Patents
Literature
244 results about "Snubber capacitor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
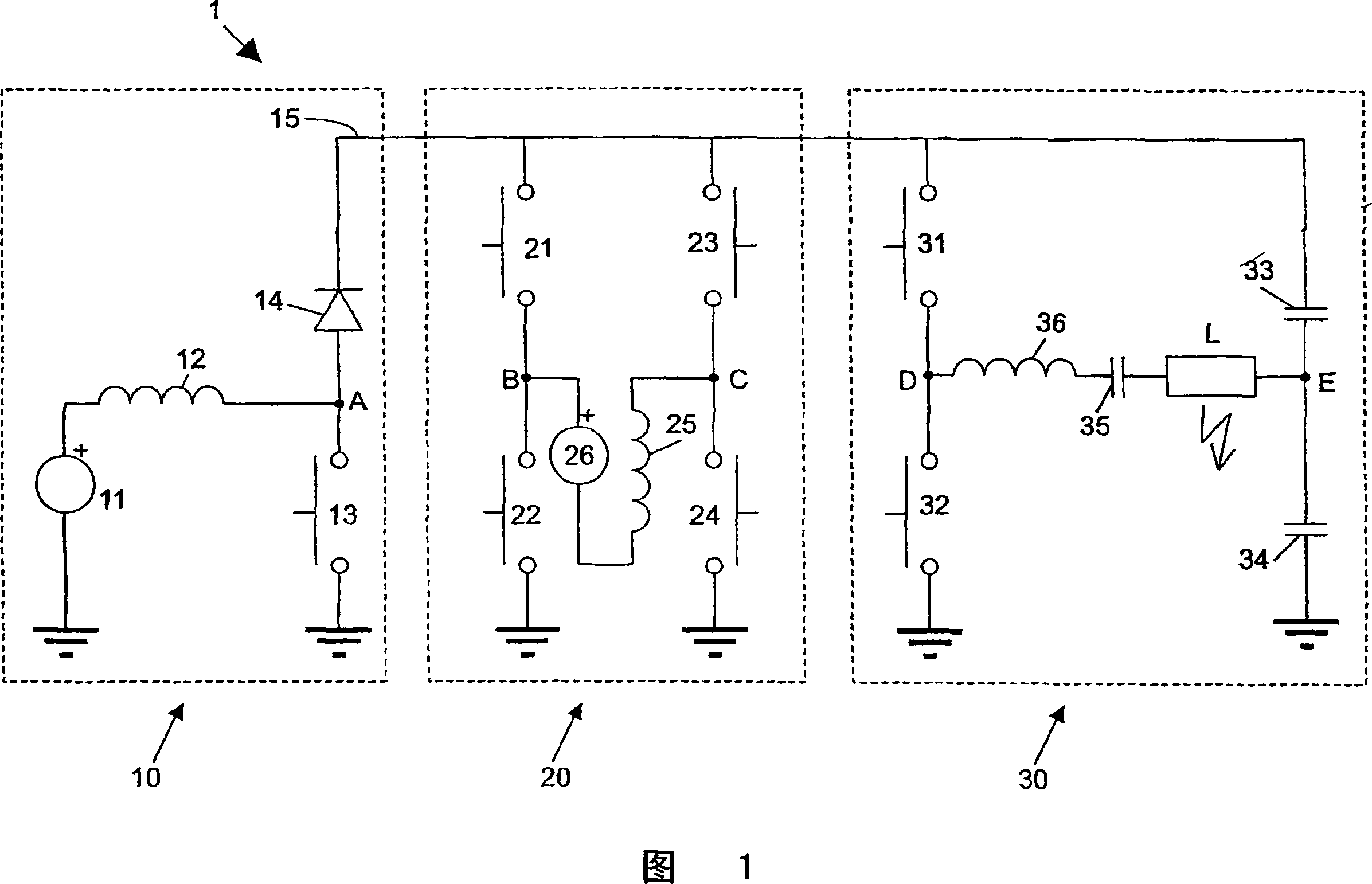
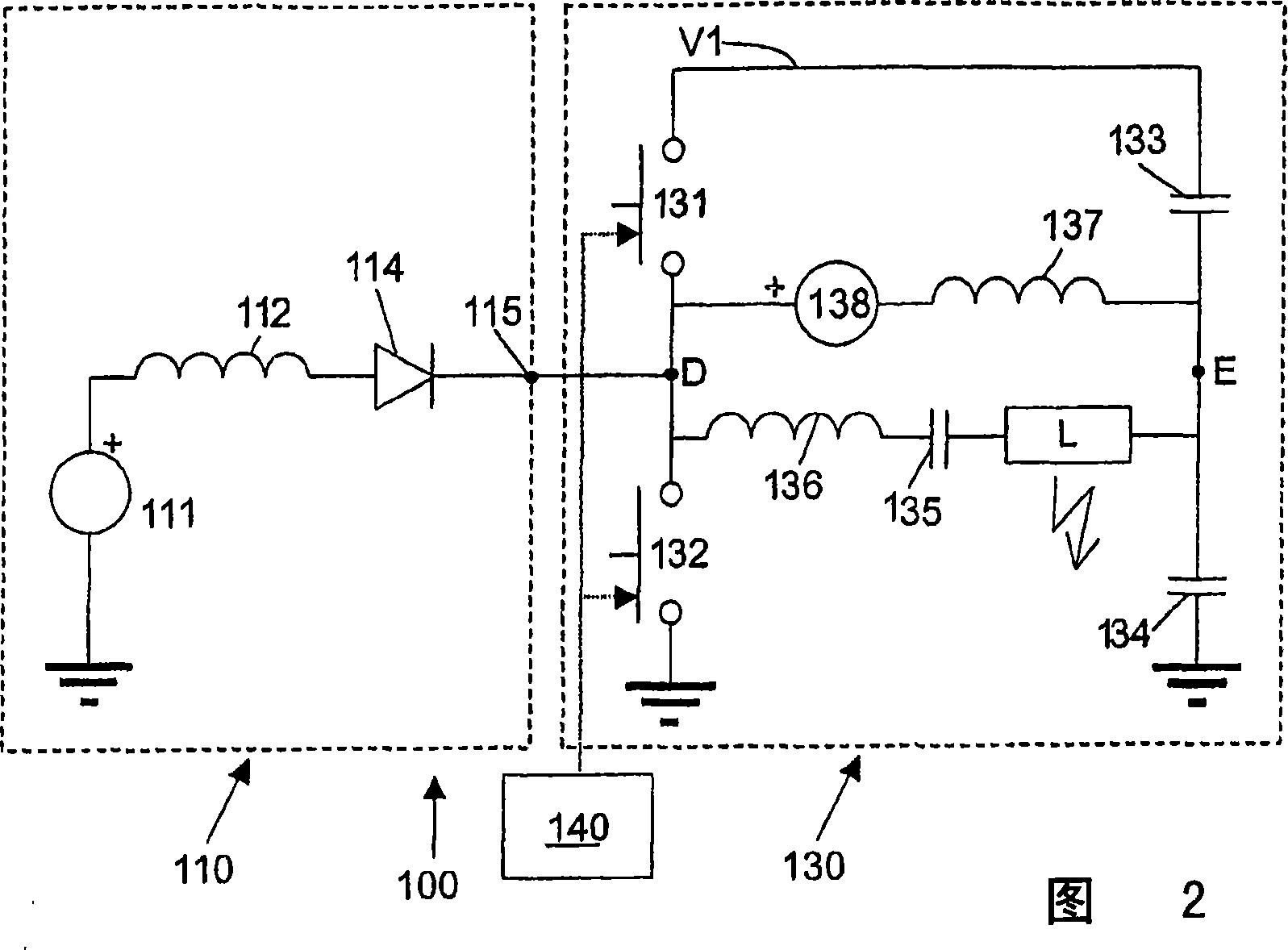
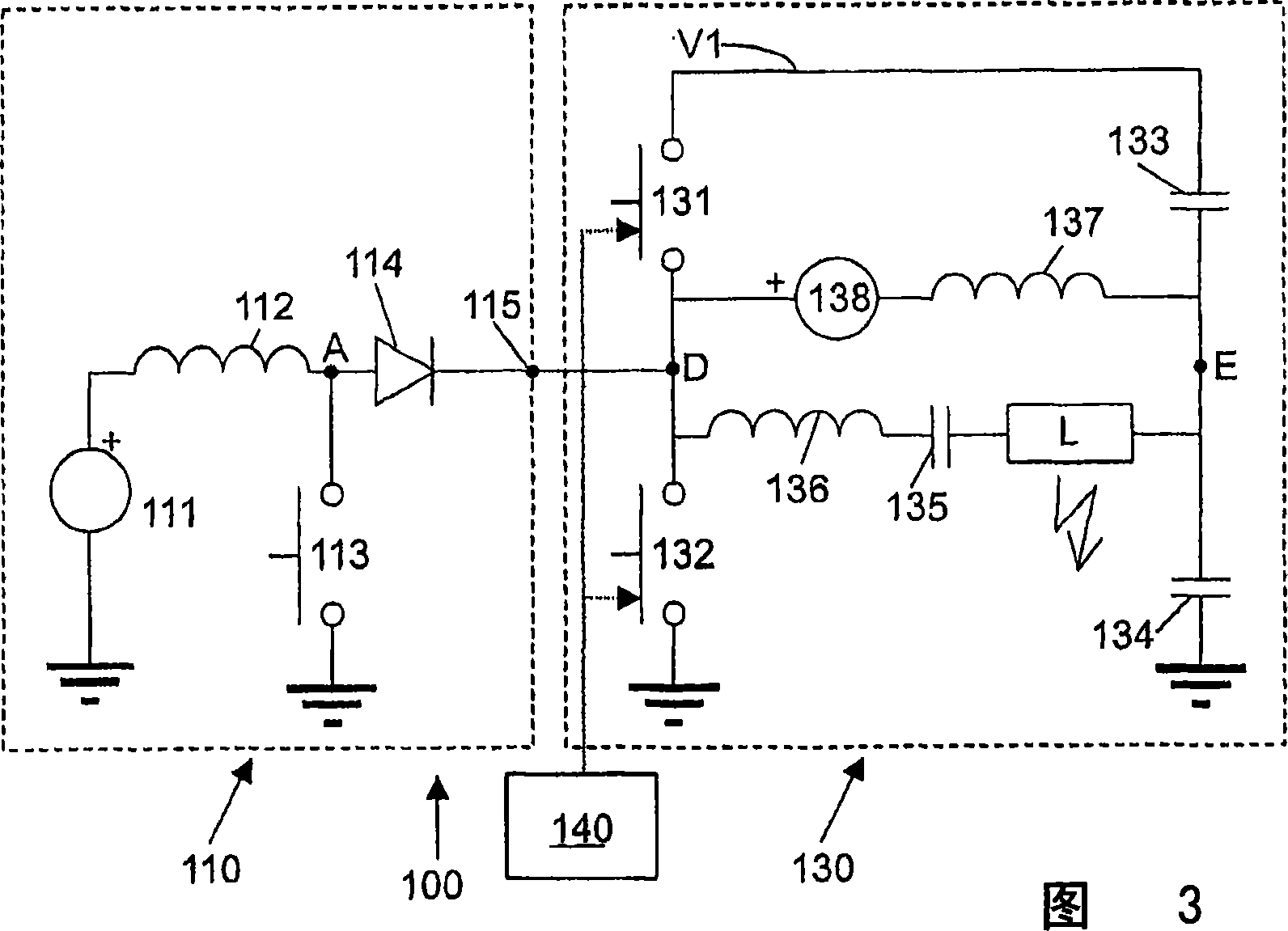
Lamp driver using solar cells
InactiveCN1930925AElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementSnubber capacitorGas-discharge lamp
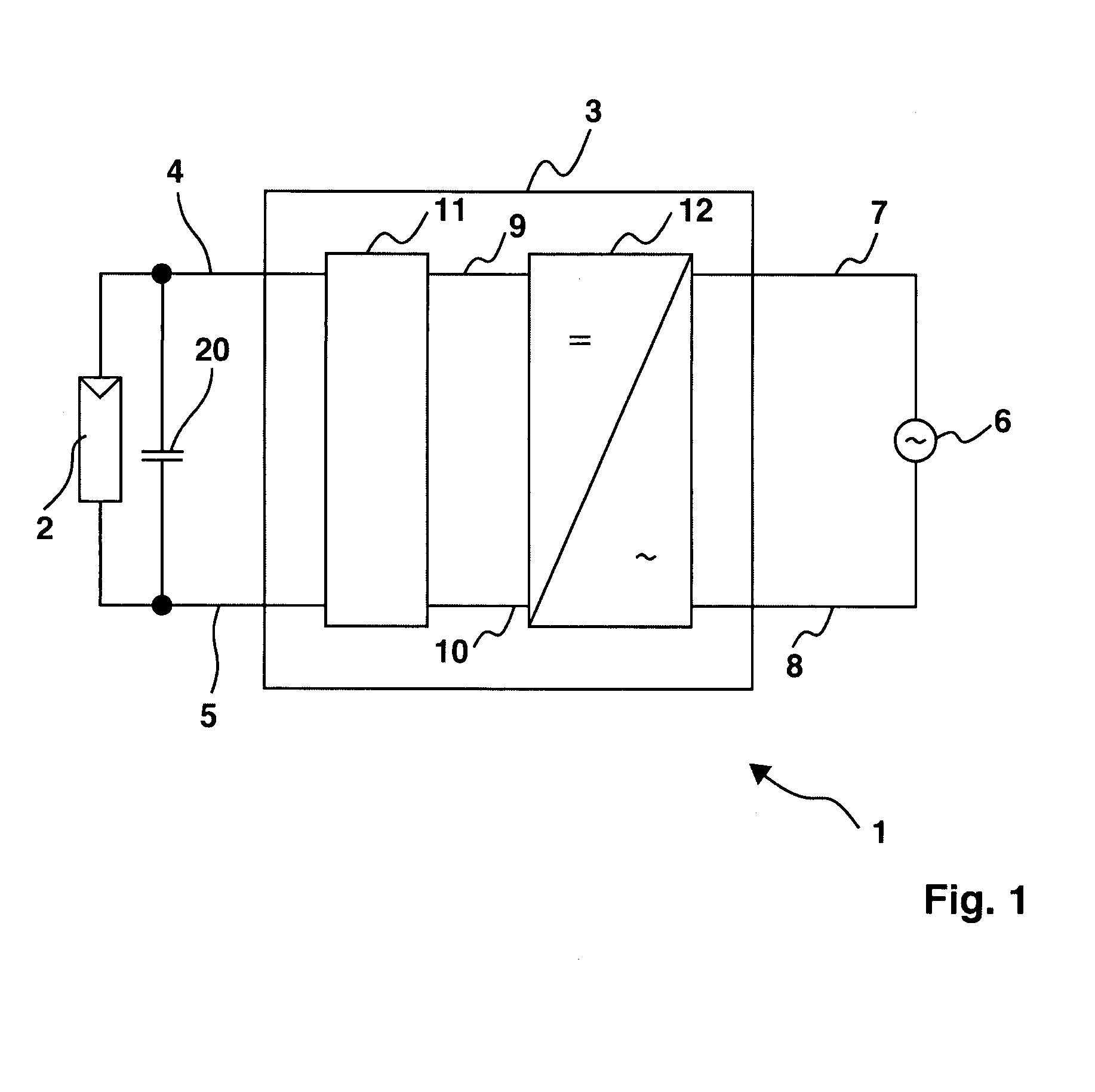
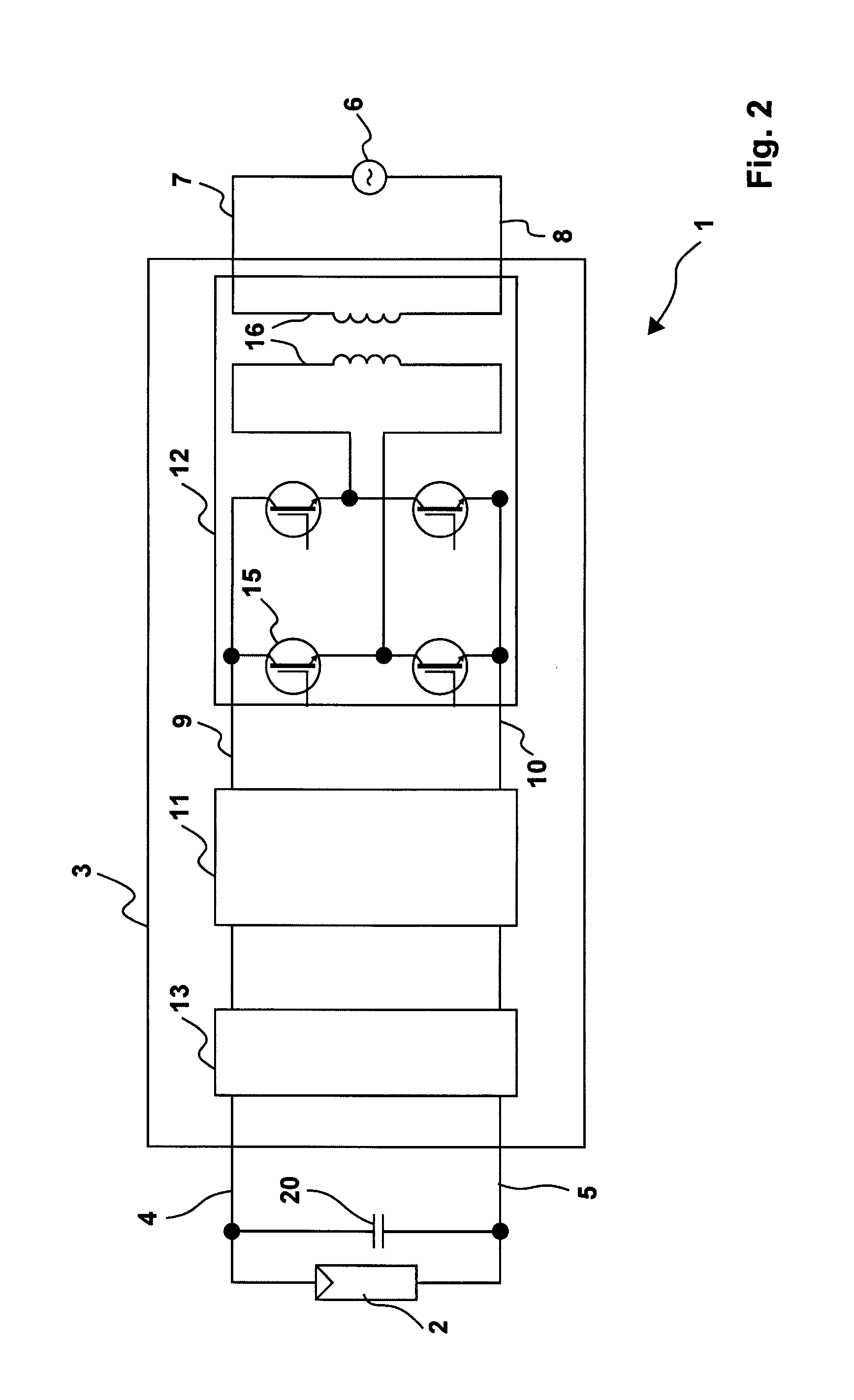
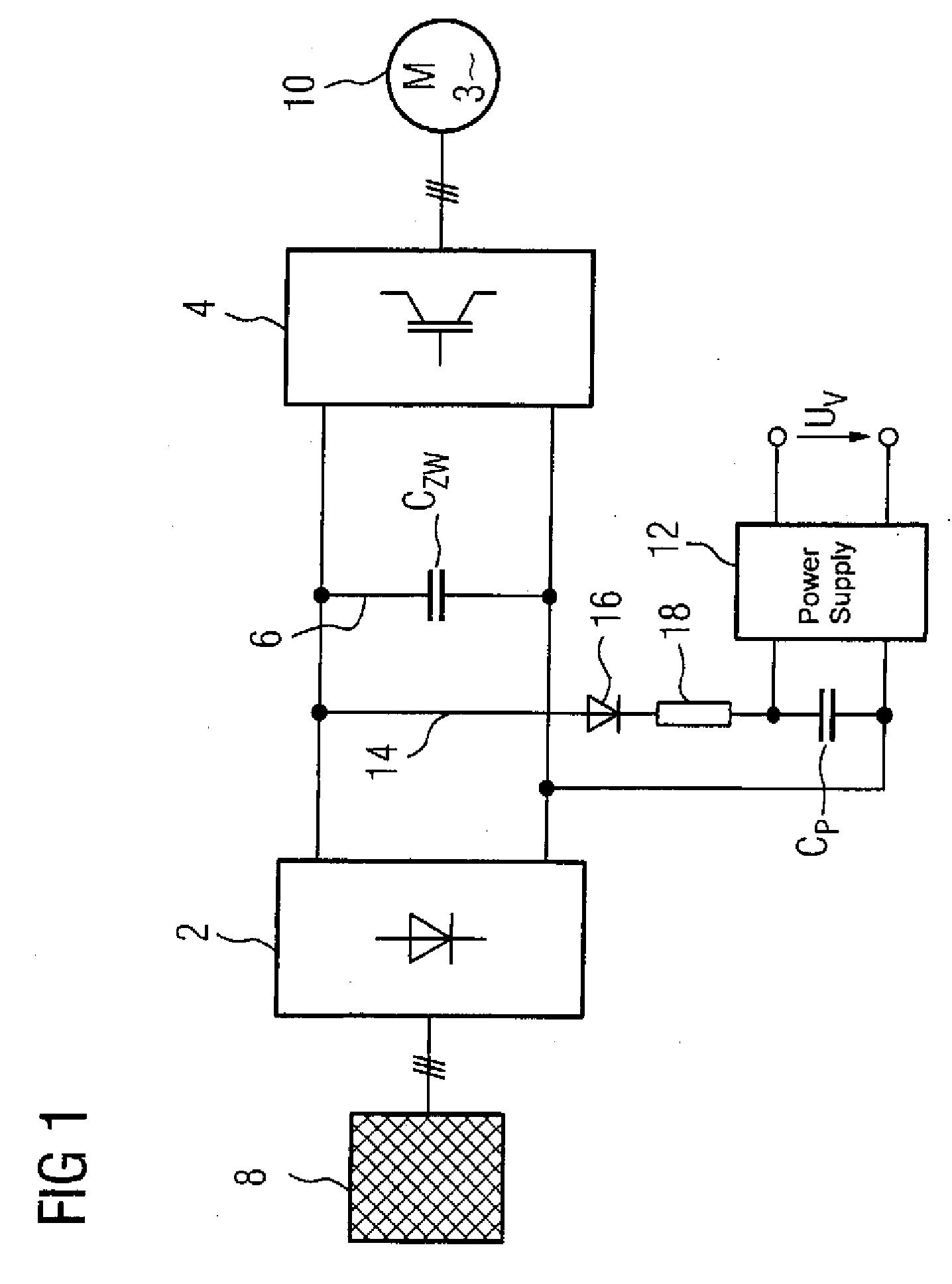
A solar energy powered lamp driver (100; 200) capable of driving a gas discharge lamp (L) comprises: - a half-bridge inverter (130), comprising: a first branch of two controllable switches (131, 132) coupled in series between a first reference node (VI) and a second reference node (mass); a second branch of two buffer capacitors (133, 134) coupled in series between said first reference node (VI) and said second reference node (mass); an output branch (DE) connected between on the one hand a first node (D) between said two controllable switches (131, 132) and on the other hand a second node (E) between said two buffer capacitors (133, 134); a boost converter (110), having an output (115) connected directly to said first node (D) between said two controllable switches (131, 132).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Switching power supply device
InactiveUS20120249059A1Reduces amount of generated heatReduce the amount requiredBatteries circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionSnubber capacitorPhase shift control
A switching power supply device includes a full-bridge circuit, a transformer, a rectifier circuit, a filter circuit, a first series connection of a snubber capacitor and a first diode, and a second diode. The full-bridge circuit includes switching elements which are controlled to be driven under phase-shift control. The first series connection