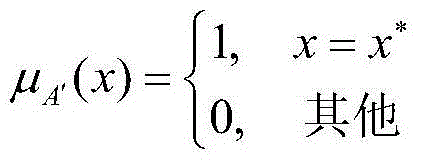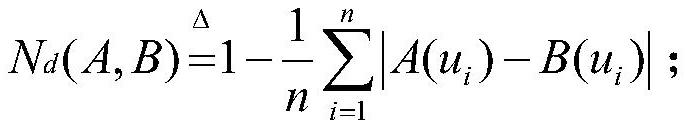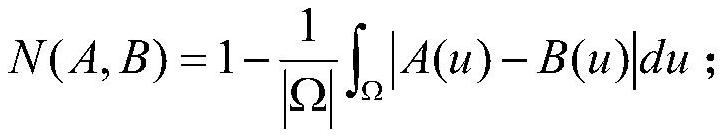Patents
Literature
35 results about "Soft computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Soft computing, as opposed to traditional computing, deals with approximate models and gives solutions to complex real-life problems. Unlike hard computing, soft computing is tolerant of imprecision, uncertainty, partial truth, and approximations. In effect, the role model for soft computing is the human mind. It was conceived by Lotfi Zadeh, pioneer of a mathematical concept known as fuzzy sets which led to many new fields such as fuzzy control systems, fuzzy graph theory, fuzzy systems, and so on. Zadeh observed that people are good at 'soft' thinking while computers typically are 'hard' thinking. People use concepts like 'some', 'most', or 'very' rather than 'hard' or precise concepts of 3.5 or 102. People want a 'warm' glass of milk, not one that is 102 degrees. In general, people are good at learning, finding patterns, adapting and are rather unpredictable. In 'hard' computing, by contrast, machines need precision, determinism and measures, and although pattern recognition happens, there is a 'brittleness' if things change - it cannot easily adapt. 'Soft' computing by contrast embraces chaotic, neural models of computing that are more pliable. Because there is no known single method that lets us compute like people, soft computing involves using a combination of methods that each bring something helpful to achieve this goal. The principal constituents of Soft Computing (SC) are Fuzzy Logic (FL), Evolutionary Computation (EC), Machine Learning (ML) and Probabilistic Reasoning (PR), with the latter subsuming belief networks and parts of learning theory.
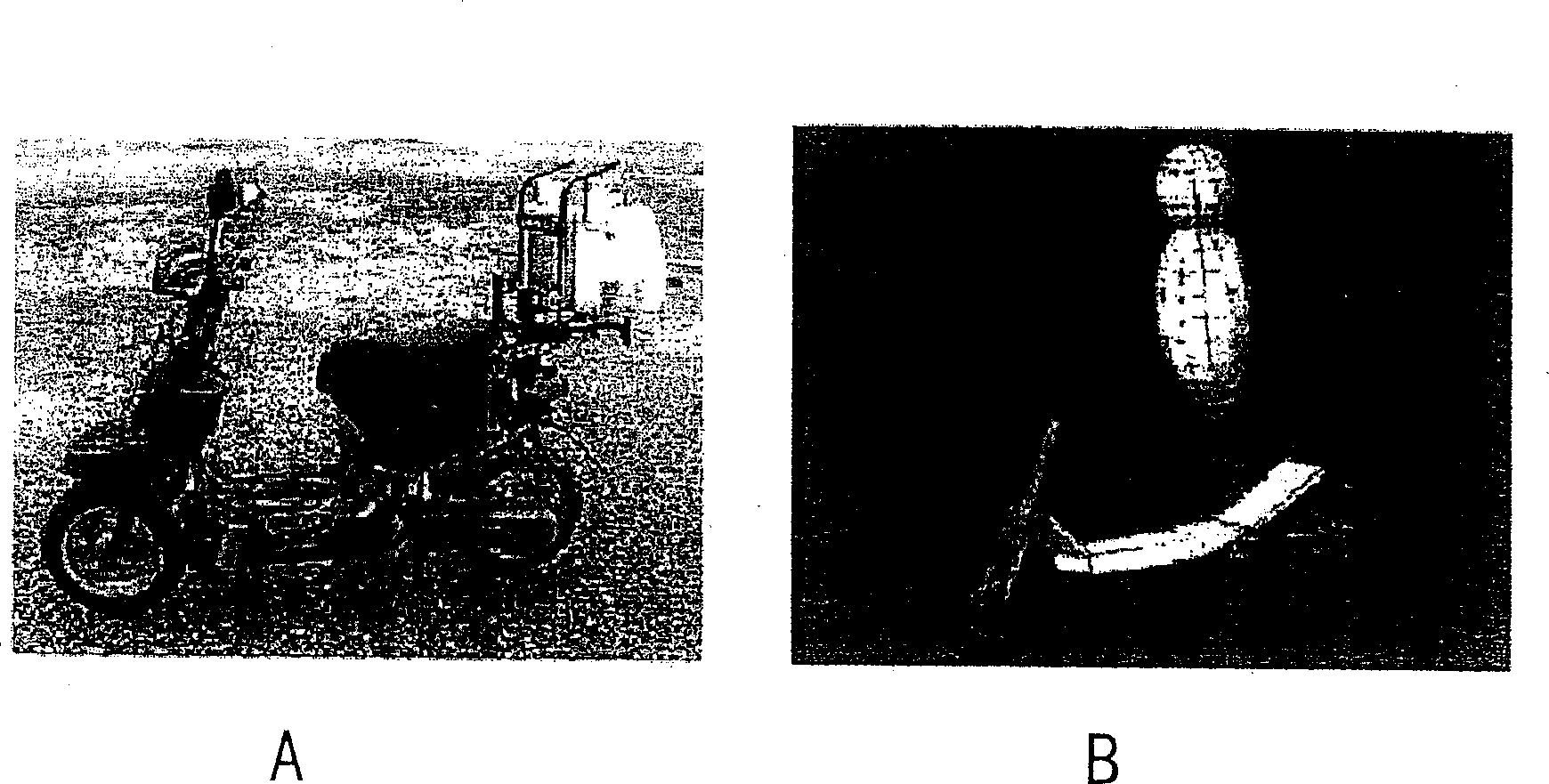
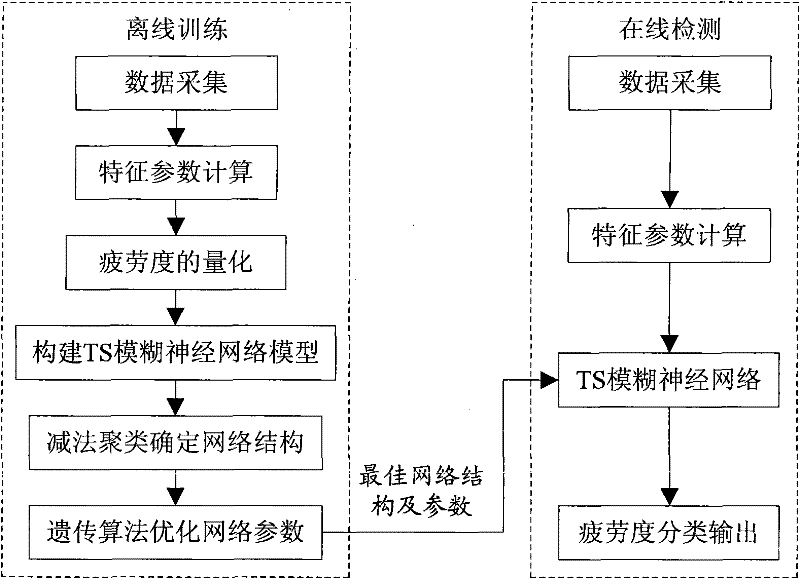
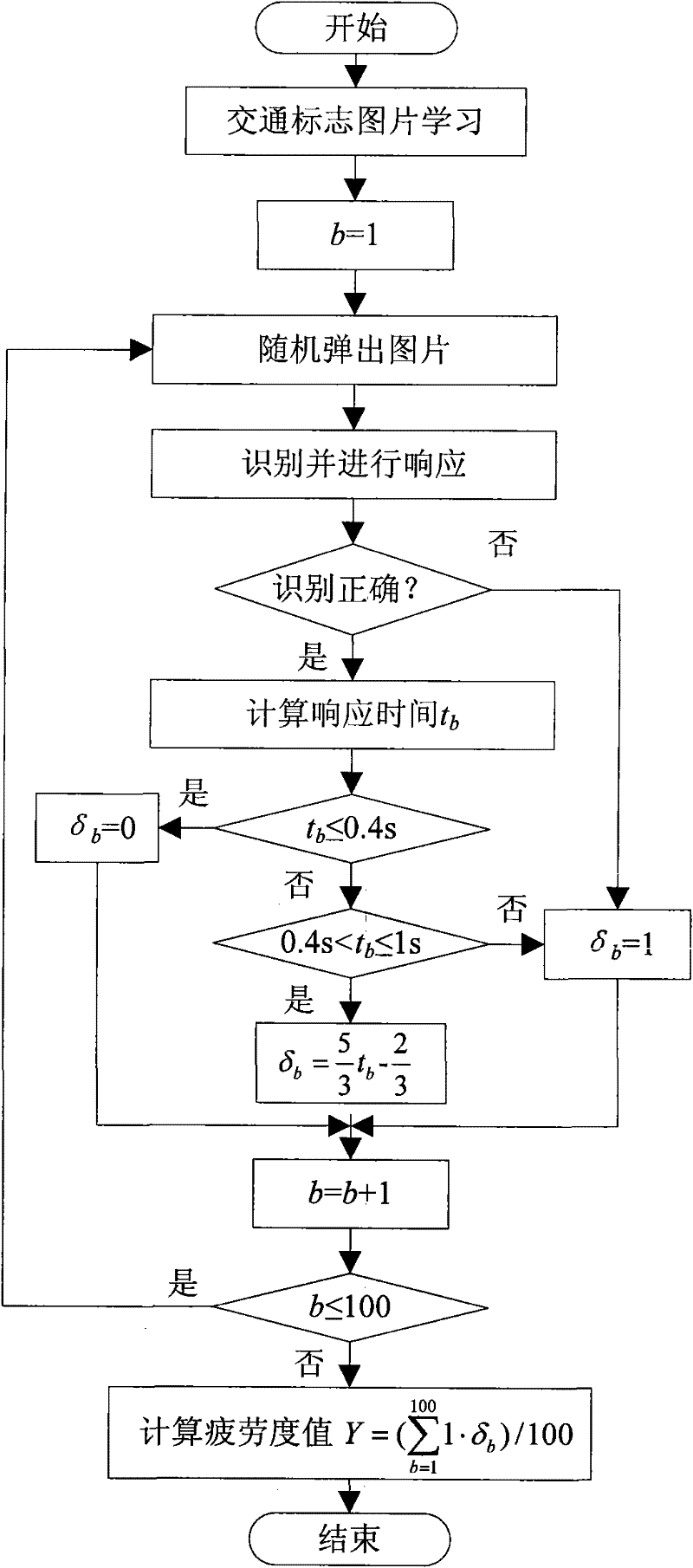
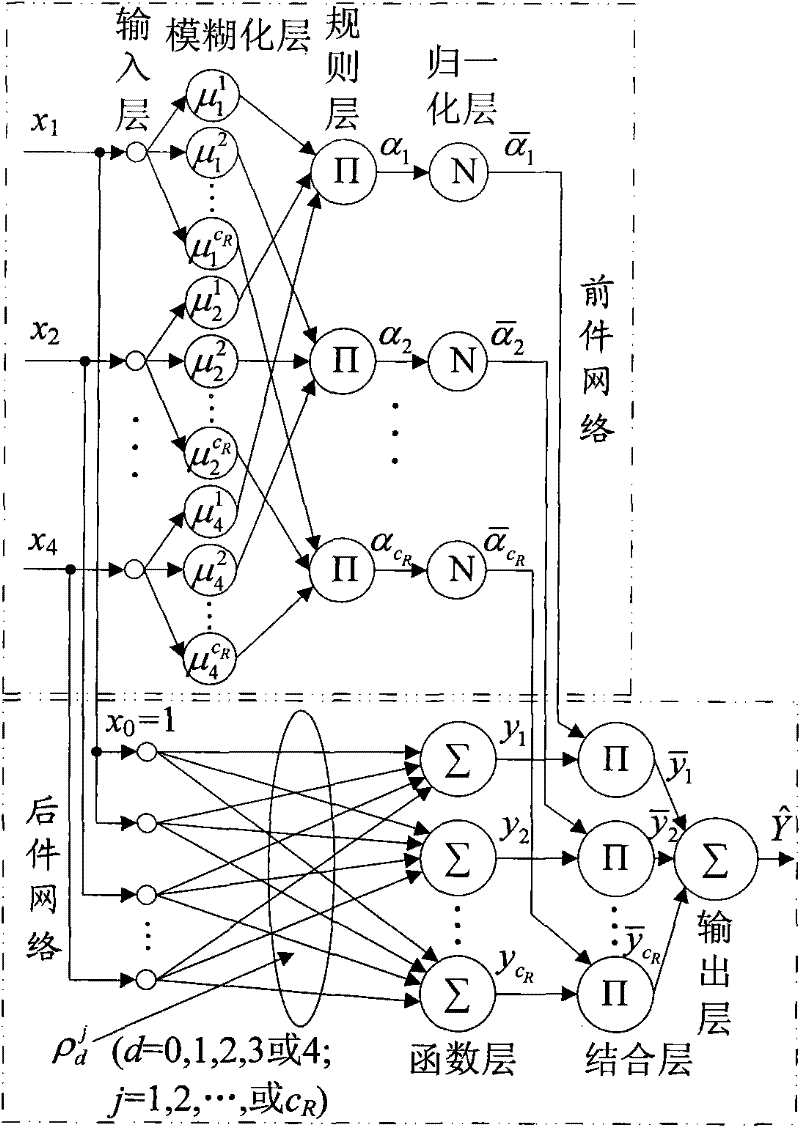
Fatigue driving fusion detection method based on soft computing
InactiveCN101746269AMeasuring Drowsy Driving BehaviorOvercome limitationsTractorsAlarmsDriver/operatorFuzzy rule
The invention discloses a fatigue driving fusion detection method based on soft computing, which can detect the fatigue driving of the driver and is characterized in that: the fatigue driving is detected in fusion mode through two aspects which include two facial characteristics for directly indicating the fatigue state of the driver and two vehicle behavior characteristics for indirectly indicating the fatigue state of the driver, wherein the two facial characteristics respectively are frequent blinking and yawning, and the two vehicle behavior characteristics respectively are abnormal vehicle lane