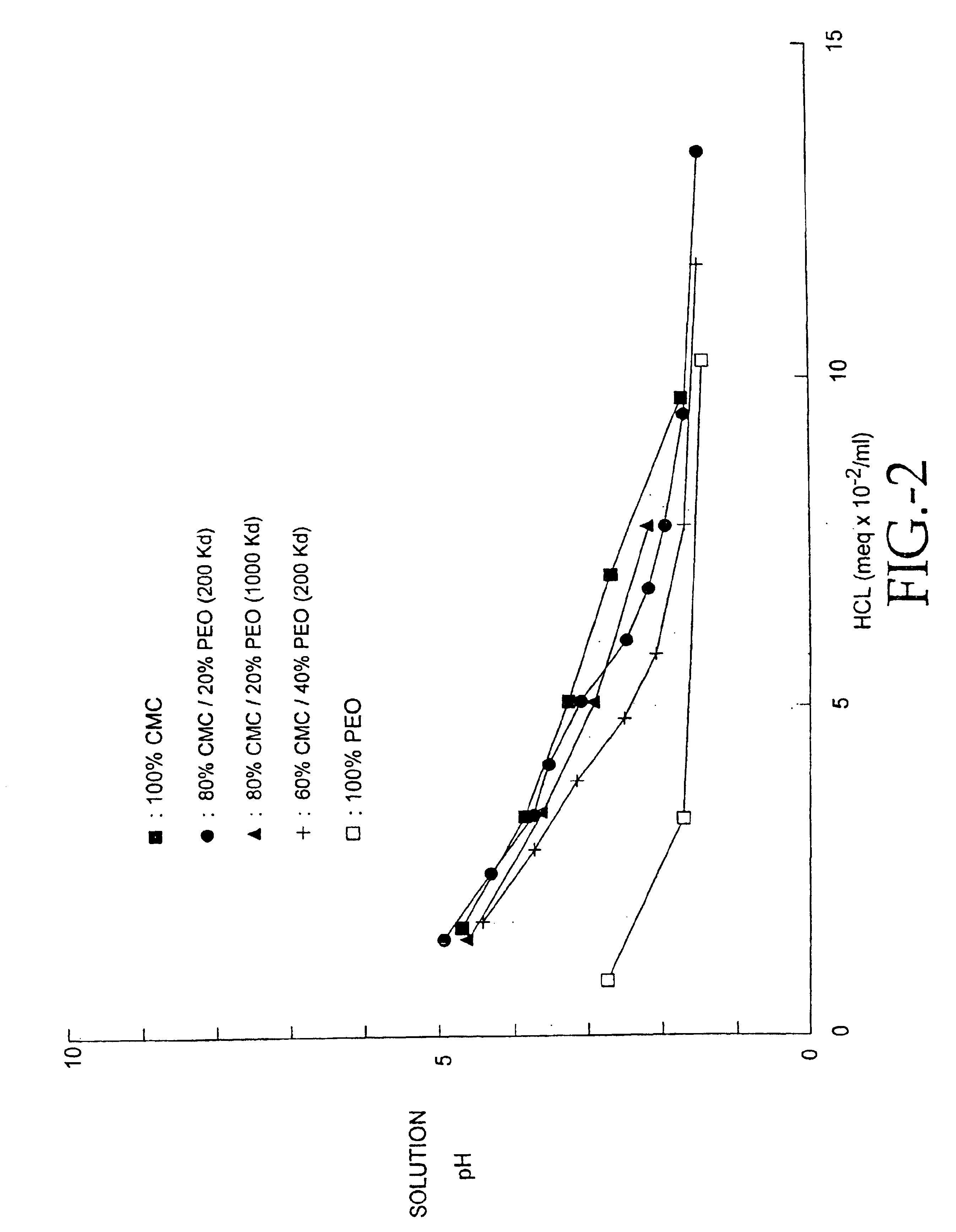
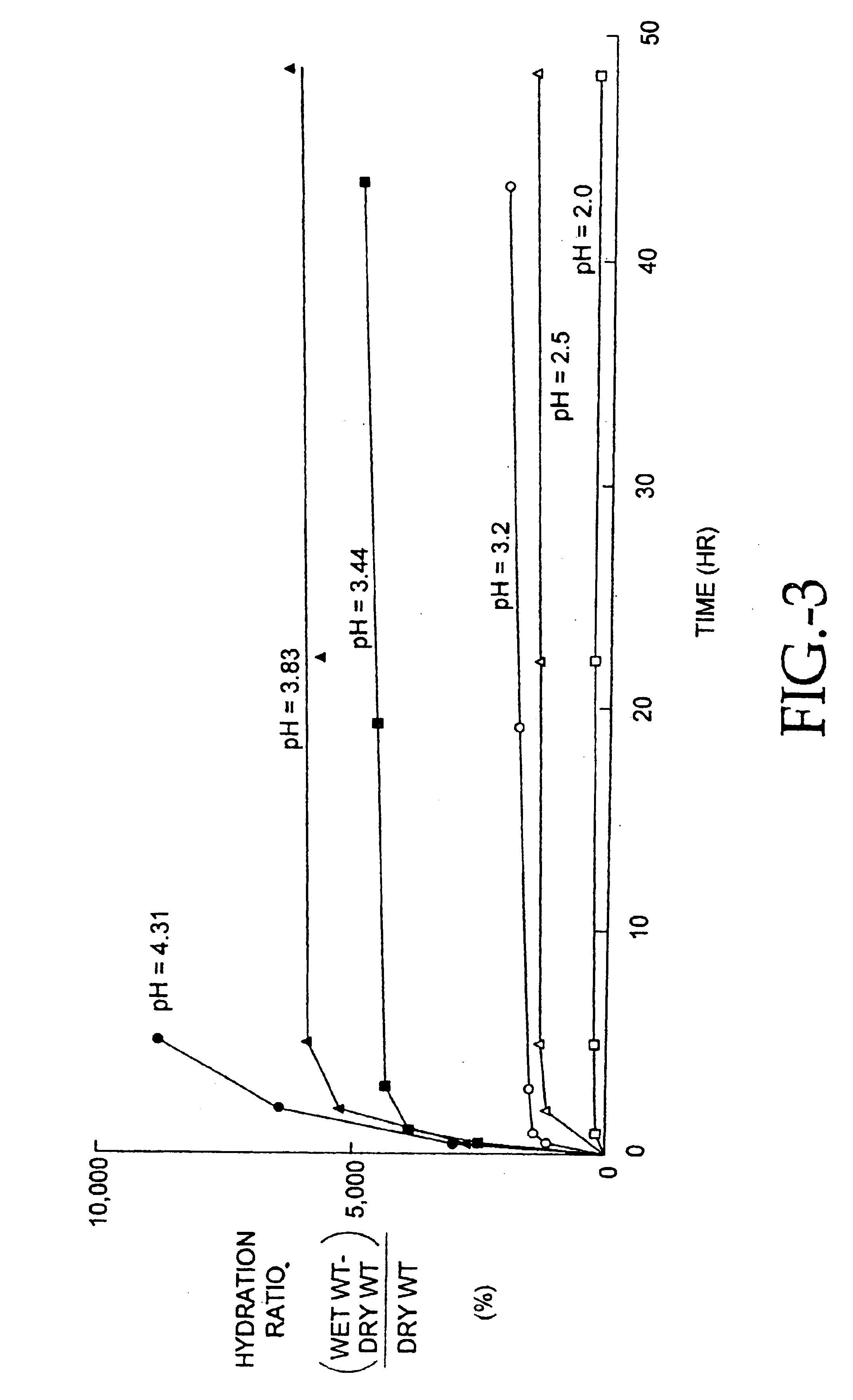
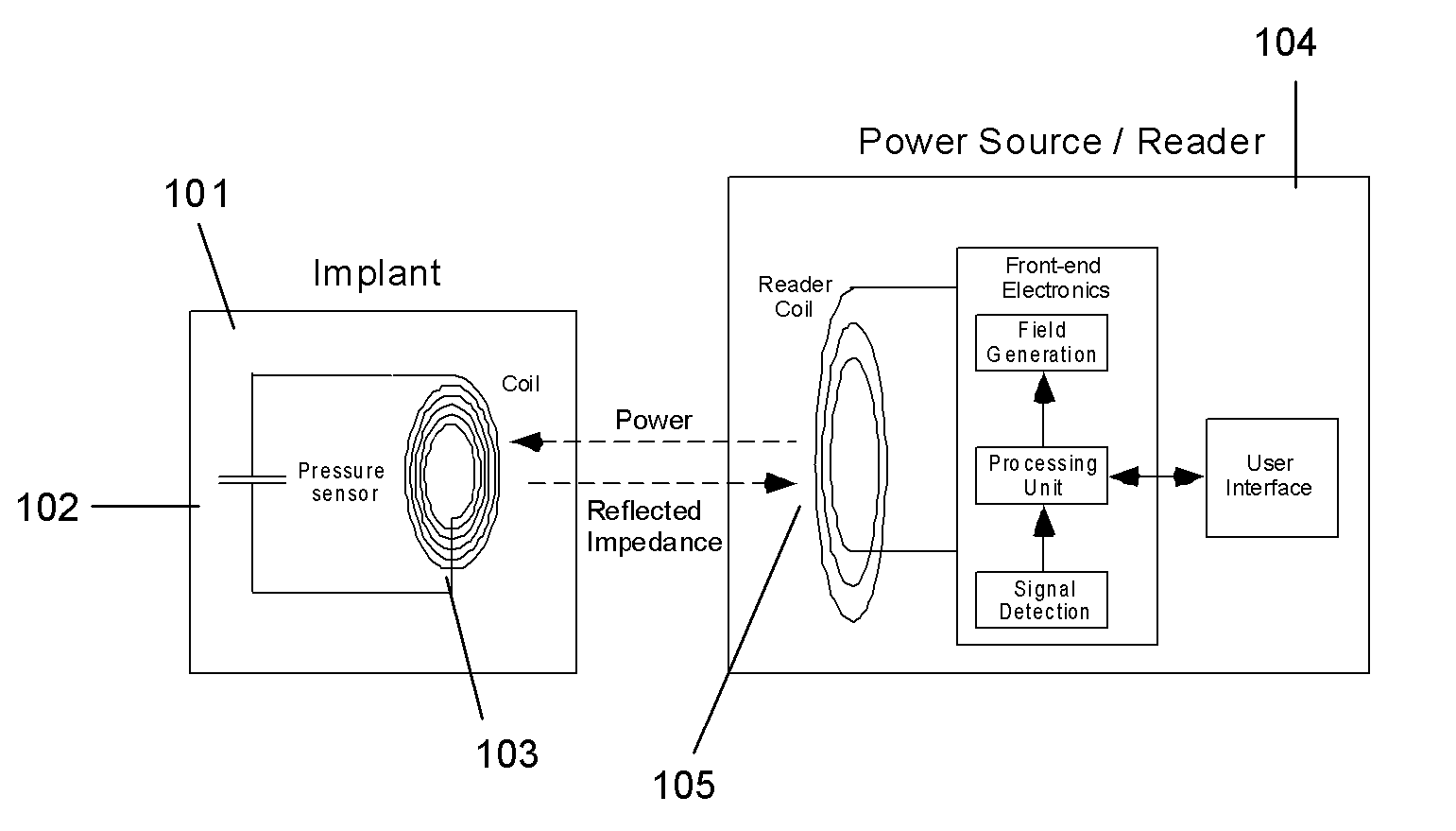
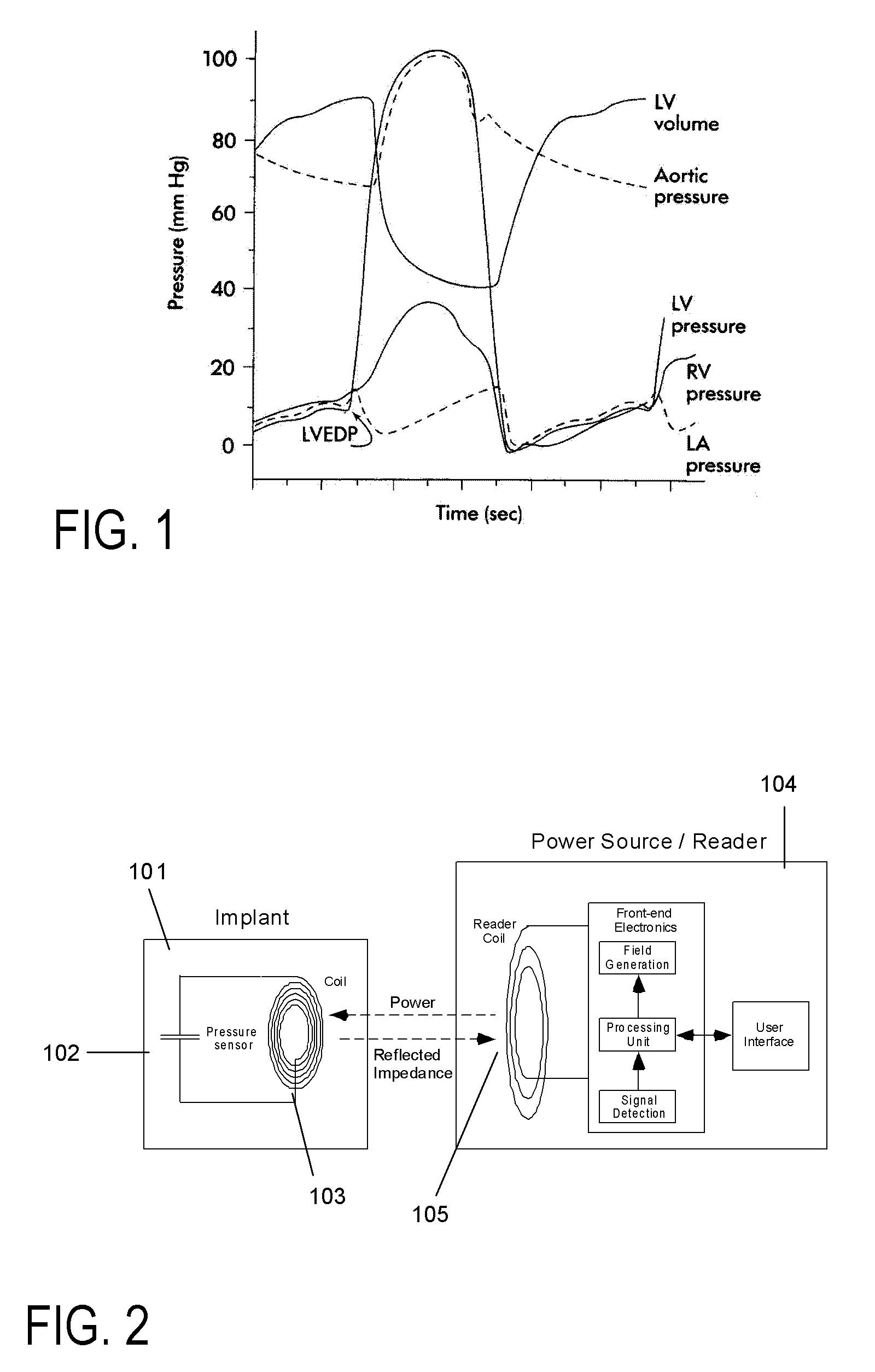
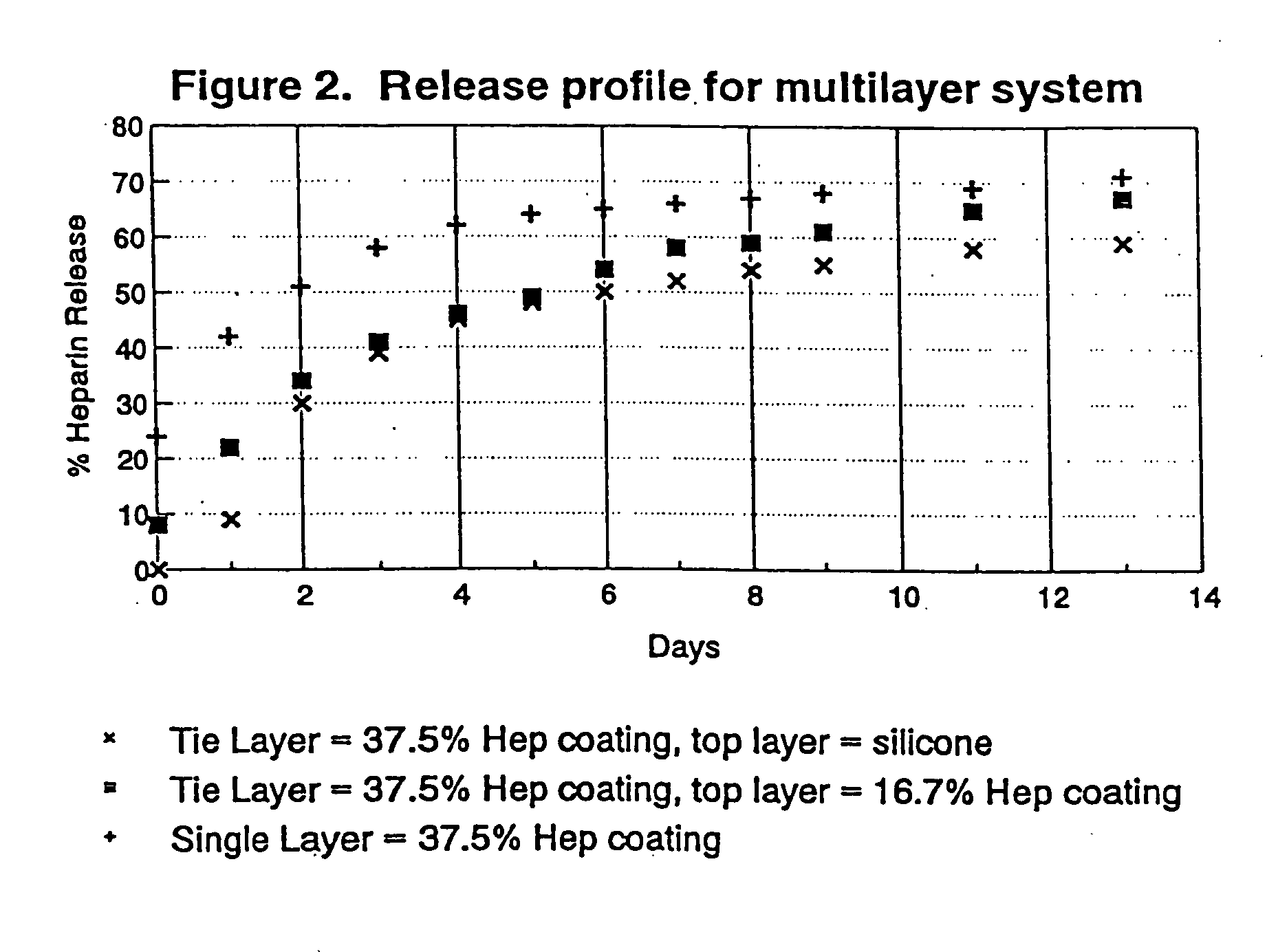
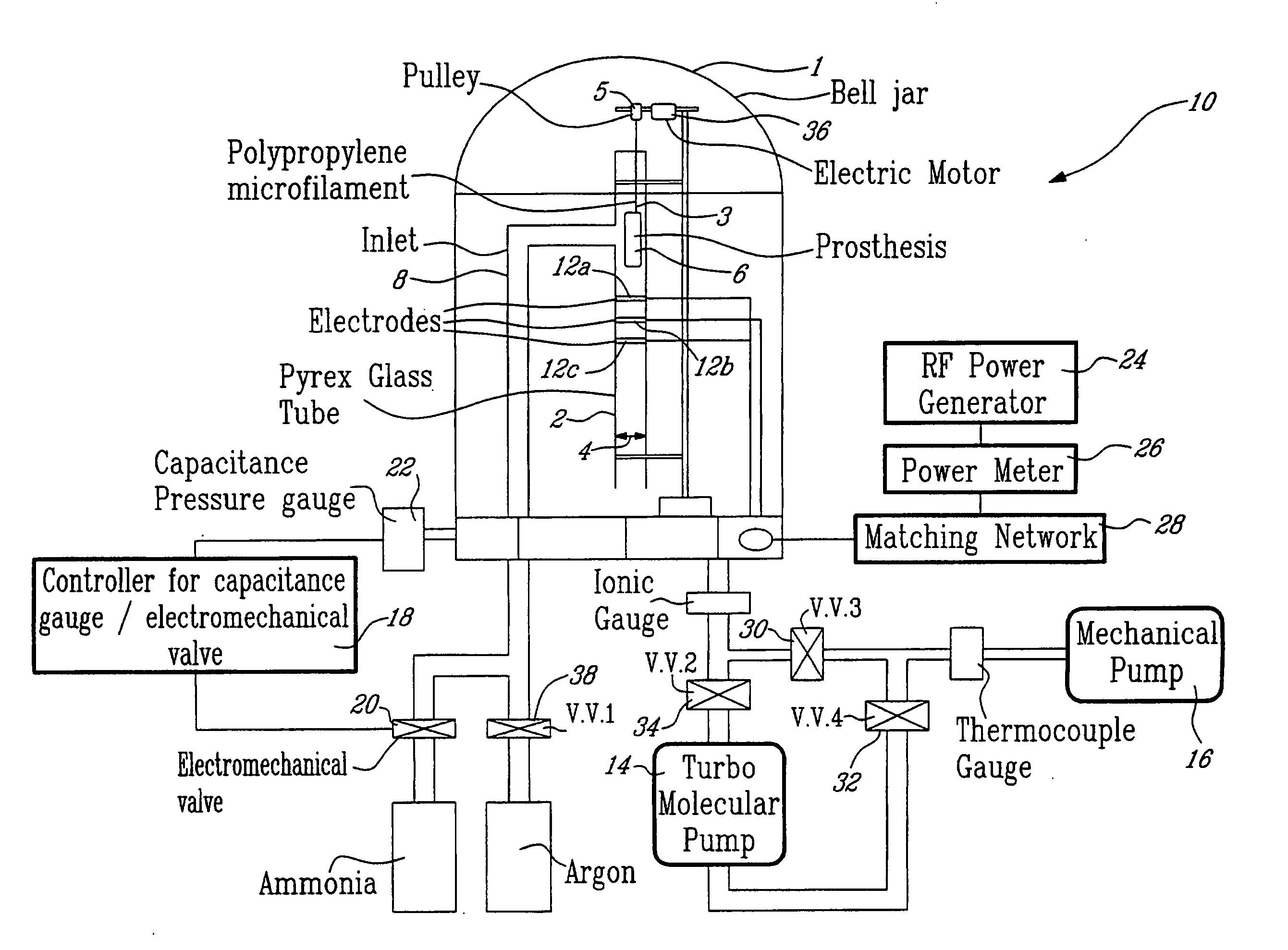
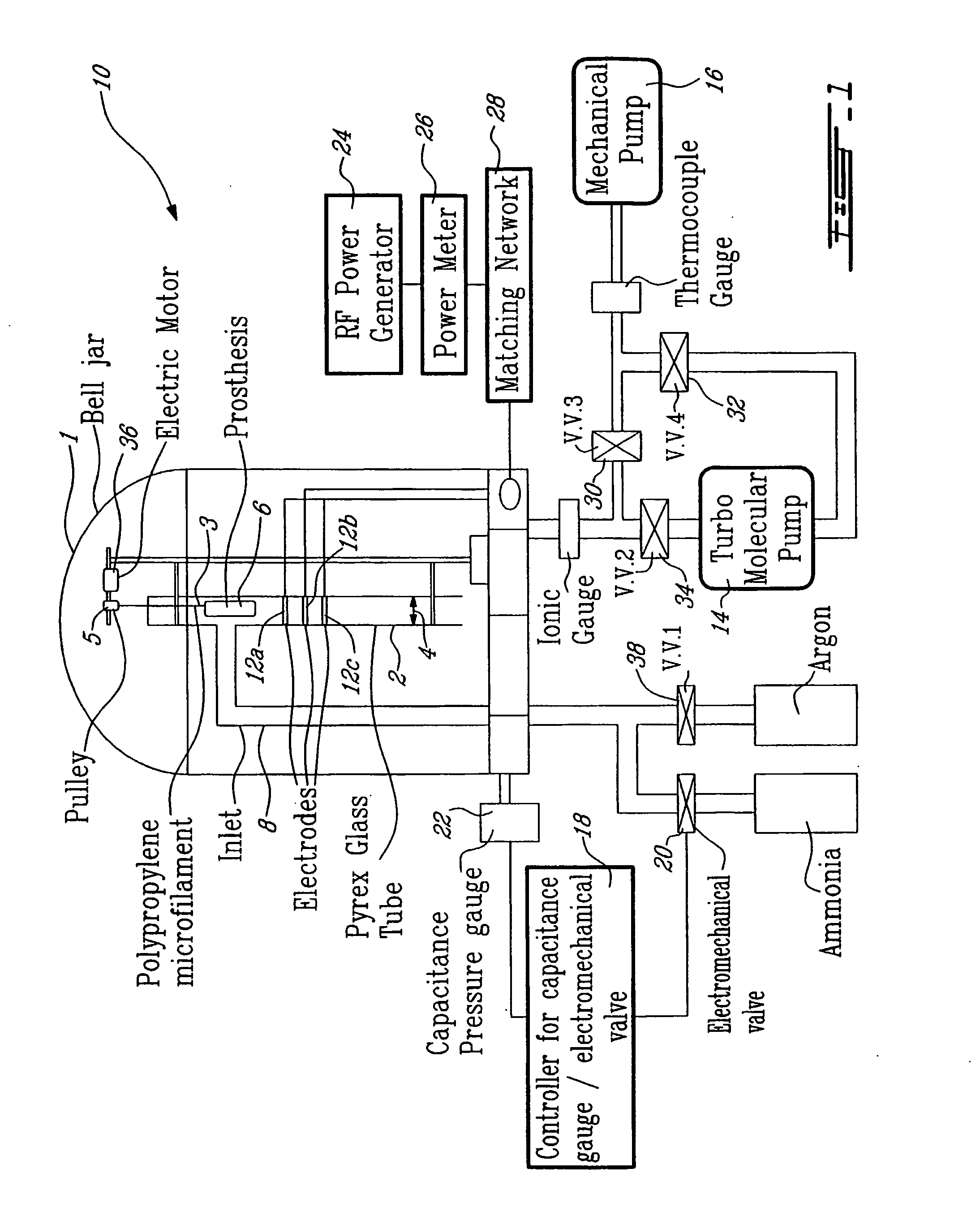
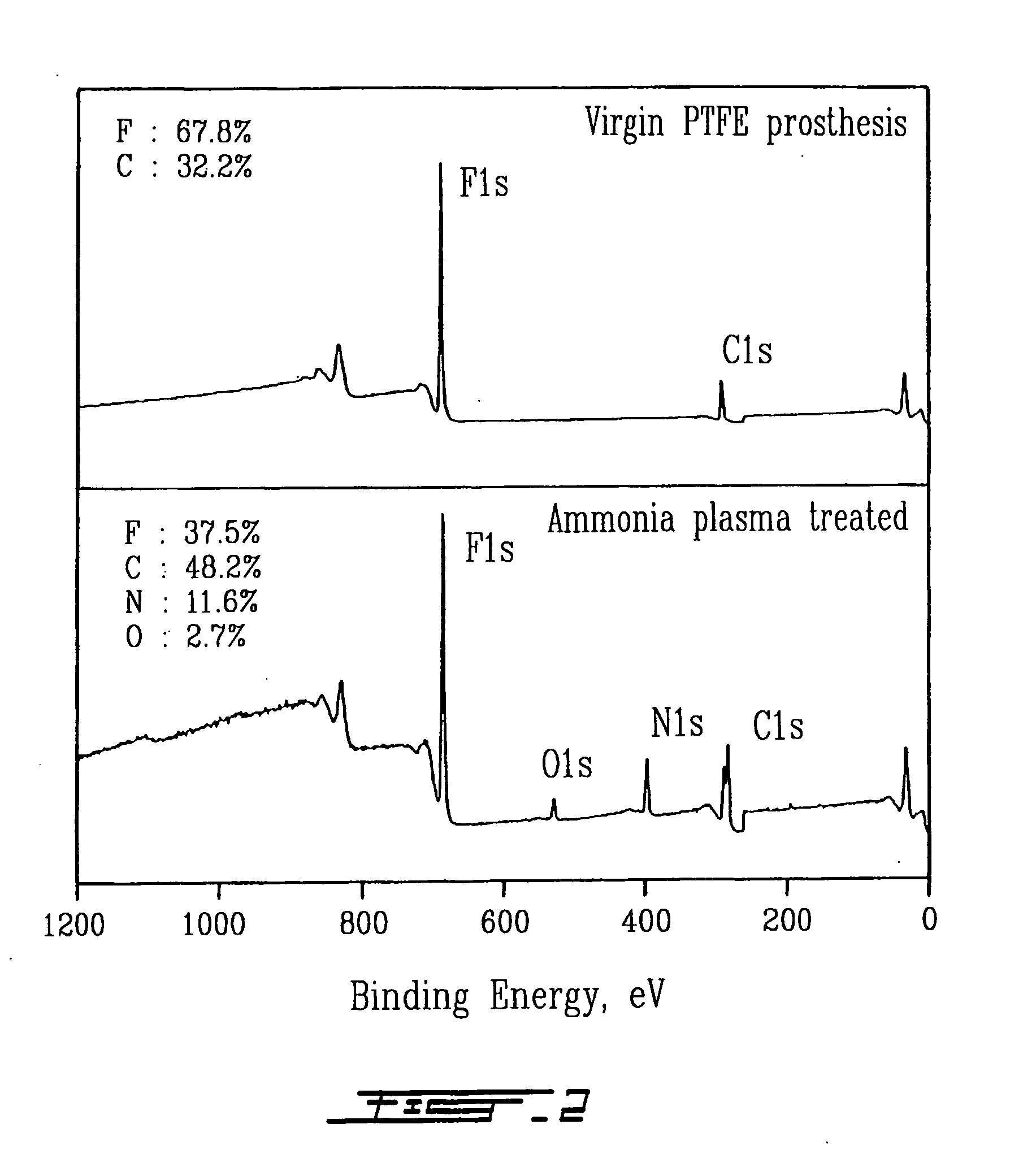
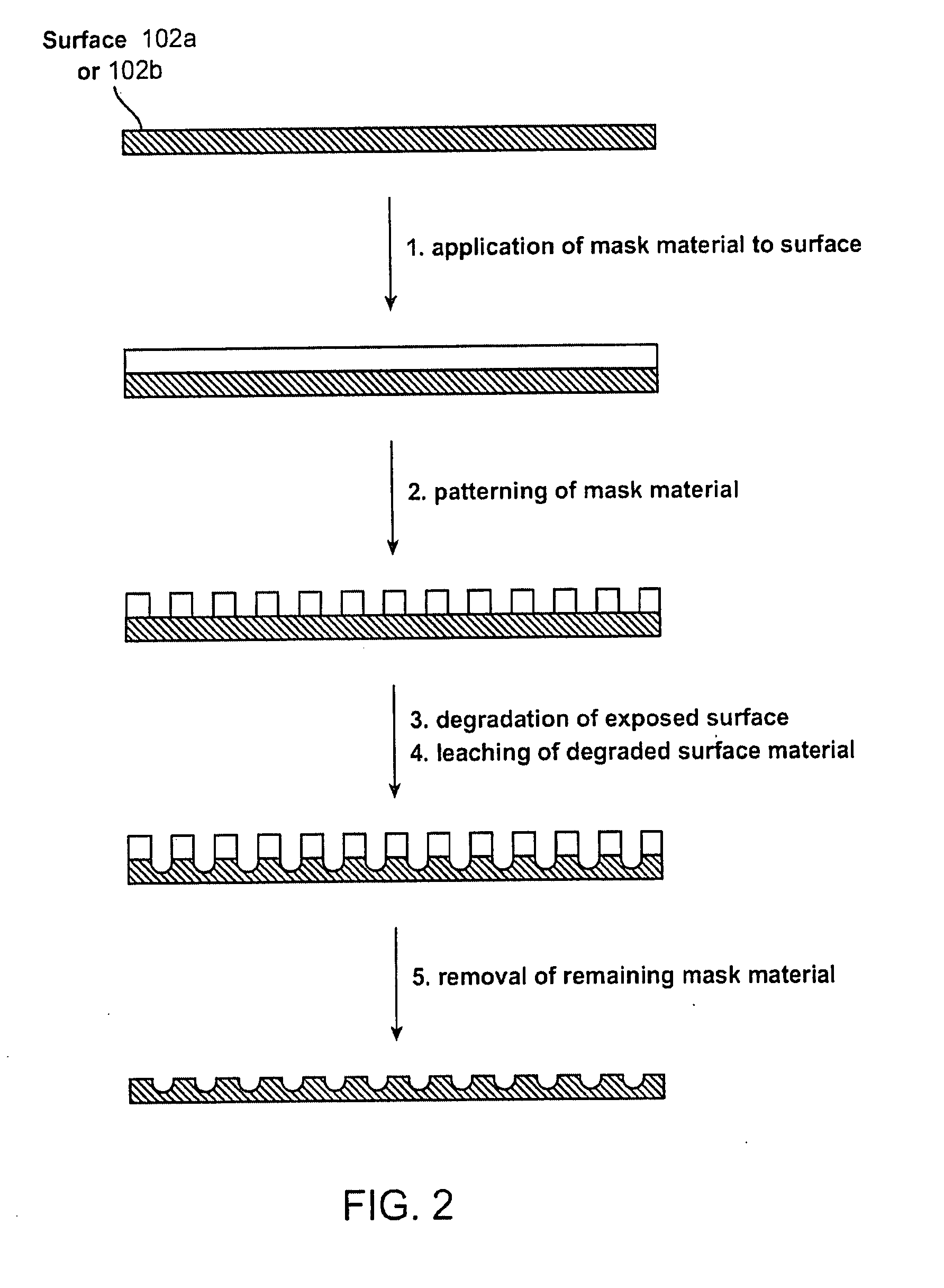
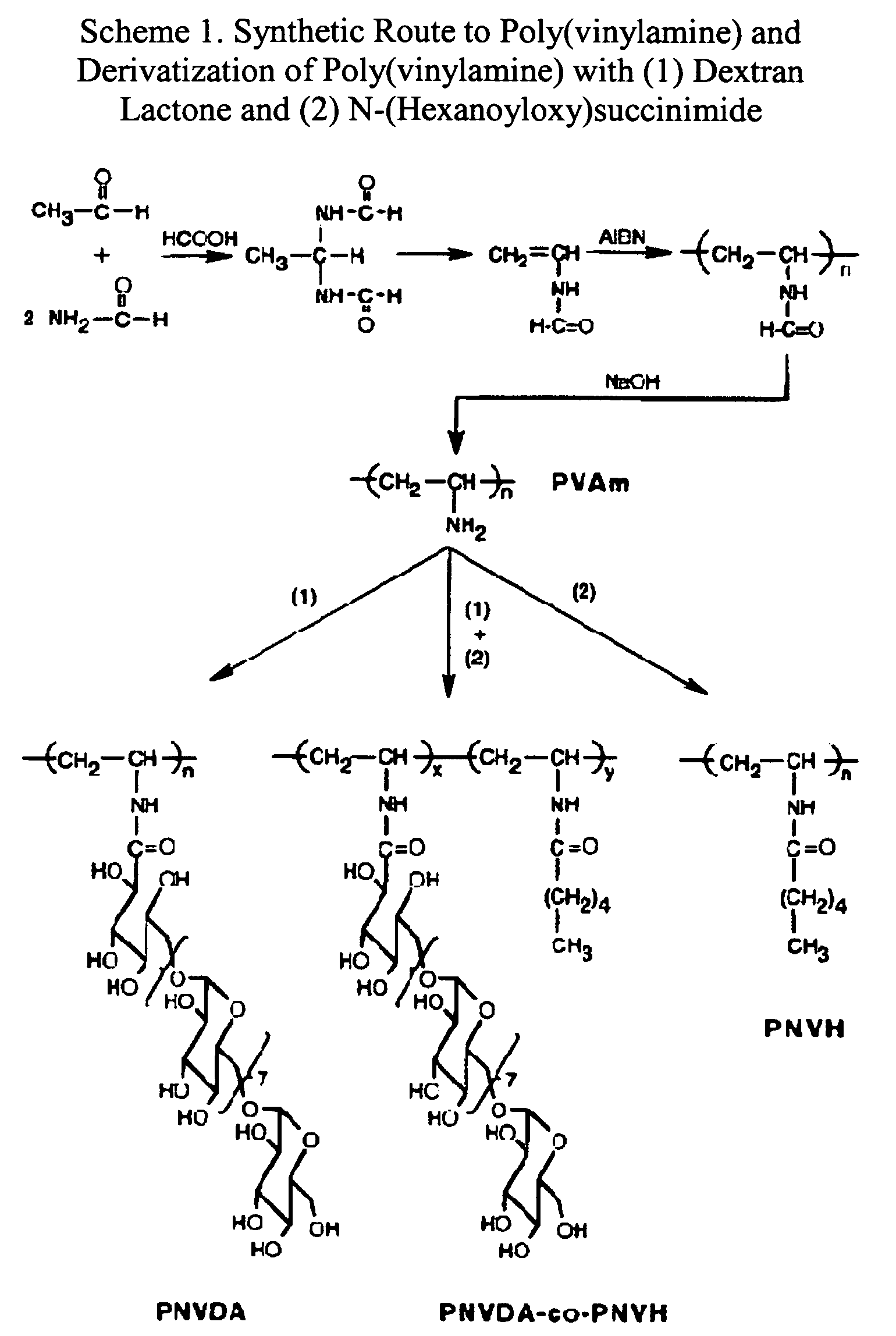
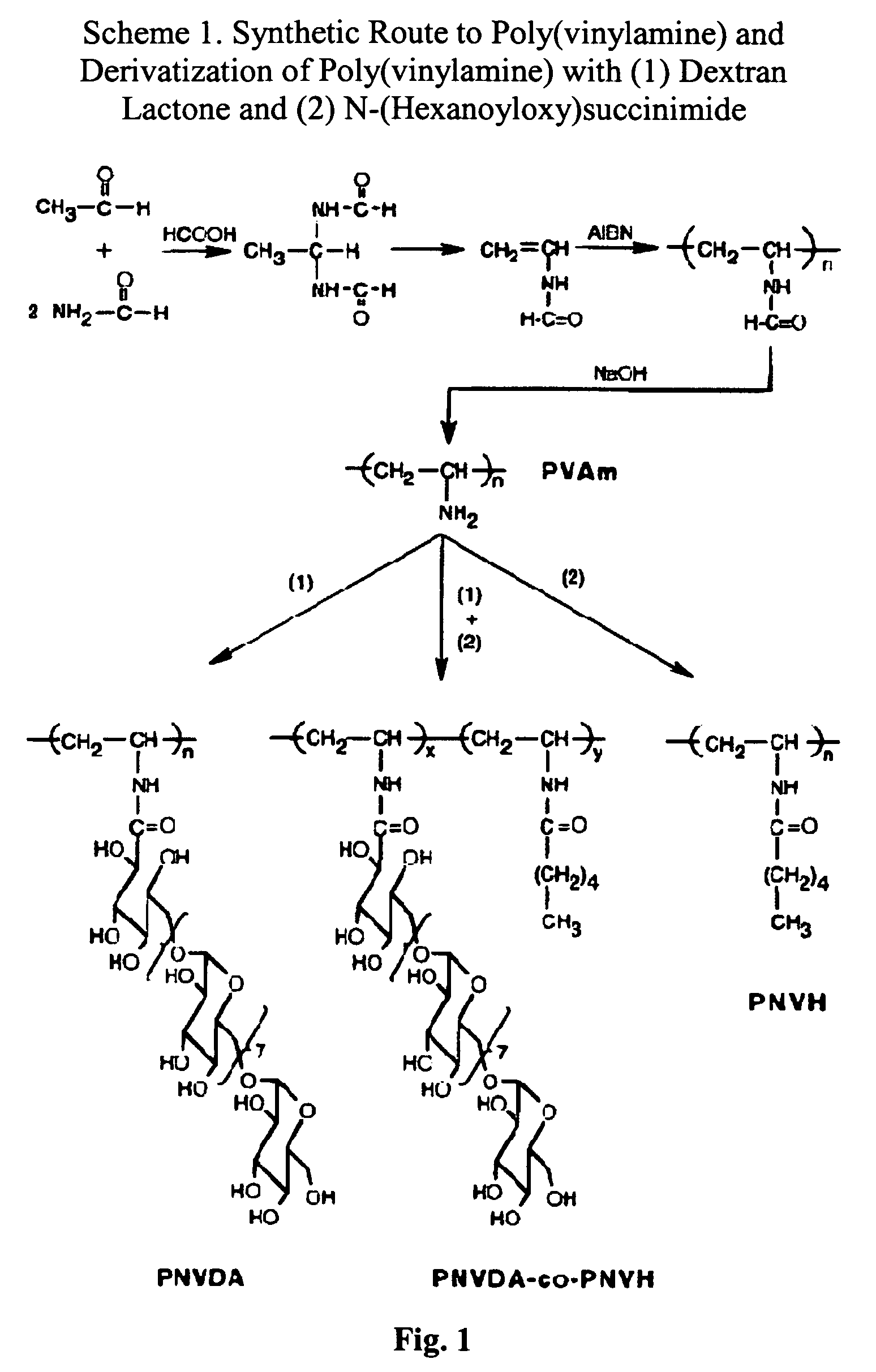
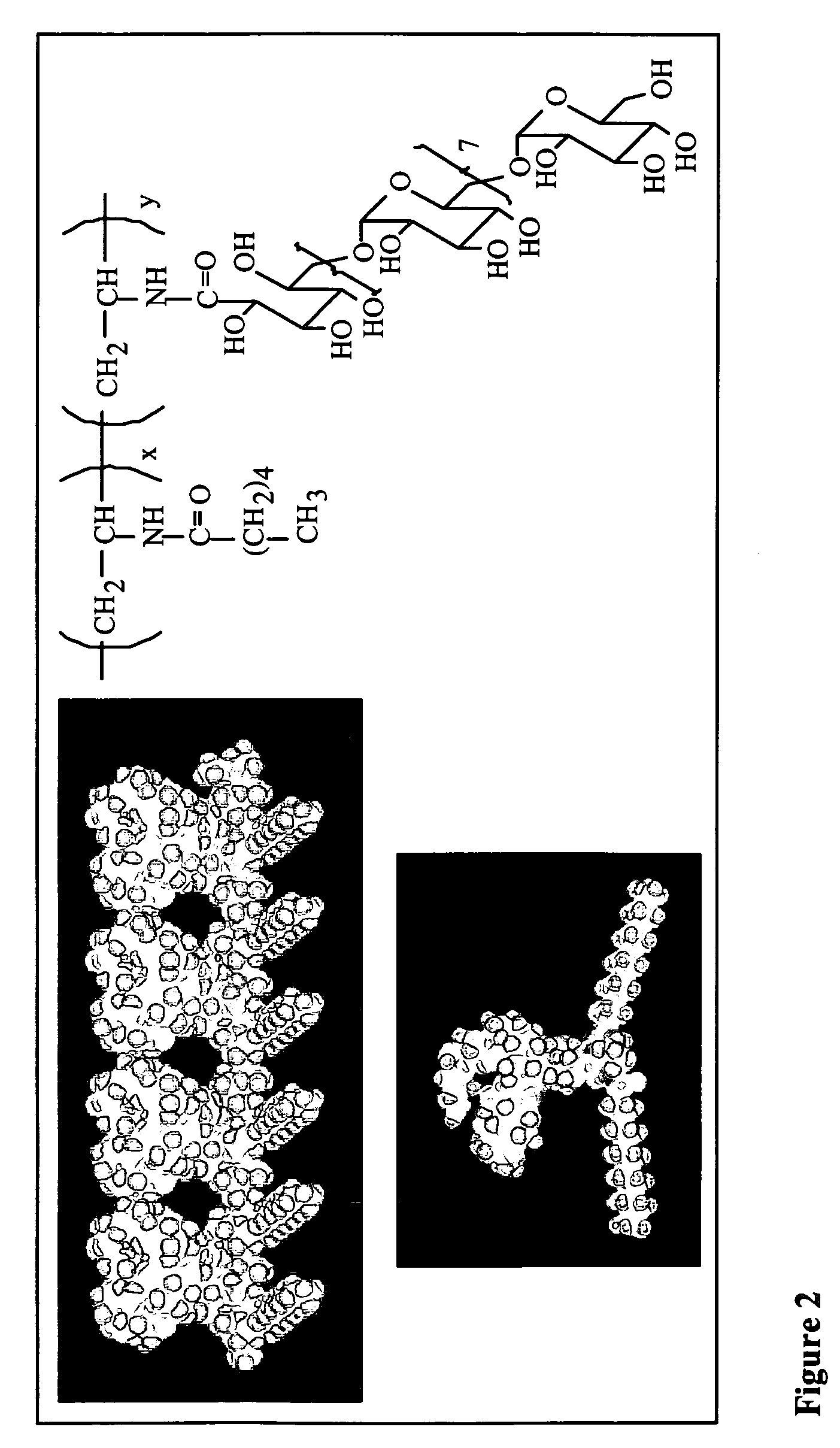
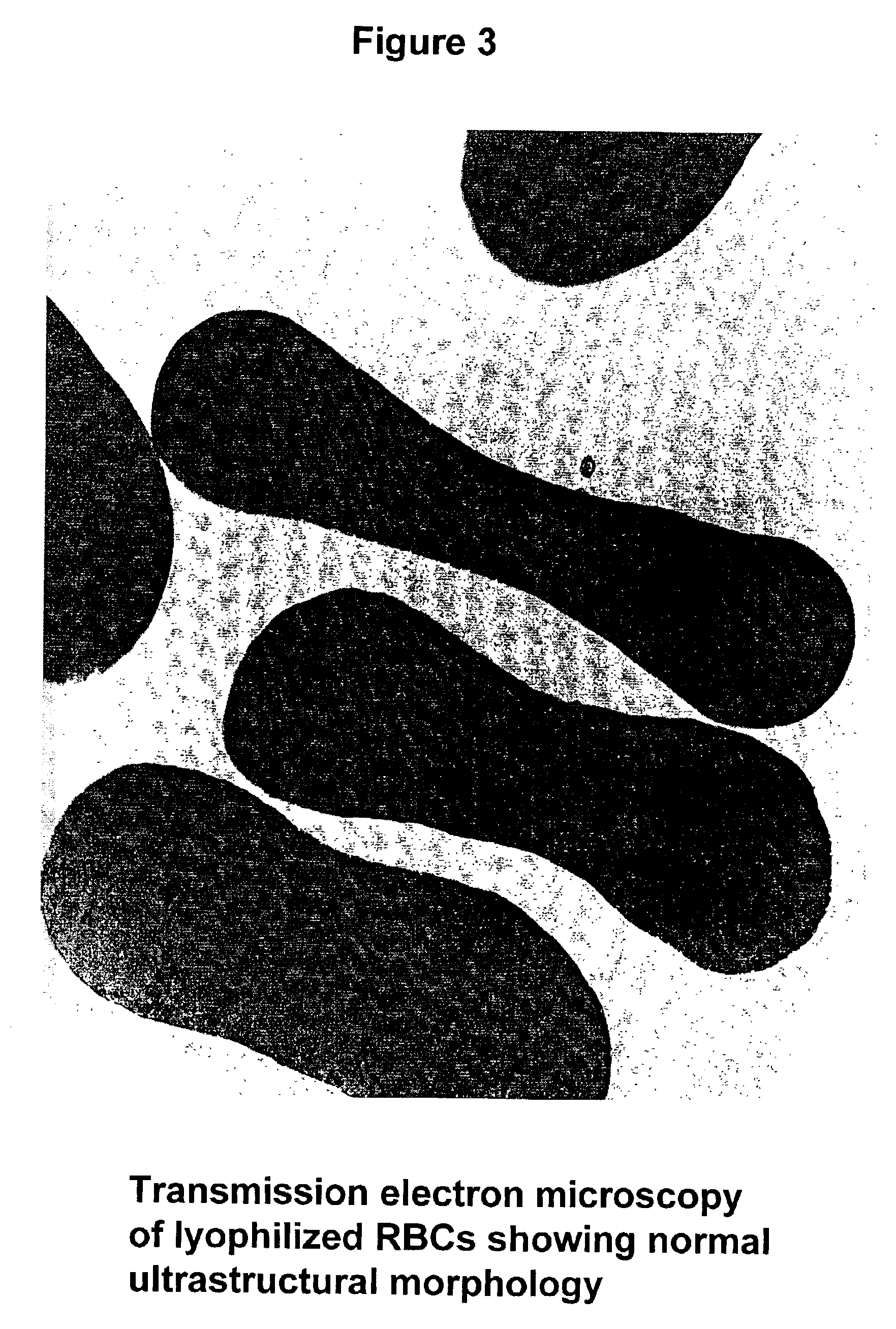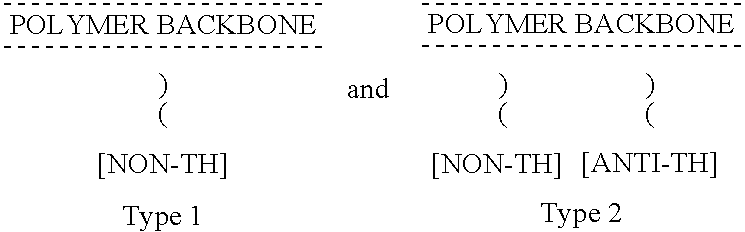Patents
Literature
83 results about "Thrombogenicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thrombogenicity refers to the tendency of a material in contact with the blood to produce a thrombus, or clot. It not only refers to fixed thrombi but also to emboli, thrombi which have become detached and travel through the bloodstream. Thrombogenicity can also encompass events such as the activation of immune pathways and the complement system. All materials are considered to be thrombogenic with the exception of the normal state of endothelial cells which line blood vessels. Certain medical implants appear non-thrombogenic due to high flow rates of blood past the implant, but in reality all are thrombogenic to a degree. Various surface treatments are available to minimize these thrombogenic effects.
