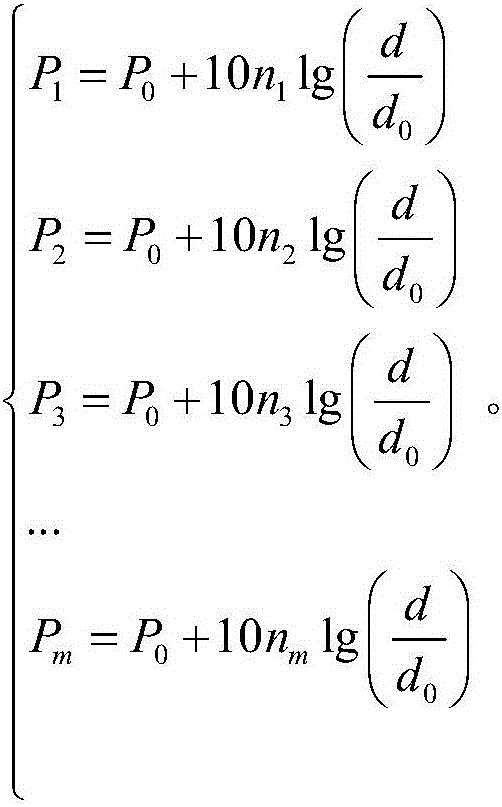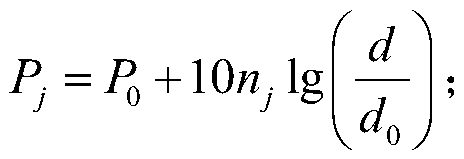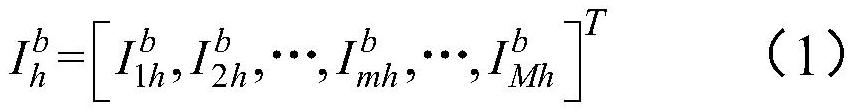Patents
Literature
31 results about "Underdetermined system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, a system of linear equations or a system of polynomial equations is considered underdetermined if there are fewer equations than unknowns (in contrast to an overdetermined system, where there are more equations than unknowns). The terminology can be explained using the concept of constraint counting. Each unknown can be seen as an available degree of freedom. Each equation introduced into the system can be viewed as a constraint that restricts one degree of freedom.
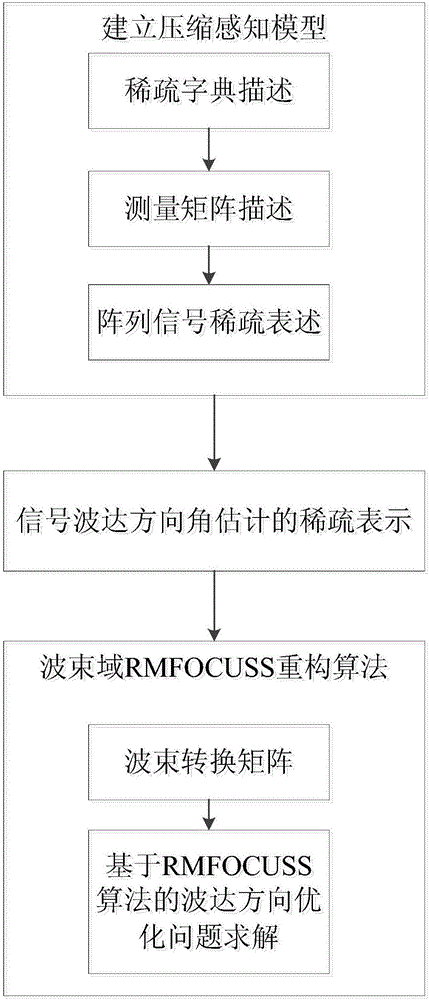
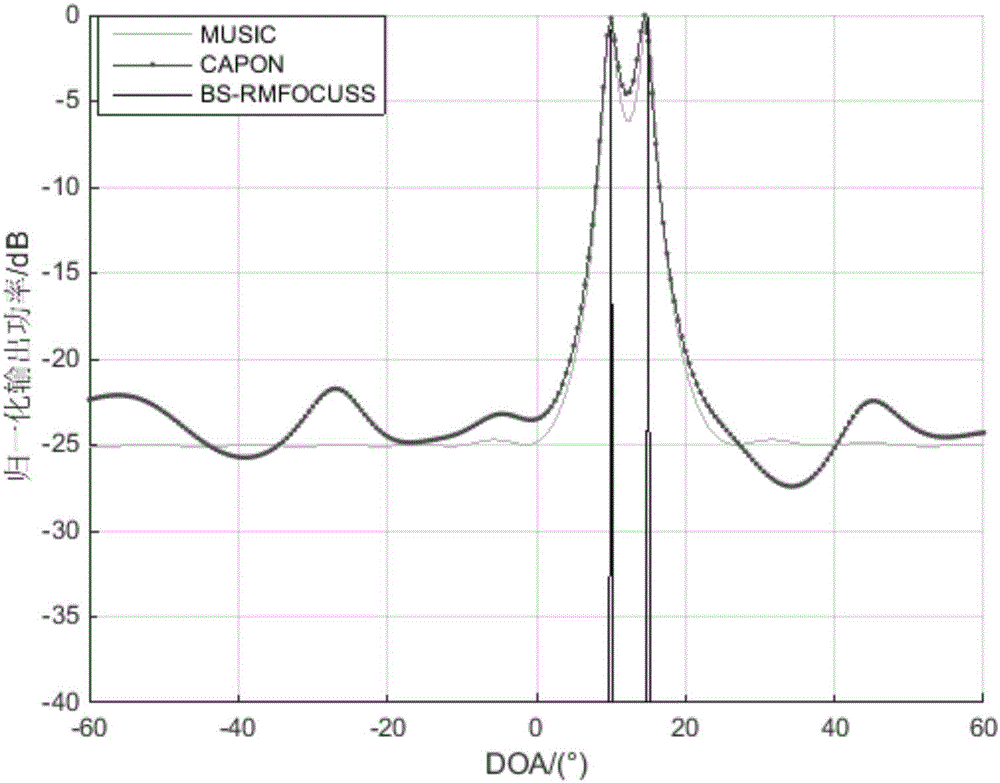
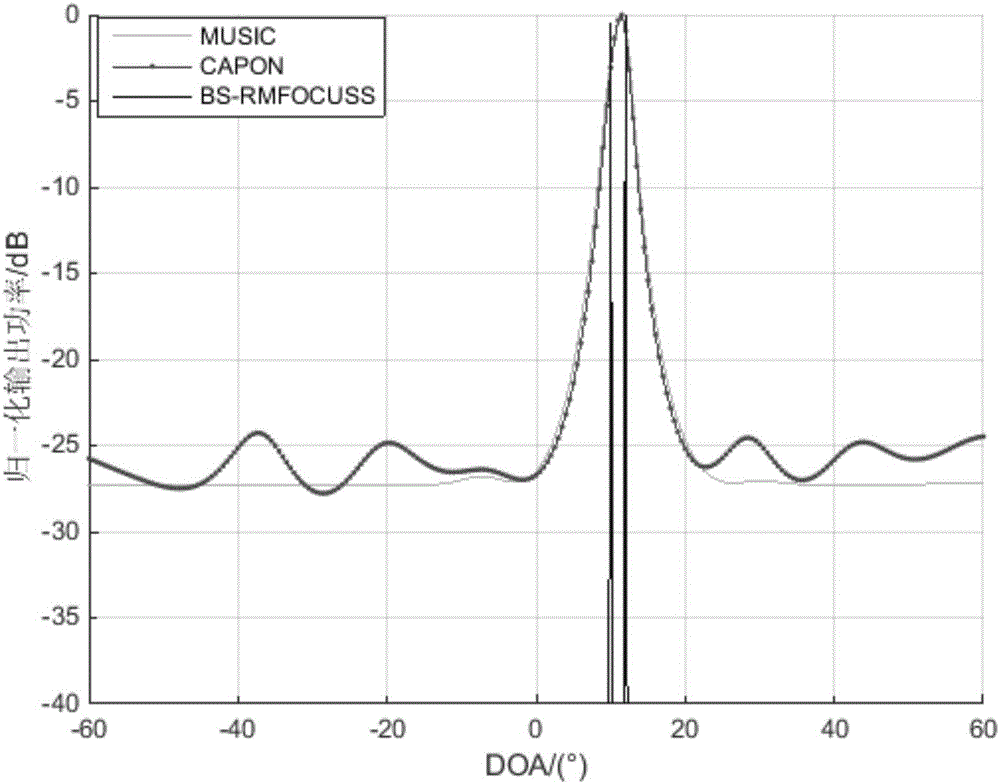
Beam domain DOA estimation based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN106772225AOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to use in low signal-to-noise ratio situationsReduce operational complexityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDirection/deviation determination systemsComputation complexitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
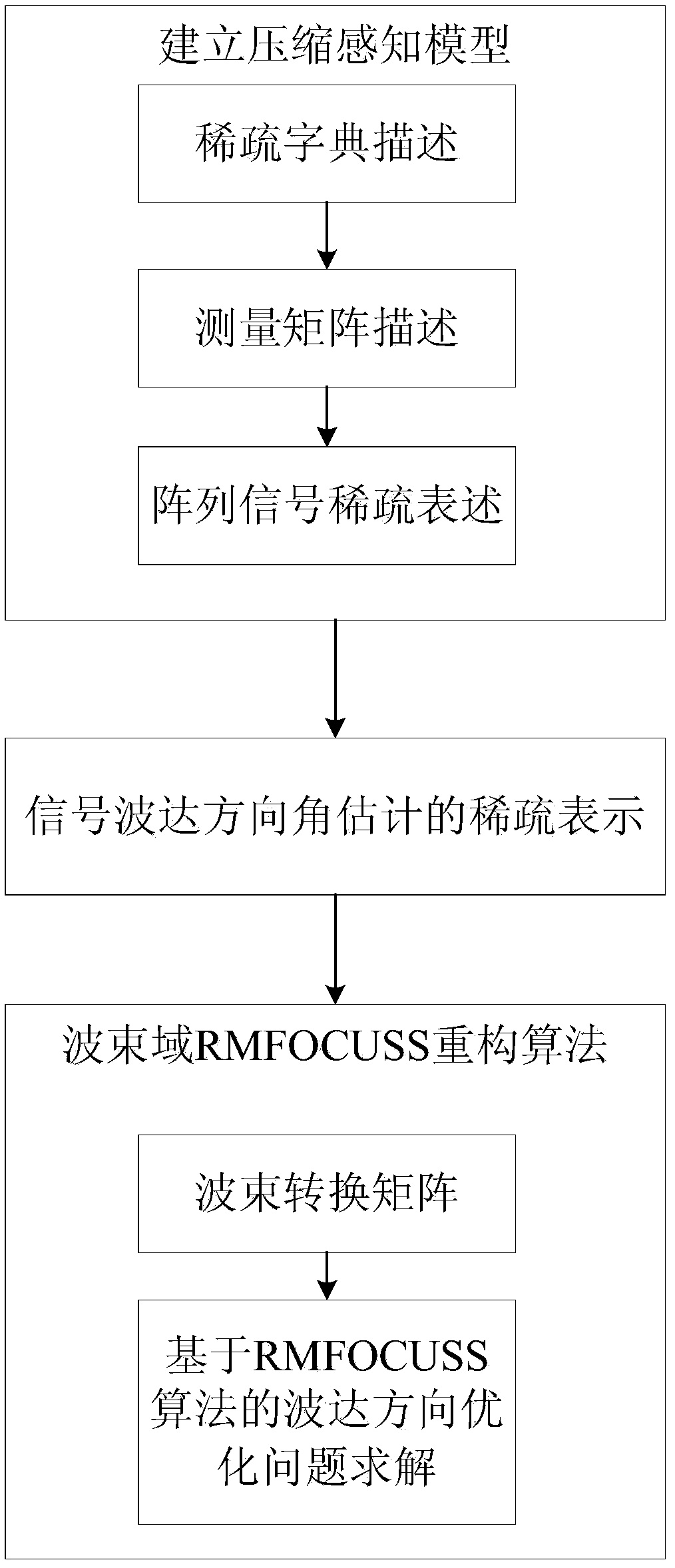
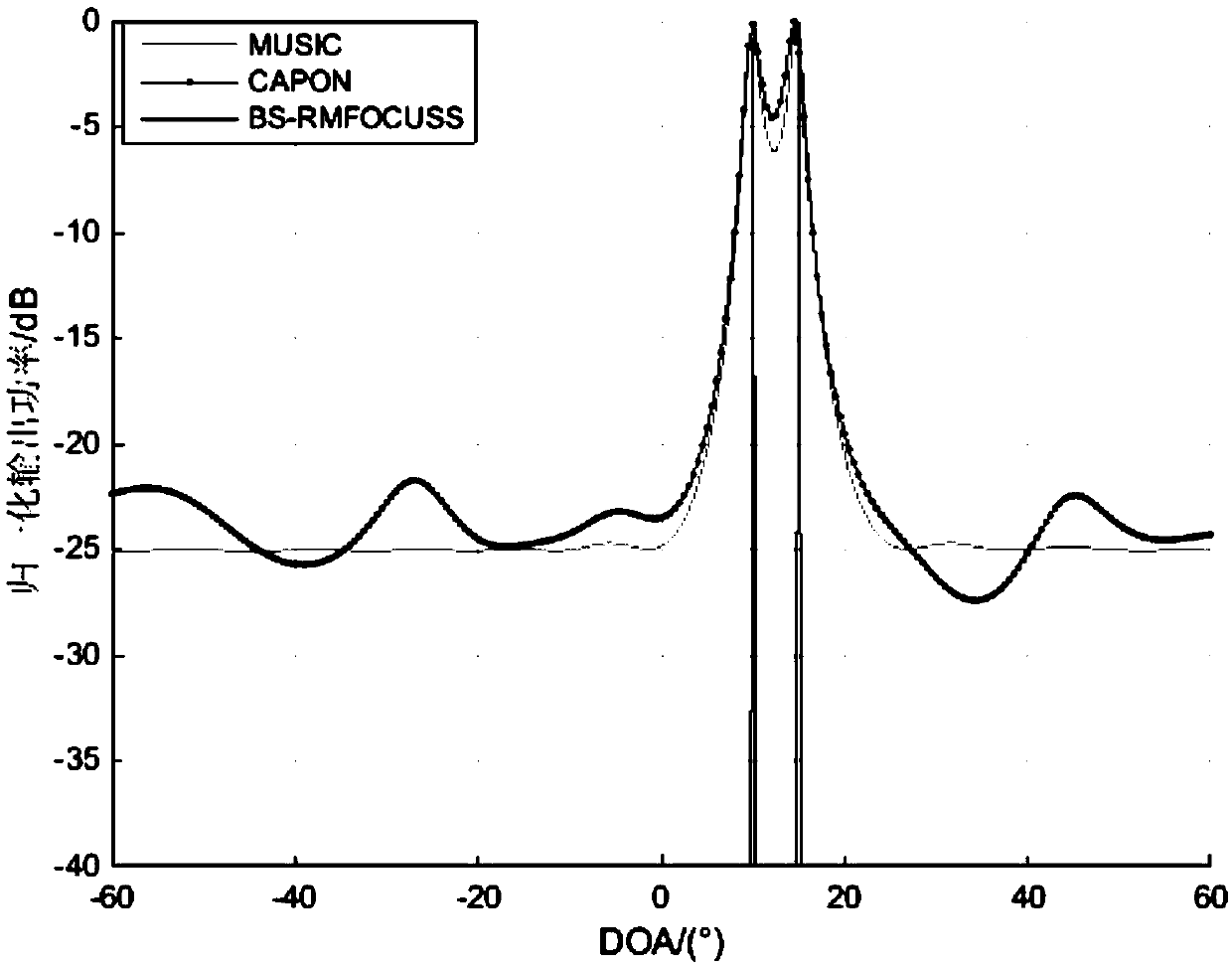
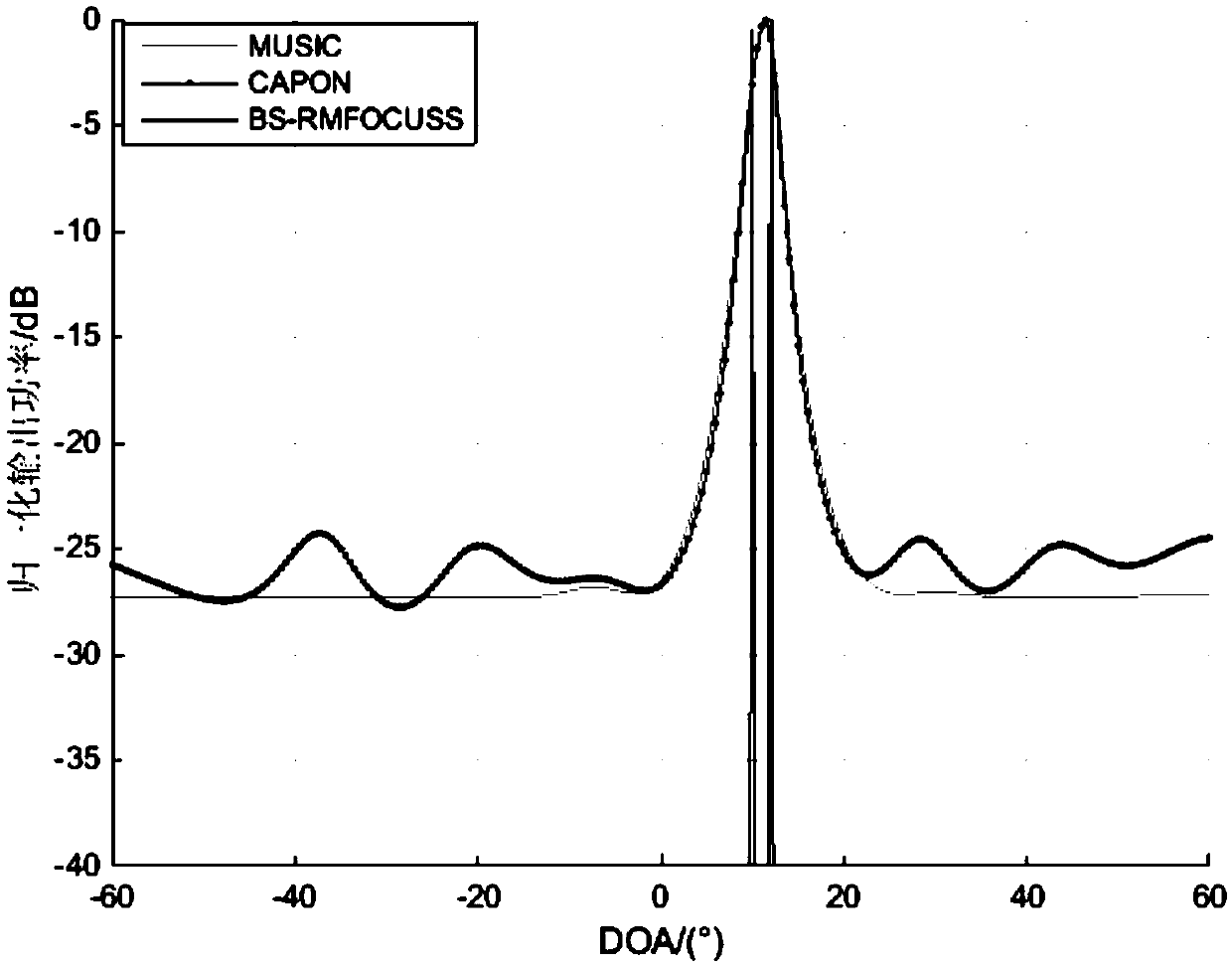
The invention belongs to the field of signal processing, aims to solve the problem that a traditional DOA (direction of arrival) estimation algorithm is large in sampling data volume to cause high computation complexity, and provides a beam-domain-based multi-measurement-vector underdetermined system regularization focusing solving (BS-RMFOCUSS) algorithm on the basis of a compressed sensing theory by using airspace sparsity of target signals. According to the algorithm, a target compressing signal is mapped to a beam domain from an element domain, the shortcoming that a sparse reconstructing algorithm cannot be used under the condition of low signal to noise ratio is overcome to a certain degree, and the algorithm complexity is low. Numerical simulation shows that the property of the algorithm is superior to that of the traditional DOA estimation algorithm, and the algorithm has high angular resolution and estimation precision, and can carrying out effective DOA estimation on coherent signals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
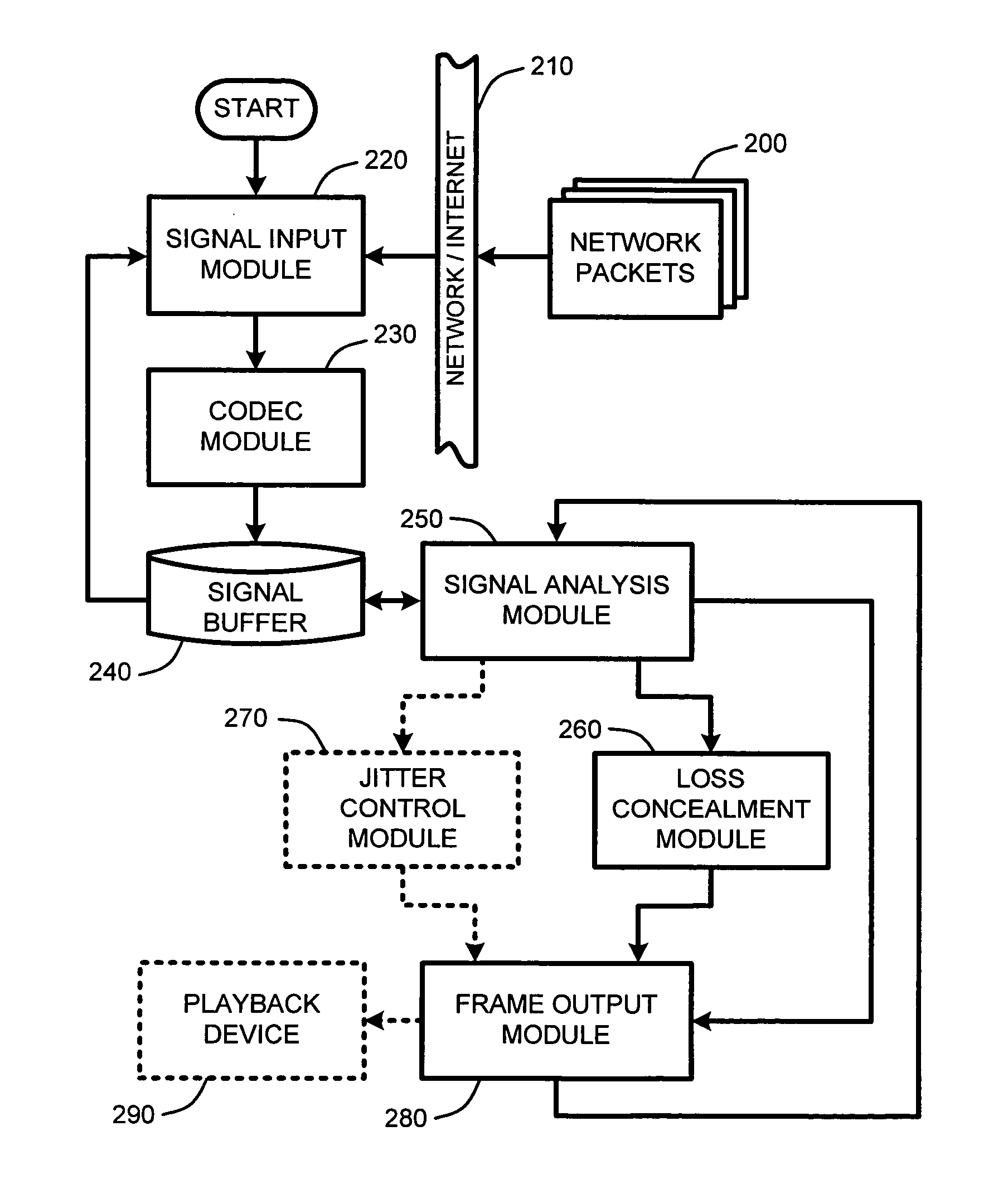
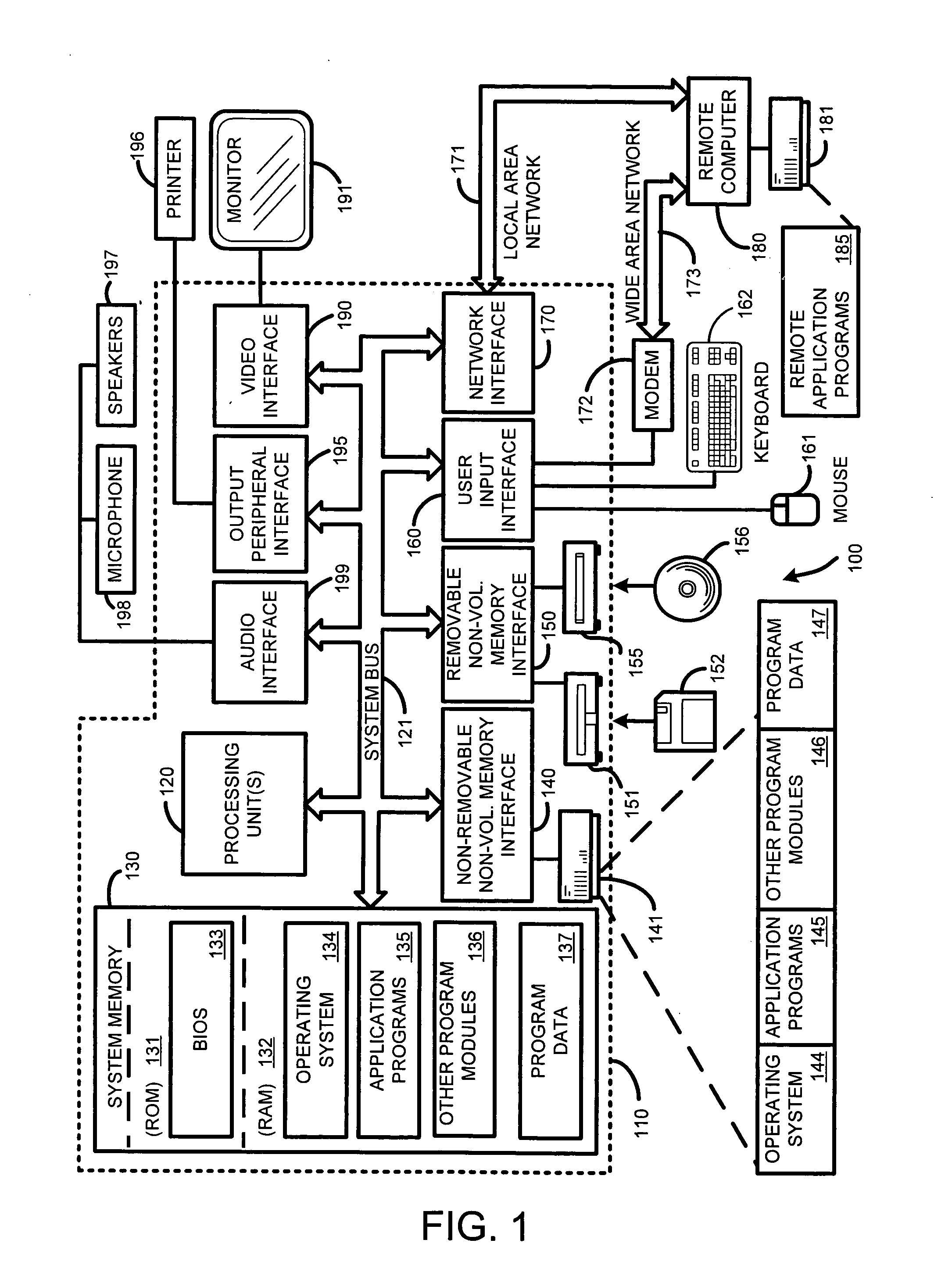
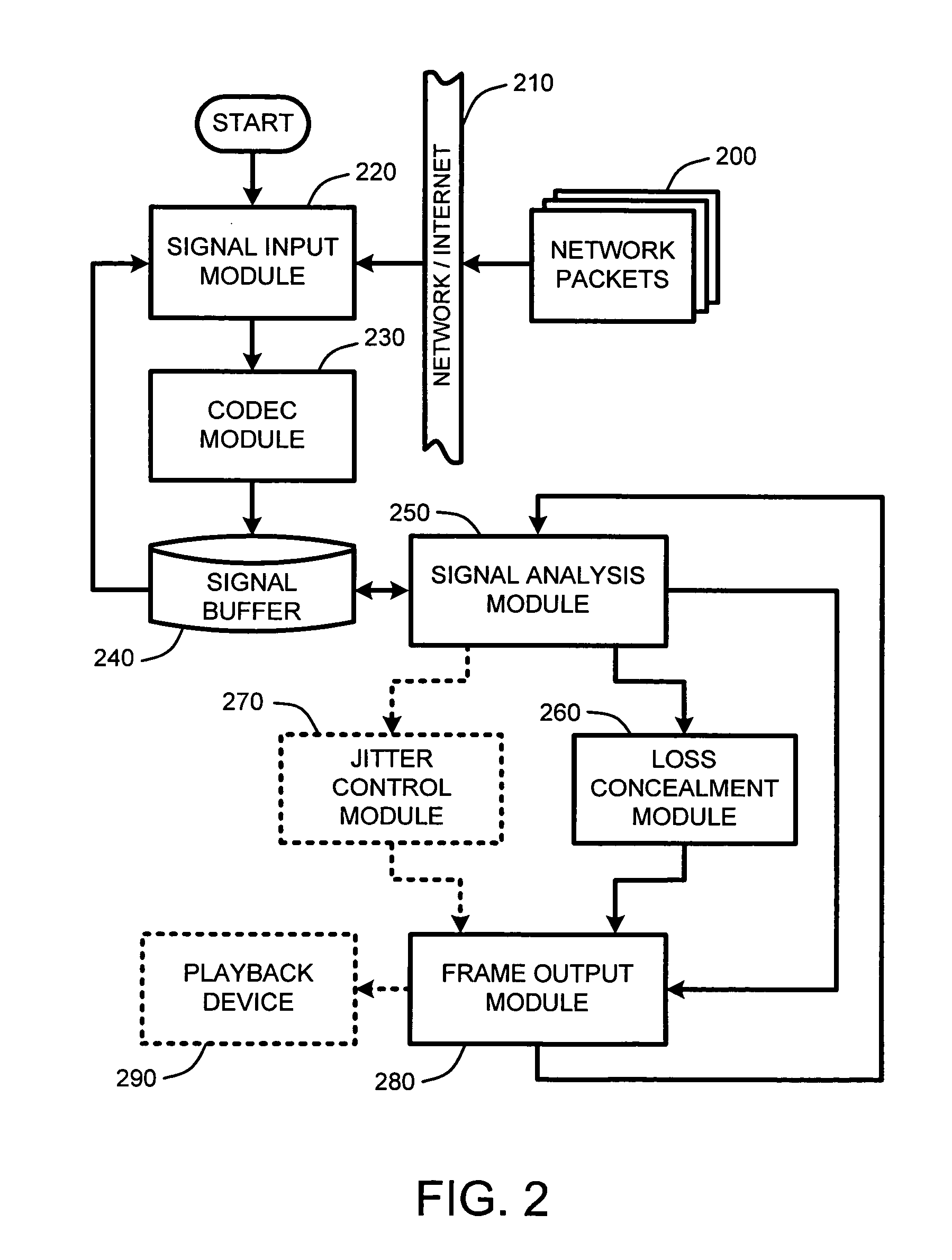
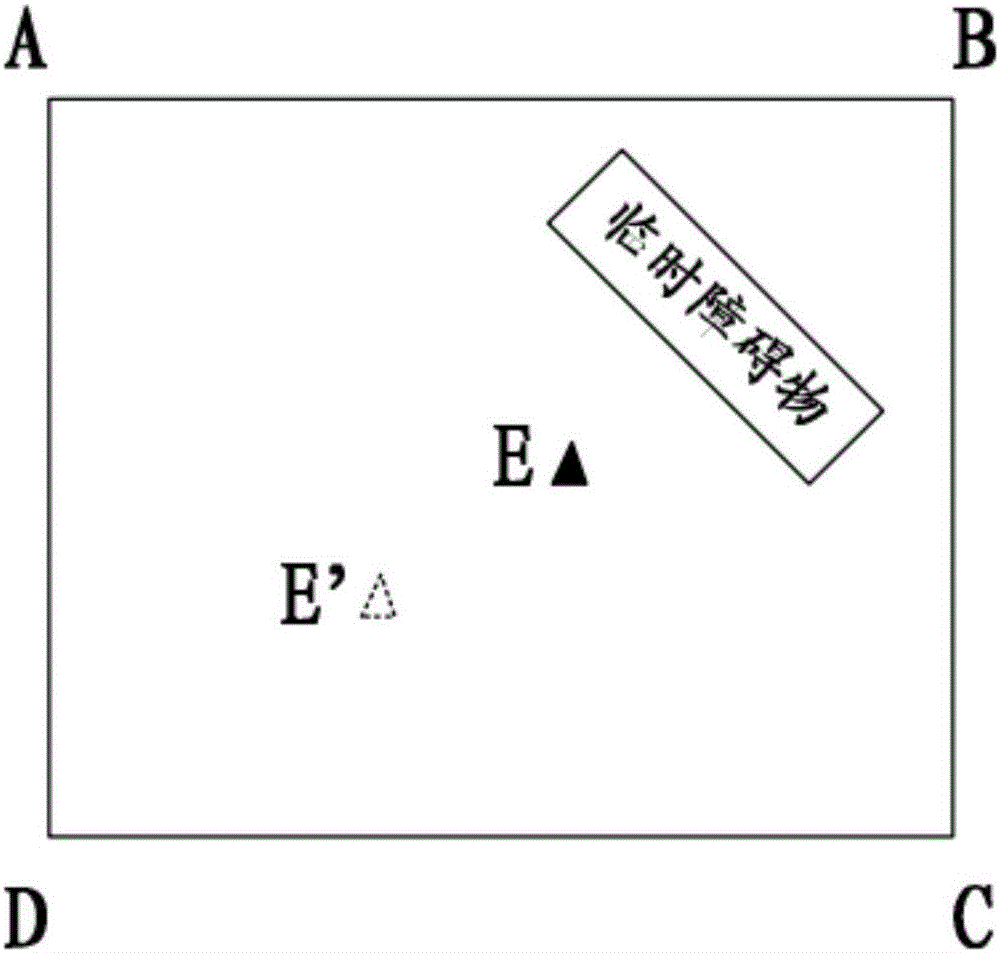
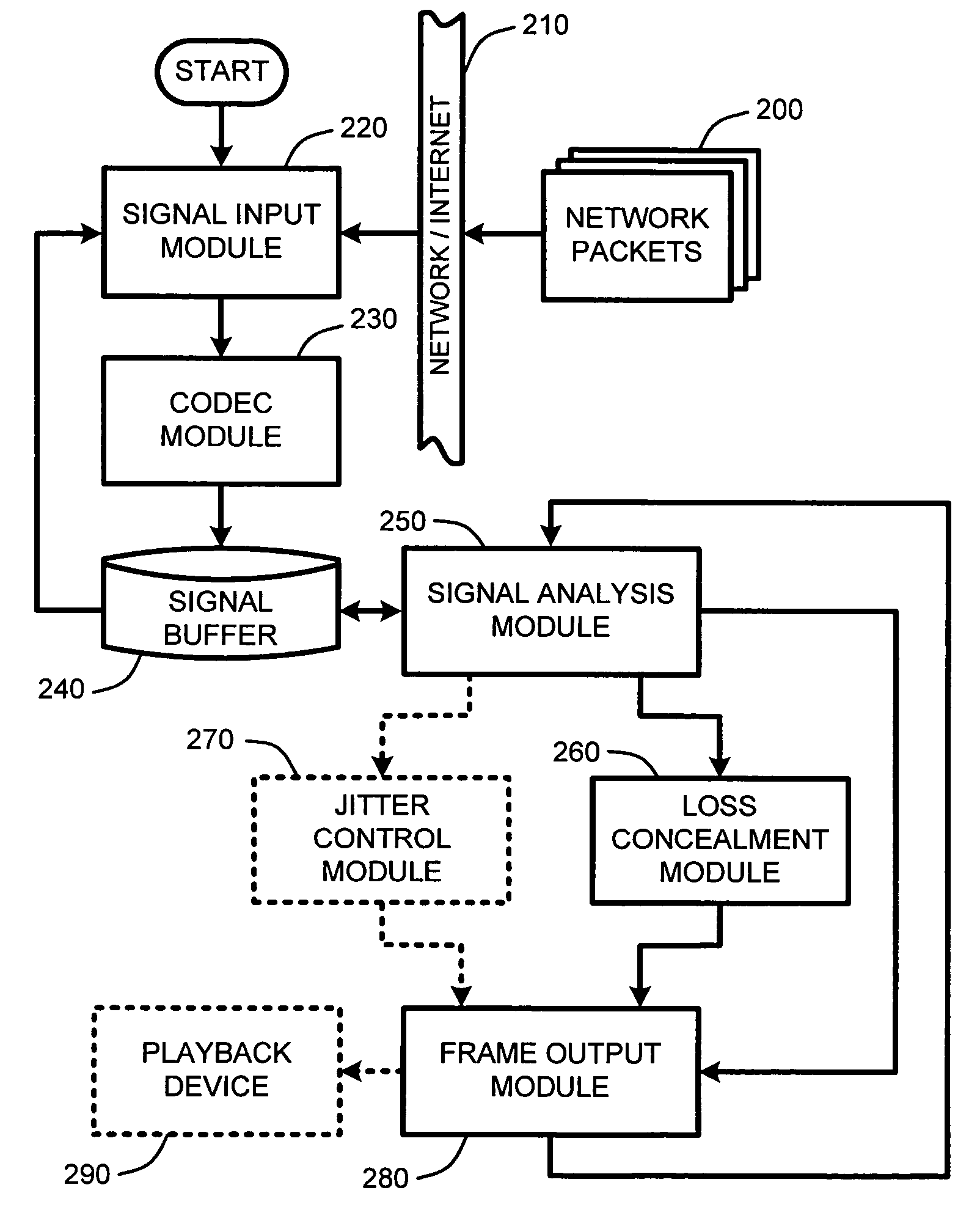
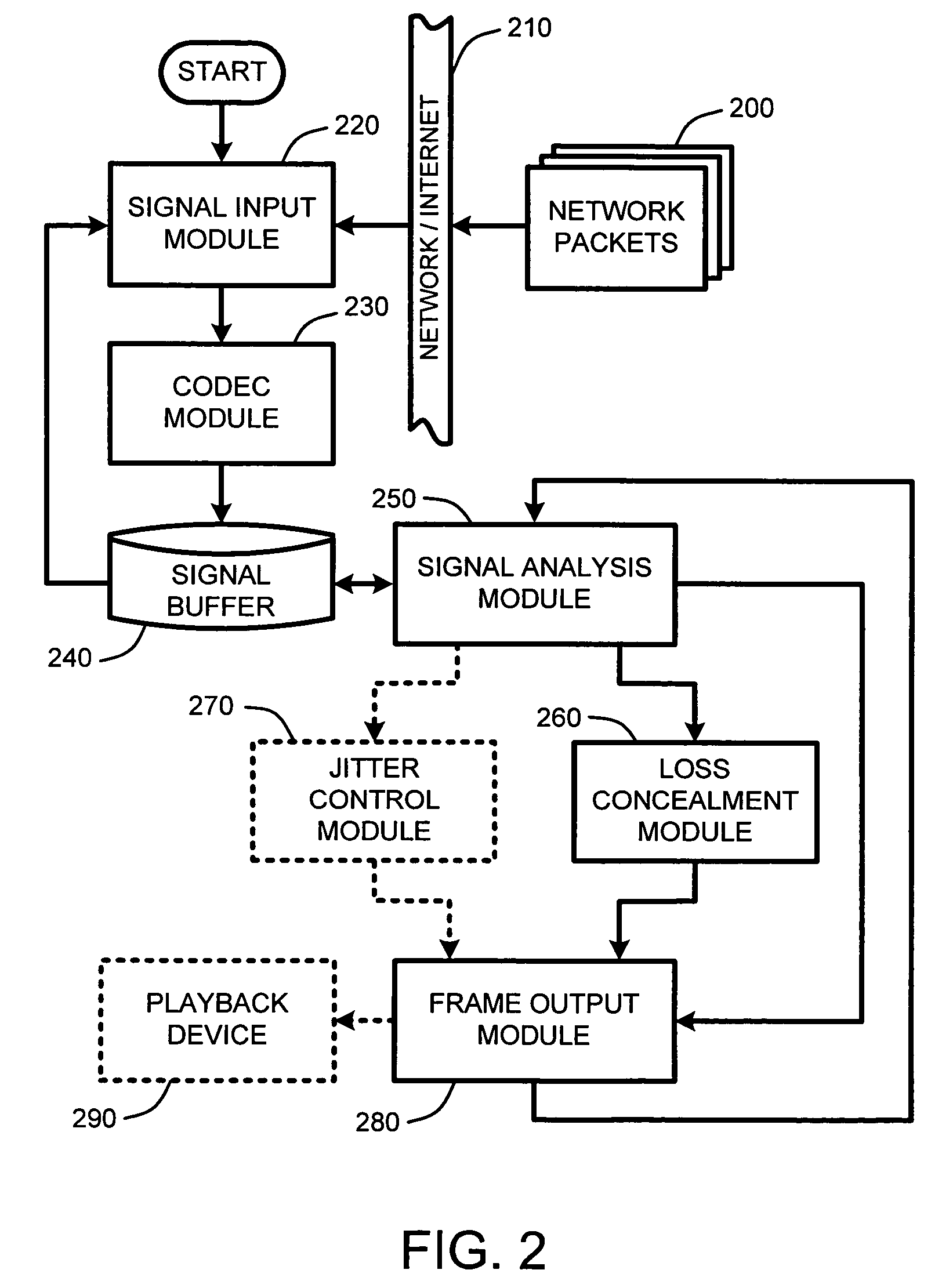
Packet loss concealment for overlapped transform codecs
InactiveUS20060209955A1Error minimizationMinimizes a model-based energy criterionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPacket loss concealmentUnderdetermined system
Real-time packet-based audio communications over packet-based networks frequently results in the loss of one or more packets during any given communication session. The real-time nature of such communications precludes retransmission of lost packets due to the unacceptable delays that would result. Consequently, packet loss concealment methods are employed to “hide” lost packets from the listener. Unfortunately, conventional loss concealment methods, such as packet repetition or stretch / overlap methods, do not fully exploit information available from partially received samples. Therefore, when a single frame of N coefficients is lost, 2N samples are only partially reconstructed, thereby degrading the reconstructed signal. To address this problem, an optimized packet loss concealment solution is identified for particular lost packets by solving an underdetermined system of linear equations representing partially received samples while minimizing a computed error based on a model of the signal obtained from neighboring blocks or frames received by the decoder.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
