Device and method for ablation of cardiac tissue
a technology of cardiac tissue and ablation device, which is applied in the field of devices for cardiac surgery, can solve the problems of disrupting the normal propagation of electrical impulses, disrupting the normal activation of atria or ventricles, and disrupting the normal path of depolarization events, so as to reduce time and invasiveness, and duplicate the effect of maze incisions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030]The following detailed description should be read with reference to the drawings, in which like elements in different drawings are numbered identically. The drawings, which are not necessarily to scale, depict selected embodiments and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention. Several forms of the invention have been shown and described, and other forms will now be apparent to those skilled in art. It will be understood that embodiments shown in drawings and described below are merely for illustrative purposes, and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention as defined in the claims which follow.
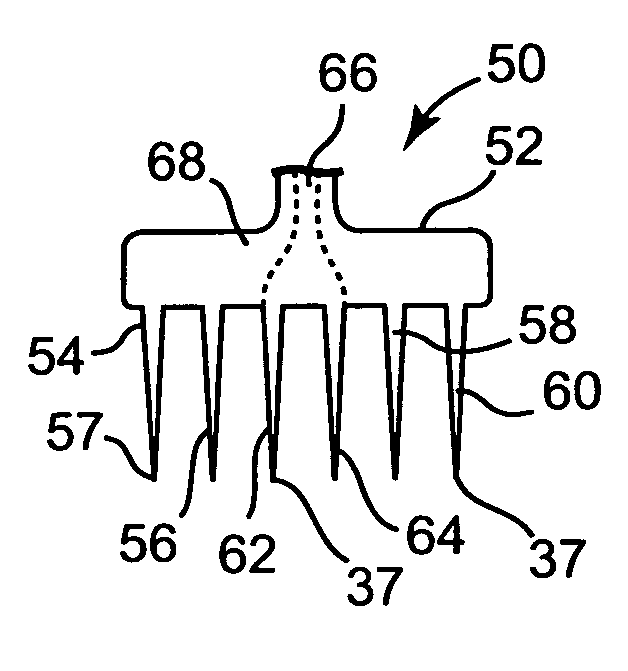
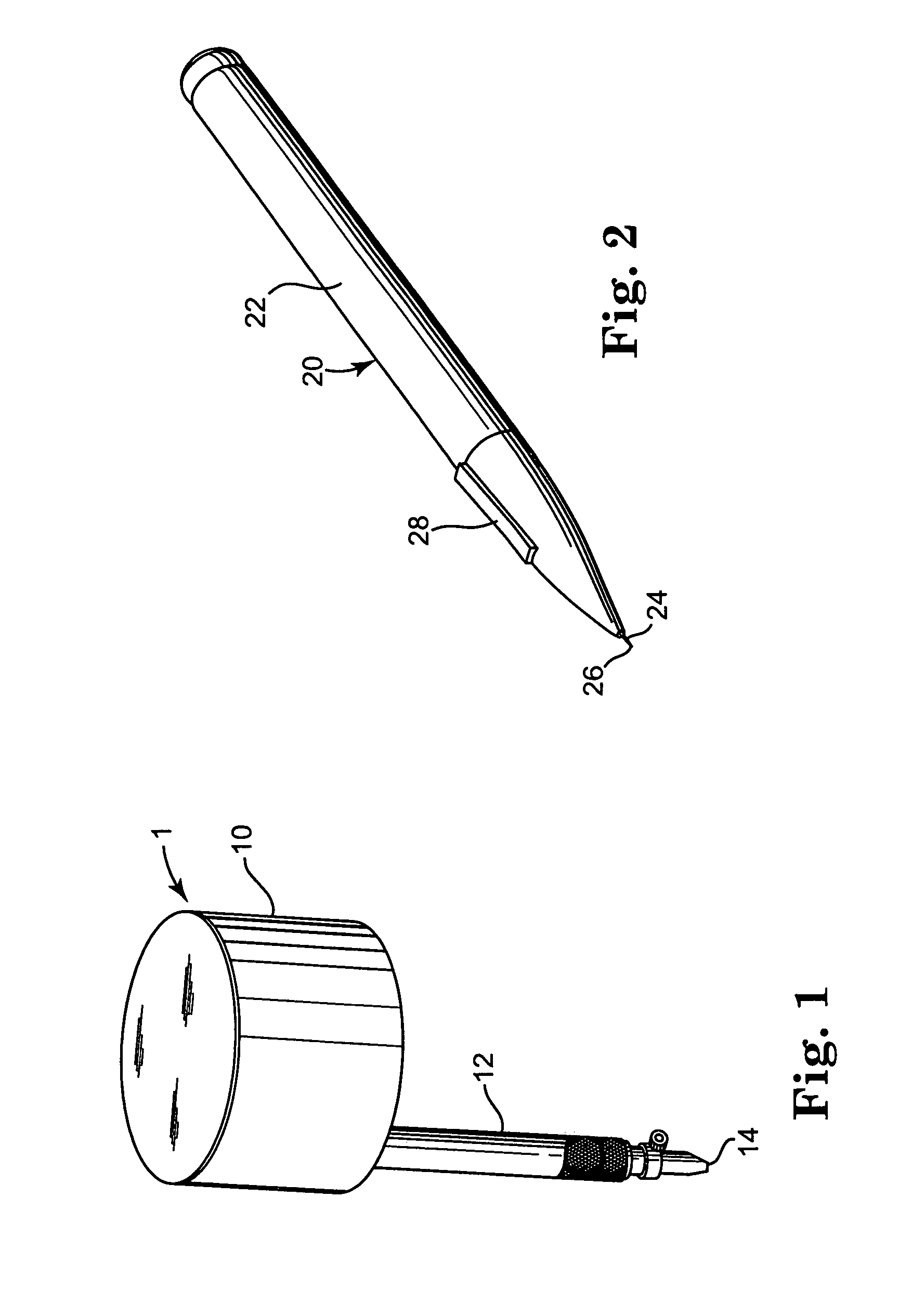
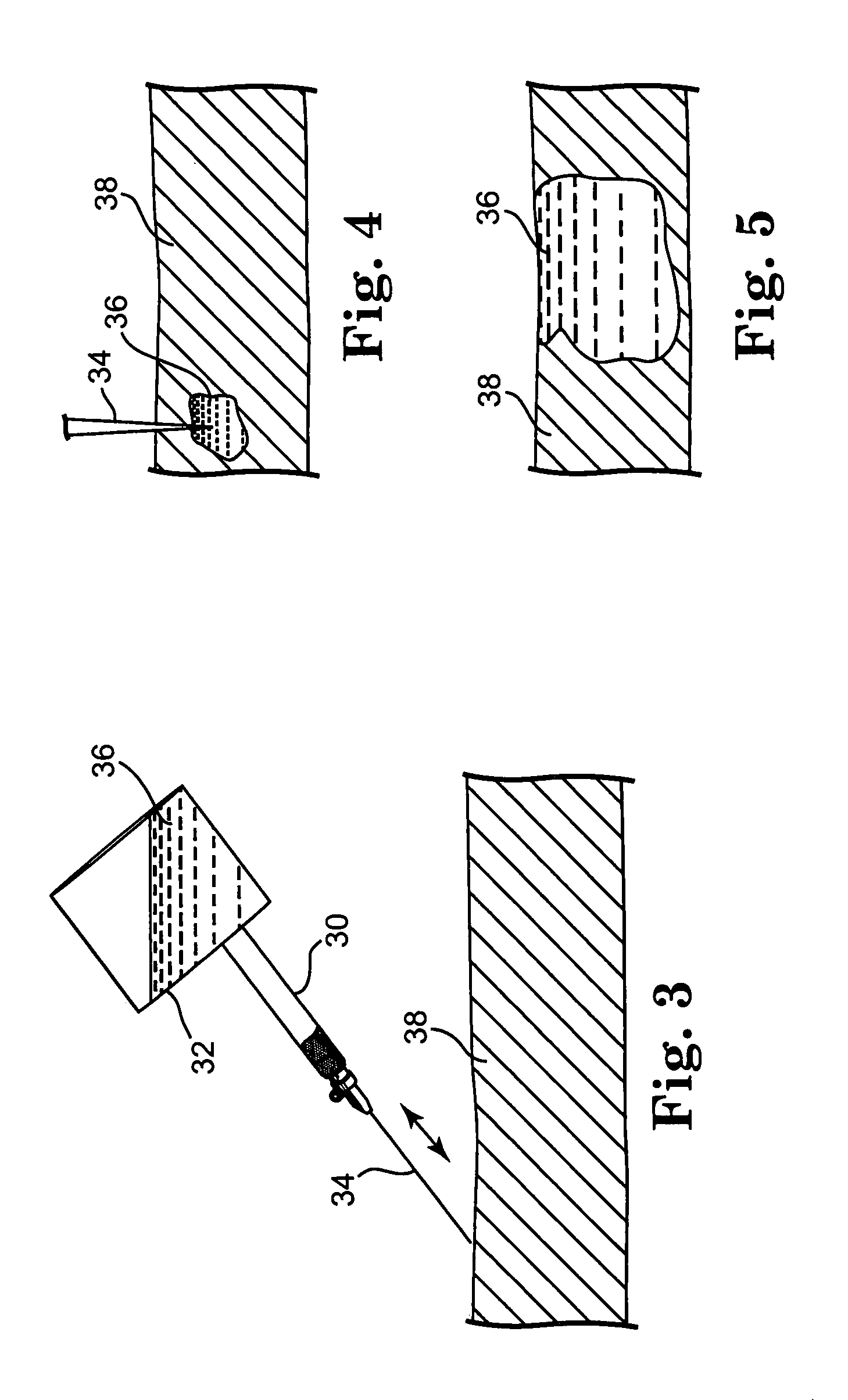
[0031]This invention relates to a device and method for ablation of cardiac tissue in which a hand-held instrument having a hollow needle is used to deliver precise amounts of liquids into cardiac tissue for purposes of ablation of the tissue along a desired lesion line. FIGS. 1 and 2 show prior art devices suitable for the practice of the present invention. FIG. 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com