Patents
Literature
411 results about "Data dependency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A data dependency in computer science is a situation in which a program statement (instruction) refers to the data of a preceding statement. In compiler theory, the technique used to discover data dependencies among statements (or instructions) is called dependence analysis.
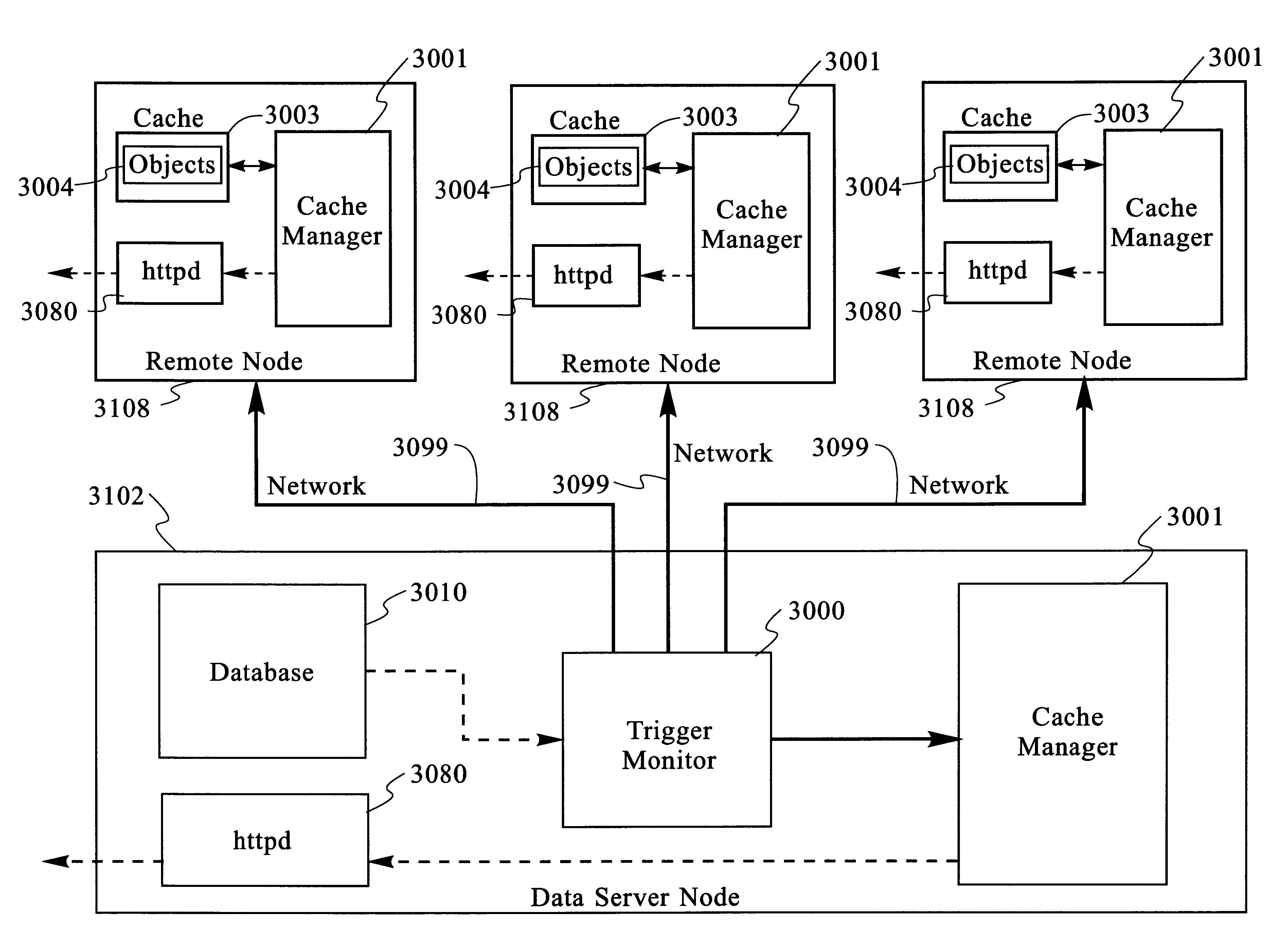
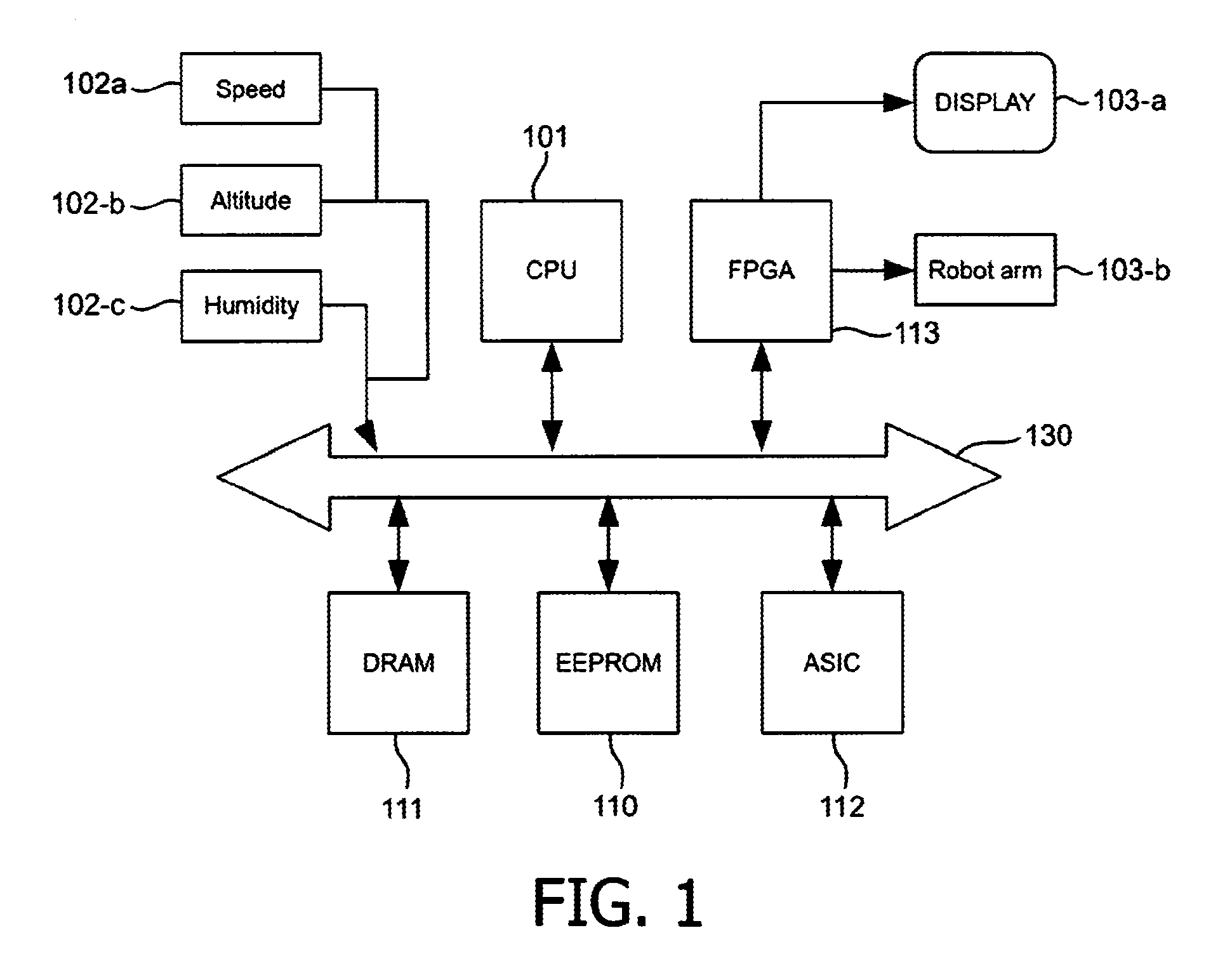
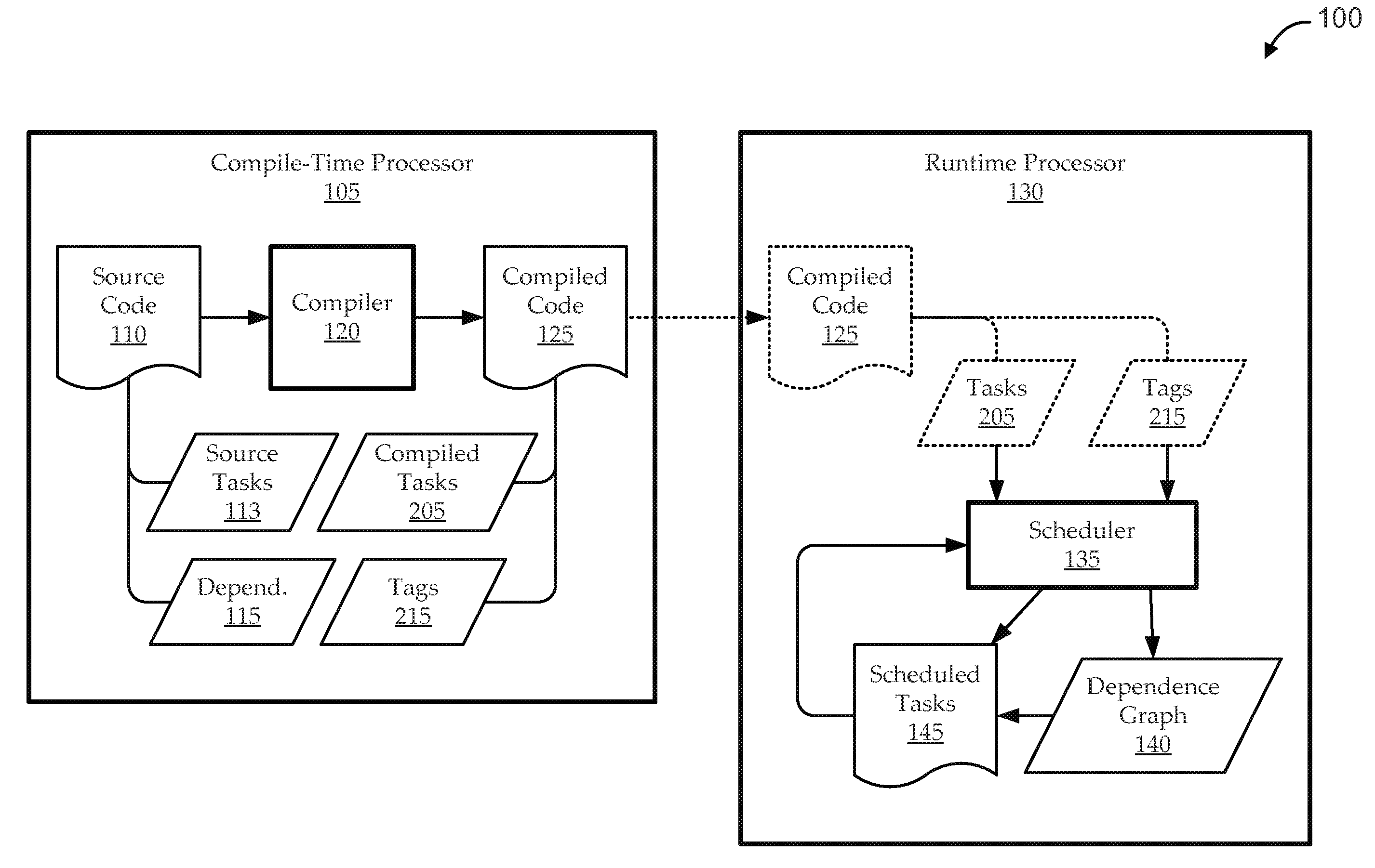
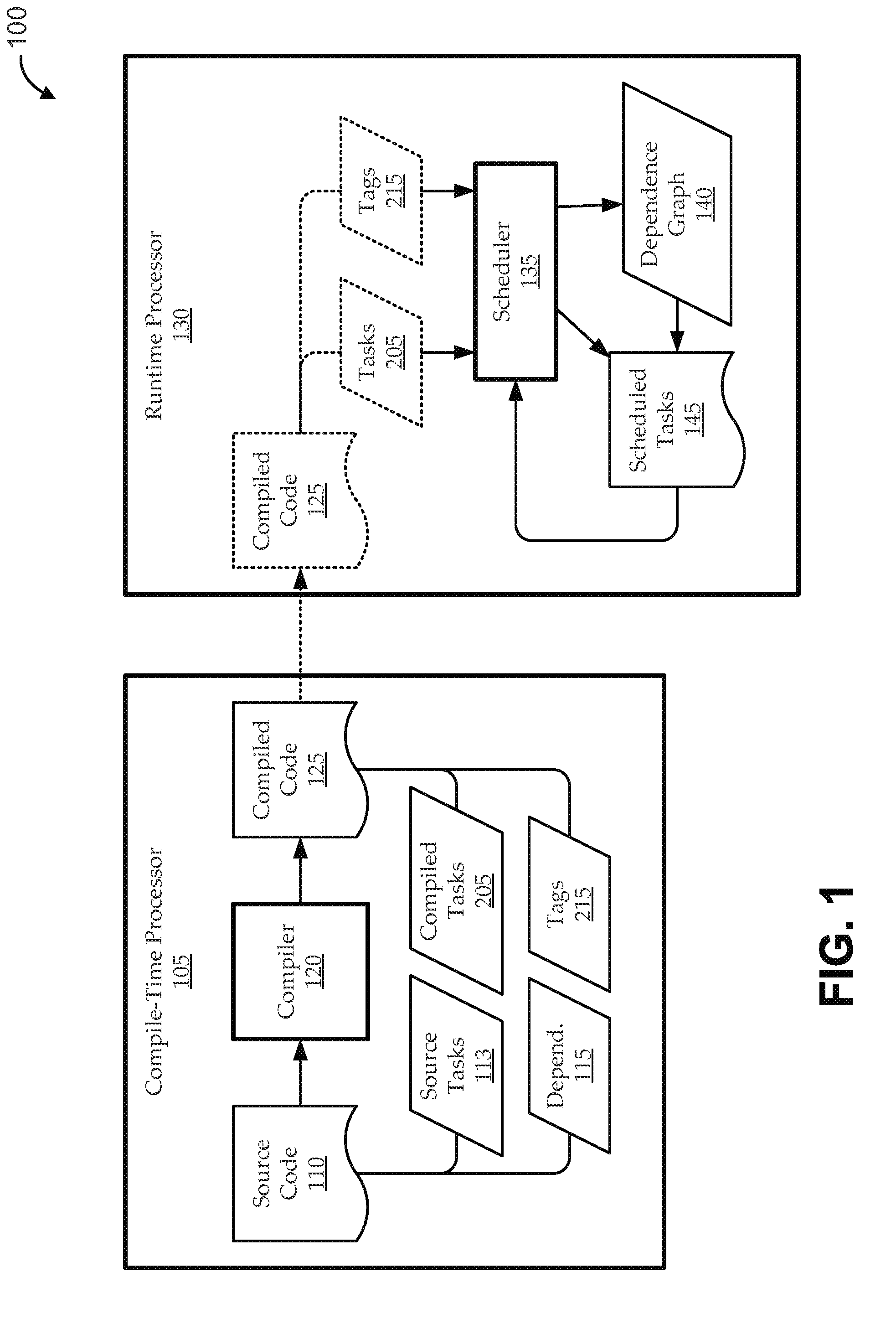
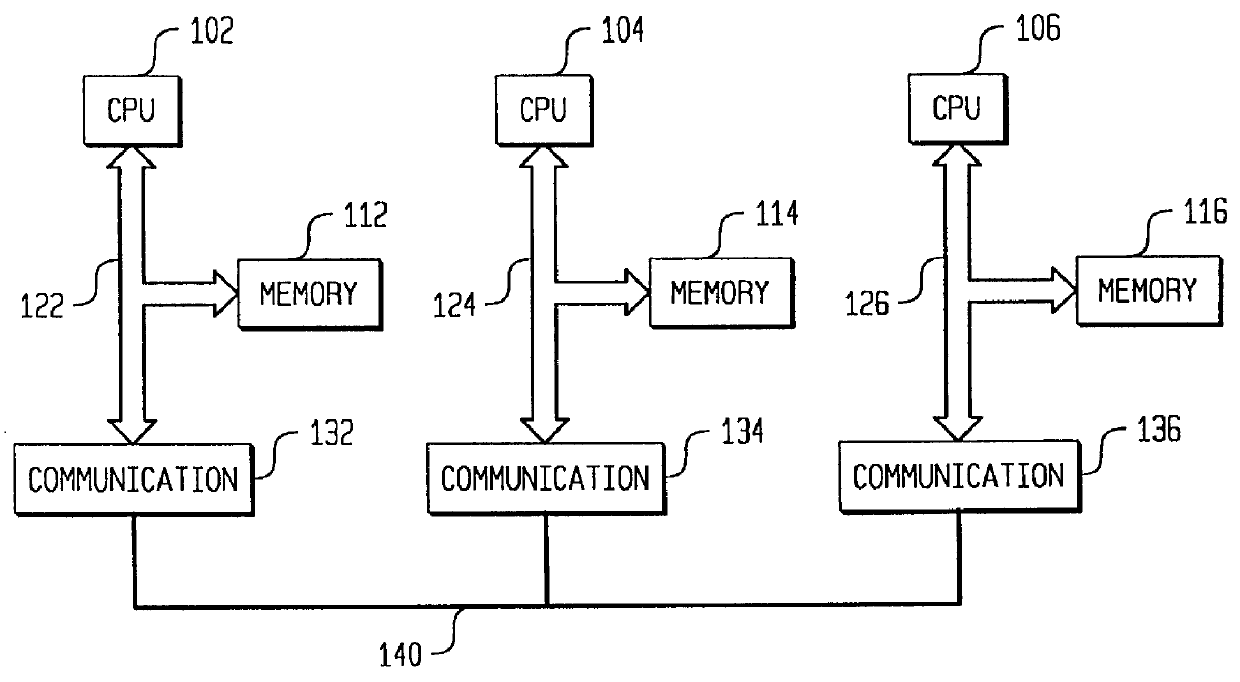
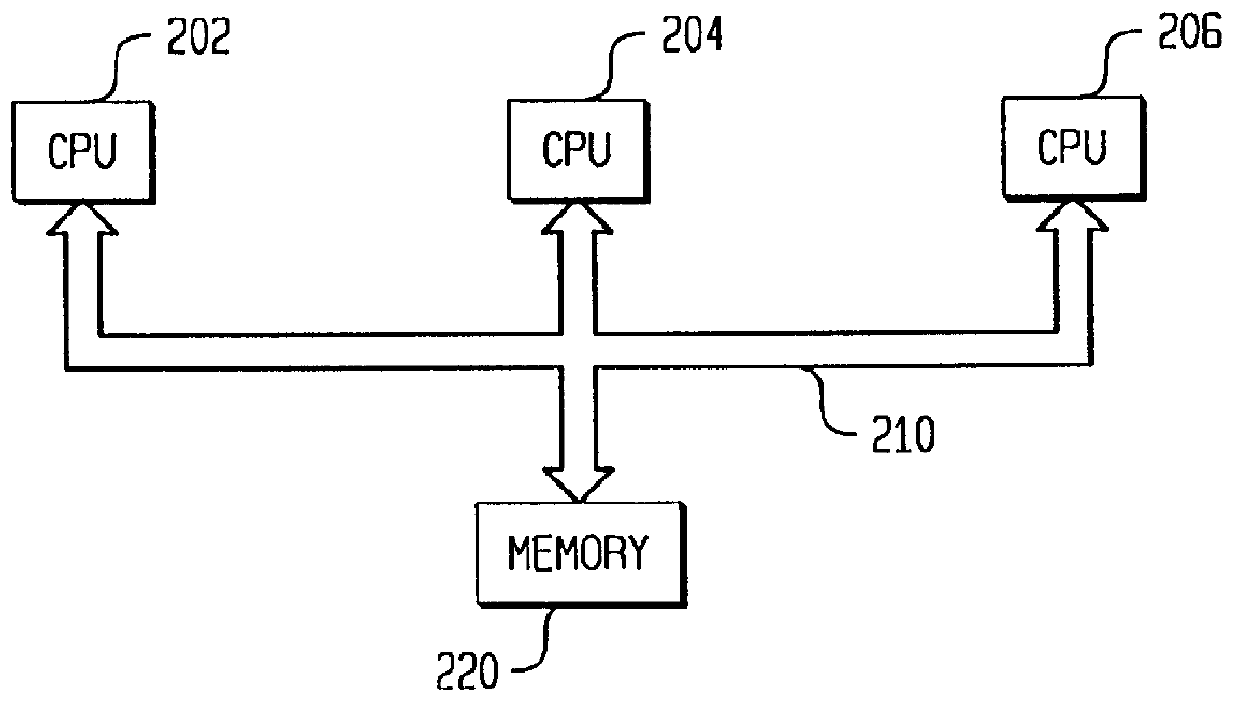
Scaleable method for maintaining and making consistent updates to caches
InactiveUS6256712B1High degreeData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData synchronizationExtensibility
A determination can be made of how changes to underlying data affect the value of objects. Examples of applications are: caching dynamic Web pages; client-server applications whereby a server sending objects (which are changing all the time) to multiple clients can track which versions are sent to which clients and how obsolete the versions are; and any situation where it is necessary to maintain and uniquely identify several versions of objects, update obsolete objects, quantitatively assess how different two versions of the same object are, and / or maintain consistency among a set of objects. A directed graph called an object dependence graph, may be used to represent the data dependencies between objects. Another aspect is constructing and maintaining objects to associate changes in remote data with cached objects. If data in a remote data source changes, database change notifications are used to "trigger" a dynamic rebuild of associated objects. Thus, obsolete objects can be dynamically replaced with fresh objects. The objects can be complex objects, such as dynamic Web pages or compound-complex objects, and the data can be underlying data in a database. The update can include either: storing a new version of the object in the cache; or deleting an object from the cache. Caches on multiple servers can also be synchronized with the data in a single common database. Updated information, whether new pages or delete orders, can be broadcast to a set of server nodes, permitting many systems to simultaneously benefit from the advantages of prefetching and providing a high degree of scaleability.
Owner:IBM CORP
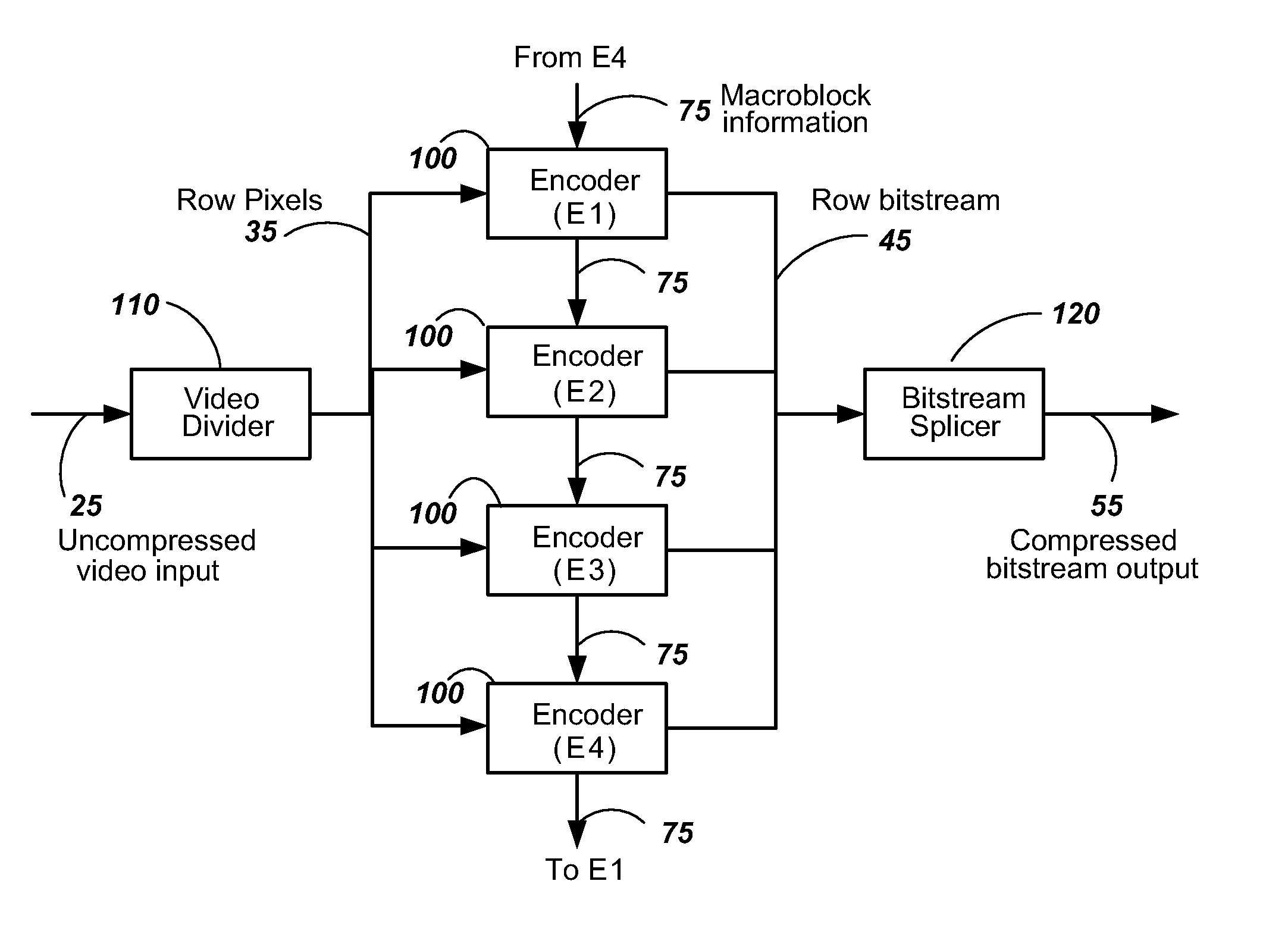
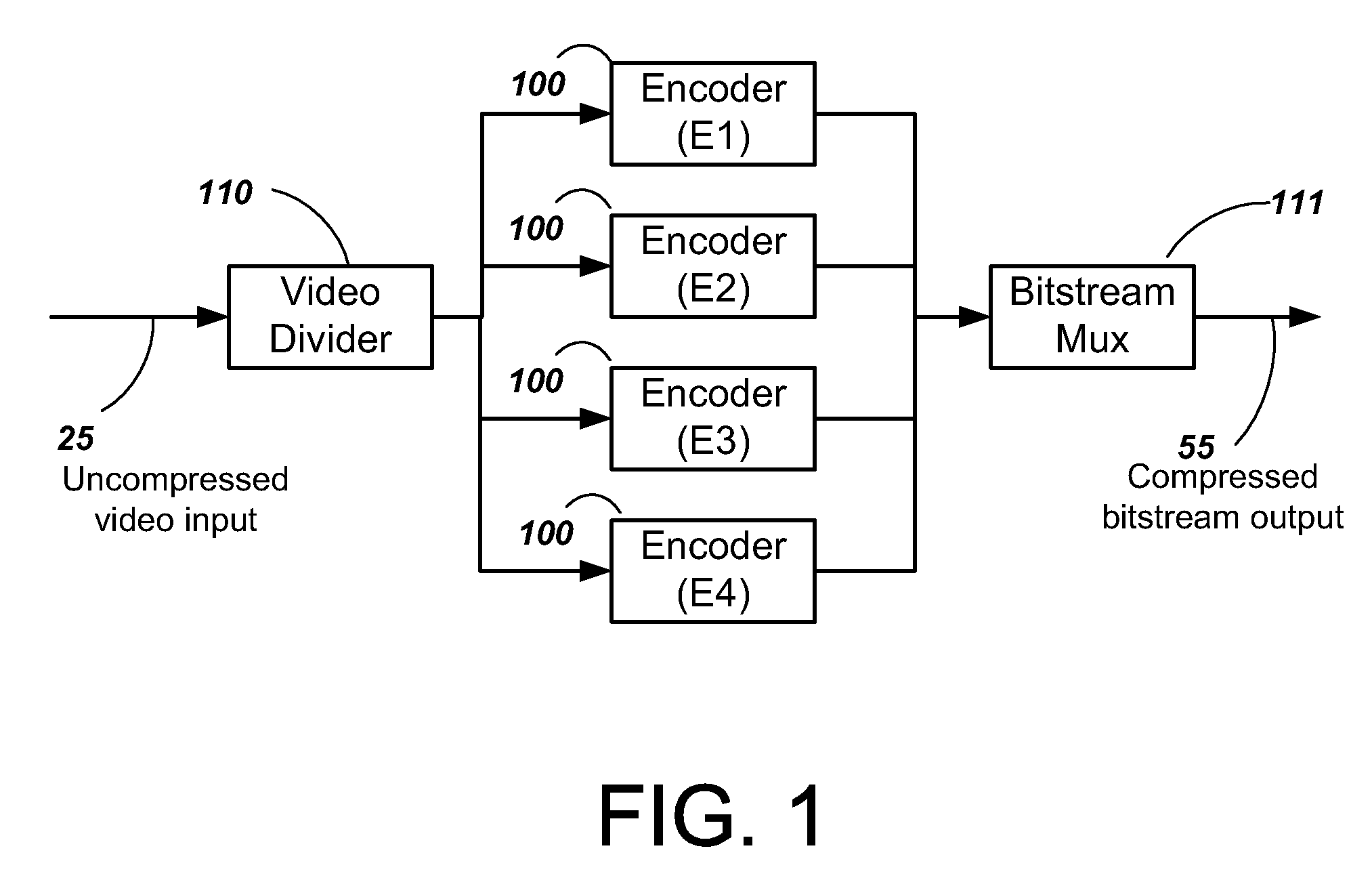
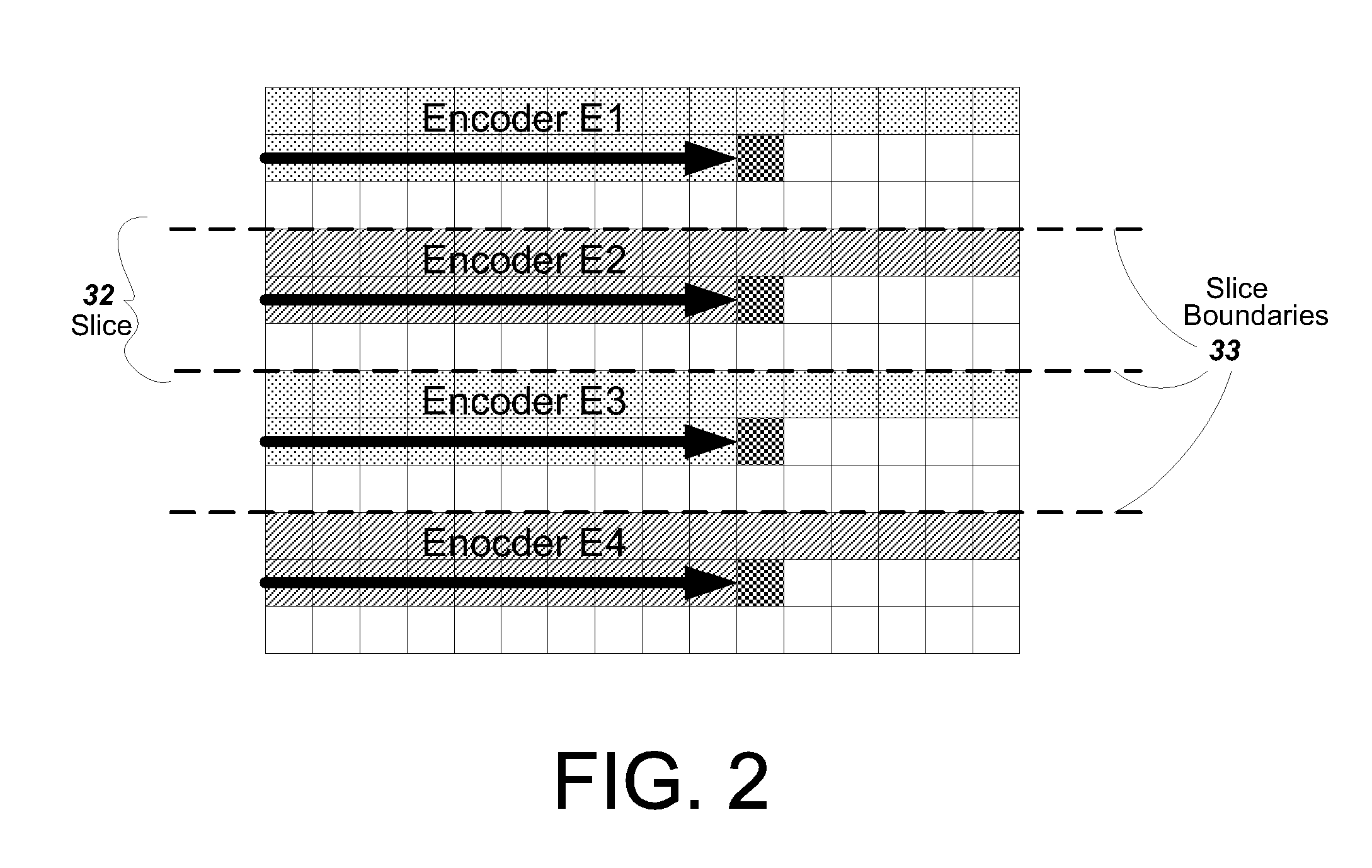
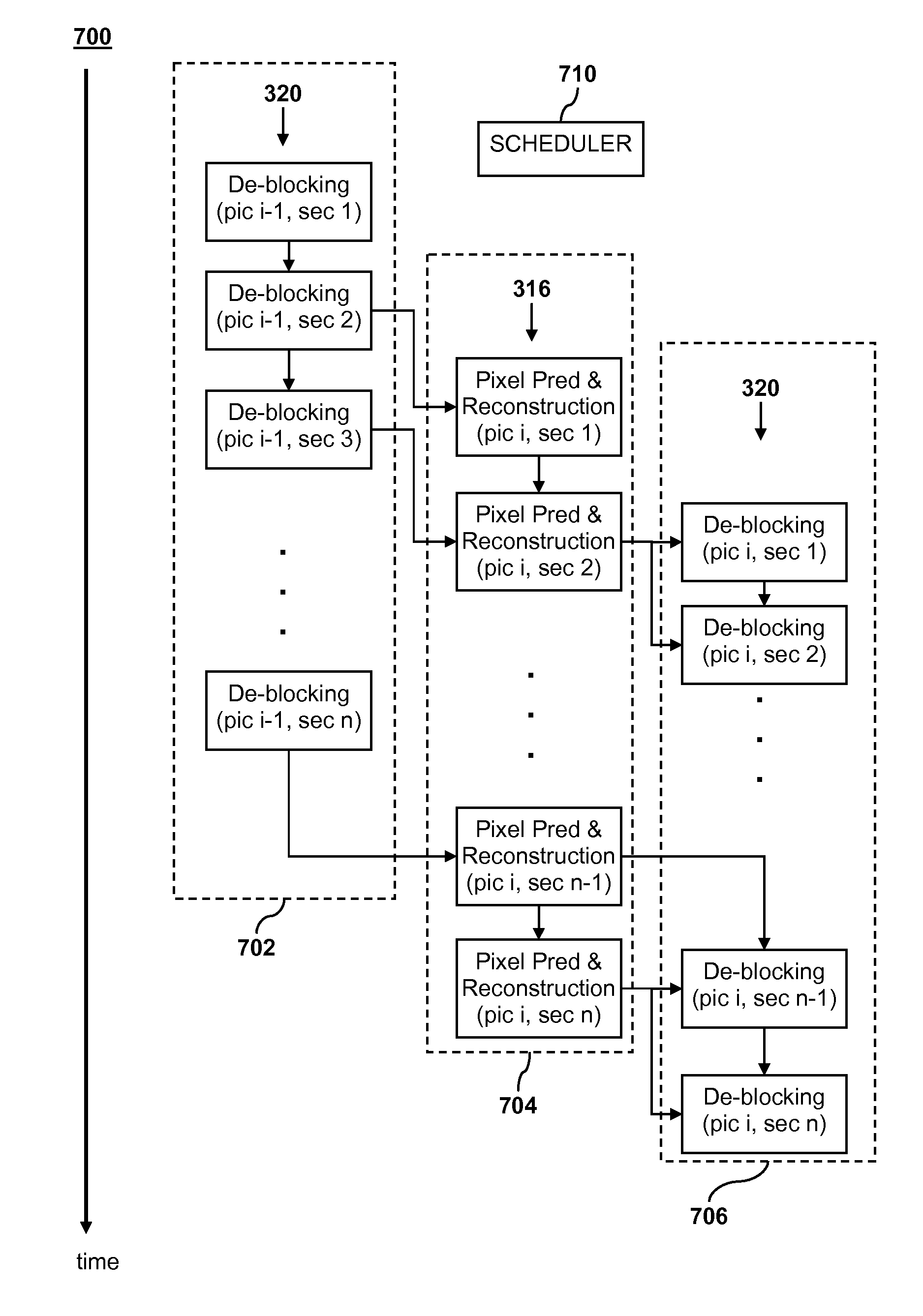
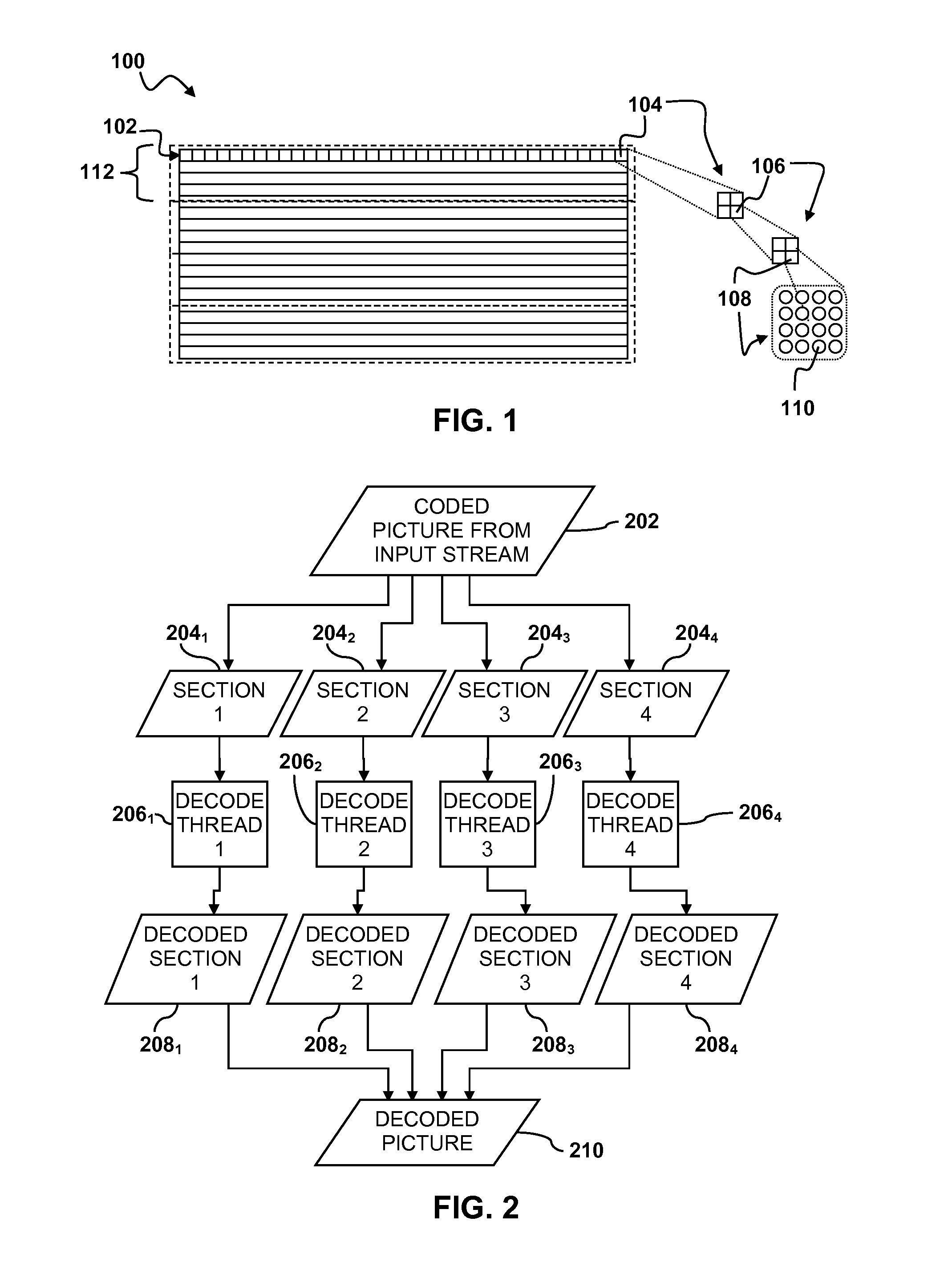
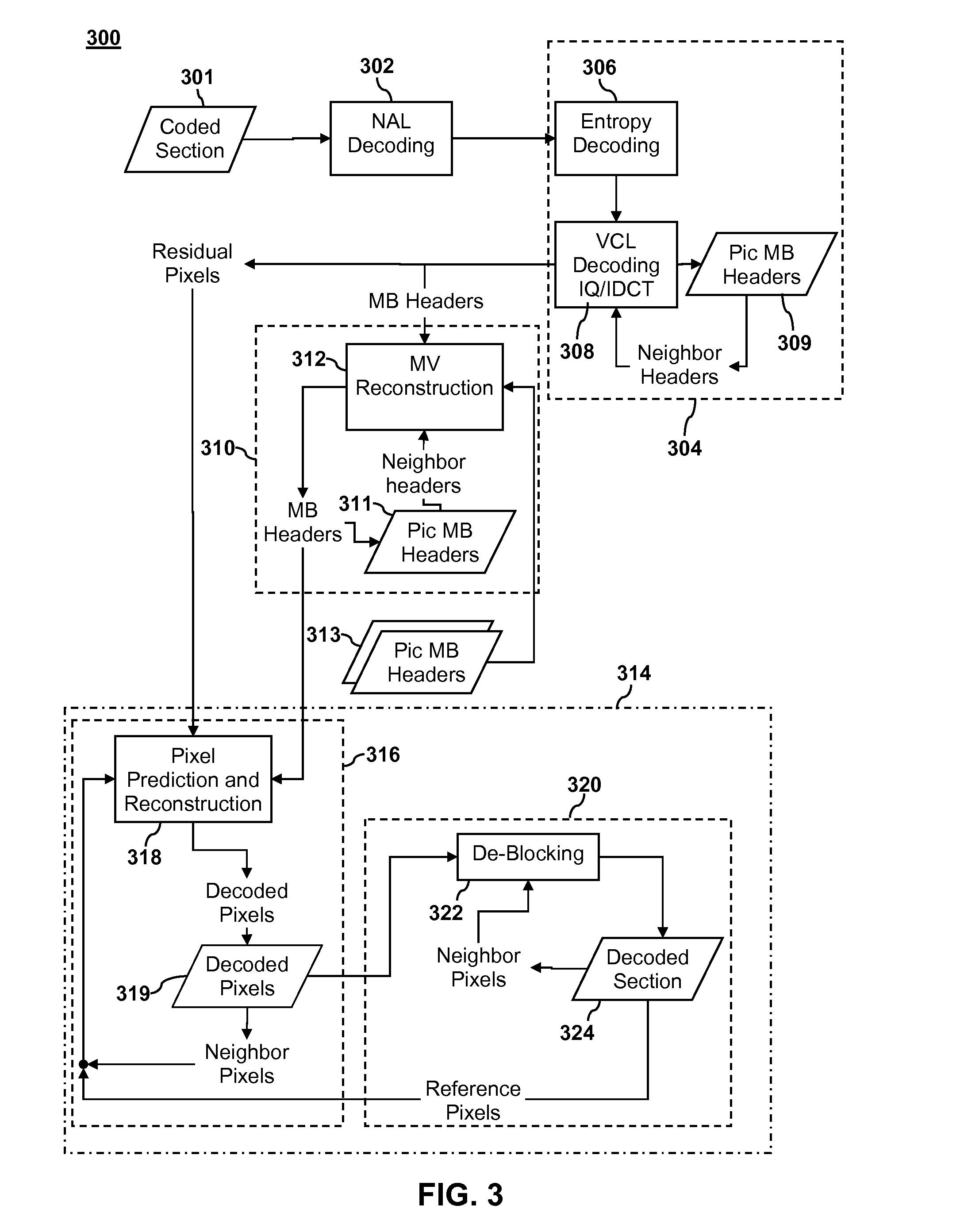
Video encoder with multiple processors
InactiveUS20070086528A1Lower latencyImprove compression efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureVideo encoding
A method and system is described for video encoding with multiple parallel encoders. The system uses multiple encoders which operate in different rows of the same slice of the same video frame. Data dependencies between frames, rows, and blocks are resolved through the use of a data network. Block information is passed between encoders of adjacent rows. The system can achieve low latency compared to other parallel approaches.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Methods and apparatus for facilitating analysis of large data sets
ActiveUS20050262108A1Facilitates recalculationDigital data processing detailsBiological testingData setRelational database
