band ratio model and solar altitude angle
ActiveUS10527542B2Accurate and convenient in applicationAccurate inversion of the vegetation informationMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionTwo bandSolar altitude
The present invention relates to a method of calculating a Topography Adjusted Vegetation Index (TAVI) based on a band ratio model and a solar altitude angle. The method includes the following steps: obtaining the apparent reflectance data of a remote sensing image through image preprocessing, analyzing the quality of the image and numerical distribution, calculating a Shadow Vegetation Index (SVI), and constructing a TAVI combinational algorithm:TAVI=BirBr+f(Δ)·1Br,calculating an adjustment factor f(Δ) with the solar altitude angle, and finally obtaining anti-topographic effect TAVI vegetation information. The TAVI in the present invention is composed of two band ratio submodels RVI and SVI, the denominators of both of which are red band data of a remote sensing image, and the adjustment factor f(Δ), which is calculated by a solar altitude angle as a parameter with a sensor factor applied, has great physical significance. The TAVI calculation method does not need digital elevation model (DEM) data and remote sensing image classification when not depending on ground survey data, and ensures that the interference of the topographic effects with the vegetation information can be effectively eliminated by the TAVI, thereby avoiding the problem of reduced inversion accuracy of ground vegetation information due to different registration accuracy of a remote sensing image and DEM data.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
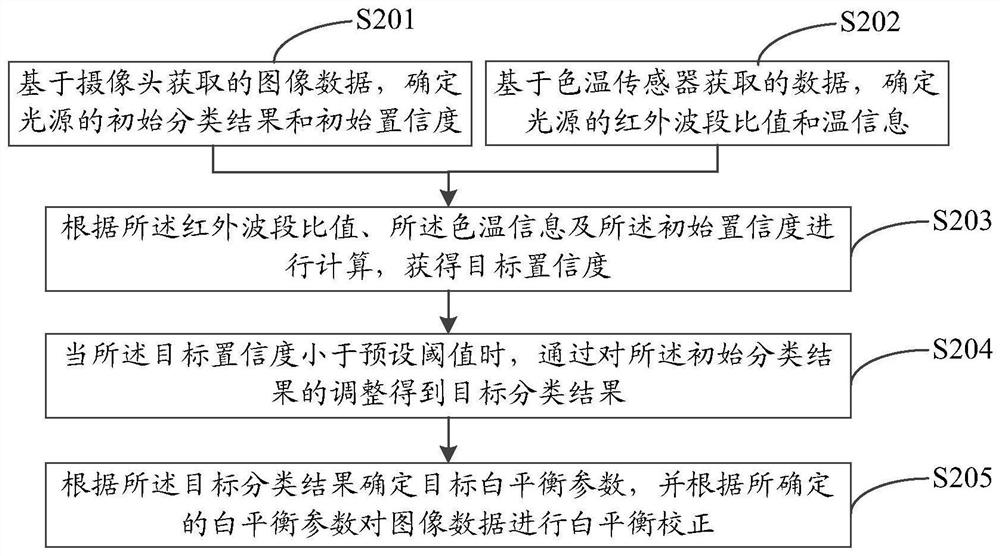
A white balance correction method, device, storage medium and terminal equipment
ActiveCN112866656BHigh color reproductionImprove accuracyColor signal processing circuitsPicture signal generatorsTerminal equipmentThresholding
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Practical atmospheric correction method for remote sensing images
InactiveCN101598543BAvoid disadvantagesHigh precisionElectromagnetic wave reradiationVegetationSatellite imagery
The invention discloses a practical atmospheric correction method for remote sensing images, which comprises three steps: a first step, inverting the optical thickness of atmospheric aerosol from MODIS data by means of a 6S model lookup table based on a dense vegetation algorithm; a second step, calculating total content of atmospheric vapor by using an MODIS data band ratio method, and then calculating the optical thickness of the atmospheric vapor; and a third step, combining the inverted optical thickness of the atmospheric aerosol, the optical thickness of the atmospheric vapor and a DOS model to invert the earth surface reflectance. The calculated earth surface reflectance has high precision; the method has strong practicability, and is applicable to various land satellite images; and the MODIS data can be acquired freely every day; therefore, the method can be used as a service atmospheric correction method for the remote sensing images.
Owner:CENT FOR EARTH OBSERVATION & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com