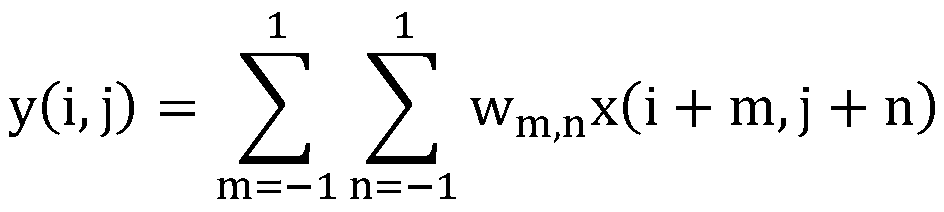Patents
Literature
53 results about "Heart motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
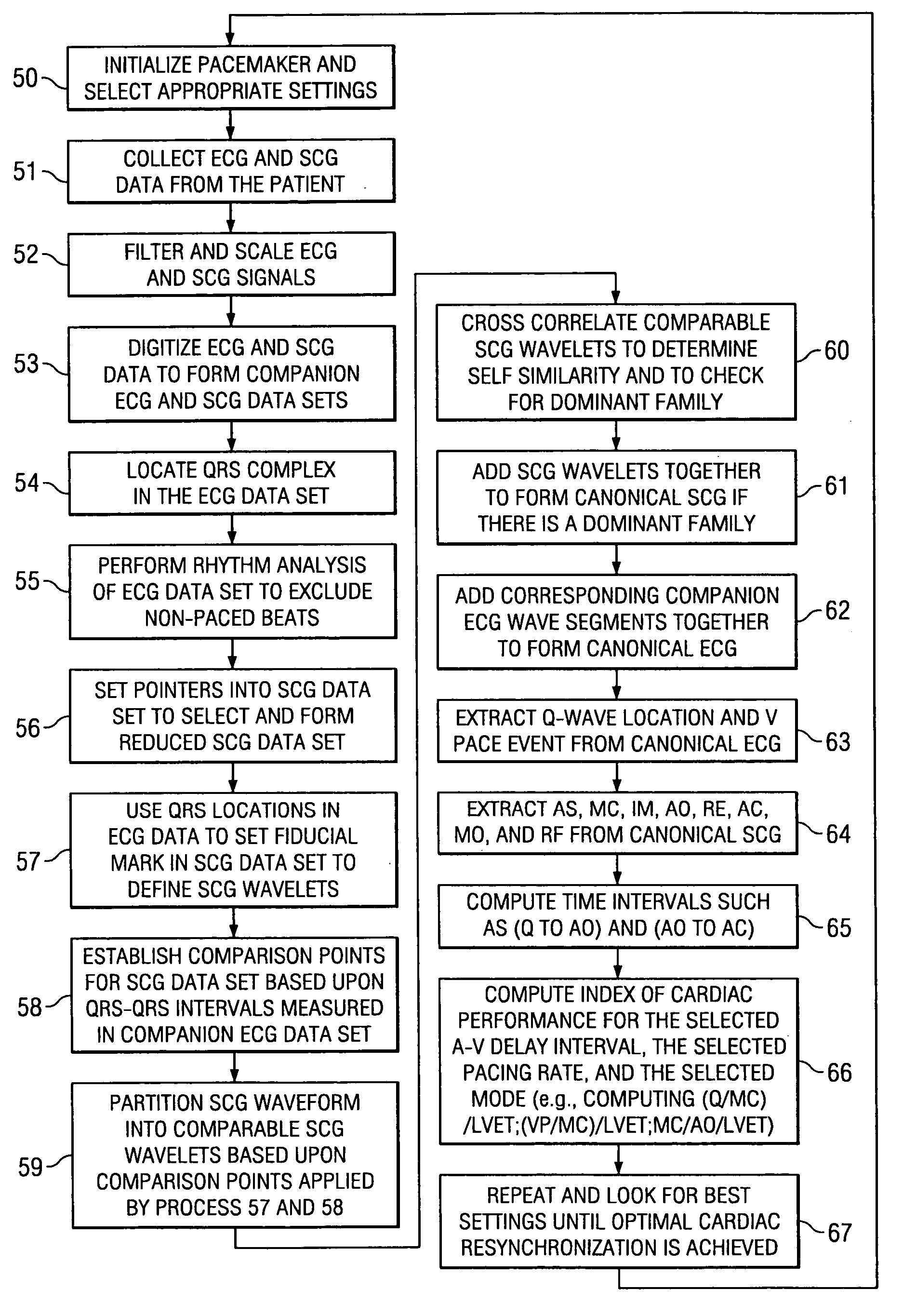
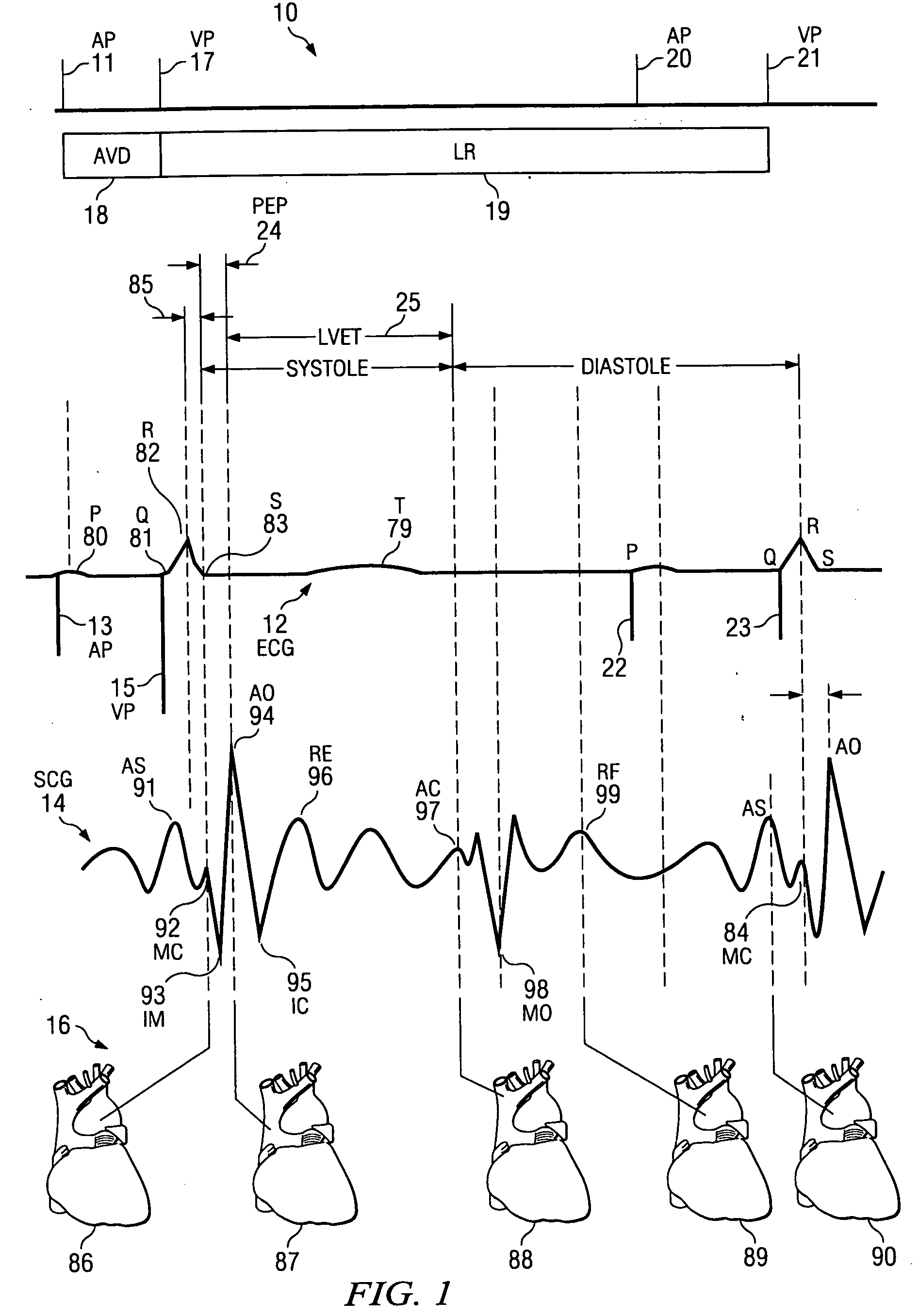
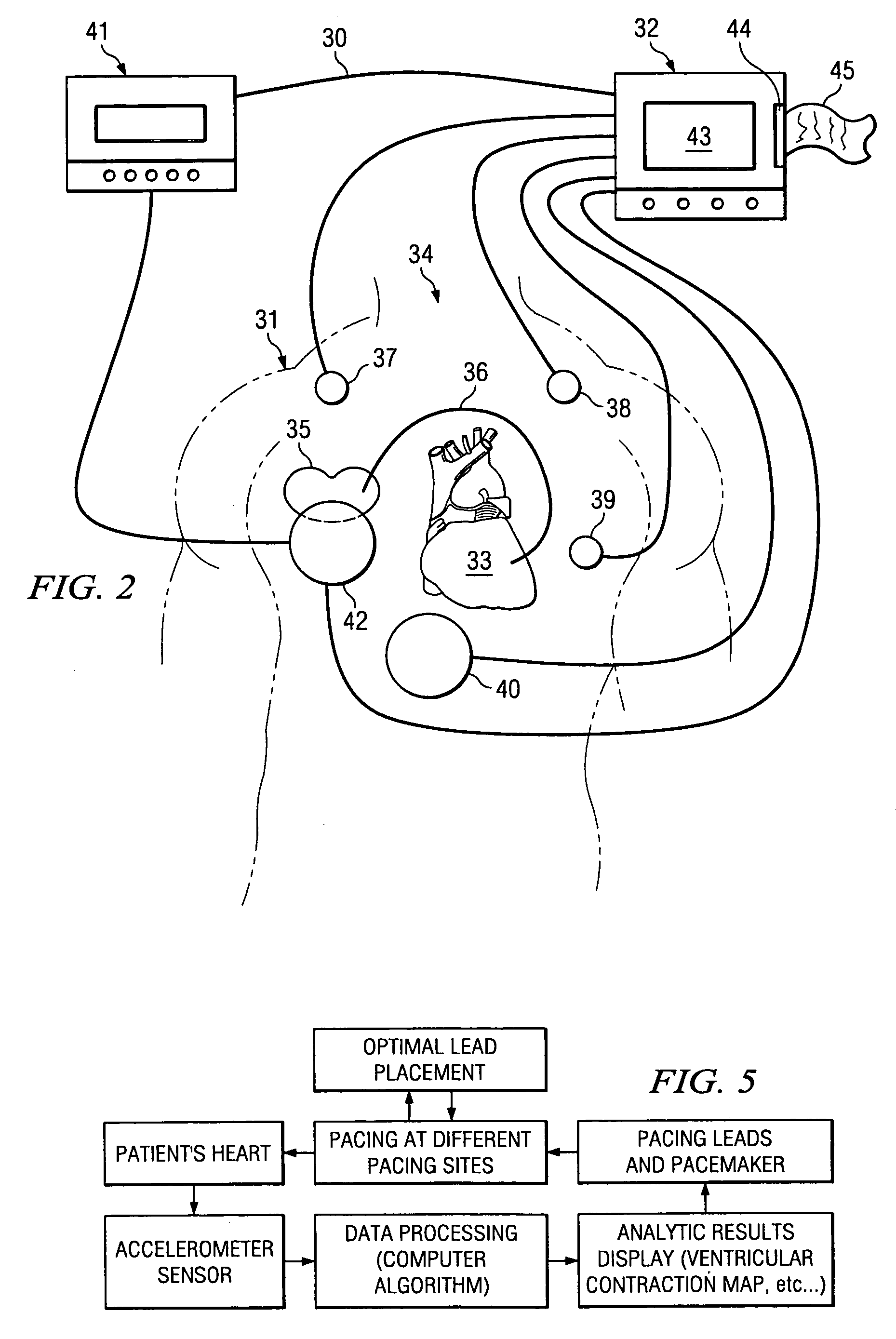
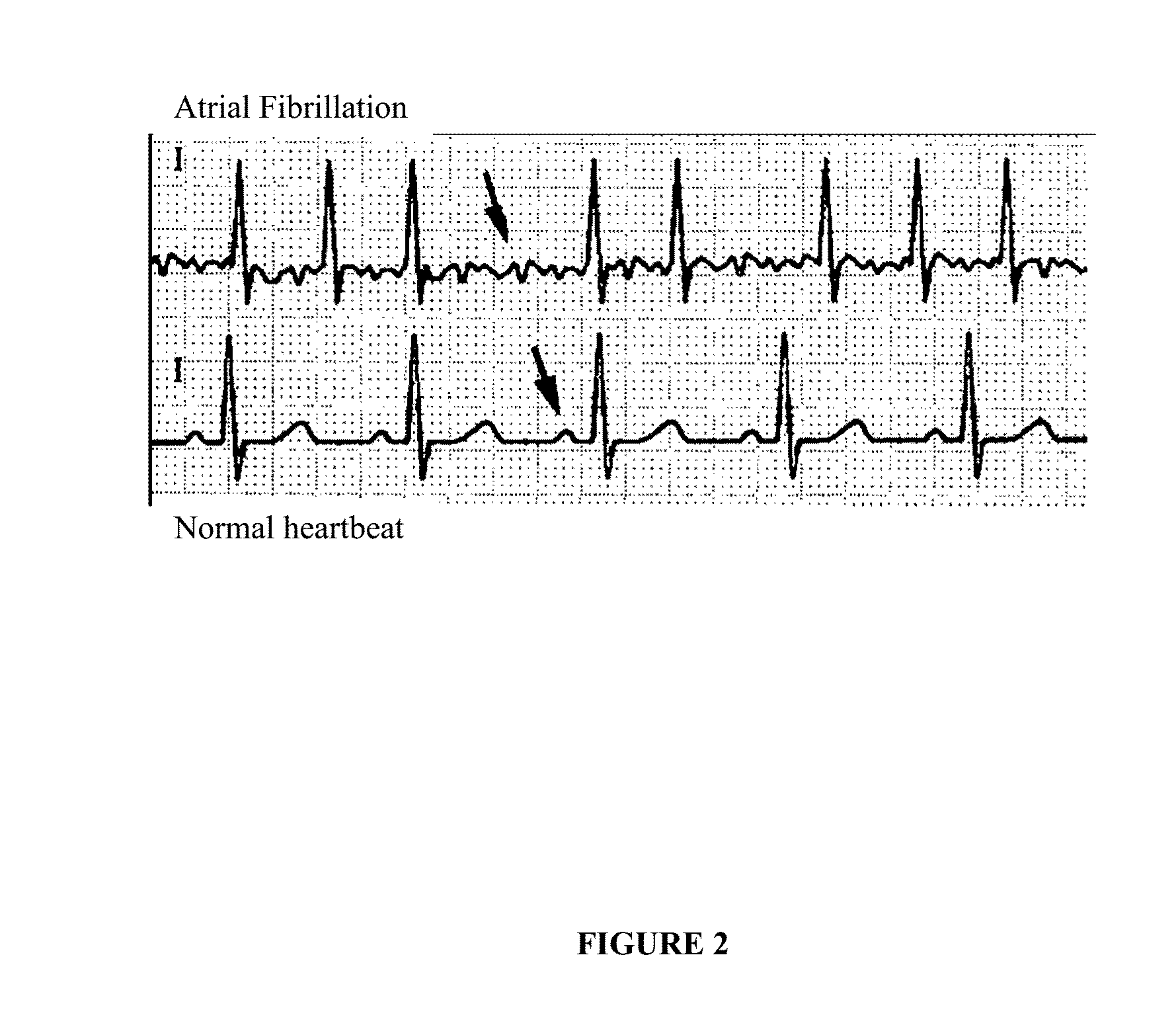
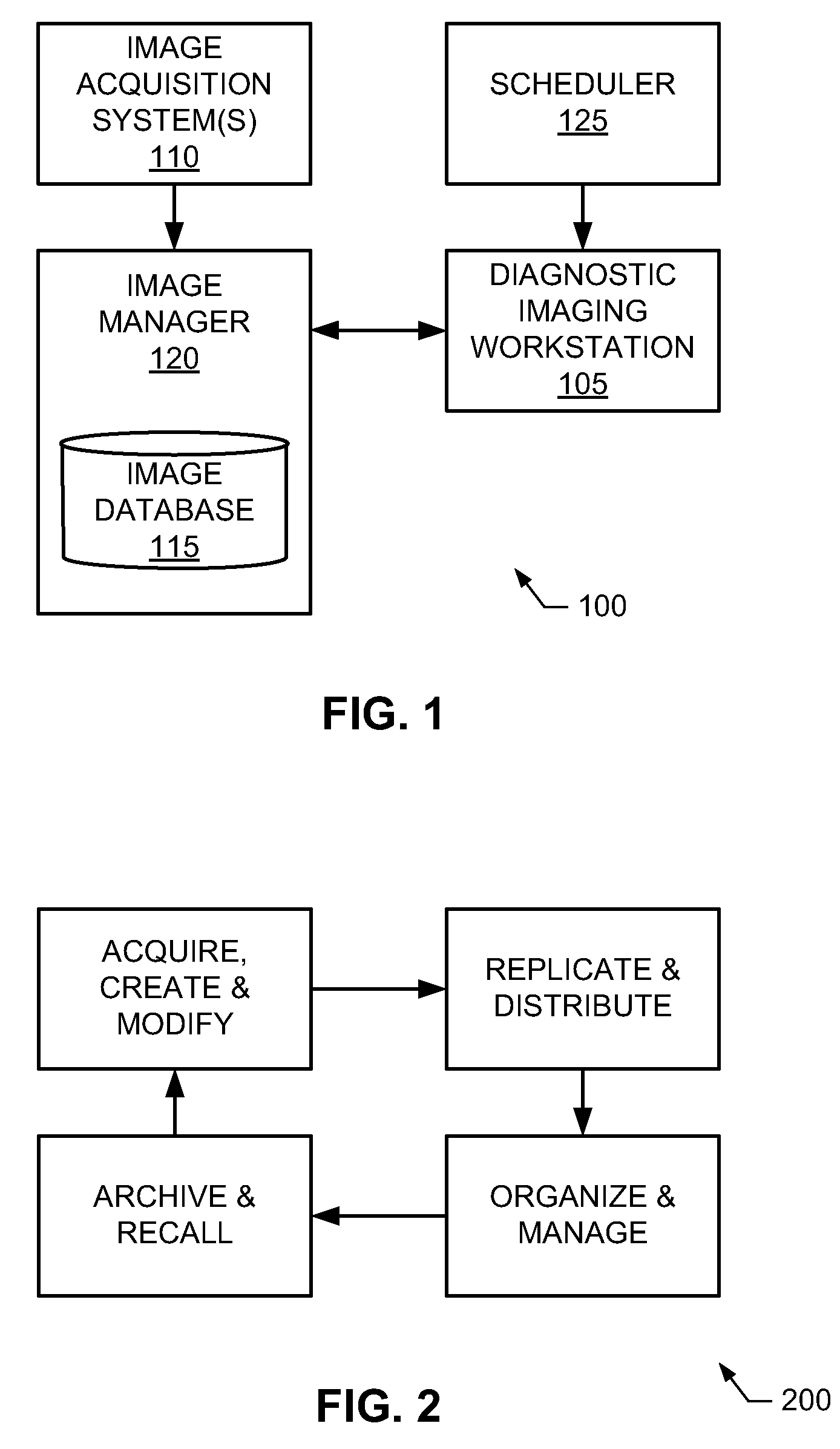
Optimization method for cardiac resynchronization therapy
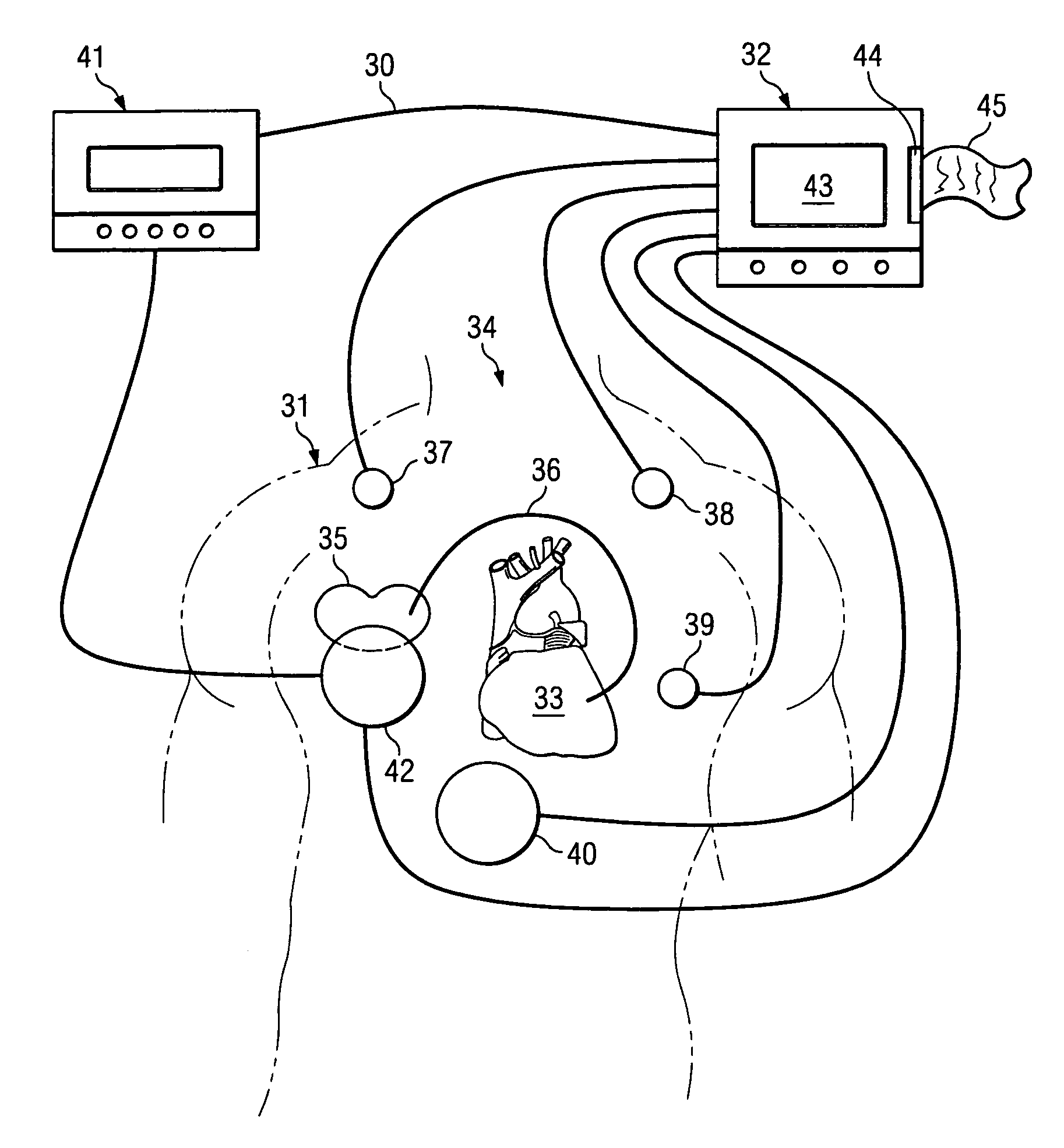
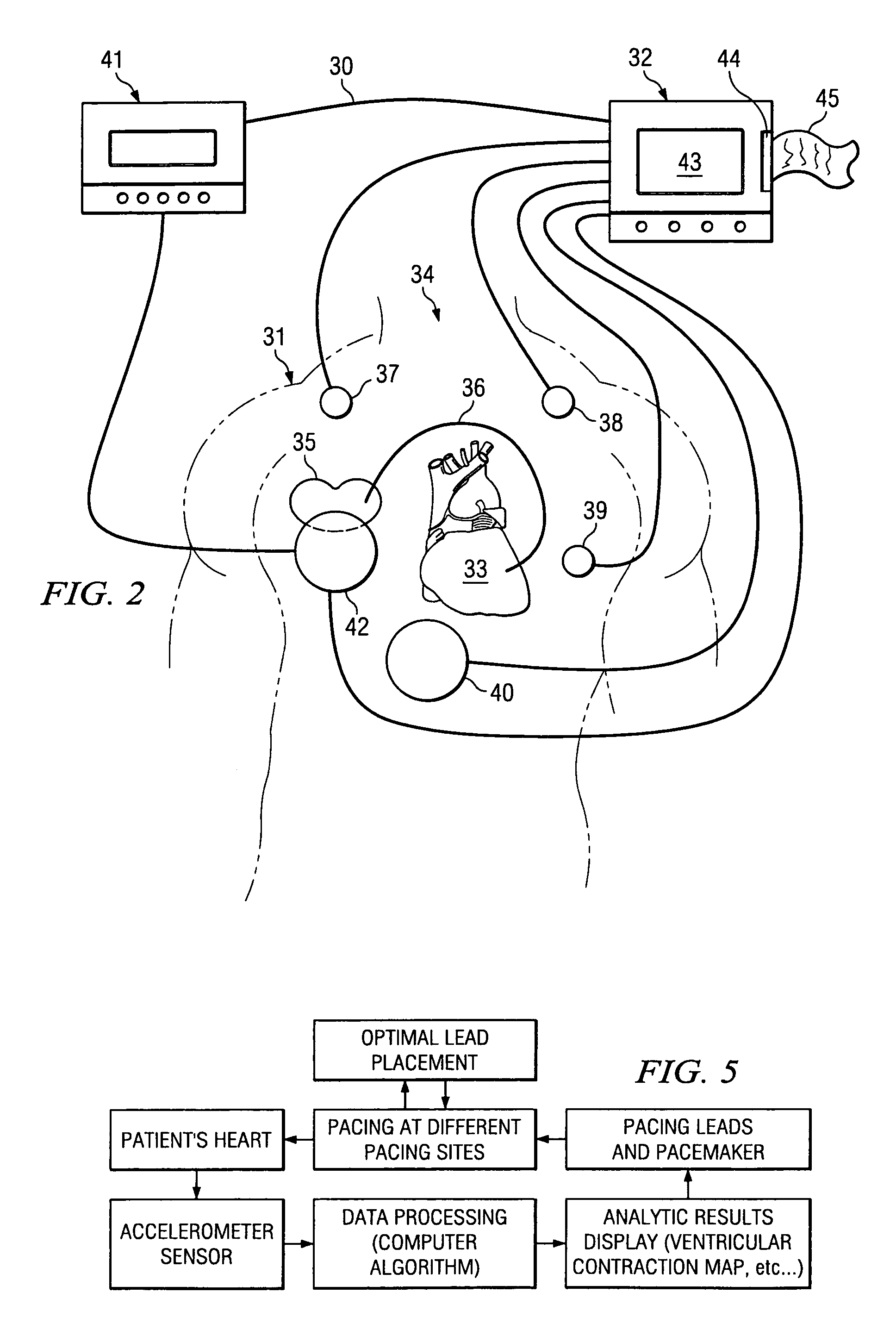
ActiveUS6978184B1Shortening of pre-ejection periodIncrease in rate of contractionInternal electrodesHeart stimulatorsAccelerometerLeft ventricular size
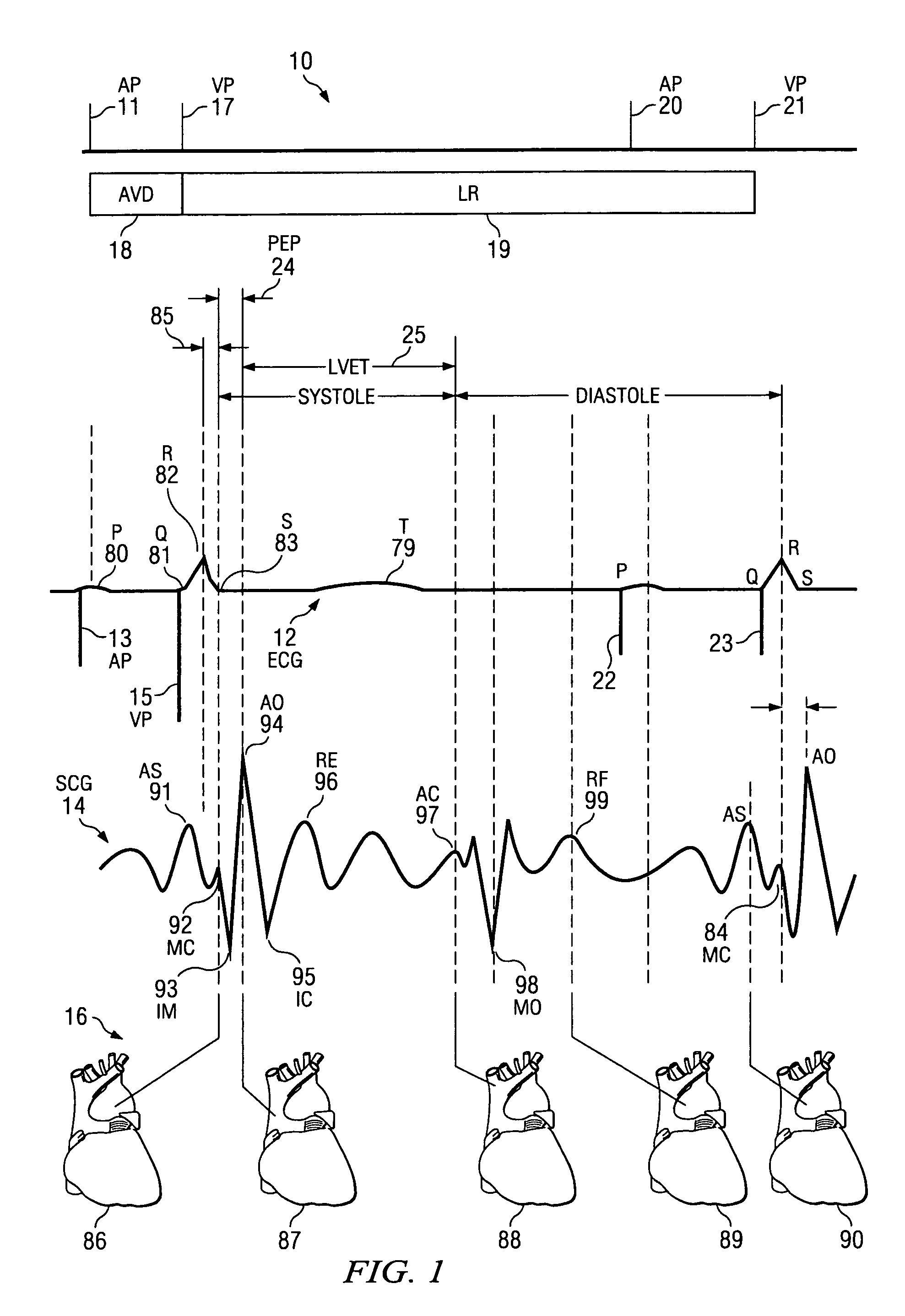
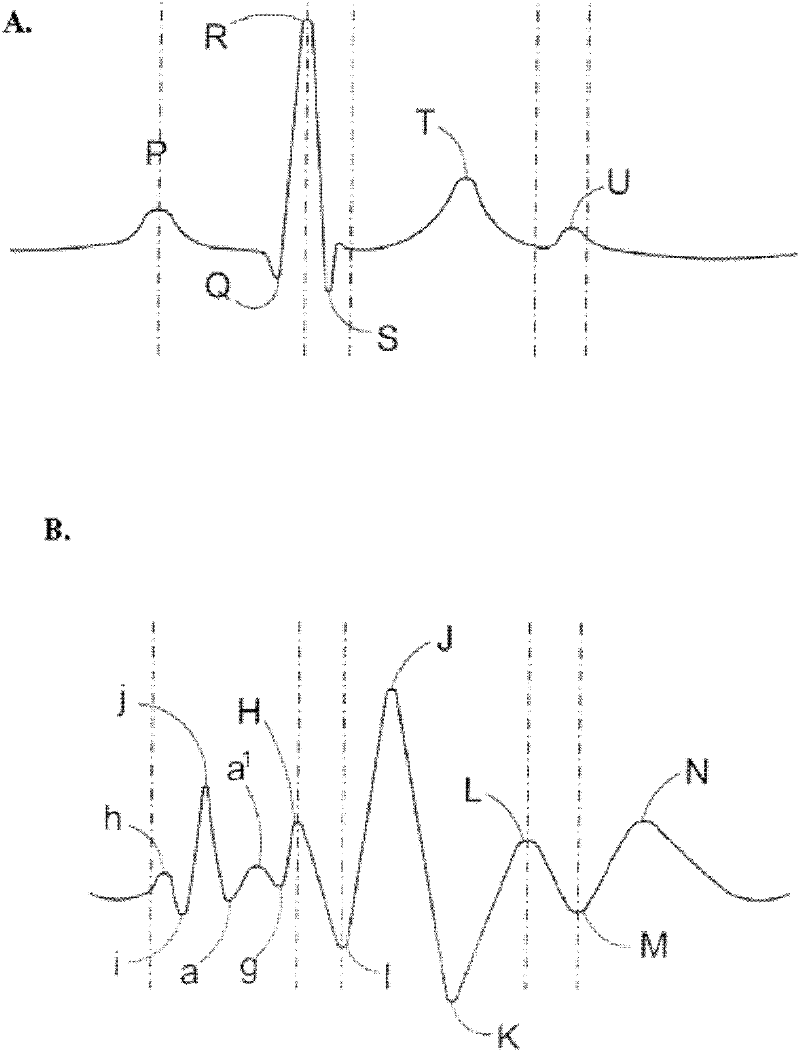
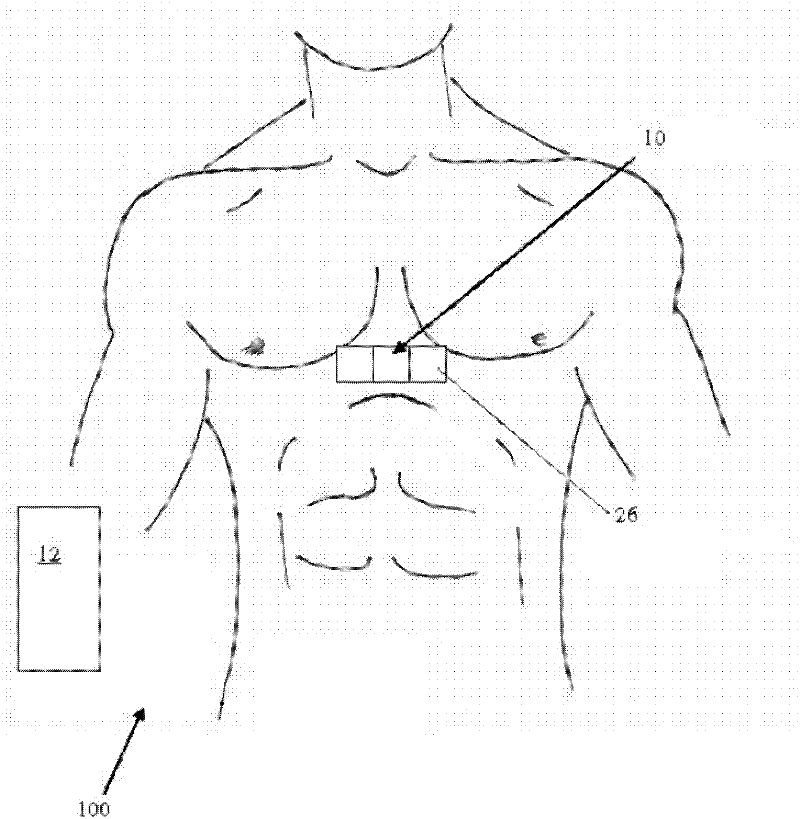
The patterns of contraction and relaxation of the heart before and during left ventricular or biventricular pacing are analyzed and displayed in real time mode to assist physicians to screen patients for cardiac resynchronization therapy, to set the optimal A-V or right ventricle to left ventricle interval delay, and to select the site(s) of pacing that result in optimal cardiac performance. The system includes an accelerometer sensor; a programmable pace maker, a computer data analysis module, and may also include a 2D and 3D visual graphic display of analytic results, i.e. a Ventricular Contraction Map. A feedback network provides direction for optimal pacing leads placement. The method includes selecting a location to place the leads of a cardiac pacing device, collecting seismocardiographic (SCG) data corresponding to heart motion during paced beats of a patient's heart, determining hemodynamic and electrophysiological parameters based on the SCG data, repeating the preceding steps for another lead placement location, and selecting a lead placement location that provides the best cardiac performance by comparing the calculated hemodynamic and electrophysiological parameters for each different lead placement location.
Owner:HEART FORCE MEDICAL +1
High intensity focused ultrasound for imaging and treatment of arrhythmias
