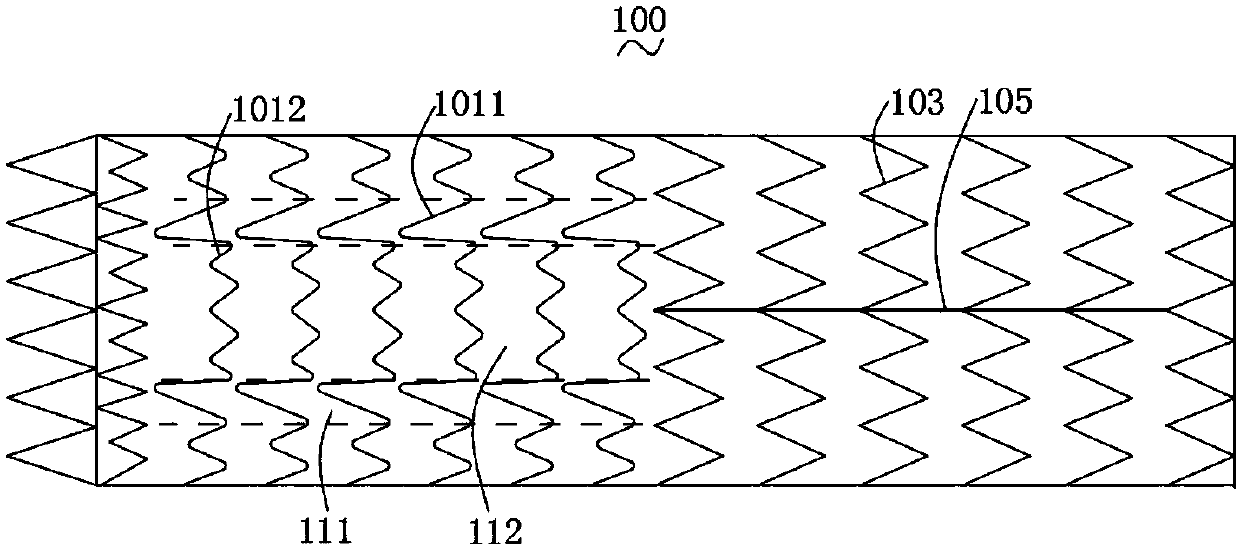
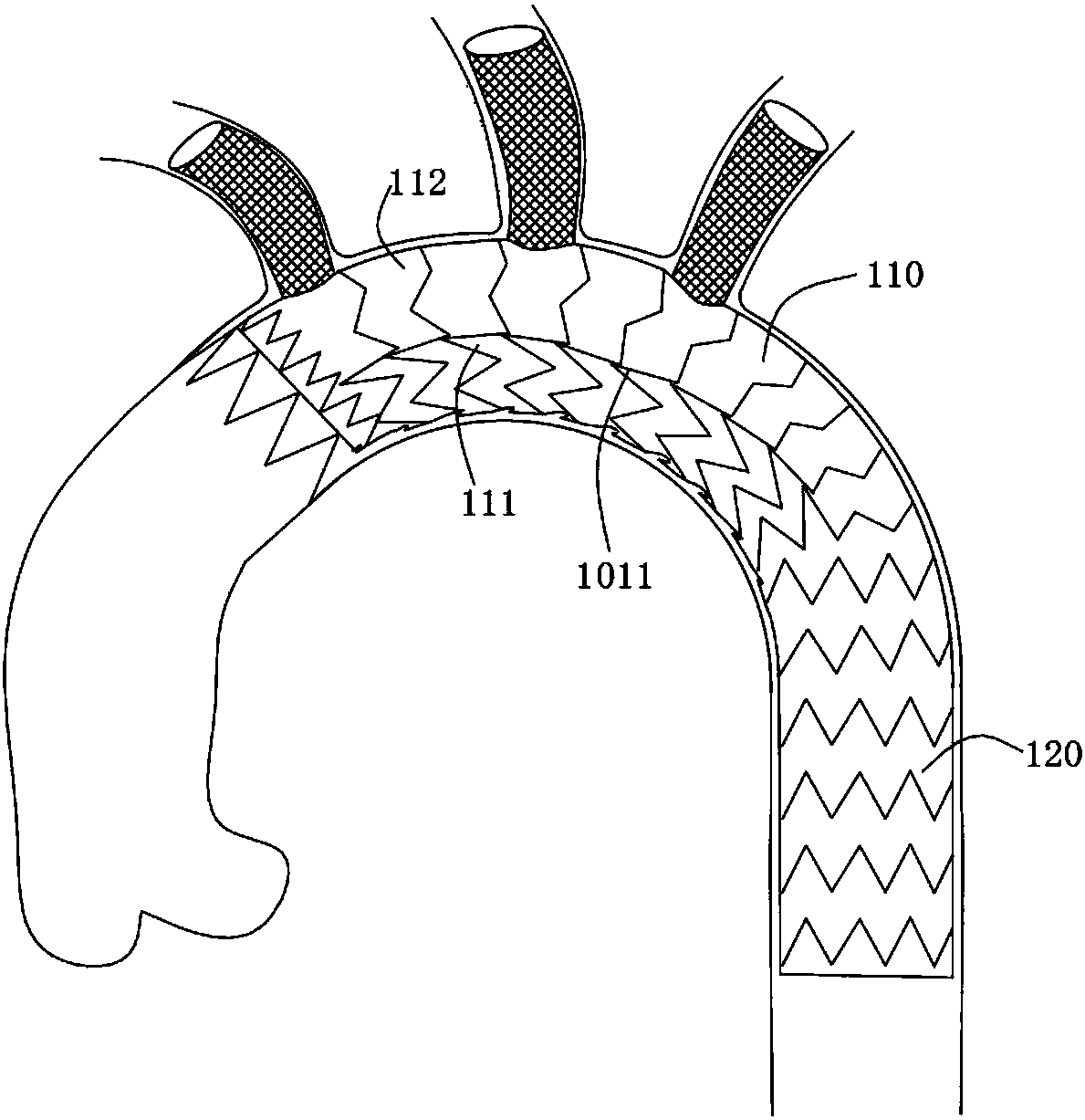
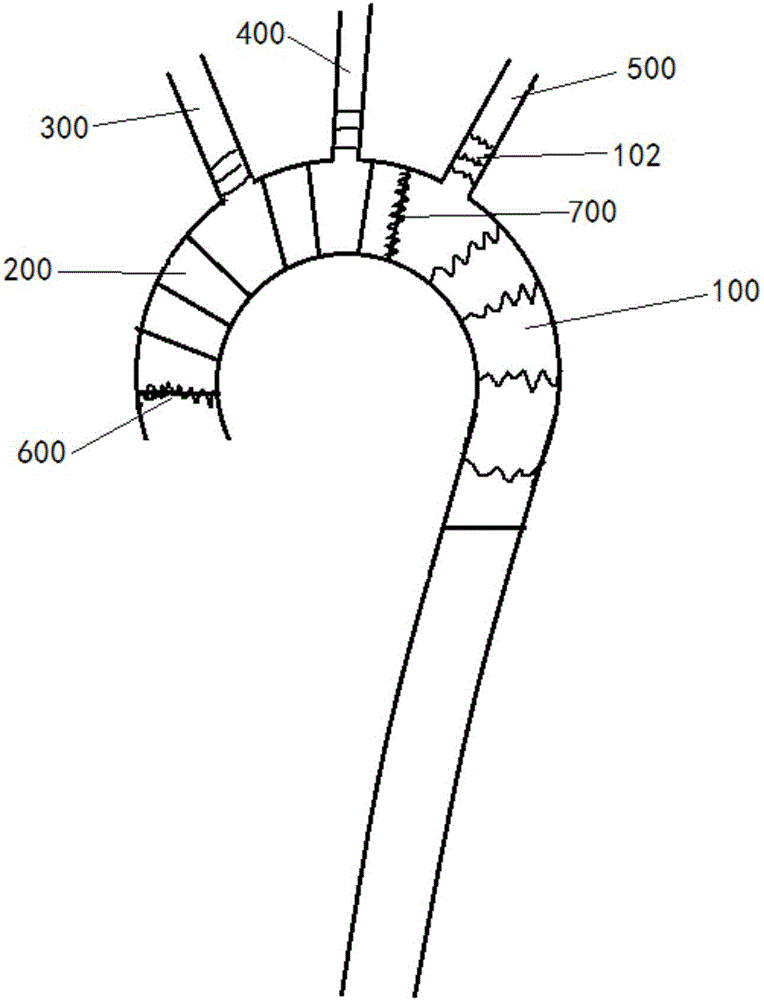
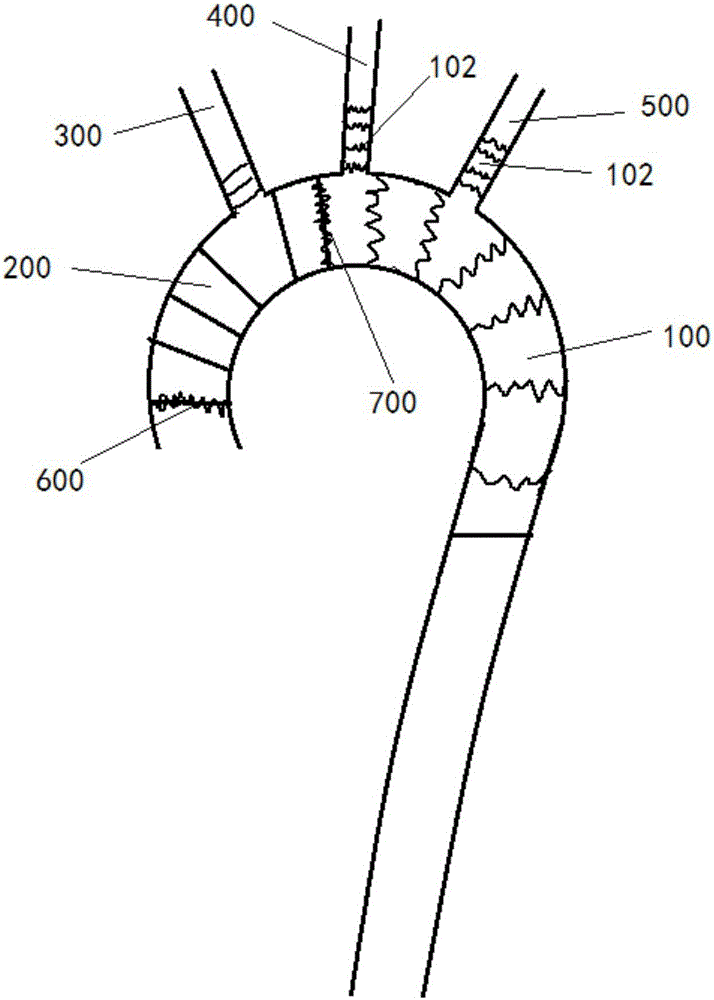
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Aortic arches" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
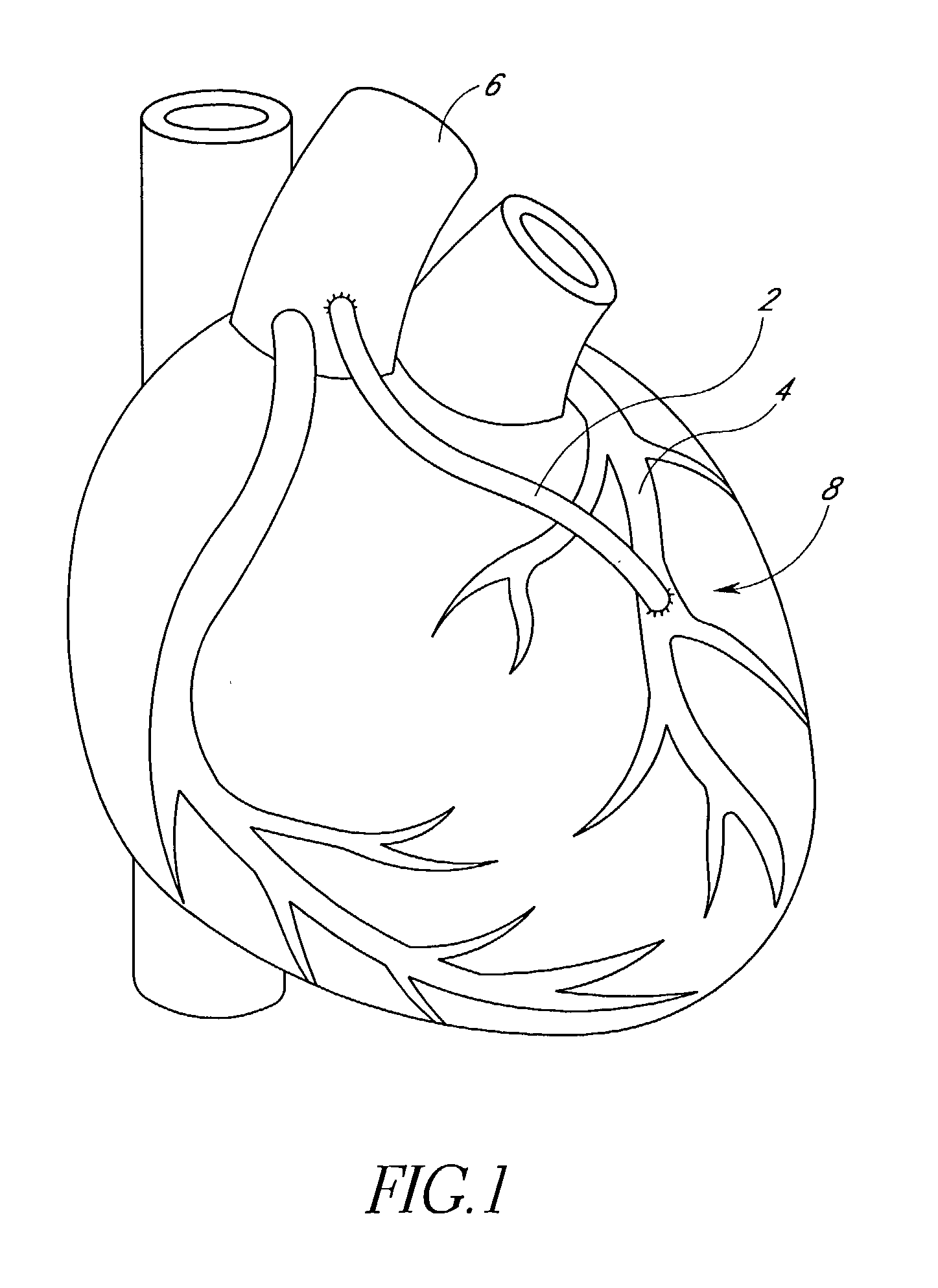
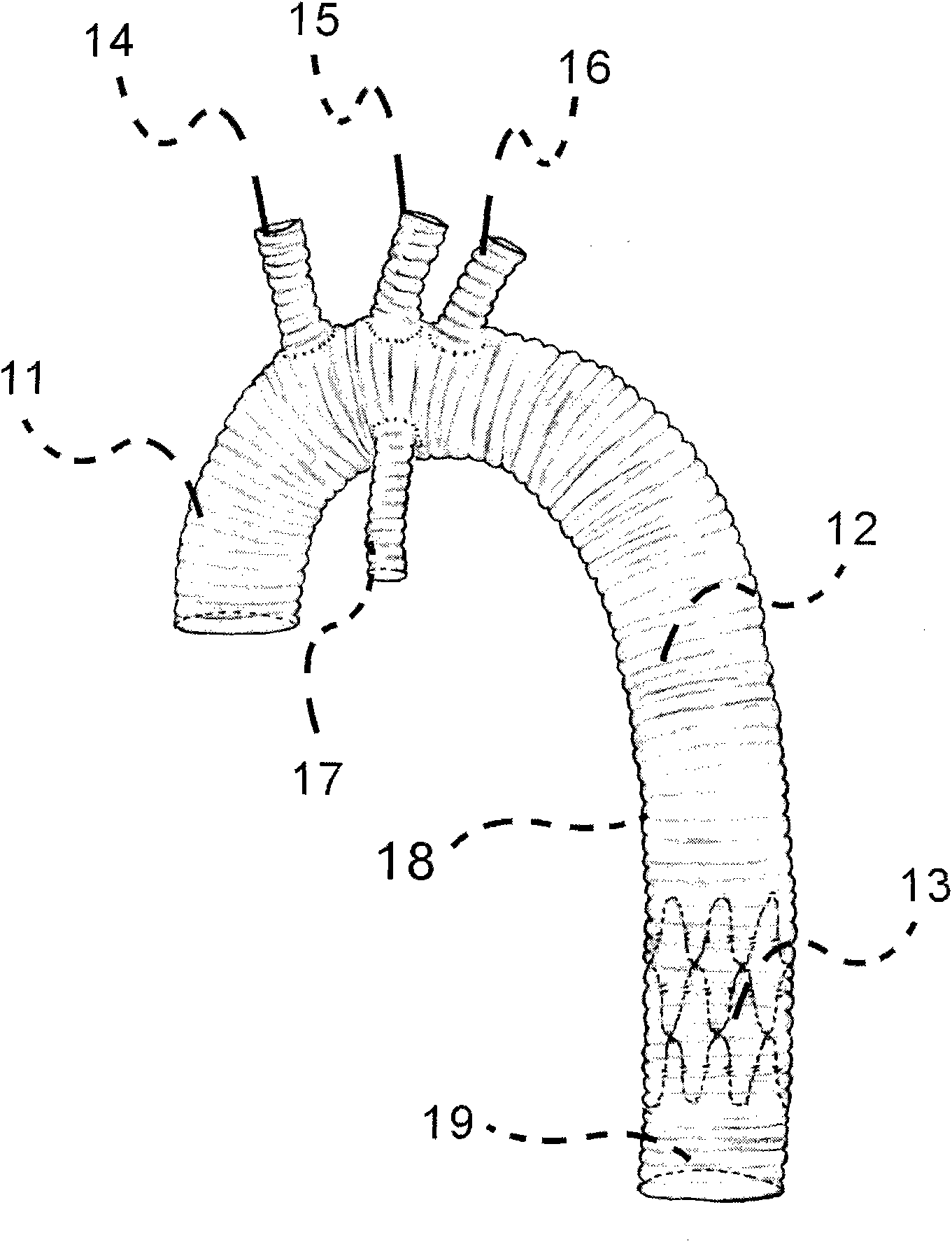
The aortic arches or pharyngeal arch arteries (previously referred to as branchial arches in human embryos) are a series of six paired embryological vascular structures which give rise to the great arteries of the neck and head. They are ventral to the dorsal aorta and arise from the aortic sac.
