Patents
Literature
177 results about "Noise induced" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
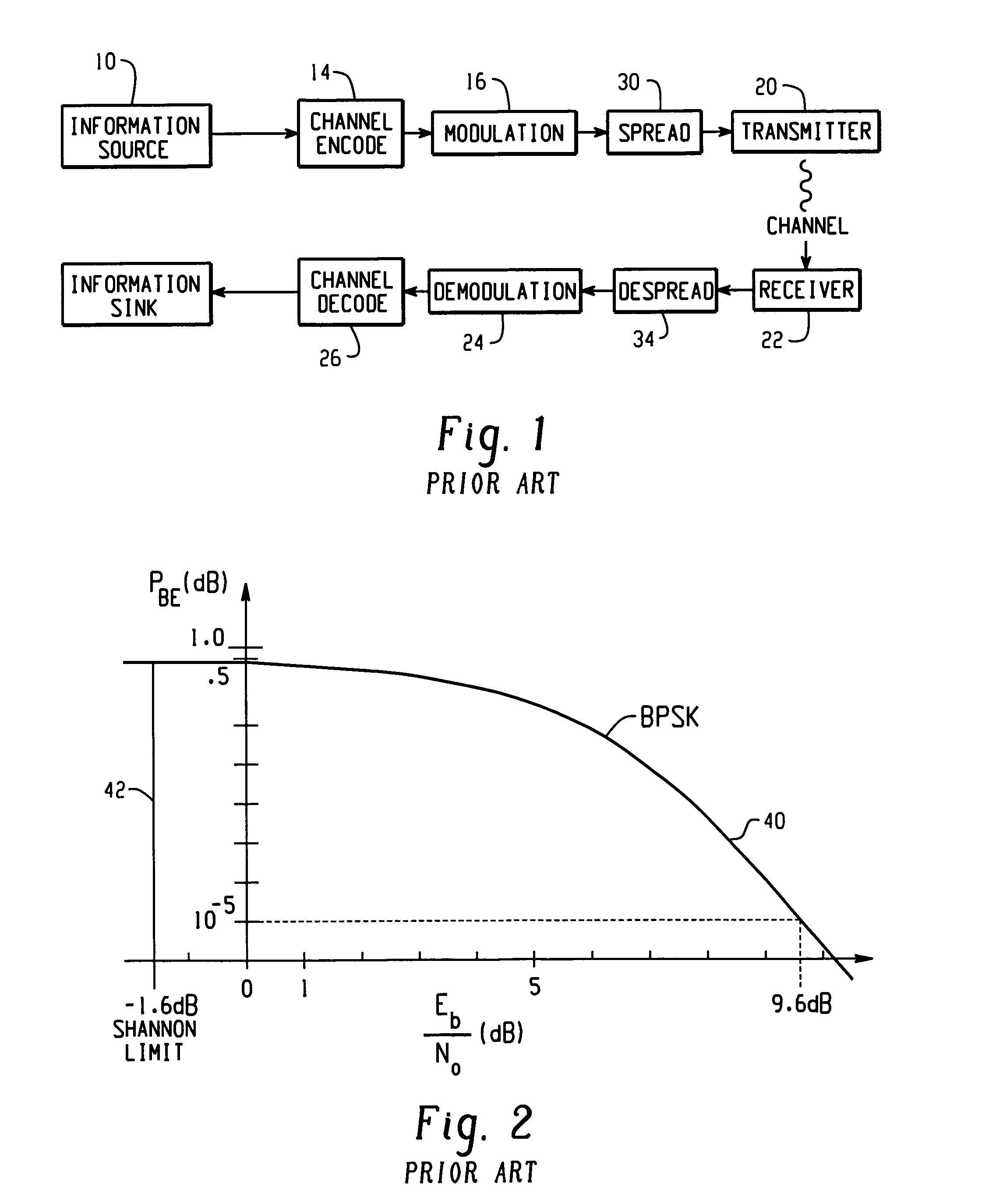
Induced noise is the noise generated in a circuit by a varying magnetic or electrostatic field produced by another circuit. Induced noise, just like any other electrical noise, degrades the useful signal and may lead to equipment errors, shutdown, or malfunction.
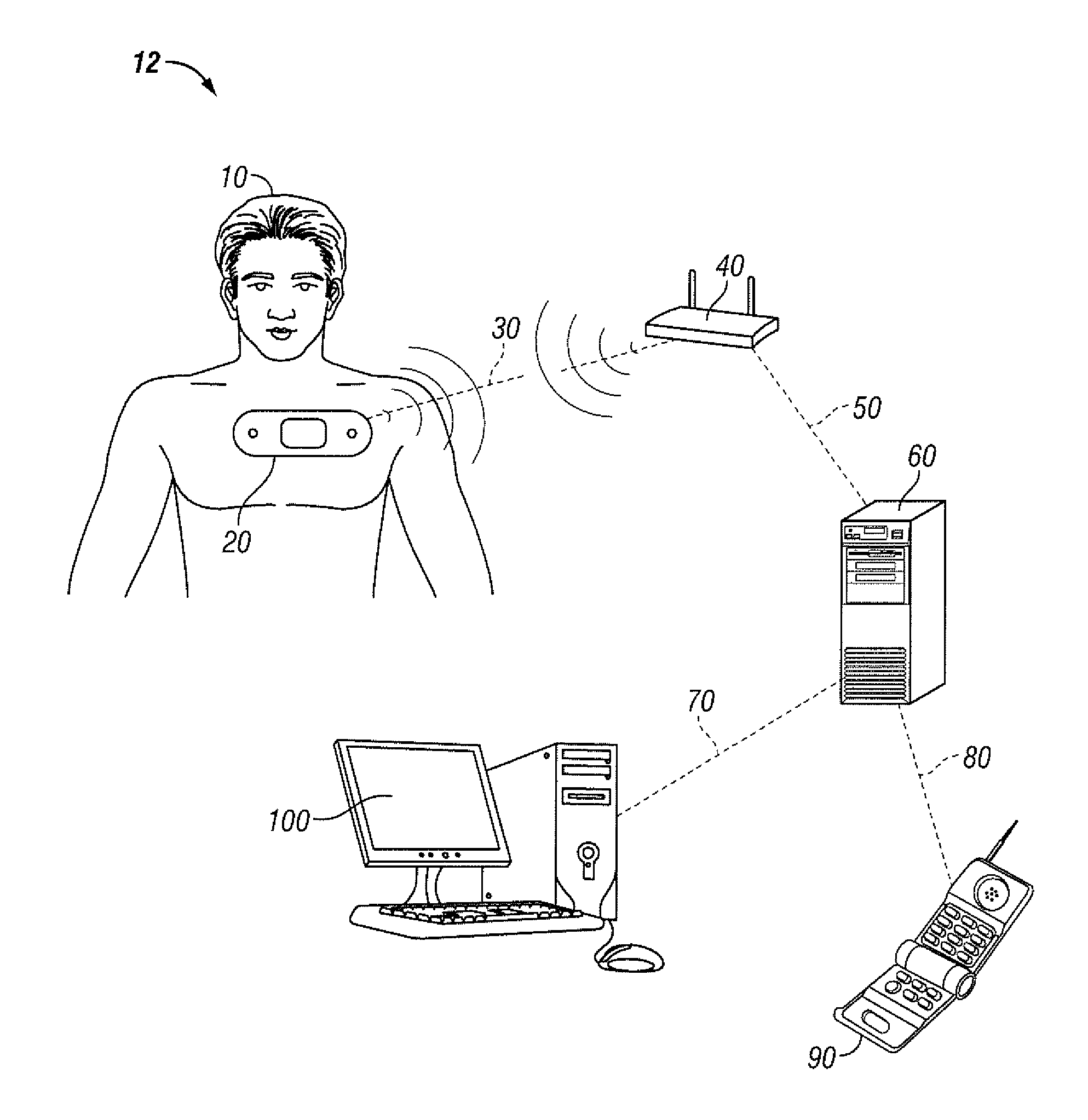
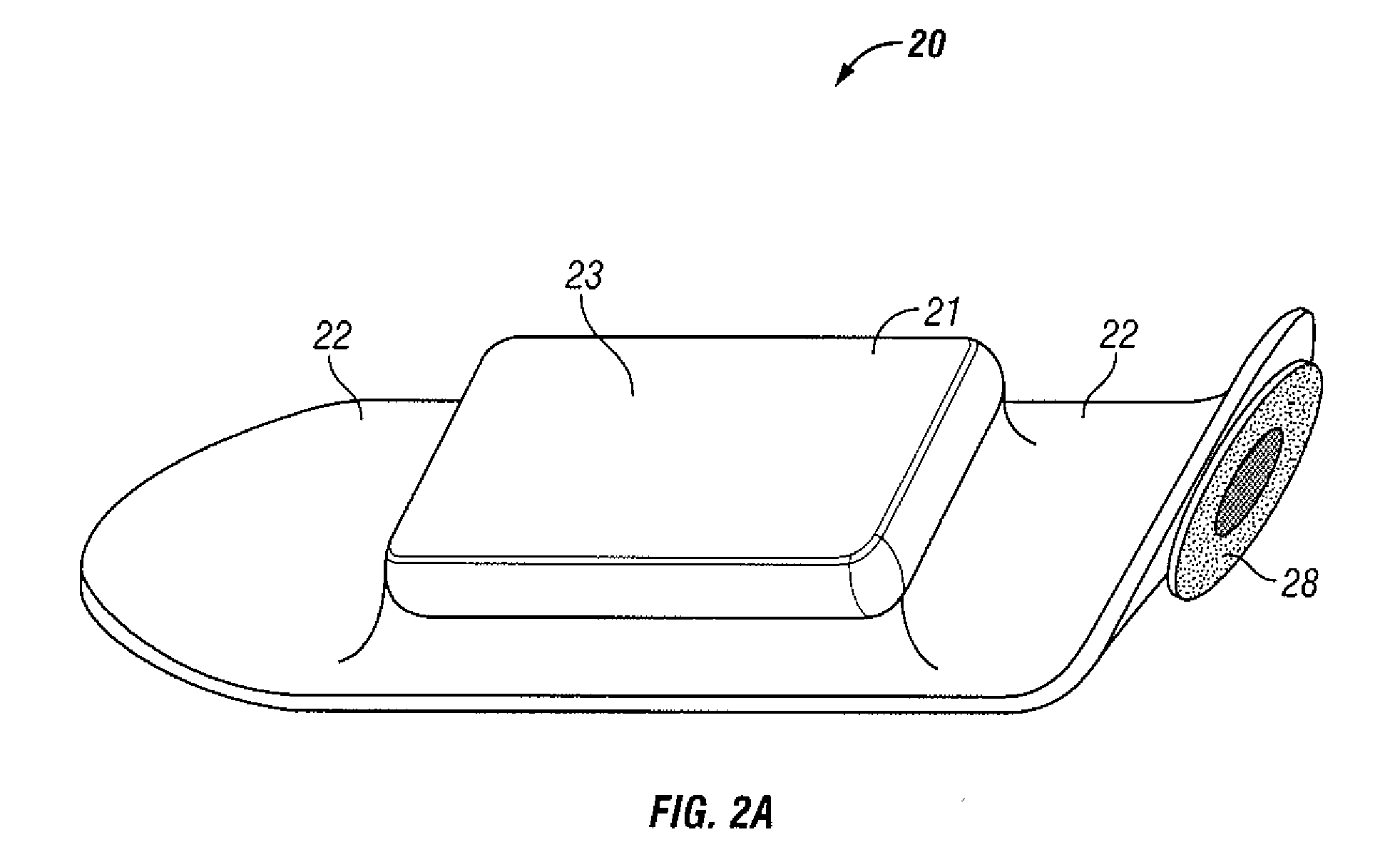
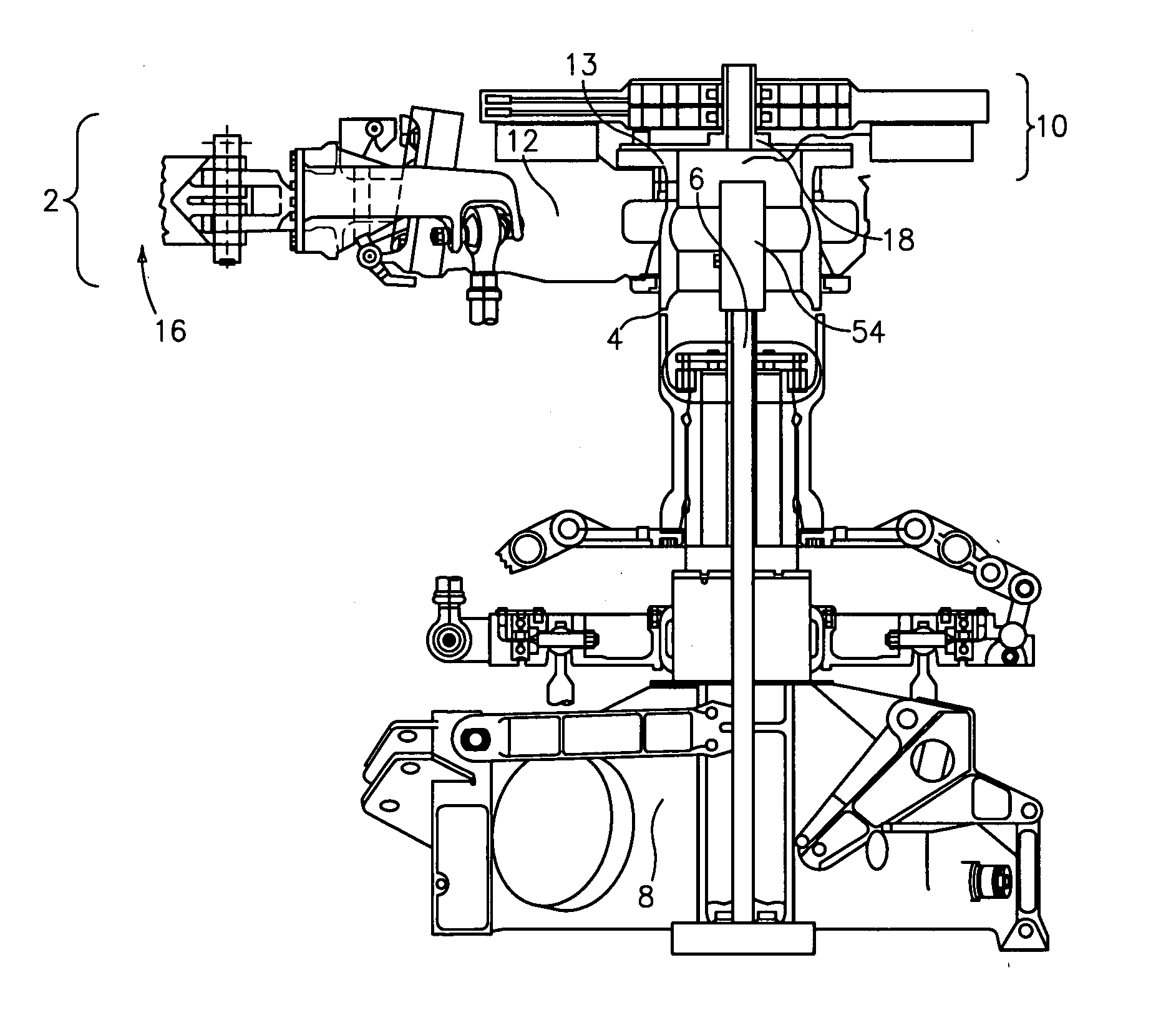
Vital-signs monitor with spaced electrodes
InactiveUS20120029307A1Control interferenceCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringVital signs monitorsVital sign monitoring
A vital-signs monitoring patch is disclosed. The patch includes at least two electrodes and a circuit assembly that periodically takes at least one measurement from the electrodes. The patch is a unitized device that contains the circuit assembly with the electrodes on the underside of the patch. The patch is attached to a patient with the electrodes in electrical contact with the patient's skin. The segments of the patch that connect the electrodes to the circuit assembly are flexible which reduces the noise induced in the measurement by stress on the contact between the electrodes and the patient.
Owner:CAREFUSION 303 INC
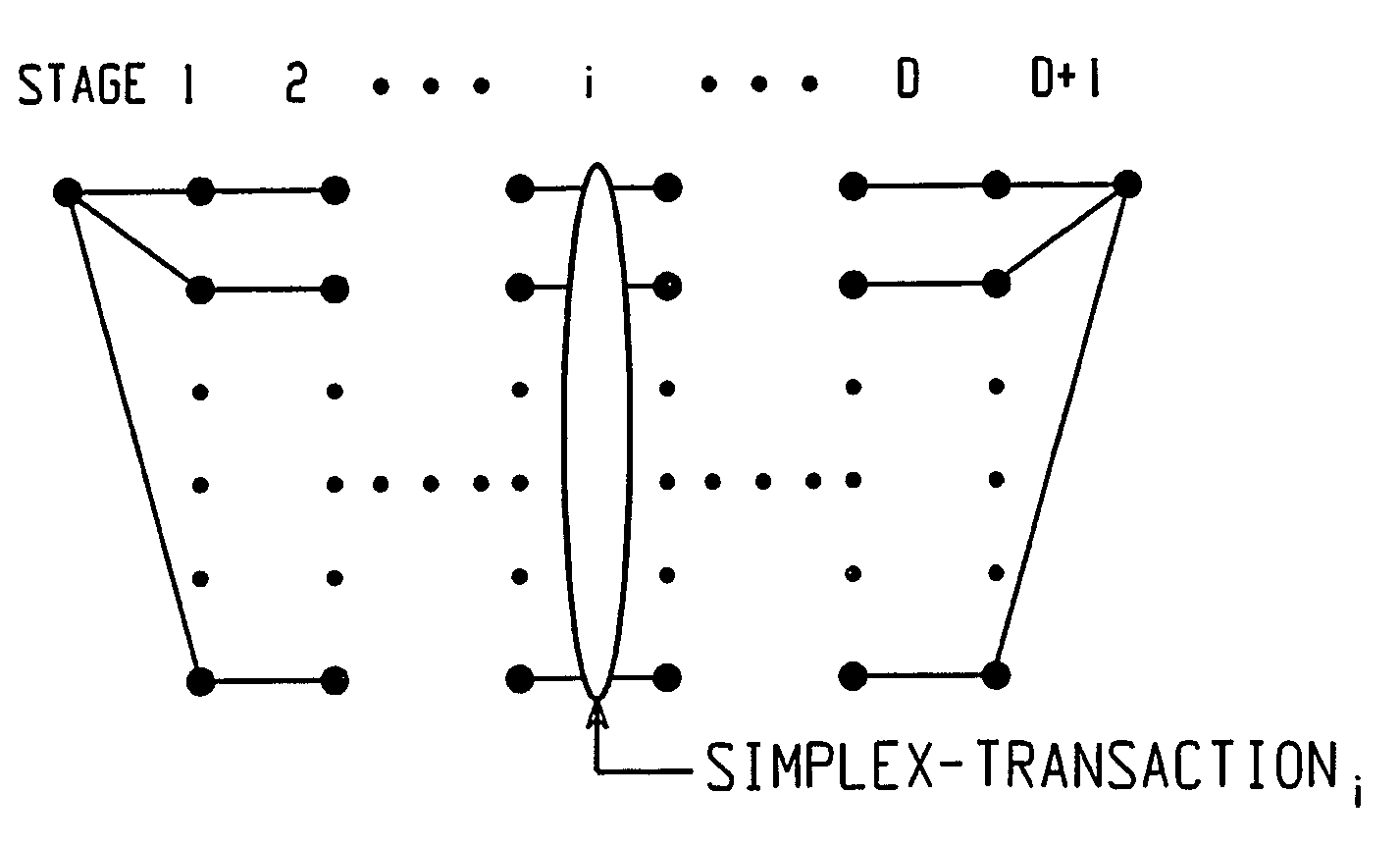
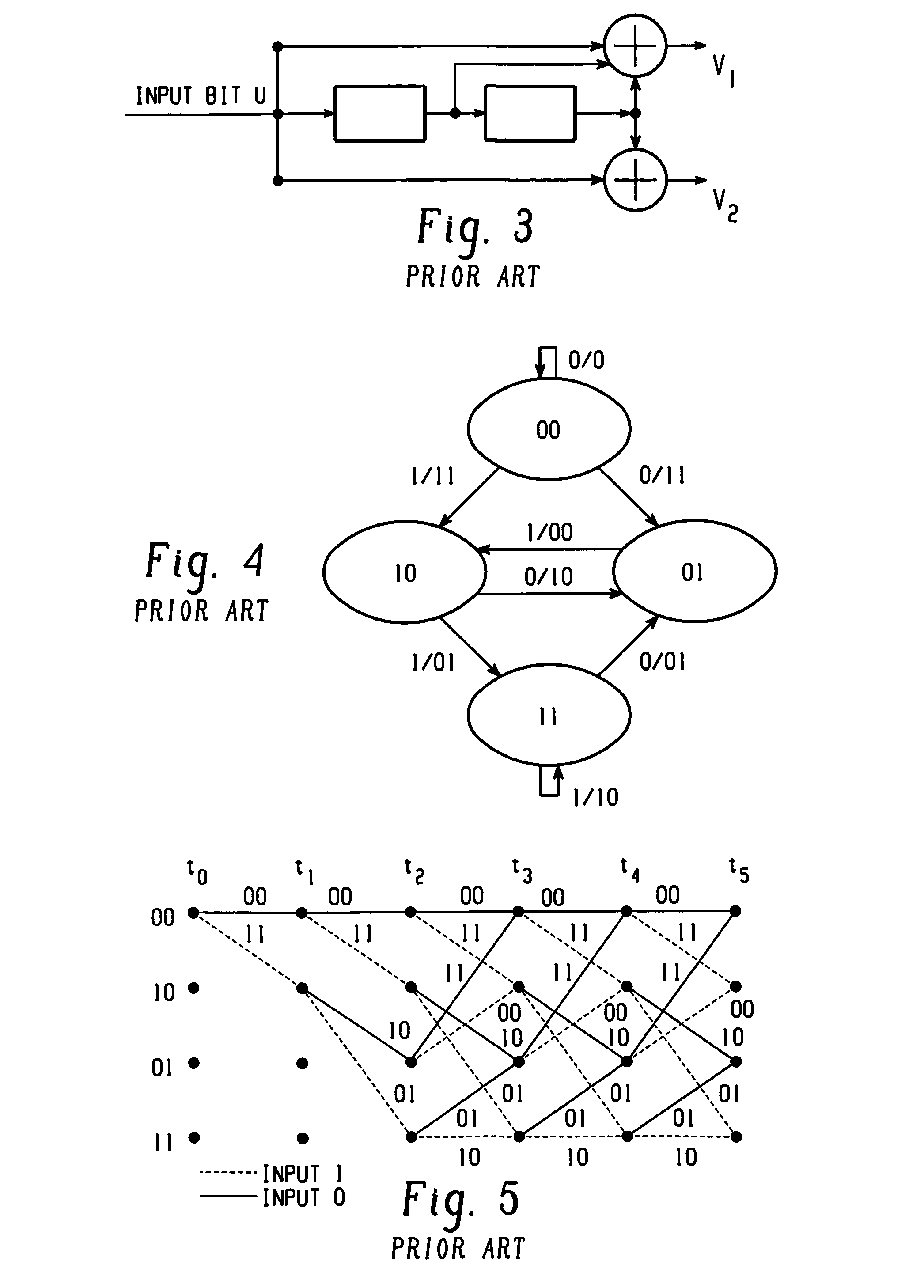
Apparatus and method of CTCM encoding and decoding for a digital communication system
InactiveUS7010052B2Improve energy efficiencyData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesCommunications systemMulti dimensional
A method of building systematically a multi-dimensional (n, D, L) circular trellis coded modulation (CTCM) encoder with properties of optimal energy efficiency, strong tail biting and maximum minimum distance (dmin) of trellis paths is disclosed. In addition, a communication system for use in a power limited channel application is disclosed comprising a circular trellis coded modulation (CTCM) encoder with permuted state structure for encoding based on a circular trellis path associated with a sequence of digital information bits and a set of simplexes identified for the path from a multi-dimensional signal constellation; a transmitter coupled to said CTCM encoder for transmitting said sequence of channel symbols over said channel; a receiver for receiving a transmission from said transmitter including said sequence of channel symbols and any noise induced therein; and a CTCM decoder coupled to said receiver for decoding the received transmission without knowledge of the starting state of the circular trellis path of the CTCM encoder to recover the sequence of information bits. Apparatus and methods of encoding and decoding are also disclosed utilizing a combination of circular trellis-coded modulation with permuted state structure and simplex signal constellation techniques for use in the digital communication system.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
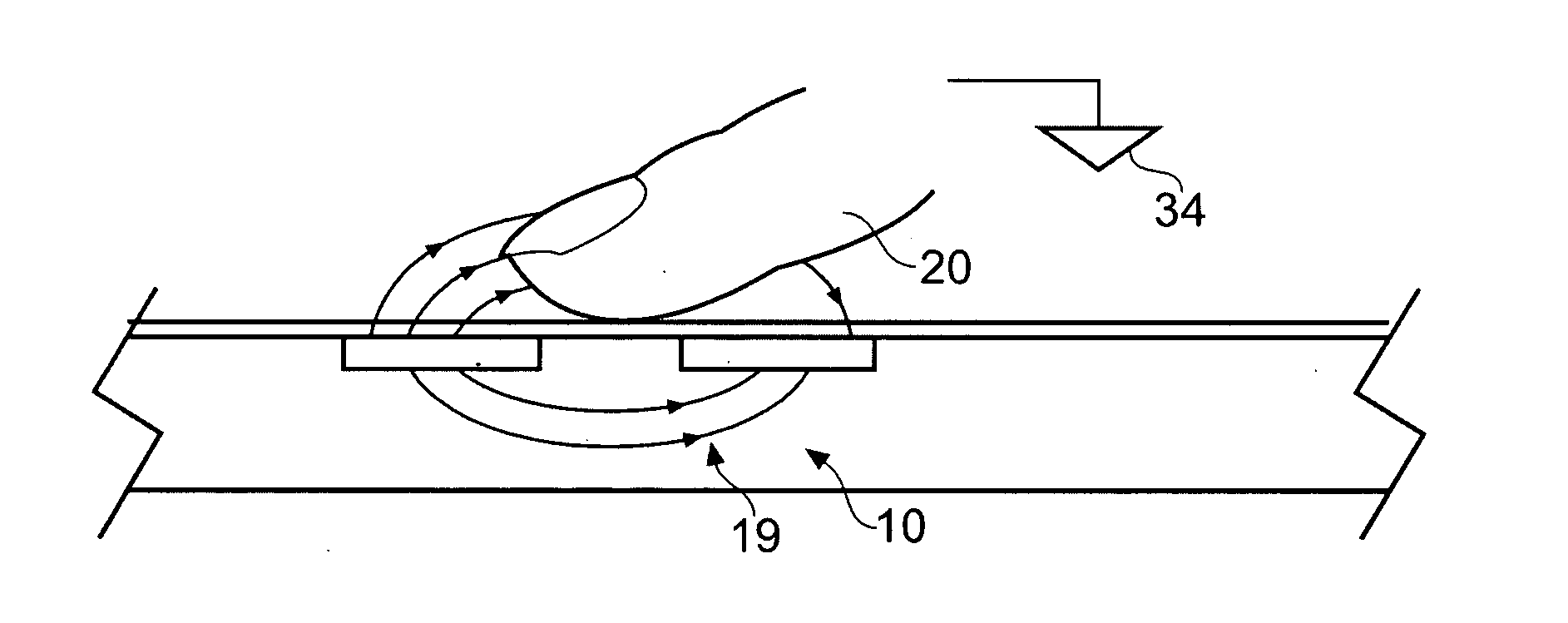
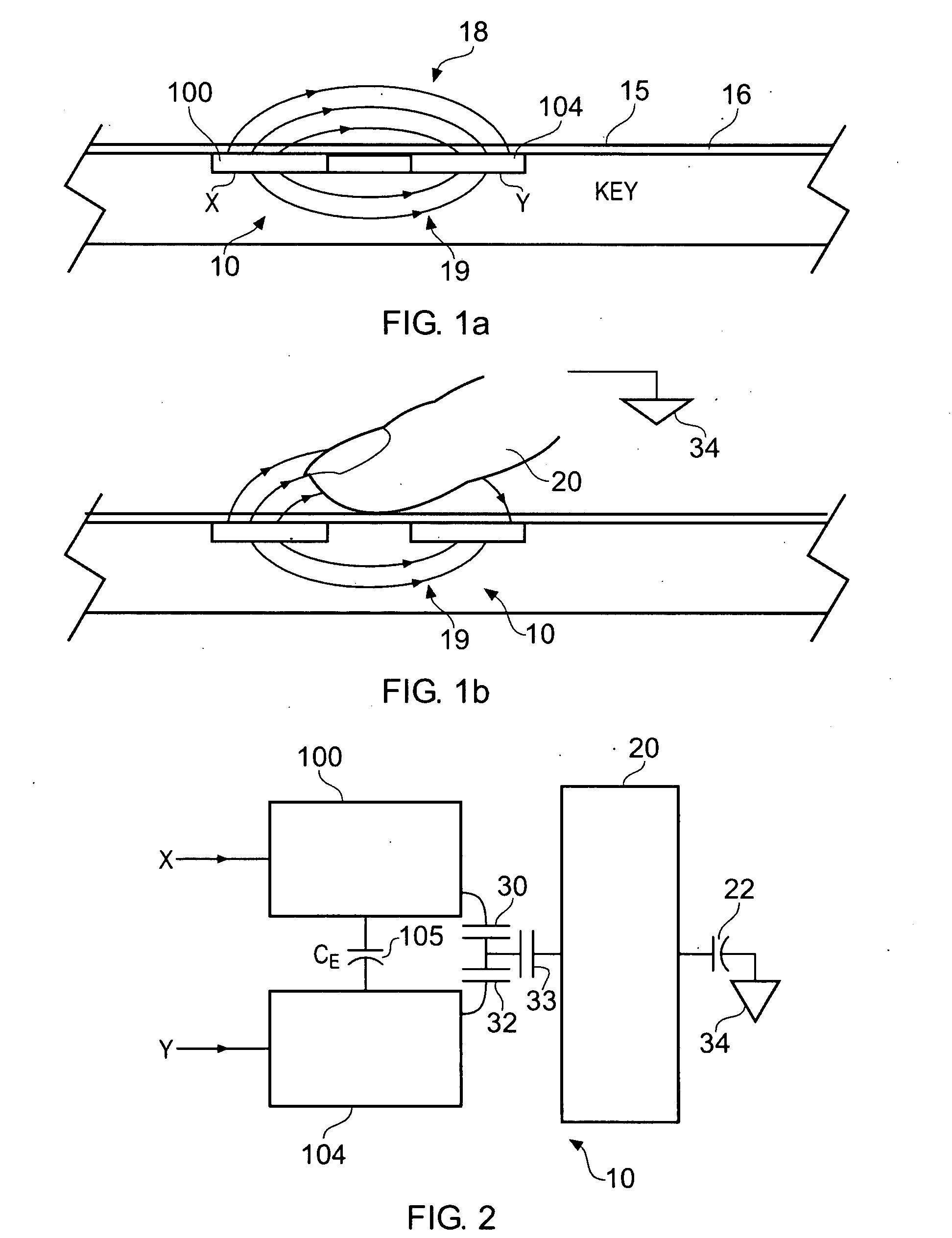
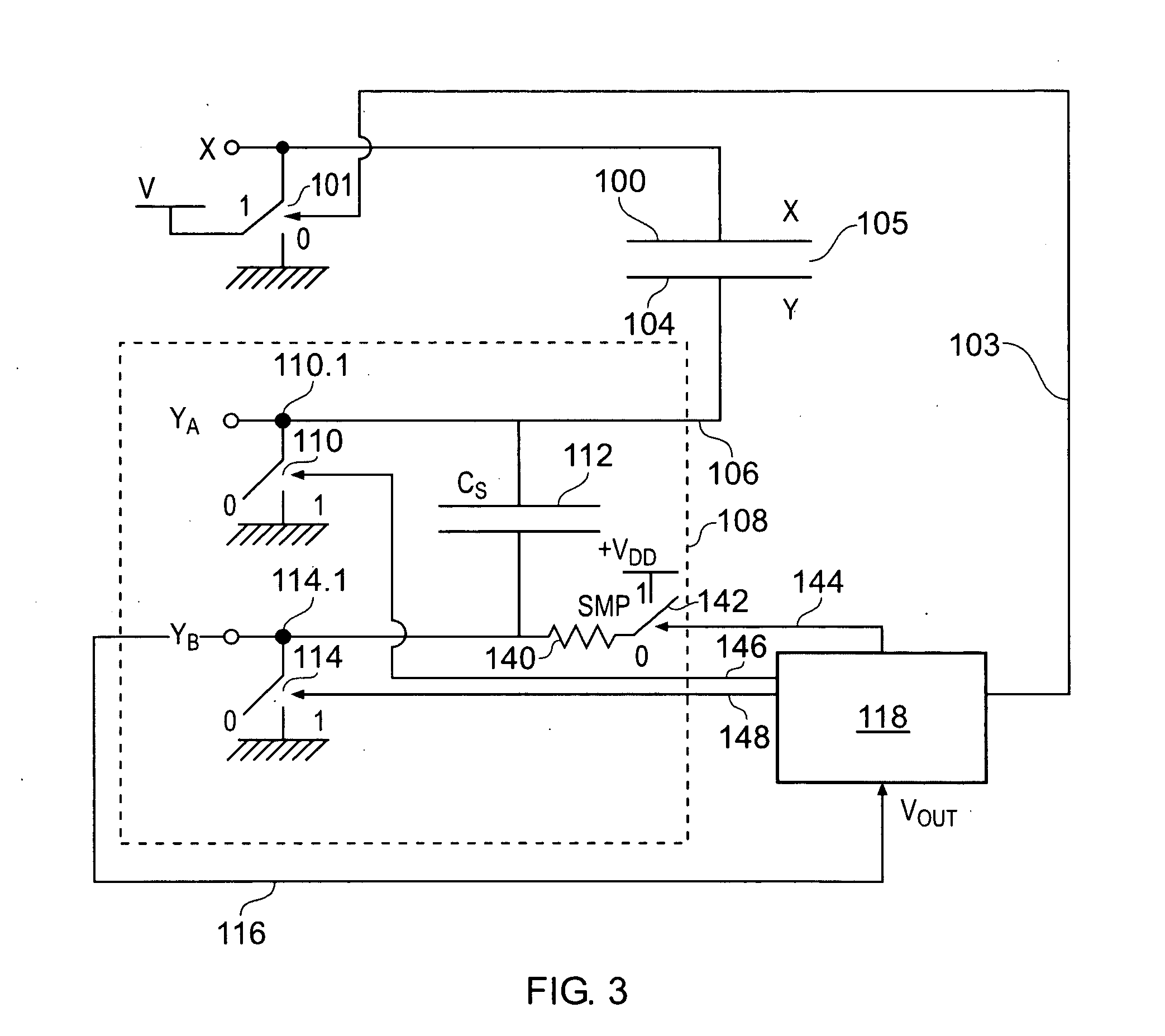
Noise Handling in Capacitive Touch Sensors
ActiveUS20100097078A1Increase the number ofCapacitance measurementsNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementAnalog signalCapacitance transducer
In a capacitive sensor of the type having X electrodes which are driven and Y electrodes that are used as sense channels connected to charge measurement capacitors, signal measurements are made conventionally by driving the X electrodes to transfer successive packets of charge to the charge measurement capacitors. However, an additional noise measurement is made by emulating or mimicking the signal measurement, but without driving the X electrodes. The packets of charge transferred to the charge accumulation capacitor are then indicative of noise induced on the XY sensing nodes. These noise measurements can be used to configure post-processing of the signal measurements.