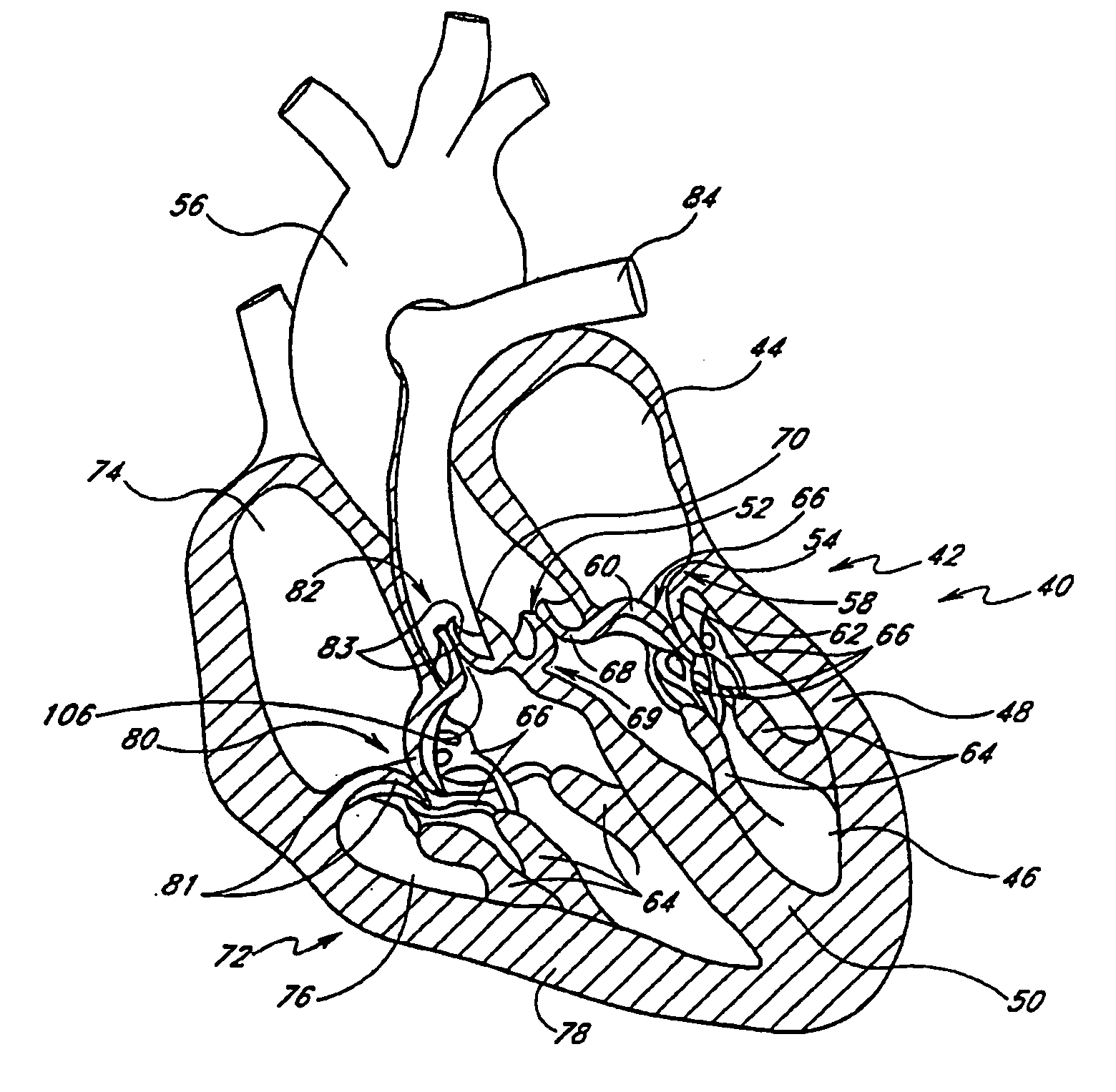
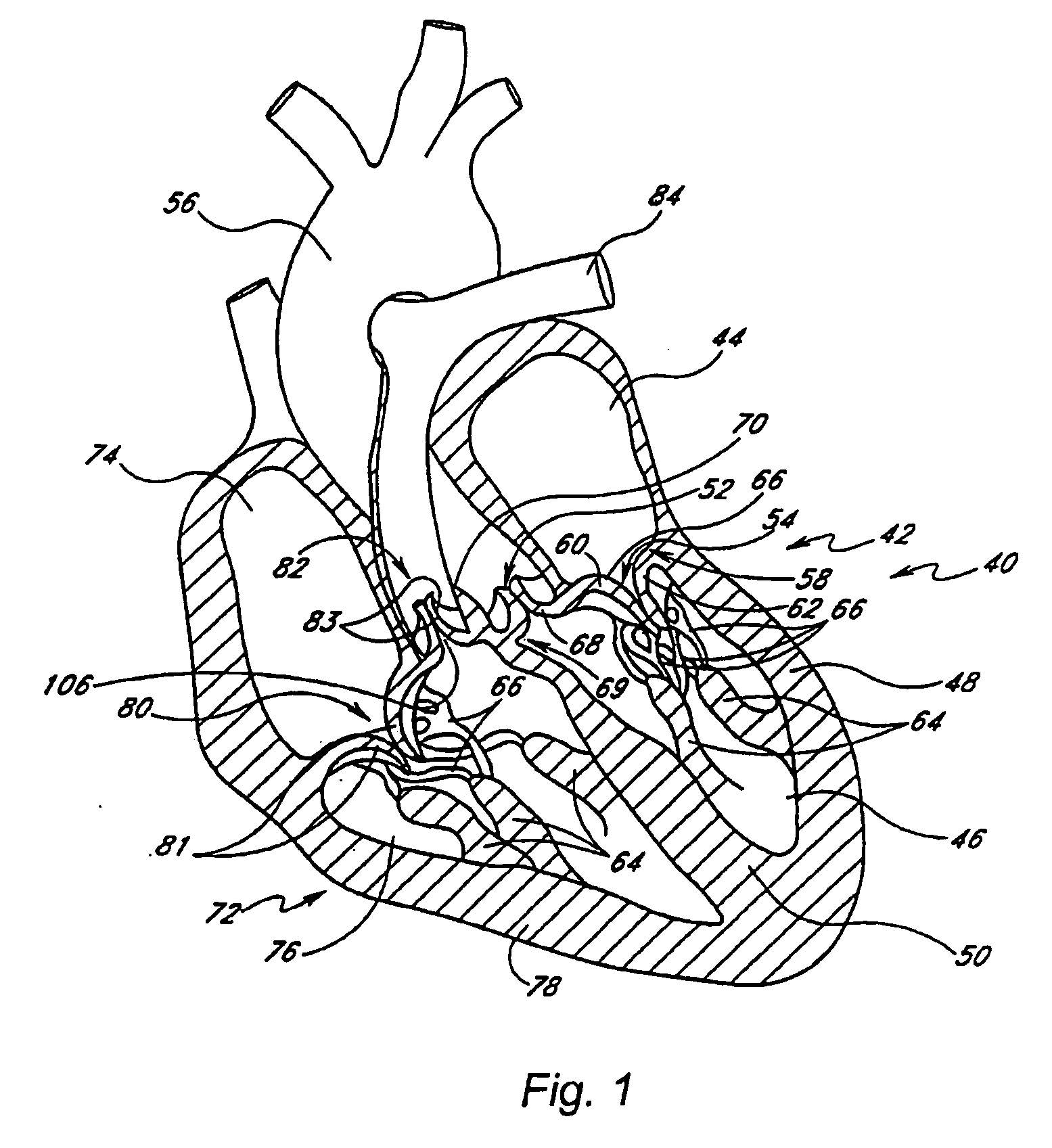
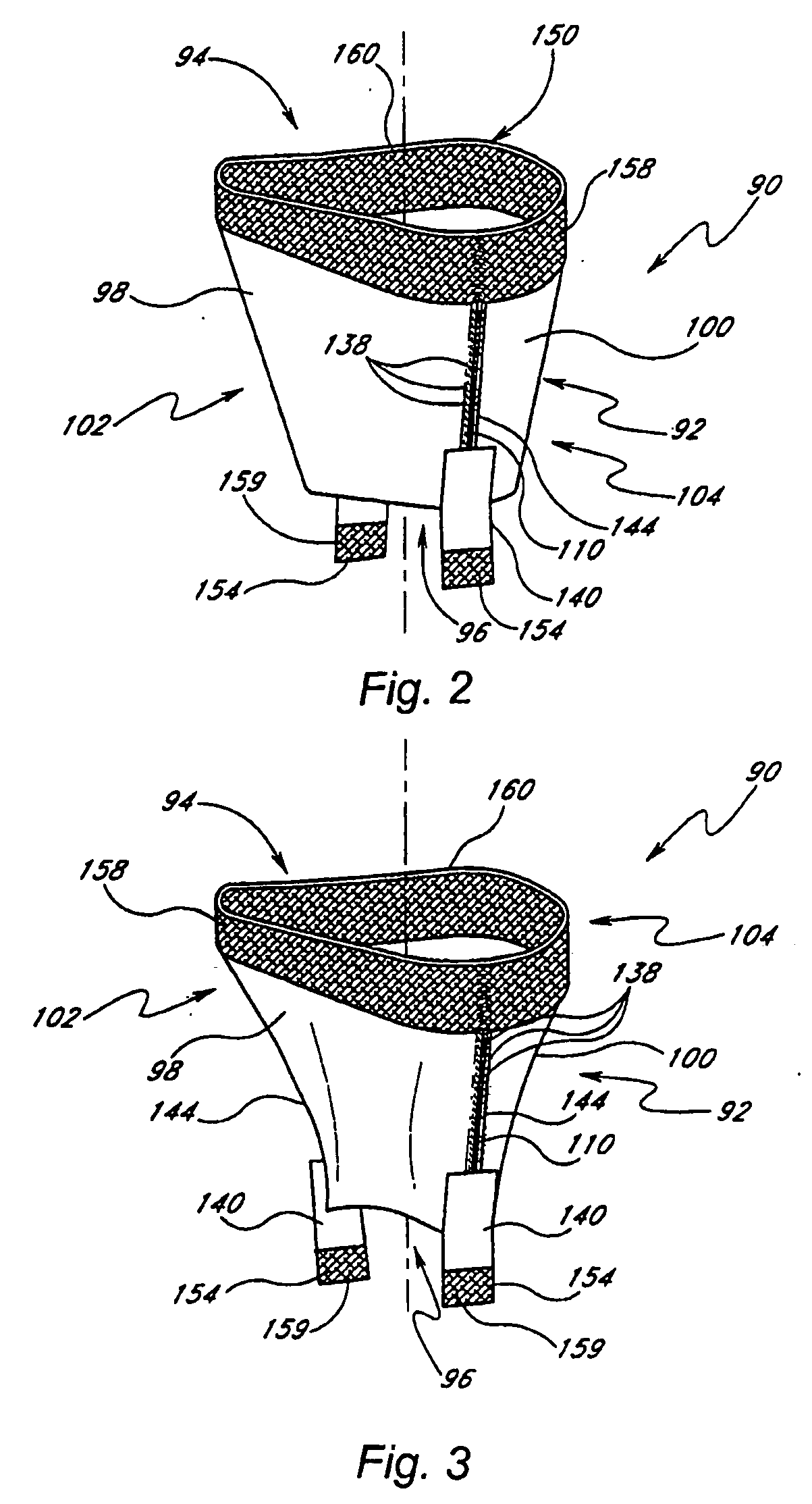
Prosthetic mitral valve
InactiveUS20070173932A1Improve performanceLow thrombogenicityHeart valvesSurgeryAnterior leafletPosterior leaflet
An improved prosthetic mitral valve is provided having advantageous hemodynamic performance, nonthrombogenicity, and durability. The valve includes a valve body having an inflow annulus and an outflow annulus. Commissural attachment locations are disposed adjacent the outflow annulus. An anterior leaflet and a posterior leaflet of the valve are shaped differently from one another. The inflow annulus preferably is scalloped so as to have a saddle-shaped periphery having a pair of relatively high portions separated by a pair of relatively low portions. The anterior high portion preferably is vertically higher than the posterior high portion.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
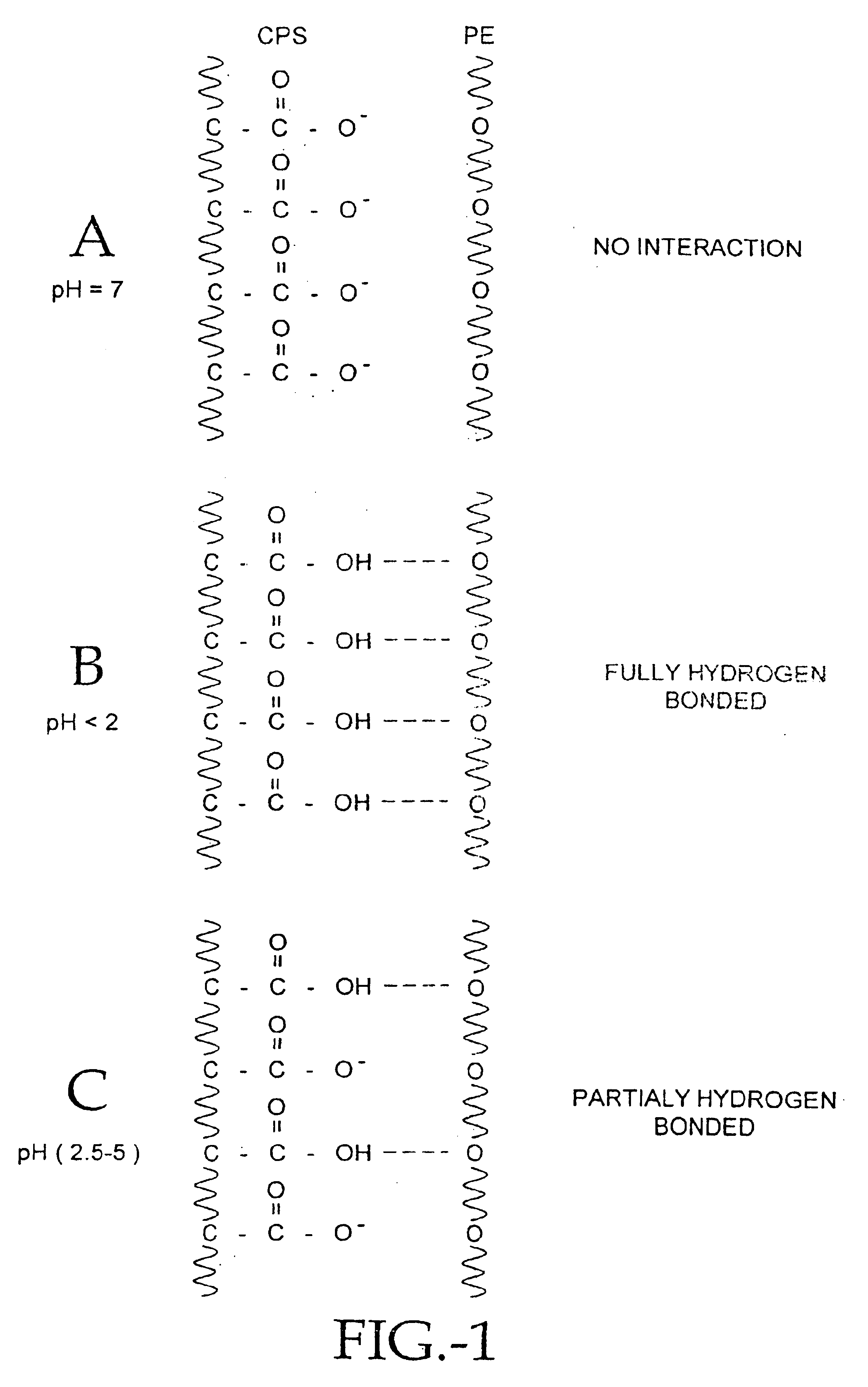
Compositions of polyacids and polyethers and methods for their use in reducing adhesions
InactiveUS6869938B1Improve anti-adhesion performancePrevent reformationBiocideSurgeryMicrosphereThrombogenicity
The present invention relates to improved methods for making and using bioadhesive, bioresorbable, anti-adhesion compositions made of intermacromolecular complexes of carboxyl-containing polysaccharides, polyethers, polyacids, polyalkylene oxides, multivalent cations and / or polycations. The polymers are associated with each other, and are then either dried into membranes or sponges, or are used as fluids or microspheres. Bioresorbable, bioadhesive, anti-adhesion compositions are useful in surgery to prevent the formation and reformation of post-surgical adhesions. The compositions are designed to breakdown in-vivo, and thus be removed from the body. Membranes are inserted during surgery either dry or optionally after conditioning in aqueous solutions. The anti-adhesion, bioadhesive, bioresorptive, antithrombogenic and physical properties of such membranes and gels can be varied as needed by carefully adjusting the pH and / or cation content of the polymer casting solutions, polyacid composition, the polyalkylene oxide composition, or by conditioning the membranes prior to surgical use. Multi-layered membranes can be made and used to provide further control over the physical and biological properties of antiadhesion membranes. Membranes and gels can be used concurrently. Antiadhesion compositions may also be used to lubricate tissues and / or medical instruments, and / or deliver drugs to the surgical site and release them locally.