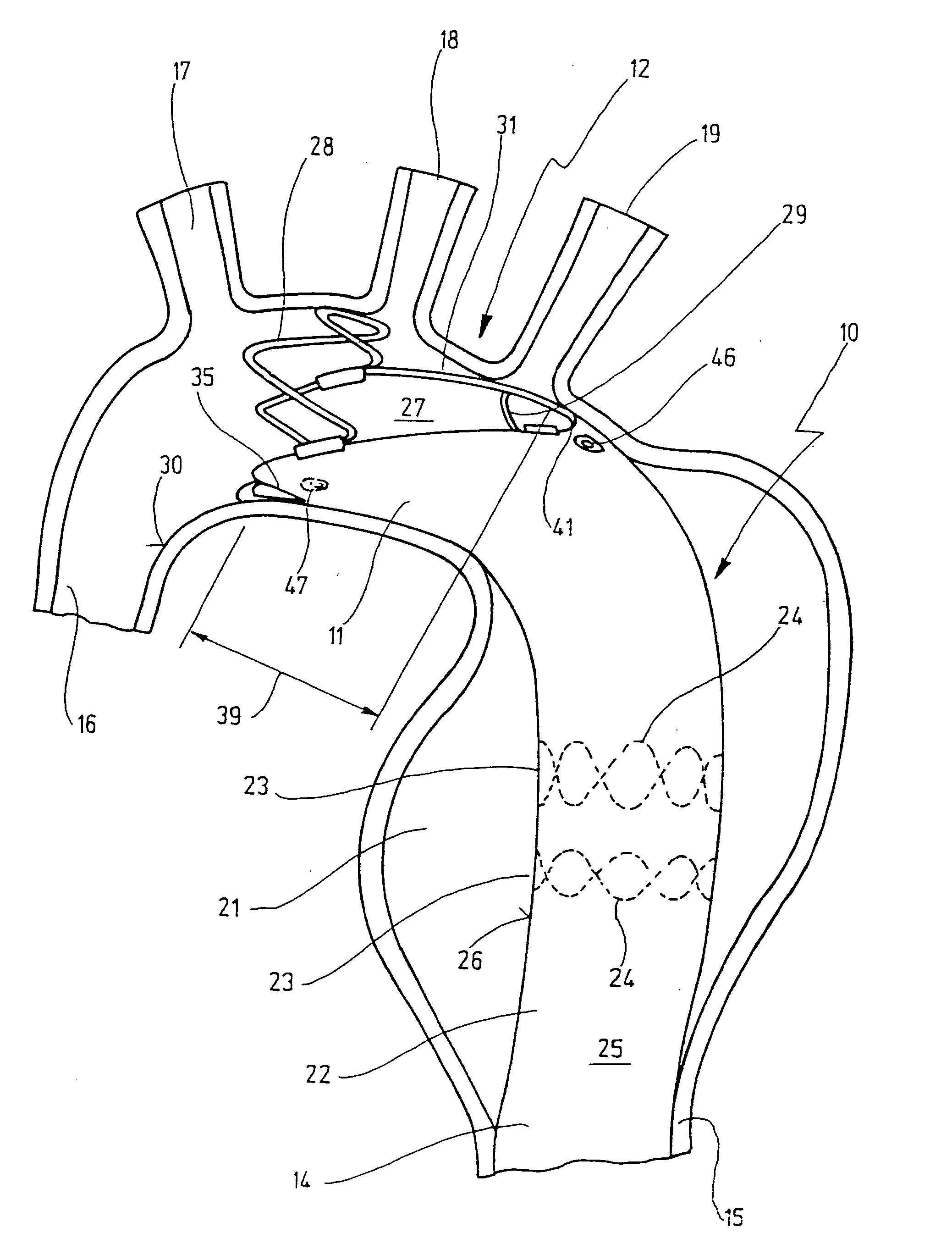
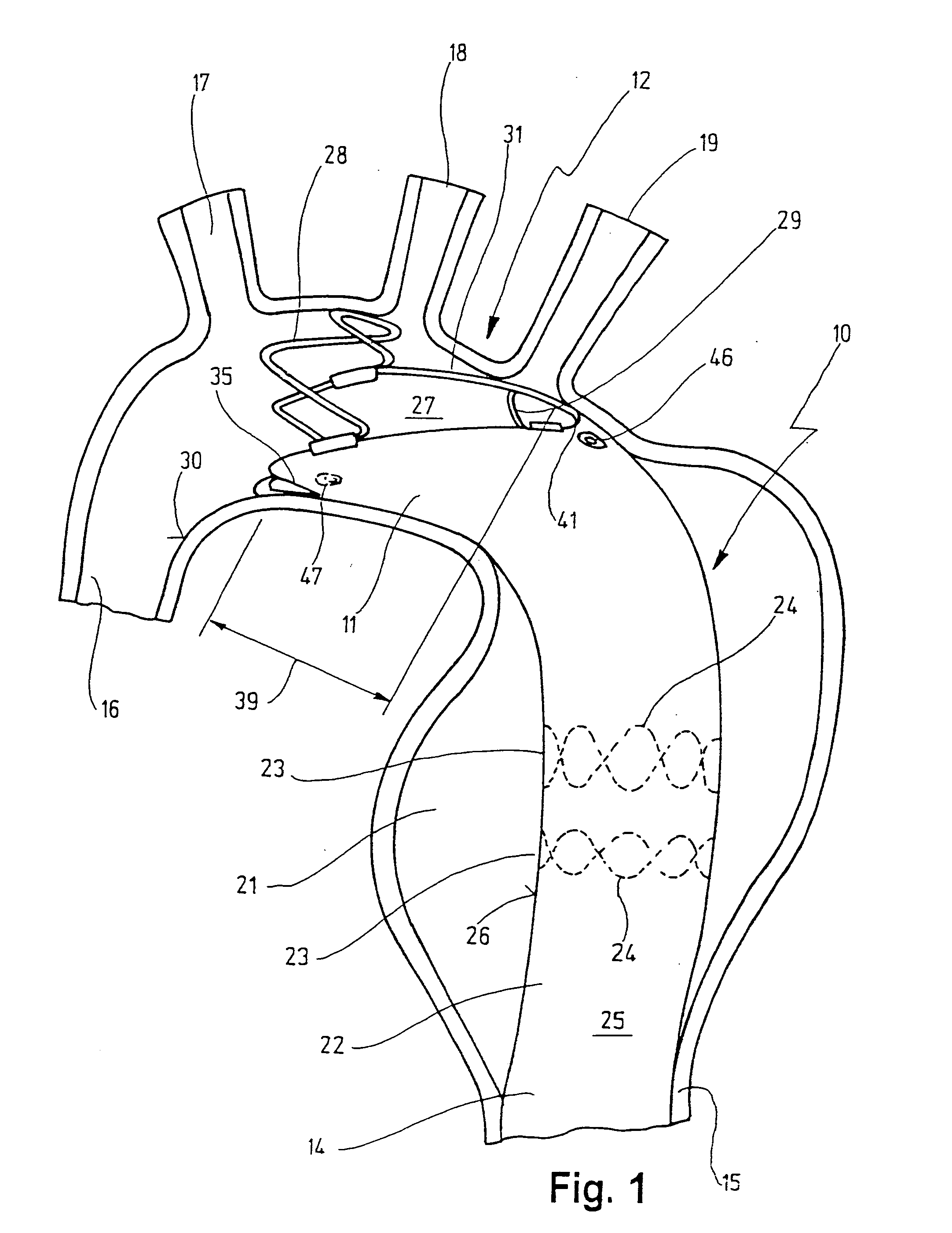
System for cardiac procedures
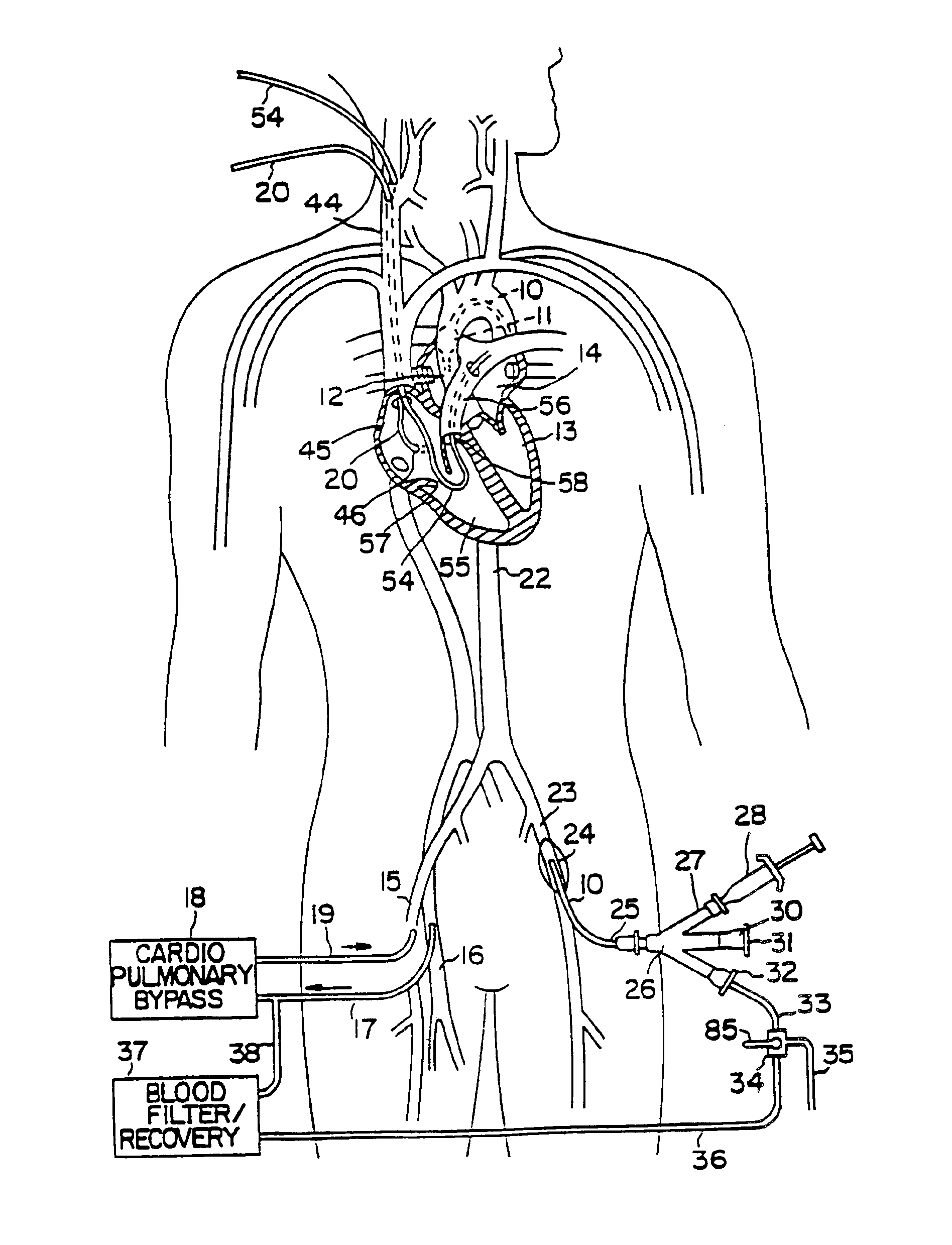
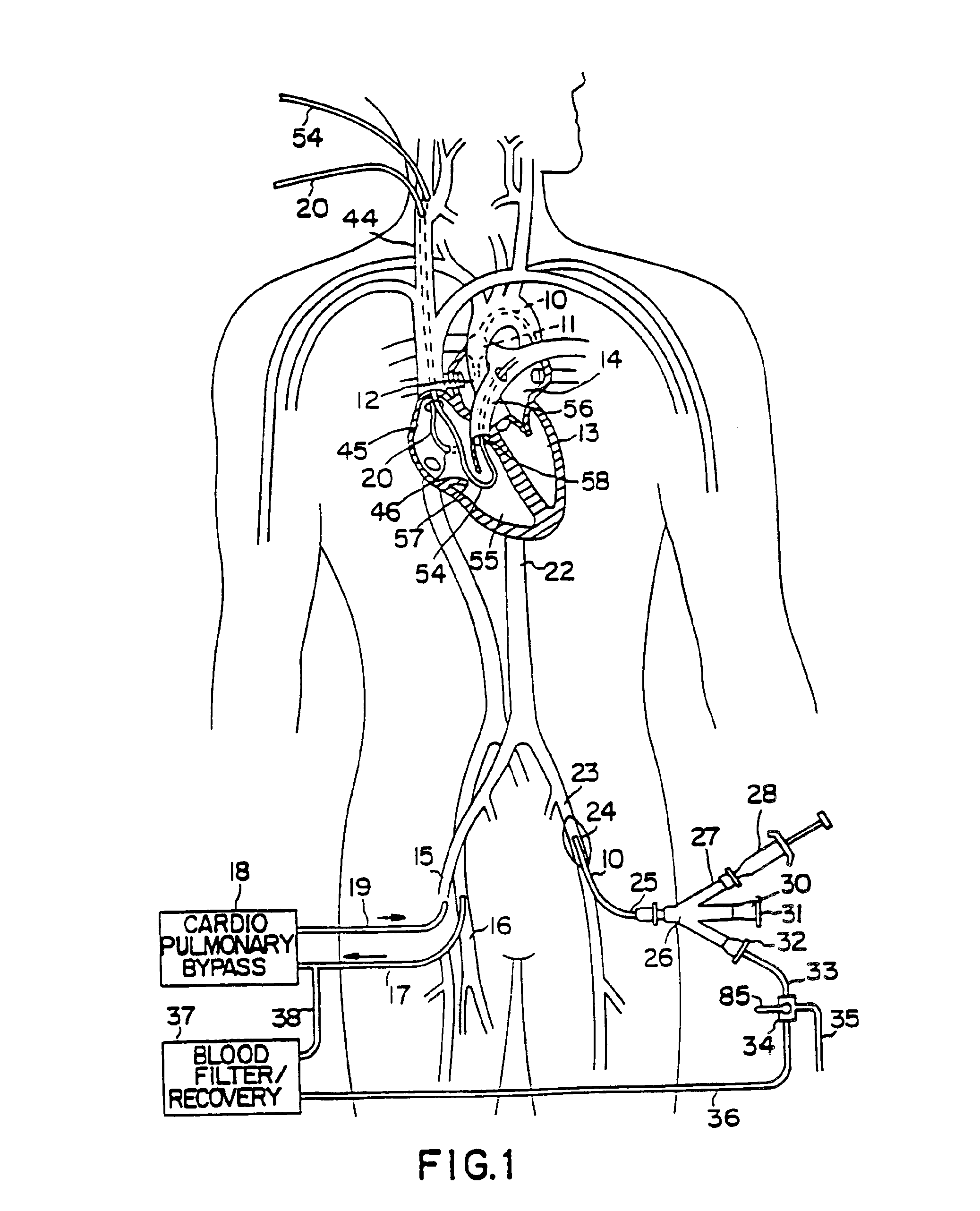
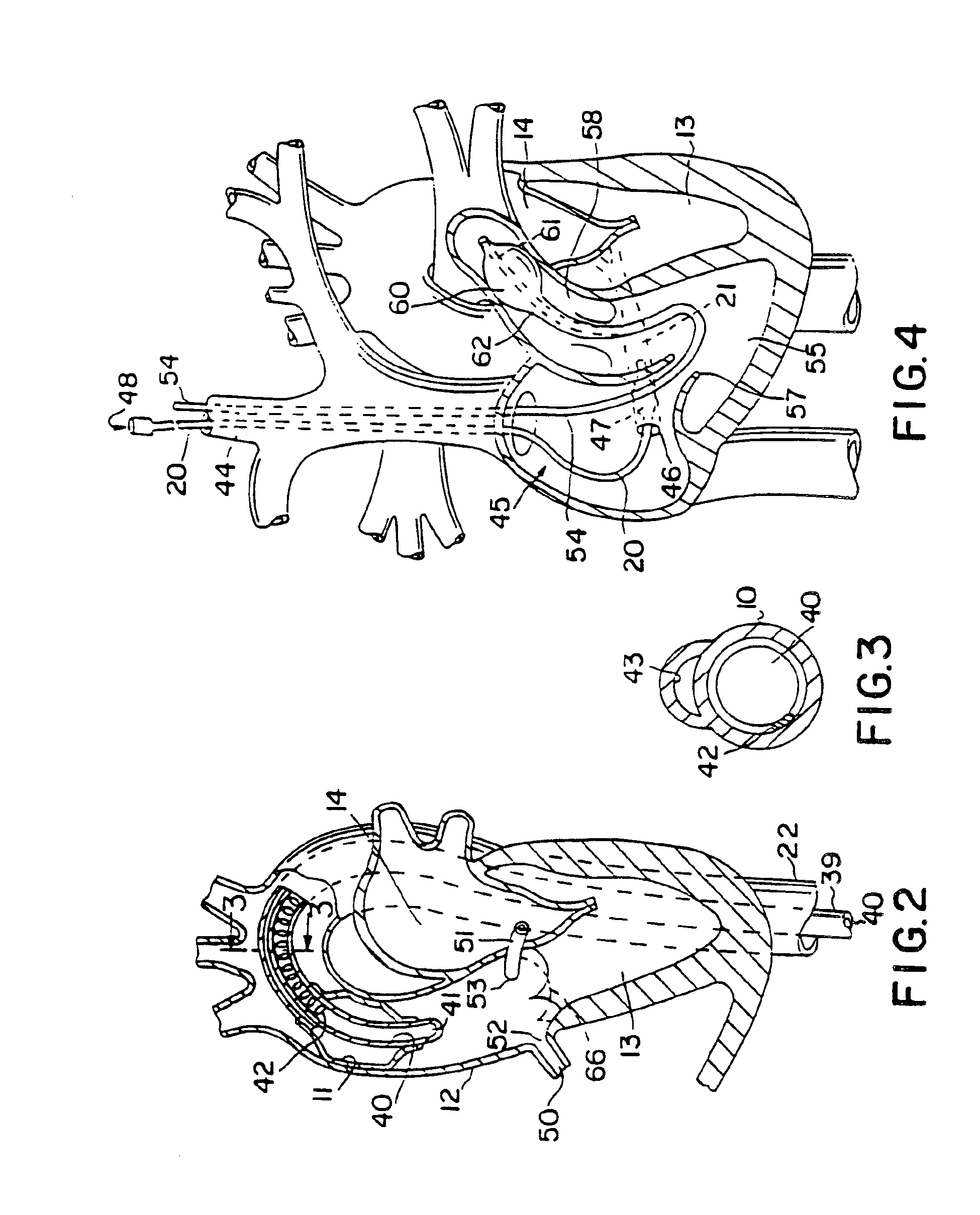
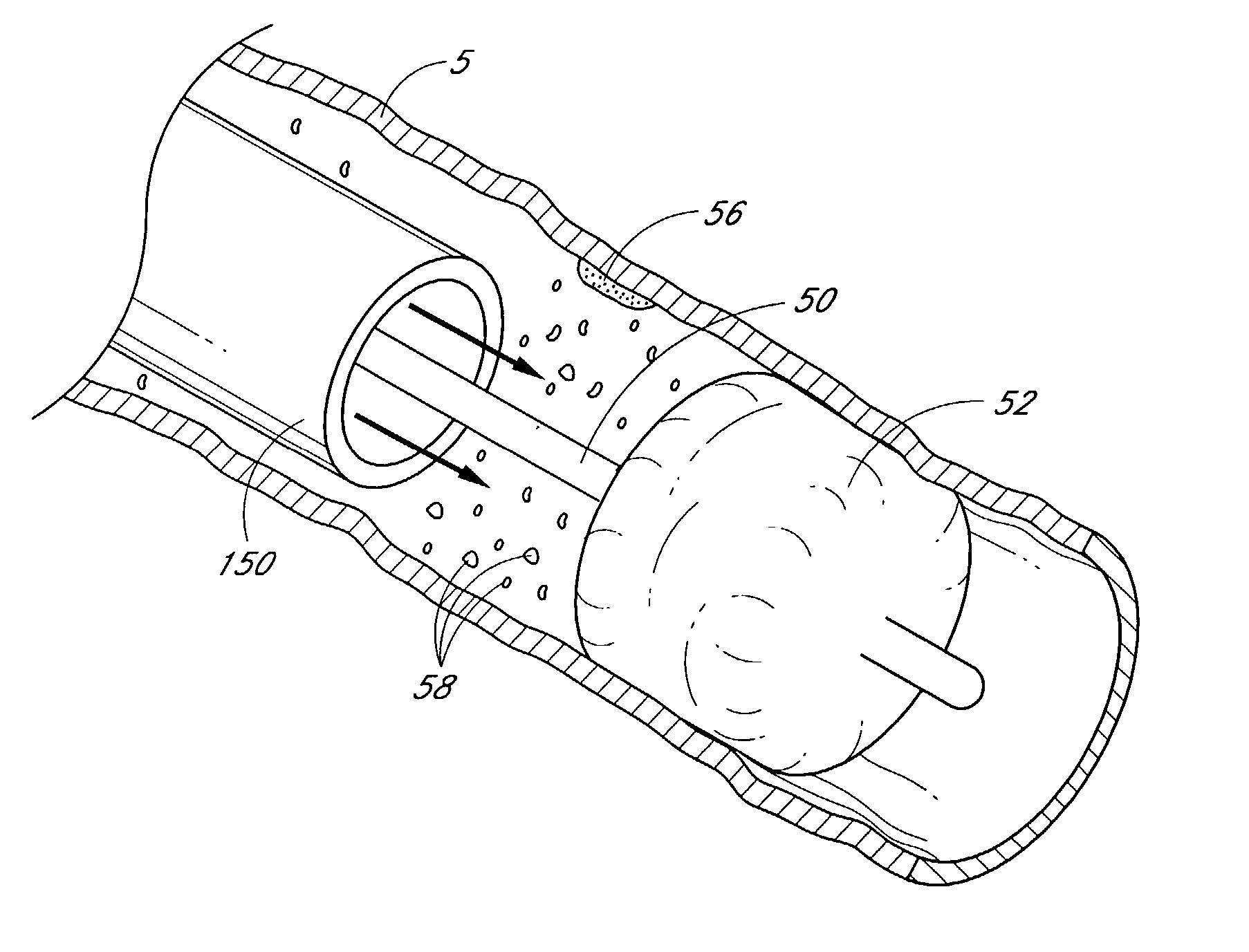
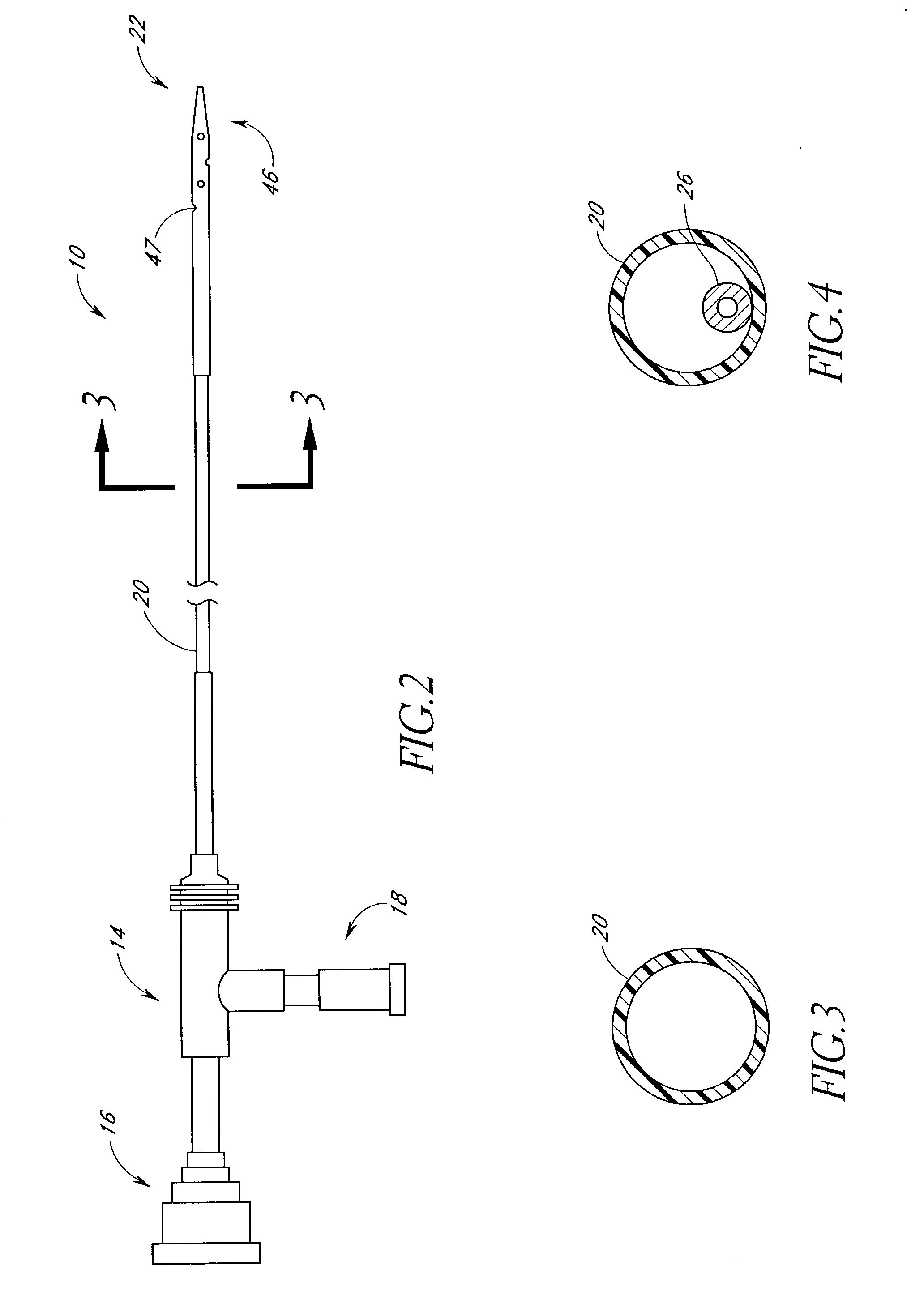
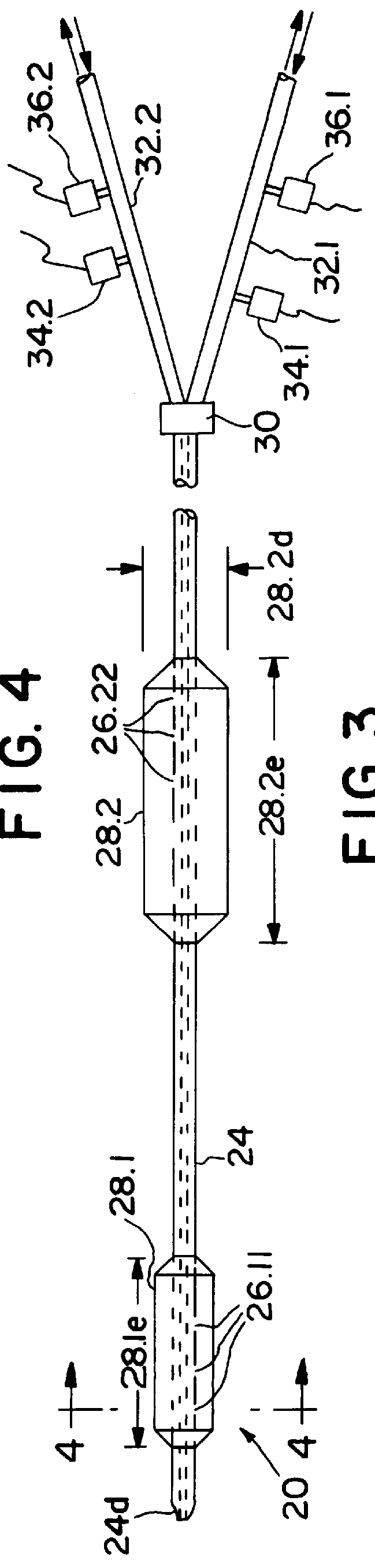
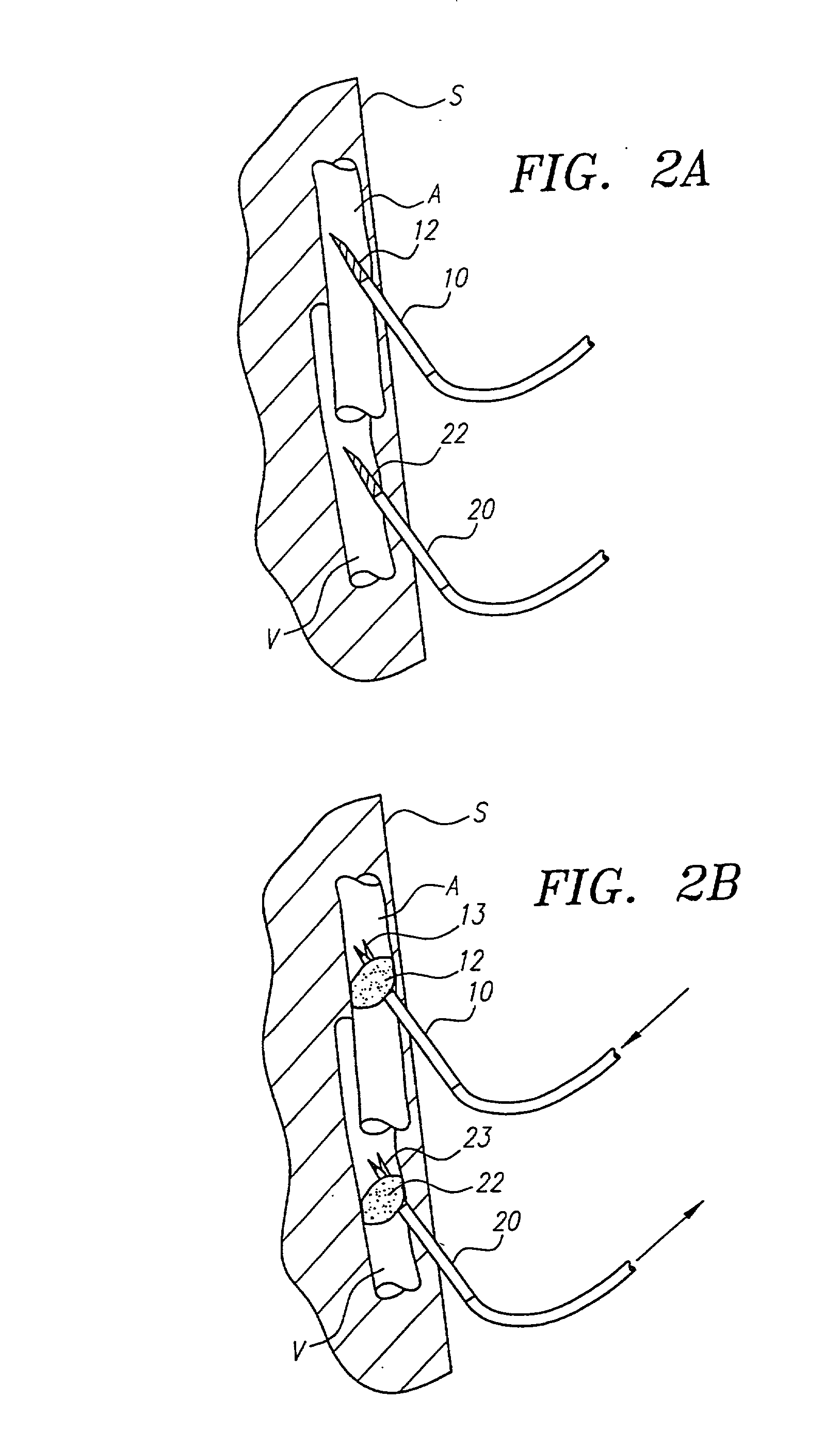
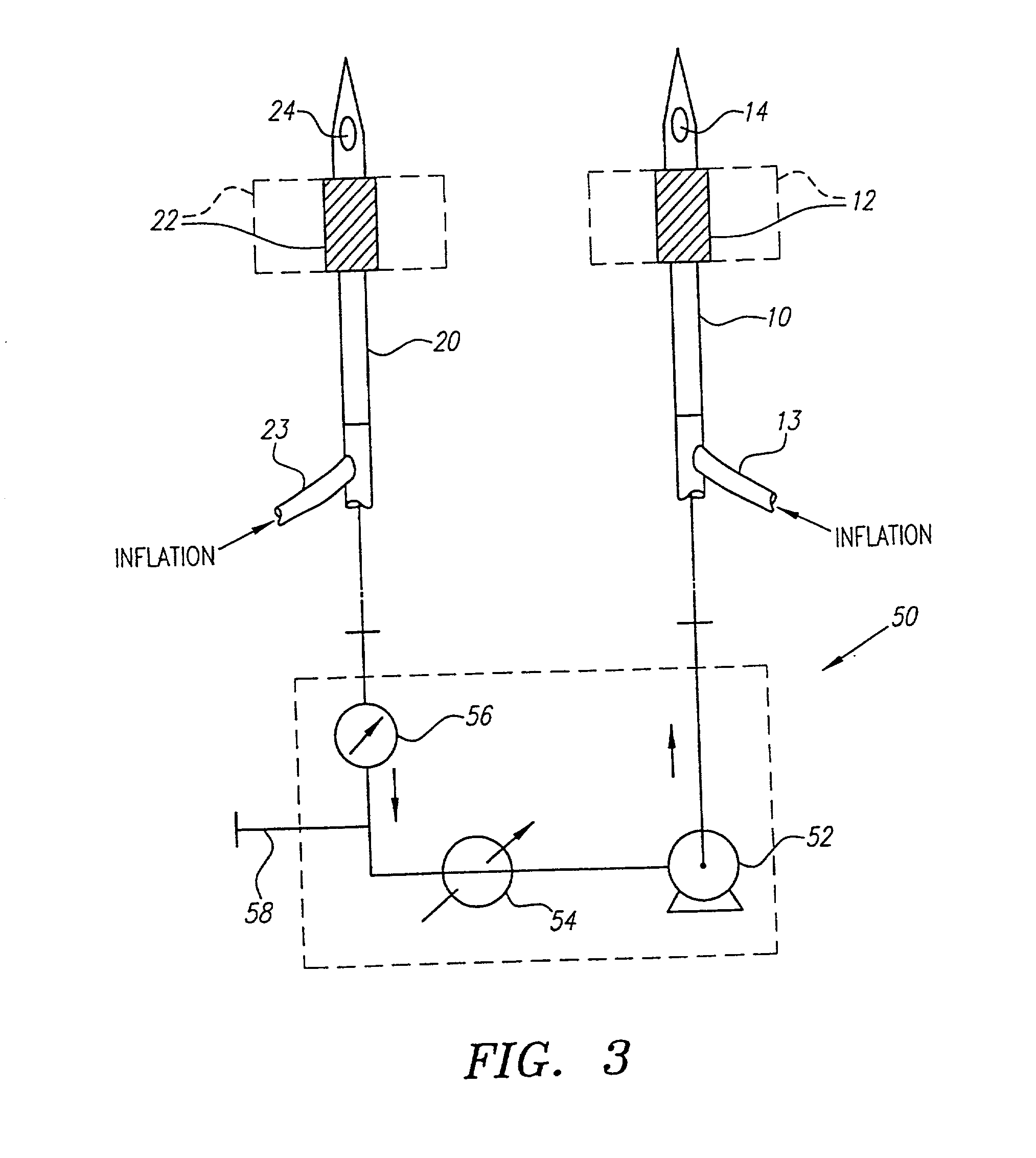
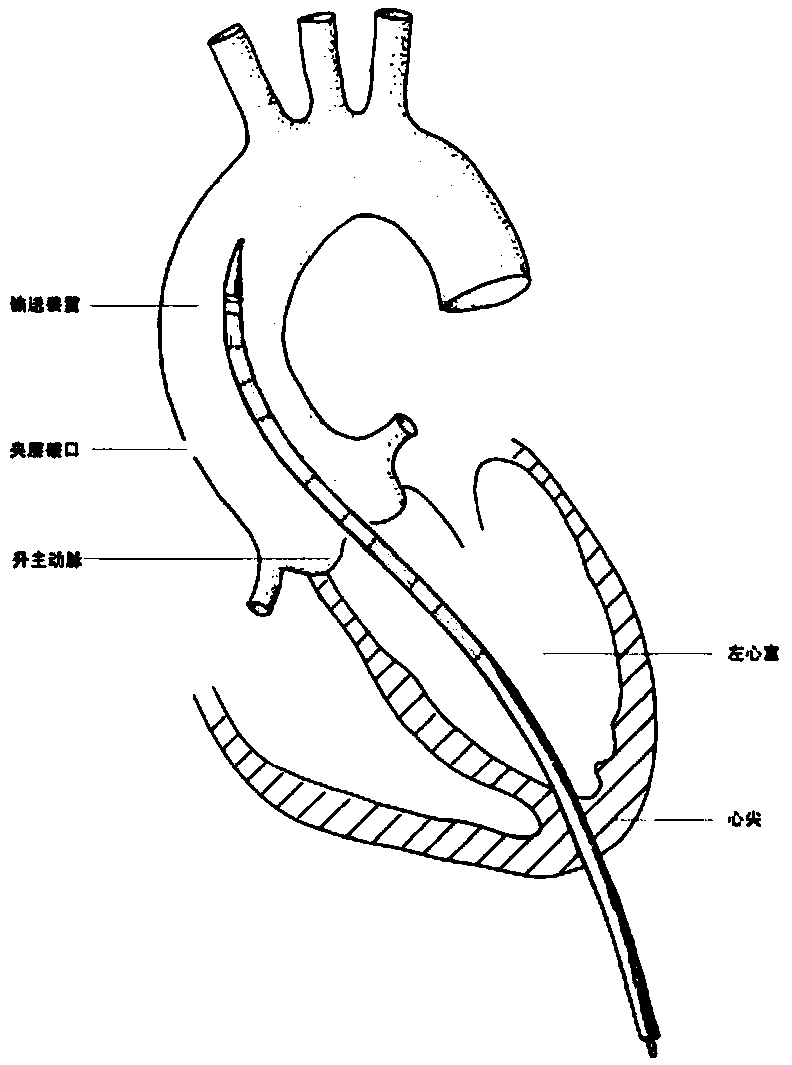
A system for accessing a patient's cardiac anatomy which includes an endovascular aortic partitioning device that separates the coronary arteries and the heart from the rest of the patient's arterial system. The endovascular device for partitioning a patient's ascending aorta comprises a flexible shaft having a distal end, a proximal end, and a first inner lumen therebetween with an opening at the distal end. The shaft may have a preshaped distal portion with a curvature generally corresponding to the curvature of the patient's aortic arch. An expandable means, e.g. a balloon, is disposed near the distal end of the shaft proximal to the opening in the first inner lumen for occluding the ascending aorta so as to block substantially all blood flow therethrough for a plurality of cardiac cycles, while the patient is supported by cardiopulmonary bypass. The endovascular aortic partitioning device may be coupled to an arterial bypass cannula for delivering oxygenated blood to the patient's arterial system. The heart muscle or myocardium is paralyzed by the retrograde delivery of a cardioplegic fluid to the myocardium through patient's coronary sinus and coronary veins, or by antegrade delivery of cardioplegic fluid through a lumen in the endovascular aortic partitioning device to infuse cardioplegic fluid into the coronary arteries. The pulmonary trunk may be vented by withdrawing liquid from the trunk through an inner lumen of an elongated catheter. The cardiac accessing system is particularly suitable for removing the aortic valve and replacing the removed valve with a prosthetic valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
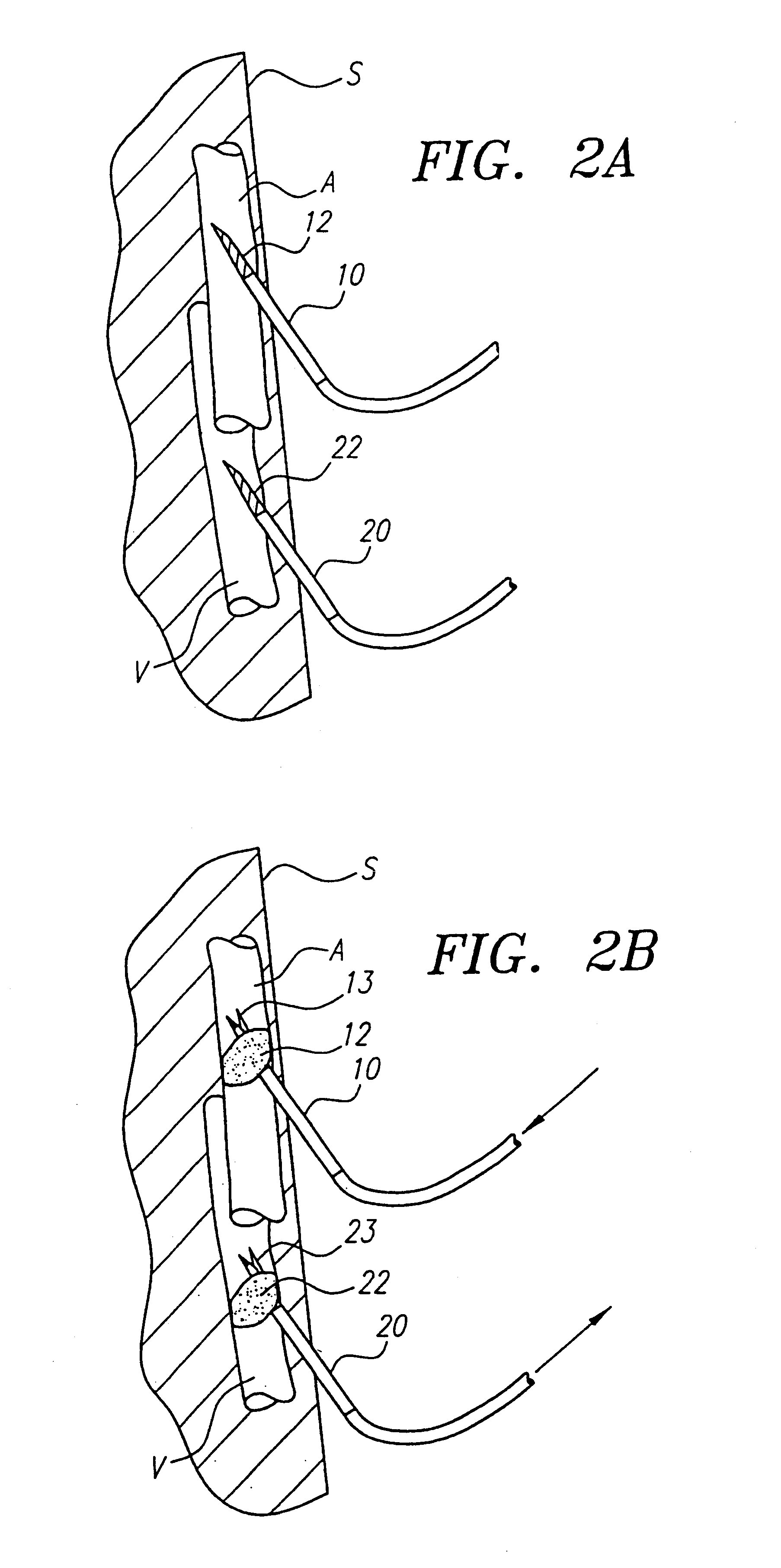
Aspiration method
InactiveUS20030009146A1Fast and efficient aspirationReduce amountBalloon catheterGuide wiresSaphenous veinsSaphenous vein graft
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
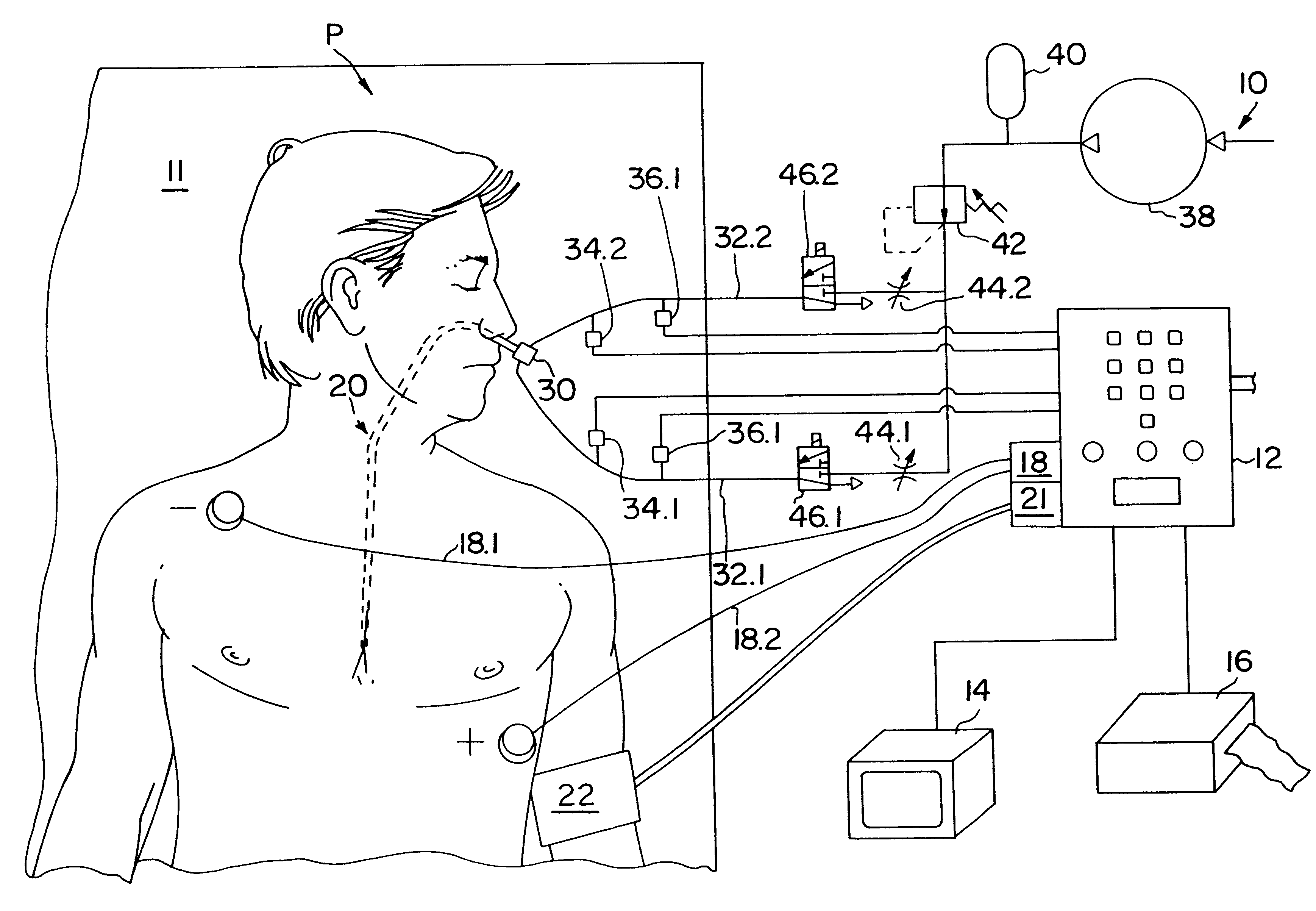
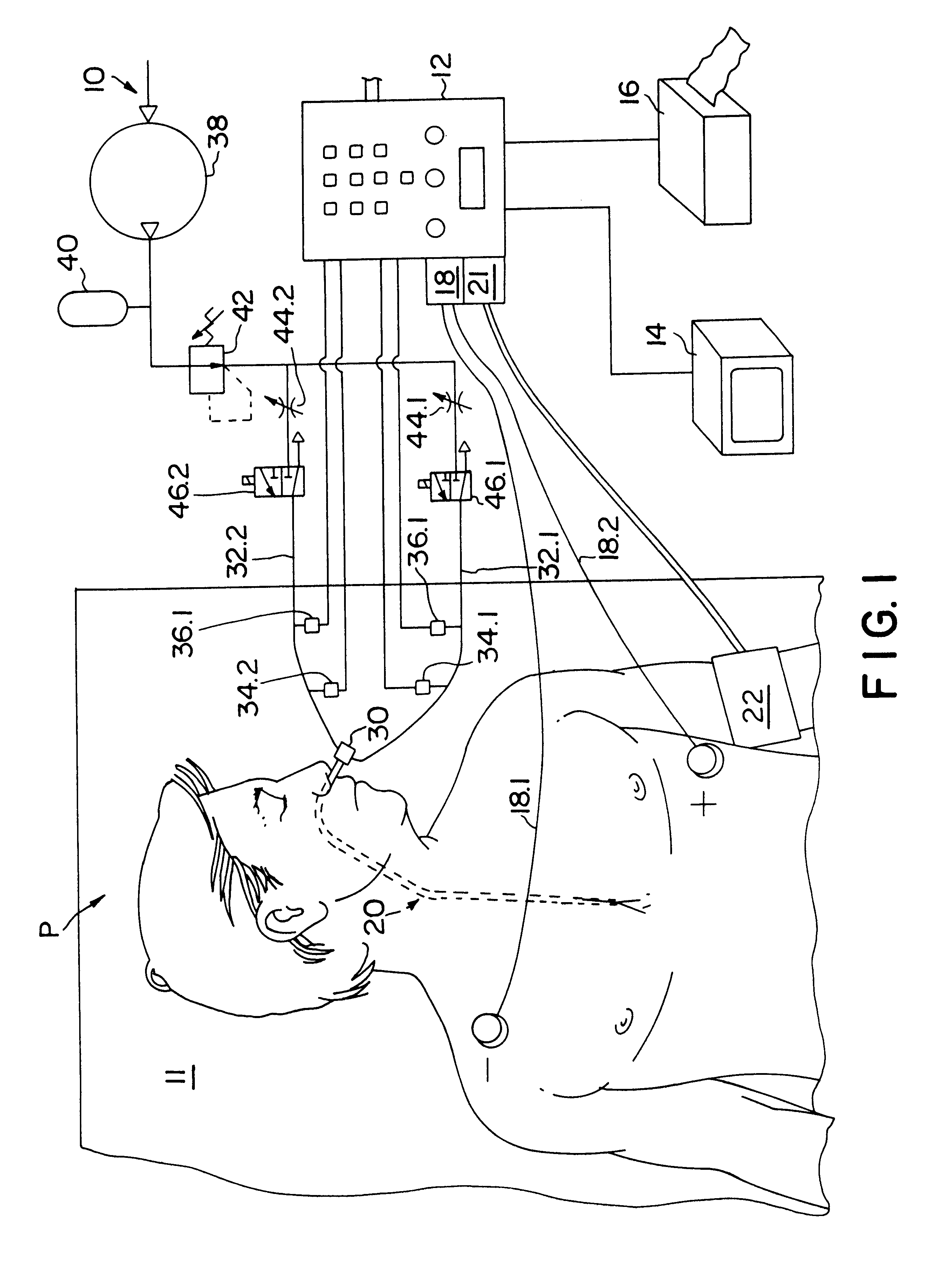
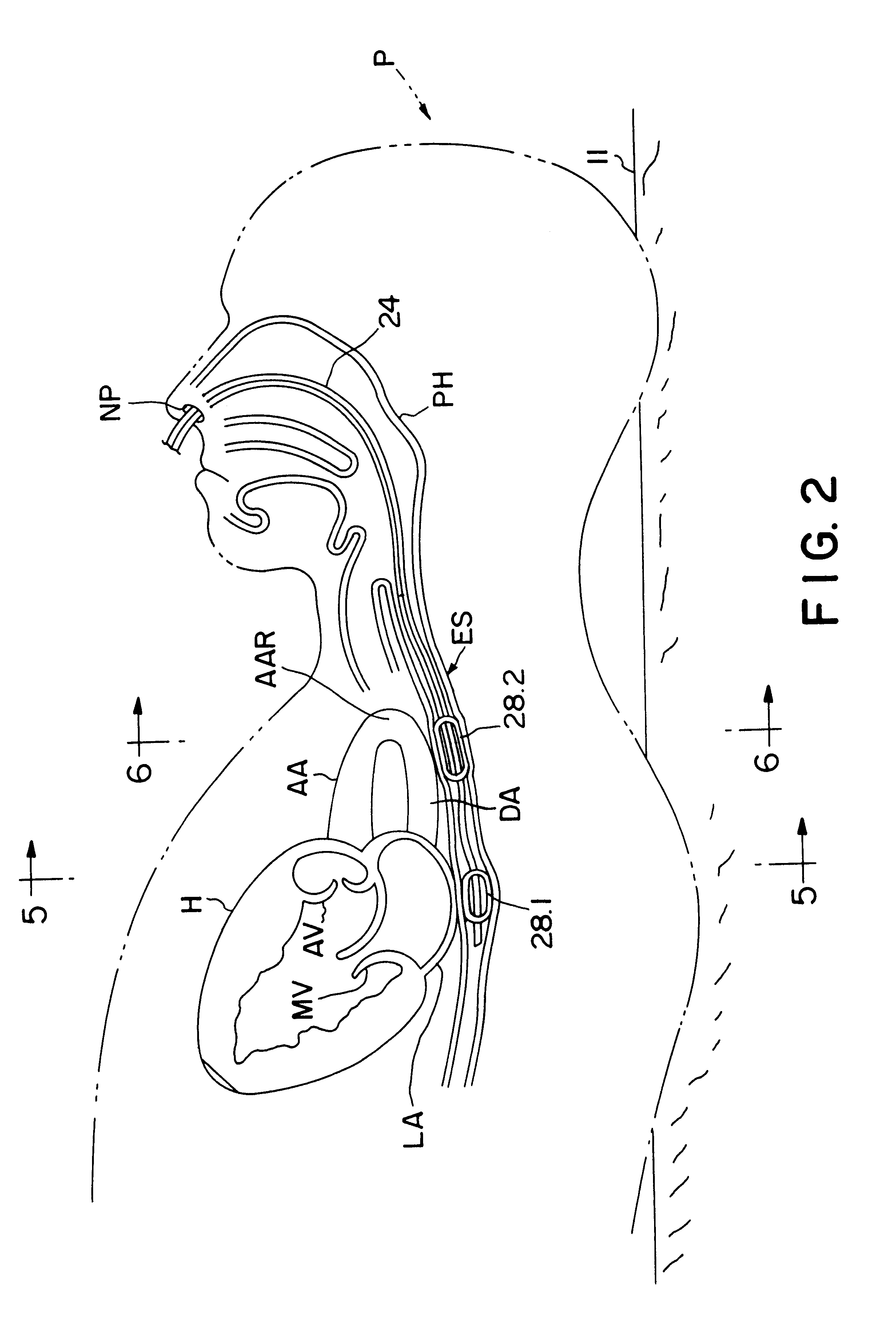
Method and apparatus for noninvasive determination of cardiac performance parameters
InactiveUS6120442AInexpensive and reliableEasy to usePerson identificationCatheterSystoleLeft atrial pressure
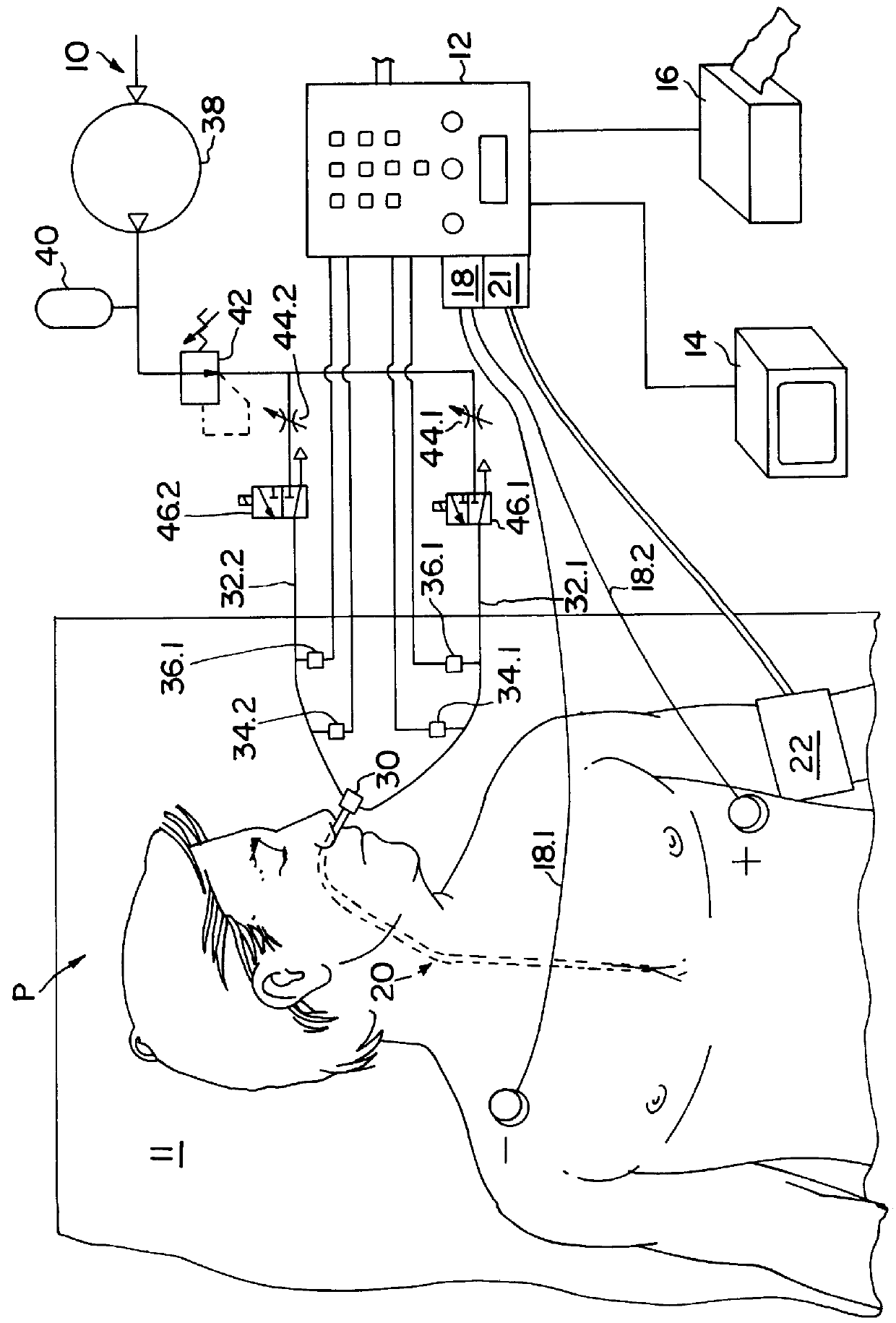
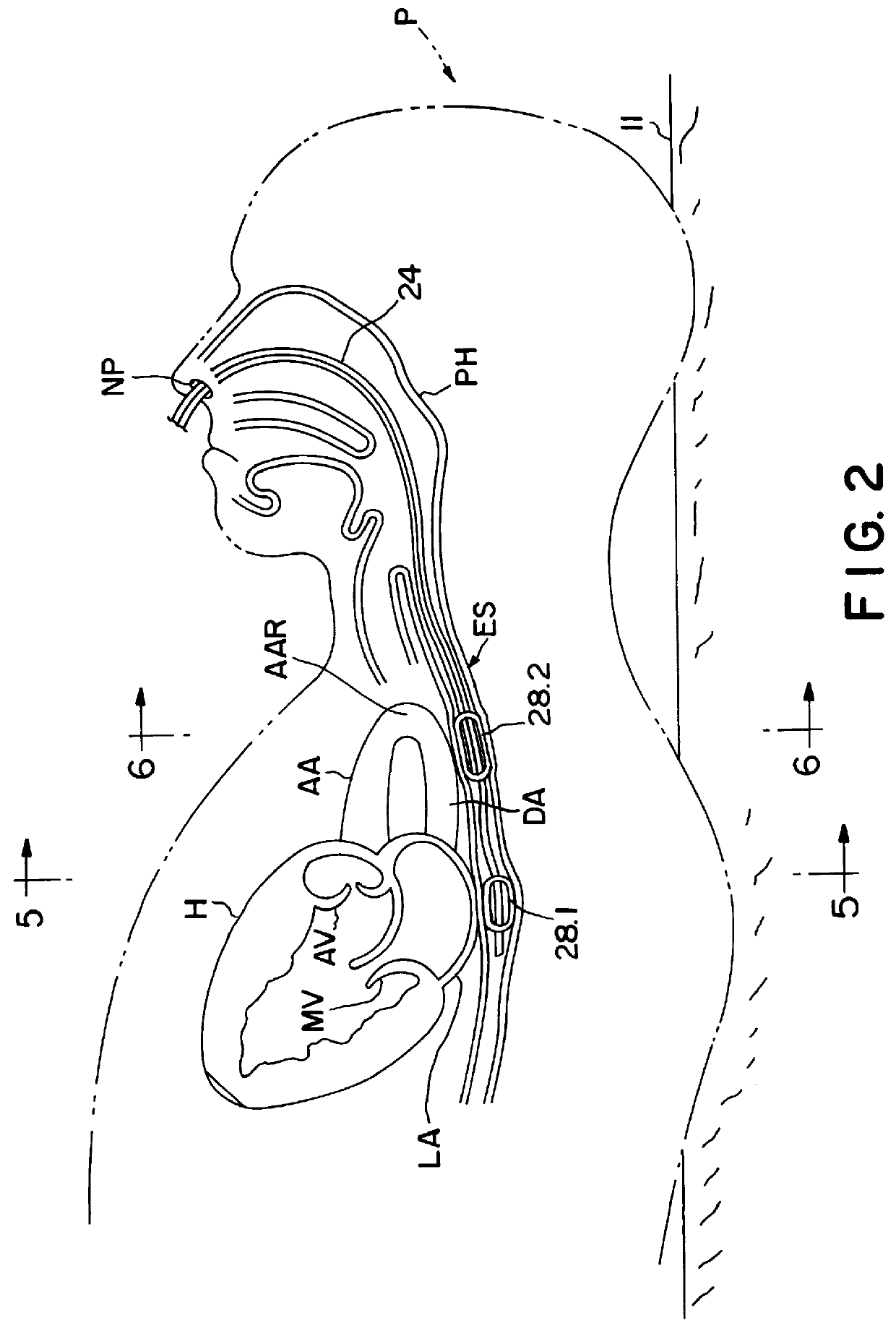
