Patents
Literature
909results about "Theodolites" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
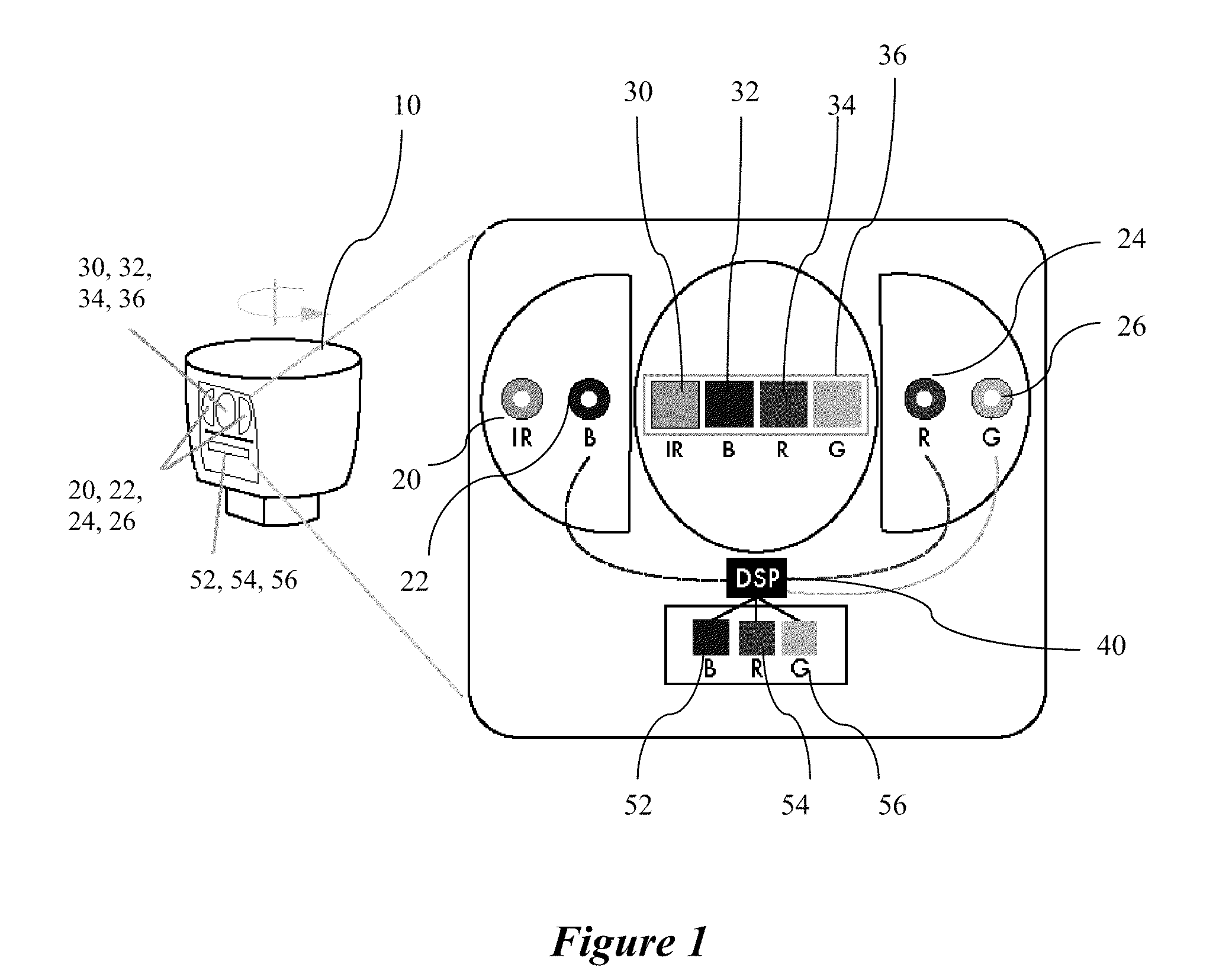
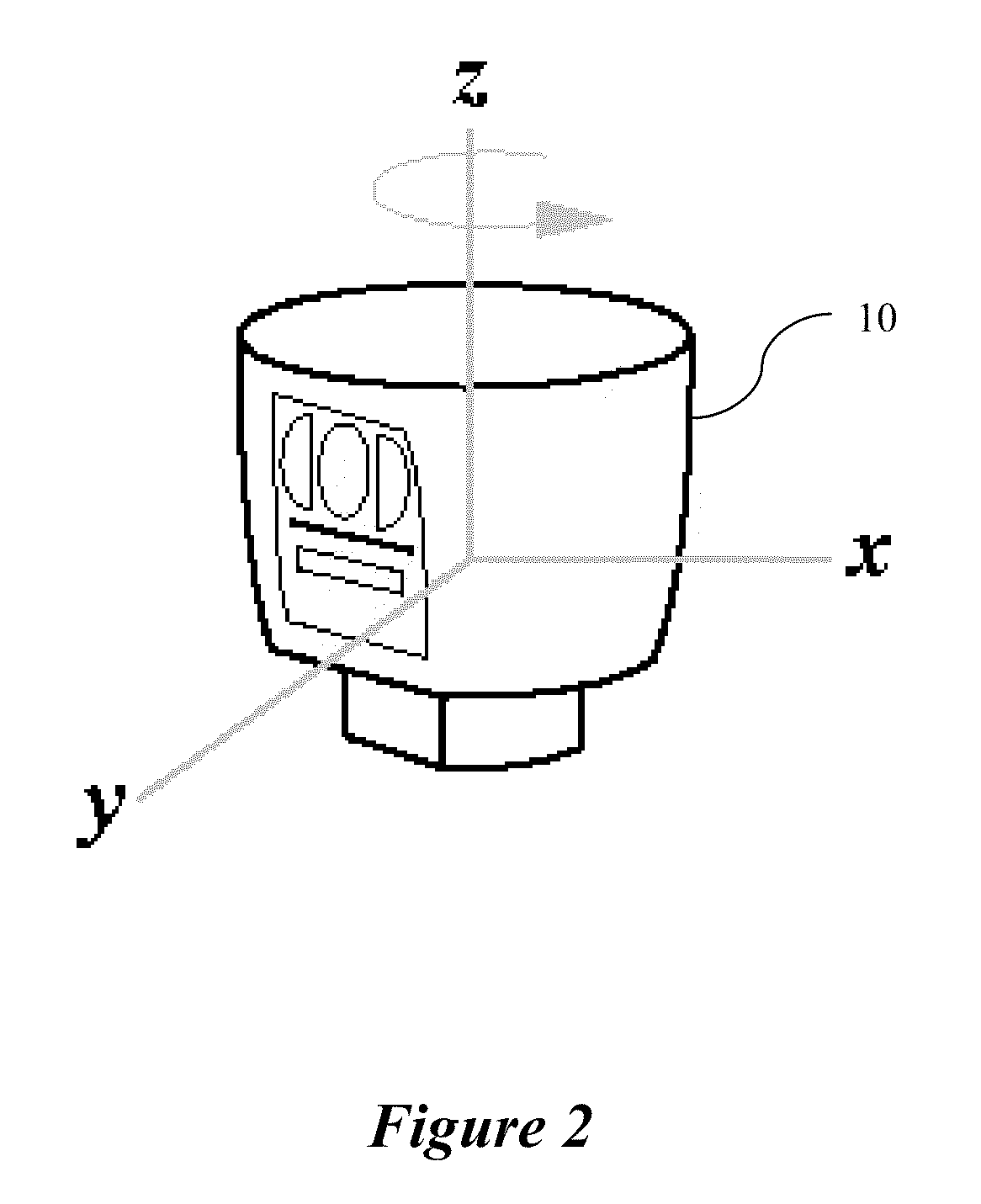
Color LiDAR scanner
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
Color lidar scanner
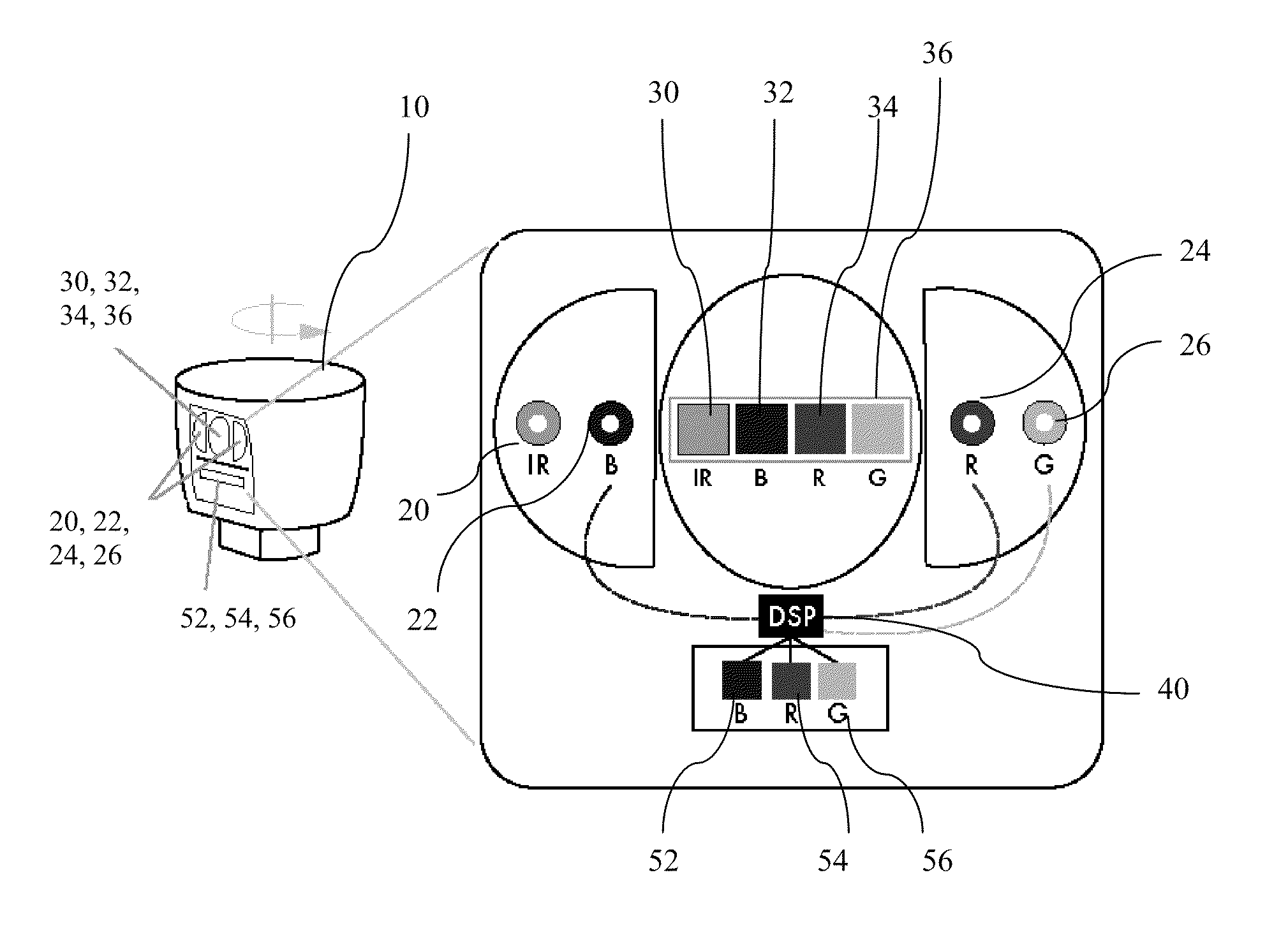
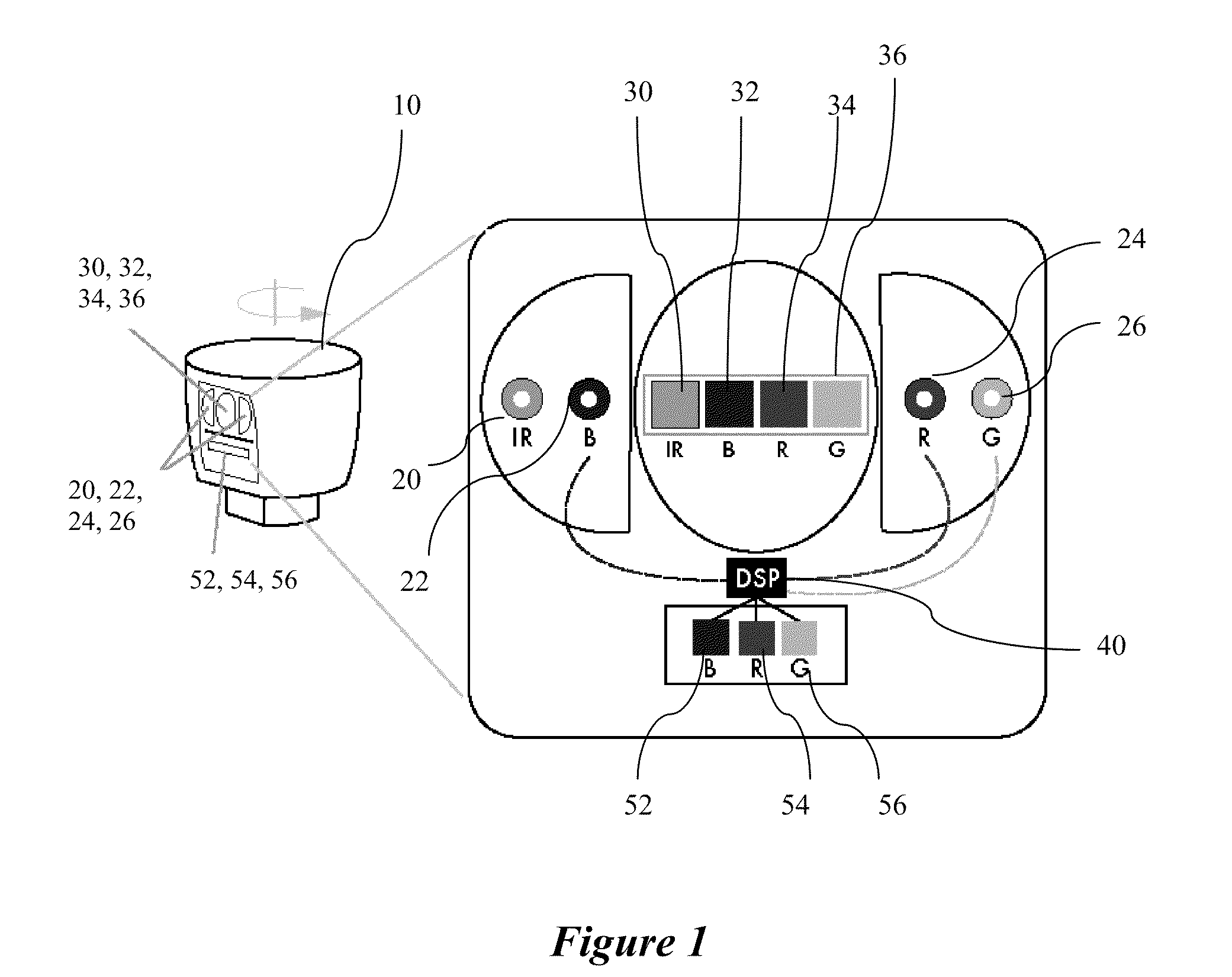
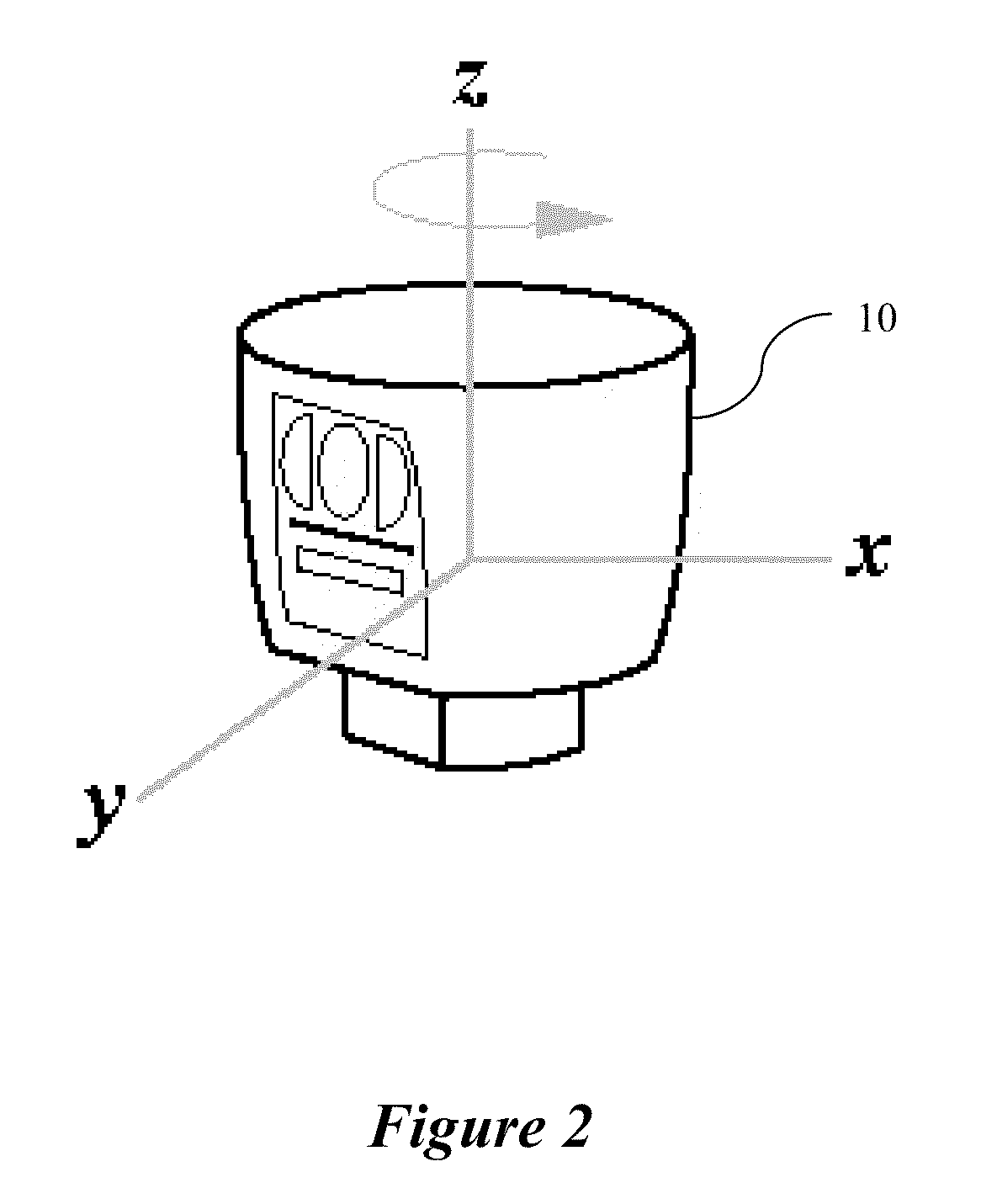
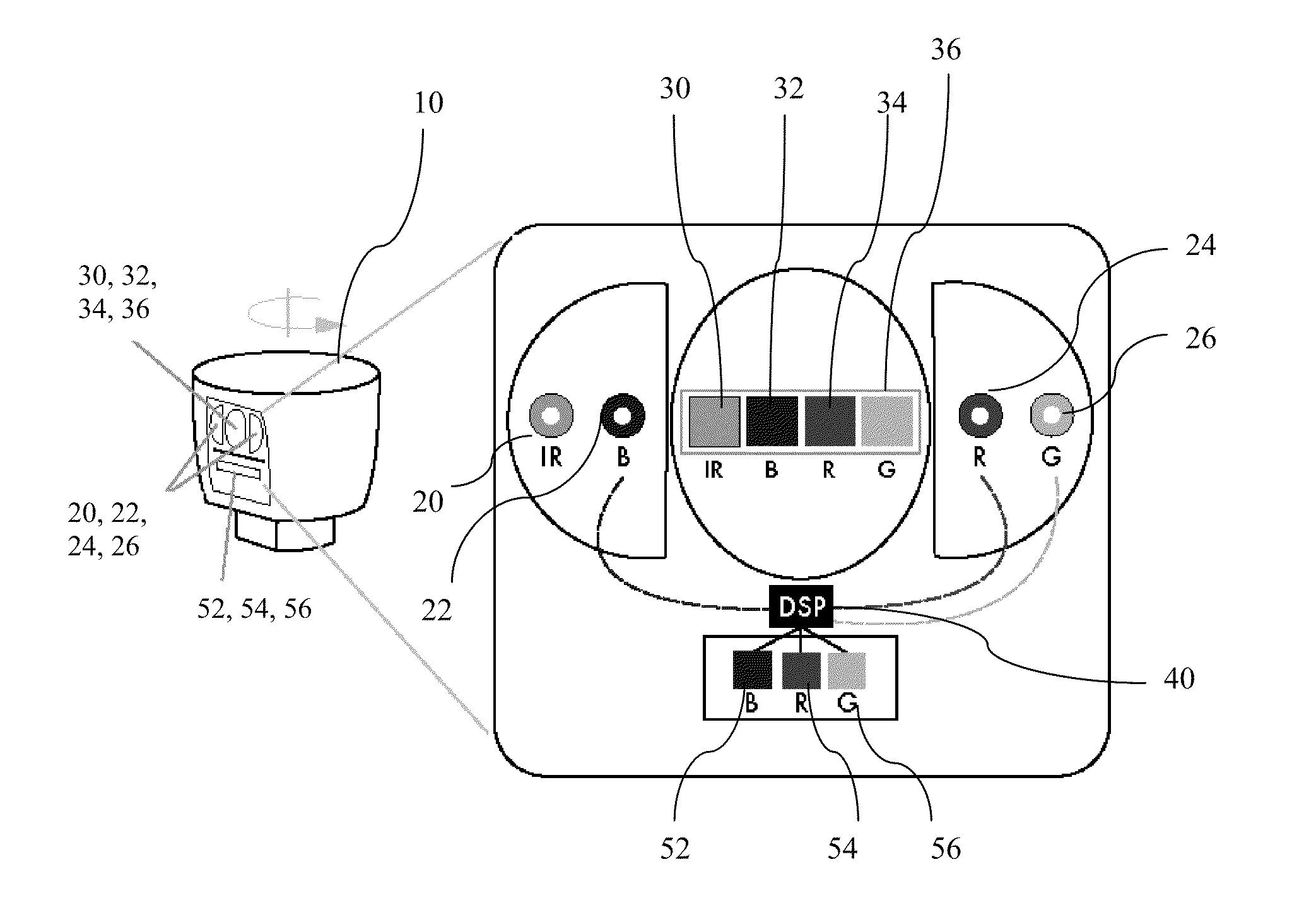
A color LiDAR scanner device includes color laser diodes (red, green, blue) and avalanche photodetector diodes (red, green, blue) that illuminate and detect the color light intensity returned from a target. In a preferred version these color laser / detectors are coupled with a single infrared laser / detector that detects the range and infrared light intensity from the same target. The combined range and color intensity information is combined to produce a single colored pixel in space. Multiple illuminations are used to create multiple pixels which can be combined to produce images. A rotating housing may be used for an entire surrounding image.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
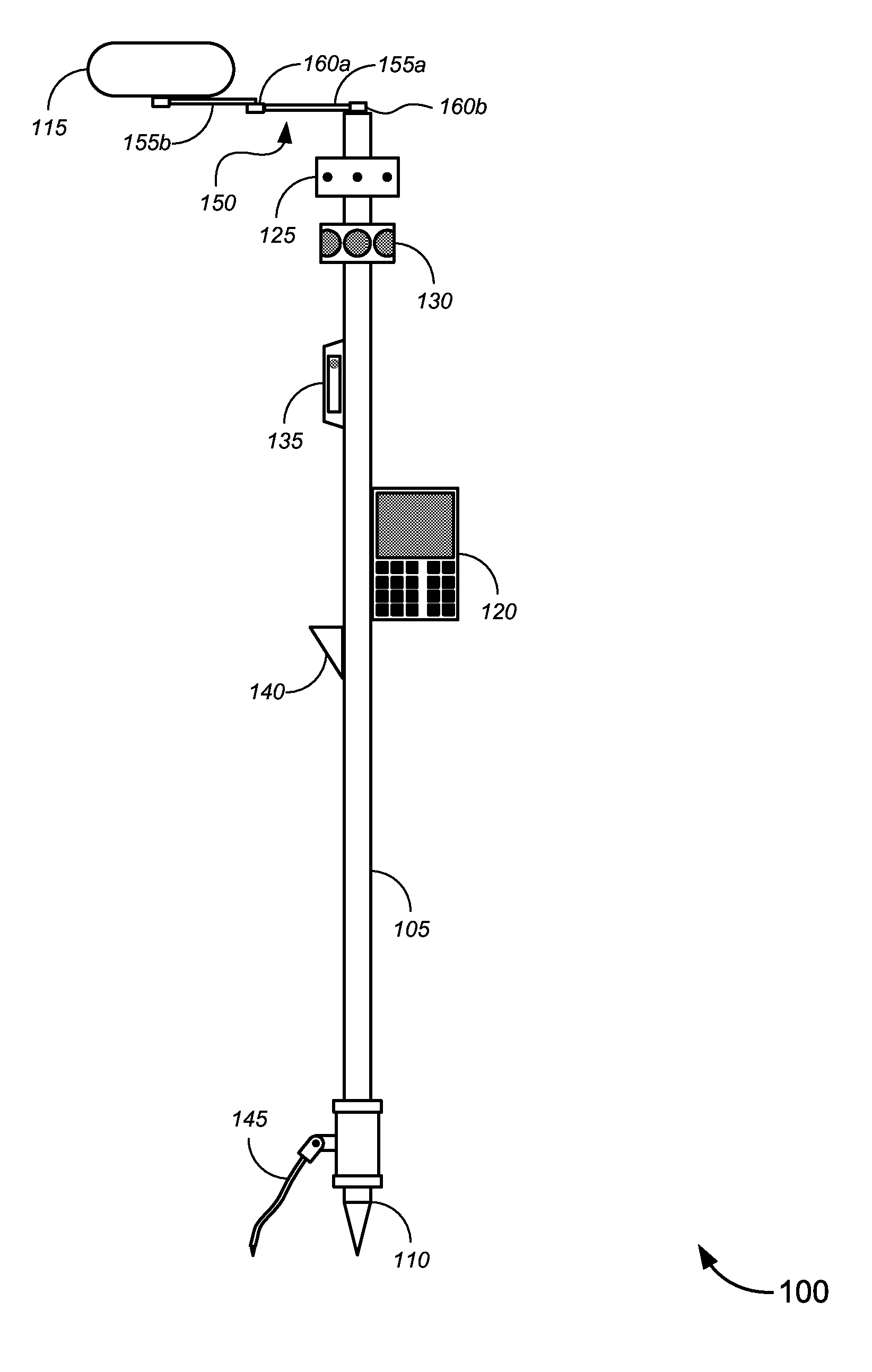
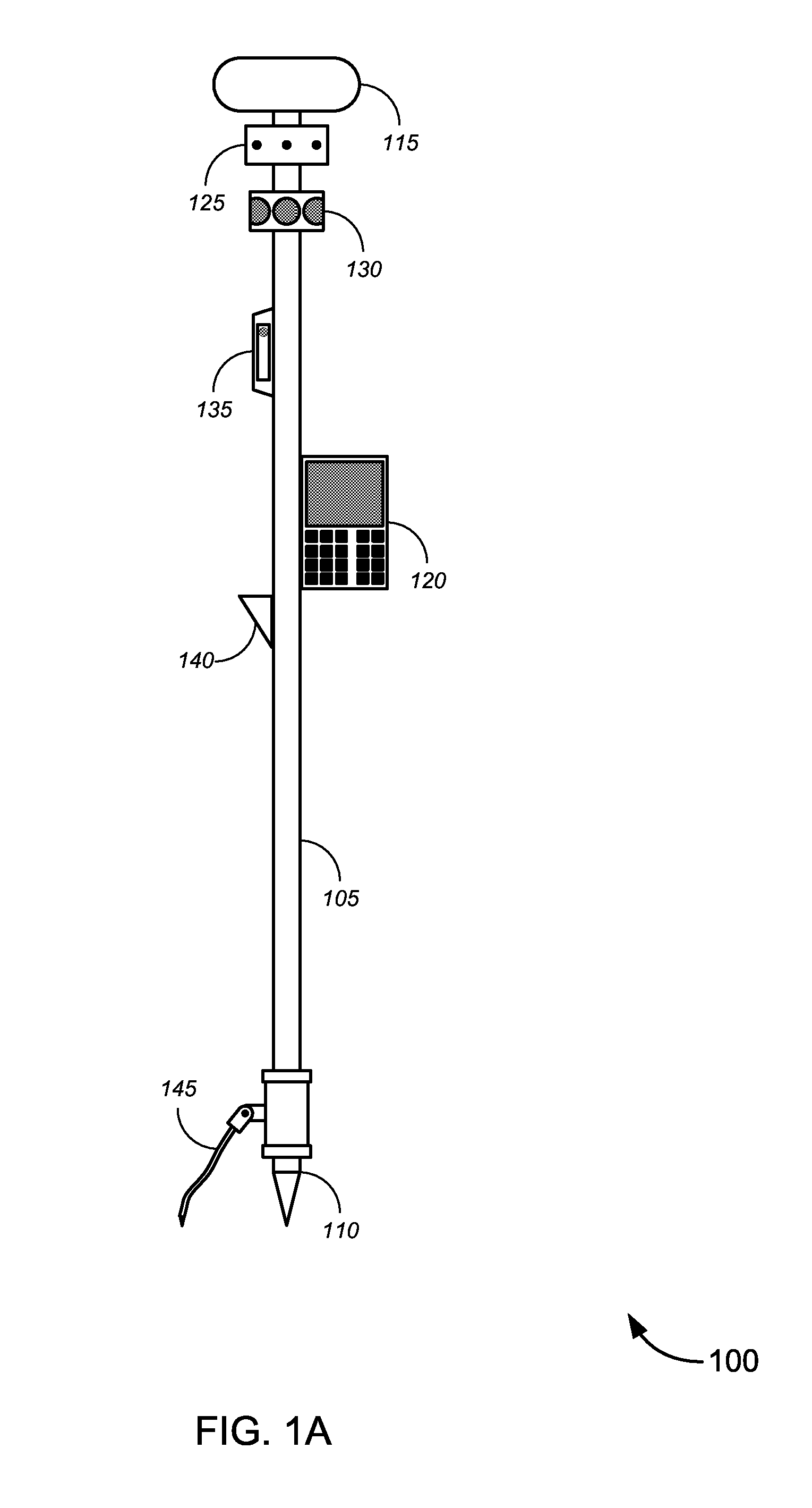
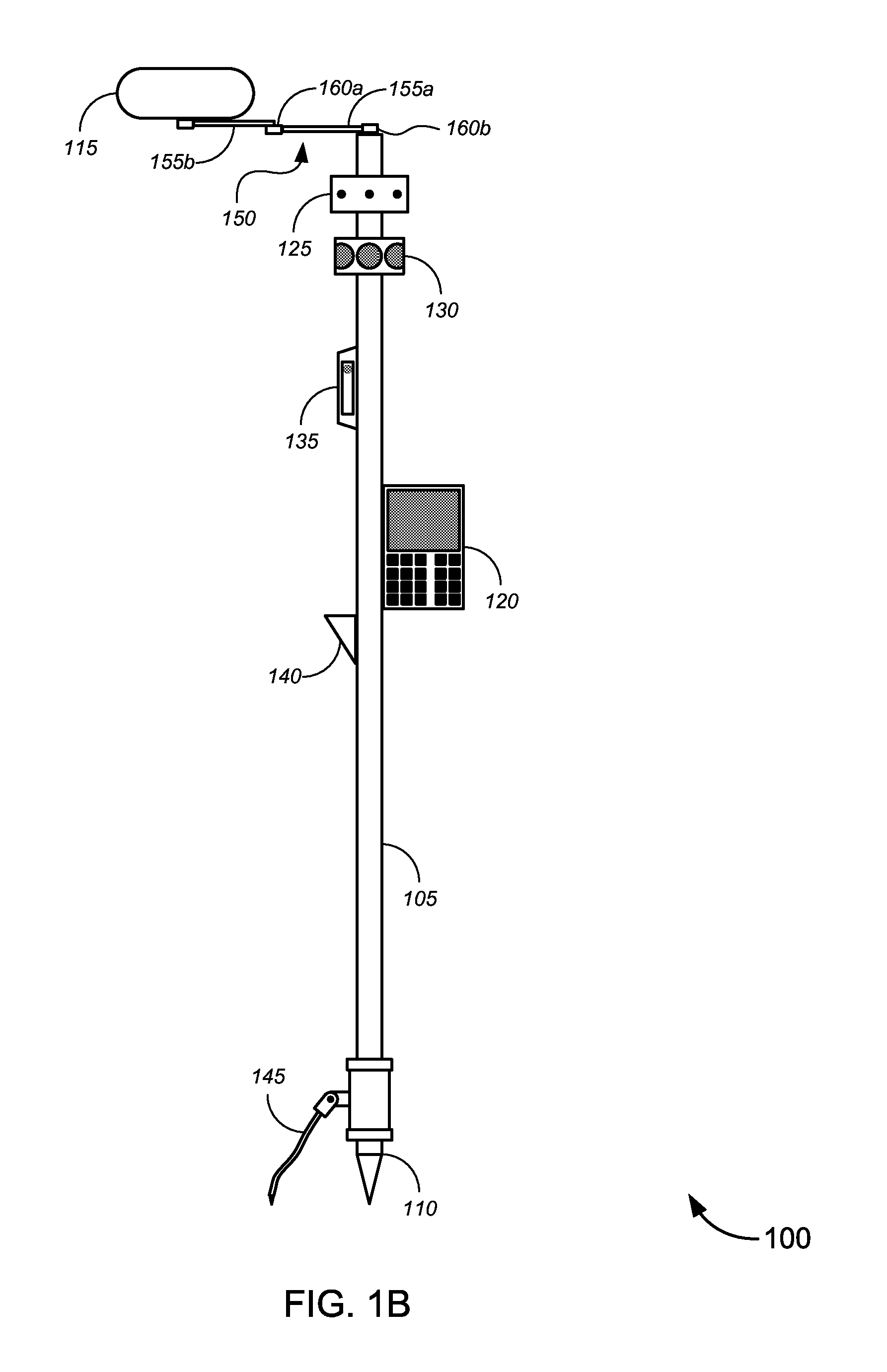
Enhanced Position Measurement Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20120166137A1Improve efficiencyImprove mobilitySurveyor's staffsMovable markersTotal stationComputer science
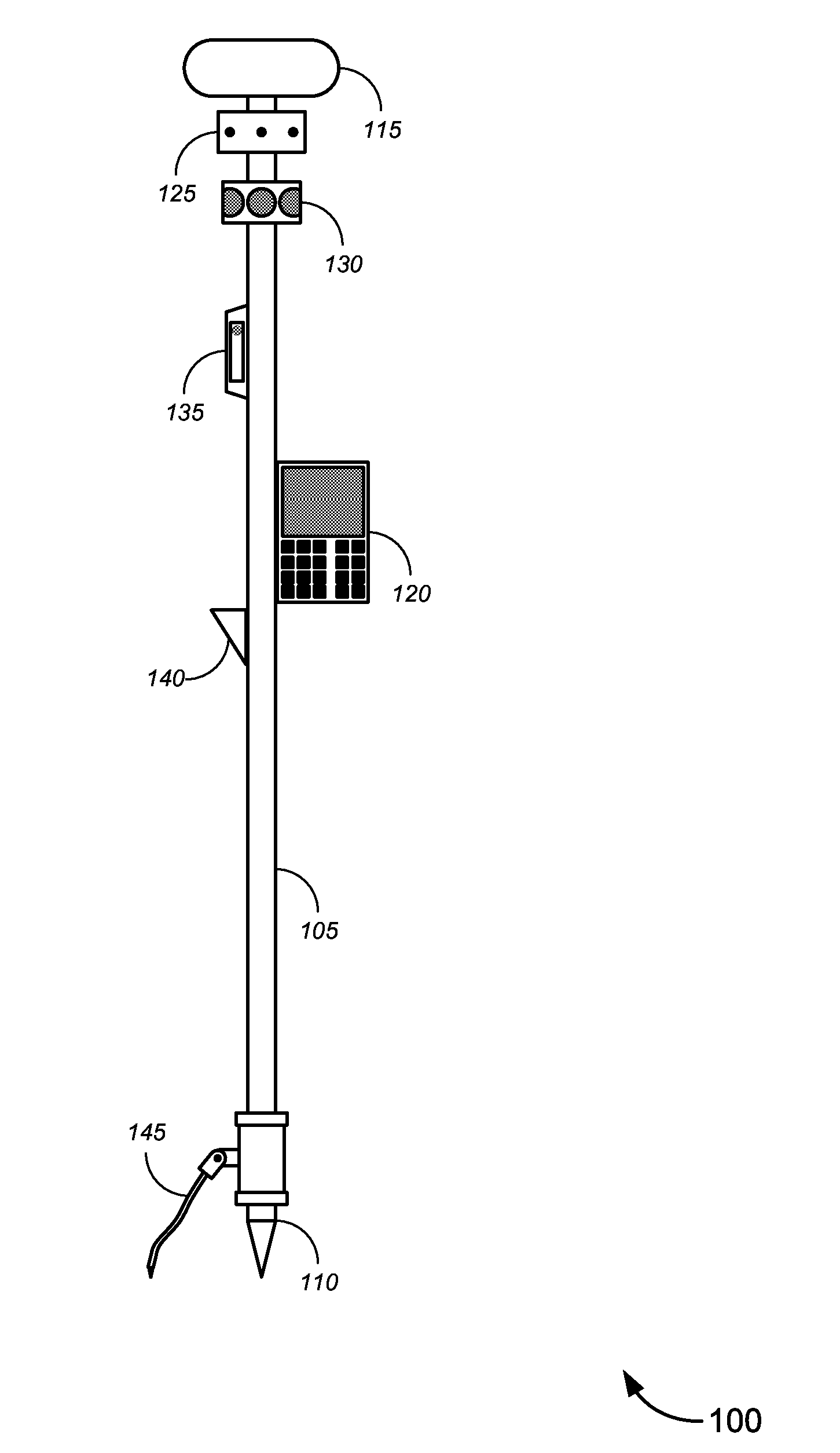
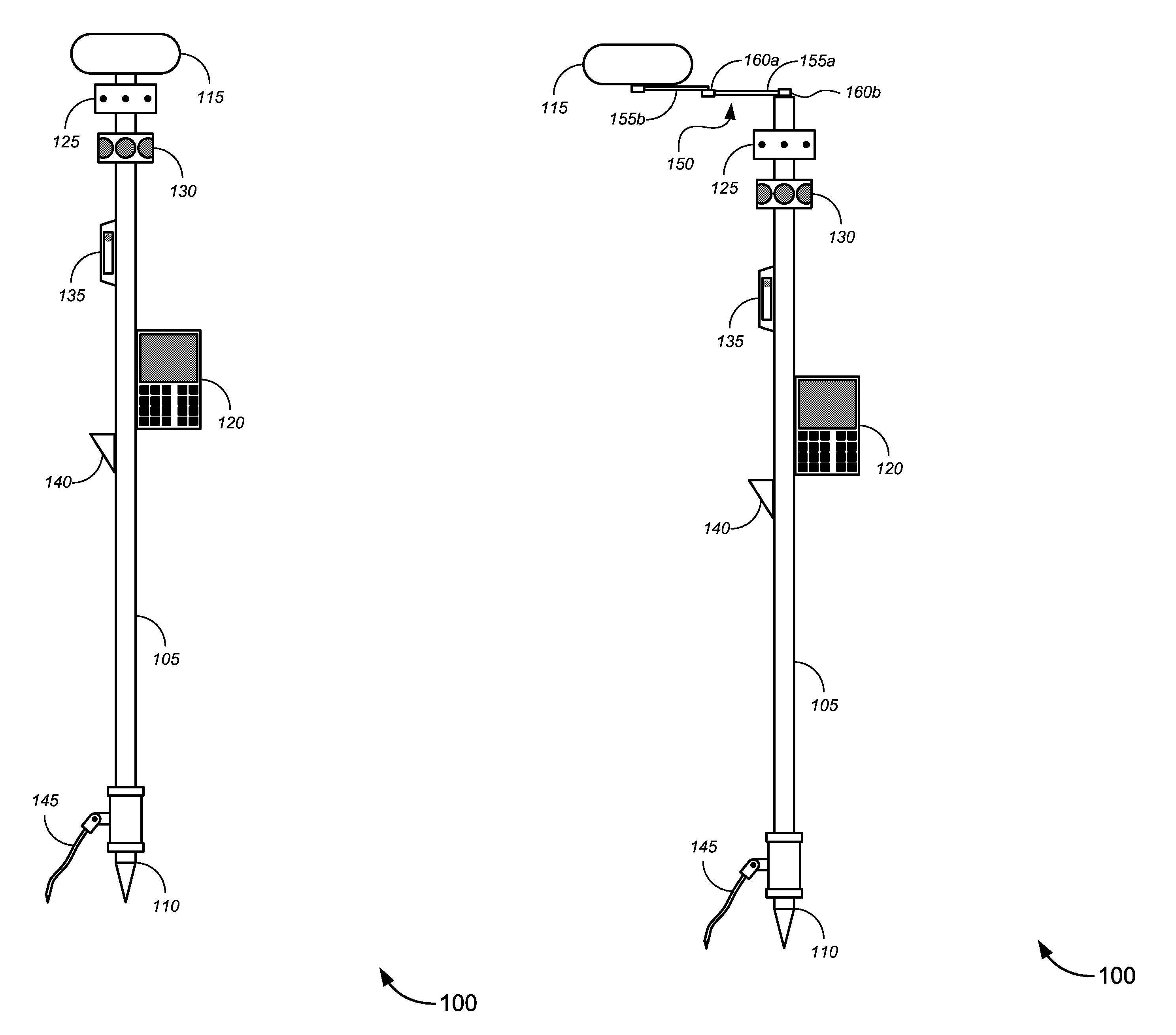
