Patents
Literature
618 results about "Gain setting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The gain setting is the amount of input voltage which will cause the amplifier to reach maximum power. Notice how much quicker the power goes toward clipping when the gain value is set at lower values. Remember that the gain tells you how much input voltage will cause the output to be driven to clipping.
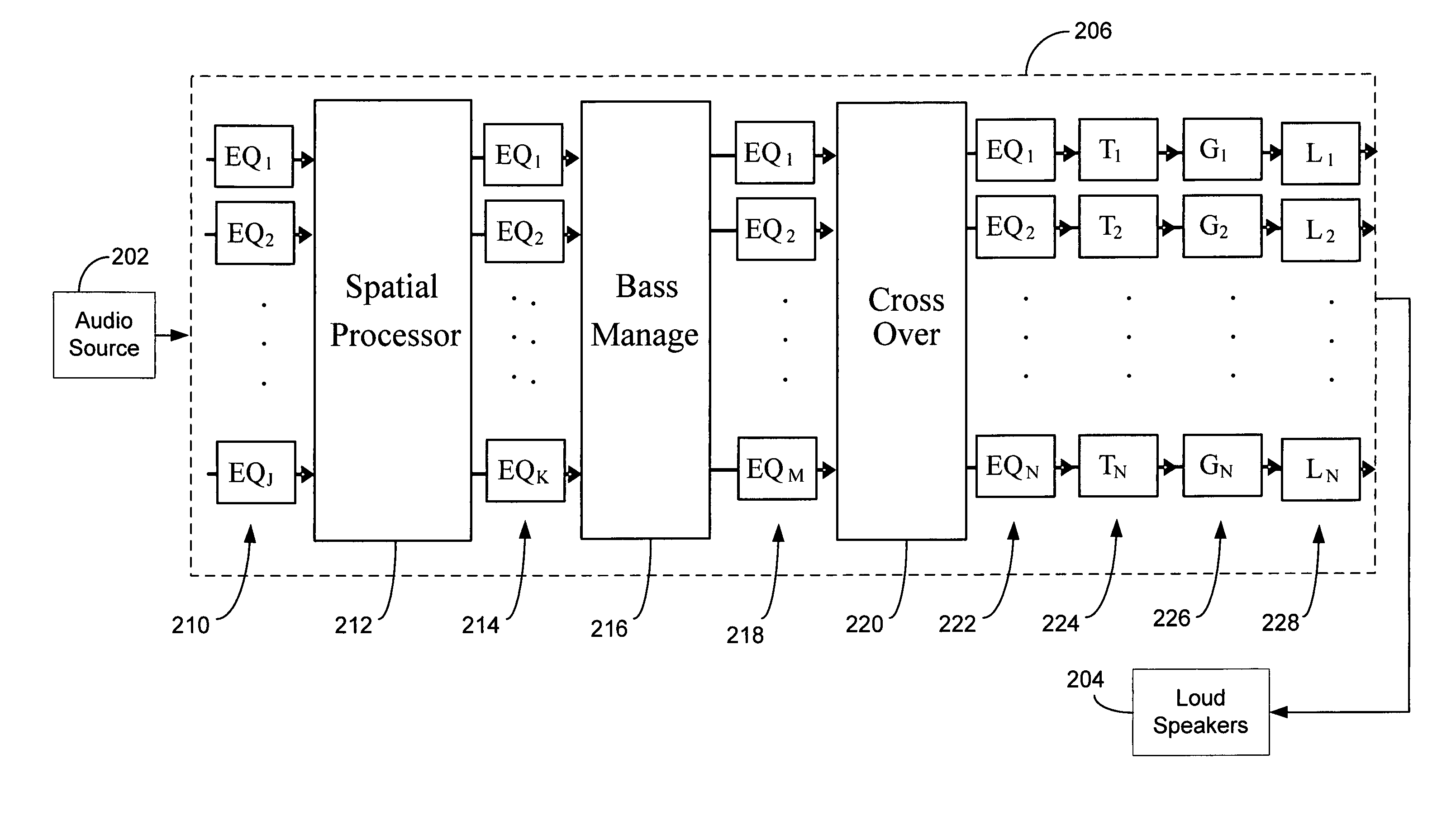
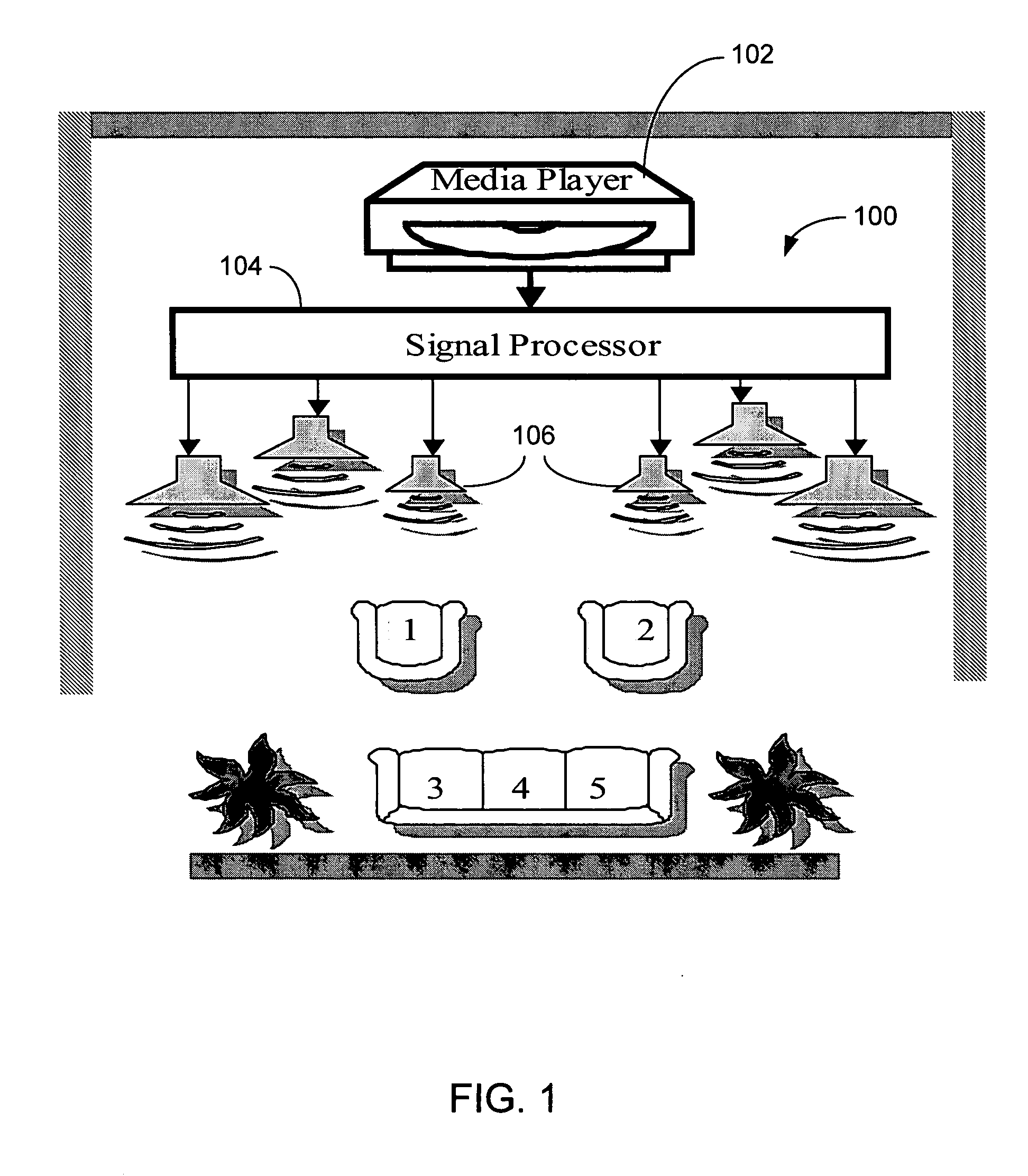
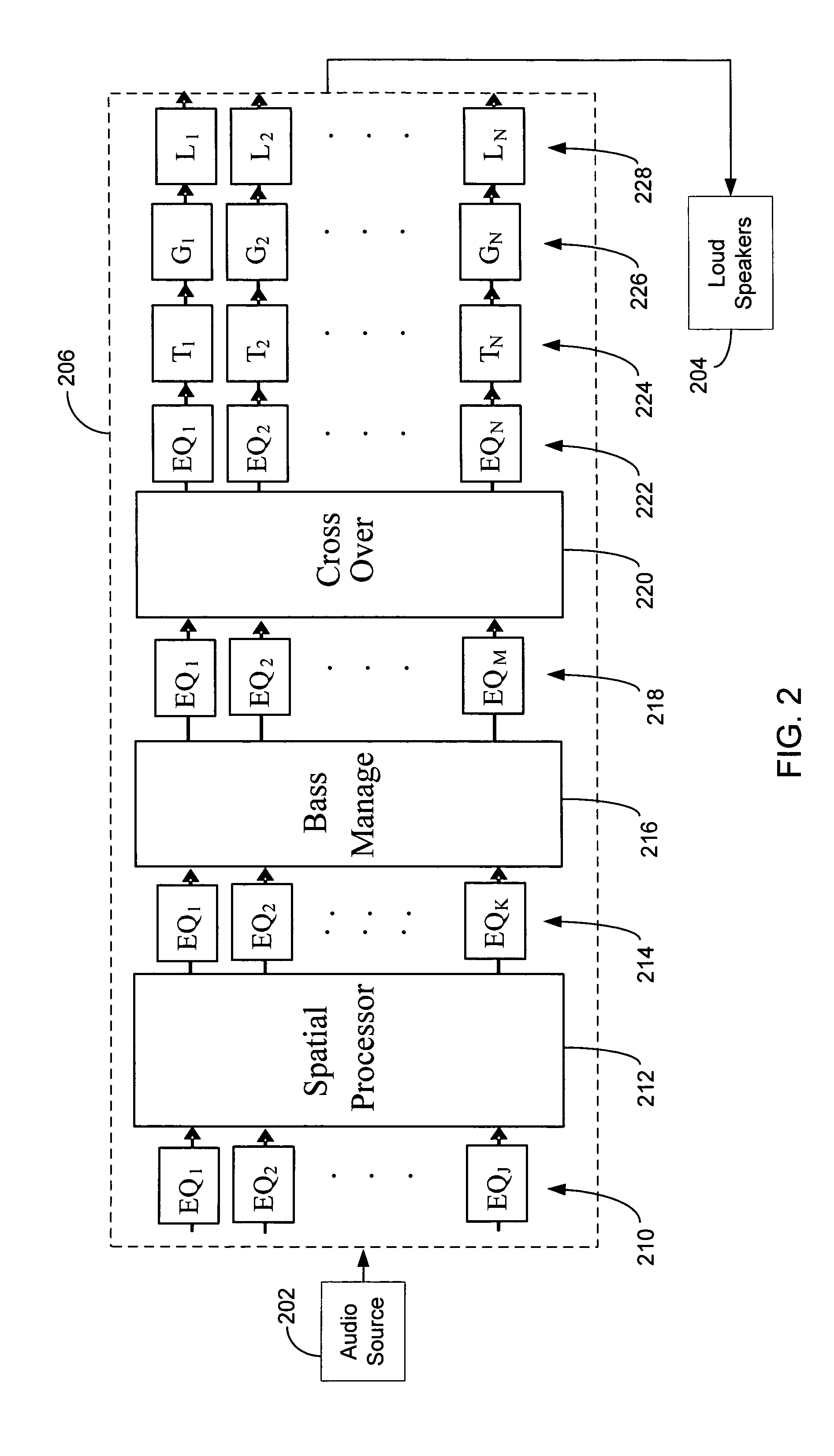
Audio tuning system
An audio system installed in a listening space may include a signal processor and a plurality of loudspeakers. The audio system may be tuned with an automated audio tuning system to optimize the sound output of the loudspeakers within the listening space. The automated audio tuning system may provide automated processing to determine at least one of a plurality of settings, such as channel equalization settings, delay settings, gain settings, crossover settings, bass optimization settings and group equalization settings. The settings may be generated by the automated audio tuning system based on an audio response produced by the loudspeakers in the audio system. The automated tuning system may generate simulations of the application of settings to the audio response to optimize tuning.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
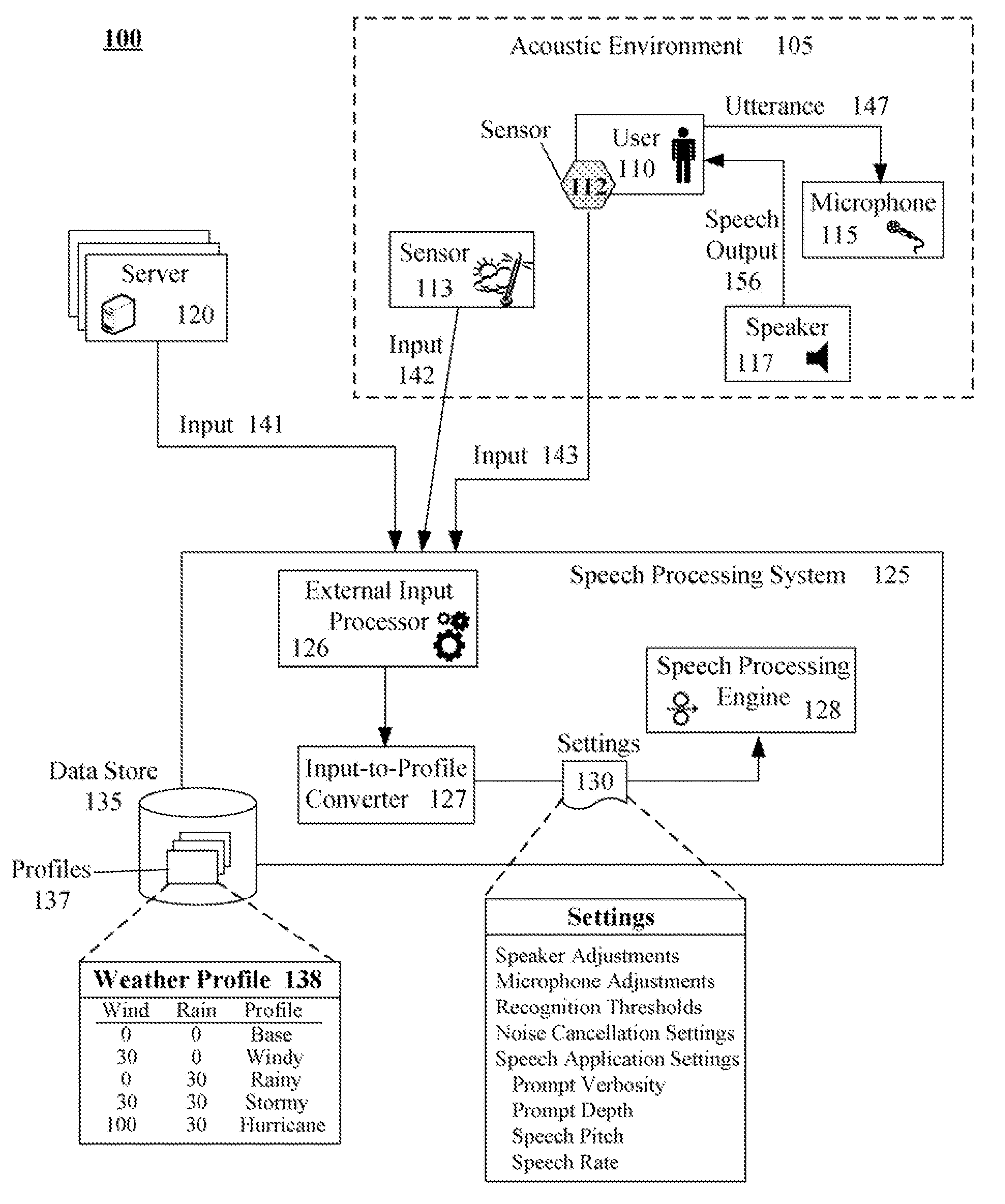
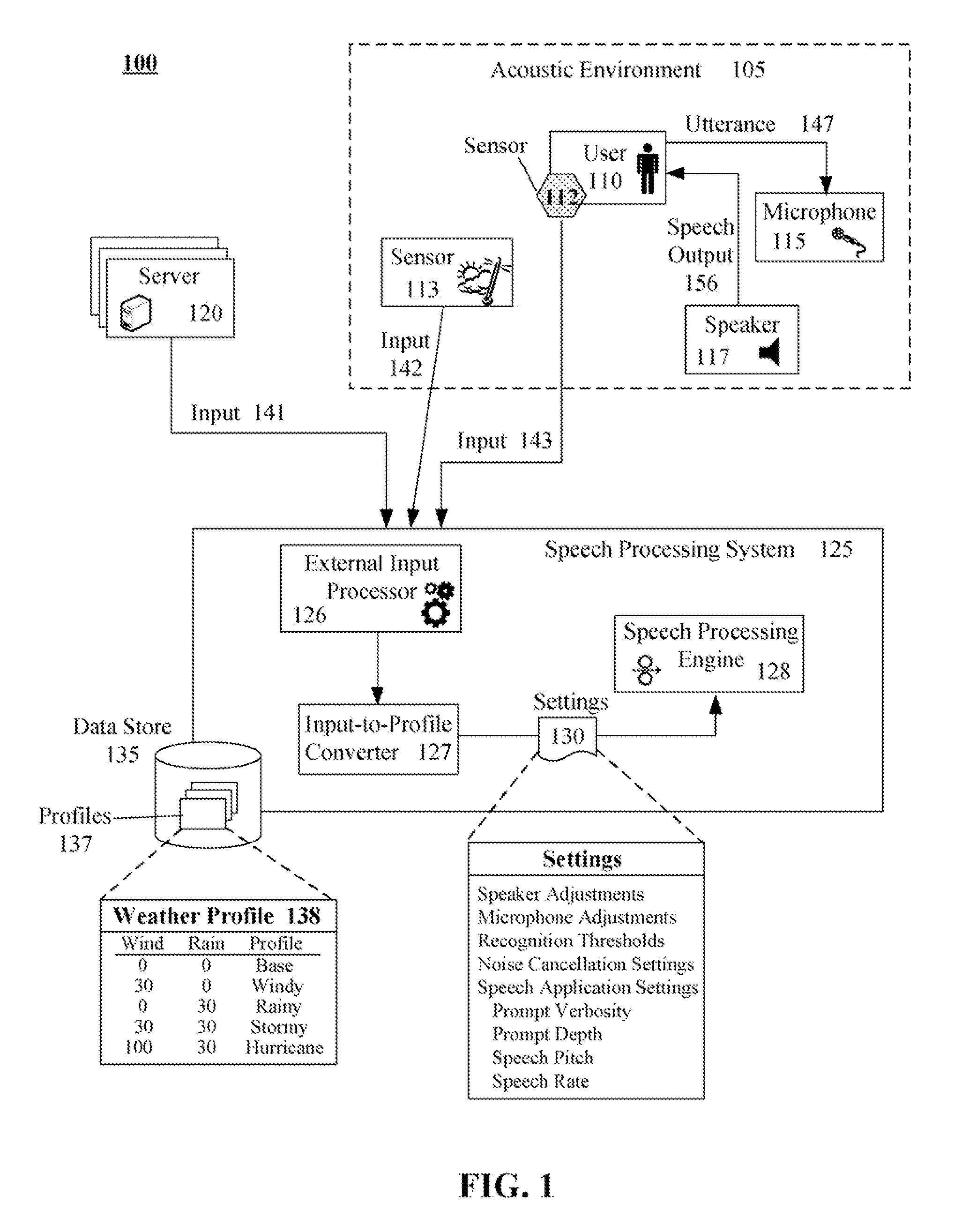
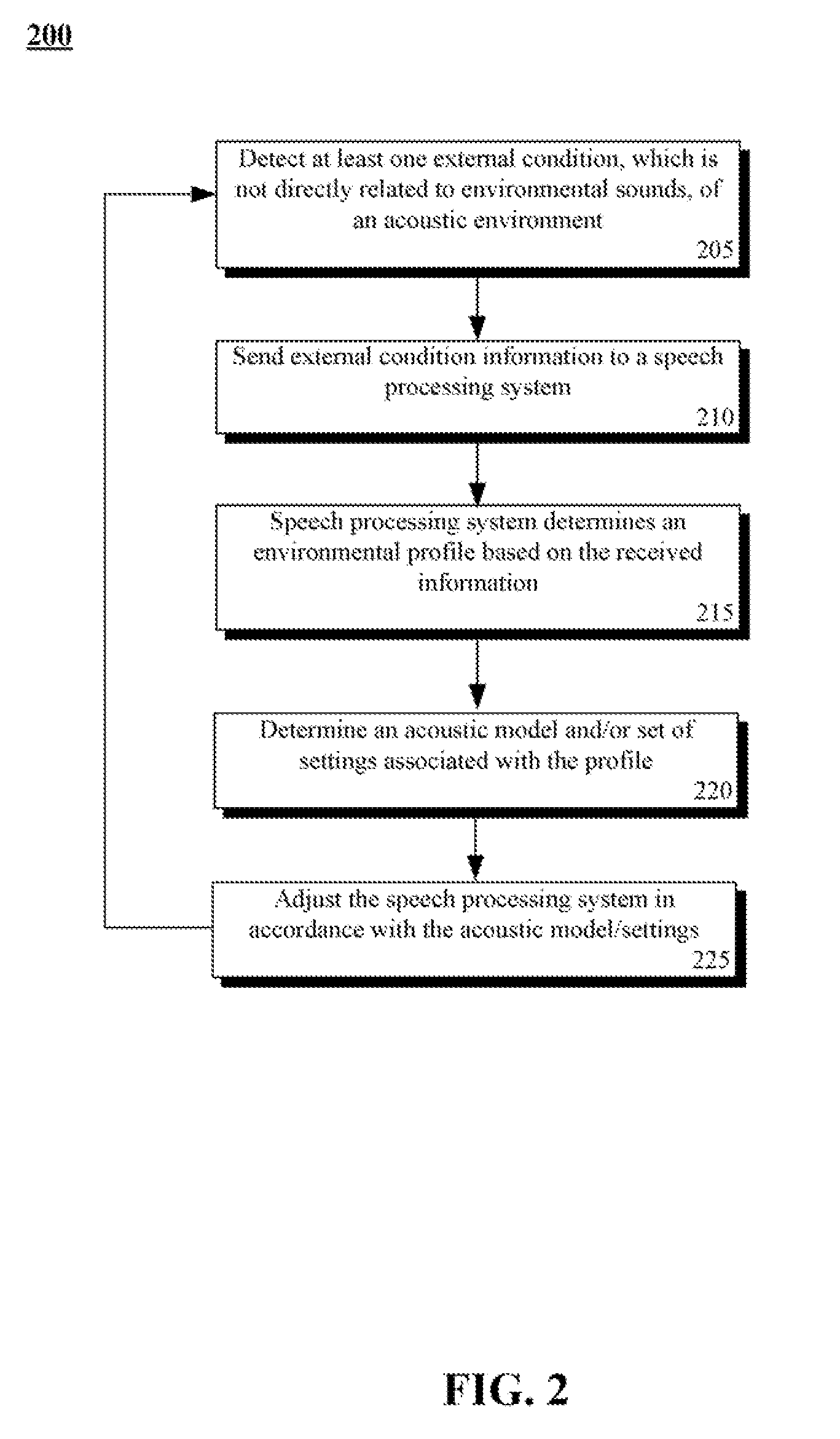
Adaptation of a speech processing system from external input that is not directly related to sounds in an operational acoustic environment
InactiveUS20080147411A1Improve system performanceImprove performanceSpeech recognitionFilter algorithmTransducer
A speech processing system that performs adaptations based upon non-sound external input, such as weather input. In the system, an acoustic environment can include a microphone and speaker. The microphone / speaker can receive / produce speech input / output to / from a speech processing system. An external input processor can receive non-sound input relating to the acoustic environment and to match the received input to a related profile. A setting adjustor can automatically adjust settings of the speech processing system based upon a profile based upon input processed by the external input processor. For example, the settings can include customized noise filtering algorithms, recognition confidence thresholds, output energy levels, and / or transducer gain settings.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
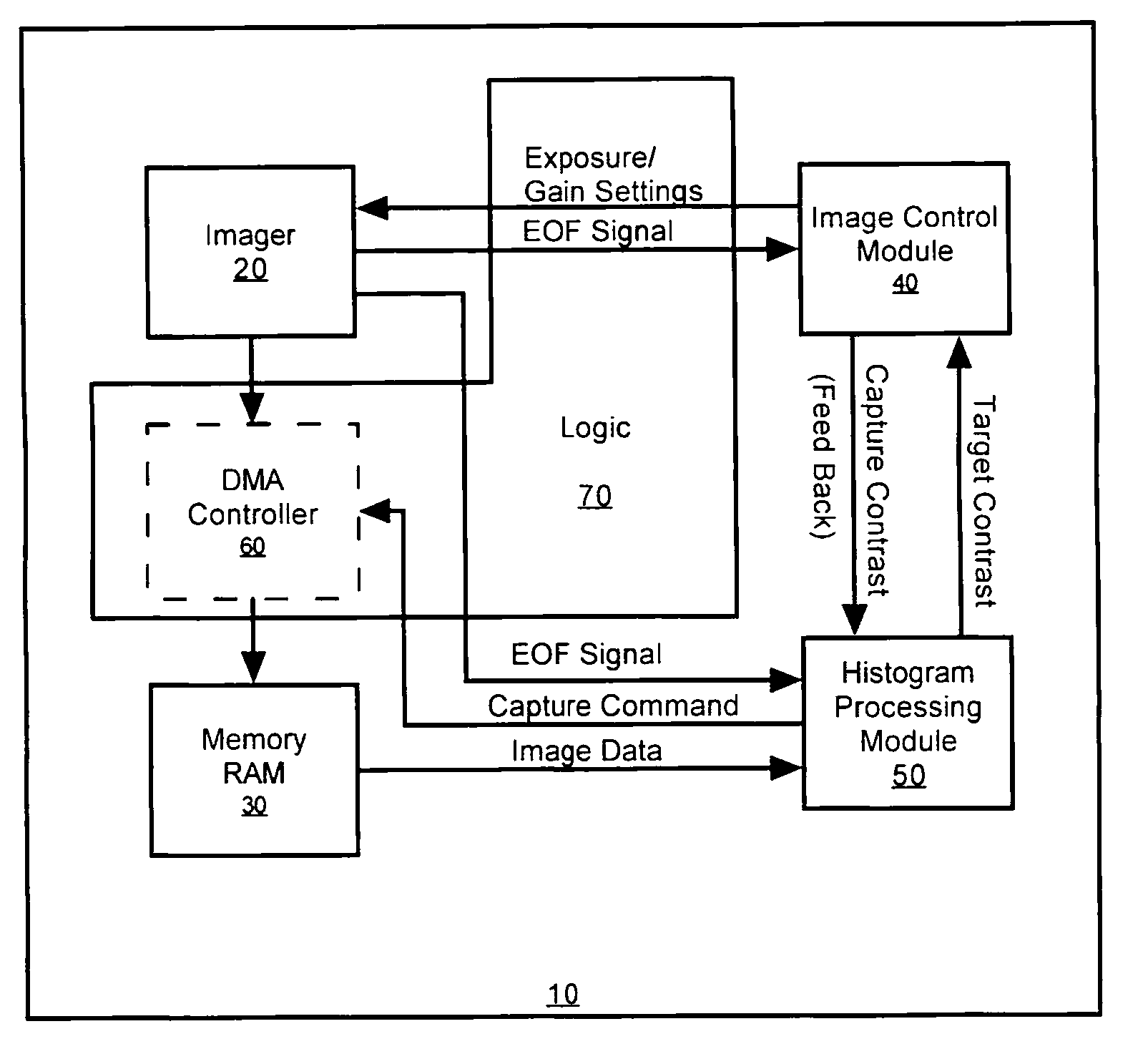
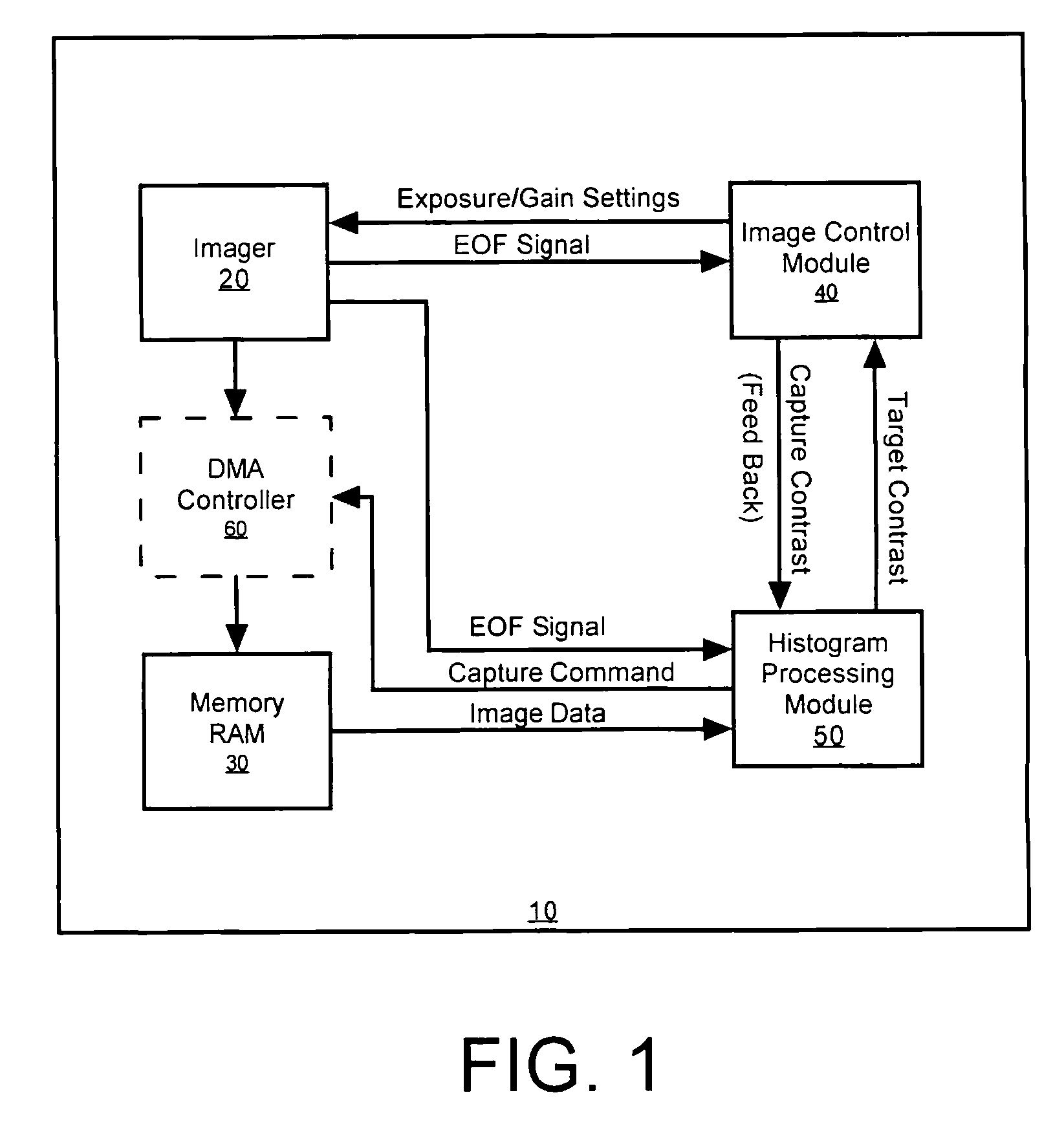
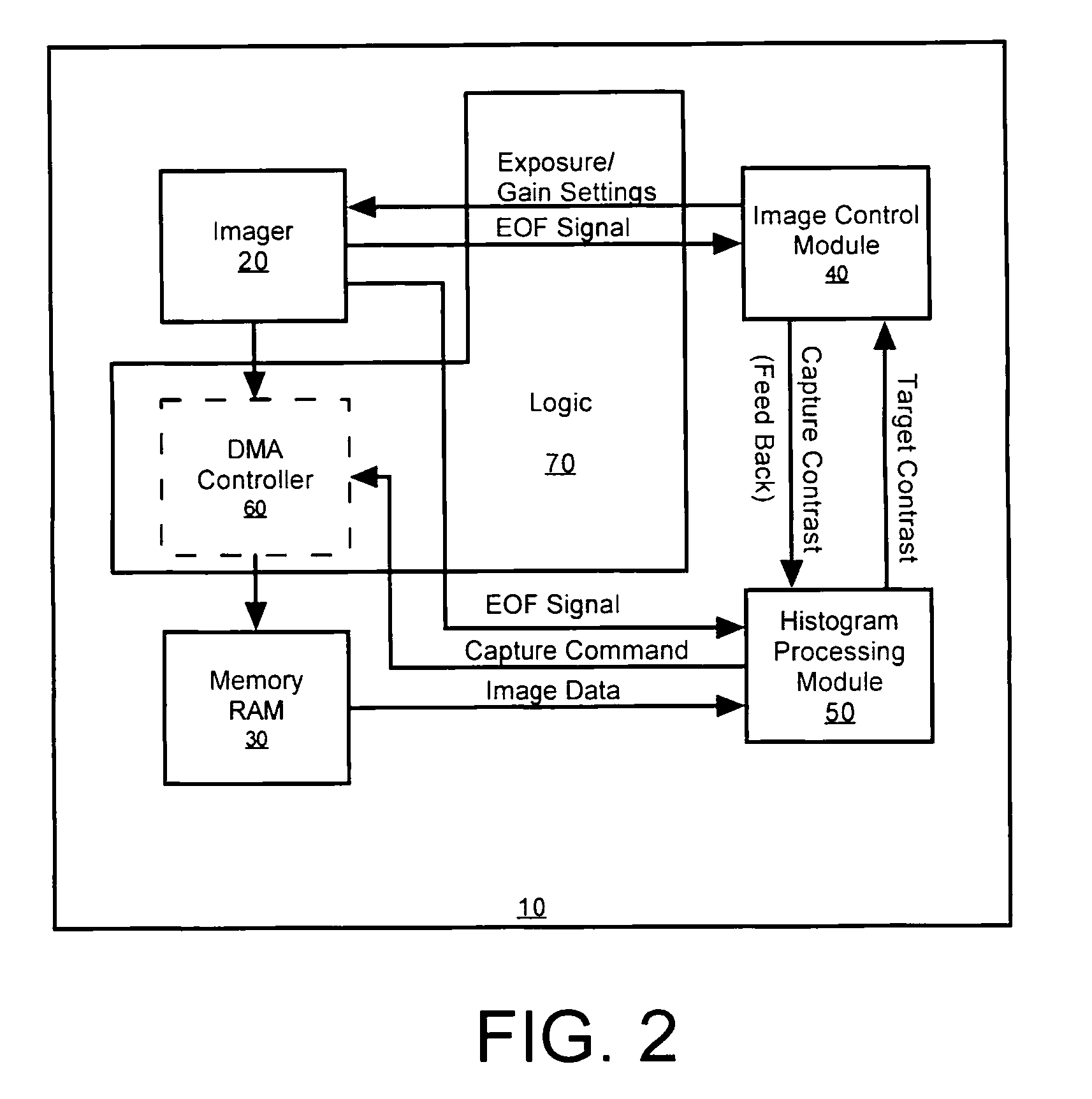
Methods and apparatus for automatic exposure control
A multi-dimensional imaging device and method for automated exposure control that implement two distinct modules to control the exposure and gain settings in the imager so that processing can occur in a multi-tasking single CPU environment. The first module, referred to herein as the imager control module, controls the exposure and gain settings in the imager. The first module is typically implemented in a high priority routine, such as an interrupt service routine, to insure that module is executed on every captured frame. The second module, referred to herein as the histogram processing module, calculates a target contrast (the product of the targeted exposure and gain settings) based on feedback data from the first module and image data from memory. The second module is typically implemented in a low priority routine, such as a task level routine, to allow for the routine to be executed systematically in accordance with priority.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
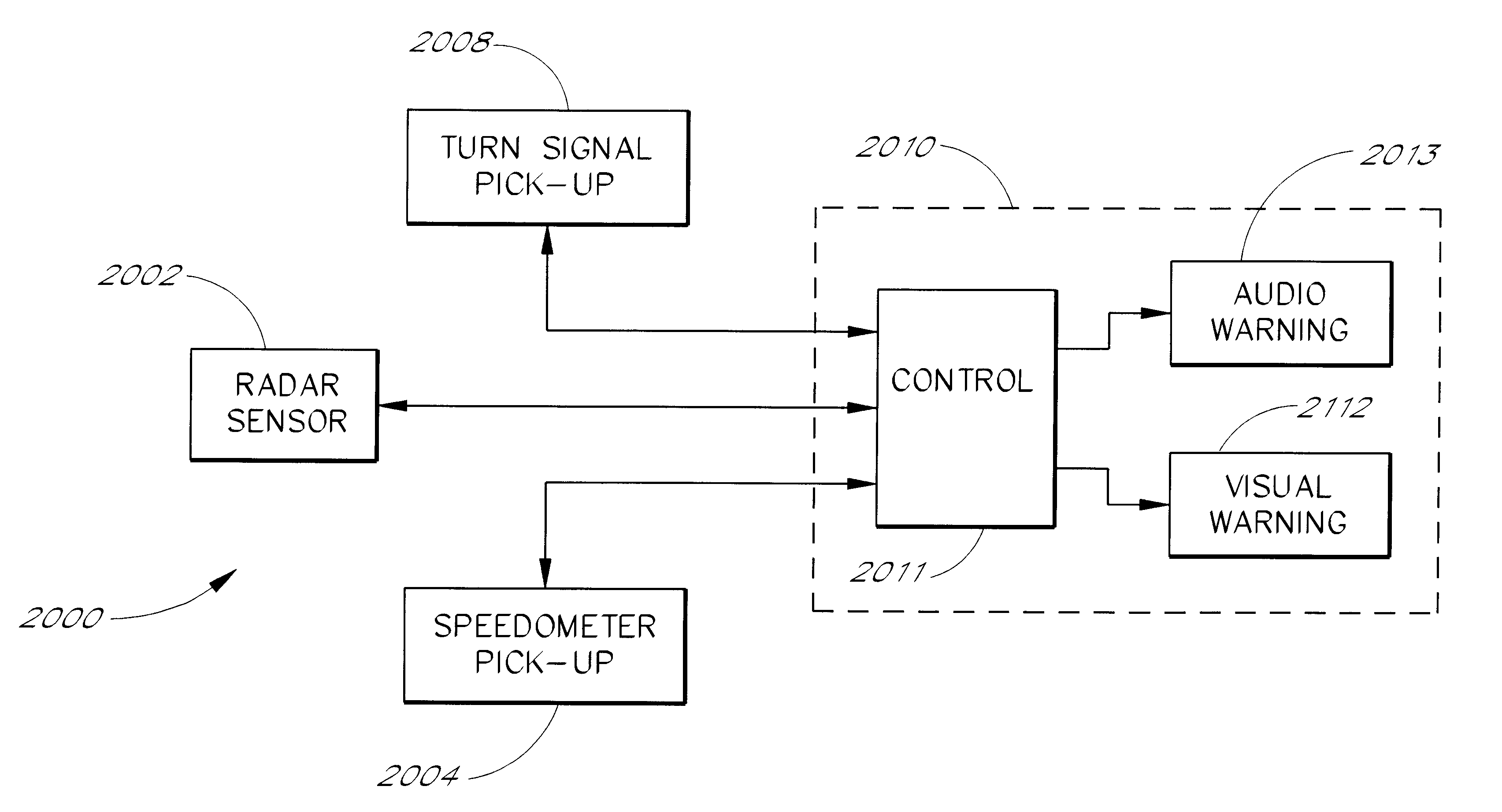
High performance vehicle radar system
InactiveUS6400308B1Road vehicles traffic controlAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesDriver/operatorRadar systems
A radar system is described for use in vehicular applications. The radar system is particularly suited to backup warning systems and lane-change warning systems. The radar minimizes many of the problems found in the prior art by providing programmable delays and programmable gain. The radar uses a range search algorithm to detect and sort targets at various ranges within the field of view of the radar. Each target range corresponds to a particular delay and gain setting. The radar searches for targets at the various ranges by running a target search algorithm. For each target range, the search algorithm causes the proper time delay and gain setting. Targets within the selected range are detected and catalogued. Speed of the targets is obtained through Doppler processing. A display is used to warn the driver of the vehicle of the presence of targets at the various ranges. The warning may be visual and / or audible. When used in a lane-change system, issuance of an audible warning is based on the speed of the vehicle.
