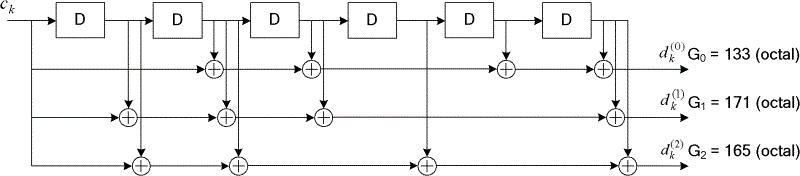
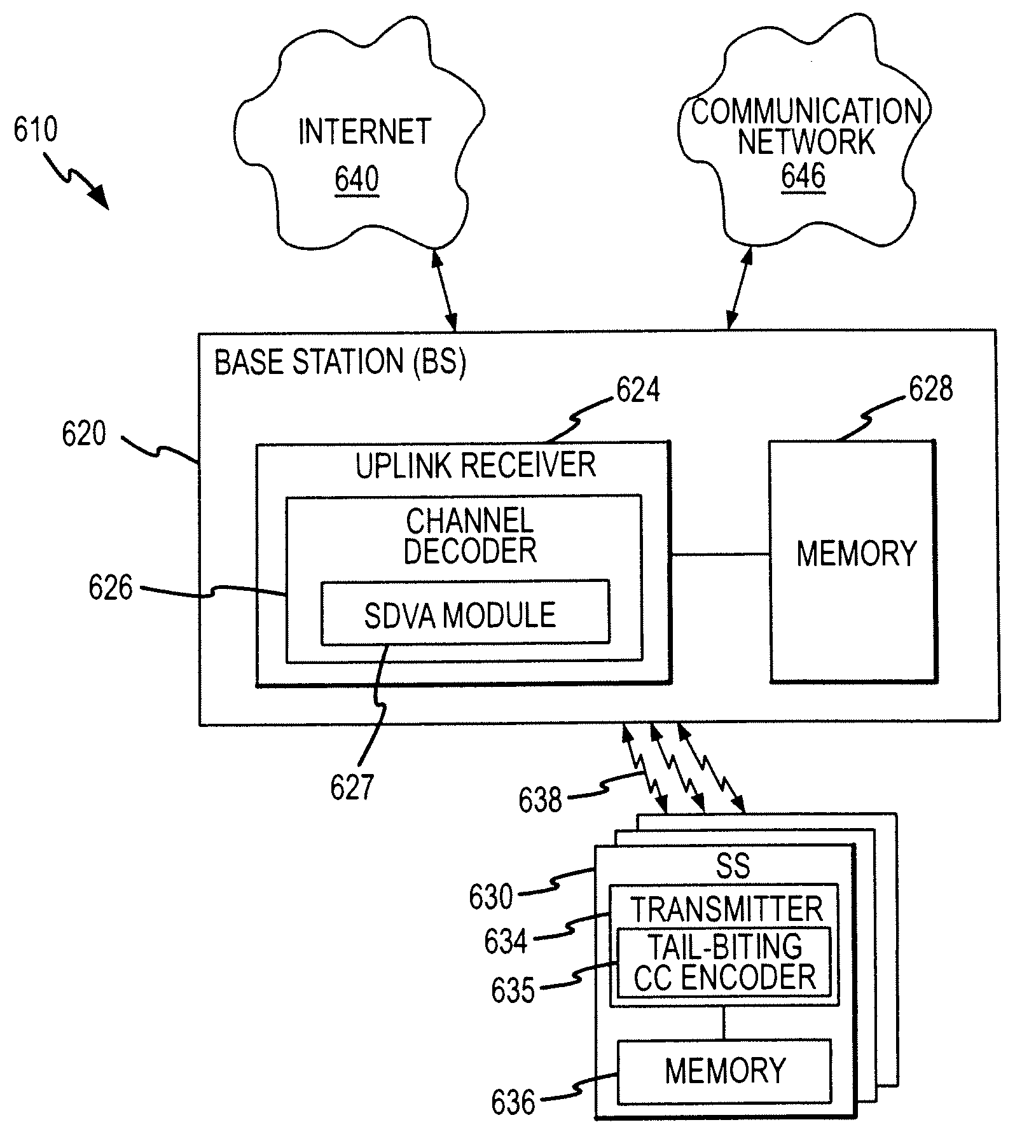
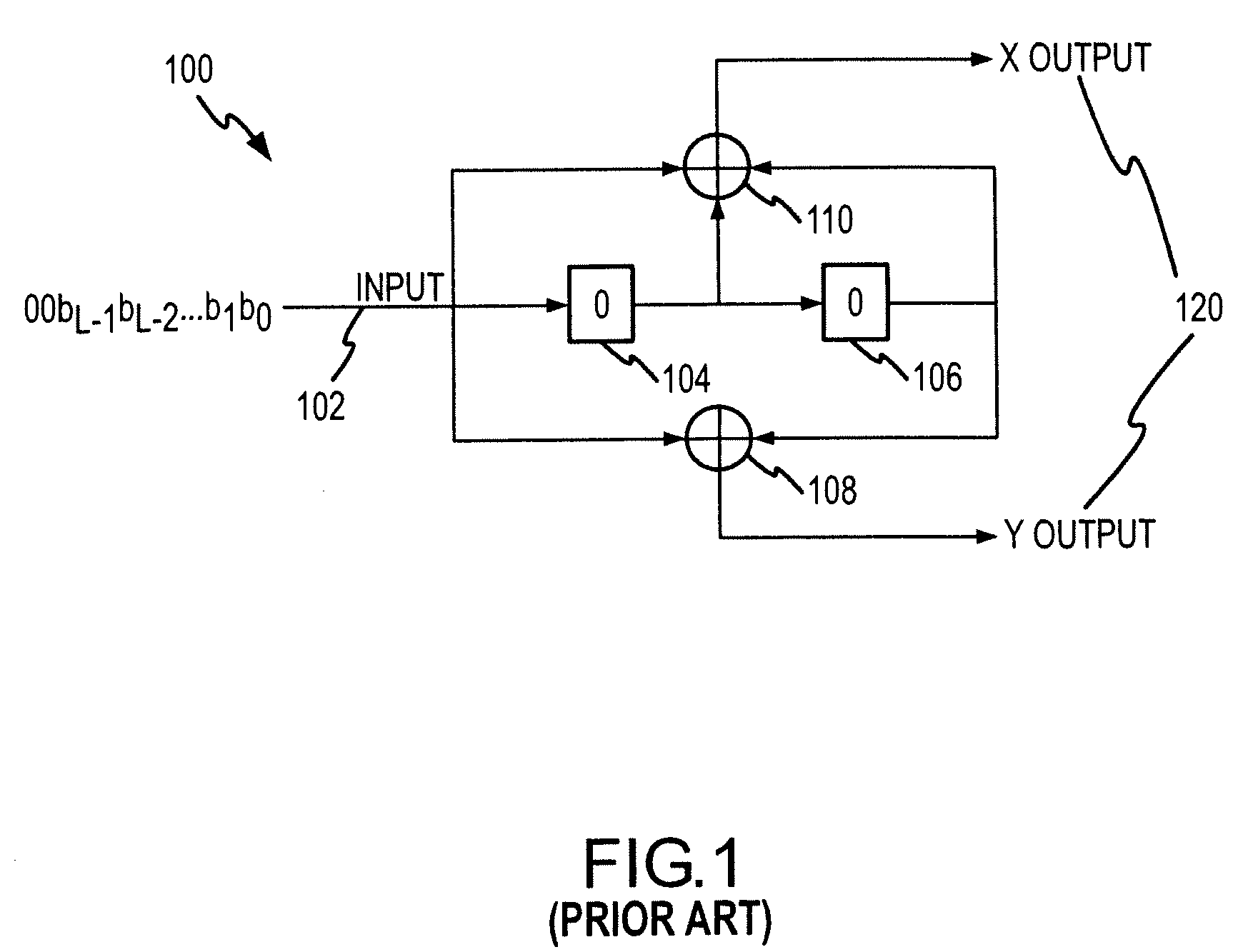
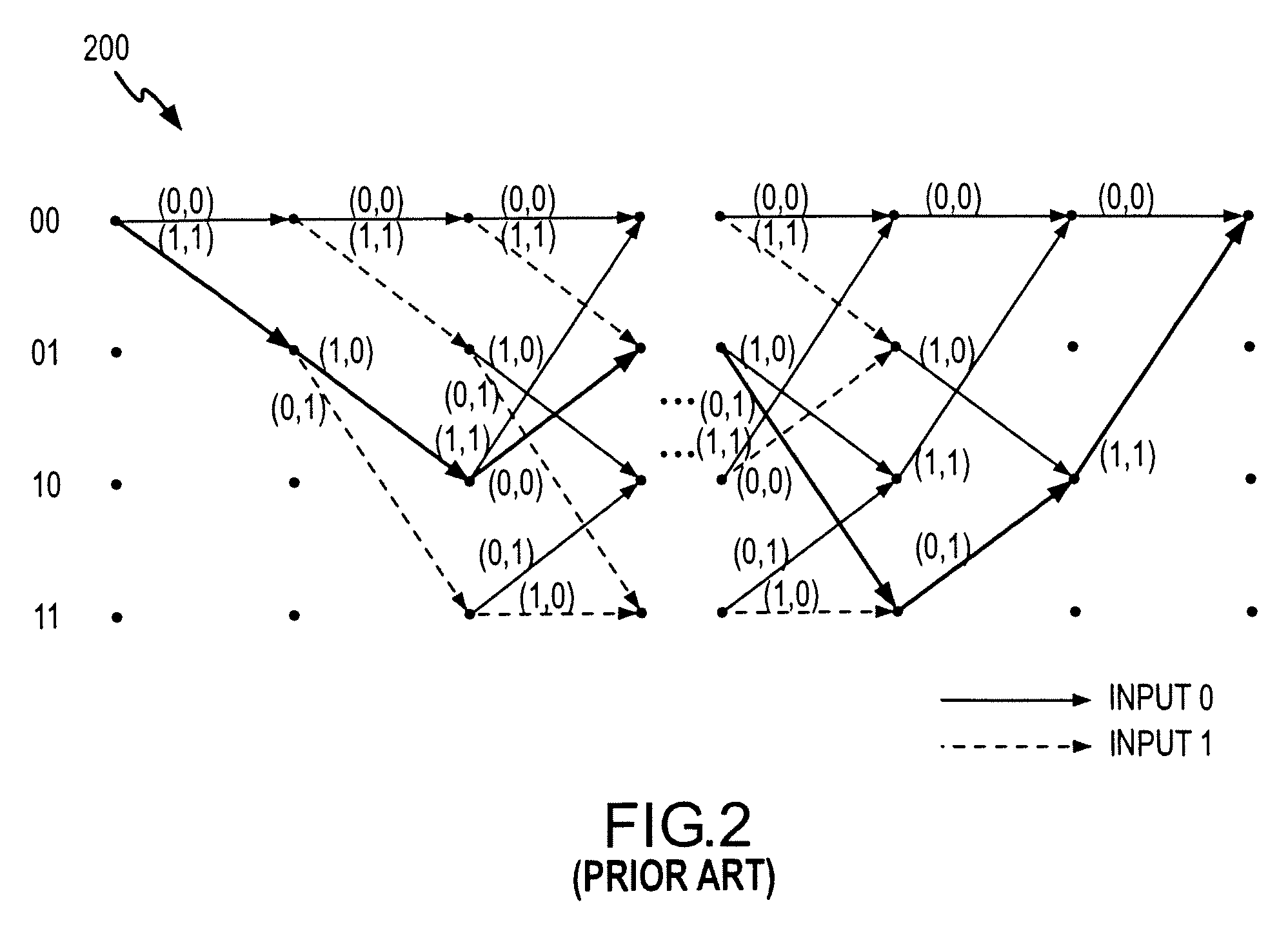
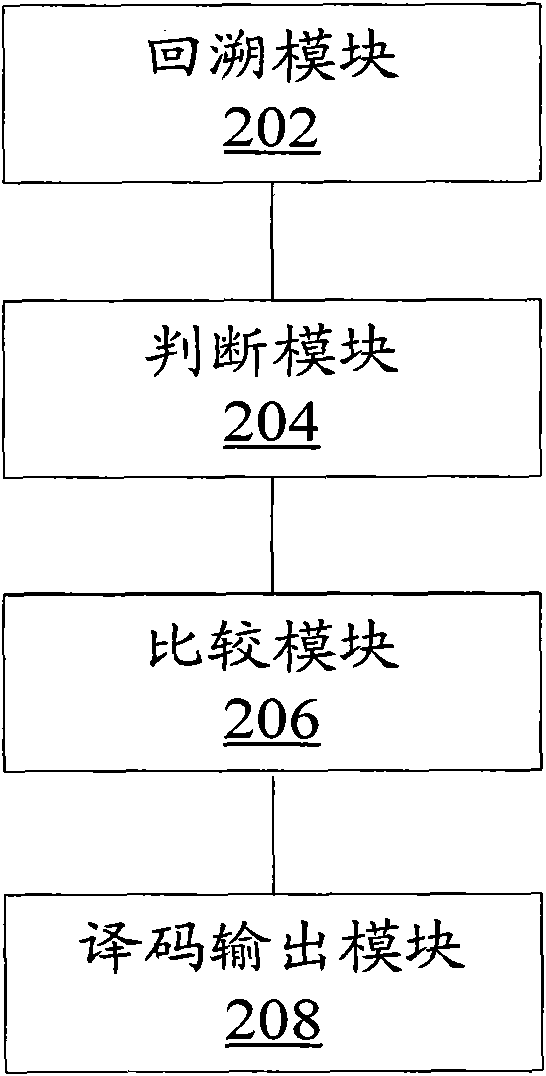
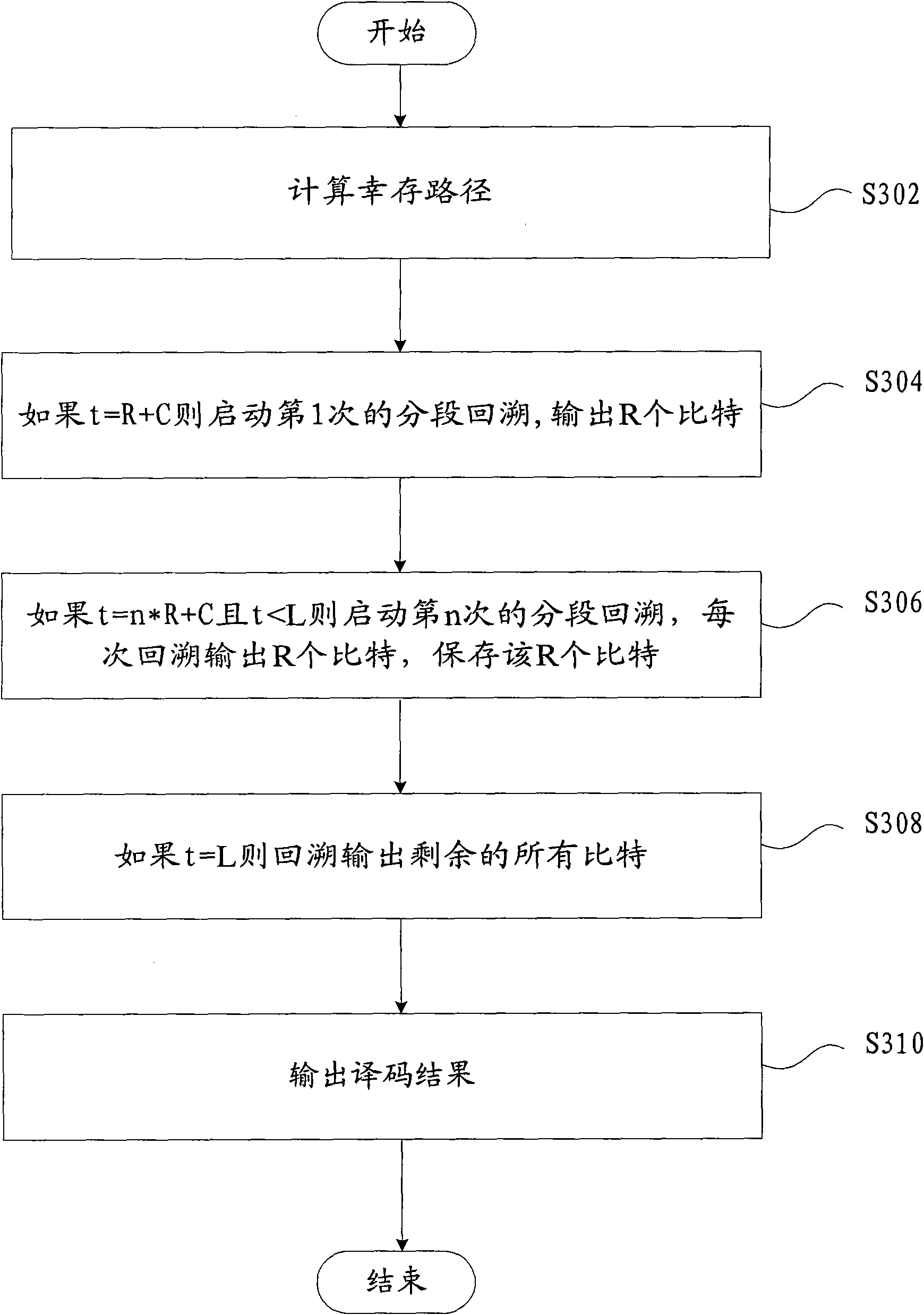
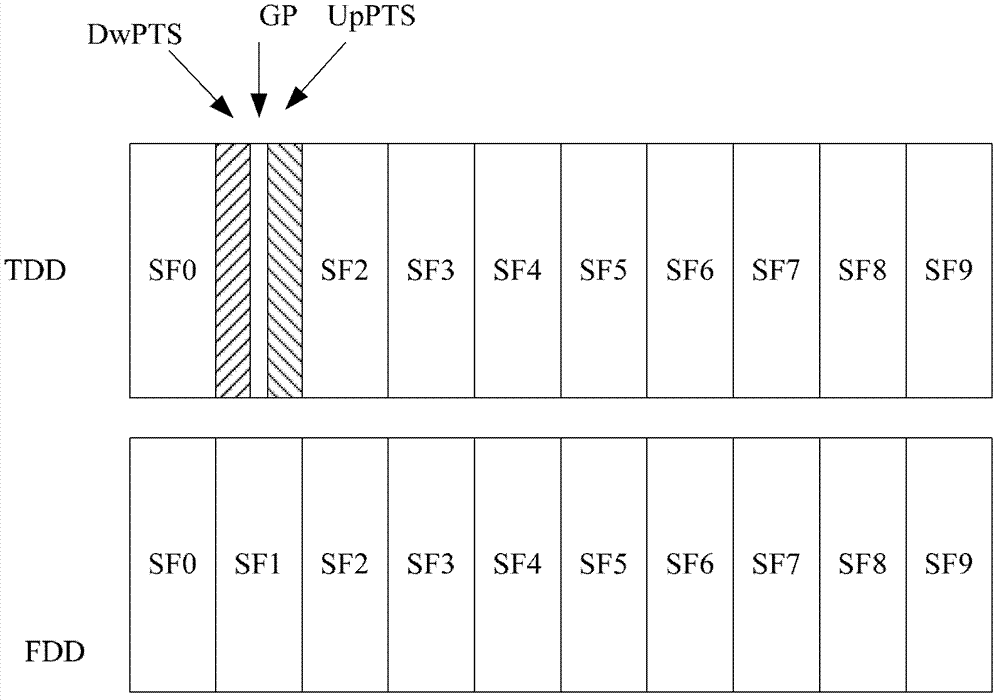
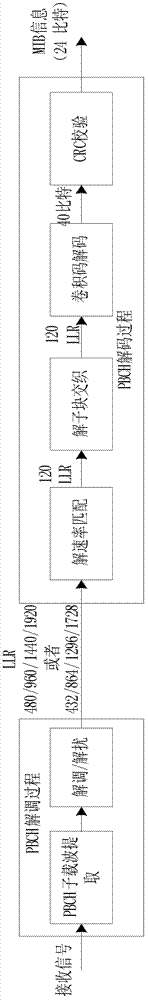
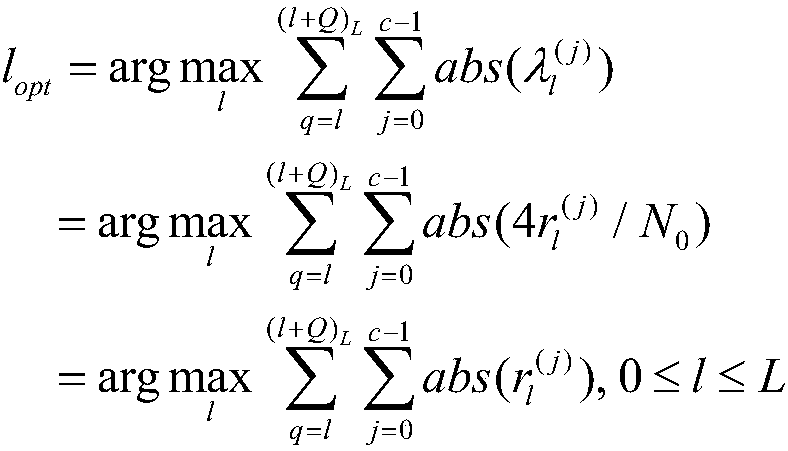Patents
Literature
116 results about "Tail-biting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
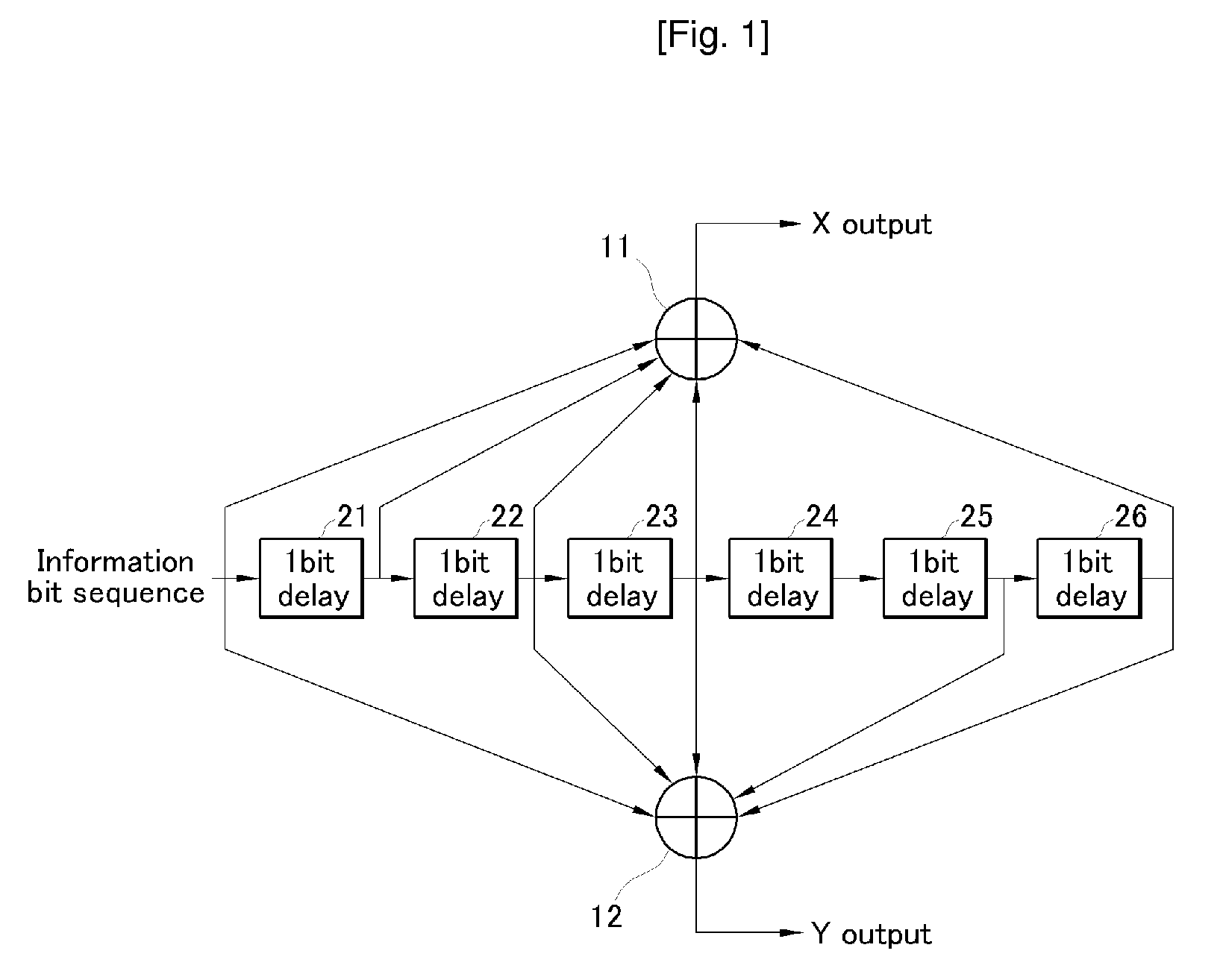
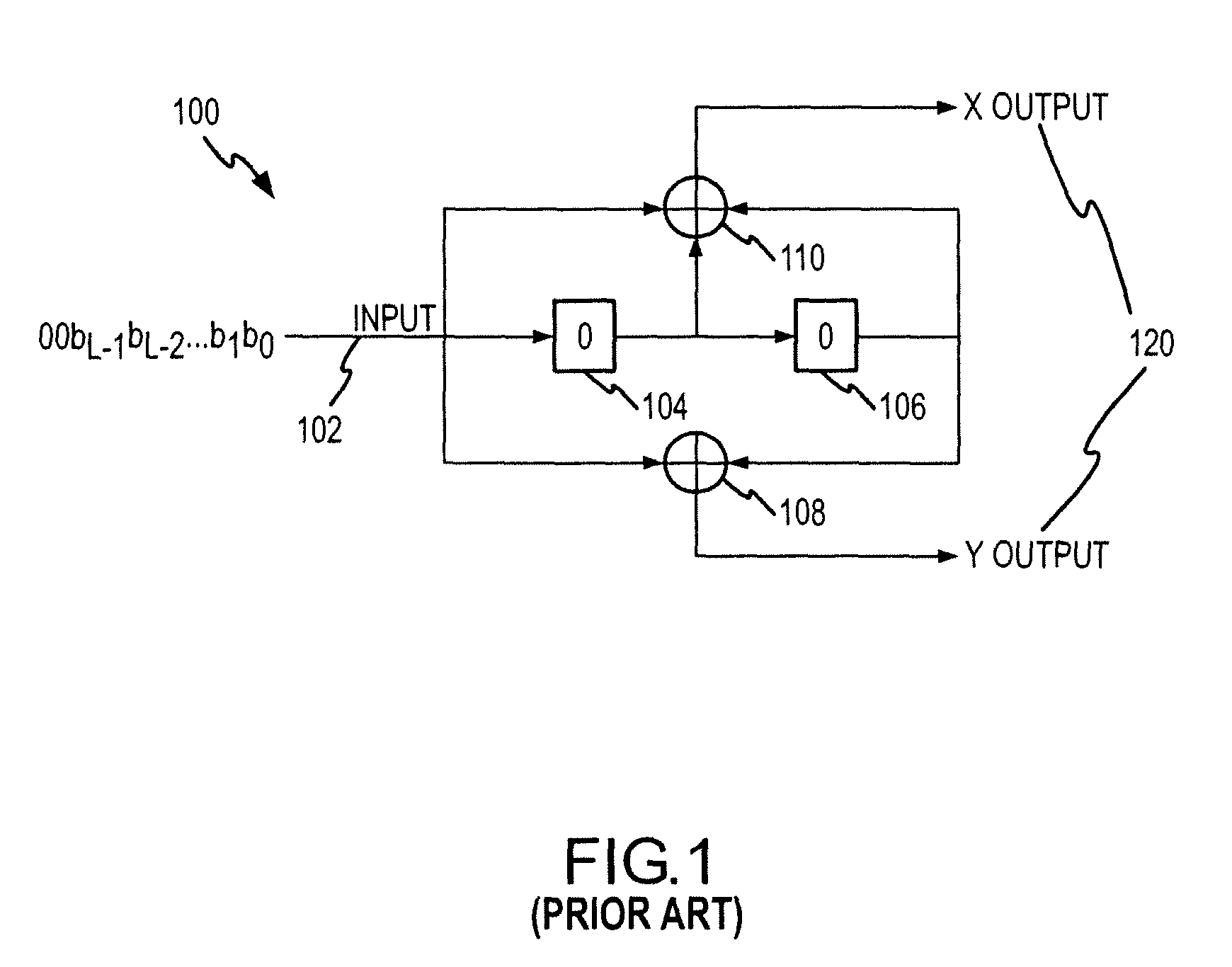
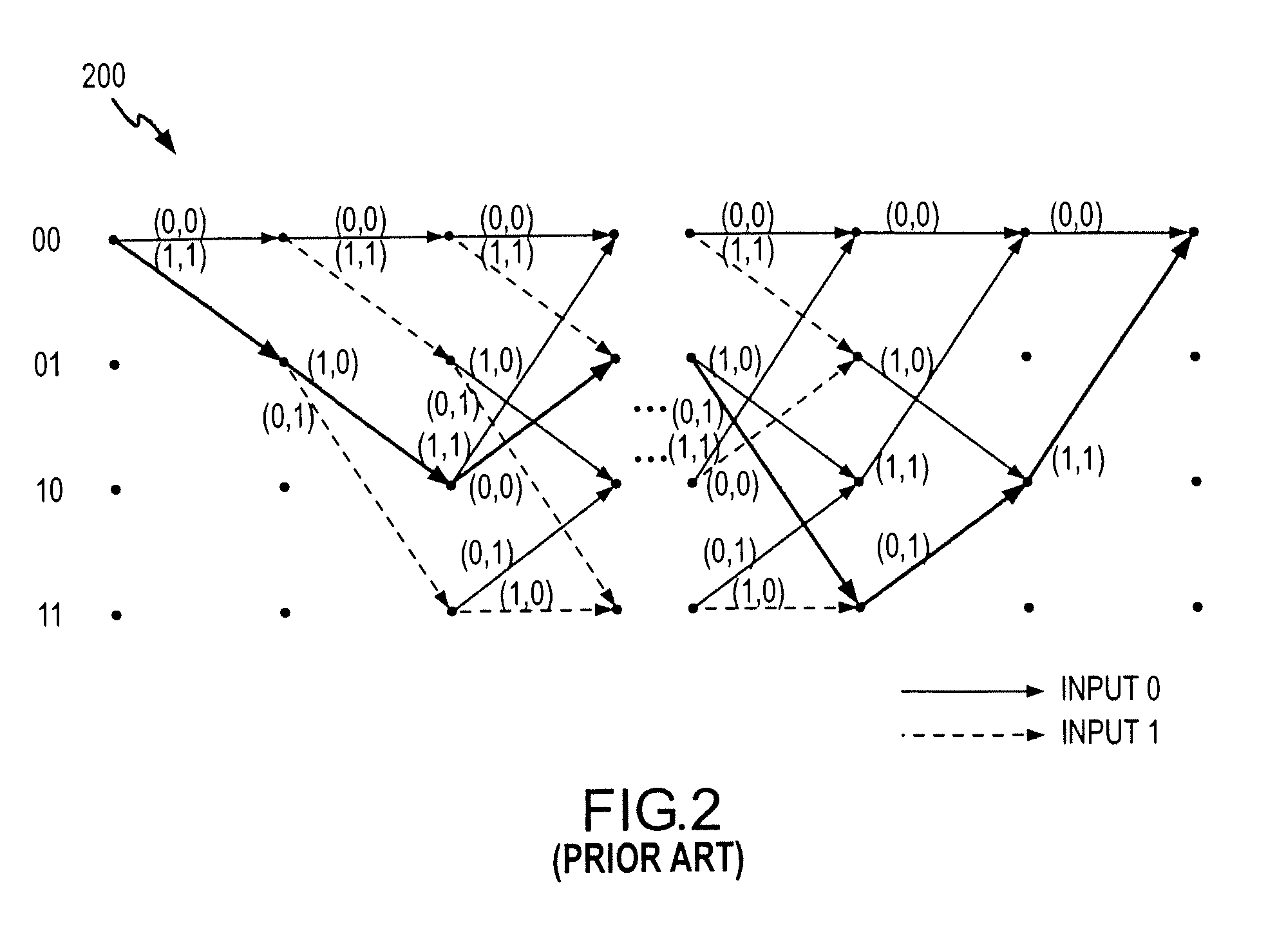
Apparatus and method of CTCM encoding and decoding for a digital communication system
InactiveUS7010052B2Improve energy efficiencyData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesCommunications systemMulti dimensional
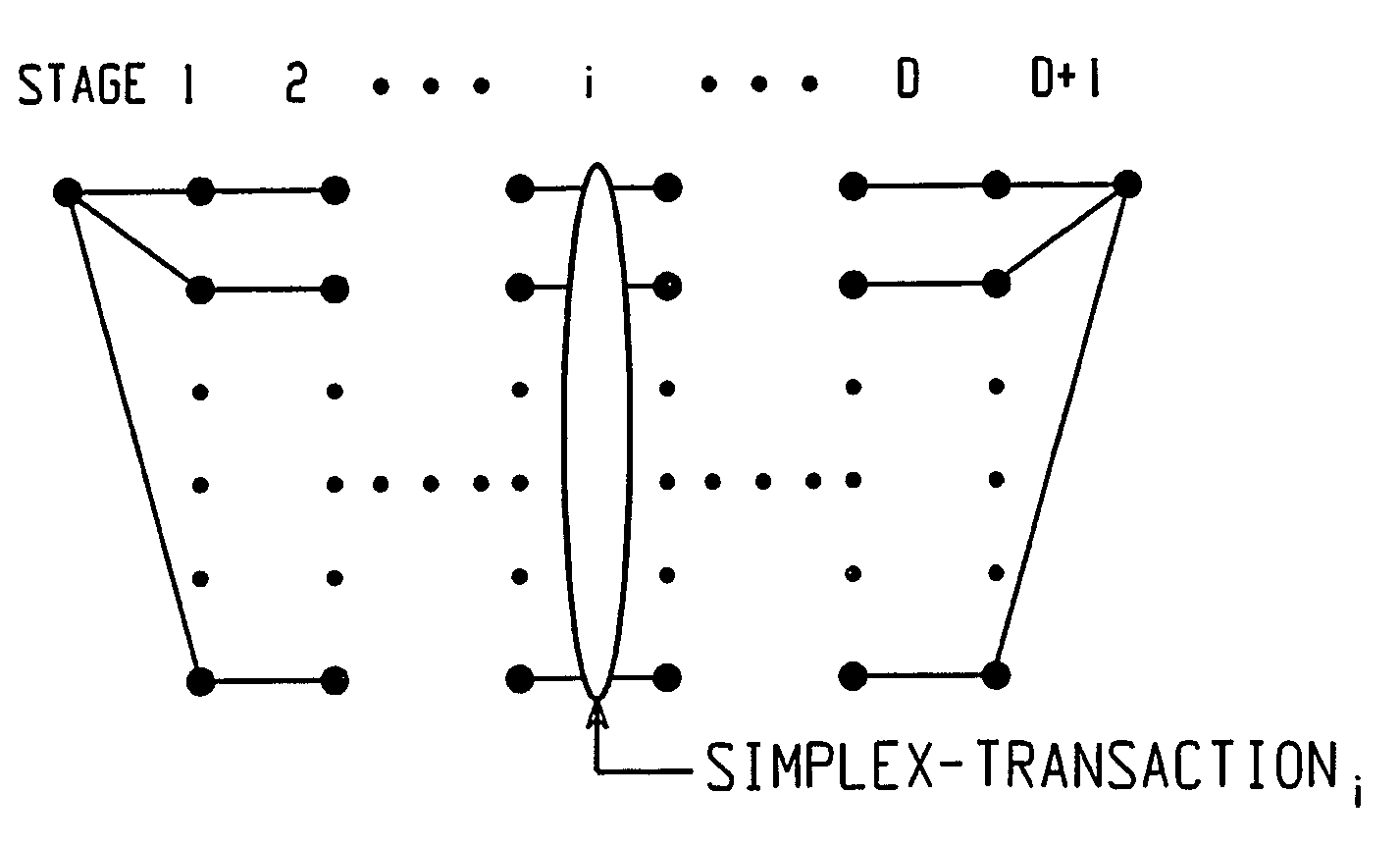
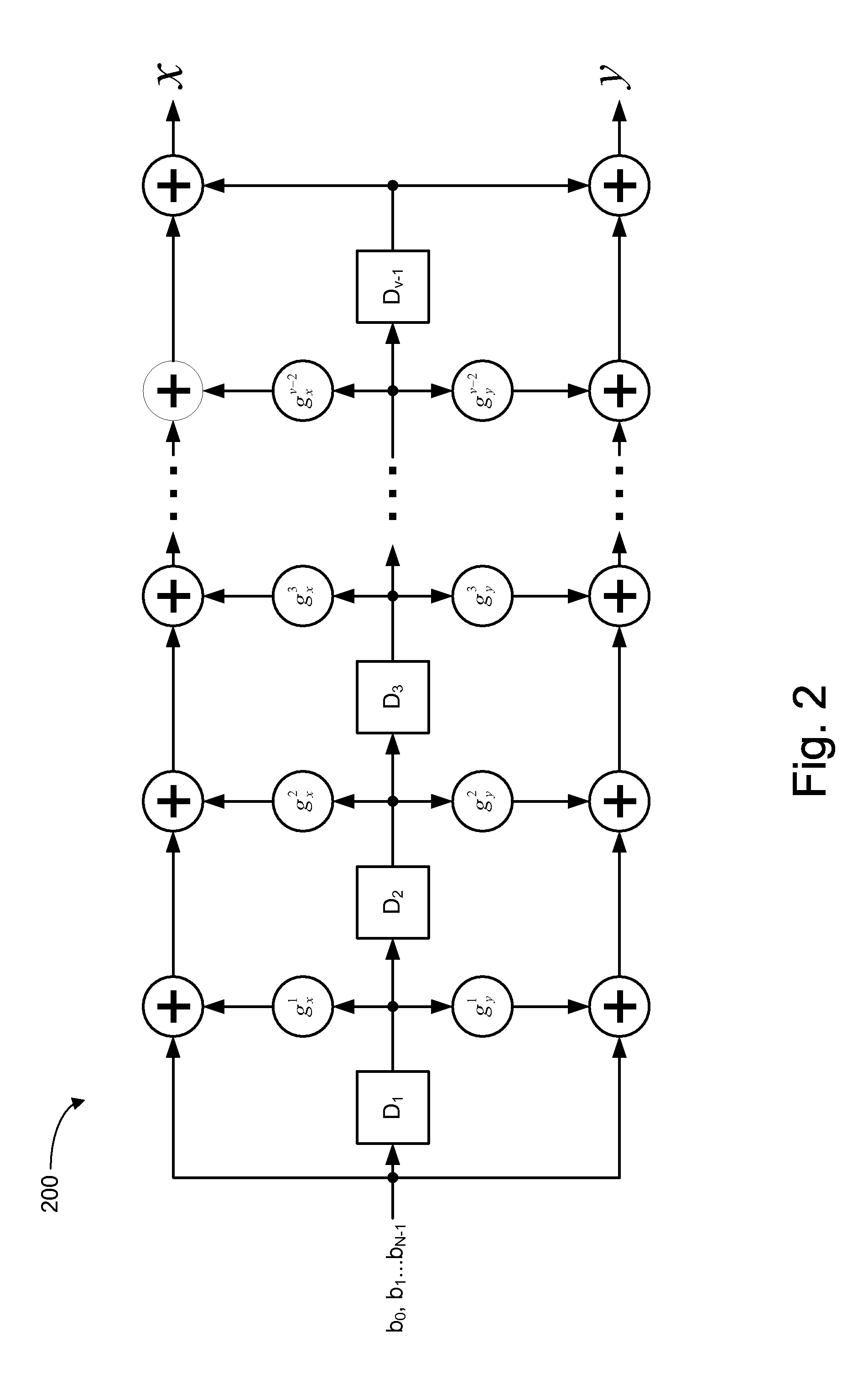
A method of building systematically a multi-dimensional (n, D, L) circular trellis coded modulation (CTCM) encoder with properties of optimal energy efficiency, strong tail biting and maximum minimum distance (dmin) of trellis paths is disclosed. In addition, a communication system for use in a power limited channel application is disclosed comprising a circular trellis coded modulation (CTCM) encoder with permuted state structure for encoding based on a circular trellis path associated with a sequence of digital information bits and a set of simplexes identified for the path from a multi-dimensional signal constellation; a transmitter coupled to said CTCM encoder for transmitting said sequence of channel symbols over said channel; a receiver for receiving a transmission from said transmitter including said sequence of channel