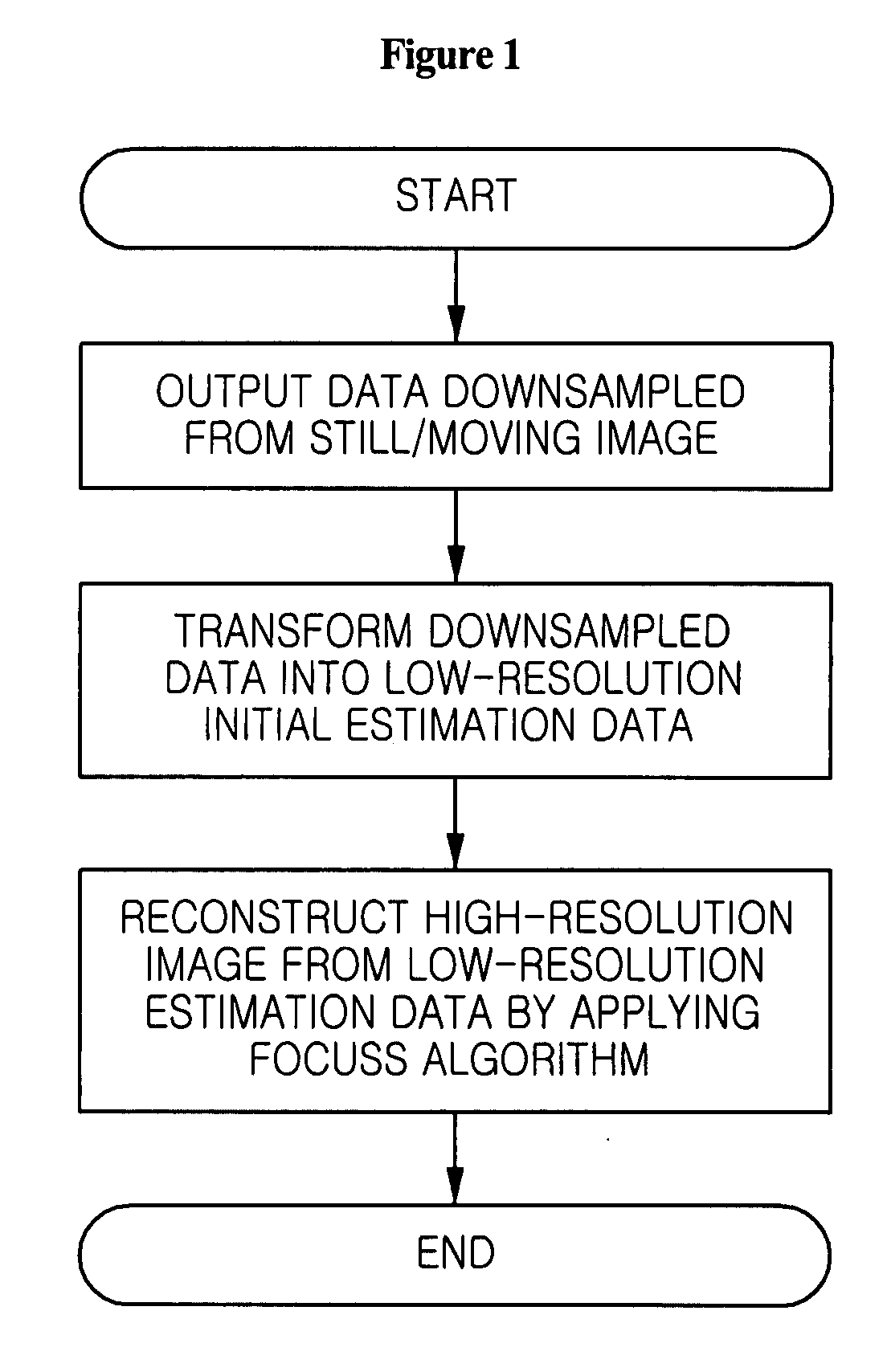
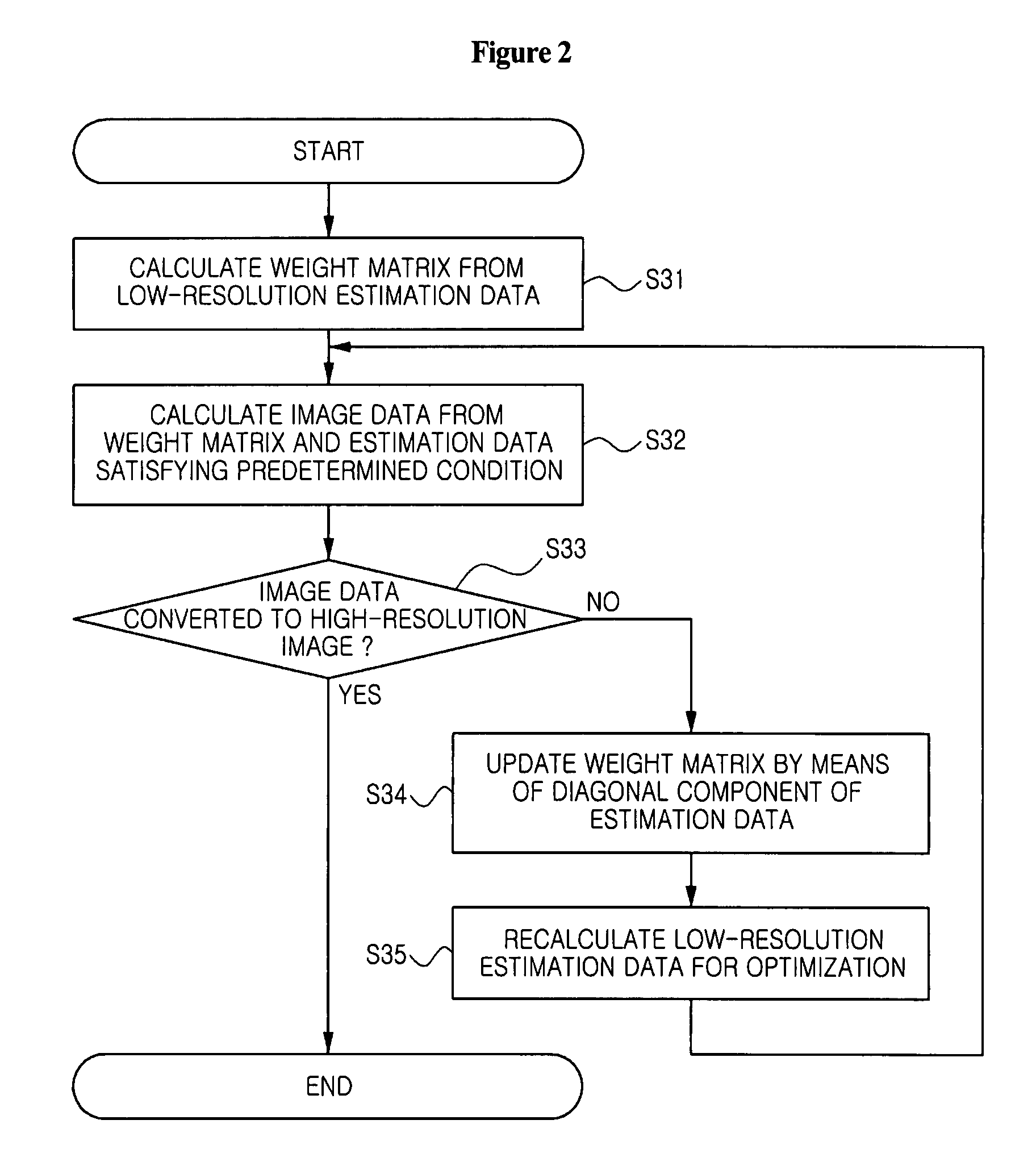
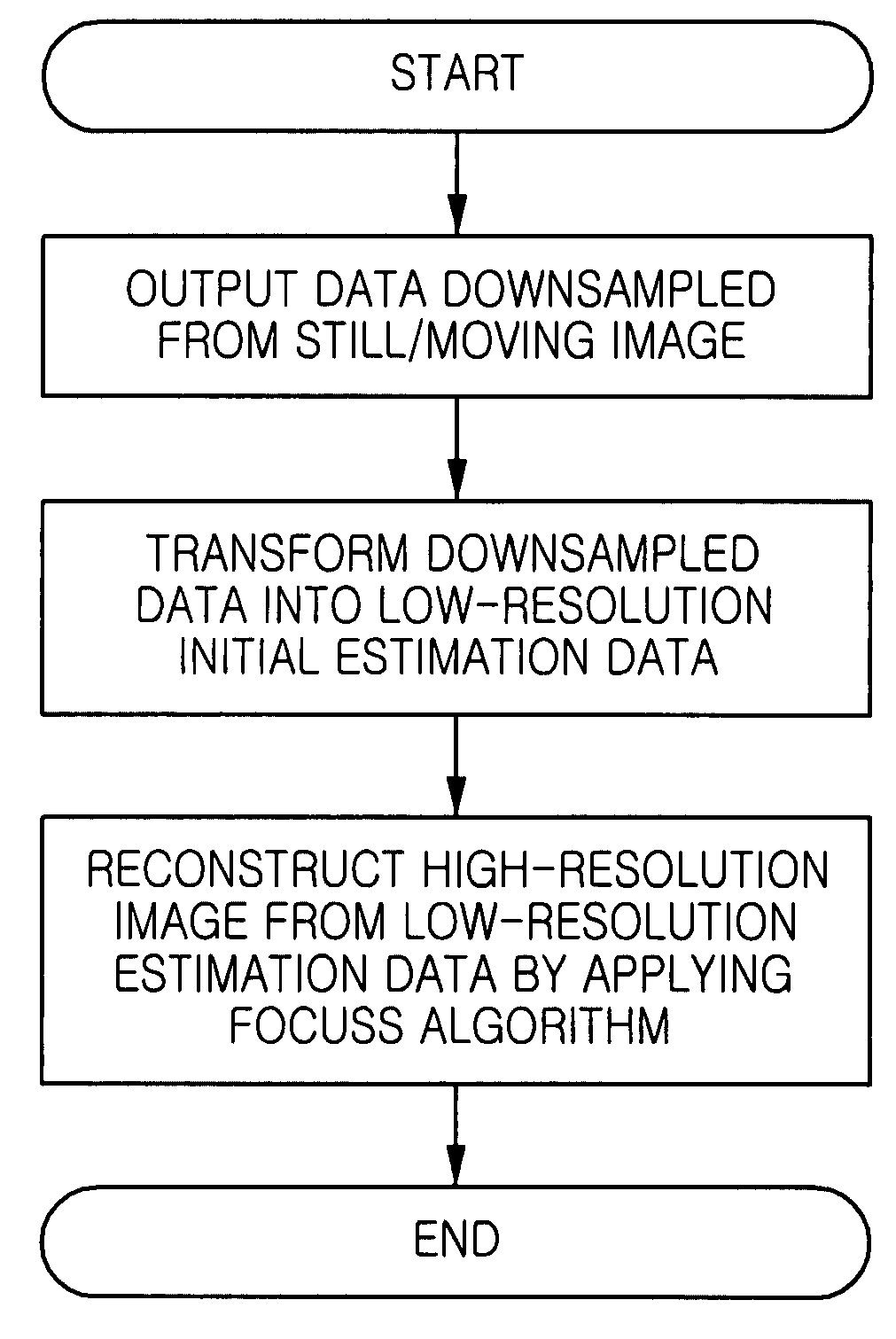
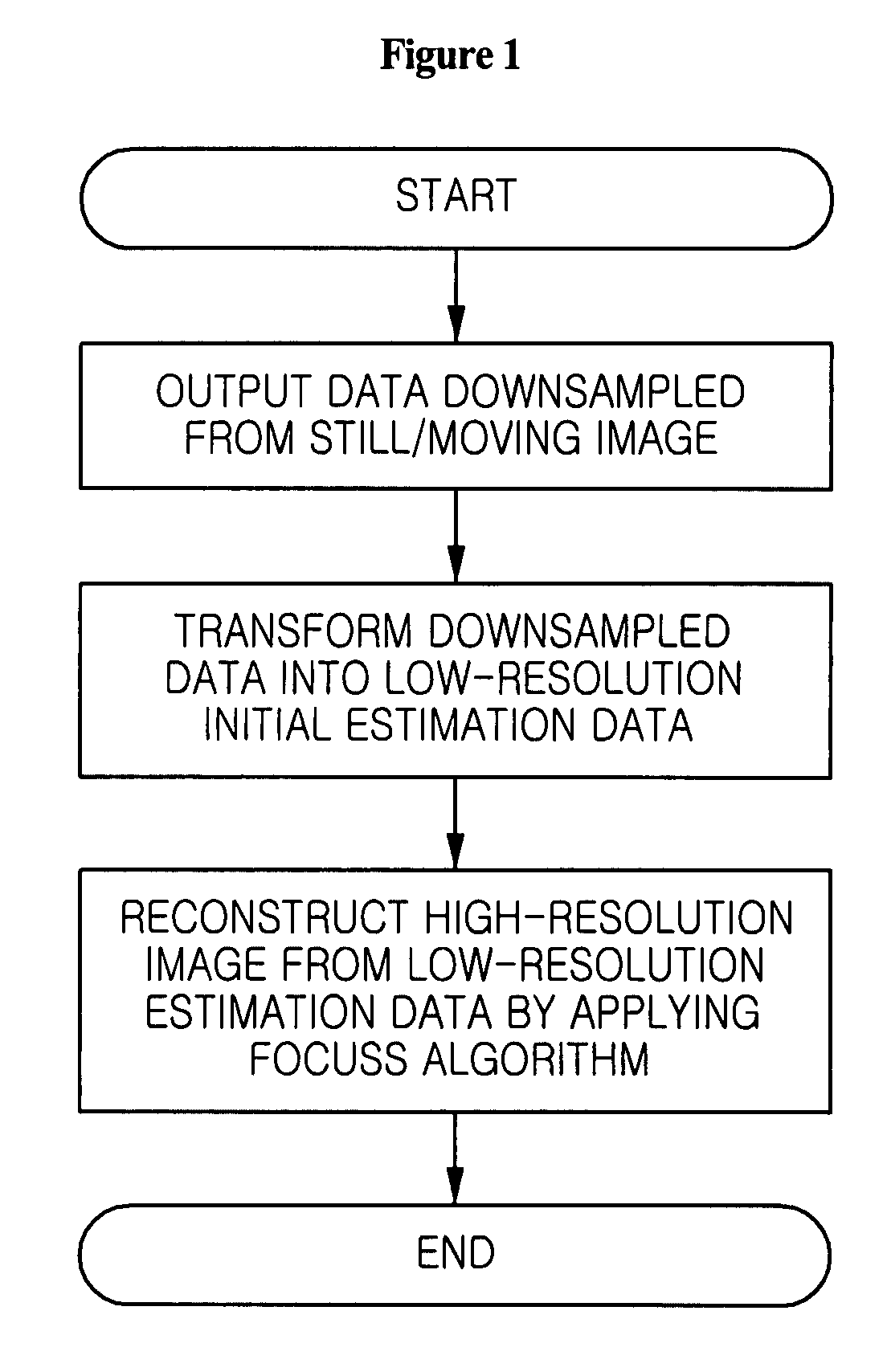
Method for super-resolution reconstruction using focal underdetermined system solver algorithm
ActiveUS20080175452A1High resolutionMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionReconstruction method
Disclosed is a high-resolution image reconstruction method using a focal underdetermined system solver (FOCUSS) algorithm. The method comprises the steps of: outputting data for an image of an object; downsampling the outputted data; transforming the downsampled data into low-resolution image frequency data; and reconstructing a high-resolution image from the transformed low-resolution image frequency data by applying focal underdetermined system solver (FOCUSS) algorithm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
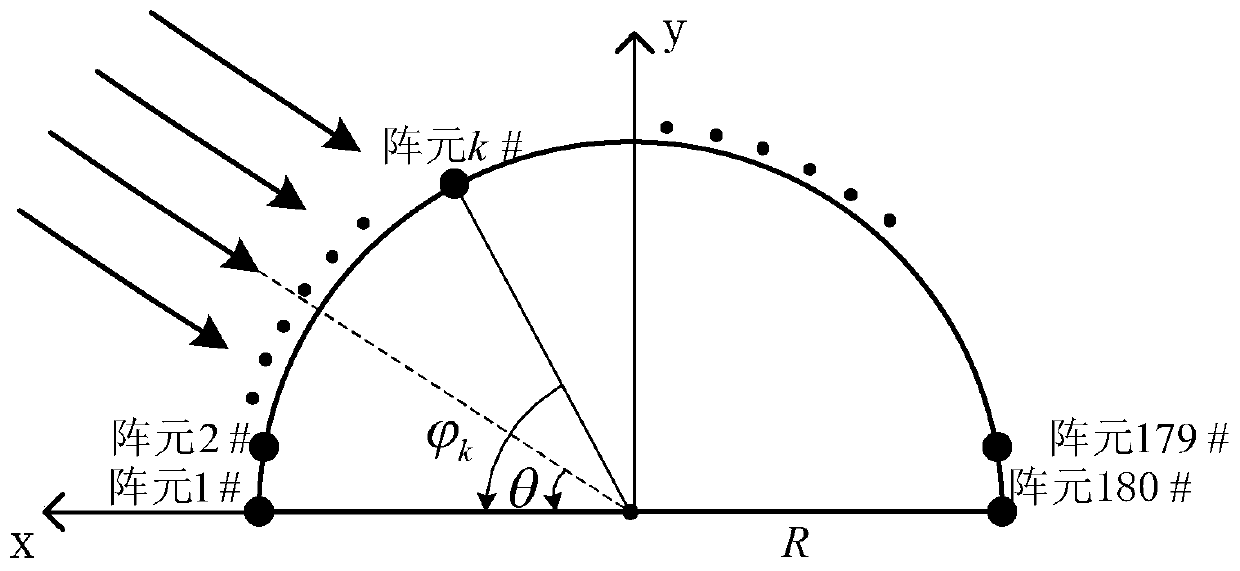
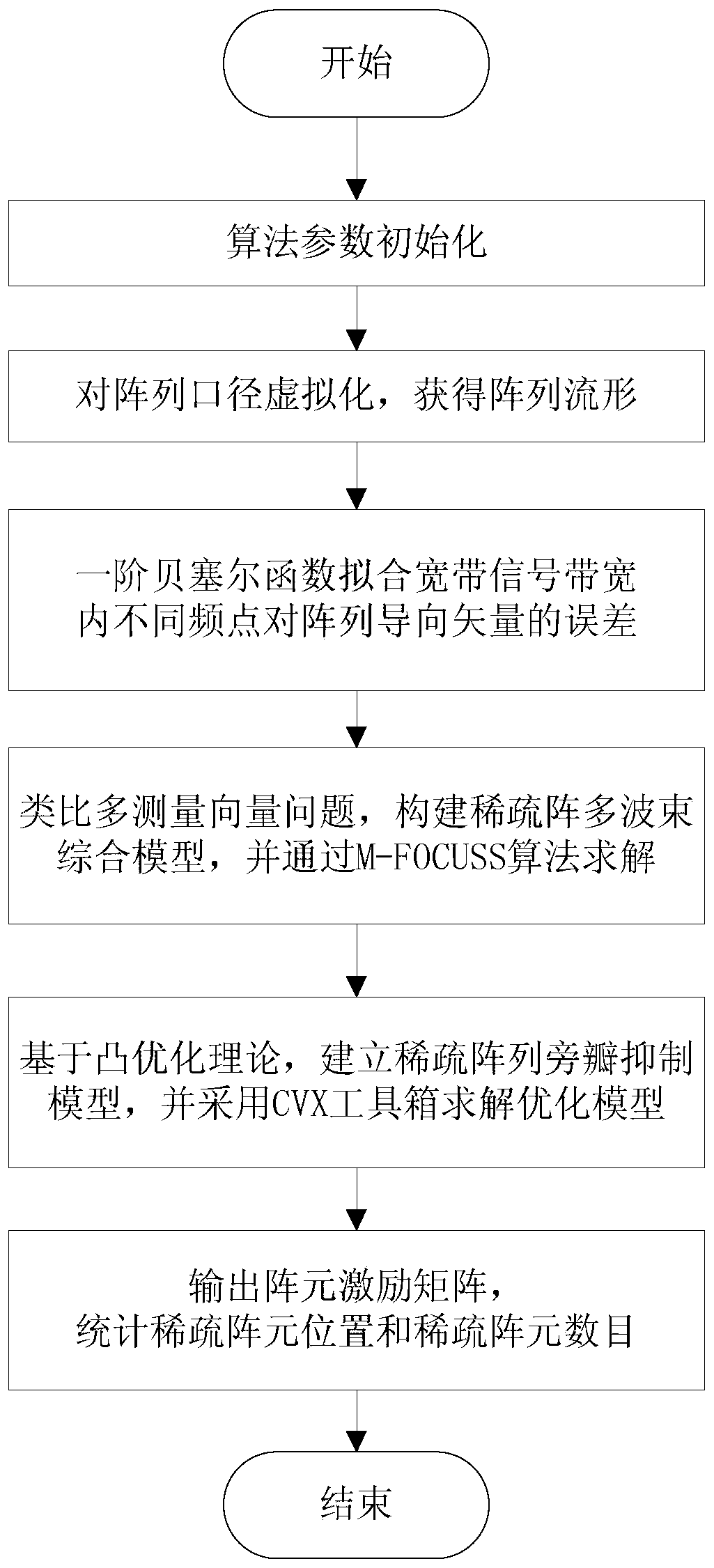
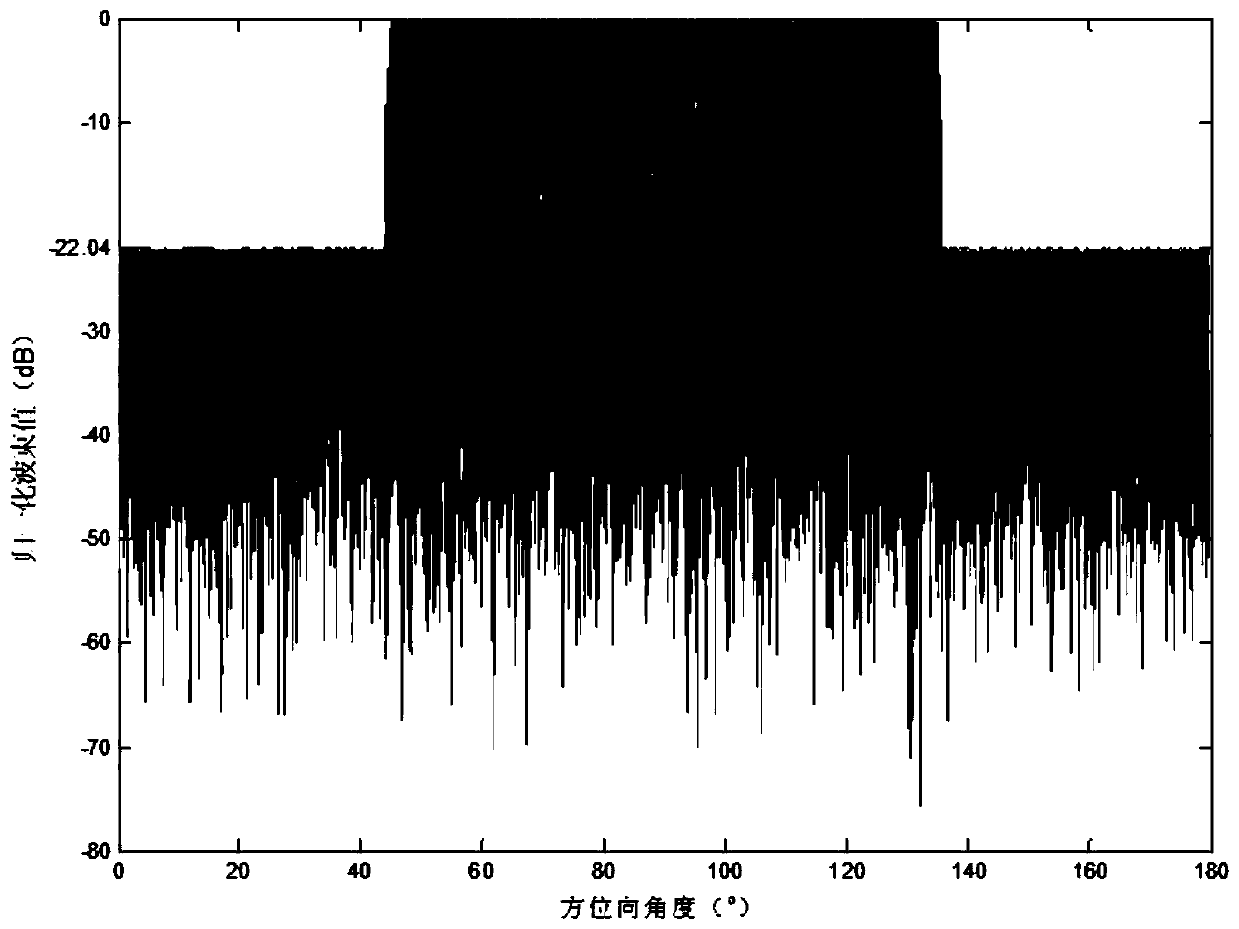
Array sparse method for broadband non-frequency-variable multi-beam imaging sonar
InactiveCN109959917AEnables wideband multi-beamformingAvoid getting stuck in local optimaWave based measurement systemsSparse methodsWeight coefficient
The invention discloses an array sparse method for a broadband non-frequency-variable multi-beam imaging sonar. With the Bessel function, fitting of influences on array guiding vectors by different frequency points in the broadband signal bandwidth is performed and a broadband signal multi-beam forming model under the far-field situation is established; on the premise that the formed multiple beams approximate a reference beam, a minimum number of effective array elements are searched and multiple sets of weighting coefficients are calculated; a highly nonlinear sparse array optimization problem is transformed into a sparse signal reconstruction problem in the compressed sensing theory, a reconstruction weighting coefficient is calculated iteratively by an underdetermined system localizedsolution algorithm, and a sparse array structure is determined; a convex optimization theory is introduced so as to form a plurality of low-side-lobe beams and a multi-beam array sparse side-lobe suppression model for array element excitation is established. According to the invention, the main lobes of a plurality of formed beams are not extended with changes of signal operating frequencies; andpeak side-lobe levels of multiple beams formed by the sparse array are reduced effectively.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
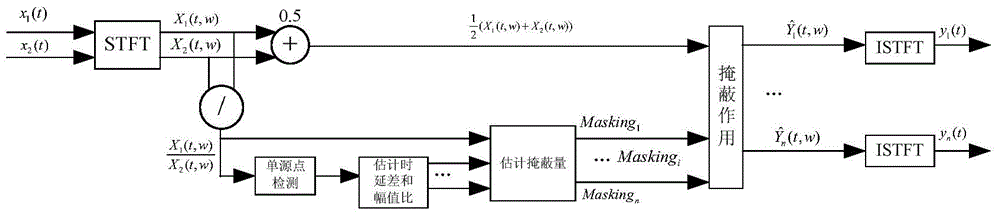
Quick source signal reconstruction method achieving blind sound source separation of two microphones
InactiveCN104167214AAvoid problemsSmall amount of calculationSpeech analysisSound source separationTime domain
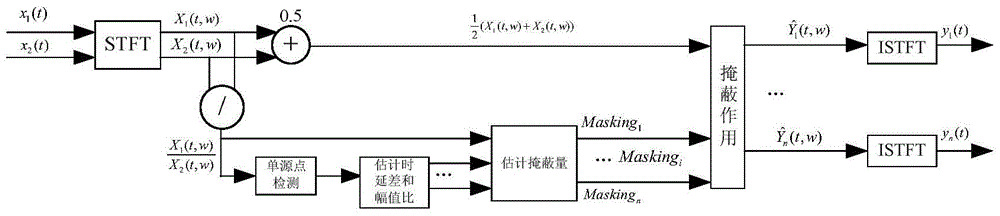
The invention discloses a quick source signal reconstruction method achieving blind sound source separation of two microphones, belongs to the field of speech signal processing, and particularly relates to a quick source signal reconstruction method achieving sound source separation of the two microphones on the situation that the number of sound sources and the surrounding environments are unknown. On the situation that temporal envelopes of reconstruction source signals are not influenced, a small additional phase is added to each frequency component of reconstruction signals, contribution of each source signal to a time-frequency point is approximately calculated to simulate the proportion of each source signal in the time-frequency point, and accordingly the source signals are restored. A traditional solving process of an underdetermined system of equations is avoided, calculation steps are simplified, and the aim of quickness is achieved. Accordingly, compared with an existing algorithm, the method has the advantages that calculation amount is little, and the signal-noise ratio is high on the situation that the number of the sound sources is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for super-resolution reconstruction using focal underdetermined system solver algorithm