Owner:NEODRON LTD
Oriented PIFA-type device and method of use for reducing RF interference
InactiveUS7230574B2Reduce radiationReduction in PWD generated noiseSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandEngineering
Owner:AERIUS INT
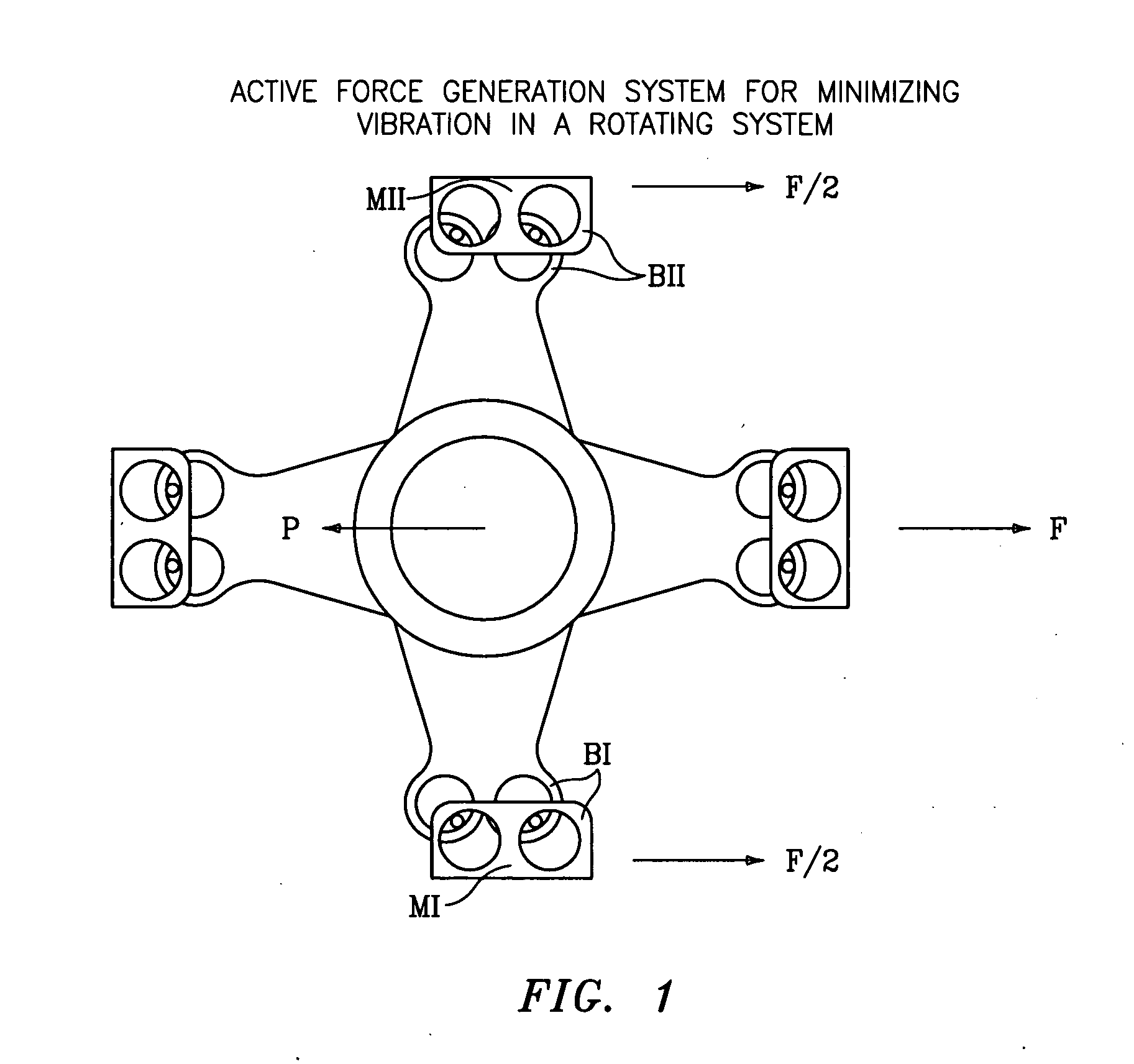
Active force generation system for minimizing vibration in a rotating system
ActiveUS20050079056A1Minimizing system weightReduce manufacturing costRotating vibration suppressionPropellersControl signalAngular velocity
A method and device for reducing vibratory noise in a system with an integral rotating member includes independently operable drive means for controlling the angular velocity of at least two masses. Control signals manipulate the drive means to allow each mass to rotate at optimal speed, direction and phase for reducing the noise induced in the system by the rotating member.
Owner:SIKORSKY AIRCRAFT CORP
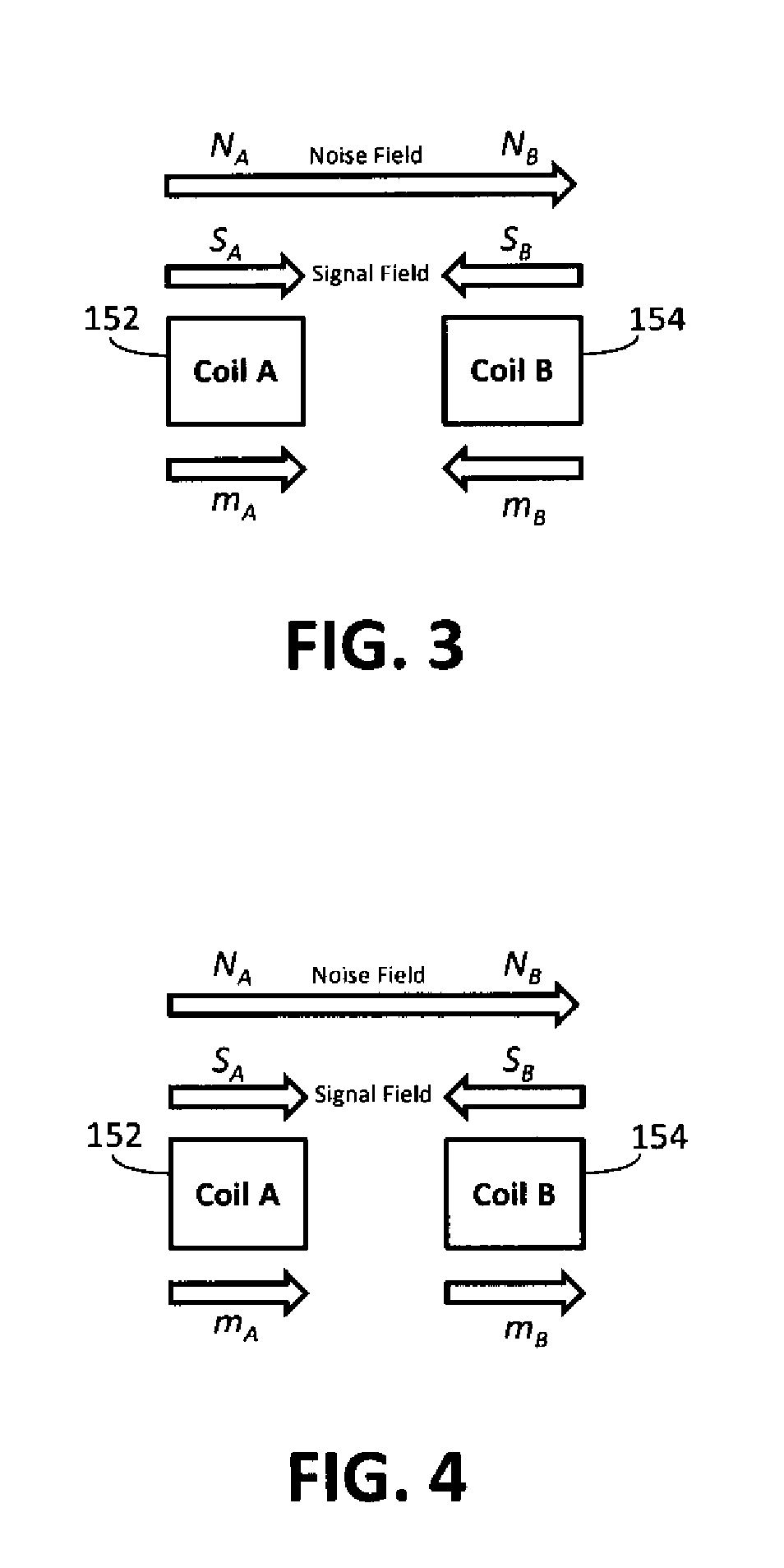
System and method for detecting magnetic noise by applying a switching function to magnetic field sensing coils
ActiveUS8893562B2Accurate measurementReduce spacingForce measurementWork measurementObservational errorNoise detection
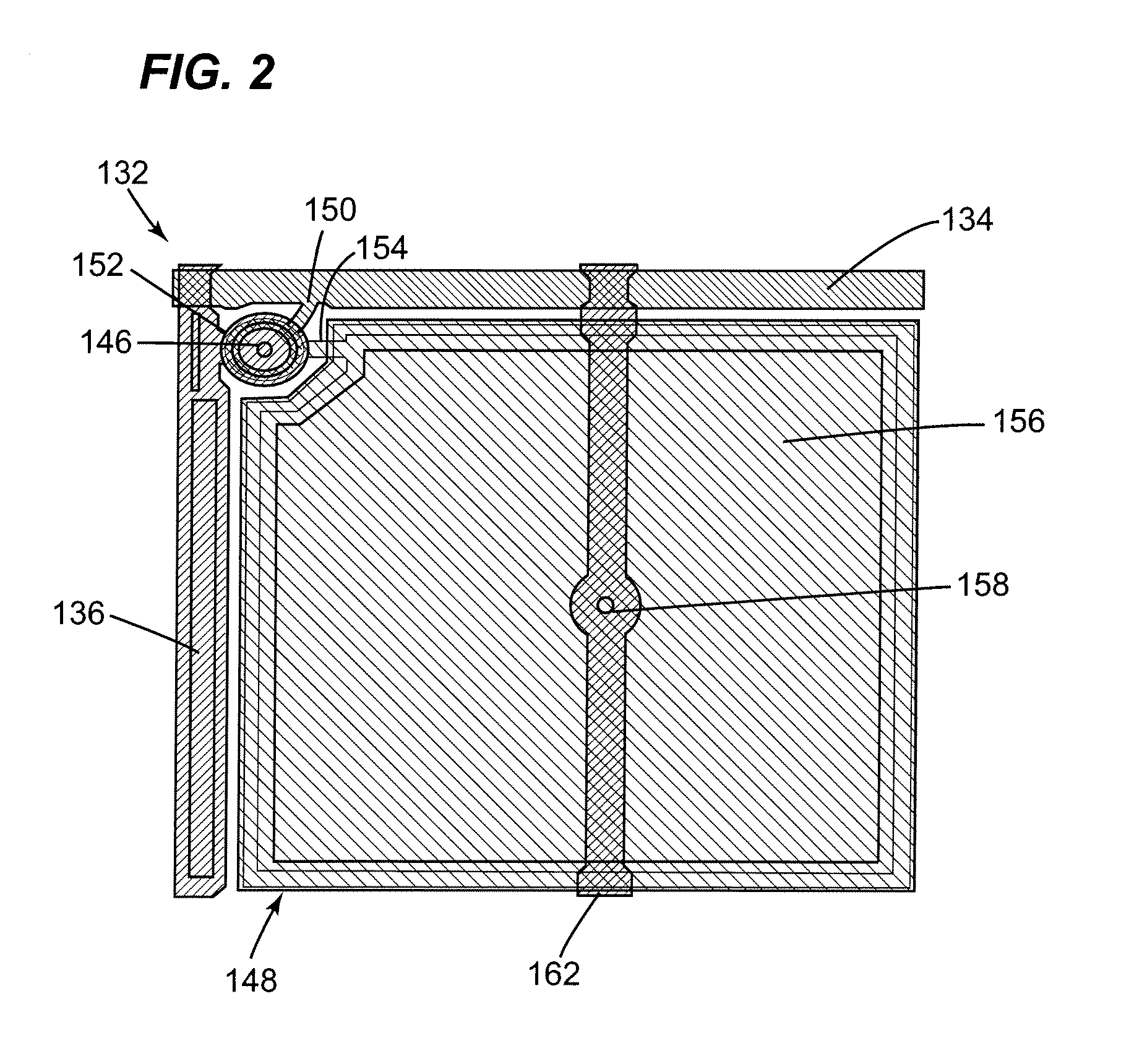
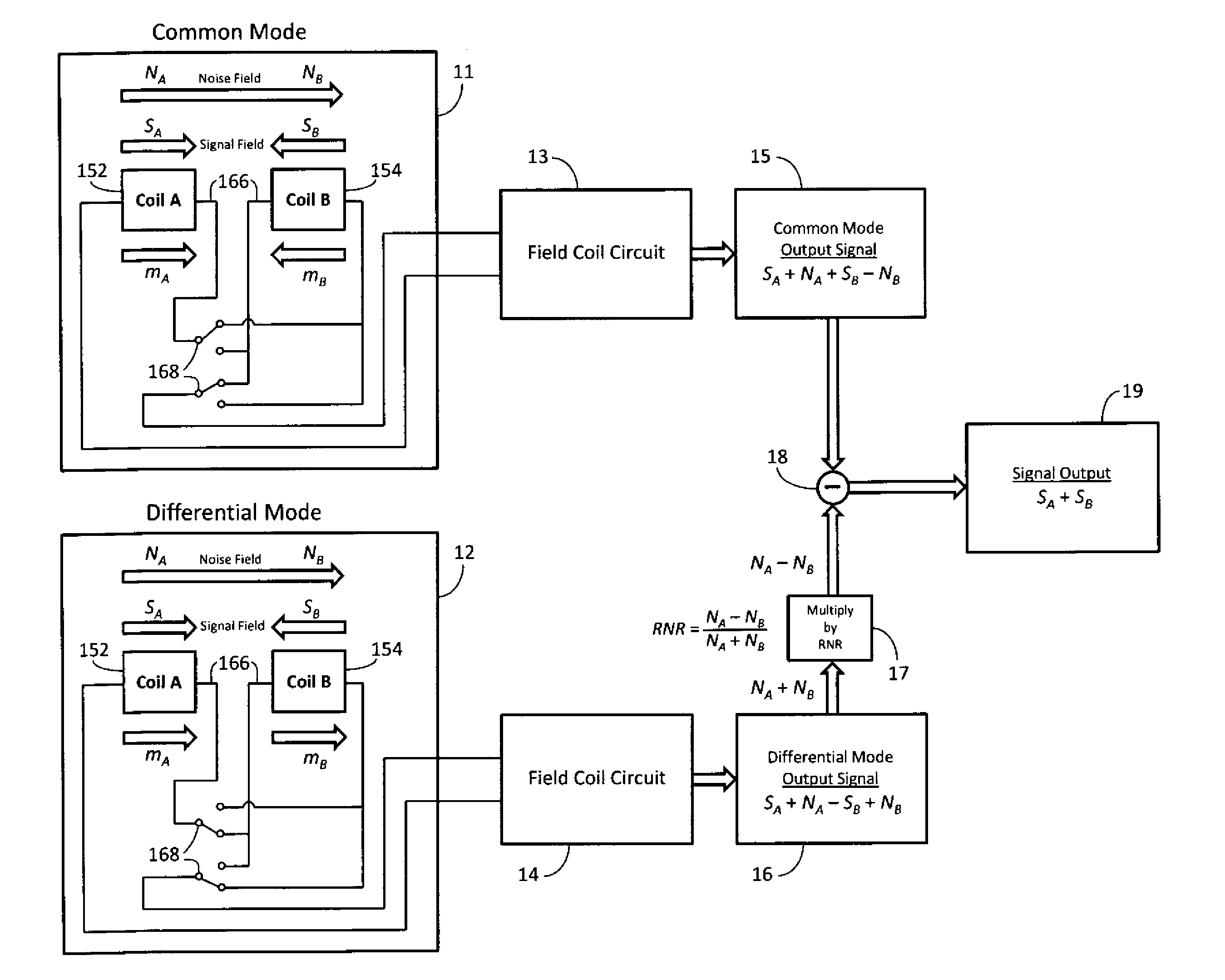
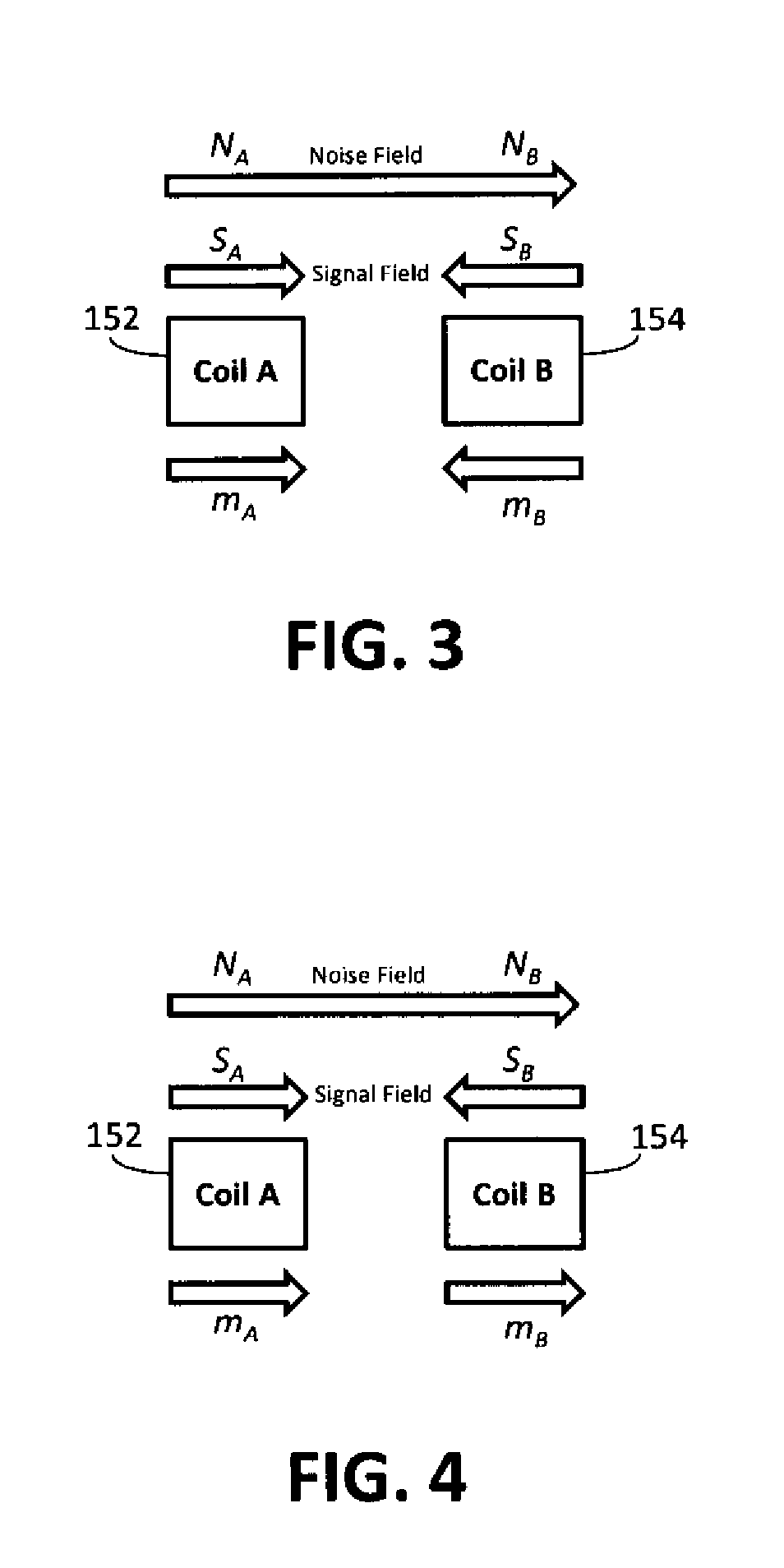
A torque sensing device for measuring the torque applied to a rotatable shaft, and also measuring the magnetic field noise affecting the device. The device incorporates a switching function thereby enabling the device to operate in a common signal detection mode and a differential noise detection mode. The device is capable of determining the torque applied to the rotatable shaft based upon output signals obtained from magnetic field sensors operating in both the common signal detection mode and the differential noise detection mode. The device is capable of accurately measuring a torque induced magnetic field and is capable of canceling measurement error resulting from noise induced magnetic fields.