Owner:AMERIGON INC
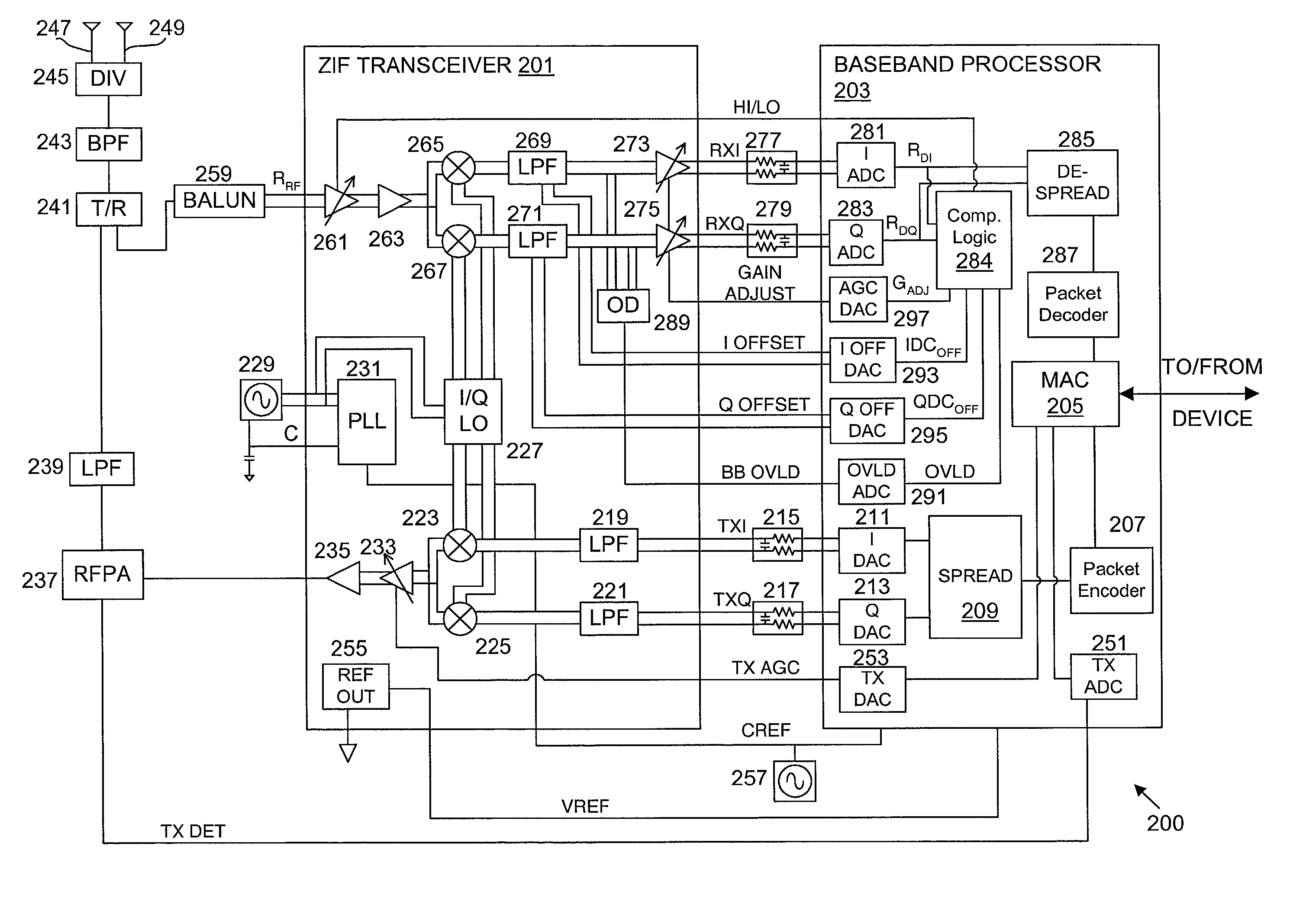
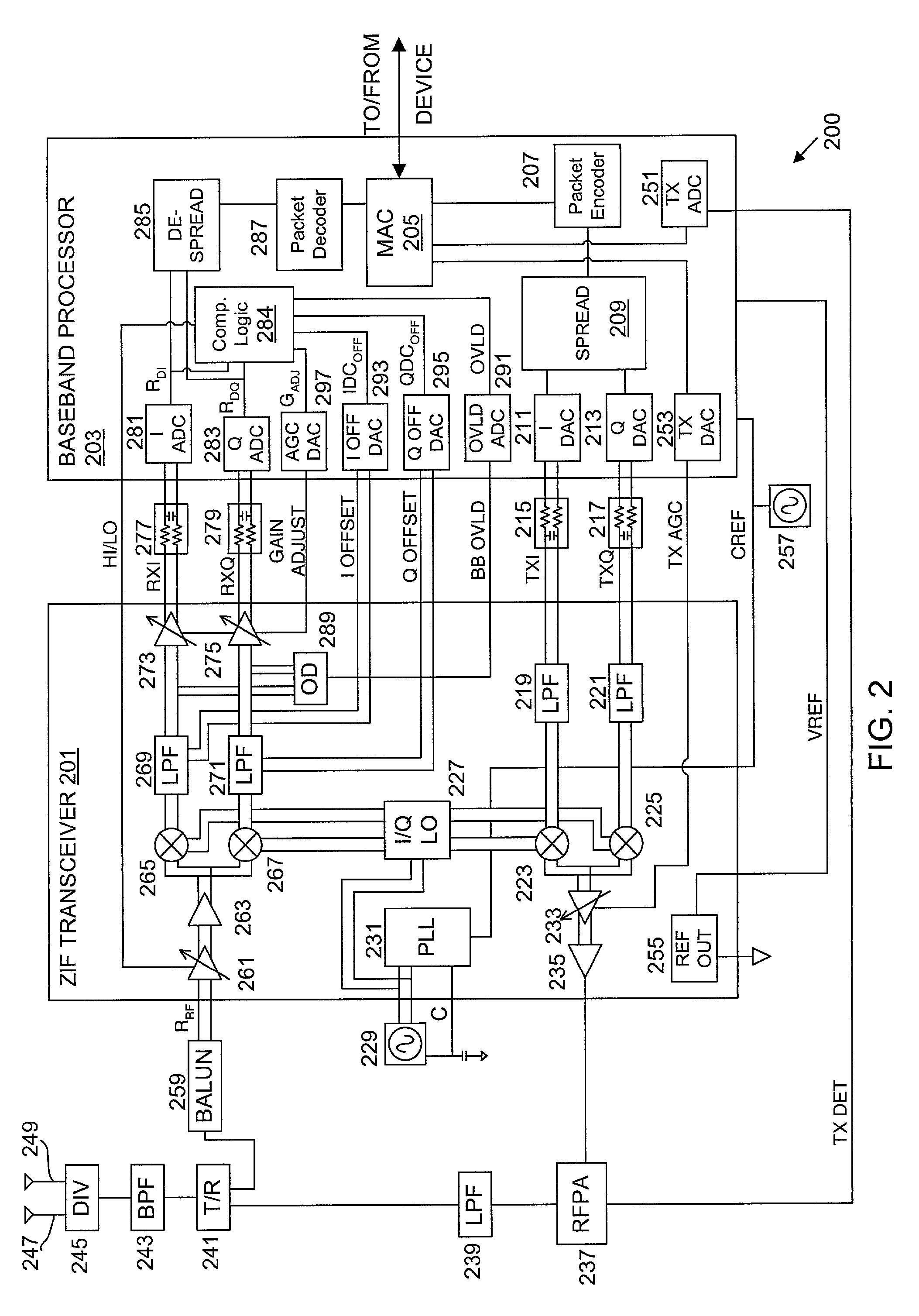
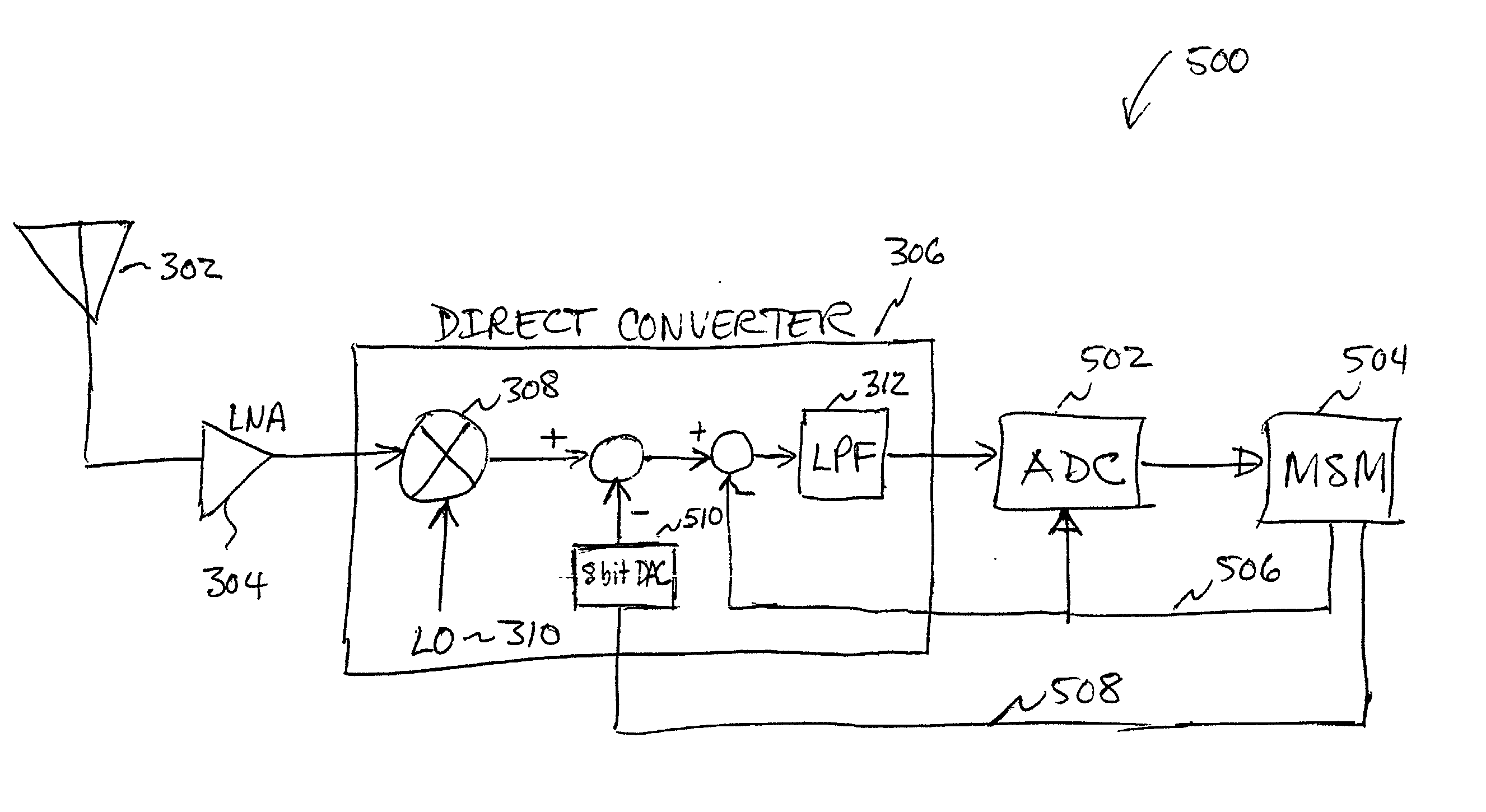
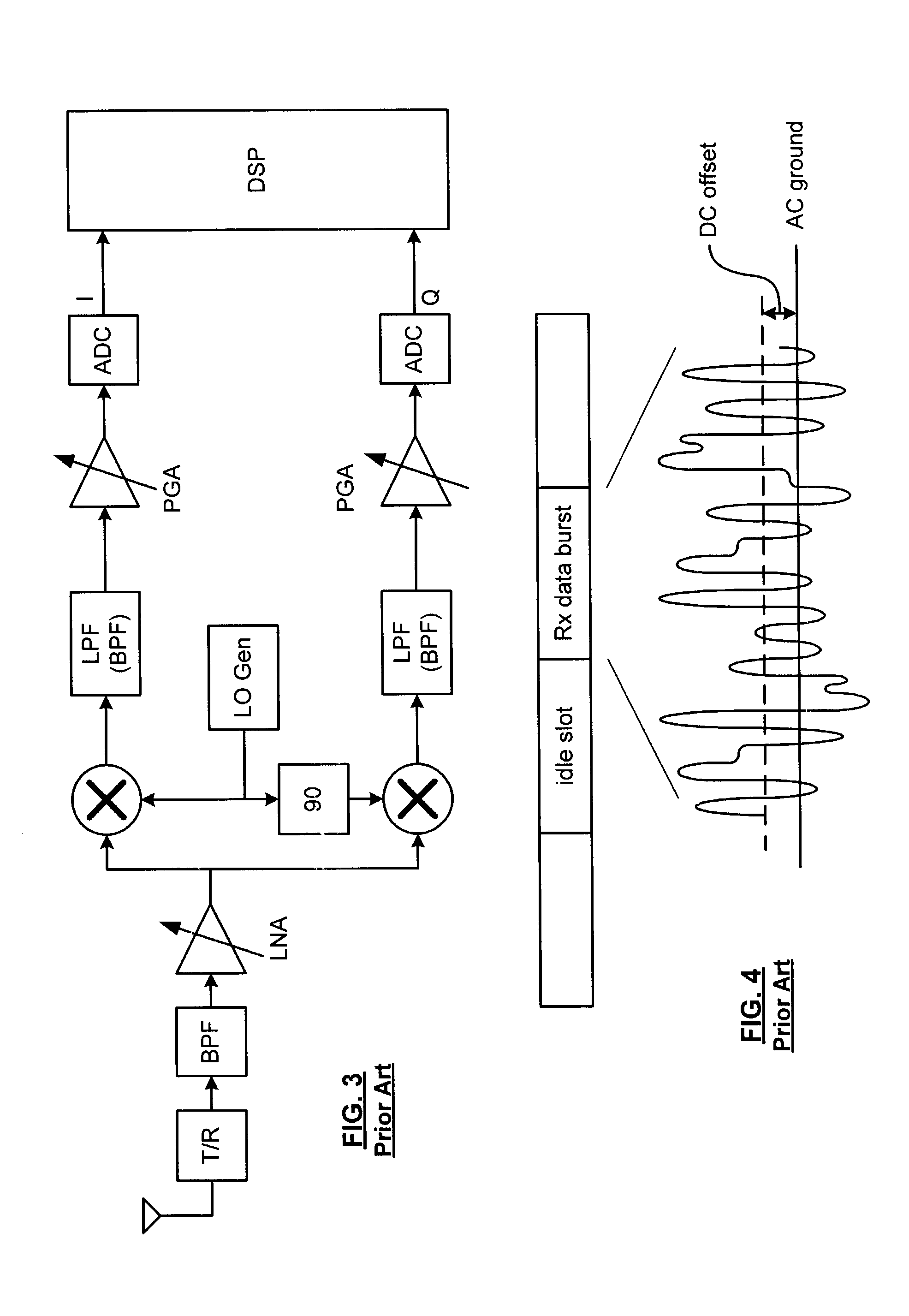
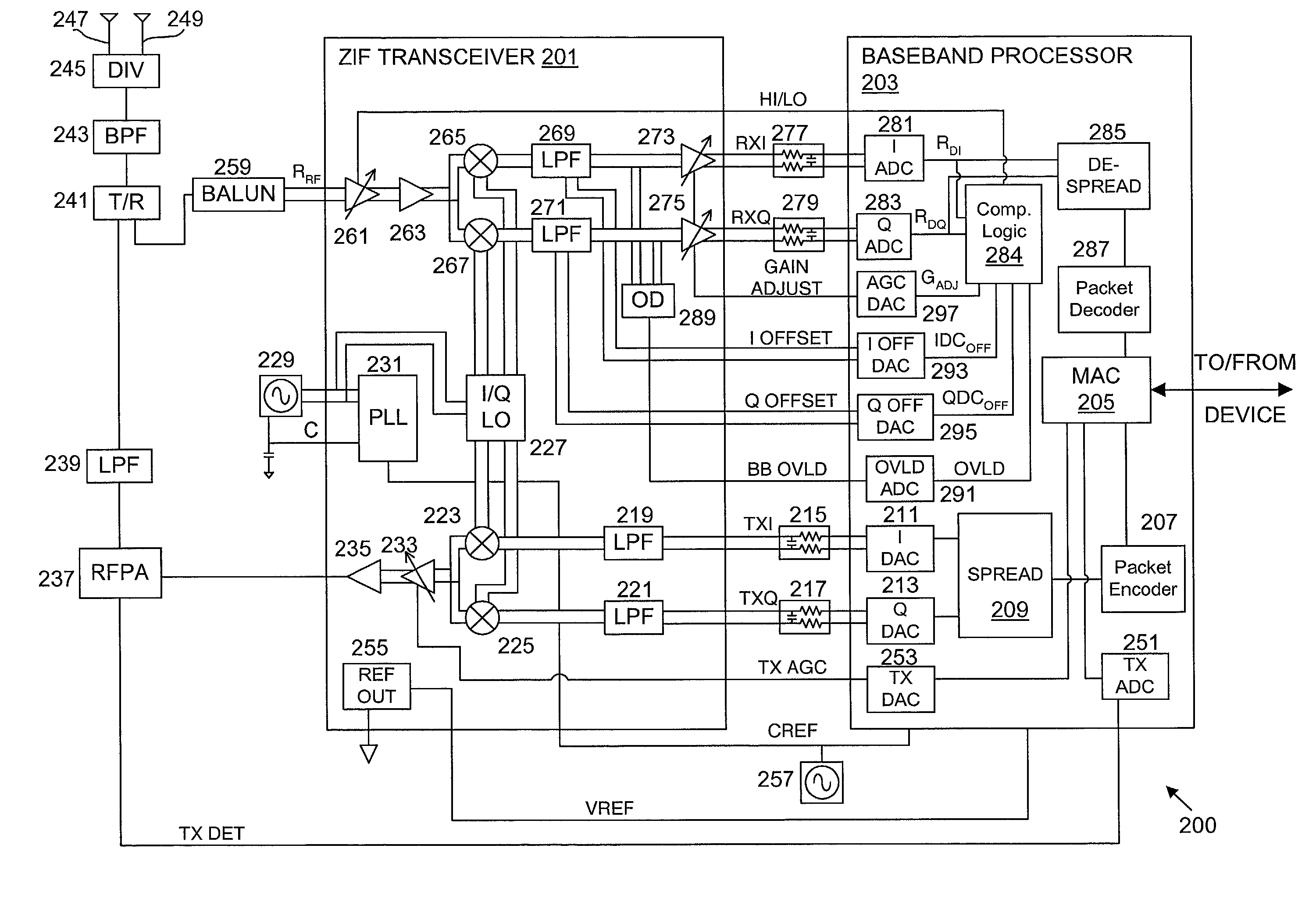
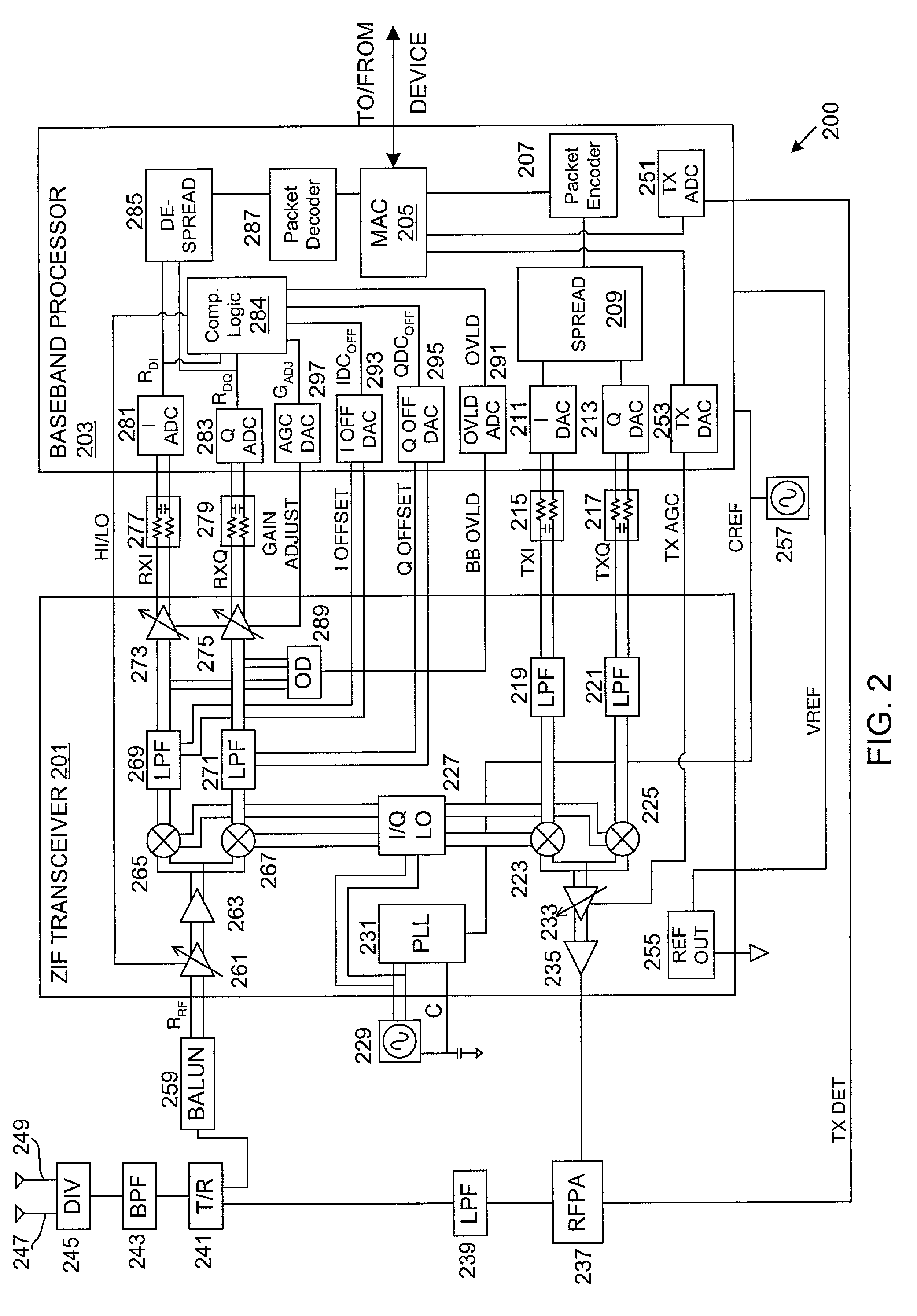
Packet acquisition and channel tracking for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
A method of controlling operation of a wireless device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture including a DC loop and a gain loop. The method includes processing energy in a wireless medium to generate a corresponding receive signal, monitoring the receive signal via a predetermined measurement window, detecting a changed condition in the channel, holding the gain feedback control loop at a constant gain level, and operating the DC loop in an attempt to search a stable DC value for the receive signal while the gain loop is held constant. A first case is DC saturation, where the gain is held constant until DC is controlled. A second case is clear channel assessment, where a prior stored gain setting is applied to the gain loop after detecting the end of the packet. A third case is preparation for receiving an expected acknowledgement packet after transmitting a packet, where again a prior stored gain setting is applied to the gain loop and DC is searched.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
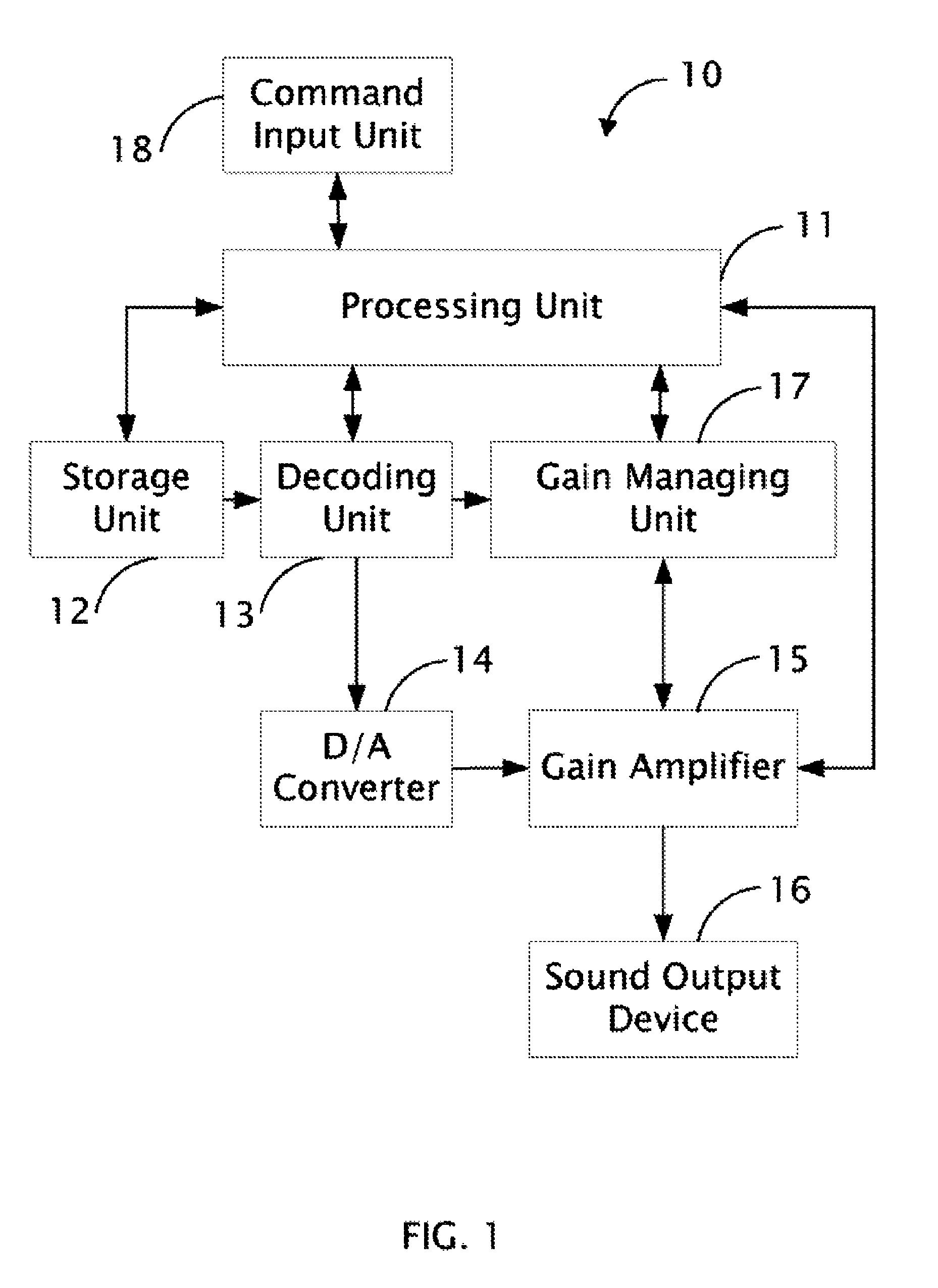
Audio processing system with function of automatic gain control and method thereof
ActiveUS8019094B2Analog signal digital controlSpecial data processing applicationsAudio power amplifierAutomatic control
The present invention relates to an audio processing system with function of automatic gain control and method thereof. The method includes steps of: receiving a playing command to play an audio file; reading a genre type of the audio file from a tag of the audio file; reading a genre gain value of the genre type from a gain setting table stored in a storage unit; decoding the audio file and generating digital audio signals; converting the digital audio signals to analog audio signals; and signaling a gain amplifier to amplify the analog audio signals by the genre gain value, thereby sounds corresponding to the analog audio signals amplified is proper to a listener's hearing.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
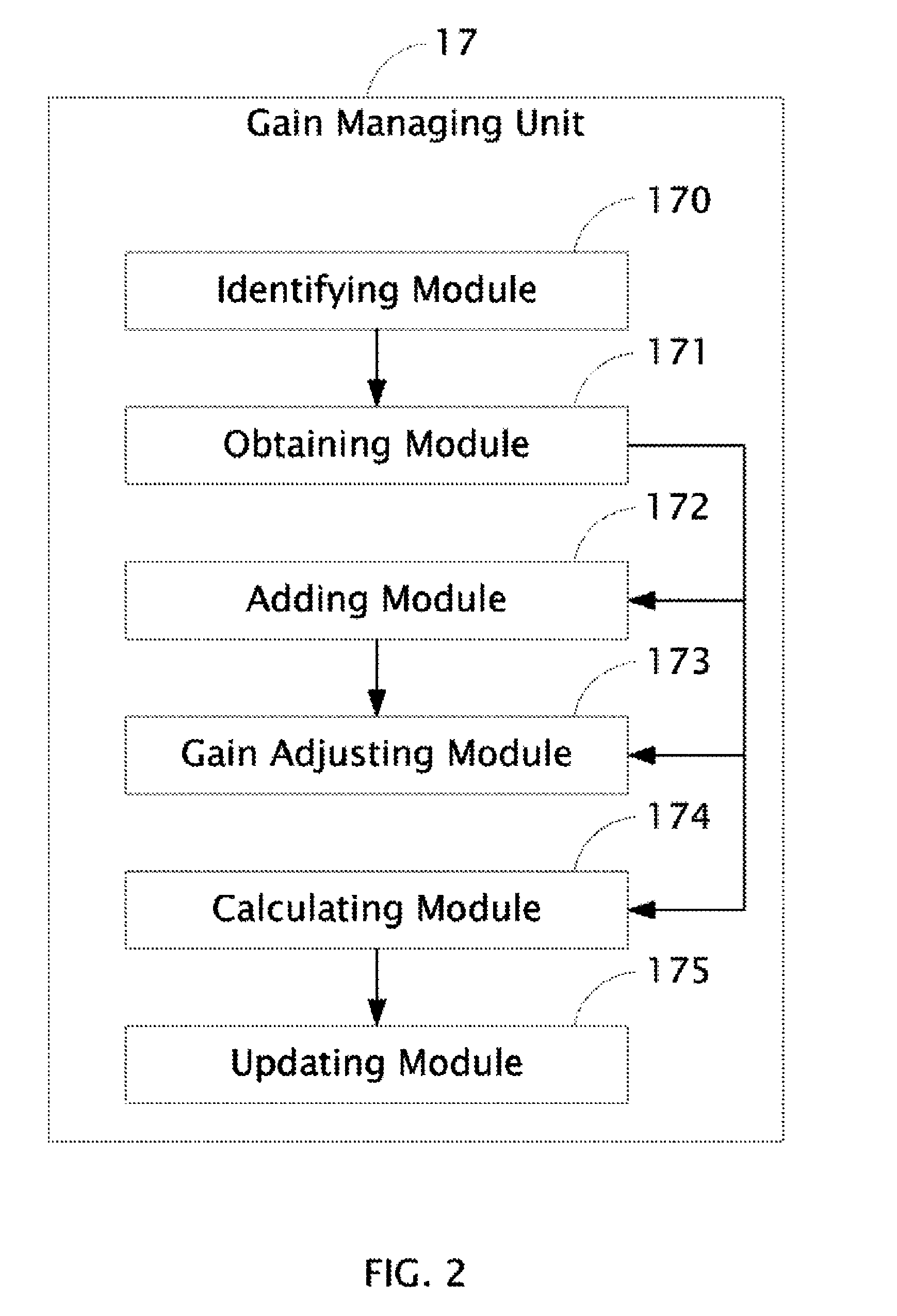
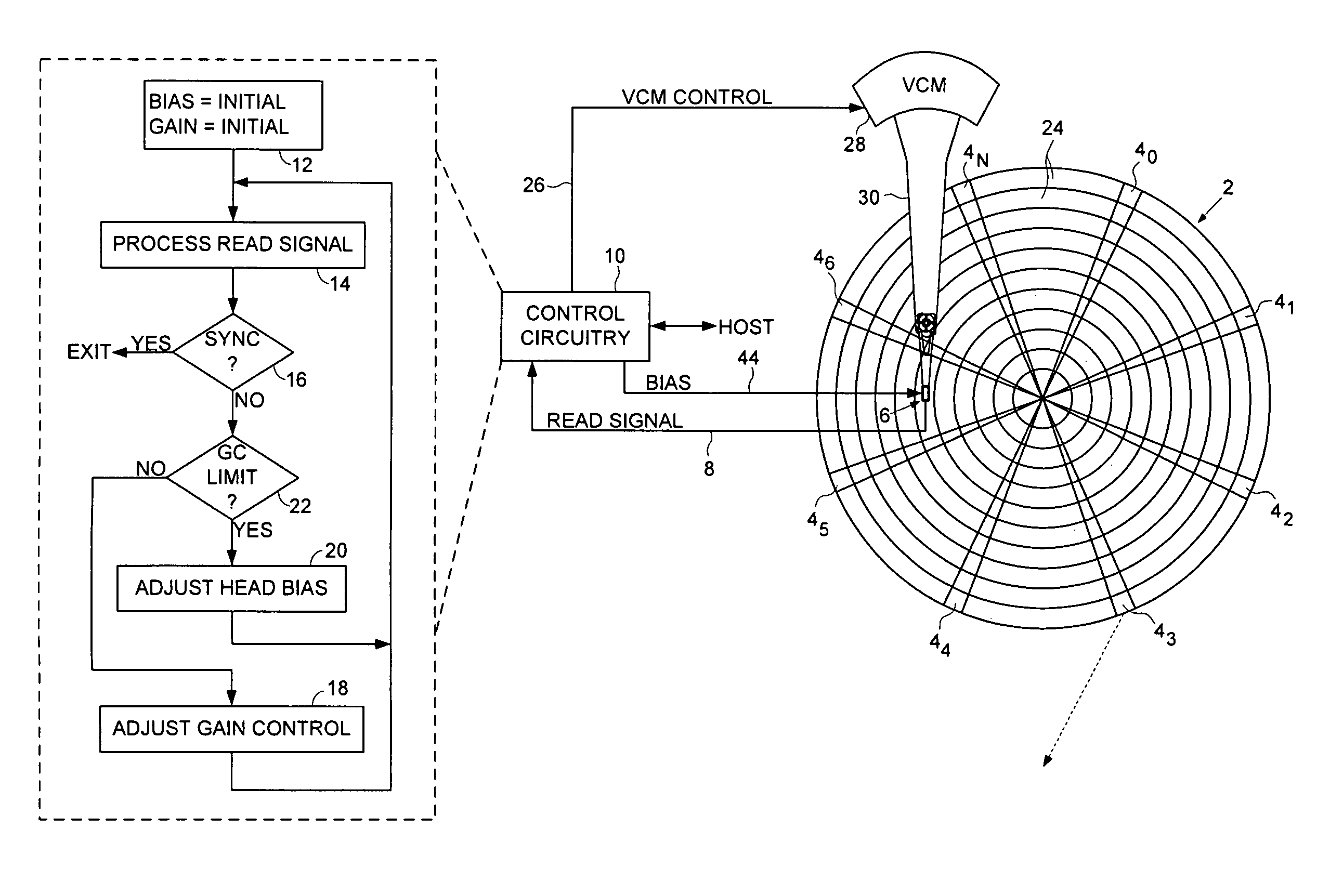
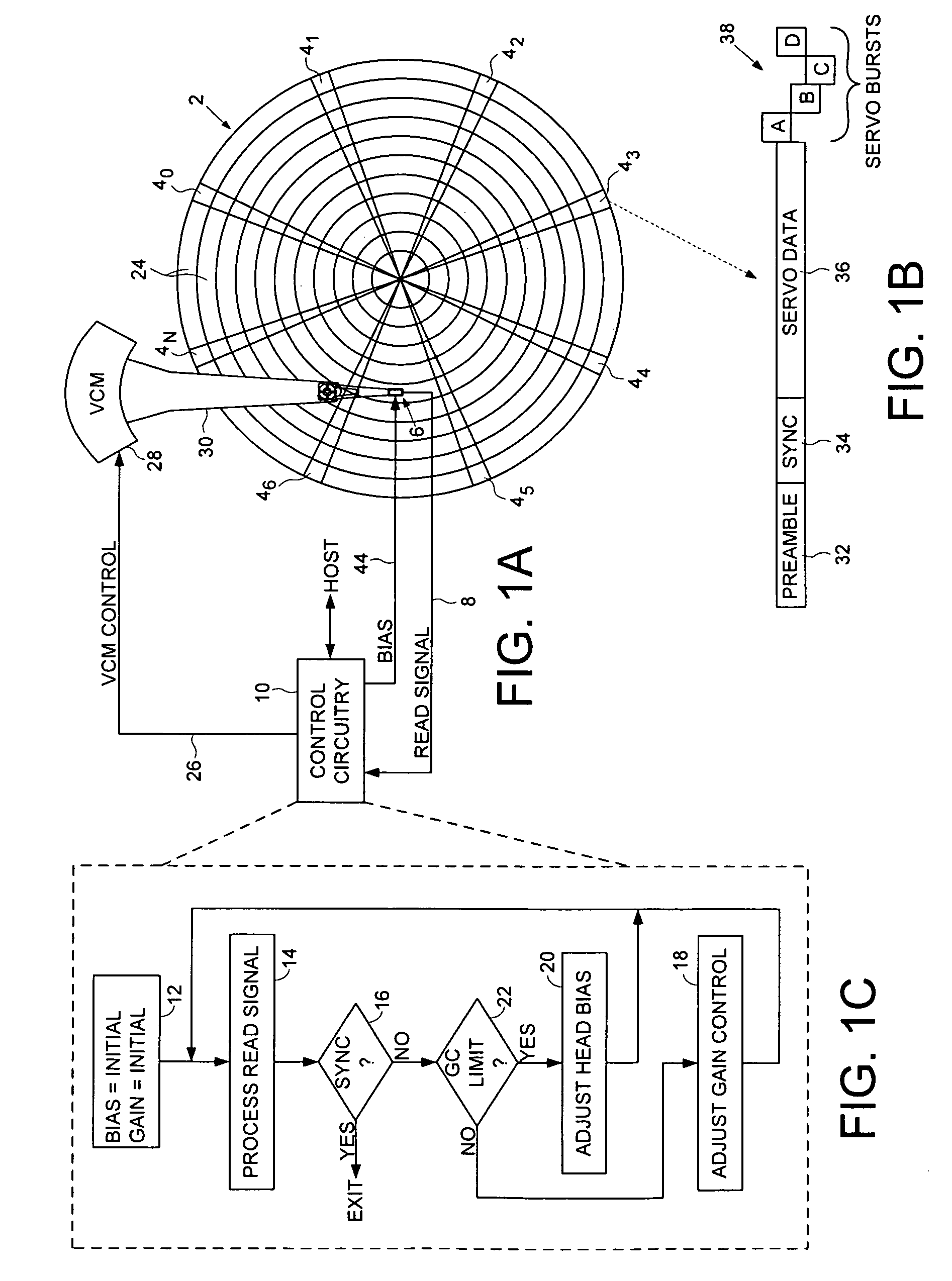
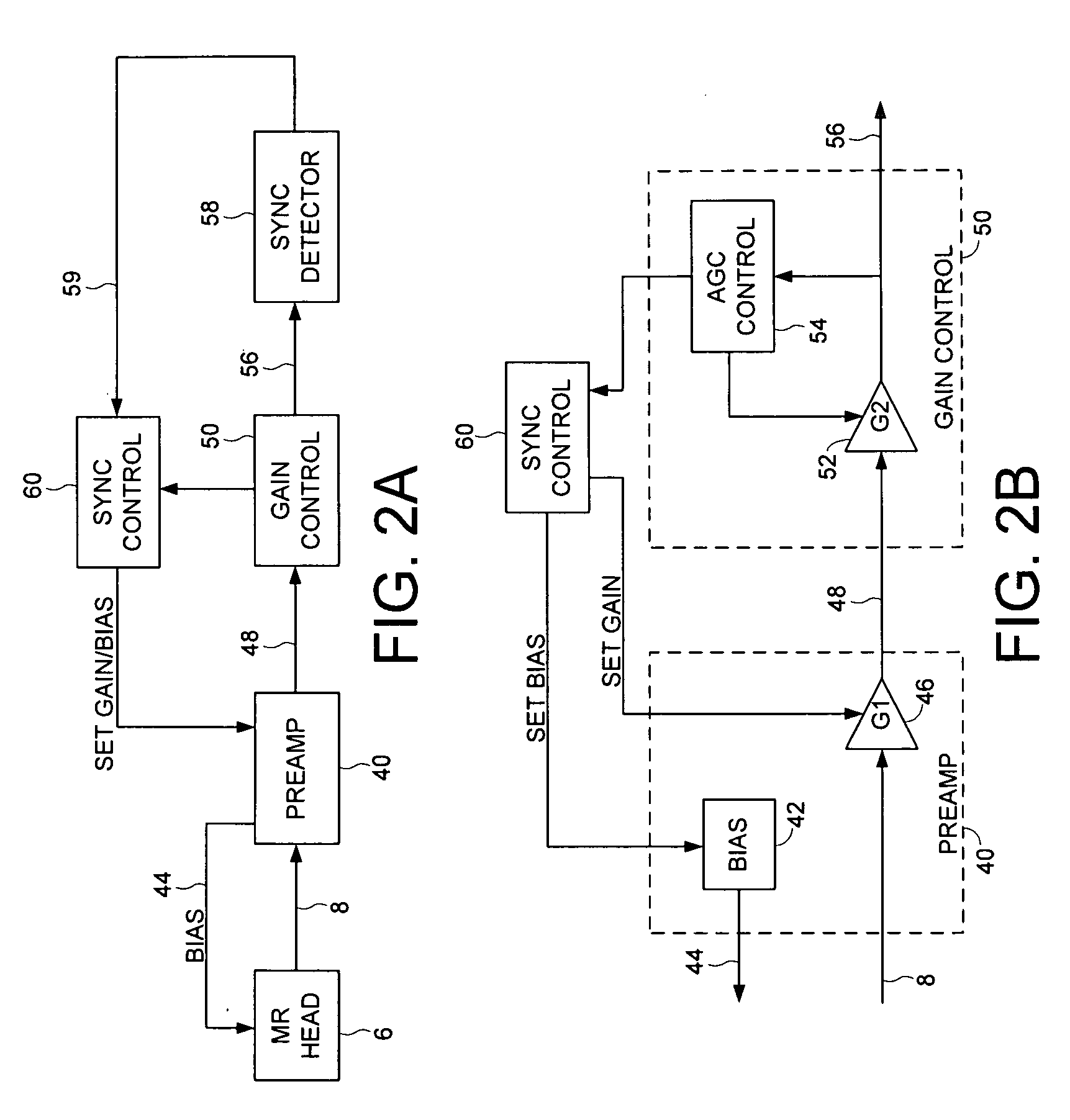
Disk drive adjusting head bias during servo synchronization to compensate for over/under sensitivity
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a disk including a plurality of servo sectors, a head actuated over the disk, the head for generating a read signal, and a gain control circuit for adjusting a gain of the read signal in response to a gain setting. A bias setting is initialized for the head, and the gain setting for the read signal is initialized. The read signal is processed to detect at least one of the servo sectors, and when at least one of the servo sectors is not detected, the gain setting is adjusted. The read signal is processed with the adjusted gain setting to detect at least one of the servo sectors, and when at least one of the servo sectors is not detected with the adjusted gain setting, the bias setting is adjusted in response to the adjusted gain setting.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
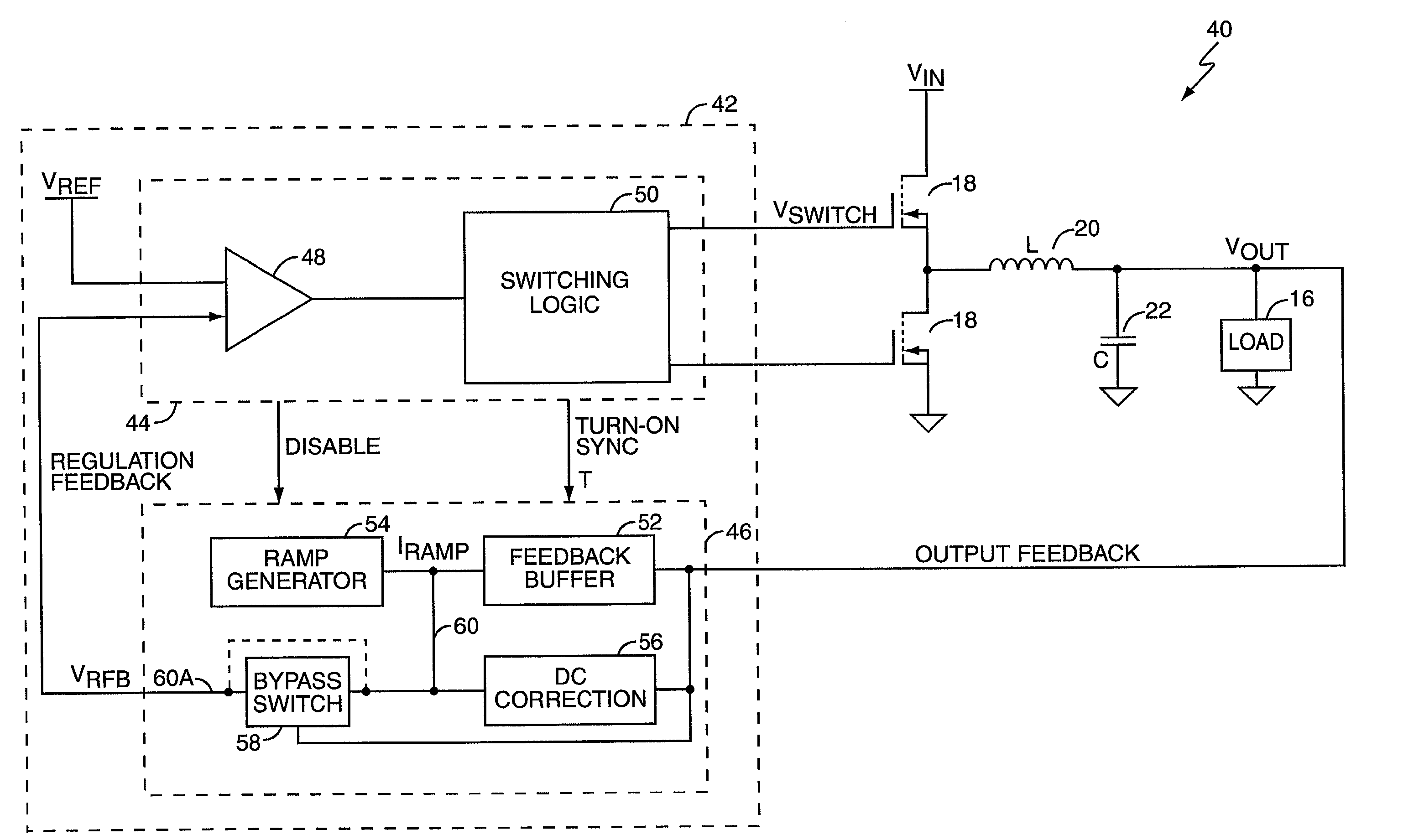
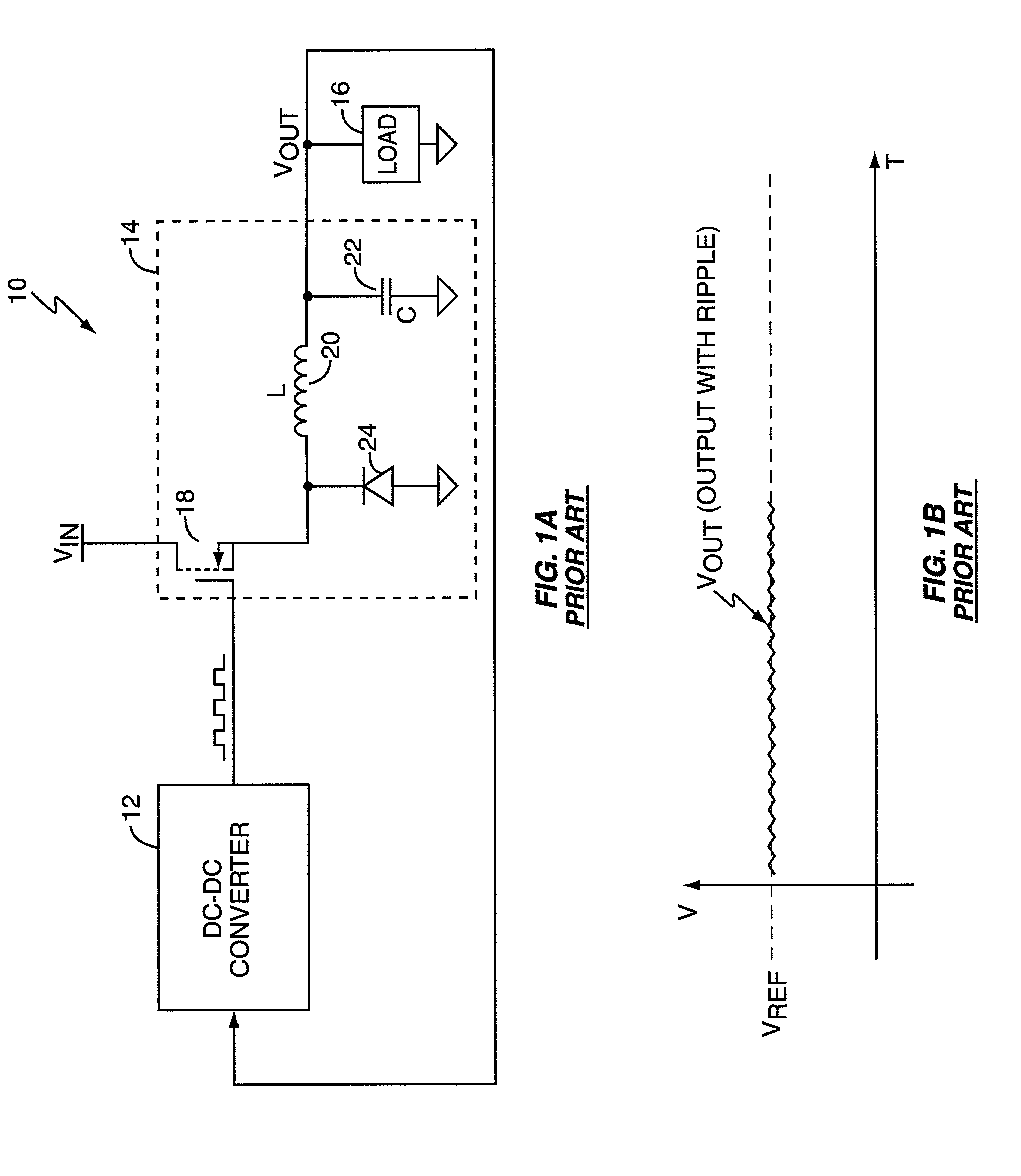
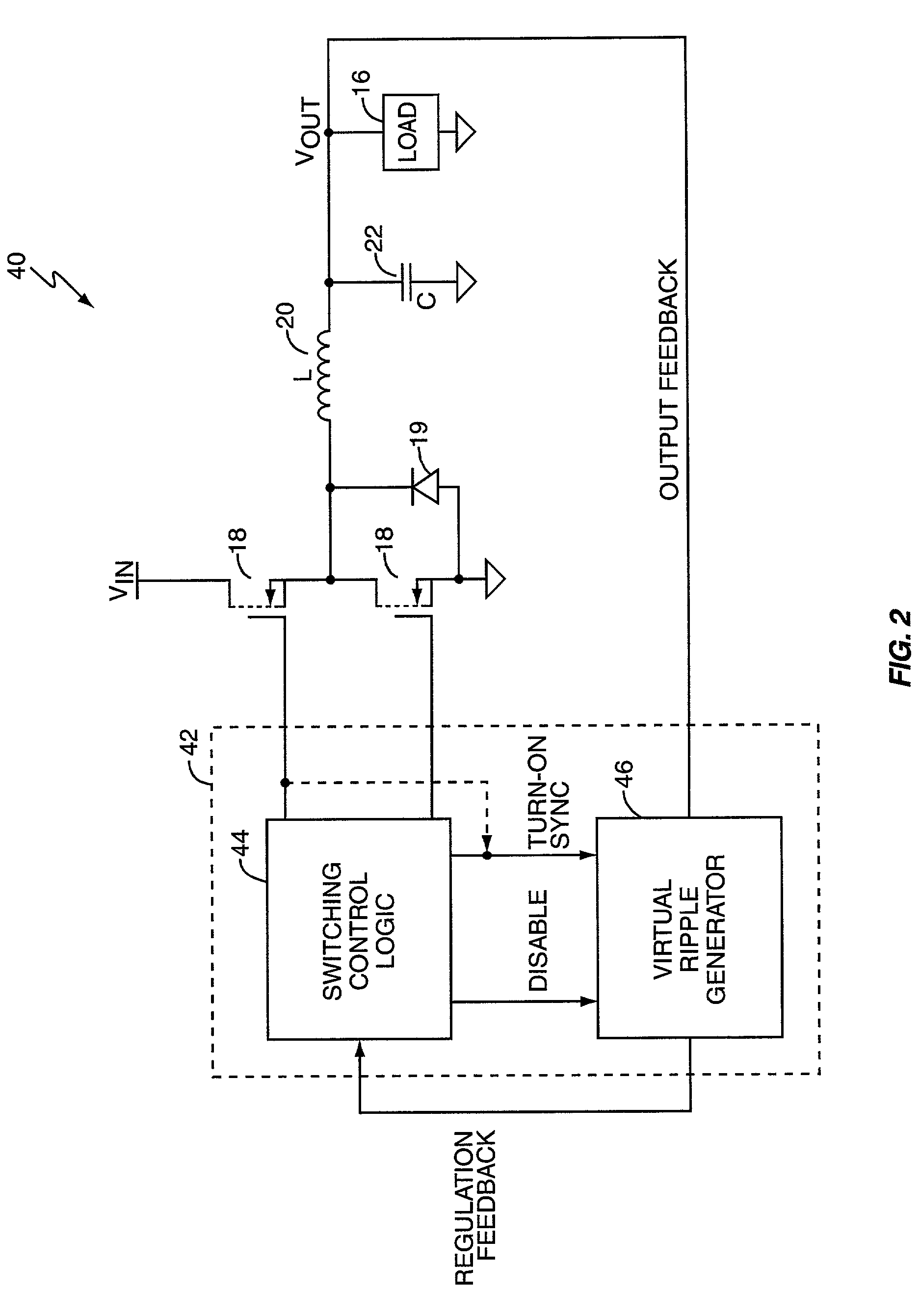
Virtual ripple generation in switch-mode power supplies
InactiveUS20020125872A1Prevent undesirable voltage overshootDroop compensationDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceVoltage regulation