Apparatus and method for noninvasively determining cardiac performance parameters including 1) lengths of systolic time intervals, (2) contractility index, (3) pulse amplitude ratios while performing the Valsalva maneuver, (4) cardiac output index, and (5) a pulse wave velocity index. A catheter having at least one balloon is inserted into the esophagus and pressurized and positioned adjacent the aortic arch to sense aortic pressure. The effects of aortic pressure on the balloon are utilized to determine at least one of the cardiac performance parameters. The catheter may include a second balloon which is spaced from the aortic balloon a distance such that when the second balloon is in a position adjacent the left atrium to sense left atrial pressure the aortic balloon is in a position adjacent the aortic arch to sense aortic pressure, this distance being related to the distance between the left atrium and aortic arch in most adult persons.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method and system for selective or isolated integrate cerebral perfusion and cooling
InactiveUS6736790B2Reduce riskImproving cerebral perfuisionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesOxygenPerfusion
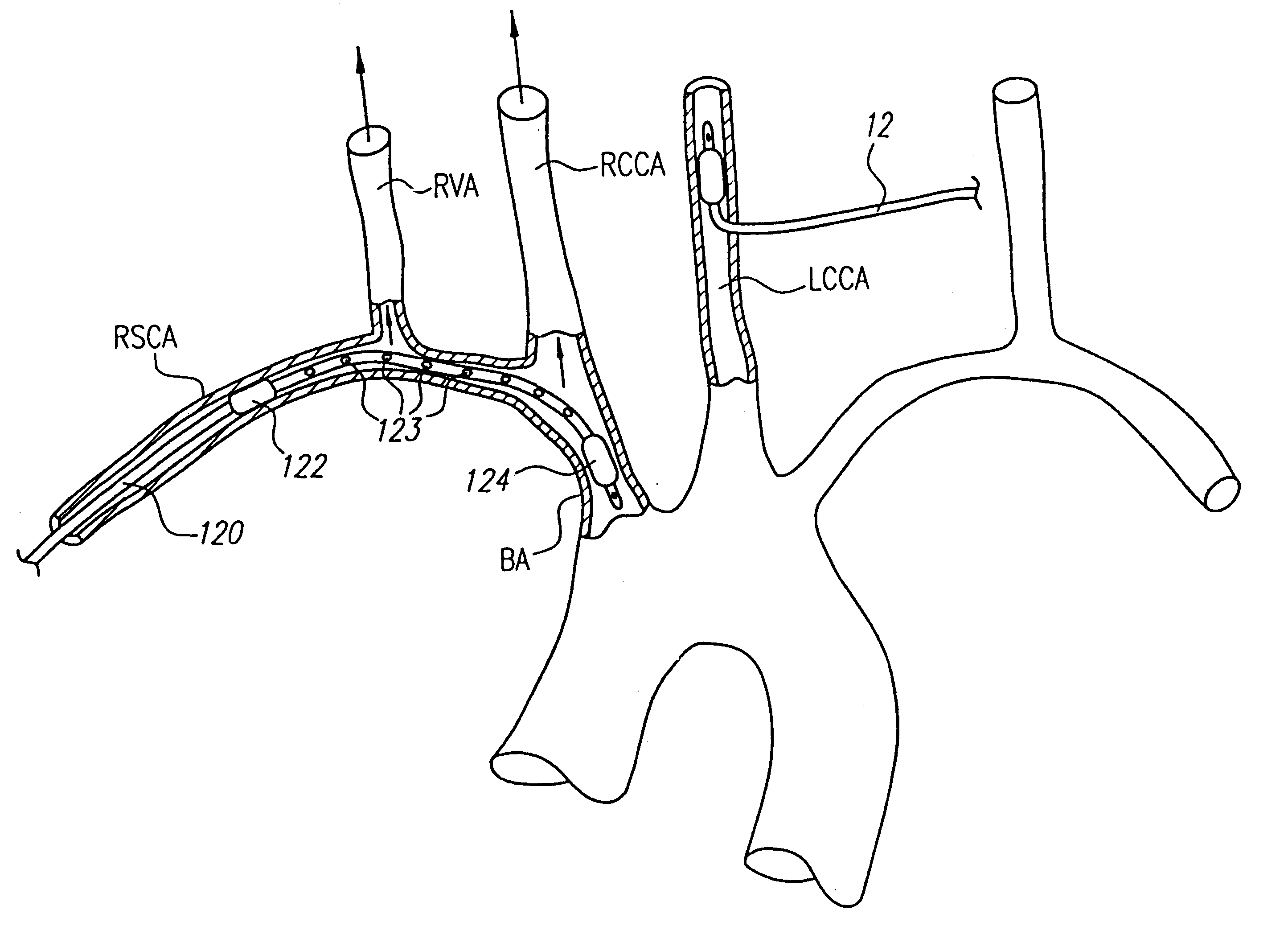
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of cardiac arrest or from other causes are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood may also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE & PATTERSON RUSSEL +1
Method and apparatus for noninvasive determination of cardiac performance parameters
InactiveUS6238349B1Inexpensive and reliableEasy to usePerson identificationCatheterSystoleLeft atrial pressure
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Methods and devices for treatging aortic atheroma
InactiveUS20080004687A1Avoid obstructionPrecise positioningStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryAortic atheroma
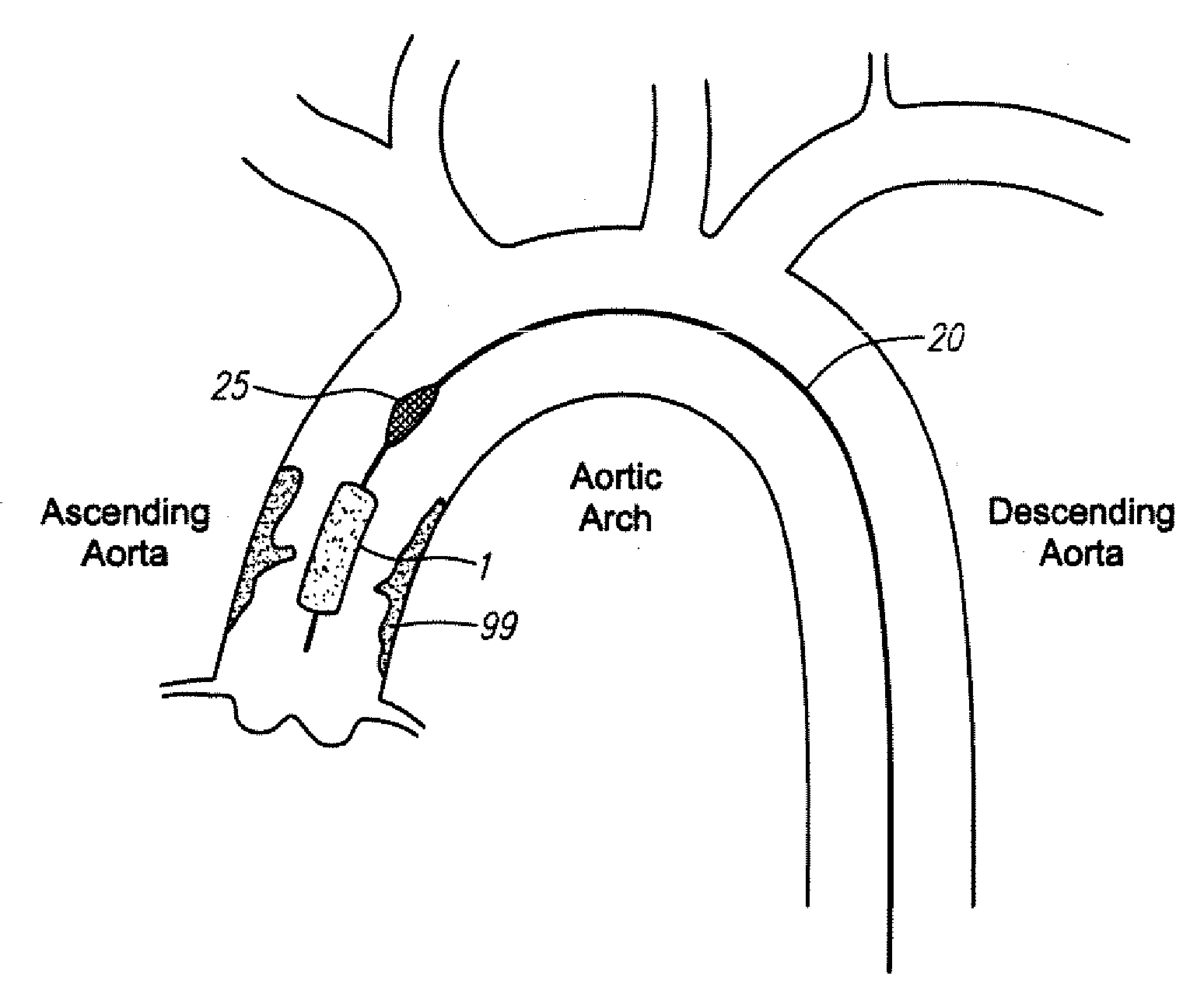
A method for treating both sessile and mobile aortic atheroma is described. A radially expanding device, such as a stent or compliant cast, comprising a generally cylindrical member expandable between a compressed state and an enlarged state is provided. The cylindrical member has a proximal opening, a distal opening, a lumen therebetween, and at least one side opening in the wall of the generally cylindrical member. The methods comprise imaging the aorta to identify position and extent of atheroma. The stent is then advanced into the aortic arch and positioned so that the at least one side-opening is aligned with the takeoff of one or more of the right brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, or the left subclavian artery. The stent is expanded into contact with the endoluminal surface of the aorta and atheroma is trapped between the stent and the endoluminal surface of the aorta.
Owner:SAGE MEDICAL TECH
Pressure-pulse therapy device for treatment of deposits
