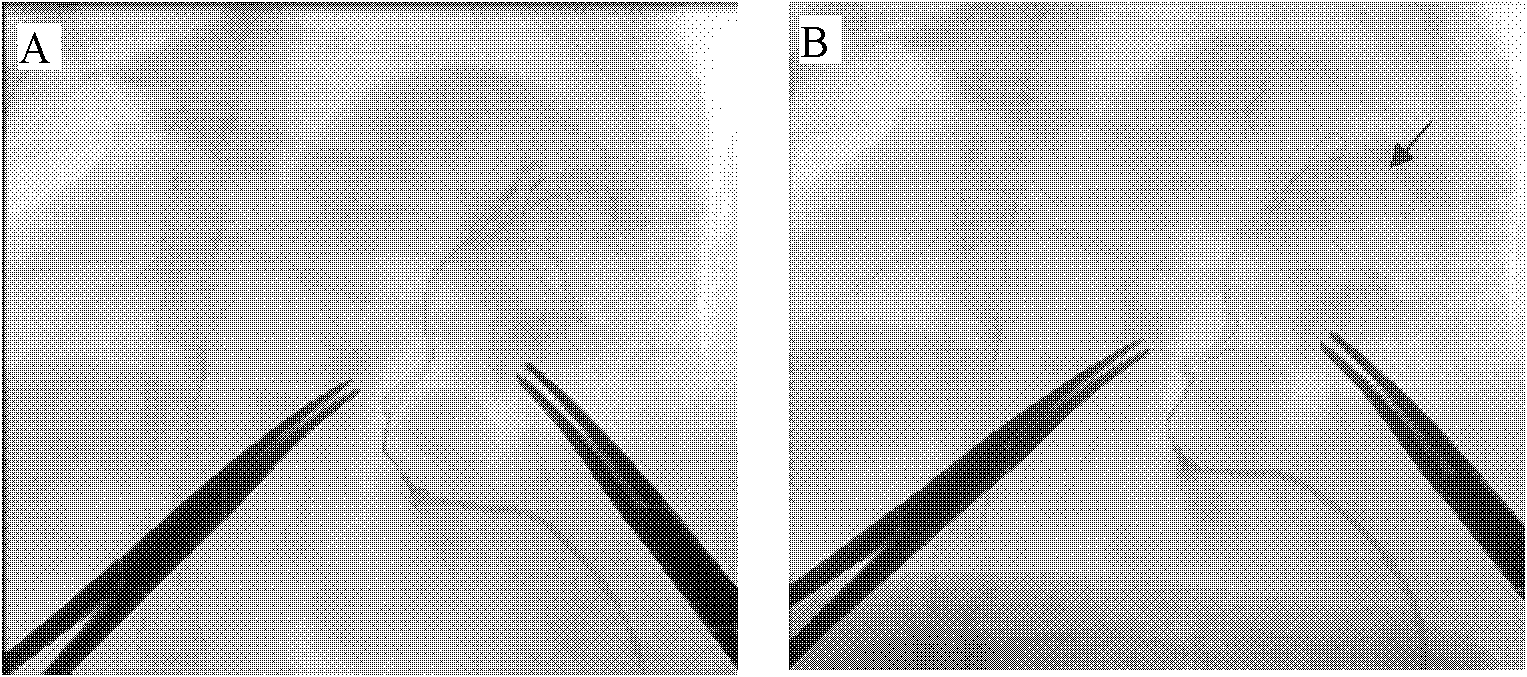
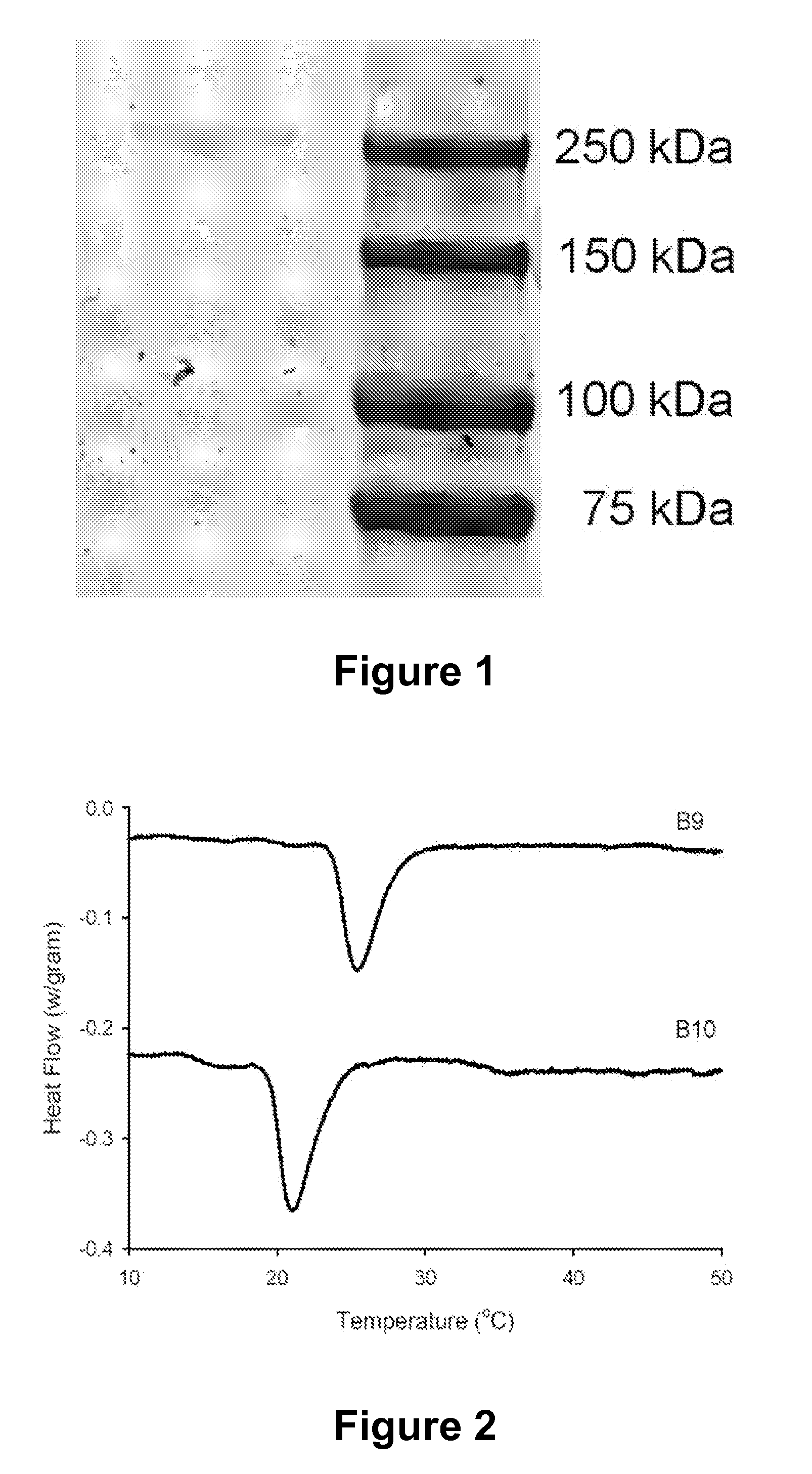
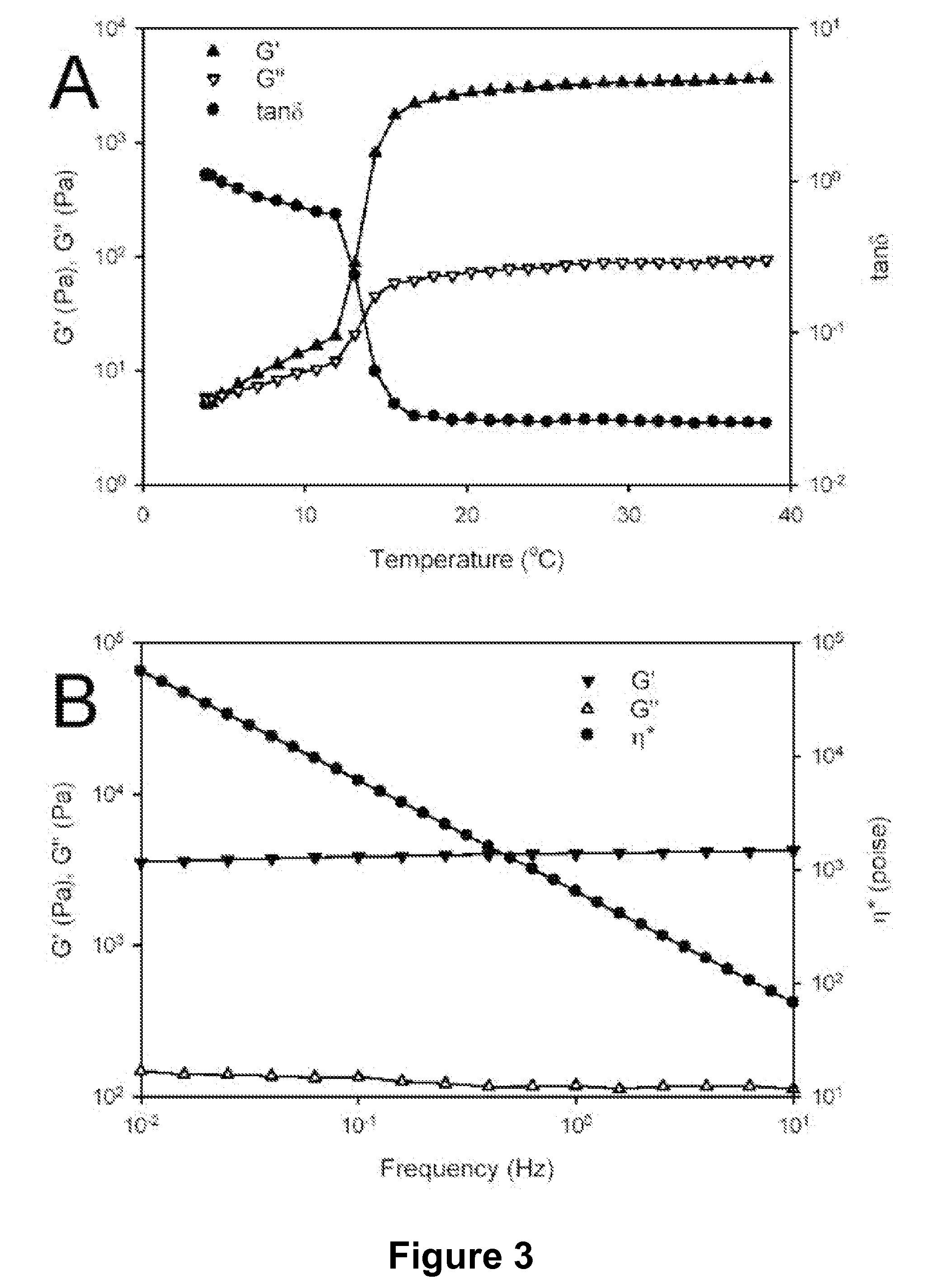
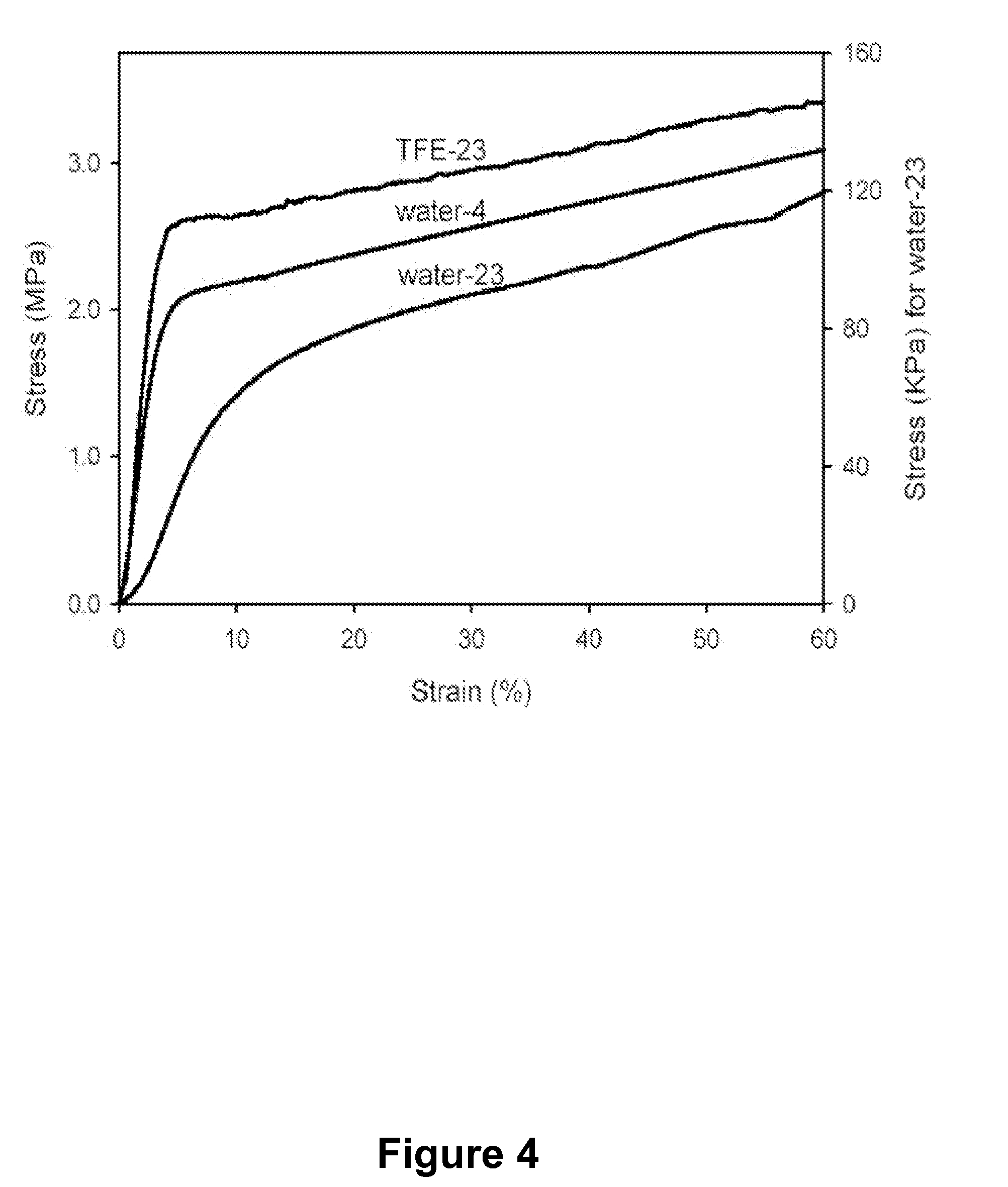
Patents
Literature
120 results about "Embolic Agent" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A substance used to block an artery, thereby eliminating the blood flow to a specific part of an organ. An embolic agent may cause permanent or temporary blockage depending on the nature of the material used.
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050149173A1Reducing perigraft leakageFacilitate “anchoring”StentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Neuro-thrombectomy catheter and method of use
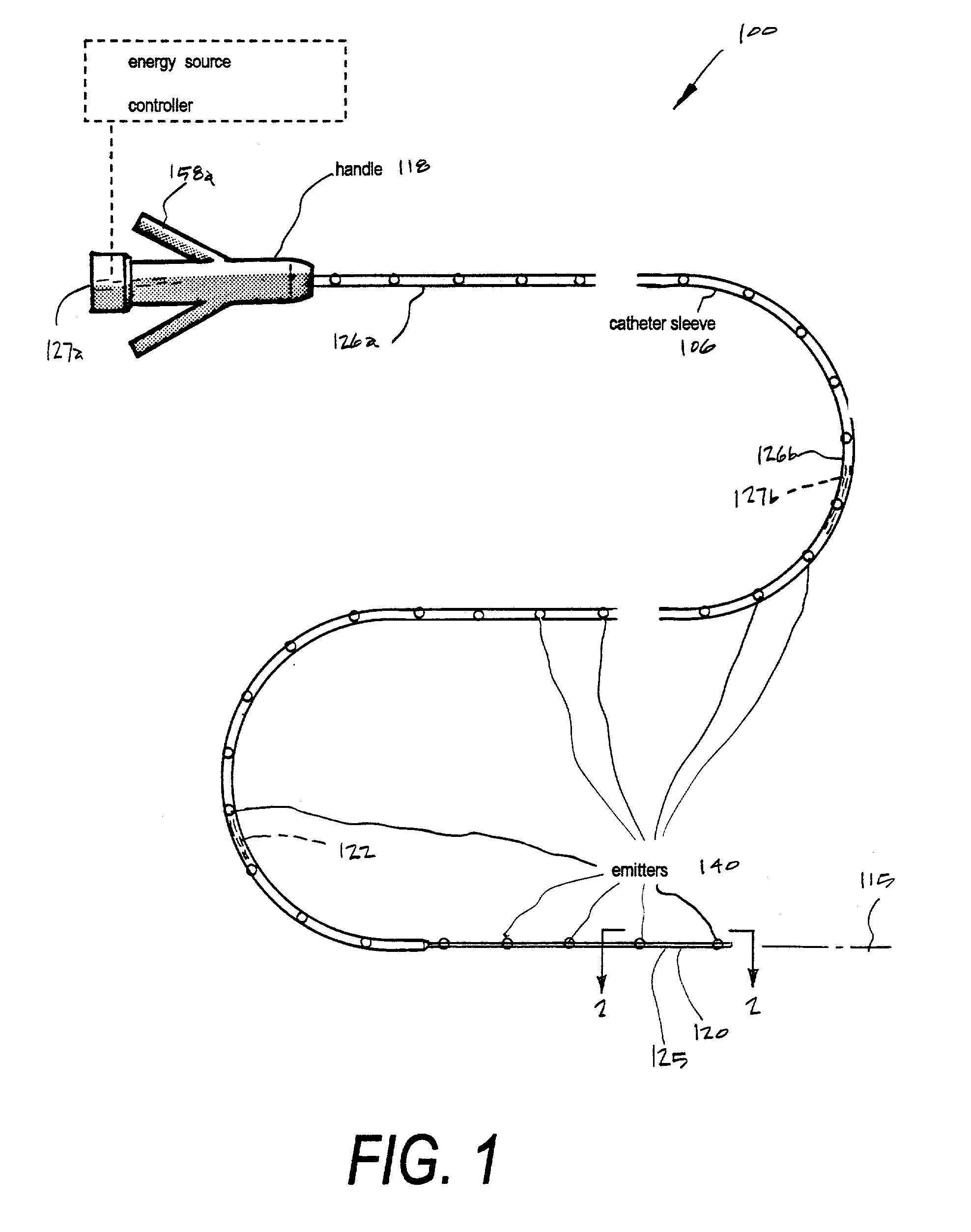
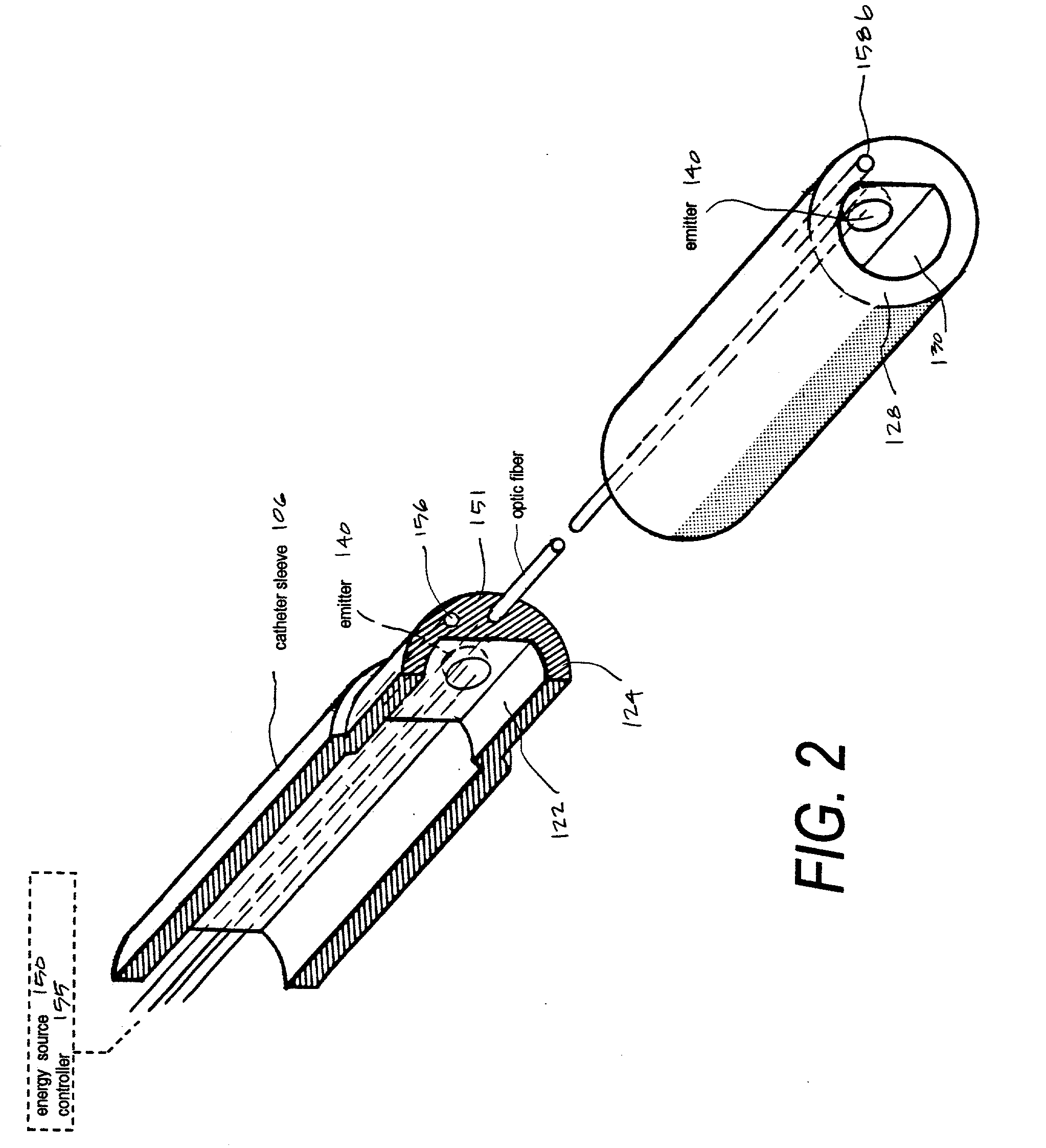
A microcatheter for removing thromboemboli from cerebral arteries in patients suffering from ischemic stroke. The microcatheter provides an extraction lumen that can be scaled to a very small diameter that is still capable of extracting and emulsifying thrombus without clogging the channel. The microcatheter of the invention uses a series of spaced apart energy application mechanisms along the entire length of the catheter's extraction lumen to develop sequential pressure differentials to cause fluid flows by means of cavitation, and to contemporaneously ablate embolic materials drawn through the extraction lumen by cavitation to thereby preventing clogging of the lumen. The catheter system thus provides a functional high-pressure extraction lumen that is far smaller than prior art catheter systems. Preferred mechanisms for energy delivery are (i) a laser source and controller coupled to optic fibers in the catheter wall or (ii) an Rf source coupled to paired electrodes within the extraction lumen. Each energy emitter can apply energy to fluid media in the extraction channel of the catheter-wherein the intense energy pulses can be sequentially timed to cause fluid media flows in the proximal direction in the channel.