A system and method provides virtual ripple signal generation for use in voltage regulation applications. Some switch-mode power converters or voltage regulators use output signal ripple to effect voltage regulation. A virtual ripple generator provides this type of voltage regulator with a virtual ripple signal comprising an offset component responsive to actual load voltage, but with a generated AC ripple component of arbitrary magnitude that is independent of actual output signal ripple. Unlike the actual output ripple signal, the generated AC ripple component is not dependent on implementation specifics, such as circuit board layout or output capacitor ESR, and may have its gain set independent of the offset component. The generated AC ripple component is synchronized to the inductor switching actions of the voltage regulator and thus reflects actual inductor phase switching in single and multi-phase regulation applications. Virtual ripple signal generation can include output (load) voltage droop compensation.
Owner:SEMTECH CORP
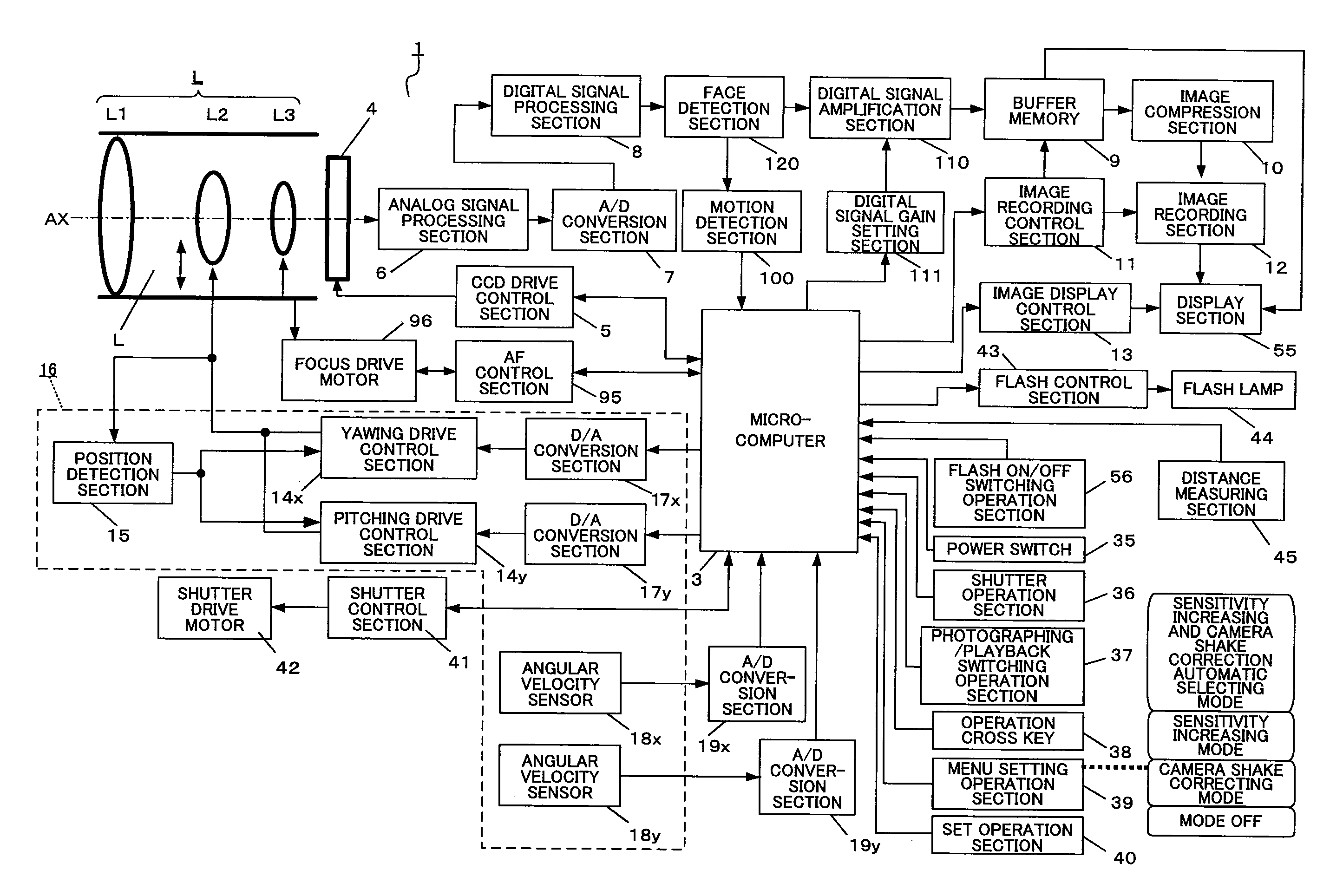
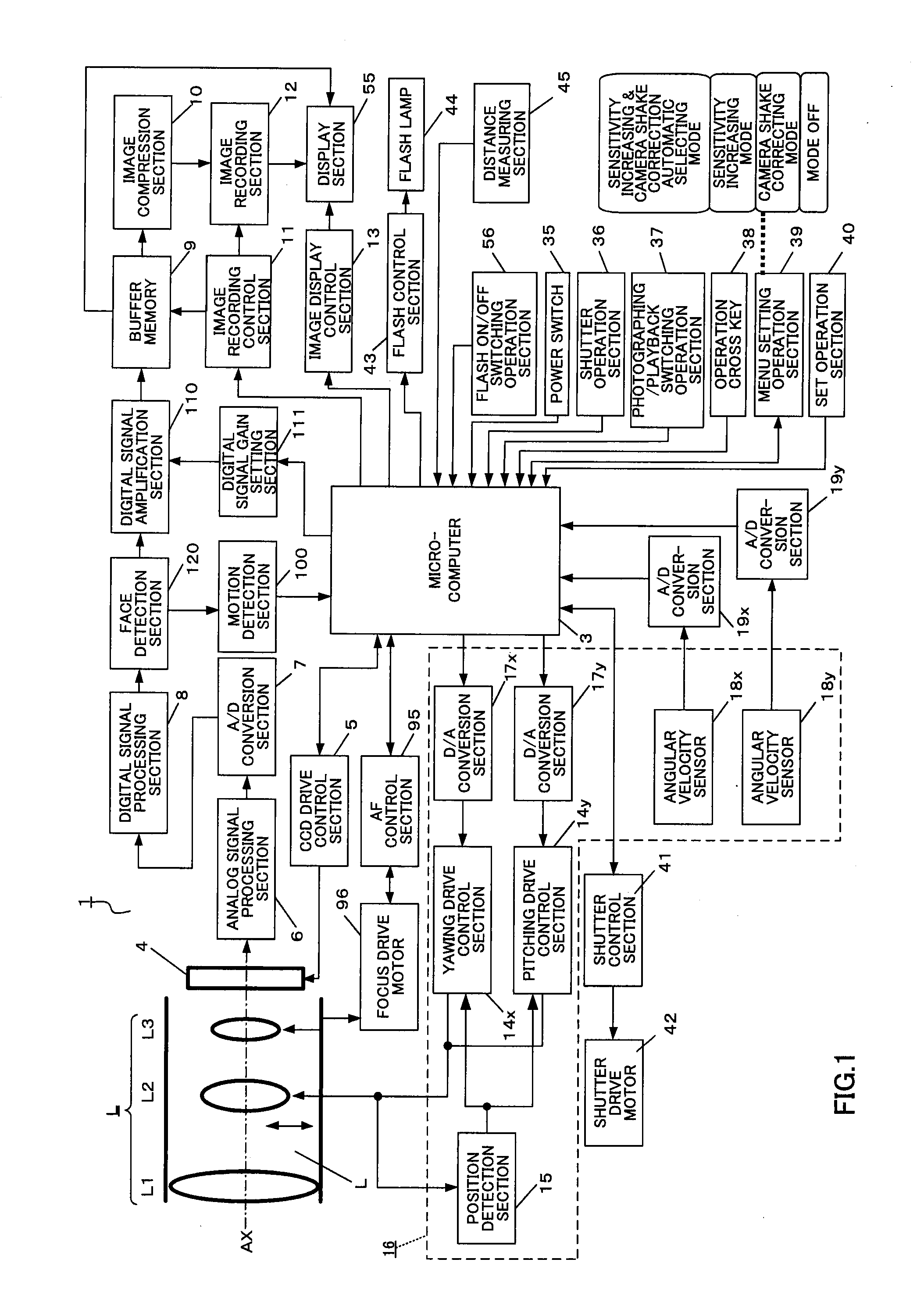
Image pickup apparatus and lens barrel
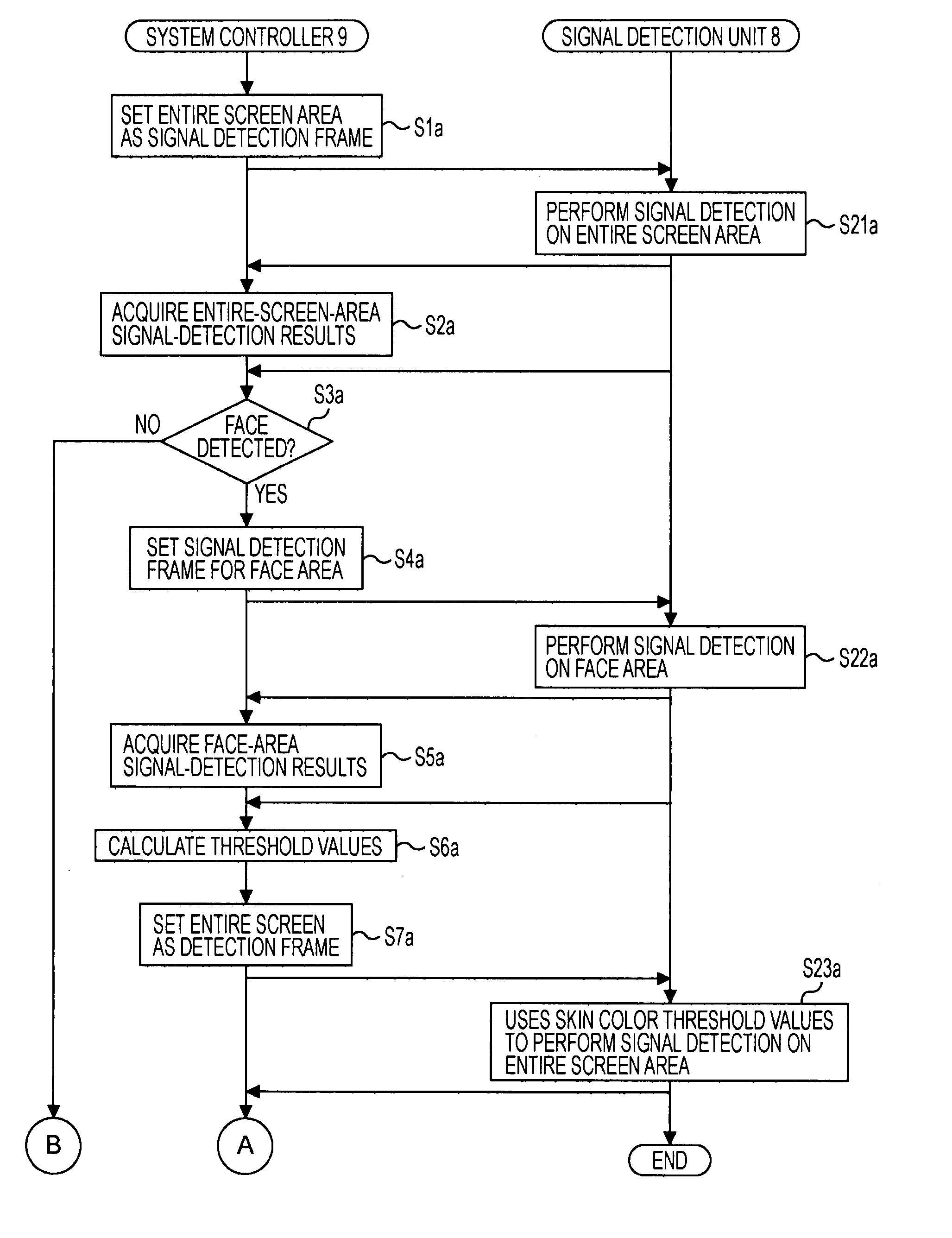
ActiveUS20080204565A1Reduce image quality degradationQuality improvementTelevision system detailsPrintersFace detectionObject based
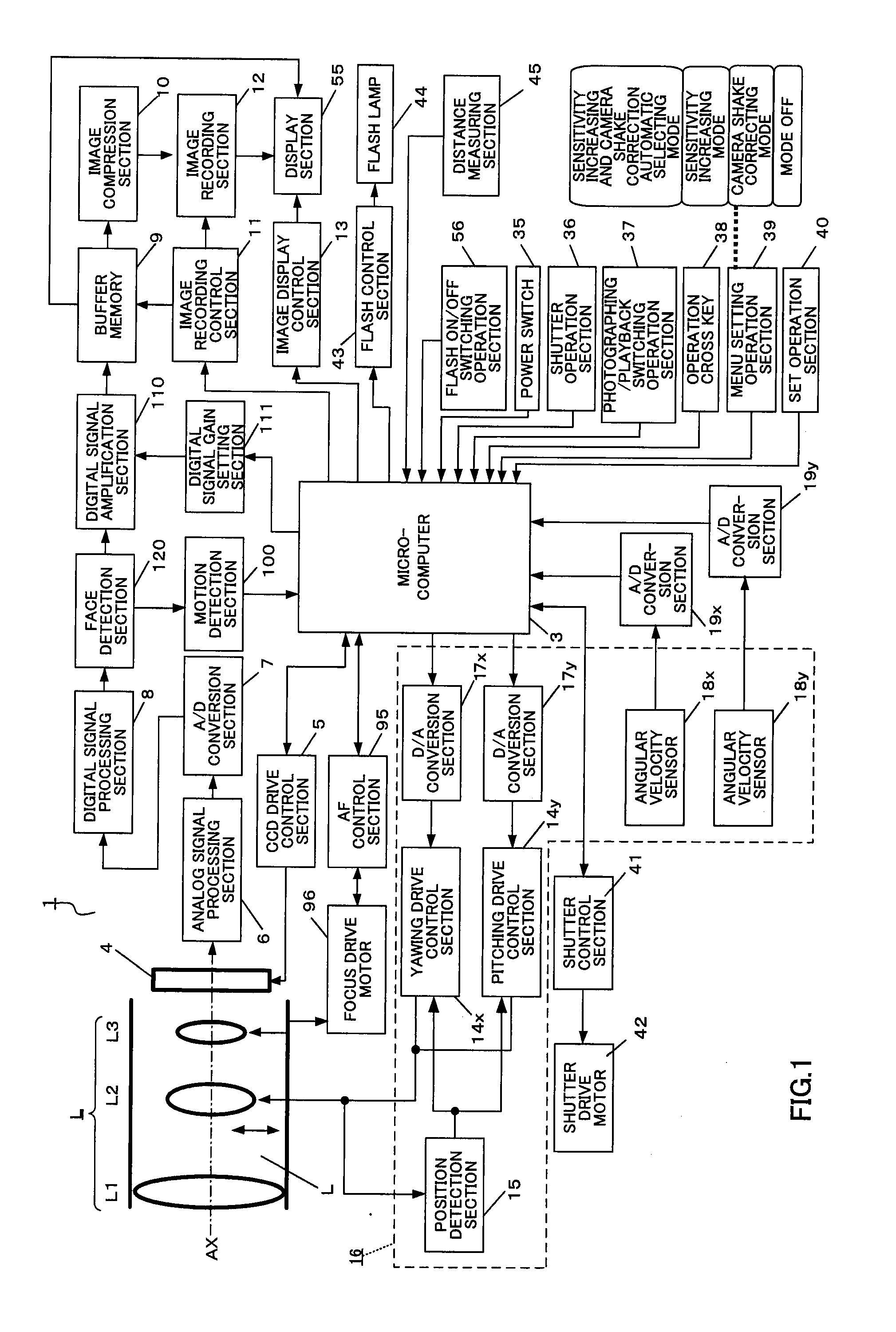
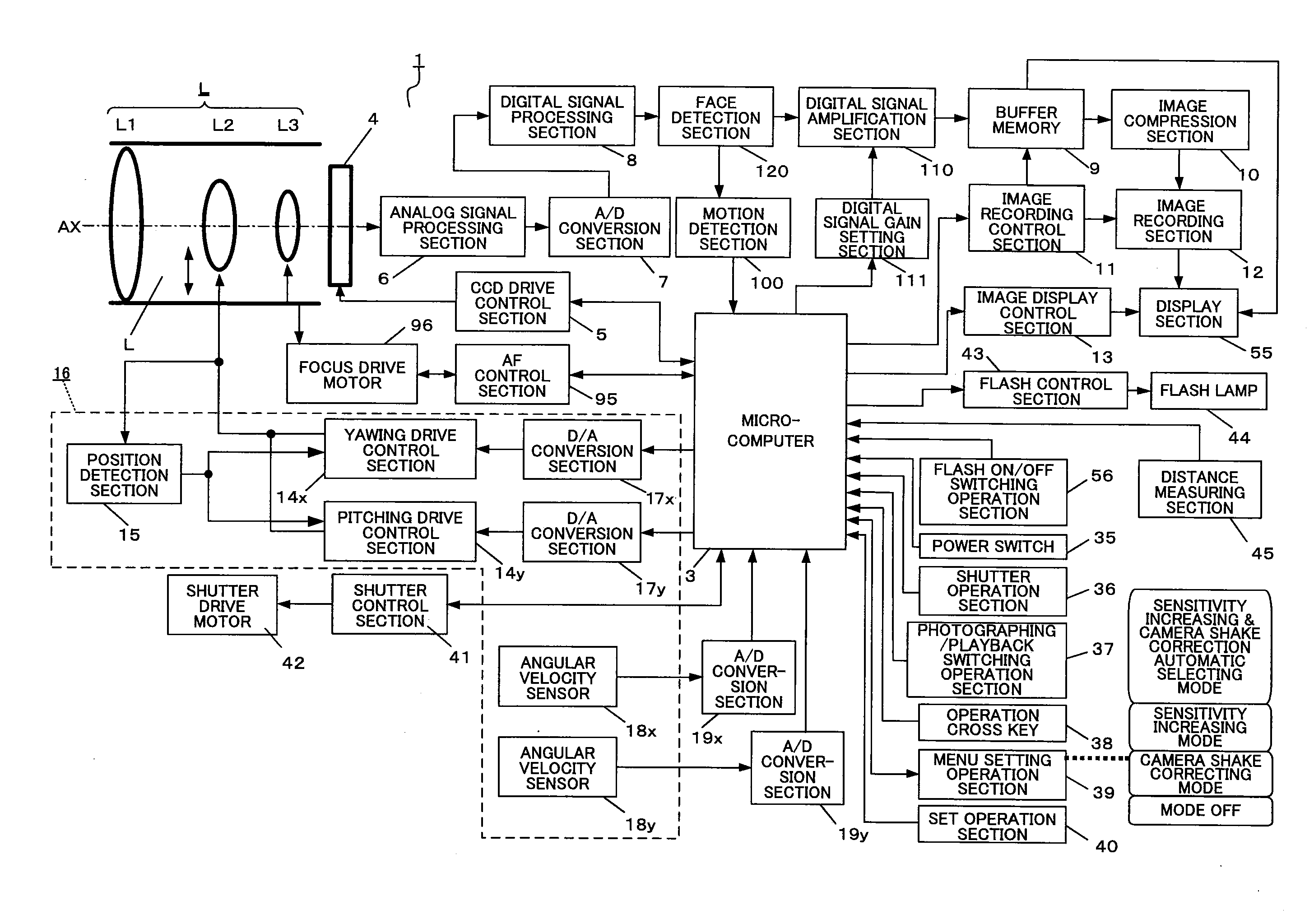
An imaging apparatus capable of preventing photographing sensitivity from being increased more than necessary, reducing image quality degradation caused by camera shake or object shake and easily photographing images in good image quality. Digital camera 1 includes image shake correcting selection 16 that corrects shake of an optical image of a photographing object formed by the imaging optical system L, digital signal amplification section 110 that amplifies an image signal with a gain set by digital signal gain setting section 111, face detection section 120 that detects a face of a fast-moving specific photographing object such as a child or pet, and motion detection section 100 that detects motion of the face of the specific photographing object based on an output of face detection section 120, wherein when a fast-moving specific photographing object such as a child or pet or the face of the specific photographing object is detected, microcomputer 3 increases the gain of a photographing sensitivity changing function compared with when no specific photographing object such as a child or pet is detected, increases ISO sensitivity, increases a shutter speed and shortens exposure time.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Frequency selective automatic gain control with dual non-symmetric attack and release times and interference detection feature
ActiveUS20070076783A1Improve errorEfficient executionGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsLoading factorFrequency-hopping spread spectrum
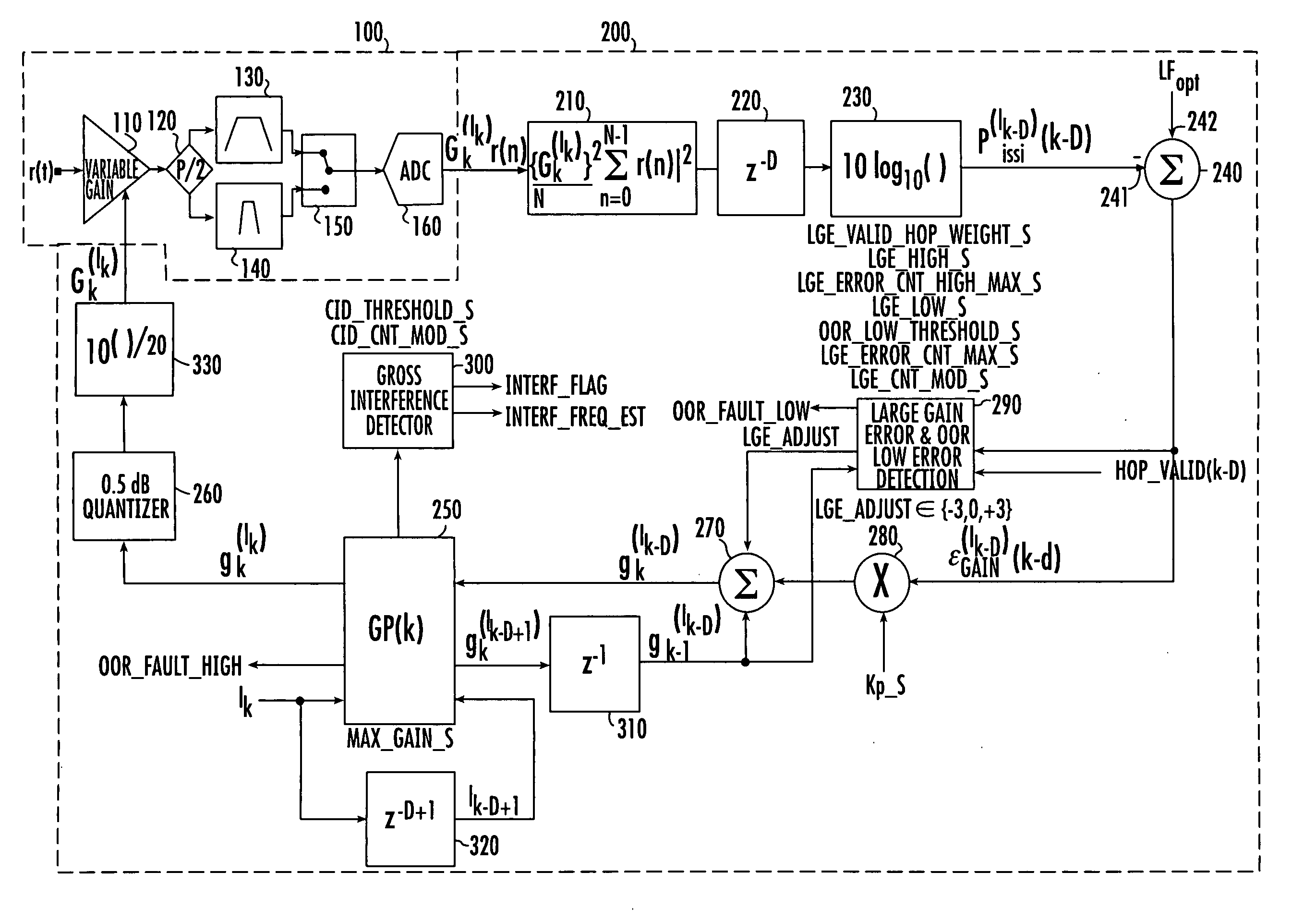
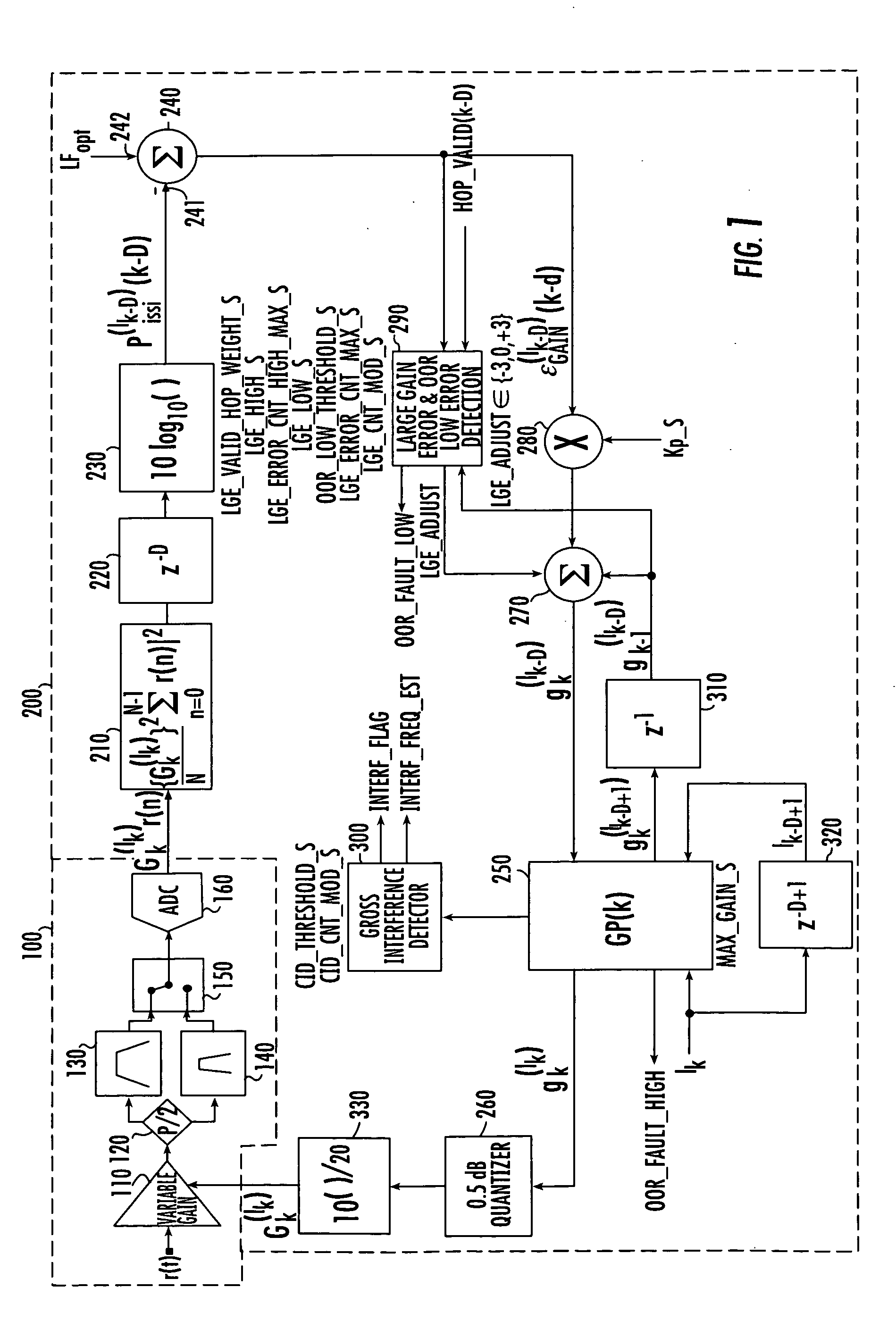
A digital signal processing-based receiver architecture performs automatic gain control (AGC) for a frequency hopping spread-spectrum communications receiver that may be subjected to one or more sources of interference or jamming. Rather than set the AGC gain at a fixed, best hoped for value, and then attempt to rely on decoding or interleaving to interpolate lost or degraded data, the present invention, through repeated but aperiodic transitions or hops across a plurality of frequency bins of interest, develops a gain profile for the plurality of frequency bins, and uses the gain profile to adjust, on a hop-by-hop basis, the gain for the channel / bin to which the receiver is listening, so as to maintain the average aggregate input signal power at an optimal ADC loading factor.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Methods for performing biometric recognition of a human eye and corroboration of same