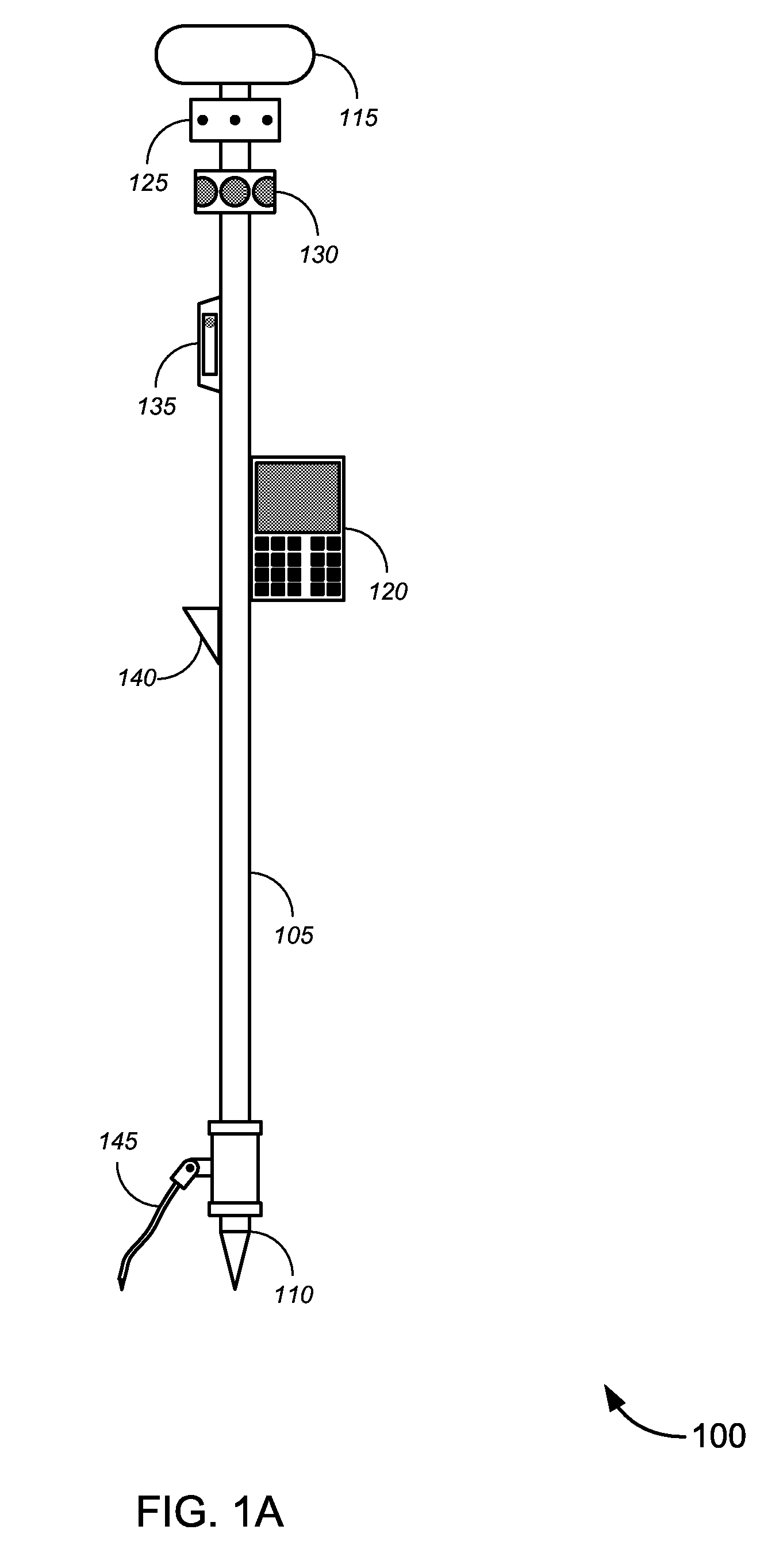
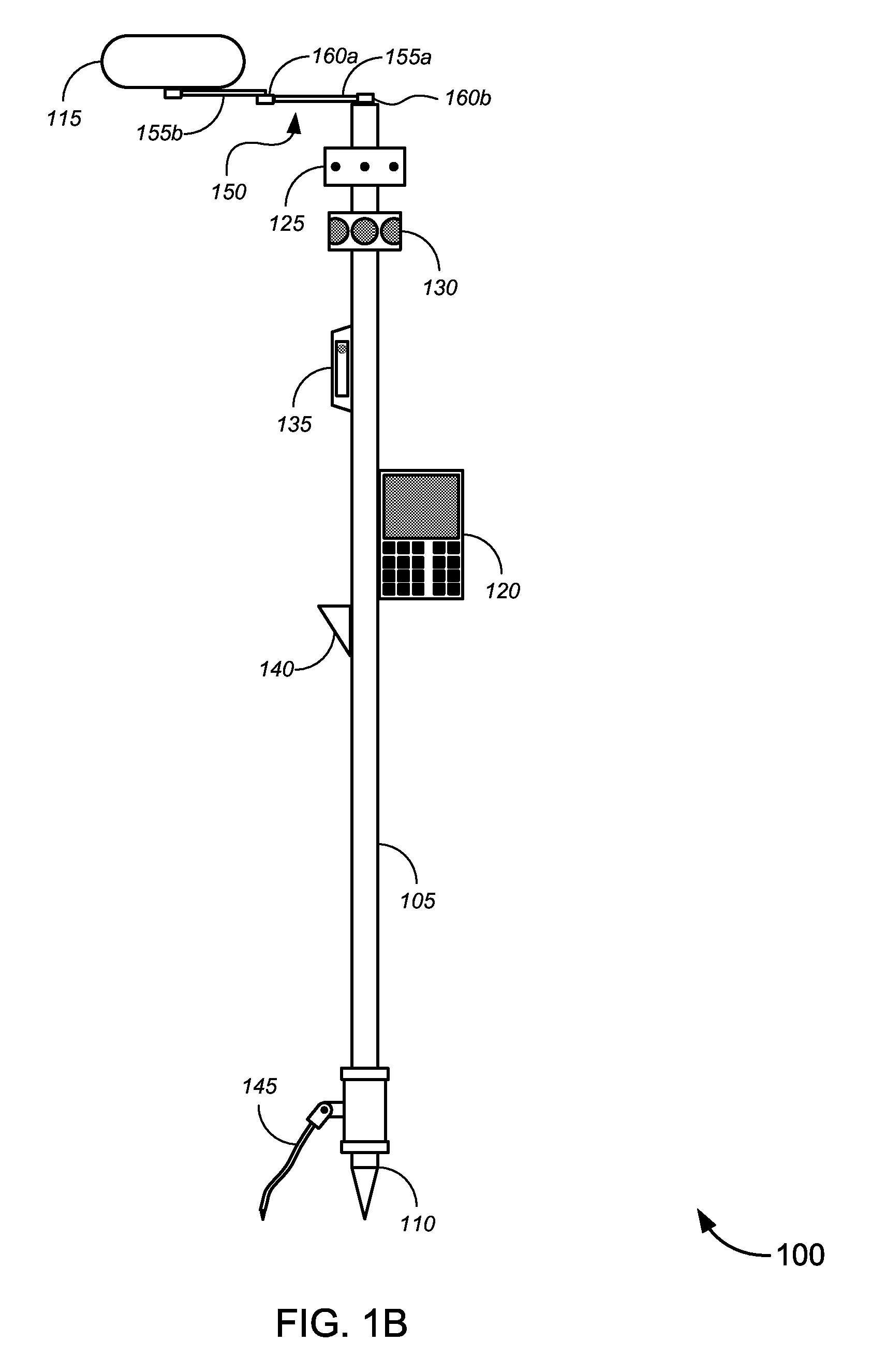
Novel solutions for position measurement, including without limitation tools and techniques that can be used for land surveying and in similar applications. One such tool is a greatly enhanced position measurement system that takes the form of a surveying rod with substantial independent functionality, which can be used with or without a total station or similar device.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
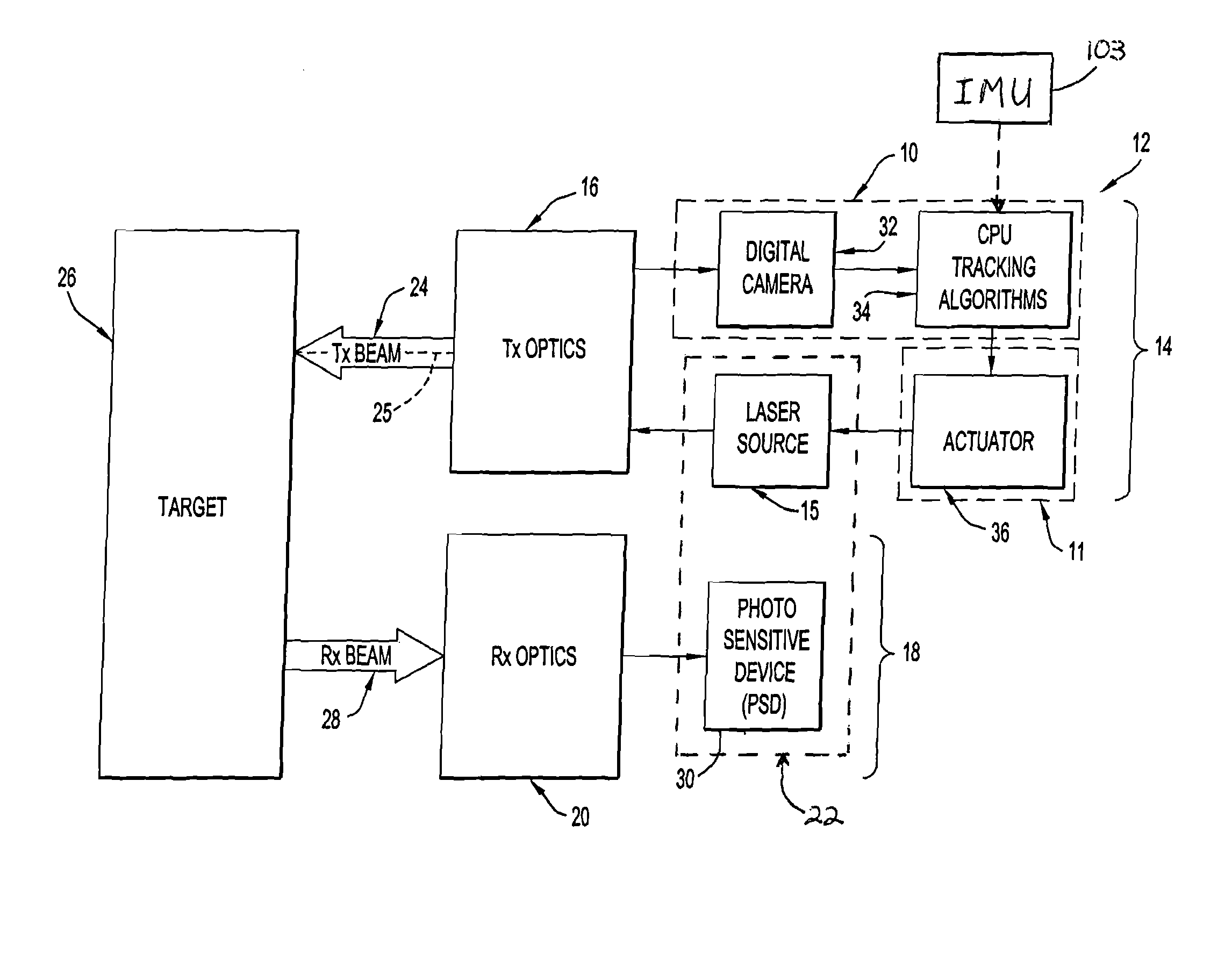
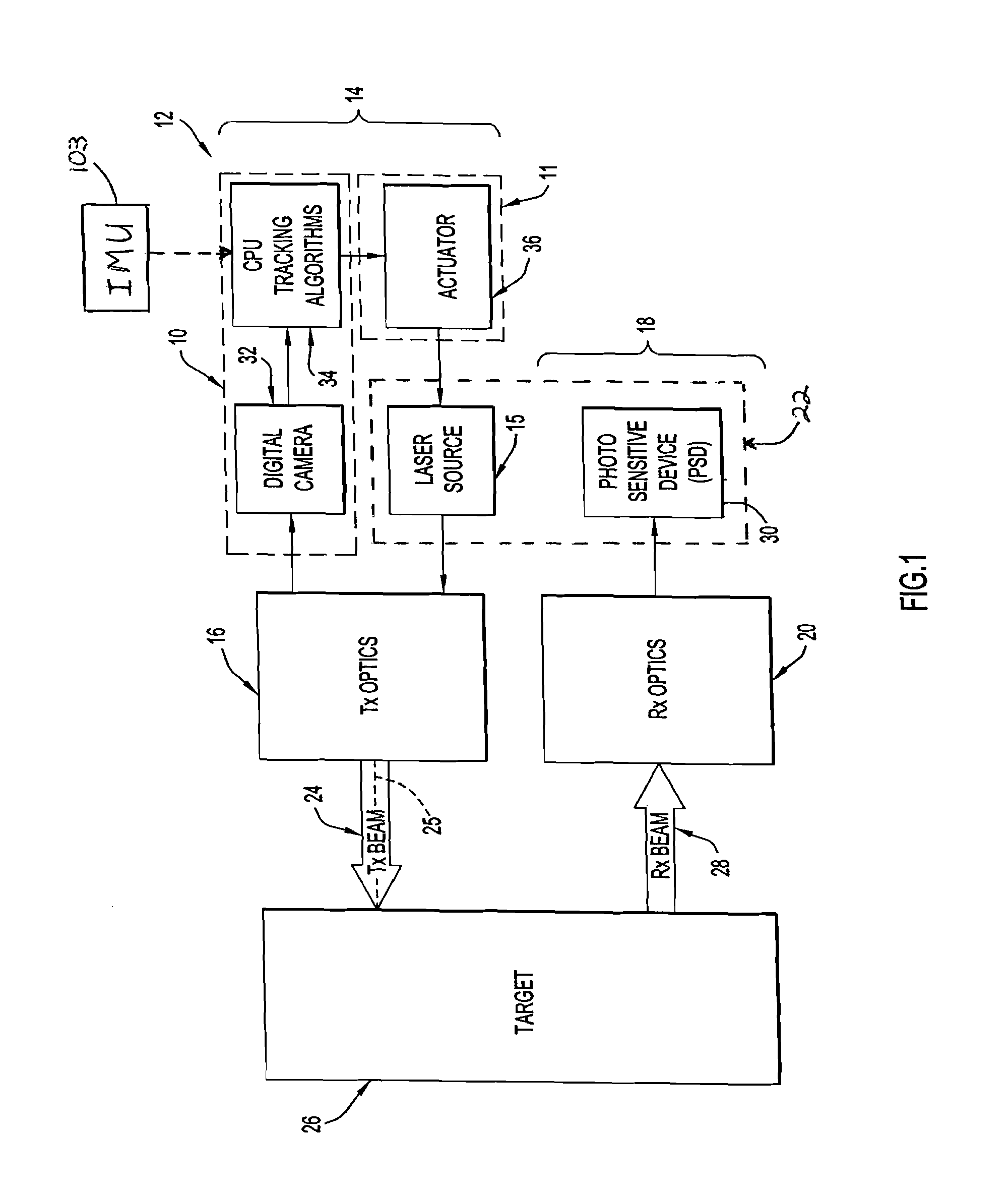
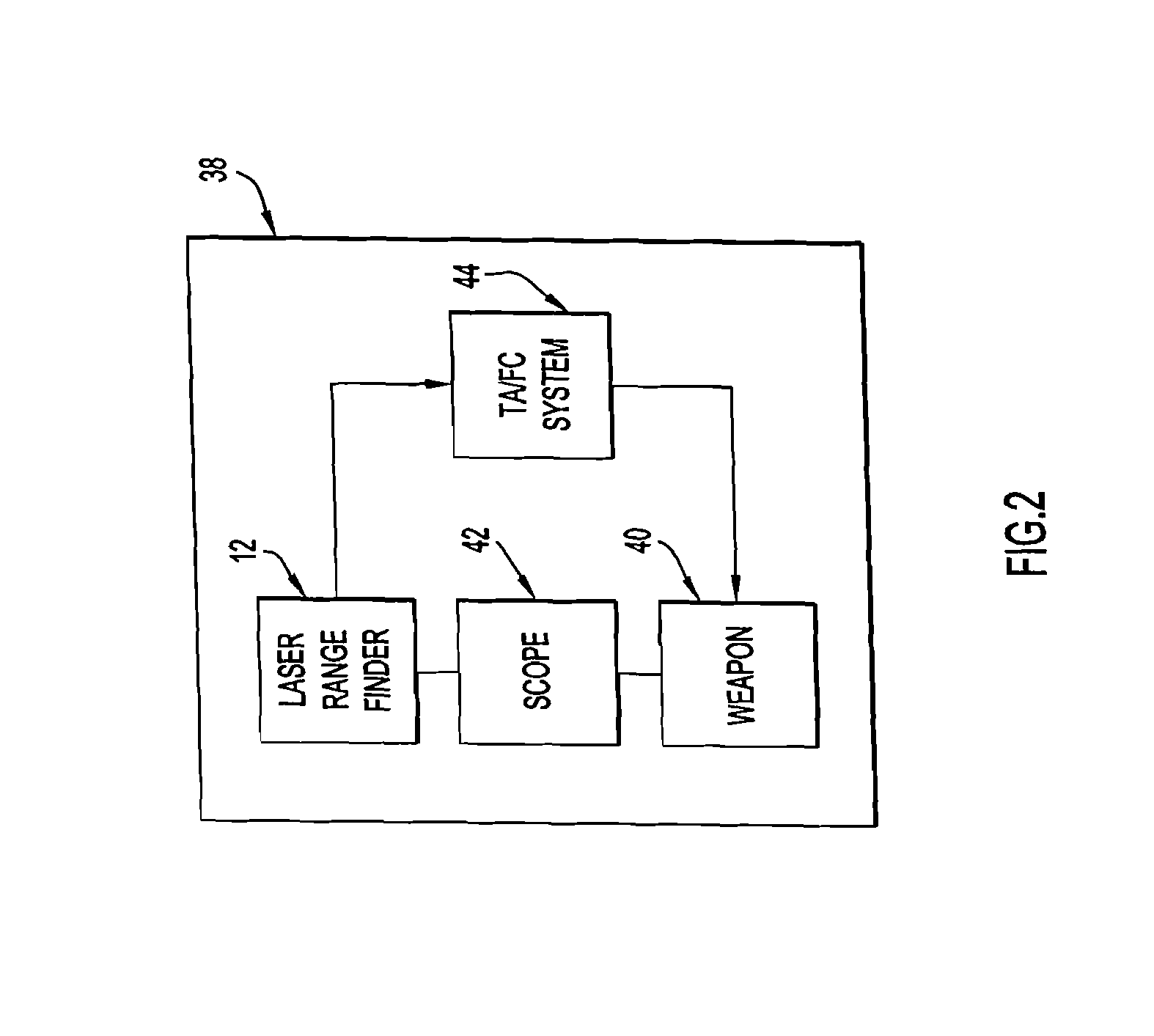
Systems and methods for automatic target tracking and beam steering
An automatic target tracking system and method employ an image capturing system for acquiring a series of images in real time of a distant area containing a remote target, and a processing system for processing the acquired images to identify the target and follow its position across the series of images. An automatic beam steering and method operate in conjunction with a laser source for emitting a laser beam to be transmitted in the form of a transmitted laser beam extending along a steerable beam transmission axis to the remote target. The beam steering system is controlled by the processing system to steer the beam transmission axis to be aimed at the target being tracked by the target tracking system, so that the transmitted laser beam will be transmitted at the appropriate angle and in the appropriate direction to be aimed at the tracked target.
