Patents
Literature
674results about "Embedding prefabricated windings" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
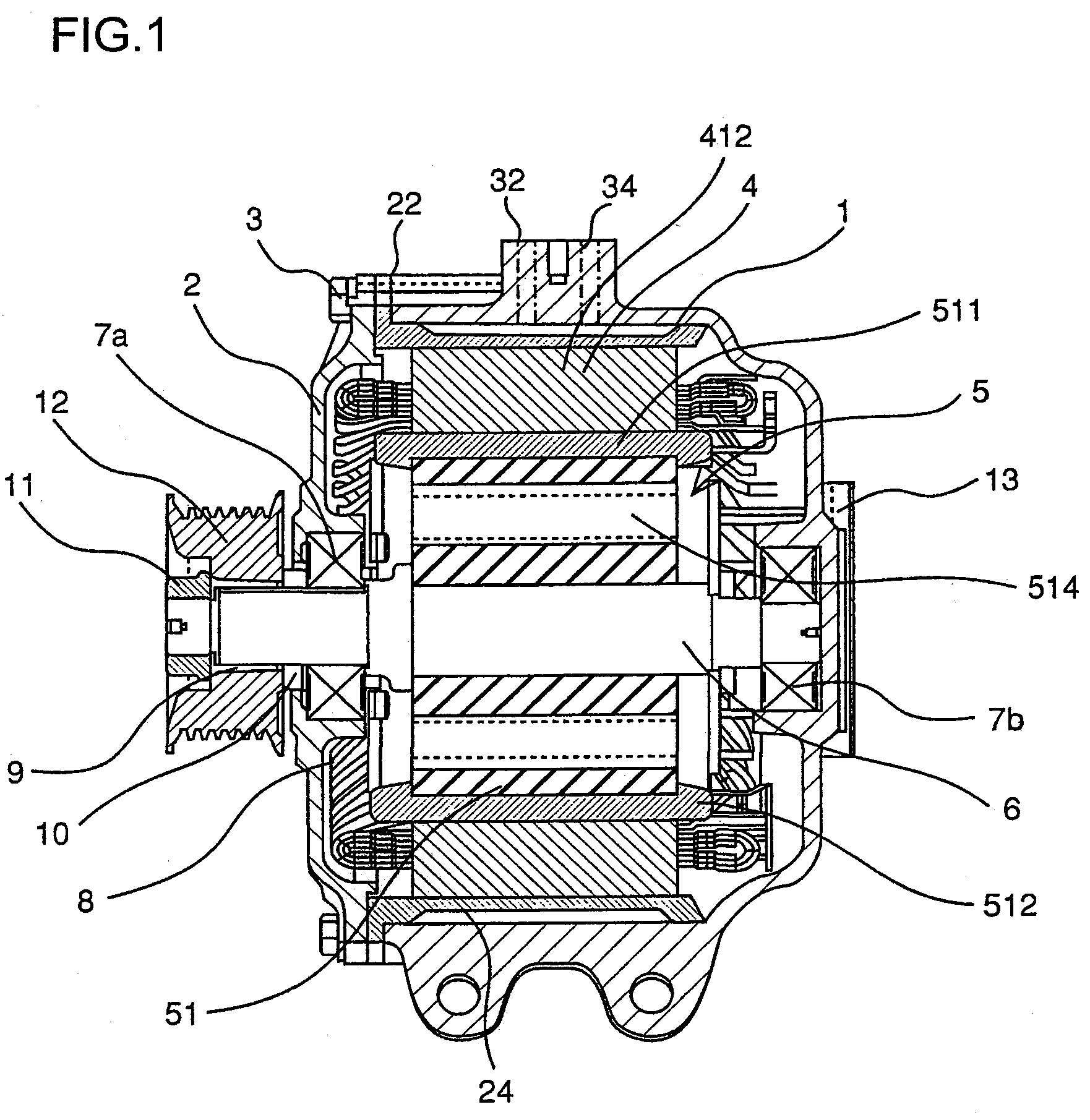
Method and apparatus for manufacturing AC-generator's stator for vehicle
InactiveUS6249956B1Positioning-accuracy can be improvedAvoid damageWire articlesForging/hammering/pressing machinesElectrical conductorEngineering
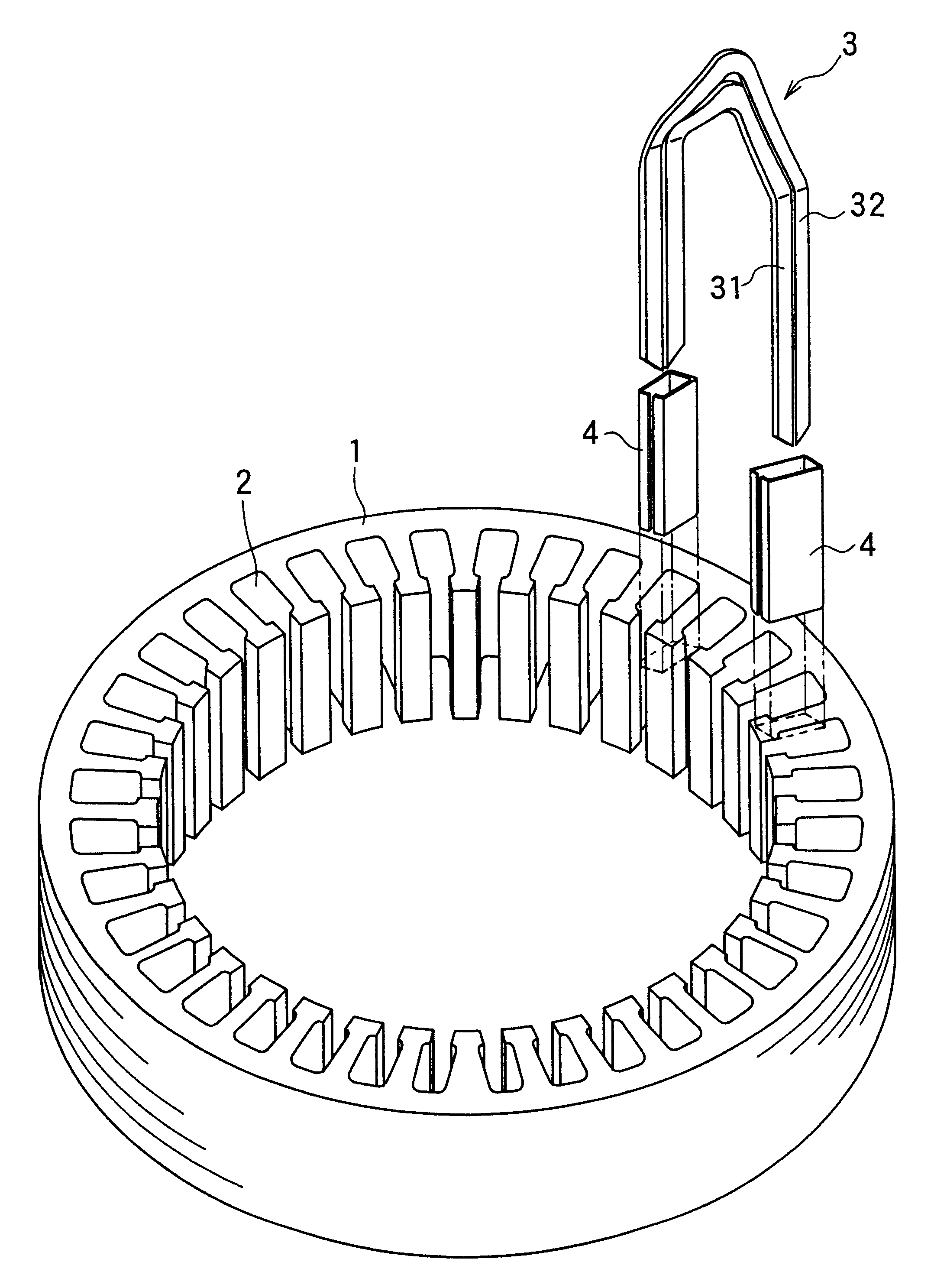
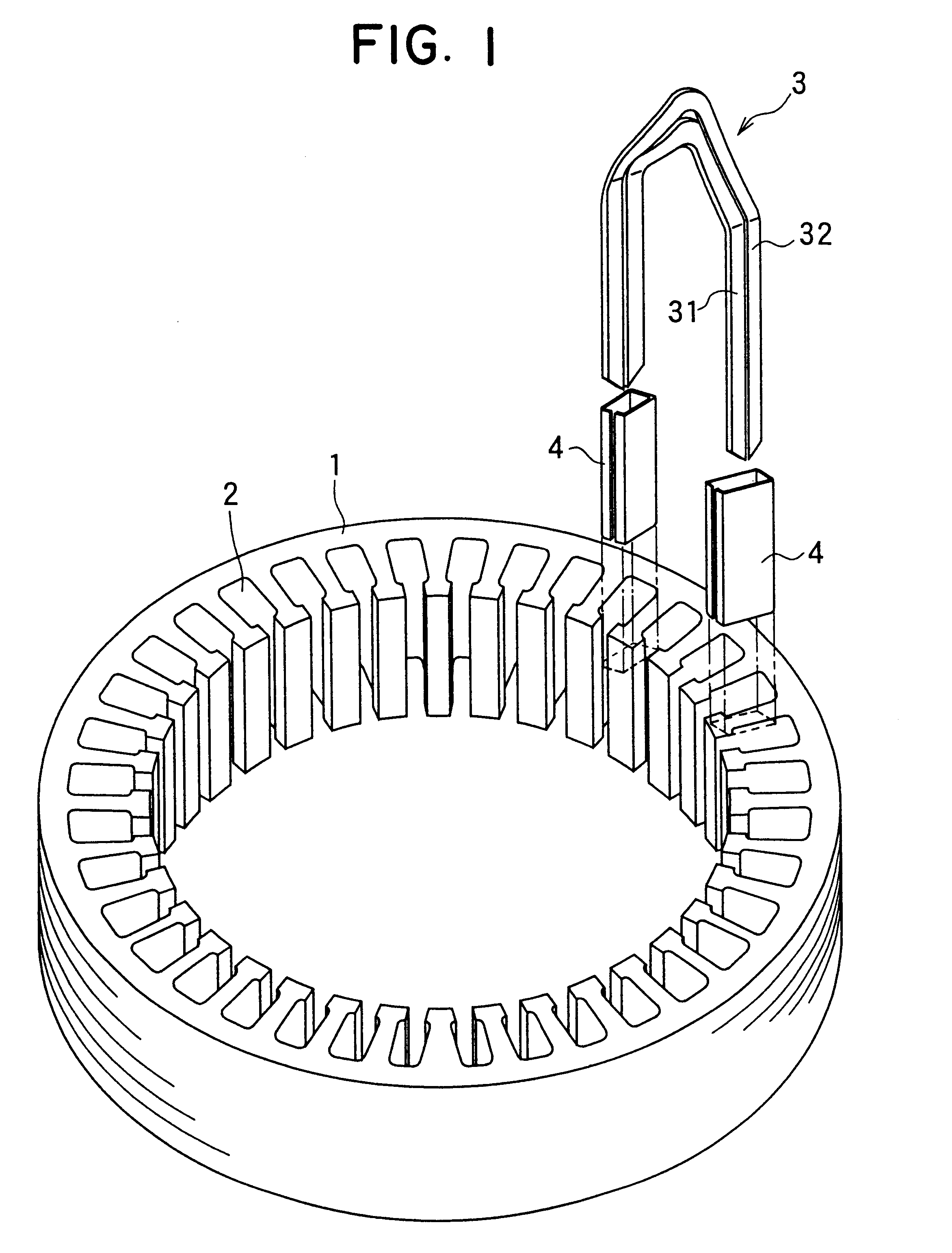
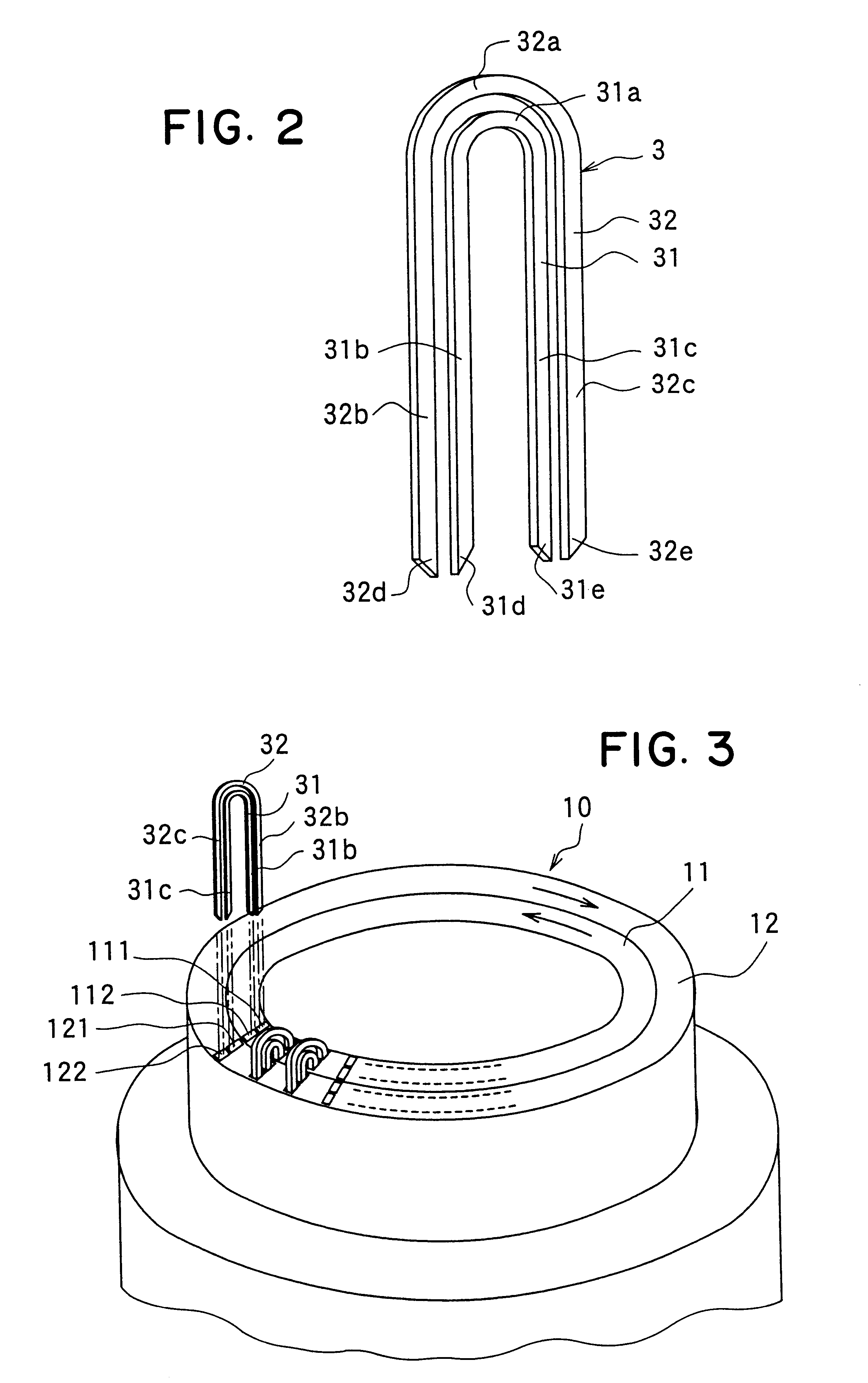
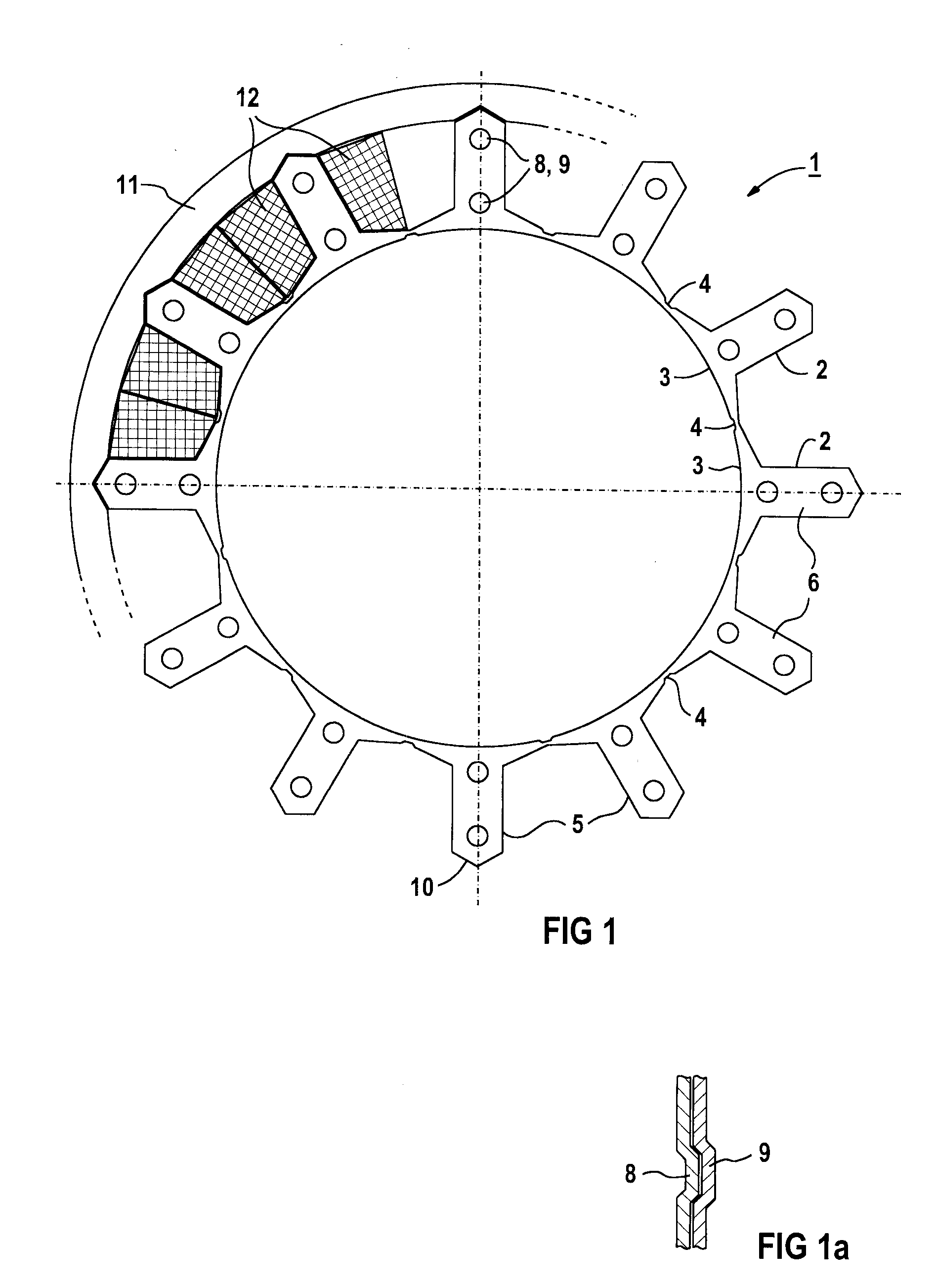
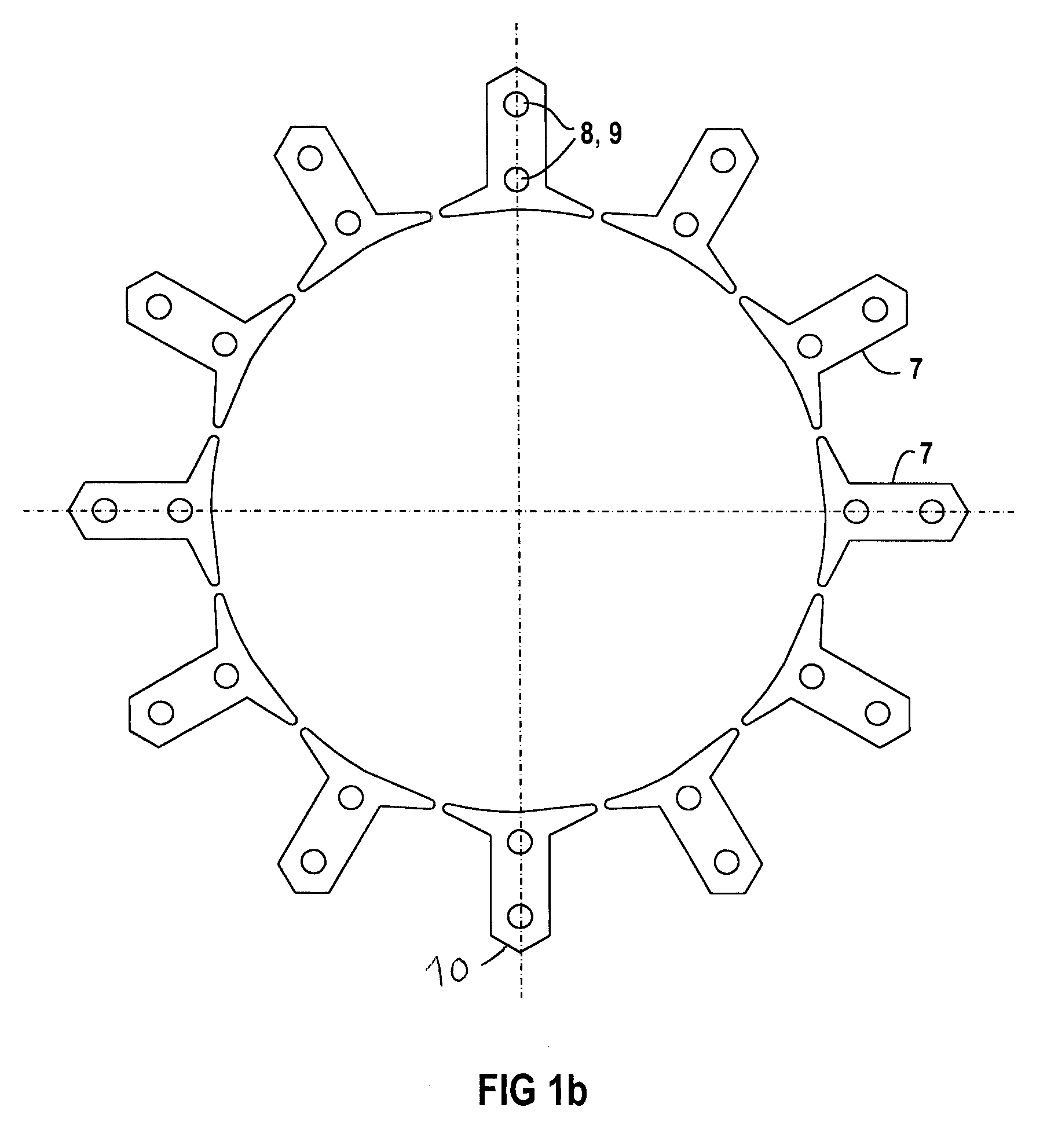
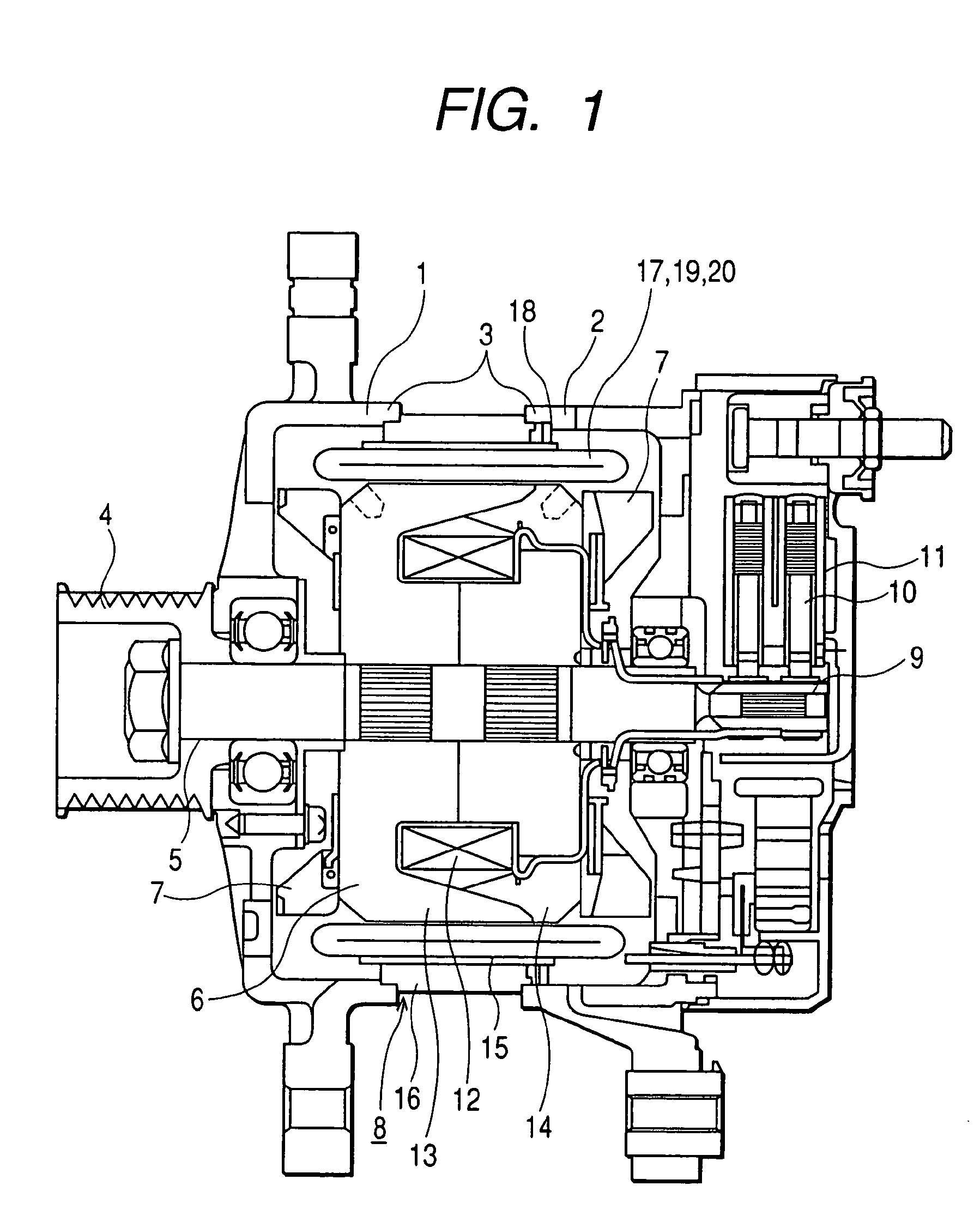
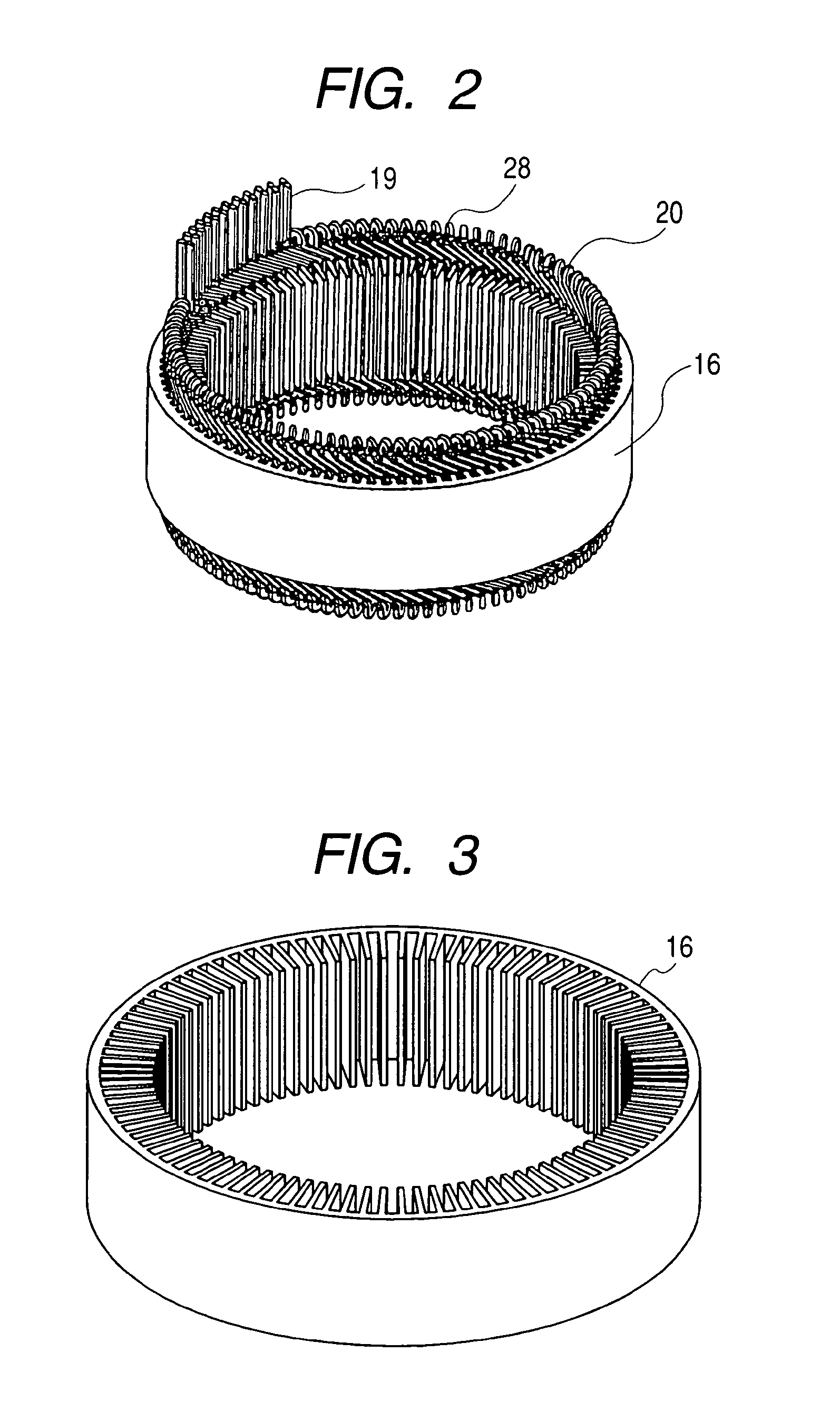