A method of biometric recognition is provided. Multiple images of the face or other non-iris image and iris of an individual are acquired. If the multiple images are determined to form an expected sequence of images, the face and iris images are associated together. A single camera preferably acquires both the iris and face images by changing at least one of the zoom, position, or dynamic range of the camera. The dynamic range can be adjusted by at least one of adjusting the gain settings of the camera, adjusting the exposure time, and / or adjusting the illuminator brightness. The expected sequence determination can be made by determining if the accumulated motion vectors of the multiple images is consistent with an expected set of motion vectors and / or ensuring that the iris remains in the field of view of all of the multiple images.
Owner:EYELOCK
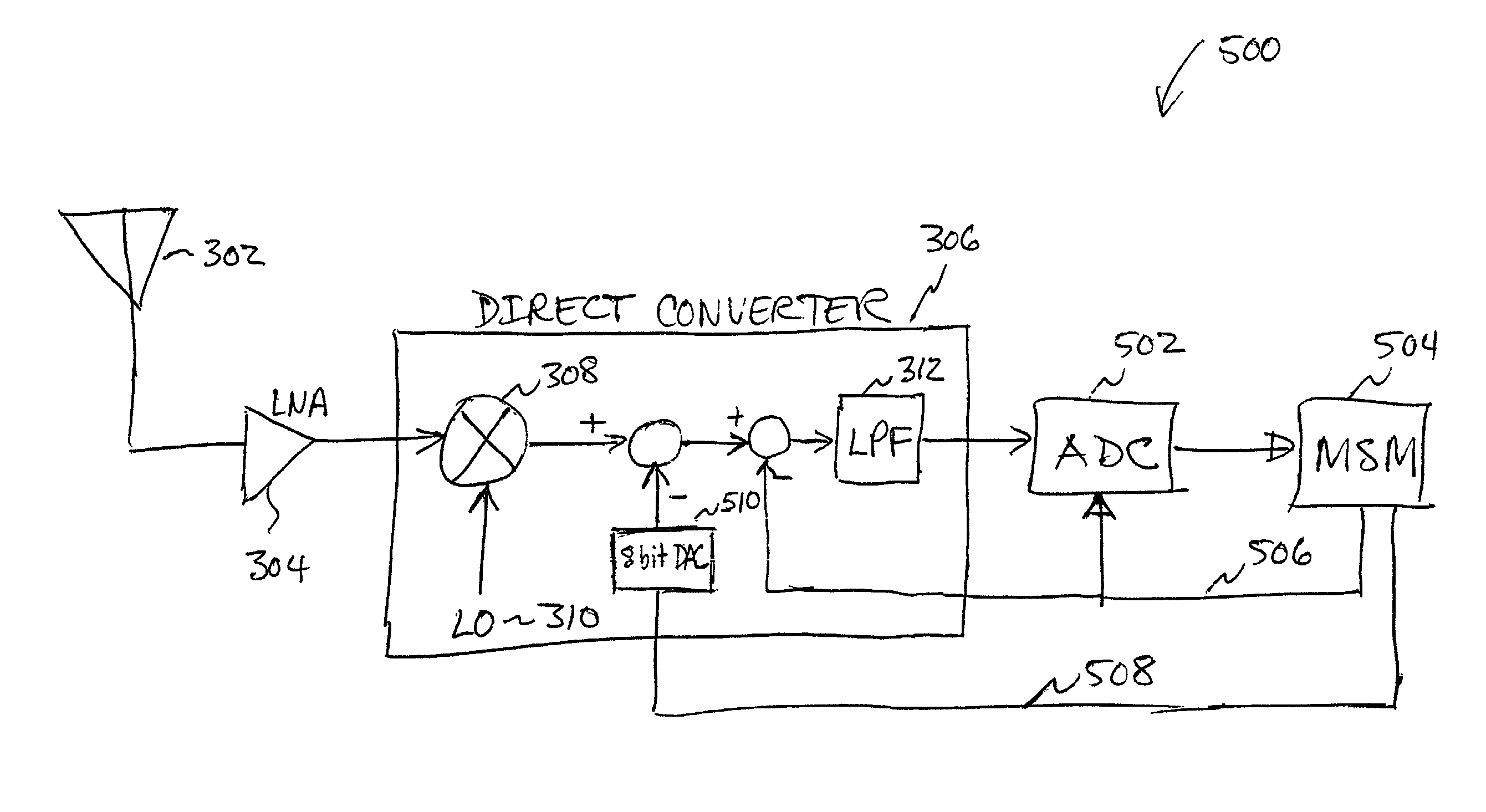
Direct current offset cancellation for mobile station modems using direct conversion
InactiveUS20030199264A1Dc level restoring means or bias distort correctionRadio transmissionModem deviceOffset cancellation
A system and method for canceling DC offset for Mobile Station Modems having direct conversion architectures. The present invention is a fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block that provides rapid and accurate DC offset estimates and cancellation techniques to support direct conversion architectures. The fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block combines four mechanisms to rapidly acquire and remove a DC offset estimate after power up, temperature changes, receiver frequency changes, and gain setting changes by increasing high pass loop bandwidth and adjusting DC offset levels at baseband. After removing the DC offset in large portions, the high pass loop bandwidth is decreased to fine tune the previous estimate and to remove any small variation in DC offset due to receiver self-mixing products.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
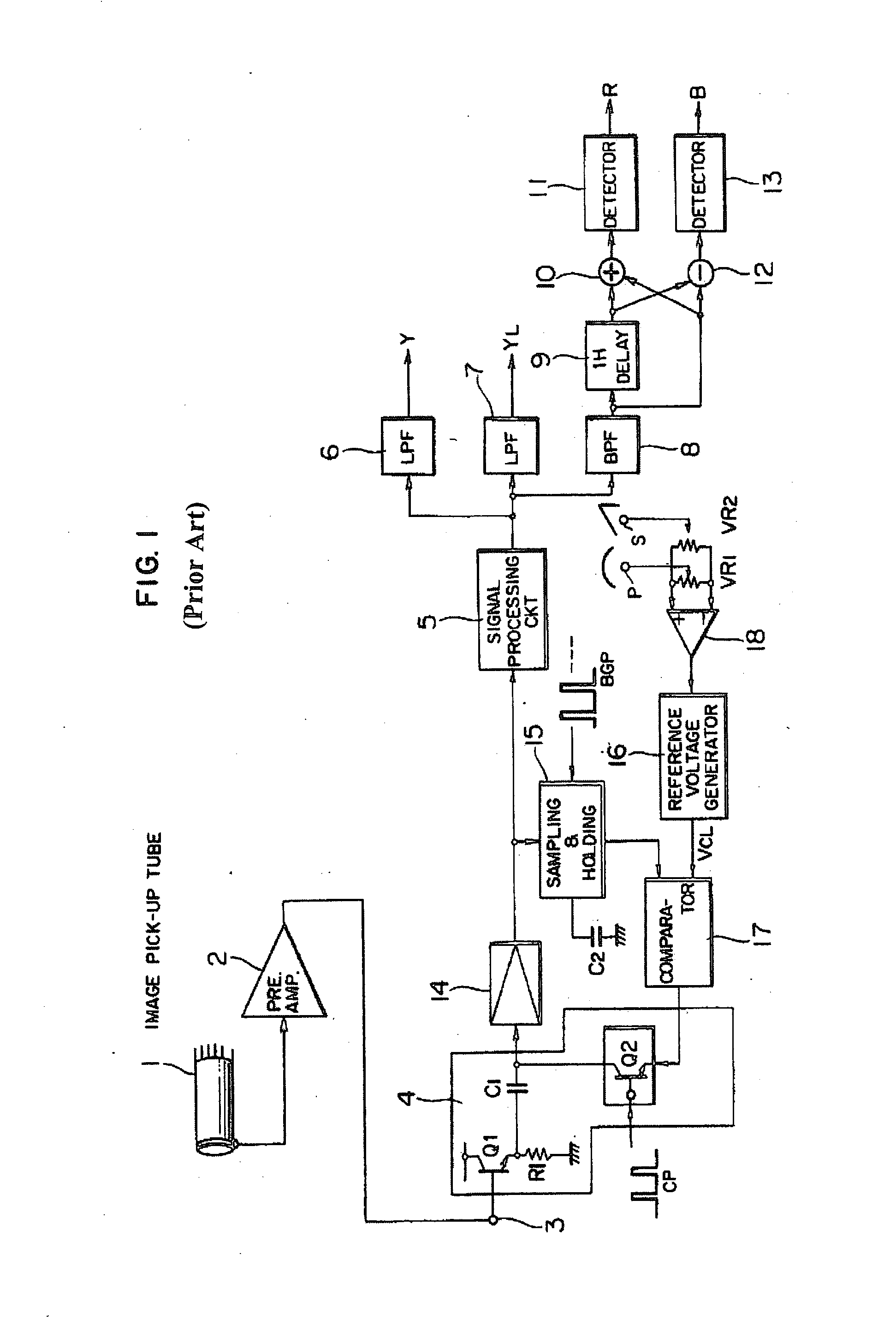
Apparatus and method for emphasizing an outline of a video signal
Video camera which emphasizes an outline of a video signal produced thereby. A detail signal of a video image represented by the video signal is generated and which represents a vertical outline emphasis signal. Edges of the video image and burst-like portions of the video signal are detected, and an edge detection signal is generated that corresponds in one manner to the detected edges and that corresponds in another manner to the detected burst portions. The detail signal is adjusted by the edge detection signal or by a cross color suppression signal generated from the vertical outline emphasis signal. The video signal then is modified by the adjusted detail signal so as to produce the outline emphasized video signal. The detail signal may also be adjusted by a gain setting signal that corresponds to the vertical outline emphasis signal and which is compressed in level when the vertical outline emphasis signal is relatively low.
Owner:SONY CORP
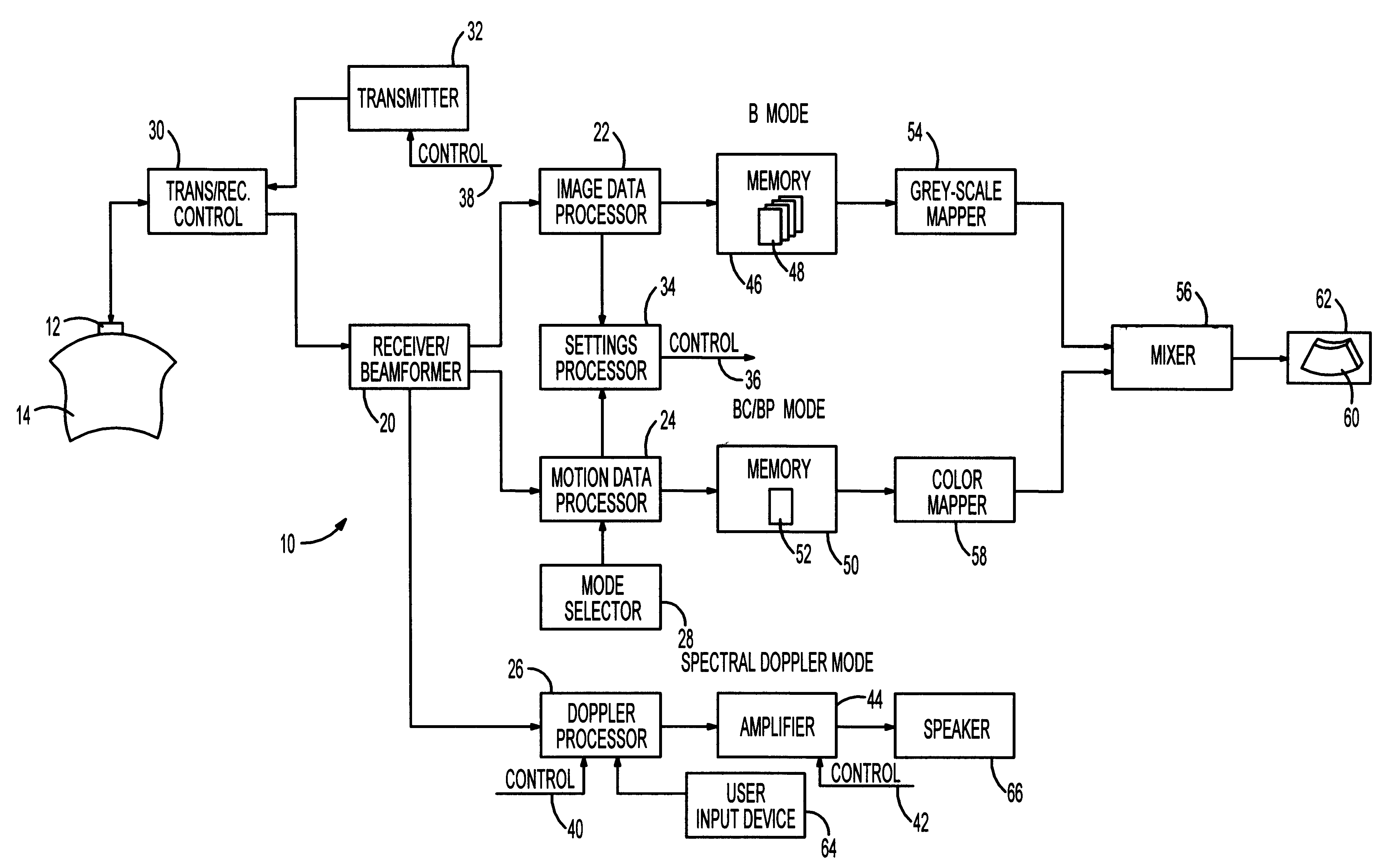
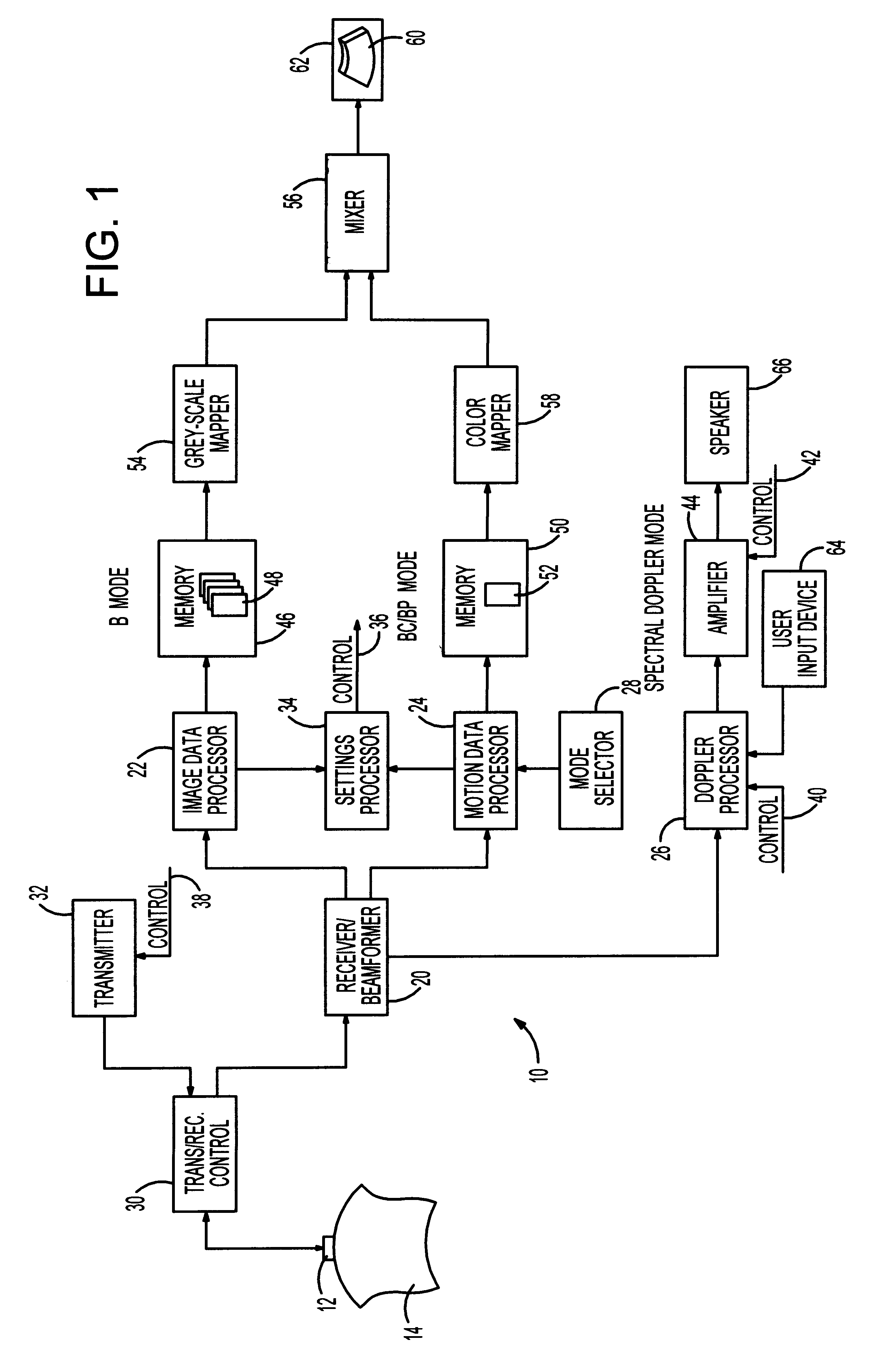
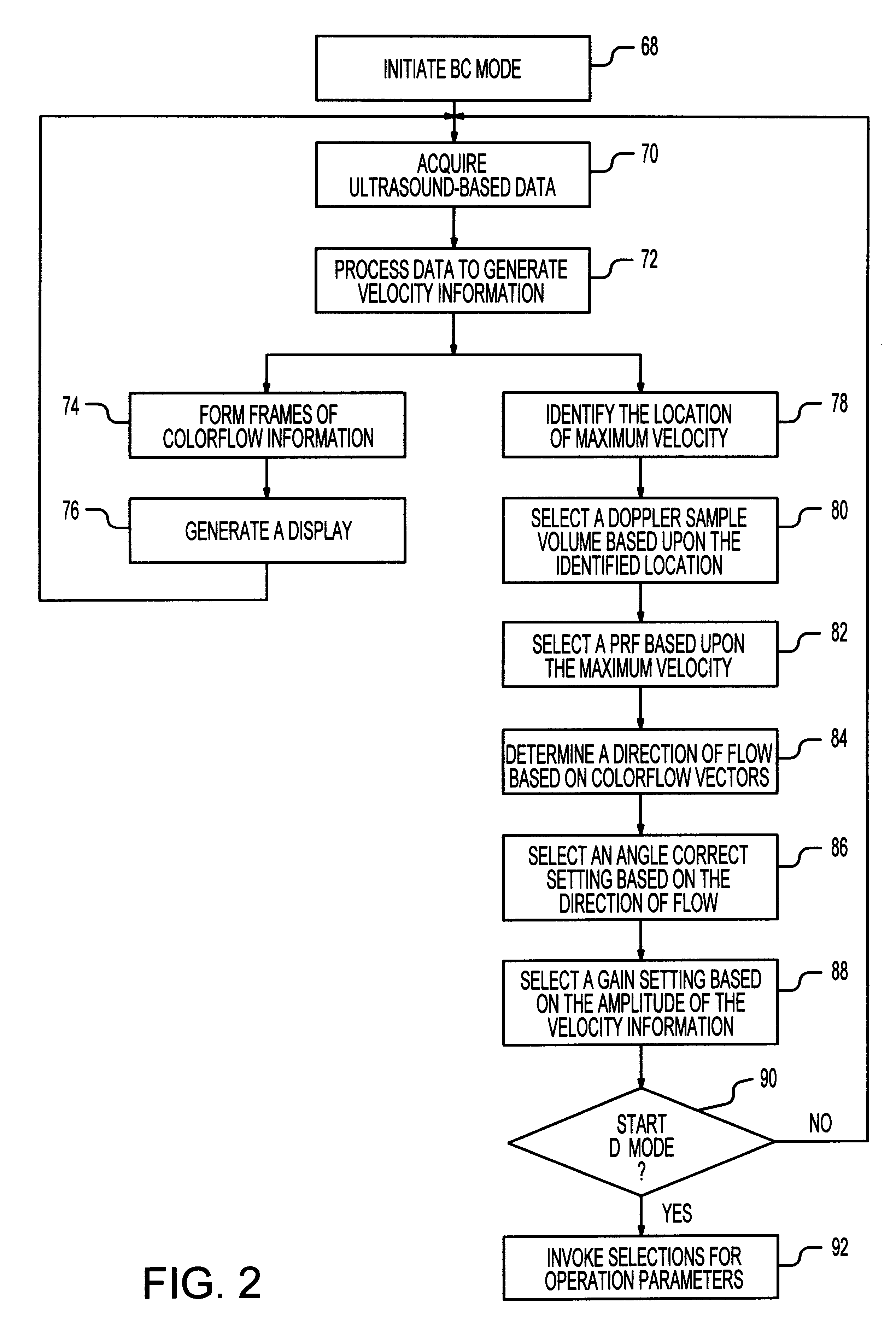
Method and system for pre-determining spectral doppler user parameters
InactiveUS6176830B1Blood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationFrequency spectrum