A device, system and method for the generation of therapeutic acoustic shock waves for at least partially separating a deposit from a vascular structure. The shock waves may optionally be generated according to any mechanism which is known in the art, including but not limited to, spark gap technology, electromagnetic shock wave generation and piezoelectric technology for generating therapeutic pressure pulses. Examples of deposits which may be treated with the present invention include, but are not limited to, atherosclerotic plaques, any type of clot, and any type of thrombus or embolus. The vascular structure itself may be any such structure for conducting blood flow, including but not limited to arteries, veins and the aortic arch.
Owner:MEDISPEC LTD
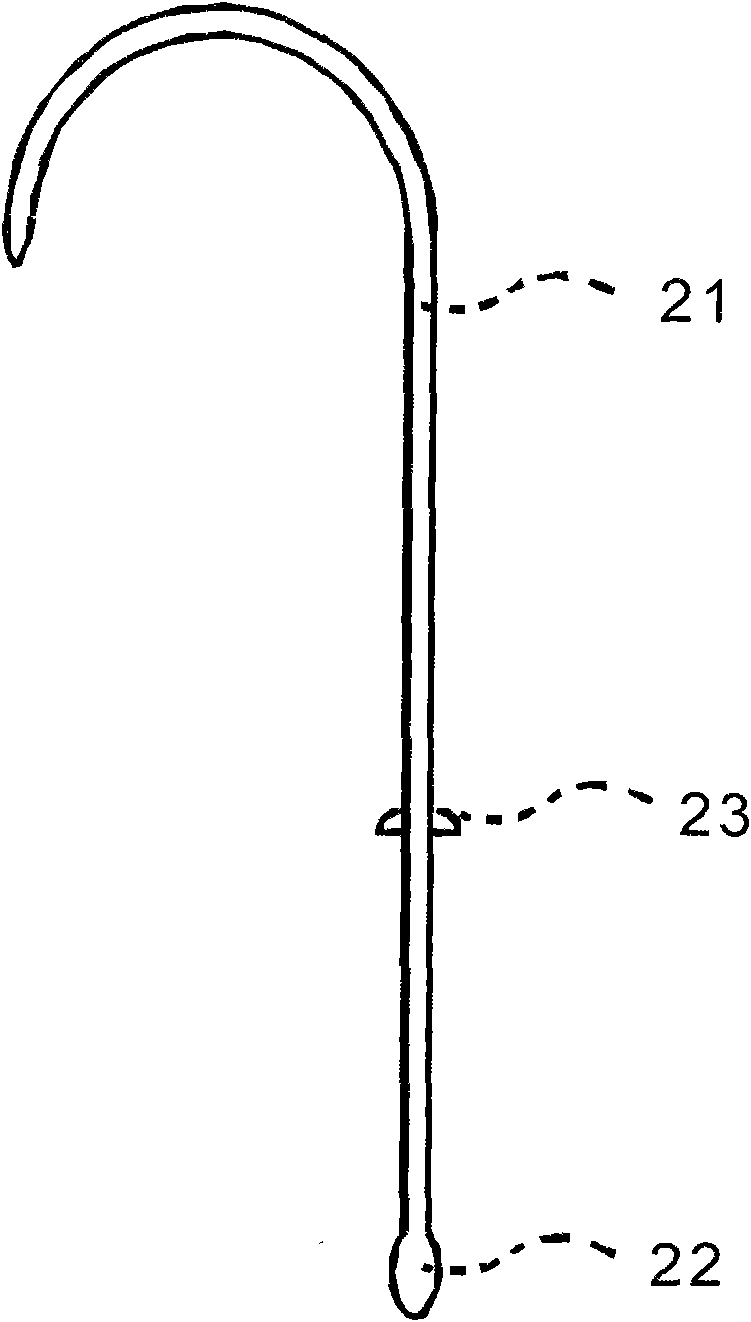
Aortic arch prosthetic graft
An implantable textile prosthesis includes a first woven section having a tubular branch wall defining a fluid passageway therethrough. The tubular branch wall includes an elongate tubular extent and an asymptotically flared tubular extent, which is asymptotic with respect to the tubular branch wall. The asymptotically flared tubular extent includes a weaving pattern having a plurality of warp yarns and fill yarns and incorporating a gradual change in the number of warp yarns with respect to the fill yarns to provide a seamless and substantially fluid-tight transition region along said flared tubular extent. The tubular branch wall may be sutured to an elongate tubular main wall to provide an implantable tubular textile prosthesis particularly useful in branched end-to-side anastomoses. The tubular main wall may be heat-settably arched to resemble the natural arch of the aorta.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
System and method for autonomic blood pressure regulation
InactiveUS20140067003A1Improve complianceReduce cardiovascular riskSpinal electrodesCatheterCervical vertebral bodyEfferent
A system for regulating blood pressure by stimulating an afferent pathway to the brain which produces an efferent output in kidneys includes a electrode device adapted for implantation in the cervical region, a stimulator generator, a cable connecting the electrode device and the stimulator generator, wherein the cervical region is generally located between a pair of common carotid arteries, above an aortic arch and in front of cervical vertebrae C2 and C3. A method of implantation includes placing the electrode device in the cervical region, selectively energizing the device in accordance with a stimulation scheme, assessing any changes in the patient's blood pressure, selectively energizing the device in accordance with another stimulation scheme, and assessing any changes in the patient's blood, for determining an optical stimulation scheme, wherein stimulation scheme involves parameters including, for example, position, placement and configuration of the electrode device in relation to surrounding tissue and / or organs, selection of electrodes energized, width, frequency and amplitude of stimulation current.