Owner:INTELLIGENT AUTOMATION LLC
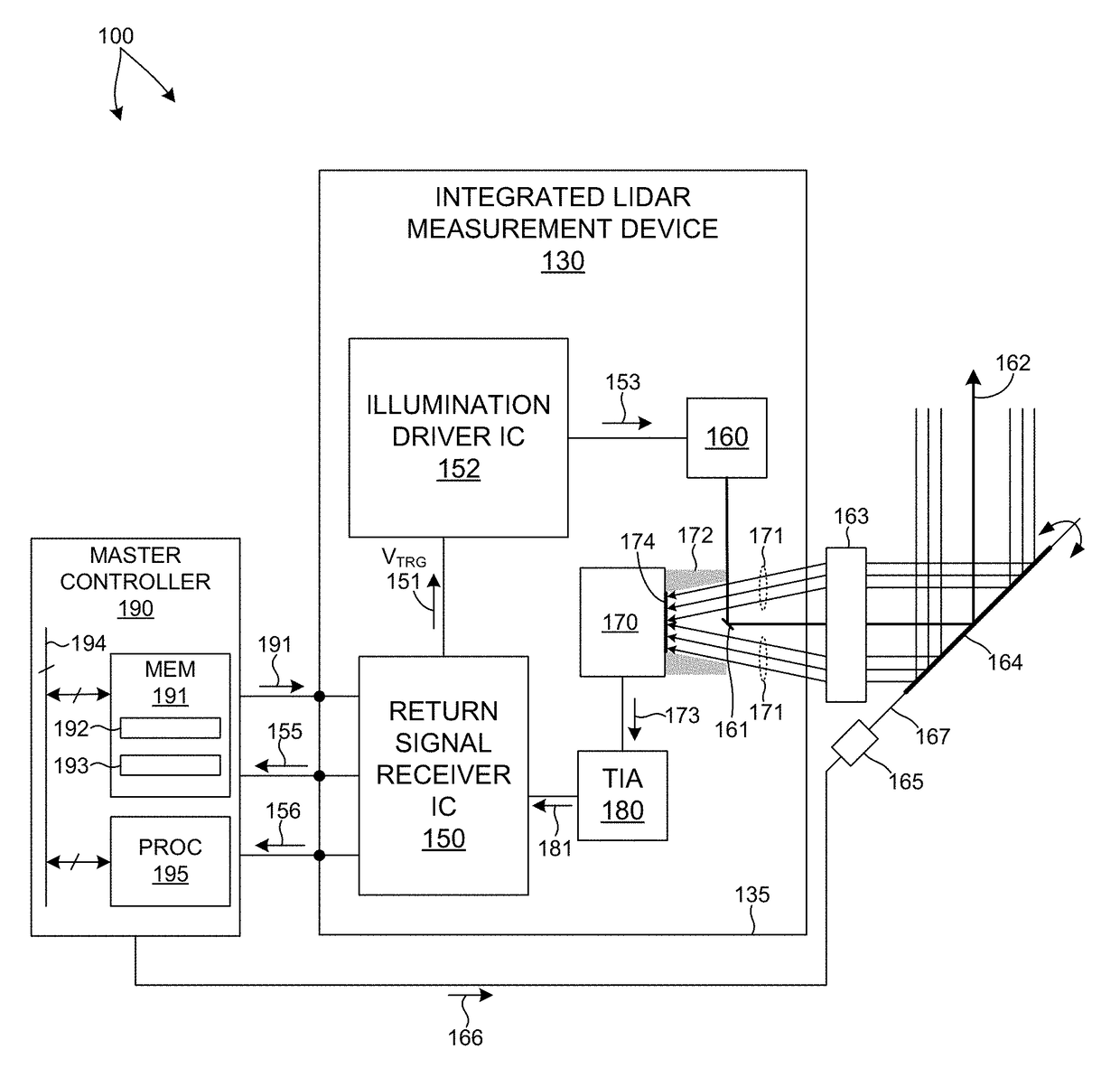
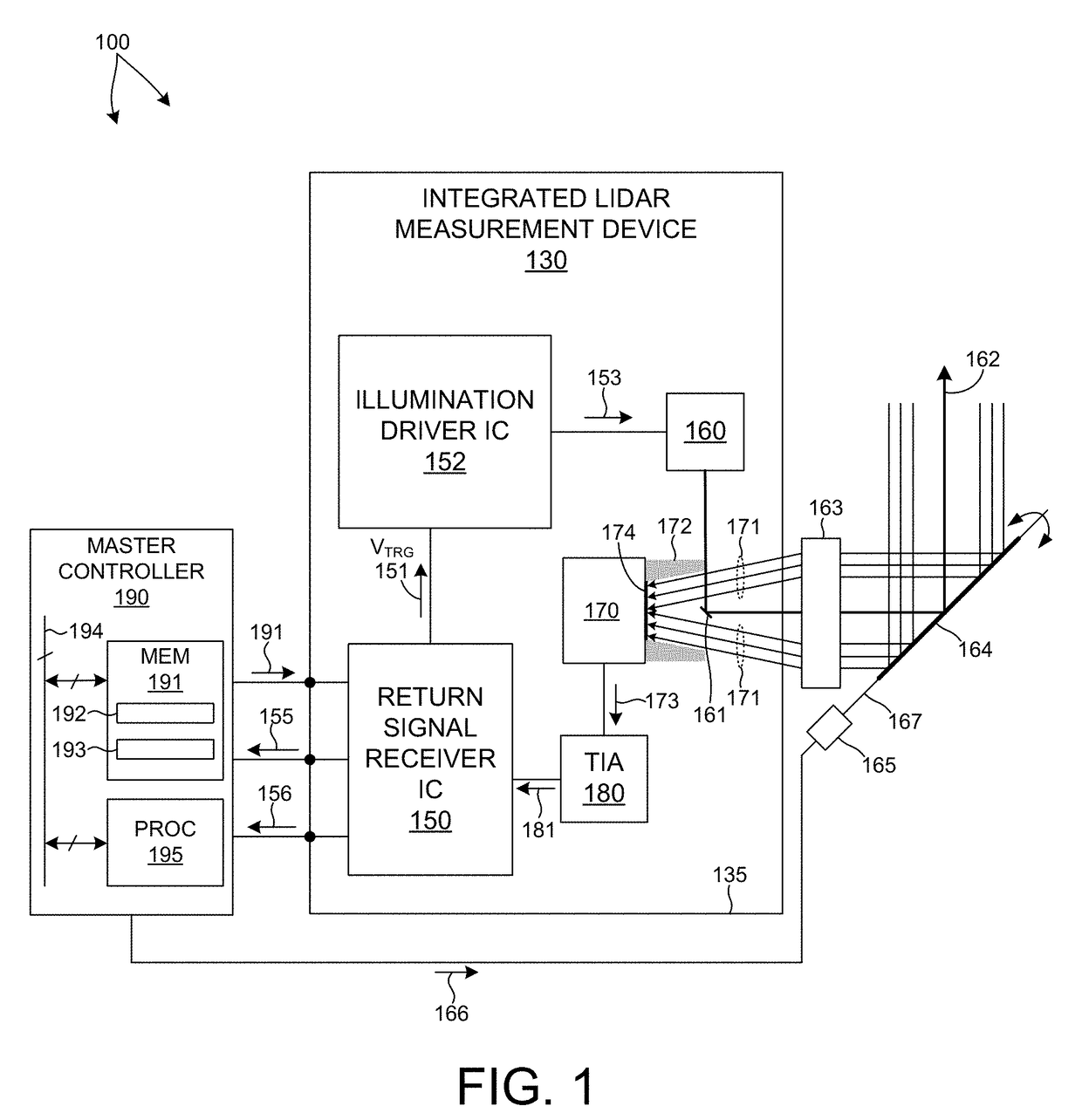
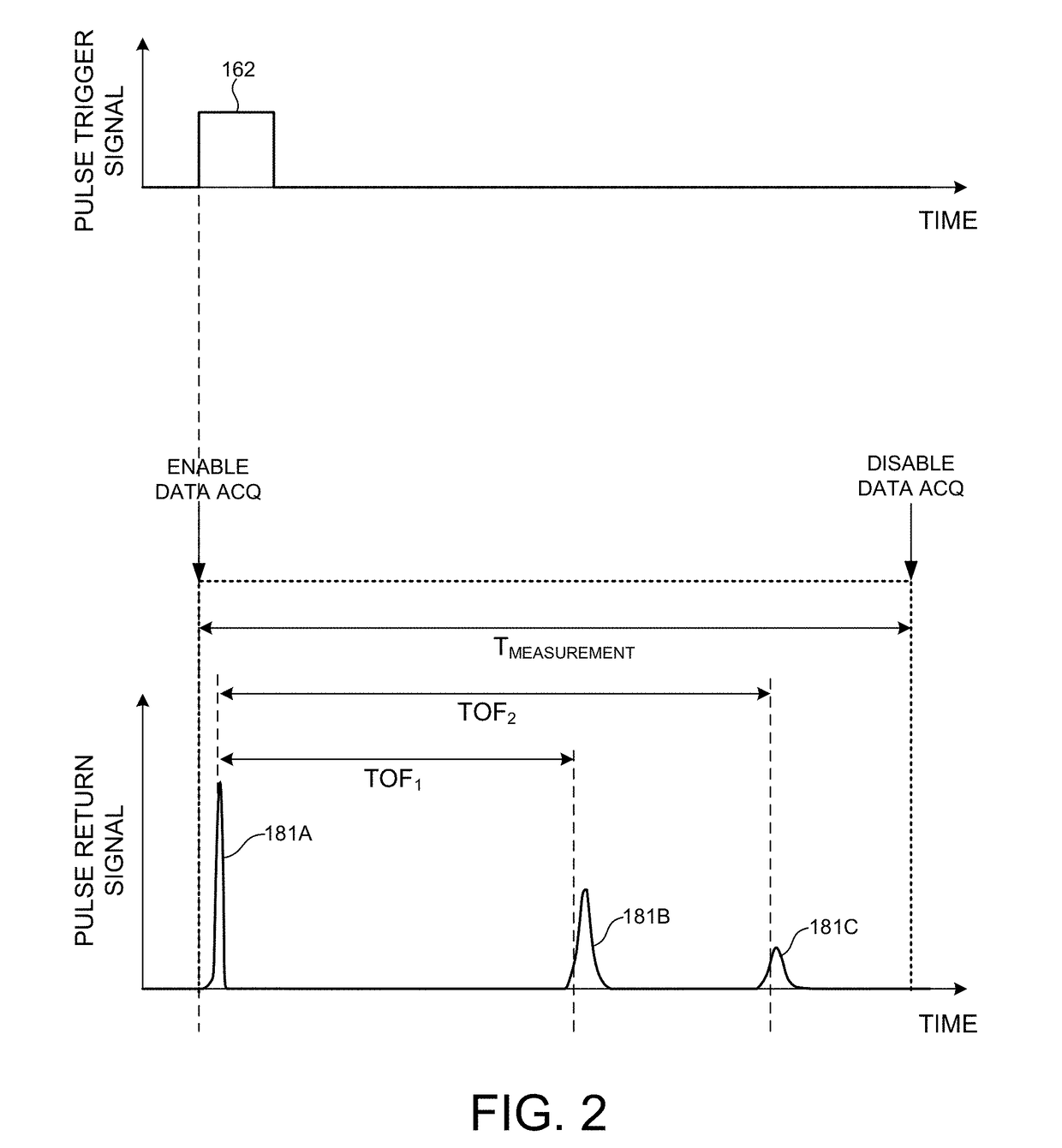
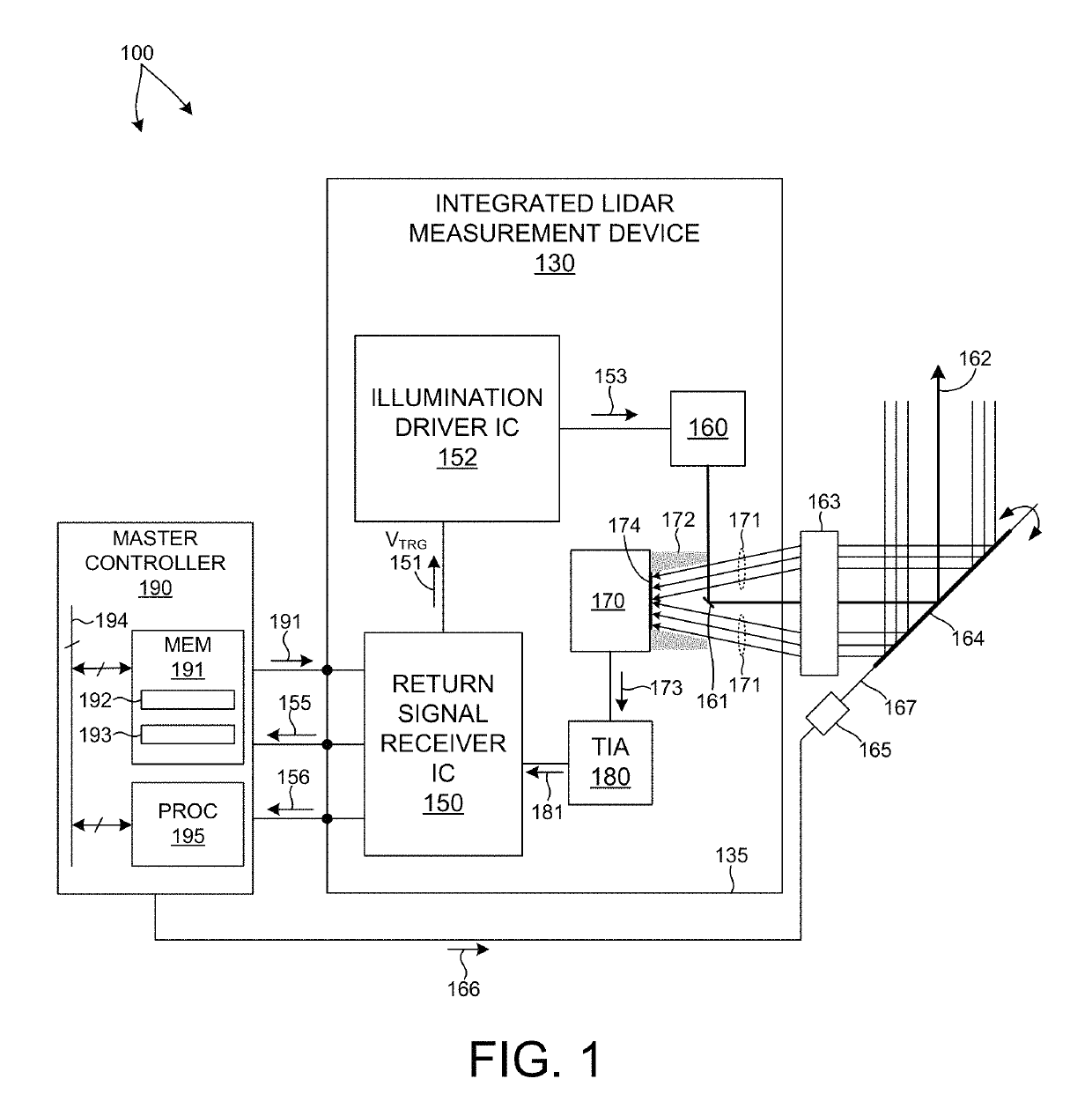
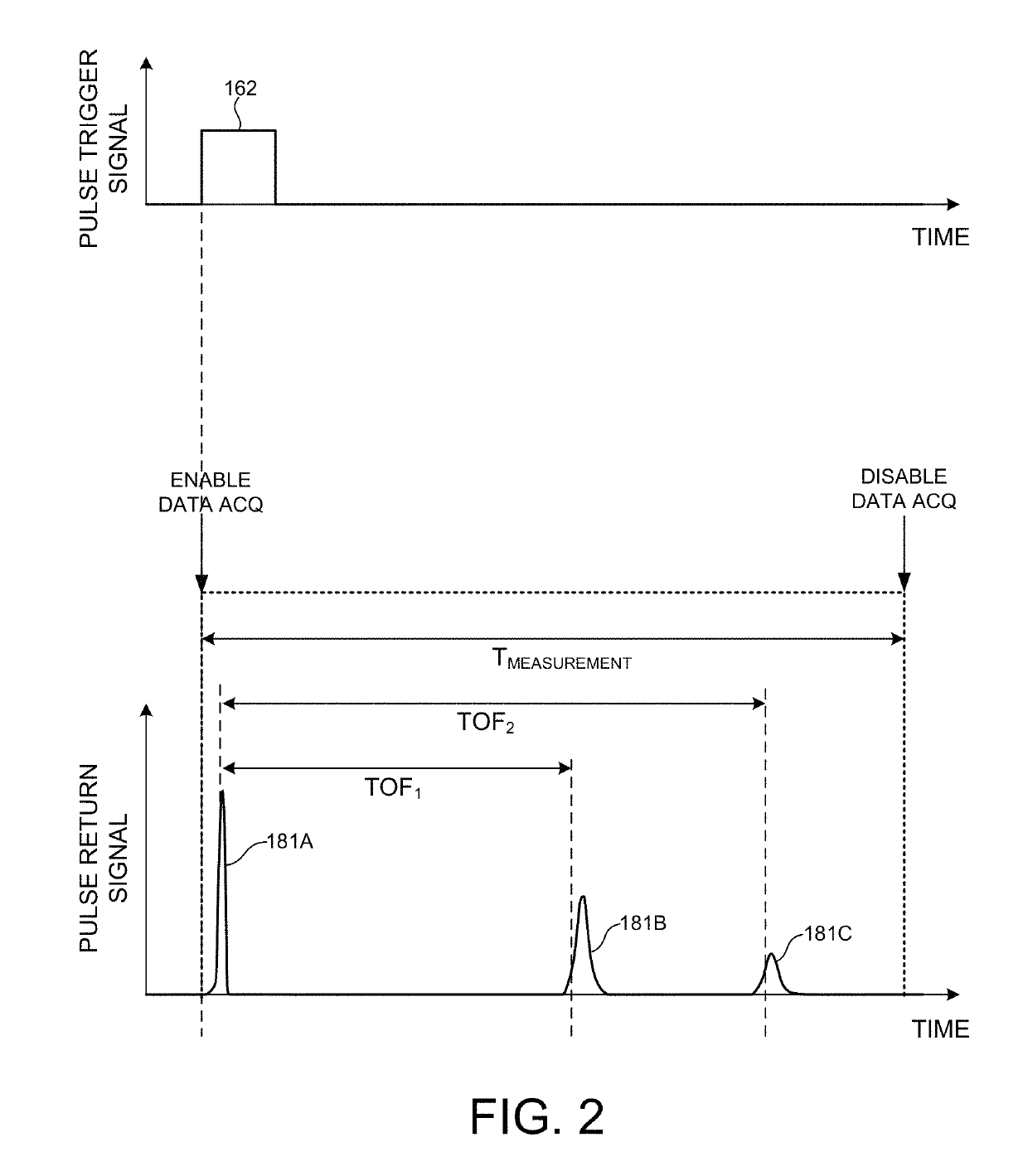
Multiple Pixel Scanning LIDAR
ActiveUS20170350983A1Expand field of viewIncrease sampling densityOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhotodetectorBeam scanning
Methods and systems for performing three dimensional LIDAR measurements with multiple illumination beams scanned over a three dimensional environment are described herein. In one aspect, illumination light from each LIDAR measurement channel is emitted to the surrounding environment in a different direction by a beam scanning device. The beam scanning device also directs each amount of return measurement light onto a corresponding photodetector. In some embodiments, a beam scanning device includes a scanning mirror rotated in an oscillatory manner about an axis of rotation by an actuator in accordance with command signals generated by a master controller. In some embodiments, the light source and photodetector associated with each LIDAR measurement channel are moved in two dimensions relative to beam shaping optics employed to collimate light emitted from the light source. The relative motion causes the illumination beams to sweep over a range of the three dimensional environment under measurement.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
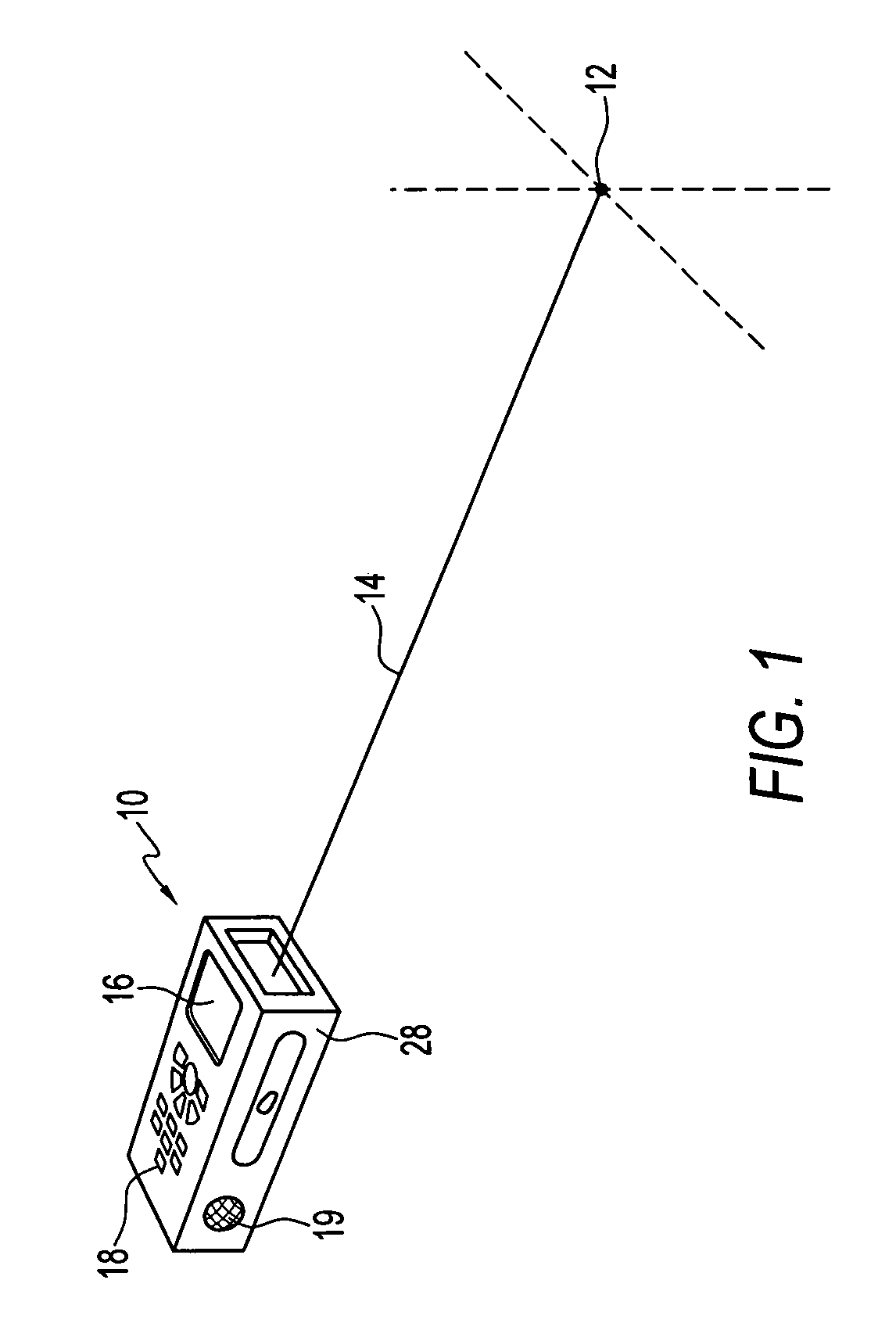
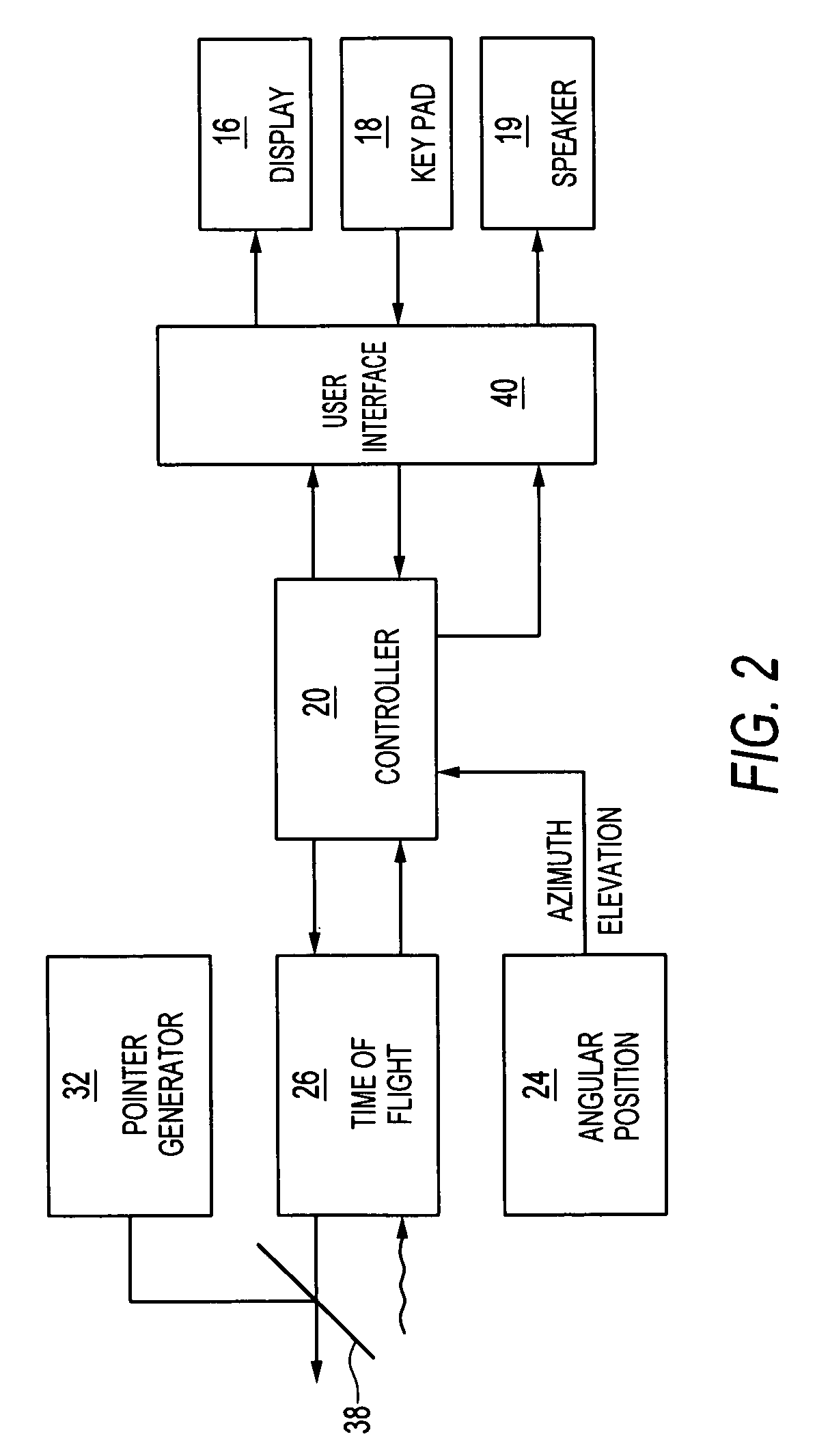
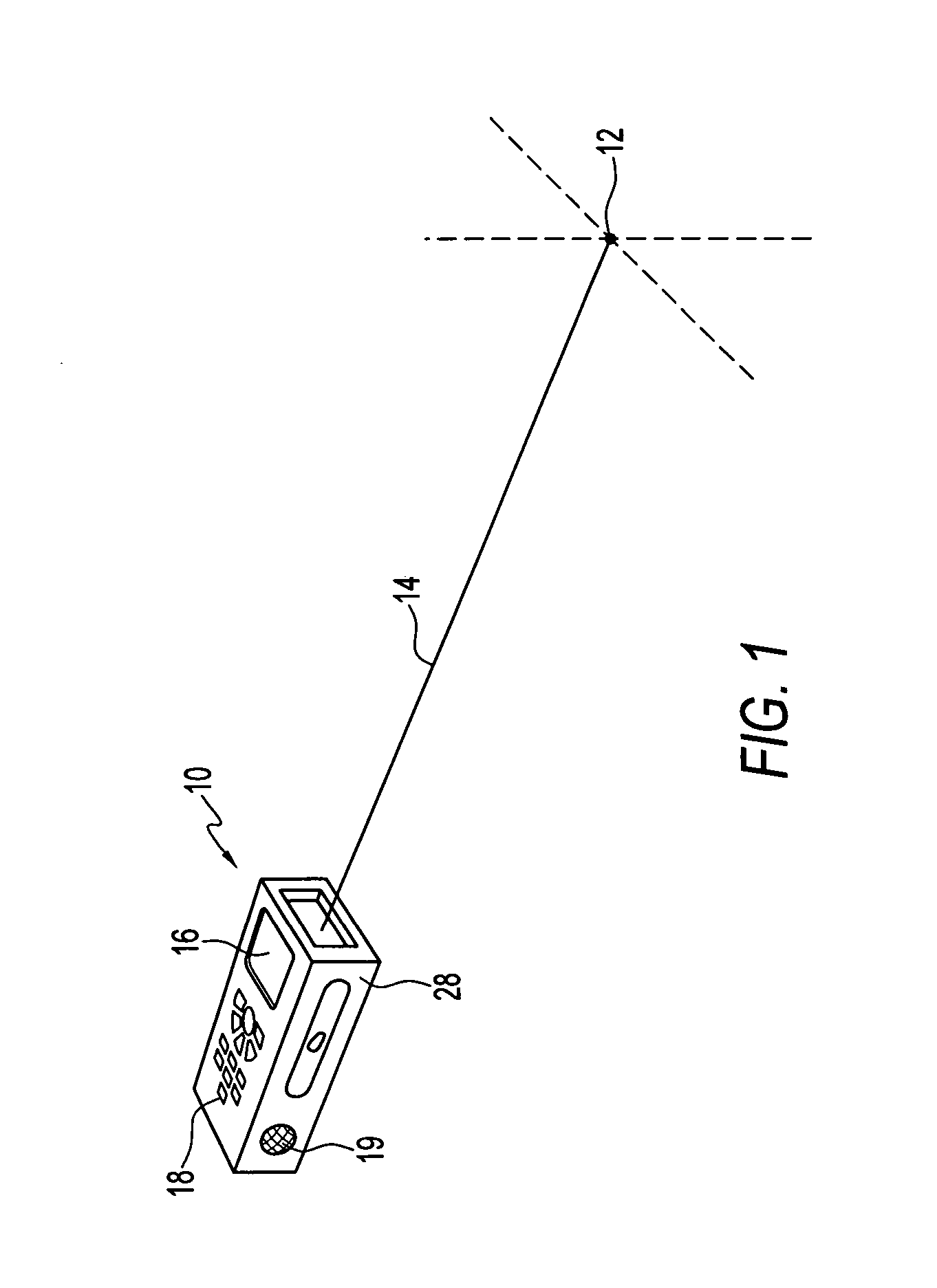
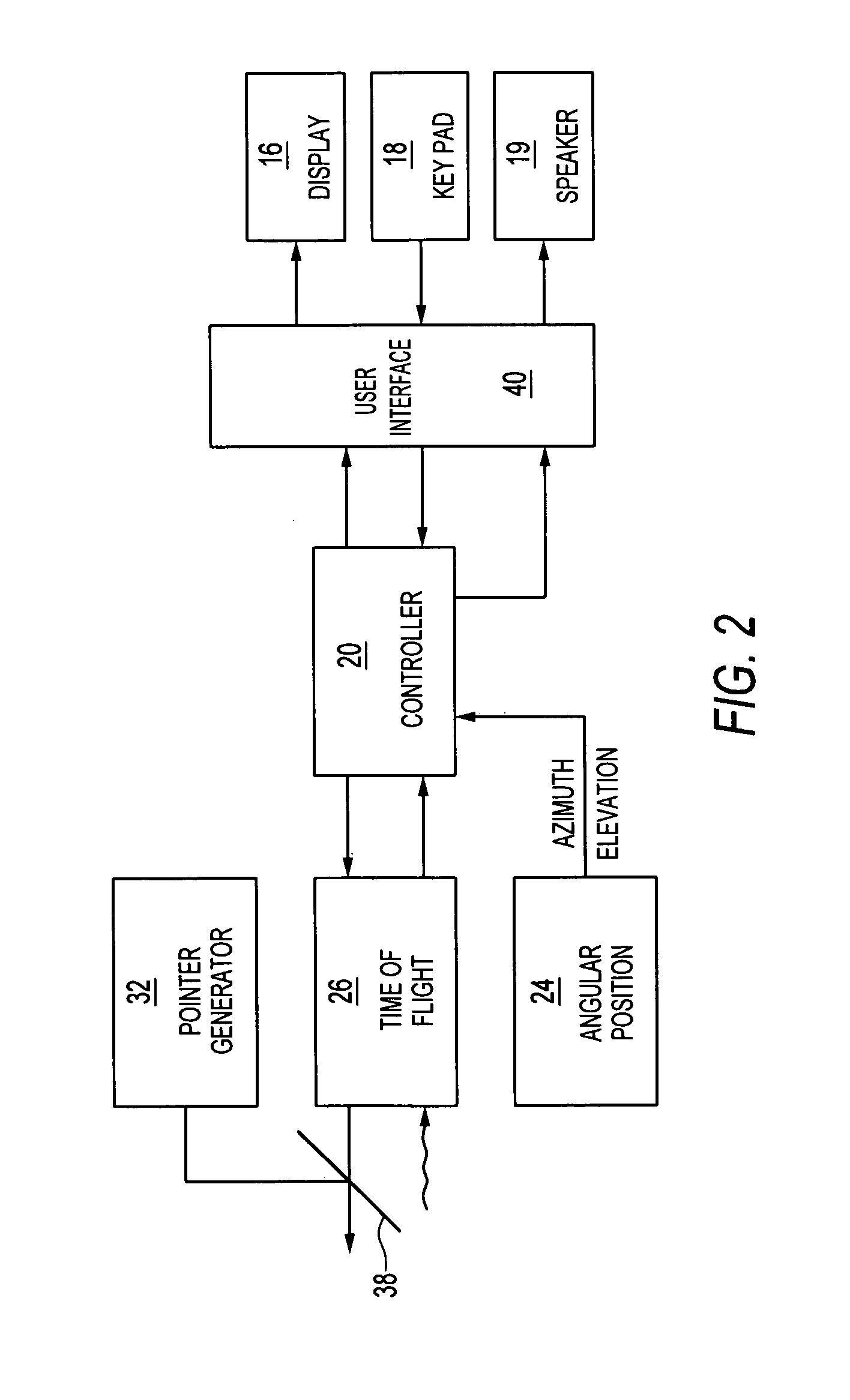
Handheld optical distance measurement device
ActiveUS7568289B2Simple and complex measurementActive open surveying meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationMeasurement deviceHand held
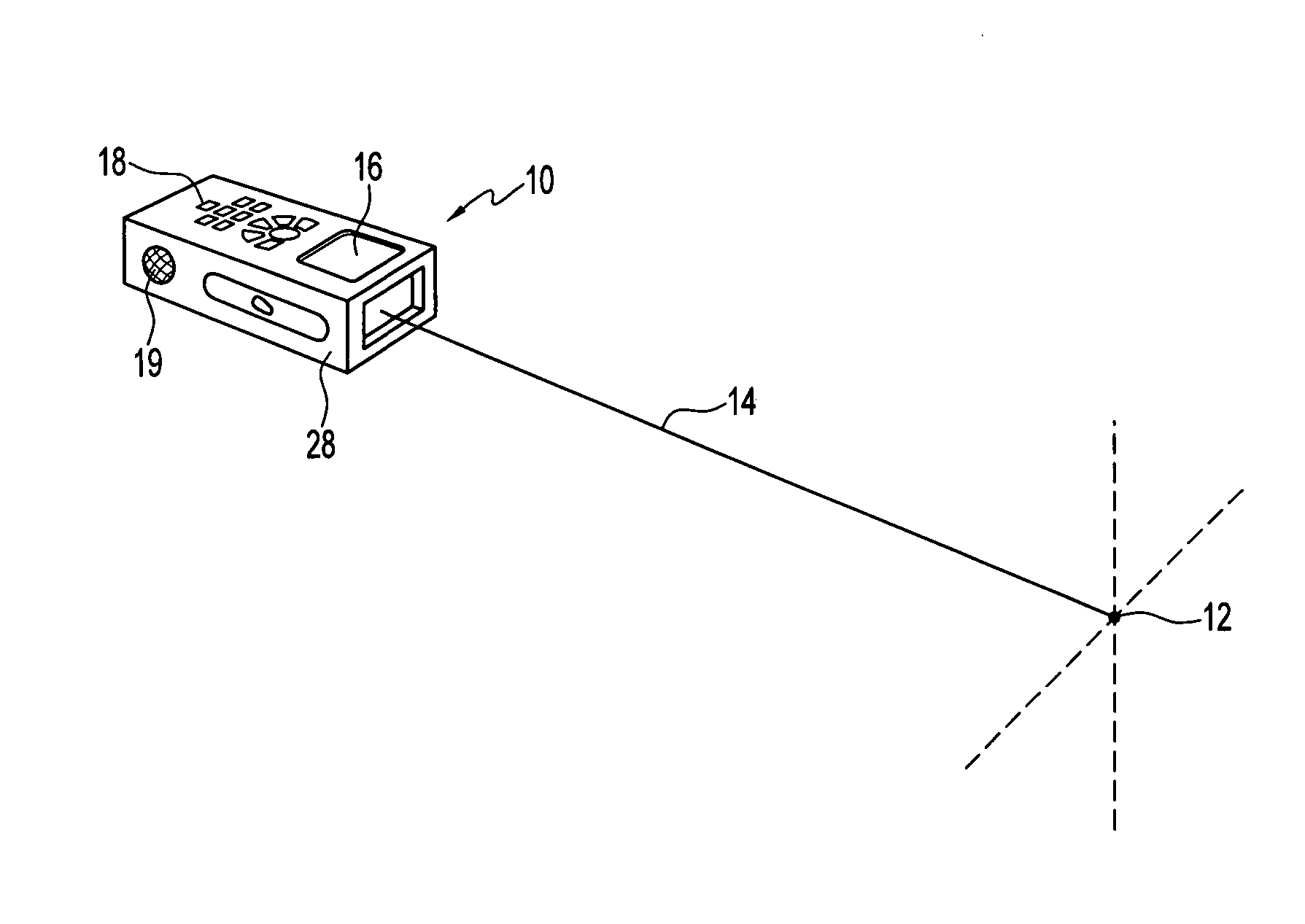
A handheld measurement device of an embodiment of the invention includes a distance measurement engine and an angular position measurement engine. A controller controls the distance measurement engine and associates an elevation, azimuth position, or relative angular position from the angular position measurement engine with distance measurements taken from the elevation engine. In preferred operations, each point measured from a target under the control of a user is automatically associated with an elevation and / or azimuth position obtained from the angular position engine. Preferably, the controller determines a set of relative coordinates in space for a plurality of related target points. The controller may then calculate a variety of useful distances, areas, volumes, etc., regarding the plurality of target points.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CO LTD
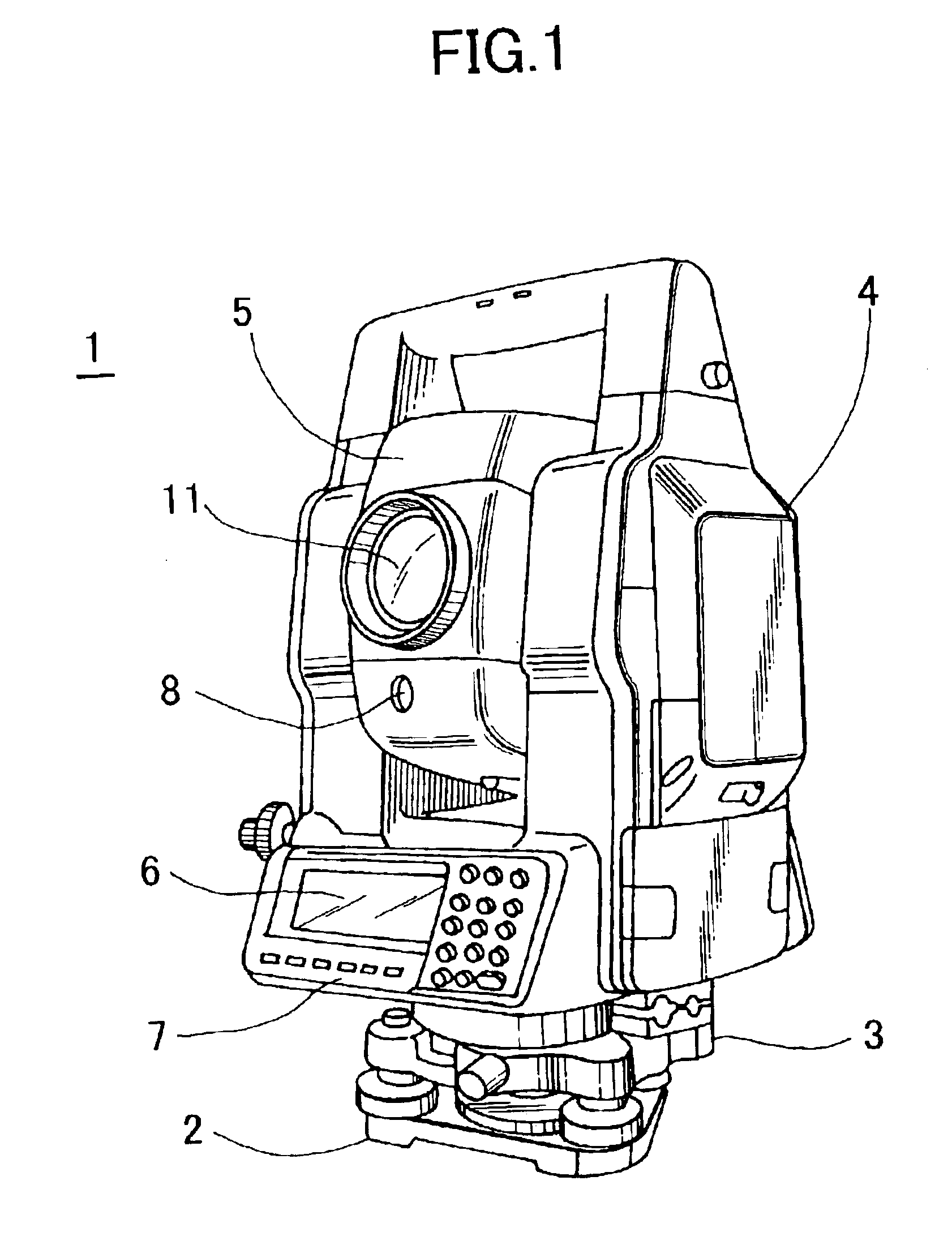
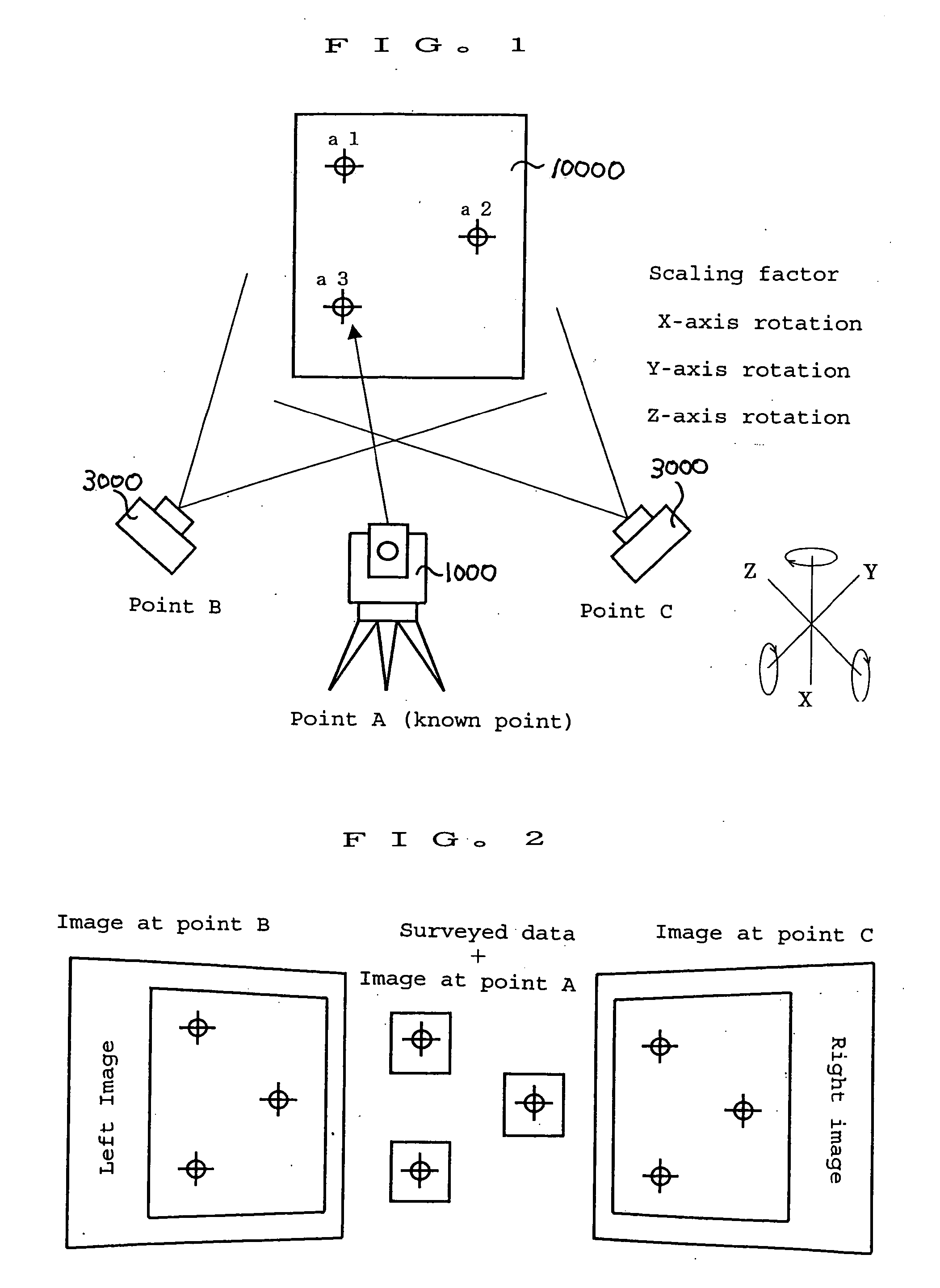
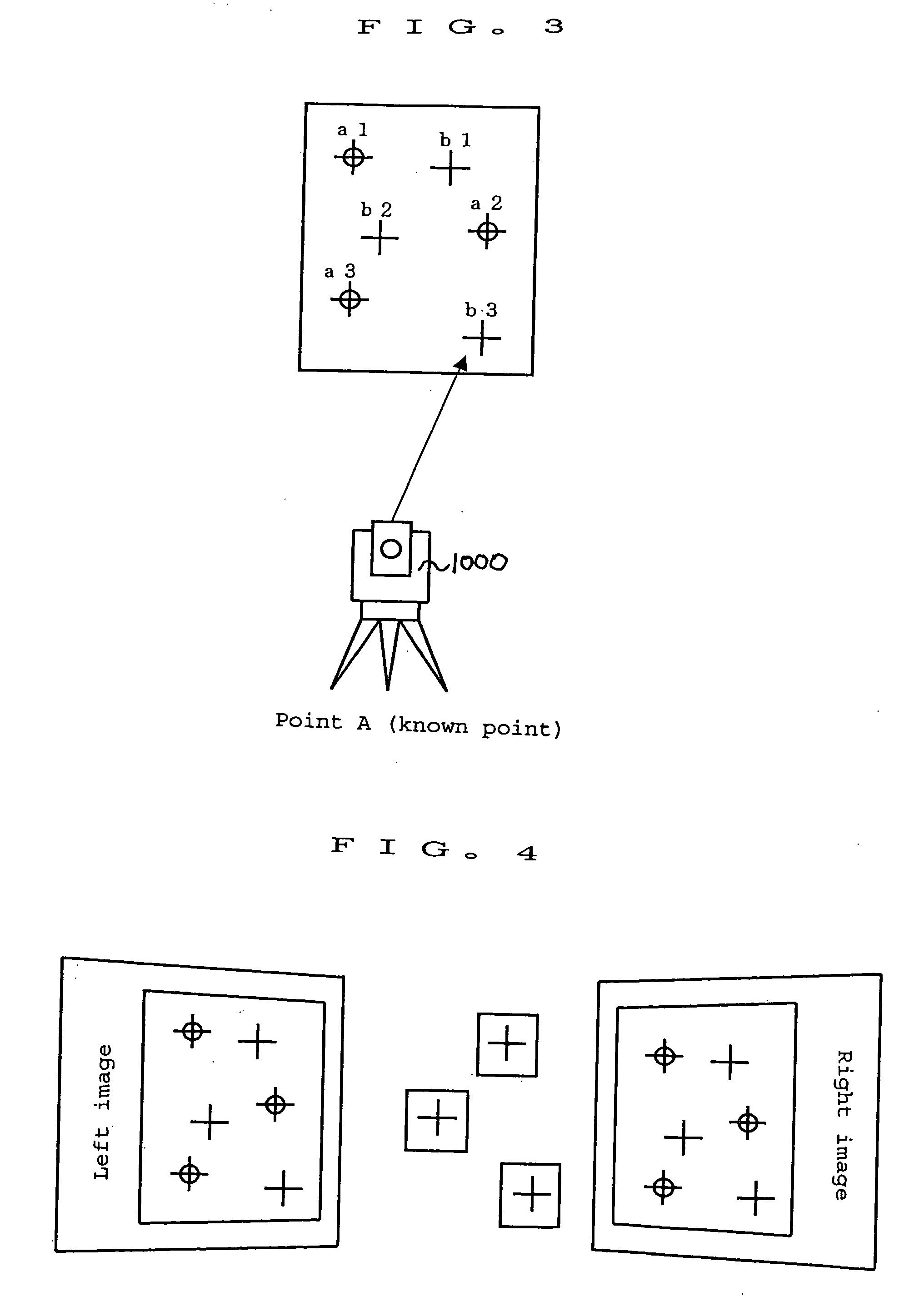
Surveying instrument and method for acquiring image data by using the surveying instrument
