Patents
Literature
260results about How to "Eliminate aberrations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
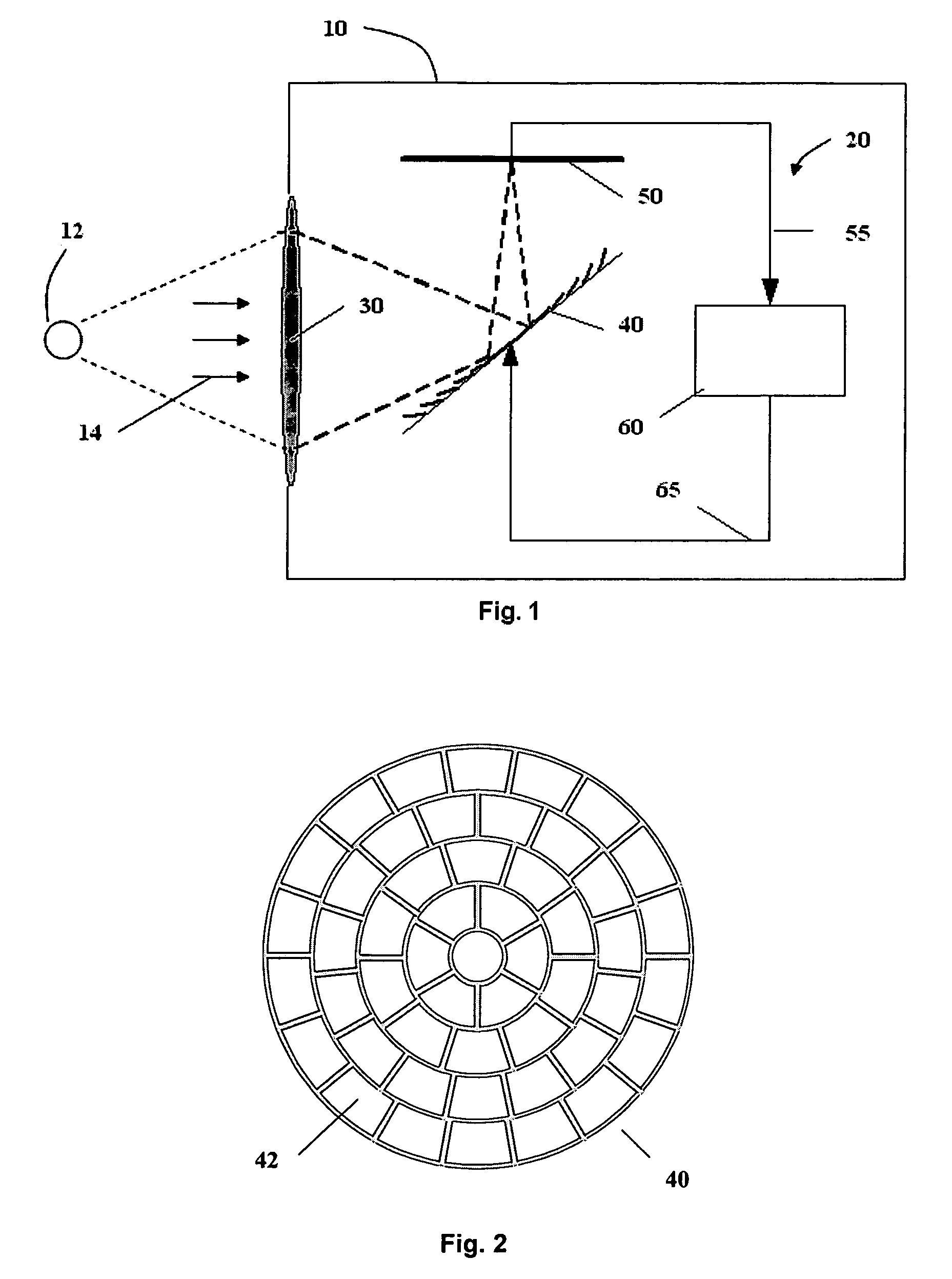
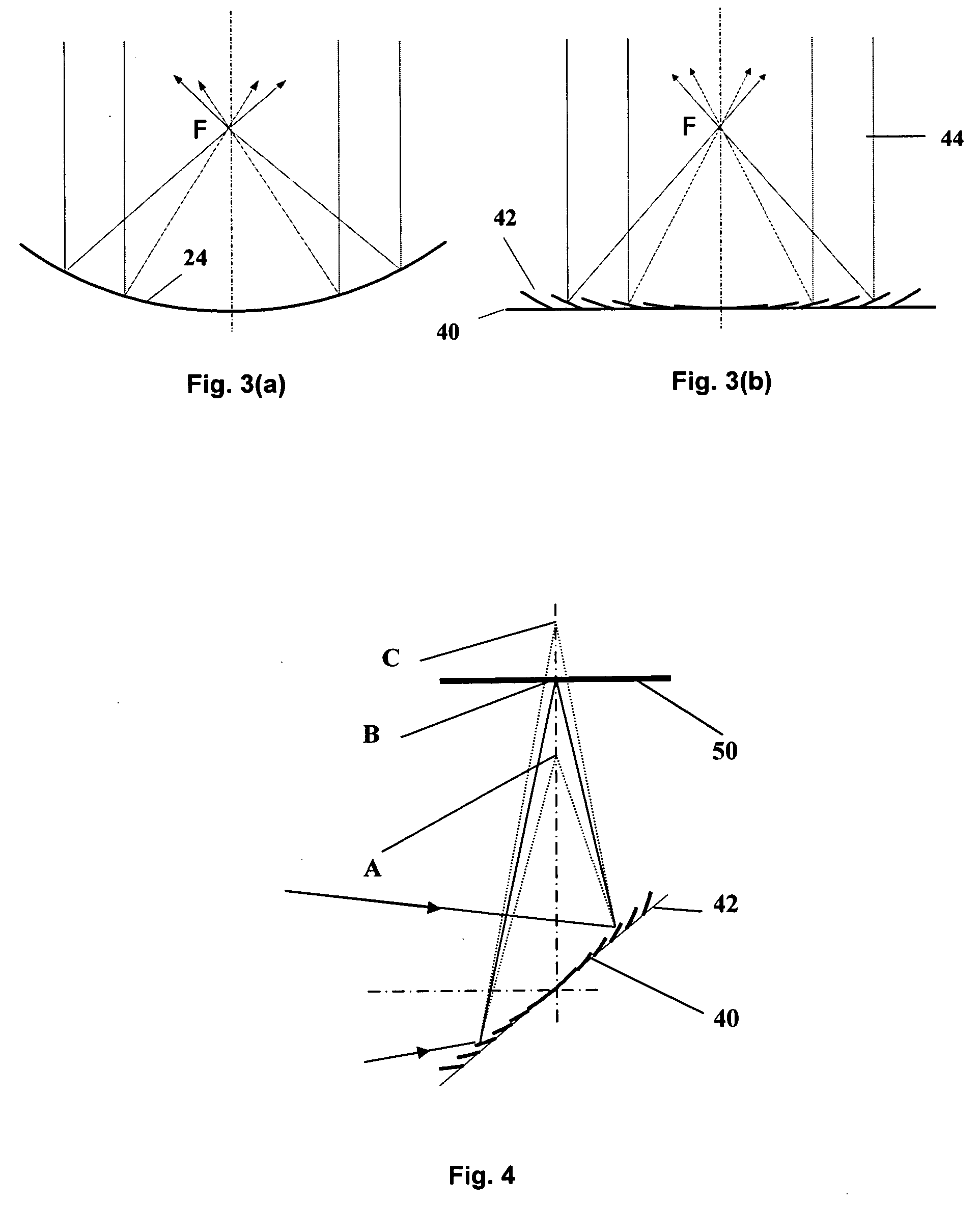
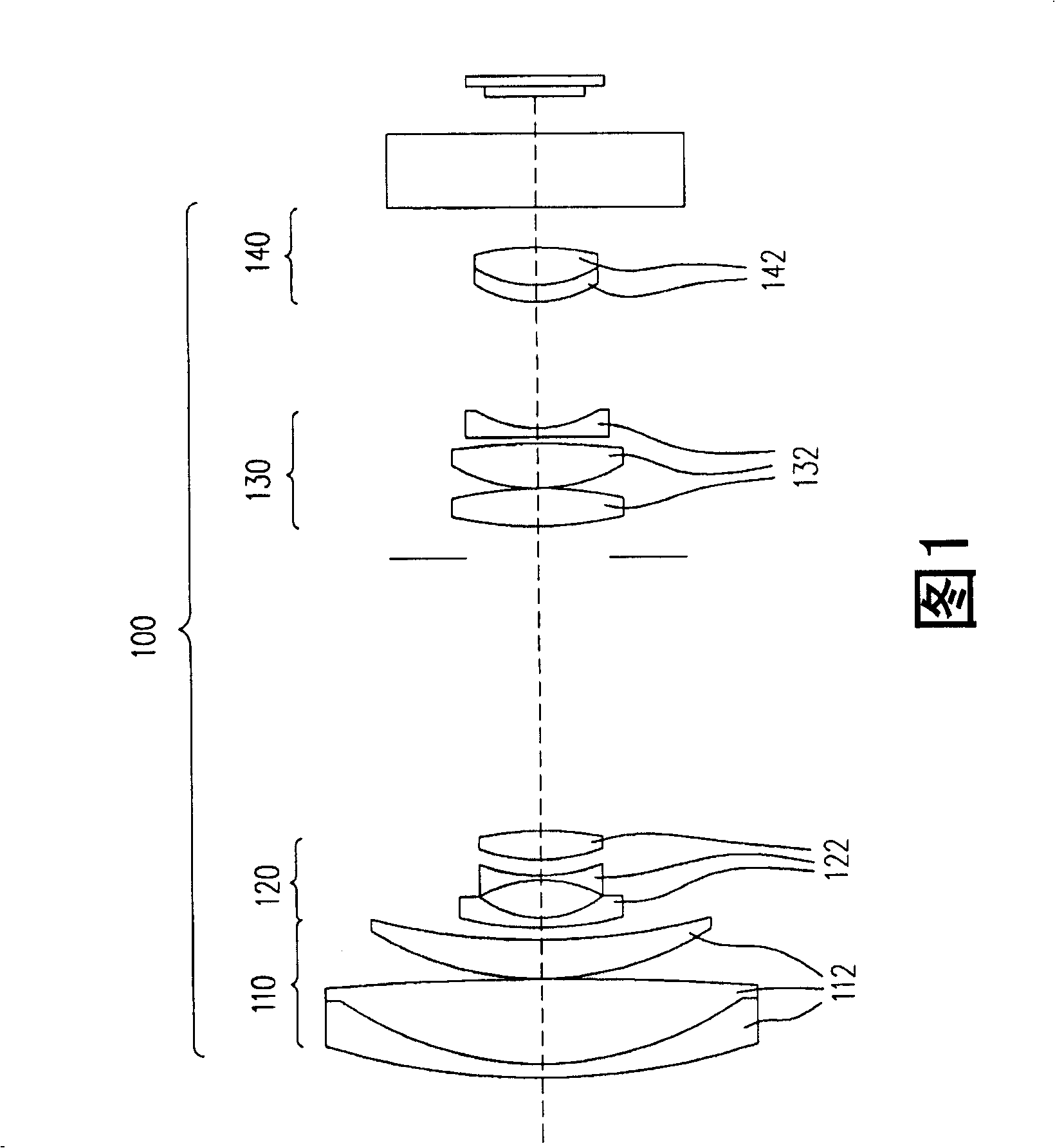
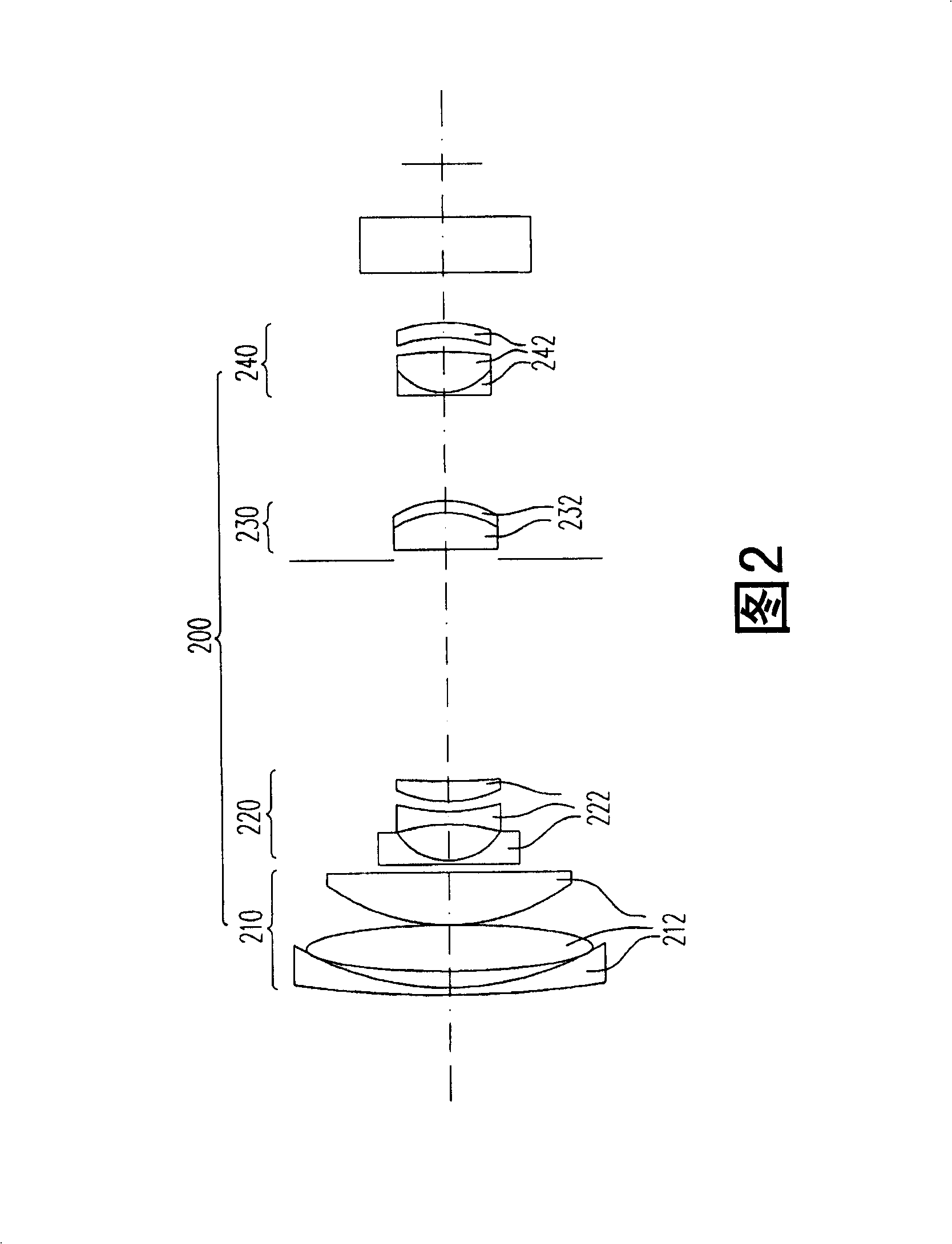
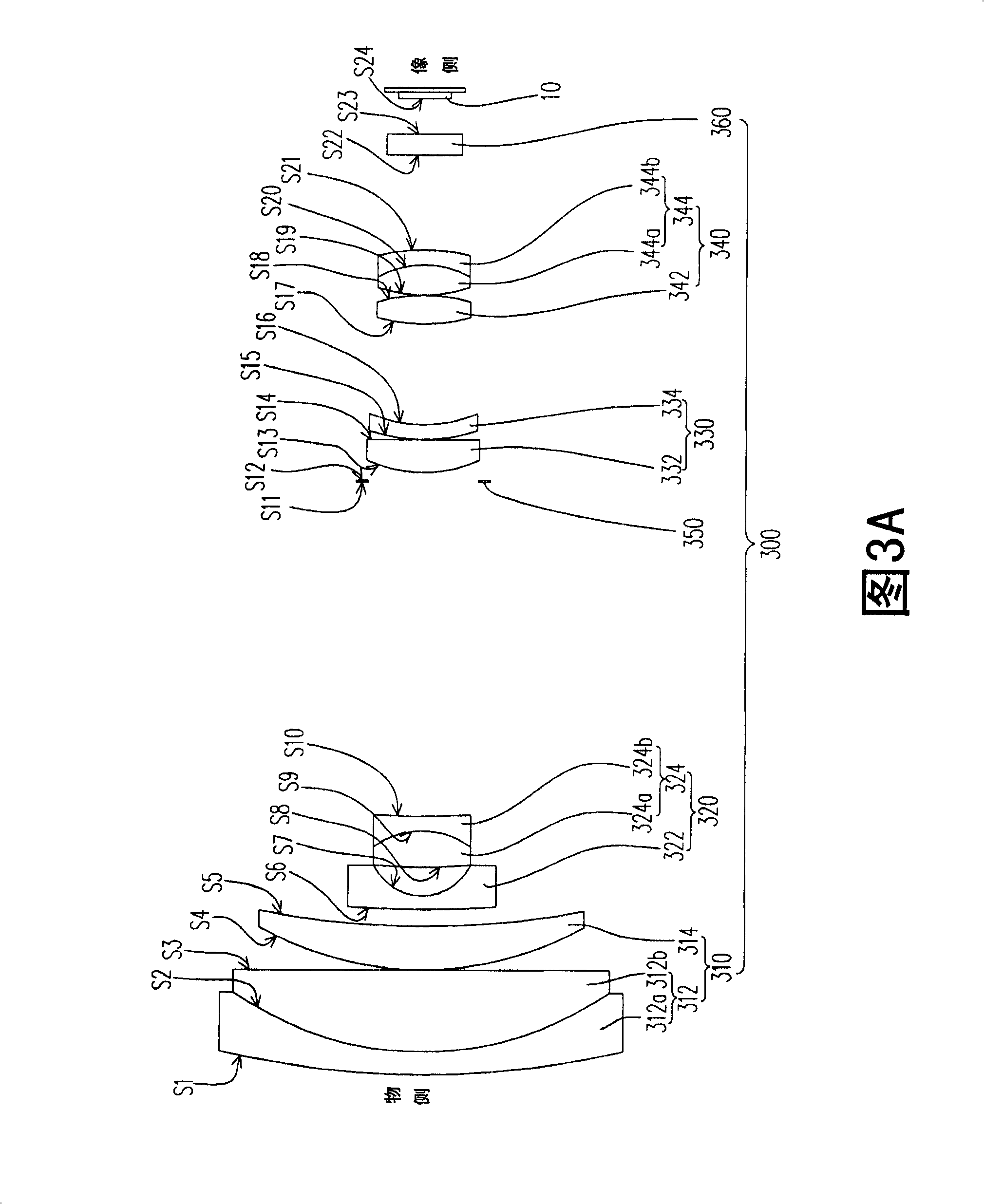
Super wide-angle panoramic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS6611282B1Without significant loss of image qualityEliminate aberrationsTelevision systemsTelescopesWide fieldViewpoints
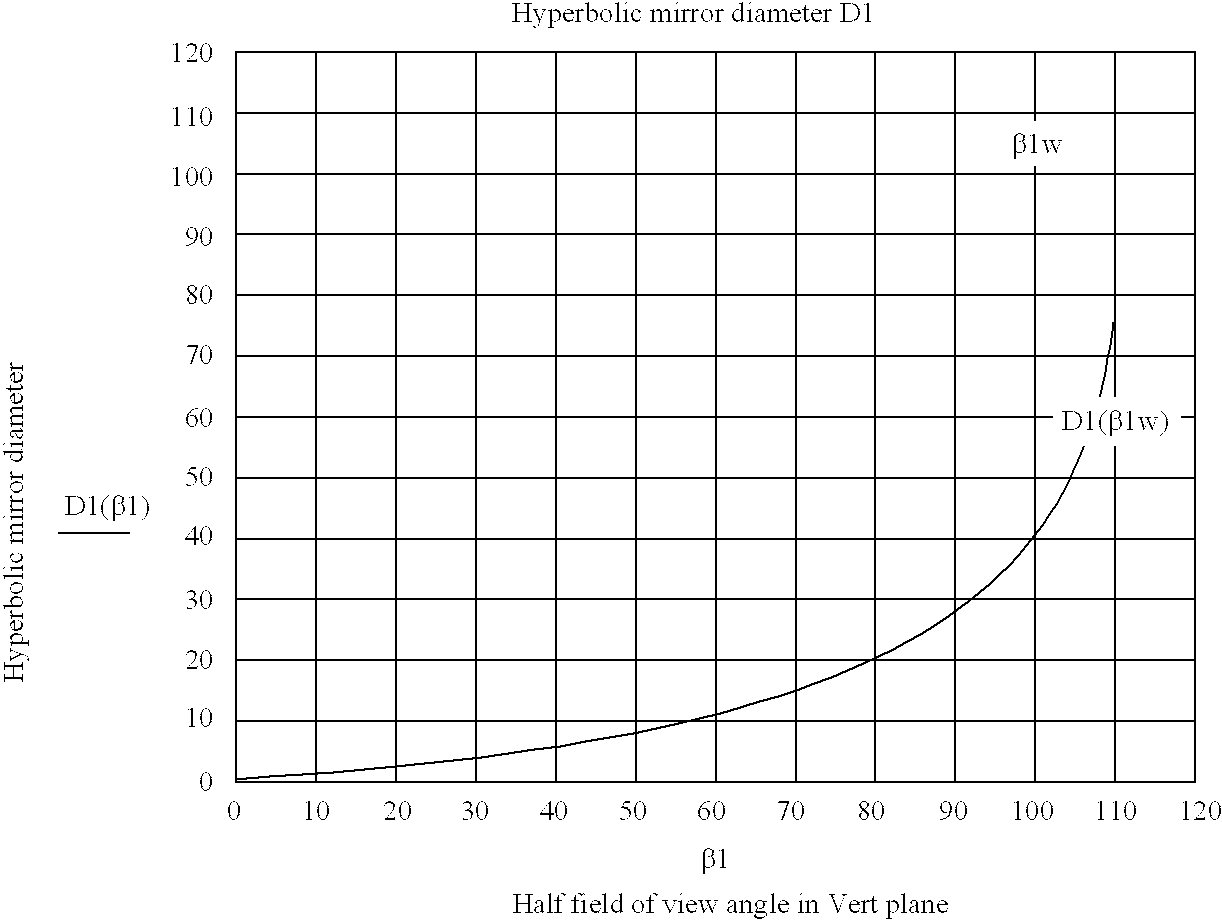
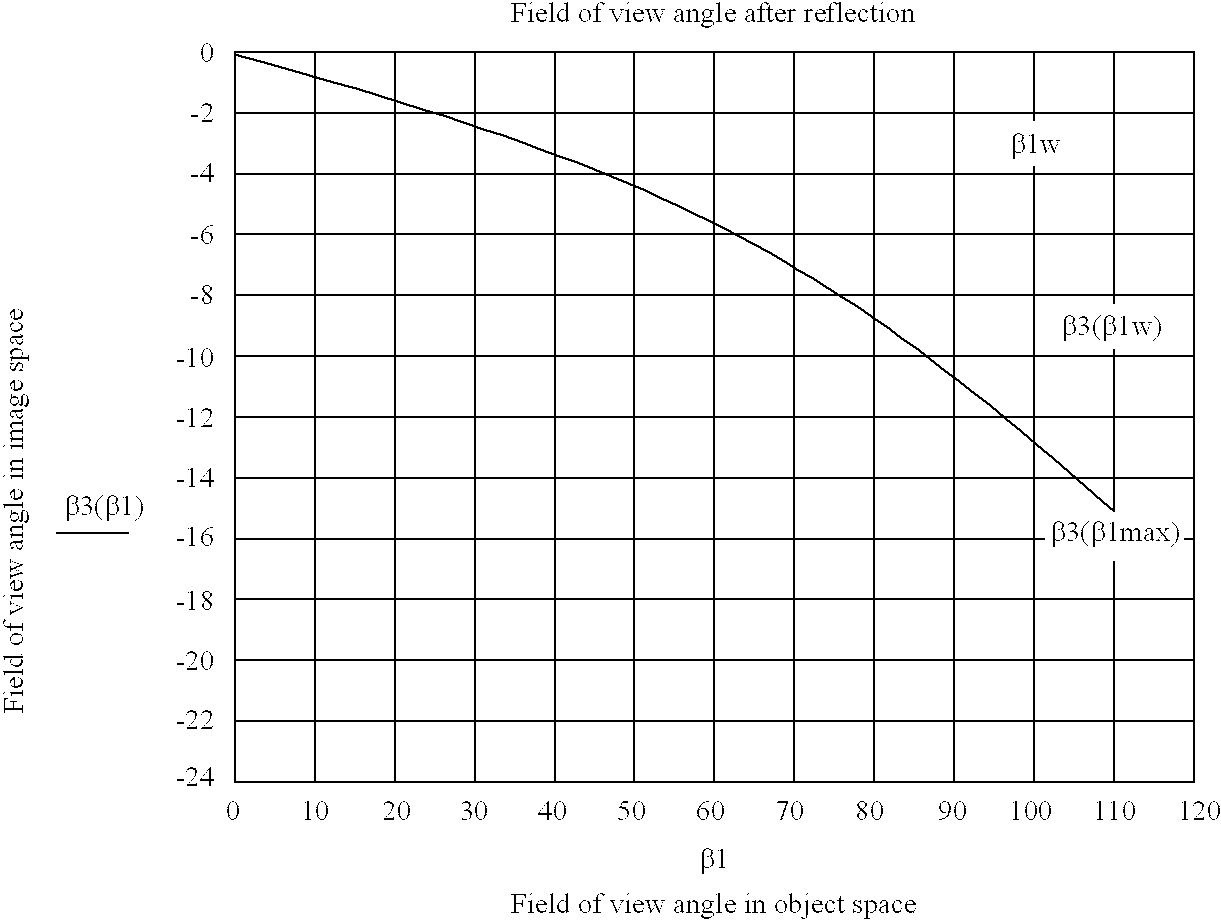
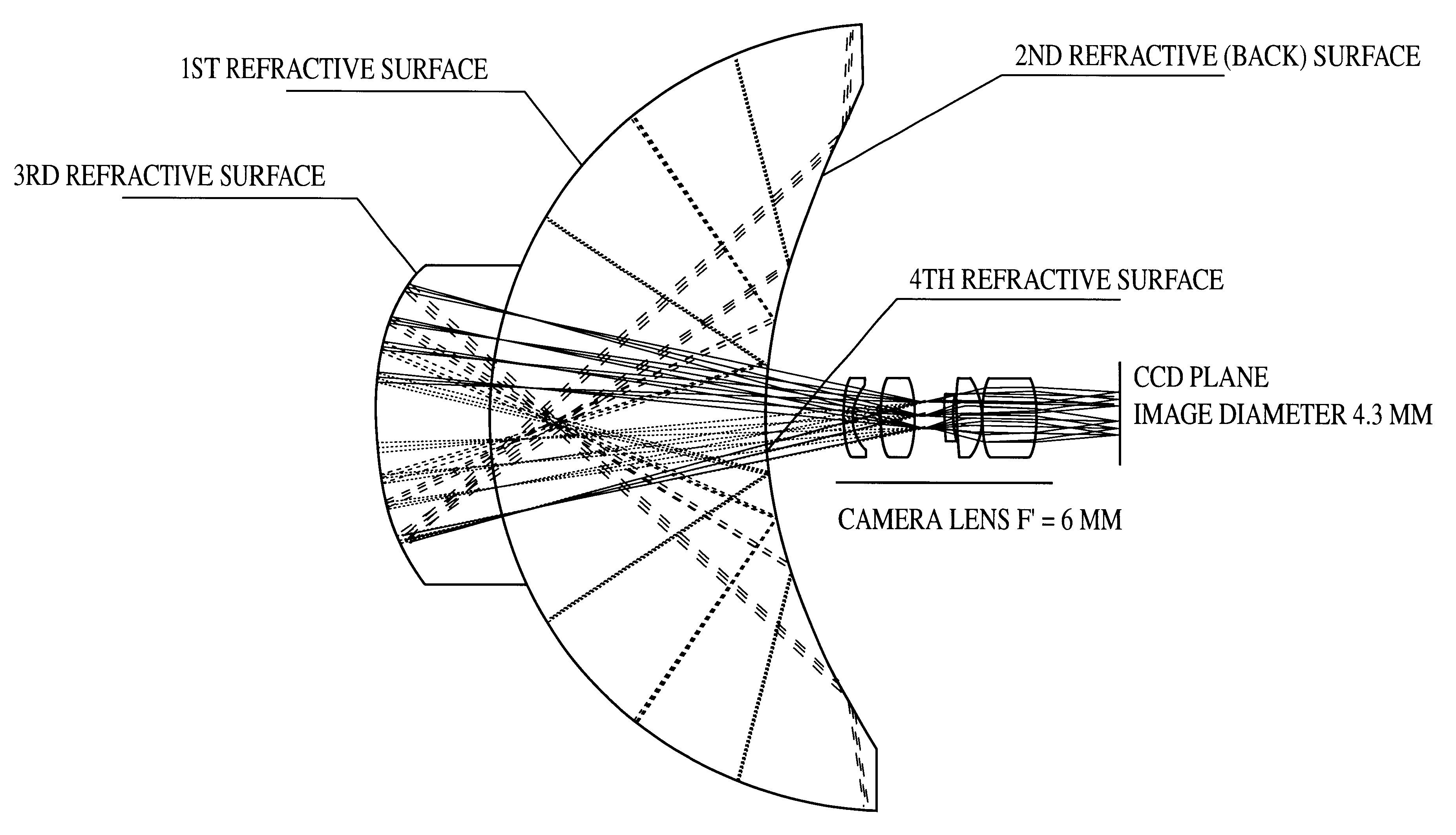
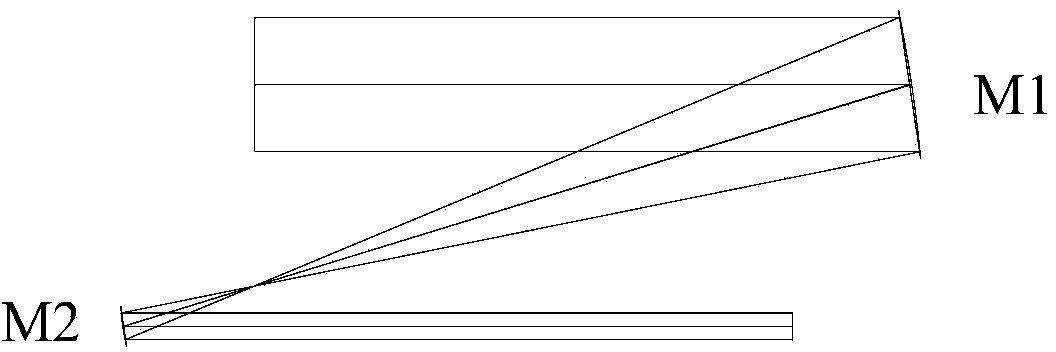
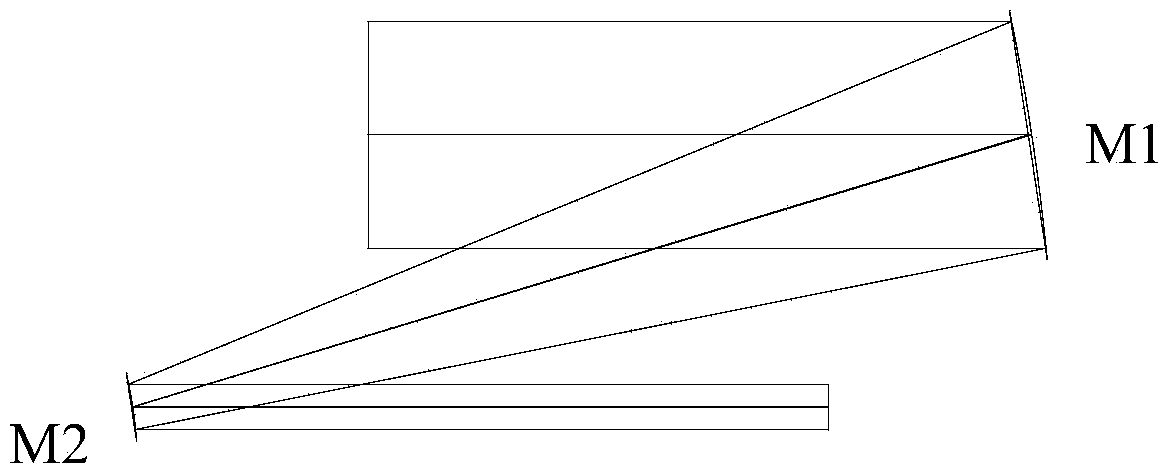
A system for capturing super wide-angle panoramic images. In particular, a two-reflector system is disclosed which is substantially self-correcting in which optical aberrations are substantially eliminated, such as field curvature, astigmatism and the like. Moreover, the super wide-angle panoramic imaging apparatus of the invention captures a super-wide field of view from a substantially single reference viewpoint. The invention provides a substantially compact viewpoint, while also having a substantially flat and stigmatic image plane, in the context of a super wide-angle panoramic system. Devices and methods for capturing panoramic images of super wide-angle scenes are provided. In a particular embodiment of the invention, two reflectors are provided (e.g., one a hyperboloidal mirror, the other a concave ellipsoidal or spherical mirror), a relay system (e.g., optics such as a mirror, a lens, a pinhole and the like) and an image sensor (e.g., an electronic photo-sensor, a film and the like).
Owner:REMOTEREALITY
Near eye wavefront emulating display
ActiveUS20180131926A1Eliminate aberrationsComfortable form factorPicture reproducers using projection devicesSteroscopic systemsSmall form factorDisplay device
A near eye display device includes a sparse array of intensity modulated light beam emission and steering points disposed on a transparent lens, capable of forming a wide field of view composite image directly on the retina with variable degrees of apparent depth controlled by an image forming timing signal. The active regions of the beam emission and steering elements is configured so as not to generate optical aberrations of transmitted ambient light that is apparent to the eye. The display may be applied to small form factor stereoscopic head worn display systems and used in conjunction with Augmented Reality software applications.
Owner:MANOR FINANCIAL INC
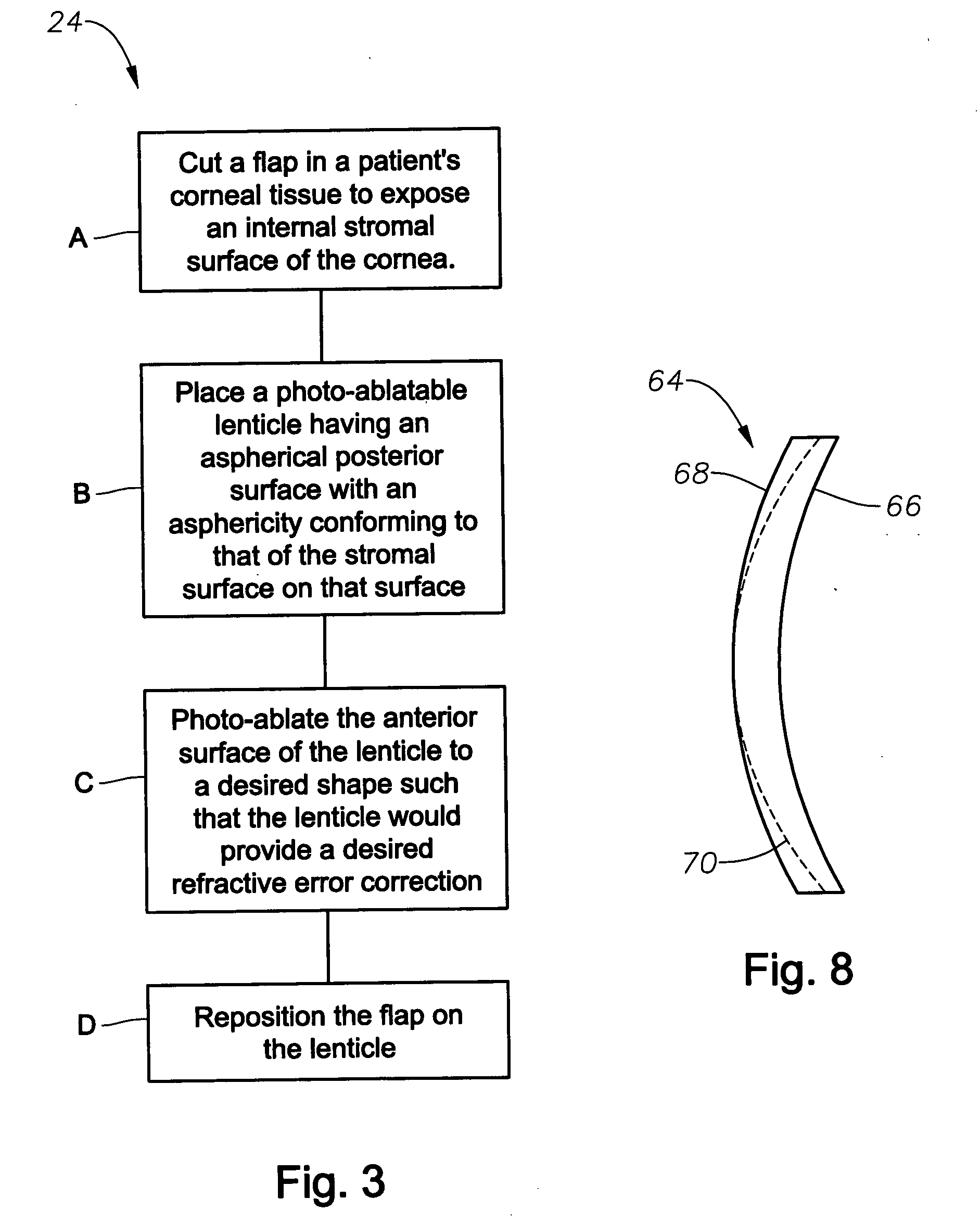
Aspheric lenticule for keratophakia
InactiveUS20060116762A1Correction errorImprove image contrastLaser surgeryEye implantsContour matchingRefractive error
Contour-matching, aspheric lenticules are disclosed for implantation in a subject's cornea to correcting refractive errors. The lenticules include a photoablatable anterior surface and a posterior surface having an aspheric profile that can substantially match the asphericity exhibited by the corneal stromal surface, on which the lenticule is placed. The posterior surface can have a generally concave shape while the anterior surface can have a generally convex shape, though other shapes can also be utilized in some embodiments. In some embodiments, the asphericity of the lenticule's posterior surface can differ from an asphericity exhibited by the corneal stromal surface by less than about 50%, or preferably by less than about 20%.