Owner:VASE ABHI +1
Guide catheter having selected flexural modulus segments
InactiveUS7674411B2Increase flexibilityPrevent guide catheter back-outGuide needlesLamination ancillary operationsFlexural modulusPliability
A guiding catheter for use in coronary angioplasty and other cardiovascular interventions which incorporates a plurality of segment of selected flexural modulus in the shaft of the device. The segments which have a different flexibility than the sections immediately proximal and distal to them, creating zones in the catheter shaft which are either more or less flexible than other zones of the shaft. The flexibility and length of the shaft in a given zone is then matched to its clinical function and role. A mid-shaft zone is significantly softer than a proximal shaft or distal secondary curve to better traverse the aortic arch shape without storing too much energy. A secondary zone section is designed to have maximum stiffness to provide optimum backup support and stability.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
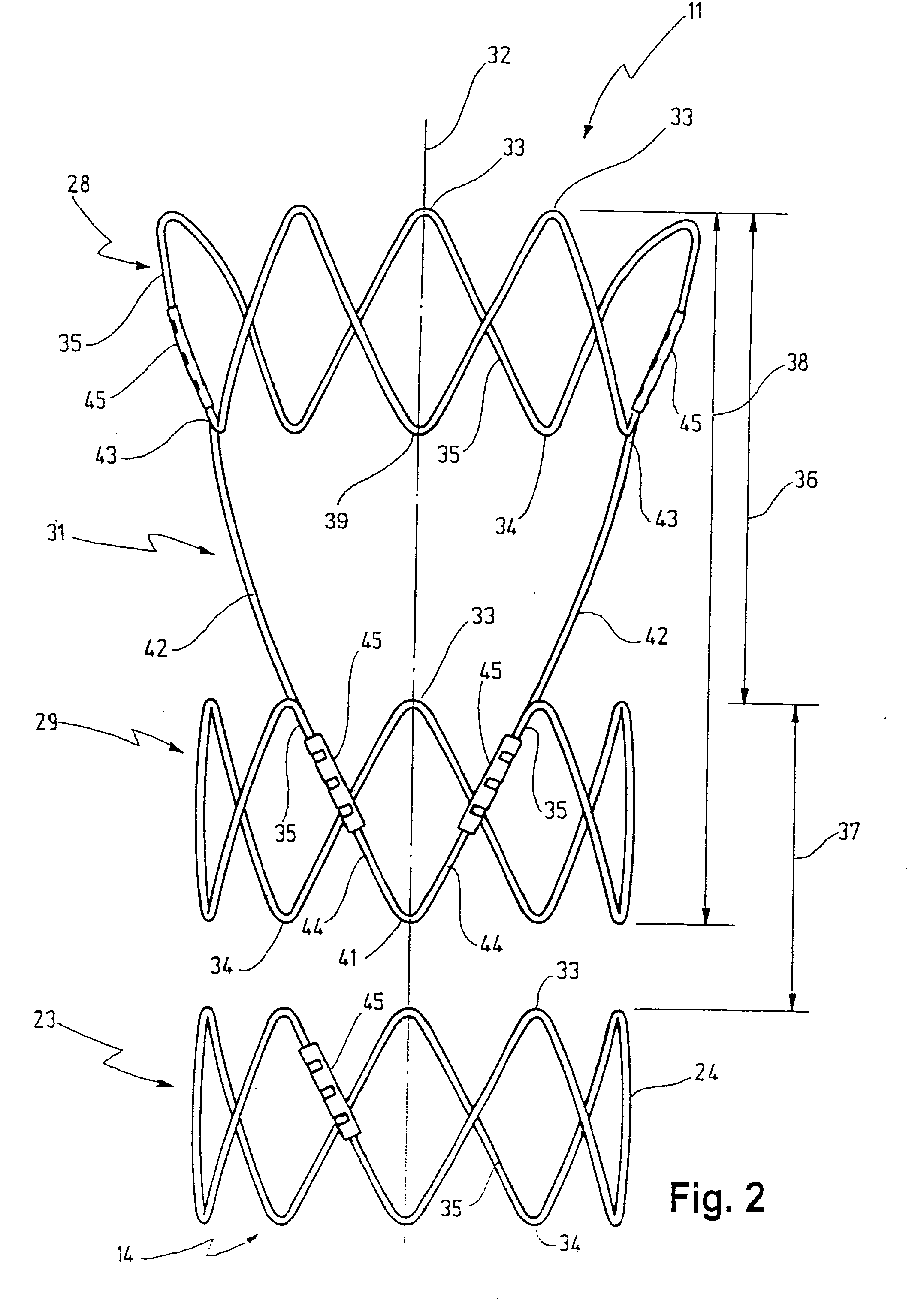
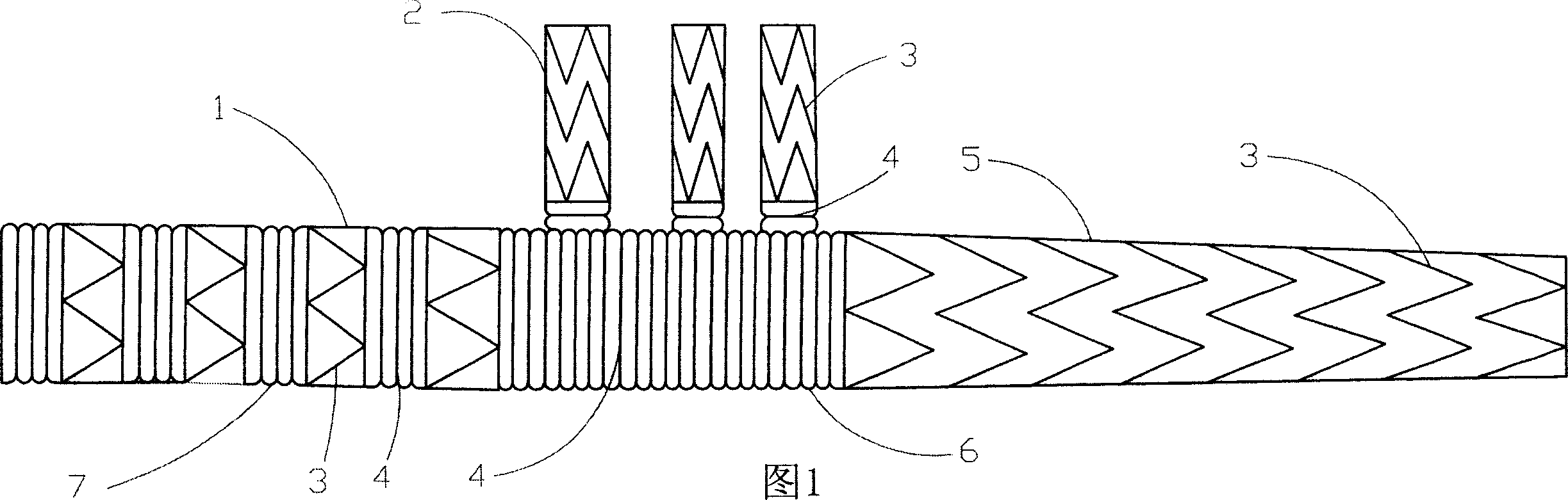
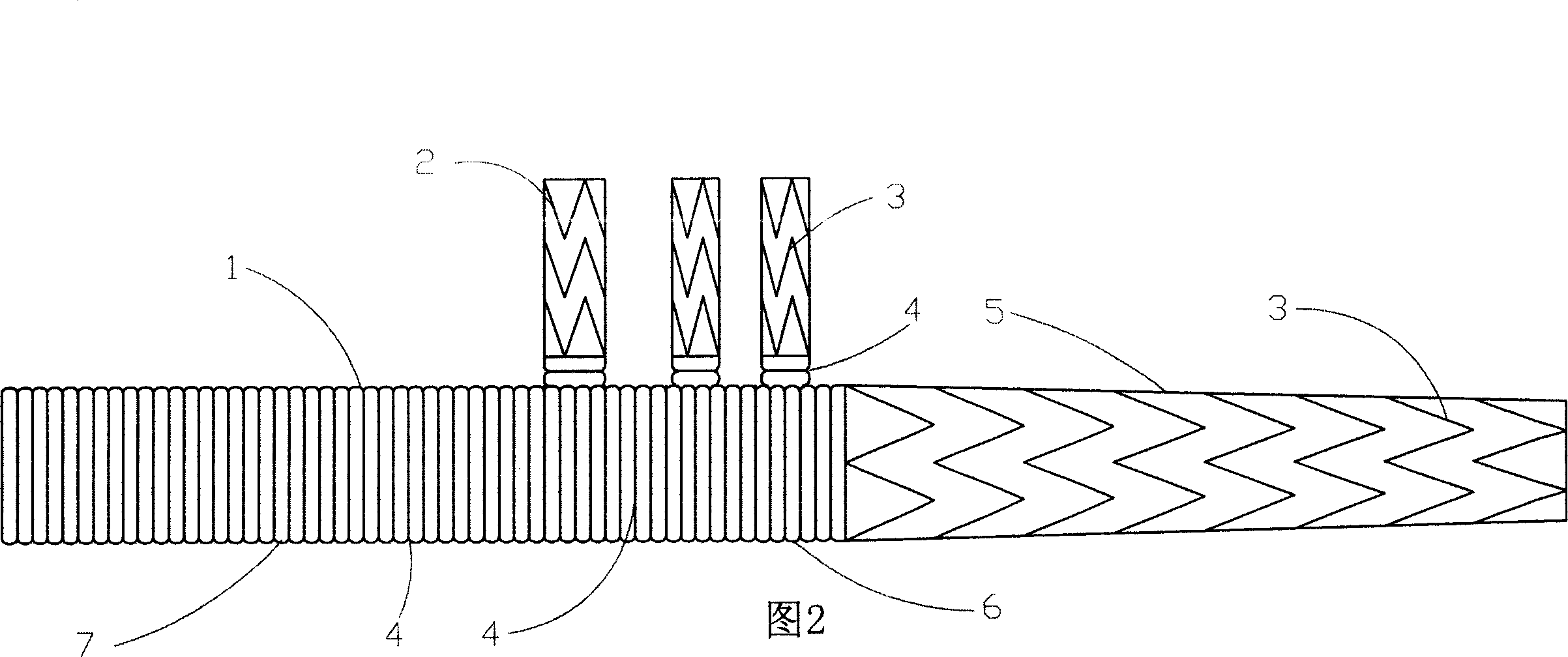
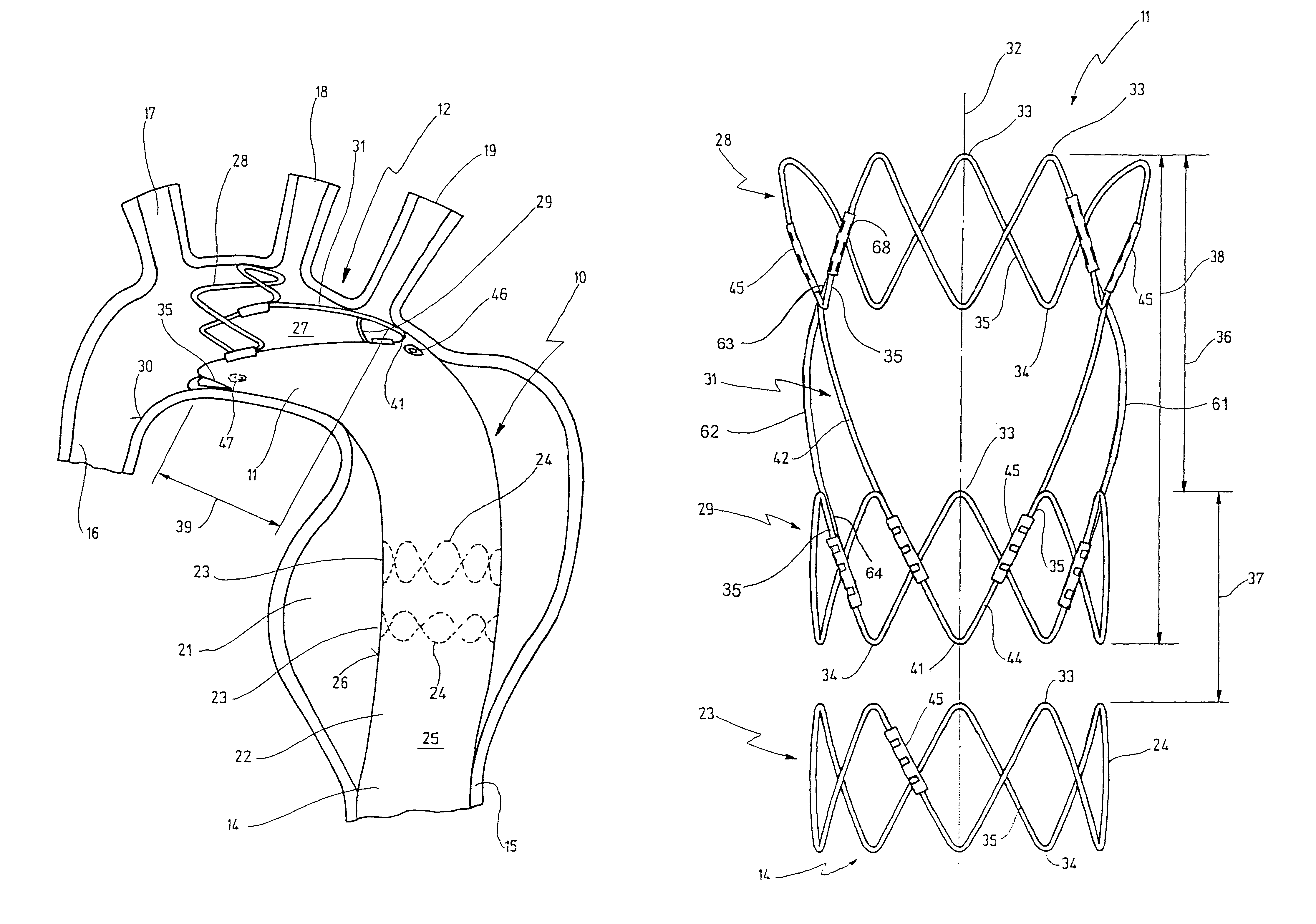
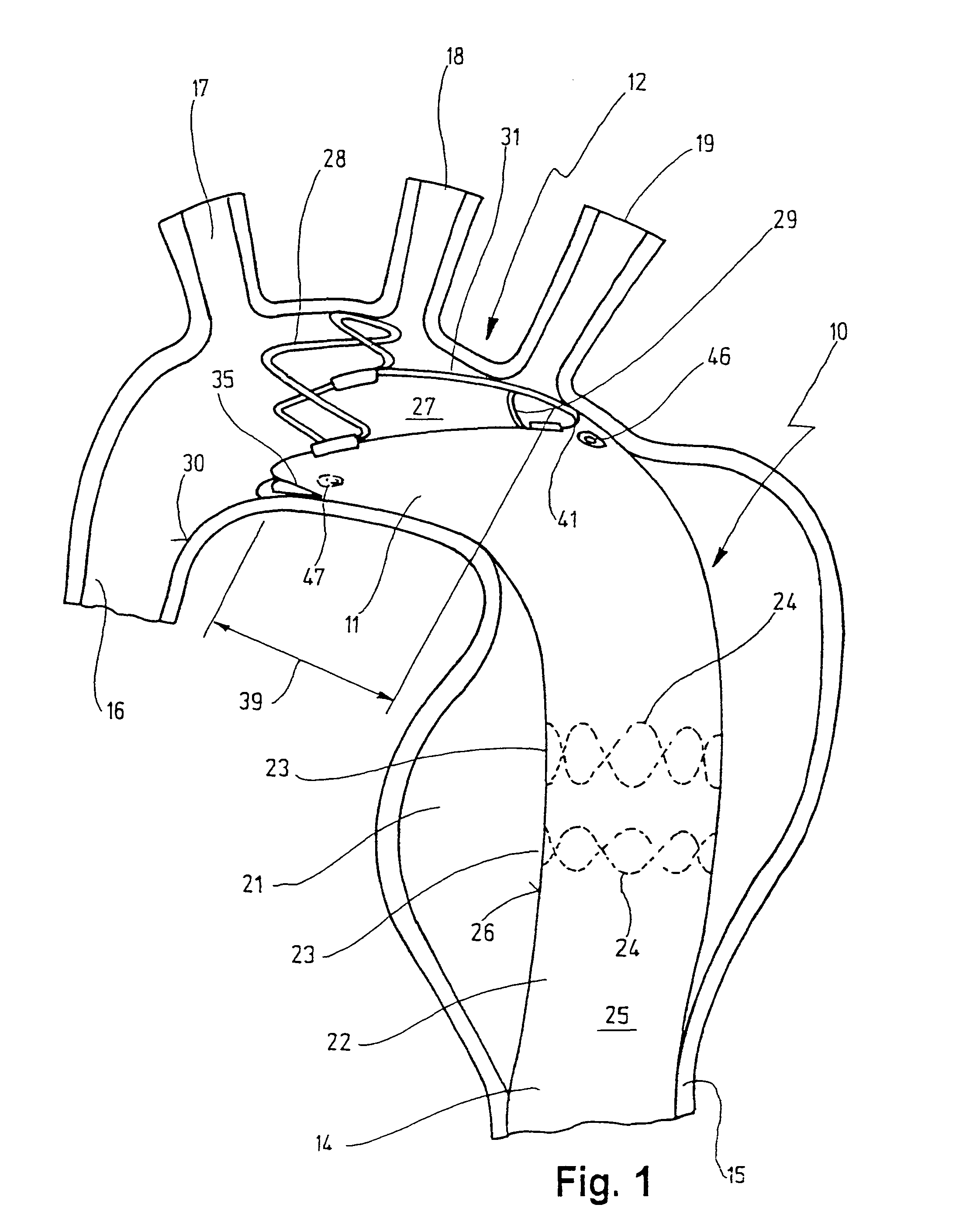
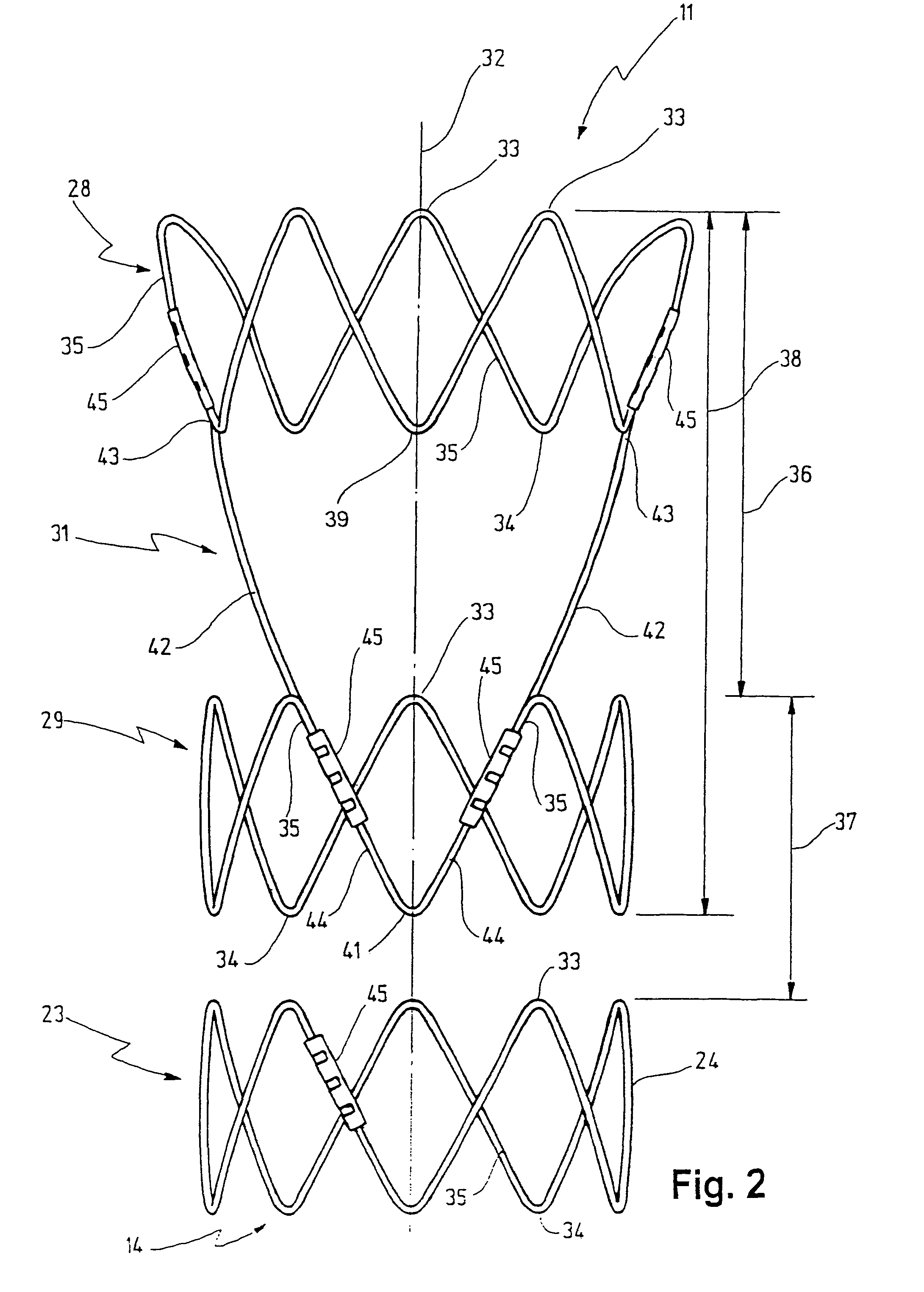
Stent for implantation in a blood vessel, especially in the region of the aortic arch
ActiveUS20060195177A1Easy to produceRapid and inexpensive but reliable productionStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentProsthesis
A stent for implantation in a blood vessel is disclosed, especially in the region of the aortic arch. The stent is comprising rings which are disposed successively in the stent's longitudinal direction and which are made up of meandering circumferential supports. The stent further comprises a prosthesis material which is fixed to the rings and which connects them, thereby forming a hollow cylindrical body with a jacket which is substantially closed on the circumference thereof. At least one connecting support is provided between the last ring and the penultimate ring at the proximal end of the stent and connects these two rings to one another.