symbols and any noise induced therein; and a CTCM decoder coupled to said receiver for decoding the received transmission without knowledge of the starting state of the circular trellis path of the CTCM encoder to recover the sequence of information bits. Apparatus and methods of encoding and decoding are also disclosed utilizing a combination of circular trellis-coded modulation with permuted state structure and simplex signal constellation techniques for use in the digital communication system.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
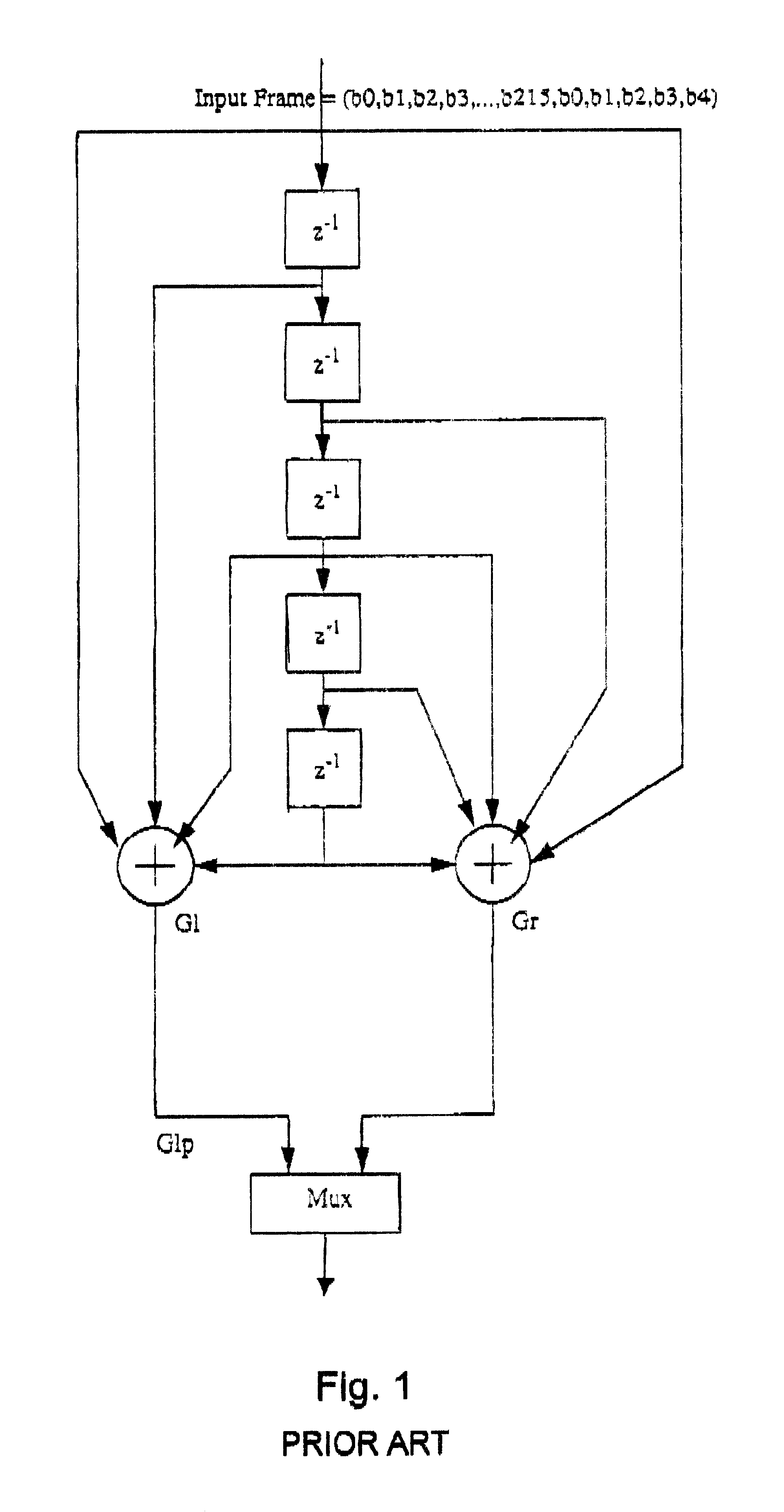
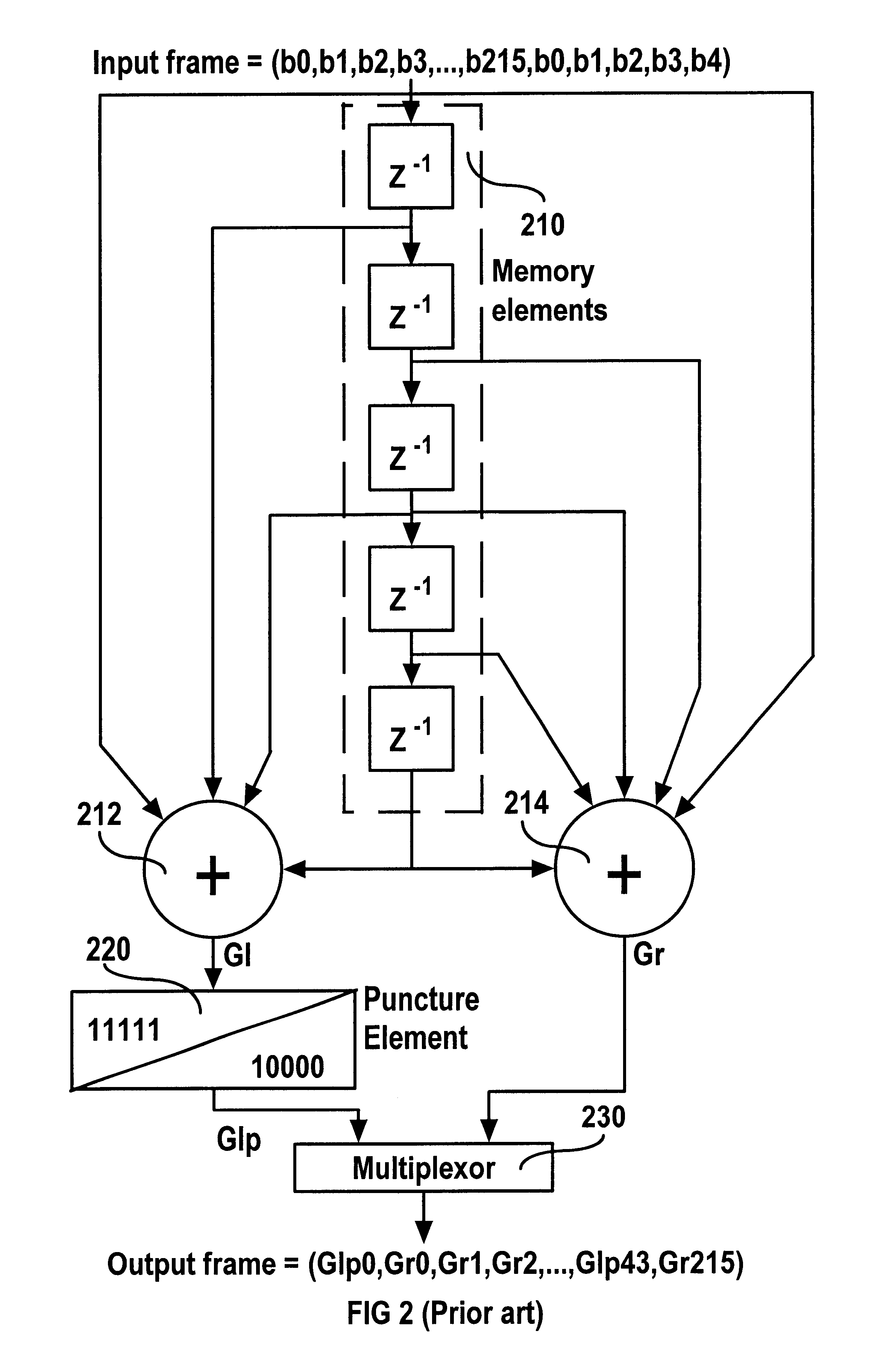
Method and apparatus for channel decoding of tail-biting convolutional codes
InactiveUS6877132B1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesMajority logic decodingMajority logic
A method for hard-decision channel decoding of tail-biting convolutional codes includes the step of receiving from a channel an input bit stream encoded by a tail-biting convolutional channel encoder. The encoder includes a number of memory elements and a rate. The input bit stream includes a series of symbols; each symbol includes a number of bits; the number of bits is related to the rate of the encoder. The method further includes the step of assuming a probability for each possible initial state of the encoder. The method further includes the step of decoding each symbol of the input bit stream using majority logic, with reference to a trellis structure corresponding to the encoder. The trellis structure represents: a number of states related to the number of memory elements of the encoder; a plurality of transitional branches; and a number of stages related to the number of symbols in the input bit stream.