InactiveUS20050267453A1Shorten treatment timeAutomate processingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationDual mode
A dual-mode, capable of imaging and ablation, ultrasound array integrated in a catheter is provided for minimally invasive treatment of arrhythmias. The catheter array is small enough for insertion through a peripheral vein and is longitudinally integrated with the catheter to have a side-view for tissue imaging and ablation. A high length / width array ratio creates a large aperture necessary for high power ablation densities. A catheter stabilization device maintains a distance between the catheter array and the wall of a heart or vein. Visualization of anatomy and imaging of ablated tissue provides a guide for placing the lesion and assists in achieving a pattern of ablated tissue. The catheter is advanced to another area by catheter rotation and / or array steering or focusing. Gating the imaging and ablation processes to a heart cycle allows for accounting and compensation of heart motion and enables automation of an arrhythmia treatment.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
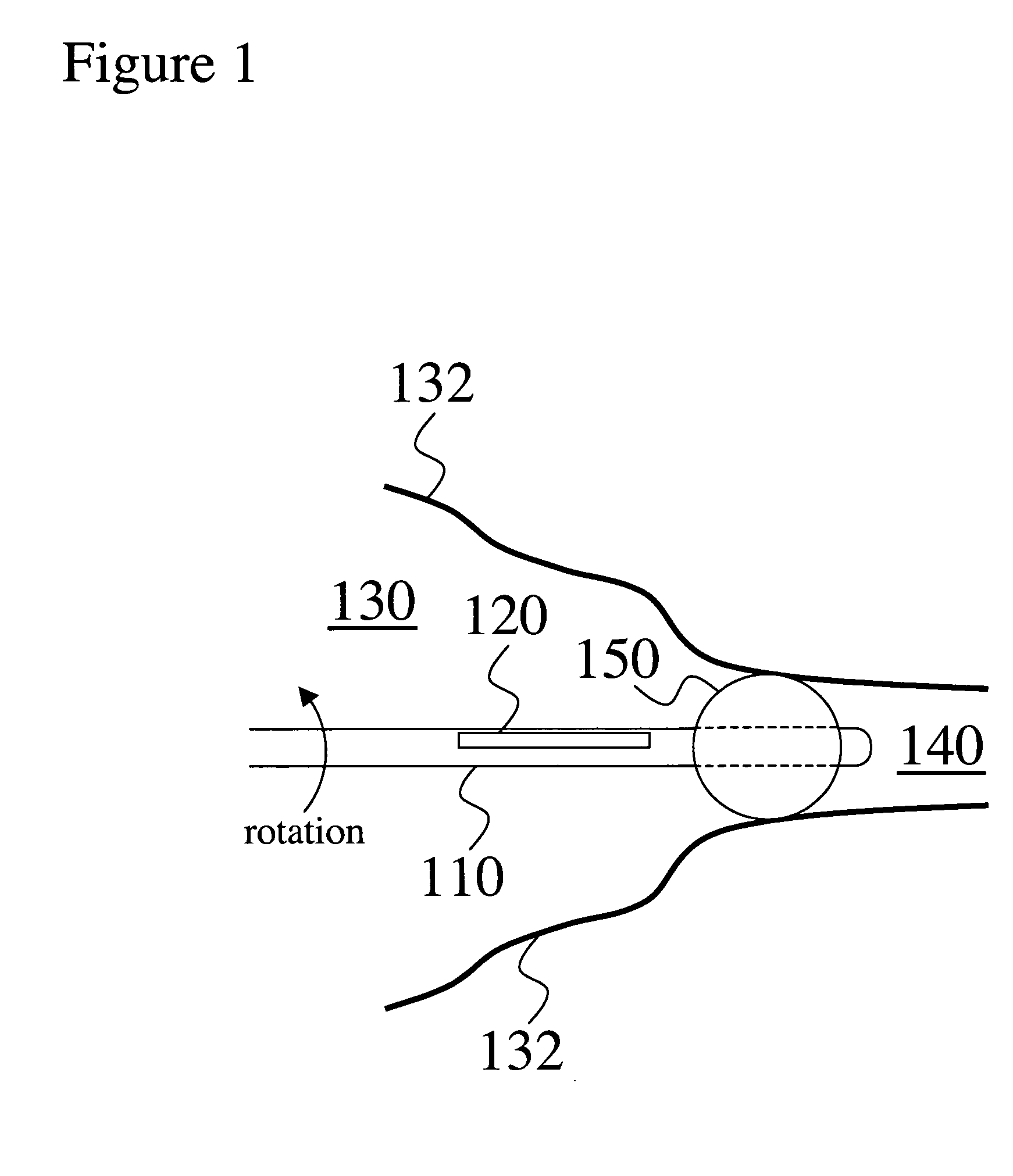
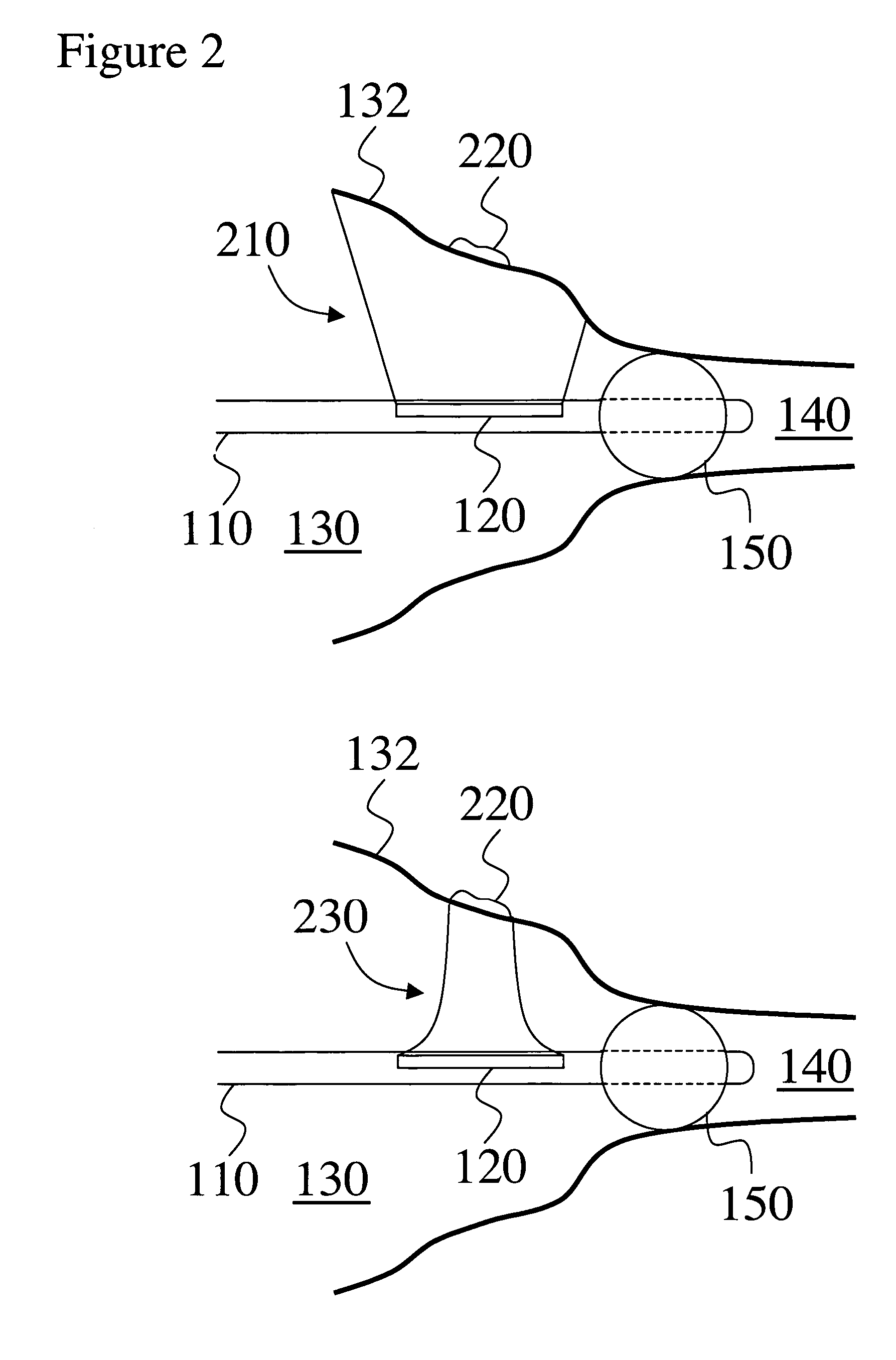
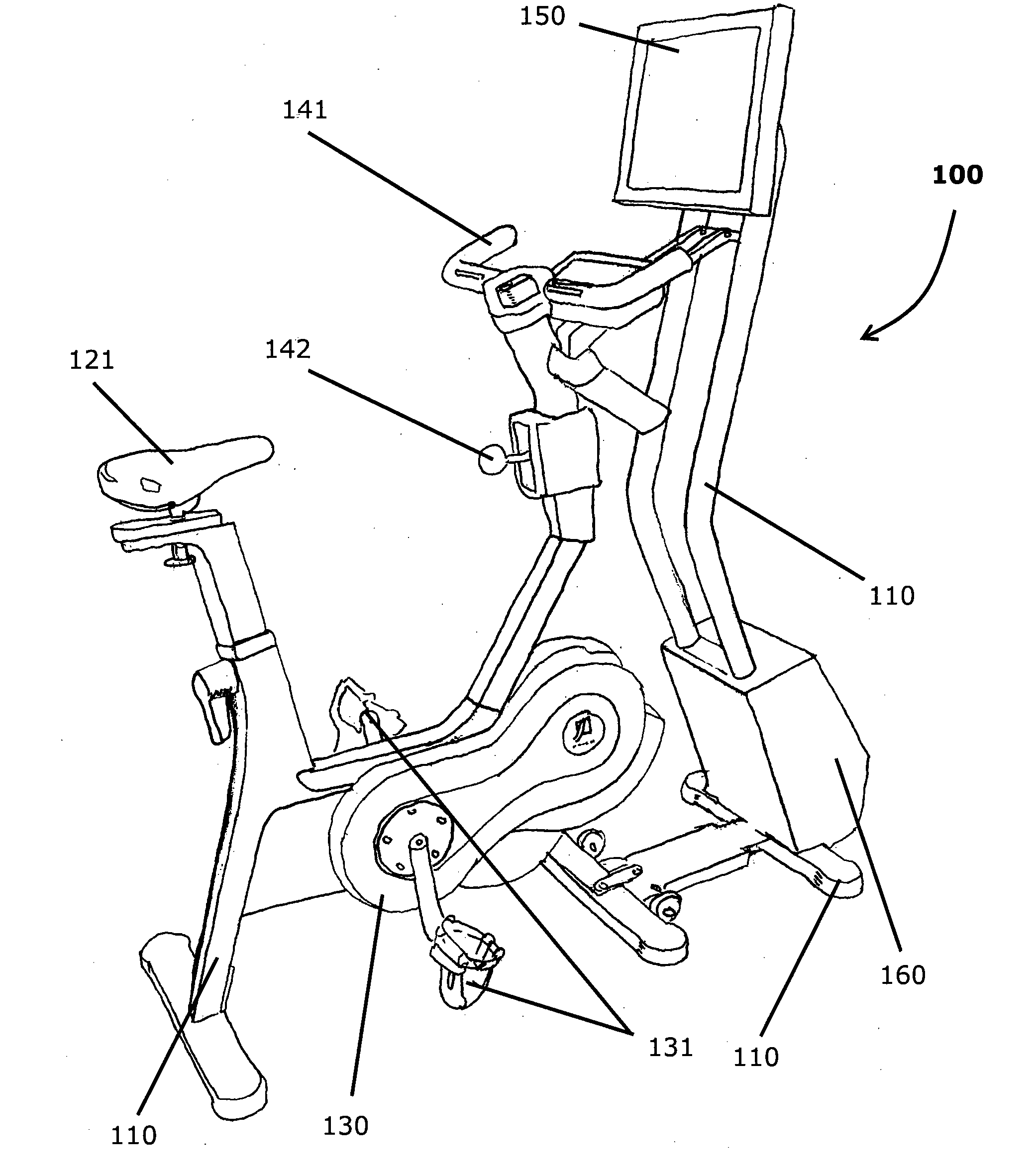
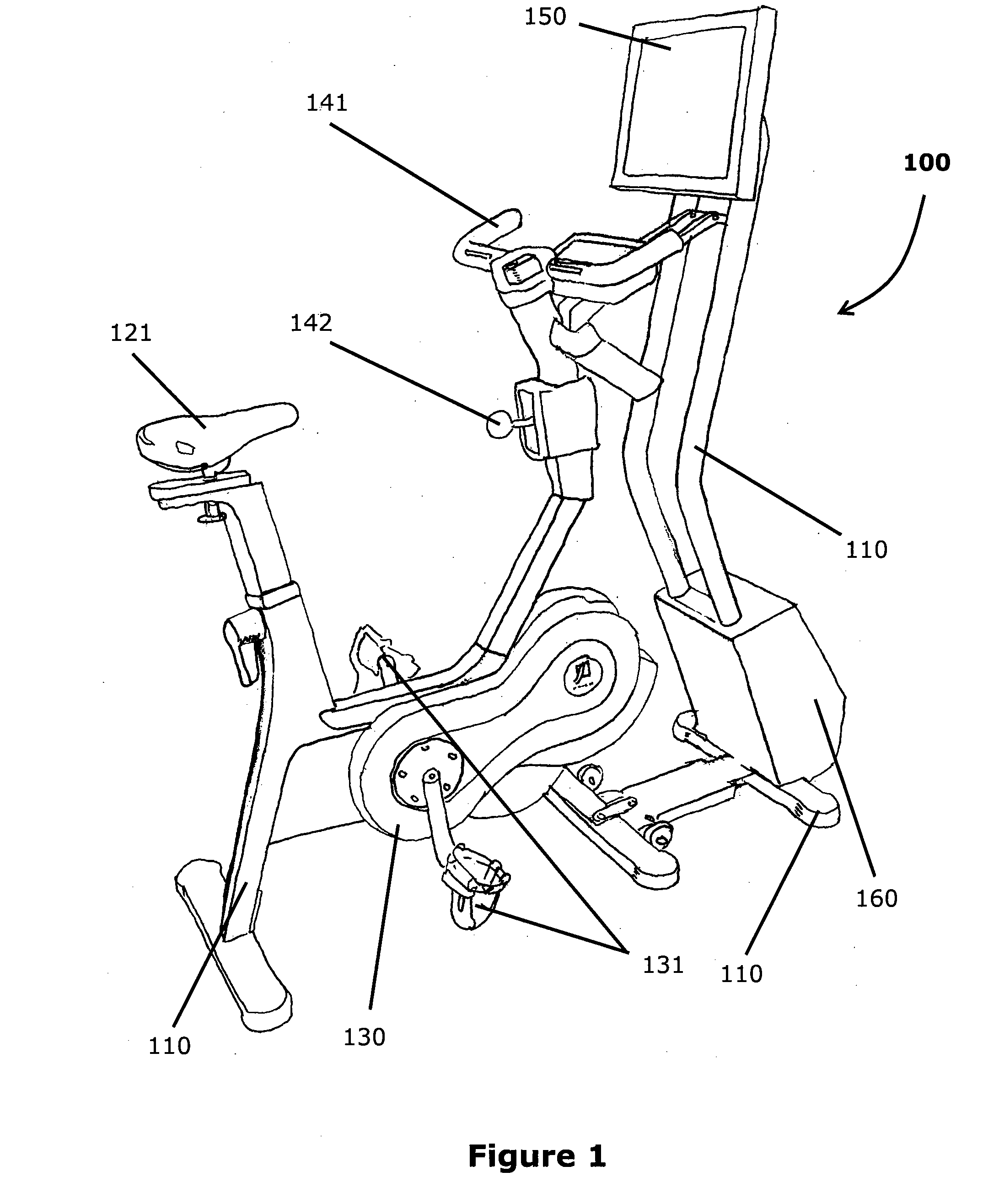
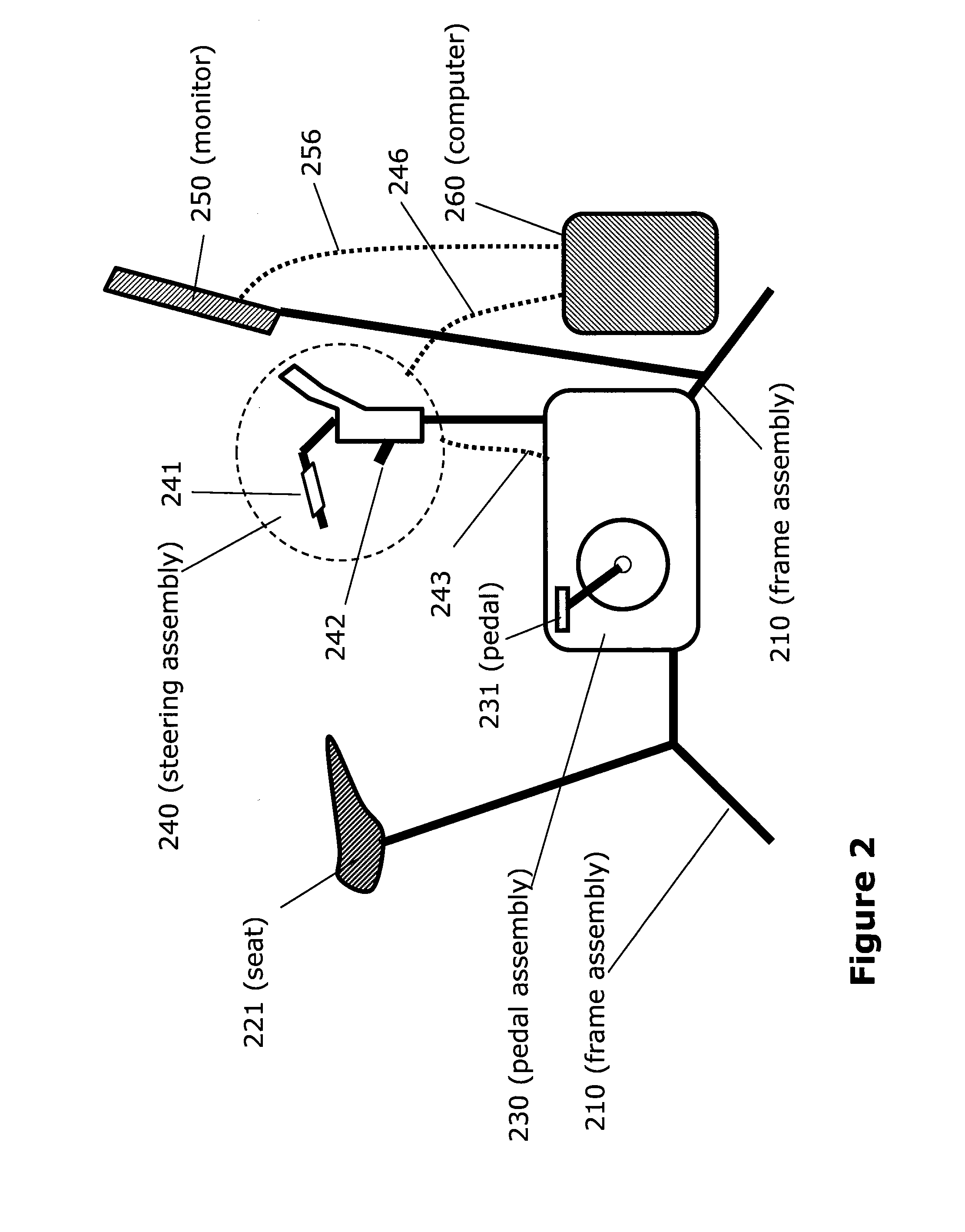
Closed-Loop Power Dissipation Control For Cardio-Fitness Equipment
InactiveUS20080207402A1Quality improvementMuscle exercising devicesMovement coordination devicesControl systemHeart motion
Various embodiments of the present invention provide (a) an inexpensive apparatus enabling the measurement of power dissipated by the rider of a cardio-fitness station (or any other stationary bicycle) that does not depend on manufacturing tolerances or machine condition variations, and (b) a method of using the data measured by such an apparatus to improve the accuracy of exercise condition settings by implementing the invented apparatus into a closed-loop control system which improves the quality of the exercise experience and enhances the adoption of exercise on a cardio-fitness station employing this as a community activity.