InactiveUS6859269B2Efficient use ofEasy to carryOptical rangefindersActive open surveying meansMeasuring instrumentSurvey instrument
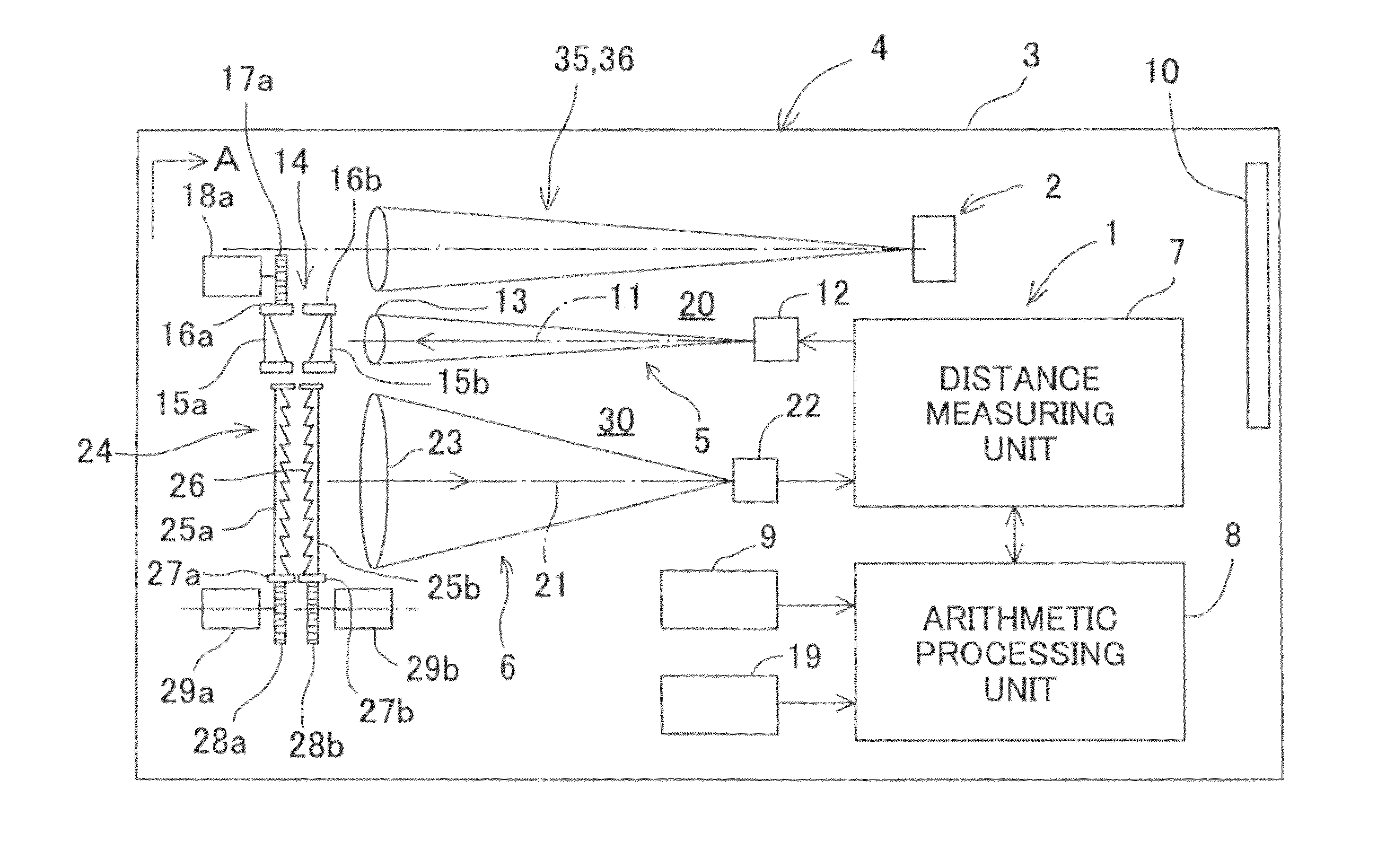
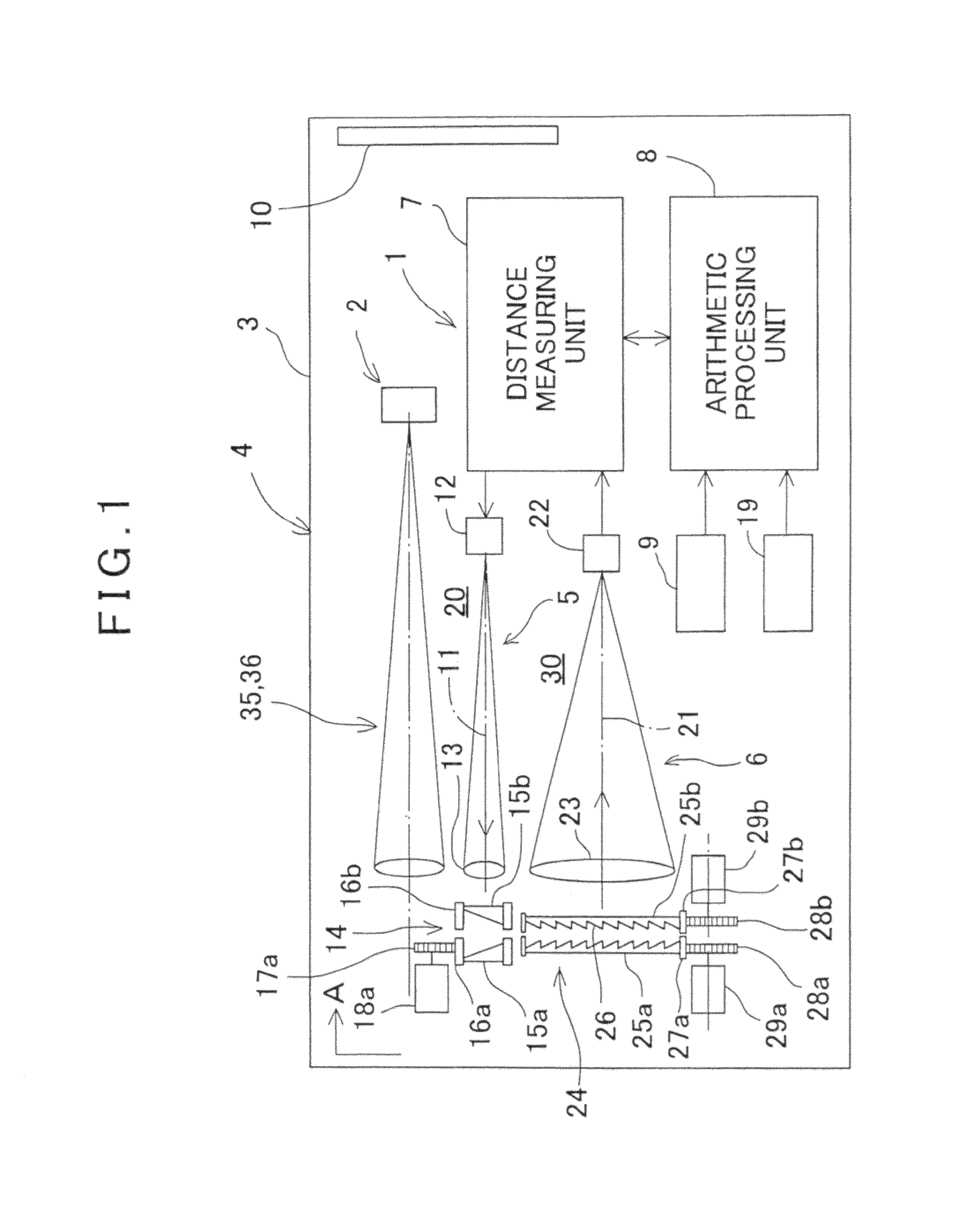
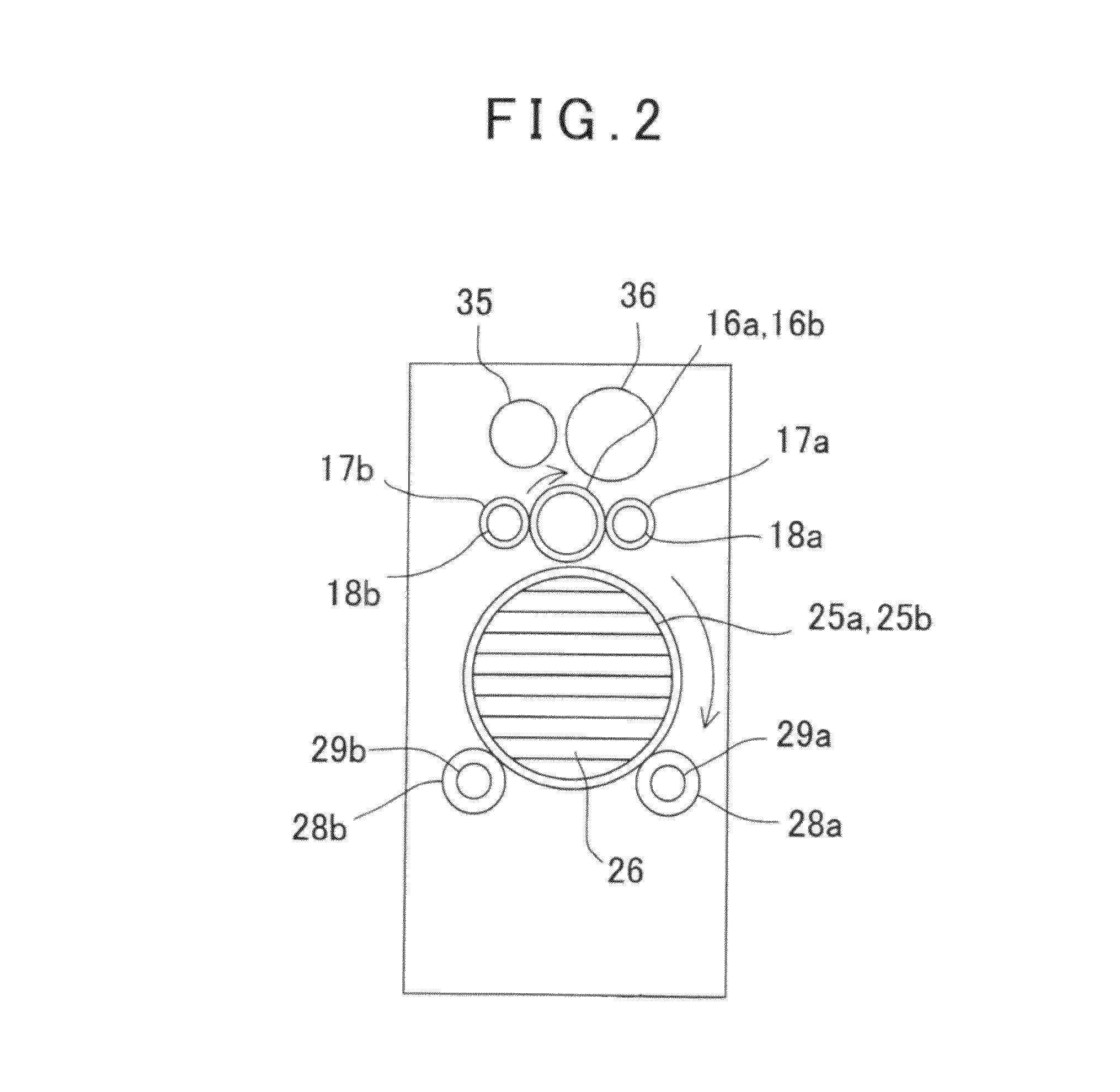
A surveying instrument, comprising a distance measuring unit for measuring a distance to a collimating point, an angle measuring unit for measuring a vertical angle and a horizontal angle of the collimating point, an image pick-up means for acquiring an image in a collimating direction, a driving unit for directing the image pick-up means in a direction of a predetermined object to be measured as selected based on an entire image data acquired by the image pick-up means, and a control arithmetic unit for recording by associating an image of an object to be measured with survey data to the object, wherein the image is picked-up in the direction directed by the driving unit and the survey data is measured by the distance measuring unit and the angle measuring unit.
Owner:KK TOPCON
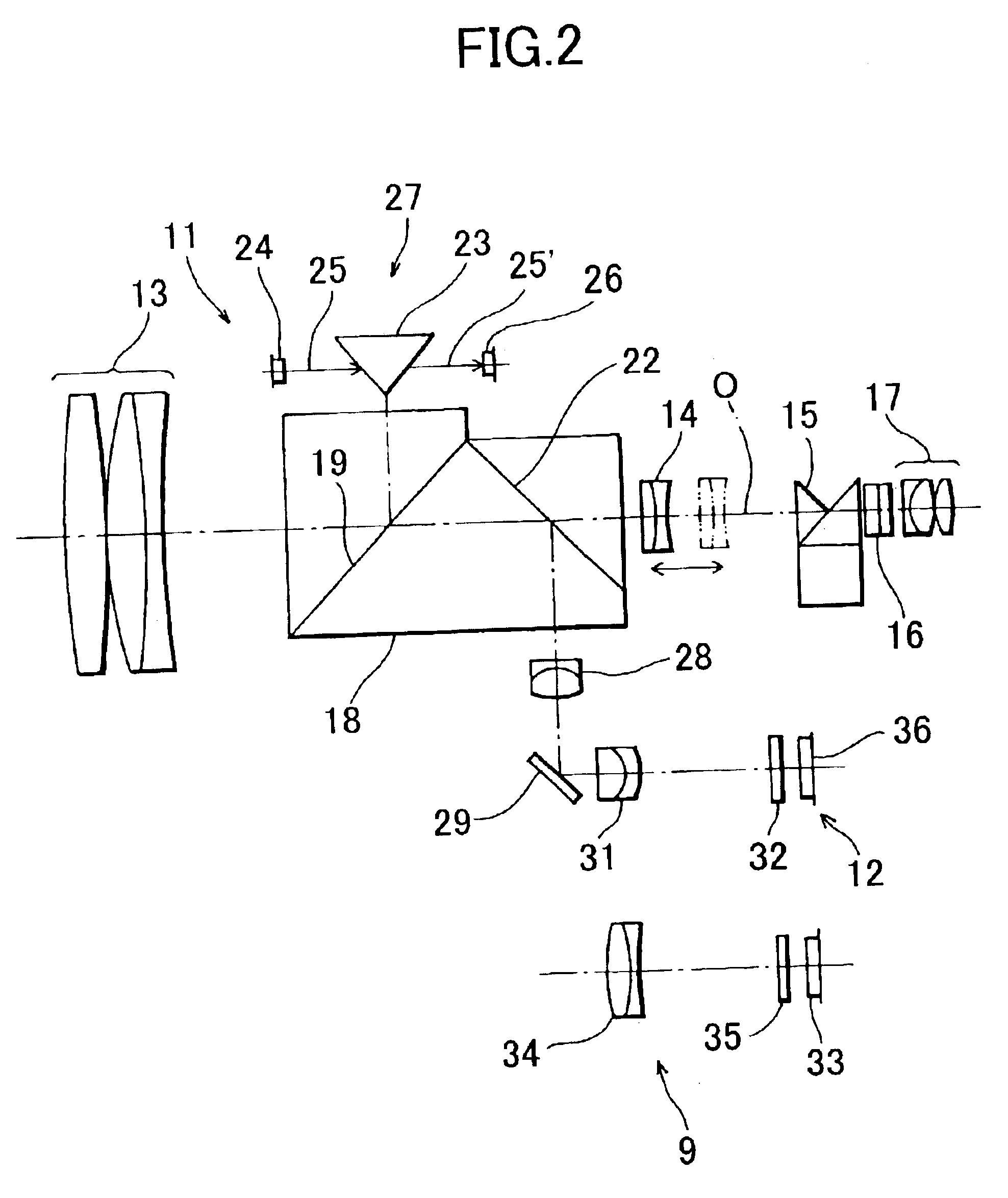
Surveying instrument
InactiveUS7055253B2Shorten the timeSurveying instrumentsHeight/levelling measurementMeasuring instrumentSurvey instrument
A surveying instrument includes a surveying instrument body rotatable about each of a vertical axis and a horizontal axis; and a first collimator optical system and a second collimator optical system each of which is positioned in the surveying instrument body to collimate the surveying instrument relative to a survey point, a viewing angle of the second collimator optical system being smaller than a viewing angle of the first collimator optical system. A first collimating operation is performed with the first collimator optical system before a second collimating operation is performed with the second collimator optical system.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Multiple pixel scanning LIDAR
ActiveUS10393877B2Expand field of viewIncrease sampling densityOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhotodetectorBeam scanning
Methods and systems for performing three dimensional LIDAR measurements with multiple illumination beams scanned over a three dimensional environment are described herein. In one aspect, illumination light from each LIDAR measurement channel is emitted to the surrounding environment in a different direction by a beam scanning device. The beam scanning device also directs each amount of return measurement light onto a corresponding photodetector. In some embodiments, a beam scanning device includes a scanning mirror rotated in an oscillatory manner about an axis of rotation by an actuator in accordance with command signals generated by a master controller. In some embodiments, the light source and photodetector associated with each LIDAR measurement channel are moved in two dimensions relative to beam shaping optics employed to collimate light emitted from the light source. The relative motion causes the illumination beams to sweep over a range of the three dimensional environment under measurement.