Owner:ALCON INC
Apparatus and methods for removing optical abberations during an optical inspection
InactiveUS6844927B2Eliminate aberrationsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationOptical apparatus testingSpatial light modulatorControl system
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for altering the phase and / or amplitude of an optical beam within an inspection system using one or more spatial light modulator(s) (SLMs). In one embodiment, an apparatus for optically inspecting a sample with an optical beam is disclosed. The apparatus includes a beam generator for directing an incident optical beam onto the sample whereby at least a first portion of the incident optical beam is directed from the sample as an output beam and a detector positioned to receive at least a portion of the output beam. The detector is also operable to generate an output signal based on the output beam. The apparatus further includes one or more imaging optics for directing the output beam to the detector and a programmable spatial light modulator (SLM) positioned within an optical path of the incident or output beam. The SLM is configurable to adjust a phase and / or amplitude profile of the incident beam or the output beam. The apparatus also has a control system operable to configure the SLM to alter the phase and / or amplitude profile of the incident beam or the output beam. For example, the SLM may be configured to alter the illumination profile of the incident beam to achieve different inspection modes. In another example, the SLM may be configured to alter the phase and / or amplitude profile of the output beam so as to substantially eliminate aberrations produced by the imaging optics. In other embodiments, the apparatus may include two or more SLM's which are configurable to alter the phase and / or amplitude profile of both the incident beam and the output beam.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Large view field angle eyepiece optical system
The invention provides a large view field angle eyepiece optical system for a head-mounted displayer, wherein the large view field angle eyepiece optical system comprises a first lens, a second lens, and a third lens which are successively and coaxially arranged along an optical axis direction from a human eye observing side to a displayer side; the first lens and the third lens are all positive lenses and the second lens is a negative lens; the surface, facing the human eye observing side, of the first lens is projected towards the human eye observing side and has a positive curvature radius; the surface, facing a diaphragm side, of the second lens is projected away from the human eye observing side and has a negative curvature radius; and at the same time, the materials, the focuses and the positions of the first lens, the second lens and the third lens should satisfy certain relationship, so that an image displayed on the displayer is imaged in human eyes after the image is amplified by an eyepiece. The eyepiece has the advantages of large hole diameter, large view field, high resolution ratio, low distortion and small size; and the eyepiece is suitable for head-mounted displayers and apparatuses similar to the head-mounted displayers.
