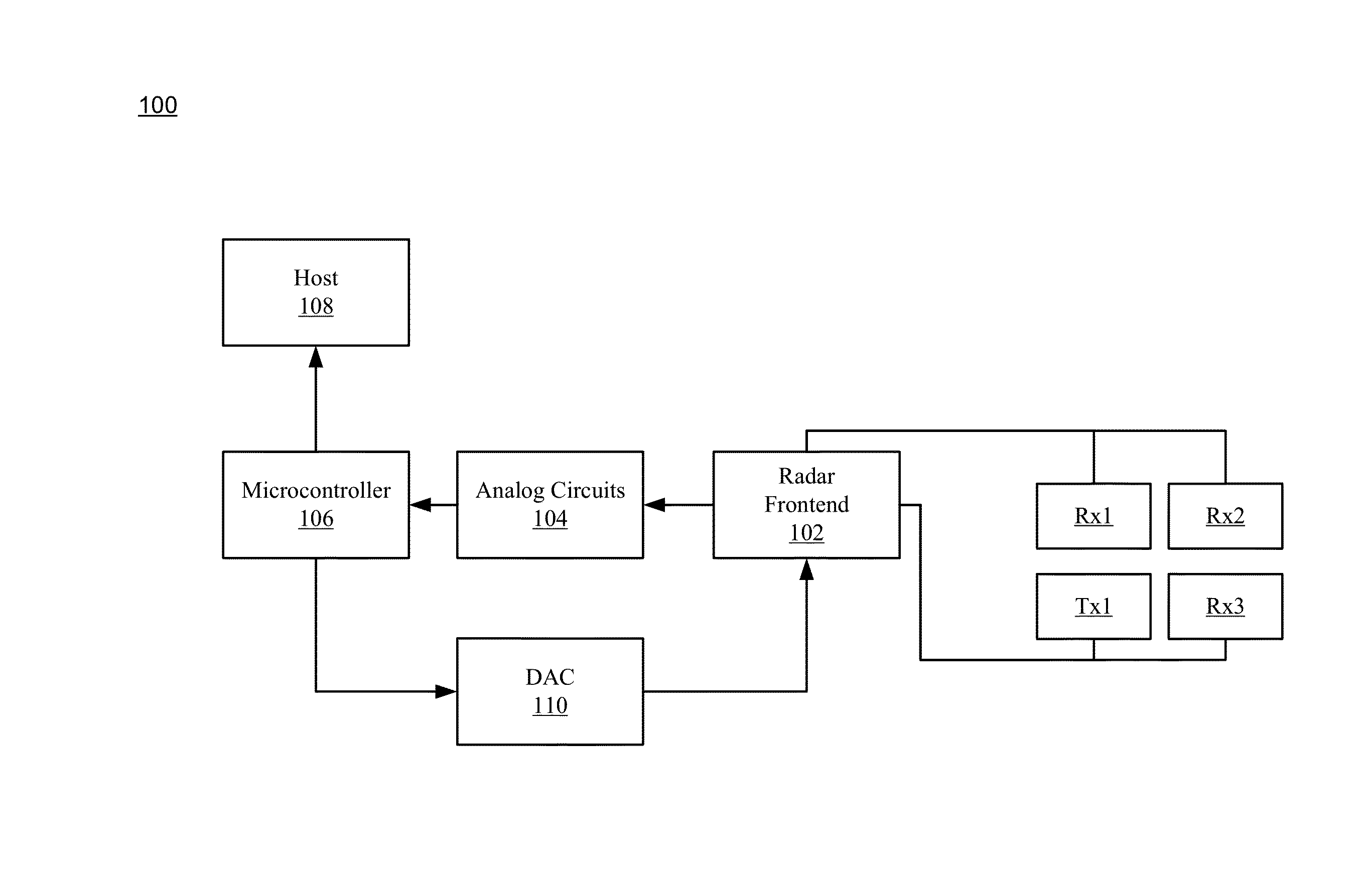
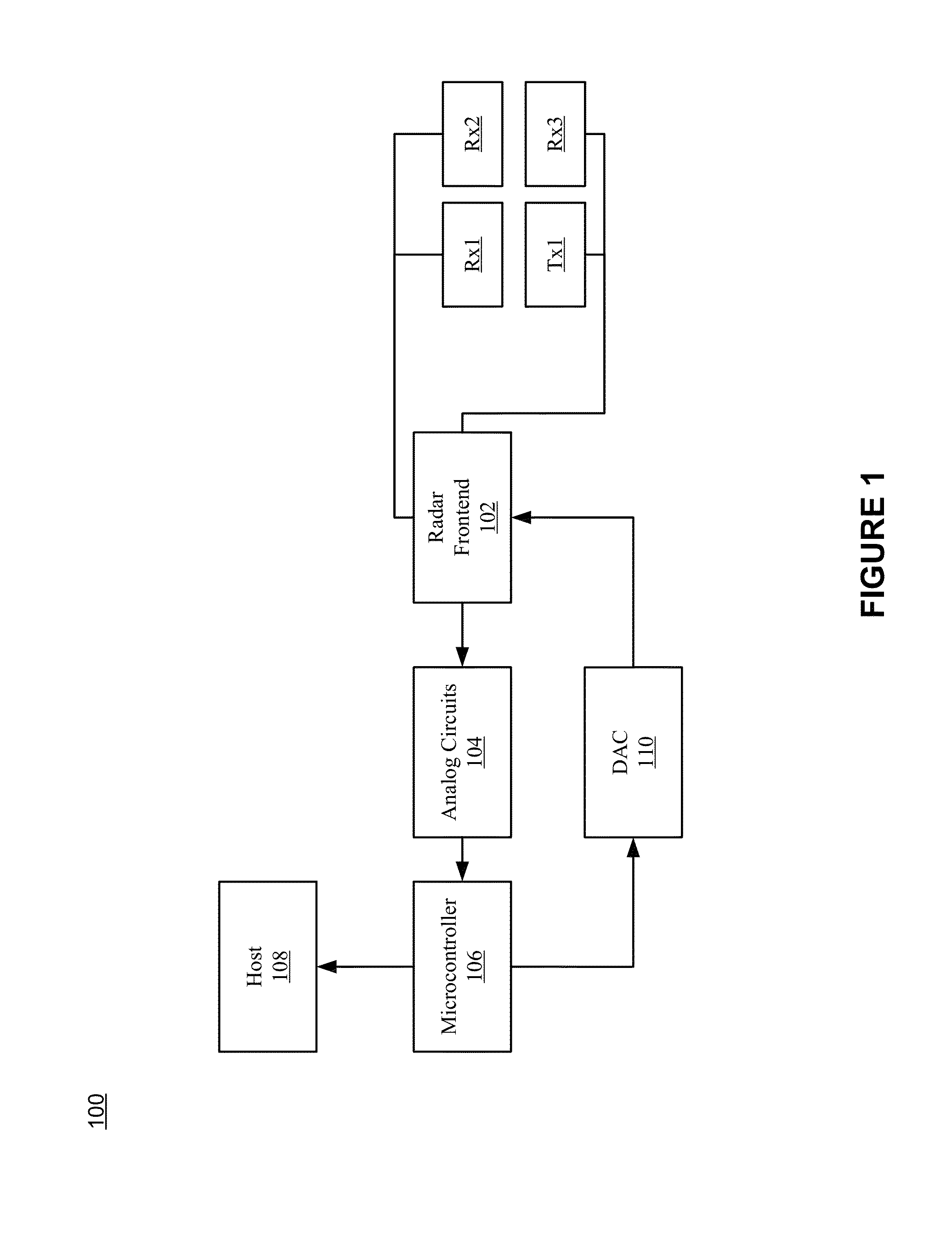
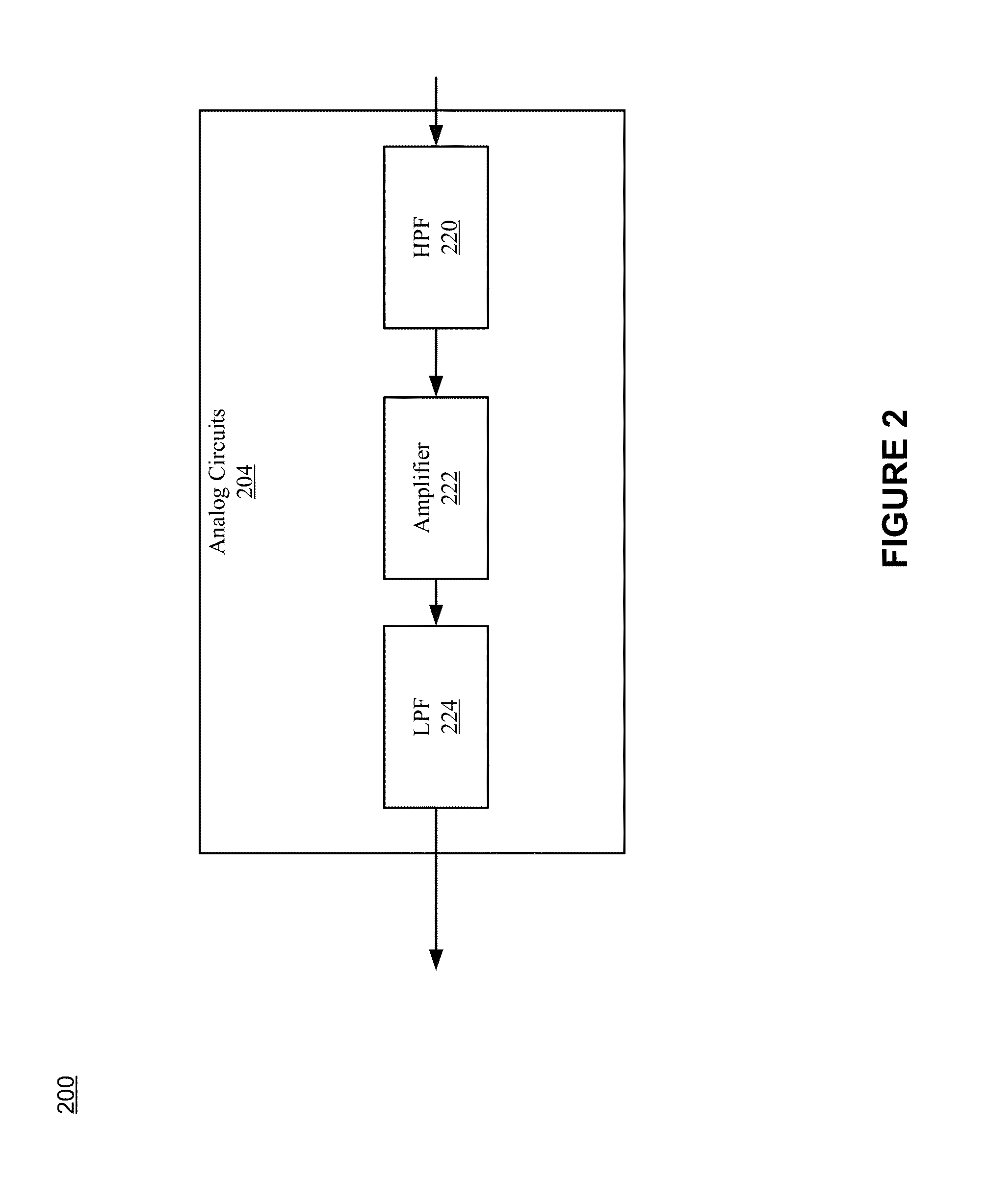
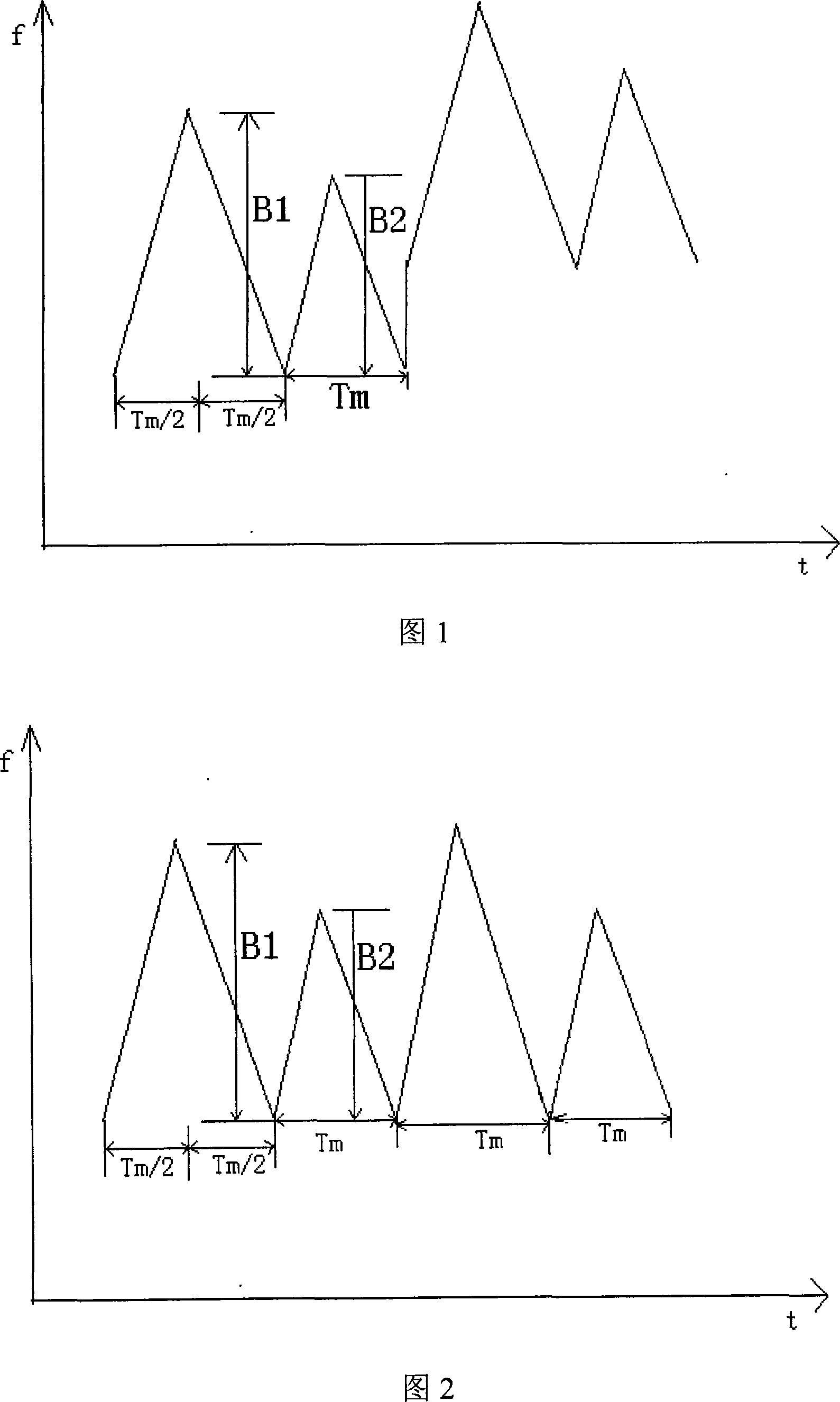Patents
Literature
3212 results about "Radar signals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Metamaterial scanning lens antenna systems and methods
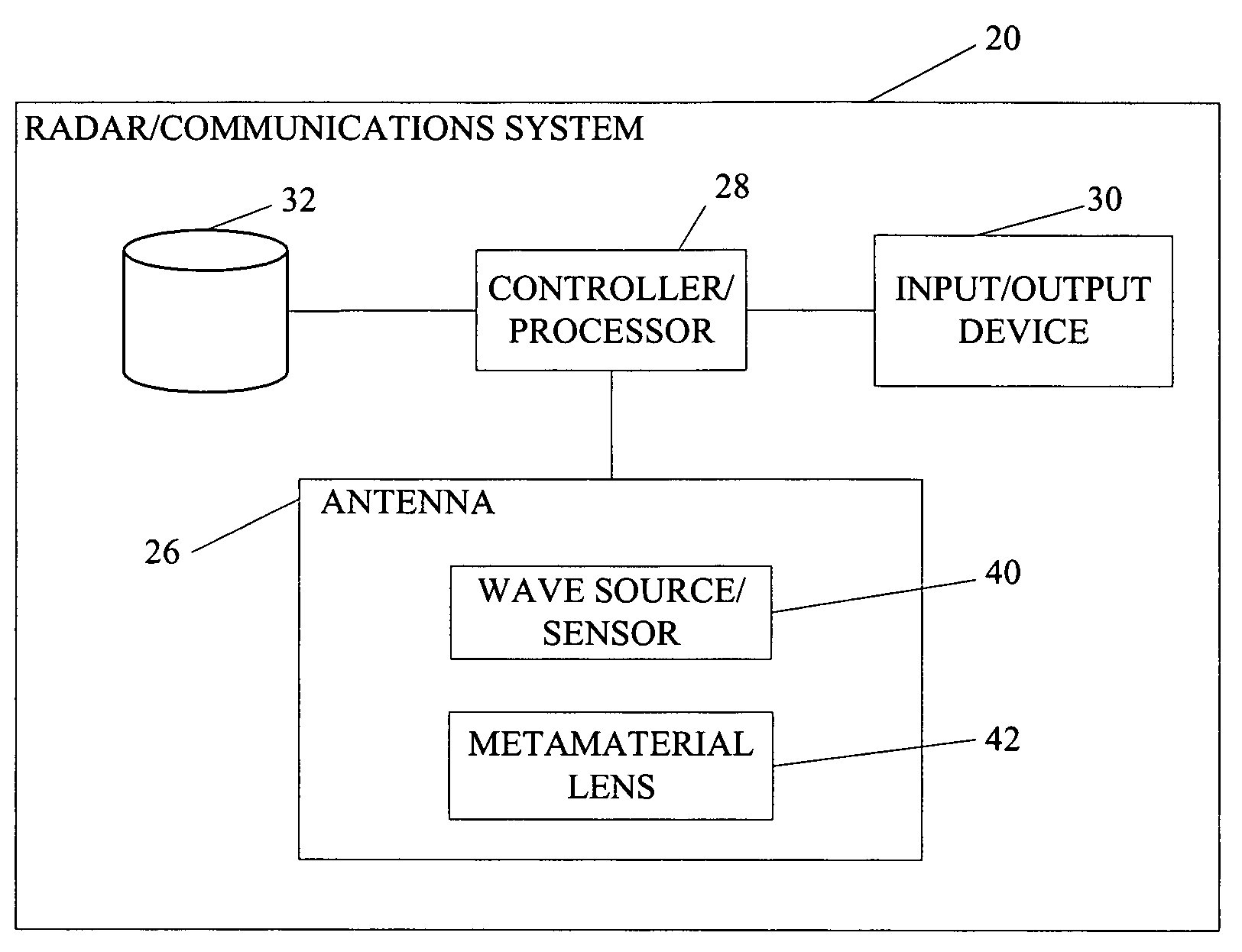
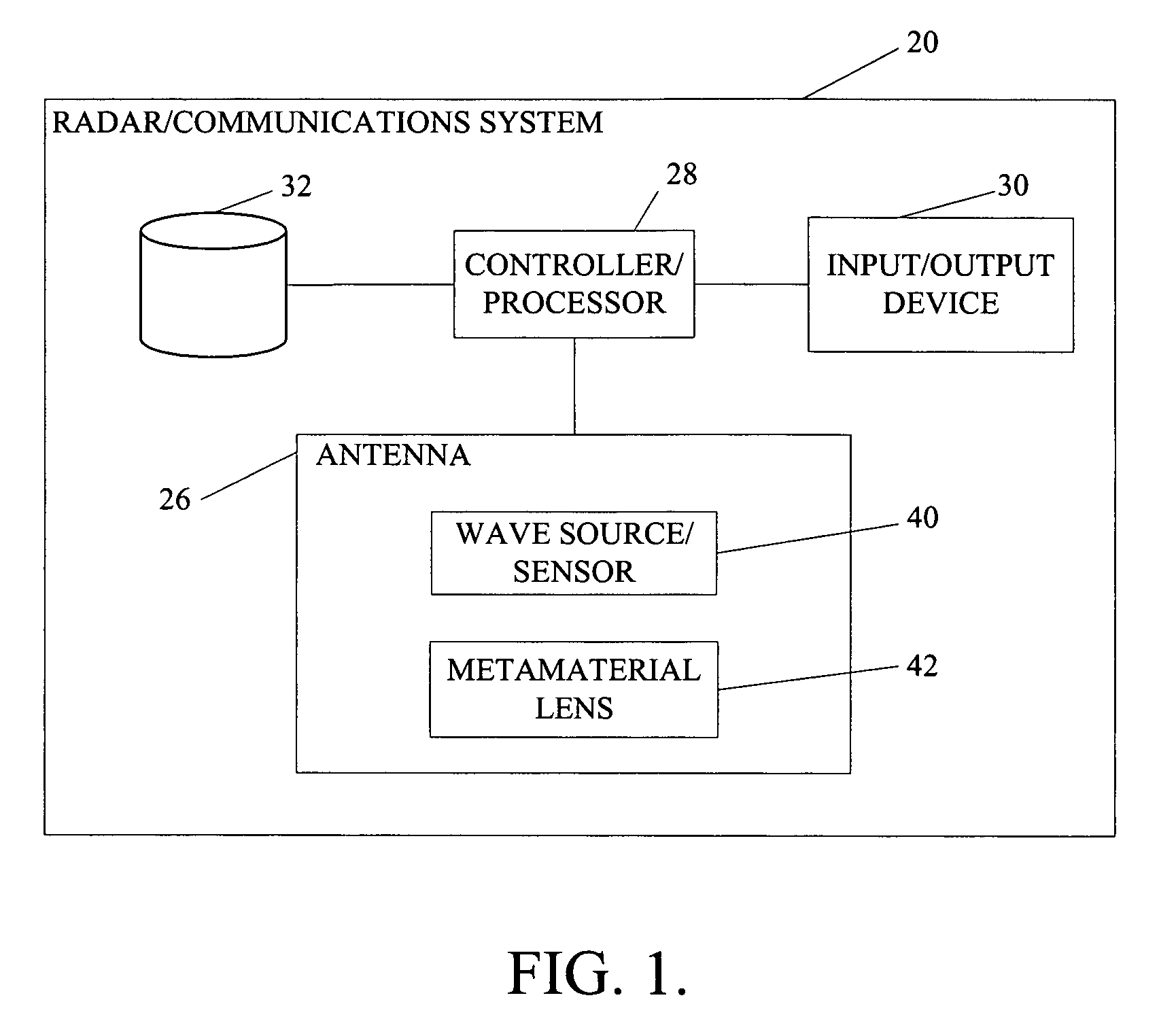
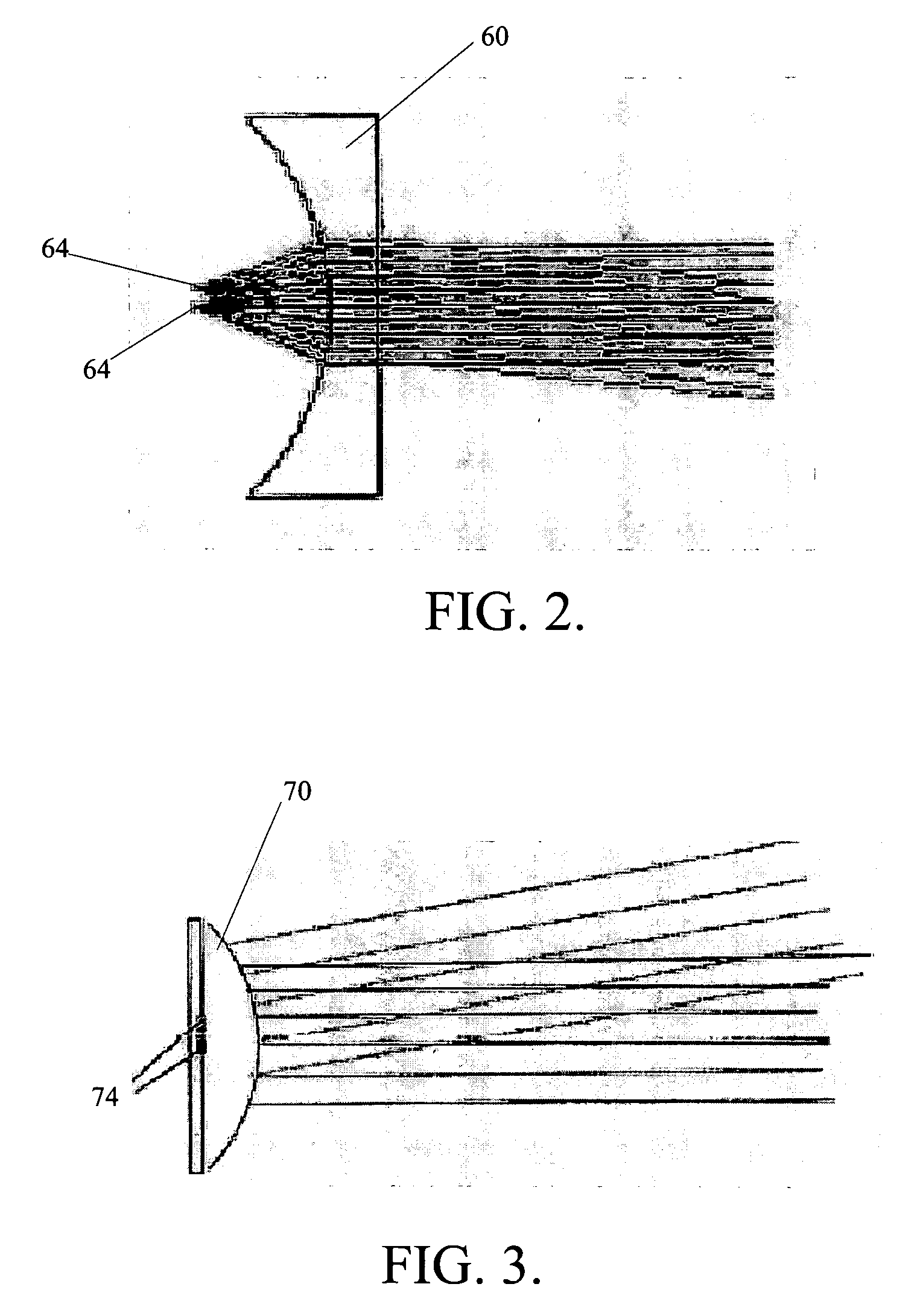
The present invention is directed to systems and methods for radiating radar signals, communication signals, or other similar signals. In one embodiment, a system includes a controller that generates a control signal and an antenna coupled to the controller. The antenna includes a first component that generates at least one wave based on the generated control signal and a metamaterial lens positioned at some predefined focal length from the first component. The metamaterial lens directs the generated at least one wave.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
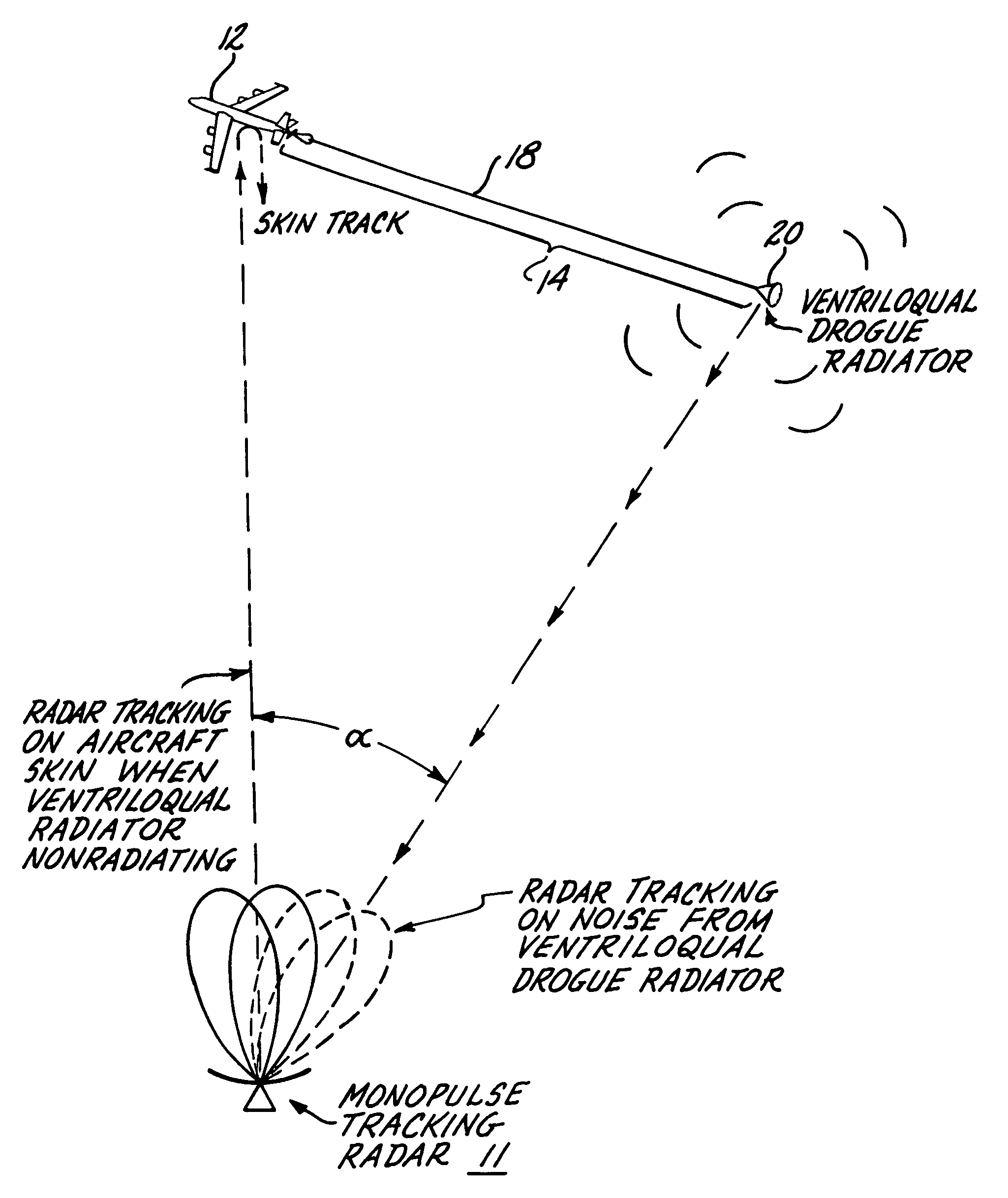
Airborne radar jamming system
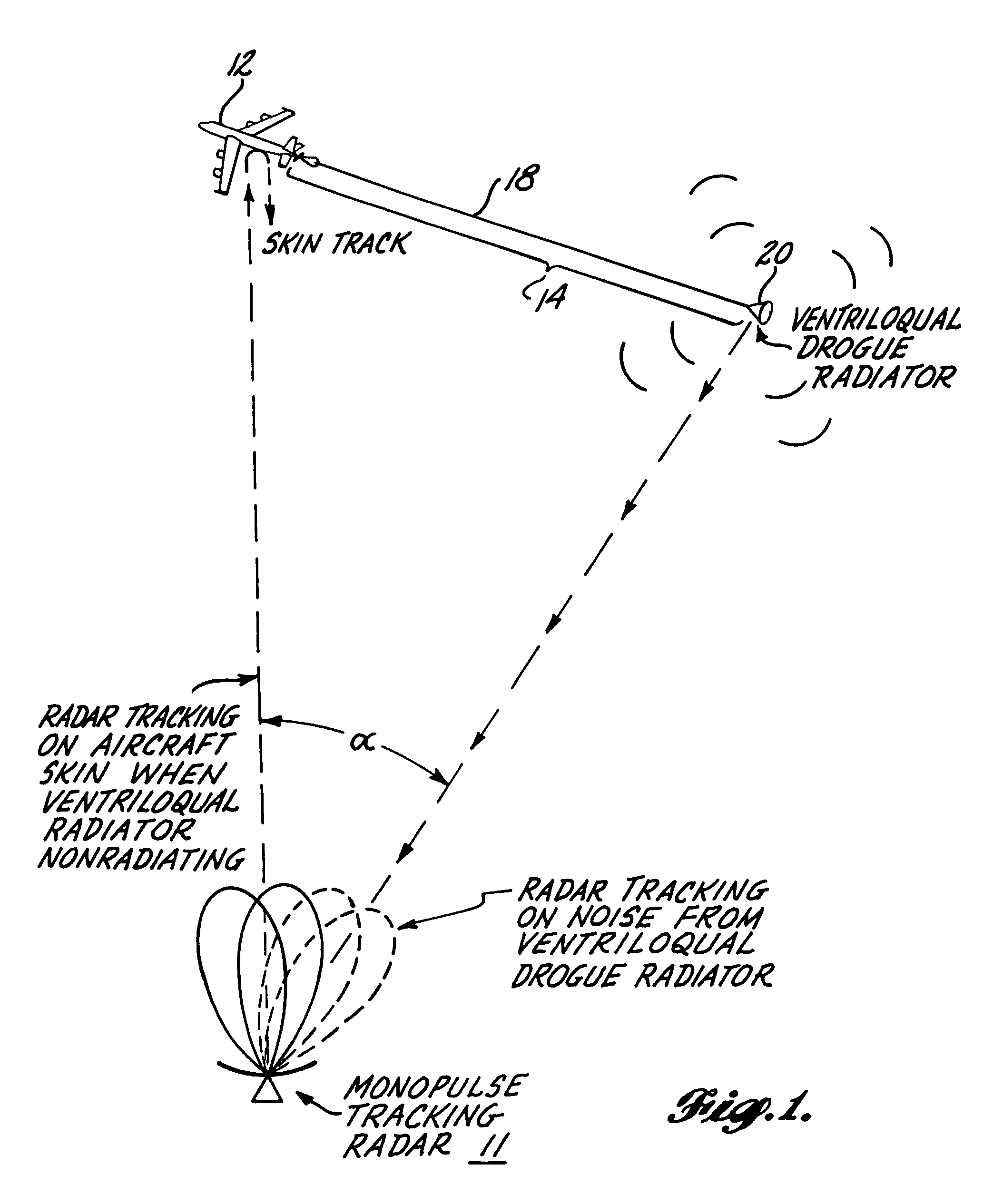
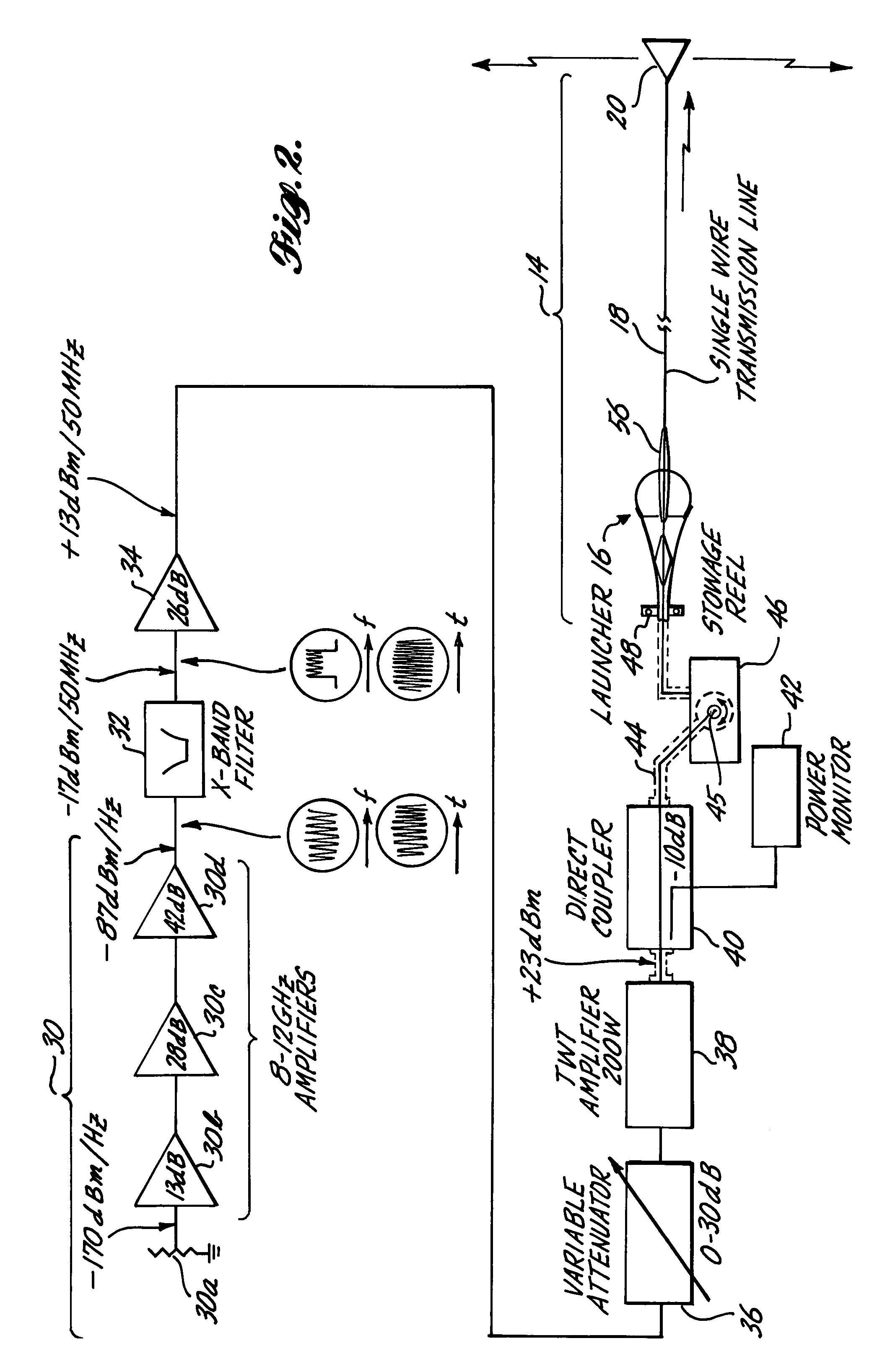
A radar jamming signal generated by equipment carried by a target aircraft, is launched onto the leading end of a towed single wire transmission line so as to travel the length of the line as a nonradiating surface wave. A drogue radiator is attached to the trailing end of the line for radiating the jamming signal transversely of the towed line so as to be received by and cause jamming of tracking and / or fire control radar. The length of the single wire transmission line is selected so that the trailing radiator causes the jamming signal to emanate from a position sufficiently behind the aircraft so as to be outside the destructive radius of weapon fire directed at the apparent source of the jamming signal by fire control radar. A ventriloqual-like deception of the radar is thus achieved. A wave launcher couples the jamming signal to the leading end of the transmission line and for this purpose includes an electrically conducted horn-shaped structure, a tunable coaxial feed end at the constricted end of the horn structure, an inner transition conductor connecting the inner conductor of the coaxial feed to a leading end of the single wire transmission line, and a plurality of annular dielectric lenses and dielectric guides cooperatively shaped and fitted to the horn structure in a manner that effectively matches the bounded electromagnetic transmission wave characteristics of the coaxial feed cable with the surface wave transmission characteristics of the single wire transmission line. Coacting with the ventriloqual-like radiation of the jamming signal from the trailing end of the transmission line is an anti-integration network that hides the return radar signal reflected off the target aircraft in a signal energy “hole” created for such purpose in a secondary low level noise signal transmitted directly from the aircraft.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Millimeter wave pulsed radar system
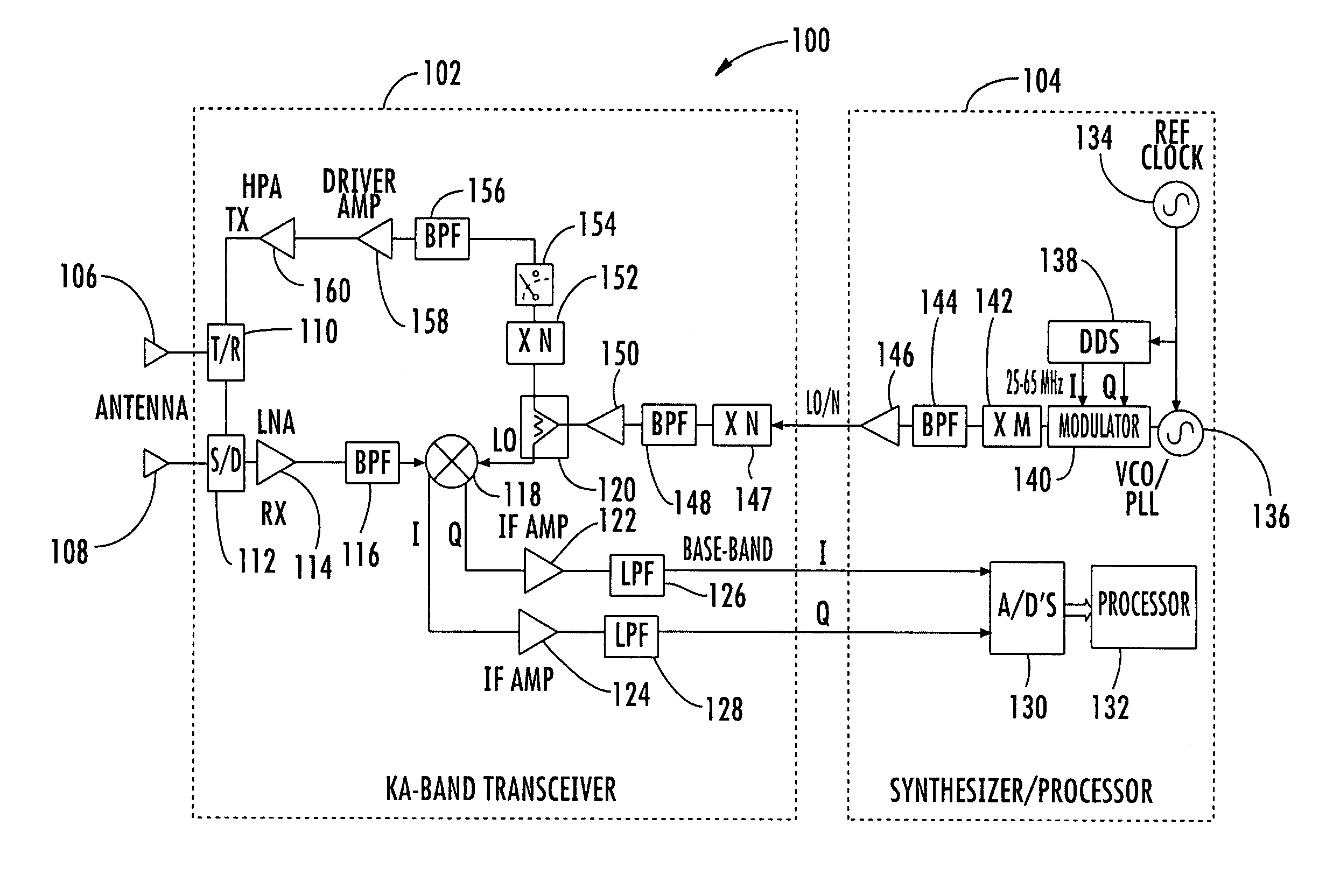
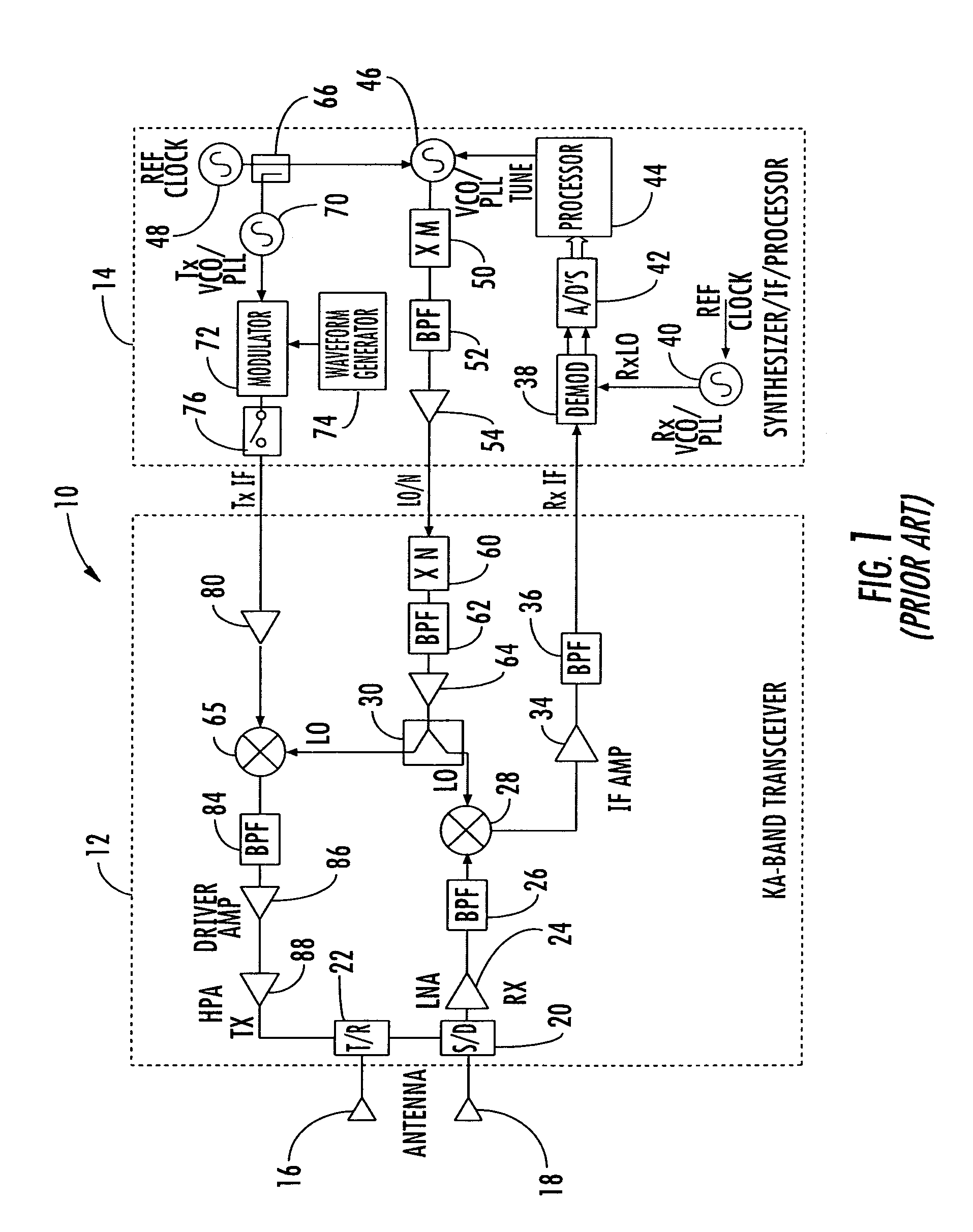