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
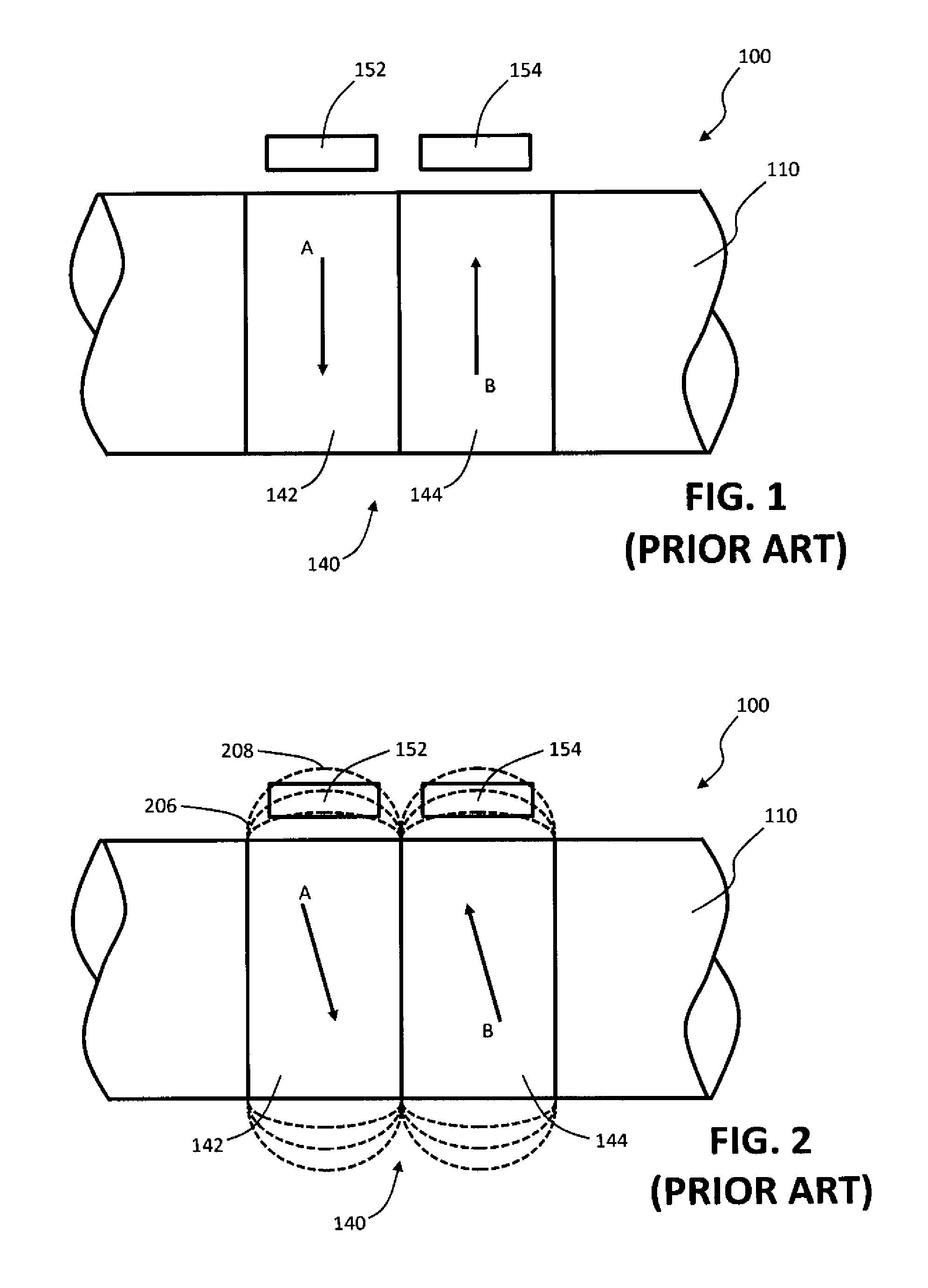
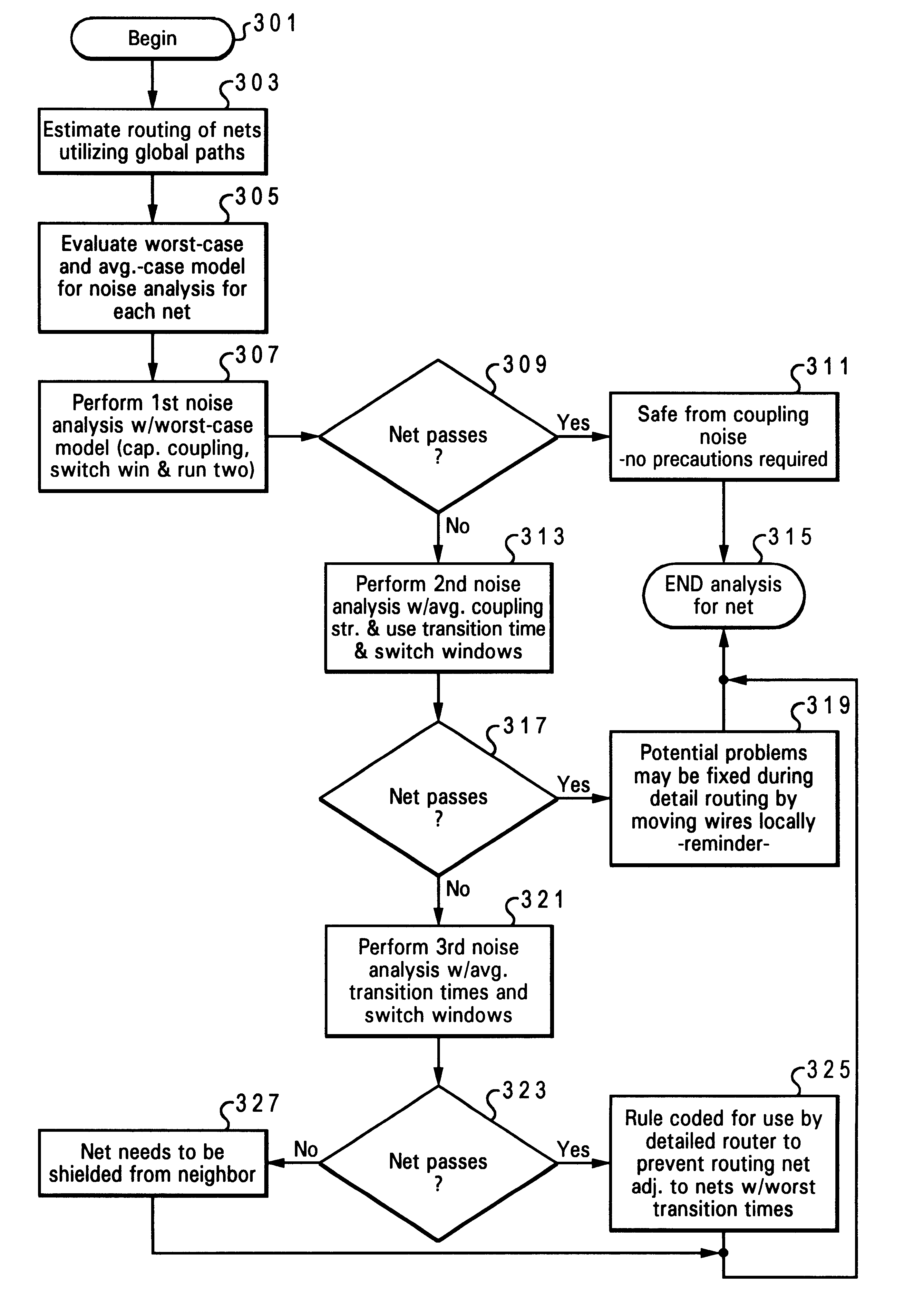
Coupled noise estimation and avoidance of noise-failure using global routing information
Disclosed is a method for pre-design estimation of coupling noise and avoidance of coupling noise failures in interconnects. An initial routing of a plurality of nets is estimated utilizing global paths. Then, the worst-case and average-case models for various parameters of each net are evaluated. With these models, a noise analysis is completed by which a determination is made whether coupling noise of any one of the nets is above a threshold level for noise-induced failure (i.e., a noise-failure threshold). When it is determined that the estimated coupling noise of a net falls below the noise-failure threshold, a response mechanism is triggered for later implementation during detailed routing of the nets to prevent the coupling noise from reaching the noise-failure threshold.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
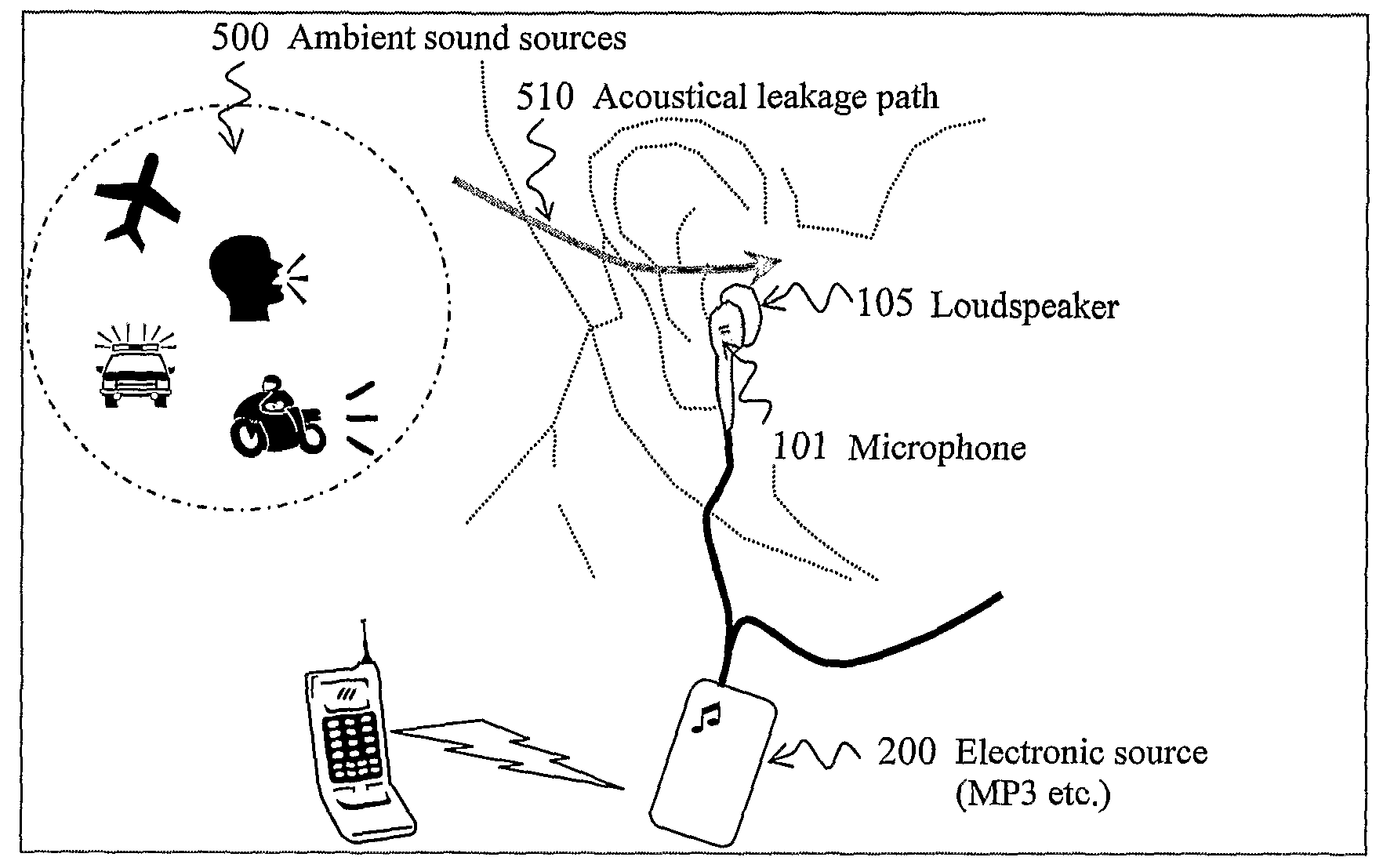
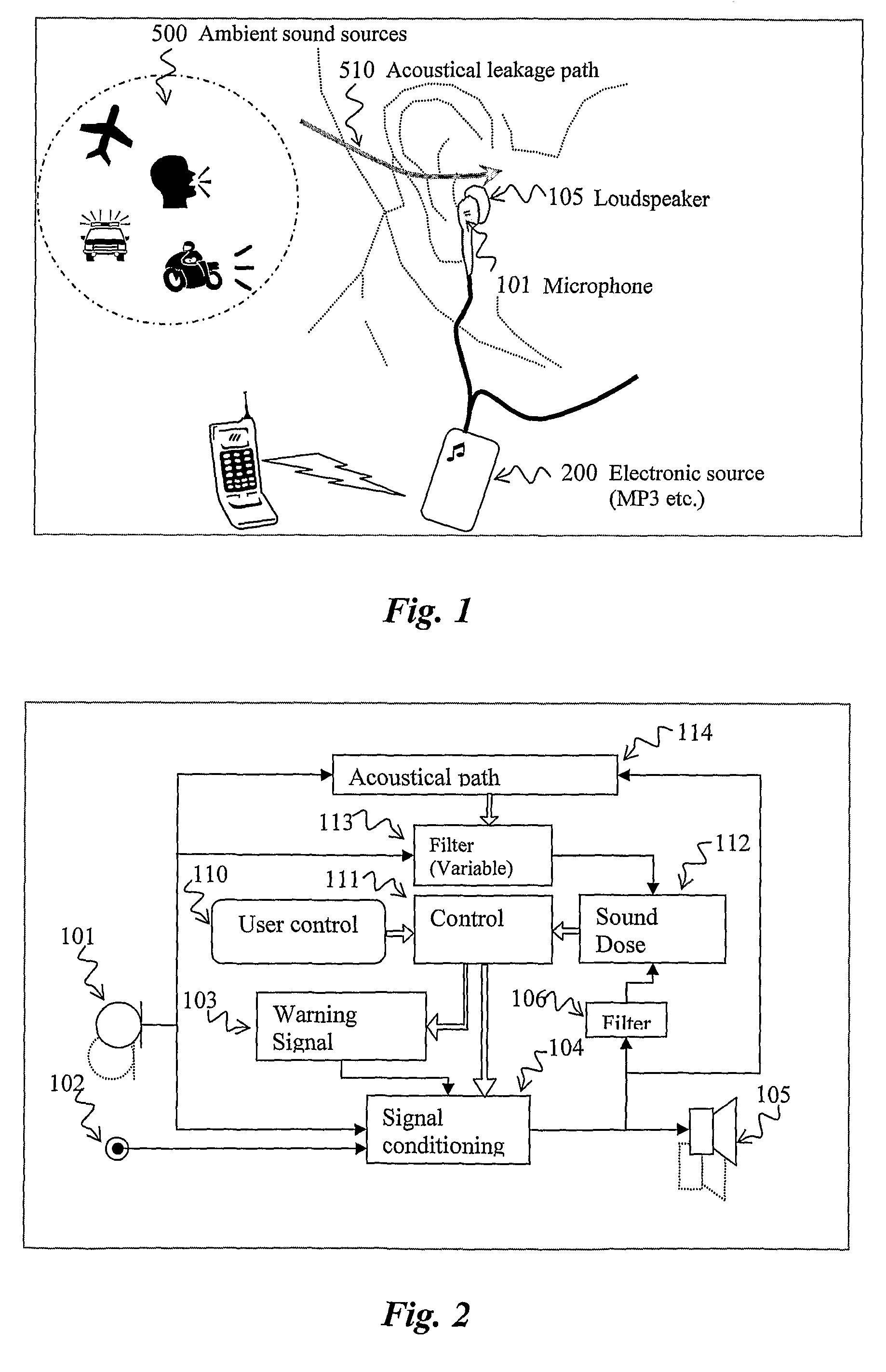
Apparatus for reducing the risk of noise induced hearing loss
InactiveUS20090208024A1Reduce riskIncreased riskVibration measurement in fluidElectrical apparatusSound energyMedicine
An apparatus is disclosed for managing the joint contribution of noise exposure of the ear of a user of the apparatus from a loudspeaker of the apparatus as well as from ambient noise so that the risk of risk of noise induced hearing losses is reduced. By assessing the joint actual sound energy delivered to the ear and feeding said assessment to a model describing the accumulated risk of hearing loss due to said sound energy accumulated over a time period, an estimate of the current risk of hearing loss is obtained. When said risk estimate passes a predetermined threshold, one or more protective measures are taken.
Owner:MICROSOUND
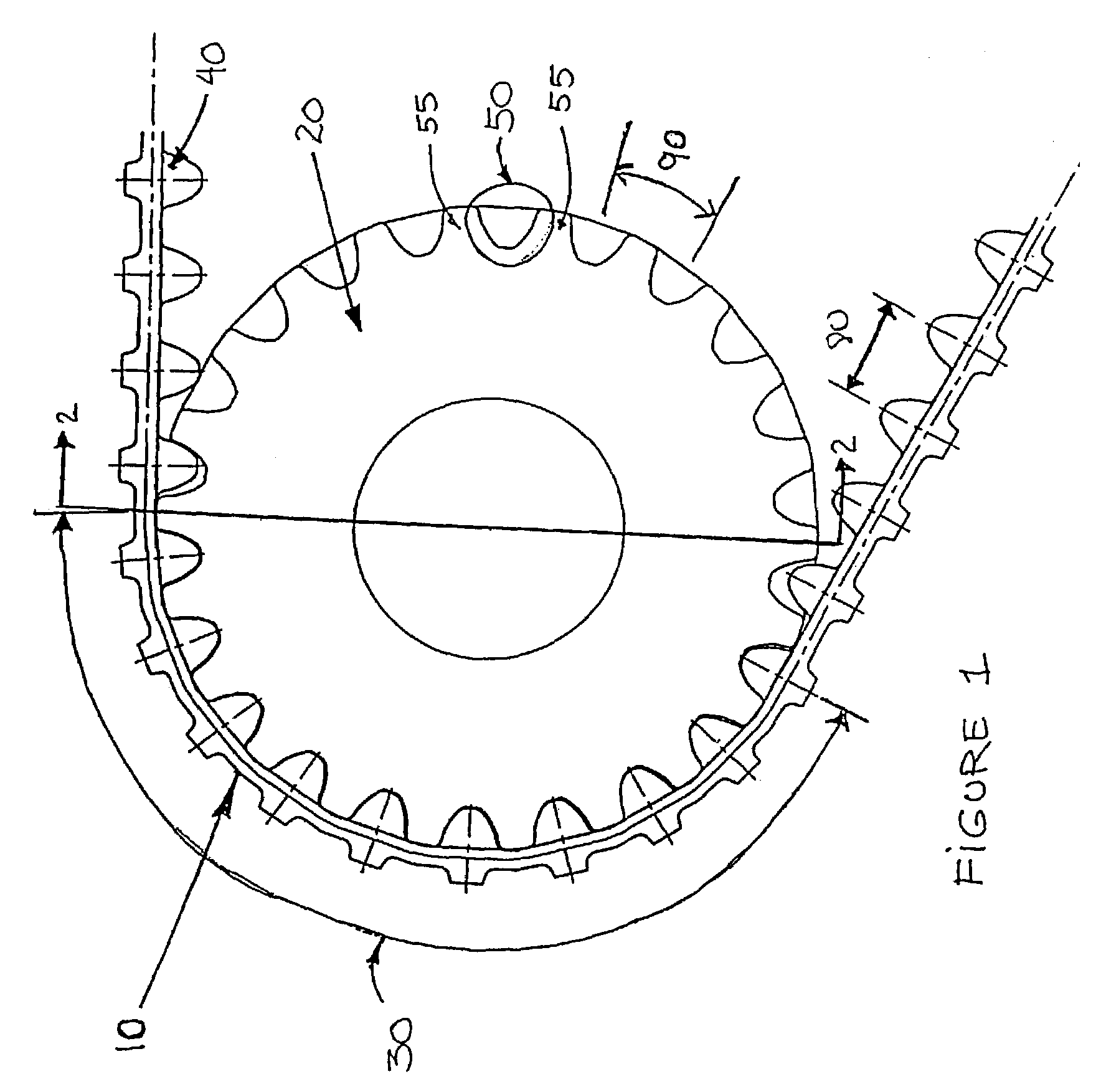
Angled traction lugs for endless band
This invention refers to the traction lugs of reinforced elastomeric endless traction bands, and more particularly to those which are used on heavy vehicles like defense vehicles or for skid steer vehicles. More specifically, the invention relates to traction lugs which are angled with respect to the transversal axis of the traction band and preferably disposed in chevrons, which optimize the band's traction while reducing the occurrences of teeth skipping and the level of vibrations and noise induced by the interaction of the traction band with the sprocket.
Owner:SOUCY INT
Dual function detector device
A dual function detector device operates in either a normal operating mode or in an EMI correction mode to suppress effects of EMI within the detector. The detector device may be a flat panel x-ray detectors used in x-ray imaging systems. The device has a pixel architecture and panel read-out technique that enables real-time, high spatial frequency measurement of noise induced by electromagnetic radiation on a digital x-ray detector. The measurement can be used to calibrate the detector in real-time to attain artifact-free imaging in all environments, including those that contain temporally and spatially changing electromagnetic fields.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for detecting magnetic noise by applying a switching function to magnetic field sensing coils
ActiveUS20130125669A1Accurate measurementReduce in quantityWork measurementTorque measurementObservational errorNoise detection
A torque sensing device for measuring the torque applied to a rotatable shaft, and also measuring the magnetic field noise affecting the device. The device incorporates a switching function thereby enabling the device to operate in a common signal detection mode and a differential noise detection mode. The device is capable of determining the torque applied to the rotatable shaft based upon output signals obtained from magnetic field sensors operating in both the common signal detection mode and the differential noise detection mode. The device is capable of accurately measuring a torque induced magnetic field and is capable of canceling measurement error resulting from noise induced magnetic fields.