Owner:SHADDUCK JOHN H
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
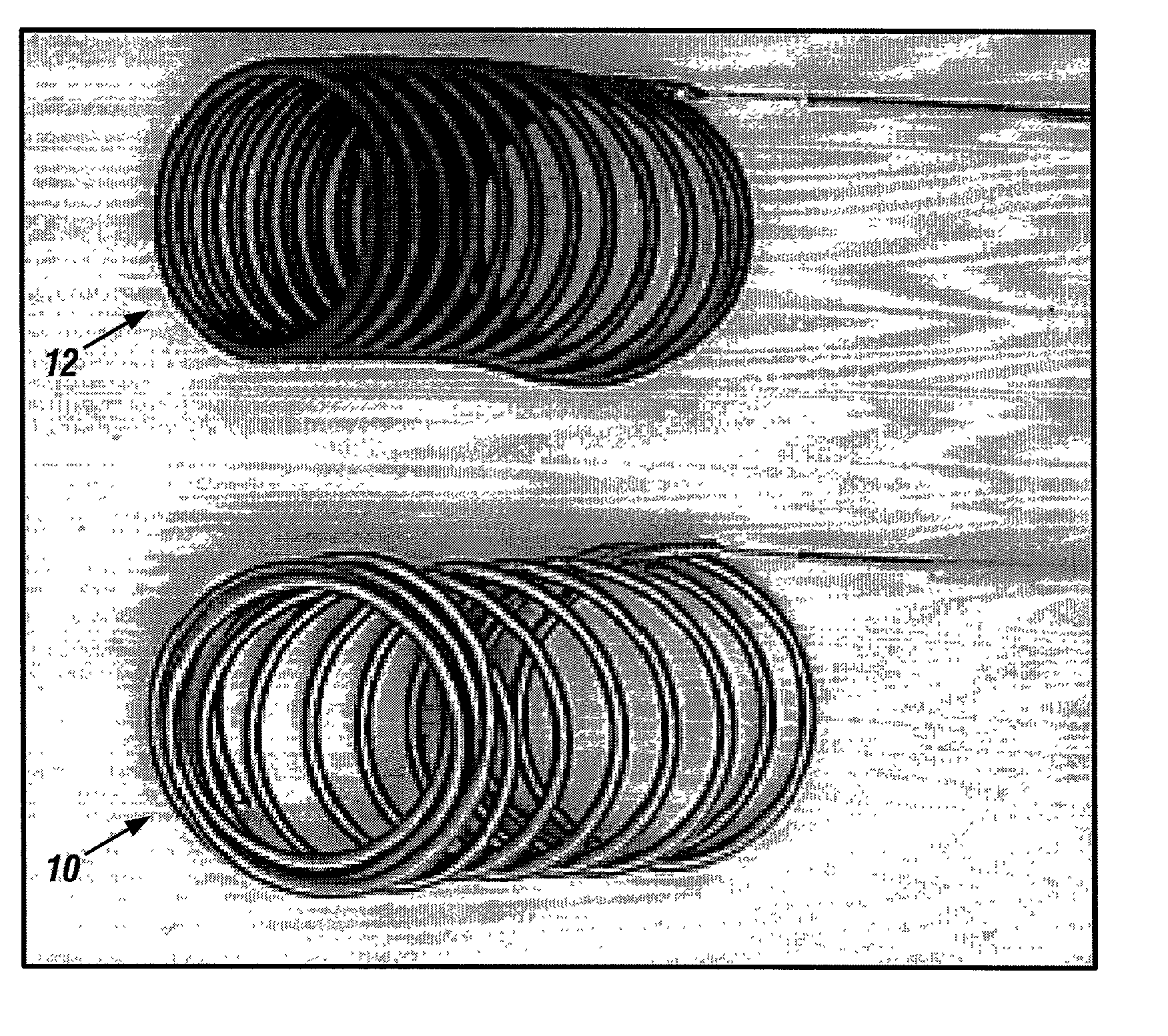
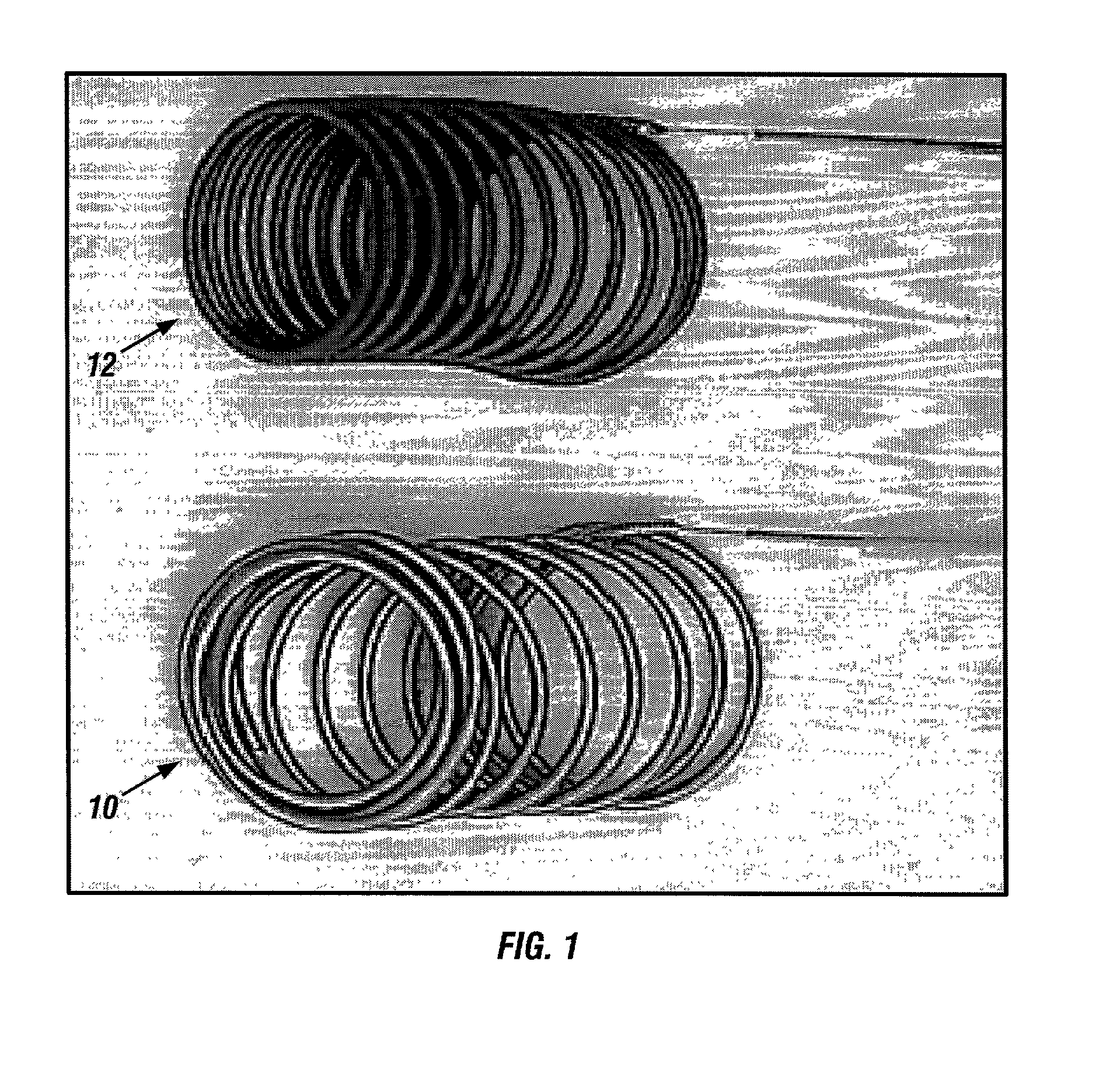
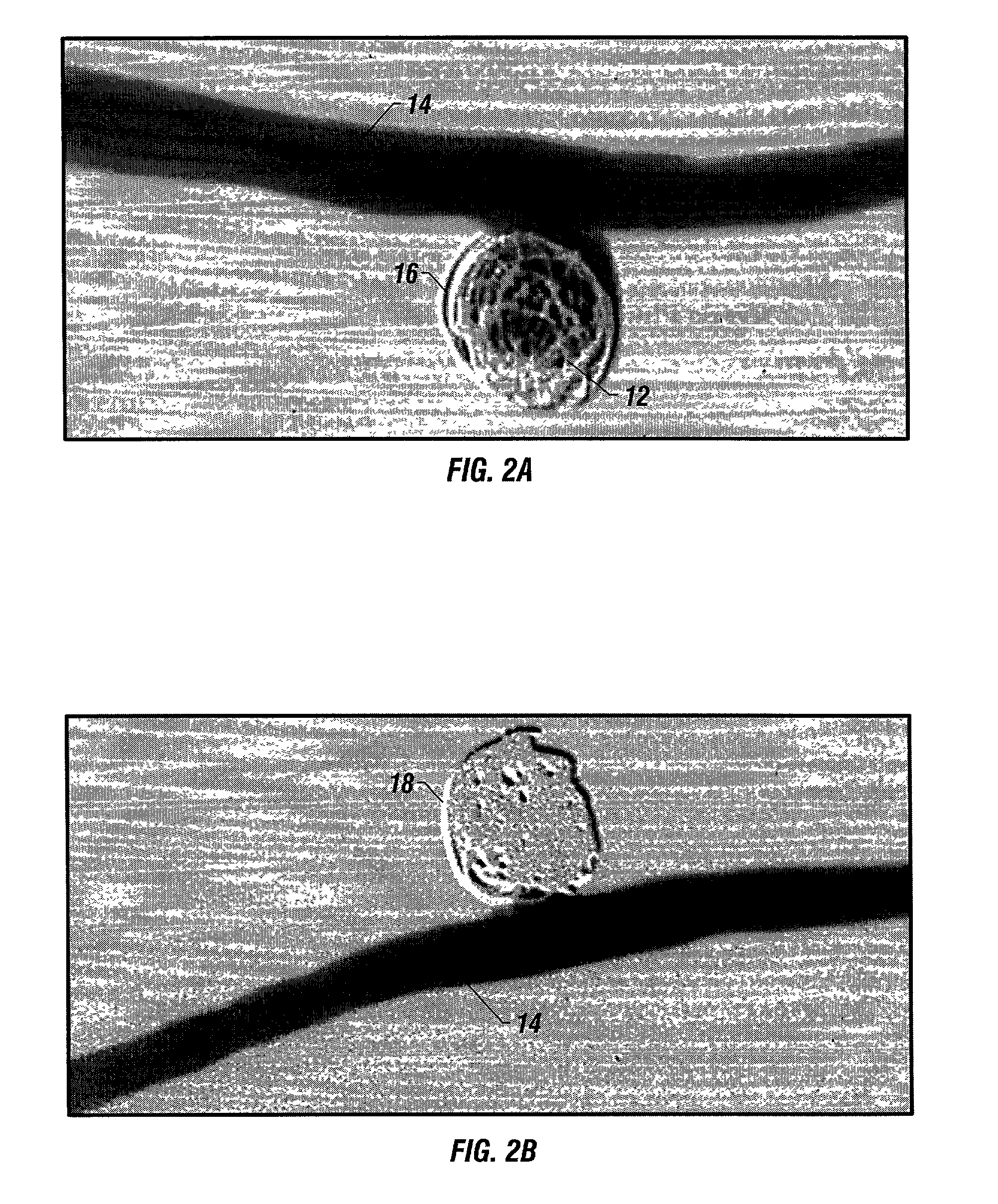
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly˜glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050149175A1Reducing perigraft leakageFacilitate “anchoring”StentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050154454A1Facilitate “anchoring”Good curative effectStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050154445A1Facilitate “anchoring”Good curative effectStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050154453A1Facilitate “anchoring”Good curative effectStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Prosthesis for reducing intra-cardiac pressure having an embolic filter
ActiveUS20120053686A1Reducing pressure necrosisImprove radiopacityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsProsthesis
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Embolic Containment
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
InactiveUS20020040239A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical containersPoly-L-lactideVascular compartment
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
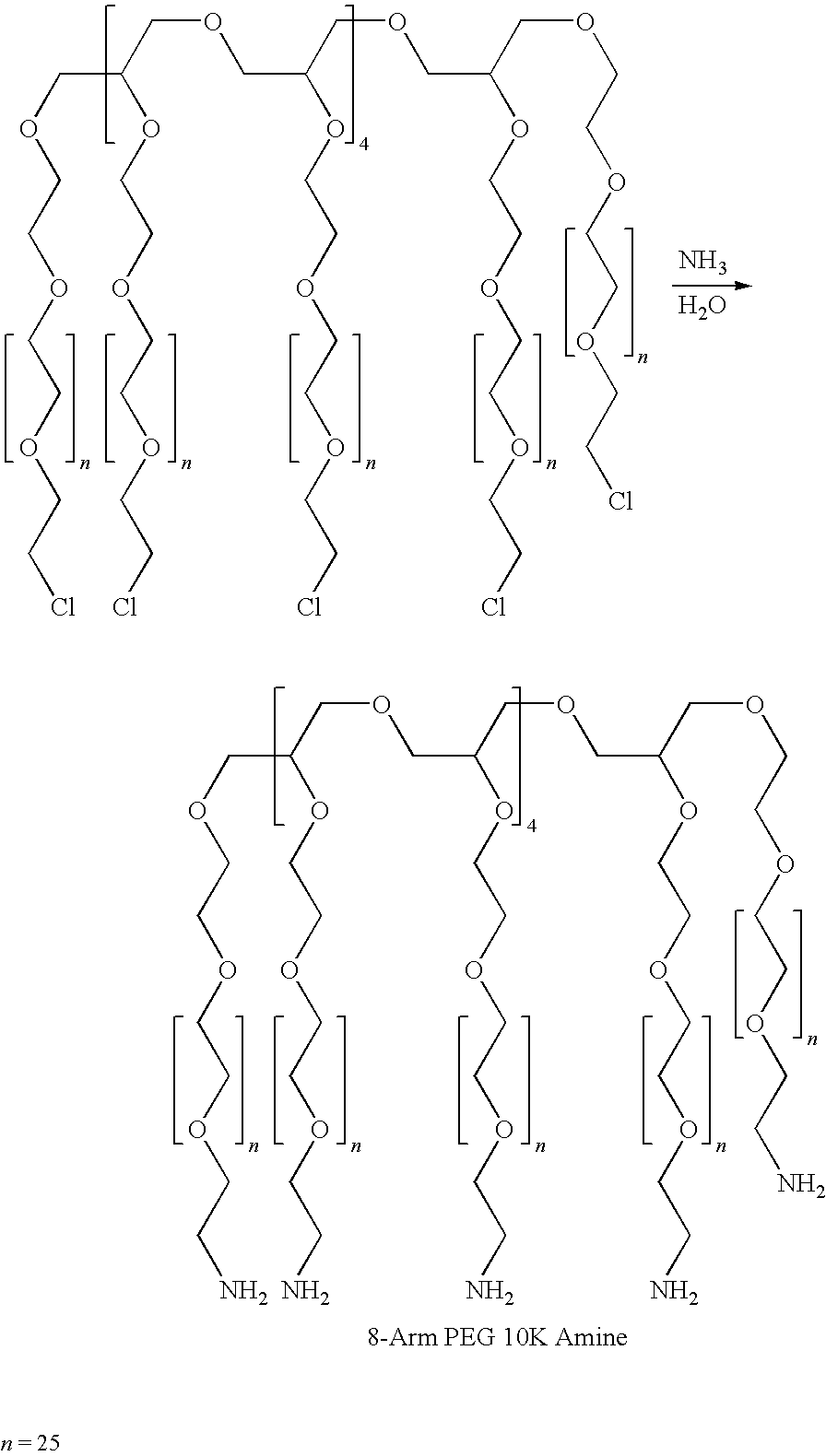
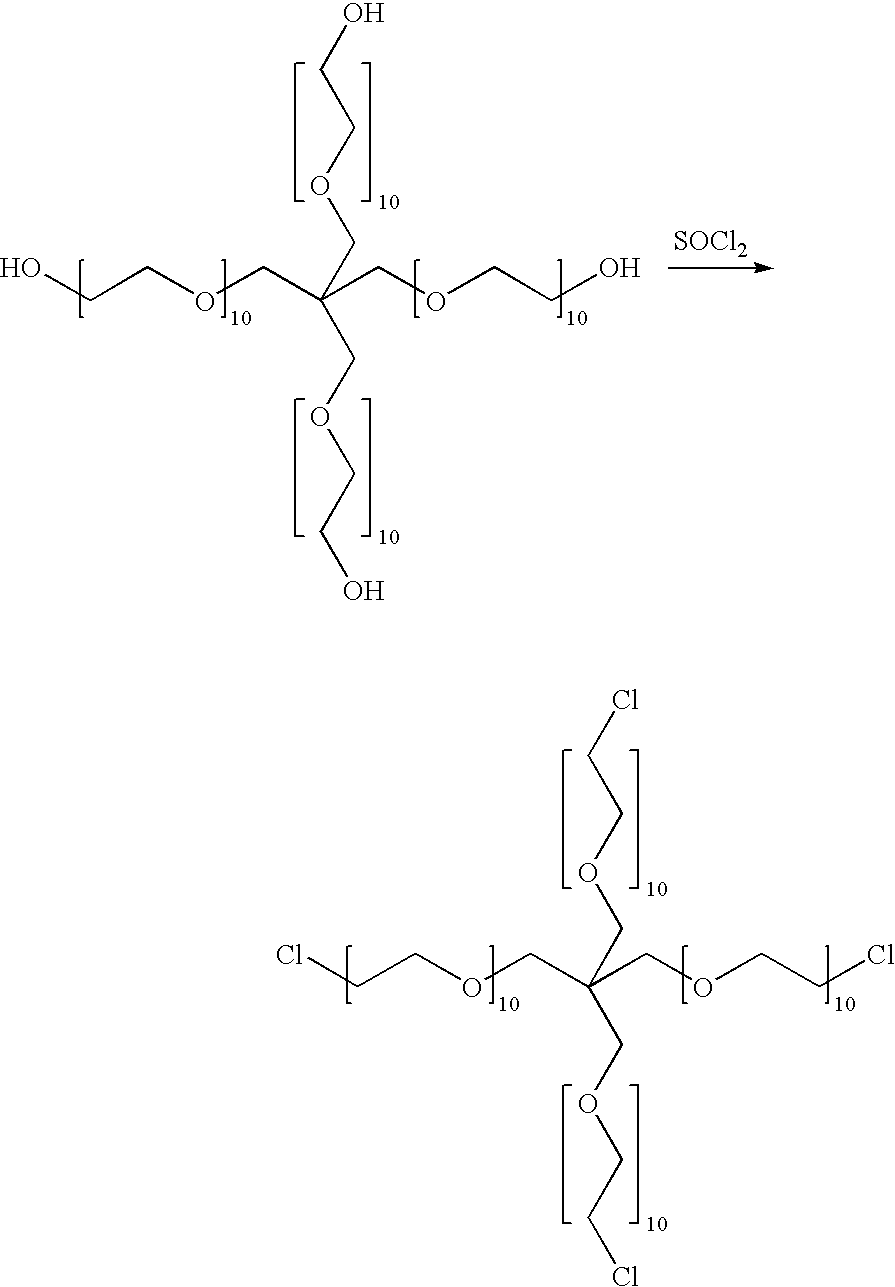
Method for embolization using liquid embolic materials
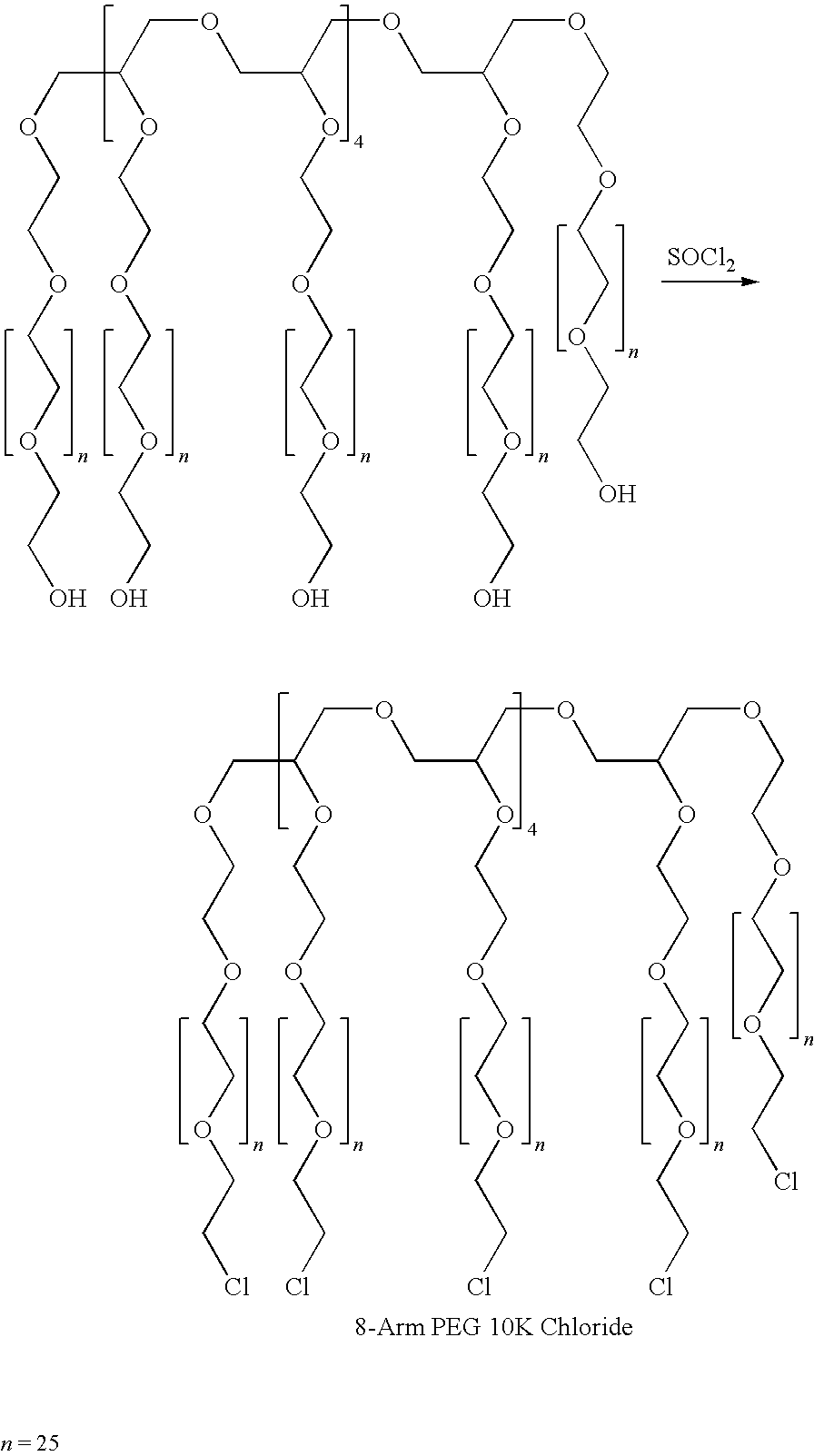
