Soft sample scaling in a turbo decoder
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
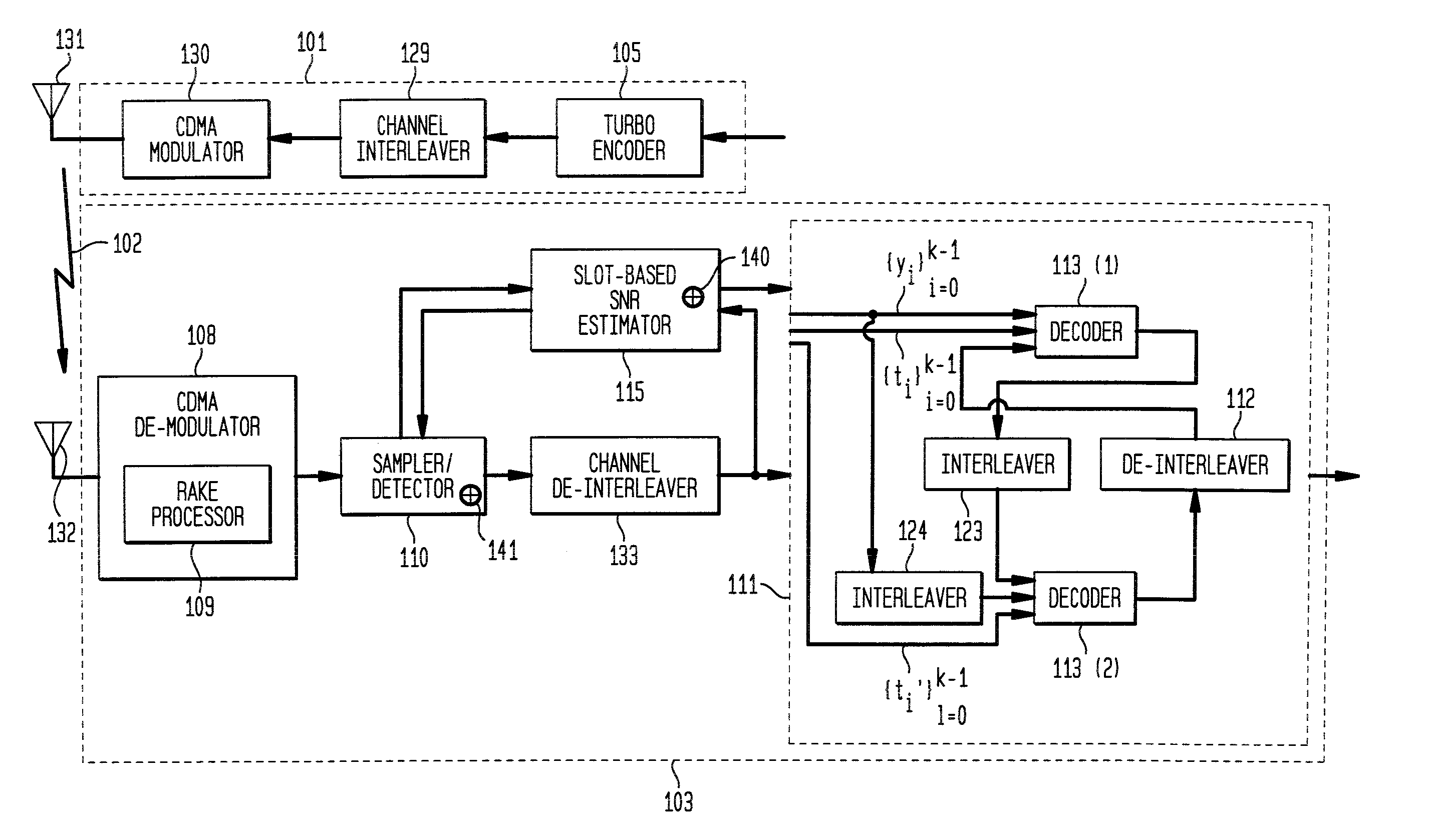
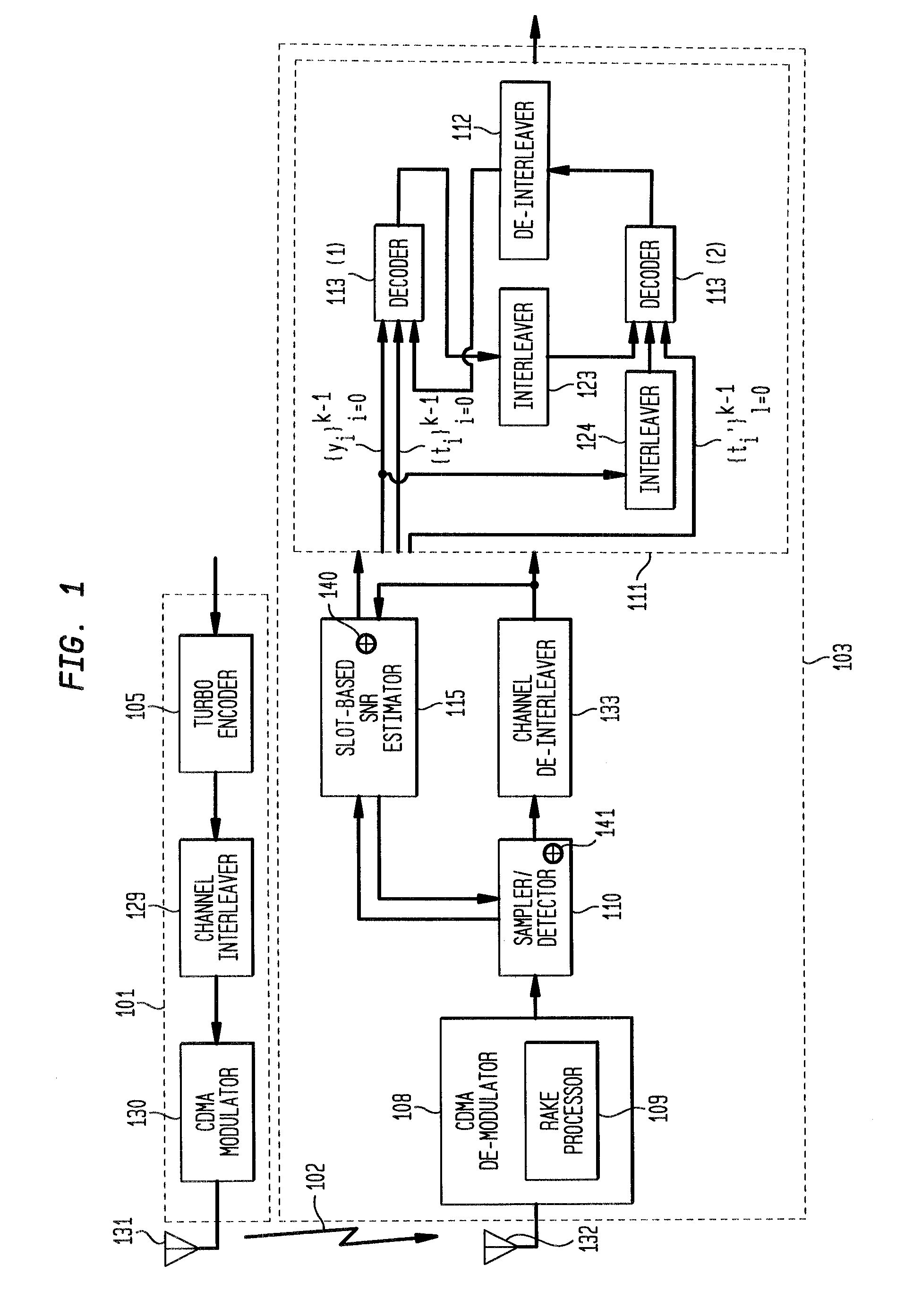
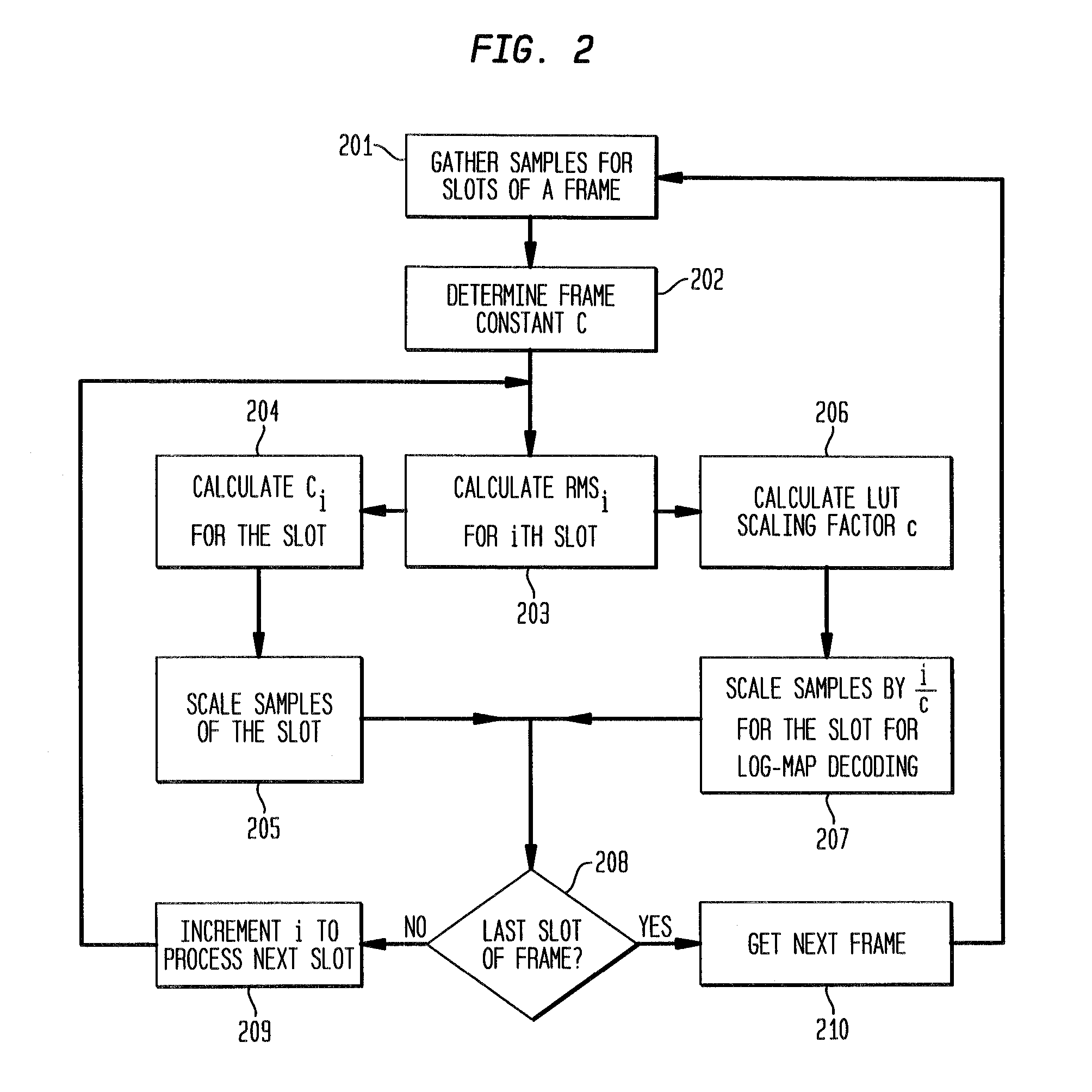
[0032] In accordance with exemplary embodiments of the present invention, a receiver for iterative decoding of a received, encoded signal employs slot-based scaling of soft samples. Iterative decoding employs a constituent maximum a priori (MAP) decoder for each constituent encoding of information of the encoded signal. Root mean square (RMS) values for soft samples over a slot are selected for dynamic range scaling. Squared RMS values are combined and equal the squared RMS value for a frame multiplied by a control constant. The RMS value with control constant serves as an SNR estimator that may be employed to scale logarithmic correction values for max* term calculation during log-MAP decoding. Slot-based RMS scaling in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention requires relatively short calculation (or access if calculated and stored in a look-up table), may be relatively easily determined during CDMA receiver processing without introducing substantial latenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com