is connected in parallel with the smoothing reactor, where one terminal is connected to a terminal on positive side of the rectifier circuit, and the other terminal is connected to an anode of the first diode. A cathode of the first diode is connected to one terminal of the smoothing capacitor which is applied with positive voltage. The second diode is provided between a terminal on negative side of the rectifier circuit and a connecting point of the snubber capacitor and the first diode. A cathode of the second diode is connected to the connecting point.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Power converter with improved control of its main switches, and application to a power converter having three or more voltage levels
InactiveUS6046920AConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSnubber capacitorCapacitive voltage divider
Owner:POWER SUPPLY SYST HLDG THE NETHERLANDS
Power supply system
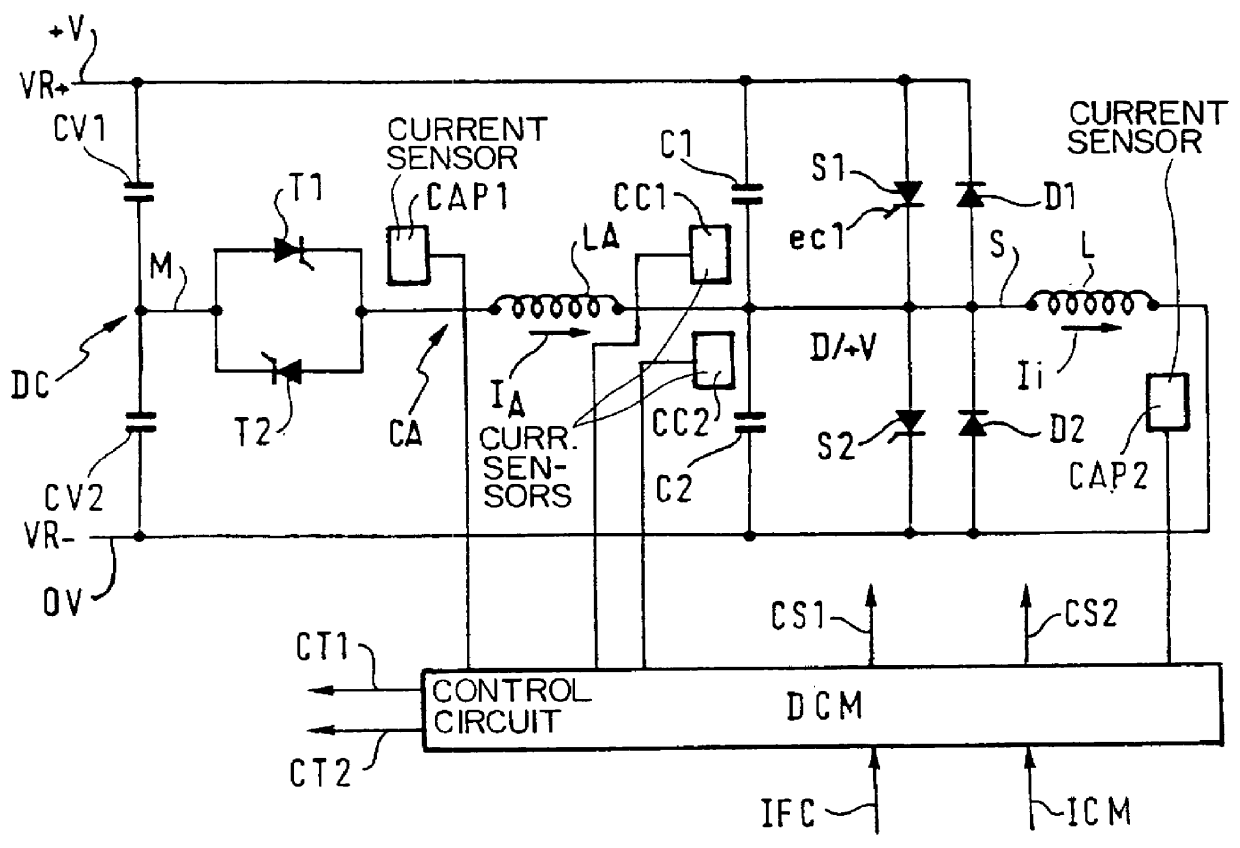
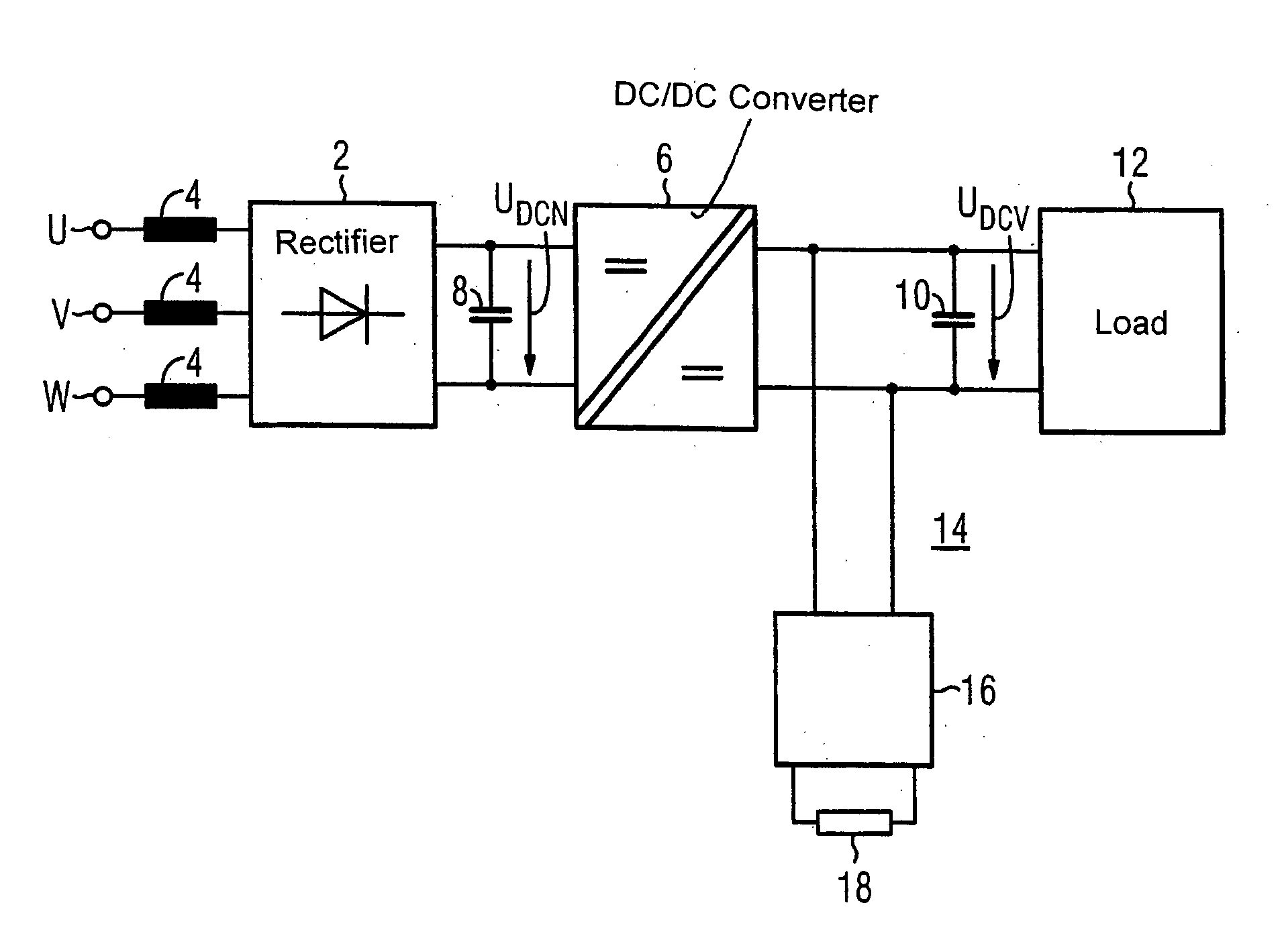
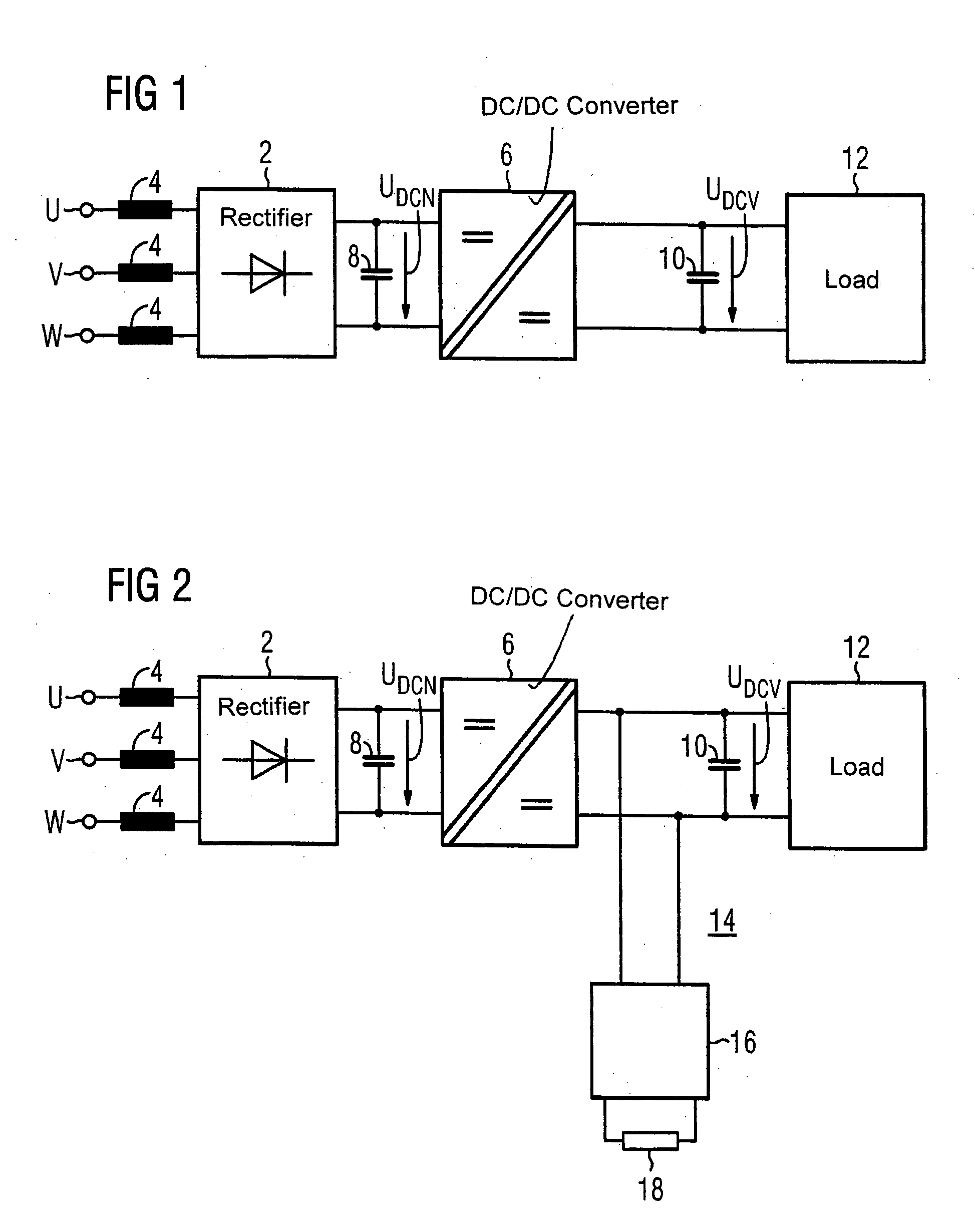
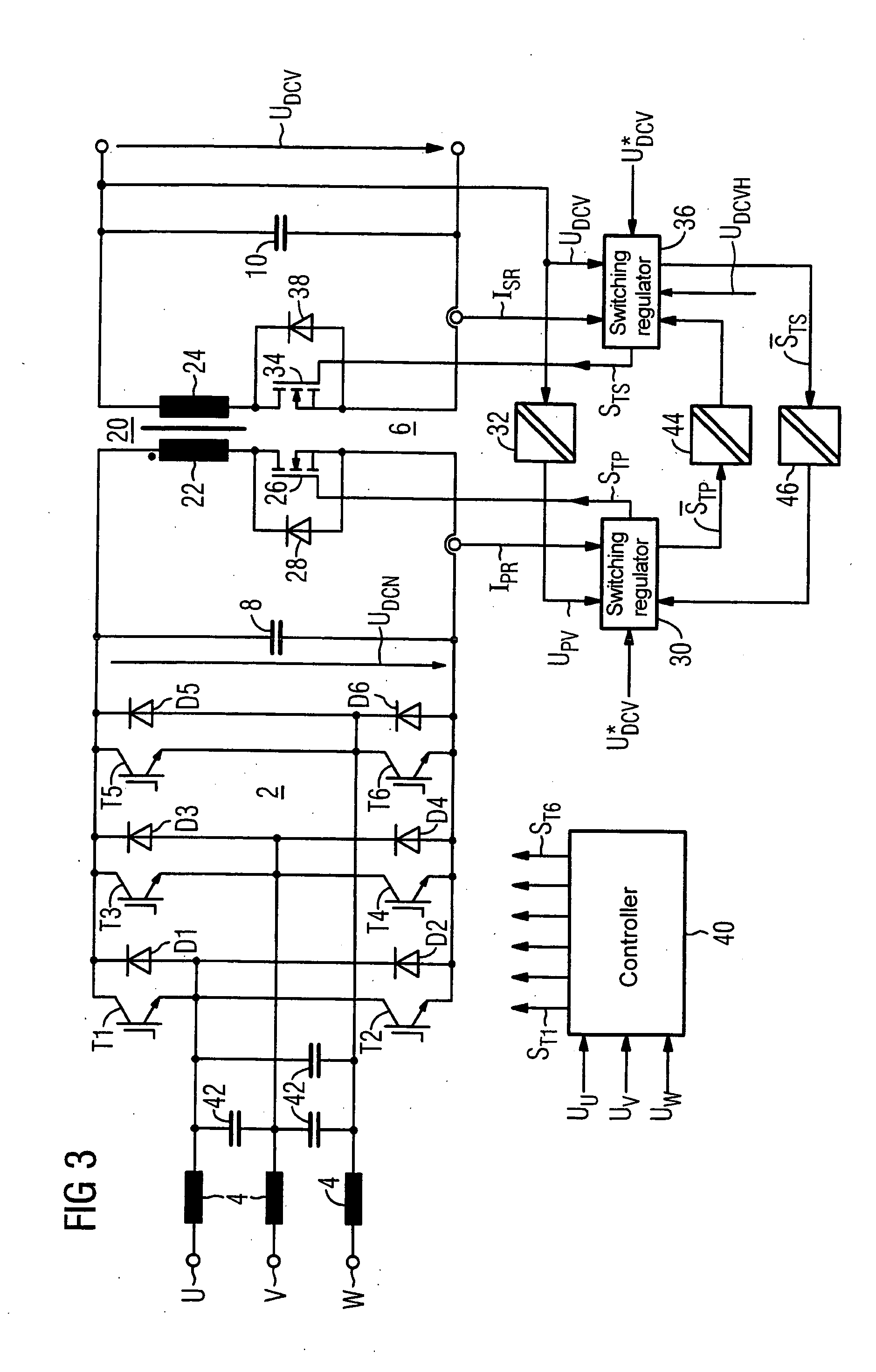
InactiveUS20050122747A1Improve energy balanceDissipate energy from the loadEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionSnubber capacitorEffective power
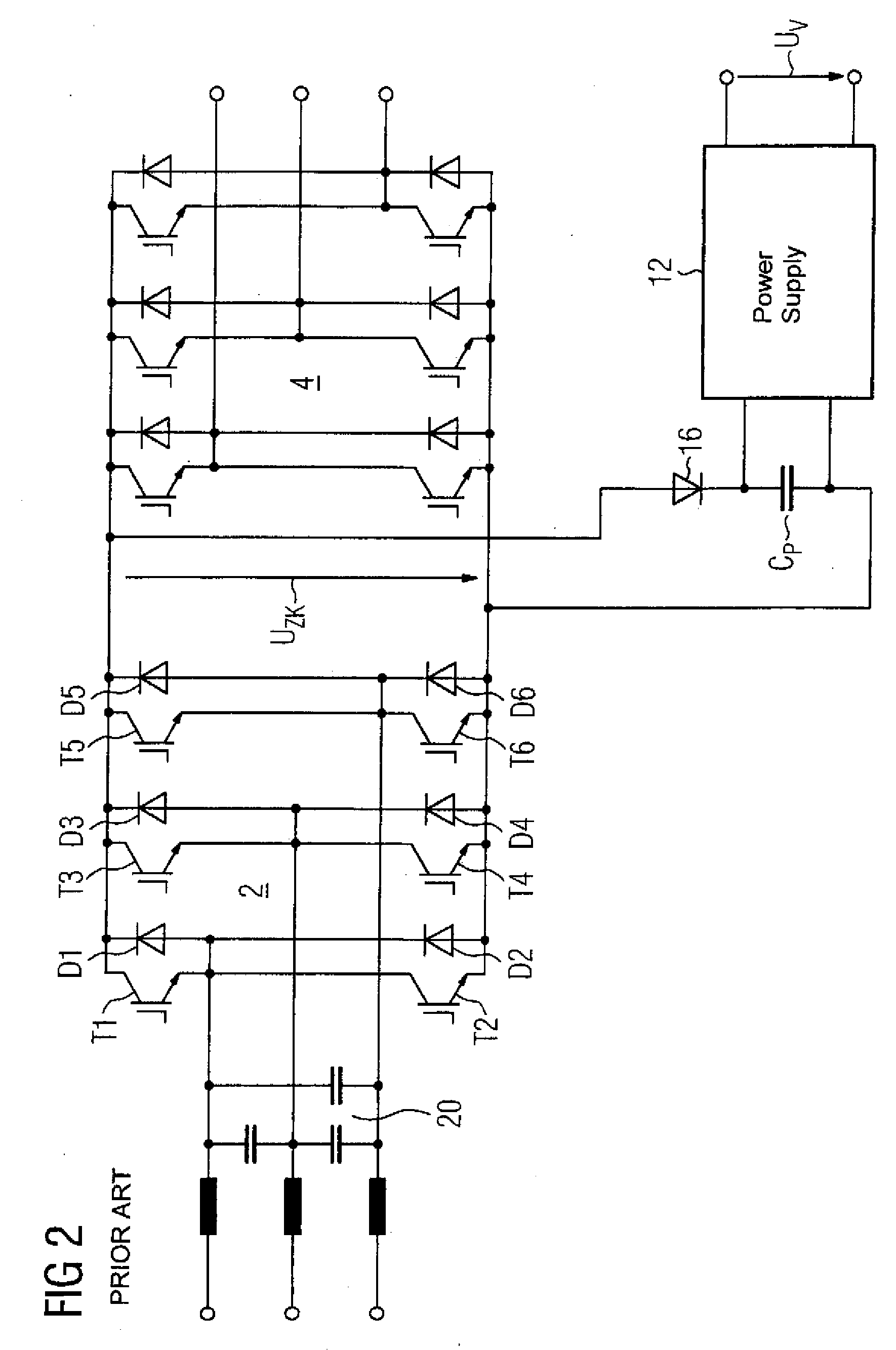
An electric power supply system includes a rectifier with an input connected to a power line and a DC output connected to a DC / DC converter. Two buffer capacitors are connected across the input and output, respectively, of the DC / DC converter. The output of the rectifier includes a plurality of diodes. An electronically controllable switch is electrically connected in parallel with a corresponding diode of the rectifier. A controller receives an input signal from a phase voltage of the power line and provides control signals to the controllable switches. The DC / DC converter is constructed symmetrically. This configuration results in a more cost-effective power supply system with an improved energy balance.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Switching power supply apparatus