A method for embolization using liquid embolic materials is described. The method comprises the use of two liquid components. The first liquid component is an aqueous solution or dispersion comprising at least one oxidized polysaccharide. The second liquid component is either an aqueous solution or dispersion comprising at least one water-dispersible, multi-arm amine, or a water-dispersible multi-arm amine in the form of a neat liquid. The two components crosslink in situ to form a hydrogel that should act as an effective embolic agent.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Collagen sponge and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102068714APromote proliferationPromote tissue repairAbsorbent padsBandagesCross-linkPorosity
The invention discloses collagen sponge and a preparation method thereof. The collagen sponge does not contain a chemical cross-linking agent, has the porosity of over 90 percent, and is prepared by performing radiation cross-linking on aqueous solution of collagen and then freeze-drying the aqueous solution of collagen; and sterilization is performed during cross-linking so that the biosafety problem caused during preparation is solved. The collagen sponge prepared by the method has no residue of chemical reagents, better biocompatibility and structural uniformity, and adjustable degradation rate and mechanical strength, and can be used as biomedical materials such as dressing, tissue engineering stents, artificial tissue components, tissue fillers, embolic agents and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Microsphere type embolic agent and preparation technology thereof
The invention provides a microsphere embolic agent, which is an elastic microsphere formed by the crosslink polymer of the functionalized macromolecules with the biocompatibility, and the particle size of the microsphere ranges from 1 Mum to 1500 Mum. The preparing technology includes the steps as follows: in a covalent link, linking a crosslinkable micromolecules with an acrylic acid structure on the polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol or polysaccharide macromolecules, forming the functionalized macromolecules; after that, the functionalized macromolecules and the monomer of the 2- acrylamide-2-methyl propanesulfonic acid undertakes opposite suspension polymerization, obtaining the crosslink polymeric microsphere embolic agent. The embolic agent has comparatively large retractility and elasticity, whose particle size is controllable and has perfect dispersiveness; moreover, the raw material is non-toxic and at the same time has good biocompatibility and stability. The preparing technology is a real chemosynthesis technology, whose material and preparing process does not produce any virus pollution, according with various requirements of the international embolic agent, which can replace various import and domestic expensive embolic agent products and is extensively applicable to various surgeries in the interventional radiology field.