Owner:JOTEC
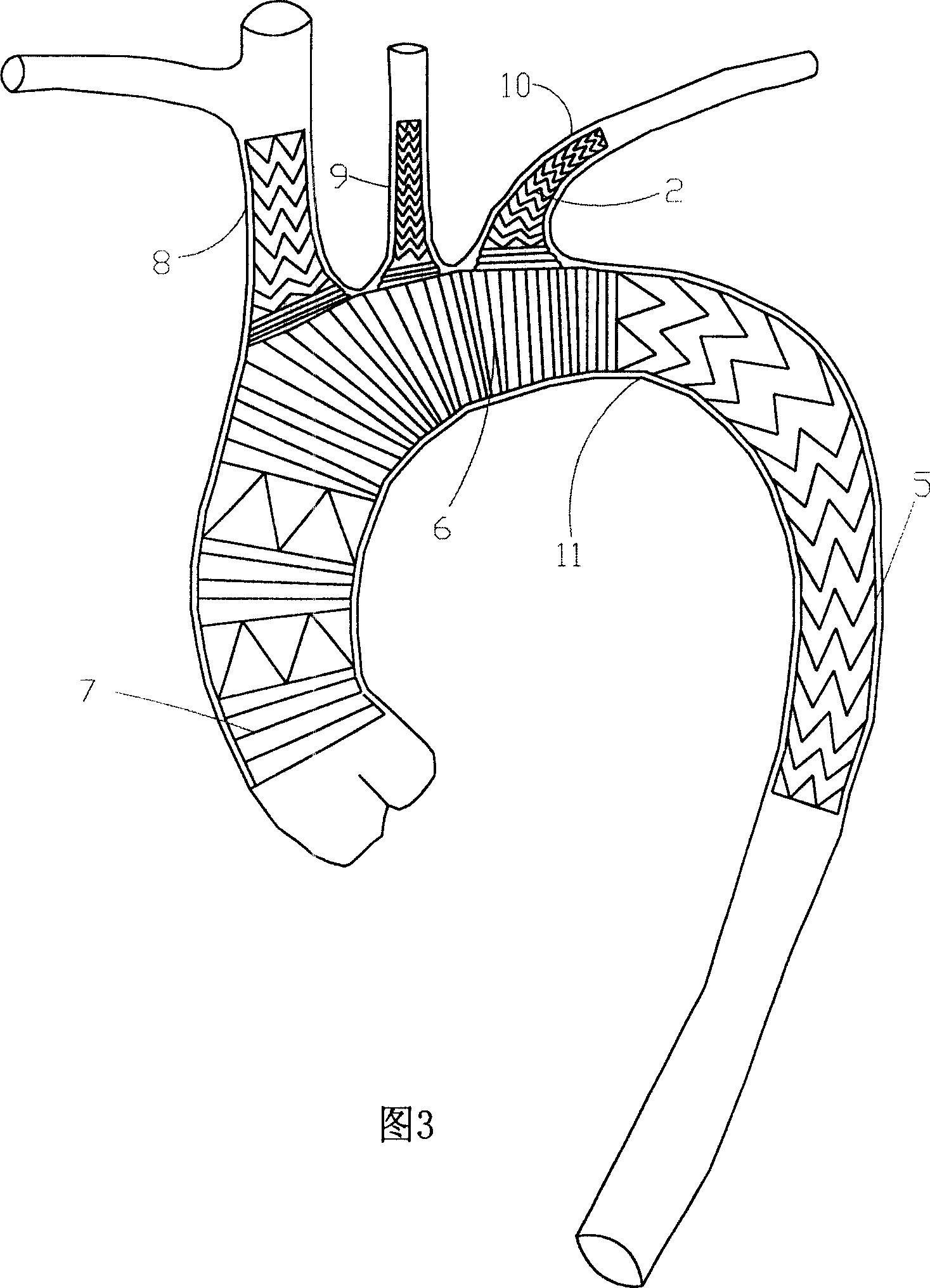
Three-collateral bracket vascellum for arcus aortae
InactiveCN101152109AReduce the incidence of injuryReduce the chance of bleedingStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryBlood vessel
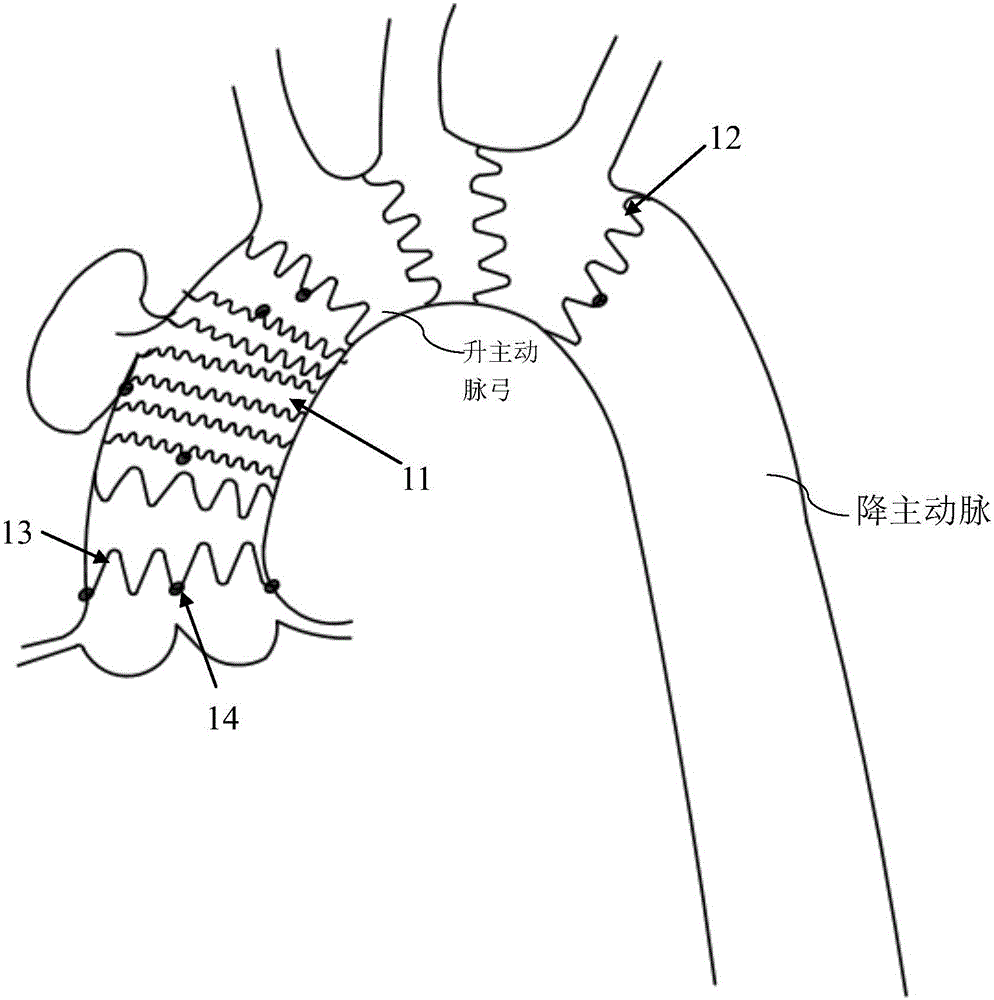
The present invention relates to aortic arch three collateral support blood vessels comprising an aorta support vascular that comprises an aorta ascenden section, an aortic arch section and an aorta section; the aorta support vascular also comprises three collateral artery support vasculars which are fixed respectively on an aortic arch section arc surface of the aorta support vascular and are formed into an five-way type. The three collateral artery support vasculars are corresponding respectively to an arteria anonyma, a left common carotid artery and a left subclavian artery. The invention is capable of greatly simplifying an operation process and greatly shortens the time of a deep hypothermia and a circulation arrest, which is characterized by not only omitting an inosculation between an artificial vascular graft and three branches of the aortic arch but also reducing bleeding rate and operation risk. In an operation, the invention changes an operation method from a partial blood vessel replacement plus partial endovascular repair to a complete endovascular repair.
Owner:黄方炯
Method and system for selective or isolated integrate cerebral perfusion and cooling
InactiveUS20010038807A1Reduce riskImproving cerebral perfuisionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesOxygenPerfusion
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of cardiac arrest or from other causes are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood may also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE & PATTERSON RUSSEL +1
Efficient and environment-friendly remains preservative and application thereof
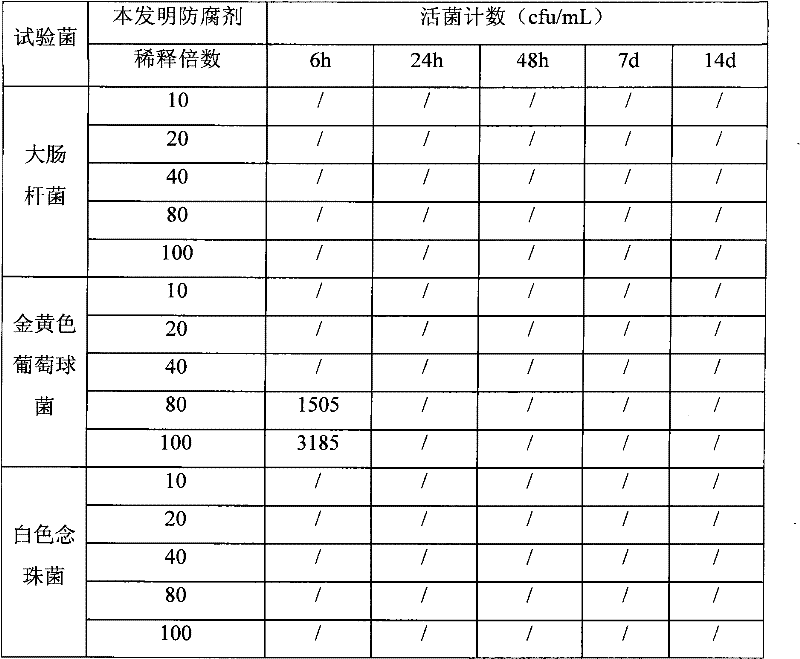
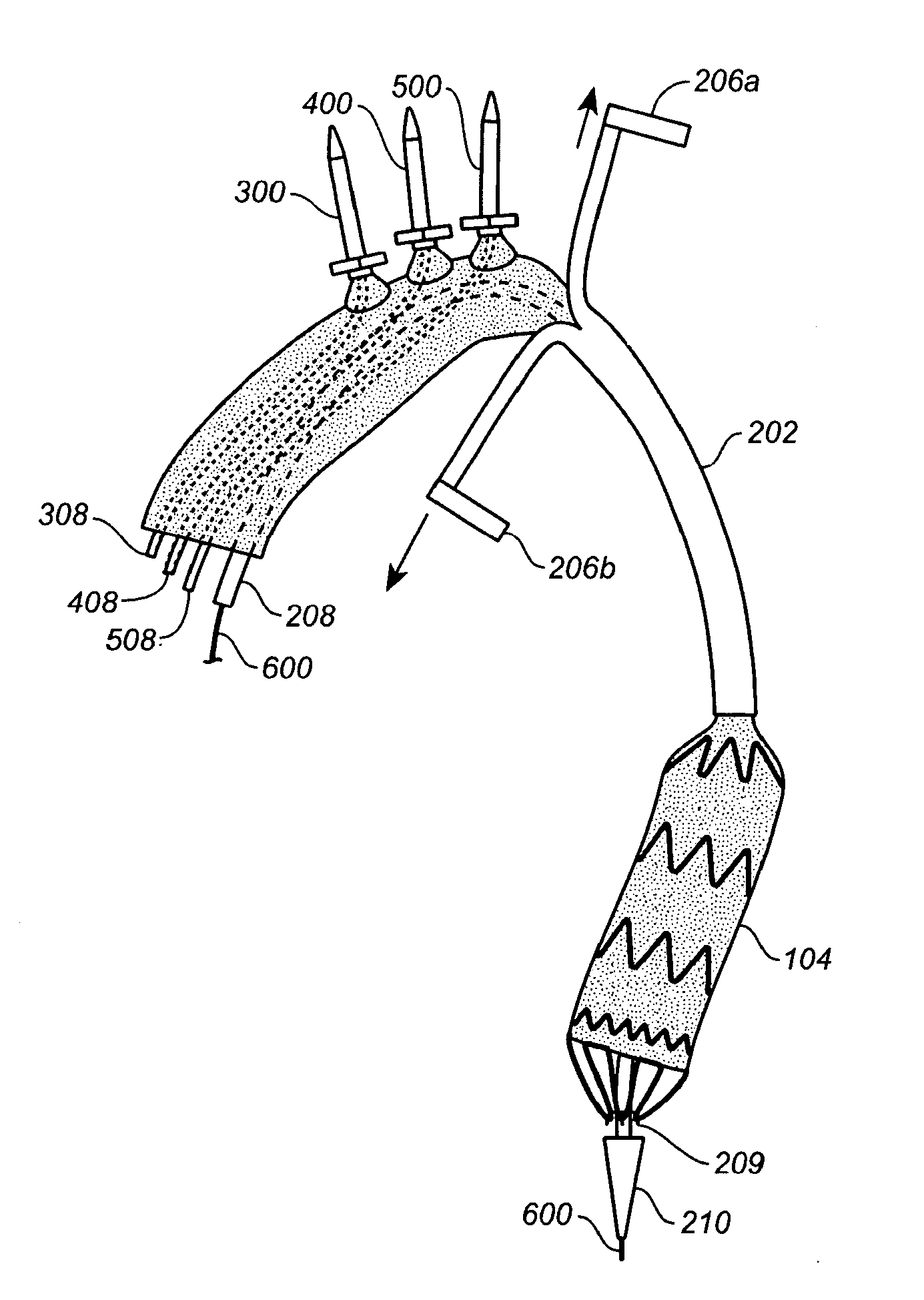
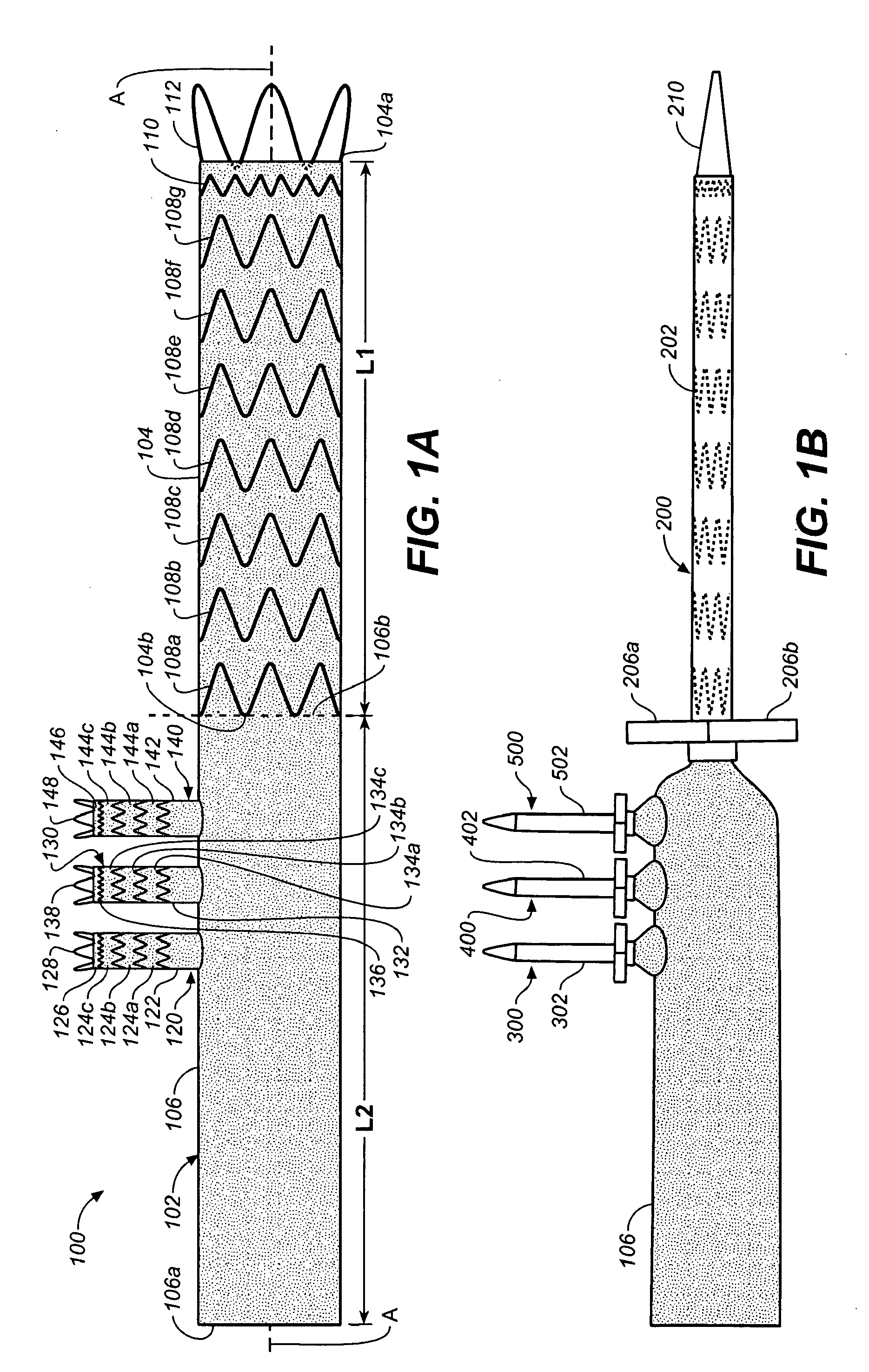
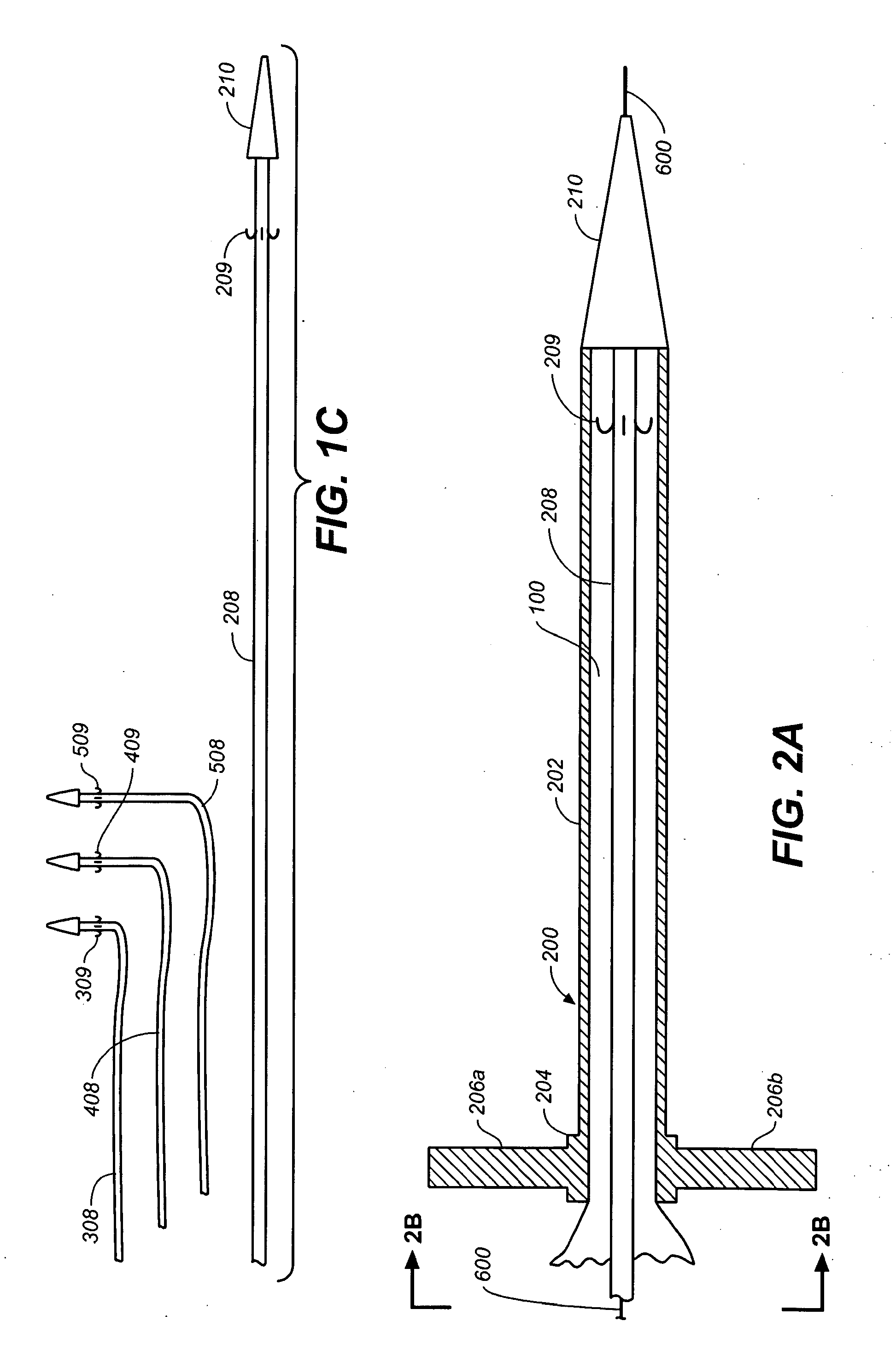
The invention relates to an efficient and environment-friendly remains preservative free of formaldehyde and application thereof. The remains preservative mainly comprises, by volume, 0.5-10% of phenoxyethanol, 0.2-1.5% of isothiazolinone, 3-15% of organic acid, 5-20% of propylene glycol, 5-30% of glycerol, 20-75% of ethanol and 5-35% of distilled water, and, by weight, 1-10% of hexamethylenetetramine and 0-2% of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt. The preservative can be poured through an aorta and an aortic arch and injected through the abdominal cavity, the thoracic cavity, the pharyngeal cavity and the cranial cavity so as to carry out antiseptic preservation, disinfection and smell removal to remains. Quantification sterilization experiments, animal experiments and funeral home field experiments prove that the remains preservative is efficient in antibacterial property, quick in action speed, low in toxicity and suitable for short-term or long-term remains antisepsis or specimen preservation of funeral homes and medical colleges at home and abroad.