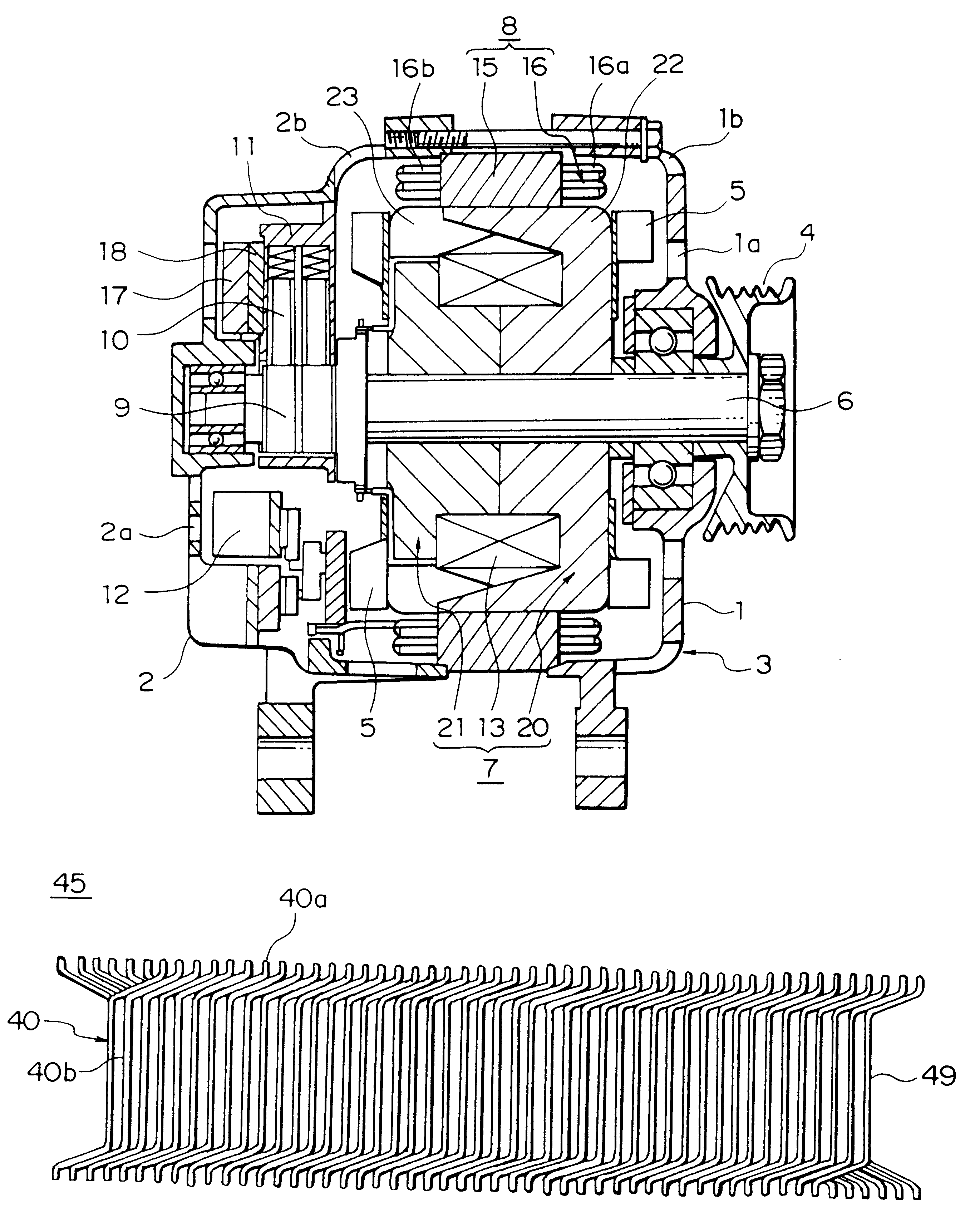
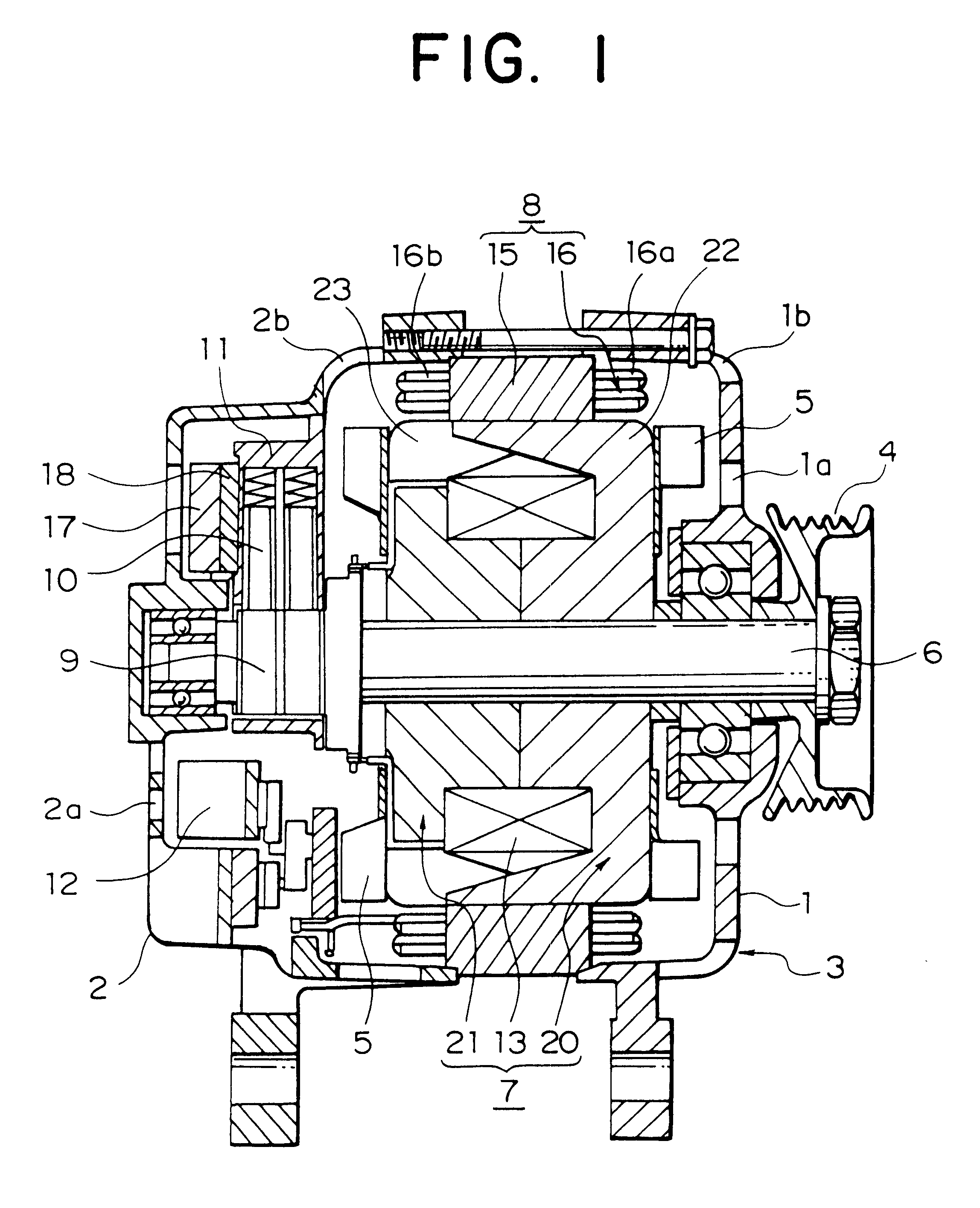
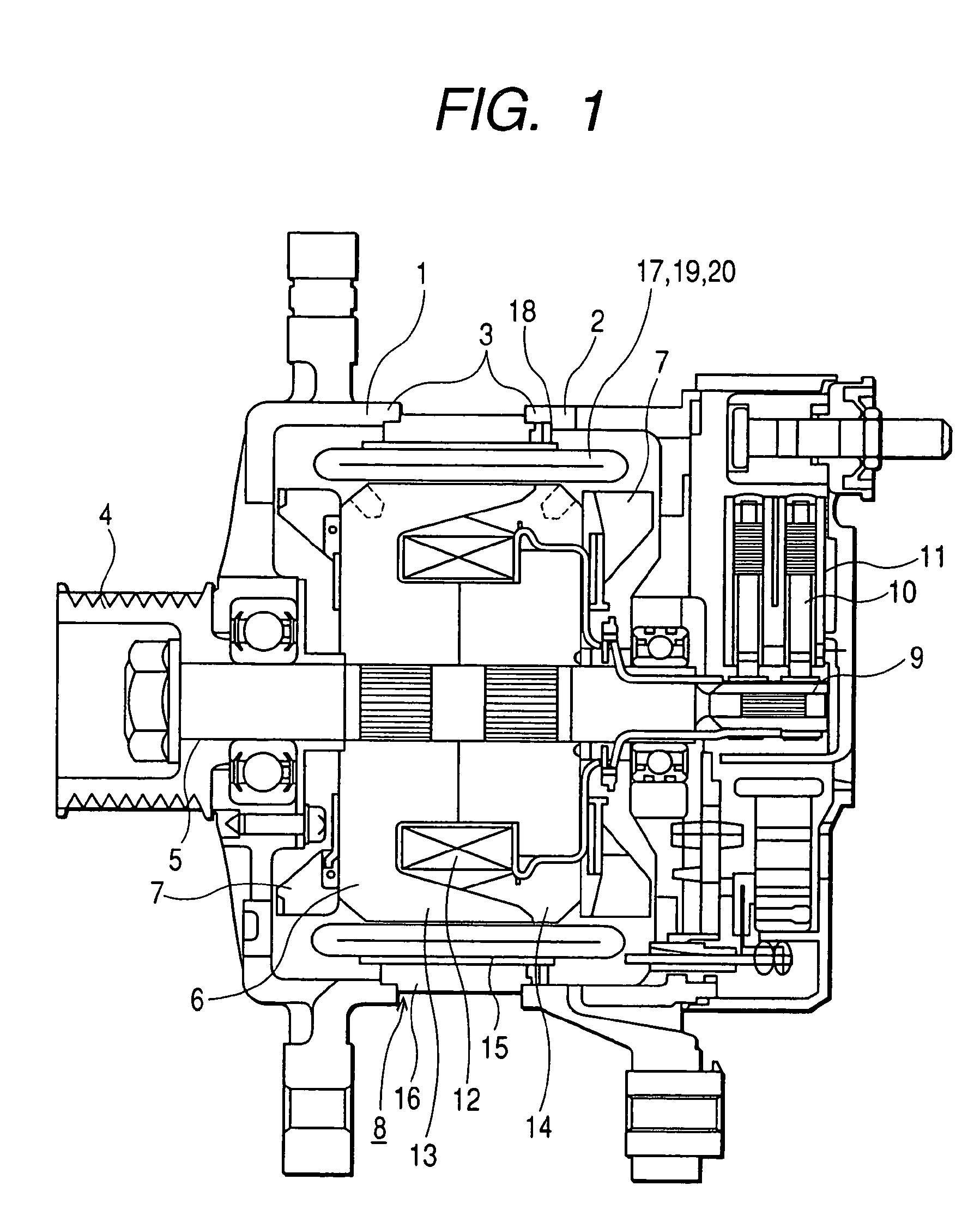
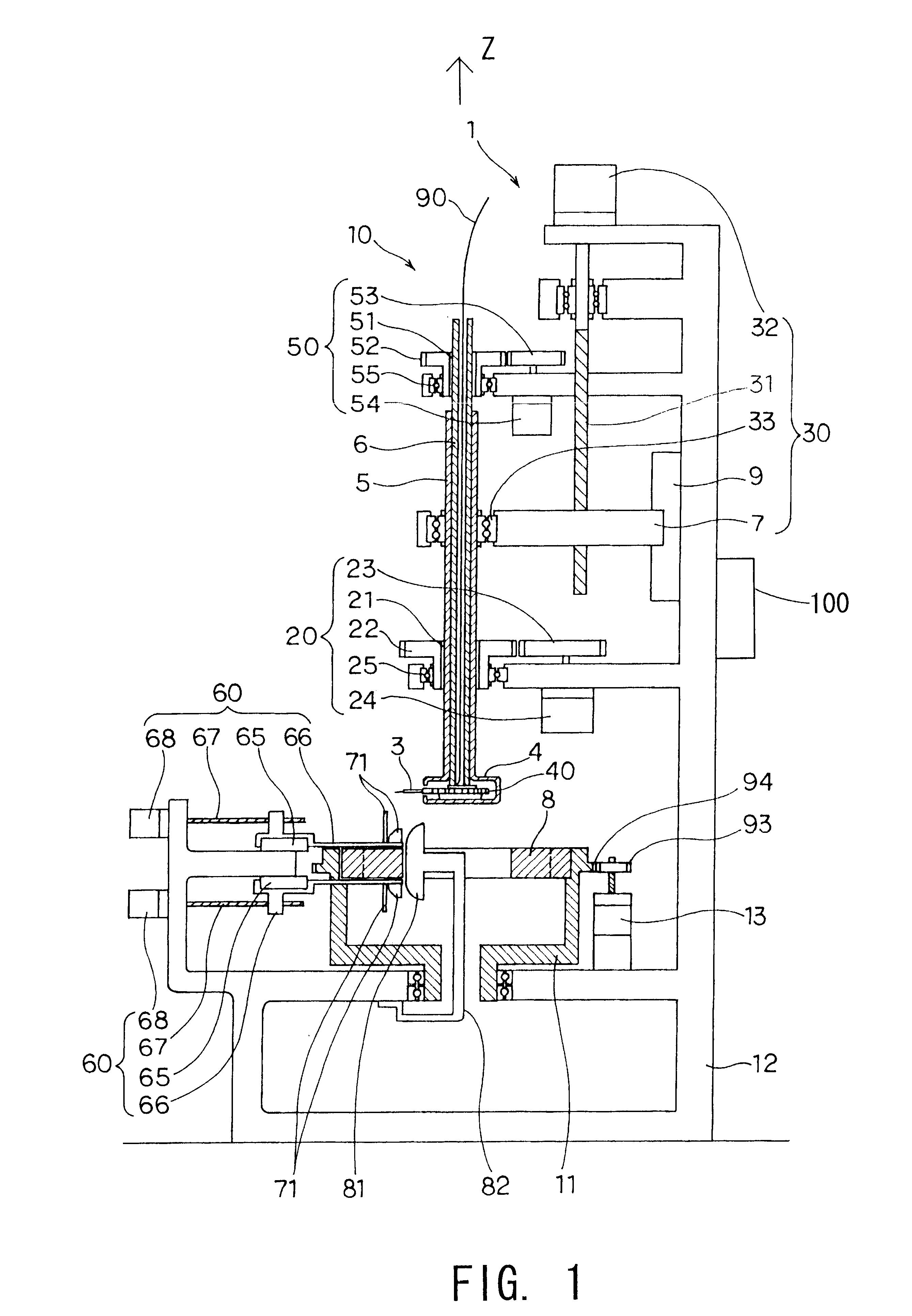
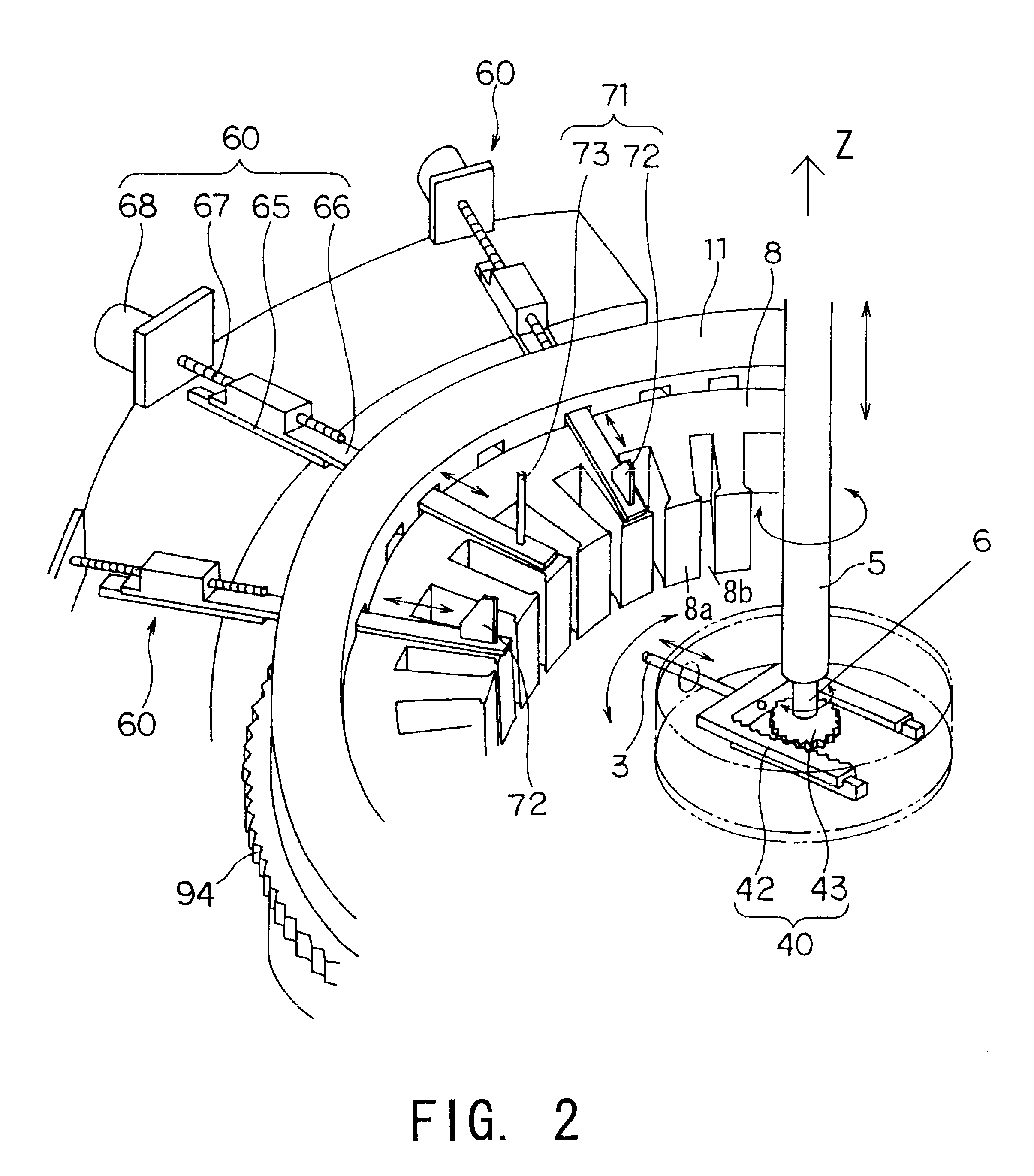
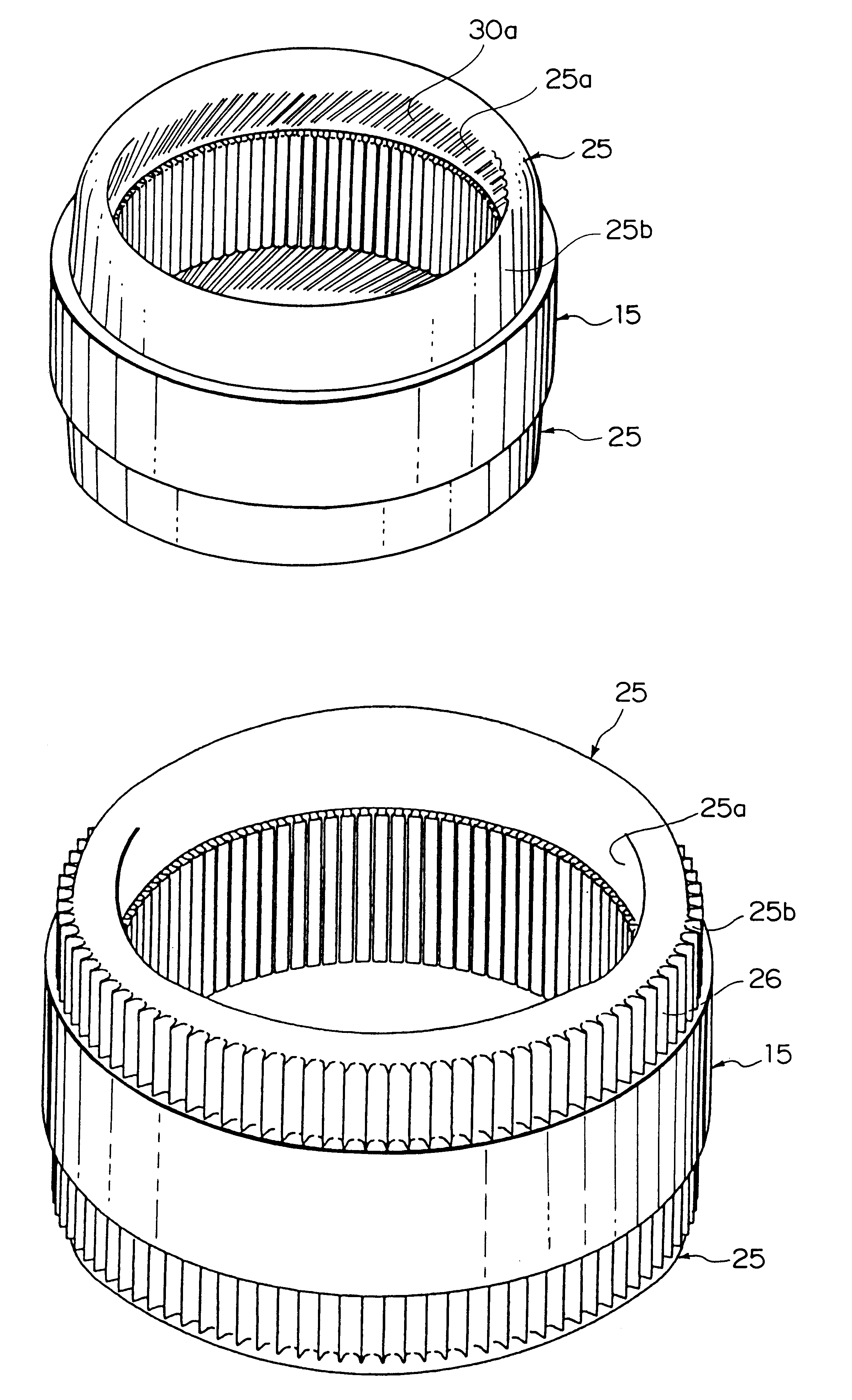
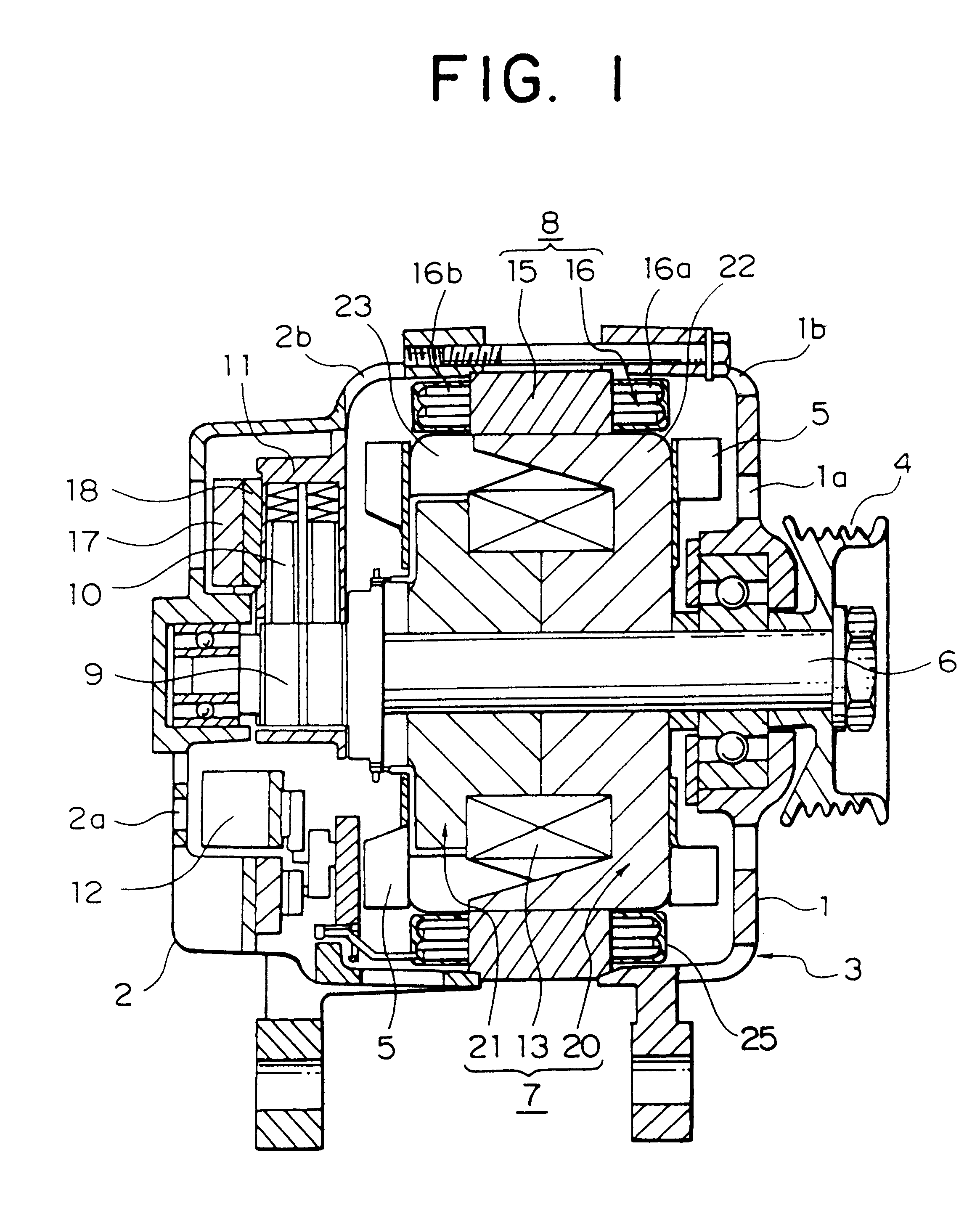
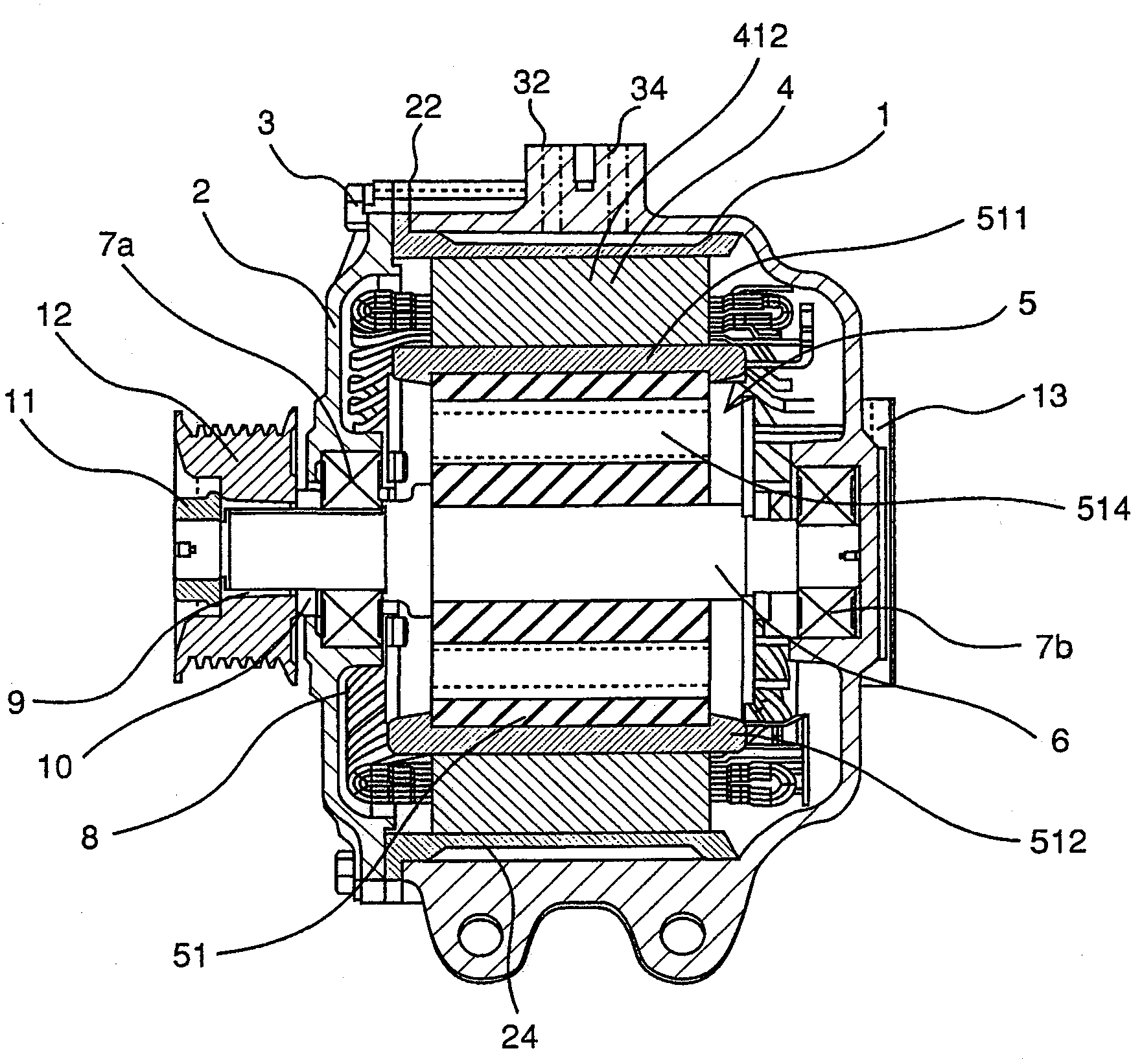
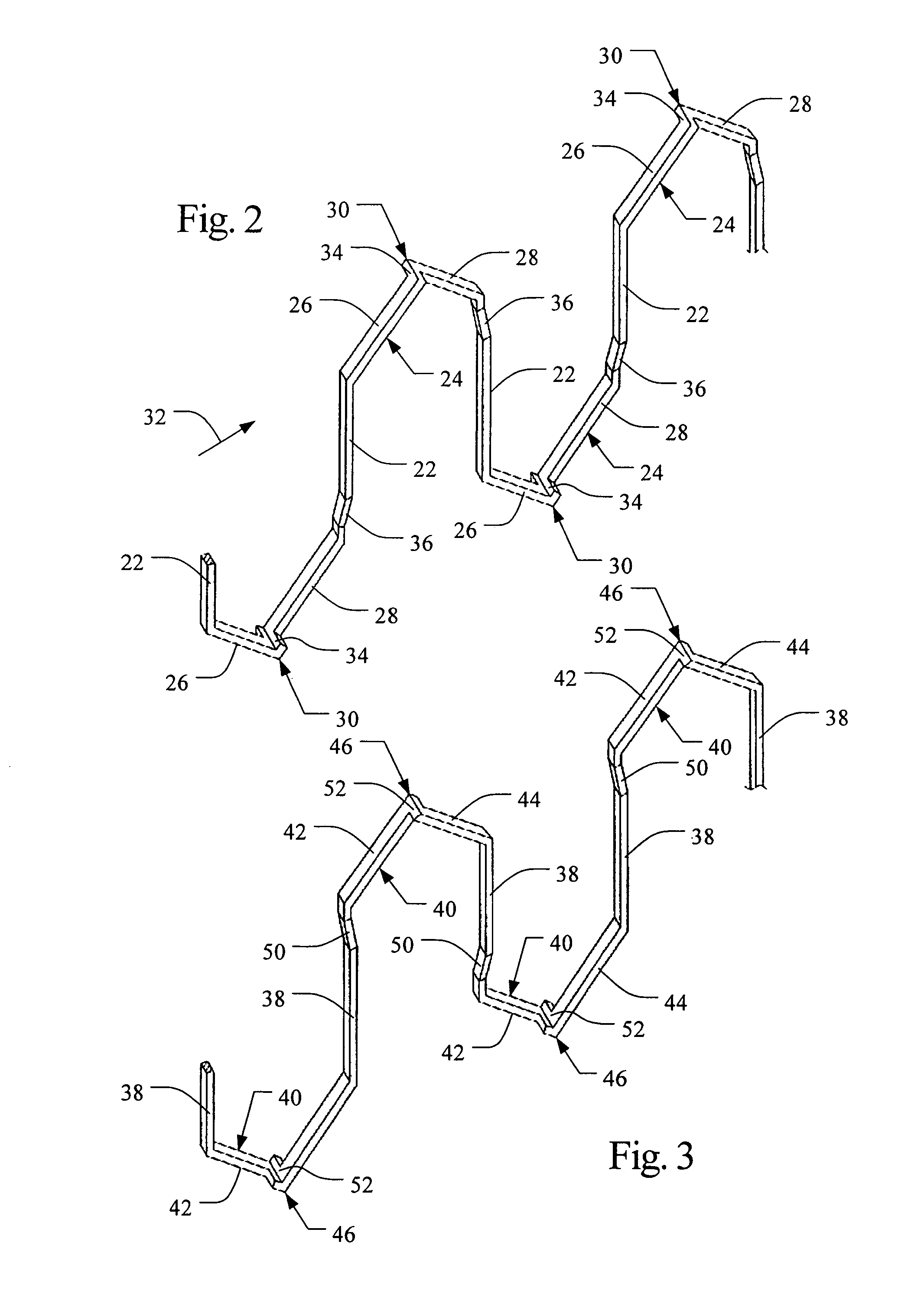
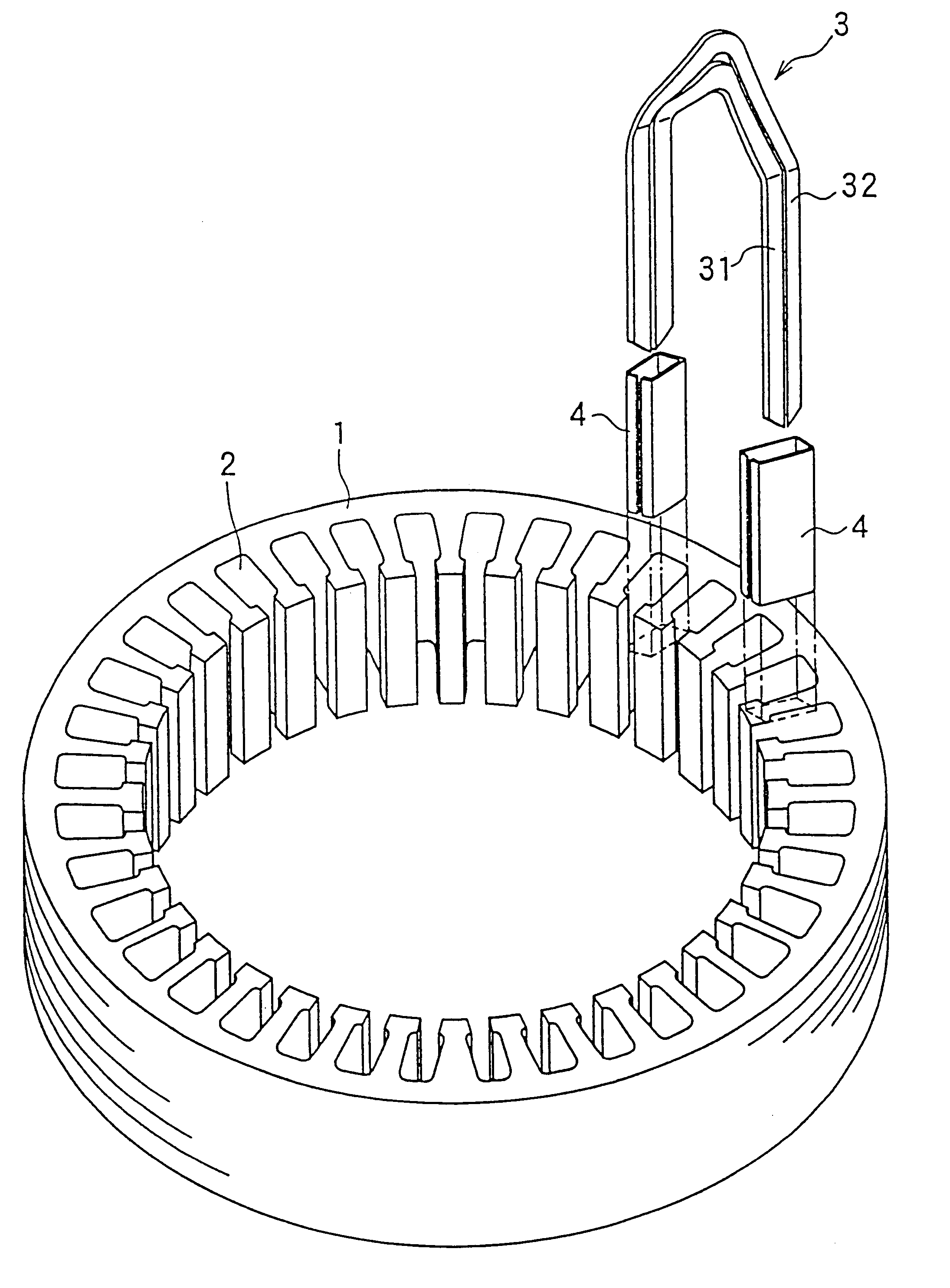
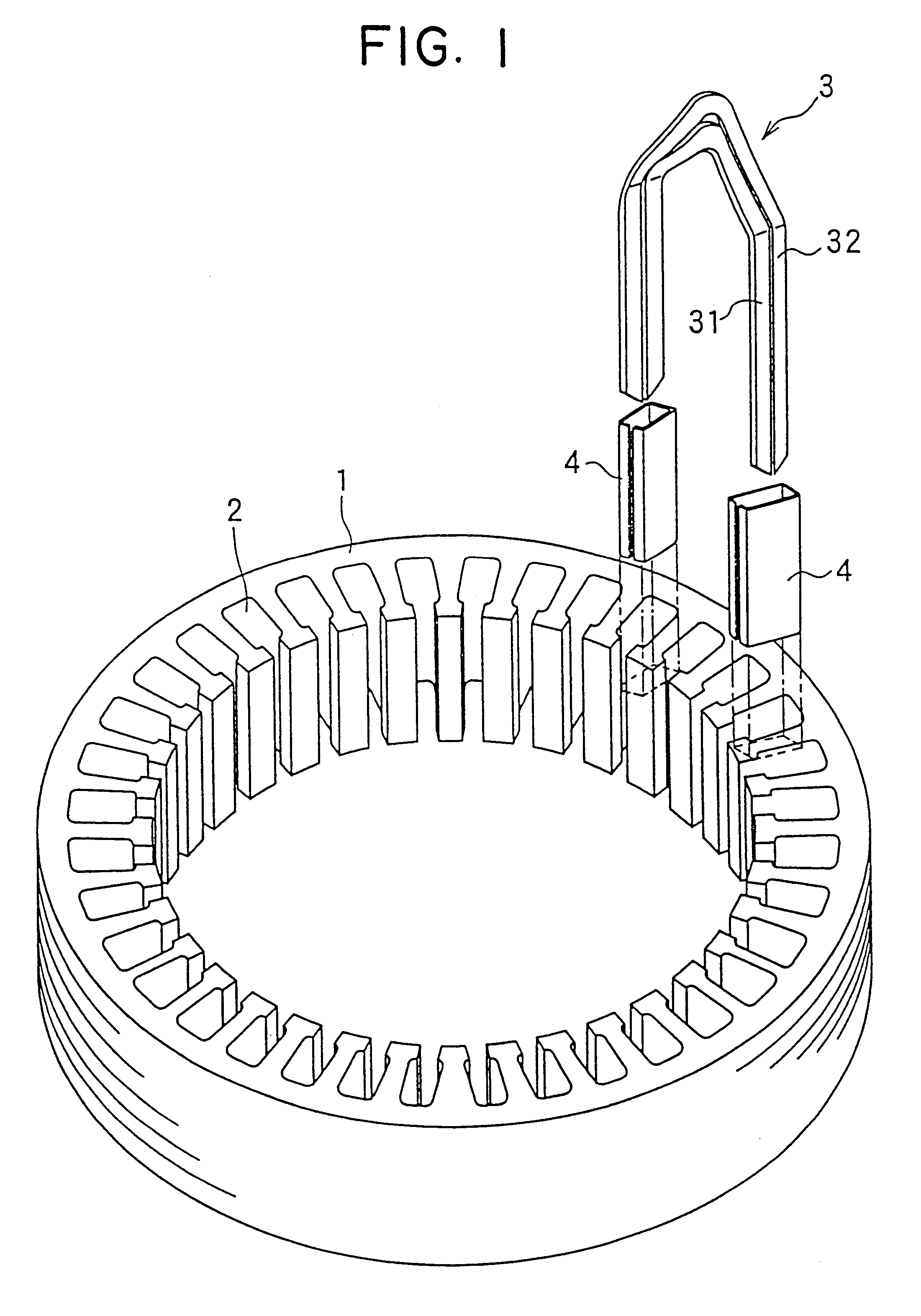
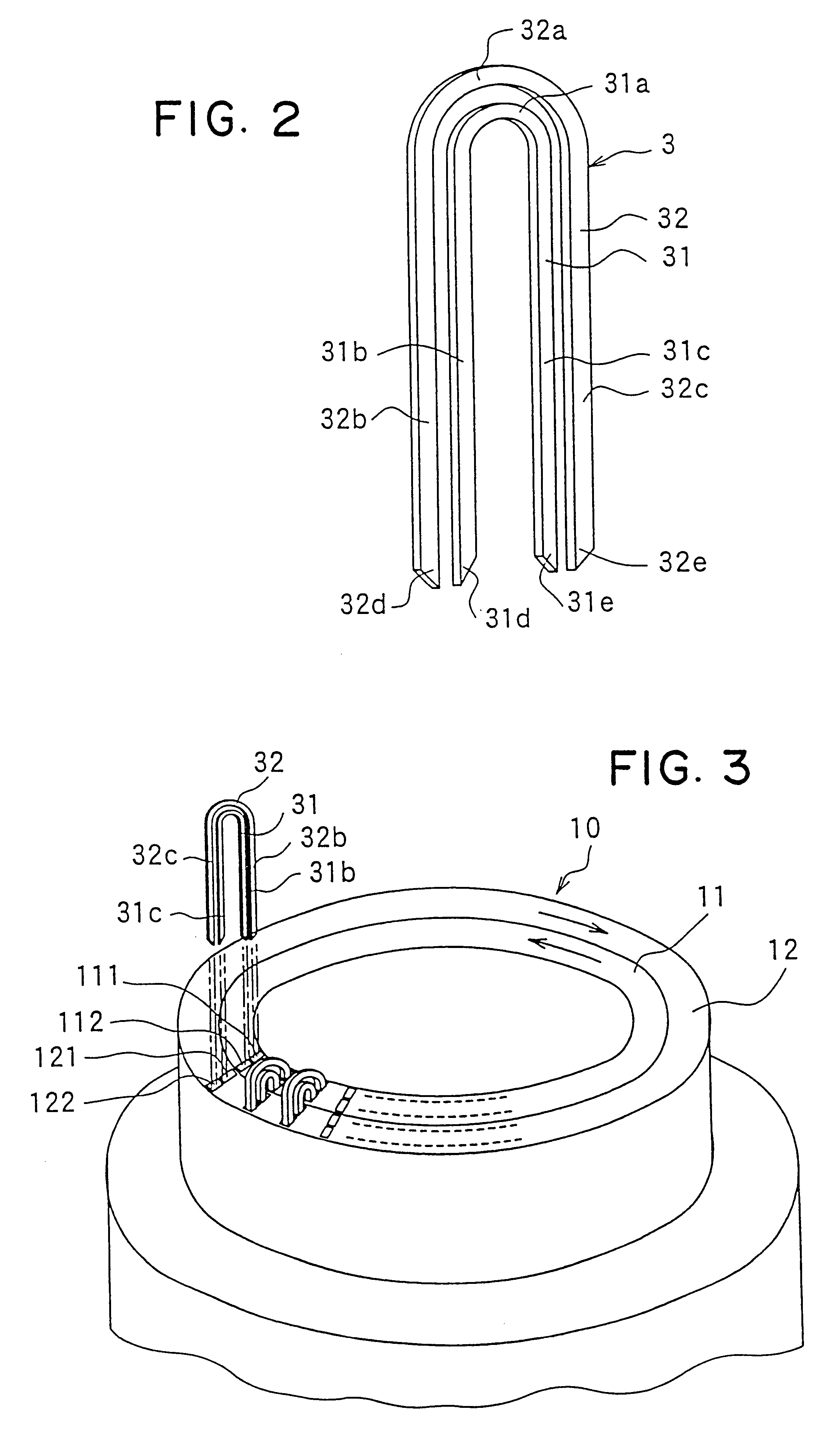
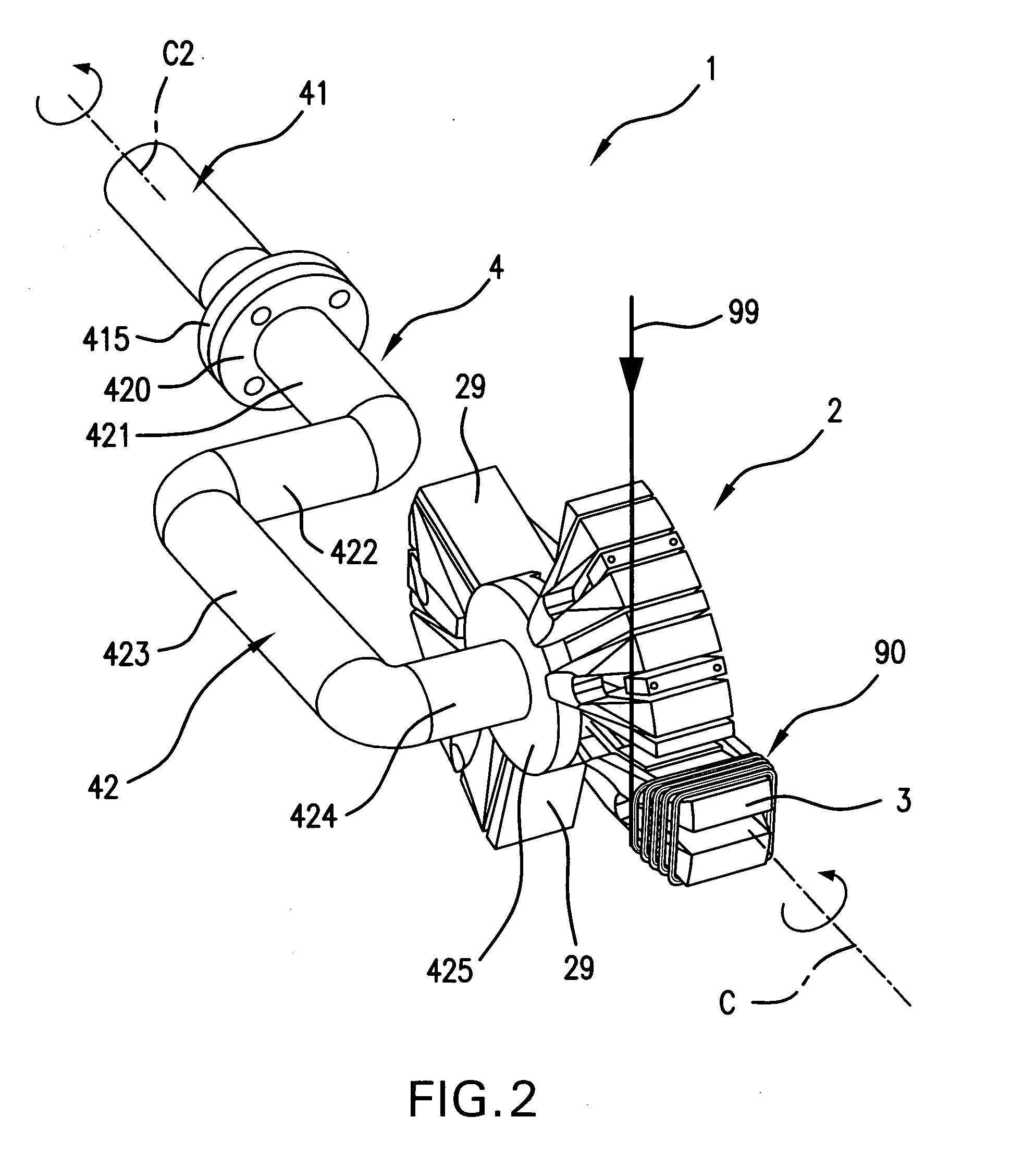
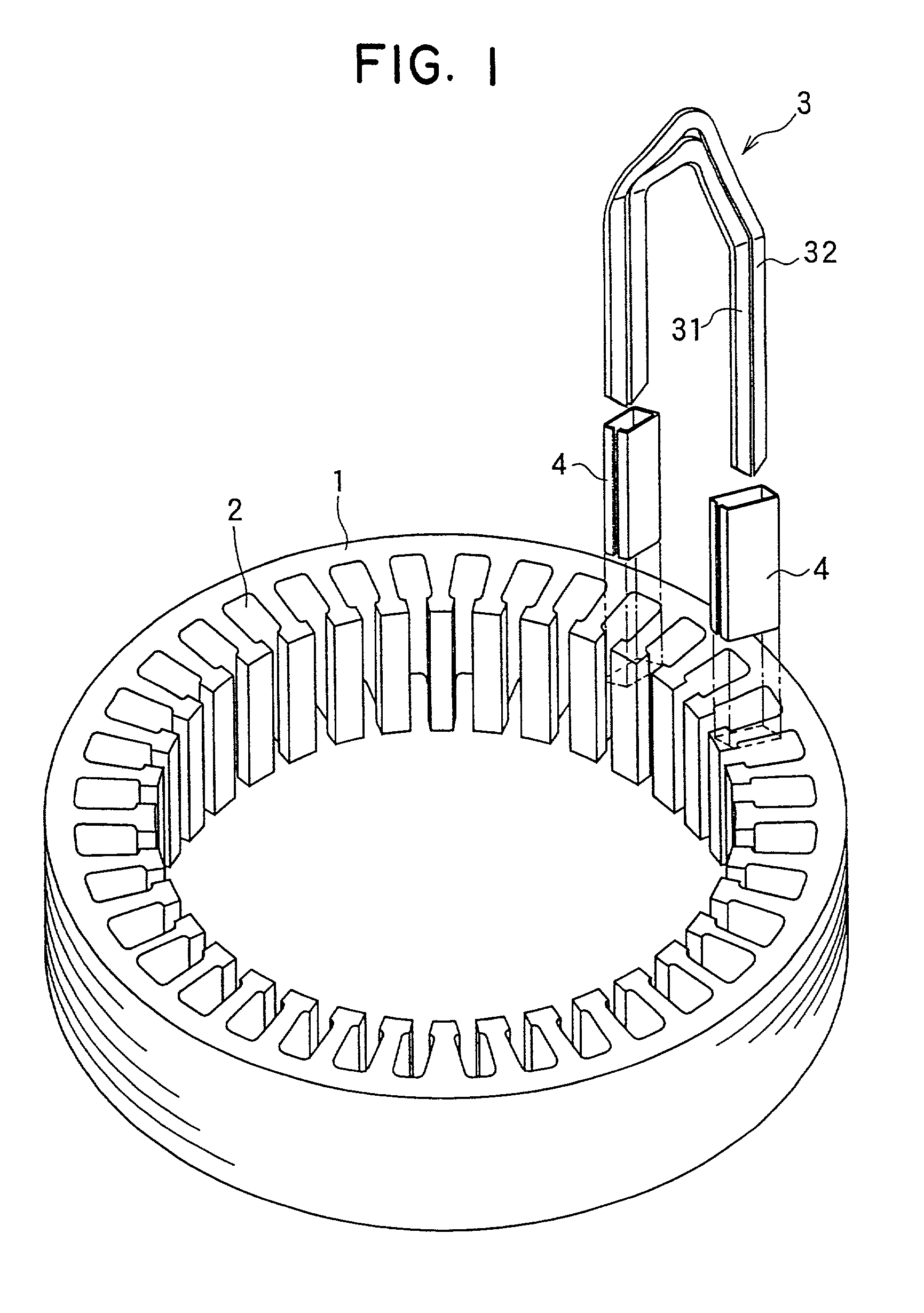
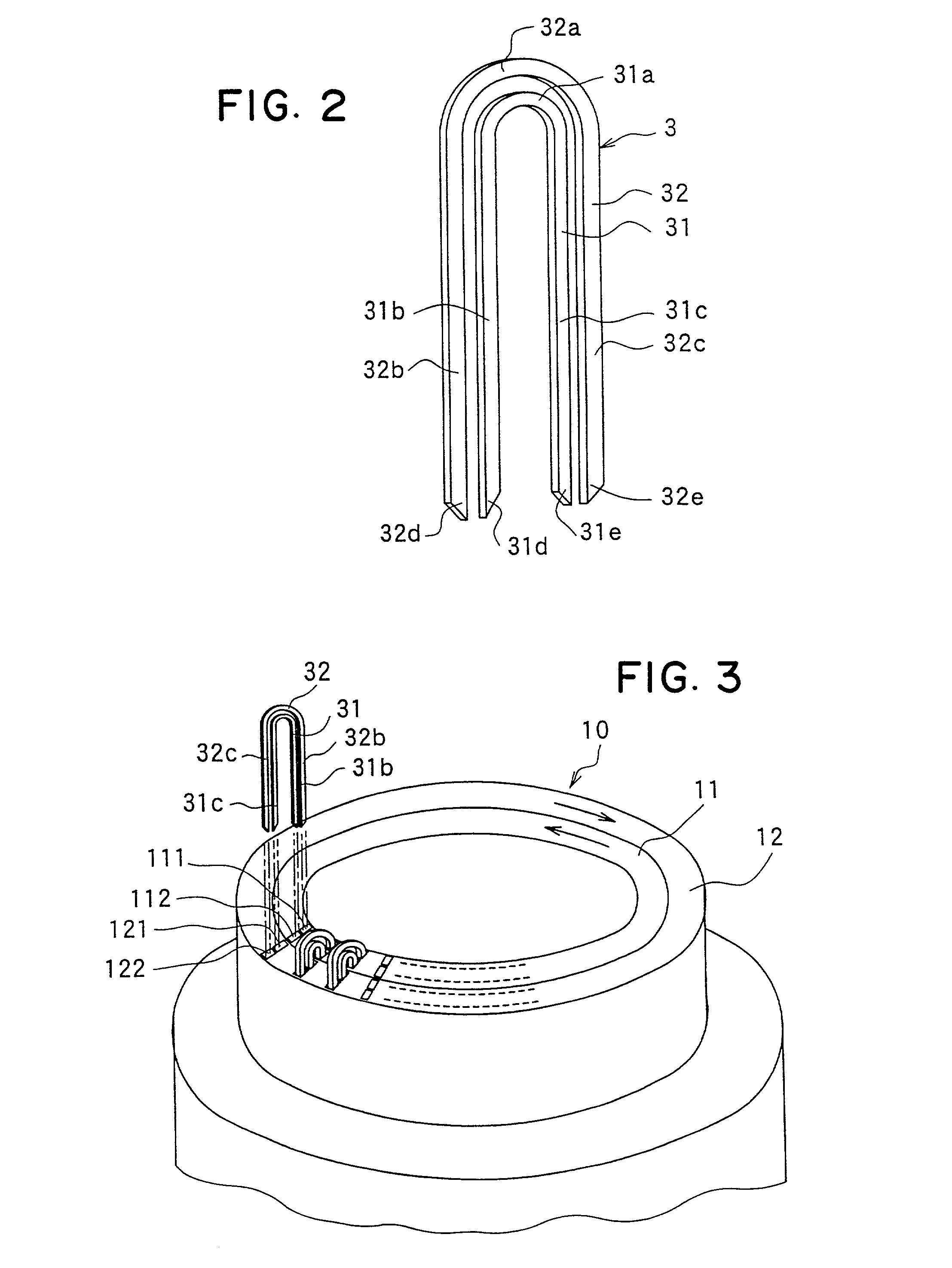
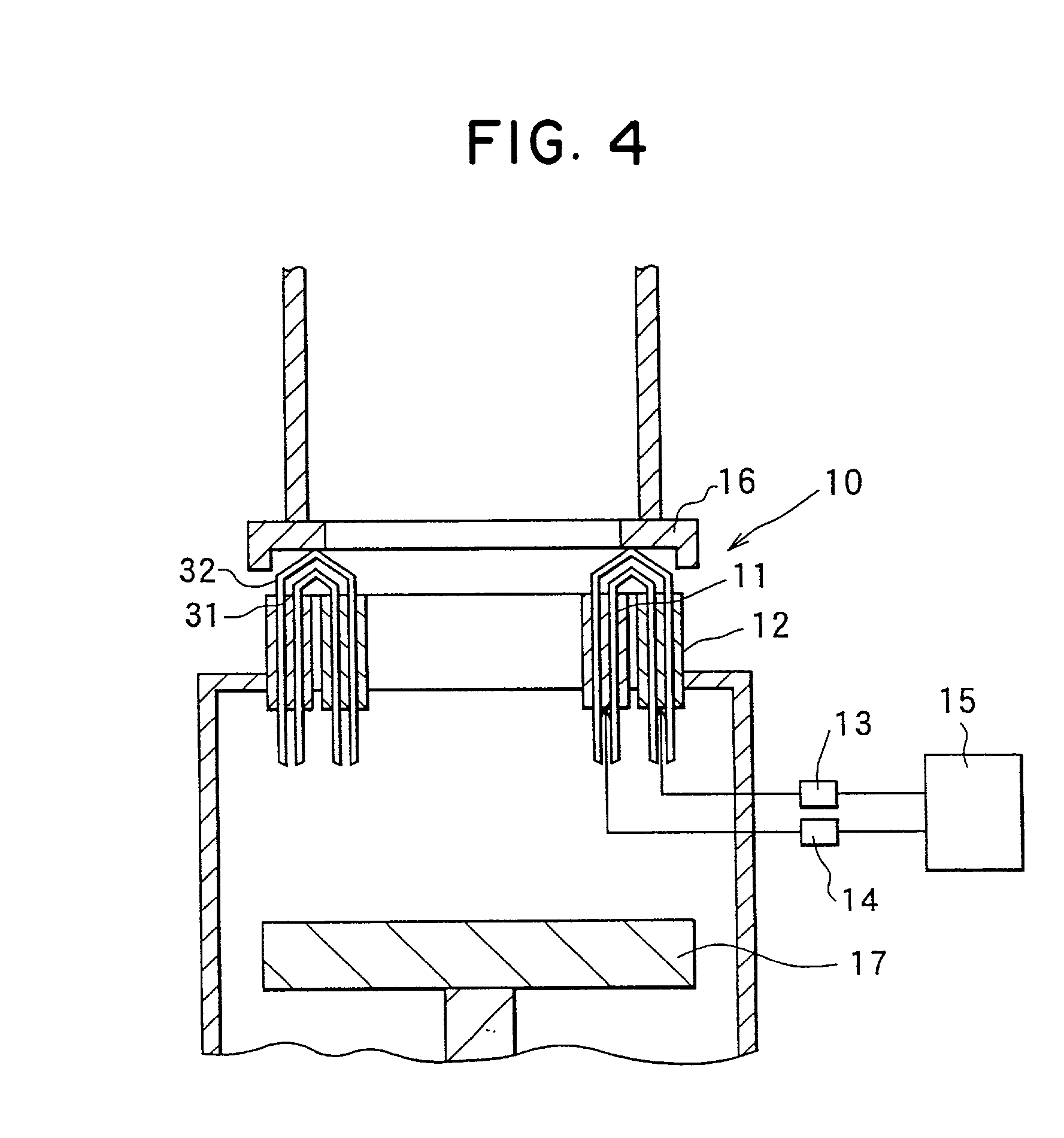
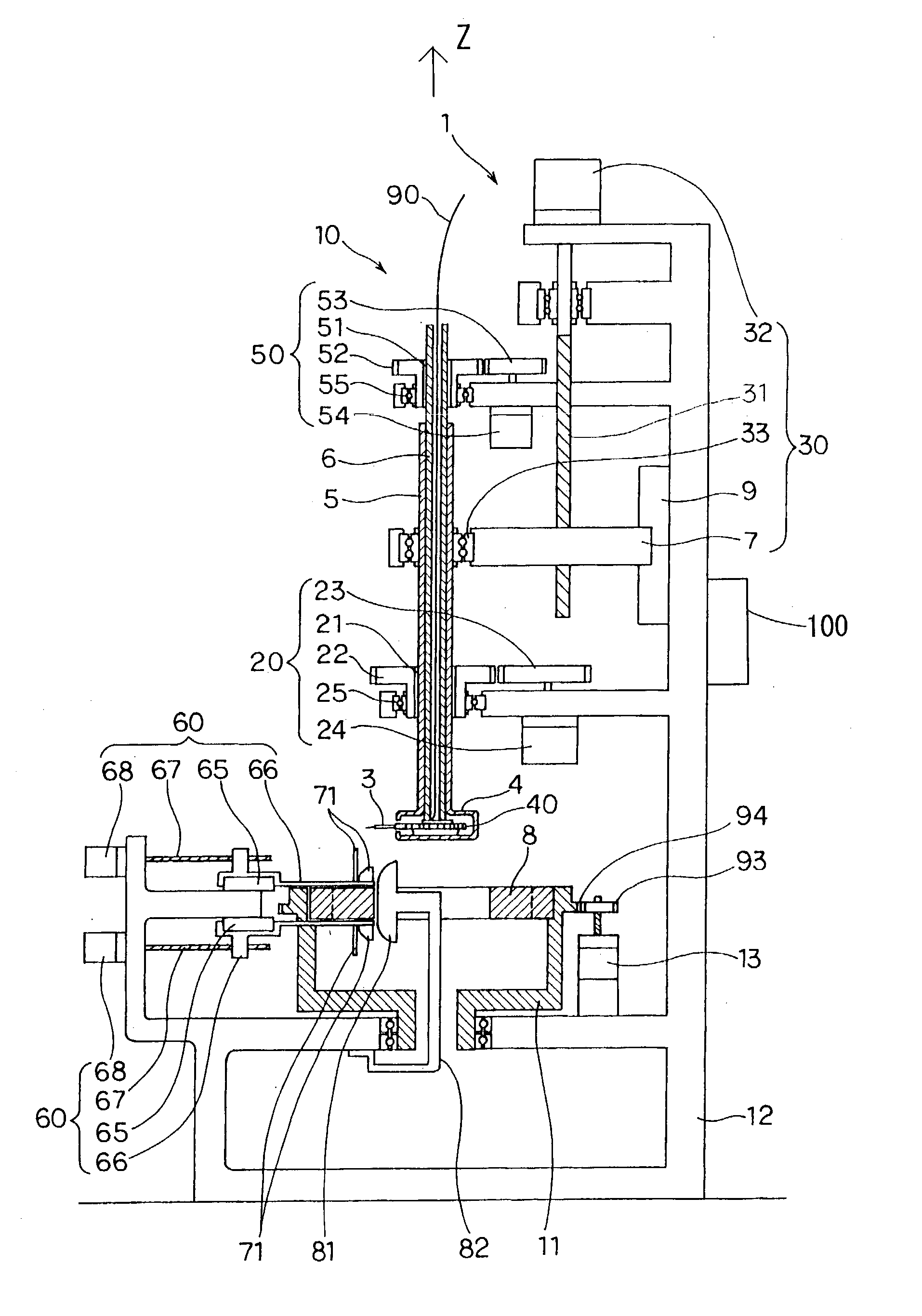
The object of the present invention is to provide a method and an apparatus for manufacturing a stator to improve accuracy in inserting conductor segments (3, 31, 32) into slots (2). The apparatus according to the present invention comprises a conductor holder (21, 22) holding the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) and an axial-moving-mechanisms (214) moving the conductor holder (21, 22) relative to a stator core (1) in an axial direction. The conductor holder (21, 22) holds straight portions (31b, 31c, 32b, 32c) of the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) to be inserted into the slots (2) from one end of the stator core (1).