Owner:SHENZHEN NED OPTICS CO LTD
High-speed automatic focusing system
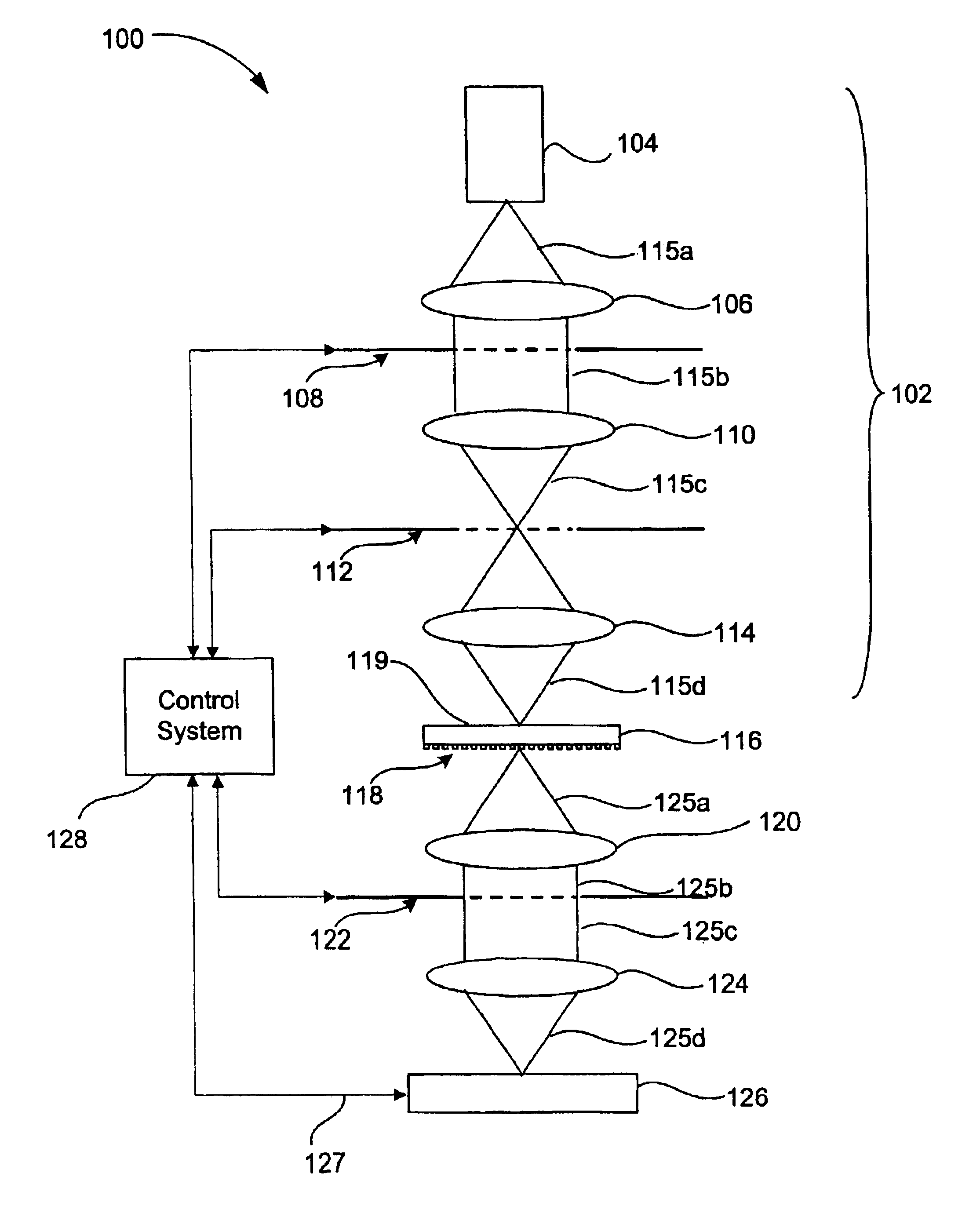
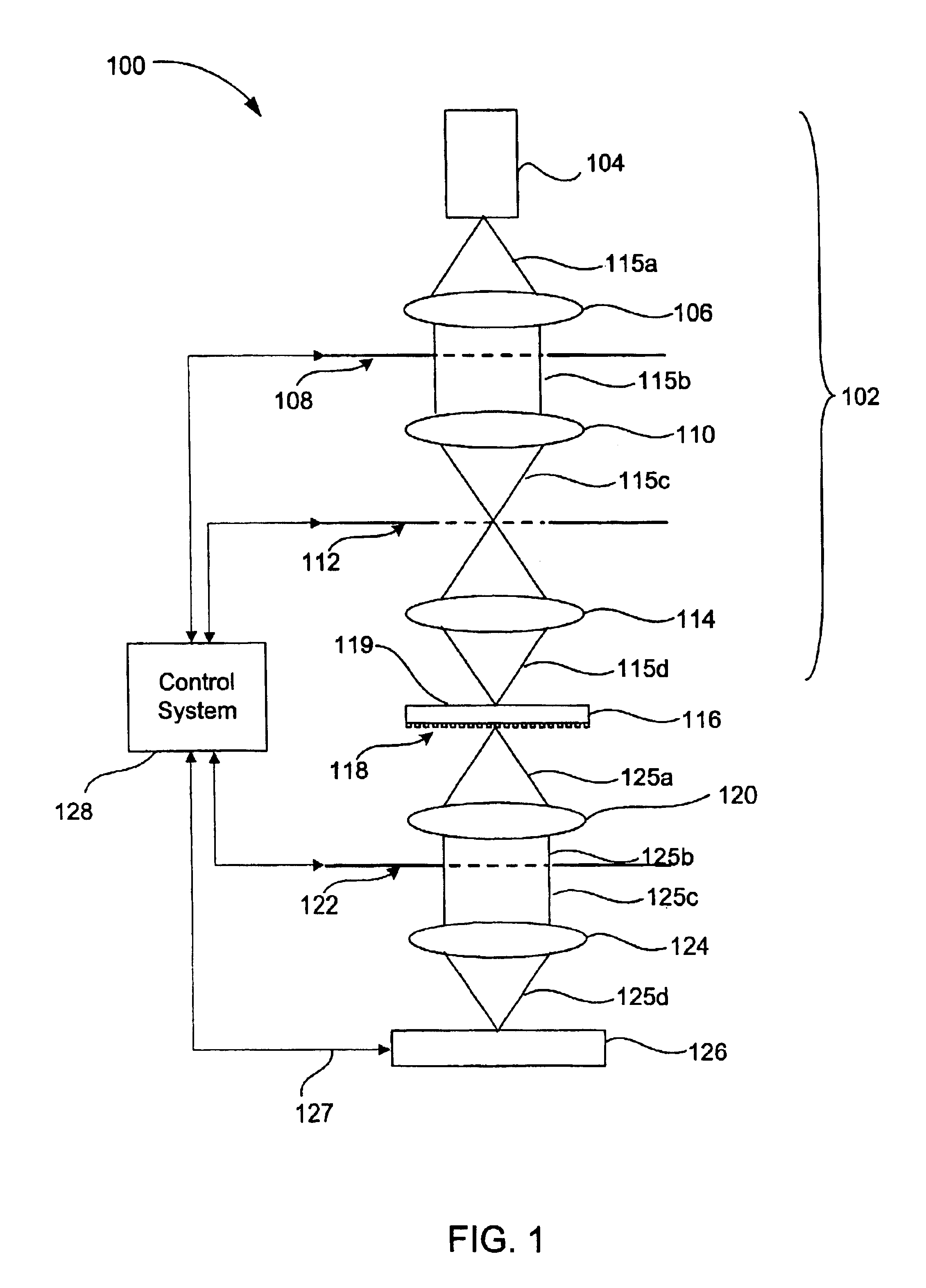
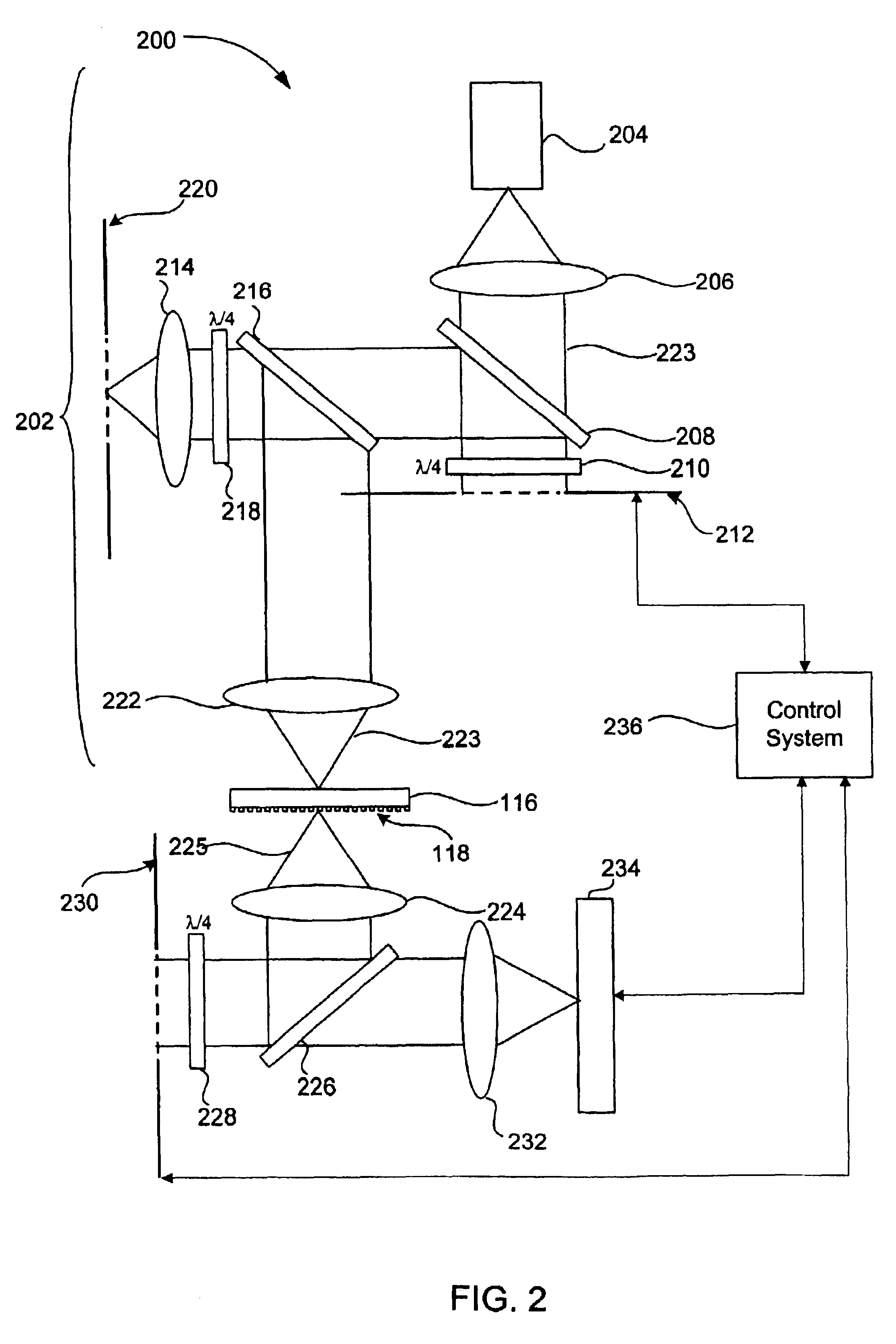
ActiveUS7215882B2Eliminate aberrationsEliminate needMirrorsProjector focusing arrangementImaging qualityLight energy
An automatic focusing system comprises at least one micromirror array lens, an image sensor, and a signal processor. The micromirror array lens images an object and focuses the image on the image sensor. The image sensor receives the light and converts the photo energy of the light to electrical energy in the form of an electrical signal. The image sensor sends the electrical signal, which carries image data concerning the object, to the signal processor. The signal processor receives the electrical signal, compares the image quality of the image data to its focus criteria, and generates a control signal, which it sends to the micromirror array lens to adjust the focal length of the micromirror array lens. This iterative process is continued until the quality of the image data meets the focus criteria, and the process is completed within the afterimage speed of the human eye.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
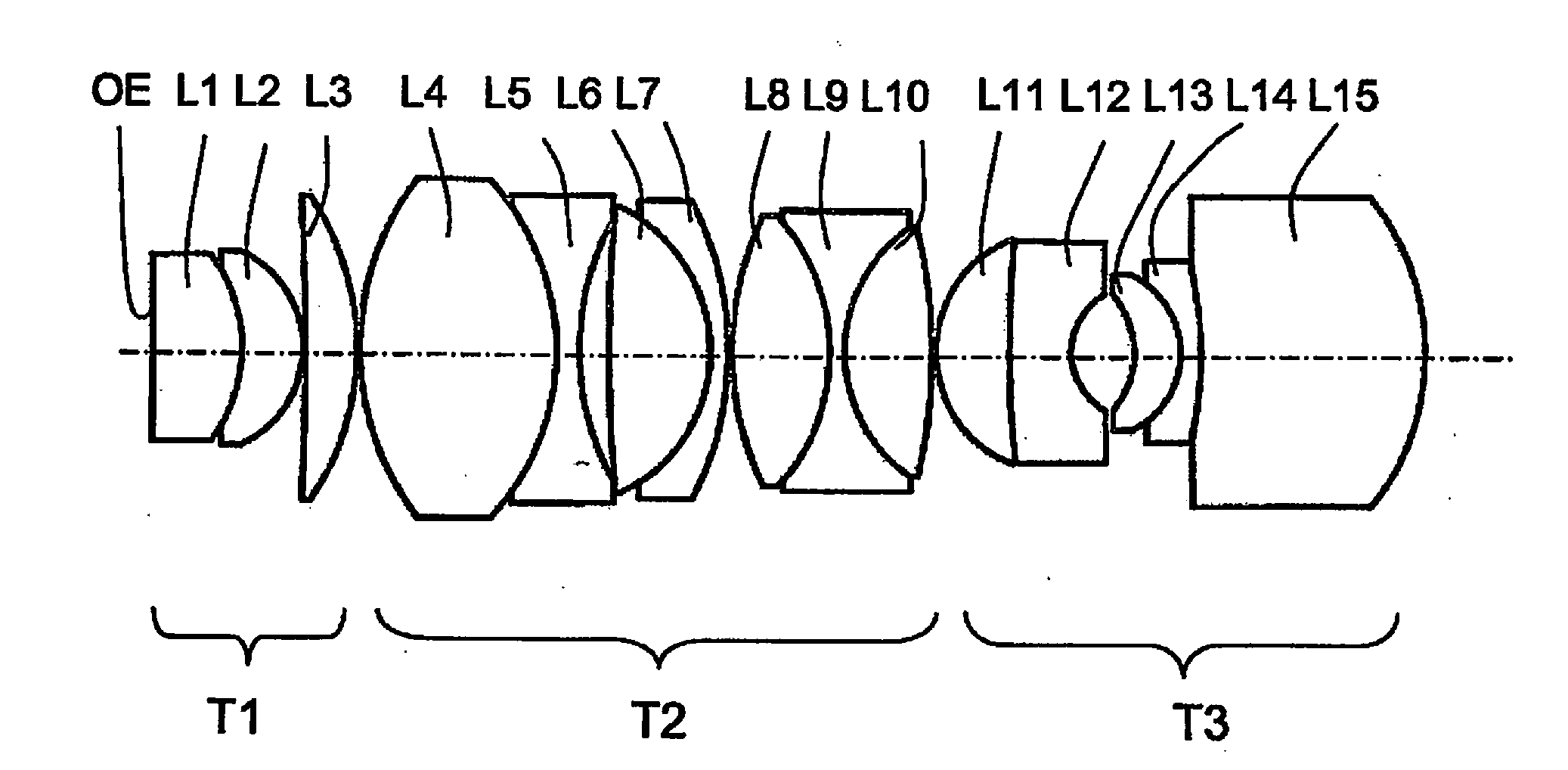
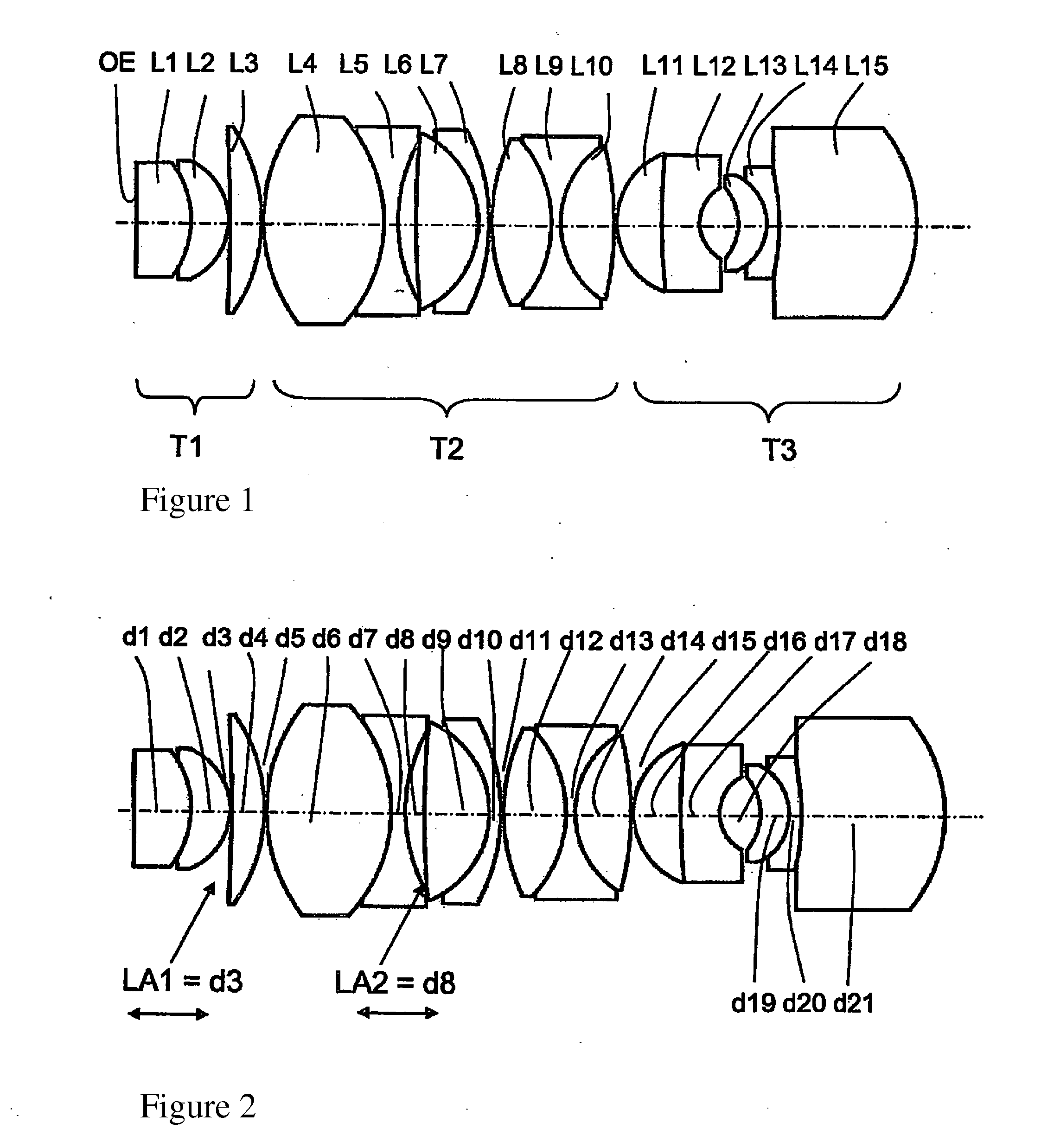
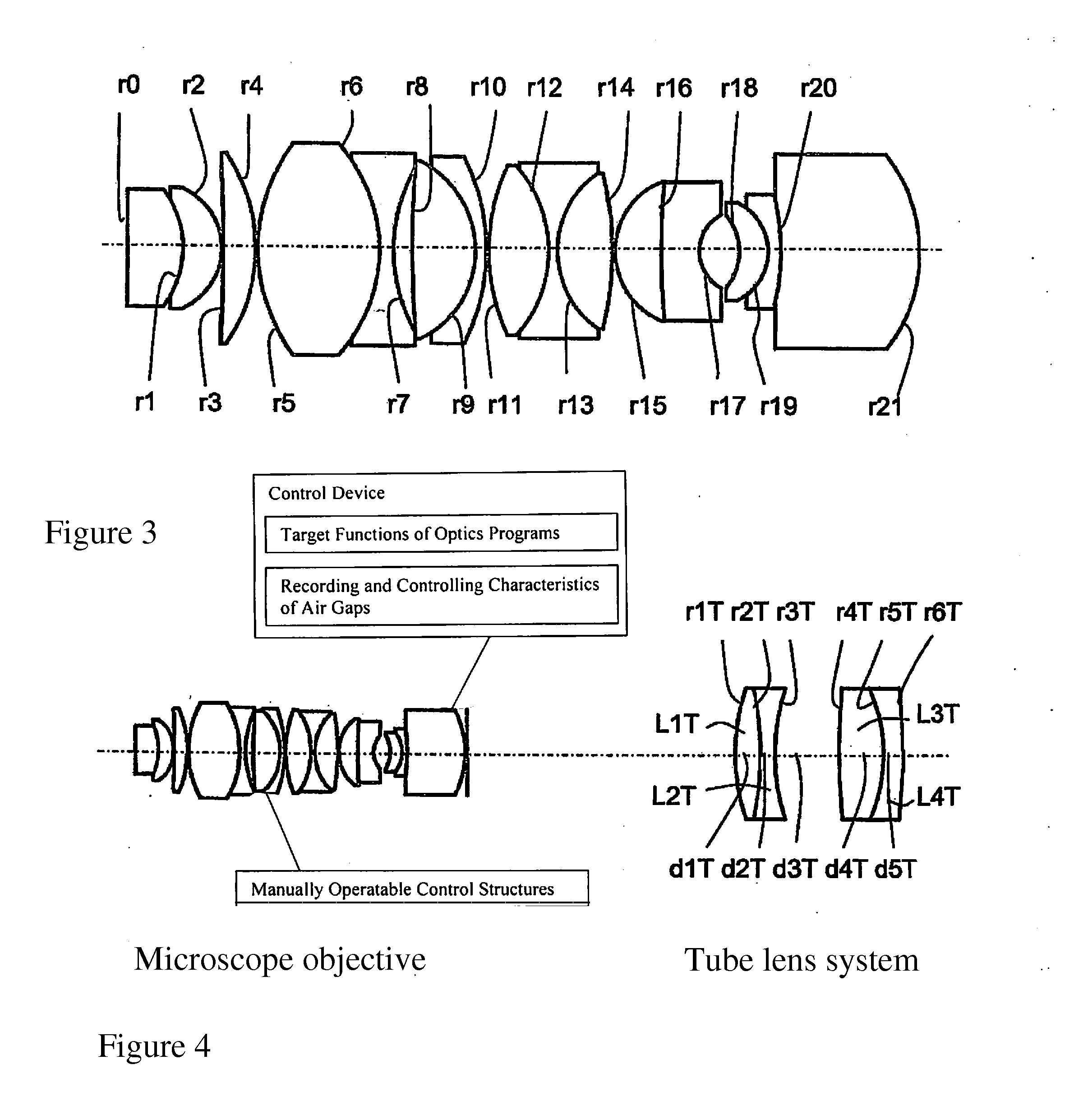
Planapochromatically-corrected microscope objective
ActiveUS20130100537A1Eliminate spherical aberrationEliminate aberrationsMicroscopesMicroscopeSpherical aberration
The invention relates to a planapochromatically-corrected immersion microscope objective for high-resolution microscopy applications with changing dispersive immersion conditions, having a plurality of lenses and / or subsystems (T1, T2, T3) comprising lens groups and a corrective function (LA2) for eliminating spherical aberrations.According to the invention, the microscope objective has an additional corrective function (LA1) for eliminating longitudinal chromatic aberrations caused by dispersive changes in the immersion by changing the air gaps between the lenses or gap combinations, wherein the influence on the longitudinal chromatic aberration corresponds to a rotation of the curve s(λ), which describes the color point (s) as a function of the wavelength (λ).
