Method and device for decoding tail-biting convolutional codes
A technology of tail-biting convolutional code and decoding device, which is applied in the direction of using convolutional code error correction/error detection, data representation error detection/correction, etc., can solve problems such as high bit error rate and reduce decoding errors. rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
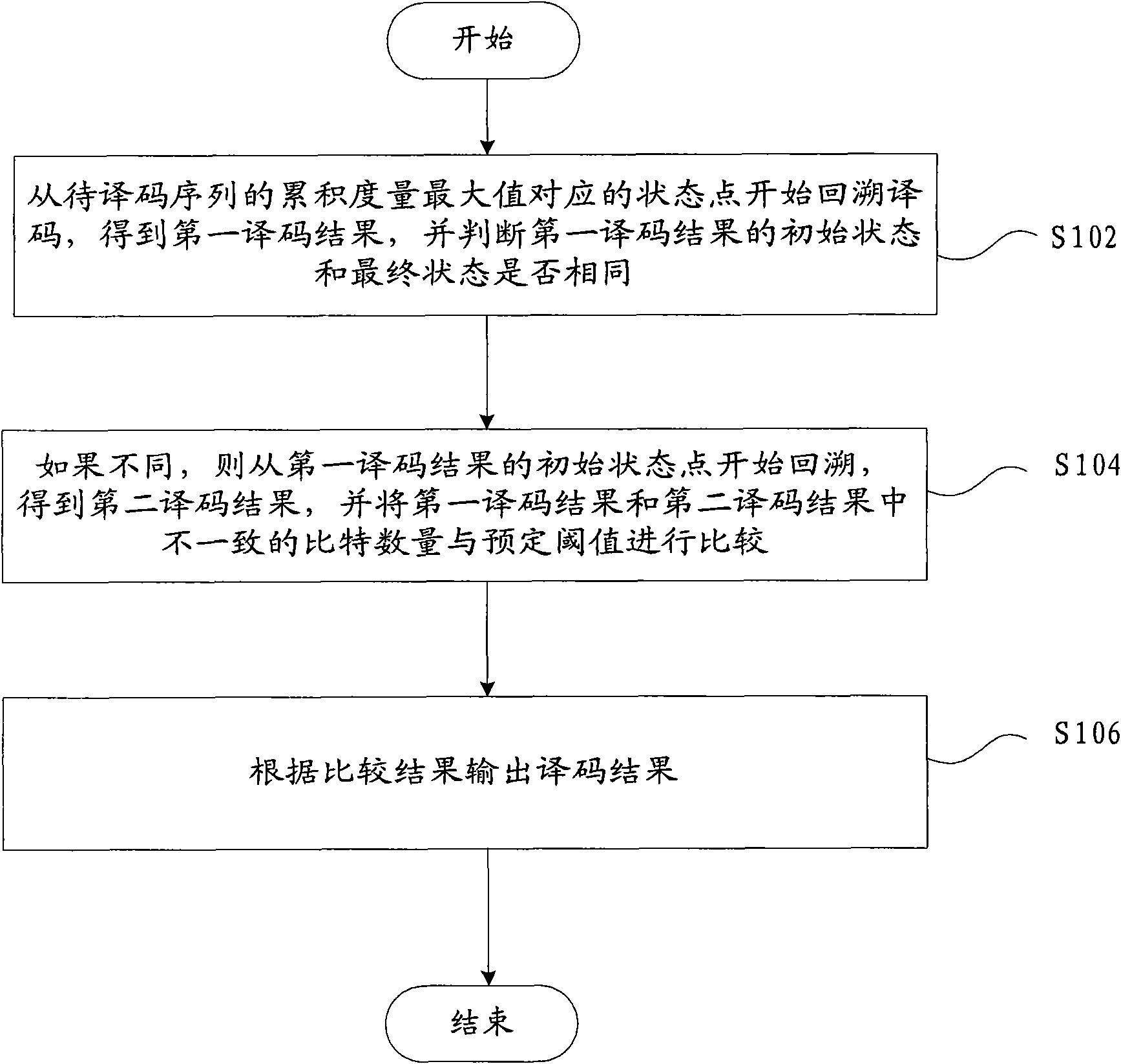
[0034] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the decoding method of the tail-biting convolutional code according to the first embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the decoding method of the tail-biting convolutional code according to the first embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0035] Step S102, start retroactive decoding from the state point corresponding to the maximum value of the cumulative metric of the sequence to be decoded, obtain the first decoding result, and judge whether the initial state and the final state of the first decoding result are the same; from the maximum value of the cumulative metric The decoding result obtained from the corresponding state (maxSts) is the first decoding result, and the value corresponding to the last N-1 bits in the first decoding result is the final state;
[0036] Step S104, if they are not the same, start backtracking from the initial state point of the first decoding result to obtain the second ...