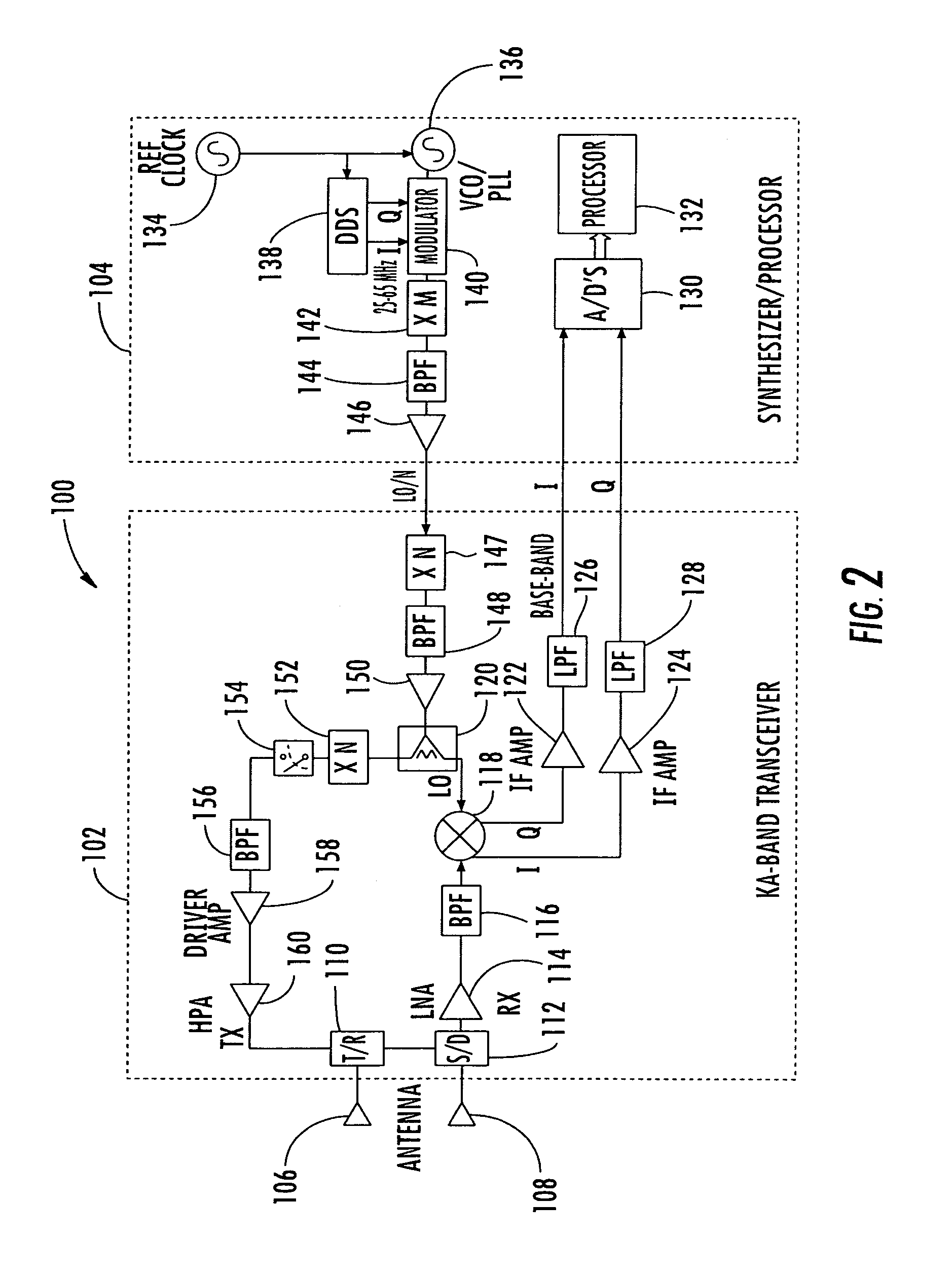
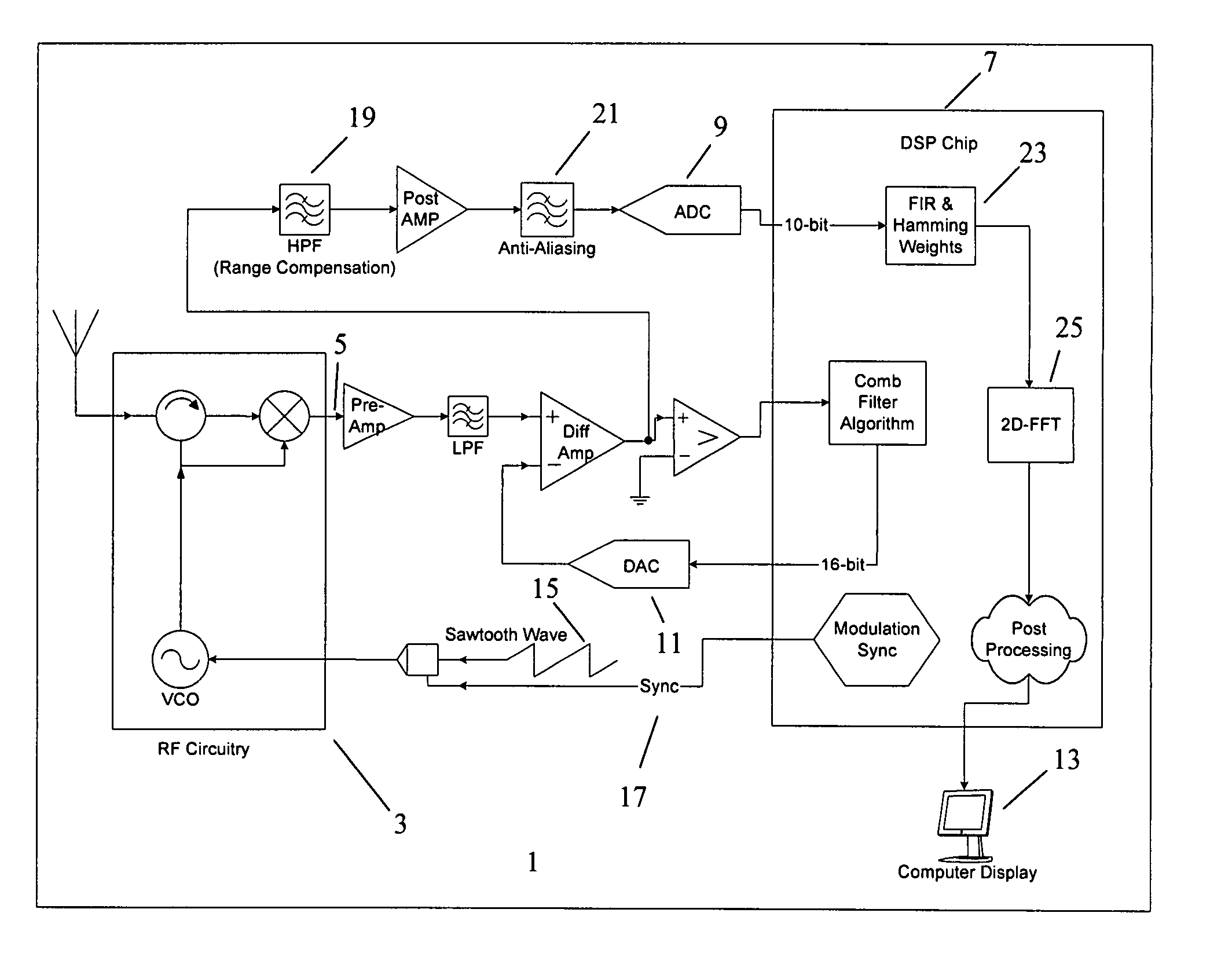
InactiveUS7002511B1Improve efficiencySimplified frequency synthesizer designRadio wave reradiation/reflectionQuadrature modulatorLocal oscillator signal
A millimeter wave pulsed radar system includes a radar synthesizer having a voltage controlled oscillator / phase locked loop (VCO / PLL) circuit, direct digital synthesizer (DDS) circuit and quadrature modulator circuit that are operative to generate an intermediate frequency local oscillator signal (IF / LO signal). A radar transceiver is operative with the radar synthesizer for receiving the IF / LO signal. A transmitter section has a frequency multiplier that multiplies the IF / LO signal up to a millimeter wave (MMW) radar signal and a receiver section and includes a direct conversion mixer that receives a MMW radar signal and the IF / LO signal to produce I / Q baseband signals that are later digitized and processed.
Owner:REVEAL IMAGING
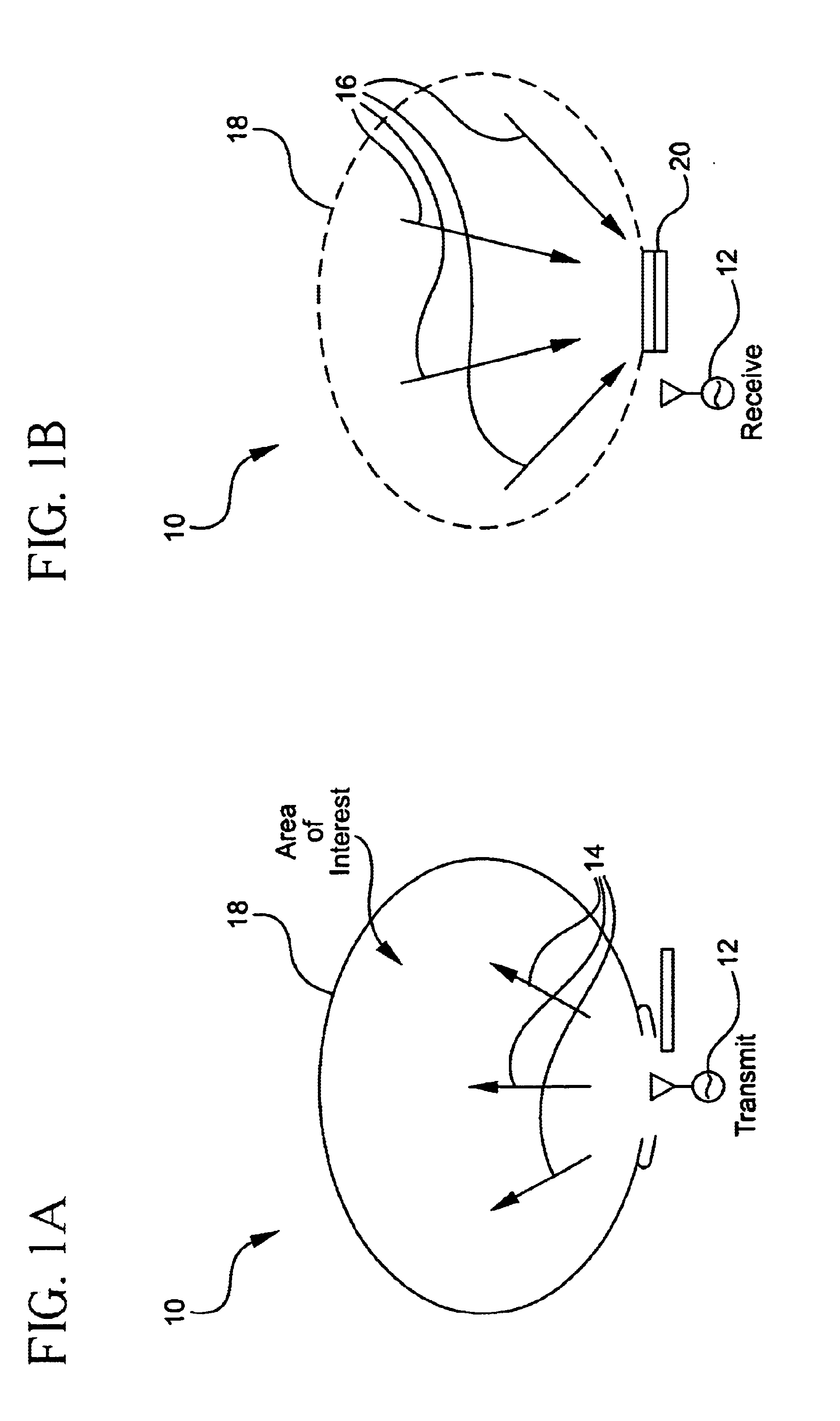
Radar system and method of manufacturing same
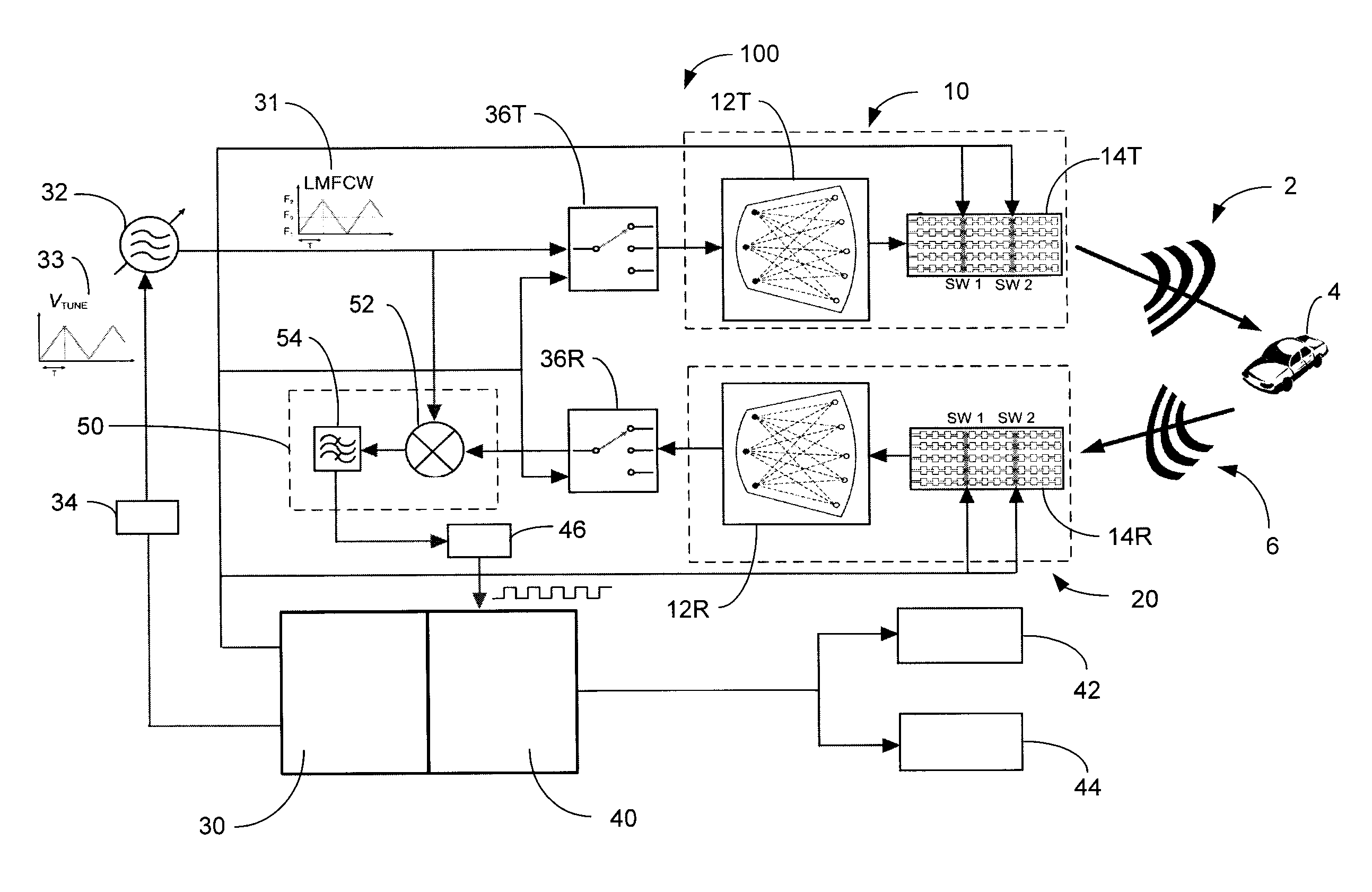
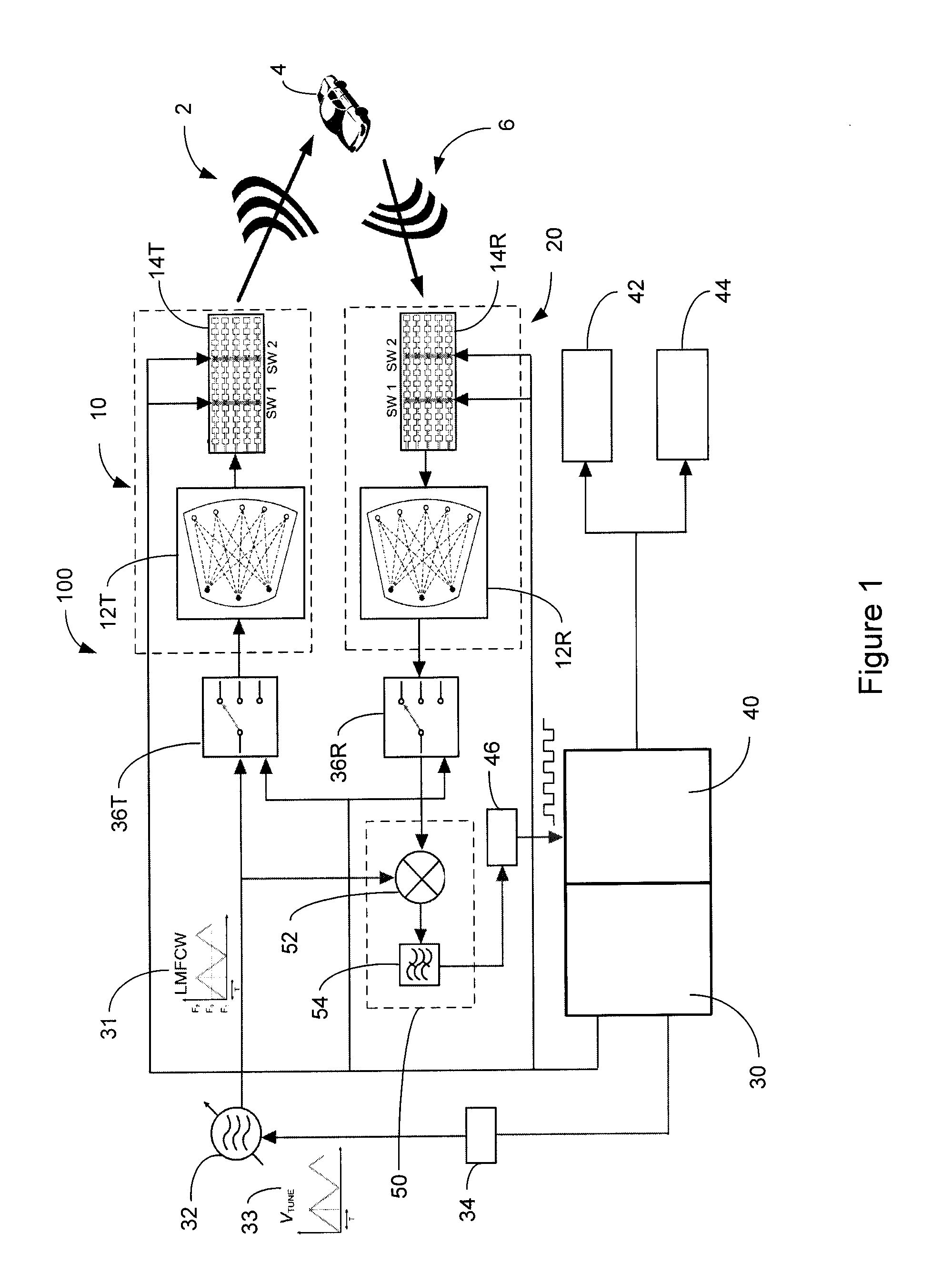
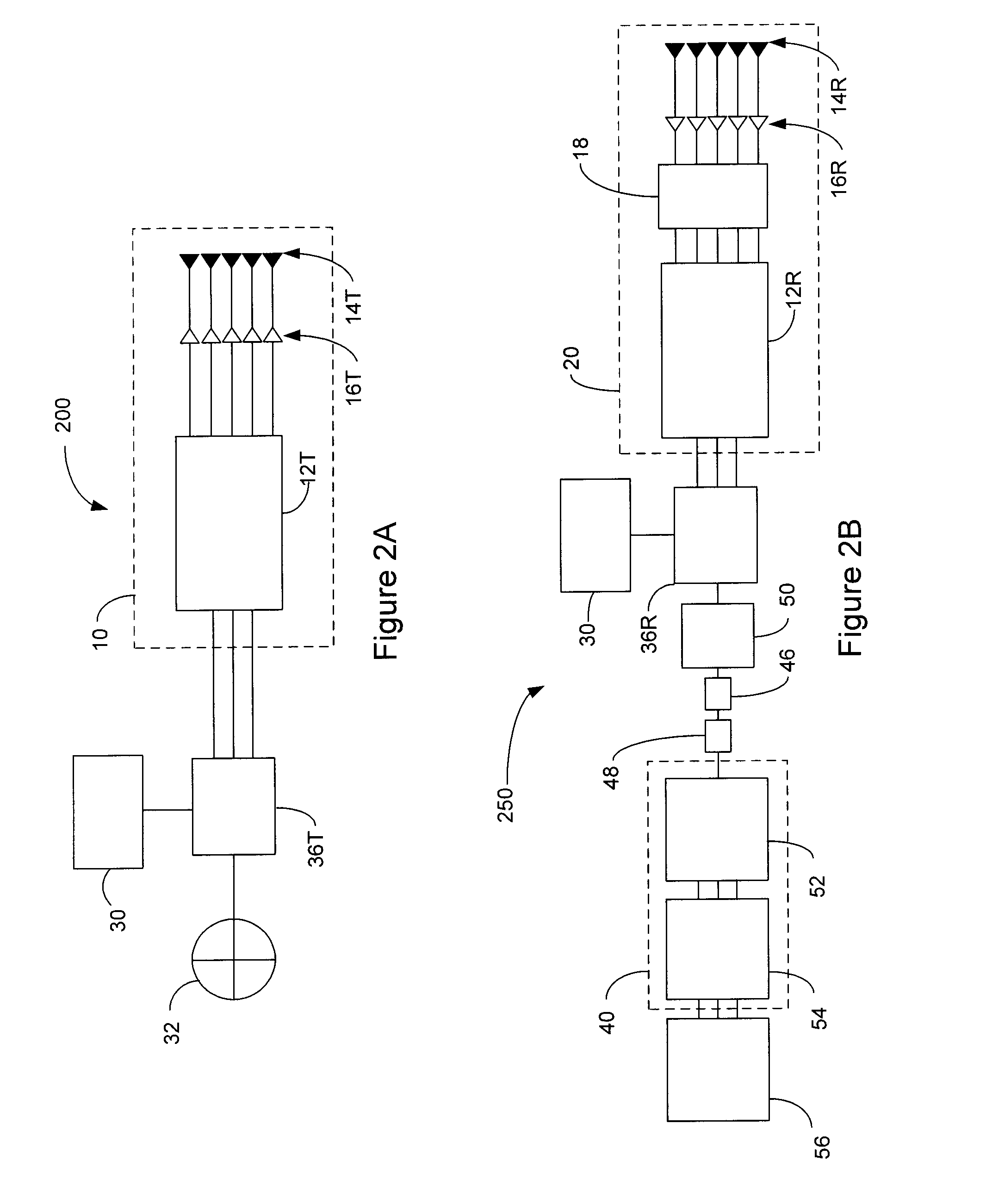
ActiveUS20130027240A1Increase speedThe signal is accurate and reliableAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesParallel-plate/lens fed arraysRadar systemsEngineering
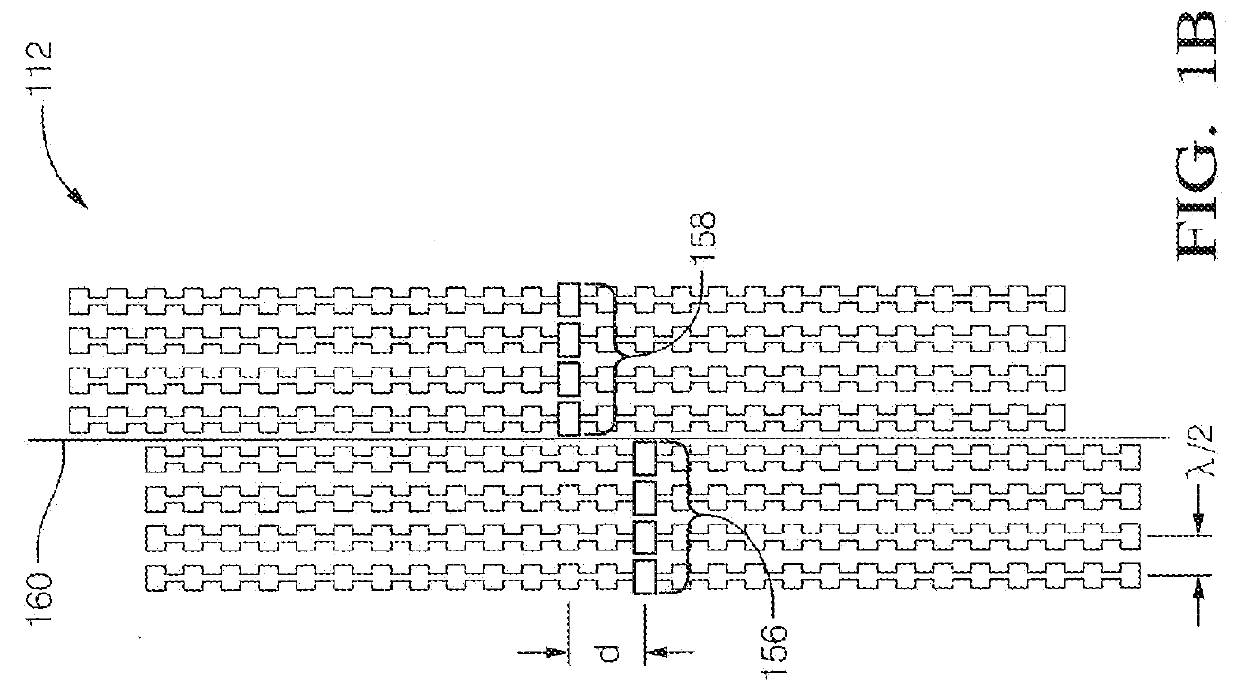
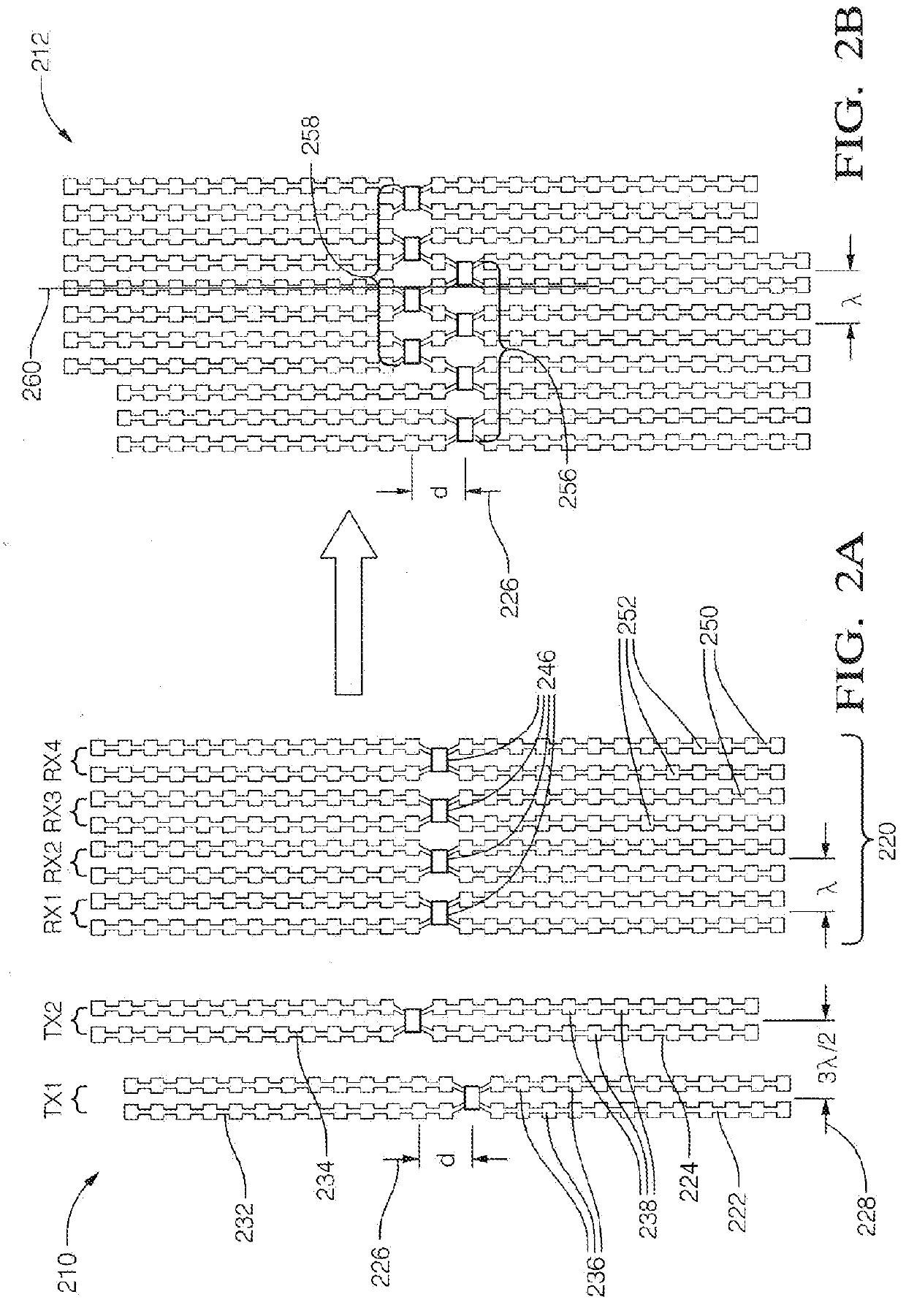
A radar system (100) is described including a transmitting assembly (10), a receiving assembly (20), a control unit (30) and a signal processing unit (40). The transmitting assembly (10) receives an input signal (31) and transmits an incident radar signal (2). The transmitting assembly (10) includes a Rotman lens (12) having a lens cavity (74), a plurality of beam ports (60), a plurality of array ports (62) and a patch antenna assembly (14). The lens cavity (74) has a lens gap (h) between 10 microns to 120 microns, and preferably 40 microns to 60 microns. The patch antenna assembly (14) includes a plurality of antenna arrays (130) operable to receive a plurality of time-delayed, in-phase signals from the Rotman lens (12) and to transmit the incident radar signal (2) towards a target (4). The receiving assembly (20) receives a reflected radar signal (6) and produces an output signal. The signal processing unit (40) compares the input signal (31) to the output signal and implements an algorithm determining the range, velocity and position of the target (4).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WINDSOR
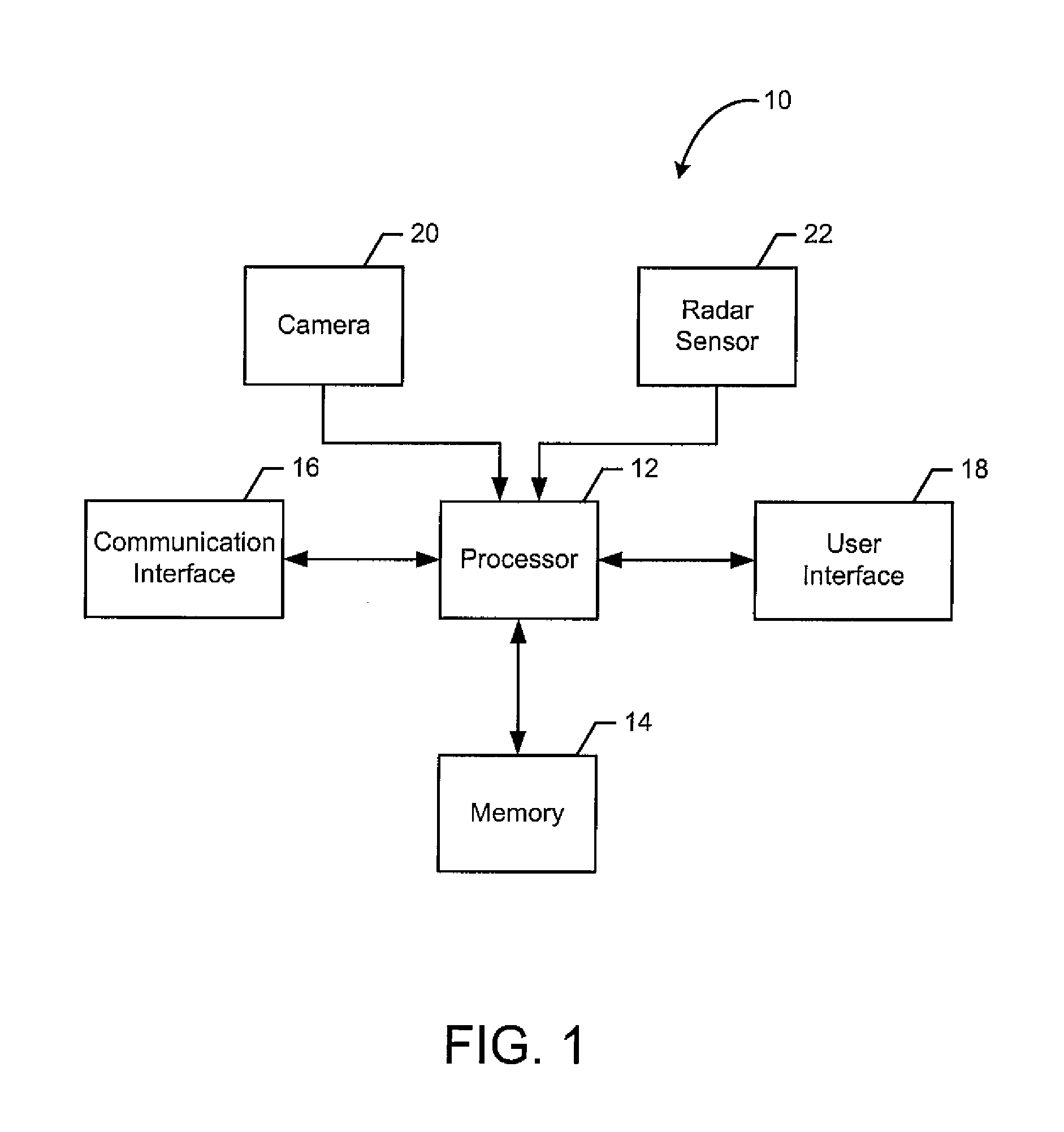
Radar based user interface
ActiveUS20160259037A1Minimize distractionImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionVehicle componentsProcessing elementUser interface
An apparatus and method for radar based gesture detection. The apparatus includes a processing element and a transmitter configured to transmit radar signals. The transmitter is coupled to the processing element. The apparatus further includes a plurality of receivers configured to receive radar signal reflections, where the plurality of receivers is coupled to the processing element. The transmitter and plurality of receivers are configured for short range radar and the processing element is configured to detect a hand gesture based on the radar signal reflections received by the plurality of receivers.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