Owner:FZIOMED
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly˜glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for monitoring a physiologic parameter of patients with congestive heart failure
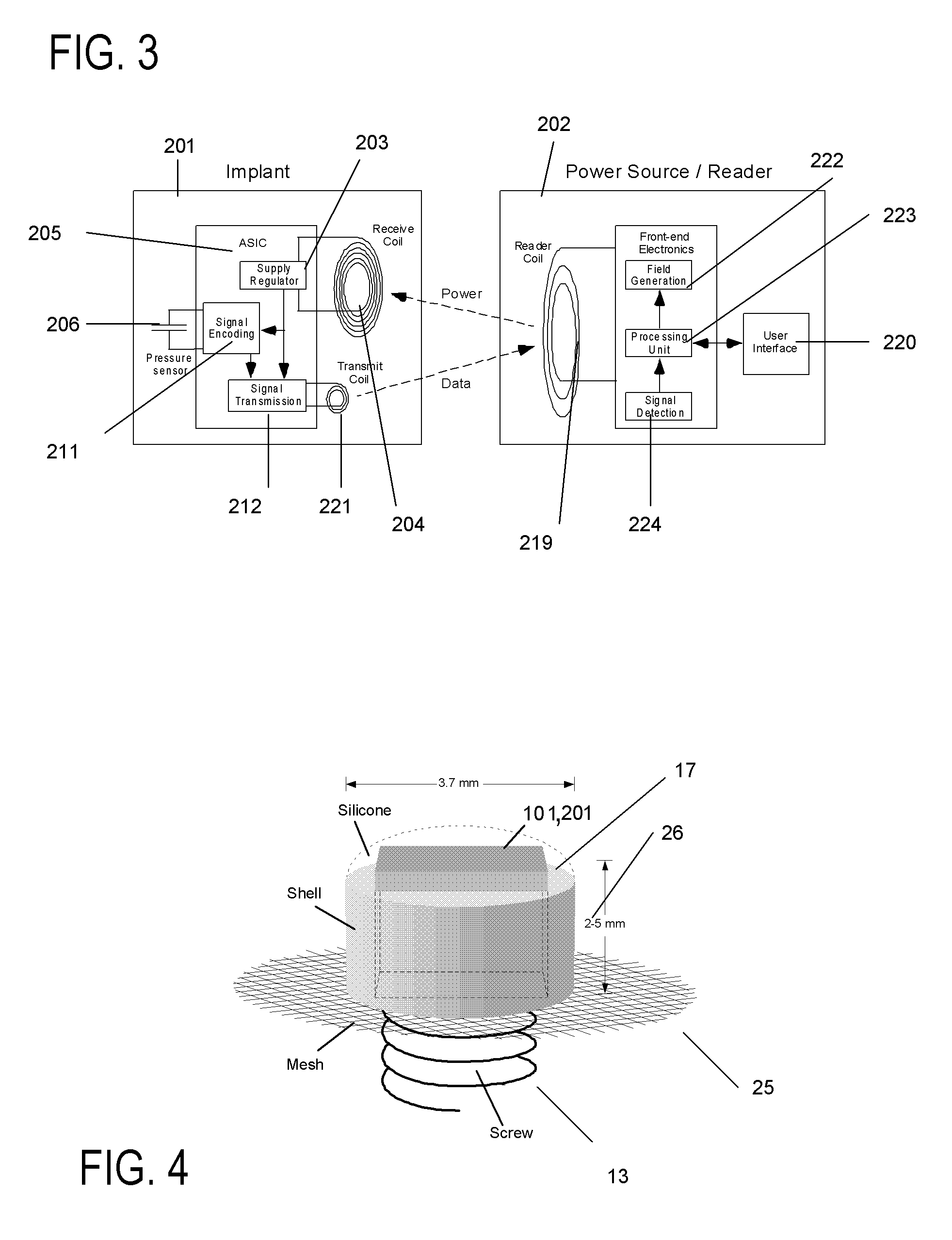
A method of monitoring physiological parameters for diagnosis and treatment of congestive heart failure in a patient. The method includes implanting at least one sensing device in a cavity of the patient's cardiovascular system, preferably so that the sensing device passes through and is anchored to a septum of the heart and, to minimize the risk of thrombogenicity, a larger portion of the sensing device is located in the right side of the heart and a smaller portion of the sensing device is located in the left side of the heart. Electromagnetic telecommunication and / or wireless powering of the sensing device is performed with an external readout device. The method can be used to perform effective monitoring, management, and tailoring of treatments for patients suffering from congestive heart failure, as well as many other diseases.
Owner:UIM PRESSURE IMPLANT INC
Implantable intraluminal protector device and method of using same for stabilizing atheromas
InactiveUS20030100940A1Process stabilityImprove propertiesStentsBlood vesselsThrombogenicityThrombus
An intraluminal device implantable in a body lumen having an atheroma therein in the vicinity of a side-branch vessel includes a mesh-like tube of bio-compatible material formed with liquid-permeable window openings. The mesh-like tube has an expanded condition in which the tube diameter is slightly larger than the diameter of the body lumen in which it is to be implanted, and the tube length is sufficient to cover the atheroma and the side-branch orifice, and to be anchored to the body lumen around the periphery of the atheroma, and a contracted condition wherein it is sufficiently flexible so as to be easily manipulatable through the body lumen to the site of the atheroma. The mesh-like tube, in its expanded condition, has window openings of a size and distribution such as to structurally stabilize the atheroma and to keep embolic material originating from the atheroma in place on the wall of the body lumen, while diverting embolic material of predetermined size present in the blood flowing through the mesh-like tube from the side-branch orifice, without substantially impeding the blood flow, or increasing the thrombogenitic properties, of the blood flowing into the side-branch orifice.
Owner:SURPASS MEDICAL
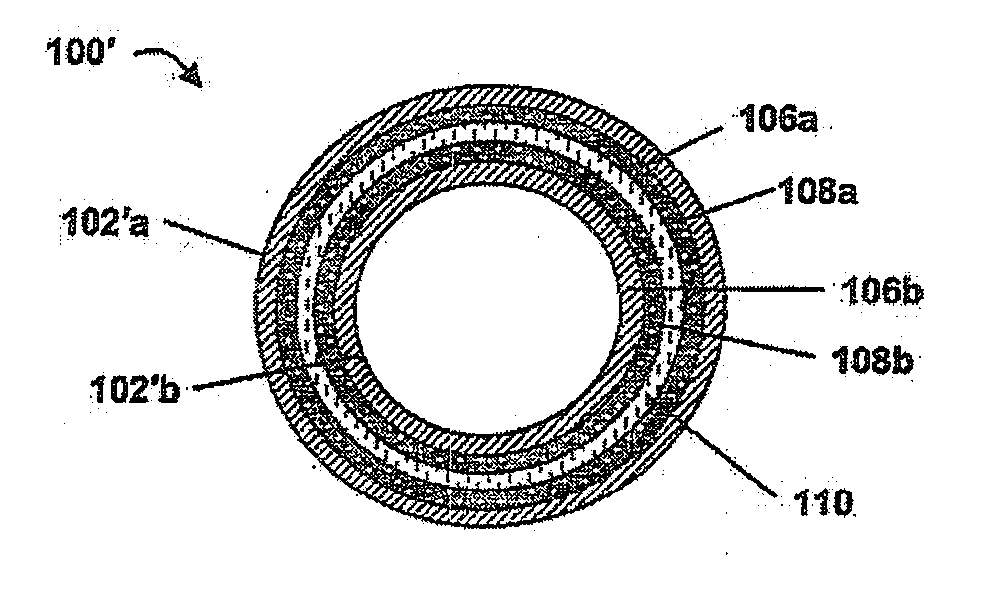
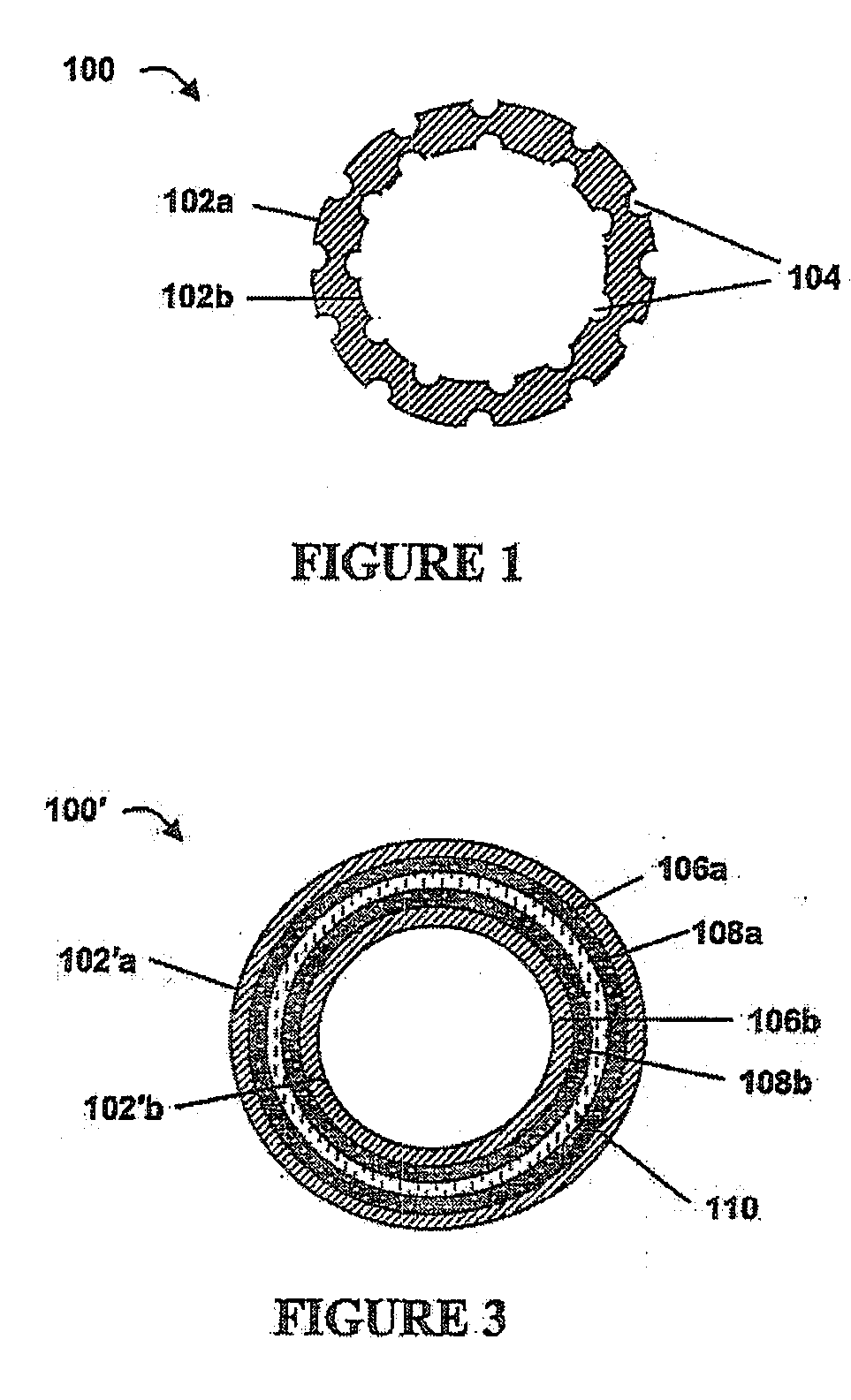
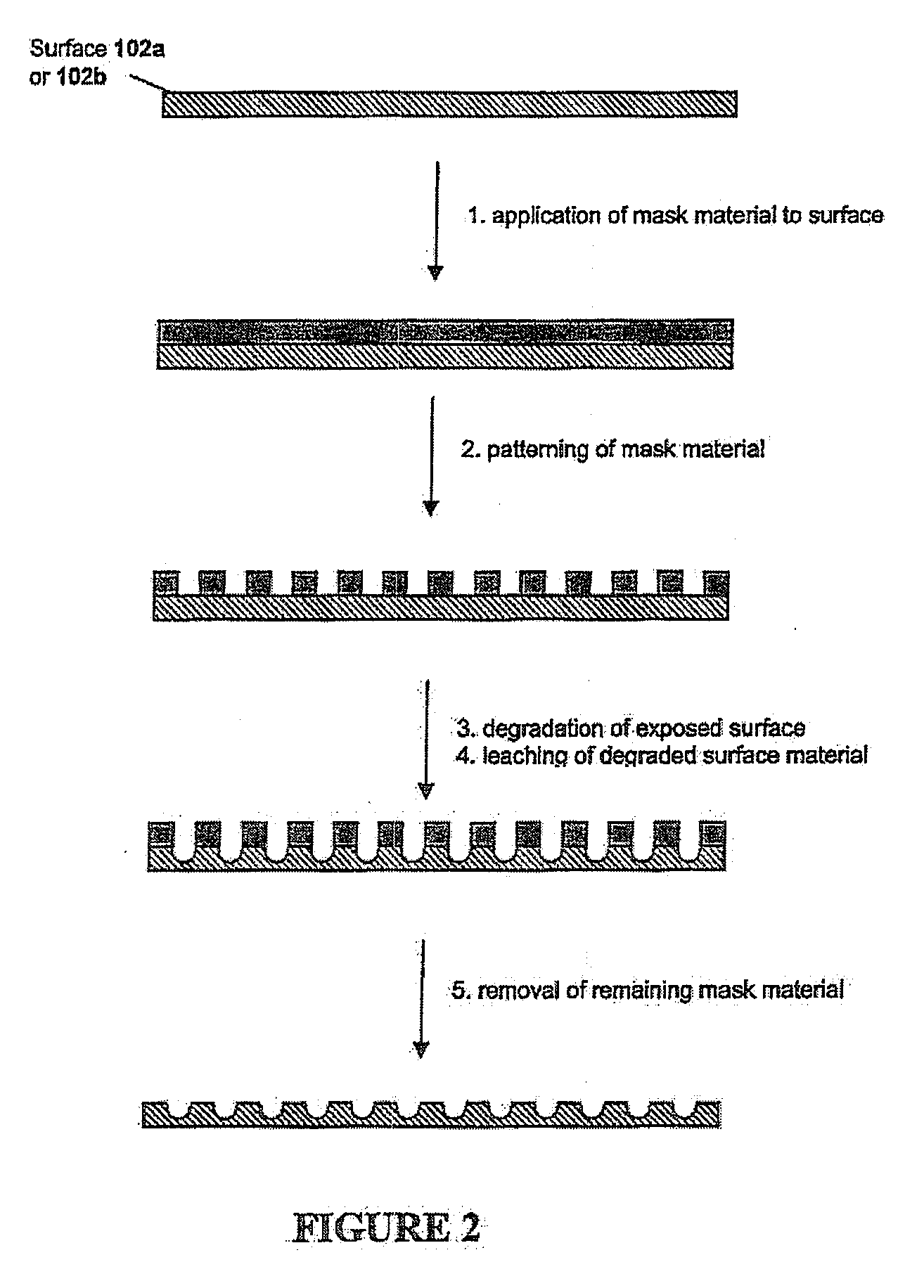
Implantable article, method of forming same and method for reducing thrombogenicity
ActiveUS20070299510A1Reduce thrombosisPromoting and enhancing endothelializationHeart valvesMedical devicesThrombogenicityThrombus
Endothelialization of a bodily fluid or tissue-contacting, particularly blood-contacting, surface may be accomplished to render that surface substantially non-thrombogenic. Thrombosis may also be mitigated or eliminated by providing an eroding layer on the surface that results in the removal of any thrombus formation as the layer erodes. An implantable device may utilize at least one surface having a plurality of nano-craters thereon that enhance or promote endothelialization. Additionally, an implantable device may have at least one first degradable layer for contacting bodily fluid or tissue and disposed about a central core, and at least one second degradable layer between the first degradable layer and the central core. The first degradable layer has a first degradation rate and the second degradable layer has a second degradation rate which degrades more slowly than the first degradable layer on contact with bodily fluid or tissue.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
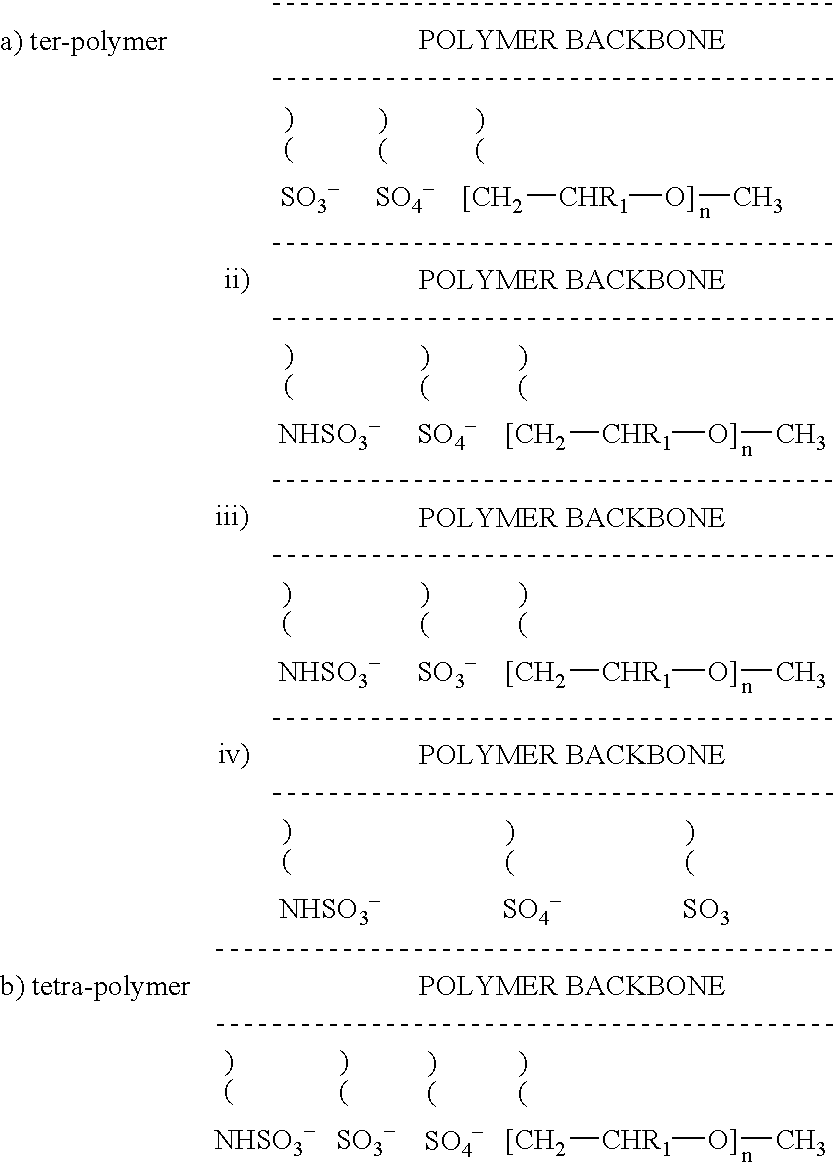
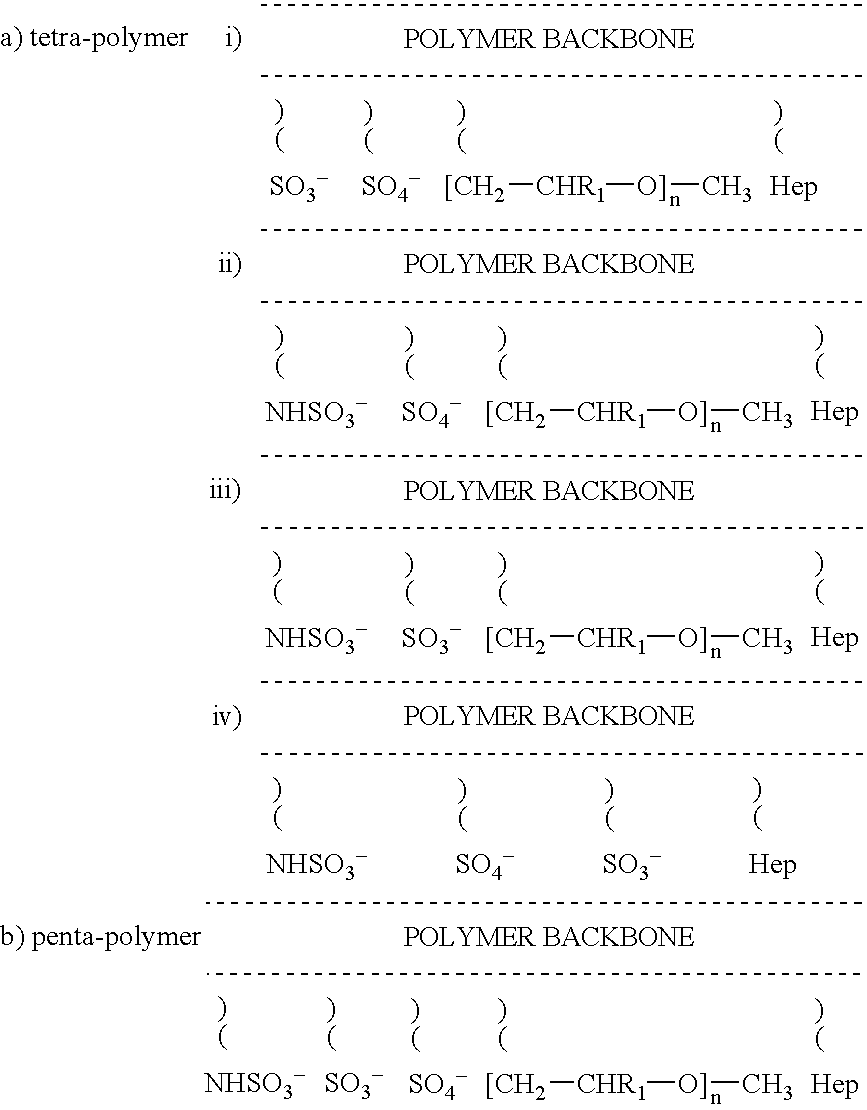
Non-thrombogenic and anti-thrombogenic polymers
InactiveUS6096798AEasy to attachReducing the thrombin-antithrombin complex concentrationCosmetic preparationsImpression capsPolymer scienceThrombogenicity
PCT No. PCT / GB97 / 01173 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 30, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 30, 1999 PCT Filed Apr. 30, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 41164 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 6, 1997Polymers having non-thrombogenic properties can be prepared by copolymerizing monomers of at least three classes selected from (a) monomers having sulphate groups, (b) monomers having sulphonate groups, (c) monomers having sulphamate groups, (d) monomers having polyoxyalkylene ether groups, and (e) monomers having zwitterionic groups. The polymers can additionally be provided with anti-thrombogenic properties by including an additional comonomer having a pendant heparin (or hirudin, warfarin or hyaluronic acid) group. The polymers can be used as coating materials for medical devices, such as tubing or connectors, in order to provide them with non-thrombogenic, and optionally anti-thrombogenic, properties.