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
High Fill-Factor Electronic Beam Steerer
InactiveUS20120081621A1Improve performanceEliminates mechanical motionNon-linear opticsOptical elementsFill factorBeam steering
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method for obtaining the image of an object, device for carrying out said method and device for delivering low coherent optical radiation
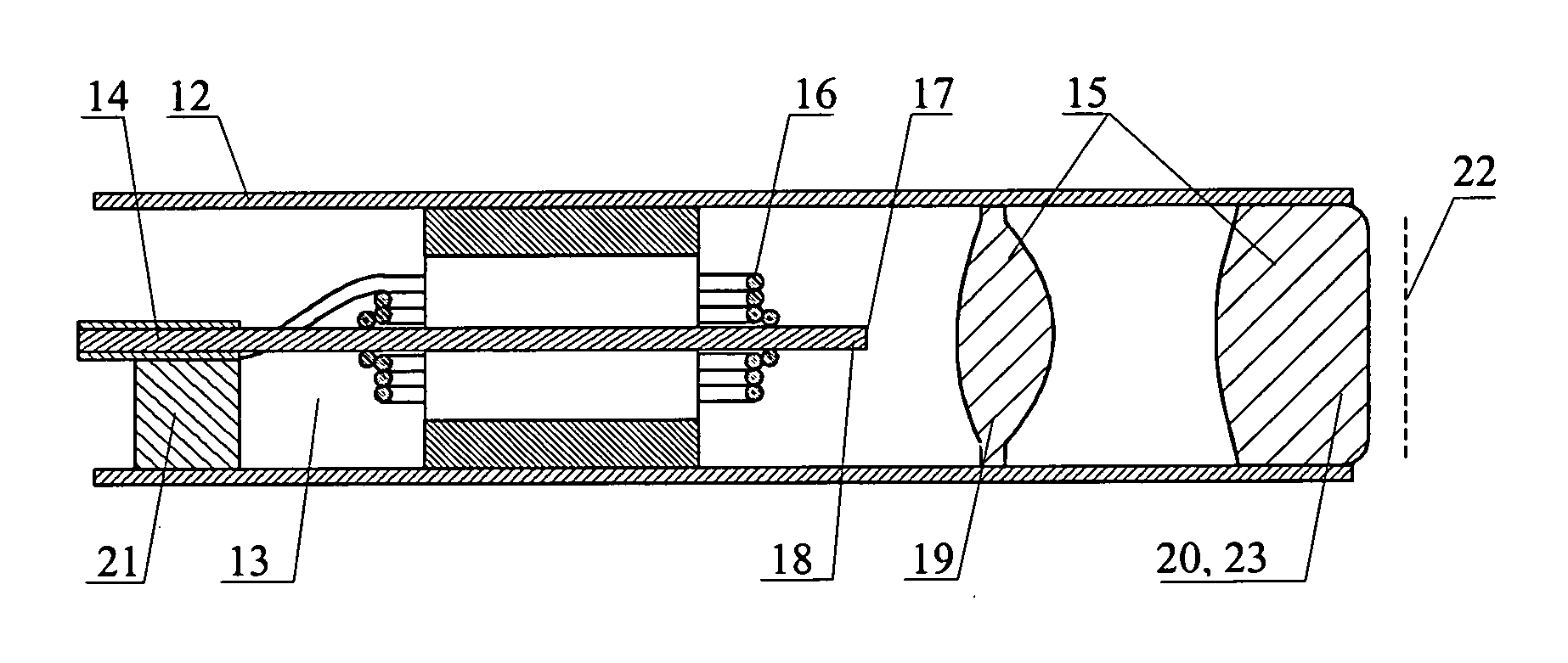
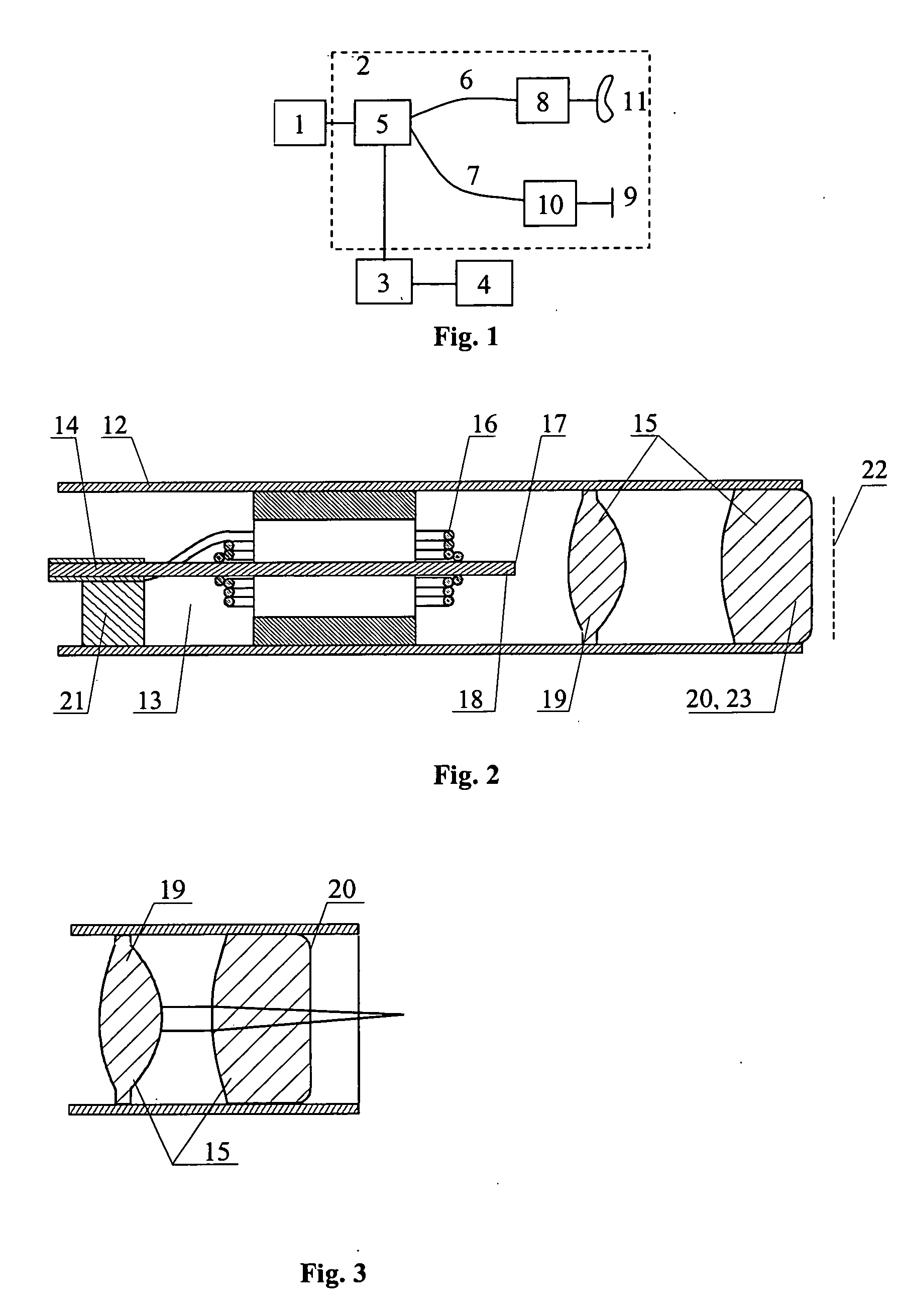
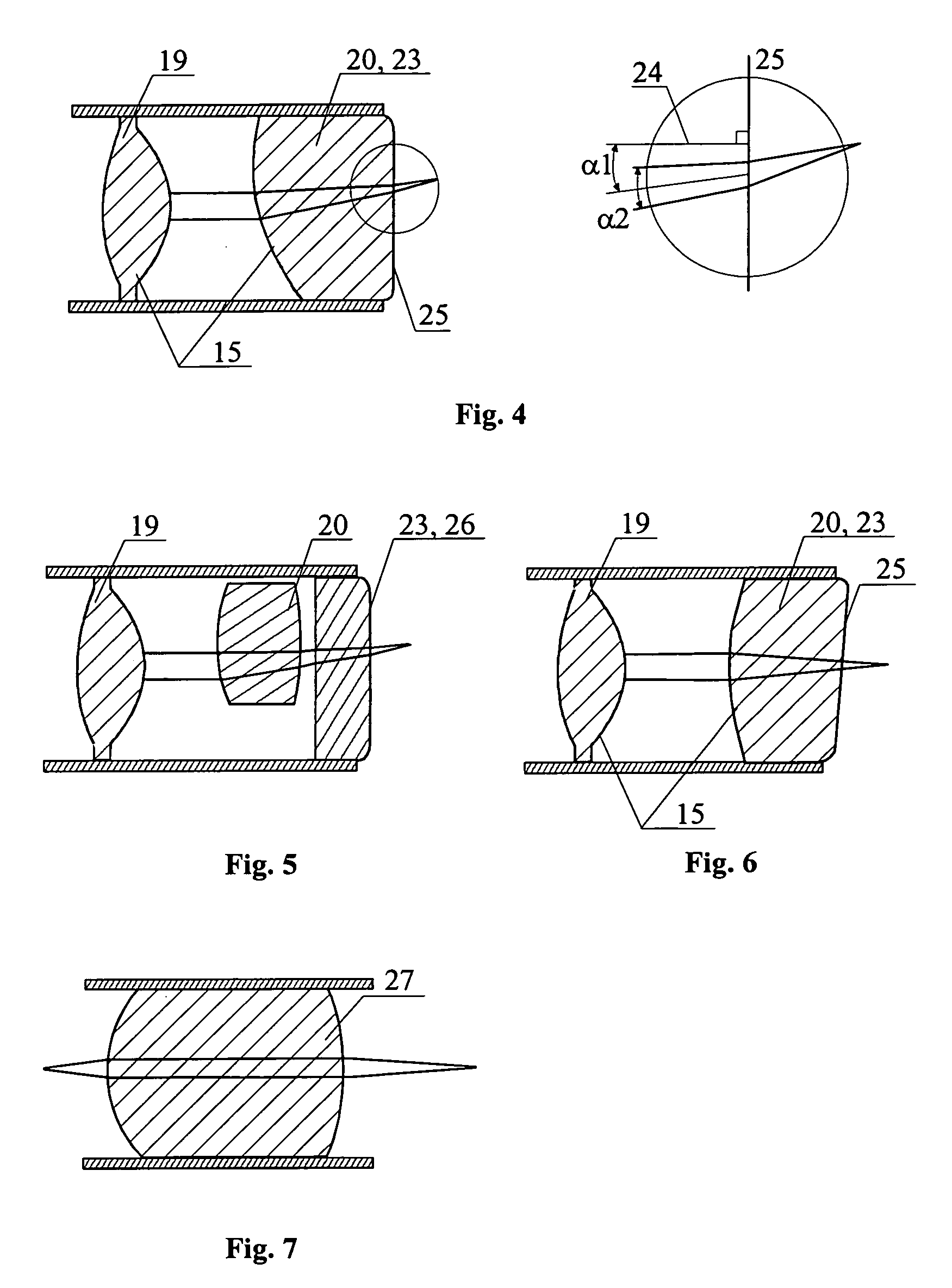
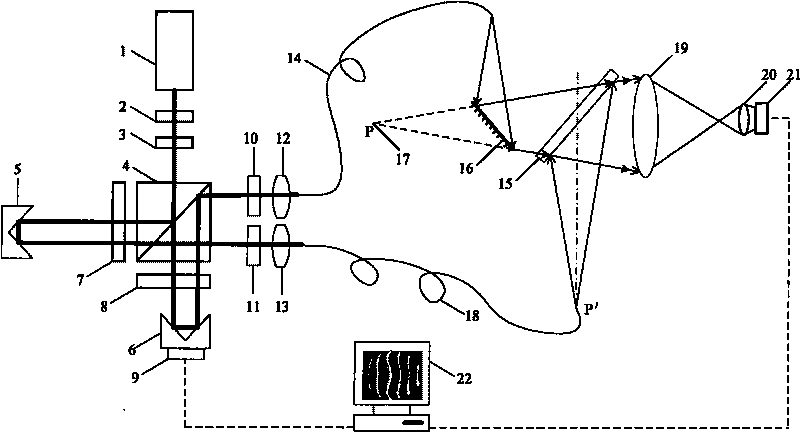
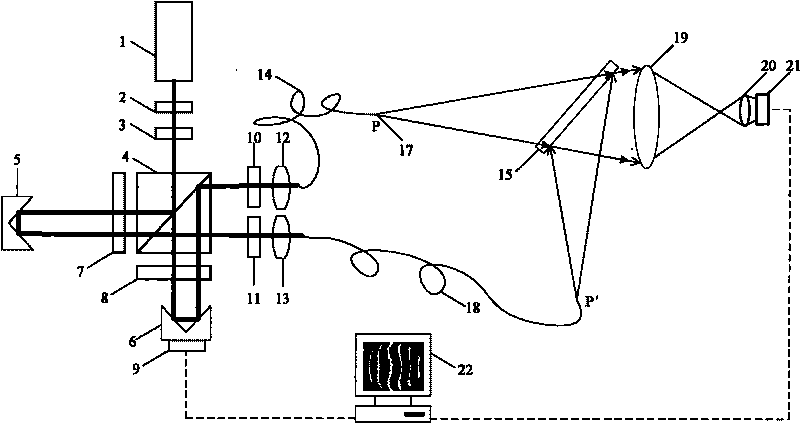
InactiveUS7515274B2High resolutionReduce light radiationInterferometersSurgeryPropagation timeOptical fiber probe
The invention relates to studies of internal structures of objects with the aid of optical means. According to the invention an optical system (15) of the delivering device for low coherence optical radiation, in a particular embodiment, an optical fiber probe (8), includes at least two lens components (19), (20), which have a positive focal power and are positioned substantionally confocally. This ensures a constant propagation time for the low coherence optical radiation propagating from a given point of the transverse scanning surface (28) or (39) to a corresponding conjugate point of the image plane (22). That provides elimination of the transverse scanning related aberration of the optical path length for low coherence optical radiation directed towards the object (11) both for a flat transverse scanning surface (28) and for a transverse scanning surface (39) having a curvature. In another embodiment, together with the substantionally confocal arrangement of lens components (19), (20), the longitudinal scanning is performed by varying the optical path length for the low coherence optical radiation propagating from the transverse scanning surface (28) to the optical system (15), i.e., from the end face (17) of the distal part (18) of the optical fiber (14) to the optical system (15). To achieve this, a device for longitudinal scanning (10) is incorporated into the optical fiber probe (8). This ensures a corresponding shift of the focusing position of the low coherence optical radiation during longitudinal scanning, i.e., allows for alignment of the focusing position of the low coherence optical radiation with the position of the coherence gate and, consequently, their simultaneous movement.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
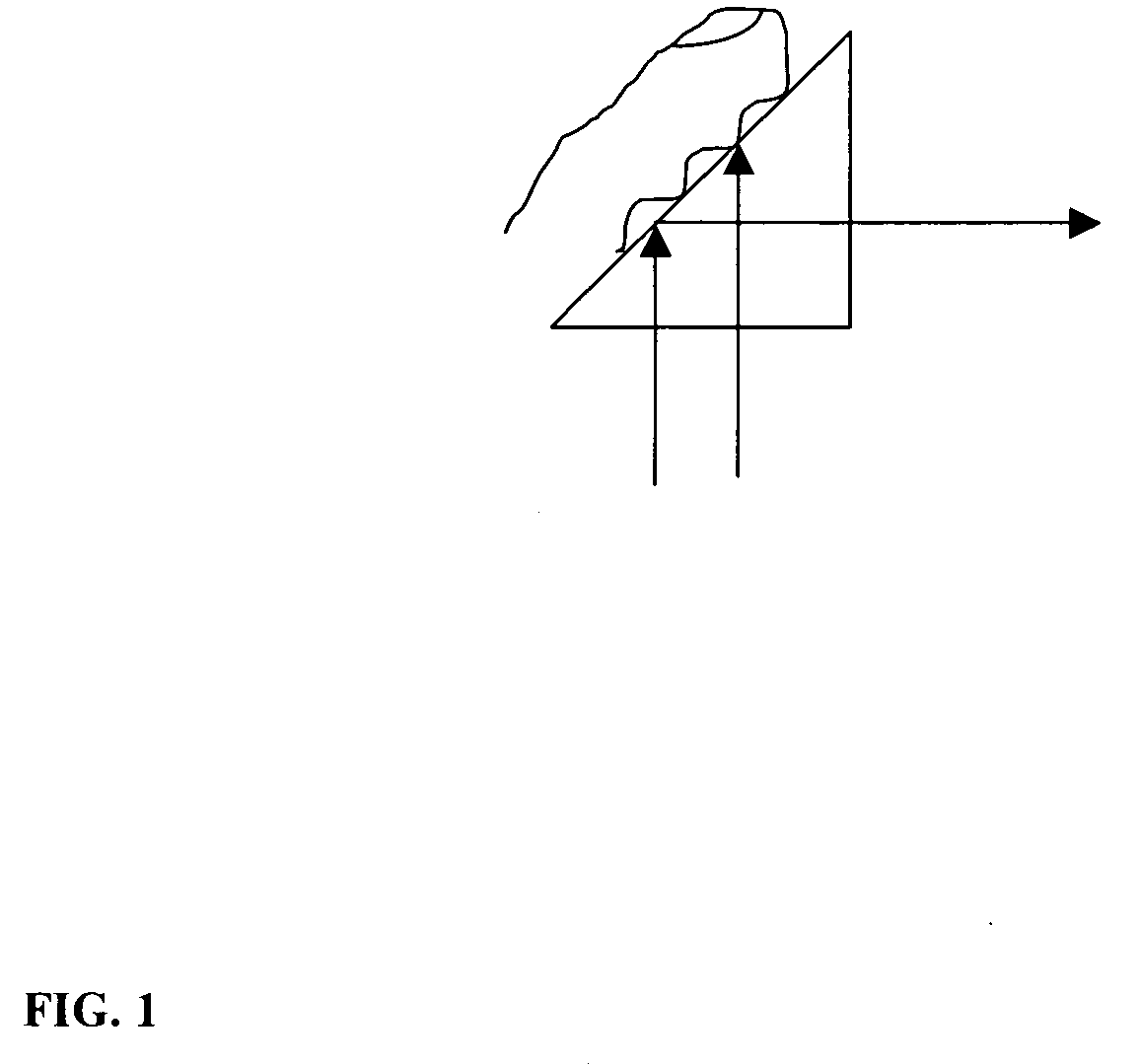
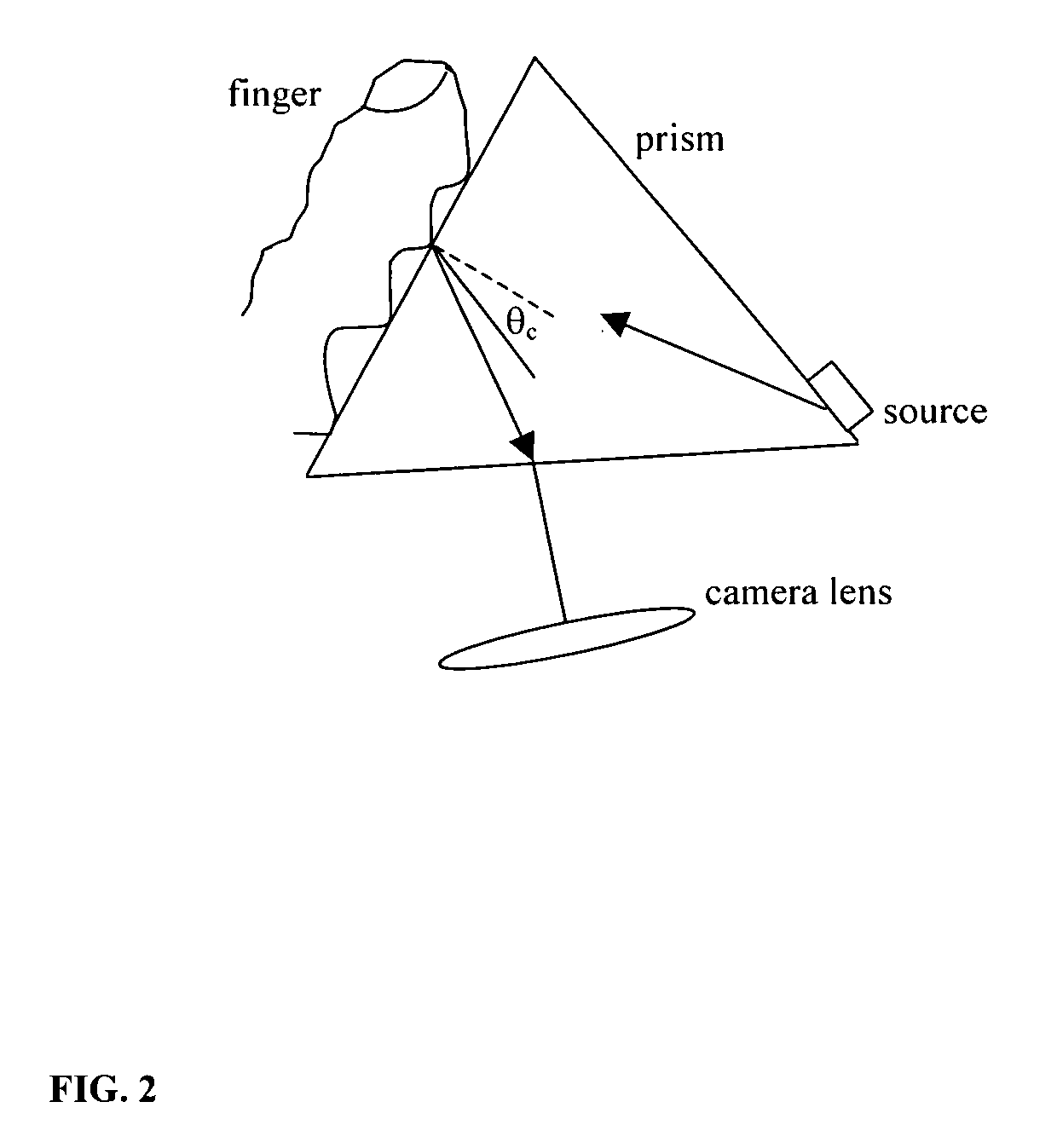
Fingerprint sensor using a spectral filter and a holographic optical element
InactiveUS20090116030A1Aberrated with astigmatismEliminate aberrationsCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansSpectral transmissionAngle of incidence
In one embodiment, a fingerprint sensing system includes a interference narrow band pass filter, a holographic optical element, a transparent slab stacked together with optical cement. The finger is placed on the filter and illuminated by a narrow band source, the center of its band shifted appropriately with respect to the pass band of the interference filter. A camera on the other side of the slab receives the fingerprint image. The light from the valleys and ridges propagating in the direction of the camera are blocked by the interference filter. The light from the ridges at steep angles are bent by the holographic optical element and then directed towards the lens. This way the ridges are seen by the camera, but not the valleys. In another embodiment, a miniaturized version, the interference filter, a modified holographic optical element, and a blocking filter (if necessary) to block room light can be sequentially attached to the image sensor. In yet another embodiment, the interference filter can be directly coated over an image sensor creating a very simple fingerprint sensor. The principle behind all of the above embodiments is the same, viz: the spectral transmission band of an interference filter shifts with change in the angle of incidence.