ActiveUS7881511B2Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionReconstruction method
Disclosed is a high-resolution image reconstruction method using a focal underdetermined system solver (FOCUSS) algorithm. The method comprises the steps of: outputting data for an image of an object; downsampling the outputted data; transforming the downsampled data into low-resolution image frequency data; and reconstructing a high-resolution image from the transformed low-resolution image frequency data by applying focal underdetermined system solver (FOCUSS) algorithm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Snow passive microwave mixed pixel decomposition method based on classified information of five types of ground features
InactiveCN102608592AAchieve decompositionImprove inversion accuracyWave based measurement systemsDecompositionAntenna gain
The invention belongs to the technical field of remotely sensed image processing, and provides a snow passive microwave mixed pixel decomposition method based on the classified information of five types of ground features. According to five types of typical underlying surfaces affecting the radiation characteristic of snow, the method acquires the classified data of the ground features with high special resolution in an observed region, utilizes the different characteristics of the microwave radiation of snow on the different underlying surfaces and selects a microwave antenna gain function and a sampling rate to build a snow passive microwave mixed pixel decomposition model, and adopts the least square method with constraint conditions to iteratively solve an underdetermined system of equations, thus realizing snow passive microwave mixed pixel decomposition. The method can effectively solve the problem of the mixed pixels of passive microwaves of snow, improves the precision of snowparameter inversion, and has a significant application value in fields such as climate and hydrological research and snow disaster assessment.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
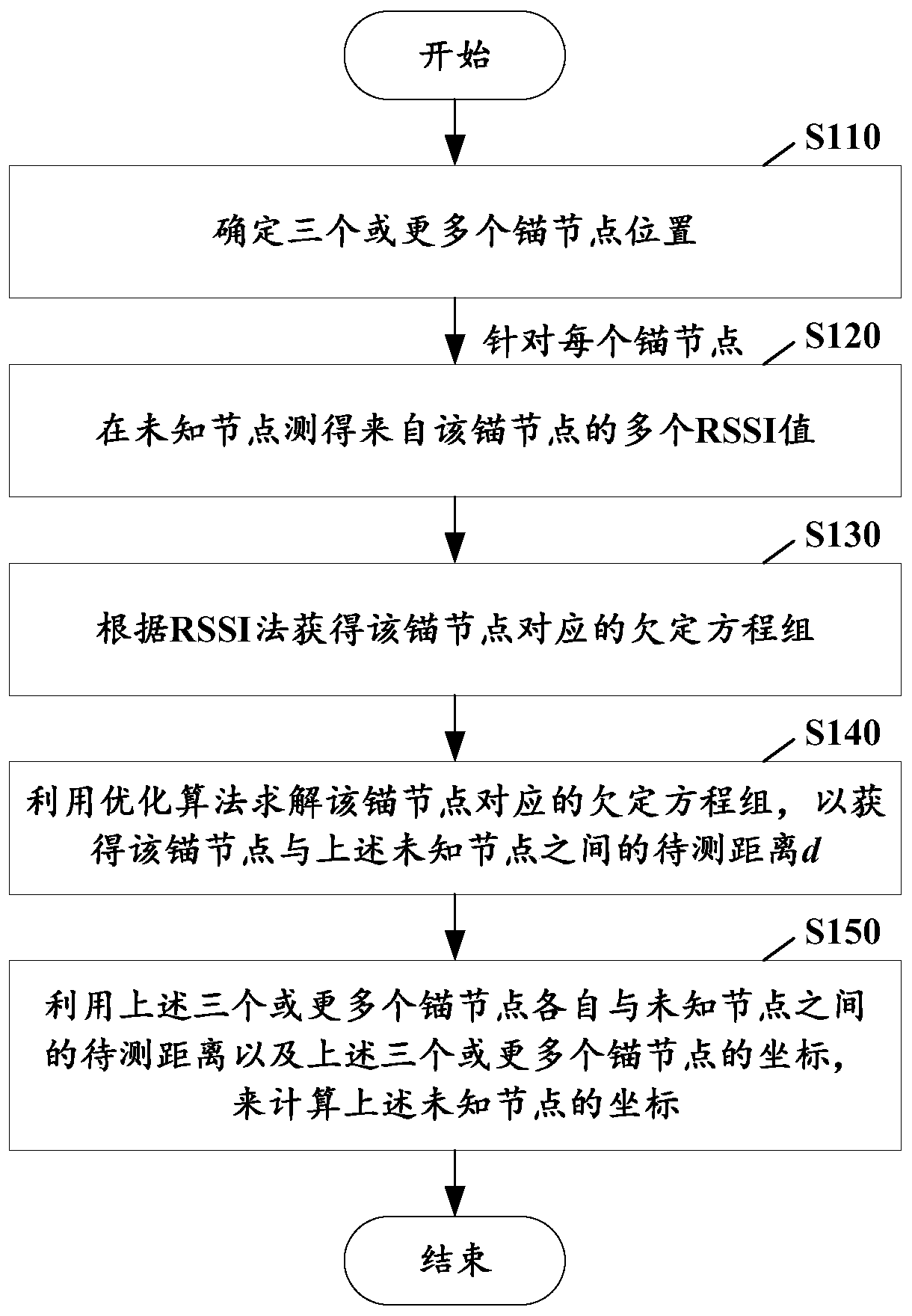
RSSI indoor multipath scattering positioning method based on optimization algorithm
ActiveCN106842120AImprove measurement errorHigh measurement accuracyPosition fixationMultipath scatteringUnderdetermined system
The invention provides an RSSI indoor multipath scattering positioning method based on an optimization algorithm. The method includes the steps that the positions of three or more anchor nodes are determined; aiming at each anchor node, an RSSI request instruction is transmitted to the anchor node from an unknown node multiple times, multiple received signal intensity values from the anchor node are measured on the unknown node, an underdetermined system of equations of the anchor node is obtained according to an RSSI method, unknown quantities in the underdetermined system of equations comprise the to-be-measured distance between the anchor node and the unknown node and m path loss coefficients, and the underdetermined system of equations corresponding to the anchor node is solved through the optimization algorithm to obtain the to-be-measured distance between the anchor node and the unknown node; coordinates of the unknown node are calculated according to the to-be-measured distances between the three or more anchor nodes and the unknown node and coordinates of the three or more anchor nodes.