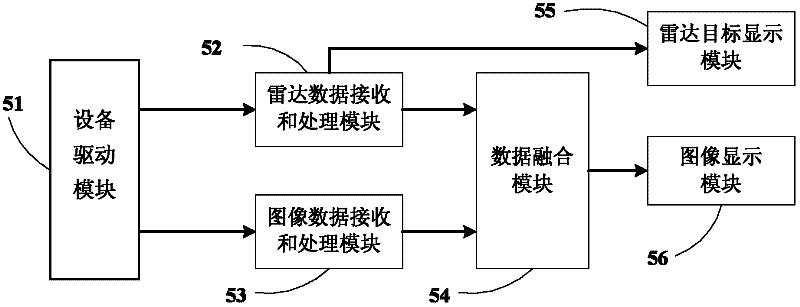
Multi-sensor information fusion-based collision and departure pre-warning device and method
InactiveCN102303605AImprove accuracyAvoid or Mitigate Collision AccidentsClosed circuit television systemsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionVisual perceptionImaging data
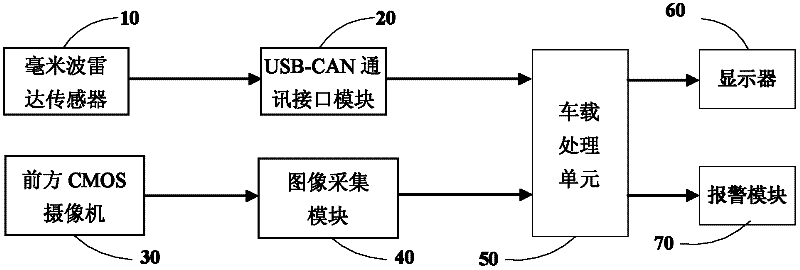
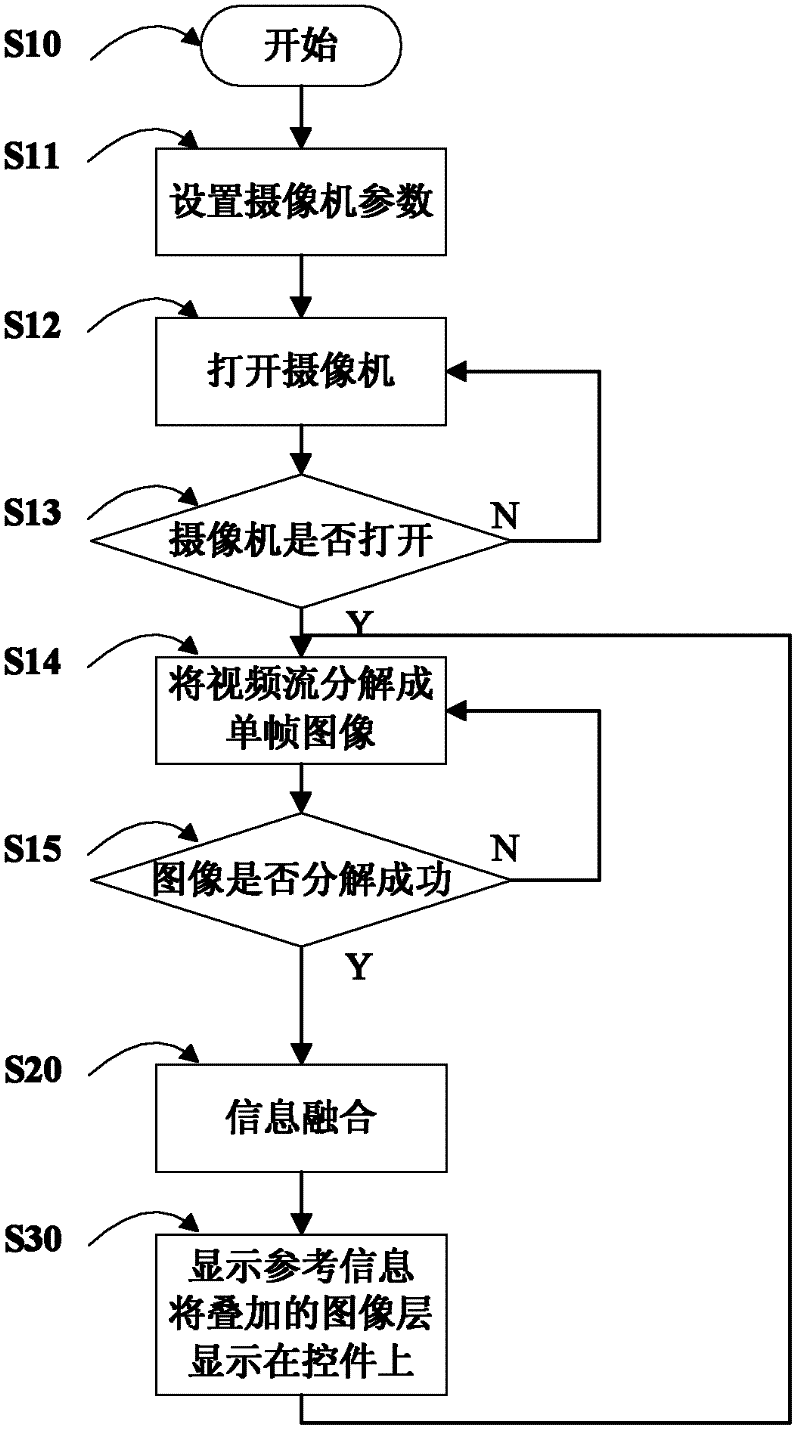
The invention discloses a multi-sensor information fusion-based forward collision and lane departure pre-warning device, which comprises a millimeter-wave radar, a communication interface module, a video camera, an image acquisition module, a display module, a warning module and a vehicle-mounted processing unit, wherein the vehicle-mounted processing unit can perform fusion processing of radar signals and machine visual information from the communication interface module and the image acquisition module. The pre-warning device is used for warning of forward collision and lane departure of a vehicle, and a pre-warning method comprises the steps of: driving devices; receiving and processing radar data and image data; fusing information; and finally displaying the fused information. According to the multi-sensor information fusion-based forward collision and lane departure pre-warning device disclosed by the invention, potential risk of collision during running of the vehicle can be found through the radar and the video camera so as to provide warning information for a driver. According to the pre-warning method disclosed by the invention, since a method of visible sensation combined with the radar is adopted, the accuracy rate of prevention of collision and lane departure of the vehicle is fundamentally improved, and the degree of accuracy can be increased by 5-20 percent as proved by experiments.
Owner:CHINA AUTOMOTIVE TECH & RES CENT
Systems, methods, and apparatus for radar-based detection of objects in a predetermined space
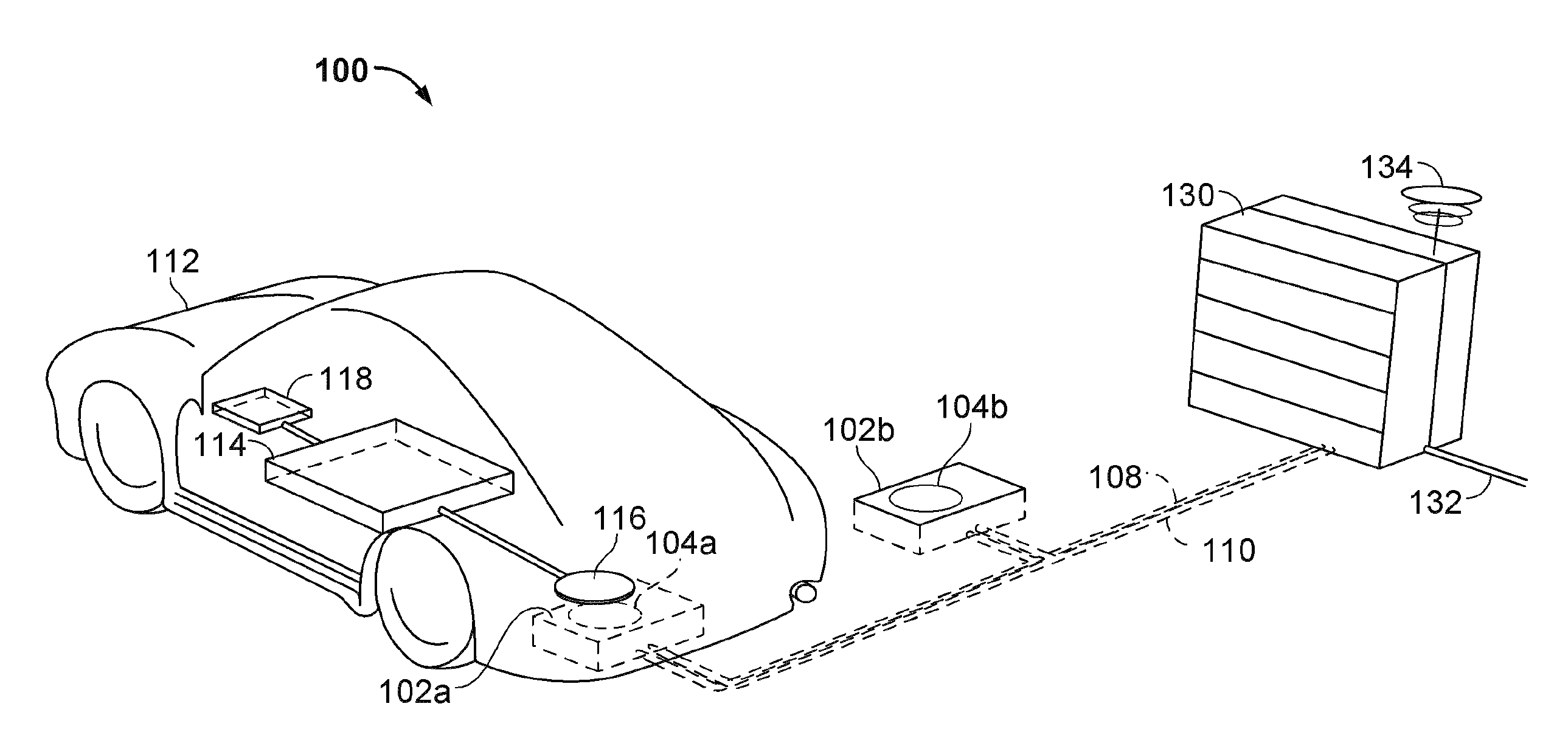
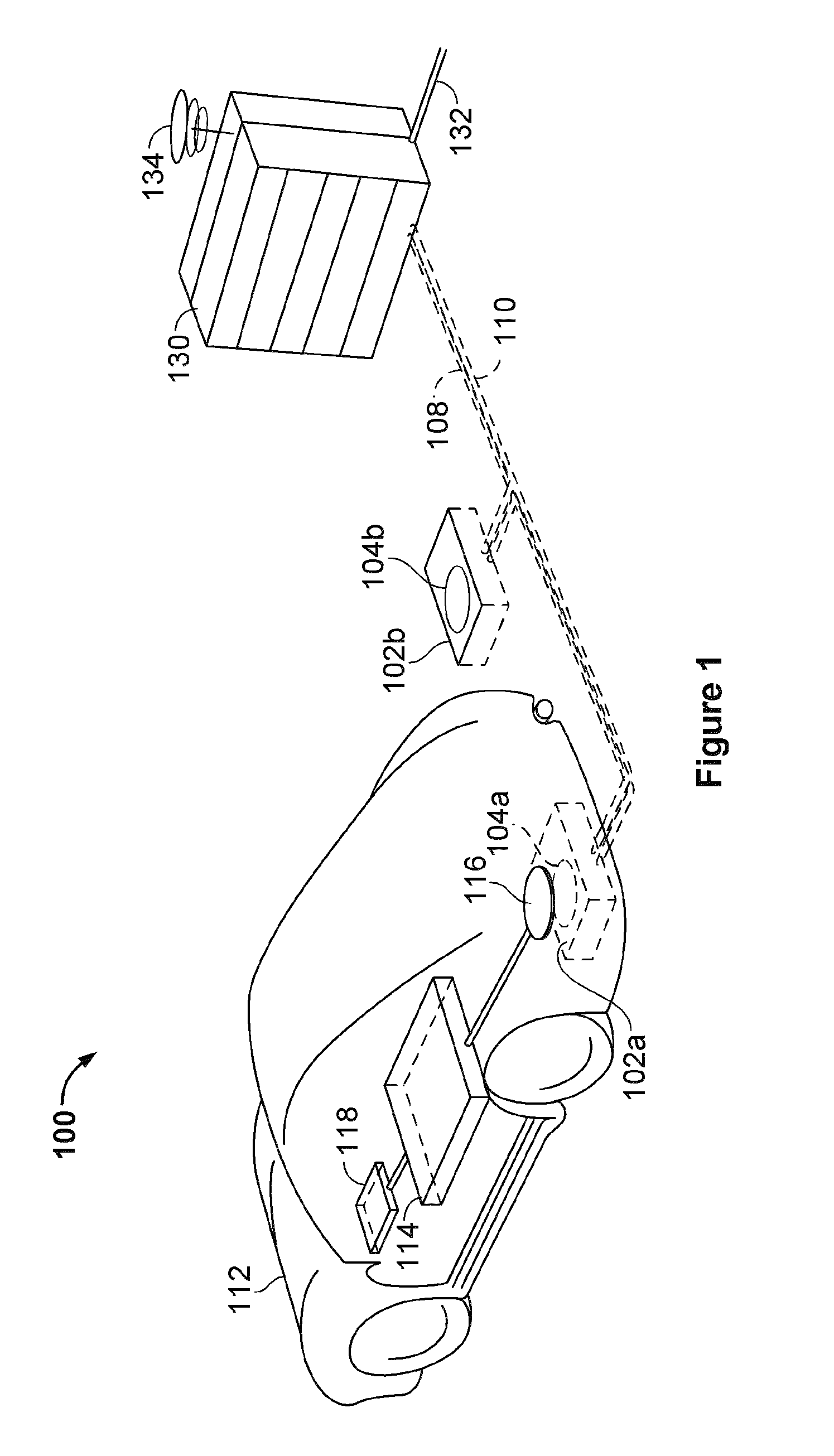
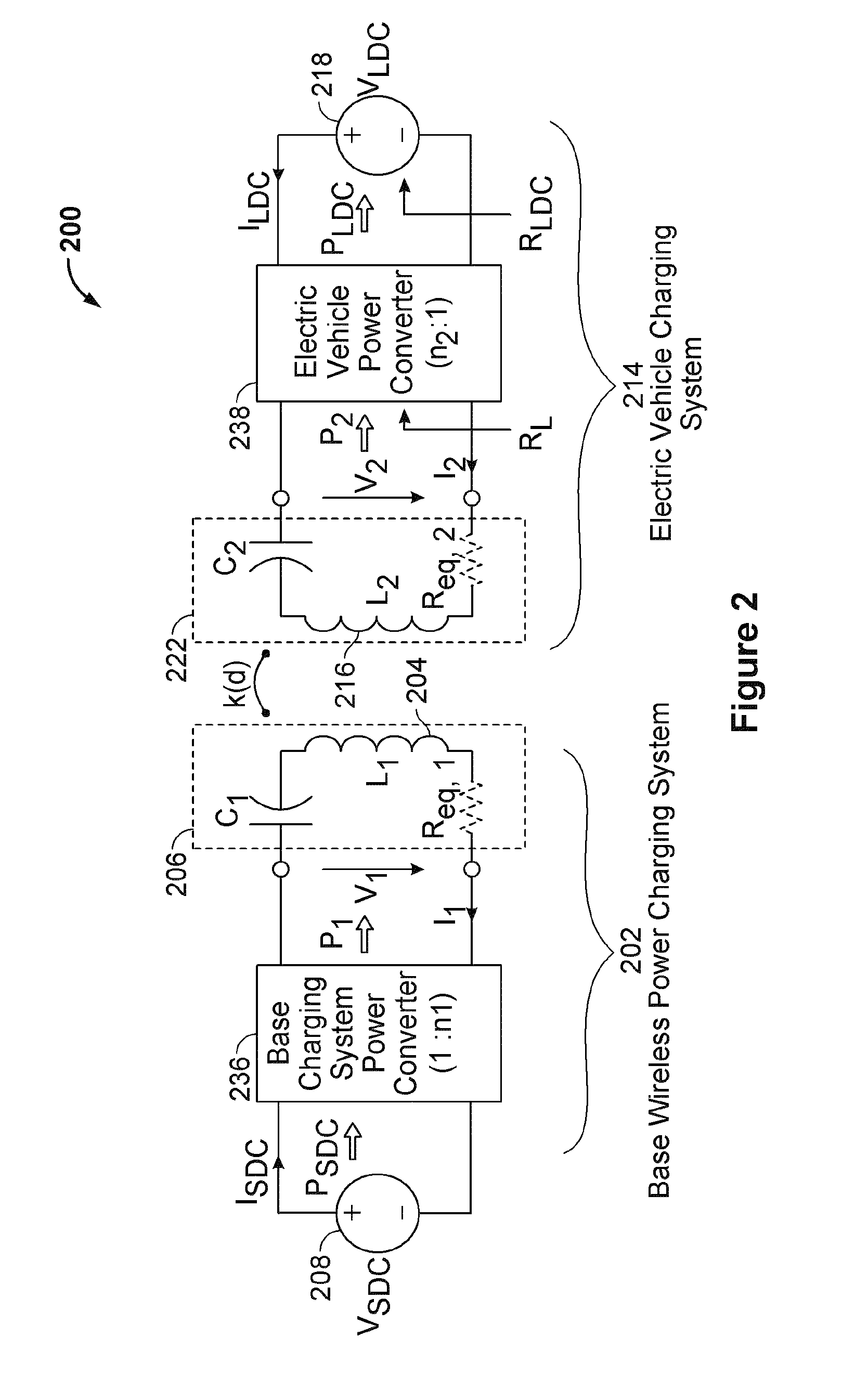
This disclosure provides apparatuses and methods for detecting foreign objects. An apparatus for detecting a presence of an object comprises at least one radar antenna attached to a wirelessly chargeable vehicle. The at least one radar antenna is configured to transmit a radar signal into a space between a wireless power receiver of the vehicle and a wireless charger as the vehicle moves in a primary direction of movement of the vehicle and receive the radar signal. The apparatus further comprises a radar processing circuit configured to determine a presence of the object in the space based on at least one characteristic of the received radar signal. The radar processing circuit is further configured to provide an indication to receive power from the wireless charger based at least in part on the determining the presence of the object.