Owner:BAHUGUNA RAMENDRA DEO
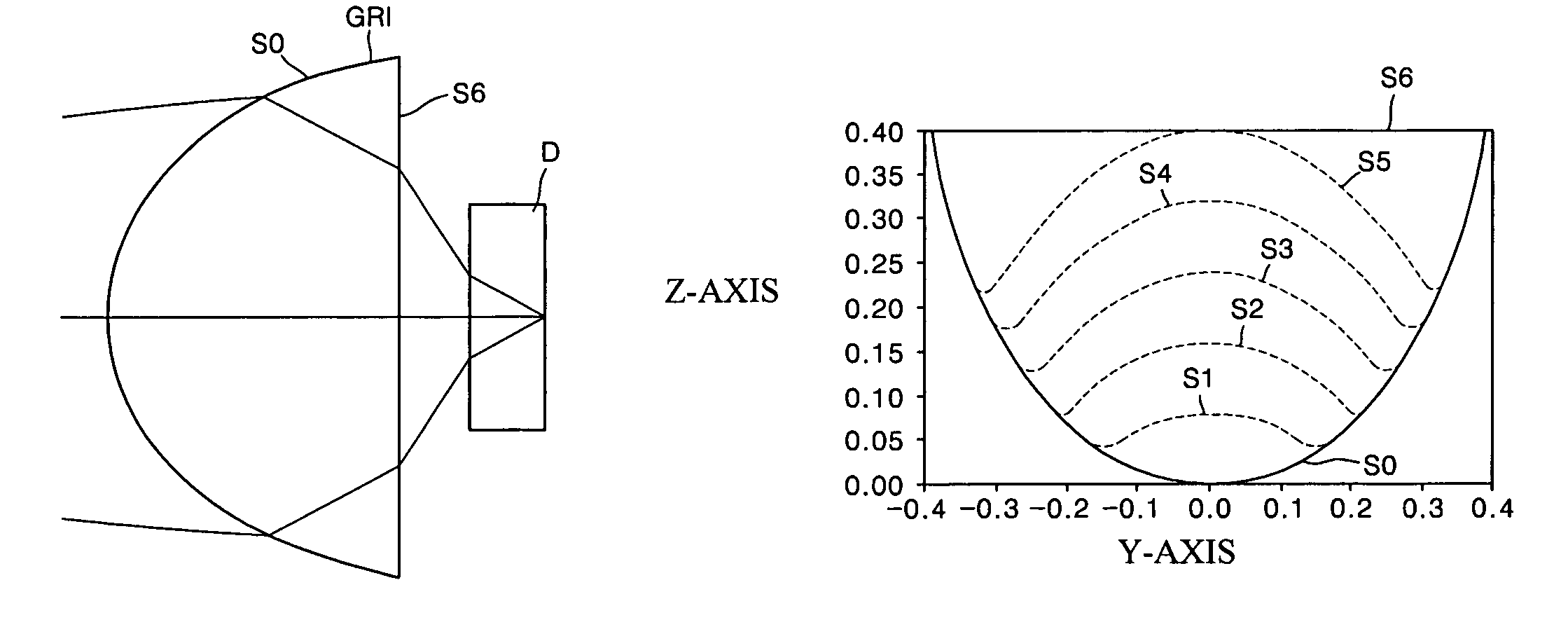
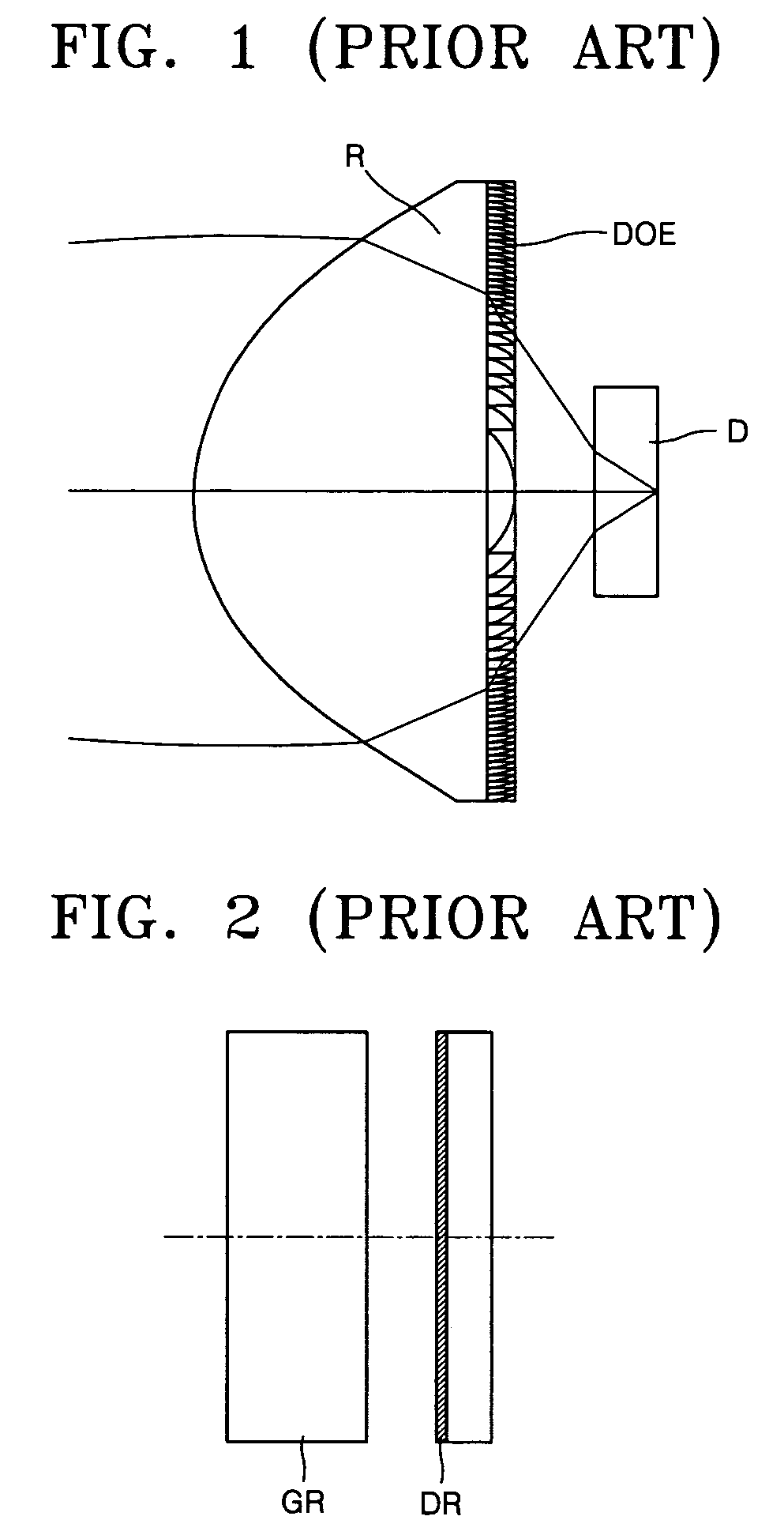
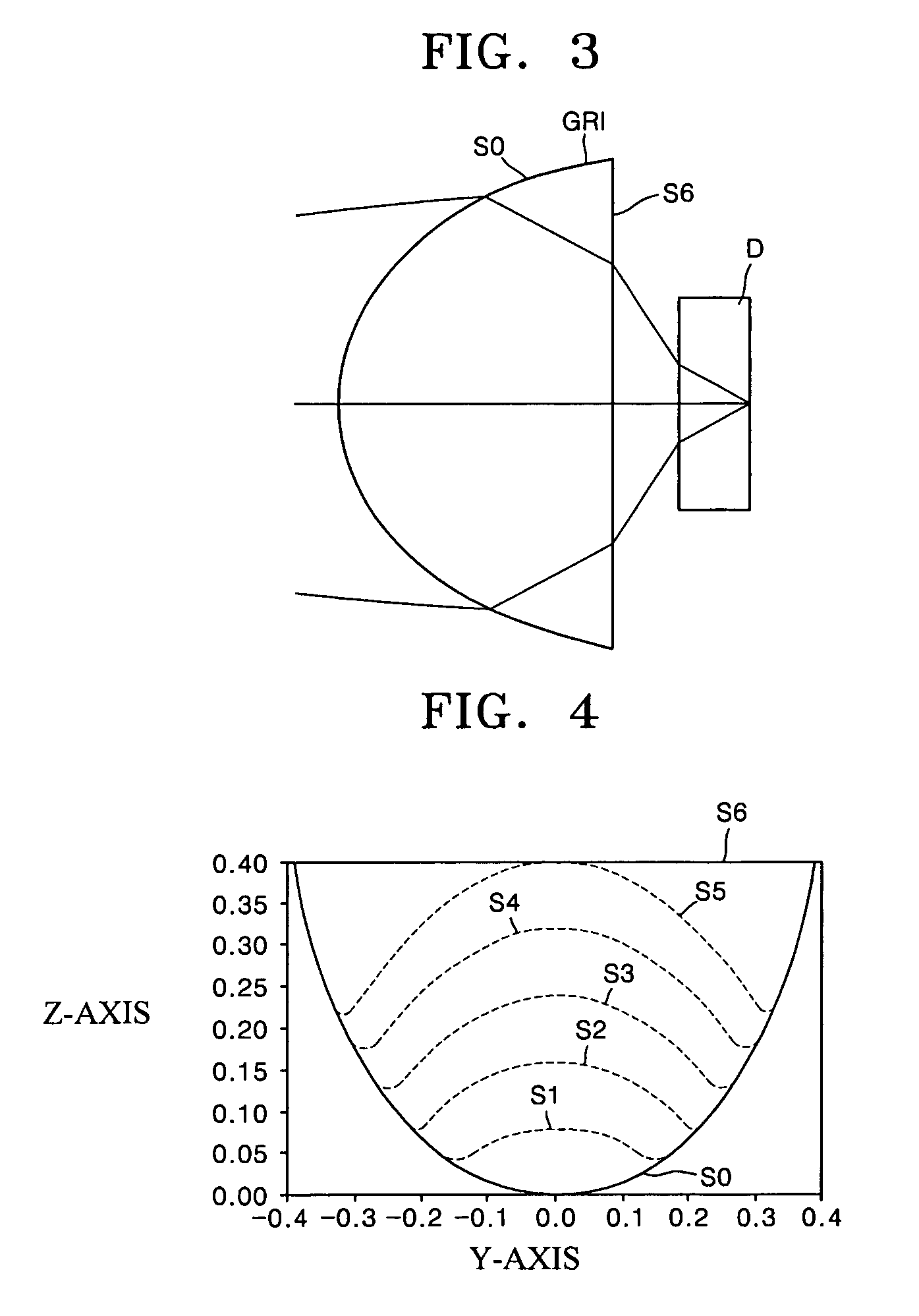
Objective optical system employing grin lens
ActiveUS7167317B2Eliminate chromatic aberrationRemove coma aberration aberrationRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansHigh numerical apertureRefractive index
Provided is an objective optical system employing a gradient index (GRIN) lens. A refractive index of the GRIN lens is changed in an axial direction and a direction perpendicular to the axial direction. The GRIN lens has a refractive index n satisfying the following equation:n(r,z)=∑i=0nr2ir2i+∑j=0nzjzjwhere z is a distance from the center of the lens in the axial direction and r is a distance from the center of the lens in the direction perpendicular to the axial direction. Thus, an objective optical system with a high numerical aperture can correct aberration.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Large-field-angle eye lens optical system
The invention provides a large-field-angle eye lens optical system used for a head worn displayer. The large-field-angle eye lens optical system comprises a first lens, a second lens and a third lens which are coaxially arranged from a human eye observation side to a displayer side in turn along an optical axis direction, and the first lens and the third lens are positive lenses and the second lens is a negative lens. The surface, which faces the human eye observation side, of the first lens convexly faces the human eye observation side, and the radius of curvature is a positive value. The surface, which faces a diaphragm, of the second lens concavely faces the human eye observation side, and the radius of curvature is a negative value. Meanwhile, the material, the focal length and the position of the first lens, the second lens and the third lens meet a certain relation so that an image displayed on a display device is enabled to be imaged in human eyes through amplification of an eye lens. The eye lens has advantages of large aperture, large field of view, high resolution, low distortion and small size so as to be suitable for the head worn displayer and similar devices.
Owner:SHENZHEN NED OPTICS CO LTD
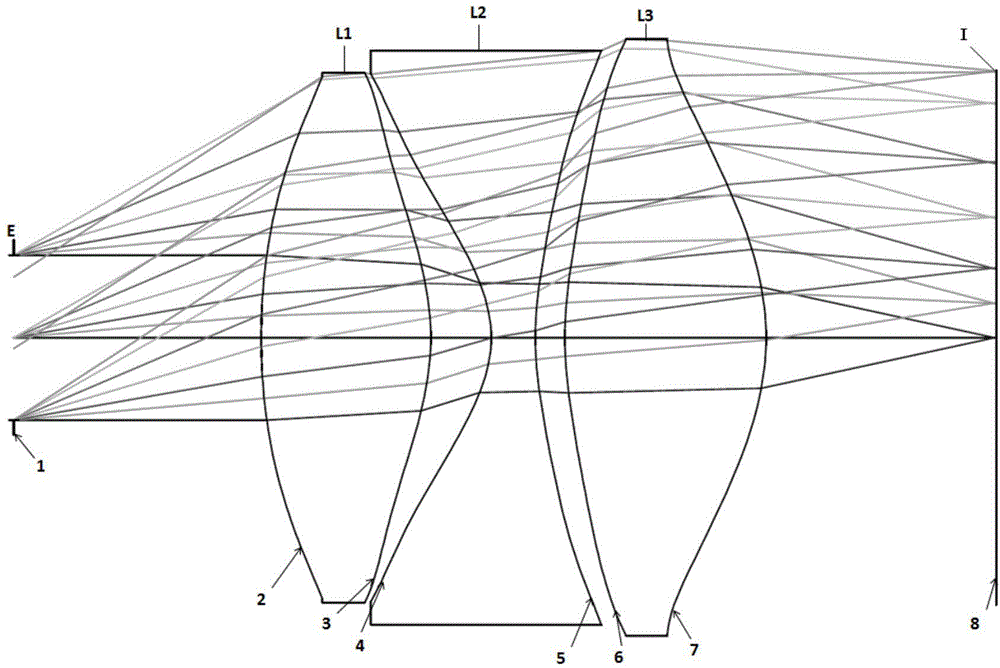
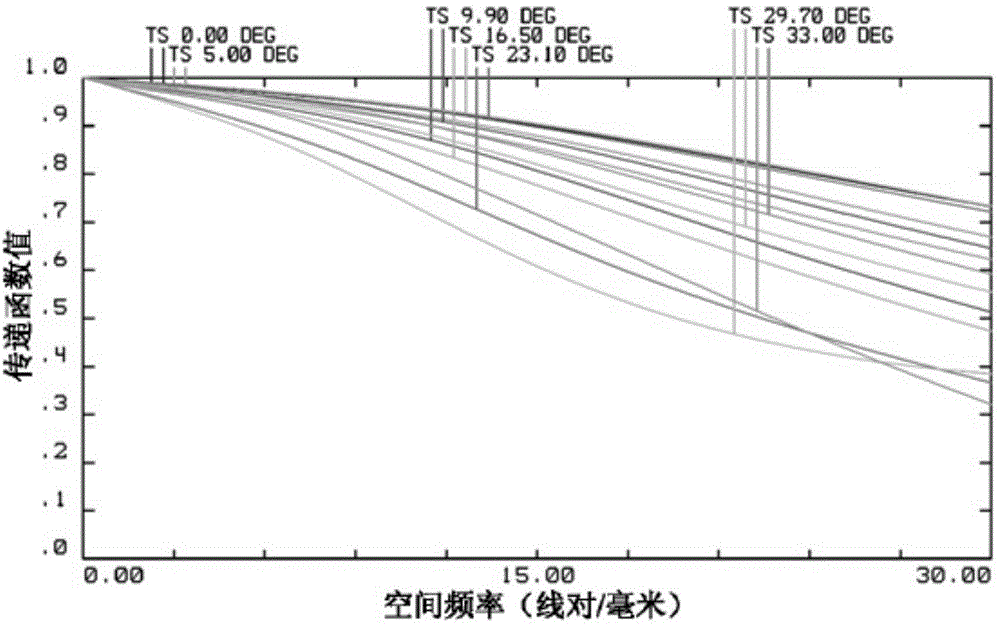
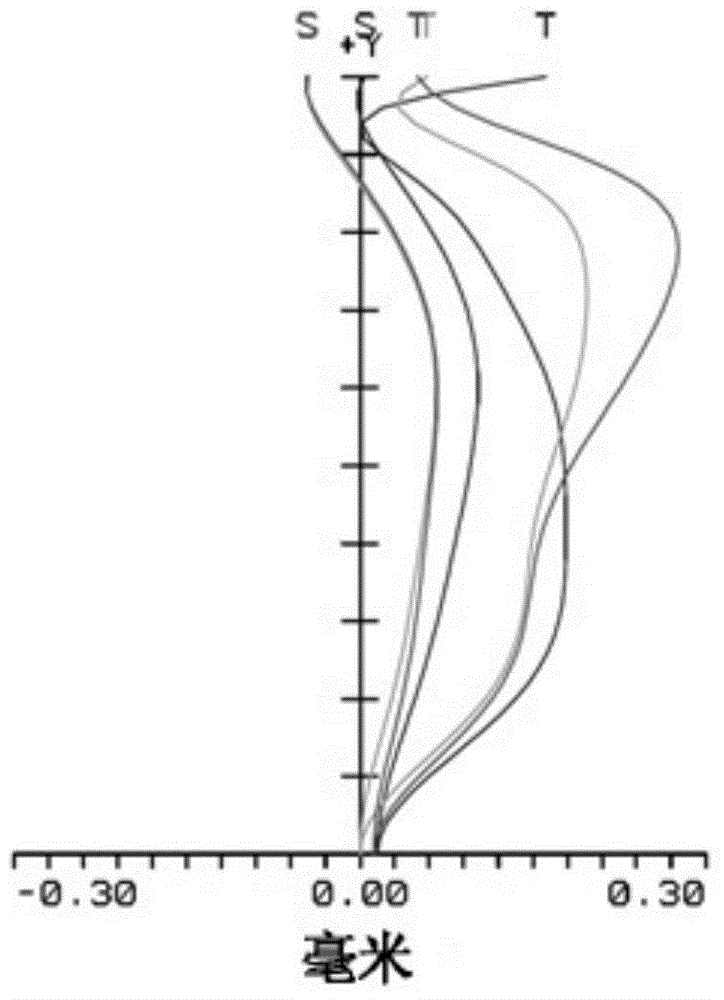
Optical lens and imaging equipment
ActiveCN109541780AReduce manufacturing costLow manufacturing cost and high manufacturing costVehicle componentsMountingsCamera lensOptoelectronics
The invention provides an optical lens which comprises the following components that are successively arranged from an object side to an imaging surface: a first lens which has negative focal power and an object-side surface that is a convex surface and an image-side surface that is a recessed surface; a second lens which has negative focal power and an object-side surface that is a recessed surface; a third lens which has positive focal power and an object-side surface that is a convex surface; a fourth lens with positive focal power; a fifth lens which has positive focal power and an object-side surface and an image-side surface that are convex surfaces; a sixth lens which has negative focal power and an object-side surface and an image-side surface that are recessed surfaces; wherein the fifth lens and the sixth lens are adhered for obtaining a adhering member; and a seventh lens with positive focal power, wherein the optical lens further comprises a diaphragm between the second lens and the third lens. The optical lens provided by the invention at least has a wide-spectrum imaging function. The invention further provides imaging equipment.
Owner:JIANGXI LIANCHUANG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Compositions and Methods for the Treatment of Presbyopia
ActiveUS20150065511A1Eliminating optical aberrationImprove visual acuityBiocideSenses disorderAdrenergicMedicine
The invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of presbyopia. The compositions preferably use aceclidine separate or together with a cycloplegic agent and / or with a nonionic surfactant and viscosity enhancer, and or with low concentrations of a selective α-2 adrenergic receptor agonist.
Owner:LENZ THERAPEUTICS INC
Zoom lens
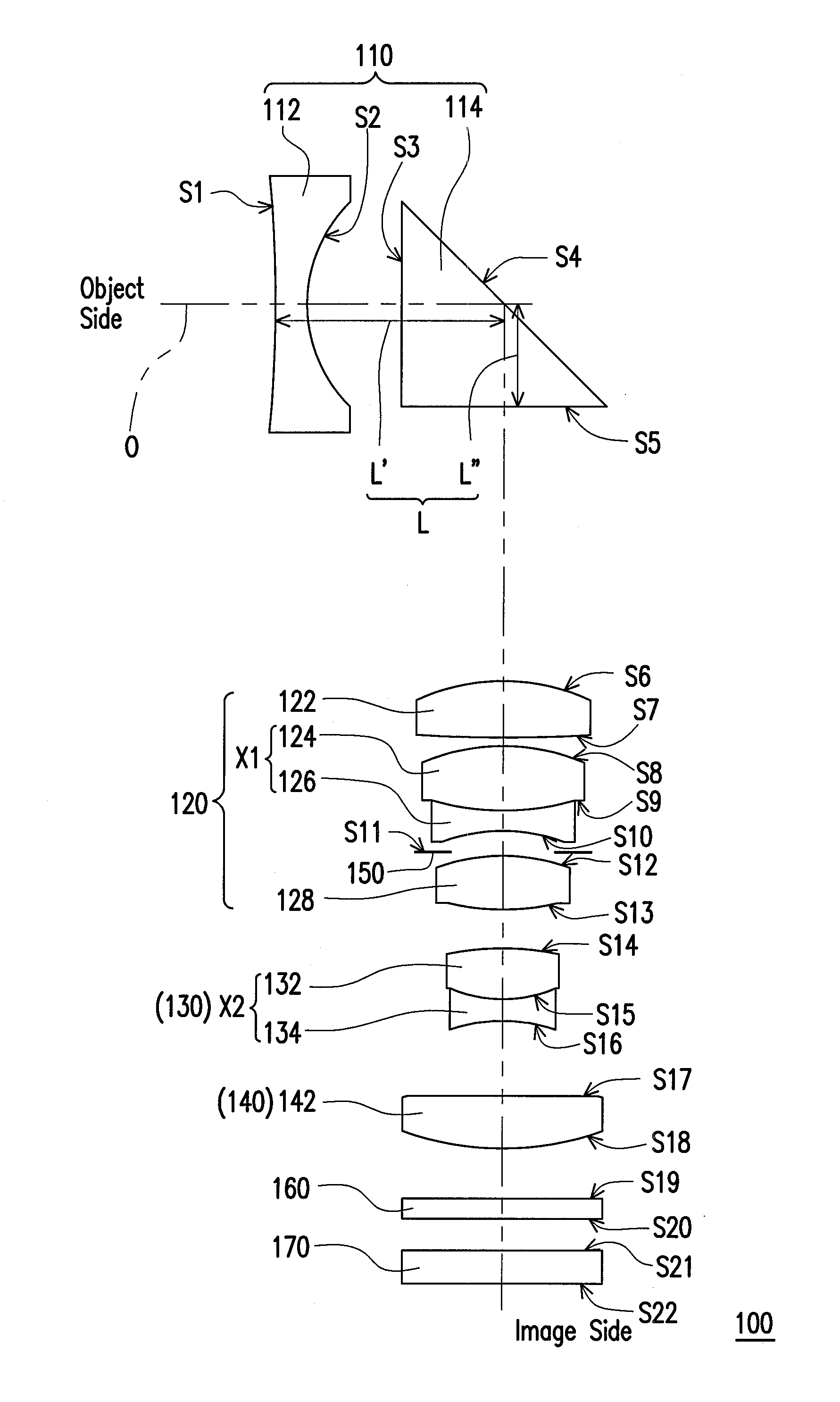
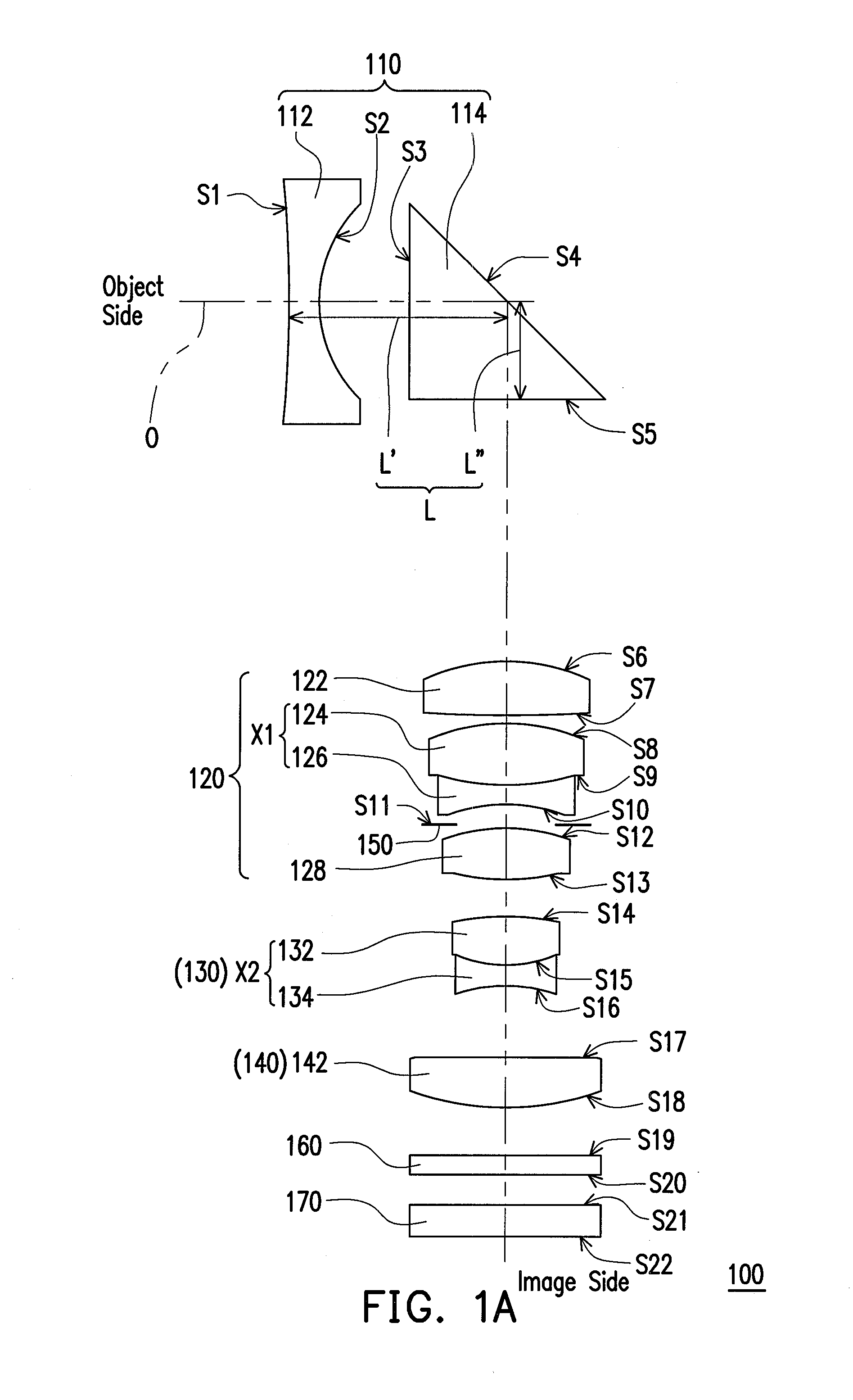
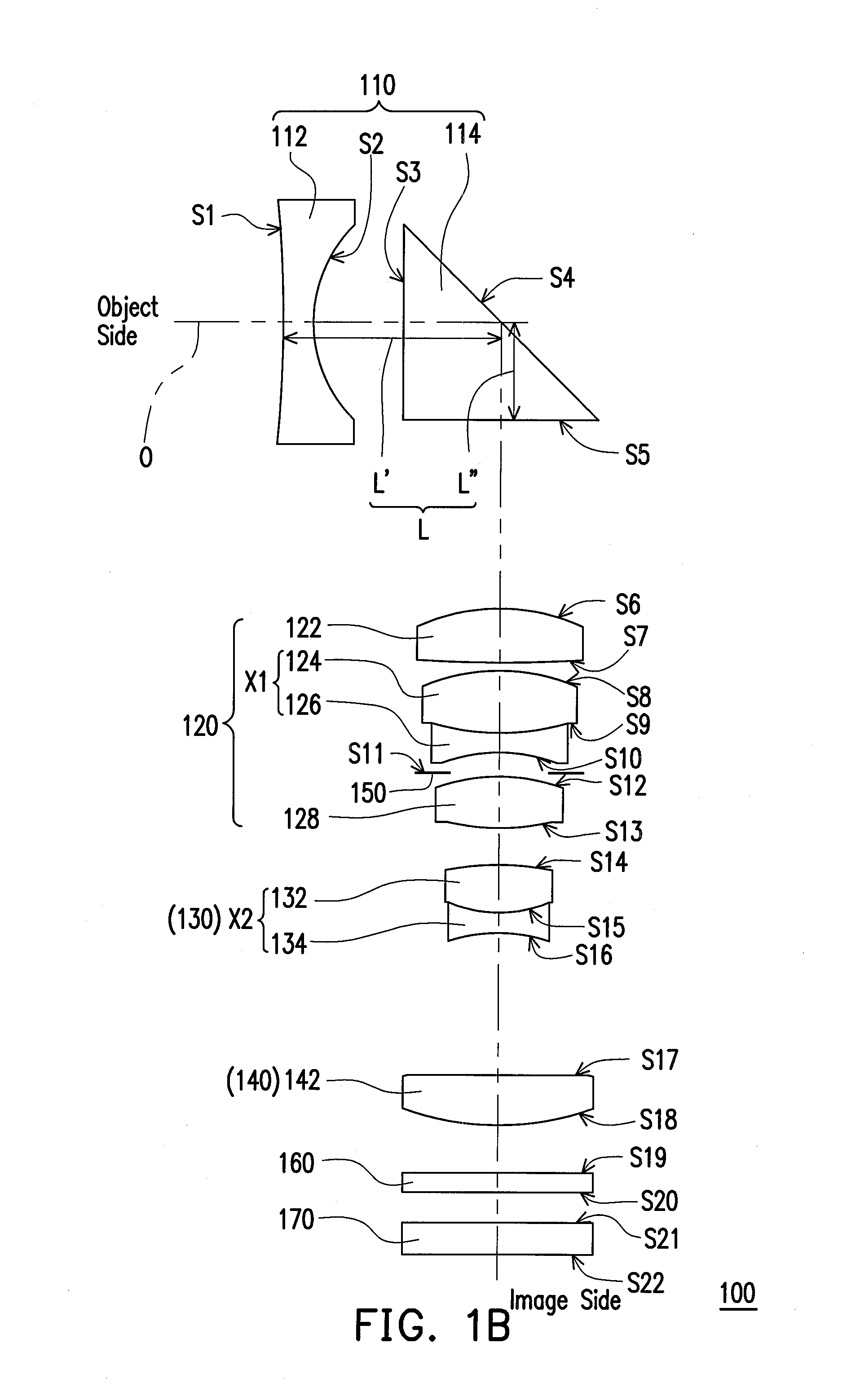
A zoom lens disposed between an object side and an image side and including a first, second, third, and fourth lens group is provided. The first lens group has a negative refractive power and includes a first lens and a prism arranged in sequence from the object side to the image side. The first lens is an aspheric lens. A distance between the first lens and the prism is L, an effective focal length of the zoom lens at a wide-end is fw, and 1.58<L / fw<1.88. The second lens group disposed between the first lens group and the image side has a positive power and includes a first double cemented lens. The third lens group disposed between the second lens group and the image side has a negative power and includes a second double cemented lens. The fourth lens group has a positive power.