Owner:山东博蓝建筑工程有限公司
Packet loss concealment for overlapped transform codecs
InactiveUS7627467B2Minimizes a model-based energy criterionMinimize artifactPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPacket loss concealmentUnderdetermined system
Real-time packet-based audio communications over packet-based networks frequently results in the loss of one or more packets during any given communication session. The real-time nature of such communications precludes retransmission of lost packets due to the unacceptable delays that would result. Consequently, packet loss concealment methods are employed to “hide” lost packets from the listener. Unfortunately, conventional loss concealment methods, such as packet repetition or stretch / overlap methods, do not fully exploit information available from partially received samples. Therefore, when a single frame of N coefficients is lost, 2N samples are only partially reconstructed, thereby degrading the reconstructed signal. To address this problem, an optimized packet loss concealment solution is identified for particular lost packets by solving an underdetermined system of linear equations representing partially received samples while minimizing a computed error based on a model of the signal obtained from neighboring blocks or frames received by the decoder.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
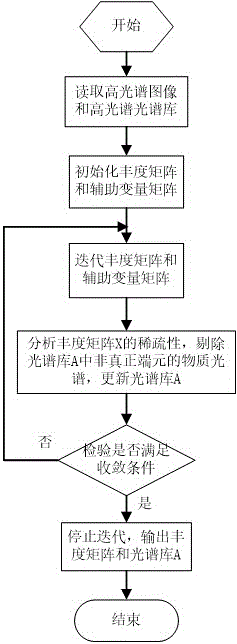
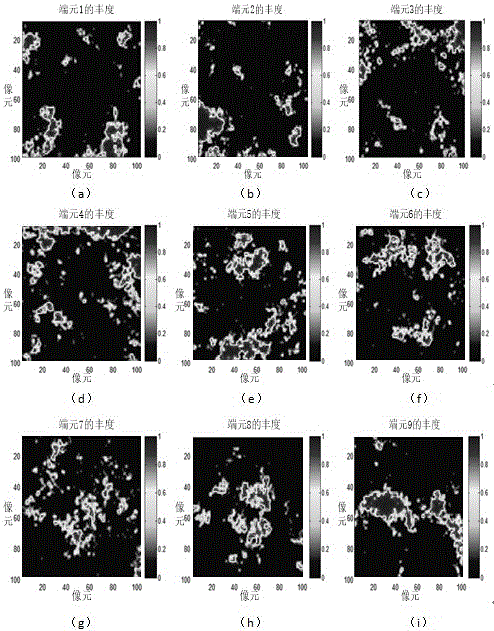
Hyperspectral image sparseness demixing method based on MFOCUSS and low-rank expression
ActiveCN105825227AOvercoming the problem of low accuracy of sparse unmixingPrevent extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural abundanceMixing effect
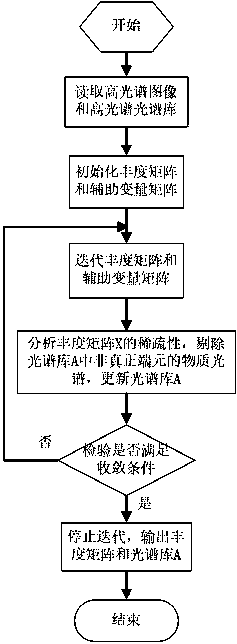
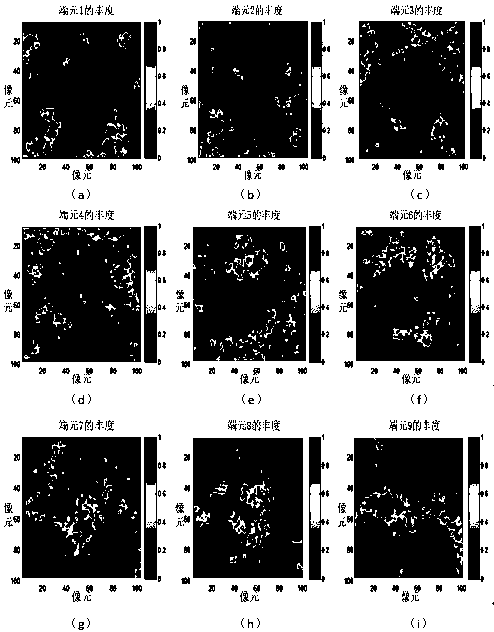
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image sparseness demixing method based on multiple focal underdetermined system solver (MFOCUSS) and low-rank expression. The method comprises: original hyperspectral data and known spectrum base data are read; and an objective function of a sparseness de-mixing model based on MFOCUSS and low-rank expression is constructed and the hyperspectral data and known spectrum base are used as input data and a dictionary of the objective function, the objective function of the MFOCUSS and low-rank expression is solved to obtain an abundance matrix of an overall spectrum library, a spectrum of a non-real end member in the spectrum library is rejected, repeated iteration is carried out on the spectrum library after non-real end member rejection to obtain a real end member matrix and a corresponding abundance matrix. According to the invention, direct end member extraction in the original hyperspectral data is avoided; the non-real end member is rejected and the spectrum library is updated; the adverse influence on the hyperspectral de-mixing effect by autocorrelation of the end member spectrum in the spectrum library is reduced; and precision of abundance estimation is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