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electric motor
InactiveUS6483221B1Simplify and reduce costsProduction be simplified and reducedMagnetic circuit stationary partsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesEngineeringMetal
A method of producing a laminated core of a stator of an electric motor, includes at least one laminated core of a stator formed by stacked sheet-metal laminates, which have mechanical individual poles and of poles connected in the circumferential direction of the stator, at least one pole shank and at least one pole shoe facing a rotor. The sheet-metal laminates are configured with indentations and protrusions and, as a result, the sheet-metal laminates form the laminated core of the stator by interengagement of the indentations and protrusions. The mechanical poles of the laminated core of the stator have windings, and webs are provided between the poles to connect the connected mechanical poles in the circumferential direction. The axial set-up of the sheet-metal laminates of the laminated core of the stator has a predeterminable alternating succession of poles with a connecting web and poles without a connecting web.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Alternator
InactiveUS6504283B1Reduce noise levelComponent with highSynchronous generatorsAsynchronous induction motorsAlternatorStator coil
An alternator includes a stator having an annular stator core provided with a number of slots extending axially disposed in lines circumferentially so as to open on an inner circumferential side and a stator coil wound into the stator core so as to be installed in the slots, a rotor having a number of claw-shaped magnetic poles for alternately forming north-seeking (N) and south-seeking (S) poles about a rotational circumference, the rotor being rotatably disposed on the inner circumferential side of the stator core, a bracket supporting the rotor and the stator, and a rectifier disposed at a first axial end of the stator and connected to end portions of the stator coil, the rectifier converting alternating current from the stator coil into direct current, wherein a number of slots is two per phase per pole, and the stator coil comprises a number of winding sub-portions in each of which a long strand of wire is wound so as to alternately occupy an inner layer and an outer layer in a slot depth direction within the slots at intervals of a predetermined number of slots by folding back the strand of wire outside the slots at axial end surfaces of the stator core.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method of manufacturing a stator for an alternator with reduced conductor portions
InactiveUS6865796B1Improve reliabilityImprove productivityWindings insulation shape/form/constructionManufacturing winding connectionsElectrical conductorAlternator
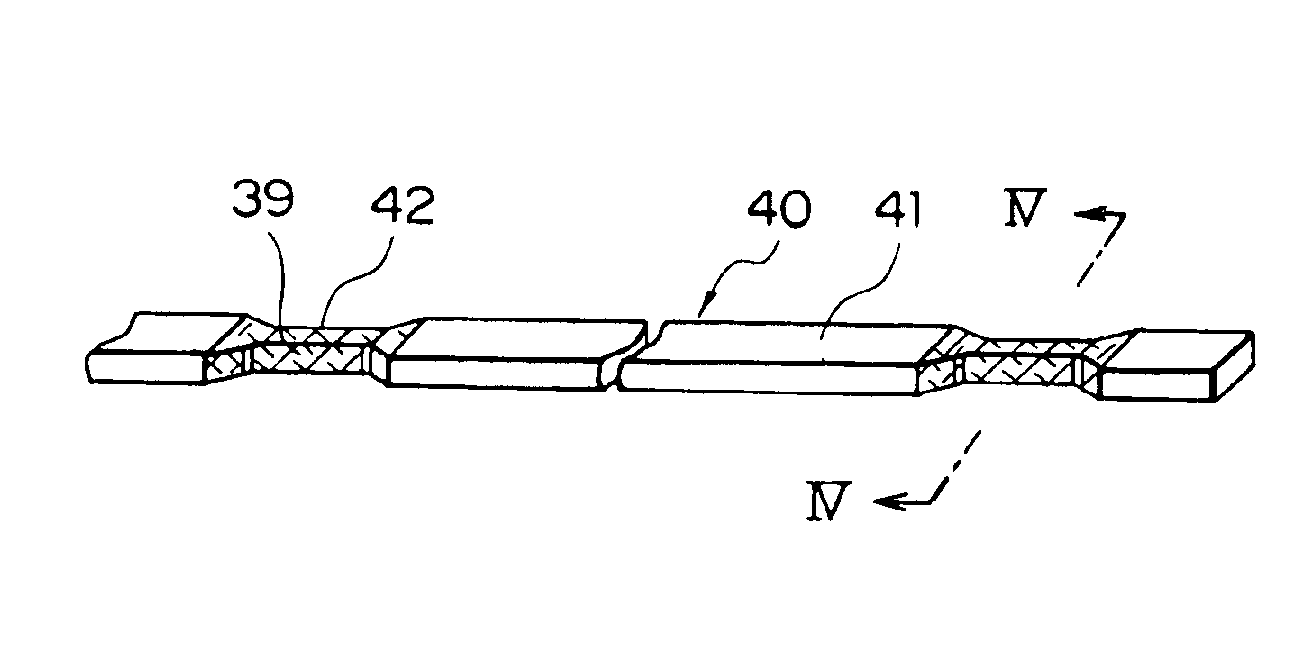
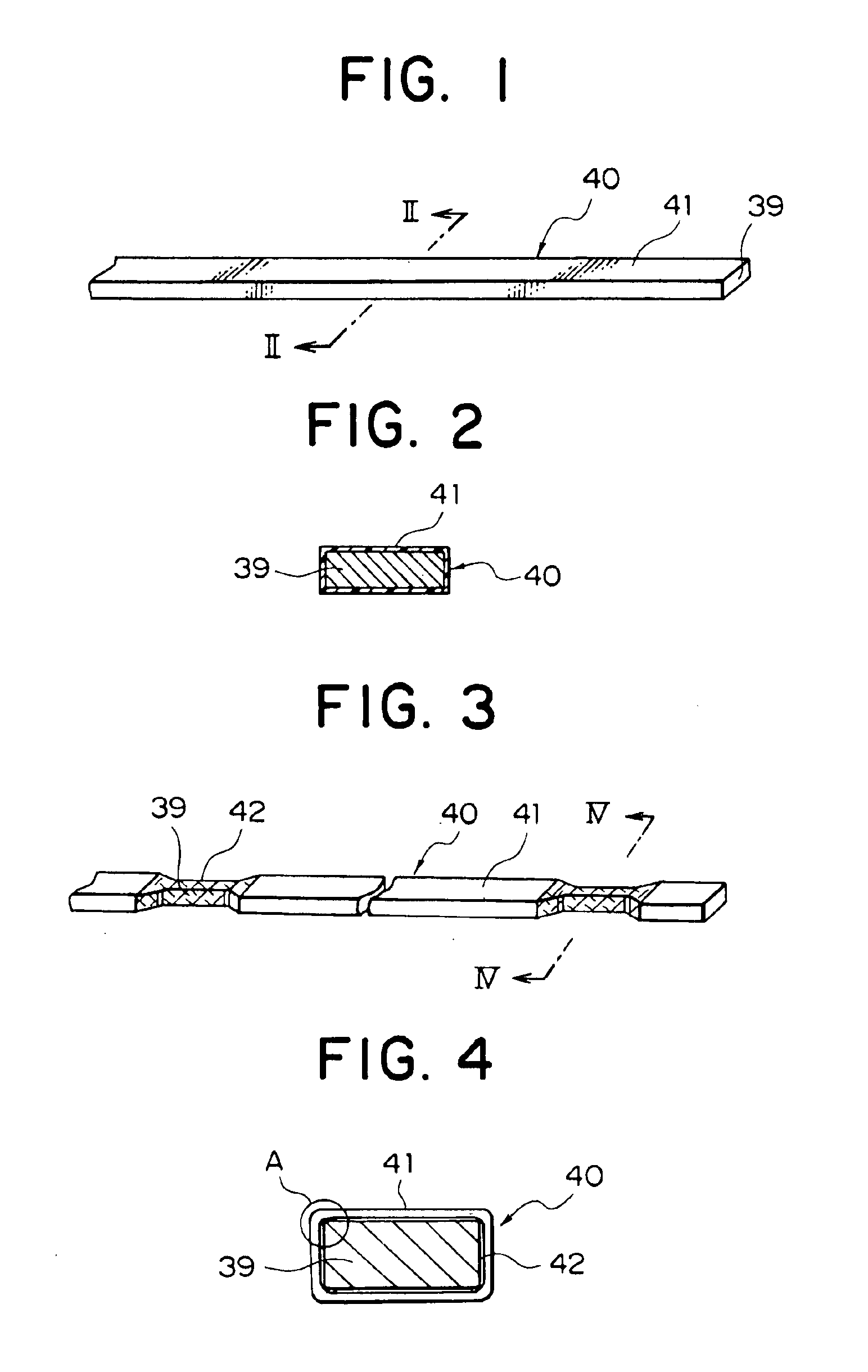
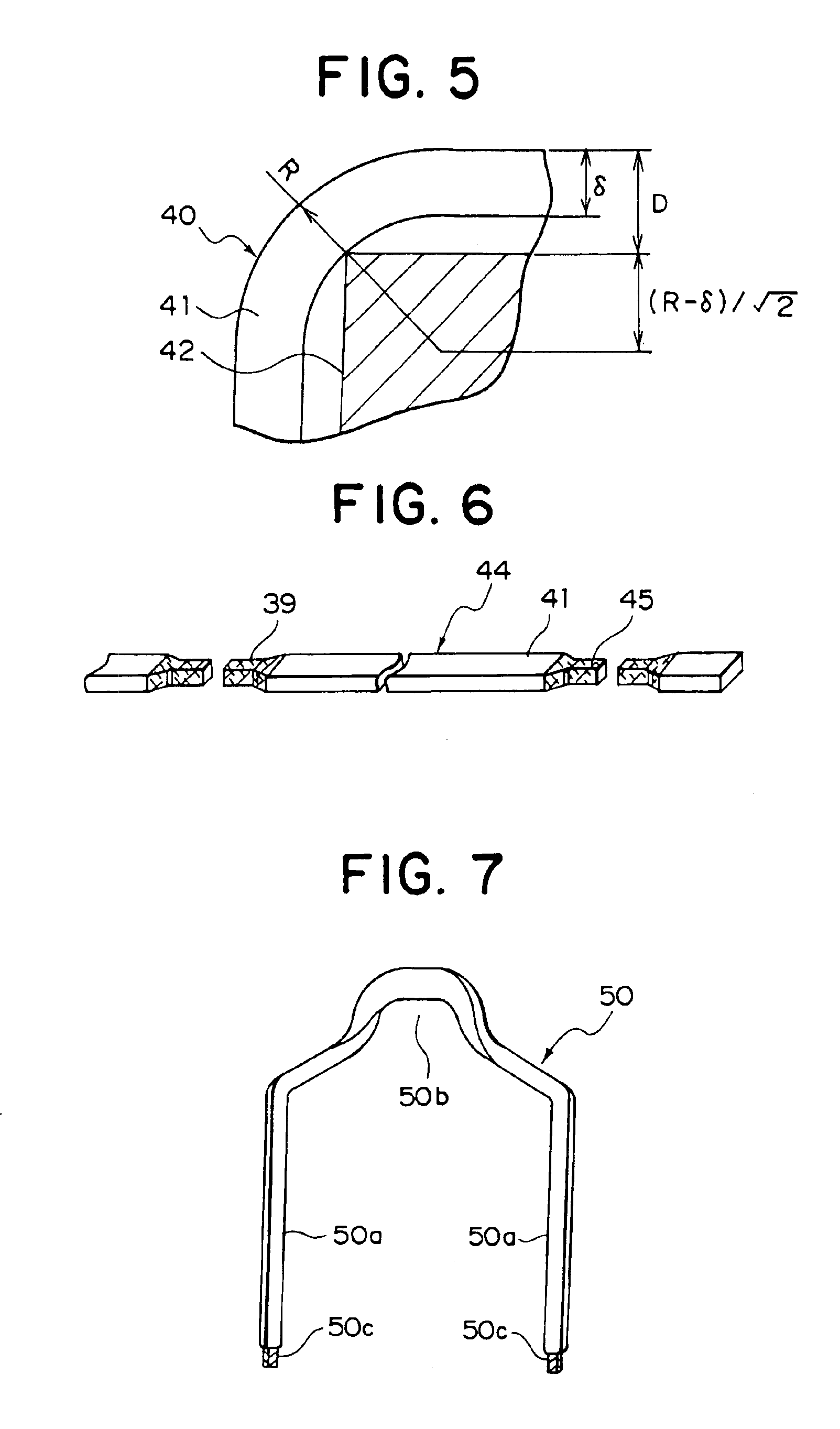
Coil members are obtained by forming width-reduced portions in a wire material over a predetermined longitudinal range generally centered on cutting positions, then removing an insulation coating from the width-reduced portions, and thereafter cutting the wire material at the width-reduced portions. Coil segments are prepared by bending the coil members into a general U shape. Then the coil segments are inserted into the slots in a stator core, and a stator is obtained by welding together the free end portions of the projecting coil segments.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Transposed winding for random-wound electrical machines operating at high frequencies
InactiveUS20020096959A1Synchronous machinesAsynchronous induction motorsElectric machineInterconnection
A random-wound winding for an electrical machine including interconnected wire layers, wherein the interconnected wire layers include randomly wound wires and are configured upon placement in the electrical machine to have substantially the same impedance. Accordingly, the random wound windings can include a first coil having layers of wires randomly wound on the first coil with the layers configured in a first layering order, a second coil having layers of wires randomly wound on the second coil with the layers configured in a second layering order transposed relative to the first layering order, and at least one electrical interconnection configured to serially connect the layers of the first coil to the layers of the second coil such that an average axial position of all interconnected layers is substantially the same. The random wound windings can include a coil having layers of wires randomly wound on the coil with one side of the coil having the layers configured in a first layering order and an opposing side of the coil having the layers configured in a second layering order transposed relative to the first layering order, wherein an average axial position of the layers substantially the same.