A method of initializing a spectral Doppler mode of operation for an ultrasonic system includes acquiring ultrasound-based data during a two-dimensional mode of operation for a particular examination session and includes automatically establishing settings for the Doppler mode operation parameters based upon the ultrasound-based data. That is, the ultrasound-based data is processed during the session to select spectral Doppler mode settings that are specific to the ongoing session. The session-specific settings are invoked when the system is switched to the spectral Doppler mode. If the two-dimensional mode is a colorflow mode, the Doppler sample volume can be based upon detecting the location of maximum velocity in the colorflow image, the angle correct setting can be based upon maximum velocities in colorflow vectors, the pulse repetition frequency setting can be based upon the maximum frequency shift detected in the colorflow data, and the gain setting can be based upon the amplitude of colorflow data. On the other hand, if the two-dimensional mode is a power mode, the Doppler sample volume is based upon detecting the region of the power mode image having the strongest signals, the angle correct setting can be based upon detecting the direction of flow, the Doppler pulse repetition frequency can be based upon a scale setting for the power mode data acquisition, and a gain setting can be based upon the amplitude of power mode data. Lastly, if the two-dimensional mode is the grey-scale imaging mode, the selection of a Doppler sample volume can be based upon identifying a dark region near the center of the grey-scale image, the angle correct setting can be based upon the orientation of the boundaries of the identified dark region, and the gain setting can be based upon the amplitude of image data.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
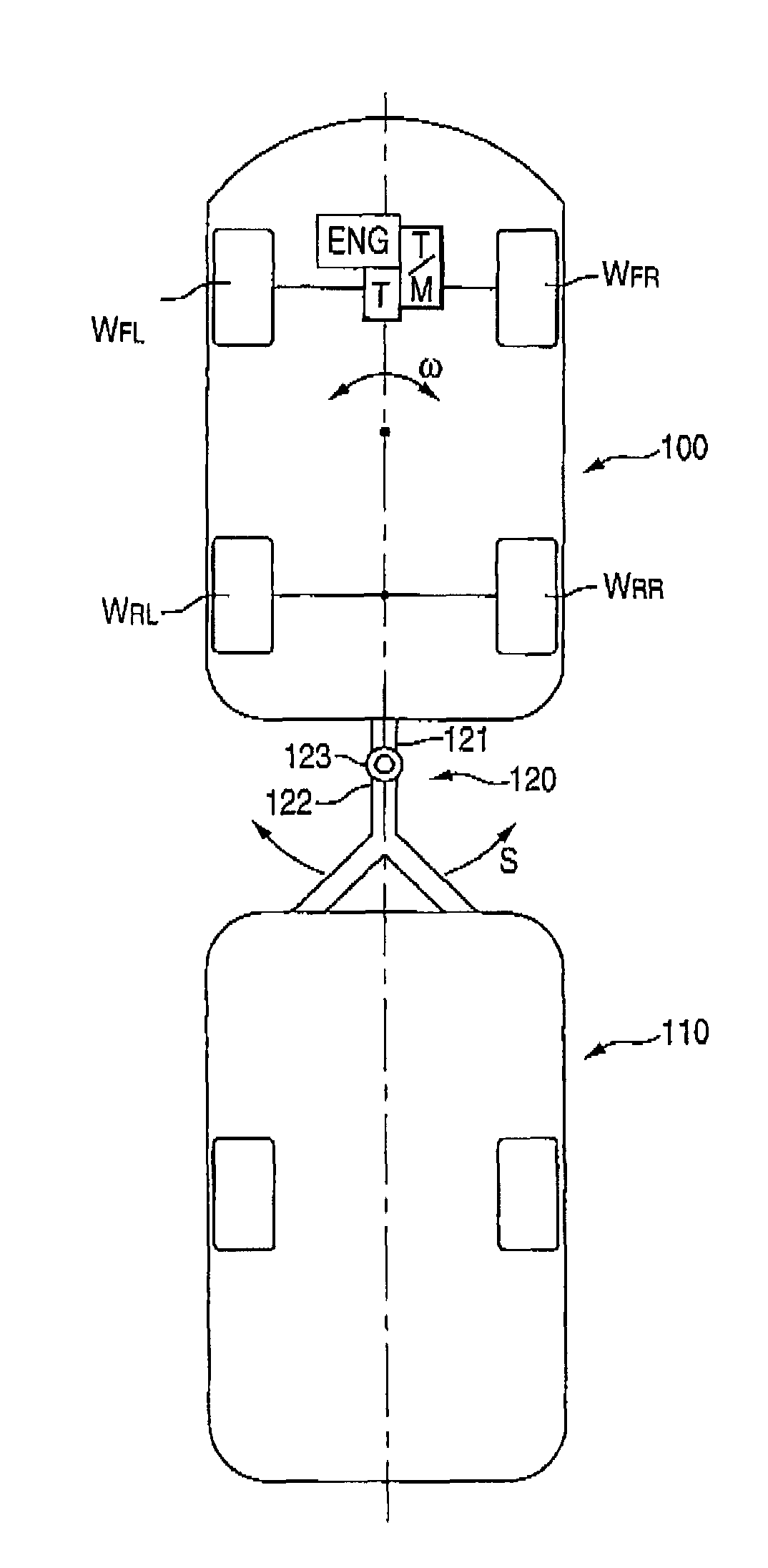
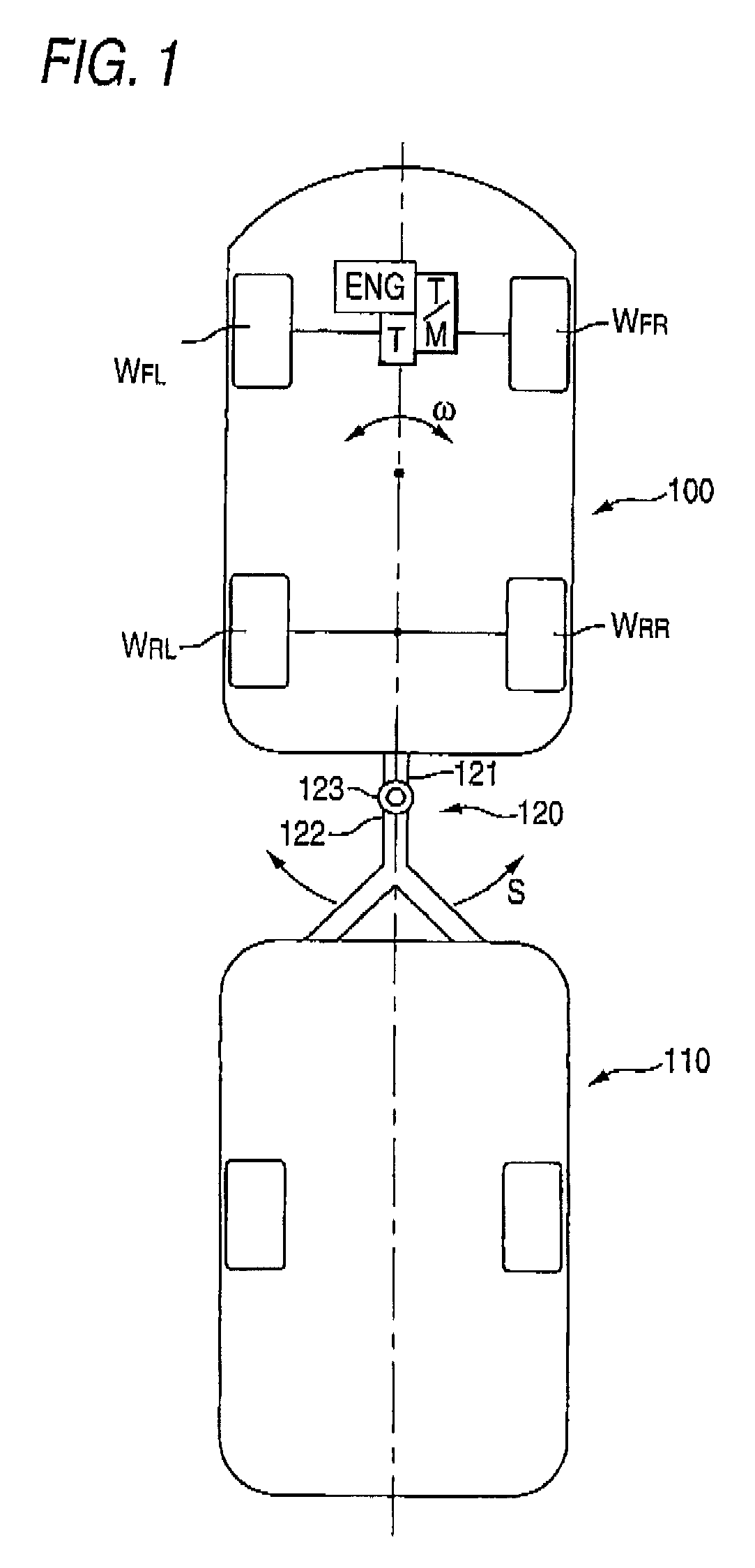
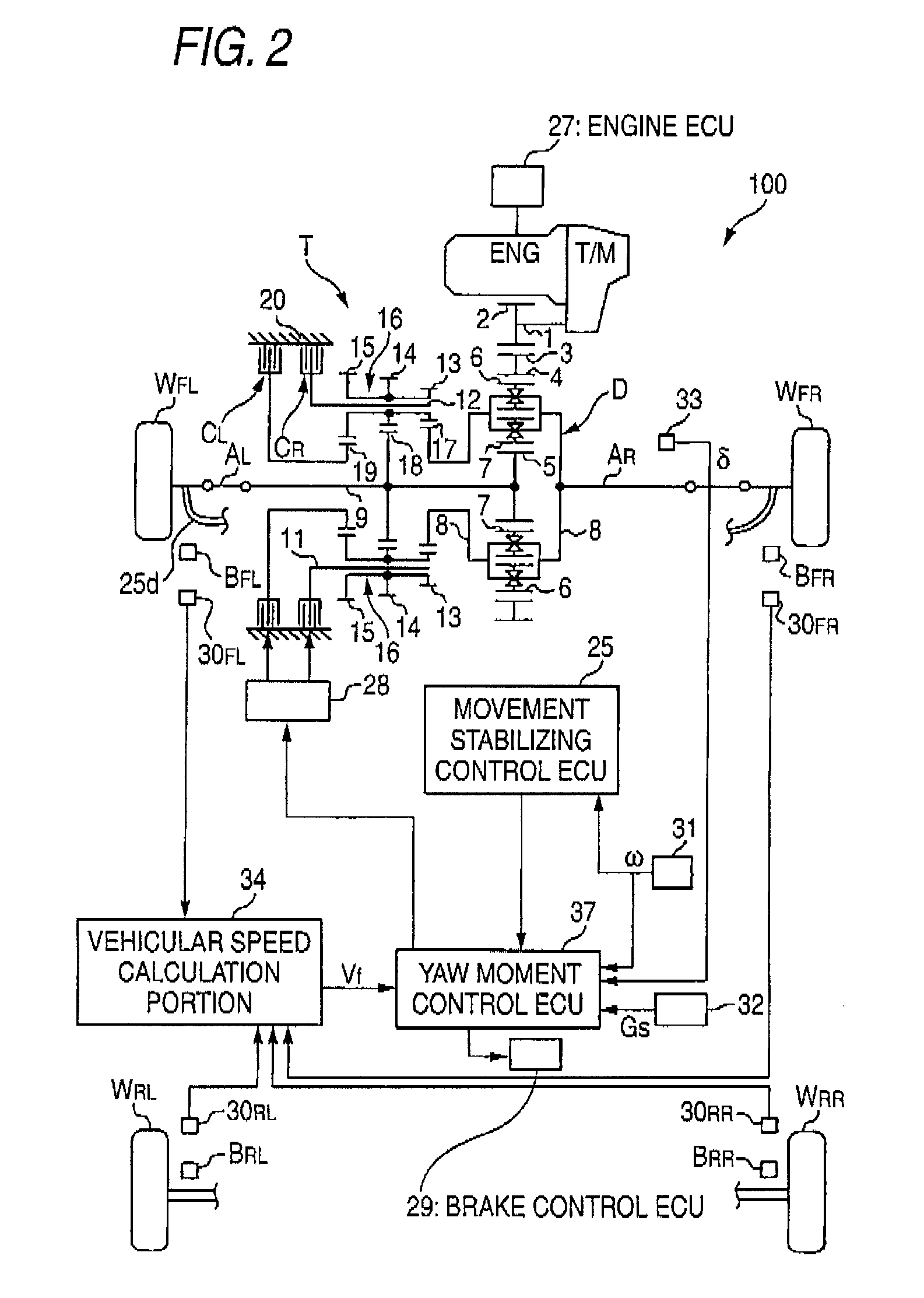
Movement stabilizing apparatus for combination vehicle
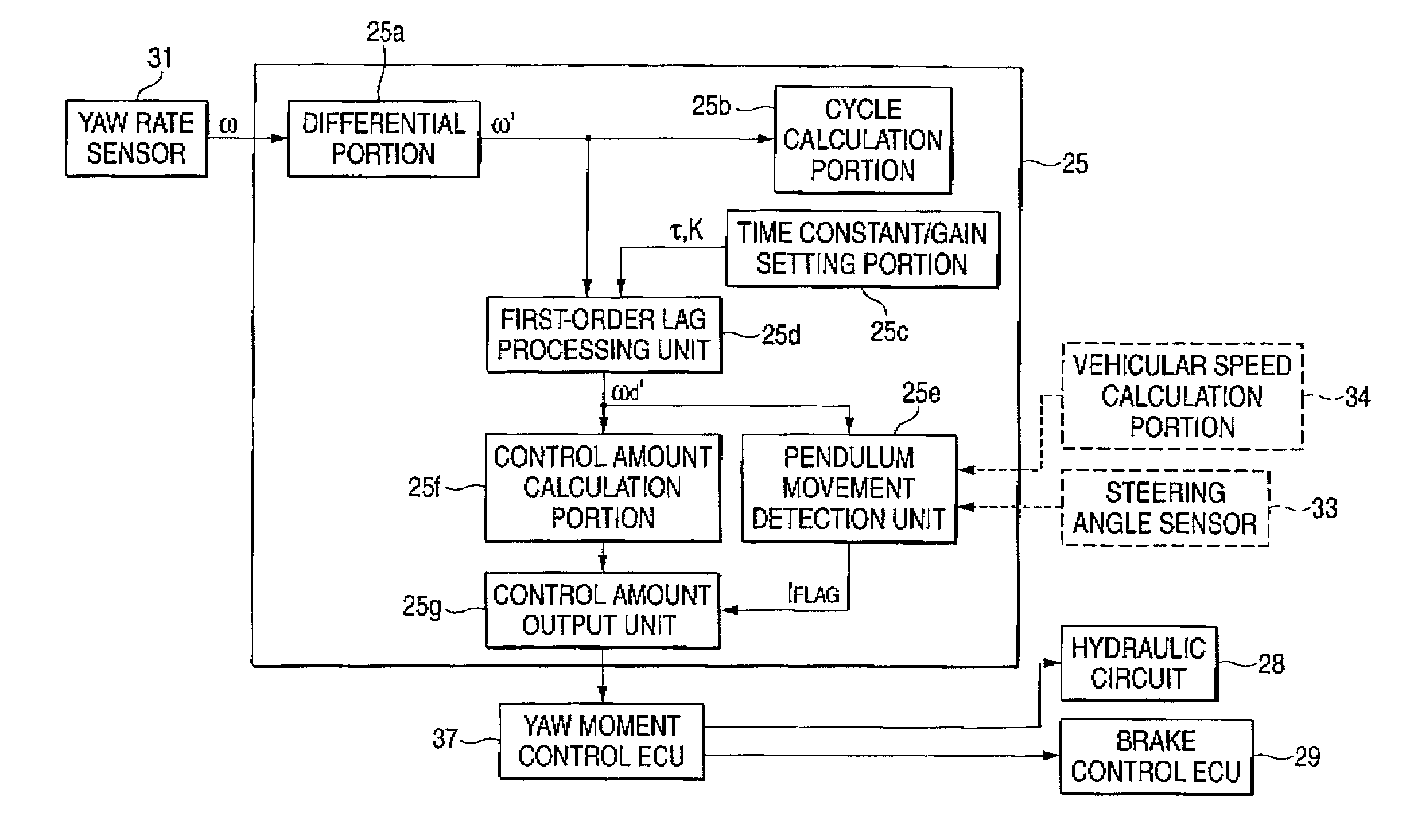
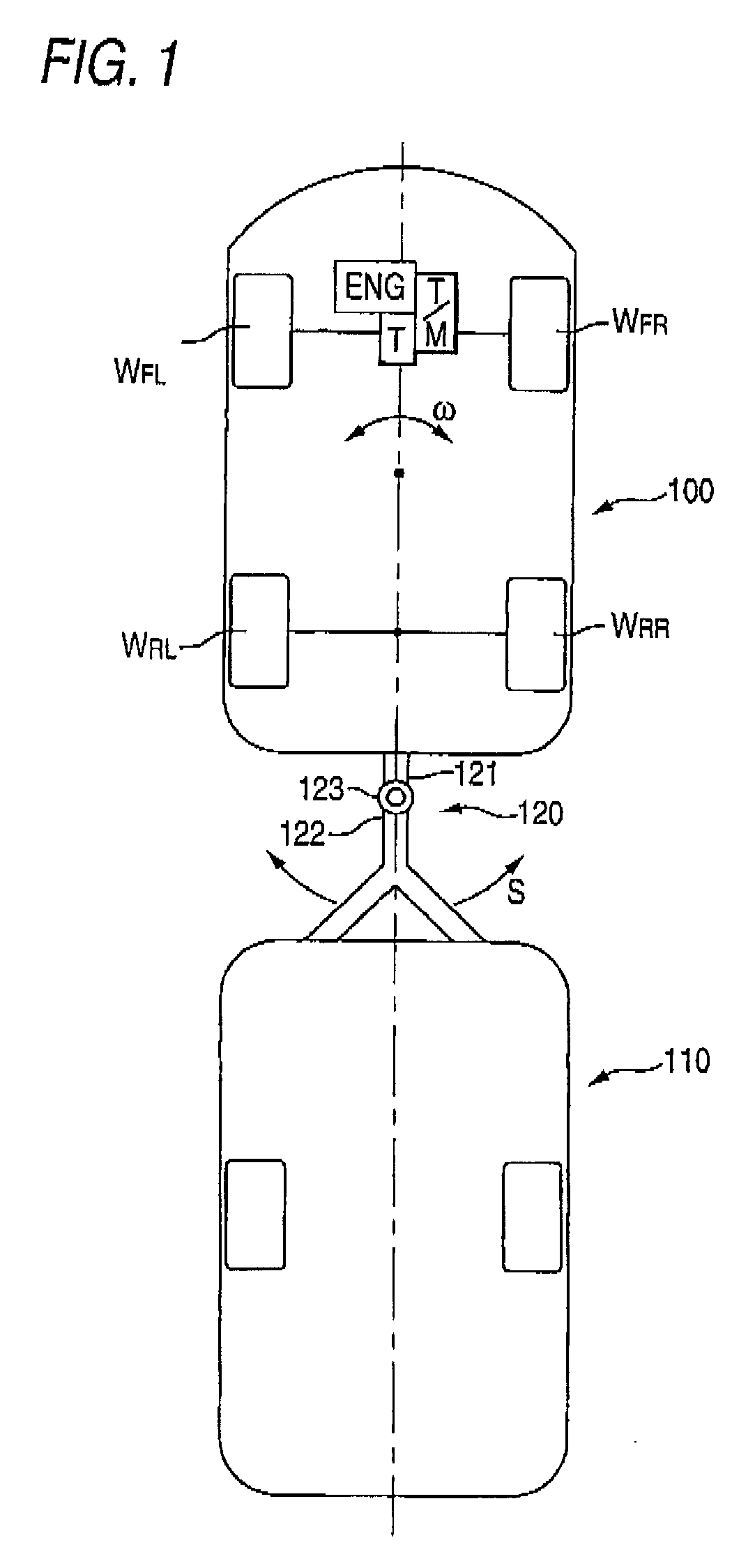
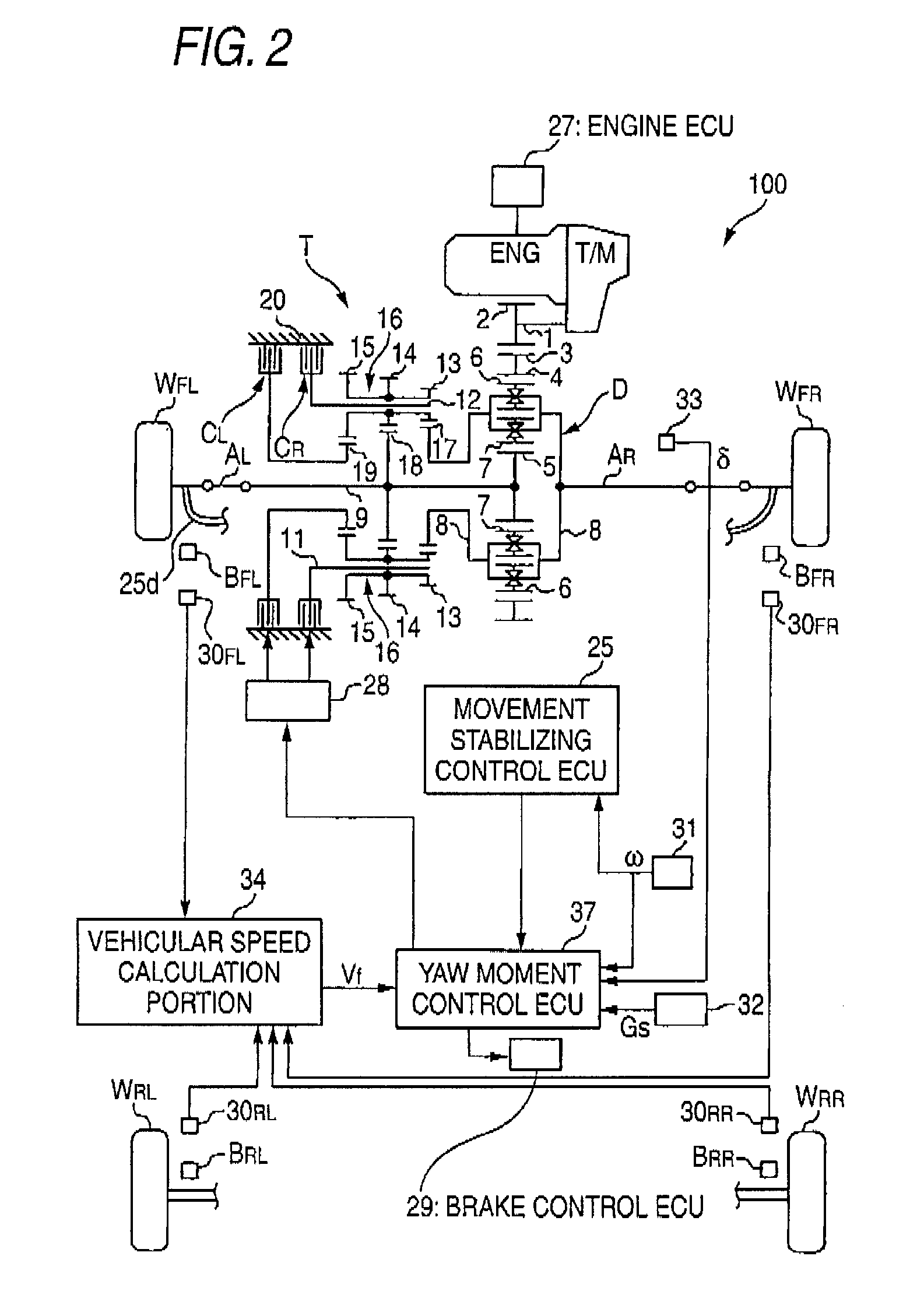
ActiveUS8180543B2Effectively suppress the pendulum movement of a vehicleAgricultural machinesAnalogue computers for trafficLagGain setting
A movement stabilizing control ECU 25 includes a differential unit 25a, a cycle calculation unit 25b, a time constant / gain setting portion 25c, a first-order lag processing unit 25d, a pendulum movement detection unit 25e, a control amount calculation portion 25f and a control amount output unit 25g. The time constant / gain setting portion 25c sets a time constant τ and a gain K used at the time of subjecting a yaw acceleration ω′ which is a time-differential value of a yaw rate ω to the first-order lag processing at the first-order lag processing unit 25d, with reference to a function or data of a look-up table, for example, depending on the cycle or the frequency of the yaw acceleration ω′ due to the pendulum movement. The control amount calculation portion 25f multiplies the amplitude of a yaw acceleration ωd′ outputted from the first-order lag processing unit 25d by a predetermined constant to calculate a yaw control amount with a phase in opposite to that of the yaw acceleration ωd′ and outputs the yaw control amount to the control amount output unit 25g.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
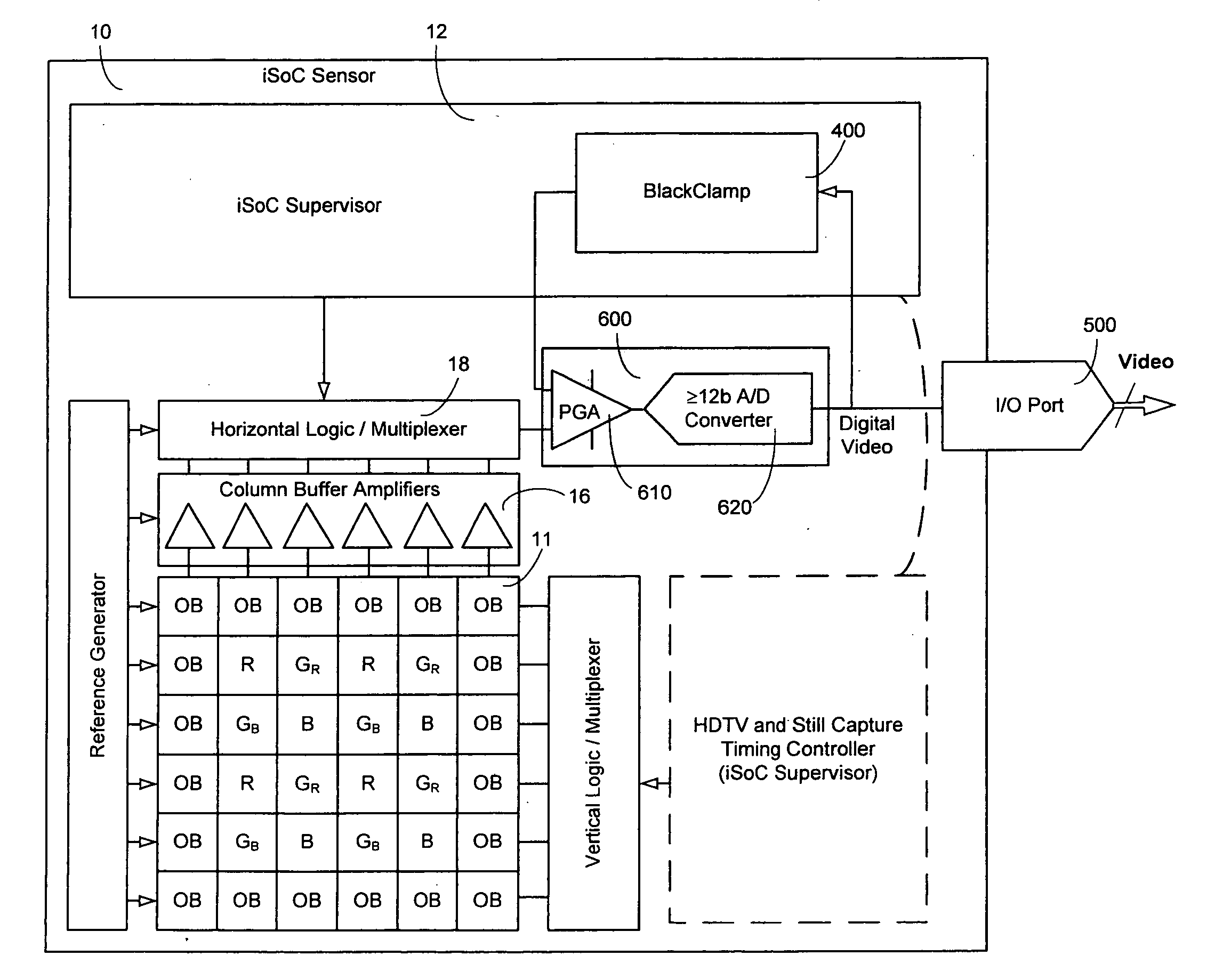
Cross-coupled differential Dac-based black clamp circuit
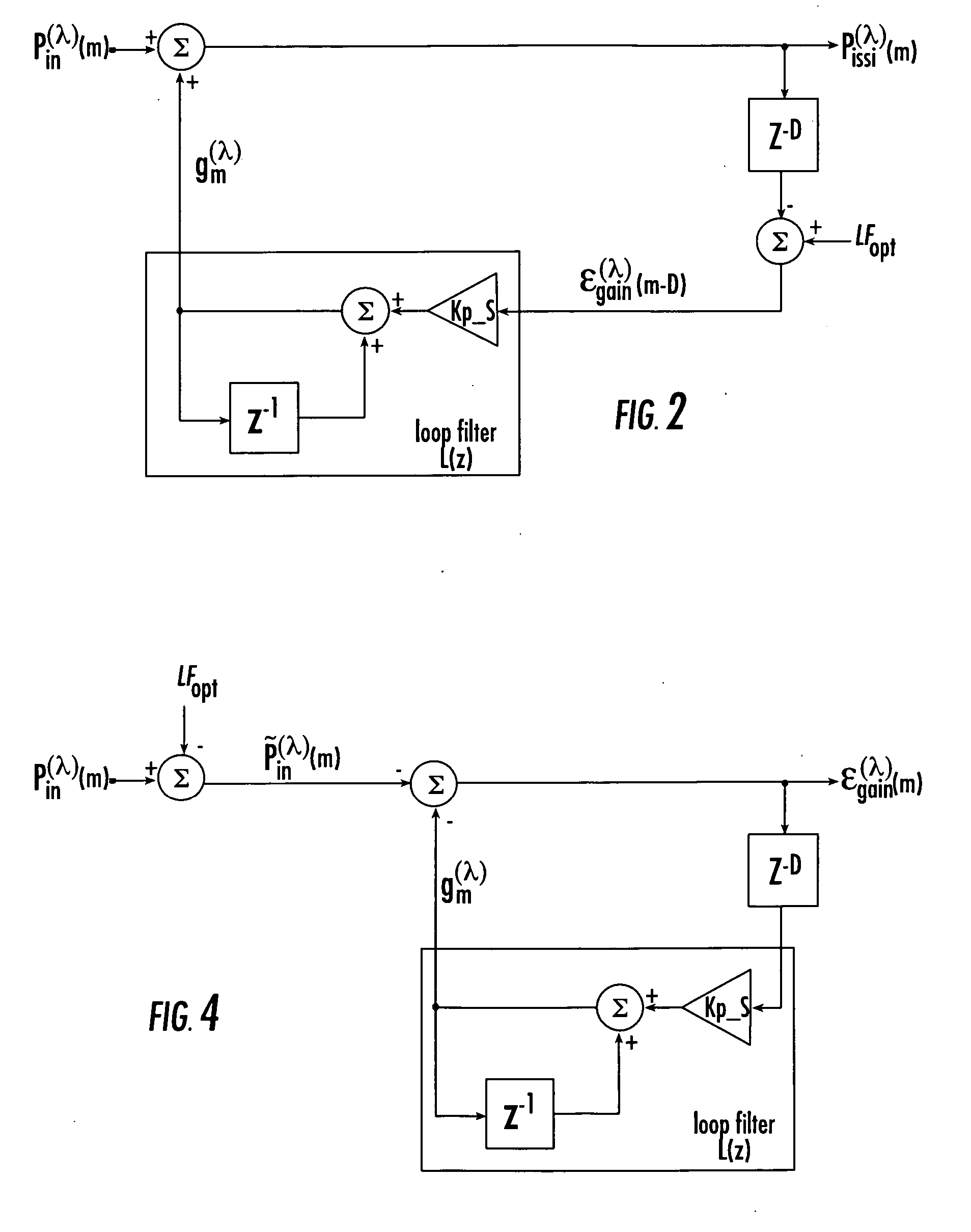
InactiveUS20080218609A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsEngineeringGain setting
A black clamp circuit for an image sensor utilizes a differential programmable gain amplifier and a feed-back loop to adjust a black level based on comparison to a reference black level. The gain (and therefore step size and range) of the feed-back loop constant for all programmable gain amplifier gain settings. The gain of the fee-back loop is kept constant by adjusting the values of programmable capacitors in the circuit.