Owner:APPLE INC
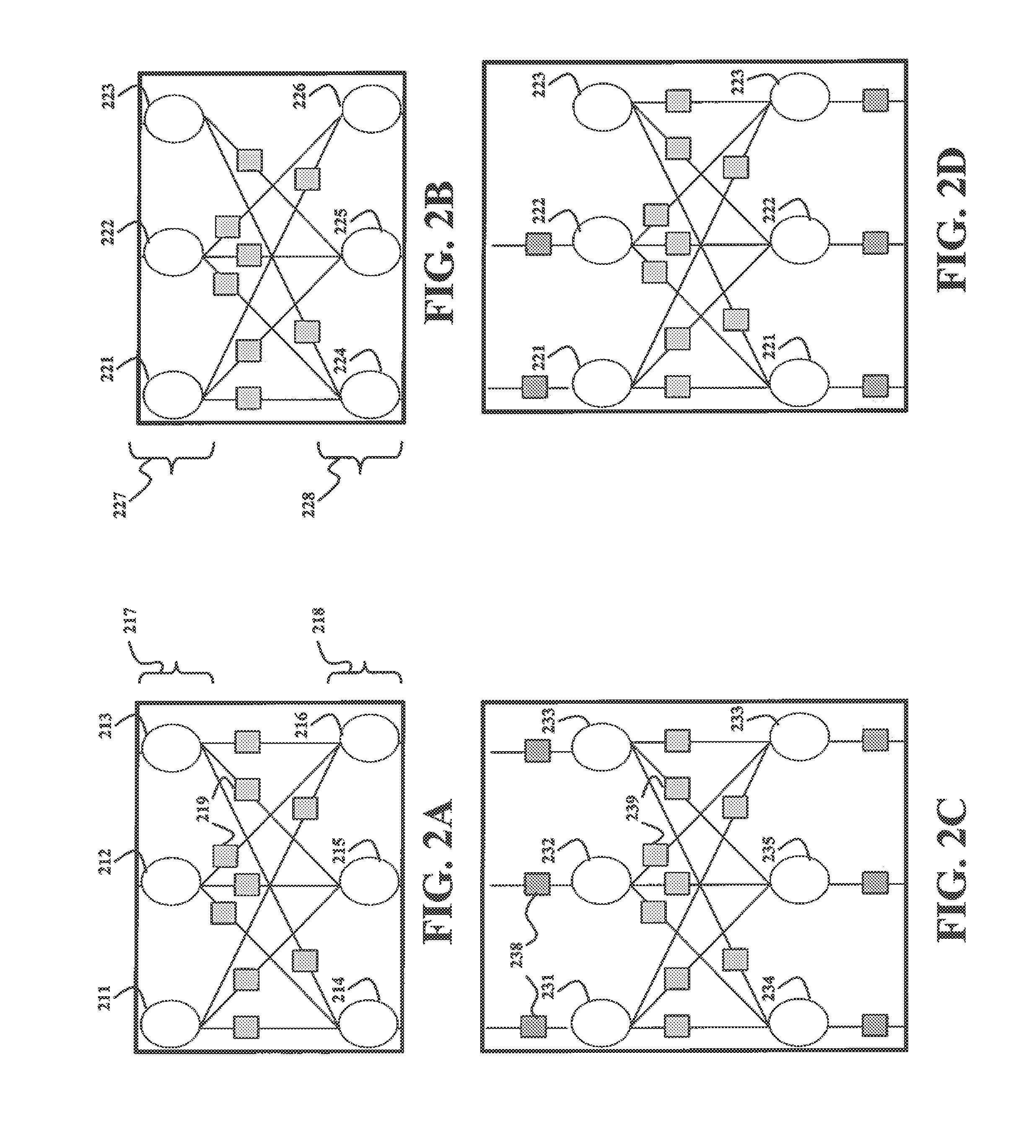
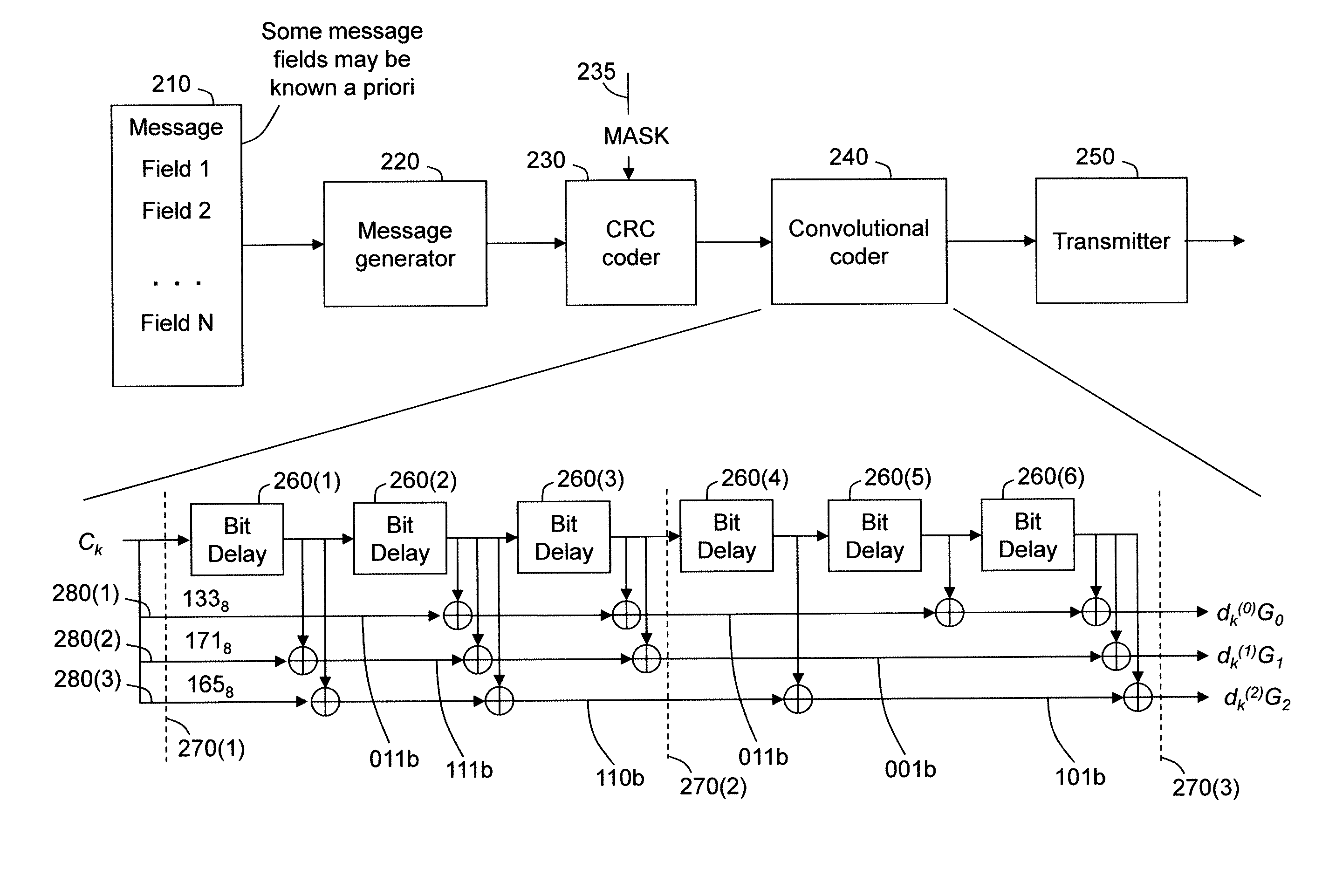
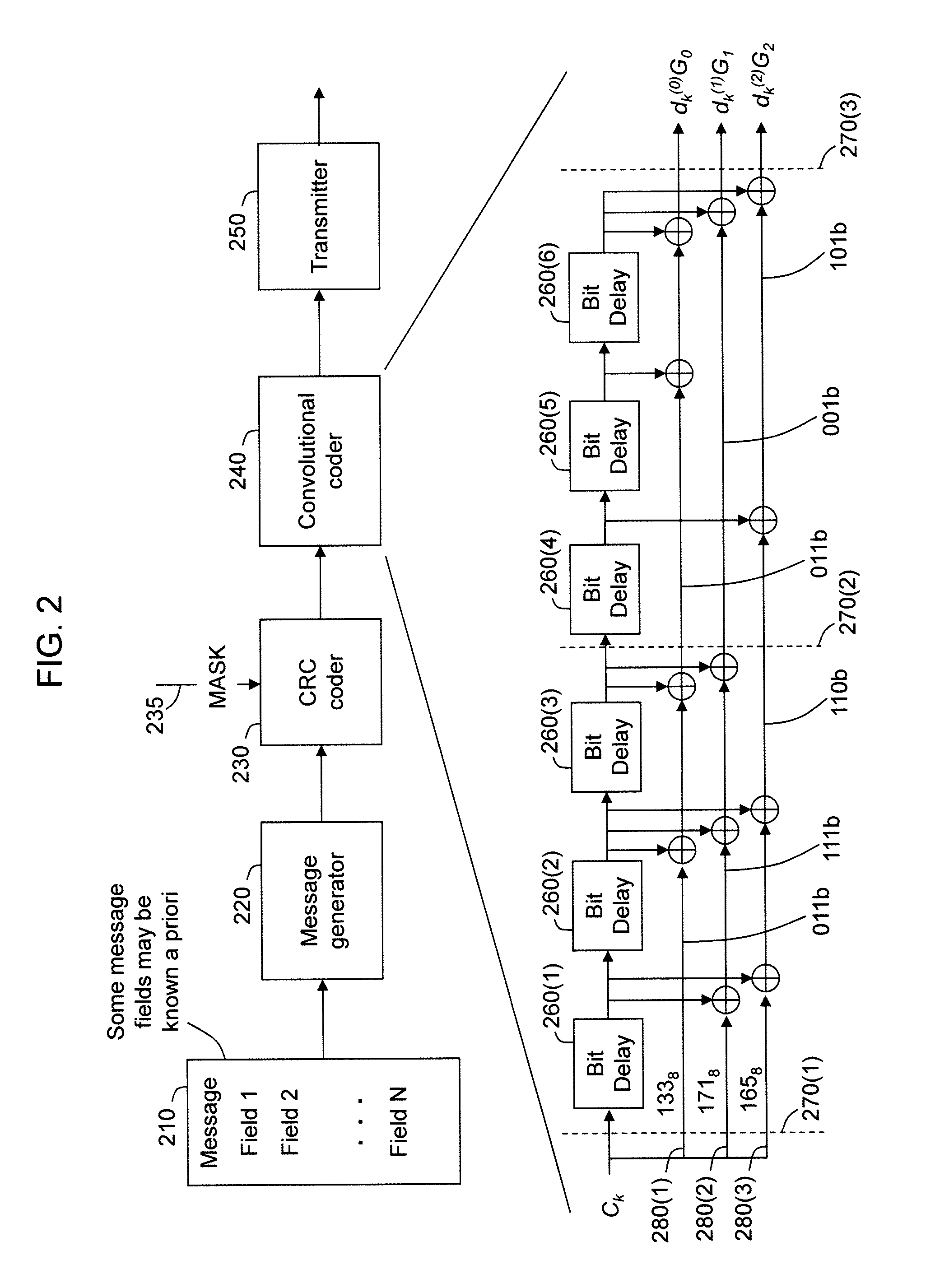
Method and apparatus to improve information decoding when its characteristics are known a priori
InactiveUS20090041166A1Reduce in quantityError preventionCode conversionComputer hardwareTail-biting
The present invention provides systems and methods for decoding received messages using a priori characteristics of selected message portions. A message which has been encoded in a particular format, such as a tail-biting convolutional coding, is received and decoded by utilizing the a priori information about the message. In one case, static-type receive bits in a portion of the message, such as a Frame Control Header, are used to reduce the number of trellis states at particular stages of the decoding process. A Viterbi-type decoding process may be employed in either a soft or hard decision mode. Reducing the number of trellis states improves the success rate for message decoding and improves receiver throughput. Power consumption may also be reduced.
Owner:MBIT WIRELESS
Method for Generating Candidates used in Turbo Coded Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing System with Selective Mapping Technique
InactiveUS20080285432A1Reduce PAPRImprove performanceError preventionModulated-carrier systemsMapping techniquesTail-biting
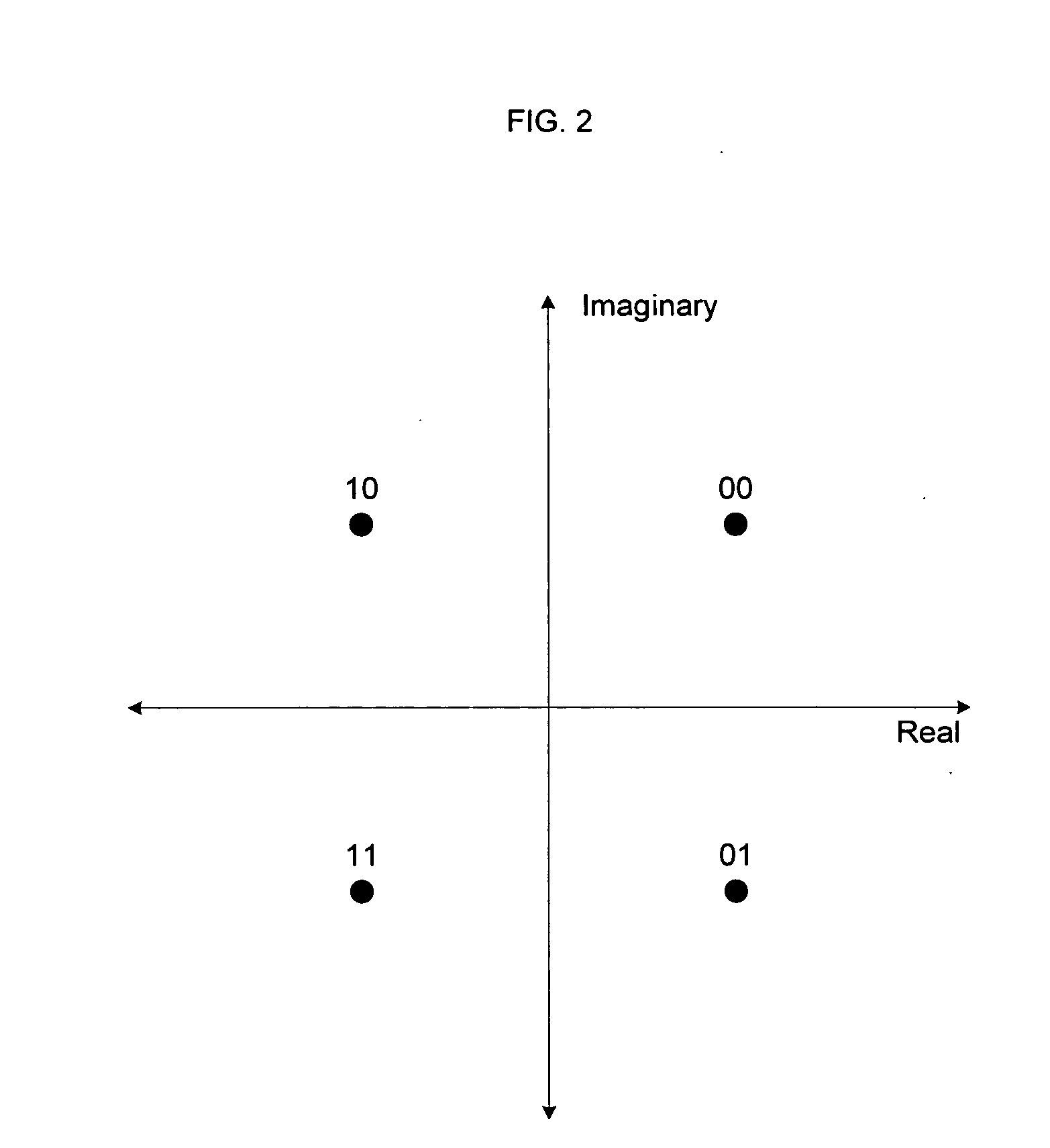
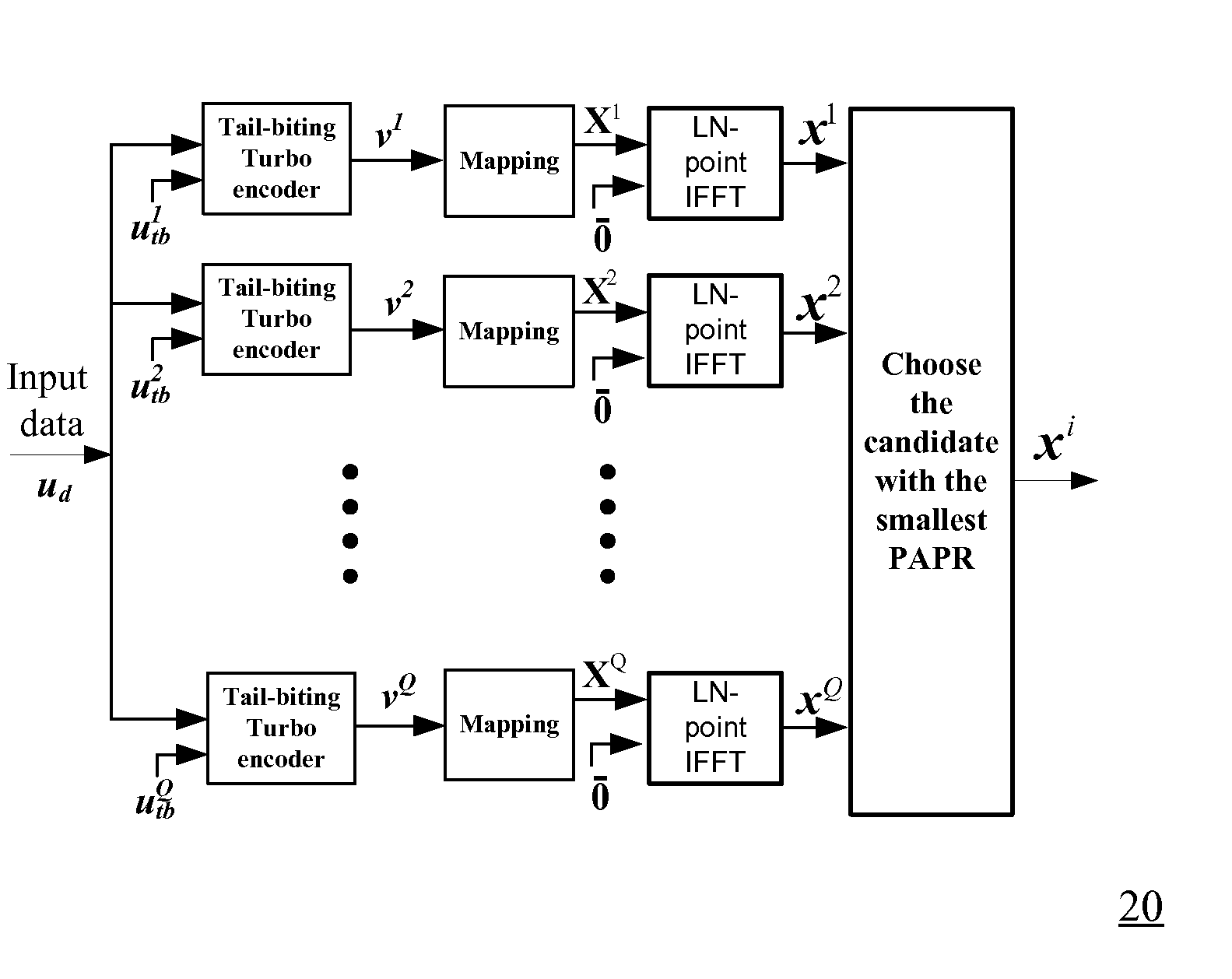
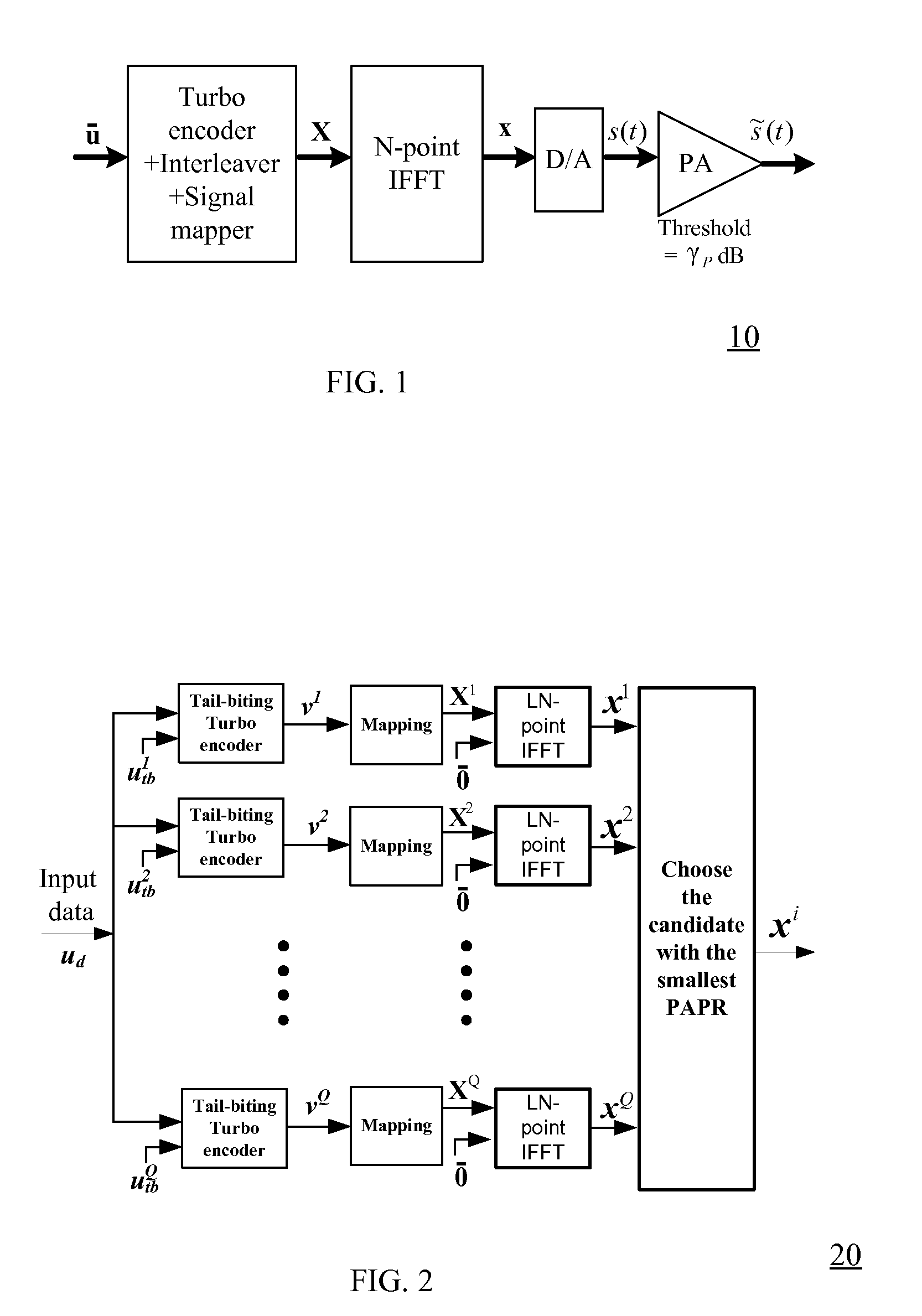
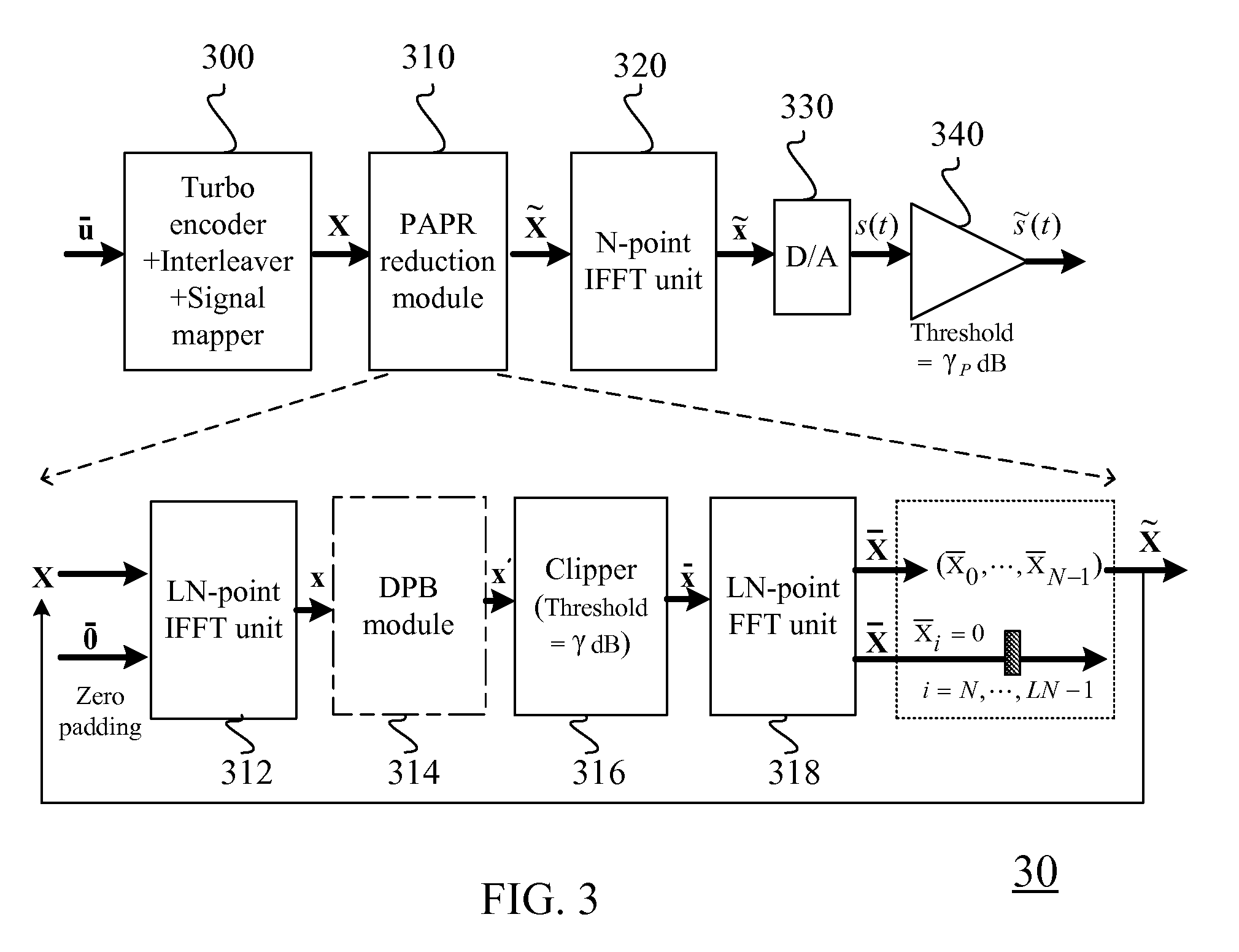
A method for generating candidate used in TCOFDM (turbo coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing) with SLM (selective mapping) technique, a user data is combined with a plurality of seeds to generate corresponding a plurality of message vectors. The method is characterized in performing tail-biting turbo encoding on the message vectors to generate corresponding turbo codewords used for generating candidates, and the seed of each message vector is different from the seeds of other message vectors.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Periodic channel state information feedback method and system
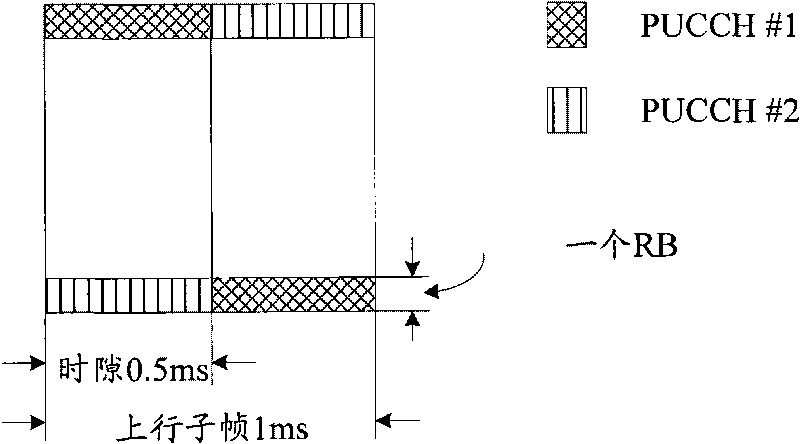
ActiveCN101702632ALoad unlimitedHigh coding gainRadio transmission for post communicationSignalling characterisationBlock codeChannel state information feedback
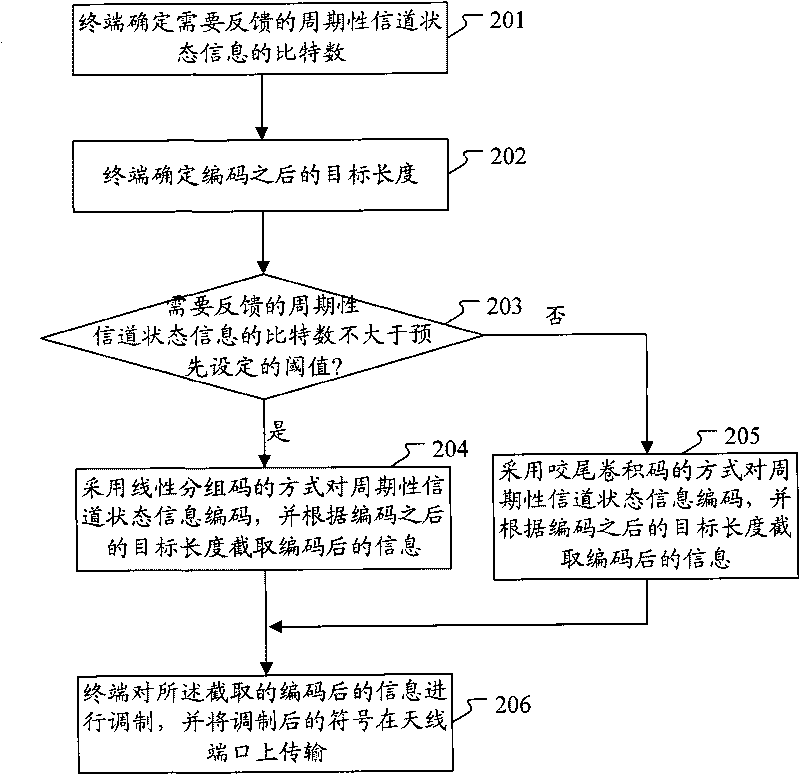
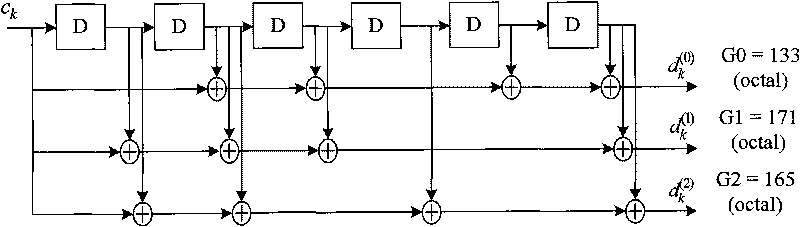
The invention discloses a periodic channel state information feedback method comprising the following steps: determining the bit number of the periodic channel state information needing to be fed back as well as the coded target length by a terminal; judging that the bit number of the periodic channel state information needing to be fed back is not more than the preset threshold value, then coding by adopting the mode of linear block code and intercepting the coded information according to the determined coded target length, or coding by adopting the mode of tail biting convolutional code, and intercepting the coded information according to the determined coded target length; and modulating the intercepted coded information by the terminal and transmitting on an antenna port. The invention correspondingly discloses a channel state information feedback system. The invention has no limitation to the load of the channel state information, thus the application range is wider. The linear block code adopted by the invention can obtain maximum coding gain, thus optimizing the performances.