deviation and abnormal steering wheel rotation; the invention utilizes the TS fuzzy neural network to recognize fatigue driving, adopts abstraction clustering for the optimized recognition of the network structure, and determines the number of fuzzy rules of the fuzzy neural network and the initial values of the relevant network parameters; genetic algorithm is utilized to train and optimize the network parameters, and determine the optimum network parameters; the TS fuzzy neural network is utilized to detect the fatigue driving of the driver in real-time according to the optimum network parameters and the four fatigue characteristic parameters.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
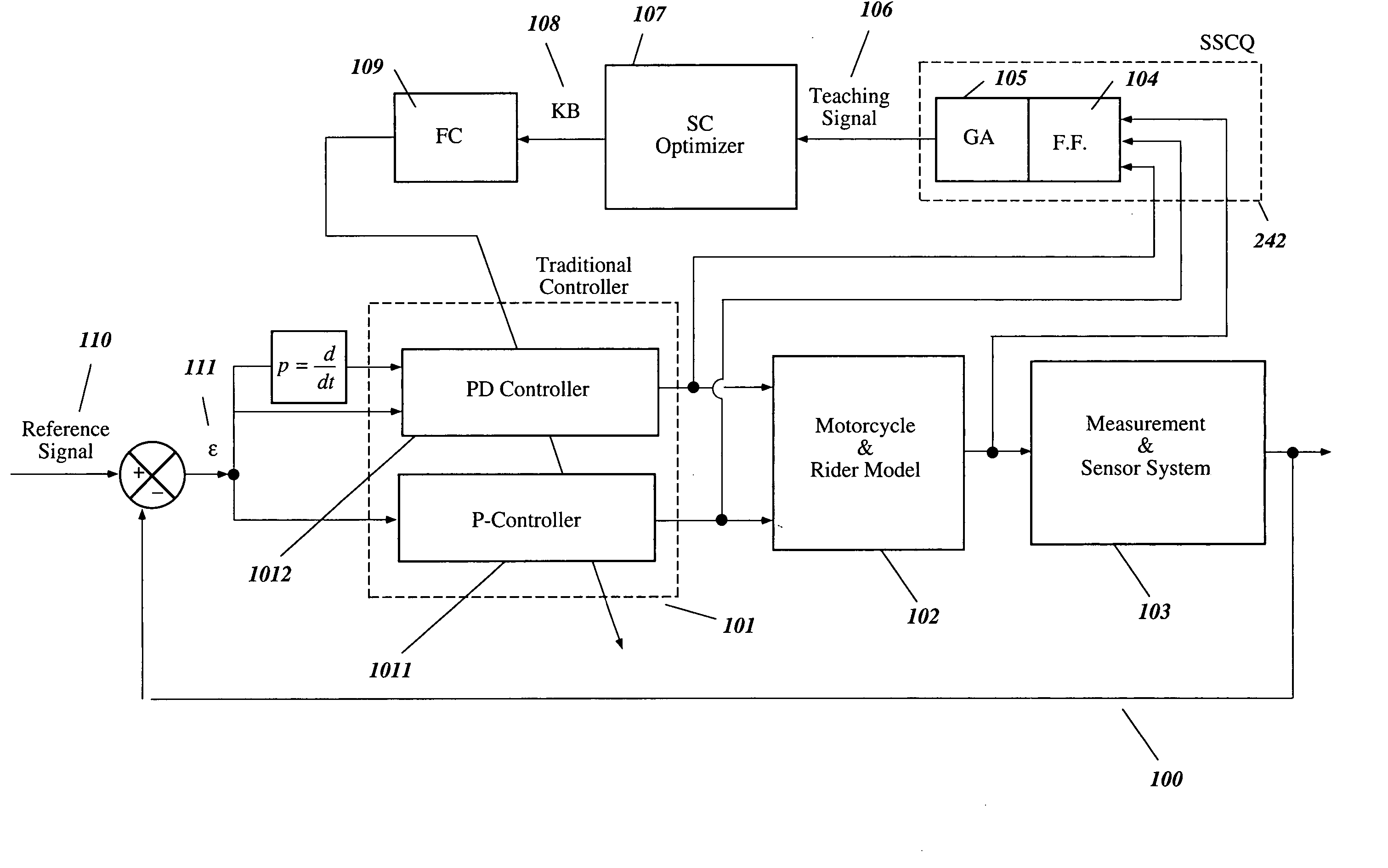
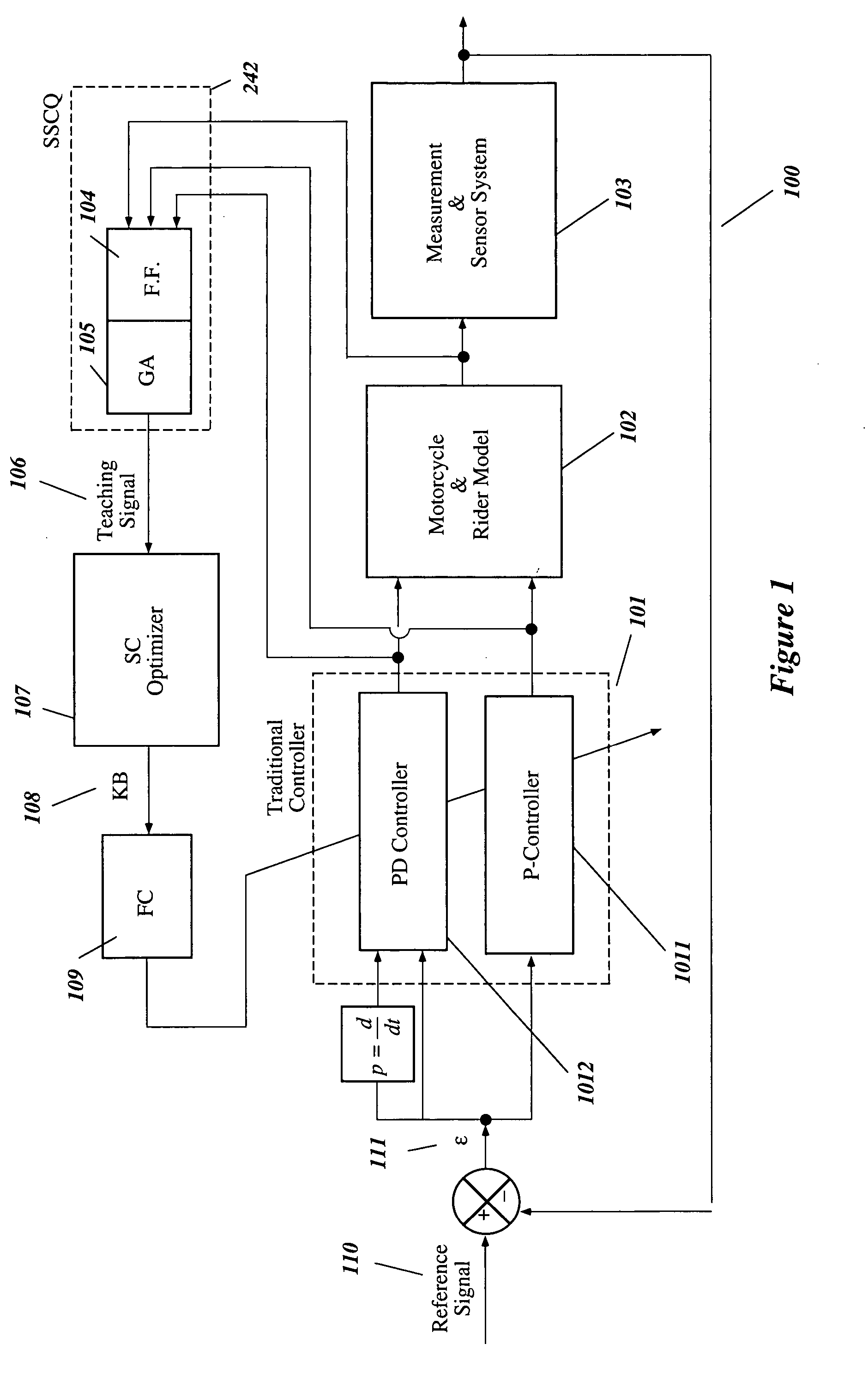
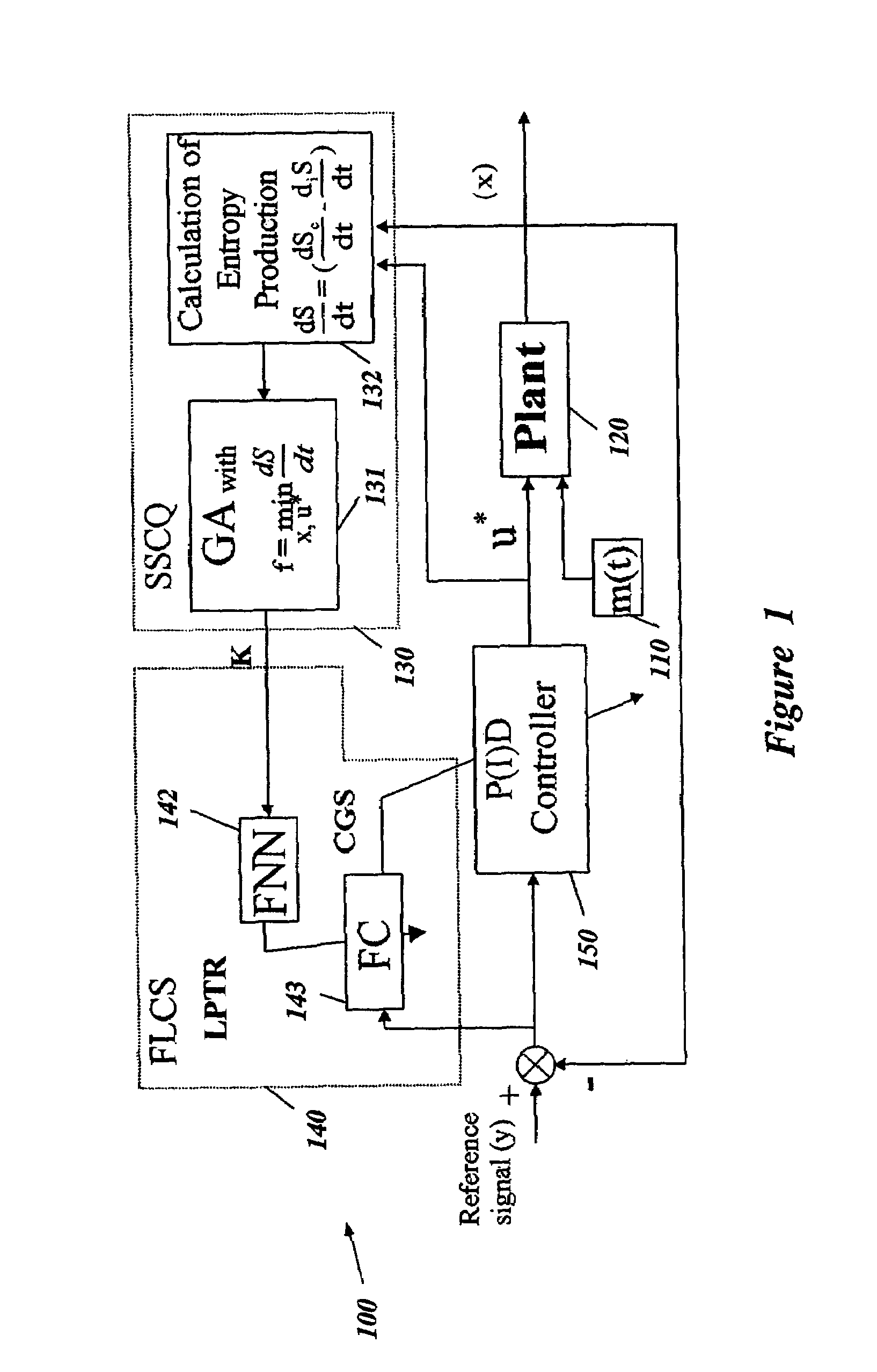
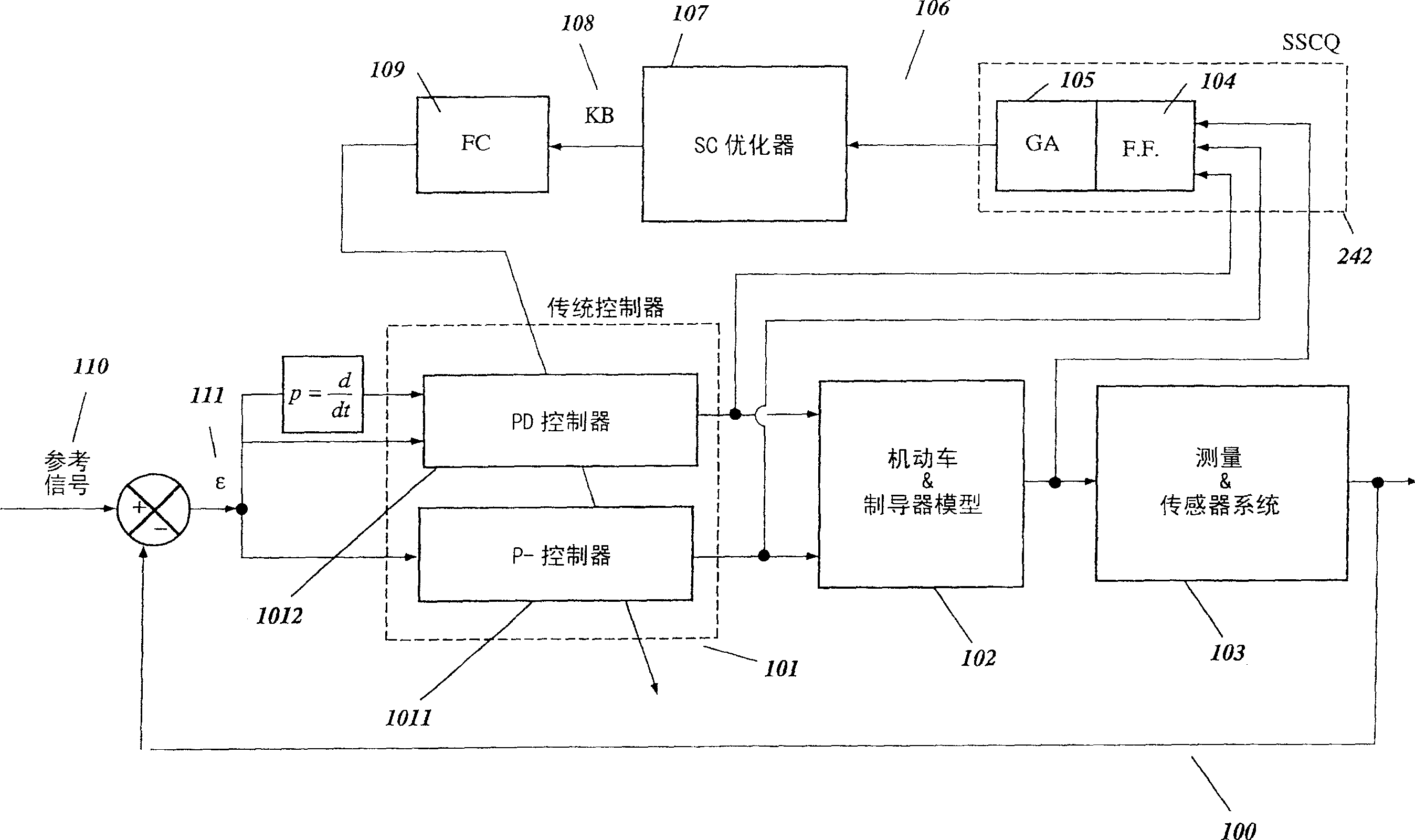
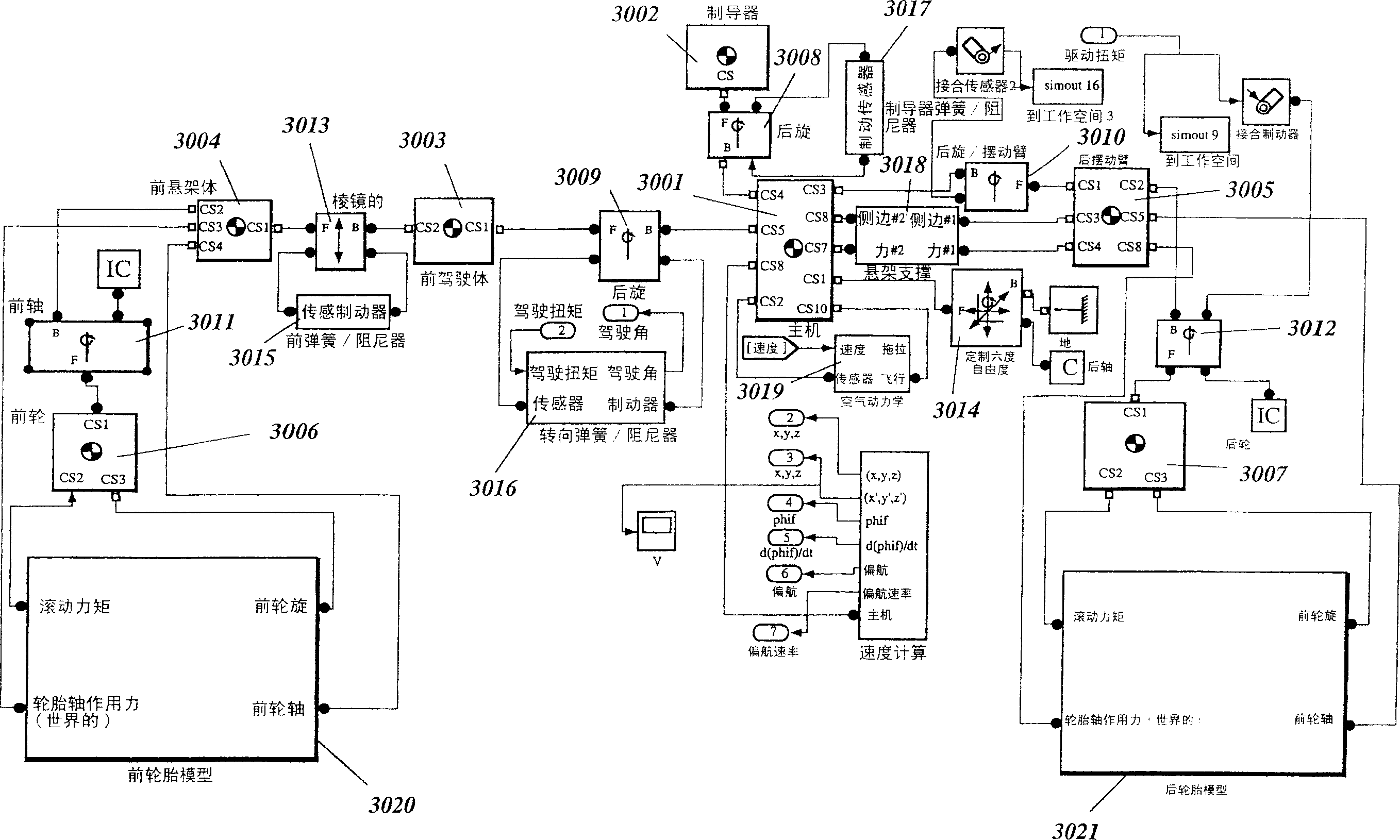
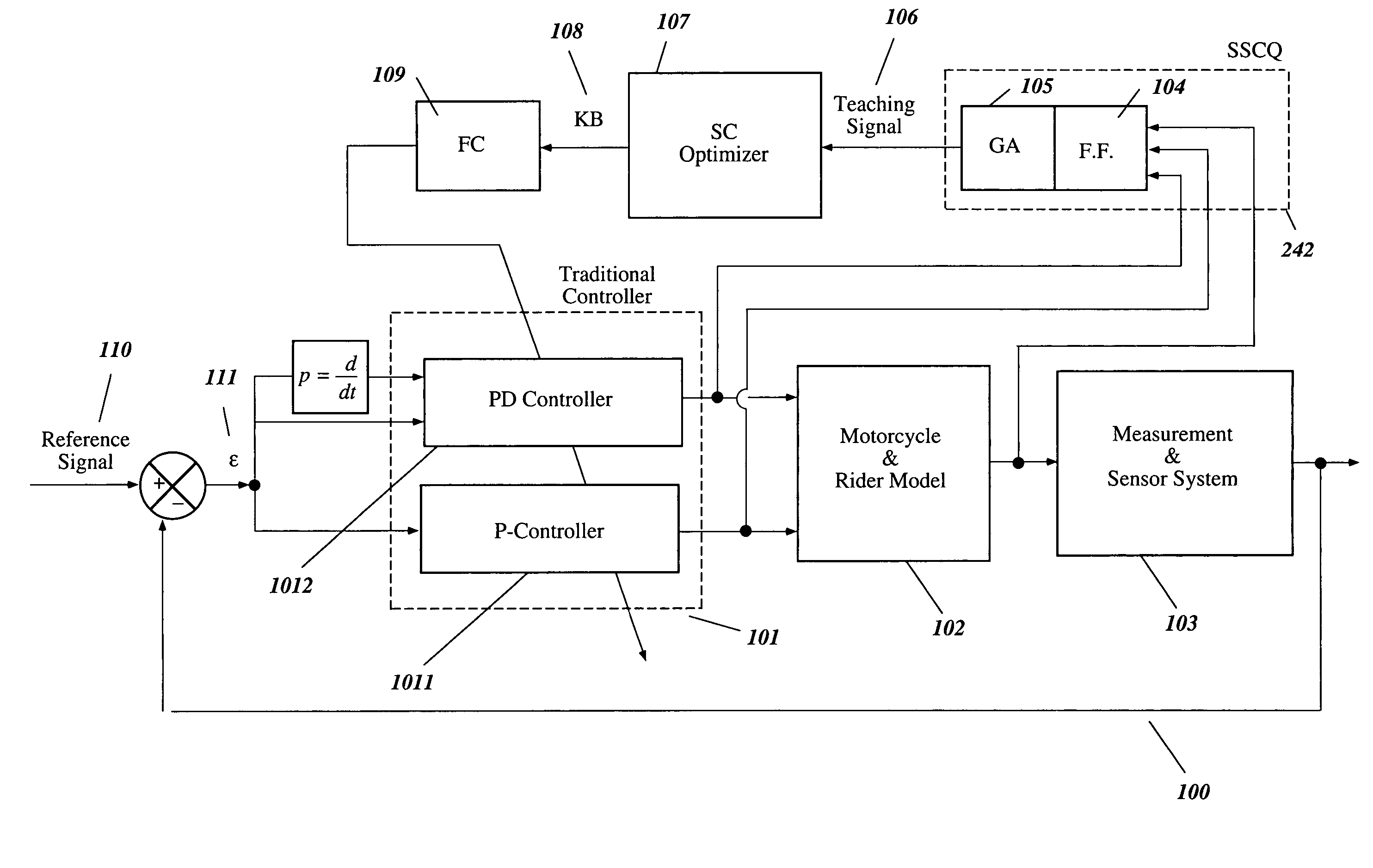
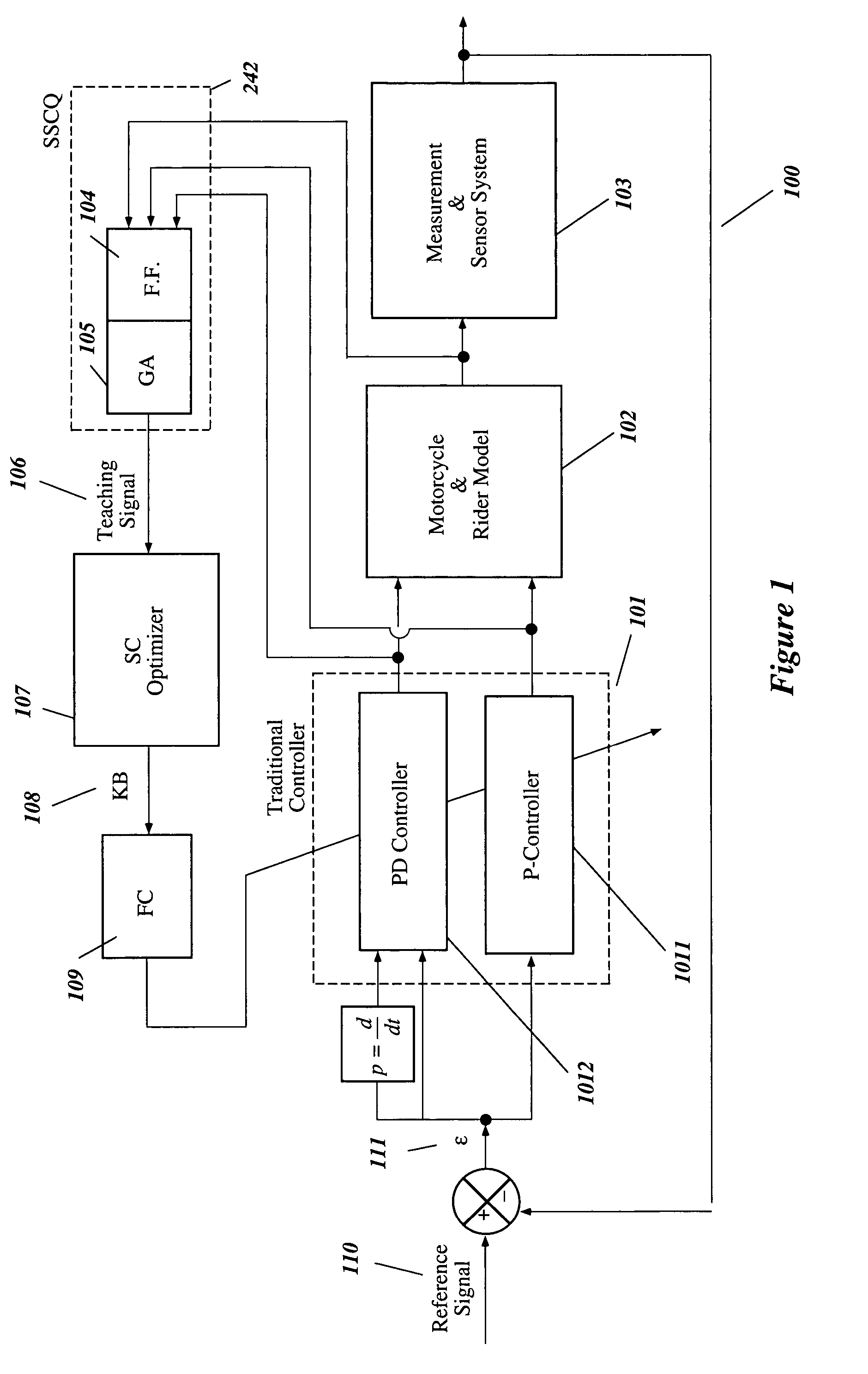
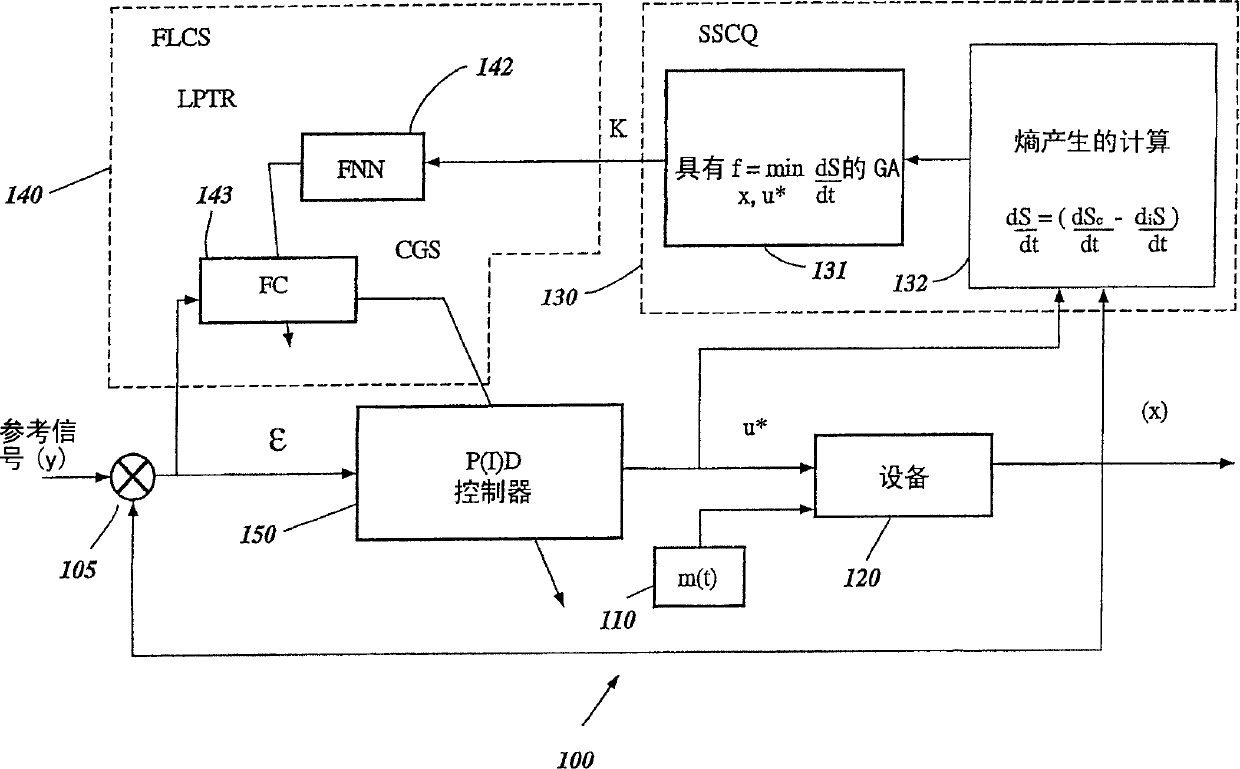
Intelligent robust control system for motorcycle using soft computing optimizer
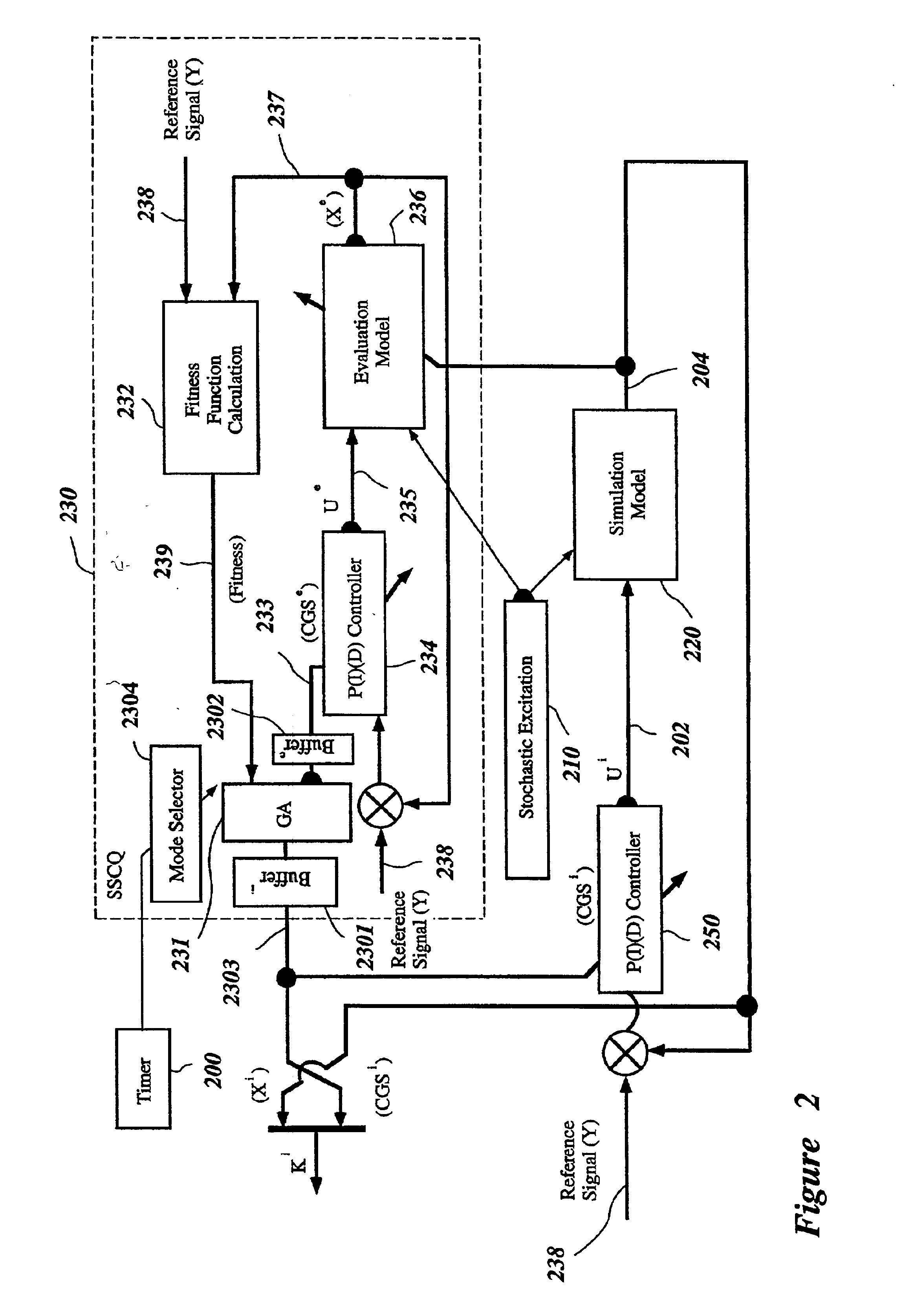
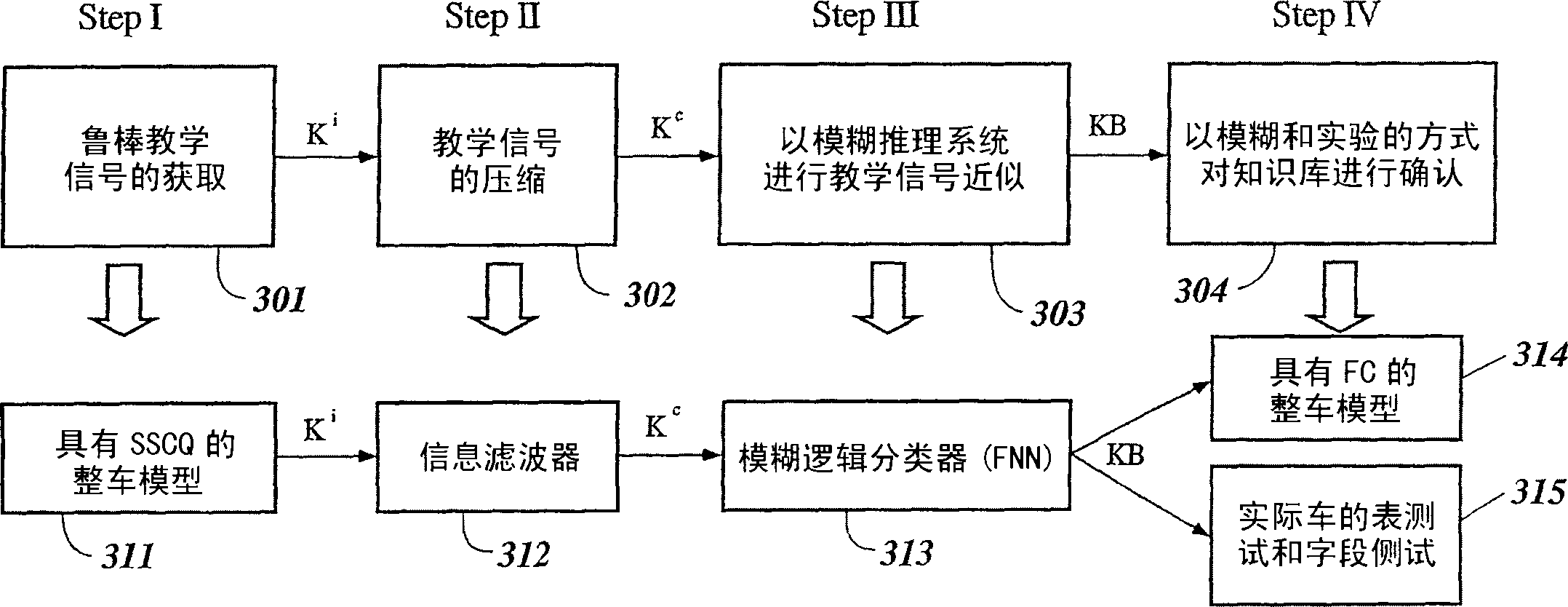
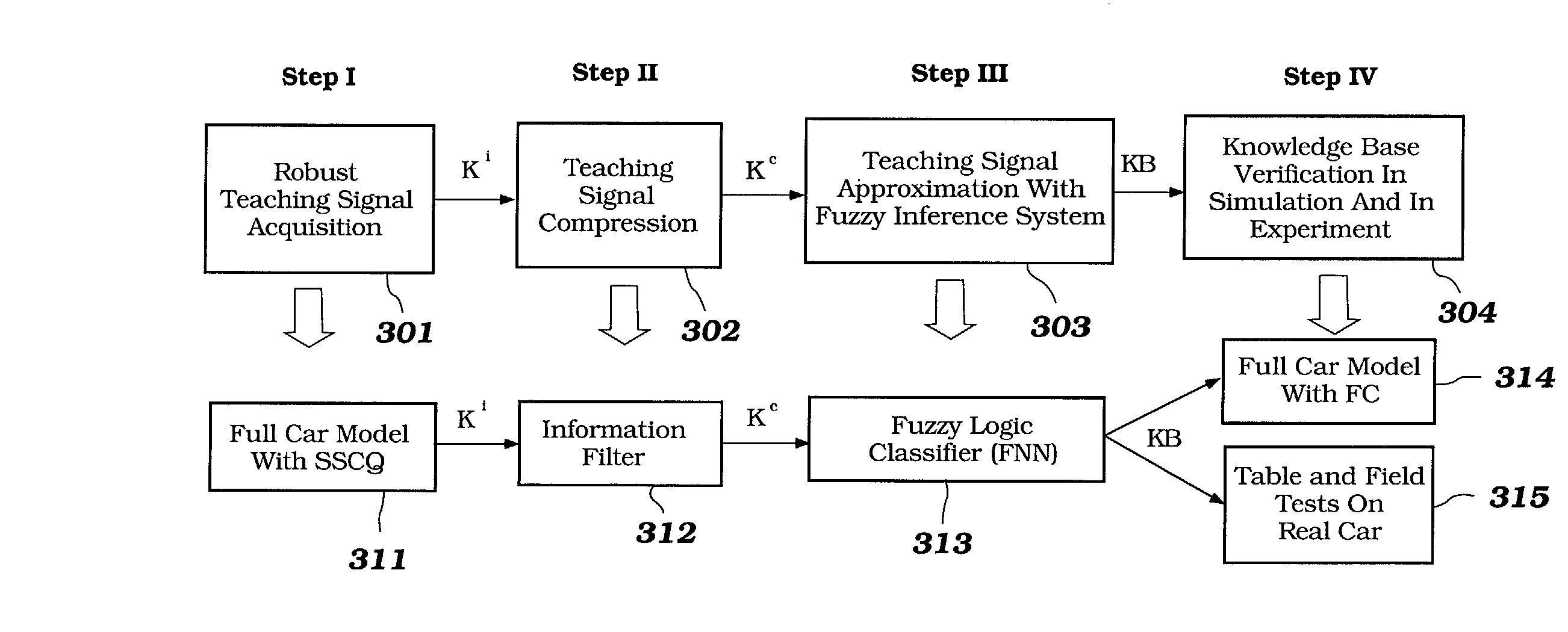
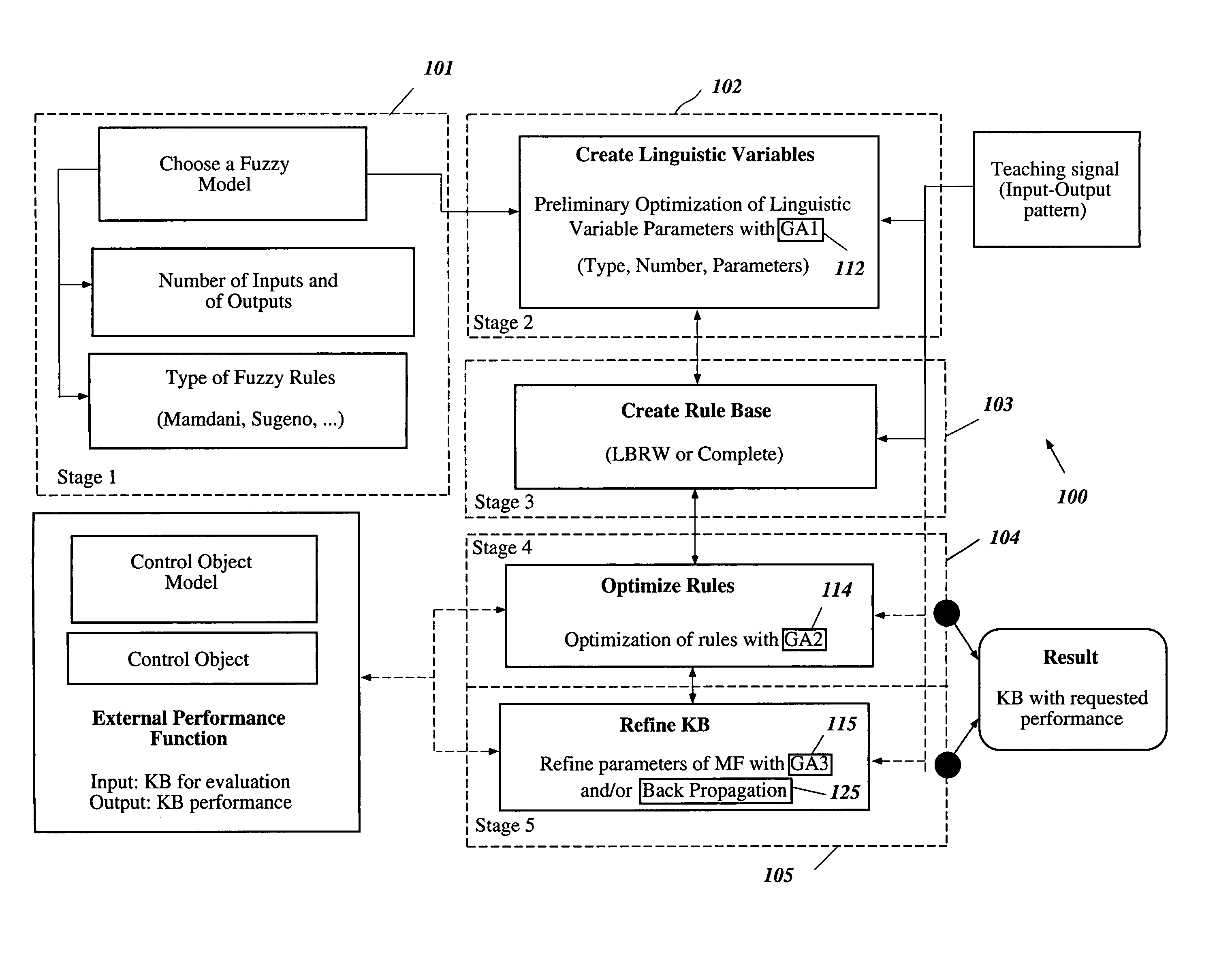
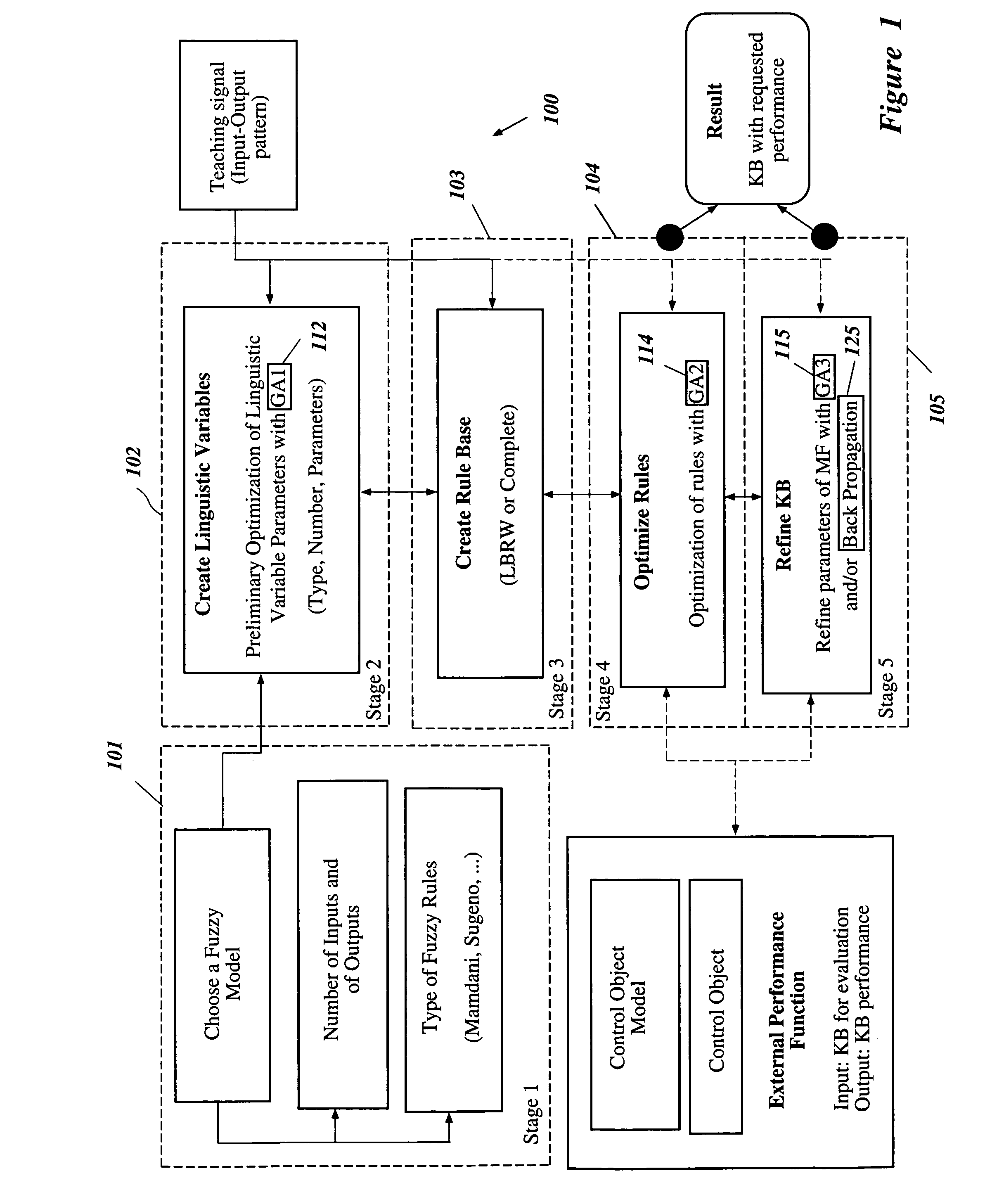
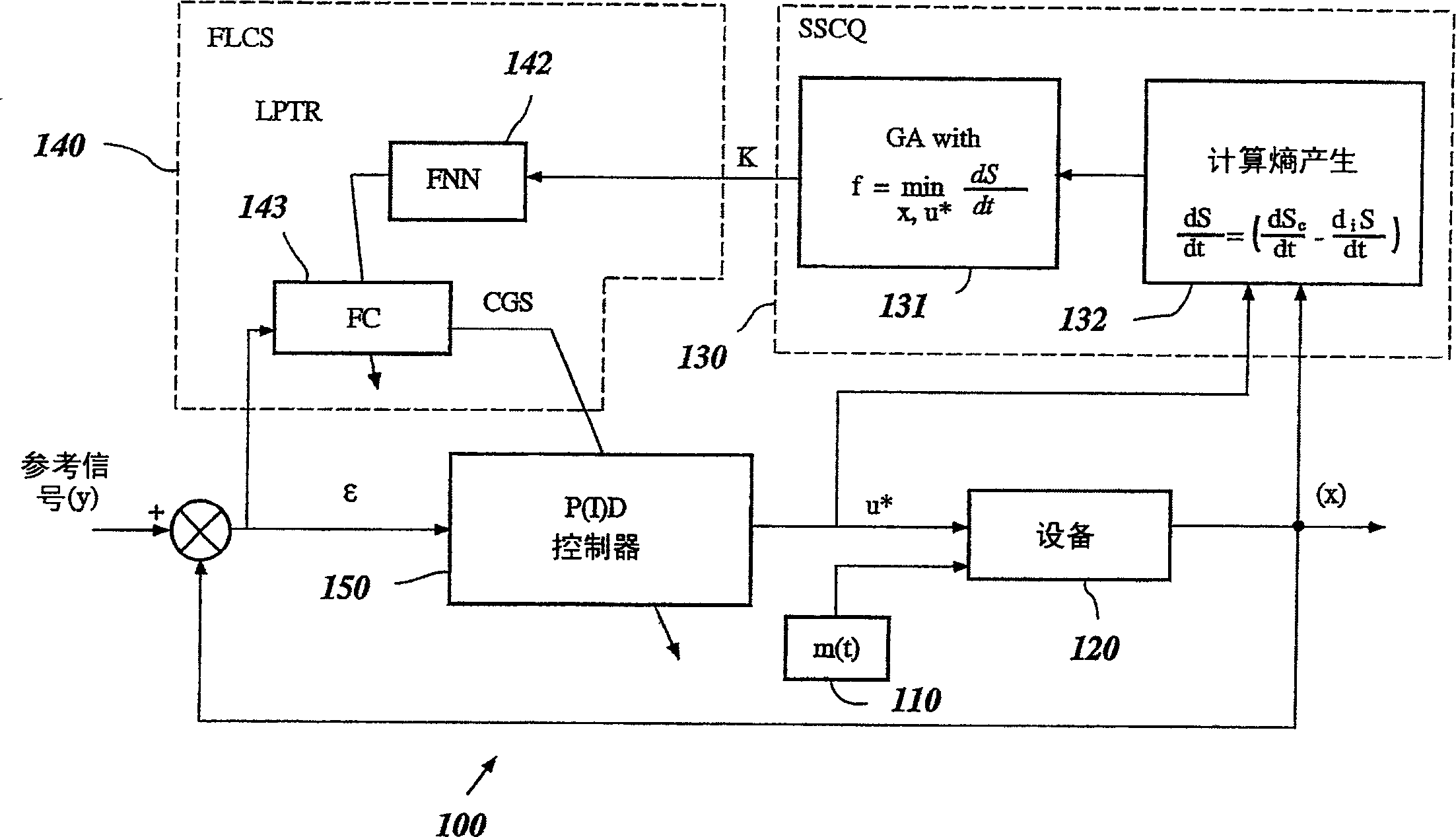
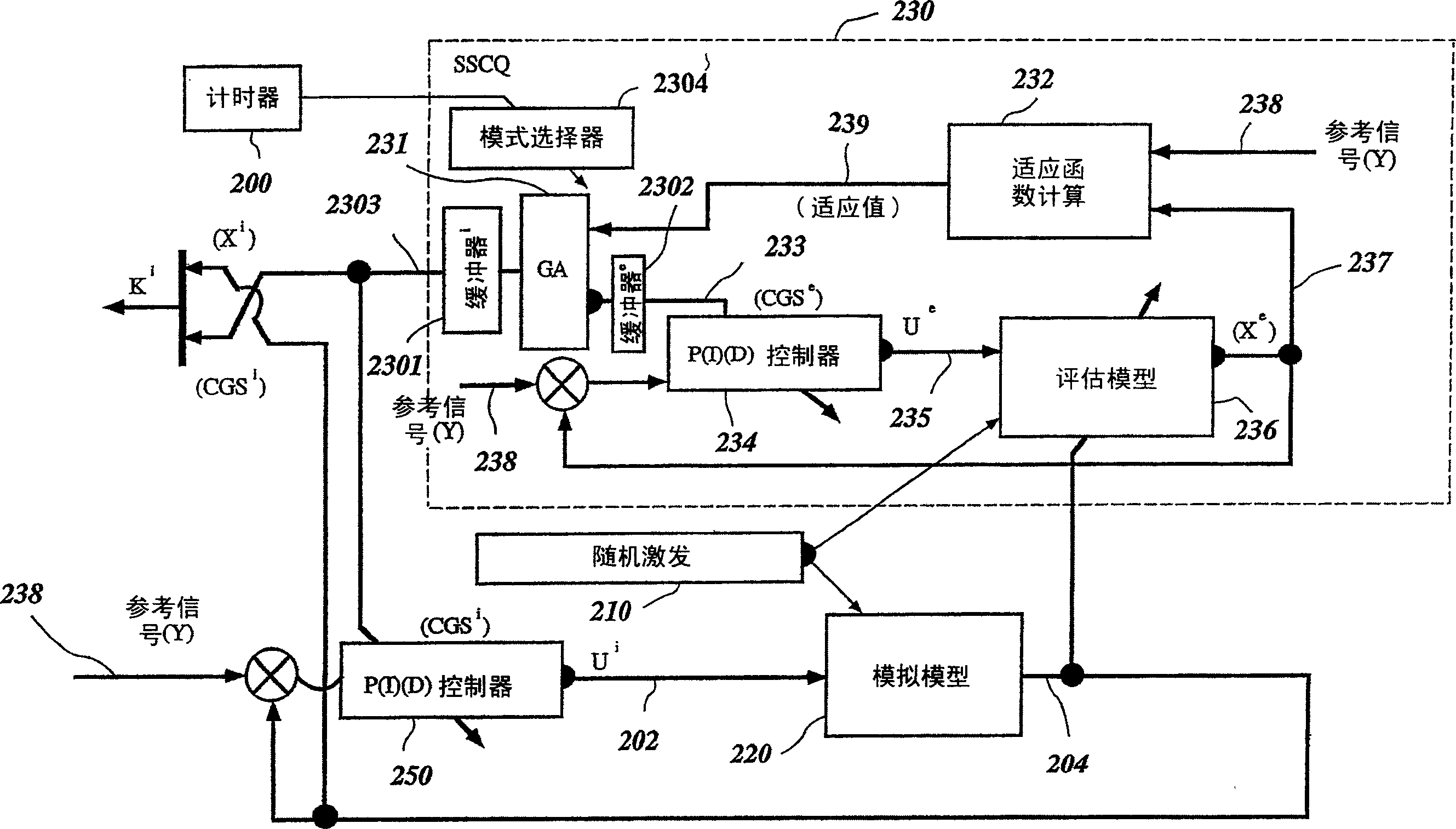
A Soft Computing (SC) optimizer for designing a Knowledge Base (KB) to be used in a control system for controlling a motorcycle is described. In one embodiment, a simulation model of the motorcycle and rider control is used. In one embodiment, the simulation model includes a feedforward rider model. The SC optimizer includes a fuzzy inference engine based on a Fuzzy Neural Network (FNN). The SC Optimizer provides Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) structure selection, FIS structure optimization method selection, and teaching signal selection and generation. The user selects a fuzzy model, including one or more of: the number of input and / or output variables; the type of fuzzy inference; and the preliminary type of membership functions. A Genetic Algorithm (GA) is used to optimize linguistic variable parameters and the input-output training patterns. A GA is also used to optimize the rule base, using the fuzzy model, optimal linguistic variable parameters, and a teaching signal. The GA produces a near-optimal FNN. The near-optimal FNN can be improved using classical derivative-based optimization procedures. The FIS structure found by the GA is optimized with a fitness function based on a response of the actual plant model of the controlled plant. The SC optimizer produces a robust KB that is typically smaller that the KB produced by prior art methods.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