Owner:CAPSTONE TURBINE
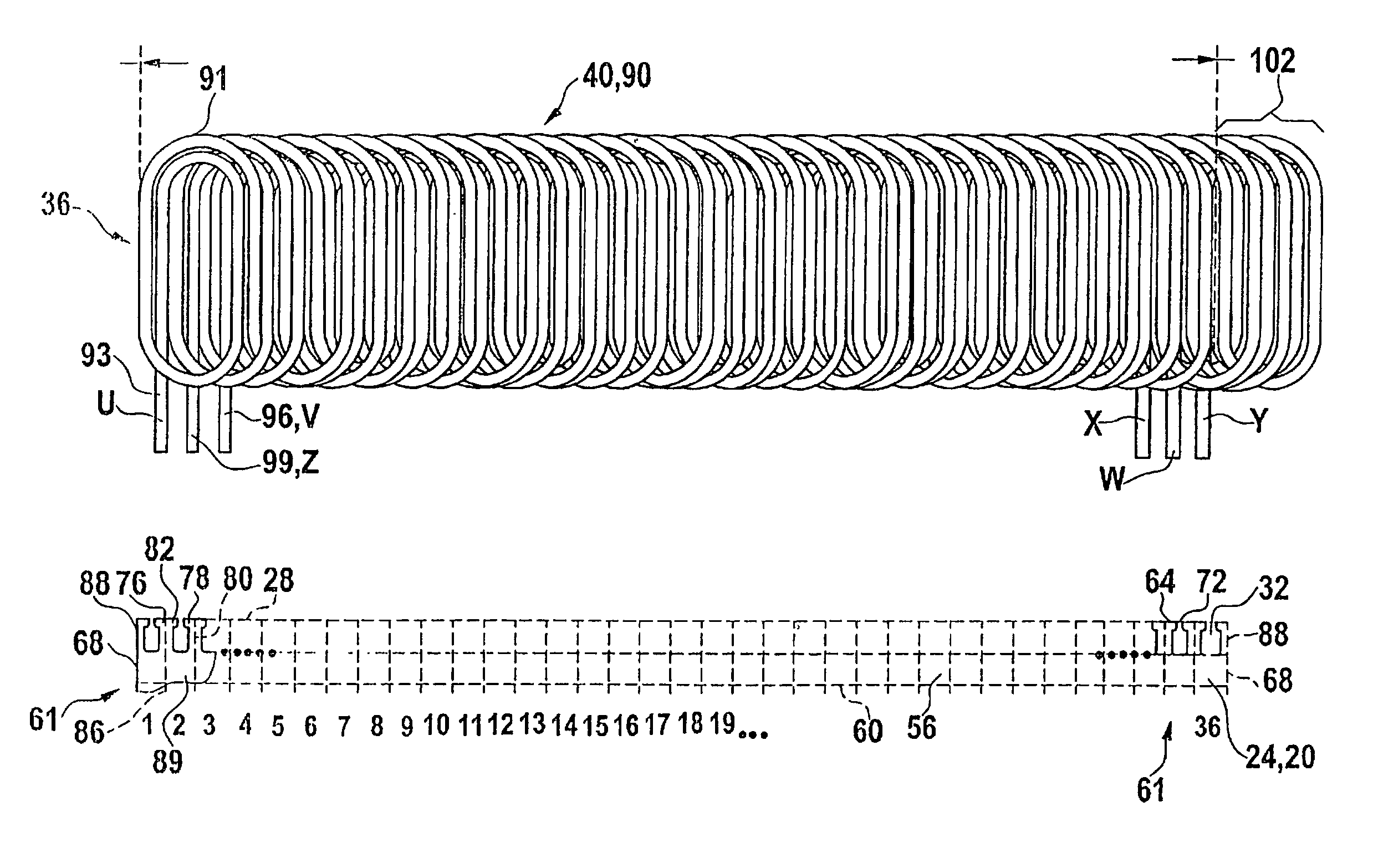
Electromagnetic device with embedded windings and method for its manufacture
InactiveUS6232681B1Maximize electromagnetic couplingGap minimizationSynchronous machinesMagnetic circuit stationary partsReduced sizeConductor Coil
A powdered magnetic material stator core with embedded stator windings and a method for its manufacture. Embedding the windings within a radially compacted powdered magnetic material stator core enables equivalent or better electromagnetic performance in a significantly reduced size. Radial compaction of the powdered magnetic material minimizes the distortion of the stator windings during compaction.
Owner:REMY TECHNOLOGIES LLC
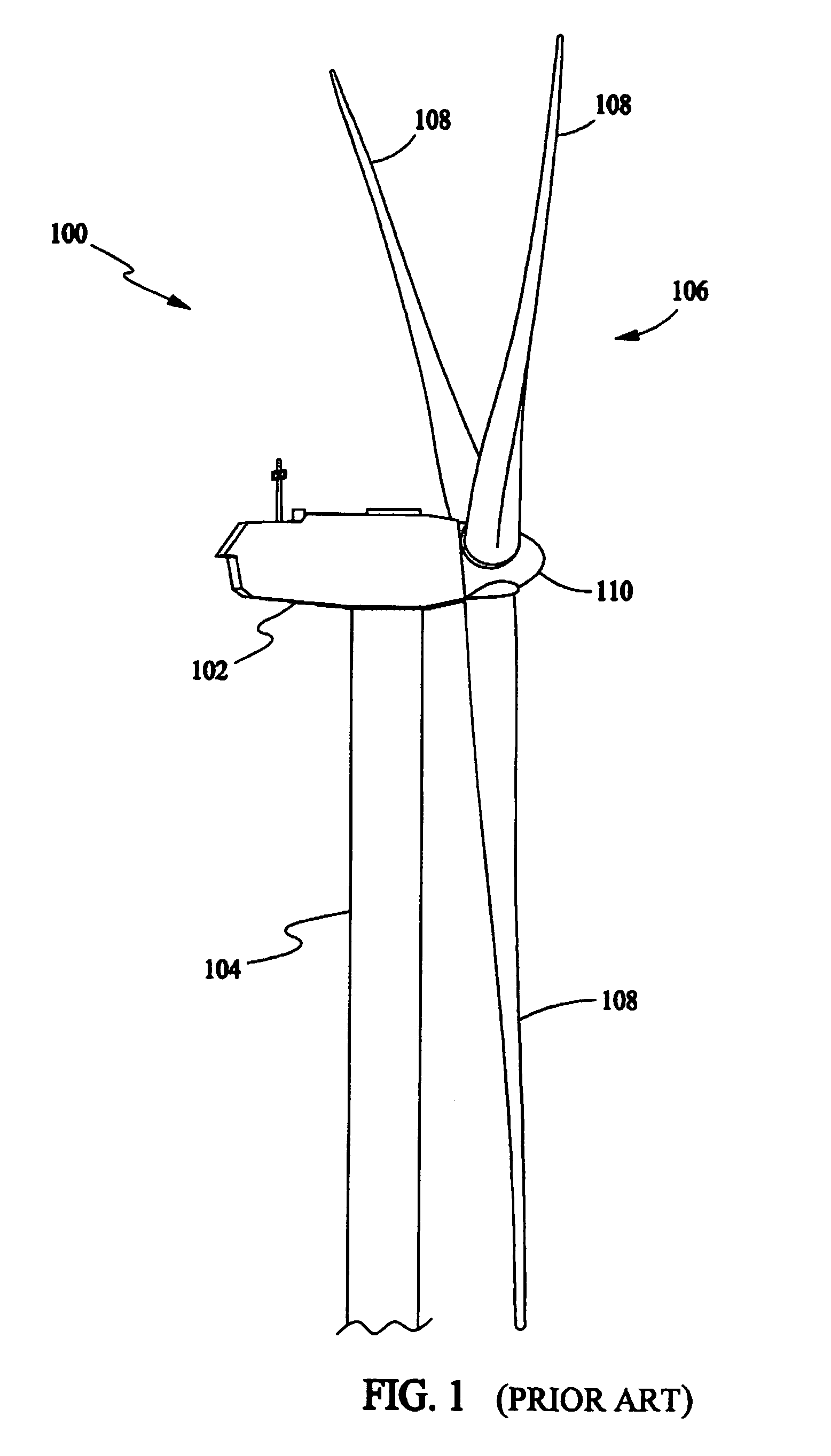
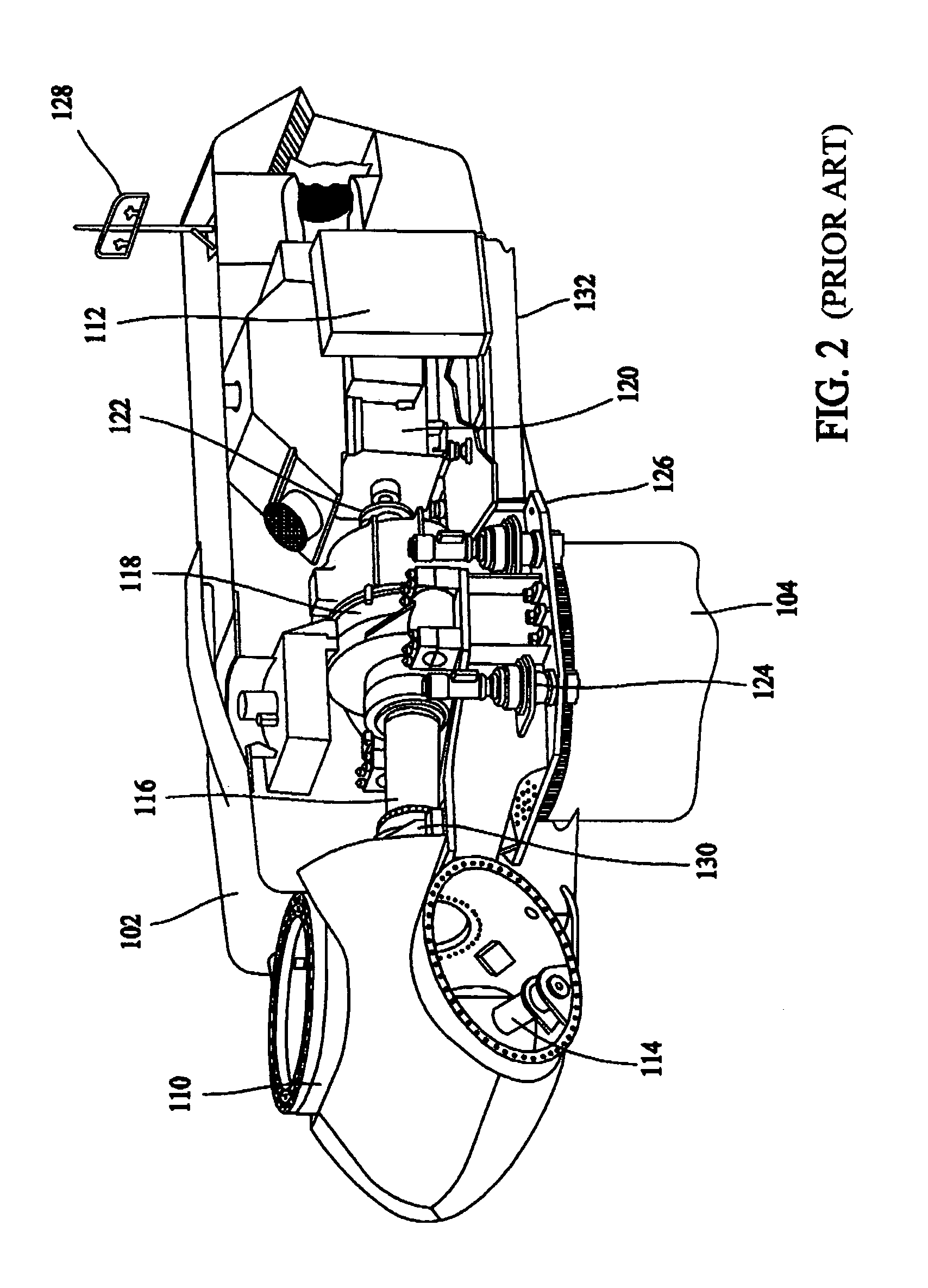
Removable bearing arrangement for a wind turbine generator
InactiveUS20070075548A1Easy to disassembleBearing repair/replacementEngine manufactureTurbineWind force
A wind generator having removable change-out bearings includes a rotor and a stator, locking bolts configured to lock the rotor and stator, a removable bearing sub-assembly having at least one shrunk-on bearing installed, and removable mounting bolts configured to engage the bearing sub-assembly and to allow the removable bearing sub-assembly to be removed when the removable mounting bolts are removed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
4-Layer type of stator winding formed of sequentially connected segments located in respective slot pairs, and method of manufacture thereof
ActiveUS20050258703A1Easy to implementFirmly connectedSynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionElectrical conductorEngineering
A phase winding of a stator winding comprises one or more pairs of interconnected partial coil, each partial coil formed of sequentially connected U-shaped segment pairs, each pair comprising a large segment and small segment. Two segment legs, of the large and small segment respectively of such a pair, constitute first and second conductor layers of a first stator slot and have their tip portions mutually connected. The remaining two segment legs respectively constitute fourth and third conductor layers of a second slot that is distant by one pole pitch, and have their respective tip portions mutually connected.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Stator for rotating electrical machine, part to be used for stator and method for manufacturing stator for rotating electrical machine
InactiveUS20090096313A1Increase spacingSuppressing deterioration of workabilitySynchronous machinesAsynchronous induction motorsElectric machineEngineering
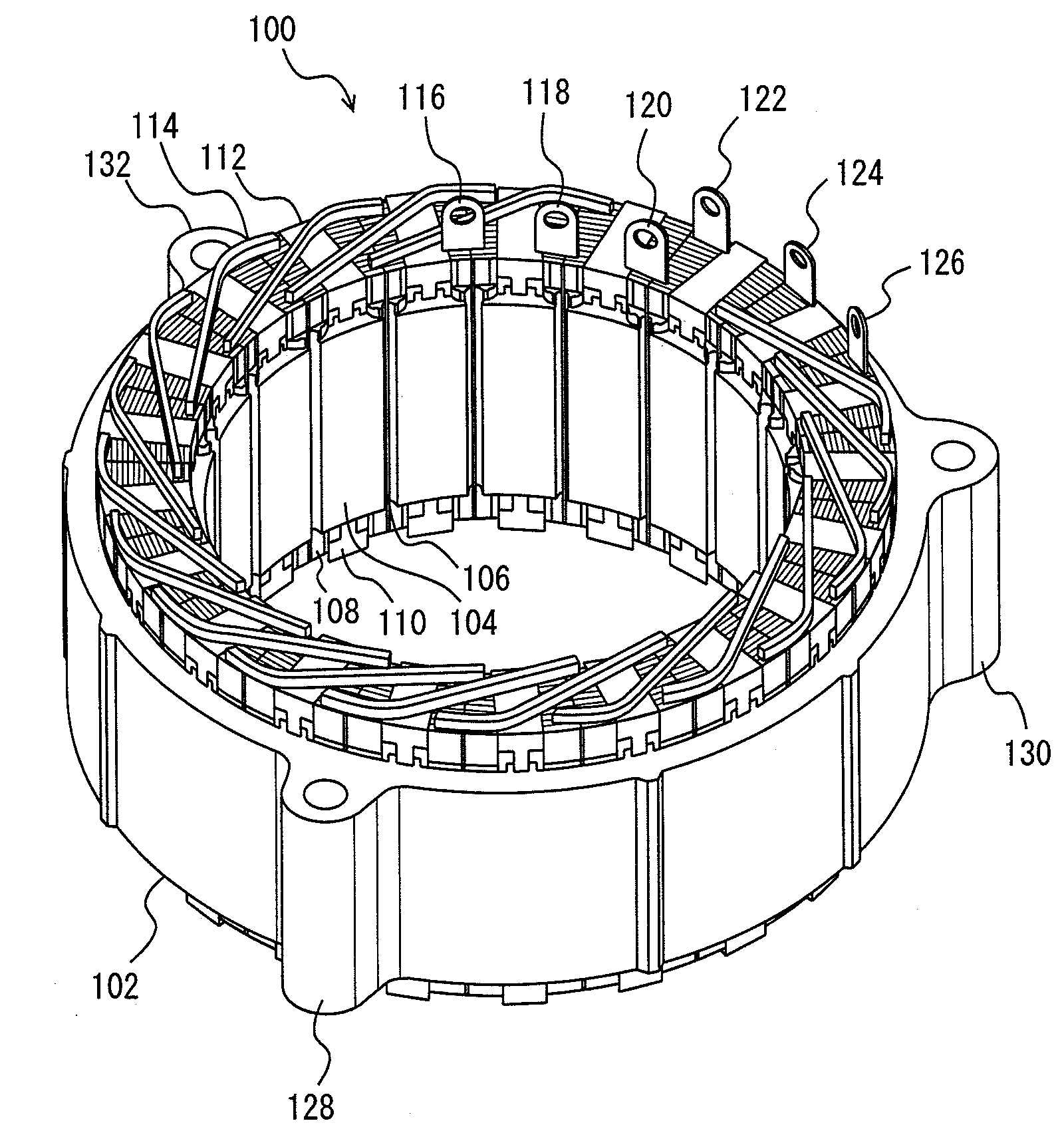
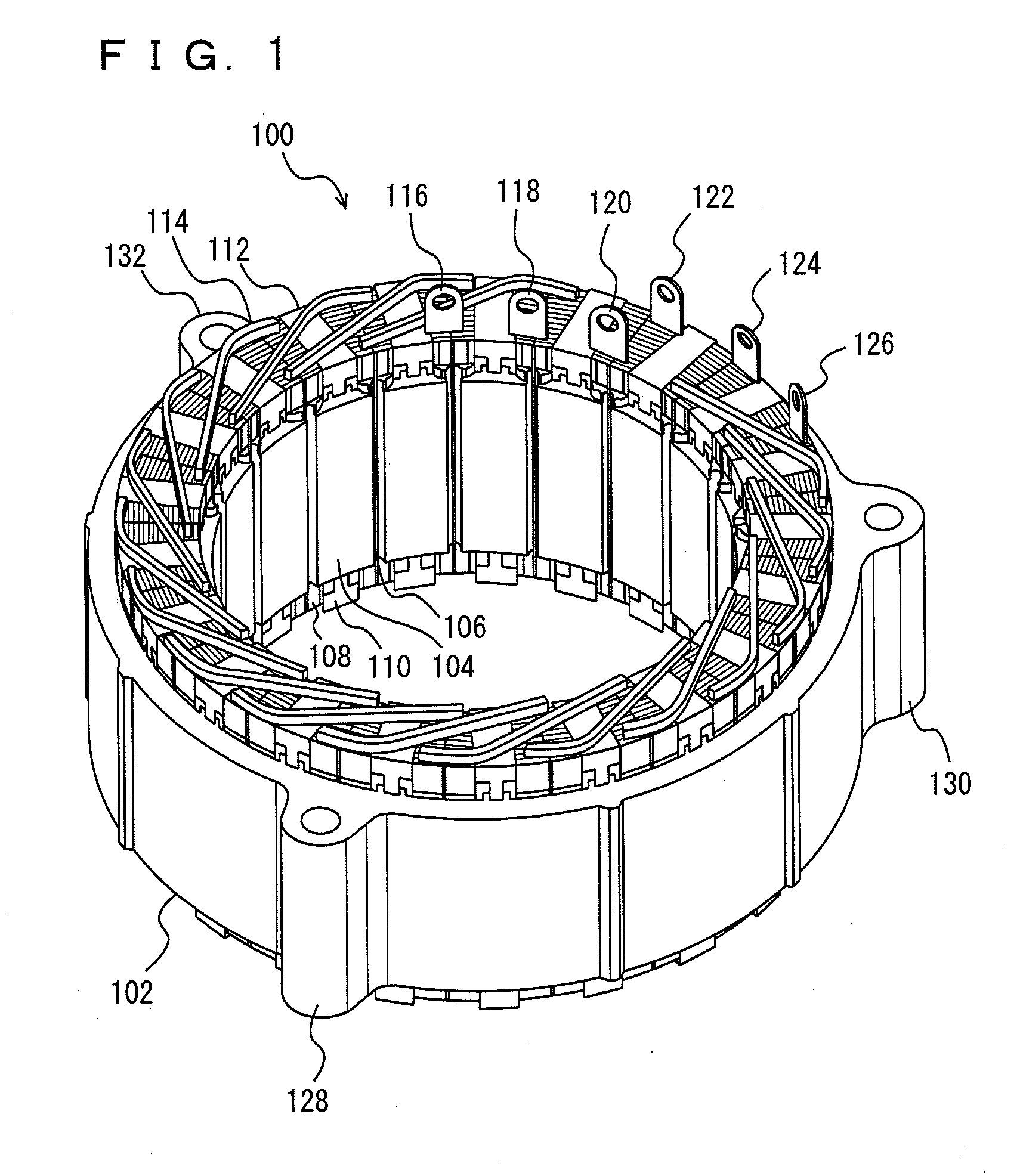
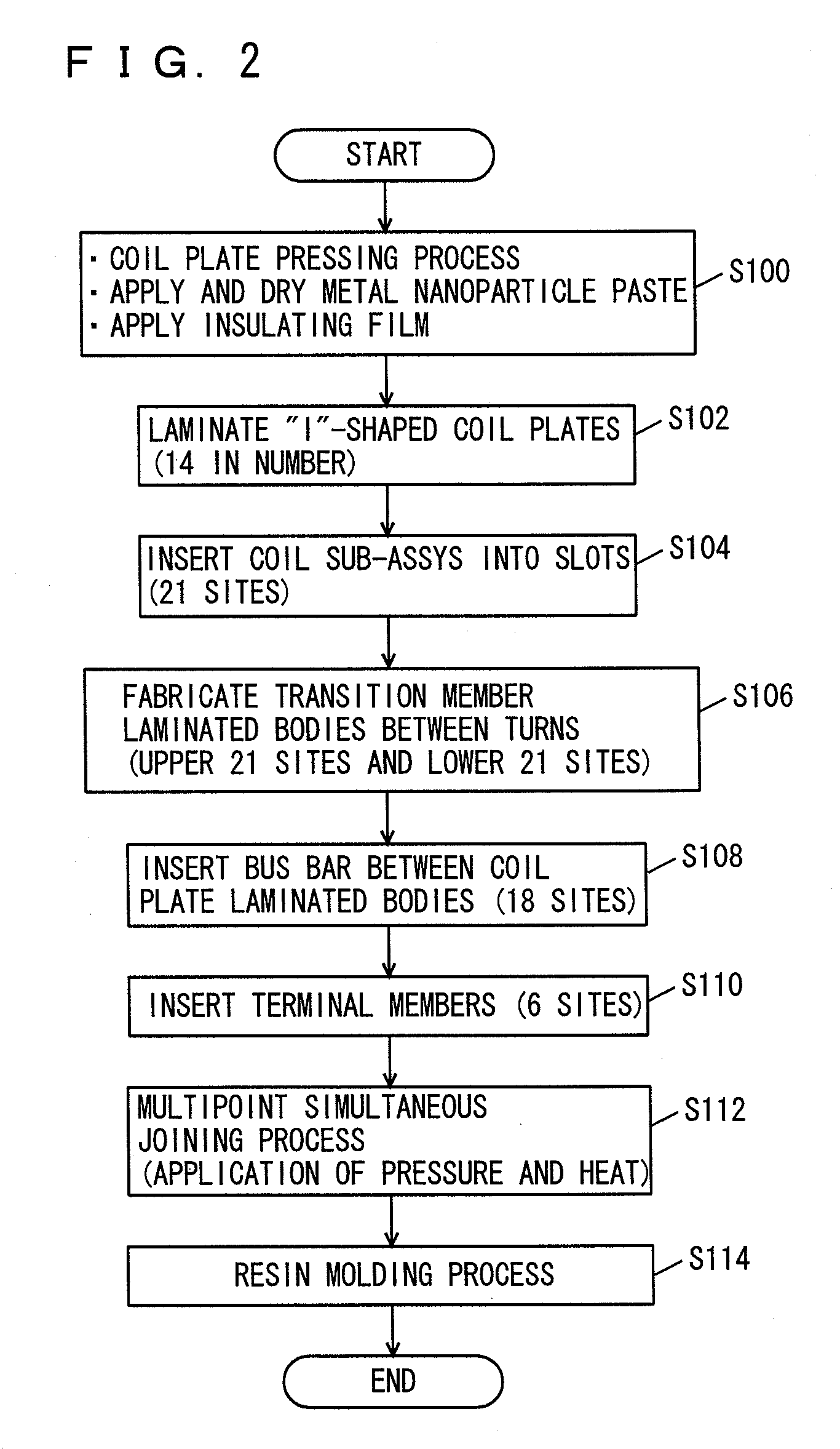
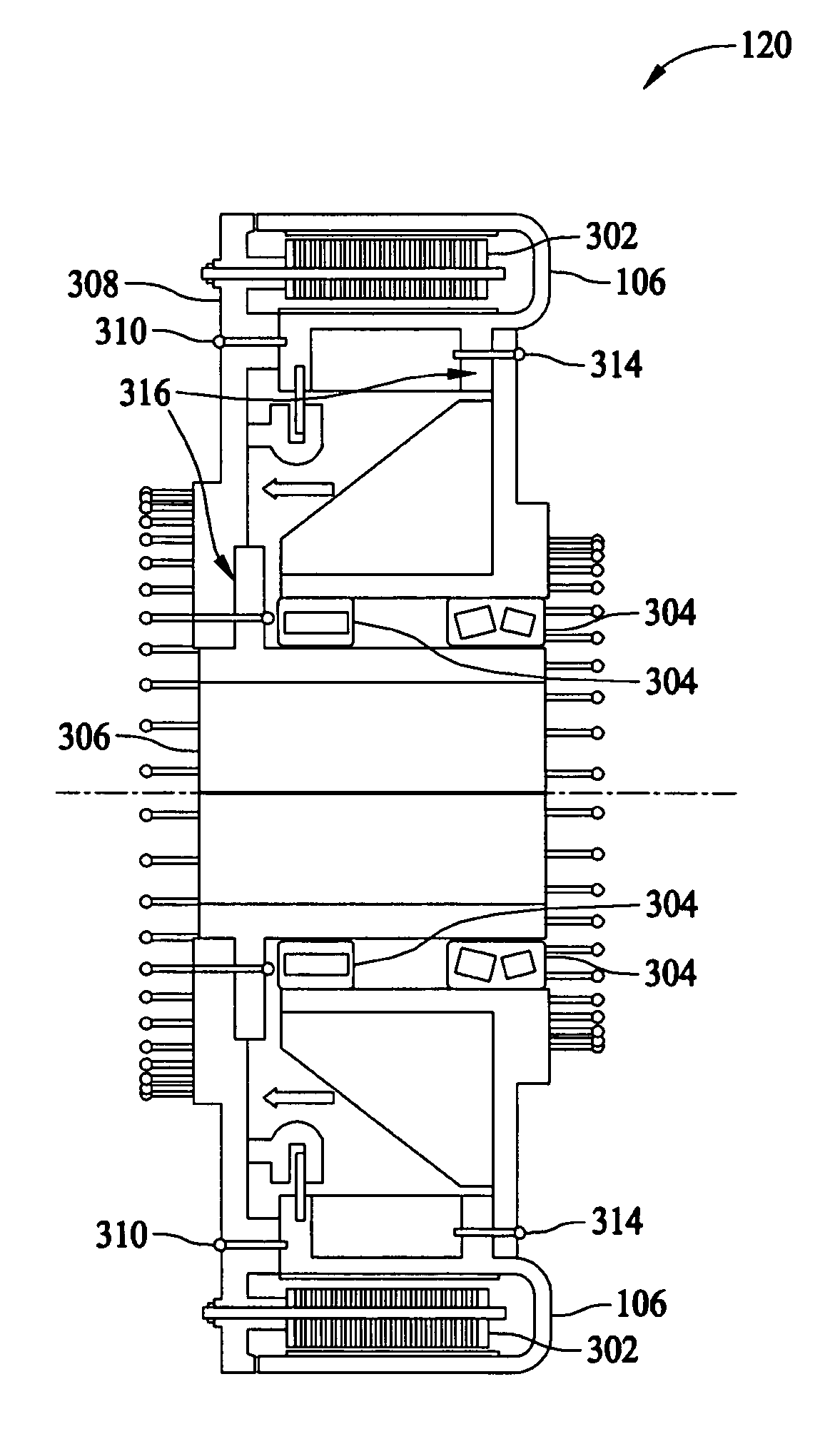
A stator includes a stator core having a plurality of slots in a direction parallel to the rotating shaft of a rotating electrical machine; and a coil plate laminated body formed by laminating a plurality of I-shaped coil plates, each of which has an insulating film adhered at least on one side, in a diameter direction. In the coil plate laminated body, a plurality of coil plates are inserted inside a resin insulator inserted into the slots so that the insulating film is arranged between the coil plates, and the coil plates are integrally held by the resin insulator. The resin insulator integrally holds the coil plate laminated body of a plurality of phases in the same slot.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for changing removable bearing for a wind turbine generator
A wind generator having removable change-out bearings includes a rotor and a stator, locking bolts configured to lock the rotor and stator, a removable bearing sub-assembly having at least one shrunk-on bearing installed, and removable mounting bolts configured to engage the bearing sub-assembly and to allow the removable bearing sub-assembly to be removed when the removable mounting bolts are removed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