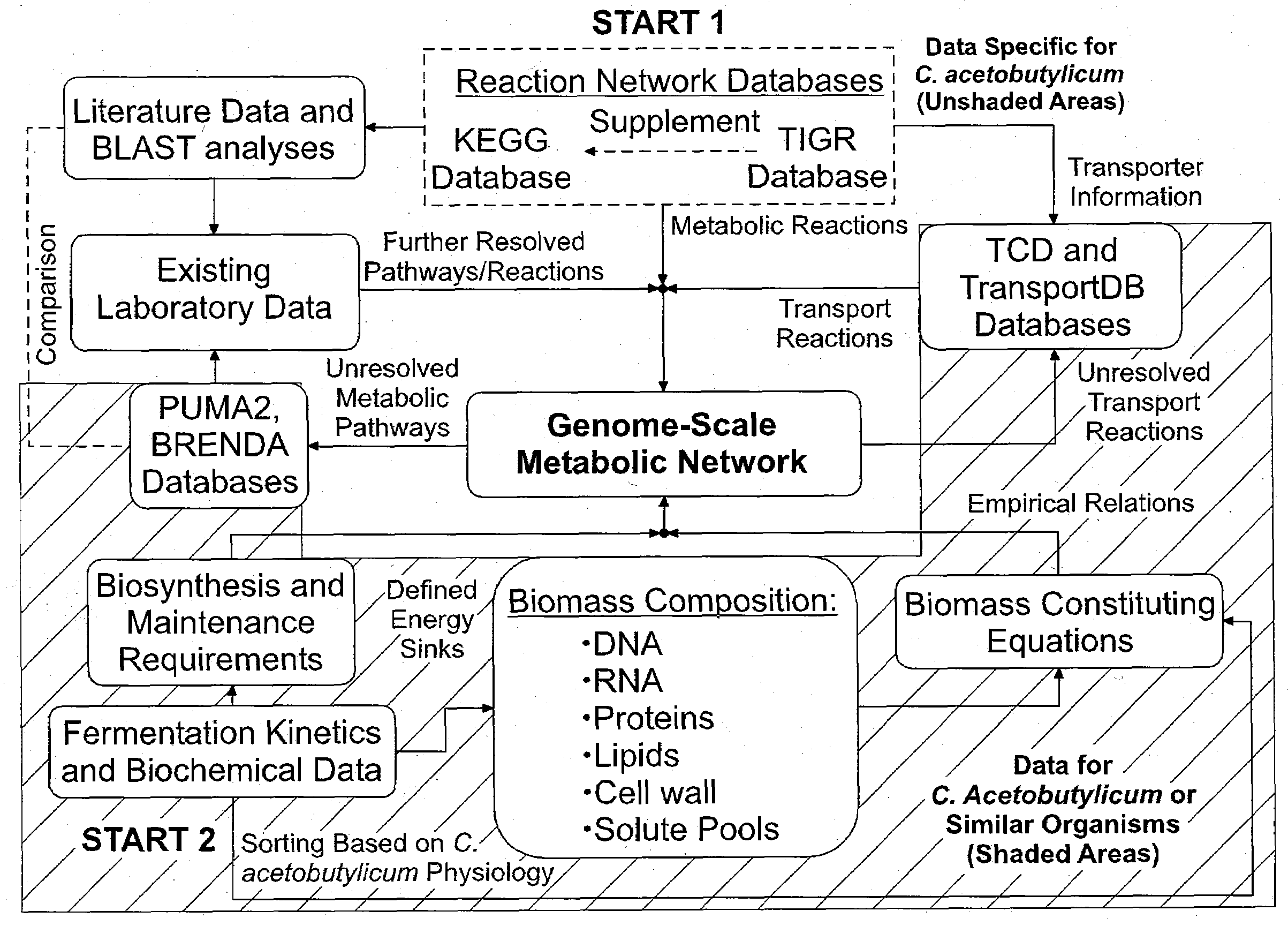
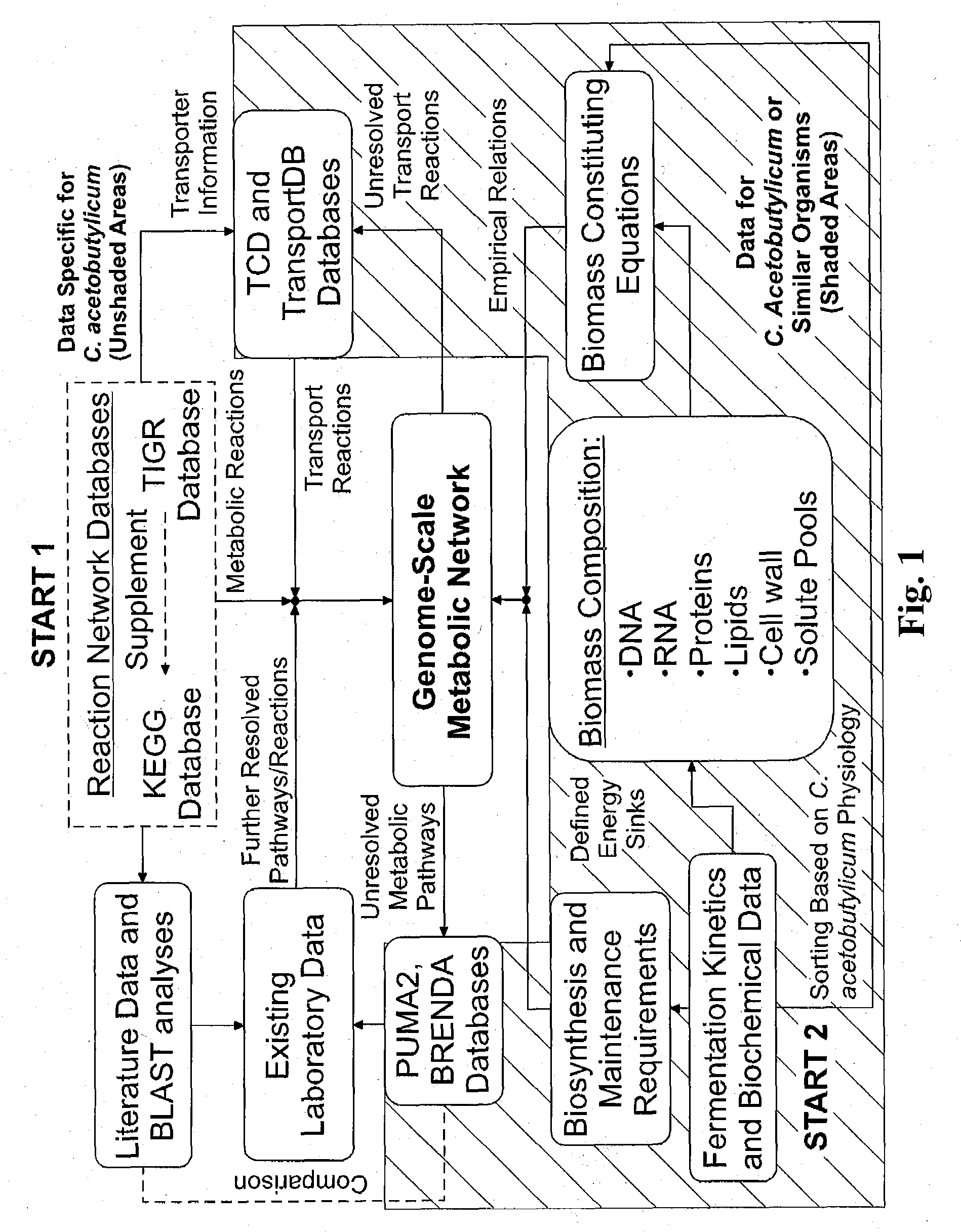
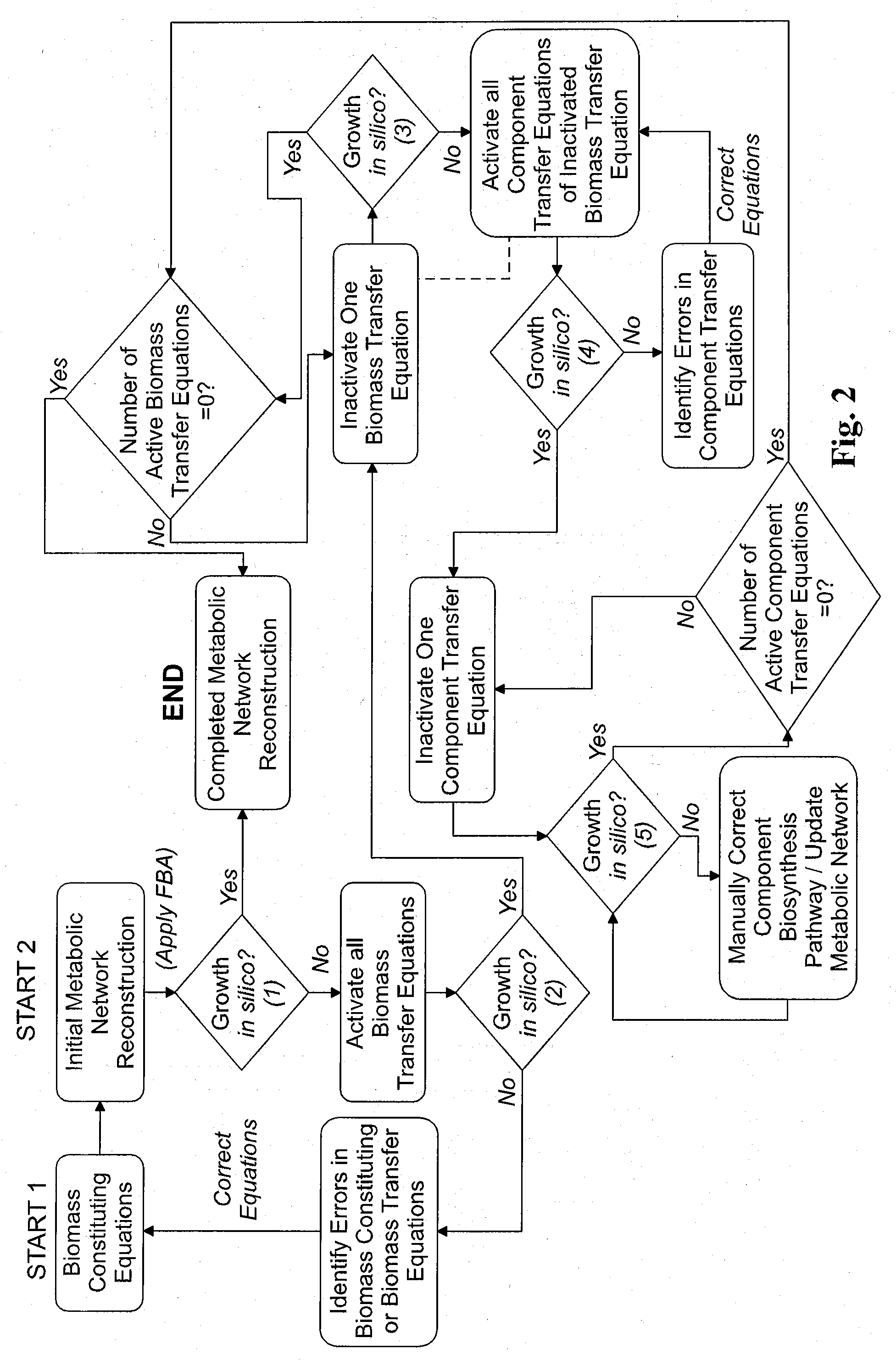
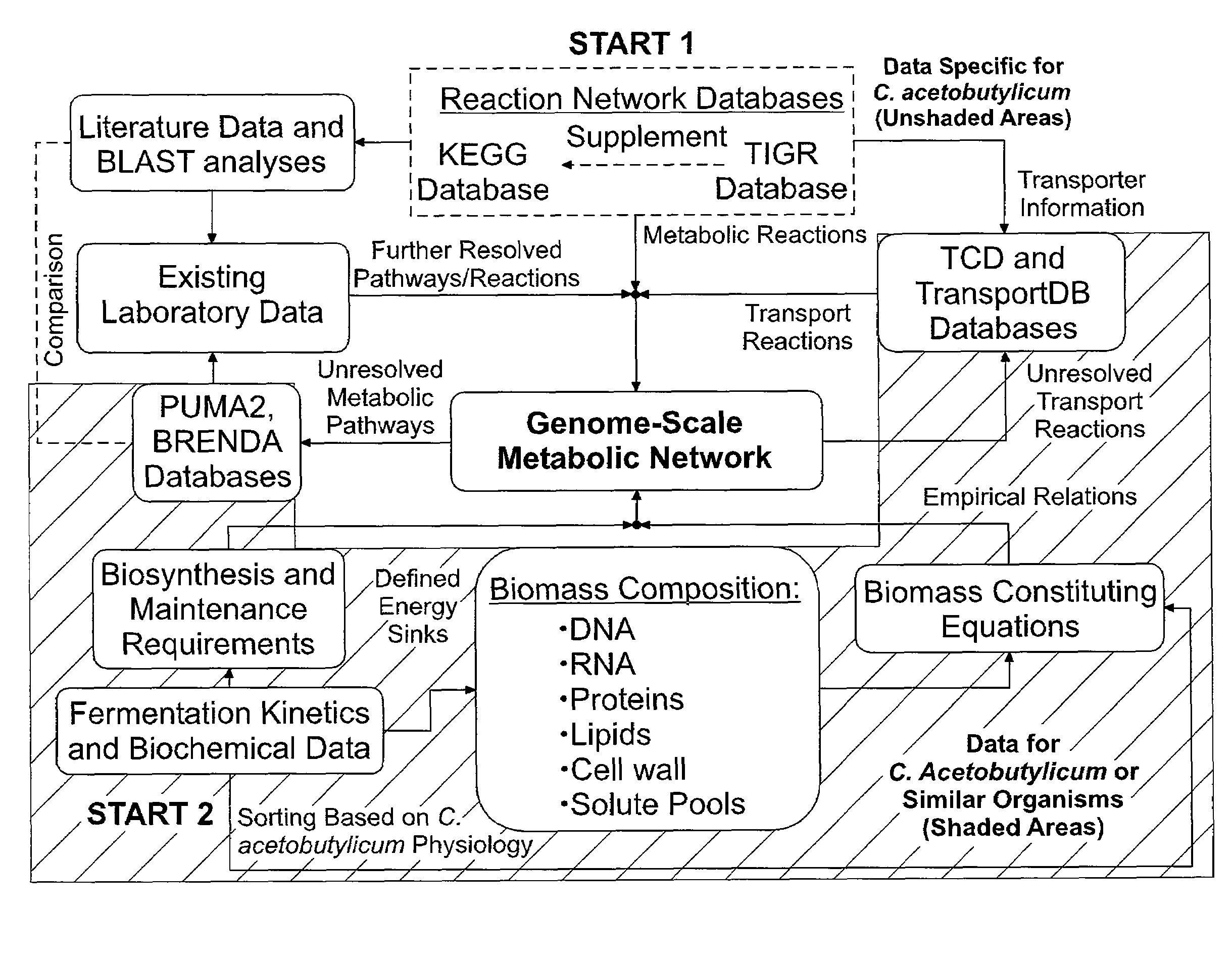
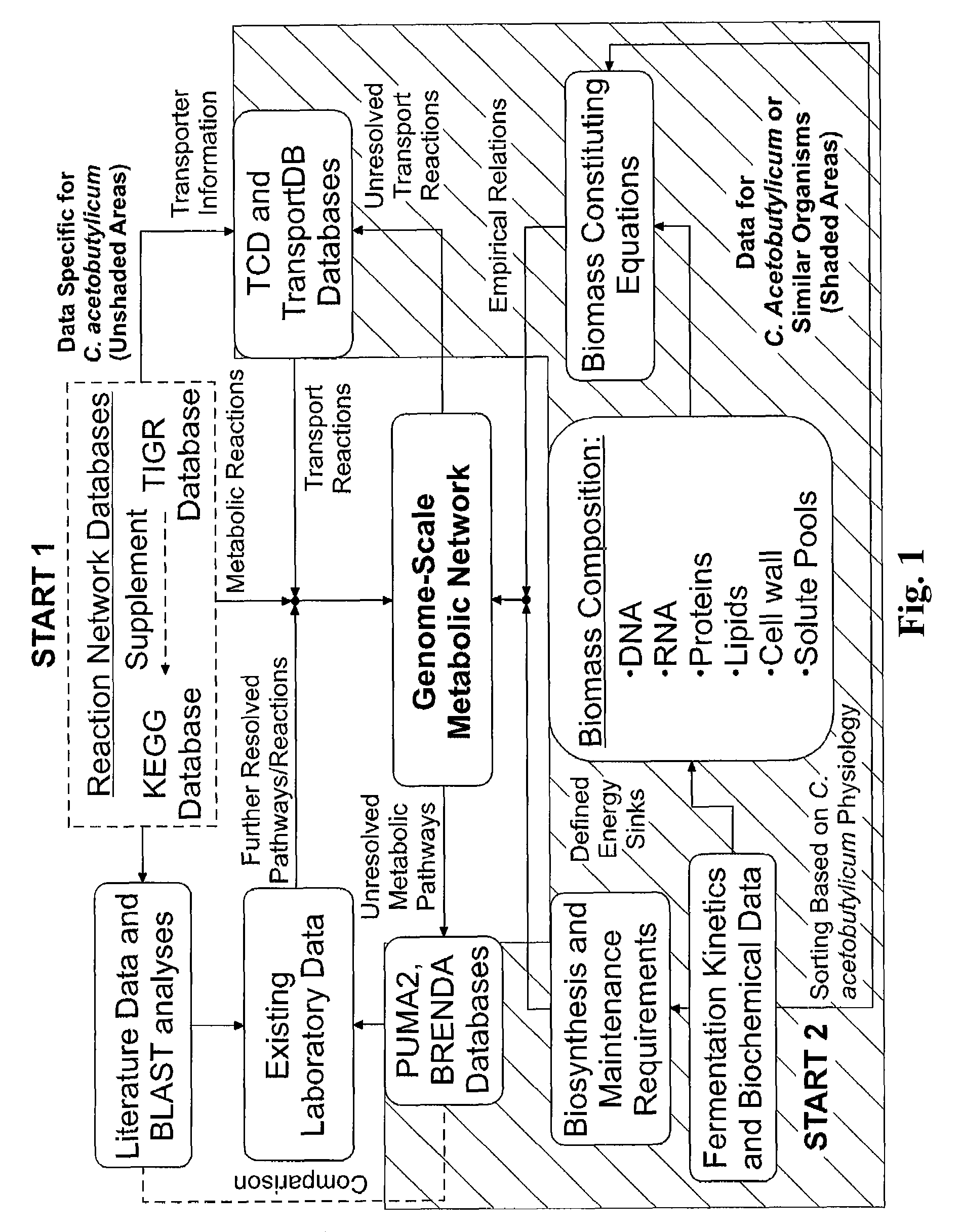
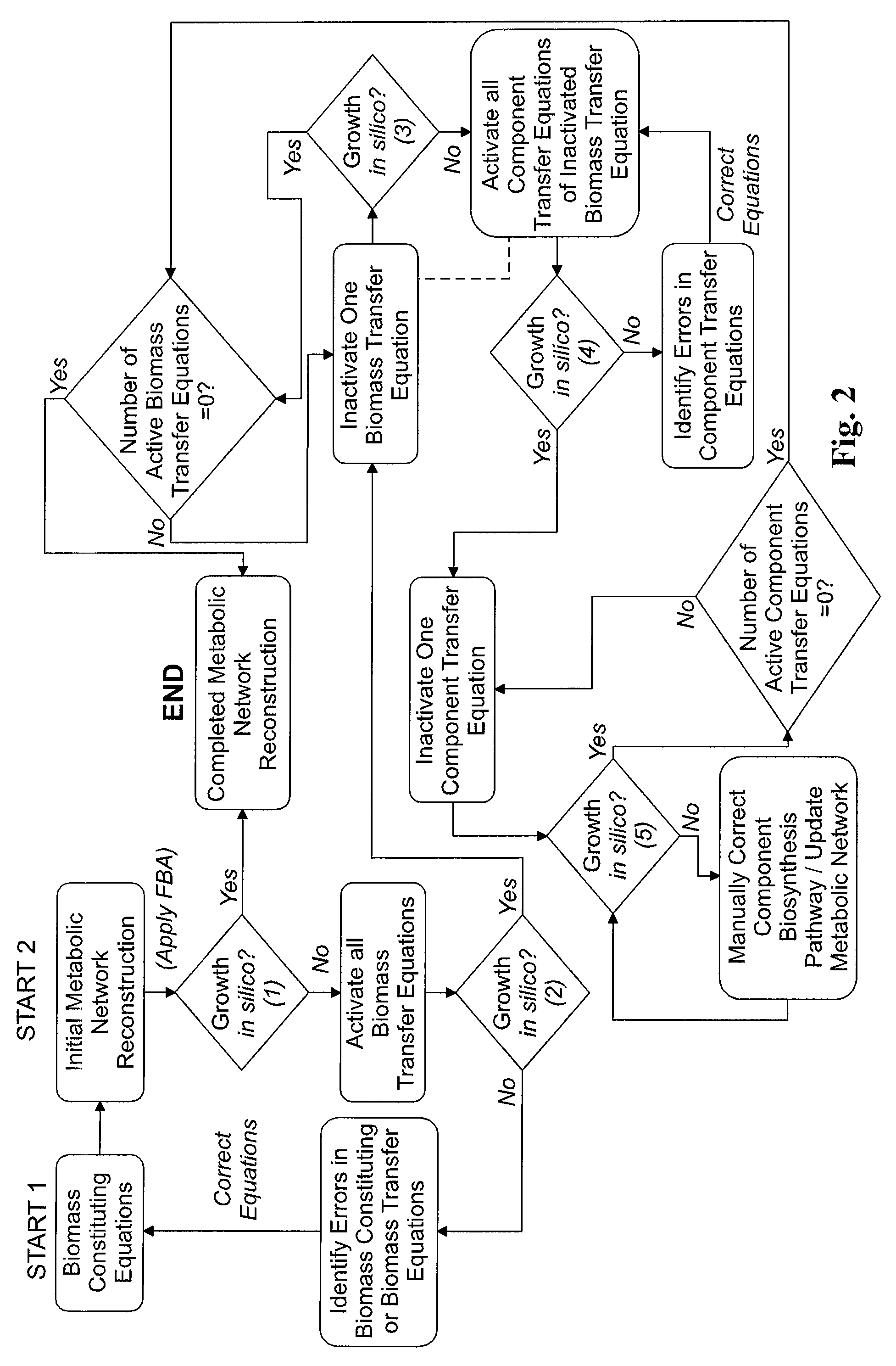
Reverse engineering genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions for organisms with incomplete genome annotation and developing constraints using proton flux states and numerically-determined sub-systems
InactiveUS20090259451A1Reduce in quantityAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingUnderdetermined systemIn silico
A genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction for Clostridium acetobutylicum (ATCC 824) was created using a new semi-automated reverse engineering algorithm. This invention includes algorithms and software that can reconstruct genome-scale metabolic networks for cell-types available through the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. This method can also be used to complete partial metabolic networks and cell signaling networks where adequate starting information base is available. The software may use a semi-automated approach which uses a priori knowledge of the cell-type from the user. Upon completion, the program output is a genome-scale stoichiometric matrix capable of cell growth in silico. The invention also includes methods for developing flux constraints and reducing the number of possible solutions to an under-determined system by applying specific proton flux states and identifying numerically-determined sub-systems. Although the model-building and analysis tools described in this invention were initially applied to C. acetobutylicum, the novel algorithms and software can be applied universally.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
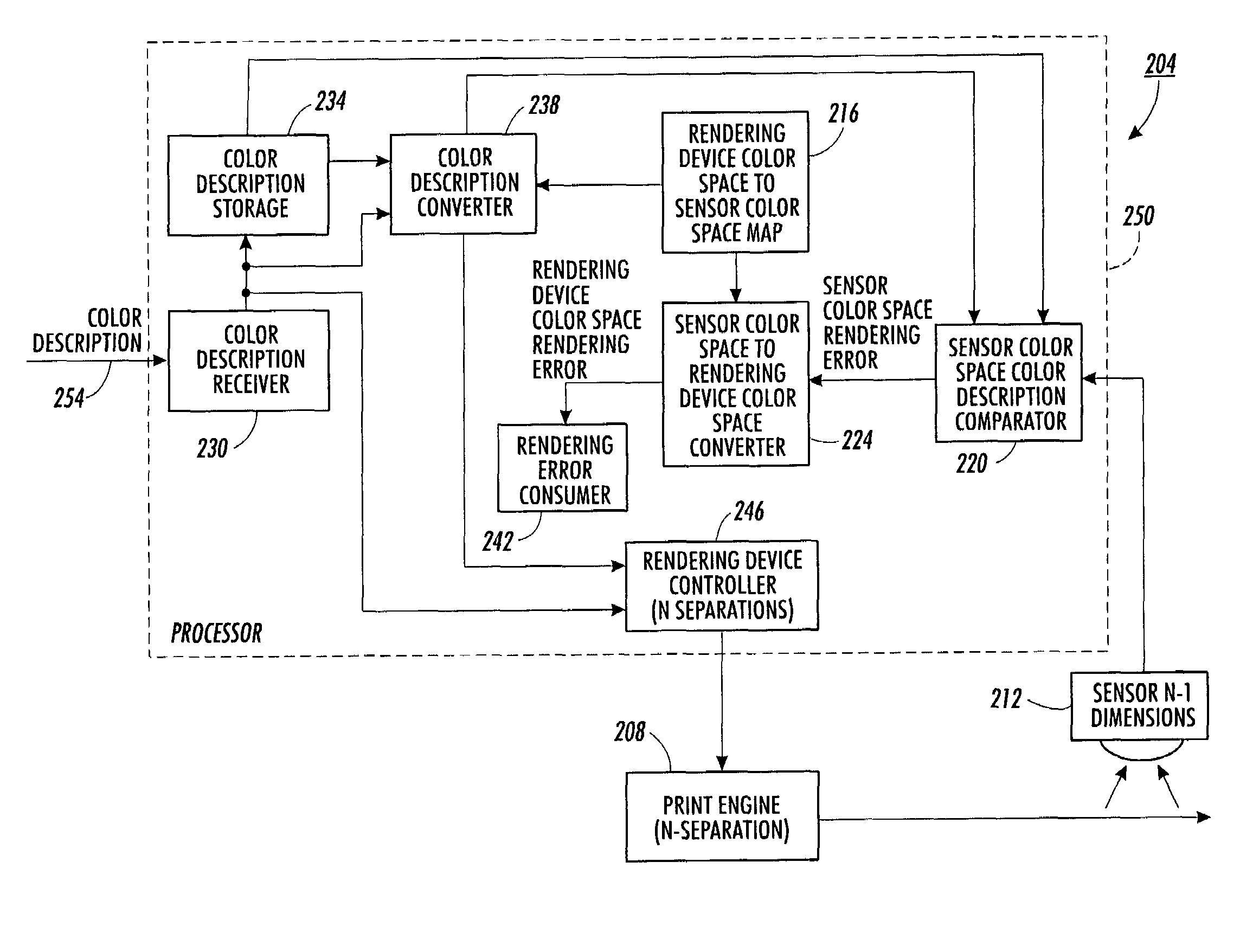
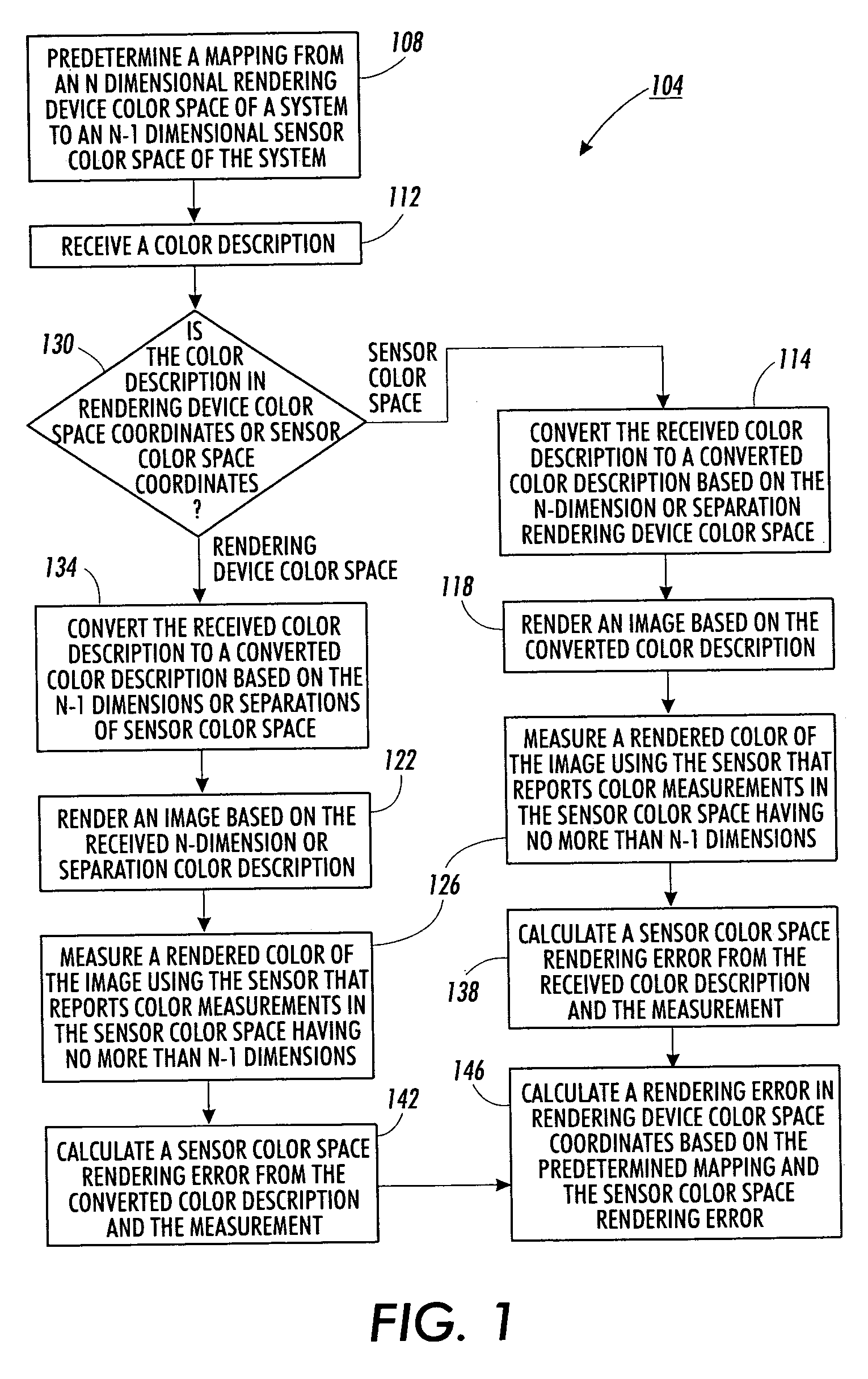
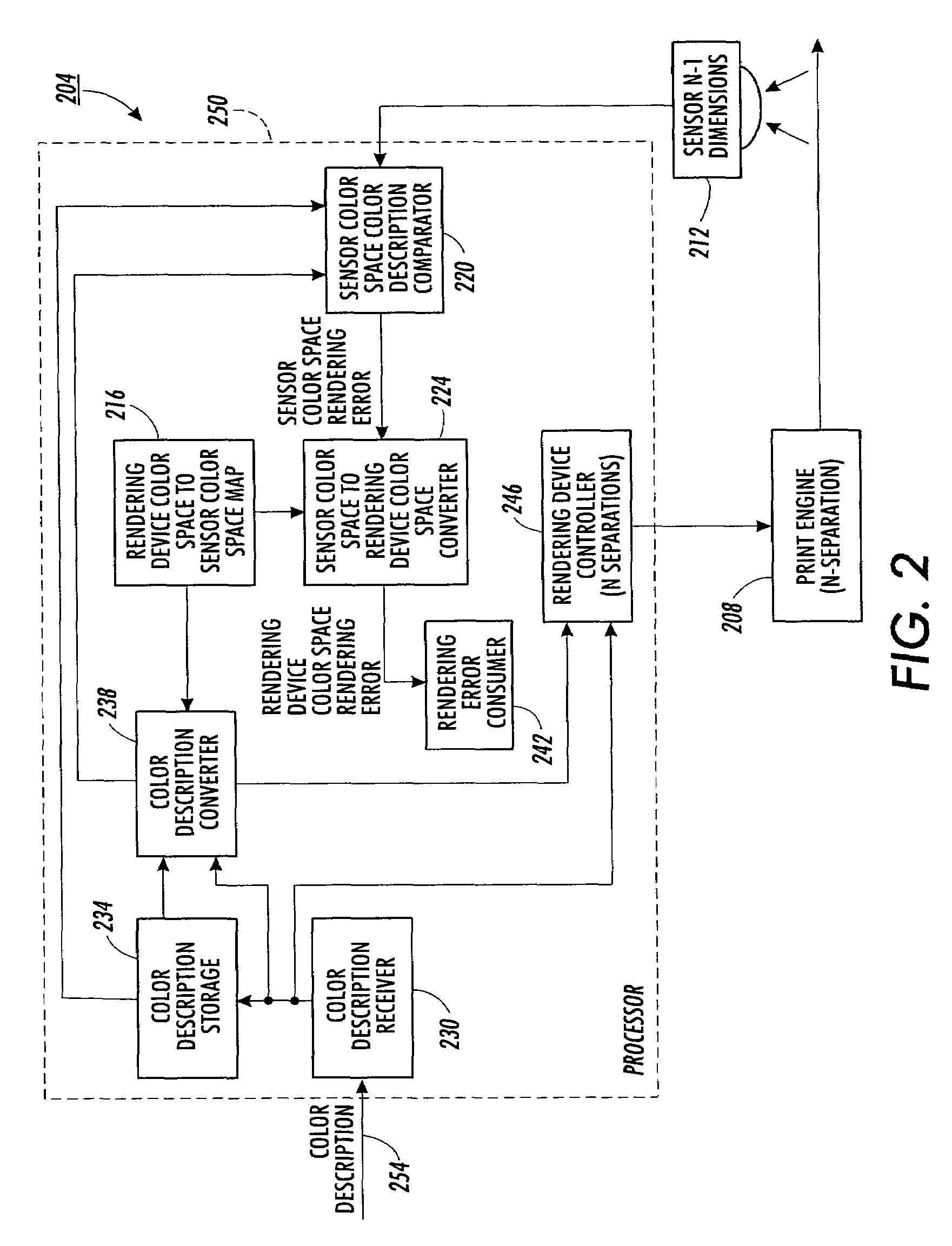
Method for calculating colorant error from reflectance measurement
InactiveUS7295215B2Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsReflectivity measurementUnderdetermined system
Color error associated with an image rendered by a rendering device is calculated in the no more than N−1 dimensions of an associated color sensor color space. The color error is assumed to be small. A differential of a mapping from an N dimensional rendering device color space to the associated color sensor color space is used to calculate a colorant error in the N dimensions of the rendering device color space. Where necessary, appropriate assumptions are used to constrain an underdetermined system of equations. Where calculated colorant error is unreasonable, the calculated colorant error is clipped and colorant error is recalculated based on the clipped value.