Methods and apparatus are described for updating a database using a multi-dimensional data model in which data corresponding to the database are organized in multi-dimensional blocks. Each block has summary information associated therewith corresponding to a current state of evolution of the associated block. Dependency information is maintained in the data model which identifies data dependencies within and among the blocks. Change information is maintained which identifies changes made to particular ones of the blocks and times at which the changes were made. The database is updated with reference to the dependency information, the summary information, and the change information. At least some of the blocks are updated without reference to all dependents thereof. In some implementations, the underlying database may be a relational database, the data from the relational database being mapped to the multi-dimensional data model.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
File input/output scheduler using immediate data chunking
An input / output (I / O) method, system, and computer program product are disclosed. An incoming I / O request is received from an application running on a processor. A tree structure including processor-executable instructions defines one or more layers of processing associated with the I / O request. The instructions divide the data in the I / O request into one or more chunks at each of the one or more layers of processing. Each instruction has an associated data dependency to one or more corresponding instructions in a previous layer. The instructions are sorted into an order of processing by determining a location of each chunk and data dependencies between chunks of different layers of processing. One or more instructions are inserted into a schedule that depends at least partly on the order of processing. The I / O request is serviced by executing the instructions according to the schedule with the processor according to the order of processing.
Owner:SONY INTERACTIVE ENTRTAINMENT LLC
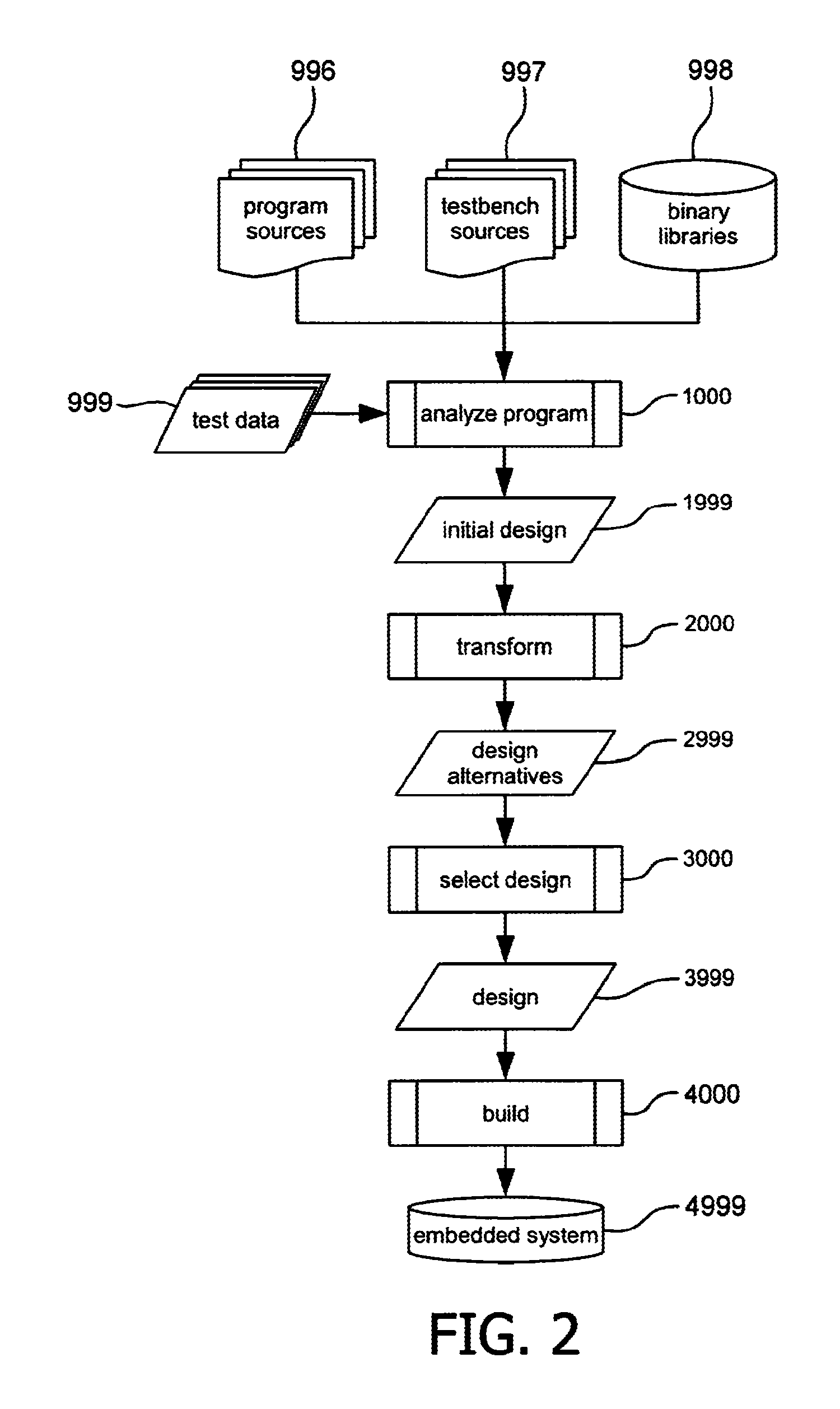
Embedded system development
InactiveUS20120144376A1Add partsLow costSoftware engineeringCAD circuit designTheoretical computer scienceDynamic data
A computer-implemented method of automatically generating an embedded system on the basis of an original computer program, comprising analyzing the original computer program, comprising a step of compiling the original computer program into an executable to obtain data flow graphs with static data dependencies and a step of executing the executable using test data to provide dynamic data dependencies as communication patterns between load and store operations of the original computer program, and a step of transforming the original computer program into an intermediary computer program that exhibits multi-threaded parallelism with inter-thread communication, which comprises identifying at least one static and / or dynamic data dependency that crosses a thread boundary and converting said data dependency into a buffered communication channel with read / write access.
Owner:VECTOR FABRICS BV
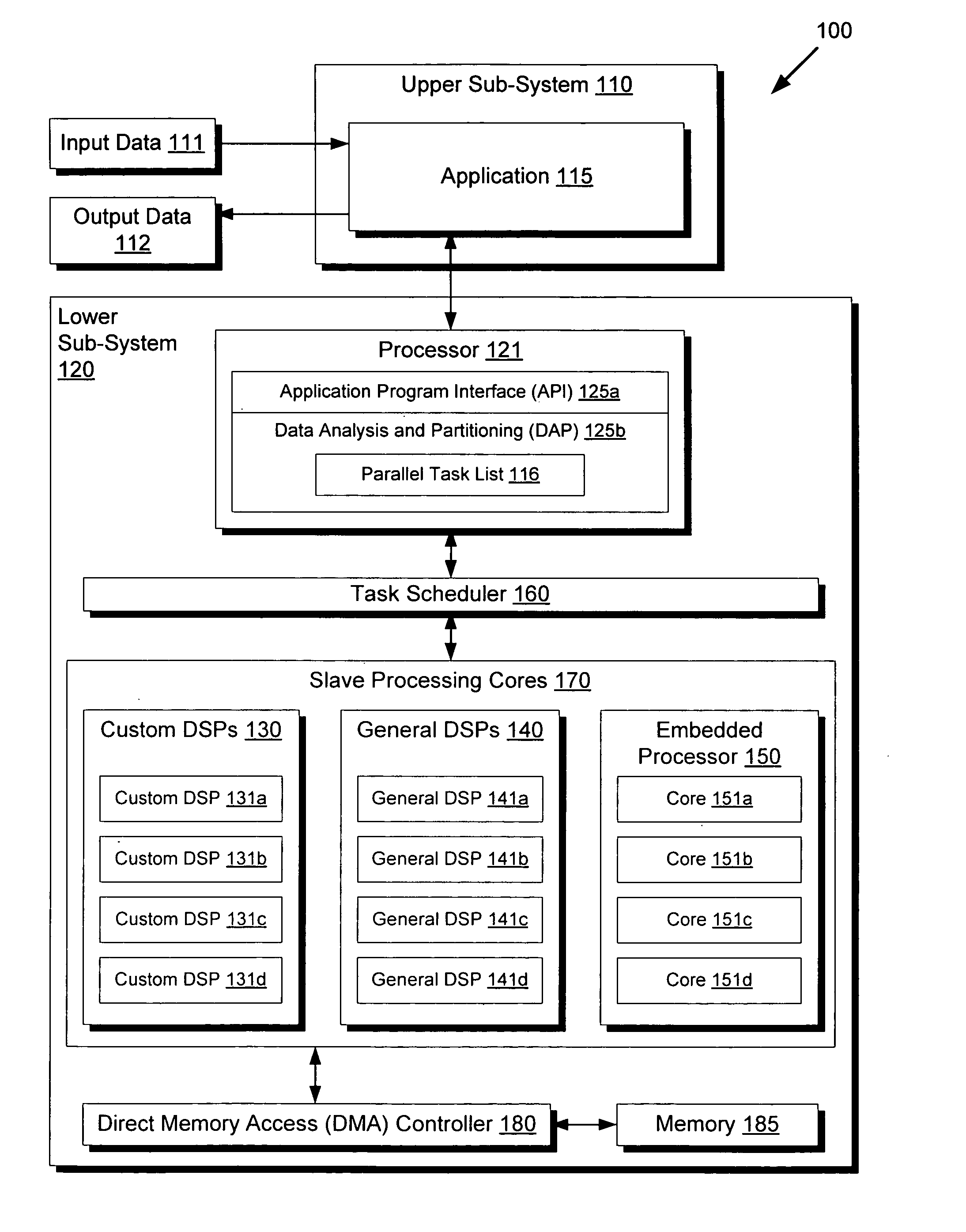
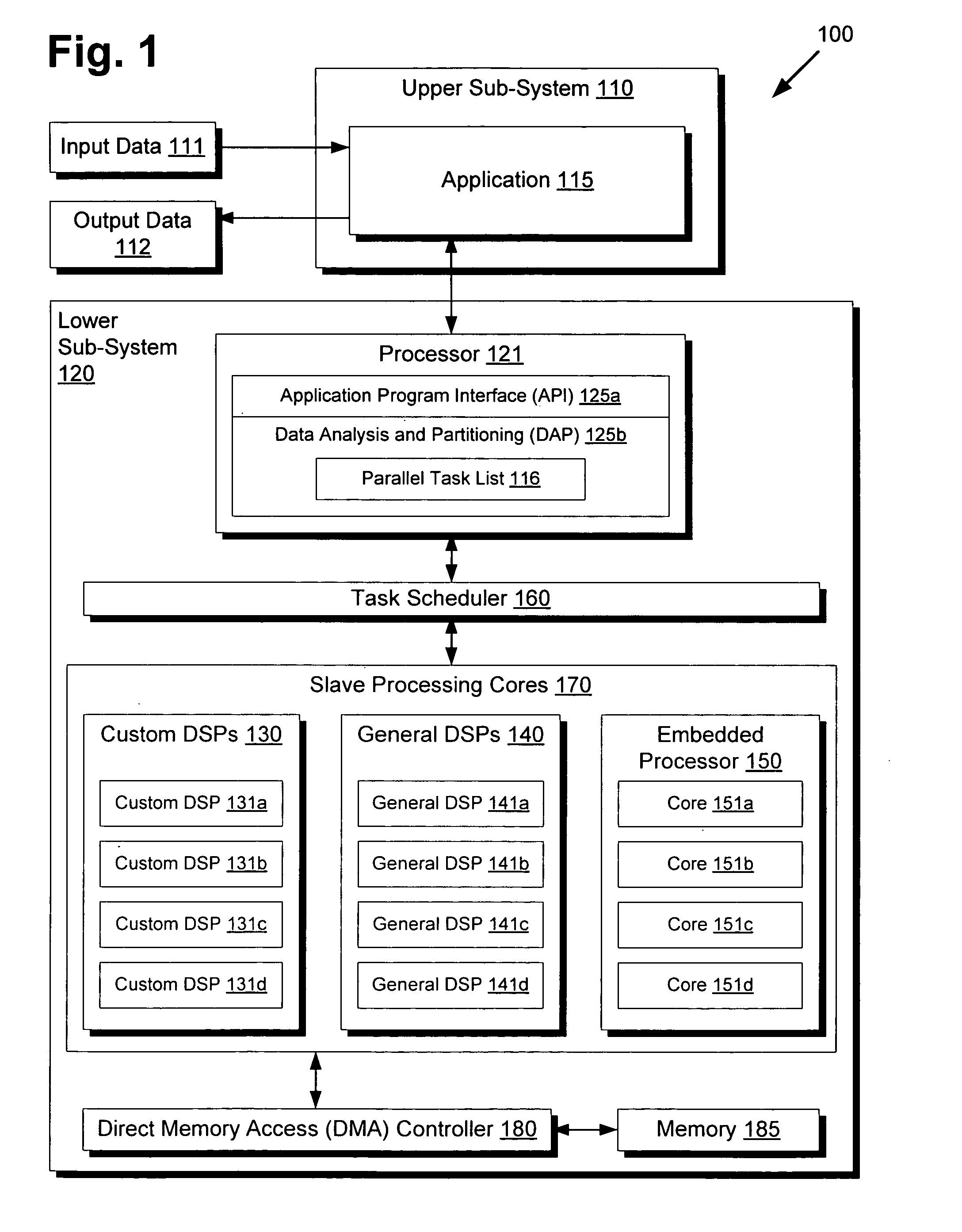
Highly distributed parallel processing on multi-core device
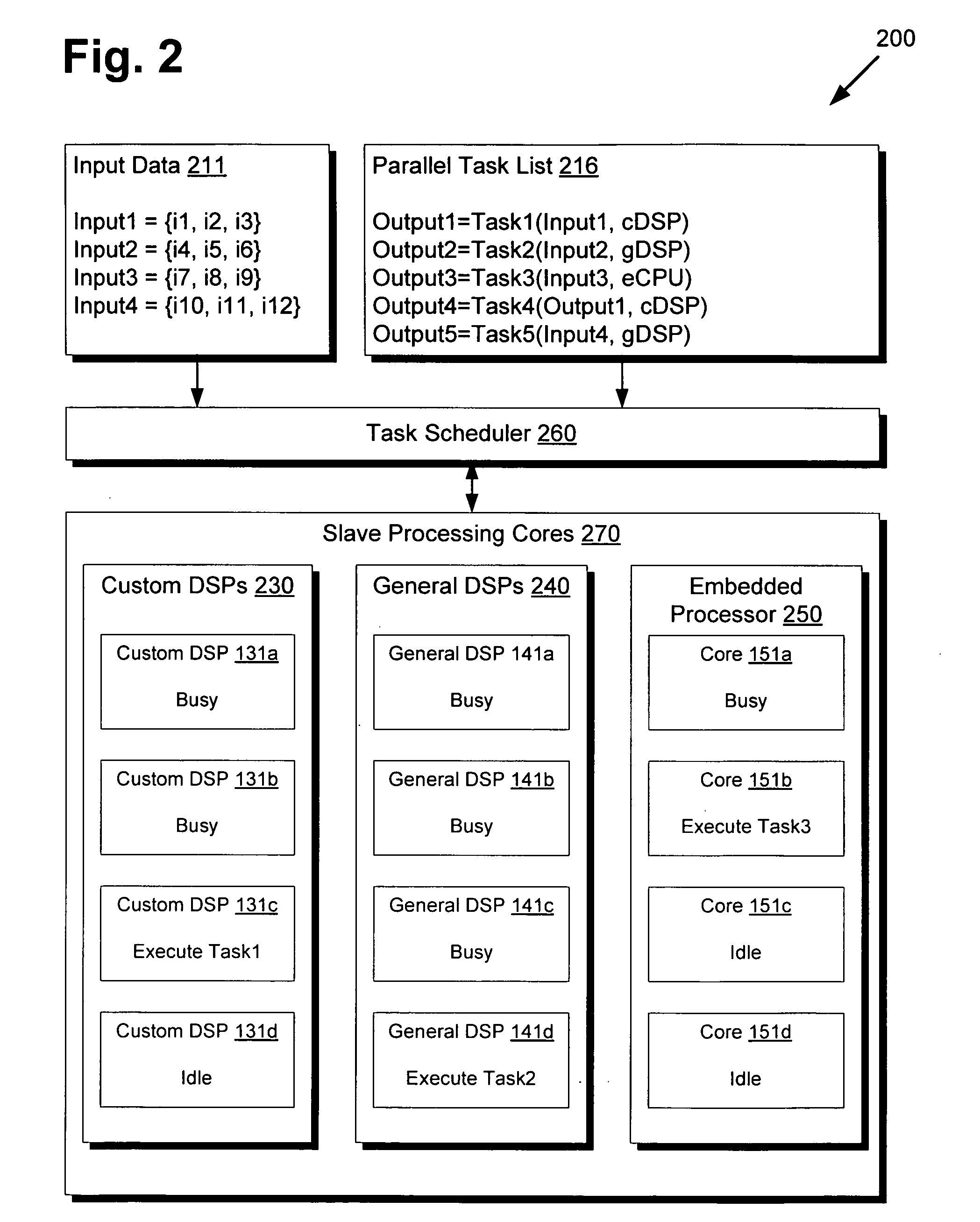
InactiveUS20100131955A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsSystem requirementsSoftware development
There is provided a highly distributed multi-core system with an adaptive scheduler. By resolving data dependencies in a given list of parallel tasks and selecting a subset of tasks to execute based on provided software priorities, applications can be executed in a highly distributed manner across several types of slave processing cores. Moreover, by overriding provided priorities as necessary to adapt to hardware or other system requirements, the task scheduler may provide for low-level hardware optimizations that enable the timely completion of time-sensitive workloads, which may be of particular interest for real-time applications. Through this modularization of software development and hardware optimization, the conventional demand on application programmers to micromanage multi-core processing for optimal performance is thus avoided, thereby streamlining development and providing a higher quality end product.
