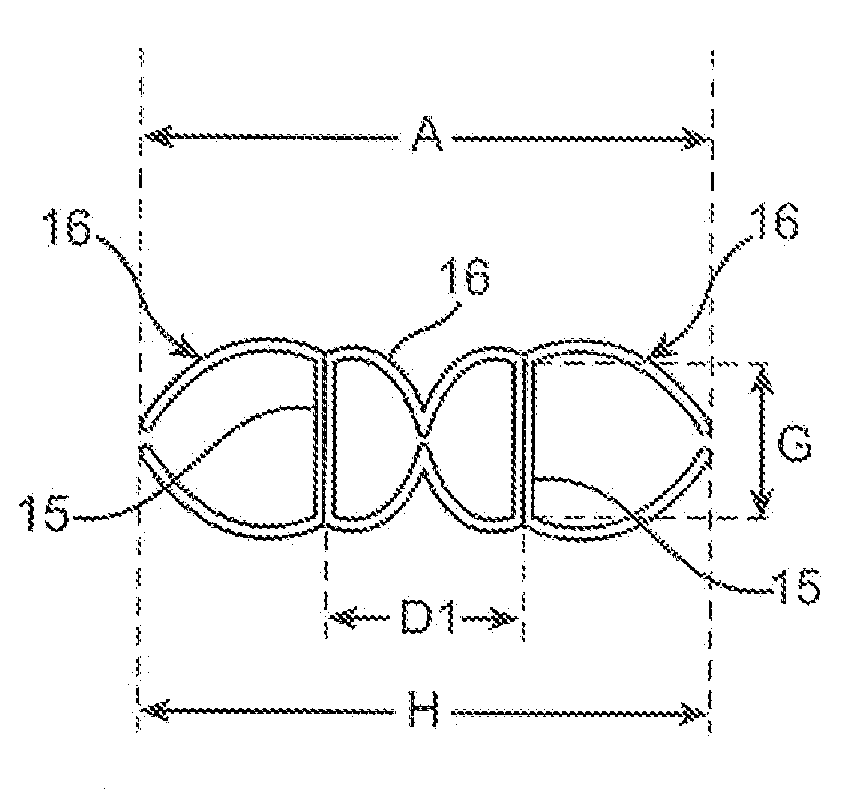
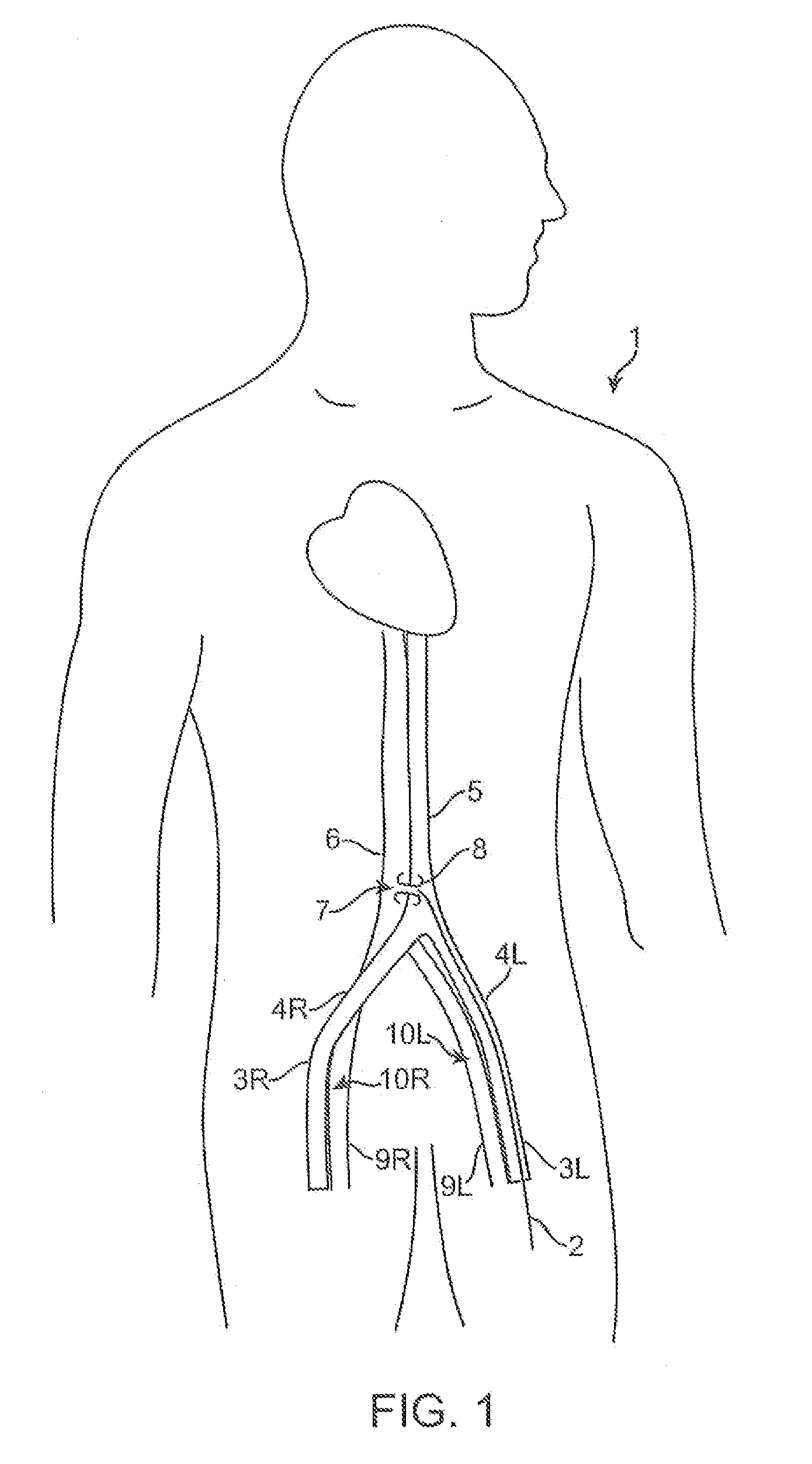
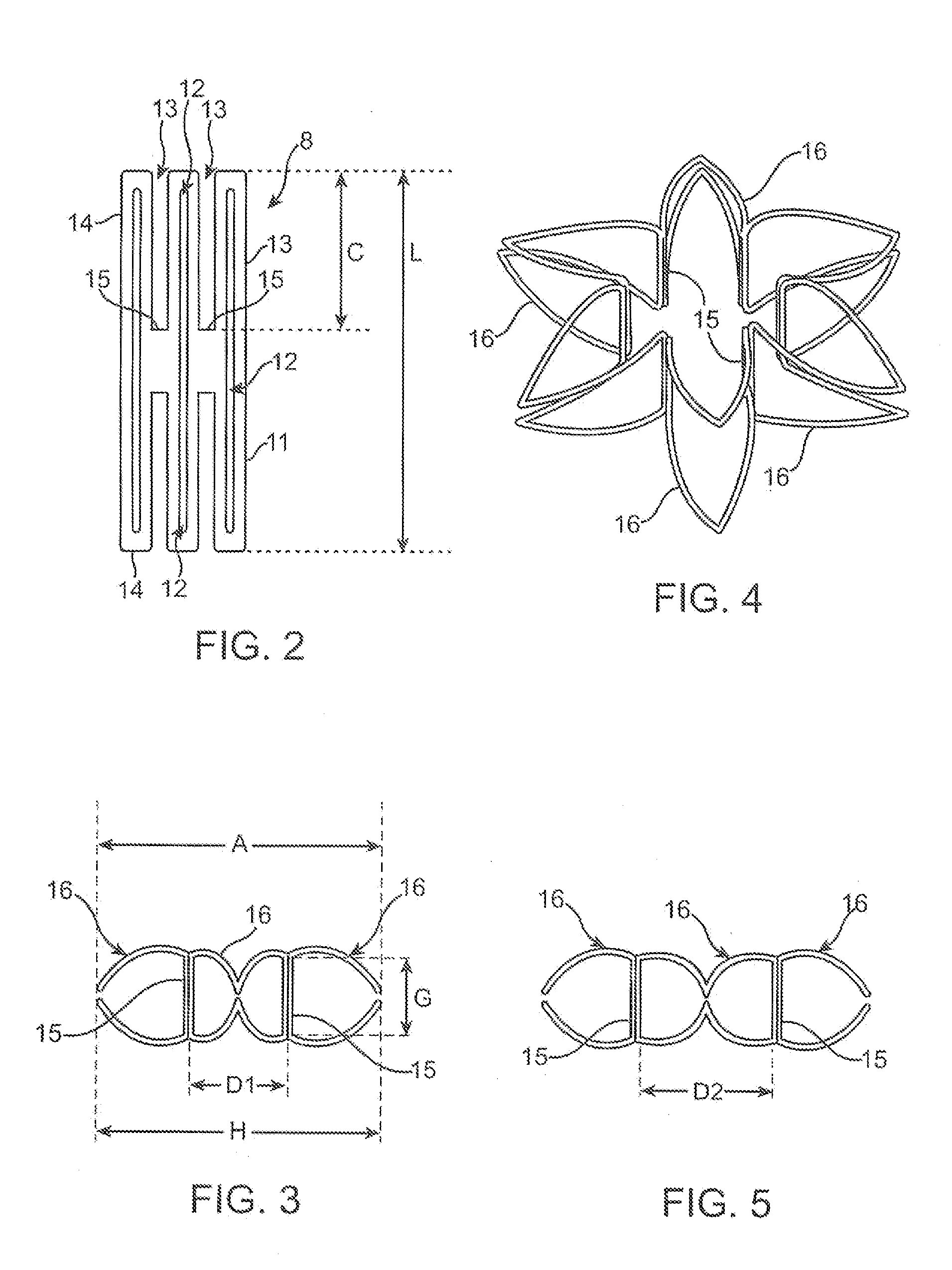
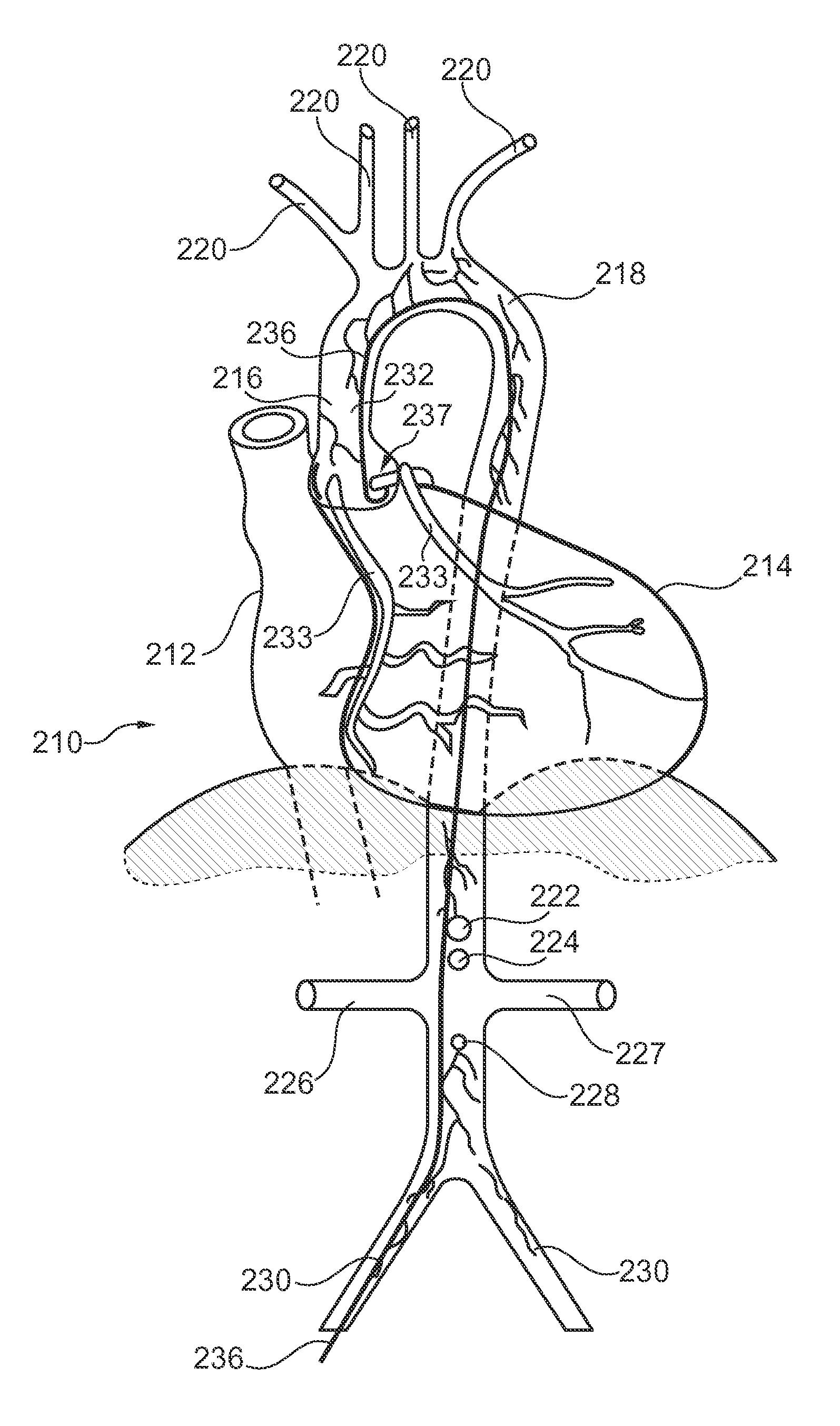
Patents
Literature
149 results about "Aorta part" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
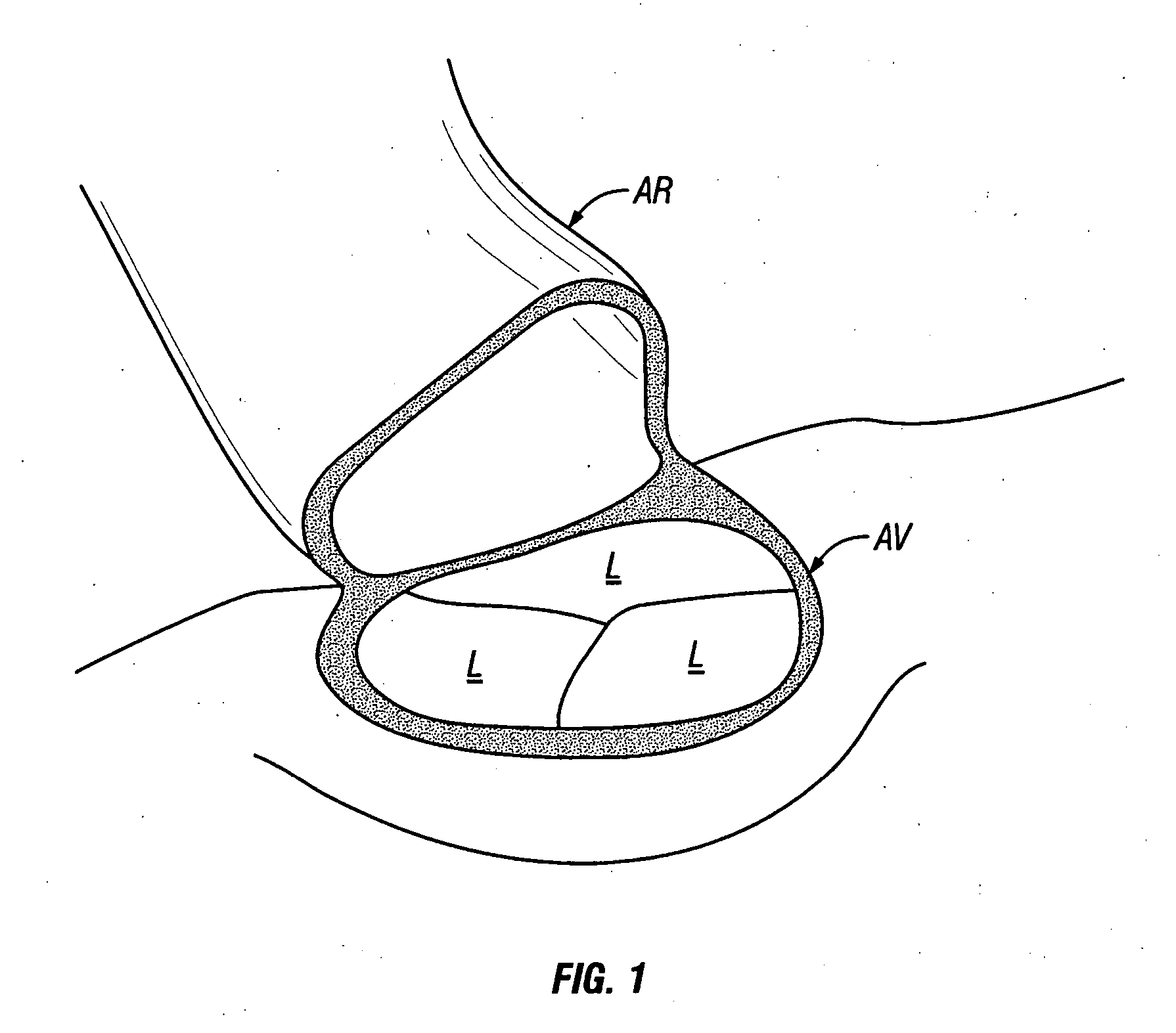
The aorta is the main artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation.
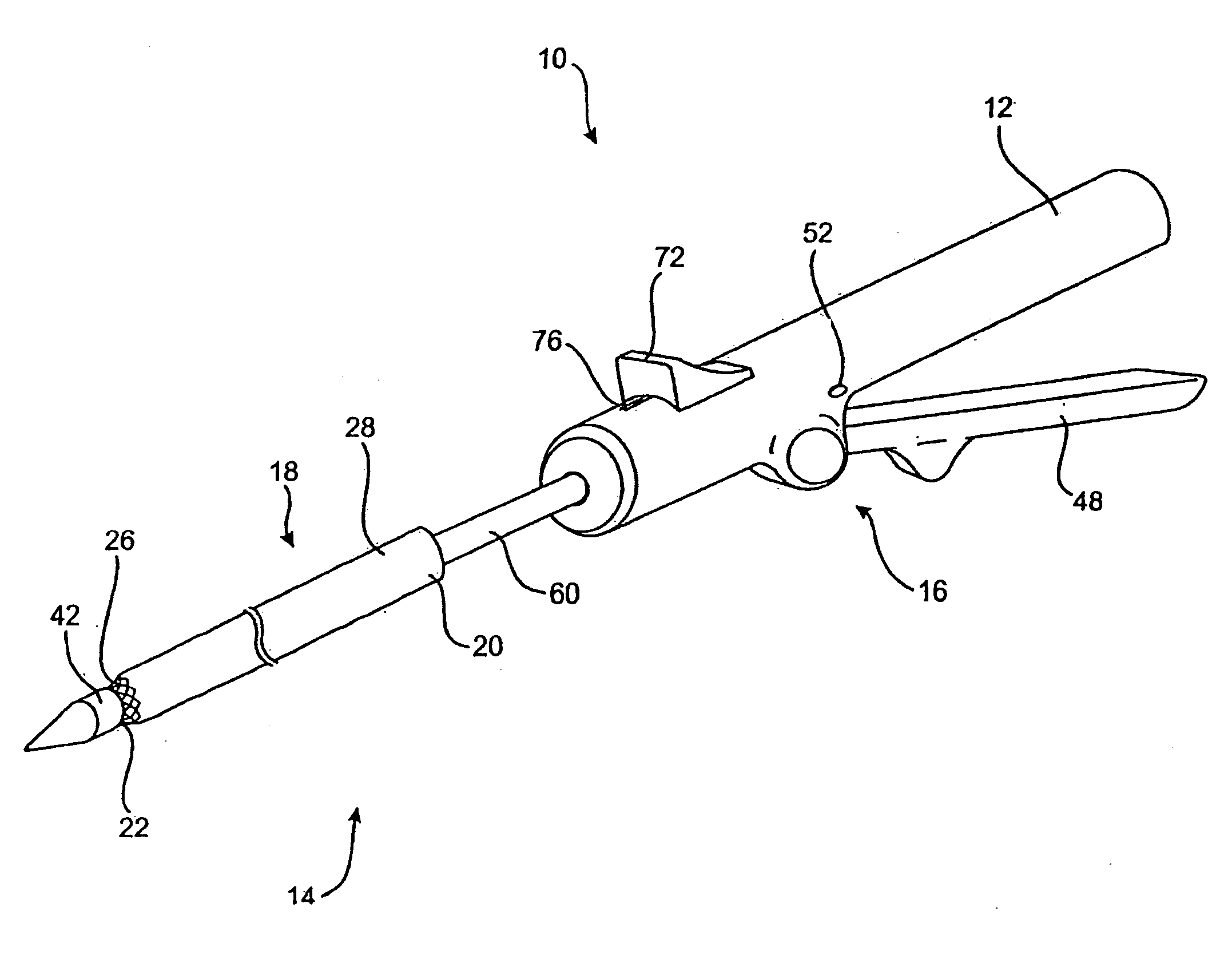
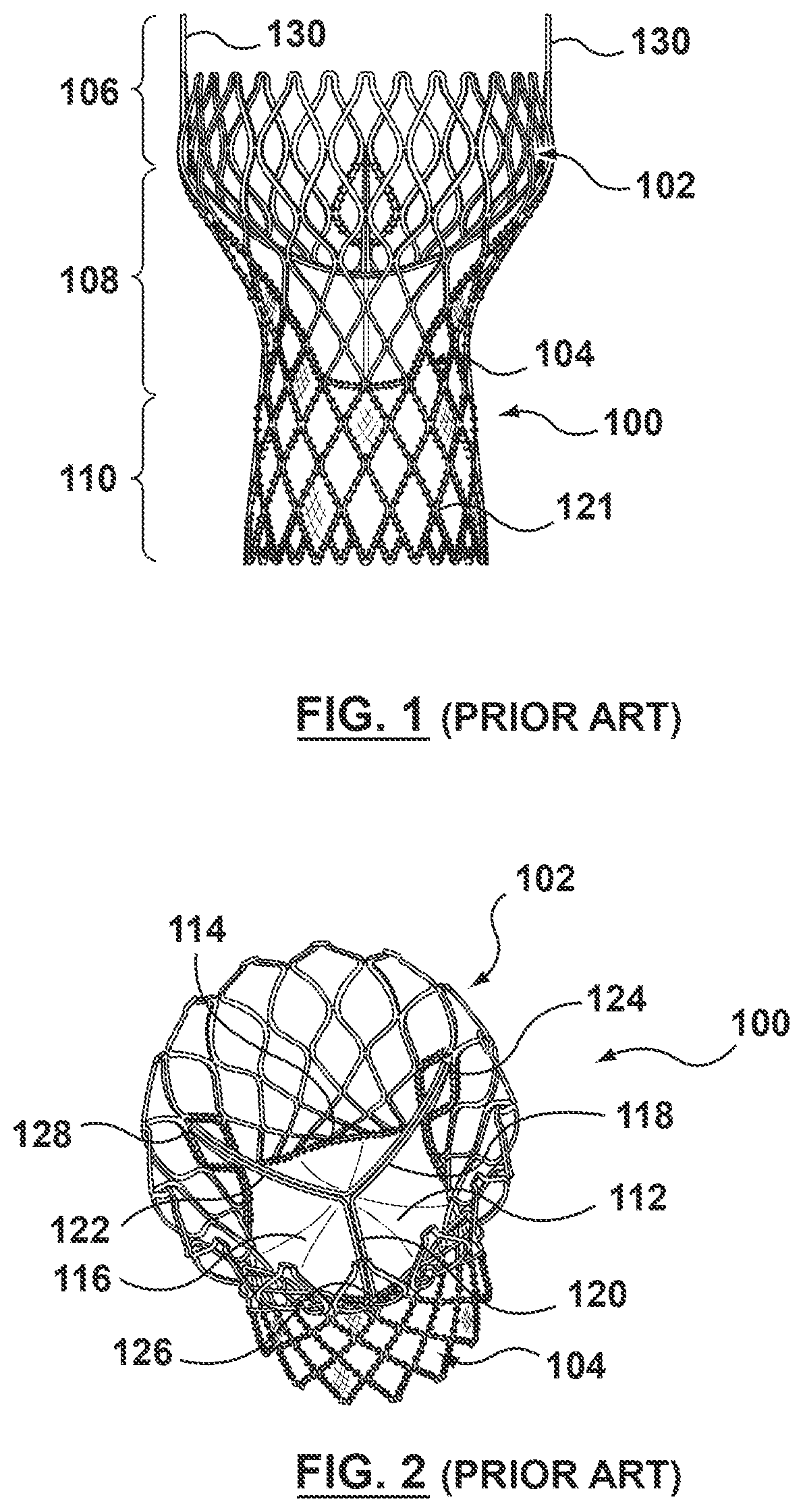
Methods and apparatus for valve repair
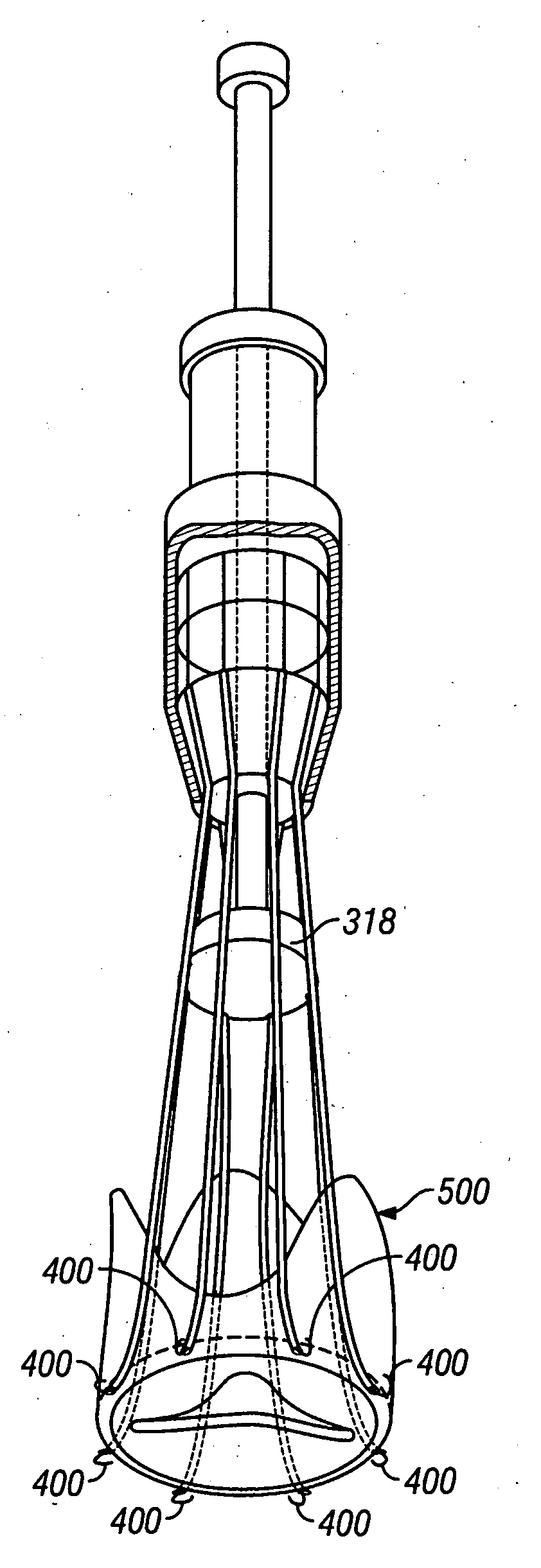
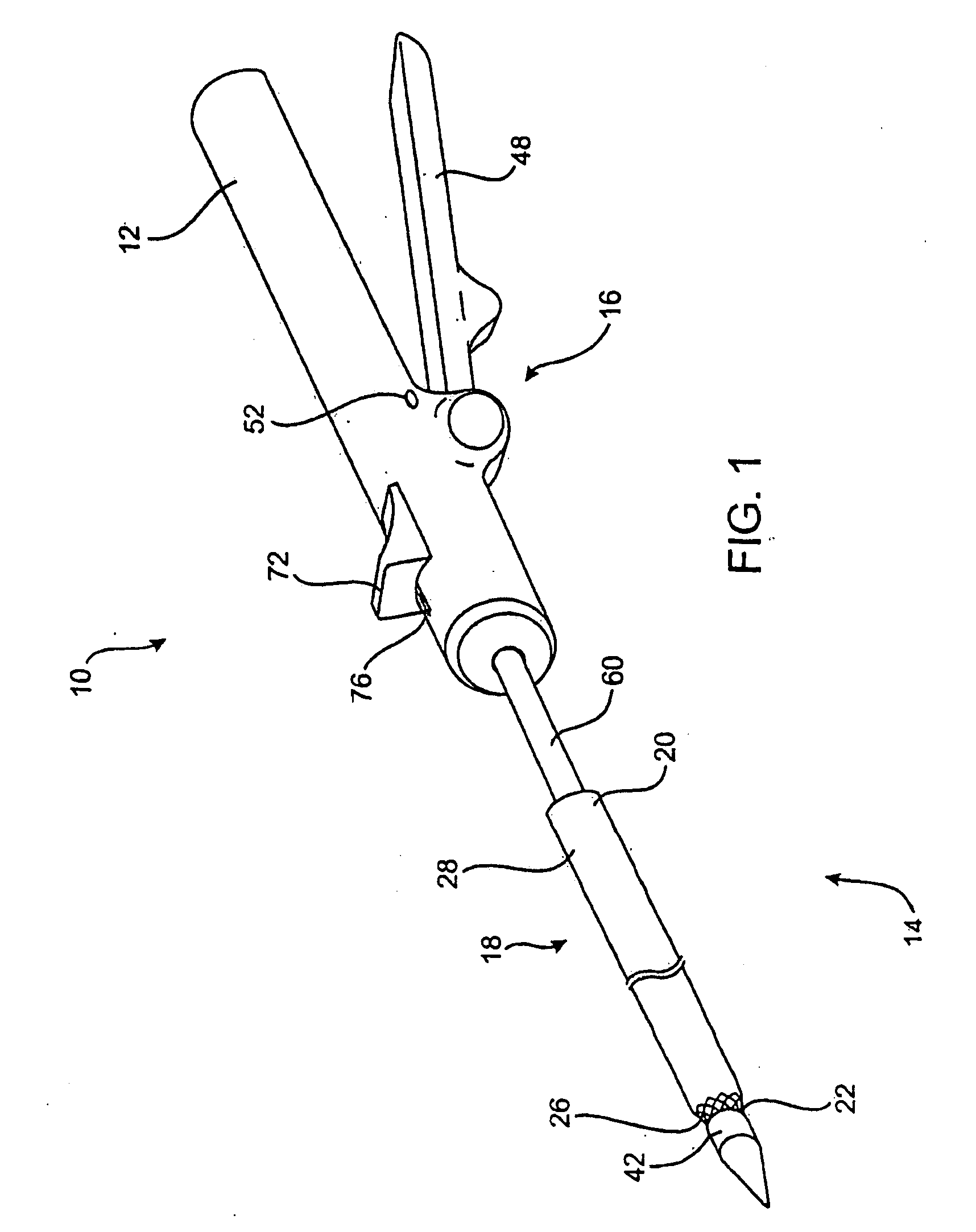
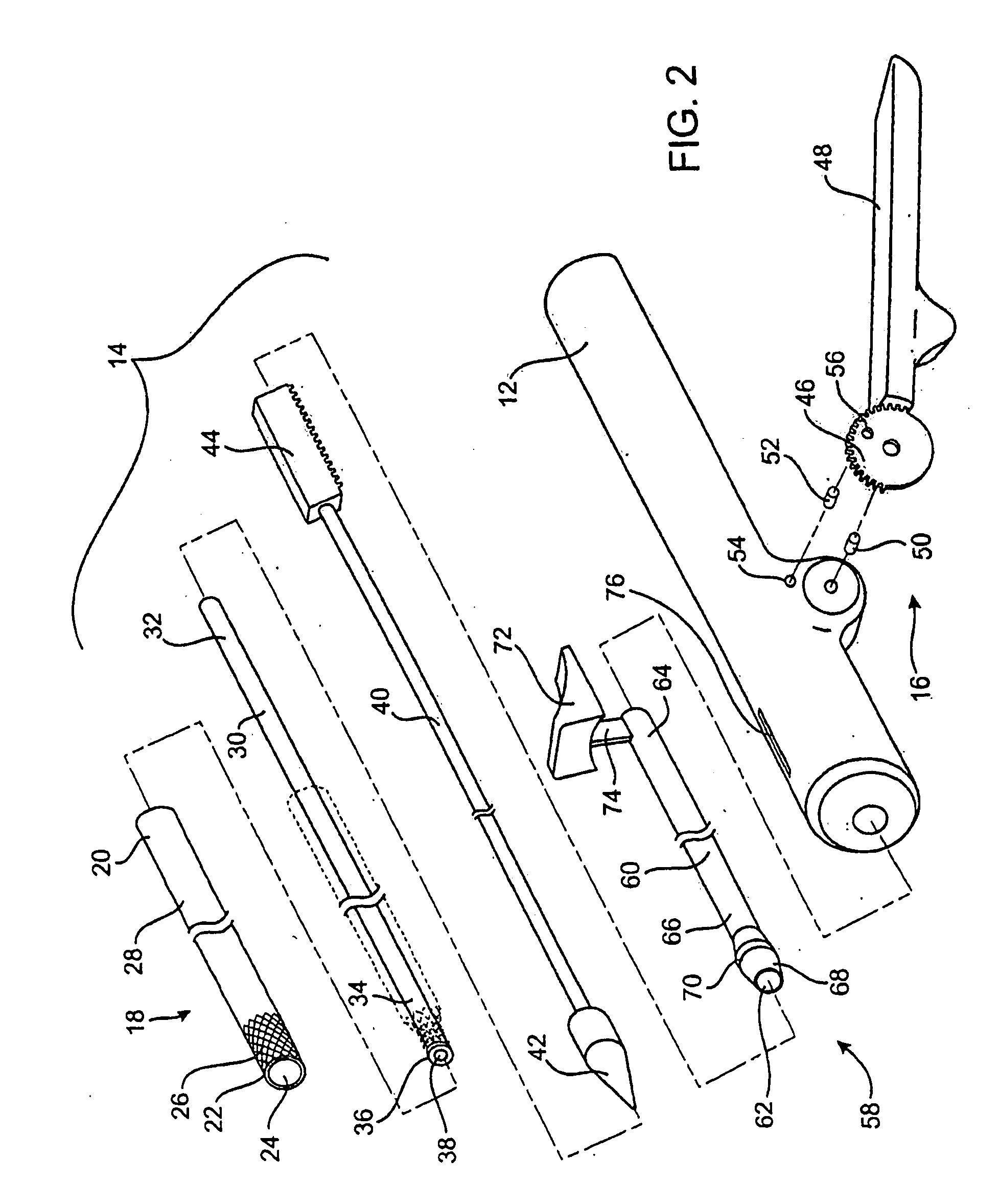
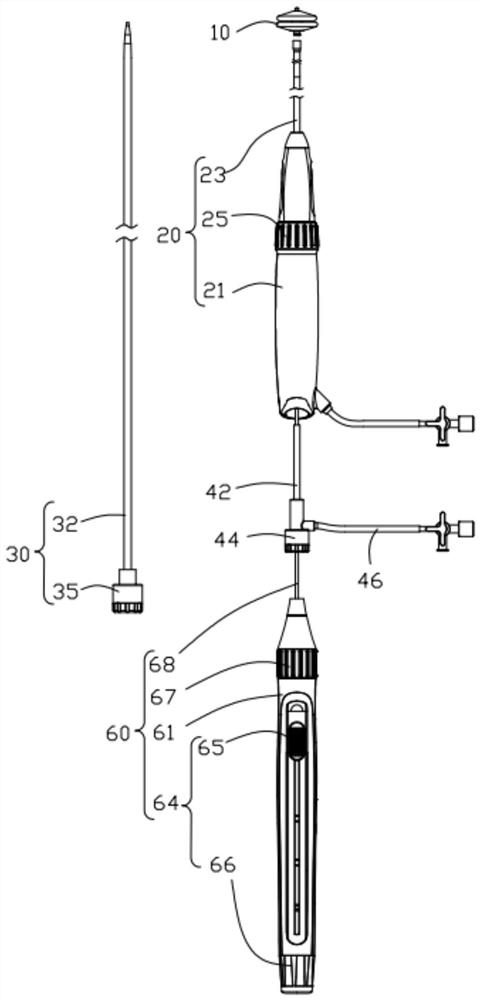
A valve delivery device is provided. The device comprises a heart valve prosthesis support having a proximal portion and a distal portion; a plurality of fasteners ejectably mounted on the support; a heart valve prosthesis being releasably coupled to said distal portion of said heart valve prosthesis support; and where the heart valve prosthesis and support are configured for delivery to the heart through an aortotomy formed in the patient's aorta. The device may include an anvil movable along a longitudinal axis of the device to engage tissue disposed between the anvil and the valve prosthesis.
Owner:REALYVASQUEZ FIDEL
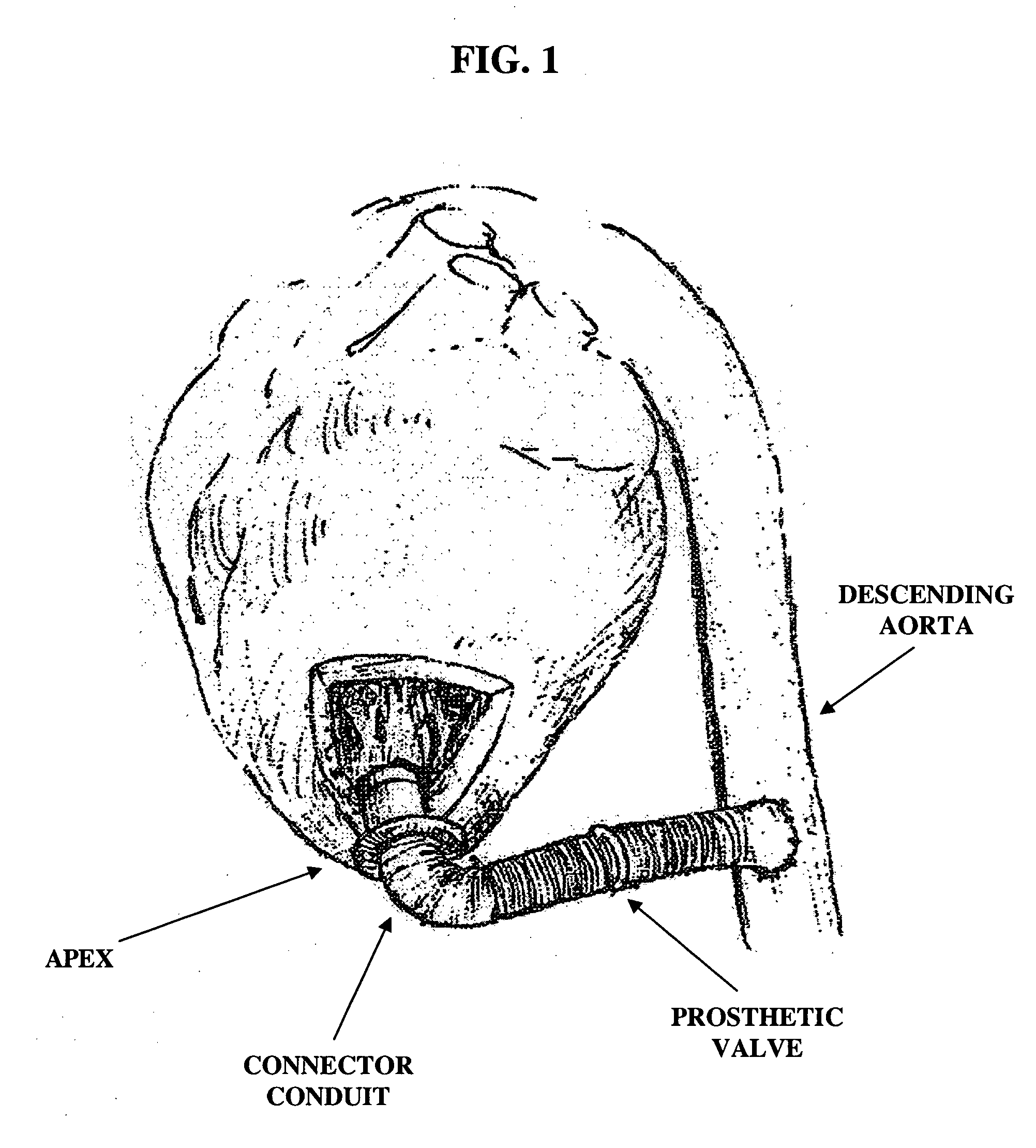
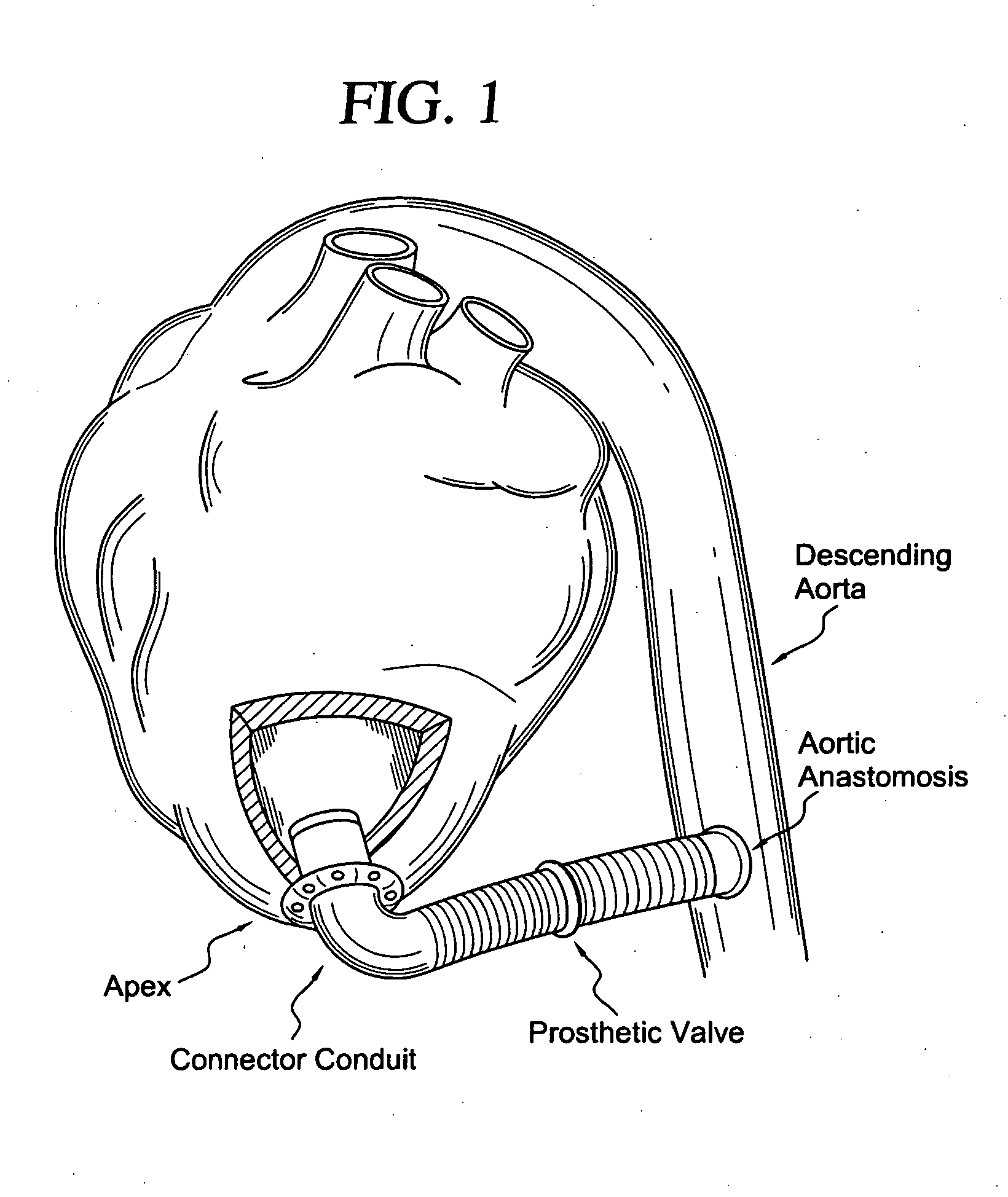
Apparatus and method for connecting a conduit to a hollow organ
InactiveUS20050251187A1Easy to optimizeReduce the possibilitySurgical instrument detailsExcision instrumentsExtracorporeal circulationProsthetic valve
An apparatus and method for connecting a first conduit to the heart without the need for cardiopulmonary bypass. The first conduit may then be attached to a second conduit that has a prosthetic device interposed. The second conduit may be connected to the aorta prior to the first conduit being attached to the heart. The prosthetic device may be a prosthetic valve or a pump, for example. The apparatus of the present invention includes