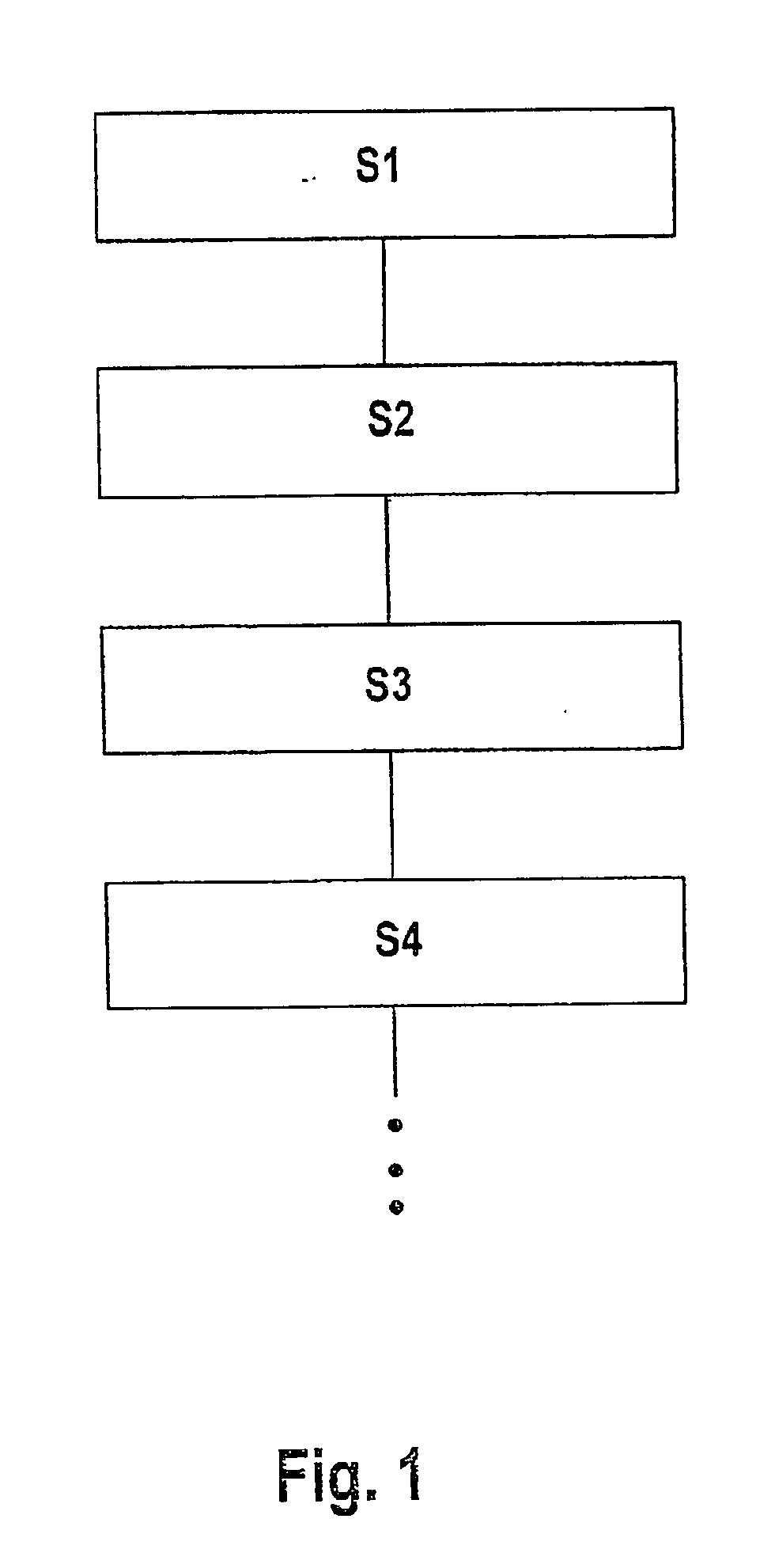
Method for producing a magnetically excitable core comprising a core winding for an electric machine
InactiveUS20030071534A1Easy to fillDifficult to joinSynchronous generatorsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineEngineering
A method for producing a magnetically excitable core (24) for an electrical machine, by which in a method step (S1), the core (24), having a substantially parallelepiped shape (20) with slots (32) extending parallel on one side, is furnished, into whose slots (32), in a method step (S2), the core winding (40) is inserted by its winding sides (36), and then in a method step (S3), the core (24) together with the core winding (40) is reshaped into a cylindrical ring shape (52) with radially inward-oriented slots (32), is proposed. The method is characterized by a further step, according to which in each case all winding sides (36) that are inserted into each slot (32) are pressed into a slot shape (119) in a tool (44) and reshaped before being inserted into the slot (32). Furthermore, a stator (150) produced by this method and an electrical machine (140) having this stator (150) are proposed.
Owner:SEG AUTOMOTIVE GERMANY GMBH
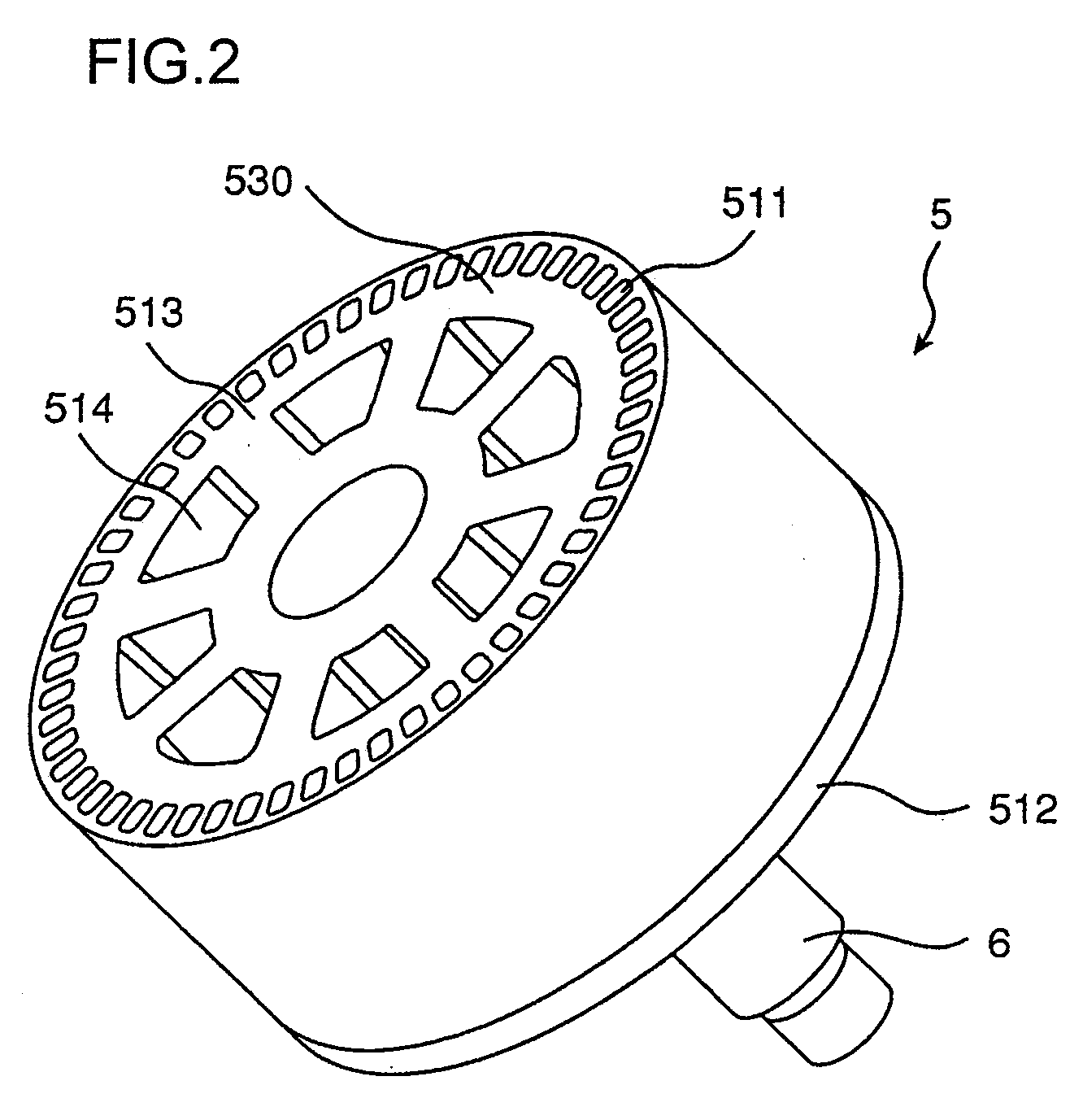
Electric Rotating Machine and Stator for the Same
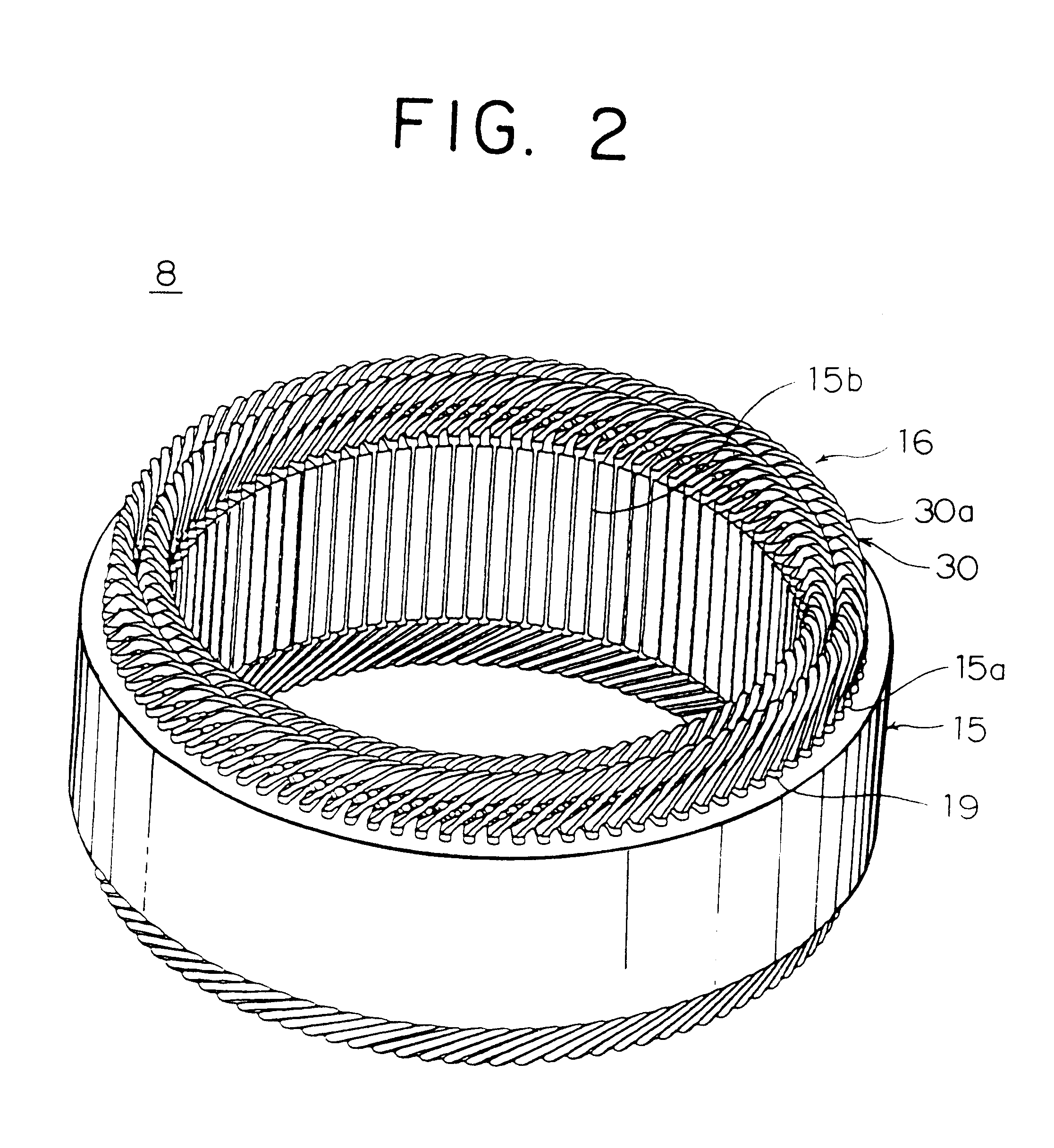
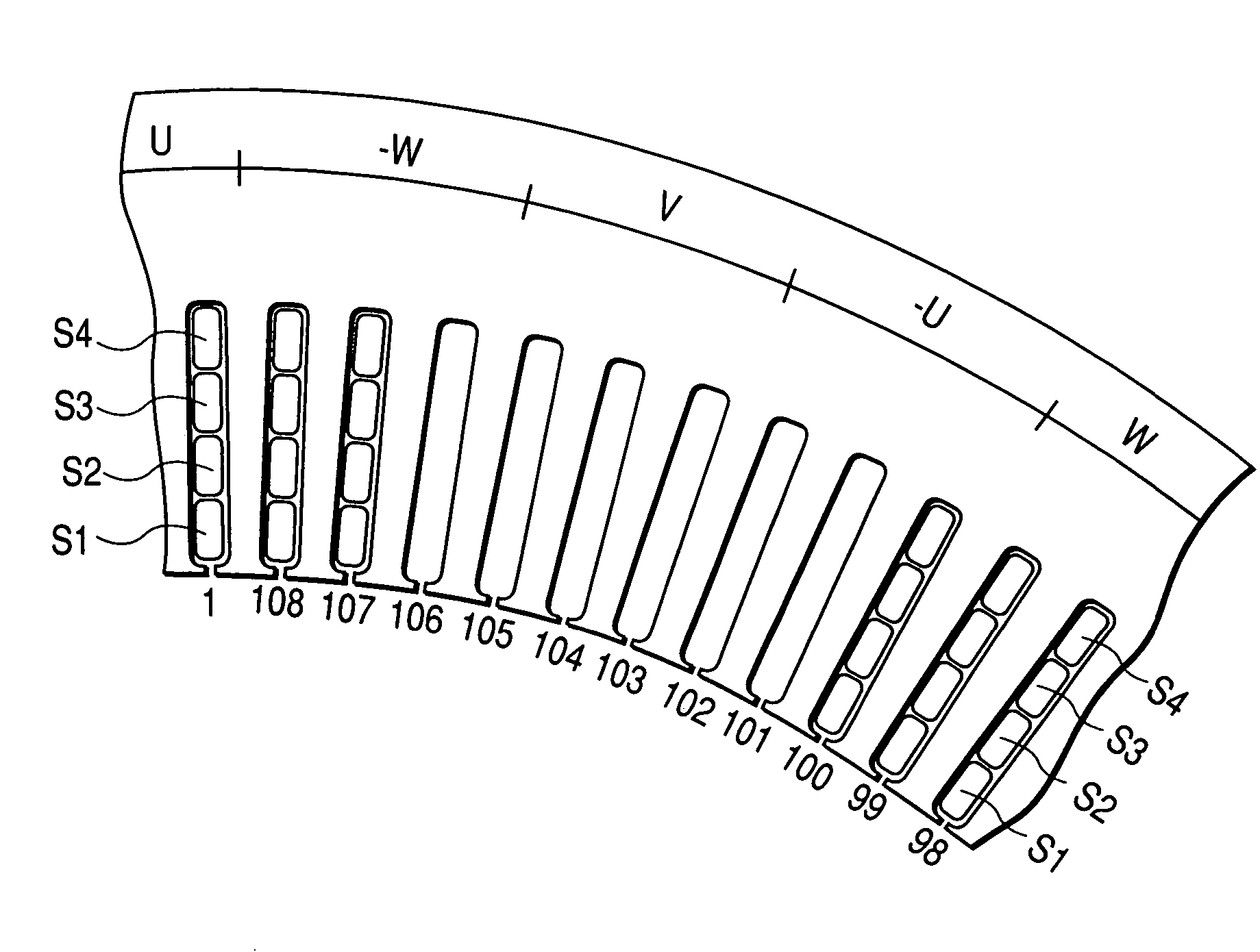
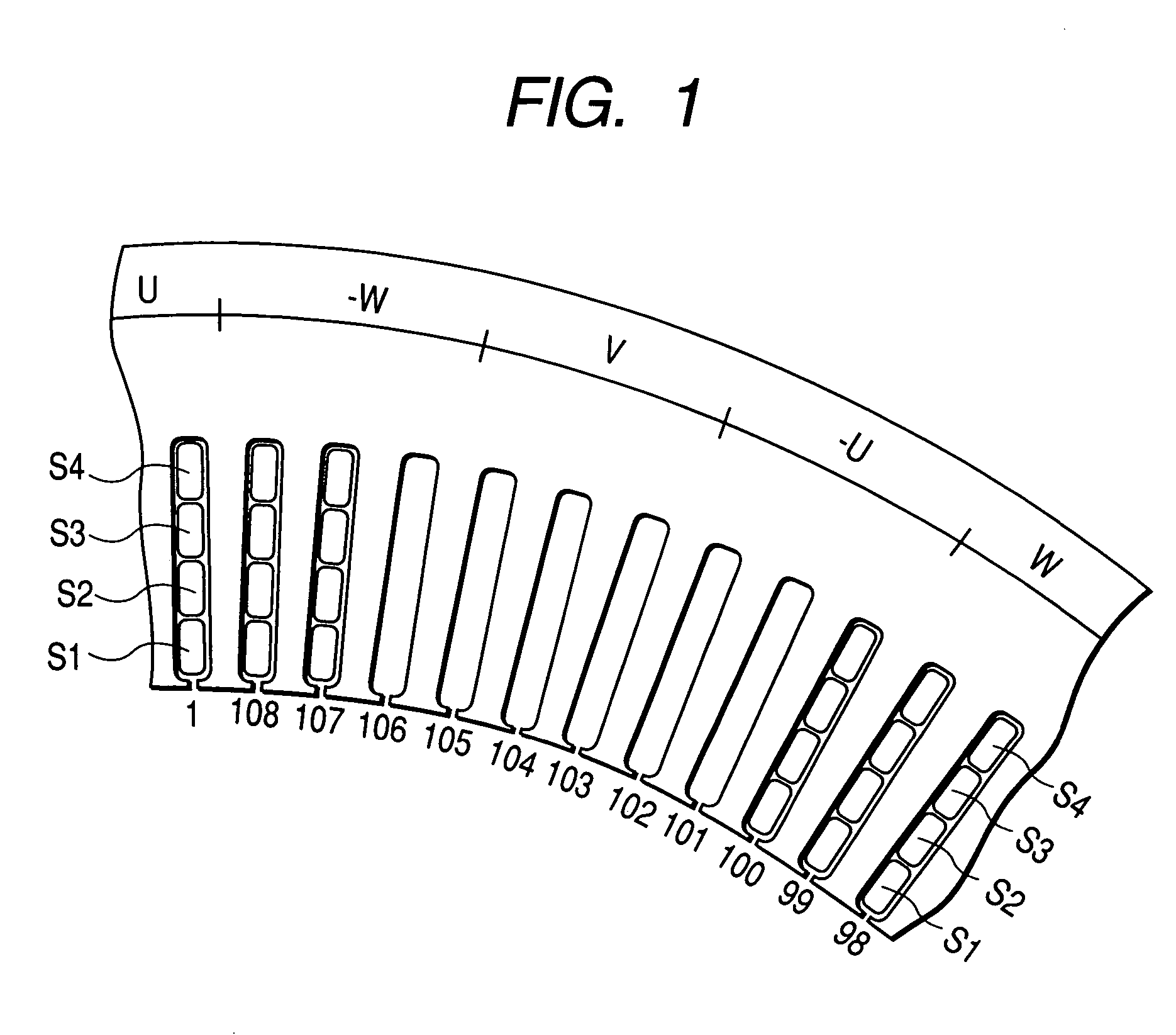
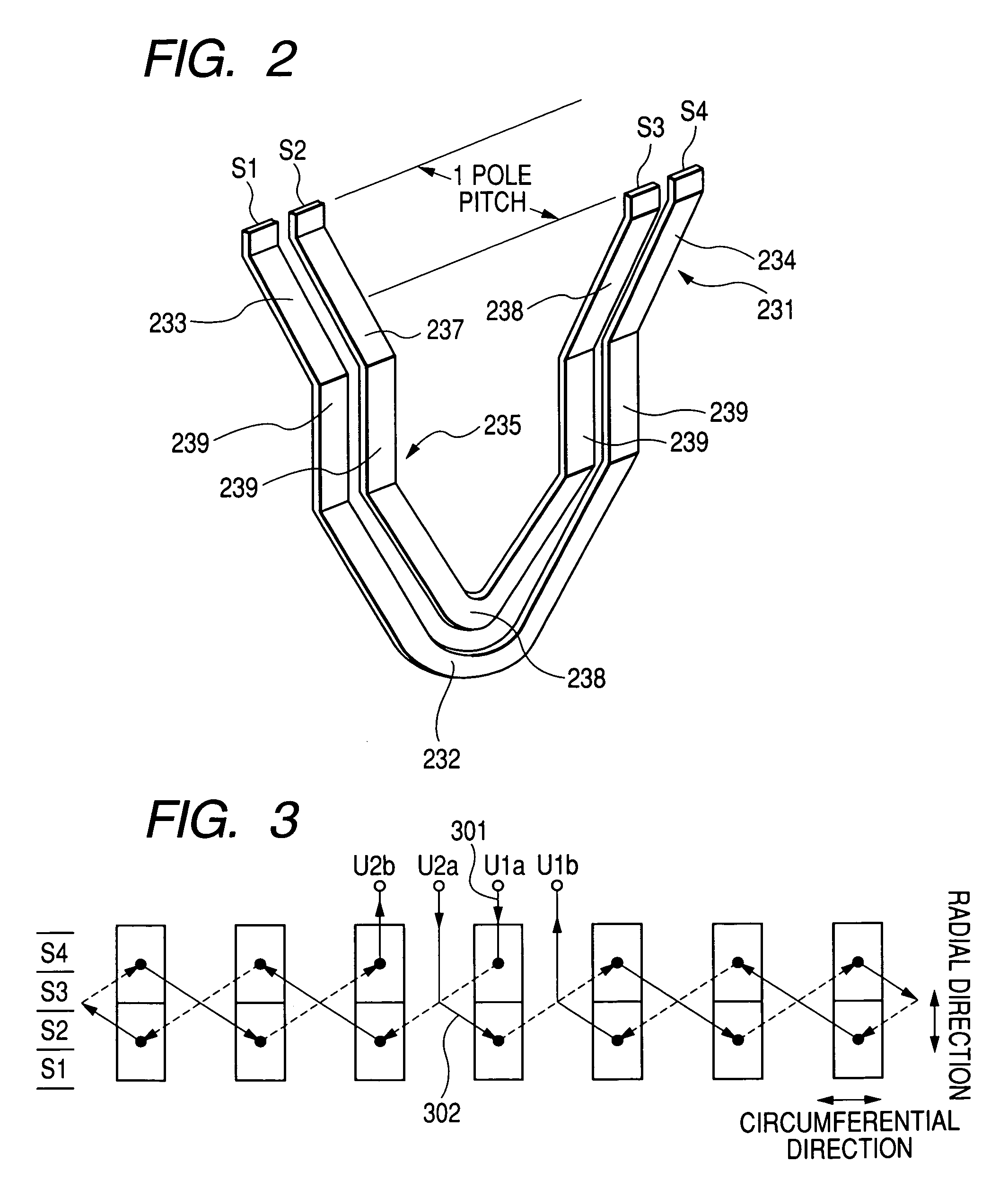
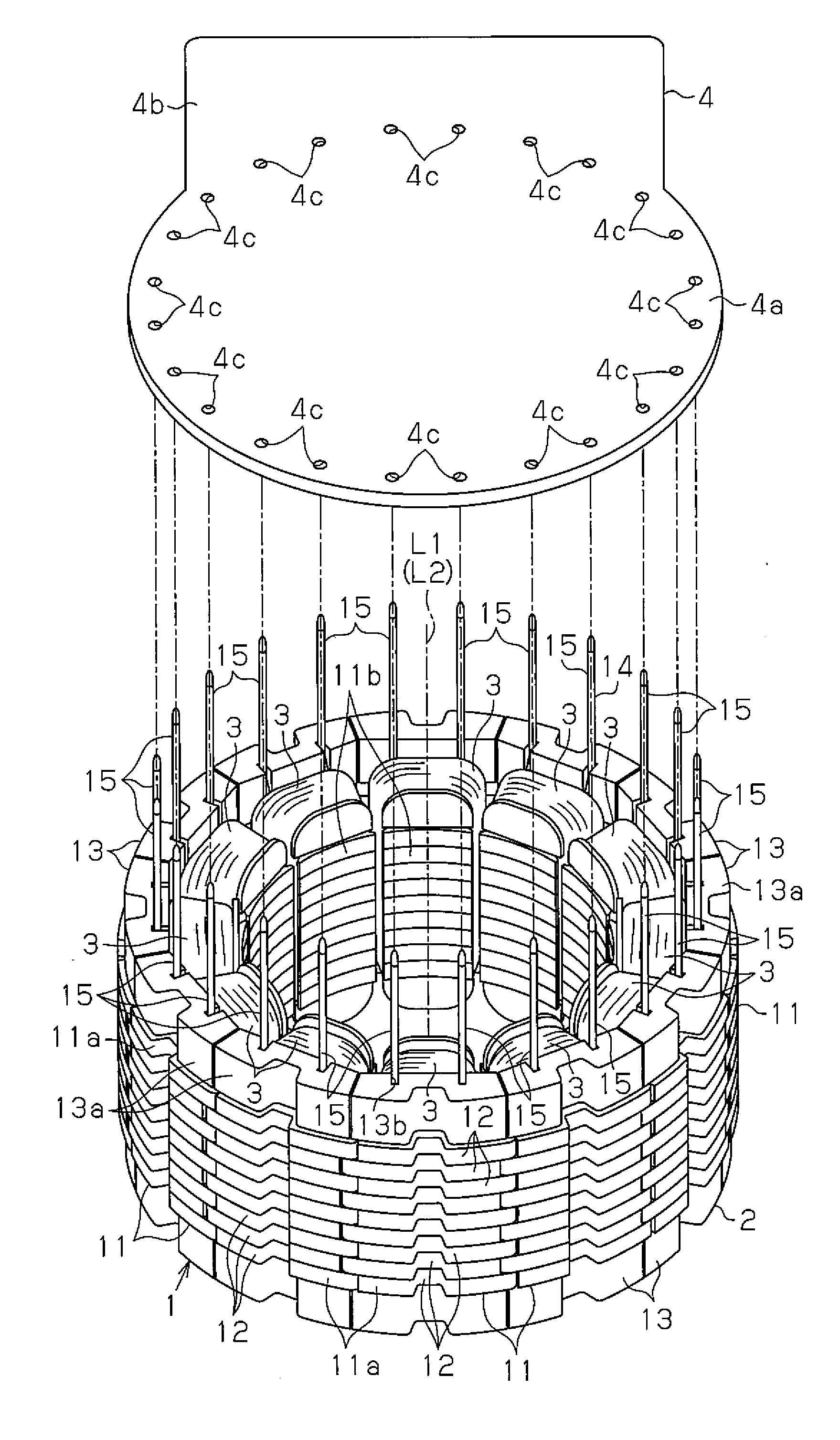
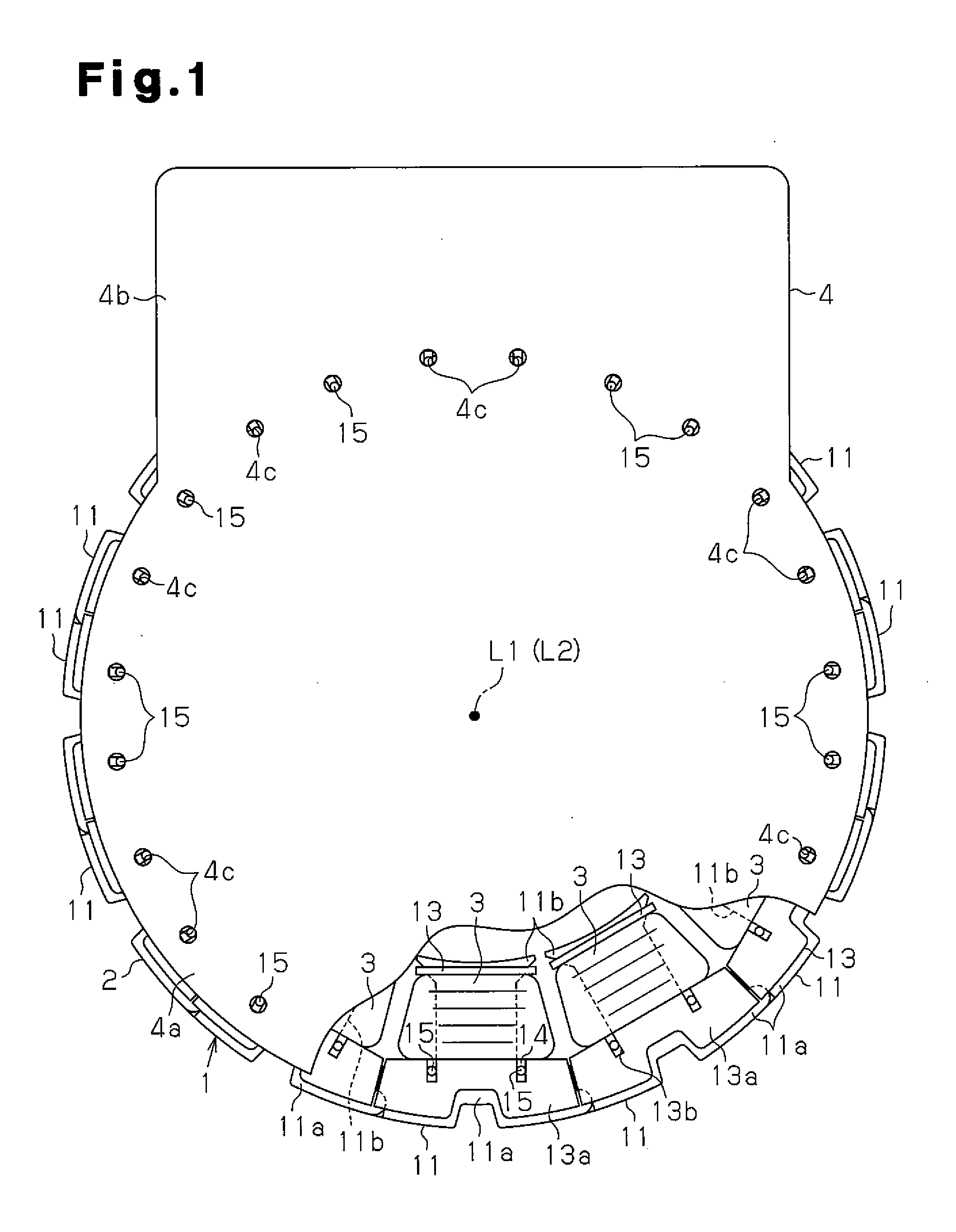
InactiveUS20070180682A1Efficient assemblyMagnetic circuit stationary partsEmbedding prefabricated windingsEngineeringFront end of line
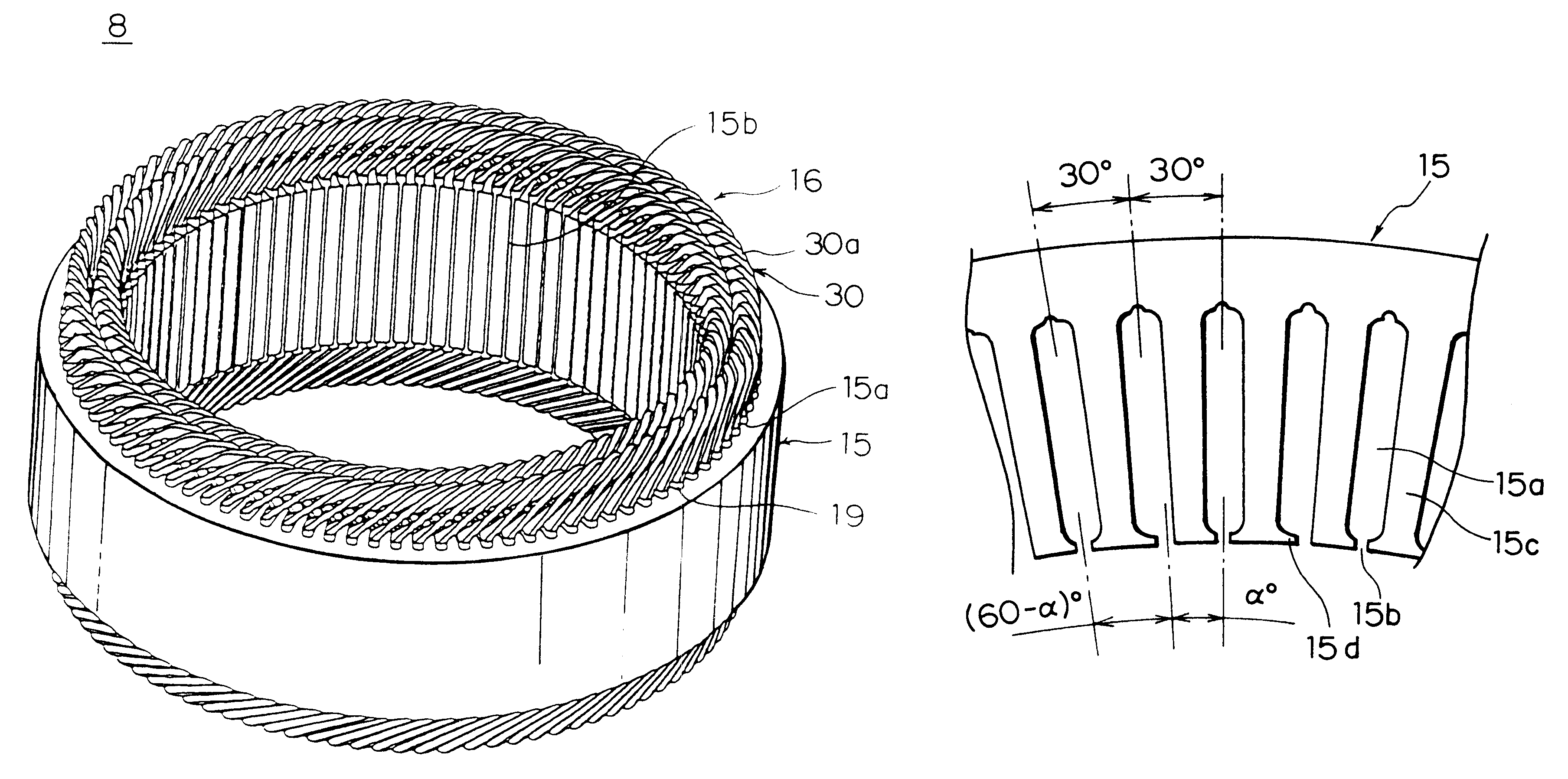
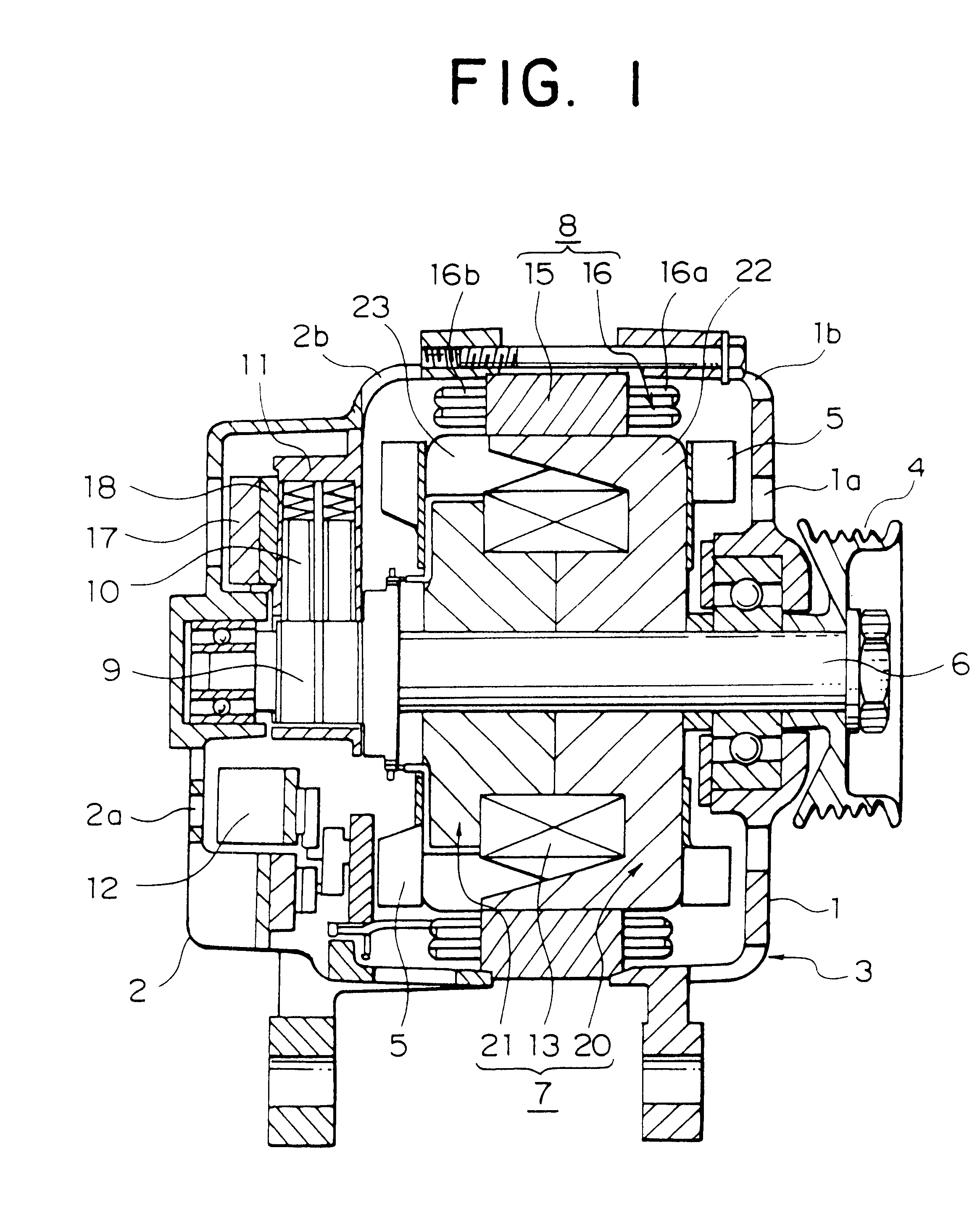
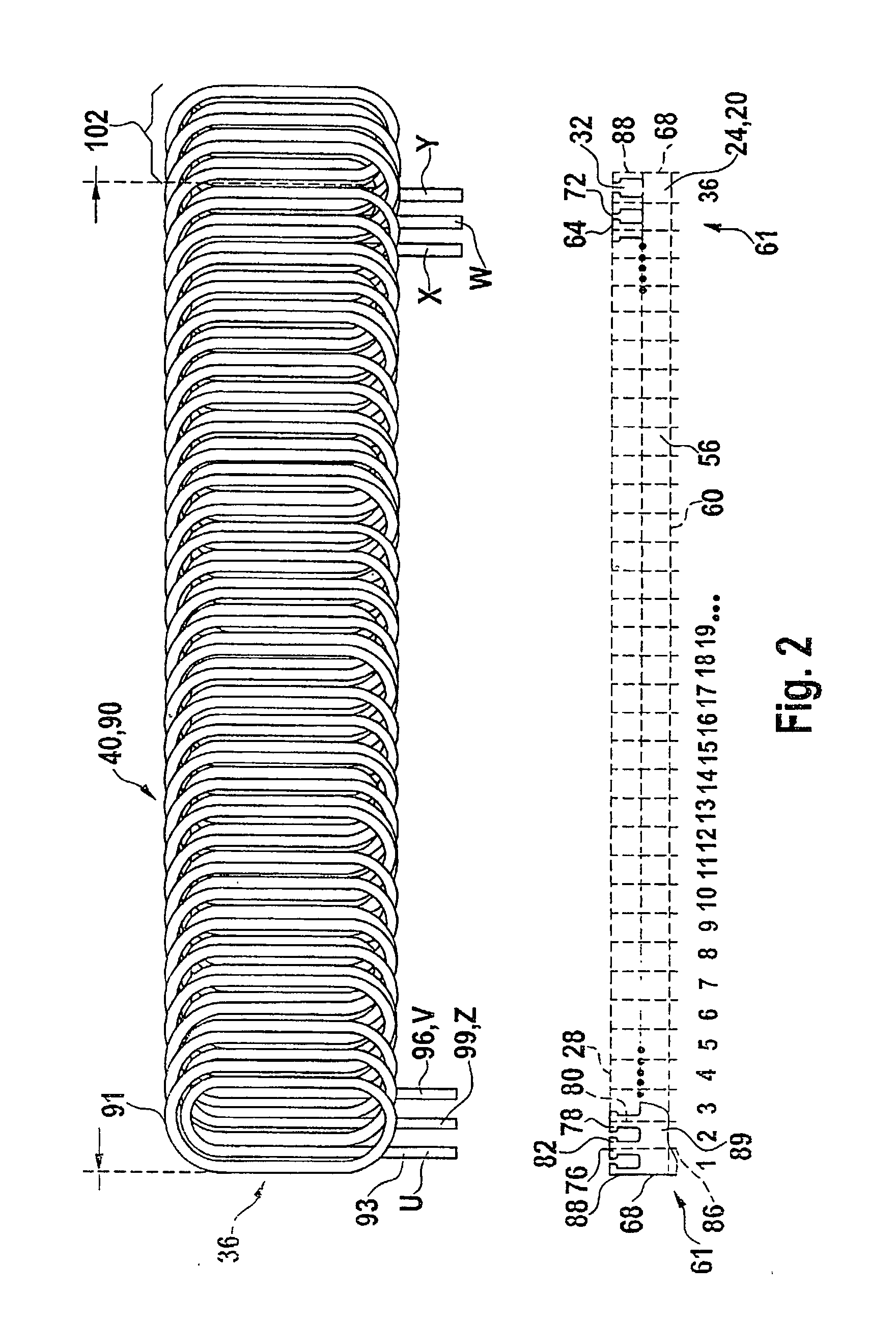
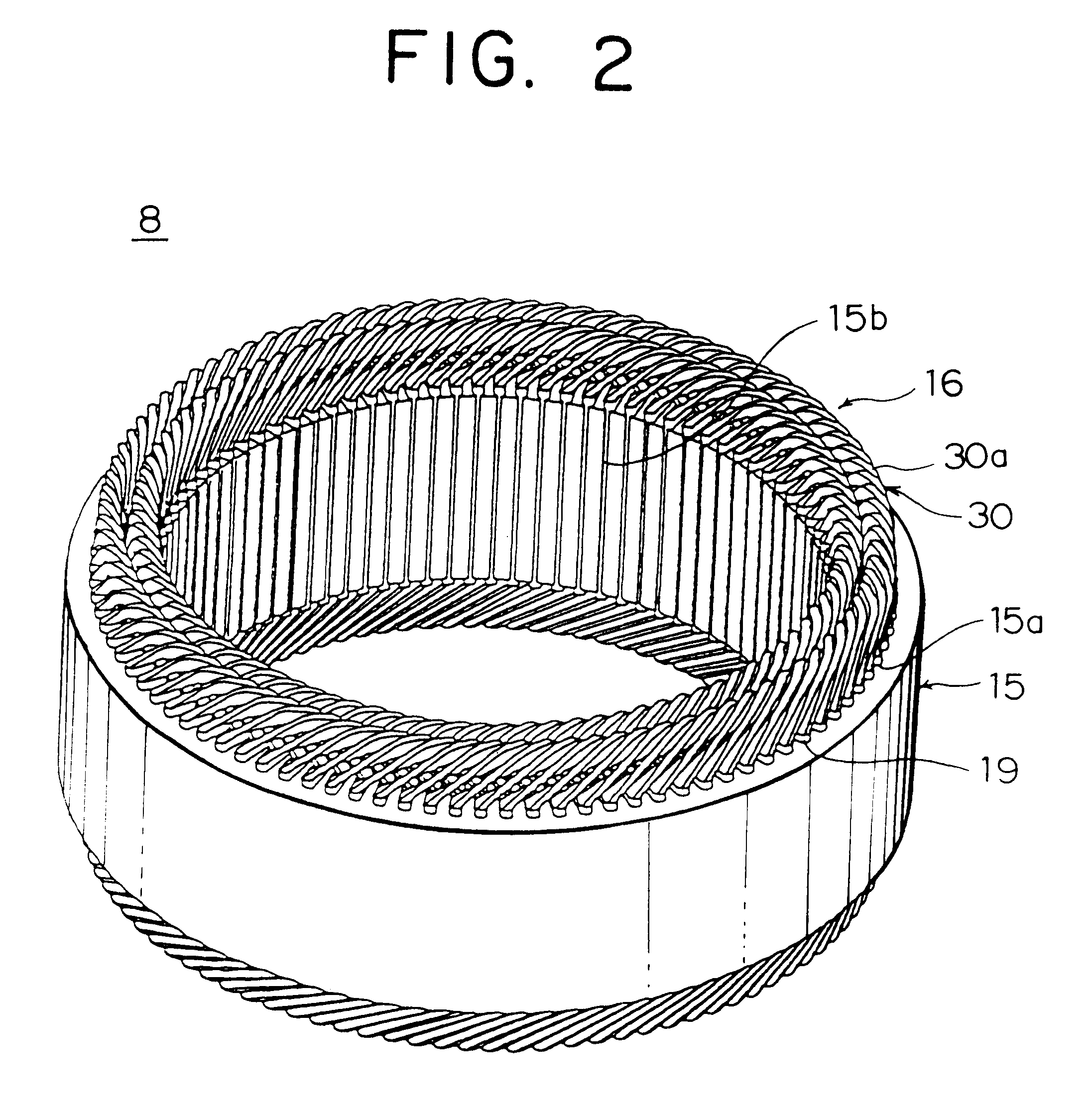
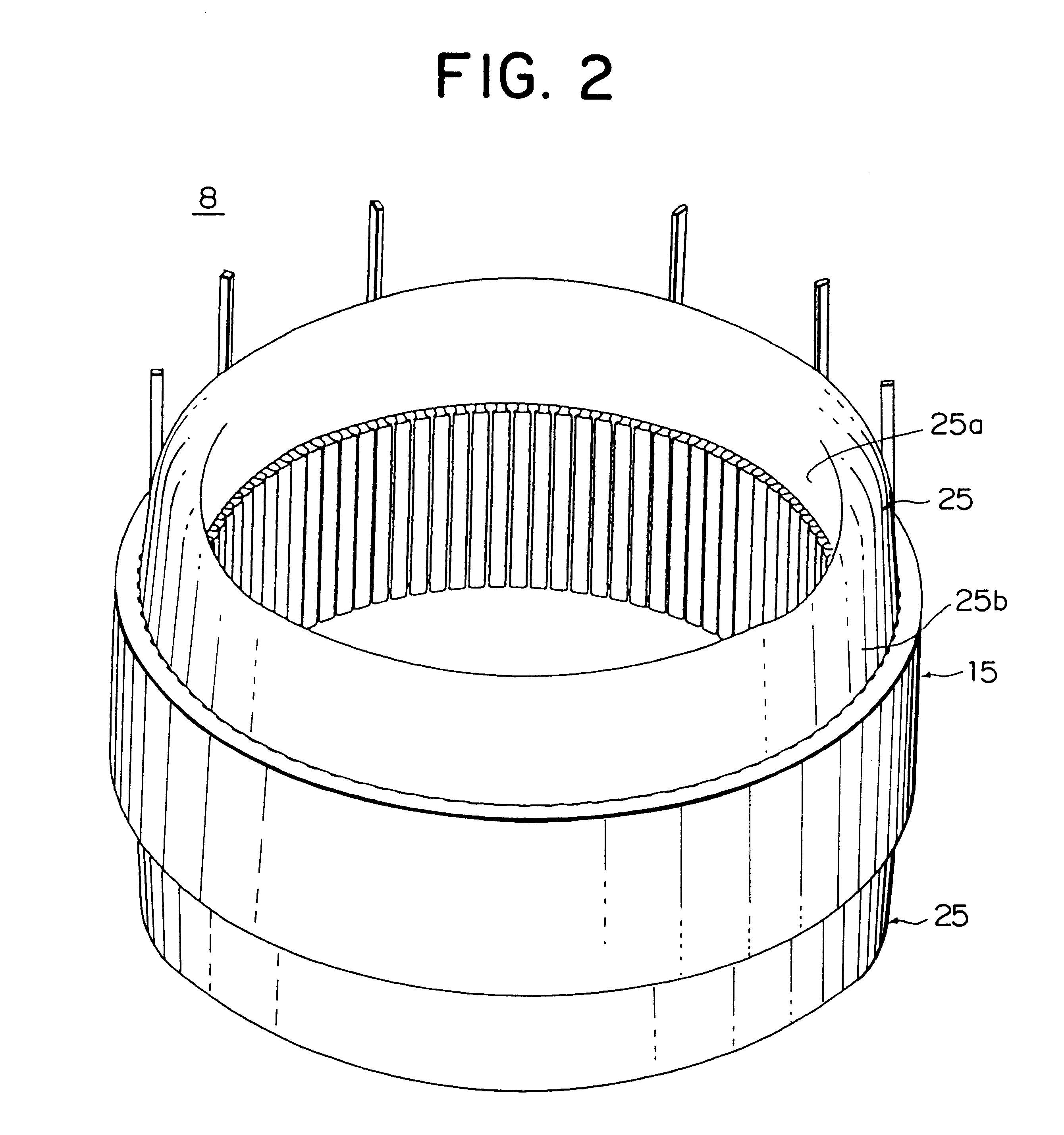
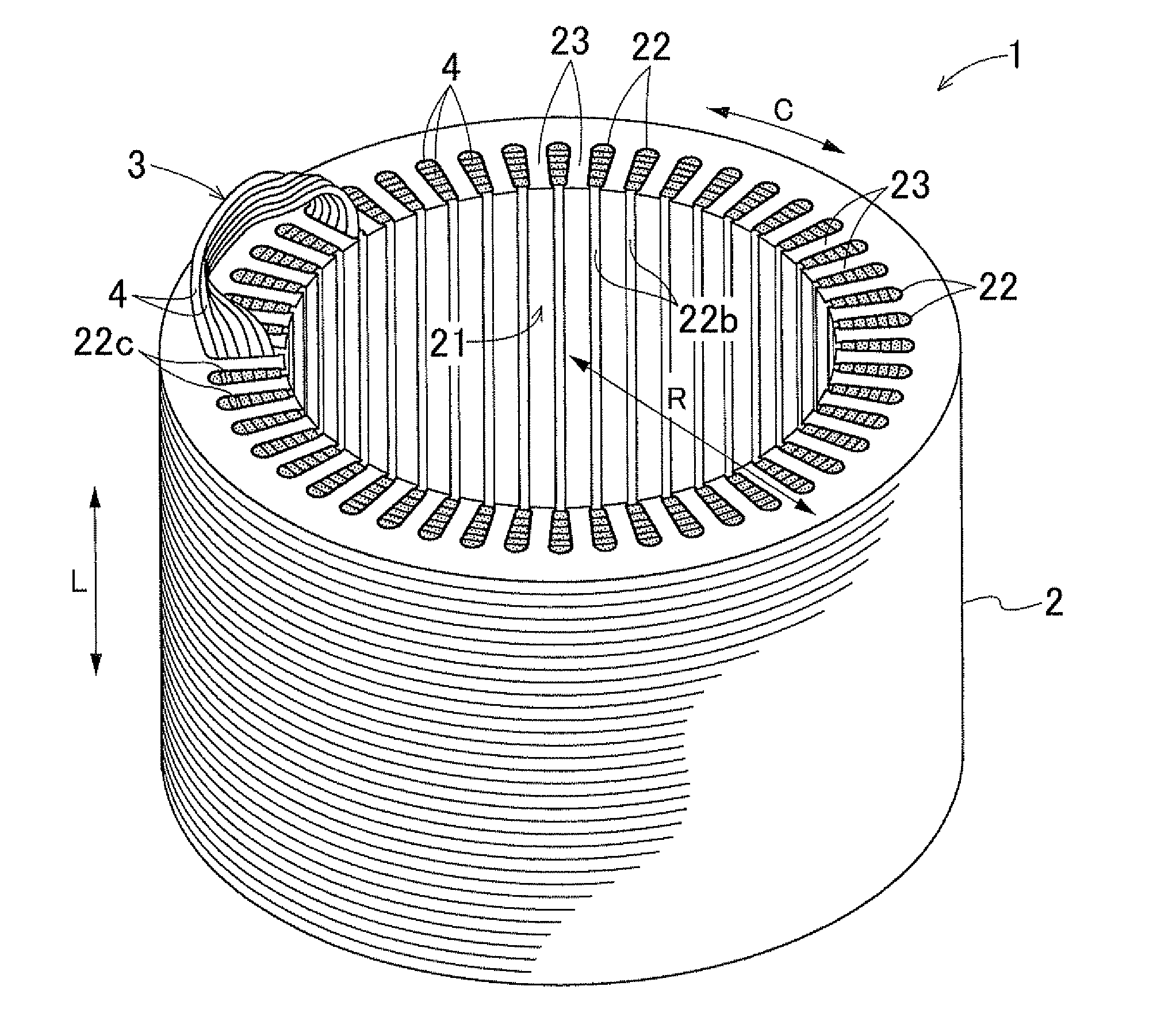
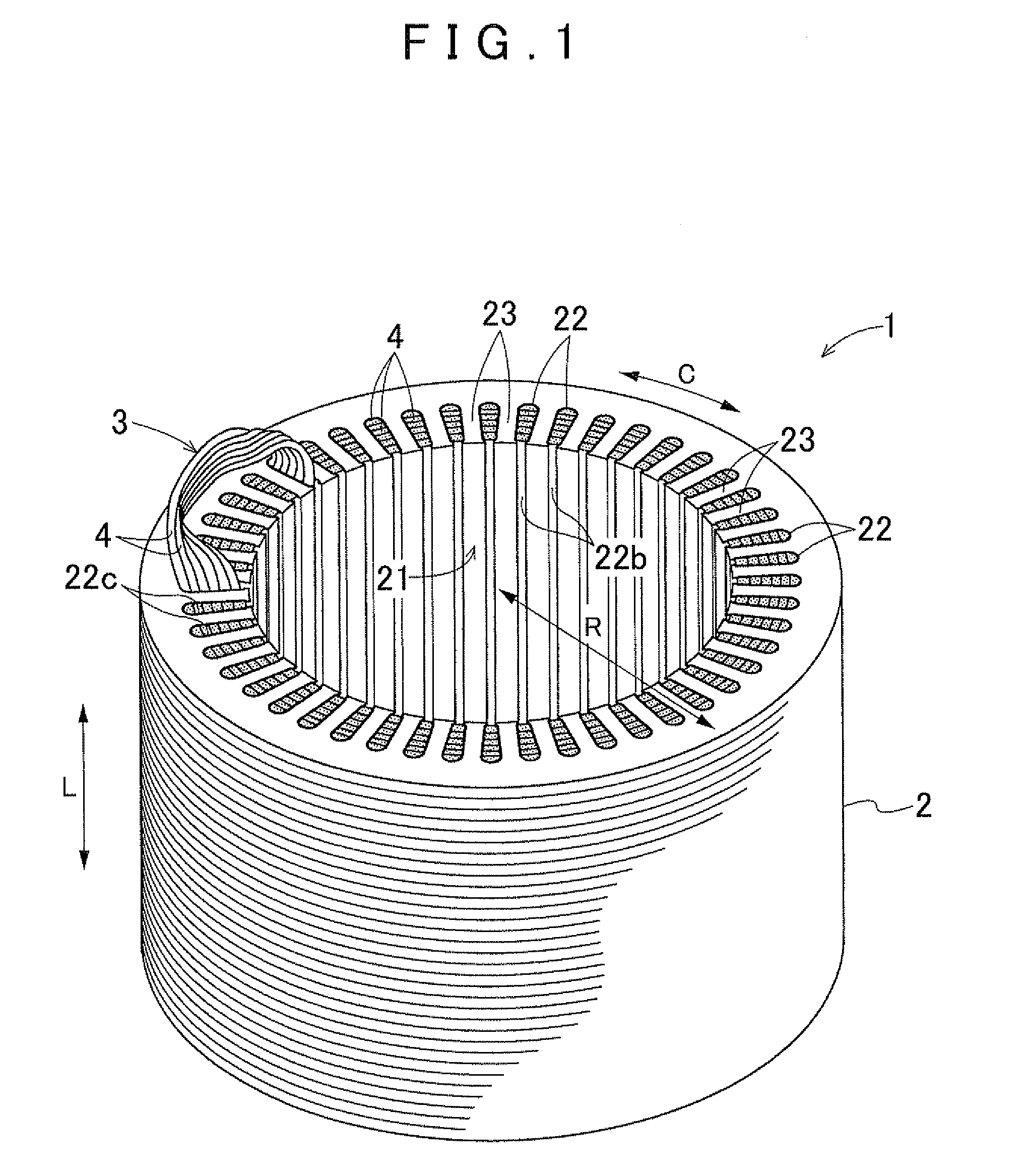
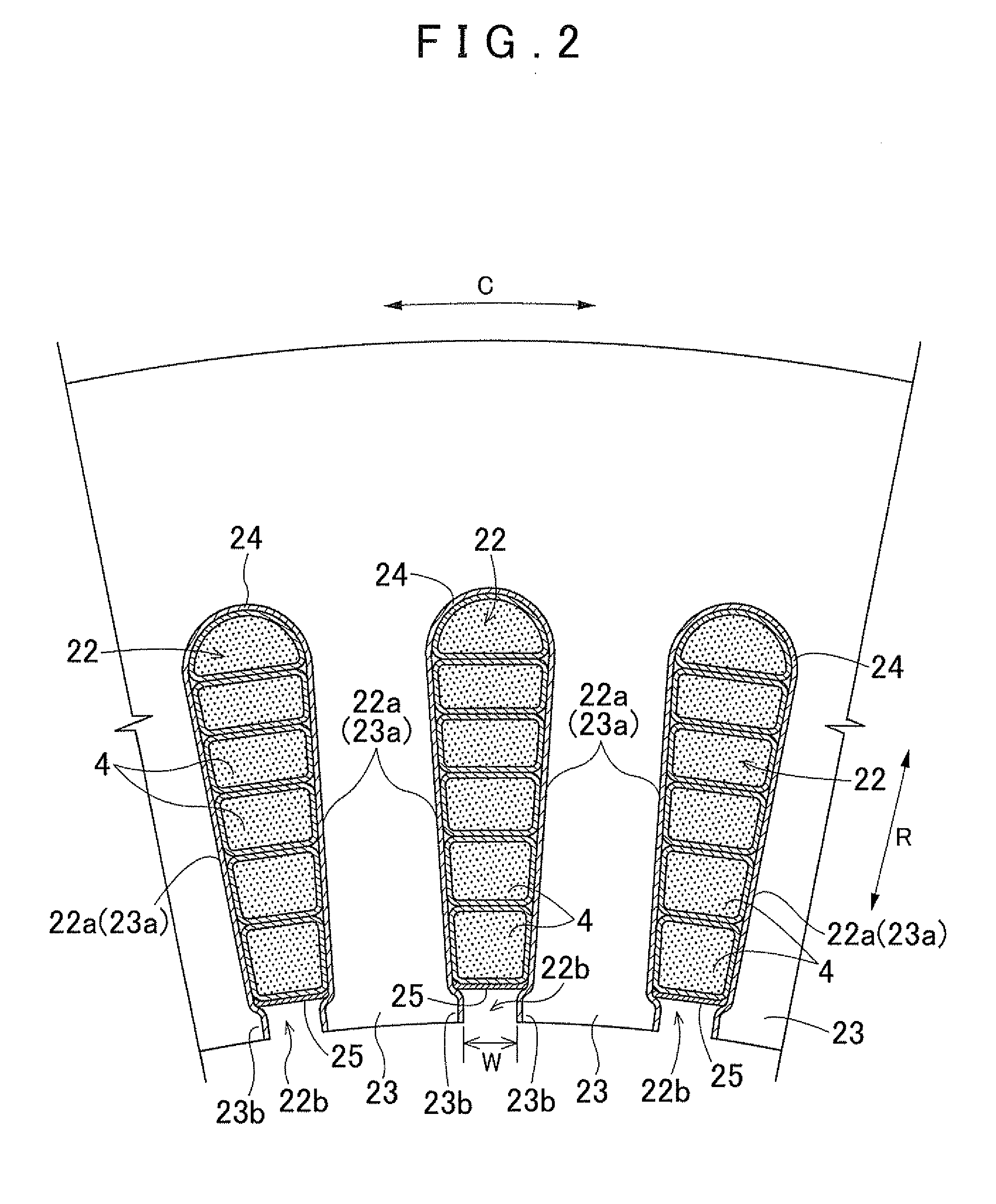
An electric rotating machine has a rotor having N and S poles and includes a stator with an annular stator core and slots. Multiple-phase stator windings are embedded in the slots, and are formed by winding continuous wires such that straight parts of the stator windings pressed in a flat shape are wound in rings around a grooved cylindrical member. The cylindrical member is inserted into a bore defined by the annular stator core so that the grooves of the cylindrical member are arranged opposite to the slots. The sets of the windings are folded back alternately outside the slots of the stator core and are wound so the sets of the windings are embedded alternately in the direction of the depth of the slots. Leading and trailing ends of the continuous wires are superposed after being wound at least one turn around the circumferentially arranged slots of the stator.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Alternator
InactiveUS6396185B1Improve serviceabilityIncrease productivitySynchronous generatorsWindings insulation materialAlternatorDepth direction
An alternator includes a rotor for forming north-seeking (N) and south-seeking (S) poles about a rotational circumference, a stator having a stator core disposed facing the rotor and a polyphase stator winding installed in the stator core, and a bracket supporting the rotor and the stator, wherein the stator core comprises a laminated iron core formed with a number of slots extending axially at a predetermined pitch in a circumferential direction, the polyphase stator winding comprises a number of winding sub-portions in each which a long strand of wire is wound so as to alternately occupy an inner layer and an outer layer in a slot depth direction within the slots at intervals of a predetermined number of slots, the strand of wire folding back outside the slots at axial end surfaces of the stator core to form turn portions, the turn portions align in a circumferential direction to constitute coil end groups at both axial end portions of the stator core, and the turn portions at both axial end portions of the stator core are provided with an insulative coating.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Stator of a dynamoelectric machine equipped with temperature detection
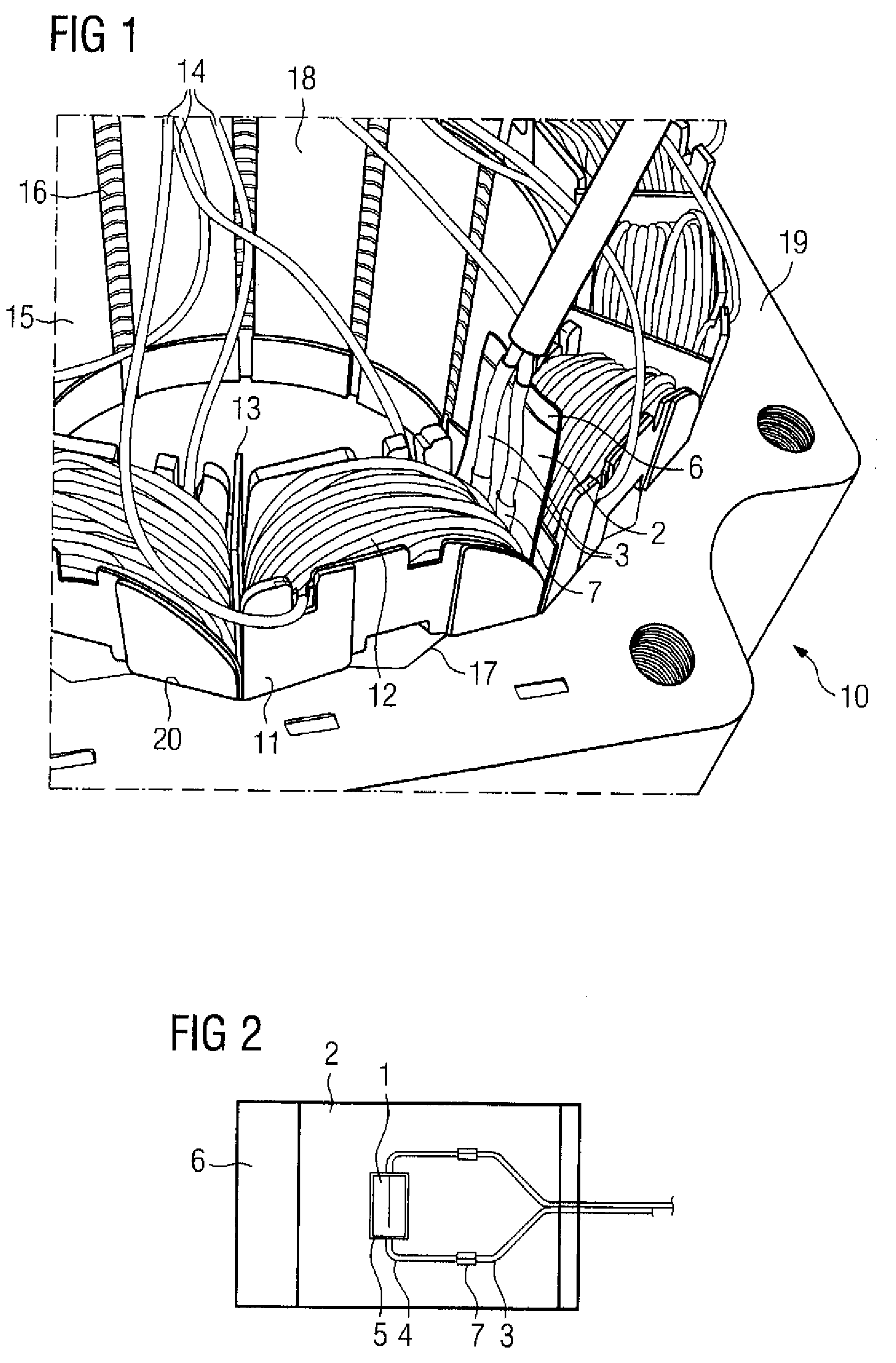
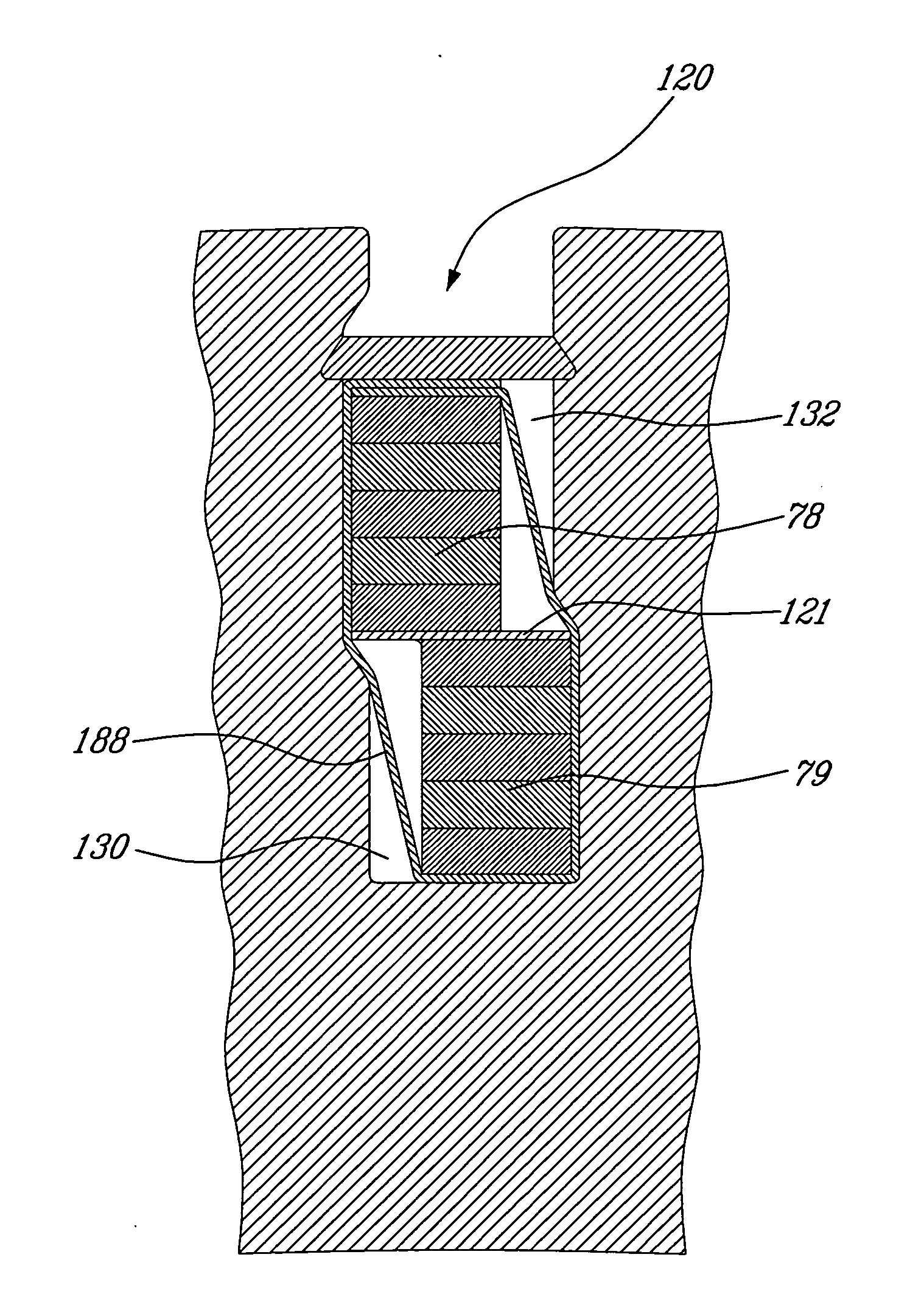
ActiveUS20090140614A1Easy to assembleEasy maintenanceWindingsEmbedding prefabricated windingsStatorConductor Coil