no. 2 example
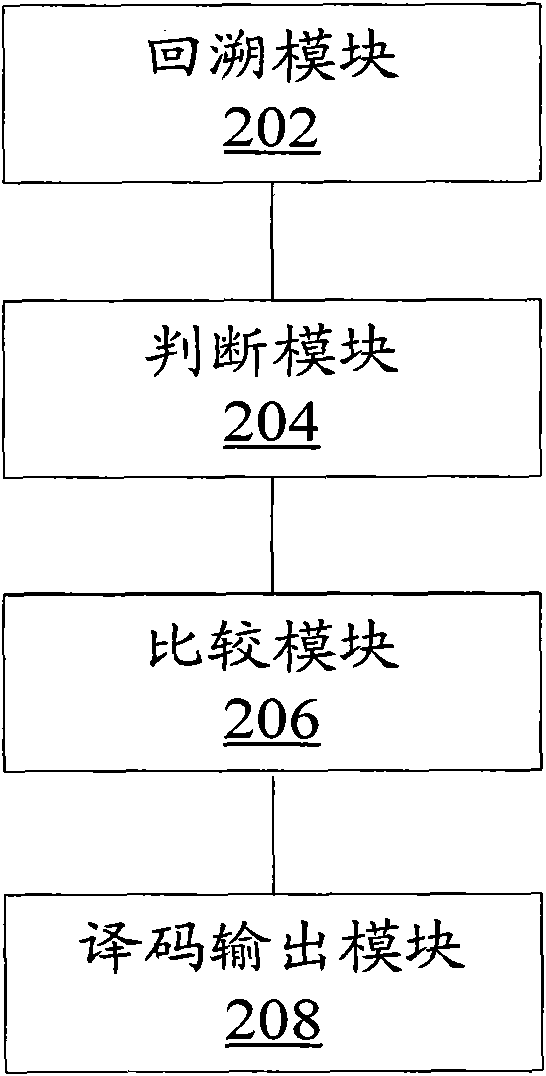
[0053] figure 2 is a block diagram of a decoding apparatus for a tail-biting convolutional code according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0054] Such as figure 2 As shown, the decoding device of the tail-biting convolutional code according to the second embodiment of the present invention includes: a backtracking module 202, which is used to backtrack from the maximum cumulative metric state of the sequence to be decoded along the direction of the maximum metric to obtain the first decoding Code result, and be used for backtracking from the initial state of the sequence to be decoded along the direction with the largest metric, to obtain the second decoding result; judging module 204, used to judge whether the initial state and the final state of the first decoding result are the same; compare The module 206 is used to compare the number of inconsistent bits in the first decoding result and the second decoding result with a predetermined threshold; the de...