Owner:METHODE ELETRONICS INC
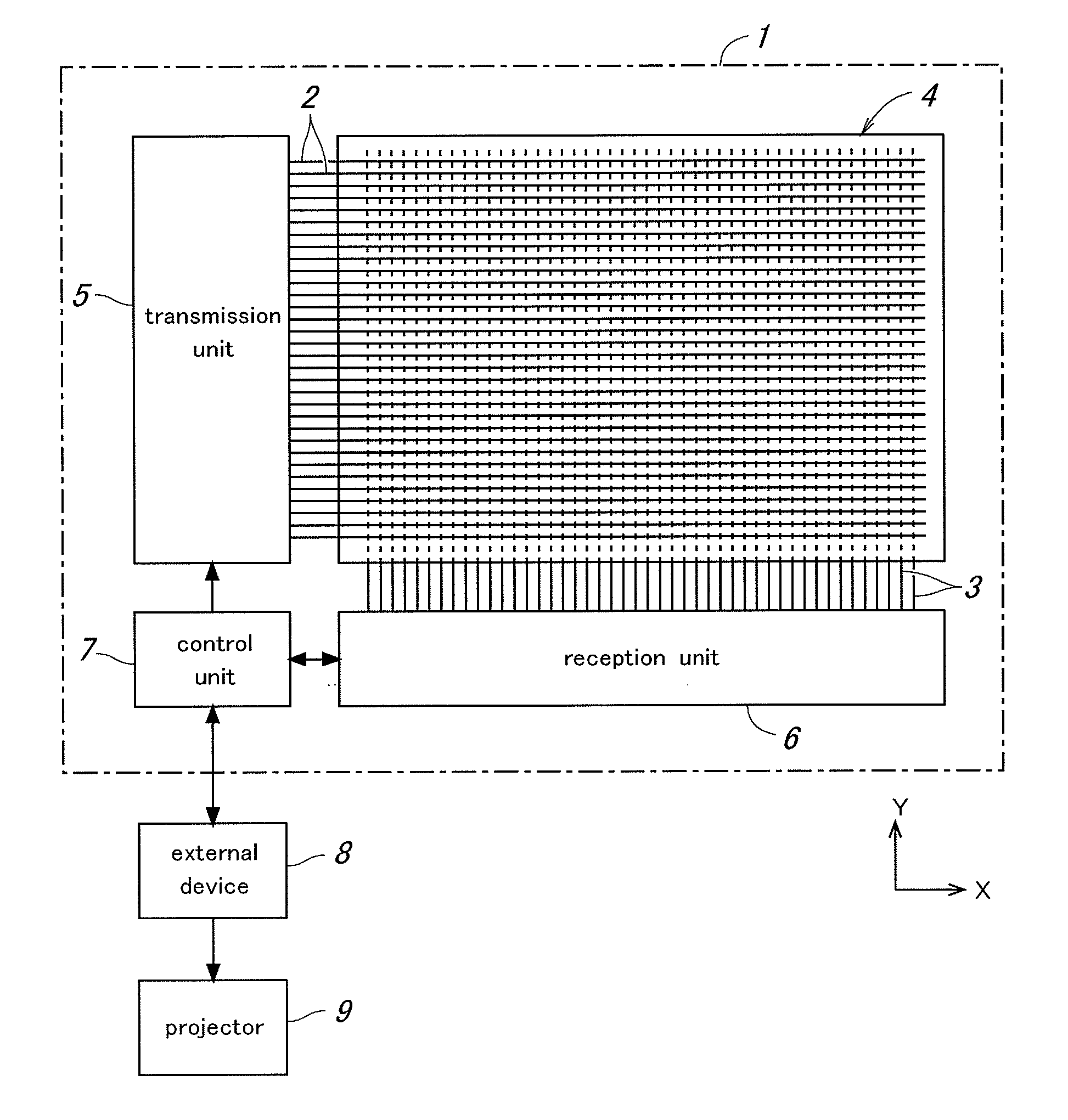
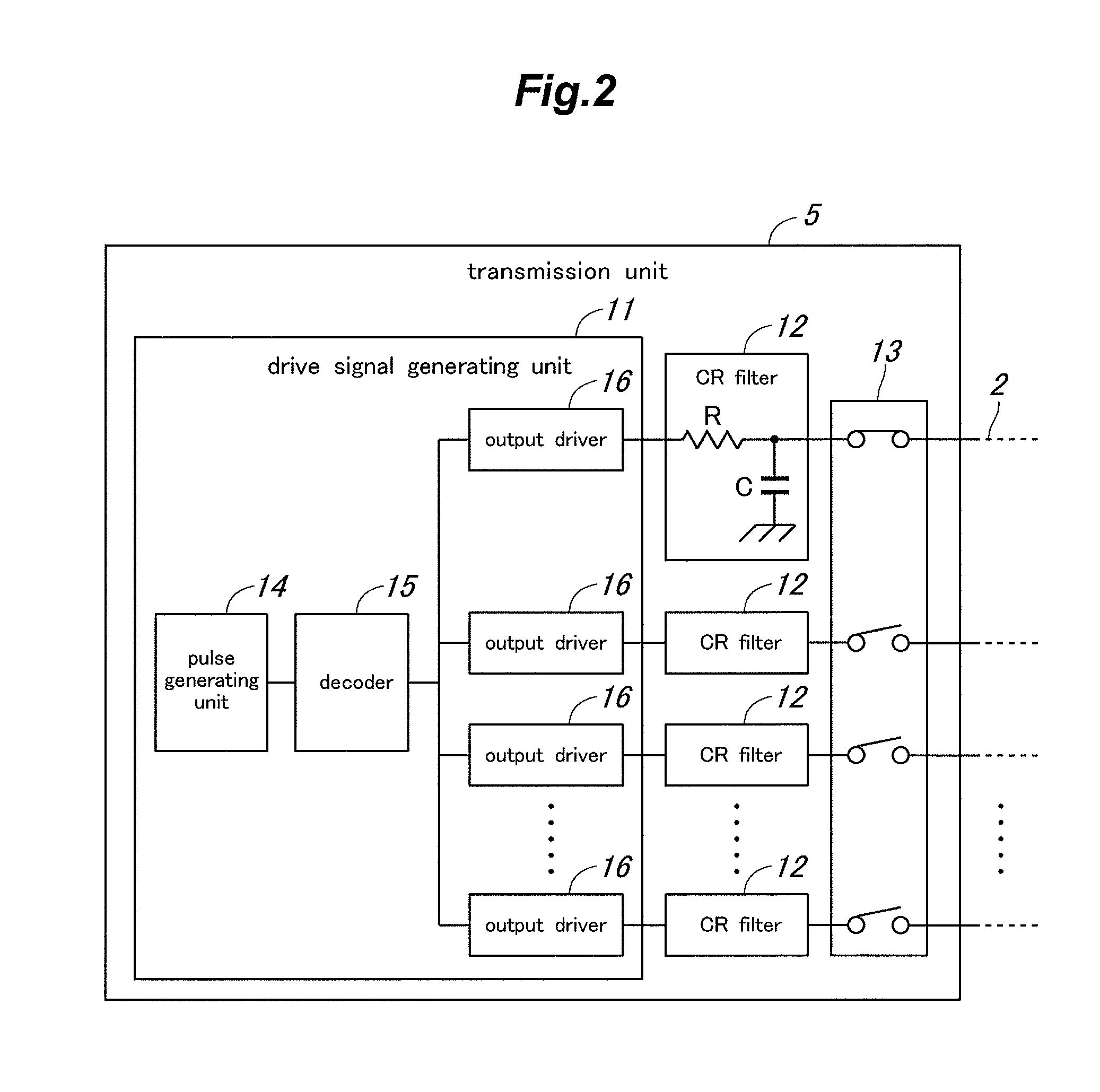
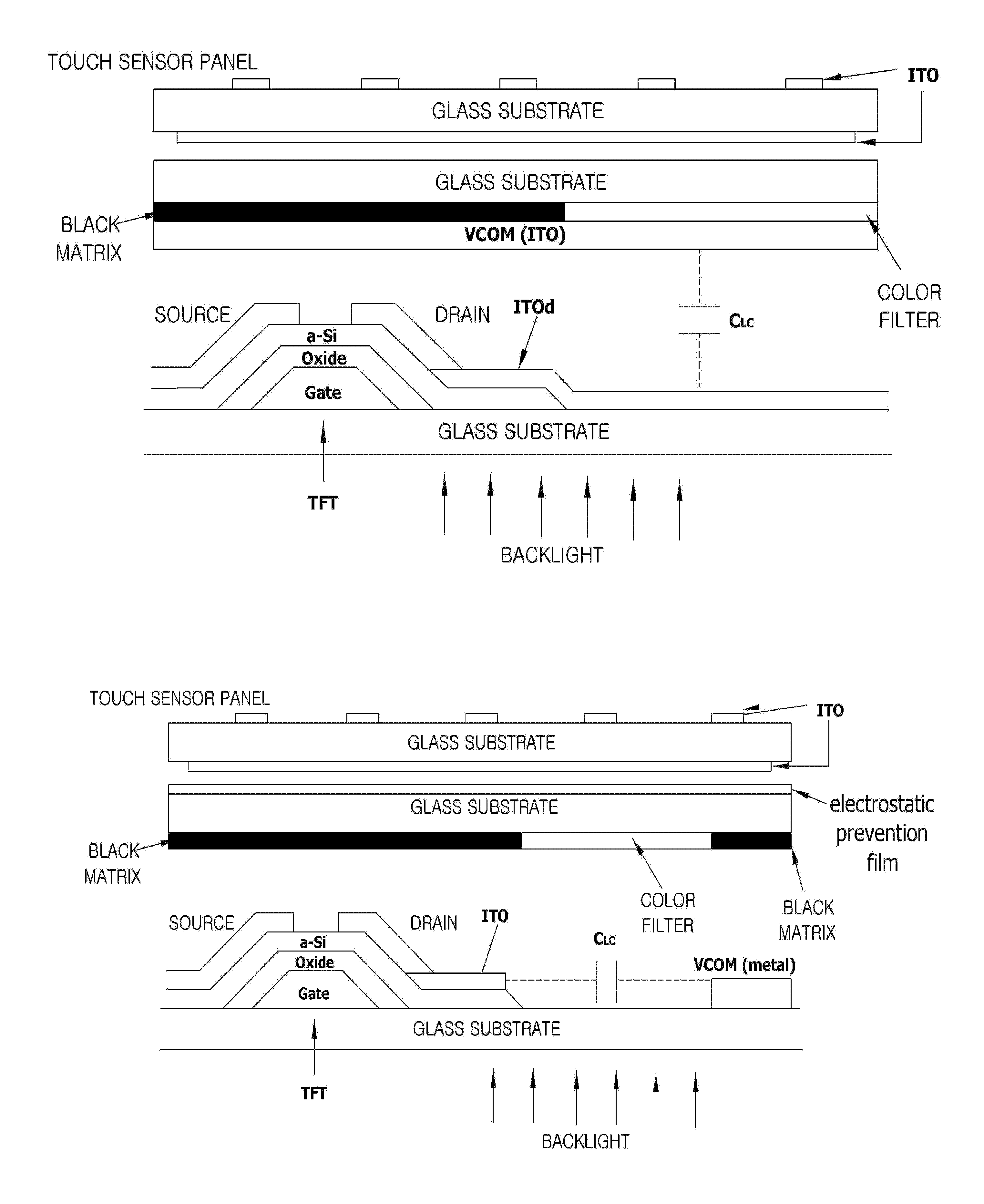
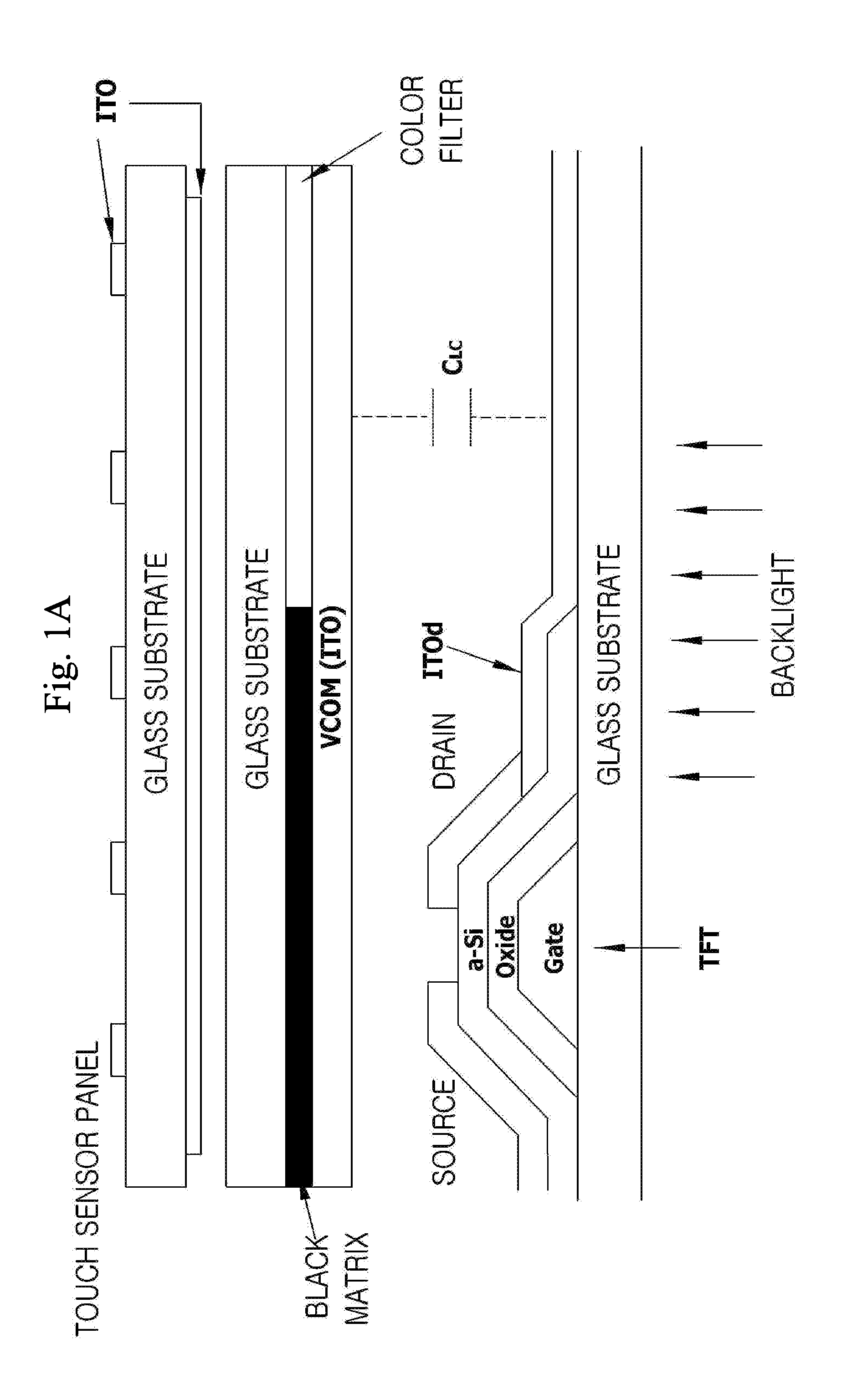
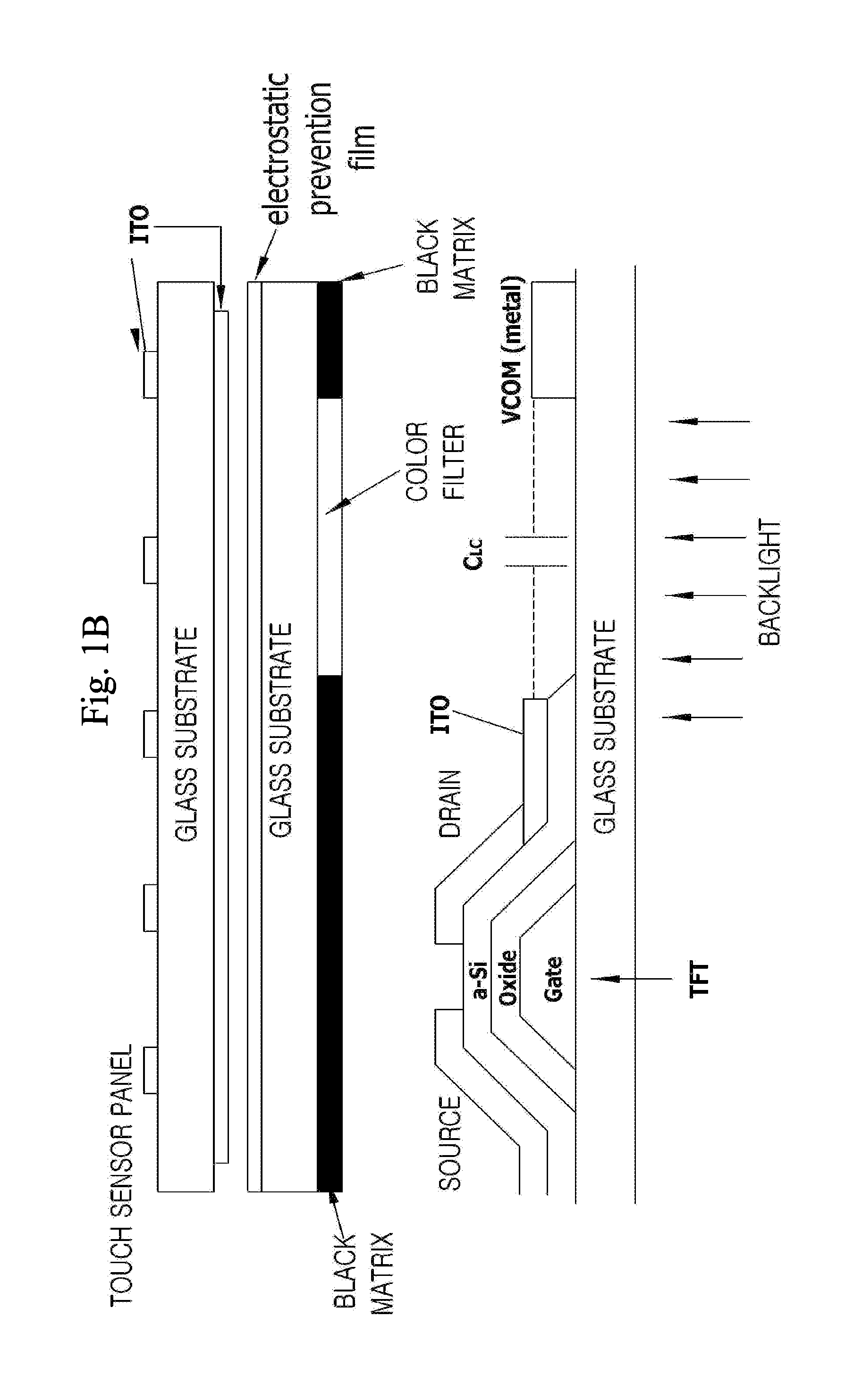
Touch panel device
InactiveUS20110254805A1Reduce noiseMinimize unevenness in positional distributionTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingRC time constantEngineering
In a touch panel device comprising a panel main body (4) including a grid array of transmission electrodes (2) and reception electrodes (3) and defining a touch surface (51), the transmission electrodes are connected to a transmission unit (5) for sequentially applying a drive signal to the transmission electrodes. A time constant element is connected to each transmission electrode via the corresponding lead wire to adjust an overall time constant of the transmission electrode, the time constant of each time constant element being selected to be greater as the length of the lead wire for the corresponding transmission electrode increases. Thereby, the induction noises induced in the reception electrodes owing to the drive signal conducted through the lead wires leading to the transmission electrodes can be minimized and homogenized among the different transmission electrodes, and the positional variations in the distribution of the sensitivity of touch position detection owing to the variations in the lengths of the lead wires leading to the transmission electrodes can be minimized.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
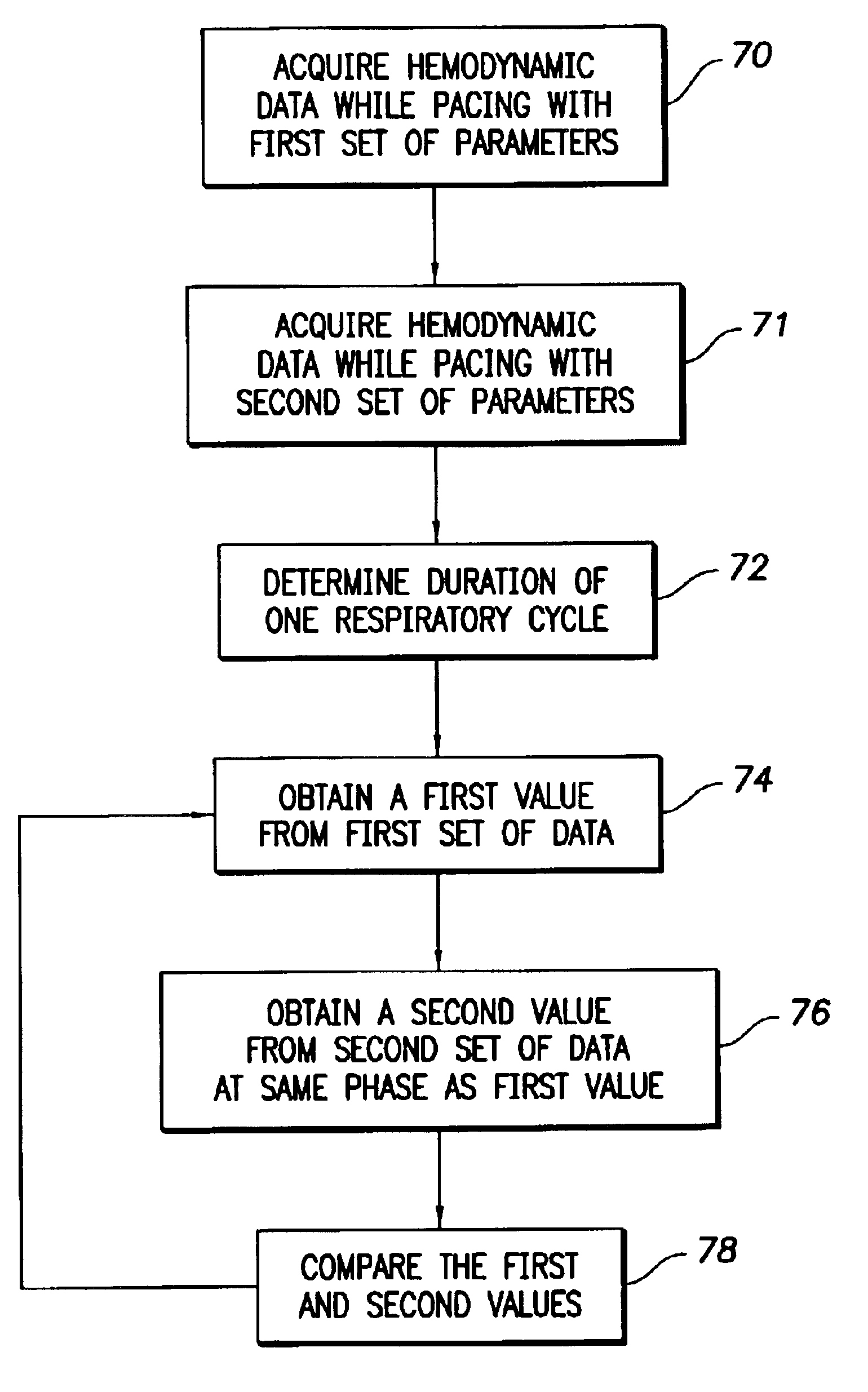
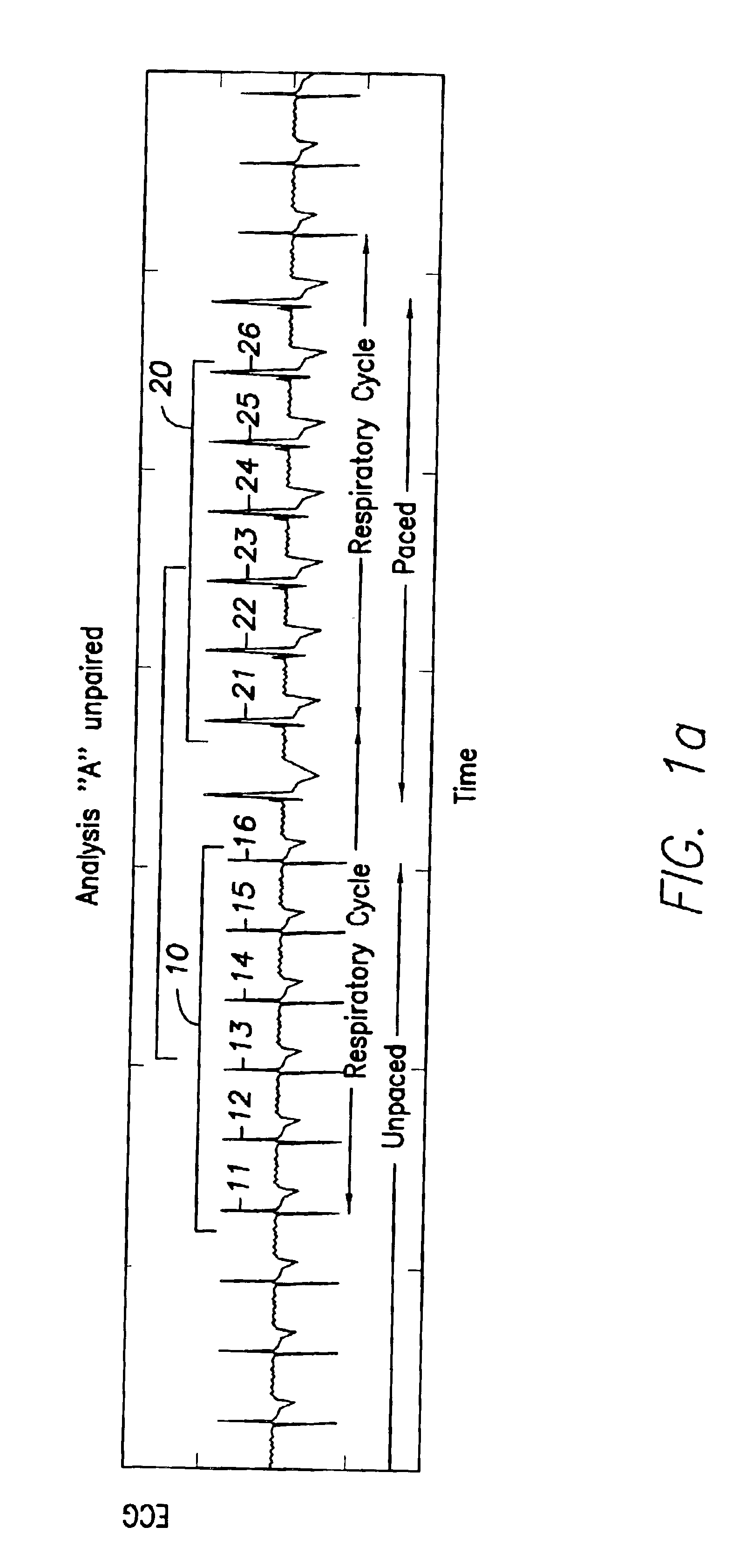
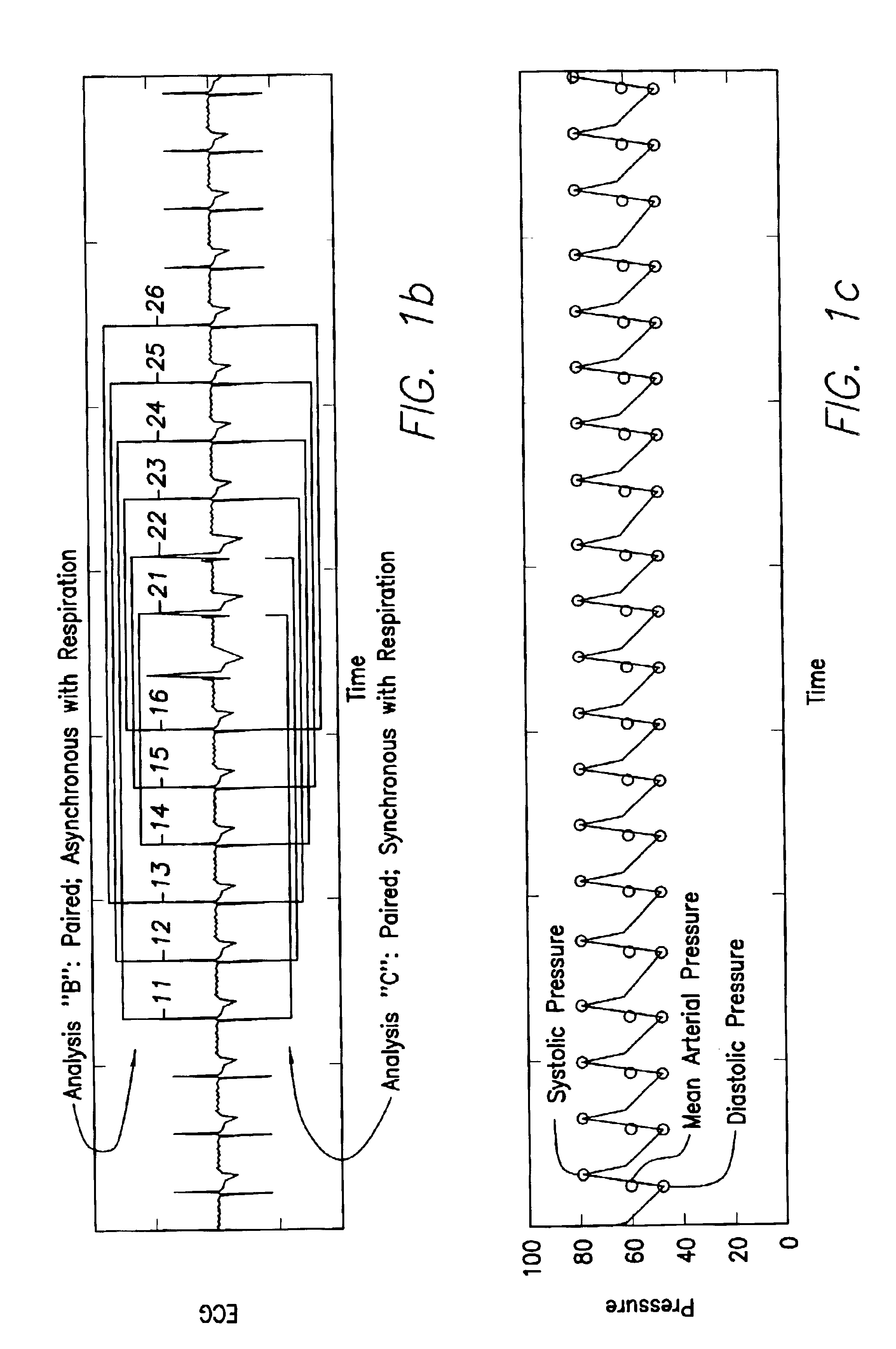
Hemodynamic analysis
To track significant changes in a hemodynamic variable of a living body regardless of measurement noise induced by cyclical functions of the body, the hemodynamic variable is measured at substantially the same instant during several cycles and the measured values compared to identify any statistically significant changes. The measurements may be discrete or continuous. The heart may be stimulated by a cardiac device during some of the cycles and parameters of the device such as the A-V delay of a pacemaker may be adjusted in accordance with the measured change in the hemodynamic variable, which may be, among others, blood pressure or blood volume.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
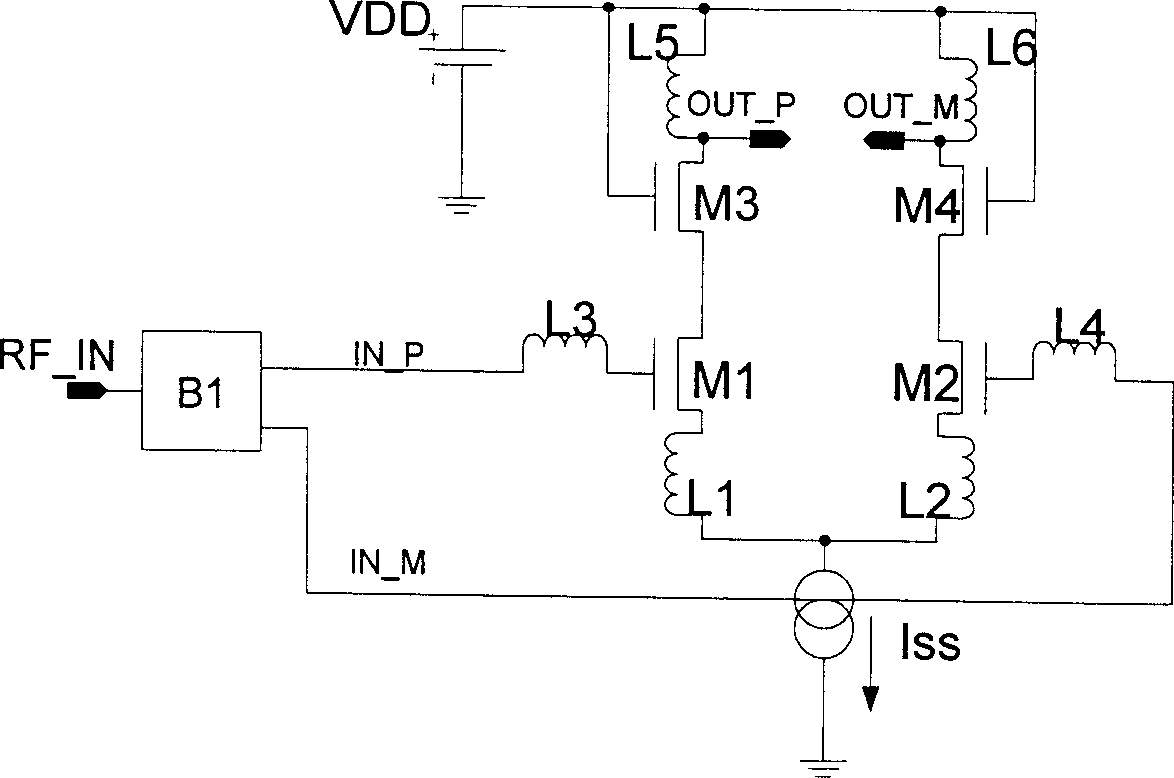
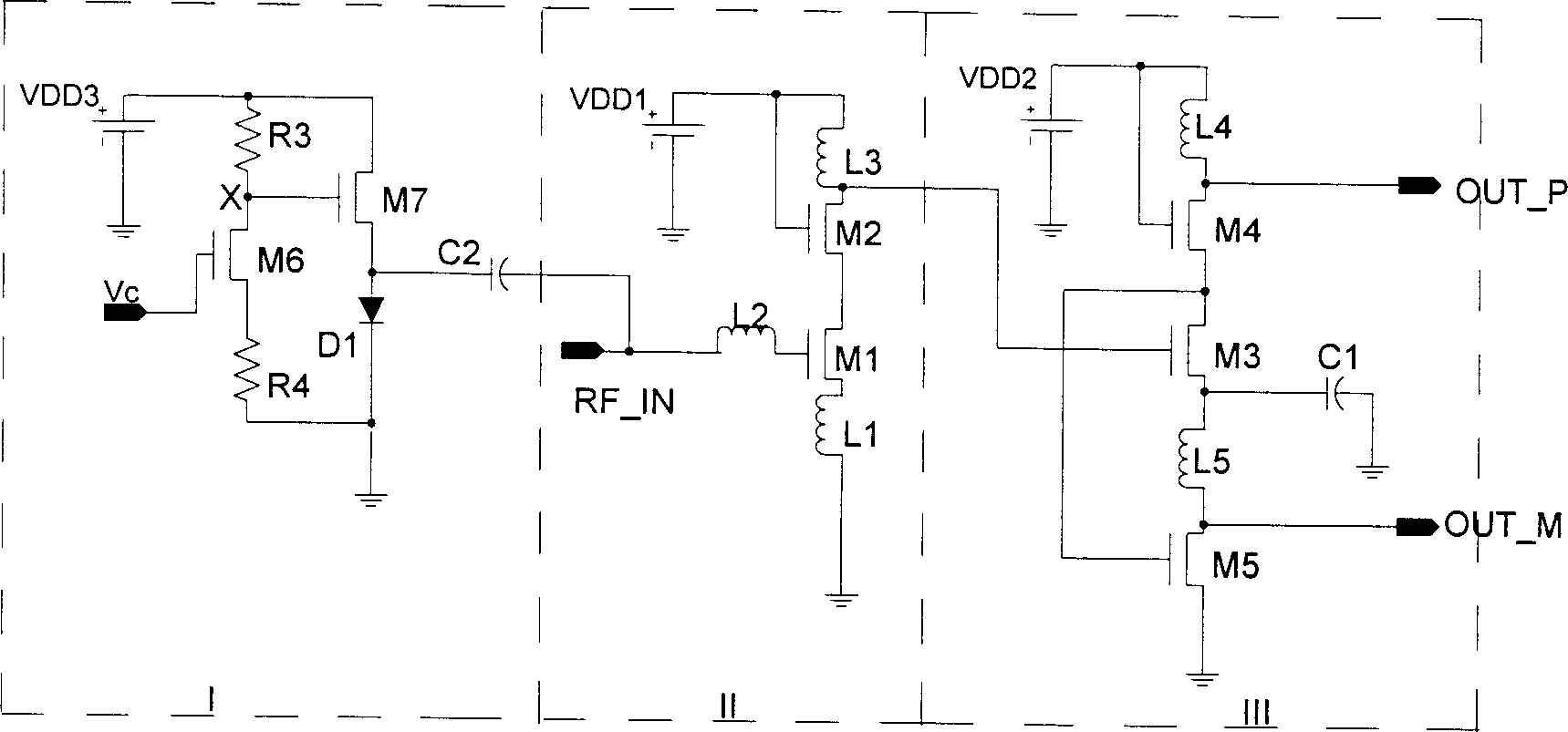
Variable-gain single-ended-to-difference radio-frequency low-noise amplifier
InactiveCN1395363AReduce power consumptionReduce noiseEnergy efficient ICTAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to the radio frequency low noise amplifier from the single end to the difference mode with variable gain belonging to the area of receiver technique in the wireless communication. The amplifier includes main amplifier circuit with single input end, the output buffer from the single end to the difference mode, which is connected to the outupt and input ends respectively, and the variable gain unit. The main amplifier consists of the 2 MOS tubes, 3 inductors. The buffer is composed of 3 MOS tubes, 2 inductors and 1 capacitor. The variable gain unit consists of 2 MOS tubes,2 resistors, capacitors and diodes. The invention provides the advantages of lowering the power consumption, improving the noise, removing the noise induced by the balum, controlling the gain as wellas lowering the requirement of the dynamic range for next stage.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
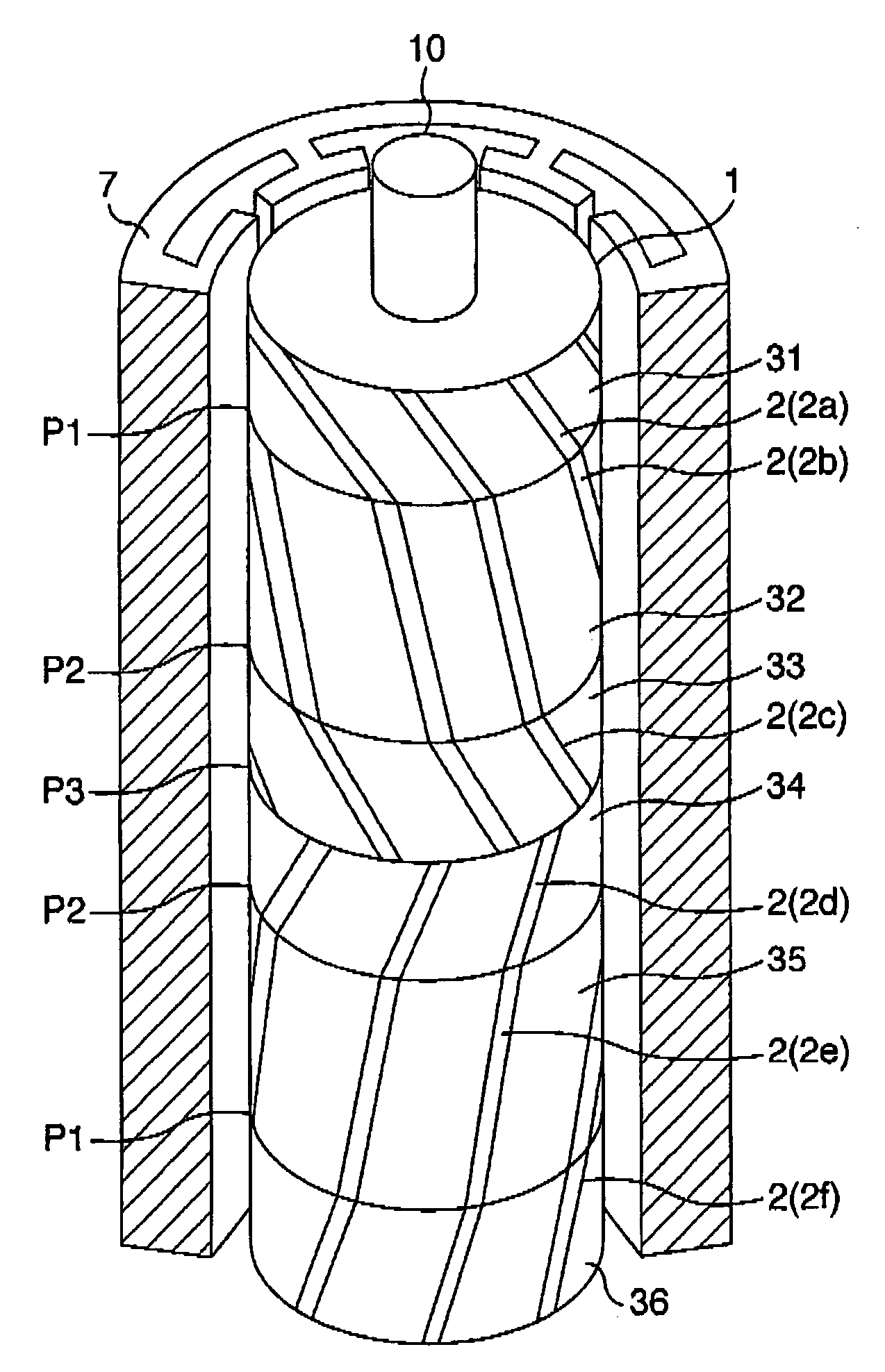
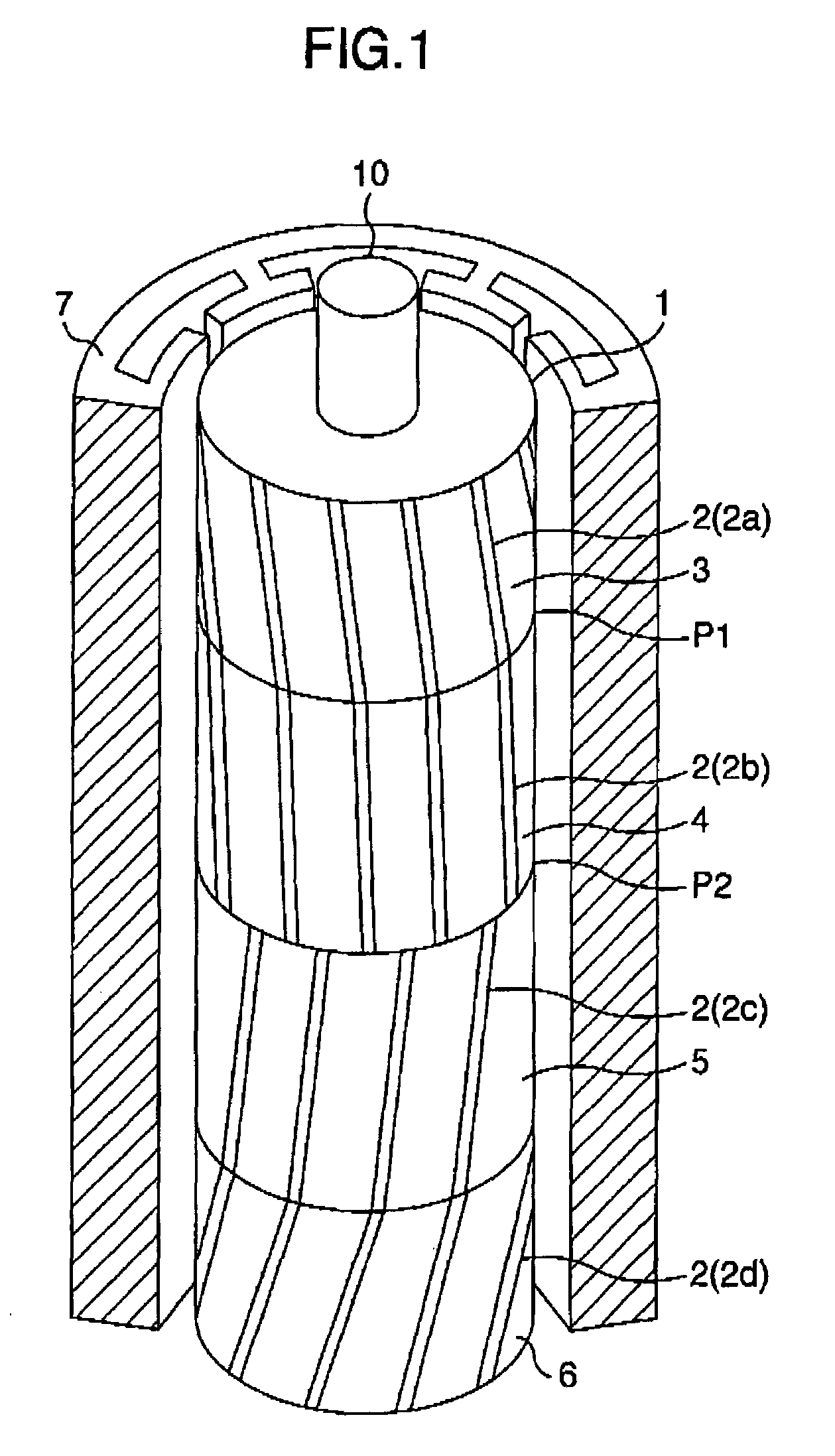
Rotating electric machine
InactiveUS20060163969A1Reduce vibrationReduce noiseMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsElectrical conductorElectric machine
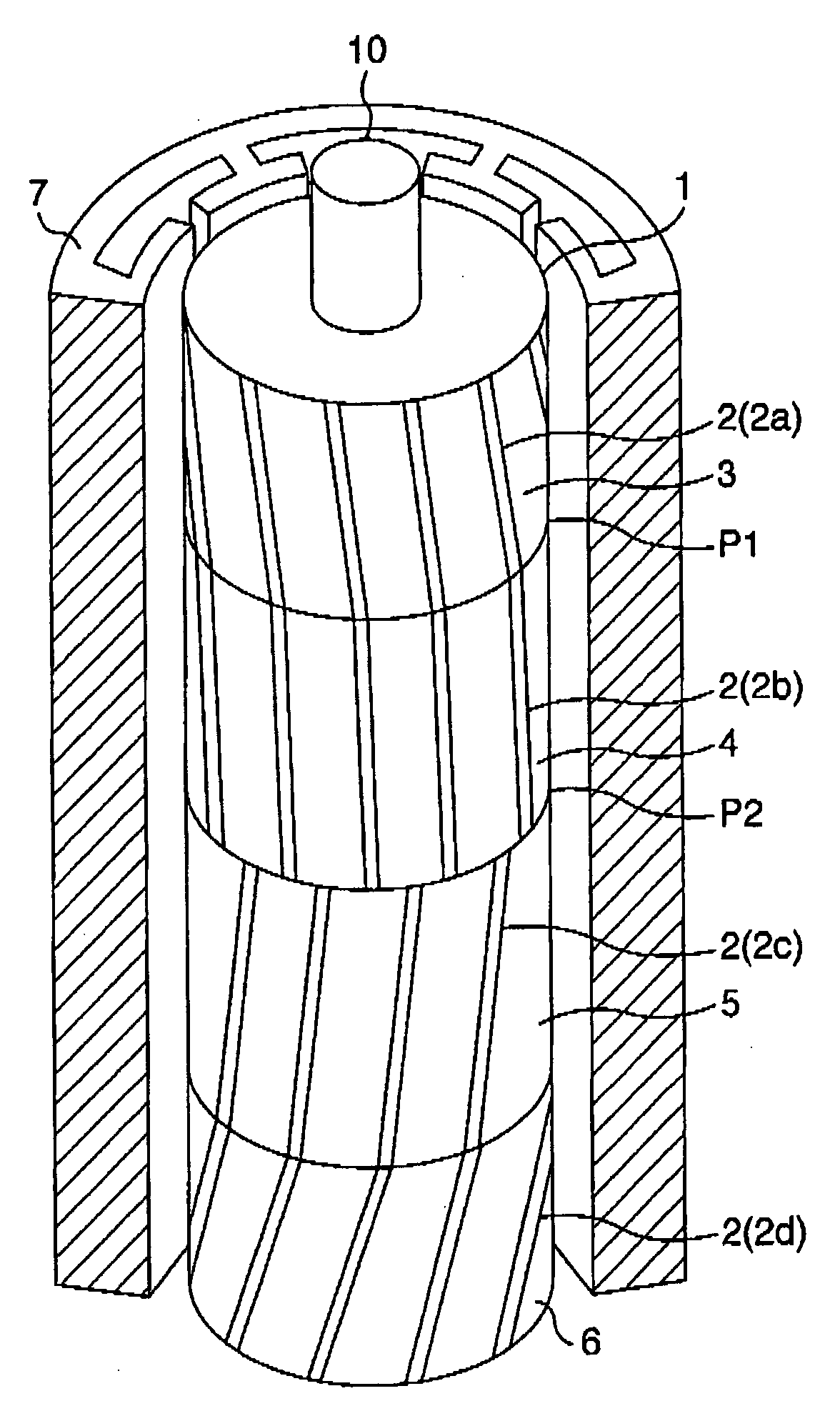
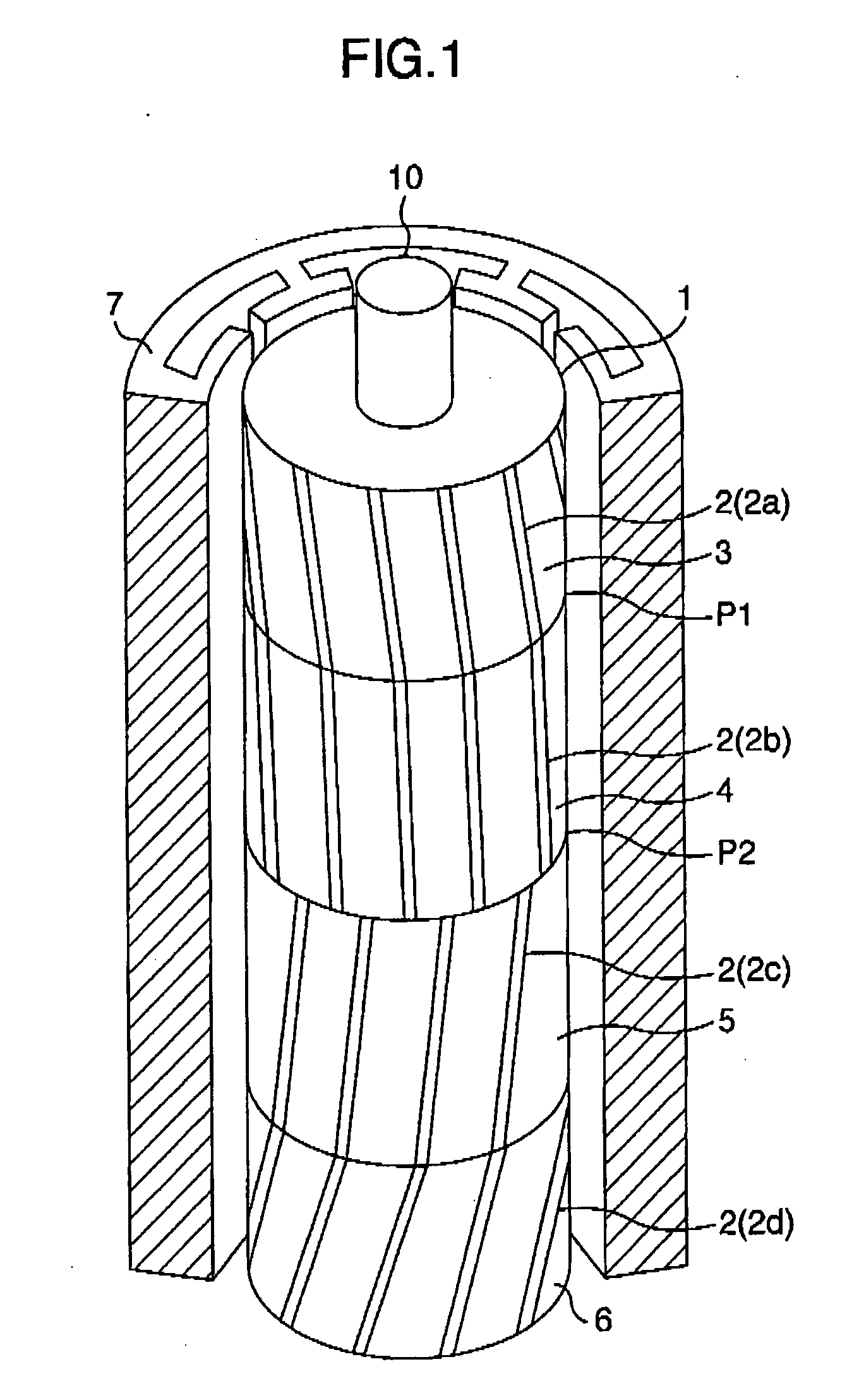
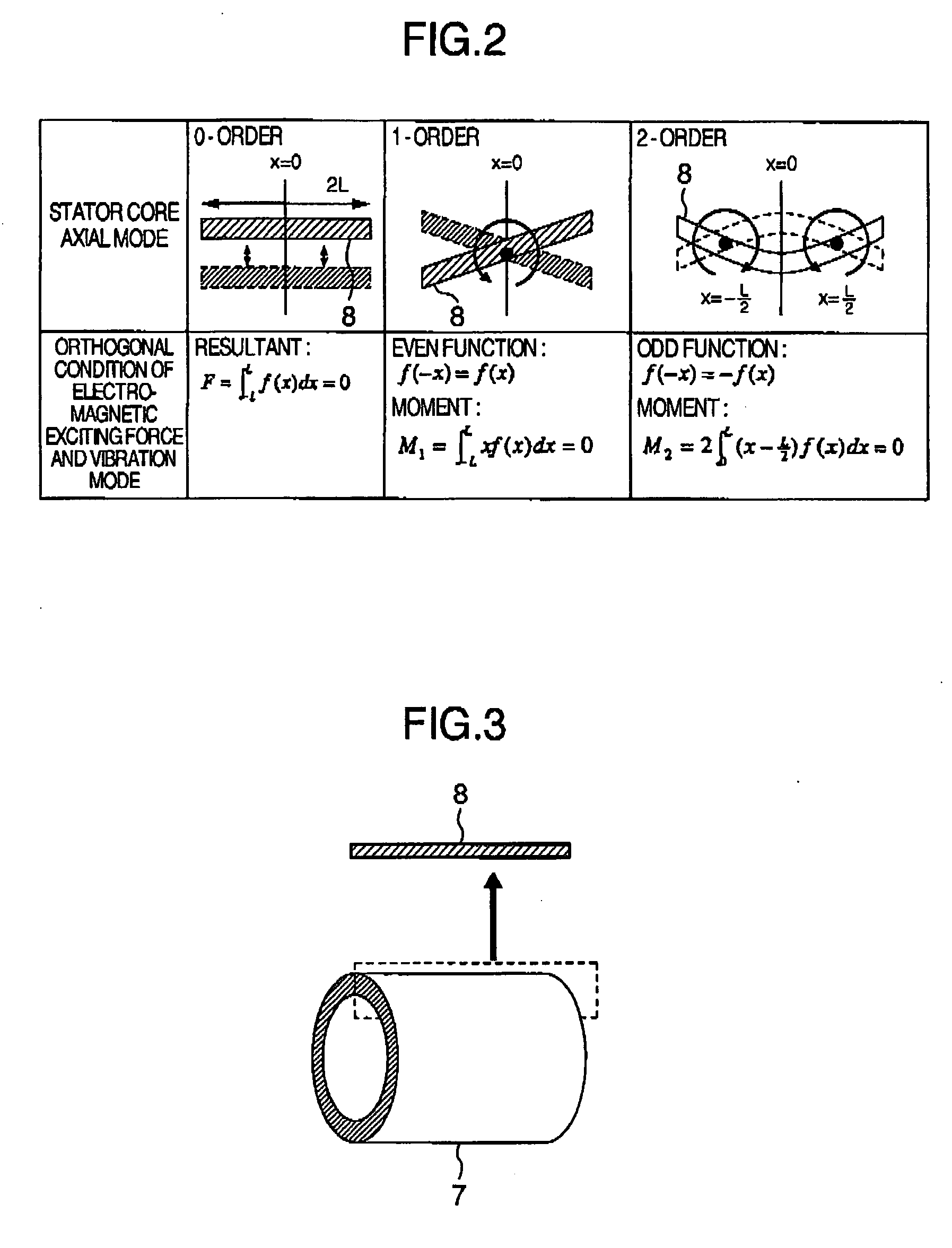