an implantable connector with first conduit component, a retractor expansion component, a coring component, and a pushing component. The retractor expansion component is slide-ably coupled to the coring component. The retractor expansion component serves to seat against and separate the inside apical wall of the left ventricle so that the coring component may cut cleanly through the myocardium to form a tissue plug without leaving any hanging attachments to the inside walls. By remaining seated against the inside wall, the retractor expansion component follows the tissue plug into the coring component. The surgeon applies force and rotary motion to the pushing component sufficient to cut the tissue plug and implant the prosthetic component.
Owner:CORREX
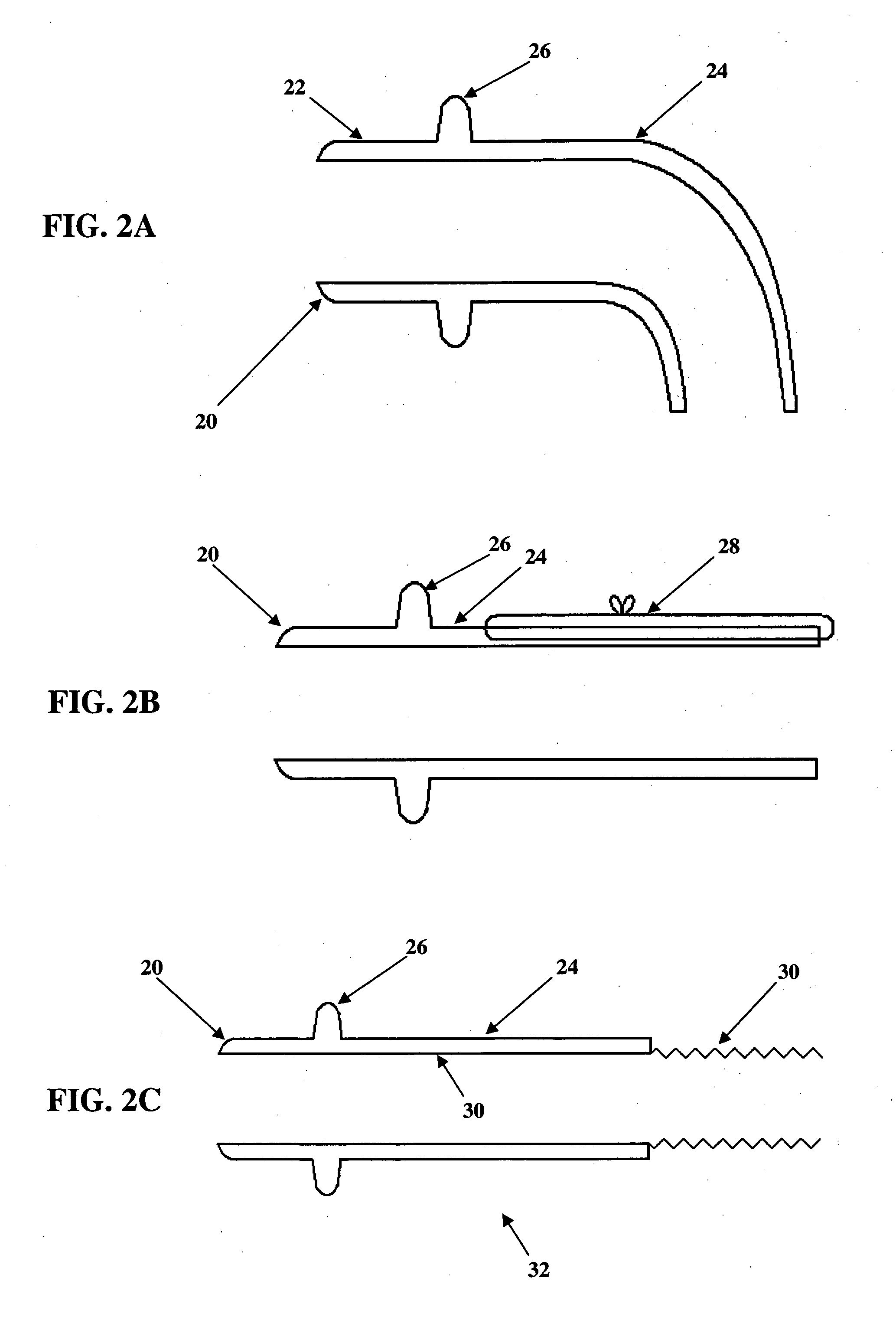
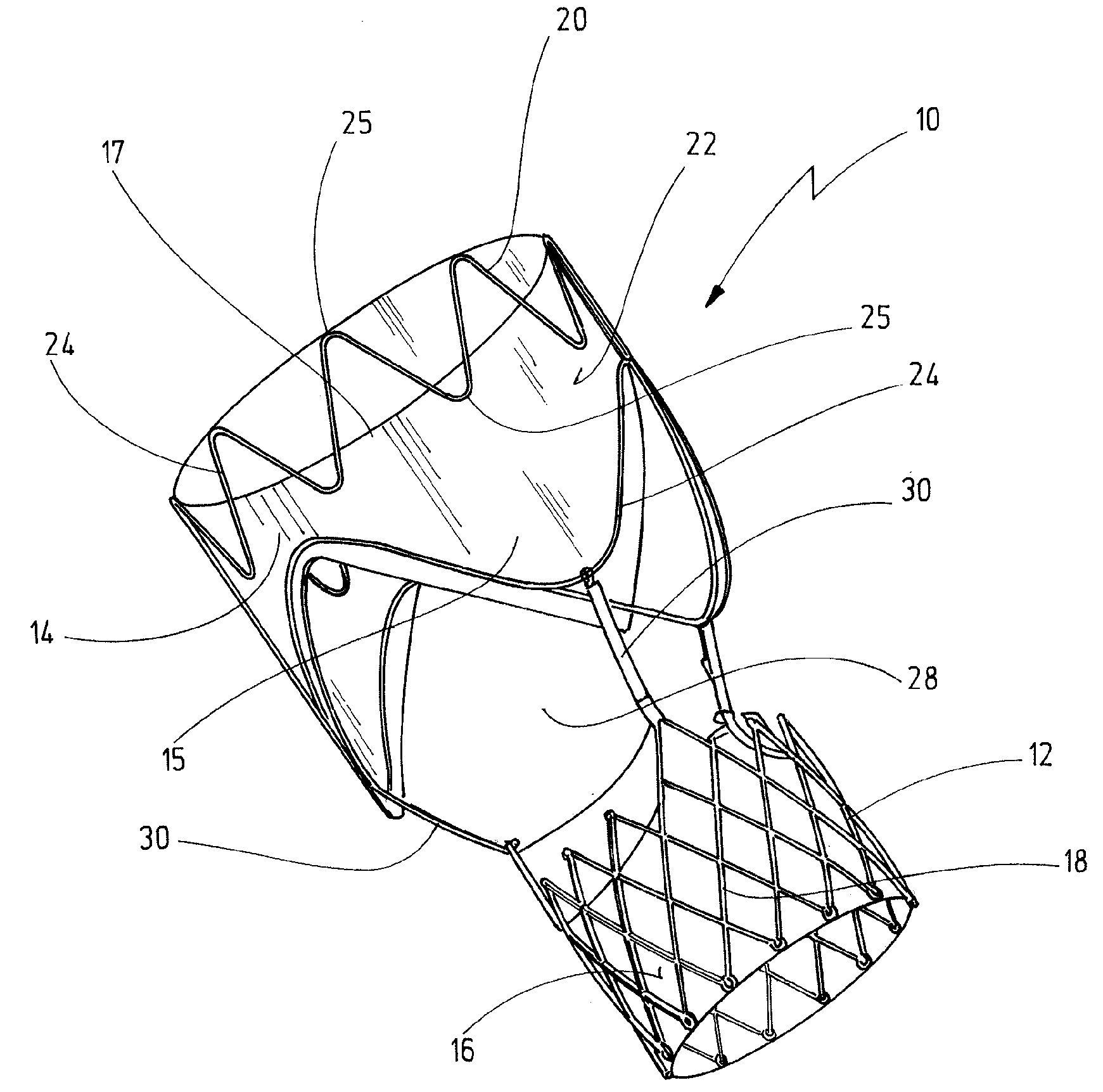
Cardiac valve prosthesis system
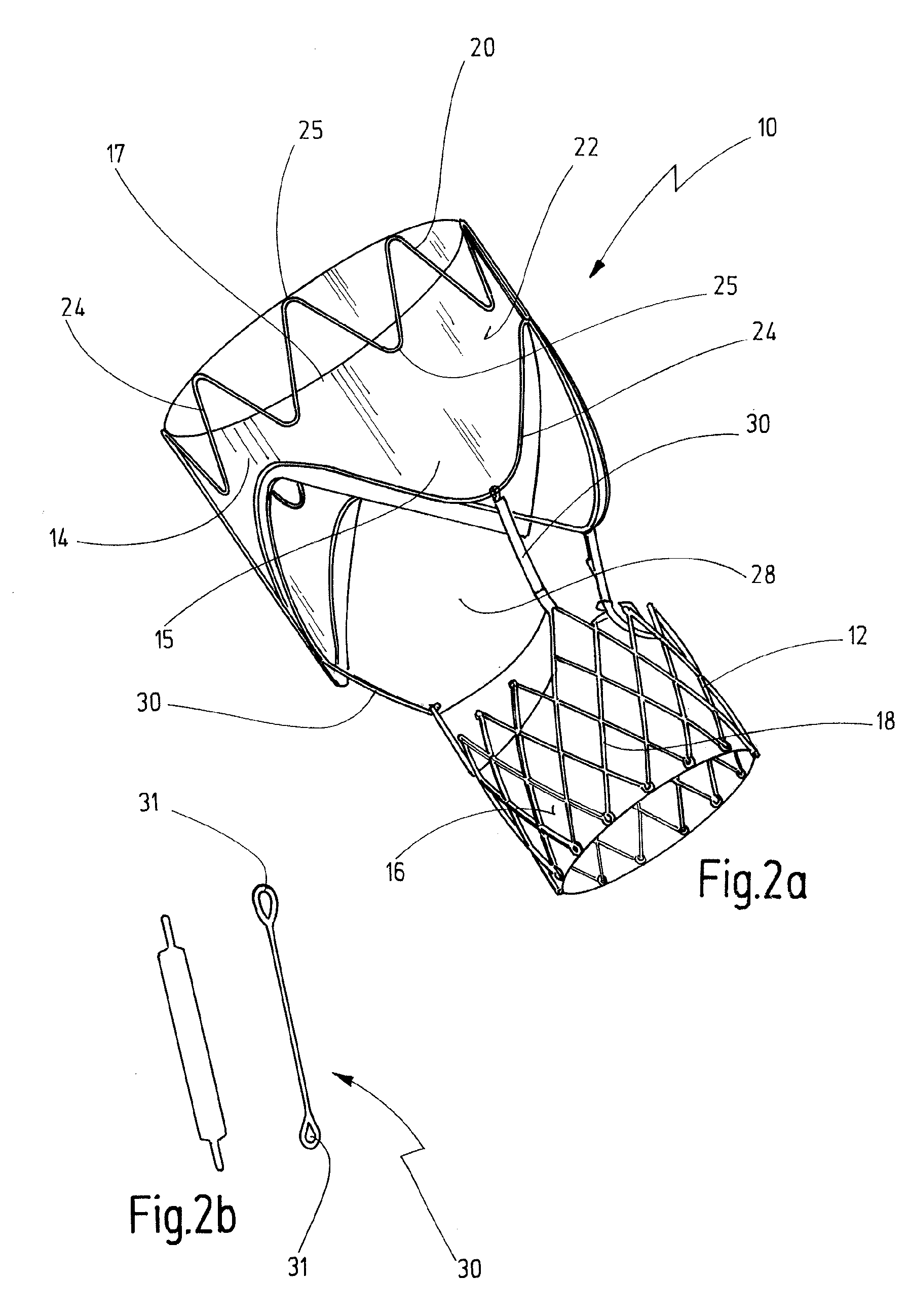
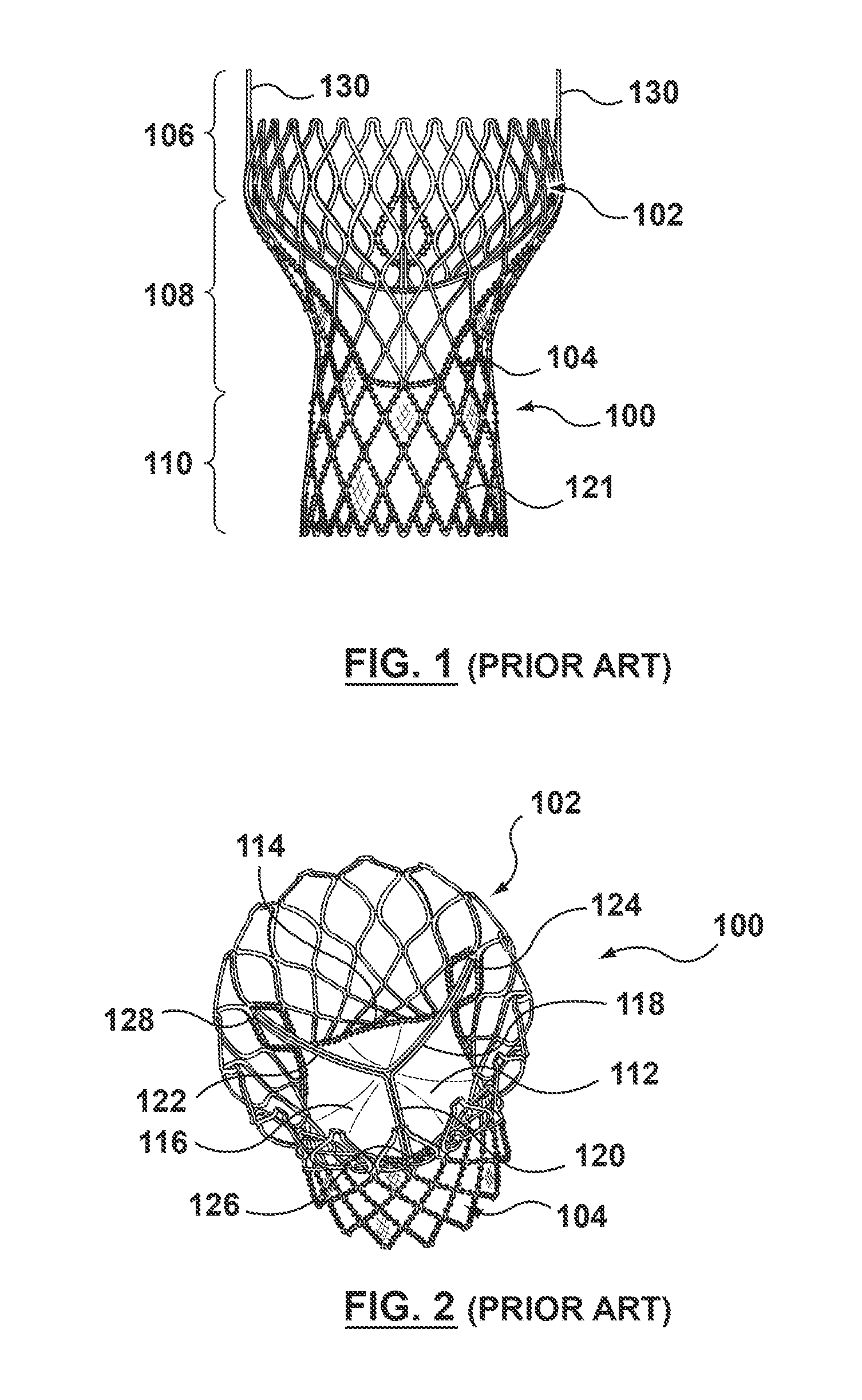
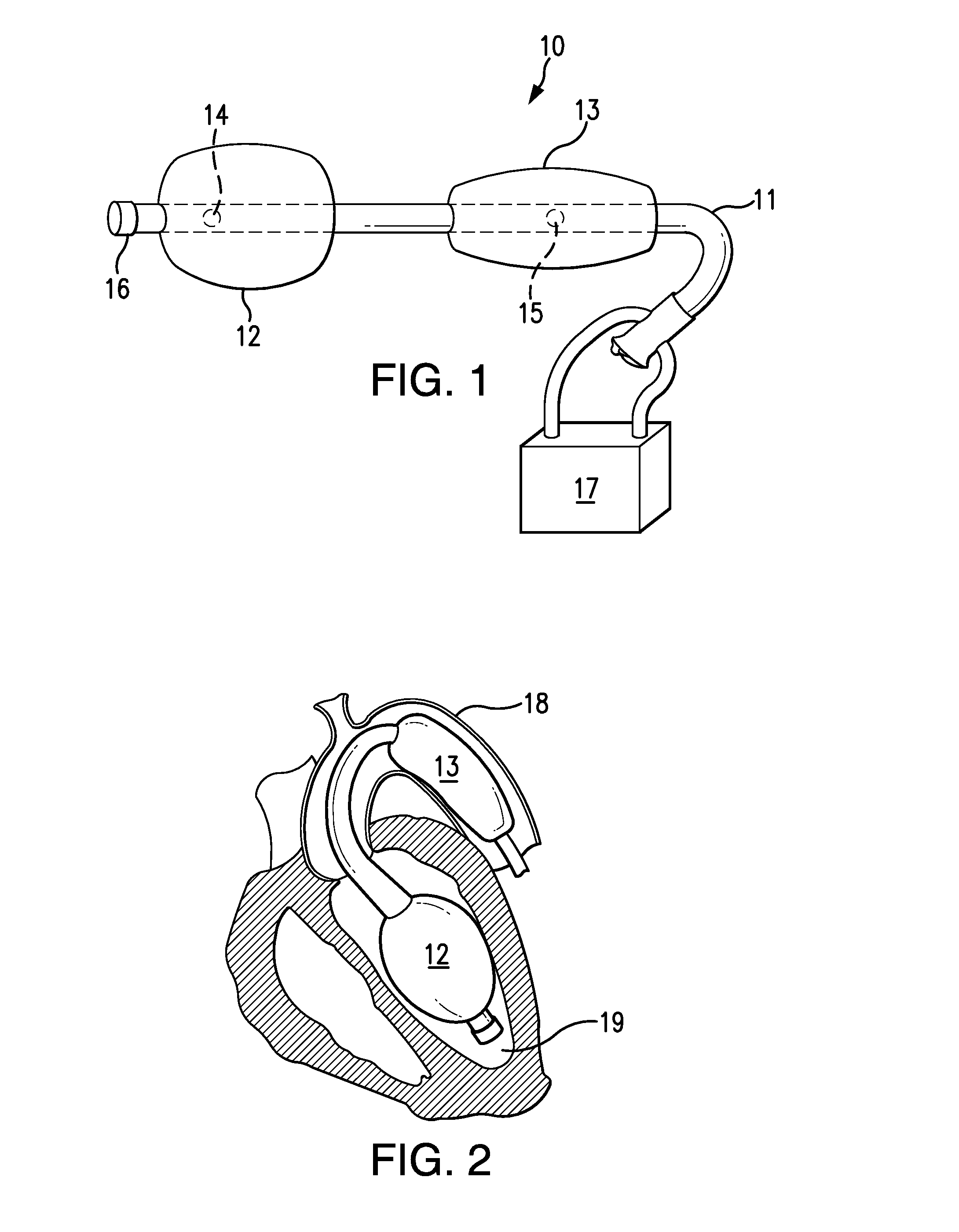
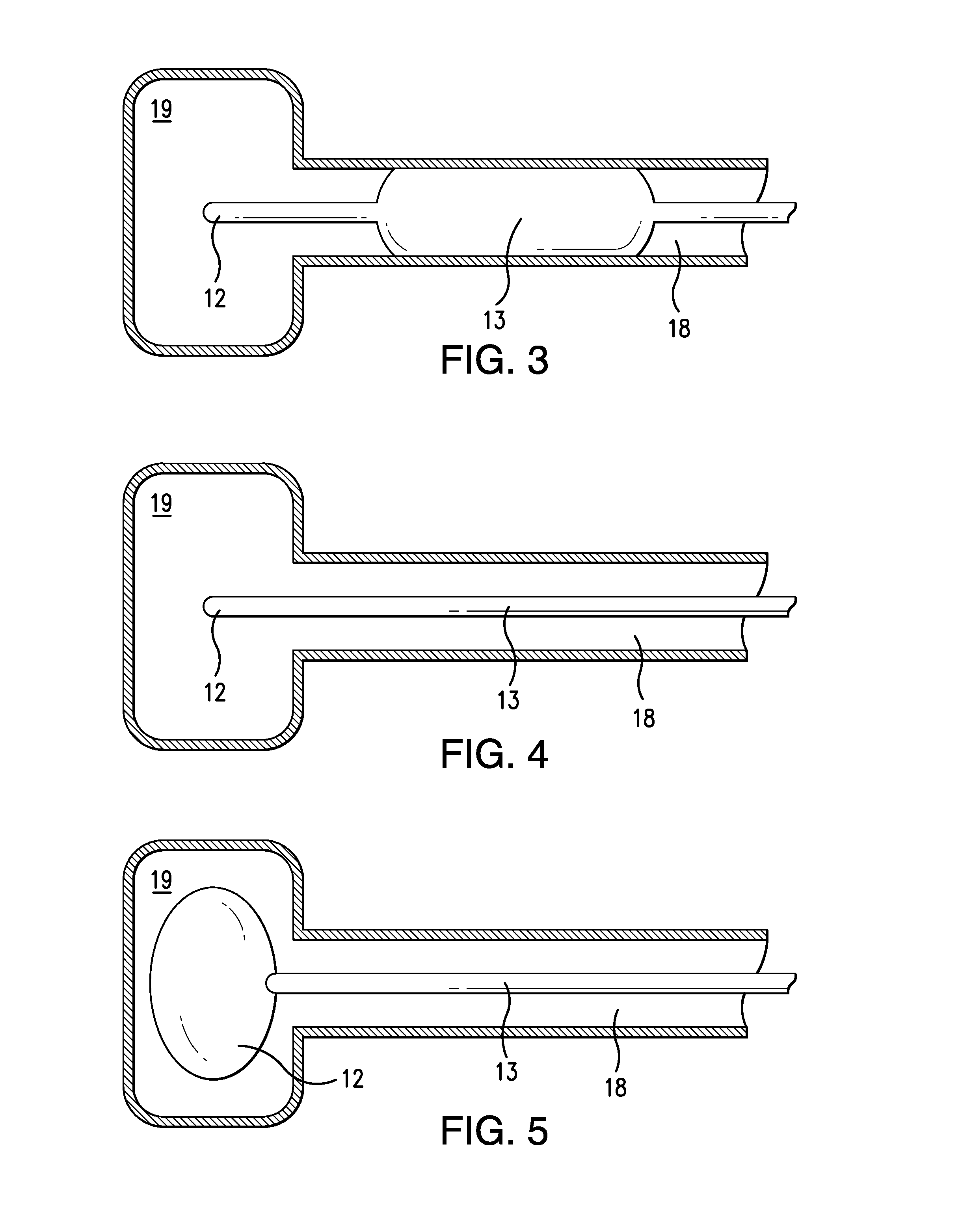
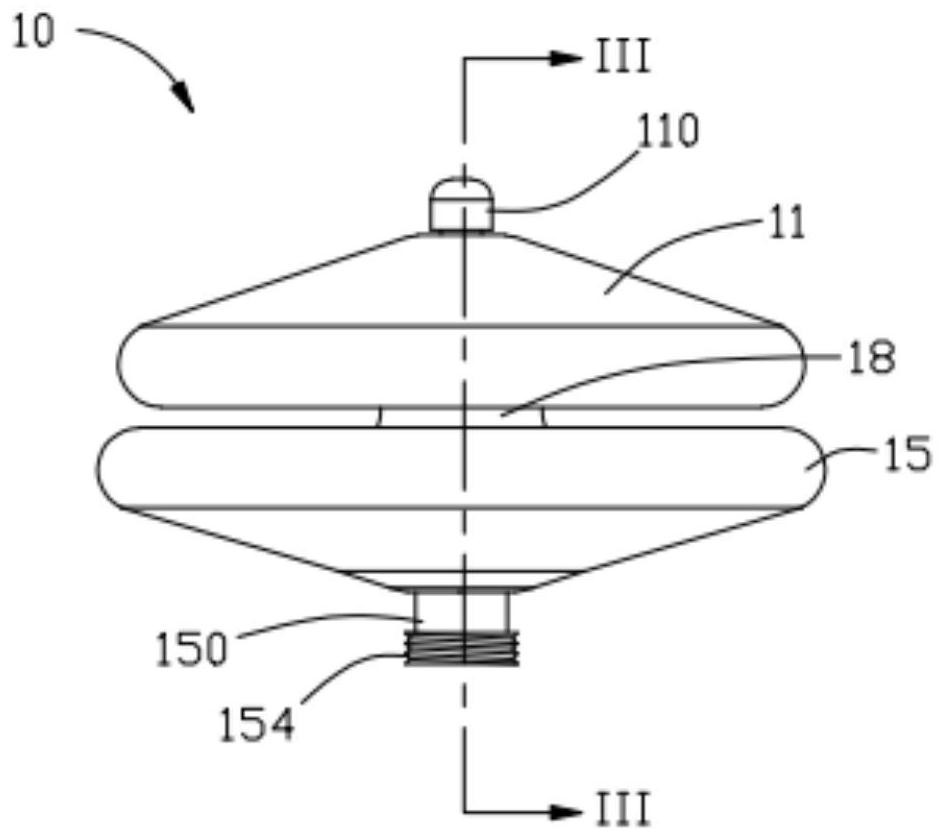
The present invention concerns a cardiac valve prosthesis system (10; 40) for implantation into the body of a mammal. The prosthesis system (19; 40) comprises a valve (16) mounted on an stent element (18) to form a stented valve element (12), and an anchoring element (14) to be arranged within the aorta of the mammal to be treated with the prosthesis and spaced-apart form the stented valve element (12). Further, the anchoring element (14) comprises a cylindrical tube element composed of fabric (22) supported by a metal mesh, and the stented valve element (12) and the anchoring element (14) represent two constructional distinctive elements being associated by ligament-like connecting means (30; 50), such, that the connecting region (28) between the stented valve element (12) and the anchoring element (14) is generally free from foreign material.
Owner:NVT
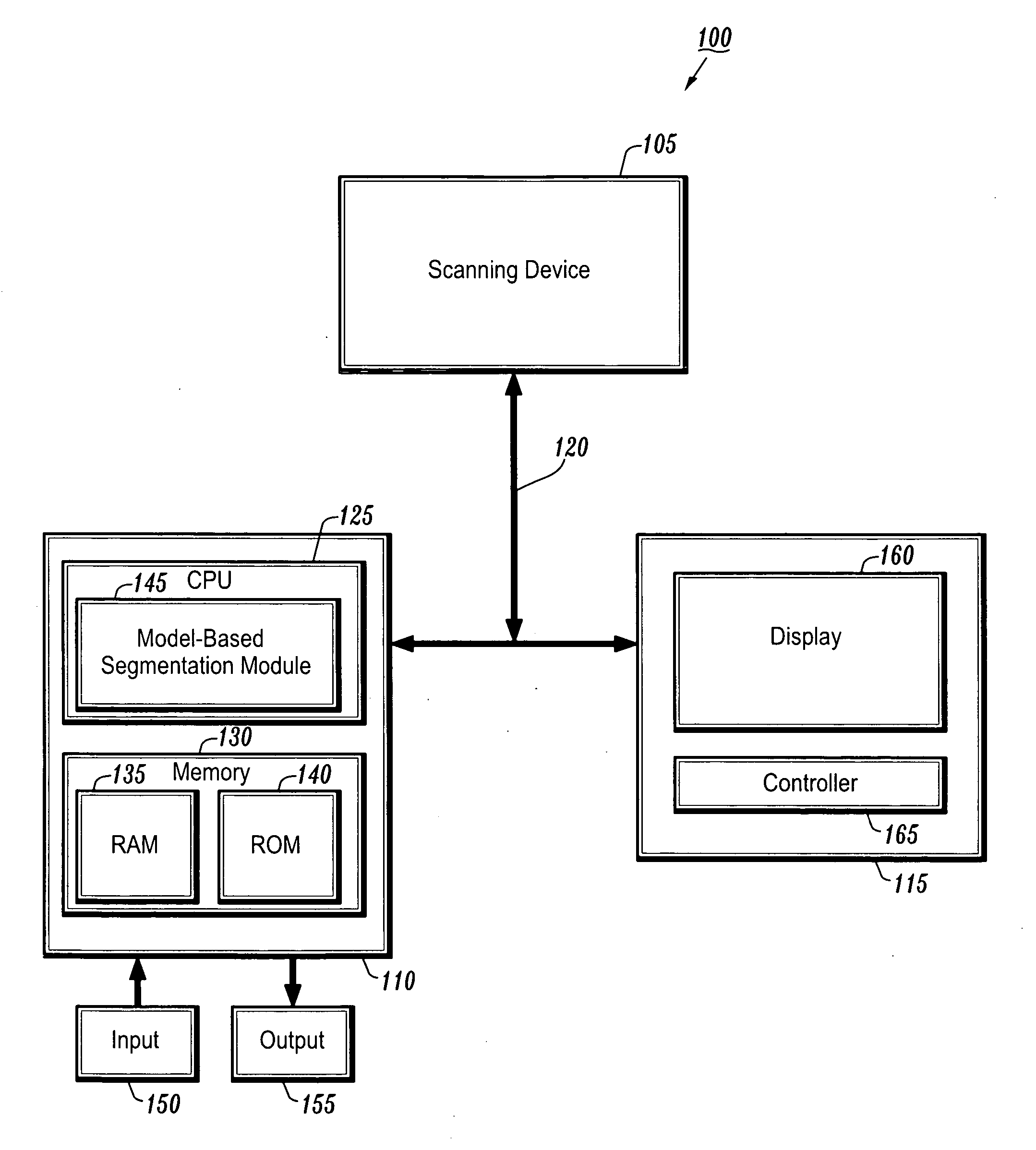
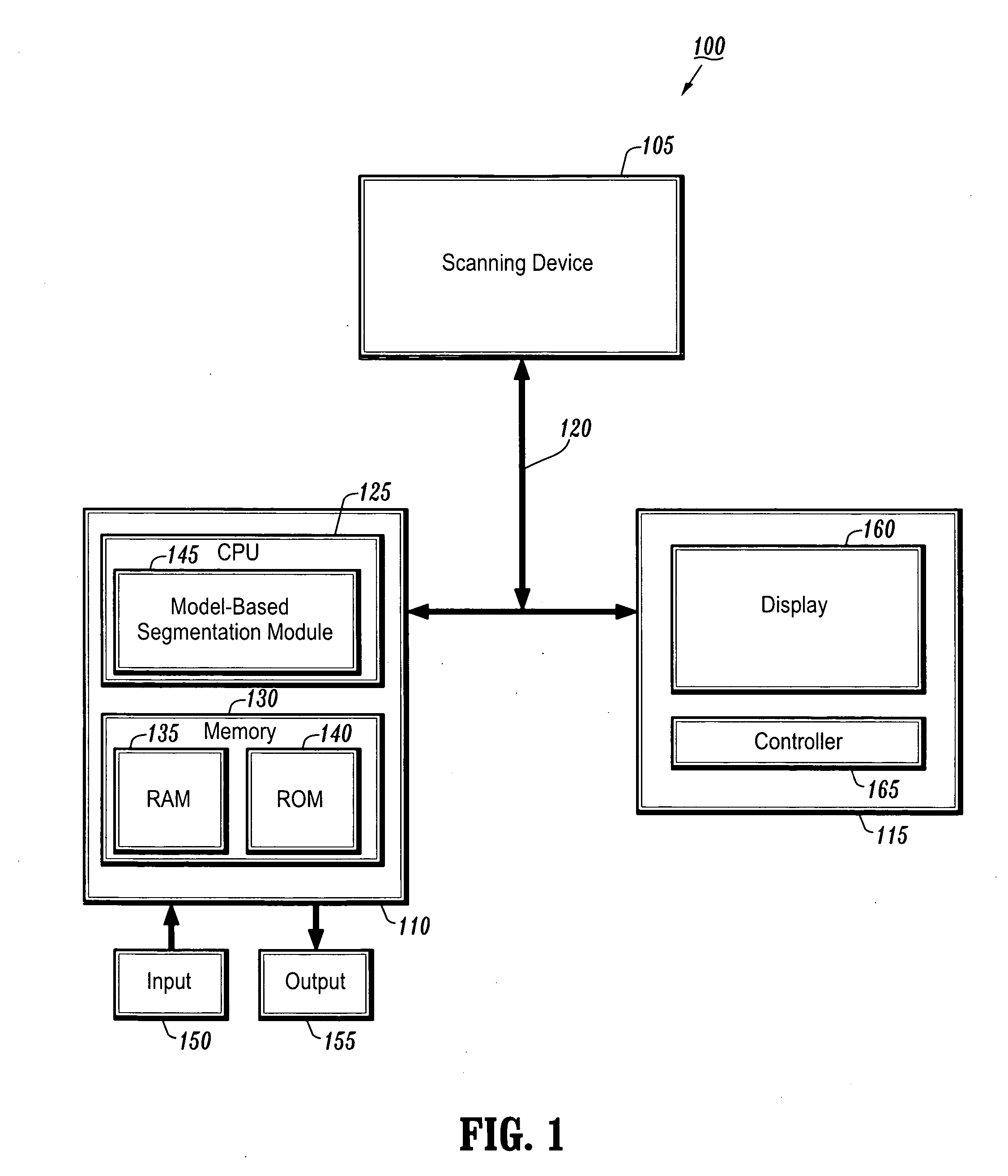