Owner:ALTASENS
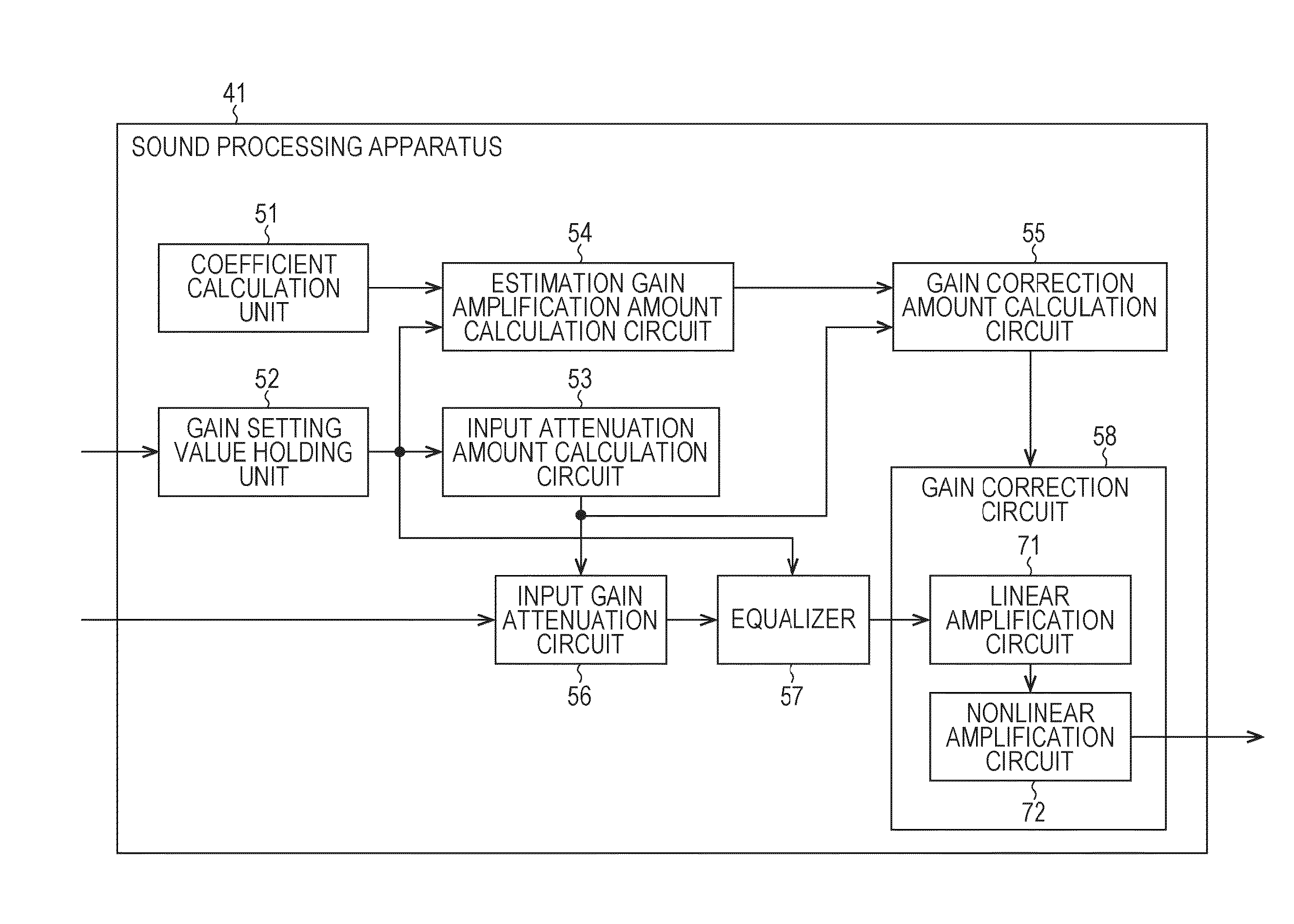
Sound processing apparatus, method, and program
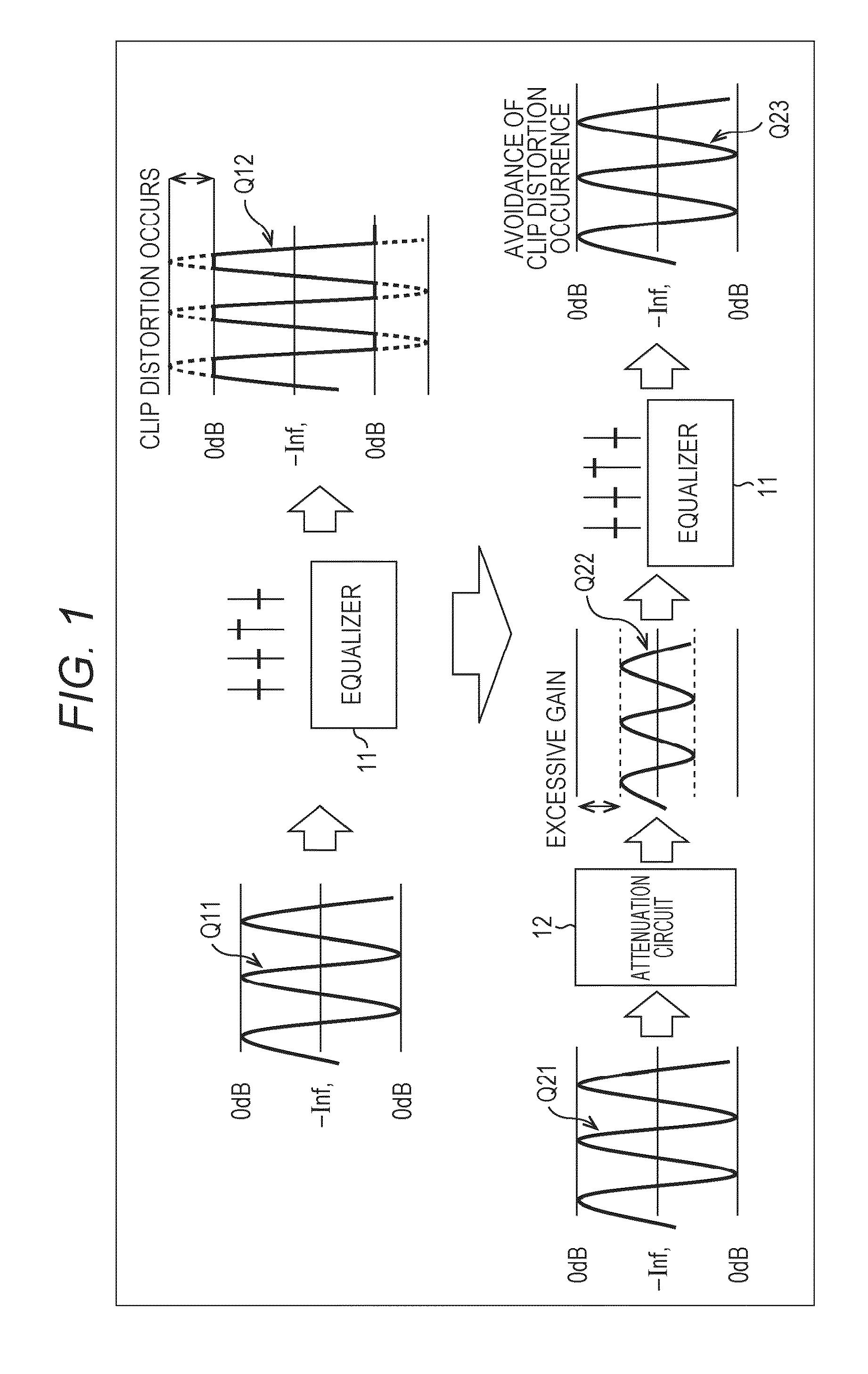
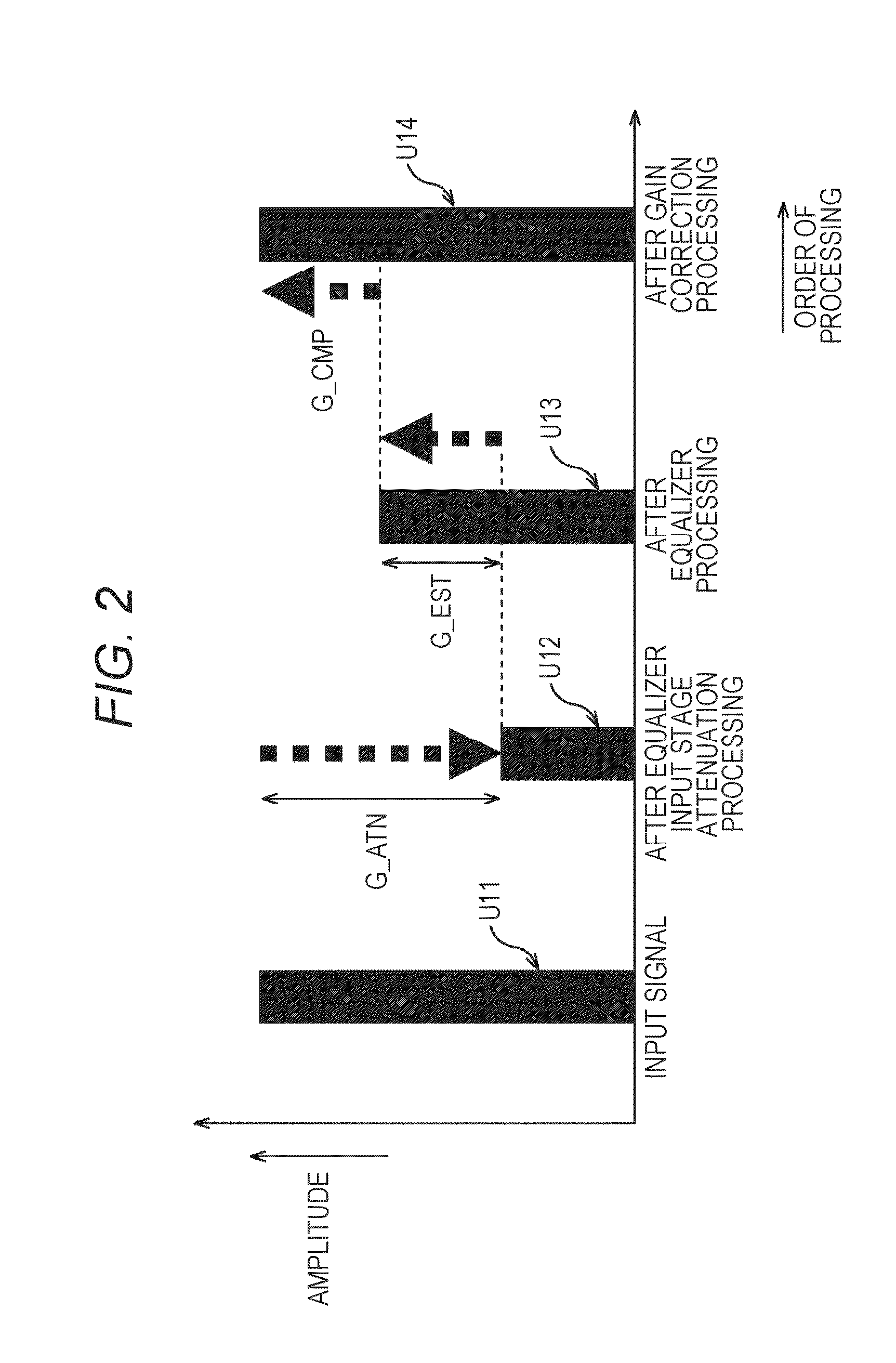
ActiveUS9294062B2Reduce quality degradationQuality improvementAnalog signal digital controlAutomatic tone/bandwidth controlUltrasound attenuationWeight coefficient
The present technique relates to a sound processing apparatus, a method, and a program capable of alleviating degradation of the quality of sound in a case where the gain of a sound signal is amplified.When equalizer processing for adjusting the gain of each frequency band of an input signal on the basis of a gain setting value is performed, an input signal is attenuated by an input attenuation amount derived from the gain setting value, and the equalizer processing is performed on the input signal attenuated. The amount of amplification of the gain of the input signal in the equalizer processing is estimated on the basis of the gain setting value and a weight coefficient of each frequency band derived from a generally-available music signal prepared in advance, and a difference of the estimation value and the input attenuation amount is calculated as a gain correction amount. Further, nonlinear amplification processing is performed on the input signal so as to actually amplify the input signal, which has been subjected to the equalizer processing, by a gain correction amount, and an output signal is obtained. The present technique can be applied to a sound processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
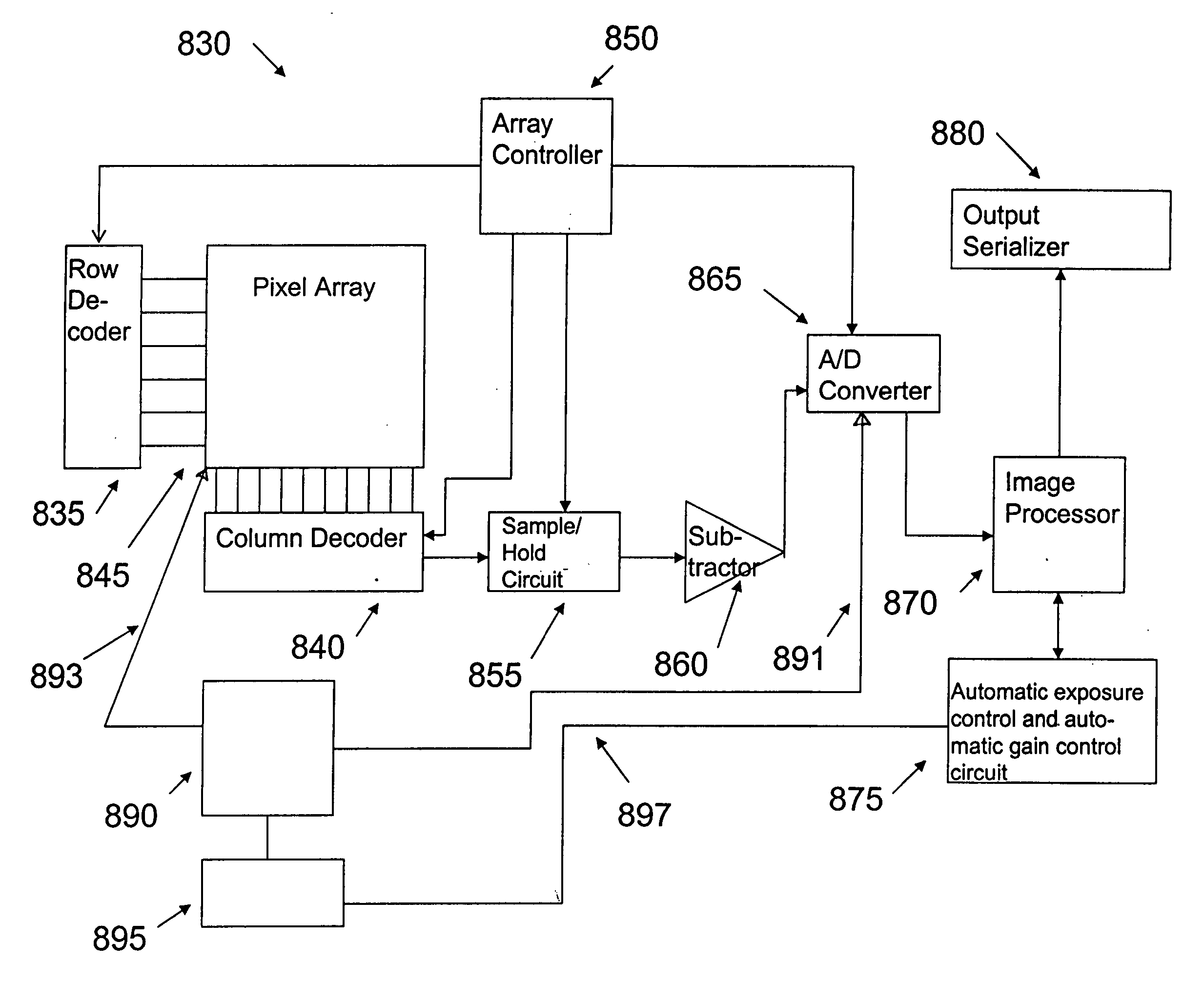
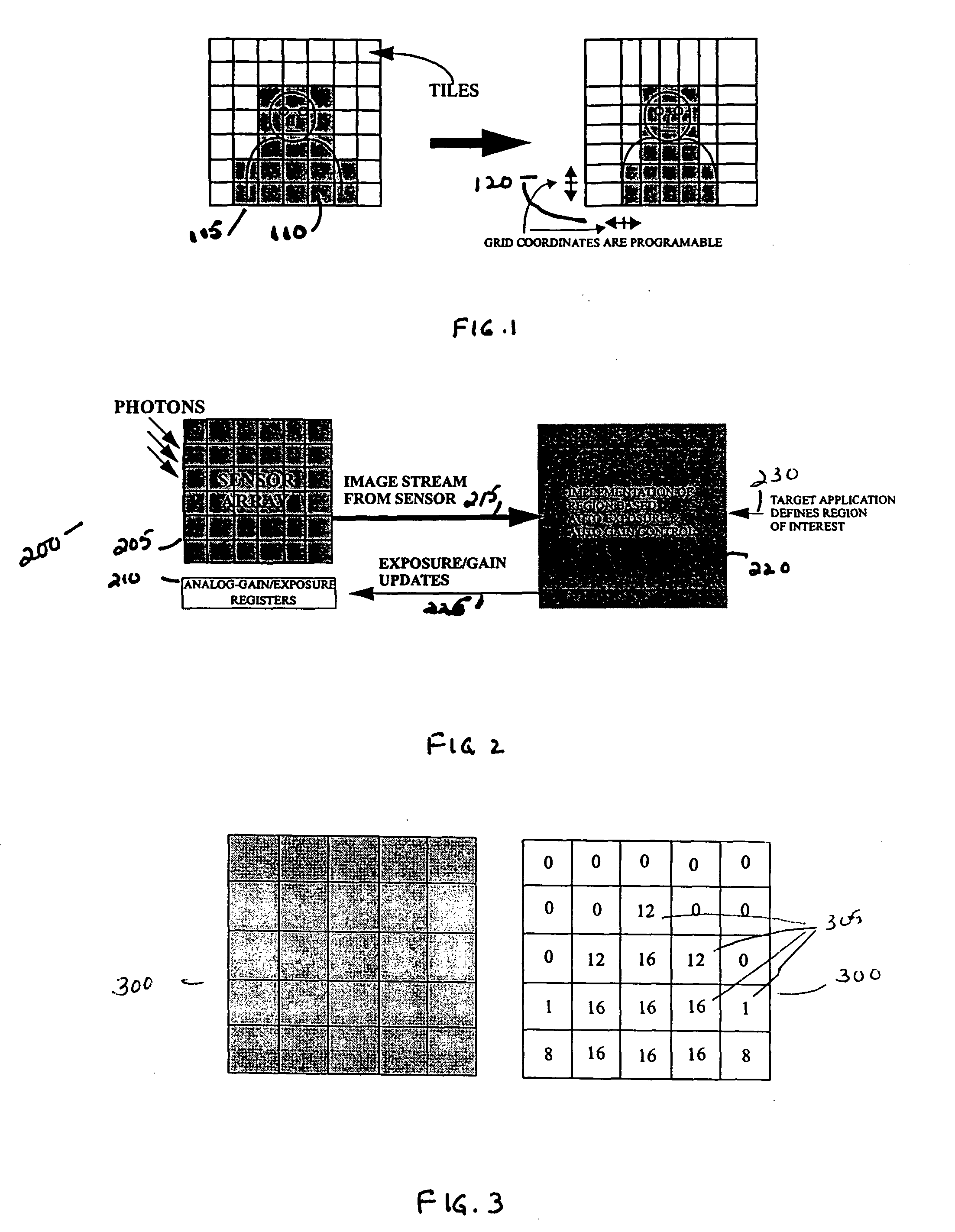
Region-based auto gain control and auto exposure control method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050057666A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSensor arrayExposure control
An apparatus and method for performing automatic exposure and gain control while minimizing oscillations as well as providing a good response time, for example, a lag time or a settling time of about one frame. The automatic exposure and gain controls are performed not only on the image as a whole but on a weighted region of interest. If the contrast in the image exceeds the dynamic range of the sensor array, then the image in the region of interest will improve at the expense of the remainder of the image. A region of interest is a selected subset of tiles upon which automatic exposure and gain control will be based. The tiles are defined by a grid system having grid coordinates, which are programmable. Image sensors have to receive feedback with regular updates of exposure and gain settings based on ever changing light conditions.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
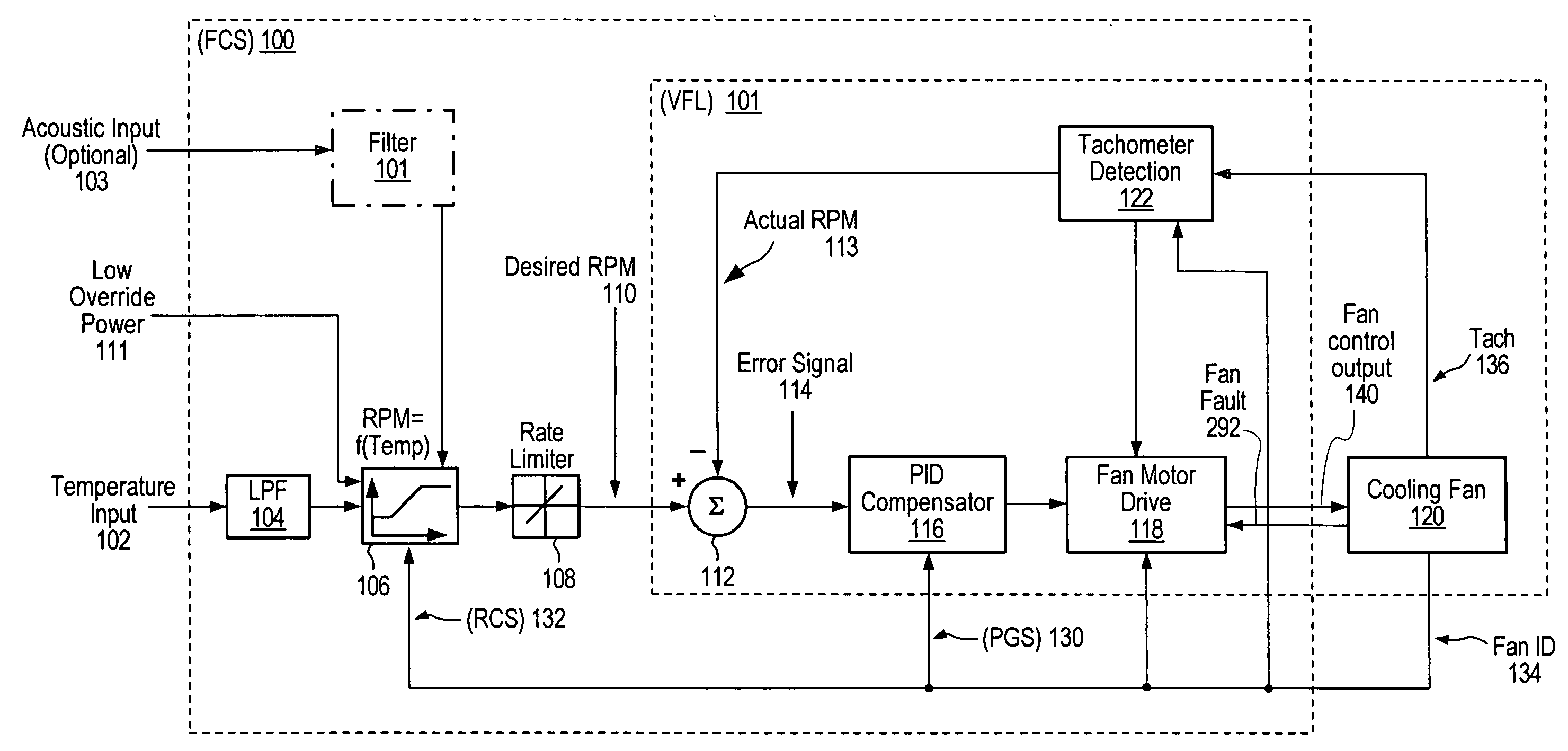
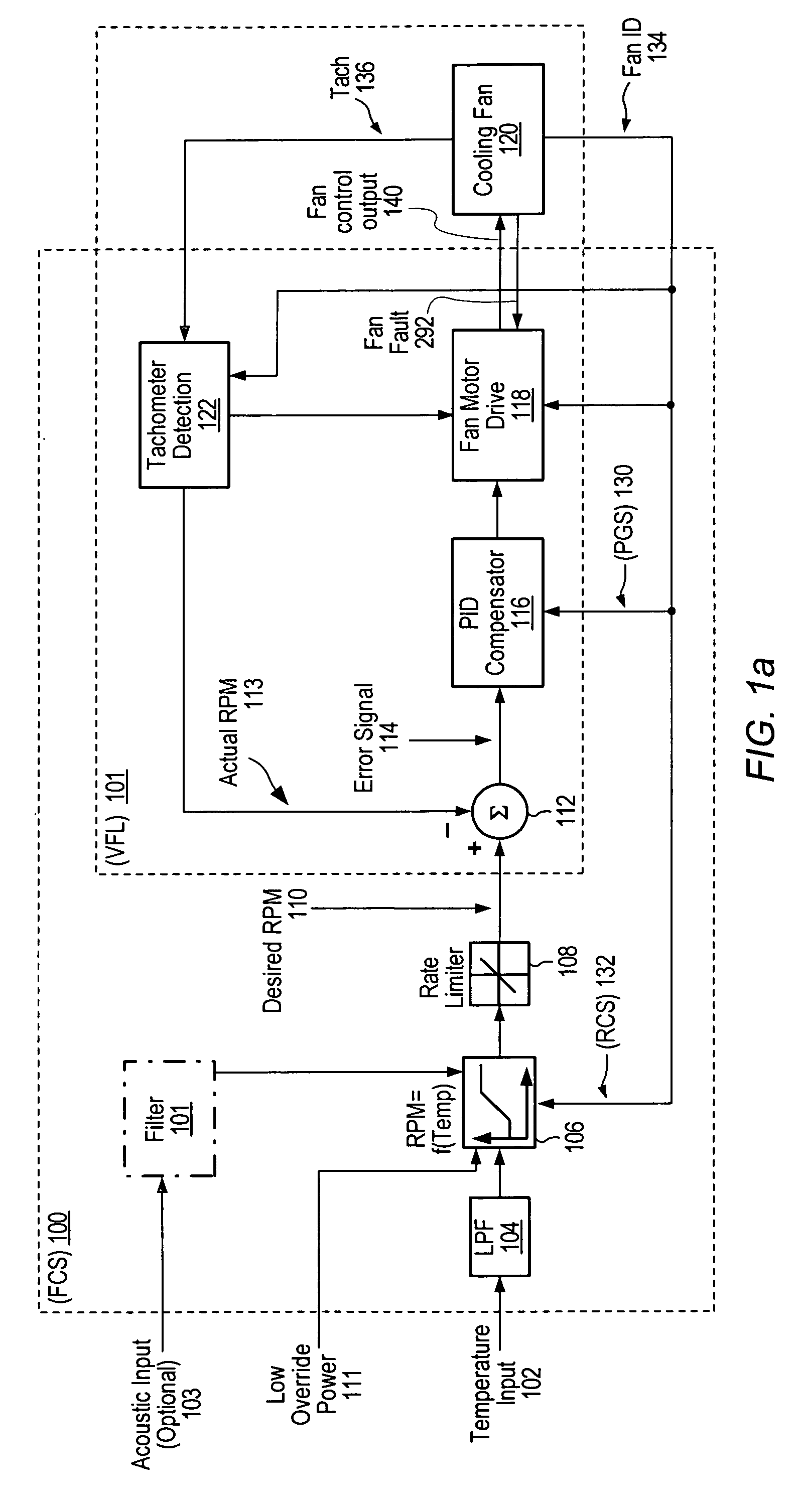
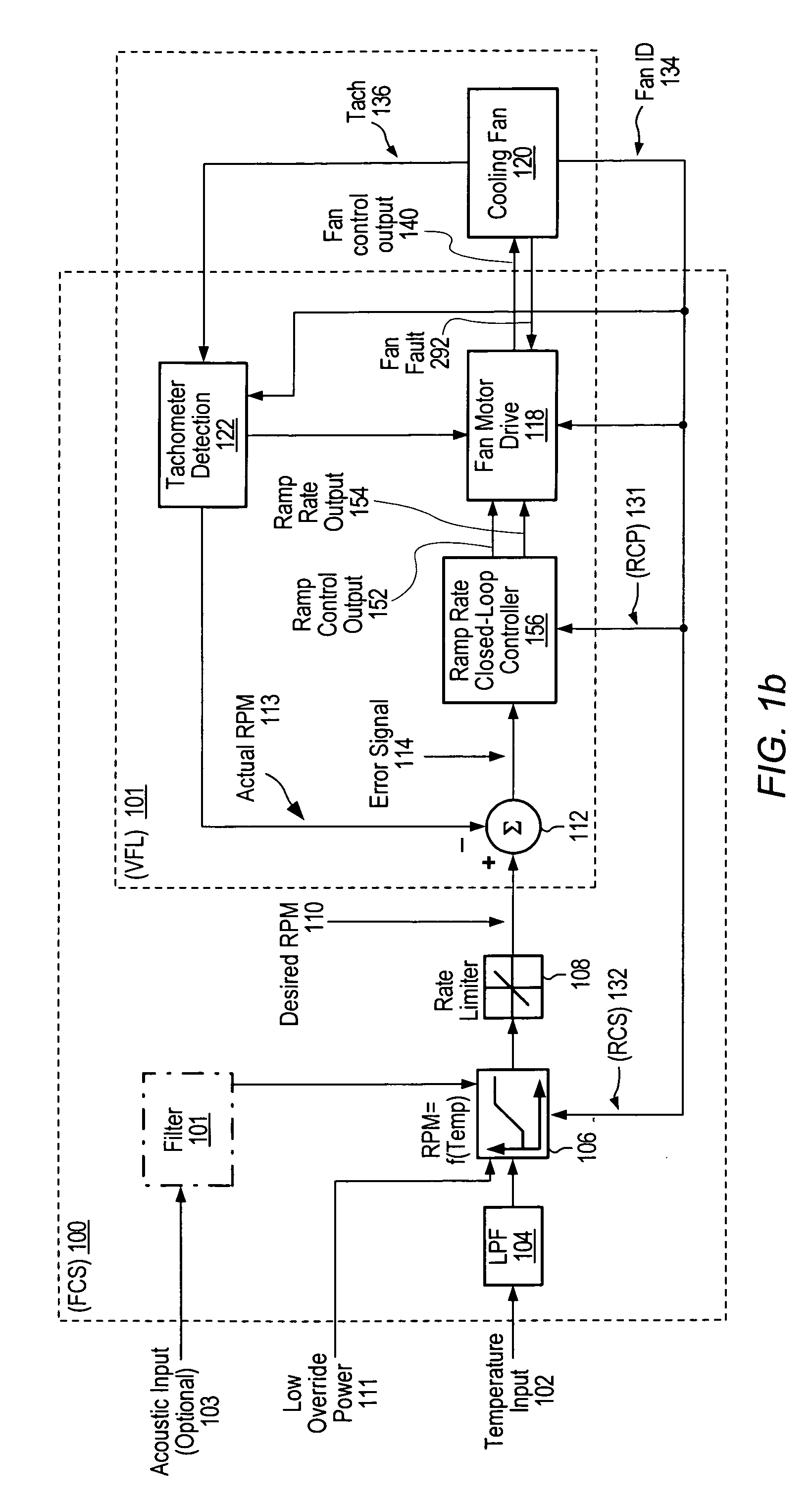
Adaptive controller for PC cooling fans
ActiveUS7138781B2Reduce complexity and costLow costSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlMicrocontrollerClosed loop
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
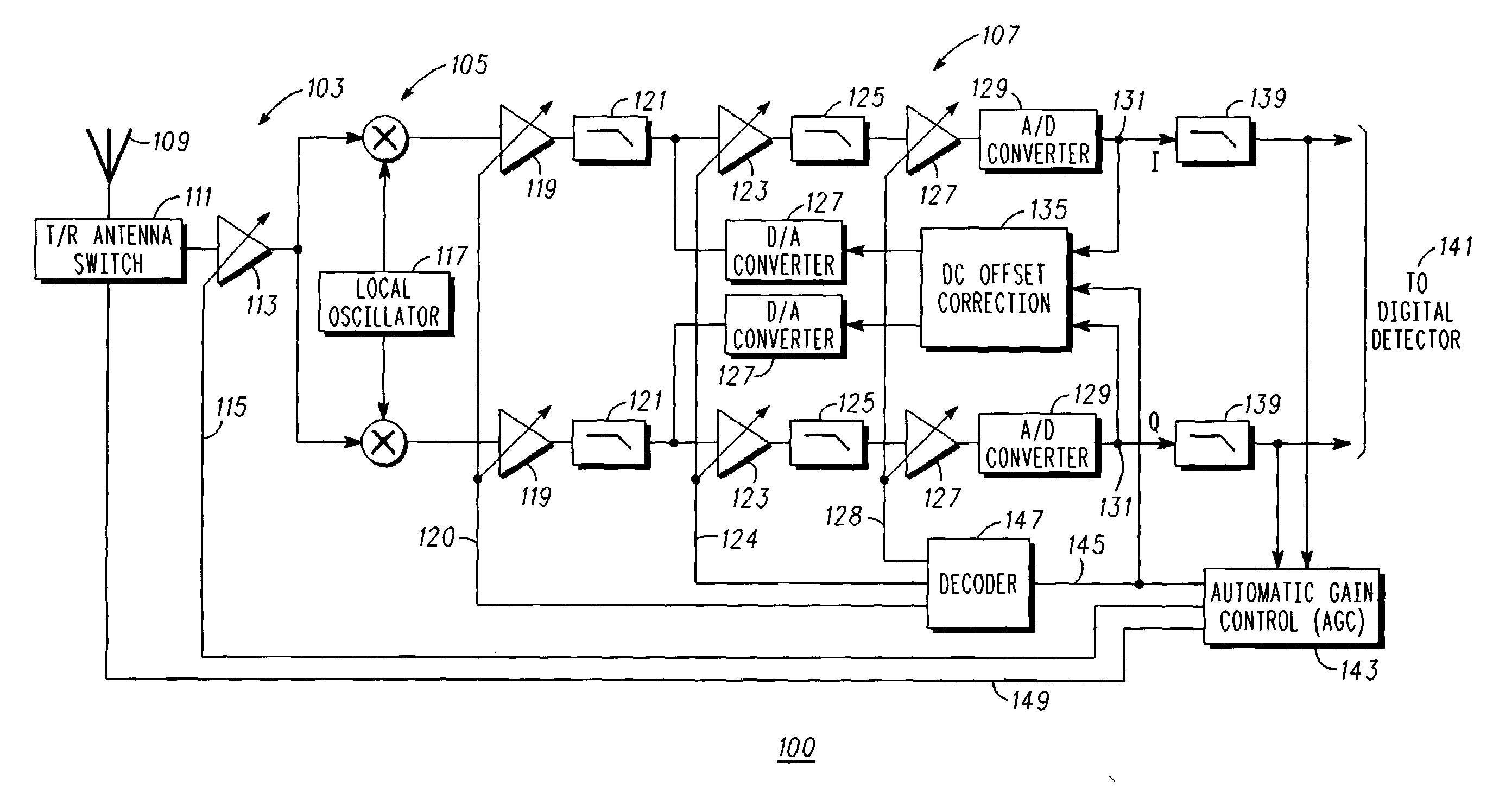
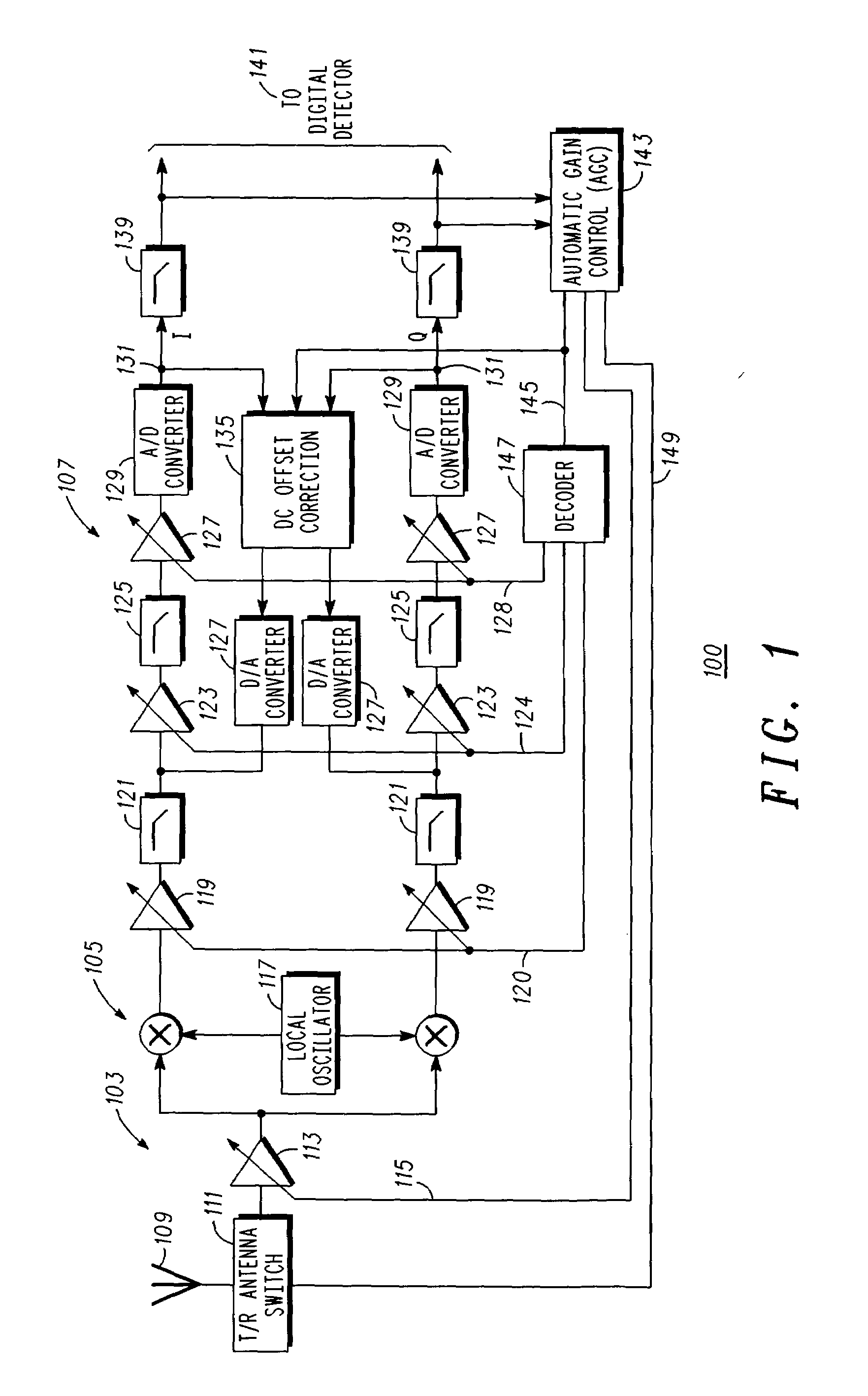
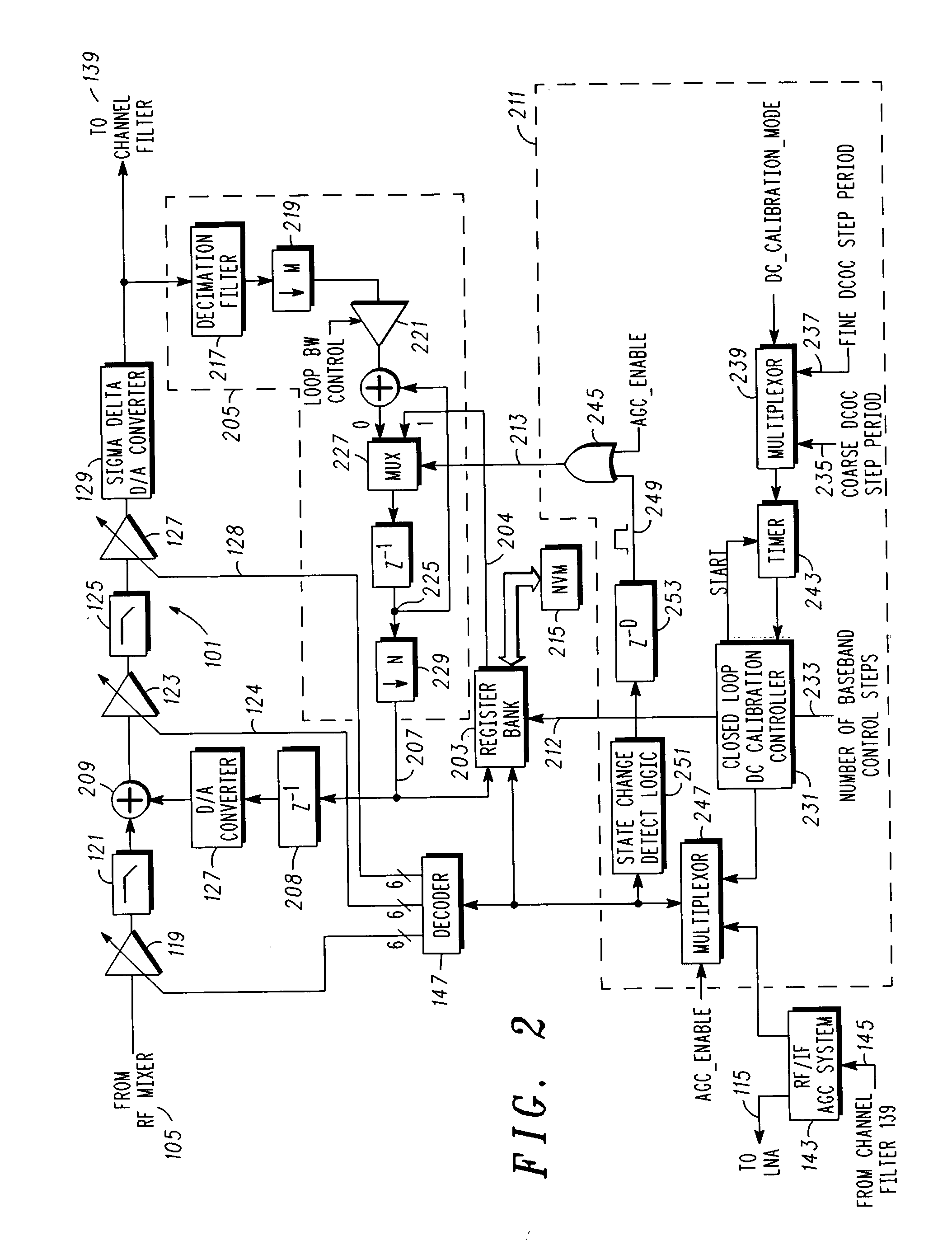
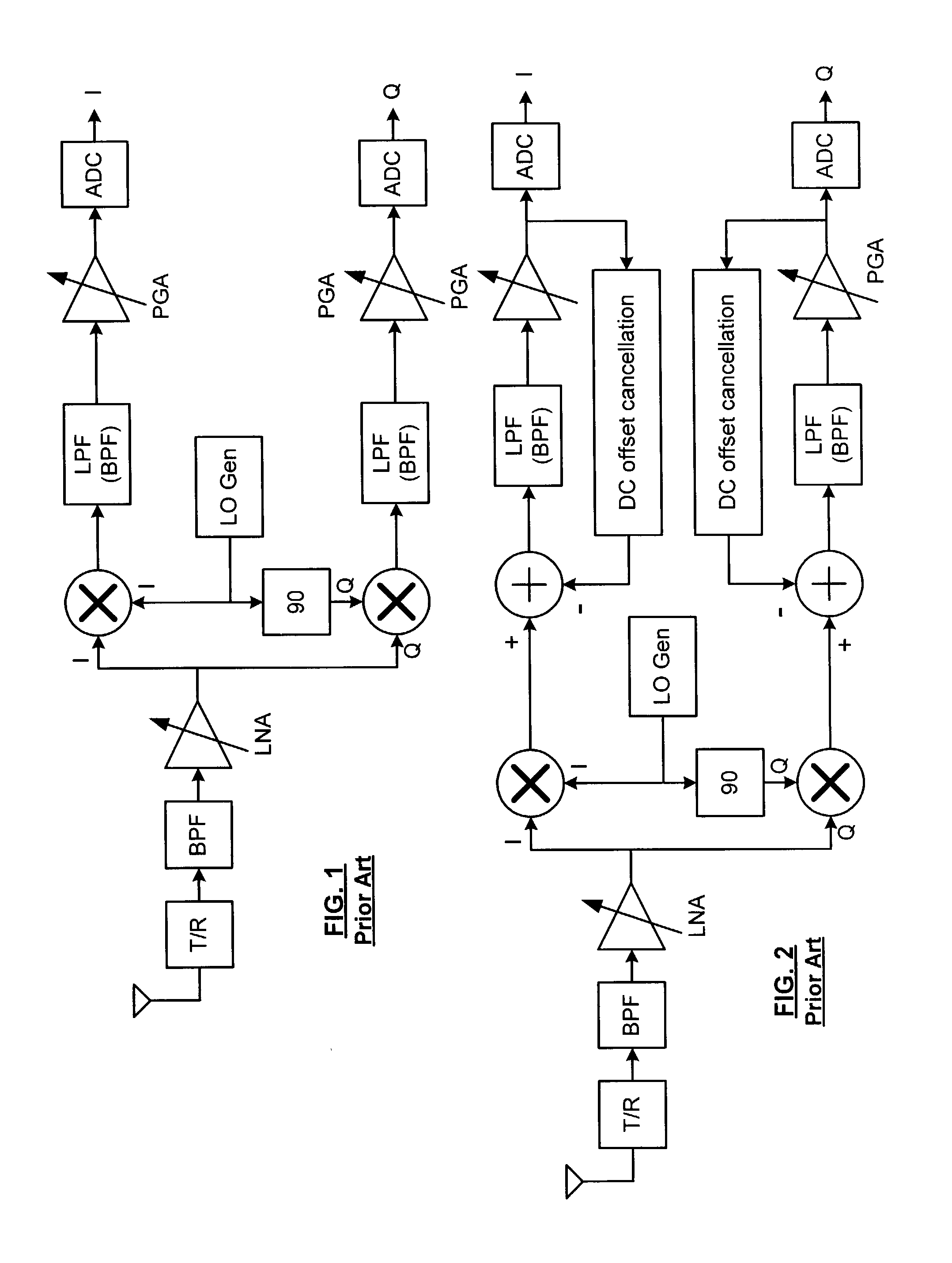
DC offset correction for direct conversion receivers
InactiveUS20070293180A1Radio transmissionAngle demodulation by oscillations conversionDirect-conversion receiverClosed loop
A direct current (DC) offset correction system for a direct conversion receiver and corresponding receiver and methods facilitate reduction of DC offsets in such receivers. One method includes calibrating a DC offset correction system in a closed loop configuration over each of a plurality of gain settings to provide a plurality of offset data for an operating mode of the direct conversion receiver; selecting one of the plurality of offset data based on a current gain setting of the direct conversion receiver as supplied, e.g., by an AGC system; and operating the DC offset correction system in an open loop configuration using the one of the plurality of offset data to correct for a DC offset in the direct conversion receiver.