Owner:EXPRESSO FITNESS CORP
Accelerometer-based method for cardiac function and therapy assessment
InactiveUS20060095085A1Improve efficiencyLarge amplitudeInternal electrodesCatheterGraphicsCardiac feature
A method for determining a change in function of a patient's heart that includes the steps of collecting seismocardiographic (SCG) data corresponding to a heart motion of the patient's heart; determining a hemodynamic parameter based on the SCG data; and comparing the parameter with a predetermined measure of cardiac performance. The system used with the method includes one or more accelerometer sensors, a computer data analysis module, and may also include a 2D and 3D visual graphic display of analytic results, i.e. a Ventricular Contraction Map.
Owner:MARCUS FR I +1
Method and apparatus for obtaining and processing ballistocardiograph data
A method and apparatus are provided for obtaining and processing ballistocardiograph data to determine a physiological condition of a subject. Ballistocardiograph data indicative of heart motion of the subject measured along a plurality of spatial axes by a sensor device which may comprise a three-axis accelerometer. The ballistocardiograph data is processed to determine processed data indicative of heart motion of the subject. Indications of physiological condition are determined based at least in part on the processed data. Processing may comprise aggregation of multidimensional data, determining magnitude of heart motion and derivative thereof, determining a thrust summation, determining an index value, outputting a report based on an index value, etc. Processing may be informed by operator input, such as a time window of interest or indications of interest.
Owner:HEART FORCE MEDICAL
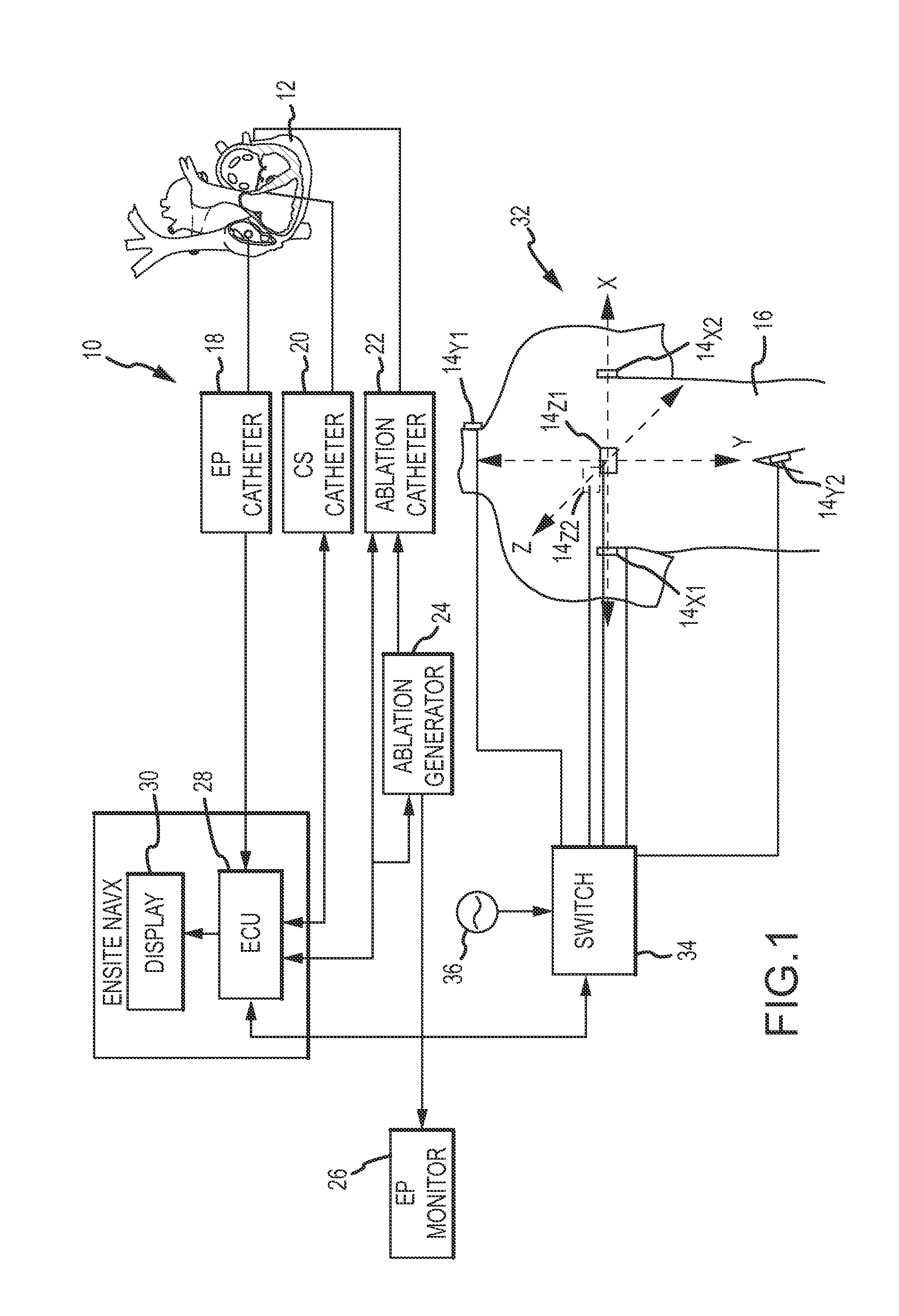
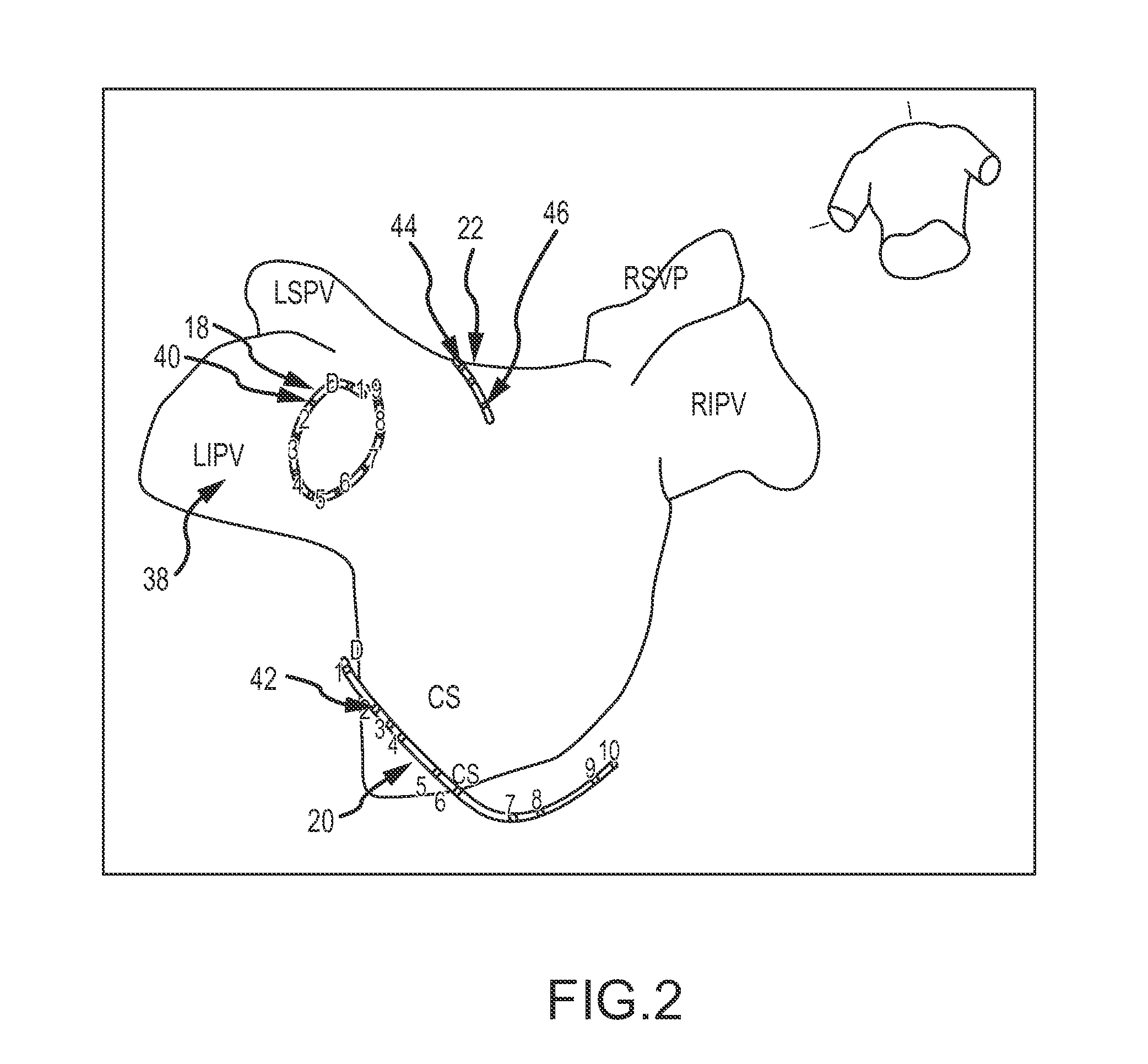
System and method for treating arrhythmias in the heart using information obtained from heart wall motion
ActiveUS9572620B2Effective measure of effectivenessGood efficacy and safety of ablation therapyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyRegimenElectromagnetic field
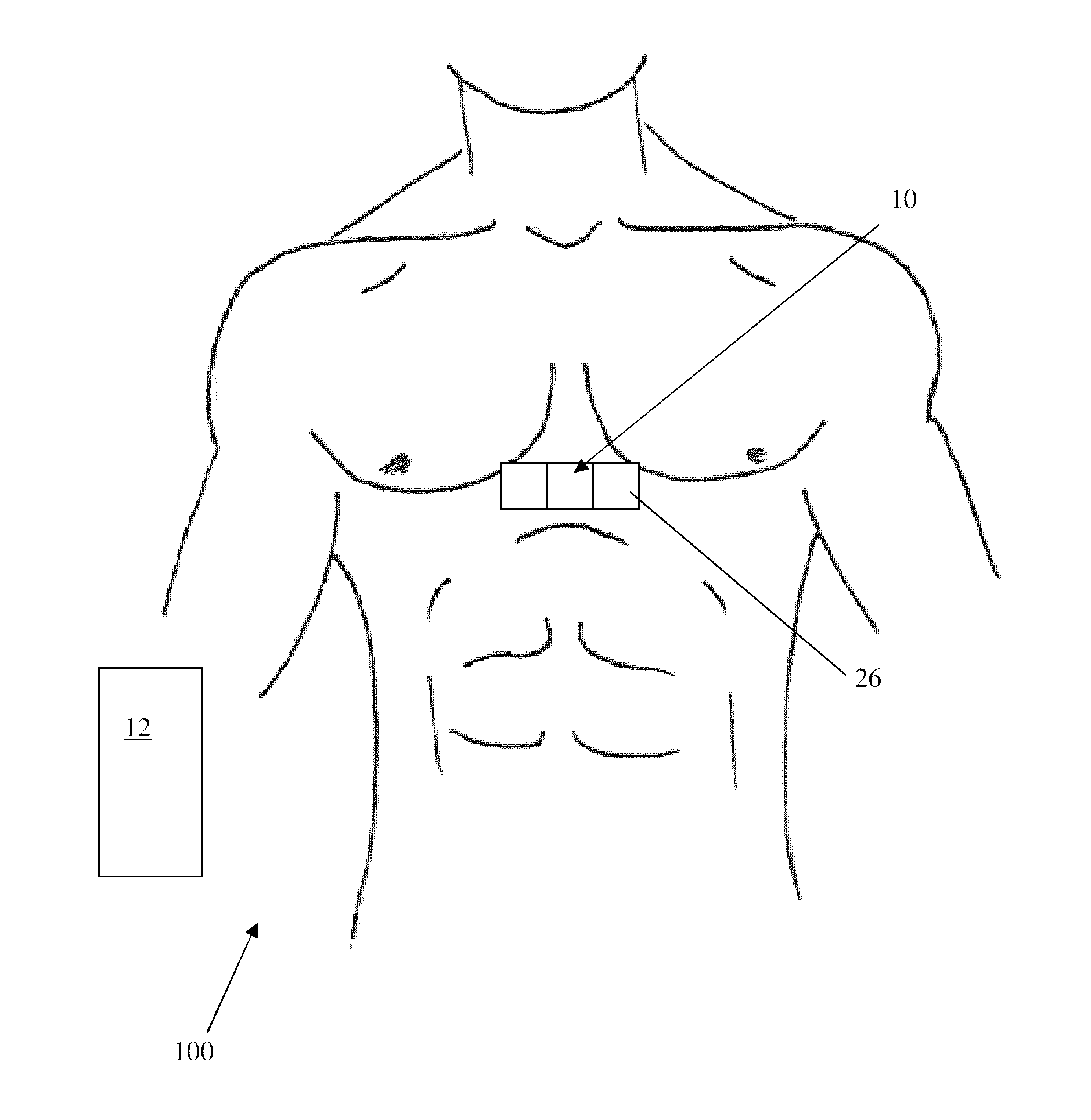
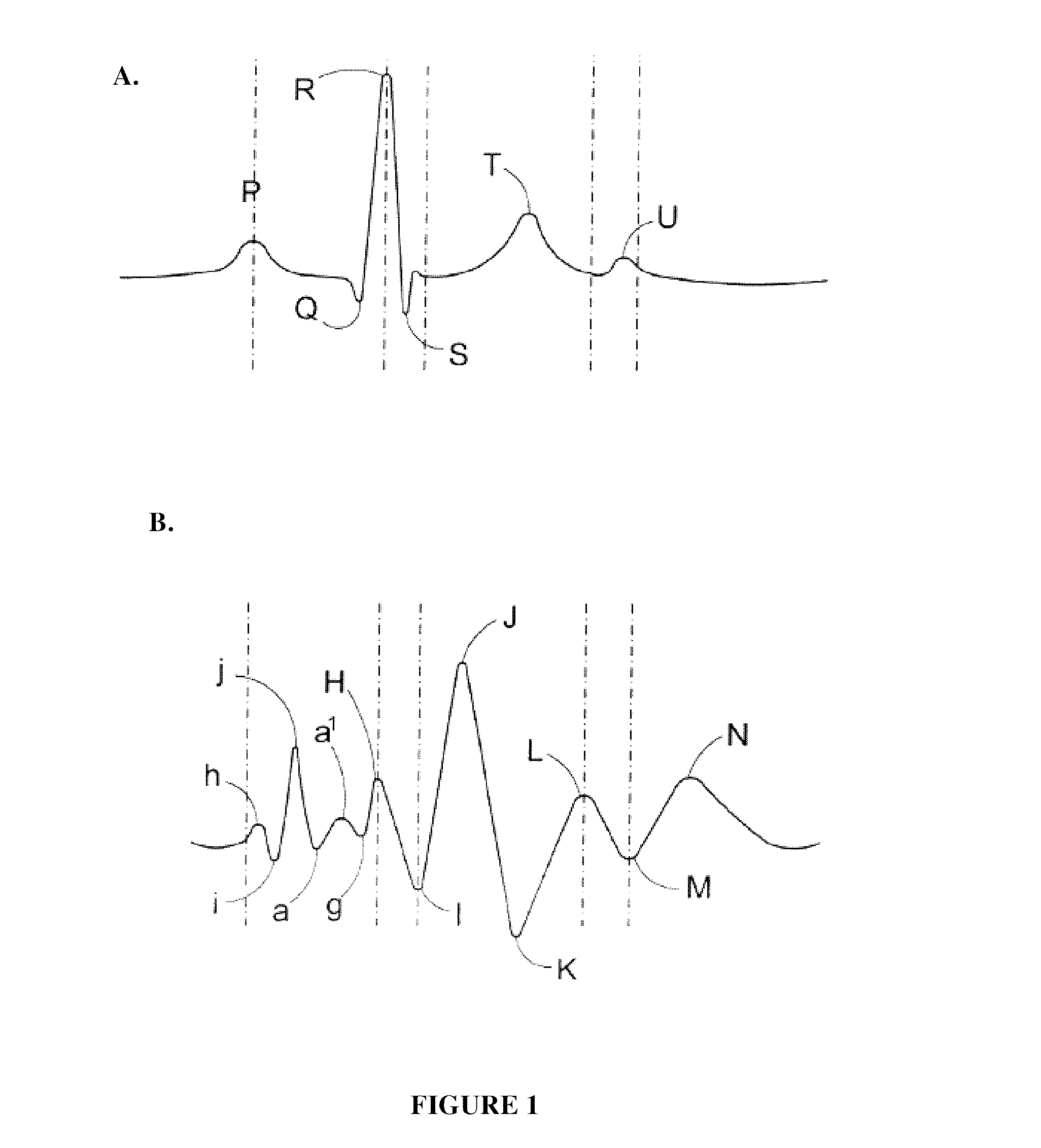
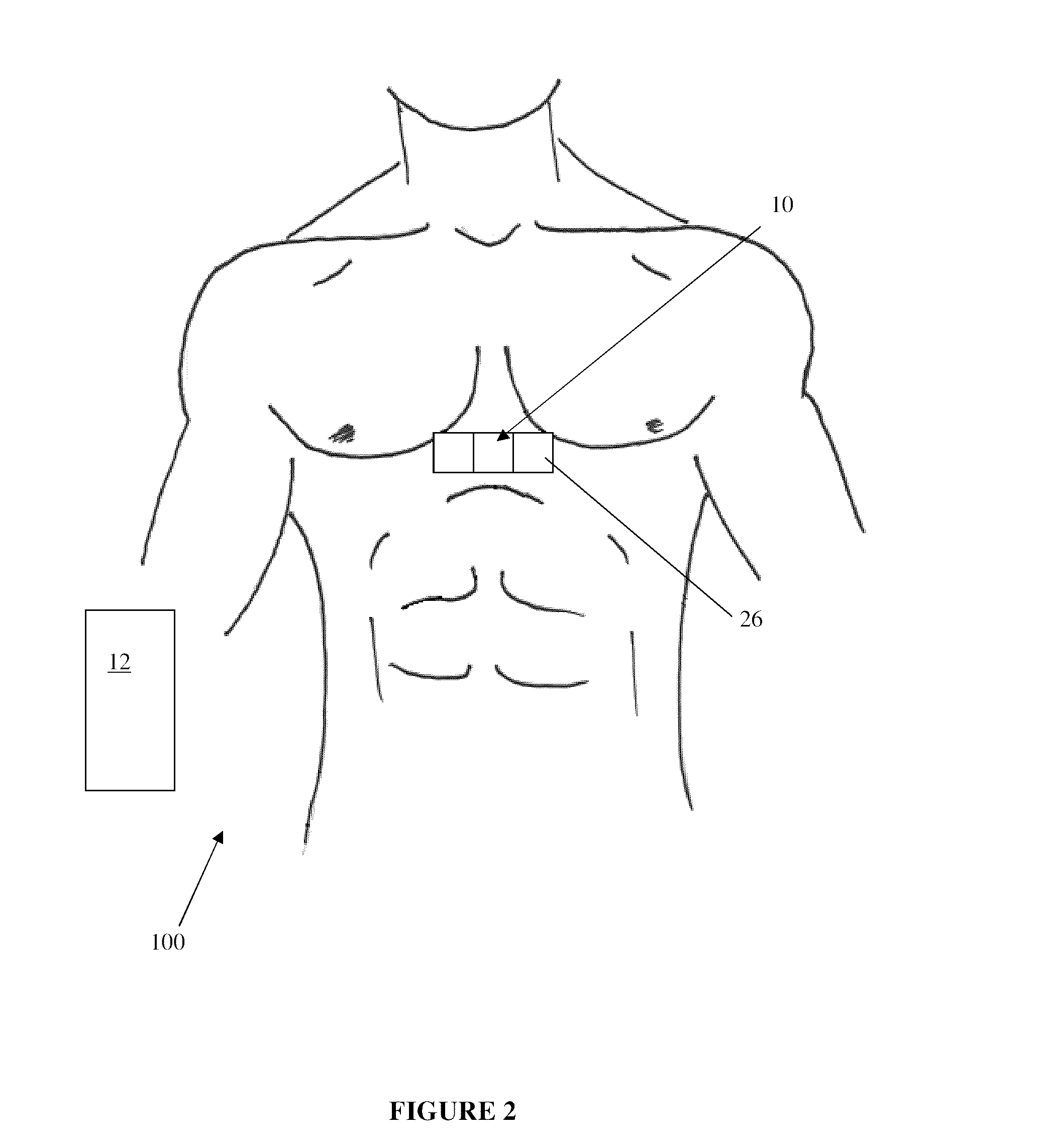
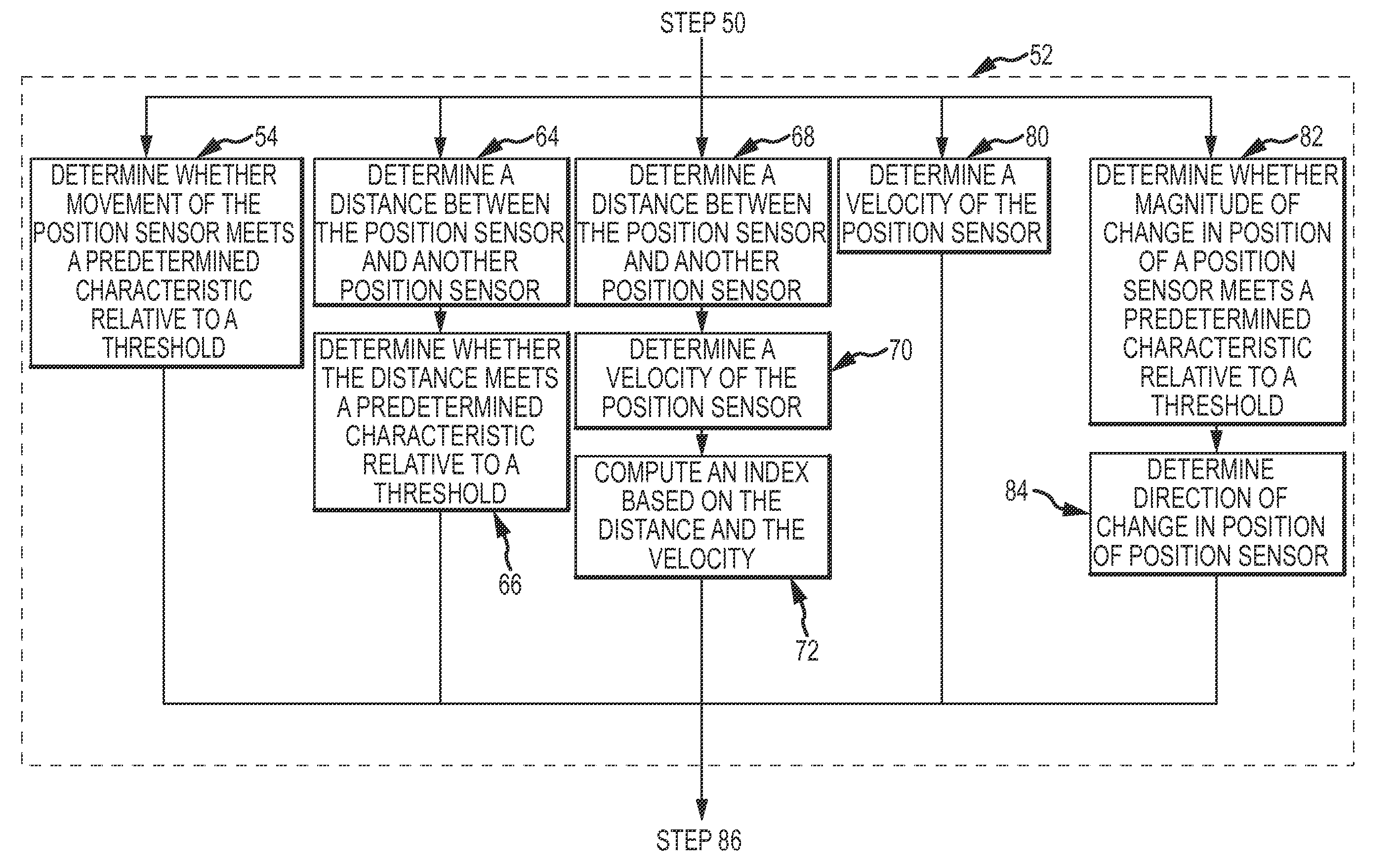
A system and method for treating an arrhythmia in a heart are provided. The system includes an electronic control unit configured to monitor movement of one or more position sensor over a period of time. The position sensors may, for example, comprise electrodes or coils configured to generate induced voltages and currents in the presence of electromagnetic fields. The positions sensors are in contact with portions of heart tissue and changes in position are representative of motion of that tissue. The electronic control unit is further configured to generate an indicator, responsive to the movements of the sensors over the period of time, of a characteristic of the heart affected by delivery of ablation energy to heart tissue. In this manner, the effectiveness and safety of cardiac tissue ablation for treatment of the arrhythmia can be assessed and a post-ablation therapy regimen determined.