Owner:WITRICITY CORP
RFID system utilizing parametric reflective technology
ActiveUS20050280539A1Optimization rangeReduce manufacturing costAntenna arraysAntenna supports/mountingsImaging algorithmRadio frequency
A system and method for encoding and decoding information by use of radio frequency antennas. The system includes one or more interrogator devices and RFID data tags. The RFID data tags include a plurality of antenna elements which are formed on a substrate or directly on an object. The antenna elements are oriented and have dimensions to provide polarization and phase information, whereby this information represents the encoded information on the RFID tag. The interrogator device scans an area and uses radar imaging technology to create an image of a scanned area. The device receives re-radiated RF signals from the antenna elements on the data tags, whereby the data tags are preferably represented on the image. The re-radiated RF signals preferably include polarization and phase information of each antenna element, whereby the information is utilized using radar signal imaging algorithms to decode the information on the RF data tag.
Owner:VUBIQ
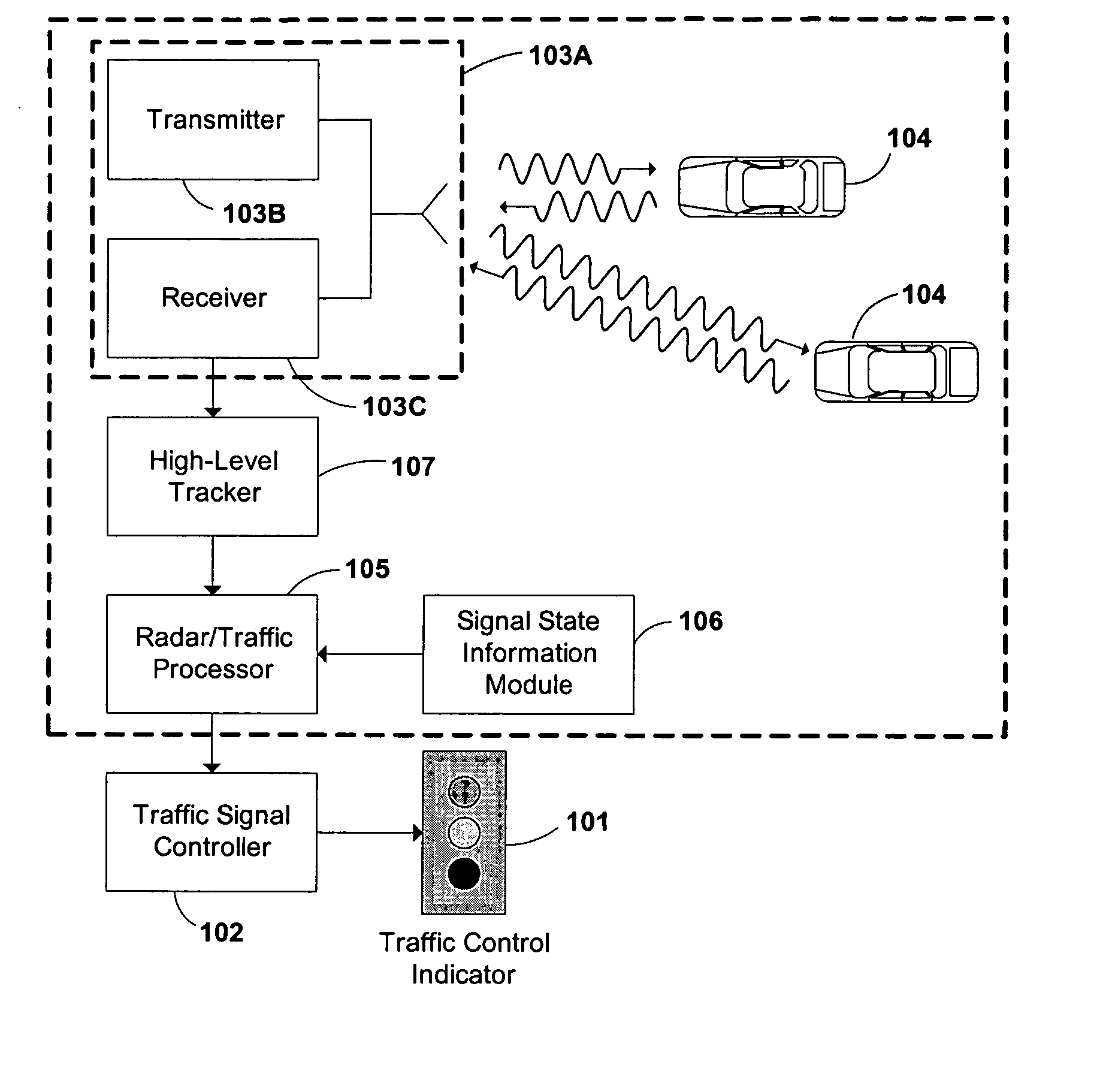
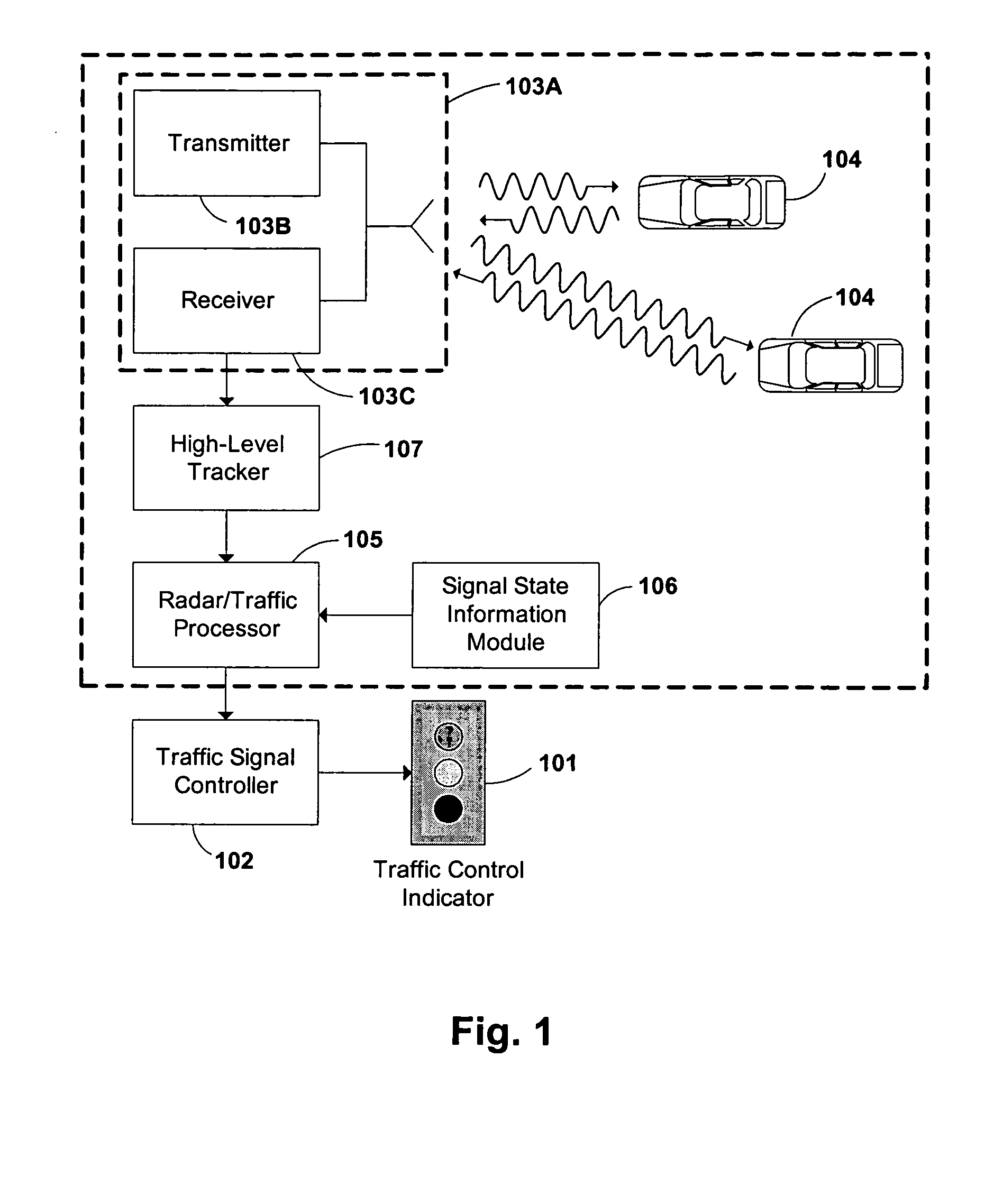
Traffic light signal system using radar-based target detection and tracking
InactiveUS20050046597A1Reduce harmSave energyControlling traffic signalsAnti-collision systemsRadar systemsTraffic signal
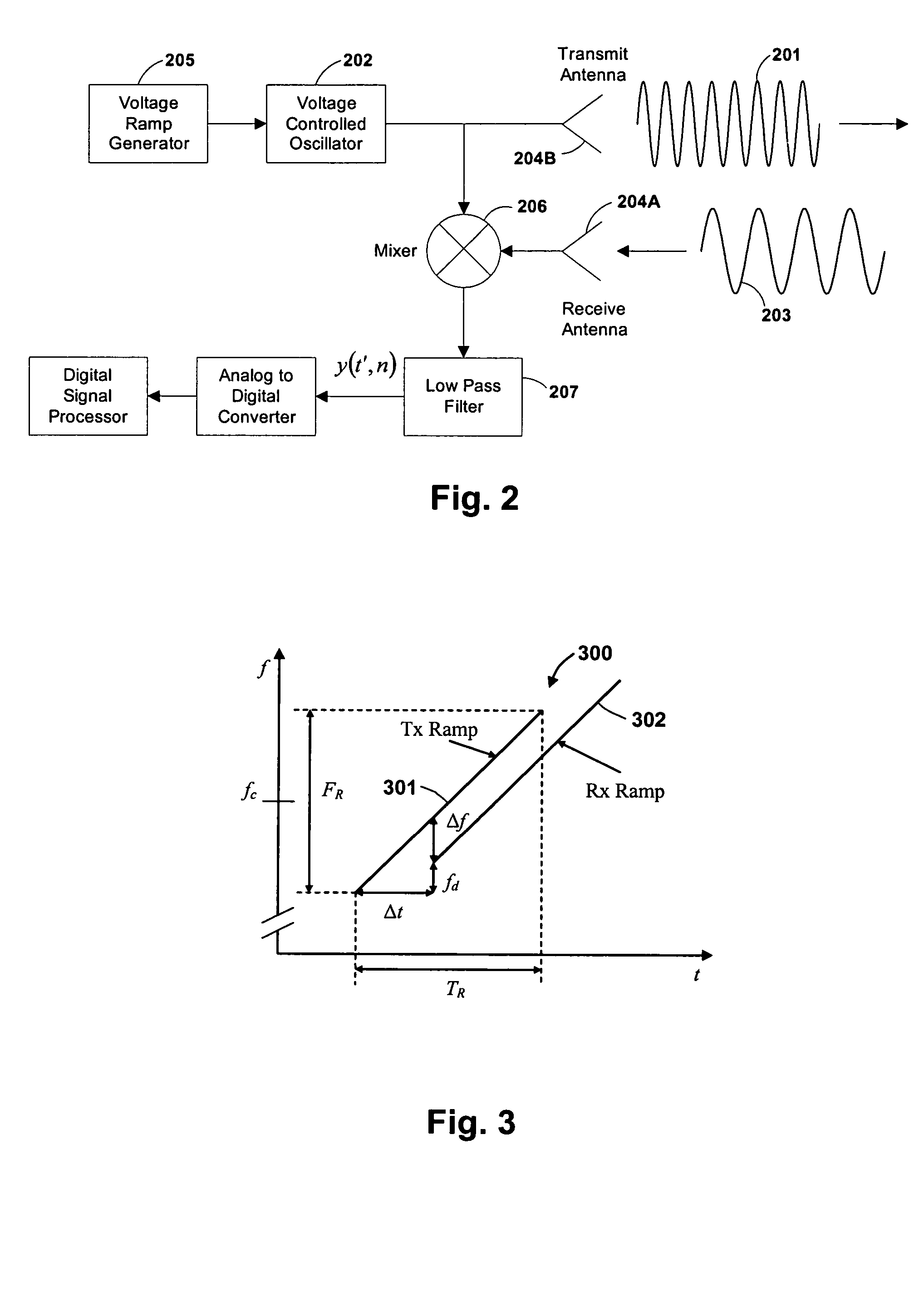
A novel system and method of integrating an RF emissions device, such as a radar system (103A), within a traffic control indicator (101) system. The system and method determines, using LFM-CW radar signals (201) and a multi-stage spectral processing algorithm (600), if one or more object / vehicle targets will enter an intersection and comprises receiving a radar echo response (203) indicating the object / vehicle target (104) is approaching the intersection, receiving range and velocity of the object / vehicle targets (104), and based on the receiving, determining if the object / vehicle target (104) will enter the intersection. The system and method can programmatically be configured to activate red-light-hold, green-light-extension, or left-turn-warning.
Owner:POWER SIGNAL TECH +1
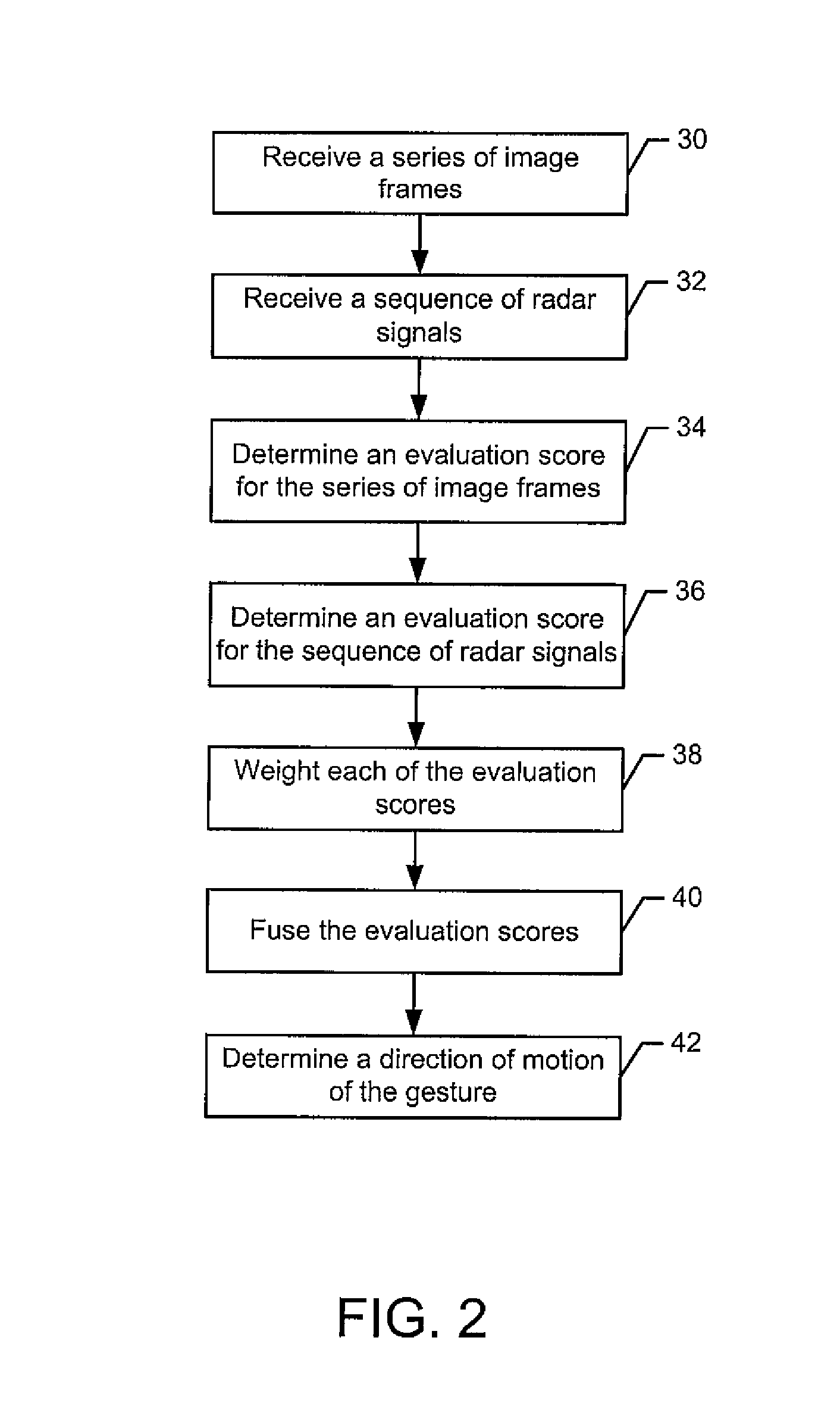
Method and Apparatus for Identifying a Gesture Based Upon Fusion of Multiple Sensor Signals
InactiveUS20140324888A1Improved gesture recognitionReliably recognizeInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsPattern recognitionMultiple sensor
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided to permit improve gesture recognition based on fusion of different types of sensor signals. In the context of a method, a series of image frames and a sequence of radar signals are received. The method determines an evaluation score for the series of image frames that is indicative of a gesture. This determination of the evaluation score may be based on the motion blocks in an image area and the shift of the motion blocks between image frames. The method also determines an evaluation score for the sequence of radar signals that is indicative of the gesture. This determination of the evaluation score may be based upon the sign distribution in the sequence and the intensity distribution in the sequence. The method weighs each of the evaluation scores and fuses the evaluation scores, following the weighting, to identify the gesture.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
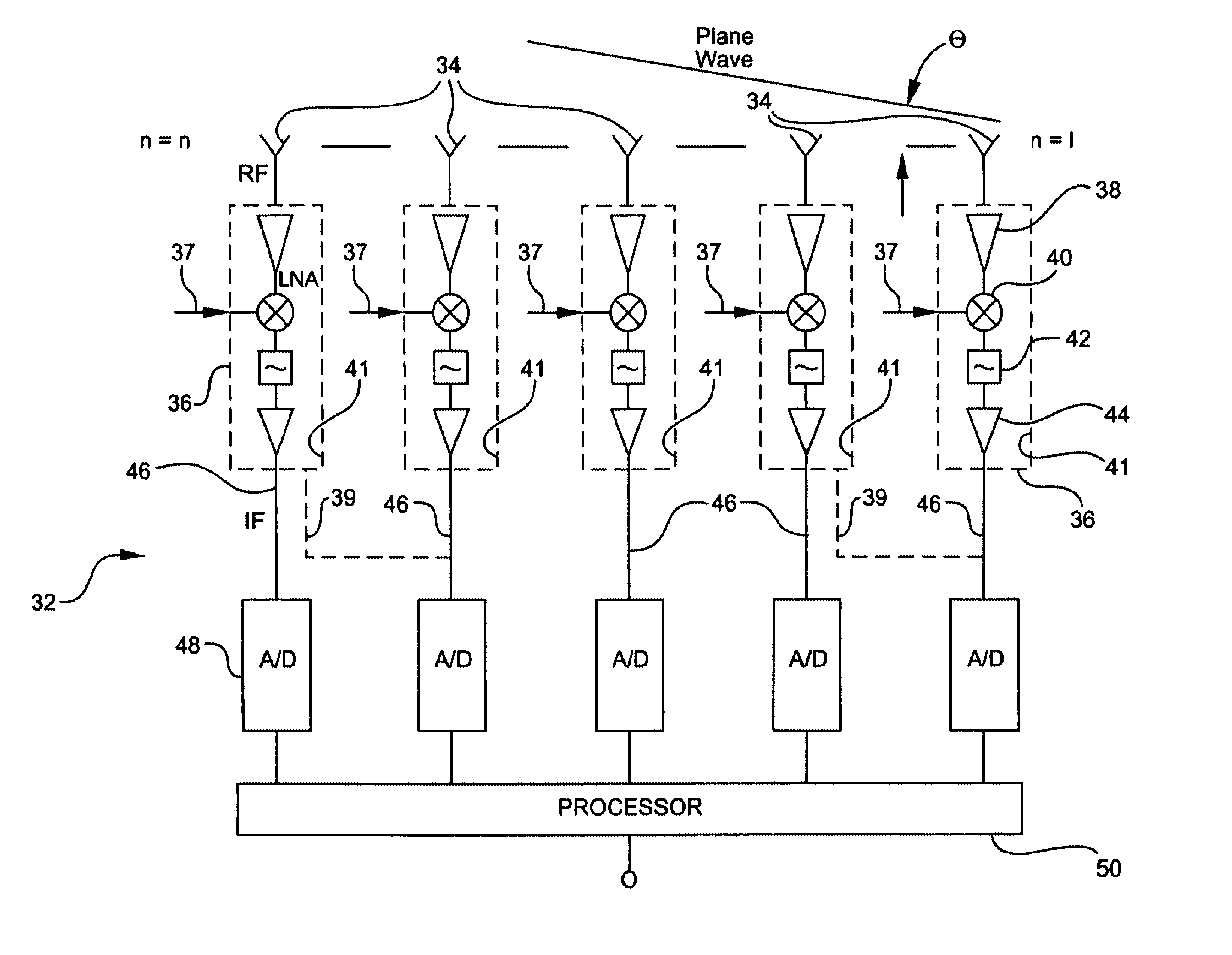
Digital beamforming radar system
InactiveUS6882311B2Less spaceEasy to manufactureModular arraysTransmissionLow noiseLocal oscillator signal
A receiver for a digital beamforming radar system includes a plurality of antenna elements, low-noise block converters, one or more analog-to-digital converters, and a processor. The antenna elements receive a radar signal and output a received signal. The low-noise block converters are modified commercially available components used in satellite television systems, respond to the received signal from a corresponding antenna element, and output an intermediate frequency signal. The low-noise block converters include at least one amplifier, a mixer, and a local oscillator input. The local oscillator input enables an external local oscillator signal to be inputted to the mixer. The analog-to-digital converters are responsive to the intermediate frequency signal of a corresponding low-noise block converter. The processor is responsive to the digital signals output by the analog-to-digital converters.
Owner:COMM & POWER IND
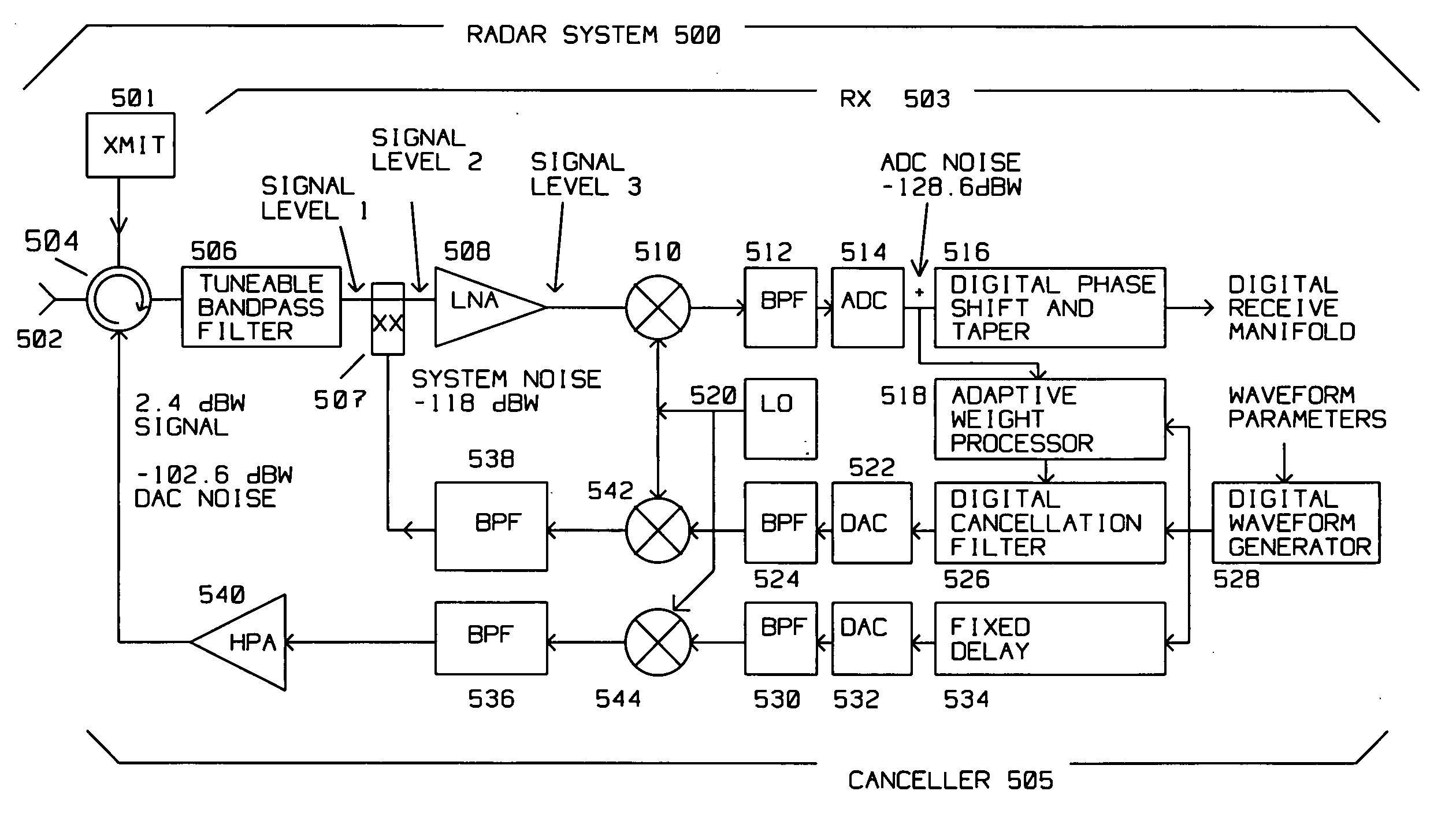
Technique for compensation of transmit leakage in radar receiver
A radar system (500) radiates a radar transmit signal, has a radar signal receiver (503) and a canceller (505) for canceling leakage of the transmit signal into the radar signal receiver (503). The canceller (505) comprises a digital waveform generator (528) for generating a first digital signal converted to an analog waveform. The analog waveform is amplified after a fixed delay (534) to generate a first cancellation signal input into a circulator (504). The circulator combines the first cancellation signal with the leakage to generate a first corrected signal. A summer (507) combines the first corrected signal from the circulator with a second cancellation signal to generate a second corrected signal. The second cancellation signal is generated by a digital cancellation filter (526). The digital cancellation filter (526) has as an input the first digital signal from the digital waveform generator (528). The digital cancellation filter (526) is controlled using weight adjustments computed by an adaptive weight processor (518). The adaptive weight processor (518) samples the second corrected signal and computes the weight adjustments to optimize the second cancellation signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
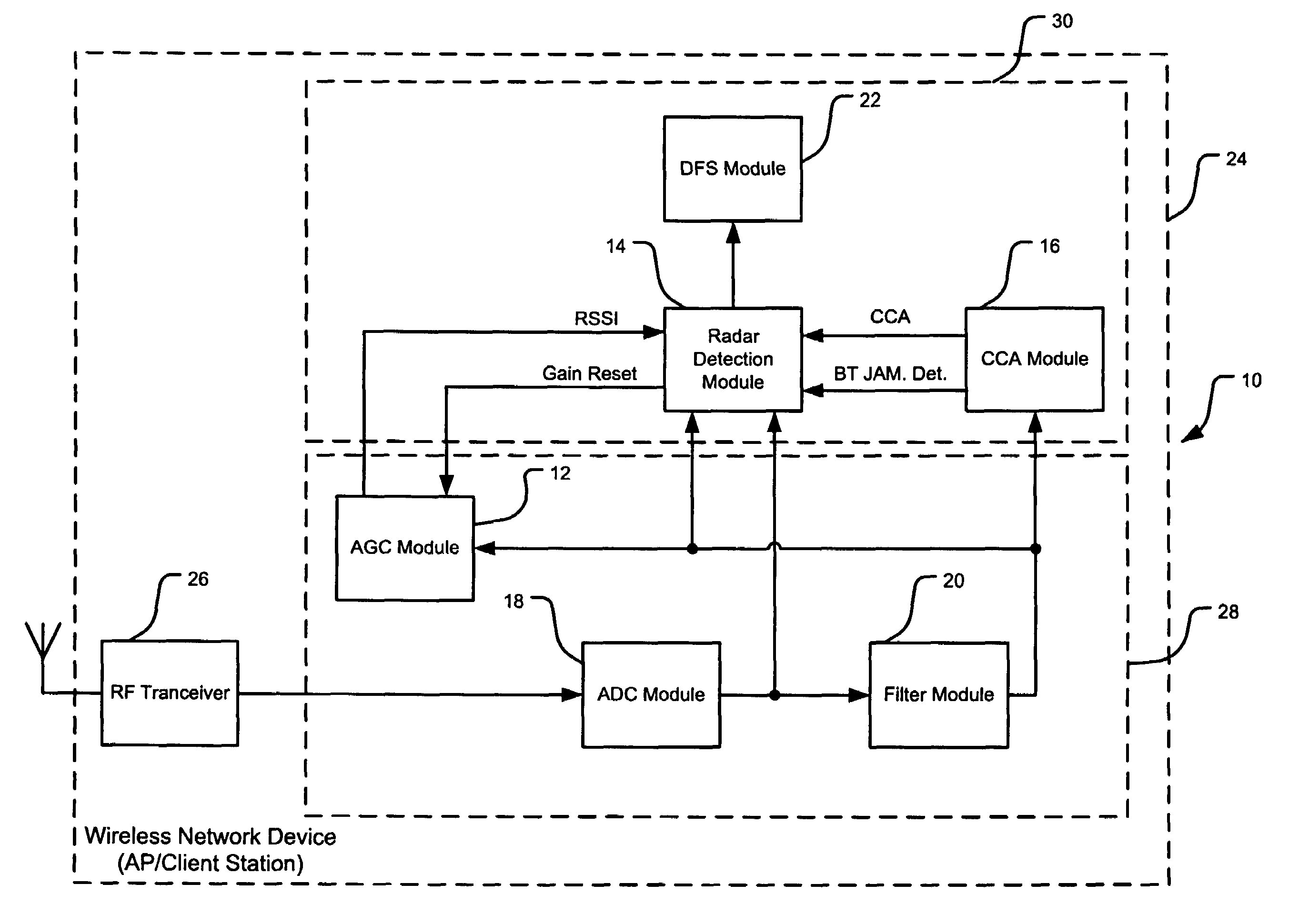
Radar detection and dynamic frequency selection
ActiveUS7702044B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsCommunication jammingAutomatic controlControl signal
A wireless network device includes a correlation module, an automatic gain control module, and a control module. The correlation module correlates a predetermined portion of a radio frequency (RF) signal and generates a correlation signal based thereon. The automatic gain control (AGC) module generates a gain control signal based on said RF signal. The control module selectively determines whether said RF signal is a radar signal based on said correlation signal and said gain control signal.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
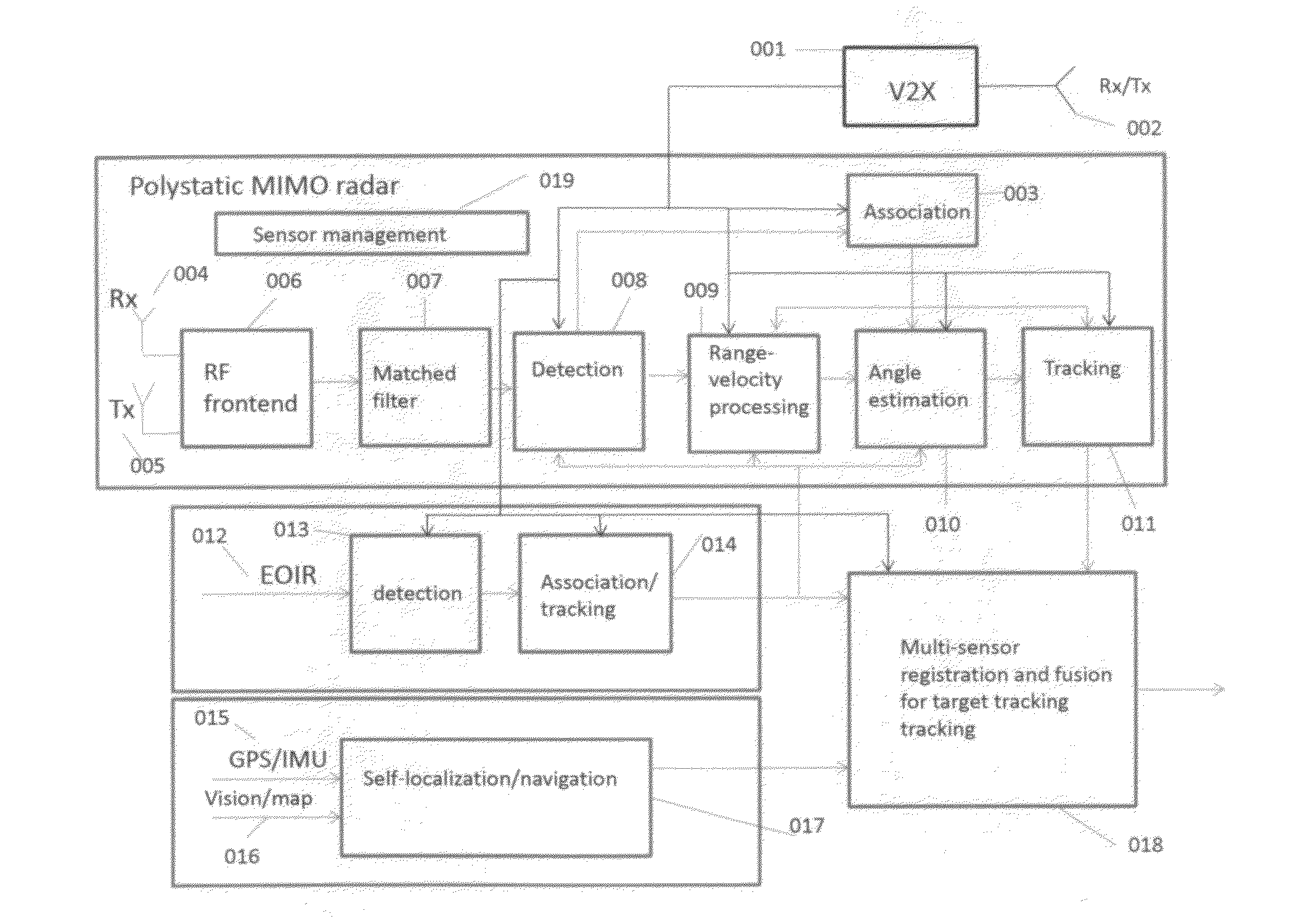
Deep Fusion of Polystatic MIMO Radars with The Internet of Vehicles for Interference-free Environmental Perception
InactiveUS20160223643A1Improve performanceSimple signal processingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputData center
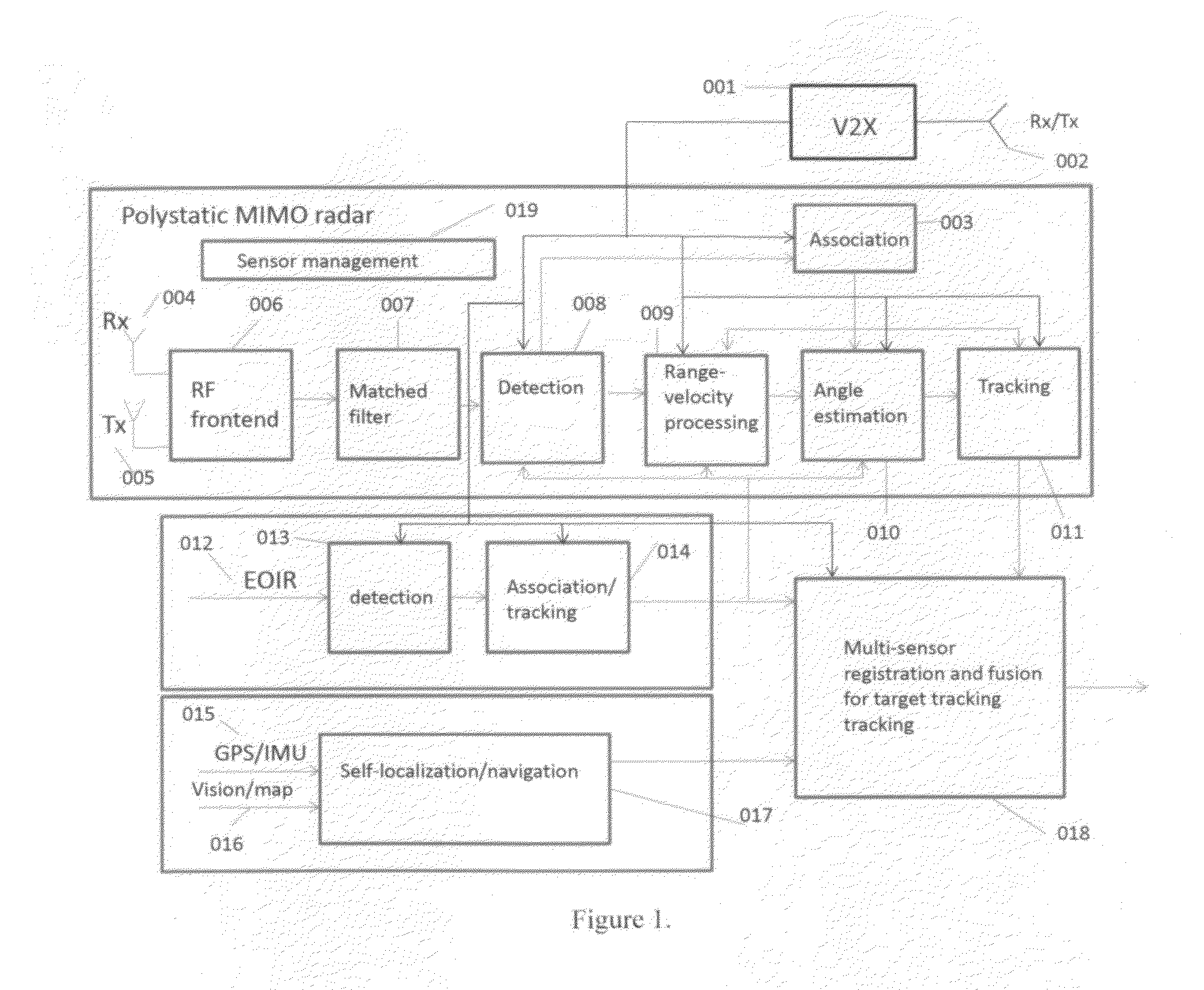
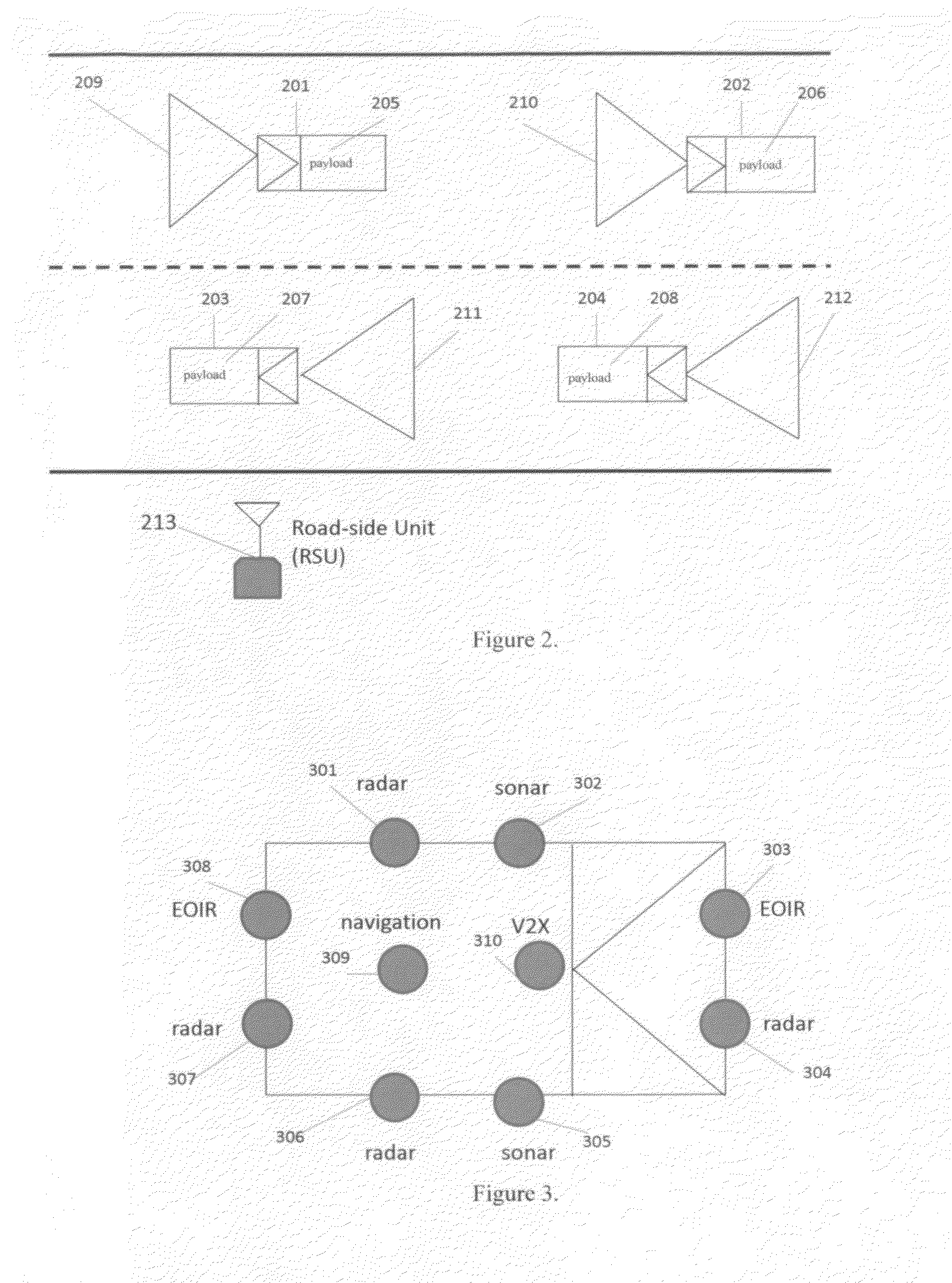
This invention is related to a deep multi-sensor fusion system for inter-radar interference-free environmental perception comprising of (1) polystatic Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) radars such as radio frequency radar and laser radar; (2) vehicle self-localization and navigation; (3) the Internet of Vehicles (IoV) including Vehicle-to-Vehicle communication (V2V), Vehicle-to-Infrastructure communication (V2I), other communication systems, data center / cloud; (4) passive sensors such as EOIR, and (5) deep multi-sensor fusion algorithms. The self-localization sensors and V2X formulate cooperative sensors. The polystatic MIMO radar on each vehicle utilizes both its own transmitted radar signals and ones from other vehicles to detect obstacles. The transmitted radar signals from other vehicles are not considered as interference or uselessness as conventional radars, but considered as useful signals to formulate a polystatic MIMO radar which can overcome the interference problem and improve the radar performance. This invention can be applied to all kinds of vehicles and robotics.