A stator for a dynamoelectric machine includes a stator body having slots and a winding system positioned in the slots of the stator body and having coils terminating in winding heads on end faces of the stator body, wherein each slot receives different coil sides of neighboring coils. Arranged between the coil sides in at least one of the slots is a temperature sensor to ascertain a temperature in the stator, in particular between the coil sides of the winding system in the slots of the stator.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Electric rotating machine and stator for the same
InactiveUS7337525B2Efficient assemblyMagnetic circuit stationary partsEmbedding prefabricated windingsFront end of lineConductor Coil
An electric rotating machine has a rotor having N and S poles and includes a stator with an annular stator core and slots. Multiple-phase stator windings are embedded in the slots, and are formed by winding continuous wires such that straight parts of the stator windings pressed in a flat shape are wound in rings around a grooved cylindrical member. The cylindrical member is inserted into a bore defined by the annular stator core so that the grooves of the cylindrical member are arranged opposite to the slots. The sets of the windings are folded back alternately outside the slots of the stator core and are wound so the sets of the windings are embedded alternately in the direction of the depth of the slots. Leading and trailing ends of the continuous wires are superposed after being wound at least one turn around the circumferentially arranged slots of the stator.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
4-layer type of stator winding formed of sequentially connected segments located in respective slot pairs, and method of manufacture thereof
ActiveUS7268455B2Easy to implementFirmly connectedSynchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionElectrical conductorEngineering
A phase winding of a stator winding comprises one or more pairs of interconnected partial coil, each partial coil formed of sequentially connected U-shaped segment pairs, each pair comprising a large segment and small segment. Two segment legs, of the large and small segment respectively of such a pair, constitute first and second conductor layers of a first stator slot and have their tip portions mutually connected. The remaining two segment legs respectively constitute fourth and third conductor layers of a second slot that is distant by one pole pitch, and have their respective tip portions mutually connected.
Owner:DENSO CORP
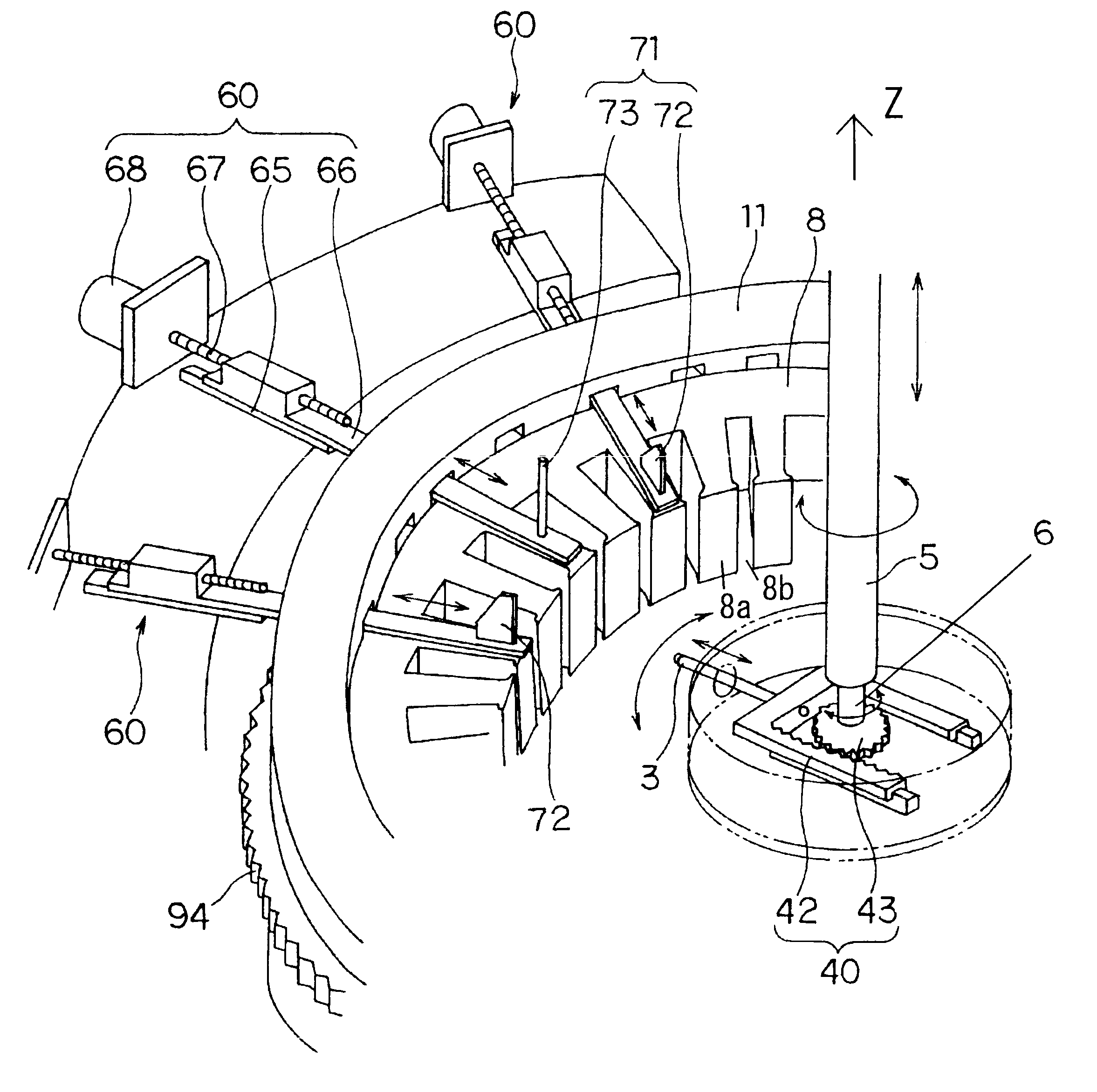
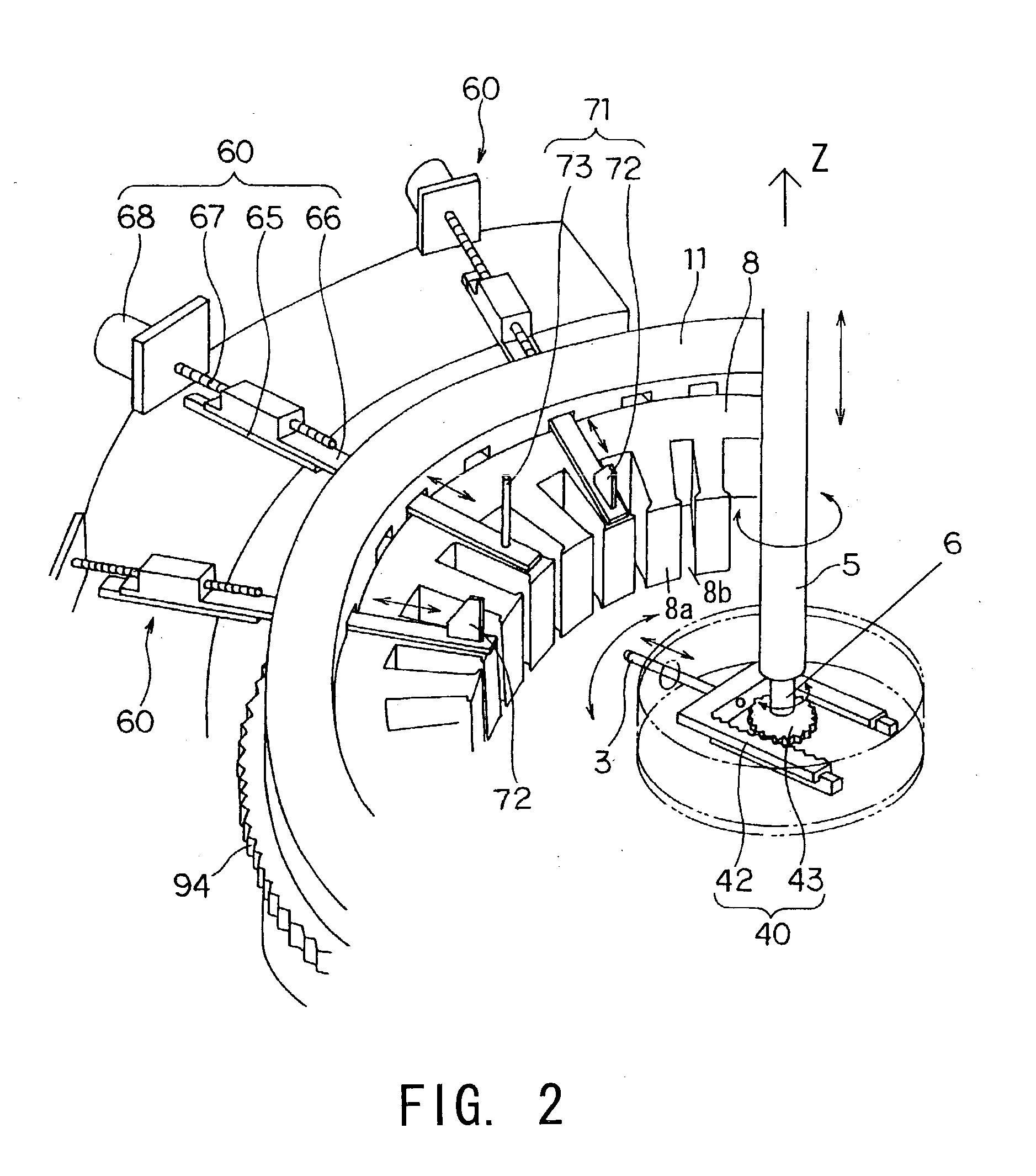
Winding method and winding device
InactiveUS6749144B2Low costSmall sizeWindingsEmbedding prefabricated windingsEngineeringRelative motion
A winding device winds a wire (90) onto a core (8) having a plurality of teeth (8b) protruding from a yoke and having slots (8a) formed between each tooth (8b). The winding device winds the wire (90) by causing a nozzle (3) which lets out the wire (90) to perform a relative motion. The winding device is provided with pusher plates (72) which guide the wire (90) into the slots (8a), and inserts the wire (90) into the slots (8a) by causing the pusher plates (72) to move relative to the core (8).
Owner:NITTOKU ENG CO LTD
Method for manufacturing stator, apparatus for manufacturing stator, and stator
InactiveUS20130162072A1Windings insulation shape/form/constructionEmbedding prefabricated windingsDistal portionLeading line
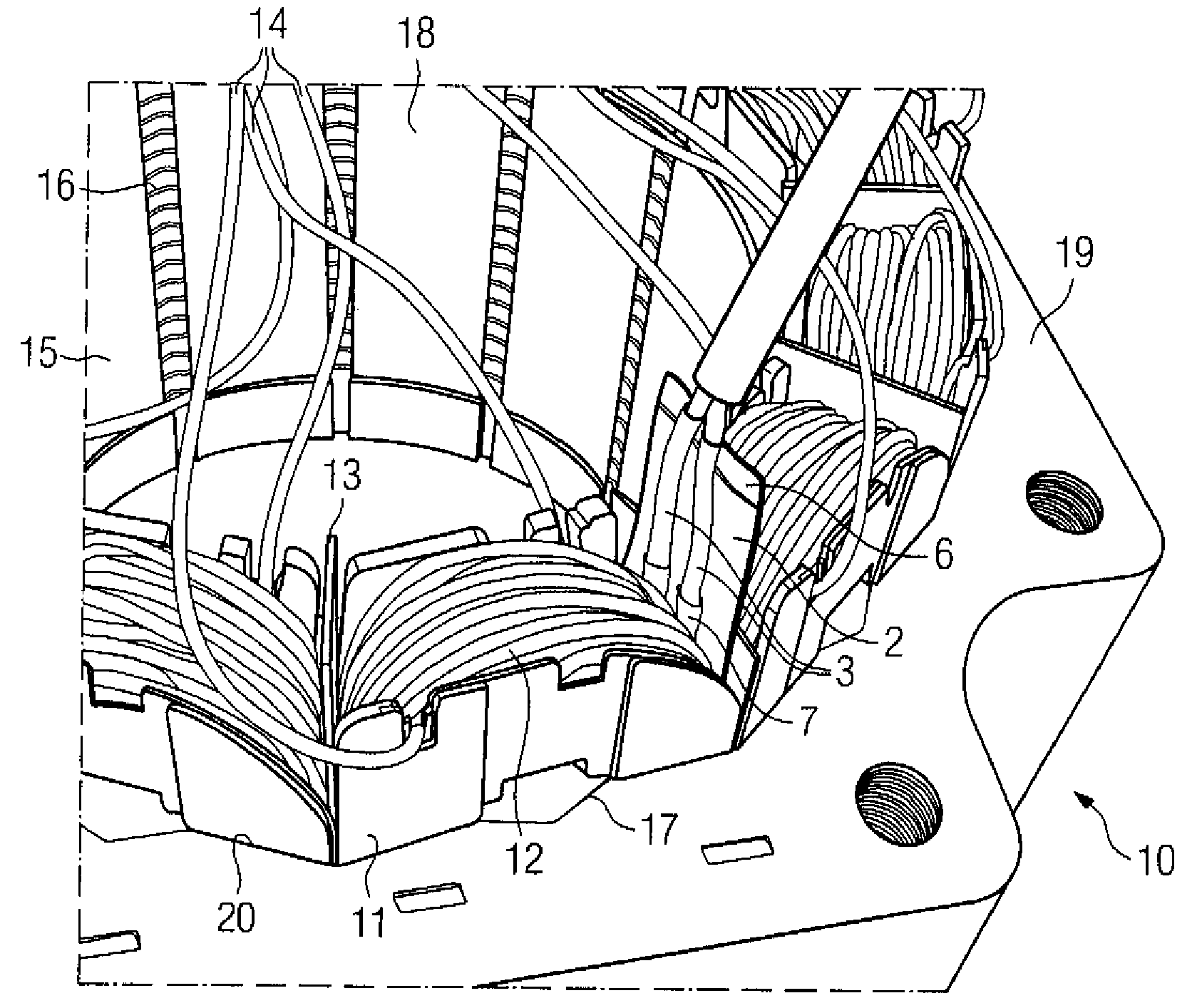
A method for manufacturing a stator includes preparing a stator core having a plurality of teeth, a plurality of coils having a plurality of lead lines, a substrate having a plurality of connecting portions, and a plurality of positioning jigs having restraining portions. The method includes positioning the substrate and the lead lines so that distal portions of the lead lines are separated from the connecting portions in at least one of a radial direction and a circumferential direction. The method further includes inserting the lead lines in the restraining portions, aligning the distal portions of the lead lines with the corresponding connecting portions using the positioning jigs, inserting the lead lines into the corresponding connecting portions, and electrically connecting the lead lines inserted in the connecting portions to the corresponding connecting portions.