Owner:SUZHOU HENGRUI CALLISYN BIOLOGICAL MEDICINE TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for the detachment of catheters or puncturing of membranes and intraluminal devices within the body
InactiveUS20070239151A1Minimal invasiveness and effortAdditional embolizationSurgical instruments for heatingOcculdersRefluxCure rate
The disclosed methods and devices utilize various techniques to detach the distal end of a catheter from an obstruction with minimal invasiveness and effort by the surgeon. As reflux of an embolic agent or hardening material over the catheter tip is a major causative factor in the increased morbidity / mortality of embolization procedures and also a technical limitation preventing a better cure rate, a method has been developed for the detachment of the distal end of catheters within the body, preferably with no regard to the amount of reflux, and preferably at the proximal edge of the reflux, in order to be able to make embolization procedures safer and more effective.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
Preparation method of mono-dispersed gelatin embolic microsphere with precisely-controlled particle size
ActiveCN104829851AOvercoming Process ComplexityOvercome granularityPowder deliverySurgeryGelatin microspheresAqueous solution
The invention provides a preparation method of a mono-dispersed gelatin embolic microsphere with a precisely-controlled particle size. In the provided method, micro water-in-oil liquid drops are formed in a micro channel reactor at first through a micro-fluidic liquid drop control technology, then a crosslinking agent and a gelatin water solution are taken as the dispersing phase and introduced into the water-in-oil system, and then the mixture is directly cured to form microspheres. By adjusting the flowing speeds of the continuous phase and the dispersing phase, and the flowing speeds of two dispersing phases, the particle size and sphericility can be precisely controlled. The preparation technology is simple and rapid, and the process is controllable. The prepared gelatin microsphere can be used as an embolic agent or an antitumor drug carrier, and can also be applied to cell culture.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
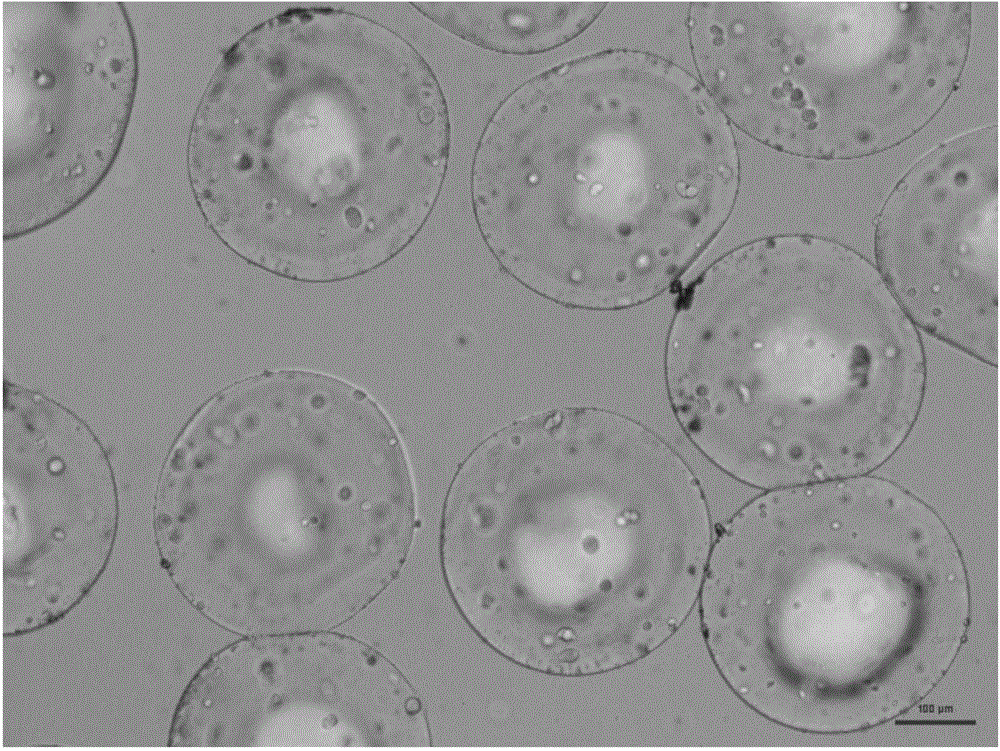
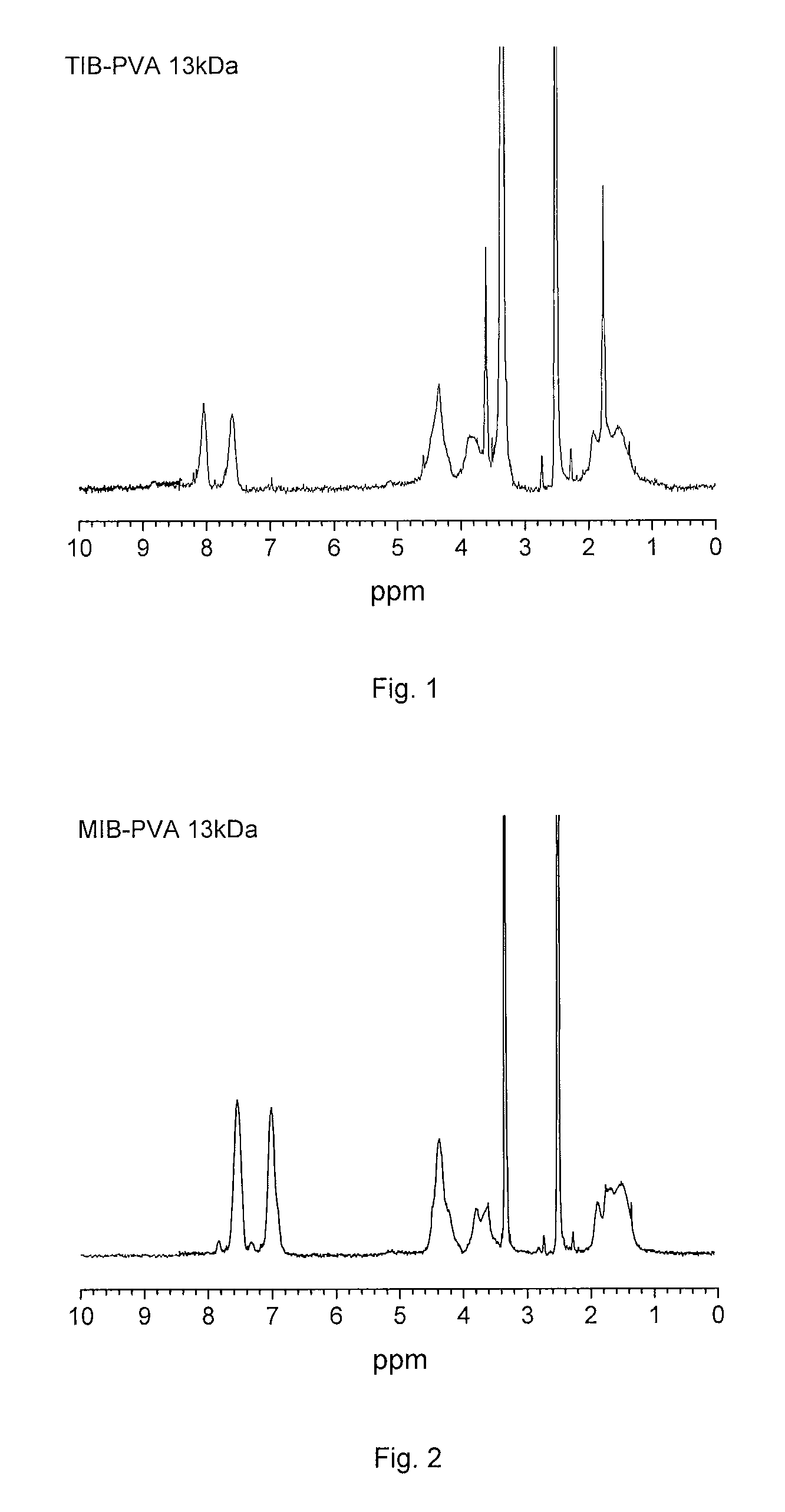
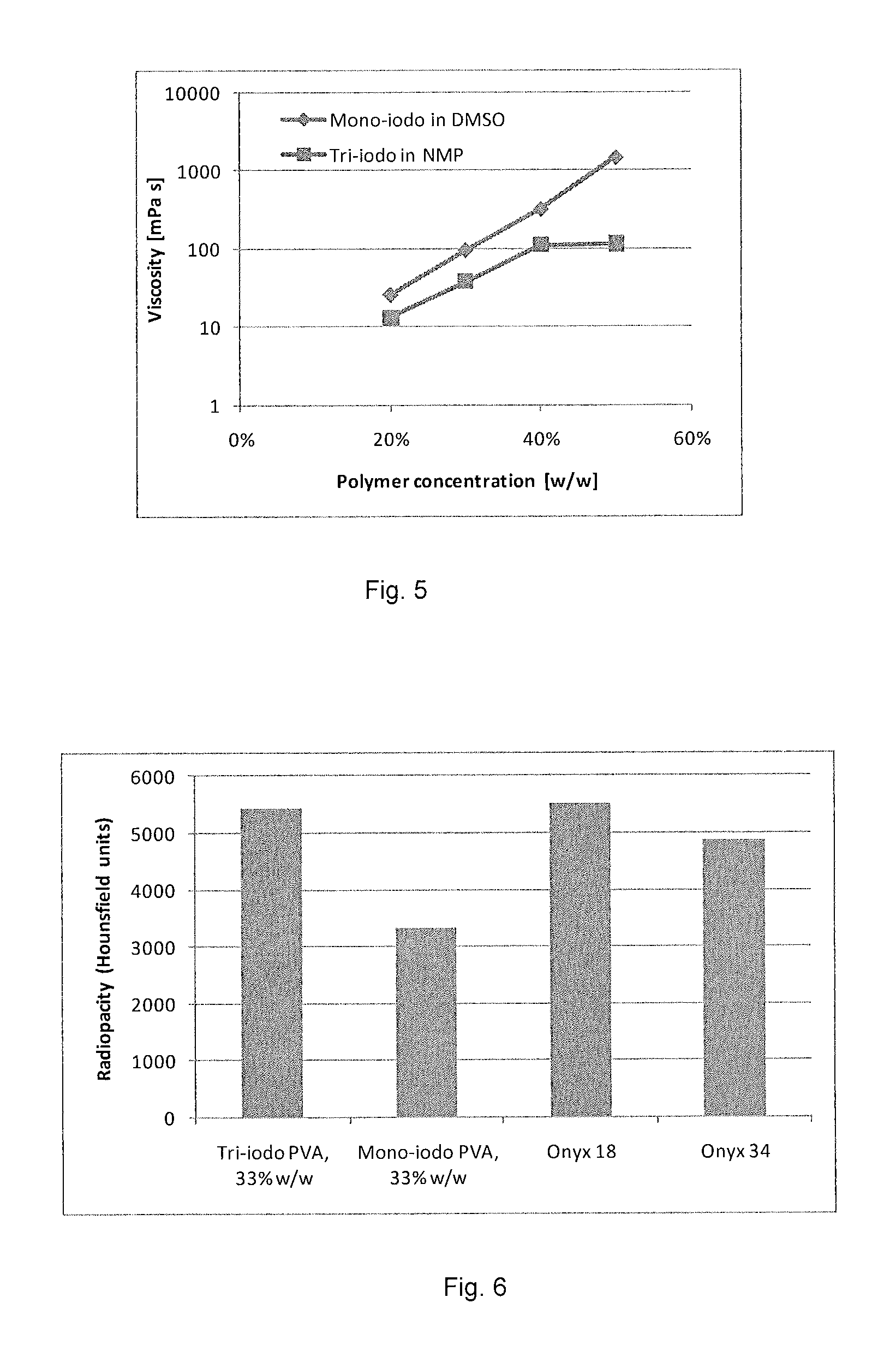
Radiopaque, non-biodegradable, water-insoluble iodinated benzyl ethers of poly(vinyl alcohol), preparation method thereof, injectable embolizing compositions containing thereof and use thereof
ActiveUS20130108574A1Surgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPolyvinyl alcoholBlood vessel
The invention concerns a radiopaque, non-biodegradable, water-insoluble iodinated benzyl ether of poly(vinyl alcohol) consisting of a PVA having covalently grafted thereon iodinated benzyl groups comprising 1-4 iodine atoms per benzyl group, a process for preparing the same comprising reacting a 0-100% hydrolyzed PVA with a iodinated benzyl derivative comprising 1-4 iodine atoms per benzyl group in a polar aprotic solvent in the presence of a base in anhydrous conditions. Said iodo-benzylether-PVA is particularly useful as embolic agent in an injectable embolizing composition. The invention also concerns an injectable embolizing composition comprising said iodo-benzylether-PVA and capable of forming a cohesive mass upon contact with a body fluid by precipitation of the iodo-benzylether-PVA. Said injectable embolizing composition is particularly useful for forming in-situ a cohesive mass in a blood vessel or into a tumor. The invention further concerns a coating composition containing said iodo-benzylether-PVA and capable of forming a radiopaque coating on a medical device. The invention further concerns particles formed of said iodo-benzylether-PVA.