Owner:RYU KYUNGMOO +8
Surgical instruments and procedures for stabilizing the beating heart during coronary artery bypass graft surgery
InactiveUS20070055108A1Less traumaMiniaturization exerciseCannulasDiagnosticsSurgical siteSurgical department
Methods and devices which a surgeon may use to stabilize the beating heart during a surgical procedure on the heart. A stabilizing device may be introduced through an opening in the chest and brought into contact with the beating heart. By contacting the heart with the device and by exerting a stabilizing force on the device, the motion of the heart caused by the contraction of the heart muscles in a vicinity of a site of surgery to be performed, is effectively eliminated. A surgeon may contact the heart with the stabilizing means, assess the degree of movement of the anastomosis site, and exert a force on the stabilizing means such that the contraction of the beating heart causes only minimal excess motion at the surgery site. The stabilizing means may be attached to a rigid support or may be attached to a semi-rigid support which is rendered motionless mechanically, chemically, or by human intervention.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Method and system for dual domain discrimination of vulnerable plaque
InactiveUS20050228295A1High sensitivityStrong specificityDiagnostics using spectroscopyCatheterFrequency spectrumRegression analysis
A method for optically analyzing blood vessel walls comprises receiving optical signals from the vessel walls and resolving a spectrum of optical signals in wavelength to generate spectral data. The spectral data is then transformed into the frequency domain. In the preferred embodiment, this transformation is achieved by applying wavelet decomposition. In other embodiments other transform techniques such as Fourier analysis is applied. The spectral data in the frequency domain are then used to analyze the vessel walls. In the typical embodiment, the spectral data are used to analyze a disease state of blood vessels walls such as the presence of atherosclerotic plaques, and their state. Dual domain method enables the spectral signals from blood vessels to be analyzed simultaneously according to frequency and wavelength (time). Dual-Domain Regression Analysis (DRDA) and Dual-Domain Discrimination Analysis (DDDA) in combination with wavelet transform (WT) enable the modeling of signals simultaneously in both domains. This provides a mechanism for isolating the non-interesting variation in spectra, making the system and analysis method more robust against variations in instrument and environmental conditions, e.g., broad-band spectral variation contributed from water, heart motion, and other non-interesting interferences. This provides higher sensitivity and specificity when compared with other models currently being used.
Owner:INFRAREDX INC
Method and apparatus for obtaining and processing ballistocardiograph data
A method and apparatus are provided for obtaining and processing ballistocardiograph data to determine a physiological condition of a subject. Ballistocardiograph data indicative of heart motion of the subject measured along a plurality of spatial axes by a sensor device which may comprise a three-axis accelerometer. The ballistocardiograph data is processed to determine processed data indicative of heart motion of the subject. Indications of physiological condition are determined based at least in part on the processed data. Processing may comprise aggregation of multidimensional data, determining magnitude of heart motion and derivative thereof, determining a thrust summation, determining an index value, outputting a report based on an index value, etc. Processing may be informed by operator input, such as a time window of interest or indications of interest.
Owner:HEART FORCE MEDICAL
Reduction of heart motion artifacts in thoracic CT imaging
InactiveUS8233691B2Reduce Motion ArtifactsLess motion artifactImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCardiac cycle
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO +1
Device, system and method for testing heart motion function
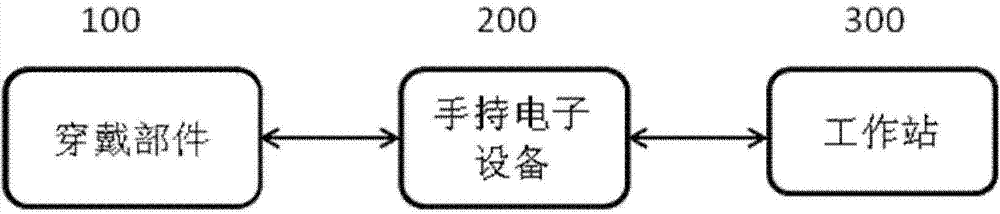
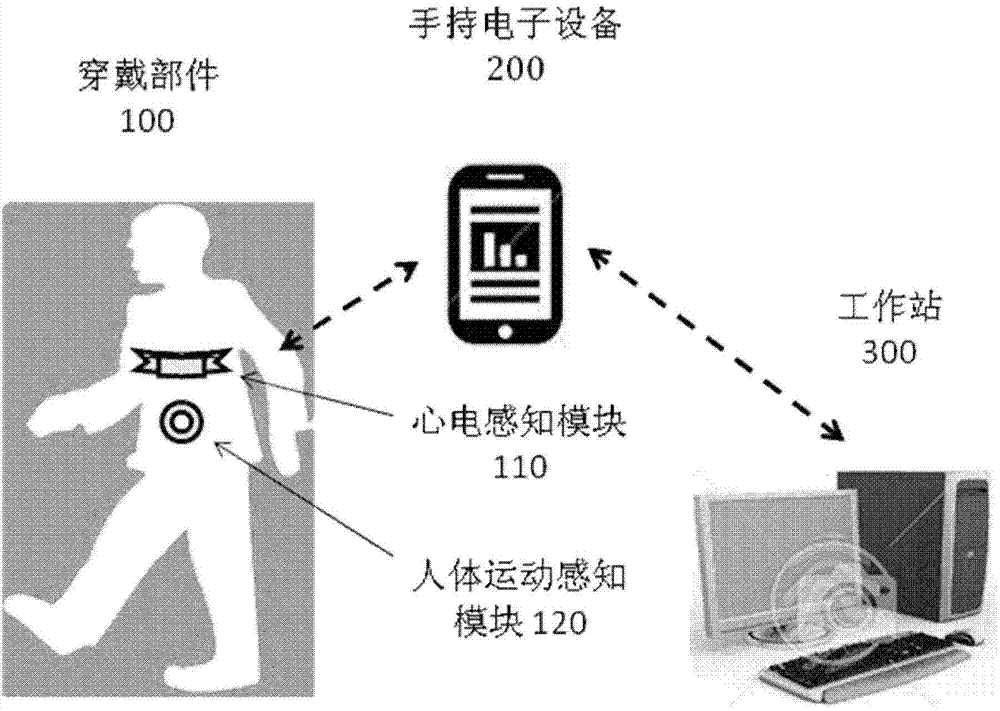
InactiveCN104840191AMedical simulationPhysical therapies and activitiesHeart motionCardiopulmonary diseases
Disclosed are a device, a system and a method for testing a heart motion function. A wearable intelligent perception technology is used to measure and perform fusion analysis on heart rate and motion of a measured person in real time, and a series of cardiopulmonary dynamic function digital indexes such as heart rate motion reaction capacity, a heart time varying index and exercise heart rate recovery are introduced. Compared with a cardiopulmonary motion test (CPX), the device, the system and the method for testing the heart motion function use the indexes distinct in index clinical significance and specific in normal reference value, are simple and convenient to use whenever and wherever possible, greatly reduce test risk, and have significance and application prospect for popularization in cardiopulmonary disease prevention and recovery.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHIHAI ELECTRONICS TECH
Quantitative analysis method for three-dimensional geometric structure of heart mitral valve device
InactiveCN102207995AOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesSupport vector machineImaging modalities
