Patents
Literature
1000results about "Centering/balancing rotors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
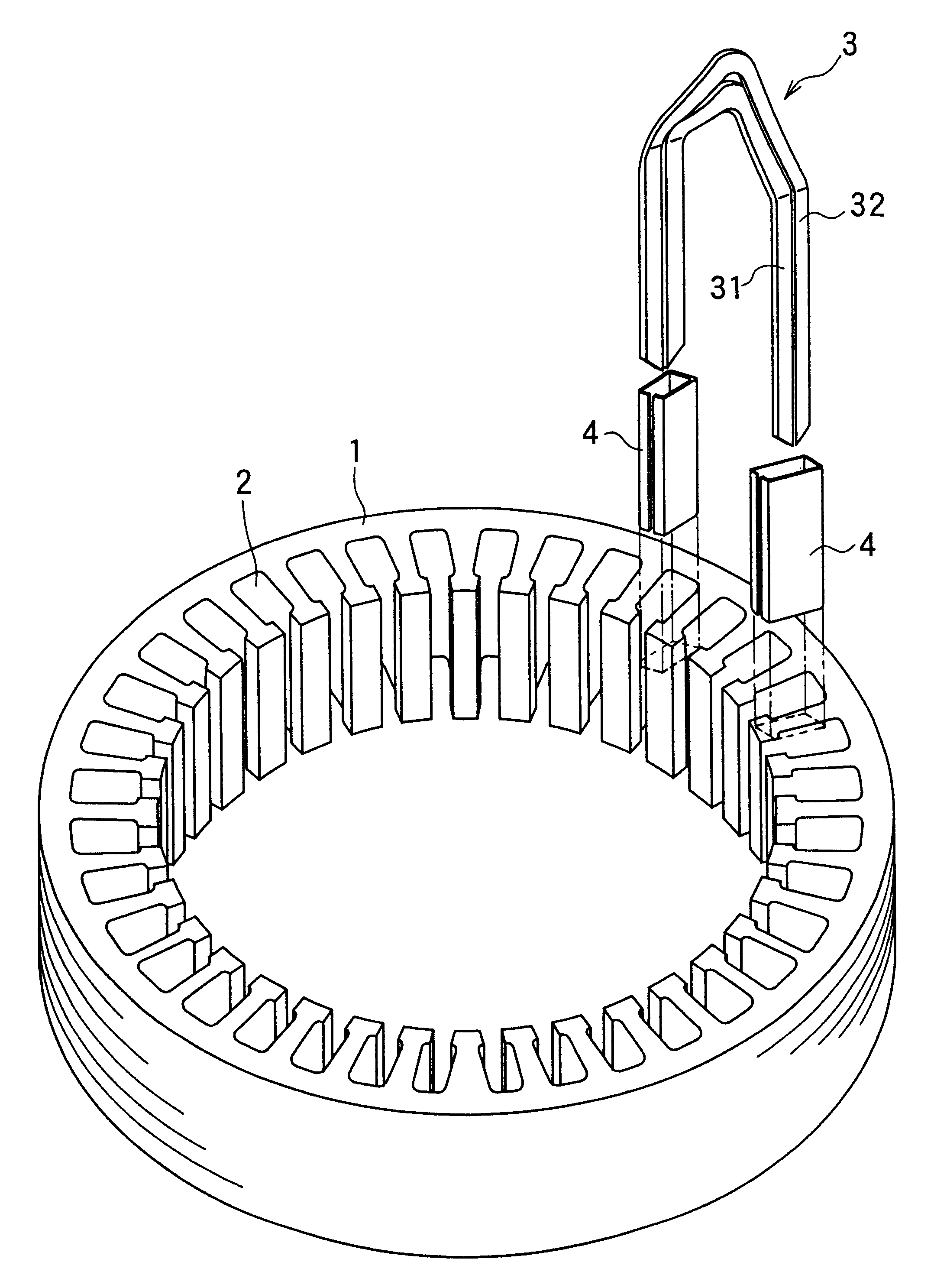
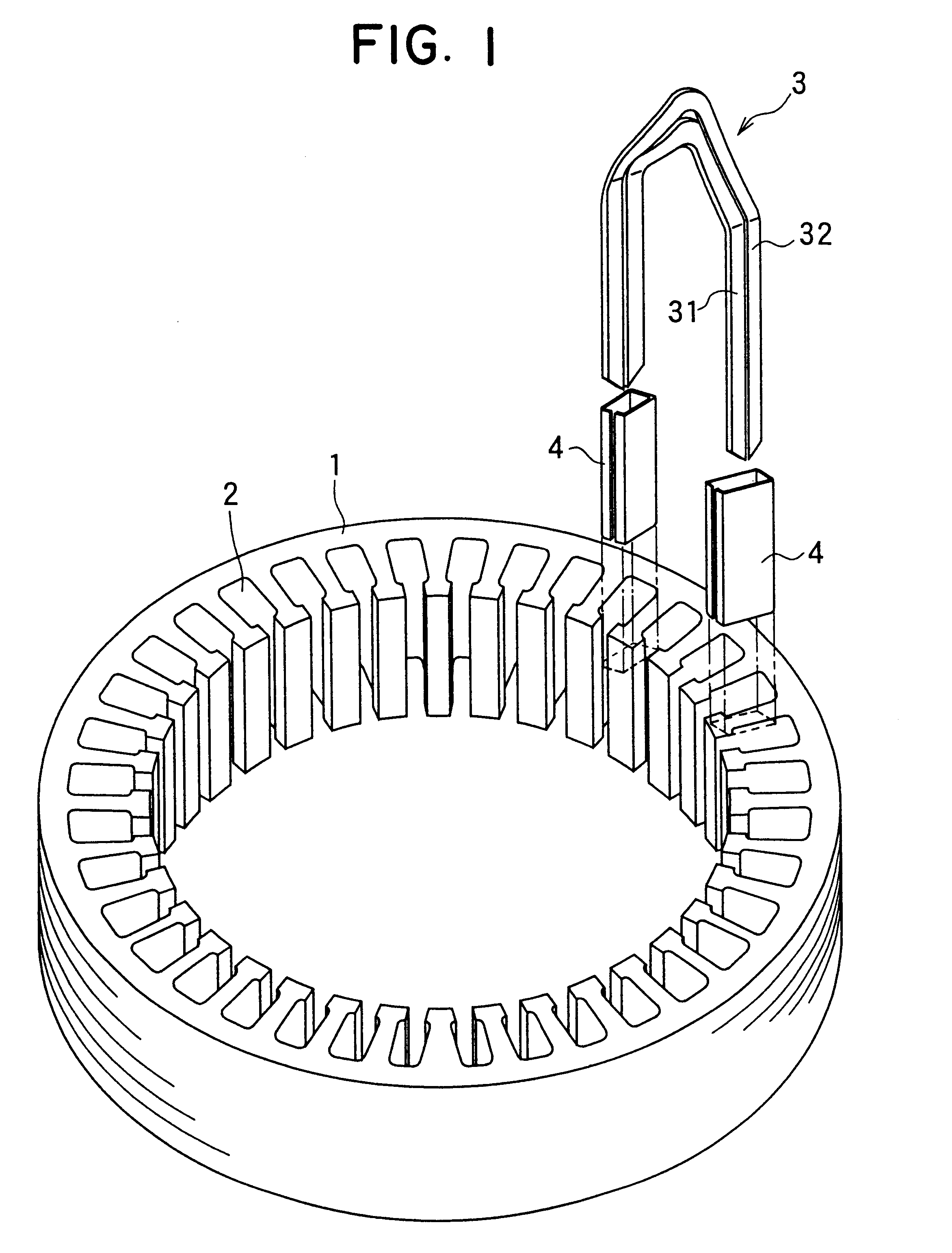
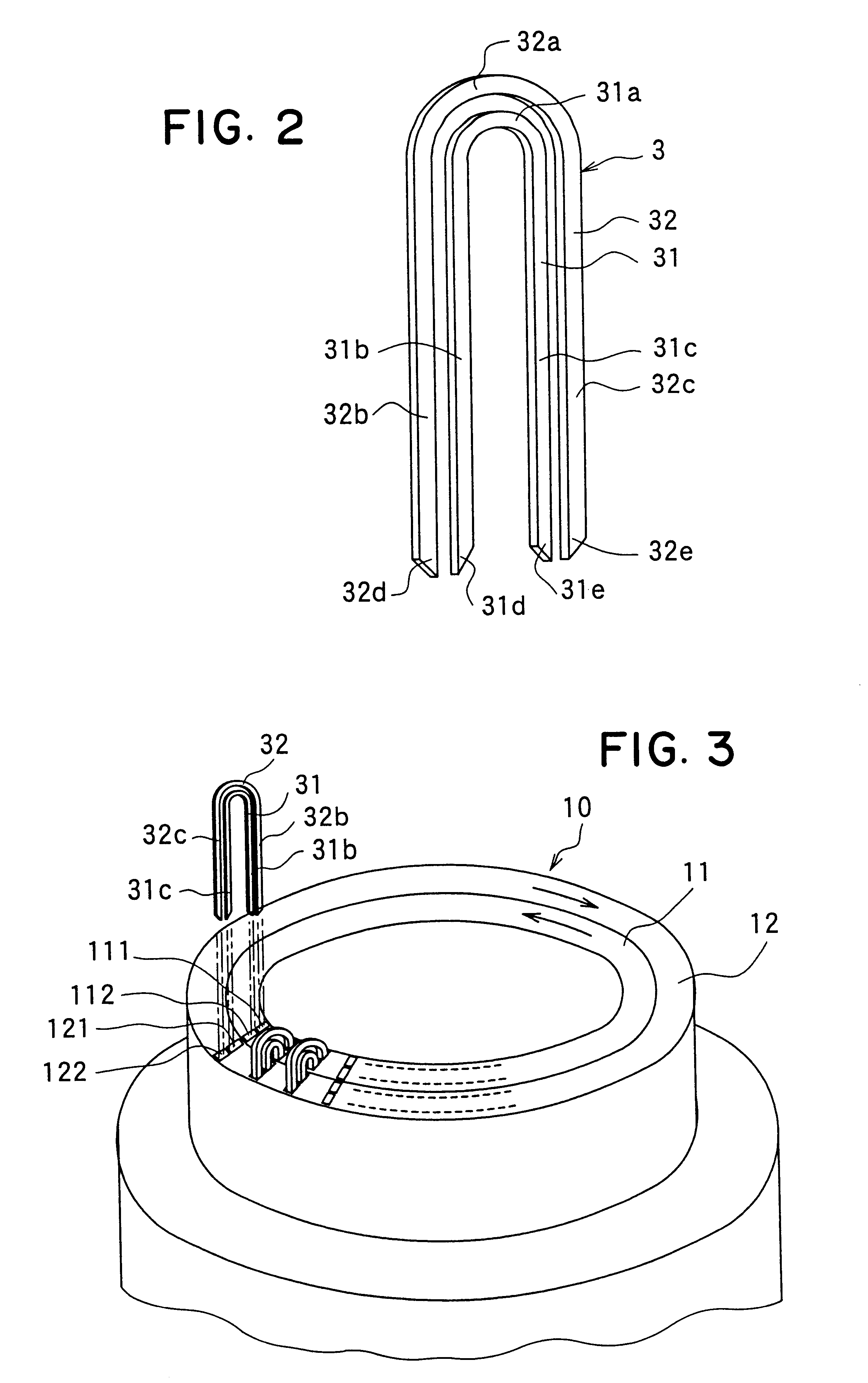
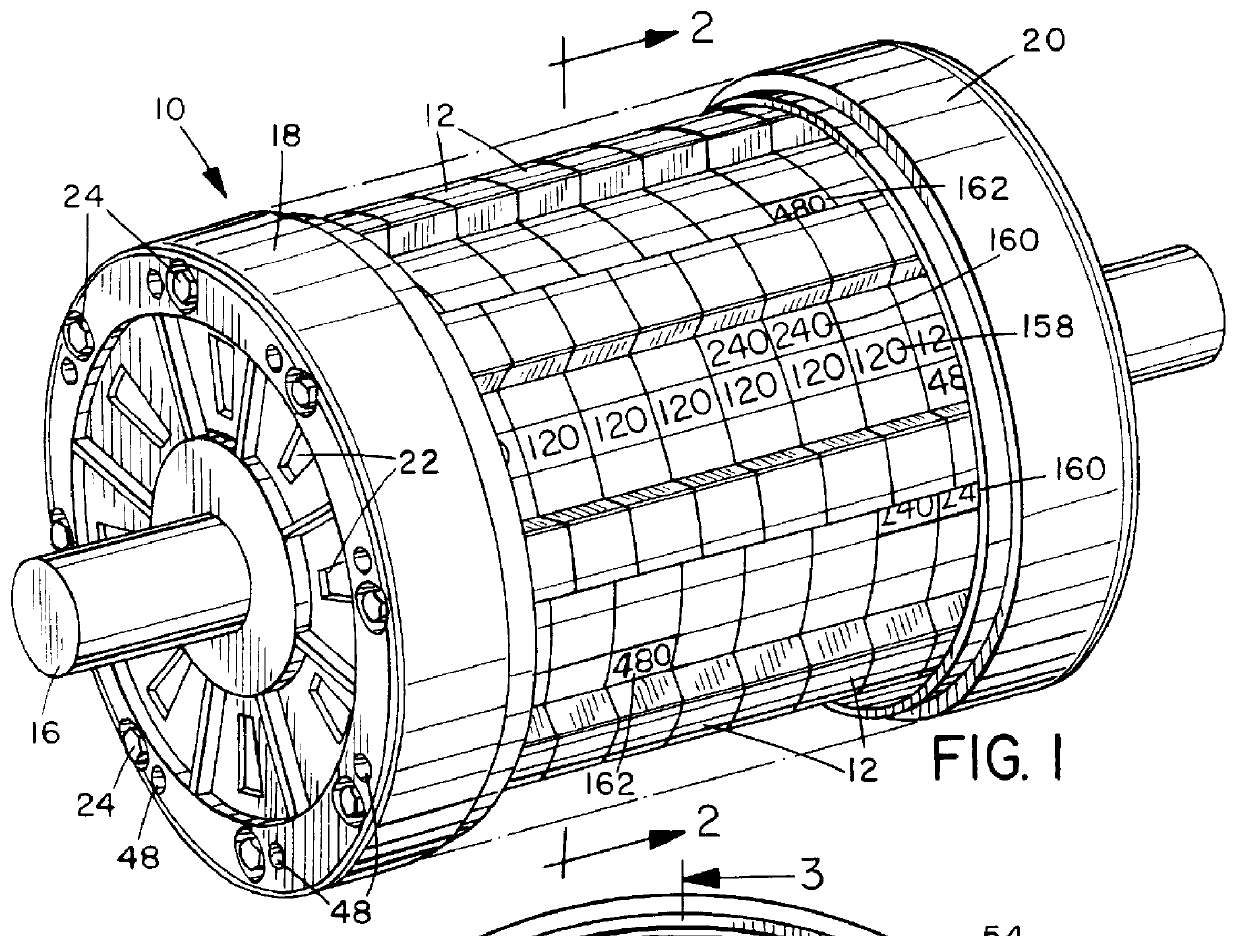
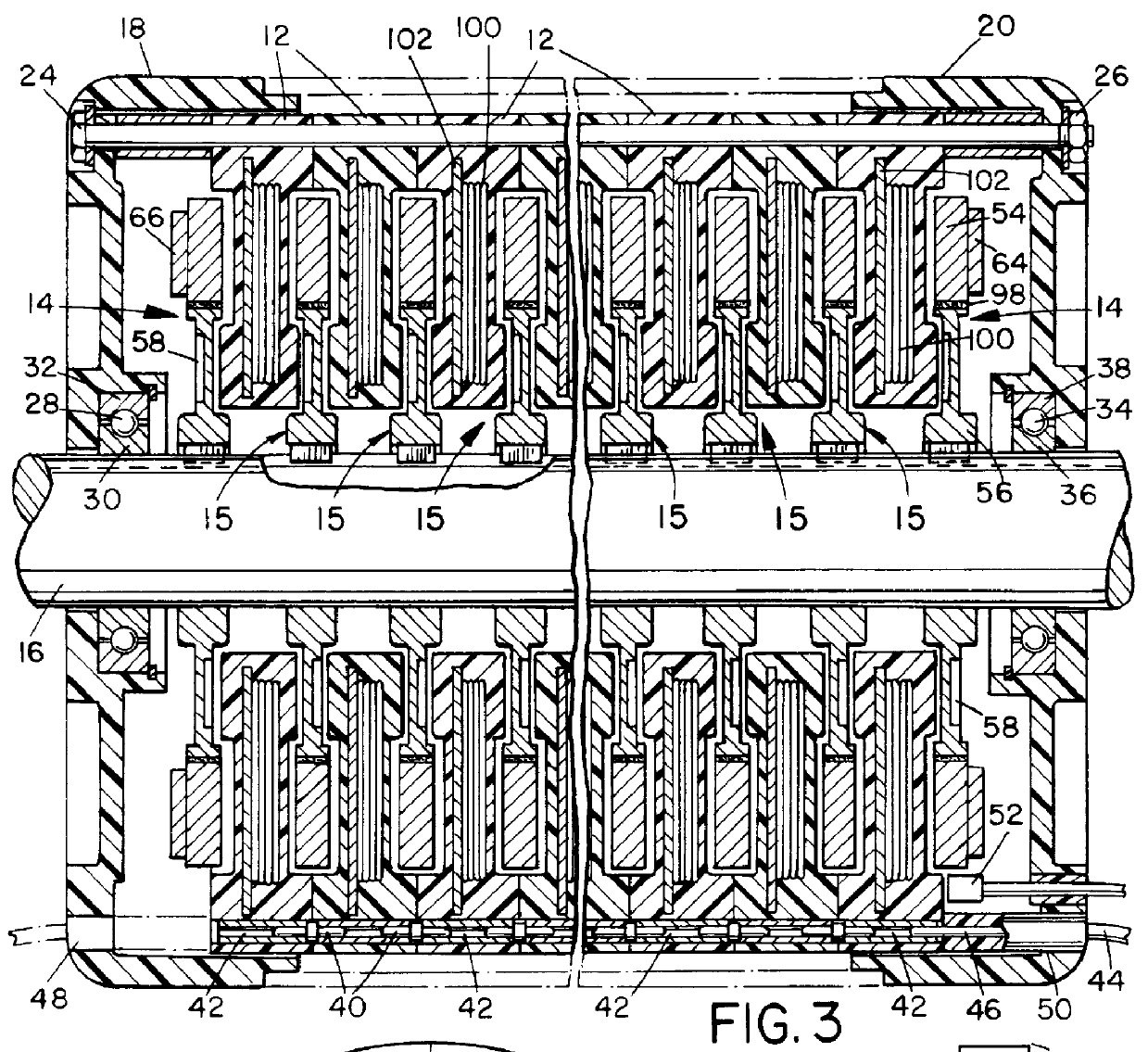
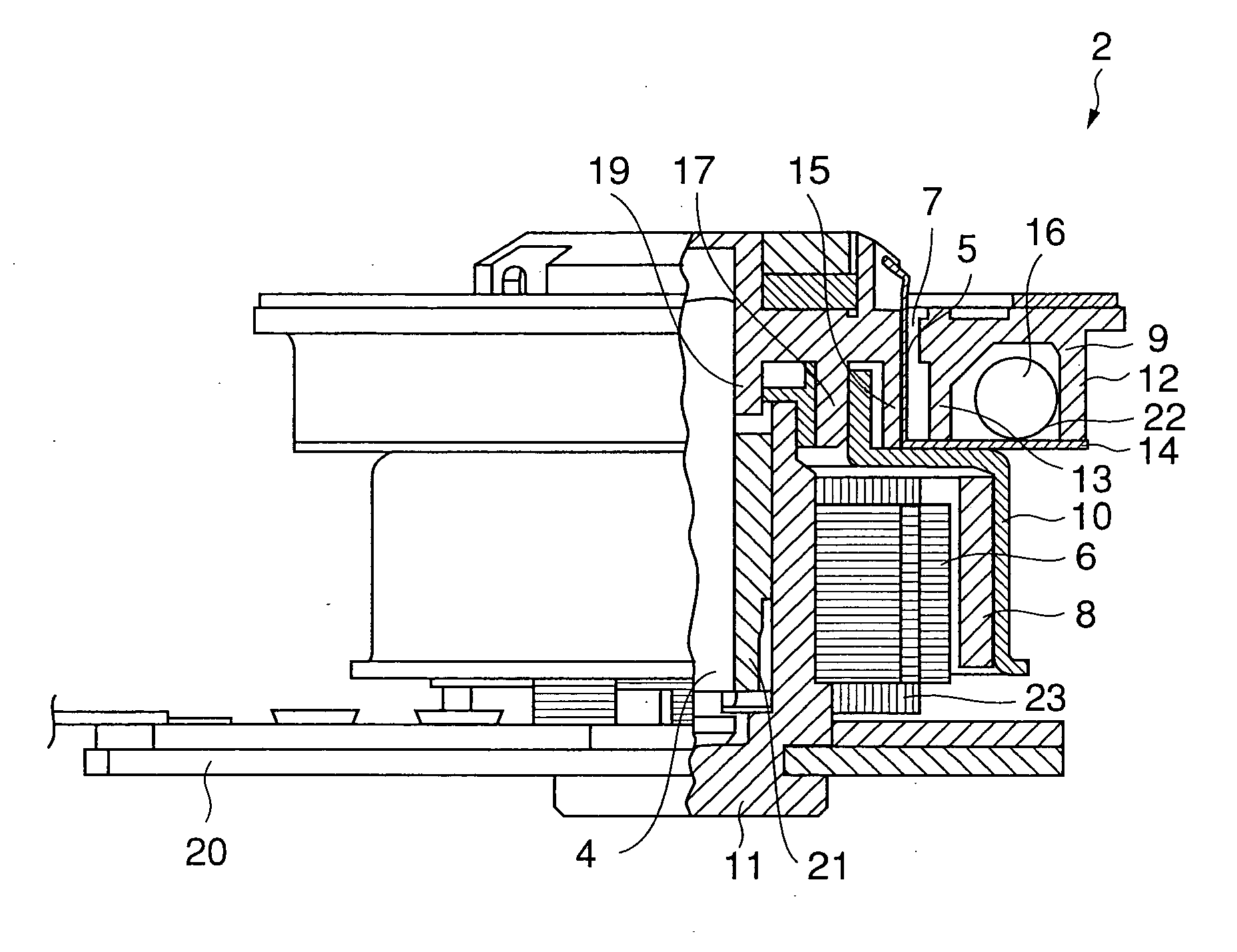
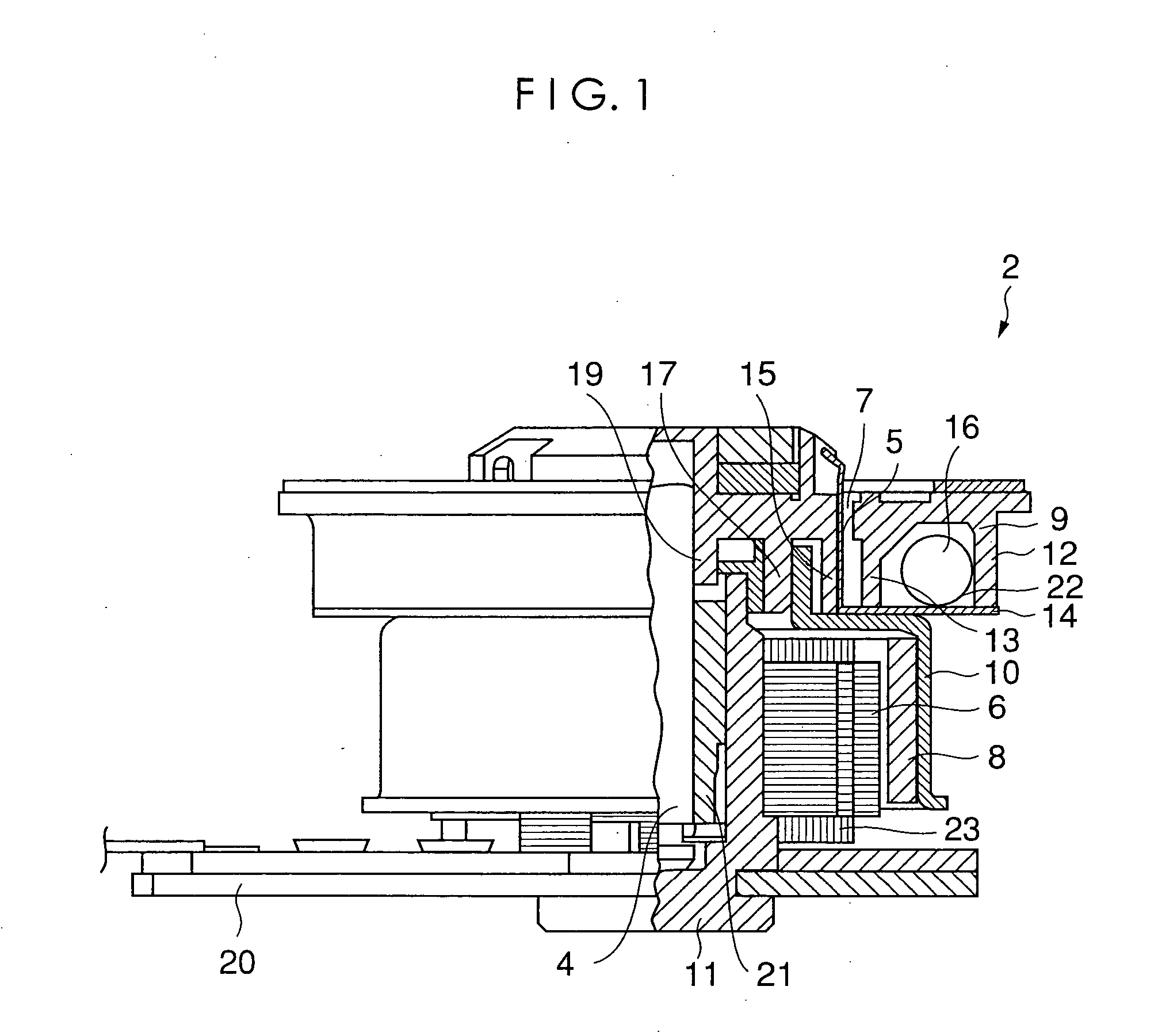
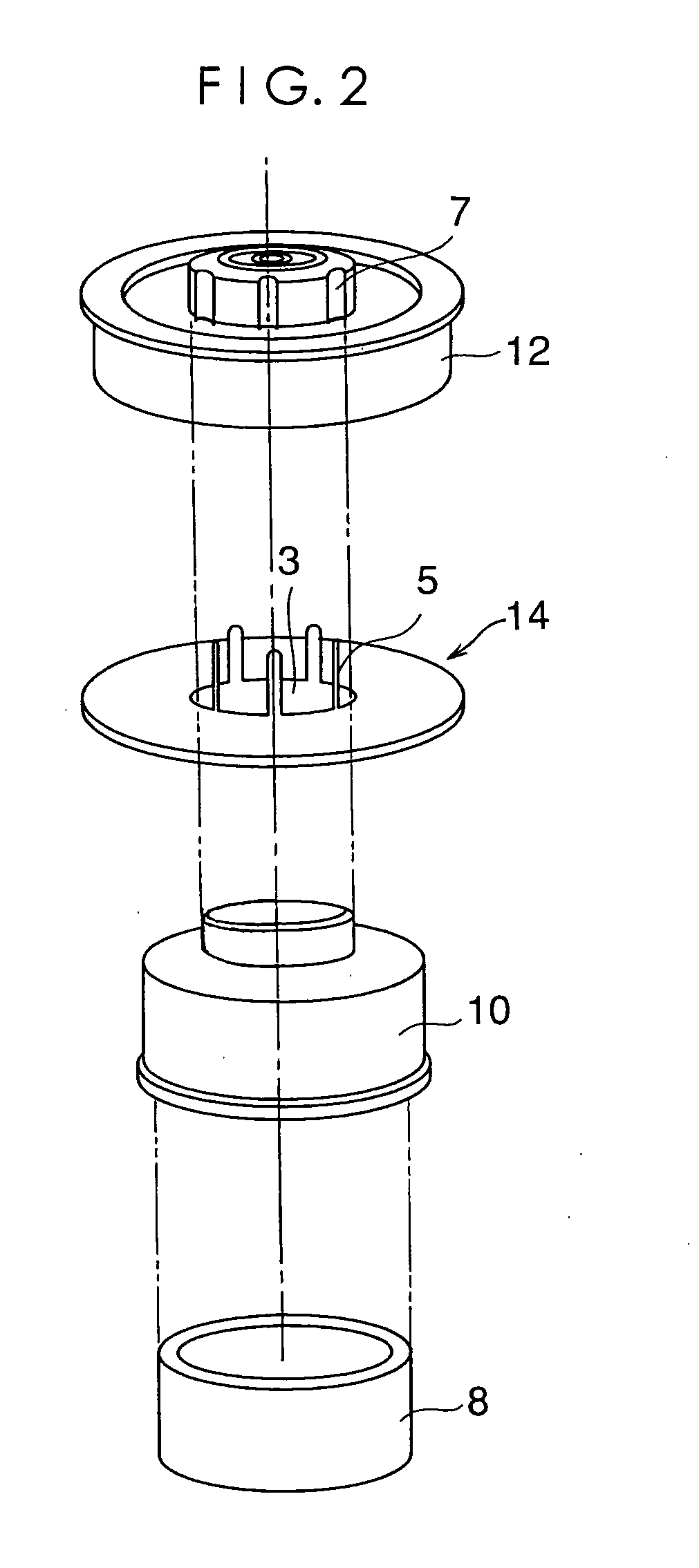
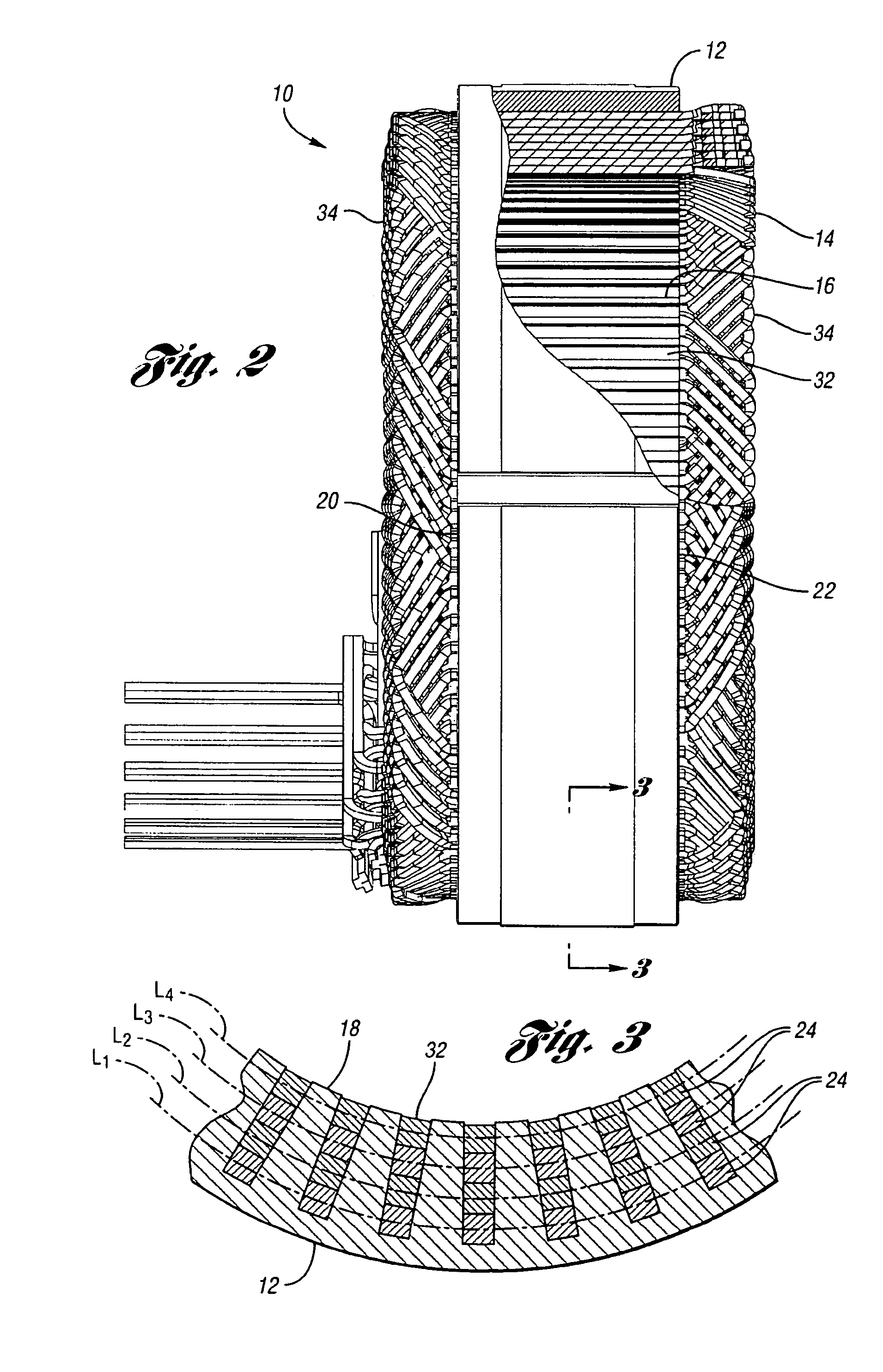
Method and apparatus for manufacturing AC-generator's stator for vehicle