Owner:ANTIA THERAPEUTICS +2
Method for preparing iodic liquid embolic agent capable of long-time self-developing
ActiveCN101513542AWith long-term developing functionRelieve painSurgeryX-ray constrast preparationsPolyvinyl alcoholBlood vessel
The invention provides a method for preparing an iodic liquid embolic agent capable of long-time self-developing. Water-soluble polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) is added with pyridine to be stirred and evaporated for removing the pyridine. Residual reactant is dehumidified and dissolved in dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) organic solvent and then is added with solution of iodic compound and dichloromethane and added with triethylamine; and an obtained iodic product (I-PVA) is poured into a mixture of butyl ether and acetone to be deposited and separated. The iodic product is washed in water, is dried and then is confected into the liquid embolic agent by the dimethyl sulphoxide or N-methyl-ketopyrrolidine organic solvent. The liquid embolic agent prepared by the invention is injectable and can develop under X-ray for a long time. When contacting with blood, the organic solvent diffuses fast for depositing and separating solid to take embolic effect. The embolic agent can be used for embolotherapy of cerebral arteriovenous malformation, tumour and other vascular disease.
Owner:山东大正医疗器械股份有限公司
Sustained-release blood vessel embolic gel used for treating tumor, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102988274AEasy to injectNot easy to refluxPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemEndovascular treatmentBlood vessel
The invention provides a sustained-release temperature-sensitive blood vessel embolic gel used for treating tumor. The sustained-release blood vessel embolic gel is prepared by entrapping a medicine by using a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The medicine is an anti-tumor medicine, and the pharmaceutically acceptable carrier comprises a gel prepared from poloxamer polymer, polyvinyl pyrrolidone, and the like or a composition thereof. The polymer material accounts for 5-65% of a gel mass. The particle size of the gel is in a range of 10nm to 150mum. The embolic agent is liquid gel under normal temperature, and can be used for direct injection through catheter. After injection into body, with the increase of temperature, the liquid gel is rapidly solidified into gel. Also, according to requirements, different medicines can be entrapped, and embolism and medication dual effect can be achieved through local sustained-release. Therefore, the gel provided by the invention can be used as an embolic agent for endovascular treatment, and can be used in various benign and malignant tumor transcatheter arterial chemoembolizations. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple, and is suitable for industrialized productions.
Owner:江苏申命医疗科技有限公司
Modified Protein Polymers
ActiveUS20100048473A1Suitable mechanical propertyDifferent mechanical propertyElectric discharge heatingPeptide/protein ingredientsMechanical propertyCopolymer
In an embodiment, a number of synthetic protein triblock copolymers are provided comprising first and second end hydrophobic blocks separated by a central hydrophilic block. In particular, the synthetic proteins are elastin-mimetic proteins having improved mechanical characteristics and related methods of making the proteins with the capability of providing precise control over the mechanical properties. Provided are proteins used in a number of medical devices such as artificial blood vessels, shunts, stents or as embolic agents in situations where it is desired to stop or reduce blood flow or pressure in a localized region.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Drug delivery from embolic agents
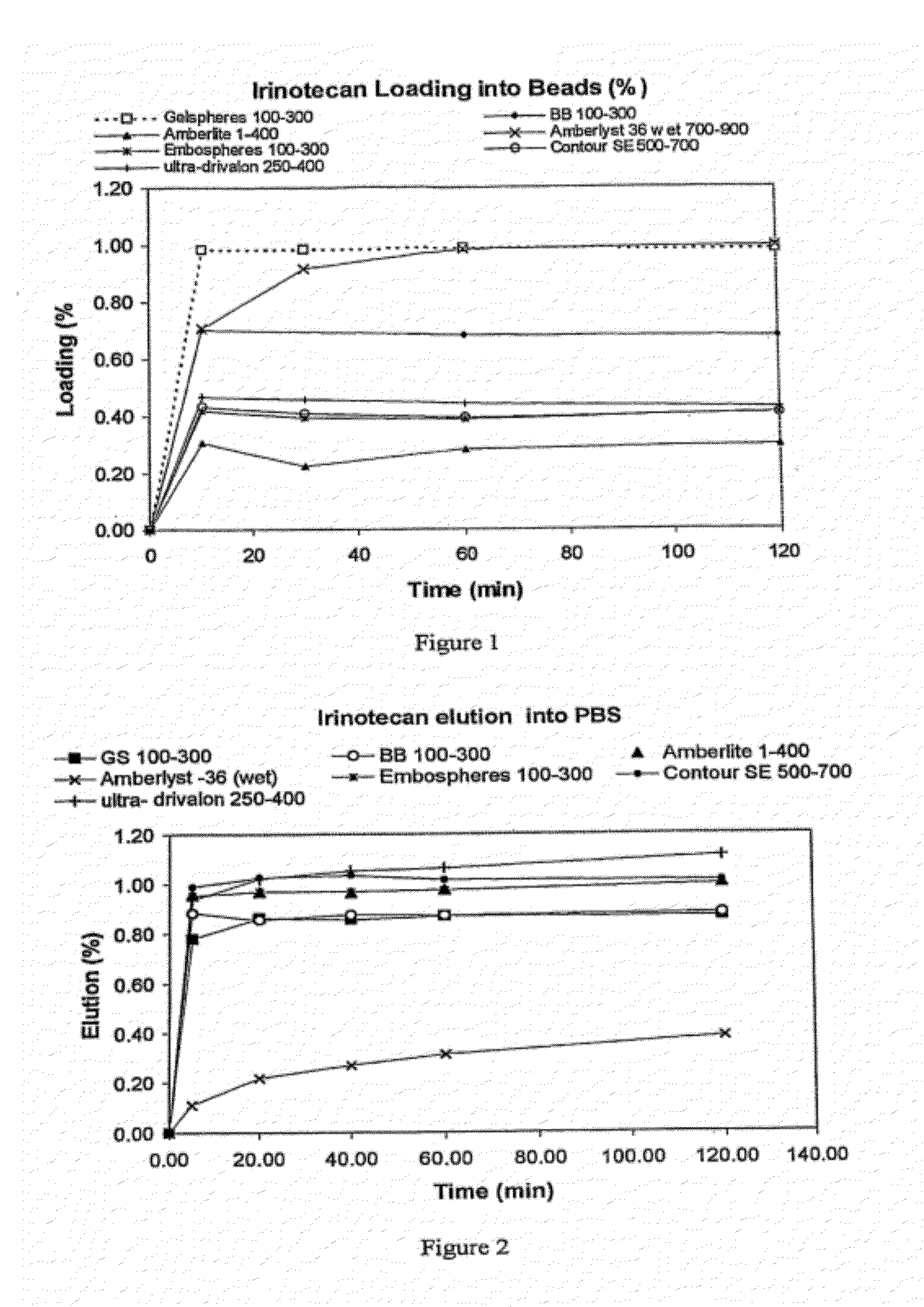
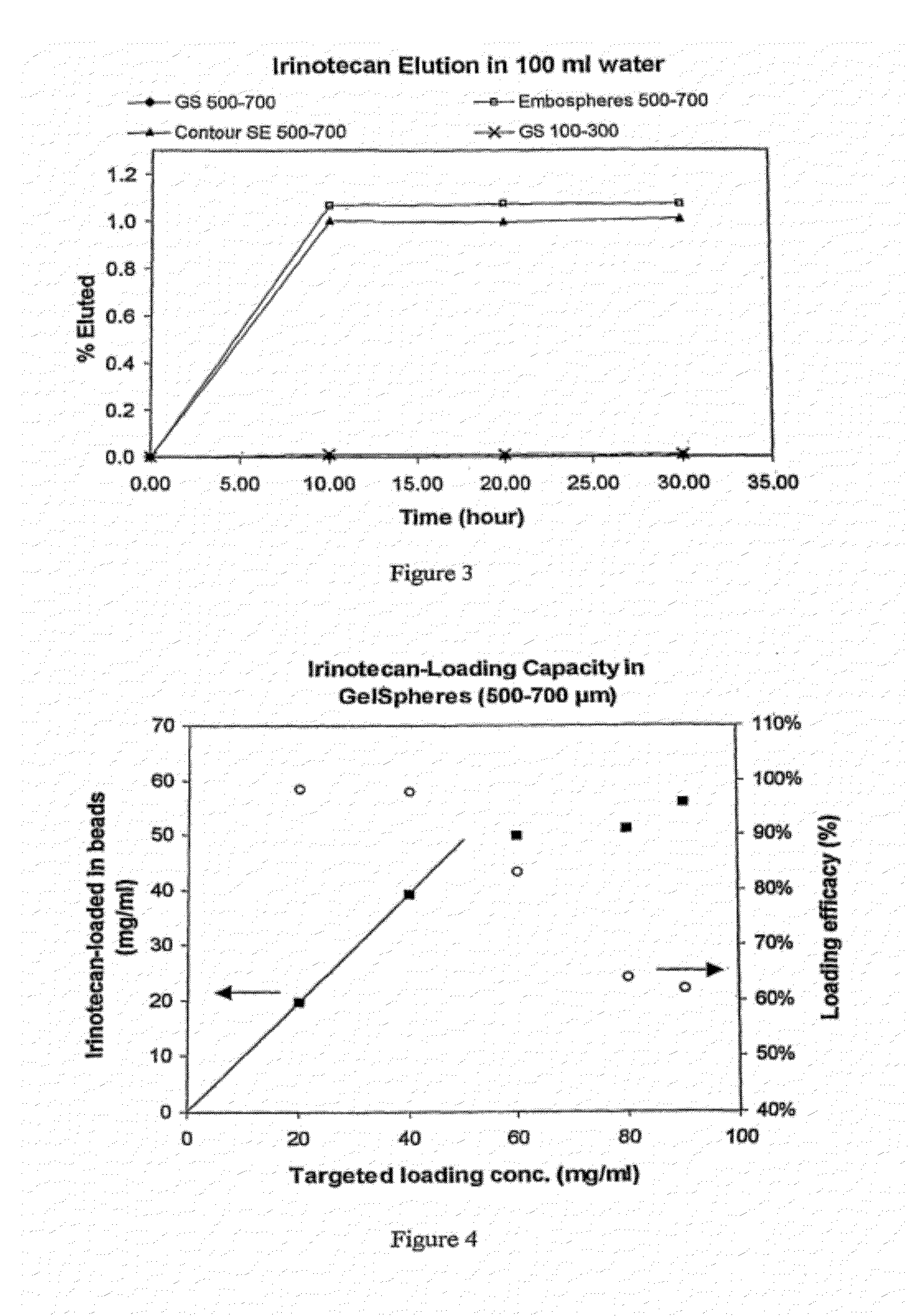
An embolic composition comprises microspheres formed of water-insoluble water-swellable anionic polymer having swollen diameter more than 100 μm and a cationic camptothecin compound, preferably irinotecan. The microspheres are preferably formed of crosslinked polyvinylalcohol, preferably of ethylenically unsaturated polyvinylalcohol macromer, crosslinked with anionic ethylenically unsaturated anionic comonomer. The compositions are used to treat hypervascular tumours for instance colorectal metastases of the liver.