Owner:MINDSPEED TECH LLC
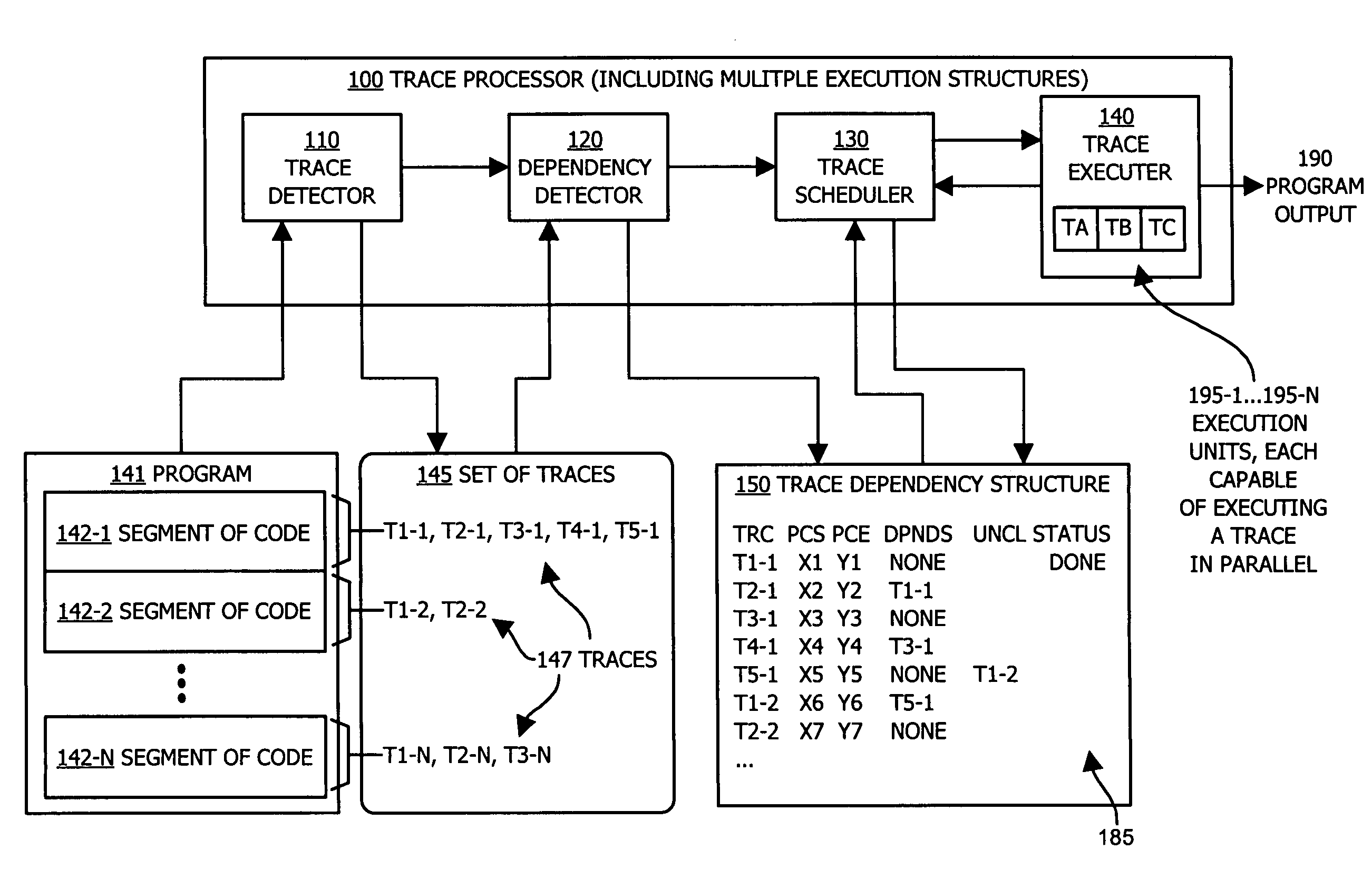
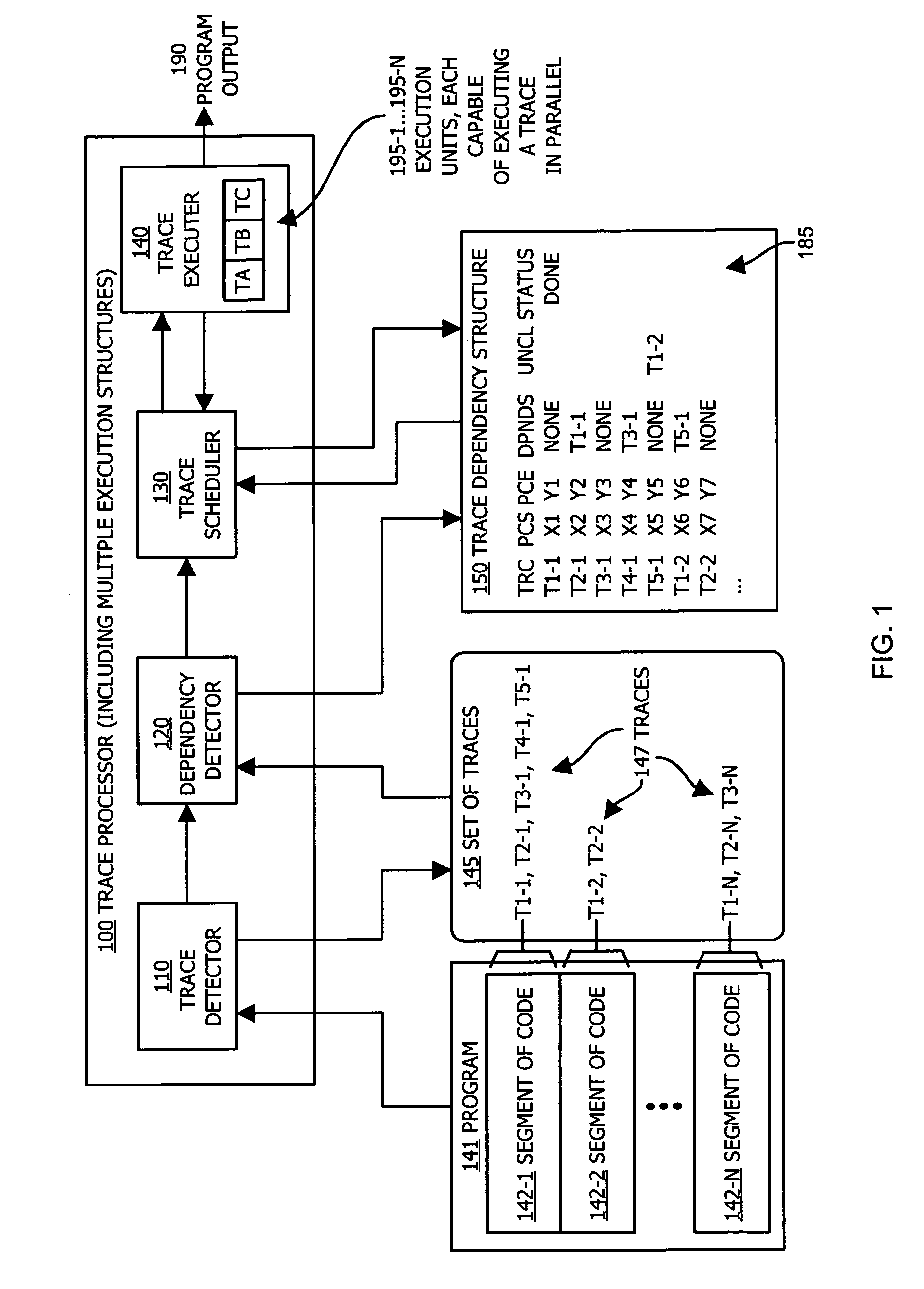
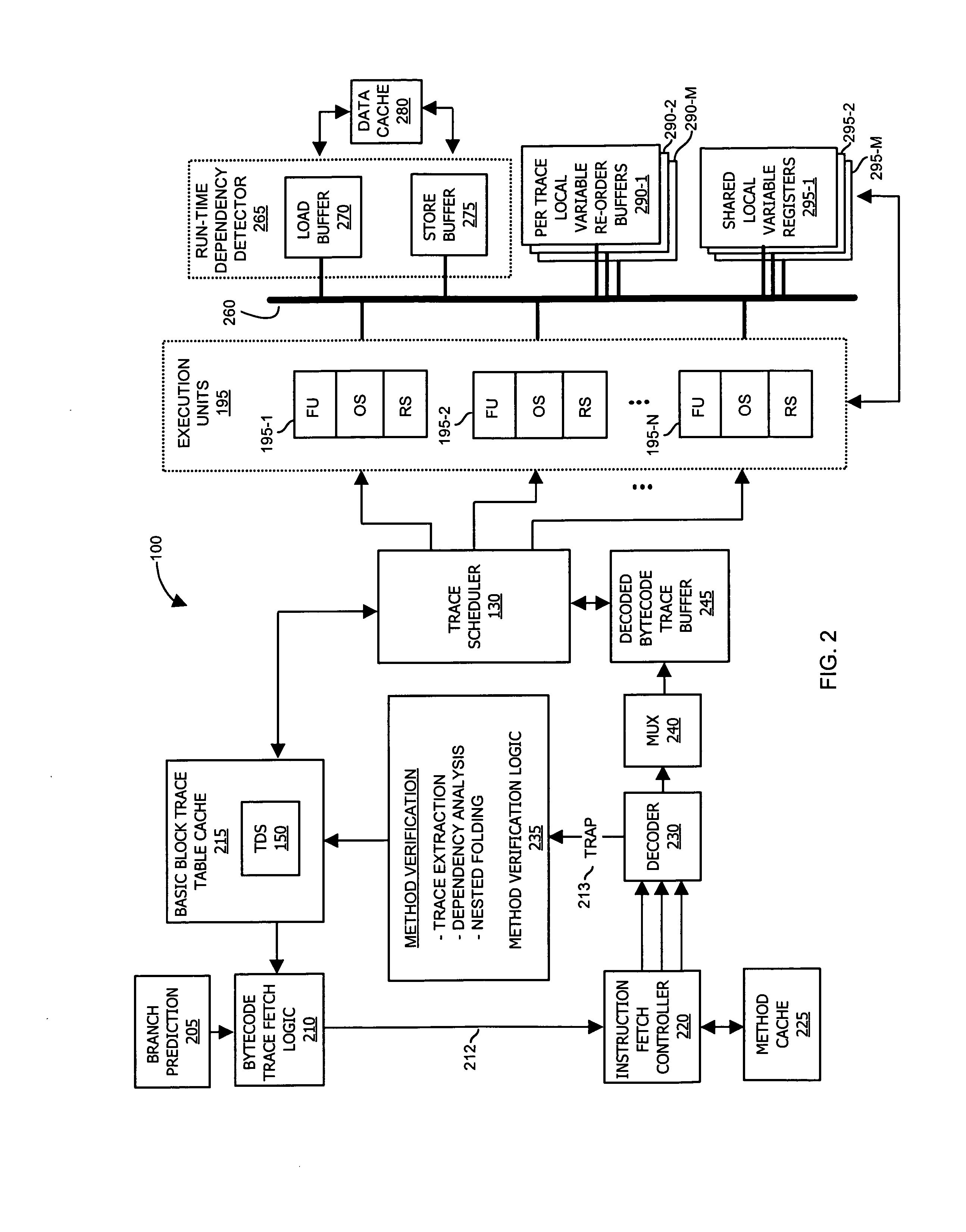
Methods and apparatus of an architecture supporting execution of instructions in parallel
ActiveUS7600221B1Improve execution speedImprove execution timeDigital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsOperandRunning time
A processing architecture supports executing instructions in parallel after identifying at least one level of dependency associated with a set of traces within a segment of code. Each trace represents a sequence of logical instructions within the segment of code that can be executed in a corresponding operand stack. Scheduling information is generated based on a dependency order identified among the set of traces. Thus, multiple traces may be scheduled for parallel execution unless a dependency order indicates that a second trace is dependent upon a first trace. In this instance, the first trace is executed prior to the second trace. Trace dependencies may be identified at run-time as well as prior to execution of traces in parallel. Results associated with execution of a trace are stored in a temporary buffer (instead of memory) until after it is known that a data dependency was not detected at run-time.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
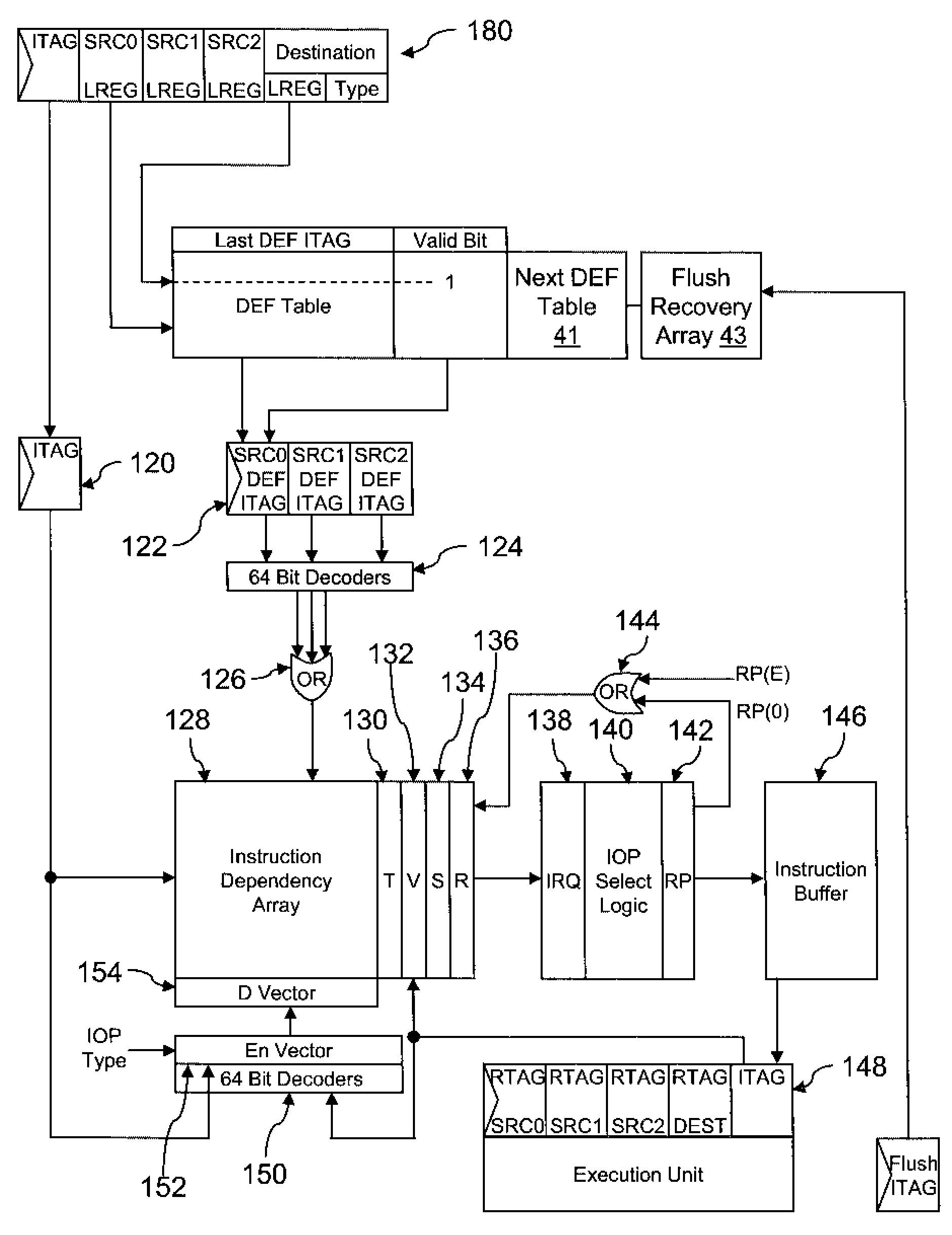
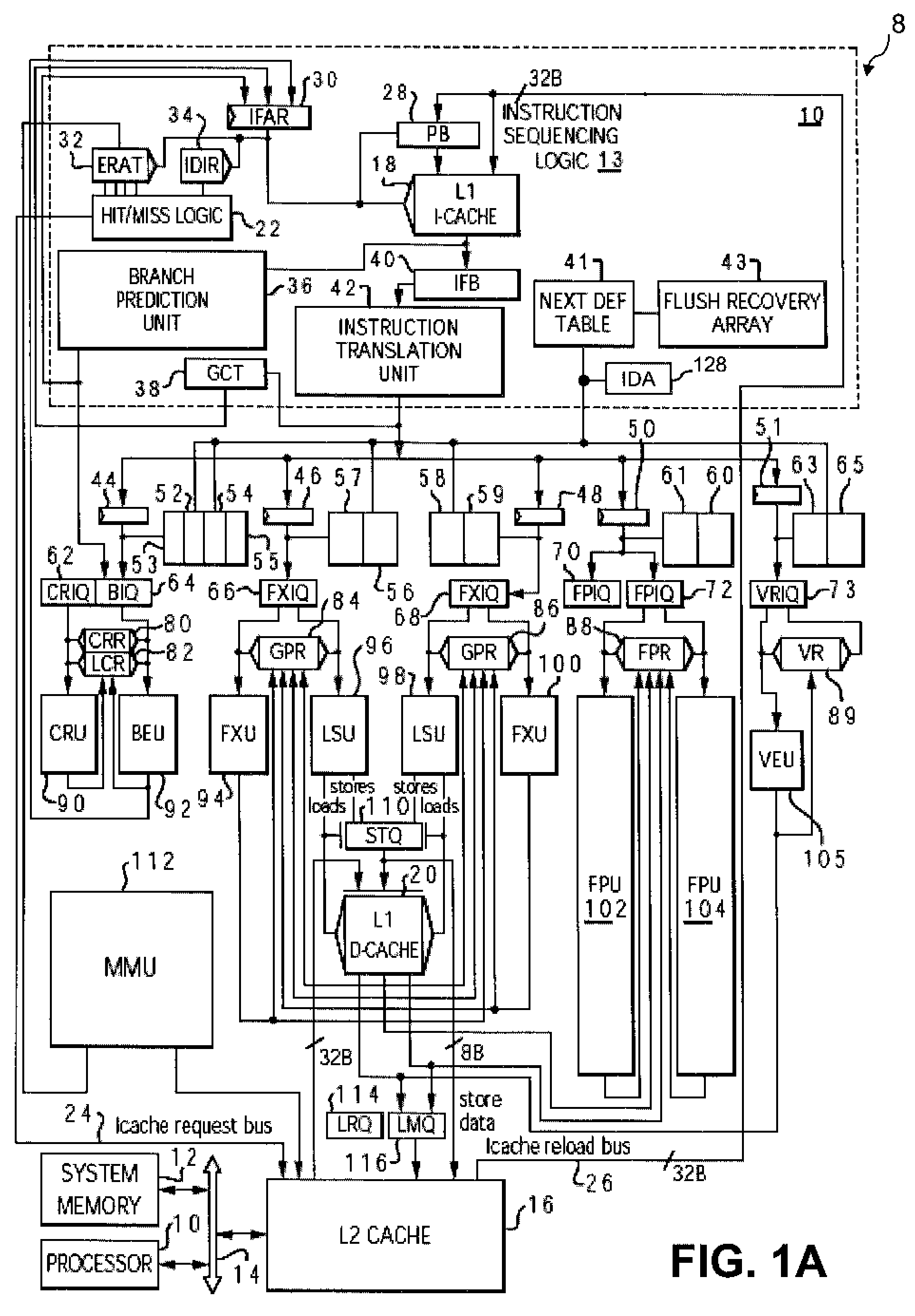
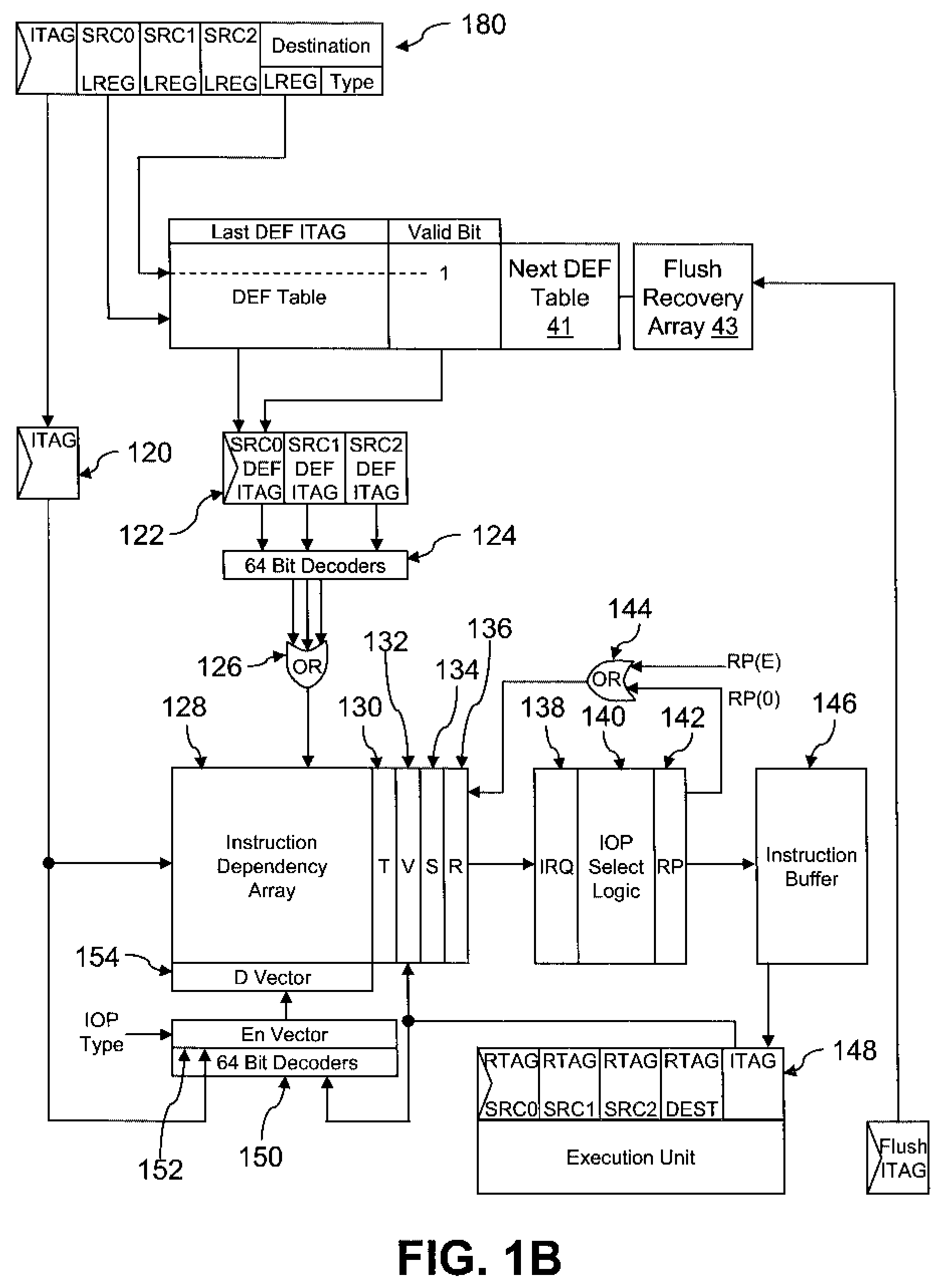
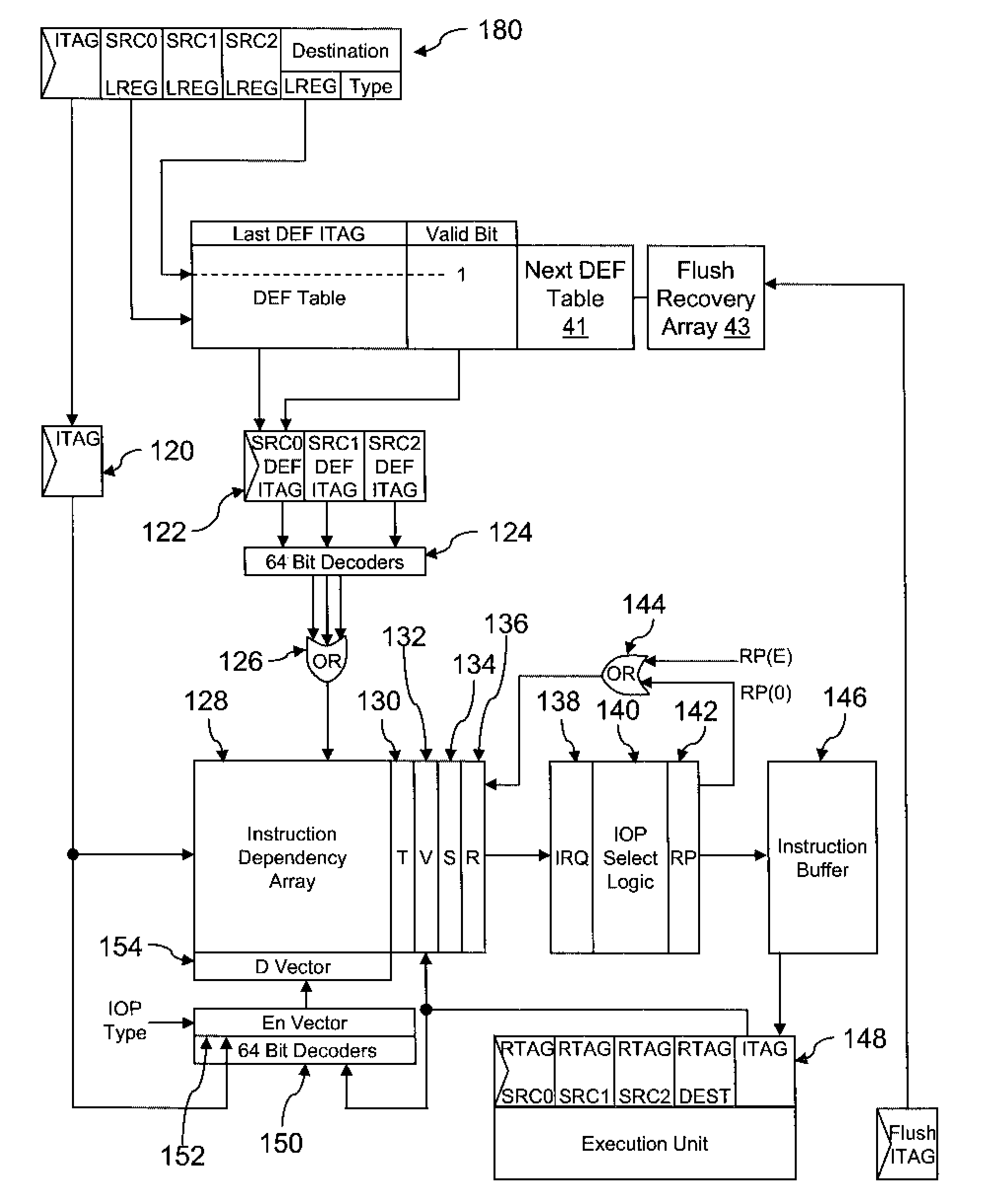
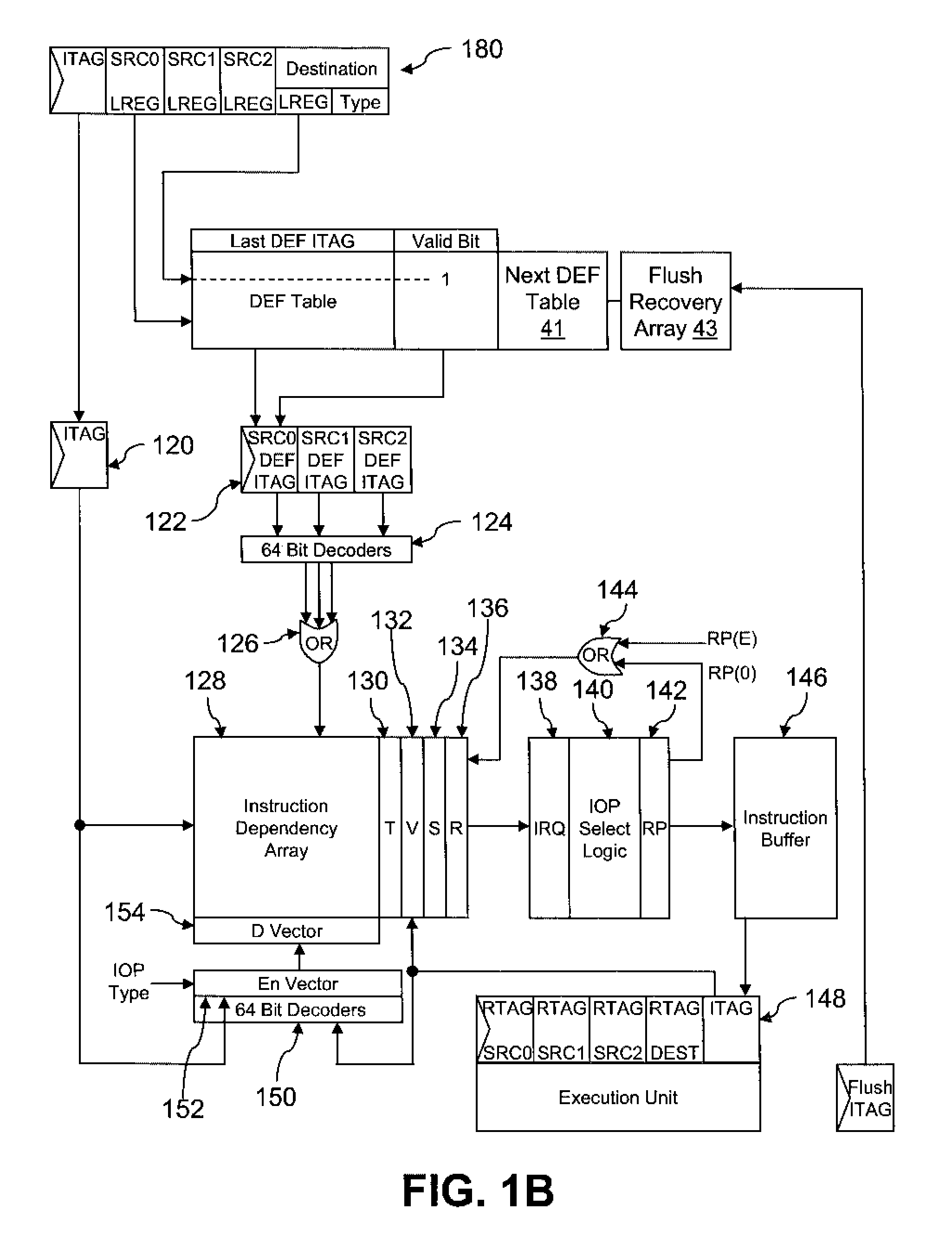
Method and system for tracking instruction dependency in an out-of-order processor
InactiveUS7711929B2Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsArray data structureData preparation
A method of tracking instruction dependency in a processor issuing instructions speculatively includes recording in an instruction dependency array (IDA) an entry for each instruction that indicates data dependencies, if any, upon other active instructions. An output vector read out from the IDA indicates data readiness based upon which instructions have previously been selected for issue. The output vector is used to select and read out issue-ready instructions from an instruction buffer.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
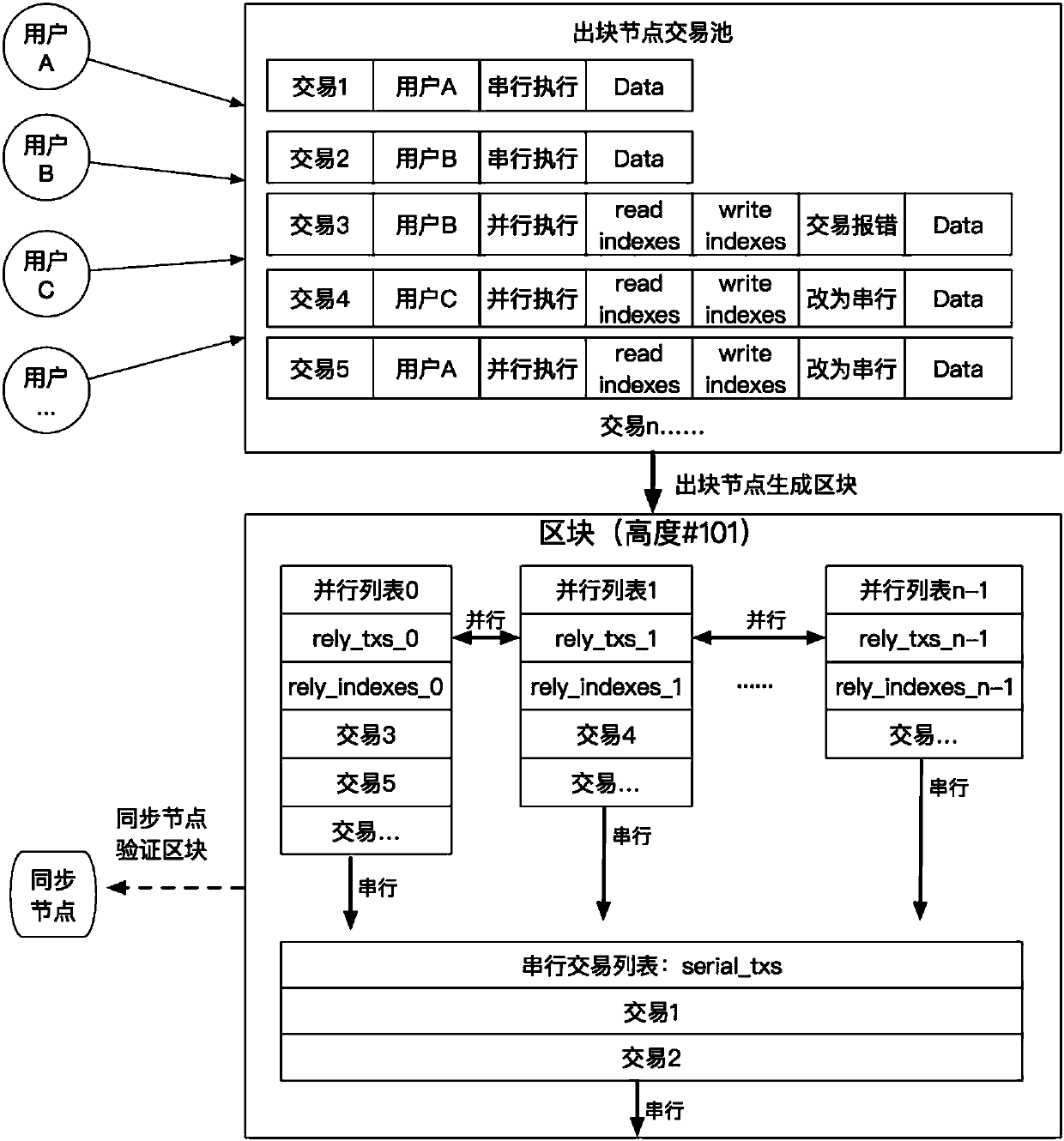
Parallel transaction execution method based on blockchain
ActiveCN107688999ASimplify concurrency difficultyImprove transaction throughputFinancePayment protocolsUser needsParallel processing
The invention discloses a parallel transaction execution method based on a blockchain. Firstly, a data unit on the datachain is subjected to index numbering, the parallel transaction of a user needs to provide a data index which needs to be read and written for transaction execution in addition to basic transaction contents. The serial transaction of the user only needs to provide the basic transaction contents. A node arranges parallel processing according to the data dependency relationship of the parallel transaction, and the transaction which can not carry out concurrence and the serial transaction can be executed in sequence.