Owner:BIOINTERACTIONS
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
InactiveUS20020040239A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical containersPoly-L-lactideVascular compartment
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly~glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Drug coating with topcoat
InactiveUS20050187611A1Long release timeReduced burst effectStentsSurgeryThrombogenicityDrug coating
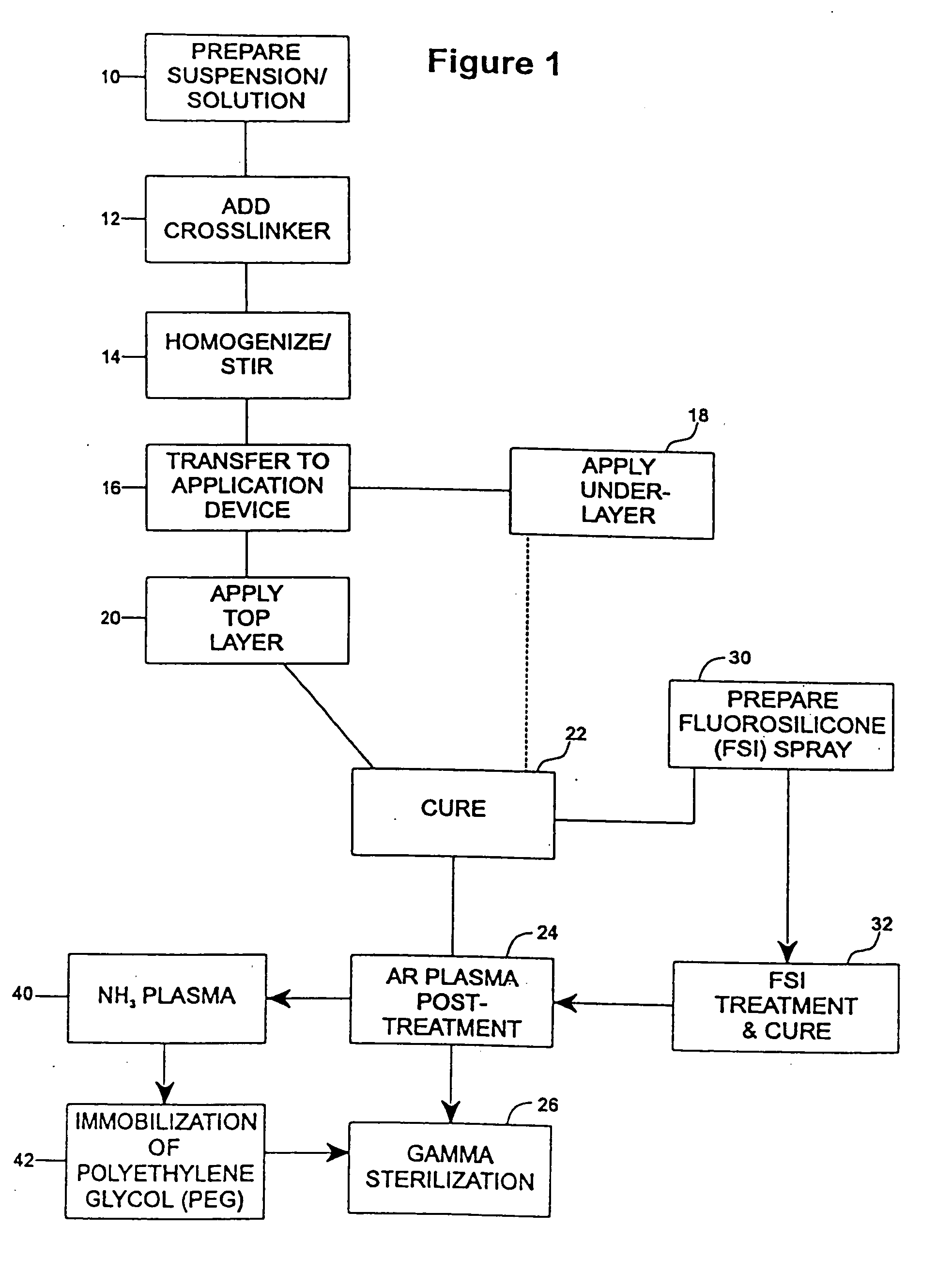
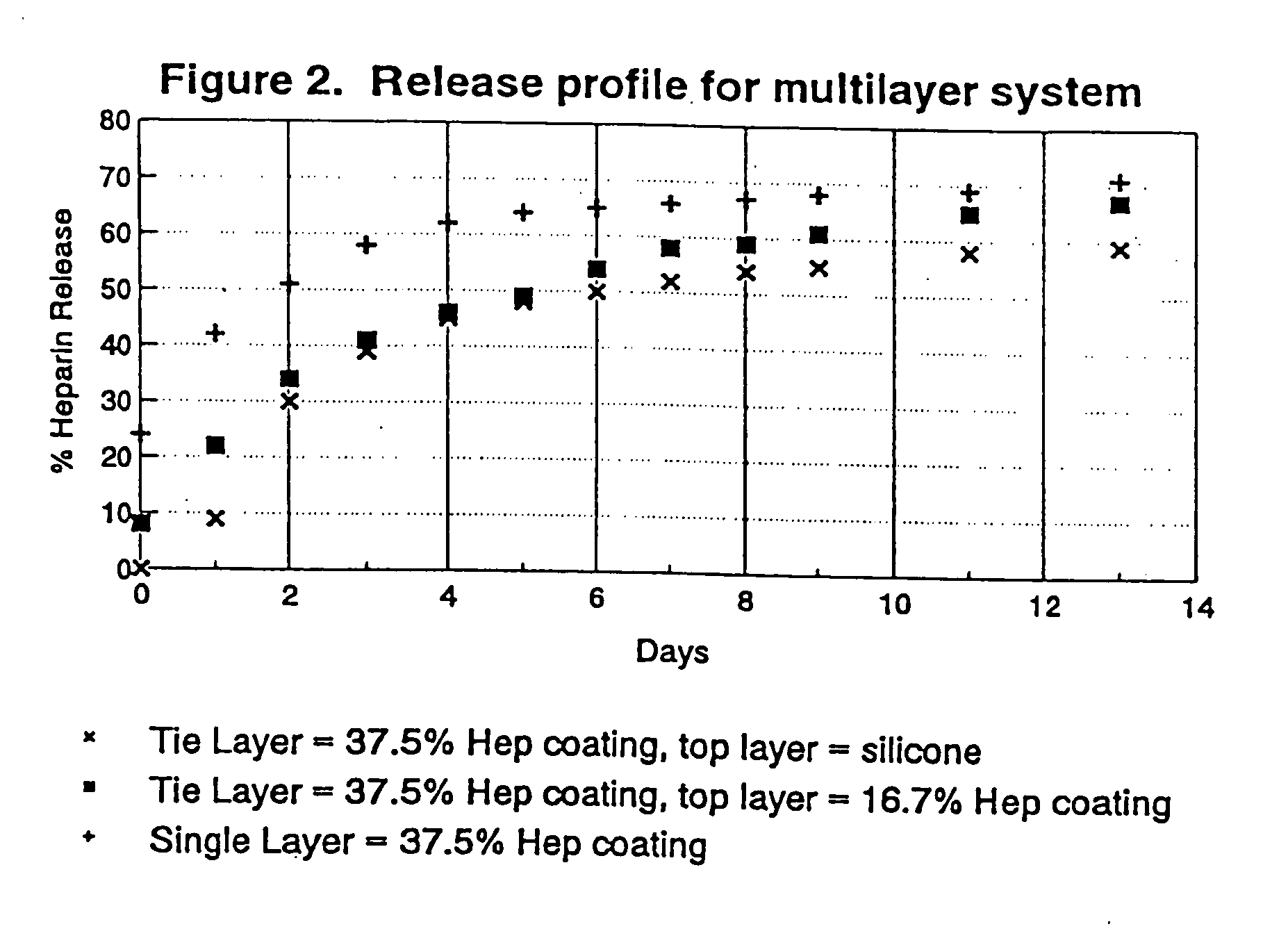
A coating and method for a coating an implantable device or prostheses are disclosed. The coating includes an undercoat of polymeric material containing an amount of biologically active material, particularly heparin, dispersed herein. The coating further includes a topcoat which covers less than the entire surface of the undercoat and wherein the topcoat comprises a polymeric material substantially free of pores and porosigens. The polymeric material of the topcoat can be a biostable, biocompatible material which provides long term non-thrombogenicity to the device portion during and after release of the biologically active material.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
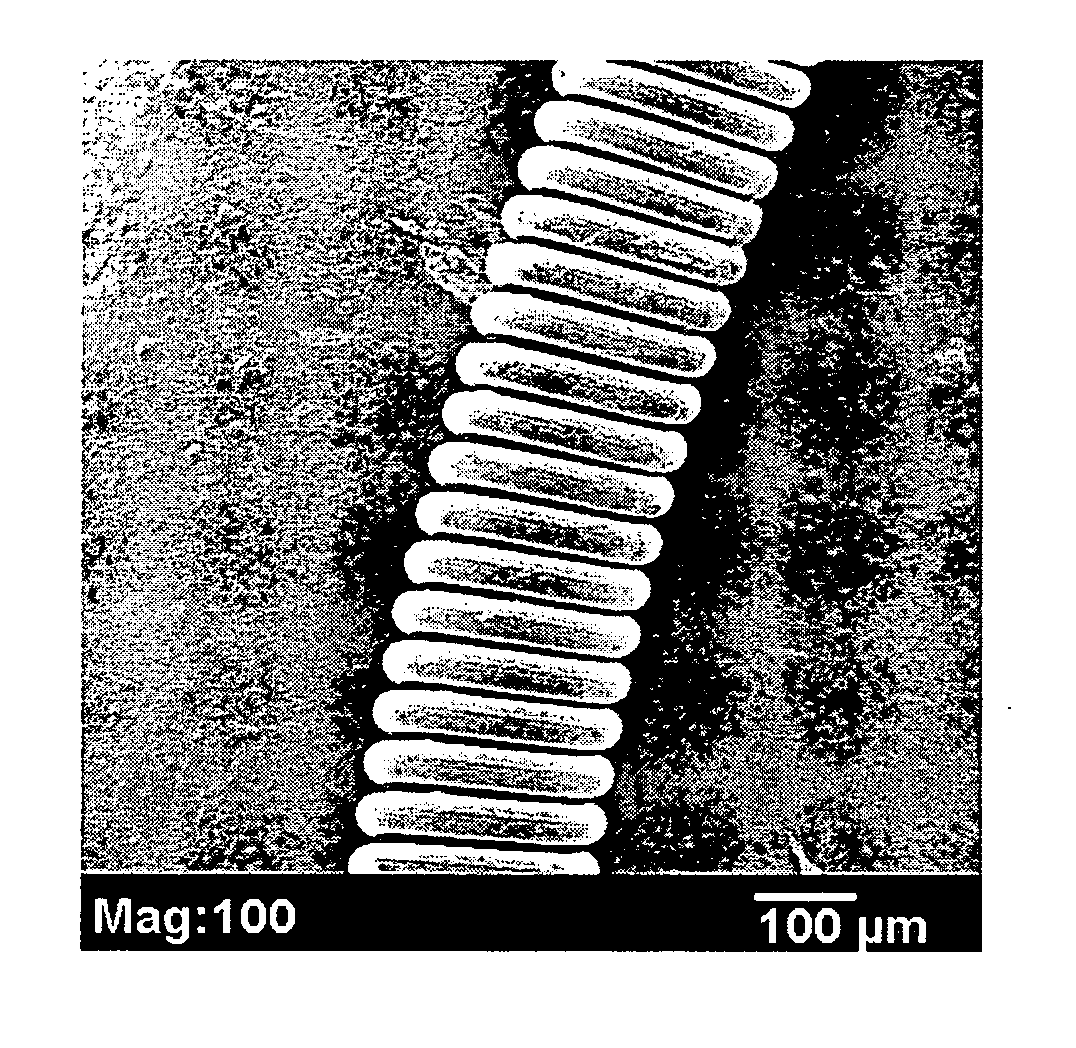
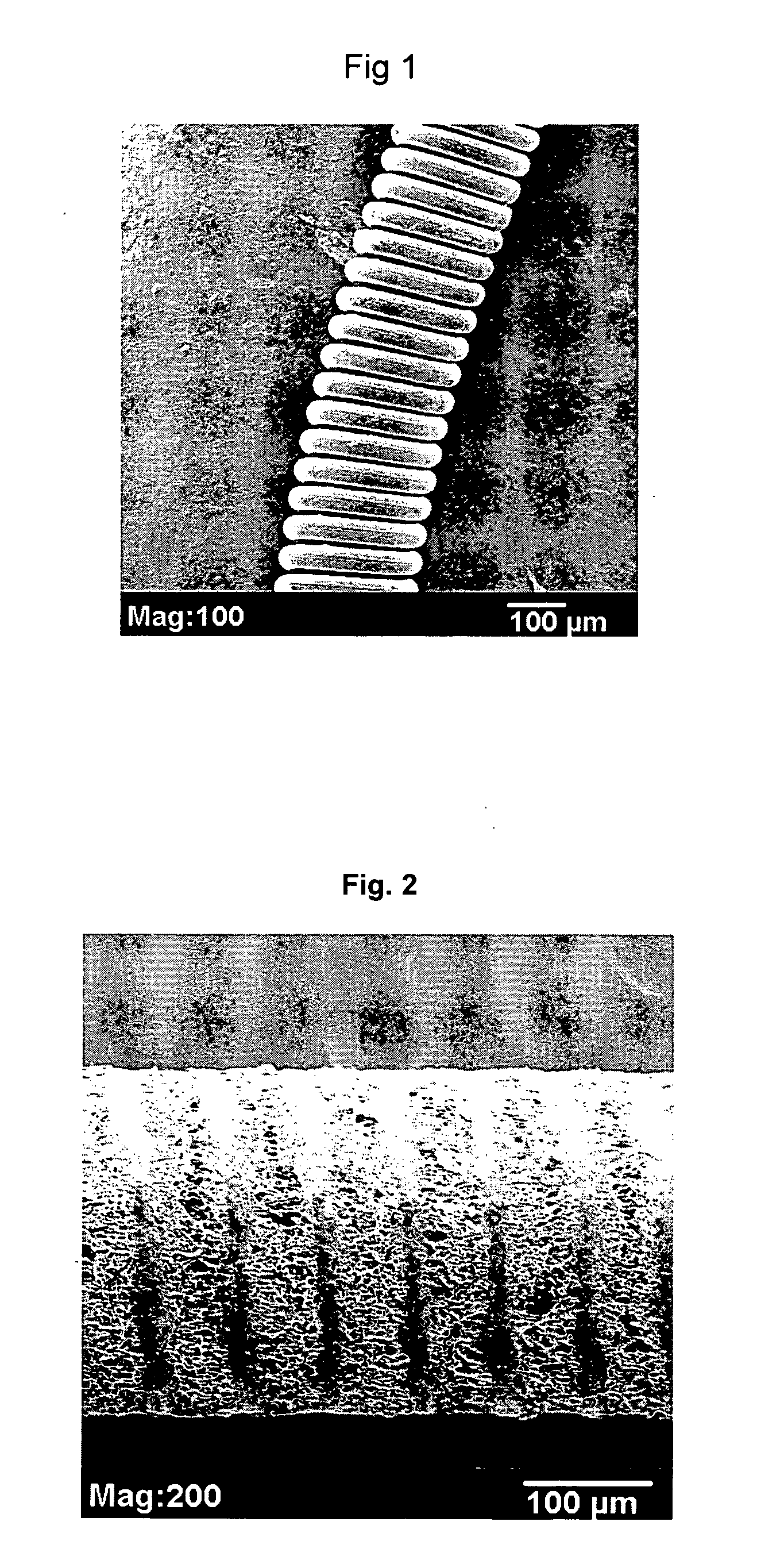
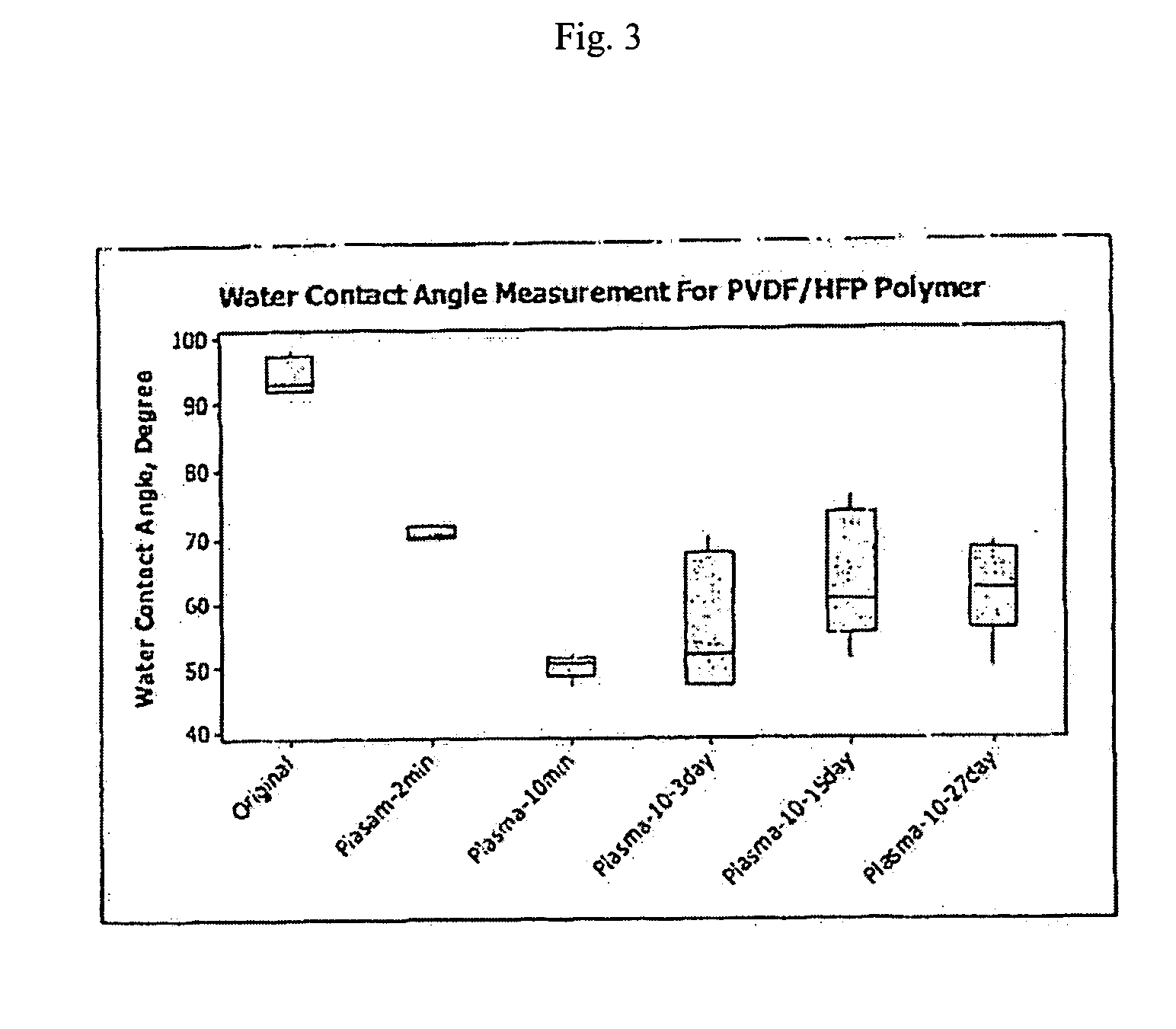
Plasma surface graft process for reducing thrombogenicity
InactiveUS20050102025A1Enhance its interfacial reaction with a biological environmentSimple designPharmaceutical containersPretreated surfacesThrombogenicityVascular prosthesis
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a novel process for modifying the surface properties of a material that is suitable for contact with animal tissue so as to enhance its hemocompatibility and make it less thrombogenic when in use. This process comprises: Exposing the surface of the material to plasma treatment conditions in order to create reactive groups on said surface; activating a molecule with an activator to produce a reactive molecular species capable of forming convalent bonds with the reactive groups created on the surface of the material to form convalent bonds. The invention further encompasses the materials produced by this process as well as devices, such as vascular prosthesis, that are comprised of these process-modified materials.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
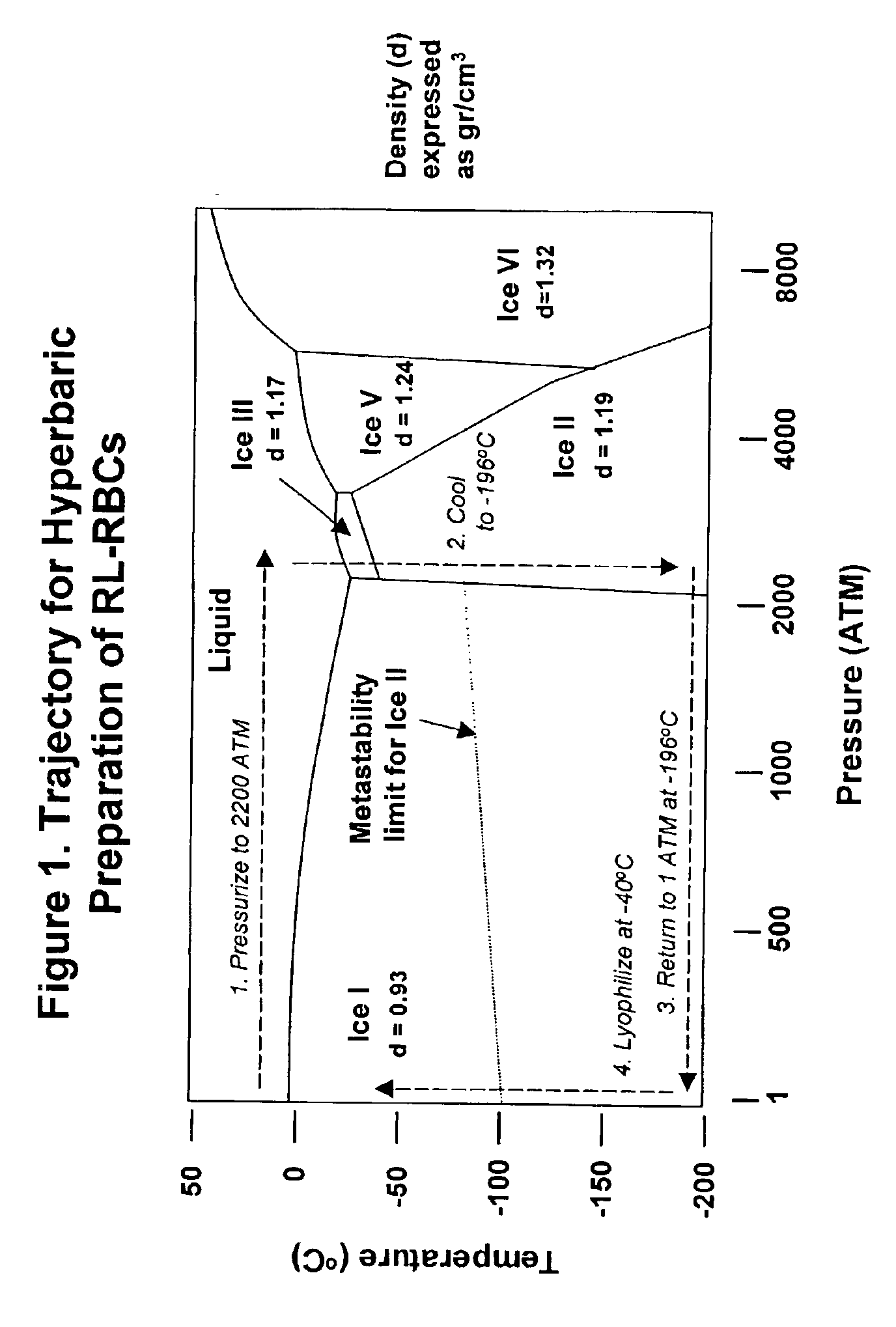
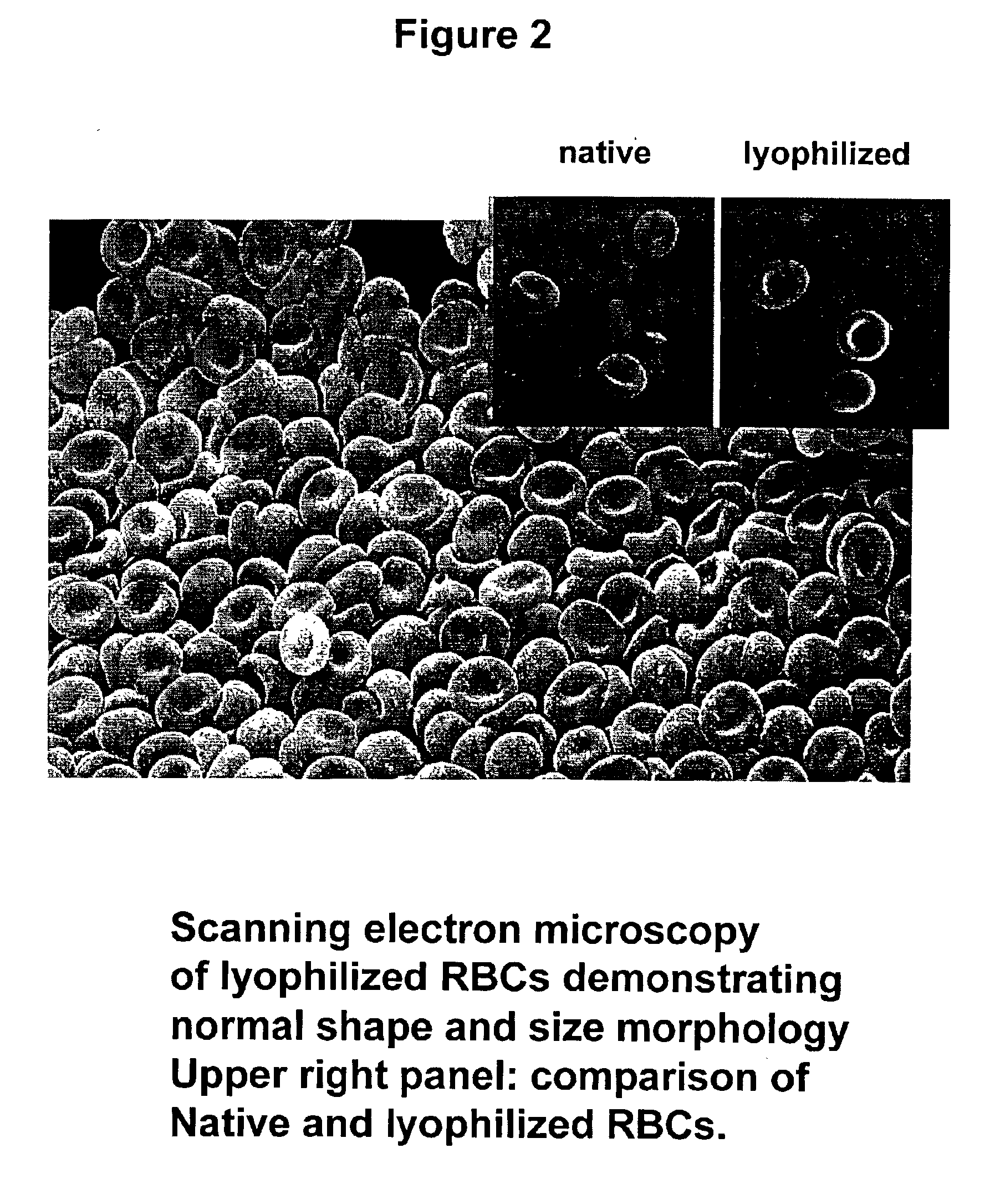
Fixed dried red blood cells and method of use
Fixed-dried red blood cells (RBCs), and processes for preparing the same are disclosed. The red blood cells, upon reconstitution with distilled water or appropriate buffer: bind oxygen with native affinities, have partial deformability, present minimal thrombogenicity to platelets, and have oblated blood group antigens. The RBCs are preferably fixed by means of cross-linkers with aldehyde functions such as paraformaldehyde or glutaraldehyde either alone or in combination. Native oxygen kinetics are achieved by preparing the red blood cells with 1,6-diphosphofructose. Blood group antigens and chemical functions that render the lyophilized RBCs thrombogenic are occluded by chemically attaching polyoxyethylene glycol polymers to the surface membrane of the red blood cells. The cross-linked red blood cells are preferably died by lyophilization.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL +1
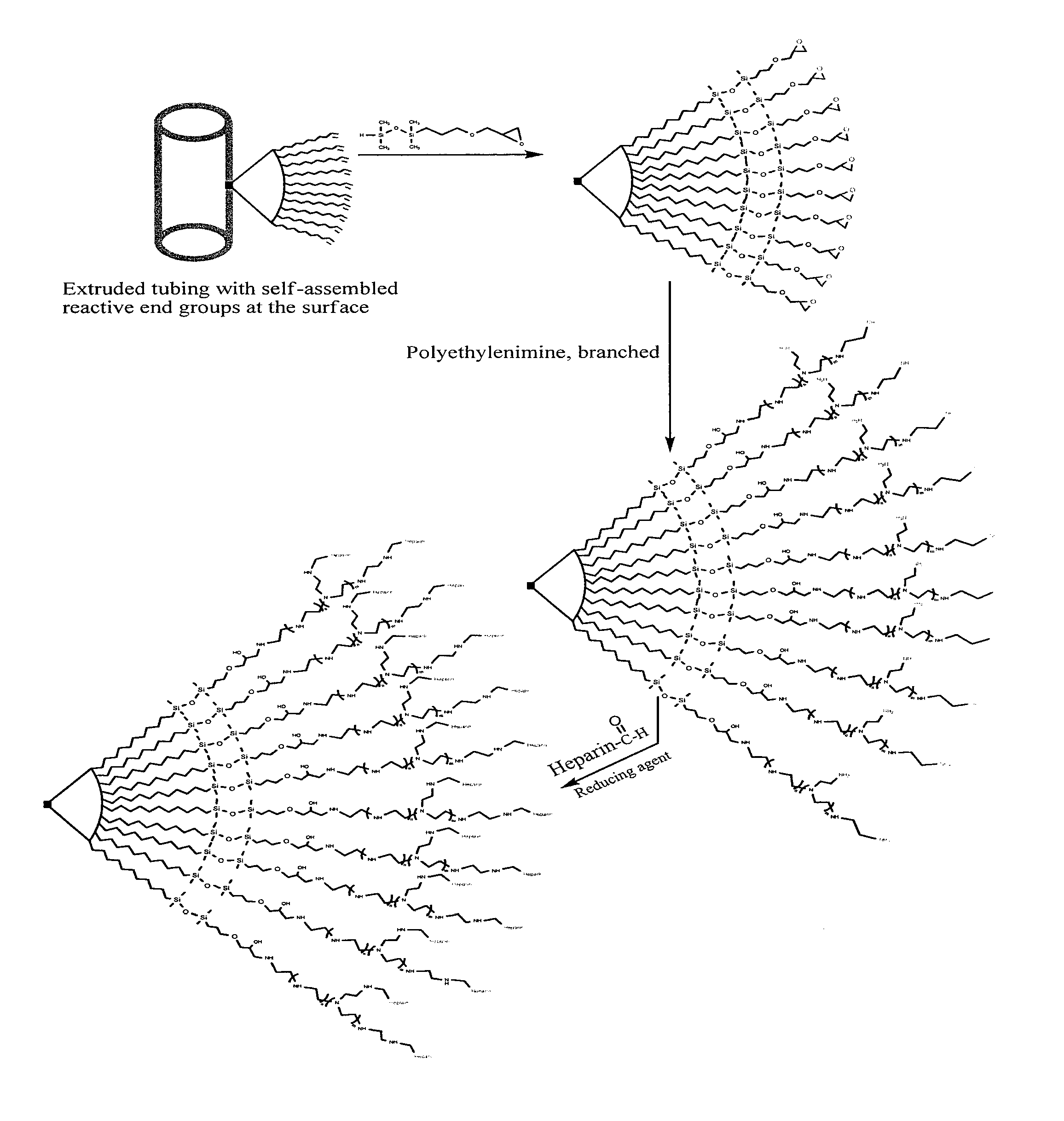
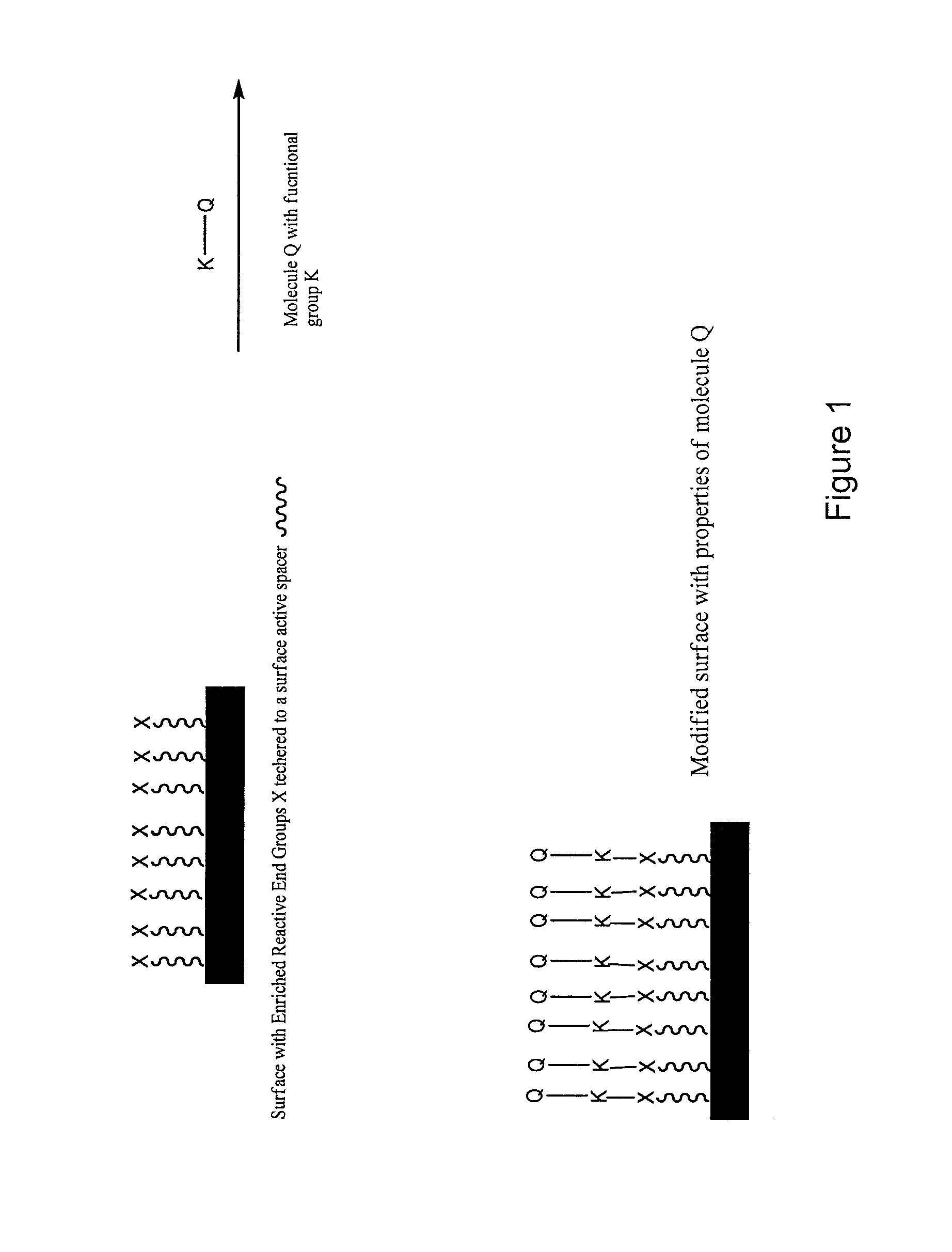
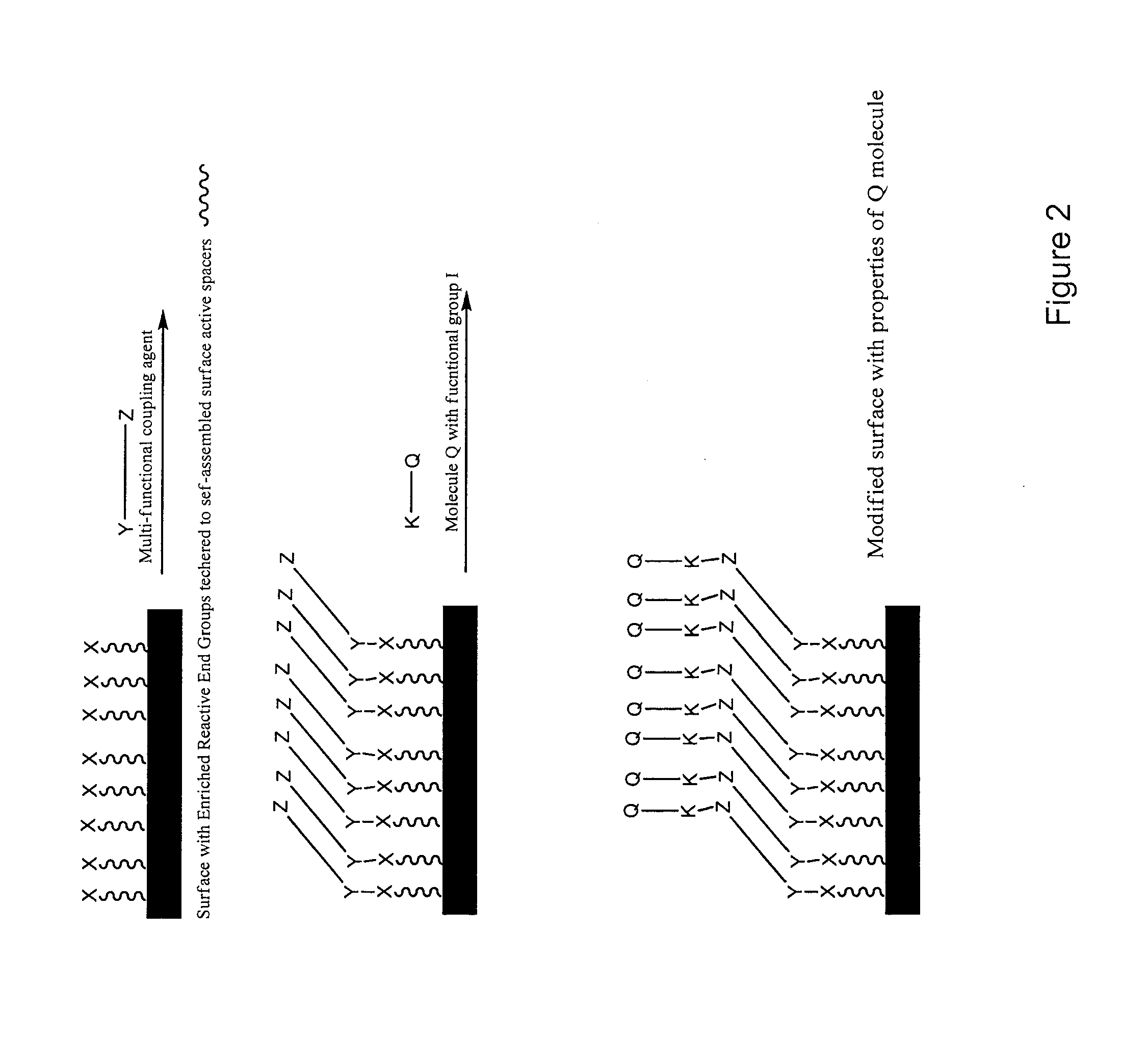
Surface modification of polymers via surface active and reactive end groups