InactiveUS6249956B1Positioning-accuracy can be improvedAvoid damageWire articlesForging/hammering/pressing machinesElectrical conductorEngineering
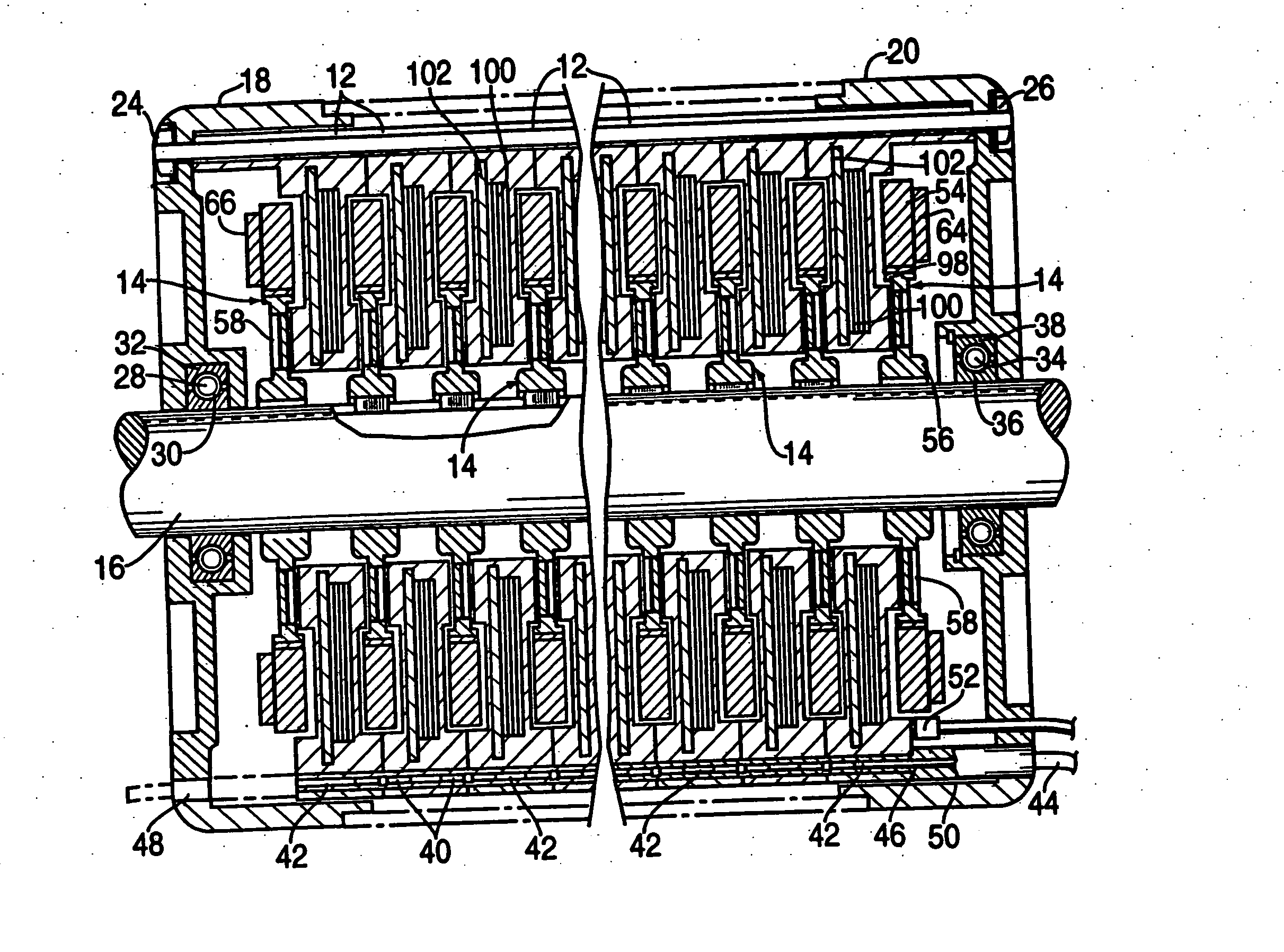
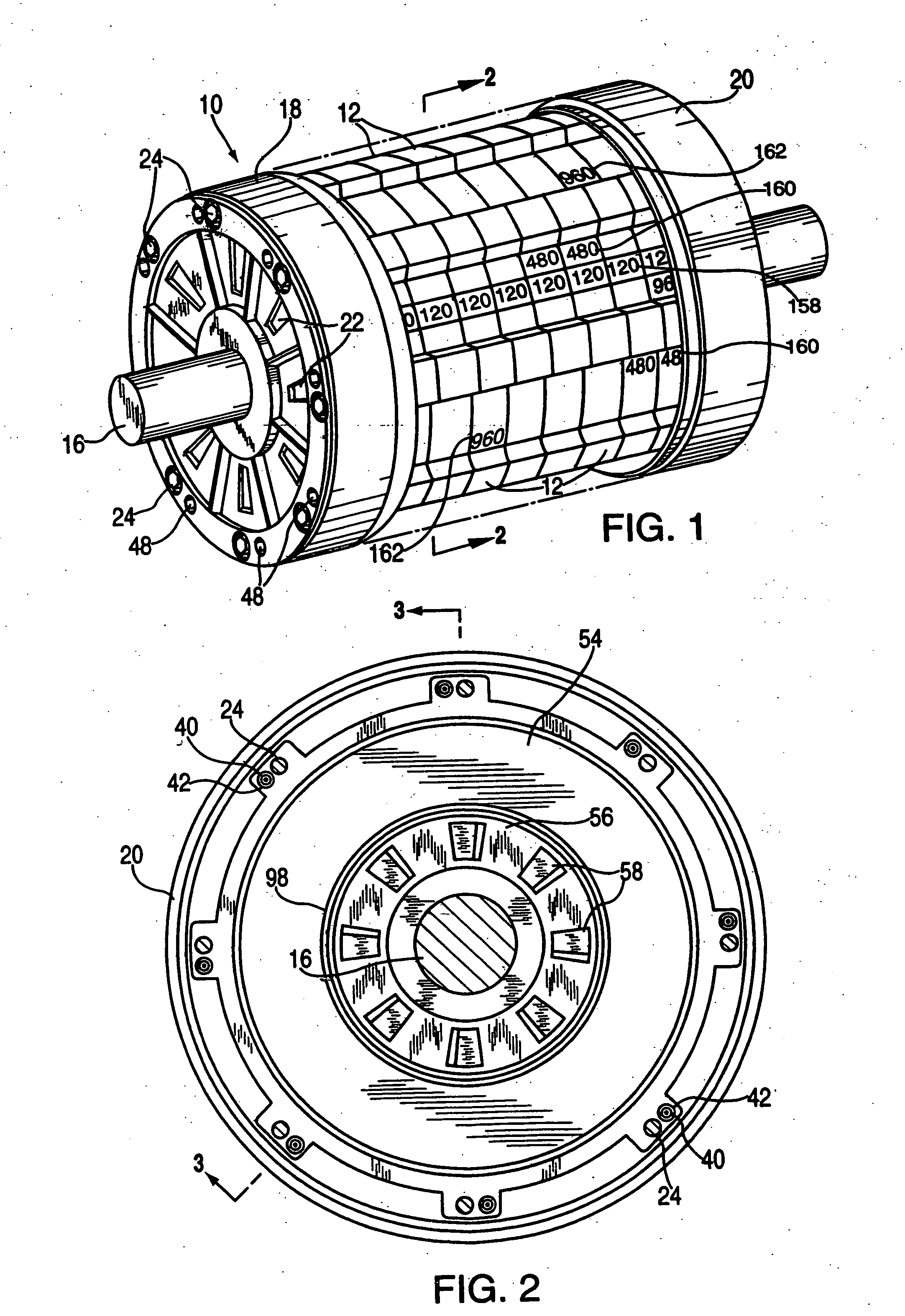
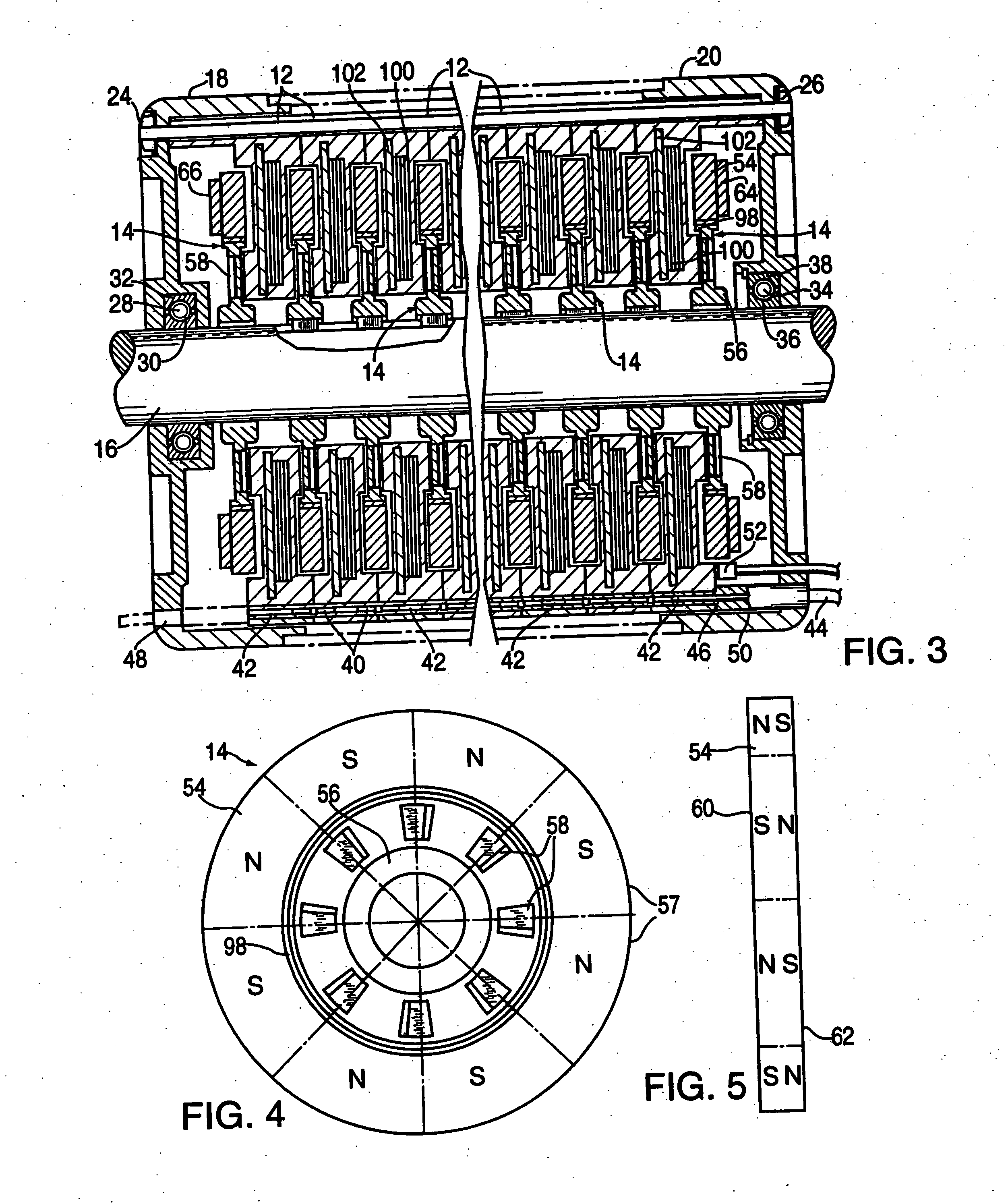
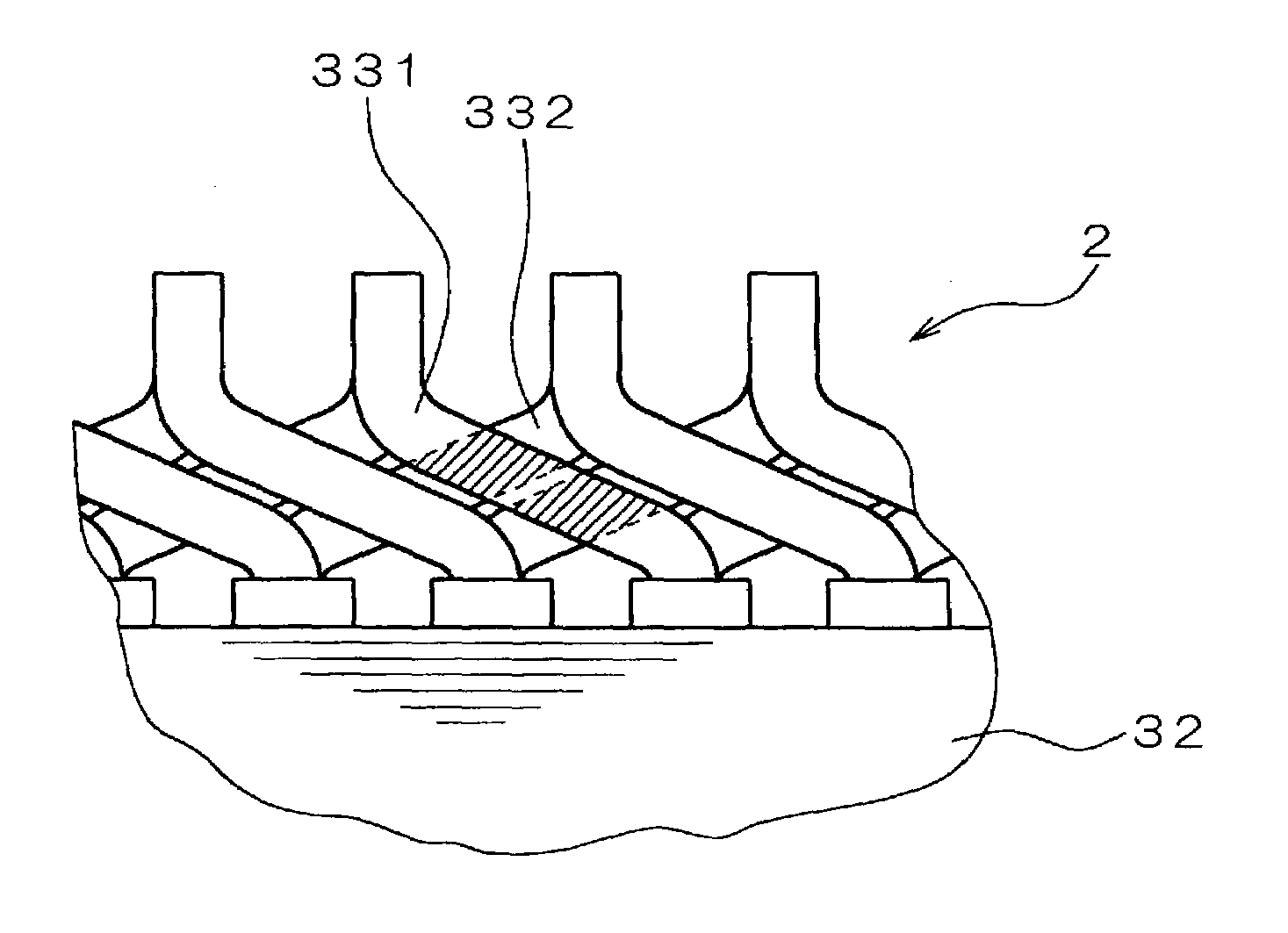
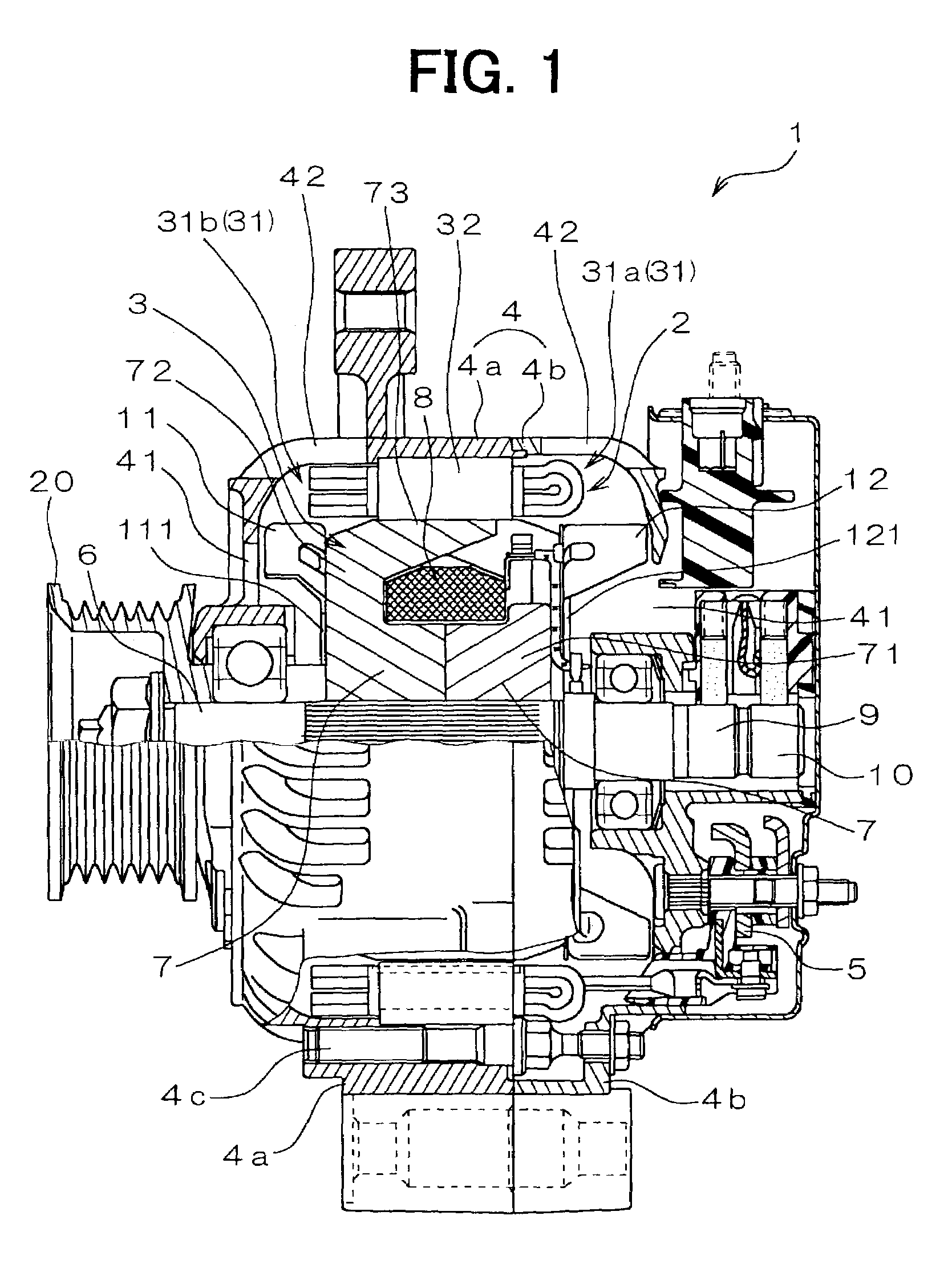
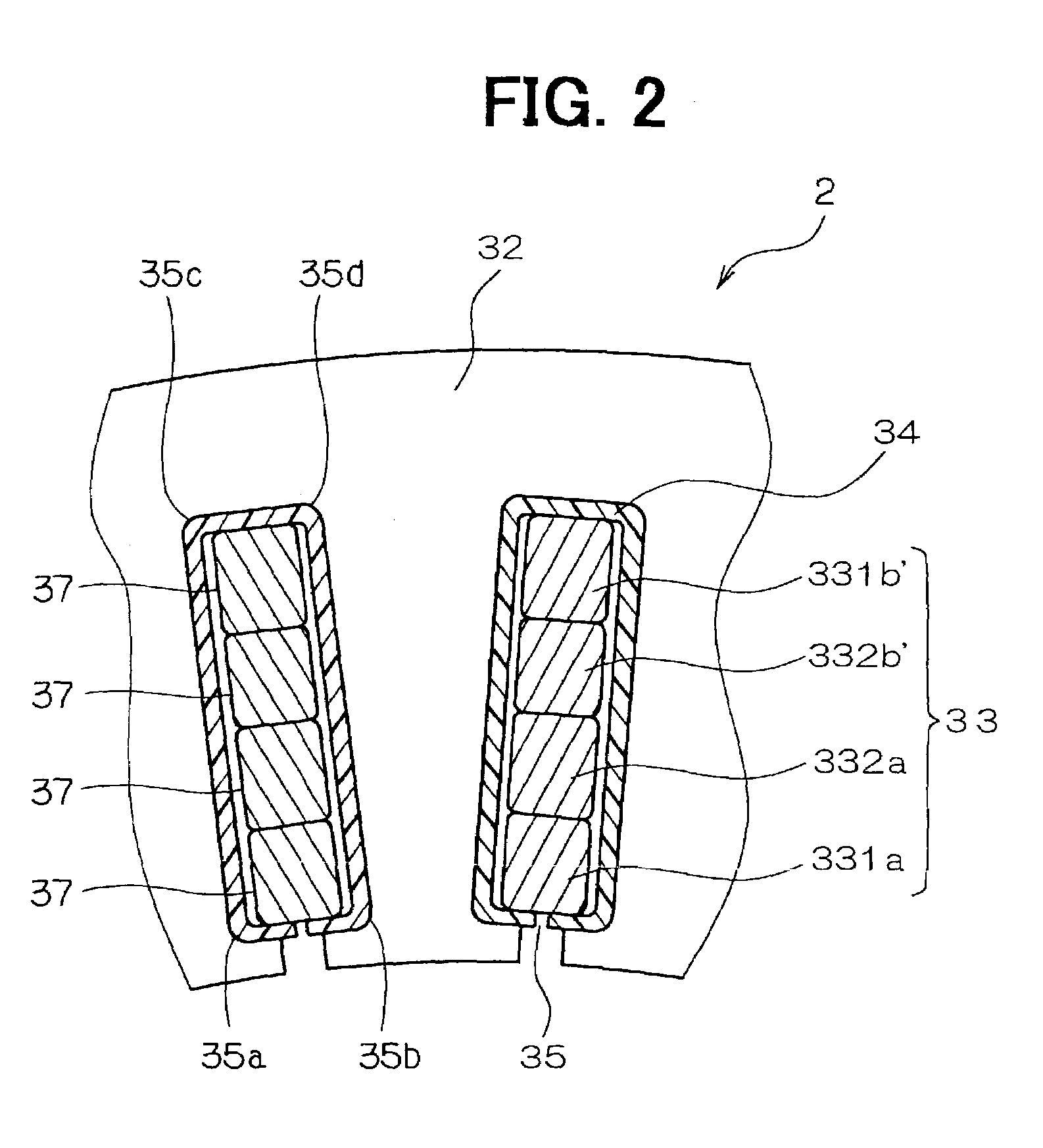
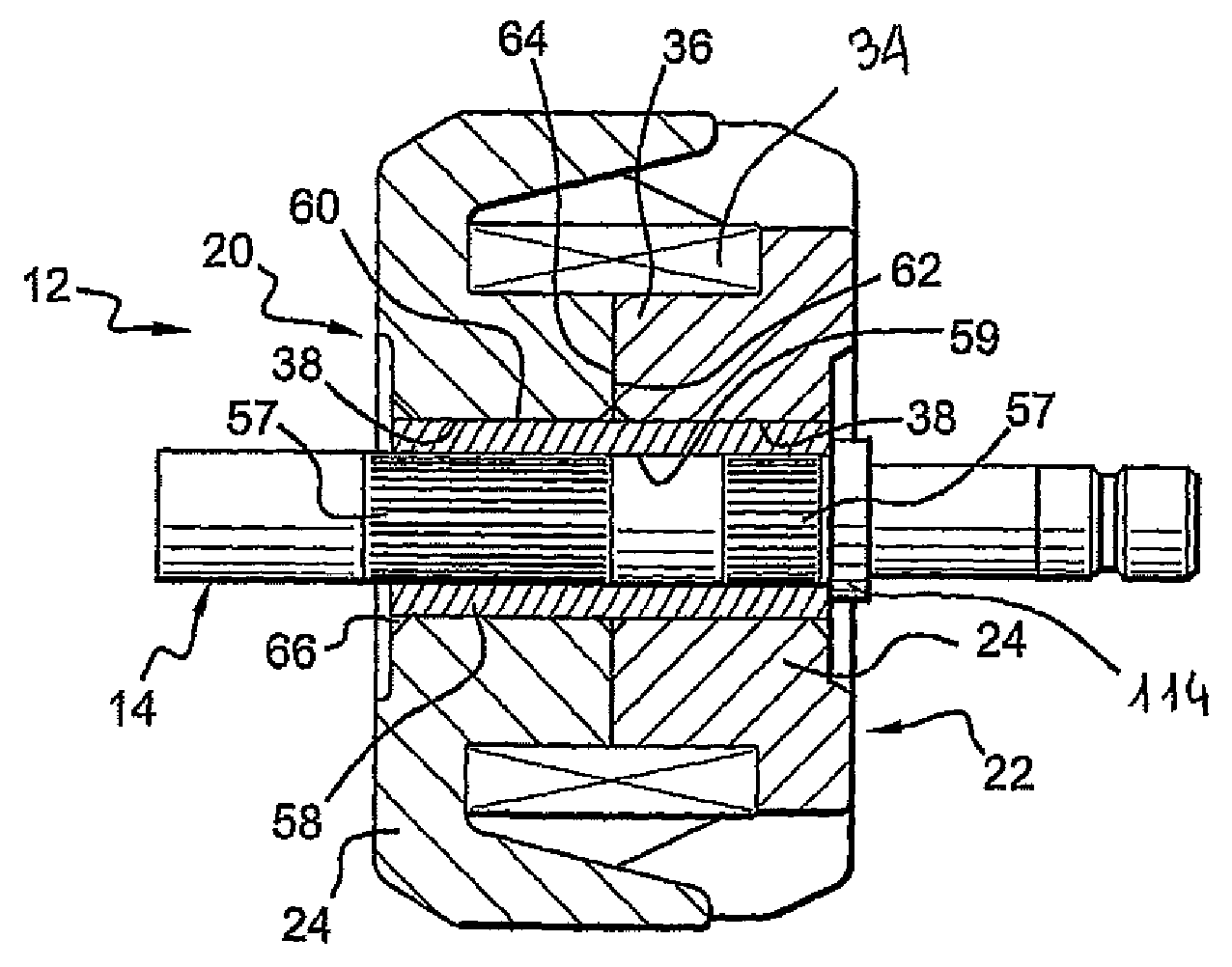
The object of the present invention is to provide a method and an apparatus for manufacturing a stator to improve accuracy in inserting conductor segments (3, 31, 32) into slots (2). The apparatus according to the present invention comprises a conductor holder (21, 22) holding the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) and an axial-moving-mechanisms (214) moving the conductor holder (21, 22) relative to a stator core (1) in an axial direction. The conductor holder (21, 22) holds straight portions (31b, 31c, 32b, 32c) of the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) to be inserted into the slots (2) from one end of the stator core (1).