Owner:HANGZHOU RIVTOWER TECH CO LTD
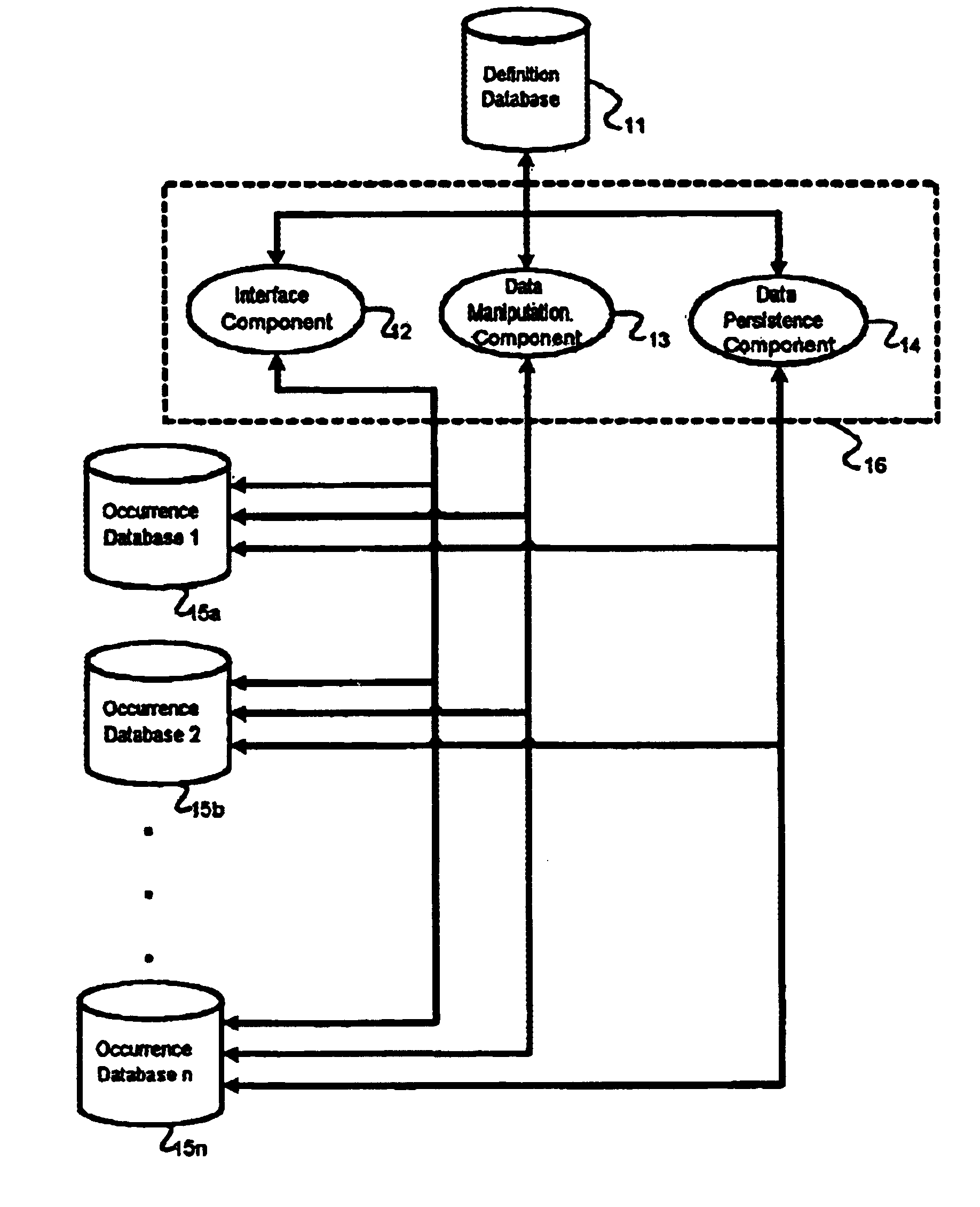
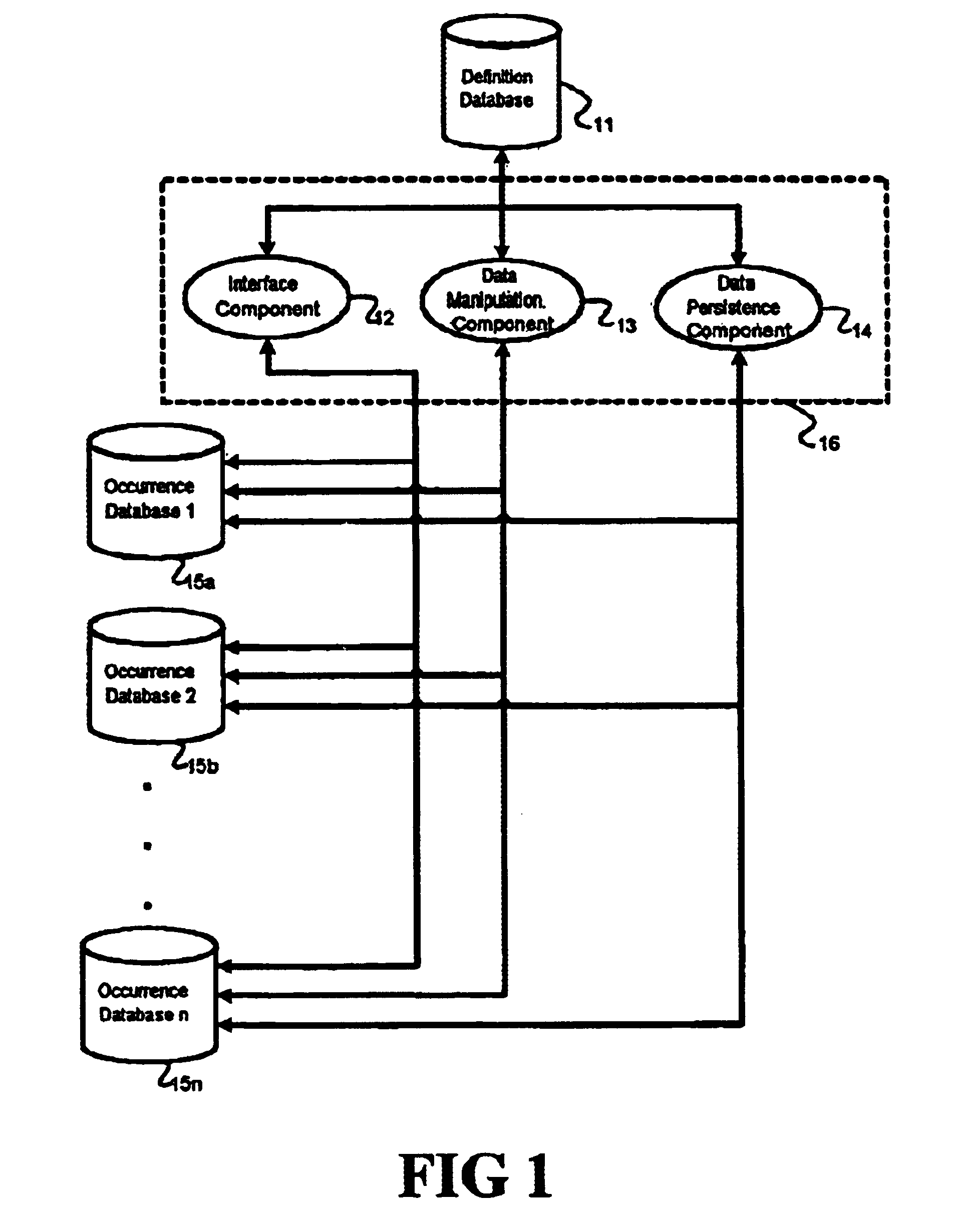
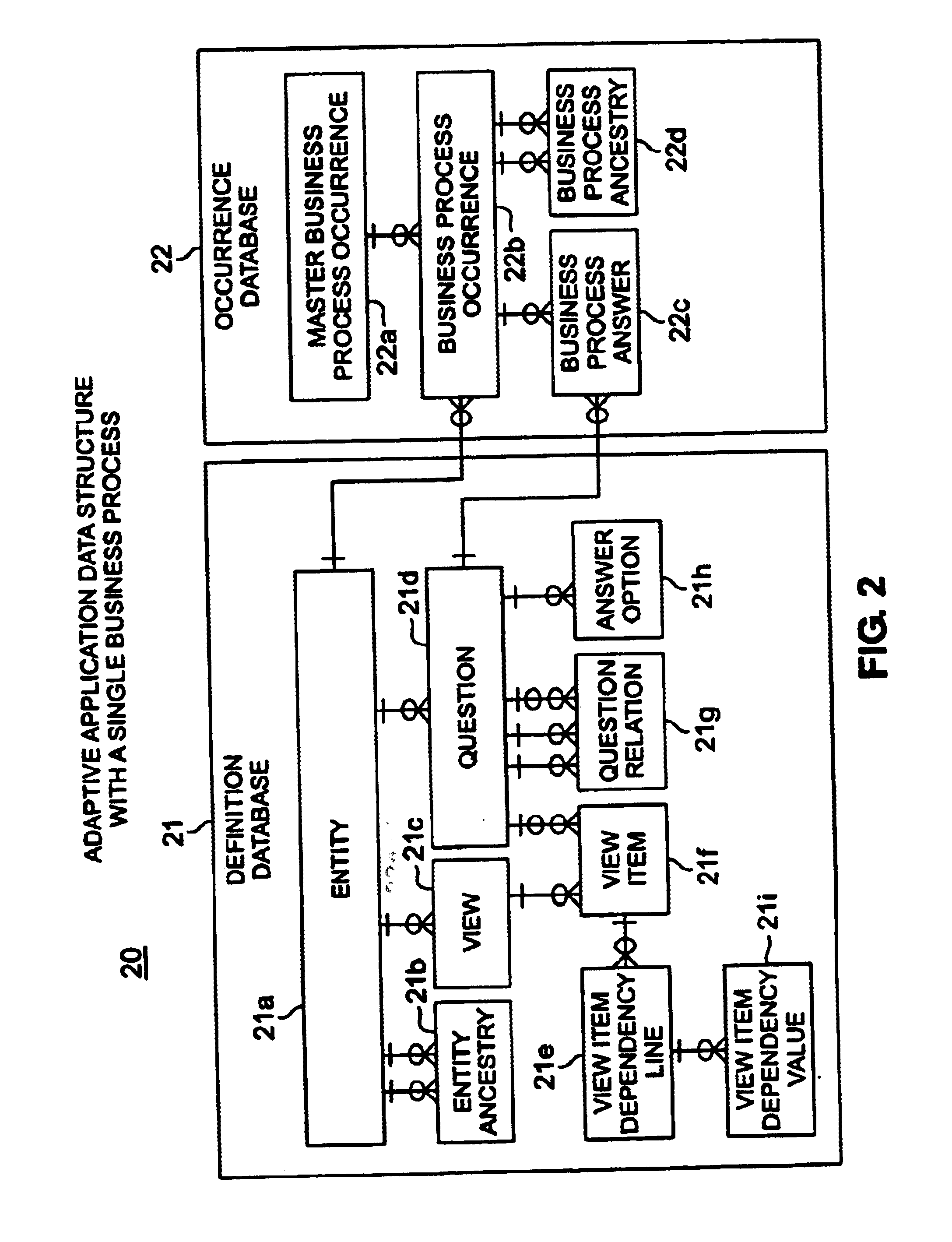
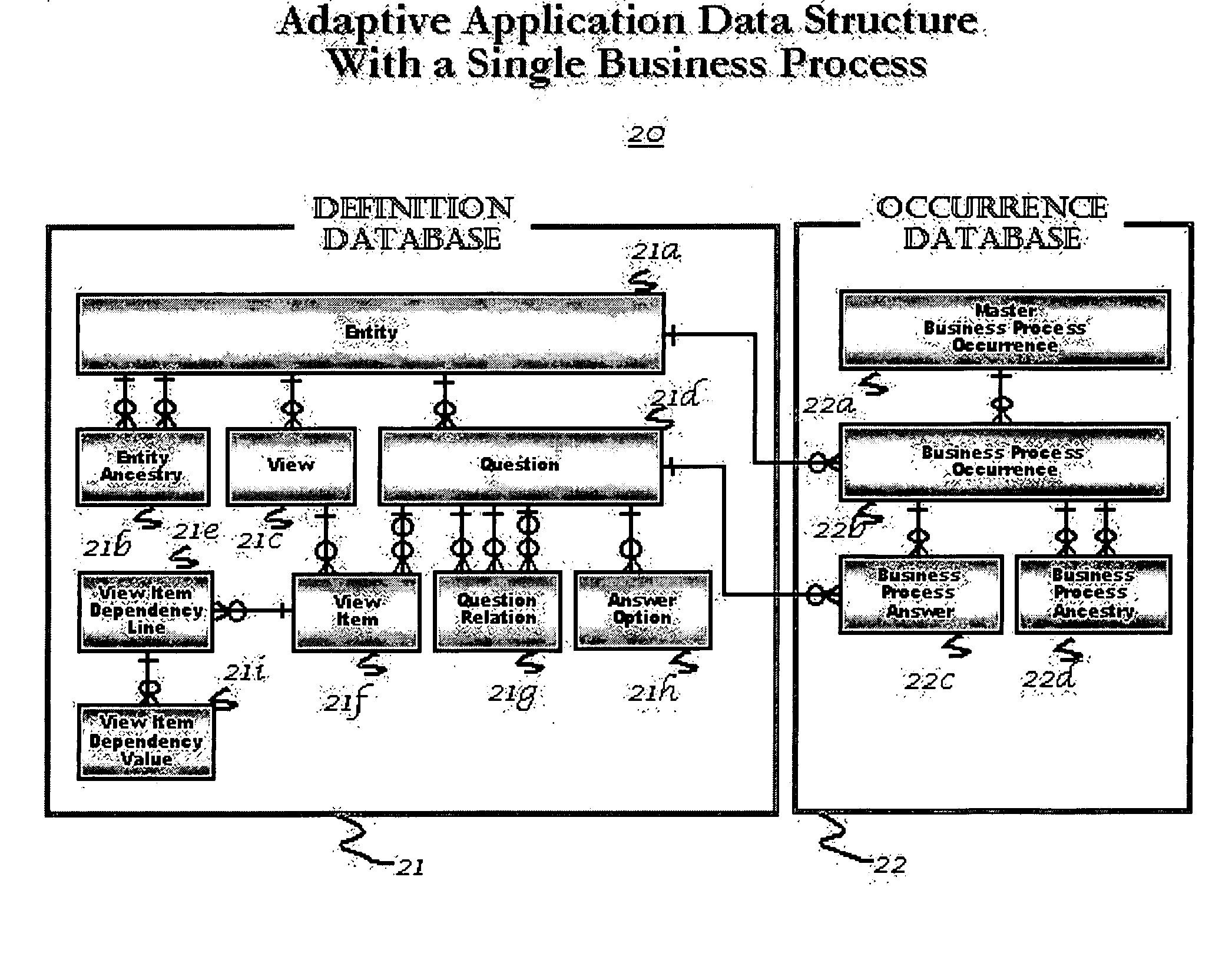
Method and apparatus for creating an adaptive application
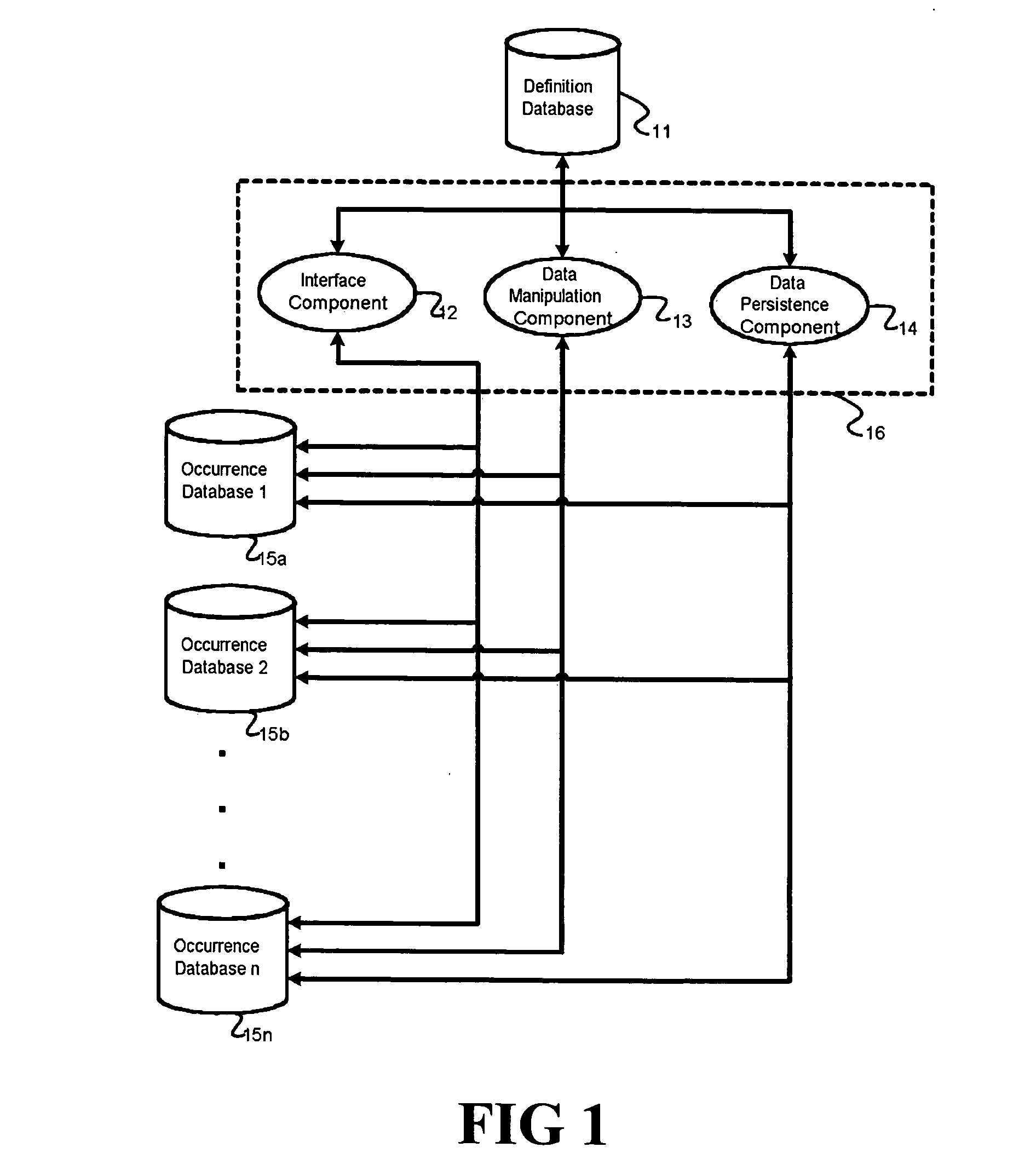
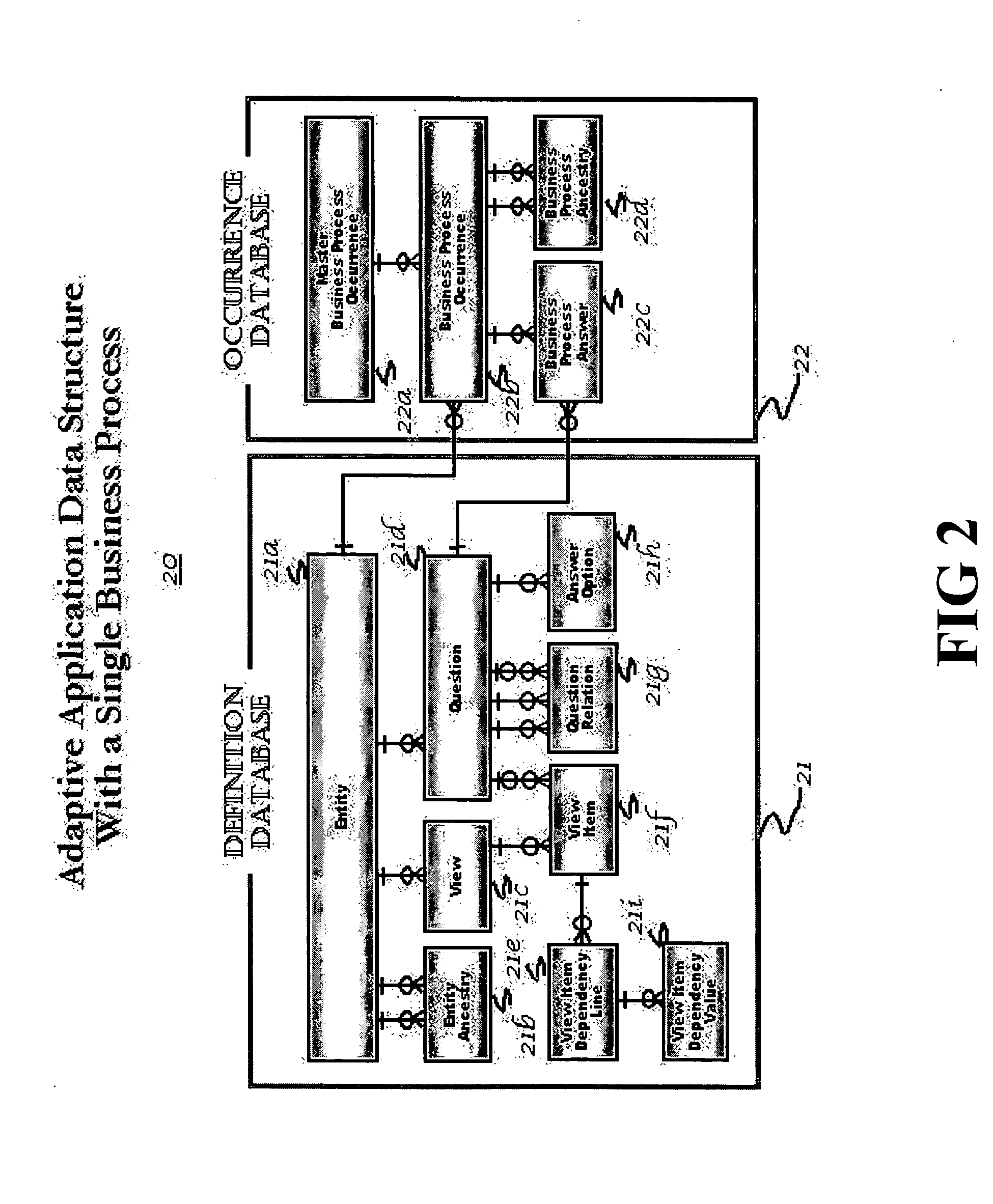
InactiveUS6895409B2Reduce system development costsQuality improvementData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsProcess logicSelf adaptive
An Adaptive Software Application consists of several types of modules, called Adaptive Units, which are highly parameterized such that they can adapt to varying business requirements by virtue of externally provided parameters. An Adaptive Application is assembled through repeated use of various combinations of different types of Adaptive Units. Large and complex business systems can be rapidly implemented through this approach. An Adaptive Unit includes interface components that can present information to and accept information from the outside world (such as a web page or a system interface), processing logic components that can manipulate and evaluate information based on received parameters received (such as comparisons and decisions including data dependency decisions), and data persistence logic components that retrieves, adds, updates, and deletes data targeting one or more Occurrence Databases. All three components of an Adaptive Unit are parameter driven. These parameters are not specific to any particular business.
Owner:ADAPTIK CORP
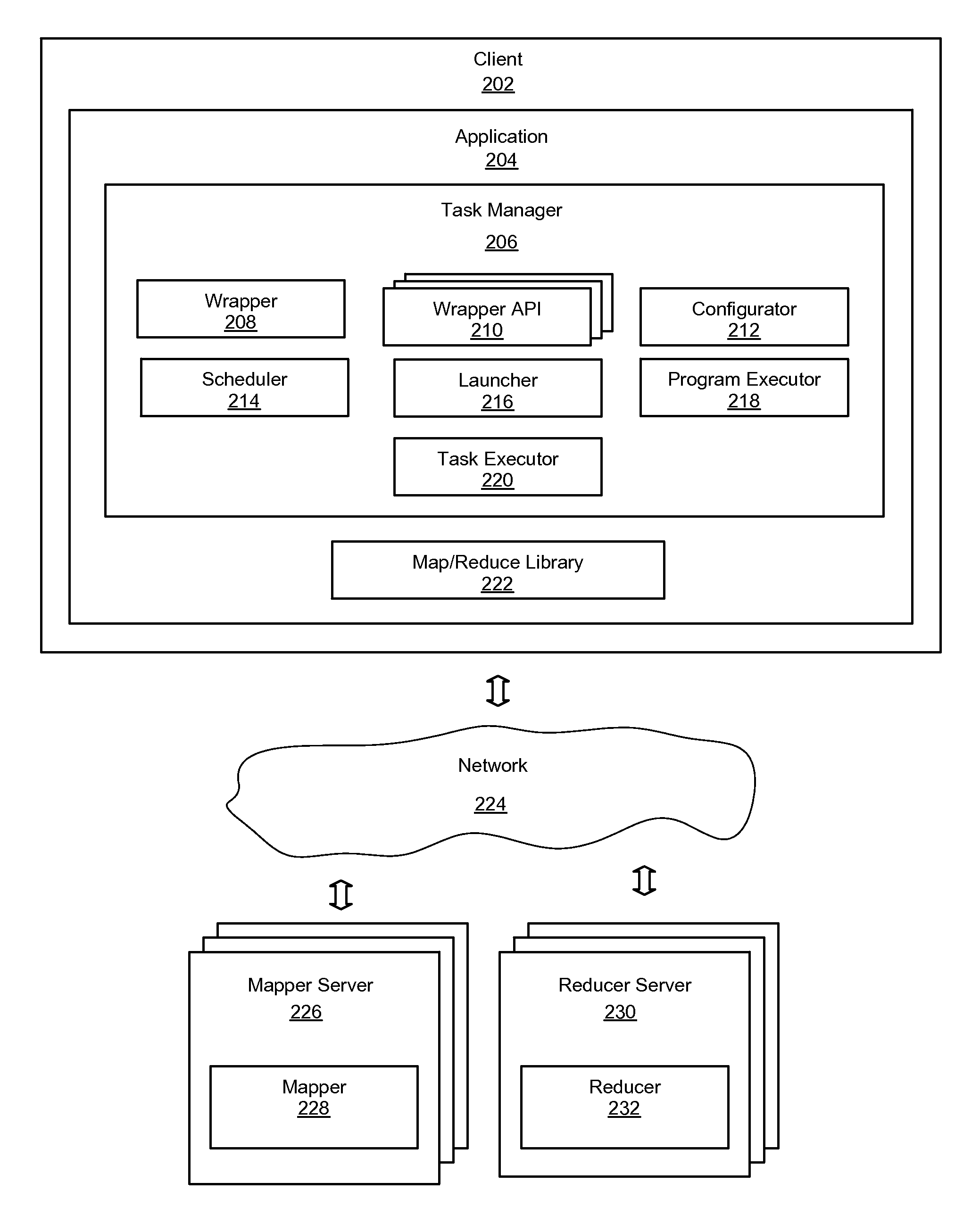
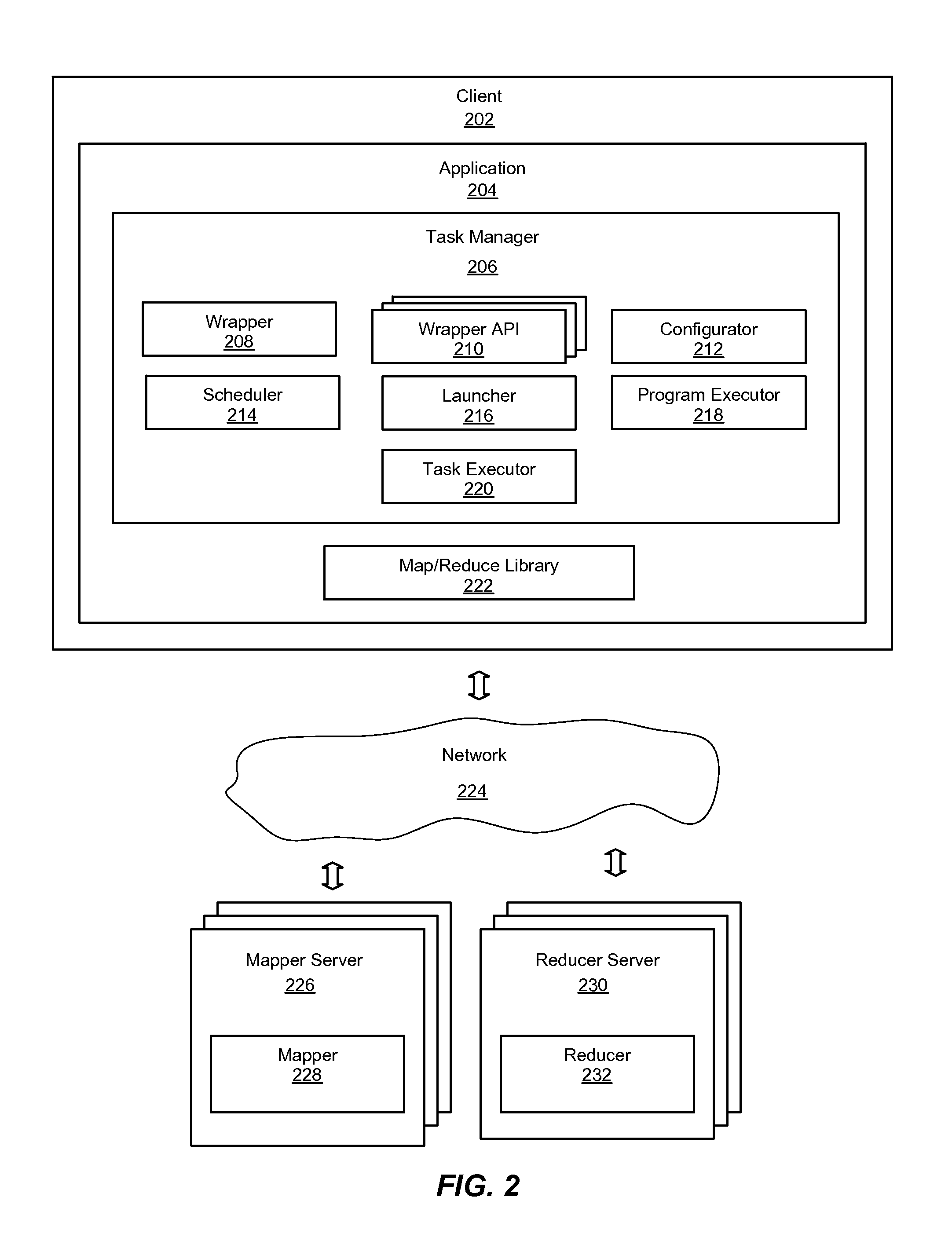
System and method for a task management library to execute map-reduce applications in a map-reduce framework
ActiveUS20110154341A1OptimizationSimple taskMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsExecution planMap reduce
An improved system and method for a task management library to execute map-reduce applications is provided. A map-reduce application may be operably coupled to a task manager library and a map-reduce library on a client device. The task manager library may include a wrapper application programming interface that provides application programming interfaces invoked by a wrapper to parse data input values of the map-reduce application. The task manager library may also include a configurator that extracts data and parameters of the map-reduce application from a configuration file to configure the map-reduce application for execution, a scheduler that determines an execution plan based on input and output data dependencies of mappers and reducers, a launcher that iteratively launches the mappers and reducers according to the execution plan, and a task executor that requests the map-reduce library to invoke execution of mappers on mapper servers and reducers on reducer servers.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
Method and System for Tracking Instruction Dependency in an Out-of-Order Processor
InactiveUS20090063823A1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsArray data structureData preparation
A method of tracking instruction dependency in a processor issuing instructions speculatively includes recording in an instruction dependency array (IDA) an entry for each instruction that indicates data dependencies, if any, upon other active instructions. An output vector read out from the IDA indicates data readiness based upon which instructions have previously been selected for issue. The output vector is used to select and read out issue-ready instructions from an instruction buffer.