Owner:民政部一零一研究所
Prosthesis for antegrade deployment
An endoluminal tubular prosthesis for use in an open surgical repair comprises a tubular graft having a longitudinal axis, a first tubular section having a plurality of self-expanding stents and extending along the longitudinal axis and a second stent-less tubular section extending from the first tubular section and along the longitudinal axis. The tubular prosthesis can include a plurality of tubular branching members branching therefrom for treating branched arteries without obstructing them, such as the branches from the aortic arch.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Adjustable human body aorta vessel model device
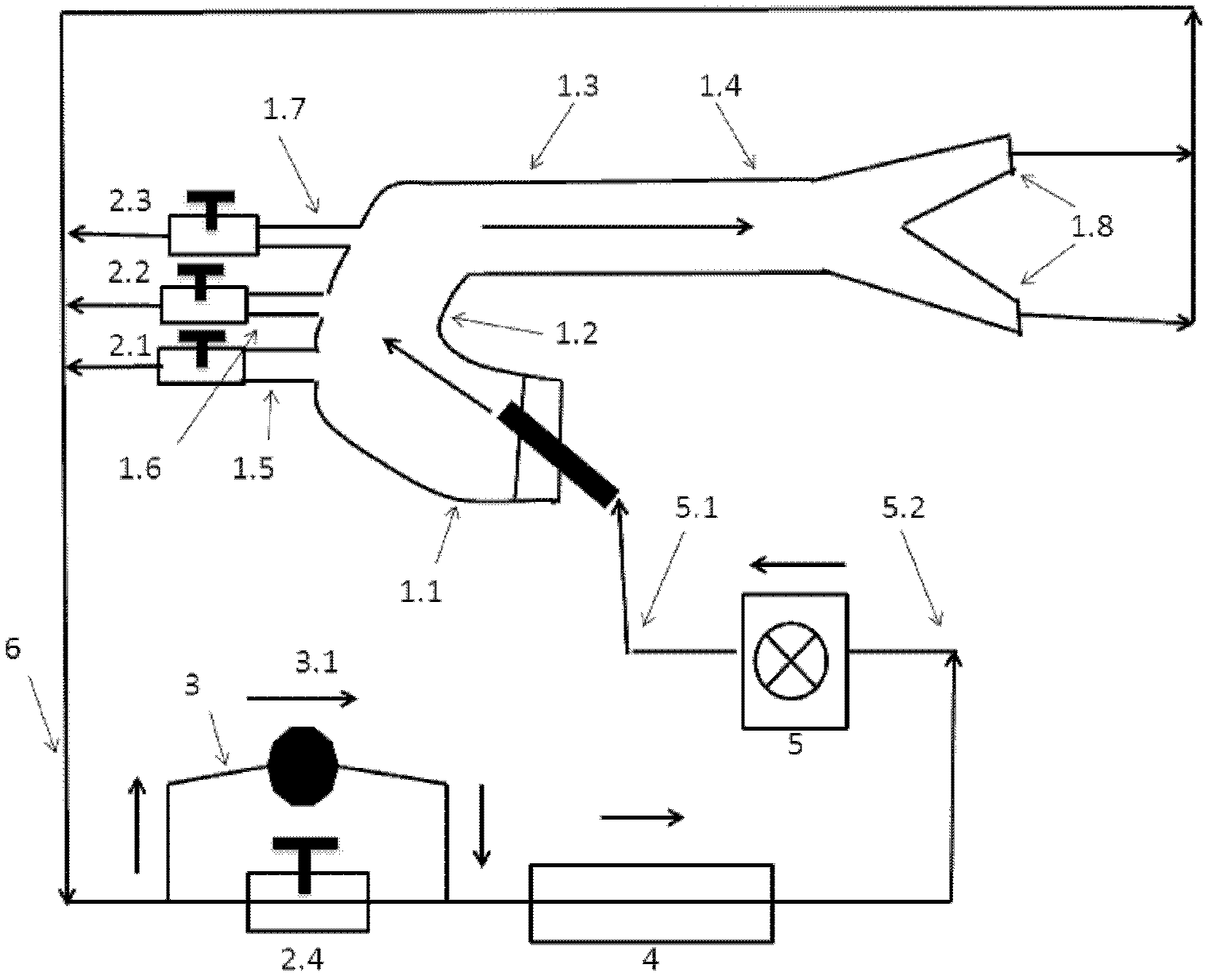
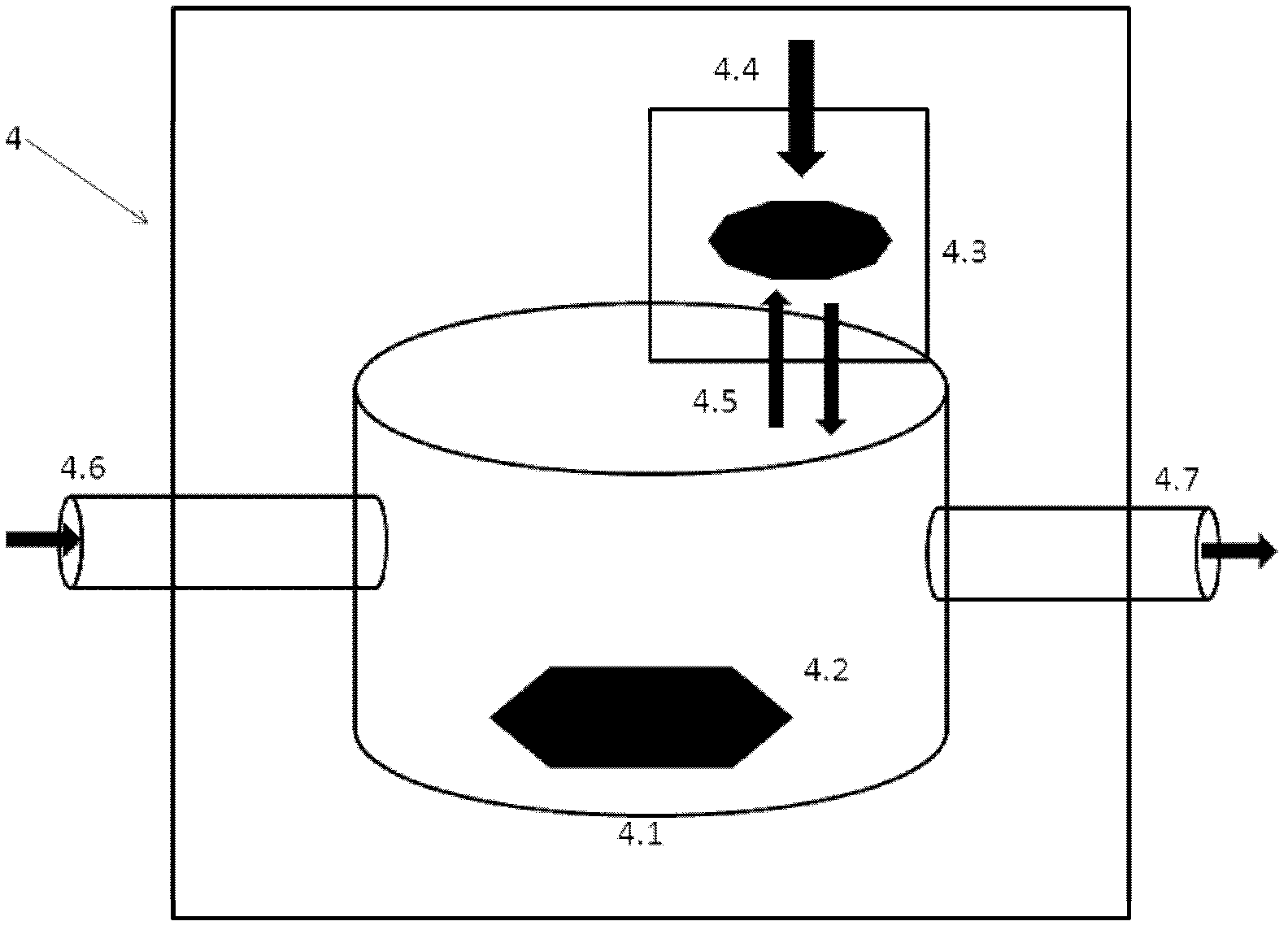
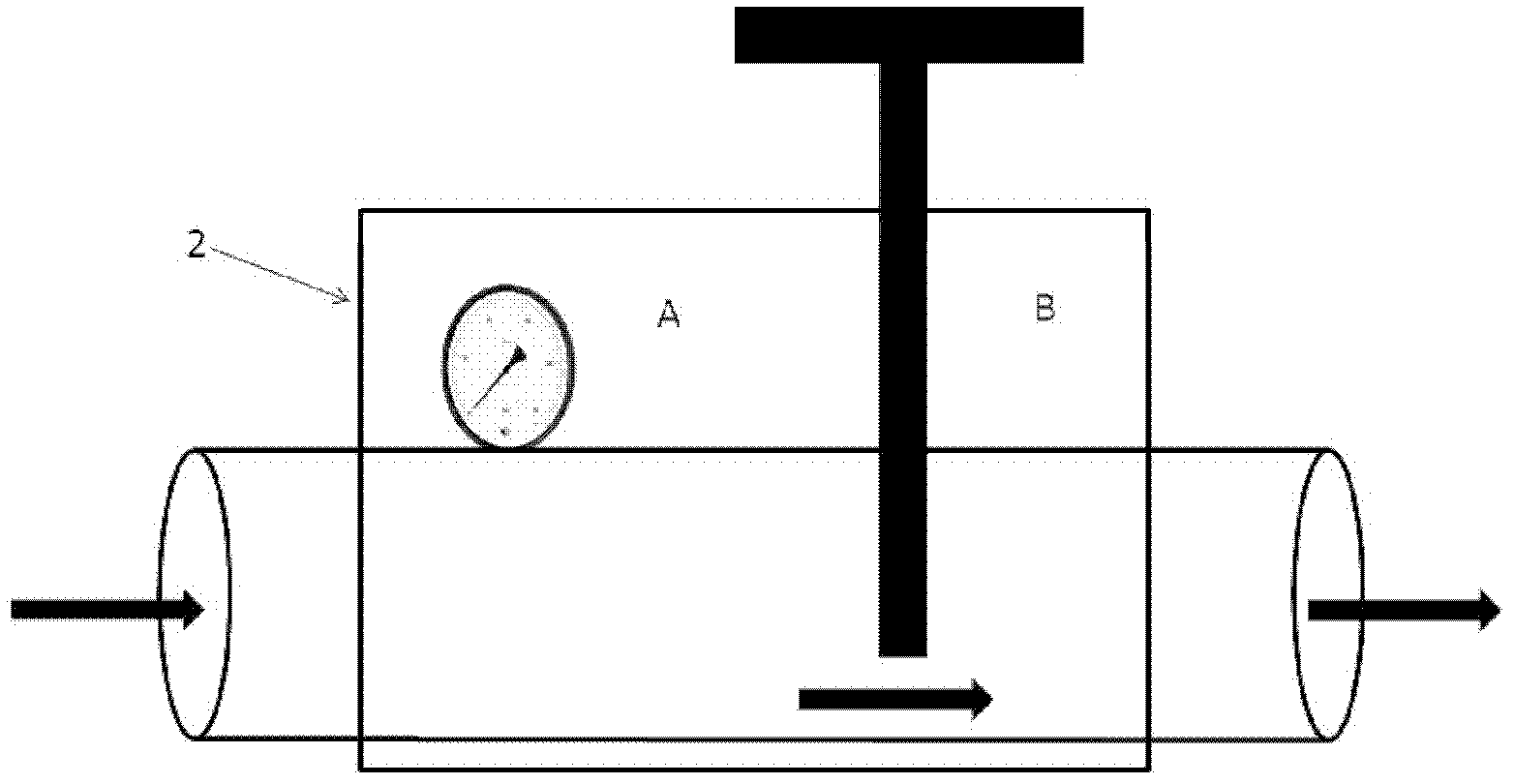
The invention relates to an adjustable human body aorta vessel model device. A aorta primary loop, three branch brachiocephalic trunk arteries of aortic arches, left common carotid artery and left subclavian artery are respectively provided with a pressure regulator (with built-in pressure gauge and regulating valve) which can regulate the loop pressure by regulating the vessel diameter size; an adjustable liquid heater and a pressure gate control channel are arranged in a liquid storage pool and can control the liquid in the pool to exchange with the outside according to the pressure magnitude; the aorta primary loop is connected with a vessel bypass in parallel; and the vessel bypass is provided with a pressure gate control channel which can automatically regulating the internal pressure in the whole vessel model. The invention can respectively regulate the pressure, temperature and circulation volume in the aorta loop to simulate the blood circulation and dynamic blood variations of human aorta under physiologic or pathological conditions in the aorta model in a more realistic way, thereby laying the foundation for clinical and scientific research related studies.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Artificial four-branch blood vessel stented elephant trunk and fixing device thereof
InactiveCN102048596AEasy to operate againImprove blockageStentsBlood vesselsHuman bodyVascular anastomosis
The invention discloses an artificial four-branch elephant trunk blood vessel with a stent and components thereof. A main body blood vessel is divided into two parts. The first part is as follows: a flexural artificial blood vessel is designed according to the anatomical characteristics of an aortic arch of a human body, three branch blood vessels are divergent from the middle part on the side of a big bend, and one branch blood vessel is divergent from the side which is near to a small bend. The second part is as follows: a section of artificial blood vessel with a stent is designed, and artificial blood vessels without stents are respectively arranged on two sides of the stent for facilitating secondary operation. An outer sheath, an inner core and a cutting knife are additionally arranged for conveying and releasing the second part of the main body blood vessel. A fixing clamp is adopted for tightening a fixing ring for performing vascular anastomosis at the distal end of the aortic arch. The device is used for the operation of adding a stented elephant trunk and replacing an aortic arch, thus the number of anastomotic stomas can be reduced, the difficulty of the operation is reduced, and convenience is provided for the secondary operation.
Owner:于存涛 +4
Stent for implantation in a blood vessel, especially in the region of the aortic arch
ActiveUS8668729B2Easy to produceRapid and inexpensive but reliable productionStentsBlood vesselsInsertion stentProsthesis
A stent for implantation in a blood vessel is disclosed, especially in the region of the aortic arch. The stent is comprising rings which are disposed successively in the stent's longitudinal direction and which are made up of meandering circumferential supports. The stent further comprises a prosthesis material which is fixed to the rings and which connects them, thereby forming a hollow cylindrical body with a jacket which is substantially closed on the circumference thereof. At least one connecting support is provided between the last ring and the penultimate ring at the proximal end of the stent and connects these two rings to one another.
Owner:JOTEC
Methods and apparatus for monitoring heart impulses
Methods and apparatus for monitoring the heart motion of a subject employ a probe which can be coupled to a portion of the anatomy of the subject. The probe may couple to the subject's aortic arch or thyroid cartilage, for example. The probe is biased into contact with the subject. The probe detects movements caused by the heart motion. The apparatus may display accelerations and displacements caused by the heart motion. Waveforms from multiple anatomic sites may be acquired, normalized in time and amplitude, and combined to produce resultant waveforms. Combining the waveforms may involve addition or subtraction.
Owner:CANFORM MEDICAL
Methods of and apparatus for monitoring heart motions
InactiveUS20070043300A1Less of noise levelReduce quality control costsElectrocardiographyStethoscopeAudio power amplifierMedicine
A method of and an apparatus for monitoring the heart motion of a subject employ a probe which can be coupled to the aortic arch or to the thyroid cartilage of the subject for detecting movements caused by the heart motion and displaying the accelerations and displacement of the heart motion on an acceleration display and a displacement display. A mechanical motion amplifier amplifies the acceleration and an optical amplifier amplifies the displacement to counteract noise.
Owner:CANFORM MEDICAL
Lattice open-window type aortic stent assembly for transplantation operation
The invention relates to a lattice open-window type aortic stent assembly for a transplantation operation. An elastic support is arranged in a main support, and a wrapping layer is arranged on the exterior of the main support; a lattice open-window plate is in an arc shape, a transverse opening fits the wrapping layer of the main support, and open-window lattice holes are formed in the lattice open-window plate; a laser pen extends into the open-window lattice holes fitting the wrapping layer and scalds the wrapping layer to form an open-window lattice; a guiding wire extends into one hole ofthe open-window lattice; one end of an inflation balloon is a balloon body, the other end of the inflation balloon is an inflation joint, the balloon body and the inflation joint are connected througha catheter, and the inflation joint conducts inflation and deflation on the balloon body through an air pump to expand the hole, where the guiding wire is located, of the open-window lattice; a branch support extends into the hole, expanded by the balloon body, of the open-window lattice. Alignment of a branch artery on the aortic arch can be easily and accurately achieved, blood supply of a branch on the aortic arch cannot be influenced, ischemia cannot be caused, and I-type internal hemorrhage cannot be caused when the assembly is released from the holes of the open-window lattice.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL
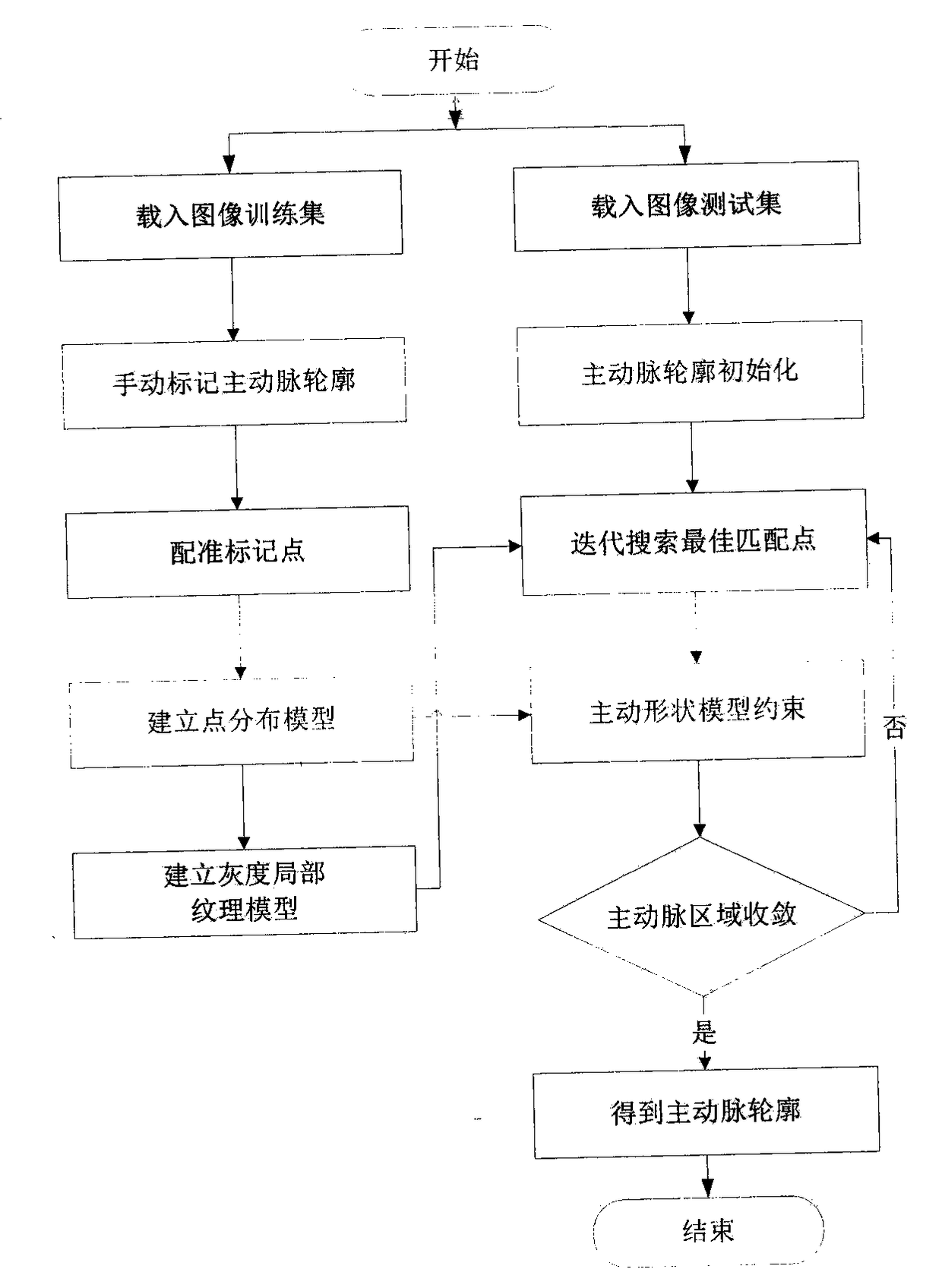
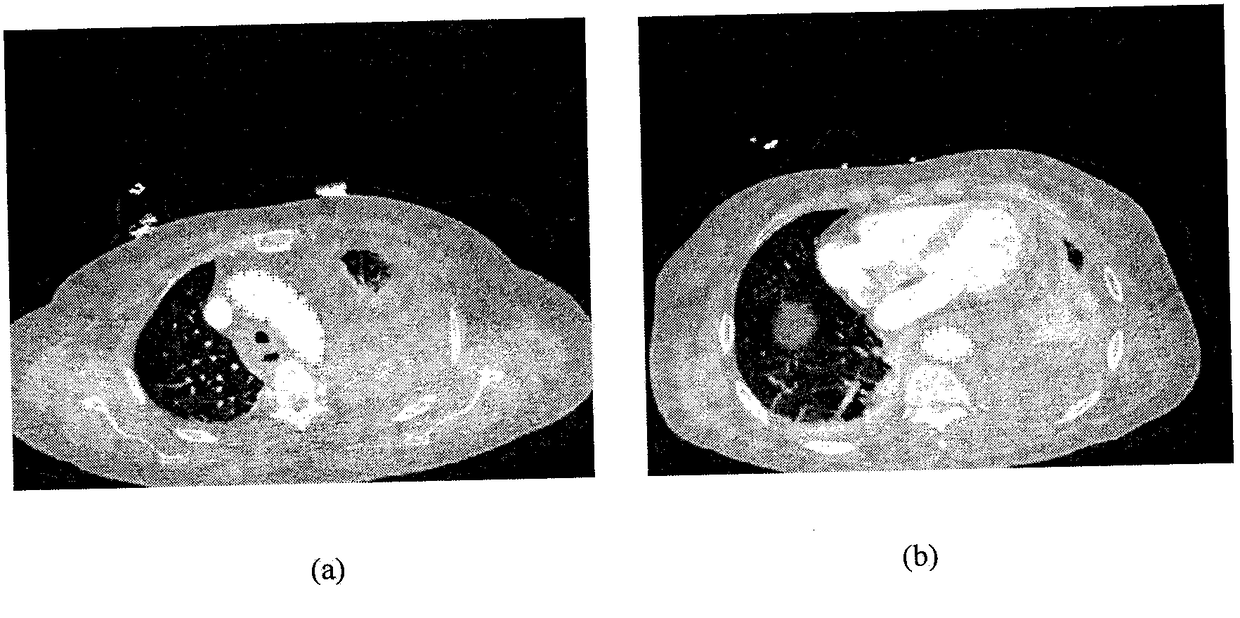
An aortic contour segmentation algorithm based on active shape model
InactiveCN109003283AImprove robustnessAvoid interferenceImage enhancementImage analysisContour segmentationEuclidean vector
The invention discloses an aortic contour segmentation algorithm based on an active shape model, which mainly overcomes the blurring or discontinuity of the aortic edge caused by the traditional method through the shape constraint, avoids the interference of other tissues, and realizes the accurate segmentation of the aortic arch part and the descending aorta part contour. The realization processis as follows: (1) marking feature points of a training set sample and performing normalizing and registration treatment on the shape vectors to establish a point distribution model; (2) sampling thegray level along the normal direction of the contour boundary of the training sample set to construct the gray level texture model of the training set; (3) searching for the best matching point of each marker point iteratively, and then uniformly performing constraining by the active shape model until the aortic contour converges.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Aortic arch filtration system for carotid artery protection
Owner:LUMEN BIOMEDICAL
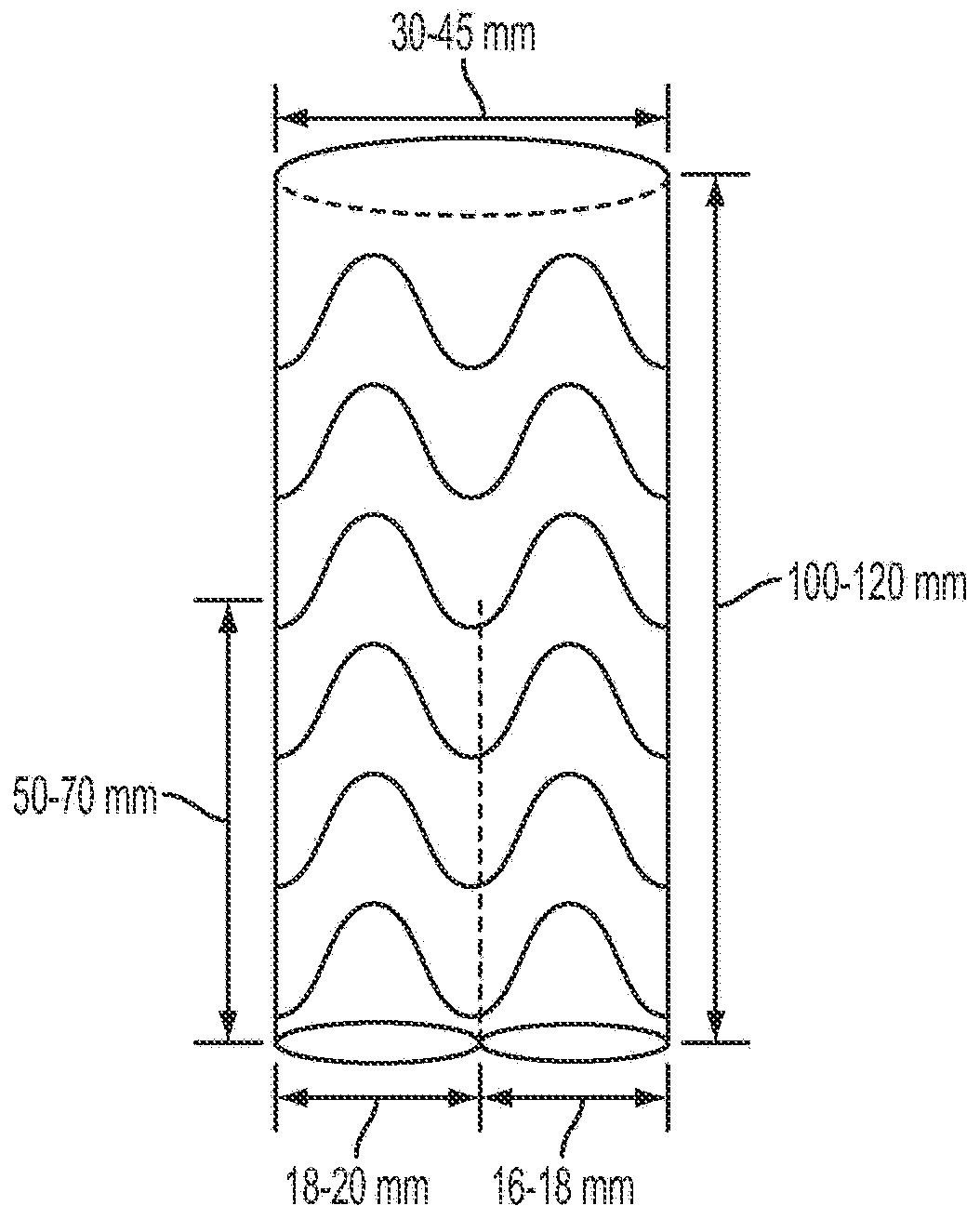