Owner:LI WENHUA +1
Short-range frequency-modulation continuous wave FMCW radar anti-interference method
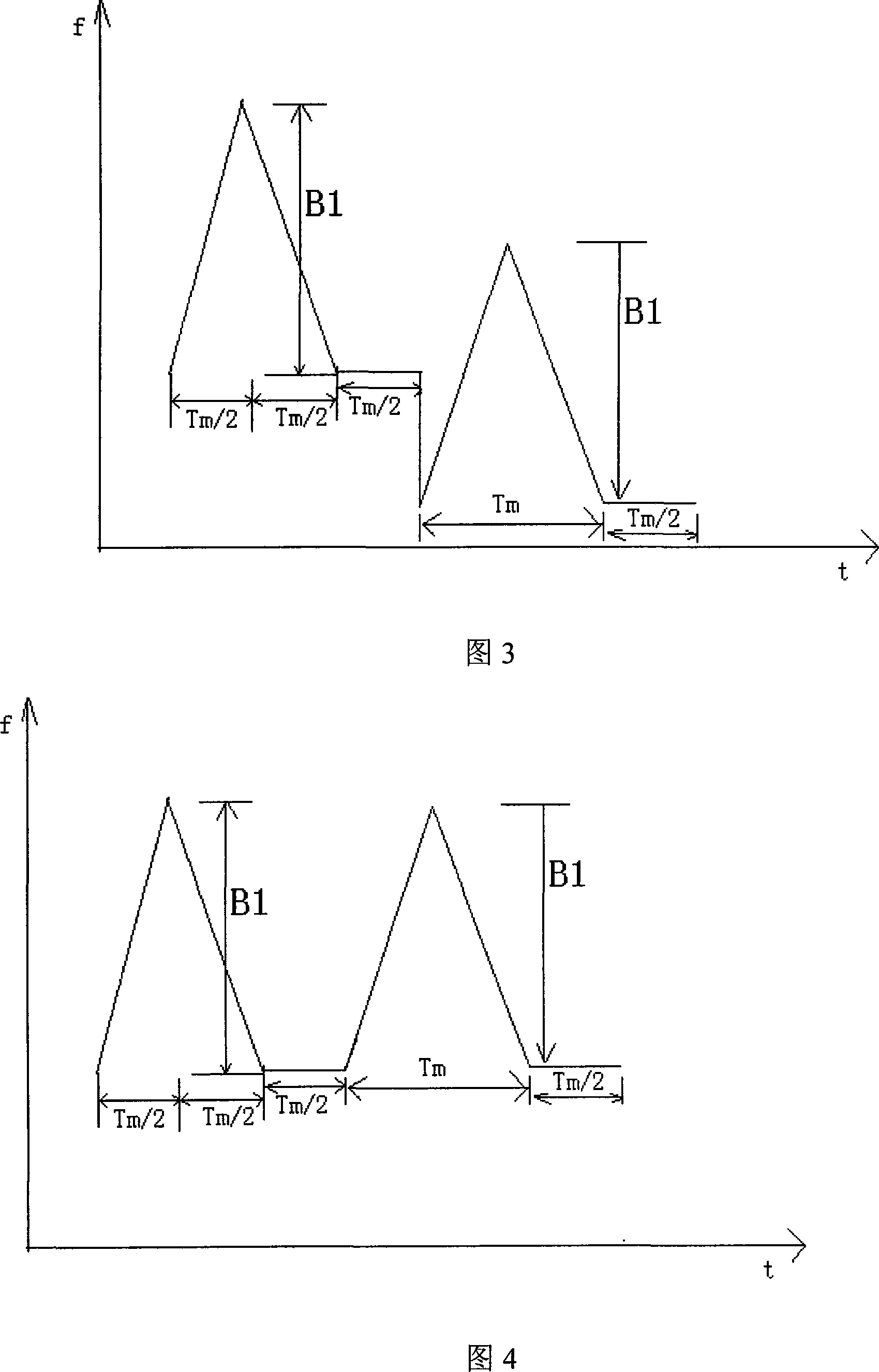
ActiveCN101089653AWork reliablyEasy to implementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionContinuous waveFrequency modulation
An anti-interfering method of short-range FMCW radar includes designing a set of pseudo-random code according to occasion of radar, distributing different pseudo-random code to different radar operated at different area, applying different pseudo-random code to modulate frequency start-point of FM emission signal for the same radar on each cycle, making frequency-mixture on received echo signal by utilizing emission signal, using filter to filter off interference signal and applying FM signal processing means to treat reserved usable signal for obtaining object distance and speed information in high resolution.
Owner:南京精益安防系统科技有限公司
Radar microsensor for detection, tracking, and classification
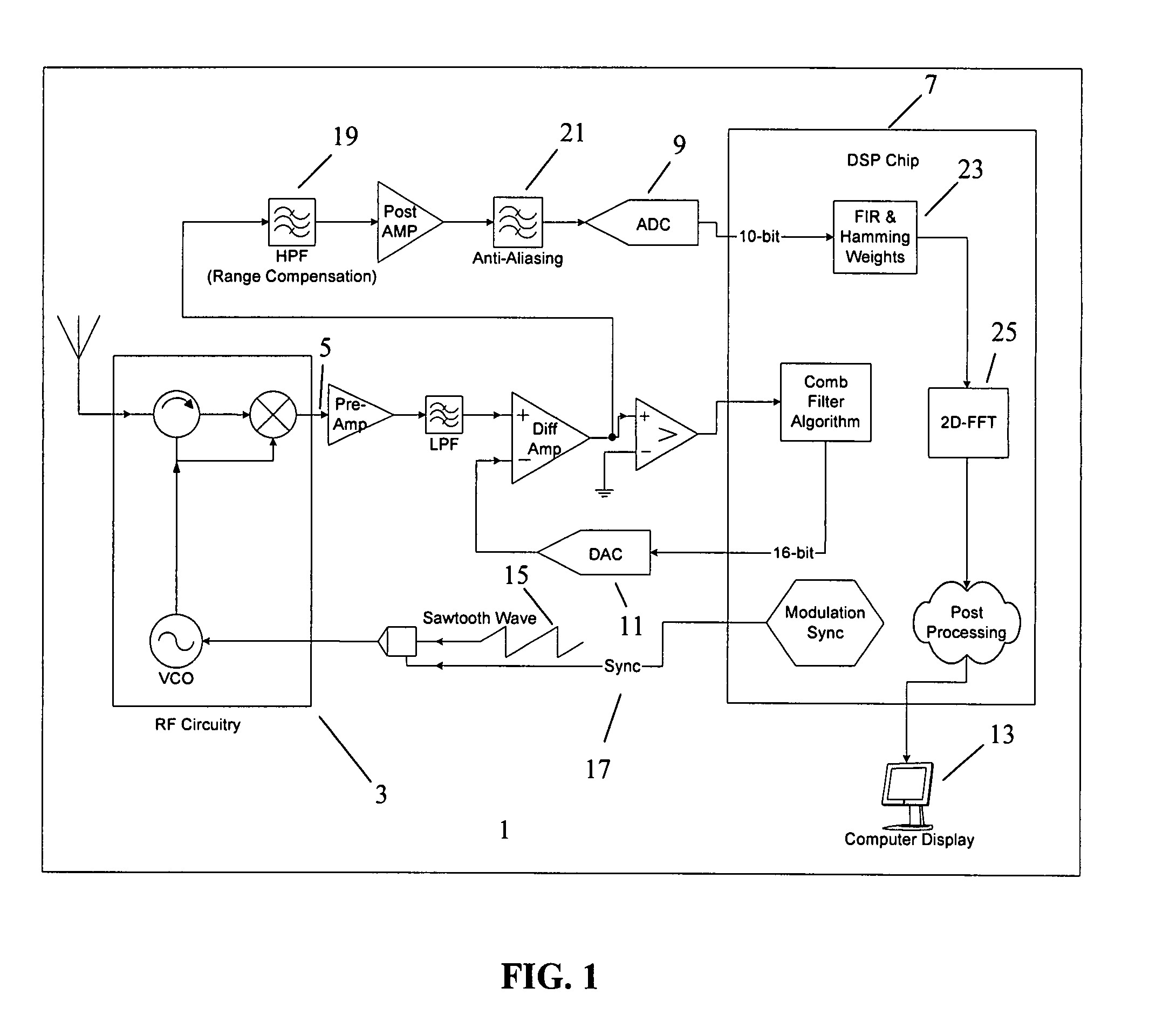
InactiveUS20080106460A1Noise minimizationRemove unwanted amplitude modulationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsImage resolution
The subject invention pertains to a frequency modulation continuous wave (FMCW) radar system. Embodiments relate to methods of improving the performance of such a FMCW system and improving the value of the information provided by such a FMCW system. In an embodiment of the subject invention, the IF level can be monitored while sweeping the frequency of the system through at least a portion of the frequency range of the system. In a specific embodiment, the system is then set to the frequency that produces the minimum IF level, which is the frequency that produces the minimum AM signal level. Embodiments of the invention pertain to techniques for expediting the adaptation of the comb filter to the signal when the system is turned on. In an embodiment, in order to reduce the number of detection calculations a processor performs every frame, a method of quickly determining the largest peaks in the RDM is implemented. Embodiments of the subject invention relate to a method for processing a radar signal that classifies two or more targets. A specific embodiment of a method for processing the radar signal classifies a human target or other target(s) using amplitude values in time-consecutive range-Doppler maps. Embodiments of the invention pertain to a method for processing a radar signal for improving the performance of FMCW detection, tracking, and classification algorithms. Embodiments improve such performance by increasing the SNR and velocity measurement resolution of slow moving targets while minimizing DSP computational and memory requirements in two-dimensional FFT range-velocity processing.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
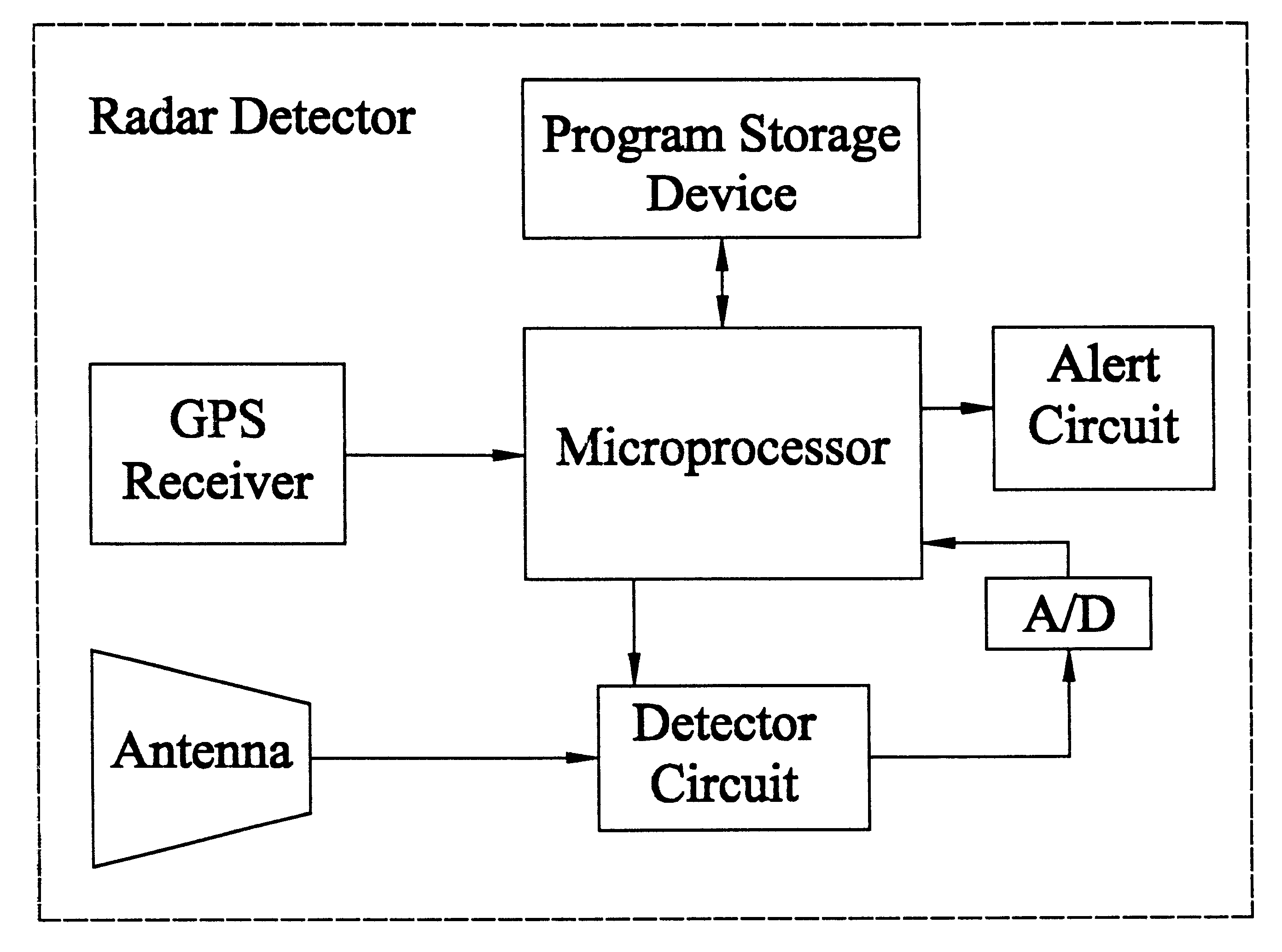
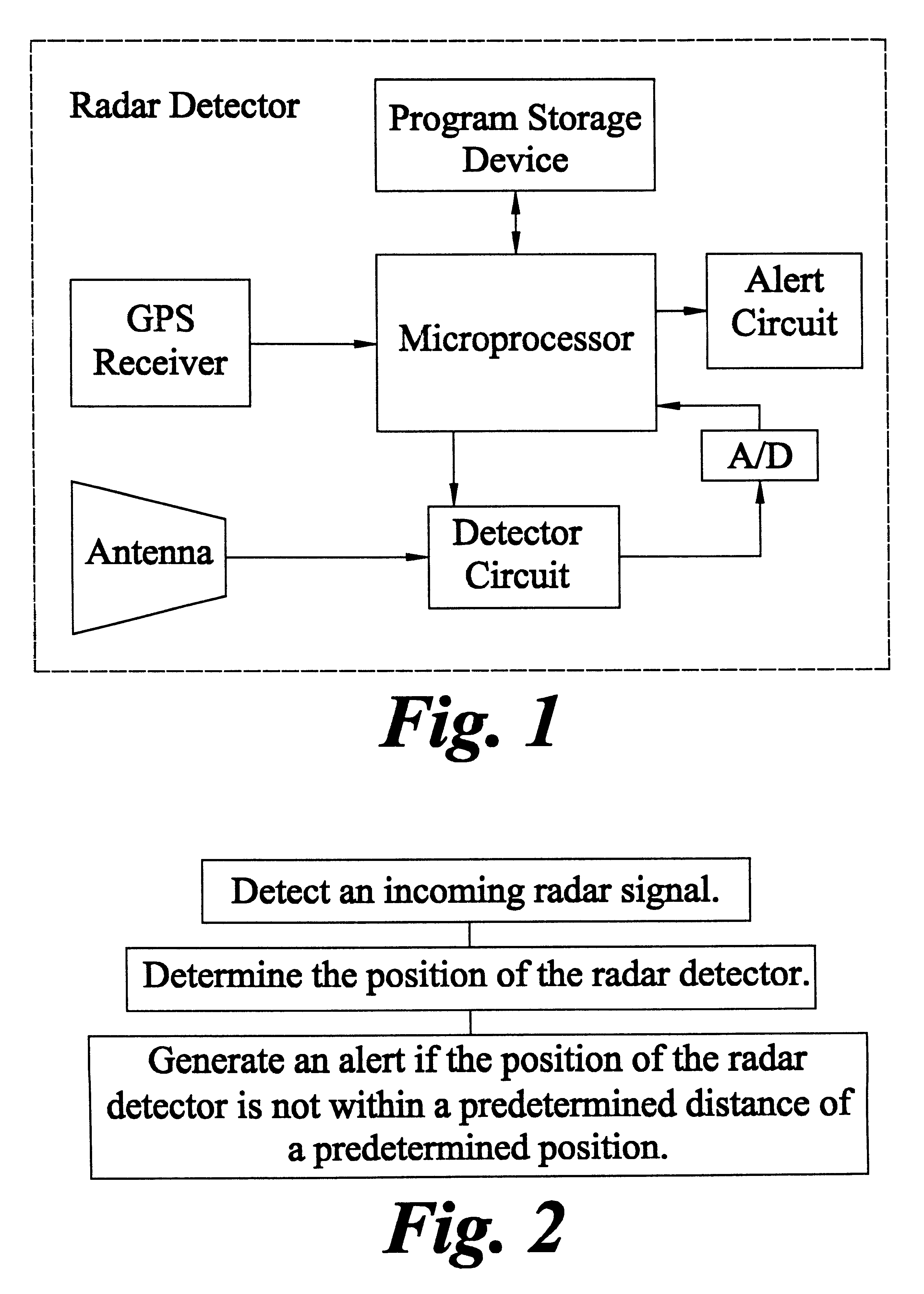
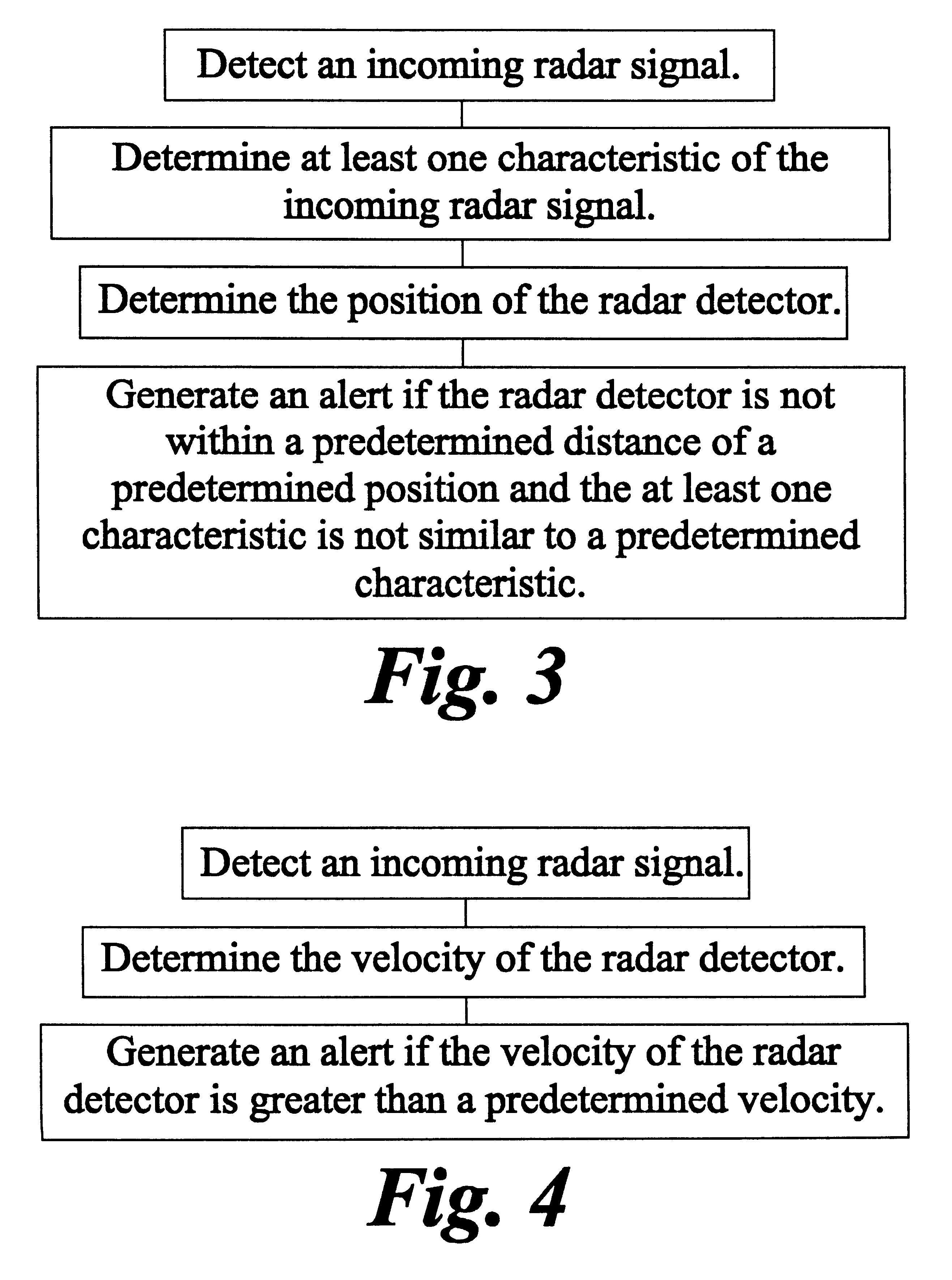
Method and apparatus for alerting an operator of a motor vehicle to an incoming radar signal
InactiveUS6204798B1Position fixationSatellite radio beaconingMobile vehicleGlobal positioning system receiver
A radar detector for alerting an operator of a motor vehicle to an incoming police radar signal. This radar detector includes a microprocessor; a circuit coupled to the microprocessor for detecting the incoming police radar signal; and a global positioning system receiver coupled to the microprocessor. Upon detection of an incoming radar signal, the radar detector can utilize the position, velocity, and / or heading data from the global positioning system receiver to determine whether to generate an alert.