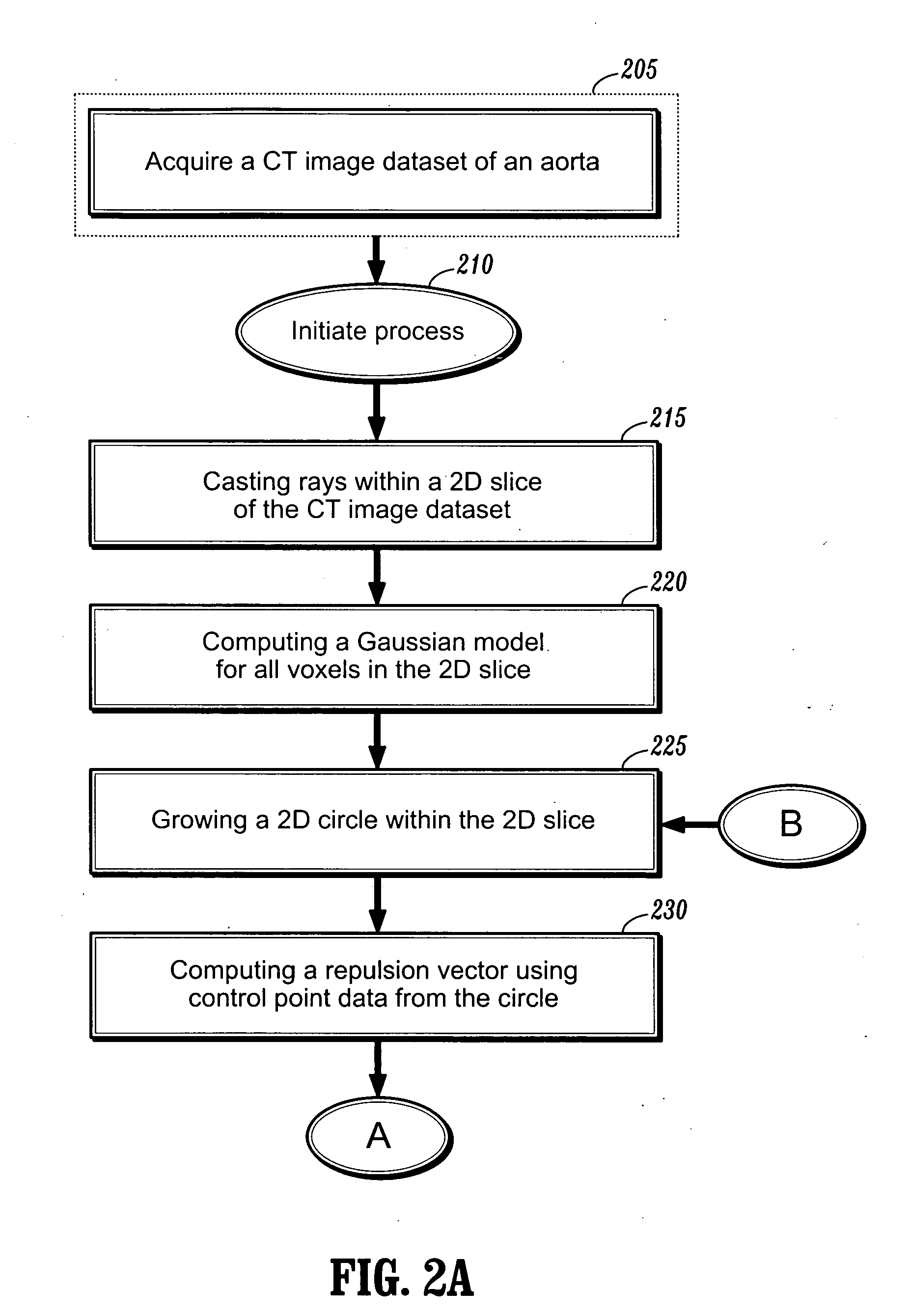
System and method for detecting the aortic valve using a model-based segmentation technique
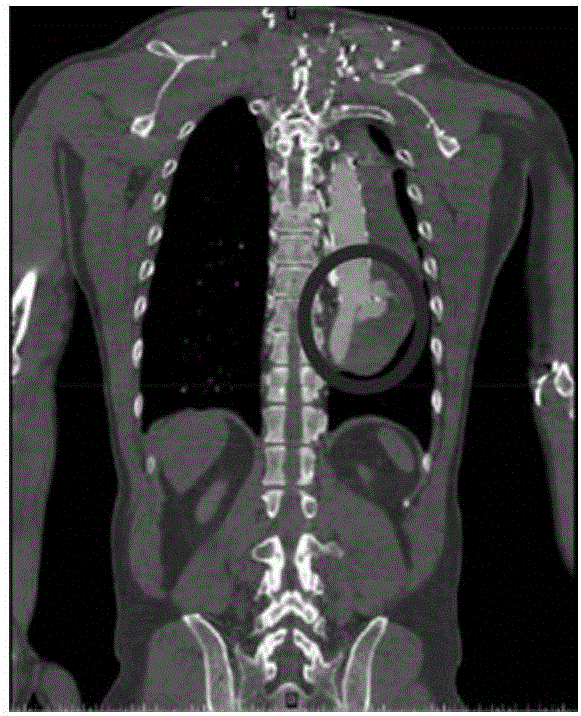
A system and method for detecting the aortic valve is provided. The method comprises: (a) casting rays on a slice of a computed tomography (CT) dataset of an aorta; (b) computing a Gaussian model for voxels on the slice, wherein the Gaussian model produces a threshold; (c) growing a circle from a point within the aorta until control points of the circle reach the threshold; (d) computing a repulsion vector for each control point reaching the threshold; (e) repositioning the circle according to an average of the repulsion vectors, wherein if the circle is within the aorta, repeating steps (c-e) until the circle is not within the aorta; (f) calculating a statistical value for the circle; (g) projecting a copy of the circle onto an adjacent slice; (h) reducing the radius of the copy of the circle; and (i) repeating steps (c-h) on remaining CT slices until the aortic valve is detected.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Two-part expanding stent graft delivery system
ActiveUS20060129224A1Reduce the possibilitySmooth connectionStentsMechanical apparatusAbdominal cavityCeliac axis
A delivery system for endovascularly delivering a prosthesis along a guidewire to a curved implantation site includes a delivery device having control handle and an inner lumen slidably disposed in the handle between a retracted position and an extended position. The inner lumen has a distal end and a tip at the distal end of the inner lumen. An intermediate lumen is slidably disposed about the inner lumen and has a distal end. A relatively flexible prosthesis sheath is connected to the distal end of the intermediate lumen and a relatively stiff outer lumen is axially fixedly connected to the handle about the intermediate lumen. The outer lumen has a length only long enough to be inserted in a patient's aorta no further than the patient's celiac axis.