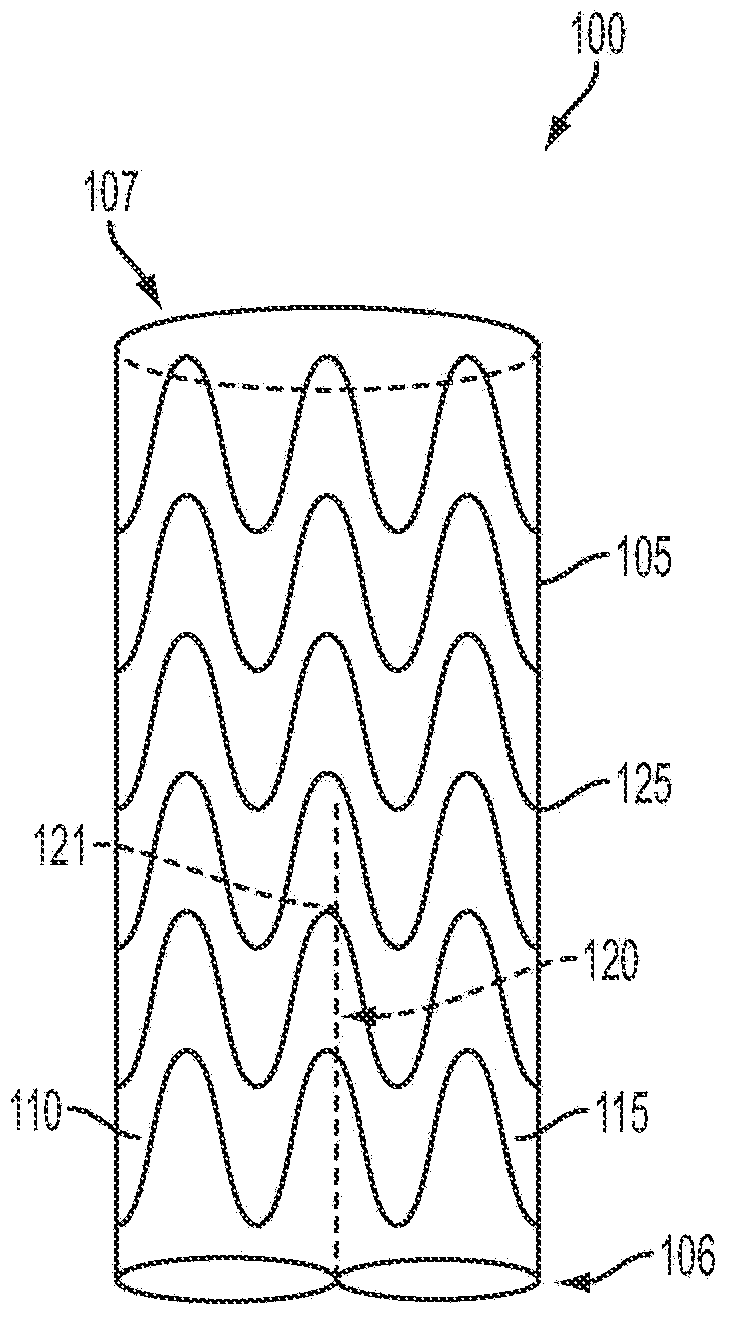
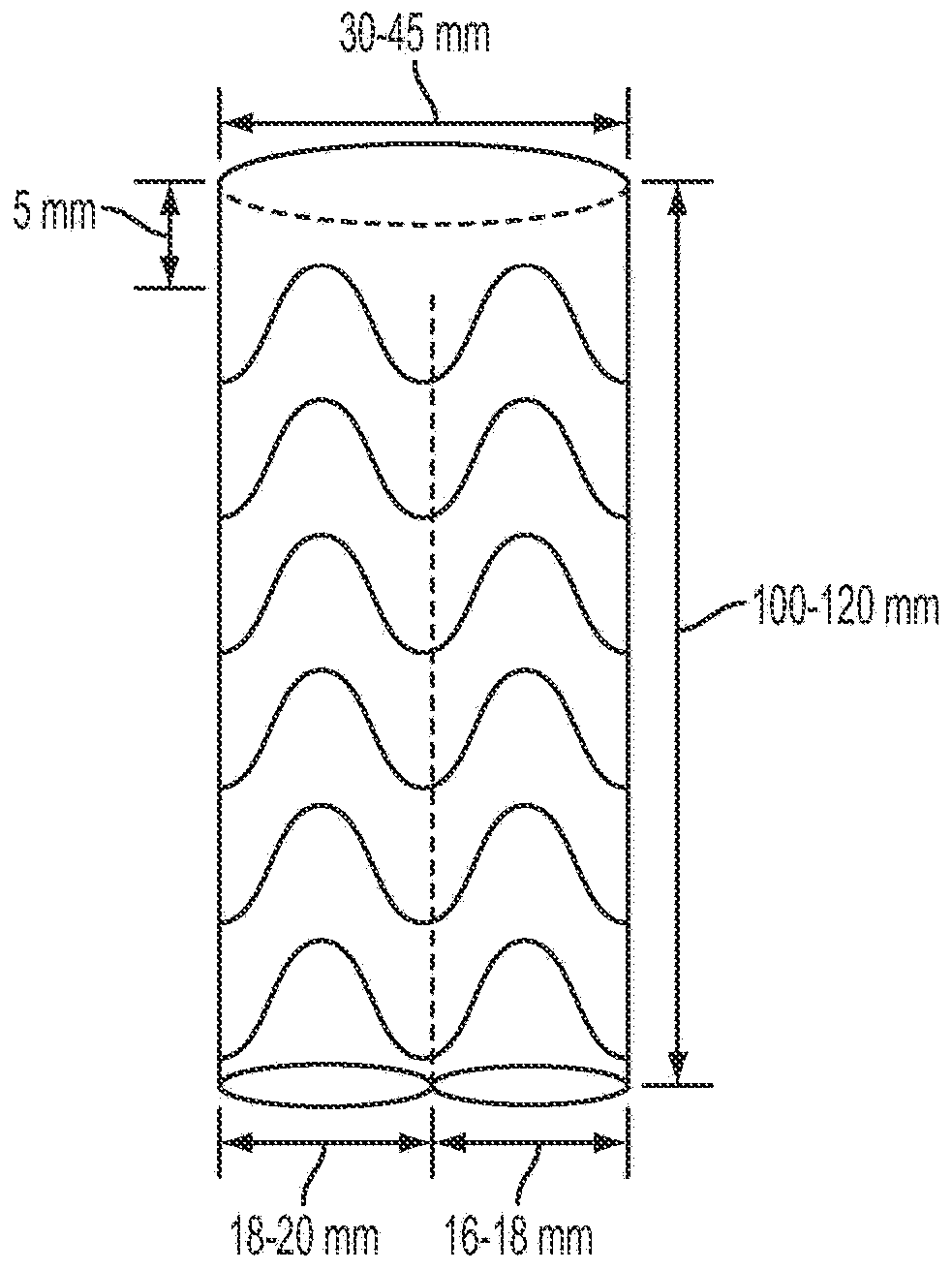
Aortic arch double-barreled main body stent graft and methods for use
A visceral double-barreled main body stent graft and methods for its use, the stent graft comprises, a main body stent graft having distal and proximal ends, the main body stent graft's length ranges from about 100-120 mm and diameter at the proximal end ranges from about 30-45 mm, first and second lumens defined at the main body stent graft's distal end, the first lumen's diameter ranges from about 18-20 mm, the second lumen's diameter ranges from about 16-18 mm, the first and second lumens have about the same length from about 50-70 mm, the first lumen is secured to the second lumen along a shared length, and the main body stent graft defines a tubular wall that is contiguous with the first and second lumens such that any fluid entering the main body must exit through one of the first or second lumens.
Owner:2031 EAST 60TH STREET NORTH SIOUX FALLS 57104 SD
Ascending aorta stent anchored by innominate artery for dissection, and delivery system
ActiveCN109172043ASecurity anchoring methodNo entry into the false cavityStentsBlood vesselsAortic dissectionThird aortic arch
The invention provides an ascending aorta repair stent anchored by innominate artery, comprising an ascending aorta stent segment and an innominate artery stent segment, wherein an innominate artery portion of the stent is first released and a body portion is then released; the distal end opening of the body portion facing the distal end of the aortic arch lumen, and the body portion of the stentcovers the dissection at the primary rupture of the ascending aorta. When the release is completed, the main body terminates above the junction of the sinus canal. The longitudinal beam structure is made of a temperature-dependent shape memory metal material extending to the great curvature side of the aortic arch of the innominate artery and to the minor curvature side of the aortic arch, and isreleased so as to satisfy the individualized ascending aortic anatomical arc of different patients to abut against the aortic wall. The stent is anchored only according to the special anatomical shapeof the ascending aorta and the innominate artery and the memory metal longitudinal beam structure. Used in patients with type A aortic dissection in the acute phase of surgical contraindication whenwaiting for the transitional phase of surgery for patients with high surgical risk of acute type A aortic dissection to provide follow-up surgical treatment opportunities.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
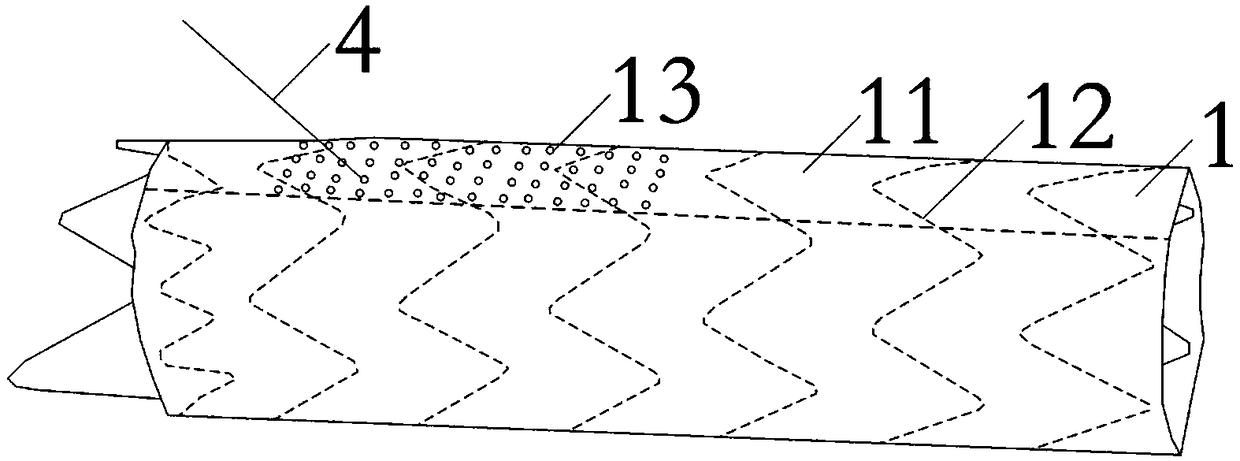
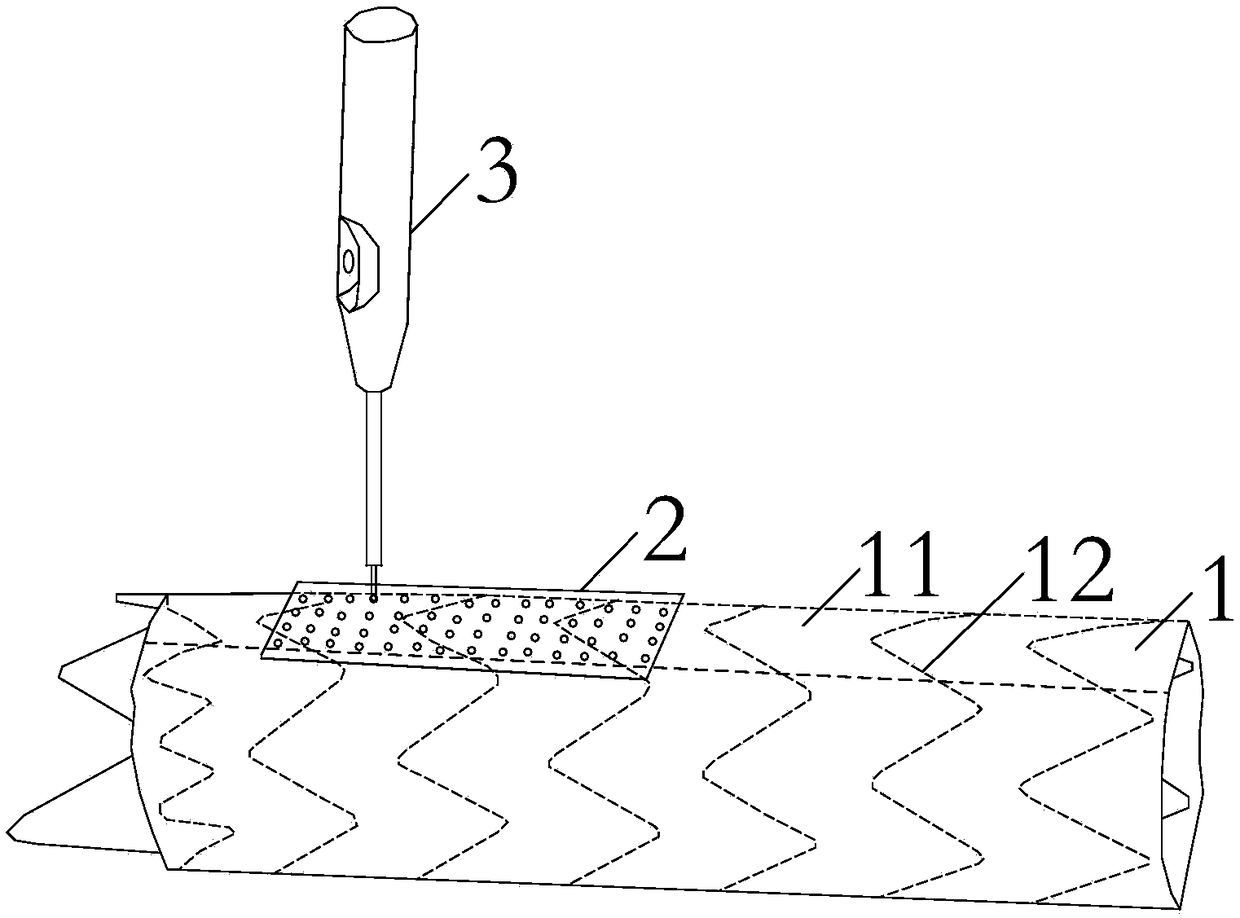
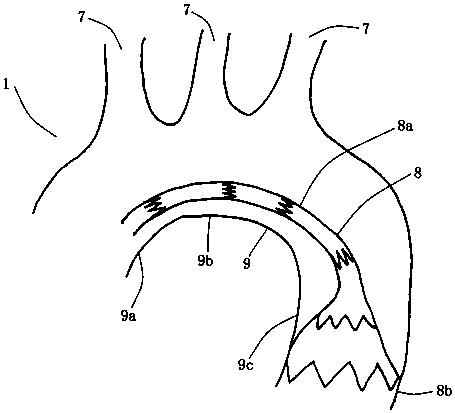
Aortic arch and branch covered stent blood vessel combined device for open operation
ActiveCN110613531AEasy to operateReduce extracorporeal circulation timeStentsBlood vesselsAortic archesCovered stent
The invention discloses an aortic arch and branch covered stent blood vessel combined device for open operation. The device comprises two artificial blood vessel assemblies: (1) an arc-shaped artificial aortic blood vessel (1) and (2) a small covered stent blood vessel (8), wherein the arc-shaped artificial aortic blood vessel (1) comprises a main blood vessel (9) and three branch blood vessels (7) on the main blood vessel (9), the main blood vessel (9) is provided with a stent (8), and a near end part (8a) of the stent (8) is a bare stent capable of being released later. By use of the blood vessel assembly, aortic arch and three branch blood vessels can be reconstructed rapidly in a total-arch replacement operation for aortic arch lesion, normal blood vessel form can be reserved to the greatest extent, the blood vessel assembly is applicable to various common blood vessels with deformed branches, has wide application range, can avoid stent customization, can be produced massively, andcan effectively reduce operation trauma and significantly simplify operation.
Owner:黄健兵
Isolating transplanting devicein aorta ascendens cavity
The invention provides an isolating transplanting device in the aorta ascendens cavity. The device is arranged in the aorta ascendens inner membrane cavity which has dissection of aorta to adjust the blood flow of the cracking holes of the dissection layer. The isolating transplanting devicein aorta ascendens cavity is a metal tubulous naked support rack, has a resetting adjustment part which is arranged in the inner membrane cavity of the dissection layer, and comprises multiple first Z-shape support rack rings which are parallelly and mutually connected through 2-5 first elastic metal rods. A anchor fixing part is arranged in an far end aortic arch cavity and upper end cavity of an aorta descendens which is communicated with the aortic arch cavity, and is connected with the far end of the resetting adjustment part through a second elastic metal rod. Multiple second Z-shape support rack rings are parallelly and mutually connected through 2-3 second elastic metal rods, wherein the wave number of each first Z-shape support rack ring is 10-24, the wave height is 2mm-10mm. The wave number of the of each second Z-shape support rack ring is 6-8, the wave height is 5mm-20mm. The gap between two adjacent first Z-shape support rack rings is -8mm-3mm. The gap between two adjacent Z-shape support rack rings is 1mm-20mm.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Covered stent
ActiveCN109966015AAvoid loweringImprove securityStentsBlood vesselsAbnormal tissue growthInsertion stent
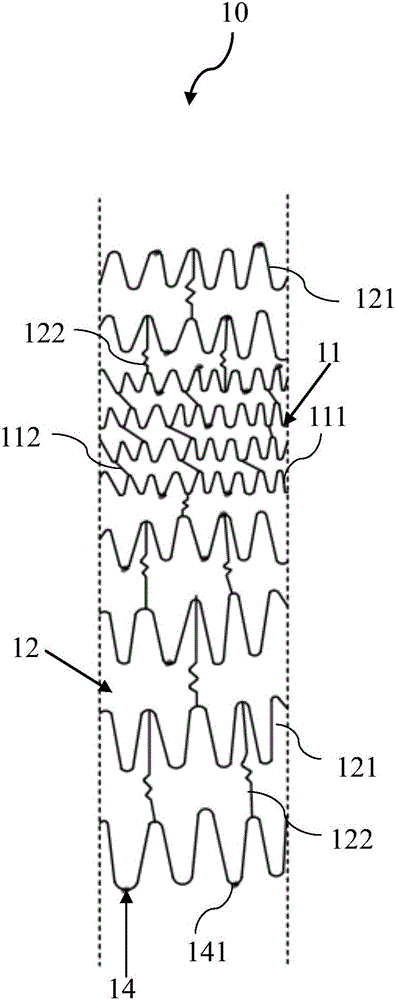
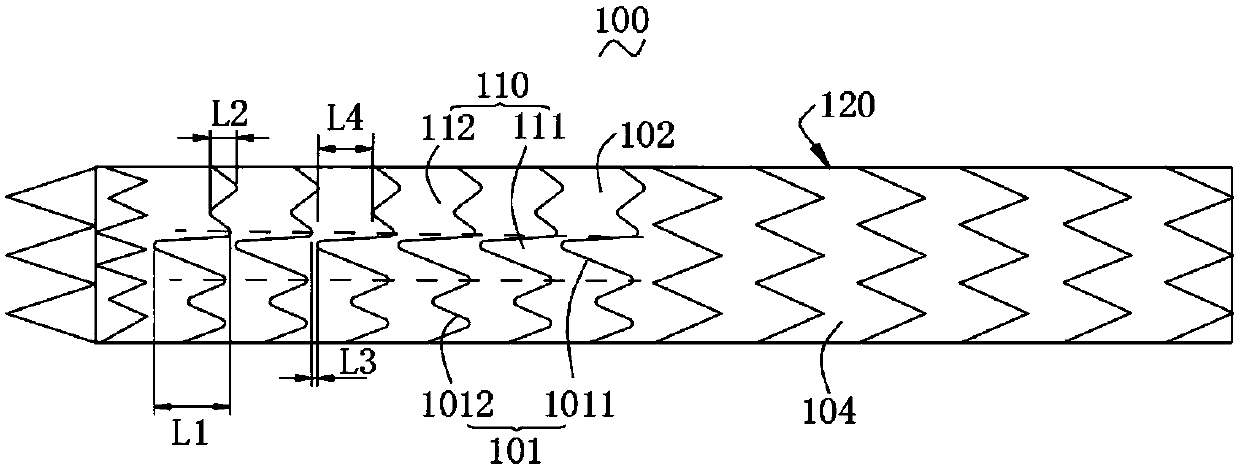
The invention relates to a covered stent. The covered stent comprises a first main body section distributed in the axial direction and a second main body section connected with the first main body section, wherein the axial shrinkage rate of the first main body section is 10%-40%, and the axial shrinkage rate of the second main body section is zero. During use of the covered stent, the first mainbody section is placed in a bent section of an aortic arch, the second main body section is placed in a straight section of the aortic arch, as the first main body section can shrink axially, that is,the first main body section has certain flexibility in the axial direction, the first main body section cannot produce straightening force when following the bending form of the aortic arch, and theoperation safety can be improved; and the second main body section cannot shrink axially, shrinkage of the second main body section under the blood flow action can be avoided, and the condition that the end of the second main body section shrinks to a tumor cavity to endanger life of a patient is avoided.
Owner:LIFETECH SCIENTIFIC (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Blood vessel prosthesis stent for Stanford type A aortic dissection
InactiveCN106308975AReduce the number of vascular anastomosisImprove the effect of surgical treatmentStentsBlood vesselsVascular anastomosisCirculatory arrest time
The invention discloses a blood vessel prosthesis stent for Stanford type A aortic dissection. The blood vessel prosthesis stent comprises a main stent body, wherein a single branch or two branches is or are fixed at a proximal end of the main stent body. With the adoption of the blood vessel prosthesis stent, the amount of vascular anastomosis of a patient with Stanford type A aortic dissection affecting the aortic arch part can be effectively reduced, the surgical procedures are simplified, the risk of hemorrhage is reduced, deep hypothermic circulatory arrest and low-flow cerebral protection time in the period of cardiovascular arrest are shortened, so that the surgical treatment effect of the patient with the Stanford type A aortic dissection is improved, and the blood vessel prosthesis stent can be popularized in primary hospitals.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
A covered stent
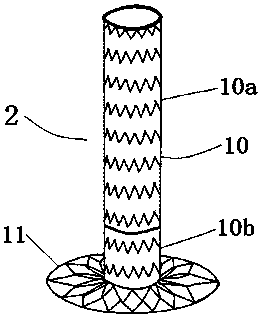
The invention belongs to the field of vascular stents, in particular to a covered stent. The covered stent comprises a frame body; a membrane disposed on the frame body to form a tubular structure. The tubular structure is in a bent state before implantation. One of the membrane and the frame body is in a bent state before implantation, and the other is in a straight state before implantation. The covered stent of the invention is simple in implantation and can be matched with a curved aortic arch.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com