Direction-of-arrival estimation method based on nested subarray array
A direction-of-arrival estimation and formula technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve the problems of limited transmission power, degree of freedom and array aperture reduction, etc., and achieve the effects of easy change of positions, strong angle resolution, and convenient mass production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
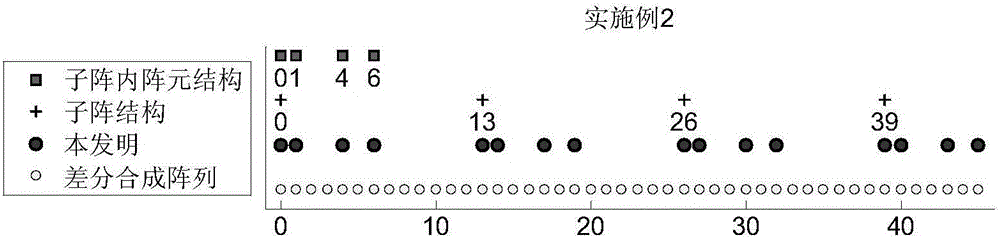
Embodiment 1
[0046] In the first embodiment, the sub-array structure and the inner element structure of the sub-array both adopt the uniform linear array ULA structure to estimate the direction of arrival of the nested sub-array array.
[0047] Step 1. Given the total number of elements S, construct the sub-array structure and the element structure in the sub-array.
[0048] The non-uniform array structure in the prior art includes three: one is the minimum redundant array MRA, the structure of which is to obtain the minimum redundant sequence and the minimum redundant array MRA according to the total number of array elements S; the second is the embedded The structure of the nested array NA is to obtain the nesting level of the array according to the total number of array elements S, and then determine the number of array elements on each level according to the nesting level, so as to obtain the array structure of the nested array NA; The three are the coprime array CA, the structure of which ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] In Embodiment 2, the sub-array structure adopts a uniform linear array ULA structure, and the inner element structure of the sub-array adopts a nested sub-array array with a minimum redundant array MRA structure to estimate the direction of arrival of the nested sub-array.
[0113] The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that the structure of the sub-array and the structure of the element in the sub-array are different in step 1, and the other steps are the same as in the first embodiment. The steps for constructing the sub-array structure and the structure of the element in the sub-array are as follows:
[0114] (1a) Given the total number of elements S, factorize S to obtain the number of elements M and the number of subarrays N:
[0115] S=M·N,
[0116] Among them, the values of M and N are the closest, and M≥2, N≥2;
[0117] (1b) According to the number M of the element in the sub-array, the structure of the element in the sub-array is desig...
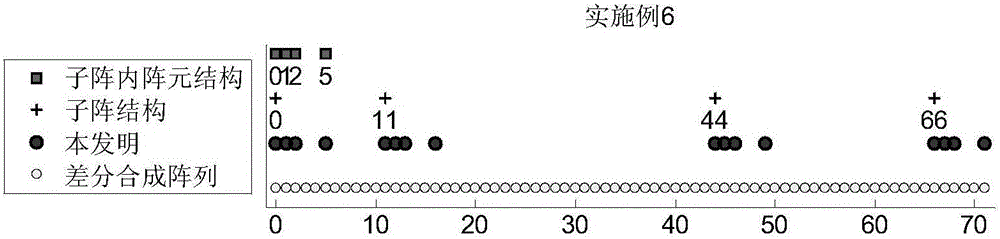
Embodiment 3
[0129] In Embodiment 3, the sub-array structure adopts the uniform linear array ULA structure, and the inner element structure of the sub-array adopts the nested linear array NA structure to estimate the direction of arrival of the nested sub-array array.
[0130] The difference between the third embodiment and the first embodiment is that the structure of the sub-array and the structure of the element in the sub-array are different in step 1, and the other steps are the same as in the first embodiment. The steps for constructing the sub-array structure and the structure of the element in the sub-array are as follows:
[0131] 1-a) Given the total number of array elements S, factorize S to obtain the number of elements M and the number of sub-arrays N:
[0132] S=M·N,
[0133] Among them, the values of M and N are the closest, and M≥2, N≥2;
[0134] 1-b) According to the number M of the elements in the sub-array, the structure of the elements in the sub-array is designed to be the sam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com