Owner:BOLTON MEDICAL INC
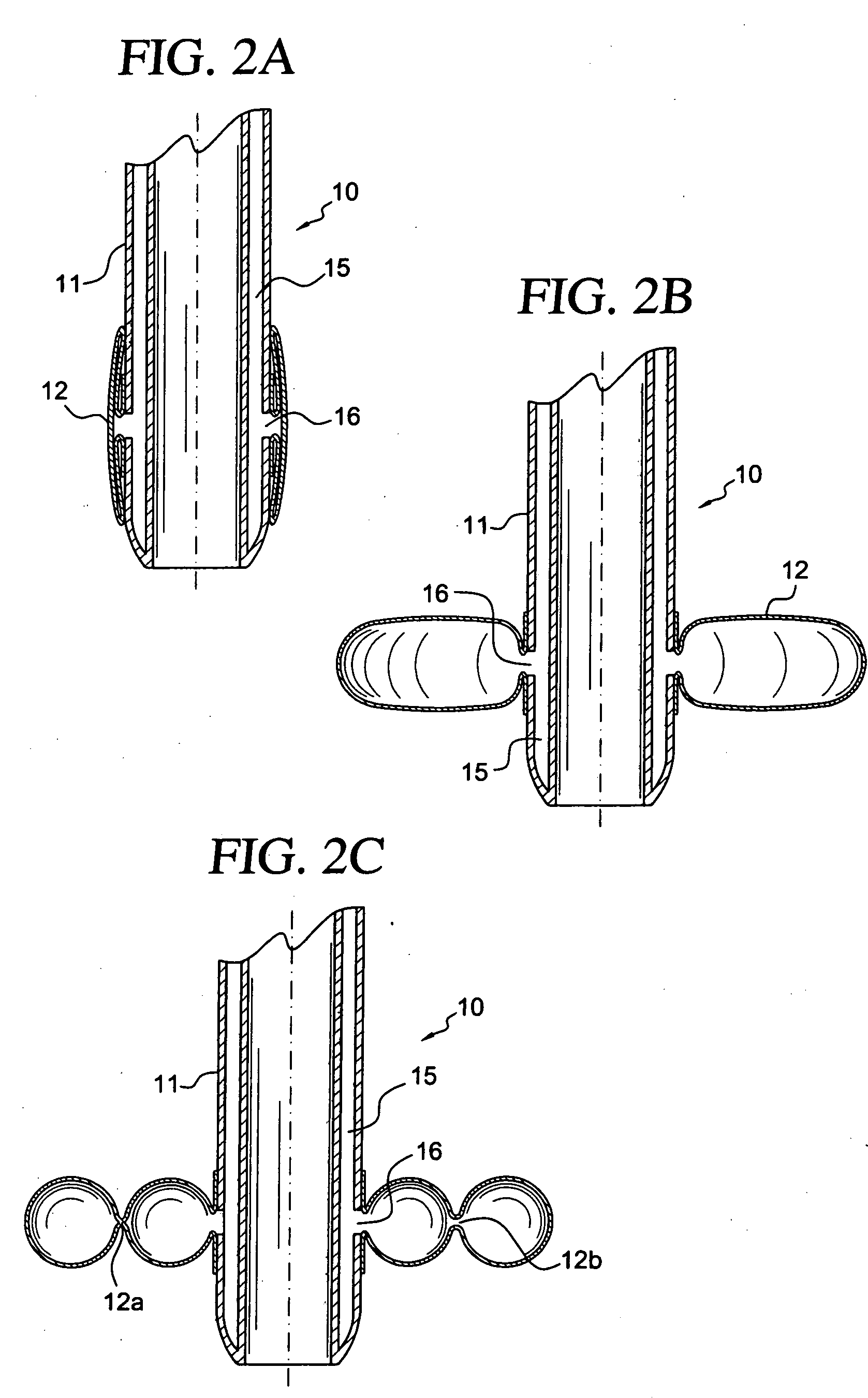
Apparatus and method for connecting a conduit to a hollow vessel
InactiveUS20060161193A1Blood lossChoose accuratelySurgical needlesExcision instrumentsAorta partEngineering
The present invention provides a system and method for forming a side branch on a hollow vessel, such as the aorta. The side branch is preferably adapted to be connected to a connector conduit, but any other suitable use is also acceptable. The system comprises a graft including a side branch portion, and an applicator comprising a hole forming element adapted to form a hole in the wall of the vessel and an insertion element adapted to be inserted through the wall of the vessel, the insertion element comprising a retraction element adapted to enter into engagement with the graft. The hole forming element may comprise a cutting element adapted to cut a hole in the wall of the vessel, and a positioning element adapted to hold the position of the applicator relative to the vessel. The system further comprises a graft protection element adapted to prevent the graft from being damaged by the cutting element. In this case, the clamping element and the graft protection element may be the same element, for example, an expansion element, which may be expandable from an unexpanded state to fully expanded state and to a partially expanded state. The expansion element may be a balloon, which may be in the shape of a circular toroid, and may include a tension member that restricts the dimensions of the balloon. In addition, the expansion element may be an umbrella mechanism.
Owner:CORREX
Implantable valve system
An implantable valve having a valve element or leaflet and a base that is attachable to a vessel wall using a connector such as a screw, pin or a staple. The valve can be implanted using a catheter to position the valve in a desired location and drive the connector into the vessel wall. The valve can be used as a venous valve to control blood flow within the veins, arteries, heart or the aorta of a patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Valve bypass graft device, tools, and method
InactiveUS20050149093A1Reduce decreasePromote quick completionSurgical needlesCatheterHeart chamberAorta part
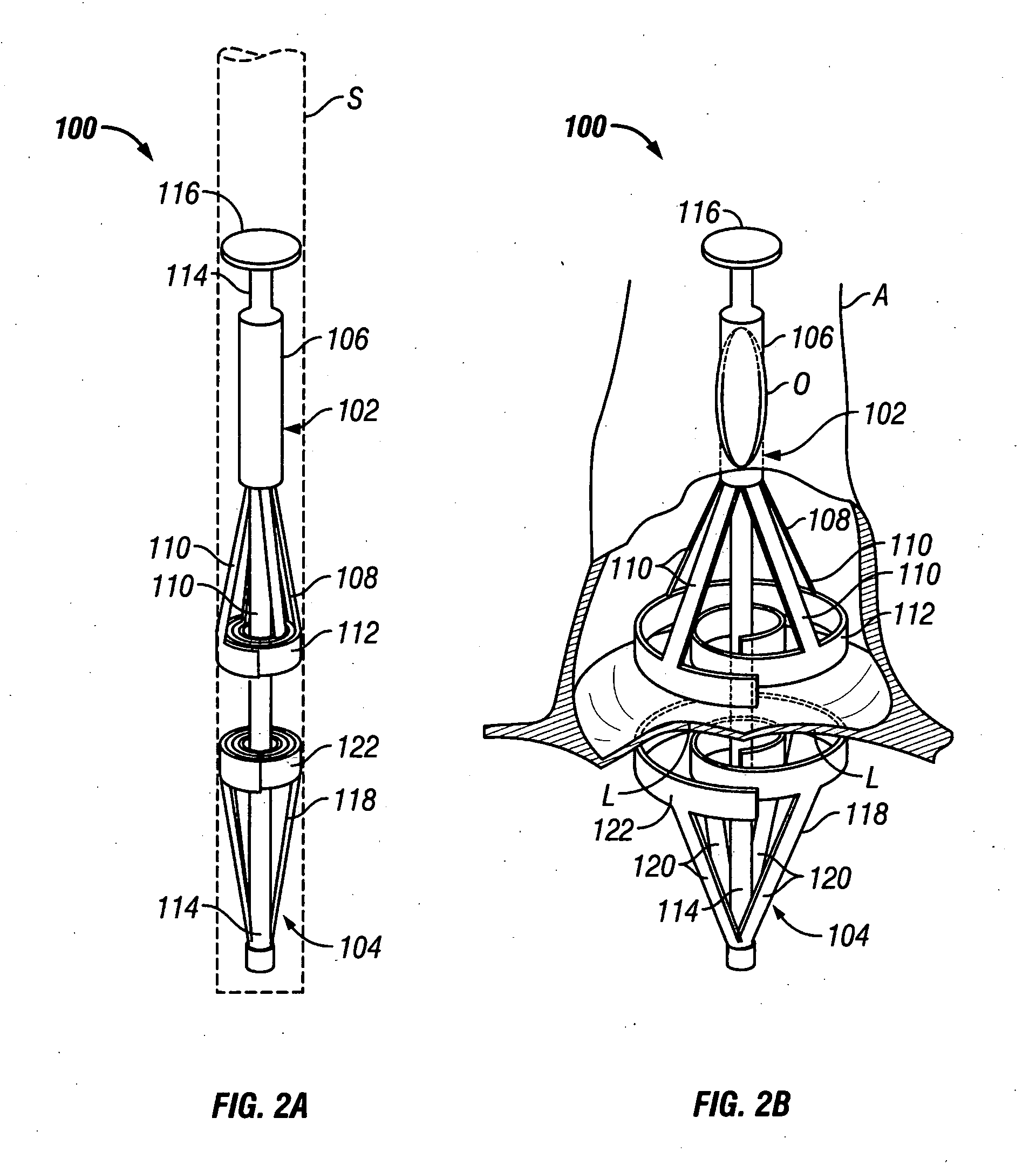
This invention relates to an implant, implant tools, and an implant technique for the interposition of an extracardiac conduit between the left ventricle of a beating heart and the aorta to form an alternative one-way blood pathway thereby bypassing the native diseased aortic valve. The implant consists of a hollow conduit having a first end opening, a second end opening, and a one-way valve located between the end openings. The valve is biased to allow one-way flow from the second end opening to the first end opening. A first slit opening is located between the first end opening and the valve and a second slit opening is located between the second end opening and the heart valve. The implant tools consist of a vessel wall cutting tool and a heart wall piercing and dilating tool. The vessel wall cutting tool is sized to closely fit through the implant's first slit opening and the first end opening. The heart wall piercing and dilating tool is sized to closely fit through the implant's second slit opening and the second end opening. The implant technique allows the surgeon to safely connect the implant between a heart chamber and a blood vessel without stopping the heart or impeding flow in the blood vessel.
Owner:CARDIOUS
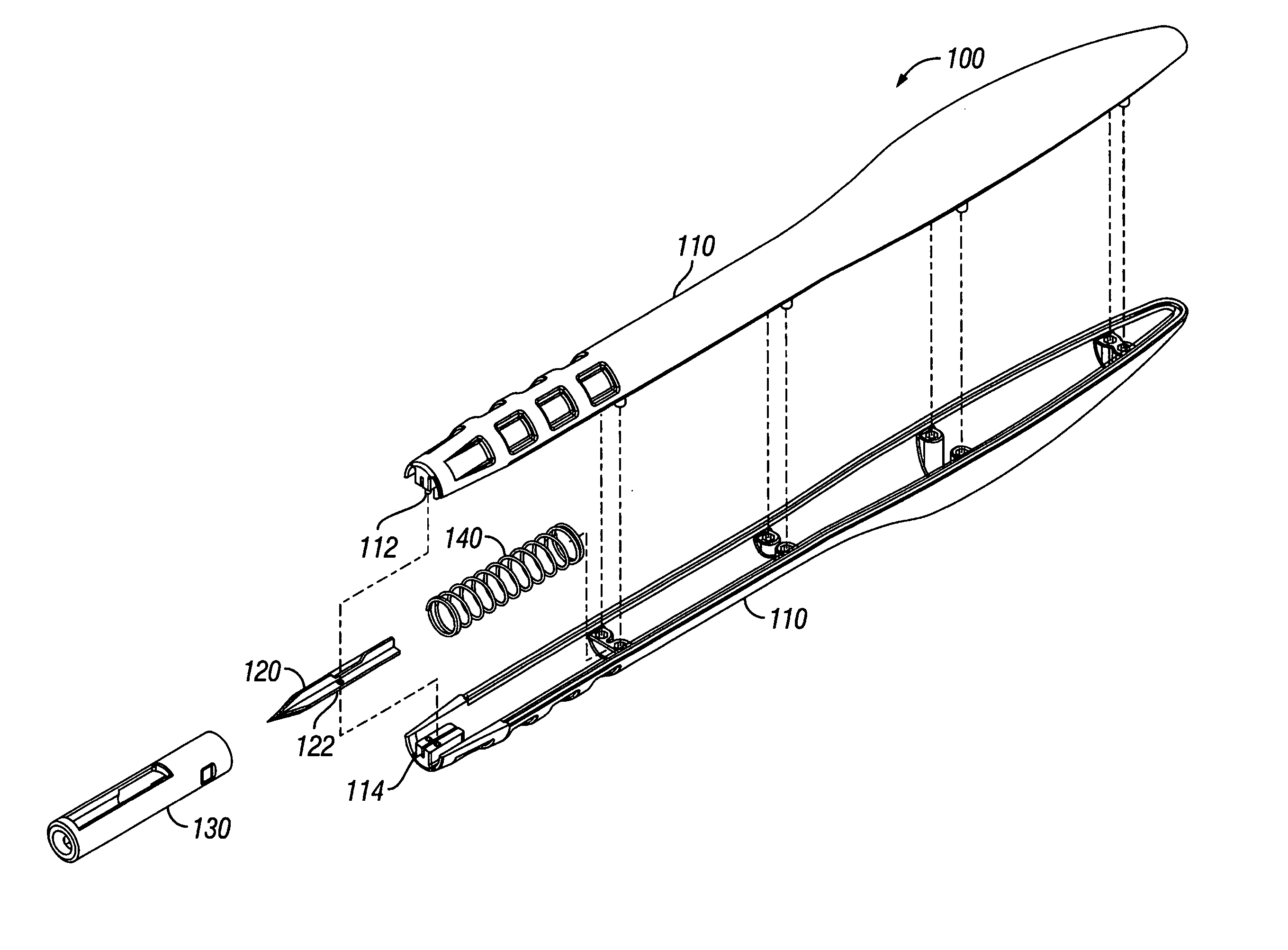
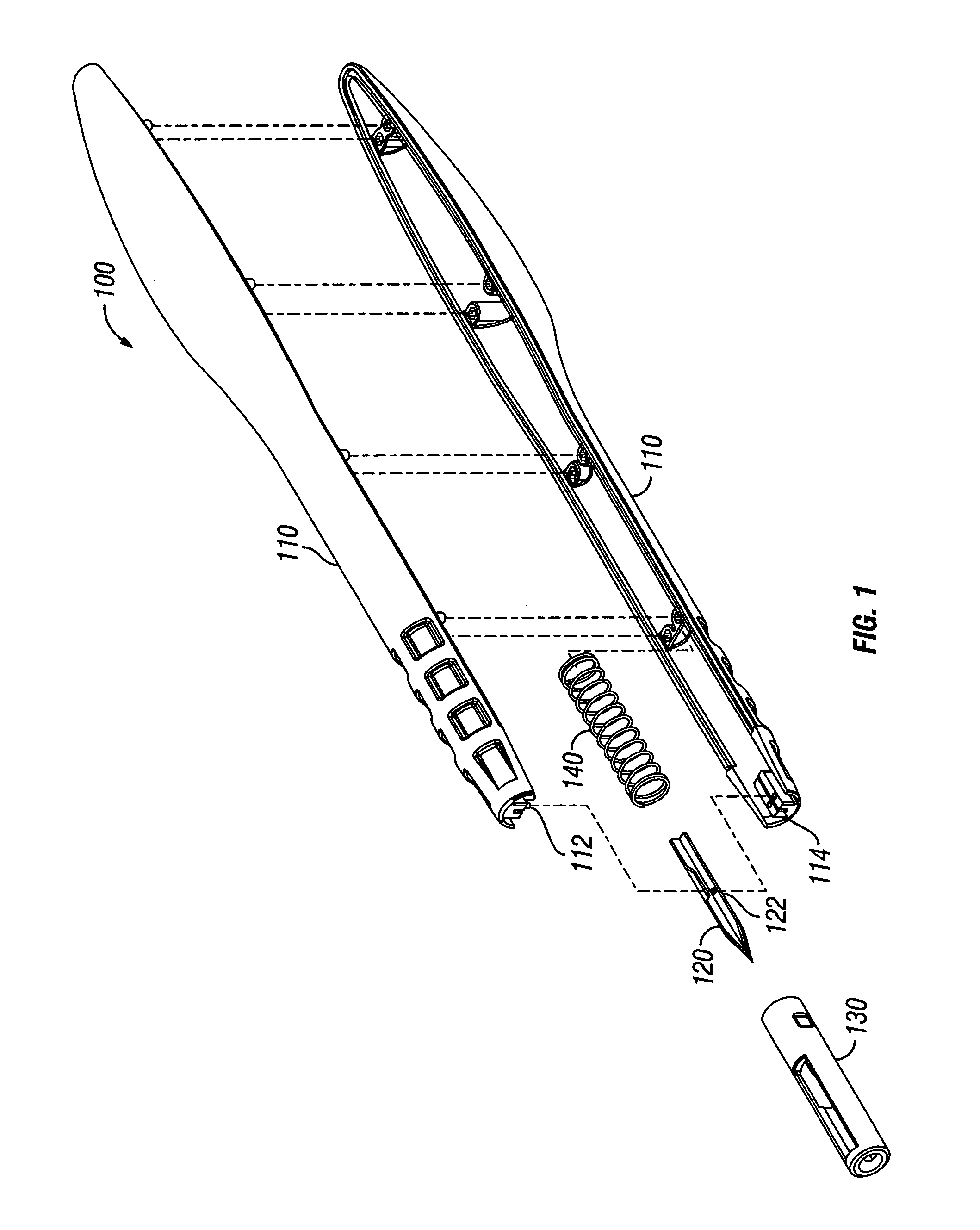
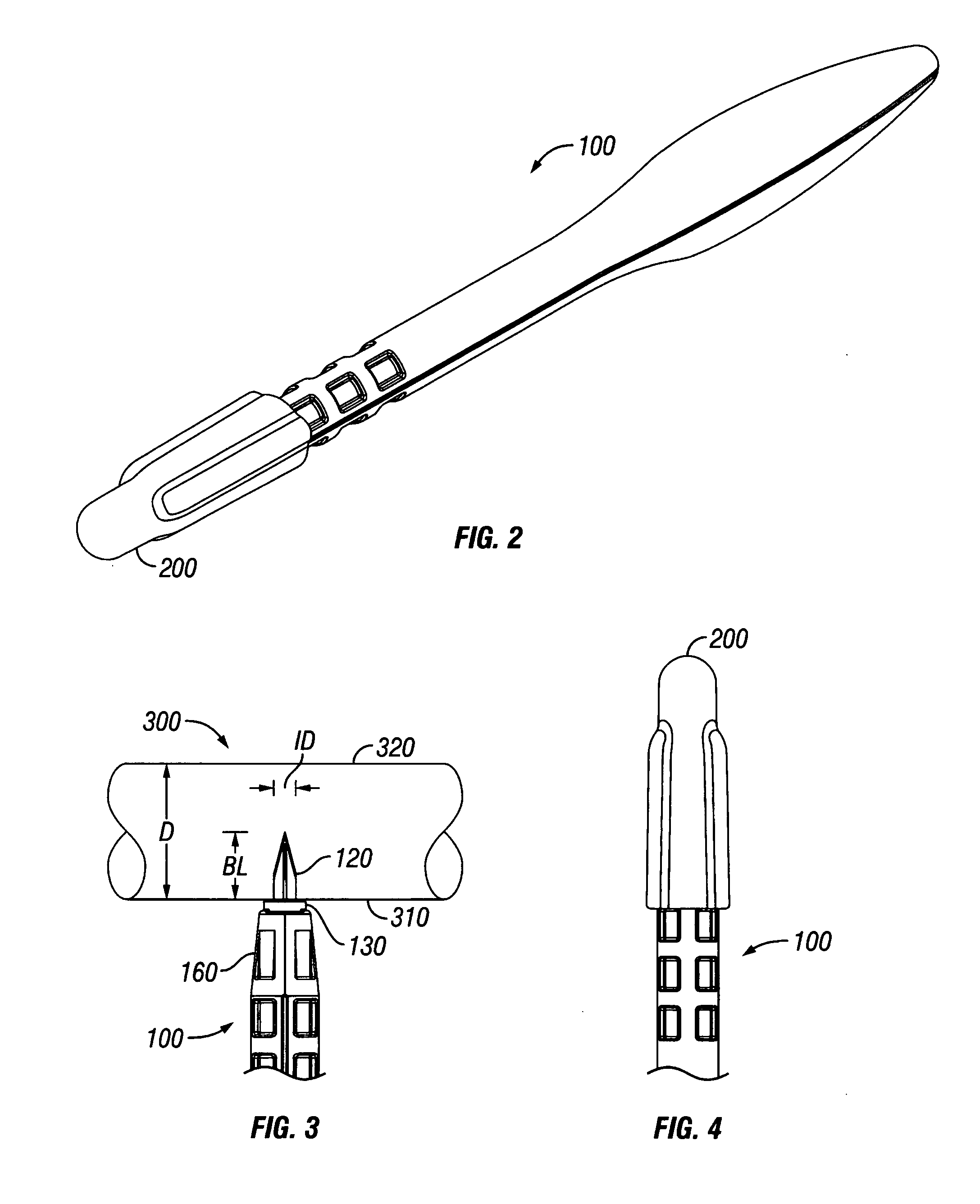
Aortic lancet
InactiveUS20070100363A1Prevent penetrationPrevent any accidental cuttingExcision instrumentsSurgical sawsAorta partEngineering
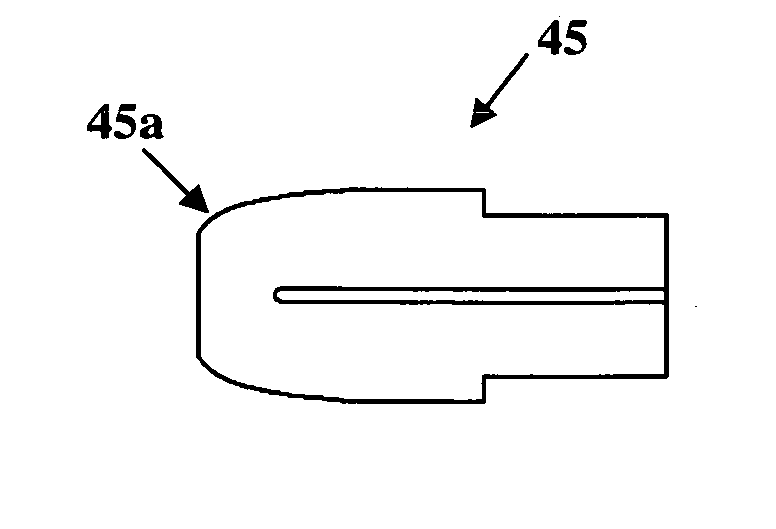
A system for making a precise incision and circular hole in a vessel wall, such as the aorta, that eliminates lateral side notches from the aortotomy. In one aspect, the system includes a surgical knife or lancet having a blade surrounded by a retractable shield. In one aspect, the system includes a tissue punch having a rotating circumferential edge for receiving a parabolic-shaped anvil having an anvil cutting edge. The anvil is placed through an incision made by a knife and actuated to produce a hole in the vessel wall.
Owner:QUEST MEDICAL
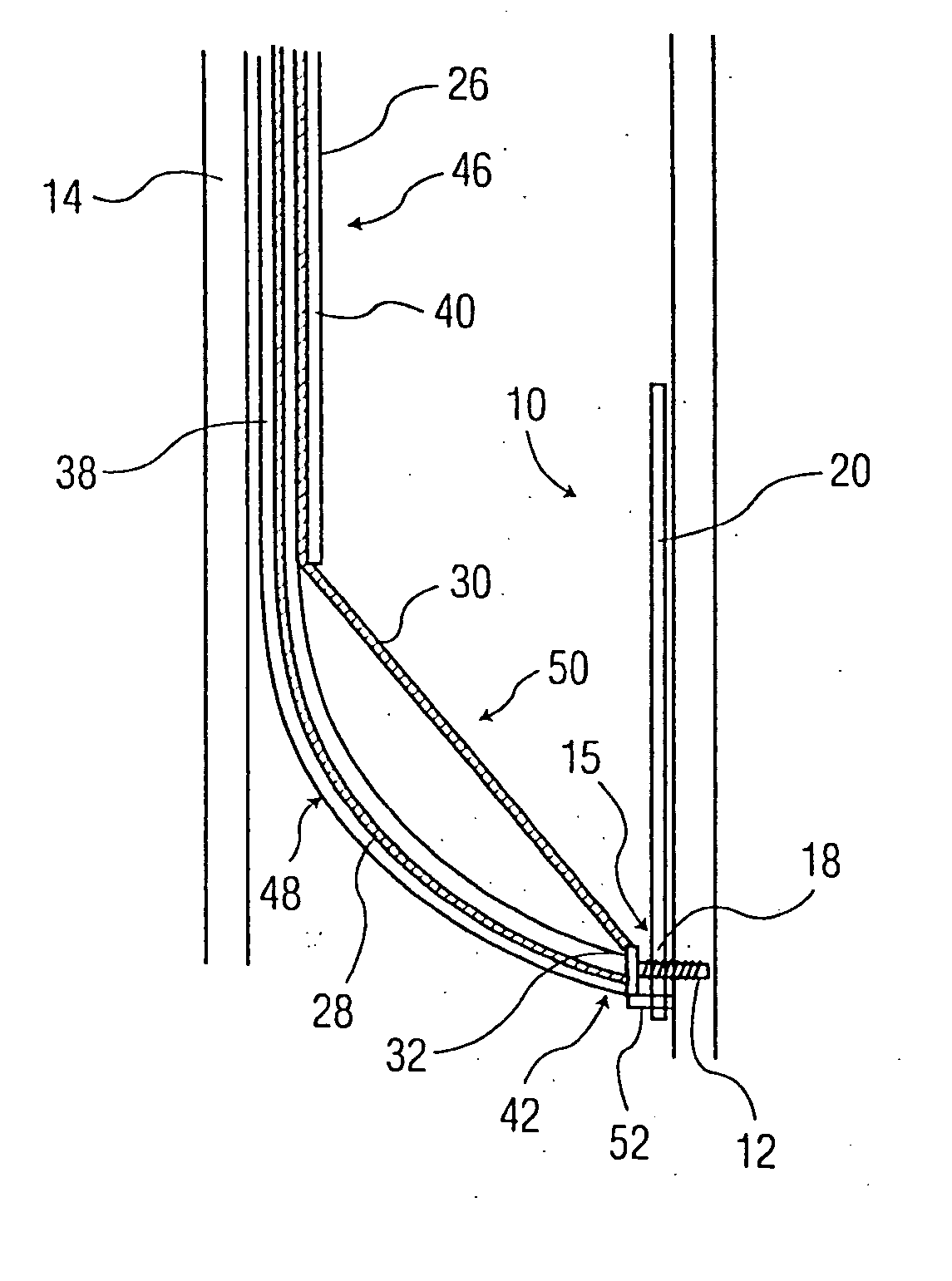
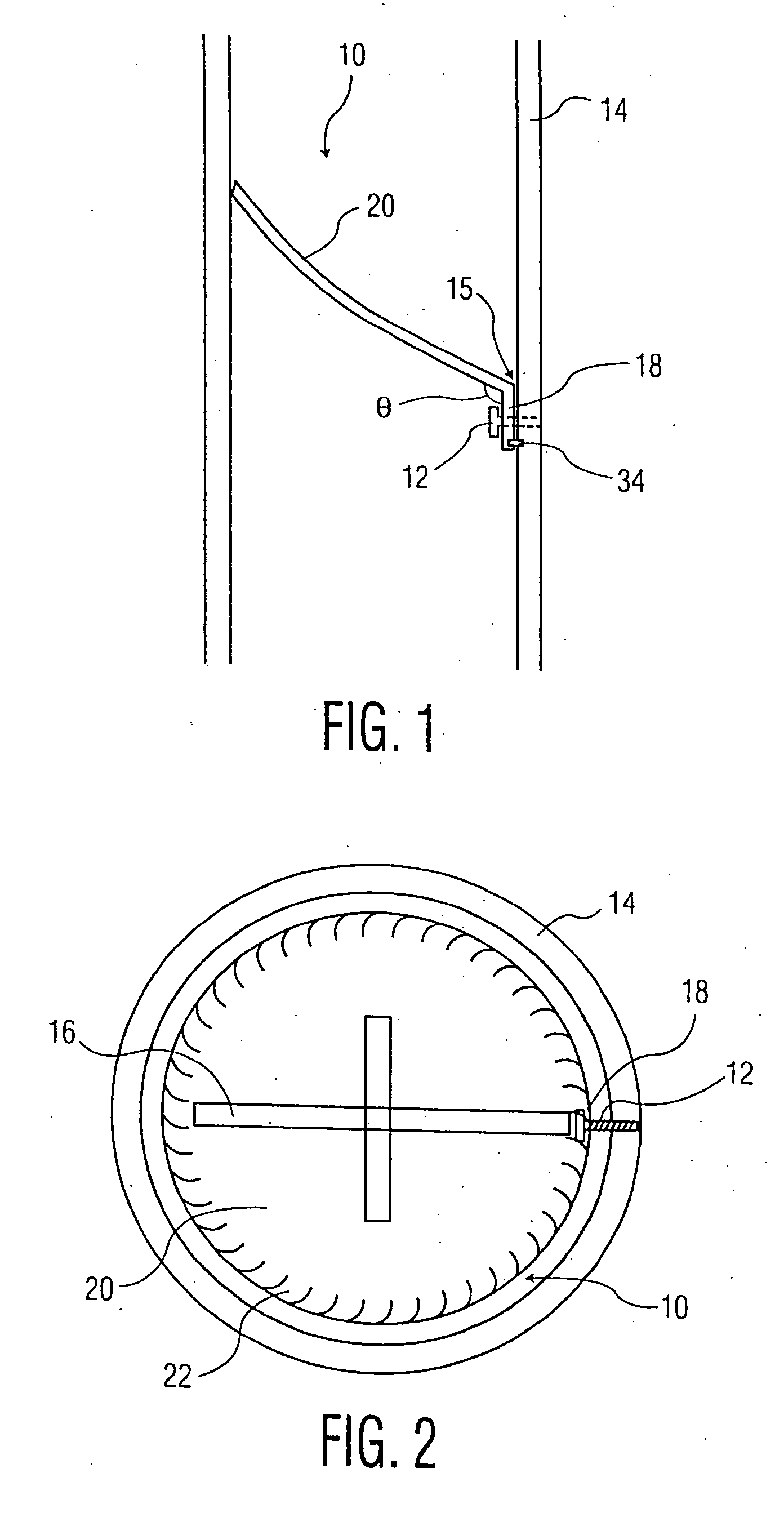
Methods and Devices for Placing a Conduit in Fluid Communication with a Target Vessel
Methods and devices for placing a conduit in fluid communication with a target vessel and a source of blood, such as the aorta or a heart chamber. The device may be actuated using one hand to place the conduit. The invention allows air in the conduit to be removed prior to placement of the conduit. The invention deploys the conduit in the target vessel by moving a sheath in a distal direction and then in a proximal direction. A conduit is provided with a reinforcing member to prevent kinking of the conduit, and a structure for preventing blockage of the conduit by tissue. A vessel coupling may be used to secure a conduit to a target vessel so as to preserve native blood flow through the vessel, and the conduit may be placed in fluid communication with a target vessel via a laparoscopic or endoscopic procedure.