Owner:福建省永阳国有资本投资集团有限公司
Coding and decoding methods of ode of tail-biting staircase codes
ActiveCN105429646AGuaranteed error correction performanceTroubleshoot issues where uncorrected errors are affecting overall performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer architectureBlock code
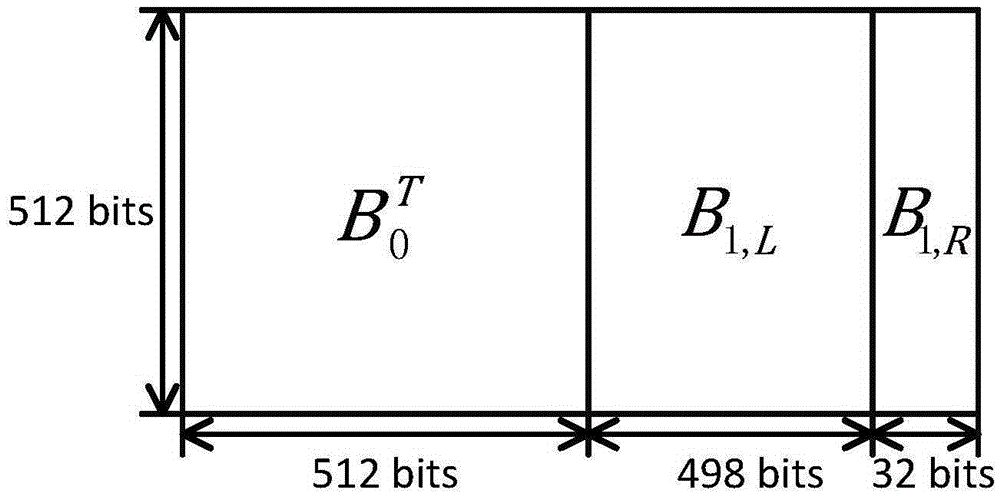
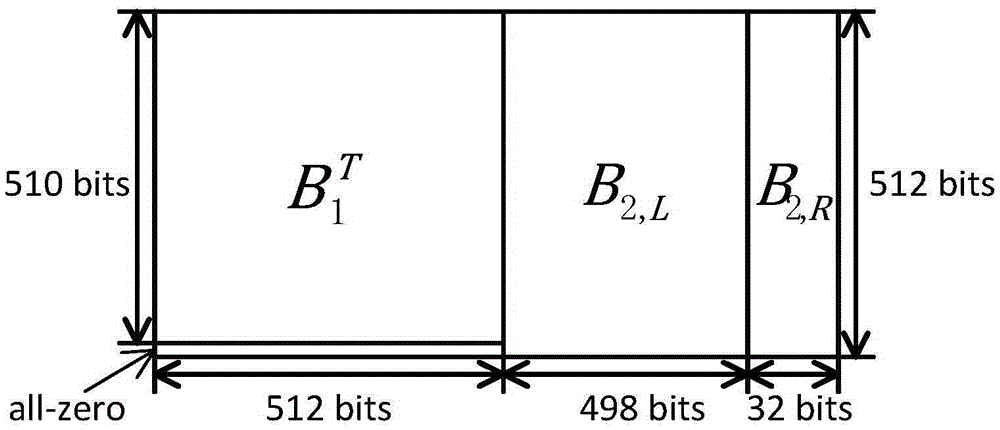
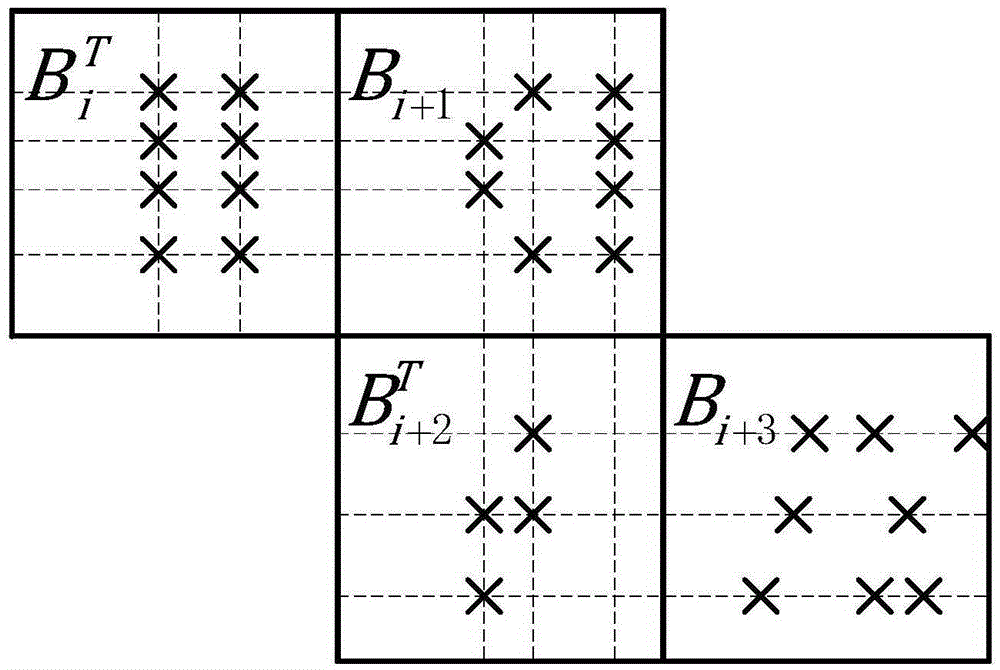
The invention relates to a tail-biting staircase code coding method. The tail-biting staircase code coding method comprises the following steps: 1) selecting an (n, k) linear block code as a component code, wherein n represents a code length, n belongs to (500, 5000), and k represents an information length before coding; and 2) grounding received information according to a mode in staircase codes, constructing a matrix B<1>, B<2>, B<3>, ..., B<n>, adding a full-zero matrix participating the coding to a lower part of B<1>, coding the residual matrix using the component code then, generating a check bit matrix while the coding, completing end-to-end connection of codes of a final matrix and a first matrix in a group then, finally replacing the full-zero matrix complemented in the B<1> with the check bit matrix, and completing the coding. The coding method is advantageous in that, through adoption of the novel coding scheme, the novel tail-biting staircase codes have a characteristic of the block code, coding processes between groups are mutually independent, information of each matrix in the groups is still contained in the two component codes, and error correction performance is guaranteed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
System and Method for Quantization of Channel State Vectors
ActiveUS20110135020A1Lower requirementExtend battery lifeSecret communicationRadio transmissionChannel state informationTelecommunications
A system and method for the quantization of channel state vectors is provided. A method for communications node operation includes measuring a communications channel between the communications node and a controller, generating channel state information based on the measurement, computing a bit representation of the channel state information, transmitting the bit representation to the controller, and receiving a transmission from the controller. The computing makes use of tail-biting trellis decoding, and the transmission makes use of the channel state information transmitted by the communications node.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Channel decoding method and channel decoding device
ActiveCN101635611ACalculation speedTake up less resourcesError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionDecoding methodsComputer science
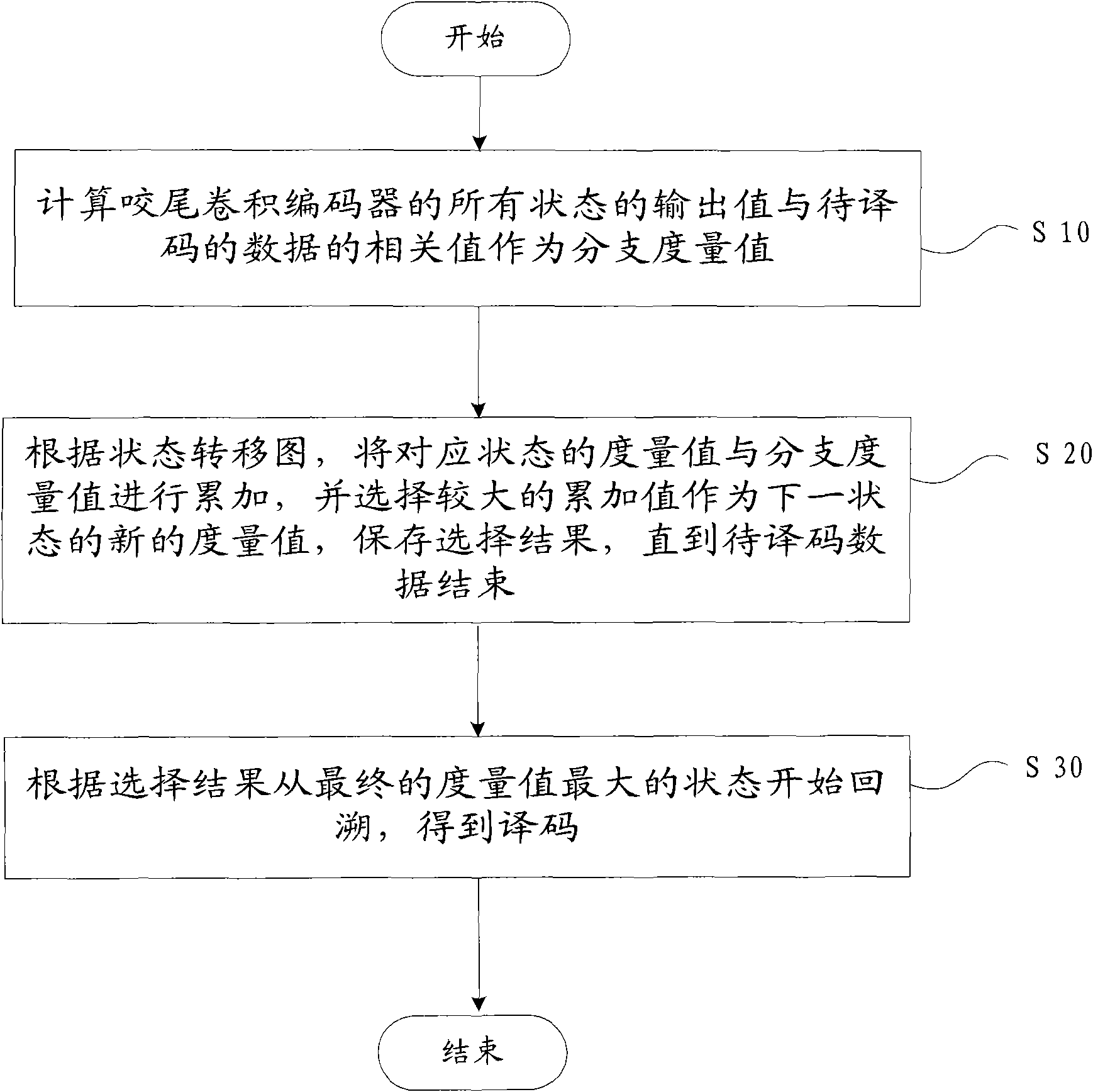
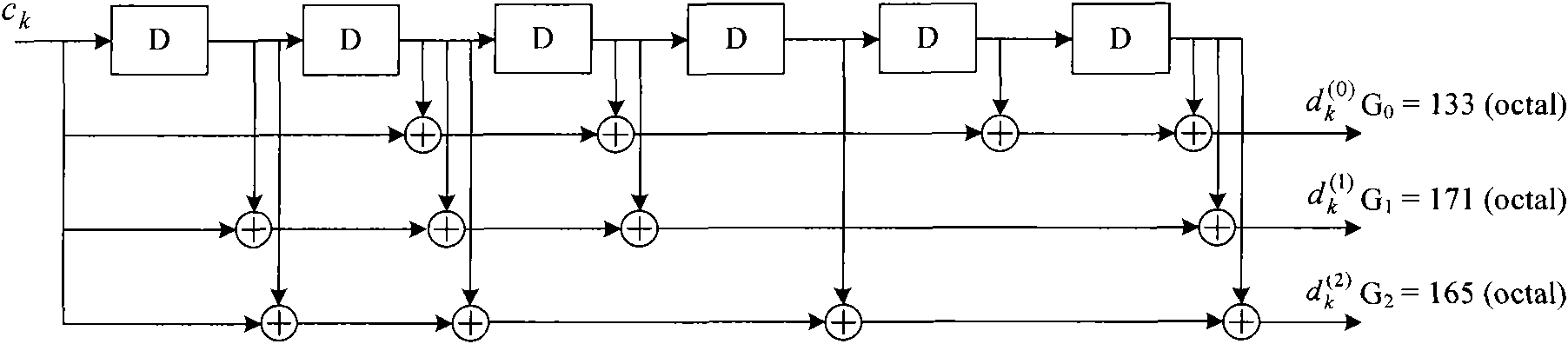
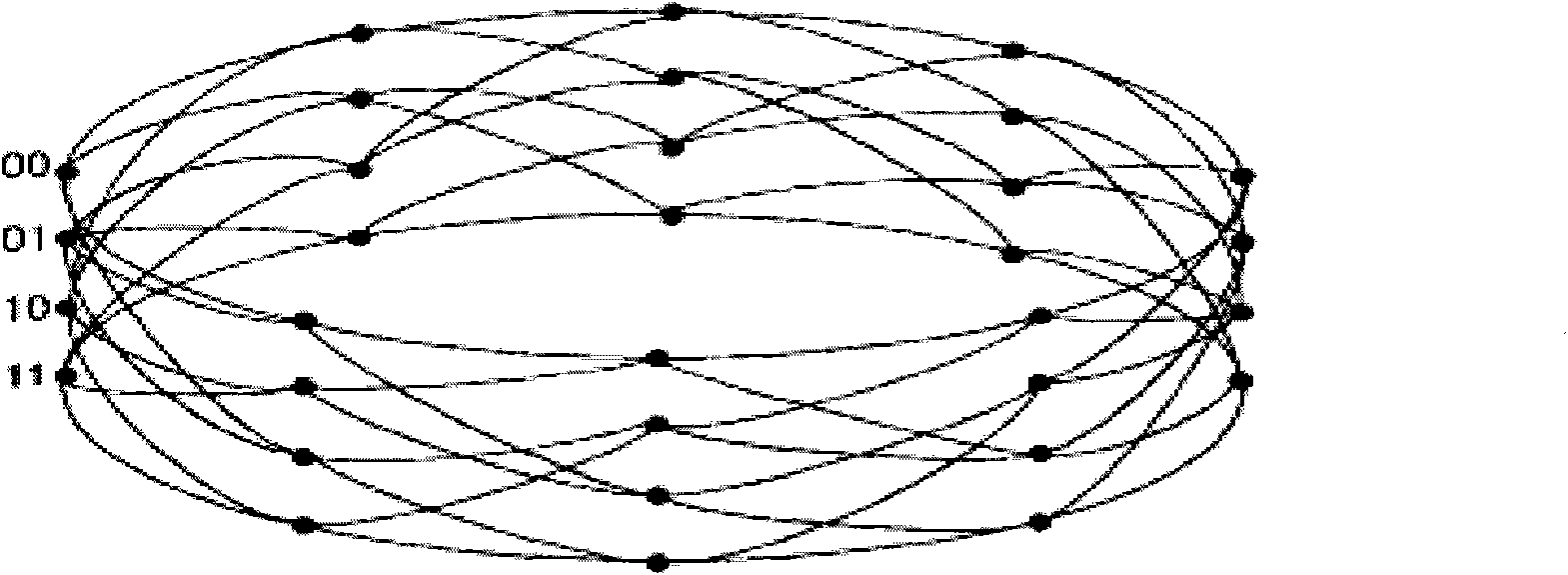
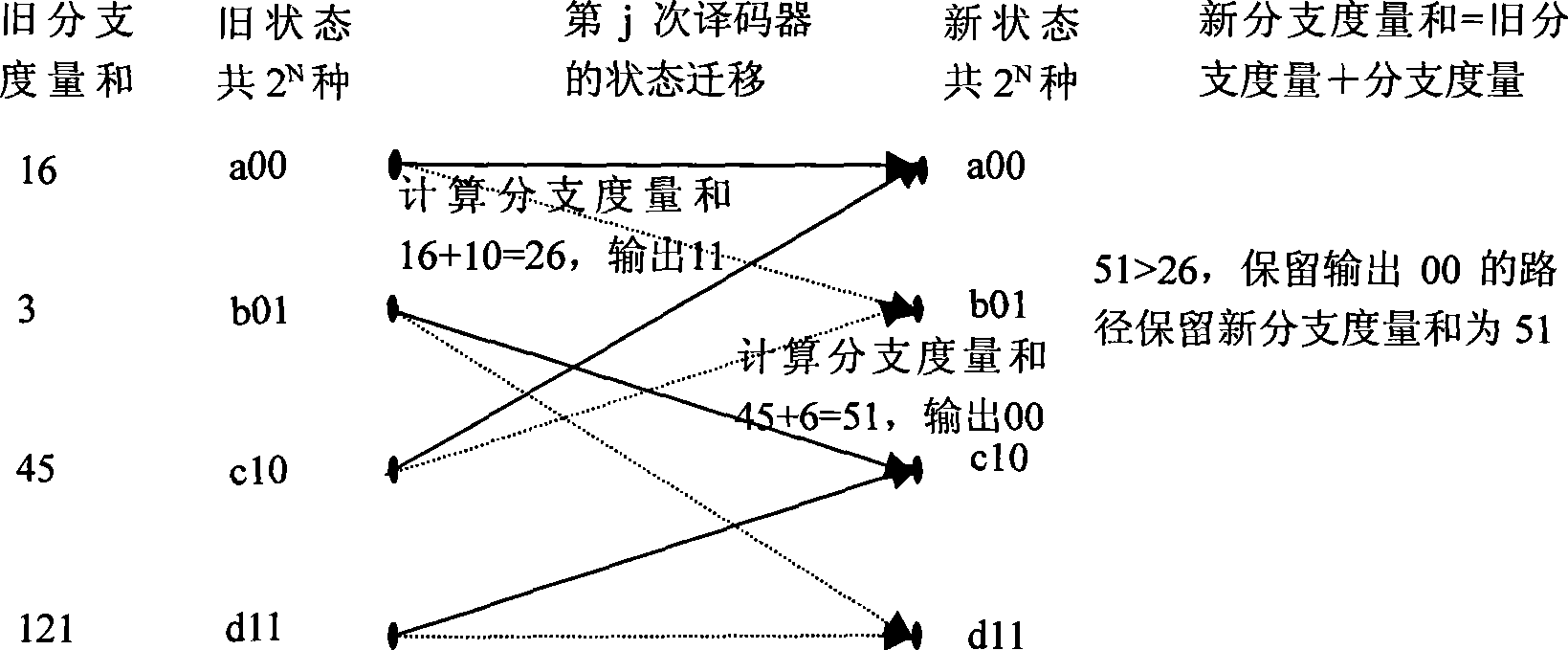
The invention provides a channel decoding method which comprises the following steps: calculating output values of all states of a tail biting convolutional encoder and correlation values of data to be decoded as branch measurement values; accumulating measurement values of corresponding states and the branch measurement values according to a state transition diagram, selecting a larger accumulated value as a new measurement value of a next state and storing selection results until the data to be decoded end up; backtracking from a final state of a maximum measurement value according to the selection results so as to obtain a decoding result. The invention also provides a channel decoding device. The invention ensures that the decoding has fewer occupied resources and high calculating speed.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
Encoding method and encoder for tailing convolution codes
InactiveCN1855732AOvercome the disadvantages of relatively high complexity and difficulty in implementationReduce computational complexityError correction/detection using convolutional codesDecoding methodsComputation complexity
The invention comprises the following steps: with the accumulating metrics of the initial window, an incorrect initial path is merged into a correct path, and a state of optimal node at the end of initial window is used as a decoding initial state of the tail-biting convolution code; in term of said decoding initial state and a delay window, through whole decoding trace-back, a Viterbi decoding is made for the tail-biting convolution code.