Owner:DENSO CORP
Motor generator including interconnected stators and stator laminations
InactiveUS6163097AMaximization of overall densityShort gapWindings insulation shape/form/constructionAsynchronous induction motorsCross-linkElectrical conductor
An axial field motor / generator having a rotor that includes at least three annular discs magnetized to provide multiple sector-shaped poles. Each sector has a polarity opposite that of an adjacent sector, and each sector is polarized through the thickness of the disc. The poles of each magnet are aligned with opposite poles of each adjacent magnet. Metal members adjacent the outermost two magnets contain the flux. The motor / generator also has a stator that includes a stator assembly between each two adjacent magnets. Each stator assembly includes one or more conductors or windings. Although the conductors may be formed of wire having a round, uniform cross-section, they may alternatively be formed of conductors having a tapered cross-section that corresponds to the taper of the sectors in order to maximize the density of the conductor in the gap between axially adjacent poles. The conductors may also alternatively be formed of traces in a printed circuit, which may have one or more layers. Each stator assembly may be removably connectable to another stator assembly to provide modularity in manufacturing and to facilitate selection of the voltage at which the motor / generator is to operate. Electrical contacts, such as pins extending from the casing, may removably connect the conductors of adjacent stator assemblies. A magnet may be dynamically balanced on the shaft by hardening a thin ring of cross-linked resin between the magnet and the shaft while the shaft is spun, using ultraviolet light to polymerize the resin.
Owner:SMITH TECH DEV LLC +1
Stator core, an electric motor in which it is utilized, and method of manufacturing a stator core
ActiveUS20050067912A1Low production costExtended service lifeMagnetic circuit stationary partsCentering/balancing rotorsEngineeringOblique line
In a stator core is formed by laminated strip-shaped straight cores including a plurality of teeth portions, bent portions being provided with V-shaped notches, which define V-shaped gaps opened to one direction and interposing between each of the teeth portions, the straight cores being formed into an annular configuration by bending the bent portions in a direction so as to close the V-shaped notches and circular holes being provided at the bent portions so as to form a series of gaps between each of the teeth portions. The straight cores further include deformation preventing portions formed on the bent portions by cutting off a part of a pair of oblique lines defining the V-shaped notches toward the circular holes so as to expand the gaps of the V-shaped notches and the circular holes for preventing the bent portions from deforming by stress of bending process.
Owner:NIDEC SHIBAURA CORP
Method for selectively coupling layers of a stator in a motor/generator
InactiveUS6181048B1Maximization of overall densityShort gapWindings insulation shape/form/constructionManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesCross-linkElectrical conductor
An axial field motor / generator having a rotor that includes at least three annular discs magnetized to provide multiple sector-shaped poles. Each sector has a polarity opposite that of an adjacent sector, and each sector is polarized through the thickness of the disc. The poles of each magnet are aligned with opposite poles of each adjacent magnet. Metal members adjacent the outermost two magnets contain the flux. The motor / generator also has a stator that includes a stator assembly between each two adjacent magnets. Each stator assembly includes one or more conductors or windings. Although the conductors may be formed of wire having a round, uniform cross-section, they may alternatively be formed of conductors having a tapered cross-section that corresponds to the taper of the sectors in order to maximize the density of the conductor in the gap between axially adjacent poles. The conductors may also alternatively be formed of traces in a printed circuit, which may have one or more layers. Each stator assembly may be removably connectable to another stator assembly to provide modularity in manufacturing and to facilitate selection of the voltage at which the motor / generator is to operate. Electrical contacts, such as pins extending from the casing, may removably connect the conductors of adjacent stator assemblies. A magnet may be dynamically balanced on the shaft by hardening a thin ring-of cross-linked resin between the magnet and the shaft while the shaft is spun, using ultraviolet light to polymerize the resin.
Owner:SMITH TECH DEV LLC +1
Axial field electric machine
InactiveUS20060012263A1Minimizes inventoryMaximize constantWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectrical conductorElectric machine
An axial field electric machine having an improved efficiency includes a number of magnetic elements (e.g., as a rotor) as annular disks magnetized to provide multiple sector-shaped poles. Each sector has a polarity opposite that of an adjacent sector, and each sector is polarized through the thickness of the disk. The poles of each disk are aligned with opposite poles of each adjacent magnet. Metal members adjacent the outermost disks contain the flux; The axial field electric machine also includes one or more conductor elements (e.g., as a stator) which include a number of conductor phases that traverse the flux emanating between poles of axially adjacent magnetic elements. The design of the axial field electric machine including the gap spacing between adjacent magnetic elements, the transition width between adjacent poles on each magnetic element, the number of poles, the number and width or conductor phases in the conductor element is based on the physical characteristics of the magnetic elements to increase efficiency.
Owner:SMITH STEPHEN H +1
Axial field electric machine
InactiveUS20020171324A1Windings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectrical conductorElectric machine
An axial field electric machine having an improved efficiency includes a number of magnetic elements (e.g., as a rotor) as annular disks magnetized to provide multiple sector-shaped poles. Each sector has a polarity opposite that of an adjacent sector, and each sector is polarized through the thickness of the disk. The poles of each disk are aligned with opposite poles of each adjacent magnet. Metal members adjacent the outermost disks contain the flux. The axial field electric machine also includes one or more conductor elements (e.g., as a stator) which include a number of conductor phases that traverse the flux emanating between poles of axially adjacent magnetic elements. The design of the axial field electric machine including the gap spacing between adjacent magnetic elements, the transition width between adjacent poles on each magnetic element, the number of poles, the number and width or conductor phases in the conductor element is based on the physical characteristics of the magnetic elements to increase efficiency.
Owner:SMITH STEPHEN H +1
Electrical machine construction using axially inserted teeth in a stator ring or armature
InactiveUS6880229B2Magnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesBobbinRadial position
An electrical machine using a plurality of separate teeth that can be axially inserted into a stator ring or armature after receiving a bobbin or form wound coil. Each tooth contains a primary locating structure and a secondary locating structure which respectively set the radial position and the angular position of the teeth in a stator ring. This construction can also be used with internal motor armatures. The primary and secondary locating structures have a size equal to or smaller than the portion of the tooth that holds the coil. This allows insertion of a pre-wound coil over these features without interference. The use of separate stator or armature teeth that are press fitted into the stator ring or armature allows the use of coil types that could not be inserted into a one piece stator or armature and tooth materials with optimum magnetic properties.
Owner:DURA TRAC MOTORS INC
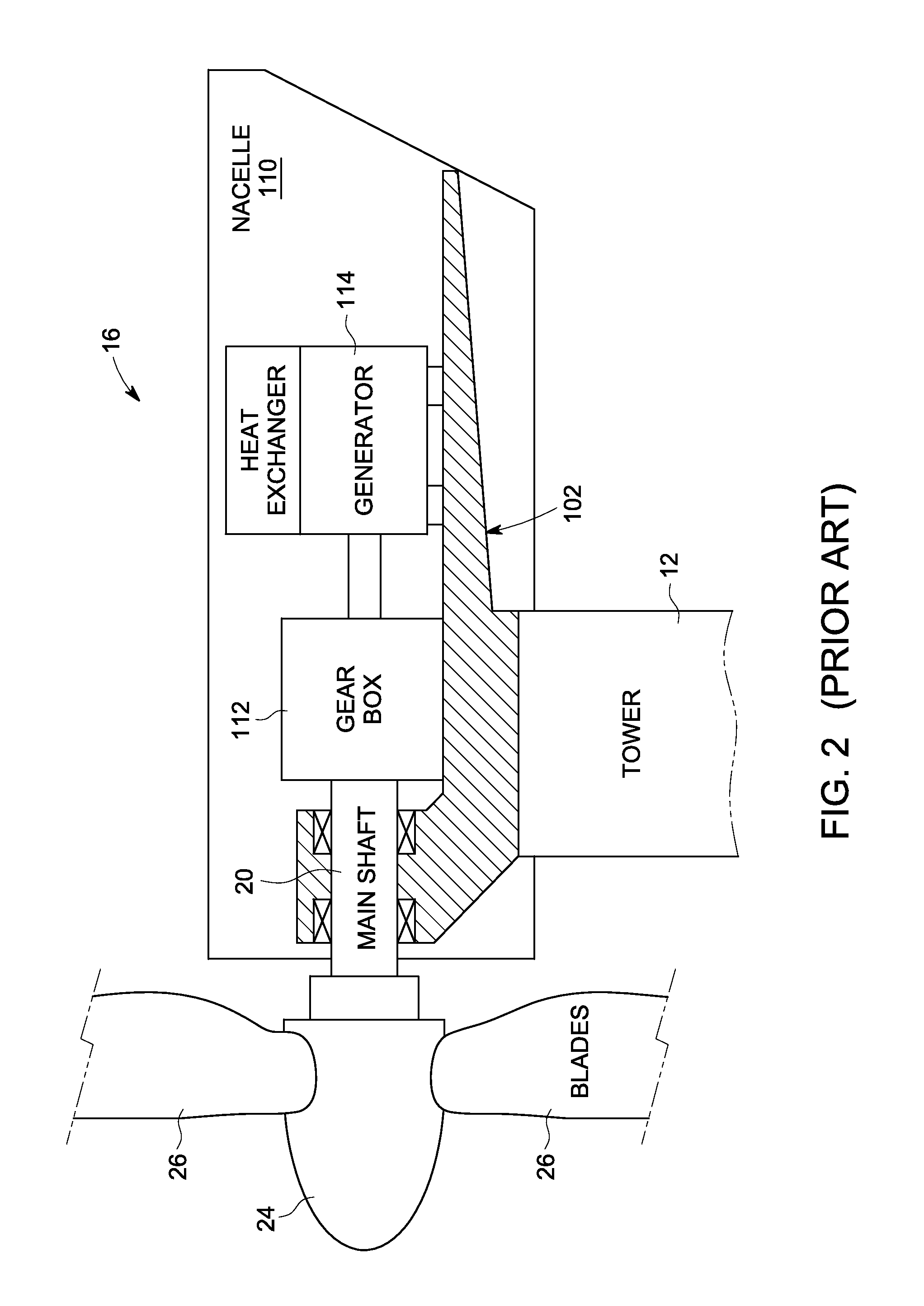
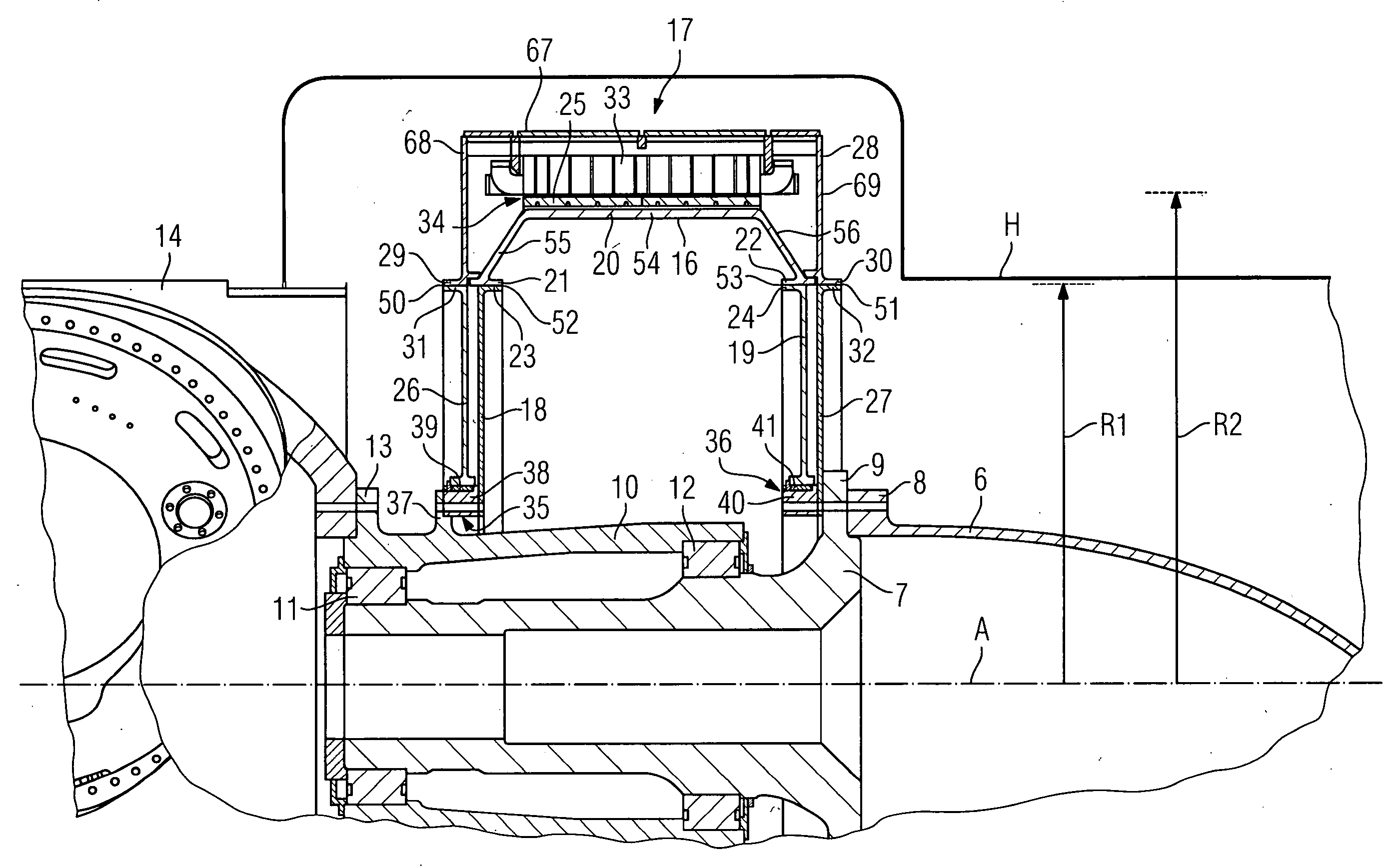
Arrangement for a direct drive generator for a wind turbine and method for the assembly of the generator
ActiveUS20090134627A1Easy to shipEasy to assembleWind motor assemblyWind motor supports/mountsTurbineWind force
The invention concerns an arrangement for a direct drive generator for a wind turbine, which generator comprises a stator with several stator segments each stator segment having at least one stator element for the power generation and which generator comprises a rotor pivotable around a centre axis of the generator and relatively to the stator with several rotor segments each rotor segment having at least one rotor element for the power generation, wherein said arrangement comprises at least one stator segment and at least one rotor segment, and wherein the at least one stator segment and the at least one rotor segment are able to be at least temporarily supported against each other. The invention concerns further a direct drive generator comprising such an arrangement, a wind turbine comprising such a direct drive generator as well as a method for the assembly of the direct drive generator.