Owner:GITTINGS DARIN C +3
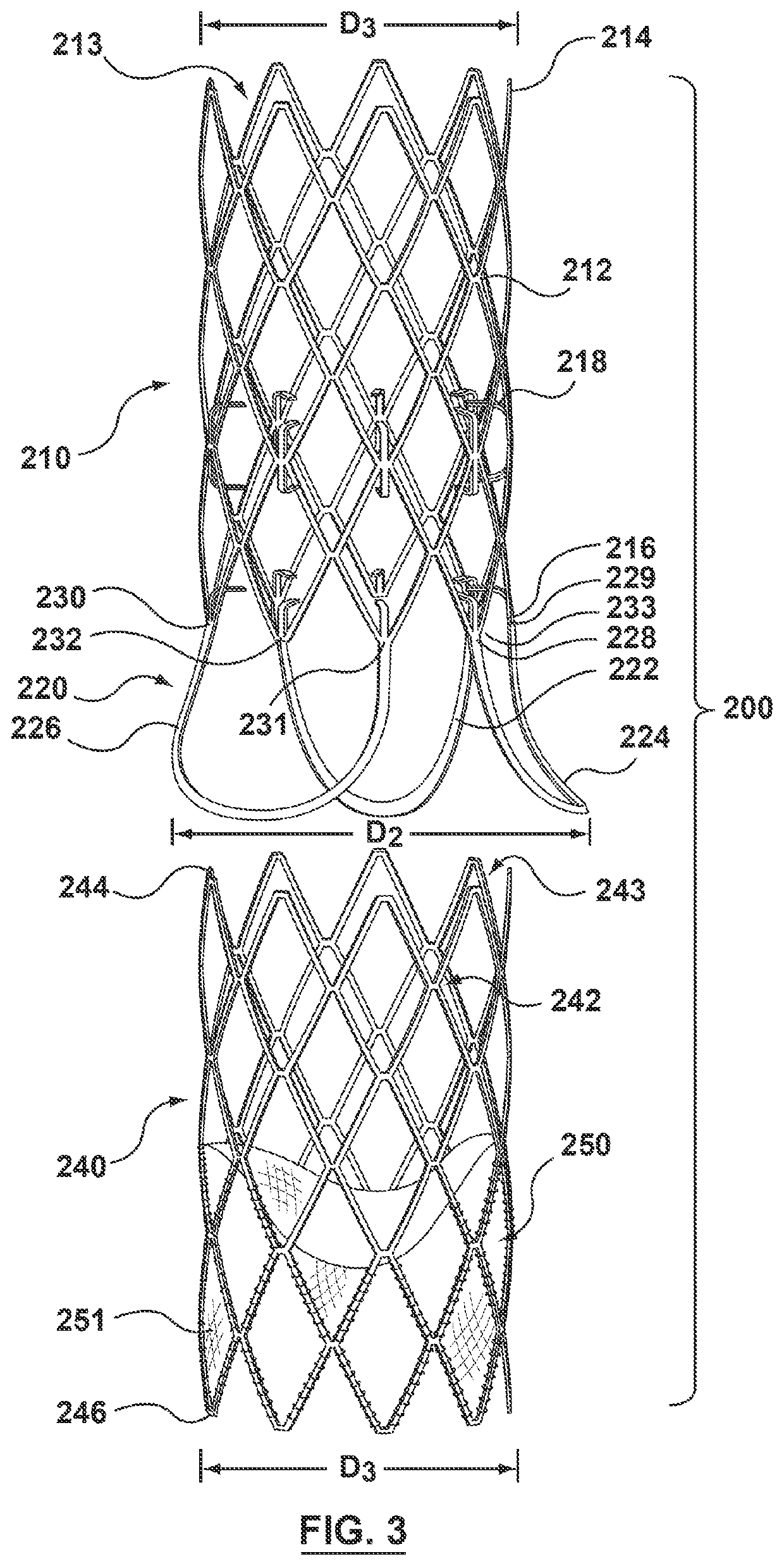
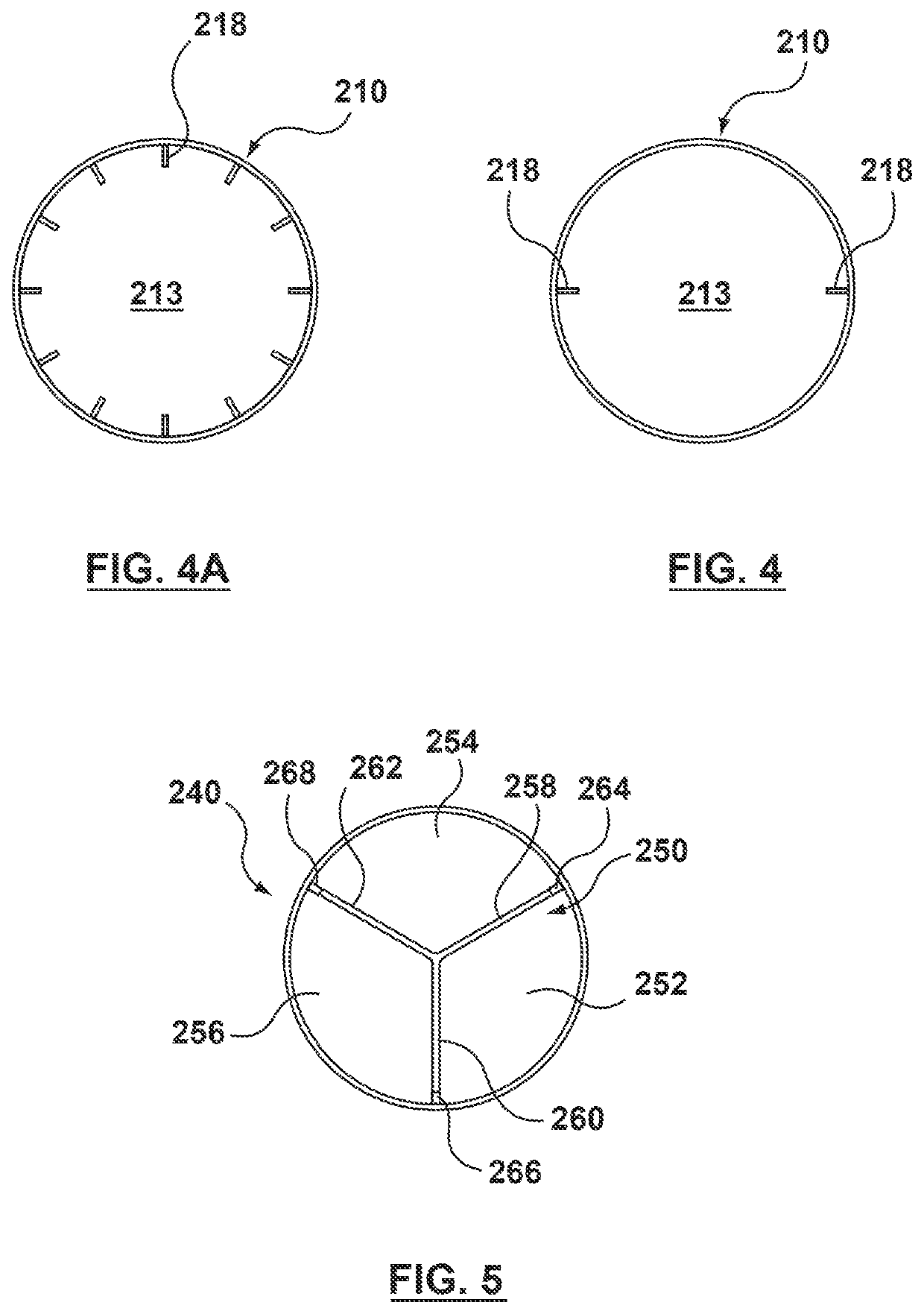
Modular valve prosthesis with anchor stent and valve component
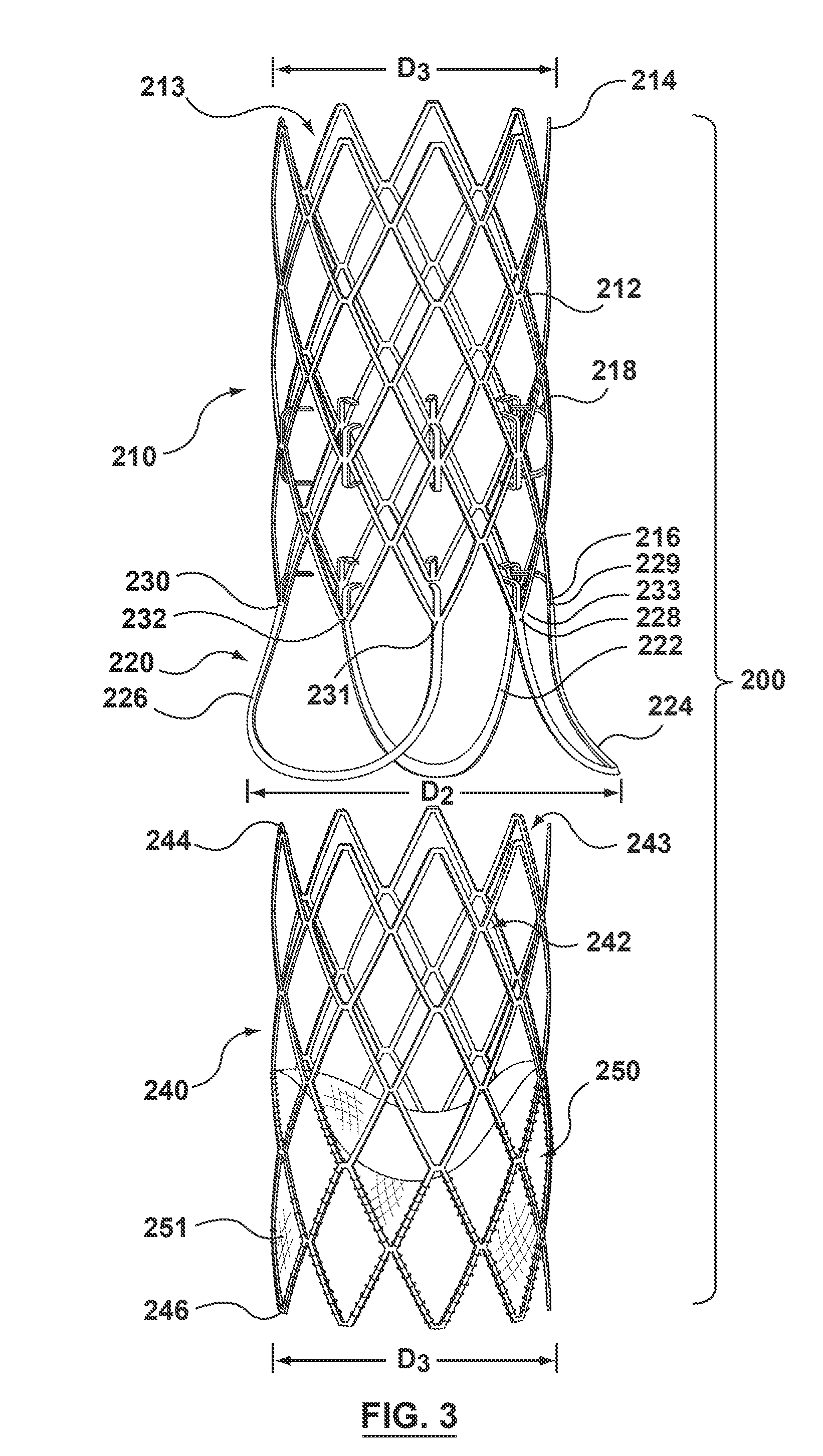
A modular valve prosthesis includes an anchor stent and a valve component. The anchor stent includes a self-expanding tubular frame member configured to be deployed in the aorta and a proximal arm component extending from a proximal end of the tubular frame member and configured to be deployed in the sinuses of the aortic valve. The anchor stent further includes attachment members extending from an internal surface of the tubular frame member. The valve component includes a valve frame configured to be deployed within the tubular frame member of the anchor stent such that the valve frame engages with the attachment members of the tubular frame member and a prosthetic valve coupled to the valve frame.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Device and method for establishing an artificial arterio-venous fistula
A shunt rivet for implantation in the aorta and inferior vena cava to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and a method of treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Device and method for establishing an artificial arterio-venous fistula
A shunt rivet for implementation in the aorta and inferior vena cava to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and a method of treating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Owner:VG GAMES +1
Image representation supporting the accurate positioning of an intervention device in vessel intervention procedures
ActiveUS9295435B2Convenient registrationPrecise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescenceX-ray
A medical imaging device and a method for providing an image representation supporting inaccurate positioning of an intervention device in a vessel intervention procedure is proposed. Therein, an anatomy representation (AR) of a vessel region of interest and at least one angiogram X-ray image (RA) and a live fluoroscopy X-ray image (LI) are acquired. The following steps are performed when a radio-opaque device is fixedly arranged within the vessel region of interest: (a) registering the anatomy representation to the at least one angiogram X-ray image in order to provide an anatomy-angiogram-registration (R1); (b) processing (DP) the at least one angiogram X-ray image and the at least one live fluoroscopy X-ray image in order to identify in each of the X-ray images the radio-opaque device; (c) registering (R2) the at least one angiogram X-ray image to the at least one live fluoroscopy X-ray image based on the identified radio-opaque device in order to provide an angiogram-fluoroscopy-registration; and (d) combining the anatomy-angiogram-registration and the angiogram-fluoroscopy-registration in order to provide an anatomy-fluoroscopy-registration (GTC; RALC). Finally, an image representation resulting from the anatomy-fluoroscopy-registration showing an overlay of live images with the anatomy representation may be output thereby helping a surgeon to accurately position for example a synthetic aortic valve within an aortic root of a heart.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for forming aortic stent graft
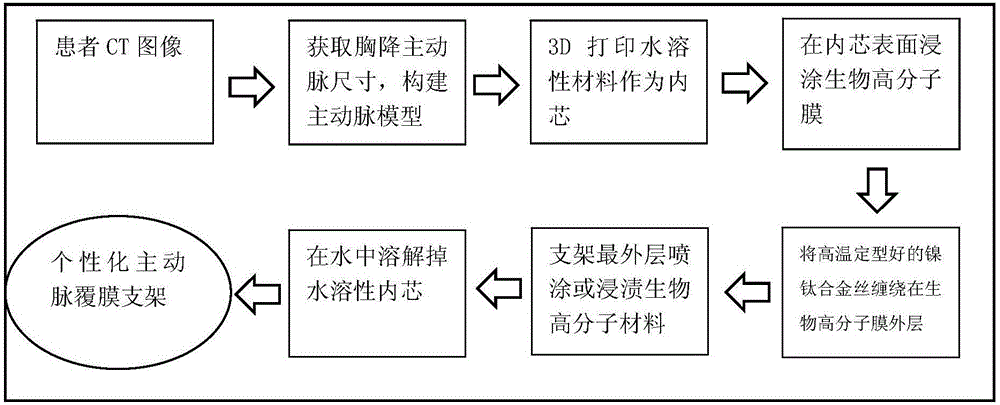
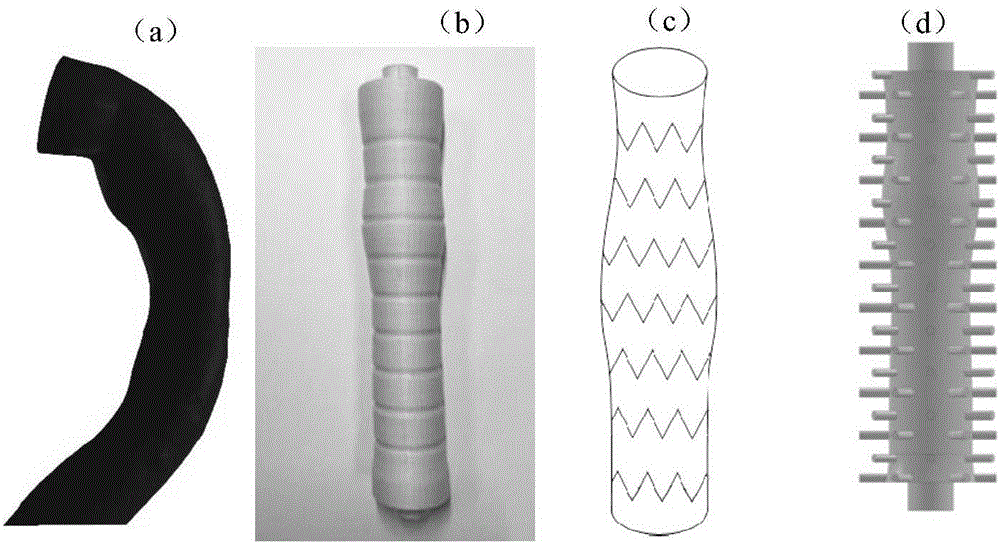
InactiveCN106491241AEfficient preparationMade preciselyStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusAorta partDip-coating
The invention discloses a method for forming an aortic stent graft. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an image of aorta, and extracting a three-dimensional (3D) model of the aorta according to the image; extracting diameter characteristics of the aorta in the axial direction of the aorta of the 3D model; reconstructing an aortic vascular model according to the extracted diameter characteristics; 3D-printing a water-soluble vascular inner core according to the aortic vascular model; dip-coating a polymer film on a surface of the water-soluble vascular inner core; spirally weaving a metal mesh outside the treated water-soluble vascular inner core as a metal stent; bonding the polymer film and the metal stent, and then removing the water-soluble vascular inner core to obtain the aortic stent graft. The method provided by the invention can efficiently and accurately manufacture a vascular stent graft according to the actual size of a thoracic descending aorta of a patient based on a 3D printing technology, can effectively solve a detect that an existing equal-diameter vascular stent does not match a true vascular size of the patient, provides an effective medical means for treatment of acute vascular aneurysm, and has important clinical value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Two-piece valve prosthesis with anchor stent and valve component
A modular valve prosthesis includes an anchor stent and a valve component. The anchor stent includes a self-expanding tubular frame member configured to be deployed in the aorta and a proximal arm component extending from a proximal end of the tubular frame member and configured to be deployed in the sinuses of the aortic valve. The anchor stent further includes attachment members extending from an internal surface of the tubular frame member. The valve component includes a valve frame configured to be deployed within the tubular frame member of the anchor stent such that the valve frame engages with the attachment members of the tubular frame member and a prosthetic valve coupled to the valve frame.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