Owner:ZTE CORP
System and Method for Non-Uniform Bit Allocation in the Quantization of Channel State Vectors
ActiveUS20130003808A1Easy to controlEnhanced informationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsChannel state informationTelecommunications
A system and method for non-uniform bit allocation in the quantization of channel state vectors is provided. A method for communications node operation includes receiving a bit-allocation profile for use in quantizing channel state information, measuring a communications channel between the communications node and a controller, generating channel state information based on the measurement, computing a bit representation of the channel state information, transmitting the bit representation to the controller, and receiving a transmission from the controller. The computing makes use of quasi-tail-biting trellis decoding, and the computing is based on the bit-allocation policy. The transmission makes use of the channel state information transmitted by the communications node.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Rapid PBCH (physical broadcast channel) decoding method for LTE (long term evolution)
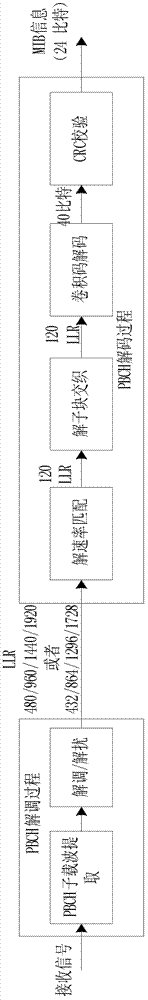
InactiveCN102904668ASimple structureReduce decoding timeError preventionBroadcast channelsResource consumption
The invention discloses a rapid PBCH (physical broadcast channel) decoding method for LTE (long term evolution). The rapid PBCH decoding method includes the steps of recording corresponding address relation before and after one hundred and twenty data sub-blocks are interleaved to obtain the position of a to-be-interleaved datum after sub-block interleaving and rate matching and a PBCH deblocked sub-block interleaved corresponding relation table indicating positions of one hundred and twenty bits of an encoded tail biting convolution code after the sub-block interleaving; performing deblocked rate matching and deblocked sub-block interleaving, wherein in the PBCH deblocked sub-block interleaved corresponding relation table, the first column indicates the positions of the first to the eighth encoded bits after the sub-blocking interleaving, the second column indicates the ninth to the sixteenth encoded bits after the sub-blocking interleaving, and so on, and the fifteenth column indicates the one hundred and thirteenth to the one hundred and twentieth encoded bits after the sub-blocking interleaving. The rapid PBCH decoding method for the LTE and a structure for decoding a PBCH of the LTE are simplified, PBCH decoding time on the premise of reaching maximum likelihood decoding performance is shortened, resource consumption for PBCH decoding is saved and realizing complexity is reduced.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
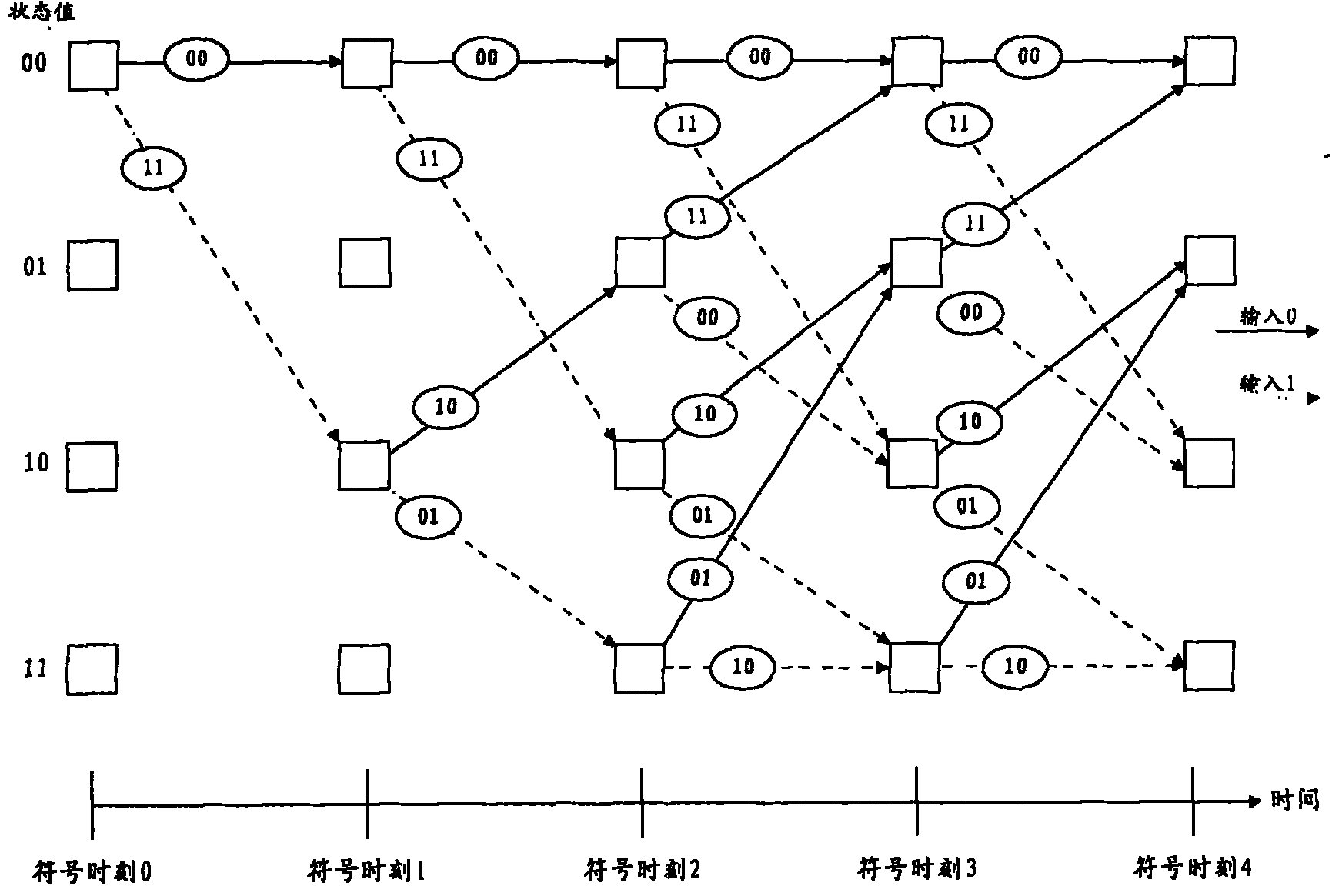
Decoding method for tail-biting convolutional codes using a search depth viterbi algorithm
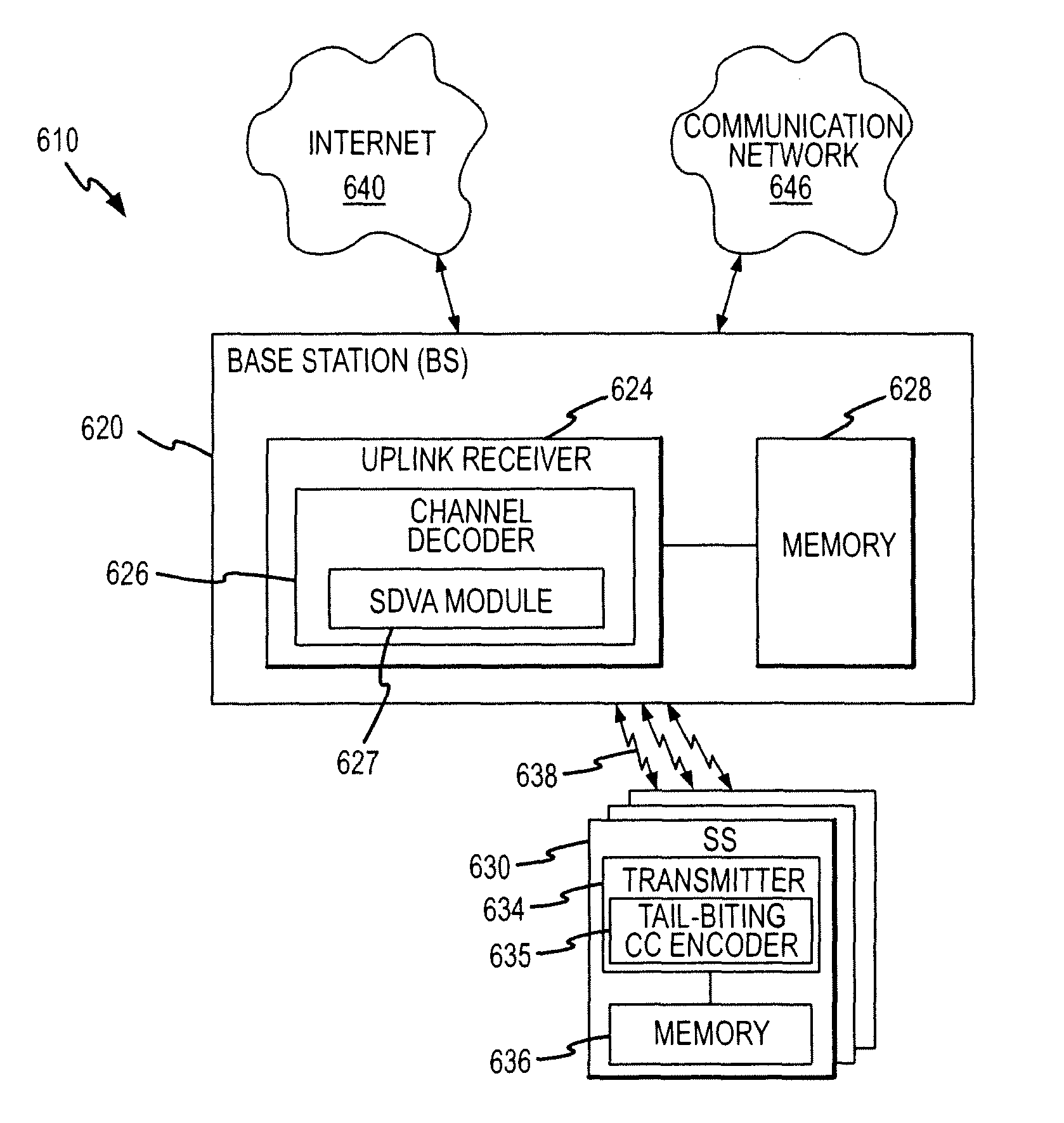
ActiveUS7856591B2Less overall consumptionReduce complexityData representation error detection/correctionError preventionTail-bitingComputer science
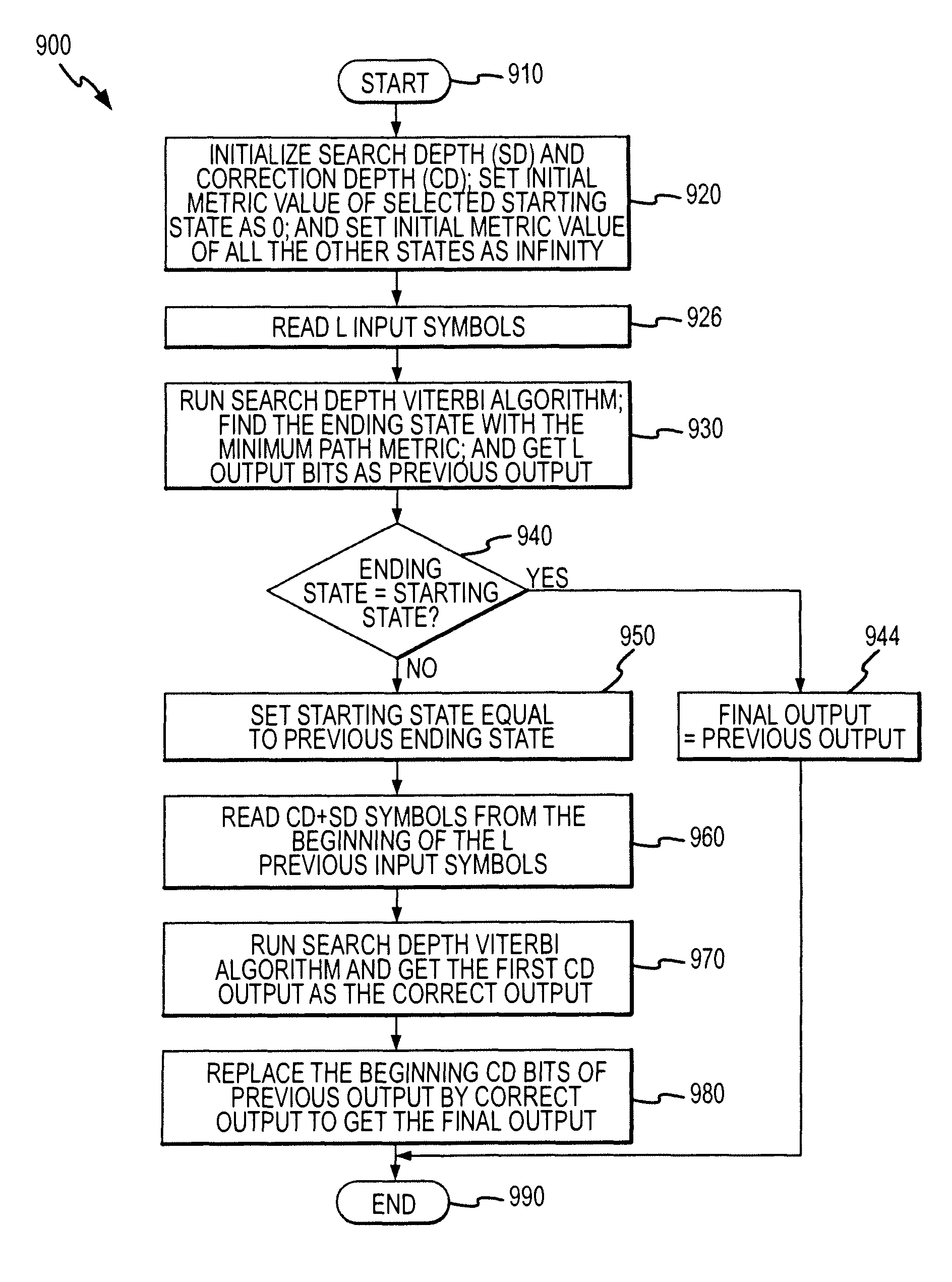
A method for decoding tail-biting convolutional codes. The method includes initializing a correction depth, selecting a first starting state from a set of encoding states, and initializing a metric value for the selected starting state as zero and the other states as infinity. The input bit stream is read and a Search Depth Viterbi algorithm (SDVA) is performed to determine path metrics and identify a minimum-metric path. The ending state for the minimum-metric path is determined and the output for this ending state is identified as “previous output.” A second starting state is set to the ending state of the minimum-metric path, and symbols equal to the correction depth from the previous output are read. The SDVA is performed on the second set of read symbols to generate a corrected output. A decoded output is generated by replacing symbols at the beginning of the previous output with the corrected output.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS BEIJING R& D
Interpretation method and apparatus for tail-biting convolutional code
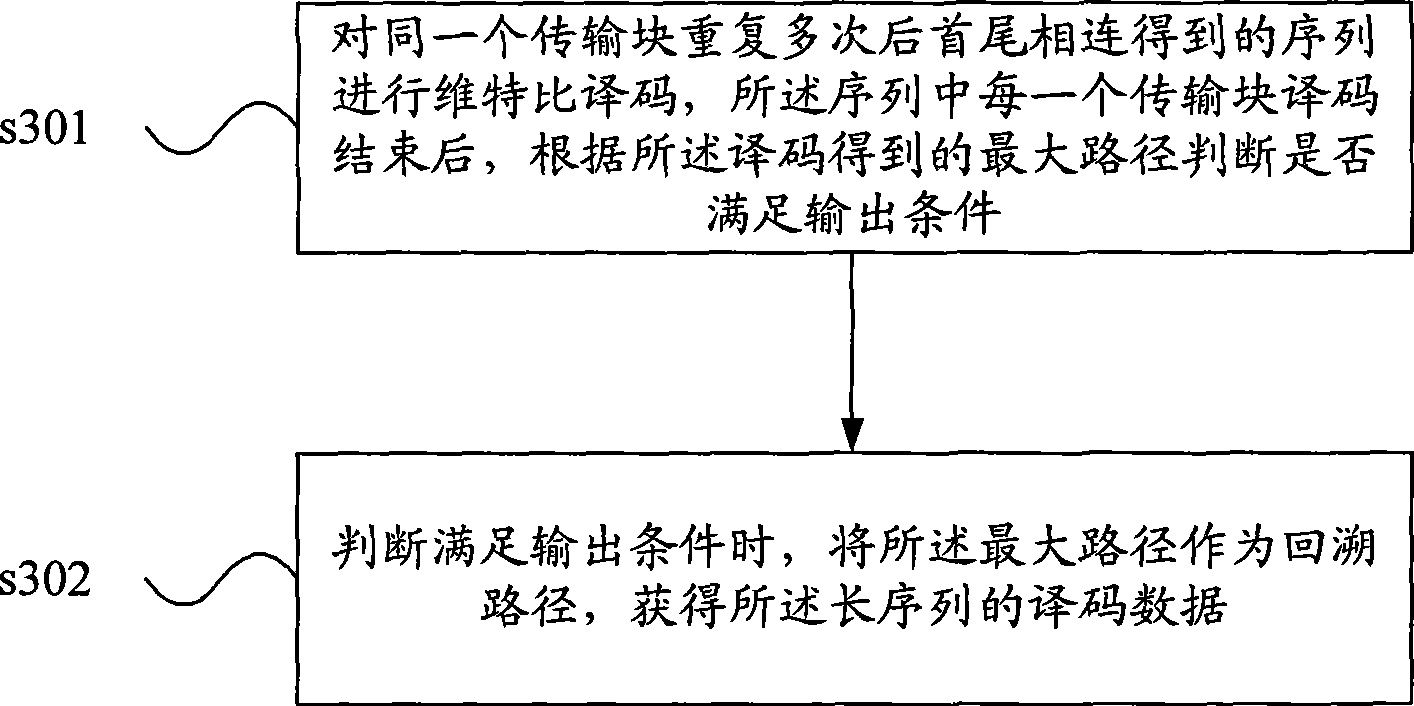
InactiveCN101369817ACorrectly decoded outputSave calculationError correction/detection using convolutional codesTail-bitingEmbedded system
Embodiment of the present invention discloses a decoding method and apparatus for tail-biting convolution code. The method includes the steps of implementing Viterbi decode to a sequence obtained by repeating a transmission block end-to-end for multiple times, wherein after decoding each transmission block of the sequence, judging whether meeting output condition based on a maximum path obtained by the decode; when meeting output condition, outputting decode data of the sequence using the maximum path as backtracking path. In the embodiment of the invention, judging the Viterbi decode of a long sequence obtained by linking a plurality of transmission blocks based on the head end status of the maximum path, when meeting presetting output condition, a decode data can be obtained directly without calculating all transmission blocks, thus it is able to obtain right decode output using less transmission blocks, and computational complexity and decode time delay are all saved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Decoding processing method and decoder
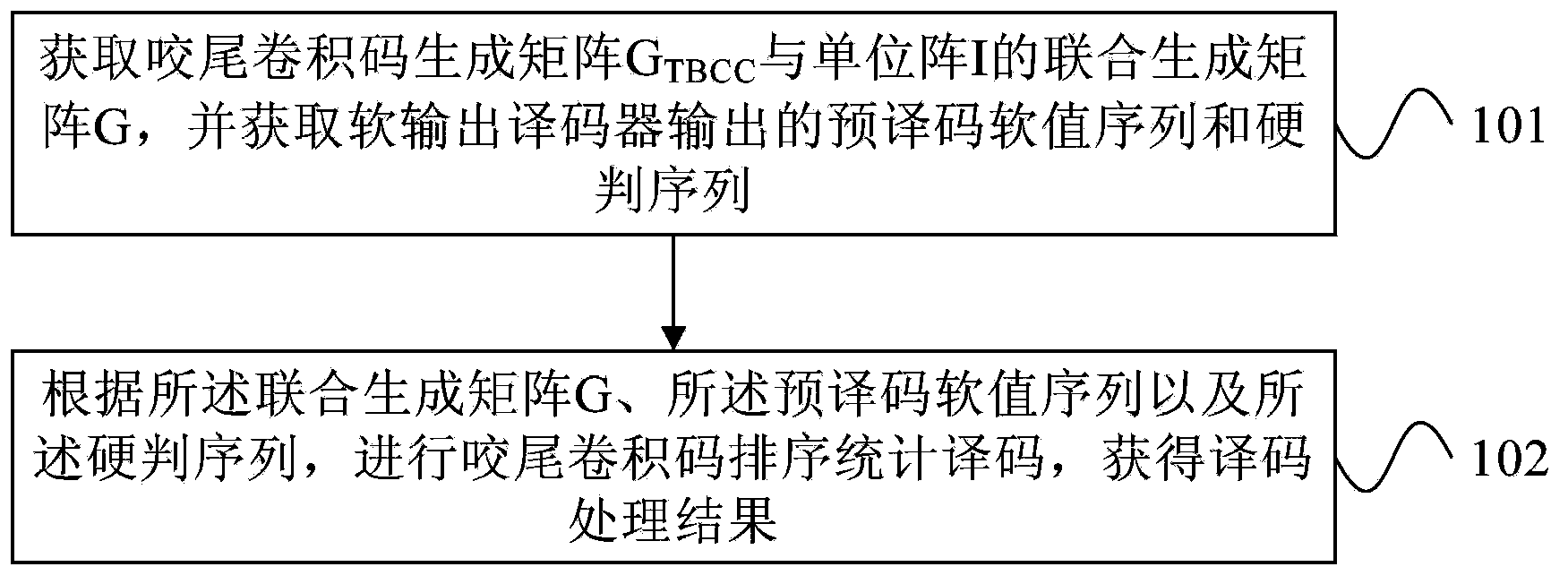
ActiveCN104242957AImprove decoding performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesTail-bitingConvolution
The embodiment of the invention provides a decoding processing method and a decoder. The method comprises the steps that union generator matrixes G of tail biting convolution code generator matrixes GTBCC and unit matrixes I are obtained, and pre-decoding soft value sequences and hard judgment sequences output by the soft output decoder are obtained; according to the union generator matrixes G, the pre-decoding soft value sequences and the hard judgment sequences, sorting statistics and decoding are carried out on tail biting convolution codes, and decoding processing results are obtained. The method can improve the decoding performance.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
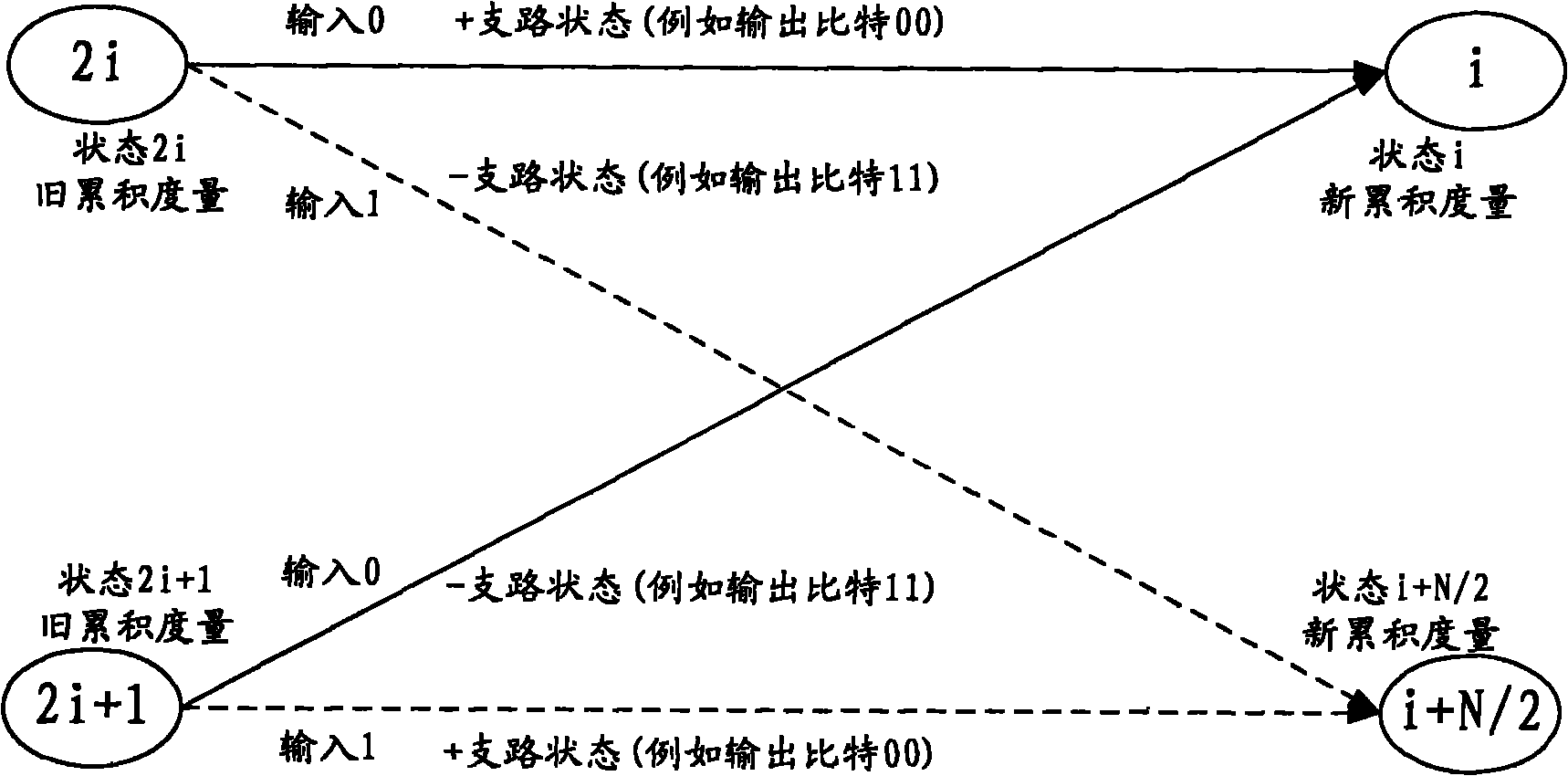
Decoding method and decoder of tail-biting convolutional code
ActiveCN102142848ASimplify decoding complexityReduce decoding costOther decoding techniquesTail-bitingComputer engineering
The invention relates to a decoding method and a decoder of a tail-biting convolutional code. The method comprises the steps of: executing a Viterbi algorithm (VA) on a sequence to be decoded, searching a preset number of accumulation measurements from obtained accumulation measurements, recalling an ending state of the sequence, and determining a reference state from obtained starting state; and determining whether a decoded sequence is directly obtained or the sequence to be decoded is subjected to executing the VA and then recalling to obtain a decoded sequence through comparing whether the ending state corresponding to the reference state is same as the reference state. The decoder comprises a VA module, a searching module, a recalling module, a state selecting module and a comparing module. The invention has the advantages of simplifying decoding complexity, reducing decoding expense and obtaining stronger decoding performance.