The invention discloses a quantitative analysis method for a three-dimensional geometric structure of a heart mitral valve device in the technical field of computer application. Quantitative analysis is realized by establishing a three-dimensional simplified model of the mitral valve device and using three-dimensional geometric structure parameters of a local coordinate system of the mitral valve device as the input of a support vector machine-based classification system. According to the method, reconstruction of the mitral valve device is not affected by an imaging mode, and the simplified three-dimensional model of the mitral valve device is obtained. The local coordinate system of the mitral valve device is established on the basis of simplified expression, so that the mitral valve device is independent of the influence factors such as the position of a sampling probe, heart motion displacement and displacement of a detected main body and the like, the three-dimensional geometric structure parameters of the mitral valve device are calculated, and the structure and the function of the mitral valve device and the spatial structure relation between the components of the mitral valve device are described.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Identity identification method based on ultrasound whole heart sequential images
ActiveCN106388832AMaintain stabilityNot easy to replaceOrgan movement/changes detectionPerson identificationGeometric propertySonification
The invention relates to an identity identification method based on ultrasound whole heart sequential images. The method comprises the steps of (1) collecting the ultrasound whole heart sequential images of the objects needed to be identified; (2) conducting segmentation on the four cavities of each image collected in the step (1), and then calculating geometric properties of the four cavities of each image; (3) arraying the geometric properties of the four cavities obtained in the step (2) according to different geometric properties and the sequential images, and obtaining a characteristic curve of the movement of the four cavities with different geometric properties; (4) processing the characteristic curve of the movement of the four cavities, and extracting key points of the characteristic curve of the movement of the heart; (5) comparing the time differences of the key points with identical characters of the characteristic changing curve of the four cavities, and obtaining synchronization information of the four cavities; (6) calculating statistics of the geometric characteristics of the four cavities of the heart in cardiac cycle; (7) conducting identification; (8) outputting the result.
Owner:XIAN SIYUAN UNIV
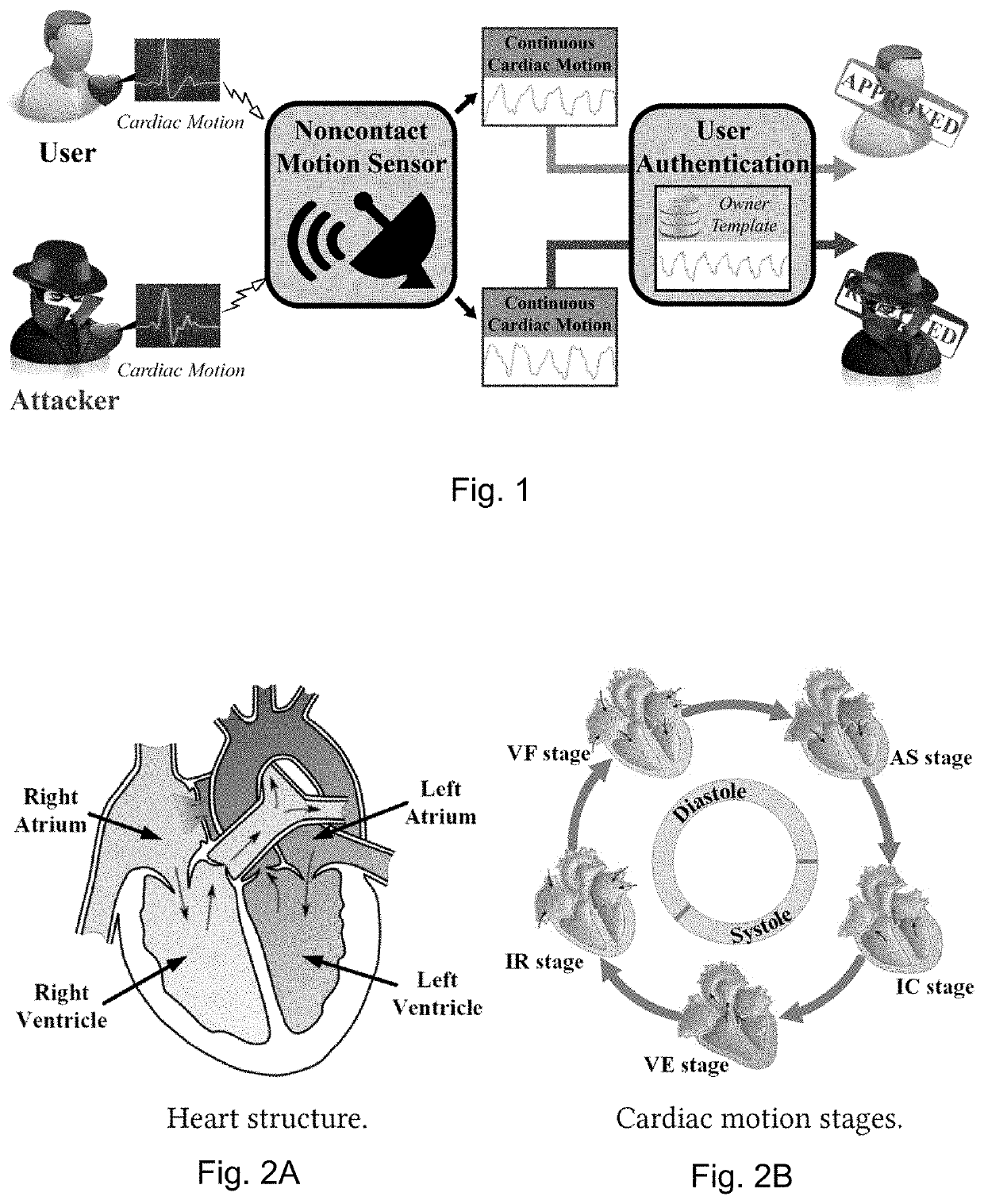
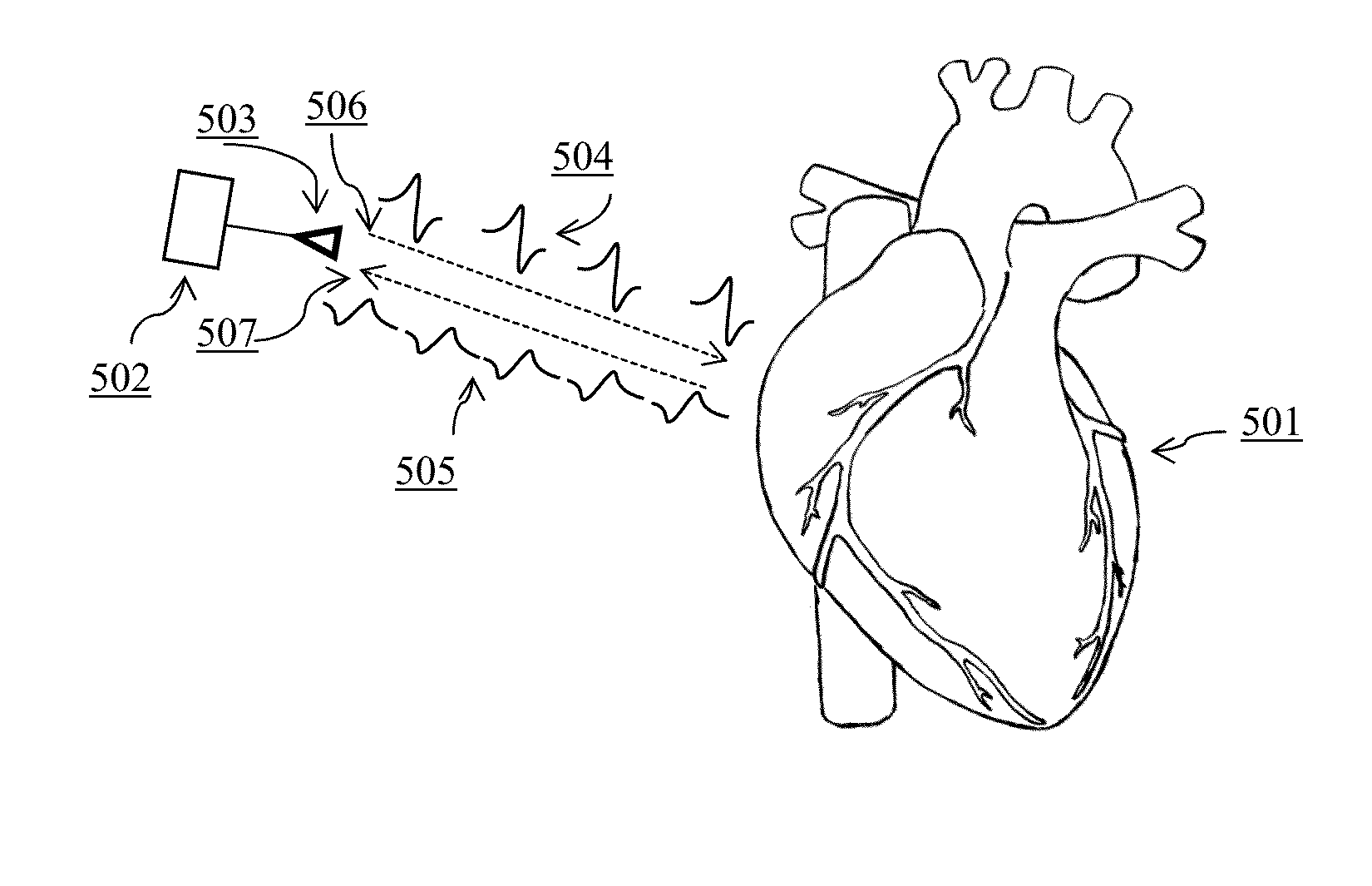
Method and system for non-contact motion-based user authentication
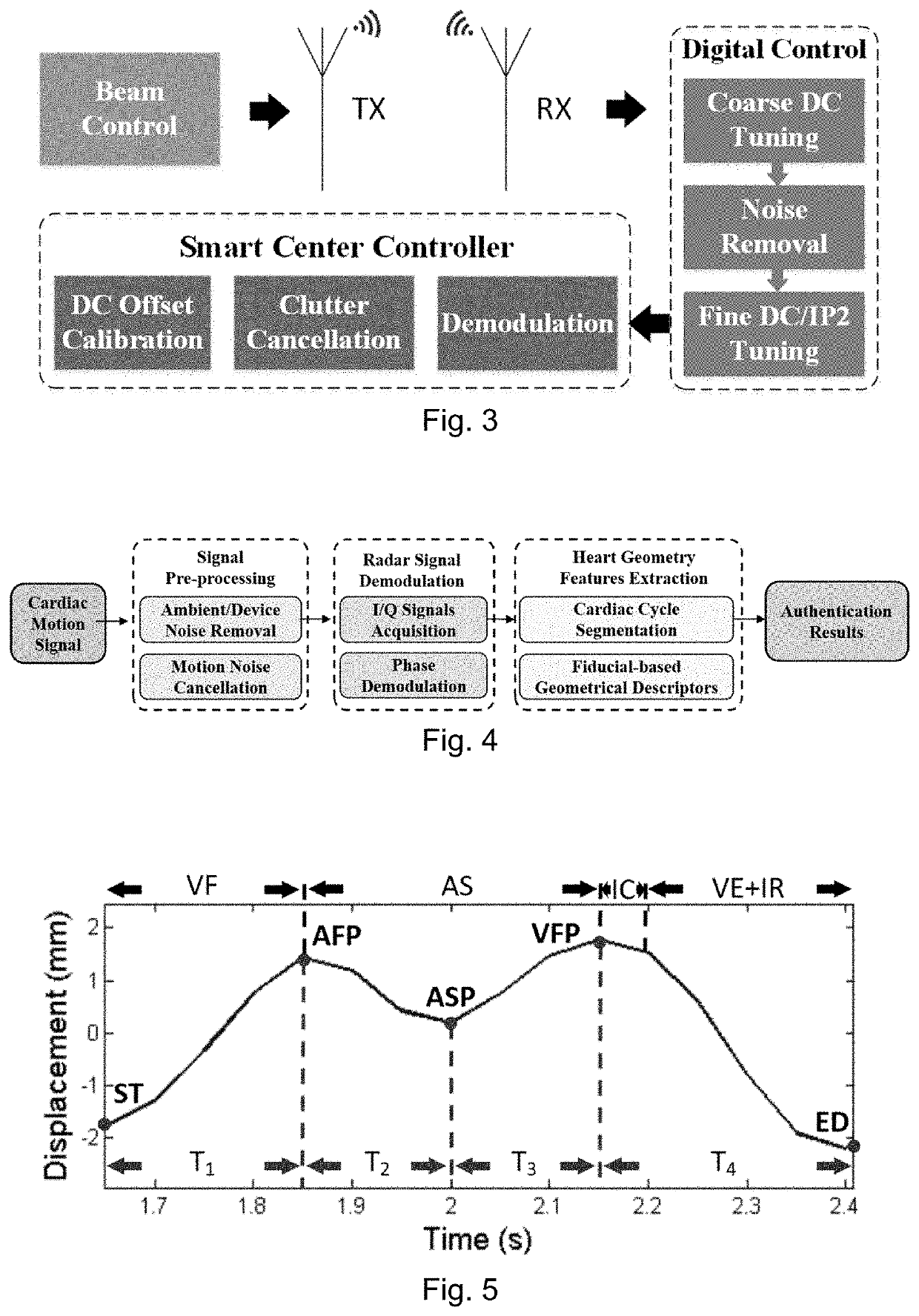
PendingUS20200236545A1Improve usabilityError rateData processing applicationsHealth-index calculationHeart motionUser authentication
Methods and systems are provided for authenticating an individual using a motion of a physiological structure. For example, an individual may be authenticated using their cardiac motion. A first radiofrequency (“RF”) signal is transmitted towards the physiological structure of the individual. A first RF return signal is received, where the first RF return signal corresponds to the transmitted first RF signal. The first RF signal and first RF return signal are processed to obtain a motion signal. One or more values are determined for each fiducial point of a set of pre-determined fiducial points in the motion signal. The set of pre-determined fiducial points corresponds to physical movements of the physiological structure. The individual is authenticated based on the values of one or more fiducial points.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
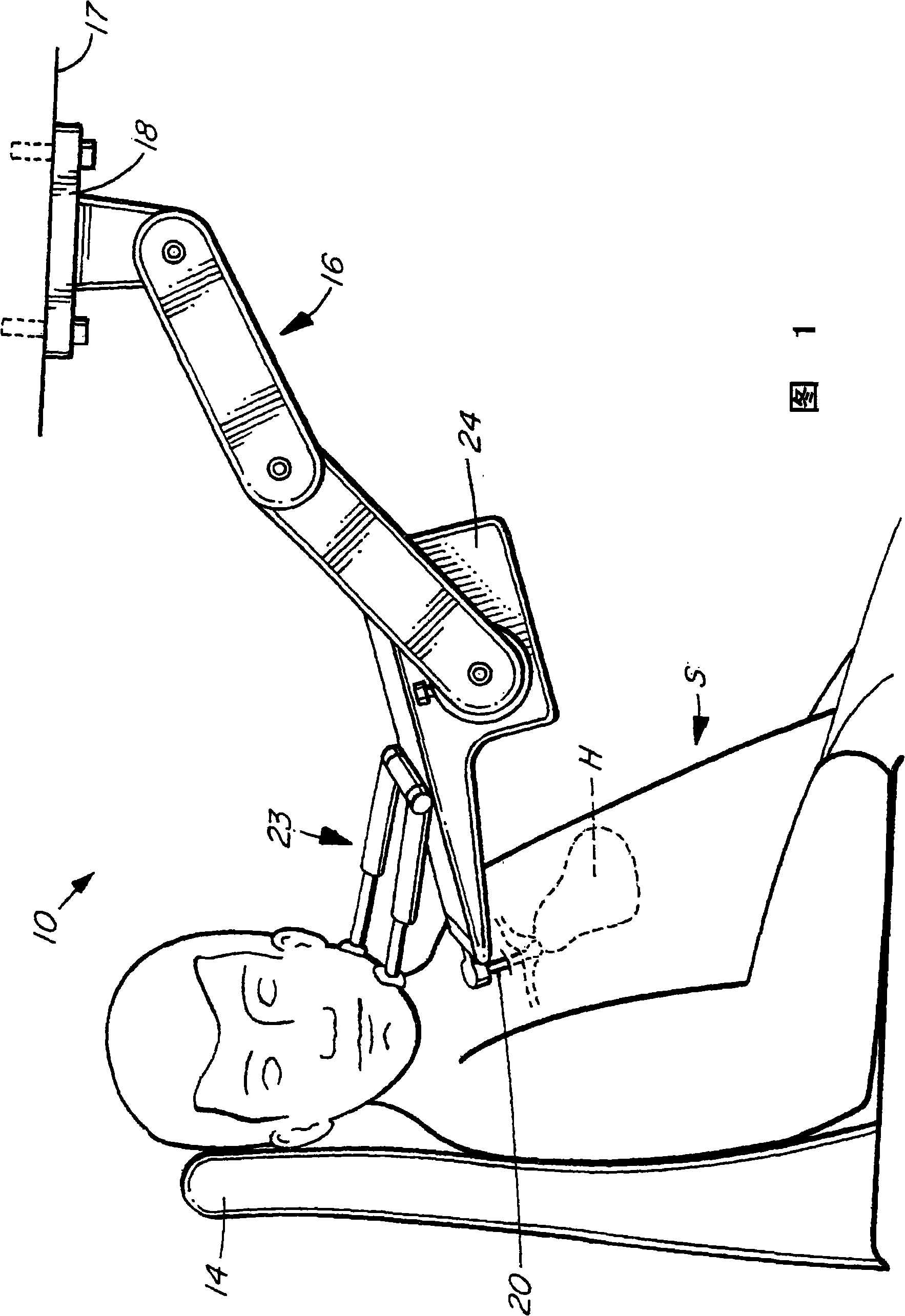
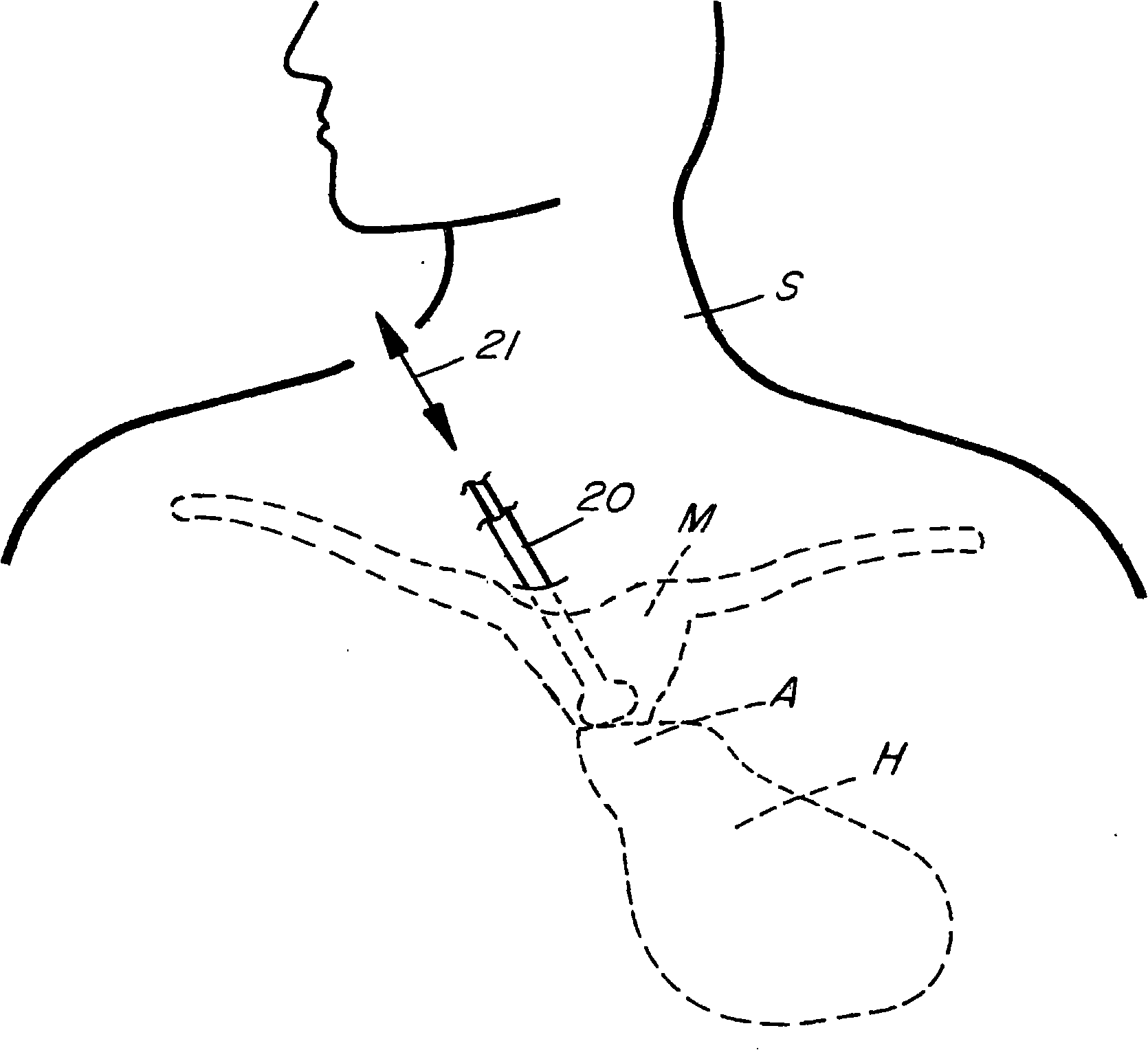
Methods and apparatus for monitoring heart impulses
Methods and apparatus for monitoring the heart motion of a subject employ a probe which can be coupled to a portion of the anatomy of the subject. The probe may couple to the subject's aortic arch or thyroid cartilage, for example. The probe is biased into contact with the subject. The probe detects movements caused by the heart motion. The apparatus may display accelerations and displacements caused by the heart motion. Waveforms from multiple anatomic sites may be acquired, normalized in time and amplitude, and combined to produce resultant waveforms. Combining the waveforms may involve addition or subtraction.
Owner:CANFORM MEDICAL
Methods of and apparatus for monitoring heart motions
InactiveUS20070043300A1Less of noise levelReduce quality control costsElectrocardiographyStethoscopeAudio power amplifierMedicine
A method of and an apparatus for monitoring the heart motion of a subject employ a probe which can be coupled to the aortic arch or to the thyroid cartilage of the subject for detecting movements caused by the heart motion and displaying the accelerations and displacement of the heart motion on an acceleration display and a displacement display. A mechanical motion amplifier amplifies the acceleration and an optical amplifier amplifies the displacement to counteract noise.
Owner:CANFORM MEDICAL
Method for removing motion from non-ct sequential x-ray images
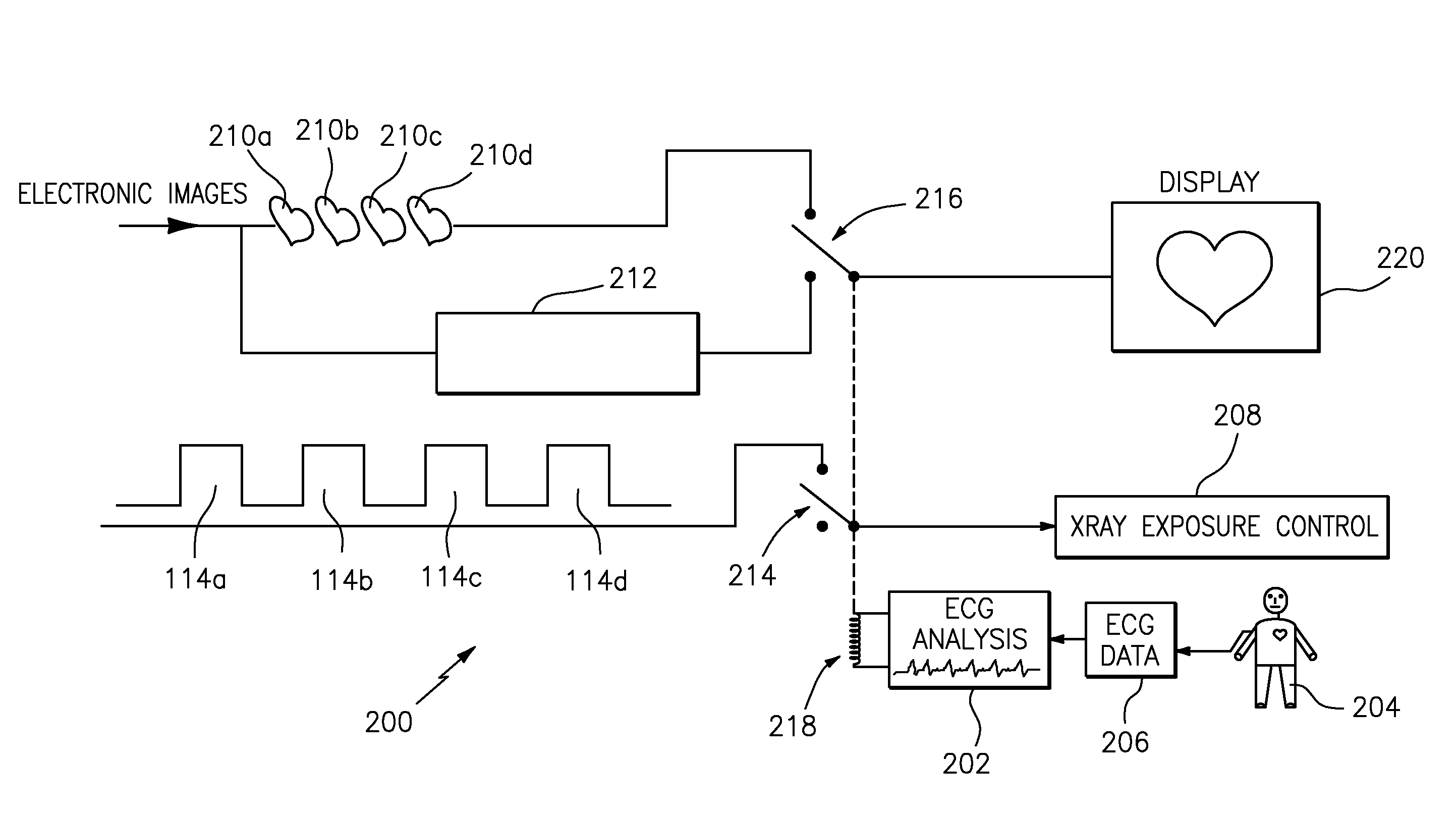
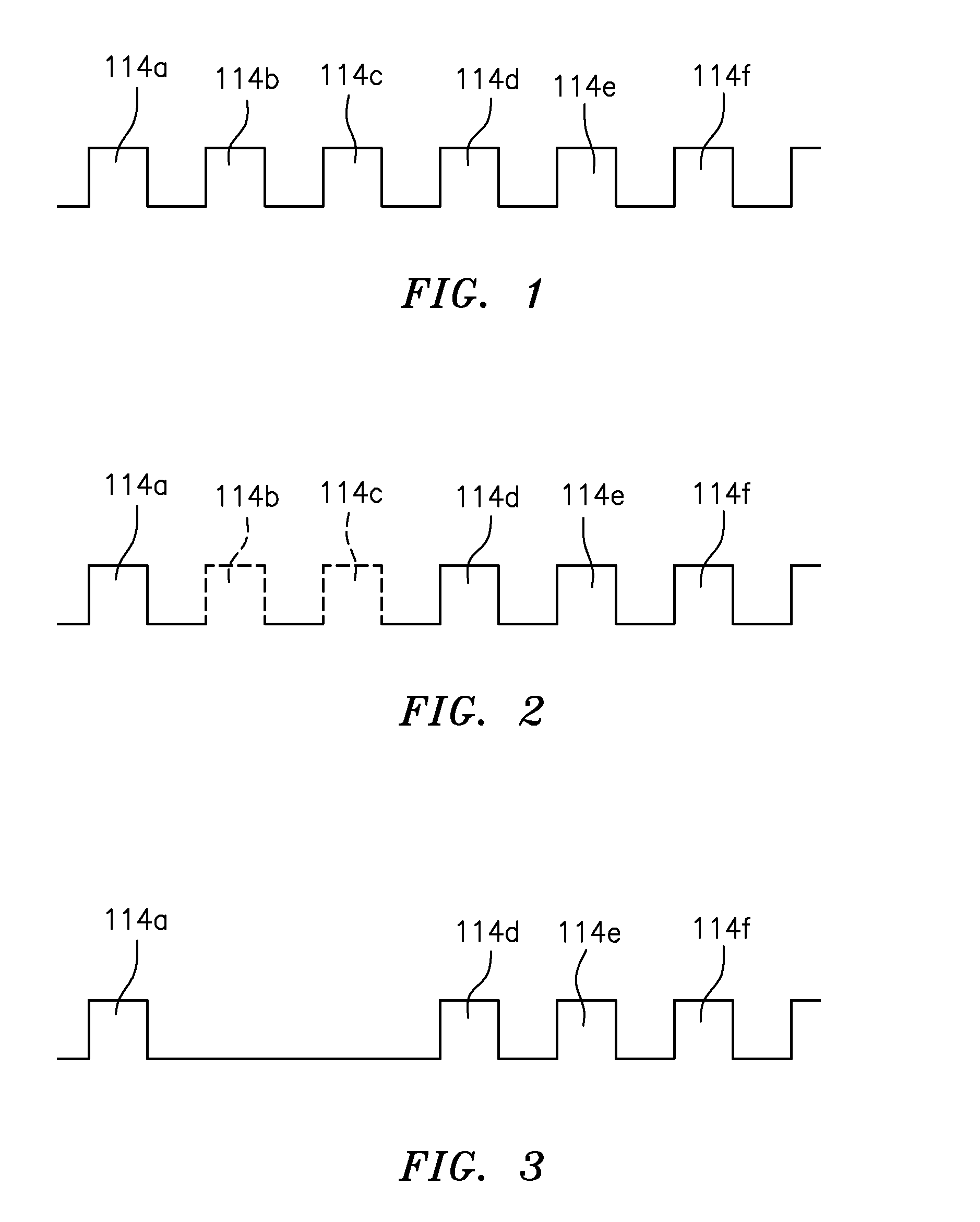
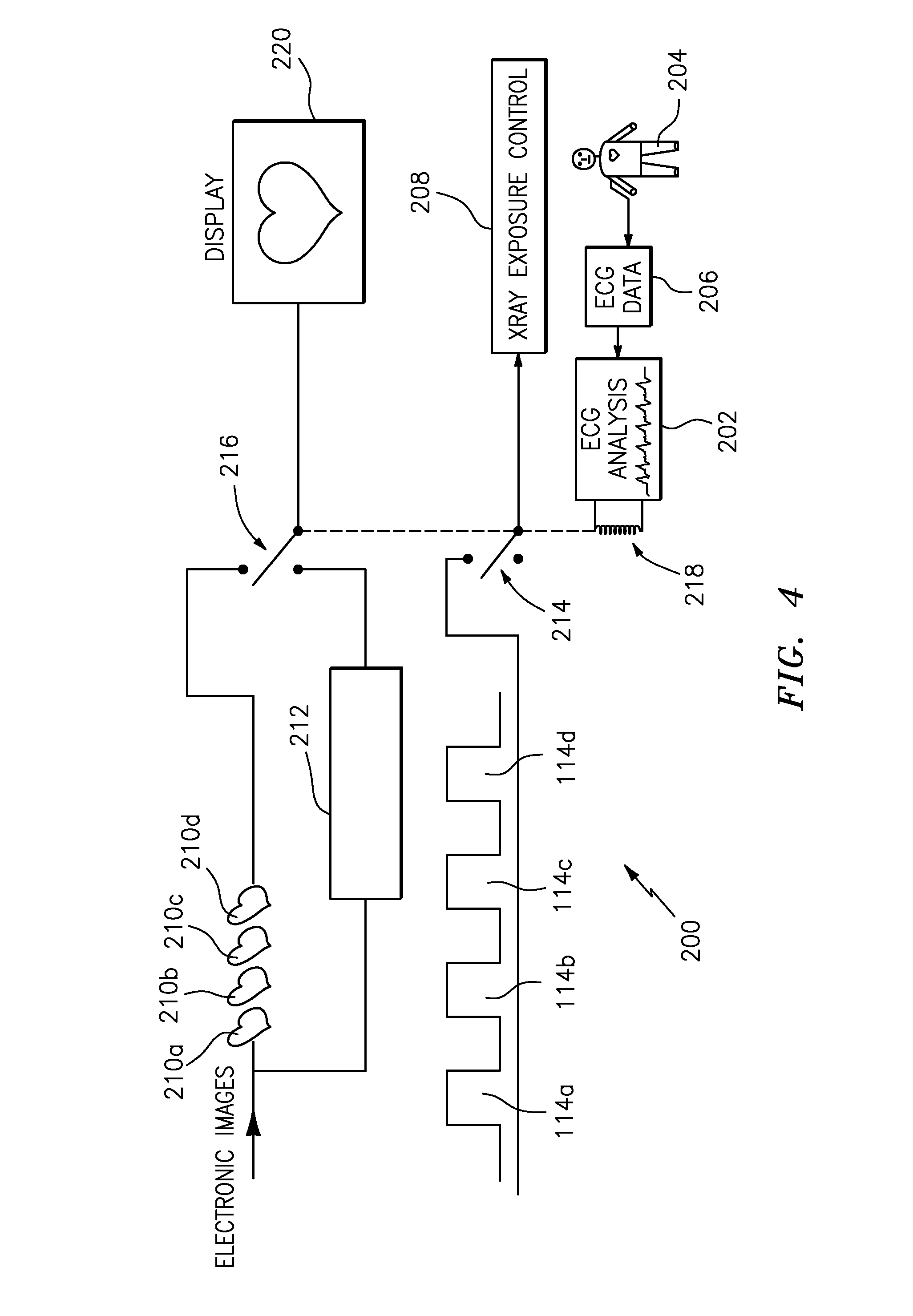
Applicant has disclosed a method for removing motion from non-CT cardiac angiographic or fluoroscopic x-ray 2-D sequential images, without using data prediction techniques in sequential CT imagery. Applicant's results are achieved by actively deleting or skipping exposure of certain 2-D flash image acquisitions during rapid heart motion (e.g., beating), the latter to reduce x-ray exposure. Applicant's preferred method comprises: positioning a person relative to a non-CT type x-ray machine, designed for fluoroscopy or angiography, with the person's heart between an x-ray source and a detector; monitoring rapid movement of the person's heart by electrocardiography; generating a series of x-ray pulses from the x-ray source; actively skipping any x-ray pulses by switching off the x-ray source during beating of the person's heart to prevent any images being generated from the skipped x-ray pulses; and generating sequential (i.e., either angiographic or fluoroscopic) 2-D cardiac images from the non-skipped x-ray pulses; wherein the motion is removed from the sequential images without using predictive algorithms and without using estimated compensation of motion.