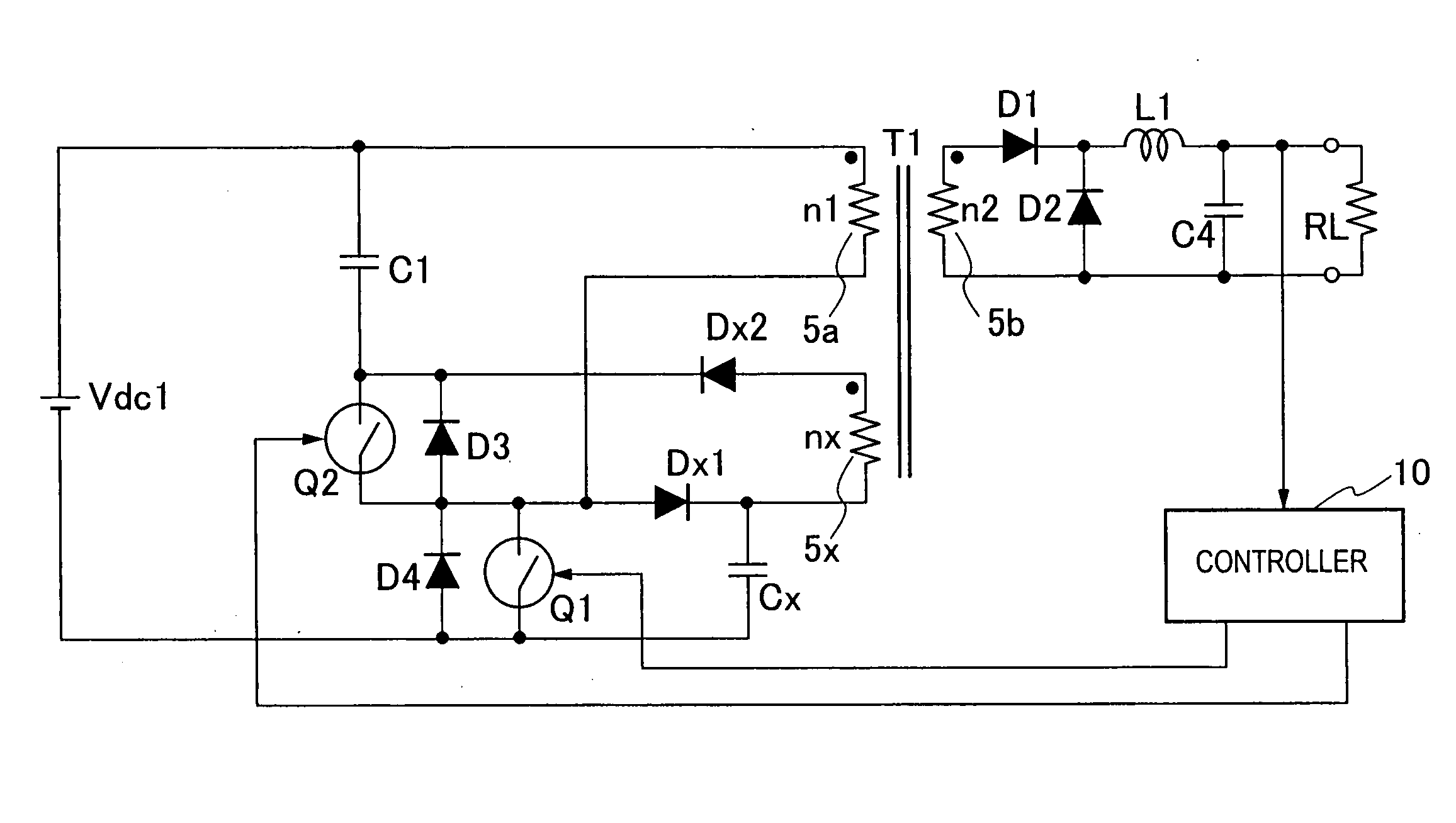
InactiveUS20060187688A1Increase usageSmall sizeEmergency protective circuit arrangementsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsClamp capacitorSnubber capacitor
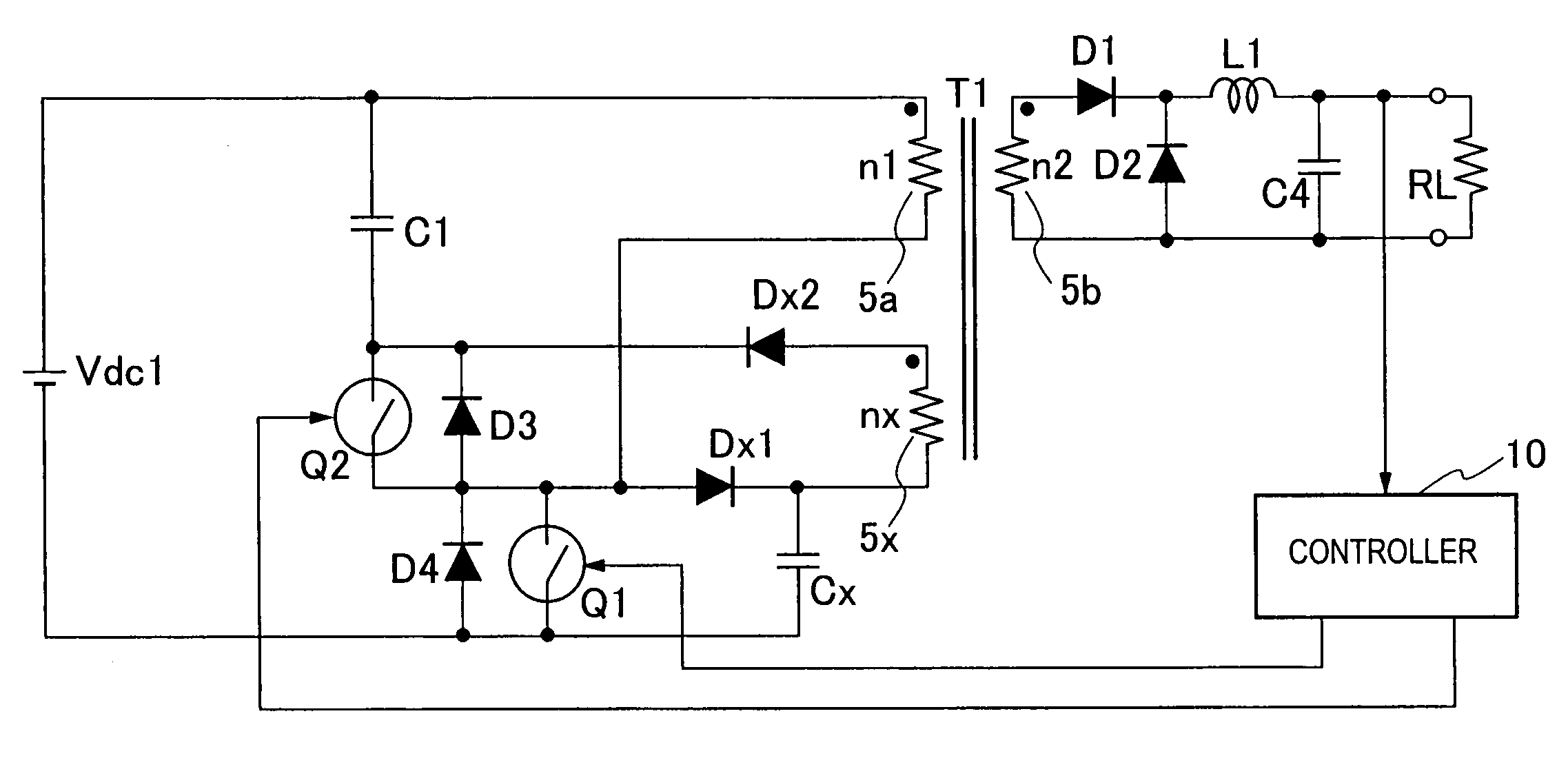
A switching power source apparatus can reduce the size of a transformer and realize the zero-voltage switching of a switch. The apparatus is compact, highly efficient, and low in noise. The apparatus has a series circuit connected to each end of a DC power source (Vdc1) and including a primary winding (5a) of a transformer (T) and a main switch (Q1), a rectifying-smoothing circuit to rectify and smooth a voltage that is outputted from a secondary winding (5b) when the main switch (Q1) is turned on, a series circuit connected to each end of the primary winding (5a) and including an auxiliary switch (Q2) and a clamp capacitor (C1), a series circuit connected to each end of the main switch (Q1) and including a diode (Dx1) and a snubber capacitor (Cx), a series circuit connected to a node between the diode (Dx1) and the snubber capacitor (Cx) and a node between the auxiliary switch (Q2) and the clamp capacitor (C1) and including an auxiliary winding (5x) and a diode (Dx2), and a control circuit (10) to alternately turn on / off the main switch (Q1) and auxiliary switch (Q2). When the main switch (Q1) is turned on, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is discharged through the auxiliary winding (5x) to the clamp capacitor (C1). When the main switch (Q1) is turned off, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is charged, to relax the inclination of a voltage increase of the main switch (Q1).