Owner:ZTE CORP
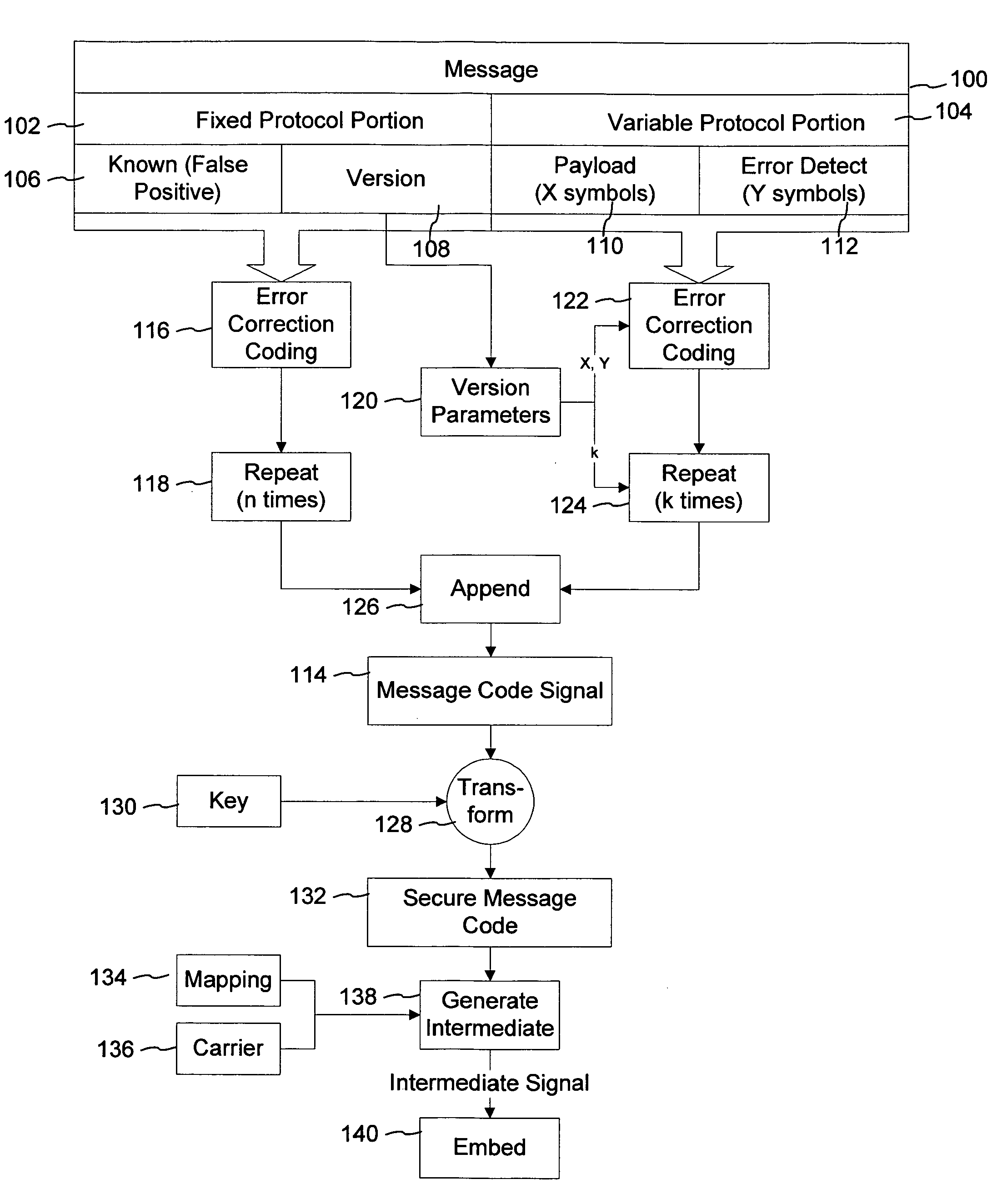
Digital watermark key generation
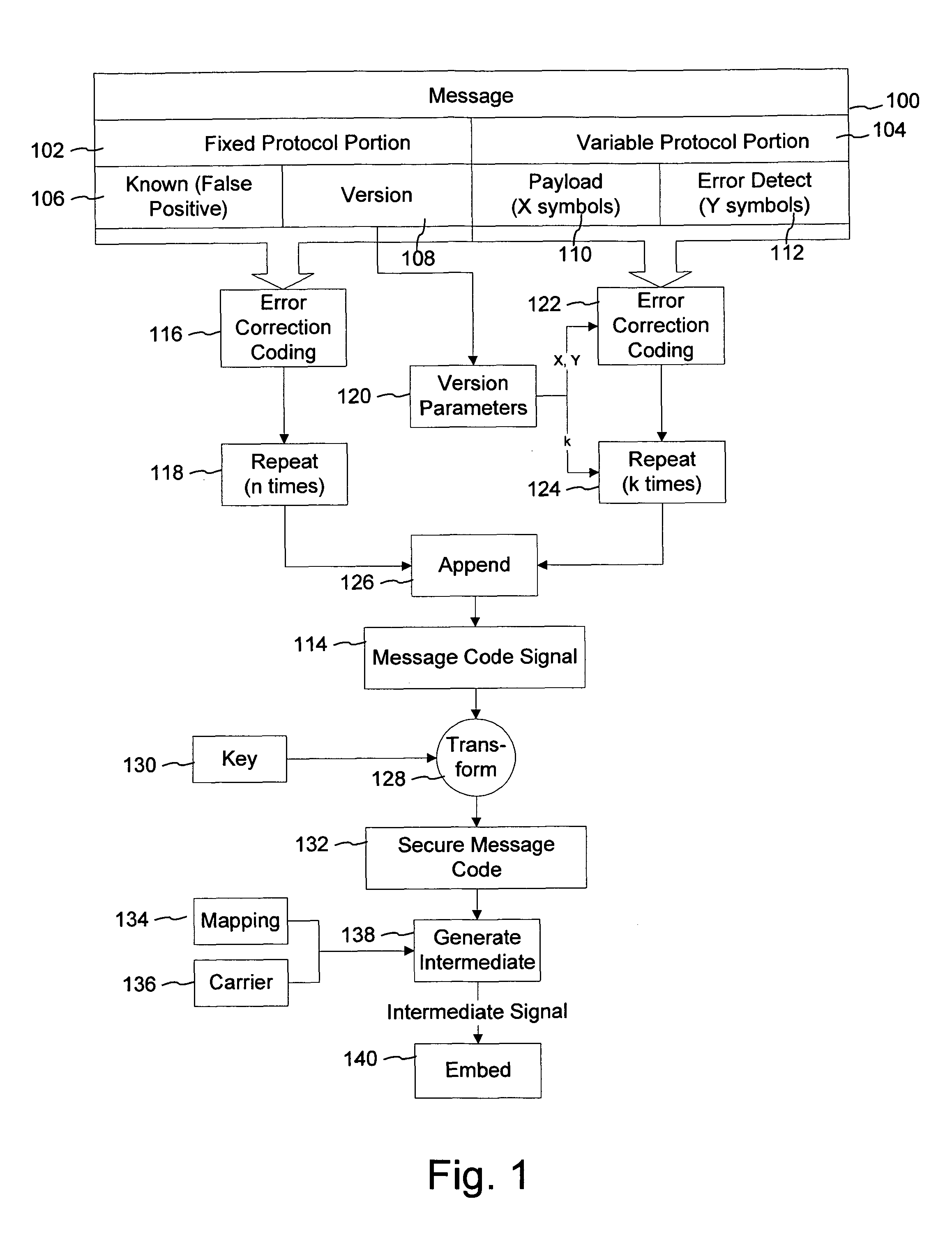
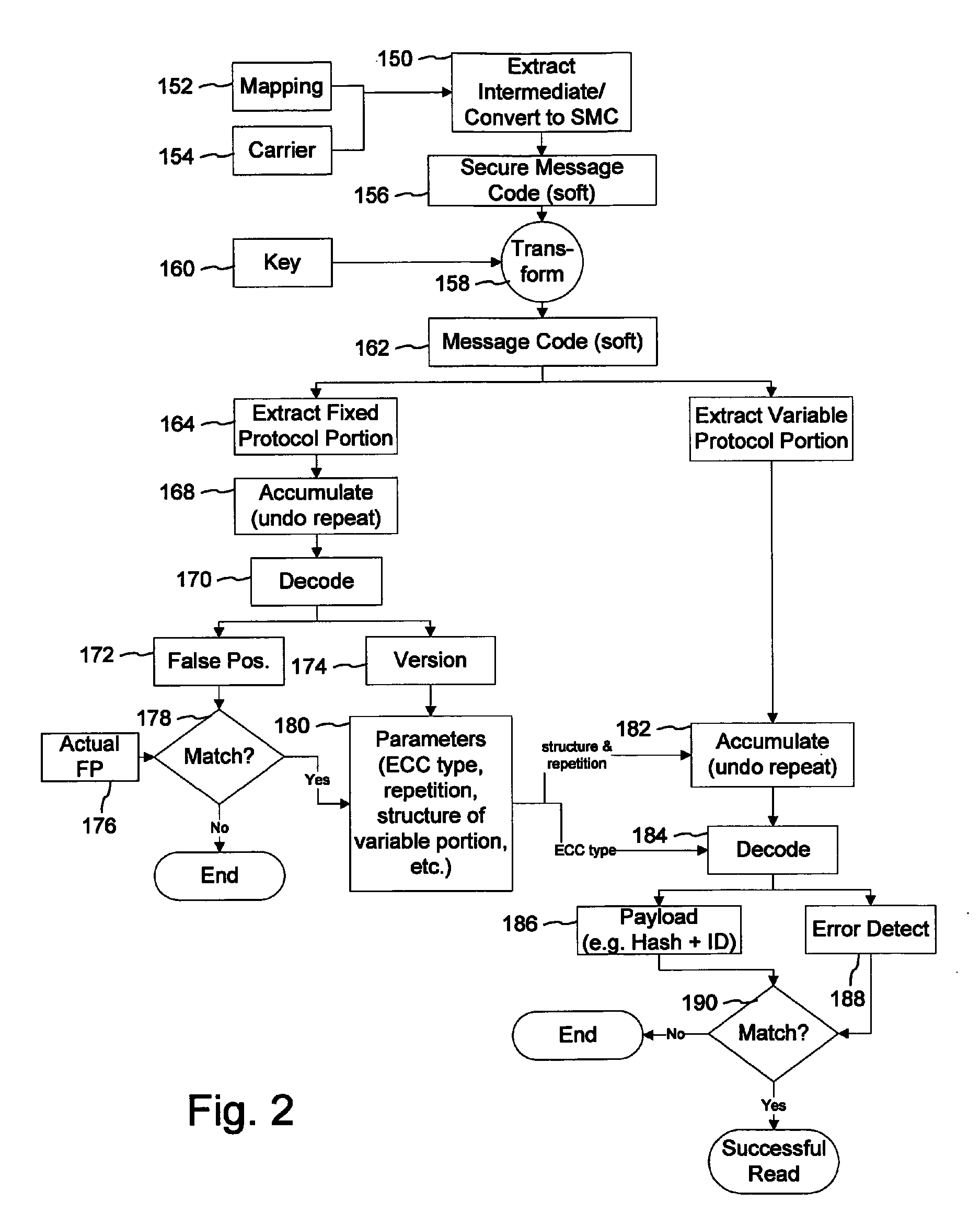
ActiveUS8140848B2User identity/authority verificationSpeech analysisComputer hardwareForward error correction
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
System and Method for Non-Uniform Bit Allocation in the Quantization of Channel State Vectors
ActiveUS20110134978A1Easy to controlEnhanced informationData representation error detection/correctionError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorChannel state informationTelecommunications
A system and method for non-uniform bit allocation in the quantization of channel state vectors is provided. A method for communications node operation includes receiving a bit-allocation profile for use in quantizing channel state information, measuring a communications channel between the communications node and a controller, generating channel state information based on the measurement, computing a bit representation of the channel state information, transmitting the bit representation to the controller, and receiving a transmission from the controller. The computing makes use of quasi-tail-biting trellis decoding, and the computing is based on the bit-allocation policy. The transmission makes use of the channel state information transmitted by the communications node.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Decoder and method for decoding a tail-biting convolutional encoded signal using viterbi decoding scheme
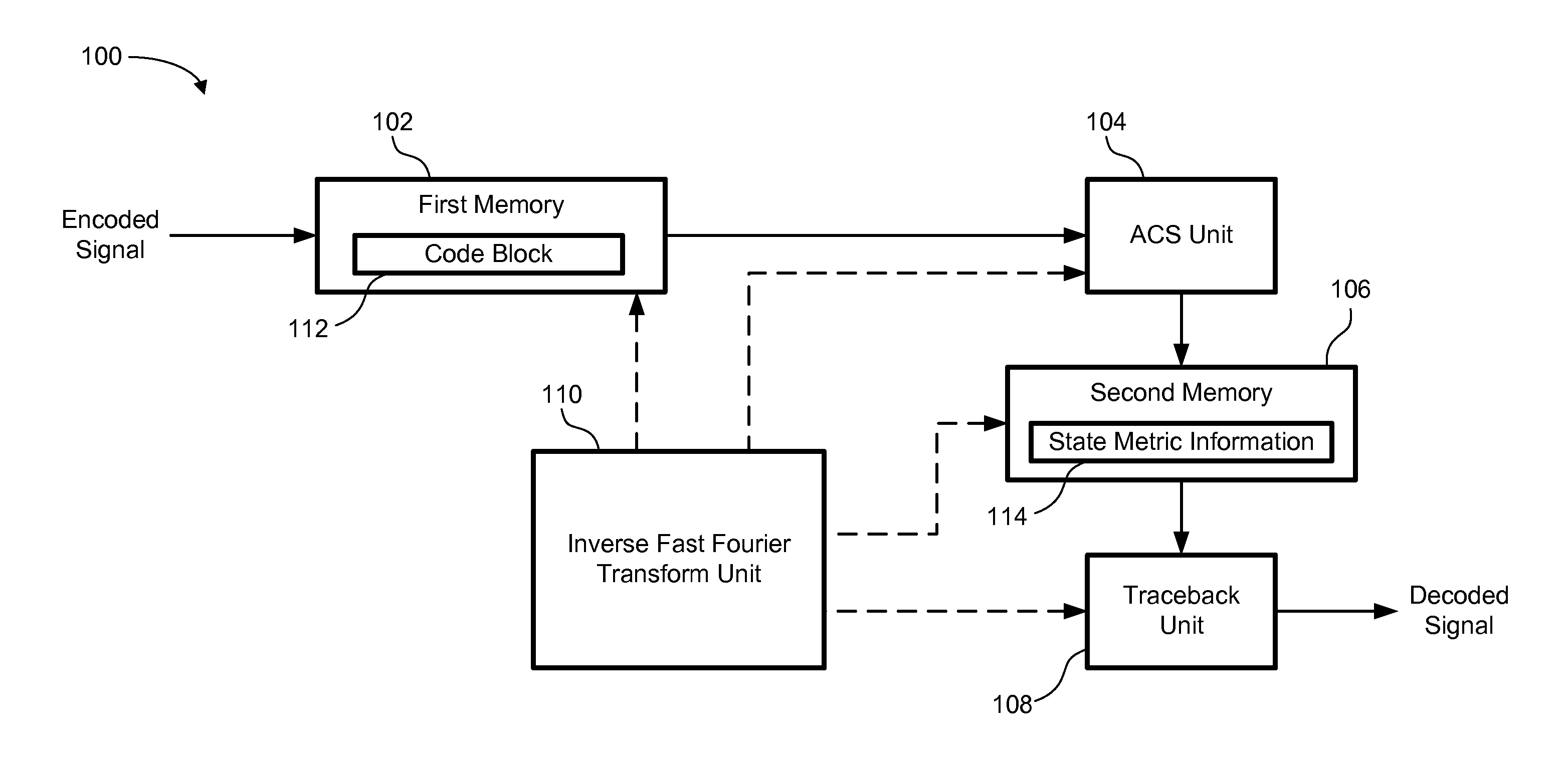
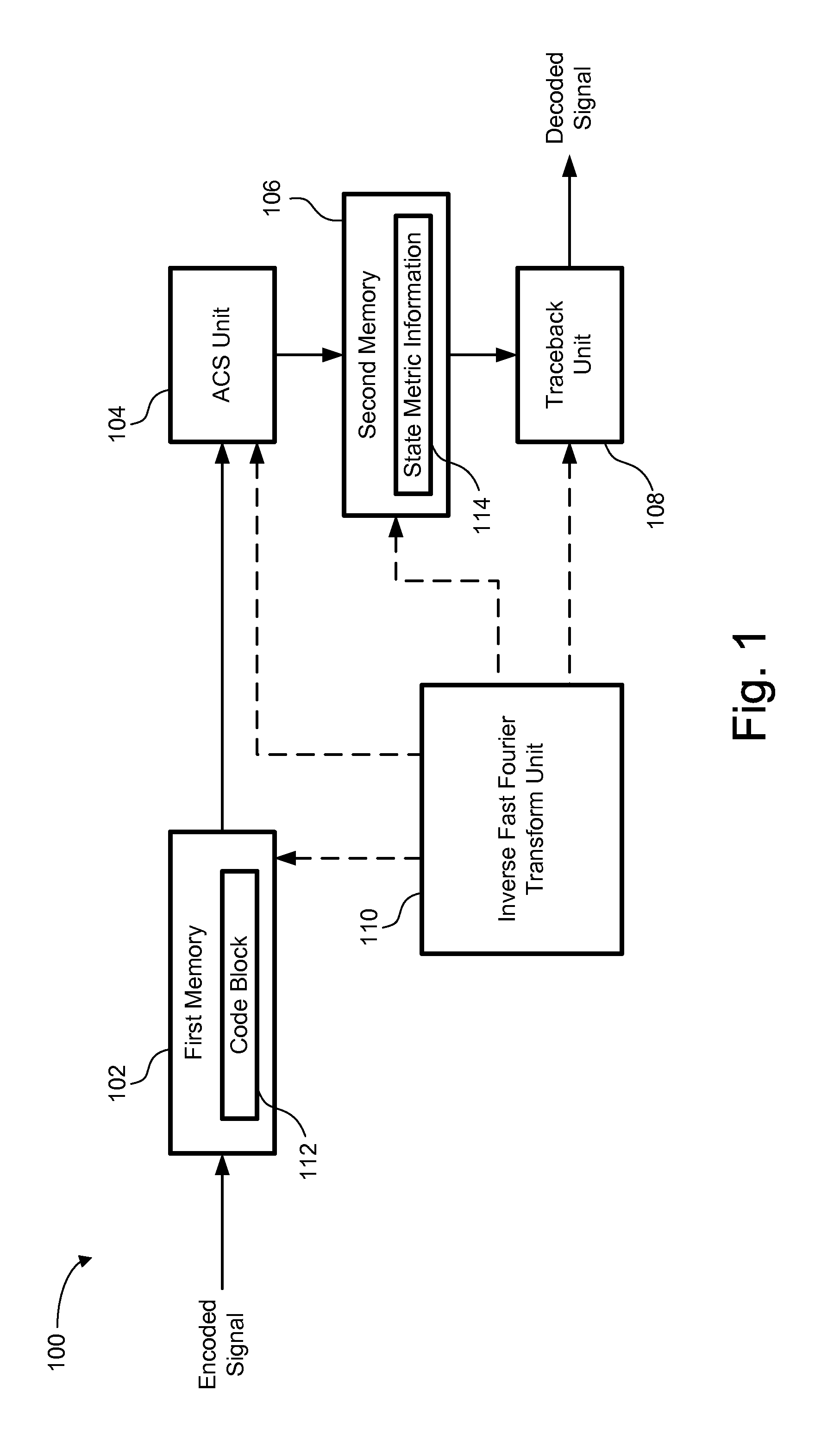
ActiveUS20070174757A1Facilitate decodingRequired memory for storing state metric information can be significantly reducedData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionComputer hardwareCoding block
A decoder and method for decoding a tail-biting convolutional encoded signal using Viterbi decoding scheme performs a traceback operation for a first portion of a total code block, which includes a code block of the tail-biting convolutional encoded signal and a padded block. During the traceback operation for the first portion, a particular state at a predefined position within the first portion is stored as a circular state. The circular state is used as a traceback starting state for at least one subsequent portion of the total code block to produce a decoded signal of the code block.
Owner:SOLID
Tail-biting convolutional code decoding checking method and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN102624404AReduce overheadNo decoding performance degradationError correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionLog likelihoodTail-biting
The invention discloses a tail-biting convolutional code decoding checking method and an apparatus thereof. The method and the apparatus are used to solve a current problem of reducing tail-biting convolutional code decoding checking processing time delay. The structure characteristic of the tail-biting convolutional code is fully used. A log-likelihood ratio (LLR) input to a decoder is reordered. Through reforming and deriving a generator polynomial of the convolutional code, the decoder can perform serial output according to a positive sequence of an information bit during a backtracking process. Thus, a first bit of an information sequence can be firstly decoded successfully, which can start cyclic redundancy check (CRC) verification as soon as possible so that parts of the backtracking process and the CRC verification can be executed in parallel. Therefore, a purpose of reducing the tail-biting convolutional code decoding checking processing time delay can be achieved. According to the invention, hardware cost is not increased; improvement can be achieved with low cost and degradation of any decoding performance can not be caused.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
Decoding method for tail-biting convolutional codes using a search depth viterbi algorithm
ActiveUS20070245209A1Reduce complexitySave memoryData representation error detection/correctionError preventionTail-bitingComputer science
A method for decoding tail-biting convolutional codes. The method includes initializing a correction depth, selecting a first starting state from a set of encoding states, and initializing a metric value for the selected starting state as zero and the other states as infinity. The input bit stream is read and a Search Depth Viterbi algorithm (SDVA) is performed to determine path metrics and identify a minimum-metric path. The ending state for the minimum-metric path is determined and the output for this ending state is identified as “previous output.” A second starting state is set to the ending state of the minimum-metric path, and symbols equal to the correction depth from the previous output are read. The SDVA is performed on the second set of read symbols to generate a corrected output. A decoded output is generated by replacing symbols at the beginning of the previous output with the corrected output.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS BEIJING R& D
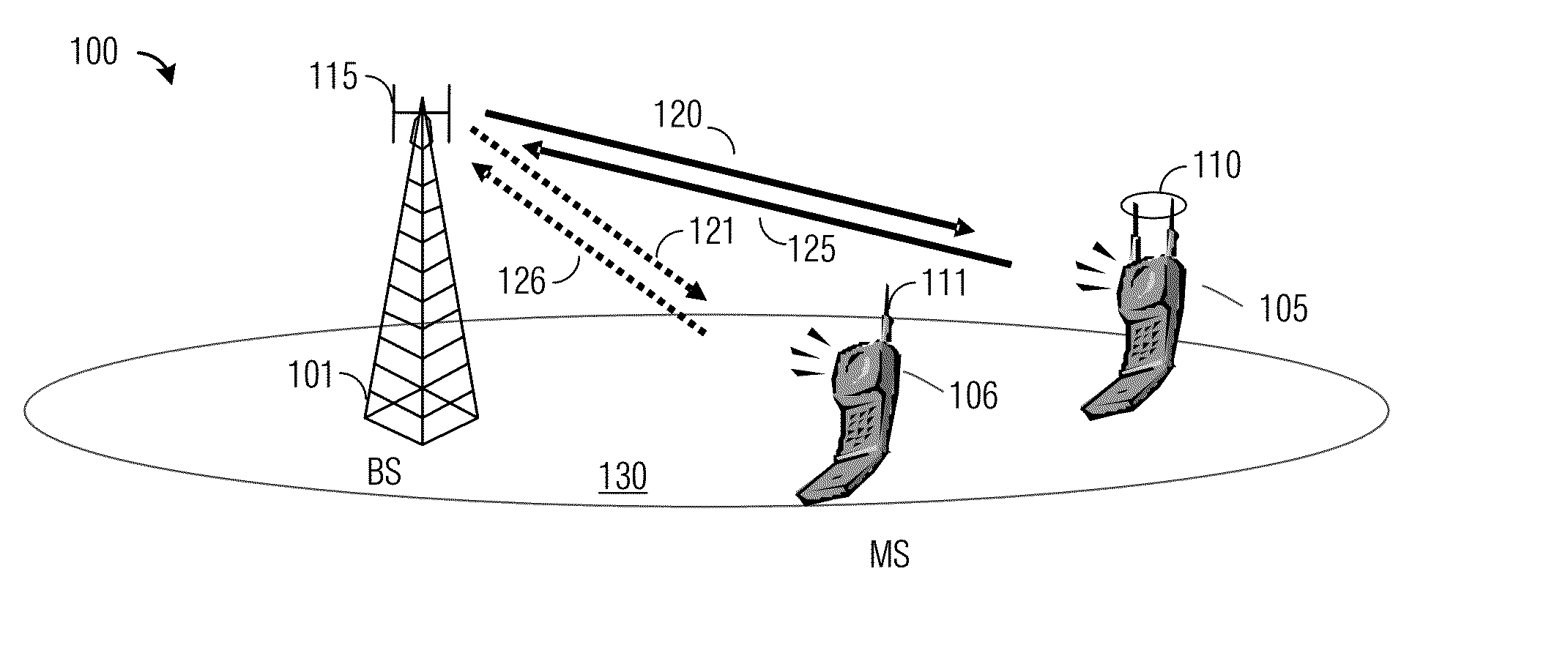
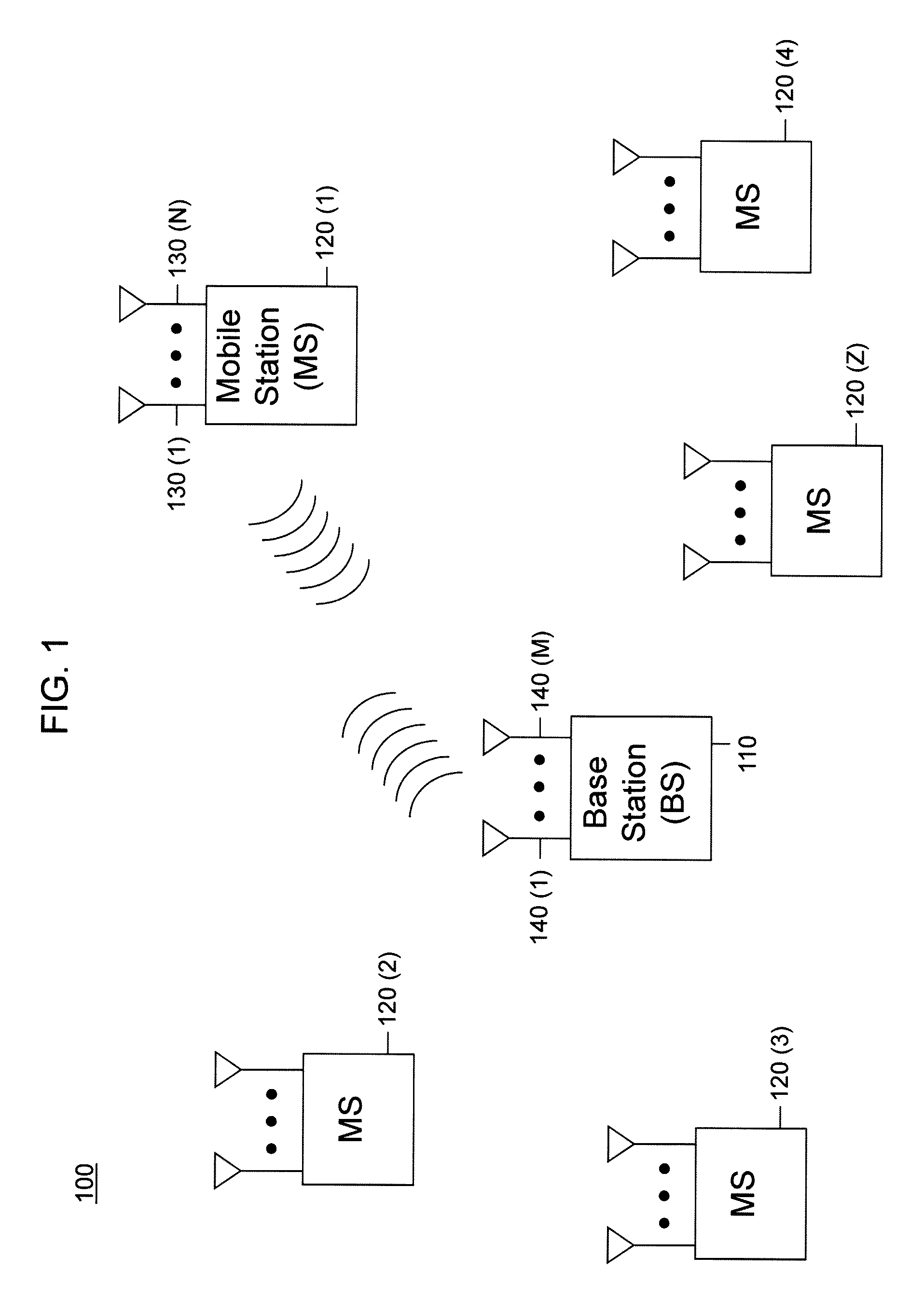