Owner:GRADY JOHN K
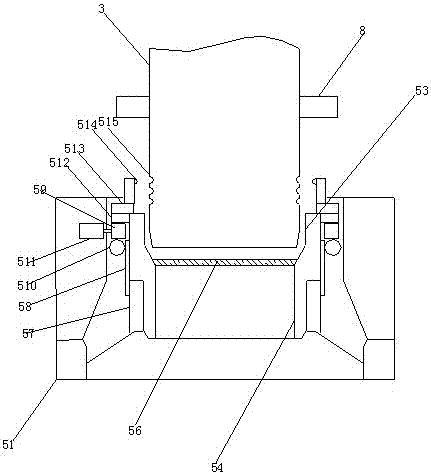
Conveniently and quickly detached and mounted infusion support
The invention discloses a conveniently and quickly detached and mounted infusion support which comprises a base, a supporting rod, a movable rod, a suspended bracket, a fixing device, a control switch, a charging interface, a limiting ring and a battery, wherein the supporting rod is arranged at the upper end of the base, the upper end of the supporting rod is connected to the movable rod through the fixing device, the suspended bracket is arranged at the upper end of the movable rod, and the control switch is arranged on one side of the fixing device. The conveniently and quickly detached and mounted infusion support has the beneficial effects that the supporting rod and the movable rod of the infusion support are fixedly connected through the fixing device, so that the control switch can be pressed, and a motor further drives a gear I to drive a gear II to move on a guide rail, and therefore, an annular gear drives a claw to perform a centered motion under rotation of the gear I so as to fixedly clamp the movable rod by the claw; and on the contrary, the motor rotates reversely to separate the fixing device from the movable rod, so that the movable rod and the supporting rod of the infusion support are conveniently detached and mounted, a patient or medical staff uses and operates the infusion support conveniently, and furthermore, the flexibility of the infusion support is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU PUJIANG KEXIAN TECH
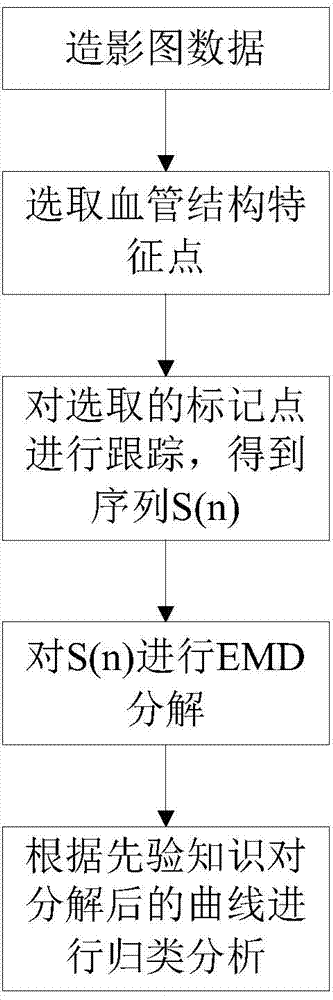
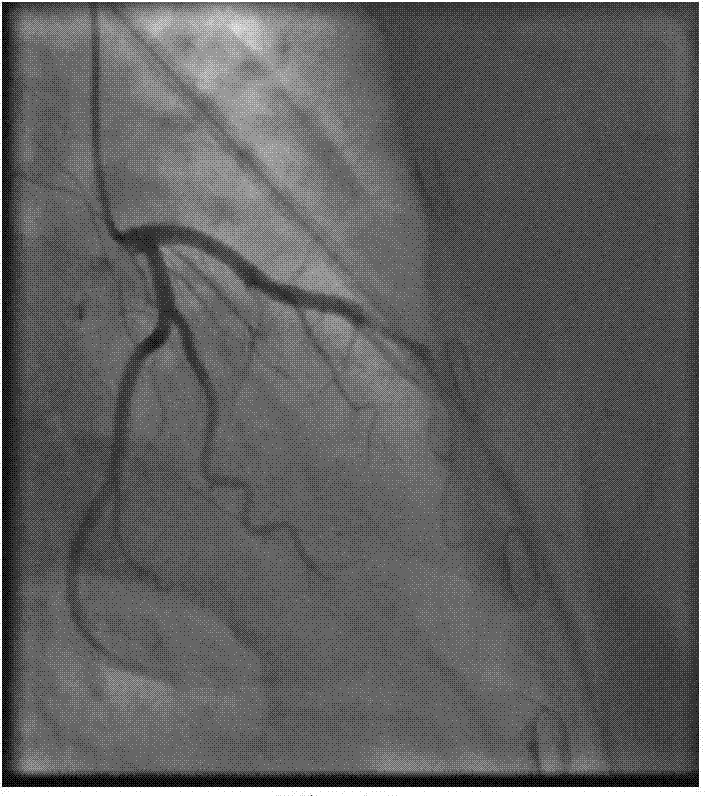
Single-arm x-ray angiography image multiple motion parameter decomposition and estimation method
InactiveCN103810721AWide applicabilityExtensive flexibilityImage enhancementImage analysisIndependent motionDecomposition
The invention discloses a single-arm x-ray angiography image sequence multiple motion parameter decomposition and estimation method. The method includes the steps: (1) automatically selecting stable vascular structure feature points; (2) automatically tracking the selected vascular structure feature points in a whole angiography image sequence; (3) selecting a sequence (img file=' DDA0000450354970000011.TIF' wi=' 92' he=' 74' / ) with the length ns=k*N1(k>1) in a point tracking sequence s(n) (the N1 refers to the cycle of heart motion); (4) decomposing (img file=' DDA0000450354970000012.TIF' wi=' 96' he=' 64' / ) into x-direction motion x(n) and y-direction motion y(n), respectively performing EMD (empirical mode decomposition) for the x(n) and the y(n) to obtain independent motion signals after EMD; (5) correspondingly classifying the independent motion signals according to priori physiological knowledge. The method has wide applicability and flexibility, higher safety and operability and better reliability and accuracy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Portable Heart Motion Monitor
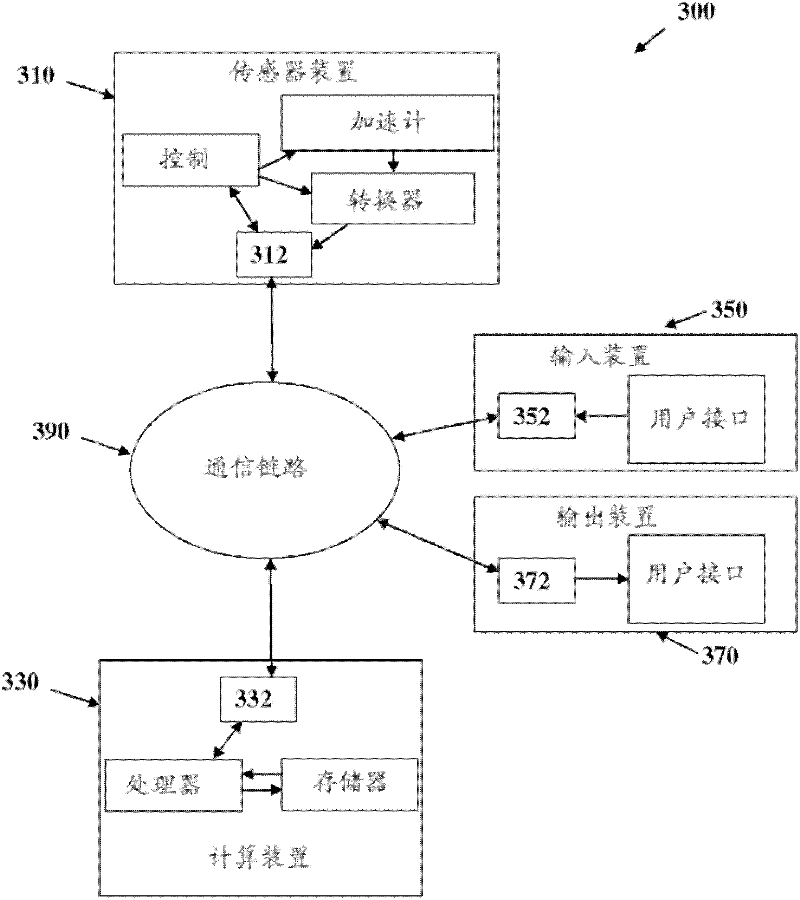
The present disclosure describes a method and device to monitor the heart of a subject using radio signals. Availability of a portable heart monitor that can be used in a subject's home can increase patient compliance and improve diagnosis rates of cardiac conditions. A mobile heart monitor can be especially useful to those subjects who are elderly, incapacitated, or do not have easy access to a clinic, doctor's office, or hospital.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
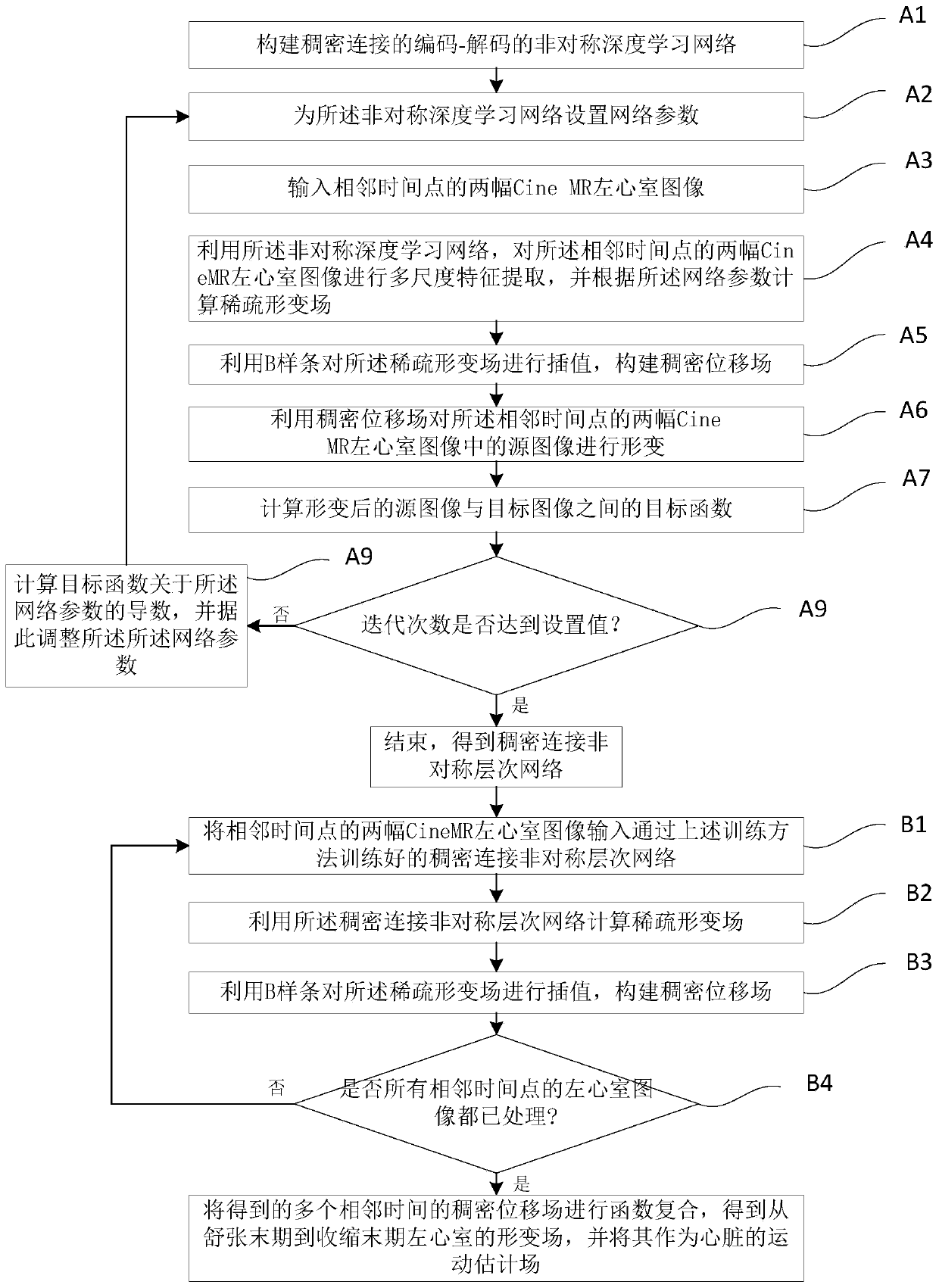
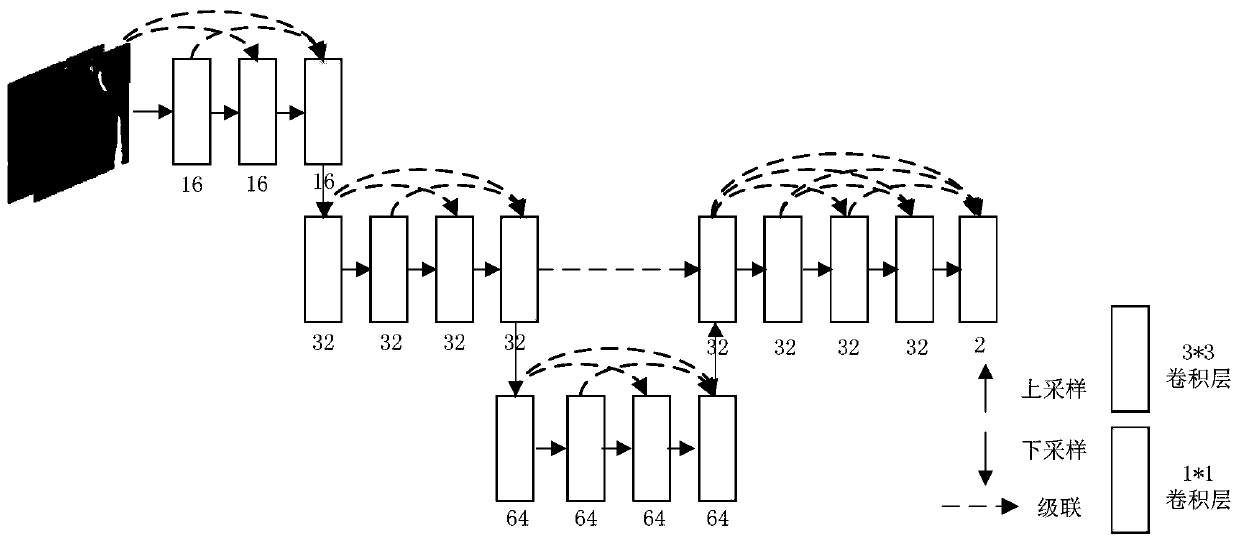
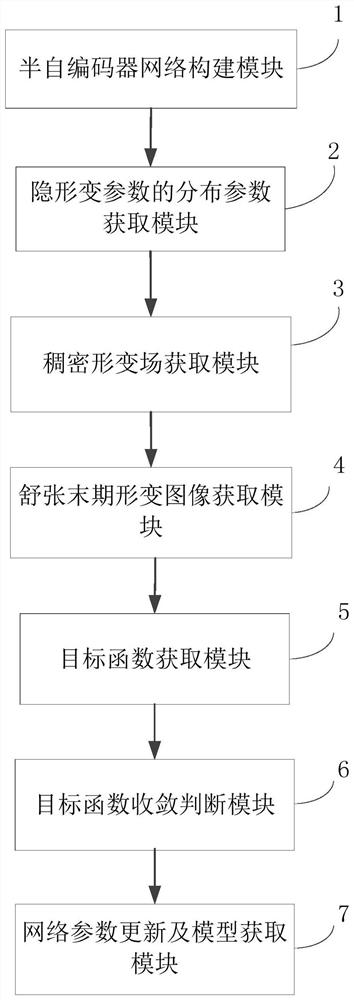
Dense connection asymmetric hierarchical network training method and cardiac motion field estimation method
ActiveCN110148150AImprove smoothnessMitigate vanishing gradient phenomenonImage enhancementImage analysisLearning networkLeft ventricle wall
The invention discloses a dense connection asymmetric hierarchical network training method and a cardiac motion field estimation method, and aims to solve the problem of cardiac motion estimation by using a dense connection coding-decoded asymmetric deep learning network to extract multi-scale characteristics of a left ventricle in two adjacent time point Cine MR images, and fusing the multi-scalecharacteristics by the coding-decoded structure network to decide the displacement of the pixel point. The introduction of the dense connection network alleviates the gradient disappearance phenomenon, the left ventricle characteristics are more effectively utilized through the fusion of the left ventricle characteristics, and fewer network parameters are provided. Wherein the asymmetric networkstructure can obtain sparse deformation fields at equal intervals, and the B spline interpolation is further utilized to obtain a smooth dense deformation field. The distortion energy constraint of the deformation field is introduced into the objective function of network training, the smoothness of the deformation field is improved, and a more stable and reasonable heart motion field can be obtained to be used for quantitative analysis of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