Owner:IBM CORP
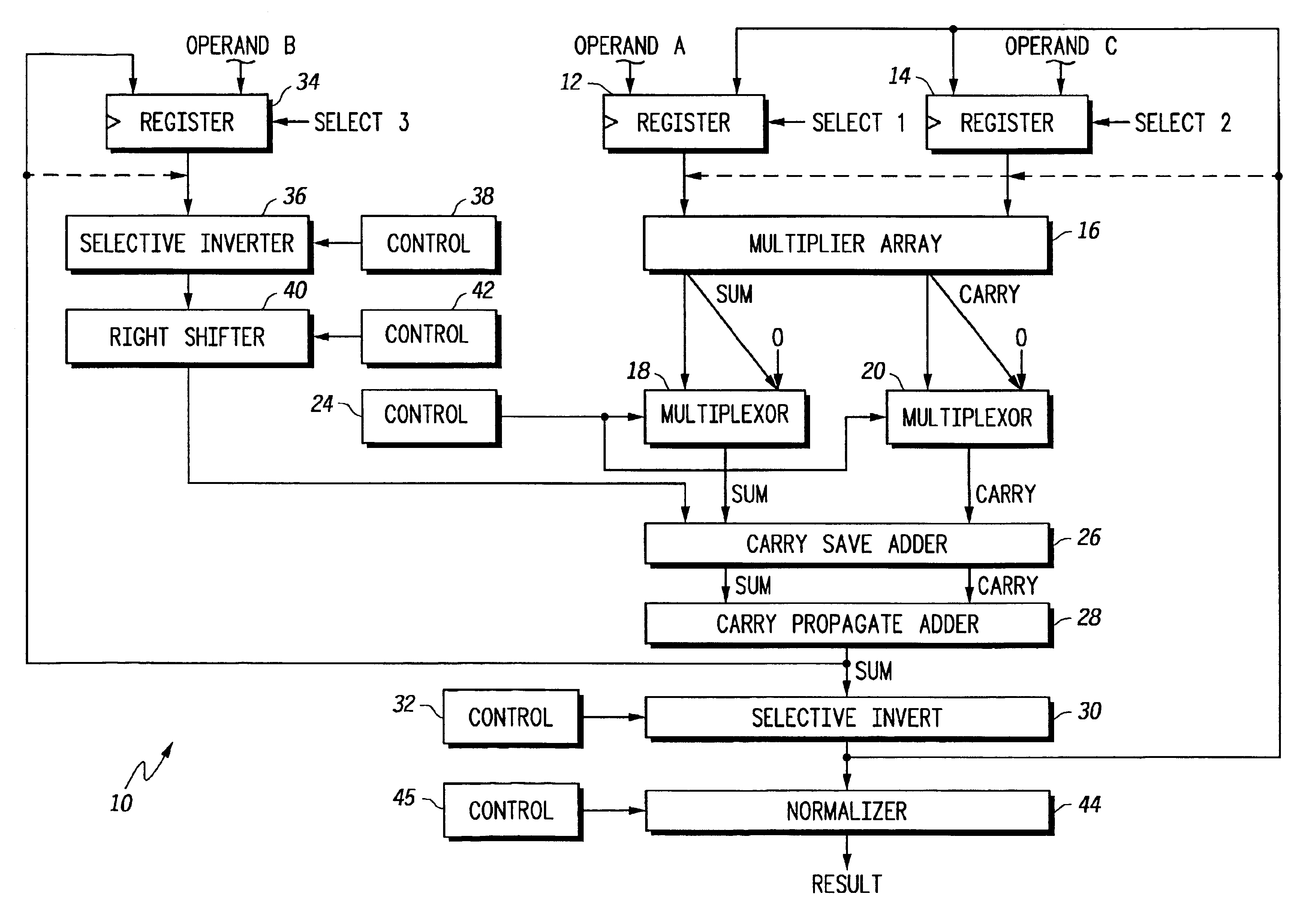
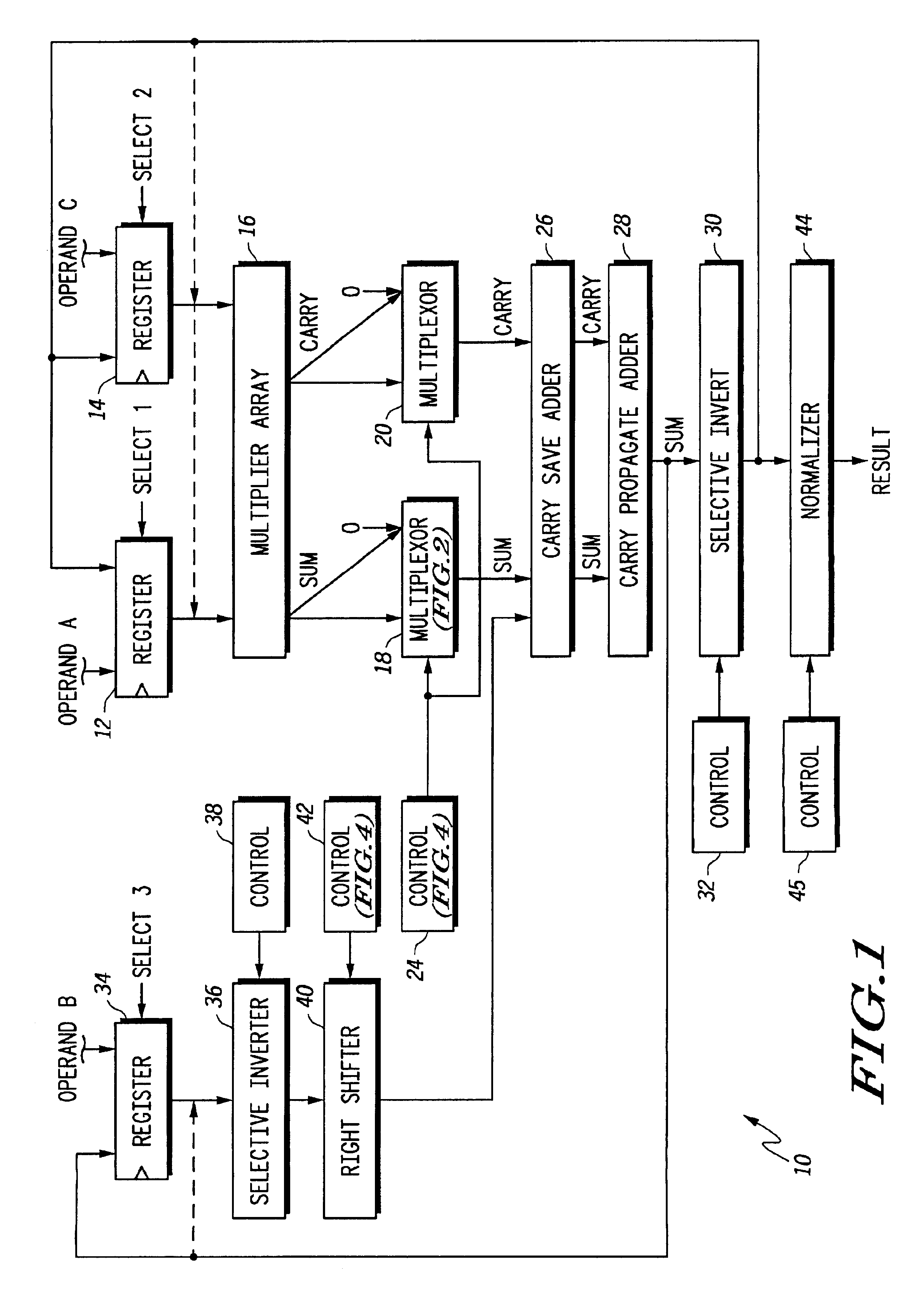
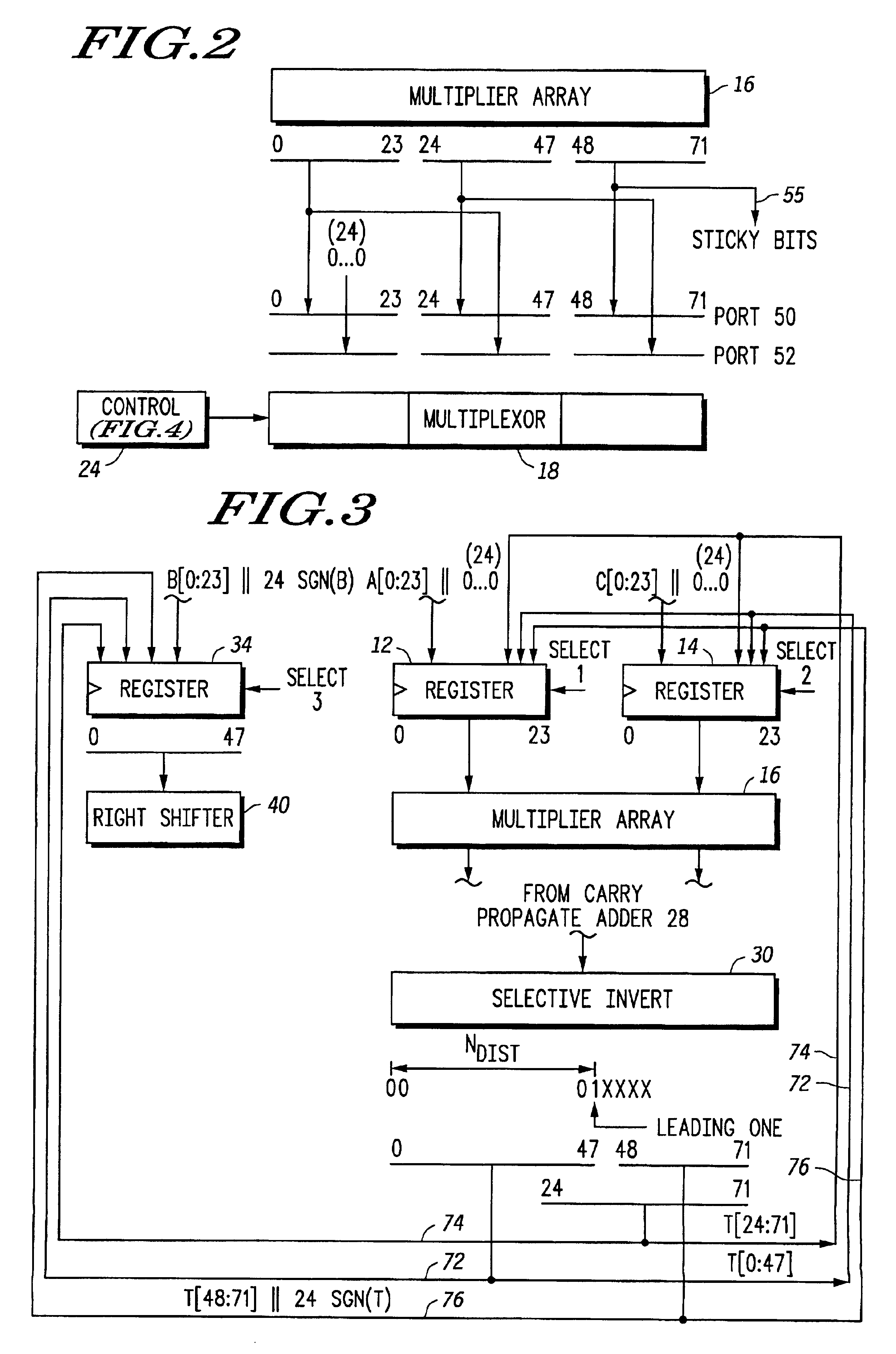
Floating point multiplier/accumulator with reduced latency and method thereof
A circuit (10) for multiplying two floating point operands (A and C) while adding or subtracting a third floating point operand (B) removes latency associated with normalization and rounding from a critical speed path for dependent calculations. An intermediate representation of a product and a third operand are selectively shifted to facilitate use of prior unnormalized dependent resultants. Logic circuitry (24, 42) implements a truth table for determining when and how much shifting should be made to intermediate values based upon a resultant of a previous calculation, upon exponents of current operands and an exponent of a previous resultant operand. Normalization and rounding may be subsequently implemented, but at a time when a new cycle operation is not dependent on such operations even if data dependencies exist.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Multi-threaded streaming data decoding
ActiveUS8213518B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor signal processing circuitsStream dataData dependency
Streaming data may be decoded by dividing a process for decoding the streaming data into two or more tasks based on data dependencies between the two or more tasks. The two or more tasks may be executed in parallel on three or more processors in a way that balances a processing load of executing the two or more tasks among the three or more processors.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Method and apparatus for creating an adaptive application
InactiveUS20050022160A1Implement extensionsReduce system development costsData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDecision takingBusiness process
An Adaptive Software Application consists of several types of modules, called Adaptive Units, which are highly parameterized such that they can adapt to varying business requirements by virtue of externally provided parameters. An Adaptive Application is assembled through repeated use of various combinations of different types of Adaptive Units. Large and complex business systems can be rapidly implemented through this approach. An Adaptive Unit includes an interface component that can present information to and accept information from the outside world (such as a web page or a system interface), a processing logic component that can manipulate and evaluate information based on received parameters received (such as comparisons and decisions as in the case of data dependency decisions), and a data persistence logic component that retrieves, adds, updates, and deletes data targeting one or more Occurrence Databases. All three components of an Adaptive Unit are parameter driven. These parameters are not specific to any particular business. One embodiment for providing parameters to these components includes a Definition Database. There may be one or more Occurrence Databases depending on the number of business processes supported by the business application for which the Adaptive Application is being adapted. The Occurrence Database includes generic (also referred to as meta model driven) tables that are not specific to any particular business.
Owner:ADAPTIK CORP
Method and apparatus for executing program code
ActiveUS20100042815A1Software engineeringGeneral purpose stored program computerControl vectorProgram code
The described embodiments provide a system that executes program code. While executing program code, the processor encounters at least one vector instruction and at least one vector-control instruction. The vector instruction includes a set of elements, wherein each element is used to perform an operation for a corresponding iteration of a loop in the program code. The vector-control instruction identifies elements in the vector instruction that may be operated on in parallel without causing an error due to a runtime data dependency between the iterations of the loop. The processor then executes the loop by repeatedly executing the vector-control instruction to identify a next group of elements that can be operated on in the vector instruction and selectively executing the vector instruction to perform the operation for the next group of elements in the vector instruction, until the operation has been performed for all elements of the vector instruction.
Owner:APPLE INC
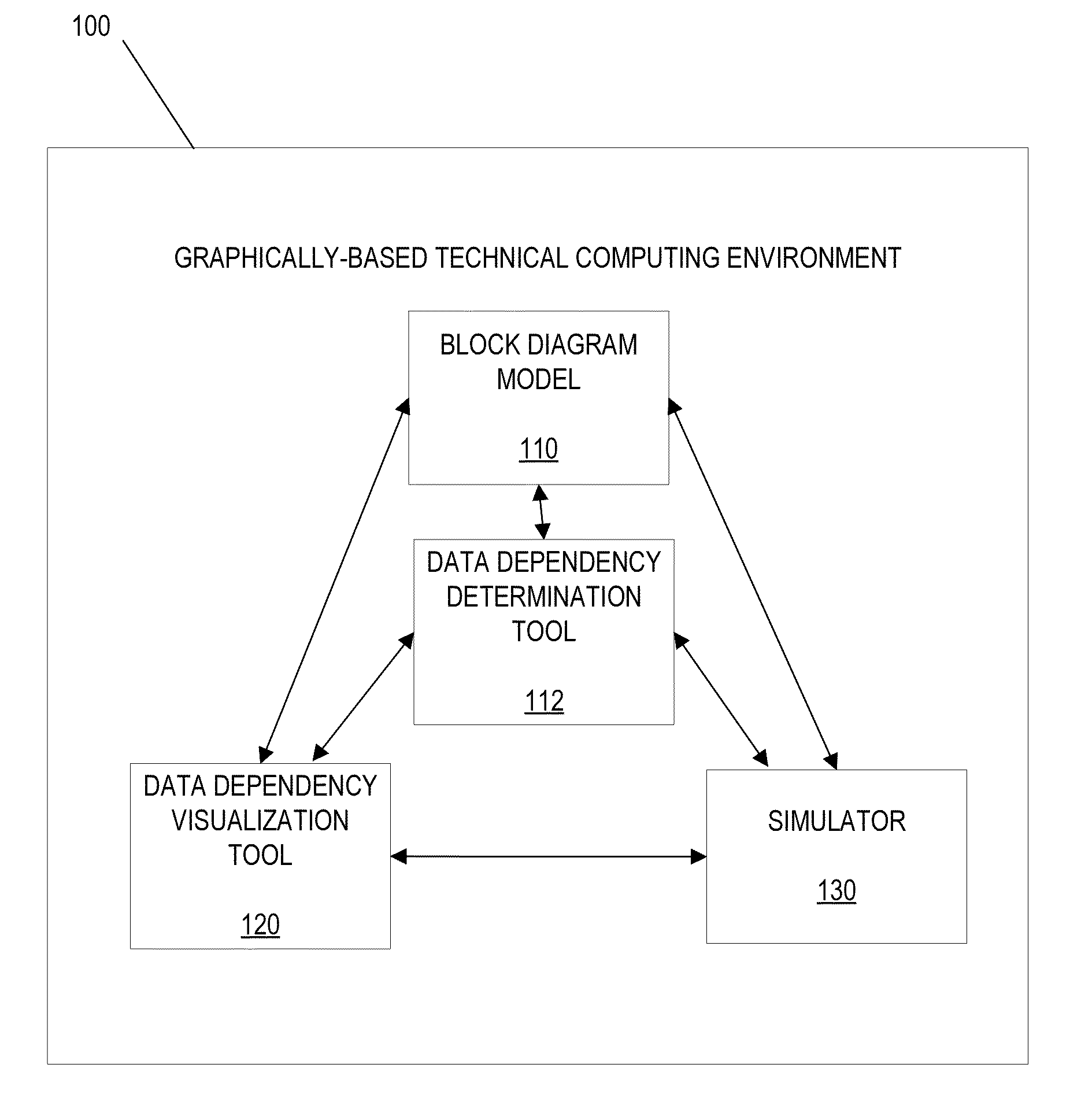
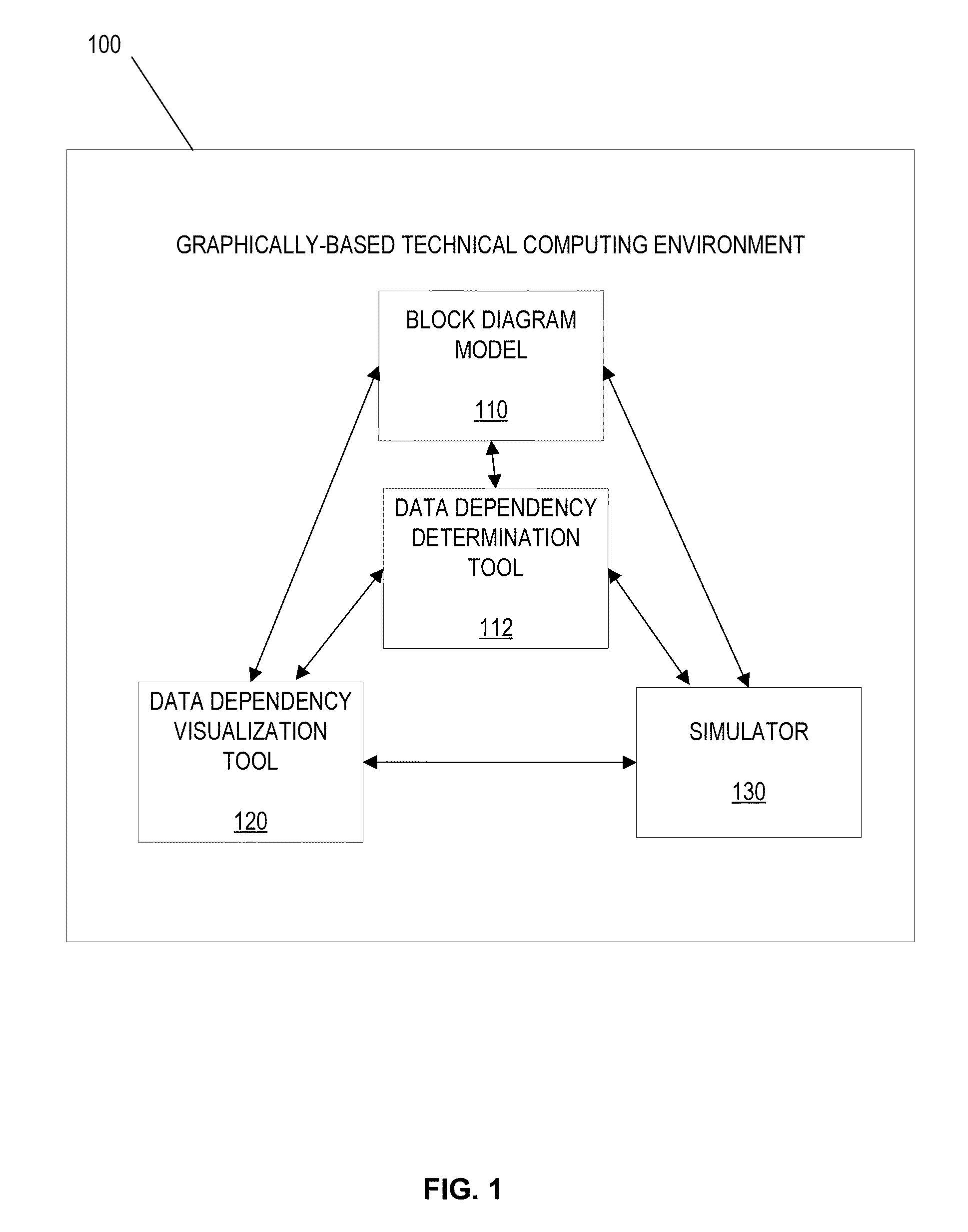
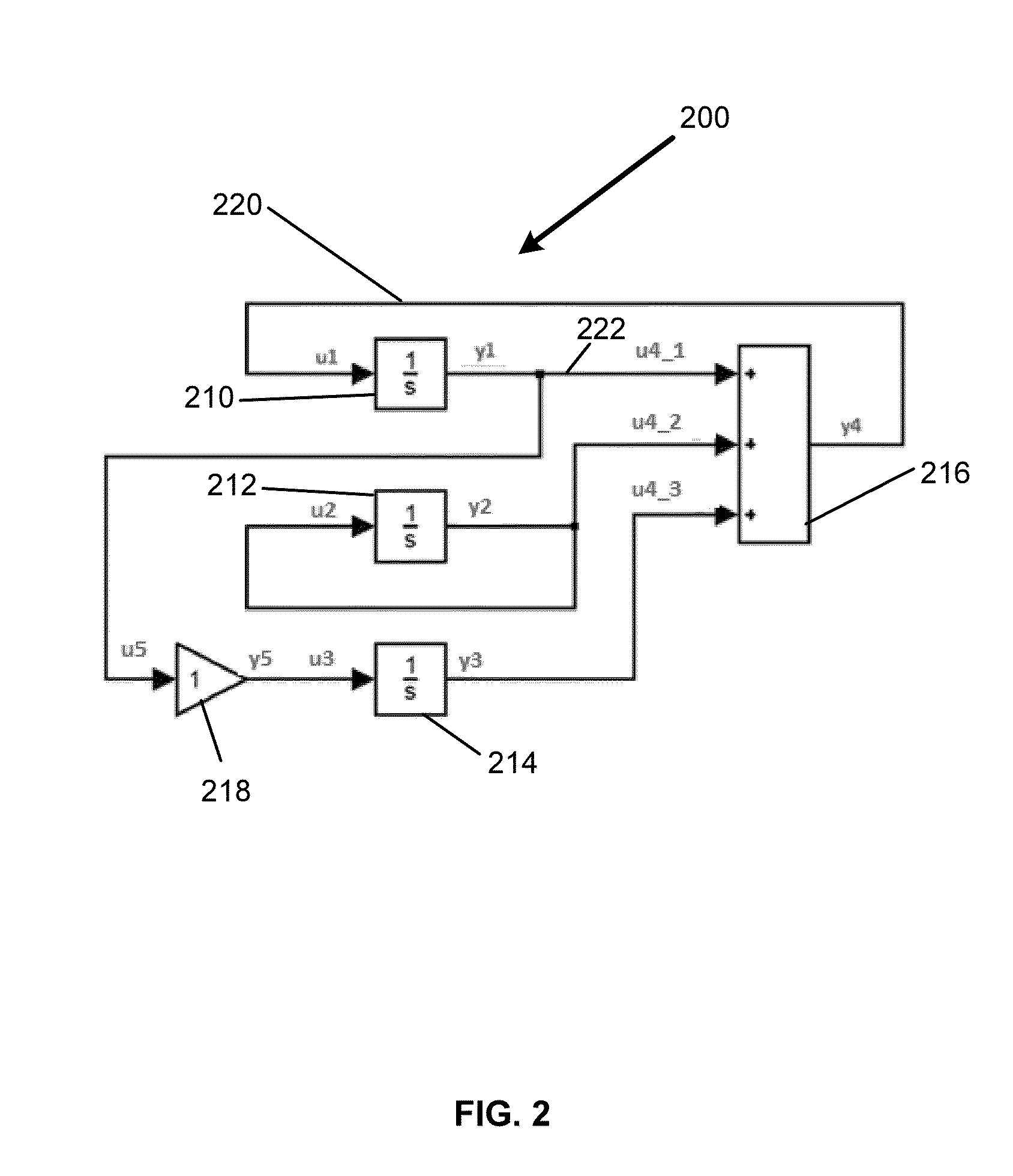
Visualization of data dependency in graphical models
ActiveUS20130116986A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationGraphicsDynamic equation
In an illustrative embodiment, an apparatus, computer-readable media, or method may be configured to suggest determine relationships. Interaction with a block diagram model may include receiving a first portion of a block diagram model. The block diagram model may include a plurality of blocks. Each of the plurality of blocks may represent a set of dynamic equations. The interacting may be performed using the computer. Relationships between a plurality of a synthesized input, a synthesized output, a synthesized state, or a synthesized derivative, may be determined. A determination may be performed for the first portion of the block diagram model. The determining may include determining a block Jacobian pattern of relationships between two or more of an input, an output, a state, or a derivative of a first block of the plurality of blocks in the graphical model.