Increasing capacity in wireless communications
ActiveCN102668612APower managementSignalling characterisationTelecommunications linkCommunications system
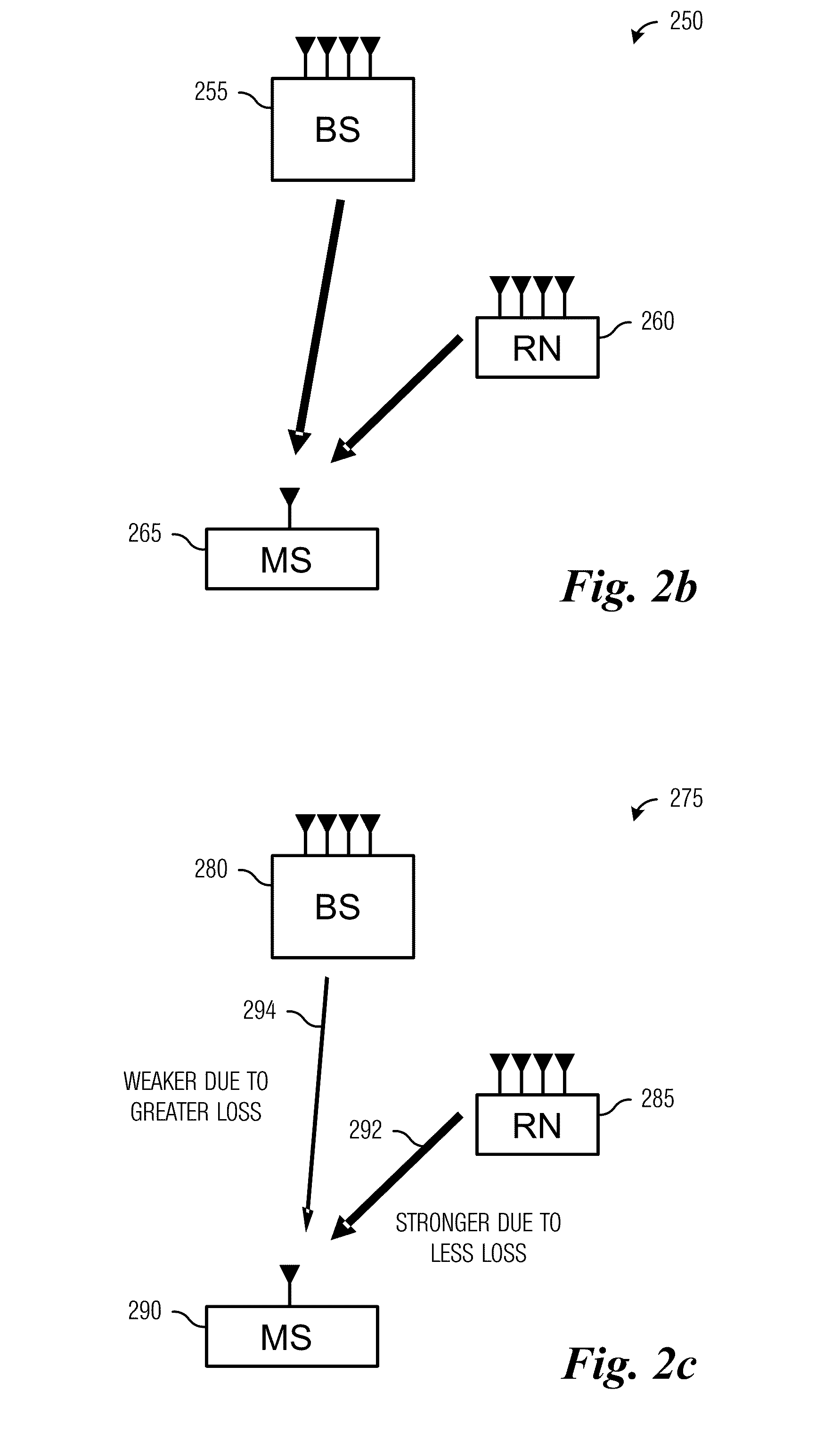
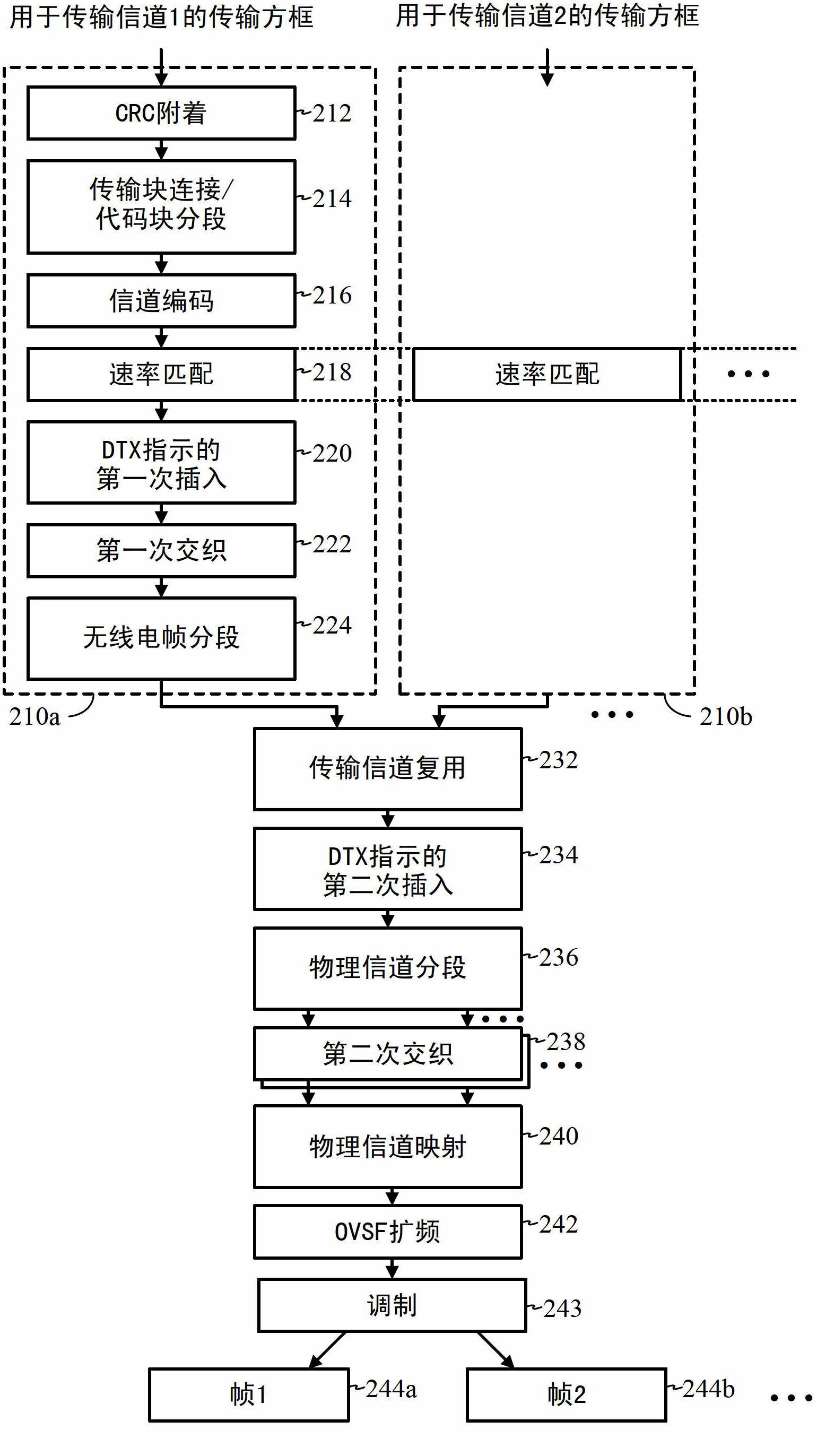
Techniques to increase the capacity of a W-CDMA wireless communications system. In an exemplary embodiment, early termination (400) of one or more transport channels on a W-CDMA wireless communications link is provided. In particular, early decoding (421, 423) is performed on slots as they are received over the air, and techniques are described for signaling (431, 432) acknowledgment messages (ACK's) for one or more transport channels correctly decoded to terminate the transmission of those transport channels. The techniques may be applied to the transmission of voice signals using the adaptive multi-rate (AMR) codec. Further exemplary embodiments describe aspects to reduce the transmission power and rate of power control commands sent over the air, as well as aspects for applying tail-biting convolutional codes (1015) in the system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and device for decoding tail-biting convolutional codes
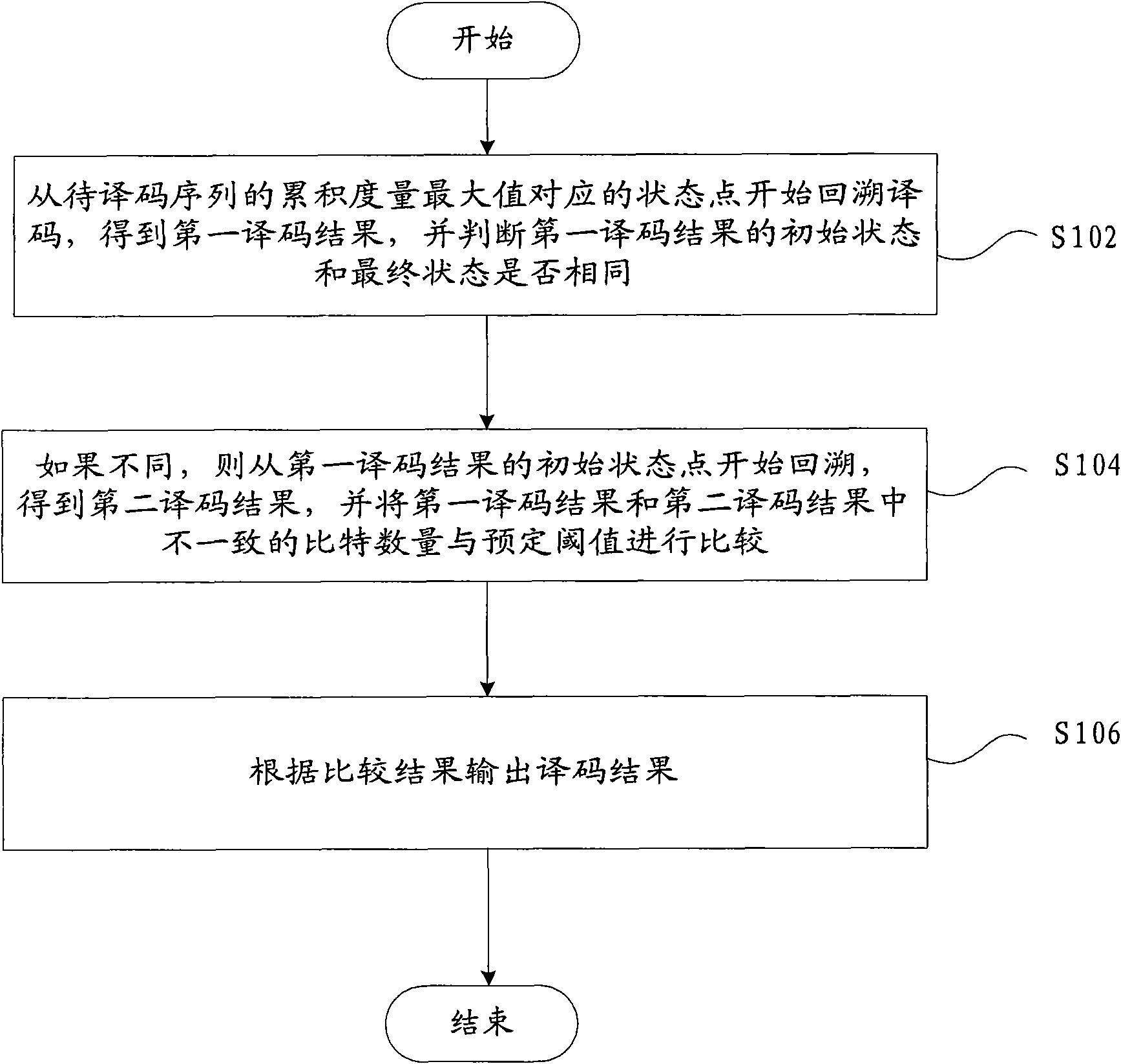
ActiveCN101969308AAvoid technical problems with high bit error rateReduce decoding error rateError correction/detection using convolutional codesTail-bitingComputer science
The invention discloses a method for decoding tail-biting convolutional codes, which comprises the following steps: carrying out backtracking decoding from a state point corresponding to the maximum cumulative metric of a code sequence to be decoded so as to obtain a first decoding result, and judging whether the initial state and final state of the first decoding result are same; if not, carrying out backtracking decoding from the initial state point of the first decoding result so as to obtain a second decoding result, and comparing the inconsistent bit quantity in the first decoding resultand the second decoding result with a preset threshold; and outputting a decoding result according to the comparison result. The method and the device of the invention solve the technical problem of large bit error rate caused by weak channel environment, thereby achieving the purpose of reducing the bit error rate of decoding.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
Method for decoding tail biting convolution codes of PBCH (physical broadcast channel) decoding in LTE (long term evolution)
InactiveCN102904667ASimplified methodSimple structureError preventionDecoding methodsBroadcast channels
The invention discloses a method for decoding tail biting convolution codes of PBCH (physical broadcast channel) decoding in LTE (long term evolution). A tail biting convolution decoder starts computing path metric from the starting position of a CRC (cyclic redundancy check) field, and a start state for computation of the path metric is zero constantly, and the computation of the path metric is separated into two situations: when SFN (system frame number) in an MIB (master information block) is unknown, computation of the path metric is ended at the sixth bit of a Spare bit field, a starting state of tracing back is zero, thirty-six decoding results are generated by the tail biting convolution decoder, and a PBCH decoding result finally with forty bits is formed by adding four '0' at the tail end of the thirty-six decoding results; when the SFN in the MIB is given, computation of the path metric is ended at the sixth bit of an SFN bit field, a starting state of tracing back is determined by the first six bits in the SFN field, twenty-eight decoding results are generated by the tail biting convolution decoder, and the PBCH decoding result finally with forty bits is formed by adding the last two bits of the SFN and ten '0' at the tail end of the twenty-eight decoding results.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
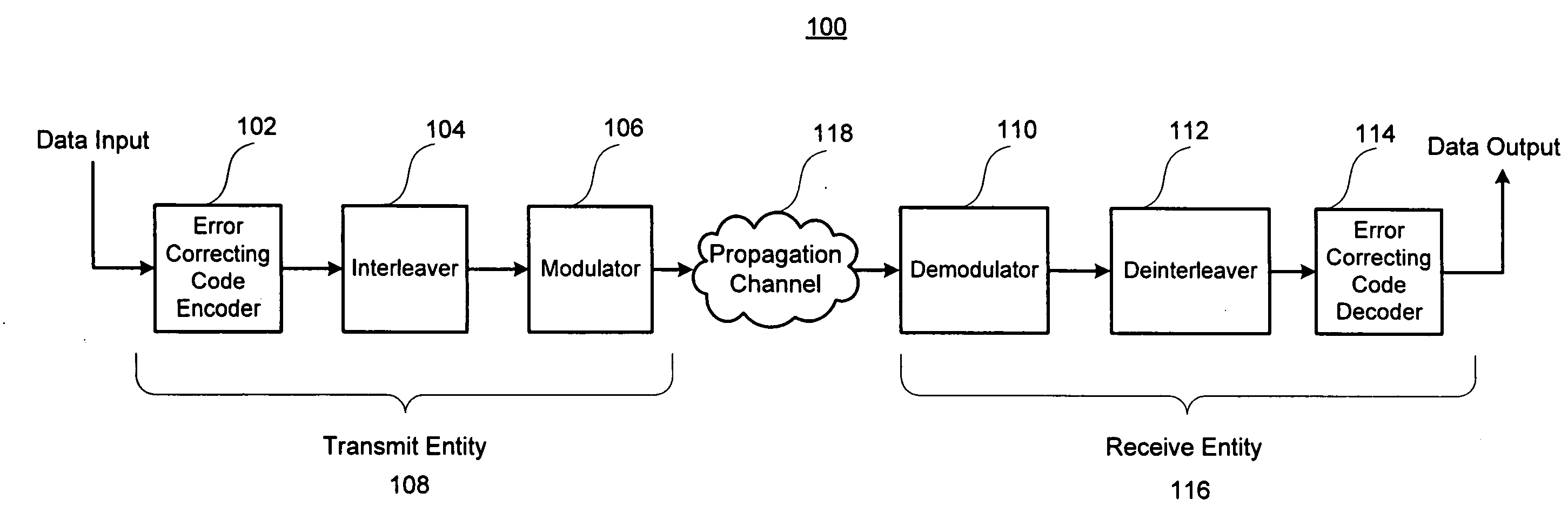
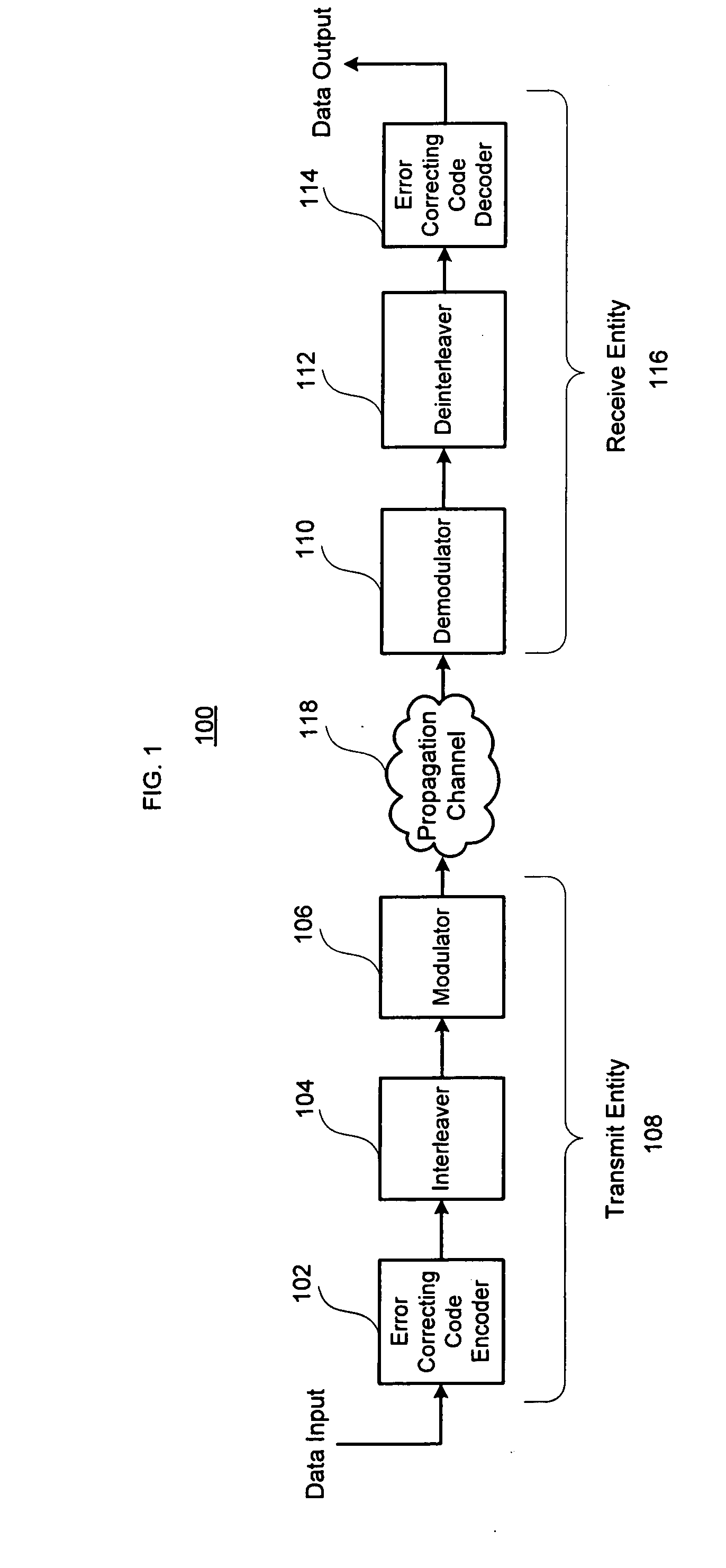
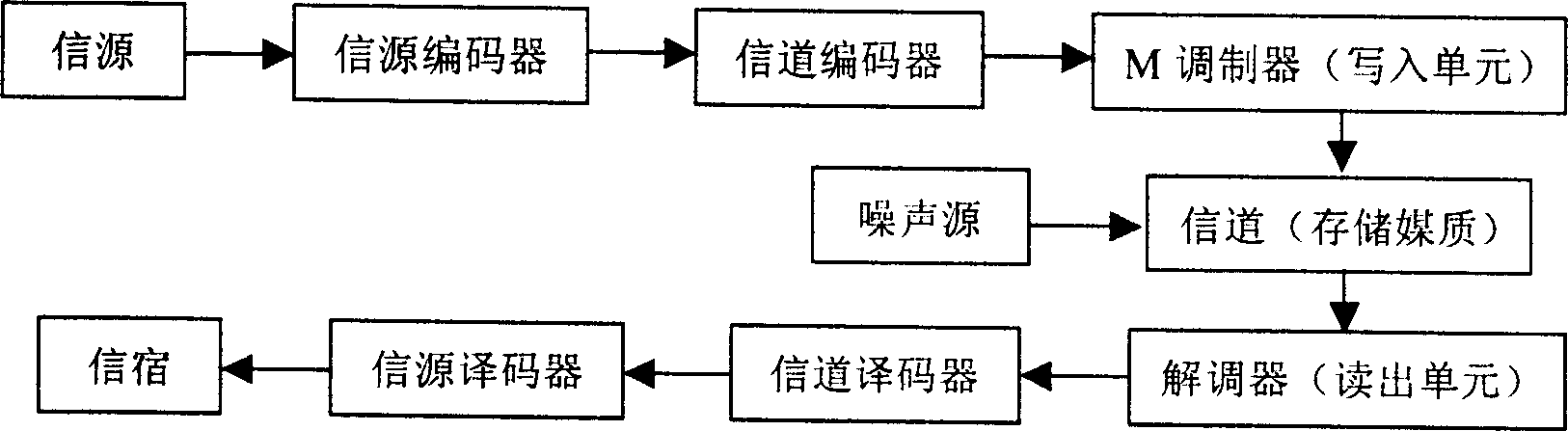
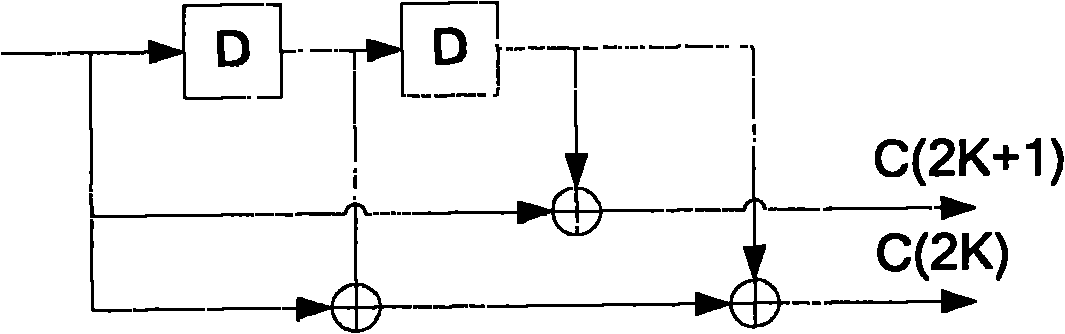
Digital communications system
InactiveUS20080310544A1Modulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionTime errorCommunications system
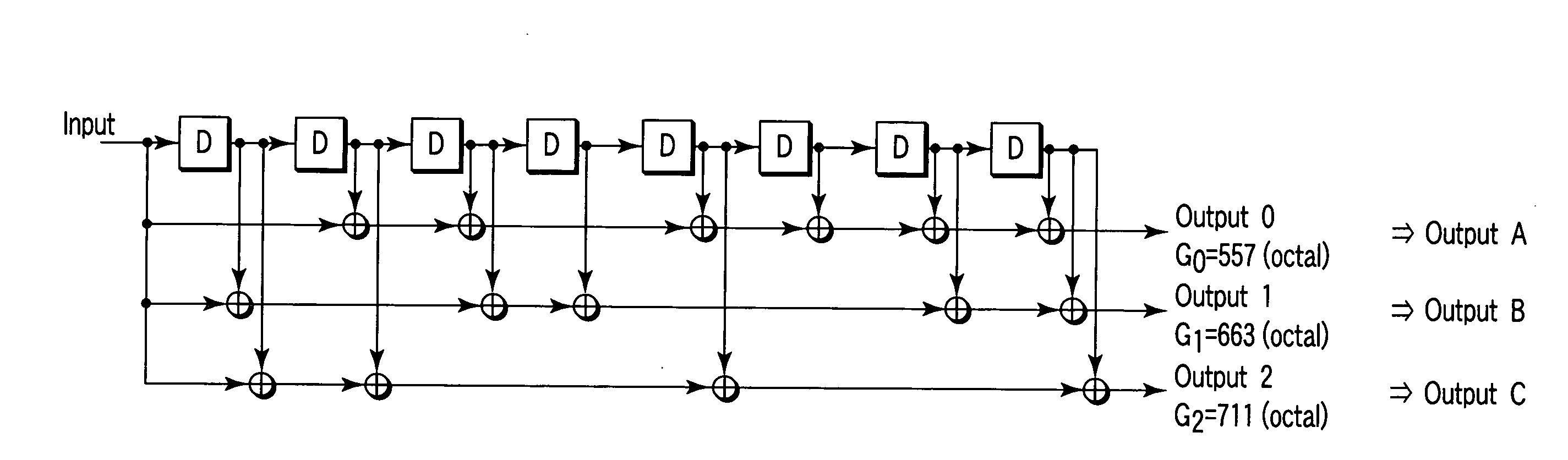
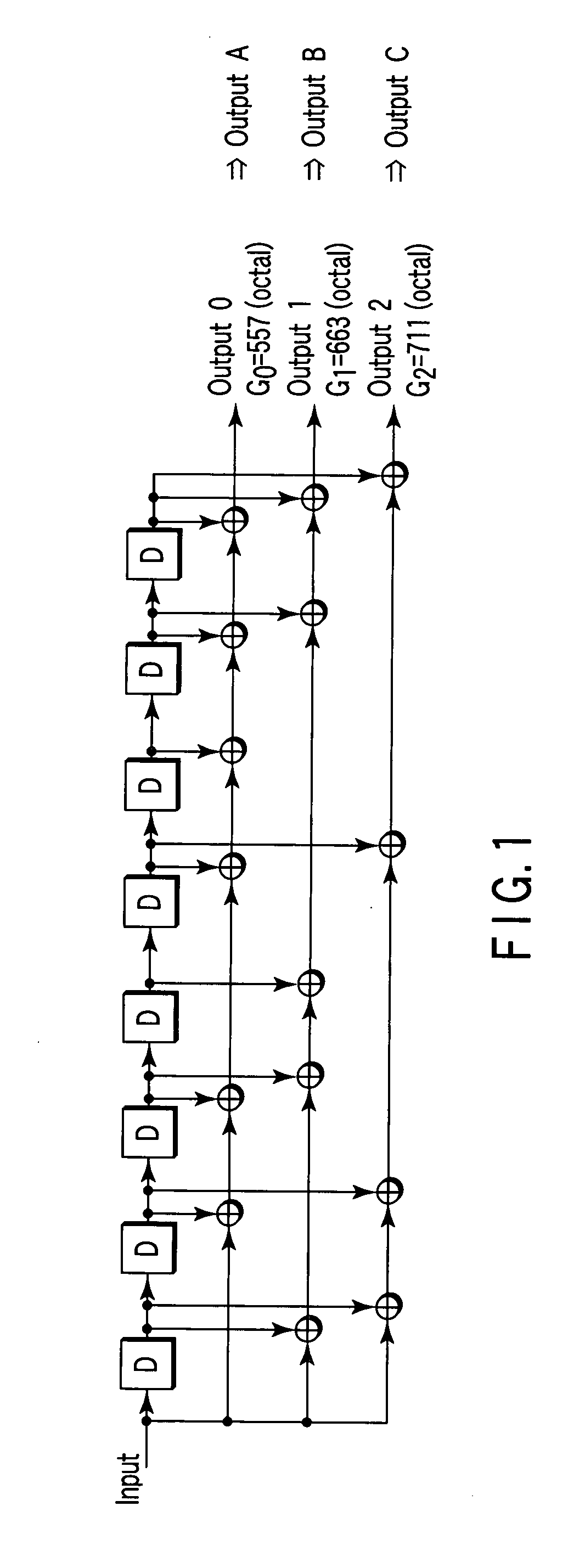
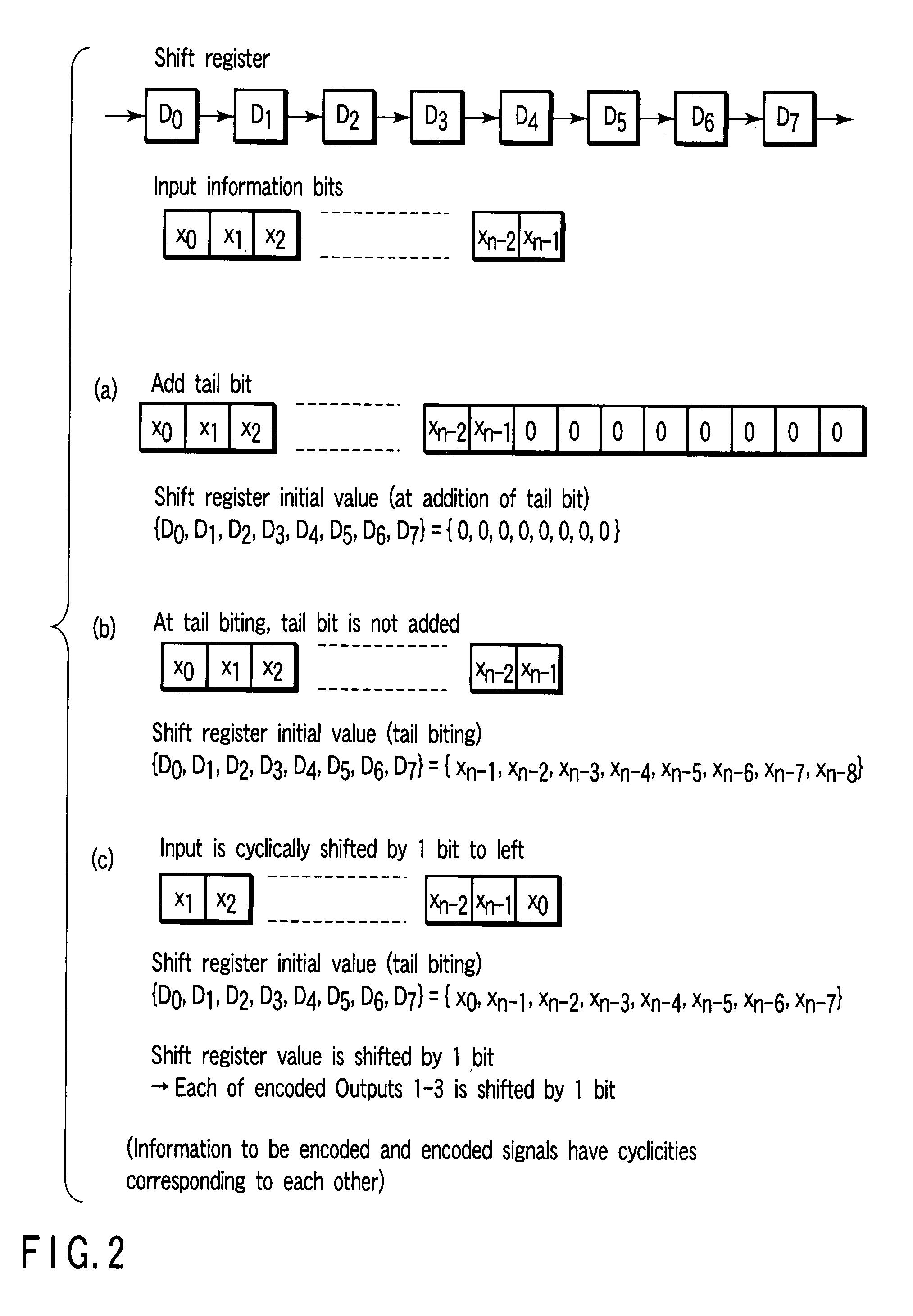
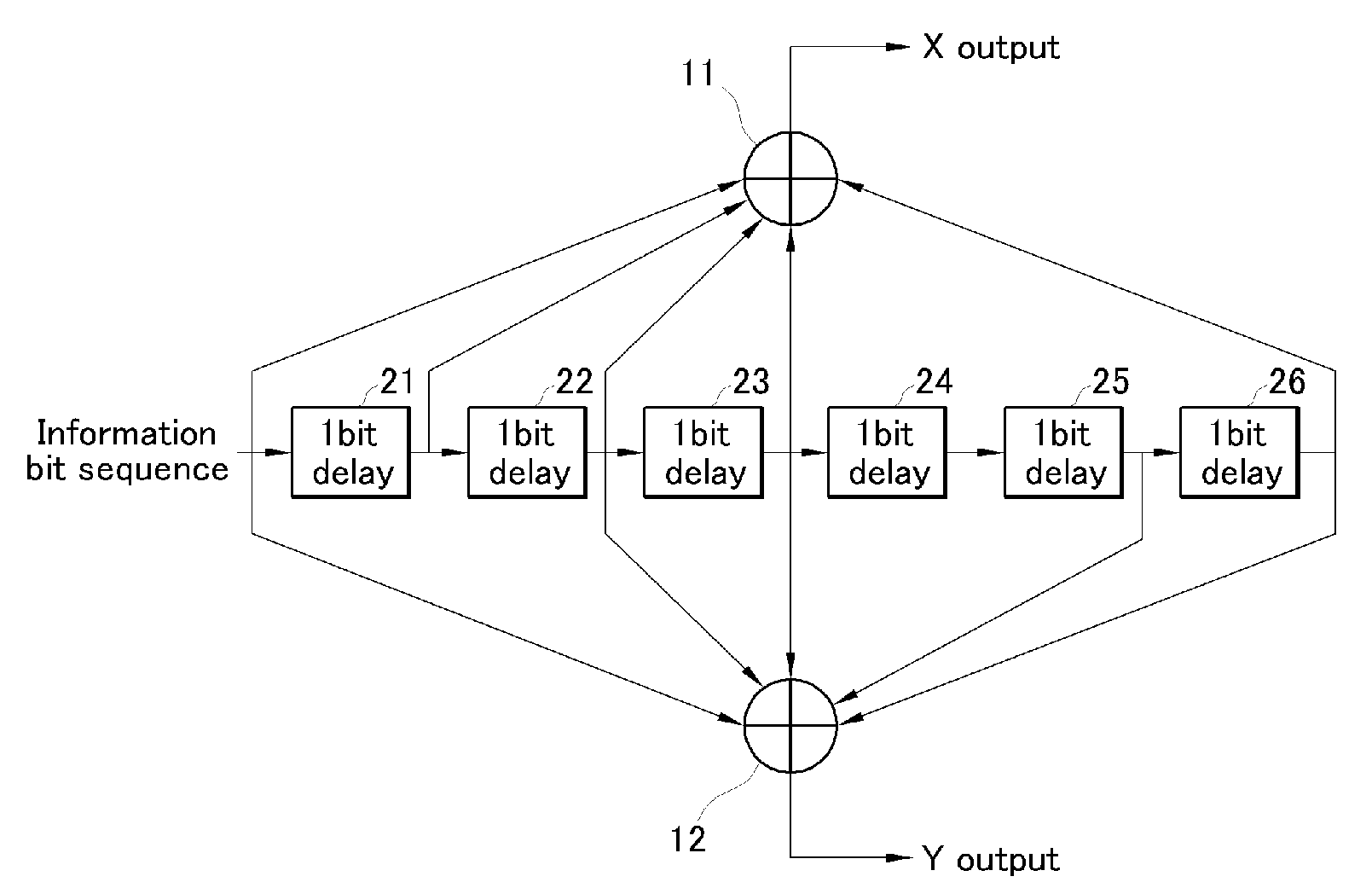
In a base station, after CRC is added to transmission data as a detection code, the transmission data is subjected to error-correcting coding using a convolutional code based on tail biting, divided into four frames of P-BCH and transmitted. For this reason, at a mobile station, even if reception (synthesis) is started from any frame of P-BCH represented as (b-1) to (b-4), a cyclic structure of the transmission signal is maintained due to the tail biting and reception data shifted by unit of frame can be obtained. For this reason, at the mobile station, even if a leading frame is unknown, decoding can be executed by one-time error-correcting decoding. A result of the decoding is subjected to CRC detection in four frame timings, the leading frame is detected and the transmission data is restored.
