Bioabsorbable marker having radiopaque constituents and method of using the same
a radiopaque and bioabsorbable technology, applied in the field of bioabsorbable markers having radiopaque constituents “ bioabsorbableradiopaque markers, can solve the problems of not being biocompatible or biostable, compromising structural integrity, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the radiopacity and the locatability of an endoprosthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
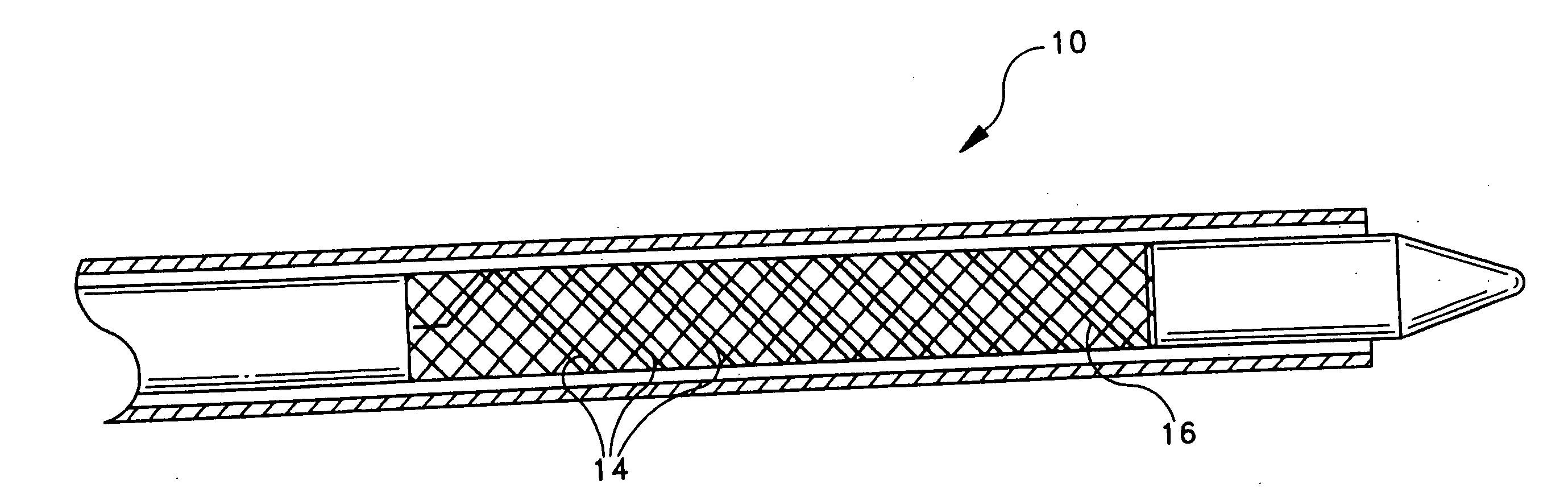
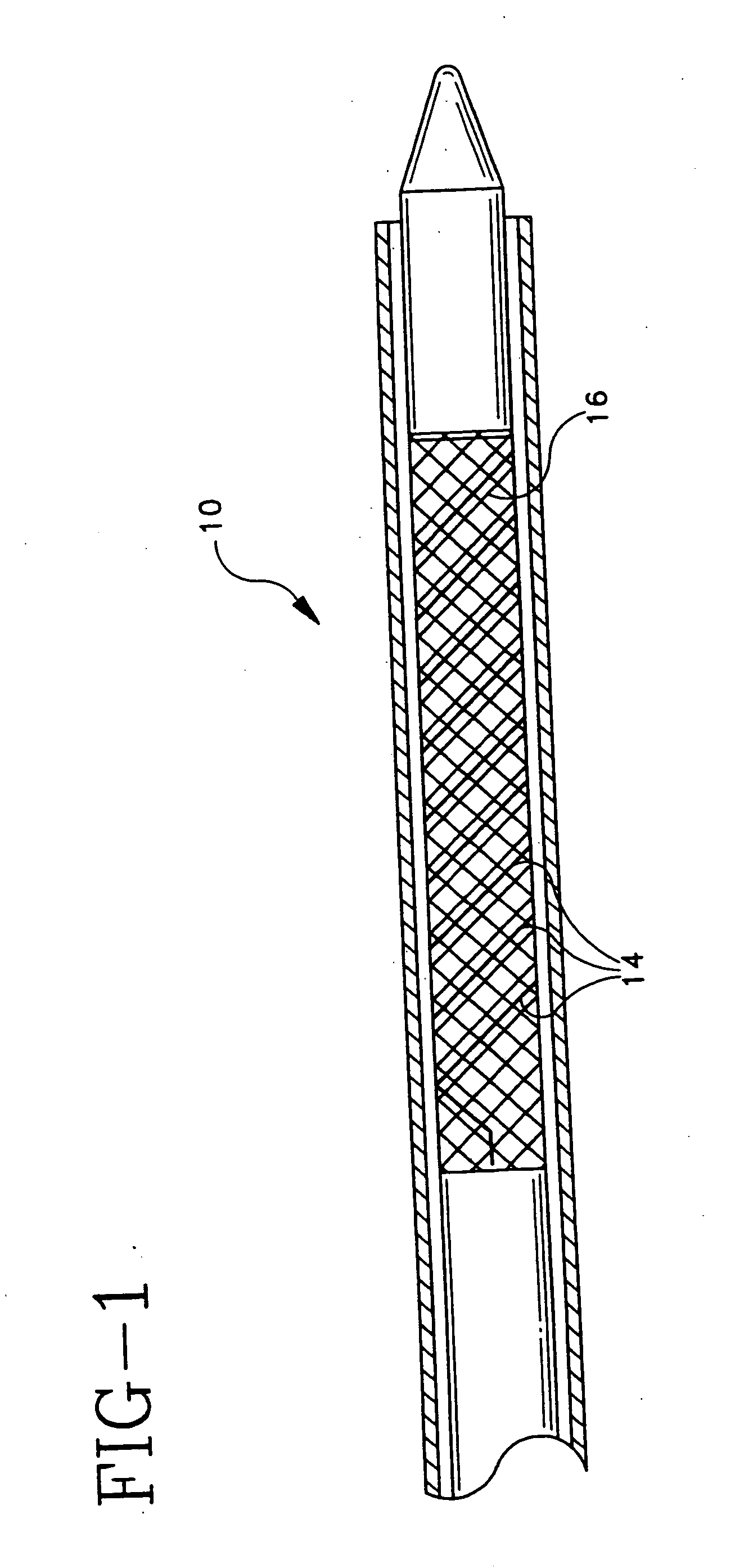
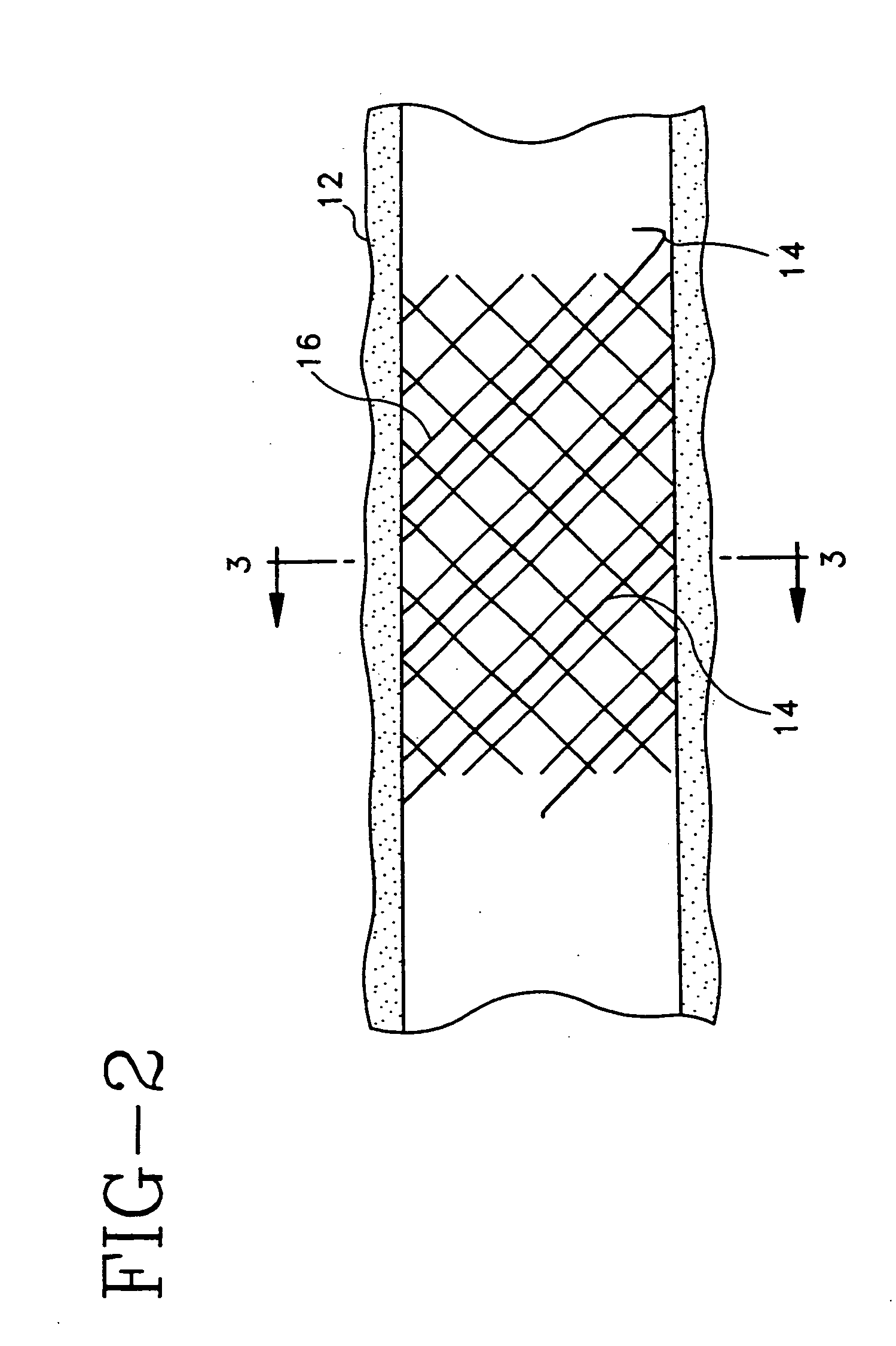
[0075] An absorbable threaded radiopaque marker can be in the form of a strand of poly (α-hydroxy acid) polymer containing radiopaque elements, oxides, or salts of elements with atomic