Owner:VELODYNE LIDAR USA INC
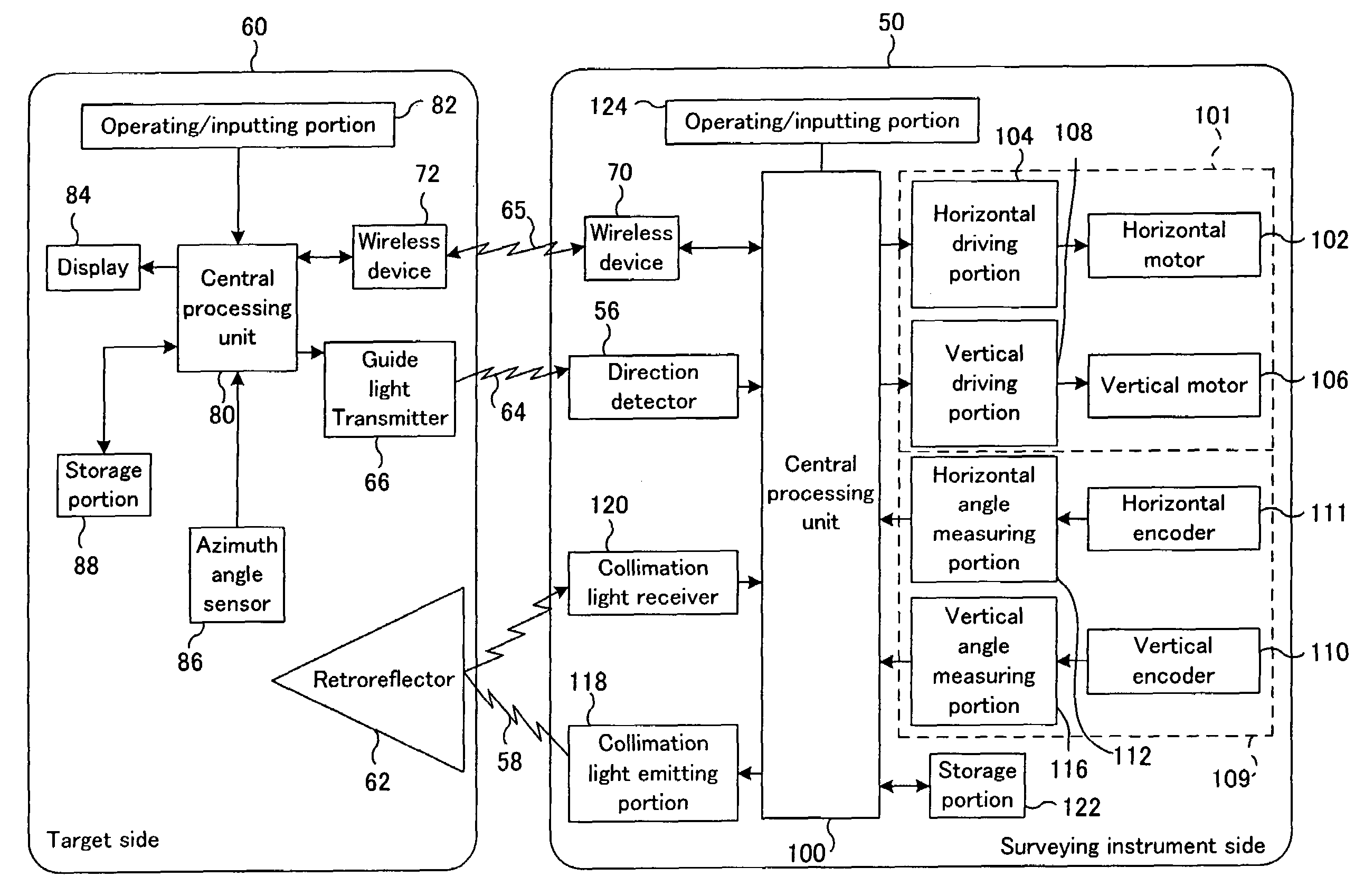
Survey system
ActiveUS7304729B2Imposing burdenShorten the timeActive open surveying meansUsing optical meansMeasuring instrumentSurvey instrument
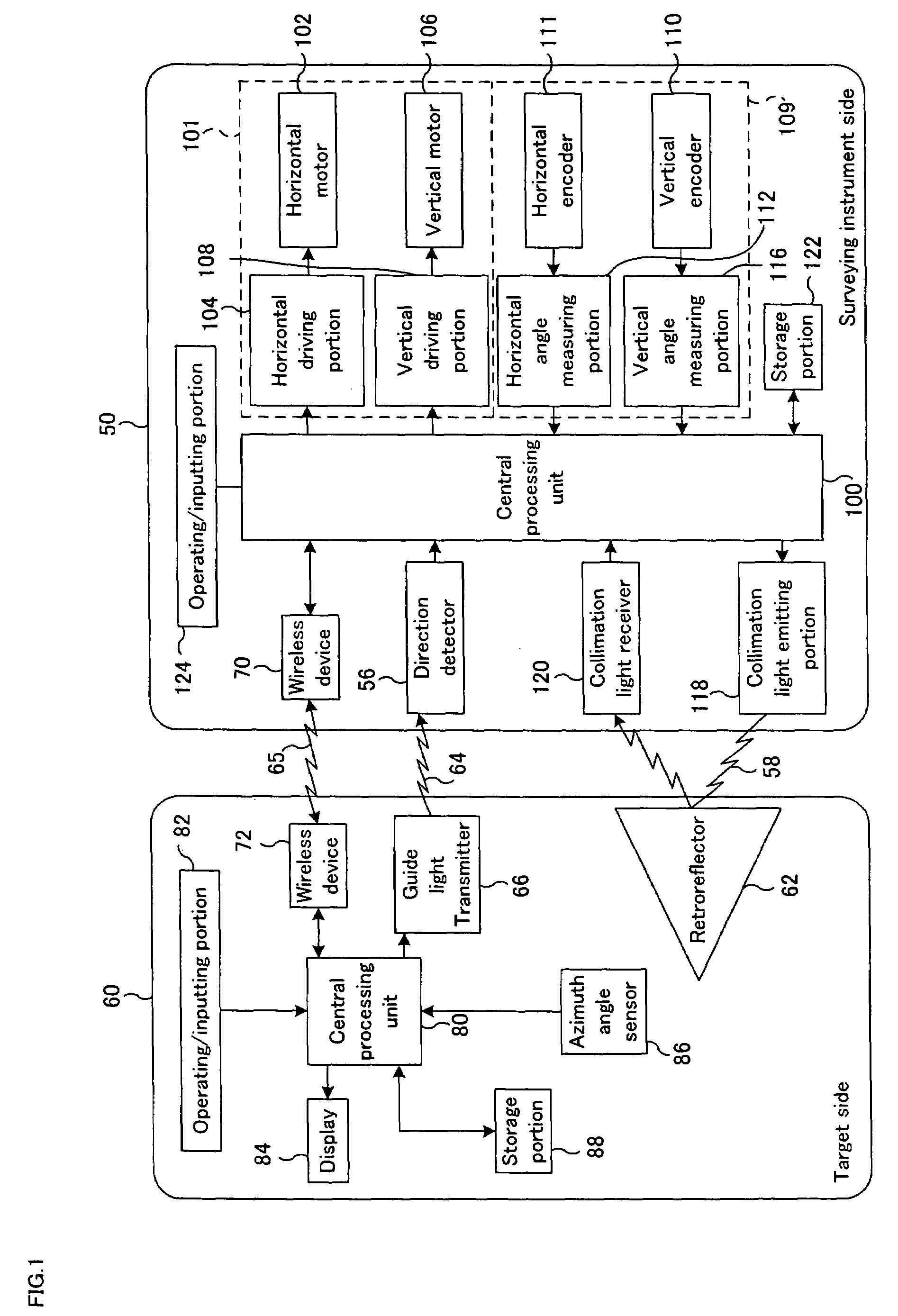
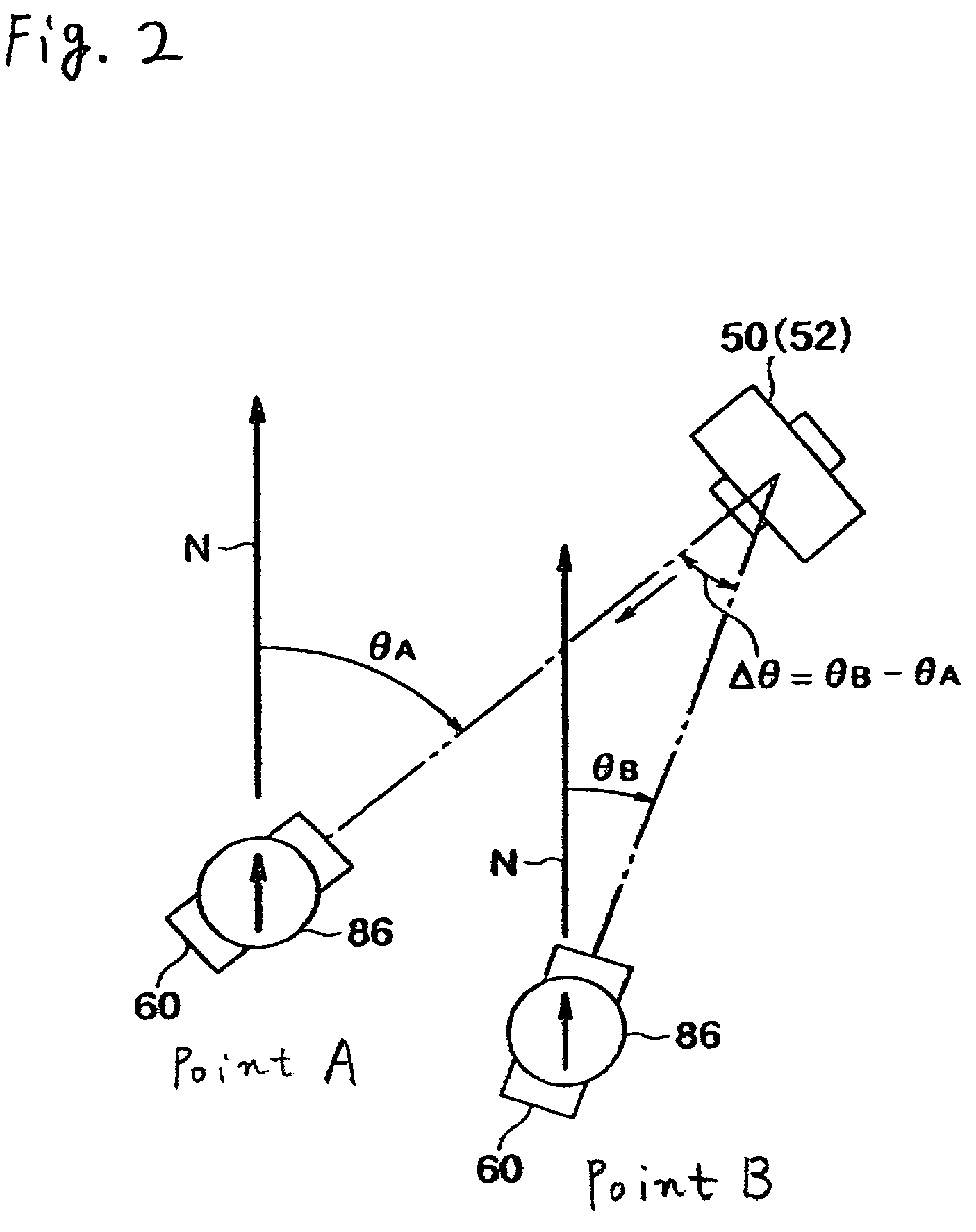
A survey system is made up of a target and a surveying instrument provided with an automatic collimator that automatically collimates the target. The target includes a guide light transmitter that emits guide light, an azimuth angle sensor that detects a direction angle (θA, θB) at which the target is directed, and a central processing unit that sends a rotation command, which includes the rotational direction of the instrument body, to the surveying instrument. The central processing unit determines the rotational direction of the instrument body based on an angular difference (θB-θA) between a direction angle (θA) obtained when the target is caused to approximately face the surveying instrument at the last measurement and a direction angle (θB) obtained when the target is caused to approximately face the surveying instrument at the present measurement.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Enhanced Position Measurement Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20150276402A1Improve efficiencyImprove mobilitySurveyor's staffsMovable markersTotal stationComputer science
Novel solutions for position measurement, including without limitation tools and techniques that can be used for land surveying and in similar applications. One such tool is a greatly enhanced position measurement system that takes the form of a surveying rod with substantial independent functionality, which can be used with or without a total station or similar device.
Owner:TRIMBLE INC
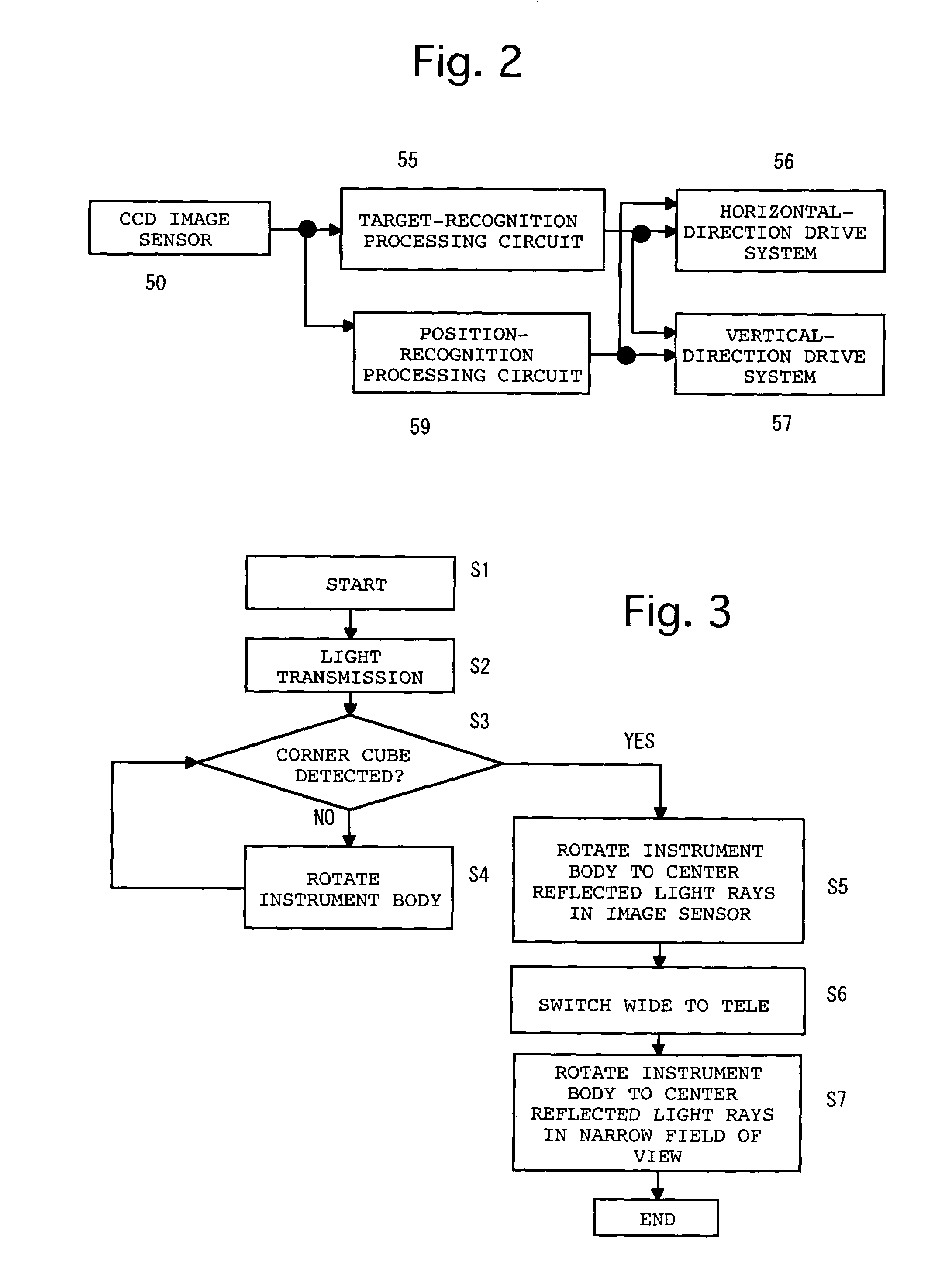
Surveying apparatus
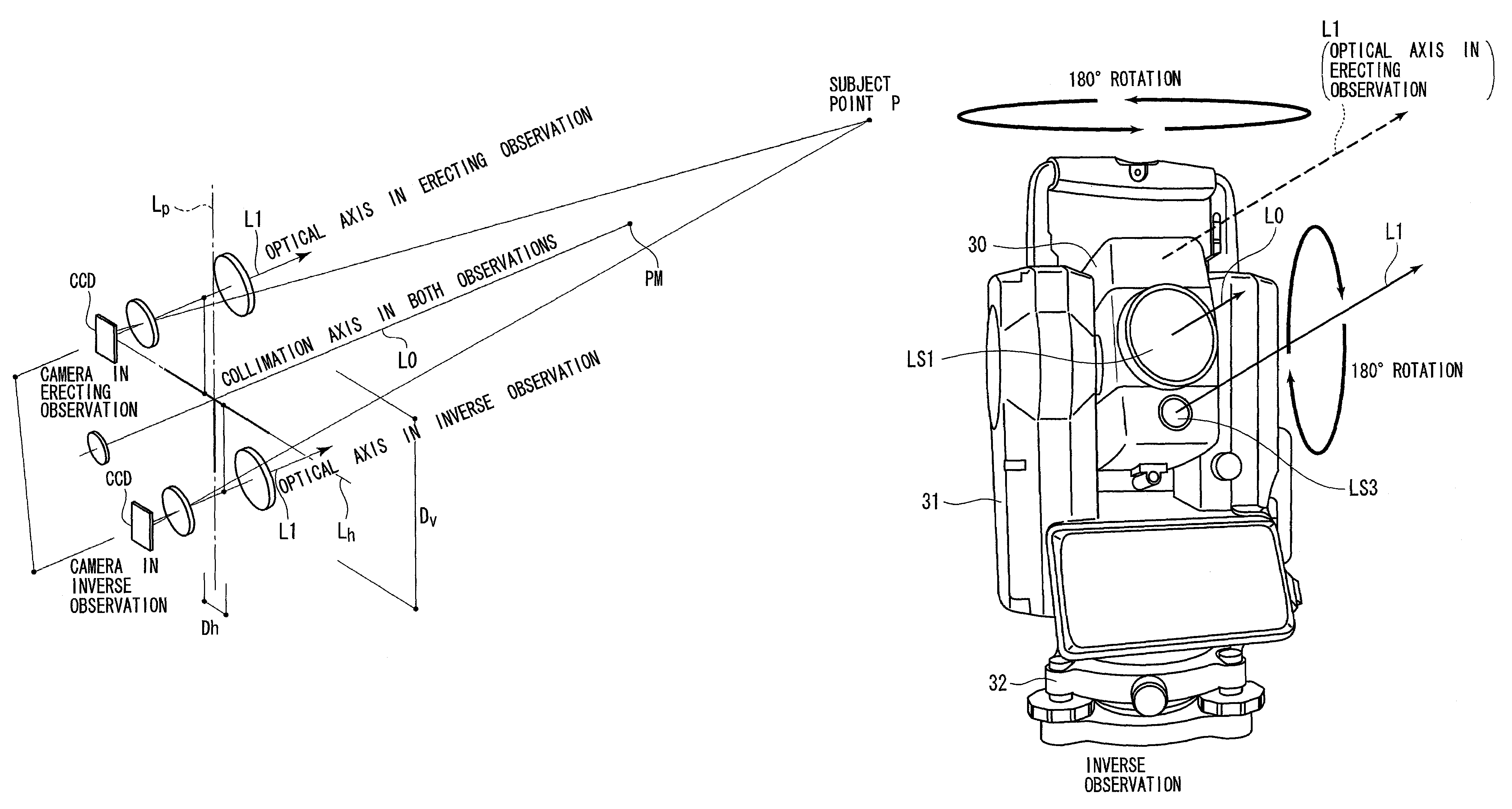
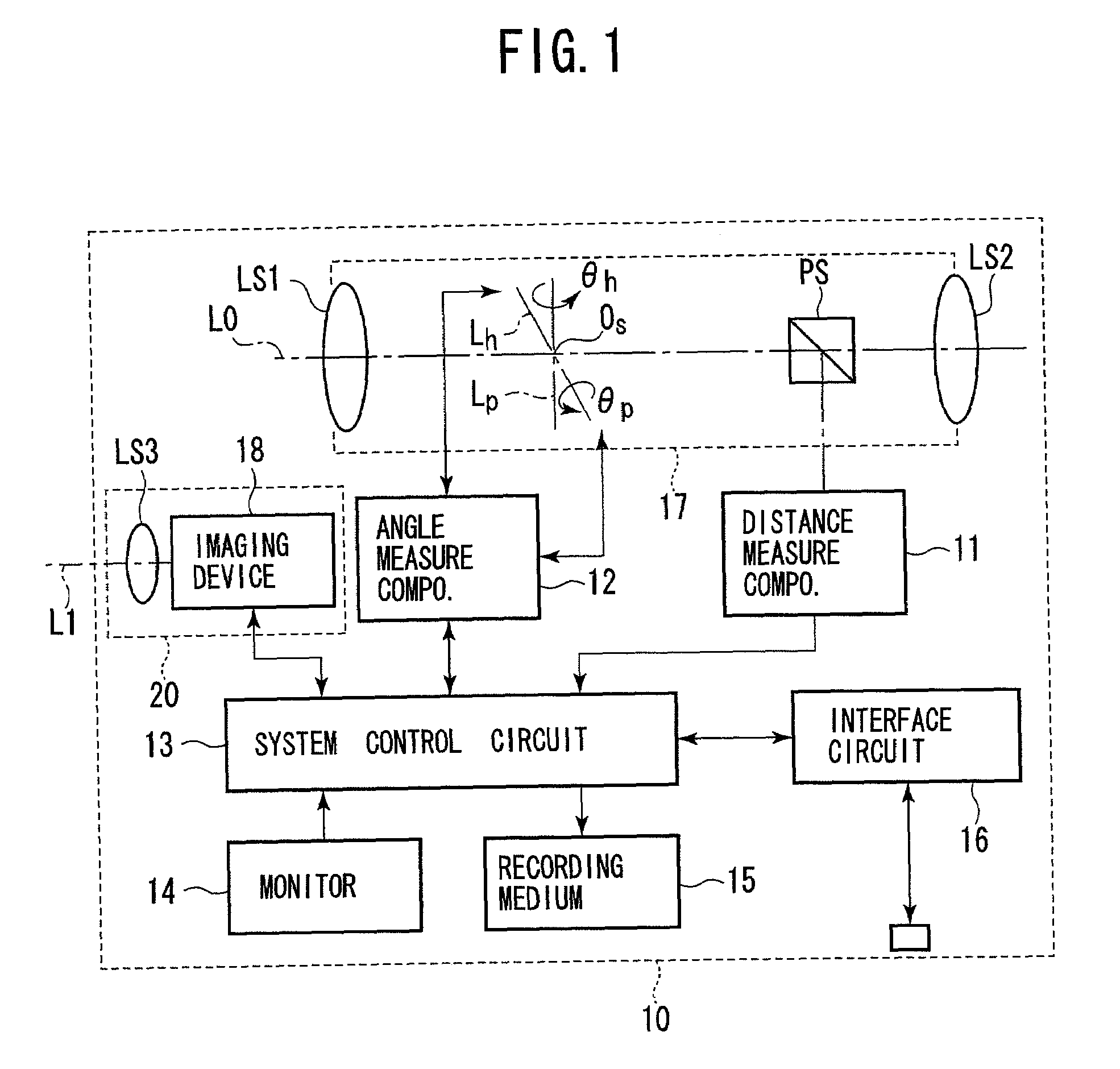
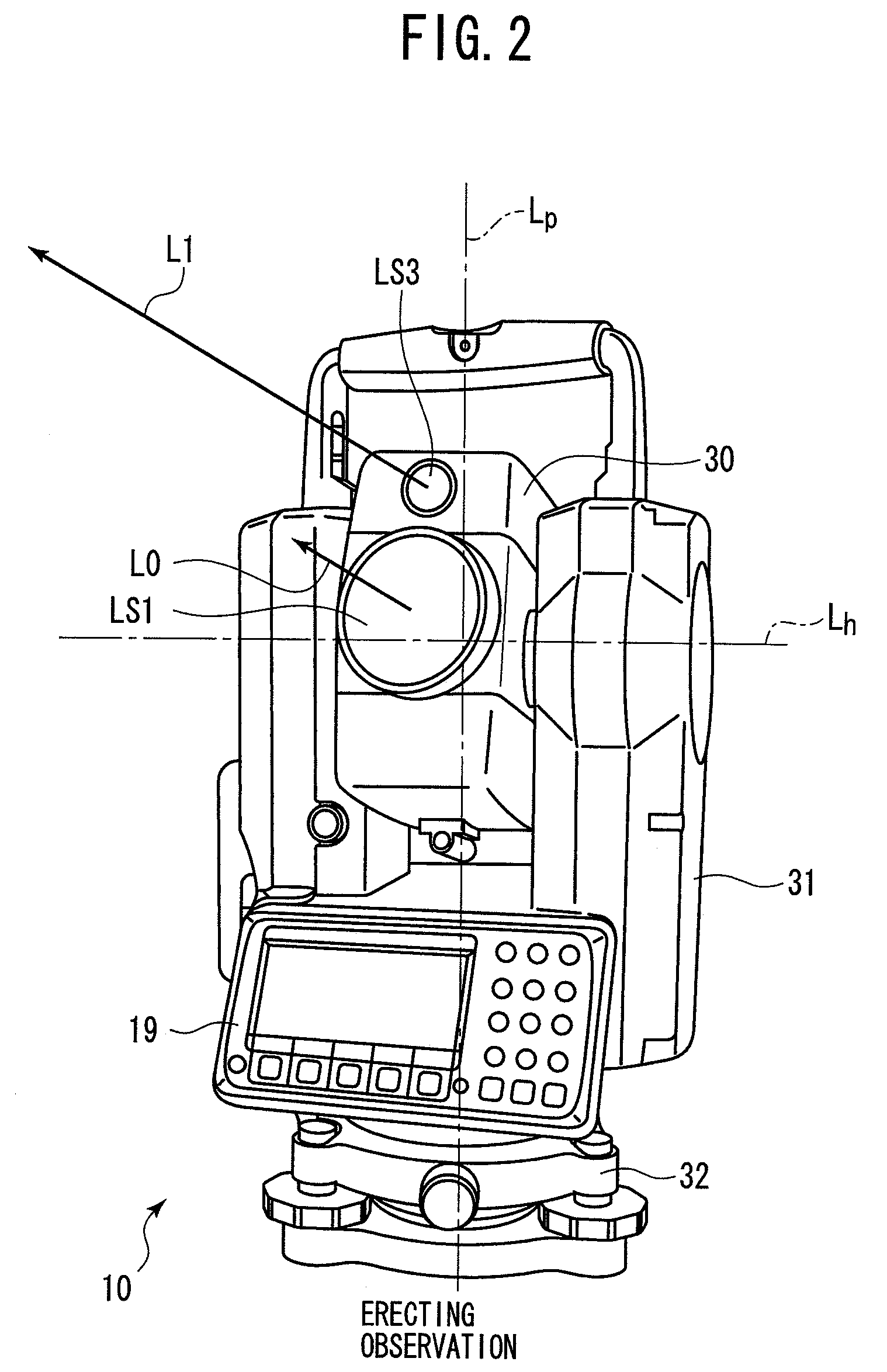
A surveying apparatus is provided that includes a sighting telescope, an imaging device, and an external orientation parameter calculator. The sighting telescope is rotatable about a horizontal axis and a vertical axis. The imaging device is integrally rotated with the sighting telescope and the imaging device has an optical axis that is different from the collimation axis. The external orientation parameter calculator calculates external orientation parameters of stereo images that are obtained by the imaging device in an erecting observation and in an inverse observation in terms of the position of the optical axis with respect to the collimation axis, and the sighting directions in the erection observation and in the inverse observation.
Owner:TAIWAN INSTR
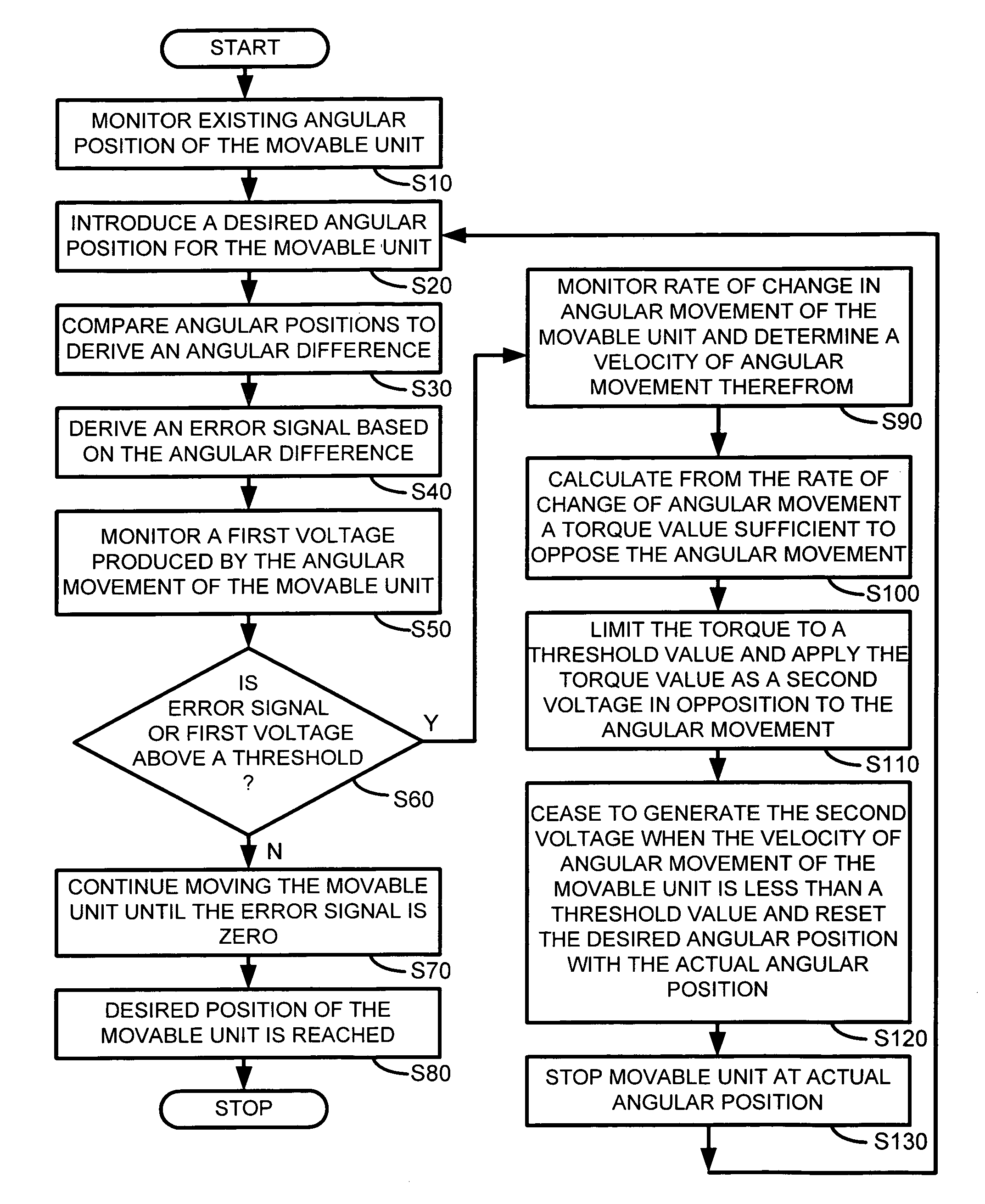
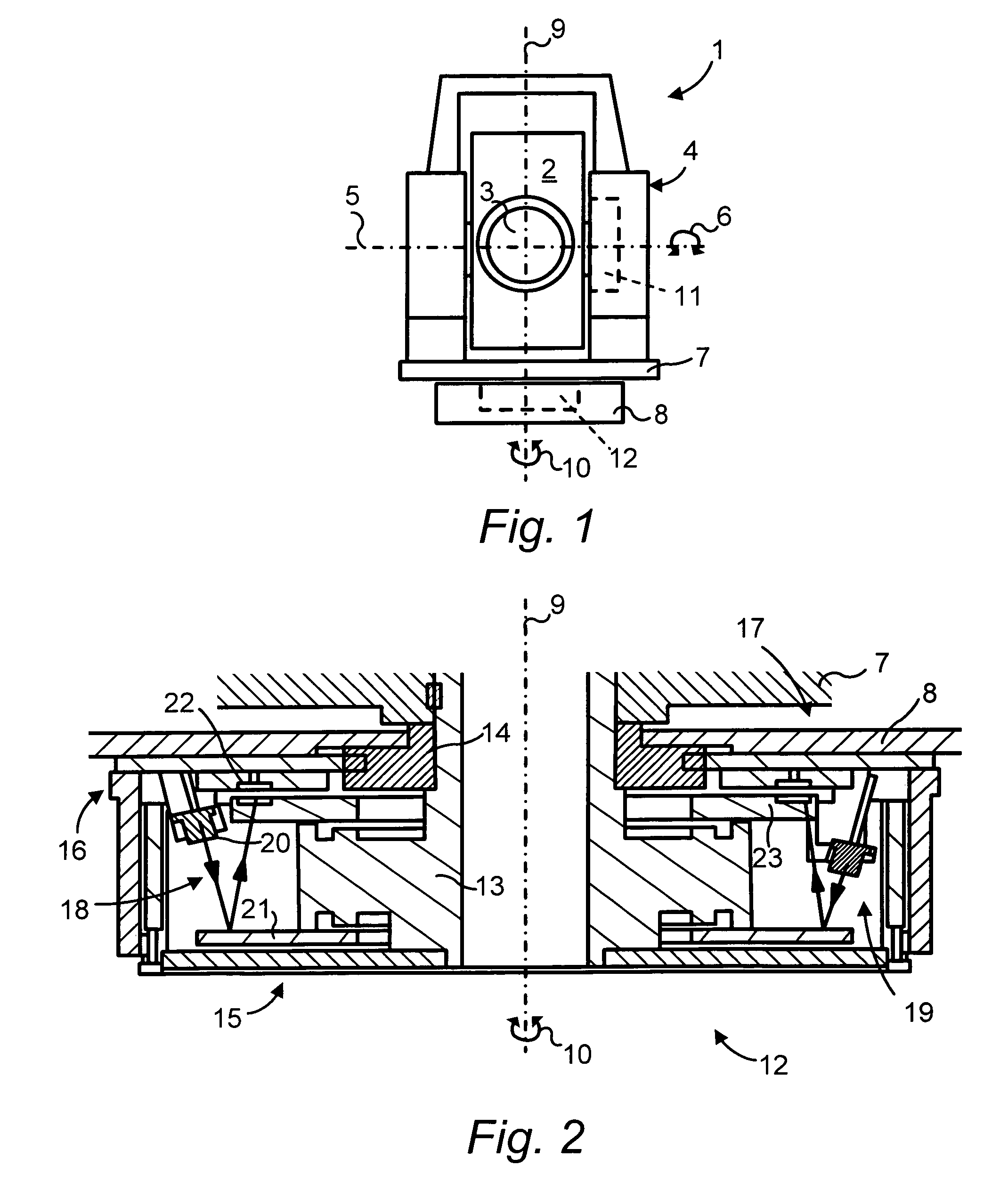
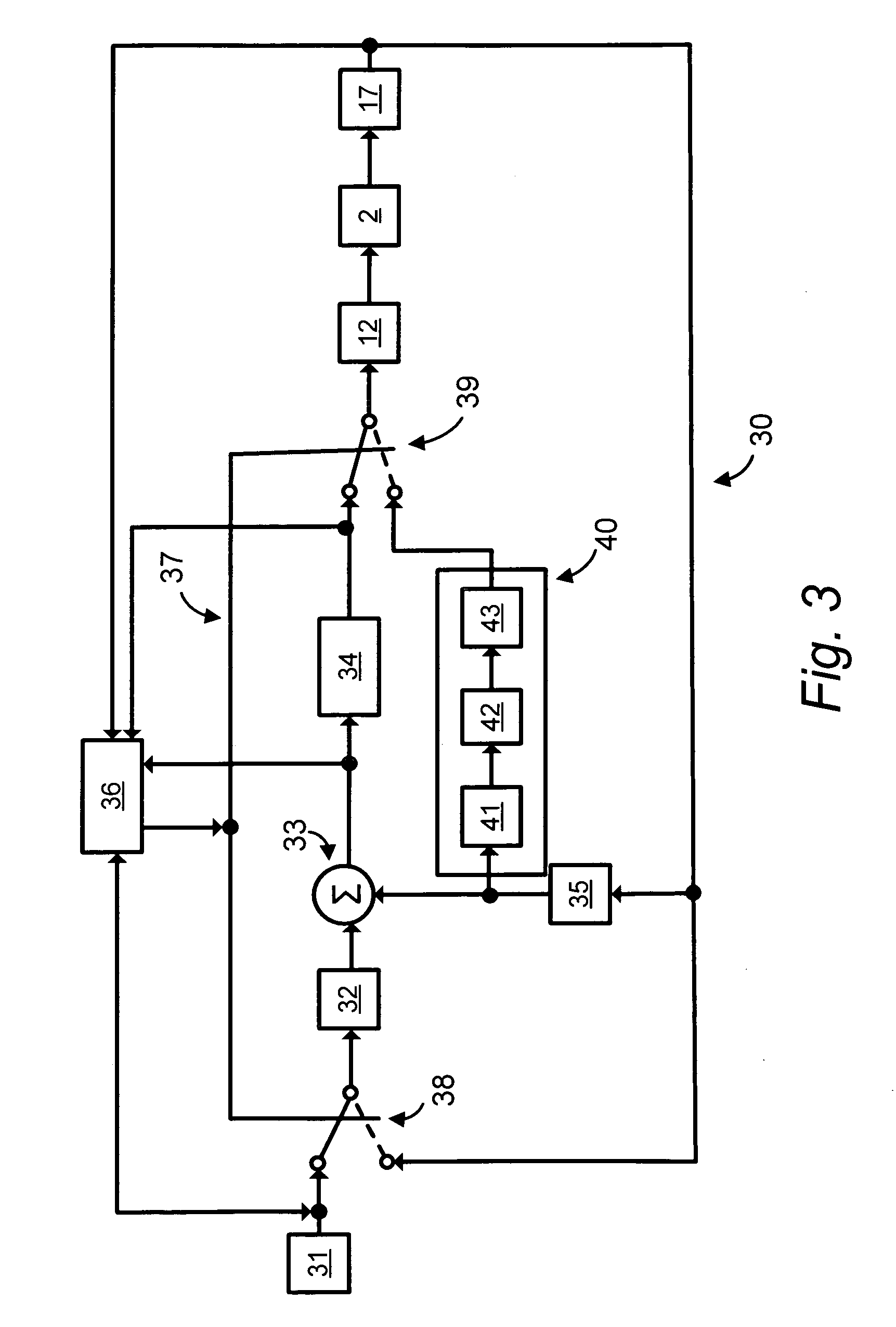
Position control arrangement, especially for a surveying instrument, and a surveying instrument
ActiveUS7634381B2Reduce manufacturing costHighly accurate in useActive open surveying meansDigital computer detailsSurvey instrumentMeasuring instrument
In a position control arrangement for controlling the rotational position of a movable unit, especially for a surveying instrument, an electric motor is arranged to rotate the movable unit around an axis of rotation, and there are controllers for enabling the motor to stop the movable unit in a desired rotational position. The motor is a direct drive motor, the shaft of which forms the axis of rotation for the movable unit, and the motor is arranged to selectively operate in either a first, normal mode for rotating the movable unit to a desired position, or in a second, friction mode for providing resistance to a forced rotation of the movable unit from a predetermined position to a new position. A control unit detects the presence of a forced rotation and automatically changes the mode of operation in response thereto.