Owner:FUJITSU TOSHIBA MOBILE COMM LTD
Viterbi Decoder and Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080250303A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionViterbi decoderTail-biting
The present invention relates to a decoder for tail-biting convolution codes and a method thereof. The decoder receives an encoding bit sequence in a convolutional encoding method from a channel, generates an expanded encoding bit sequence, Viterbi decodes the expanded encoding bit sequence, and generates decoded data. In addition, the decoder selects a central bit sequence of the decoded data, rearranges the central bit sequence, and generates final decoded data. Accordingly, the decoder has a simplified configuration for decoding the bit sequence encoded in the tail biting convolutional encoding method, and the decoder also decodes a bit sequence encoded in a zero-tail convolutional encoding method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +4
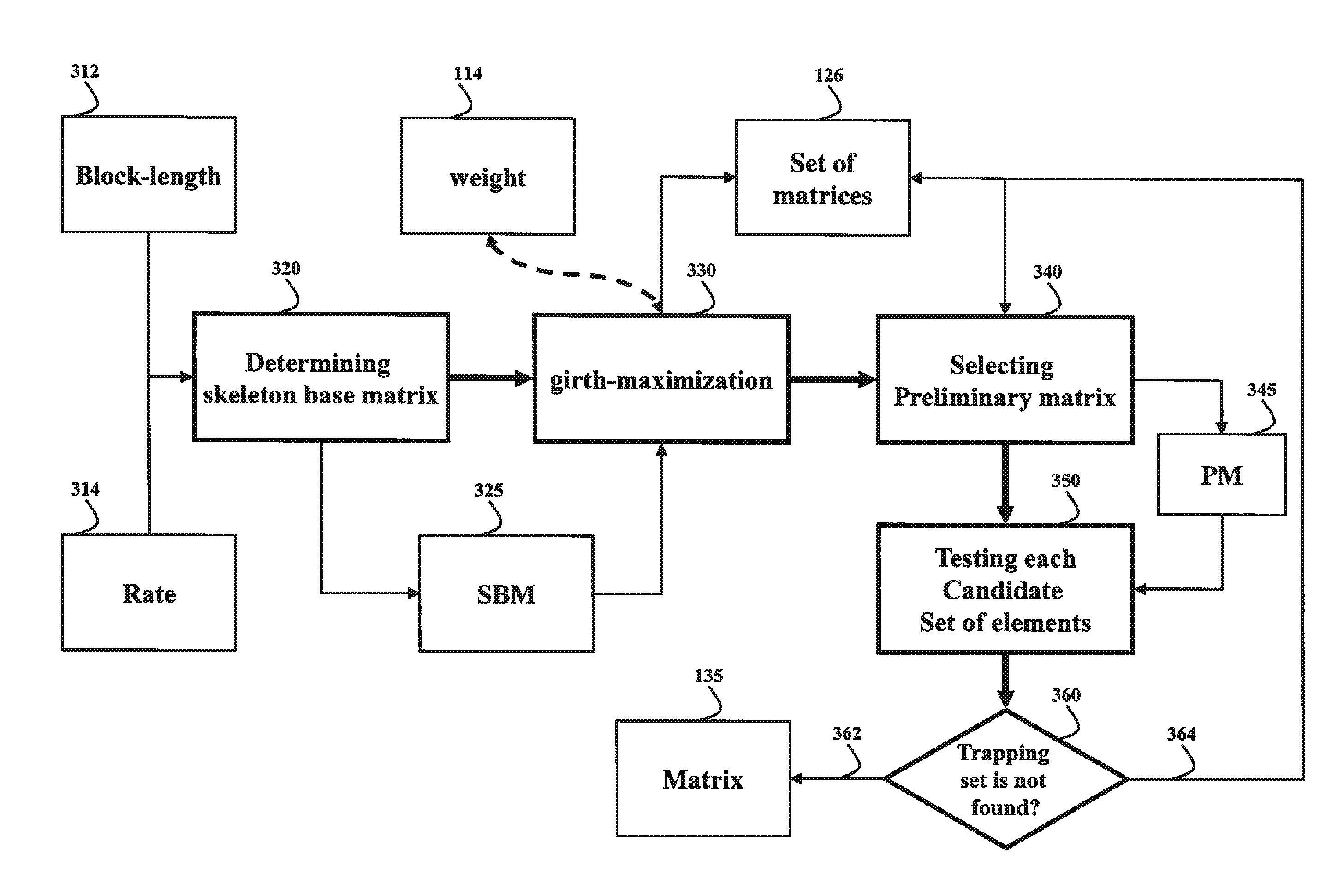
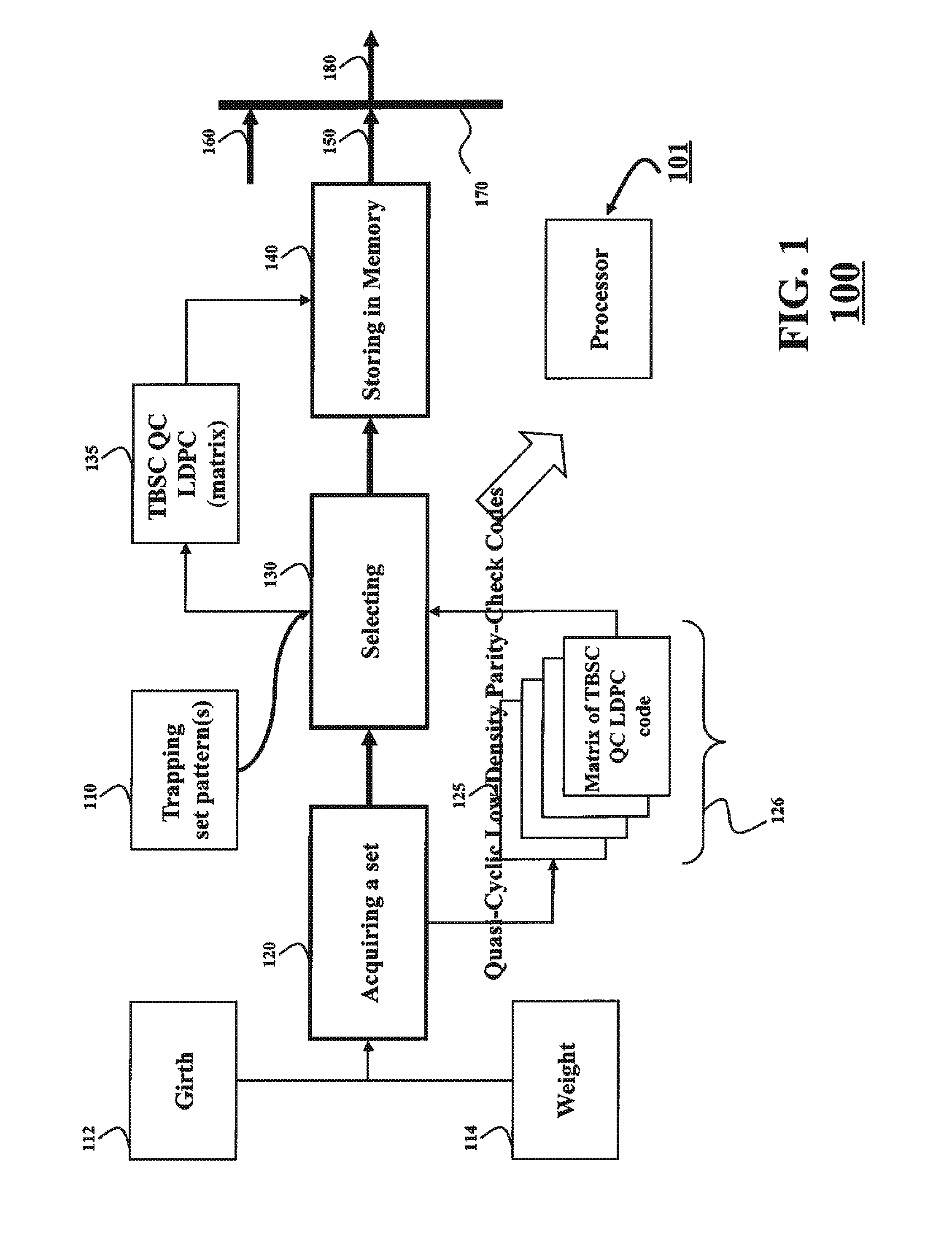
Quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check codes
ActiveUS8595589B2Improve performanceAvoid mistakesCode conversionCoding detailsTheoretical computer scienceLow density
A system and a method for determining a quasi-cyclic (QC) low-density parity-check (LDPC) code, such that the QC LDPC code has no trapping sets are disclosed. A set of matrices representing a family of QC LDPC codes are acquired, wherein each QC LDPC code is a tail-biting spatially-coupled code of girth not less than eight, and wherein each column of each matrix in the set has a weight not less than four. Based on a trapping set pattern, a matrix from the set of matrices is selected such that the matrix represents the QC LDPC code with no trapping sets. The matrix can be stored into a memory.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Tail-biting convolutional decoder and decoding method
InactiveUS20130124947A1Reduce implementation complexityReduce error rateError correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionData streamParallel computing
Techniques are provided for decoding tail-biting convolutional codes by using information within the received data stream that traditionally has not been used or been available to the convolutional decoder, e.g., cyclic redundancy check (CRC) and bit information known by both the transmitter and receiver. Further, a single parallel trace-back is used that reduces implementation complexity. In addition, the least reliable decisions made during forward processing may be reversed in order to generate additional possible codeword candidates. These techniques can be used to reduce false detection rates (FDRs) and / or detection error rates (DERs).
Owner:MSTAR SEMICON INC +2
CVA-based tail-biting convolutional code channel decoding method
ActiveCN107911195AReduce decoding delayImprove decoding efficiencyError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionDependabilityTail-biting
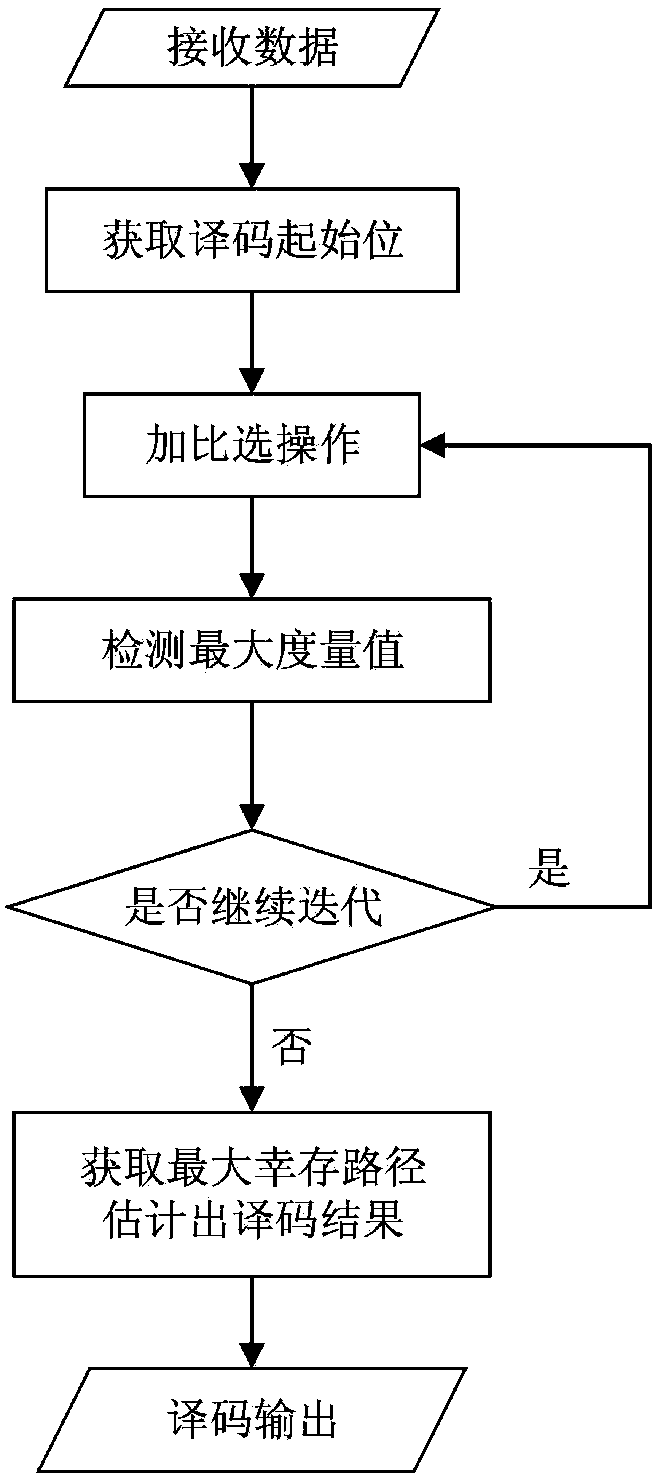
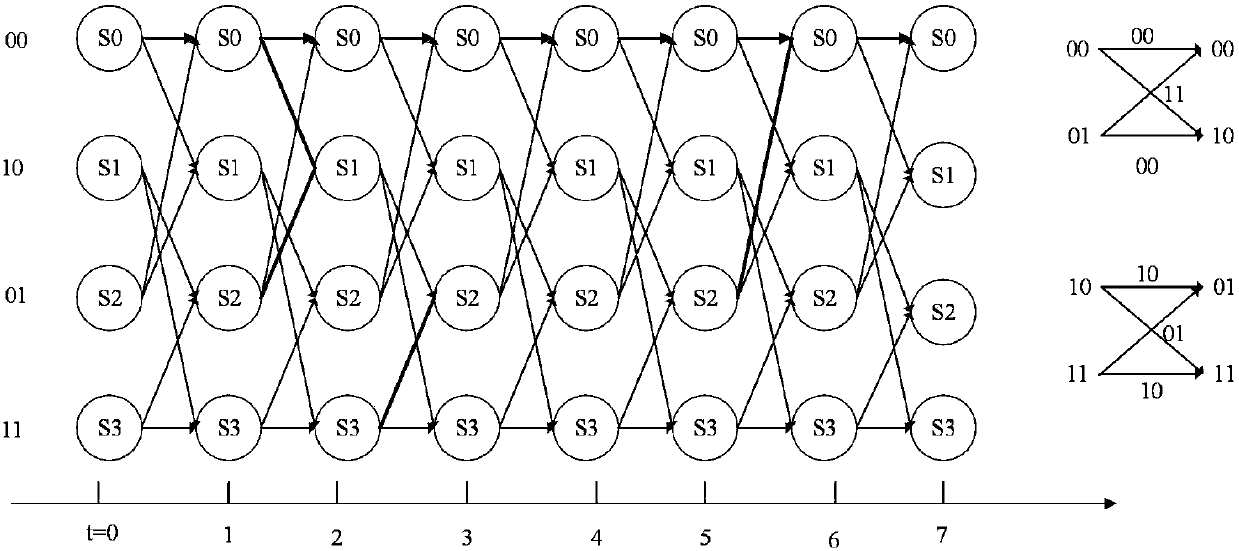
The invention claims a CVA-based tail-biting convolutional code channel decoding method, which relates to the field of mobile communication technology. In order to reduce the decoding complexity and increase the decoding efficiency, the present invention proposes a decoding algorithm based on the Circular Viterbi Algorithm (CVA). The decoding start position of the highest reliability is determinedbased on the likelihood ratio information of a received information sequence. The Viterbi decoding is modified from the start position, by adding a comparison and selection process, impossible statepositions are deleted, and after several iterations of search, less surviving states converge in surviving paths, the state of the largest measurement value is selected as the start position of the final decoding, and a decoding result is estimated according to its corresponding surviving path. The algorithm has a faster convergence speed, the decoding efficiency is further improved, and the decoding delay is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Decoding method for tail-biting convolutional codes using a search depth viterbi algorithm
ActiveUS20110060972A1Less overall consumptionReduce complexityError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionComputer scienceTail-biting
A method for decoding tail-biting convolutional codes. The method includes initializing a correction depth, selecting a first starting state from a set of encoding states, and initializing a metric value for the selected starting state as zero and the other states as infinity. The input bit stream is read and a Search Depth Viterbi algorithm (SDVA) is performed to determine path metrics and identify a minimum-metric path. The ending state for the minimum-metric path is determined and the output for this ending state is identified as “previous output.” A second starting state is set to the ending state of the minimum-metric path, and symbols equal to the correction depth from the previous output are read. The SDVA is performed on the second set of read symbols to generate a corrected output. A decoded output is generated by replacing symbols at the beginning of the previous output with the corrected output.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS BEIJING R& D
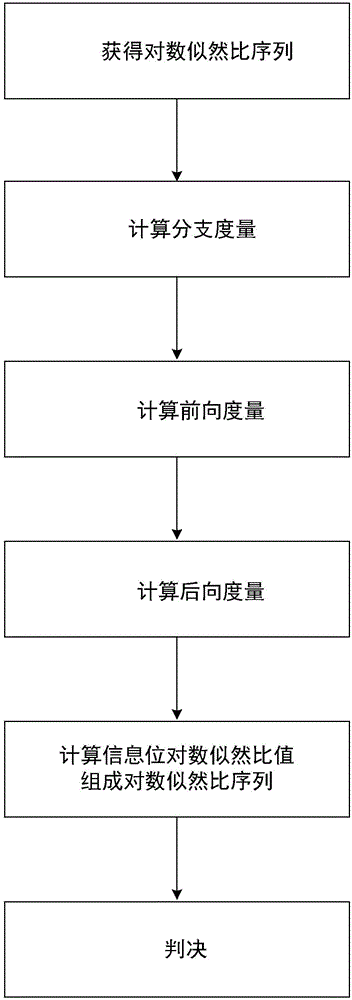
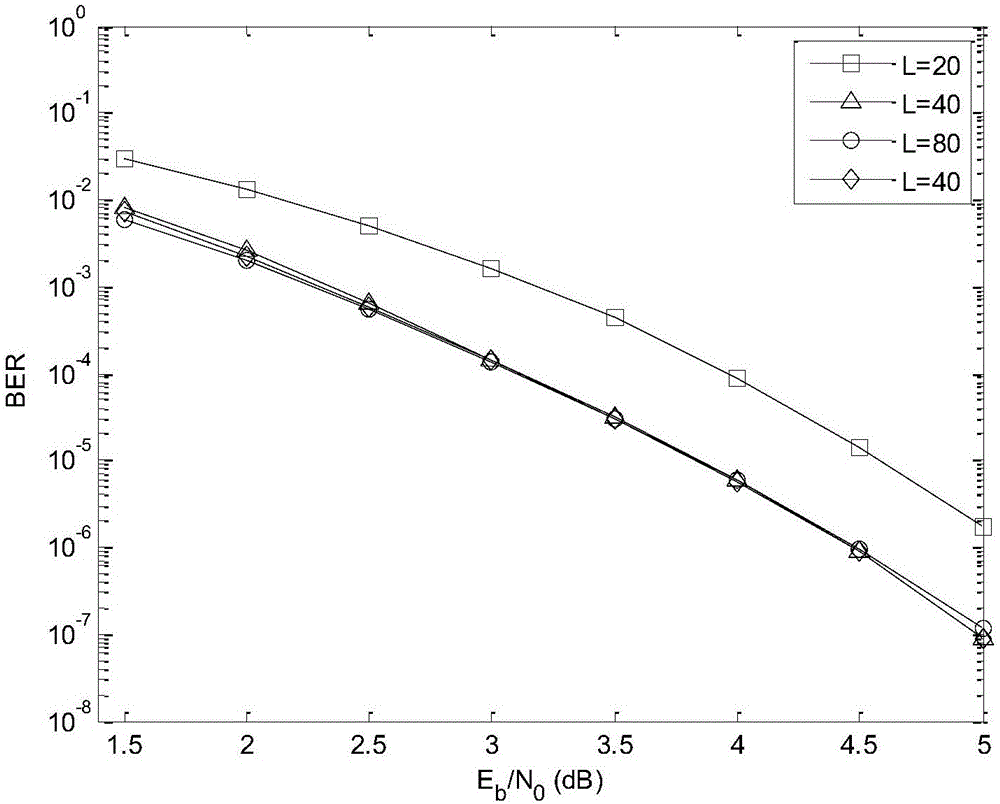
Improved soft output tail biting convolution code decoding method
ActiveCN106301391AOvercome the disadvantages of high computational complexityReduce operational complexityError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesRatio SequenceCoding decoding
The invention discloses an improved soft output tail biting convolution code decoding method. The method comprises the following steps of (1) acquiring a logarithmic likelihood ratio sequence; (2) calculating a branch metric; (3) calculating a forward metric; (4) calculating a backward metric; (5) calculating an information-bit logarithmic likelihood ratio to form the logarithmic likelihood ratio sequence; and (6) deciding. In the invention, the branch metric is calculated for one time, the forward metric and the backward metric are calculated for twice, and through using splicing, combination calculating is performed on a logarithmic likelihood ratio, a complexity is low and decoding performance is increased. In the invention, the information-bit logarithmic likelihood ratio sequence is calculated and is served as soft output, a tail biting convolution code can be served as an internal code which can carry out iteration with an external code in a whole system and an application value is expanded.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com