Owner:YOUNG OPTICS
Method for obtaining the image of an object, device for carrying out said method and device for delivering low coherent optical radiation
InactiveUS20060165350A1Increase horizontal resolutionHigh resolutionSurgeryInterferometersOptical radiationPropagation time
The invention relates to studies of internal structures of objects with the aid of optical means. According to the invention an optical system (15) of the delivering device for low coherence optical radiation, in a particular embodiment, an optical fiber probe (8), includes at least two lens components (19), (20), which have a positive focal power and are positioned substantionally confocally. This ensures a constant propagation time for the low coherence optical radiation propagating from a given point of the transverse scanning surface (28) or (39) to a corresponding conjugate point of the image plane (22). That provides elimination of the transverse scanning related aberration of the optical path length for low coherence optical radiation directed towards the object (11) both for a flat transverse scanning surface (28) and for a transverse scanning surface (39) having a curvature. In another embodiment, together with the substantionally confocal arrangement of lens components (19), (20), the longitudinal scanning is performed by varying the optical path length for the low coherence optical radiation propagating from the transverse scanning surface (28) to the optical system (15), i.e., from the end face (17) of the distal part (18) of the optical fiber (14) to the optical system (15). To achieve this, a device for longitudinal scanning (10) is incorporated into the optical fiber probe (8). This ensures a corresponding shift of the focusing position of the low coherence optical radiation during longitudinal scanning, i.e., allows for alignment of the focusing position of the low coherence optical radiation with the position of the coherence gate and, consequently, their simultaneous movement.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
Three-dimensional imaging device for retina
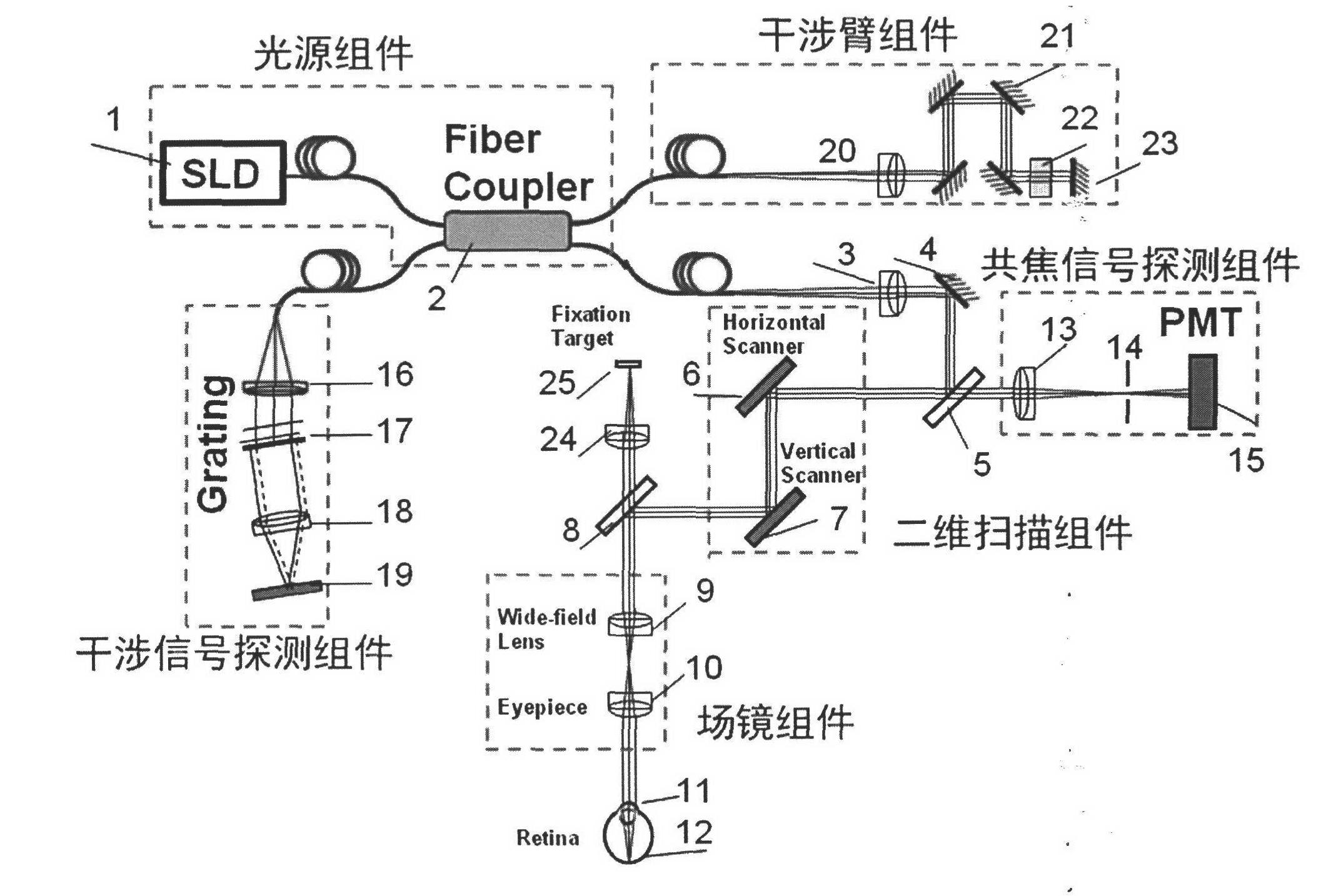
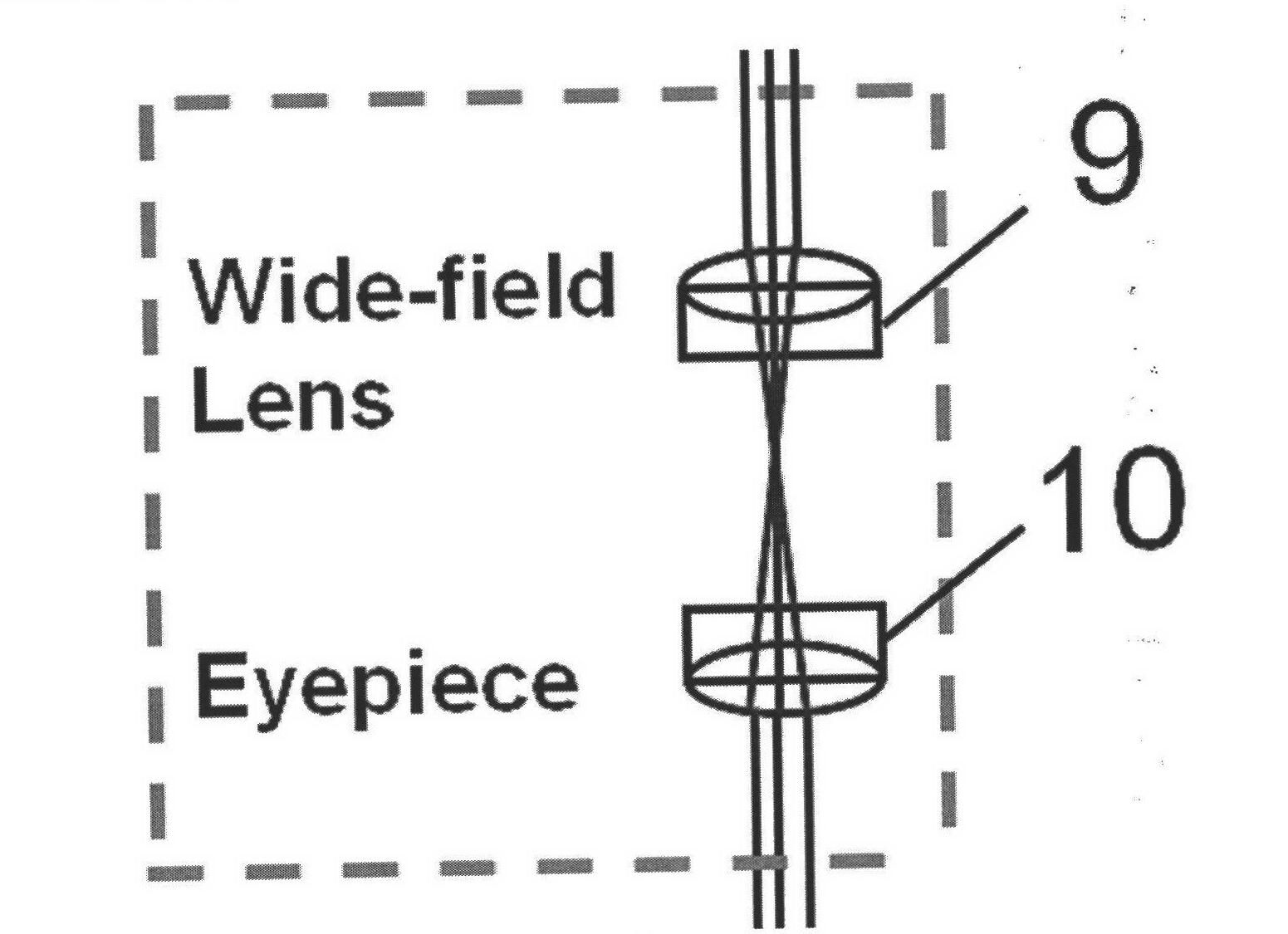
InactiveCN102525406AEliminate aberrationsEliminate non-uniformityOthalmoscopesImage resolutionOptical fiber coupler
The invention discloses a three-dimensional imaging device for a retina. The device consists of a light source component, an interference arm component, a two-dimensional scanning component, a field lens component, a confocal signal detection component and an interference signal detection component. The three-dimensional imaging device for the retina finishes scanning on the retina of a human eye by using the two-dimensional scanning component, extracts a surface image of the retina by using the confocal signal detection component and depth information of the retina by using the interference signal detection component, and jointly finishes the reconstruction of a three-dimension image of the retina through a confocal signal and an interference signal; the system is compact by adopting the design of optical fiber access and an optical fiber coupler; the influence of curvature of field and aberration in the imaging process is reduced through the design of a field lens so as to acquire a large-field-of-view three-dimensional image of the retina of the human eye; and the three-dimensional imaging device for the retina which is compactly designed and is high in imaging resolution and large in imaging field of view is realized, so that the imaging effect of the traditional fundus imaging instrument is greatly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROCLEAR MEDICAL INSTR
Method and device for shielding a high-power laser apparatus and high-power-laser optical system employing such a device
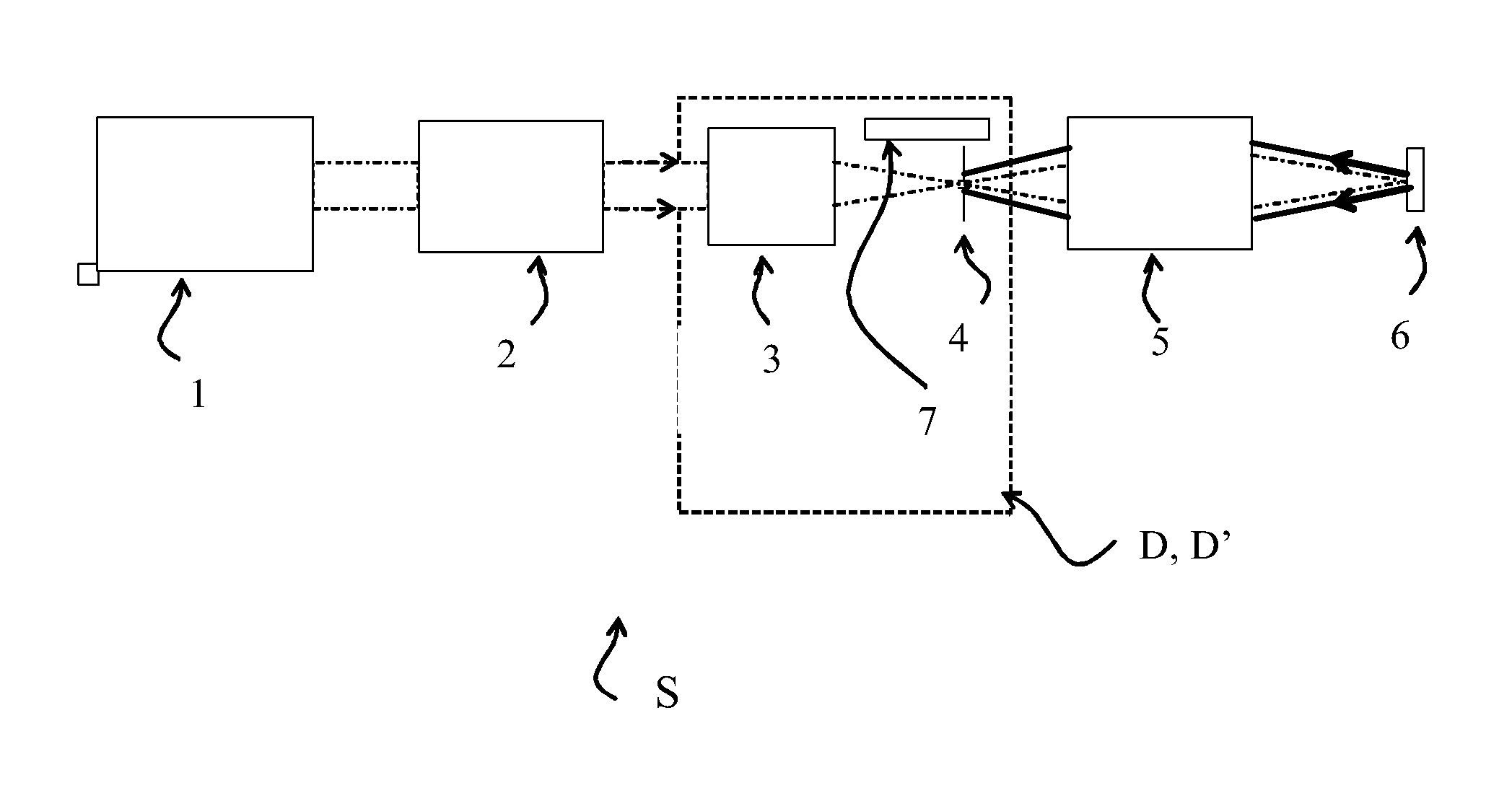
InactiveUS8971363B2Control damageEasy to controlLaser arrangementsOptical devices for laserPhase correctionHigh power lasers
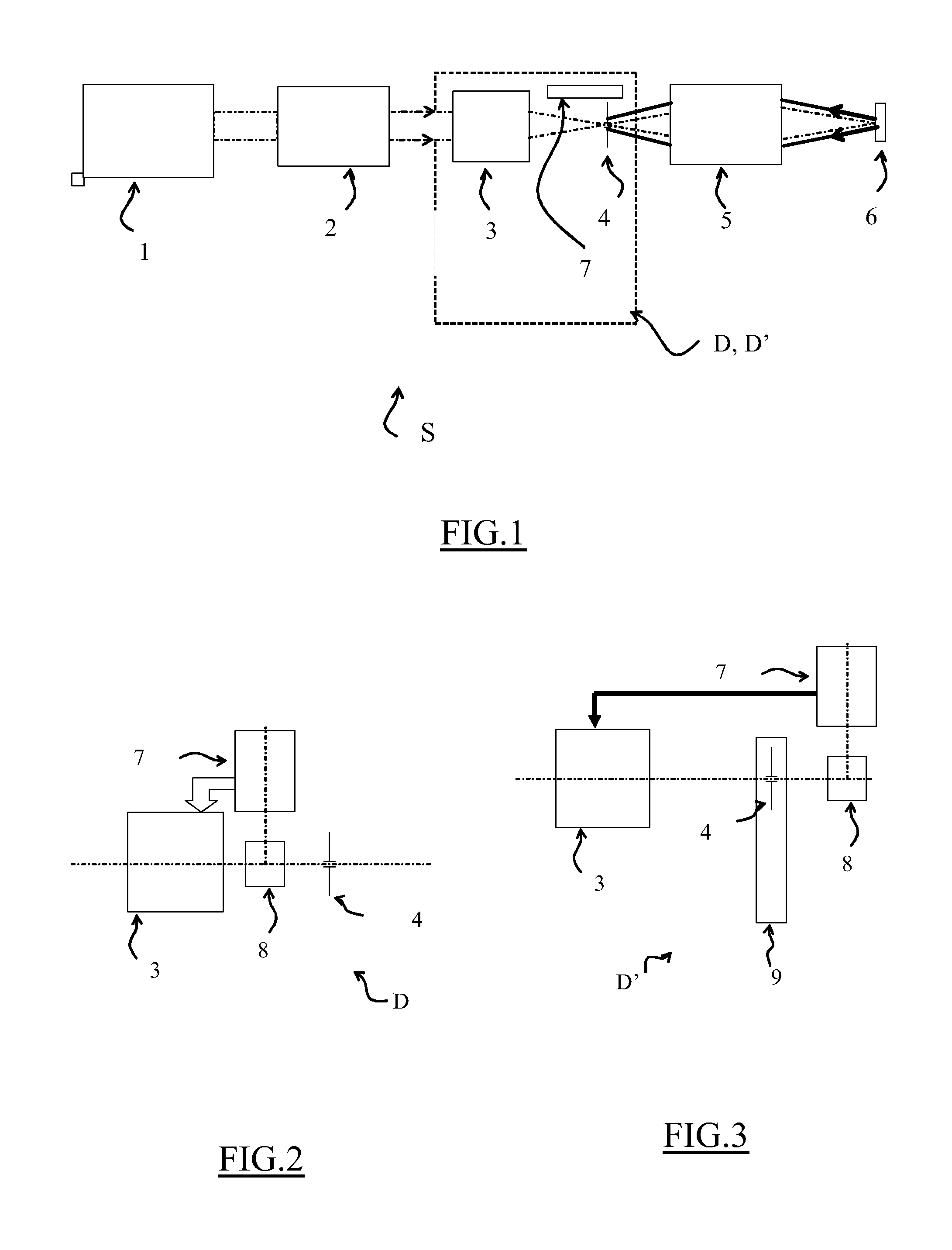
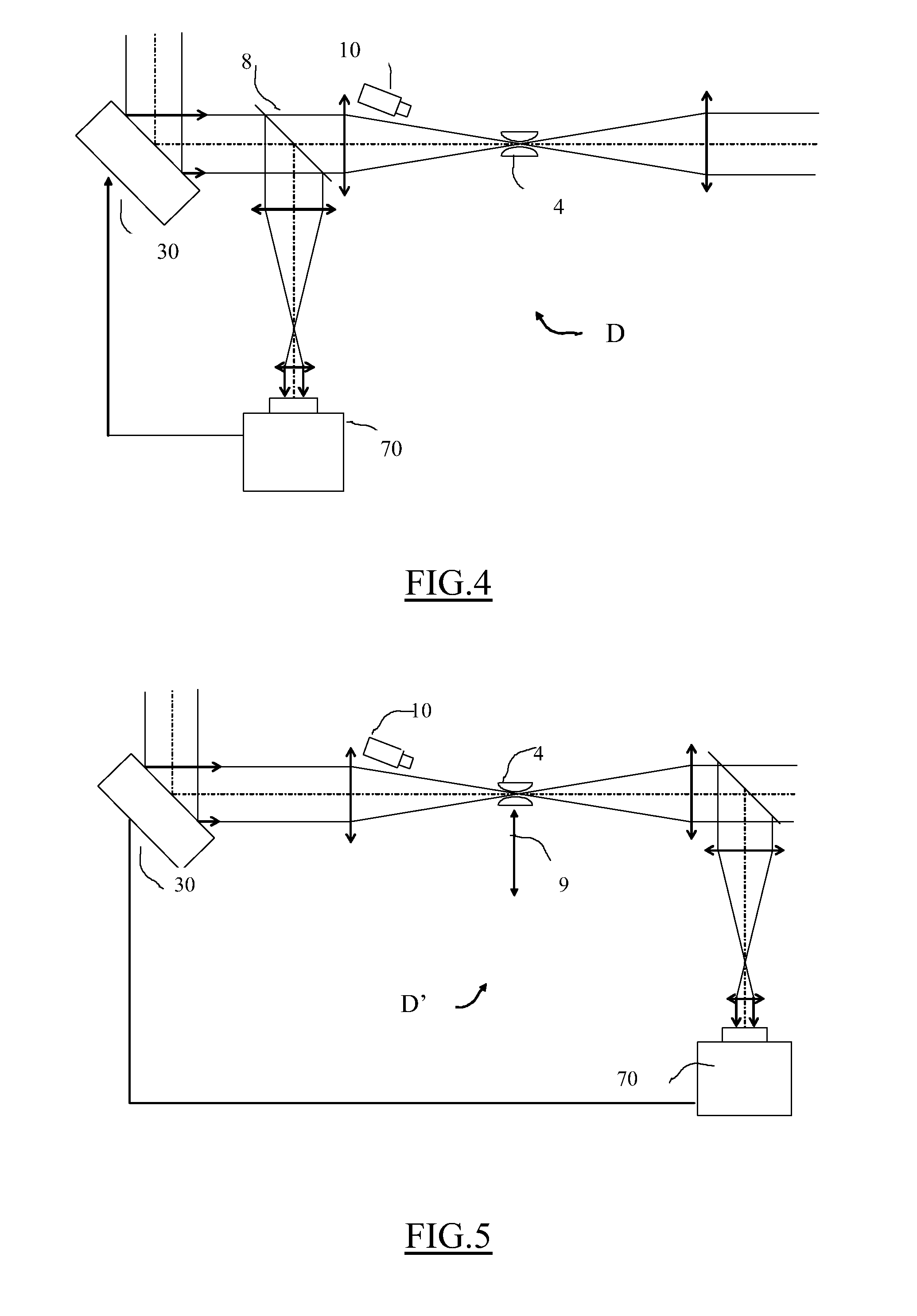
Method for shielding a high-power laser apparatus (S) in which a laser beam is generated and then amplified in at least a first amplification stage, including spatial filtering (4) of the amplified laser beam, phase correction (3) carried out on the laser beam before it is spatially filtered, and a measurement of the aberrations (7) on the laser beam. The phase of the beam is corrected so as to produce a beam having minimal aberrations after spatial filtering. The shielding device (D, D′) implementing this method may in particular be employed in apparatus using an intense laser beam of high (terawatt) peak power and in proton therapy units.