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Switching device and method, in particular for photovoltaic generators
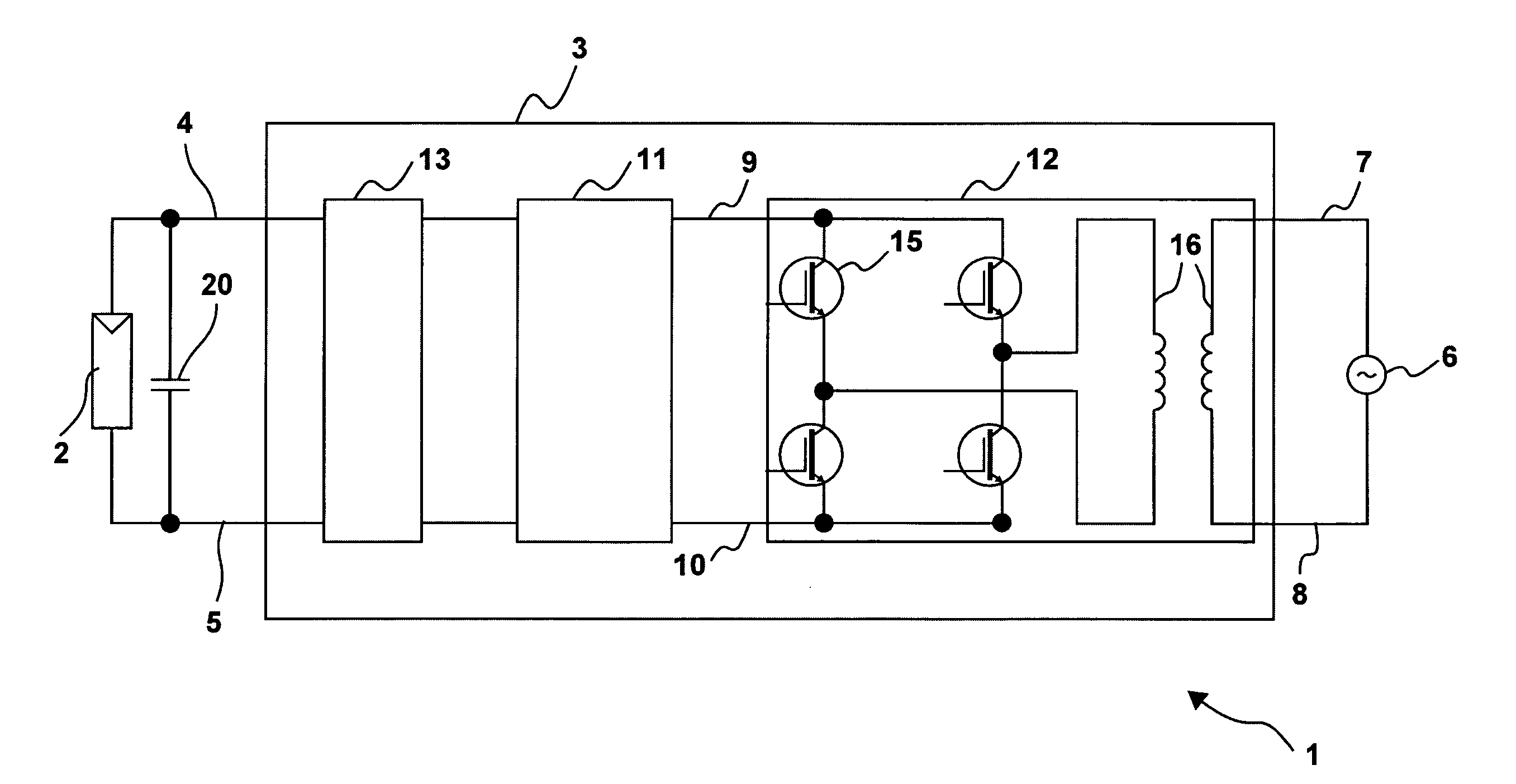
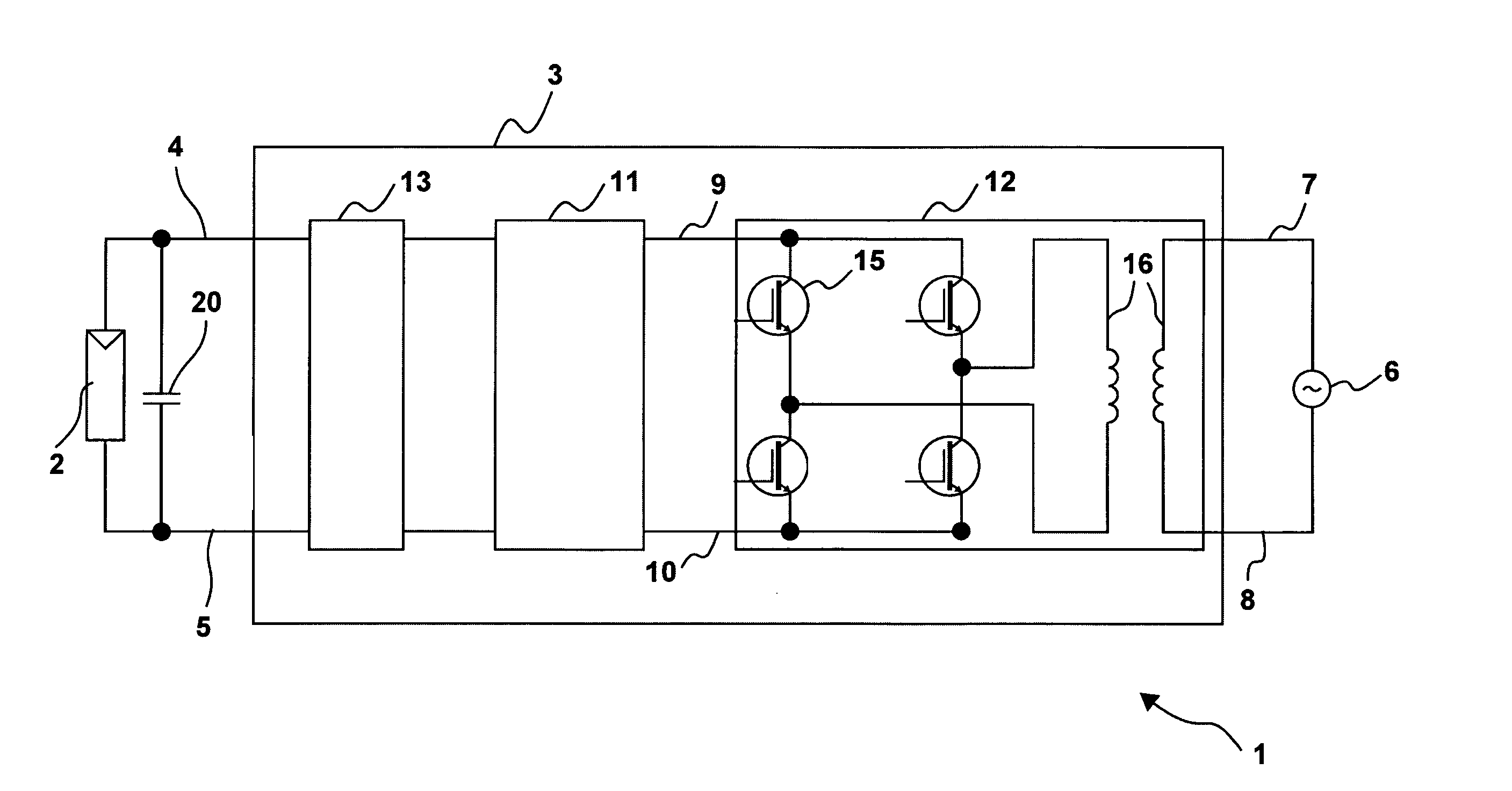
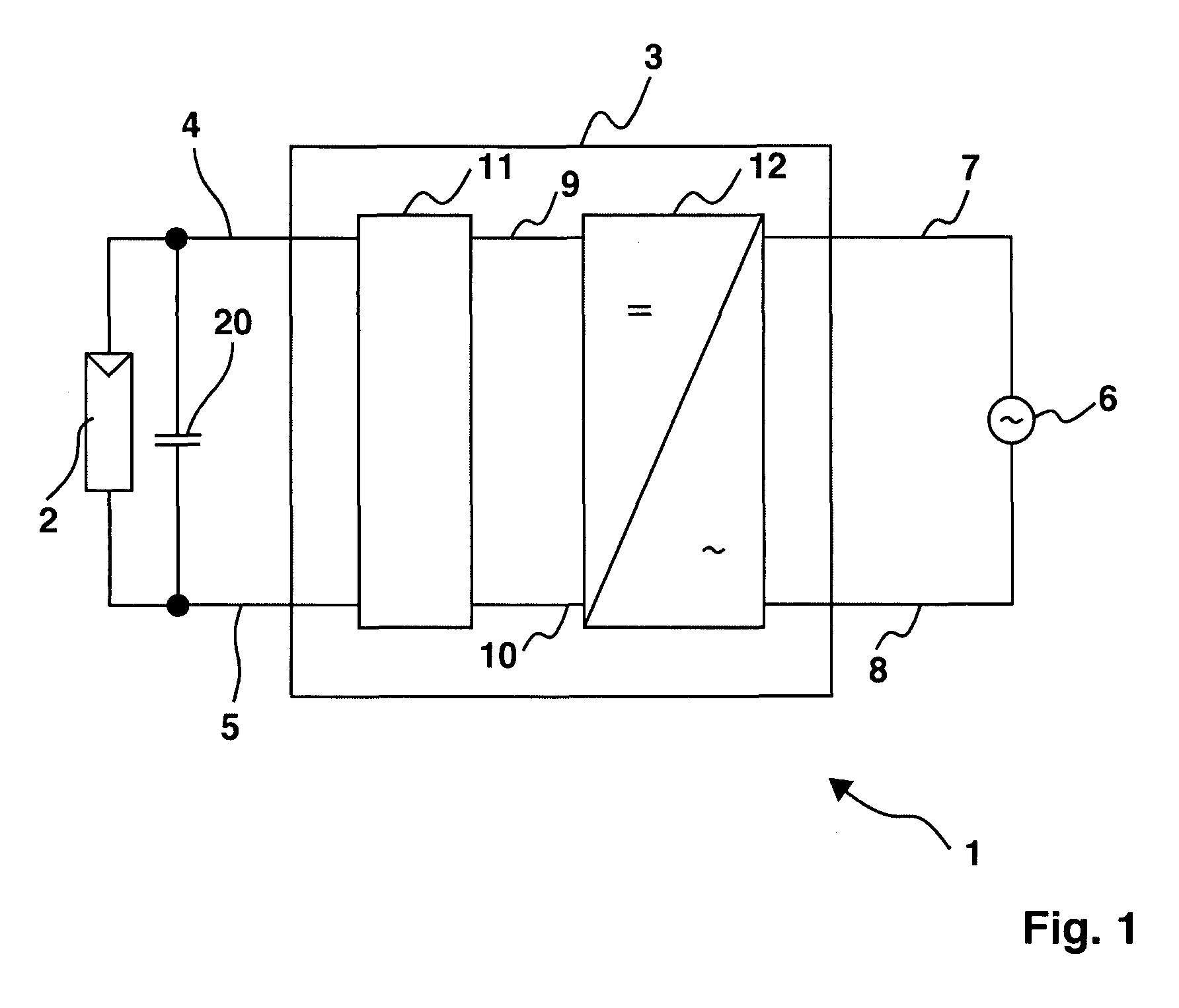
ActiveUS20080094867A1Quick correctionElegant simplificationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower supply linesDc ac converterEngineering
The subject matter of the invention is an inverter (3), more specifically for use in a photovoltaic plant (1) with a direct voltage input (connection terminals 4; 5) for connection to a generator (2) and an alternating voltage output (connection terminals 7; 8) for feeding into an energy supply network (6) as well as with a DC-AC converter (12) with semiconductor switch elements (15) and an intermediate circuit (11), at least one short-circuit switch element (18) being connected in parallel to the generator (2), so that the voltage will not exceed a maximum voltage value neither at the connection terminals (4; 5) of the generator (2) nor between the connection terminals (9; 10) of the inverter. This is achieved in that the inverter (3) comprises, in the intermediate circuit (12), a buffer capacitor (14) that is connected to the generator (2) through a protection diode (17) so that said buffer capacitor (14) will not be discharged upon actuation of the short-circuit switch element (18), the generator (2) working according to a clock rate in the short-circuit mode of operation.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
Liquid crystal display device with a buffer capacitor electrode disposed in a non-pixel electrode region
ActiveUS7688393B2Improve display characteristicsStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsSnubber capacitorLiquid-crystal display
The invention relates to a substrate for a liquid crystal display, a liquid crystal display having the substrate, and a method of driving the display and provides a substrate for a liquid crystal display which allow high display characteristics to be achieved, a liquid crystal display having the substrate, and a method of driving the display.The substrate includes two TFTs having gate electrodes connected to a gate bus line and drain electrodes connected to a drain bus line, a pixel electrode connected to a source electrode, a pixel electrode connected to another source electrode and separated from the pixel electrode, another TFT having a gate electrode connected to another gate bus line and a source electrode connected to the pixel electrode, and a buffer capacitor portion having a buffer capacitor electrode connected to another drain electrode and another buffer capacitor electrode connected to a storage capacitor bus line.