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
Method for transcatheter intra-arterial perfusion magnetic resonance imaging
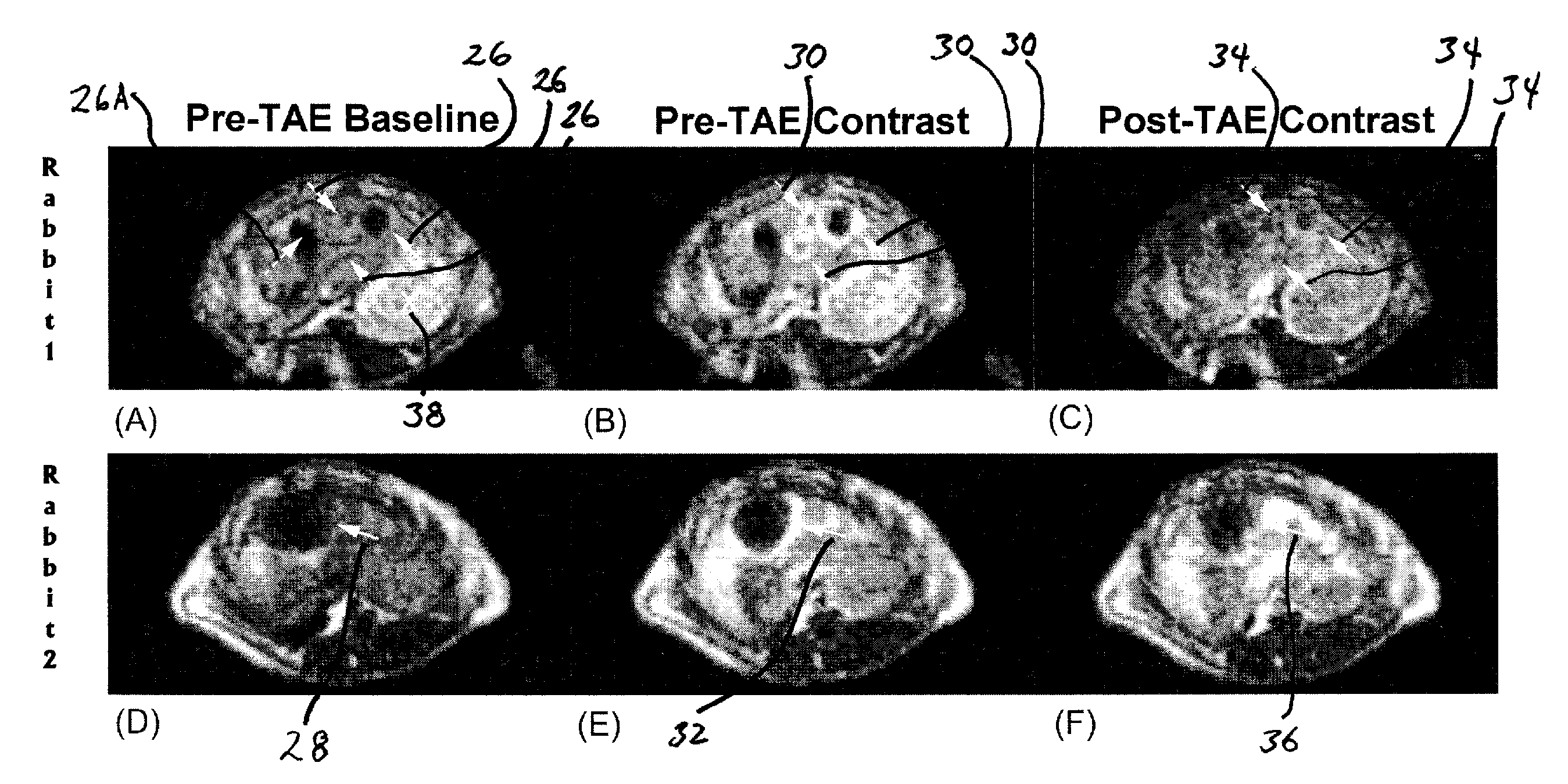
A method to serially determine changes in perfusion to tissues is provided. This method involves injecting contrast material into a catheter that is positioned in the blood supply proximal to the targeted tissue of interest, acquiring a time series of images that depicts the uptake of this contrast material within the tissue, deriving semi-quantitative or quantitative perfusion metrics based upon the time series of perfusion images, altering perfusion to the targeted tissue by means of injecting pharmacologic agents or embolic agents into the blood vessels supplying the targeted tissue, repeating the acquisition of perfusion images to serially monitor changes in tissue perfusion after each alteration, and calculating changes in perfusion metrics after each series of perfusion images. This method is used to monitor changes in perfusion to various tissues, including a diverse array of tumors. The perfusion imaging method can be acquired using magnetic resonance, x-ray computed tomography, or radionuclide imaging. The perfusion metric is serially measured during an embolization procedure as a means of measuring changes in tissue perfusion or to target an endpoint based upon a specific alteration in the calculated perfusion metric.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Color-Coded Polymeric Particles of Predetermined Size for Therapeutic and/or Diagnostic Applications and Related Methods
InactiveUS20100028260A1Minimizes probabilityPowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsPolyphosphazeneMedicine
Various embodiments are directed to color-coded and size-calibrated polymeric particles comprising an acrylate-based hydrogel core incorporating one or more chromophores of interest, and an outer shell comprising polyphosphazenes of formula I, useful for various therapeutic and / or diagnostic procedures. In various embodiments, the color-coded and size-calibrated polymeric particles can be employed in any particle-mediated procedure, including as embolic agents, dermal fillers, and various implantable devices for a broad range of clinical and cosmetic applications. The incorporation of a particular chromophore formulation that correlates with a pre-determined size specificity for implantable and loadable polymeric particles (“color-coded and size-calibrated”) enables the visual detection and identification of particles exhibiting a particular size of interest, and minimizes the probability of user-introduced or procedural errors.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Blood vessel embolization method using balloon catheter and balloon catheter for blood vessel embolization method
A blood vessel embolization method includes inserting a balloon catheter into a blood vessel of a human or an animal having a lesion site and disposing a balloon of the balloon catheter at a portion located at a proximal side of the blood vessel and in a neighborhood of the lesion site thereof; shutting off a blood flow in the blood vessel by expanding the balloon; discharging a glucose solution from a distal end of the balloon catheter in a state in which the blood flow in the blood vessel is shut off; discharging a cyanoacrylate-based embolization substance-containing liquid from the distal end of the balloon catheter after the glucose solution injection step; hardening an embolization substance by maintaining a blood flow shut-off state of the blood vessel after the embolization substance injection step; and removing the balloon catheter from the blood vessel after the embolization substance-hardening step.
Owner:ST MARIANNA UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly˜glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Vascular embolic agent as well as injection device and application thereof
ActiveCN103315945AControl lengthLiquidHeavy metal active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsAfter treatmentChemotherapeutic drugs
The invention relates to a vascular embolic agent, which is composed of liquid metal and / or liquid metal alloy. The liquid metal and liquid metal alloy have the melting points below 60 DEG C and density larger than that of blood, are non-toxic. The vascular embolic agent can be mixed with nano particles or radioactive elements or chemotherapeutics. The invention also provides an injection device of the vascular embolic agent, which has heating and temperature measuring functions. The vascular embolic agent can be used as an imaging equipment contrast agent or a tumor thermotherapy sensitizer, and can be used for preparing tumor radiotherapy and chemotherapeutics drugs. The vascular embolic agent can be extracted from the blood vessel after treatment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Flow Directional Infusion Device
A flow directional infusion device includes a filter valve located at the distal end of a catheter. The filter valve constrains delivery of an embolic agent through the catheter to the locus of the aneurysm. In order to provide such delivery, the valve includes a longitudinal opening, radial opening or is otherwise partially permeable in a direction of the aneurysm so that the embolic agent or a delivery element for such agent is limited toward the aneurysm. In addition, the filter valve permits and directs blood flow within the blood vessel about the aneurysm during the treatment without obstructing the vessel and without allowing retrograde flow of the embolic agent in the vessel upstream of the aneurysm.
Owner:TRISALUS LIFE SCI INC
Embolic Containment
ActiveUS20180070955A1Allow useUseful in treatmentDiagnosticsOcculdersMedicineArteriovenous malformation
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Detachable tip microcatheter
A microcatheter for delivering embolic agent to a vascular site is provided. The microcatheter has a biocompatible or biocompatible and biodegradable tip which can be detachably engaged to the microcatheter body by a thermoplastic sleeve. Once the embolic agent is delivered to the desired vascular site, the tip of the microcatheter is often entrapped within the mass of the liquid embolic fluid. Using the microcatheter, the clinician can retract the microcatheter at a predetermined retraction force thereby disengaging the tip from the microcatheter body allowing for easier removal of the microcatheter.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Preparation technique of protein microsphere suppository
InactiveCN101332175APharmaceutical delivery mechanismMacromolecular non-active ingredientsManufacturing technologyVegetable oil
The present invention relates to a manufacture technology of an embolic agent, in particular to a manufacture technology of a protein microsphere embolic agent. The manufacture technology is realized by the following steps: protein aqueous solution is added into vegetable oil for emulsification under the temperature of 40 DEG C to 70 DEG C; protein microspheres are obtained after deoiling and drying, wherein, the volume ratio of the protein aqueous solution and the vegetable oil is 1 to 2:5; then, the obtained protein microspheres are subject to thermal crosslinking to be solidified; the protein microspheres obtained after solidification are sieved and graded or are deoiled, dried, sieved and graded to obtain a microsphere embolic agent in different particle diameters. An emulsification method is used, so the manufactured protein microspheres have regular shapes; the protein microspheres which are heated and solidified can take effect of the protein microspheres which are solidified by a cross linker and do not contain residual cross linker, and the protein microsphere embolic agent is safer to human body and is fit for the interventional therapy better.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Non-viscous medical use liquid embolic agent
ActiveCN1947803AReduce usageTo achieve the purpose of permanent embolismSurgeryWater insolubleArteriovenous malformation
A non-adhesive liquid-state embolizing agent for treating cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) and aneurysm is composed of the water-insoluble organic polymer soluble to organic solvent containing alcohol and the medical developer.
Owner:SAIKE SAISI BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com