Owner:ESCORT INC
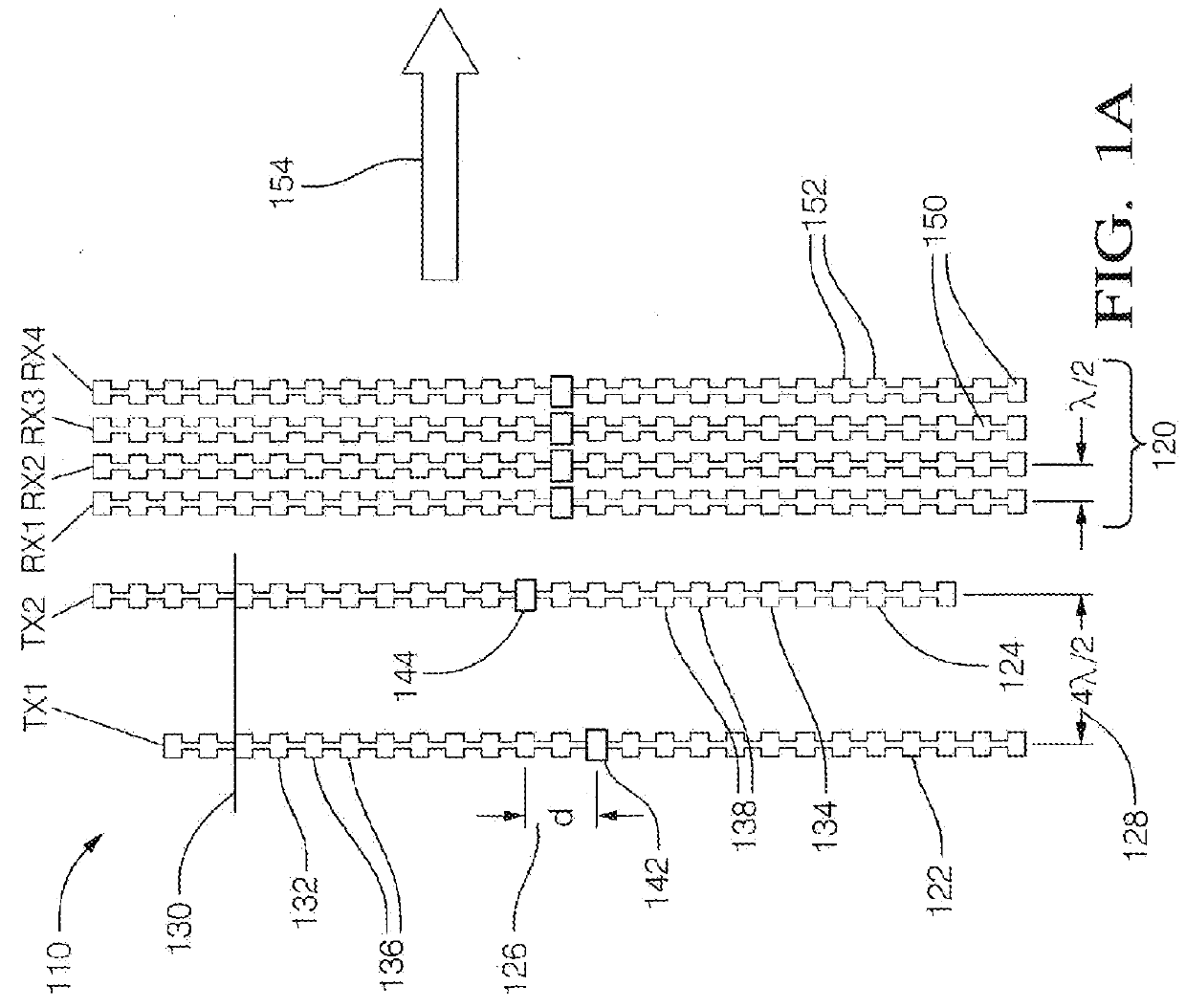
MIMO antenna with elevation detection
A multiple input multiple output (MIMO) antenna for a radar system includes a receive antenna, a first transmit-antenna-arrangement, and a second transmit-antenna-arrangement. The receive-antenna is configured to detect radar-signals reflected by a target toward the receive-antenna. The first transmit-antenna-arrangement includes a first vertical-array of radiator elements and a second vertical-array of radiator elements. The first transmit-antenna-arrangement is configured so the first vertical-array can be selectively coupled to a transmitter independent of the second vertical-array. The second transmit-antenna-arrangement includes a third vertical-array of radiator elements and a fourth vertical-array of radiator elements. The second transmit-antenna-arrangement is configured so the third vertical-array can be selectively coupled to a transmitter independent of the fourth vertical-array. The second transmit-antenna-arrangement is vertically offset from the first transmit-antenna-arrangement by a vertical offset distance selected so an elevation angle to the target can be determined by the receive-antenna.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Finite harmonic oscillator
InactiveUS20090204627A1Code conversionHandling data according to predetermined rulesFeature vectorData set
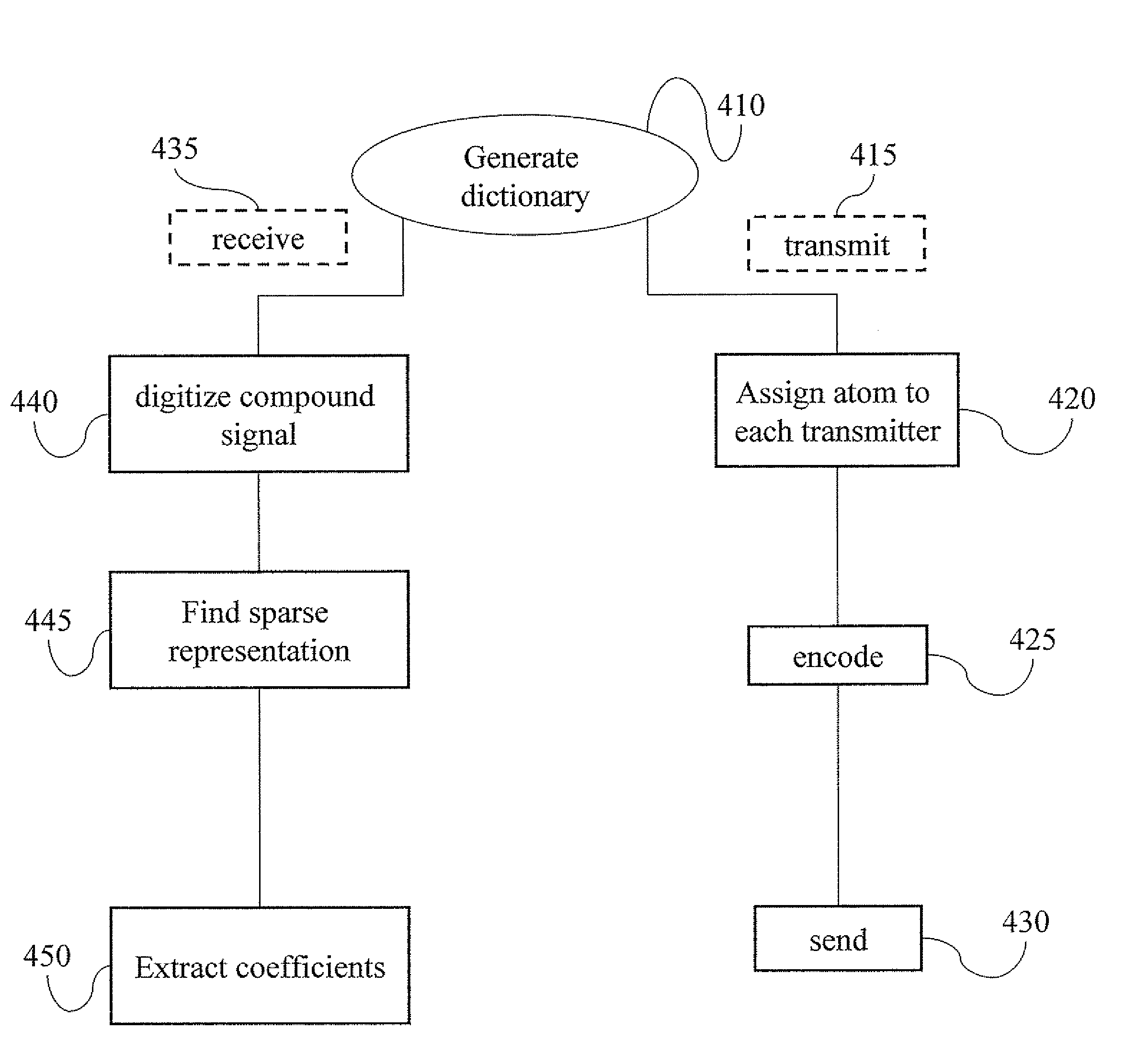
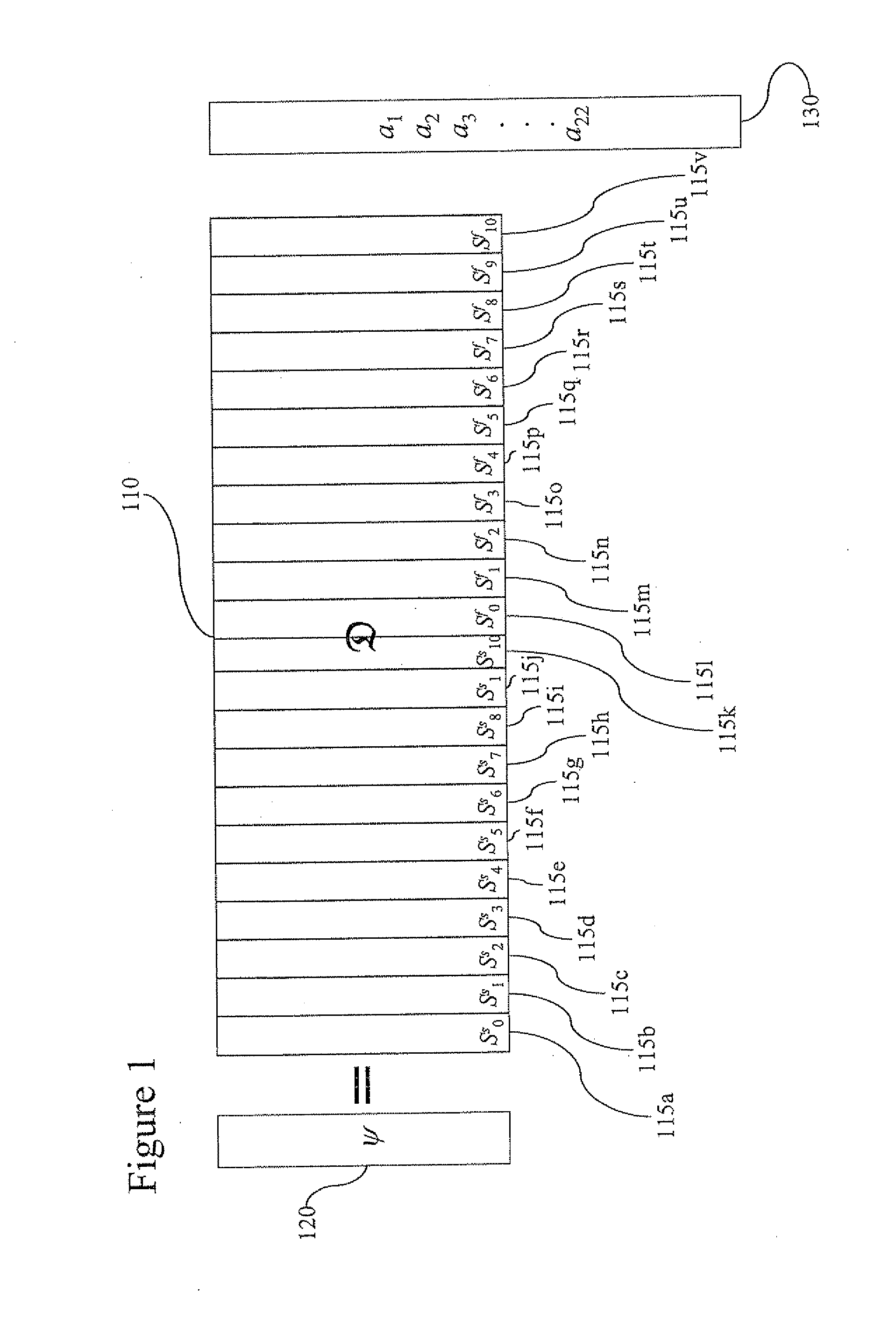
A dictionary at least partially spans a set of discrete q-length signals. The atoms of the dictionary are eigenvectors of a representation of a commutative subgroup of a finite symplectic group. The dictionary may be used for interpreting a radar signal, denoising a signal, compressing data, finding a sparse representation, deblurring at a signal finding a sparse representation of a signal, encoding a signal for communication, encoding a symbol for CDMF communication, classifying a data set and generating a random number.
Owner:SOCHEN NIR ASHER +2
Logging device with down-hole transceiver for operation in extreme temperatures
ActiveUS20080062036A1Information can be usedLow loss signal transport mechanismsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid removalTransceiverRadar systems
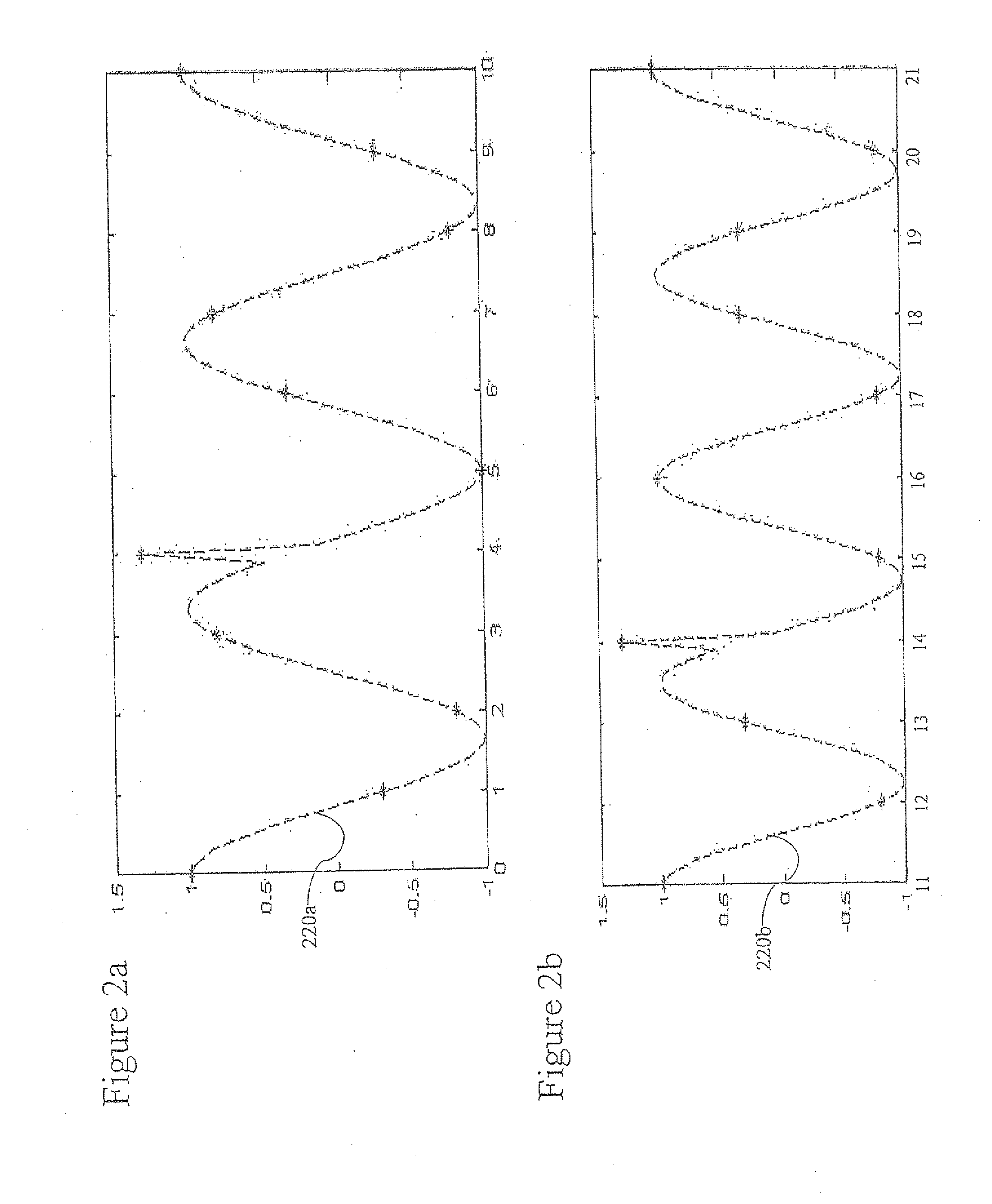
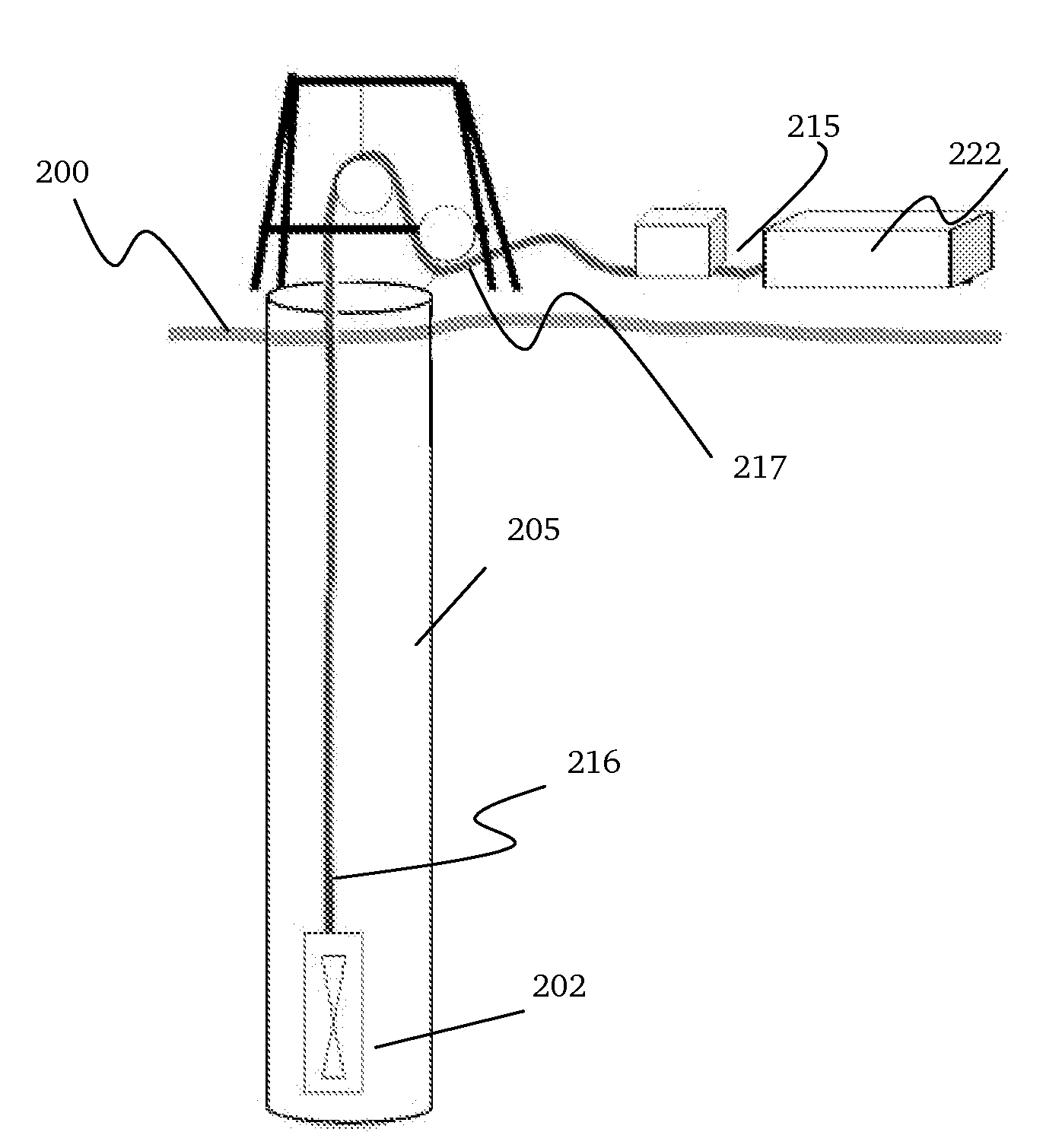
A logging radar system and method for measuring propped fractures and down-hole formation conditions in a subterranean formation including: a radar source; an optical source; an optical modulator for modulating an optical signal from the optical source according to a signal from the radar source; a photodiode for converting the modulated optical signal output from the optical modulator to the source radar signal; a transmitter and receiver unit; and a mixer. The transmitter and receiver unit receives the source radar signal from the photodiode, transmits the source radar signal into the formation and receives a reflected radar signal. The mixer mixes the reflected radar signal with the source radar signal to provide an output. This technology can be used to describe all fractures connected to the wellbore and differentiate between the dimensions of the two vertical wings of a propped fracture.
Owner:HEXION INC
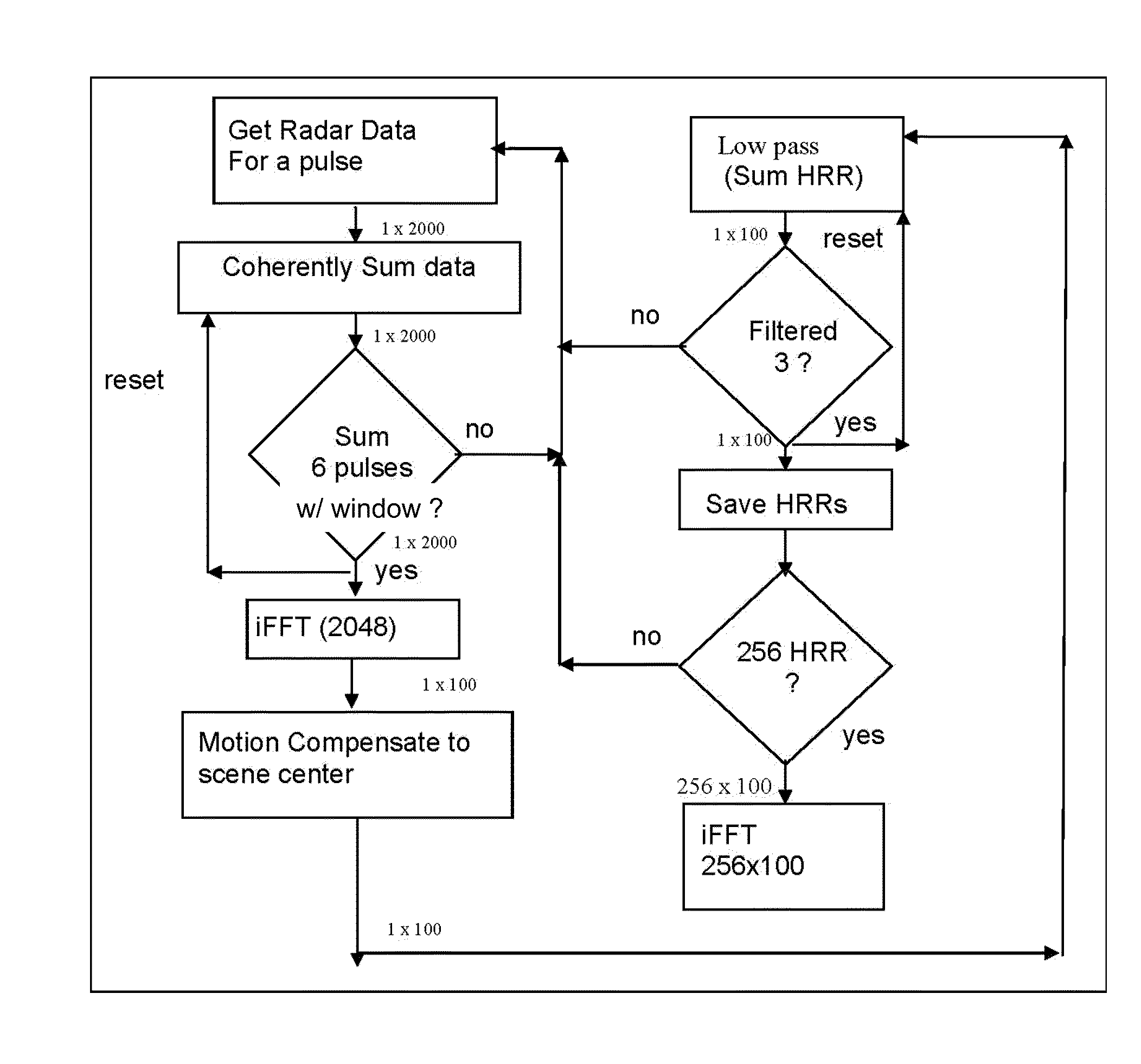
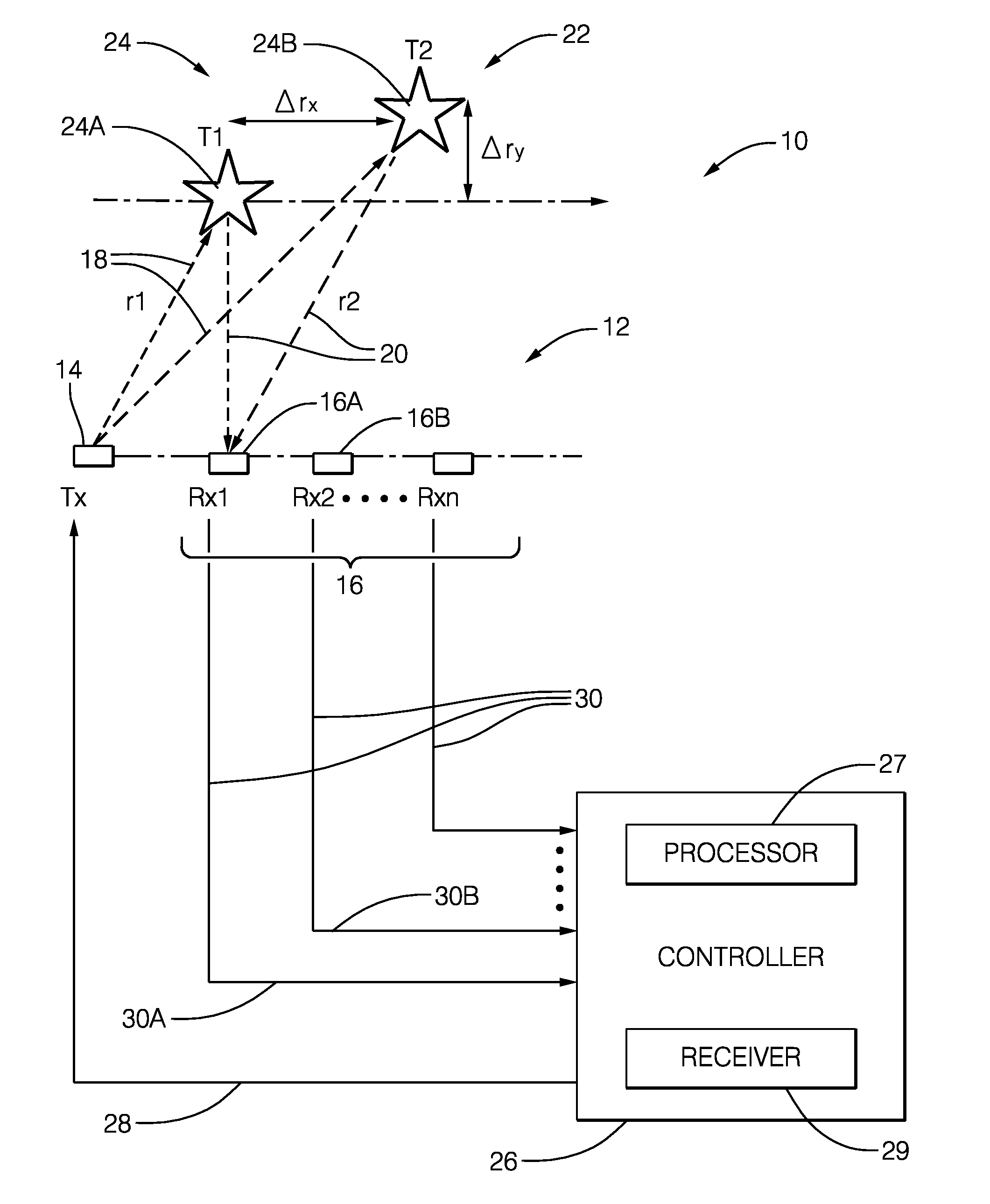
Computationally efficent radar processing method and sytem for SAR and gmti on a slow moving platform
A method and system for processing radar data obtained from a platform which is subjected to non-uniform movement, the distance the platform travels during the formation of an image comprising an aperture; the system comprising software programming for performing a subroutine for building up an average pulse representing a single point on the aperture; the subroutine comprising the steps of inputting radar data from a radar antenna; passing the radar signal through low noise amplifier to reduce impact of electronic noise from the radar system; down converting the signal with a mixer to obtain a lower frequency; filtering out harmonics from the higher frequency range; sampling the radar data using an analog to digital converter at least at Nyquist down range frequency; based upon the IF of the radar; determining a scene center (center of SAR imagery) for the purpose of motion compensation; performing a two stage averaging scheme of the received signals with a variable window function; determining a window function based upon the velocity and acceleration of the platform and scene center; the window function comprising a first stage window; coherently averaging N pulses together to create an average pulse; performing an inverse Fourier transform; compensating to the scene center by multiplying by a complex exponential based upon both the GPS and inertial navigational system; summing the average pulses using low pass filter; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building up an average pulse a first predetermined number of times for a time period that is less than the Nyquist sample time interval; the software programming operating to repeat the step of building an average pulse for a predetermined number of times to generate a second predetermined number of average pulses; the software programming operating to perform a two dimensional inverse Fourier transform to obtain SAR image; outputting the SAR image on a display screen; and a display for displaying the outputted SAR image.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Radar system with phase based multi-target detection