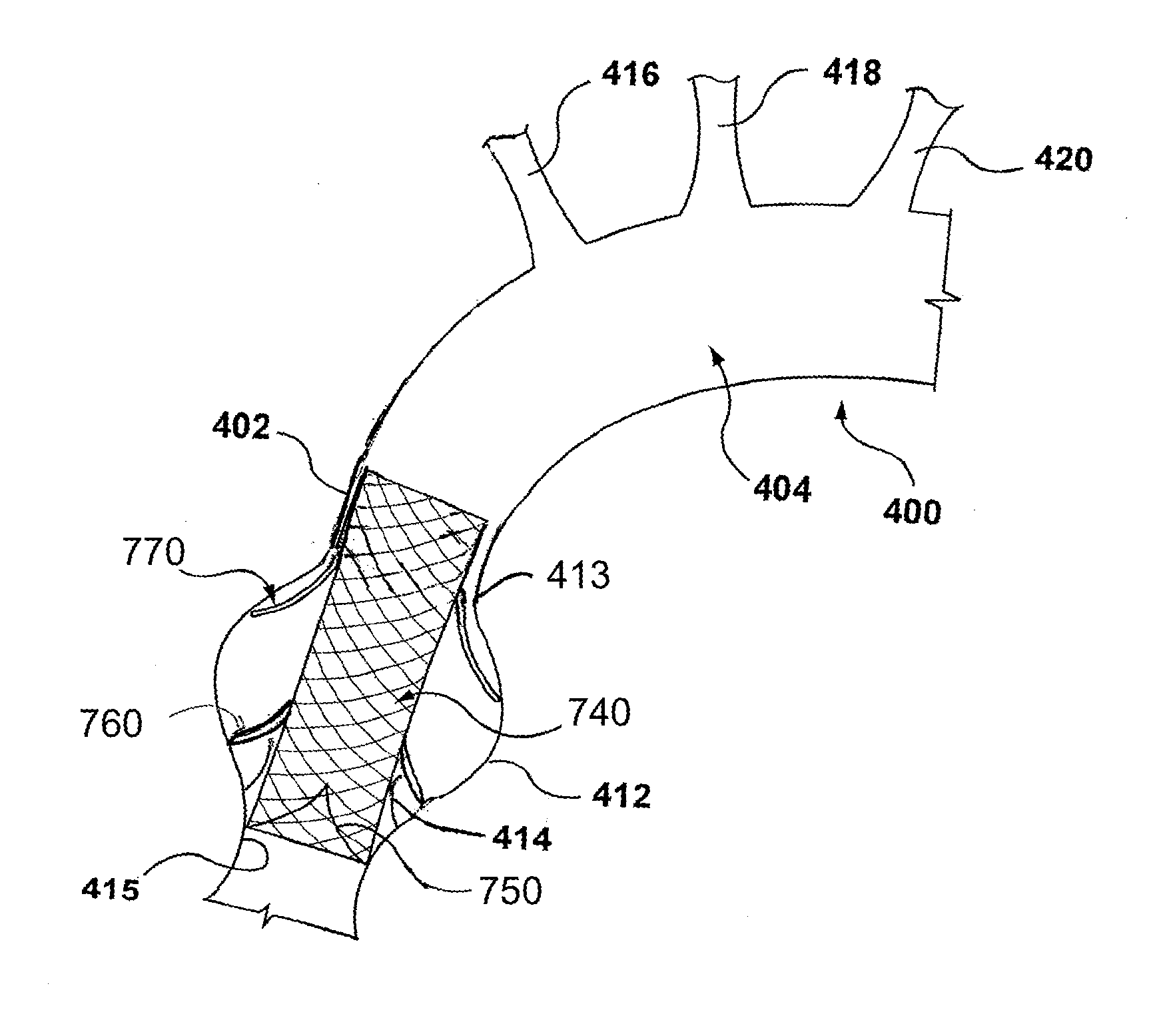
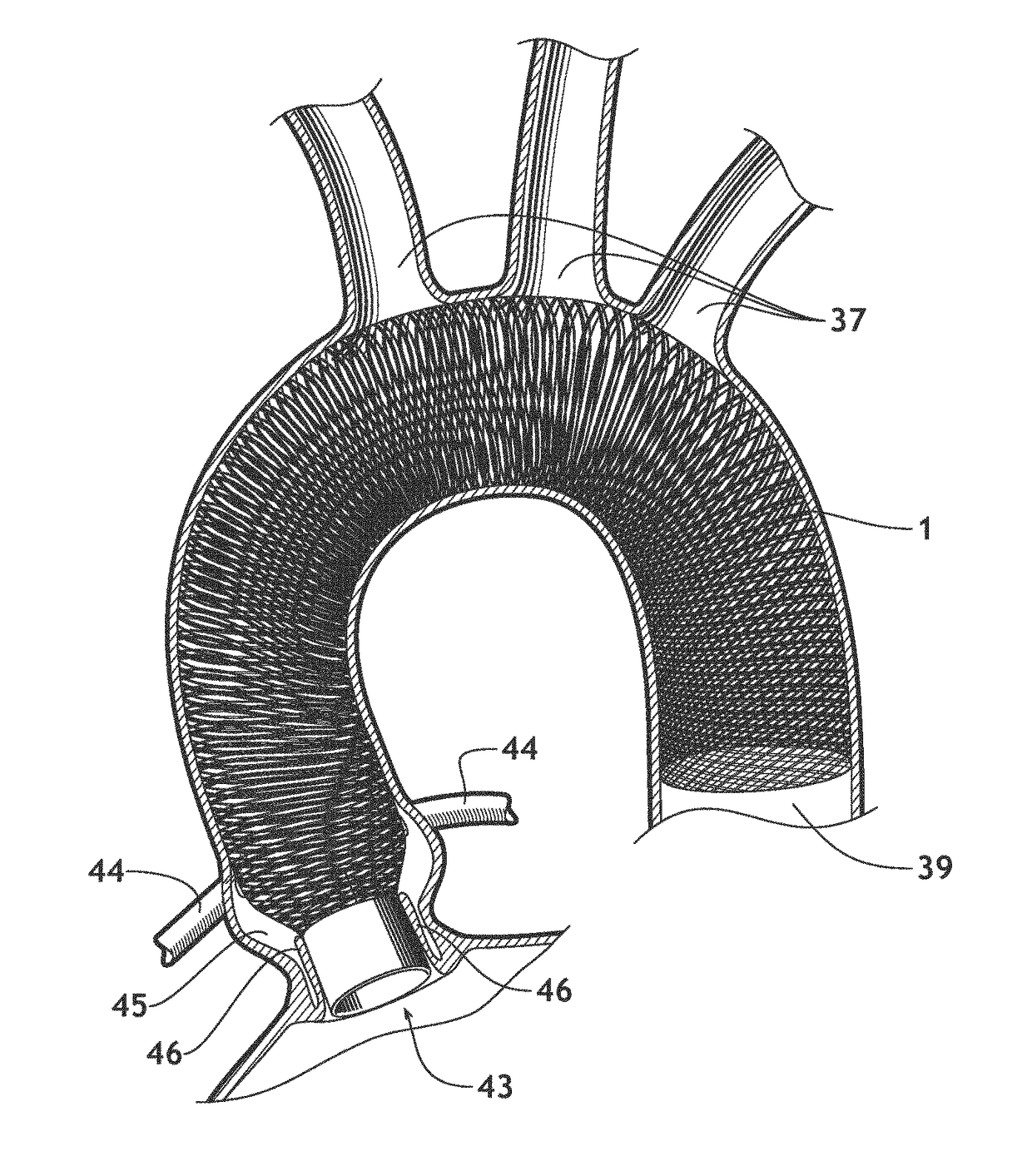
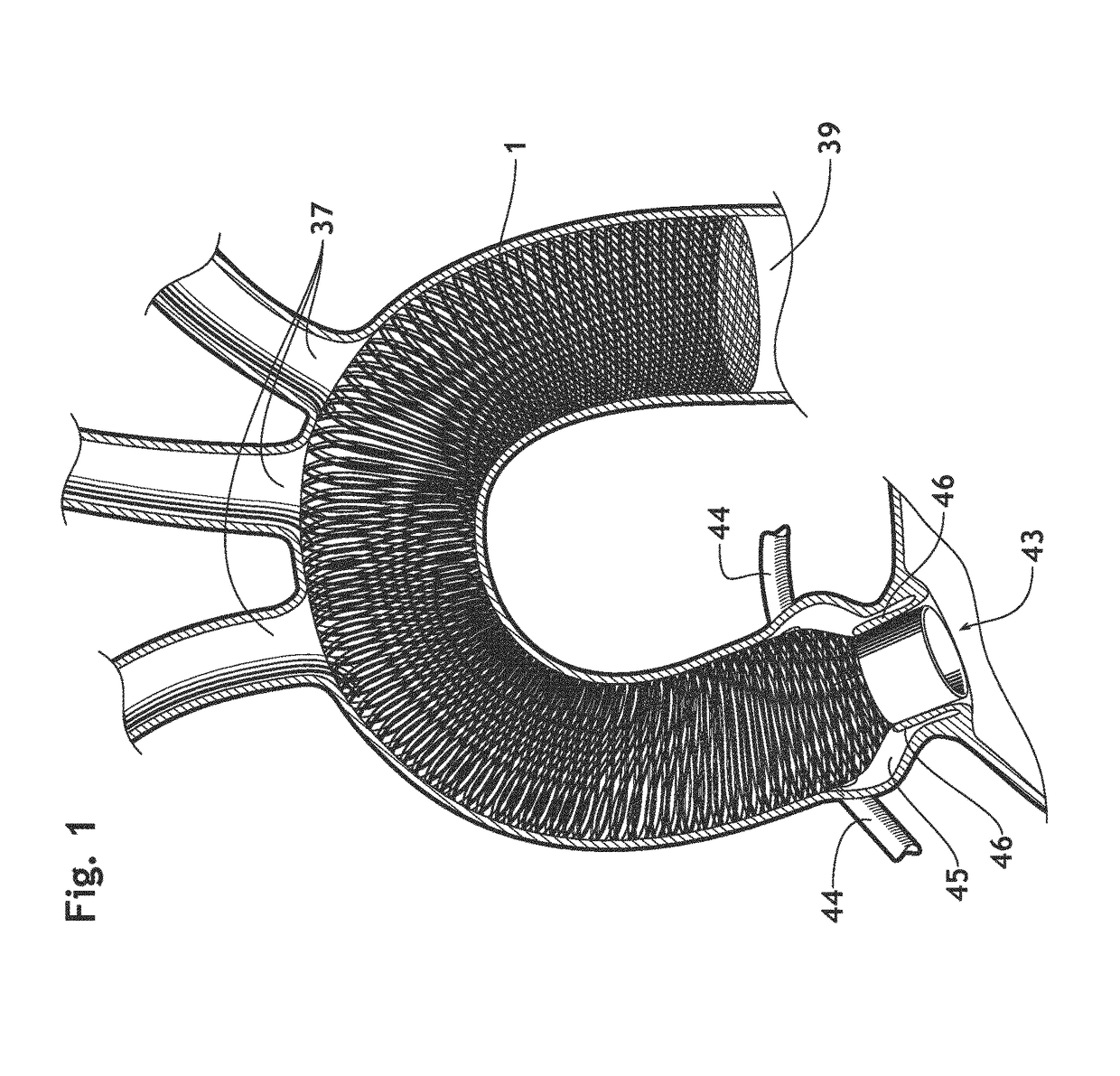
Ascending aorta stent-graft system
InactiveUS20160193029A1Easy transitionInhibition of translationStentsBlood vesselsAscending aortaStent grafting
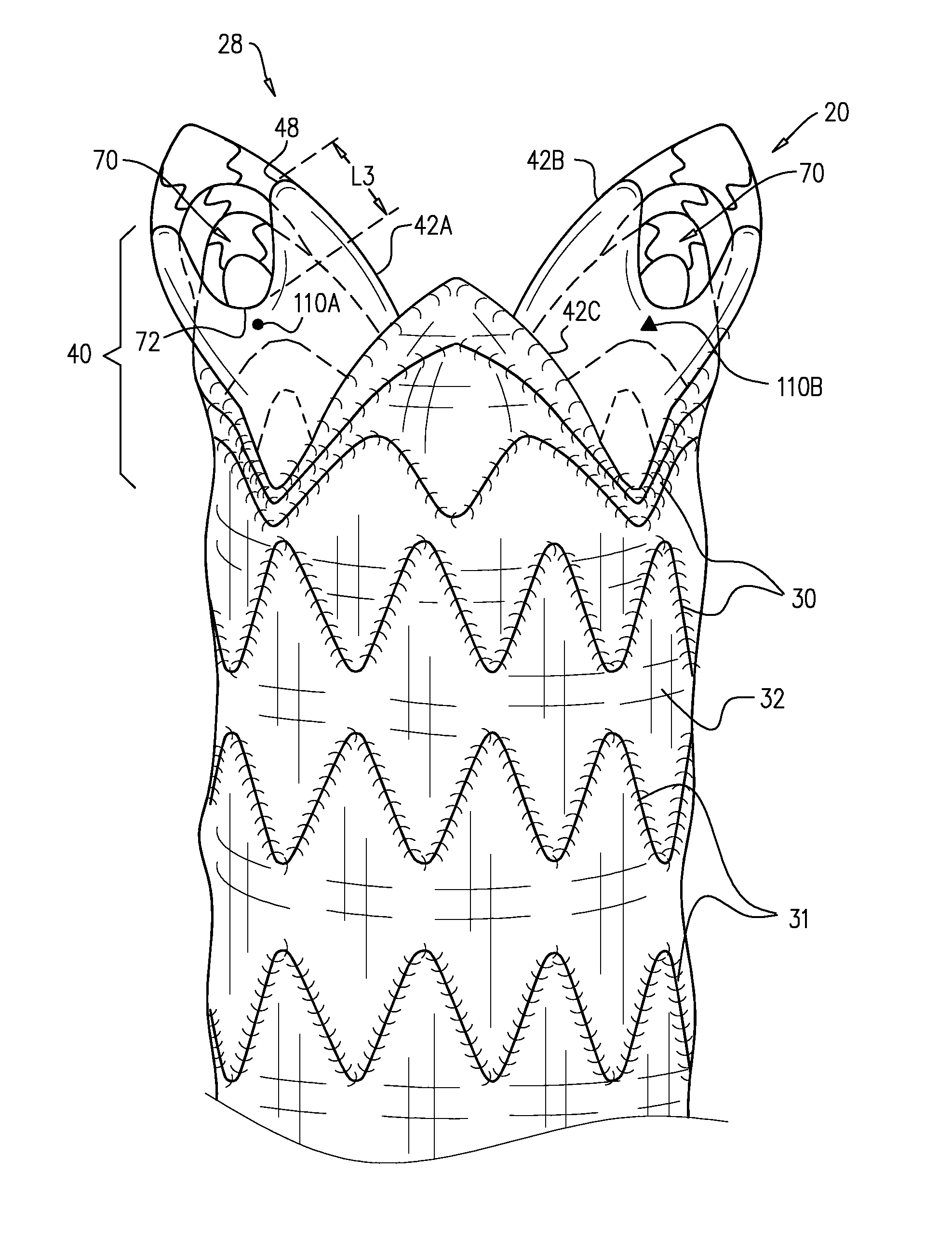
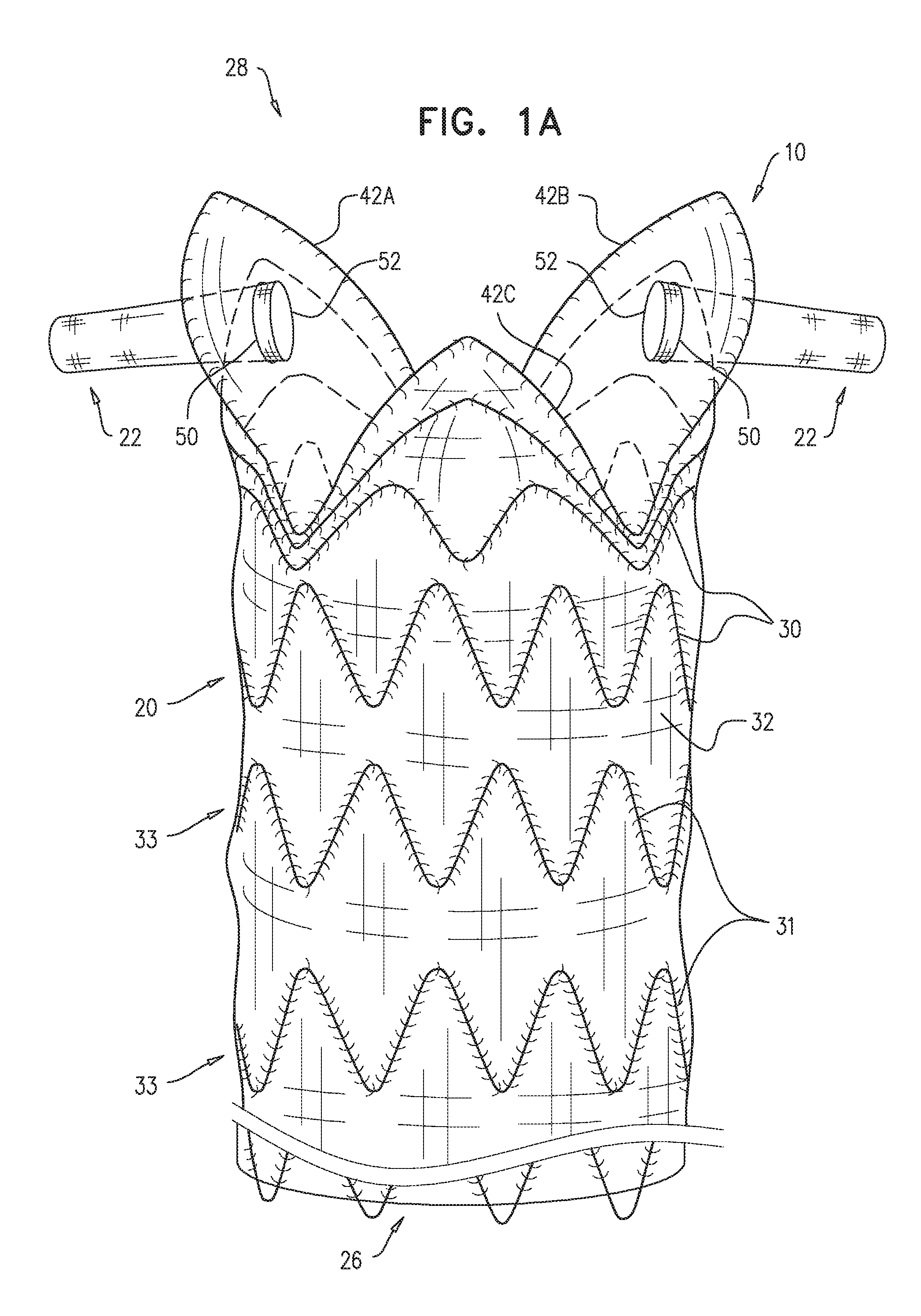
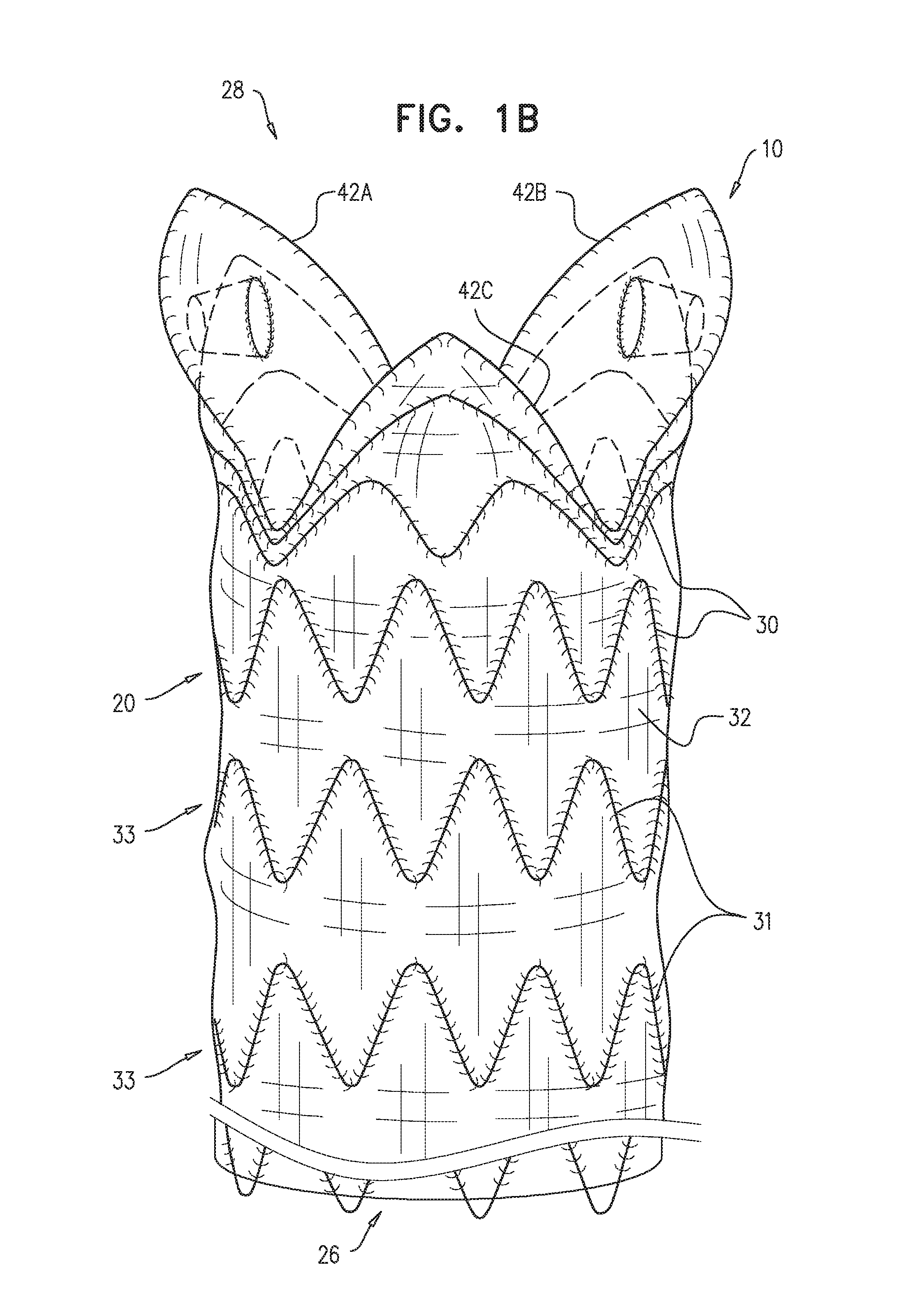
A generally tubular stent-graft (20) includes a generally tubular support element (30) and a covering element (32) that is attached to and at least partially covers the support element (30). When the stent-graft (20) is unconstrained in a radially-expanded state, a proximal end portion (40) of the covering element (32) is shaped so as to define at least first and second proximally-extending pieces (42A, 42B). When the stent-graft (20) is unconstrained in the radially-expanded state and the proximally-extending pieces (42A, 42B) are fully proximally extended, the proximally-extending pieces (42A, 42B) (a) are shaped so as to define respective distal bases (46), which (i) have respective base lengths (L1) measured circumferentially around the stent-graft (20), and (ii) circumferentially circumscribe respective base arcs (a) of between 100 and 140 degrees, (b) are shaped so as to define respective proximal-most portions (48) more proximal than all other respective portions of the covering element (32) that circumscribe the respective base arcs (a), and (c) have respective axial lengths (L2) that equal between 50% and 150% of the respective base lengths (L1).
Owner:ENDOSPAN
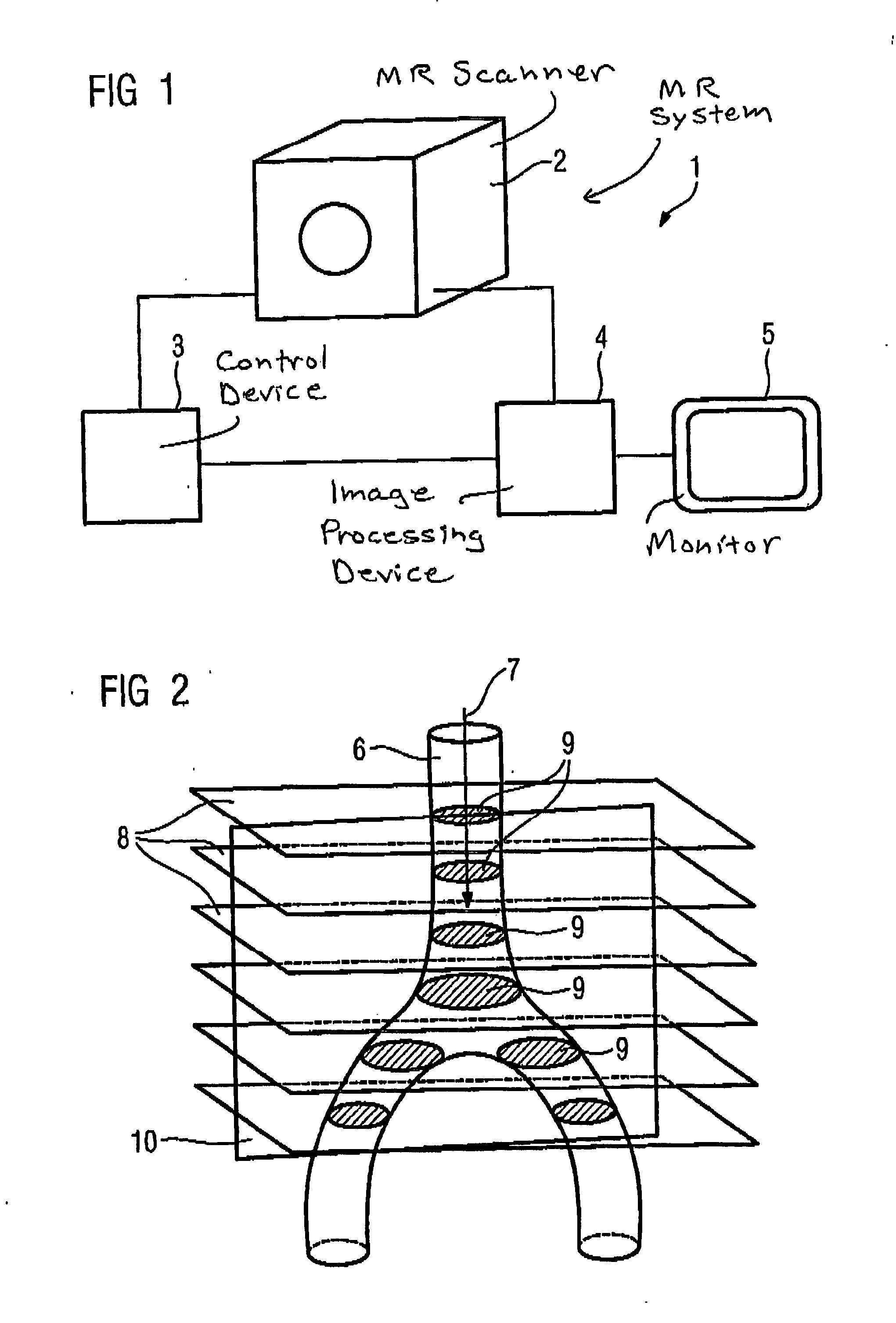
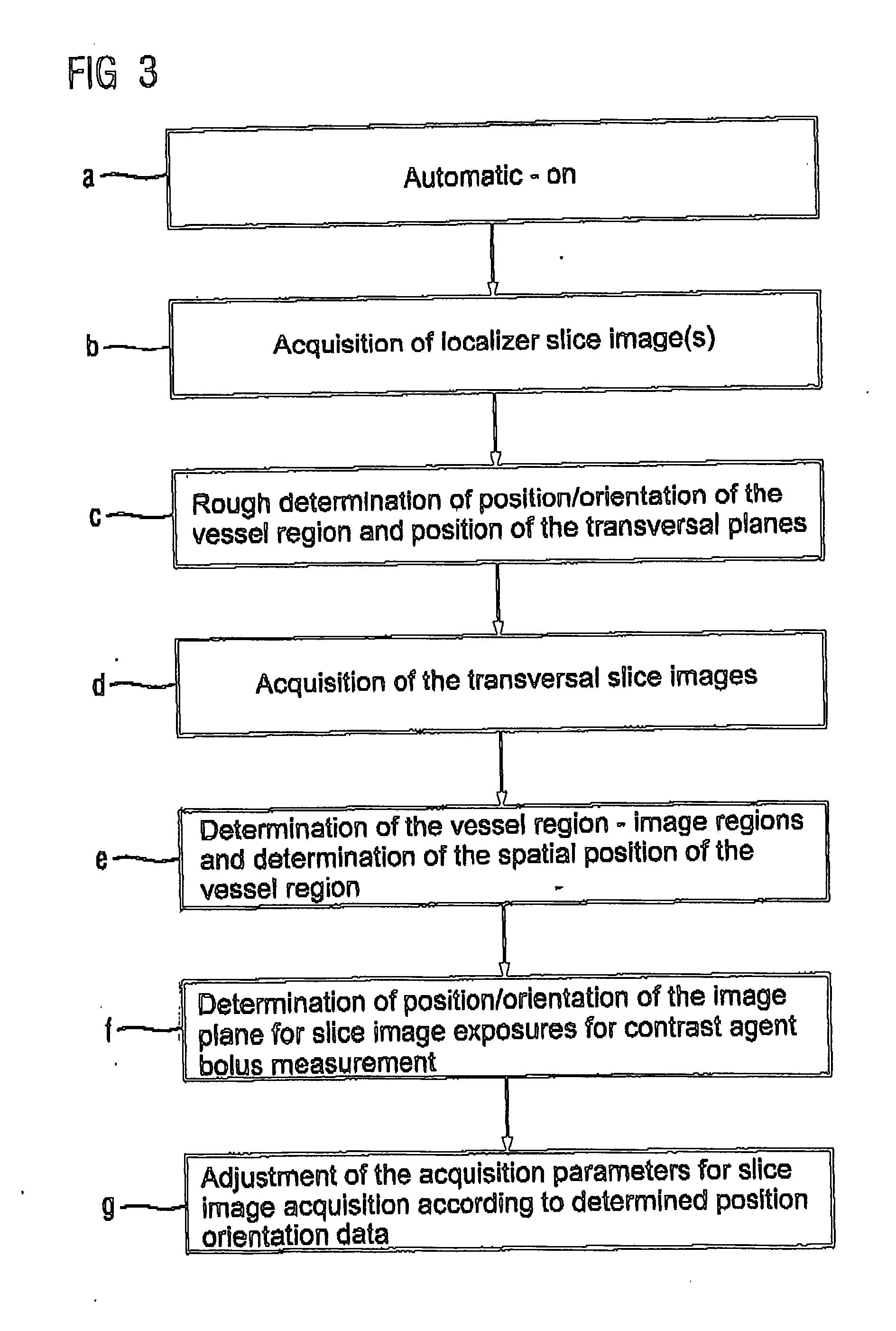
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for determining the position and/or orientation of the image plane of slice image exposures of a vessel region in a contrast agent bolus examination
InactiveUS20050203381A1Favorable for determinationShorten the timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging processingResonance
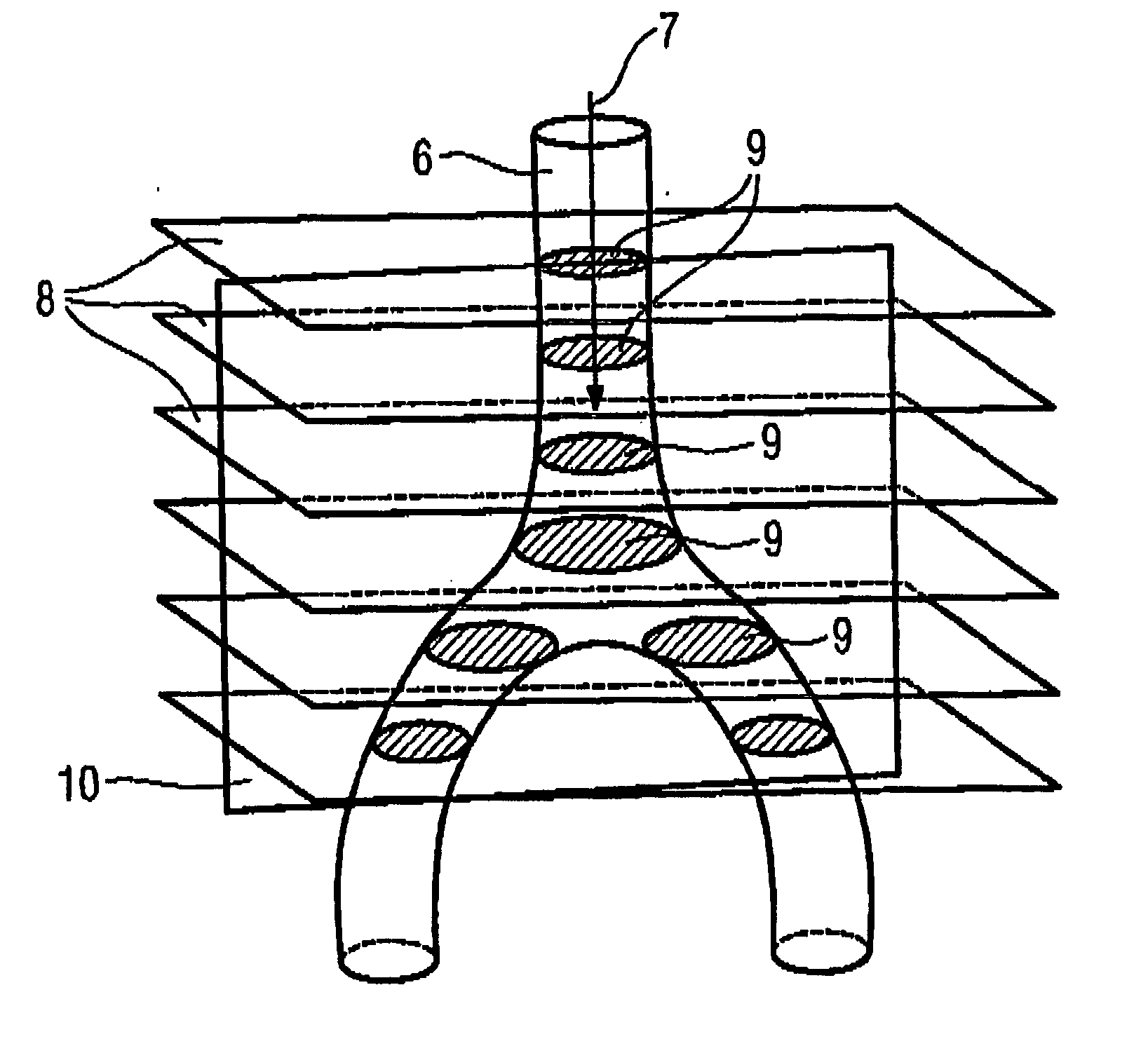
In a method and a magnetic resonance system for determining the position and / or orientation of the image plane of slice image exposures of a vessel region in a contrast agent bolus examination, in particular in the region of the aorta bifurcation or the aorta arch, wherein the image plane traverses the vessel region in the longitudinal section, initially a group of slice image exposures disposed essentially orthogonal to the vessel is automatically acquired from different planes of the vessel region lying parallel to one another, and the image regions showing the vessel region are automatically determined within the orthogonal slice image exposures in an image-processing device, and using the determined image regions the spatial position of the vessel region is determined. The position and / or orientation of the image plane disposed essentially orthogonal to the planes of the slice image exposures and traversing the vessel region in the longitudinal section is determined automatically using the position information, such that the image plane lies in the center of the vessel region.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
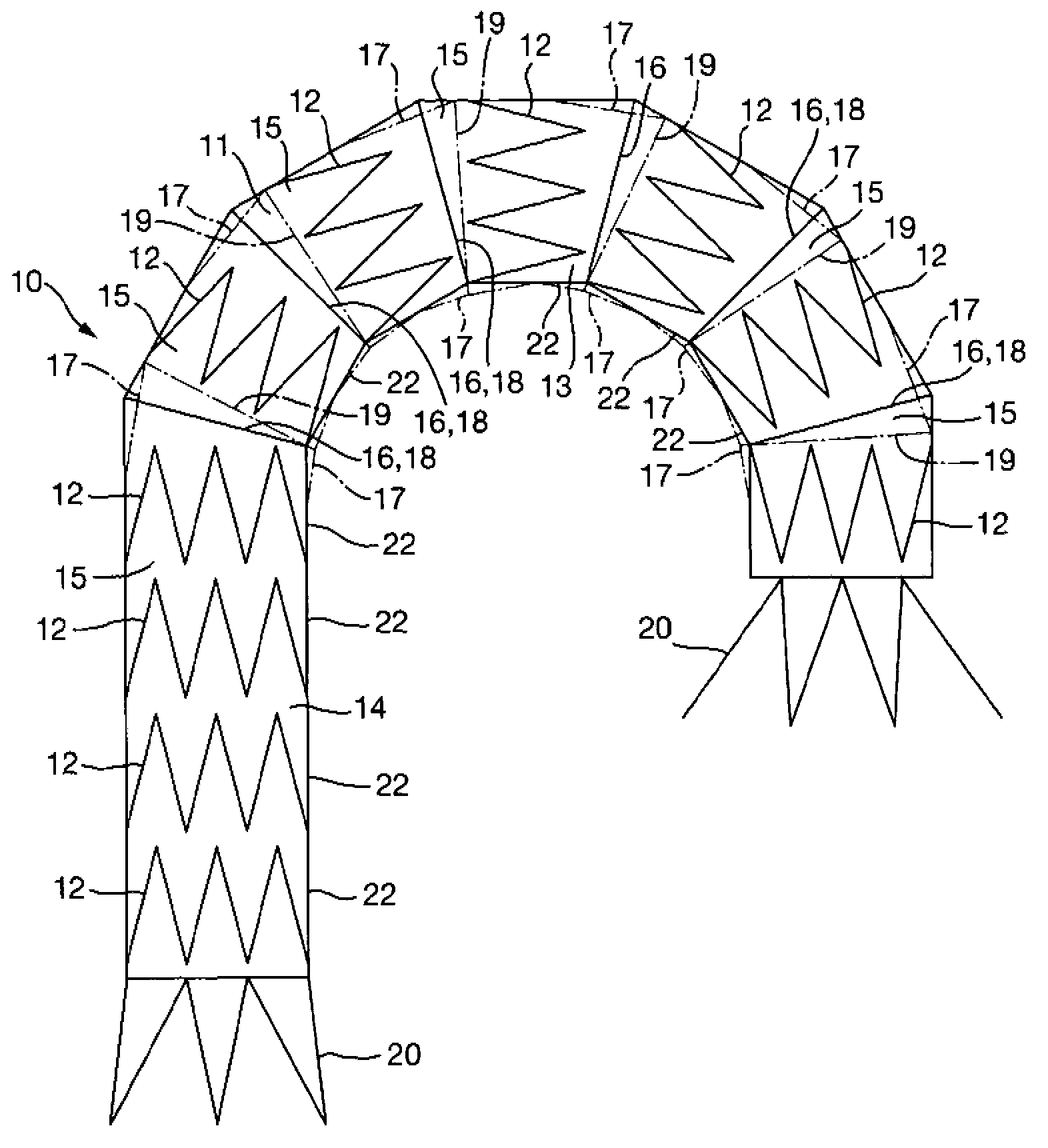
Curved stent graft assembly
A stent graft assembly comprises a graft of flexible material supported by a stent frame that is configured to be deformable between an expanded state and a radially collapsed state. The graft of flexible material has the shape of a tube that is curved along a longitudinal axis of the tube when the graft is in an expanded, undeformed state. The stent graft assembly is deformable into a state in which the graft is deformed into the shape of a tube that is straight. The stent graft assembly may be designed for treatment of a thoracic aorta aneurysm.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
Method of deriving a quantitative measure of a degree of calcification of an aorta
ActiveUS20060280350A1Increase the areaImage enhancementImage analysisDigital dataPattern recognition
A method of deriving a quantitative measure of a degree of calcification of a blood vessel such as an aorta by processing an image such as an X-ray image of at least a part of the blood vessel containing said calcification comprises: taking a starting set of digital data representative of an image of at least part of a blood vessel containing a calcification set against a background; estimating the boundary of the calcification; using inpainting to replace digital data in said starting set representing the calcification with data extrapolating the boundary of the background to extend over the area of calcification, and so generating an inpainted set of digital data; and computing the difference between the starting set of digital data and the inpainted set of digital data to obtain a quantitative measure of the degree of calcification of the blood vessel.