Owner:ASMO CO LTD
Electric motor
InactiveUS20090251024A1Reduced useful lifeImpairs its traveling comfortMagnetic circuit rotating partsAsynchronous induction motorsEngineeringConductor Coil
The present invention relates to an electric motor and to a method for manufacturing an electric motor. The electric motor comprises at least a stator (24), a rotor (25) and an air gap (26) between these, in which motor the stator and / or rotor comprises slots (4) and teeth (5) between slots, and in which the stator and / or rotor has a concentrated winding fitted in the slots. In the method of the invention, the phase windings are fitted as a concentrated fractional-slot winding.
Owner:KONE CORP
Alternator
InactiveUS6366000B1Windings insulation shape/form/constructionAsynchronous induction motorsAlternatorEngineering
An alternator includes a rotor for forming north-seeking (N) and south-seeking (S) poles about a rotational circumference, a stator including a stator core disposed facing the rotor, and a stator winding installed in the stator core, a bracket supporting the rotor and the stator, and a cooling means for cooling the stator winding by moving together with the rotor and generating a flow of cooling air inside the bracket, wherein the stator core includes a laminated core formed with a number of slots extending axially at a predetermined pitch in a circumferential direction, the stator winding includes a number of winding sub-portions in each of which a long strand of wire is wound so as to alternately occupy an inner layer and an outer layer in a slot depth direction within the slots at intervals of a predetermined number of slots, the strand of wire folding back outside the slots at first and second axial end surfaces of the stator core to form turn portions, the turn portions align in a circumferential direction to constitute coil ends, an electrically-insulative resin portion is disposed so as to completely cover the coil ends, and at least one surface of the electrically-insulative resin portion selected from a rotor-facing surface and a bracket-facing surface is formed into a smooth surface.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Rotating Electrical Machine and Method for Manufacturing the Same
InactiveUS20090085421A1Synchronous generatorsWindings insulation shape/form/constructionStator coilElectrical and Electronics engineering
A rotating electrical machine includes: a stator that has a stator core and a stator coil; and a rotor disposed rotatably on an inner circumferential side of the stator core. The stator core includes a plurality of slots opening on the inner circumferential side and the slots are each formed as an open slot with a width of an inner circumferential-side opening thereof ranging along a circumferential direction set substantially equal to or greater than a width of a bottom side measured along the circumferential direction. The stator further includes a slot insulator disposed between inner wall of each of the slots at the stator core and the stator coil and a holding member constituted with a nonmagnetic material and inserted in each of the slots at the stator core so as to hold the slot insulator between two side surfaces present along the circumferential direction at the slot. The stator is formed by winding the stator coil through the plurality of slots.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
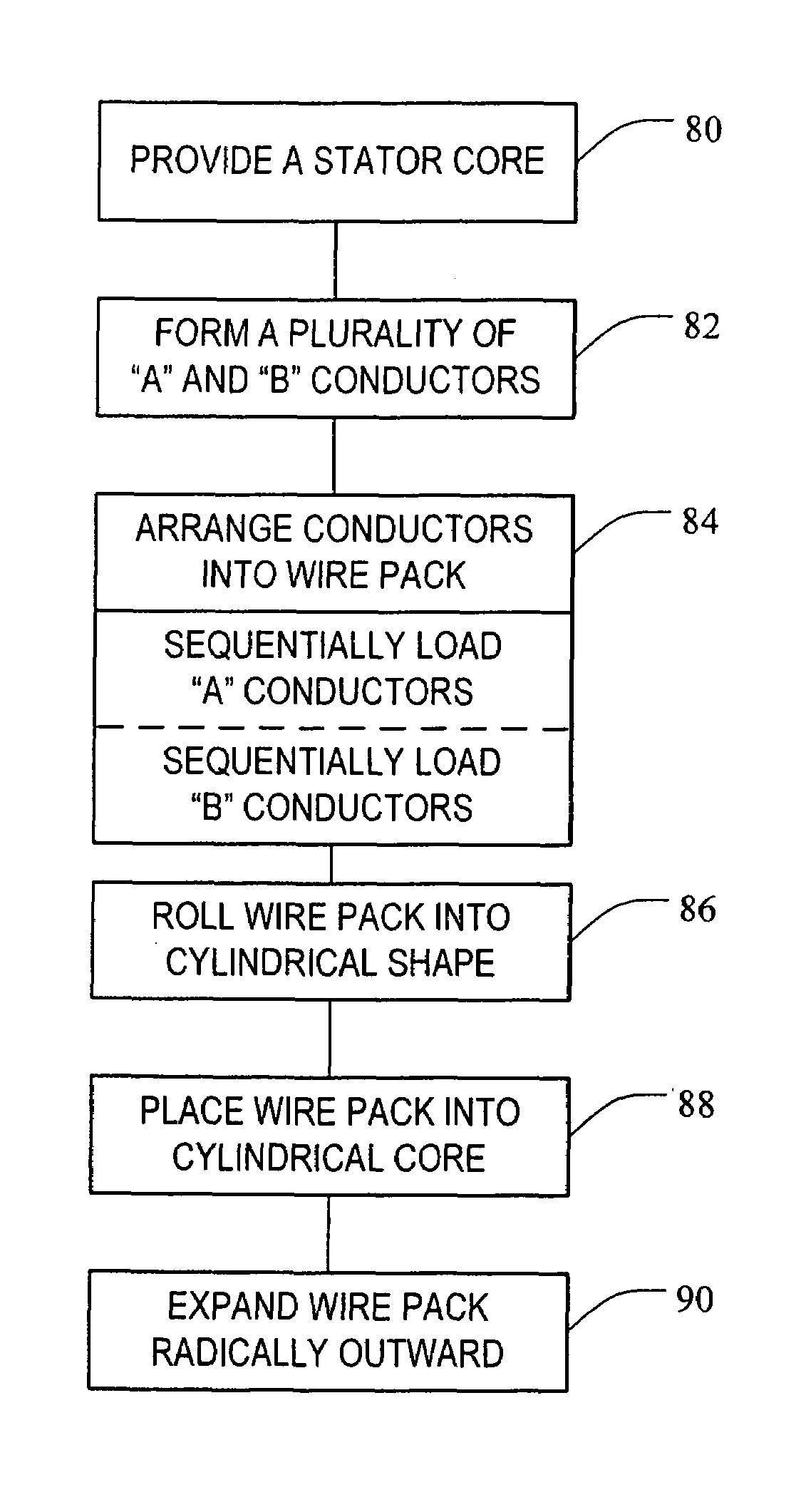
Method of forming cascaded stator winding
ActiveUS7386931B2Synchronous machinesAsynchronous induction motorsElectrical conductorElectric machine
A method of forming a stator for an electric machine having a cascaded winding includes the steps of: providing a stator core having a plurality of circumferentially spaced and axially-extending core slots in a surface thereof, forming a plurality of A conductors and a plurality of B conductors, arranging the A and B conductors into a wire pack, rolling the wire pack into a cylindrical shape and inserting the wire pack within the stator core, and expanding the wire pack radially outward such that the wire pack is inserted within the slots of the stator core.
Owner:REMY TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Stator for rotating electrical machine
InactiveUS20120274172A1Simple processIncrease spacingWindings insulation shape/form/constructionSynchronous machinesElectrical conductorMechanical engineering
A stator for a rotating electrical machine includes a stator core with a plurality of slots; and coils attached to the stator core. The coils are each structured by winding a covered conductor wire bundle around the stator core. The covered conductor wire bundle is structured by covering an outer circumference of a conductor wire bundle with a flexible insulating cover, the conductor wire bundle consisting of an assembly of a plurality of conductor wires. A plurality of the covered conductor wire bundles is disposed in each slot such that adjacent pairs of the covered conductor wire bundles are in contact with each other.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Dynamoelectric machine stator and method for mounting prewound coils thereunto
InactiveUS20050110361A1Easy to insertReduce needWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectrical conductorRadial position
A dynamoelectric machine stator core for receiving a pre-formed stator winding includes a core body defining a cylindrical core main peripheral surface. A plurality of axially extending stator slots are circumferentially spaced in the core body. Each of the stator slots defines a slot first section extending radially from the slot base to a slot intermediate radial position and a slot second section extending radially from the slot intermediate radial position towards the core main peripheral surface. The slot first and second sections communicate with each other and are circumferentially offset relative to each other. The slot first and second sections are positioned, configured and sized to facilitate insertion therein of a corresponding conductor section of the stator winding with reduced needs for deforming the latter.
Owner:TM4 INC
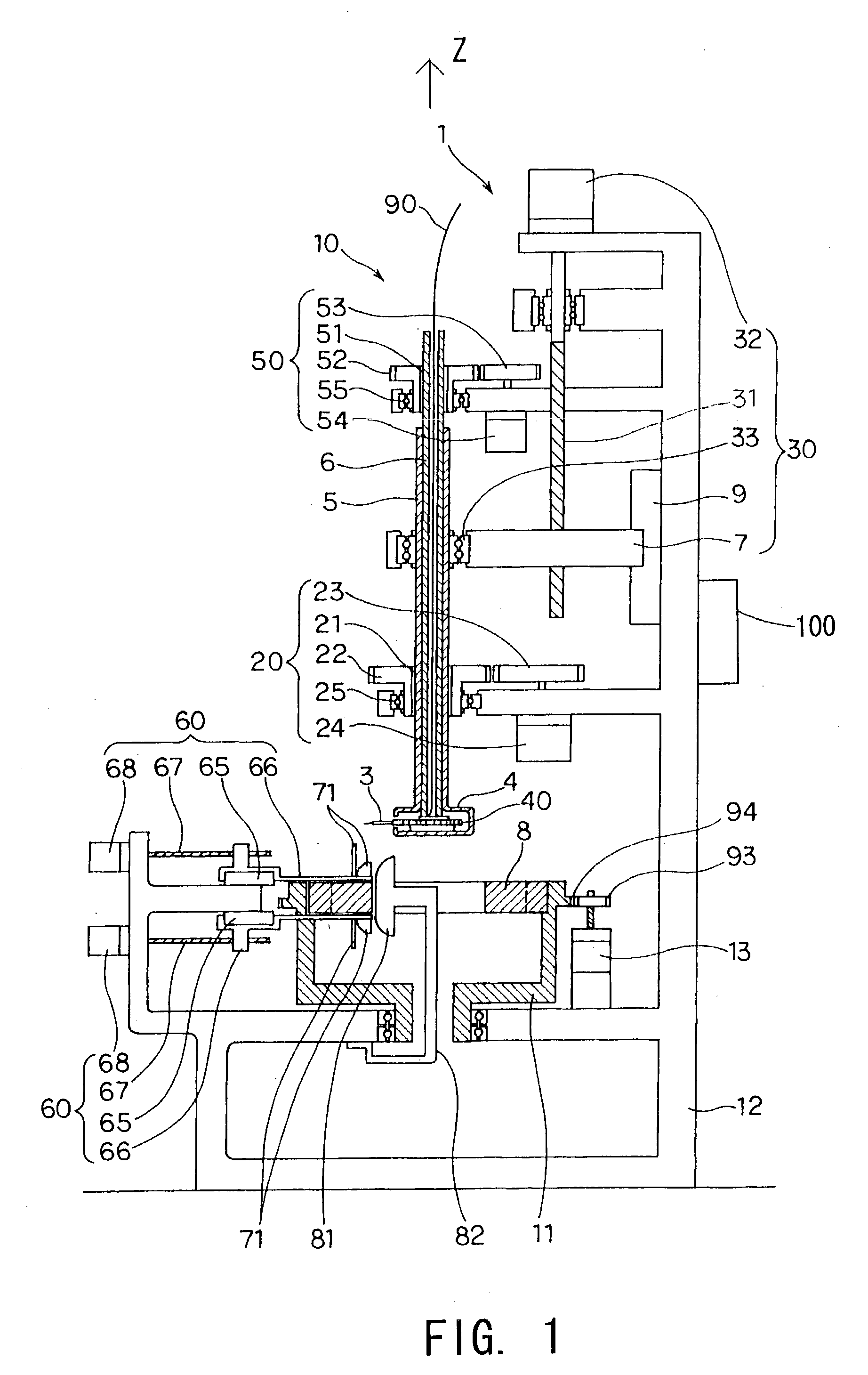
Method and apparatus for manufacturing AC-generator's stator for vehicle
InactiveUS6530140B2Positioning-accuracy can be improvedAvoid damageLine/current collector detailsEmbedding prefabricated windingsElectrical conductorEngineering
The object of the present invention is to provide a method and an apparatus for manufacturing a stator to improve accuracy in inserting conductor segments (3, 31, 32) into slots (2). The apparatus according to the present invention comprises a conductor holder (21, 22) holding the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) and an axial-moving-mechanisms (214) moving the conductor holder (21, 22) relative to a stator core (1) in an axial direction. The conductor holder (21, 22) holds straight portions (31b, 31c, 32b, 32c) of the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) to be inserted into the slots (2) from one end of the stator core (1).
Owner:DENSO CORP
Coil forming method and coil forming device
InactiveUS20050133655A1Easy feedingWell formedManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesEmbedding prefabricated windingsBobbinReciprocating motion
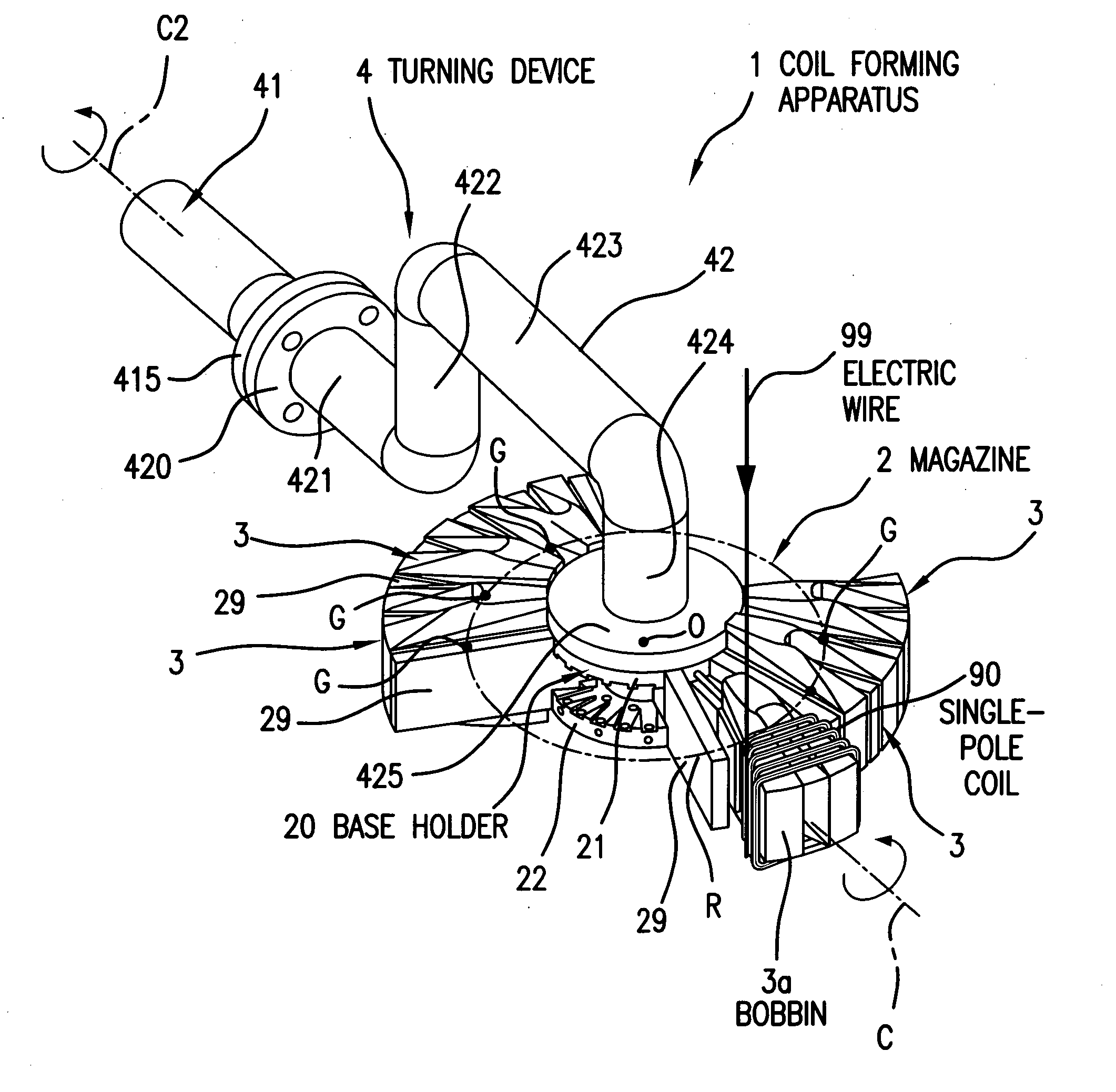
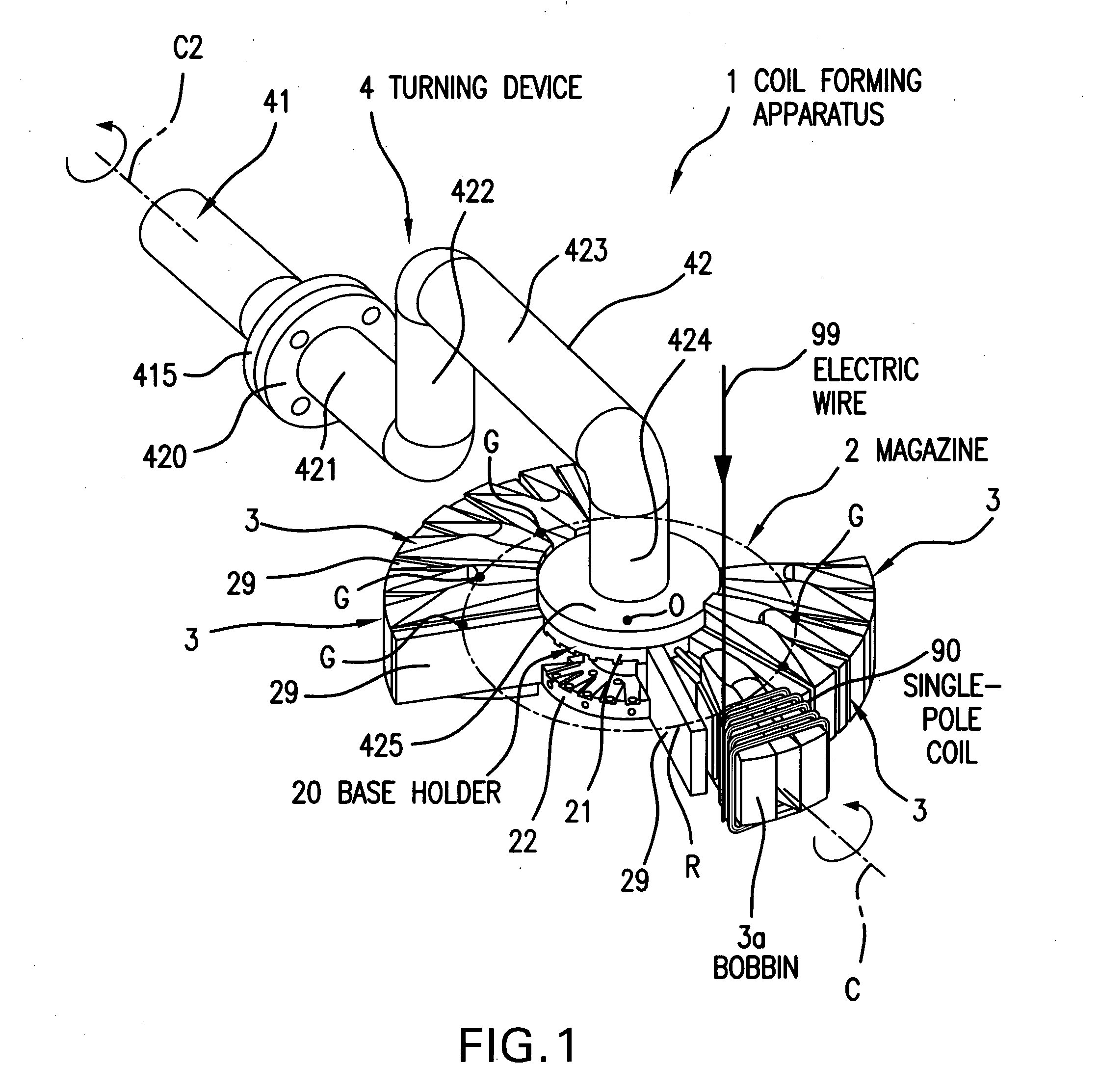
A coil forming apparatus for forming a continuous-pole coil having a plurality of single-pole coils includes a winding jig rotatable around a center swing axis. The winding jig includes: a holder rotatable around a center axis of rotation different from center swing axis; and a plurality of coil bobbins arranged around said holder and mounted for reciprocal movement between advanced and retracted positions relative to the holder. Each individual coil bobbin has a winding axes which can be aligned with the center swing axis by turning the winding jig around the center axis of rotation. The single-pole coils having little twist can be stably formed for any coil bobbin to thereby form the continuous-pole coil.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Fault tolerant permanent magnet machine
InactiveUS20100090557A1Increase in sizeWeight increaseWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuitEngineeringLeakage inductance
A PM machine is provided. The PM machine includes a stator including a stator core, wherein the stator core defines multiple step-shaped stator slots. The stator includes multiple fractional-slot concentrated windings wound within the step-shaped stator slots. The stator also includes at least one slot wedge configured to close an opening of a respective one of the step-shaped stator slots, wherein the slot wedge is further configured to adjust the leakage inductance in the PM machine. The PM machine also includes a rotor having a rotor core and disposed outside and concentric with the stator, wherein the rotor core includes a laminated back iron structure disposed around multiple axially-segmented magnets.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for manufacturing AC-generator's stator for vehicle
InactiveUS20010013167A1Positioning-accuracy can be improvedAvoid damageLine/current collector detailsEmbedding prefabricated windingsElectrical conductorAlternator
The object of the present invention is to provide a method and an apparatus for manufacturing a stator to improve accuracy in inserting conductor segments (3, 31, 32) into slots (2). The apparatus according to the present invention comprises a conductor holder (21, 22) holding the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) and an axial-moving-mechanisms (214) moving the conductor holder (21, 22) relative to a stator core (1) in an axial direction. The conductor holder (21, 22) holds straight portions (31b, 31c, 32b, 32c) of the conductor segments (3, 31, 32) to be inserted into the slots (2) from one end of the stator core (1).
Owner:DENSO CORP
Winding method and winding device
A winding device winds a wire (90) onto a core (8) having a plurality of teeth (8b) protruding from a yoke and having slots (8a) formed between each tooth (8b). The winding device winds the wire (90) by causing a nozzle (3) which lets out the wire (90) to perform a relative motion. The winding device is provided with pusher plates (72) which guide the wire (90) into the slots (8a), and inserts the wire (90) into the slots (8a) by causing the pusher plates (72) to move relative to the core (8).
Owner:NITTOKU ENG CO LTD
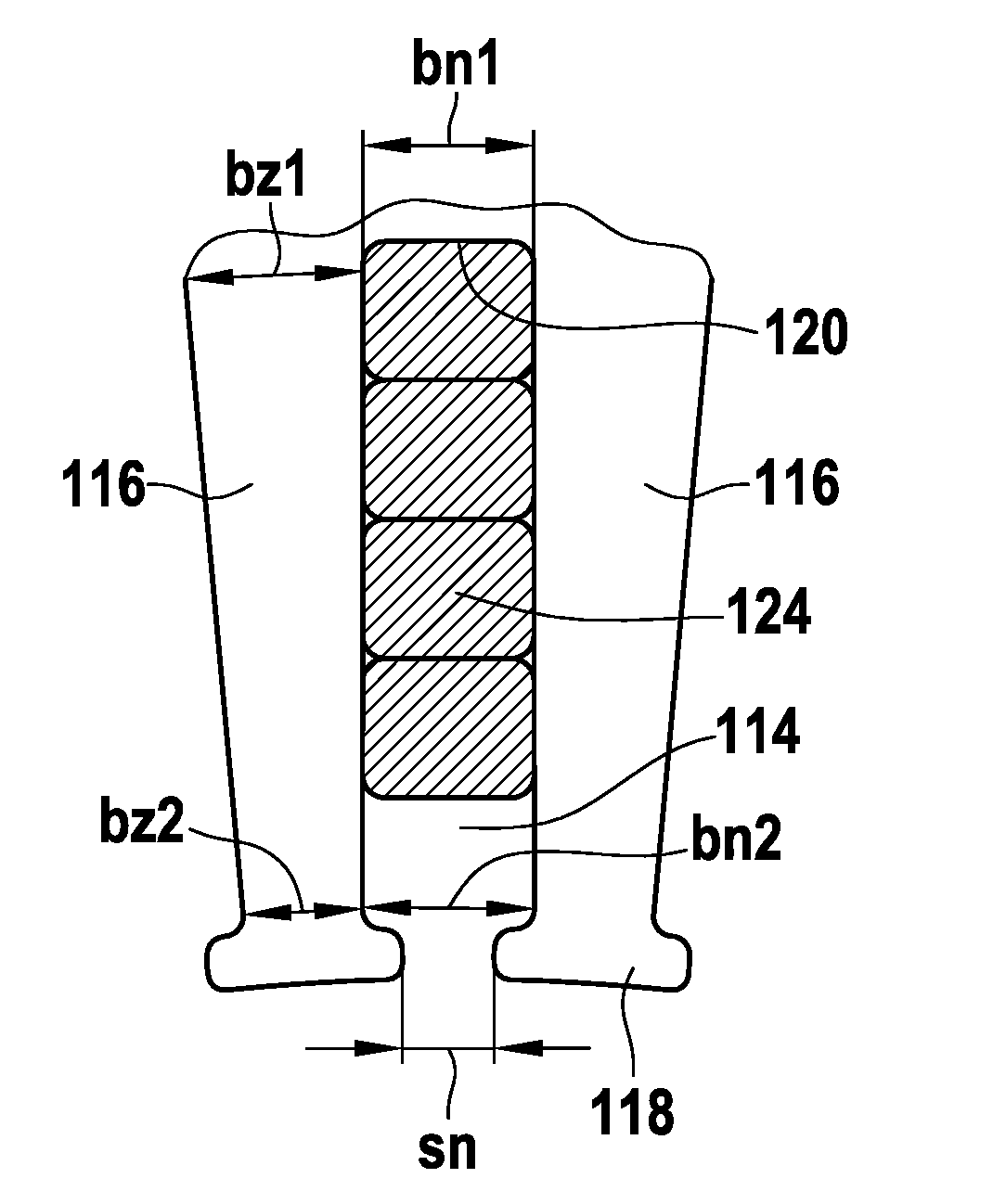
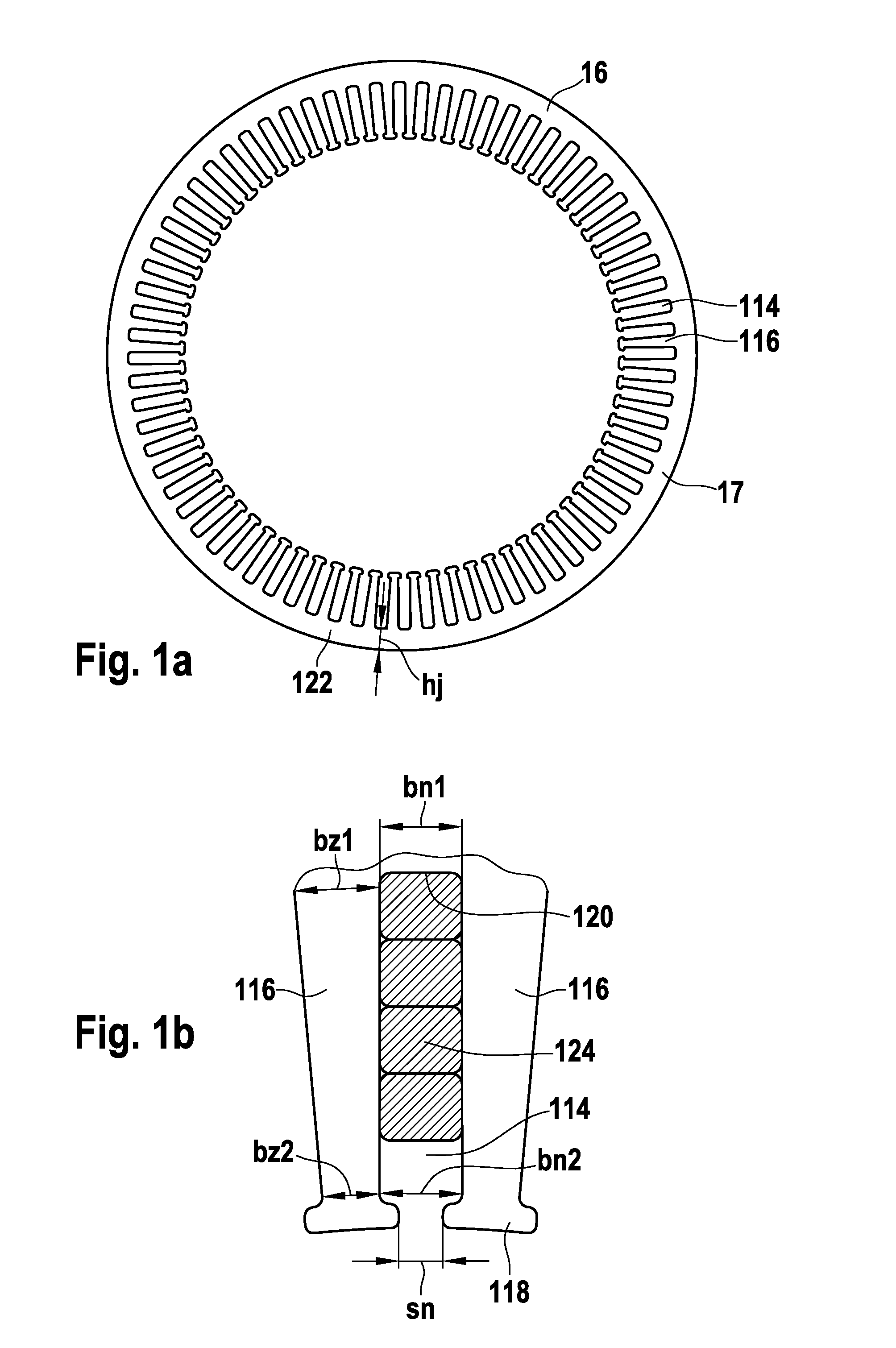
Stator for a polyphase electric machine and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20100295390A1Easy to attachAvoid huge wasteMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machineEngineering
A stator (16) is proposed for a polyphase electric machine, having a core body (17), which is provided with slots (114), which are situated in the radial direction with respect to an axis of rotation of the electric machine on one side of the core body (17) parallel to the longitudinal axis of the core body (17), having a slot width (bn1, bn2) and a stator yoke (122) being provided on the opposite side, with two slots (114) each being separated from one another by a tooth (116) having a tooth width (bz1, bz2) and extending from a slot base (120) to a tooth head (118), these slots (114) being provided to receive at least one coil winding having a plurality of coils that is electrically connected in series and are manufactured from at least one continuous wire (124) without interruption, the ratio (bz2 / hj) of the tooth width (bz2) to the yoke height (hj) at the tooth head (118) being between 0.3 and 0.8 and / or the ratio (bz2 / bn2) of the tooth width (bz2) at the tooth head (118) to the slot width (bn2) at the tooth head (118) being between 0.3 and 3, and / or the ratio (mCu(slot) / mCu(total)) of the copper mass of the wire (124) in the slot (114) to the total copper mass of the wire (124) being between 0.43 and 0.55
Owner:SEG AUTOMOTIVE GERMANY GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com