Owner:XEROX CORP
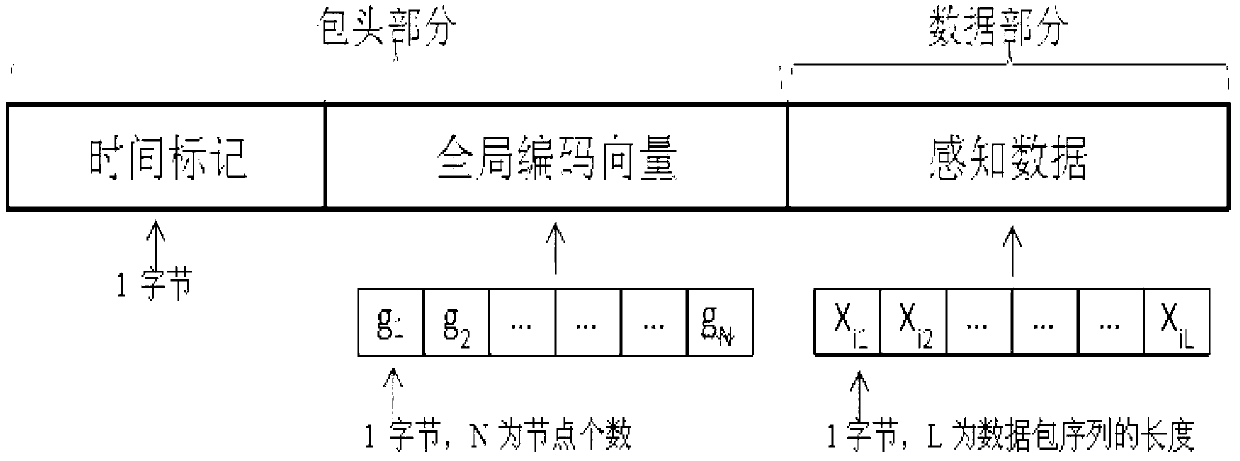
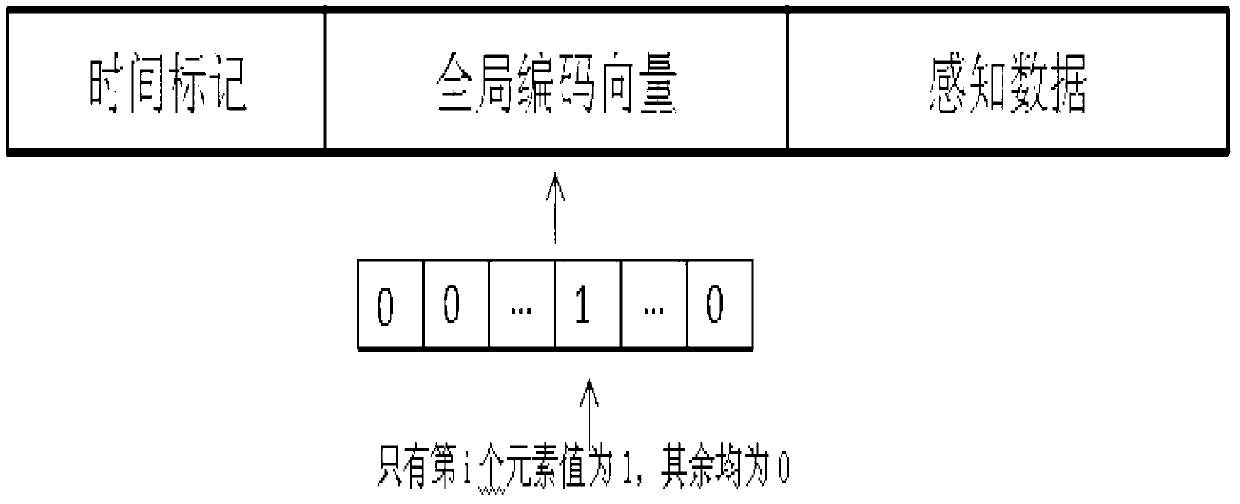
Data processing method and system suitable for wireless distributed perception system
InactiveCN103346864ASolve the \"allSolve the nothing problemError preventionNetwork topologiesL1 minimizationSensor node
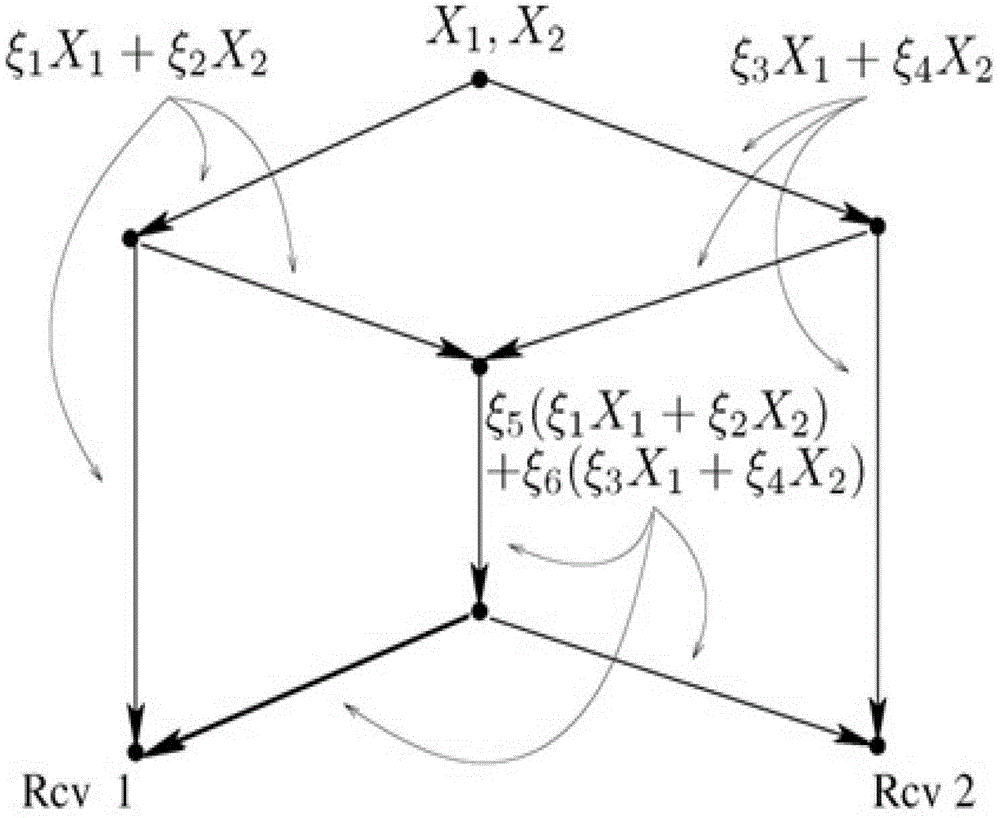
The invention provides a data processing method and system suitable for a wireless distributed perception system. The data processing method includes the following steps that sensor nodes collect perception data with relevance; intermediate nodes process the perception data by utilizing random linear network codes; the number of the sensor nodes is N, the number of aggregation nodes is m, source data are supposed to be x, data received by the aggregation nodes are y, the aggregation nodes combine received input vectors to acquire a system of linear equations, and due to the fact that m (N and the system of linear equations) is underdetermined, the problem of solving the underdetermined system of equations is converted to the problem of minimizing l1, and original perception data are reconstructed; a receiving terminal receives the original perception data. The data processing method and system suitable for the wireless distributed perception system have the advantages that due to the fact that the compressed perception theory is introduced to the decoding stage of the aggregation nodes, the problem of 'all or nothing' is effectively solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
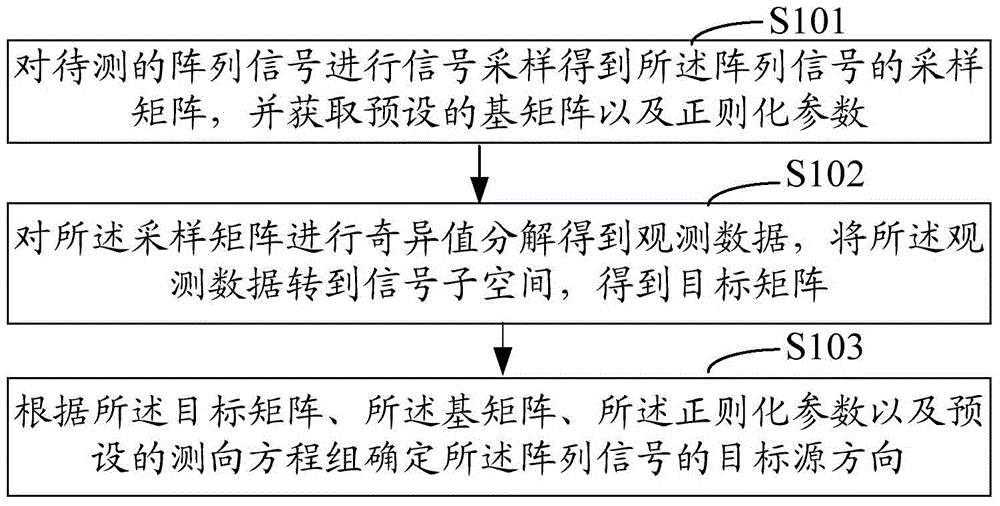
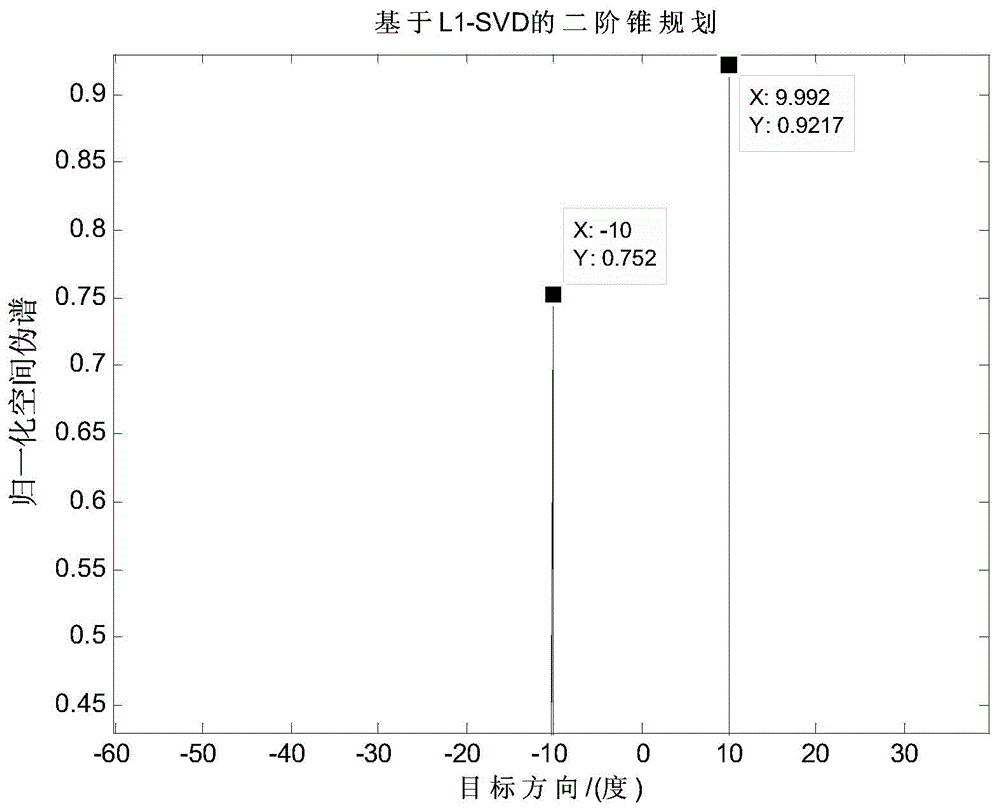
Method and system for finding direction of target source of array signal
InactiveCN104407319AEasy to follow upReduce processing costsRadio wave finder detailsSingular value decompositionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention provides a method and a system for finding a direction of a target source of an array signal. The method comprises the following steps: performing signal sampling on the array signal to be detected to obtain a sampling matrix of the array signal, and acquiring a preset base matrix and a regularization parameter; performing singular value decomposition on the sampling matrix to obtain observation data, transferring the observation data into a signal subspace to obtain a target matrix; determining a target source direction of the array signal according to the target matrix, the base matrix, the regularization parameter and a preset direction finding equation set. According to the scheme, the target source direction finding of a high-dimensional signal can be abstracted into solution of underdetermined system of equations, so that effects of lower reconstruction error and higher success rate can be achieved within a larger signal-to-noise ratio range, and signals with higher correlation can be identified.
Owner:POWER DISPATCHING CONTROL CENT OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID CO LTD
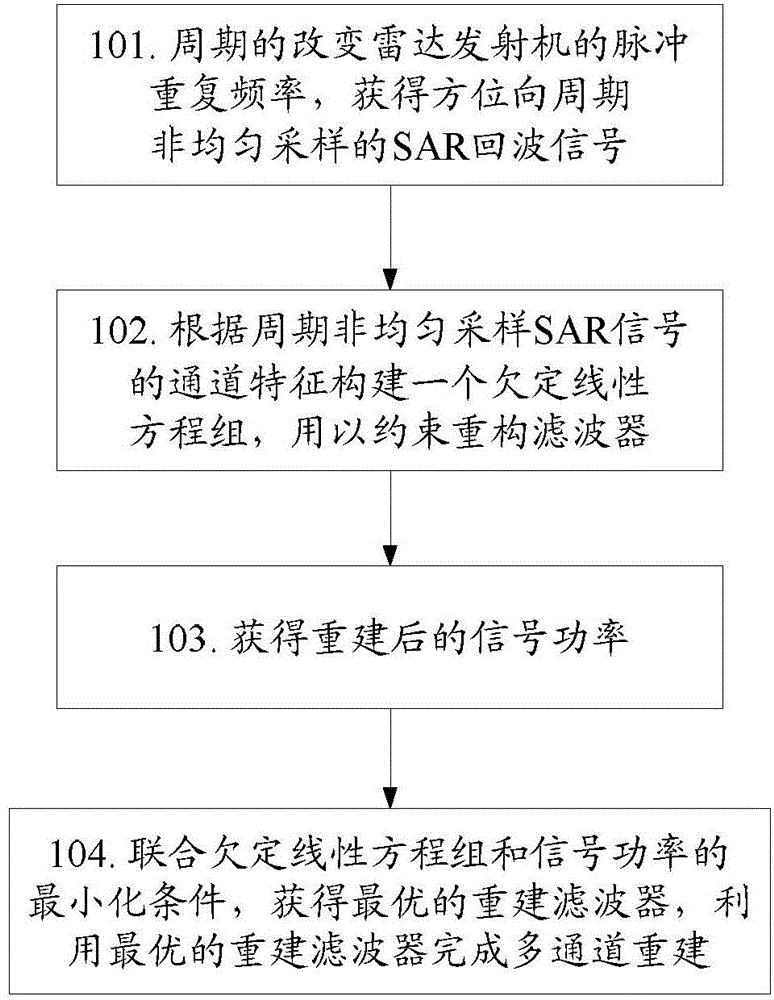
Multichannel reconstruction method and device for periodical non-uniform sampling SAR (synthetic aperture radar) signals
InactiveCN104008270AMinimize powerImprove performanceSpecial data processing applicationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionReconstruction filterSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a multichannel reconstruction method for periodical non-uniform sampling SAR (synthetic aperture radar) signals. The method includes: periodically changing pulse repetition frequency of a radar transmitter to acquire a periodical non-uniform sampling SAR echo signal, constructing a constraint underdetermined system of linear equations of a reconstruction filter according to channel features of the periodical non-uniform sampling SAR echo signal to acquire signal power after multichannel reconstruction, combining the underdetermined system of linear equations and minimum conditions of the signal power to acquire the optimal reconstruction filter, and using the optimal reconstruction filter to complete multichannel reconstruction.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reverse engineering genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions for organisms with incomplete genome annotation and developing constraints using proton flux states and numerically-determined sub-systems
InactiveUS8311790B2Analogue computers for chemical processesSystems biologyInformation repositoryMetabolic network
A genome-scale metabolic network reconstruction for Clostridium acetobutylicum (ATCC 824) was created using a new semi-automated reverse engineering algorithm. This invention includes algorithms and software that can reconstruct genome-scale metabolic networks for cell-types available through the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. This method can also be used to complete partial metabolic networks and cell signaling networks where adequate starting information base is available. The software may use a semi-automated approach which uses a priori knowledge of the cell-type from the user. Upon completion, the program output is a genome-scale stoichiometric matrix capable of cell growth in silico. The invention also includes methods for developing flux constraints and reducing the number of possible solutions to an under-determined system by applying specific proton flux states and identifying numerically-determined sub-systems. Although the model-building and analysis tools described in this invention were initially applied to C. acetobutylicum, the novel algorithms and software can be applied universally.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
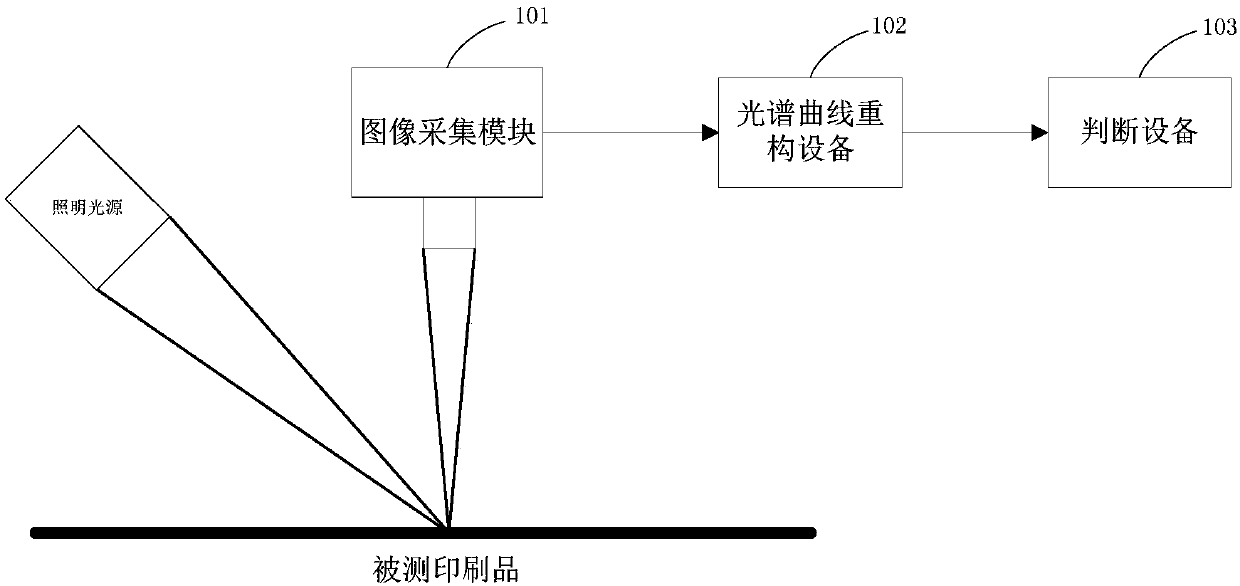
Spectrum curve reconstructing method and device
ActiveCN107907215AAvoid the number of sampling pointsLow costImage enhancementImage analysisArray data structureSpectral response
The invention provides a spectrum curve reconstructing method and device. A sampling result of a first sampling point of a to-be-detected object is acquired. The sampling result of the first samplingpoint includes sampling information of M channels of the sampling point. M sampling functions are determined according to products of a light source output spectrum function and spectral response functions of M sampling information of a sampling device respectively. A sampling array matrix is determined according to an impulse function group and the sampling functions. An underdetermined system ofequations is determined according to the sampling array matrix and the sampling results. A coefficient S is determined according to the impulse function group and a prior spectrum function. Through aconstraint condition of taking the minimal value of the variant S, a spectrum function of the first sampling point is determined from a plurality of solutions of the underdetermined system of equations. According to the invention, the prior spectrum function substitute into a spectrum sampling reconstruction process so as to make up sampling deficiency of a to-be-measured spectrum curve. Therefore, use of excessive sampling points is avoided, cost is saved and system complexity is furthermore reduced.
Owner:BEIJING LUSTER LIGHTTECH
Single image camera calibration method based on compressed sensing
ActiveCN107644444AImprove calibration qualityImprove calibration efficiencyImage analysisSingle imageLoop optimization
The invention relates to the technical field of camera calibration and in particular discloses a single image camera calibration method based on compressed sensing. The method is just required to photograph a calibration plate once, and solves the optimal solution of a single image by using a compressed sensing reconstruction algorithm by setting qualification conditions for six unknown quantitiesin a underdetermined system of equations of the single image via a Zhang's planar calibration method, thereby greatly simplifying the process of solving the internal matrix and the foreign matrix ofthe single image. The used compressed sensing reconstruction algorithm is subjected to self loop optimization and high camera calibration quality and high calibration efficiency are achieved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH +1
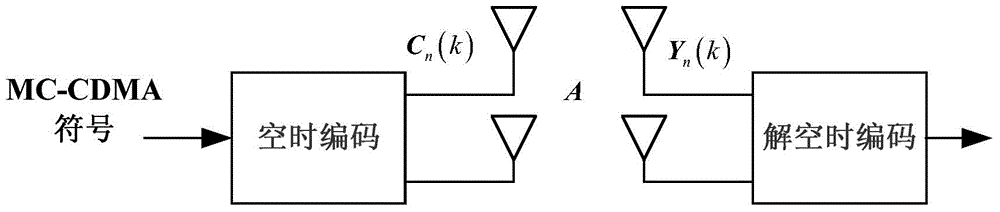
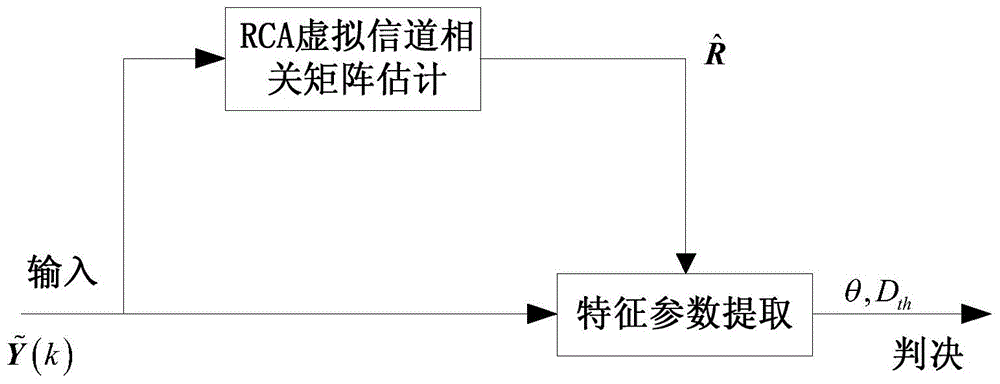
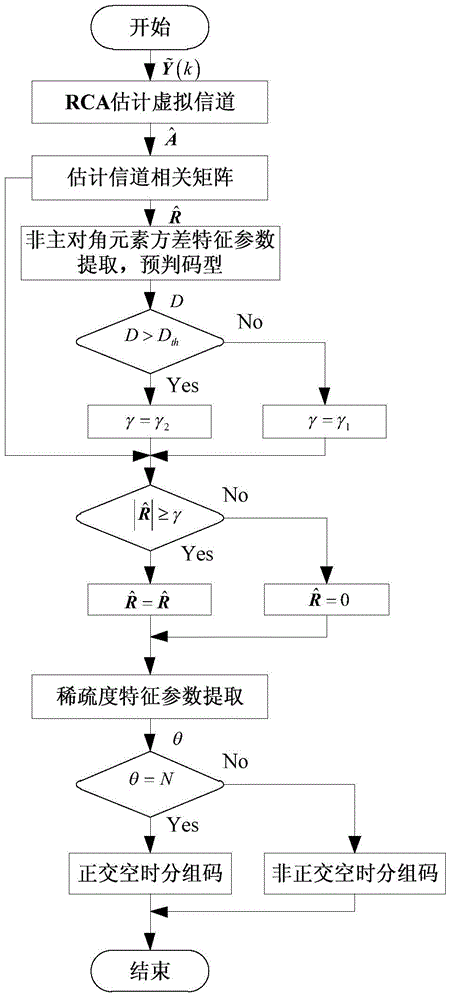
Underdetermined system real orthogonal space-time block code blind identification method based on robust competitive clustering
ActiveCN104363078ABlind recognition worksEfficient identificationReceiver specific arrangementsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMain diagonalSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to an underdetermined system real orthogonal space-time block code blind identification method based on robust competitive clustering, and belongs to the technical field of signal processing. The method comprises the steps of modeling a signal receiving model relevant to a virtual channel matrix, wherein the virtual channel matrix comprises space-time code information and can be used for identifying the space-time code; then carrying out blind estimation on the virtual channel matrix by using a robust competitive clustering algorithm; extracting the sparseness of the relevant matrix of the virtual channel matrix and an identification characteristic parameter of an energy ratio of non-main diagonal element energy to main diagonal element energy; and finally performing orthogonal space-time block code identification according to the parameter. By the adoption of the algorithm, a real orthogonal space-time block code signal is subjected to effective blind identification under low complexity, and the real orthogonal space-time block code signal can well work under a condition of a low input signal-to-noise ratio, so that the system performance is improved; moreover, the robust competitive clustering algorithm can be also used for carrying out blind estimation on the number of source signals, and the underdetermined system real orthogonal space-time block code blind identification method has a wide application prospect.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
RSSI Indoor Multipath Scattering Location Method Based on Optimal Algorithm
ActiveCN106842120BImprove measurement errorHigh measurement accuracyPosition fixationMultipath scatteringUnderdetermined system
The invention provides an RSSI indoor multipath scattering positioning method based on an optimization algorithm. The method includes the steps that the positions of three or more anchor nodes are determined; aiming at each anchor node, an RSSI request instruction is transmitted to the anchor node from an unknown node multiple times, multiple received signal intensity values from the anchor node are measured on the unknown node, an underdetermined system of equations of the anchor node is obtained according to an RSSI method, unknown quantities in the underdetermined system of equations comprise the to-be-measured distance between the anchor node and the unknown node and m path loss coefficients, and the underdetermined system of equations corresponding to the anchor node is solved through the optimization algorithm to obtain the to-be-measured distance between the anchor node and the unknown node; coordinates of the unknown node are calculated according to the to-be-measured distances between the three or more anchor nodes and the unknown node and coordinates of the three or more anchor nodes.