Owner:APPLE INC
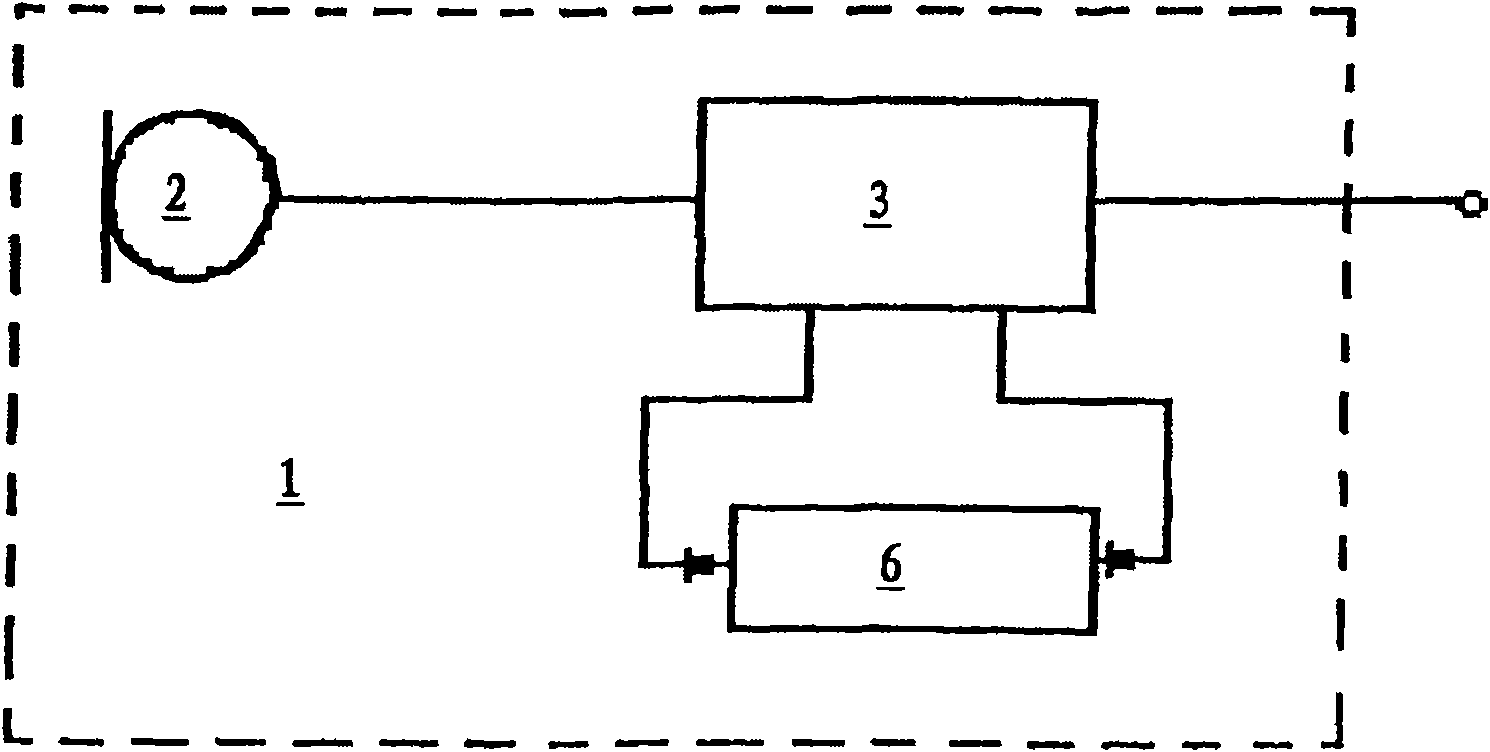
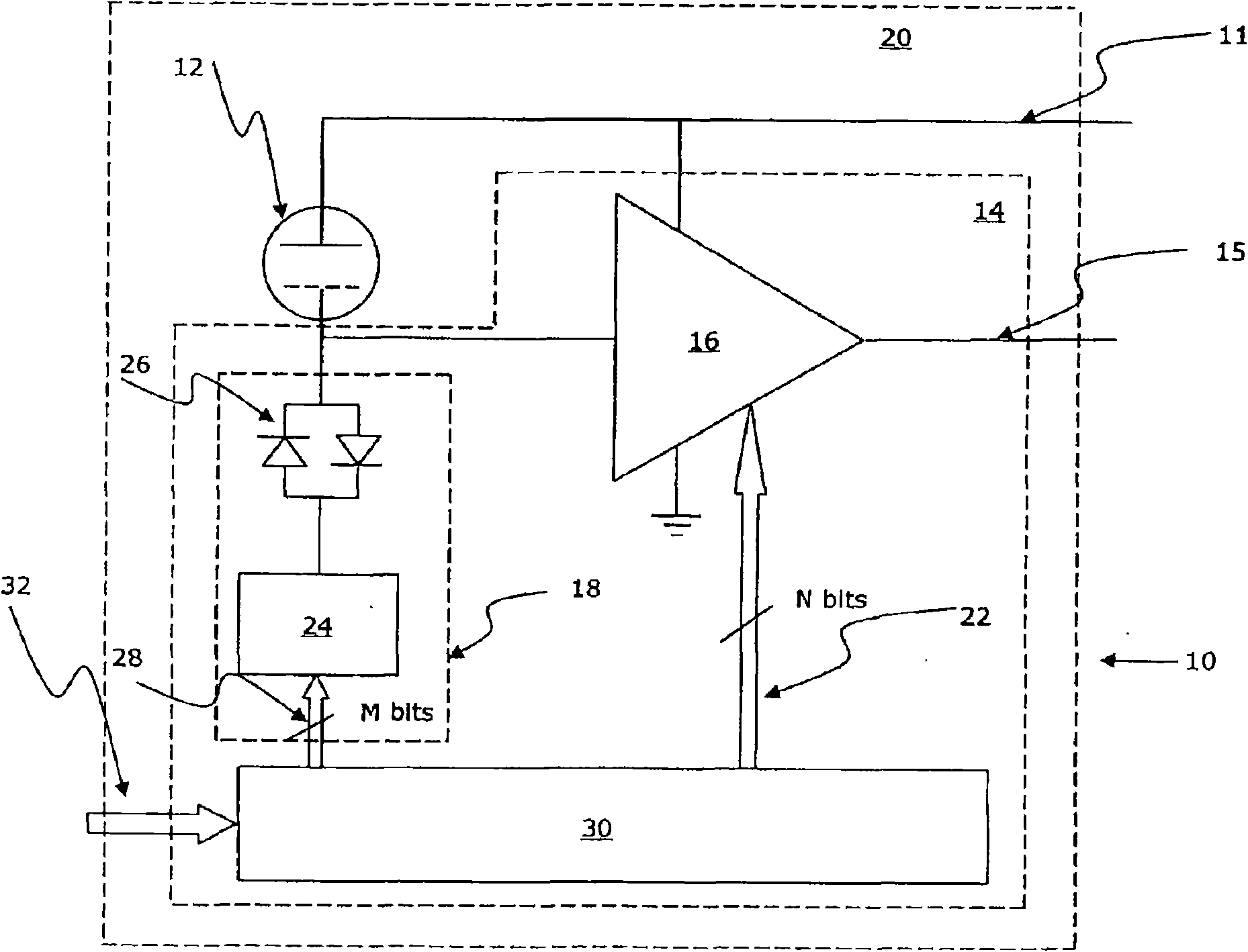
Method and device for calibrating sensitivity of microphone
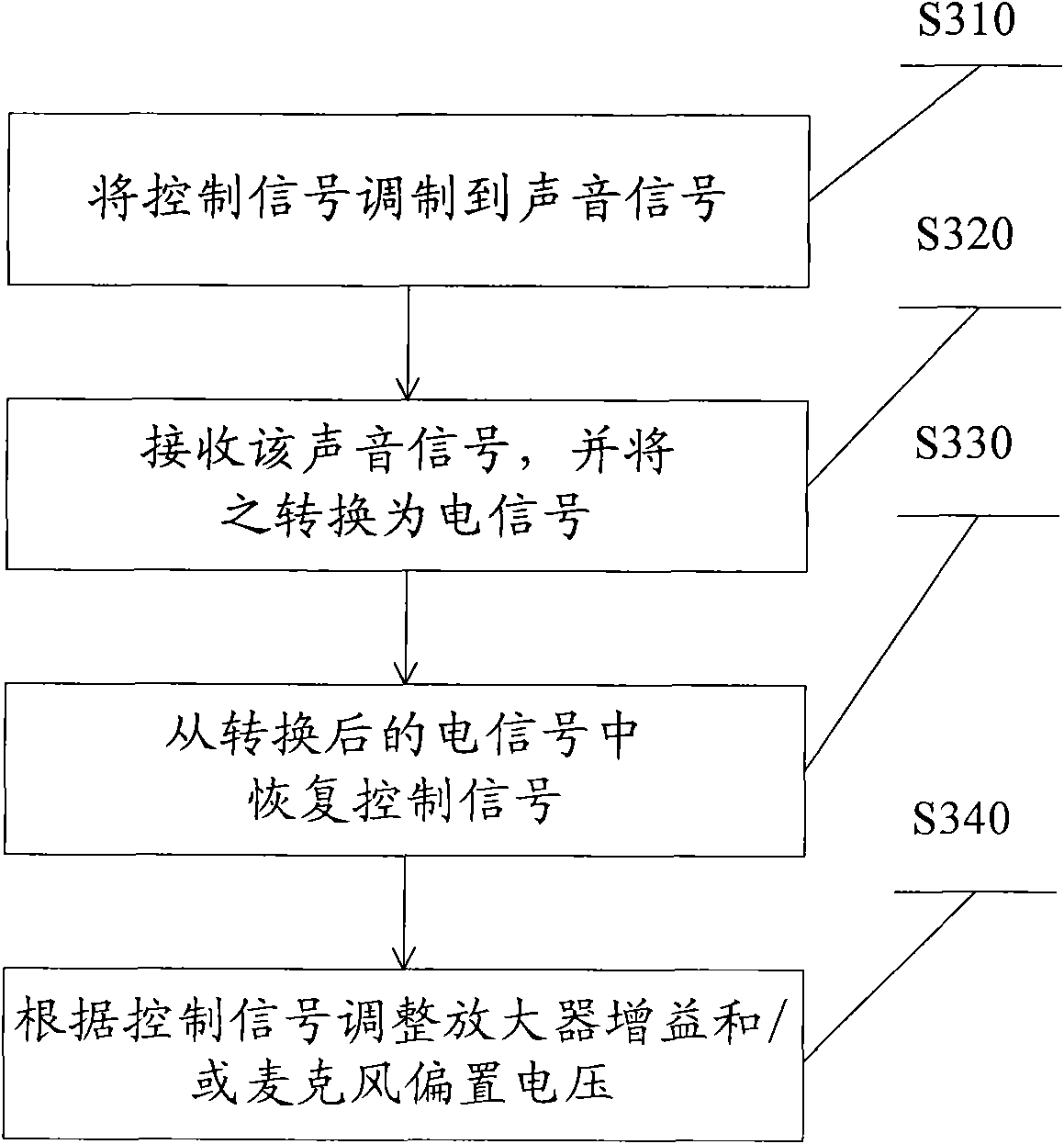
ActiveCN101621728AFree pin connectionQuick calibrationElectrical apparatusElectricityAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a method for calibrating sensitivity of a microphone, comprising the following steps: receiving a power supply voltage signal and a sound input signal; judging whether the power supply voltage signal meets a preset condition or not, if so, entering a calibrating mode to continue, and otherwise, stopping; restoring a clock signal from a sound signal; restoring a data signal from the power supply voltage signal; and regulating the amplifier gain and / or microphone bias voltage according to the clock signal and the data signal. A microphone calibrating circuit applying the method comprises a clock restoring module, a data signal restoring module, a gain regulating and controlling and register interface module and a storage, wherein the clock restoring module is used for restoring the clock signal from an output signal of a sound / electricity switching assembly; the data signal restoring module is used for restoring the data signal from the power supply voltage signal, the gain regulating and controlling and register interface module is used for writing amplifier gain regulating data into the storage according to the output of the clock restoring module and the data signal restoring module, and the storage is used for receiving the amplifier gain regulating data from the gain regulating and controlling and register interface module and is used as the grain arrangement when an amplifier normally operates.
Owner:SHANDONG GETTOP ACOUSTIC
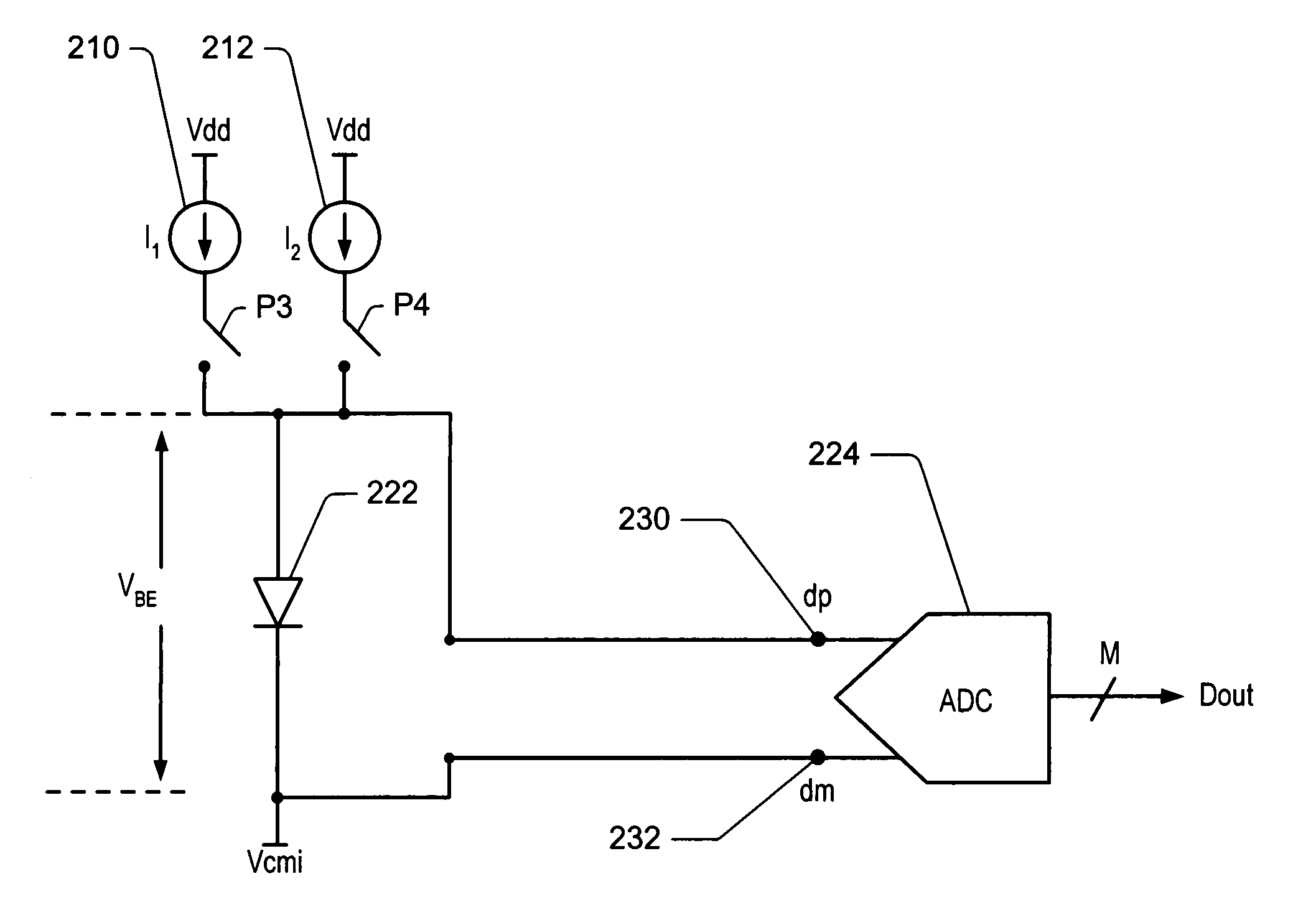
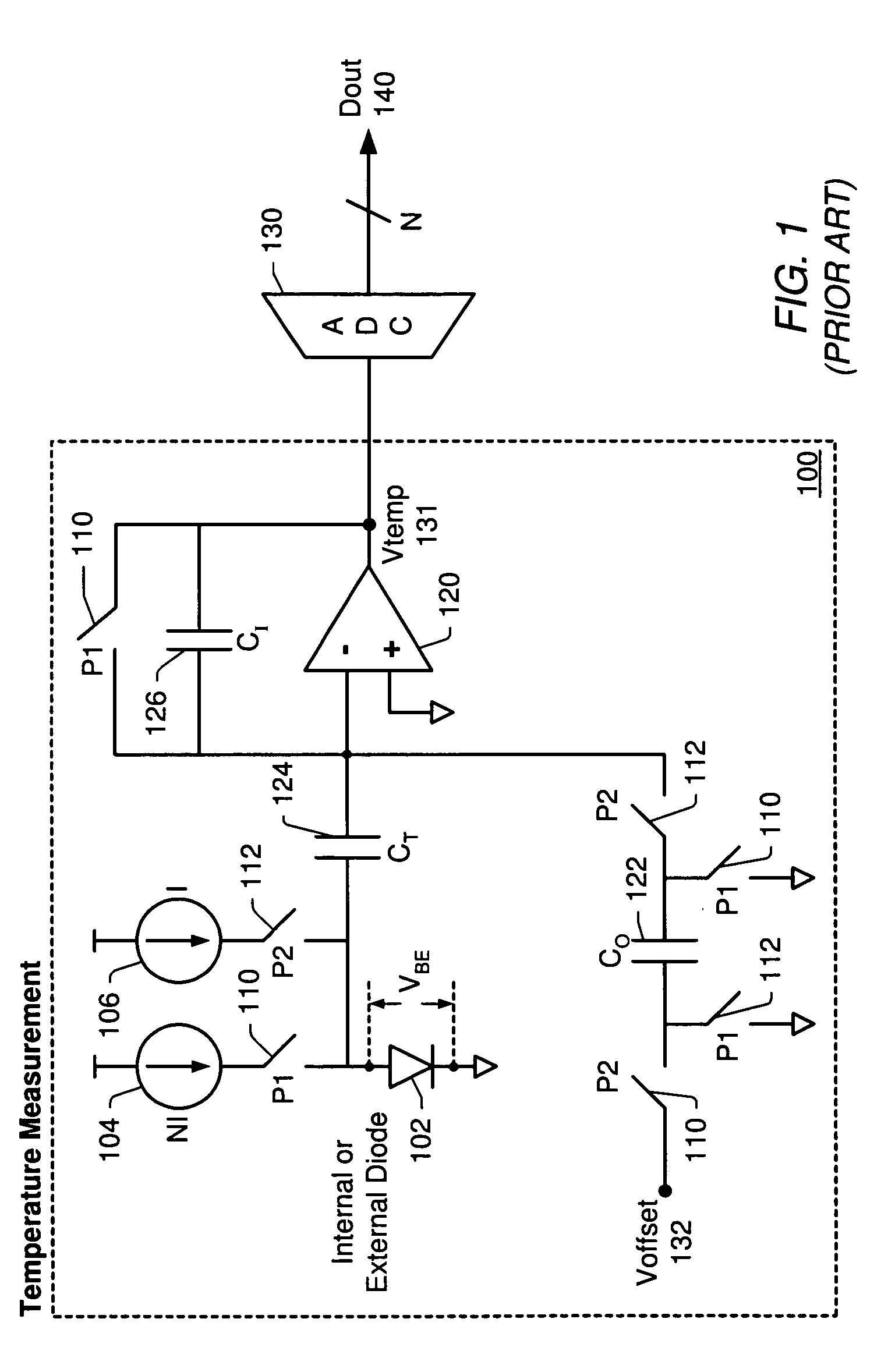
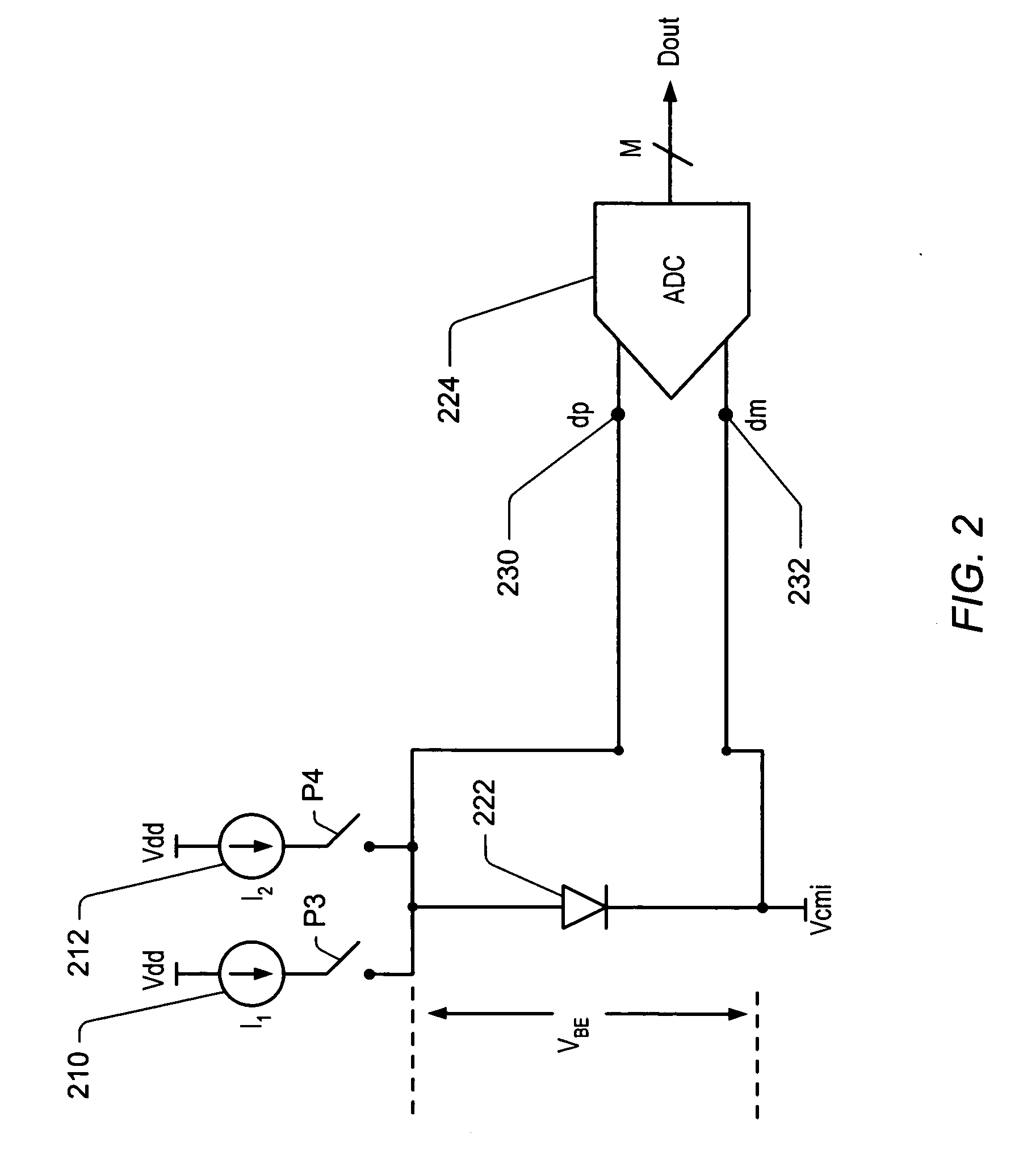
Programmable ideality factor compensation in temperature sensors
ActiveUS20060093016A1Accurate temperature measurementError freeThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsSignal conditioningVoltage reference
A temperature sensor circuit and system providing accurate readings using a temperature diode whose ideality factor may fall within a determined range. In one set of embodiments a change in diode junction voltage (ΔVBE) proportional to the temperature of the diode is captured and provided to an ADC, which may perform required signal conditioning functions on ΔVBE, and provide a numeric value output corresponding to the temperature of the diode. Errors in the measured temperature that might result from using diodes with ideality factors that differ from an expected ideality factor may be eliminated by programming the system to account for differing ideality factors. The gain of the temperature sensor may be matched to the ideality factor of the temperature diode by using an accurate, highly temperature stable reference voltage of the ADC to set the gain of the temperature measurement system. The reference voltage may have a trim capability to change the gain setting voltage by a digital address comprising a determined number of bits, with the programmable range for the reference voltage corresponding to a determined range of ideality factors.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Direct current offset cancellation for mobile station modems using direct conversion
InactiveUS6985711B2Easy accessRapid and accurate DC offset estimates and cancellation techniquesDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionRadio transmissionModem deviceOffset cancellation
A system and method for canceling DC offset for Mobile Station Modems having direct conversion architectures. The present invention is a fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block that provides rapid and accurate DC offset estimates and cancellation techniques to support direct conversion architectures. The fast acquiring DC offset cancellation block combines four mechanisms to rapidly acquire and remove a DC offset estimate after power up, temperature changes, receiver frequency changes, and gain setting changes by increasing high pass loop bandwidth and adjusting DC offset levels at baseband. After removing the DC offset in large portions, the high pass loop bandwidth is decreased to fine tune the previous estimate and to remove any small variation in DC offset due to receiver self-mixing products.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for normalizing sound recording loudness
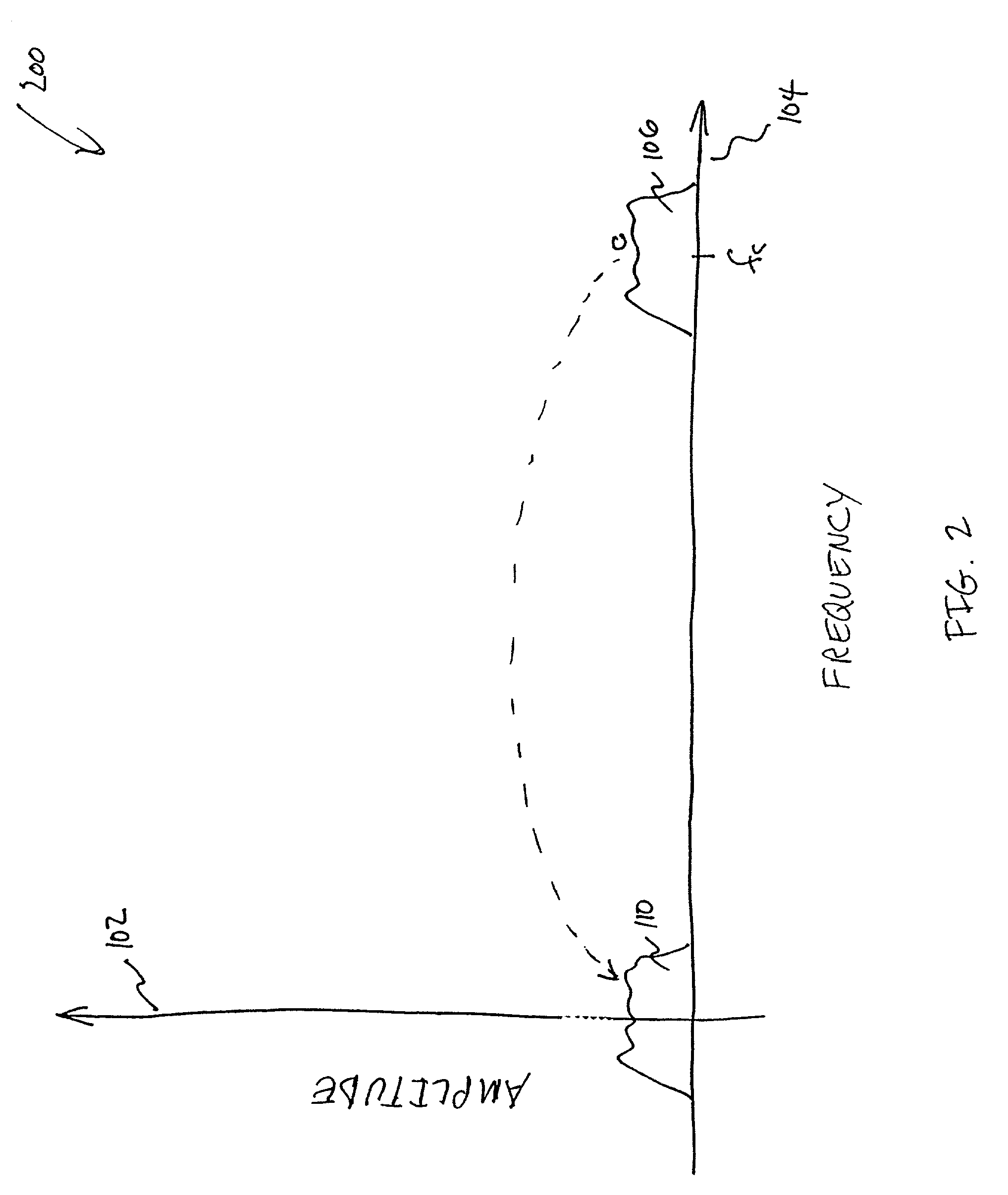
InactiveUS20060106472A1Maximum flexibilityNormalize playback loudnessSpeech amplifier applicationsDigital/coded signal controlLoudnessGain setting
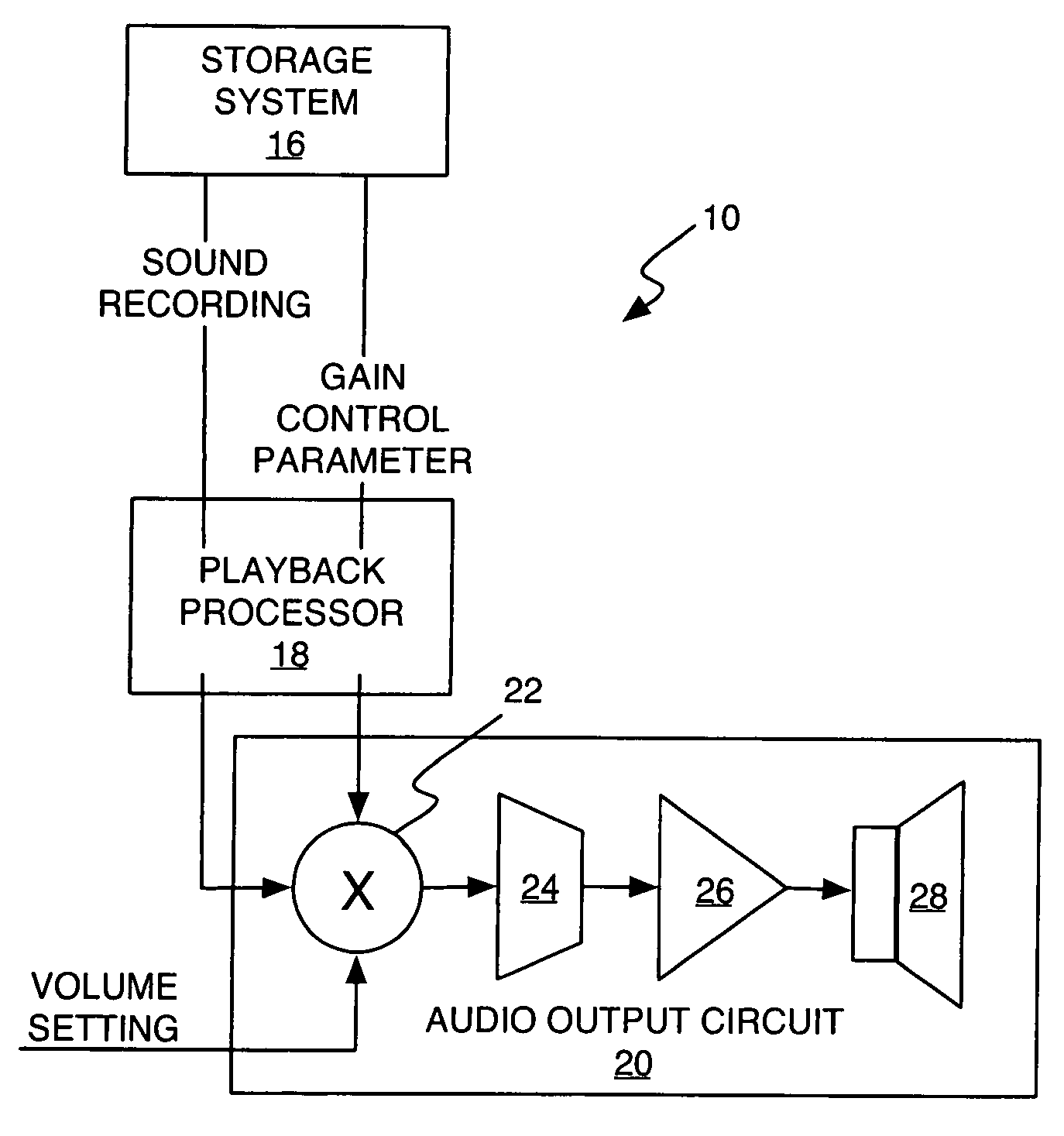
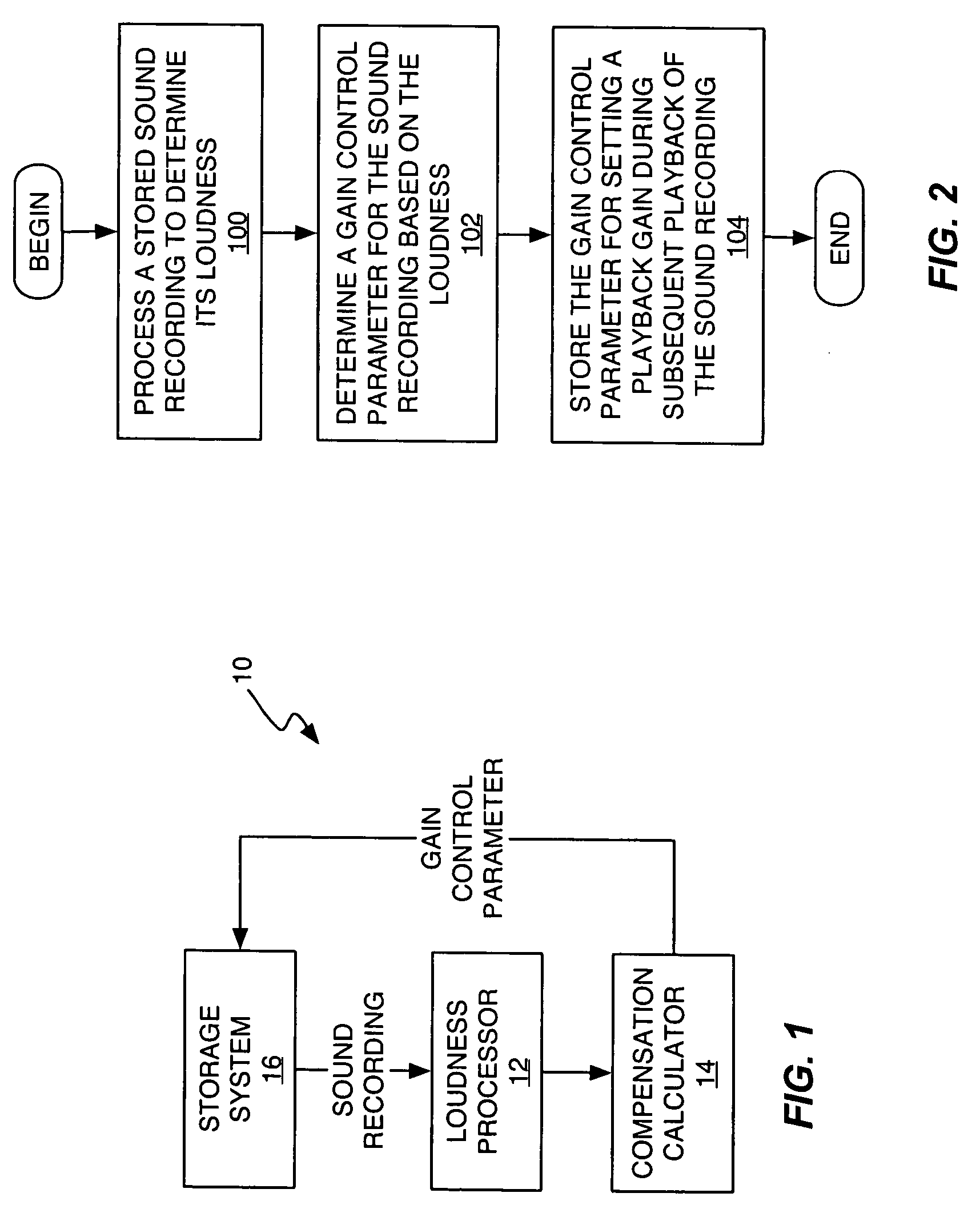
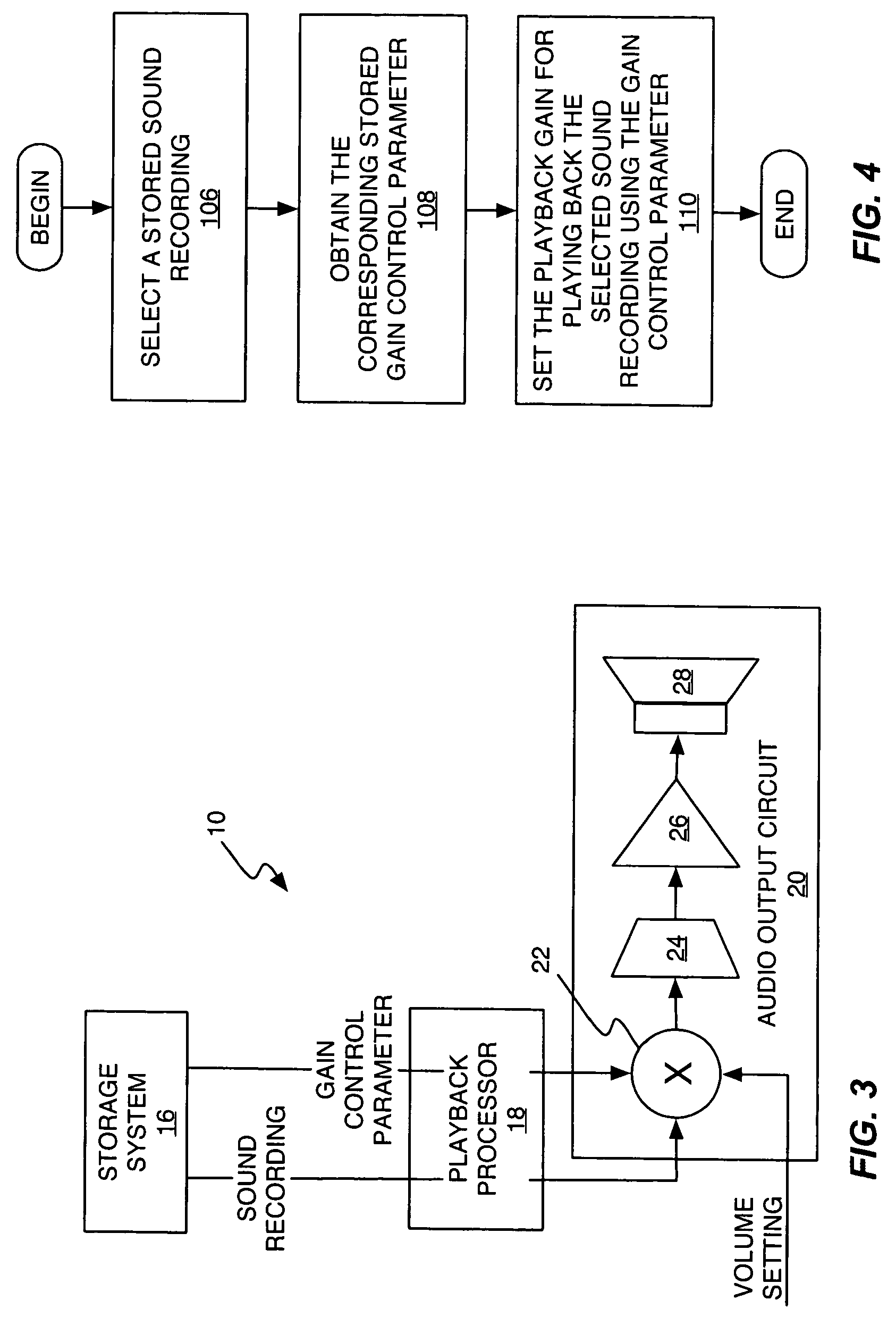
A method and apparatus normalizes the playback loudness of stored sound recordings to avoid objectionable variations in perceived loudness between different sound recordings at the same volume setting. In an exemplary processing method, a stored sound recording is processed to determine its loudness. That loudness, or some value derived from it, is then used to set the playback gain used for playing back the sound recording. Thus, for a given volume setting, the playback gain can be set lower for louder recordings, and higher for quieter recordings. In one or more exemplary embodiments, sound recordings are processed as received, or at least some time in advance of their first playback, so that a loudness-based gain compensation parameter can be calculated and stored for them. The corresponding stored gain control parameter can then be selected and used responsive to selecting a particular sound recording for playback.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Method of monitoring a broadcast channel for a page at a mobile communication device
InactiveUS7047050B1Extension of timeSacrificing operating effectivenessPower managementEnergy efficient ICTBroadcast channelsBattery charge
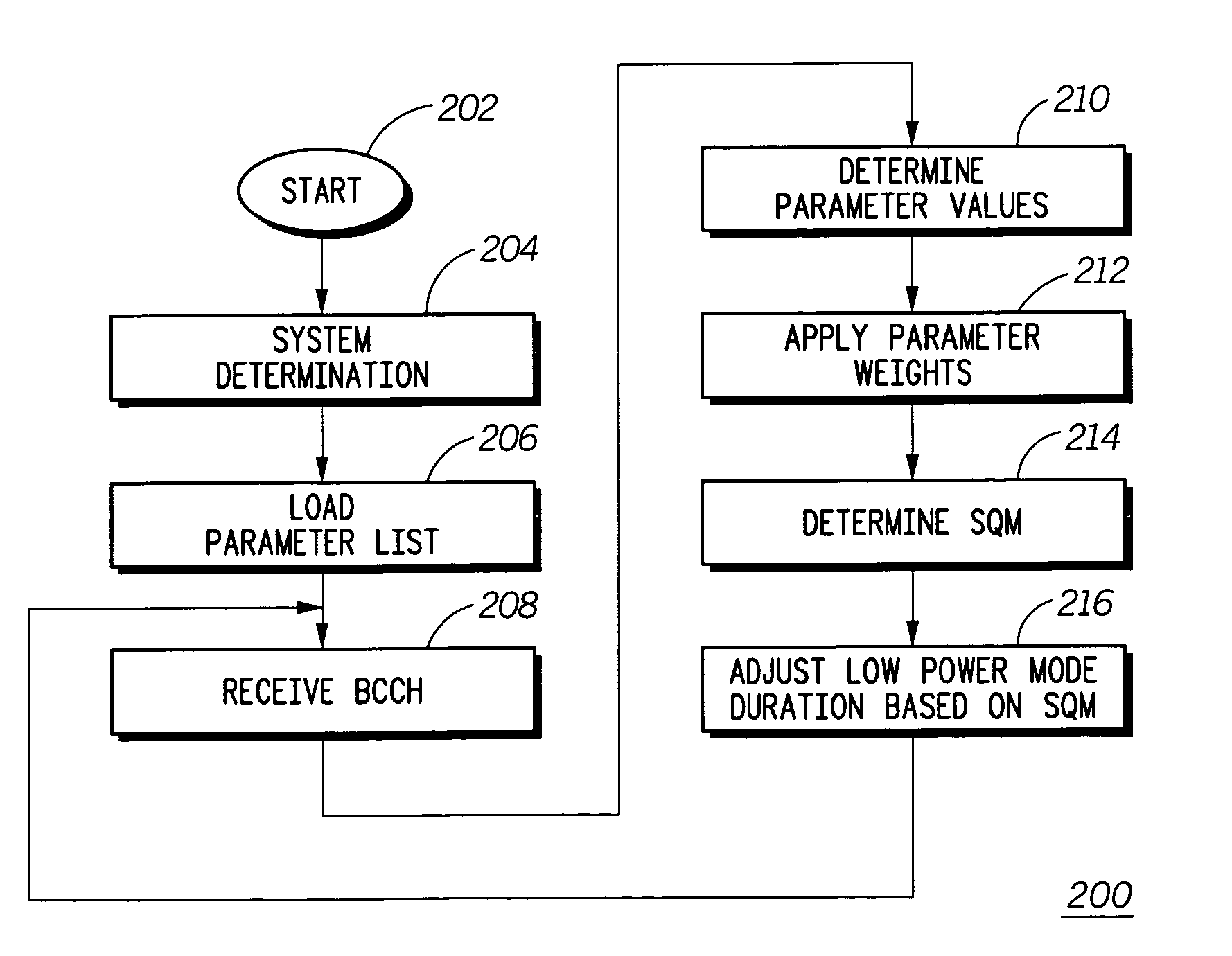
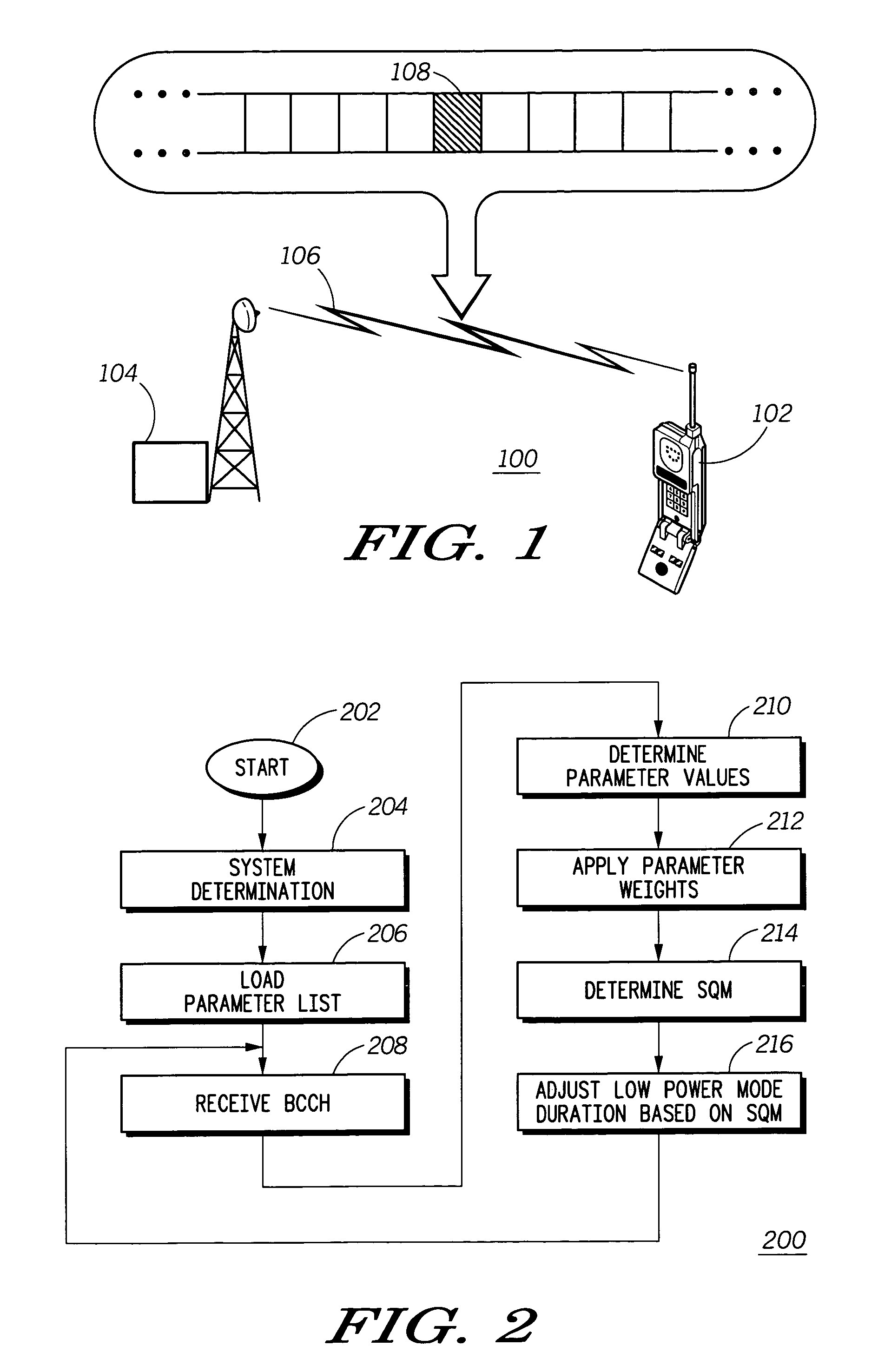