Owner:TRIMBLE A B A CORP OF SWEDEN
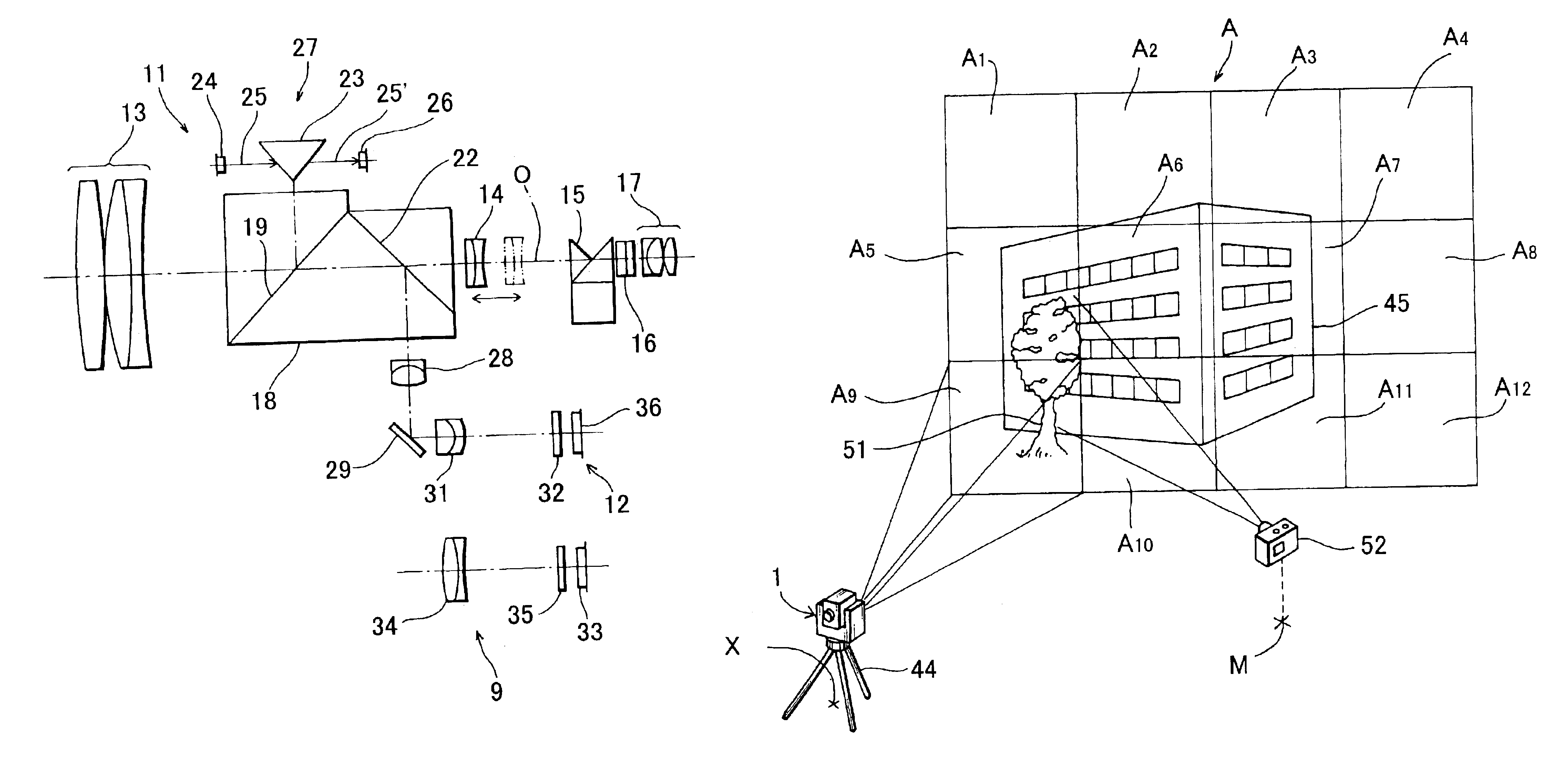
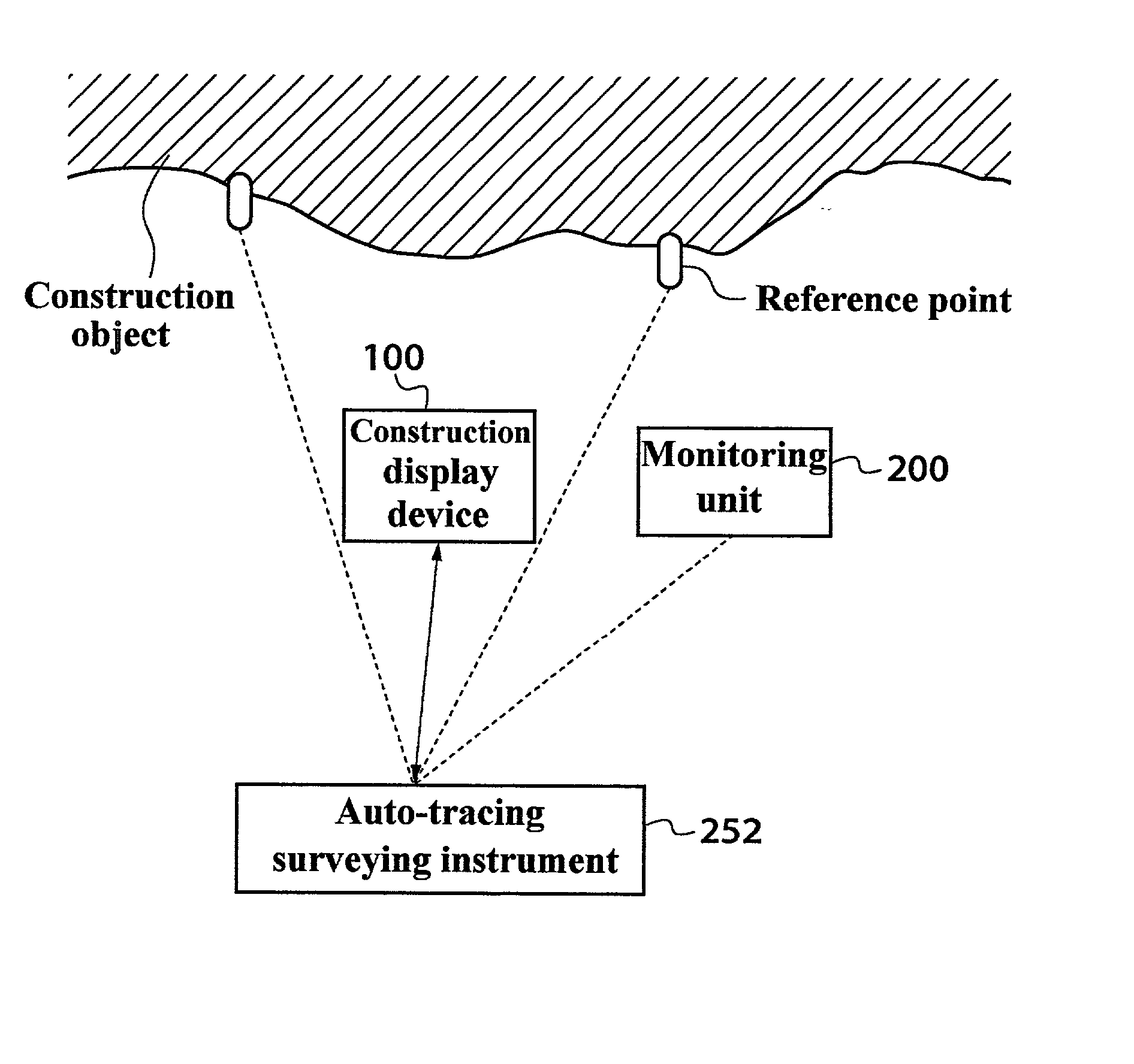
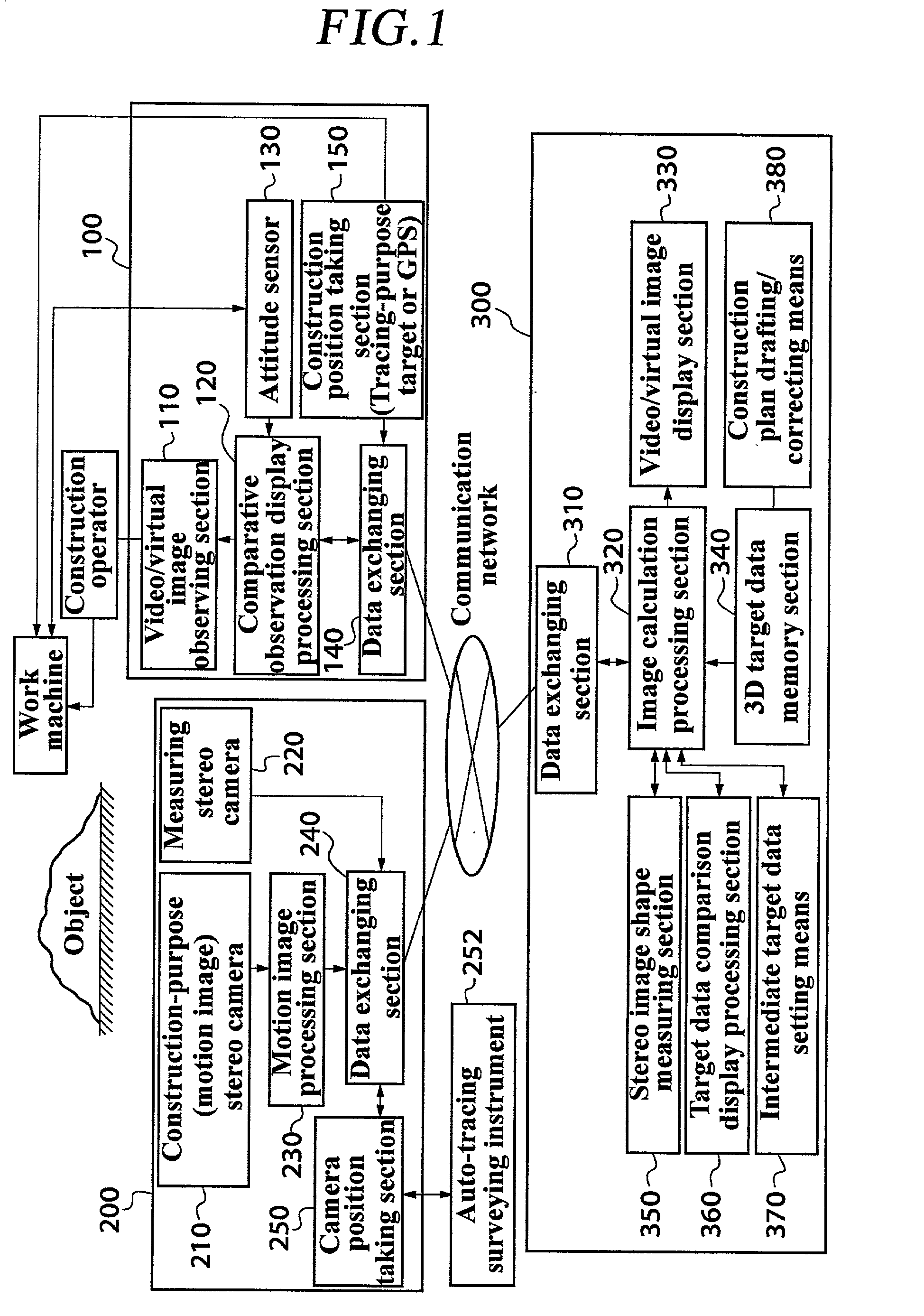
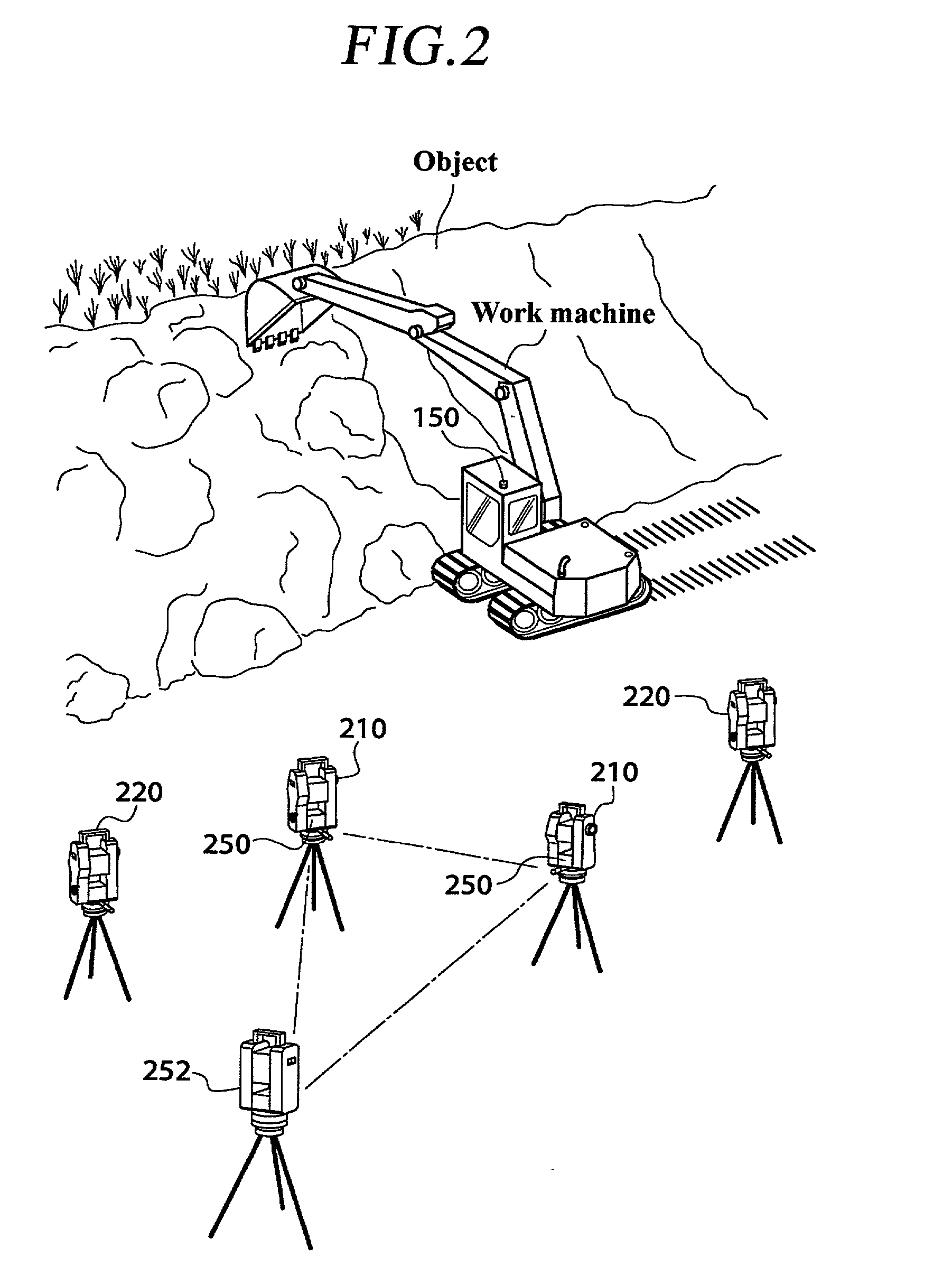
Image measurement and display device, image measurement and display system, construction management method, and construction status monitor system
A device comprises: a shape measuring section 350 for measuring shape data from a pair of stereovision images of an object taken with an image taking section 220; a memory section 340 for storing target data related to the images of the object; an image display section 330 for superposing the paired stereovision images of the object and the stereovision target data image based on the target data and for displaying the images; and a comparison display processing section 360 for comparing the shape data of the object measured by the shape measuring section 350, with the target data and reflecting the results of the comparison on the superposed display on the image display section 330.
Owner:KK TOPCON
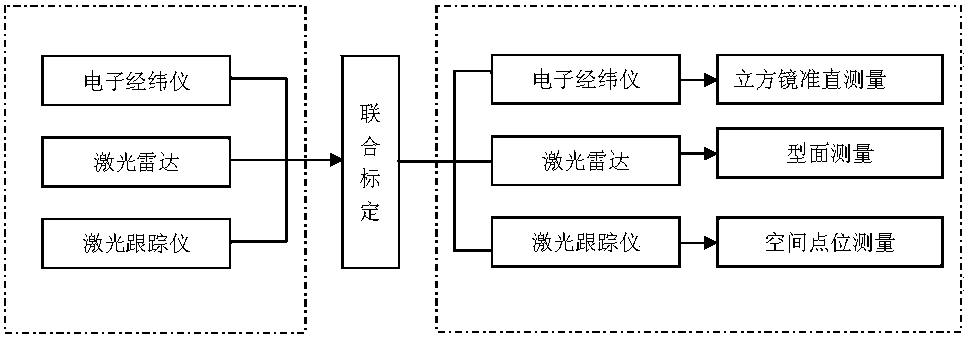
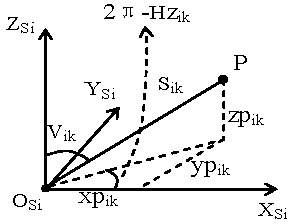
Mixed measurement analysis method for satellite antenna
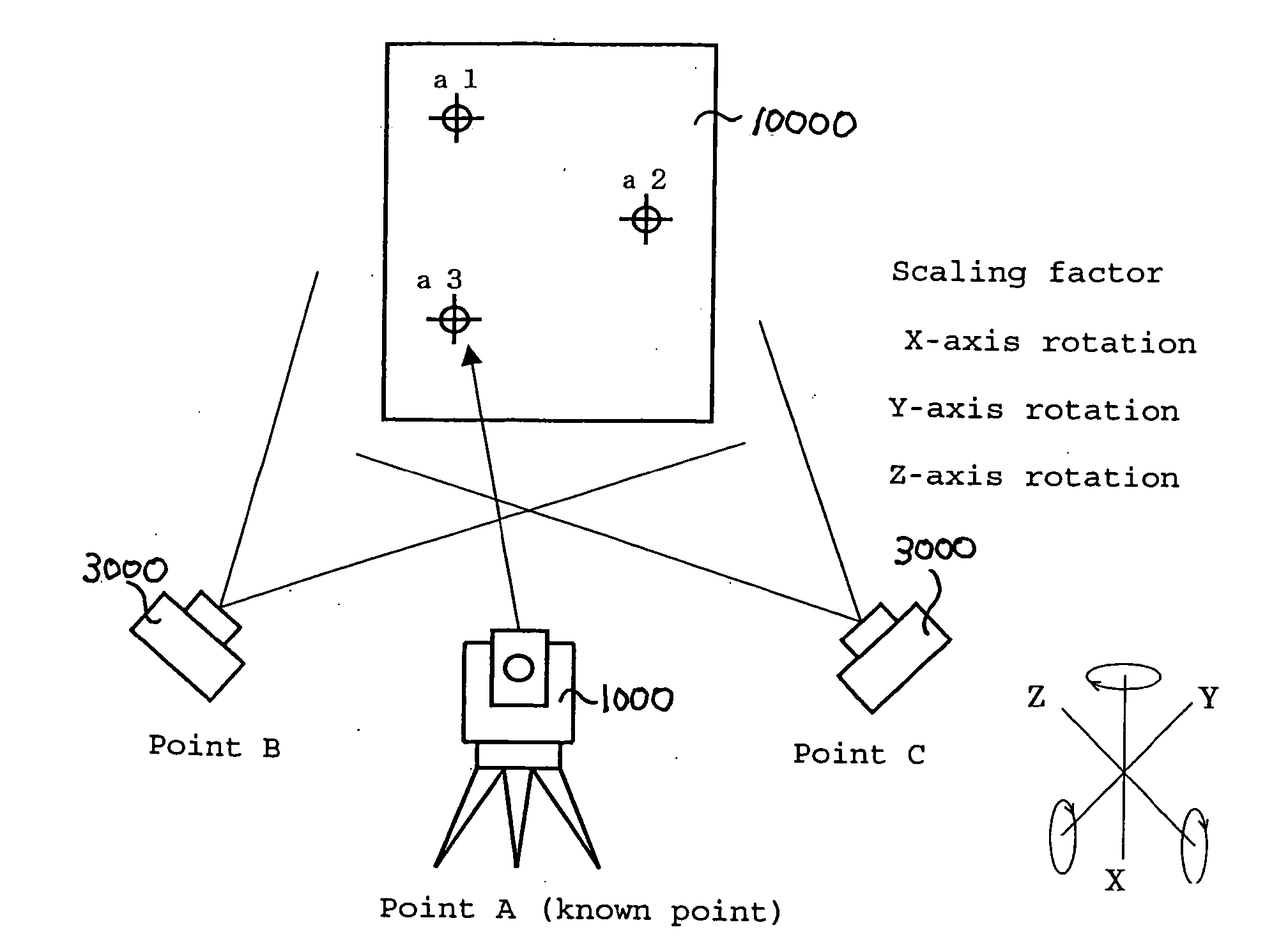
The invention relates to a mixed measurement analysis method for a satellite antenna. The method effectively solves the problems that various measurement devices are used for co-measurement to reduce detection difficulty and improve detection efficiency during a measurement process of the satellite antenna. The method comprises the steps: cubic mirror collimating measurement is carried out by electronic theodolites during antenna installation and detection processes, scanning measurement of an antenna shaped surface is carried out by a laser radar, a space point position is measured by a laser tracker, and thus the measurement of the satellite antenna is jointly completed by the various measurement devices; union calibration algorithm of 'six freedom degree measurement station three-dimensional network' is employed, a conversion relationship between measurement station coordinates and measurement coordinates is utilized, various observed value error equations are directly listed, so as to overcome shortcomings of a traditional algorithm and improve adaptability of the algorithm. The method provided by the invention is simple, is easy to operate, enables an initial value to be fast acquired, has low requirements for precise degree of the initial value, has a few iteration times, is quick in convergence speed, theoretically is an optimal solution, and has strong algorithm adaptability, high measuring efficiency, fast speed and high precision.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE MFG FACTORY +1
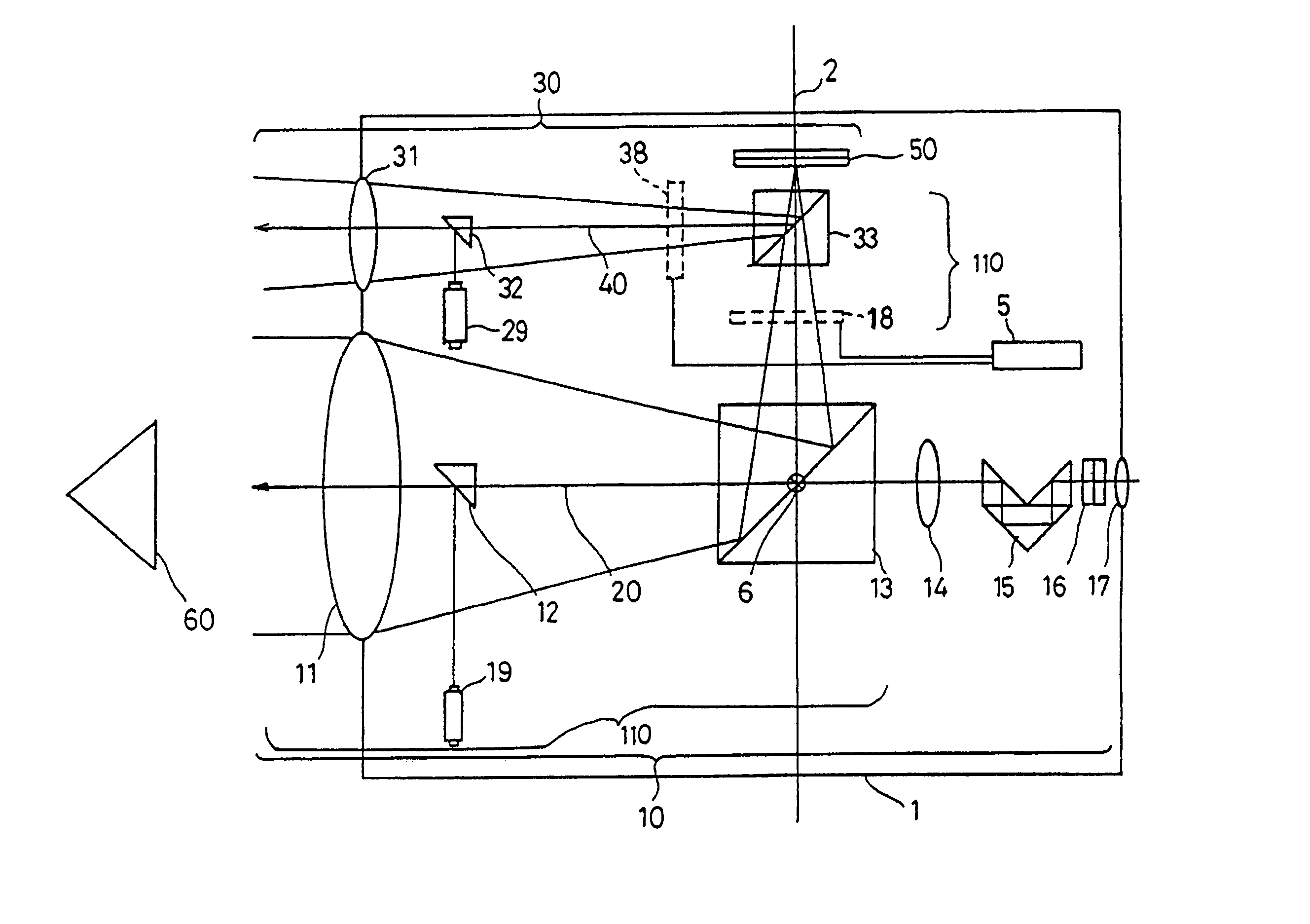
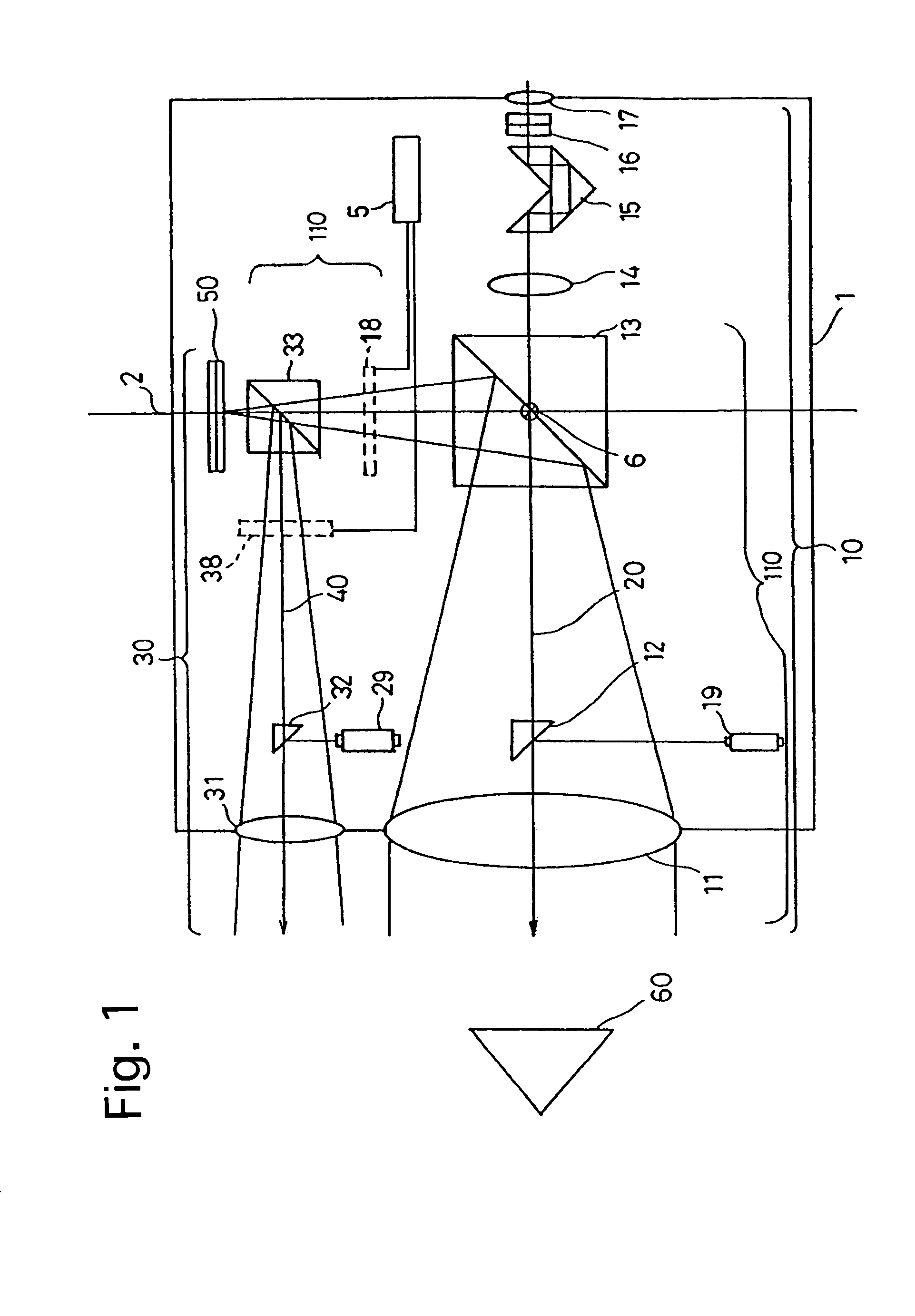
Calibration of a surveying instrument
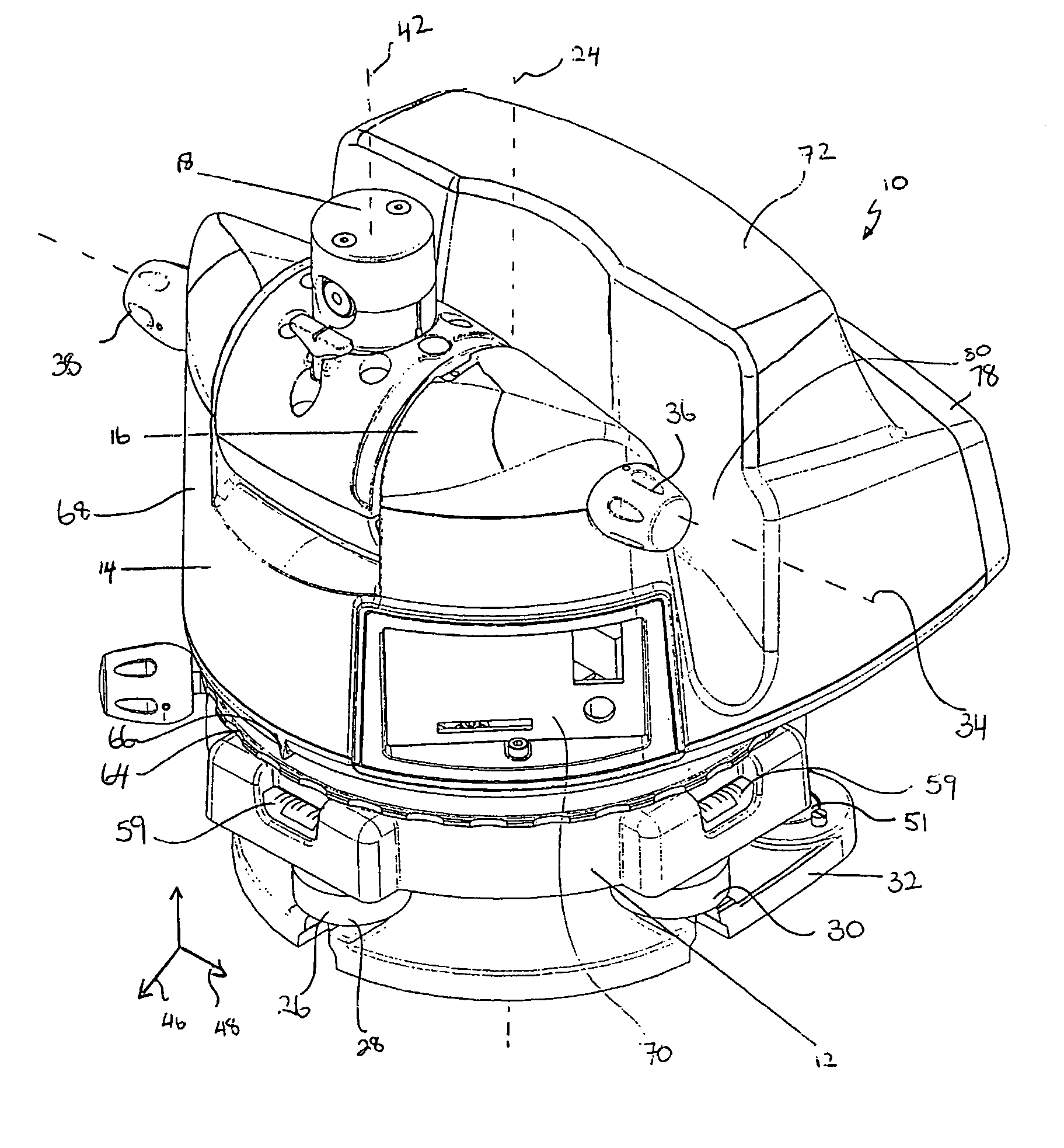
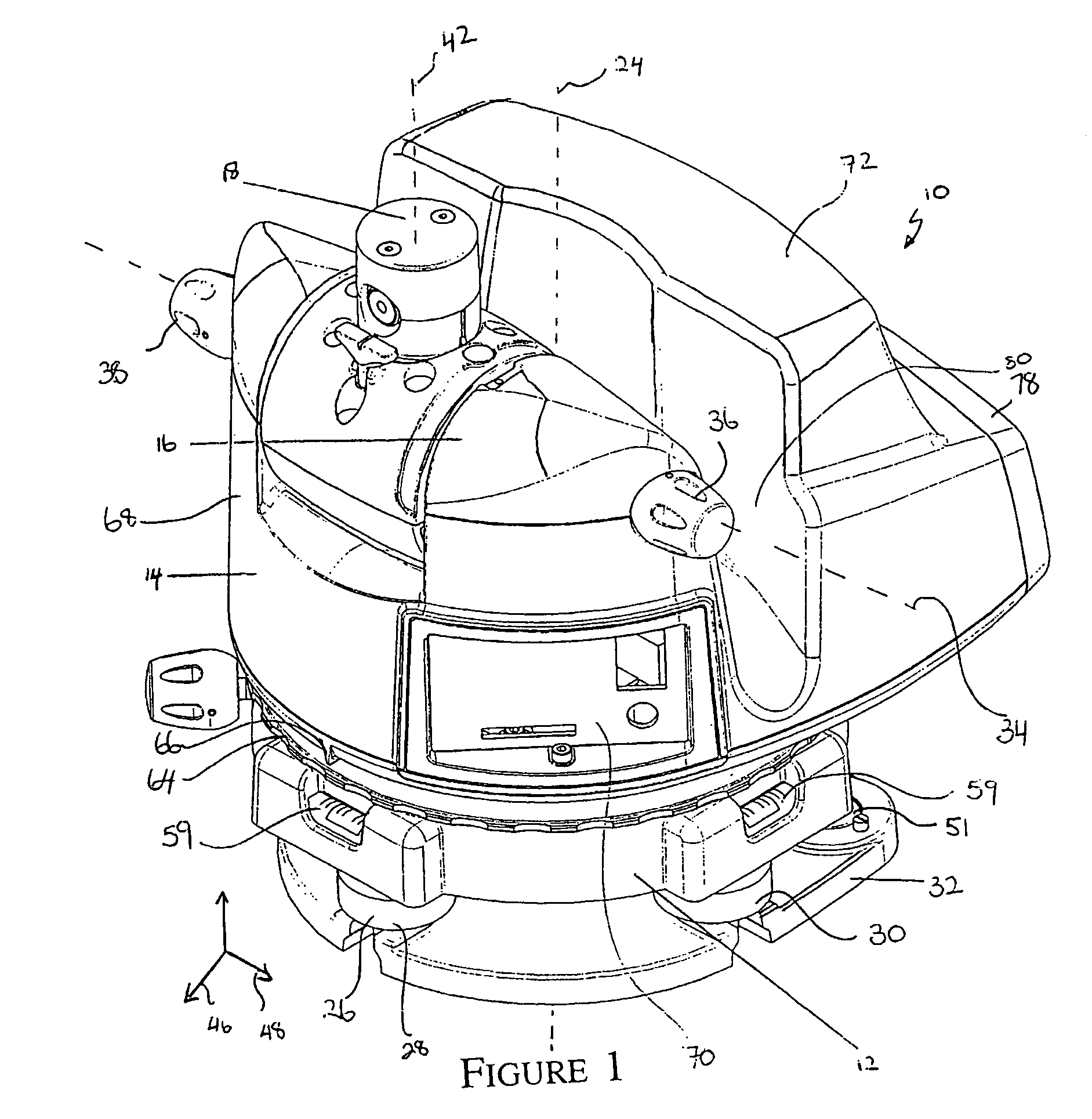
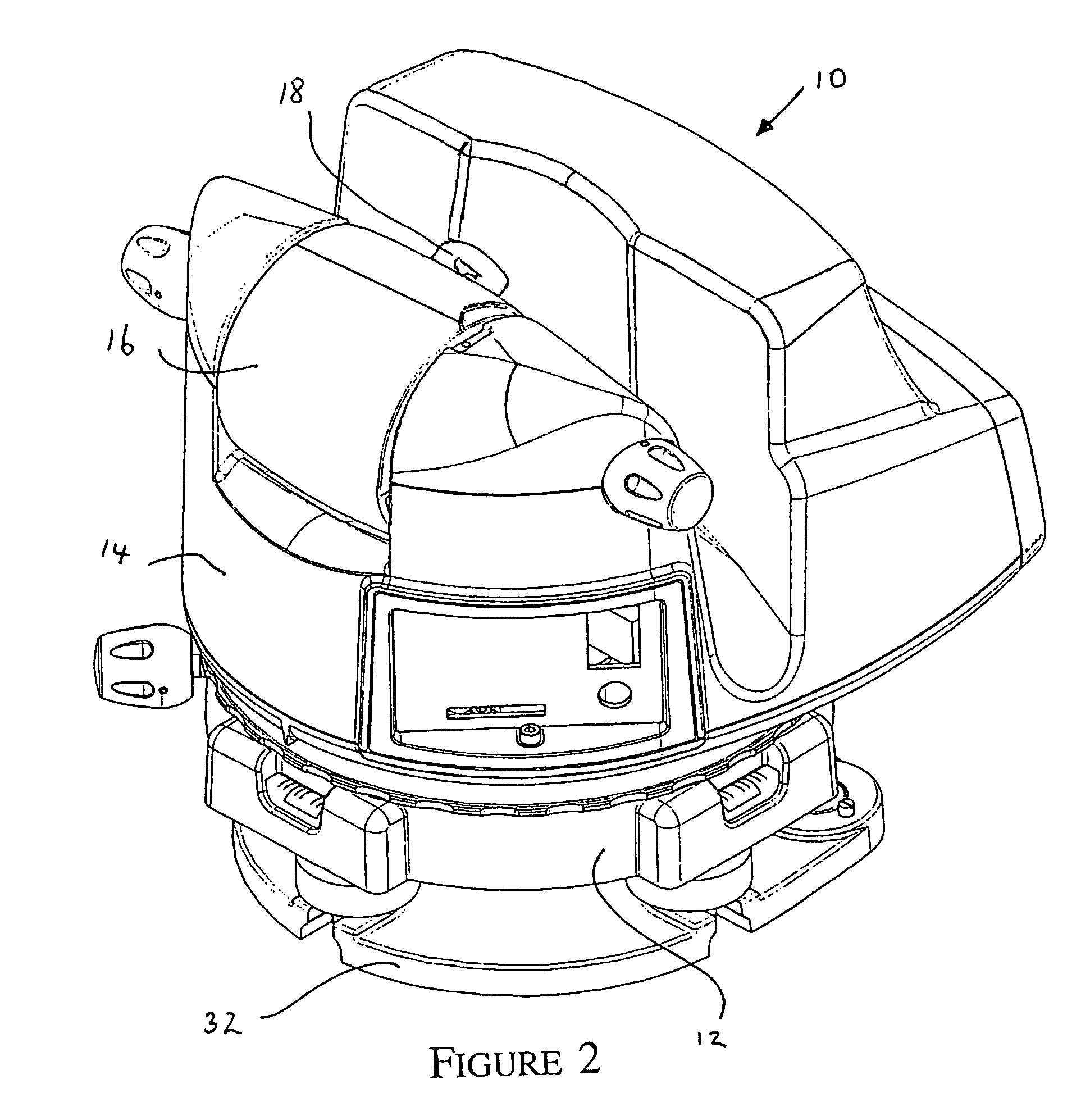
ActiveCN1894557AAccurate CalibrationQuick calibrationSurveying instrumentsTheodolitesOptical propertySurvey instrument
A method for calibrating a surveying instrument is disclosed the survey instrument comprising a base element (3) and a camera with an image sensor (10), the camera being rotatable about a vertical axis (2) fixed with respect to said base element and being rotatable about a tilting axis (4), the tilting axis being rotated about the vertical axis with rotation of the camera about the vertical axis, In the method, data associated with calibration points (P) and images (P1) of the calibration points on the image sensor captured in different faces are used, the data for each of said calibration points comprising distance data and the data for each of the images of each said calibration point comprising image position data and orientation data. Further, on the basis of the distance data for each of the calibration points and the image position and orientation data for each of the images of the calibration points the surveying instrument is calibrated simultaneously taking into account at least one optical property of camera and at least one of the relative orientation of the vertical axis and the tilting axis and the orientation of the camera relative to one of the base element, the vertical axis and the tilting axis.