Owner:THE MATHWORKS INC
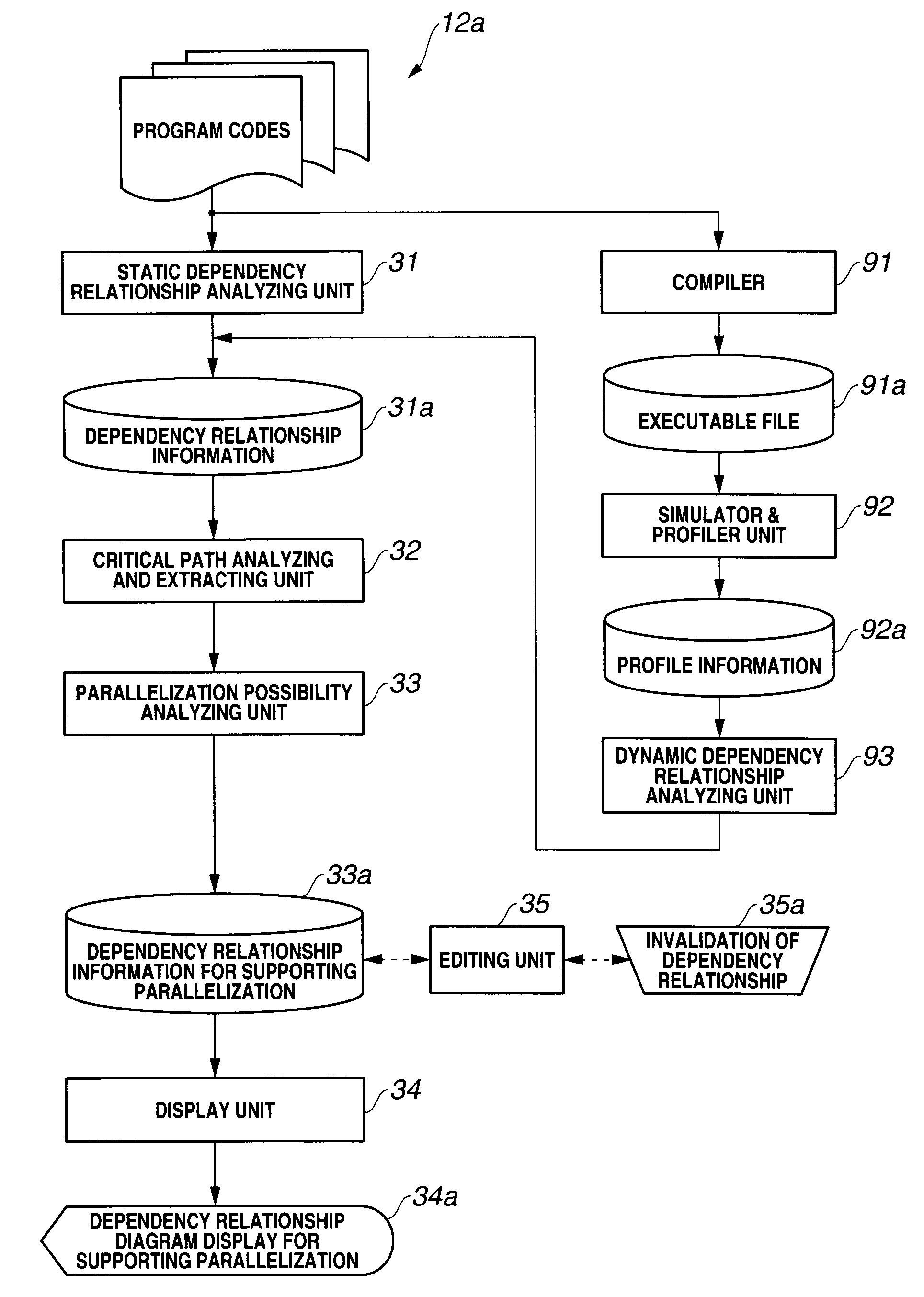
Program parallelization supporting apparatus and program parallelization supporting method
InactiveUS20090138862A1Reduce in quantitySoftware engineeringProgram controlProcessing InstructionCritical path method
A program parallelization supporting apparatus determines a determinacy in at least one dependency relationship of a data dependency, a control dependency and a pointer dependency in a program, extracts a critical path in the program, and extracts a processing instruction which exists on the critical path and has a non-deterministic determinacy in the dependency relationship. Furthermore, if a process related to a path of the extracted non-deterministic processing instruction is parallelized and the path of the non-deterministic processing instruction is deleted, the program parallelization supporting apparatus outputs parallelization labor hour information depending on the number of dependency relationships disturbing the parallelization and parallelization effect information depending on the number of processing instructions which are shortened by the parallelization.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
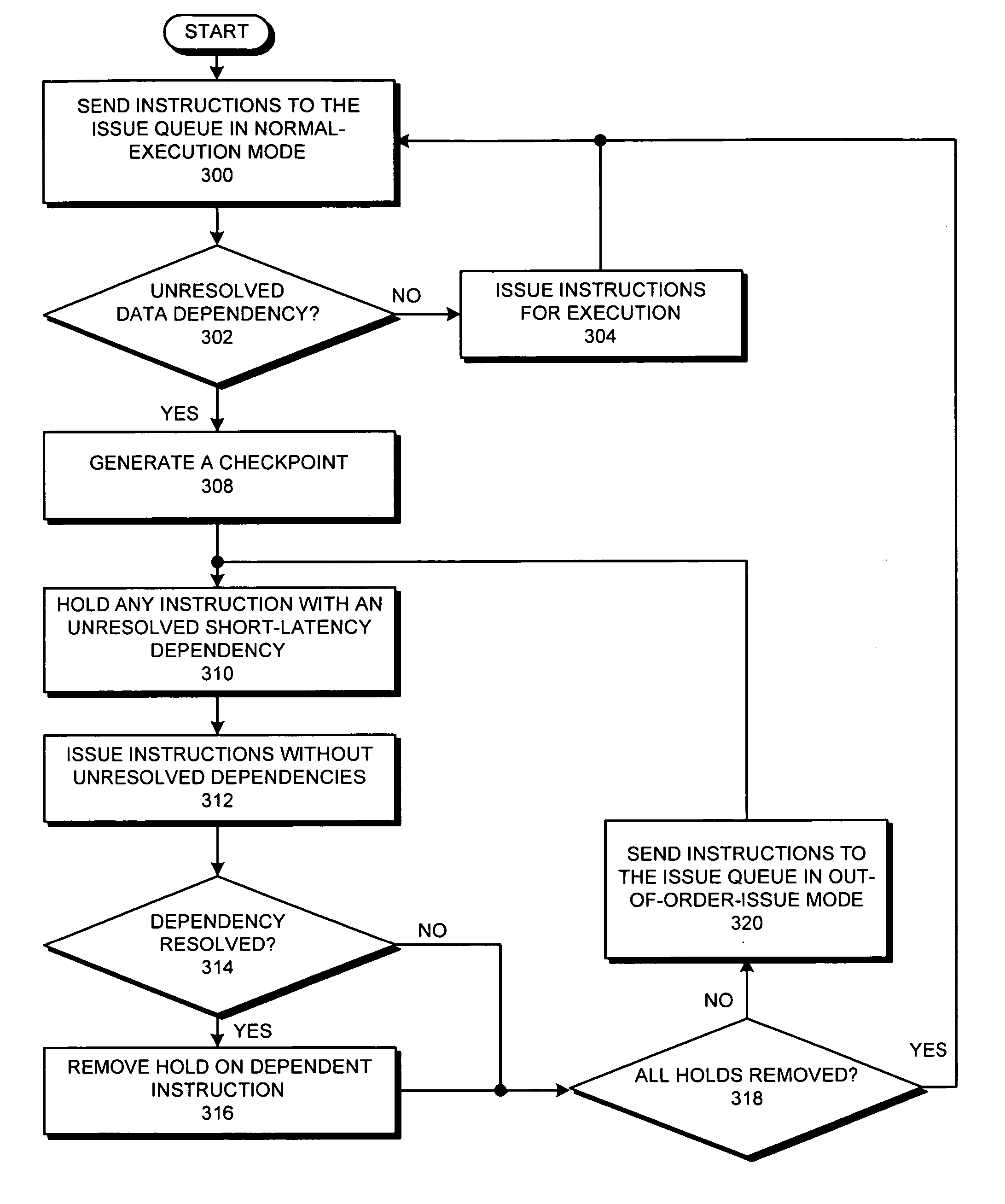
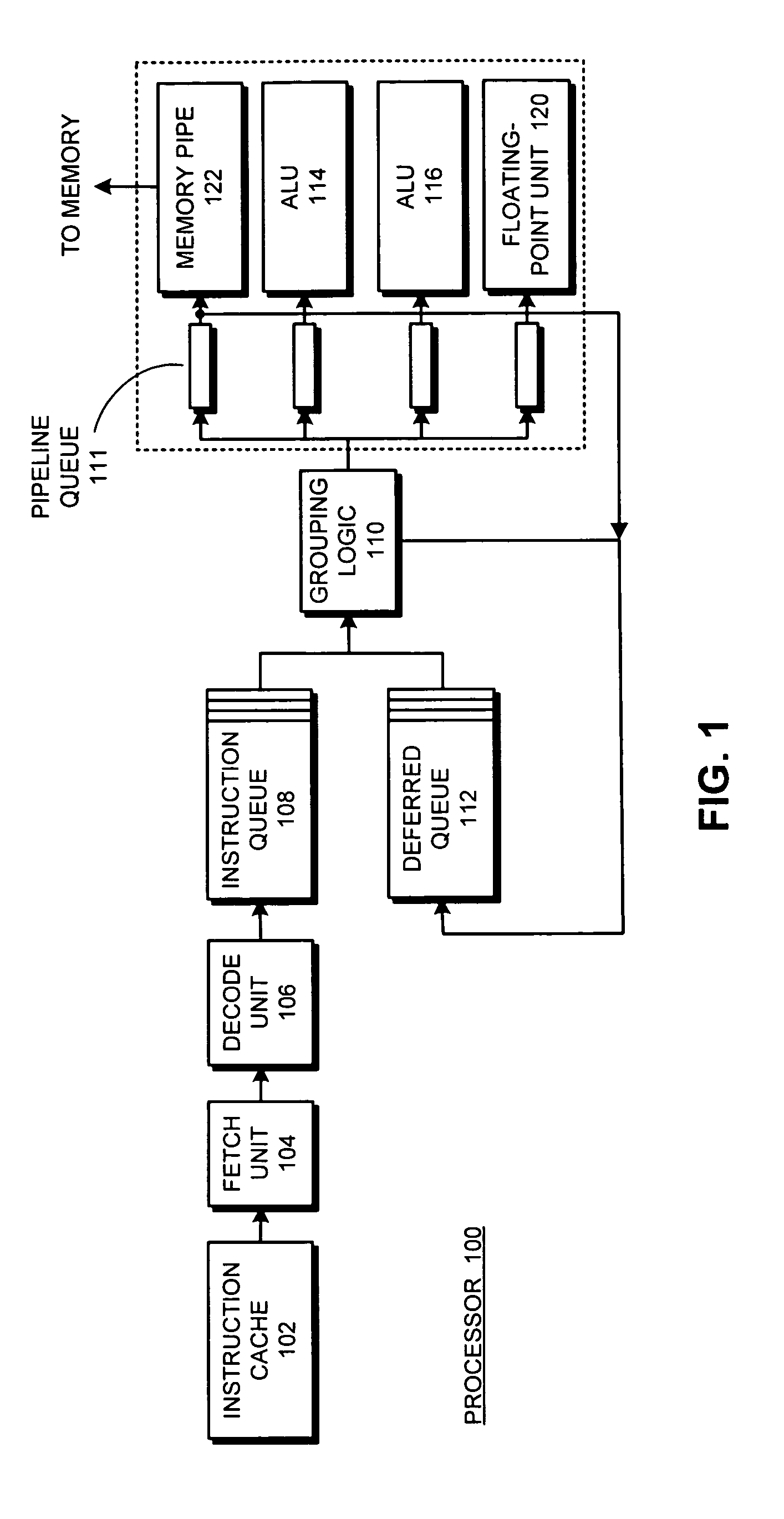
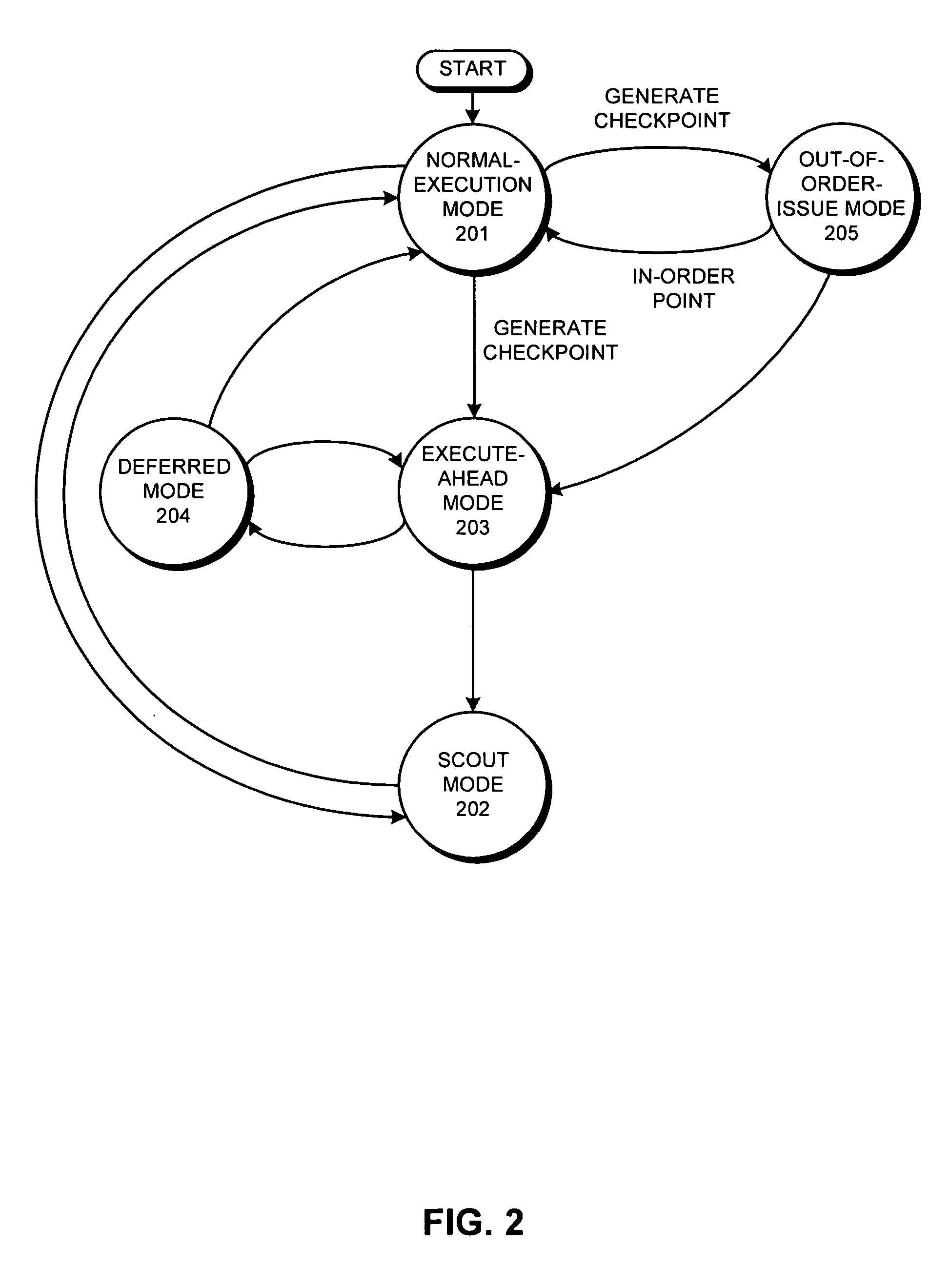
Supporting out-of-order issue in an execute-ahead processor
InactiveUS20070186081A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsWaiting timeProcedure sequence
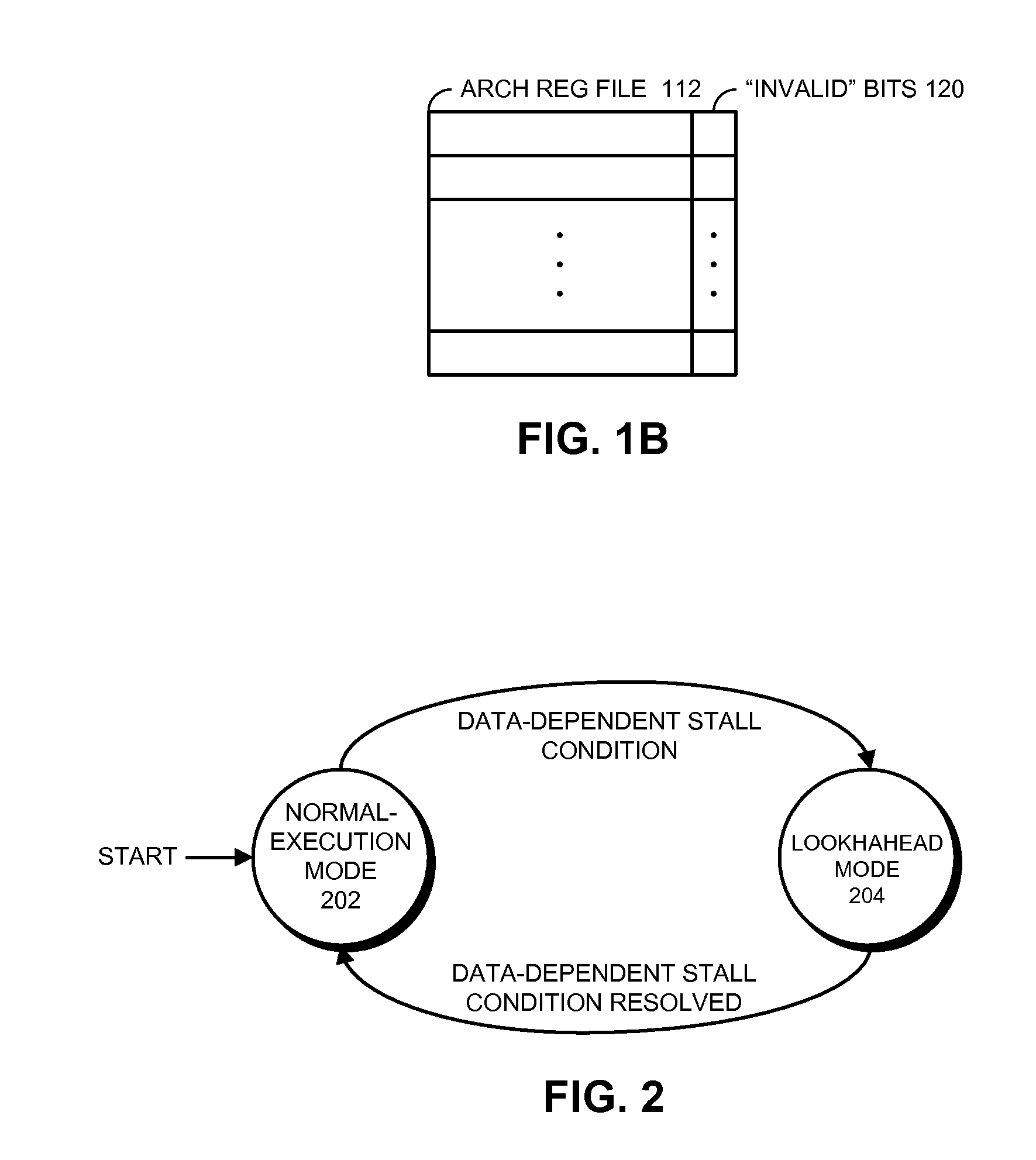
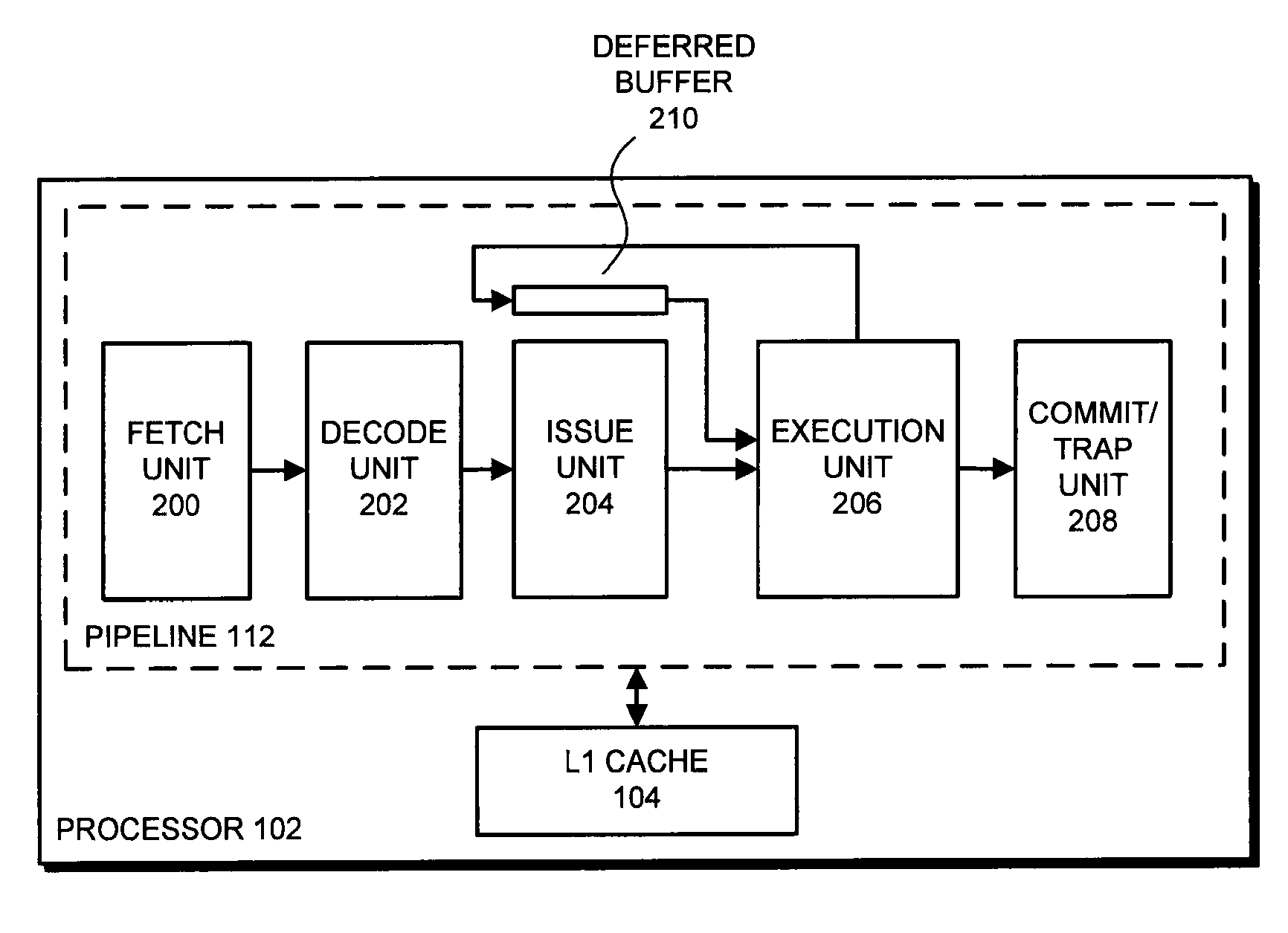
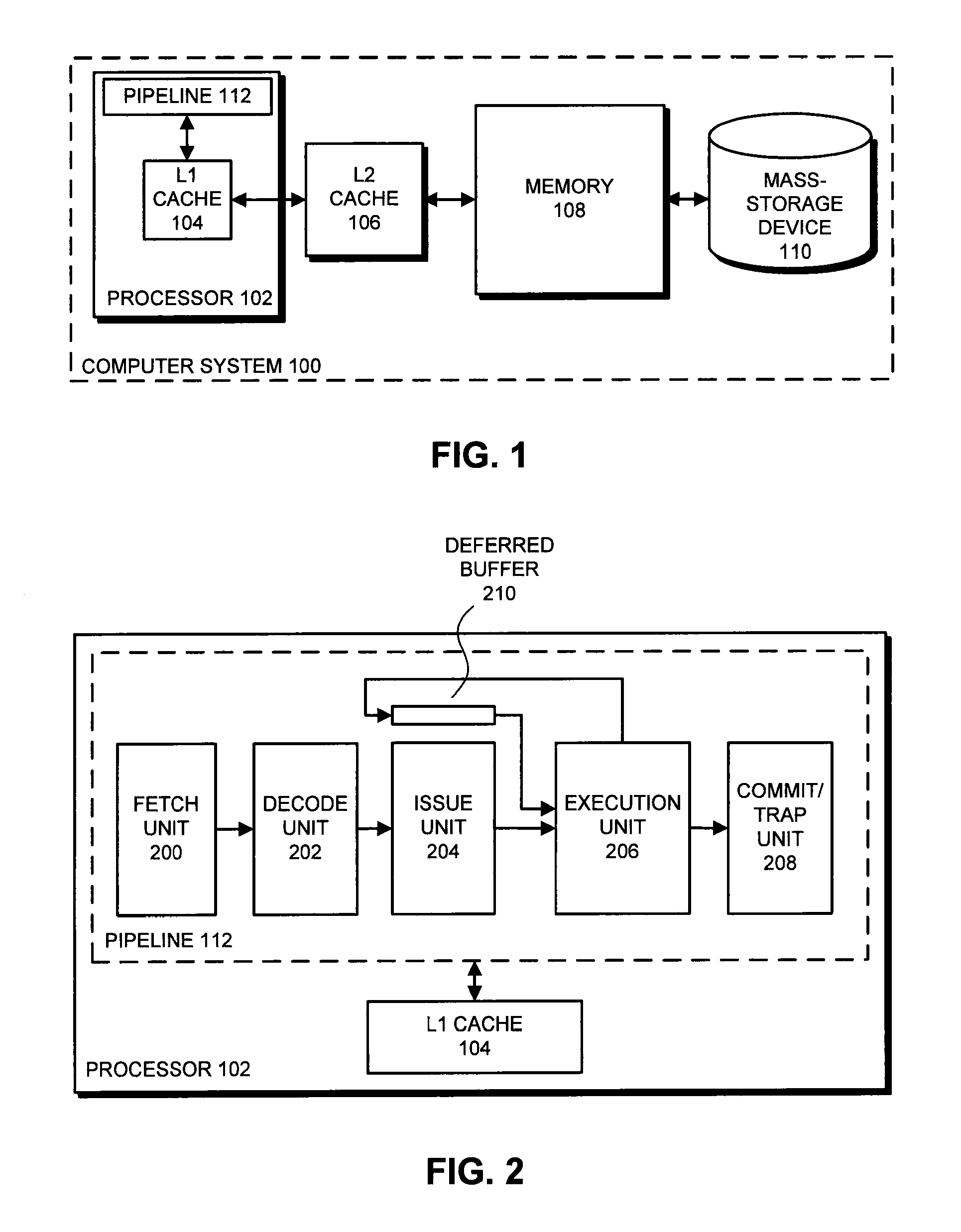
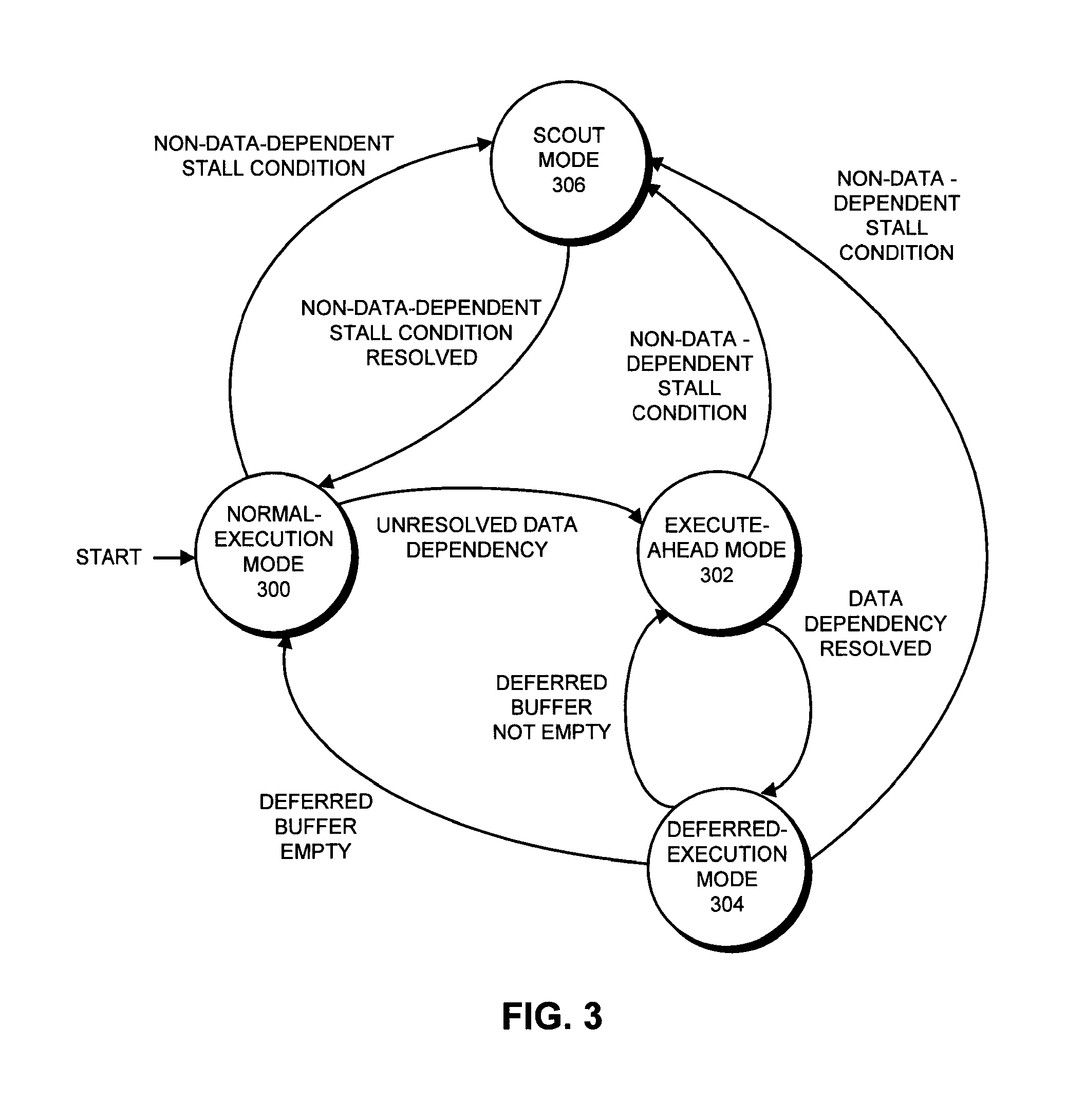
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system which supports out-of-order issue in a processor that normally executes instructions in-order. The system starts by issuing instructions from an issue queue in program order during a normal-execution mode. While issuing the instructions, the system determines if any instruction in the issue queue has an unresolved short-latency data dependency which depends on a short-latency operation. If so, the system generates a checkpoint and enters an out-of-order-issue mode, wherein instructions in the issue queue with unresolved short-latency data dependencies are held and not issued, and wherein other instructions in the issue queue without unresolved data dependencies are allowed to issue out-of-order.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
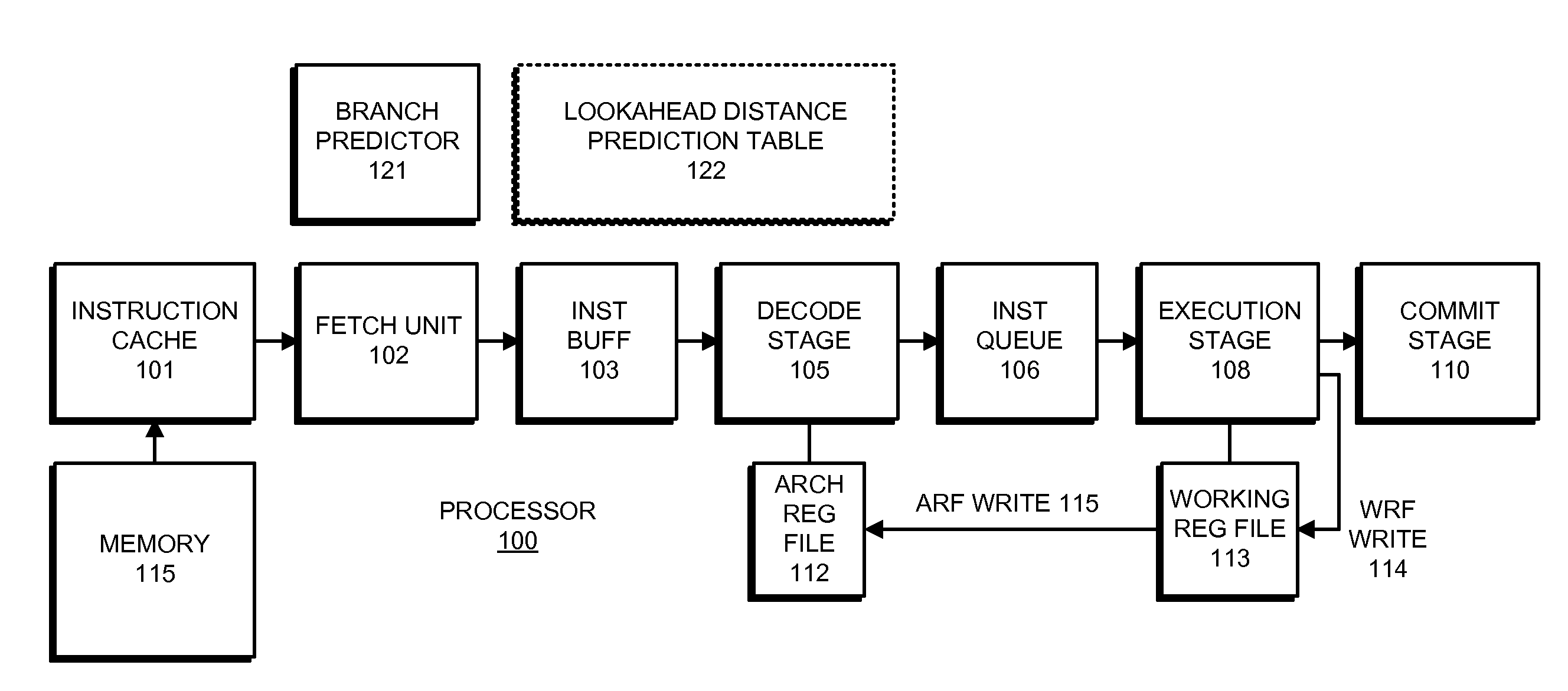
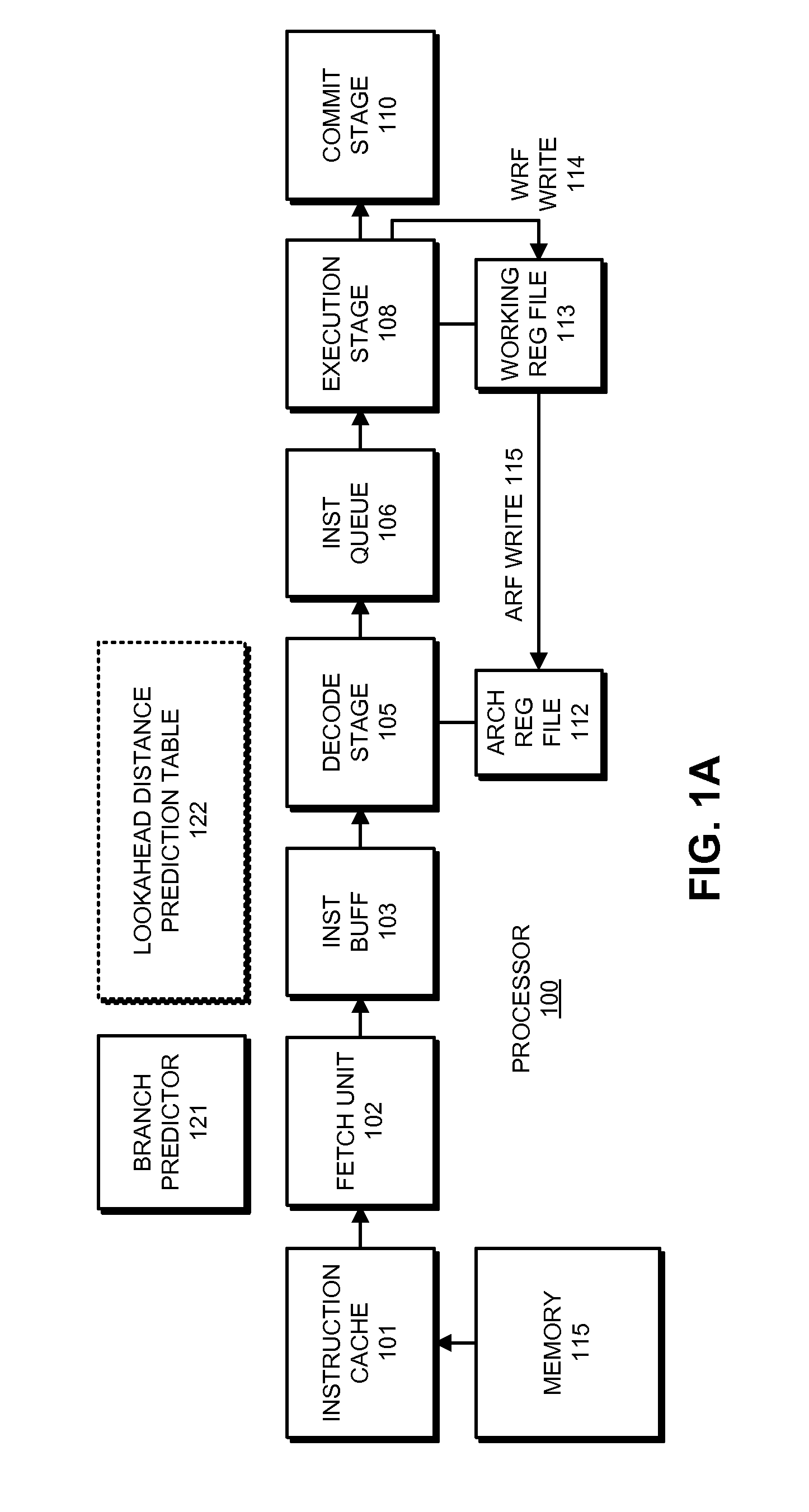
Reducing power consumption and resource utilization during miss lookahead
ActiveUS20130124829A1Eliminate needEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsProgram instructionResource utilization
The disclosed embodiments relate to a system that executes program instructions on a processor. During a normal-execution mode, the system issues instructions for execution in program order. Upon encountering an unresolved data dependency during execution of an instruction, the system speculatively executes subsequent instructions in a lookahead mode to prefetch future loads. While executing in the lookahead mode, if the processor determines that the lookahead mode is unlikely to uncover any additional outer-level cache misses, the system terminates the lookahead mode. Then, after the unresolved data dependency is resolved, the system recommences execution in the normal-execution mode from the instruction that triggered the lookahead mode.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
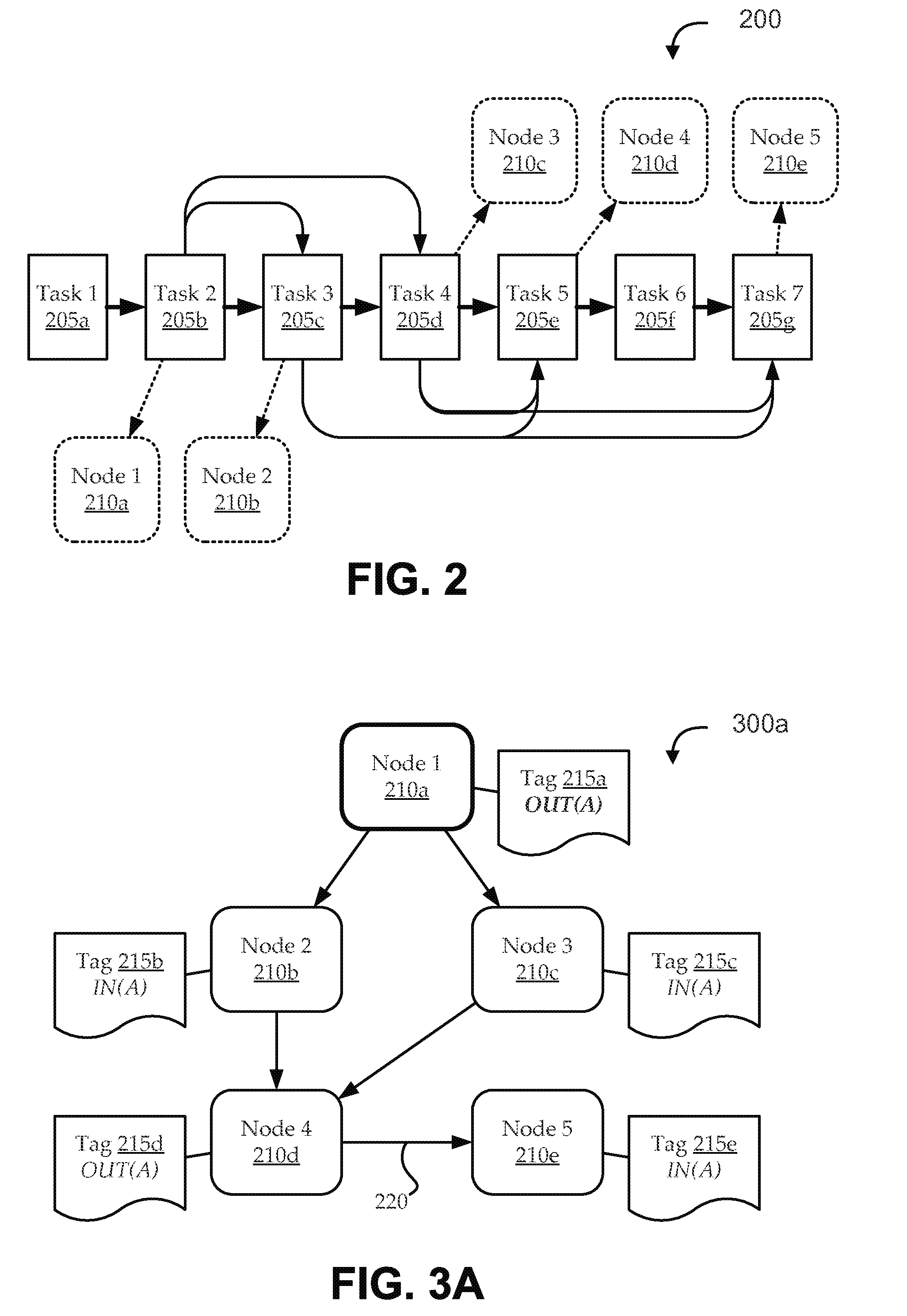
Runtime handling of task dependencies using dependence graphs
ActiveUS20150268992A1Preserves task dependenciesProgram initiation/switchingMemory systemsTask dependencyRuntime library
Embodiments include systems and methods for handling task dependencies in a runtime environment using dependence graphs. For example, a computer-implemented runtime engine includes runtime libraries configured to handle tasks and task dependencies. The task dependencies can be converted into data dependencies. At runtime, as the runtime engine encounters tasks and associated data dependencies, it can add those identified tasks as nodes of a dependence graph, and can add edges between the nodes that correspond to the data dependencies without deadlock. The runtime engine can schedule the tasks for execution according to a topological traversal of the dependence graph in a manner that preserves task dependencies substantially as defined by the source code.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Data security in a semantic data model
InactiveUS20060149739A1Simple definitionComplete security measuresDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsGranularitySemantic search
A data dependency path calculator for a semantic search engine is provided. A body of semantically related data is modeled according to a semantic data model. A user is presented a list of data elements from which they may select desired data elements. The system automatically calculates all of the possible paths through the database that may be used to retrieve meaningful data based on the selected data elements. The available data dependency paths are returned to the user for selection. The system further provides a type of data permission that allows restricted data elements to be used as a pass-through data element for relating, connecting and retrieving non-restricted data. Thus, a user can use restricted data to create data dependency paths to retrieve meaningful data. The system further provides for defining access privileges for all levels of data structures, allowing data to be secured with an increased level of granularity than previously possible.