Owner:BIOCLINICA
Surgical conduit leak testing
ActiveUS10119882B2Quick testEasy to set upMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateNon destructiveValved conduit
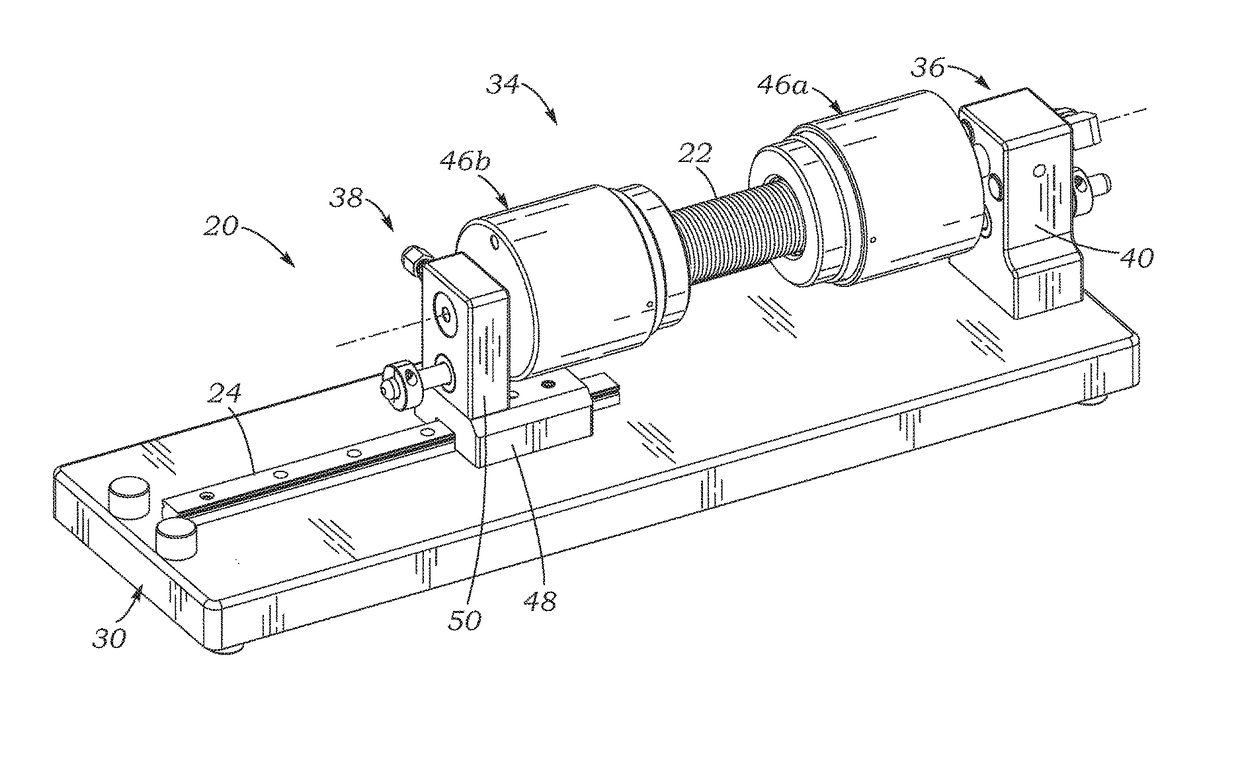
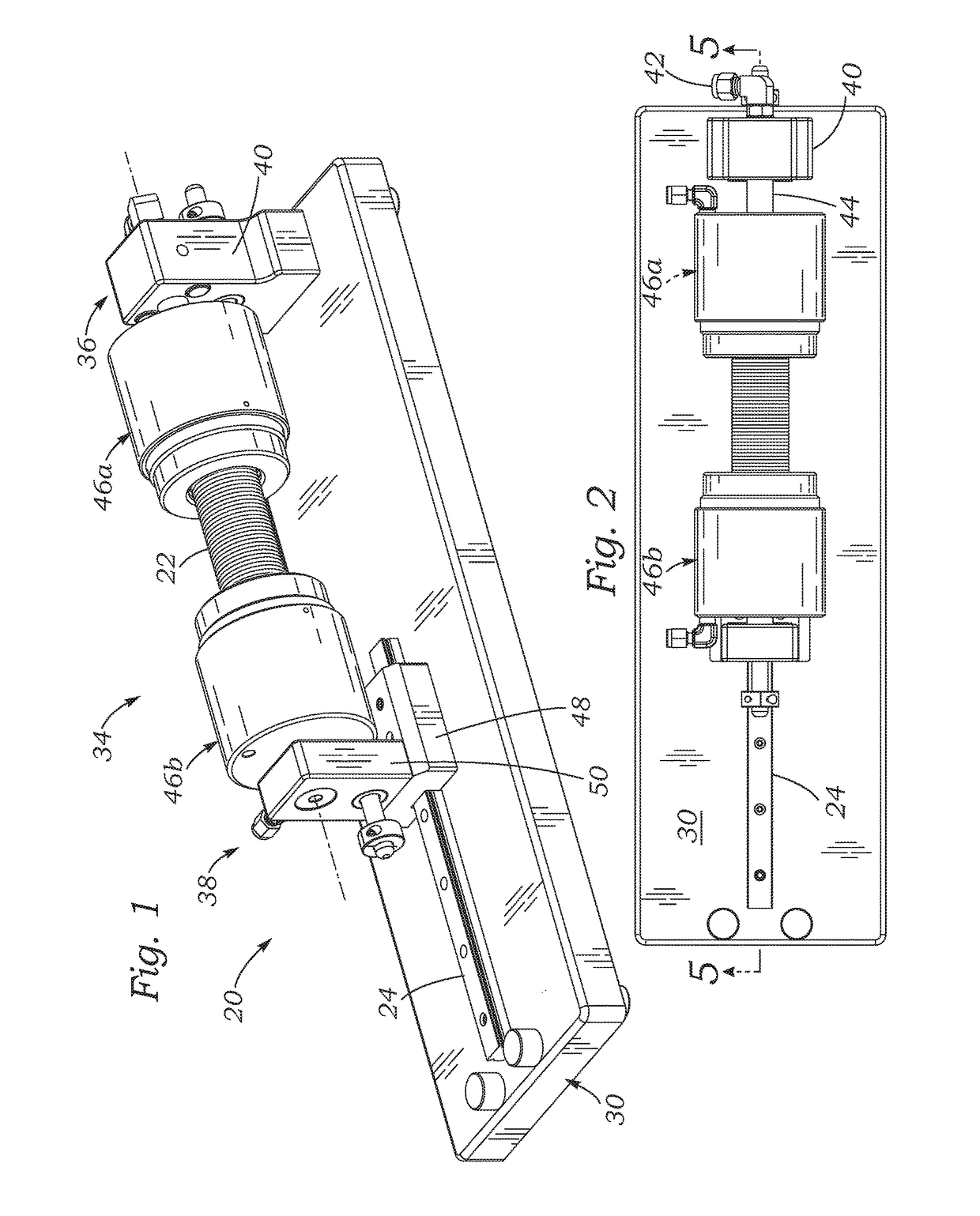
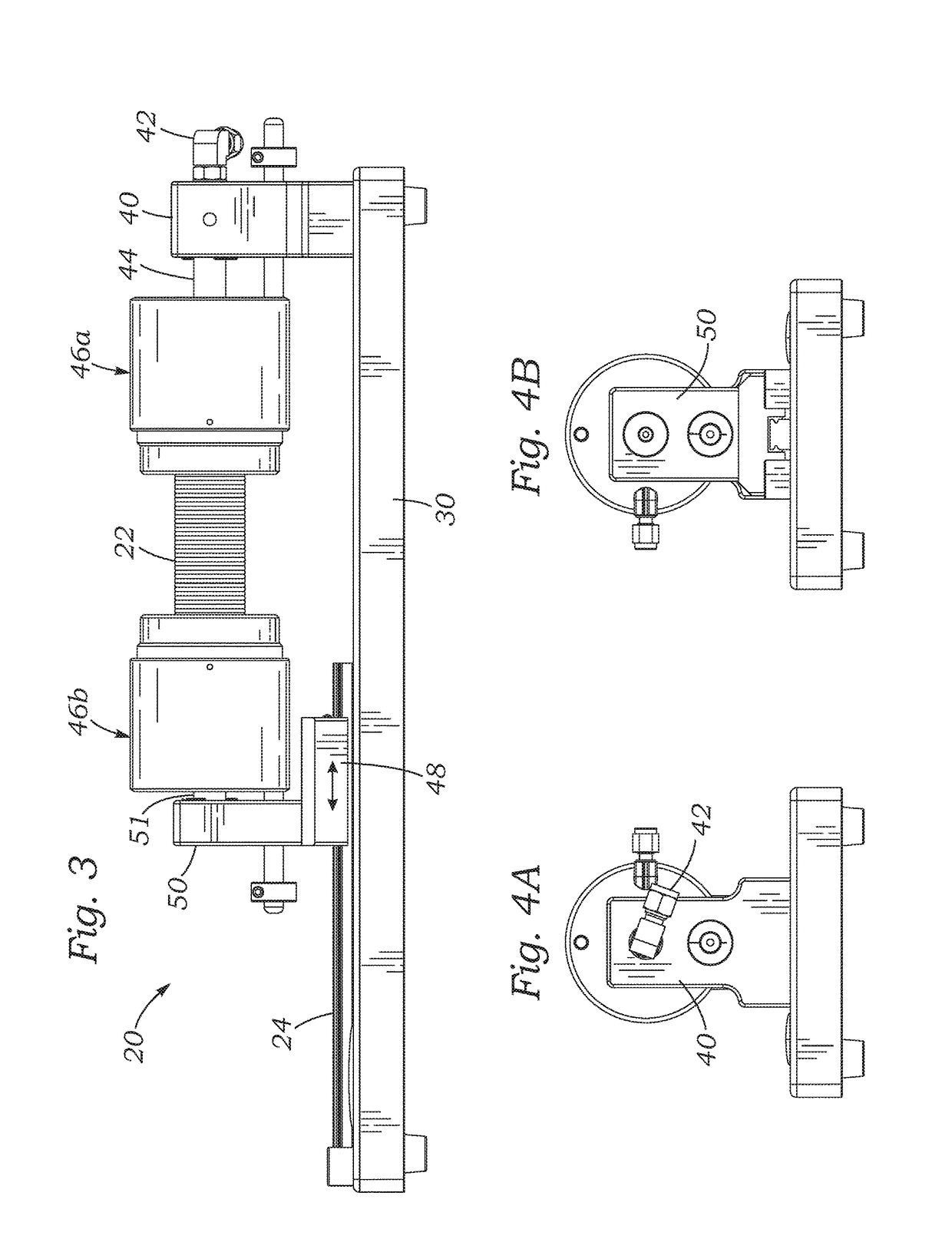
Systems, devices, and methods for leak testing surgical conduit grafts or valved conduits such as aortic-valved conduits with a pressurized gas such as air. Air is non-destructive and especially useful for leak testing conduits that have coatings or sealants that may be functionally impacted when exposed to fluids such as water or saline. Open ends of the conduit are clamped and sealed, and a pressurized gas introduced into an inner lumen thereof. A change in mass flow rate is measured to quantify the leakage. One end of a tubular conduit may be clamped to a fixed manifold, and the opposite end to a manifold slidably mounted to accommodate any conduit elongation when pressurized. The clamping and sealing structure may be pneumatic and / or mechanical, and complementary contoured clamp members may be used to seal a scalloped external sealing ring of an aortic conduit.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
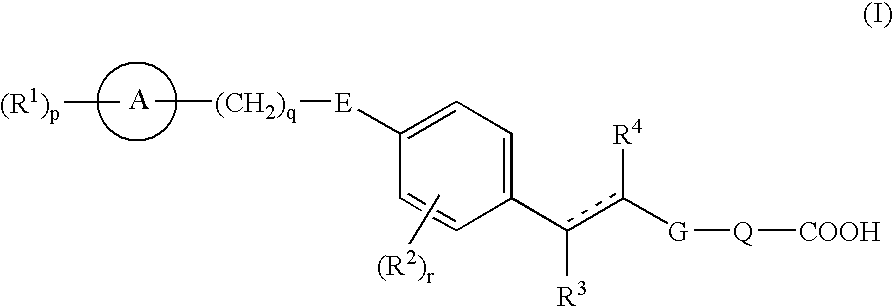
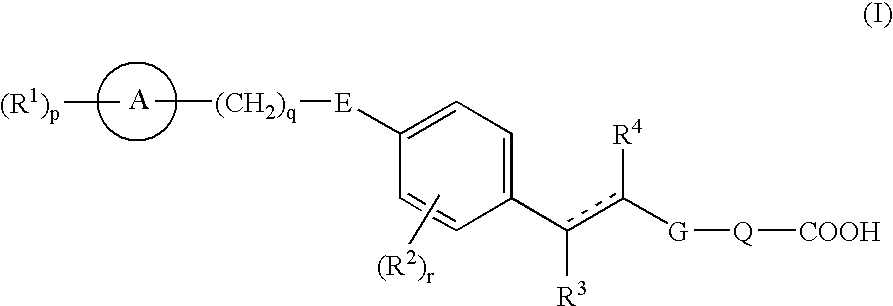
Carboxylic acid derivatives and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same as an active ingredient
Compounds represented by formula (I), prodrugs thereof and salts thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same as an active ingredient (wherein each symbol has the meaning as defined in the specification.). Because of having an EDG-1 agonism, the compounds represented by formula (I) are useful in preventing and / or treating peripheral arterial disease such as arteriosclerosis obliterans, thromboangiitis obliterans, Buerger's disease or diabetic neuropathy, sepsis, angiitis, nephritis, pneumonia, stroke, myocardial infarction, edematous state, atherosclerosis, varicosity such as hemorrhoid, anal fissure or fistula ani, dissecting aneurysm of the aorta, angina, DIC, pleuritis, congestive heart failure, multiple organ failure, bedsore, burn, chronic ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, heart transplantation, renal transplantation, dermal graft, liver transplantation, osteoporosis, pulmonary fibrosis, interstitial pneumonia, chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, chronic renal failure, or glomerular sclerosis.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
3D filter for prevention of stroke
InactiveUS20180064525A1Easy to replaceLimiting and preventing spreadingStentsHeart valvesMedicineProsthesis
The present invention relates to implantable endoluminal prostheses and methods of using such devices in preventing clots migration to avoid ischemic strokes. The implantable endoluminal prosthesis is suitable for deployment from the aortic annulus to the aorta and comprises a self-expandable braided framework able to expand from a radially compressed state in a delivery configuration to a radially expanded state, and a radially collapsible valve body comprising an impermeable material. The self-expandable braided framework is formed of braided wires having a given diameter, and has a proximal end configured to extend toward the heart and a distal end configured to extent toward away from the heart and extending along an axis. The braided framework comprises a main tubular body at the distal end of the self-expandable braided framework, a neck at the proximal end of the self-expandable braided framework, a transition portion extending between the proximal end of the main tubular body and the distal end of the neck. The main tubular body 3 and the neck comprise a lumen in a cylindrical form with a circular cross-section and a constant diameter respectively, and the diameter of the main tubular body is larger than the one of the neck. The main tubular body, the neck and the transition portion consist of an integrated structure comprising plurality of layers of made of biocompatible material, being devoid of any impermeable cover layer, and forming a wall having a thickness. The valve body is placed within the lumen of the neck.
Owner:FRID MIND TECH
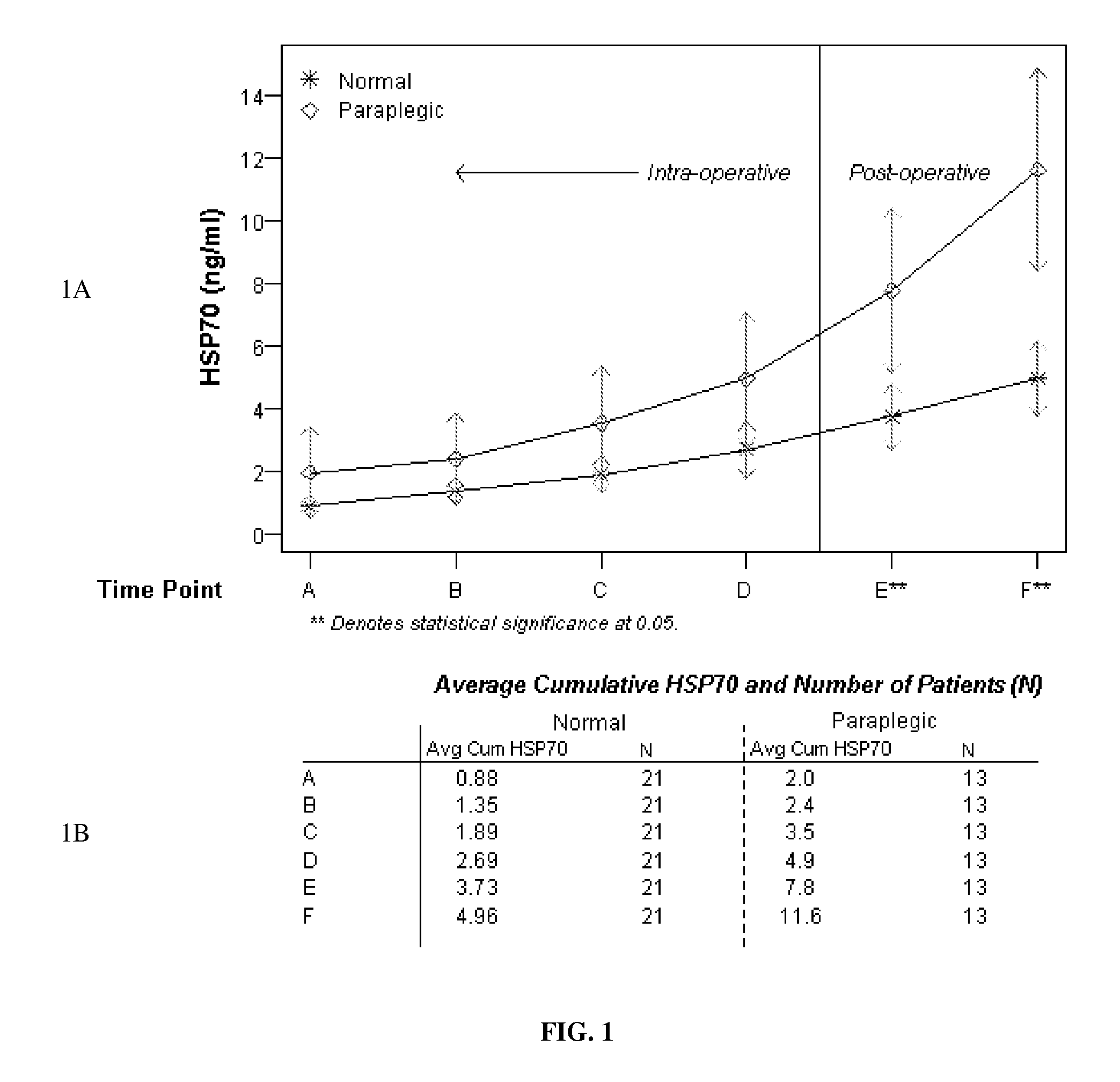
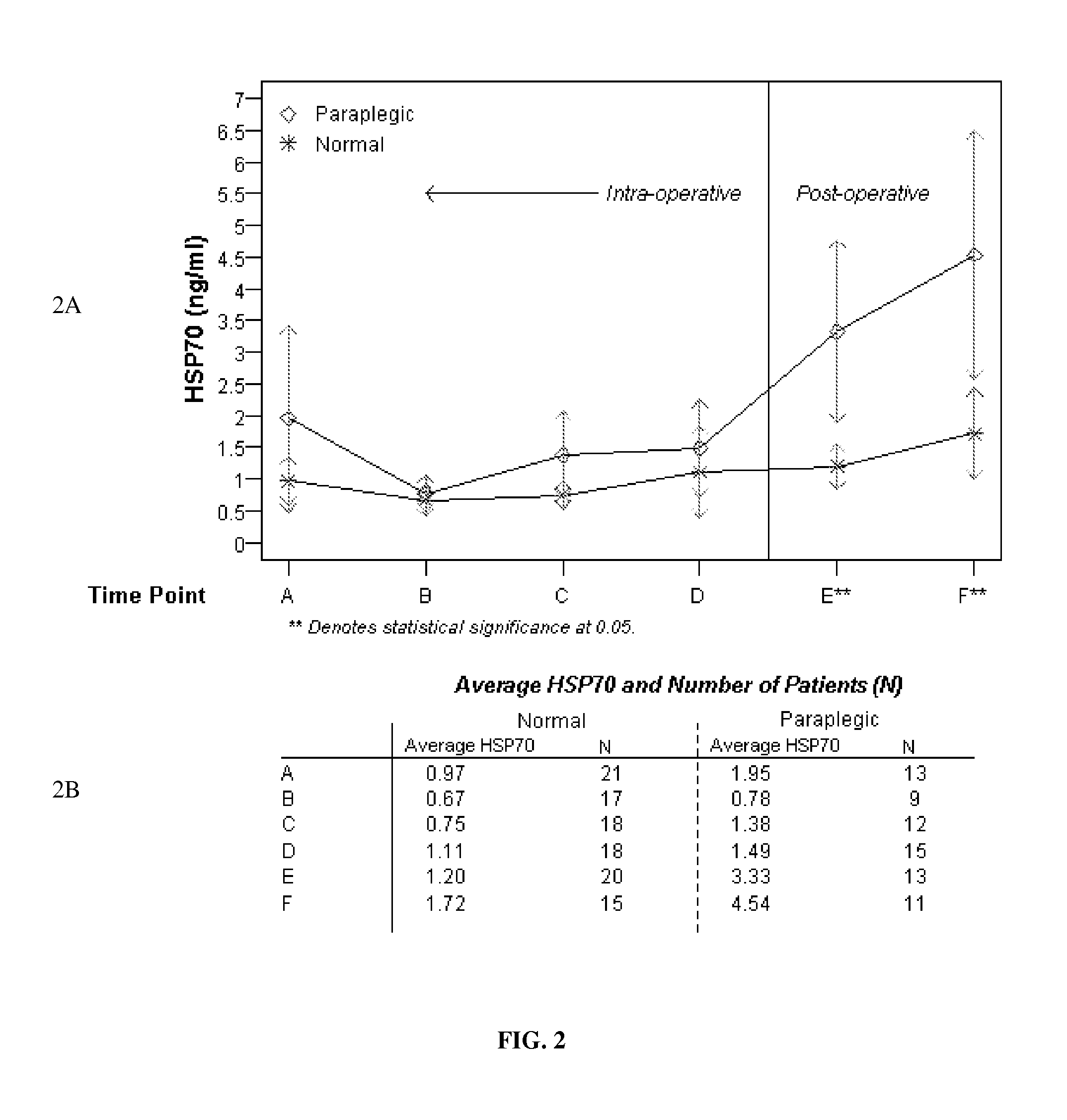
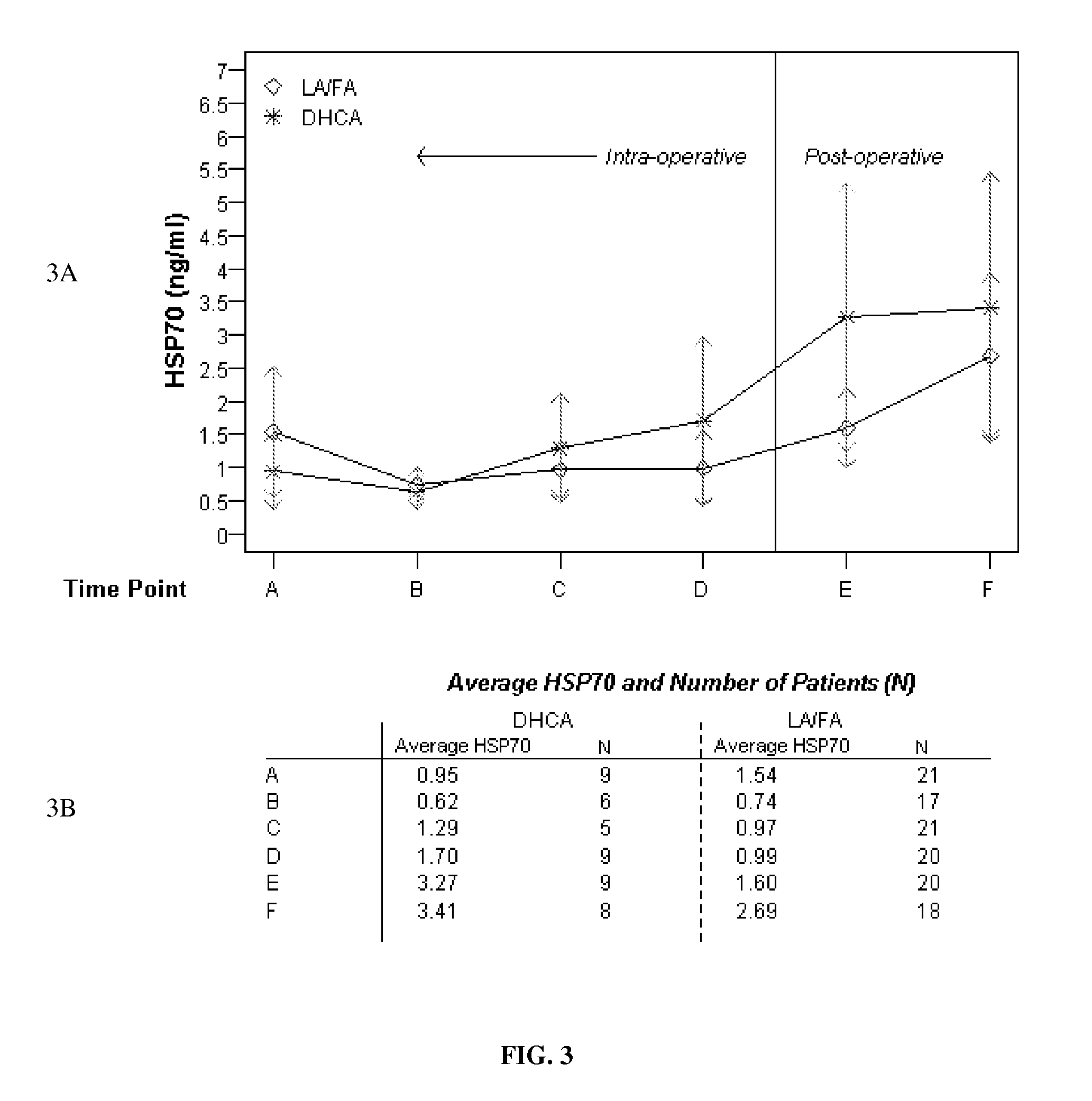
Elevation of Induced Heat Shock Proteins in Patient's Cerebral Spinal Fluid: A Biomarker of Risk/Onset of Ischemia and/or Paralysis in Aortic Surgery
Provided are methods for intra-operatively predicting, detecting or diagnosing the risk or onset of spinal cord ischemia and / or associated permanent paralysis in a patient, based upon the stress-induced elevation of levels of heat shock proteins, specifically HSP70 and / or HSP27 in the cerebral spinal fluid of the patient, as measured during thoracic-aorta surgery, particularly thoracic aneurysm repair surgery, that will permit intra-operative medical intervention to try to prevent or attenuate severe, and often fatal, complications. Further provided are kits, assay devices and methods of analyzing biomarker data for use in pre-, intra- or post-operatively detecting the stress-induced elevations of the measured levels of HSP70 and / or HSP27, and the biomarker itself.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Dual-Balloon Cardiac Pump
A dual-balloon cardiac pump comprises a flexible catheter tube in pneumatic communication with inflatable ventricular and aortic balloons, which are inflated and deflated in accordance with a programmed sequence of pressurized inert gas into the catheter tube as regulated by a control unit. The programmed sequence rapidly inflates and deflates the ventricular balloon after left ventricular contraction is completed. The programmed sequence inflates the aortic balloon after the aortic valve closes and deflates it just before the next systolic cycle begins.