ActiveUS20160084941A1Suppresses noise variationImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsObject based
A radar system includes a plurality of antennas and a controller. The plurality of antennas is configured to detect a reflected radar signal reflected by an object in a field-of-view of the system. Each antenna of the plurality of antennas is configured to output a detected signal indicative of the reflected radar signal detected by the antenna. The controller is configured to receive detected signals from the plurality of antennas, and determine if a target is present in the field-of-view based on the detected signals. The controller is also configured to determine if the target includes more than one object based on an analysis of phases of the detected signals.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
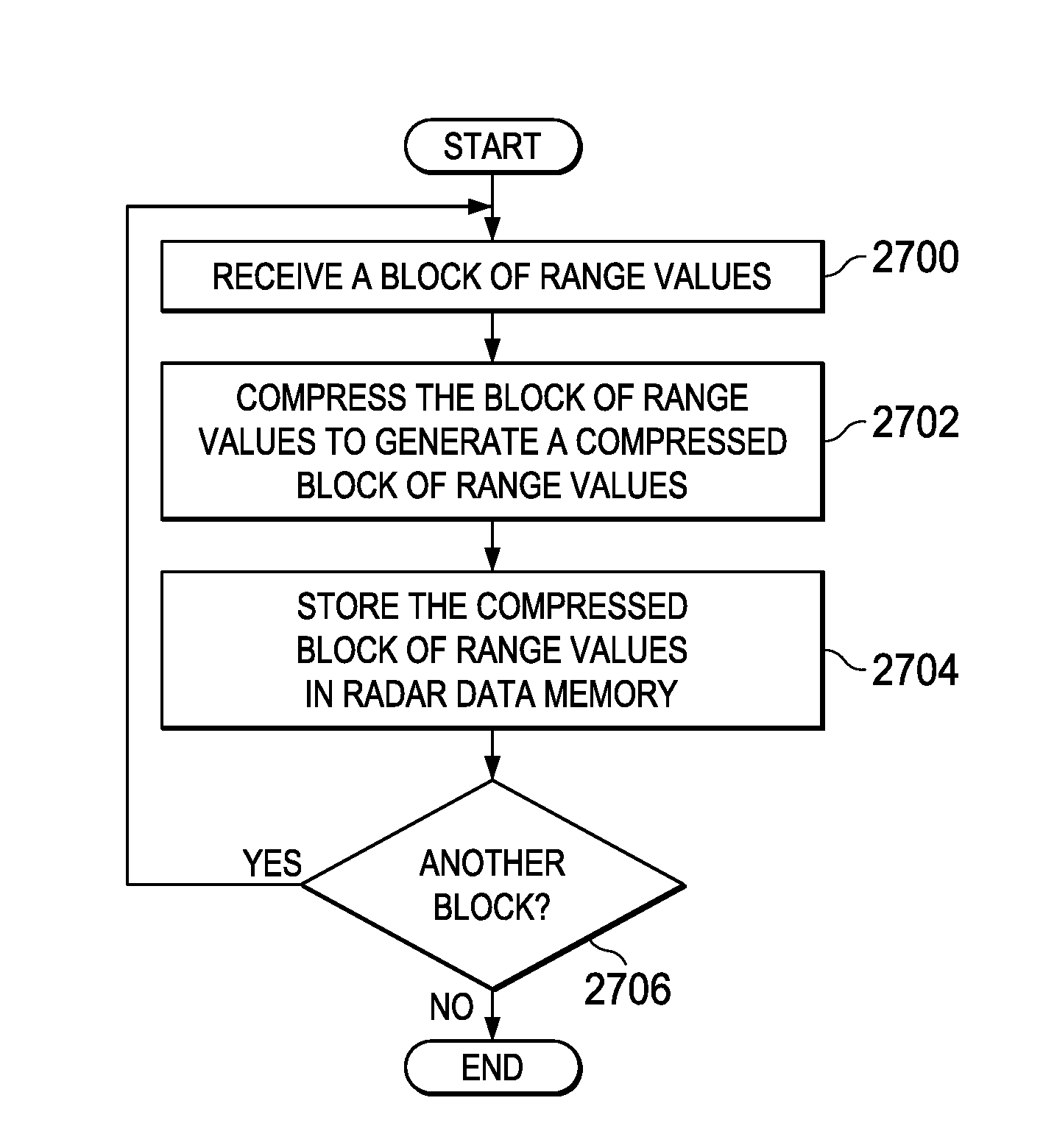
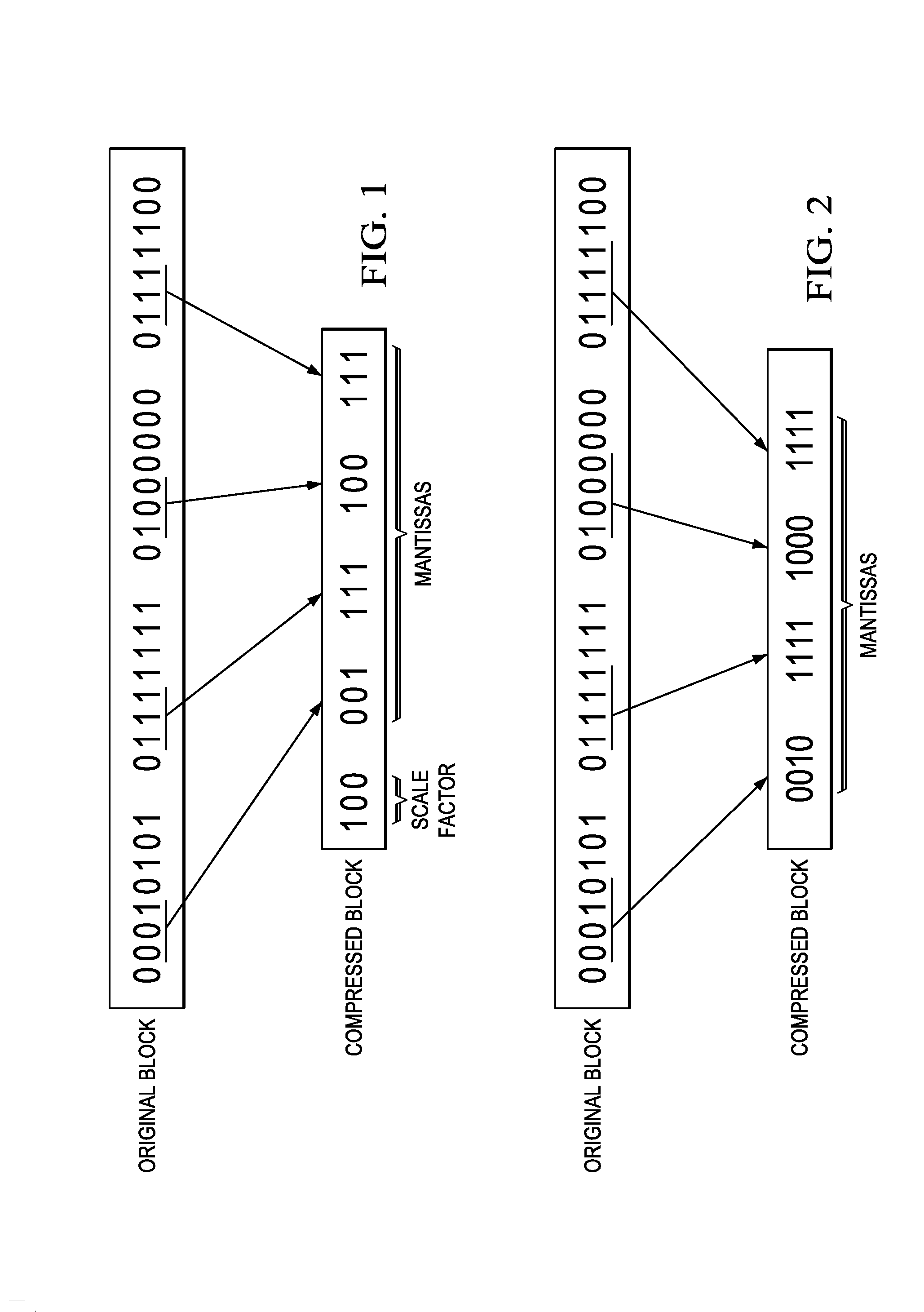
Method and System for Compression of Radar Signals
A radar system is provided that includes a compression component configured to compress blocks of range values to generate compressed blocks of range values, and a radar data memory configured to store compressed blocks of range values generated by the compression component.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Millimeter wave quick frequency conversion radar target simulator
InactiveCN101082667ALow costImprove confidentialityCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsFrequency changerBandpass filtering
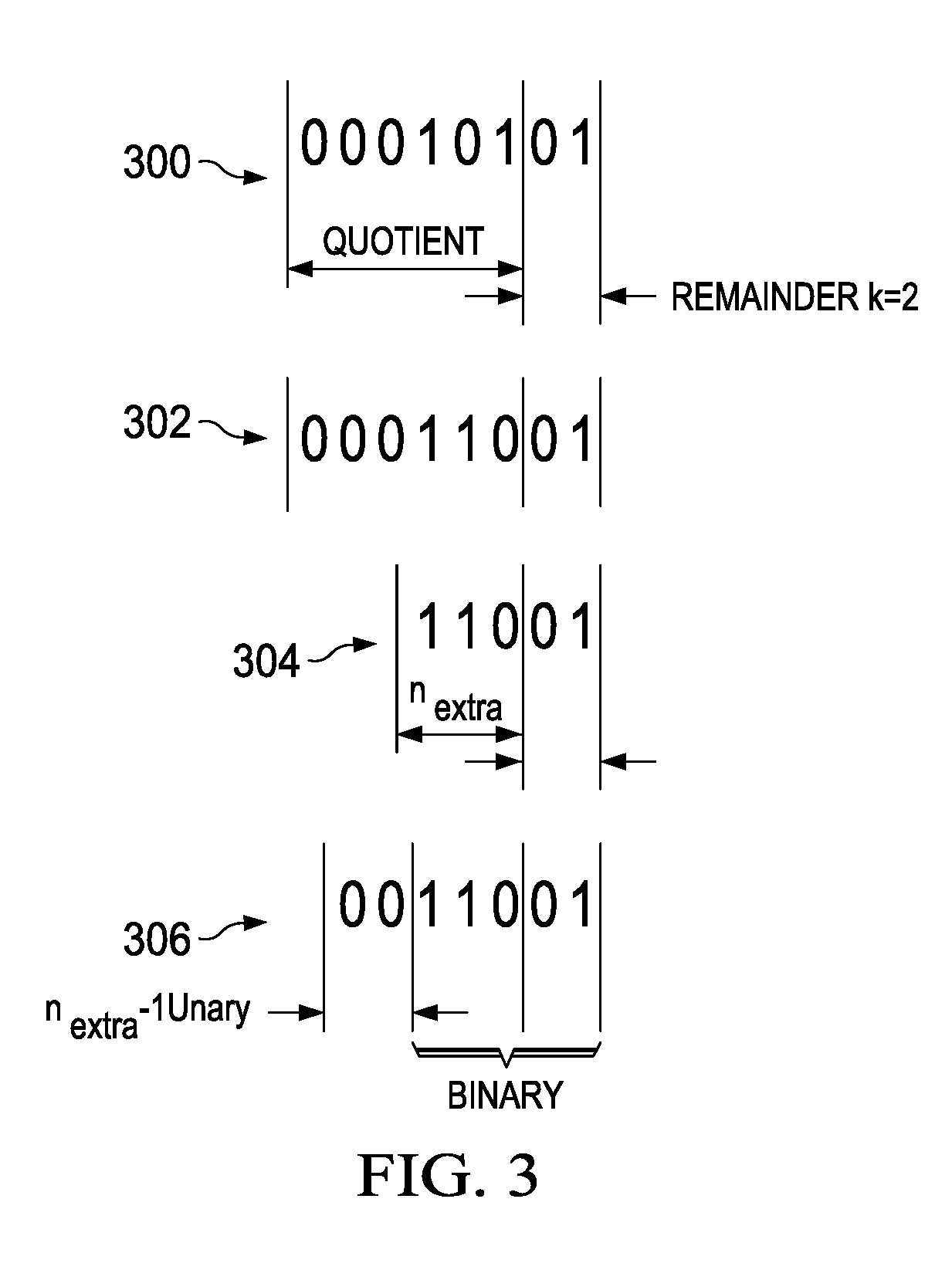
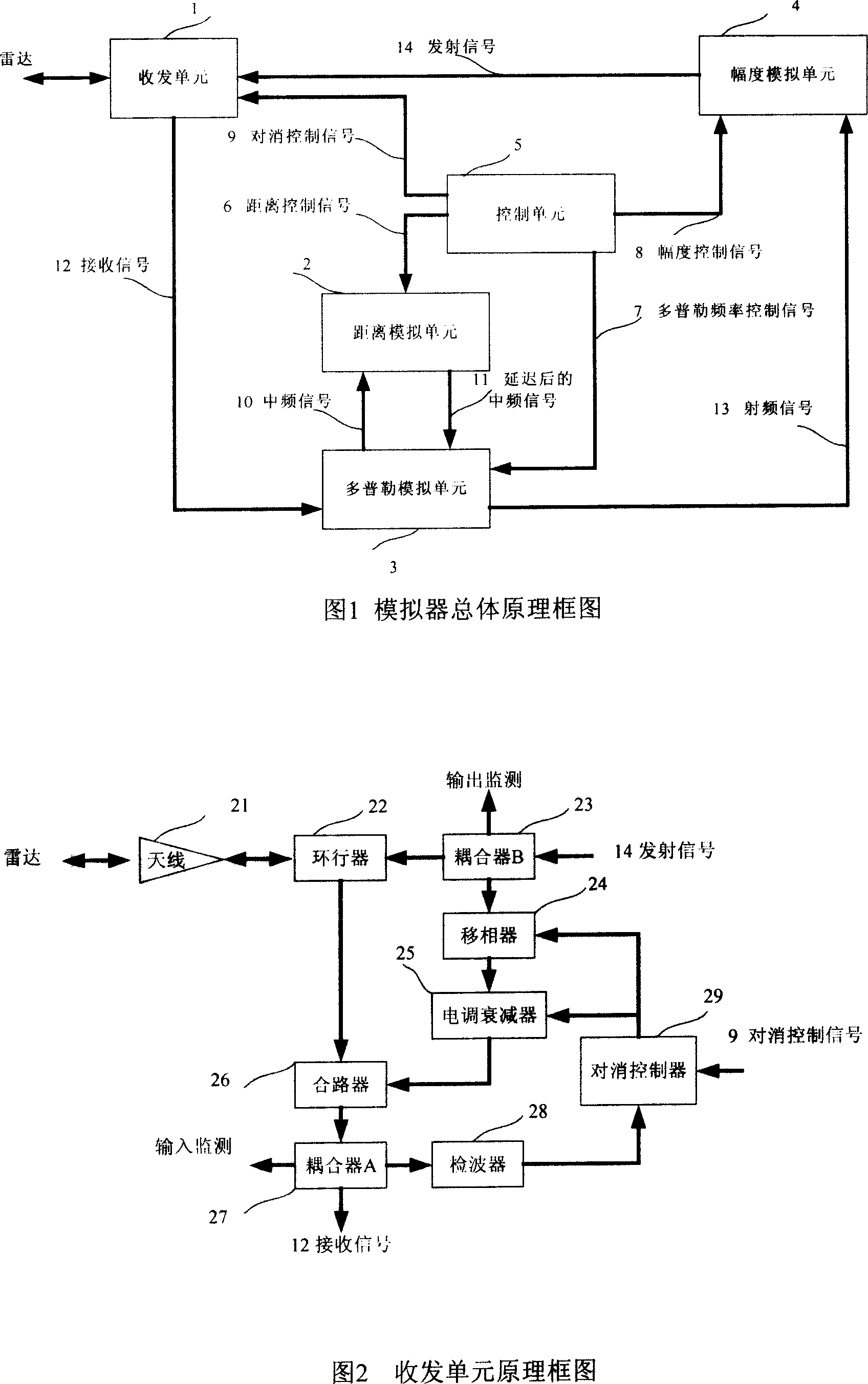
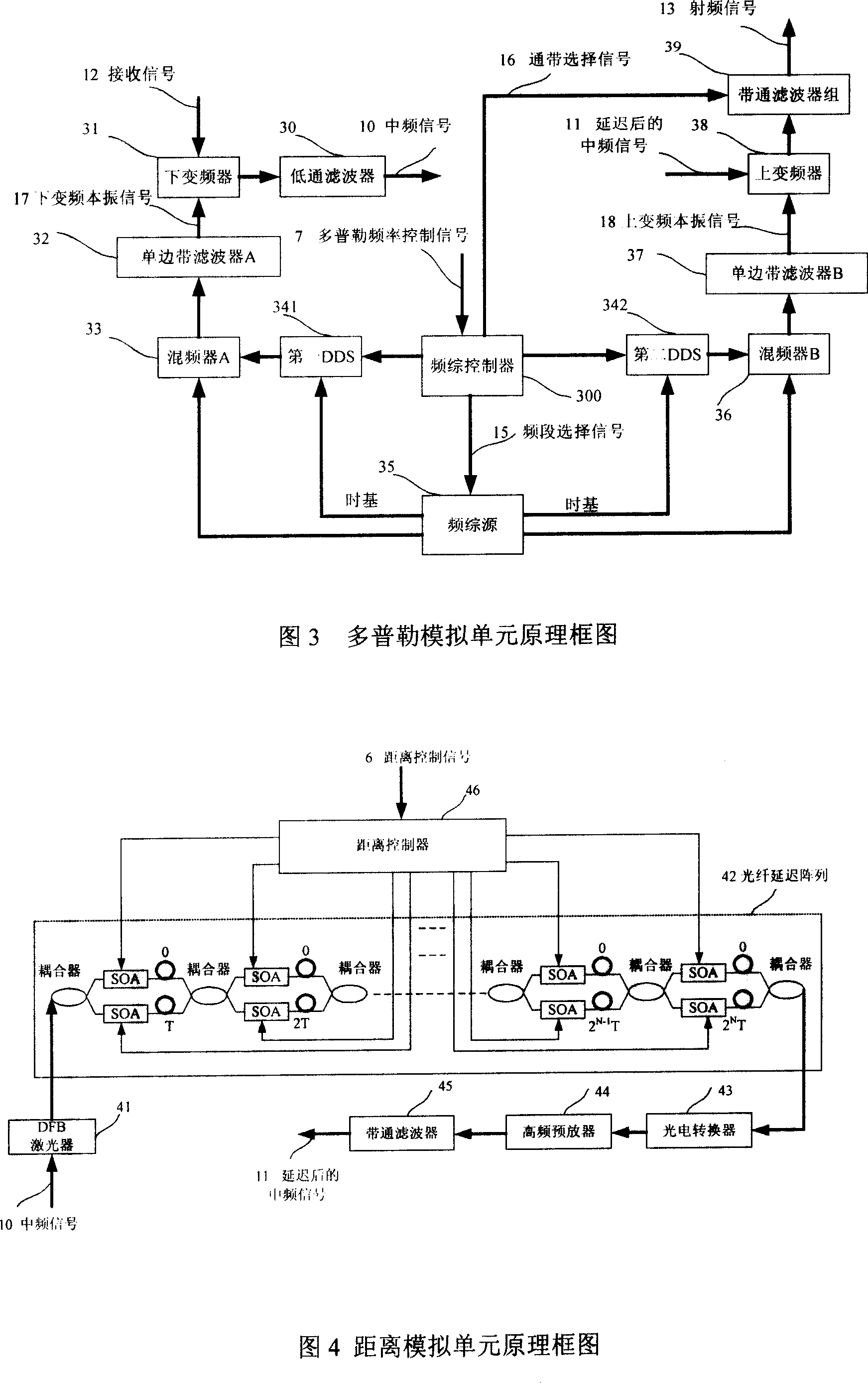
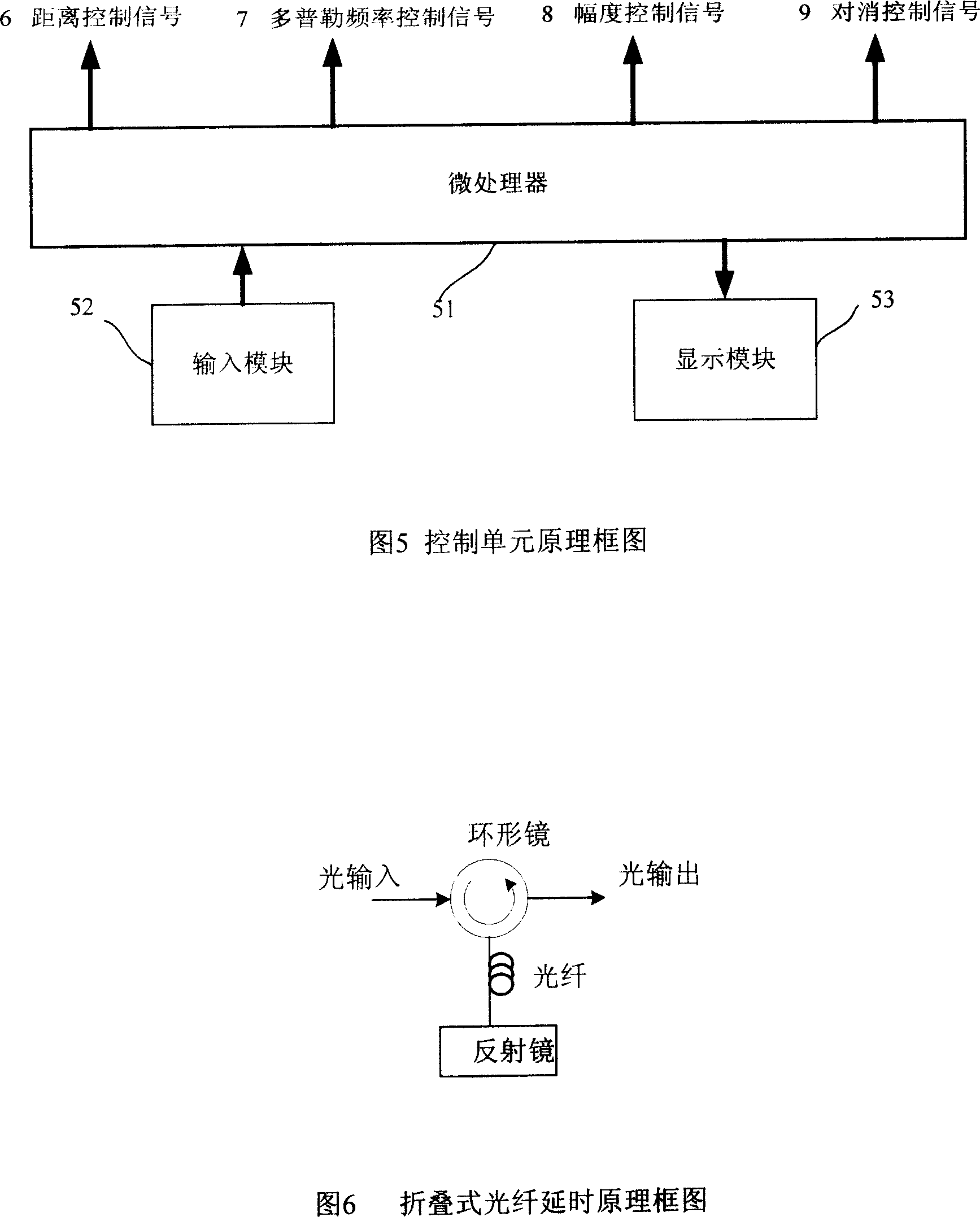
The invention discloses a frequency-change radar goal emulator of millimeter wave, which comprises the following parts: control unit, transceiver unit, Doppler analog unit, distant analog unit and amplitude analog unit, wherein the radar signal enters into the Doppler analog unit through transceiver unit, which produces middle-frequency signal through lower frequency-changer and low-pass filter of the Doppler analog unit; the upper frequency-changer and band-pass filter group of Doppler analog unit produces RF signal; the difference of local oscillator frequency of upper and lower frequency-changers analogs the Doppler frequency shift of goal; the RF signal generates launching signal through changing the echo amplitude of goal simulated by amplitude analog unit, which is transmitted by transceiver unit; the control unit transmits control signal for other four units according to the analog parameter such as input distance, speed and amplitude; the radar signal passes the emulator to provide an analog signal with Doppler frequency shift, signal amplitude fluctuation and distant delay to radar, which provides estimating platform for working property testing for radar.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Radar System For Automated Vehicle With Phase Change Based Target Catagorization
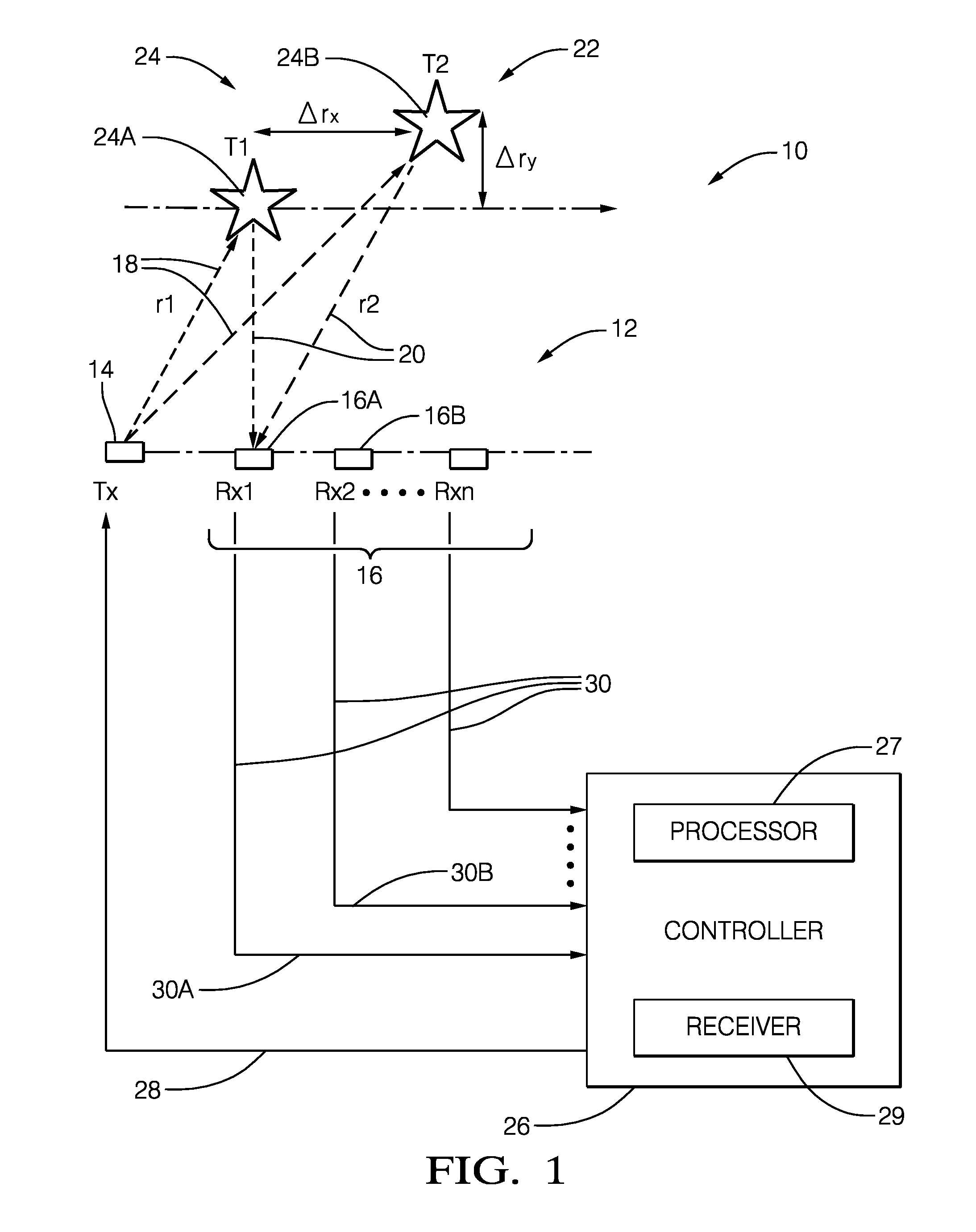
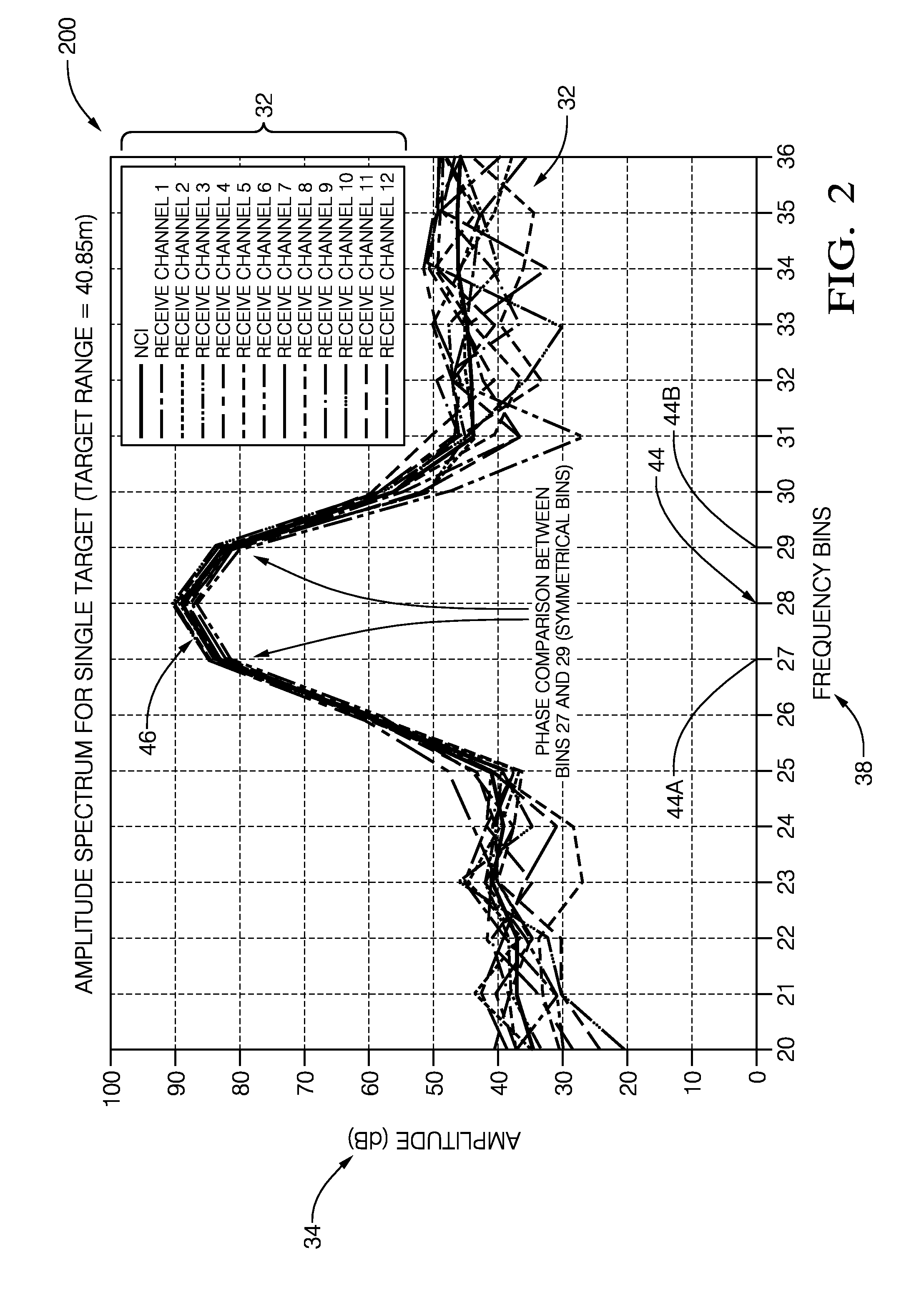
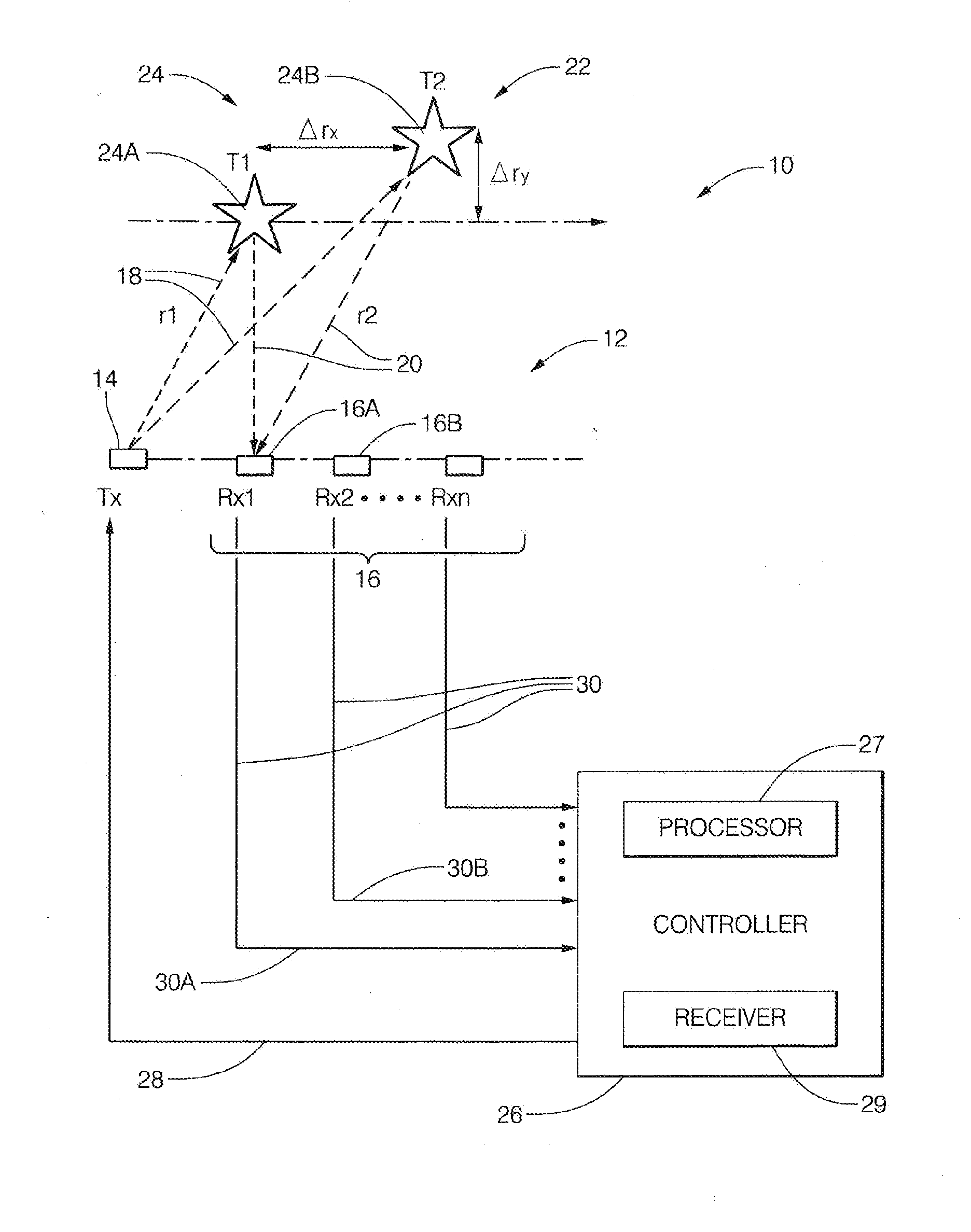
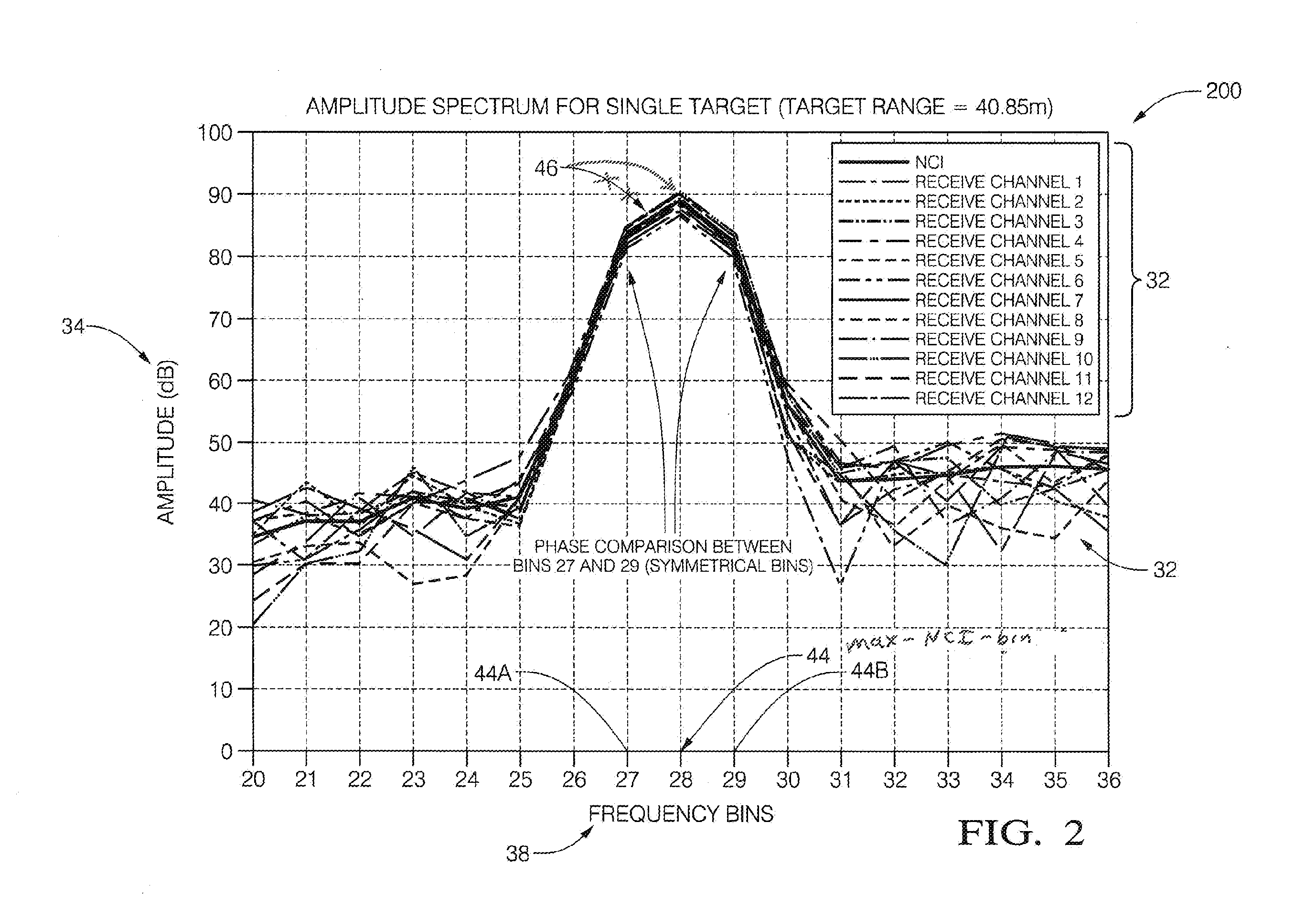
A radar system suitable for an automated vehicle includes a plurality of antennas configured to detect a reflected radar signal reflected by an object in a field-of-view of the system. Each antenna of the plurality of antennas is configured to output detected signals indicative of the reflected radar signal detected by each of the plurality of antennas. The system also includes a controller configured to receive the detected signals from the plurality of antennas, determine if the object is present in the field-of-view based on the detected signals, and determine a phase-difference between symmetrical-frequency-bins for each antenna. The symmetrical-frequency-bins are symmetrically offset from a maximum-amplitude non-coherent-integration detection-frequency-bin (max-NCI-bin). The controller is further configured to determine a classification of the object based on a time-domain-analysis of the phase differences across the plurality of antennas.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
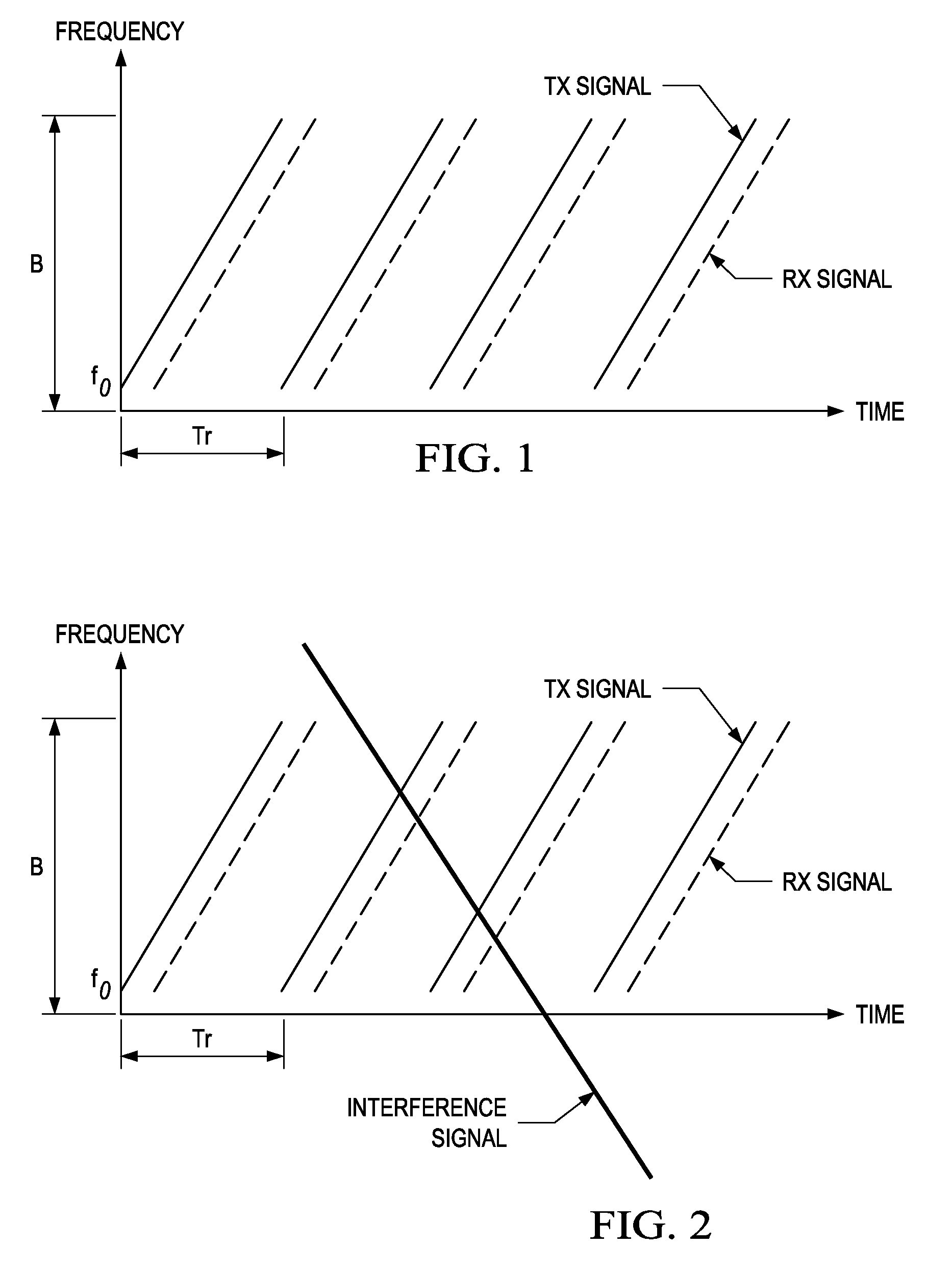
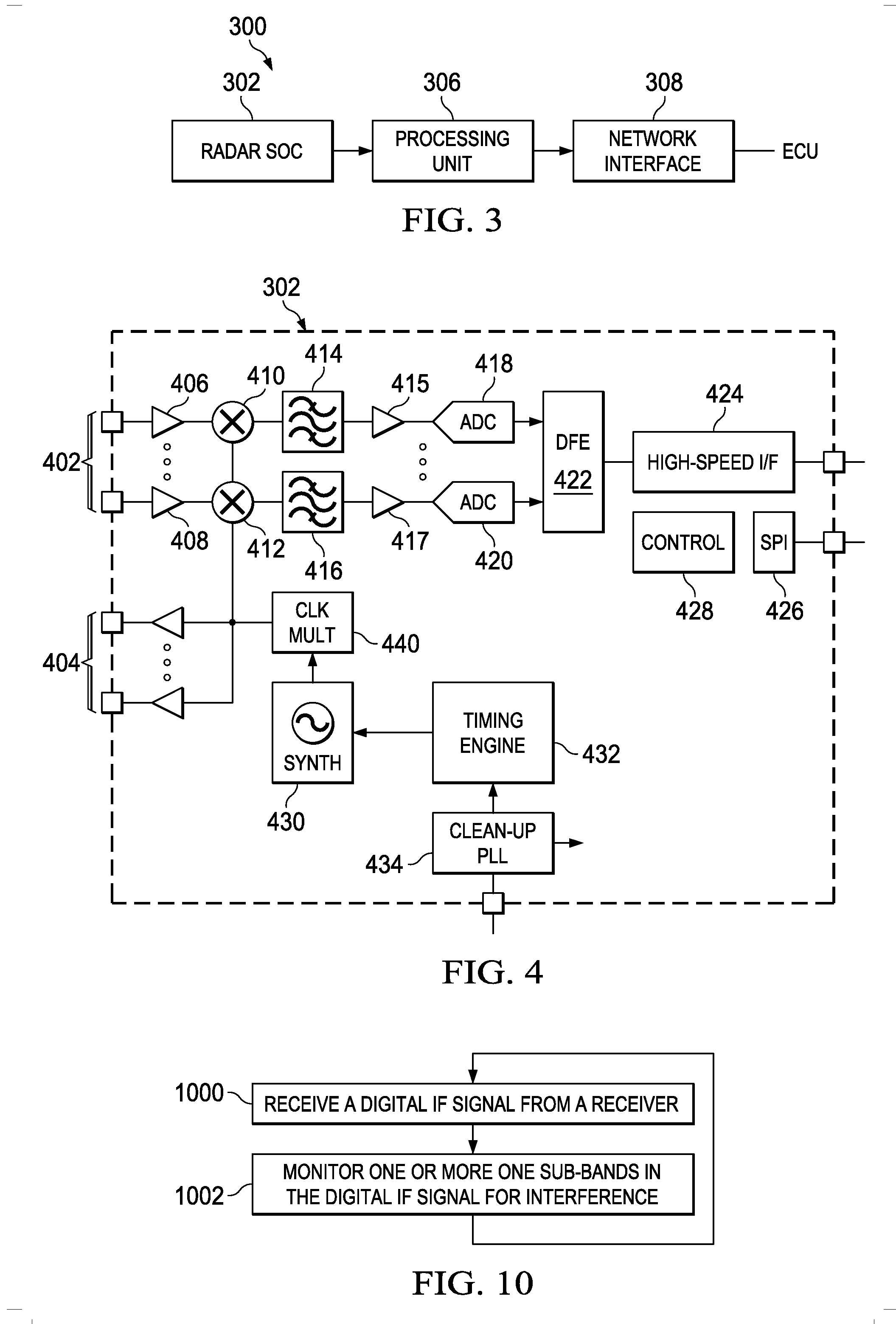
Interference Detection in a Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) Radar System
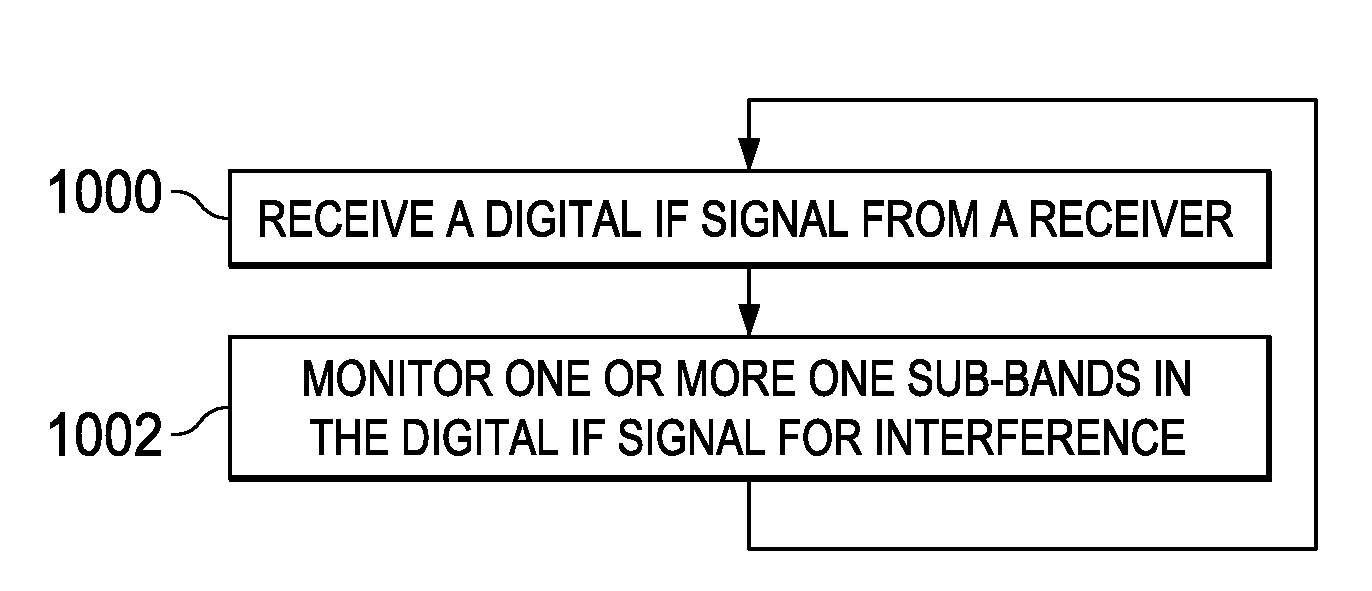