Owner:SHARP KK
DC-DC Converter And Its Controlling Method
InactiveUS20110013437A1Reduction dimension/weightLarge capacityAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionSnubber capacitorDc dc converter
A unidirectional DC-DC converter and method of control thereof. The converter includes a DC power-supply, a buck converter circuit having a first main switching element, a boost converter circuit having a second main switching element, a first snubber capacitor, a first inversely-parallel diode, a control device, and an output diode.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Power semiconductor module
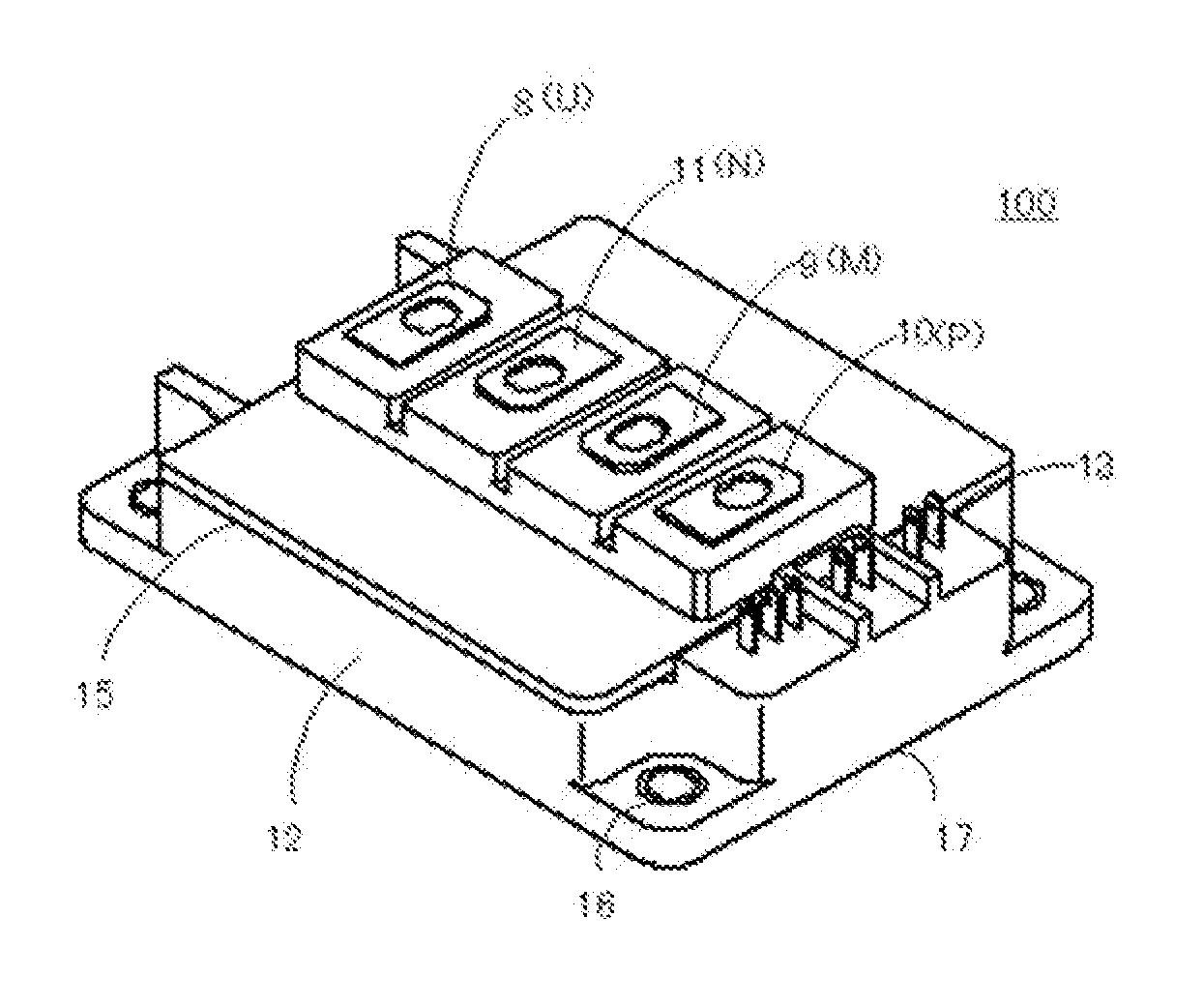
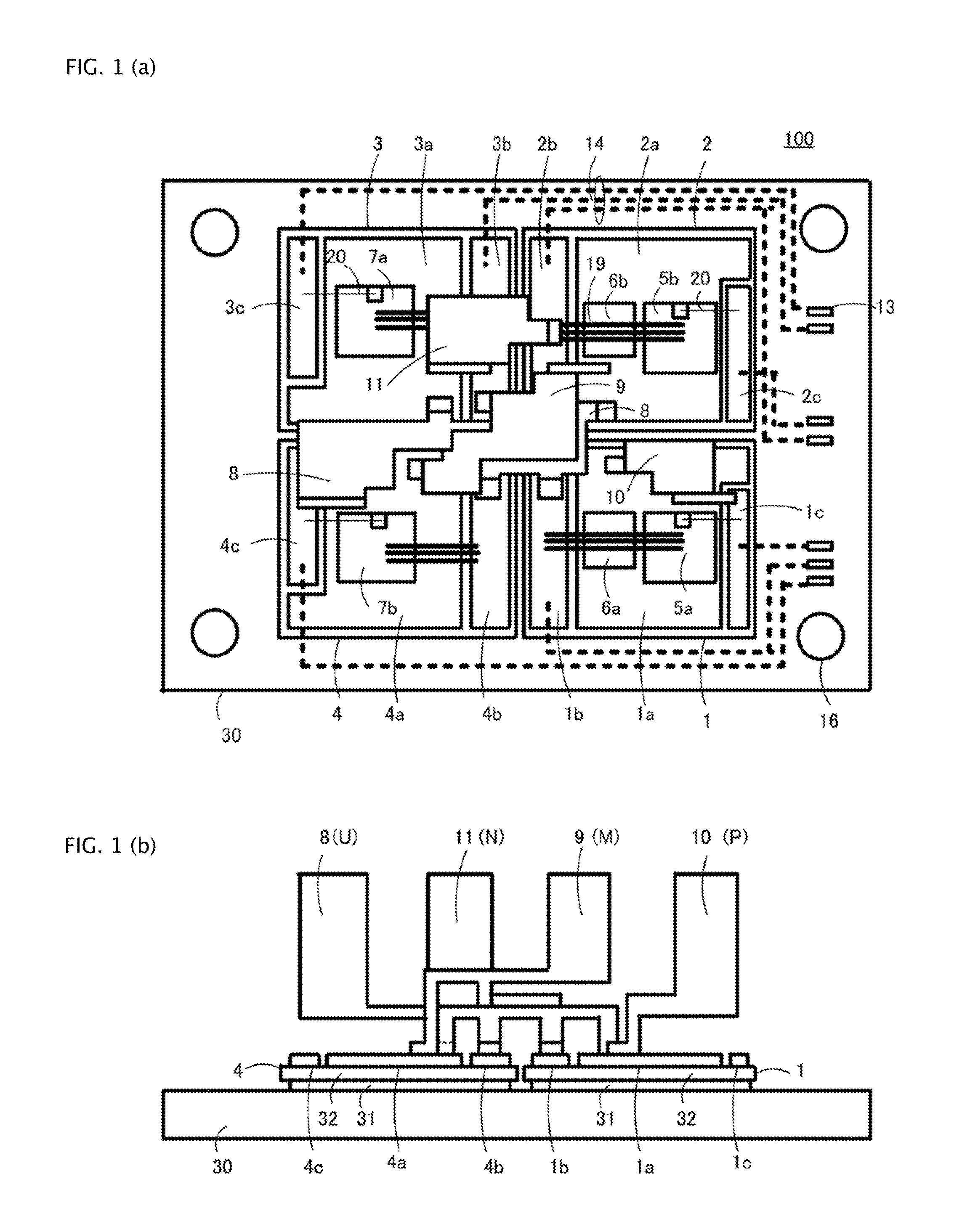
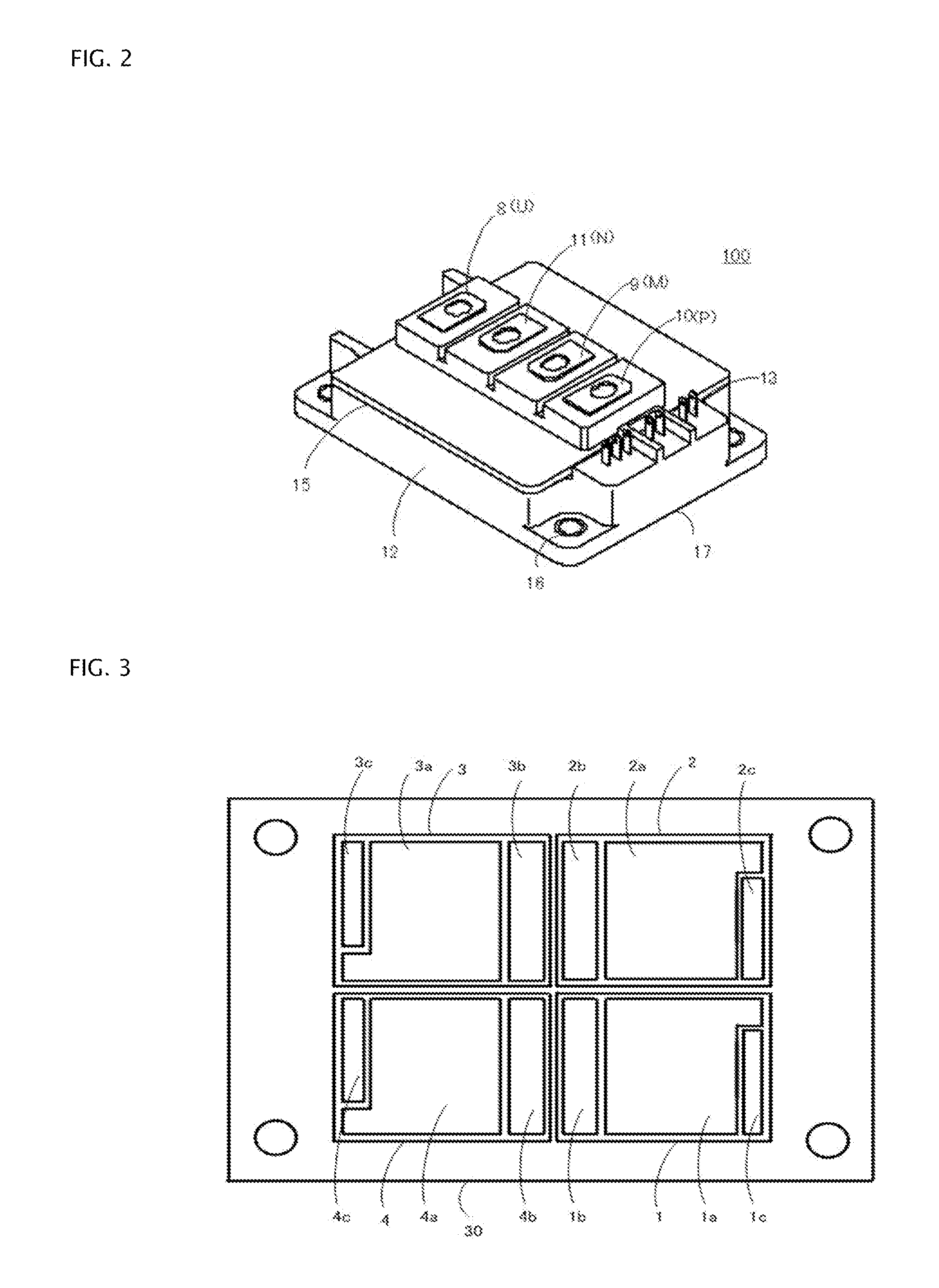
ActiveUS20120119256A1Reduce manufacturing costFacilitates reducing mutual inductanceAc-dc conversionSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceSnubber capacitor
In a semiconductor module according to certain aspects the invention, a U-terminal and an M-terminal overlap each other in a manner to reduce inductance and to further to reduce the size of snubber capacitor. In certain aspects of the invention, a P-terminal, M-terminal, N-terminal, and U-terminal are arranged such that the U-terminal, through which currents flow in and out, is arranged farthest away from control electrodes to reduce the noises superposed to control electrodes, and the P-terminal, M-terminal, N-terminal, and U-terminal are aligned to facilitate attaching external connection bars thereto. A power semiconductor module according to aspects of the invention can facilitate reducing the wiring inductance inside and outside the module, reducing the electromagnetic noises introduced into the control terminals, and attaching the external wirings to the terminals thereof simply and easily.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Frequency converter having an intermediate circuit without any capacitors
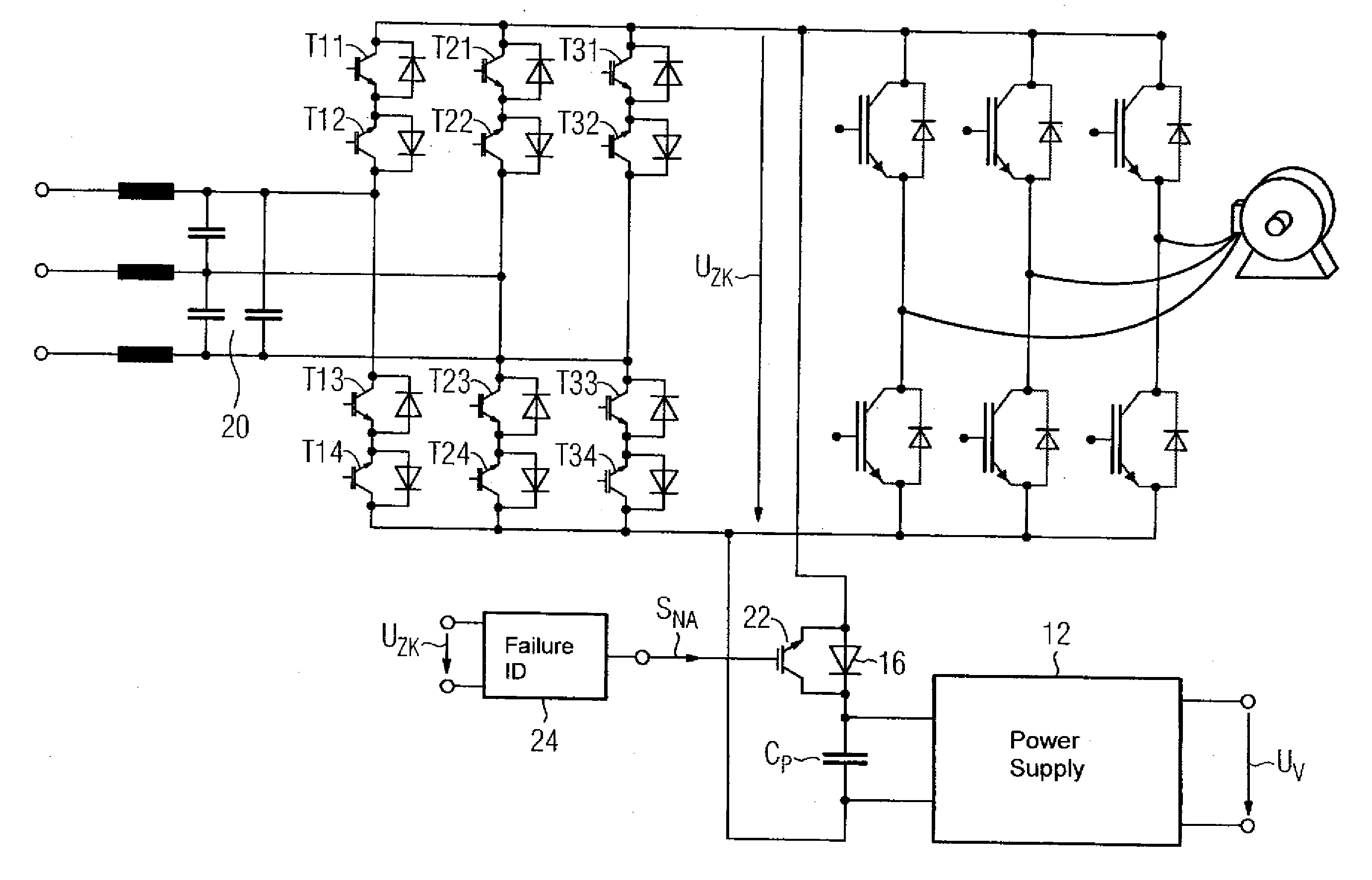
InactiveUS20070177407A1Simple wayAc-ac conversionEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentFrequency changerCapacitance
A frequency converter includes an intermediate circuit without any capacitors and an electronics which is supplied with power from a power supply device. The power supply device has a buffer capacitor which is disposed on an input side of the power supply device and connected electrically in parallel with the intermediate circuit. Connected to the buffer capacitor is a supply line in which a decoupling diode is disposed. A semiconductor adapted to be switched off is connected electrically back-to-back in parallel with the decoupling diode and has a control output which is connected to an output of an identification device for recognizing a power-line failure.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Integrated circuit and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100013047A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSnubber capacitorDielectric layer
An integrated circuit on a substrate comprises a buffer capacitor in a buffer region. The buffer capacitor comprises a buffer electrode arranged at least partially in a recess, and a dielectric layer disposed between the buffer electrode and the substrate.