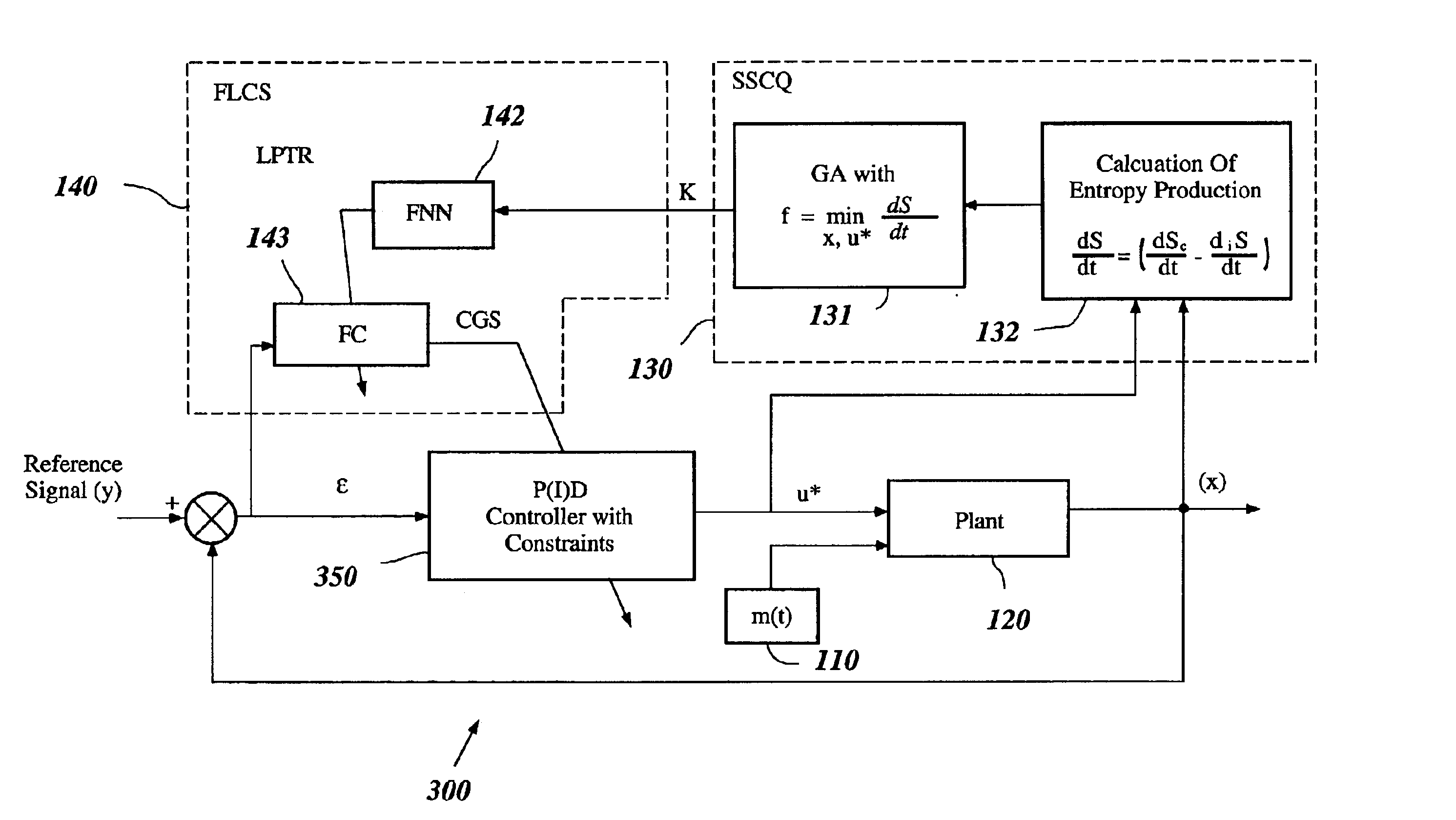
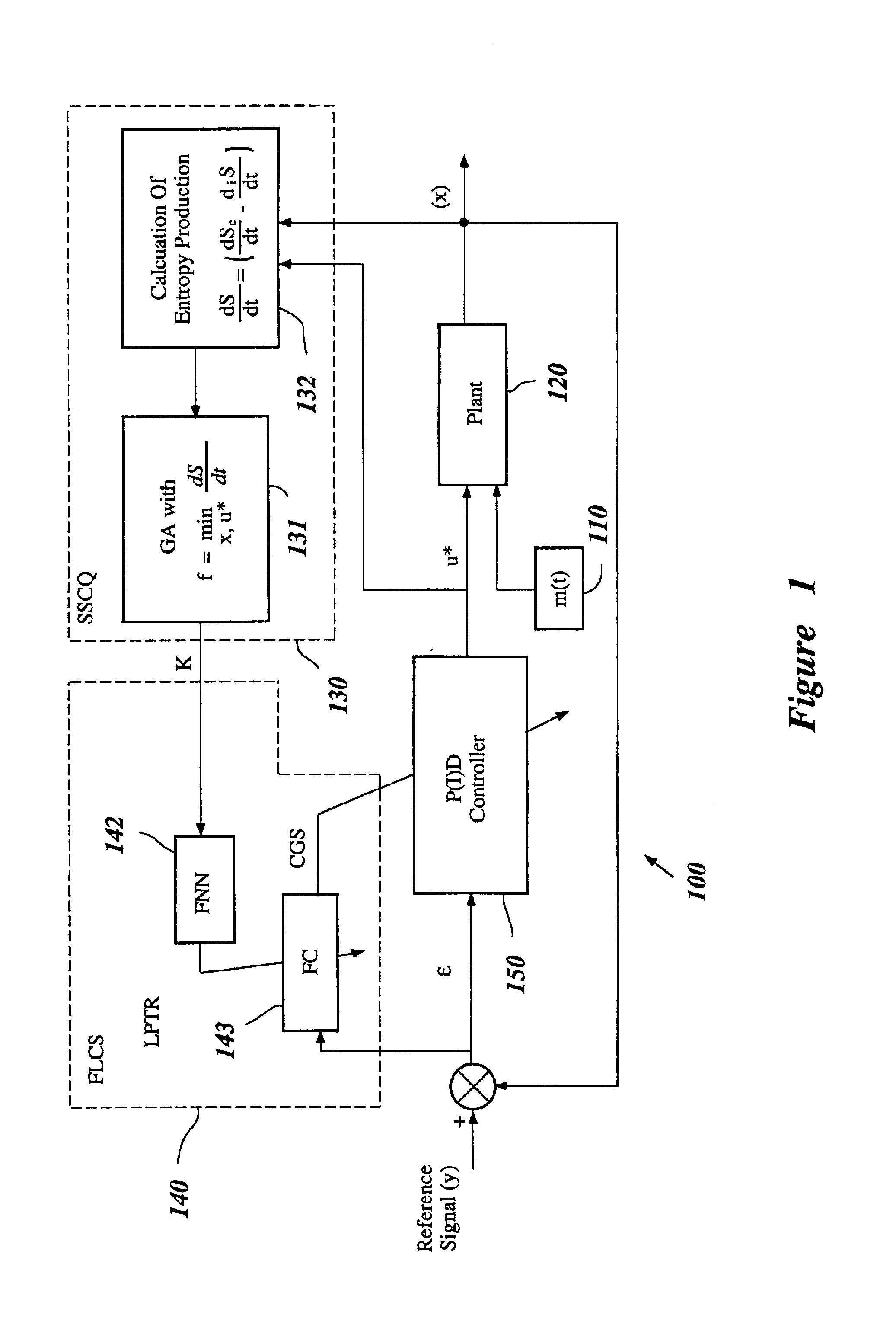
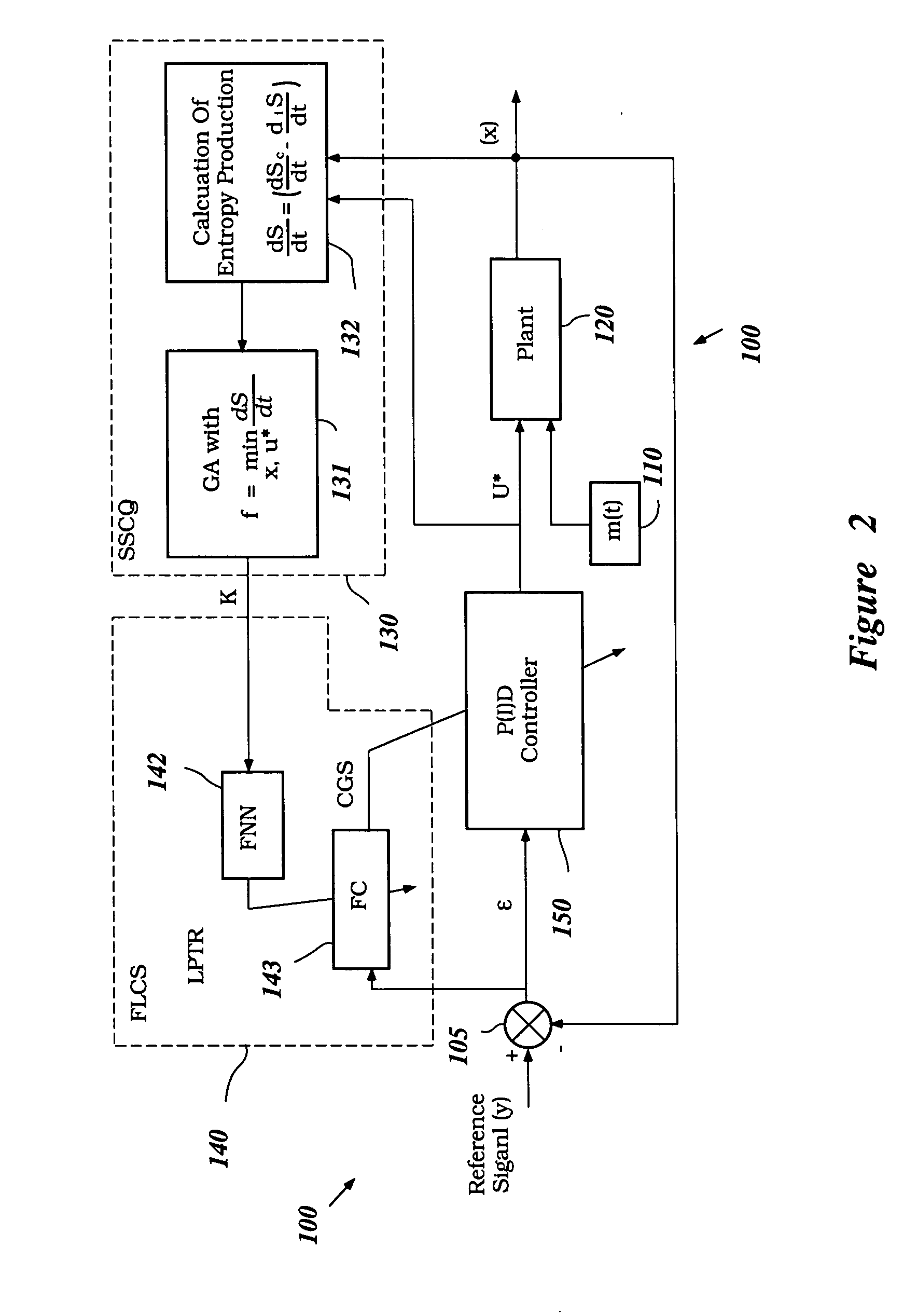
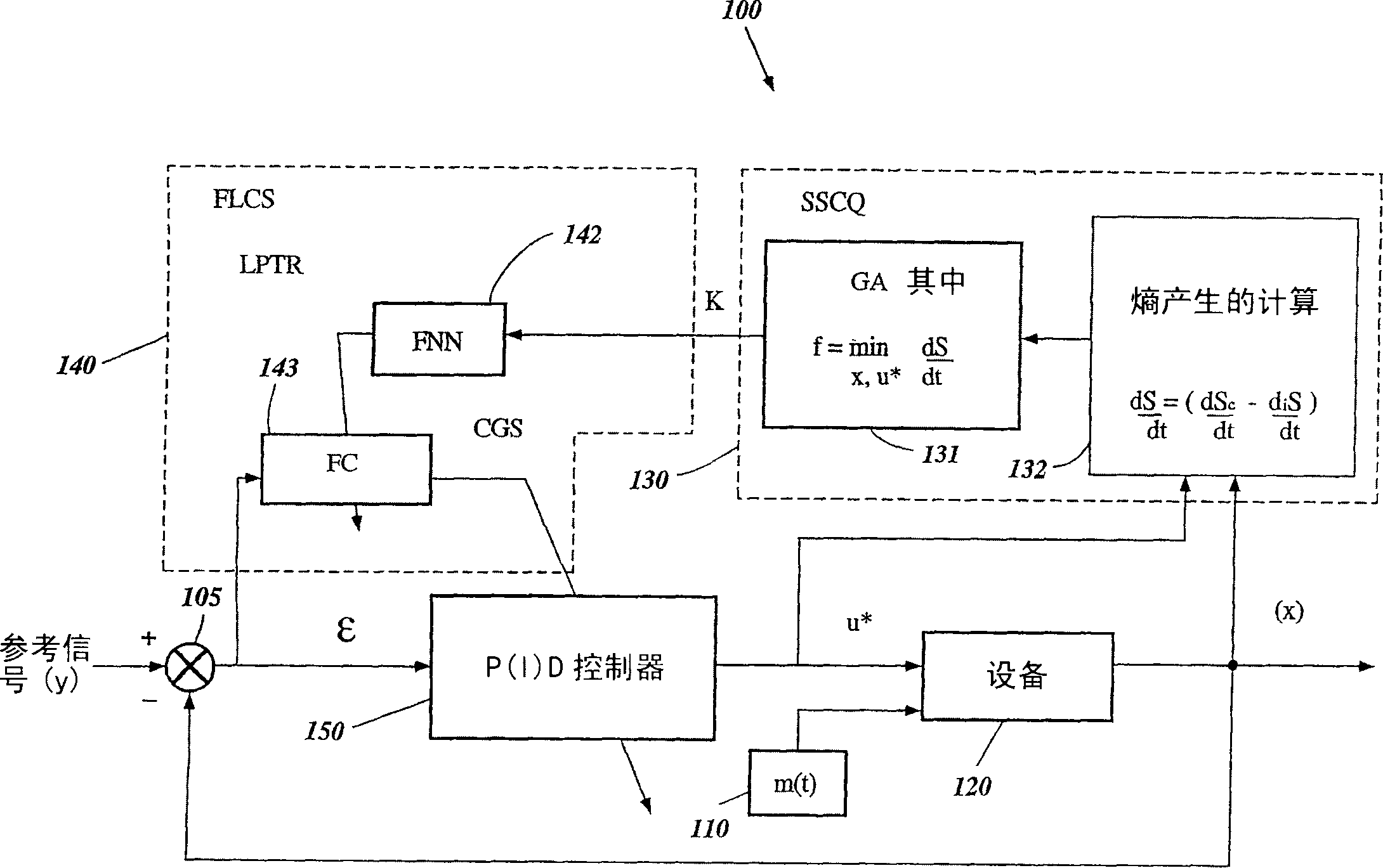
System and method for nonlinear dynamic control based on soft computing with discrete constraints
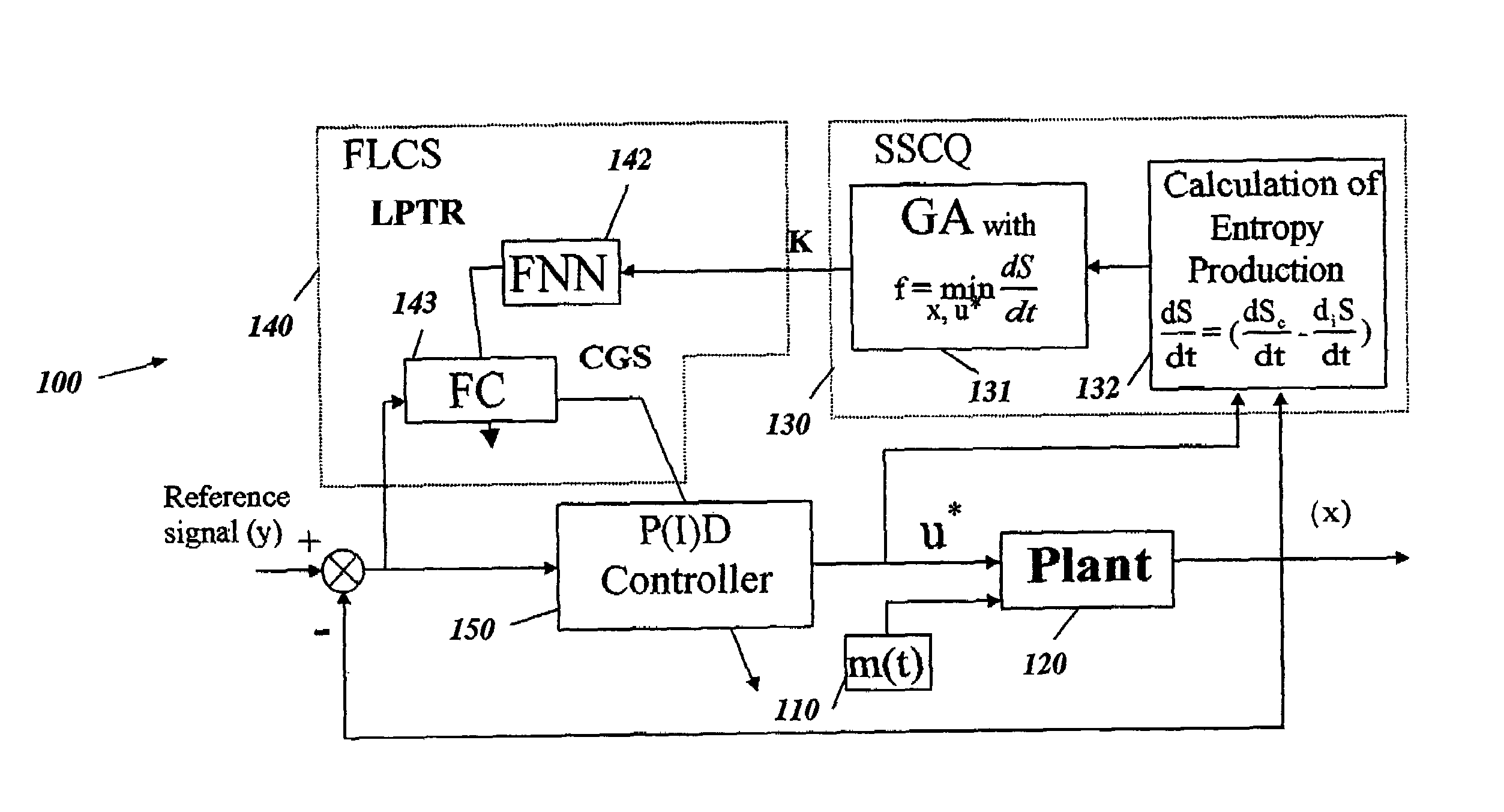
InactiveUS6950712B2Minimizes entropyMaximizes sensor information contentDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesNon linear dynamicMinimum entropy
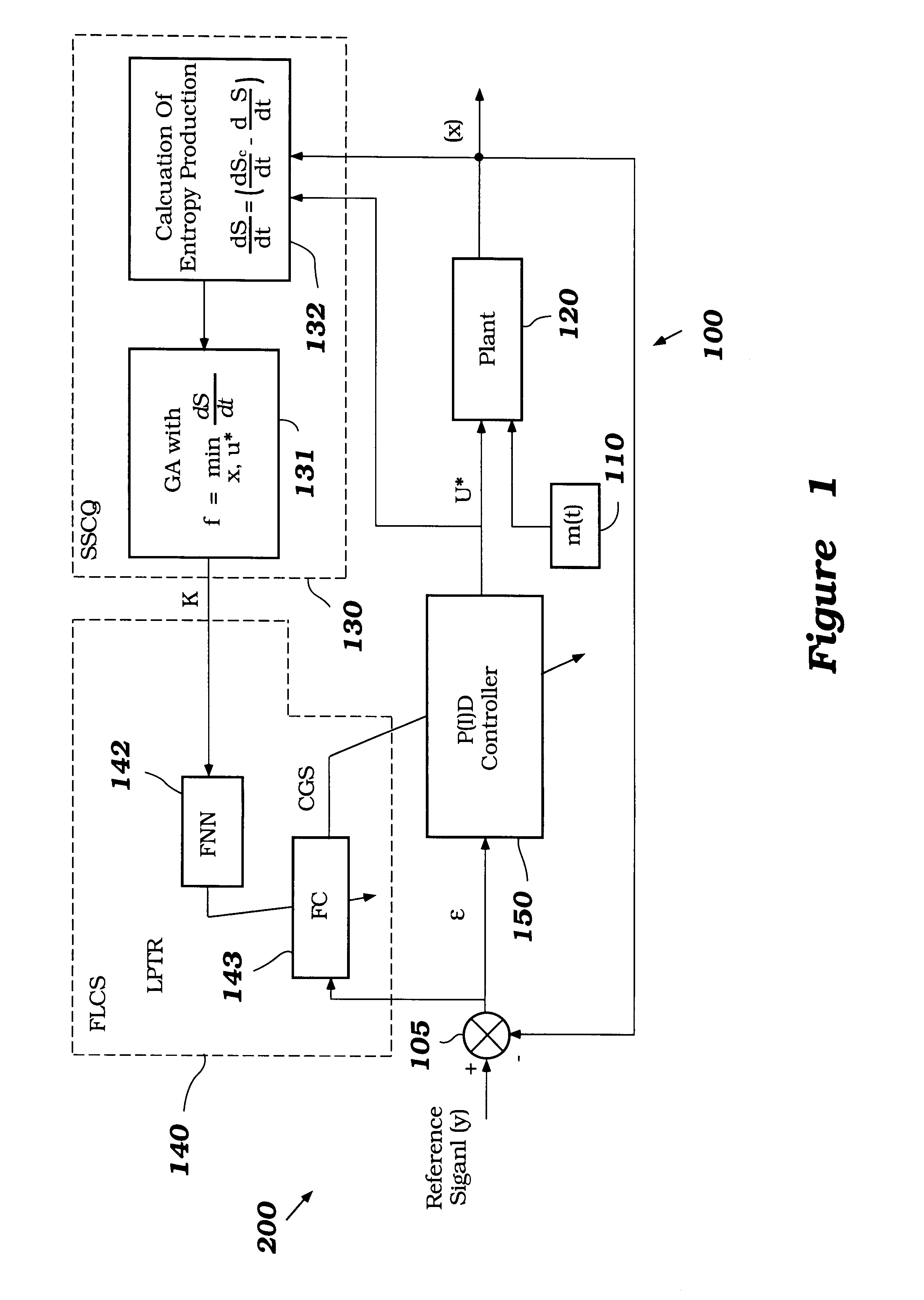
A control system using a genetic analyzer based on discrete constraints is described. In one embodiment, a genetic algorithm with step-coded chromosomes is used to develop a teaching signal that provides good control qualities for a controller with discrete constraints, such as, for example, a step-constrained controller. In one embodiment, the control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy. In one embodiment, the genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal for a fuzzy logic classifier system that develops a knowledge base. The teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from the knowledge base. The control system can be used to control complex plants described by nonlinear, unstable, dissipative models. In one embodiment, the step-constrained control system is configured to control stepping motors.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
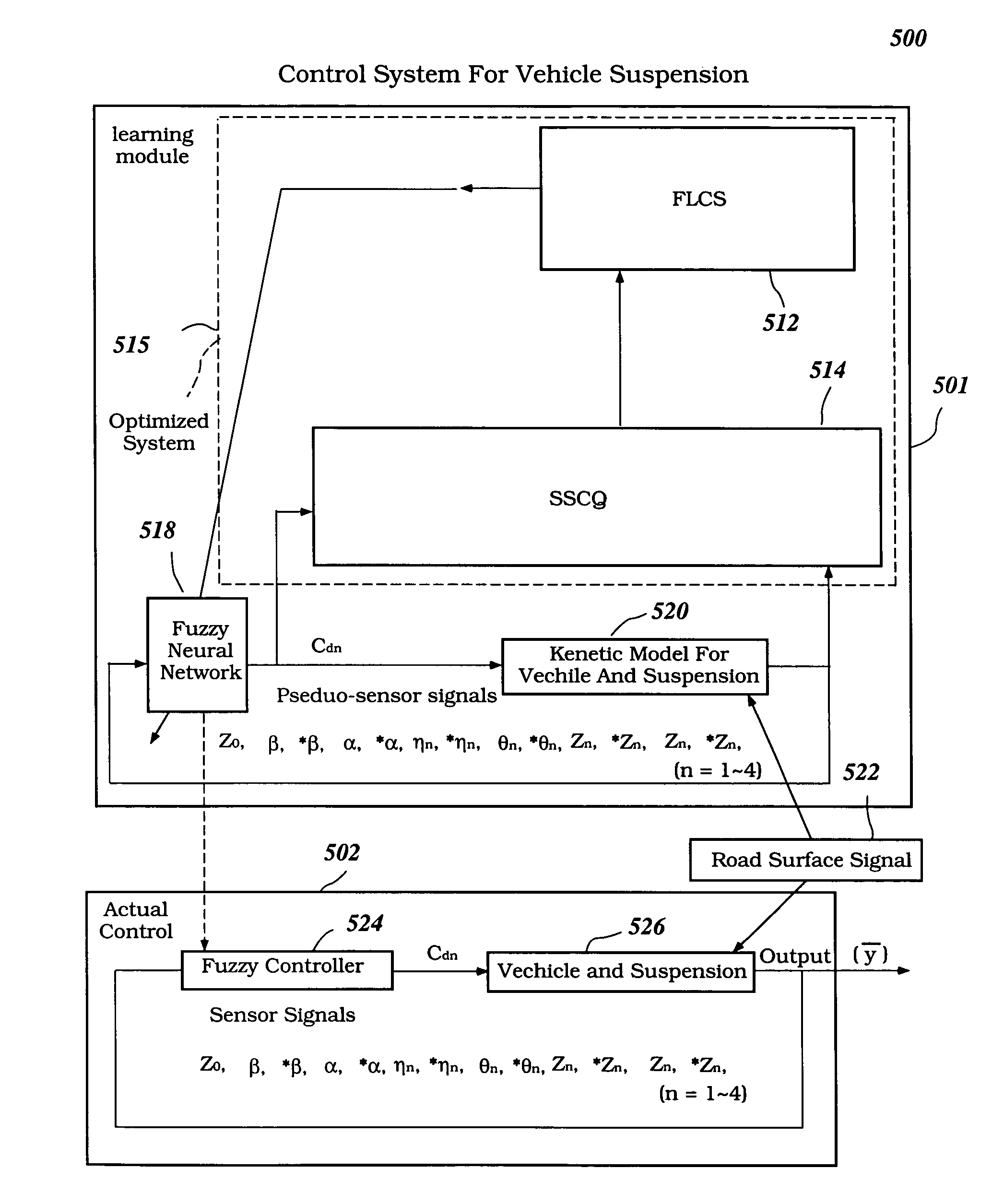
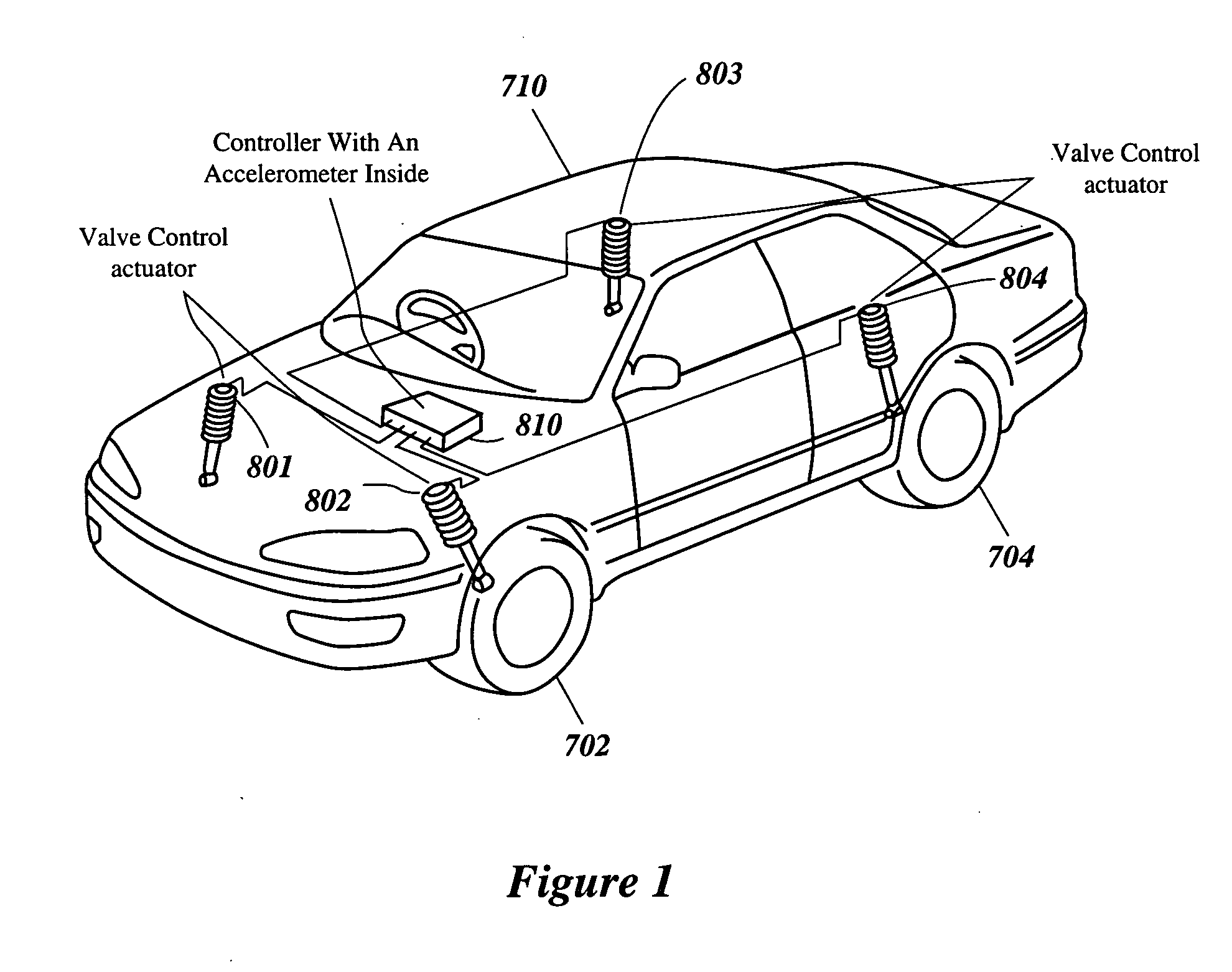
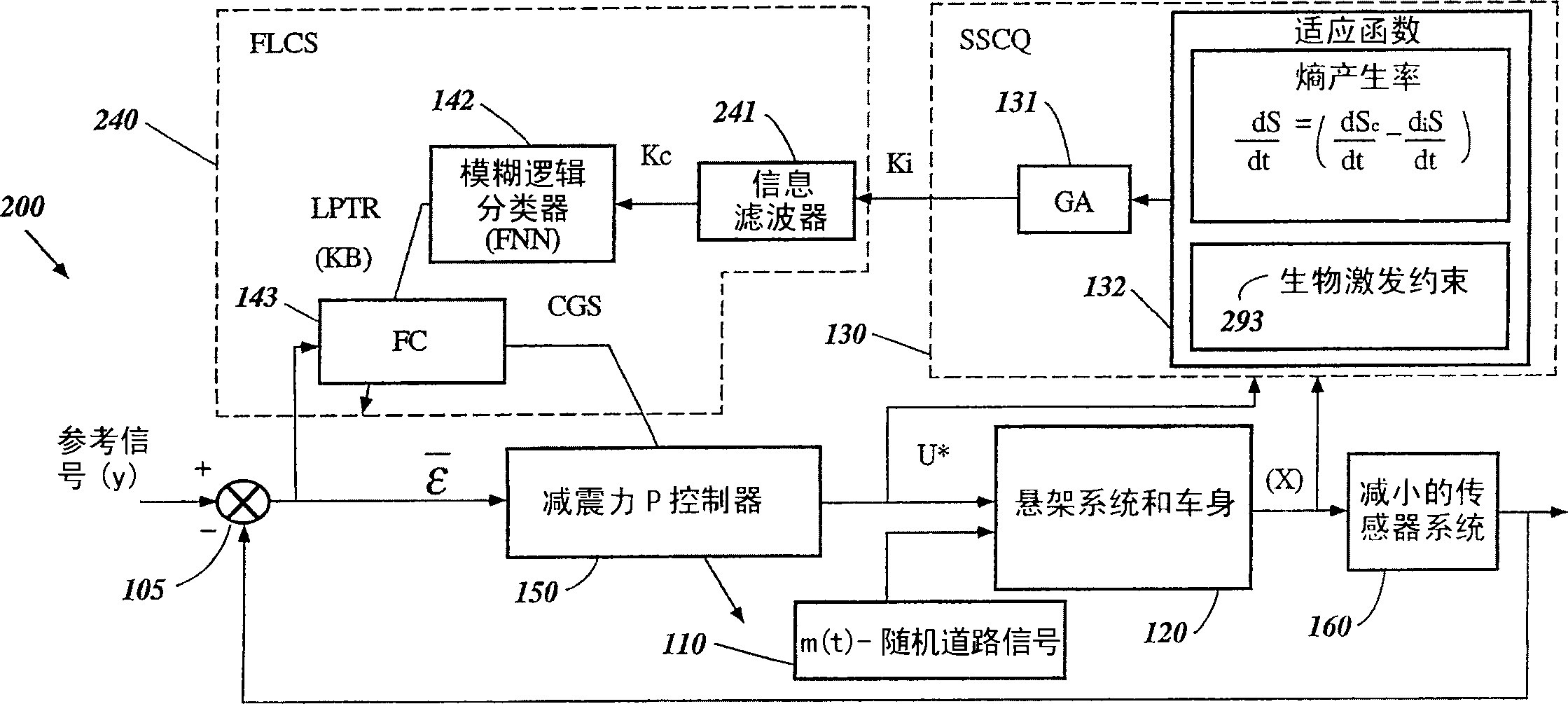
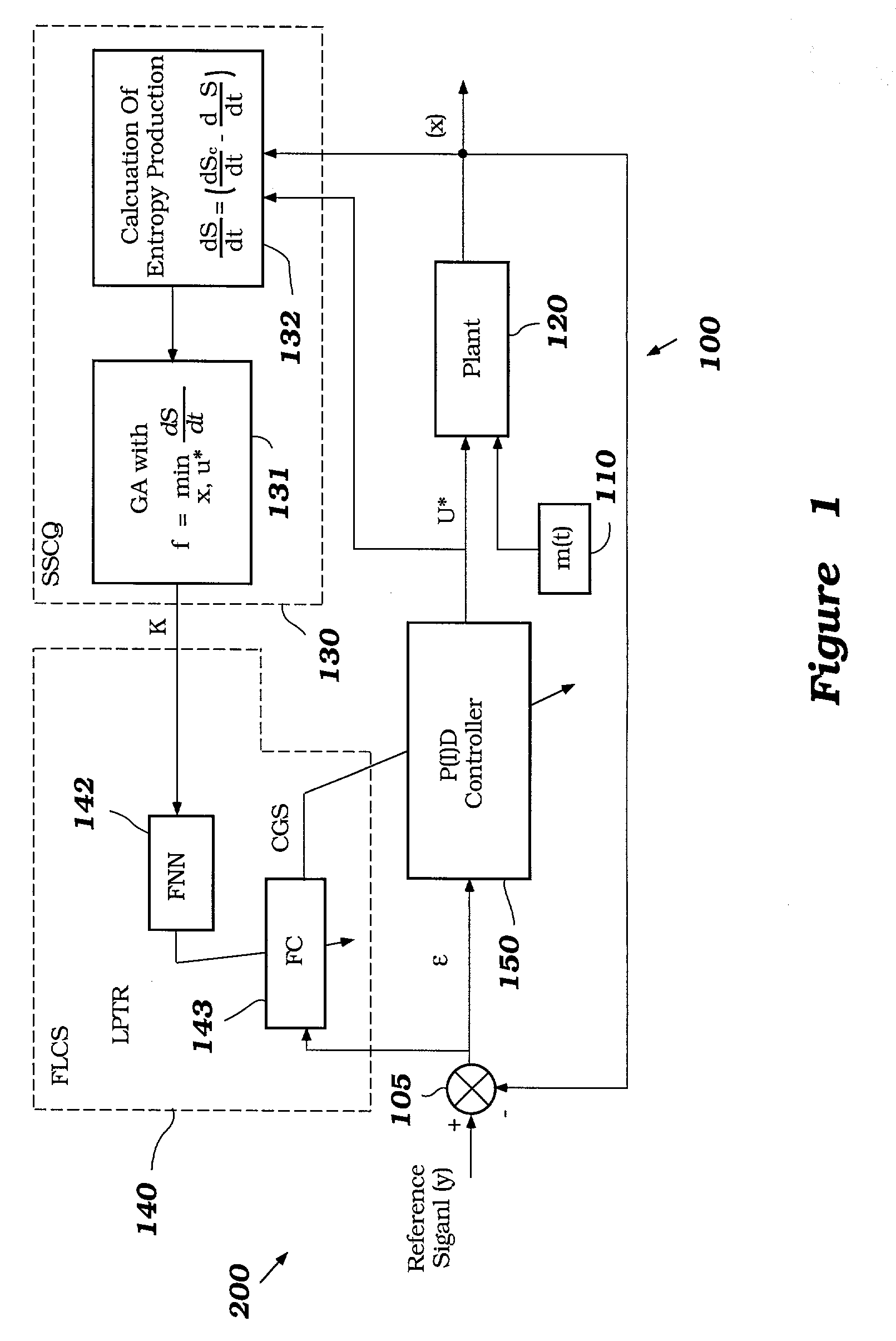
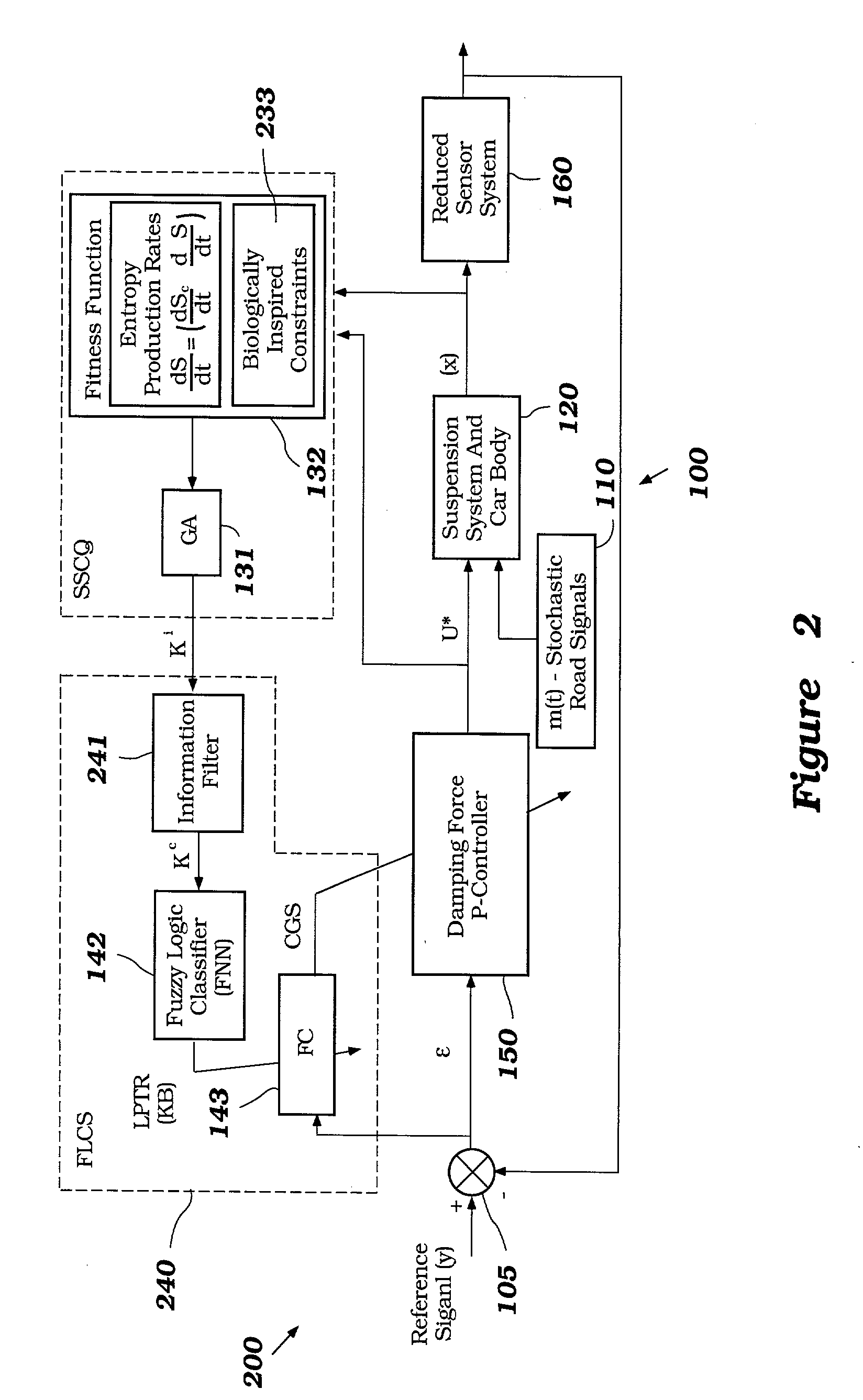
Intelligent mechatronic control suspension system based on soft computing
InactiveUS6701236B2Maximises informationLightweight productionSpringsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemFuzzy control system
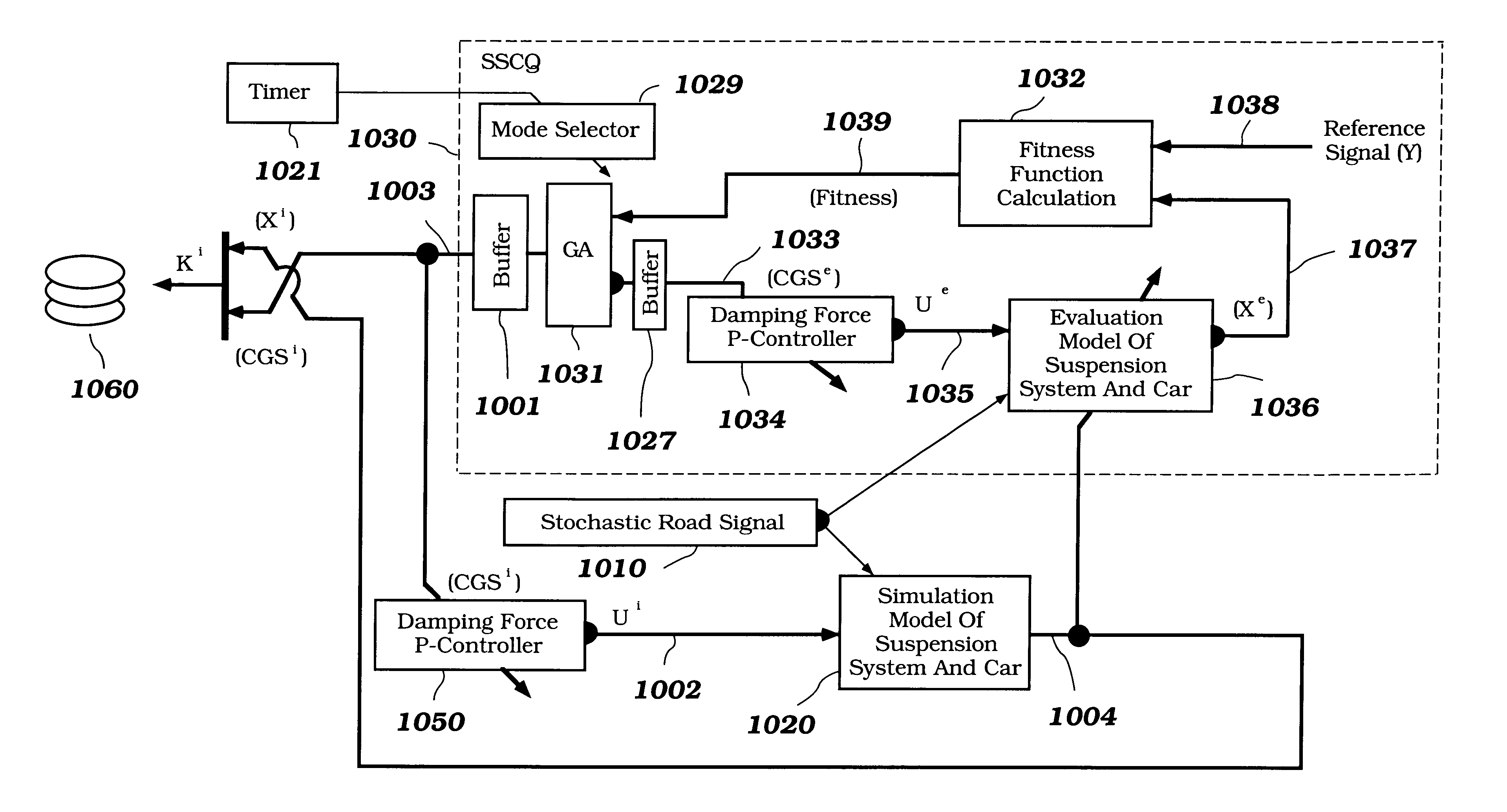
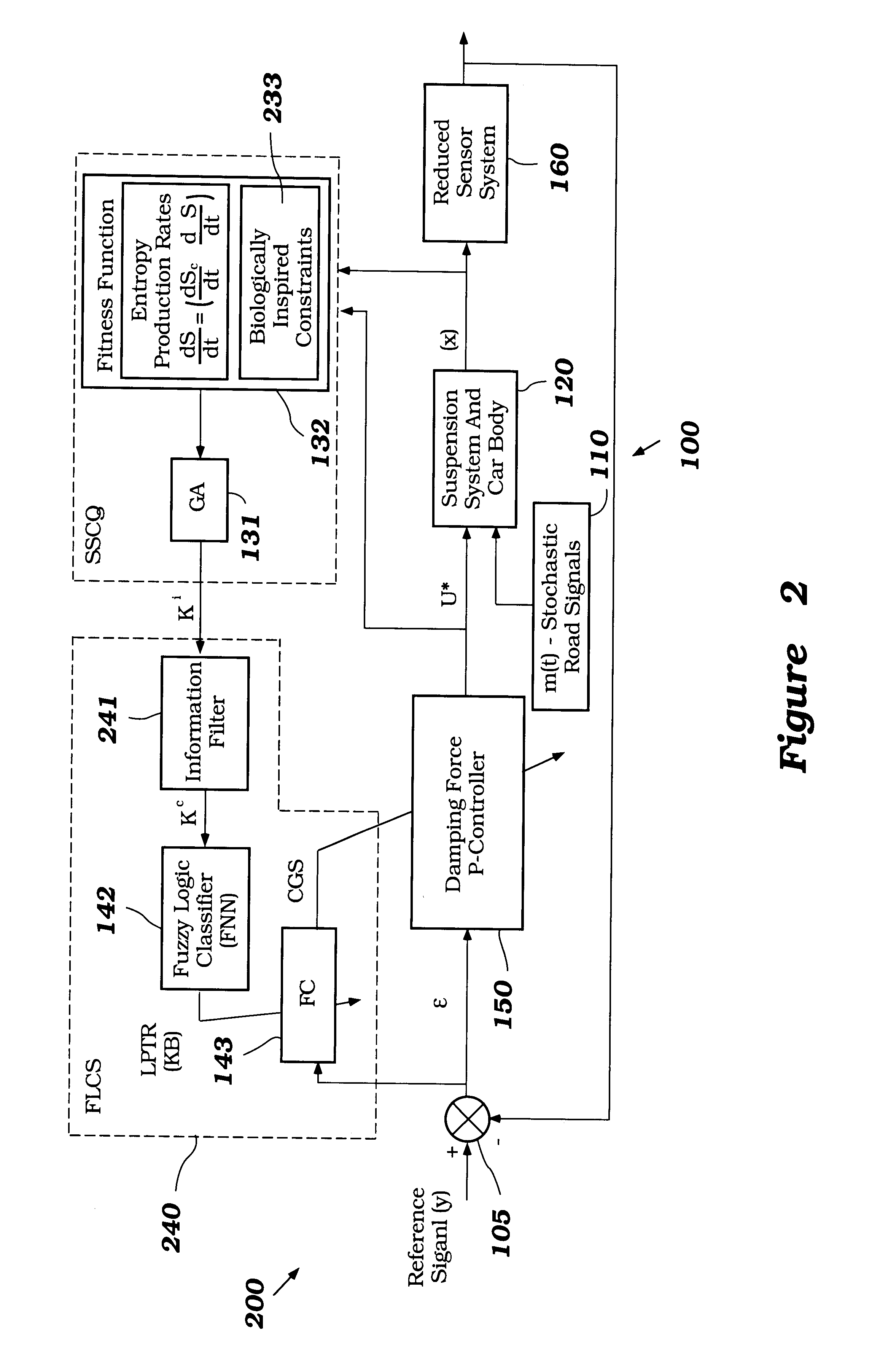
A control system for optimizing a shock absorber having a non-linear kinetic characteristic is described. The control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy and biologically inspired constraints relating to mechanical constraints and / or rider comfort, driveability, etc. In one embodiment, a genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal. An information filter is used to filter the teaching signal to produce a compressed teaching signal. The compressed teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from a knowledge base. In one embodiment, the control system includes a learning system, such as a neural network that is trained by the compressed training signal. The learning system is used to create a knowledge base for use by an online fuzzy controller. The online fuzzy controller is used to program a linear controller.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