Provided is a rotating electric machine which can restrain vibration and noise induced by a radial electromagnetic force of the rotating electric machine, and in which a rotor is divided into first to fourth four rotating pieces having axial lengths of 0.29 L, 0.71 L, 0.71 L and 0.29 L where 2 L is an axial length of a rotor or stator core, and secondary conductors defining effective magnetic pole opening angles, are arranged being shifted by a value which is equal to a phase difference of electric angle between axial sections of the rotator pieces in order to define skews so that phase differences of electric angles are continuous between axial sections of the first and second rotor pieces, the skews being continuous between the third and fourth rotor pieces but being not continuous between the second and third rotor piece.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Signal generation apparatus and method for seafloor electromagnetic exploration
InactiveUS7187569B2Quality improvementEasy to monitorAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFrequency stabilizationOcean bottom
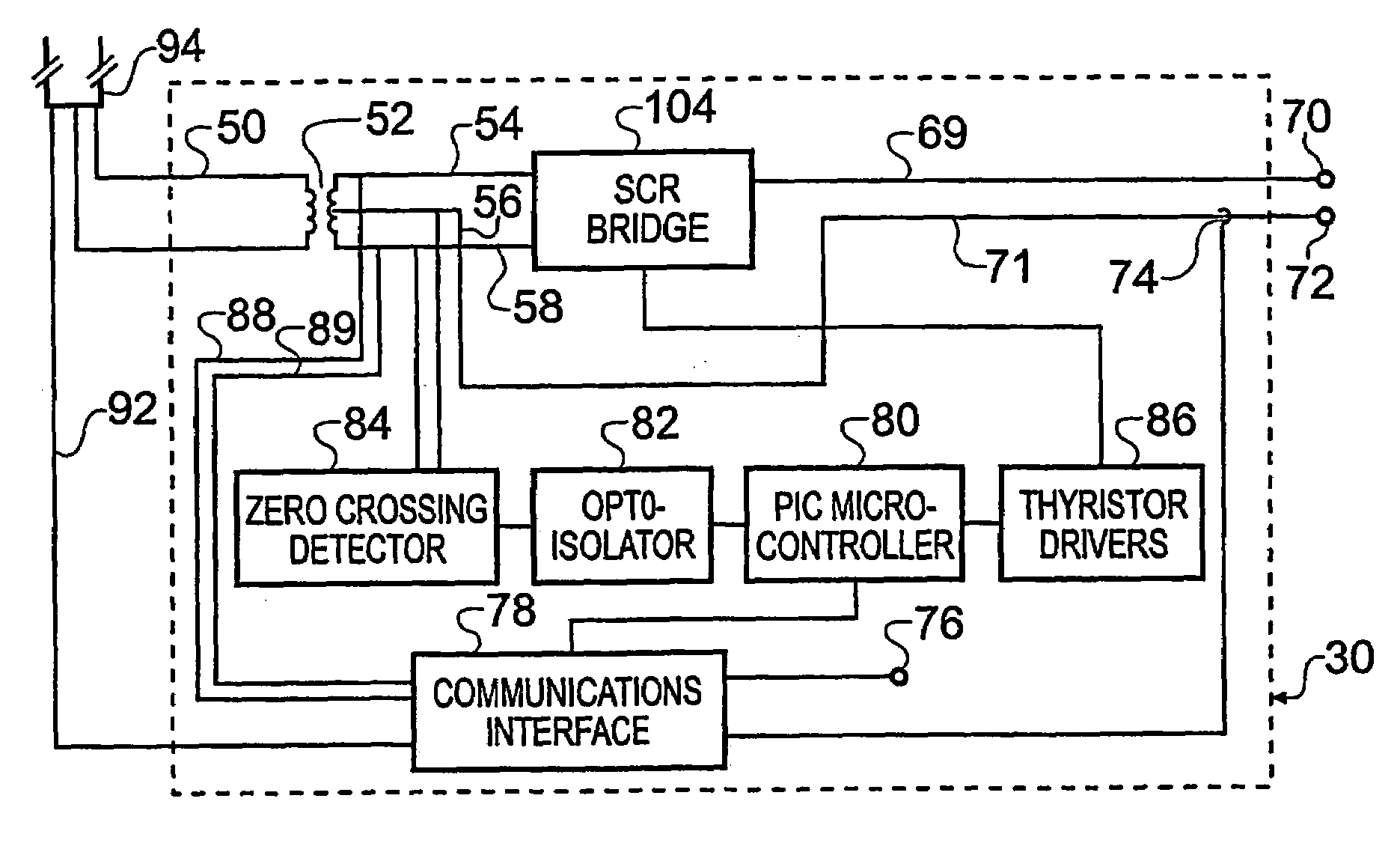
An apparatus for generating electronic signals for application in subsea electromagnetic exploration. A surface generated high-voltage low-current source signal stabilized at a first frequency is supplied to a deep-tow vehicle (18) via an umbilical cable (16). The high-voltage low-current signal is transformed at the deep-tow vehicle to a high-current low-voltage a.c. signal by a transformer (52) within a cycloconverter (30). A semiconductor relay bridge (104) provides switchable rectification of the high-current low-voltage a.c. signal to provide a quasi-square wave at a second frequency, lower than the first frequency, for supply to a transmitting antenna (22) towed by the deep-tow vehicle. The times of the rectification switching are dependent on zero crossings of the high-current low-voltage a.c. signal. Allowable rectification switching times may be gated to occur only within pre-determined time windows to avoid noise-induced zero-crossing switching. The apparatus allows multiple transmission frequencies to be derived from a single stabilized source and improves spectral integrity by avoiding rectification switching at zero-crossings not occurring at the first frequency.
Owner:OHM
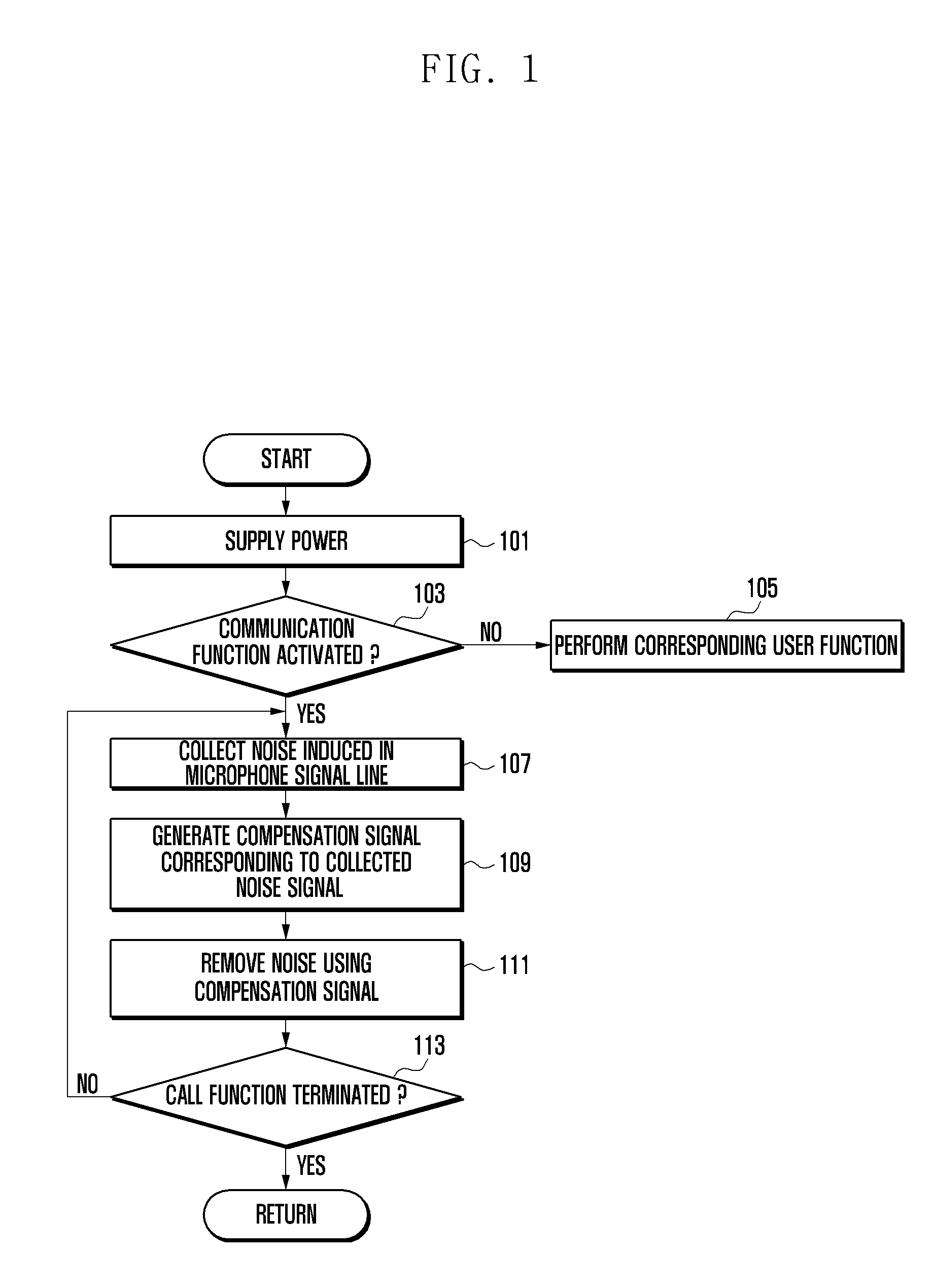
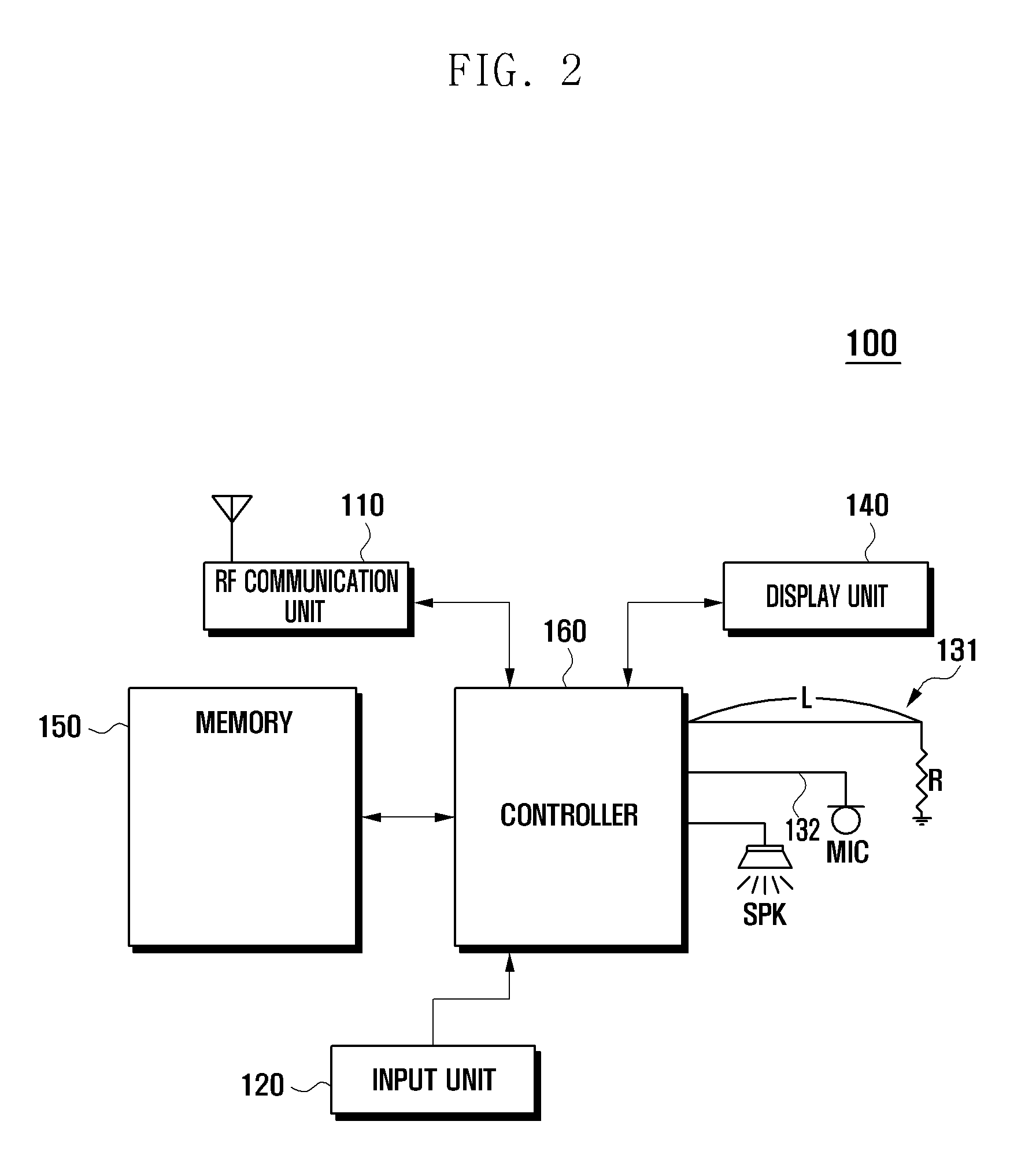
Method of removing microphone noise and portable terminal supporting the same
InactiveUS20130051574A1Cancel noiseImprove call qualityEar treatmentMicrophone structural associationSupport removalEngineering
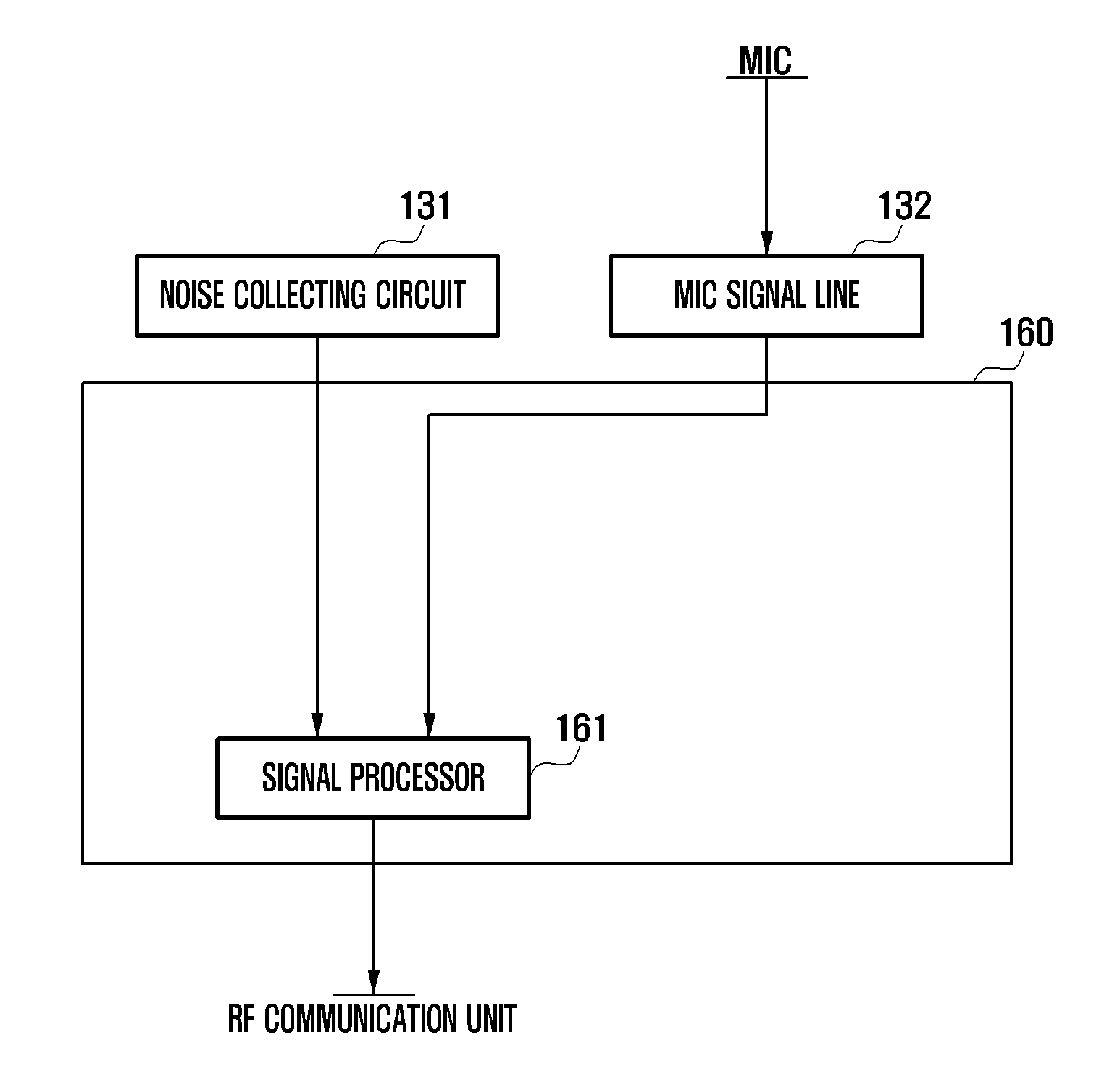
A method of removing a microphone noise and a portable terminal supporting the same are provided. The portable terminal supporting removal of a microphone noise includes a microphone for collecting an audio signal, a controller for processing the audio signal collected by the microphone, a microphone signal line for transferring a microphone signal collected by the microphone to the controller, and a noise collecting circuit disposed at a neighboring region of the microphone signal line for collecting and providing a noise signal similar to a noise induced in the microphone signal line to the controller, wherein the controller controls such that the noise induced in the microphone signal line is removed based on the noise signal collected by the noise collecting circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Oriented PIFA-type device and method of use for reducing RF interference
InactiveUS20060033667A1Reduce radiationLong rangeSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsMulti bandEngineering
An oriented PIFA-type apparatus for reducing hearing aid radio frequency (RF) interference including a directional multi-band and / or single band antenna for use with PWDs such as digital cellphones is disclosed. The apparatus greatly reduces or eliminates the audio noise induced in hearing aids by the PWDs and allows operation of a hearing aid during PWD operation. In operation, the apparatus may be provided on the PWD side away from the user's head. The apparatus may be integrated into the PWB during its manufacture or provided as an after market assembly for a PWD that has a port for connection of an external antenna. The apparatus provides for improved front-to-back ratio as compared to antennas currently in use on PWD's, and therefore also reduces SAR (specific absorption rate), the level of RF energy received into the head by a PWD.