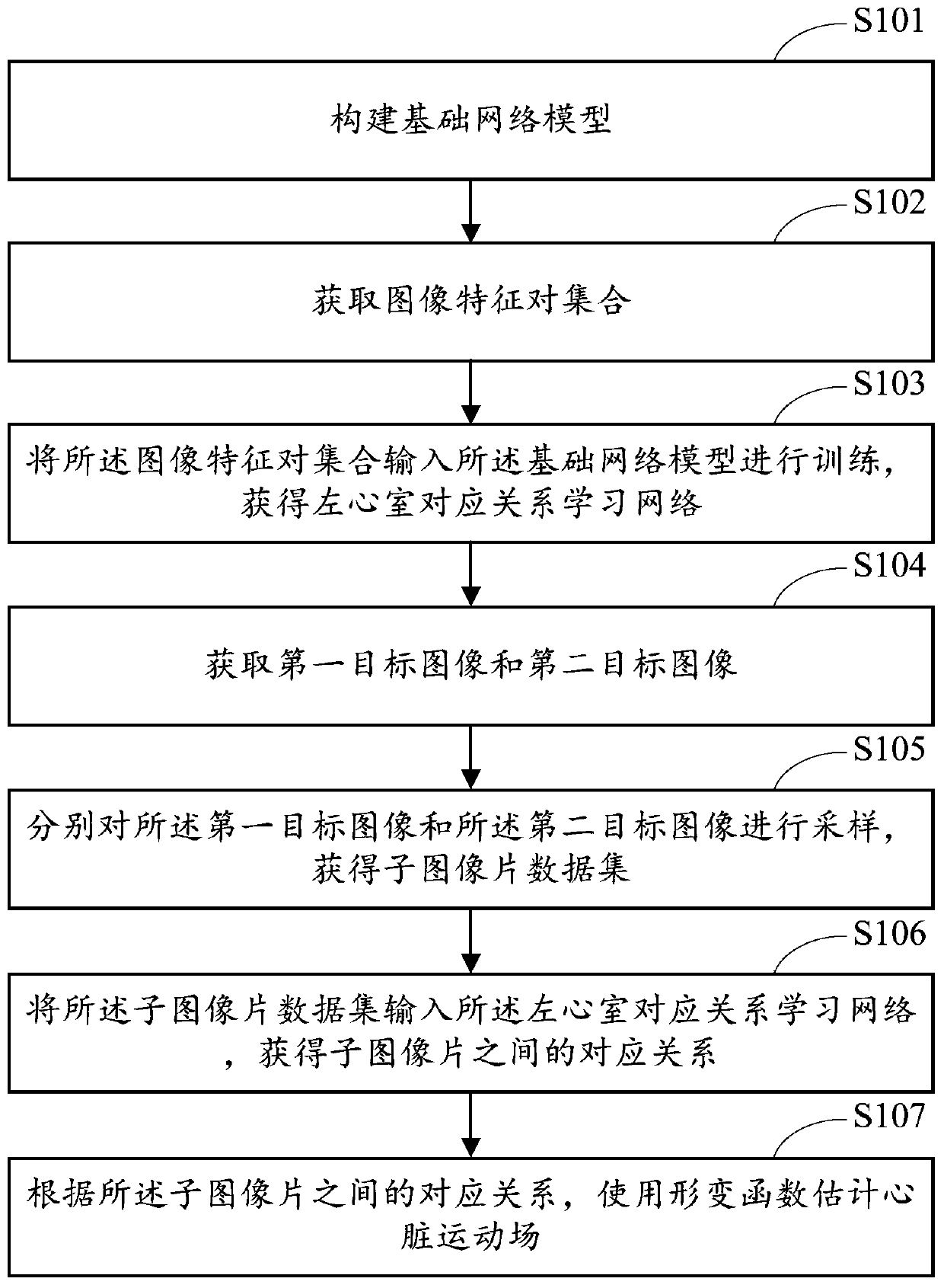
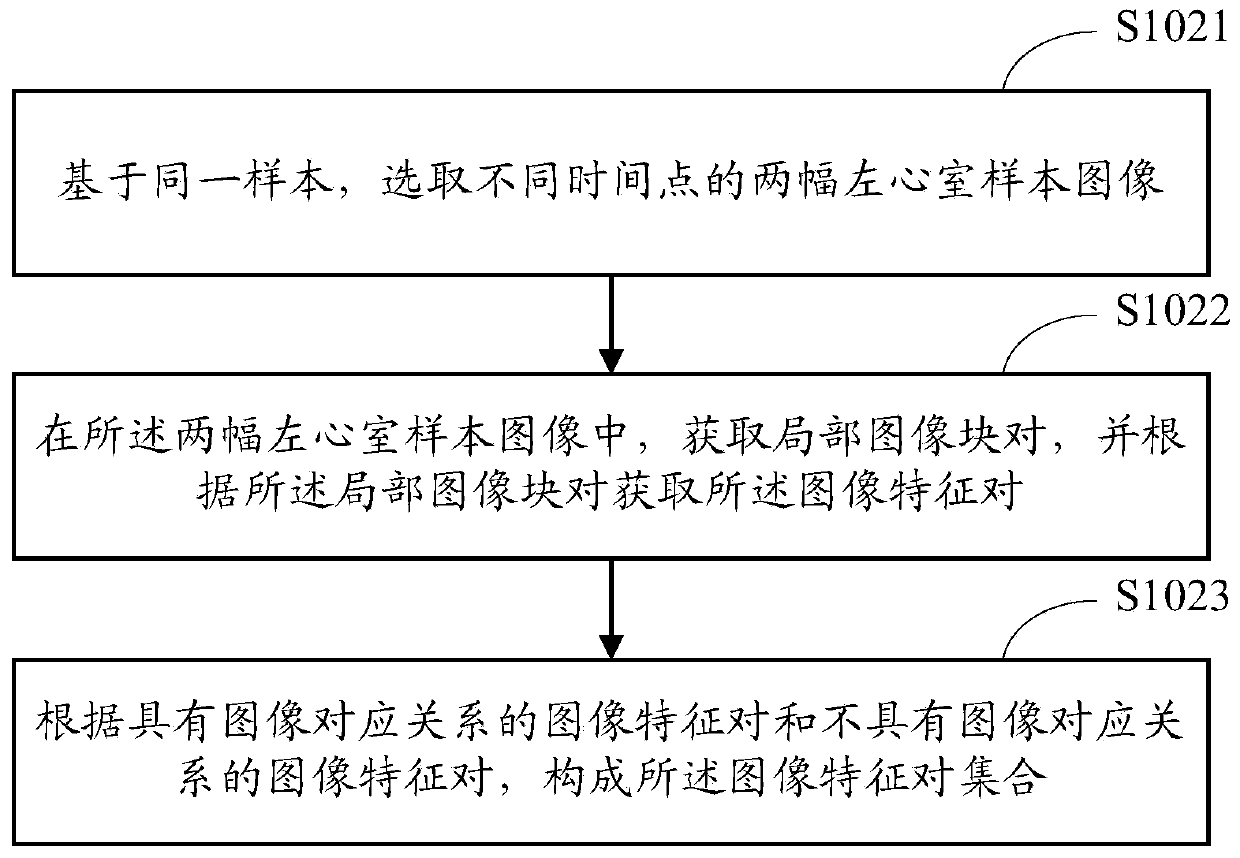
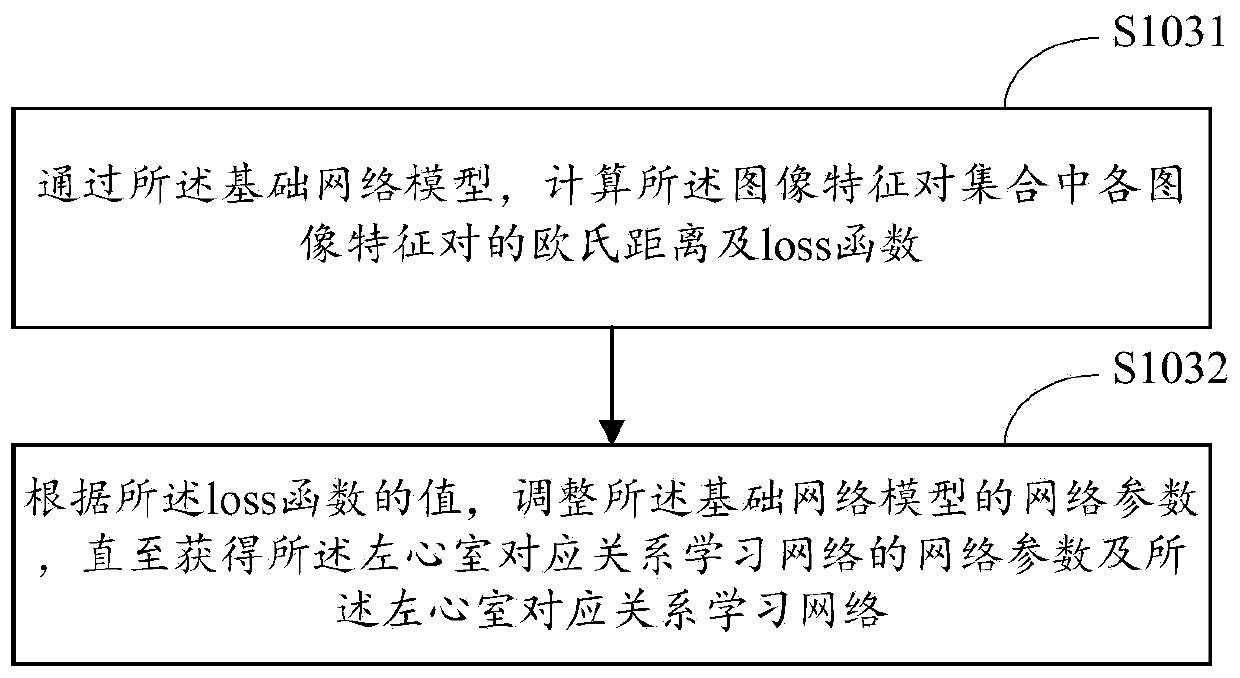
Heart motion estimation method and system and terminal equipment
ActiveCN110136111AAccurate analysisOvercome the mismatch problemImage enhancementImage analysisData setSample image
The invention is applicable to the technical field of image processing, and provides a heart motion estimation method and system and terminal equipment, and the method comprises the steps: building abasic network model which is a deep learning network of dense connection mixed hole convolution; obtaining an image feature pair set according to the left ventricle sample image; inputting the image feature pair set into a basic network model for training to obtain a left ventricle corresponding relation learning network; obtaining a first target image and a second target image; respectively sampling the first target image and the second target image to obtain a sub-image slice data set; inputting the sub-image slice data set into a left ventricle corresponding relation learning network to obtain a corresponding relation between sub-image slices; and estimating the heart motion field by using a deformation function according to the corresponding relationship between the sub-image patches.By means of the method, a stable and reasonable heart motion field can be obtained on the premise that the cardiac muscle layer is not segmented.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
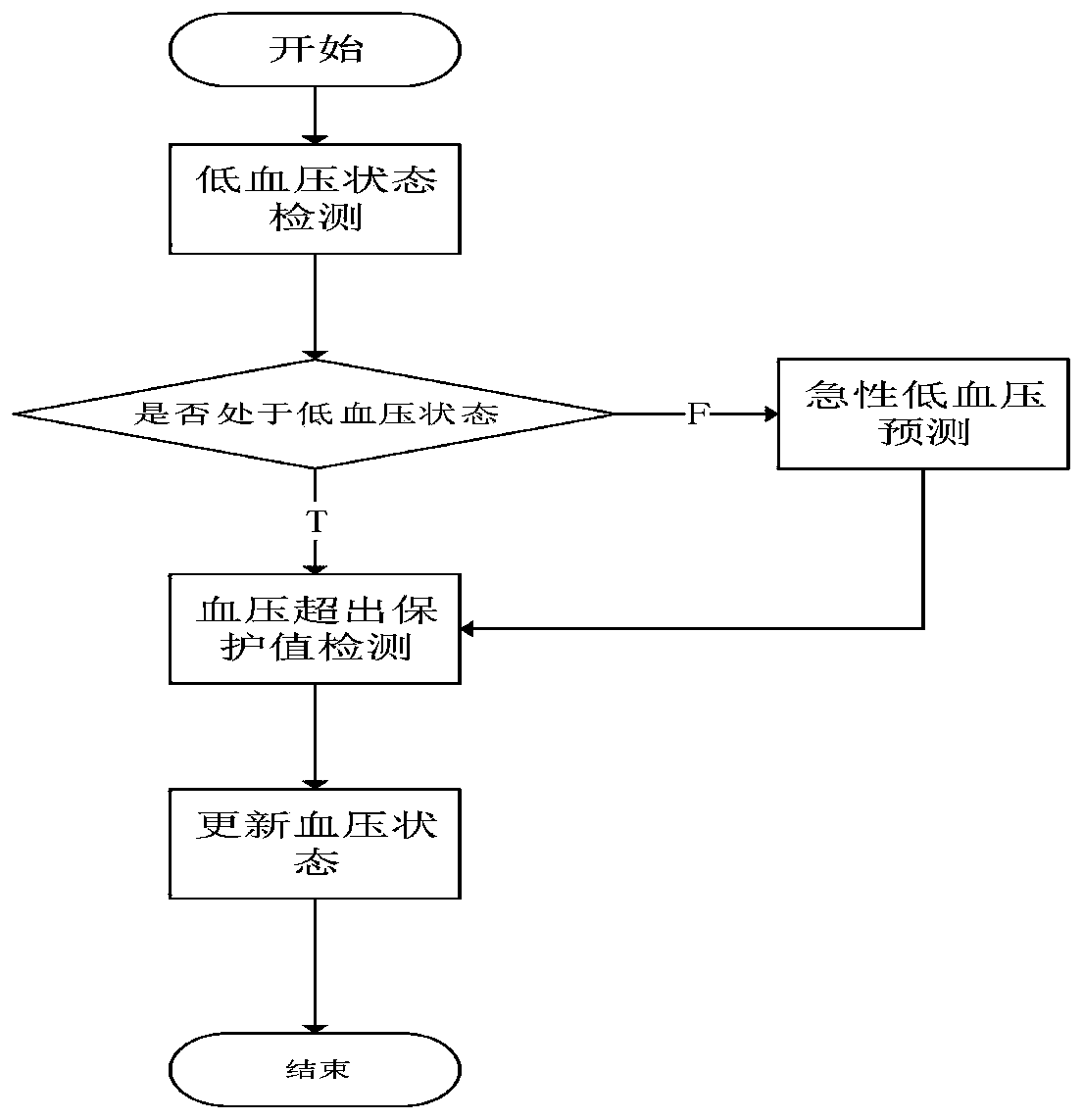
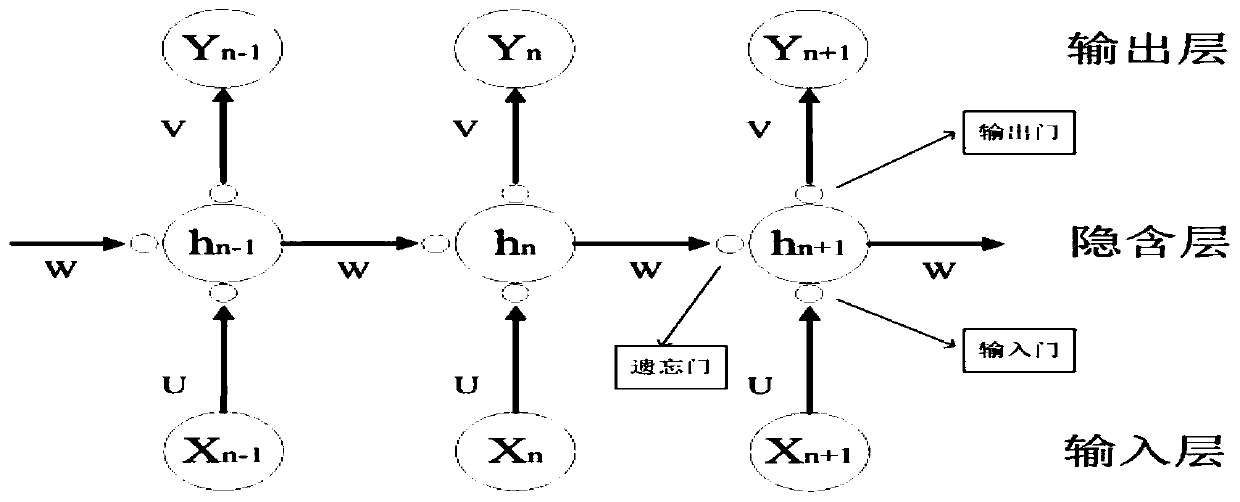
Acute hypotension hybrid early warning method based on LSTM network
PendingCN110507296AEfficient and safe rehabilitation exerciseAvoid accidentsMedical imagingEvaluation of blood vesselsHeart motionBlood pressure
The invention discloses an acute hypotension hybrid early warning method based on an LSTM network. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, a collected physiological data sequence is imported; hypotension event detection is carried out; if a patient is in a hypotension state at present, a result is output for hypotension early warning, if the patient is not in the hypotension state at present, predicting of an acute hypotension event is carried out, if the acute hypotension is predicted to occur in a next time period, the result is output for hypotension prediction early warning, then a blood pressure protection value is detected, and if the blood pressure exceeds the protection value, returning to two results is carried out for early warning. The prediction and early warning canbe carried out on acute hypotension, so that time is bought for monitoring personnel, the safety of the patient during rehabilitation training is guaranteed, and cardiac exercise rehabilitation becomes more scientific, efficient and safer.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
A prosthetic valve prosthesis
ActiveCN109199640AFits uneven contoursGood effect on preventing paravalvular leakageHeart valvesProsthetic valveHeart motion
A prosthetic valve prosthesis including stents and valves, the stent comprises a valve seam segment and an atrial segment, a valve is fixedly attached to the seam of the valve, a suture segment of that valve is connected with an atrial segment, the atrial segment consists of radial rod-shaped supports, a rod-shaped support include two main supports and at least one auxiliary support, one end of the rod-shaped support is fixedly connected with the valve sewing section as a fixing end. The other end of the rod-shaped support is dissociated as a free end, a flexible skirt is arranged between adjacent rod-shaped supports, and the atrial segment can be adapted into a D-shaped structure when the atrial segment is completely released. The connecting line of the free end of the main support constitutes a straight section of the D-shaped structure, and the free end of the auxiliary support is located on an arc section of the D-shaped structure. On the basis of guaranteeing reliable fixation, the invention not only reduces the influence of valve convection, but also reduces the pressure on heart tissue and the influence on heart motion, and has better leakage prevention effect.
Owner:NINGBO JENSCARE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Method for acquiring x-ray data, x-ray device, computer program and electronically readable storage medium
A method and device for acquiring at least a part of an x-ray data set with at least one x-ray device. The x-ray data set includes at least one first x-ray image data set and at least one second x-ray image data set acquired separated in time that are to be evaluated together. Both x-ray image data sets show a region of interest of a patient that is subject to heart motion at different phases of a heart cycle. The second x-ray image data set is acquired triggered at a beginning of each heart cycle covered by the acquisition and with an acquisition rate such that the phases of the acquired x-ray image data set match phases of the first x-ray image data set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