Owner:METADATA
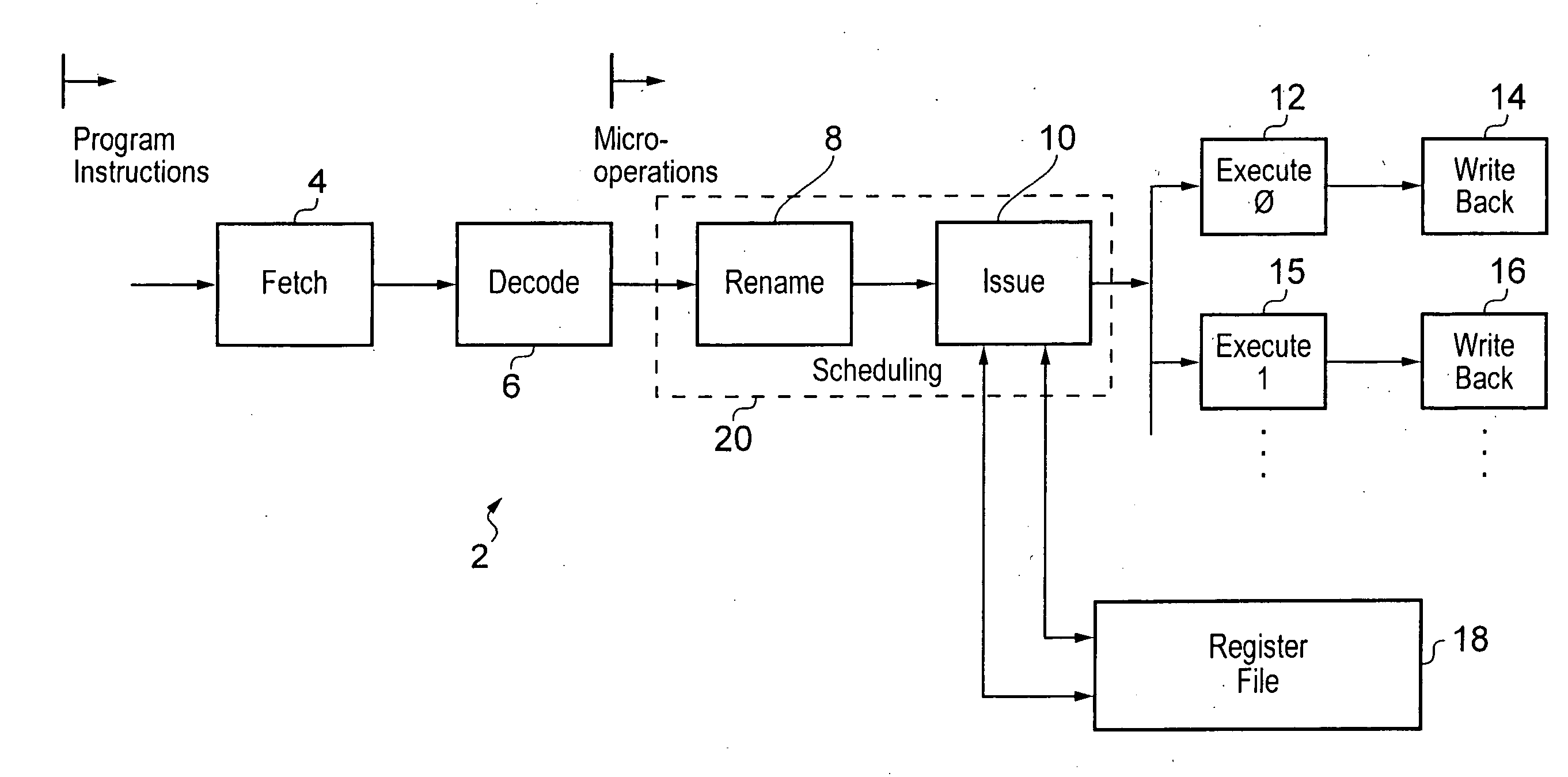
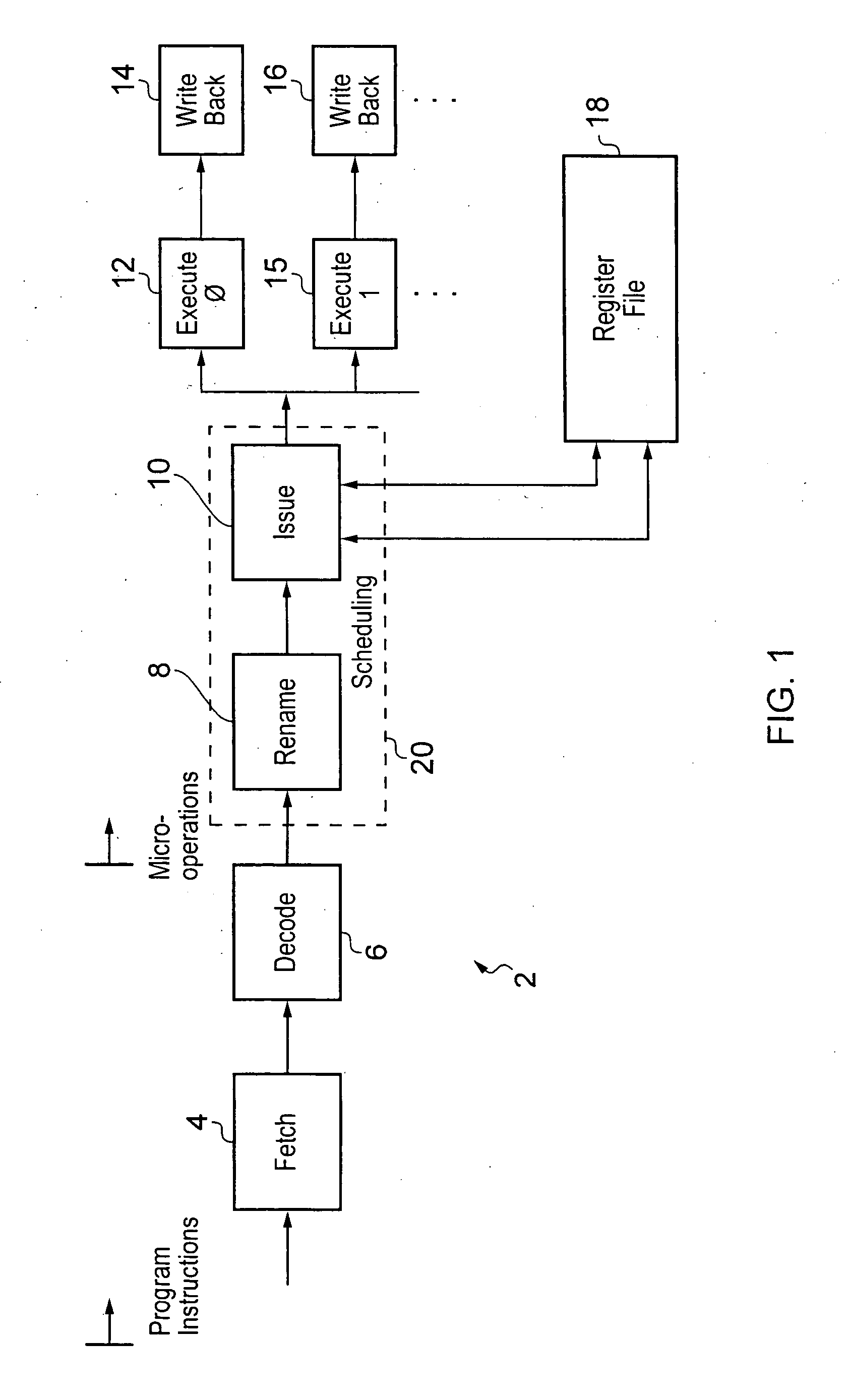
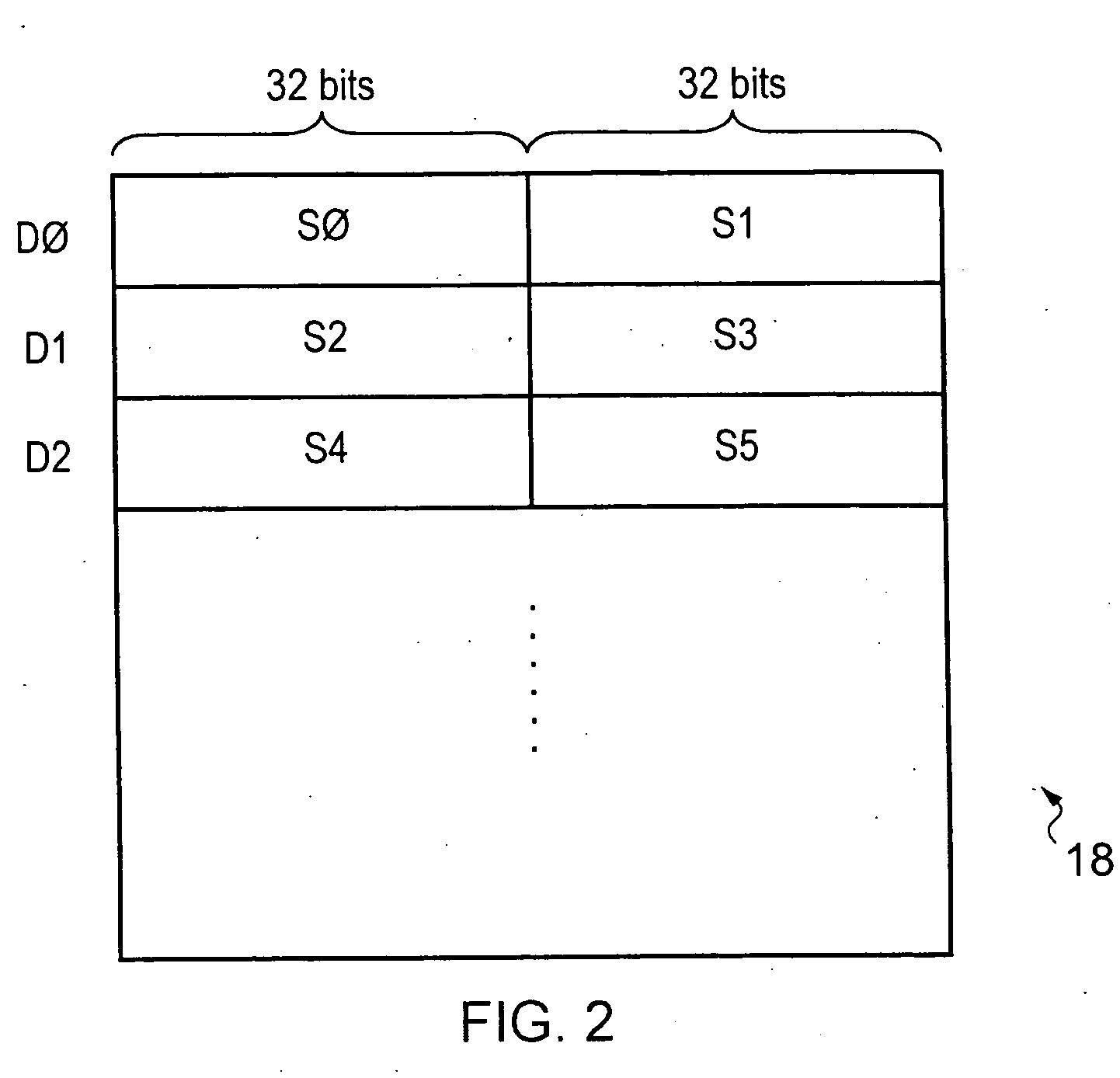
Remapping source Registers to aid instruction scheduling within a processor
ActiveUS20100332805A1Rapidly dealEfficient mechanismInstruction analysisRuntime instruction translationProgram instructionMicro-operation
An out-of-order renaming processor is provided with a register file within which aliasing between registers of different sizes may occur. In this way a program instruction having a source register of a double precision size may alias with two single precision registers being used as destinations of one or more preceding program instructions. In order to track this data dependency the double precision register may be remapped into a micro-operation specifying two single precision registers as its source register. In this way, scheduling circuitry may use its existing hazard detection and management mechanisms to handle potential data hazards and dependencies. Not all program instructions having such data hazards between registers of different sizes are handled by this source register remapping. For these other program instructions a slower mechanism for dealing with the data dependency hazard is provided. This slower mechanism may, for example, be to drain all the preceding micro-operations from the execution pipelines before issuing the micro-operation having the data hazard.
Owner:ARM LTD
Controlling multi-pass rendering sequences in a cache tiling architecture
ActiveUS20170053375A1Optimize arbitrarily complexReduces memory bandwidth consumptionImage memory managementCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsTiled rendering
In one embodiment of the present invention a driver configures a graphics pipeline implemented in a cache tiling architecture to perform dynamically-defined multi-pass rendering sequences. In operation, based on sequence-specific configuration data, the driver determines an optimized tile size and, for each pixel in each pass, the set of pixels in each previous pass that influence the processing of the pixel. The driver then configures the graphics pipeline to perform per-tile rendering operations in a region that is translated by a pass-specific offset backward—vertically and / or horizontally—along a tiled caching traversal line. Notably, the offset ensures that the required pixel data from previous passes is available. The driver further configures the graphics pipeline to store the rendered data in cache lines. Advantageously, the disclosed approach exploits the efficiencies inherent in cache tiling architecture while honoring highly configurable data dependencies between passes in multi-pass rendering sequences.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Issuing instructions with unresolved data dependencies
The described embodiments include a processor that determines instructions that can be issued based on unresolved data dependencies. In an issue unit in the processor, the processor keeps a record of each instruction that is directly or indirectly dependent on a base instruction. Upon determining that the base instruction has been deferred, the processor monitors instructions that are being issued from an issue queue to an execution unit for execution. Upon determining that an instruction from the record has reached a head of the issue queue, the processor immediately issues the instruction from the issue queue.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
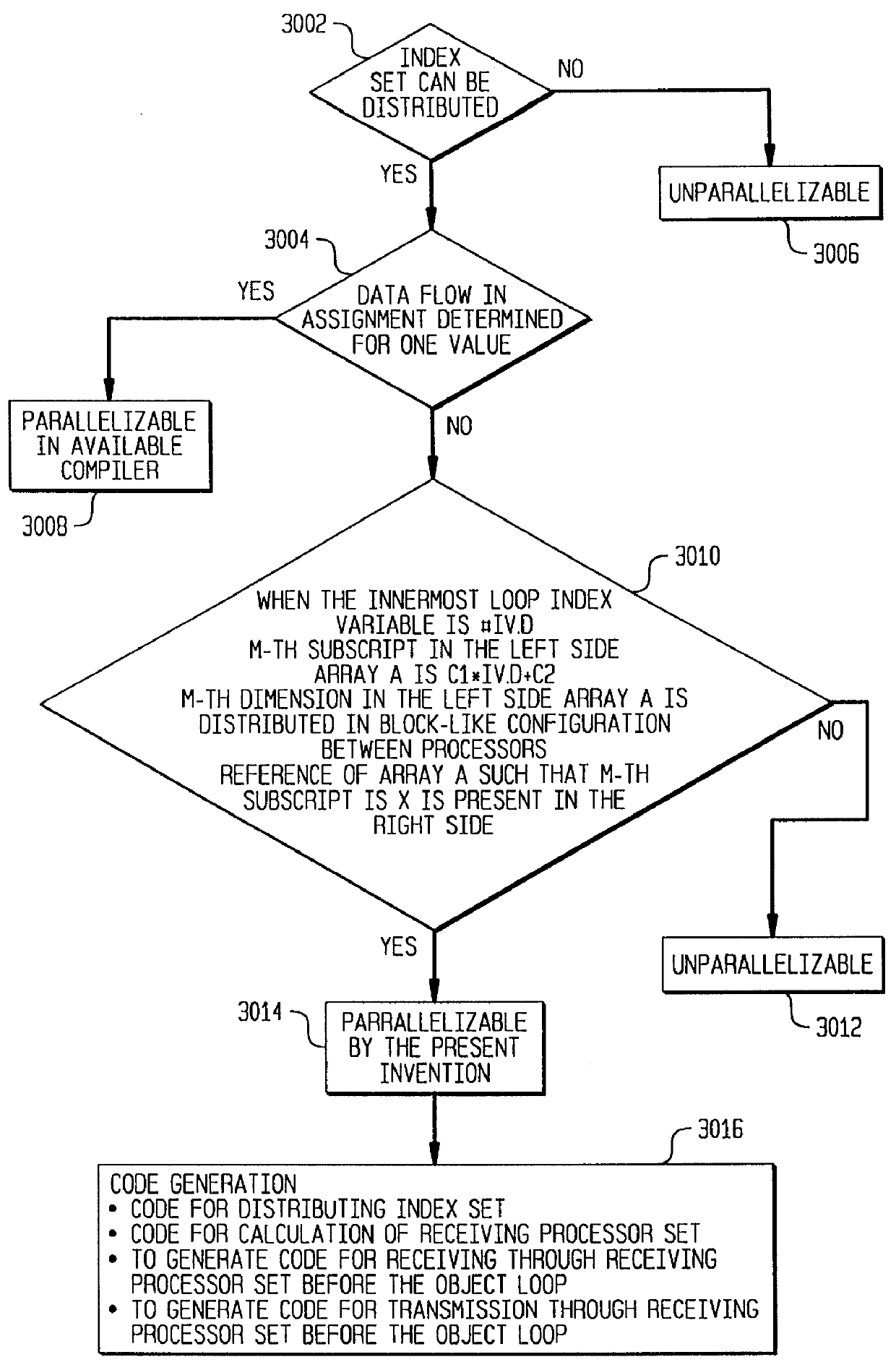
Method and apparatus for compilation of a data parallel language
InactiveUS6016397AReduce processing speedShorten speedProgram control using stored programsSoftware engineeringHuman languageParallel language
A loop having an index set that can be distributed but with data dependency on the right side of an assignment expression that is indefinite can be parallelized. The index set of the loop is distributed to a plurality of processors. A processor set that uses values that are defined before the loop and a processor set using values defined after the loop is calculated. Code is interpolated that enables these processors to engage in communication before and after loops, thereby eliminating communication between processors in the loop and improving the execution speed of the program.