Owner:QIMONDA
Direct-Current Converter
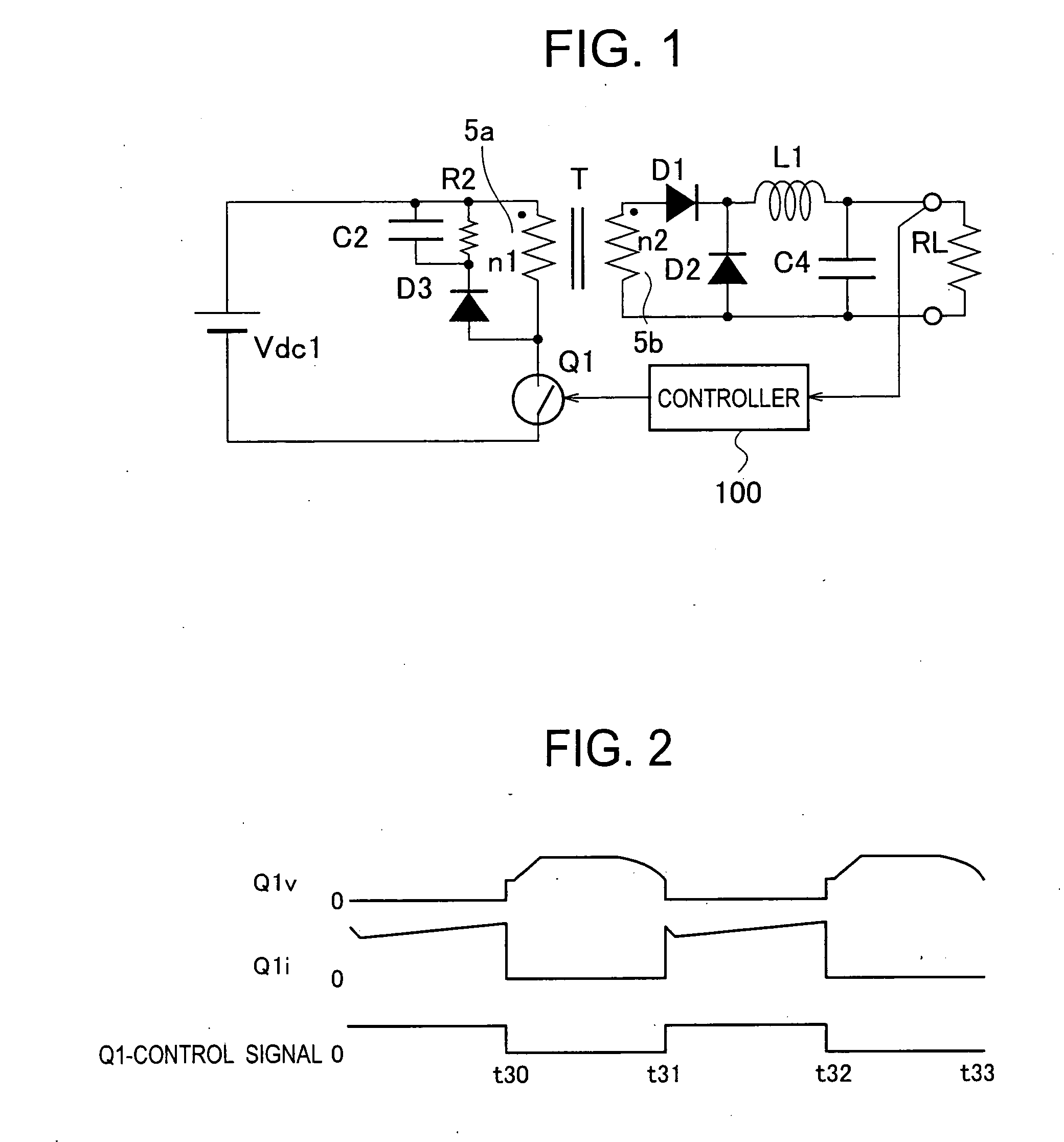
InactiveUS20060013021A1Reduce power consumptionReduce switching lossesEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionSnubber capacitorSwitching frequency
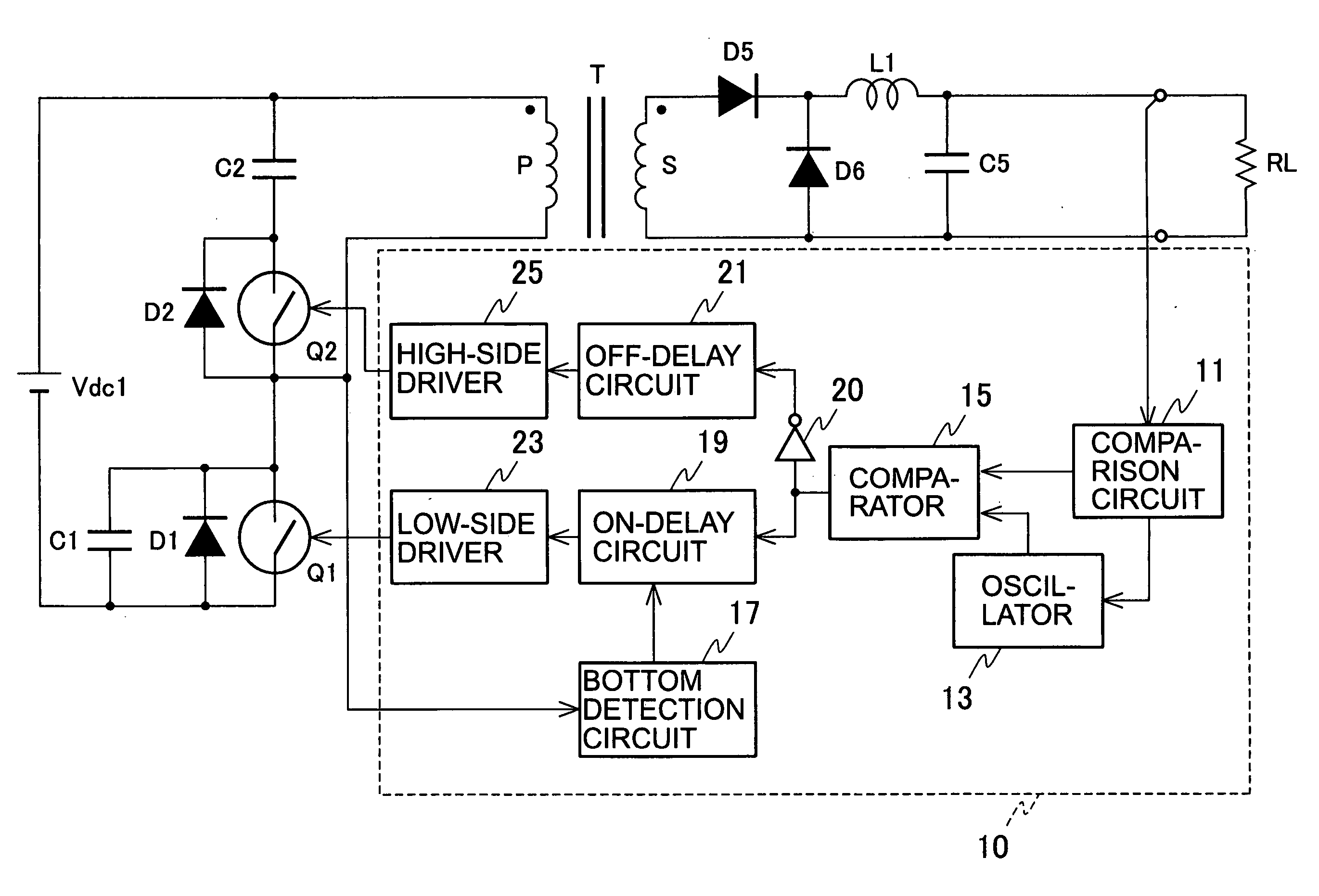
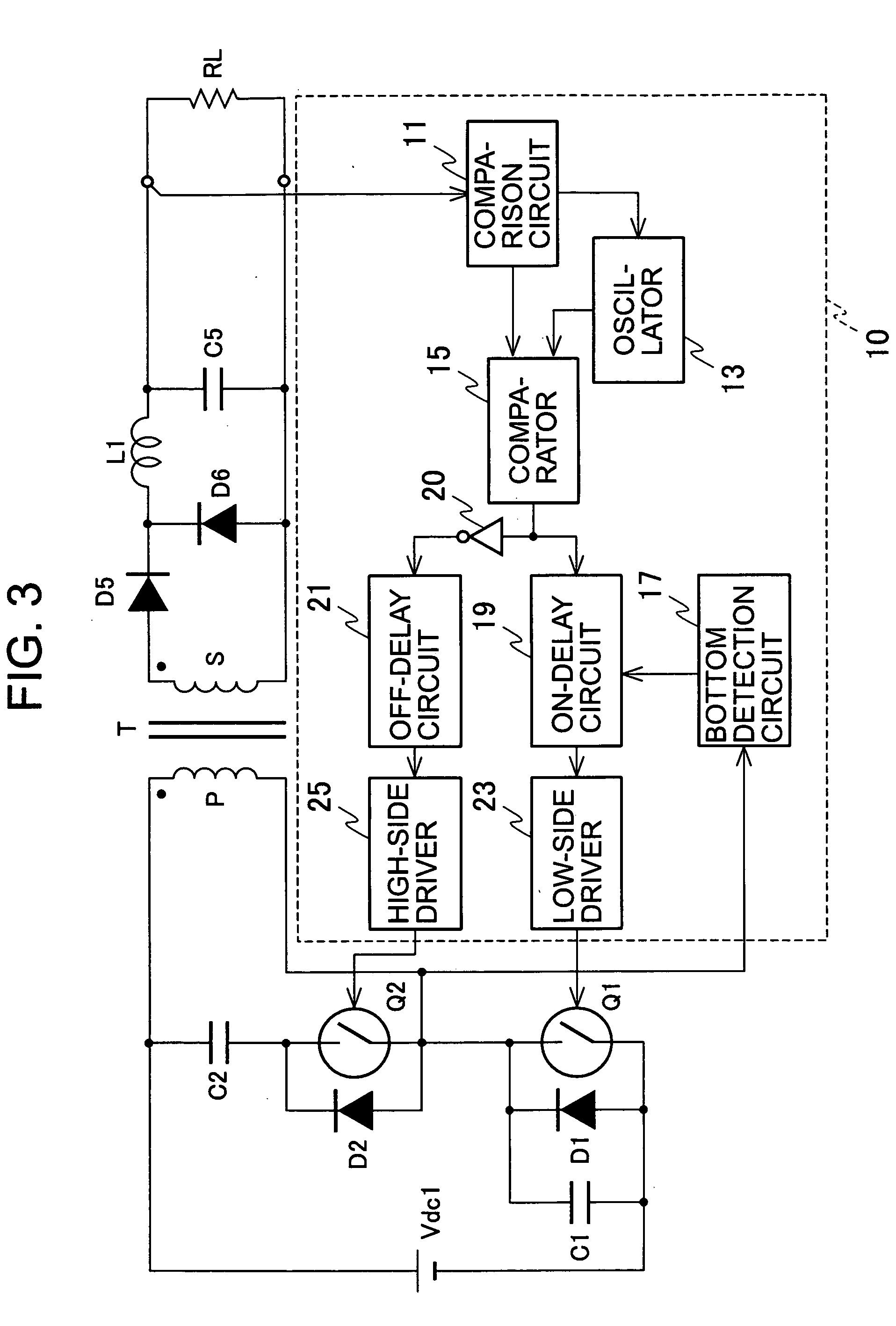
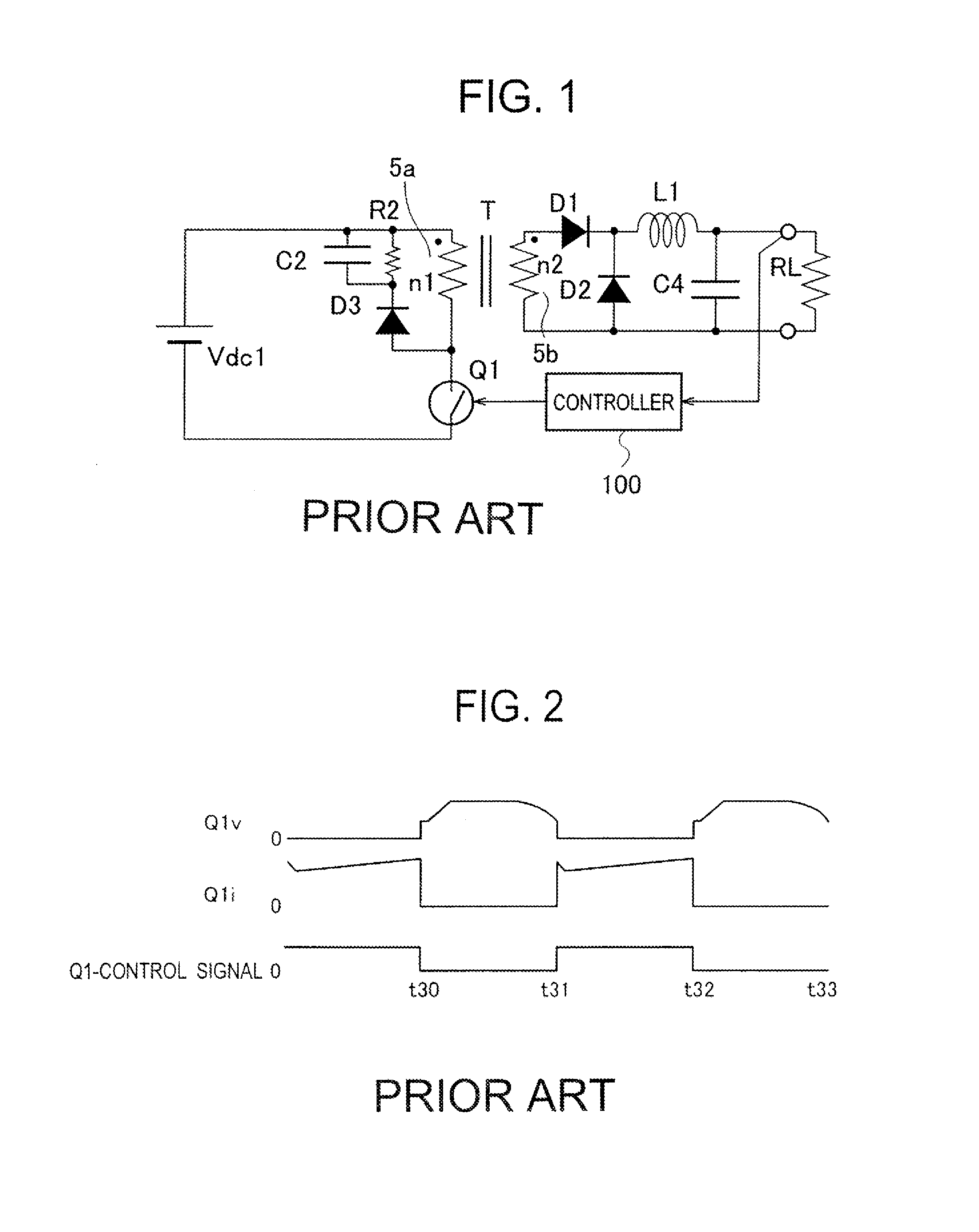
Provided is a direct-current converter which can reduce power consumption at light load by reducing switching losses of a main switch. The direct-current converter is provided with: a first serial circuit which is connected to both ends of a direct current power supply Vdc1 and in which a primary winding P of a transformer T and a main switch Q1 are serially connected to each other; a second serial circuit which is connected both ends of the primary winding P of the transformer T and in which an auxiliary switch Q2 and a snubber capacitor C2 are serially connected to each other; rectifying / smoothing circuits D5, D6, L1 and C5 which rectify and smooth a voltage generated in a secondary winding S of the transformer T by energy supplied from the primary winding P of the transformer T when the main switch Q1 is turned on; and a control circuit 10 which turns on / off the main switch Q1 and the auxiliary switch Q2 alternately using a signal with predetermined switching frequency. The control circuit 10 reduces the switching frequency during light load.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
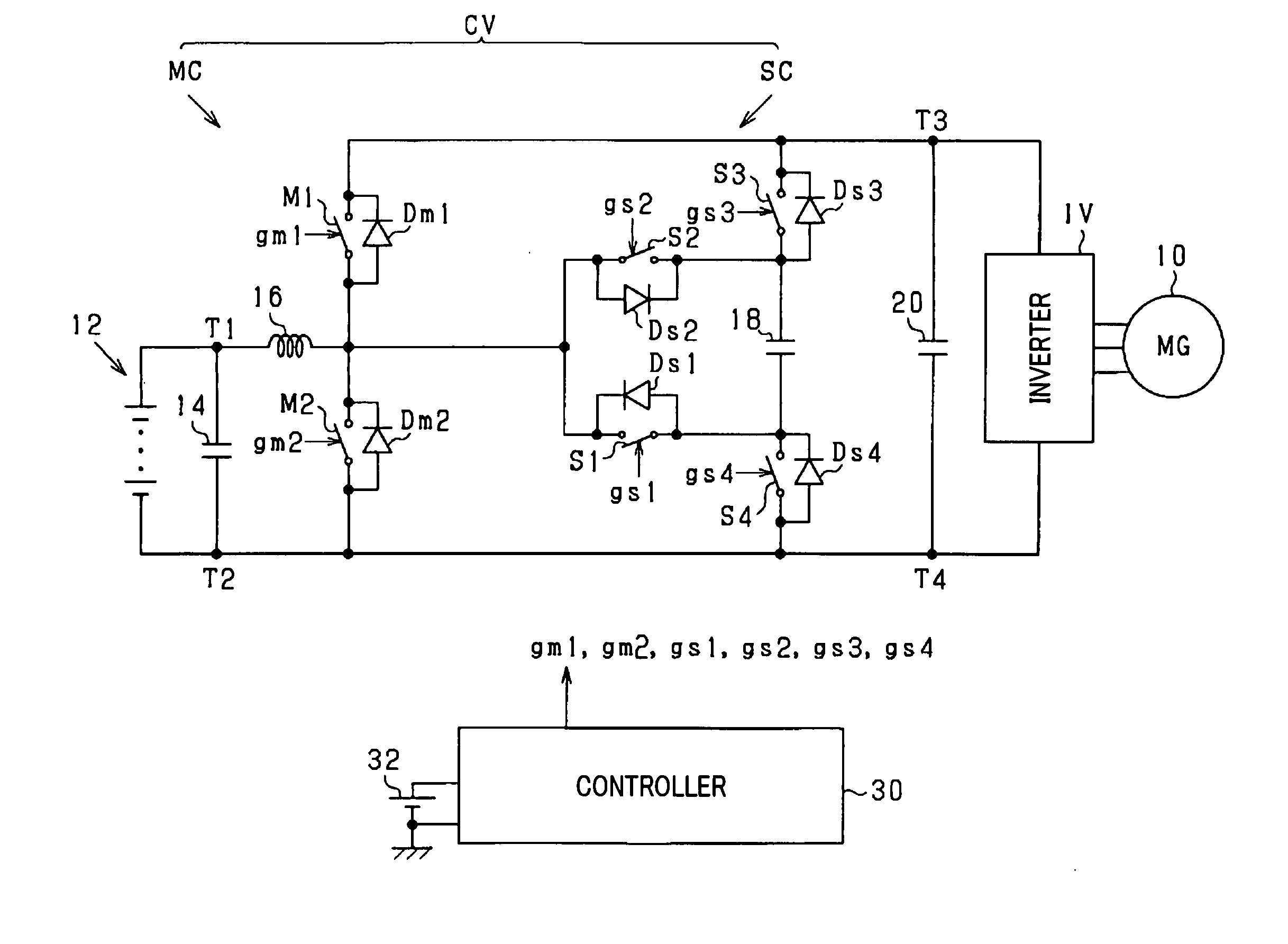
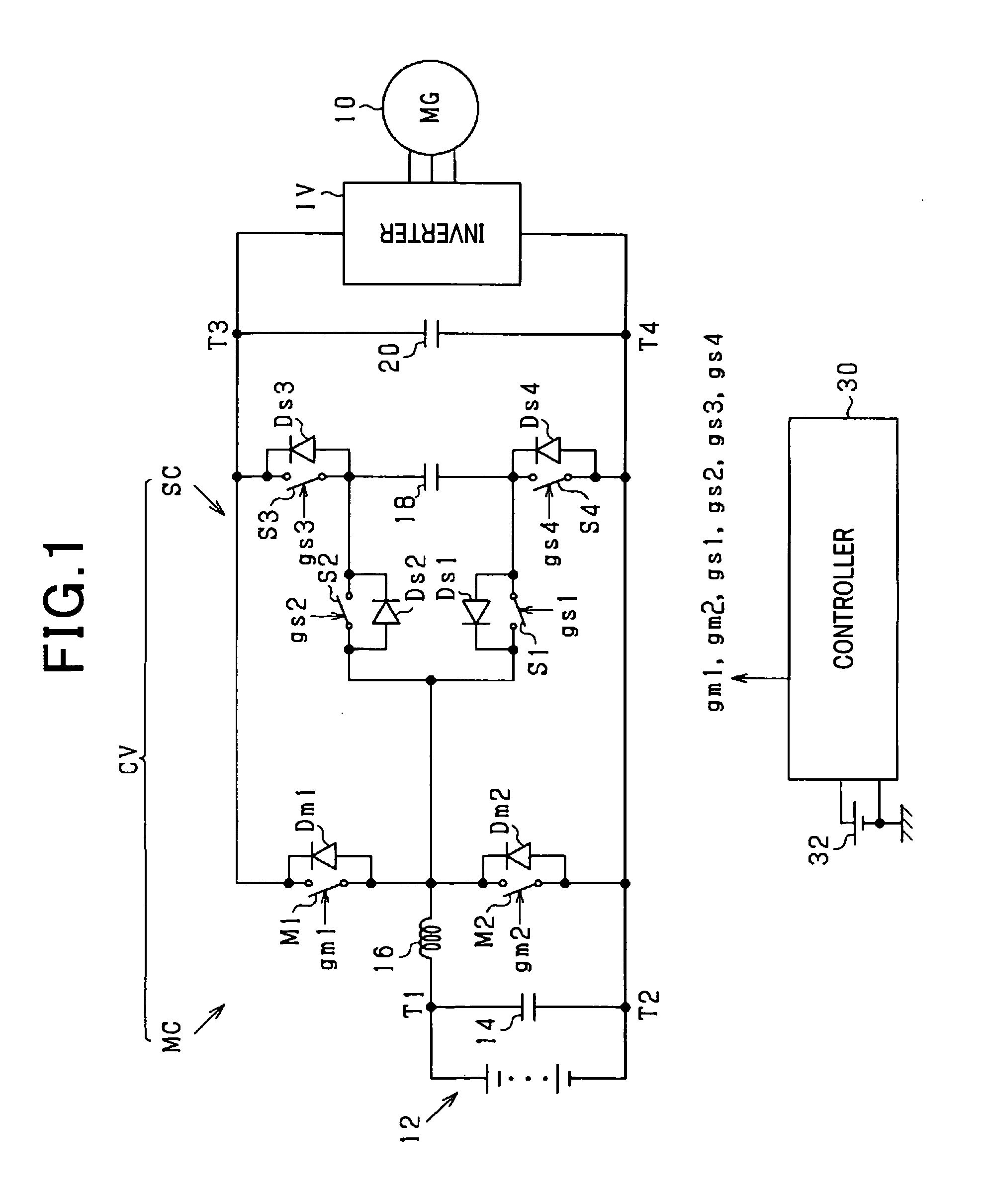
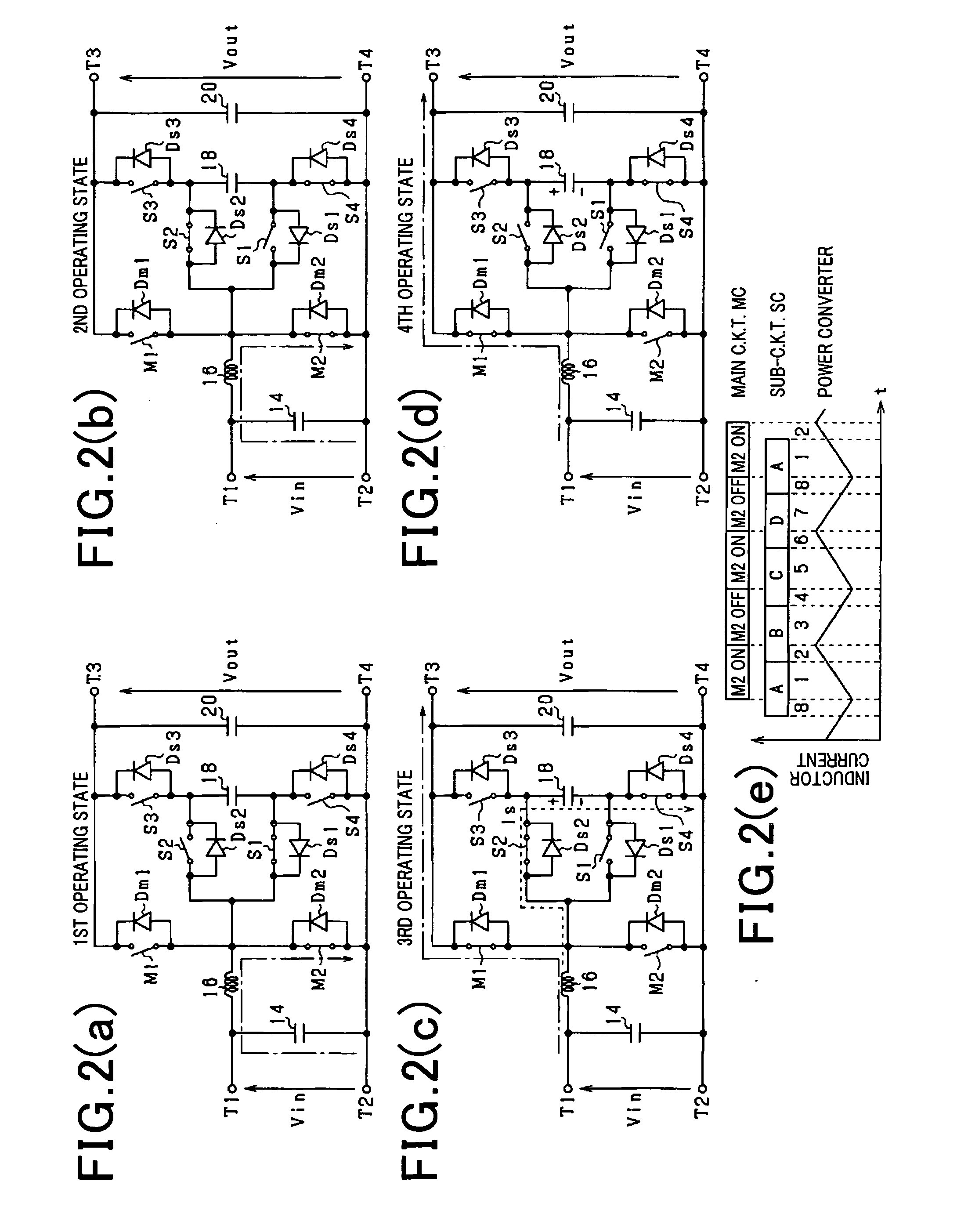
Compact power converter with high efficiency in operation
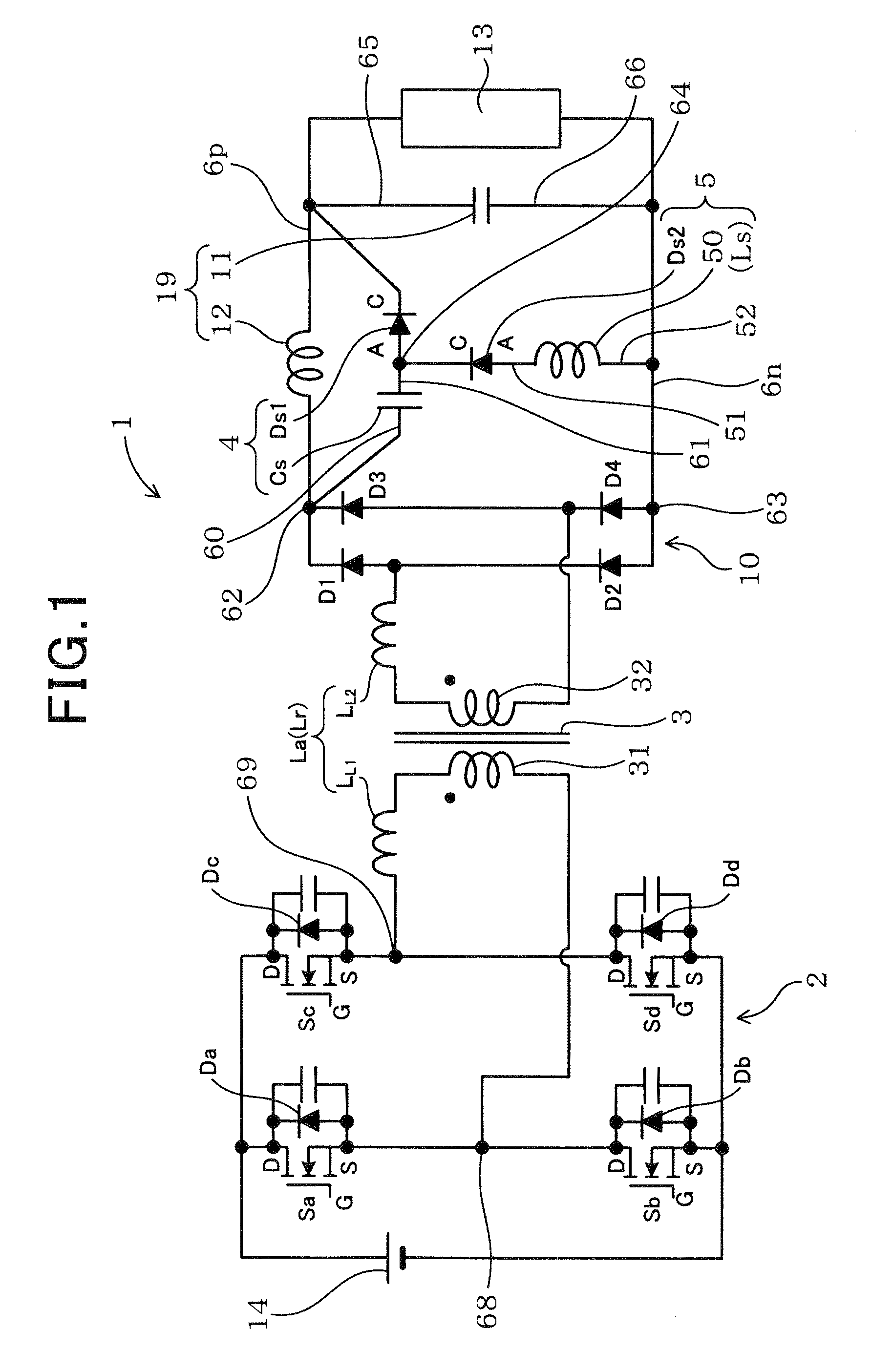
InactiveUS20120069604A1Small sizeImprove operational efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionSnubber capacitorSoft switching
A power converter including a main circuit and a sub-circuit. The main circuit serves as a step-up / down chopper circuit including a series-connected assembly of main switches, an inductor coupled to a joint of the main switches, and a capacitor connected in parallel to the series-connected assembly. The sub-circuit is designed to establish the soft-switching and includes a snubber capacitor, a first sub-switch coupled to the joint of the series-connected assembly and a negative terminal of the snubber capacitor, a second sub-switch coupled to the joint and a positive terminal of the snubber capacitor, a third sub-switch coupled to the positive terminal of the snubber capacitor and a high-potential terminal of the main circuit, and a fourth sub-switch coupled to the negative terminal of the snubber capacitor and a low-potential terminal of the main circuit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Cooling structure of capacitor and inverter device
InactiveUS20120020025A1Improve reliabilityInhibit temperature riseEfficient power electronics conversionFixed capacitor terminalsSnubber capacitorElectronic component