Owner:MAROTTA CHARLES
Occluder, occluder locking system and occluder locking method
PendingCN111803167AExtended service lifeImprove the blocking effectOcculdersAortic dissectionPostoperative complication
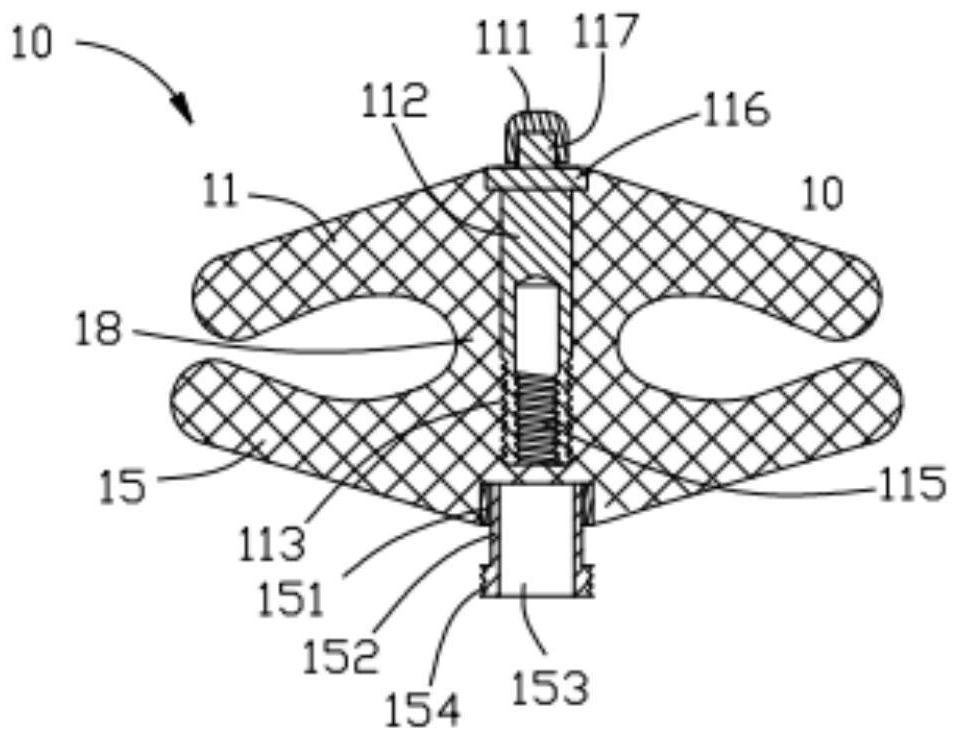
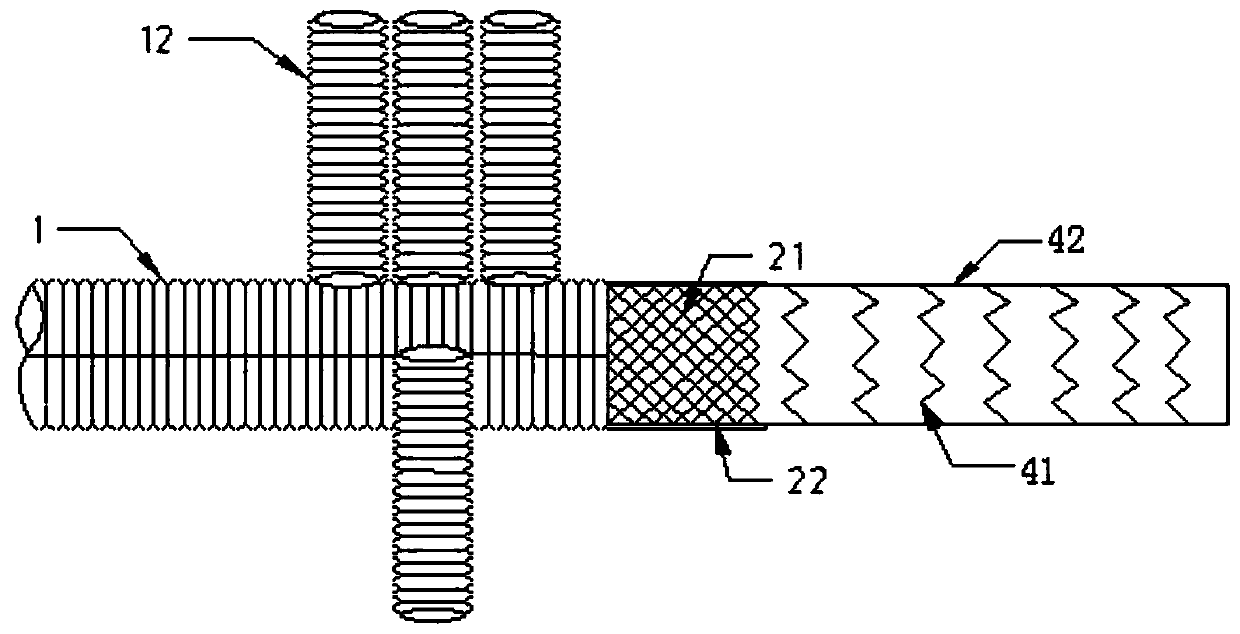
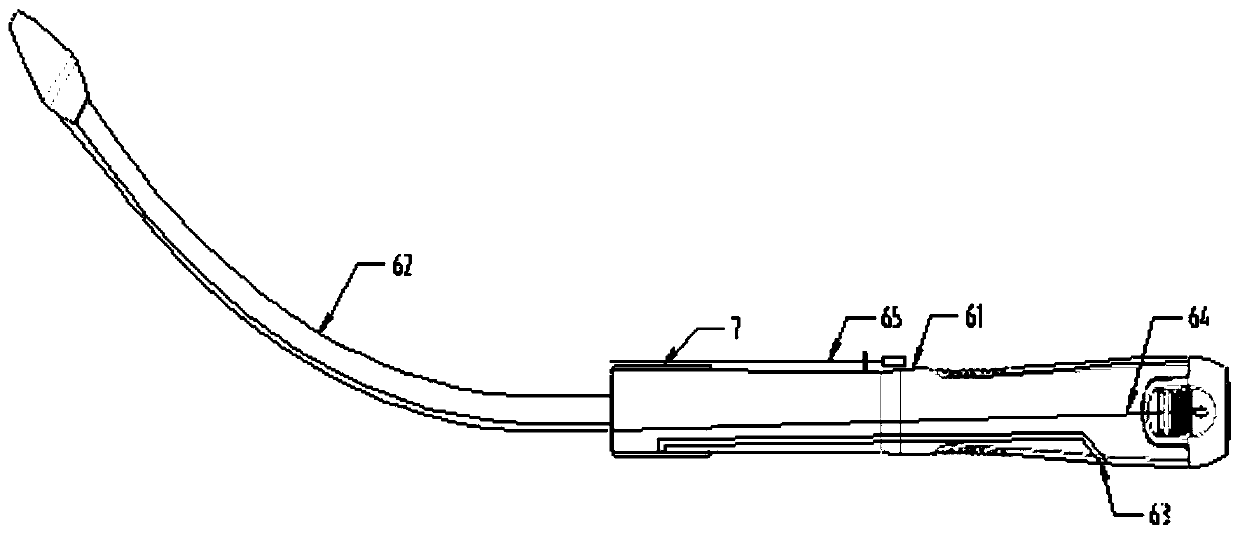
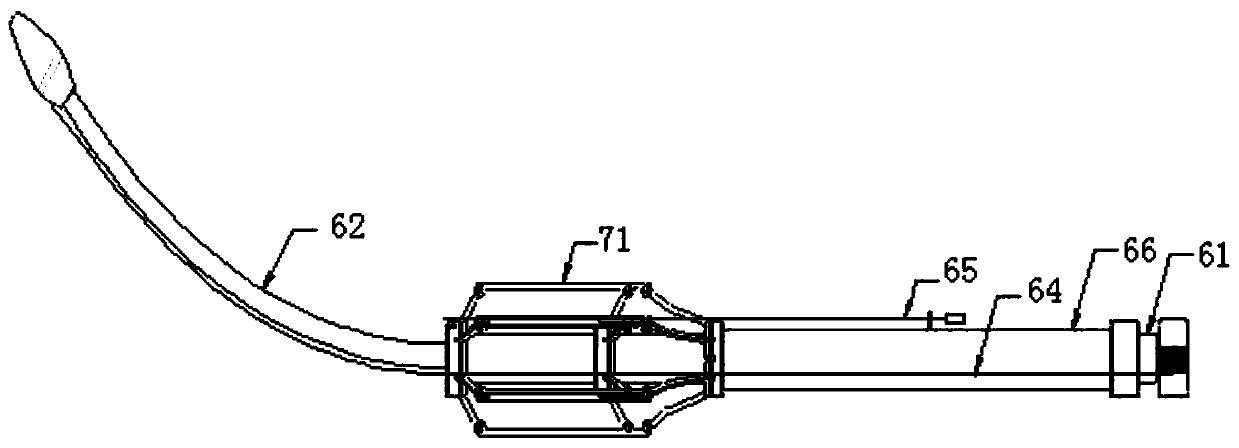
The invention provides an occluder. The occluder comprises a first occluding part and a second occluding part, a connecting bolt is arranged at the far end of the first occluding part along the direction of the second occluding part, a first external thread is arranged on the side wall of the connecting bolt, a protruding part is arranged at the near end of the second occluding part, a through hole is formed in the protruding part, a second external thread is arranged on the side wall of the protruding part, the thread direction of the first external thread is opposite to that of the second external thread, and the near end of the connecting bolt can penetrate through the through hole to be in threaded connection with a nut. The invention further provides an occluder locking system and a locking method thereof. According to the structure of the occluder, efficient, stable and reliable locking can be achieved under the combined action of a pushing device, so that the service life and the occluding effect of the occluder are prolonged, the risk of postoperative complications is reduced, and the occluder is particularly suitable for occluding treatment of aortic dissection crevasses.
Owner:HANGZHOU WEIQIANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
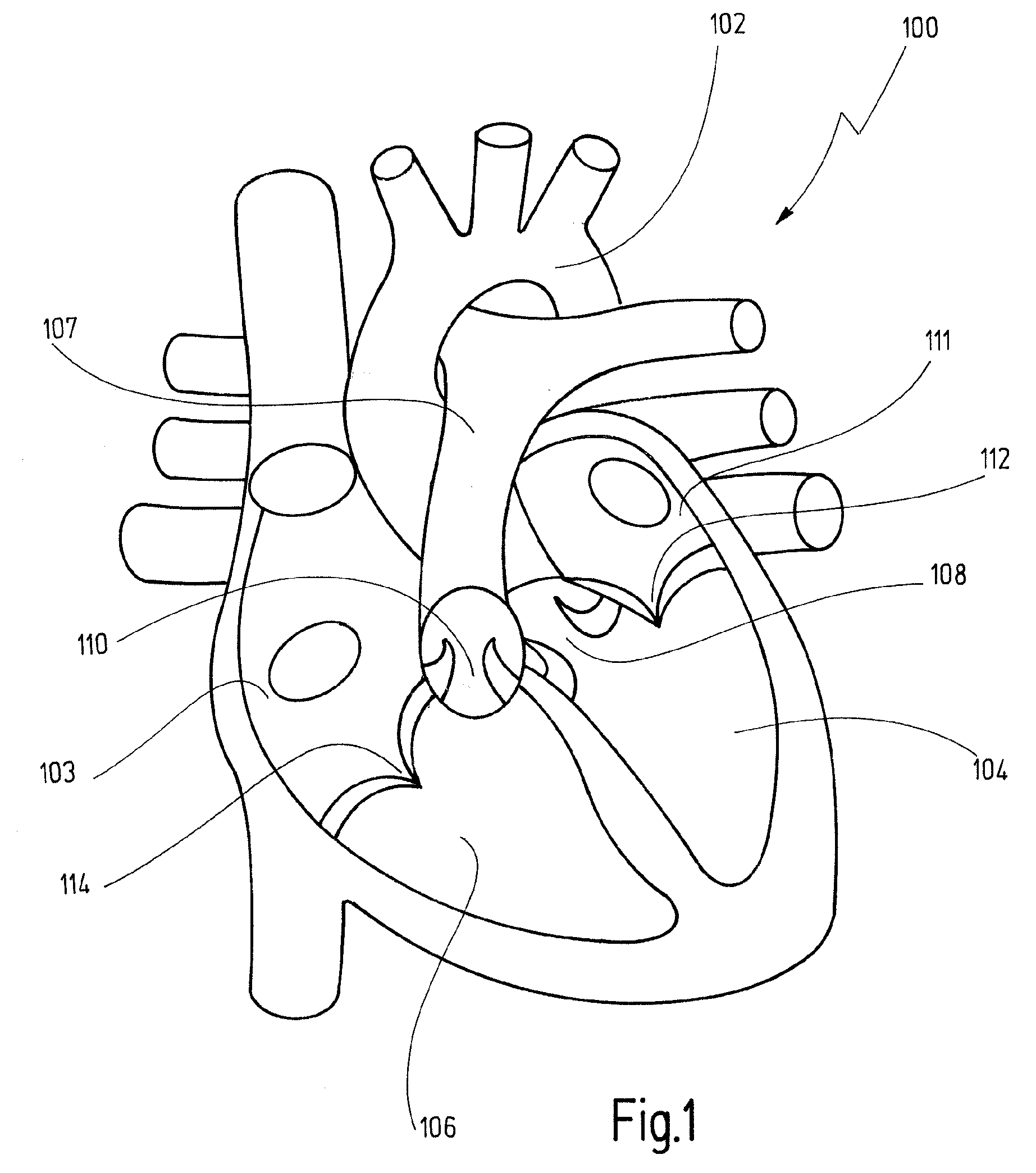
Method and system for pericardium based model fusion of pre-operative and intra-operative image data for cardiac interventions
A method and system for model based fusion pre-operative image data, such as computed tomography (CT), and intra-operative C-arm CT is disclosed. A first pericardium model is segmented in the pre-operative image data and a second pericardium model is segmented in a C-arm CT volume. A deformation field is estimated between the first pericardium model and the second pericardium model. A model of a target cardiac structure, such as a heart chamber model or an aorta model, extracted from the pre-operative image data is fused with the C-arm CT volume based on the estimated deformation field between the first pericardium model and the second pericardium model. An intelligent weighted average may be used improve the model based fusion results using models of the target cardiac structure extracted from pre-operative image data of patients other than a current patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Quick-connection thoracotomy vascular stent and conveying system
The invention discloses a quick-connection thoracotomy vascular stent system. The quick-connection thoracotomy vascular stent system comprises an artificial blood vessel, a laminating membrane stent and a support piece, wherein the laminating membrane stent comprises a stent body and a laminating membrane for covering the outside of the stent body, and the laminating membrane is longer than the stent body; the artificial blood vessel and the laminating membrane for covering the outside of the stent body are integrally woven, and a section of stent-less laminating membrane is arranged between the distal end of the artificial blood vessel and the proximal end of the laminating membrane stent; the support piece comprises a support ring and a tectorial membrane for wrapping the outer layer ofthe support ring; the support ring is located on the outer layer of the stent-less laminating membrane; and the support ring and the distal end of the tectorial membrane are matched on the laminatingmembrane in an anastomosis mode. A conveying system of the thoracotomy vascular stent comprises a conveying rod, a support structure, a conveying handle, a first control component, a second control component, and a fixing band. According to the vascular stent and the conveying system provided by the invention, the anastomosis between the proximal end of the descending aorta and the proximal end ofthe laminating membrane stent placed therein is avoided, and the surgical time is shortened.
Owner:JIANGSU BIODA LIFE SCI CO LTD
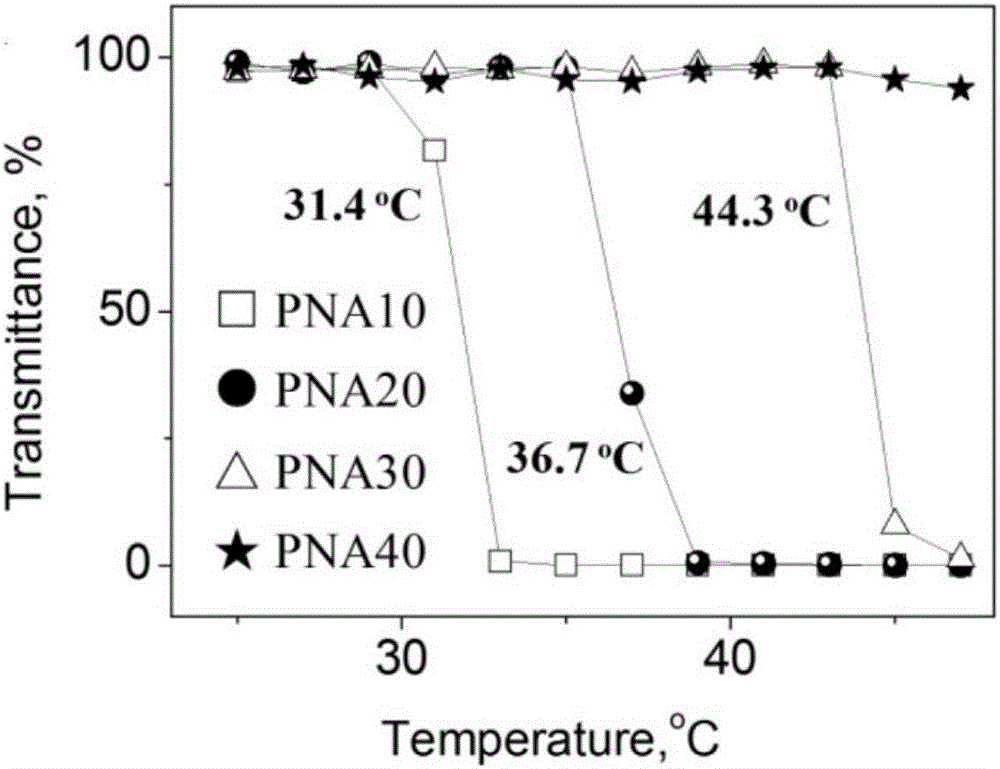
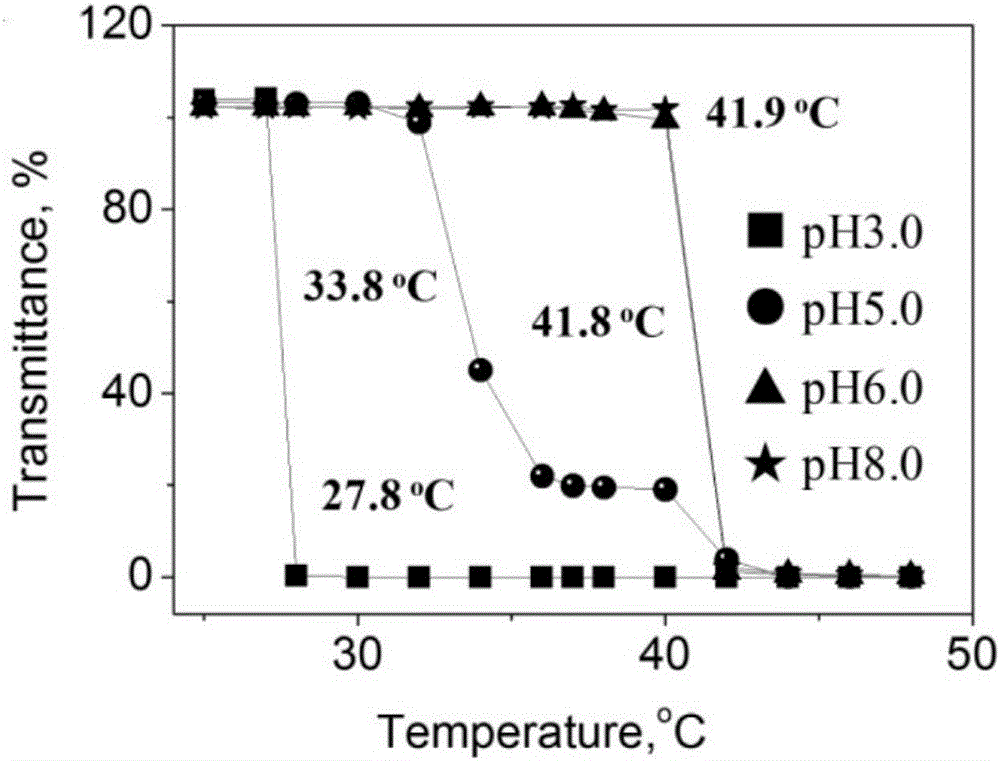
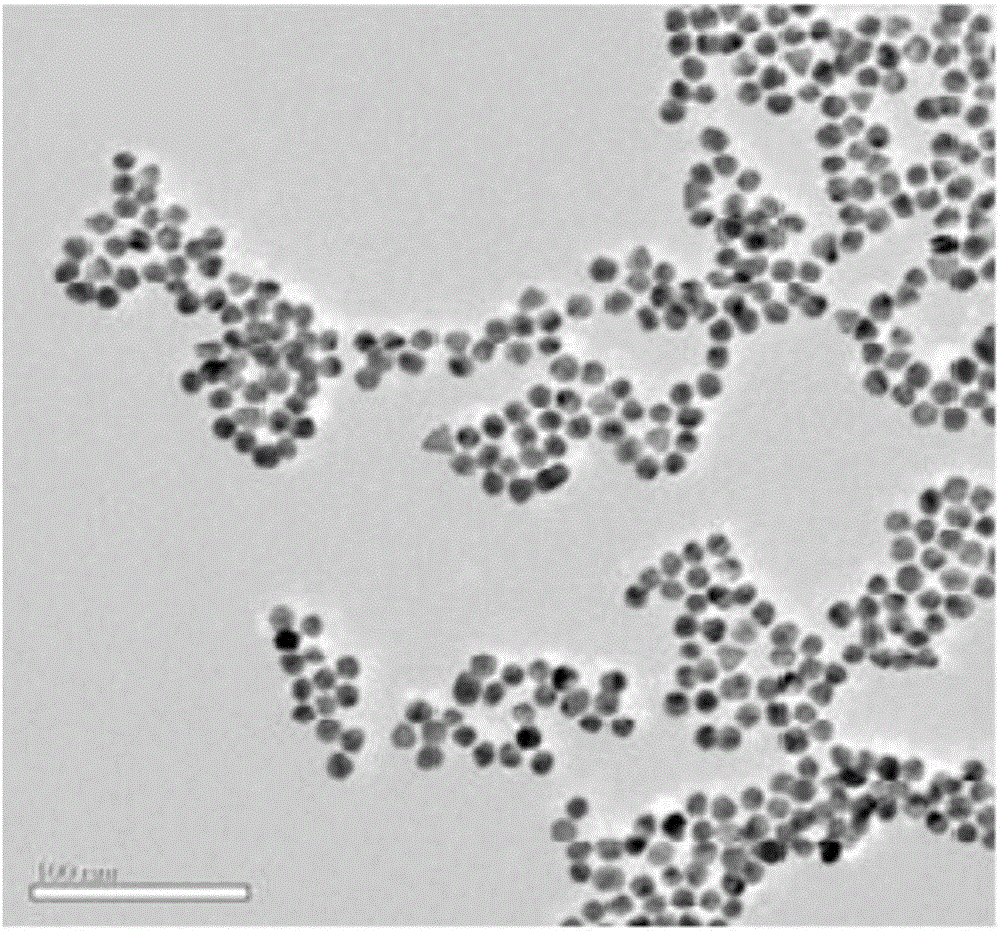
Temperature-sensitive vascular thrombosis material capable of performing long-term self-development and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106620826AGood biocompatibilityEmbolization achievedSurgical adhesivesTissue regenerationAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
The invention provides a temperature-sensitive vascular thrombosis material capable of performing long-term self-development and a preparation method thereof. The vascular thrombosis material contains gold nano gel and a dispersion medium, wherein the gold nano gel comprises a gold nano particle cytochalasin and a polyacrylamide amide compound temperature-sensitive polymer housing layer coated on the surface of the gold nano particle cytochalasin. The vascular thrombosis material only uses temperature as a phase change regulating and controlling factor, has good biocompatibility, can achieve long-term thrombosis in the blood vessel, has the capability of long-term development, can be used for vascular thrombosis of multiple tumor sites, achieves thrombosis of the aorta and terminal blood vessel, completely blocks blood and cuts off cancer cell blood supply to achieve the tumor suppression purpose.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com