Owner:FLENDER GMBH
Method of making a composite electric machine component of a desired magnetic pattern
InactiveUS6889419B2More powerLow costManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesApplying solid insulationElectric machineNon magnetic
A method of making composite electric machine components. Magnetic segments and non-magnetic segments are separately formed to green strength, and then arranged adjacent to each other in a desired magnetic pattern. A small amount of powder material is added in-between the segments, and the whole assembly is then sintered to form a sinterbonded composite component of high structural integrity.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Centring method in process of mounting generator rotor in threading mode
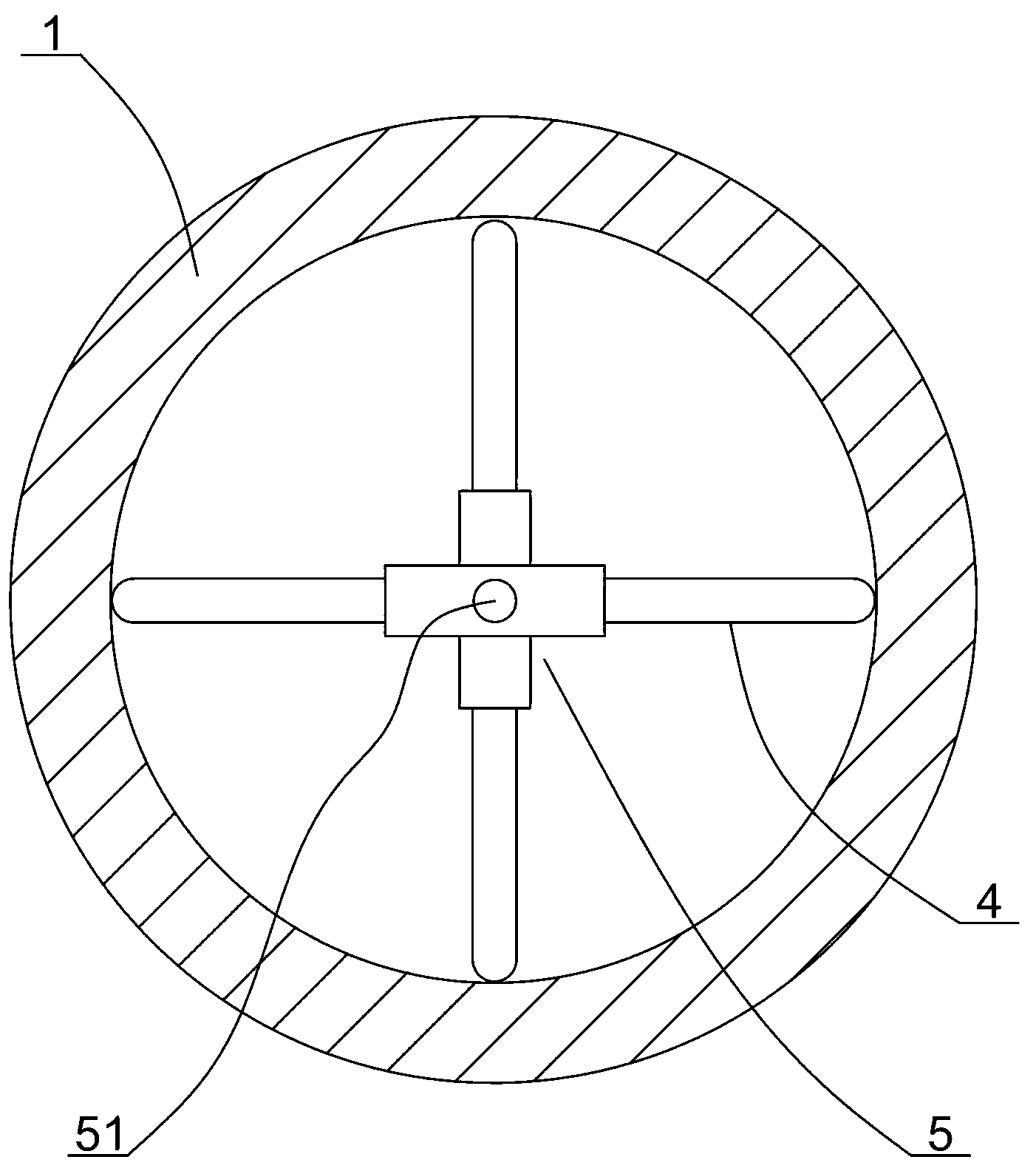
ActiveCN103296845AImprove coordinationLower requirementUsing optical meansCentering/balancing rotorsLaser transmitterEngineering
The invention discloses a centring method in the process of mounting a generator in a threading mode. The centring method comprises the steps of arranging a laser emitter on each side of the rotor, enabling the two laser emitters to be opposite to each other, adjusting the positions of the laser emitters to enable the laser beams emitted by the laser emitters to be located on the central line of a stator, arranging centring target boards at the two ends of the rotor correspondingly, arranging a circular centring ring at the position corresponding to the rotor central line, and keeping the imaging points of the laser beams on the centring target boards to be in the circular centring ring when the rotor is mounted in the threading mode. Therefore, the rotor is kept to be coaxial with the stator, and friction and collision are avoided. By means of the centring method in the process of mounting the generator in the threading mode, the coaxiality of the rotor and the stator can be observed and confirmed rapidly and conveniently, on-site coordination and command can be conducted conveniently when the rotor is mounted, and the rotor is guaranteed not to rub or collide with the stator in the whole mounting process.
Owner:NINGBO FUSHIDA ELECTRIC ENG
Split-pole magnetic module for electric machine rotors
InactiveUS20120133230A1Easy to insertMany of manufacturing complexityMagnetic circuit rotating partsElectronic circuit testingElectric machineMagnetic flux
A split-pole magnetic module for use in large permanent magnet machines. The split-pole magnetic module has at least two permanent magnets positioned within a lamination stack at an angle relative to each other so that magnetic flux enters a first portion of an outer surface of the lamination stack and exits a second portion of the outer surface of the lamination stack. Consequently, little if any magnetic flux passes through, or is carried by, the support structure of a rotor or a stator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
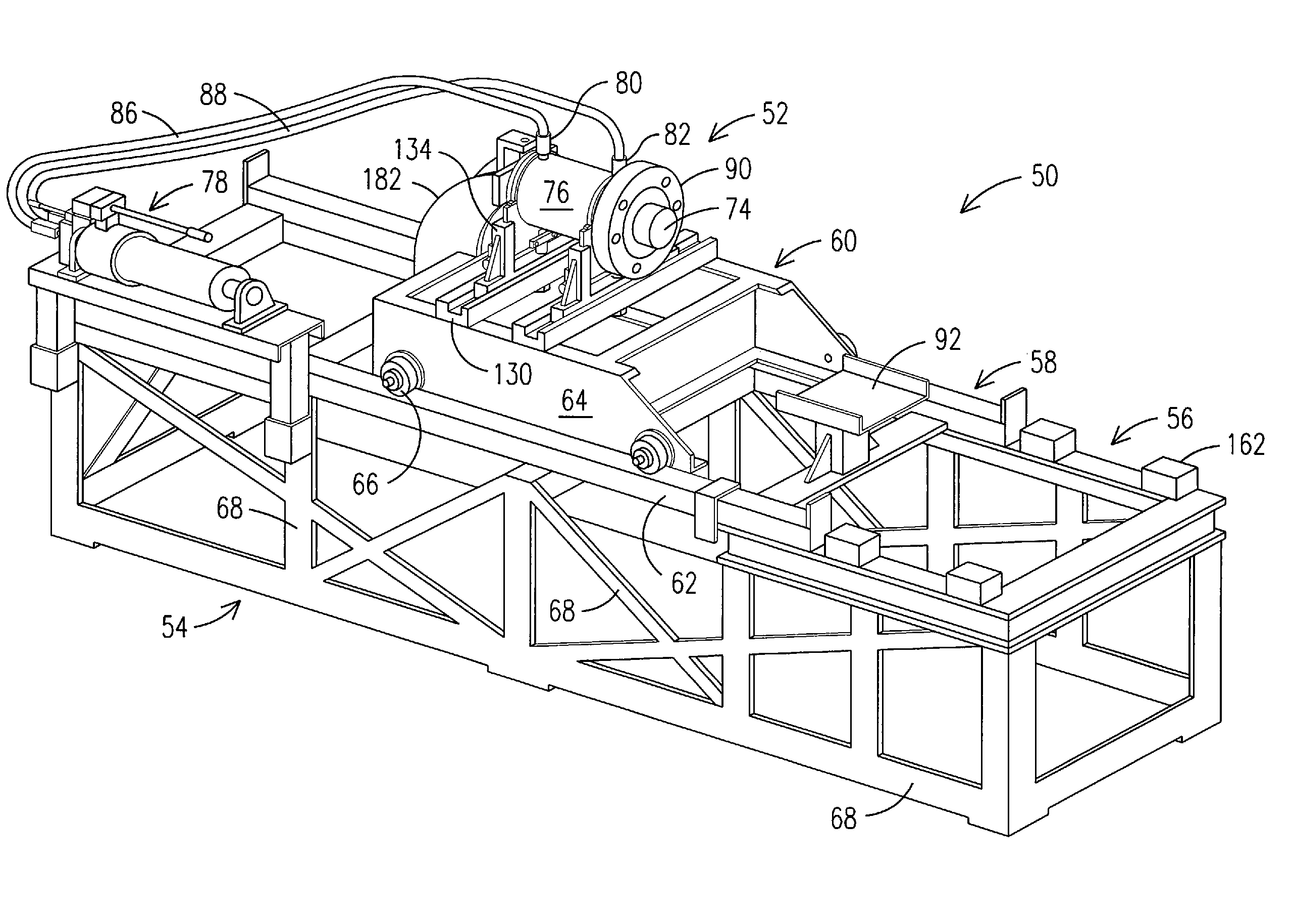
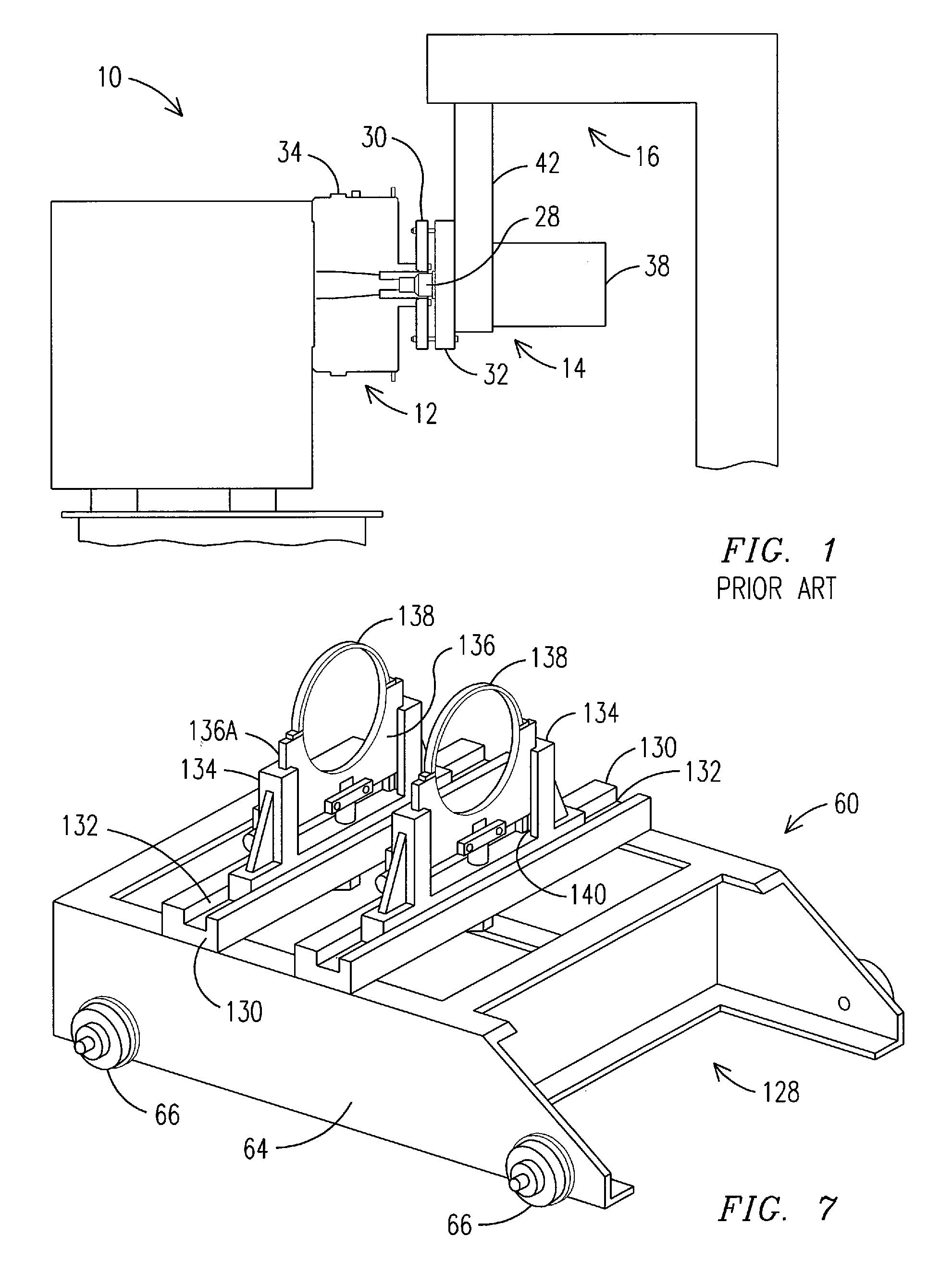
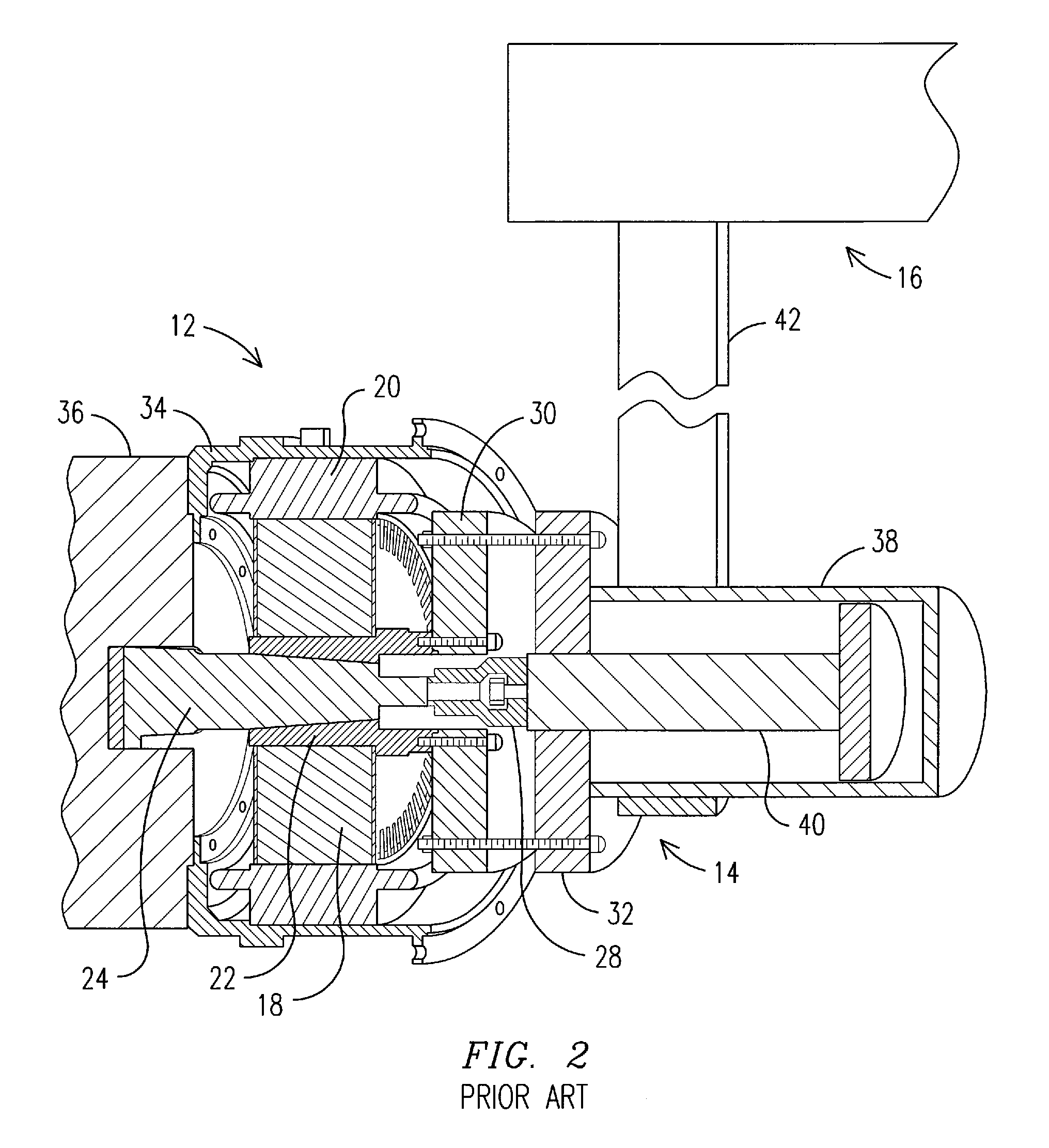
Apparatus and method for the disassembly and installation of electric motor components
An apparatus for removing and installing a rotor in an electric motor that coupled to a shaft of a machine comprises a table having a support area for supporting and mounting the machine and motor. A tool is positioned on the table to move back and forth relative to the machine and motor, and engages the rotor to remove and install the rotor. A flange on the tool is secured to a temporary flange on a rotor sleeve. The tool also includes a piston concentrically aligned with the rotor and shaft to engage the shaft. A driving mechanism is linked to the piston to actuate the piston in a backward or forward direction relative to the machine and motor. The tool housing, responsive to movement of the piston, moves on the table in a direction opposite to the direction of movement of the piston to remove or install the rotor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method of improving the overall operating efficiency of an electric motor-powered assembly
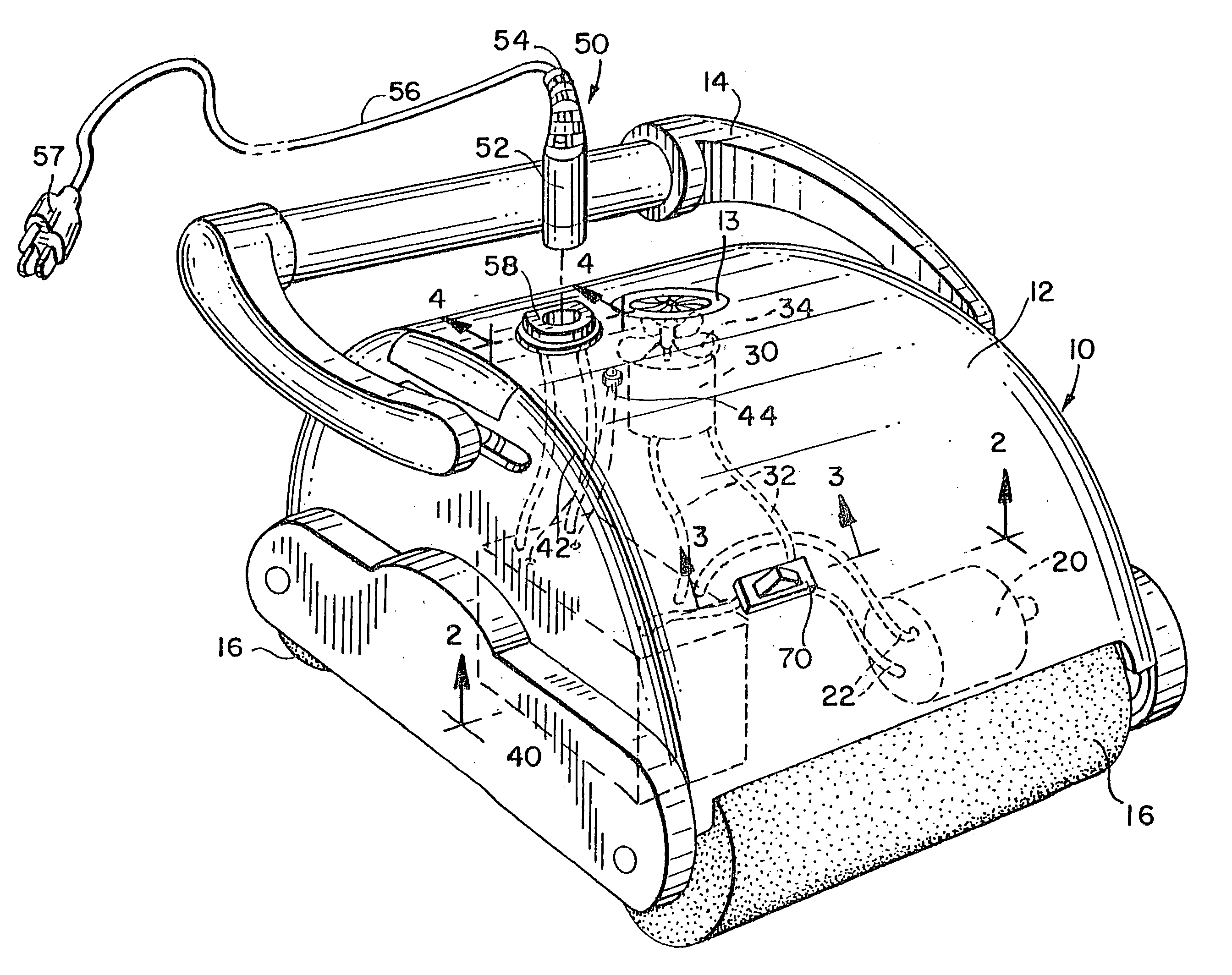
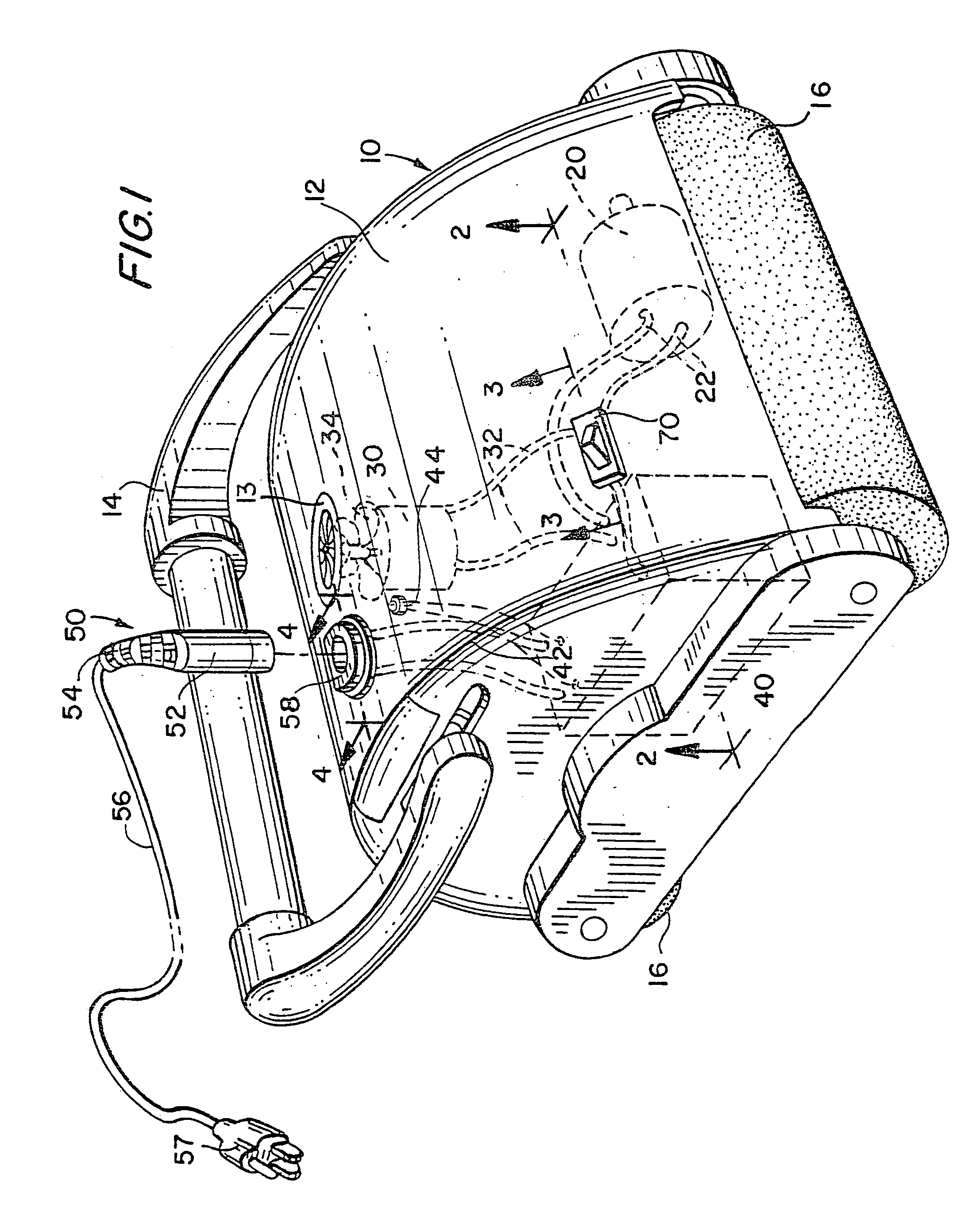
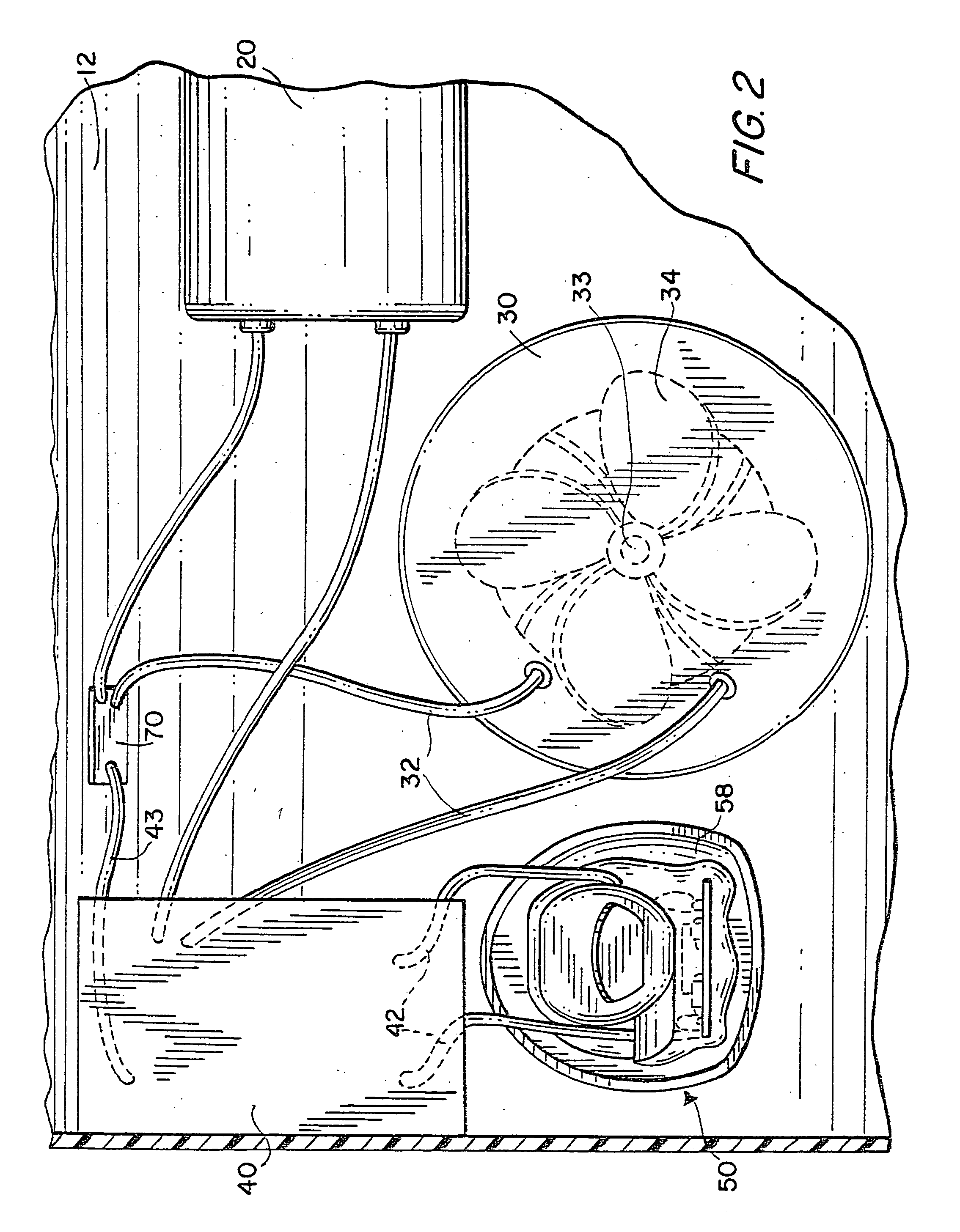