Owner:TRIMBLE JENA
Laser leveling apparatus
InactiveUS7099000B2Improve accuracyEasy to controlOptical rangefindersActive open surveying meansBody axisLight beam
A laser levelling apparatus includes a platform, a base assembly, a body assembly, a head assembly and a laser assembly. The body assembly is rotatable about a body axis relative to the base assembly, the head assembly is rotatably supported by the body and rotatable about a head assembly axis transverse to the body axis and the laser assembly supported by the head assembly and rotatable about a laser assembly axis which is transverse the head assembly axis. The laser assembly has a laser diode and focusing elements and laser collimator the laser beam with the laser assembly. The head assembly is mounted between a first shaft end mounted at a first position of the body and a second shaft end mounted at the second position of the body opposed to the first position. A head assembly collimator is used to adjust the axis of rotation of the head assembly. A base assembly leveller is used to adjust the level of the base relative to the platform in at least two transverse directions. The base leveller, laser collimator and head assembly collimator together and head assembly collimator together provide for collimator of the beam along three orthogonal axes.
Owner:CONNOLLY MICHAEL
Three-dimensional surveying instrument and electronic storage medium
InactiveUS20060017938A1Surveying instrumentsUsing optical meansSurvey instrumentMeasuring instrument
Owner:KK TOPCON
Survey system capable of remotely controlling a surveying instrument
ActiveUS7345748B2Shorten the timeMeasuring points markingOptical rangefindersMeasuring instrumentSurvey instrument
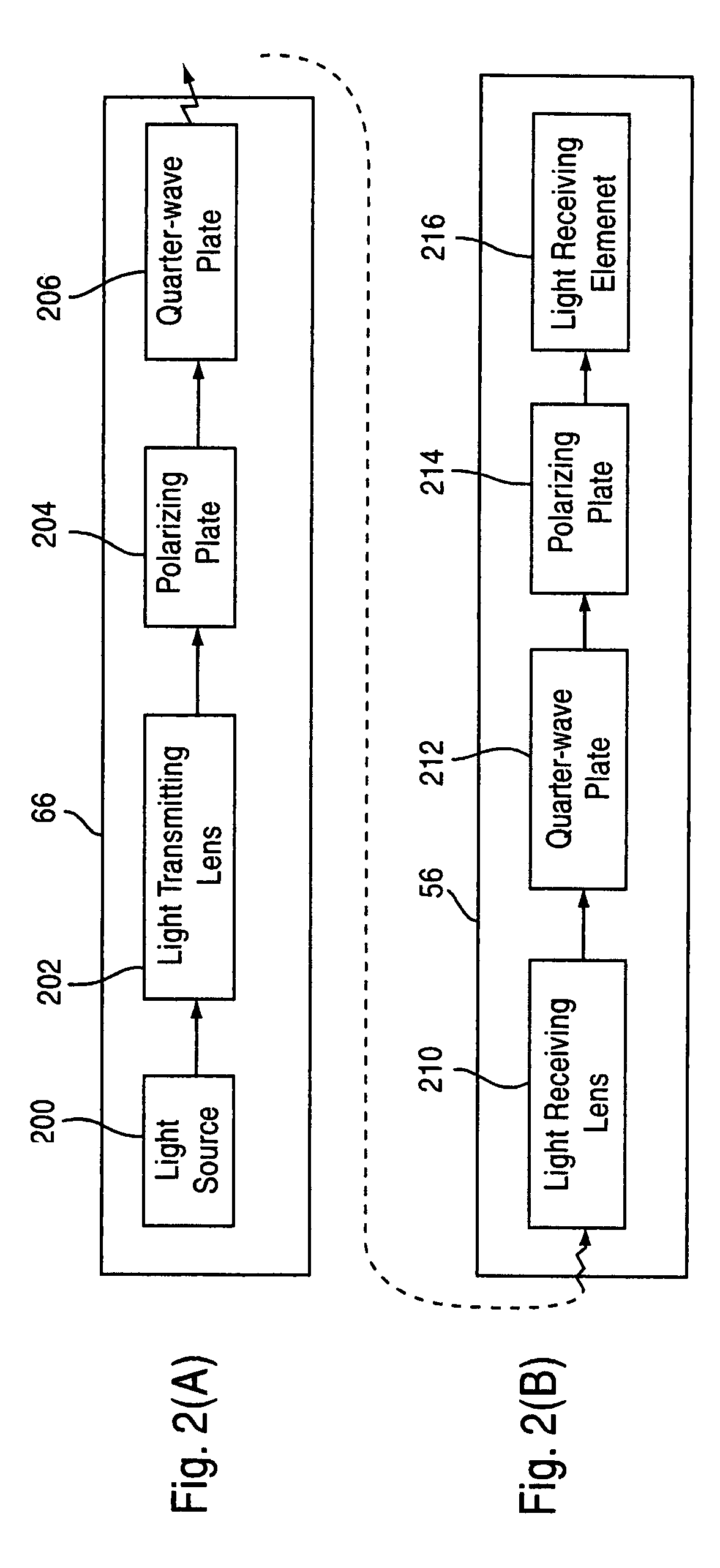
In a survey system in which guide light is emitted from the side of a target, and, on the side of a surveying instrument, a telescope is directed roughly toward the target by receiving the guide light so as to shorten the time required for automatic collimation, the automatic collimation of the surveying instrument can be reliably performed by removing guide light reflected by reflective objects such as windowpanes. The target has a guide light remitter that emits guide light The guide light transmitter includes a light source, a polarizing plate that changes light emitted from this light source into linearly polarized light, and a quarter-wave plate that changes this nearly polarized light into circularly polarized guide light The surveying instrument includes a direction detector and a collimation preparing means. The direction detector includes a quarter-wave plate and a polarizing plate.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Surveying instrument
InactiveUS20090119050A1Improve accuracyExclude influenceActive open surveying meansCharacter and pattern recognitionElevation angleSurvey instrument
There are provided a horizontal angle detector for detecting a horizontal angle, an elevation angle detector for detecting an elevation angle, a dynamic displacement detecting means 10 for detecting posture displacement of a surveying instrument main unit in two horizontal directions, and a calculating unit, wherein said dynamic displacement detecting means detects displacement with respect to standard posture of the surveying instrument main unit 1, said calculating unit calculates the horizontal angle and the elevation angle corresponding to dynamic displacement detected by said dynamic displacement detecting means, and compensates the horizontal angle and the elevation angle obtained by the horizontal angle detector and the elevation angle detector respectively are compensated based on the calculated horizontal angle and the calculated elevation angle.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Position control arrangement, especially for a surveying instrument, and a surveying instrument
InactiveUS7765084B2Reduce manufacturing costHighly accurate in useActive open surveying meansDigital computer detailsSurvey instrumentMeasuring instrument
Owner:TRIMBLE A B A CORP OF SWEDEN
Multidirectional laser indicator
A laser indicator includes a weight mechanism having a bracket with a weight secured to the bracket in a manner where the weight is suspended by gravity. A plurality of laser generators are arranged about the weight, including a horizontal beam generator, a center laser generator arranged at the axial center of the bottom of the weight for emitting a laser point coaxial to the axial line of the weight, and a plurality of vertical beam generators positioned in spaced-apart manner around the axial center of the weight at the top of the weight. The laser indicator can include a stand that includes a seat having a plurality of legs, and a rotary table having a plurality of legs, with the weight mechanism coupled to the rotary table, and the rotary table removably coupled to the seat so that altitude of the weight mechanism can be adjusted. In addition, the laser indicator can include a securing mechanism for coupling the weight to the upper bracket of the bracket.
Owner:QUARTON
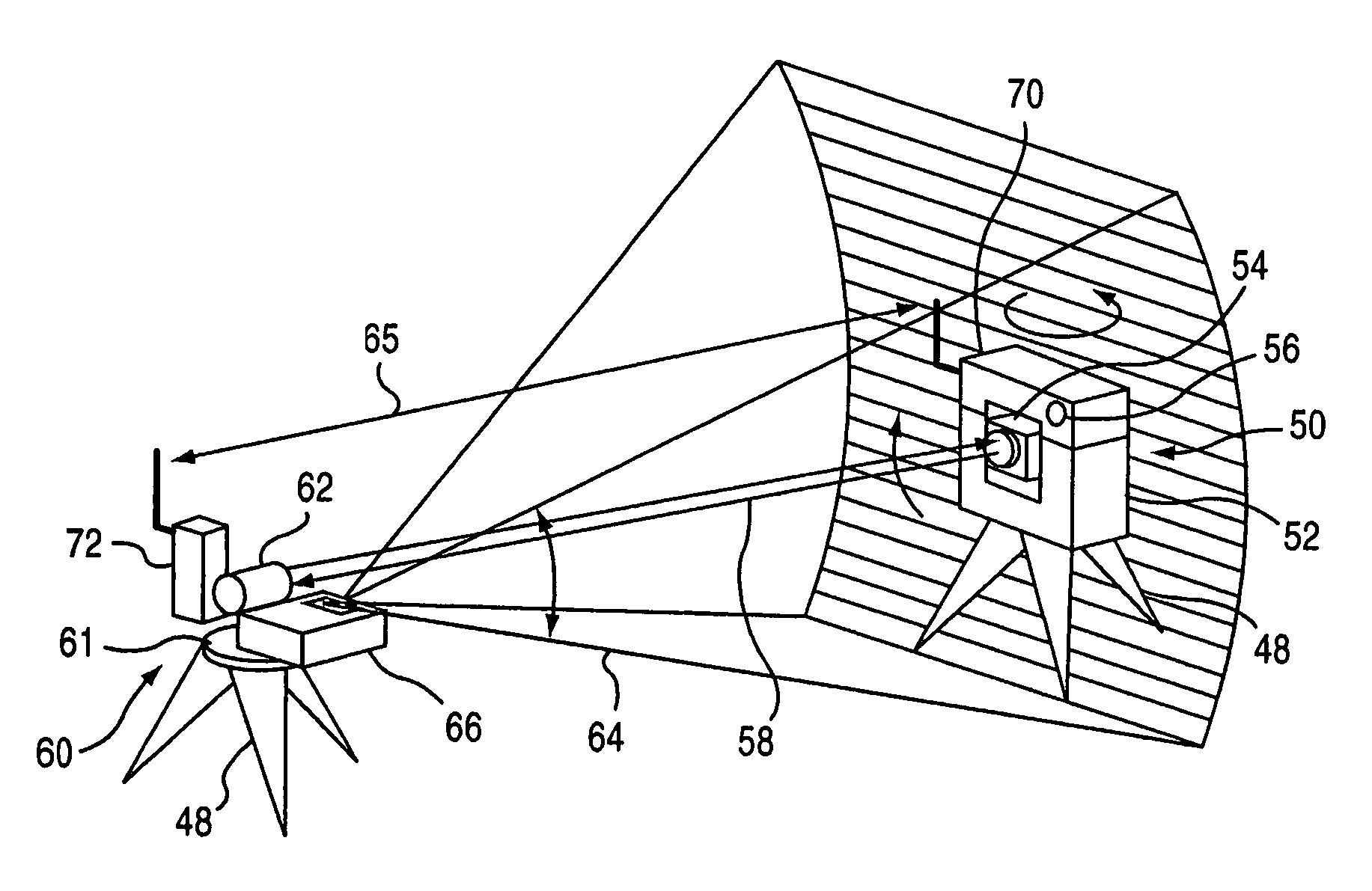
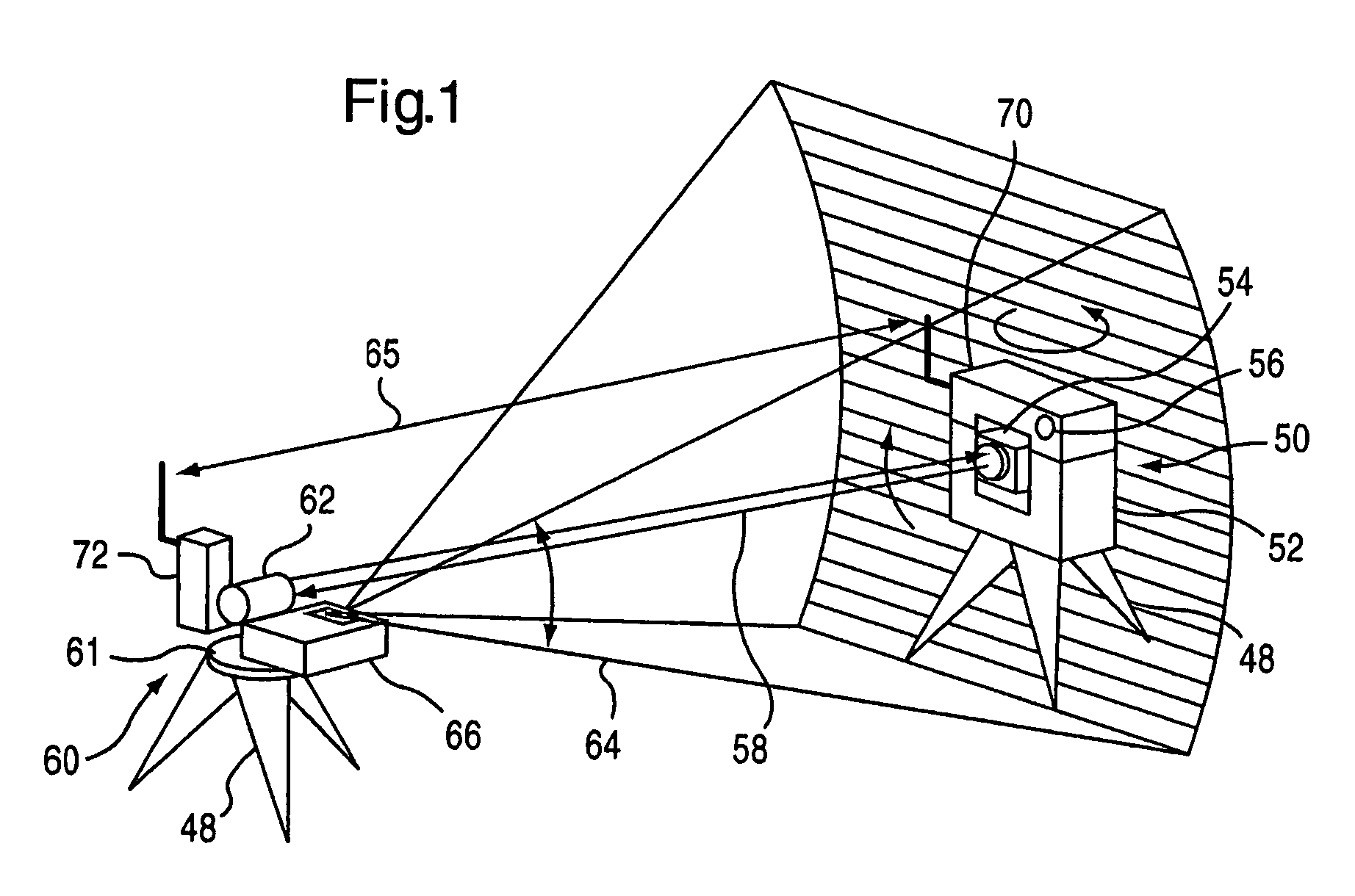
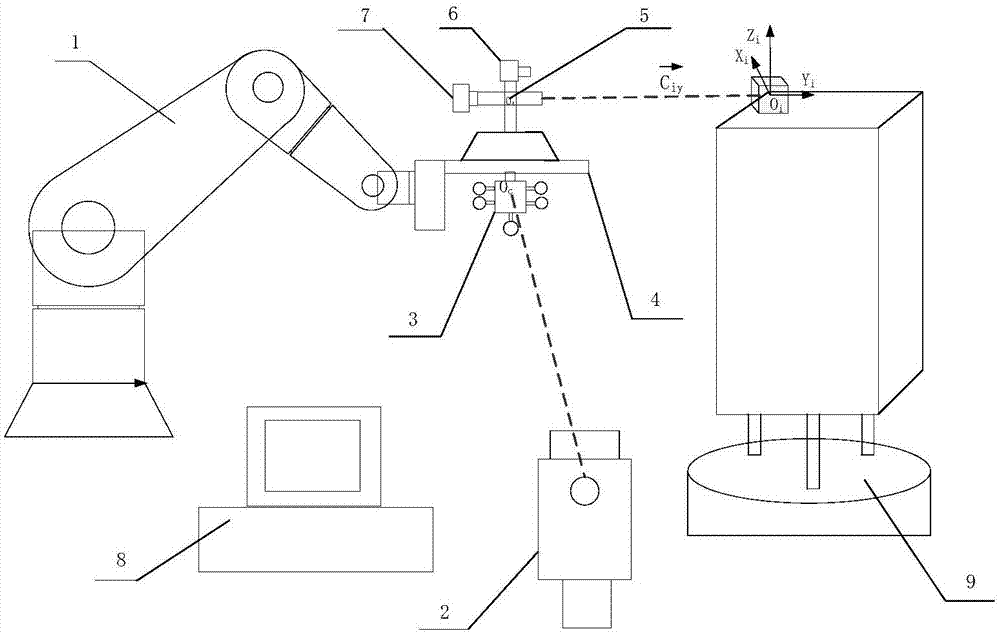
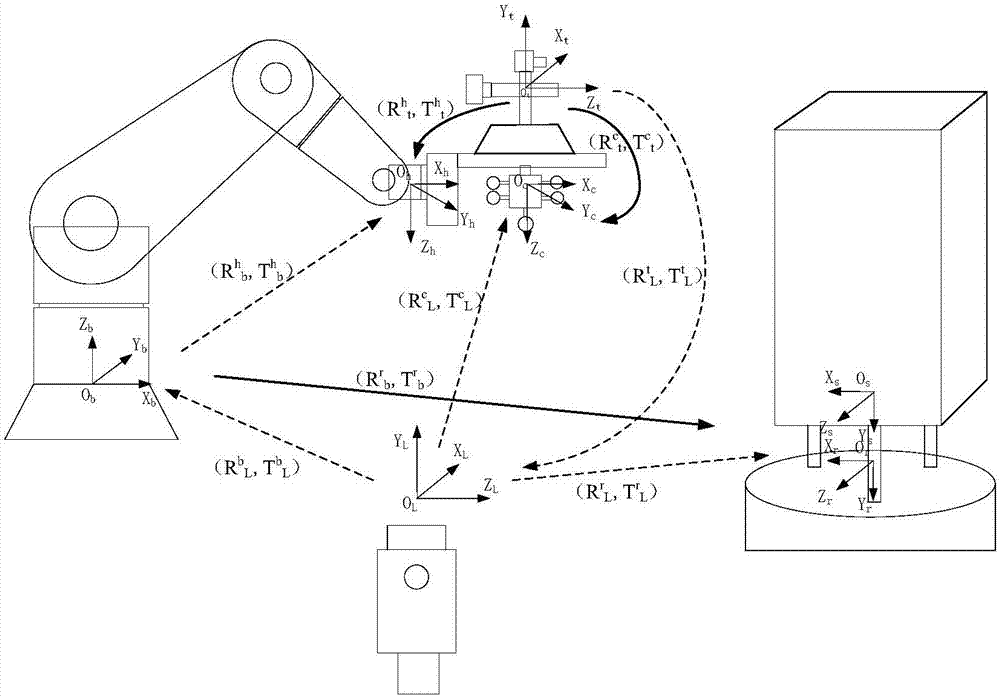
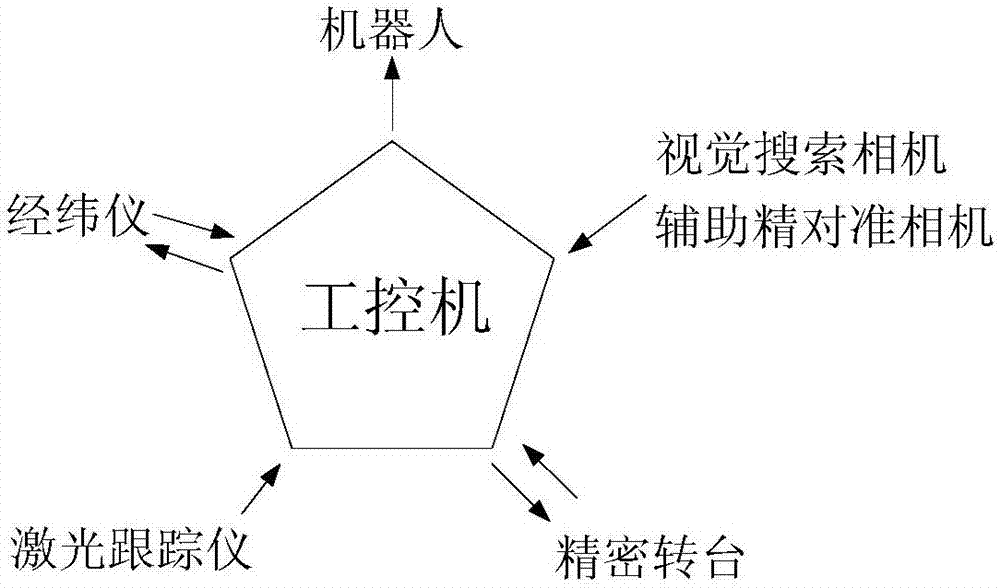
Automatic collimation measurement system, collimation method and measurement method for spacecraft devices
ActiveCN107543495ARealize automatic levelingExcellent leveling accuracyUsing optical meansTheodolitesTheodoliteAutocollimation
The invention discloses a collimation measurement system for attitudes and angles among spacecraft devices based on the combination between a robot and a theodolite. The system herein includes a robot, a laser tracker, a laser tracking target (T-MAC), a robot terminal tool, and the like. The system searches a to-be-tested datum cube mirror which is disposed on a spacecraft device by conducting mode identification, and computes the relations of phase position and direction of the datum cube mirror with respect to the theodolite. The laser tracker is intended for calibrating the relative direction relation in a coordinate system of respective spacecraft devices and integrating the measurement results of the theodolite at different measurement positions to the same coordinate system. Based onthe calibration relation and the relative relation, the laser tracker is guided to real-timely track the robot terminal tool and establish the relative relation between the laser track and the robotterminal tool. And eventually, the attitude relation matrix of the spacecraft is computed. According to the invention, the automatic measurement of the attitude relation among different devices is realized, the measurement efficiency can reach one time per half-minute, the measurement precision can be higher than 30'', on-site measurement flexibility is higher, and construction and measurement indifferent places can be much easier.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Survey system
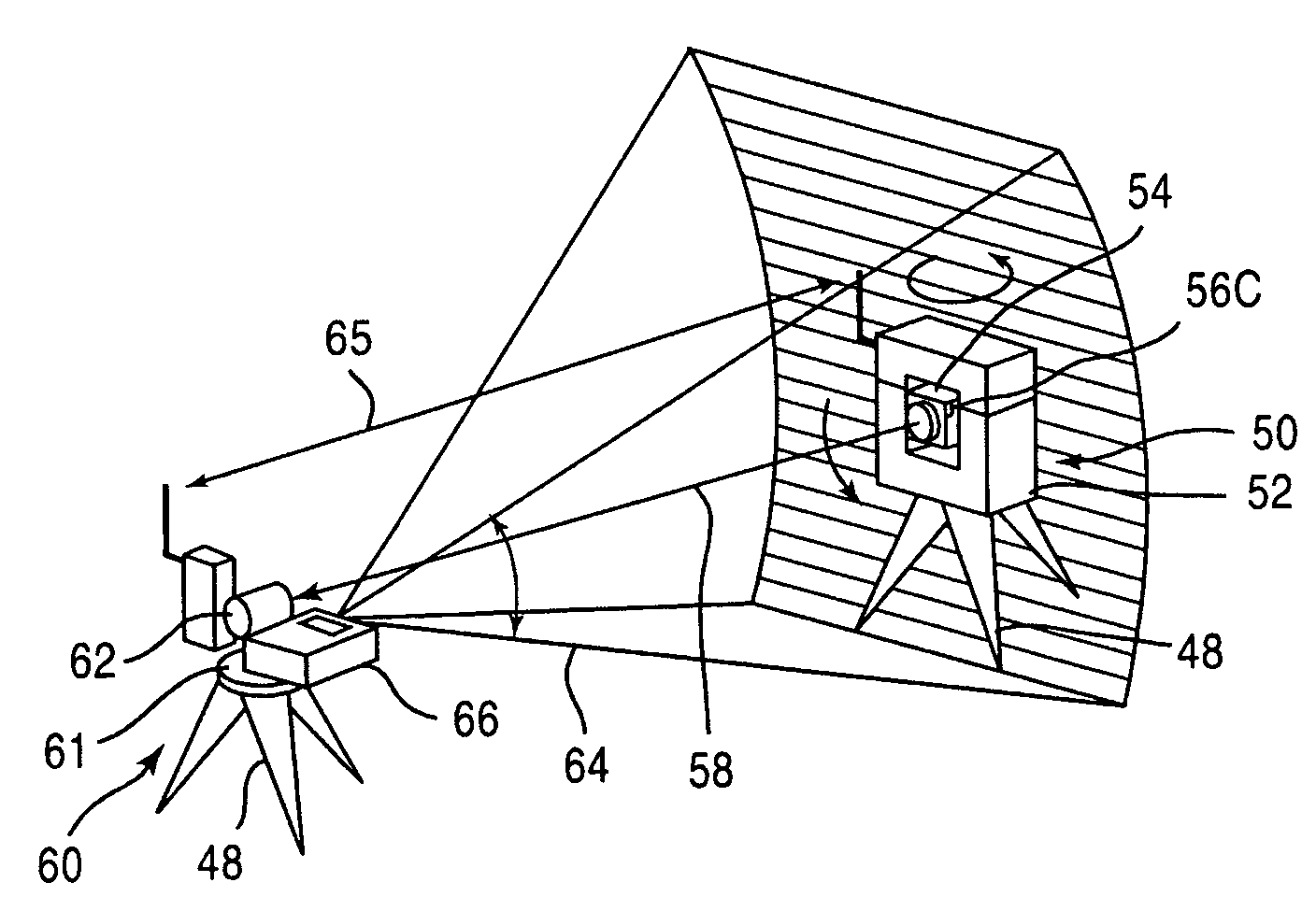
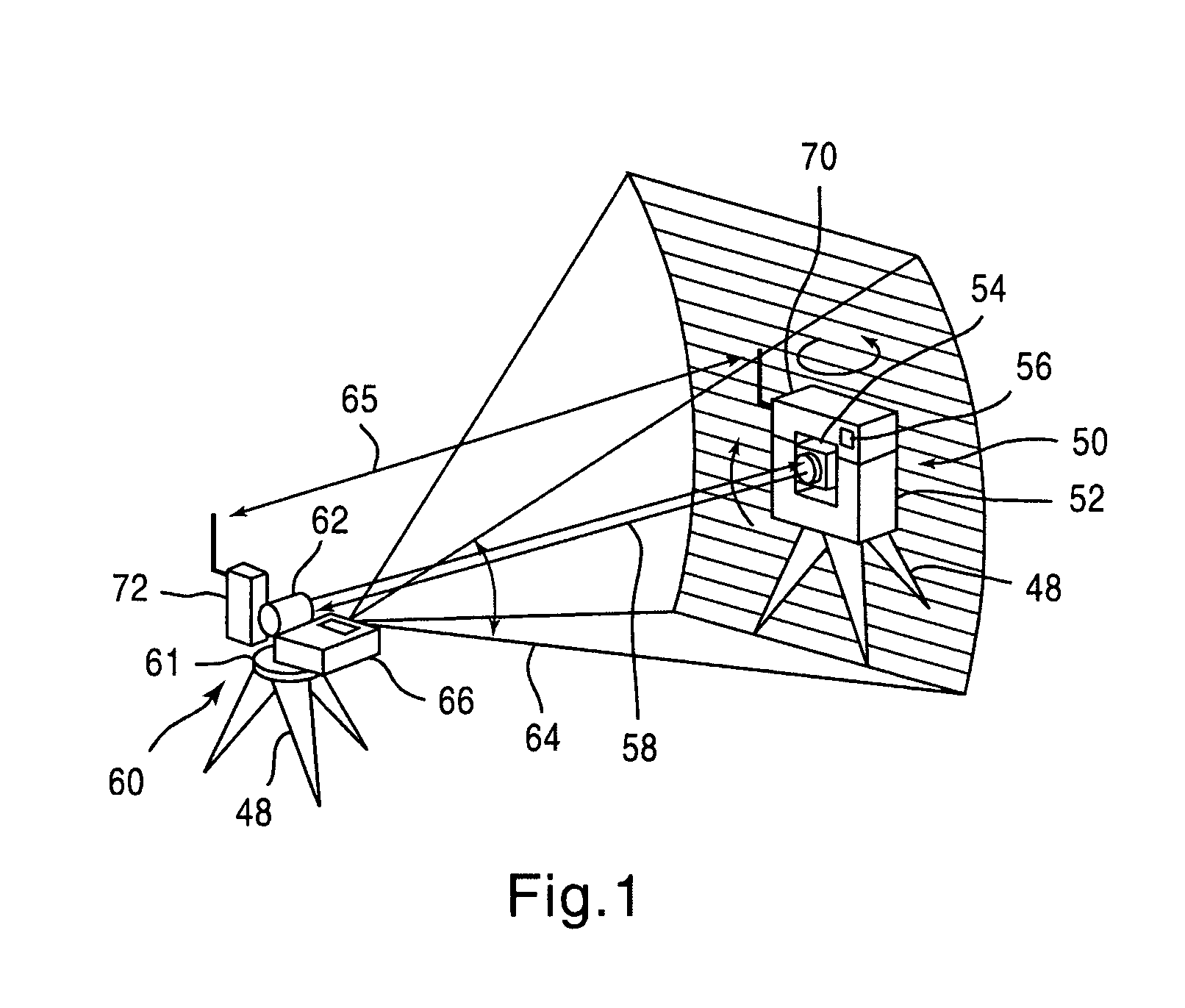
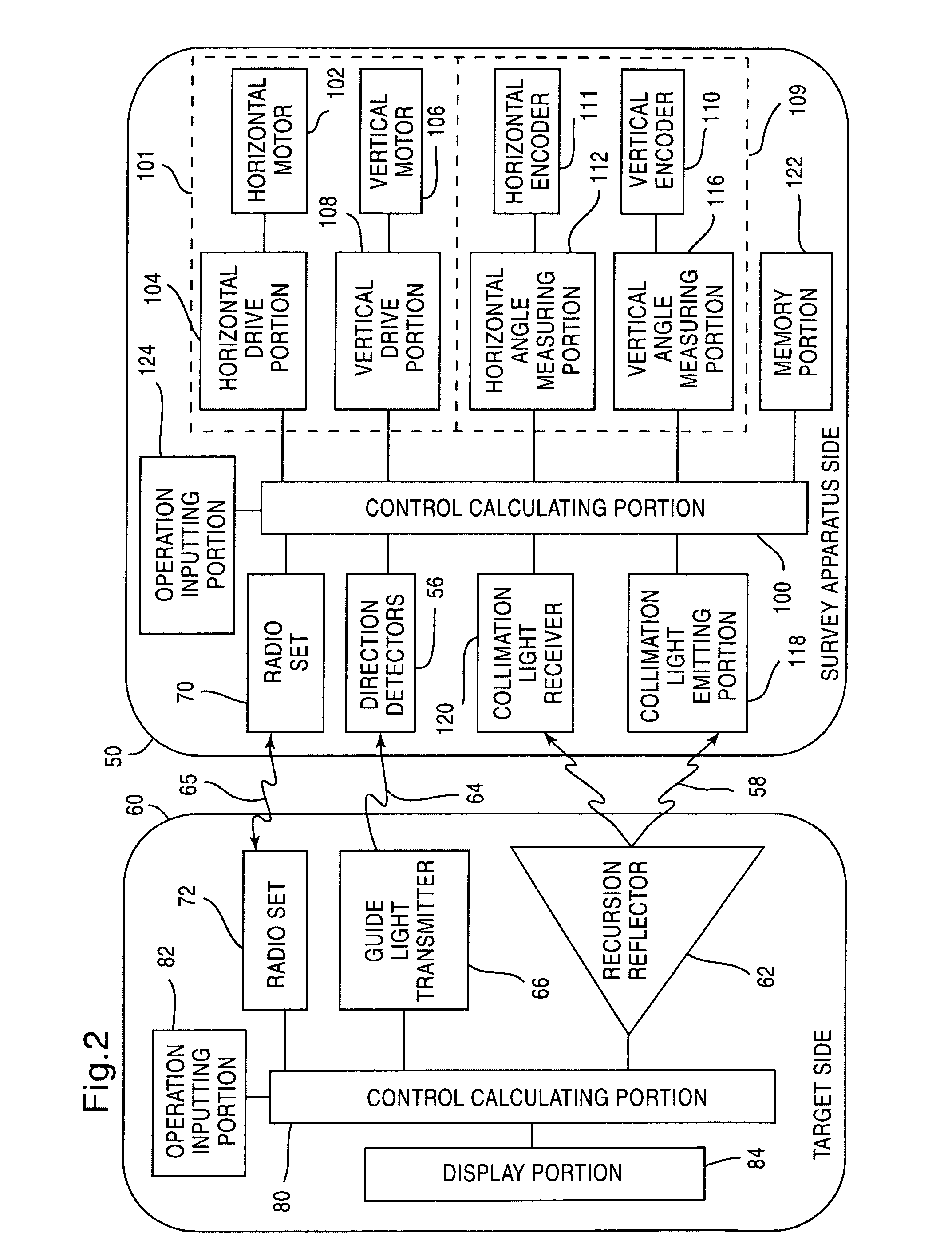
A survey system for transmitting guide light for instructing the direction of a target, the guide light having a wide range with small power. The survey system includes a target having a recursion reflector for reflecting light and a survey apparatus having an automatic collimation device for automatically coinciding the collimation axis of the recursion reflector with that of a telescope. The target includes a guide light transmitter for emitting guide light and scans a fan beam that is wide in the horizontal direction and narrow in the vertical direction in the vertical direction as guide light. The survey apparatus includes a direction detector for receiving guide light and detecting the direction of the guide light transmitter and also includes a collimation preparing device for turning the telescope roughly to the recursion reflector based on an output signal from the direction detector prior to commencing the automatic collimation.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Surveying Instrument And Three-Dimensional Camera