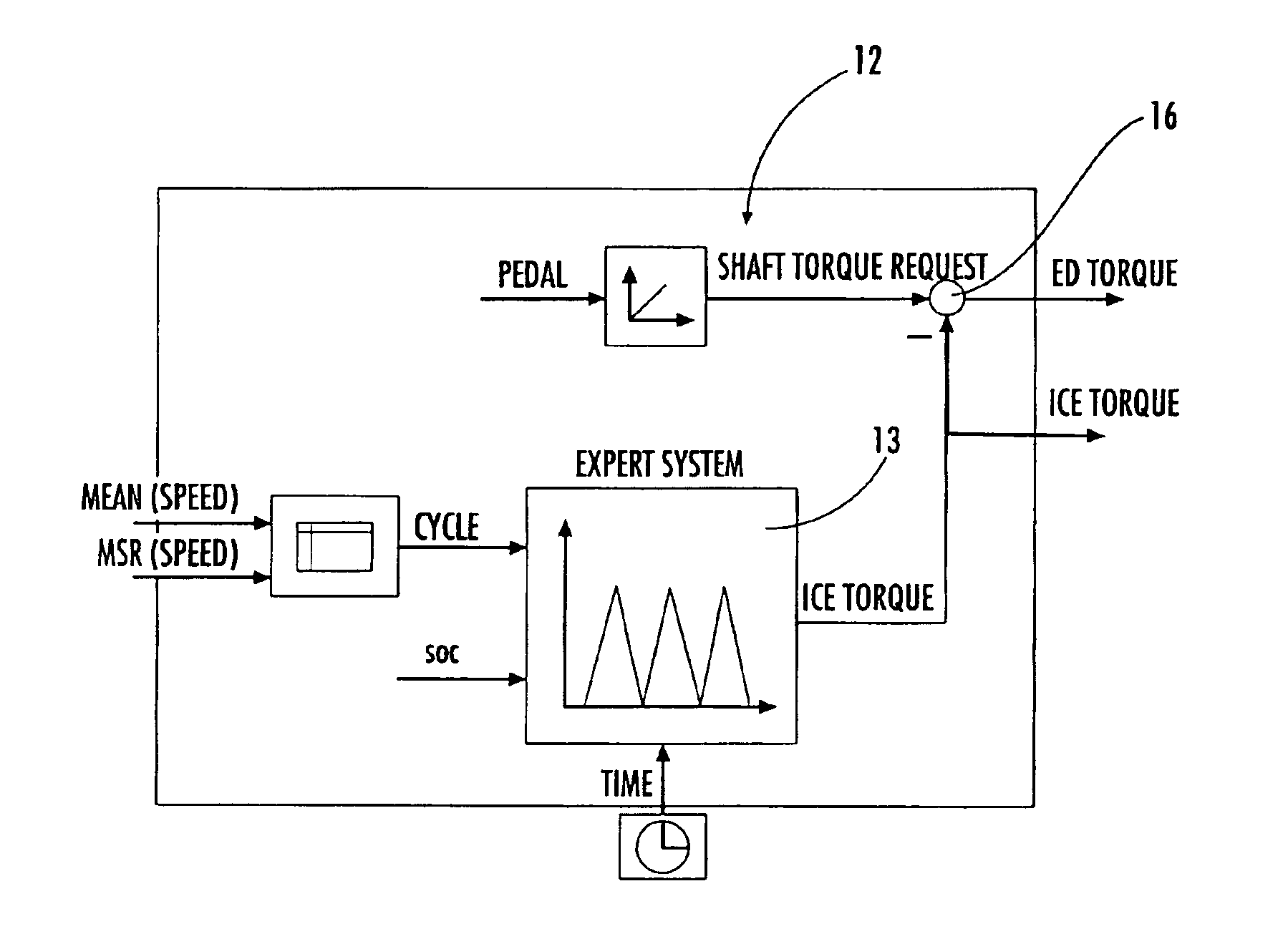
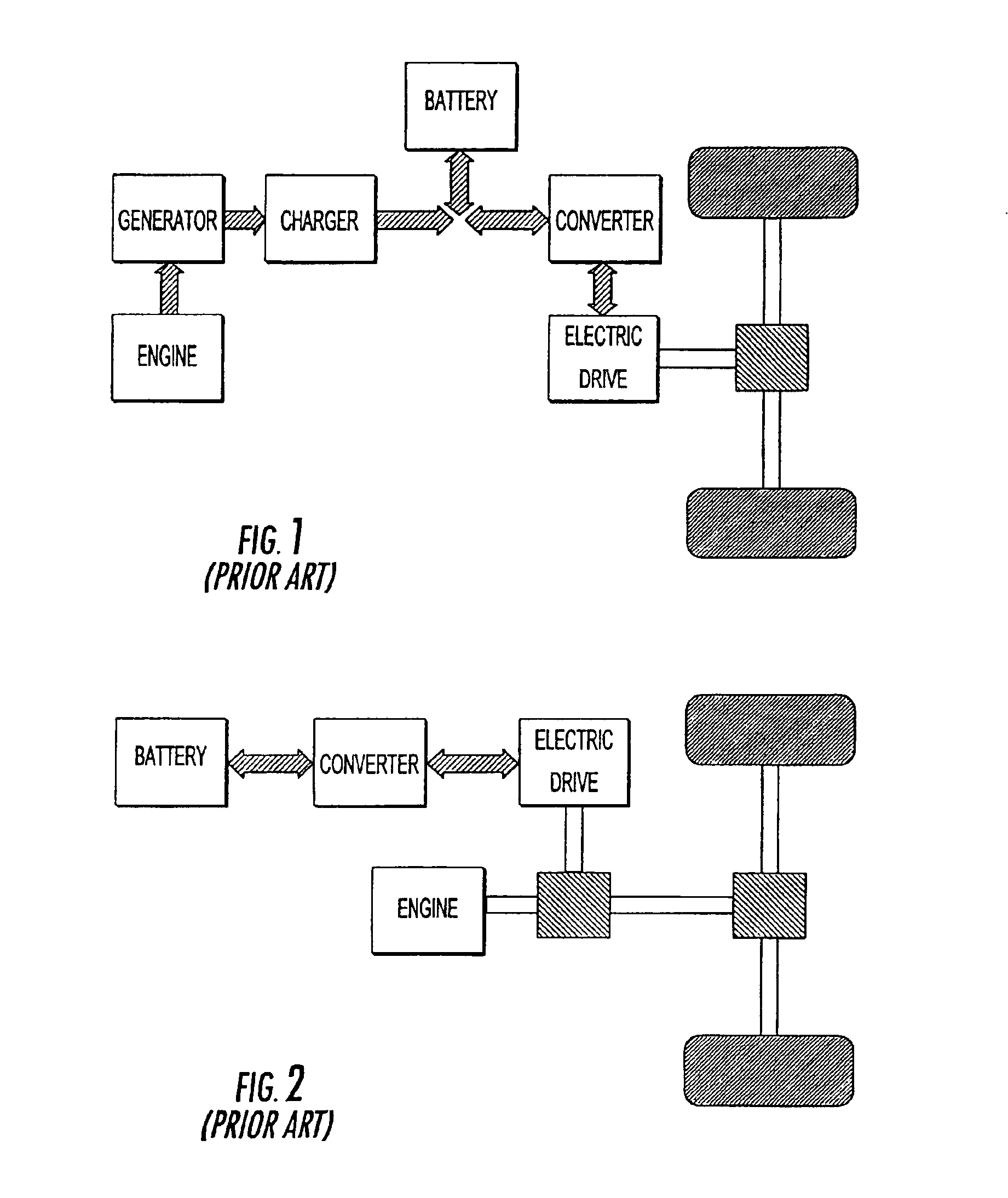
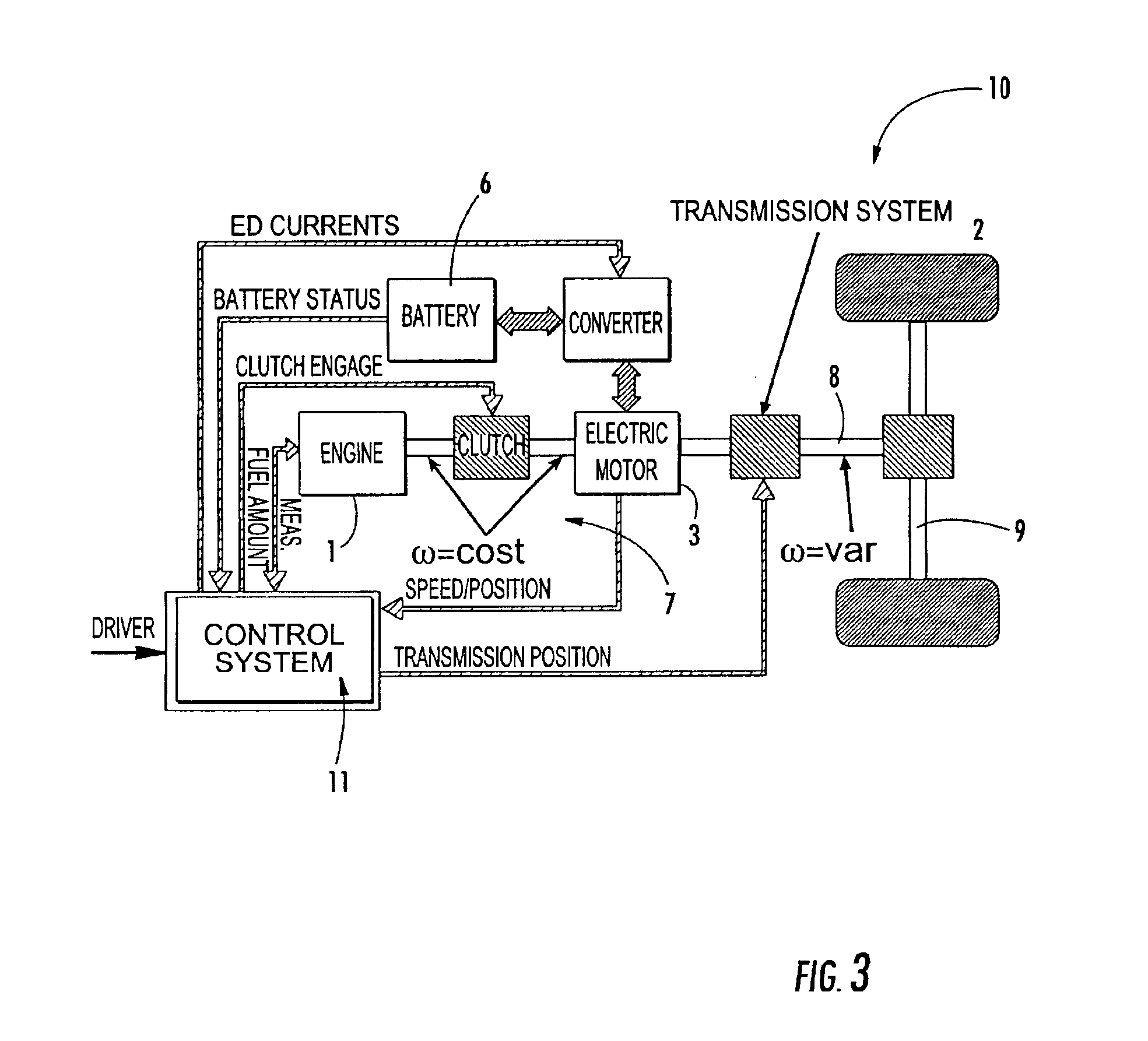
Electronic control system for torque distribution in hybrid vehicles
ActiveUS6853893B2Improving hybrid propulsion vehicle performanceOvercome limitationsInternal combustion piston enginesDigital data processing detailsExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
An electronic torque control and distribution system is provided for a hybrid propulsion vehicle. The drive thrust of the hybrid propulsion vehicle is distributed between an electric engine and an internal combustion engine through a transmission system. The transmission system delivers the torque of both engines to the vehicle wheels. The electronic torque control and distribution system is slaved to a control unit, and includes a controller for incorporating a fuzzy logic processor to predict through soft computing techniques the torque contributions of the electric engine and of the internal combustion engine. A sensor estimates the vehicle polluting emissions. The controller and the sensor are both connected to the control unit.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
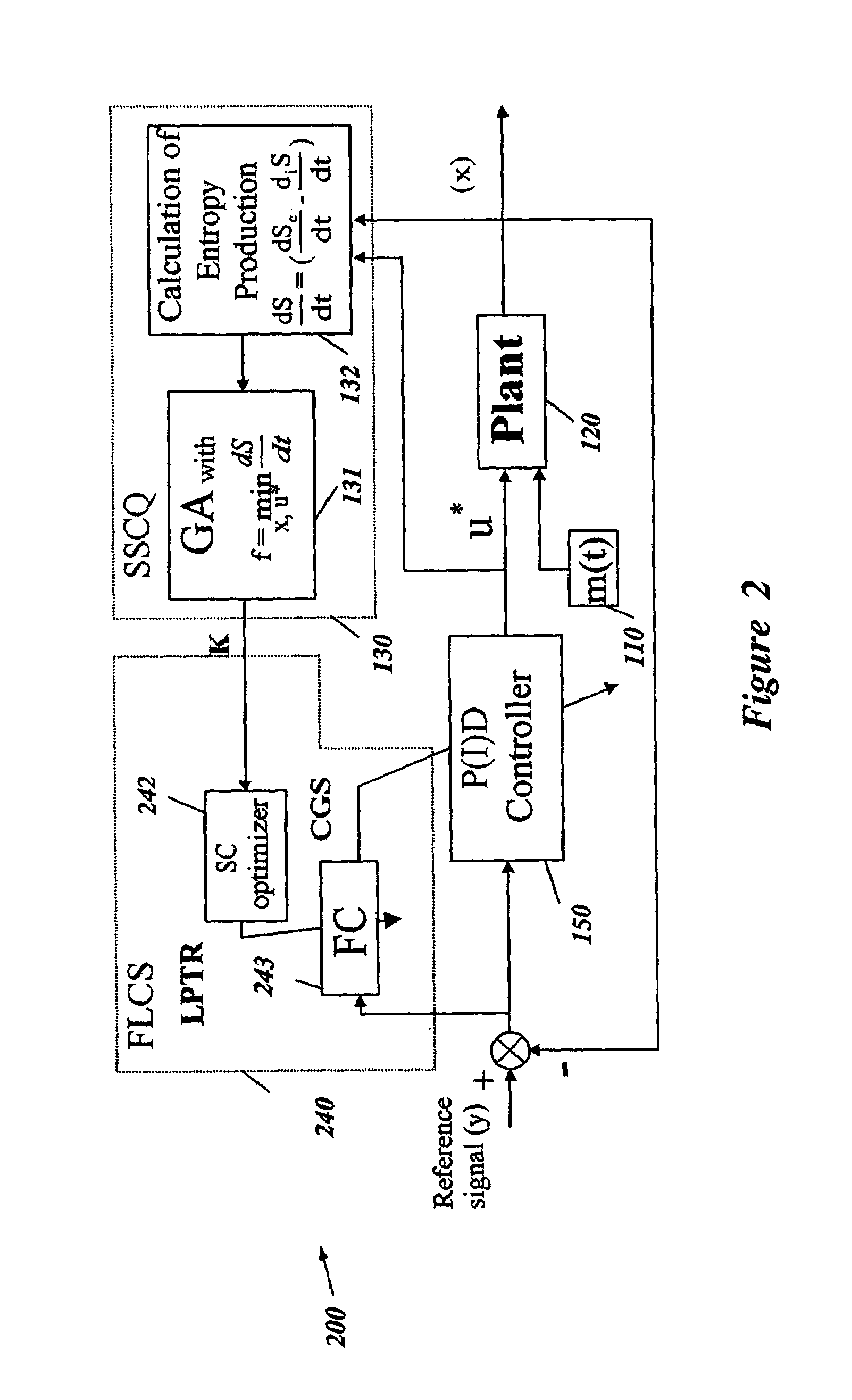
Intelligent electronically-controlled suspension system based on soft computing optimizer
InactiveUS20060293817A1Near-optimal FNNMaximises informationDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesInput/outputSoft computing
A Soft Computing (SC) optimizer for designing a Knowledge Base (KB) to be used in a control system for controlling a suspension system is described. The SC optimizer includes a fuzzy inference engine based on a Fuzzy Neural Network (FNN). The SC Optimizer provides Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) structure selection, FIS structure optimization method selection, and teaching signal selection and generation. The user selects a fuzzy model, including one or more of: the number of input and / or output variables; the type of fuzzy inference model (e.g., Mamdani, Sugeno, Tsukamoto, etc.); and the preliminary type of membership functions. A Genetic Algorithm (GA) is used to optimize linguistic variable parameters and the input-output training patterns. A GA is also used to optimize the rule base, using the fuzzy model, optimal linguistic variable parameters, and a teaching signal. The GA produces a near-optimal FNN. The near-optimal FNN can be improved using classical derivative-based optimization procedures. The FIS structure found by the GA is optimized with a fitness function based on a response of the actual suspension system model of the controlled suspension system. The SC optimizer produces a robust KB that is typically smaller that the KB produced by prior art methods.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Intelligent mechatronic control suspension system based on quantum soft computing