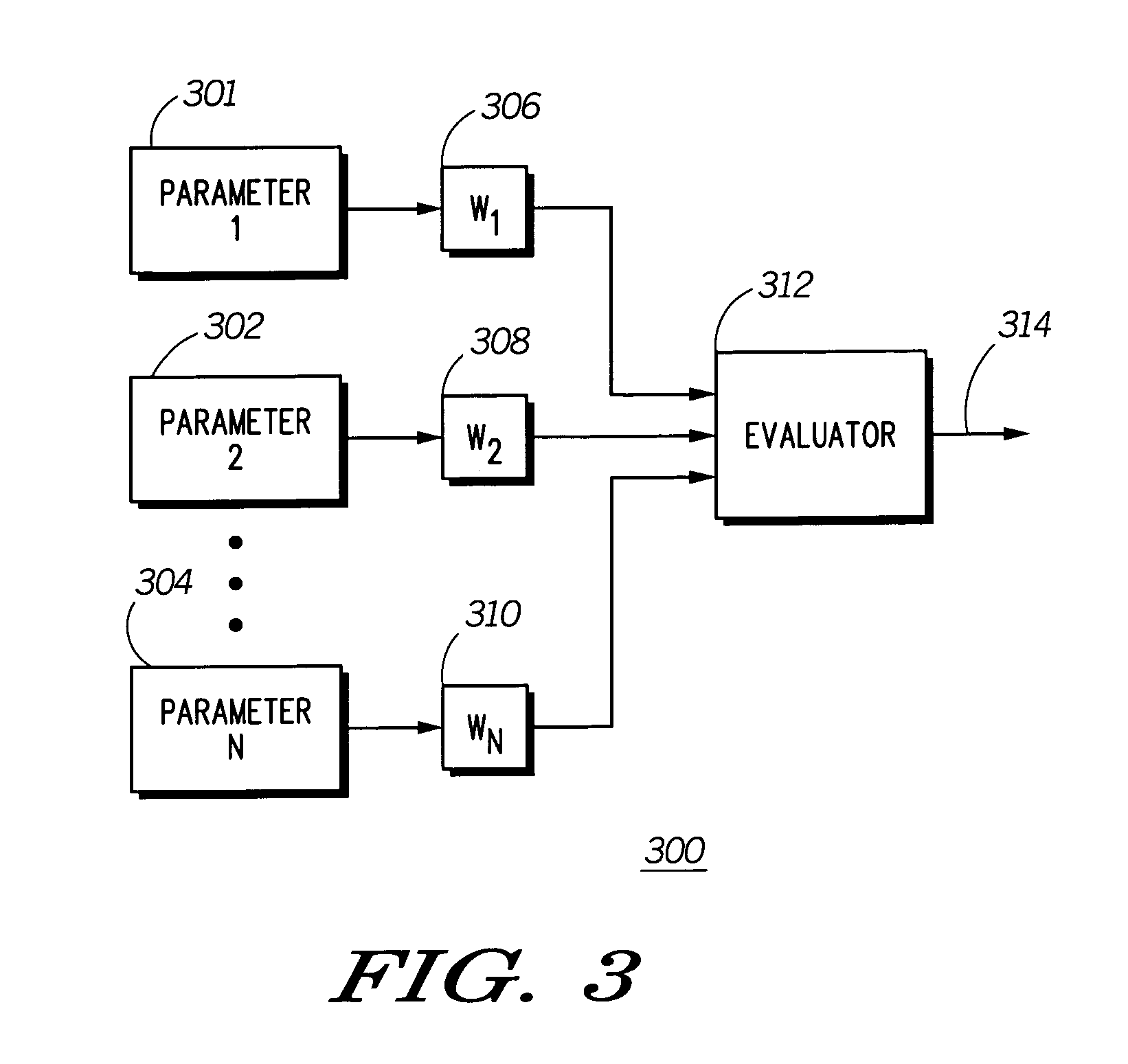
A mobile communication device (102) receives information in a broadcast control channel (108) including a page message (108). The mobile communication device measures certain parameters (210) of the control channel, such as received signal strength, channel quality, and the present automatic gain setting. These parameters are scored and weighted (300) to produce a signal quality metric (314) to determine the duration of time the mobile communication device can remain in a low power state to conserve battery charge before checking for page alert message in the broadcast control channel next.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
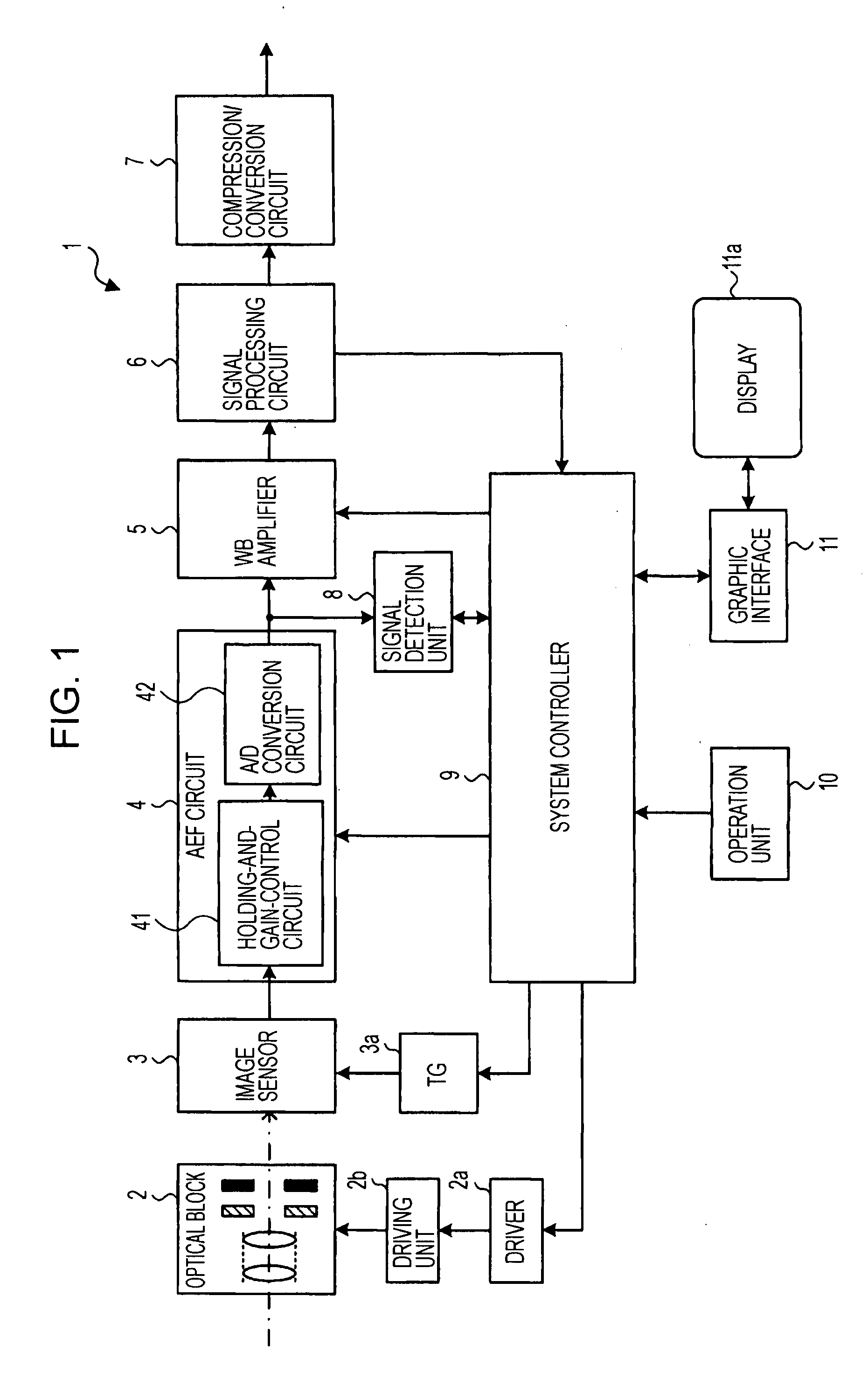
Imaging pickup apparatus, image pickup method, image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program
ActiveUS20080094485A1White balance control is facilitatedHighly accurate white balance controlColor signal processing circuitsFace detectionImaging processing
Owner:SONY CORP
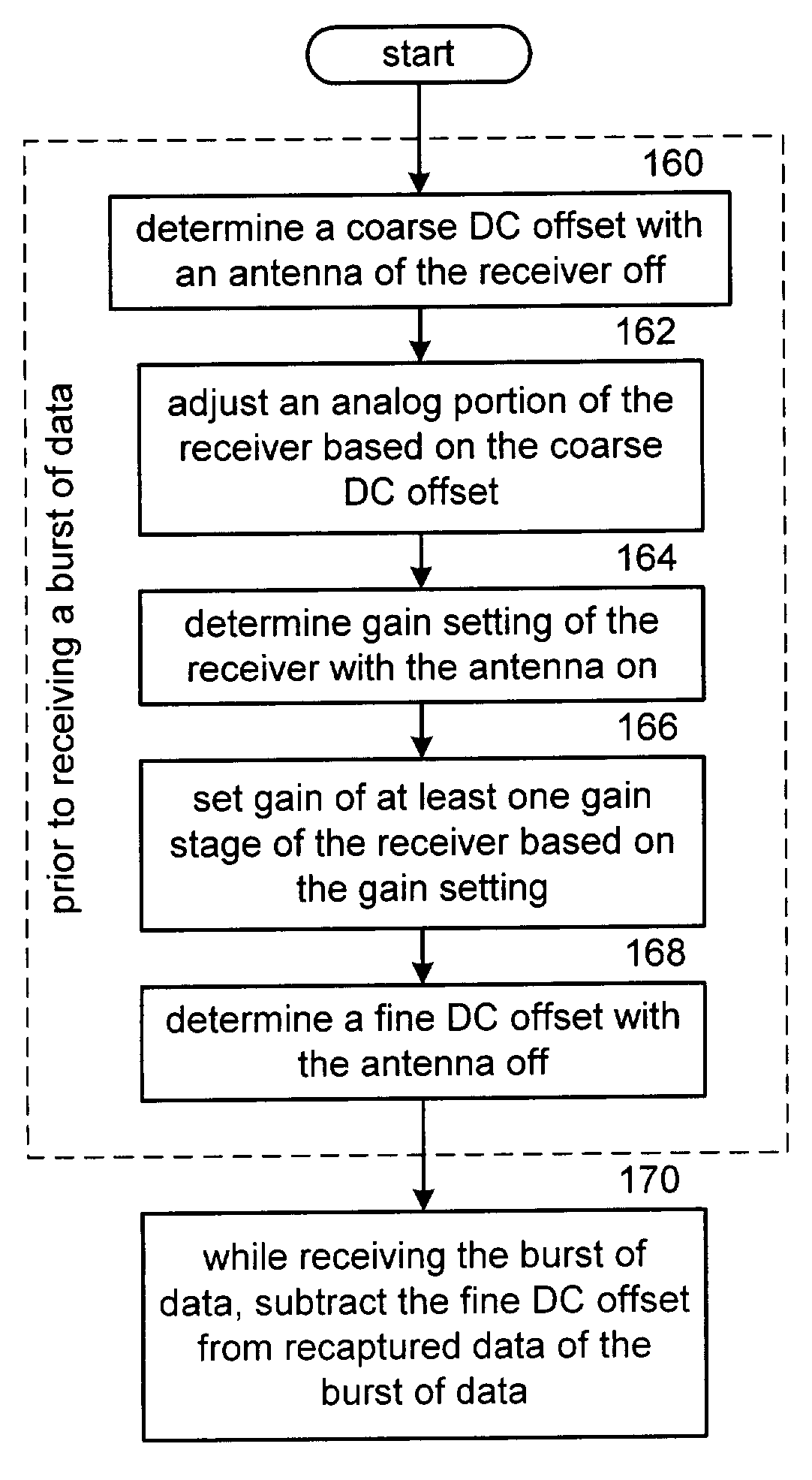
DC offset correcting in a direct conversion or very low IF receiver
InactiveUS7136431B2Reduce cancellationDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionLine balance variation compensationEngineeringLow IF receiver
A direct conversion or VLIF receiver corrects DC offset by, prior to receiving a burst of data, the receiver determines a coarse DC offset with the antenna of the receiver switched off. The receiver then adjusts an analog portion of the receiver (e.g., the output of the mixers) based on the coarse DC offset. The receiver then determines a gain setting of the receiver (e.g., for the low noise amplifier and / or programmable gain amplifiers) with the antenna on. The receiver then sets the gain of at least one gain stage of the receiver based on the gain setting. The receiver then determines a fine DC offset with the antenna off. The receiver then, while receiving a burst of data, subtracts the fine DC offset from the digital baseband or low IF signal prior to data recovery.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Packet acquisition and channel tracking for a wireless communication device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture
InactiveUS7068987B2Easy to implementPulse automatic controlGain controlIntermediate frequencyData acquisition
A method of controlling operation of a wireless device configured in a zero intermediate frequency architecture including a DC loop and a gain loop. The method includes processing energy in a wireless medium to generate a corresponding receive signal, monitoring the receive signal via a predetermined measurement window, detecting a changed condition in the channel, holding the gain feedback control loop at a constant gain level, and operating the DC loop in an attempt to search a stable DC value for the receive signal while the gain loop is held constant. A first case is DC saturation, where the gain is held constant until DC is controlled. A second case is clear channel assessment, where a prior stored gain setting is applied to the gain loop after detecting the end of the packet. A third case is preparation for receiving an expected acknowledgement packet after transmitting a packet, where again a prior stored gain setting is applied to the gain loop and DC is searched.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Movement stabilizing apparatus for combination vehicle
ActiveUS20090005946A1Effectively suppress the pendulum movement of a vehicleAgricultural machinesAnalogue computers for trafficLagGain setting
A movement stabilizing control ECU 25 includes a differential unit 25a, a cycle calculation unit 25b, a time constant / gain setting portion 25c, a first-order lag processing unit 25d, a pendulum movement detection unit 25e, a control amount calculation portion 25f and a control amount output unit 25g. The time constant / gain setting portion 25c sets a time constant τ and a gain K used at the time of subjecting a yaw acceleration ω′ which is a time-differential value of a yaw rate ω to the first-order lag processing at the first-order lag processing unit 25d, with reference to a function or data of a look-up table, for example, depending on the cycle or the frequency of the yaw acceleration ω′ due to the pendulum movement. The control amount calculation portion 25f multiplies the amplitude of a yaw acceleration ωd′ outputted from the first-order lag processing unit 25d by a predetermined constant to calculate a yaw control amount with a phase in opposite to that of the yaw acceleration ωd′ and outputs the yaw control amount to the control amount output unit 25g.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Image pickup apparatus and lens barrel
InactiveUS20080204564A1Quality improvementReduce image quality degradationTelevision system detailsPrintersFace detectionImaging equipment
An imaging apparatus capable of preventing photographing sensitivity from being increased more than necessary, reducing image quality degradation caused by camera shake or object shake and easily photographing images in good image quality. Digital camera 1 includes image shake correcting selection 16 that corrects shake of an optical image of a photographing object formed by an imaging optical system L, digital signal amplification section 110 that amplifies an image signal with a gain set by digital signal gain setting section 111, and face detection section 120 that detects a face of a photographing object, and microcomputer 3 calculates an object speed based on the detected motion of the face of the photographing object, decides whether or not the object speed is equal to or higher than a threshold A, and operates, when the object speed is lower than the threshold A, image shake correction by controlling image shake correcting section 16 or increases, when the object speed is equal to or higher than the threshold A, the gain of digital signal gain setting section 111, increases ISO sensitivity to increase the shutter speed and shorten the exposure time.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com