Owner:AERIUS INT
Low noise line powered DAA with differential feedback
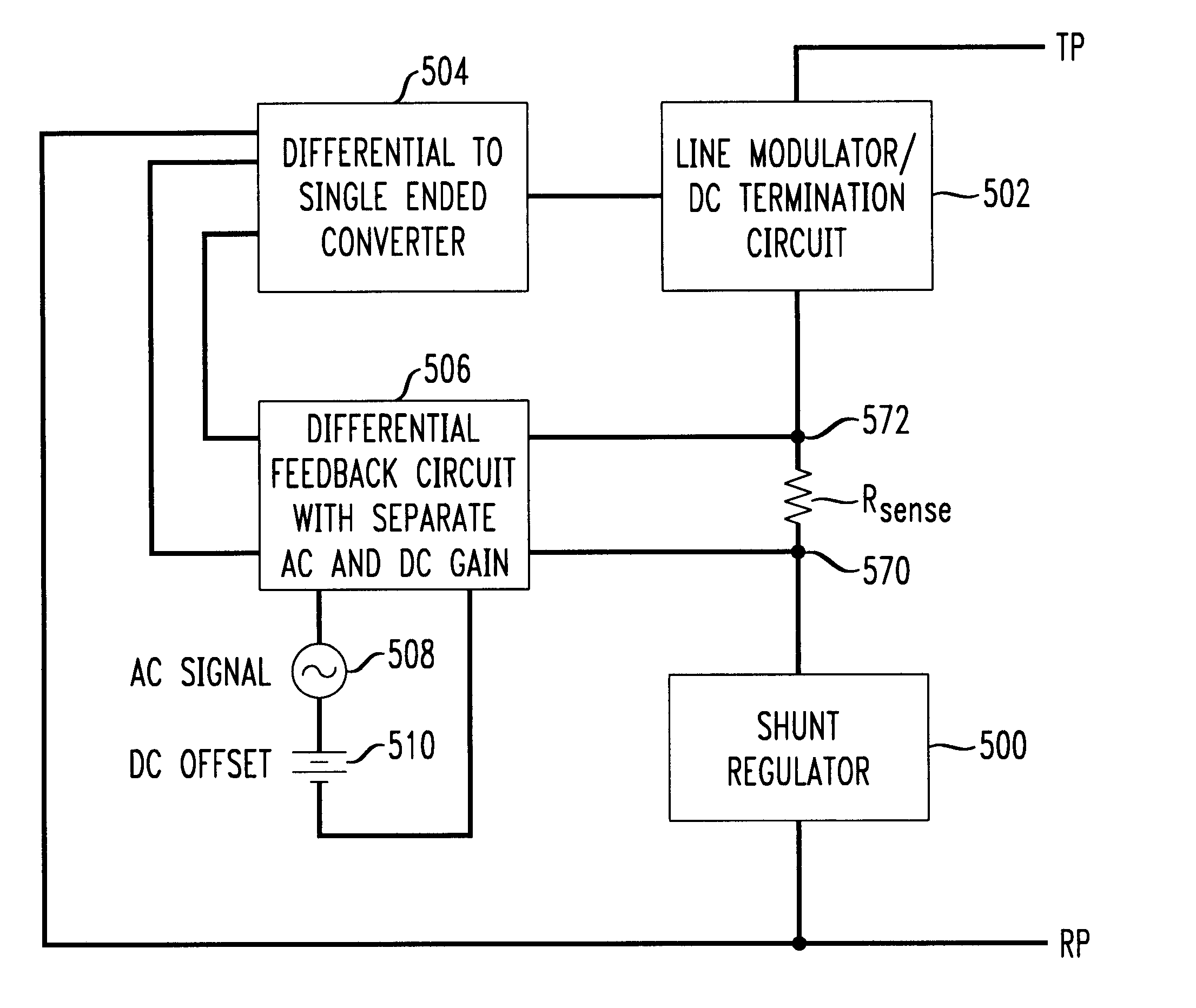
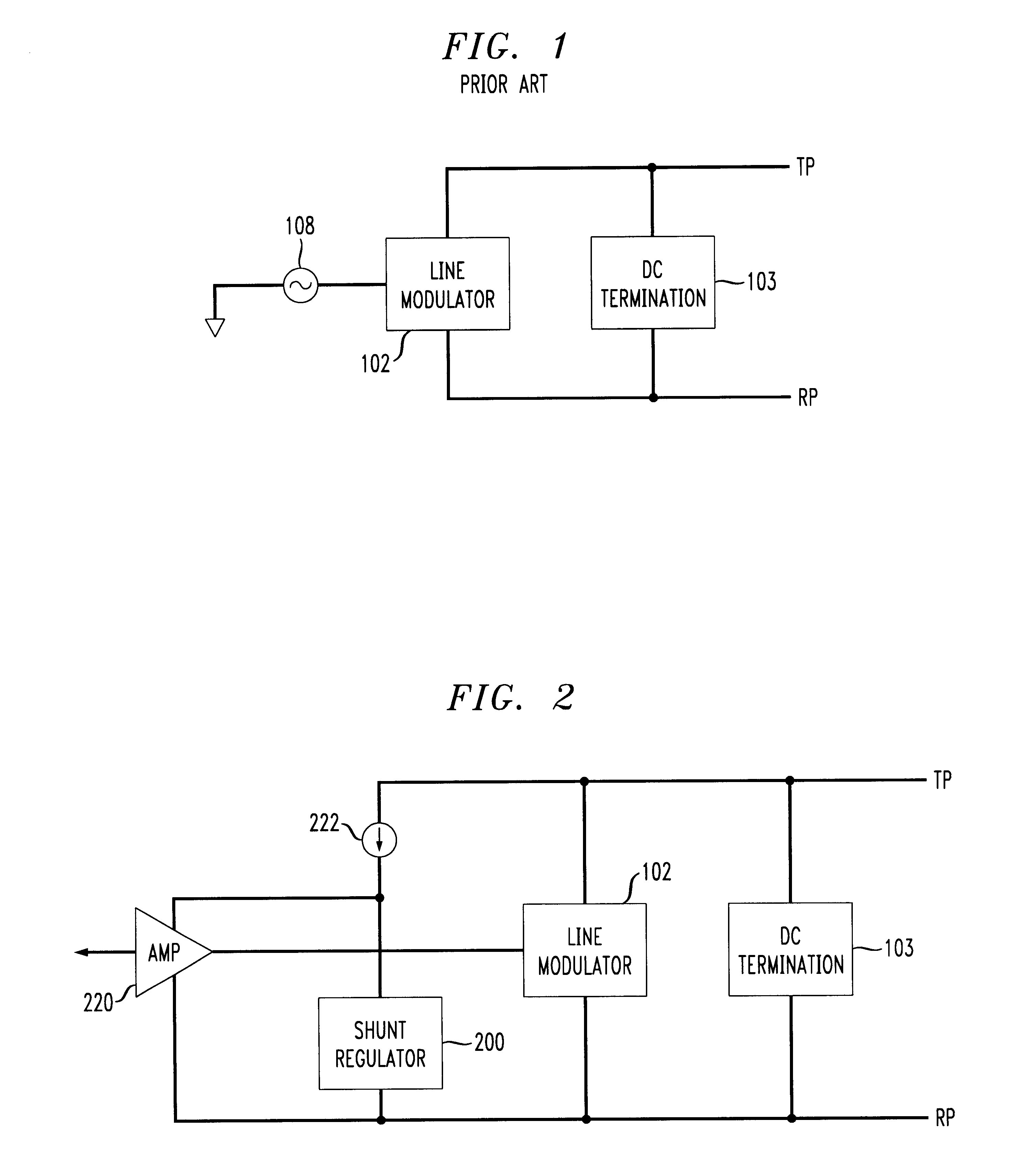
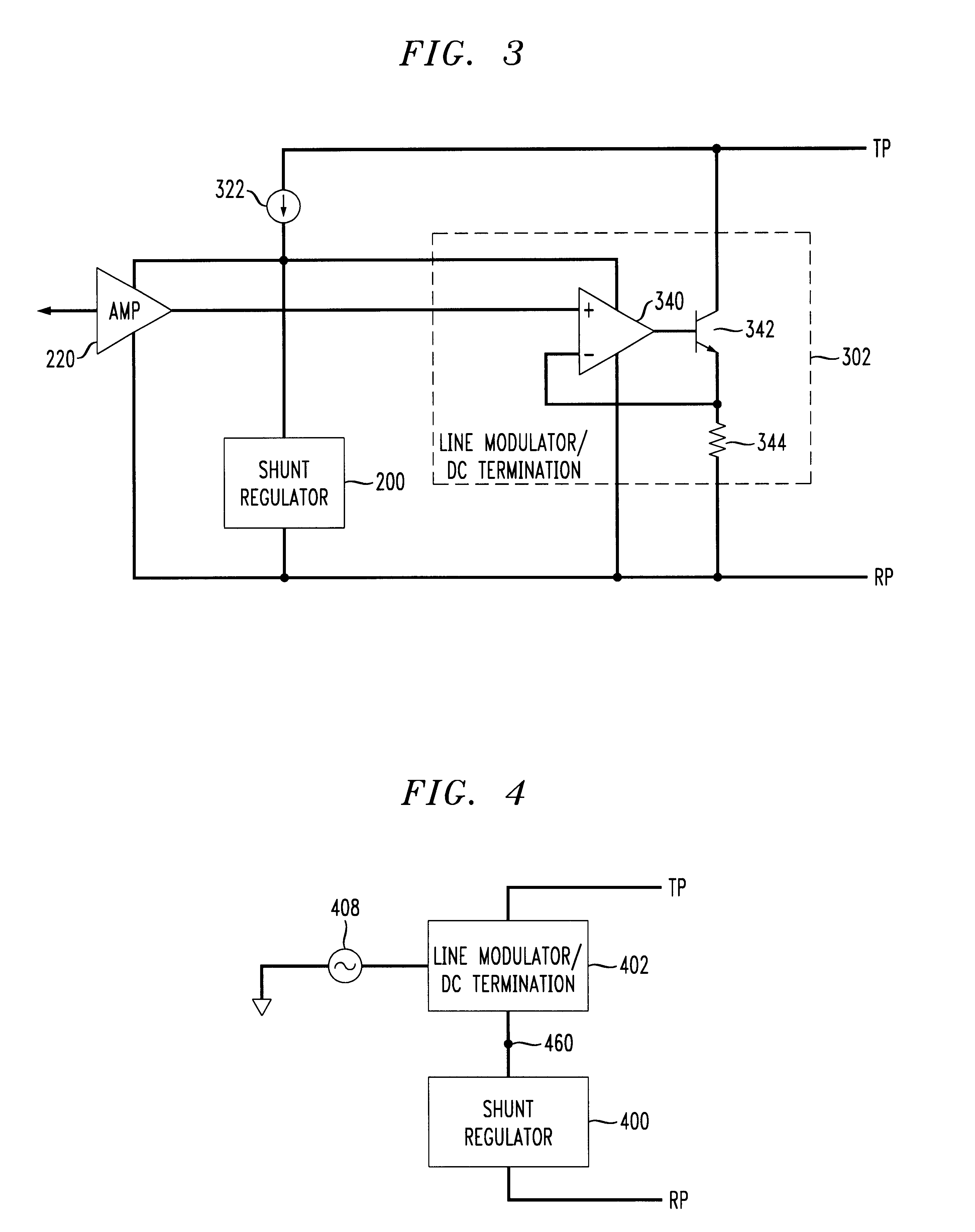
A telephone line interface or data access arrangement (DAA) is provided which draws power for the customer premises equipment from the telephone line. The DAA includes a shunt regulator as the power source drawing power from the telephone line, and a line modulator in series with the shunt regulator. A sense resistor is placed in series between the line modulator and shunt regulator to sense the line current. Accordingly, DC termination and AC modulation characteristics as presented by the DM to the telephone line can be adjusted by variation of an AC signal with DC offset input to the amplifier driving the line modulator without requiring a different DAA for use in regions or countries having various DC termination and AC modulation requirements. The differential feedback from a sense resistor reduces the noise induced in the circuit from the shunt regulator.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
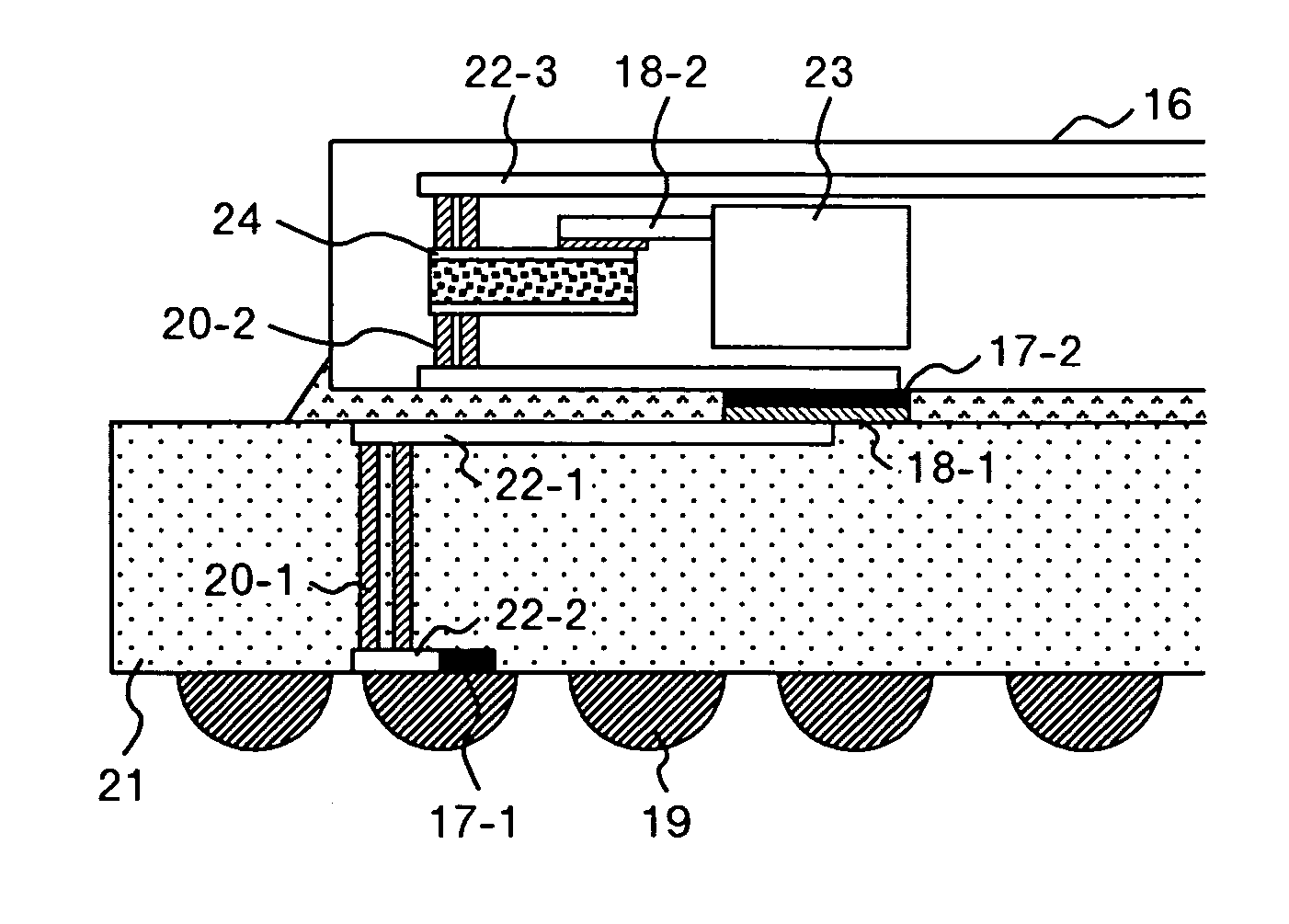
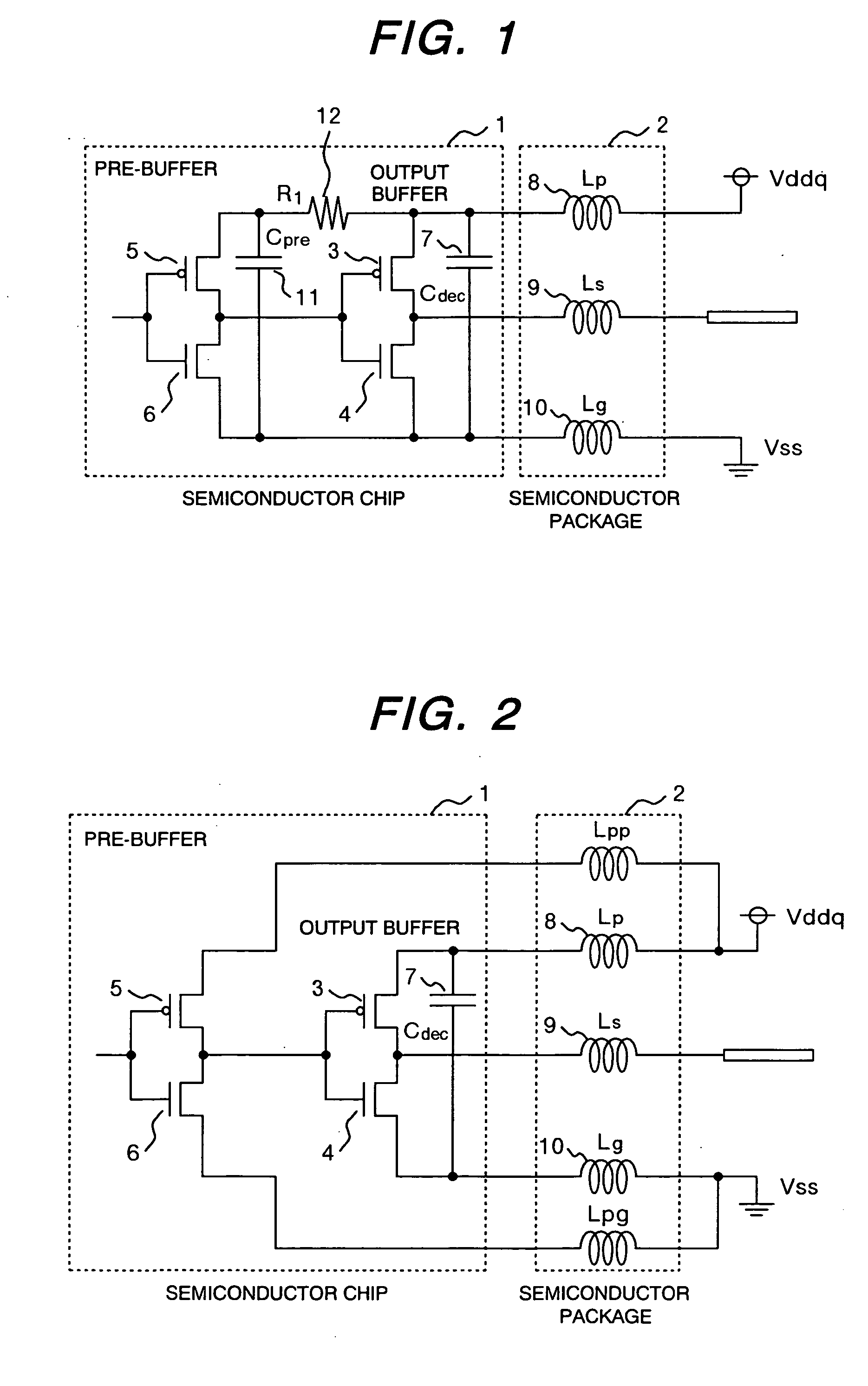
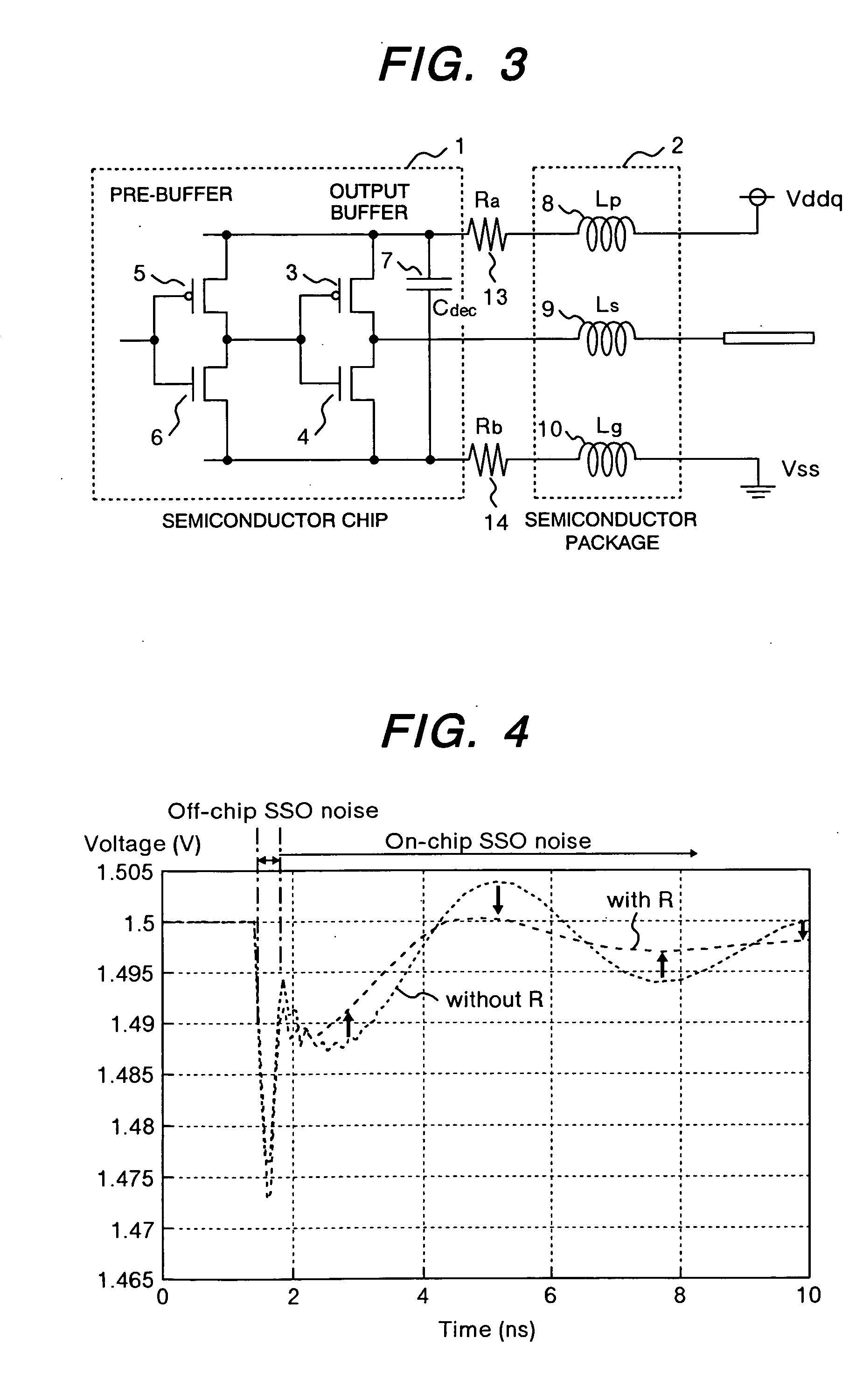
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060017144A1Increase the number ofAvoid noiseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSnubber
The present invention provides a technique which, without causing two problems, i.e., (1) increased number of power supply / grounding pins and (2) increased power feed line inductance, prevents the noise causing a problem in a control circuit, from becoming routed around and induced into an output buffer. More specifically, the above can be realized by using either of two methods: (A) providing an on-chip bypass capacitor for the control circuit and isolating a power feed route of the control circuit from that of the output buffer in an AC-like manner, or (B) designing electrical parameters (inserting resistors) such that the oscillation mode of any electrical parameter noise induced into the power feed routes will change to overdamping.
Owner:LONGITUDE LICENSING LTD
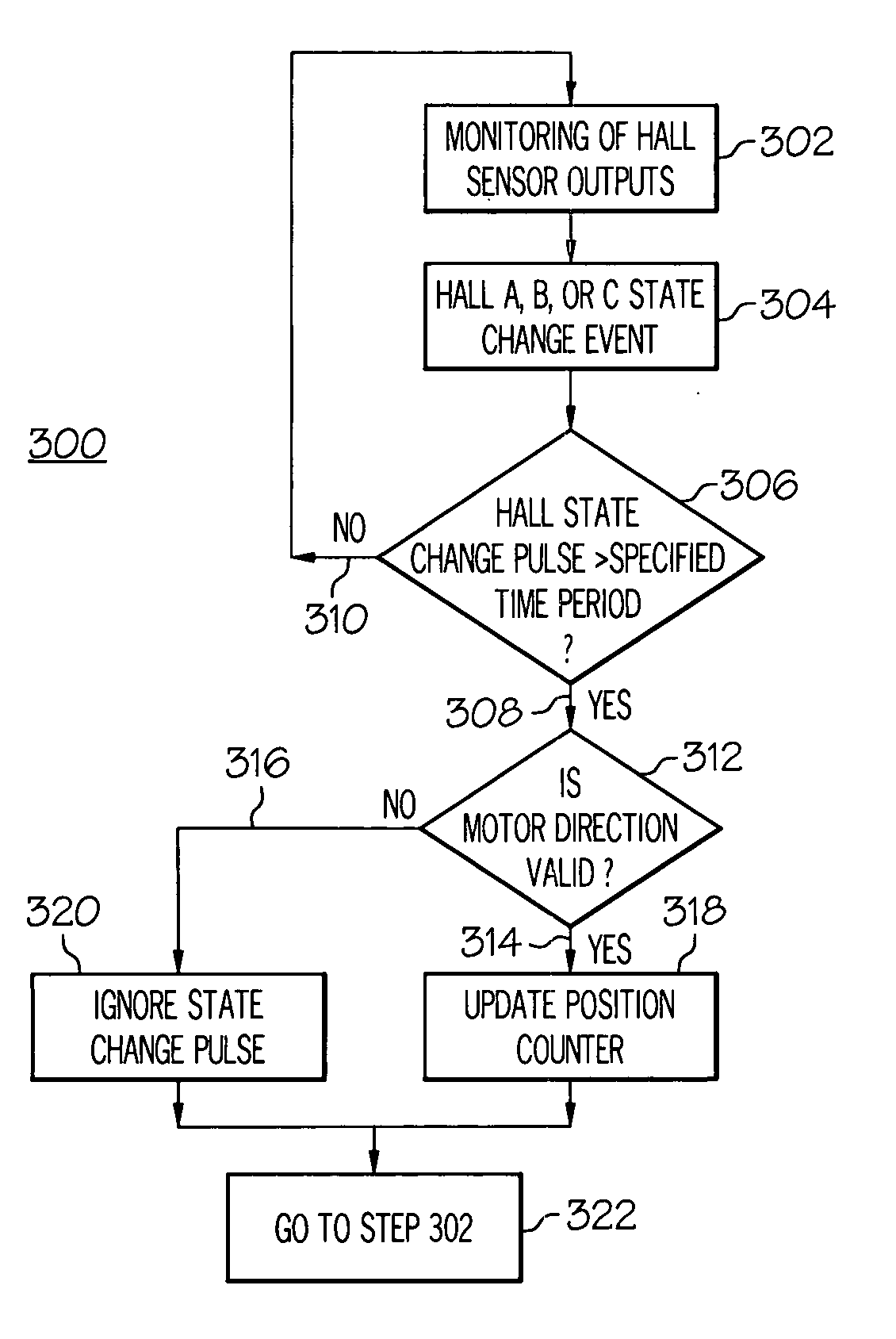
Motor state counting
ActiveUS20050152489A1Magnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesCounting objects on conveyorsPermanent magnet motorArtificial intelligence
Systems, methods, and computer-readable media are disclosed for error-compensated counting of Hall states for motor position feedback and / or commutation. An indicated Hall state is detected by digital Hall state sensors and a duration of the Hall state is compared to a specified time period. When the duration exceeds the specified time period, the indicated Hall state is compared to one or more valid Hall states and a position counter is changed for valid states. When the indicated Hall state is invalid, the position counter is not changed. The Hall state sensors may be connected to logic means and may detect the position of a rotor of a permanent magnet motor relative to a stator. When noise induces a change in an indicated Hall state, corresponding noise-induced effects on the position counter may be may be removed through error-compensated counting.