A cooling structure of a capacitor includes a snubber capacitor in which lead terminals are joined to external electrodes of a laminated ceramic electronic component; a circuit board which is for mounting the snubber capacitor and semiconductor switching elements; and a heat dissipation plate which is made of metal that dissipates the heat generated in the circuit board. The cooling structure of the capacitor is configured such that an insulating member having a high coefficient of thermal conductivity intervenes between the snubber capacitor and the heat dissipation plate.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Drive system
ActiveUS7026783B2Improve efficiencyLess expensiveBatteries circuit arrangementsSynchronous motors startersSnubber capacitorEnergy recovery
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Dc-dc converter
ActiveUS20120068678A1Reducing not only the turn-off loss but also the turn-on lossEasily realizedEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSnubber capacitorDc dc converter
Provided is a DC-DC converter capable of reducing not only a turn-off loss but also a turn-on loss. A snubber capacitor has one end connected to an anode of a step-up diode, a current input end of a step-up switching element and a main reactor. A first snubber diode has a cathode connected to other end of the snubber capacitor, and an anode connected to a cathode of the step-up diode. A second snubber diode has an anode connected to the cathode of the first snubber diode and other end of the snubber capacitor. A snubber reactor has one end connected to the anode of the first snubber diode, and other end connected to a cathode of the second snubber diode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Switching power source apparatus
InactiveUS7130204B2Reduce rateIncrease in sizeTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsClamp capacitorCapacitance
A switching power source apparatus can reduce the size of a transformer and realize the zero-voltage switching of a switch. The apparatus is compact, highly efficient, and low in noise. The apparatus has a series circuit connected to each end of a DC power source (Vdc1) and including a primary winding (5a) of a transformer (T) and a main switch (Q1), a rectifying-smoothing circuit to rectify and smooth a voltage that is outputted from a secondary winding (5b) when the main switch (Q1) is turned on, a series circuit connected to each end of the primary winding (5a) and including an auxiliary switch (Q2) and a clamp capacitor (C1), a series circuit connected to each end of the main switch (Q1) and including a diode (Dx1) and a snubber capacitor (Cx), a series circuit connected to a node between the diode (Dx1) and the snubber capacitor (Cx) and a node between the auxiliary switch (Q2) and the clamp capacitor (C1) and including an auxiliary winding (5x) and a diode (Dx2), and a control circuit (10) to alternately turn on / off the main switch (Q1) and auxiliary switch (Q2). When the main switch (Q1) is turned on, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is discharged through the auxiliary winding (5x) to the clamp capacitor (C1). When the main switch (Q1) is turned off, the snubber capacitor (Cx) is charged, to relax the inclination of a voltage increase of the main switch (Q1).