InactiveUS7143502B2Reduce frictionReduced Power RequirementsShrinkage connectionsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesMotor driveElectrical battery
A submersible robotic pool cleaner is provided with an integral sealed rechargeable battery and an inductive charging assembly, a first portion of which is mounted in the pool cleaner housing and during the charging, receives a second separate portion that is connected by a cable to a conventional power source. The pump motor drive shaft is treated with a specialized anti-friction lubricant composition to minimize frictional energy losses where the shaft contacts the seal(s) and any shaft bearing(s), to maximize efficiency and minimize the power consumption of the pump motor assembly and permit the pool cleaner to completely traverse the surfaces to be cleaned within the fully-charged power capacity of the battery.
Owner:AQUATRON
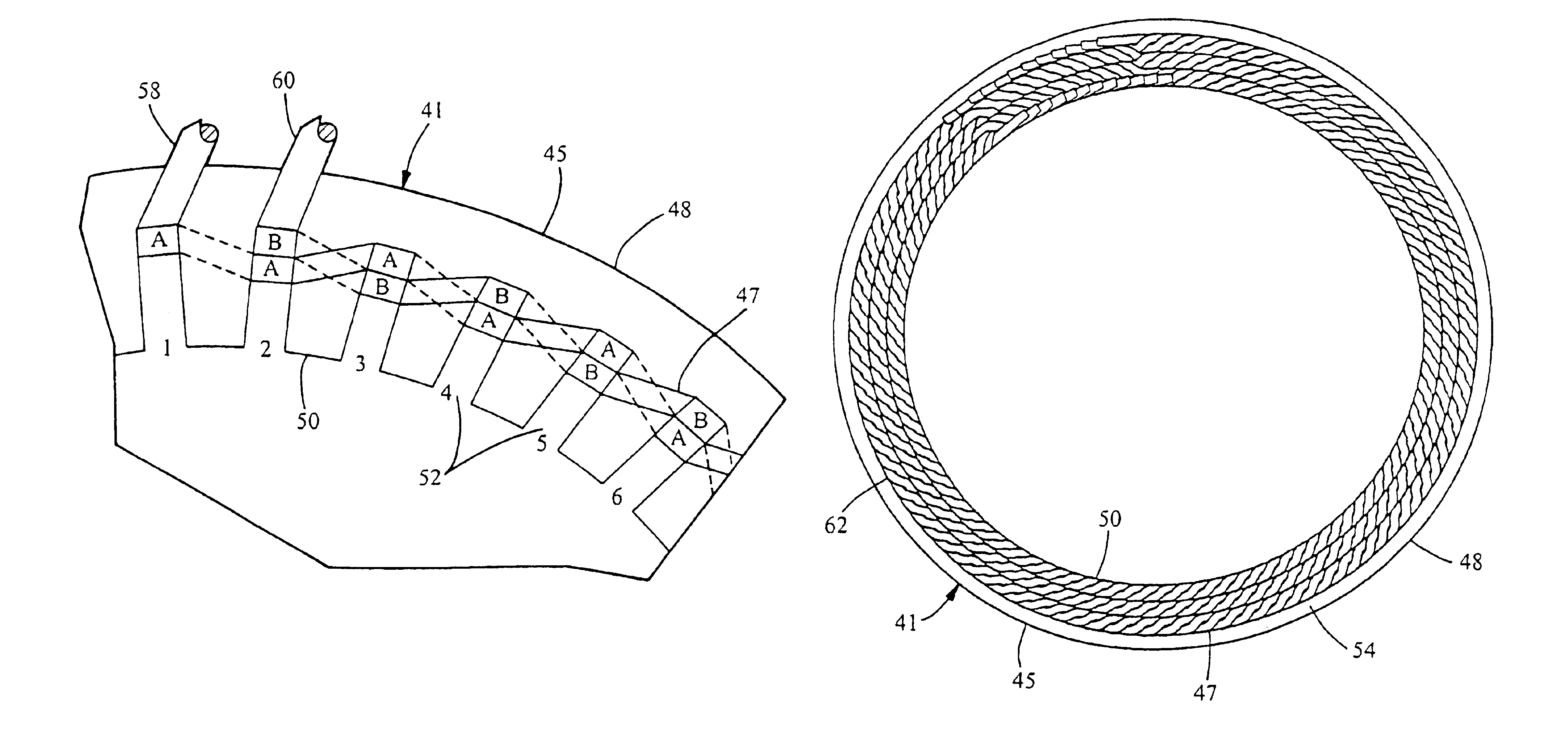
Automotive alternator stator assembly with rectangular continuous wire
InactiveUS6862797B2High slot space utilizationLow-end loop heightSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuitElectrical conductorAlternator
A method of forming a stator core assembly for an electric machine includes: providing two electrical conductors designated as conductor A and conductor B and winding the conductors into the winding slots.
Owner:VISTEON GLOBAL TECH INC
Method and assembling device for assembling and disassembling stator and rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN102097896ASimple structureSimple control structureCentering/balancing rotorsPermanent magnet synchronous motorRocker arm
The invention provides a method and assembling device for assembling and disassembling a stator and a rotor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method is characterized by adopting a rocker arm vertical permanent magnet synchronous motor stator and rotor assembling and disassembling method to fix a rotor on a rocker arm by a floating positioning seat, with the excircle and end face at the shaft extension end or the excircle and end face at the extension end of the rotor as the positioning surfaces, plugging a tapered positioning pin after the floating positioning seat is fixedly positioned, ensuring the axis of the rotor to be vertical to the horizontal plane and on the same straight line with the center line of a stator and arranging a pilot rod at the front end of the rotor; fixing the stator on a stator positioning disc by a bolt, with a bearing chamber at the end where the end cover is assembled and the end face of the bearing chamber as the positioning surfaces; installing the stator positioning disc on which the stator is installed in the center of a stator fixing station and ensuring the central axis of the stator to be vertical to the horizontal plane and coaxial with the floating positioning seat of the rotor; installing the rocker arm on a column, driving the rocker arm to move up and down via a screw drive mechanism and driving the rotor installed on the rocker arm to move up and down together when the rocker arm moves up and down to realize assembly and disassembly of the stator and the rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:襄阳中车电机技术有限公司 +1
Dynamoelectric machine stator and method for mounting prewound coils thereunto
InactiveUS20050110361A1Easy to insertReduce needWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectrical conductorRadial position
A dynamoelectric machine stator core for receiving a pre-formed stator winding includes a core body defining a cylindrical core main peripheral surface. A plurality of axially extending stator slots are circumferentially spaced in the core body. Each of the stator slots defines a slot first section extending radially from the slot base to a slot intermediate radial position and a slot second section extending radially from the slot intermediate radial position towards the core main peripheral surface. The slot first and second sections communicate with each other and are circumferentially offset relative to each other. The slot first and second sections are positioned, configured and sized to facilitate insertion therein of a corresponding conductor section of the stator winding with reduced needs for deforming the latter.