Owner:HR TEXTRON
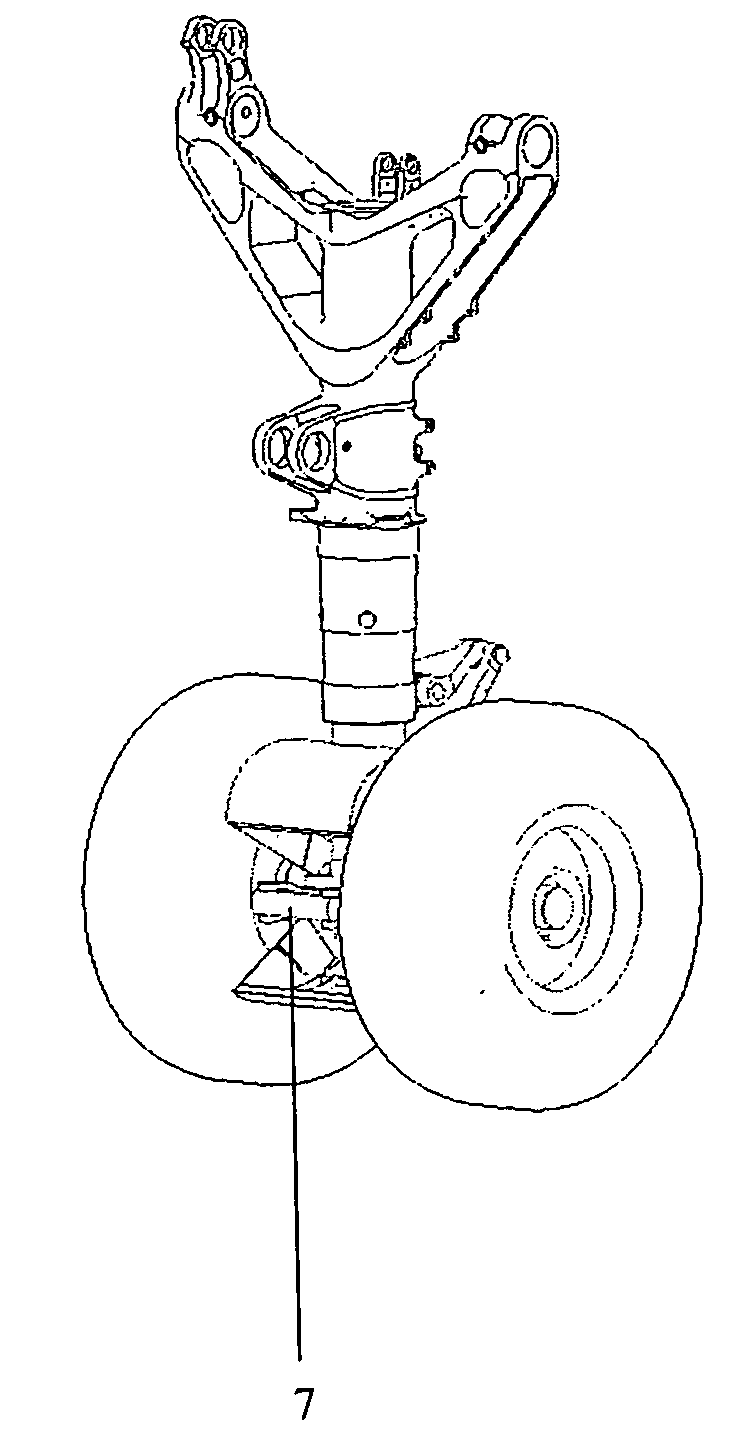
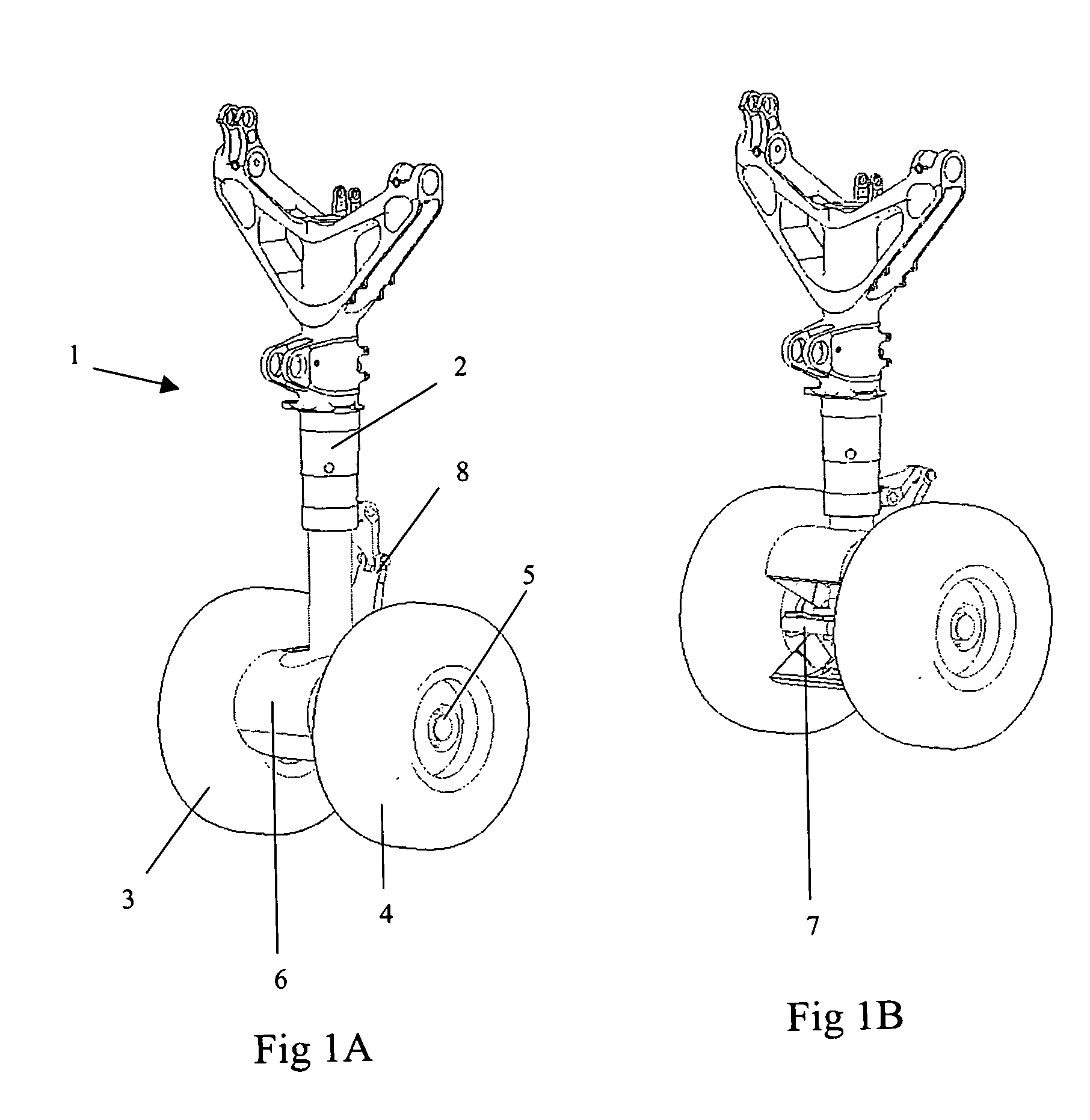
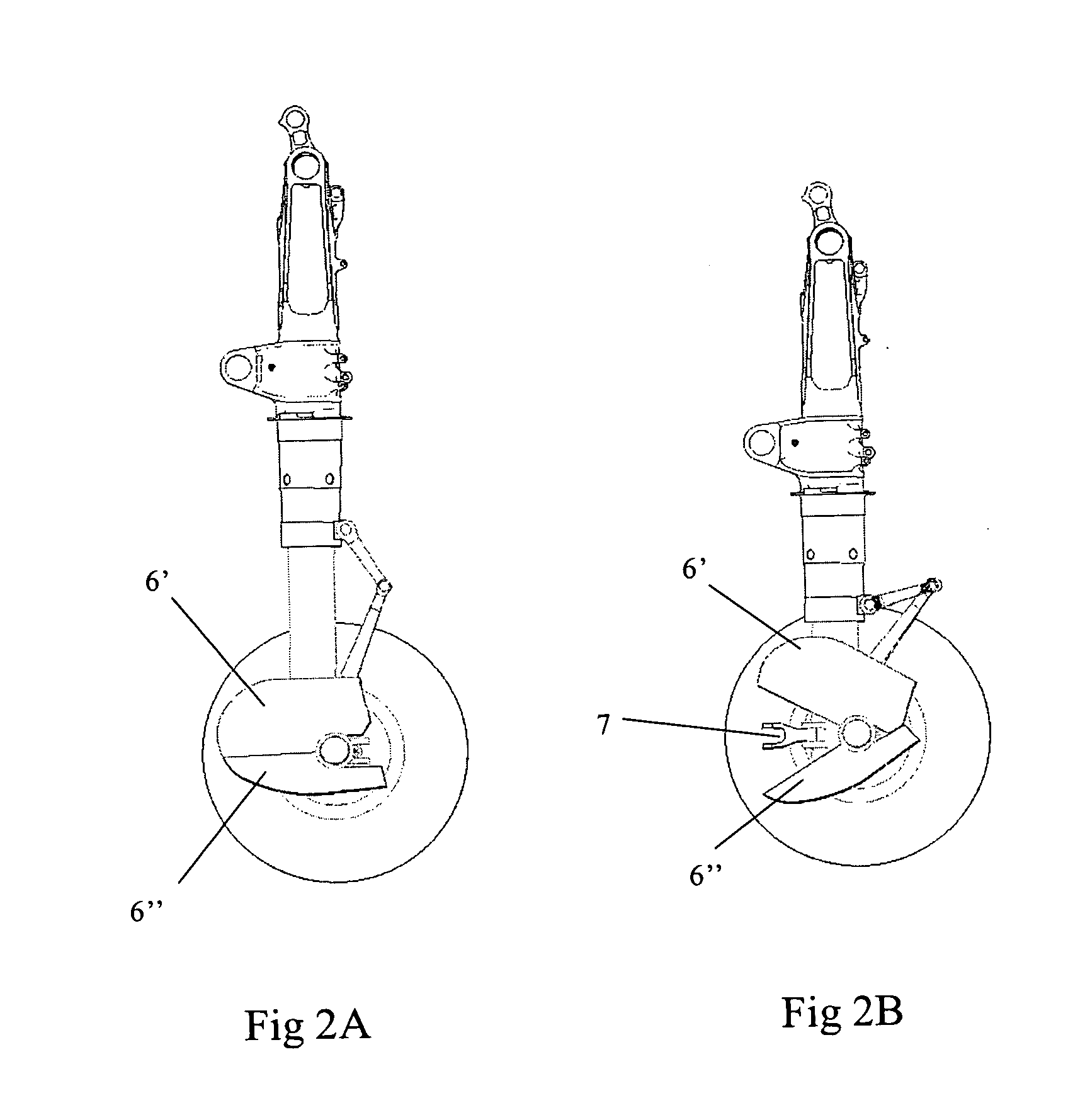
Aircraft noise reduction apparatus
InactiveUS20090321559A1Easy accessReducing aircraft noiseFuselage insulationAir-flow influencersAircraft landingNoise reduction
The invention relates to aircraft noise reduction apparatus, in particular, but not exclusively, to noise reduction apparatus on an aircraft landing gear. The aircraft noise reduction apparatus comprises a noise reduction attachment for a landing gear of an aircraft. The noise reduction apparatus is movable between a first position in which it deflects air away from a noise inducing component of the landing gear and a second position in which it allows access to the noise inducing component. The movement of the noise reduction attachment between the first and second positions is actuated by a part of the landing gear.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Rotating electric machine
InactiveUS7541710B2Reduce vibrationReduce noiseMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous motorsElectrical conductorElectric machine
Provided is a rotating electric machine which can restrain vibration and noise induced by a radial electromagnetic force of the rotating electric machine, and in which a rotor is divided into first to fourth four rotating pieces having axial lengths of 0.29L, 0.71L, 0.71L and 0.29L where 2L is an axial length of a rotor or stator core, and secondary conductors defining effective magnetic pole opening angles, are arranged being shifted by a value which is equal to a phase difference of electric angle between axial sections of the rotor pieces in order to define skews so that phase differences of electric angles are continuous between axial sections of the first and second rotor pieces, the skews being continuous between the third and fourth rotor pieces but being not continuous between the second and third rotor pieces arranged being shifted by a value which is equal to a phase difference of electric angle between axial sections of the rotor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
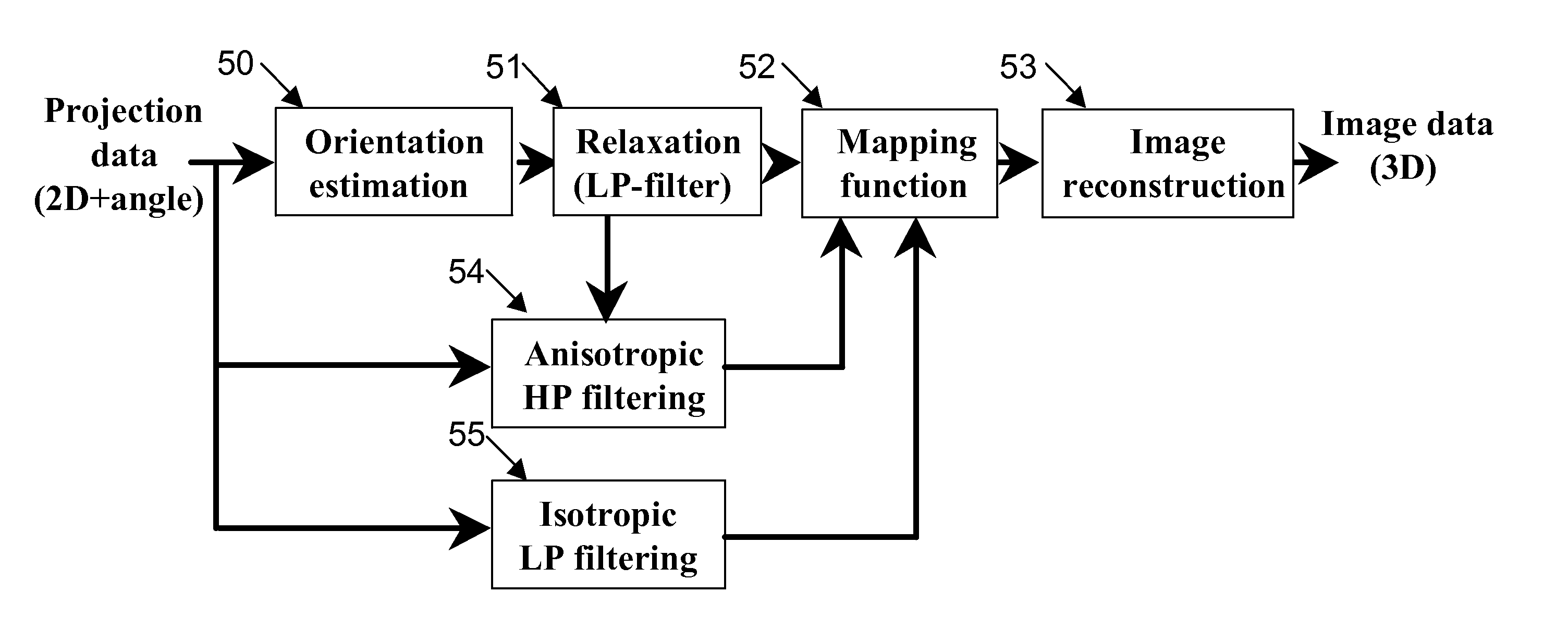
Adaptive anisotropic filtering of projection data for computed tomography
ActiveUS20080069294A1Reduce high frequency noiseReduce radiation doseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionLow-pass filterImaging quality
CT imaging is enhanced by adaptively filtering x-ray attenuation data prior to image reconstruction. Detected x-ray projection data are adaptively and anisotropically filtered based on the locally estimated orientation of structures within the projection data from an object being imaged at a plurality of rotation positions. The detected x-ray data are uniformly low pass filtered to preserve the local mean values in the data, while the high pass filtering is controlled based on the estimated orientations. The resulting filtered data provide projection data with smoothing along the structures while maintaining sharpness along edges. Image noise and noise induced streak artifacts are reduced without increased blurring along edges in the reconstructed images. The enhanced image allows reduced x-ray dose while maintaining image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
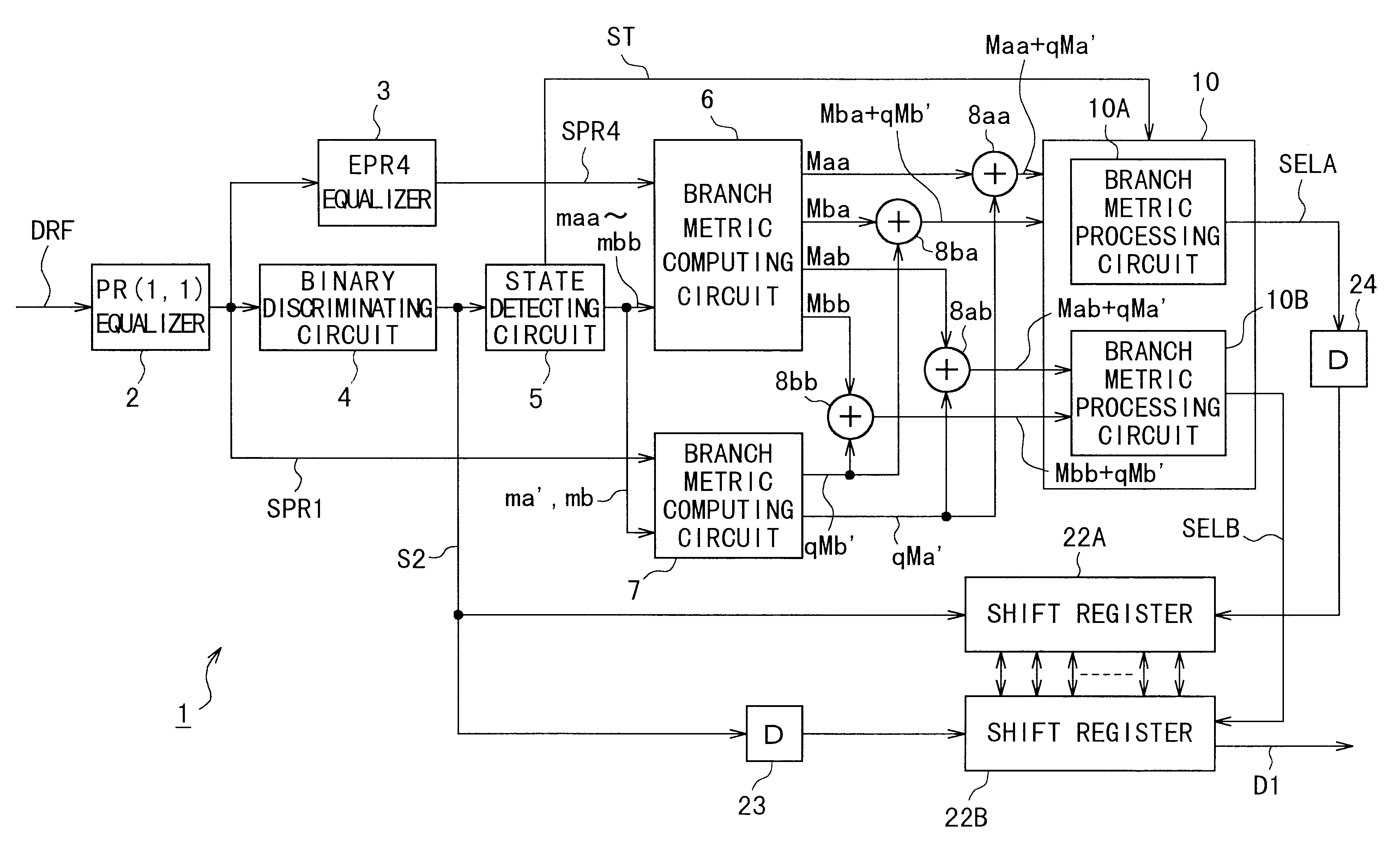
Digital signal reproducing apparatus
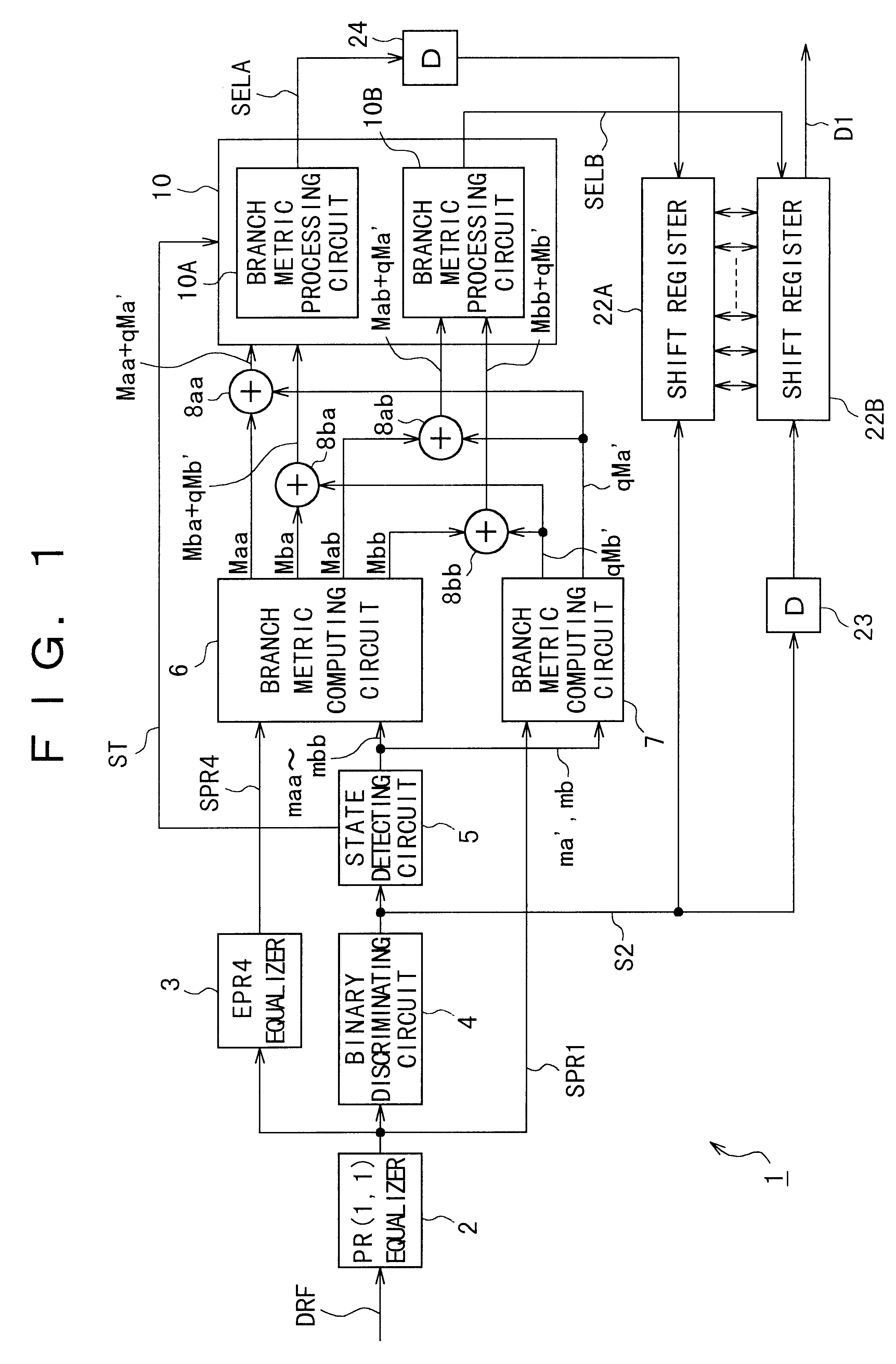
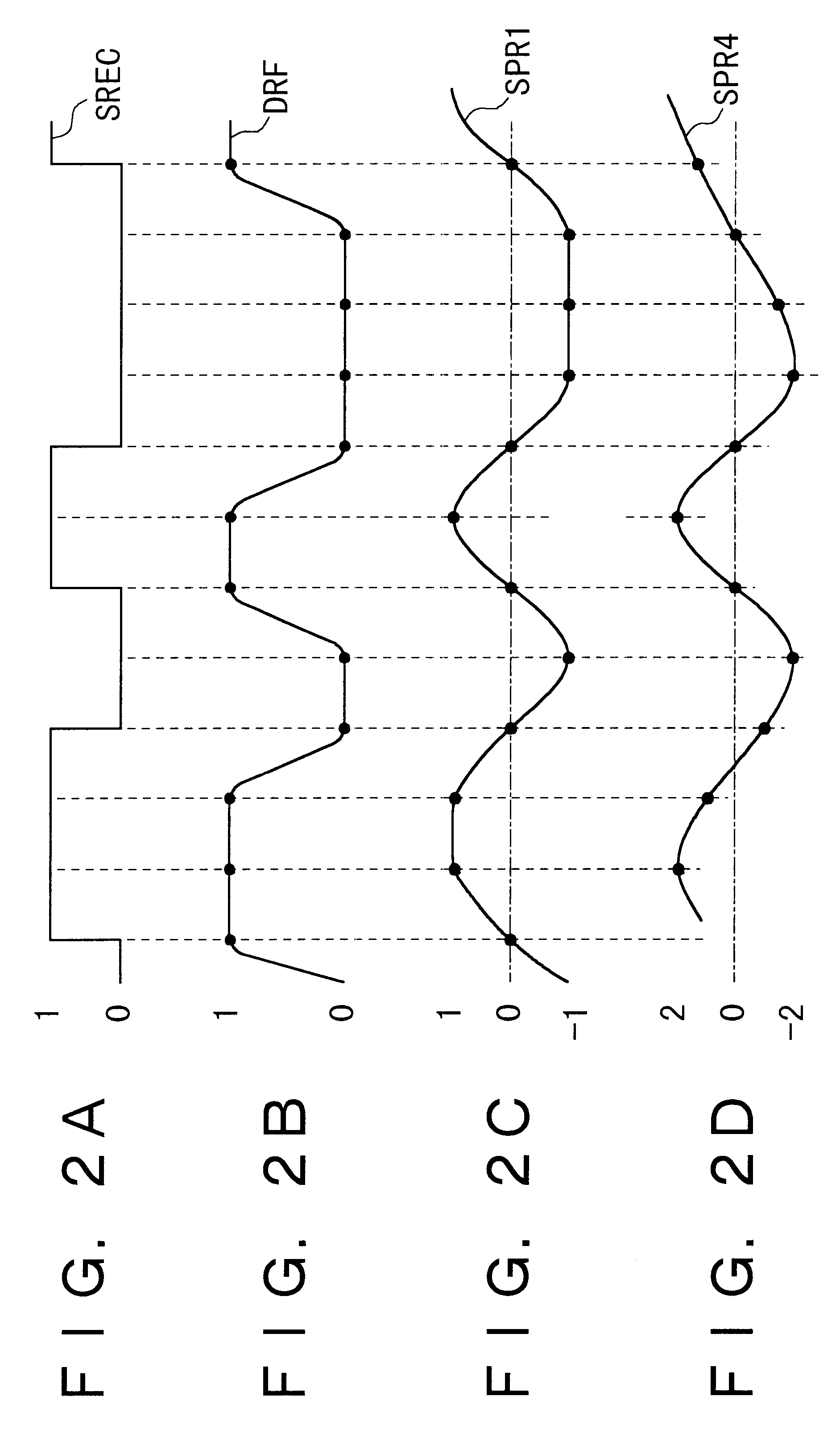
InactiveUS6378107B1Improve fitAvoid lowering discriminatory levelModification of read/write signalsTransmission control/equlisationViterbi decoderVideo Tape Recording
This invention relates to a digital signal reproducing apparatus. This invention is applicable to an apparatus such as a video tape recorder and an optical disk drive, using a Viterbi decoder therein. Noise characteristics are equalized at points of discrimination by adding an equalized signal SPR4 of a differential system and an equalized signal SPR1 of an integrating system in a weighted manner, or by adding up metrics Maa-Mbb, (Ma', Mb') relative to amplitude reference values calculated for the two equalized signals SPR4 and SPR1, over each of relevant paths in a weighted fashion. The arrangements allow the inventive apparatus to avert noise-induced deterioration of discrimination accuracy.