Owner:山东博蓝建筑工程有限公司
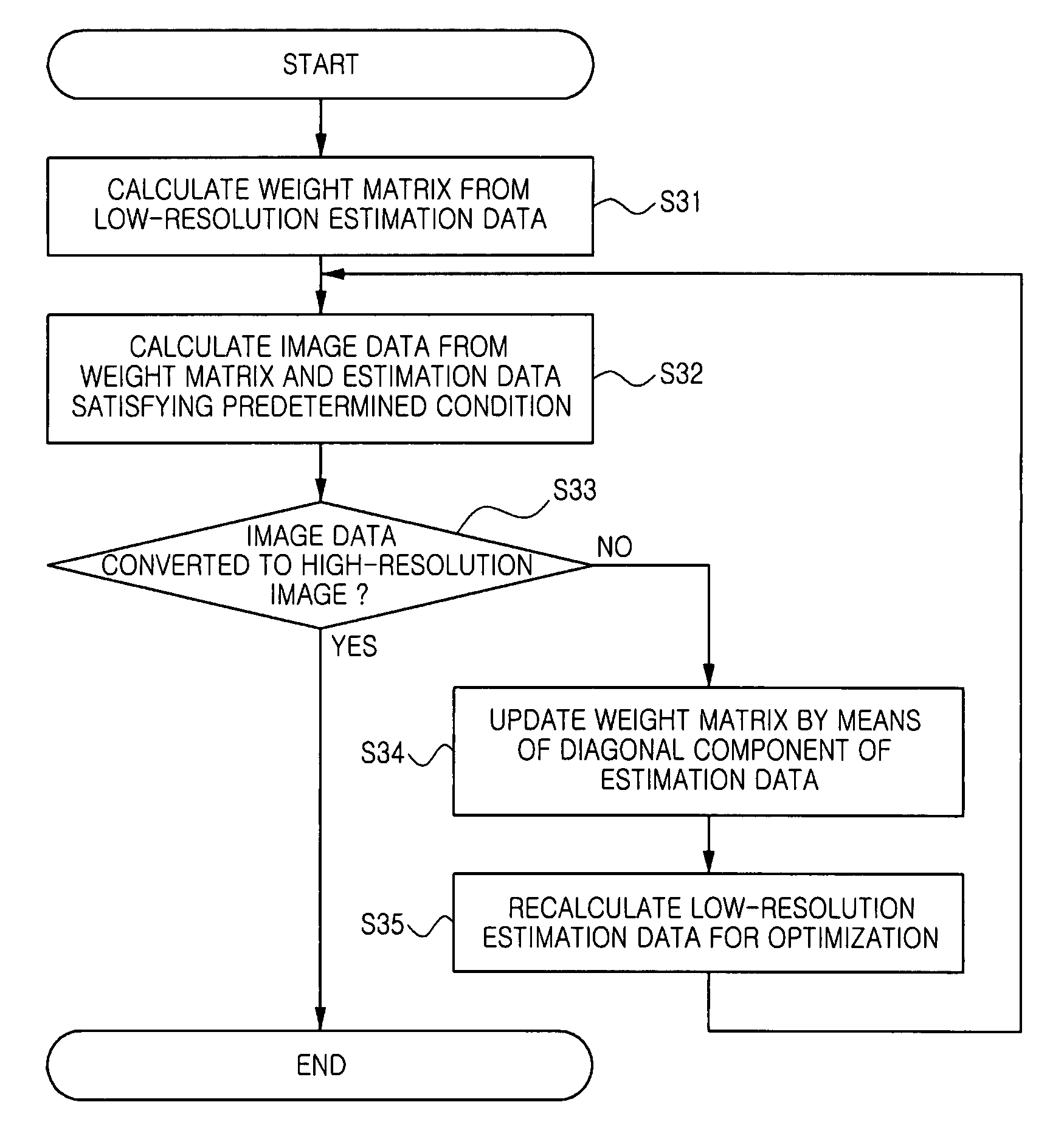
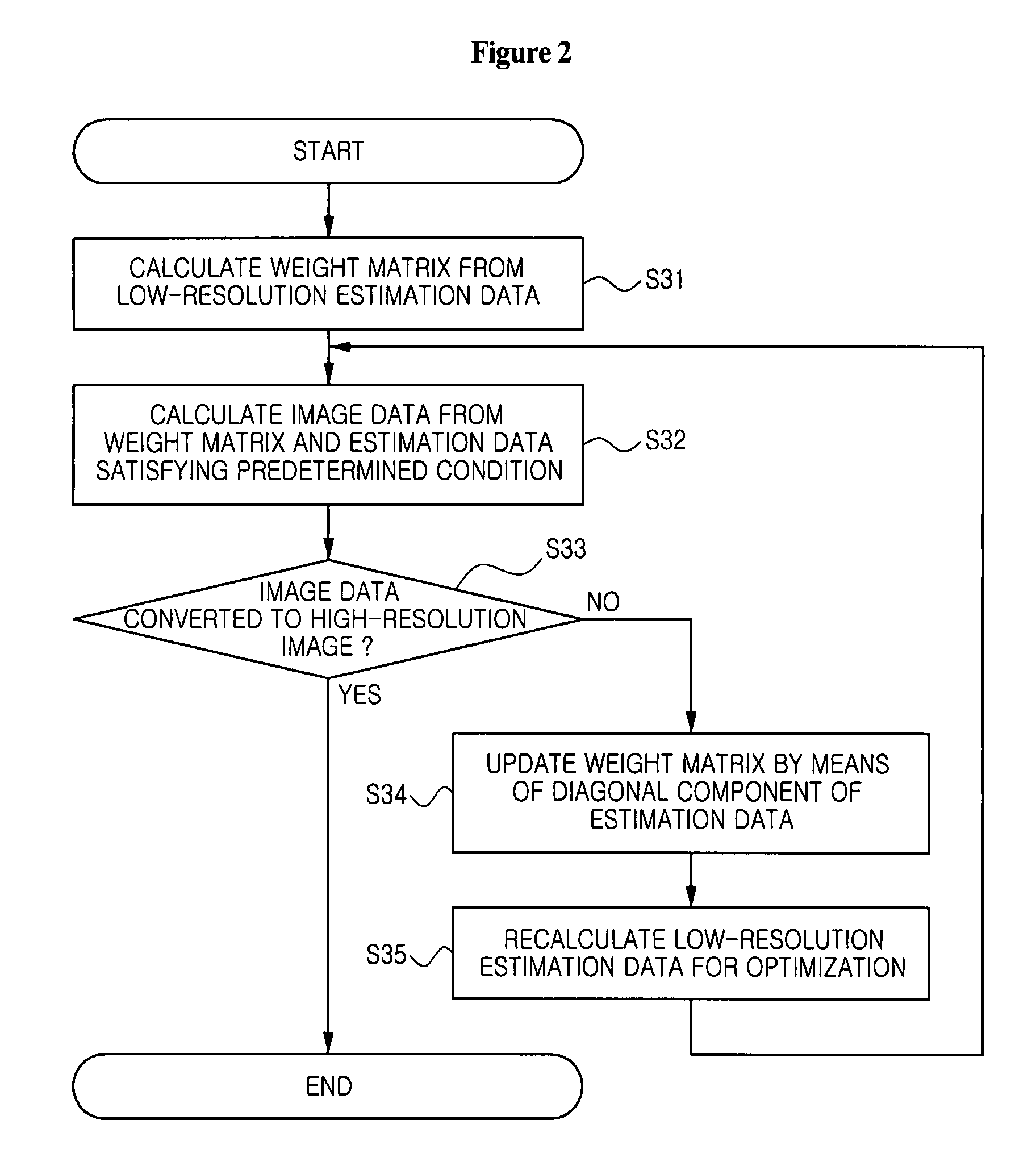
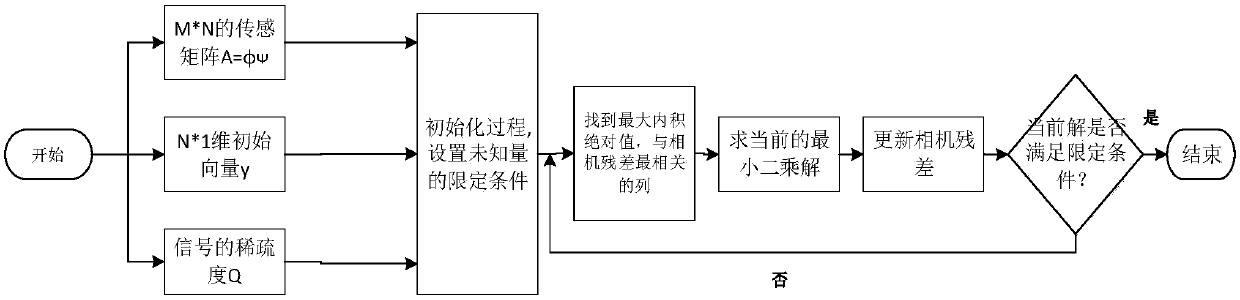
Solution method and solution apparatus for underdetermined system of linear equations
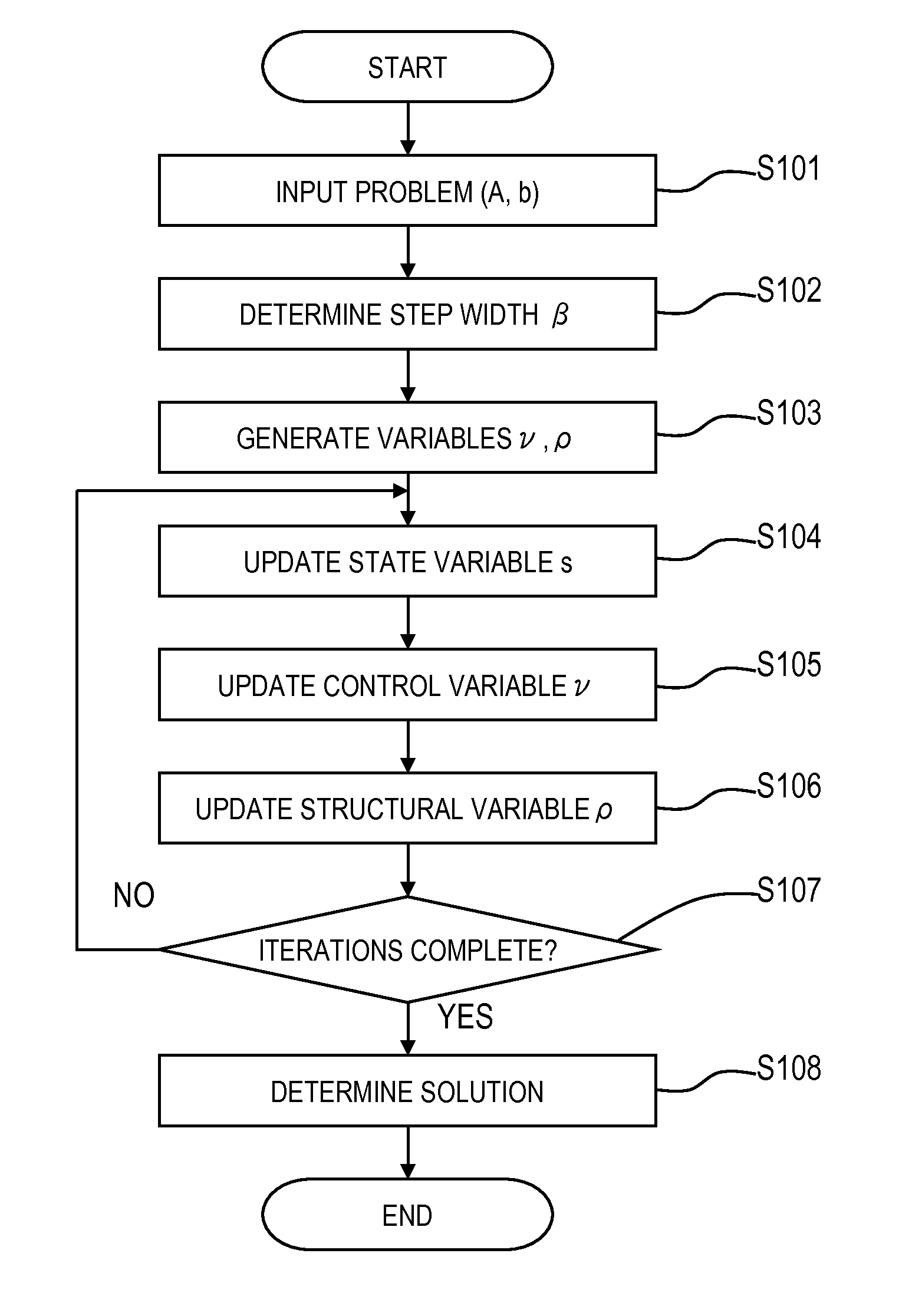
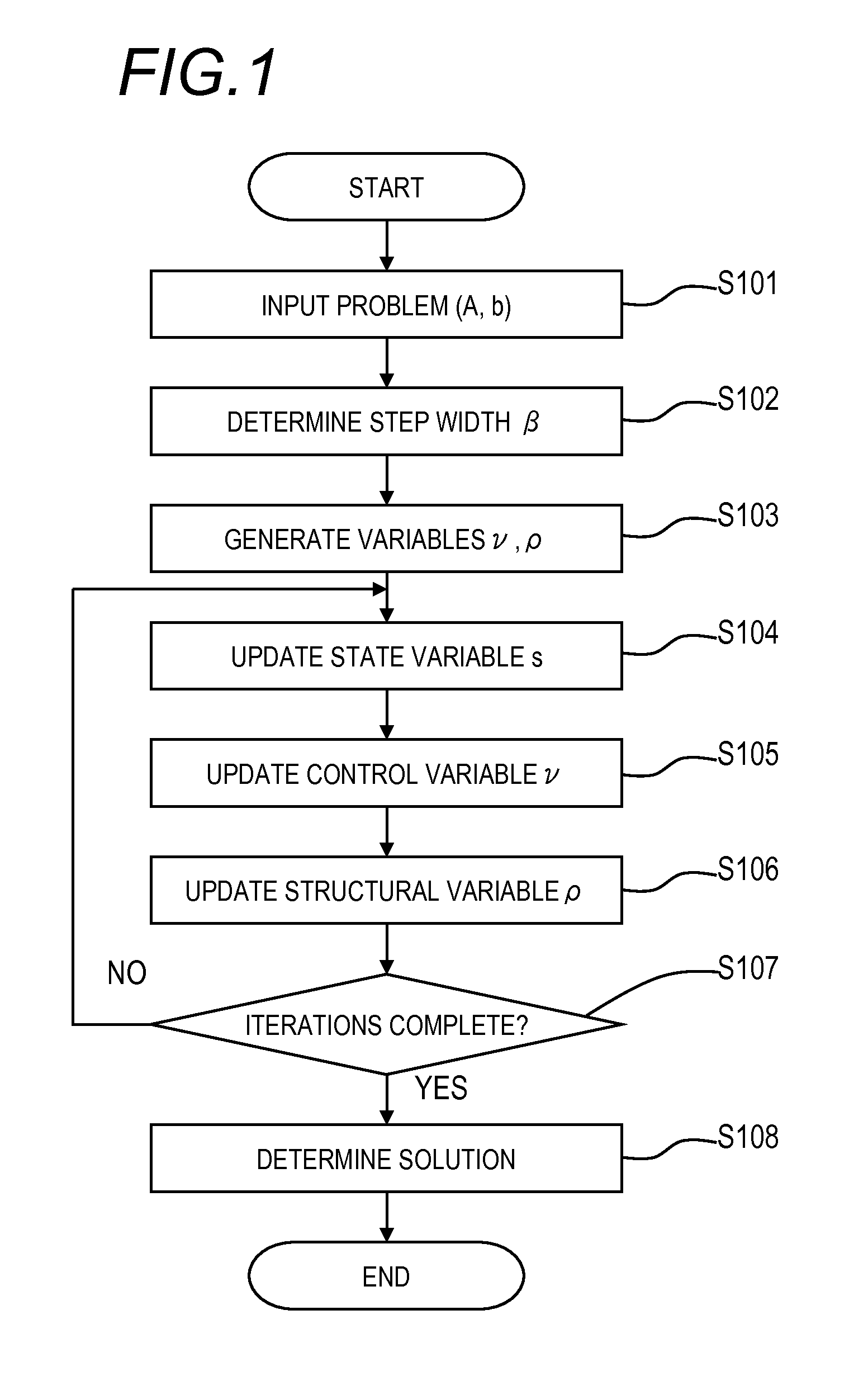
InactiveUS20150161076A1High degree of estimation precisionSmall observation rateComplex mathematical operationsComputation using denominational number representationState variableTheoretical computer science
A variable to be determined is expressed as a product of a state variable and a structural variable for each element. The structural variable is a monotonically increasing function of a control variable that takes a real number value, and is thus limited to a real number of 0 to 1. An objective function defined as a function of the state variable and structural variable or the state variable and control variable is used. In each iteration, a computer executes: a state variable updating step of updating a value of each element of the state variable on the basis of information of the objective function with respect to the state variable; and a structural variable updating step of updating a value of each element of the structural variable on the basis of information of the objective function with respect to said structural variable.
Owner:CANON KK
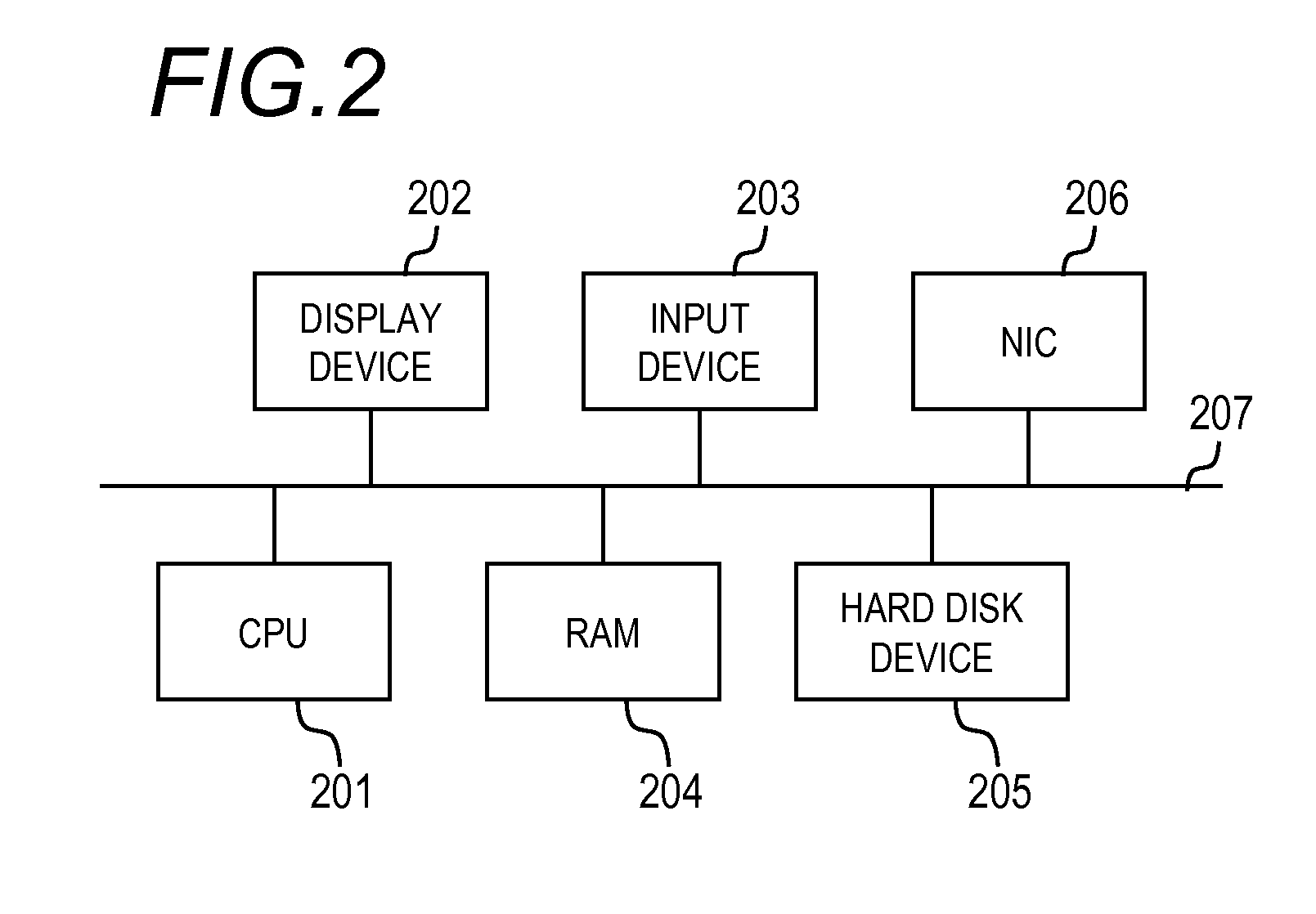
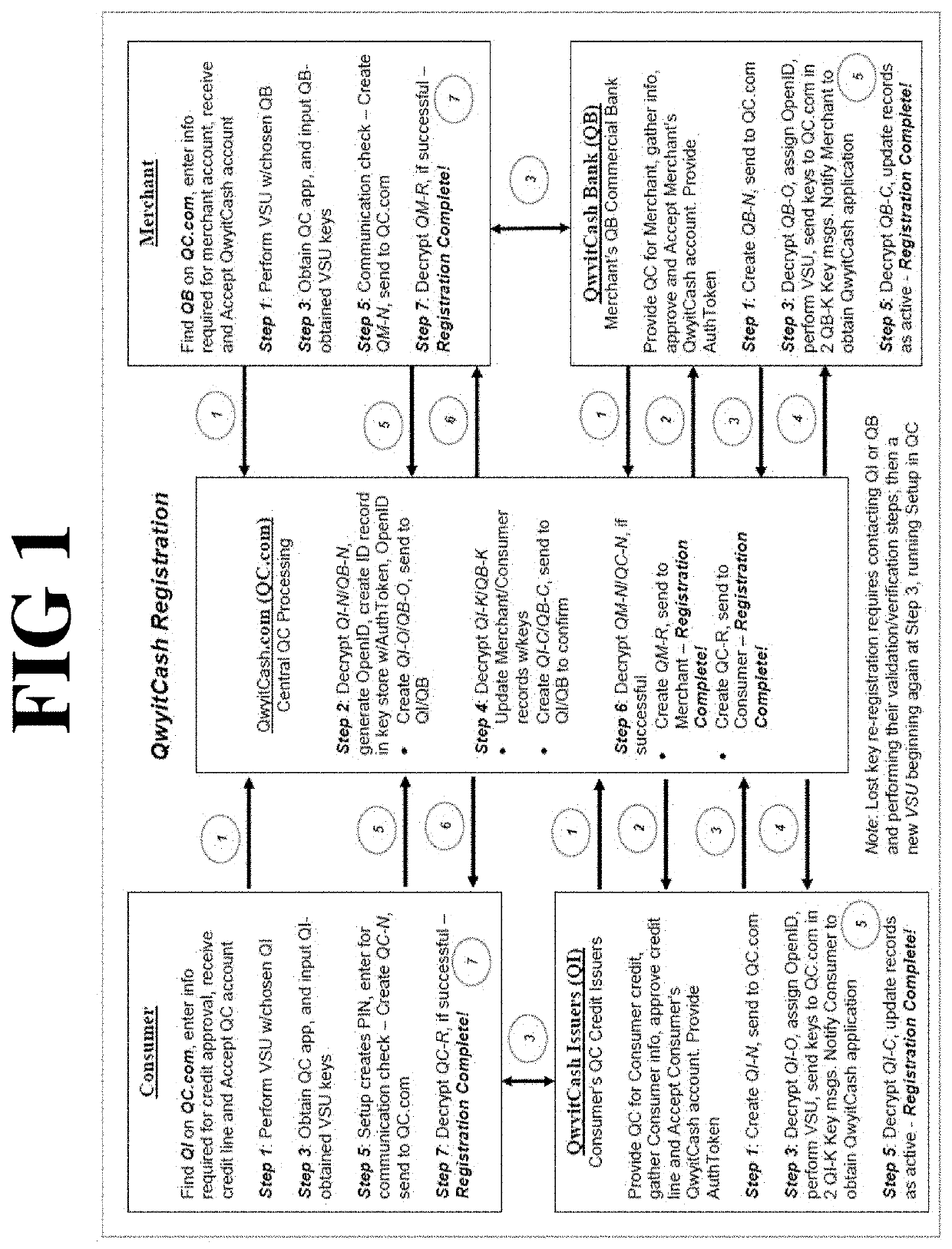
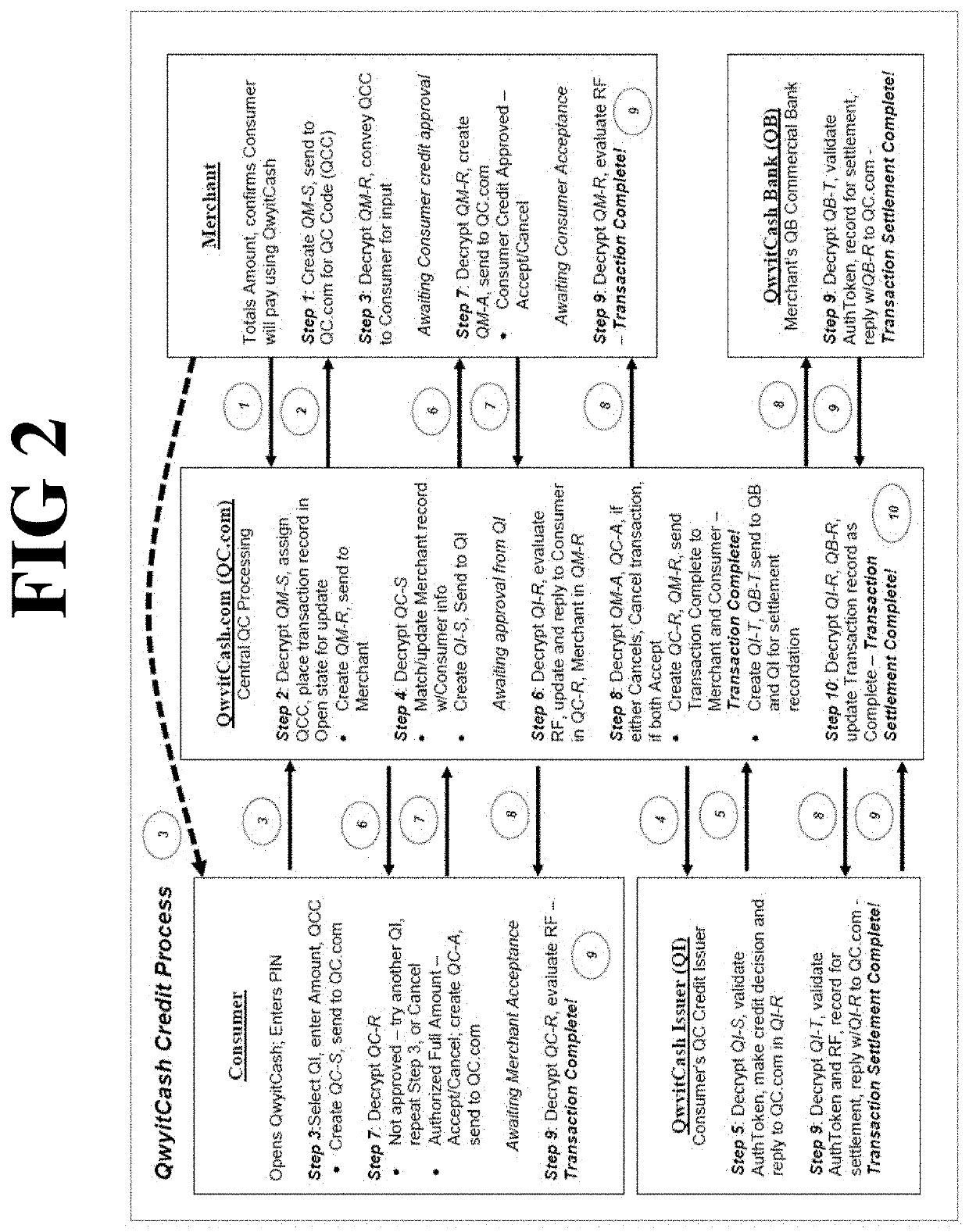
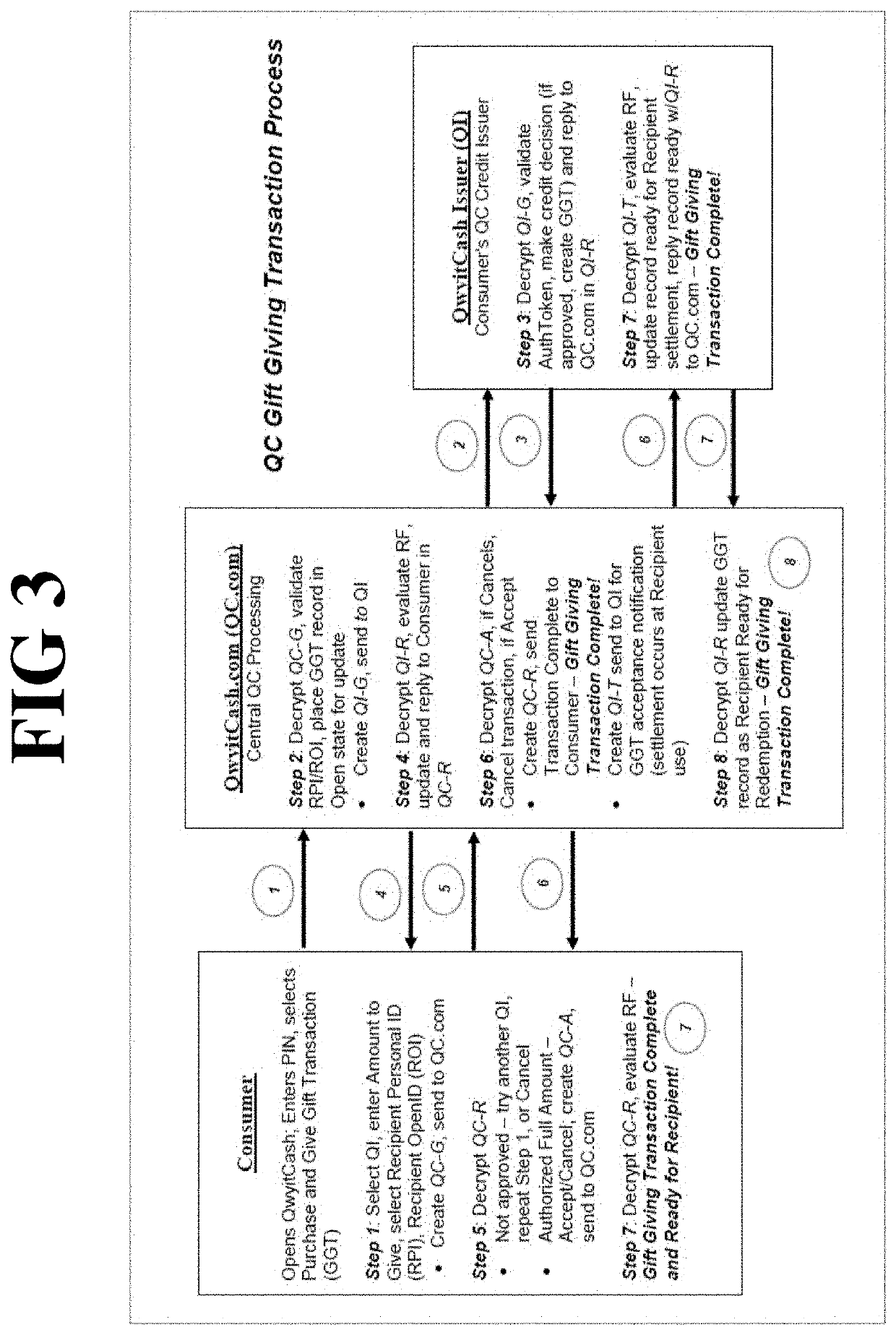
Method and apparatus for credit transaction employing unbreakable encryption
PendingUS20200051054A1Easy to optimizeLow costKey distribution for secure communicationFinanceCredit cardFinancial transaction
A method and apparatus for a streamlined electronic credit transaction that provides more security in a streamlined transaction process than any current deferred net settlement system. The removal of the physical credit card restores the proper risk balance to all participants and performs processing in real time, faster than any current system. The method relies on secure authentication and encryption security communications, based on the provably secure unbreakable mathematics of underdetermined systems of equations, which are maintained everywhere throughout the transaction process.