InactiveUS20110293522A1AntiinfectivesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymeric surfacePolymer modified
Polymer surface modification method comprising the steps of first forming a surface of primary reactive end groups tethered to the polymer chain ends during fabrication of an article, and then modifying the reactive surface with bio-active molecules, hydrophilic and hydrophobic monomers, oligomers, or polymers to attain specific surface properties. Alternatively, a multifunctional coupling agent can be used to couple the primary reactive group to a second reactive group capable of reacting with a functional group associated with bio-active molecules, hydrophilic and hydrophobic monomers, oligomers, and polymers to attain specific surface properties. The invention involves bringing reactive endgroups to the surface with surface active spacer attached to the polymer chain end. The surface active spacer allows the migration and enrichment of reactive end groups to the surface during fabrication. The invention provides medical devices having a bio-interface with anti-thrombogenic properties, lubricity, selective adsorption, and antimicrobial properties.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Diagnostic assay
The present invention relates generally to a diagnostic device including a prognostic assay for parameters which are indicative of a condition or event associated with the systemic vasculature. More particularly, the present invention provides an assay to detect parameters associated with a vascular disease including cardiovascular, stroke, pulmonary, renovascular, cerebrovascular, thrombotic or generalized arterial or venous condition or event including acute coronary syndrome such as but not limited to acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, atheromoma or a thrombotic condition. The identification of these parameters or more particularly a pattern of parameters enables the diagnosis of a condition or event or the determination of the risk of development of a condition or event associated to the systemic vasculature. Still more particularly, the present invention is directed to a diagnostic device comprising a set of members wherein one or more of said members has or have specific or generic binding partners in a biological sample from an animal including human subject wherein the pattern of binding of the members to the binding partners is indicative, predictive or otherwise associated with a likelihood of a condition or event within the systemic vasculature. The absence of detection of specific or generic binding partners is also of indicative or predictive value. This is particularly important in cases where patients are unable to communicate advice to a physician on their own condition, such as during surgery or for patients in a coma. It is also useful in determining the risk of a vascular disease including cardiovascular, stroke, pulmonary, renovascular, cerebrovascular, thrombotic or generalized arterial or venous conditions or events in a healthy subject or a subject entering into an exposure to risk such as surgery or chemotherapy. The present invention is useful inter alia for the identification and / or quantitation of biochemical markers of conditions or events in the systemic vasculature such as heart disease, heart disorders, infections of the heart, stroke and thrombosis as well as the determination of a risk of development of these conditions including the absence of disorders or absence of risk of the development of a disorder. The assessment of such conditions may be made in a clinical setting, as part of triage, as part of a routine testing protocol and / or as a laboratory procedure.