InactiveCN1672171AGood precisionImprove reliabilityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsQuantum search algorithmMinimum entropy
A control system for optimizing a shock absorber having a non-linear kinetic characteristic is described. The control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy and biologically inspired constraints relating to mechanical constraints and / or rider comfort, driveability, etc. In one embodiment, a genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal. The teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from a knowledge base. A learning system is used to create the knowledge base for use by the online fuzzy controller. In one embodiment, the learning system uses a quantum search algorithm to search a number of solution spaces to obtain information for the knowledge base. The online fuzzy controller is used to program a linear controller.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
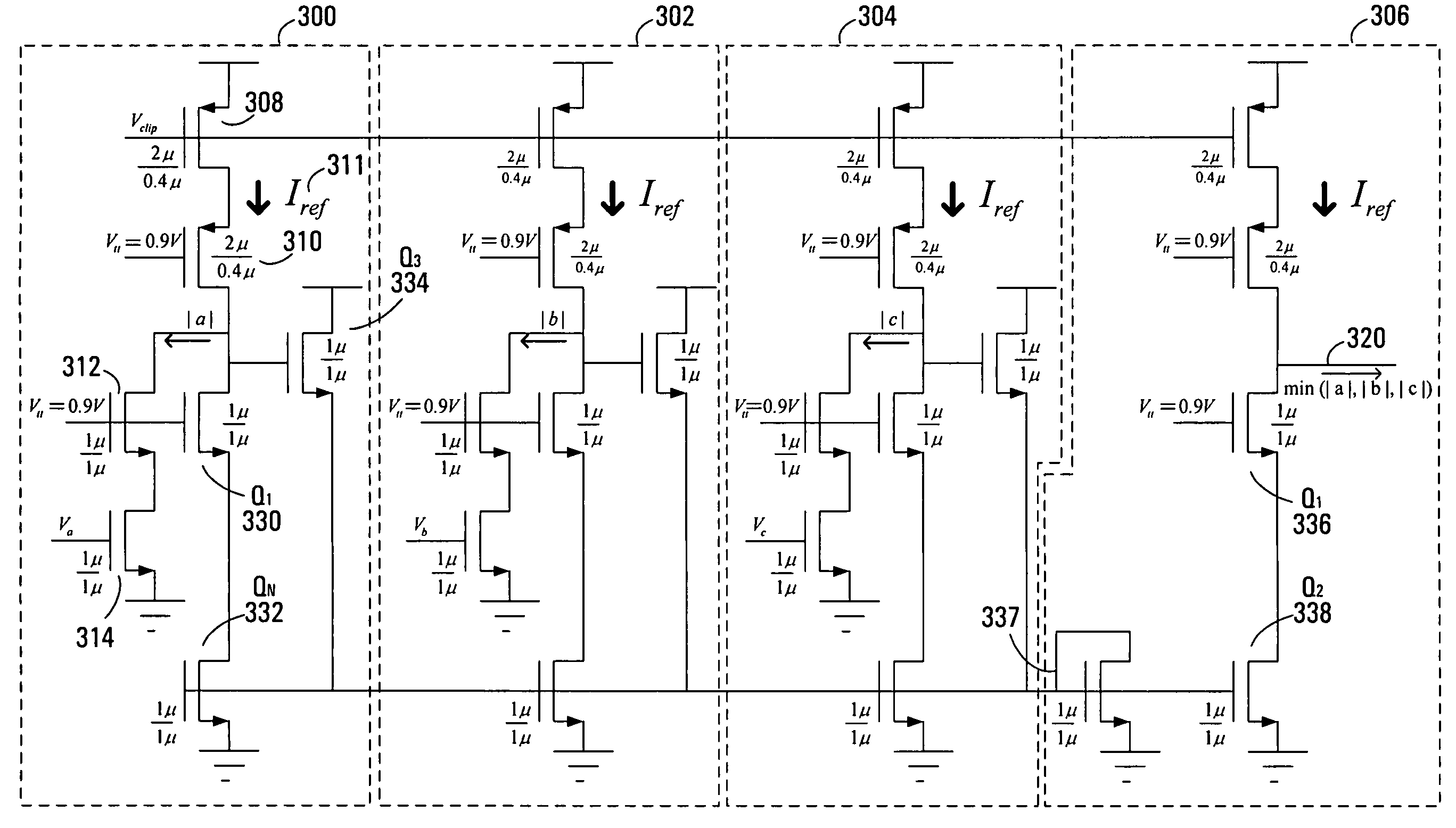
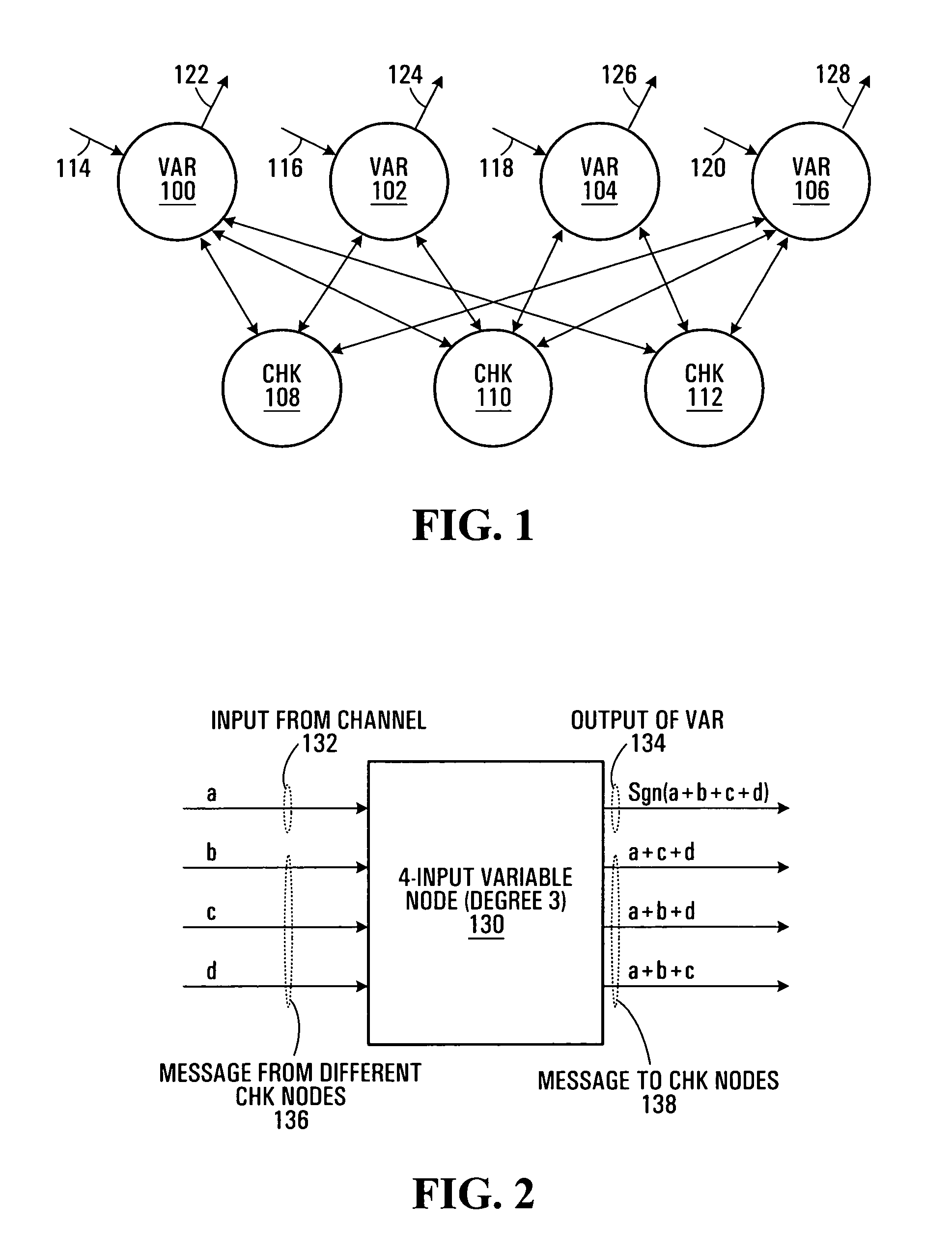
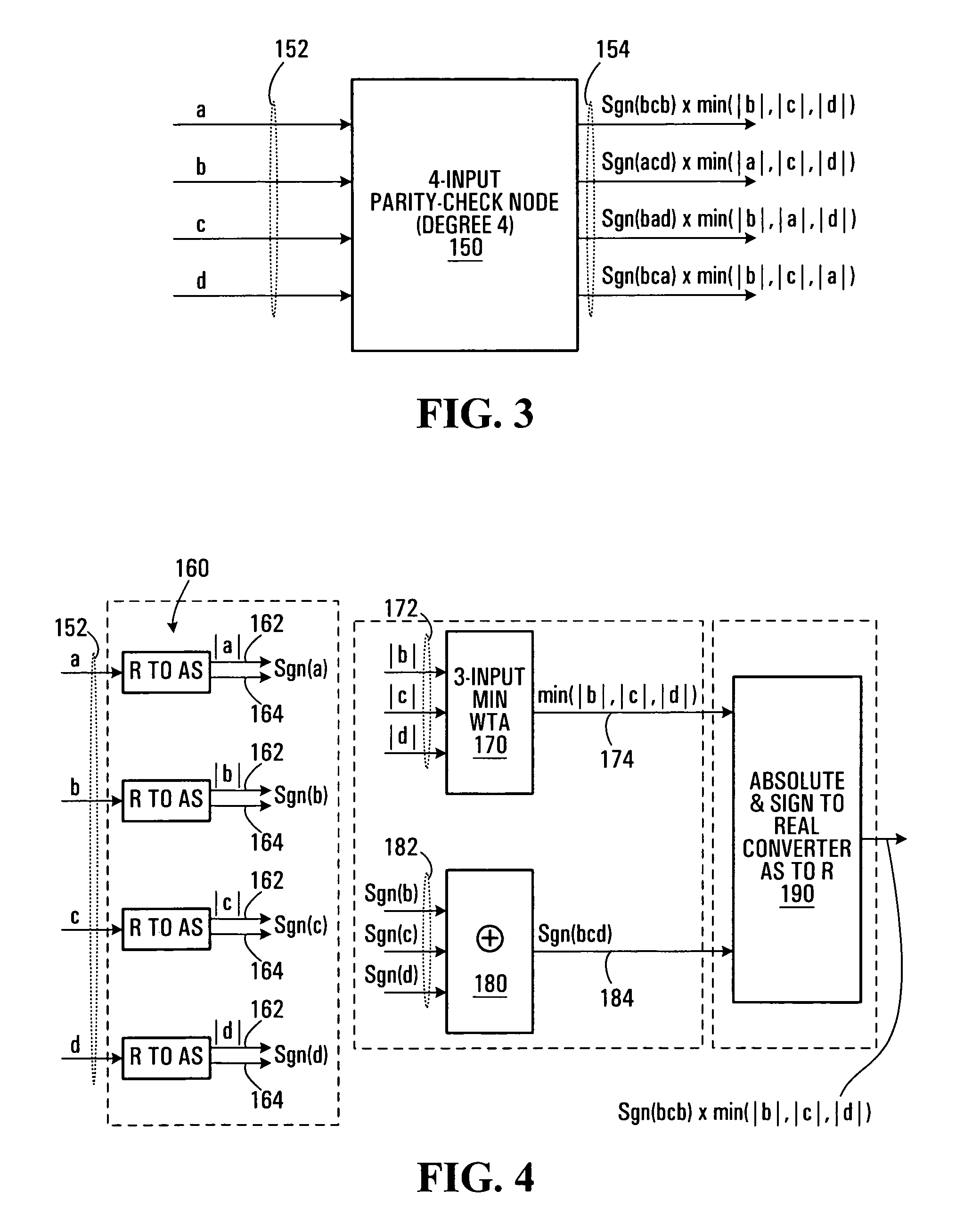
Full CMOS min-sum analog iterative decoders
InactiveUS20050240647A1Reduce manufacturing costSimple designDigital data processing detailsError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsMOSFETCMOS
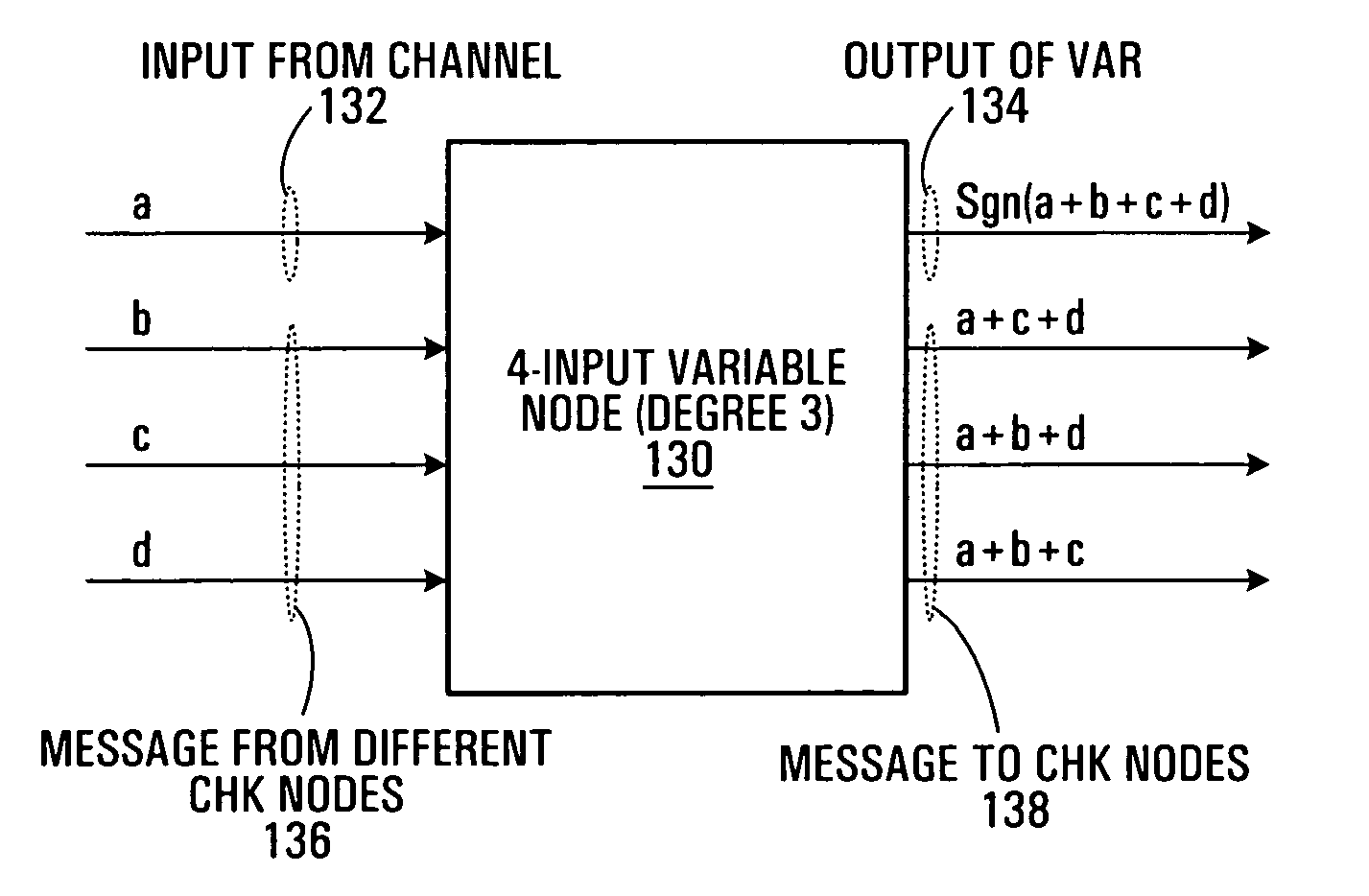
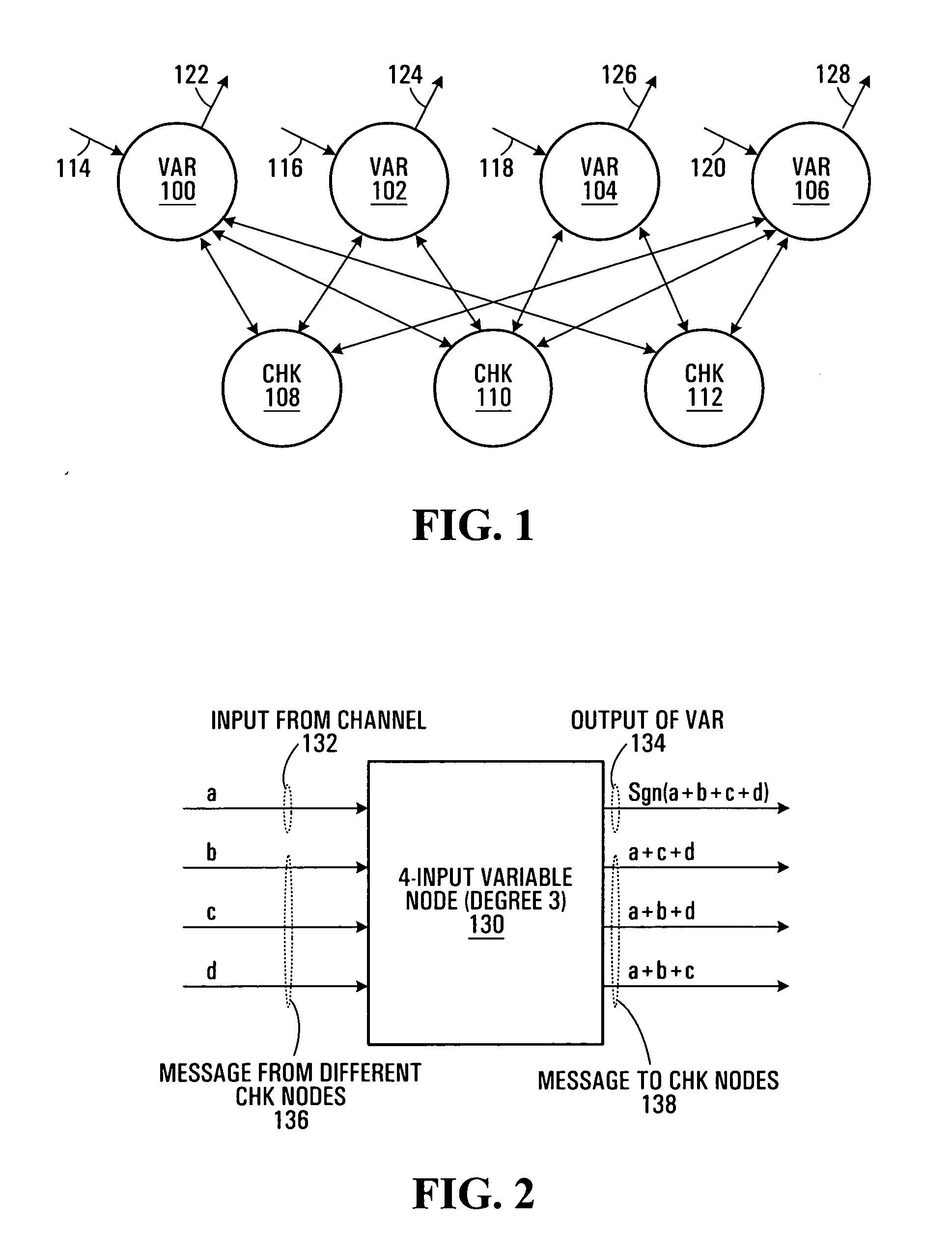
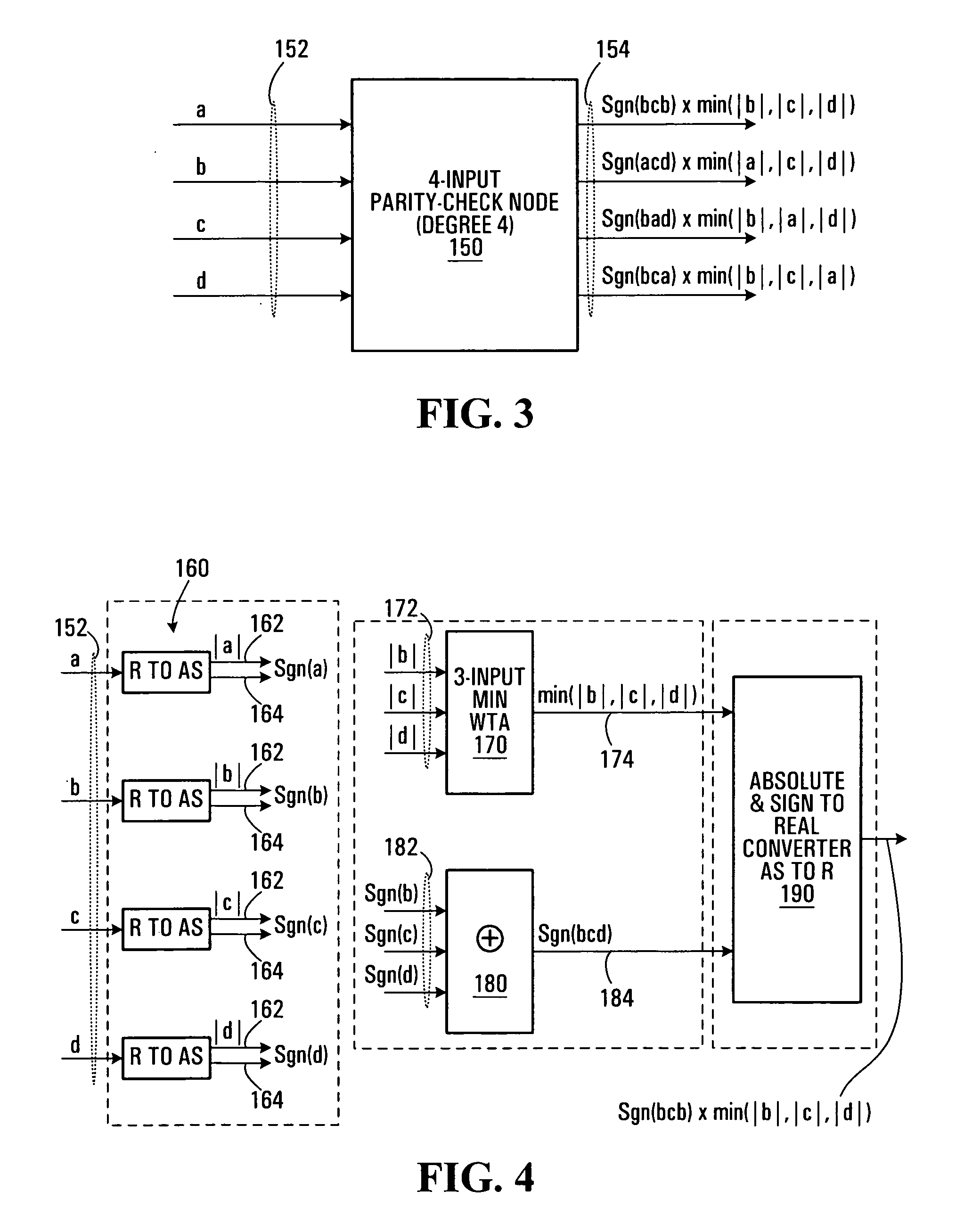
Analog iterative decoders are provided that are based on the so-called min-sum algorithm (also referred to as max-sum or max-product, Max-Log-MAP or BP-based decoding) and can be used to decode powerful coding schemes such as low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes and turbo codes. The circuits can be implemented by standard CMOS technology, which means lower fabrication cost and / or simpler design compared to previously reported analog iterative decoders that are based on BiCMOS or sub-threshold CMOS technology. Soft information is passed among variable nodes and parity-check nodes. A low-voltage high-swing Max WTA circuit is also provided. The circuit can be implemented by short channel MOSFET transistors and yet provide a reasonably high degree of accuracy. Applications include soft computing, and analog signal processing, in general. A Min WTA circuit can also be built based on this circuit by subtracting the input currents from a large reference current.