no. 3 example
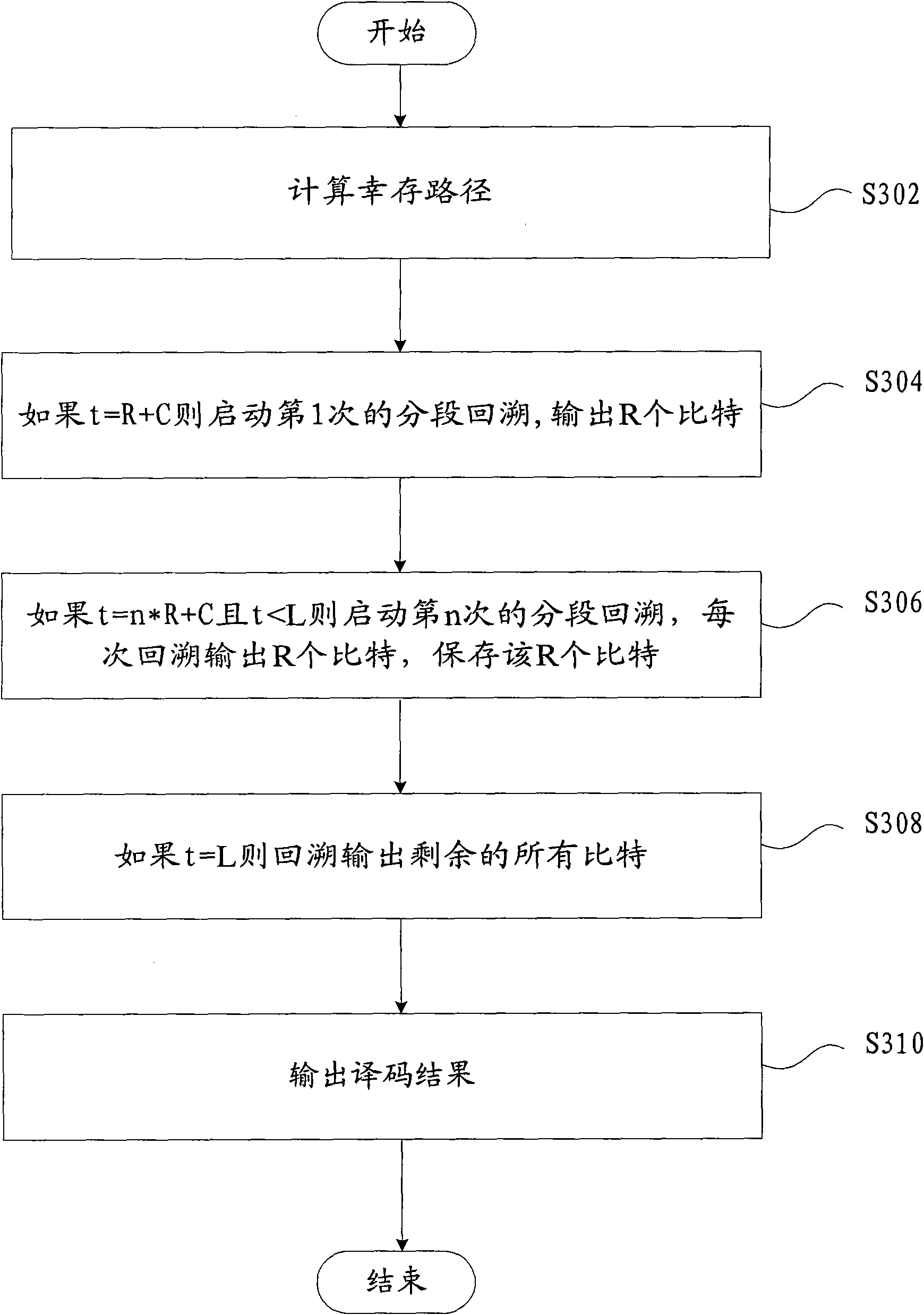
[0064] In this embodiment, a decoding method of a tail-biting convolutional code according to the third embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail by taking the decoding process of an LTE tail-biting convolutional code as an example.
[0065] image 3 It is a flowchart of a decoding method of a tail-biting convolutional code according to the third embodiment of the present invention. Such as image 3 As shown, the decoding method of the tail-biting convolutional code according to the third embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0066] Step 302, calculate the surviving path; the principle of calculating the surviving path is as follows Figure 4 As shown, first calculate the 4 newly added cumulative metrics corresponding to the 4 paths of K=0 from T=0 (that is, from t0 to t1), and then calculate the 4 cumulative metrics, and then select two paths to the S2k state point The path with the larger cumulative metric in the S2k+1 state point is select...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com