Owner:SYDNEY UNIV OF
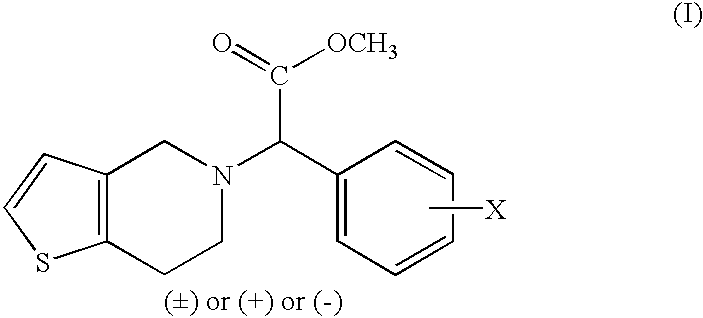
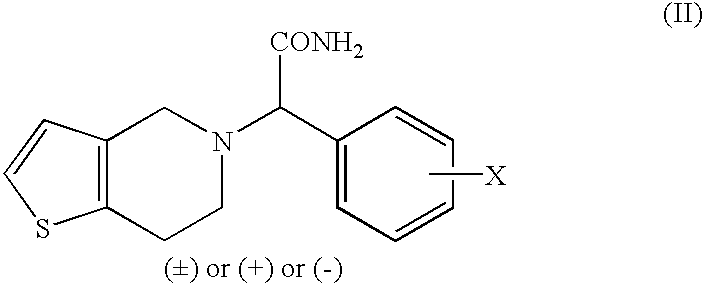
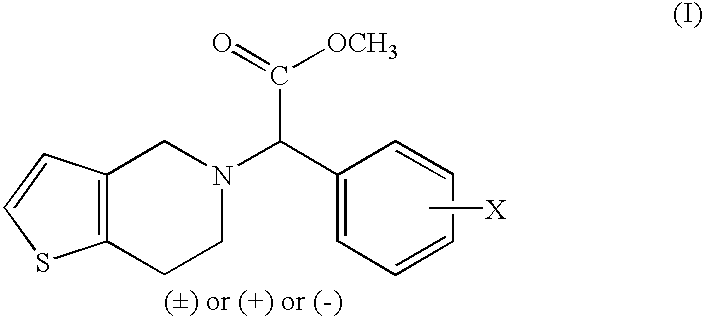
Process to prepare clopidogrel
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of thieno[3,2-c]pyridine derivatives having pharmacologically significant anti-aggregating and anti-thrombotic properties.
Owner:CADILA HEALTHCARE LTD
Amorphous oxide surface film for metallic implantable devices and method for production thereof
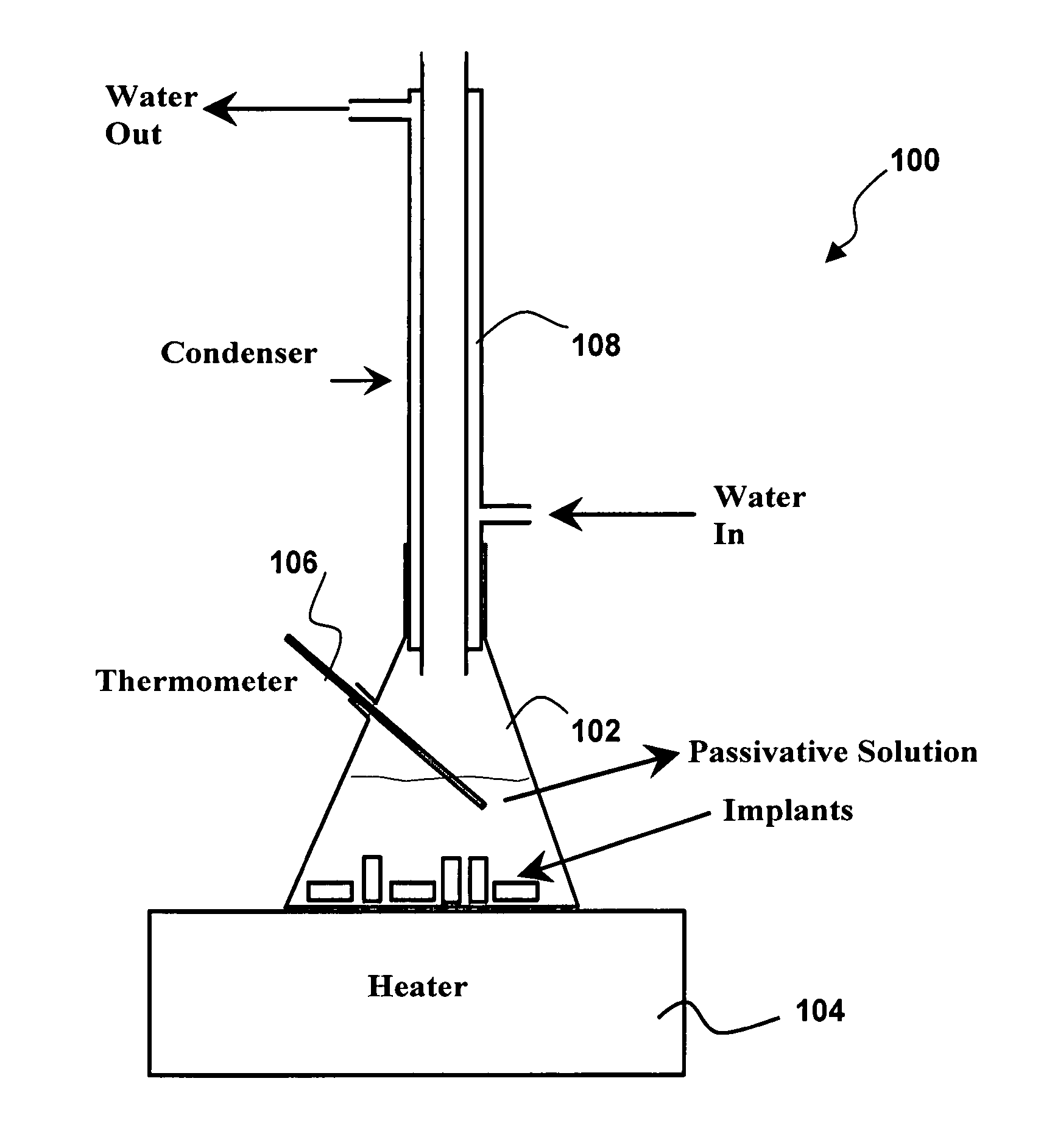
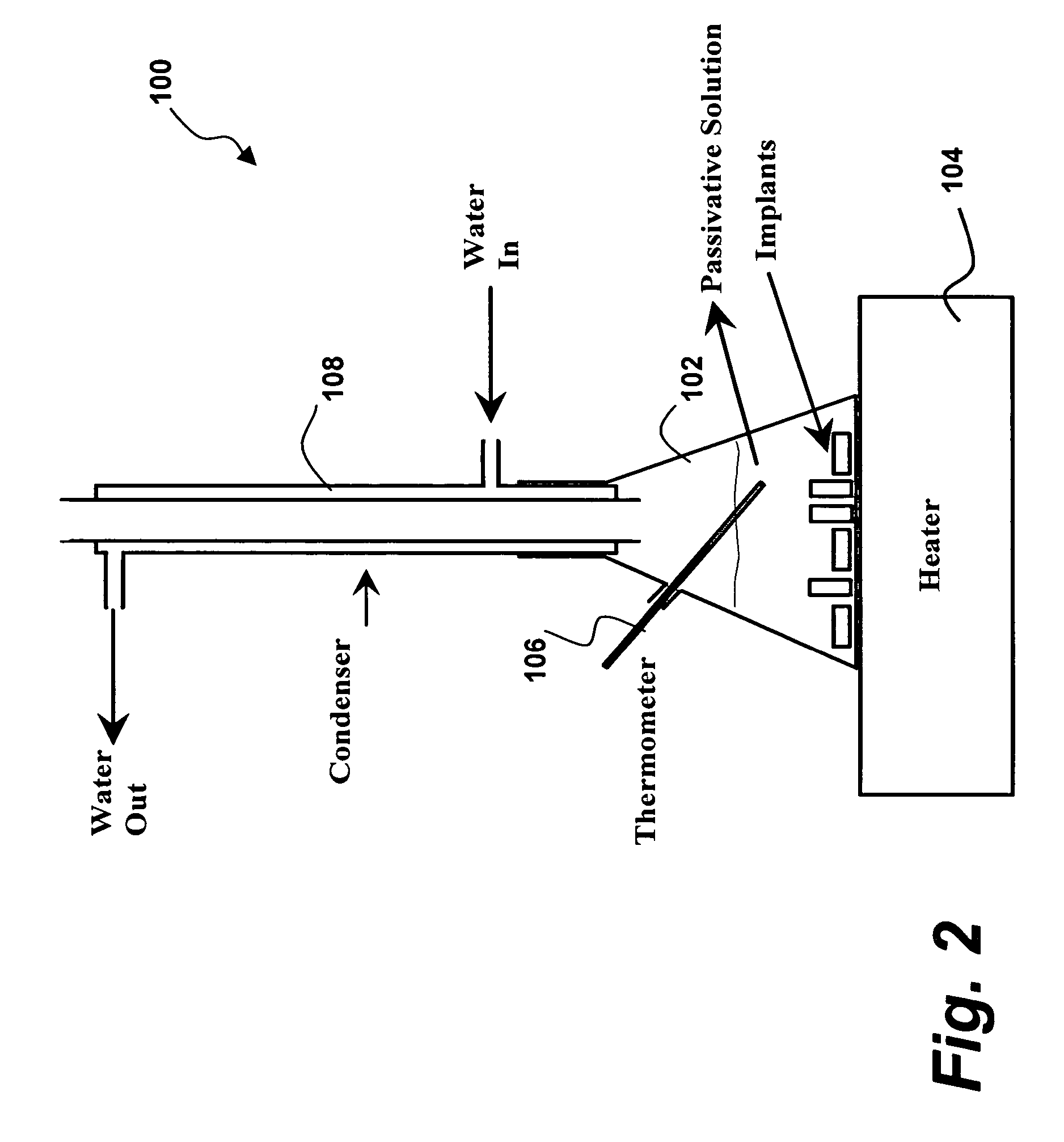
InactiveUS20050234545A1Improve corrosion resistanceStable open-circuit potentialStentsSurgeryHigh concentrationThrombogenicity
An amorphous oxide surface film for metallic implantable devices and method for production thereof, wherein the amorphous oxide film is characterized by a high concentration of oxygen, chromium and hydroxyl ions within the film so as to form a non-stoichiometric chromium oxide with significant negative charge; thereby, improving the corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of the metallic implantable device, and thus significantly reducing the degree of thrombogenicity and restenosis.
Owner:SU YEA YANG +3
Biocompatible substrates and uses thereof
A new substrate makes it possible to modify surface properties relating to biocompatibility. Said substrate has an electron donating surface, characterized in having metal particles on said surface, said metal particles comprising palladium and at least one metal chosen from gold, ruthenium, rhodium, osmium, iridium, and platinum, wherein the amount of said metal particles is from about 0.001 to about 8 μg / cm2. The substrate is suggested for different uses, such as for modifying the hydrophobicity, protein adsorption; tissue ingrowth, complement activation, inflammatory response, thrombogenicity, friction coefficient, and surface hardness.