numbers of from about 22 to about 83 interwoven or interbraided along a helical, circumferentail, or axial orientation on an endoprosthesis such as a stent, stent-graft, graft, filter, occlusive device, and valve. The radiopaque material has a linear attenuation coefficient of from about 10 cm−1 at 50 KeV to about 120 cm−1 at 50 KeV.
example 2
[0076] An absorbable threaded radiopaque marker can be in the form of a strand of poly (α-hydroxy acid) polymer containing radiopaque elements, oxides, or salts of elements with atomic numbers of from about 22 to about 83 disposed on one or more surfaces of an endoprosthesis such as a stent, stent-graft, graft, filter, occlusive device, and valve. The radiopaque material has a linear attenuation coefficient of from about 10 cm−1 at 50 KeV to about 120 cm−1 at 50 KeV.
example 3
[0077] An absorbable threaded radiopaque marker can be in the form of a strand of poly (α-hydroxy acid) polymer containing radiopaque elements with atomic numbers of from about 22 to about 83, loaded into hollow cores, cavities, or pores of the polymer portion and disposed on an endoprosthesis such as a stent, stent-graft, graft, filter, occlusive device, and valve. The radiopaque material has a linear attenuation coefficient of from about 10 cm−1 at 50 KeV to about 120 cm−1 at 50 KeV.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| linear attenuation coefficients | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| atomic numbers | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| atomic numbers | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com