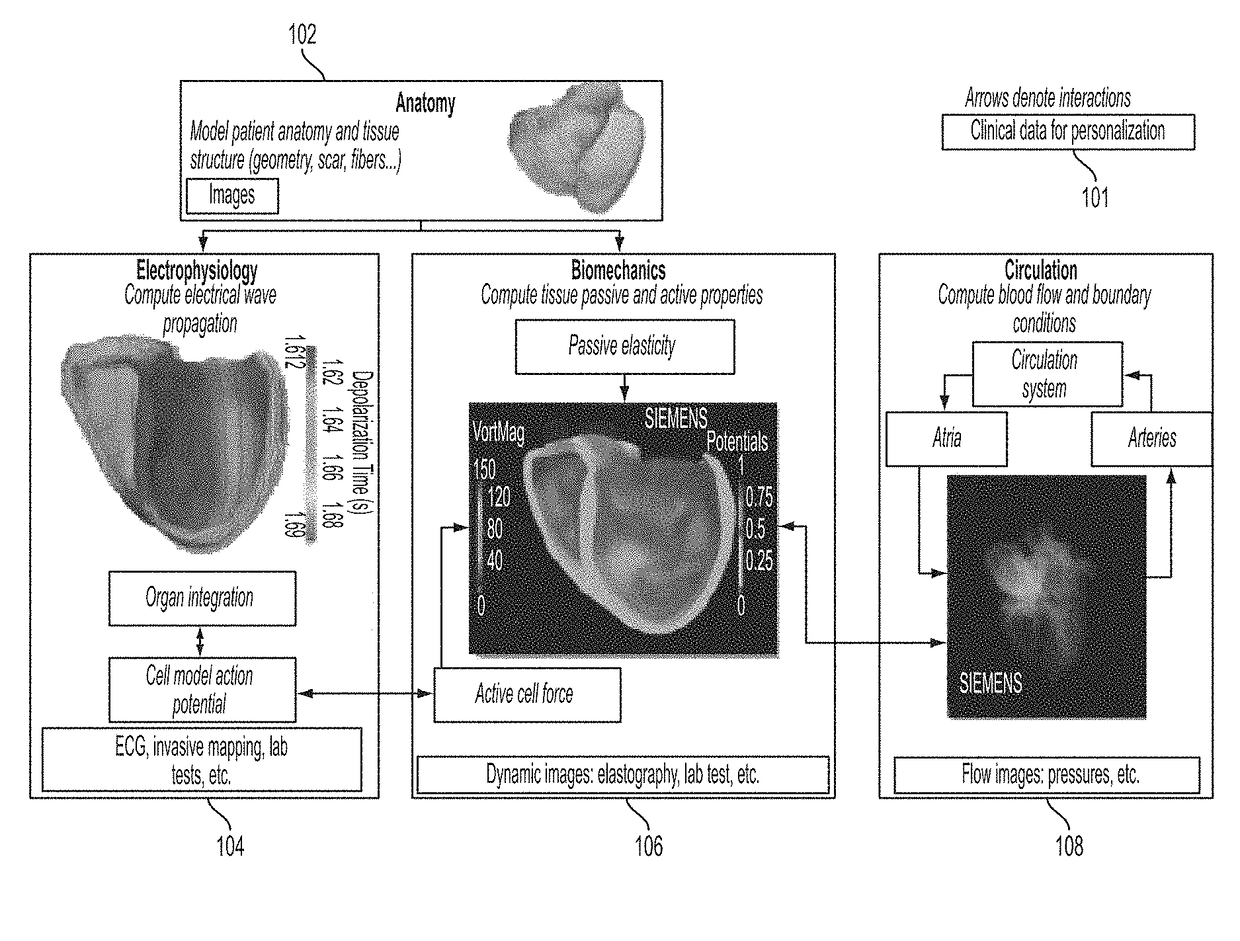
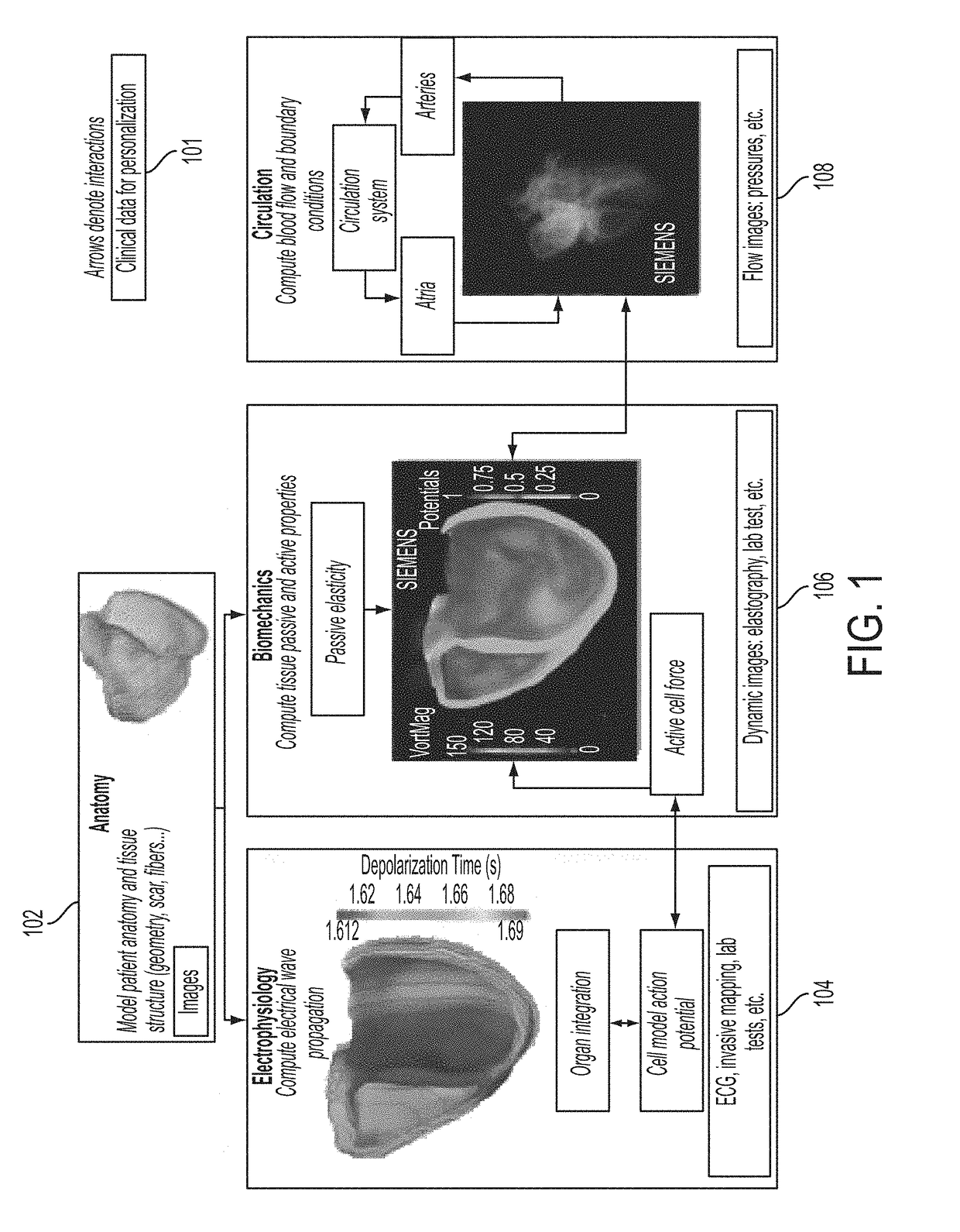
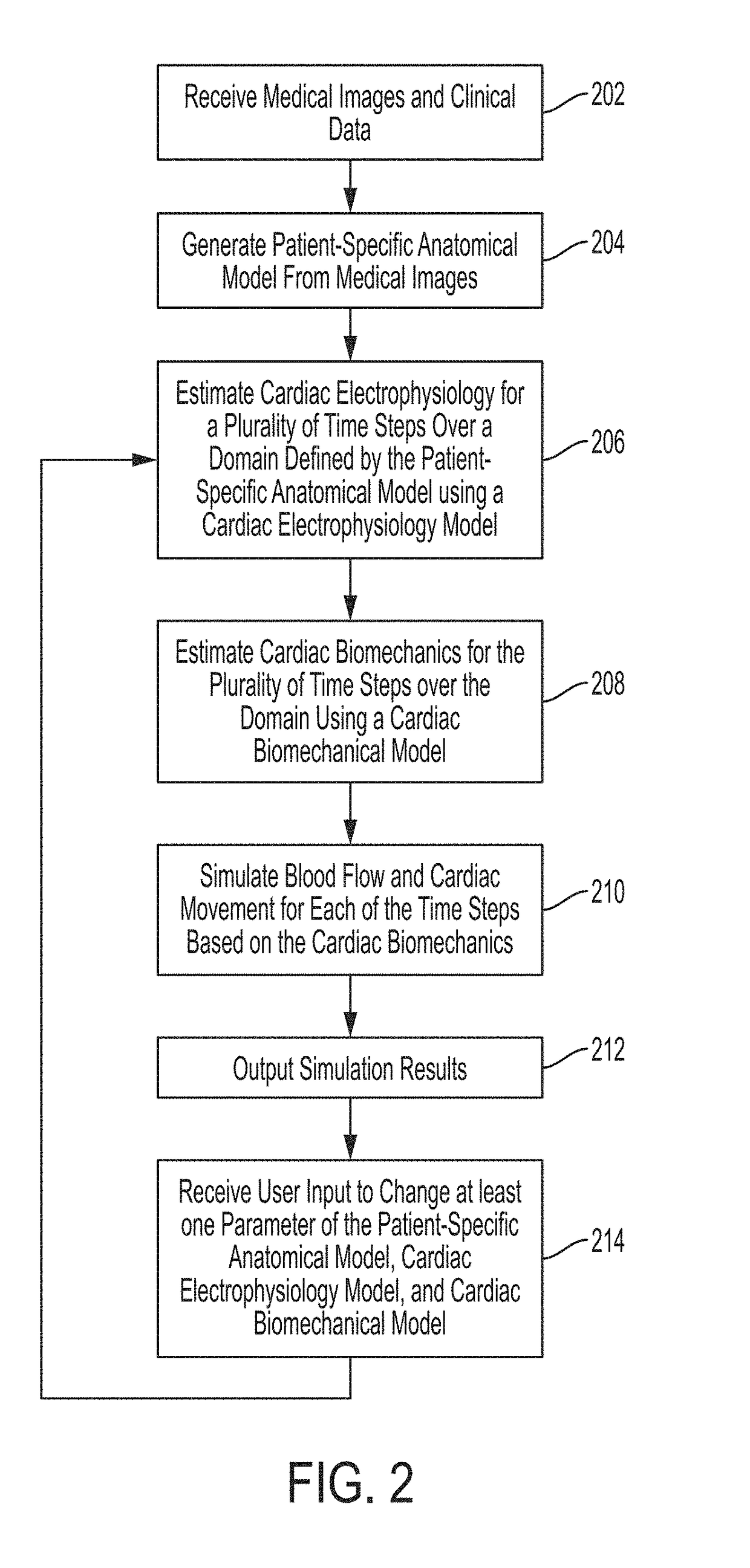
Method and system for interactive computation of cardiac electromechanics
A method and system for simulating cardiac function of a patient. A patient-specific anatomical model of at least a portion of the patient's heart is generated from medical image data. Cardiac electrophysiology potentials are calculated over a computational domain defined by the patient-specific anatomical model for each of a plurality of time steps using a patient-specific cardiac electrophysiology model. The electrophysiology potentials acting on a plurality of nodes of the computational domain are calculated in parallel for each time step. Biomechanical forces are calculated over the computational domain for each of the plurality of time steps using a cardiac biomechanical model coupled to the cardiac electrophysiology model. The biomechanical forces acting on a plurality of nodes of the computational domain are estimated in parallel for each time step. Blood flow and cardiac movement are computed at each of the plurality of time steps based on the calculated biomechanical forces.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
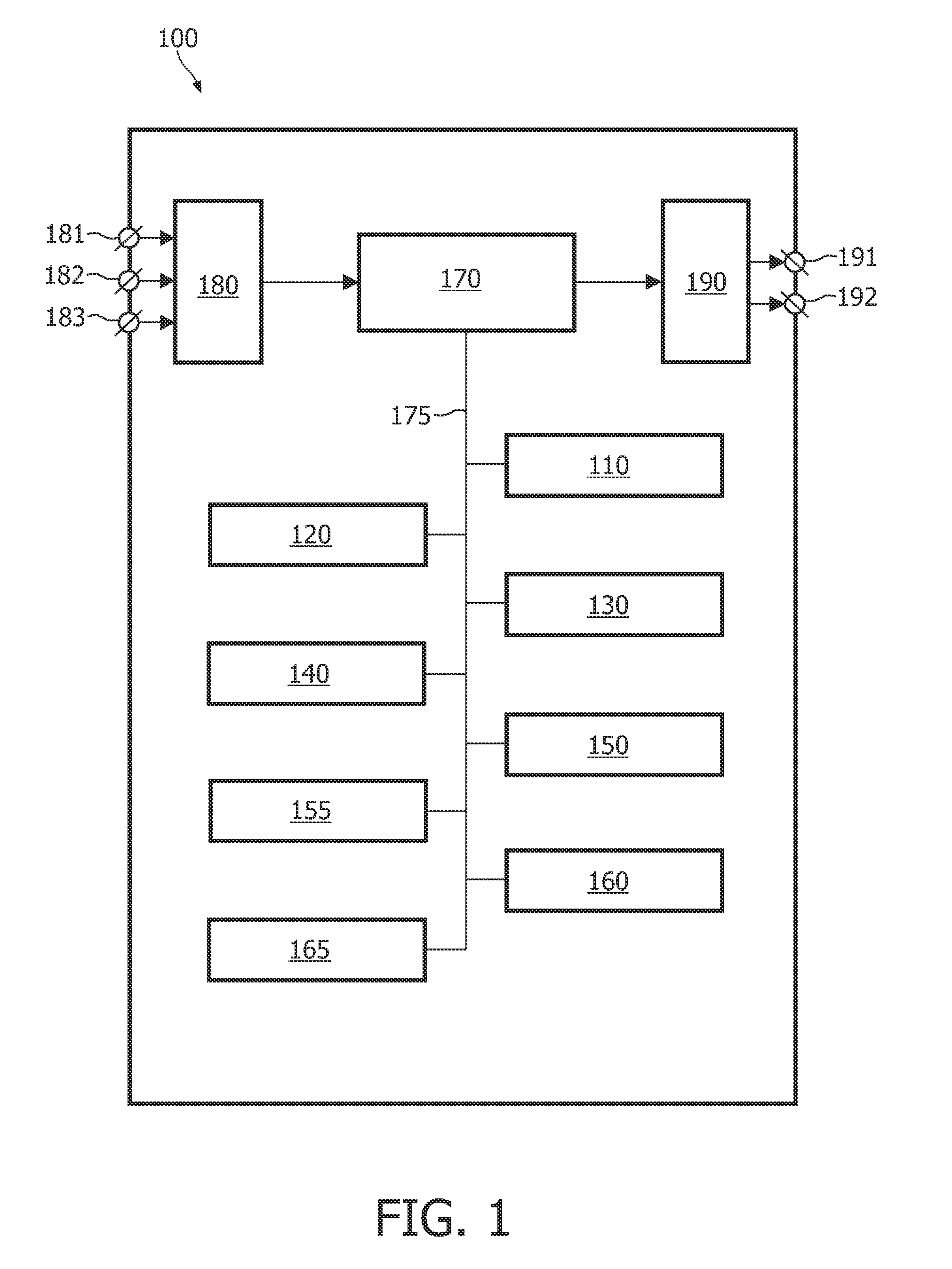
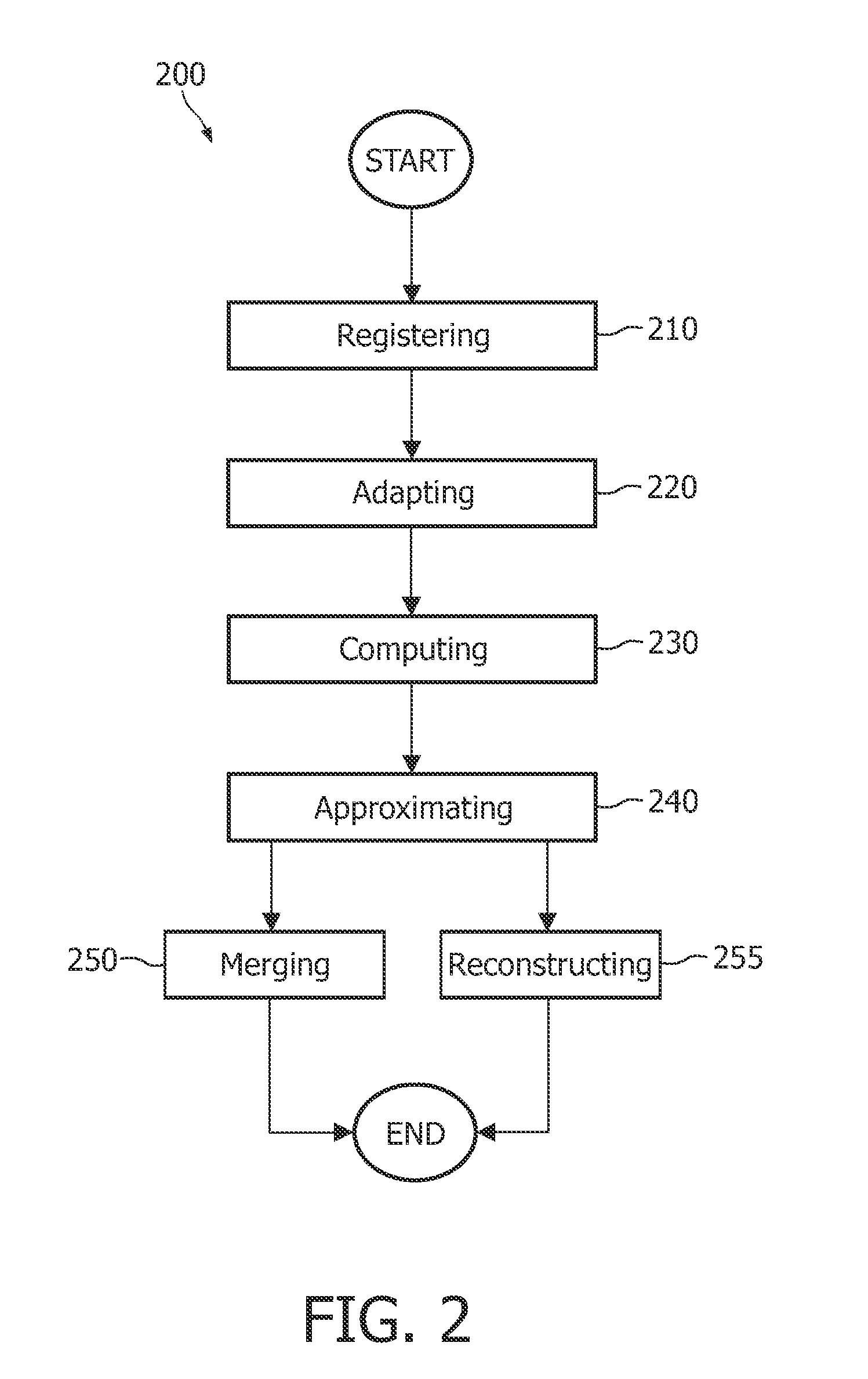
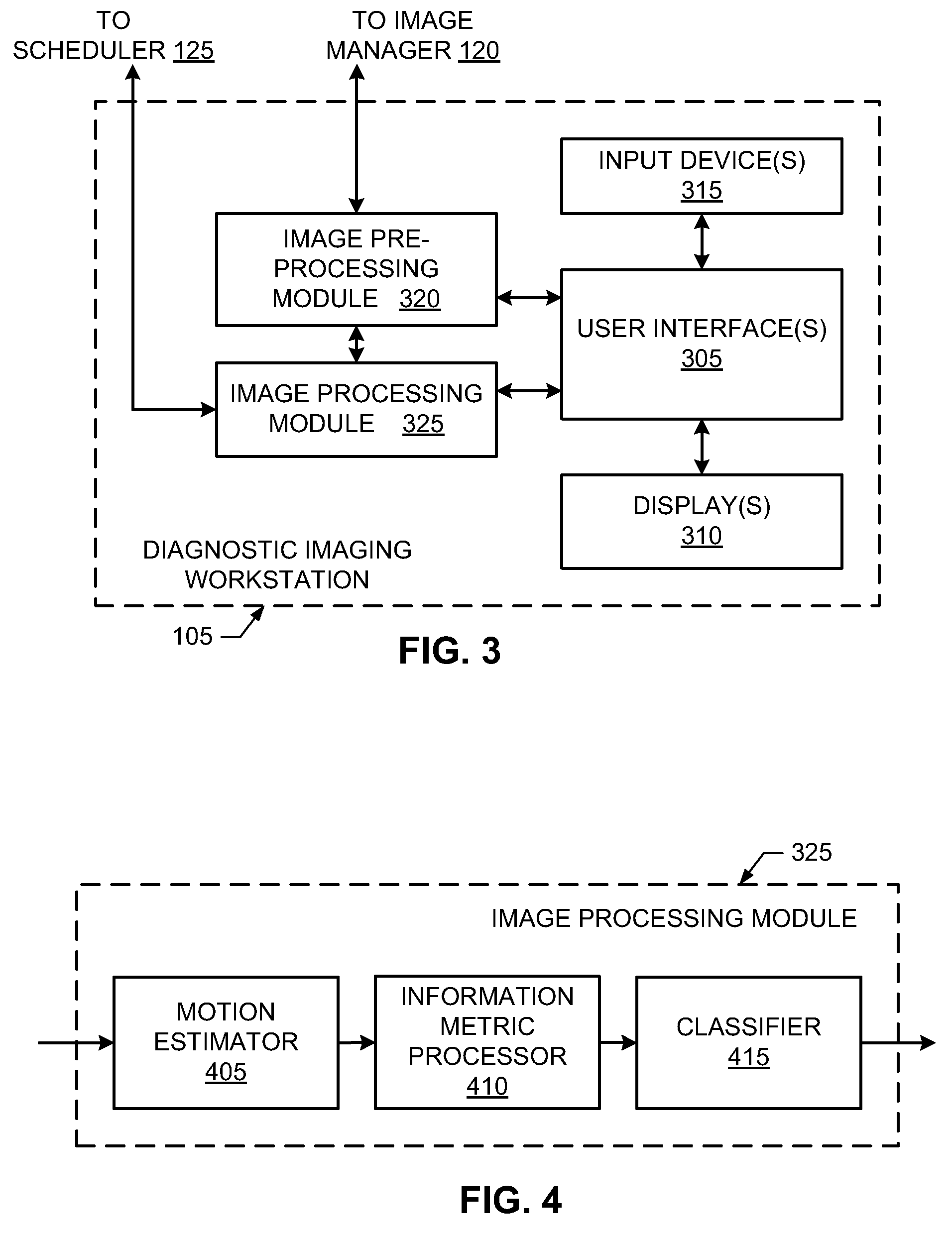
Methods, apparatus and articles of manufacture to process cardiac images to detect heart motion abnormalities
ActiveUS20110064284A1Reducing interReducing intra-observer variabilityImage enhancementImage analysisHeart motionRat heart
Example methods, apparatus and articles of manufacture to process cardiac images to detect heart motion abnormalities are disclosed. A disclosed example method includes adapting a state of a state-space model based on a plurality of cardiac images to characterize motion of a heart, computing an information-theoretic metric from the state of the state-space model, and comparing the information-theoretic metric to a threshold to determine whether the motion of the heart is abnormal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
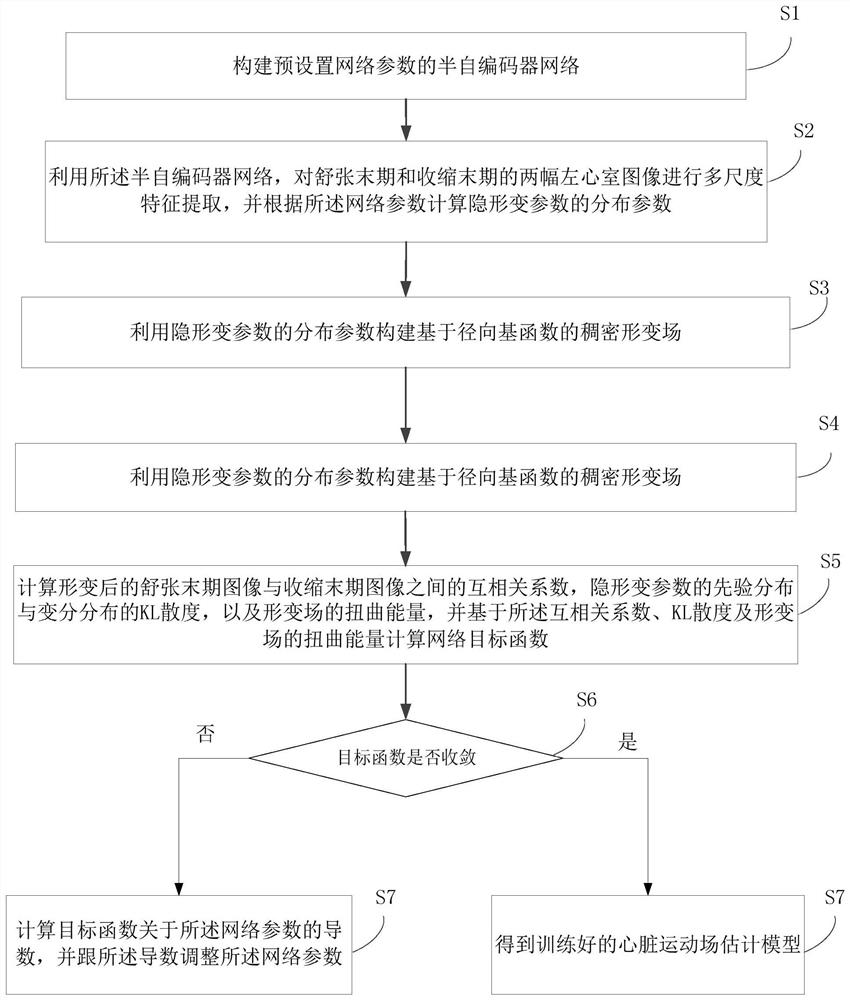
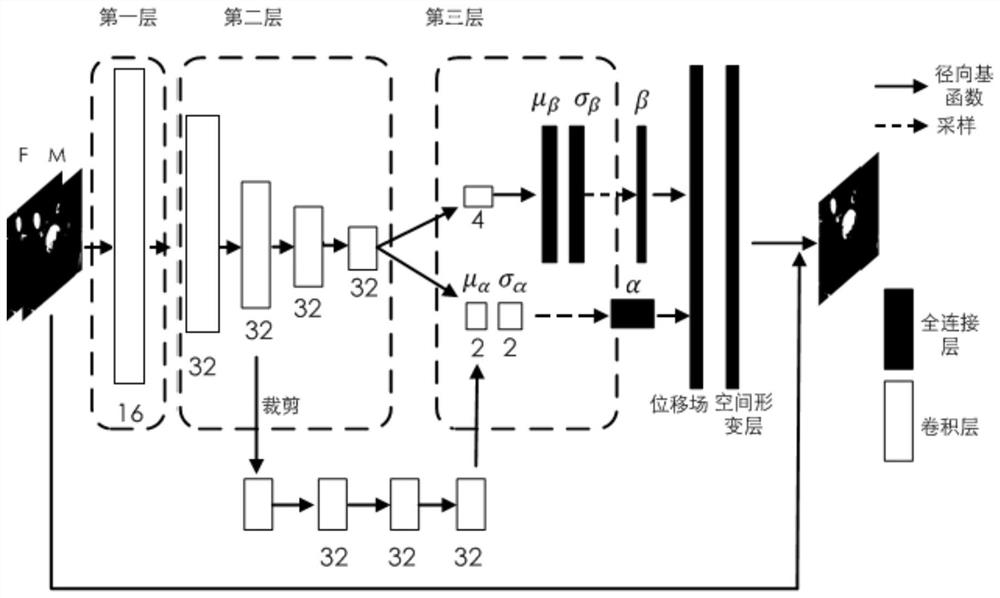
Method and system for training heart motion field estimation model and method and system for heart motion field estimation
PendingCN111784732AOvercome the defect of low estimation accuracyHigh deformation accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisLeft ventricle wallAutoencoder
The invention discloses a method and a system for training a heart motion field estimation model and a method and a system for heart motion field estimation. According to the method and the system fortraining a heart motion field estimation model, a semi-auto-encoder network is used to extract multi-scale features of the left ventricle in a Cine MR images at the end of diastole and the end of systole, different scale features are fused through an encoding network so as to decide distribution parameters of deformation parameters of control points, a deformation model of a radial basis functionis introduced into an auto-encoder, and a decoding process is not needed in an auto-encoder network structure, so that the network is lightened. The non-uniformly distributed control points are adopted, so that the deformation field of the area where the left ventricle is located is easier to control, and the deformation precision is higher; and meanwhile, invisible variable parameters have definite physical significance, the smoothness of a deformation field is easier to control, and a more stable and reasonable heart movement field is obtained to be used for quantitative analysis of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
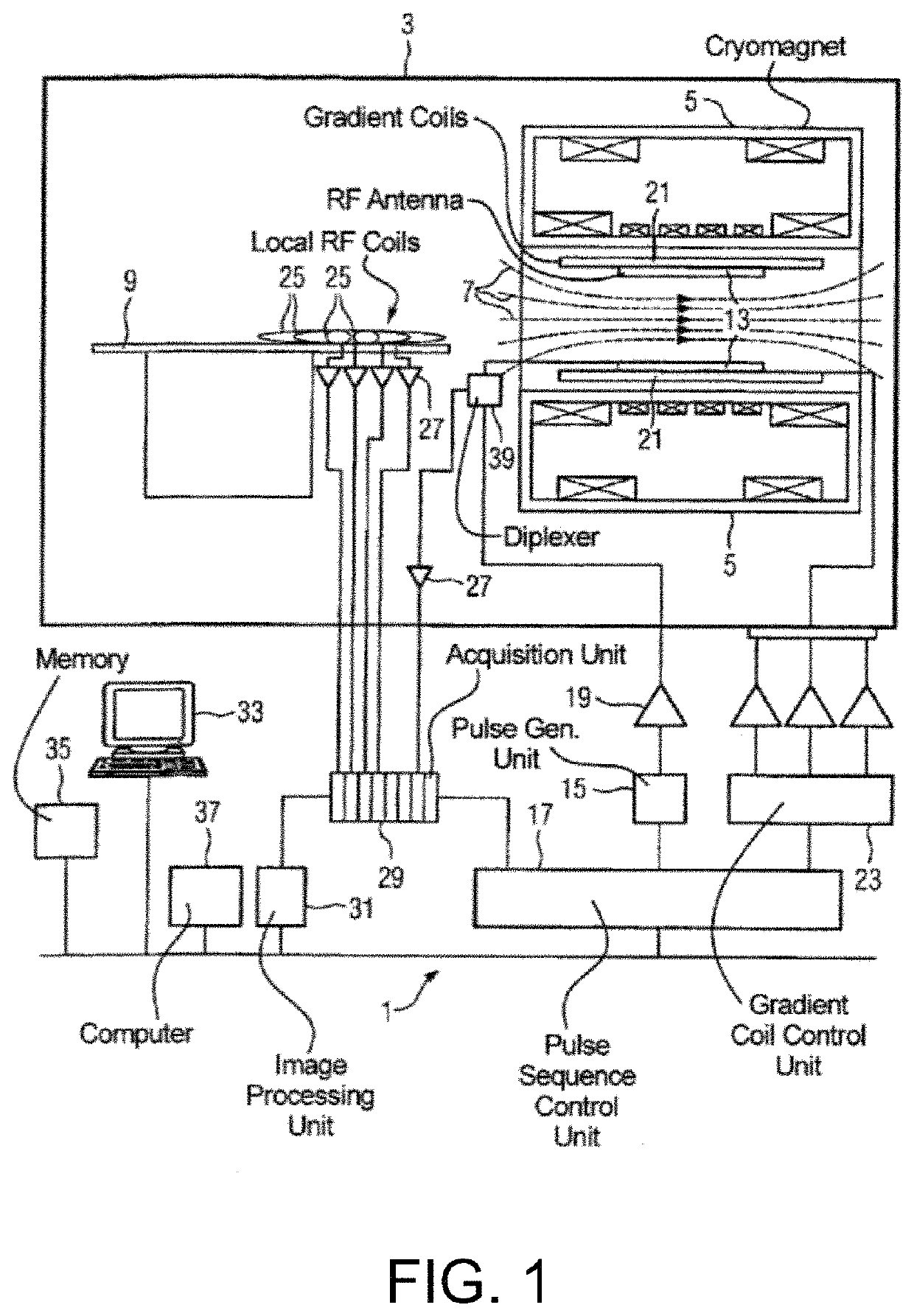
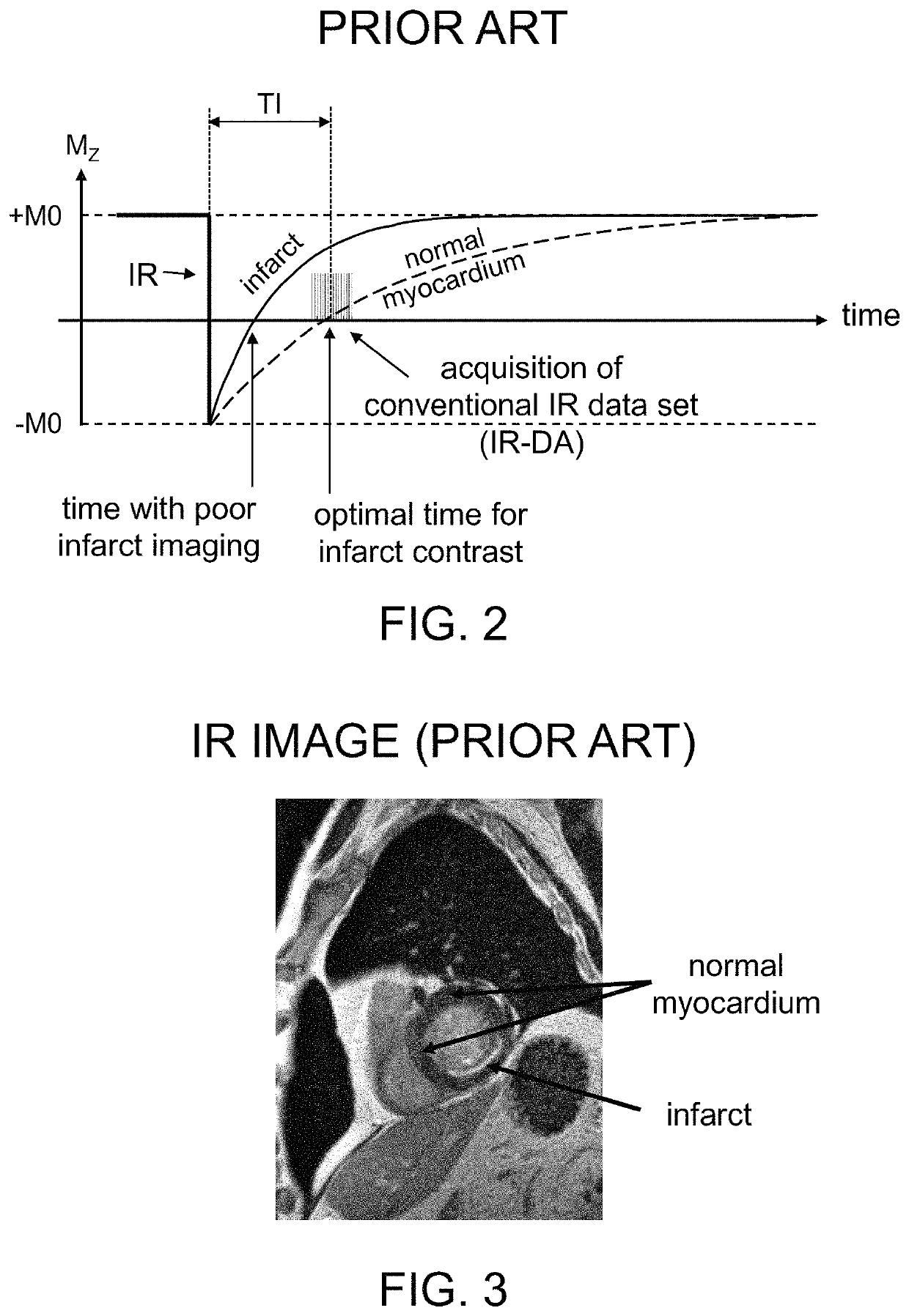
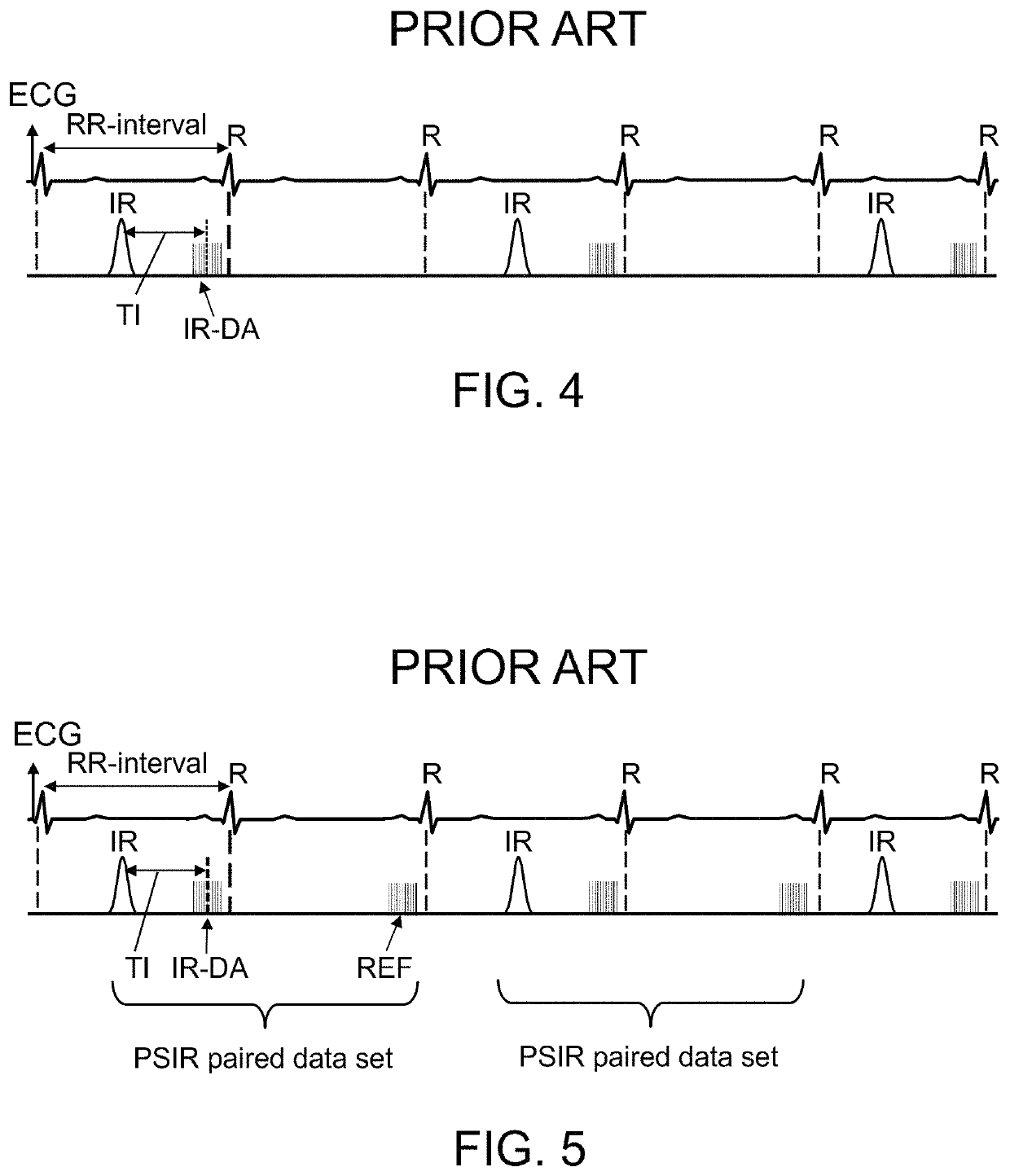
Systems and methods for phase-sensitive inversion recovery MR imaging with reduced sensitivity to cardiac motion
ActiveUS10591568B2Reduce misregistrationReduce scan timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsInversion recoveryData set
A magnetic resonance imaging system and method are provided for improved phase-sensitive magnetic resonance imaging of tissues affected by cardiovascular pulsatile motion. A magnetically-prepared image dataset and corresponding reference image dataset (for phase sensitivity) are obtained within the duration of a single cardiac cycle. The paired datasets can be single-shot or segmented datasets and a navigator sequence can optionally be provided with each paired dataset. The system and method take advantage of the shape symmetry of the cardiac cycle to acquire the paired dataset in a shorter time interval, thereby reducing misregistration artifacts. The magnetic preparation can include inversion recovery pulses, FIDDLE sequences, other magnetic preparation sequences, or combinations thereof. The reference dataset can be acquired at a lower resolution than the corresponding magnetically-prepared dataset without compromising image quality.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com