Owner:BACTIGUARD AB
Bioabsorbable polymeric implants and a method of using the same to create occlusions
A new embolic agent, bioabsorbable polymeric material (BPM) is incorporated to a Guglielmi detachable coil (GDC) to improve long-term anatomic results in the endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The embolic agent, comprised at least in part of at least one biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer and growth factors, is carried by hybrid bioactive coils and is used to accelerate histopathologic transformation of unorganized clot into fibrous connective tissue in experimental aneurysms. An endovascular cellular manipulation and inflammatory response are elicited from implantation in a vascular compartment or any intraluminal location. Thrombogenicity of the biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is controlled by the composition of the polymer. The coil further is comprised at least in part of a growth factor or more particularly a vascular endothelial growth factor, a basic fibroblast growth factor or other growth factors. The biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer is in the illustrated embodiment at least one polymer selected from the group consisting of polyglycolic acid, poly˜glycolic acid / poly-L-lactic acid copolymers, polycaprolactive, polyhydroxybutyrate / hydroxyvalerate copolymers, poly-L-lactide. Polydioxanone, polycarbonates, and polyanhydrides.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
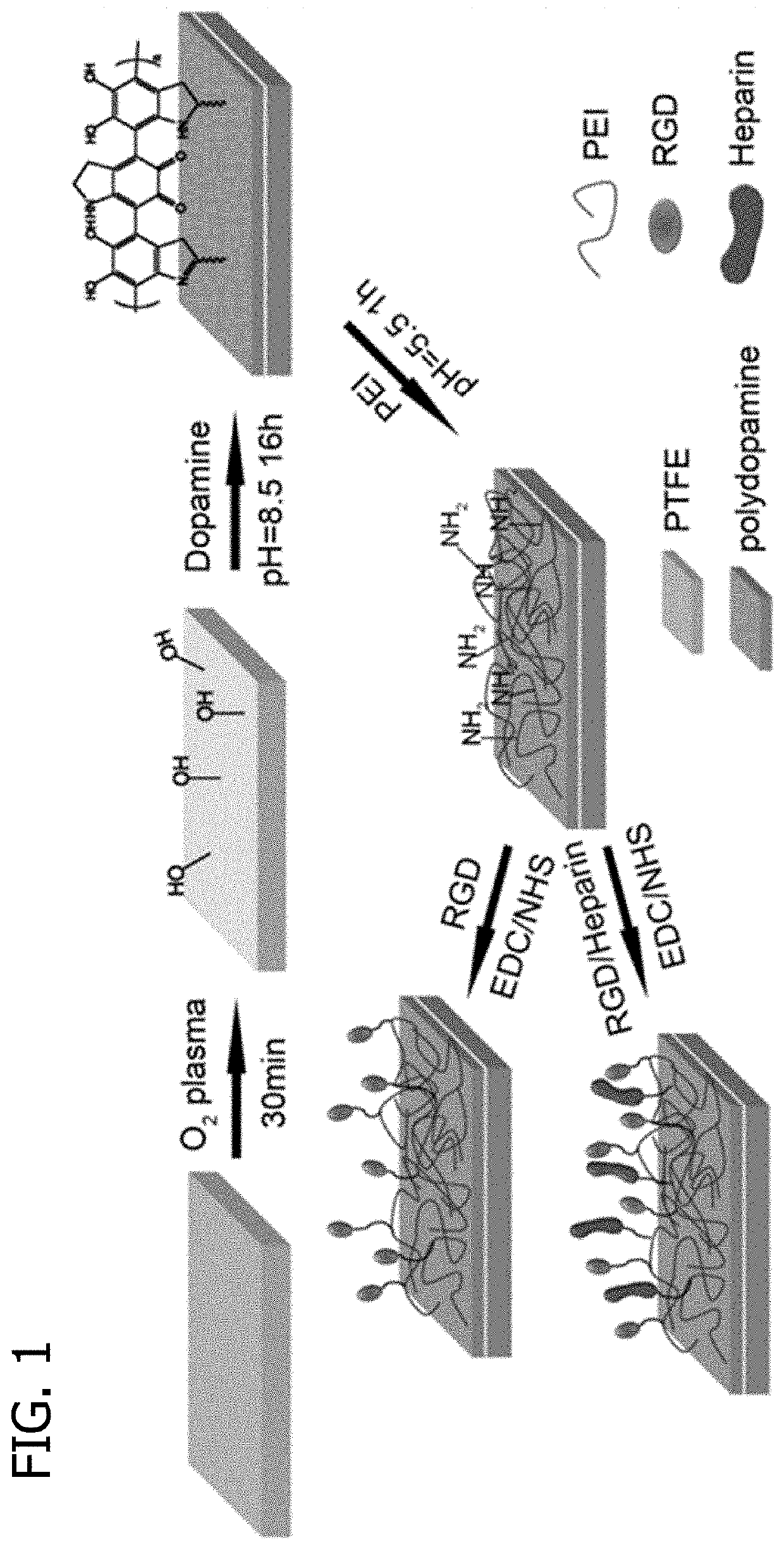
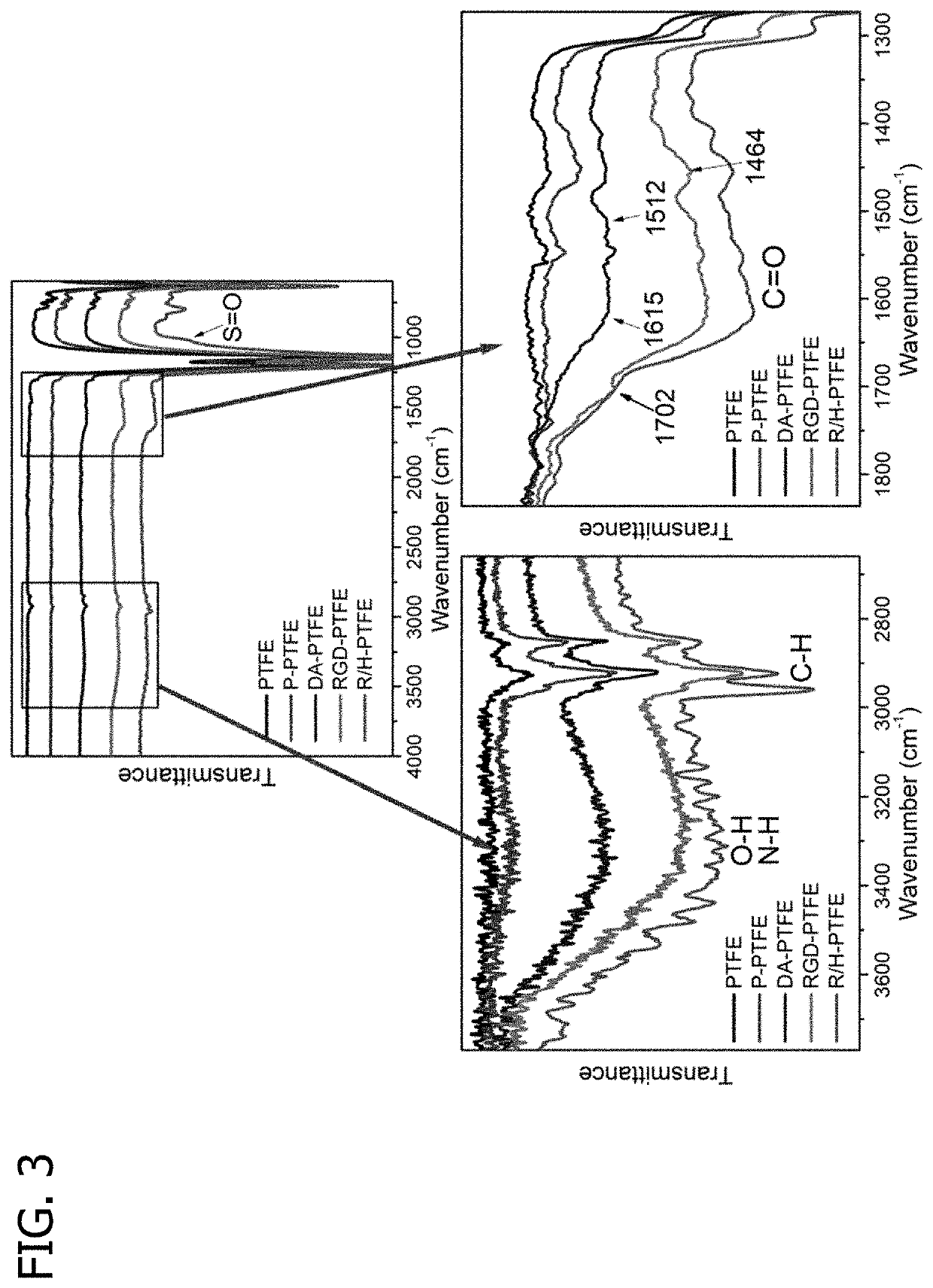
Promoting endothelial cell affinity and antithrombogenicity of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) by mussel-inspired modification and rgd/heparin grafting
ActiveUS20190365954A1Promote cell affinityReduce thrombosisPharmaceutical containersPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCrystallographyThrombogenicity
Disclosed herein are methods for modifying a substrate having a hydrophobic surface. Also disclosed are modified hydrophobic substrates. The modified hydrophobic substrates and methods disclosed herein advantageously improve cell affinity and antithrombogenicity of hydrophobic surfaces.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Non-thrombogenic and anti-thrombogenic polymers
InactiveUS7034061B1Improve attachment stabilityPreferential ionic bondingPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsWarfarinPolymer science
Polymers having non-thrombogenic properties can be prepared by copolymerizing monomers of at least three classes selected from (a) monomers having sulphate groups, (b) monomers having sulphonate groups, (c) monomers having sulphamate groups, (d) monomers having polyoxyalkylene ether groups, and (e) monomers having zwitterionic groups. The polymers can additionally be provided with anti-thrombogenic properties by including an additional comonomer having a pendant heparin (or hirudin, warfarin or hyaluronic acid) group. The polymers can be used as coating materials for medical devices, such as tubing or connectors, in order to provide them with non-thrombogenic, and optionally anti-thrombogenic, properties.
Owner:BIOINTERACTIONS
Composition consisting of heparin fractions having reproducible characteristics with average molecular weight equal to 5200d
Composition consisting of heparin fractions having reproducible characteristics with average molecular weight of 5,200 D obtained by depolymerization with gamma radiation and subsequent fractionation by gel permeation, having high antithrombotic properties and particularly suitable for the prophilaxis and the therapy of the alterations of the plasmatic homeostasis.
Owner:LAB DERIVATI ORGANICI
Drug coating with topcoat
InactiveUS20050208200A1Increase coating thicknessLow drug loadStentsSurgeryThrombogenicityDrug coating
A coating and method for a coating an implantable device or prostheses are disclosed. The coating includes an undercoat of polymeric material containing an amount of biologically active material, particularly heparin, dispersed therein. The coating further includes a topcoat which covers less than the entire surface of the undercoat and wherein the topcoat comprises a polymeric material substantially free of pores and porosigens. The polymeric material of the topcoat can be a biostable, biocompatible material which provides long term non-thrombogenicity to the device portion during and after release of the biologically active material.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Implantable article, method of forming same and method for reducing thrombogenicity
InactiveUS20080097620A1Reduce thrombosisPromoting and enhancing endothelializationPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAntithrombogenic treatmentThrombogenicityThrombus
Endothelialization of a bodily fluid or tissue-contacting, particularly blood-contacting, surface may be accomplished to render that surface substantially non-thrombogenic. Thrombosis may also be mitigated or eliminated by providing an eroding layer on the surface that results in the removal of any thrombus formation as the layer erodes. An implantable device may utilize at least one surface having a plurality of nano-craters thereon that enhance or promote endothelialization. Additionally, an implantable device may have at least one first degradable layer for contacting bodily fluid or tissue and disposed about a central core, and at least one second degradable layer between the first degradable layer and the central core. The first degradable layer has a first degradation rate and the second degradable layer has a second degradation rate which degrades more slowly than the first degradable layer on contact with bodily fluid or tissue.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Methods of making and using surfactant polymers
InactiveUS20080262614A1Reduce packaging processReduce colonizationPeptide/protein ingredientsLigamentsThrombogenicityBackbone chain
Comblike, surfactant polymers for changing the surface properties of biomaterials are provided. Such surfactant polymers comprise a polymeric backbone of repeating monomeric units having functional groups for coupling with side chains, a plurality of hydrophobic side chains linked to the backbone via the functional groups, and a plurality of hydrophilic side chains linked to said backbone via the functional groups. Medical devices coated with the surfactant polymers are also provided. The surfactant polymers may be used to decrease the thrombogenic properties, encapsulation, and bacterial colonization of medical devices.
Owner:NANOMIMETICS
Graft copolymers, methods for grafting hydrophilic chains onto hydrophobic polymers, and articles thereof
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Biocompatible, biomimetic ampholyte materials
ActiveUS20130053470A1Good biocompatibilityHigh haemocompatibilityCosmetic preparationsImpression capsHydrophilic polymersThrombogenicity
New ampholyte biomaterial compounds containing ampholyte moieties are synthesized and integrated into polymeric assemblies to provide hydrophilic polymers exhibiting improved biocompatibility, haemocompatibility, hydrophilicity non-thrombogenicity, anti-bacterial ability, and mechanical strength, as well as suitability as a drug delivery platform.
Owner:BIOINTERACTIONS
Block copolymer and antithrombotic coating agent
ActiveUS20140235748A1Improve balanceImprove solubilityPharmaceutical containersDead animal preservationPolymer scienceMeth-
The object of the present invention is achieved by providing a copolymer, in particular, a block copolymer which has excellent coating formation ability, adhesive properties to a substrate, and does not adsorb protein; an antithrombotic coating agent which has superior antithrombotic properties and adhesive properties to a substrate to those of the conventional antithrombotic coating agent; and a medical instrument which is obtained by coating the antithrombotic coating agent, and the block copolymer includes a polymer (A) containing a (meth)acrylic ester monomer and a polymer (B) containing a (meth)acrylamide monomer and has excellent coating formation ability and high adhesive properties to a substrate.
Owner:KAWAMURA INST OF CHEM RES +1
Functional chitosan derivative
InactiveUS7125968B2Overcome problemsIncrease moisture contentCosmetic preparationsBiocideSolubilityThrombogenicity
A functional chitosan derivative which comprises a chitin / chitosan, which is a natural polysaccharide, and incorporated therein at least one of a carbohydrate, a photo-reactive functional group, an amphipathic group, e.g. a polyoxyethylene alkyl ether, and a glycosaminoglycan and which, due to the incorporation, has solubility in a neutral medium, self-crosslinking ability, the property of highly containing water or healing wounds, and antithrombotic properties. Namely, the derivative has various properties required of health care materials such as medical products and cosmetics.
Owner:NETECH
Plasma-treated vascular occlusion devices and methods
ActiveUS20070239205A1Promote thrombosisImproves thrombogenic propertyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsMedicineThrombogenicity
Vaso-occlusive devices are provided that have a polymer foam disposed about them. The polymer is treated with a plasma to facilitate thrombogenicity. A method for making and using such devices also is provided. The preferred polymer is a copolymer of a halogenated vinylidene and a halogenated alkene.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
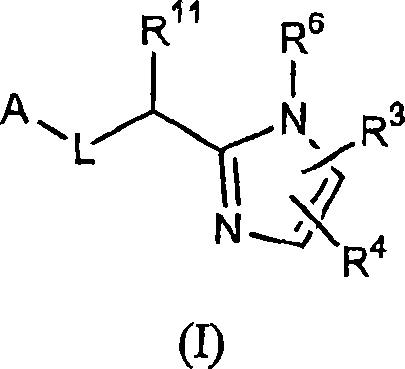
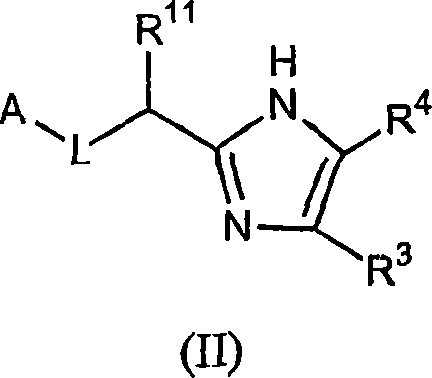
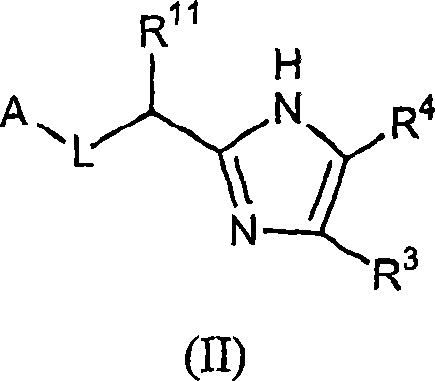
Five-membered heterocycles useful as serine protease inhibitors.
The present invention provides a method for treating a thrombotic or an inflammatory disorder administering to a patient in need thereof a therapeutically effective amount of at least one compound of Formula (I) or Formula (V): (I) or a stereoisomer or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate form thereof, wherein the variables A, L, Z, R<3>, R<4>, R<6>, R<11>, X<1>, X<2>, and X<3> are as defined herein. The compounds of Formula (I) are useful as selective inhibitors of serine protease enzymes of the coagulation cascade and / or contact activation system; for example thrombin, factor Xa, factor XIa, factor IXa, factor VIIa and / or plasma kallikrein. In particular, it relates to compounds that are selective factor XIa inhibitors. This invention also provides compounds within the scope of Formula I and relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
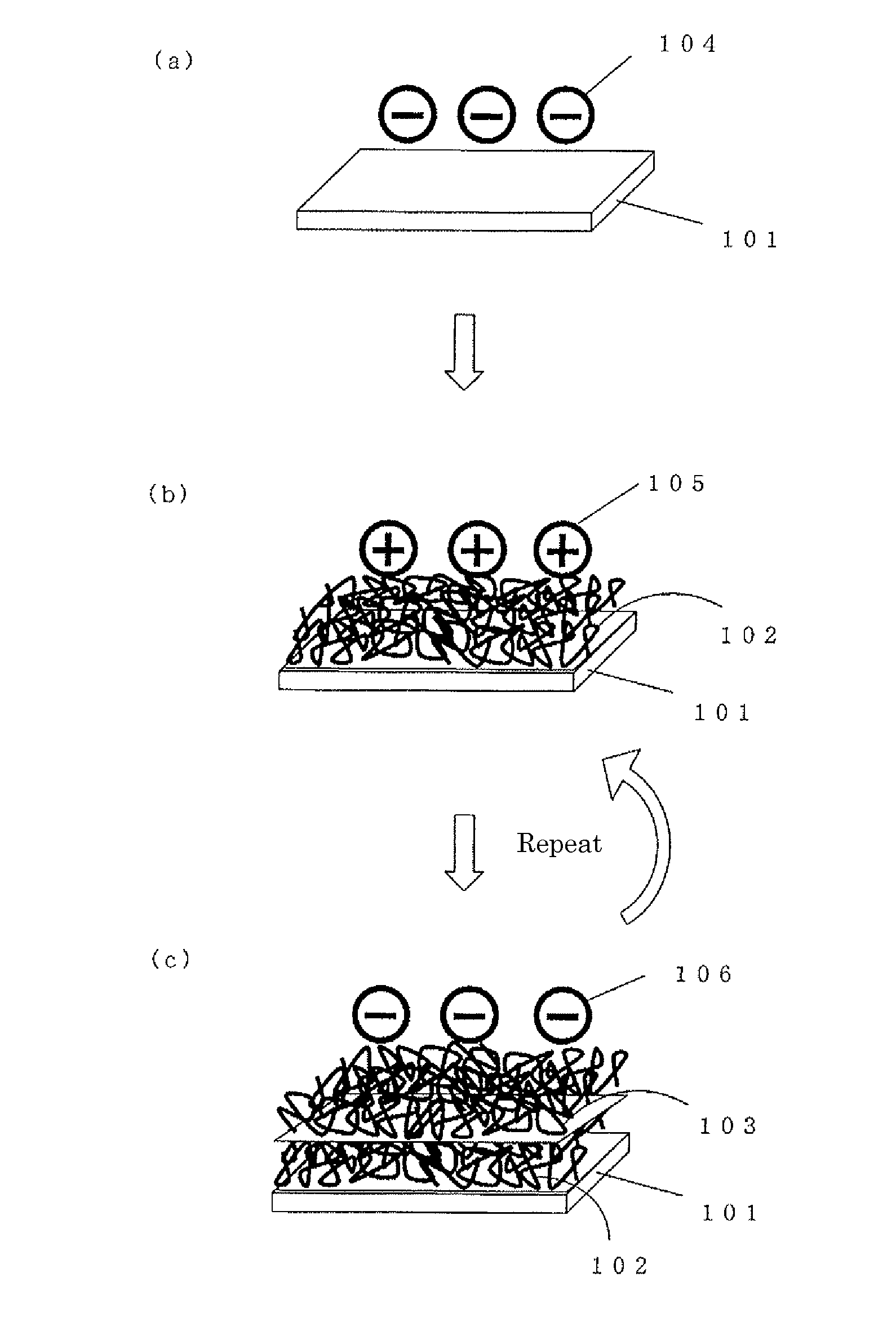
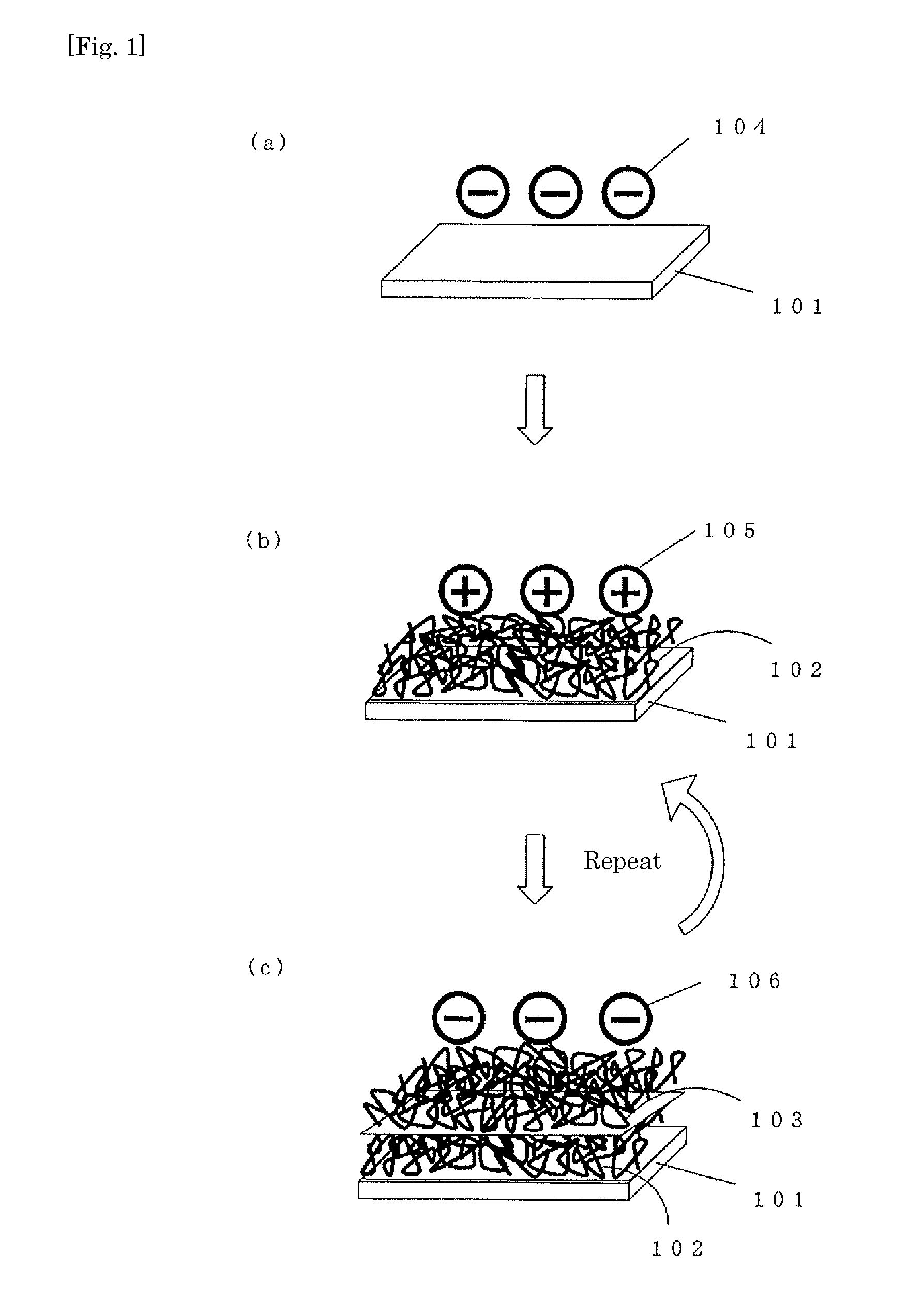
Antithrombogenic surface
InactiveUS20110084019A1High in antithrombogenicityReduce thicknessRecord information storageAntithrombogenic treatmentThrombogenicityAntithrombogenic surface
Provided is a surface showing excellent antithrombotic properties. Also provided is a medical device having the same. An antithrombotic surface comprising polymer layers which are in different charged states and alternately layered, characterized by having three-dimensional peaks and valleys formed thereon. The antithrombotic surface as described above which is further characterized in that the peaks and valleys are 15 nm or more but not more than 200 nm in height and depth respectively. A medical device characterized by being provided with the antithrombotic surface as described above. Thus, a thin and highly antithrombotic surface or medical device can be obtained by a relatively convenient method.
Owner:KANEKA CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com