ActiveUS20160238385A1Low costOptical rangefindersActive open surveying meansOptical axisSurvey instrument
The invention provides a surveying instrument, which comprises a light emitting element for emitting a distance measuring light, a distance measuring light projecting unit for projecting the distance measuring light, a light receiving unit for receiving a reflected distance measuring light, a photodetection element for receiving the reflected distance measuring light and for producing a photodetection signal and a distance measuring unit for performing a distance measurement based on a light receiving result from the photodetection element, further comprises a first optical axis deflecting unit disposed on a projection optical axis of the distance measuring light for deflecting an optical axis of the distance measuring light at a deflection angle as required and in a direction as required, a second optical axis deflecting unit disposed on a light receiving optical axis for deflecting the reflected distance measuring light at the same deflection angle and in the same direction as the first optical axis deflecting unit and a projecting direction detecting unit for detecting a deflection angle and a deflecting direction by the first optical axis deflecting unit, wherein it is so arranged that the distance measuring light is projected through the first optical axis deflecting unit and the reflected distance measuring light is received by the photodetection element through the second optical axis deflecting unit and a three-dimensional data of a measuring point is obtained based on a distance measuring result of the distance measuring unit and a detection result of the projecting direction detecting unit.
Owner:KK TOPCON
Handheld optical distance measurement device
ActiveUS20060201006A1Simple and complex measurementActive open surveying meansPlumb lines for surveyingElevation angleMeasurement device
A handheld measurement device of an embodiment of the invention includes a distance measurement engine and an angular position measurement engine. A controller controls the distance measurement engine and associates an elevation, azimuth position, or relative angular position from the angular position measurement engine with distance measurements taken from the elevation engine. In preferred operations, each point measured from a target under the control of a user is automatically associated with an elevation and / or azimuth position obtained from the angular position engine. Preferably, the controller determines a set of relative coordinates in space for a plurality of related target points. The controller may then calculate a variety of useful distances, areas, volumes, etc., regarding the plurality of target points.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH CO LTD
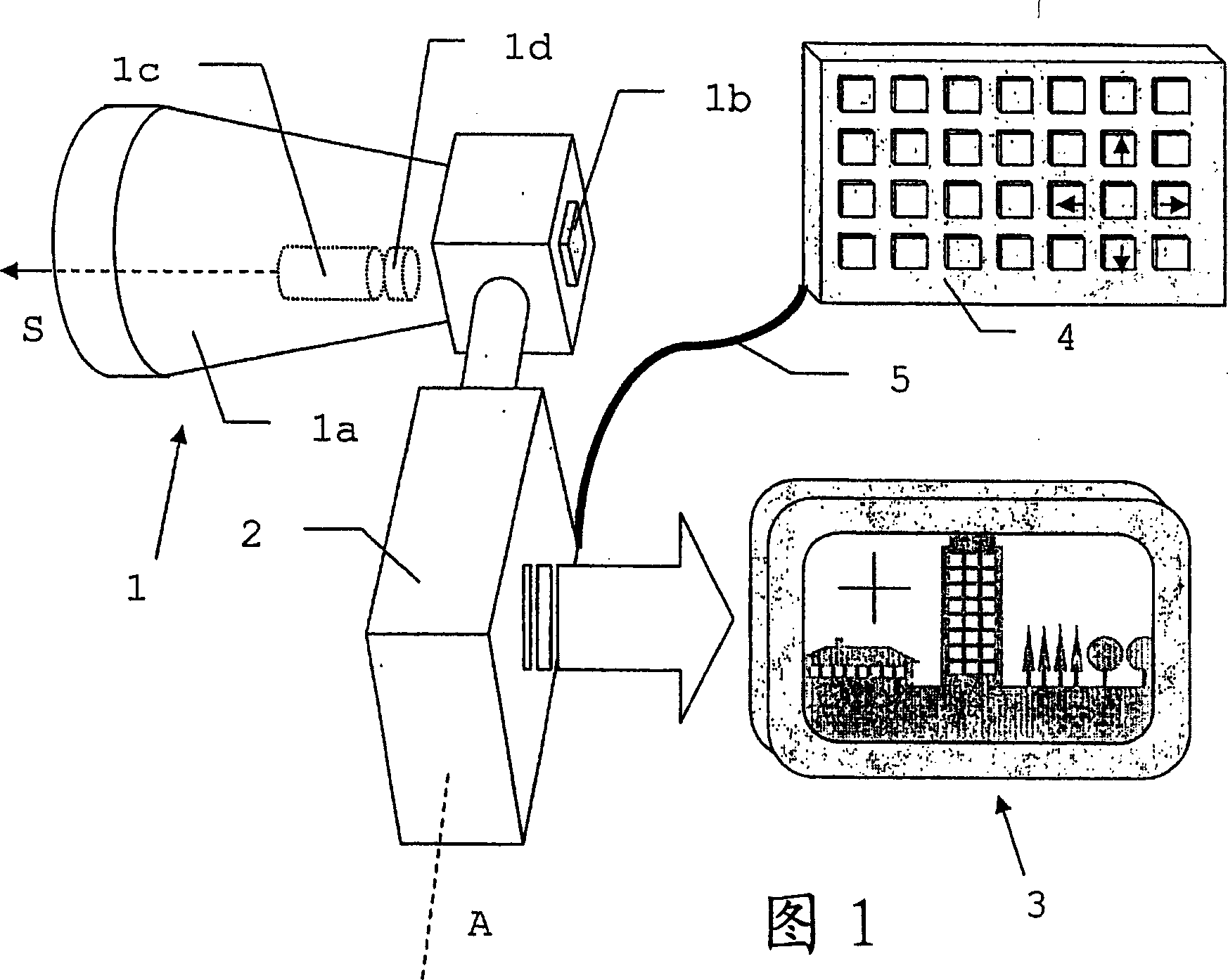
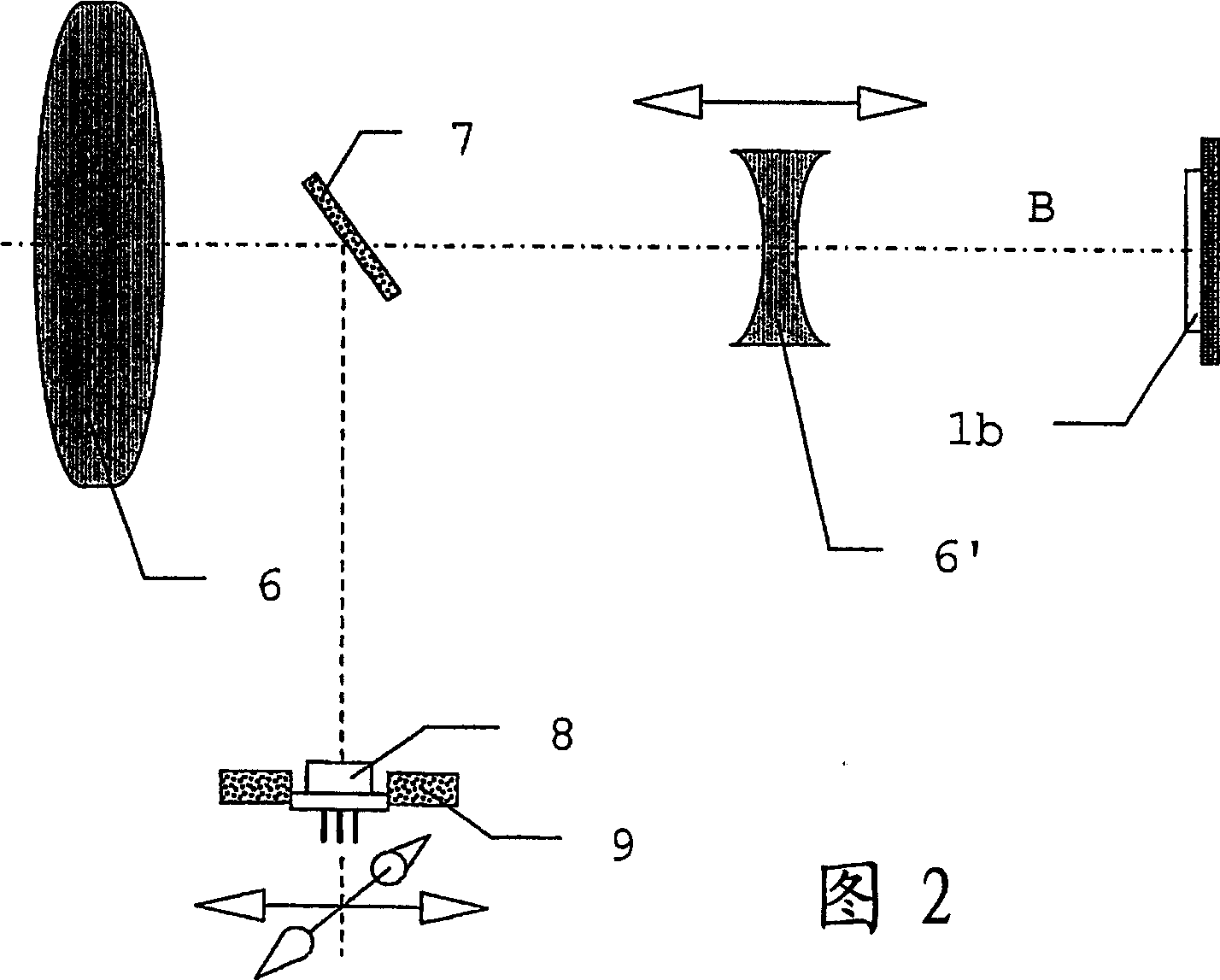
Electronic display and control device for a measuring instrument
InactiveCN1688867AEasy to measureWave based measurement systemsActive open surveying meansRemote controlMeasuring instrument
The invention relates to an electronic display and control device for a geodesic measuring device (12) containing capturing means (1') and representation means for detecting and reproducing a measuring range (11) together with input means for controlling the measuring processes. The radiation beam (S) necessary for said measuring processes is emitted by a radiation source and is influenced in the direction of emission thereof by orientating means such that it can be orientated onto a selected target within the measuring range (11) without the capturing means being displaced. Determining the target and initiating the measuring process occurs by displacing a position mark (3a) on a screen. A suitable operating module can be produced by suitably combining the representation means with means for inputting data. Said module can also be used independently from and separately from a measuring device (12,12') which is connected thereto by communication means. The use of said module together with a plurality of measuring devices as sensor components, enables the formation of remote-controlled geodesic measuring systems.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS AG
Calibration method of inertial unit optical aiming prism installation error
The invention provides a calibration method of inertial unit optical aiming prism installation errors. The calibration method is characterized in that prism lines of the inertial unit optical aiming prism rotate for several positions; a self calibration theodolite and an inertial unit optical aiming prism collimator which are fixed in the one position is used in each position. The relative posture of the inertial unit is provided through inertial navigation solution; the relative posture of the theodolite collimation axis can be obtained through reading and calculation via a dial. According to the initial conditions of the self calibration theodolite and the inertial unit optical aiming prism collimator in each position, a multivariate overdetermined equation including inertial unit optical aiming prism installing error Z0 (deflection quantity) and Y0 (inclination quantity) is built; the installing errors Y0 and Z0 of the inertial unit optical aiming prism can be obtained through solving the multivariate overdetermined equation. The posture in the inertial unit rotationprocess is given through inertial navigation solution; the rotation process can be manually completed on an ordinary platform; the requirements on test equipment is low; the realization is easy; the calibration parameters are comprehensive; high universality is realized.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
Enhanced position measurement systems and methods
ActiveUS9182229B2Improve efficiencyEasy to set upSurveyor's staffsMovable markersTotal stationComputer science
Novel solutions for position measurement, including without limitation tools and techniques that can be used for land surveying and in similar applications. One such tool is a greatly enhanced position measurement system that takes the form of a surveying rod with substantial independent functionality, which can be used with or without a total station or similar device.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
Scanner vis
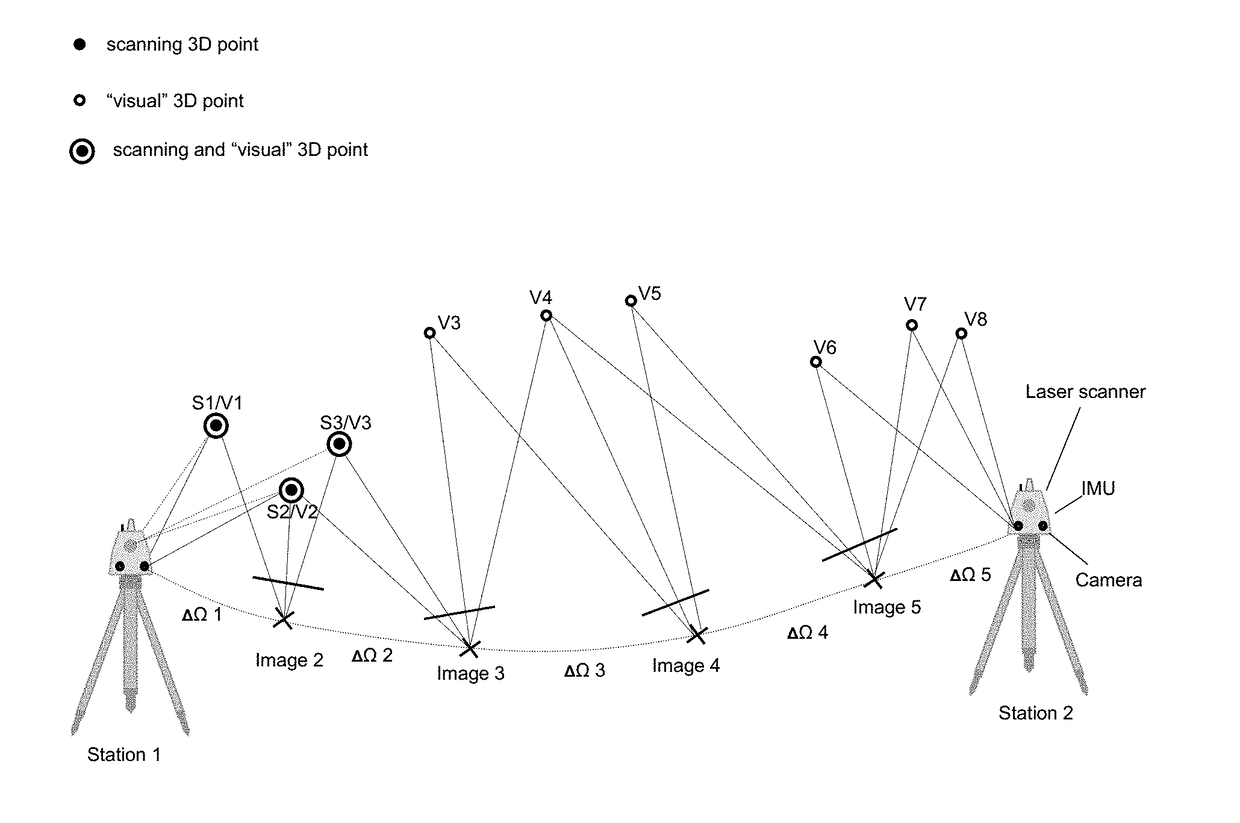
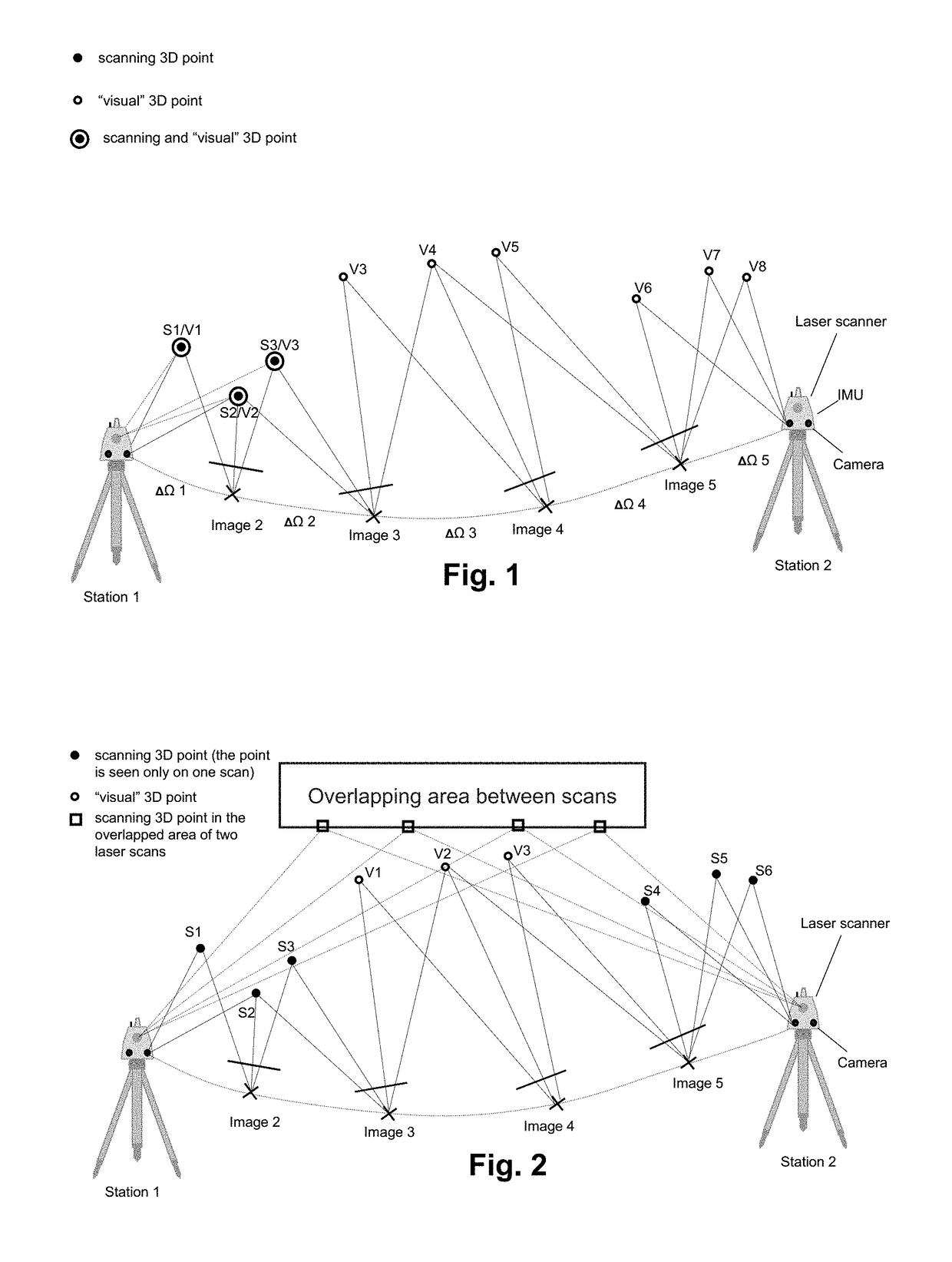
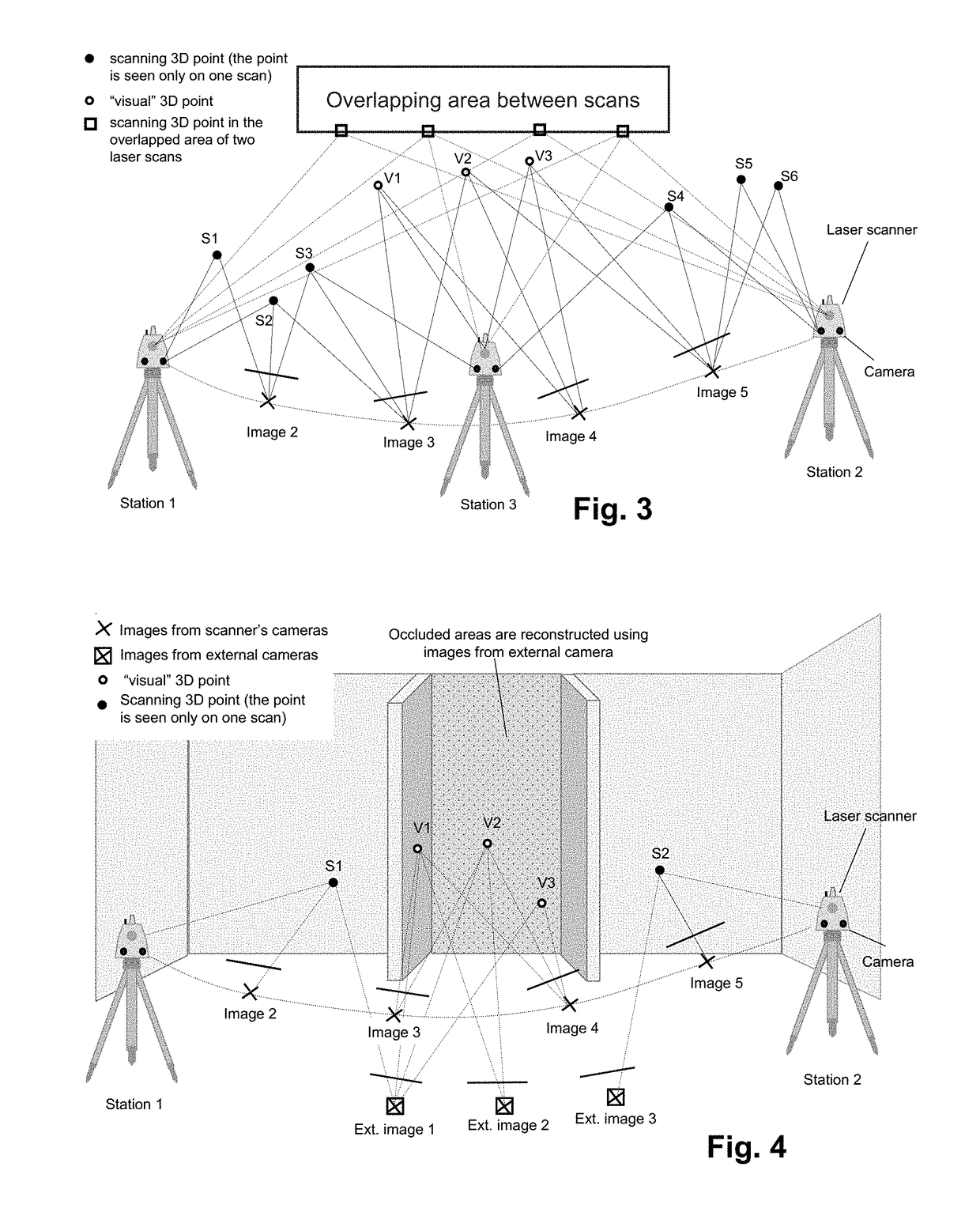
ActiveUS20180158200A1Distance minimizationReduce driftImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPoint cloudSurvey instrument
A method for registering two or more three-dimensional (3D) point clouds. The method includes, with a surveying instrument, obtaining a first 3D point cloud of a first setting at a first position, initiating a first Simultaneous Localisation and Mapping (SLAM) process by capturing first initial image data at the first position with a camera unit comprised by the surveying instrument, wherein the first initial image data and the first 3D point cloud share a first overlap, finalising the first SLAM process at the second position by capturing first final image data with the camera unit, wherein the first final image data are comprised by the first image data, with the surveying instrument, obtaining a second 3D point cloud of a second setting at the second position, and based on the first SLAM process, registering the first 3D point cloud and the second 3D point cloud relative to each other.
Owner:HEXAGON TECH CENT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com