Owner:SONY CORP
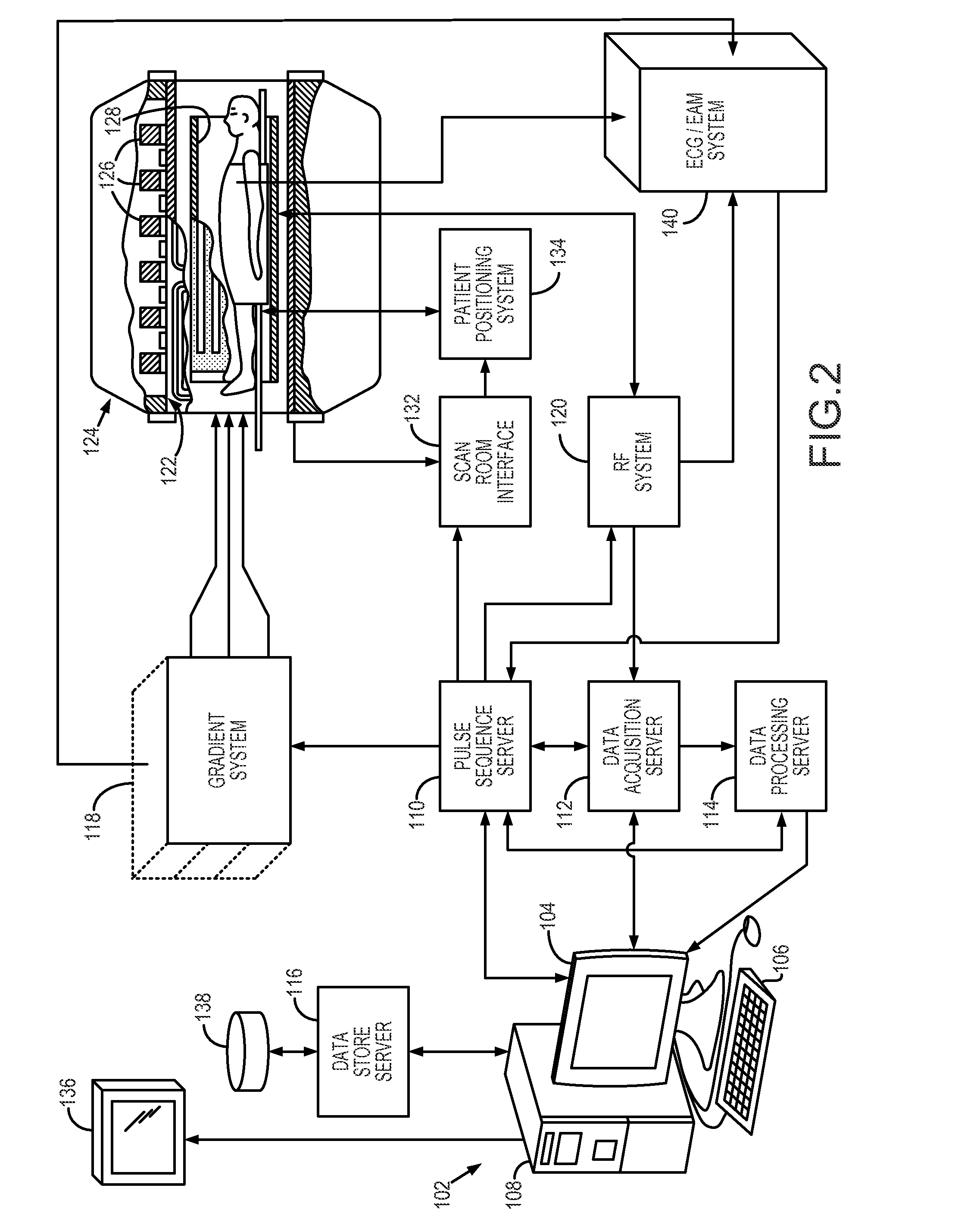
Noise tolerant localization systems and methods
A system and method for tracking catheter electrode locations with the body of a patient during an MRI scan sequence includes mitigation logic configured to identify one or more impedance measurements that were taken during potentially noise-inducing conditions (i.e., magnet gradients, RF pulses), and were thus subject to corruption by noise. The mitigation logic is configured to replace the potentially corrupt impedance measurements with previously-obtained impedance measurements taken from an immediately preceding acquisition cycle (e.g., from a previous time-slice).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Sensing apparatus
InactiveUS20150293636A1High SNR valueReduce the impact of noiseStatic indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingSmall amplitudeSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The present invention relates to a sensor circuit method for securing a sufficient Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) by reducing the influence of noise induced from a sensor element which appears in the final output signal of a reception unit although an input signal having a relatively small amplitude is used in a sensing apparatus in which a time-periodic signal having a relatively higher frequency as compared with the speed of change of a behavior of a user or a movement of an object to be sensed, such as a capacitive sensor or an inductive sensor, is used as an input signal. Power consumption of a touch sensor chip can be reduced even without increasing the amplitude of a touch sensor panel driving signal, and a production cost for a touch sensor chip can be reduced by removing a high voltage driver.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
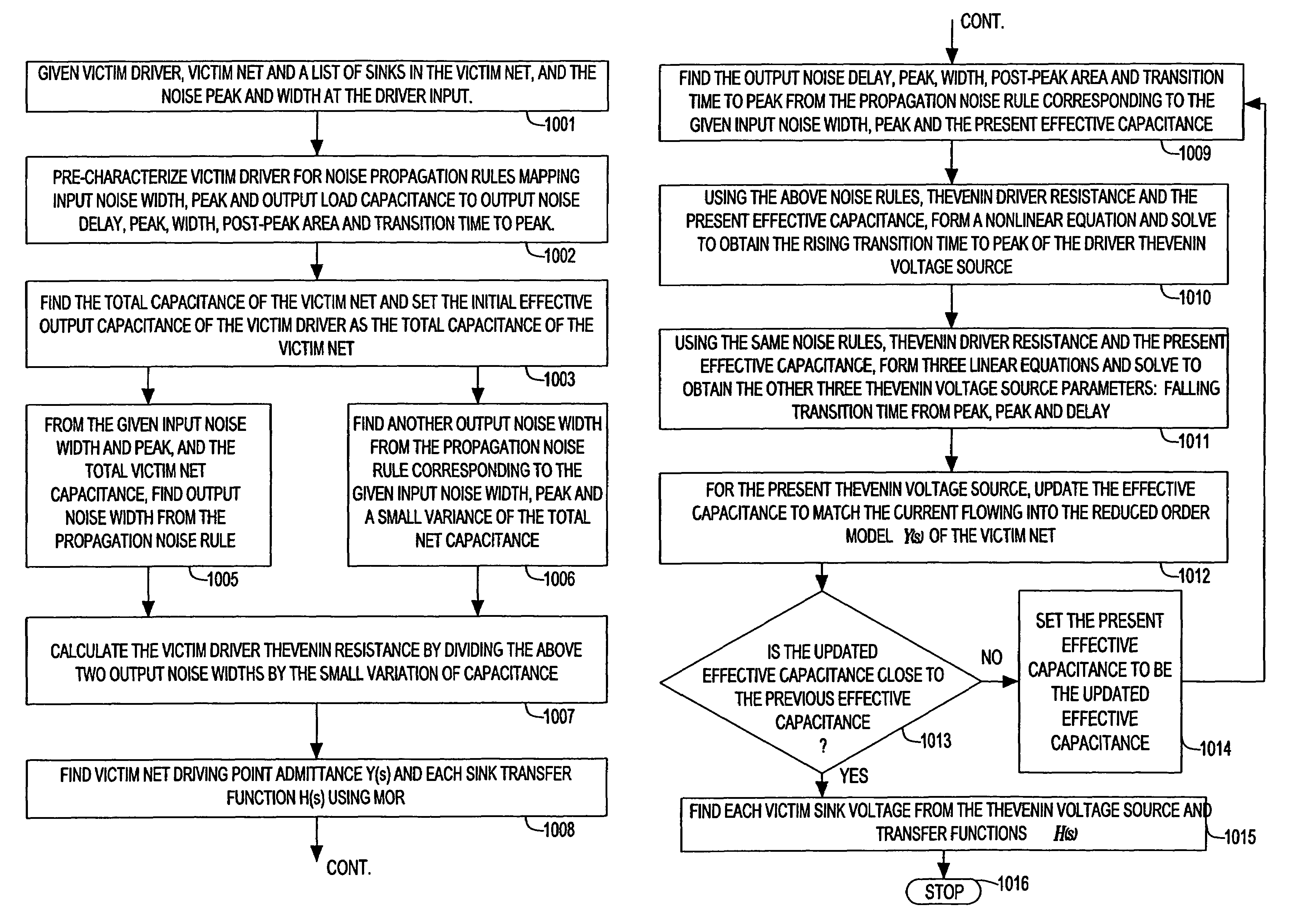
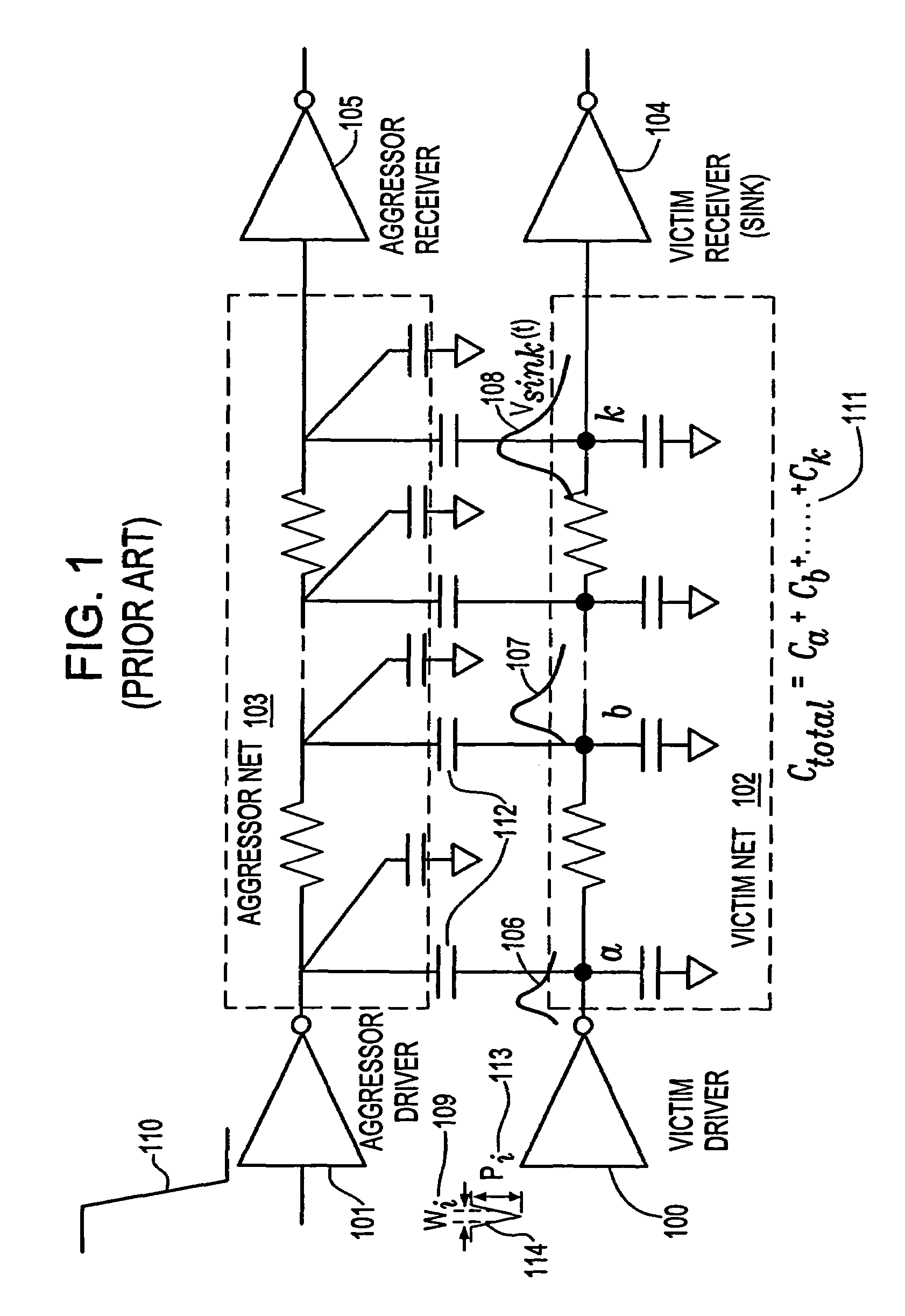
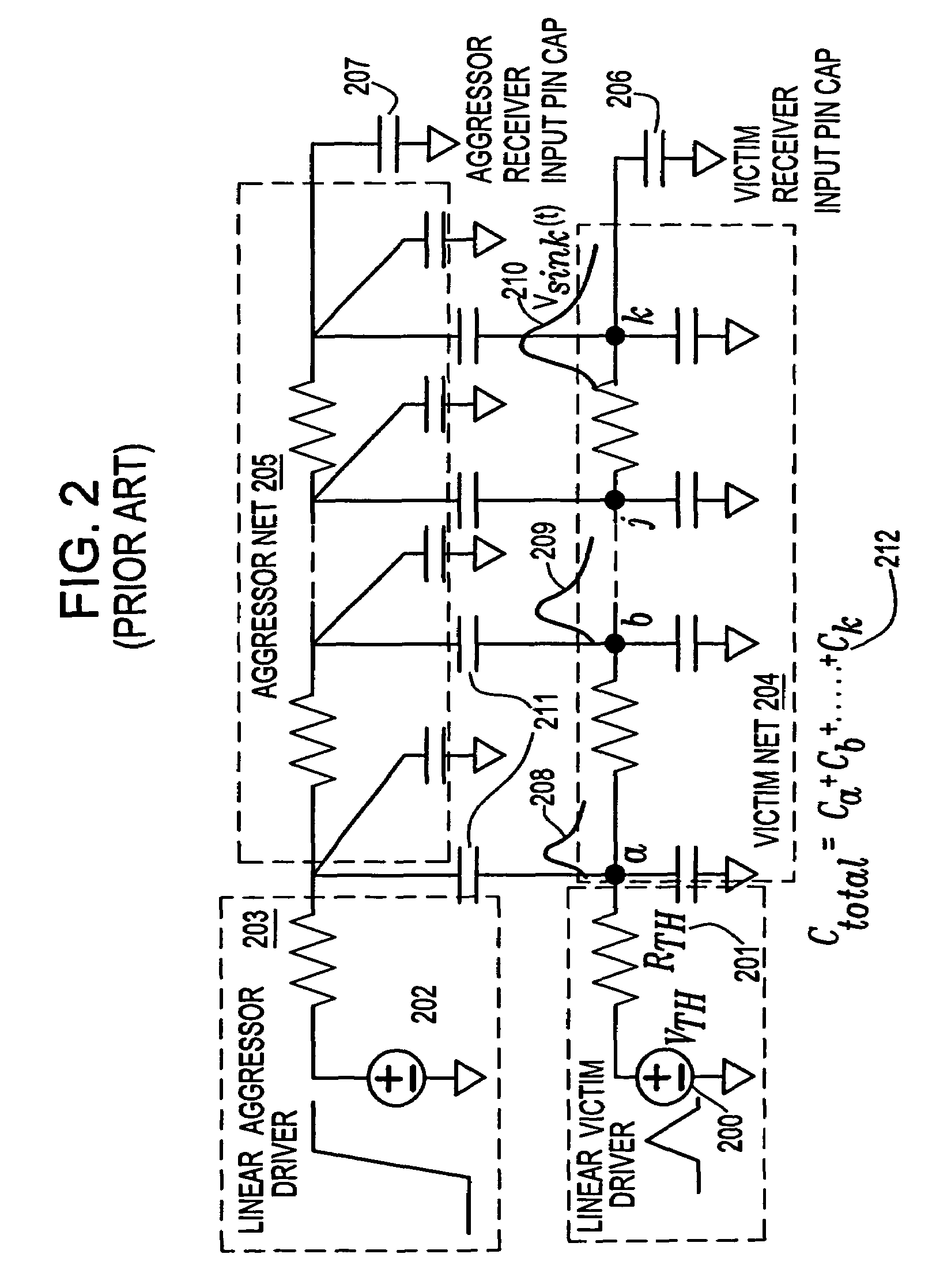
Method for estimating propagation noise based on effective capacitance in an integrated circuit chip
InactiveUS7346867B2Improve accuracySolve the real problemComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsDriver circuitElectrical resistance and conductance
A system and method for estimating propagation noise that is induced by a non-zero noise glitch at the input of the driver circuit. Such propagation noise is a function of both the input noise glitch and the driver output effective capacitive load, which is typically part of the total wiring capacitance due to resistive shielding in deep sub-micron interconnects. The noise-driven effective capacitance solution provided herein also estimates the propagation noise induced by a non-zero noise glitch at the input of the driving gate. Gate propagation noise rules describing a relationship between the output noise properties and the input noise properties and the output loading capacitance are used within the noise-driven effective capacitance process to determine the linear Thevenin model of the driving gate. The linearized Thevenin driver model is then employed to analyze both the propagation noise and the combined coupling and propagation noise typically seen in global signal nets.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
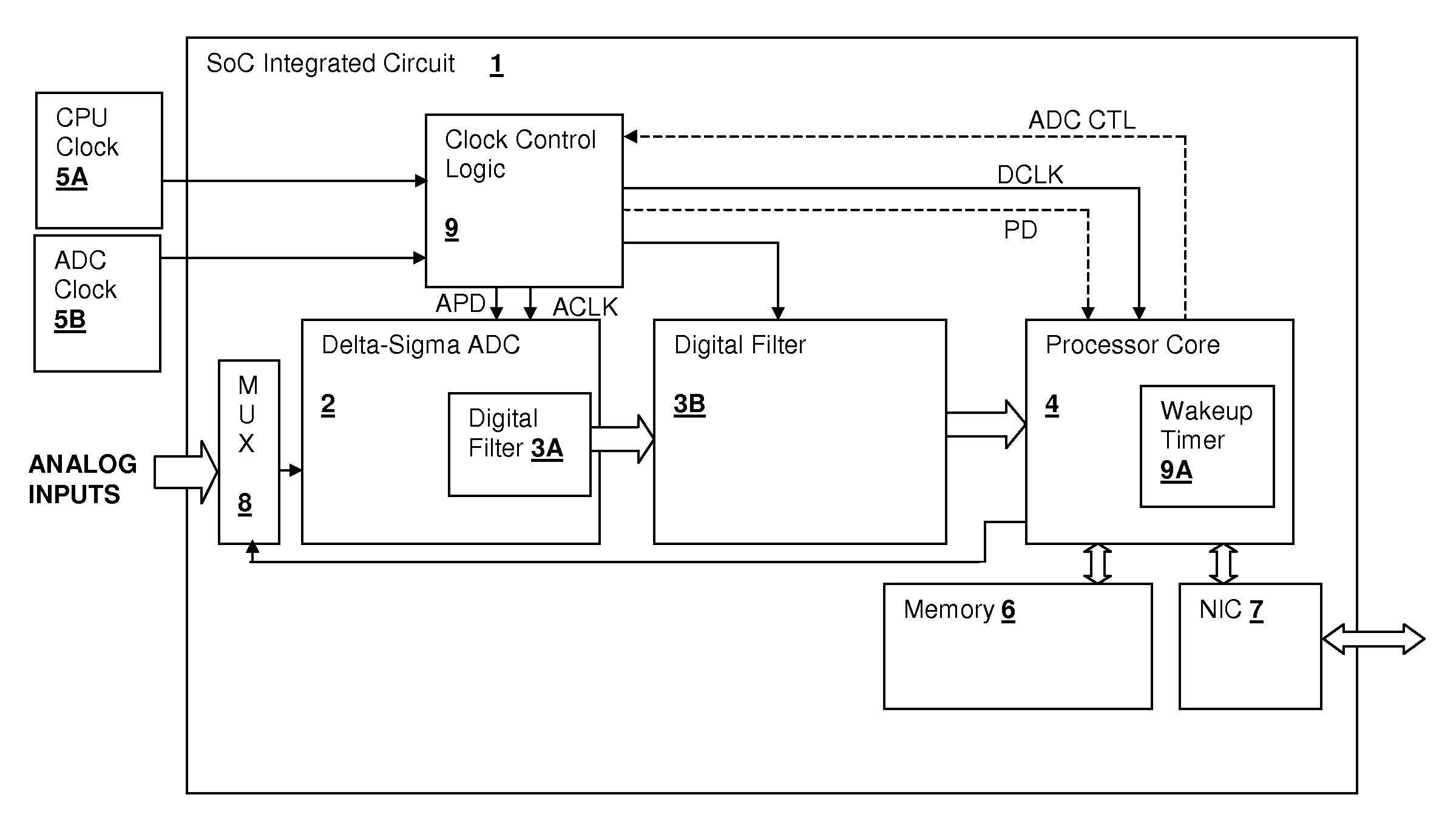
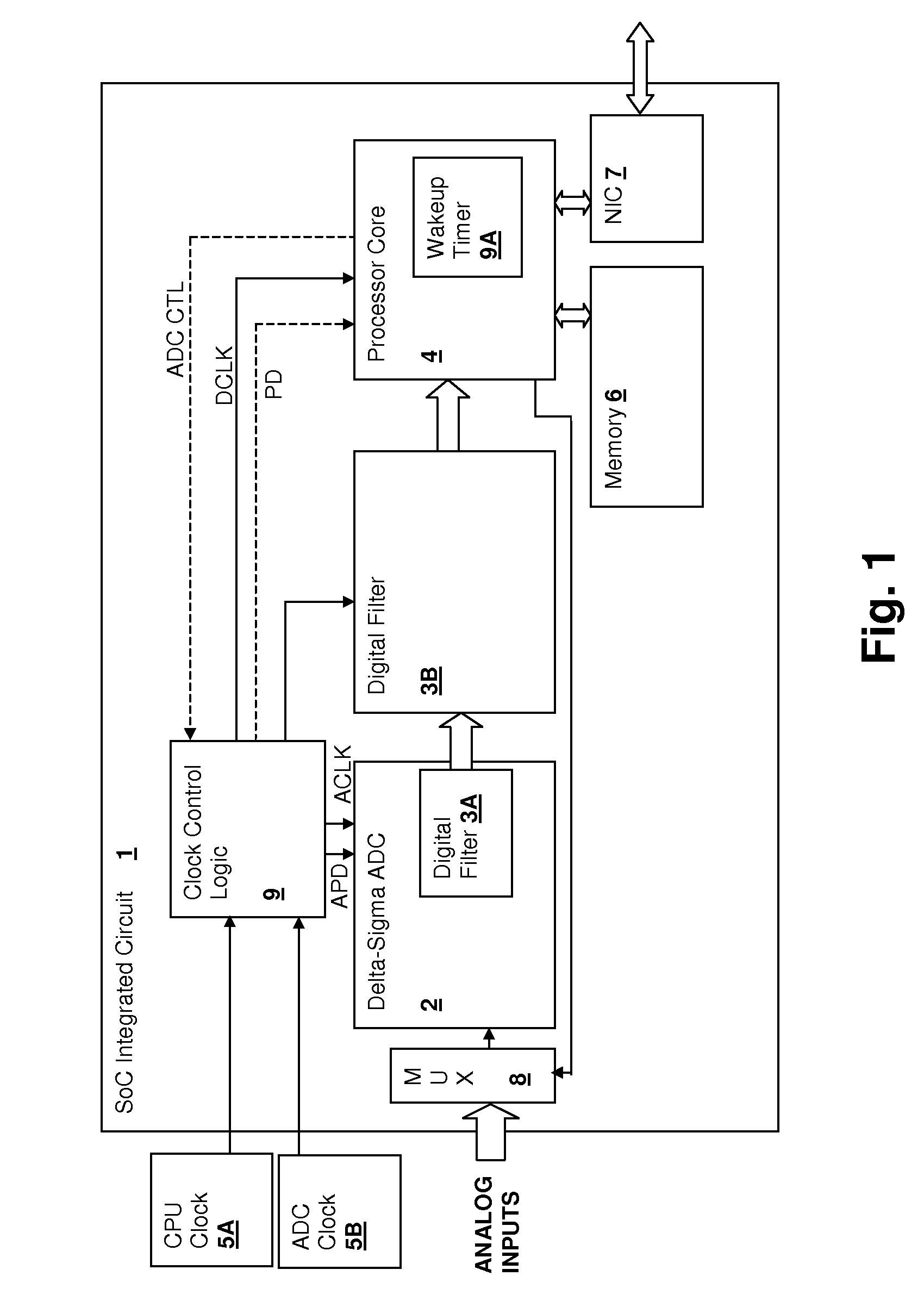
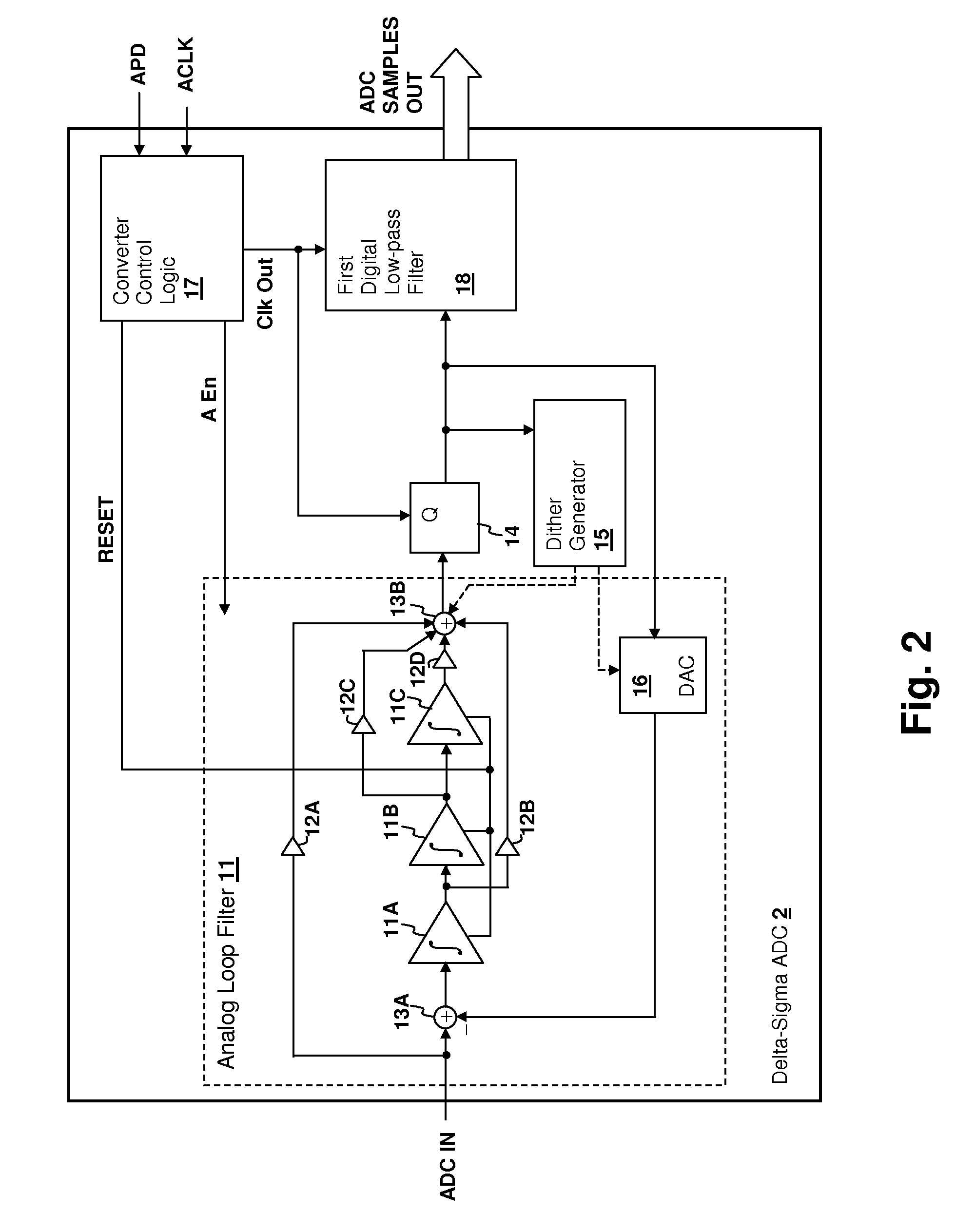
System-on-chip (SoC) integrated circuit including interleaved delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
ActiveUS7382300B1Cancel noiseReduce the impactElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital down converterLow-pass filter
A system-on-chip (SoC) integrated circuit including an interleaved delta-sigma analog to digital converter (ADC) provides for reduced noise in the ADC conversions. The ADC is operated intermittently and the balance of the digital circuits forming the system are halted while the conversions take place. The halted portion of the system may include an output low-pass filter of the ADC. The system may include a processor core or other logic having a clock frequency unrelated to the ADC modulator clock frequency that is not otherwise clock-managed to reduce noise induced in the converter output by the operation of the core or other logic.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Acoustic wave sensor with EMAT drive
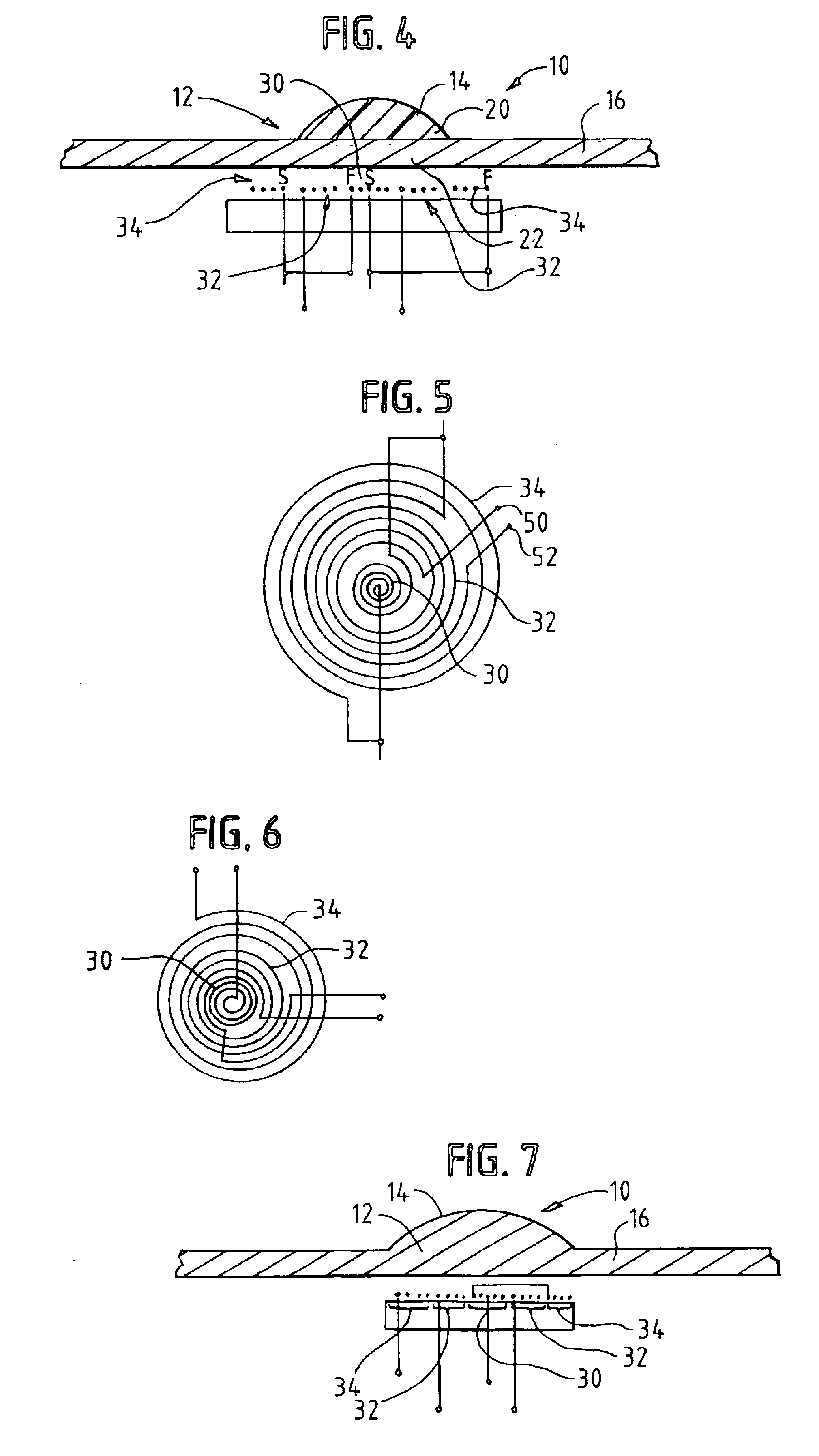
InactiveUS6933932B2Electronic switchingCathode-ray tube indicatorsSurface acoustic wave sensorElectromagnetic acoustic transducer
An acoustic wave sensor includes an electromagnetic acoustic transducer to generate a resonant acoustic wave substantially trapped in an acoustic wave cavity. The acoustic wave cavity is defined by a radially symmetric raised surface. The electromagnetic acoustic transducer includes a spiral primary coil to generate the acoustic wave in the acoustic wave cavity and a concentric spiral pickup coil to pick up an electrical signal representing the acoustic wave in the cavity. A noise canceling coil portion is used to cancel spurious noise induced by the primary coil from the pickup coil to provide an output signal representing the acoustic wave energy in the cavity 12.
Owner:TEXZEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com