Owner:IBM CORP
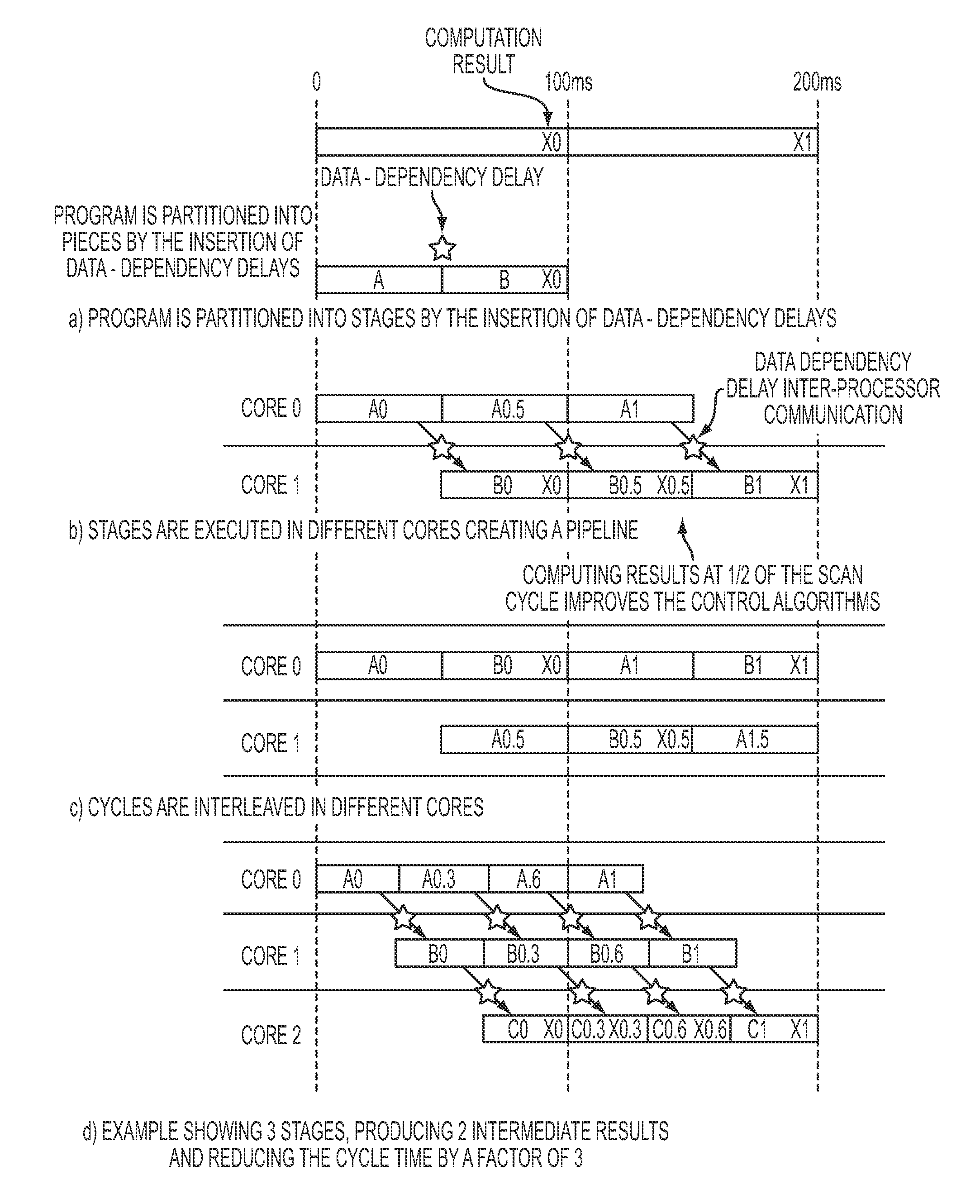
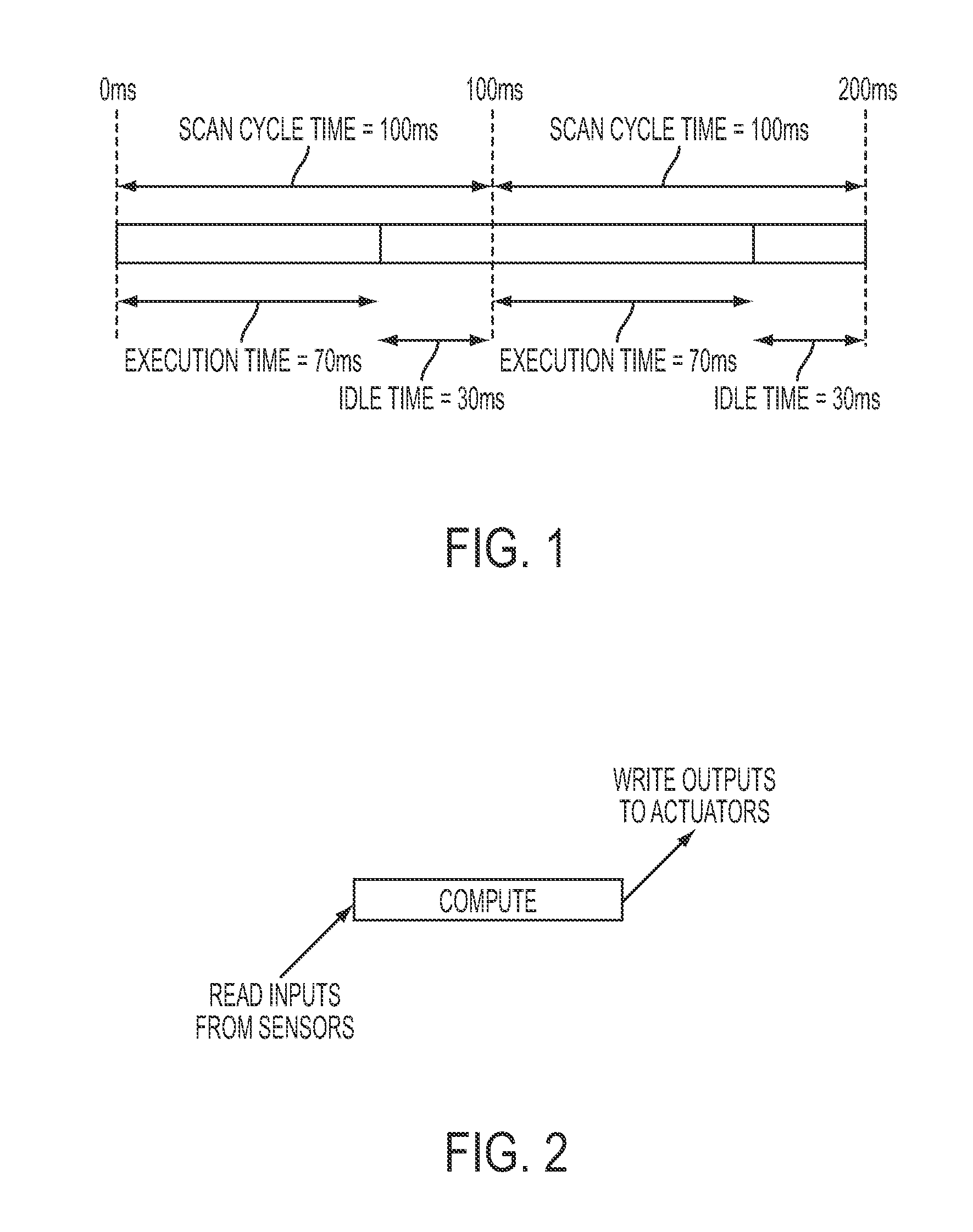
Reducing The Scan Cycle Time Of Control Applications Through Multi-Core Execution Of User Programs
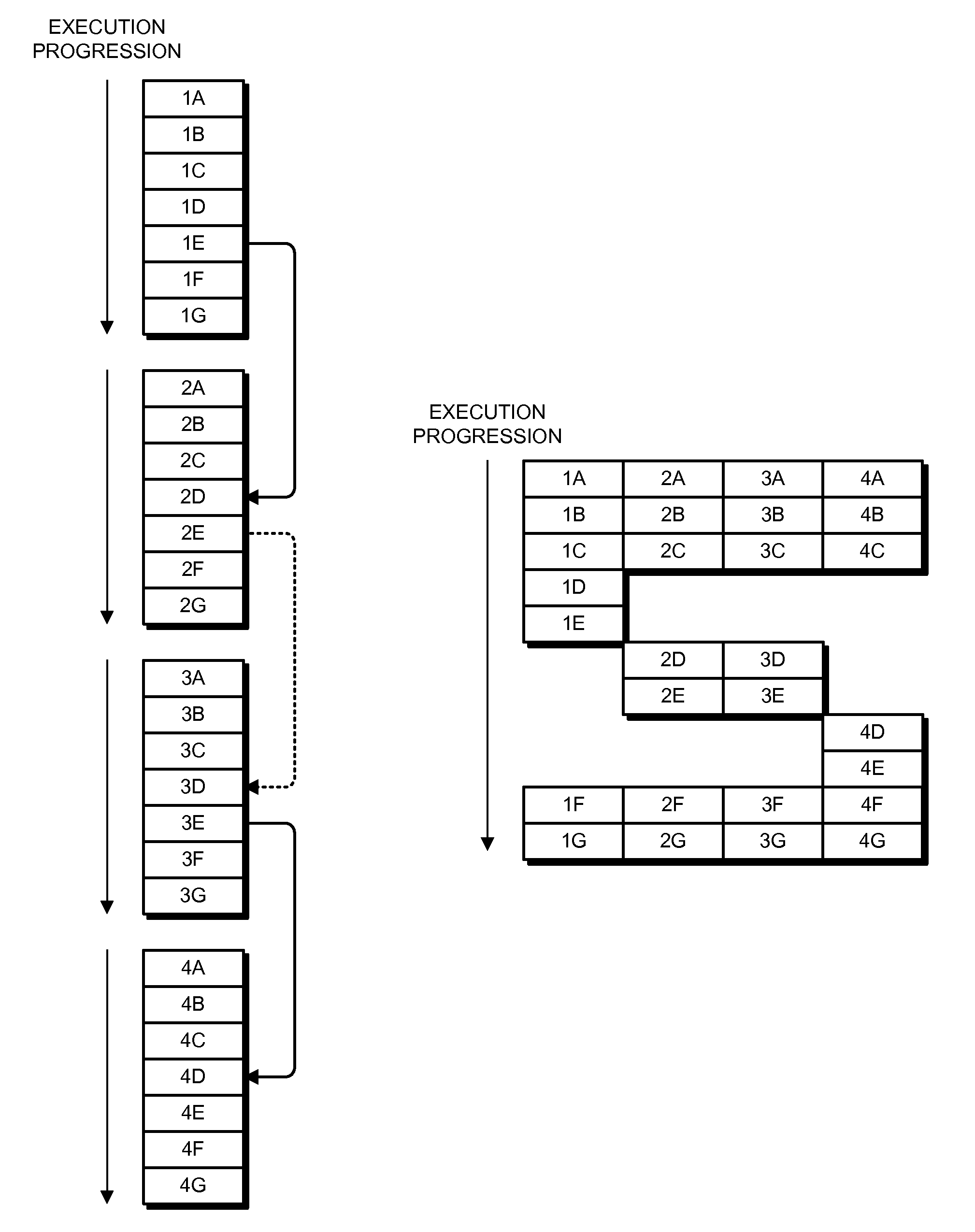
ActiveUS20140165077A1Reducing scan cycle timeShorten cycle timeProgramme controlProgram initiation/switchingData dependency analysisCycle time
A method for pipeline parallelizing a control program for multi-core execution includes using (12) data dependency analysis on a control program to identify tasks that can be performed in parallel, identifying (13) a largest task Tmax requiring the most execution time of the identified tasks, identifying (14) cut-points in the largest task Tmax where data dependency delays decouple the task, inserting (15) delayed data dependencies into cut-points of the largest task Tmax to create N pipeline sub-tasks, in which N is a number of cores available to a processor on which the control program will be executed, and scheduling (16) the tasks and pipeline sub-tasks to the available processor cores.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Modeling trends in crop yields
ActiveUS20170228475A1Character and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationDigital dataCrop yield
A method and system for modeling trends in crop yields is provided. In an embodiment, the method comprises receiving, over a computer network, electronic digital data comprising yield data representing crop yields harvested from a plurality of agricultural fields and at a plurality of time points; in response to receiving input specifying a request to generate one or more particular yield data: determining one or more factors that impact yields of crops that were harvested from the plurality of agricultural fields; decomposing the yield data into decomposed yield data that identifies one or more data dependencies according to the one or more factors; generating, based on the decomposed yield data, the one or more particular yield data; generating forecasted yield data or reconstructing the yield data by incorporating the one or more particular yield data into the yield data.
Owner:THE CLIMATE CORP
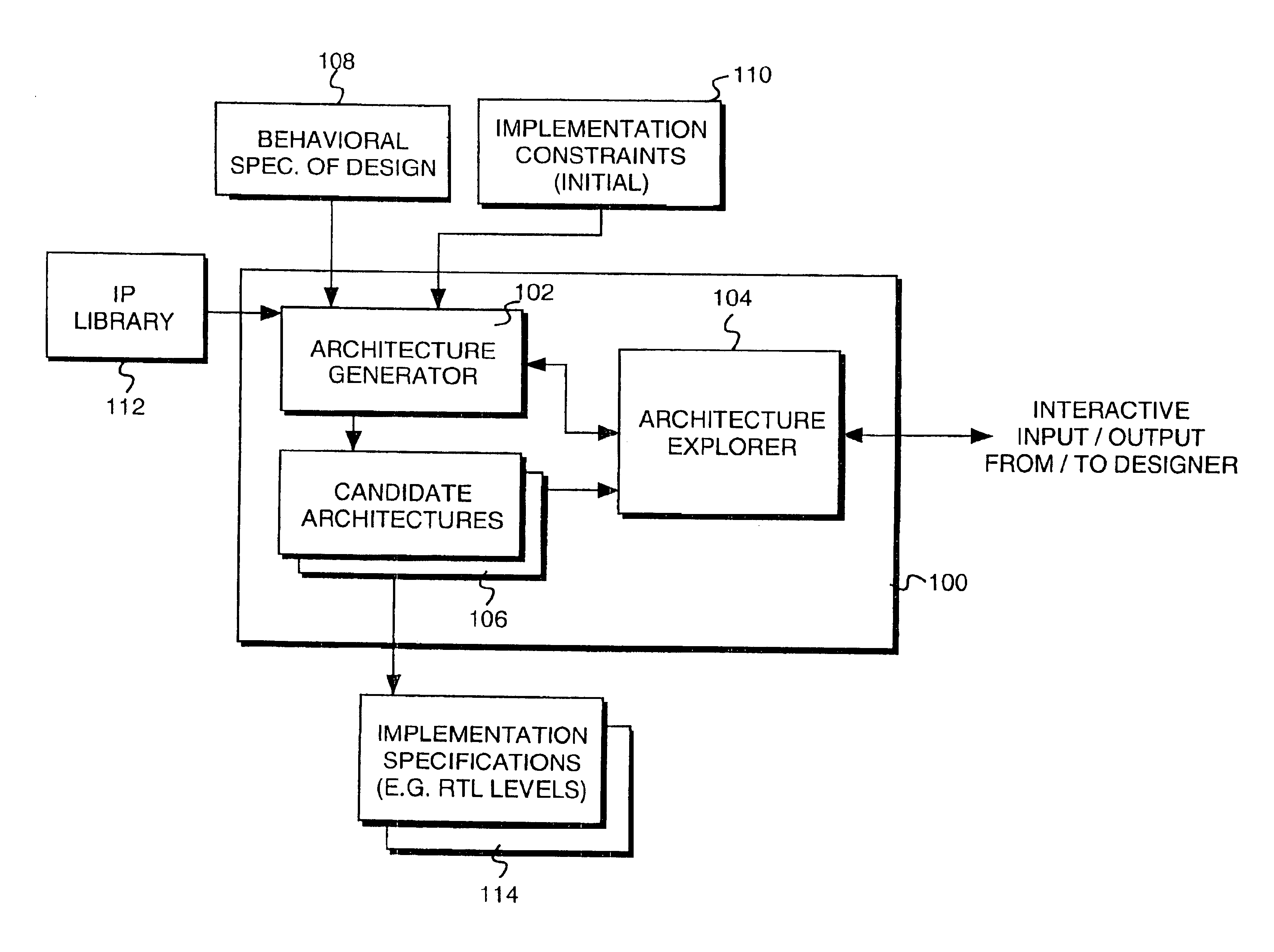
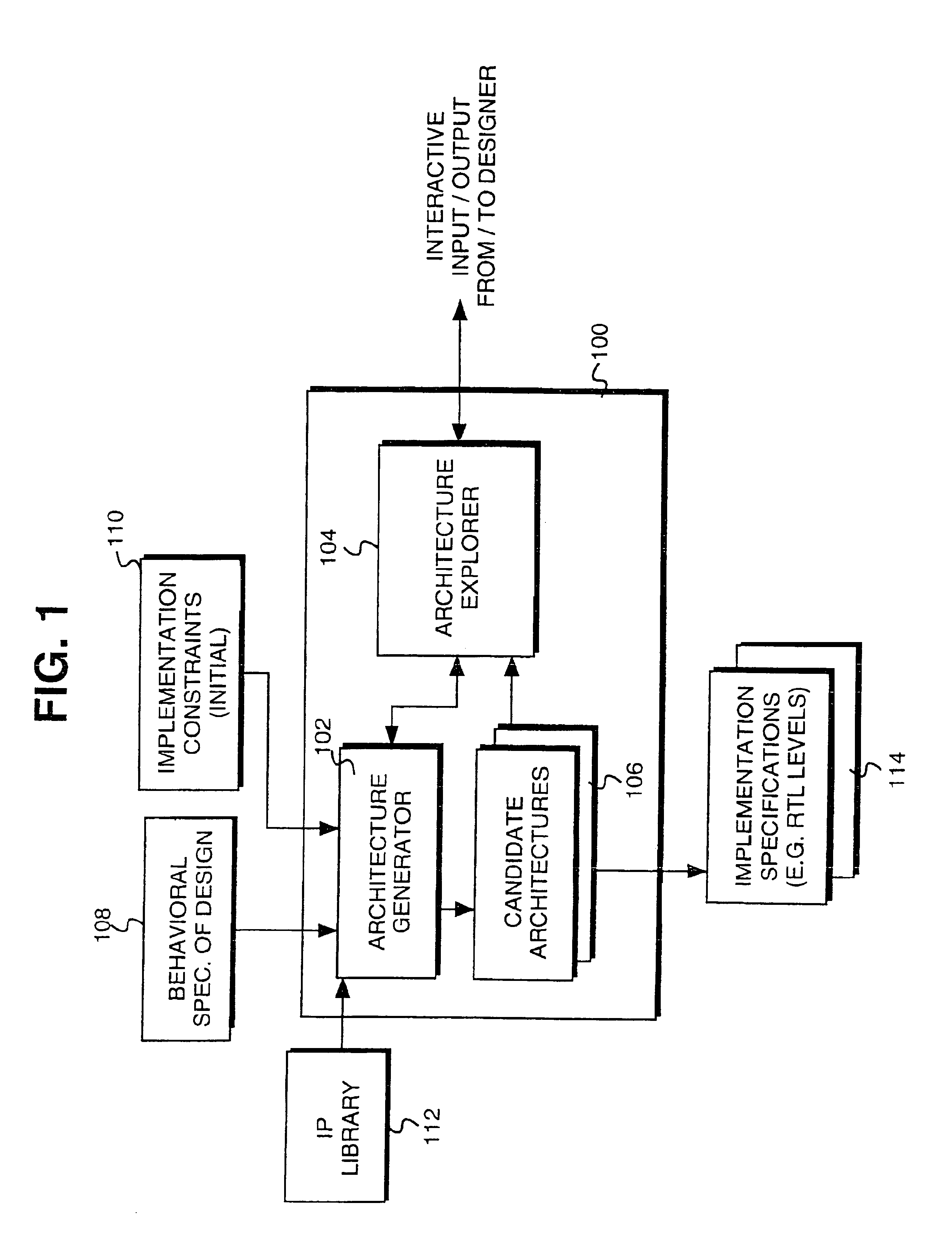
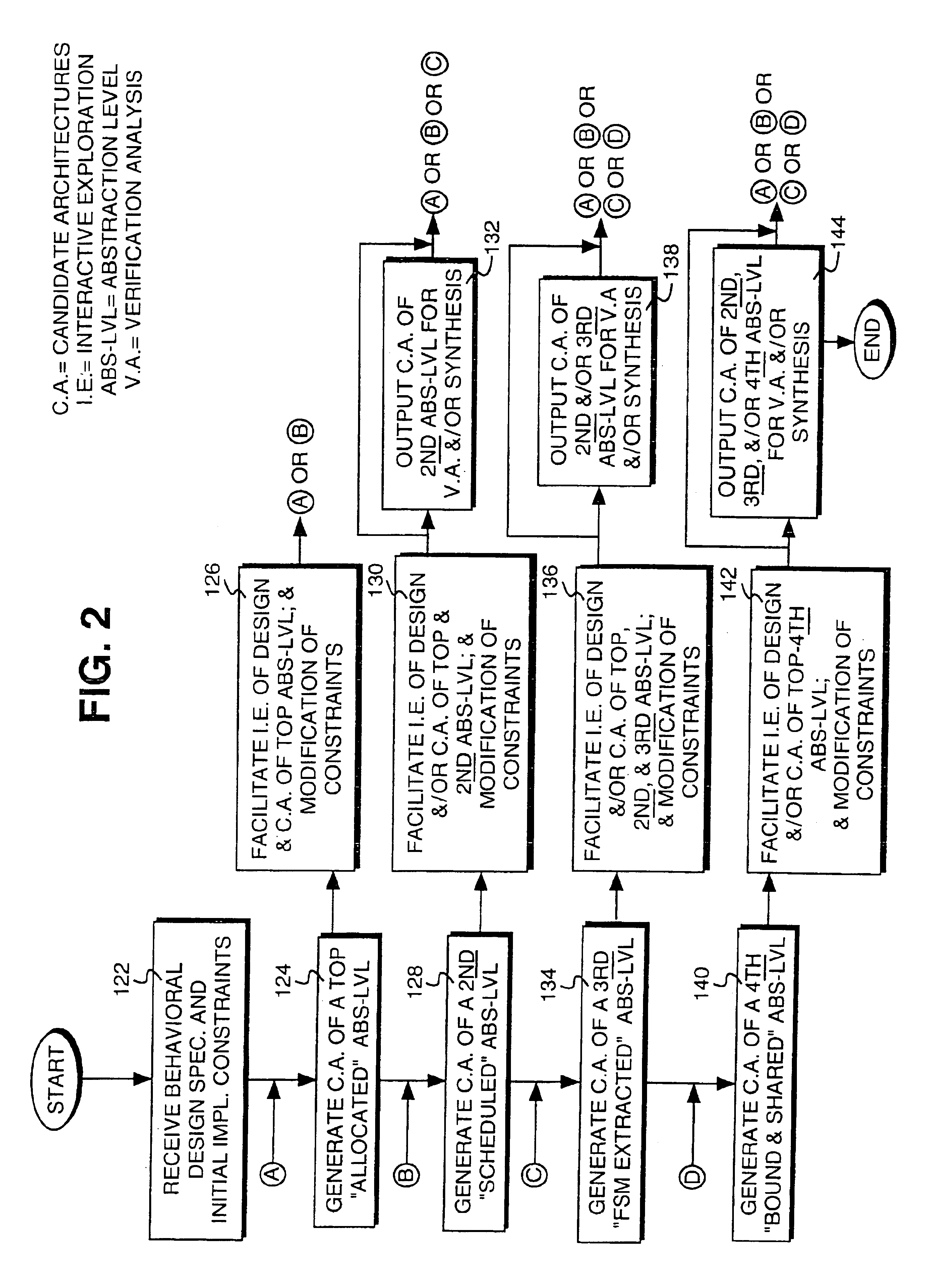
Facilitating guidance provision for an architectural exploration based design creation process
InactiveUS6917909B1To offer comfortComputation using non-denominational number representationCAD circuit designGraphicsGantt chart
Guidance provision to the creation of an electronic design is facilitated through a method that includes facilitating interactive exploration of the electronic design by a designer to aid the designer in formulating his / her guidance, and facilitating the designer in interactively providing the formulated guidance. In one embodiment, facilitation of interactive exploration by the designer include facilitating interactive cross-probing into a number of issues about the design, including generated candidate architectures for the design. In one embodiment, the issues available for cross probing include inter-dependencies of data and mobility of operations of the design, as well as occupation of hardware resources for the generated candidate architectures. In one embodiment, Gantt diagrams are employed to facilitate navigation by the designer in performing the interactive cross probing. Gantt diagrams graphically representing the generated candidate architectures are selectively presented to the designer. Data dependencies may be graphically depicted on the Gantt diagrams. Additionally, various aspects of the generated candidate architectures may be correlated back to the behavioral specification of the electronic design for the designer. In one embodiment, the designer may also modified the constraints on the electronic design interactively, applying the information the designer learned through the interactive exploration.
Owner:MENTOR GRAPHICS CORP
Data dependency detection using history table of entry number hashed from memory address
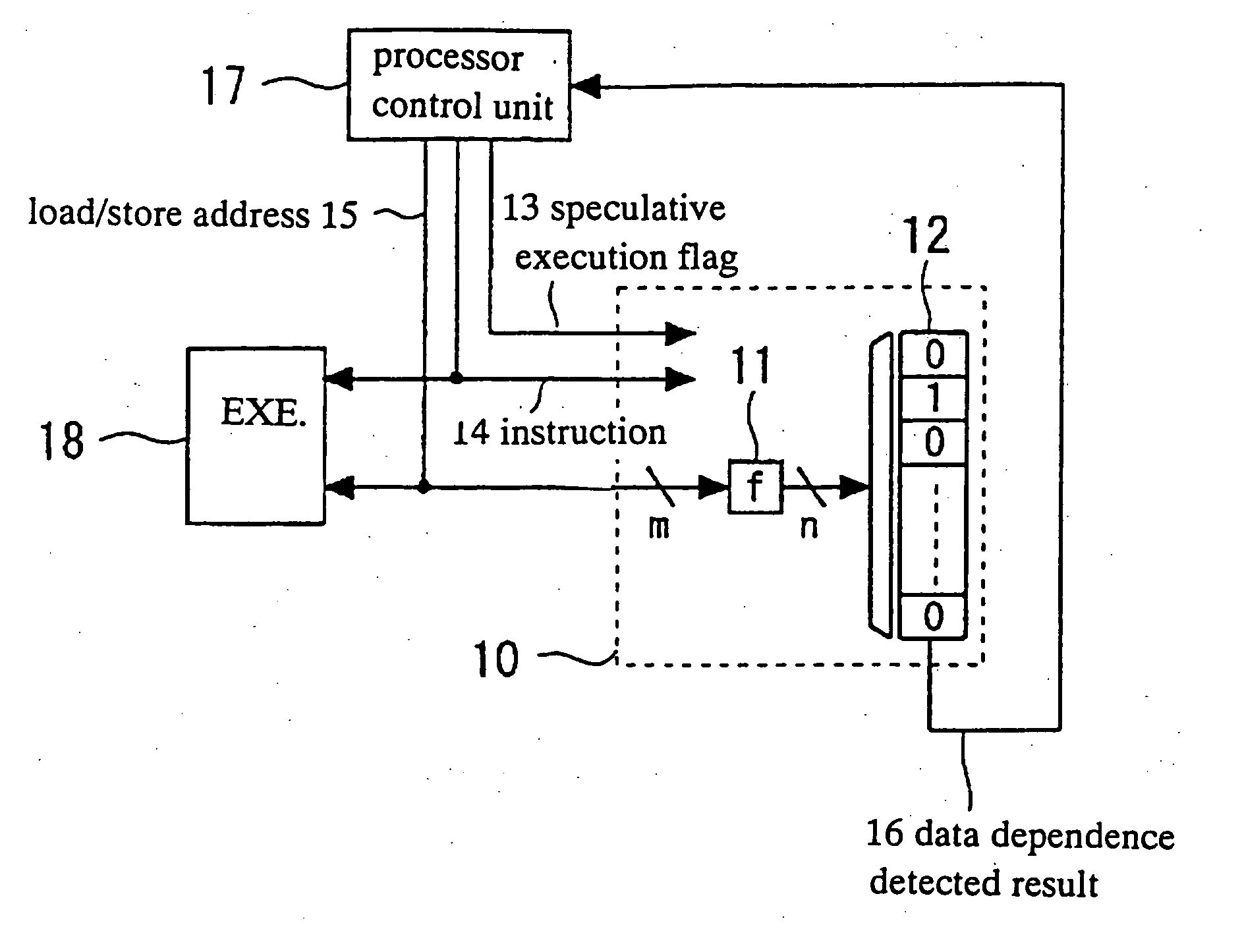
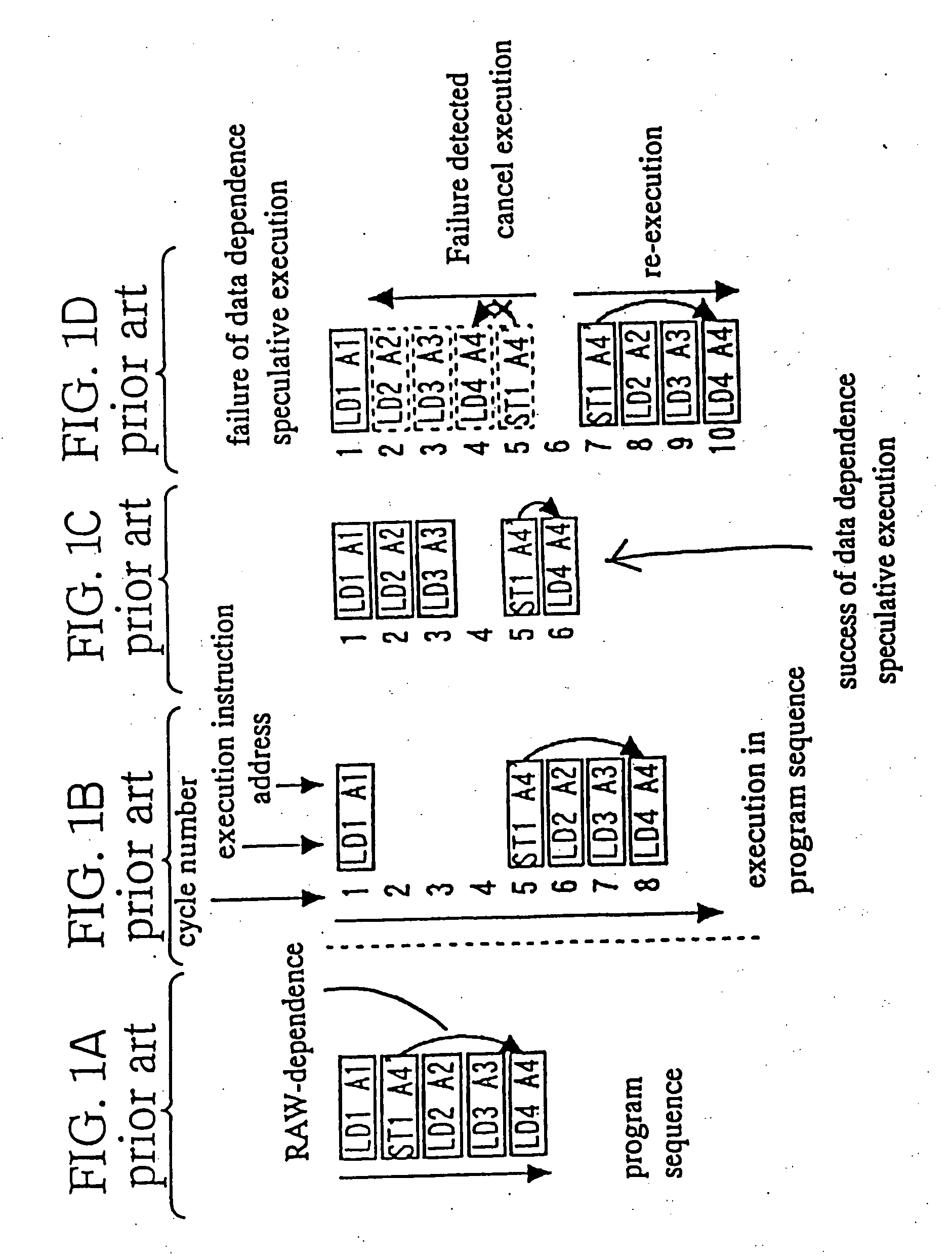
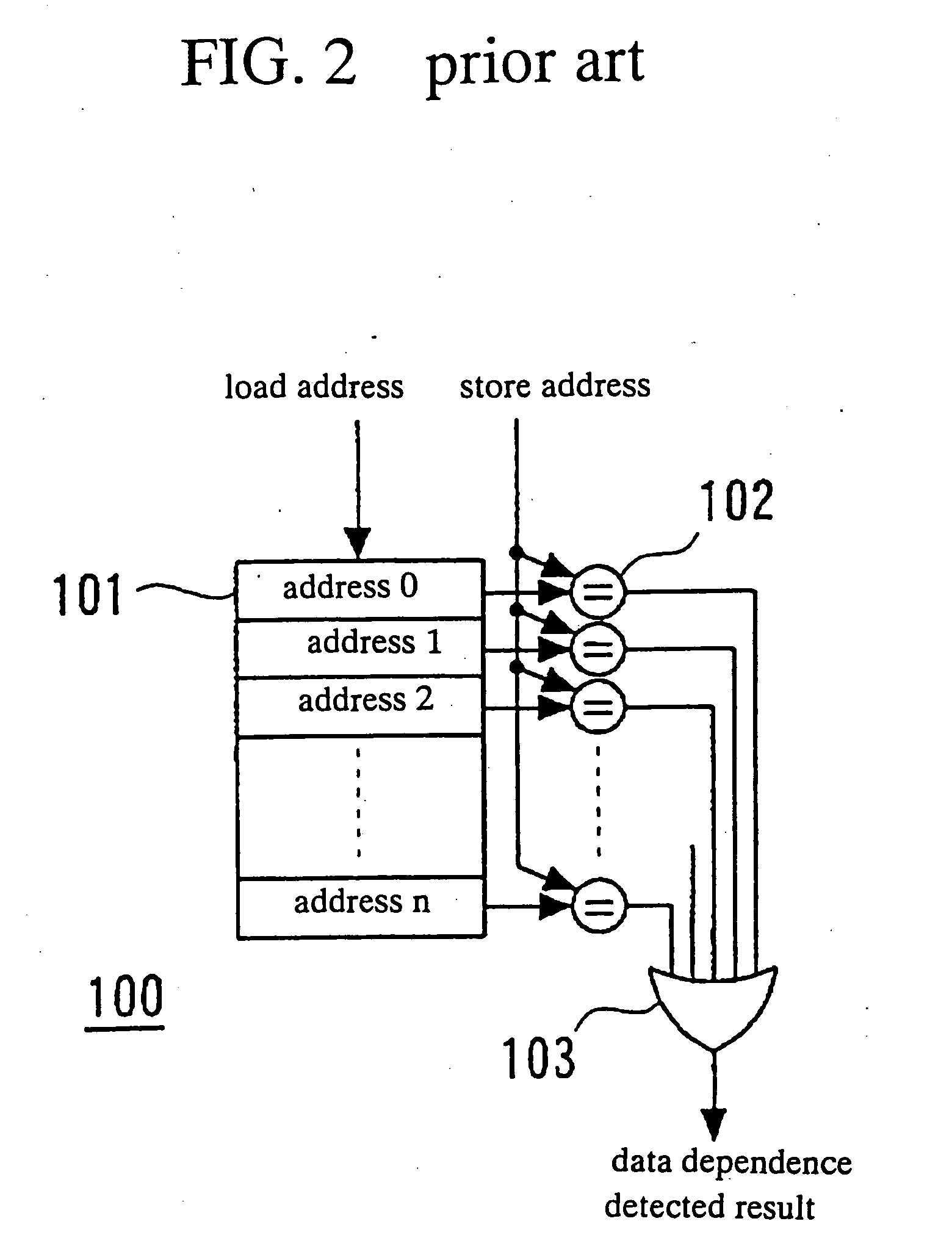
InactiveUS20050216705A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsProgramming languageMemory address
A detector detects at least one kind of dependence in address between instructions executed by at least a processor, the detector being adopted to detect a possibility of presence of the at least one kind of dependence, wherein if the at least one kind of dependence is present in fact, then the detector detects a possibility of presence of the at least one kind of dependence, and if the at least one kind of dependence is not present in fact, then the detector may detect a pseudo presence of the at least one kind of dependence. The detector has an execution history storing unit with a plurality of entries and an address converter for converting an address of a memory access instruction into an entry number, where different addresses may be converted into entry numbers that are the same.
Owner:NEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com