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Switching power supply with a snubber circuit
InactiveUS7130203B2Reduce lossImprove efficiencyEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionCapacitanceSnubber capacitor
Owner:DET INT HLDG LTD
Drive system
ActiveUS20050122082A1Reduce complexityImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsDC motor speed/torque controlSnubber capacitorEngineering
A drive system includes a central power supply with a line-commutated converter and a DC / DC converter connected downstream of the line-commutated converter, and a plurality of inverters, each inverter having an output connected a load, for example a motor, and a DC input connected to a regulated DC voltage output of the central power supply. Buffer capacitors are connected across the respective input and output of the DC / DC converter. The drive system further includes an energy recovery device with an input connected to the controlled voltage output of the central power supply and an output connected to at least two input terminals of the line-commutated converter. This type of drive system eliminates a bulky brake circuit.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
DC power supply
ActiveUS20120300501A1Reduce electromagnetic noiseAccurate estimateEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionVoltage sourceFilter capacitor
A DC power supply including a resonant circuit on a secondary side of a transformer suppresses a surge voltage during power recovery of diodes constituting a rectifier circuit, correctly estimates a load current from a secondary current of the transformer, and adjusts supplied power when a load is light. The DC power supply includes a DC voltage source, a converter, a transformer, a rectifier circuit, a resonant circuit composed of a resonant switch and a resonant capacitor, a filter reactor, a filter capacitor, a snubber diode, a snubber capacitor, a load, first and second voltage sensors, a current sensor, and a controller for controlling gate pulses of semiconductor devices constituting a converter and the resonant switch and a signal for adjusting operation timings of A / D converters converting the signals of these sensors.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Induction heating device
InactiveCN1874621AEfficient supplyInduction current sourcesInduction heating controlCapacitanceLoad circuit
The invention a magnetoelectric induction heating device which comprises a harmonic oscillation loading circuit including subjects to be heated for converting direct current voltage into alternative current voltage to provide power to the oscillation loading circuit; and a power source circuit for generating direct current voltage. The inverter comprise at least two semi-conductor switch elements connected in series to form up-down branches; a buffer capacity switching unit for switching buffer capacity according to the material of objects to be heated, and a oscillation capacity switching unit for switching oscillating capacity according to the material of the objects to be heated.
Owner:HITACHI HOME & LIFE SOLUTIONS INC
Monolithically integrated active snubber
A semiconductor device containing an extended drain MOS transistor with an integrated snubber formed by forming a drain drift region of the MOS transistor, forming a snubber capacitor including a capacitor dielectric layer and capacitor plate over the extended drain, and forming a snubber resistor over a gate of the MOS transistor so that the resistor is connected in series between the capacitor plate and a source of the MOS transistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Dc-dc converter circuit
ActiveCN101842971ANo heat lossImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionSnubber capacitorDc dc converter
A DC-DC converter circuit comprises a switching circuit for switching a DC power supply with a primary switch element, a transformer having primary winding to which the output from the switching circuit is applied and secondary winding for outputting a voltage transformed at a predetermined transformation ratio, and a secondary diode for rectification connected with the secondary winding of the transformer. The circuit further comprises a regenerative snubber circuit, which is connected between the rectification outputs of the secondary diode and includes a series circuit of a discharge prevention diode and a snubber capacitor and a switch element for regeneration connected in parallel with the discharge prevention diode, and a control section for turning on the switch element for regeneration for a predetermined time from the off timing of the primary switching element. The predetermined time is set to a time for substantially discharging the snubber capacitor due to a reverse recovery time when the secondary diode is turned off.
Owner:SANSHA ELECTRIC MFG
Dc-dc converter circuit
ActiveUS20110280048A1Improve efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSnubber capacitorDc dc converter
This DC-DC converter circuit includes a switching circuit which switches a DC power supply with a primary side switching element, a transformer to a primary side winding whereof the output of the switching circuit is applied and which outputs a voltage which has been changed by a predetermined voltage change ratio to a secondary side winding, and secondary diodes for current adjustment connected to the secondary side winding of the transformer. Moreover, it includes a regeneration snubber circuit connected in parallel with the secondary diode circuit and including a series circuit of a discharge blocking diode and a snubber capacitor and a switching element for regeneration connected in parallel with the discharge blocking diode, a filter circuit connected between rectification outputs of the secondary diode circuit, and a control unit which turns the switching element for regeneration ON a predetermined time period after the timing of turning the primary side switching element OFF. The predetermined time period is set to approximately the time period during which the charge, accumulated in the snubber capacitor due to reverse recovery time when one of the secondary diodes has been turned OFF, discharges.
Owner:SANSHA ELECTRIC MFG
Lc snubber circuit
InactiveUS20140362613A1Reduce circulating currentEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSnubber capacitorTransformer
The present disclosure relates to an LC snubber circuit for a switching converter, wherein the switching converter includes an inductor and a switching device connected in series. The LC snubber circuit can include a first snubber diode, a snubber capacitor, a second snubber diode, and a snubber transformer having a primary winding and a secondary winding. The secondary winding of the snubber transformer is connected to an output of the switching converter.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Hybrid inductive-capacitive charge pump with high diode driving capability
InactiveUS7034601B2High diode driving capabilityAvoid threshold lossAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionSnubber capacitorEngineering
A hybrid inductive-capacitive charge pump provided with a driving stage that comprises a step-up converter and a buffer capacitor, and a cascade of charge pump stages; the first stage of the stage cascade is connected to a power supply and the last stage of the stage cascade is connected to an output of the charge pump circuit; the charge pump circuit comprises elements for activating alternately the charge pump stages, transferring charge from one stage of the cascade to the next stage of the cascade, each stage of the cascade of charge pumping stages comprising a pass transistor and a capacitor.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
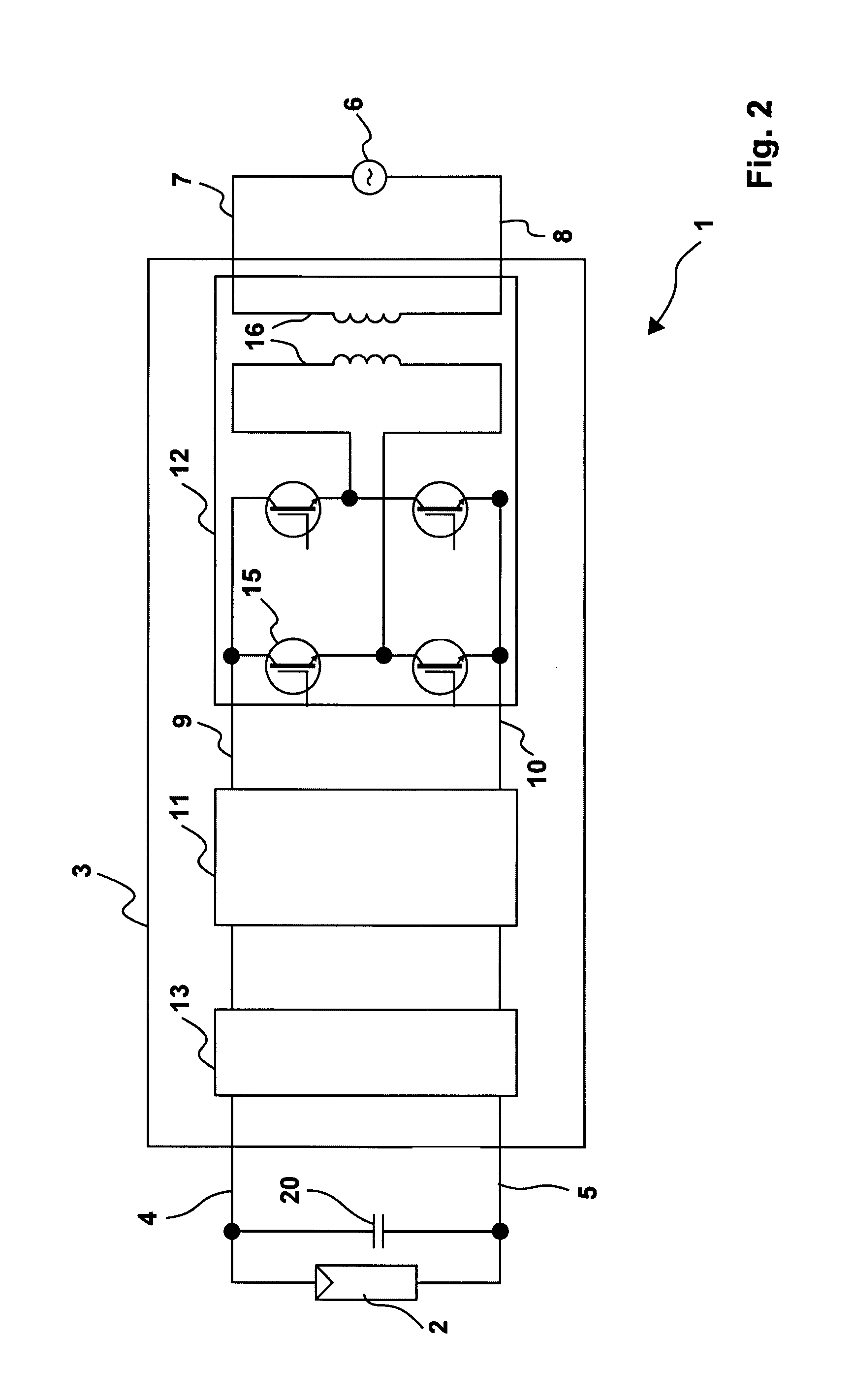
Switching device and method, in particular for photovoltaic generators
ActiveUS7924582B2Increase flexibilityReduce in quantityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower supply linesSnubber capacitorClock rate
The subject matter of the invention is an inverter (3), more specifically for use in a photovoltaic plant (1) with a direct voltage input (connection terminals 4; 5) for connection to a generator (2) and an alternating voltage output (connection terminals 7; 8) for feeding into an energy supply network (6) as well as with a DC-AC converter (12) with semiconductor switch elements (15) and an intermediate circuit (11), at least one short-circuit switch element (18) being connected in parallel to the generator (2), so that the voltage will not exceed a maximum voltage value neither at the connection terminals (4; 5) of the generator (2) nor between the connection terminals (9; 10) of the inverter. This is achieved in that the inverter (3) comprises, in the intermediate circuit (12), a buffer capacitor (14) that is connected to the generator (2) through a protection diode (17) so that said buffer capacitor (14) will not be discharged upon actuation of the short-circuit switch element (18), the generator (2) working according to a clock rate in the short-circuit mode of operation.
Owner:SMA SOLAR TECH AG
Low-voltage IC-circuit
InactiveUS7710192B2Keep energy smallUniform voltage dropBatteries circuit arrangementsPulse automatic controlSnubber capacitorLow voltage
An integrated circuit is partitioned into two or more sub-circuits, each sub-circuit including two supply terminals across which to receive supply voltage. The sub-circuits are connected in series with the first sub-circuit receiving input voltage at its first supply terminal, and the voltage level output at the second supply terminal of the first sub-circuit being used as input voltage level in a second sub-circuit. Further, a control-circuit is configured to balance voltage drops across the sub-circuits and to maintain constant voltage-drops over the sub-circuits. The control-circuit includes two buffer capacitors, each coupled in parallel over one of the two sub-circuits respectively. The control-circuit also includes at least one bucket capacitor alternately coupled in parallel over the first and the second buffer capacitor through a switching system controlled by a toggling signal.
Owner:BERNAFON
Power converting device
InactiveCN1383605ATurn-off losses do not increaseEasy to controlEfficient power electronics conversionDc-ac conversion without reversalSnubber capacitorResonance
Disclosed is a power conversion device that does not generate ripples, including a control circuit that generates a switching signal at a timing capable of realizing soft switching. The first main switch (Q1) and the second main switch (Q2) connected in series are connected to the positive terminal of the DC power supply at the end of the first switch, and connected to the negative terminal of the DC power supply at the end of the second main switch. Diodes (D1, D2) are connected in parallel on each main switch to make it reverse biased relative to the DC power supply. On each main switch, the main switch buffer capacitors (C1, C2) are connected in parallel. The connection point of the circuit is connected to the load, and the output is generated by controlling the on and off of the main switch according to the switching signal from the control circuit. The first auxiliary resonant circuit composed of the first auxiliary switch and the second auxiliary switch (Q3, Q4, Q5, Q6) connected in series and the resonant inductor (L1) connected in series on the second auxiliary switch is connected to the positive terminal of the DC power supply Between its connection point and the two main switches, connect diodes to the first and second auxiliary switches so that they are reverse biased relative to the DC power supply. The control circuit takes the voltage signals from the voltage detection part representing the voltages at both ends of the main switch and the above-mentioned auxiliary switch as input, and supplies the first and second auxiliary switches with an on-signal as a switch signal before supplying the first main switch Turn on the signal.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Adaptive rcd snubber and method for switching converter
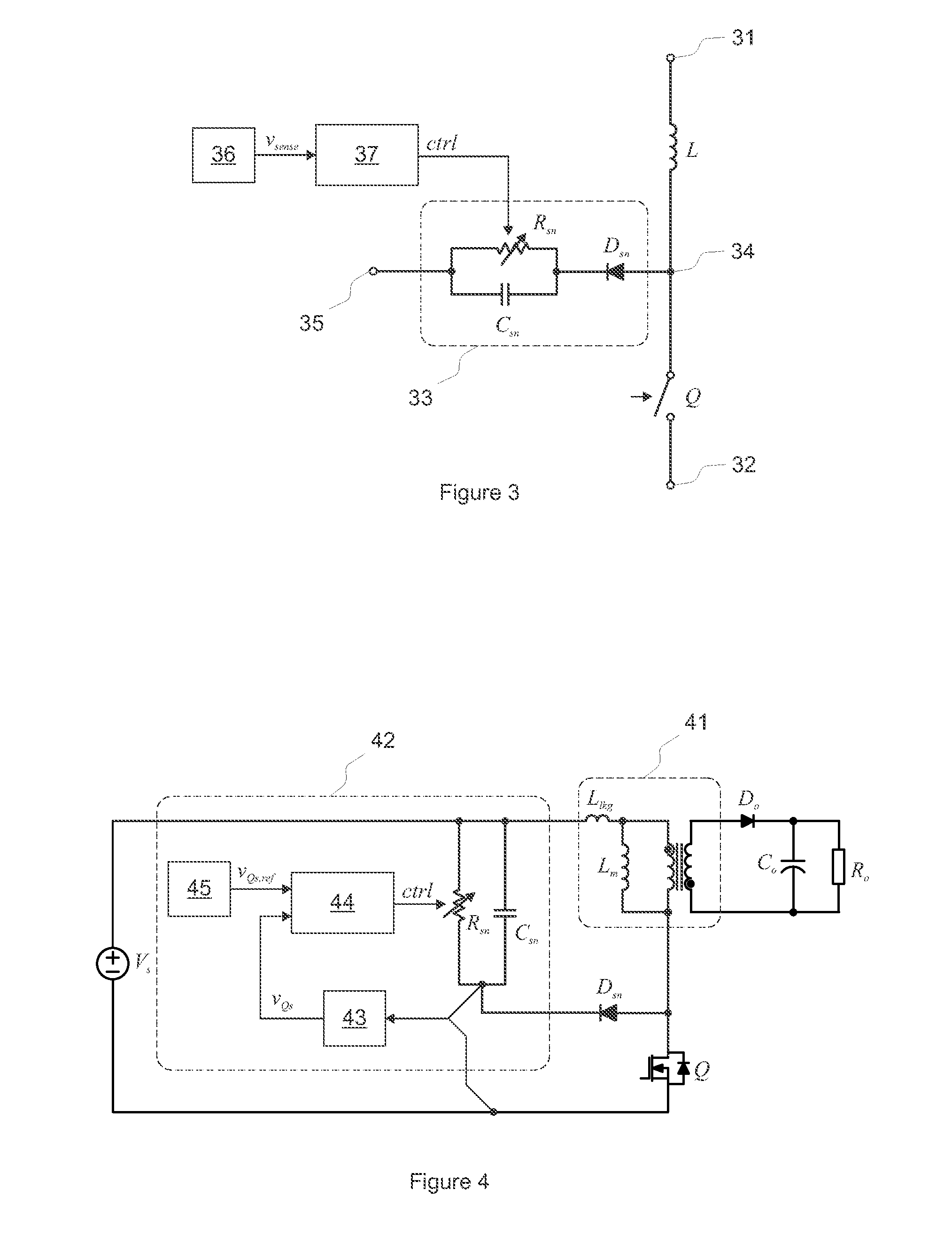
InactiveUS20140369093A1Suppressing additional voltage stressSimple structureEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionSnubber capacitorInductor
Exemplary embodiments provide a method and an adaptive RCD snubber circuit for a switching converter having a series-connection of a main inductor and a main switching device. A voltage stress of the main switching device is sensed, and the sensed voltage stress is controlled to a reference level by controlling a snubber capacitor voltage, wherein the snubber capacitor voltage is controlled by adjusting the snubber resistance of the RCD snubber.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com