A frequency modulated continuous wave (FMCW) radar system is provided that includes a receiver configured to generate a digital intermediate frequency (IF) signal, and an interference monitoring component coupled to the receiver to receive the digital IF signal, in which the interference monitoring component is configured to monitor at least one sub-band in the digital IF signal for interference, in which the at least one sub-band does not include a radar signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
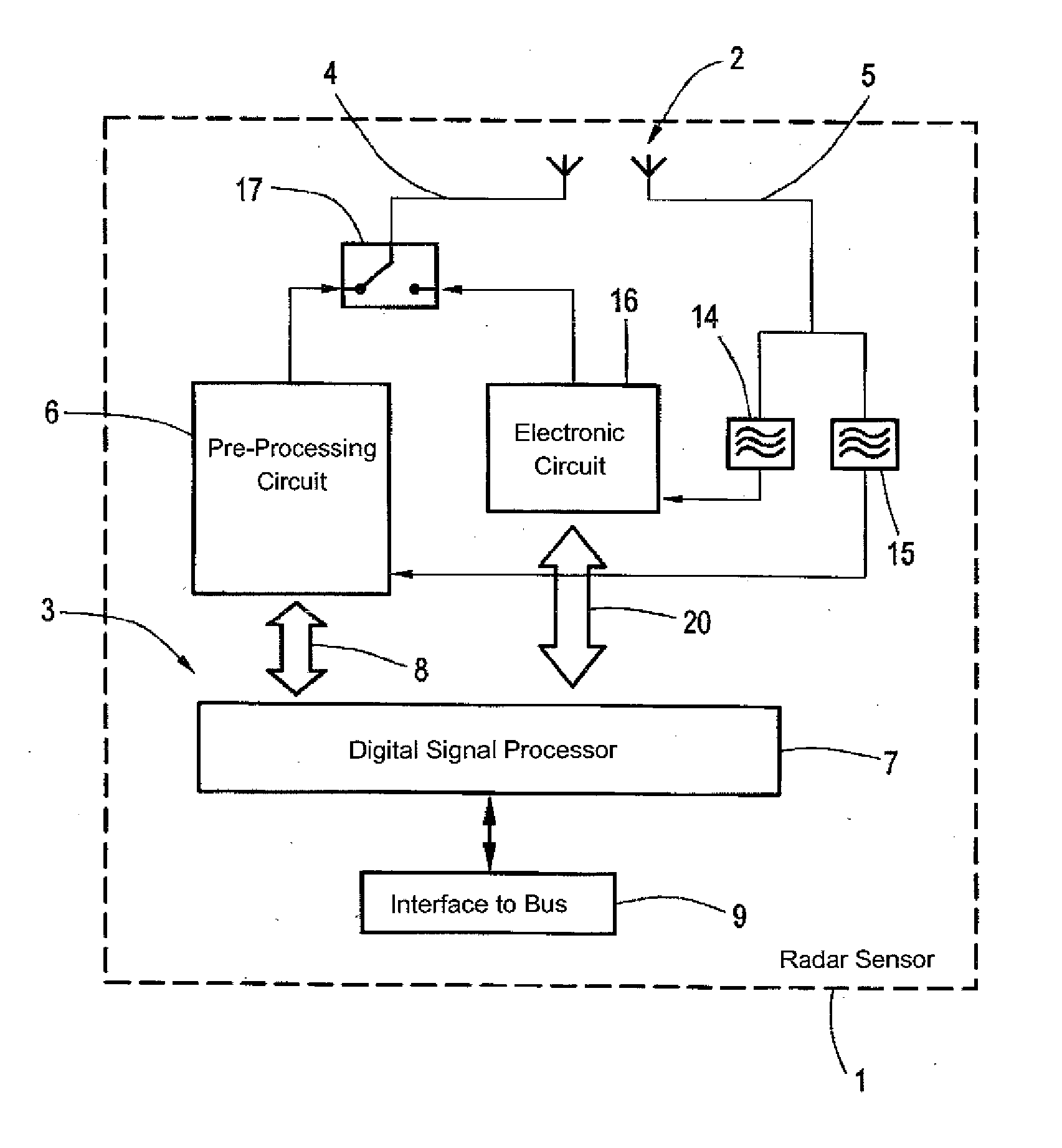
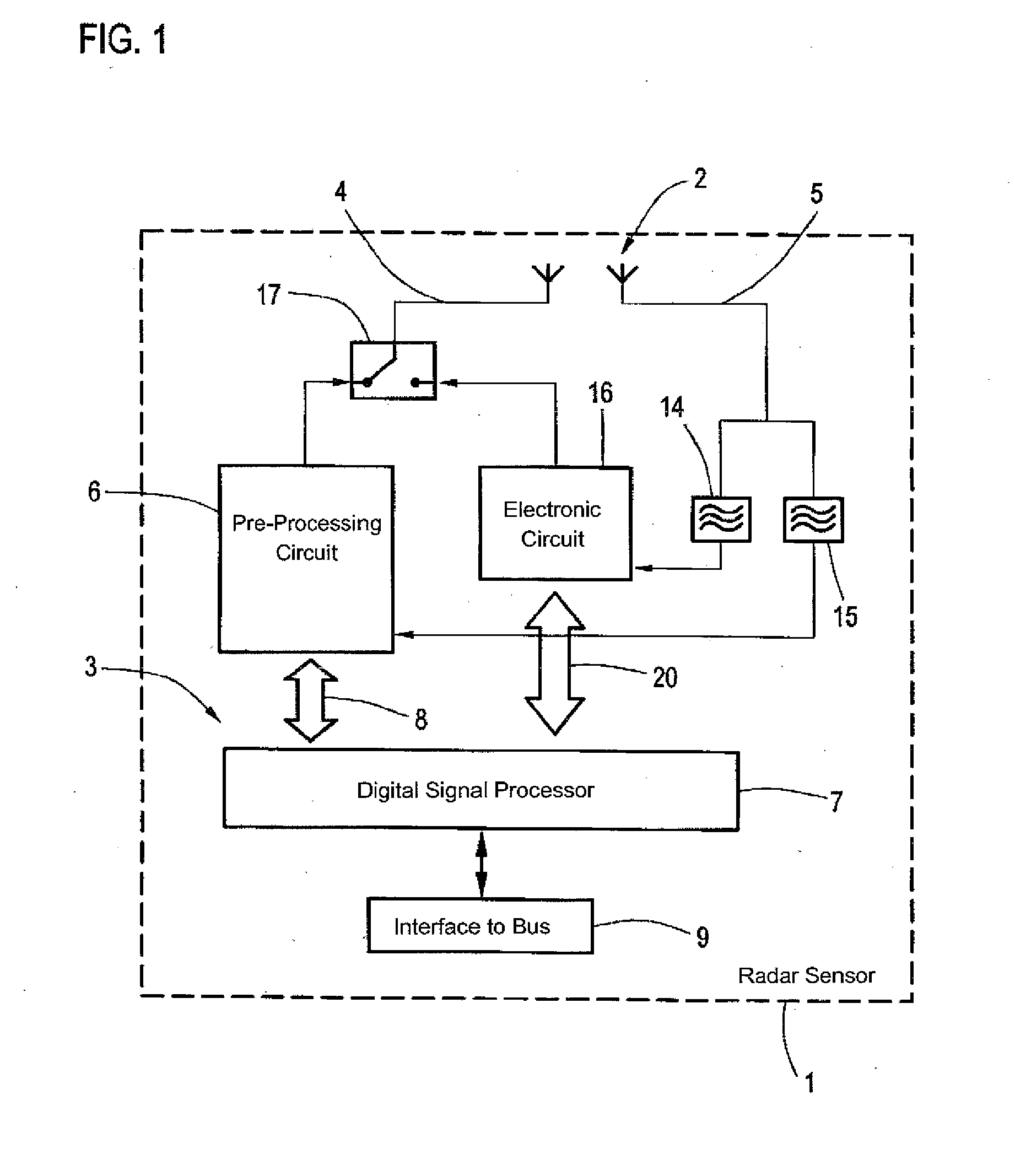
Radar sensor for a motor vehicle, motor vehicle and communication method
ActiveUS20140035774A1Latencies caused by the transmission in the bus systemReduce hardware complexityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMobile vehicleMotorized vehicle
A radar sensor for a motor vehicle has at least one antenna arrangement for transmitting and receiving radar signals and a controller for controlling the operation of the antenna arrangement. The controller evaluates the received radar signals. The controller also operates the antenna arrangement to transmit and / or receive messages in a car-to-car communication.
Owner:AUDI AG
System and method of using absorber-walls for mutual coupling reduction between microstrip antennas or brick wall antennas
InactiveUS7427949B2Reduce signalingReduce horizontal sizeAntenna detailsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMicrostrip patch antennaBrick
A multi-element antenna with sufficiently small return loss and mutual coupling signals to allow the simultaneous transmission of powerful radar signals and the reception of faint target return signals. The microstrip patch antenna has radio frequency absorbing material place between neighboring antenna elements to reduce the mutual coupling leakage signals.
Owner:COBHAM DEFENSE ELECTRONICS SYST CORP
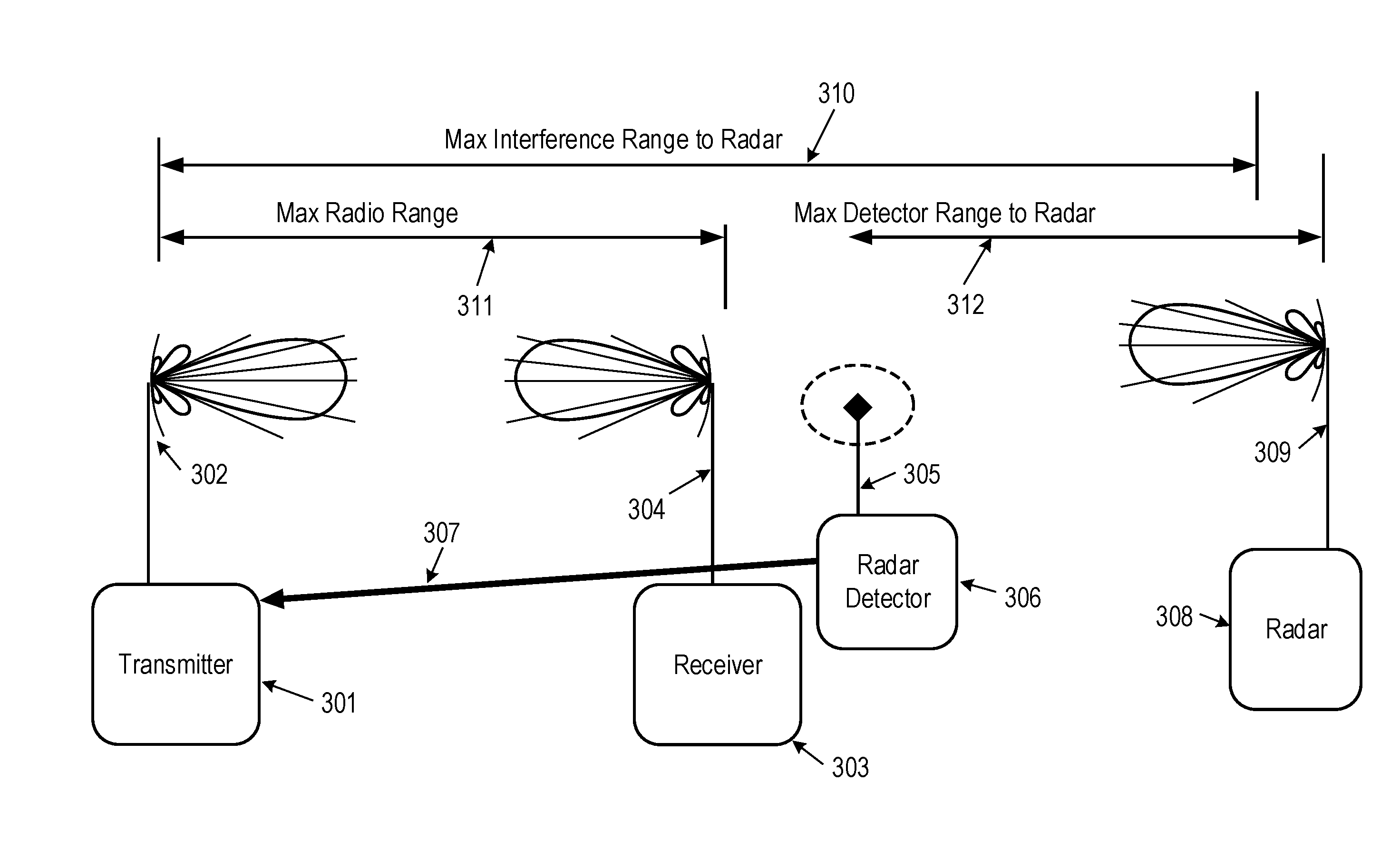
Radio with oobe victim detection
InactiveUS20160285611A1Improve performanceMitigating the losses from multipath fadingPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementWideband radarTransmitted power
A radar detector is used with a radio link, the radio link characterized by high duty factor operation of a radio transmitter. The radar detector is located a sufficient distance from the radio transmitter that the radar detector is not overwhelmed by the radio transmission signal in that channel and can detect sufficiently low level radar signals to ascertain potential radio interference at the radar from said radio transmitter. The results of the radar detection are communicated to the transmitter in a way that impacts the transmitter's use of the sensed channel. This communication can occur reactively when a radar detection is achieved (the absence of which indicates no radar has been detected) and / or can be a periodic or event-driven indication that the channel is available for operation (the information expiring if the result is not refreshed). A highly sensitive radar detector apparatus that can detect wideband radar signals at very low levels and overcome the disparity of detection range versus interference range is described. A signal detector is also described that detects energy from other users that is not in the operating channel or operating band of the transmitter to determine if the out of band emissions or out of channel emissions of the operating transmitter's signal need to be adjusted through such settings as transmit power, operating channel, filtering, or a combination.
Owner:SKYLINE PARTNERS TECH LLC
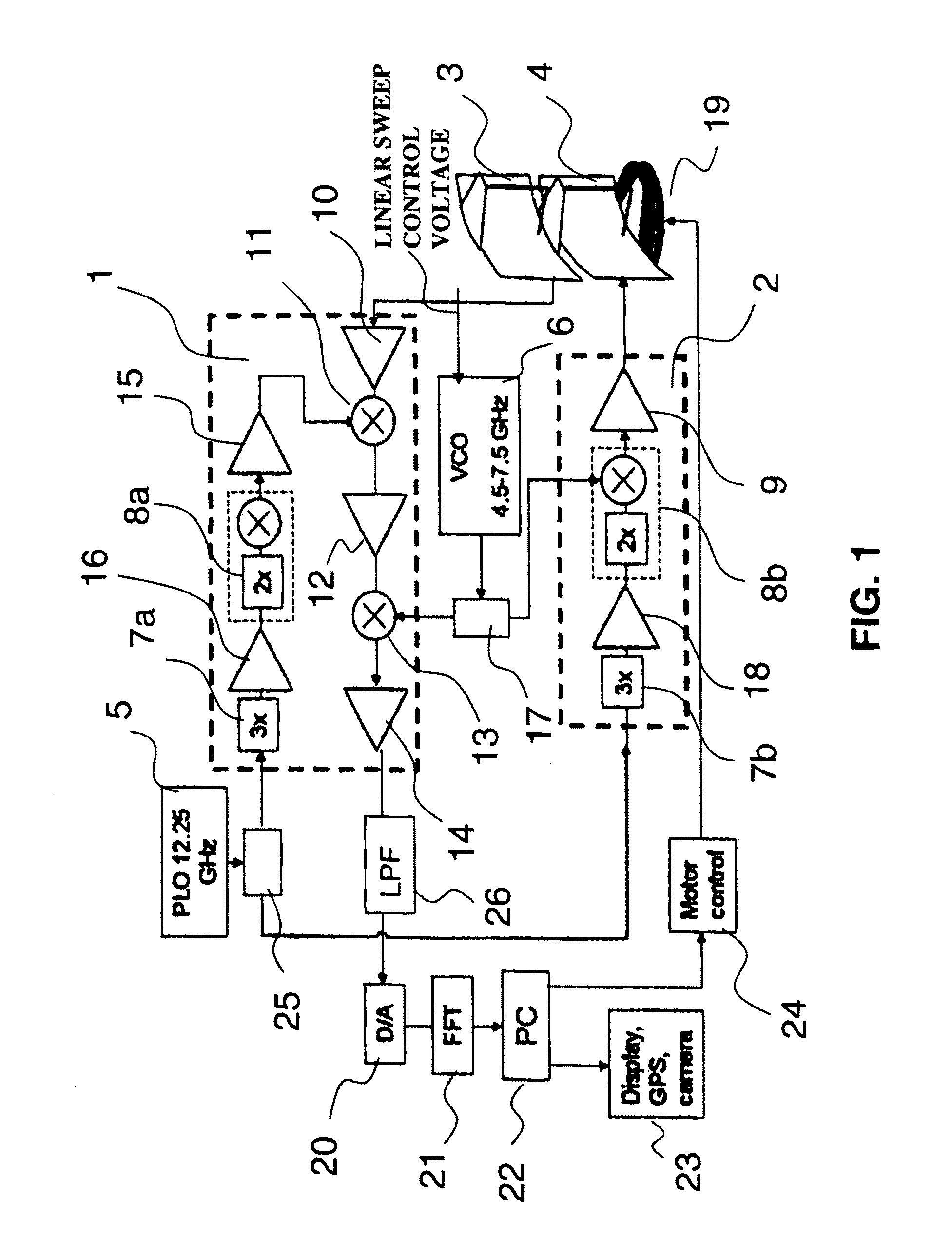
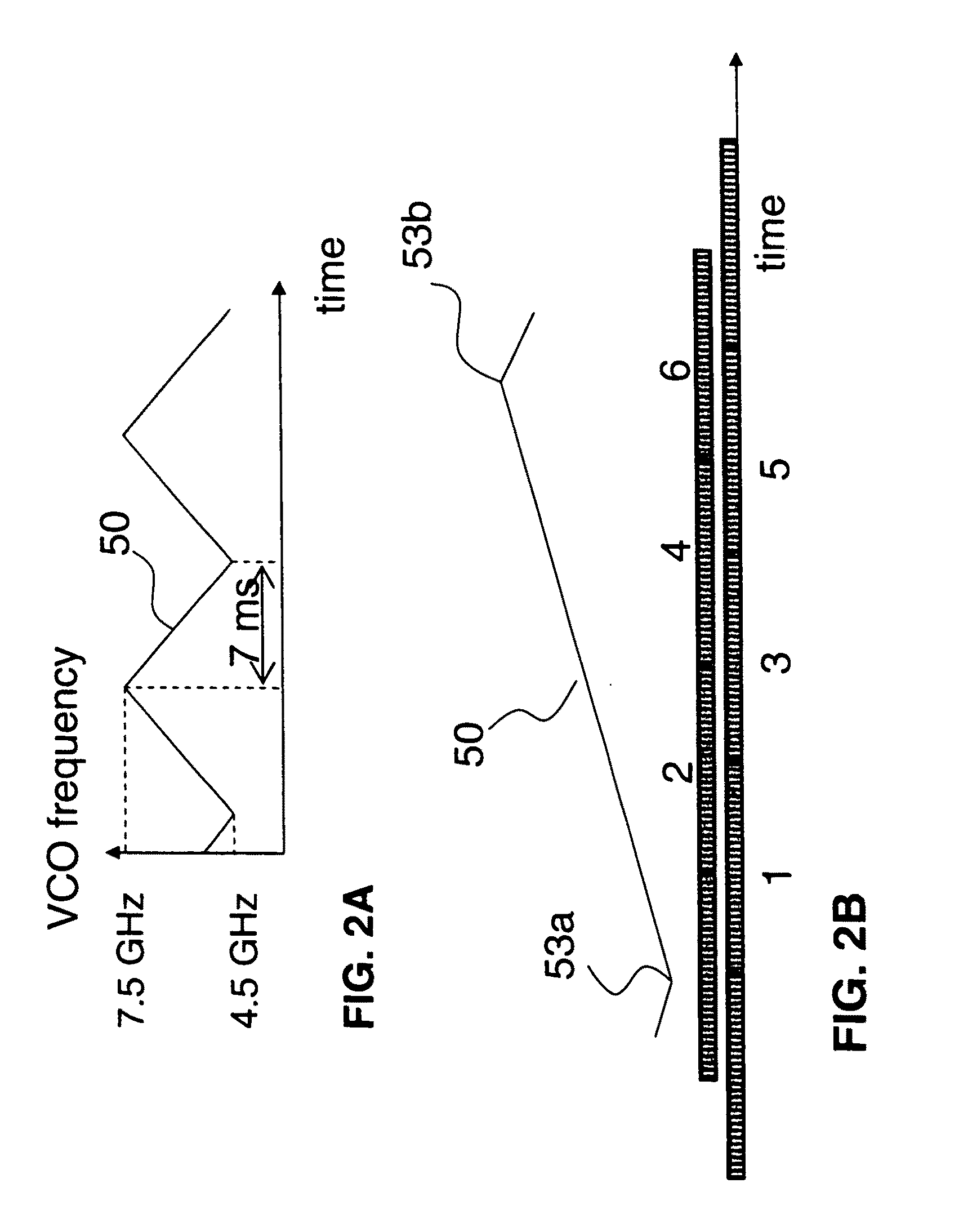
Millimeter wave surface imaging radar system
InactiveUS20110199254A1Ample scan coverageReliable and effective FOD detectionAntenna arraysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar imagingMillimetre wave
A short range millimeter wave surface imaging radar system. The system includes electronics adapted to produce millimeter wave radiation scanned over a frequency range of a few gigahertz. The scanned millimeter wave radiation is broadcast through a frequency scanned transmit antenna to produce a narrow transmit beam in a first scanned direction (such as the vertical direction) corresponding to the scanned millimeter wave frequencies. The transmit antenna is scanned to transmit beam in a second direction perpendicular to the first scanned direction (such as the horizontal or the azimuthal direction) so as to define a two-dimensional field of view. Reflected millimeter wave radiation is collected in a receive frequency scanned antenna co-located (or approximately co-located) with the transmit antenna and adapted to produce a narrow receive beam approximately co-directed in the same directions as the transmitted beam in approximately the same field of view. Computer processor equipment compares the intensity of the receive millimeter radar signals for a pre-determined set of ranges and known directions of the transmit and receive beams as a function of time to produce a radar image of at least a desired portion of the field of view. In preferred embodiment the invention is mounted on a truck and adapted as a FOD finder system to detect and locate FOD on airport surfaces.
Owner:TREX AVIATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com