Owner:IMAGINE OPTIC +1
Variable distortion aberration image pickup device
InactiveUS20050105822A1Eliminate aberrationsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementEngineeringElectronic feedback
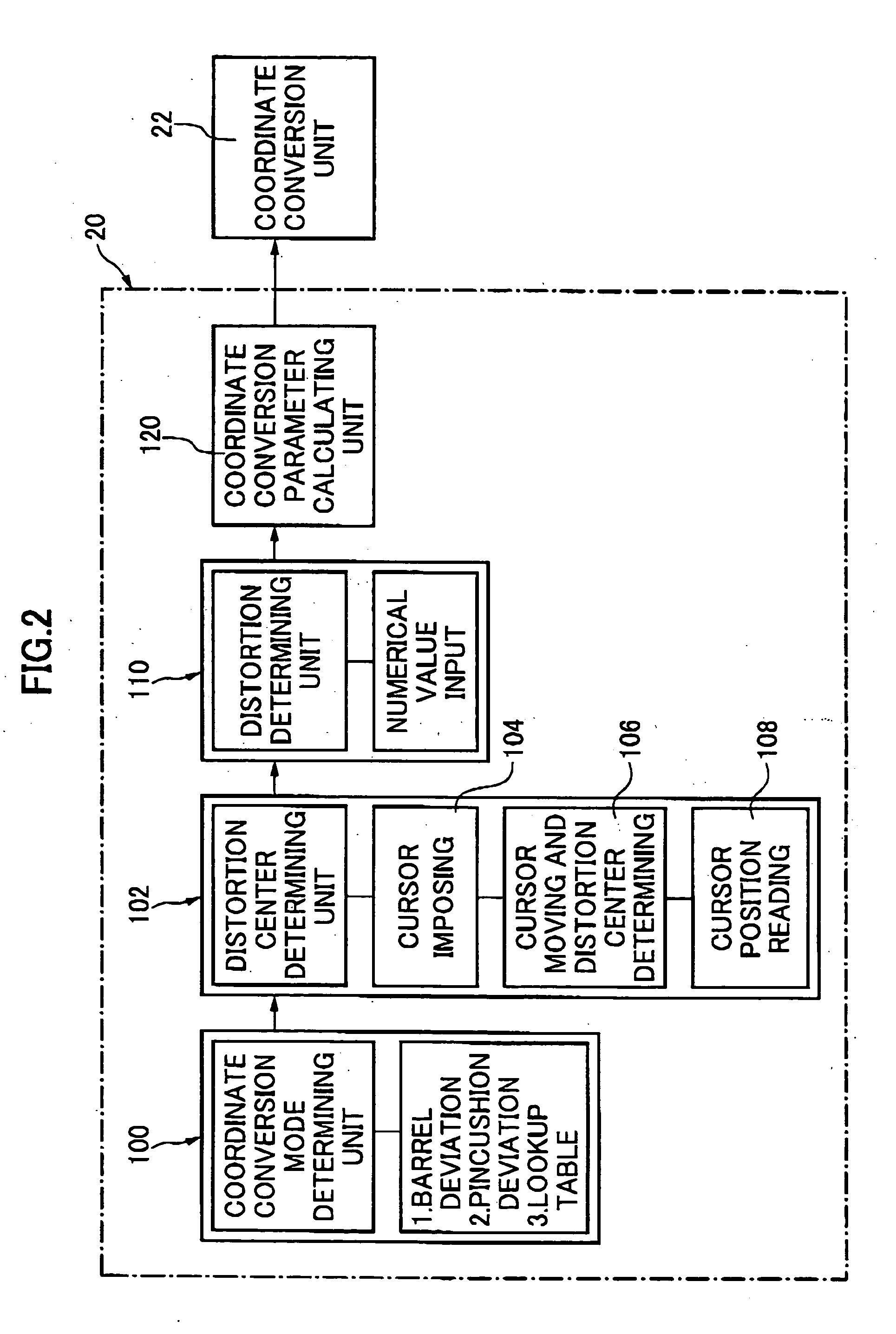
The present invention is directed to a variable distortion aberration image pickup device that is capable of varying distortion aberration with its center at any desired point either inside or outside an image where, specifically, distortion aberration is effectively developed and / or eliminated with the distortion center at any desired point both inside and outside the image as desired, and such an image pickup device is also capable of varying distortion aberration with its center at a desired point either inside or outside the image, separately in individual directions, where specifically an image is processed so as to have distortion aberration with its center at any desired point both inside and outside the image, with varied distortion ratios from one direction to another. For that purpose, the variable distortion aberration image pickup device is comprised of a photograph lens, two-dimensional opto-electronic feedback elements, and a distortion aberration conversion circuit that receives output image signals from the two-dimensional opto-electronic feedback elements to dislocate a desired point of an image in some direction(s) from the given center of distortion.
Owner:TAMRON
Discretely controlled micromirror array device with segmented electrodes
ActiveUS20080137173A1Effective structureEliminate aberrationsMirrorsStatic indicating devicesDevice formEngineering
This invention provides a discretely controlled micromirror array device comprising a plurality of micromirrors. The discretely controlled micromirror array device forms multiple surface profiles, wherein the rotational and translational motion of each micromirror is discretely controlled by selectively activating different groups of segmented electrodes using a control circuitry. The discretely controlled micromirror array device is compatible with known semiconductor electronics technologies and provides structural stability and efficiency in motion.
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Optical fiber laser and collimator thereof
InactiveCN102135668AReduce processing costsSimple preparation processActive medium shape and constructionMountingsOptical axisLight beam
The invention discloses a collimator of an optical fiber laser, comprising a lens cone, an output tail fiber and an optical lens, wherein the output tail fiber is fixed on the front end of the lens cone; the optical lens is fixed in the lens cone; the rear end surface of the output tail fiber is positioned on a focal point of the optical lens; and the optical lens comprises a biconcave lens and abiconvex lens which are sequentially arranged along a light path and positioned on a same optical axis. The optical lens of the collimator is mainly a double-lens group comprising the biconcave lens with positive spherical aberration and the biconvex lens with negative spherical aberration, the double-lens group can eliminate system aberration, thereby ensuring that the quality of collimated and expanded output light beams is basically not reduced and keeping the advantage of high light beam quality of the optical fiber laser; and the double-lens group has simple manufacturing process and lowcost, therefore the processing cost of the collimator is reduced. In addition, the invention also discloses the optical fiber laser with the collimator.
Owner:INST OF IND TECH GUANGZHOU & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Off-axis blocking-free parallel light system capable of eliminating six types of aberrations
InactiveCN103869491AEliminate aberrationsSolve chromatic aberrationMirrorsBeam expanderOptoelectronics
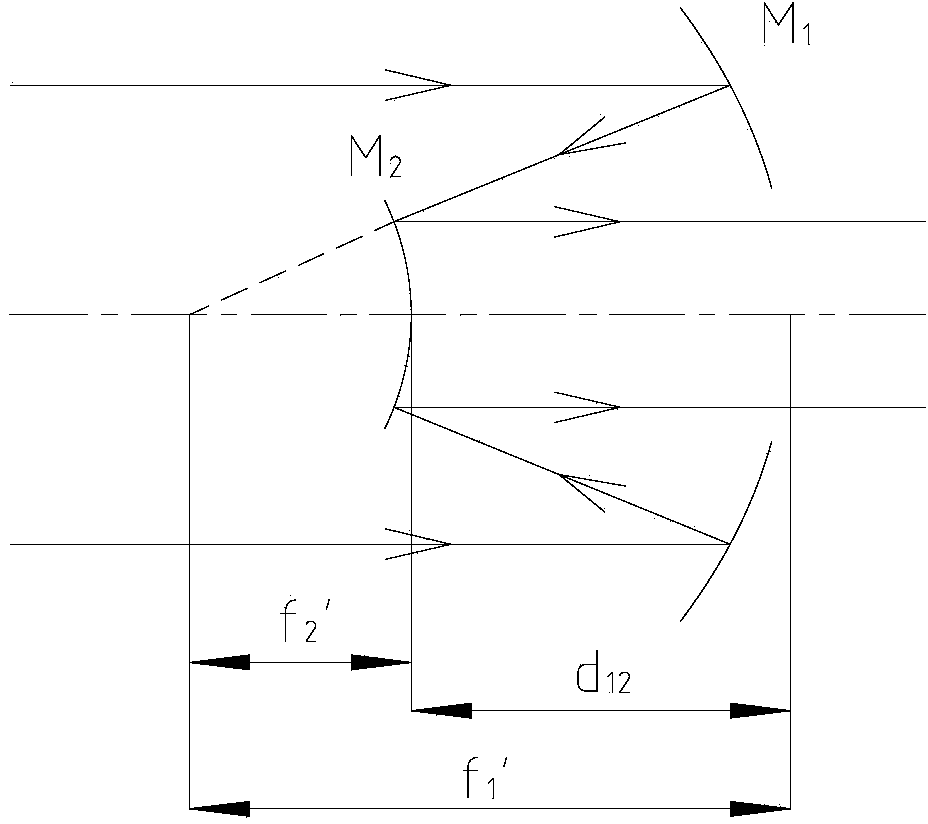
The invention relates to an off-axis blocking-free parallel light system capable of eliminating six types of aberrations. The off-axis blocking-free parallel light system capable of eliminating six types of aberrations comprises a first reflecting mirror and a second reflecting mirror, the second reflecting mirror is arranged on a reflected light path after reflection of the first reflecting mirror; the first reflecting mirror is arranged on an incident light path; the first reflecting mirror and the second reflecting mirror are paraboloidal reflecting mirrors. The off-axis blocking-free parallel light system capable of eliminating six types of aberrations can be used for a beam expander system or a beam shrinking system or a telescopic system and is capable of simultaneously eliminating six types of aberrations.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for a self-referencing interferometer
ActiveUS8462349B1Reduce size and complexity of componentImprove assemblyInterferometersUsing optical meansPhysicsSignal beam
Systems and methods are described herein for a self-referencing interferometer. The interferometer can comprise an improved spatial phase shifter that reduces the number of components, size and complexity of the spatial phase shifter and maintains a common path for a combined reference beam and signal beam. The self-referencing interferometer further comprises a single mode fiber shunt for filtering the reference beam and further reducing the size of the interferometer. The angle of the reference beam can be tilted before being recombined with the single beam which further simplifies the spatial phase shifting component of the interferometer.
Owner:LEIDOS
Super-large-aperture wide-angle lens of single lens reflex camera
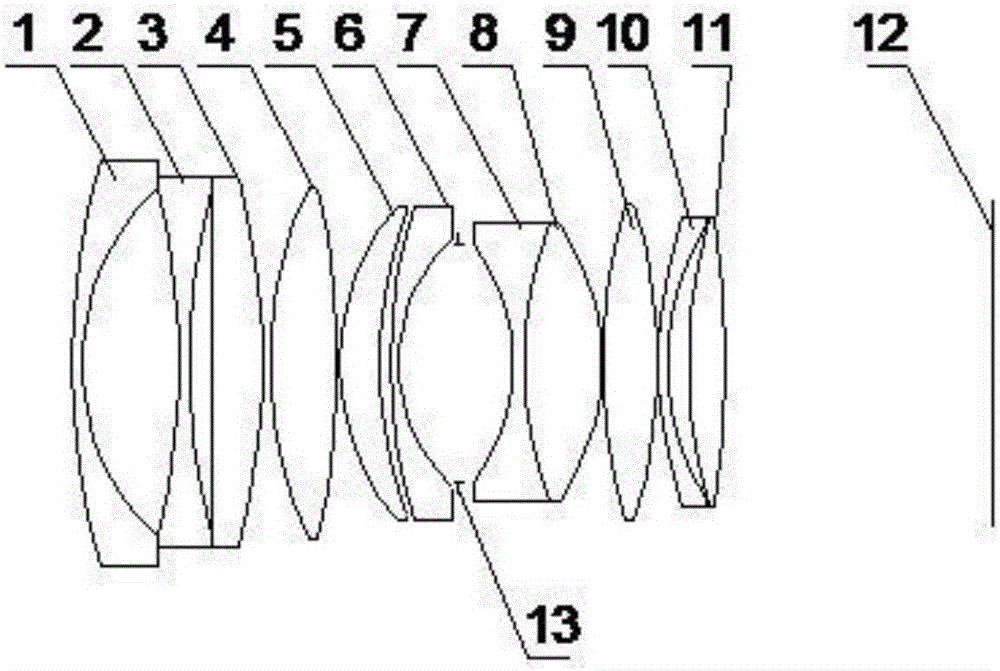
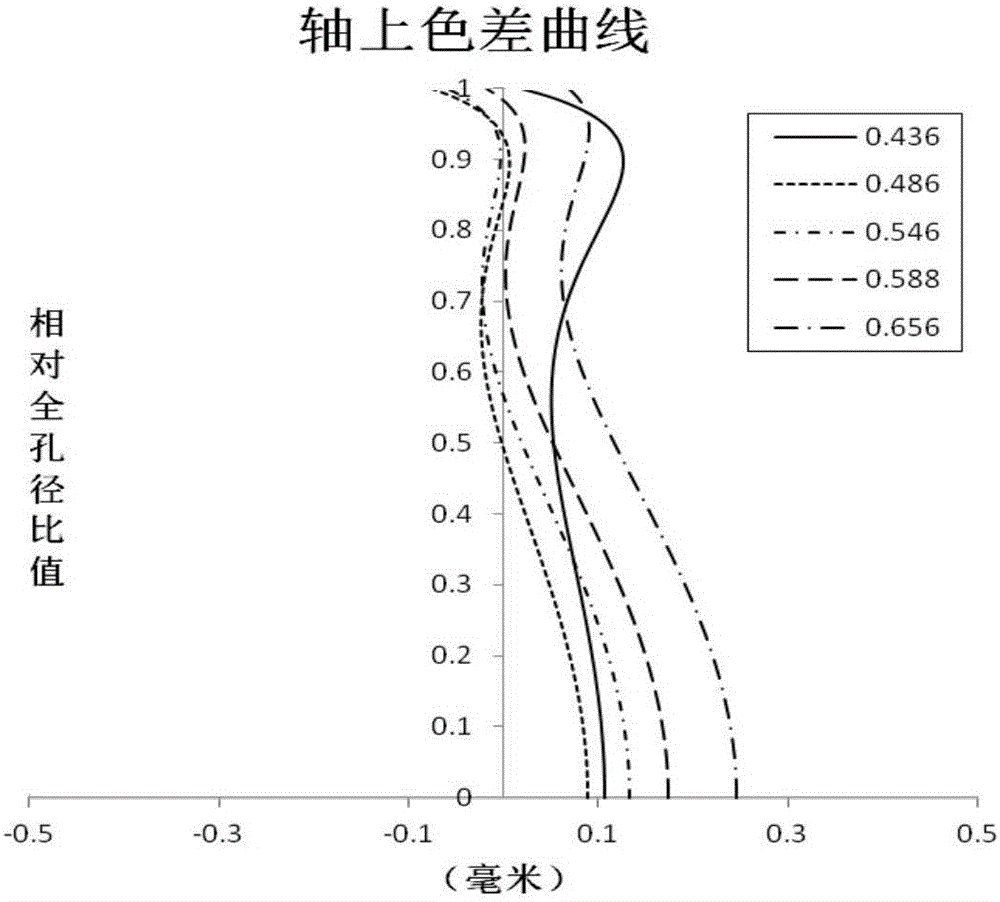
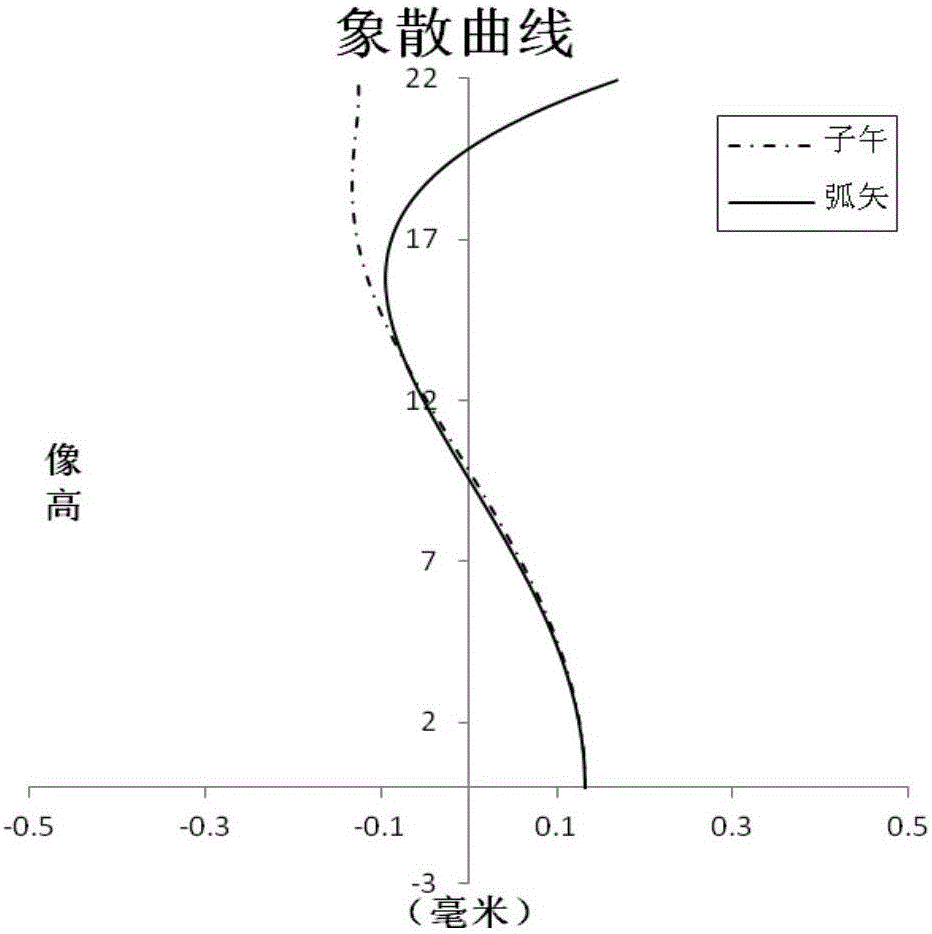
The invention discloses a super-large-aperture wide-angle lens of a single lens reflex camera.The super-large-aperture wide-angle lens comprises an optical lens which sequentially comprises 11 lenses from the object side to the image side; the first lens has negative power, and the object side face of the first lens is a convex face; the second lens has negative power, and the object side face of the second lens is a concave face; the third lens has positive power, and the object side face of the third lens is a plane; the fourth lens has positive power, and the object side face of the fourth lens is a convex face; the fifth lens has positive power, and the object side face of the fifth lens is a convex face; the sixth lens has negative power, and the object side face of the sixth lens is a convex face; the seventh lens has negative power, and the object side face of the seventh lens is a concave face; the eighth lens has positive power, and the object side face of the eighth lens is a convex face; the ninth lens has positive power, and the object side face of the ninth lens is a convex face; the tenth lens has negative power, and the object side face of the tenth lens is a convex face; the eleventh lens has positive power, and the object side face of the eleventh lens is a convex face.The super-large-aperture wide-angle lens of the single lens reflex camera can correct various aberrations and is compact in structure, good in imaging effect, long in back focal length, low in cost and high in cost performance ratio.
Owner:SHENZHEN DONGZHENG OPTICAL TECH CO LTD
Zoom lens
The invention relates to a zoom lens, comprising a first lens group, a second lens group, a third lens group and a fourth lens group arranged in sequence from an object side to an image side, wherein, the second lens group is suitable to move between the first lens group and the third lens group, and the fourth lens group is suitable to move between the third lens group and the image side. In addition, the first lens group has positive refraction, and comprises at least one first composite lens. The second lens group has negative refraction, and comprises at least one second composite lens. Meanwhile, the second composite lens comprises at least one aspheric lens, wherein, the adhesive surface of one of the aspheric lens is a concave face, and the adhesive surface faces the object side. The third lens group has positive refraction, and comprises at least one aspheric lens. The fourth lens group has positive refraction, and comprises at least a pair of convex lenses and a third composite lens from the object side to the image side. The zoom lens has the advantages of high rate and compact size.