Owner:BANIHASHEMI AMIR +1
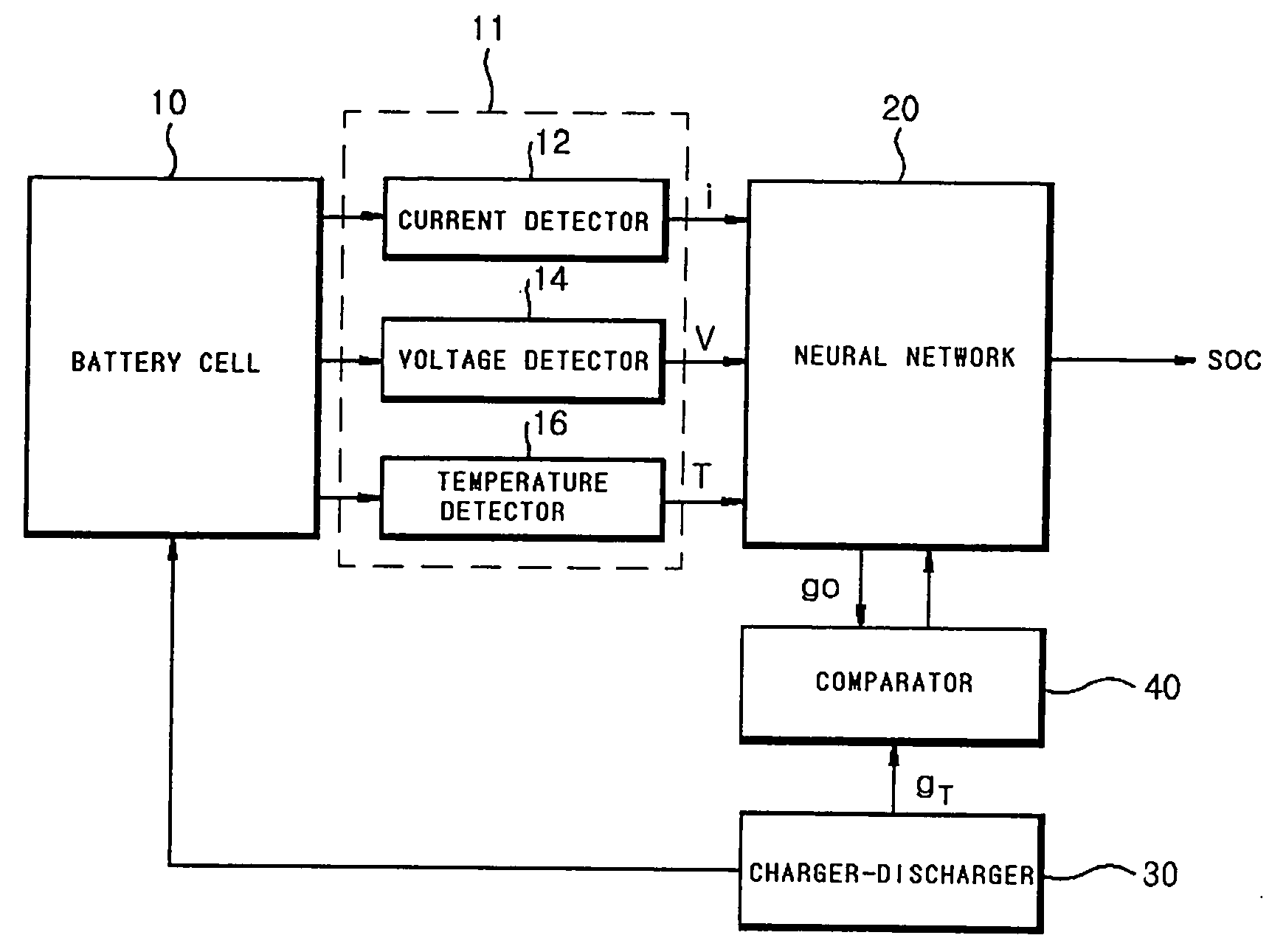
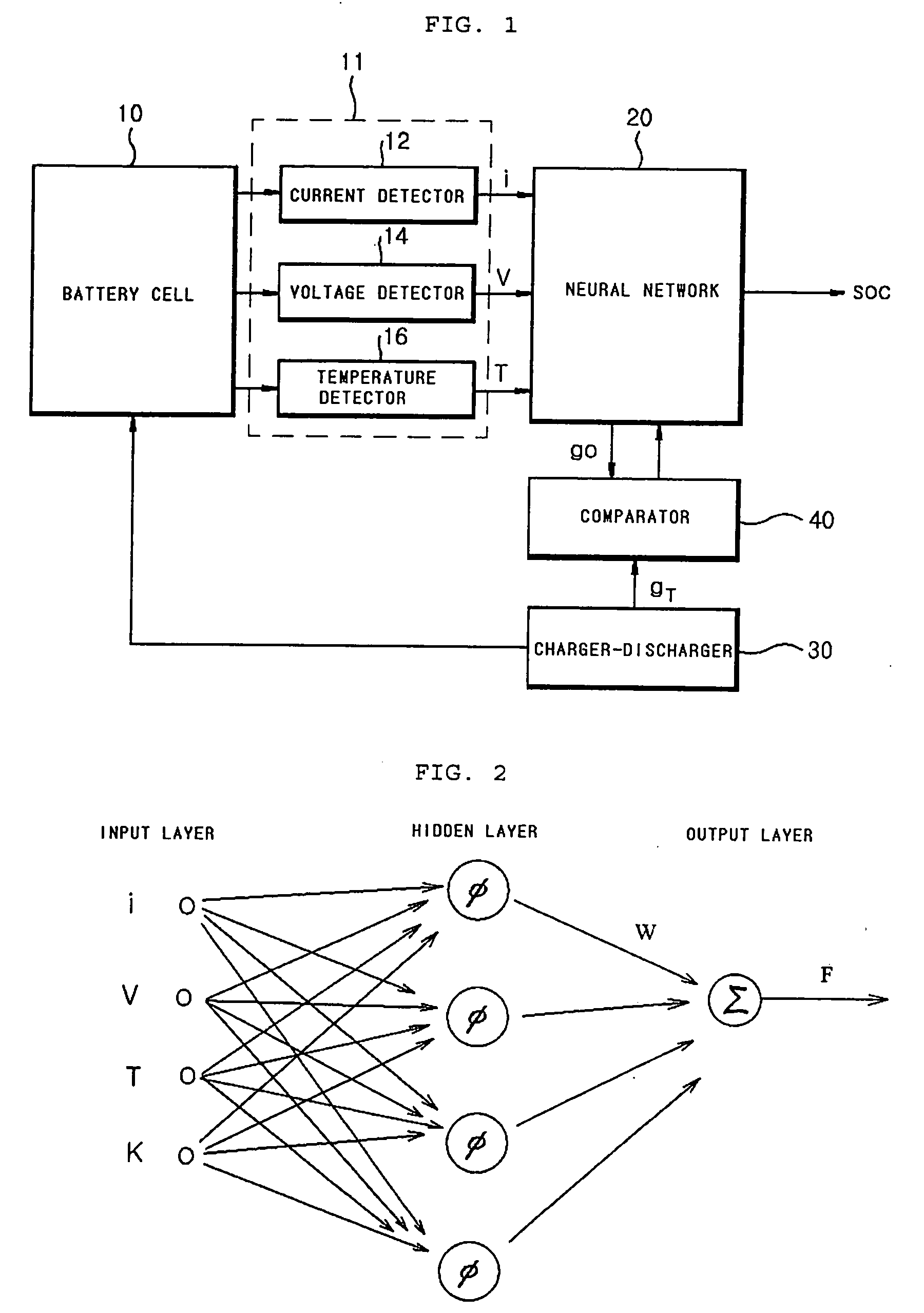
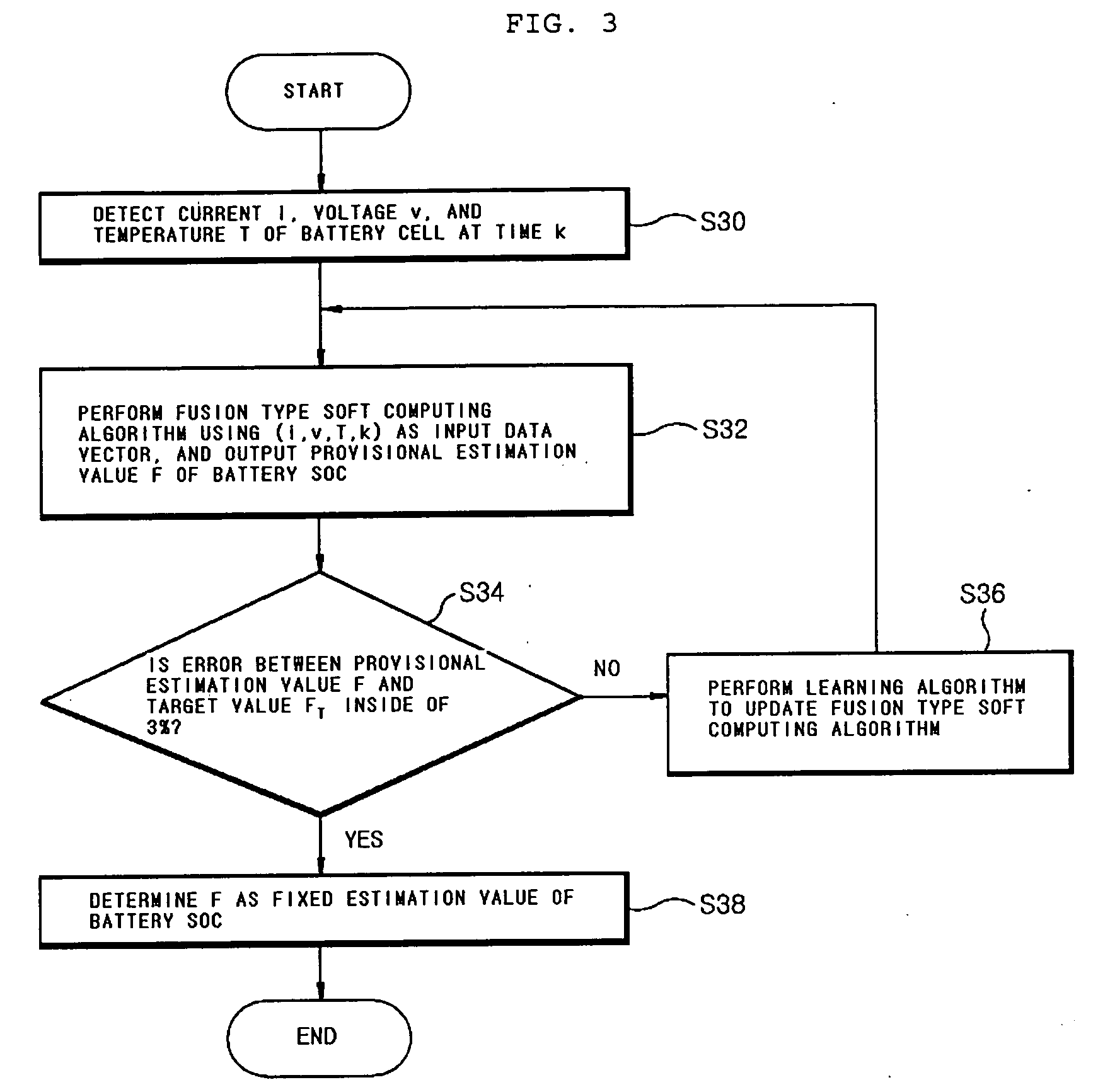
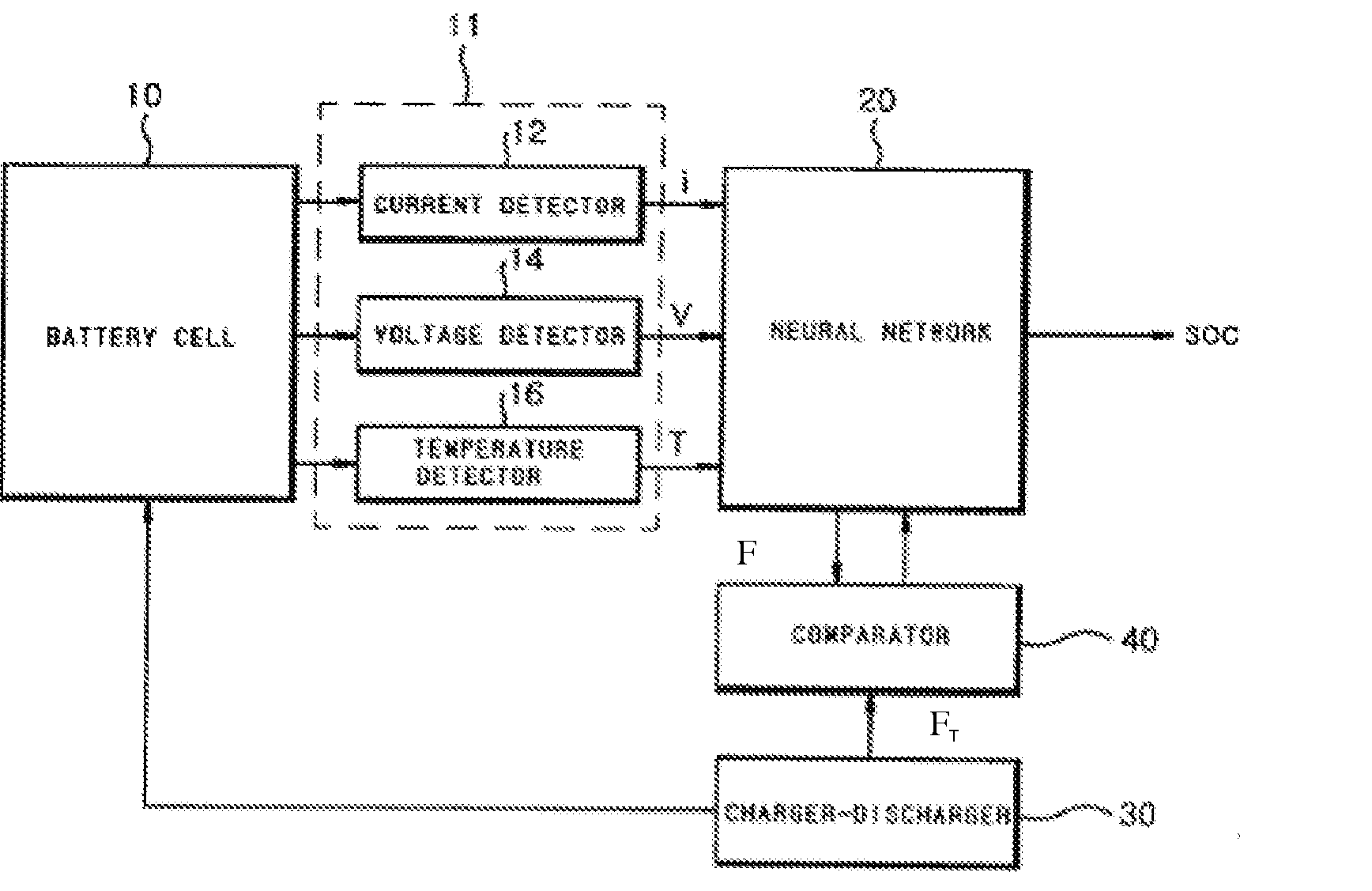
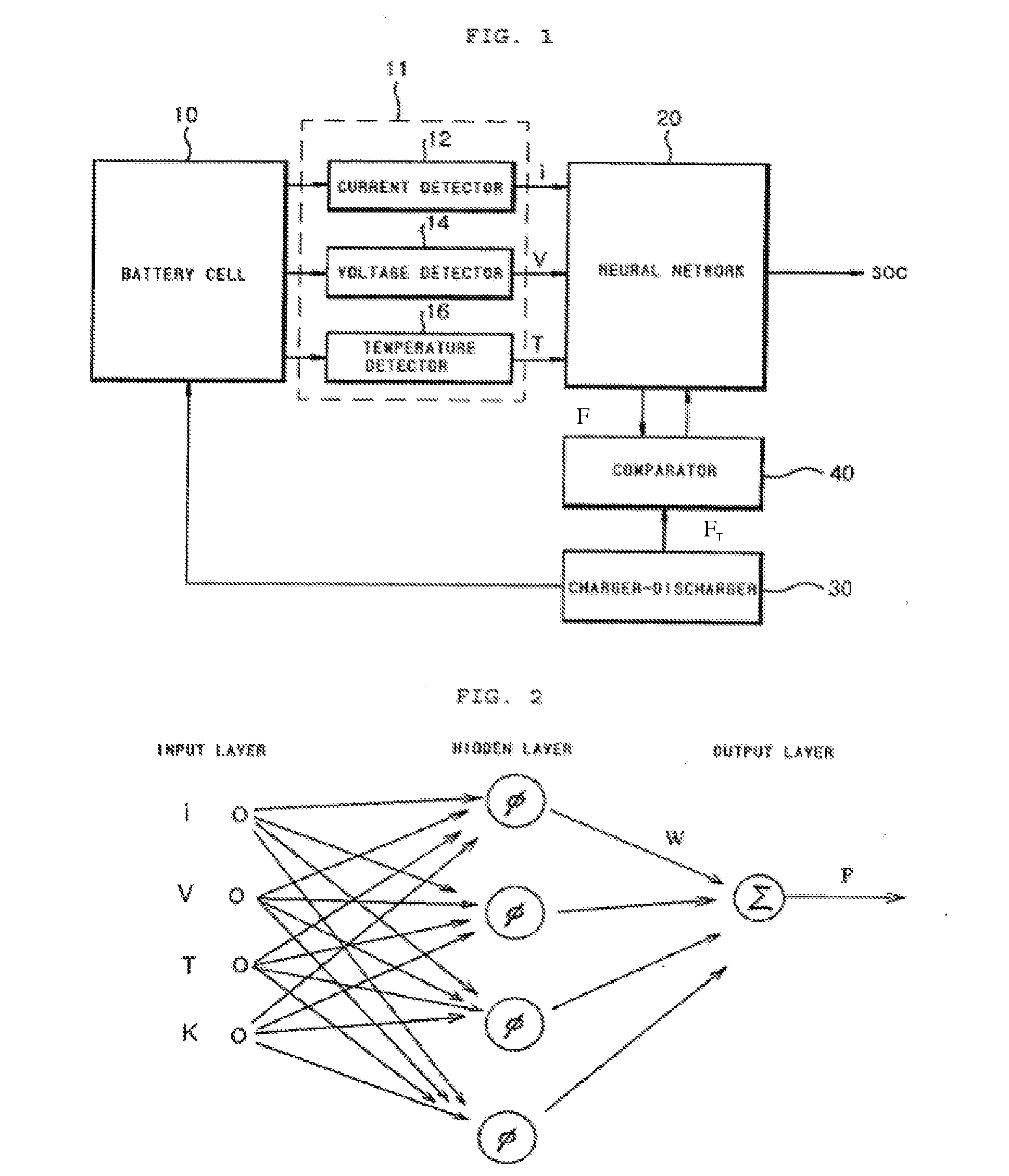
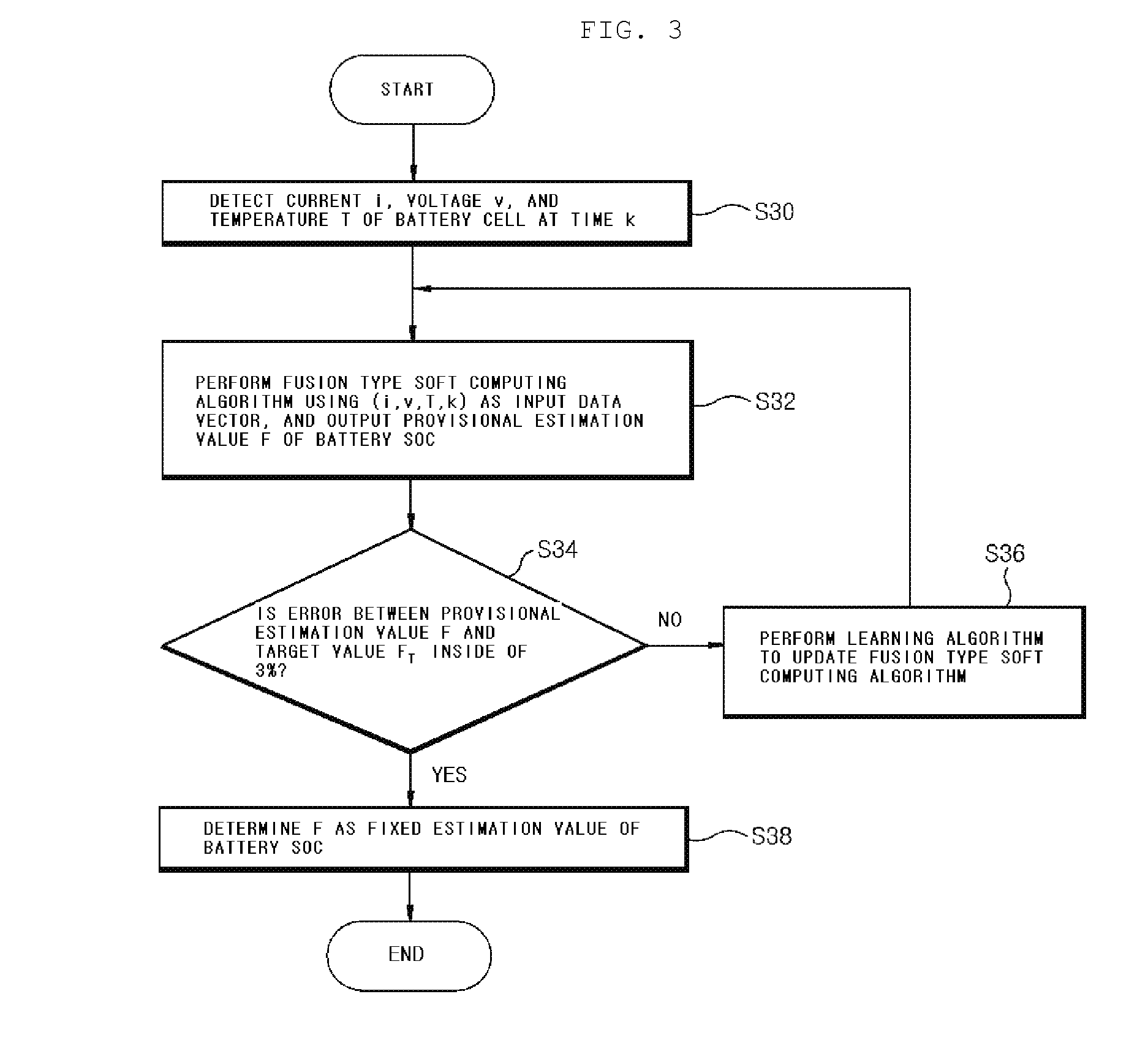
Apparatus and method for testing state of charge in battery
InactiveUS20070005276A1Accurate estimateImprove the environmentElectric devicesOperating modesState of chargeGenetic algorithm
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for estimating a state of charge (SOC) in a battery, in which the battery SOC is estimated using a fusion type soft computing algorithm, thereby accurately estimating the battery SOC in a high C-rate environment. The apparatus includes a detector unit for detecting current, voltage and temperature of a battery cell; and soft computing unit for outputting a battery SOC estimation value of processing the current, the voltage and the temperature detected by the detector unit using a radial function based on a neural network algorithm. Especially, the soft computing unit combines the neural network algorithm with any one of a fuzzy algorithm, a genetic algorithm (GA), a cellular automata (CA) algorithm, an immune system algorithm, and a rough-set algorithm, and thereby adaptively updates the parameters of the neural network algorithm.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Soft computing optimizer of intelligent control system structures
InactiveUS7219087B2Near-optimal FNNTelevision system detailsChaos modelsEngineeringInternal combustion engine
The present invention involves a Soft Computing (SC) optimizer for designing a Knowledge Base (KB) to be used in a control system for controlling a plant such as, for example, an internal combustion engine or an automobile suspension system. The SC optimizer includes a fuzzy inference engine based on a Fuzzy Neural Network (FNN). The SC Optimizer provides Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) structure selection, FIS structure optimization method selection, and teaching signal selection and generation. The user selects a fuzzy model, including one or more of: the number of input and / or output variables; the type of fuzzy inference model (e.g., Mamdani, Sugeno, Tsukamoto, etc.); and the preliminary type of membership functions. A Genetic Algorithm (GA) is used to optimize linguistic variable parameters and the input-output training patterns. A GA is also used to optimize the rule base, using the fuzzy model, optimal linguistic variable parameters, and a teaching signal. The GA produces a near-optimal FNN. The near-optimal FNN can be improved using classical derivative-based optimization procedures. The FIS structure found by the GA is optimized with a fitness function based on a response of the actual plant model of the controlled plant. The SC optimizer produces a robust KB that is typically smaller that the KB produced by prior art methods.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Apparatus and method for testing state of charge in battery
ActiveUS20100324848A1Accurate estimateImprove the environmentElectric devicesOperating modesCellular automationState of charge
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for estimating a state of charge (SOC) in a battery, in which the battery SOC is estimated using a fusion type soft computing algorithm, thereby accurately estimating the battery SOC in a high C-rate environment. The apparatus includes a detector unit for detecting current, voltage and temperature of a battery cell; and soft computing unit for outputting a battery SOC estimation value of processing the current, the voltage and the temperature detected by the detector unit using a radial function based on a neural network algorithm. Especially, the soft computing unit combines the neural network algorithm with any one of a fuzzy algorithm, a genetic algorithm (GA), a cellular automata (CA) algorithm, an immune system algorithm, and a rough-set algorithm, and thereby adaptively updates the parameters of the neural network algorithm.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Intelligent mechatronic control suspension system based on soft computing
A control system for optimizing a shock absorber having a non-linear kinetic characteristic is described. The control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy and biologically inspired constraints relating to mechanical constraints and / or rider comfort, driveability, etc. In one embodiment, a genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal. An information filter is used to filter the teaching signal to produce a compressed teaching signal. The compressed teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from a knowledge base. In one embodiment, the control system includes a learning system, such as a neural network that is trained by the compressed training signal. The learning system is used to create a knowledge base for use by an online fuzzy controller. The online fuzzy controller is used to program a linear controller.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
System for soft computing simulation
InactiveUS20060218108A1Near-optimal FNNGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsFuzzy inferenceAlgorithm
The present invention involves a Soft Computing Optimizer (SCOptimizer) for designing a Knowledge Base (KB) to be used in a control system for controlling a plant. The SC Optimizer provides Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) structure selection, FIS structure optimization method selection, and training signal selection and generation. The user selects a fuzzy model, including one or more of: the number of input and / or output variables; the type of fuzzy inference model (e.g., Mamdani, Sugeno, etc.); and the preliminary type of membership functions. A Genetic Algorithm (GA) is used to optimize linguistic variable parameters and the input-output training patterns. A GA is also used to optimize the rule base, using the fuzzy model, optimal linguistic variable parameters, and a teaching signal.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Automatic estimation method for antenna pattern relative to high-frequency ground wave radar
InactiveCN102707270AIncreased complexityIncrease costWave based measurement systemsSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioOperating cost