Owner:TM4 INC
Brushless motor
ActiveUS20100133935A1High positioning accuracyProlonging permanent magnetWindingsMechanical energy handlingBrushless motorsMagnetic poles
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and Arrangement to Adjust an Air-Gap
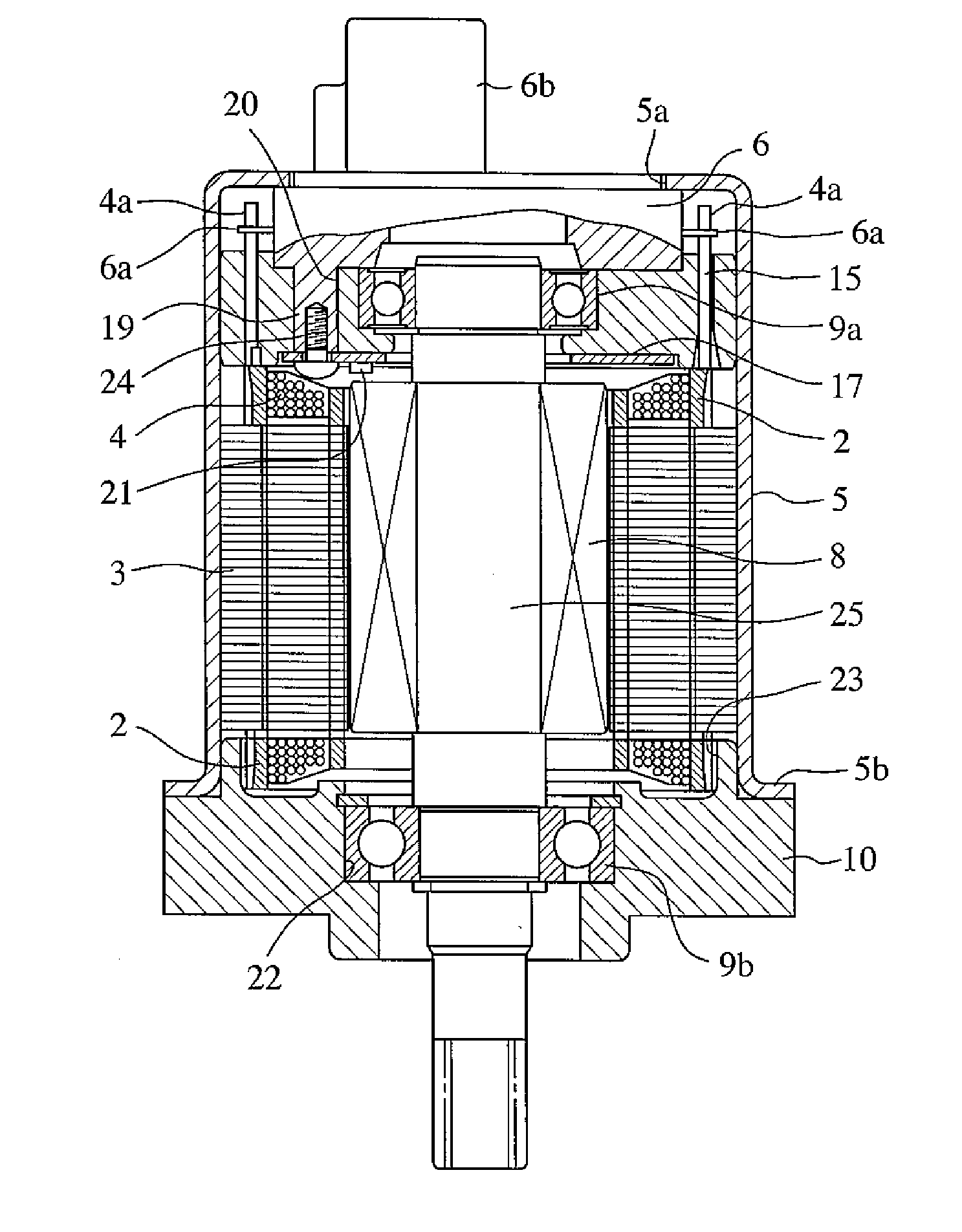
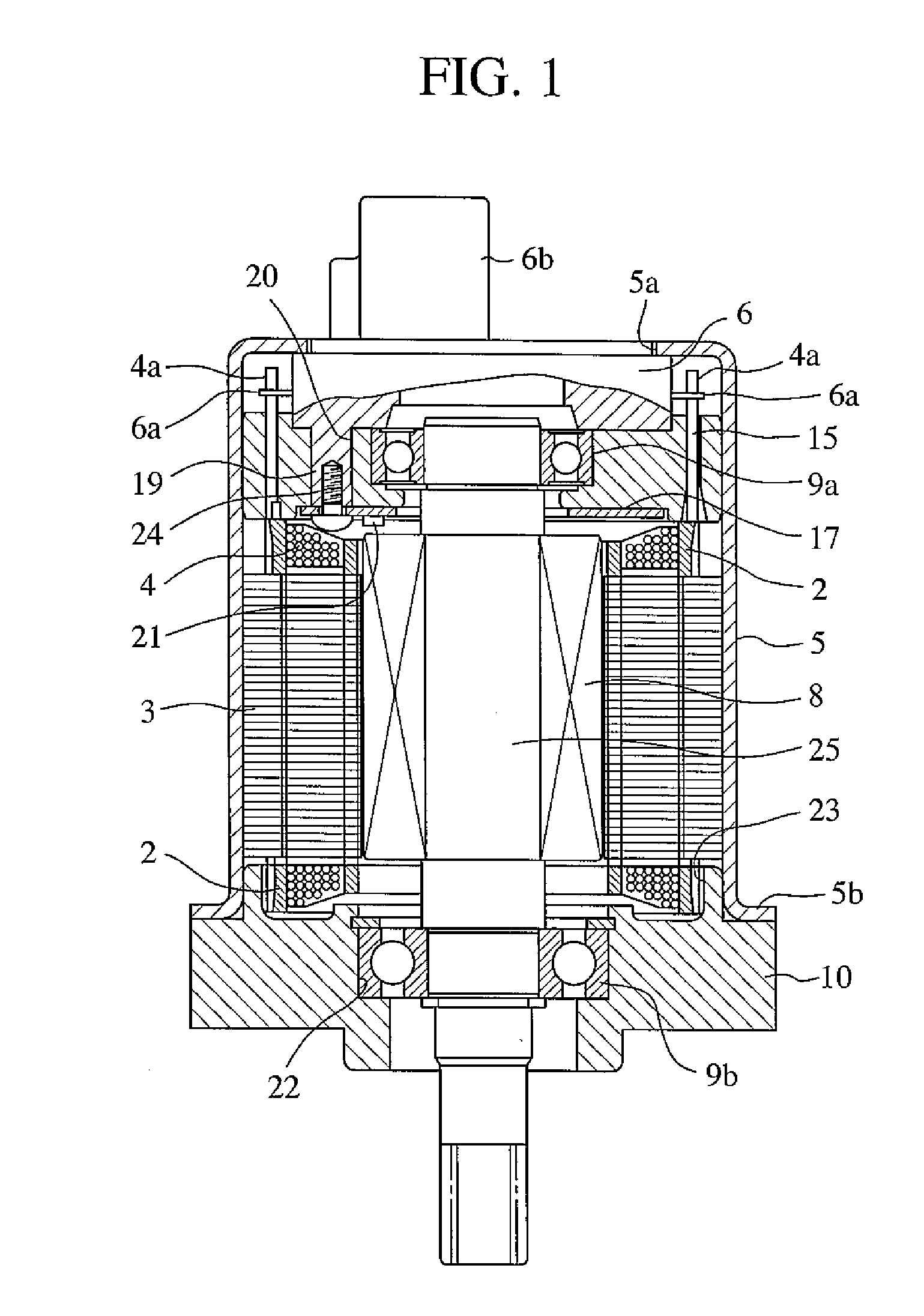
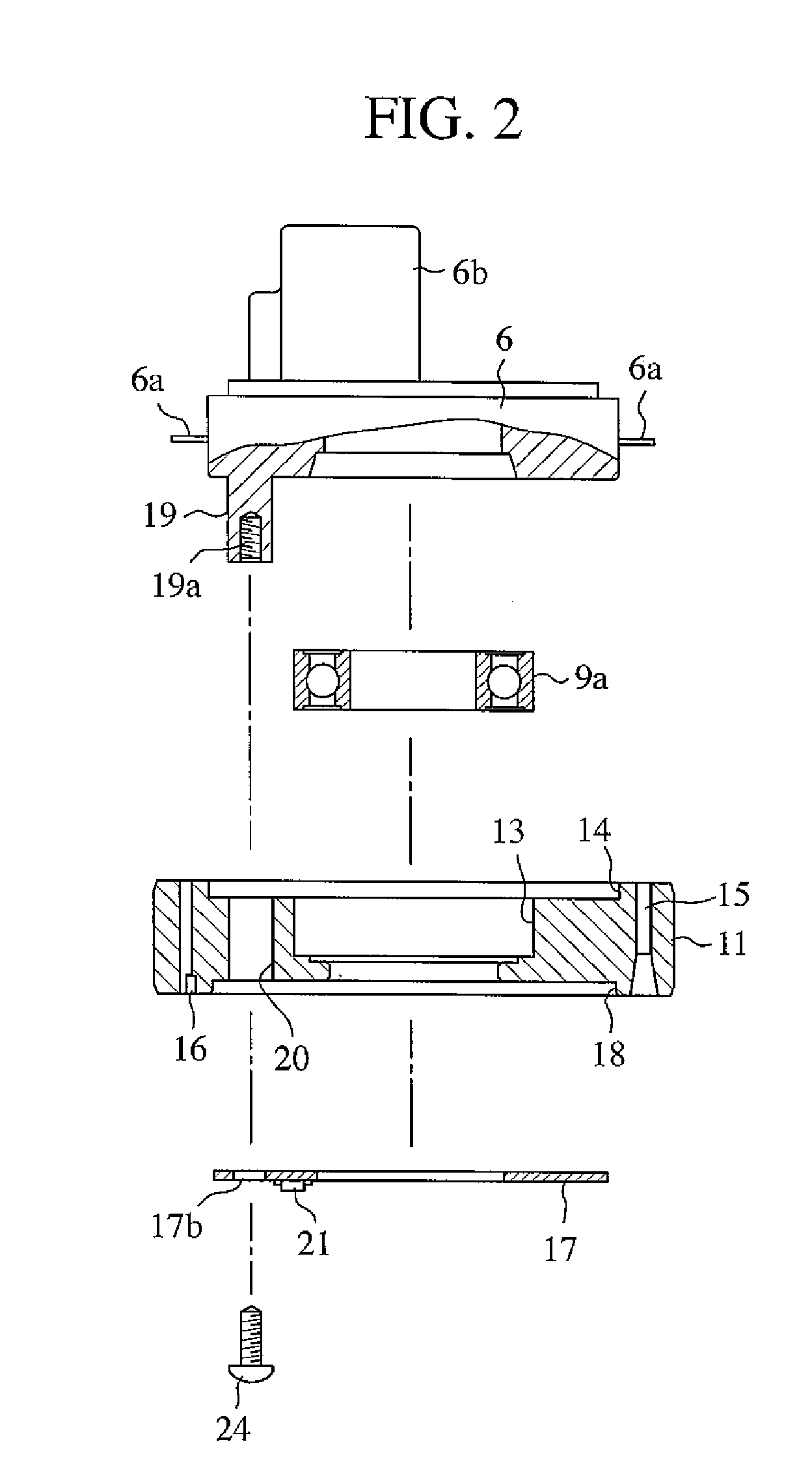
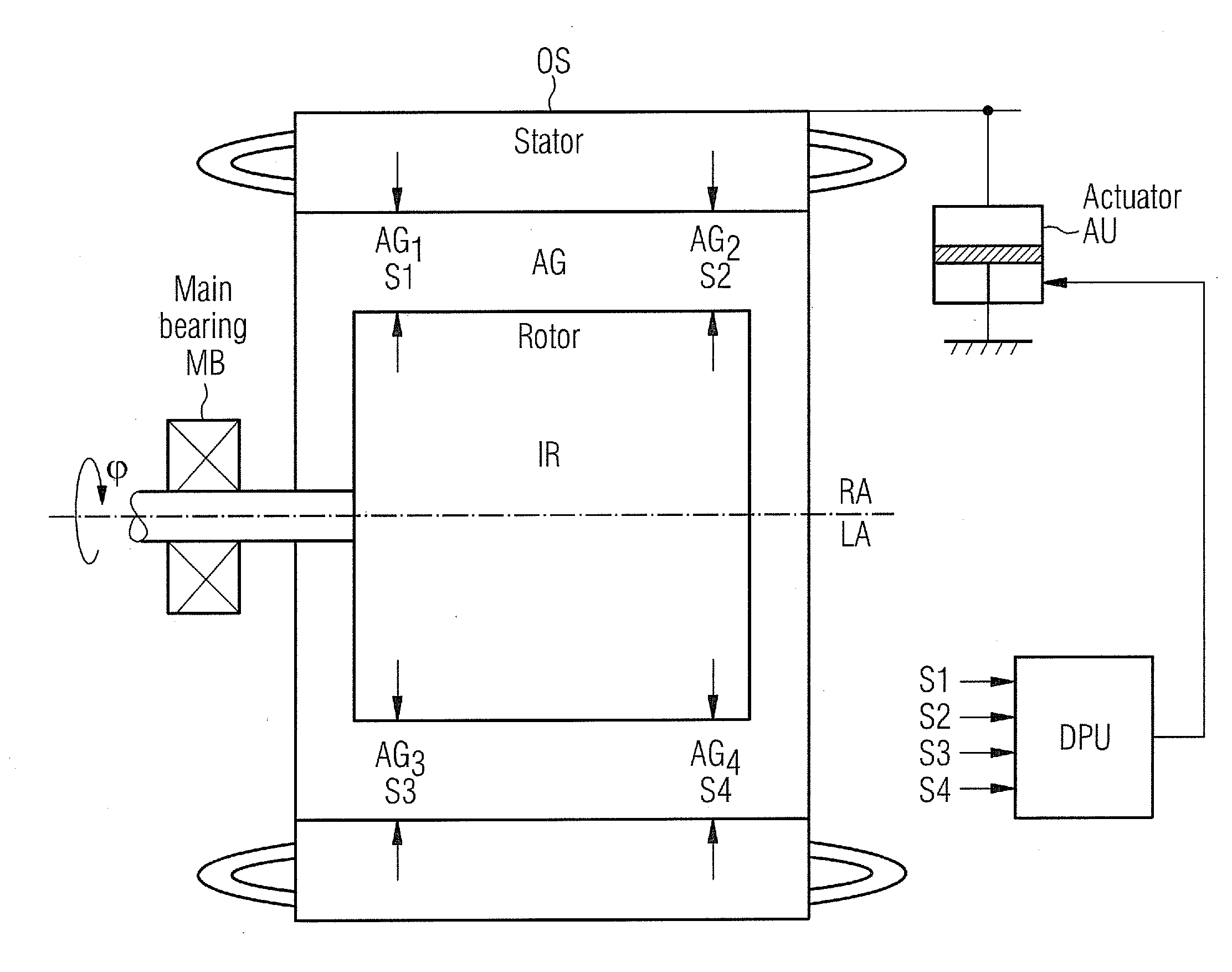
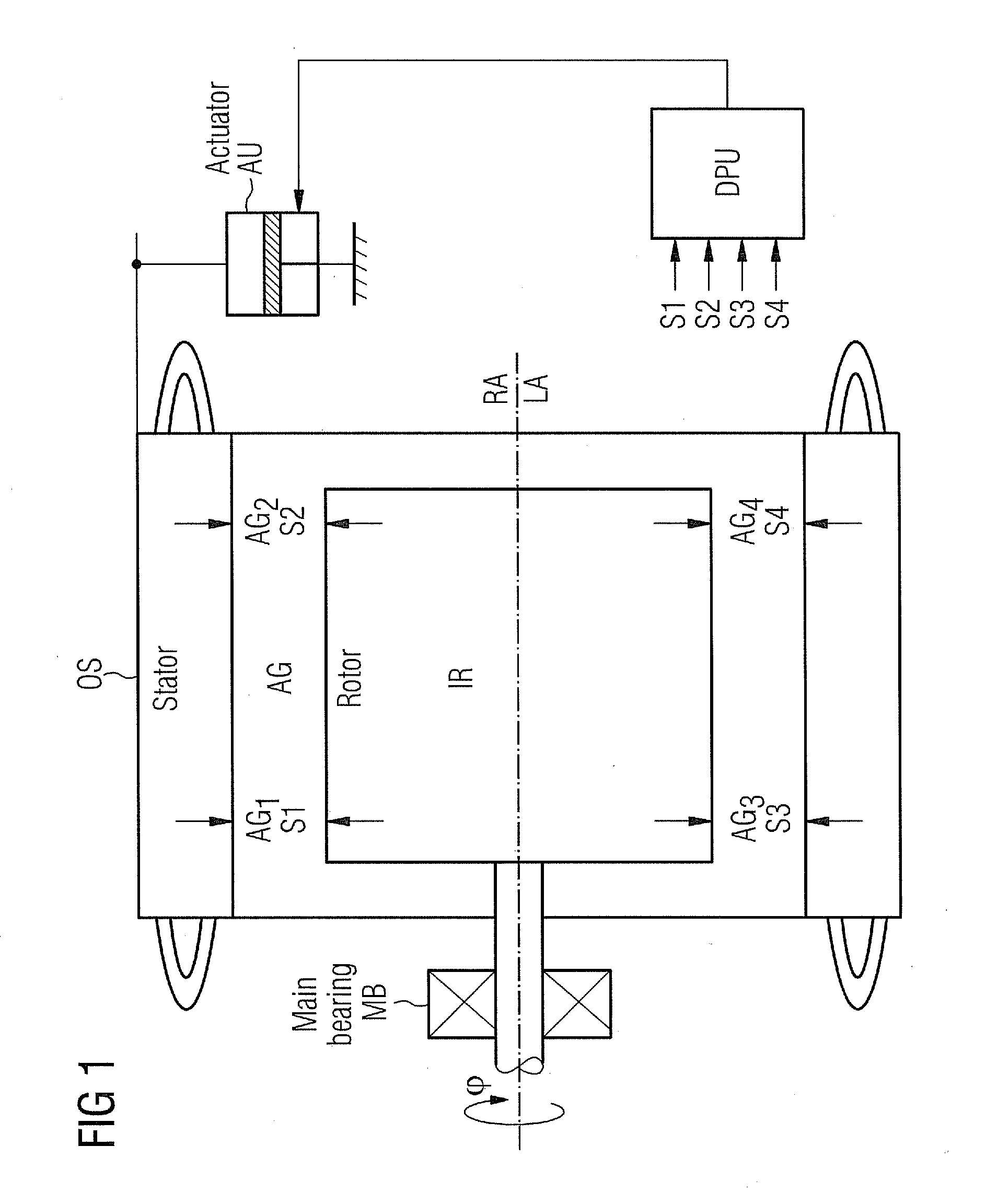
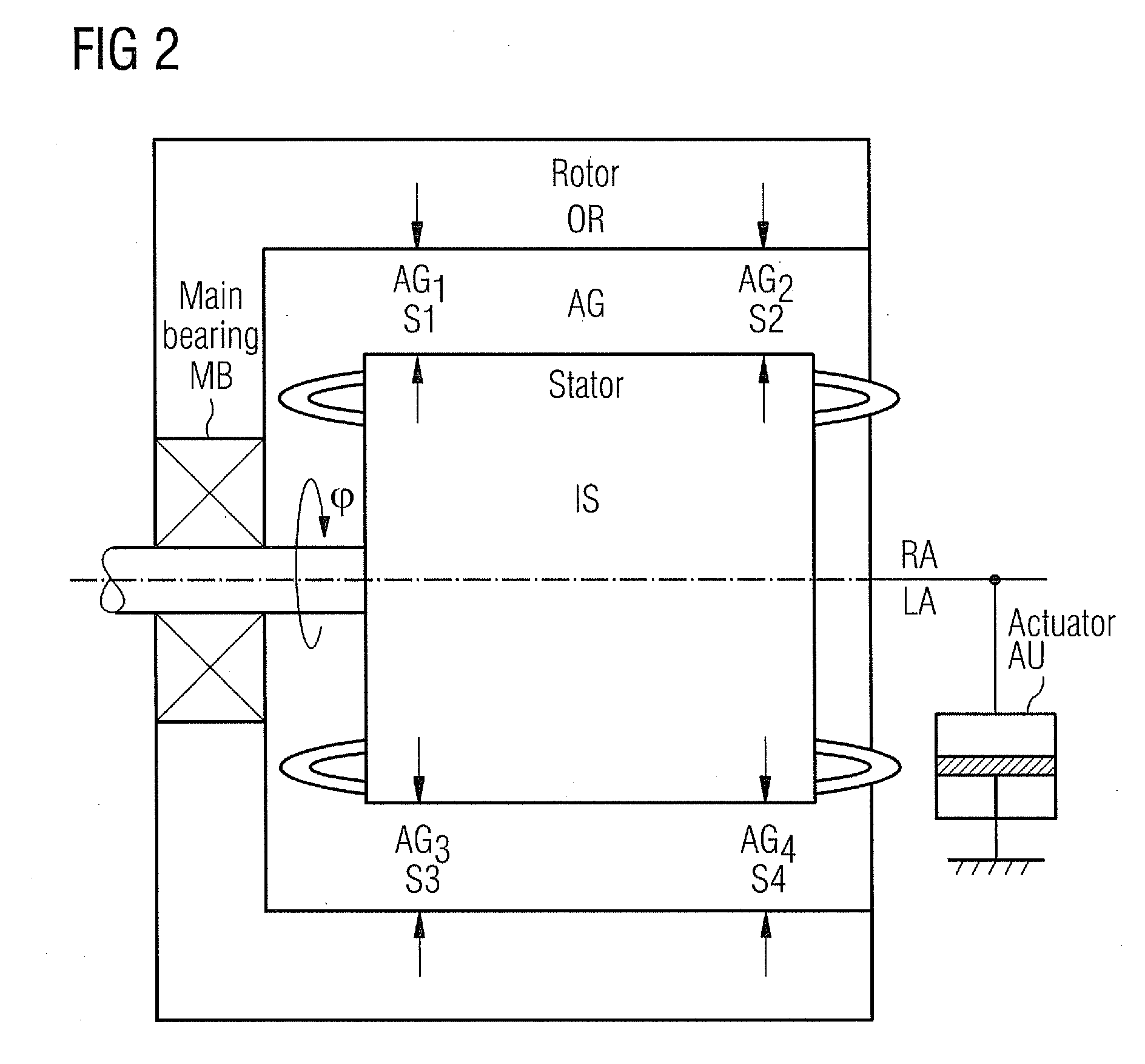
InactiveUS20100253272A1Reduce machine loadLife time is improvedDC motor speed/torque controlMachines/enginesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The electrical machine includes a movable part and a static part. The movable part rotates in relation to the static part around a dedicated rotary axis. An air-gap is located between the rotating and the static part of the machine. A device is positioned and used to measure the spacing of the air-gap. The static part and / or the movable part is coupled with an actuating-unit, which changes the relative position of the static part in relation to the movable part to adjust the spacing of the air-gap.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Manufacturing method of a coil member
InactiveUS6951054B2Easy to changeEasy to adjustSynchronous generatorsShaping toolsMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Dynamoelectric machine winding joining method
InactiveUS6990724B2Improving joining operationBroaden the fieldMagnetic circuitContainer/bottle contructionTorchEngineering
An intermediate holding member is inserted between a second free end and a third free end from an inner circumferential side in a radial direction, a first radial restraining member presses against a free end at an innermost circumference from radially inside, and a second radial restraining member presses against a free end at an outermost circumference from radially outside. Next, a voltage is supplied between a torch and the members, an inert gas is supplied to the torch, and an arc discharge is generated between the torch and the free ends, welding the radially-adjacent free ends.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Spindle motor
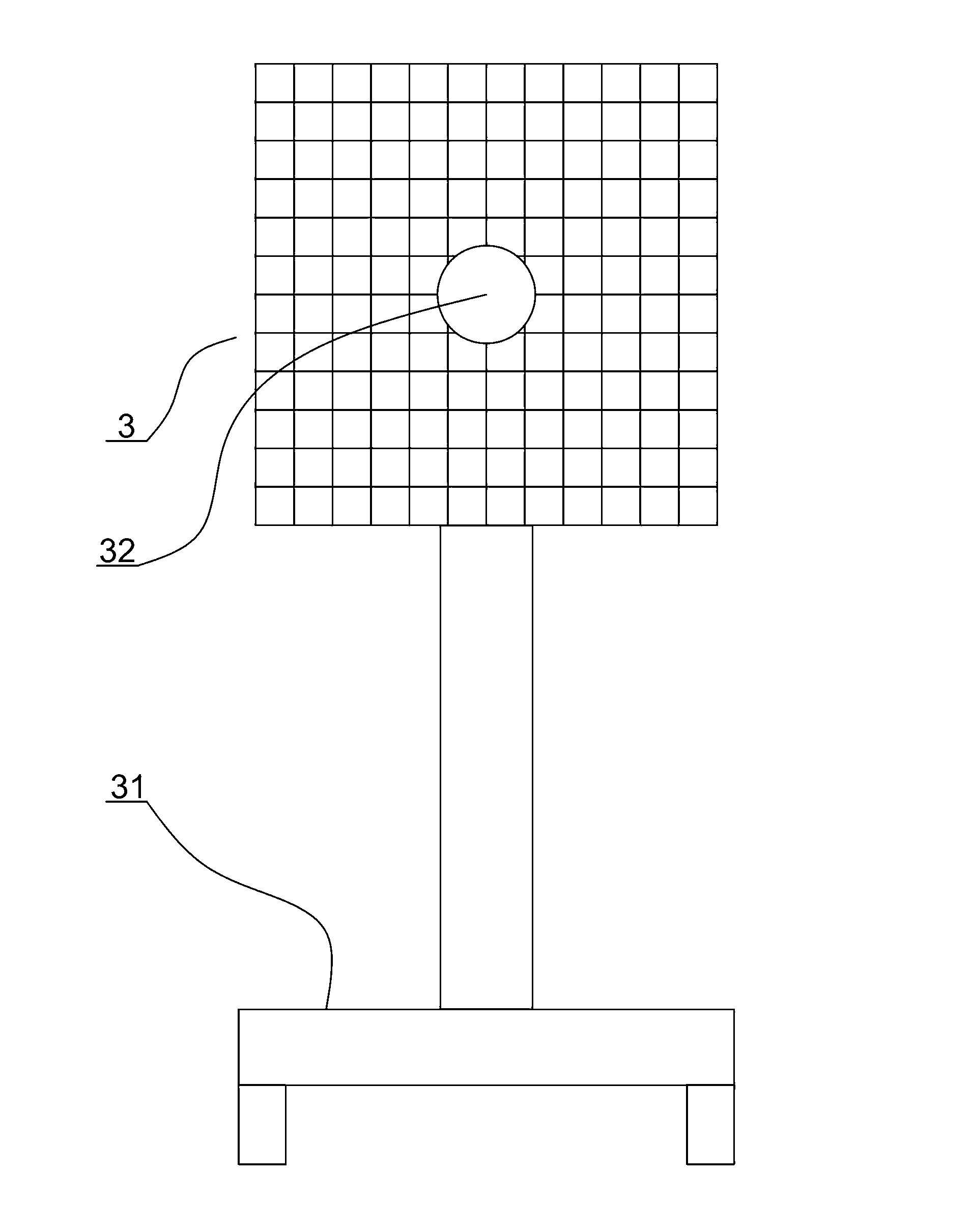
InactiveUS20050223400A1Accurate centerReduce in quantityRecord information storageMechanical energy handlingEngineeringSteel ball
A spindle motor, in which the number of parts is kept from increasing and the number of assembling processes is reduced, and which has mechanisms for self-balancing and centrally aligning a disk, comprises a motor assembly (31) for rotating a disk (30) as a recording medium, a turntable (12) for mounting the disk (30), and a holder plate (14) disposed under the turntable (12). The mechanism for self-balancing is structured such that a plurality of steel balls (16) are disposed within an annular space (22) defined by the turntable (12) and the holder plate (14), and the mechanism for centrally aligning the disk (30) is constituted by a plurality of claw-shaped aligning members (5) formed at the inner circumference of the holder plate (14).
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
Direct drive generator and wind turbine
ActiveUS20090134628A1Easy to shipSufficient roundnessWind motor assemblyWind motor supports/mountsEngineeringTurbine
The invention concerns a direct drive or directly driven generator for a wind turbine comprising a stator having at least one stator element for power generation and a rotor pivotable around a centre axis of the generator having at least one rotor element for power generation, the generator having an air gap between the stator element and rotor element, wherein the stator comprises a front and a rear ring-shaped supporting element and stator segments being attached to the front and rear ring-shaped supporting elements of the stator, wherein junctions between the front and rear ring-shaped supporting elements of the stator and stator segments are located substantially at a radius in relation to the centre axis of the generator which is smaller than the radius of the air gap between the stator element and rotor element. Furthermore the invention concerns a wind turbine comprising such a direct drive generator.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Electric motor and an actuator having the same
In an electric motor of an SBW actuator, a rotor shaft is rotated upon energization of the motor. A rotor core is rotated integrally with the rotor shaft. A resilient member enables tilting or decentering of the rotor shaft upon application of a decentering force on the rotor shaft. A stator core contacts the rotor core when the rotor shaft is tilted or decentered.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Drive device and device manufacturing method
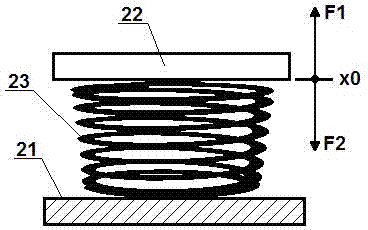
ActiveCN104753303AImprove efficiencyReduce power consumptionPrintersPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical engineeringBalance point
A driving apparatus comprises a stator (21), a rotor (22) and a deformation connector (23). The rotor is connected to the stator through the deformation connector. An external driving force drives the deformation connector to have deformation so that the rotor changes its position with respect to the stator. Under the condition that no external driving force is applied, the deformation connector remains at a force balanced position (x0). The force on the deformation connector comprises a deformation force (F1) of the deformation connector and a first primitive force (F2) in opposite direction to the deformation force (F1). Also provided is a device fabrication method. Because the deformation connector keeps balance under the effect of the deformation force and the first primitive force, a small external driving force is required when the driving apparatus operates near the balance point, thereby reducing power consumption.