Owner:YOUNG OPTICS
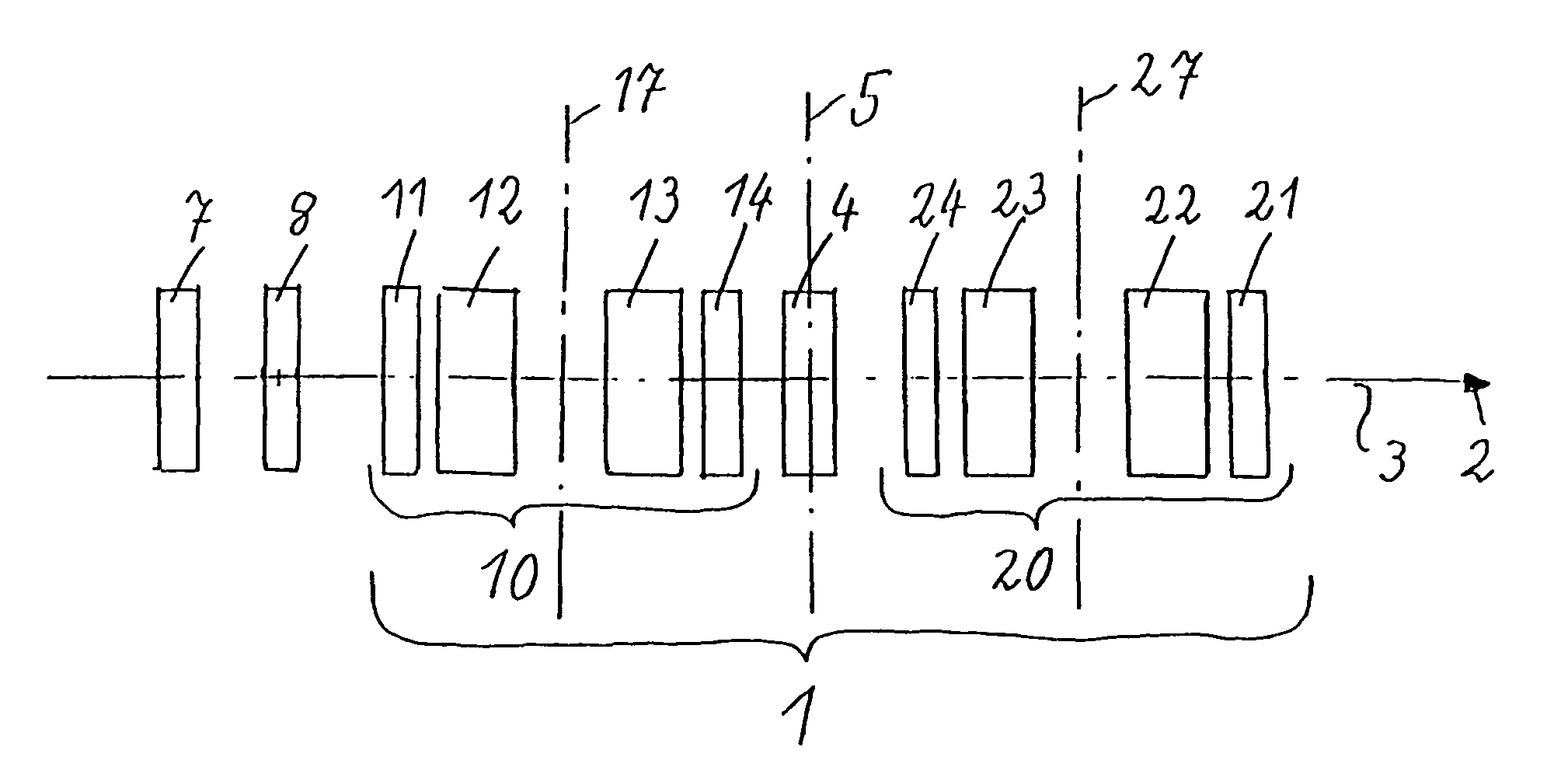
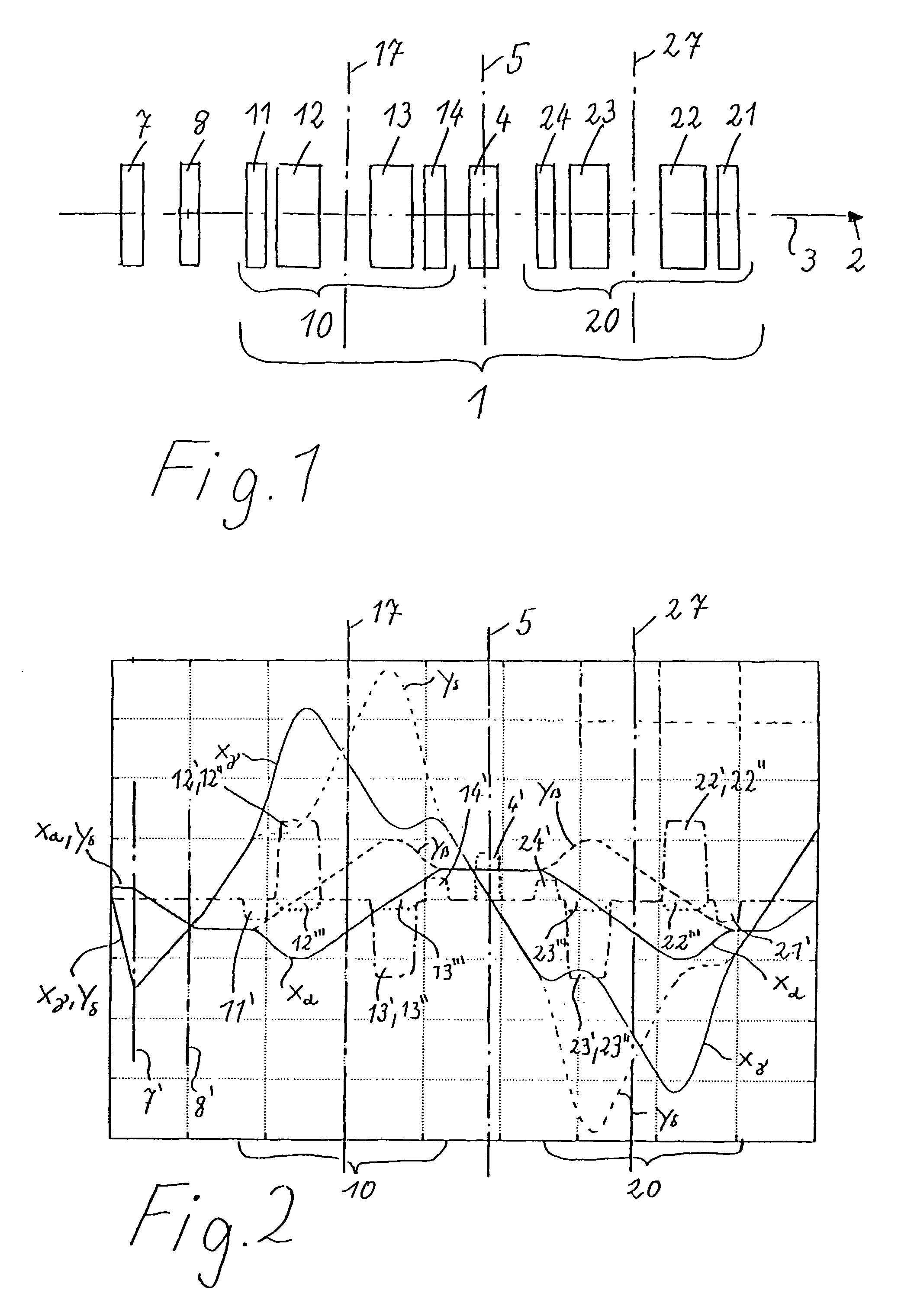
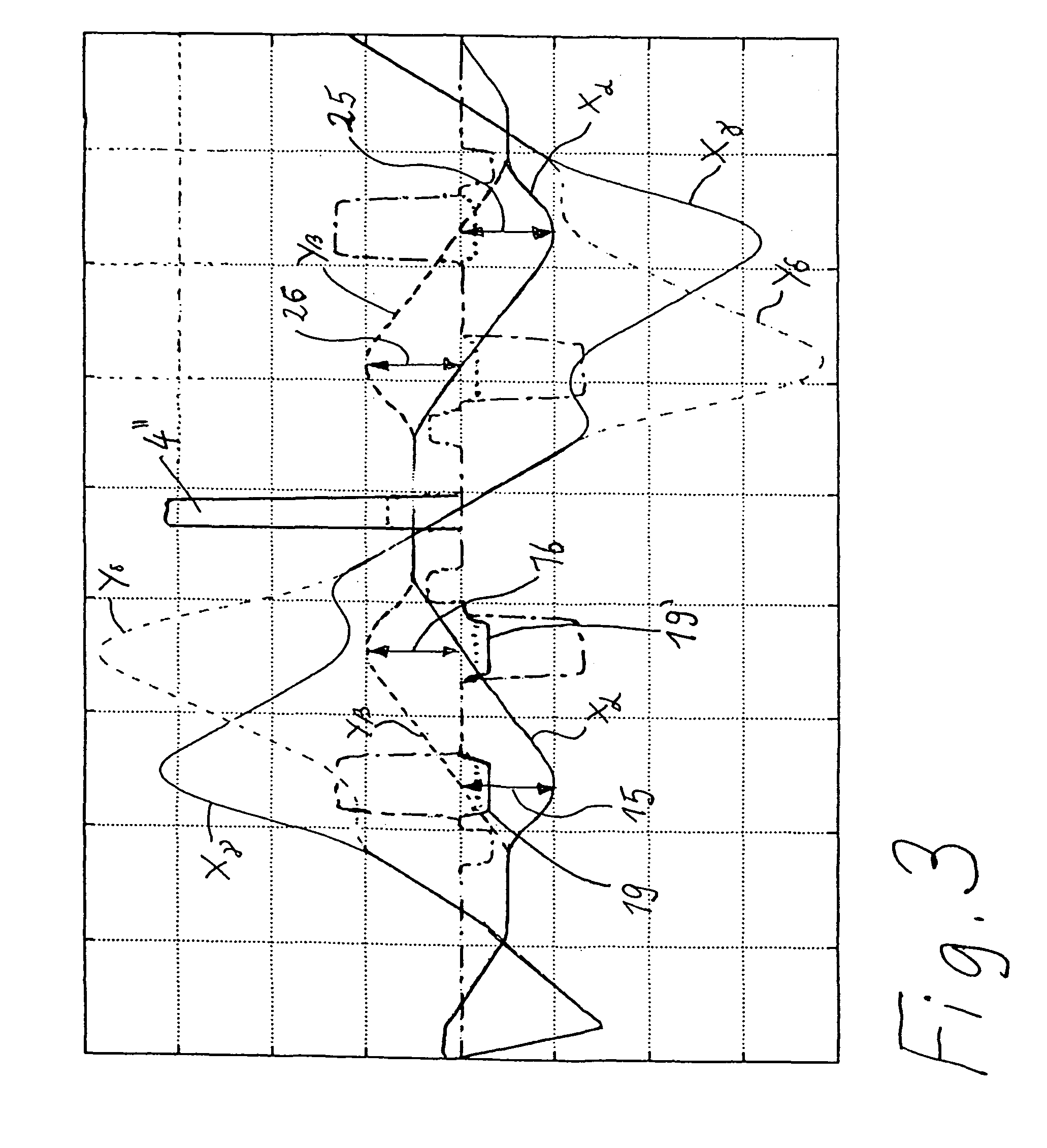
Corrector for axial and off-axial beam paths
InactiveUS7807965B2Eliminate astigmatismEliminate aberrationsStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationQuadrupole fieldOptical axis
A corrector (1) for the axial and off-axial beam path of a particle-optical system, comprises a first (10) and a second (20) correction piece, which are disposed one behind the other in the beam path (2) on an optical axis (3). Each correction piece (10, 20) comprises four successive multipole elements (11, 12, 13, 14; 24, 23, 22, 21) disposed symmetrically with respect to a center plane (5) and with the following fields: wherein the first (11; 24) and the fourth (14; 21) multipole elements of the multipole elements (11, 12, 13, 14; 24, 23, 22, 21) are used to generate quadrupole fields (11′, 14′; 24′, 21′) and the second (12; 23) and third (13; 22) are used to generate octupole fields (12′″, 13′″; 23′″,22′″) and quadrupole fields (12′, 13′; 23′,22′), wherein the latter are superposed magnetic (12′, 13′; 23′, 22′) and electric fields (12″, 13″; 23″, 22″), wherein the quadrupole fields (11′, 12′, 13′, 14′; 24′, 23′, 22′, 21′) of all four multipole elements (11, 12, 13, 14; 24, 23, 22,21) are rotated from one to the next through 90°. An astigmatism of third order is corrected by a central multipole element disposed in the center plane and generating an octupole field.
Owner:CEOS CORRECTED ELECTRON OPTICAL SYST
Absolute interference measurement method for plane shape of optical plane
The invention relates to an absolute interference measurement method for a plane shape of an optical plane, belonging to the technical field of the optical measurement. The method is as follows: firstly, spherical waves diffracted from a measuring fiber are reflected by a plane mirror to be detected, deflects and penetrates a plane beam splitter, are converged with spherical wavefront diffracted by a reference optical fiber and reflected by the plane beam splitter and the interference happens; an interference pattern is analyzed and processed by a standard method; and the optical aberration introduced by the plane mirror to be detected and the plane beam splitter is obtained in the first step. And then, the plane mirror to be detected is removed; the end face of the measuring optical fiber is moved to the conjugation position of the plane mirror to be detected; and the spherical waves diffracted from the measuring fiber and the reference optical fiber are converged and interference happens again; and the aberration introduced by the plane beam splitter is obtained by measurement in the second step; the optical aberration introduced by the plane mirror to be detected is obtained by subtracting the measuring results in the first step and the second step and is corrected according to the incident angle of the spherical wavefront to obtain the plane shape of the plane mirror to be detected. The absolute interference measurement method realizes the holohedral form point-to-point and high accuracy interference measurement of the optical plane and is the plane absolute interference measurement method.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Wide-view-field high-resolution image pickup apparatus and method based on calculation aberration compensation
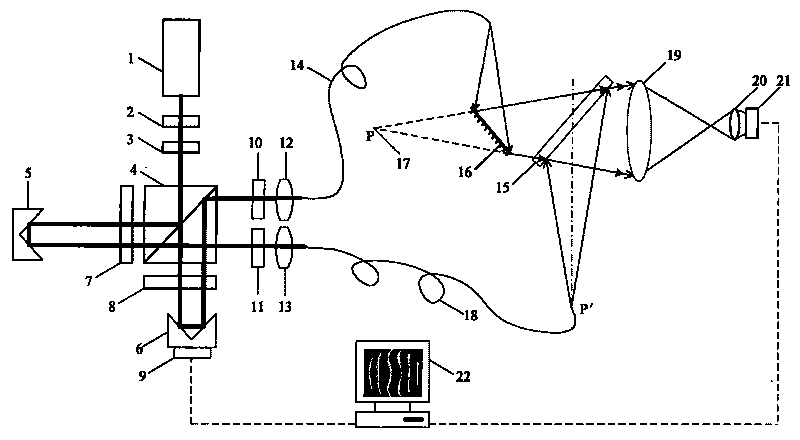
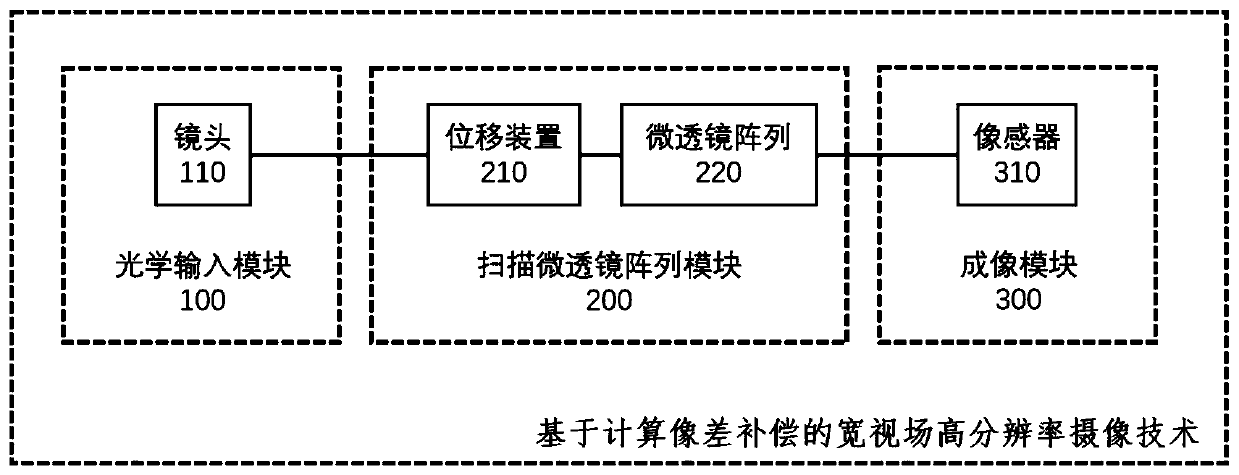
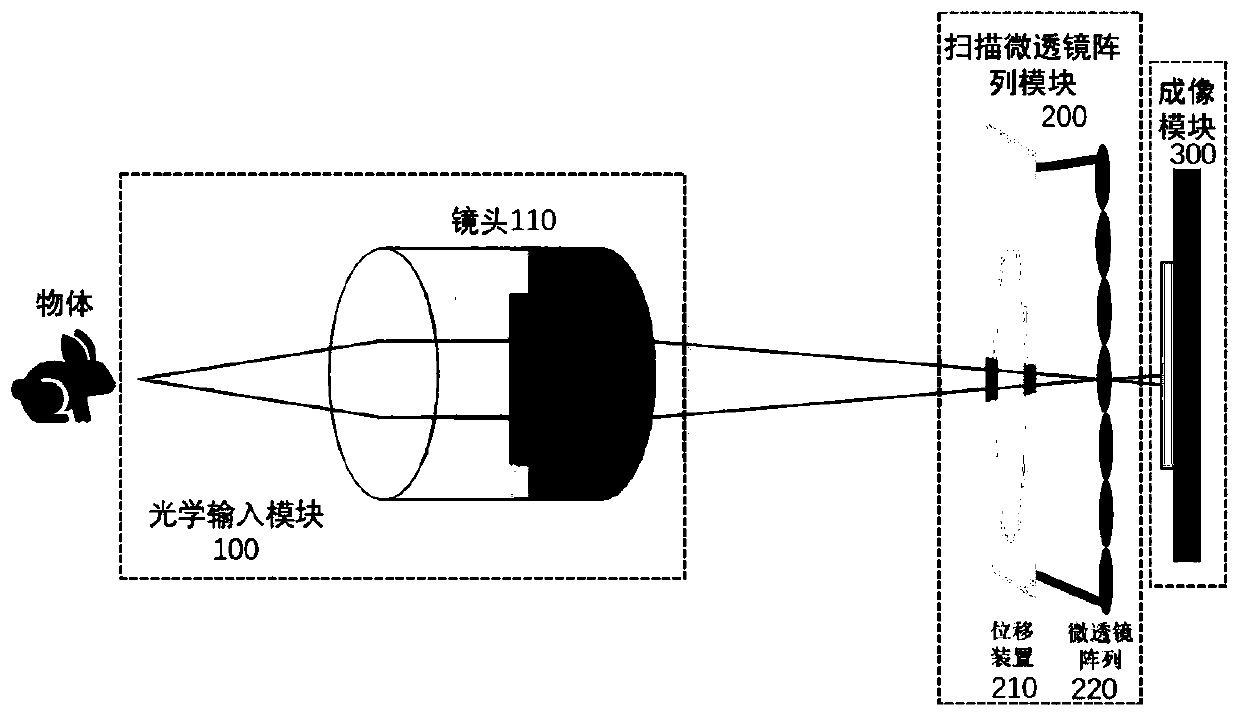
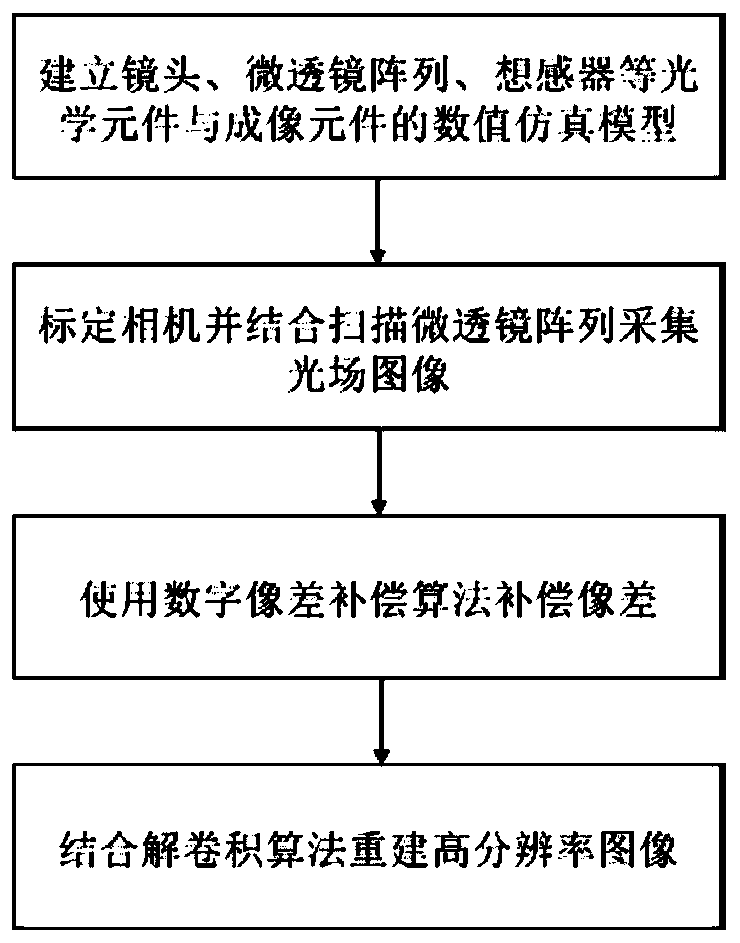
ActiveCN111182191AIncrease the number of pixelsHigh number of pixelsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMicro lens arrayComputer science
The invention provides a wide-view-field high-resolution camera shooting device and method based on calculation aberration compensation. The wide-view-field high-resolution camera equipment based on calculation aberration compensation comprises an optical input module, a scanning micro-lens array module and an imaging module, wherein the optical input module comprises an optical lens; the scanningmicro-lens array module comprises a displacement device and a micro-lens array; the imaging module comprises an image sensor; the optical input module shoots a scene through any optical lens to collect optical information; and the scanning micro-lens array module drives the micro-lens array to perform periodic movement scanning through the displacement device, and further transmits the optical information collected by the optical lens to the image sensor in the imaging module.
Owner:浙江荷湖科技有限公司
Large-visual-field-angle high-image-quality eyepiece optical system and head-mounted display device
The invention relates to a large-visual-field-angle high-image-quality eyepiece optical system and a head-mounted display device. The large-visual-field-angle high-image-quality eyepiece optical system comprises a first lens group and a second lens group which are coaxially and sequentially arranged from a human eye to an image source along an optical axis direction, wherein the first lens group and the second lens group satisfy a certain focal length relationship. The effective focal length of the first lens group is a negative value, and the first lens group is composed of a first lens close to the human eye and a second lens away from the human eye. The effective focal length of the second lens group is a positive value, and the second lens group is composed of one or two pieces of lenses. The first lens is in a biconvex shape, the optical surface, close to the human eye, of the second lens is recessed towards the human eye, and the first lens and the second lens are each of an aspheric surface type. The distance between the first lens and the second lens, a focal length relationship between lenses in the second lens group, and material characteristics of the lenses satisfy certain relationships, and the second lens group further comprises a fourth lens. The large-visual-field-angle high-image-quality eyepiece optical system has the advantages of large aperture, large field of view, high resolution, low distortion, small size and the like, and is suitable for the head-mounted display and similar devices.
Owner:SHENZHEN NED OPTICS CO LTD
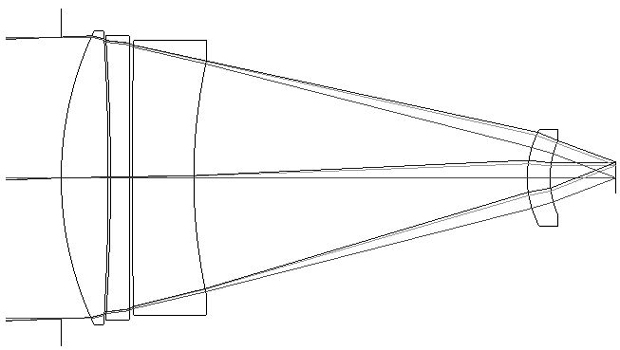
Long-wave long-focus uncooled thermalization-free infrared optical system
ActiveCN102033316AImprove image qualitySimple structureMountingsLensImaging qualityThermal expansion
The invention relates to a long-wave long-focus uncooled thermalization-free infrared optical system, belonging to the technical field of optics. The optical system comprises an aperture diaphragm, a first lens, a second lens, a third lens and a fourth lens which are sequentially and axially arranged along a light incident direction, wherein the first lens, the second lens and the third lens forma converging group used for correcting primary aberration, the lenses are in a positive-negative-negative-positive symmetrical structure, the first face of the second lens is a rotating and symmetrical diffractive face, and thermal expansion coefficients of the optical elements and the structural materials of the four lens and the intervals and the curvature radii of the four lenses all satisfy aformula. By utilizing different temperature characteristics and linear expansion coefficients of various optical materials and combining with a lens cone material, the self adaptation to the environment is realized to realize a thermalization-free function, which can effectively simplify the structure of an optical machine, reduce system weight, shorten system volume and improve the imaging quality of the optical system in different temperature environments.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF ELECTRO OPTICAL EQUIP OF AVIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com