The invention provides an automatic estimation method for an antenna pattern relative to high-frequency ground wave radar. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting single arrival angle echo spectral points with higher signal-to-noise ratios than a predetermined signal-to-noise ratio from radar echo signals; modifying a current antenna pattern by utilizing the amplitude ratios and the arrival angles of various selected signal arrival angle echo signal spectral points to obtain a modified antenna pattern; judging whether the modified antenna pattern is converged relative to the current antenna pattern; if the modified antenna pattern is converged relative to the current antenna pattern, taking the modified antenna pattern as the obtained antenna pattern; and if the modified antenna pattern is not converged relative to the current antenna pattern, repeating the modifying step by taking the modified antenna pattern as the current antenna pattern. By the method provided by the invention, each antenna pattern is estimated from the radar echo signals in a soft computing mode completely; the conventional measurement mode which adopts an additional transponder or beacon equipment is abandoned; and the complexity and the operating cost of a high-frequency ground wave radar system are reduced greatly.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Intelligent robust control system for motorcycle using soft computing optimizer
The invention describes a vehicular intelligent touch control system using a soft computing (SC) optimizer, and the SC is used to design a knowledge base (KB) used in the vehicular control system. A user selection fuzzy model comprises one or a plurality of input and / or output variable numbers, fuzzy inference models, and the primary models of membership functions. A genetic algorithm (GA) is used to optimize language variable parameters and an input-output training mode. The GA is used to optimize a rule base through the fuzzy model, the optimized language variable parameters and teaching signals. The GA produces an approximately optimal fuzzy nerve network (FNN). The approximately optimal FNN can be improved through examples based on a derivative optimization procedure. The fuzzy inference systems (FIS) constructed by the GA can be optimized through the adaptation function of a controlled-shop-based real shop model response. The touch KB produced by the SC optimizer is usually smaller than the KB produced by the prior art.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Intelligent robust control system for motorcycle using soft computing optimizer
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
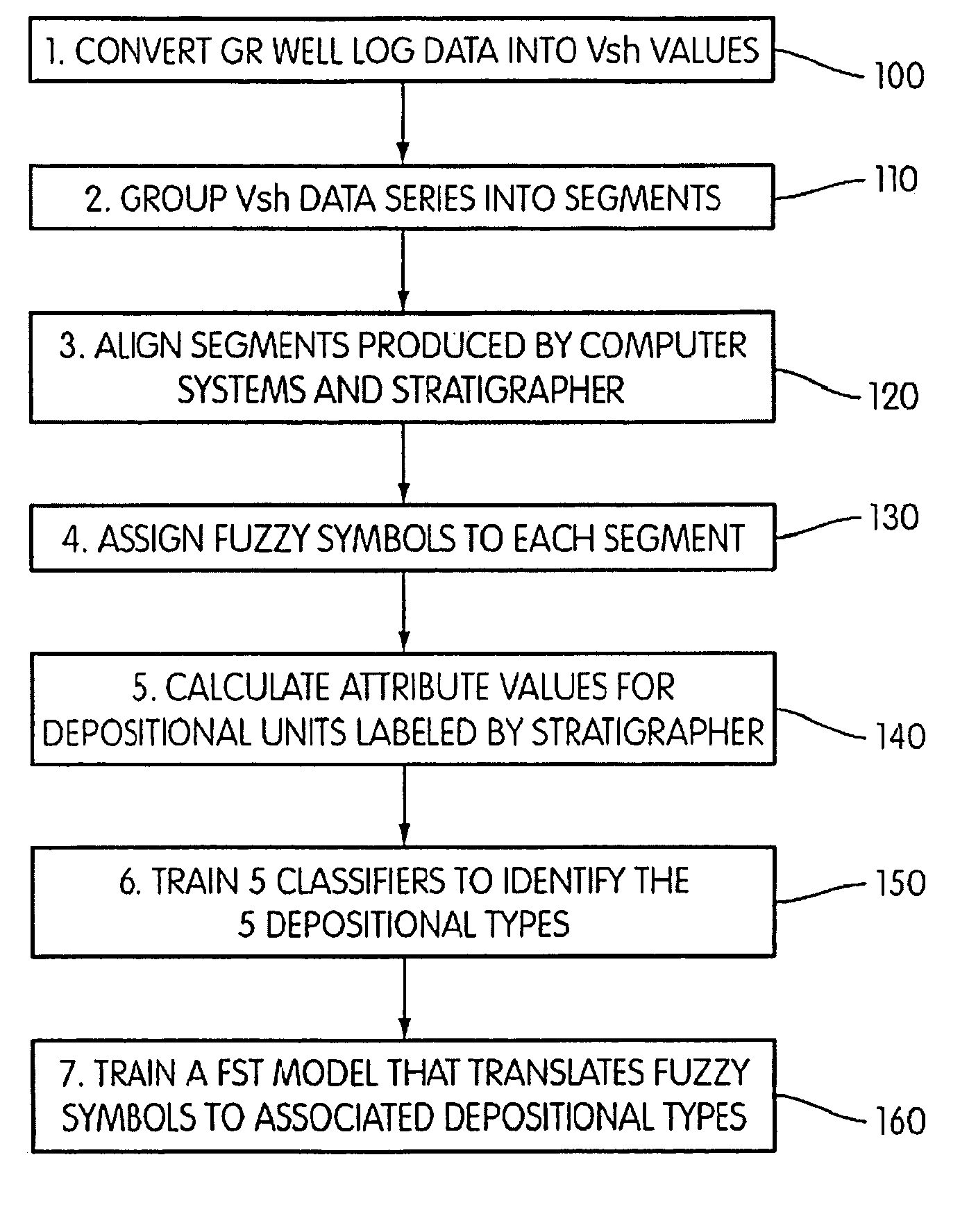
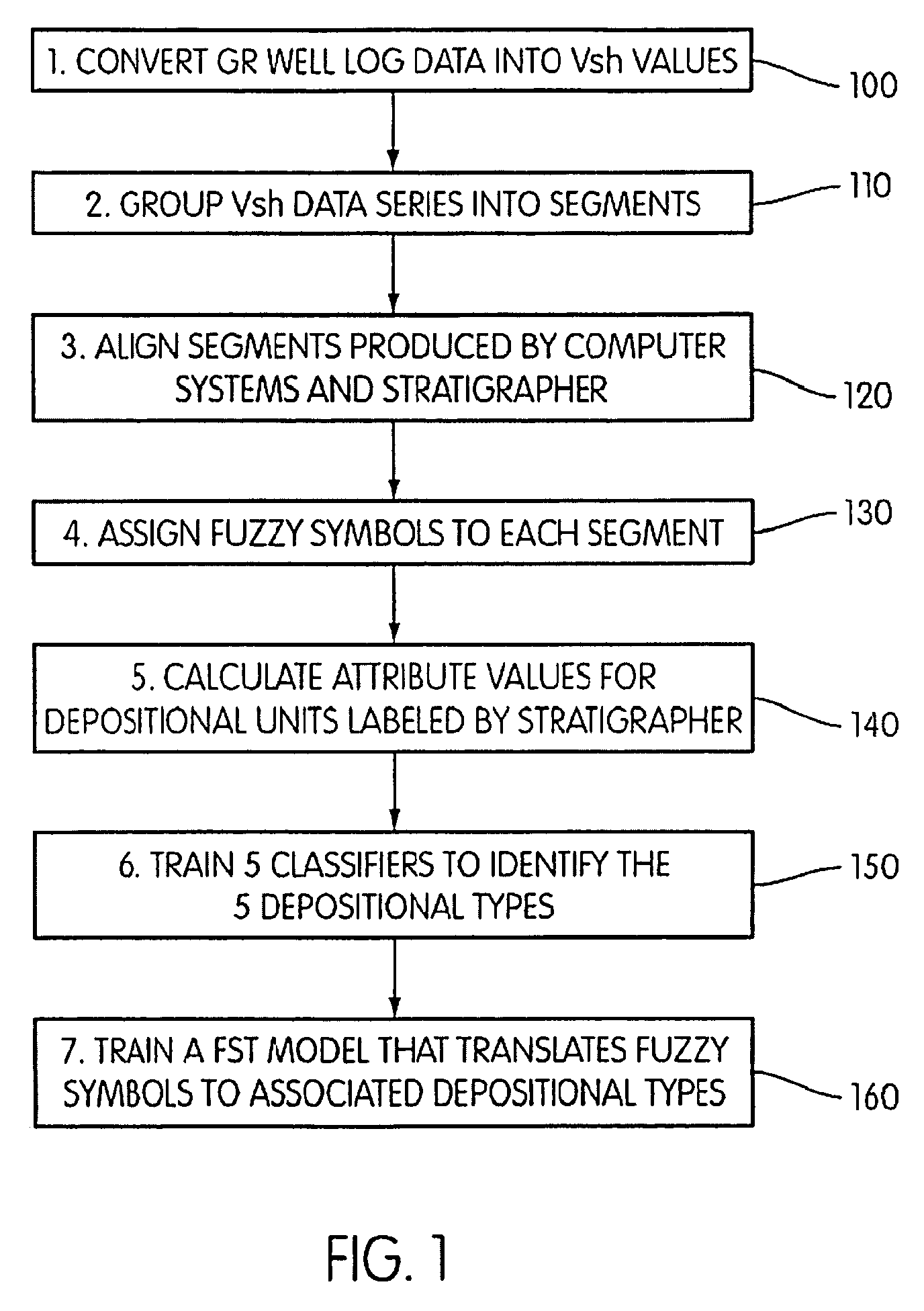
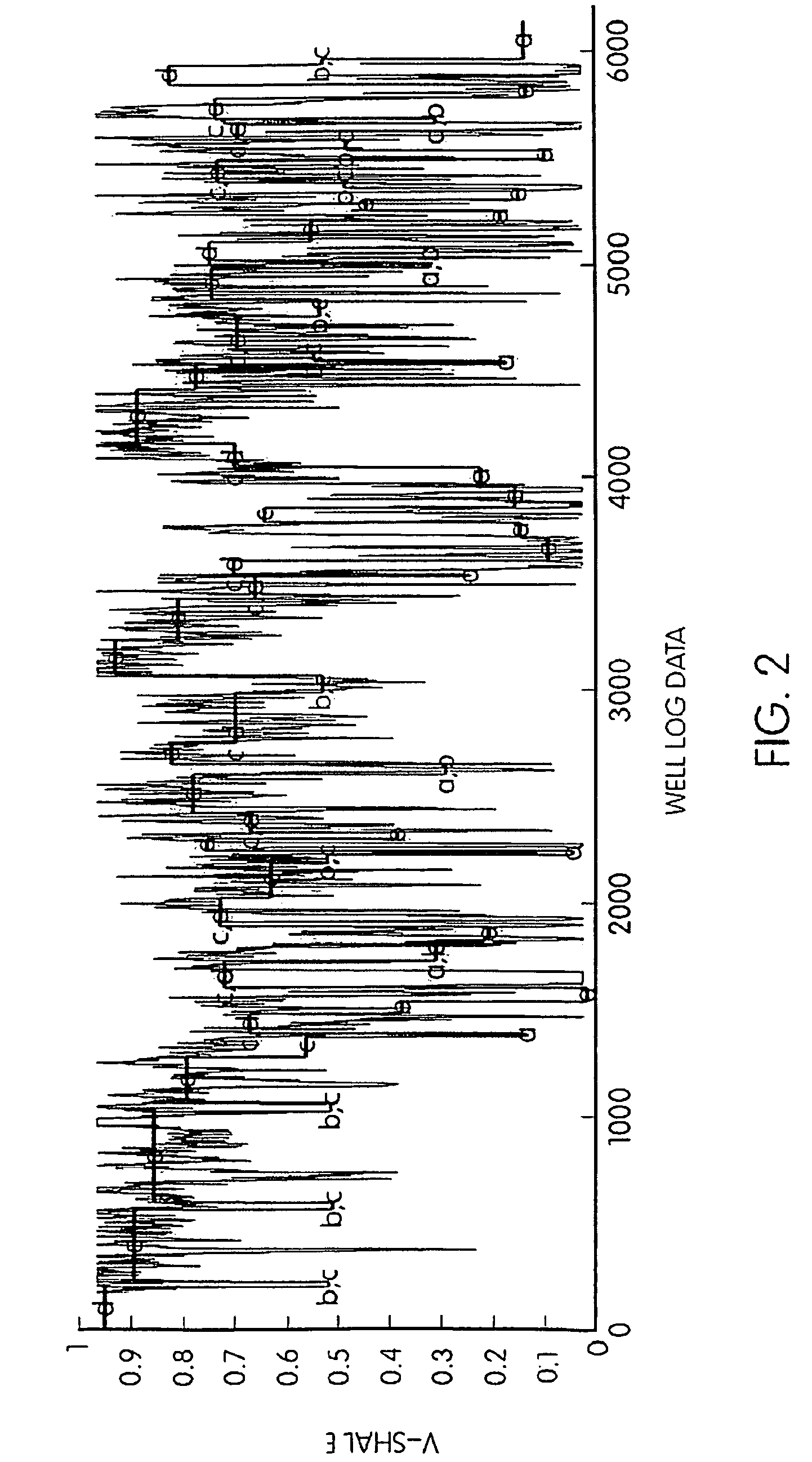
System and method for interpretation of well data
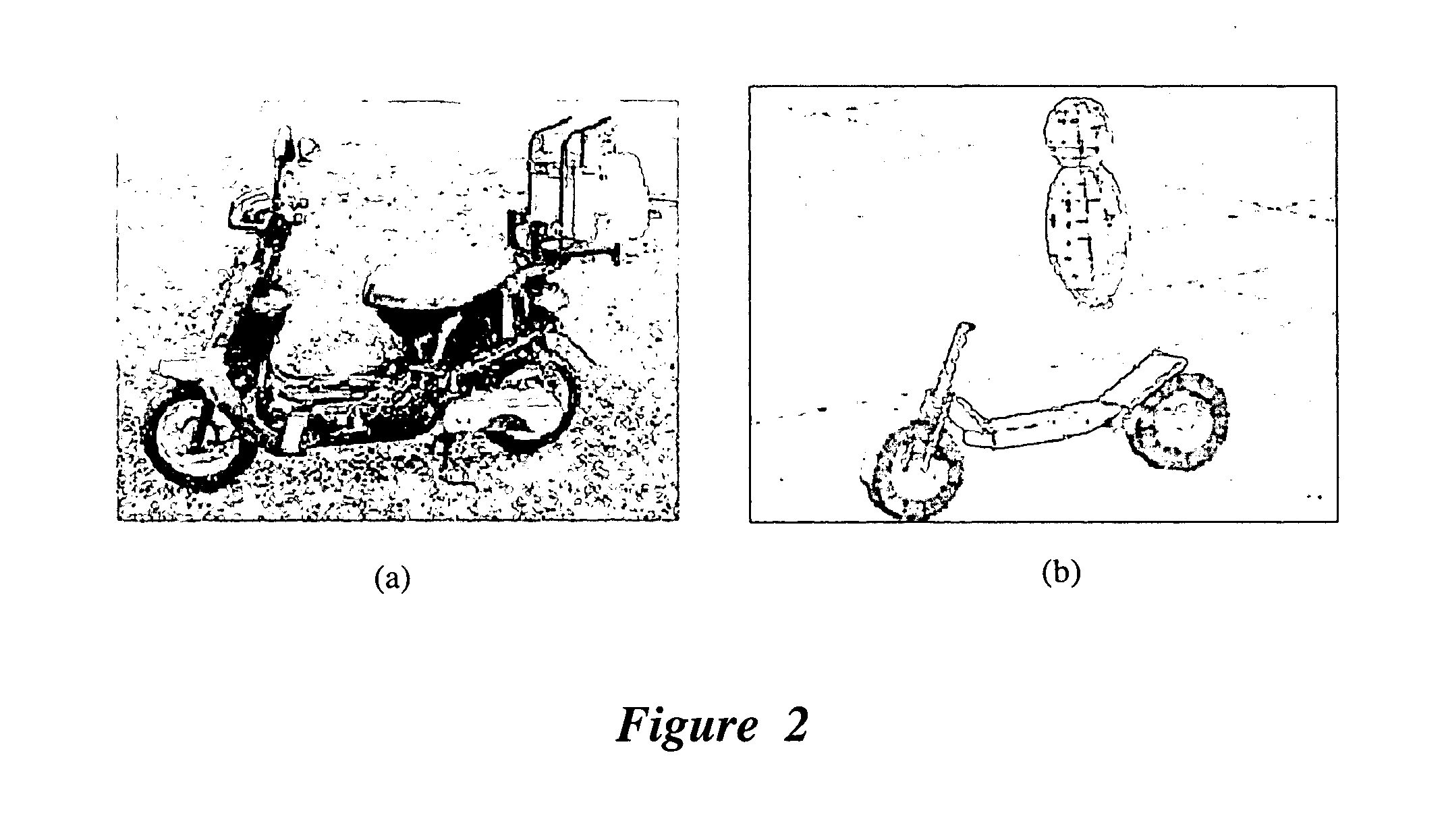
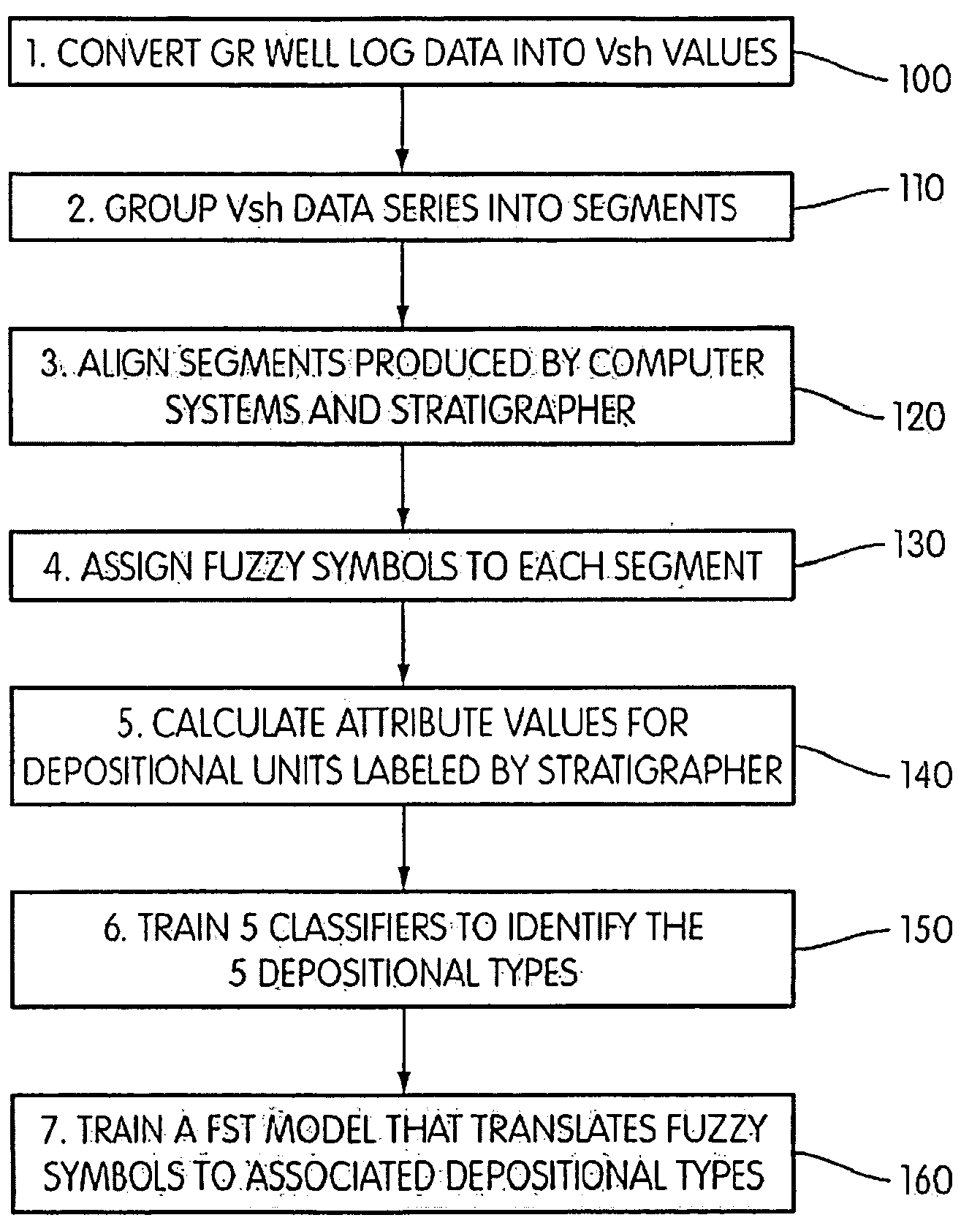
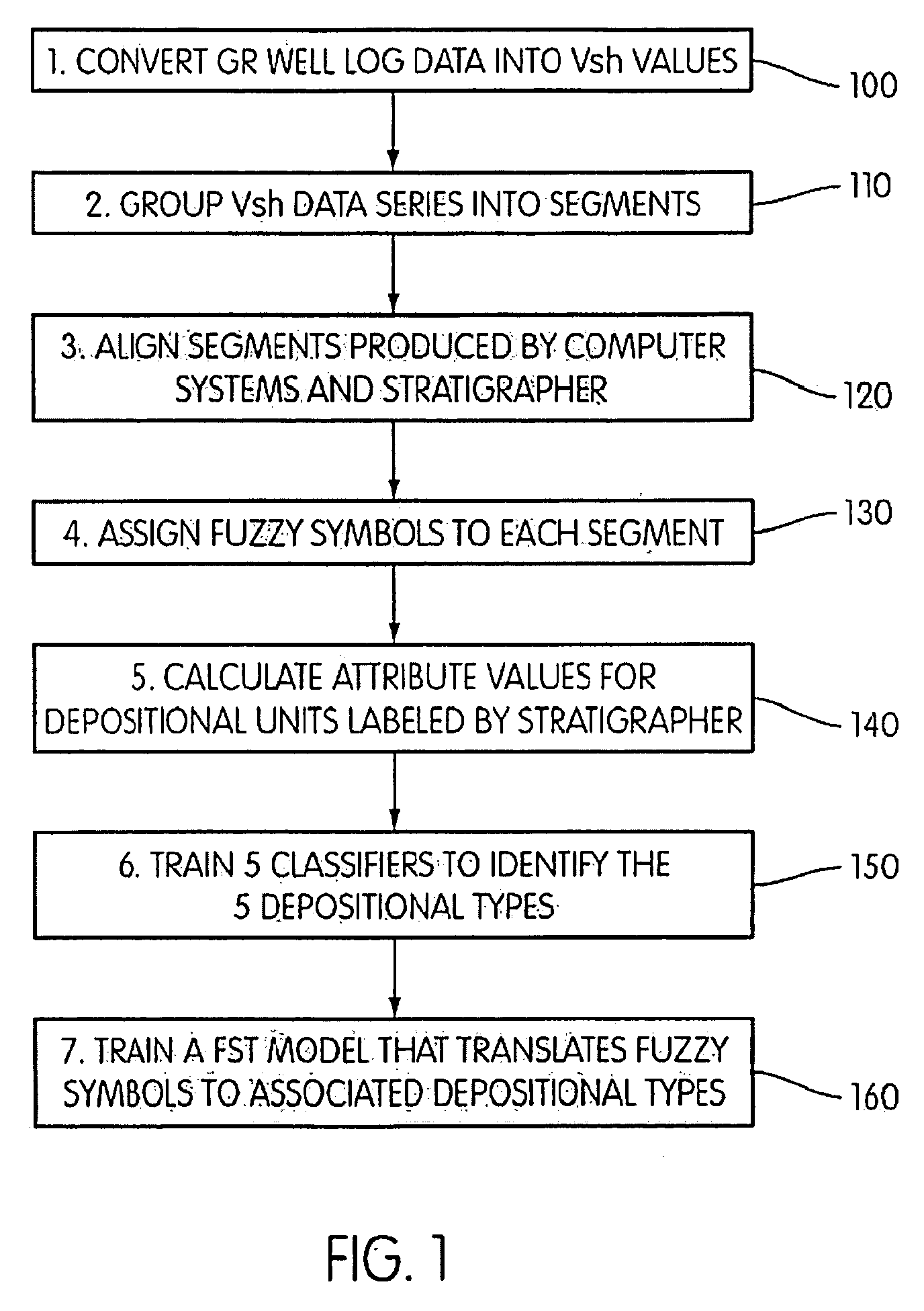
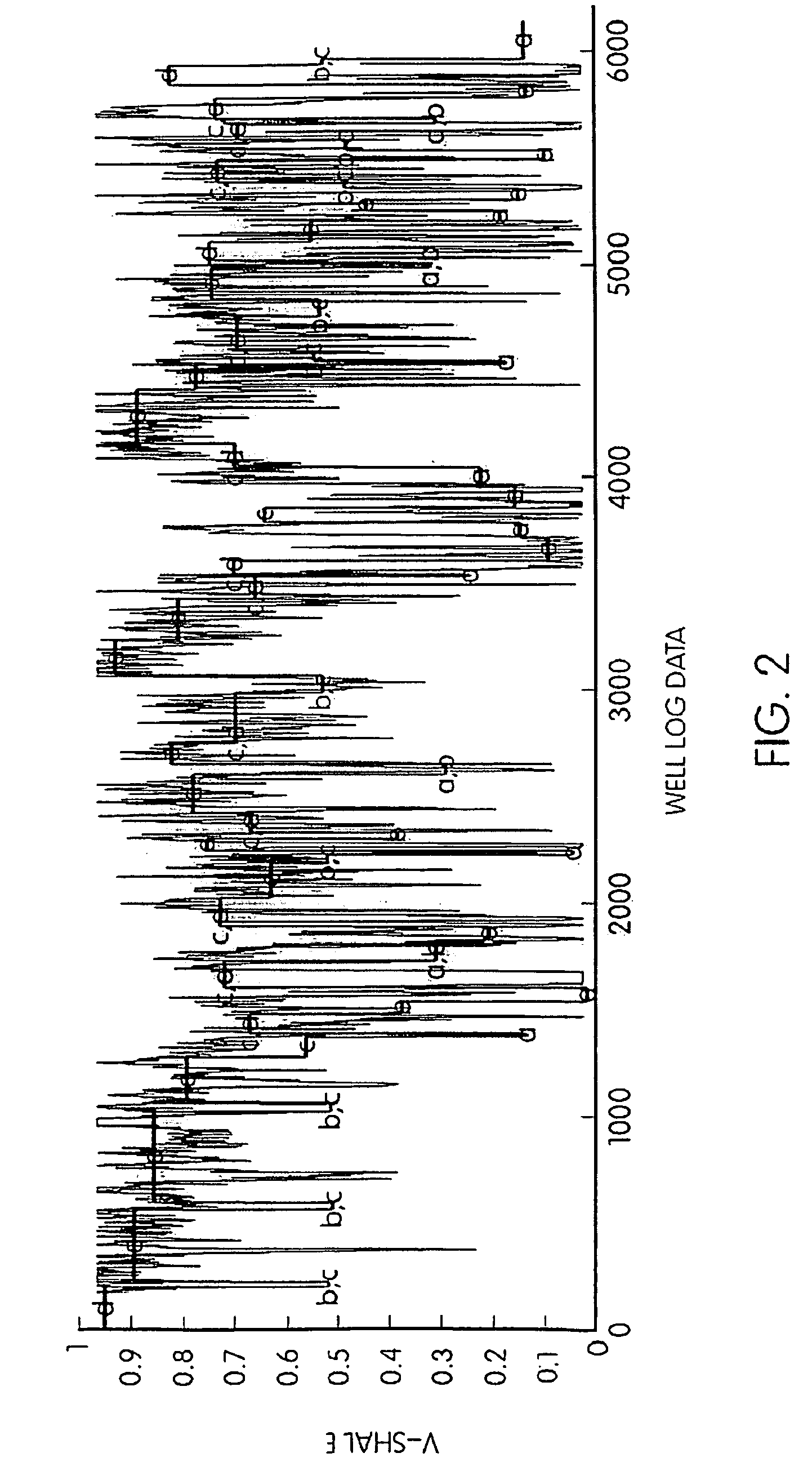
ActiveUS20090276157A1Provide controlElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingWell loggingData mining
Well log data is assigned depositional labels by a soft computing method. A model is trained on an expert-interpreted well log by segmenting, assigning fuzzy symbols to the segments, and calculating attribute values for units labeled by the expert. From these values, classifiers are trained for each of a number of depositional types. Finally, a model is developed for translating fuzzy symbols into depositional labels. Once trained, the model is applied to well log data.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
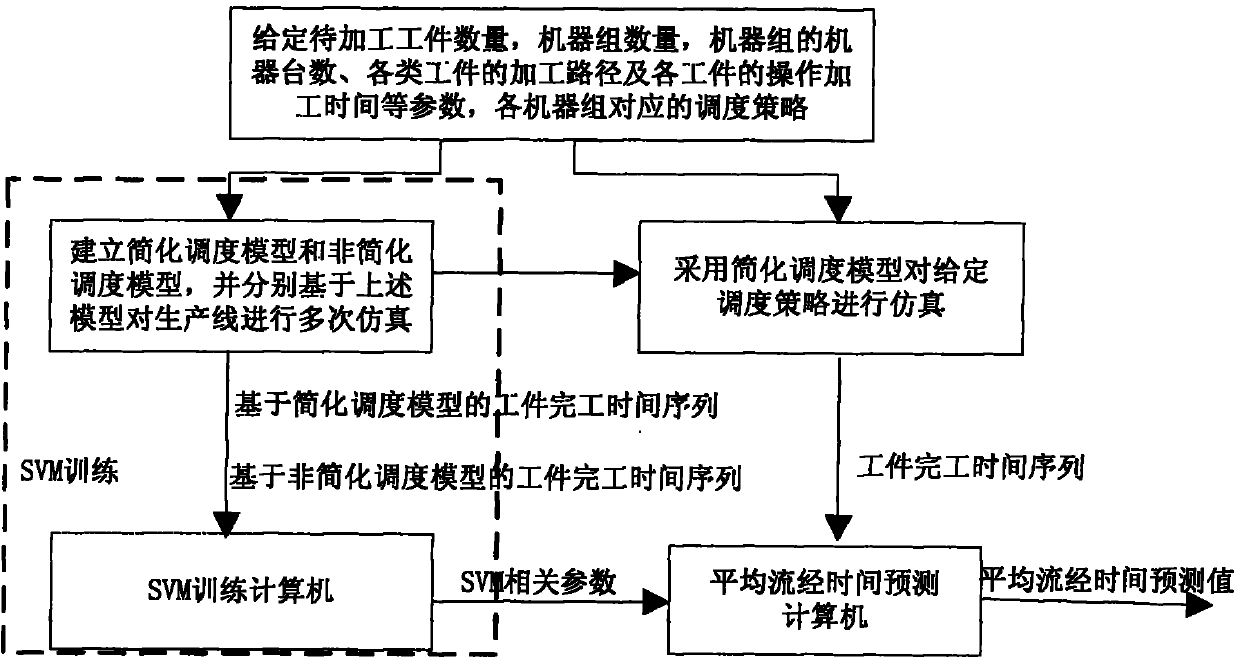
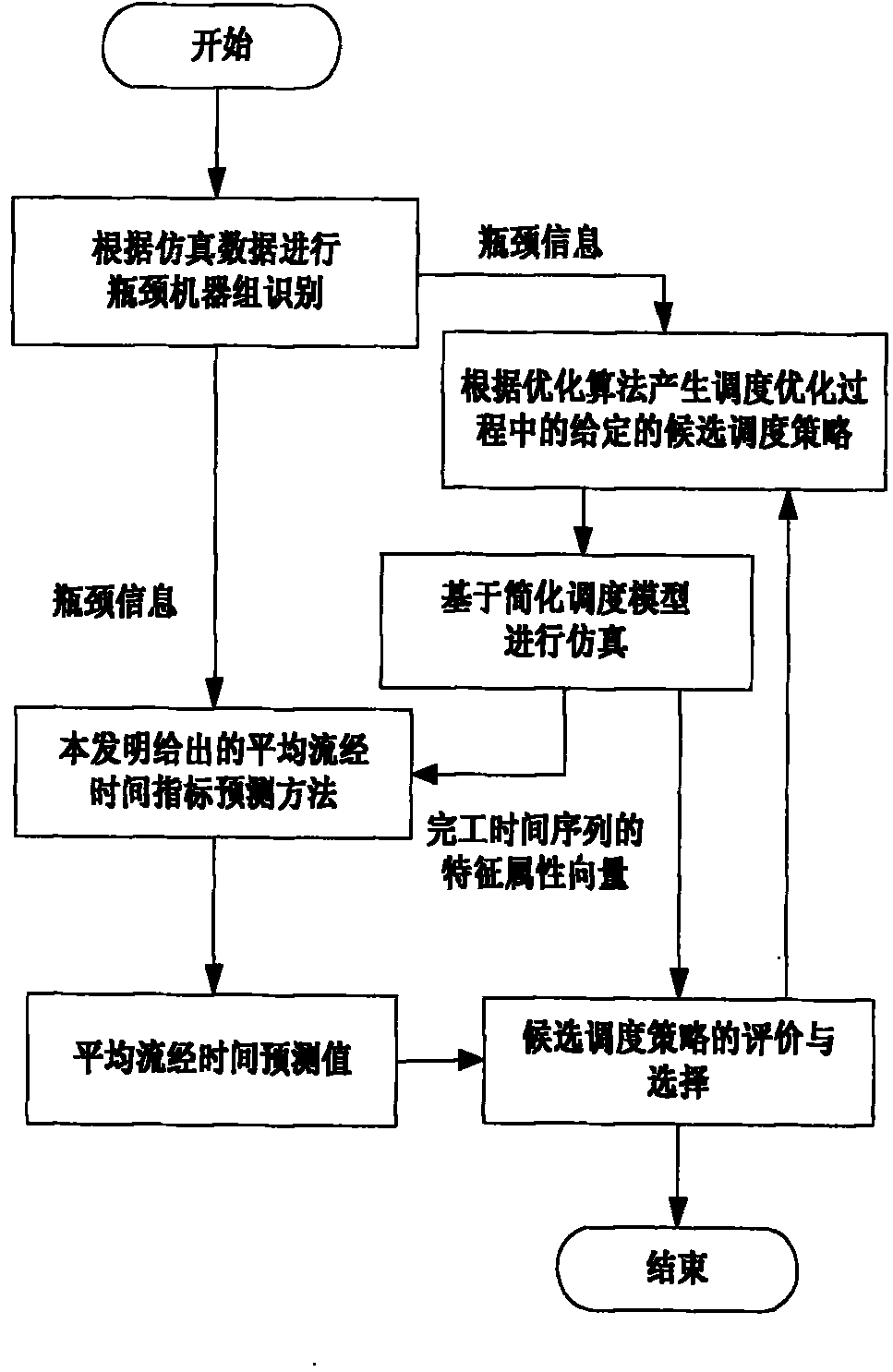
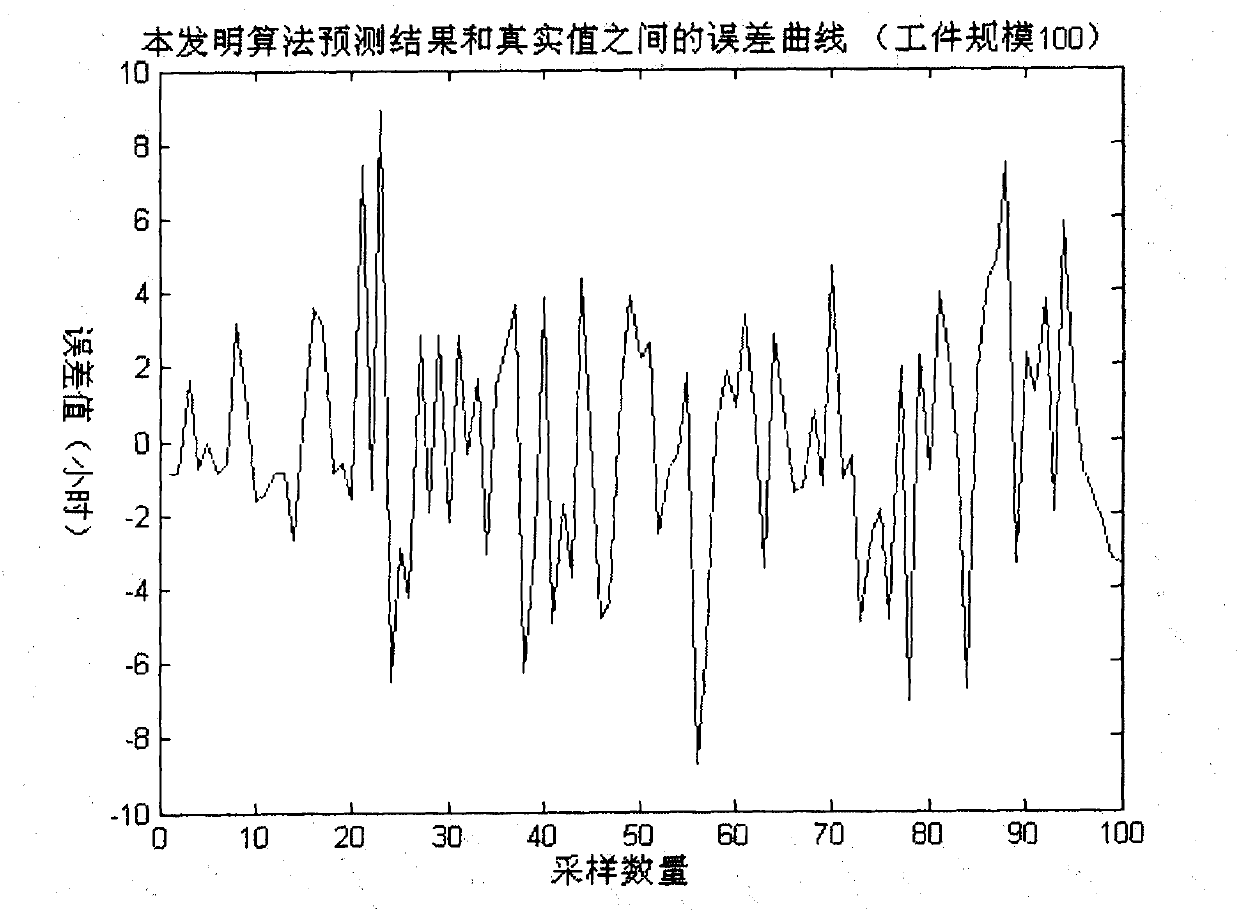
Quick prediction method of average flowing-through time on basis of index compensation
InactiveCN101782769AImprove performanceProgramme total factory controlSupport vector machinePredictive methods
Average flowing-through time is an important scheduling index to which enterprises pay attention. When a dispatching method based on soft computing and the like is used for optimizing dispatch, global simulation is required to be carried out on a dispatching strategy to obtain a corresponding average flowing-through time index; the process needs to be carried out several times; the process consumes longer time if used for building an accurate simulation model for a whole larger scale production line as well as used for global simulation on the dispatching strategy; thus, quick prediction of the average flowing-through time index has the important meaning for improving the performance of the dispatching algorithm. The invention discloses a quick prediction method of average flowing-through time on basis of index compensation, which divides a machine group into a bottleneck machine group and a non-bottleneck machine group so as to loosen the working capability of the non-bottleneck machine group to build a simplified dispatching model; then, an SVM (support vector machine) is used for obtaining the compensation relationship between the corresponding average flowing-through time indexes of the simplified dispatching model and a non-simplified dispatching model, thus realizing the quick prediction of the average flowing-through time index.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Full CMOS min-sum analog iterative decoders
InactiveUS7769798B2Reduce manufacturing costSimple designDigital data processing detailsError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsMOSFETLow voltage
Analog iterative decoders are provided that are based on the so-called min-sum algorithm (also referred to as max-sum or max-product, Max-Log-MAP or BP-based decoding) and can be used to decode powerful coding schemes such as low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes and turbo codes. The circuits can be implemented by standard CMOS technology, which means lower fabrication cost and / or simpler design compared to previously reported analog iterative decoders that are based on BiCMOS or sub-threshold CMOS technology. Soft information is passed among variable nodes and parity-check nodes. A low-voltage high-swing Max WTA circuit is also provided. The circuit can be implemented by short channel MOSFET transistors and yet provide a reasonably high degree of accuracy. Applications include soft computing, and analog signal processing, in general. A Min WTA circuit can also be built based on this circuit by subtracting the input currents from a large reference current.