Owner:BOLY MEDIA COMM SHENZHEN
Dynamoelectric machine having encapsulated coil structure with one or more of phase change additives, insert molded features and insulated pinion
InactiveUS6946758B2Increase stiffnessIncrease critical speedWindings insulation materialWindings insulation shape/form/constructionAdhesivePinion
Magnet wires wound in slots in a lamination stack of a dynamoelectric machine are encapsulated, in whole or in part, with thermally conductive plastic. Pre-formed features having a thermal conductivity higher than the thermally conductive plastic are insert molded when the plastic is molded. The pre-formed features may include a finned end cap and a fan. Alternatively, end domes of the plastic over end coils of the wound magnet wires have a metallic layer on them, such as by being metallized. The end domes can be formed with features which are also metallized. The thermally conductive plastic can have a phase change additive in it. The magnet wires can have a layer of heat activated adhesive that is activated when the plastic is molded. Slots in the lamination stack can include slot liners formed of thermally conductive plastic. A fan can be formed when the thermally conductive plastic is molded to encapsulate the magnet wires.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Method of making an electric motor
InactiveUS7146706B2Windings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit stationary partsPole pieceNet shape
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Method for forming an armature for an electric motor for a portable power tool
InactiveUS7013552B2Resists extreme temperatureHeat dissipationWindings insulation materialManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesAdhesiveEngineering
An electric motor having an armature which includes a coating of thermally conductive plastic applied in a conventional injection molding process. The armature also includes a fan which is integrally formed from the thermally conductive plastic applied to the armature. This completely eliminates the need to apply one or more coatings of a trickle resin to the armature. It also eliminates the need to separately form and secure a fan by a suitable adhesive to the armature, which together significantly simplifies the manufacturing and cost of the armature. The plastic coating also better fills the spaces between the magnet wires, thus promoting even more efficient cooling and better holding of the magnet wires stationary relative to one another. The thermally conductive plastic coating may be mixed with other suitable materials to provide a density approximately equal to the magnet wires. This eliminates the need to balance the armature after the injection molding step.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
Method of manufacturing winding of rotary electric machine
ActiveUS6971153B2Reduced dimensionControl deformationSynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionElectric machineEngineering
A method of manufacturing a winding of a rotary electric machine includes steps of pressing a portion of a conductor segment in a predetermined direction to reduce its dimension in the direction, inserting the conductor segment into a slot of a stator core, bending the conductor segments and joining ends of the conductor segments. In the pressing step, the conductor segment is pressed with a punch in a condition that it is held in a die that has curved inside corner portions to restrict deformation of corners of the pressed portion.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electrical Rotating Machine Comprising an Intermediate Sleeve Interposed Between the Shaft and the Polar Wheels and Method for Making the Rotor
InactiveUS20080315714A1High concentricityEasy to processWindingsMagnetic circuit rotating partsEngineeringMotorized vehicle
An electrical rotating machine rotor, in particular for a motor vehicle, comprising a central shaft, an annular core coaxial with the shaft and two polar wheels which are axially arranged on either side of the core, of the type wherein the shaft includes at least one drive section which is axially force-fitted into a fixing bore of at least one component of the rotor so as to secure in rotation at least one of the two polar wheels of the rotor to the shaft, an intermediate sleeve being radially interposed between each polar wheel and the central shaft, and on which sleeve is mounted said polar wheel. The invention also concerns a method for making such a rotor.
Owner:VALEO EQUIP ELECTRIC MOTEUR
Method of making cascaded multilayer stator winding with interleaved transitions
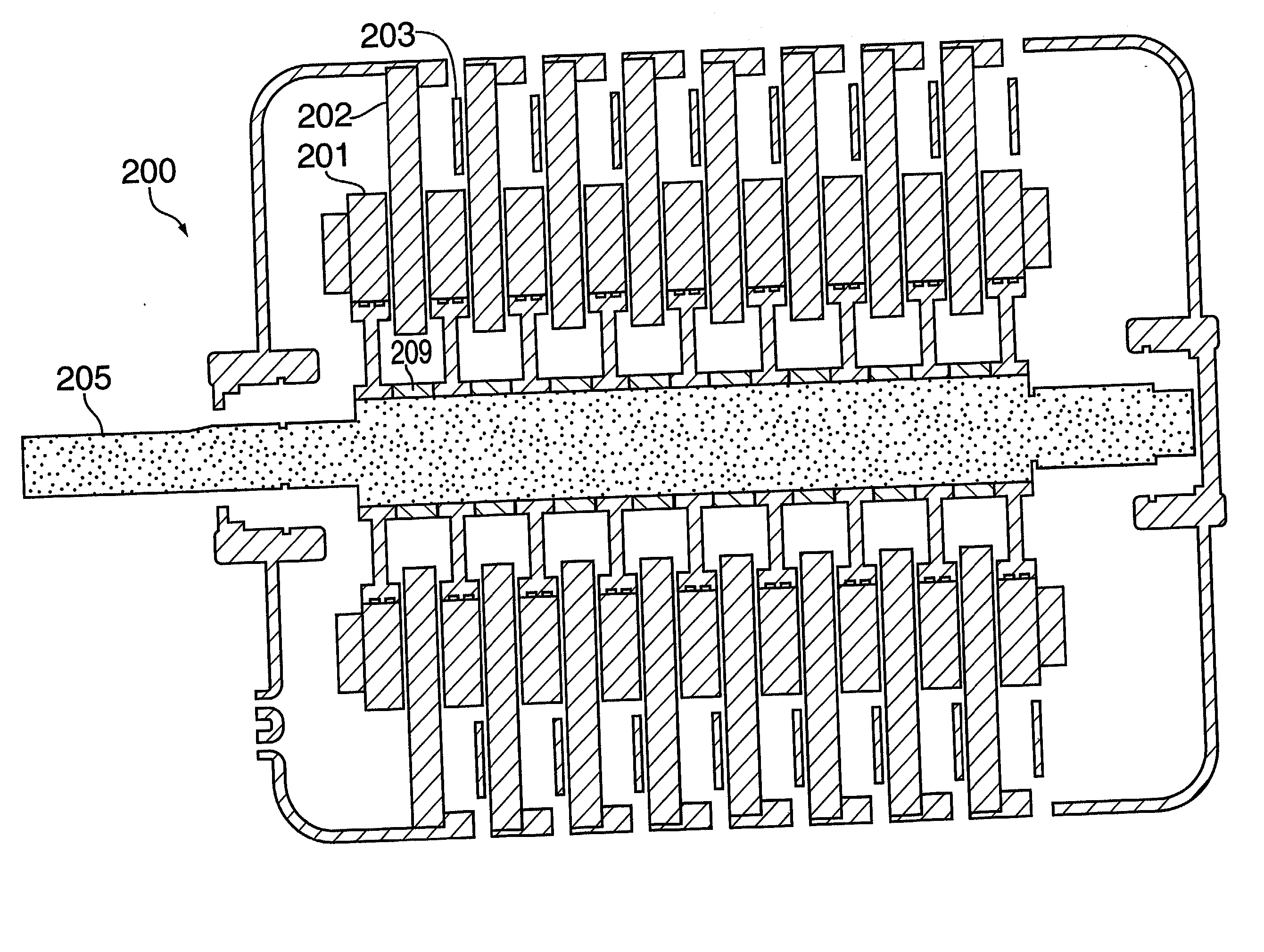
A method for making a stator assembly includes forming several continuous conductors with generally-coplanar parallel-spaced straight segments interconnected by end loop segments, as by winding each of several conductors on a peg board, and then pressing the conductors to form either one, two, or three generally-orthogonal “jogs” in a given end loop segment. The conductors are interpositioned with their straight segments staggered and with a first leg of each subsequent conductor's end loop segments generally overlying a second leg of the immediately-prior conductor's end loop segments, except for the two end loop segments following the first conductor's “nth” straight segment, and multiples thereof, where the stacking order is reversed (“n” being equal to the number of stator core slots divided by the number of conductors that will form a given winding layer). The resulting preform is inserted into the core slots over multiple revolutions to thereby obtain a multilayer cascaded stator winding with interleaved transitions.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com