Owner:QWYIT LLC
A Fast Source Signal Reconstruction Method for Blind Sound Source Separation with Two Microphones
InactiveCN104167214BAvoid problemsSmall amount of calculationSpeech analysisSound source separationTime domain
The invention discloses a fast source signal reconstruction method for double-microphone blind sound source separation, which belongs to the field of speech signal processing, and is especially used for fast source signal reconstruction for double-microphone sound source separation where the number of sound sources and the surrounding environment are unknown. method. This invention adds a small additional phase to each frequency component of the reconstructed signal without affecting the time-domain envelope of the reconstructed source signal, and simulates it by approximately calculating the contribution of each source signal to the time-frequency point. The proportion of the time-frequency points is used to restore the source signal, which avoids the usual process of solving underdetermined equations, simplifies the calculation steps, and achieves the purpose of speed. Therefore, compared with the existing algorithm, the method has the advantages of small calculation amount and high signal-to-noise ratio when the number of sources increases.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A Compressive Sensing Method for Multi-source Shock Load Identification of Mechanical Structures
InactiveCN105912504BTake advantage of sparsityBreak through the bottleneck that cannot be solvedComplex mathematical operationsUnderdetermined systemCompressed sensing
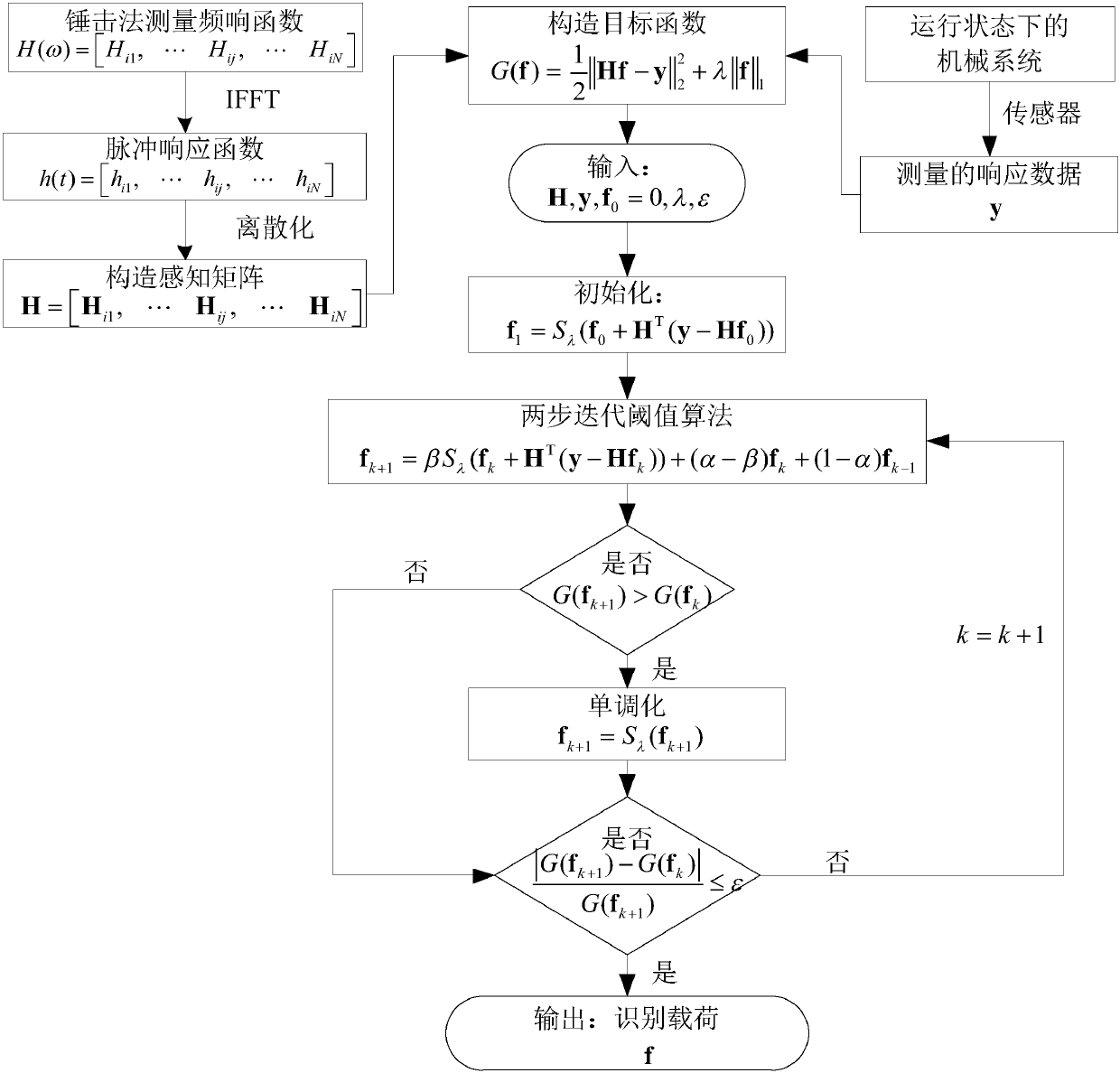
The present invention relates to a compressed sensing method for multi-source impact load identification of a mechanical structure for solving ill-posed natures of the multi-source impact load identification inverse problem of a highly underdetermined system. The method comprises the following steps of (1) measuring a frequency response function between an action point of impact load of the mechanical structure and a response point of the mechanical structure, and furthermore constructing a sensing matrix; (2) measuring signals generated by dynamic load of the structure by using a sensor; (3) constructing an underdetermined equation of the multi-source impact load identification; (4) constructing an L1-norm-based compressed sensing convex optimization model of the multi-source impact load identification; and (5) solving the compressed sensing optimization model by using a two-step iteration threshold algorithm, and obtaining a compressed sensing solution of multi-source impact load. Time and space combined sparsity of the impact load is fully utilized, the method is suitable for identifying and positioning the multi-source impact load acting on the mechanical structure, and the choke point that the underdetermined system cannot be solved by a traditional regularization method based on L2 norm is overcome.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
A Harmonic Source Location Method Based on Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Algorithm
ActiveCN110308366BEffective positioningAccurate estimateCircuit arrangementsFault location by conductor typesHarmonic controlPower grid
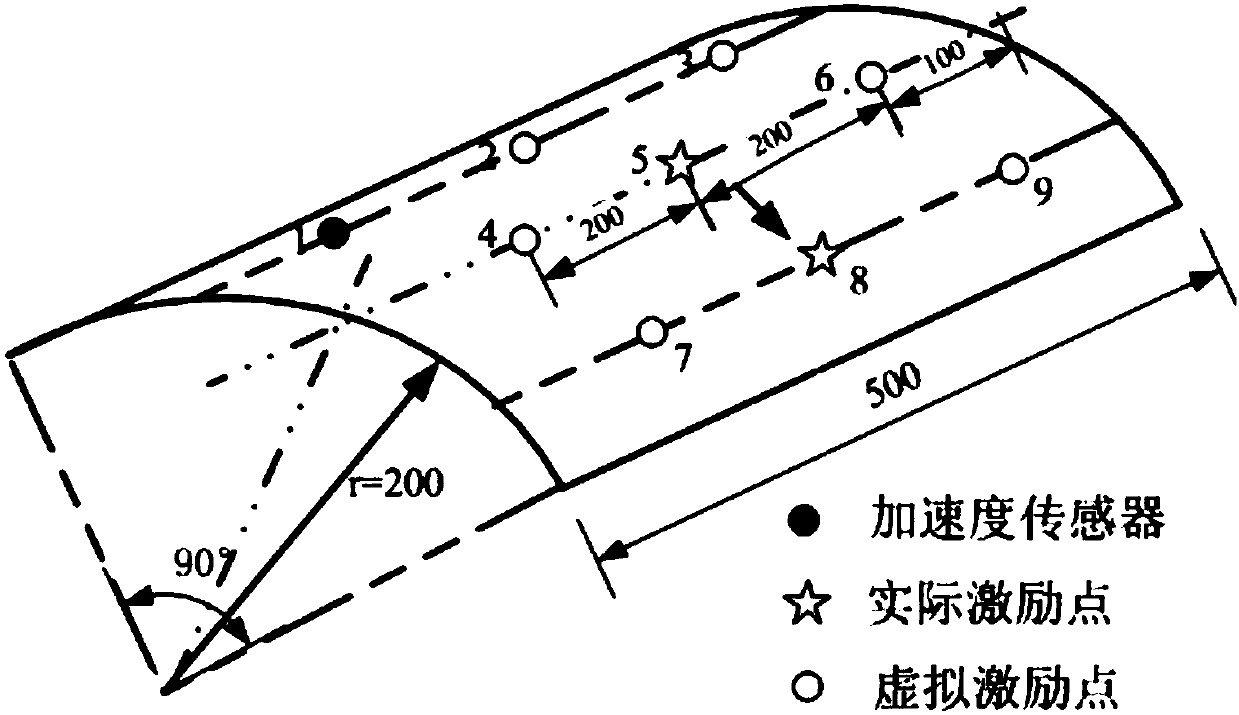
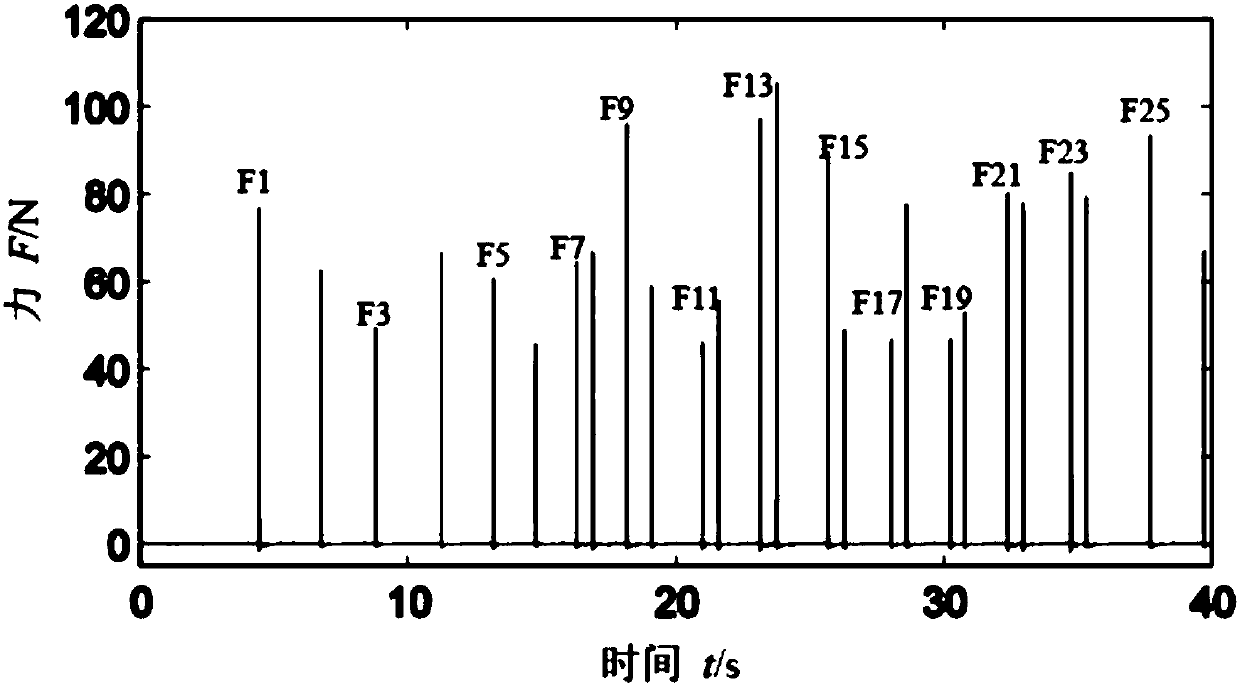
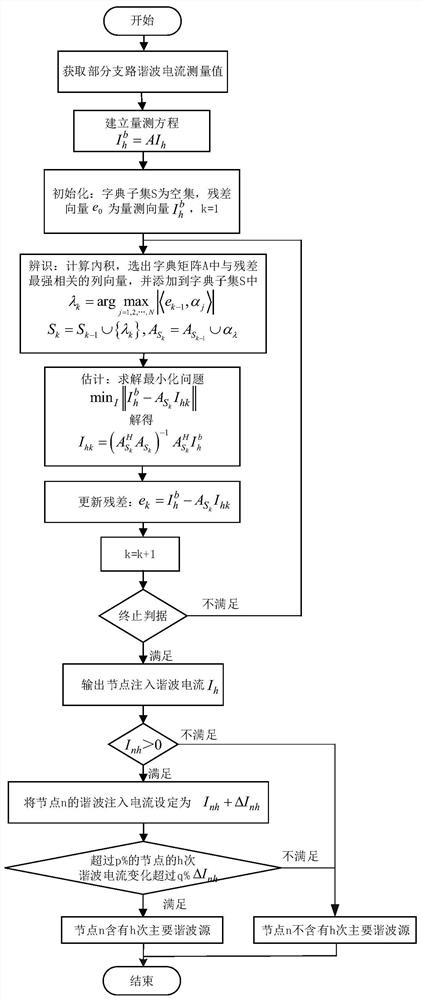
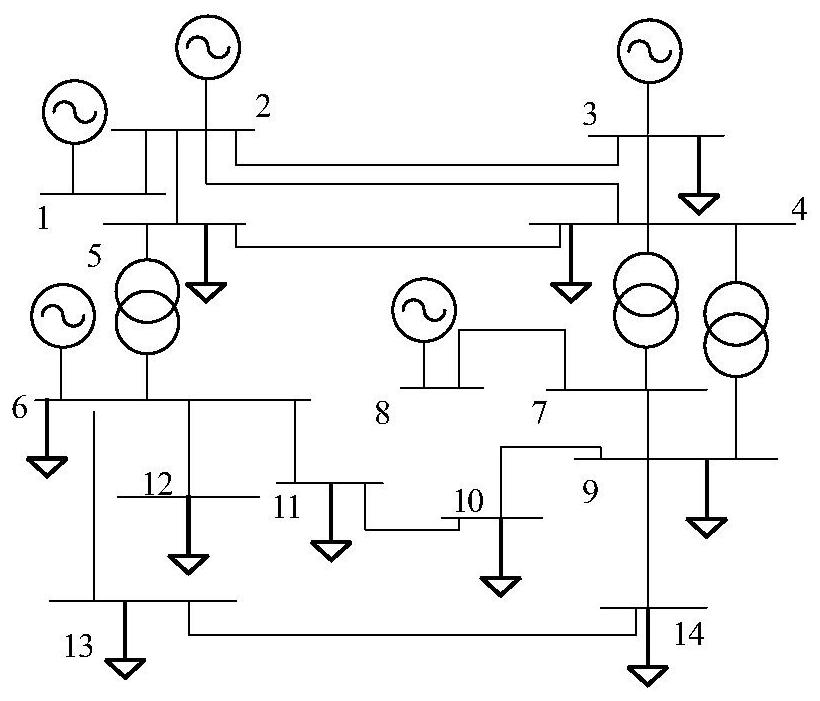
The invention discloses a harmonic source positioning method based on an orthogonal matching tracking algorithm. The harmonic source positioning method is suitable for effective positioning of harmonic source positioning in an actual system, including steps: A. Establishing a measurement based on measurement information Equation; B. Estimation of node injection harmonic current based on orthogonal matching pursuit algorithm; C. Locating the main harmonic source based on the estimation result. The invention overcomes the problems of underdetermined measurement equations and non-global objectivity of the system caused by less configuration of existing measurement devices, and can accurately measure each node of the network under the condition of obtaining partial branch harmonic currents of the system network Estimating the injected harmonic current, effectively locating the harmonic source in the distribution network, reducing the investment cost, providing a basis for the division of harmonic responsibilities and harmonic governance, and improving the power quality of the power grid, reducing economic losses, and improving User satisfaction is of great significance.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST STATE GRID SHANXI ELECTRIC POWER +2
Mixed pixel adaptive decomposition method based on multi-scale window
InactiveCN106529473ABreak down smoothlyImprove spatial resolutionScene recognitionPicture interpretationLinear correlationHigh spatial resolution
The present invention relates to a mixed pixel adaptive decomposition method based on a multi-scale window. The method comprises the steps of gathering the components and the abundances thereof within a mixed pixel space range, and establishing an initial window scale; b constructing a system of linear equations which takes the pixel values and the abundances as the known numbers and the component values as the unknown numbers; c calculating the linear correlation of the equations in the system of equations, and determining whether the system of equations belongs to an underdetermined system of equations; d if the constructed system of equations belongs to the underdetermined system of equations, increasing the window scale by two pixel units as the new window scale, and repeating the steps b and c; e according to the calculated component values, constructing the high-spatial resolution component value images within the mixed pixel space range. By calculating the number of the to-be-decomposed mixed pixel components on the image, the multi-scale window is obtained, a calculation system of equations of the mixed pixels is constructed adaptively, an underdetermined problem can be avoided, the mixed pixels on the image can be decomposed smoothly, and the component images of higher spatial resolution can be obtained.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A data processing method and system suitable for a wireless distributed sensing system
InactiveCN103346864BGood refactorabilityError preventionNetwork topologiesL1 minimizationPattern perception
The invention provides a data processing method and system suitable for a wireless distributed perception system. The data processing method includes the following steps that sensor nodes collect perception data with relevance; intermediate nodes process the perception data by utilizing random linear network codes; the number of the sensor nodes is N, the number of aggregation nodes is m, source data are supposed to be x, data received by the aggregation nodes are y, the aggregation nodes combine received input vectors to acquire a system of linear equations, and due to the fact that m (N and the system of linear equations) is underdetermined, the problem of solving the underdetermined system of equations is converted to the problem of minimizing l1, and original perception data are reconstructed; a receiving terminal receives the original perception data. The data processing method and system suitable for the wireless distributed perception system have the advantages that due to the fact that the compressed perception theory is introduced to the decoding stage of the aggregation nodes, the problem of 'all or nothing' is effectively solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Beam domain doa estimation based on compressive sensing
ActiveCN106772225BOvercome the disadvantage of not being able to use in low signal-to-noise ratio situationsReduce operational complexityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDirection/deviation determination systemsComputation complexitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
A hyperspectral image sparse unmixing method based on mfocuss and low-rank representation
ActiveCN105825227BOvercoming the problem of low accuracy of sparse unmixingPrevent extractionCharacter and pattern recognitionNatural abundanceUnderdetermined system
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image sparse unmixing method based on MFOCUSS and low-rank representation. The specific steps of the invention include: reading original hyperspectral data and known spectral library data; constructing a sparse solution based on MFOCUSS and low-rank representation The objective function of the mixed model, and the hyperspectral data and the known spectral library are used as the input data and dictionary of the objective function, and the abundance matrix of the entire spectral library is obtained by solving the objective function of MFOCUSS and the low-rank representation model, and the spectral library is eliminated. The spectrum of the non-true endmembers, the spectral library after removing the non-real endmembers, iterates repeatedly to finally obtain the real endmember matrix and the corresponding abundance matrix; this method avoids directly extracting the endmembers from the original hyperspectral data, and eliminates The non-true endmembers and the spectral library were updated, which reduced the adverse effect of the autocorrelation of the endmember spectra in the spectral library on the hyperspectral unmixing effect, and improved the accuracy of the abundance estimation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Snow passive microwave mixed pixel decomposition method based on classified information of five types of ground features
InactiveCN102608592BTimely processingAccurate processingWave based measurement systemsSnowpackDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of remotely sensed image processing, and provides a snow passive microwave mixed pixel decomposition method based on the classified information of five types of ground features. According to five types of typical underlying surfaces affecting the radiation characteristic of snow, the method acquires the classified data of the ground features with high special resolution in an observed region, utilizes the different characteristics of the microwave radiation of snow on the different underlying surfaces and selects a microwave antenna gain function and a sampling rate to build a snow passive microwave mixed pixel decomposition model, and adopts the least square method with constraint conditions to iteratively solve an underdetermined system of equations, thus realizing snow passive microwave mixed pixel decomposition. The method can effectively solve the problem of the mixed pixels of passive microwaves of snow, improves the precision of snowparameter inversion, and has a significant application value in fields such as climate and hydrological research and snow disaster assessment.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com