Owner:BANIHASHEMI AMIR +1
System and method for nonlinear dynamic control based on soft computing with discrete constraints
InactiveCN1672103ABiological modelsSpecial data processing applicationsMinimum entropyNon linear dynamic
A control system using a genetic analyzer based on discrete constraints is described. In one embodiment, a genetic algorithm with step-coded chromosomes is used to develop a teaching signal that provides good control qualities for a controller with discrete constraints, such as, for example, a step-constrained controller. In one embodiment, the control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy. In one embodiment, the genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal for a fuzzy logic classifier system that develops a knowledge base. The teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from the knowledge base. The control system can be used to control complex plants described by nonlinear, unstable, dissipative models. In one embodiment, the step-constrained control system is configured to control stepping motors.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Method and circuit for controlling an electric power plant
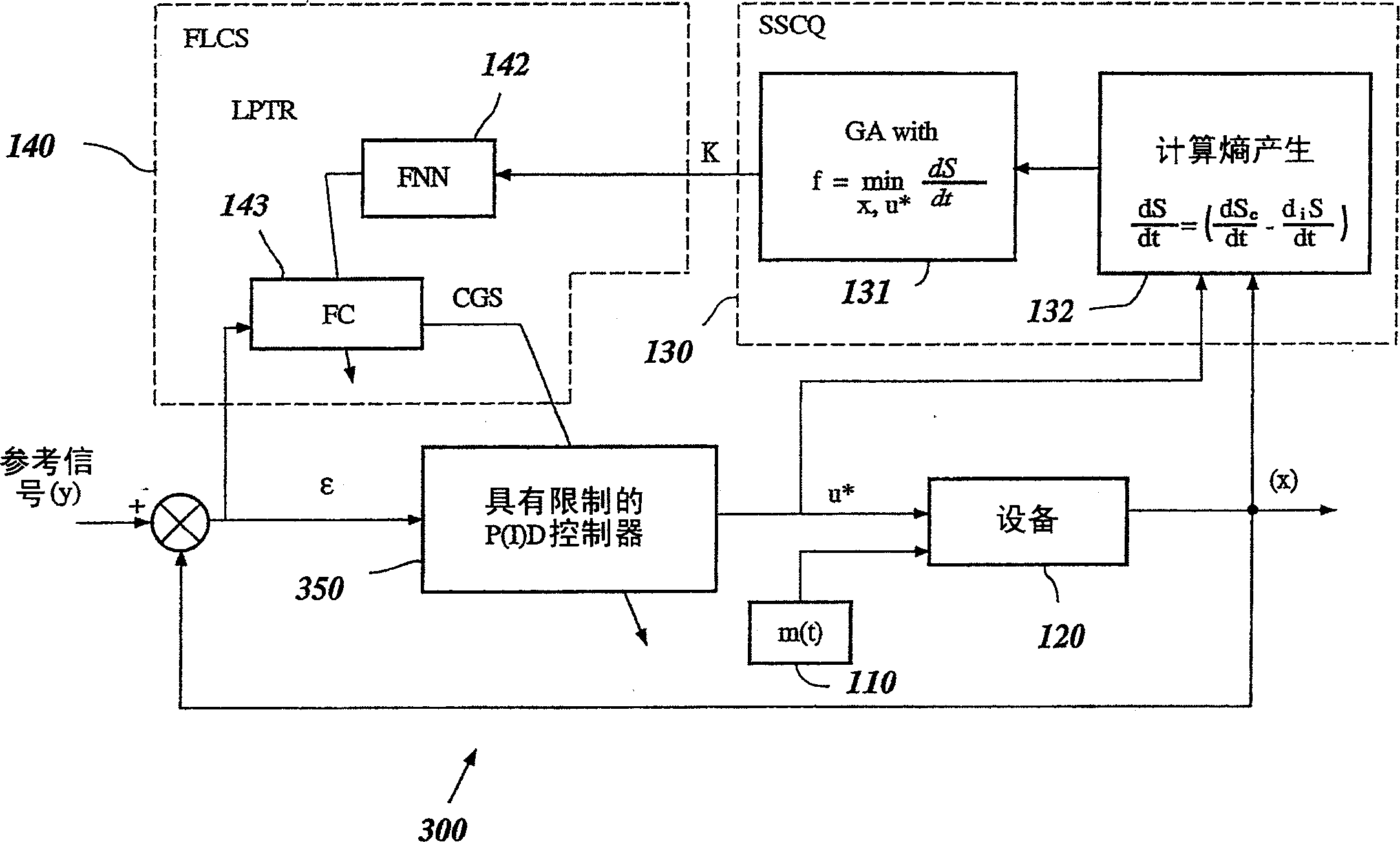
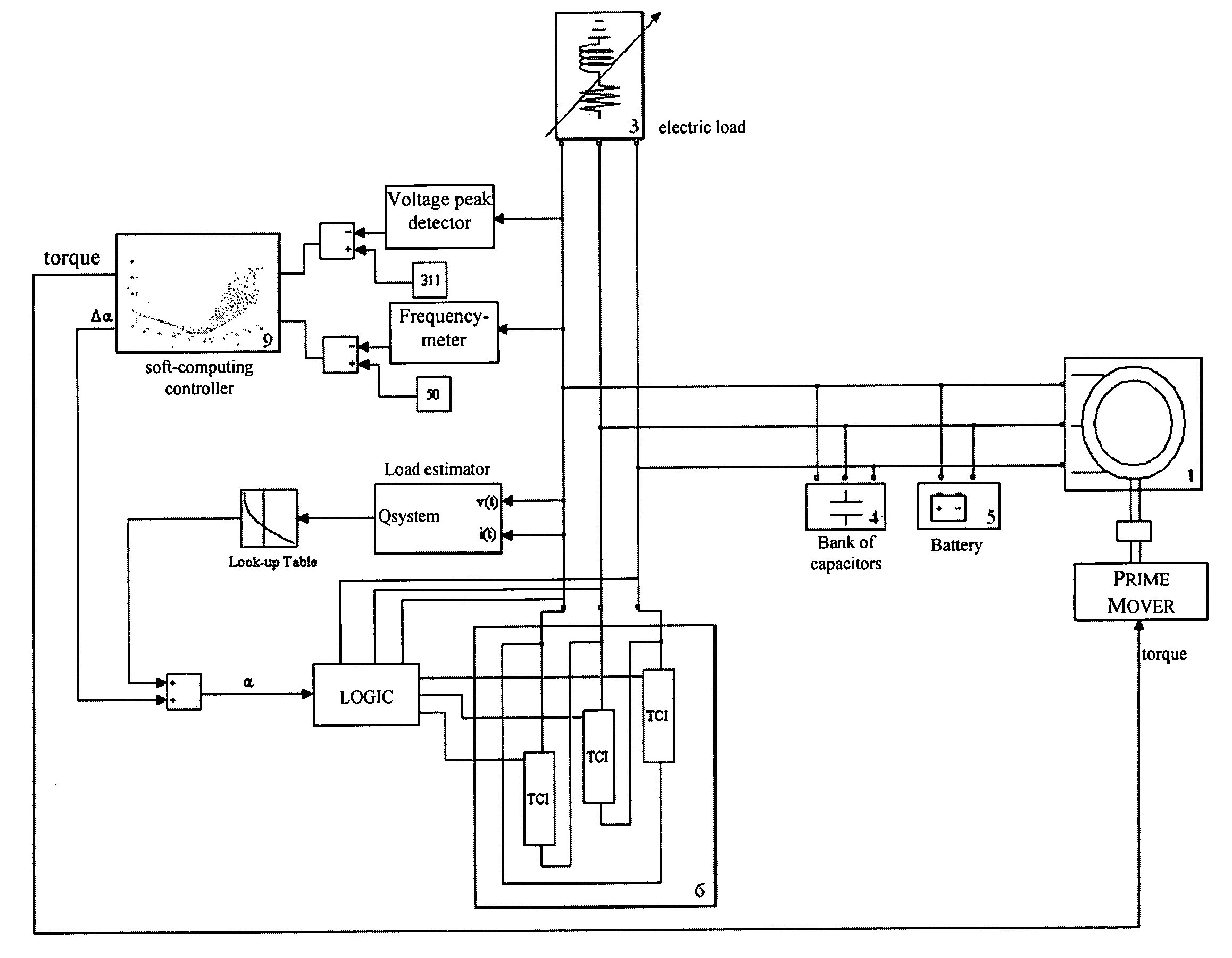
InactiveUS7459890B2High precisionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlCapacitancePower station
A control circuit is for an electric power plant including an asynchronous generator of an AC voltage, a motor to rotate a rotor of the asynchronous generator as a function of a first control signal of a developed motor torque, and a bank of capacitors coupled to the asynchronous generator and having a total capacitance varying as function of a second control signal. The control circuit may include a monitor circuit to monitor at least one parameter of the AC voltage, and a control signal generator circuit cooperating with the monitor circuit to generate the first and second control signals by soft-computing techniques both as a function of the frequency and of a representative value of an amplitude of the AC voltage to make the AC voltage have a desired amplitude and frequency.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Fuzzy forecasting model based method for detecting pulp concentration in ore grinding process of dressing plant
ActiveCN104978484AReliable measurementImprove adaptabilitySpecial data processing applicationsImage resolutionField data
The present invention discloses a fuzzy forecasting model based method for detecting pulp concentration in an ore grinding process of a dressing plant. The ore grinding concentration and overflow concentration are predicted and estimated online by using a fuzzy model construction method based on soft computing, a characteristic variable set in a forecasting model is established based on applying an attribute set evaluation metric based on neighborhood decision resolution and a characteristic set selection method on field record data, a fuzzy scheme is established based on applying the fuzzy scheme construction method based on an effective information rate on the field record data, and a prediction rule is obtained by performing fuzzy prediction rule extraction on the field data. By means of the method provided by the present invention, the subjectivity and limitation of a conventional fuzzy modeling method are avoided, a stable and reliable prediction result can be provided for the detection of a key parameter in the ore grinding process of the dressing plant, and a basis is established for the optimization control and process monitoring of the ore grinding process.
Owner:陕西广林汇程能源科技有限公司
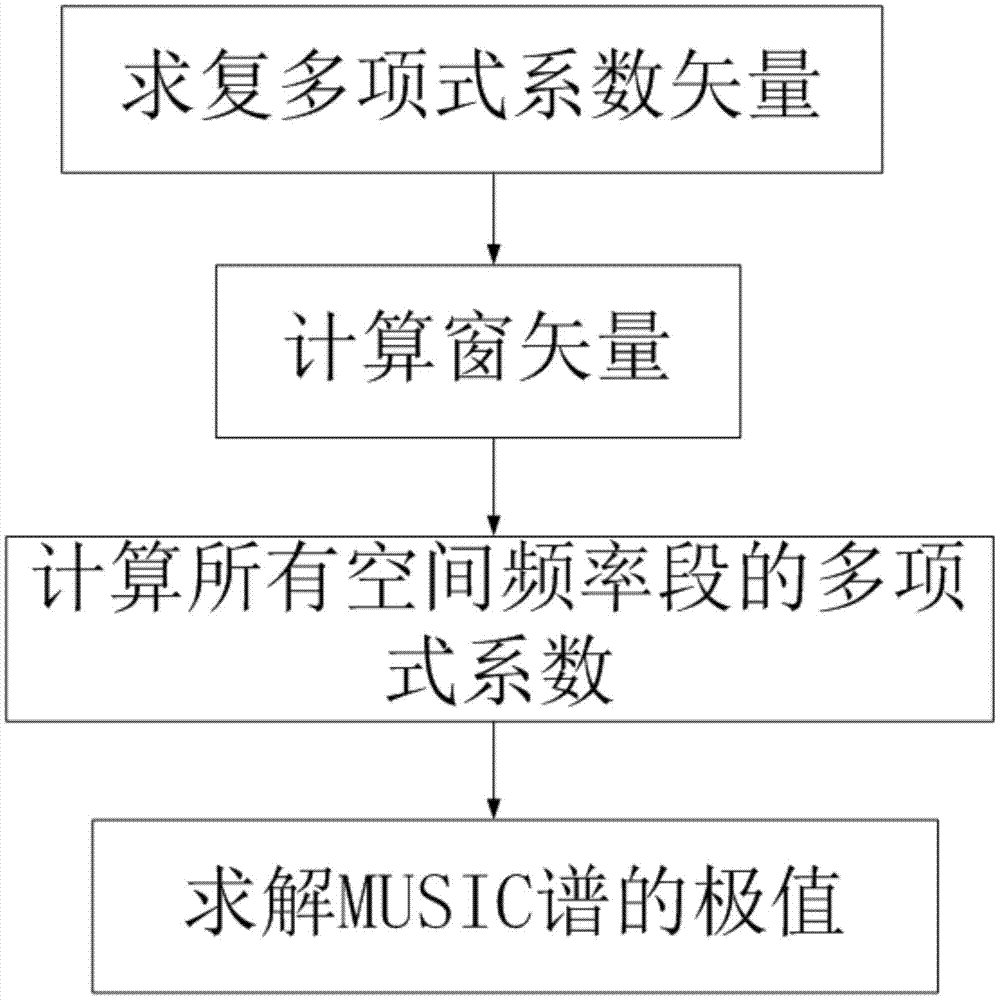
Spectrum MUSIC method for achieving uniform linear array by means of root computing of real polynomials
InactiveCN104123462AComputationally efficientReduce computational complexityWave based measurement systemsSpecial data processing applicationsNumerical stabilityComputation complexity
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar signal processing, and particularly relates to a spectrum MUSIC method for achieving a uniform linear array by means of root computing of real polynomials. The spectrum MUSIC method includes the following steps of (1) computing coefficient vectors of the complex polynomials, (2) computing a window vector, (3) computing coefficients of the polynomials of all intervals, and (4) computing extreme values of MUSIC spectrums. According to the method, the coefficient vectors of the complex polynomials are computed quickly through Fourier transformation, the method of computing the extremities of the MUSIC spectrums is changed into the method of computing roots of multiple sets of low-order polynomials, and windowing Fourier transformation is carried out on related vectors of a signal subspace so that the coefficients of all the sets of the polynomials can be obtained. The defects that in the prior art, elaborate angle searching algorithms are needed, computation complexity is high and value stability is poor are overcome, and the method has the advantages that computation complexity is low and value stability is good and has great potential in estimation of the direction of arrival in low complexity.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
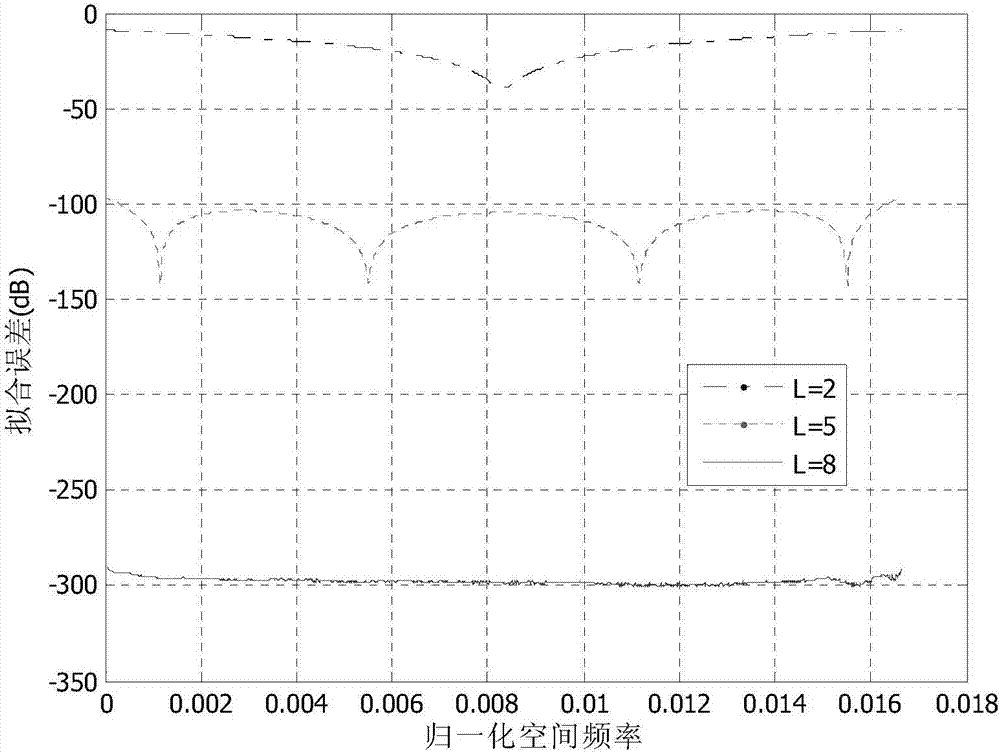
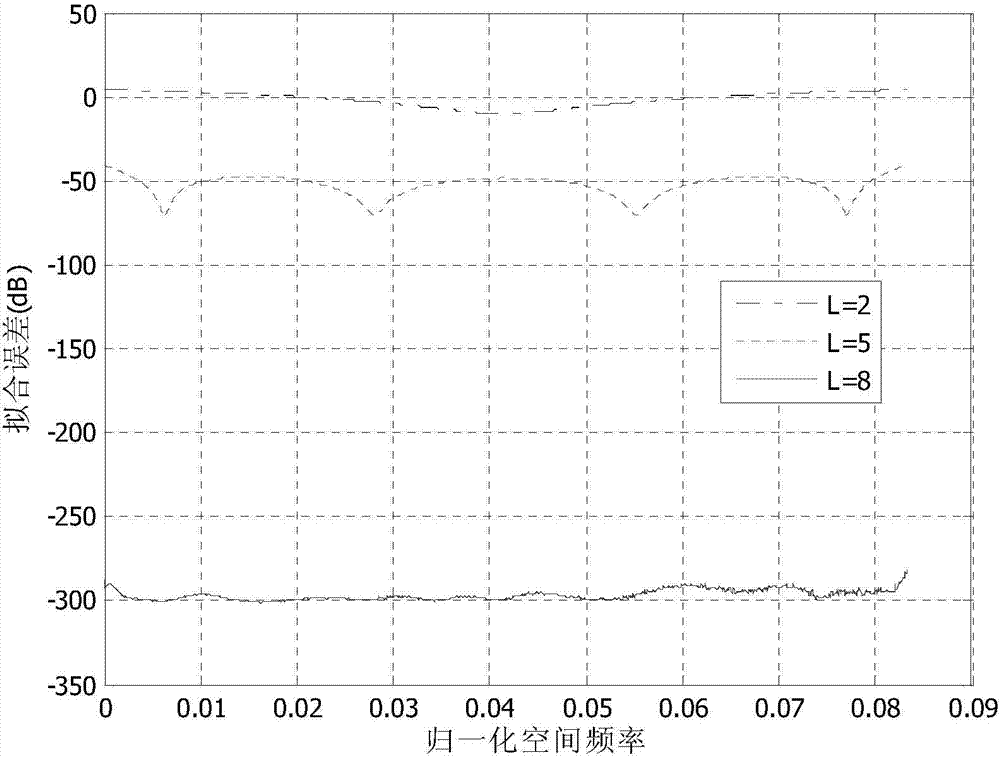
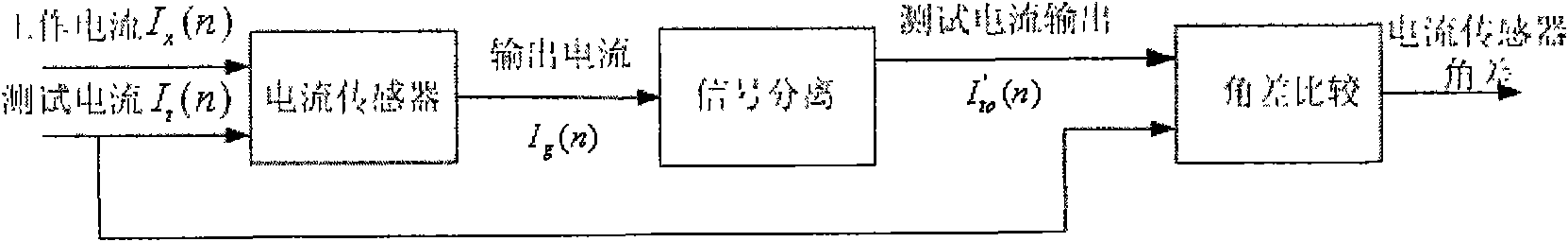
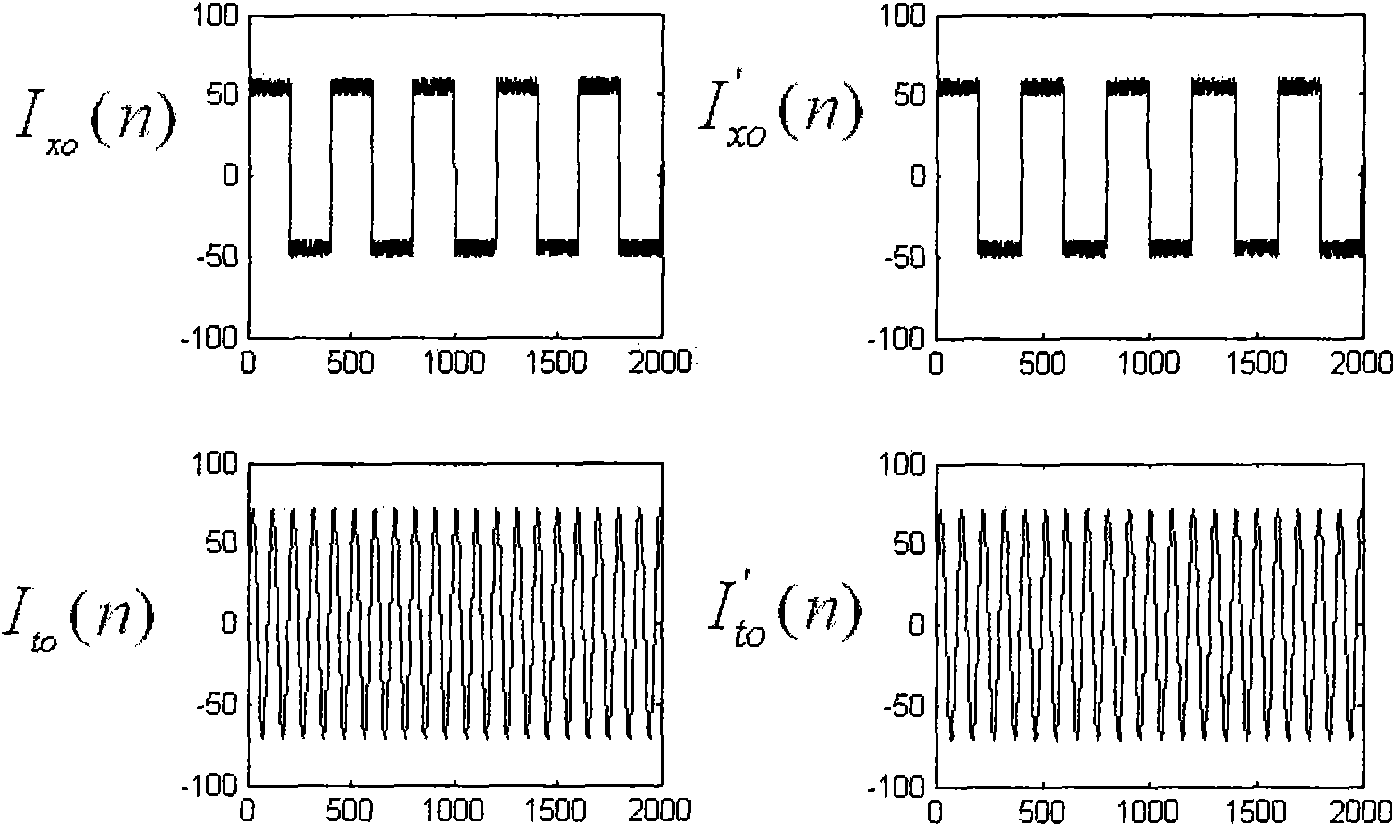
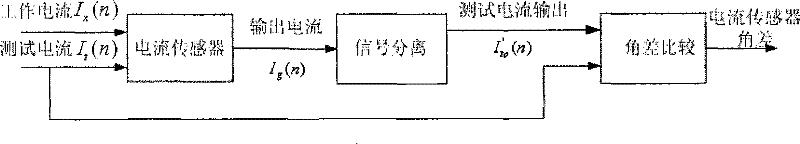
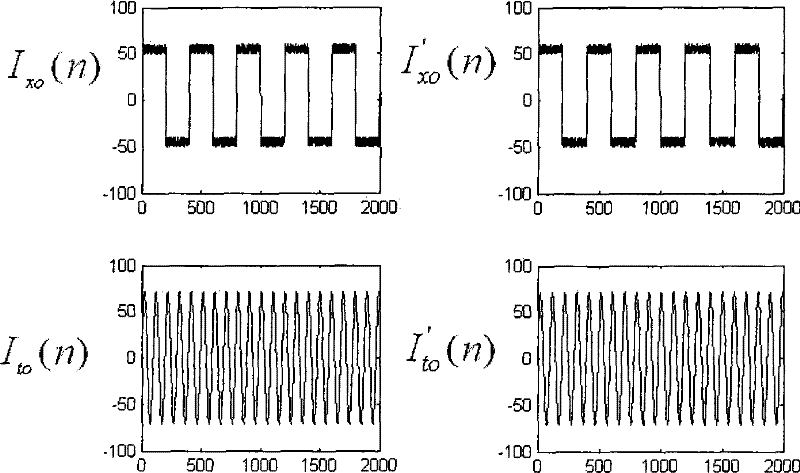
Method for monitoring current sensor angular difference online based on kernel independent component analysis
InactiveCN101576611AHigh separation precisionImprove robustnessVoltage-current phase angleCurrent sensorIndependent component analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of current signal high-precision separation and angular difference measurement, and in particular discloses a method for monitoring current sensor angular difference online based on kernel independent component analysis. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a sine-wave current test signal and normal working current into a current sensor together, and sampling a mixed signal output by the current sensor to obtain a mixed sampled signal; inputting the mixed sampled signal into a signal separation module which removes mean values of and whitens the mixed sampled signal, and applies the kernel independent component analysis to extract a test signal from the mixed sampled signal; and inputting the former sine-wave current test signal and the extracted test signal into an angular difference comparison module together, wherein the angular difference comparison module performs angular difference computation and calibrates the angular differences according to the result of the computation. The method uses a soft computing mode to achieve online calibration and check on the angular difference of the current sensor, and the algorithm has the advantages of high separation precision, good robustness and the like.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
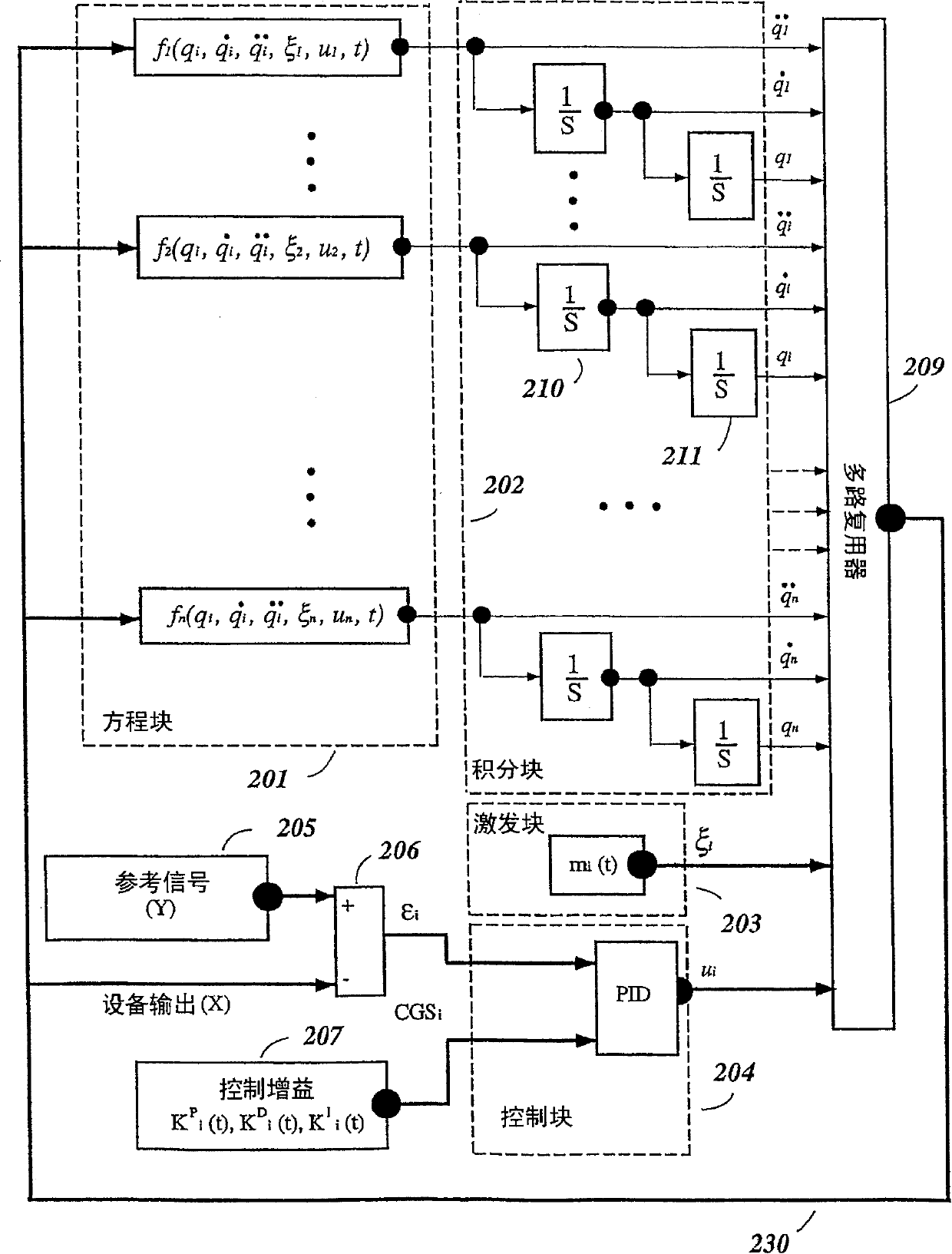
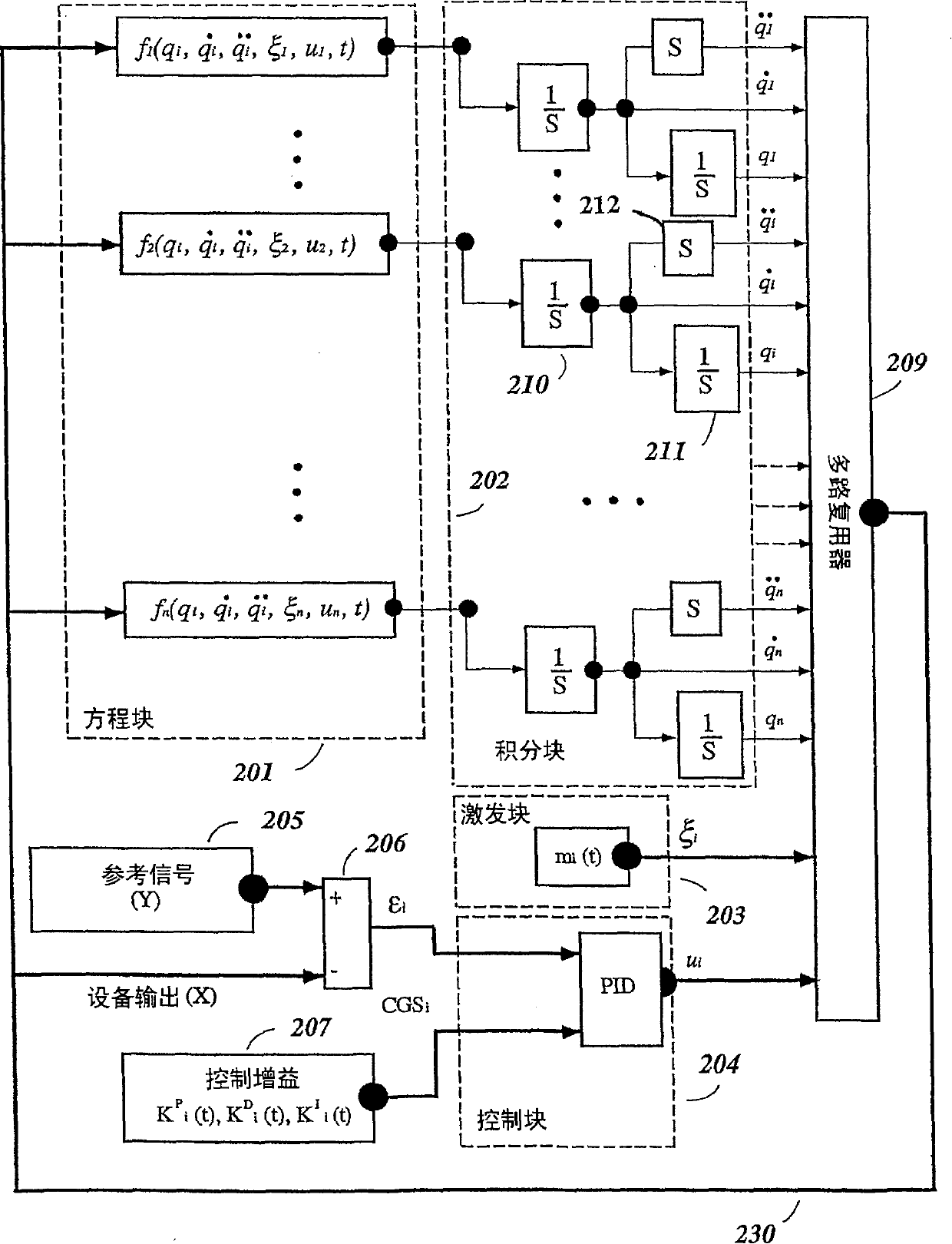
System and method for simulation of nonlinear dynamic systems applicable within soft computing
A system and method for efficient stochastic simulation of dynamic systems is described. Since analytic solutions cannot usually be found for stochastic differential equations, complete analysis requires numerical simulations. These simulations are most commonly done with first-order Euler-type algorithm. The efficiency of these algorithms is improved by removing algebraic loops in the simulation. An algebraic loop occurs when an output variable of the system of equations is also in an input variable to one or more of the equations describing the system. In one embodiment, the algebraic loops are removed by formulating a simulation wherein an output variable that gives rise to an algebraic loop is integrated to produce an integrated output. The integrated output is later provided to a differentiator to reconstruct the output variable as needed.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for interpretation of well data
ActiveUS8090538B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingWell loggingData mining
Well log data is assigned depositional labels by a soft computing method. A model is trained on an expert-interpreted well log by segmenting, assigning fuzzy symbols to the segments, and calculating attribute values for units labeled by the expert. From these values, classifiers are trained for each of a number of depositional types. Finally, a model is developed for translating fuzzy symbols into depositional labels. Once trained, the model is applied to well log data.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
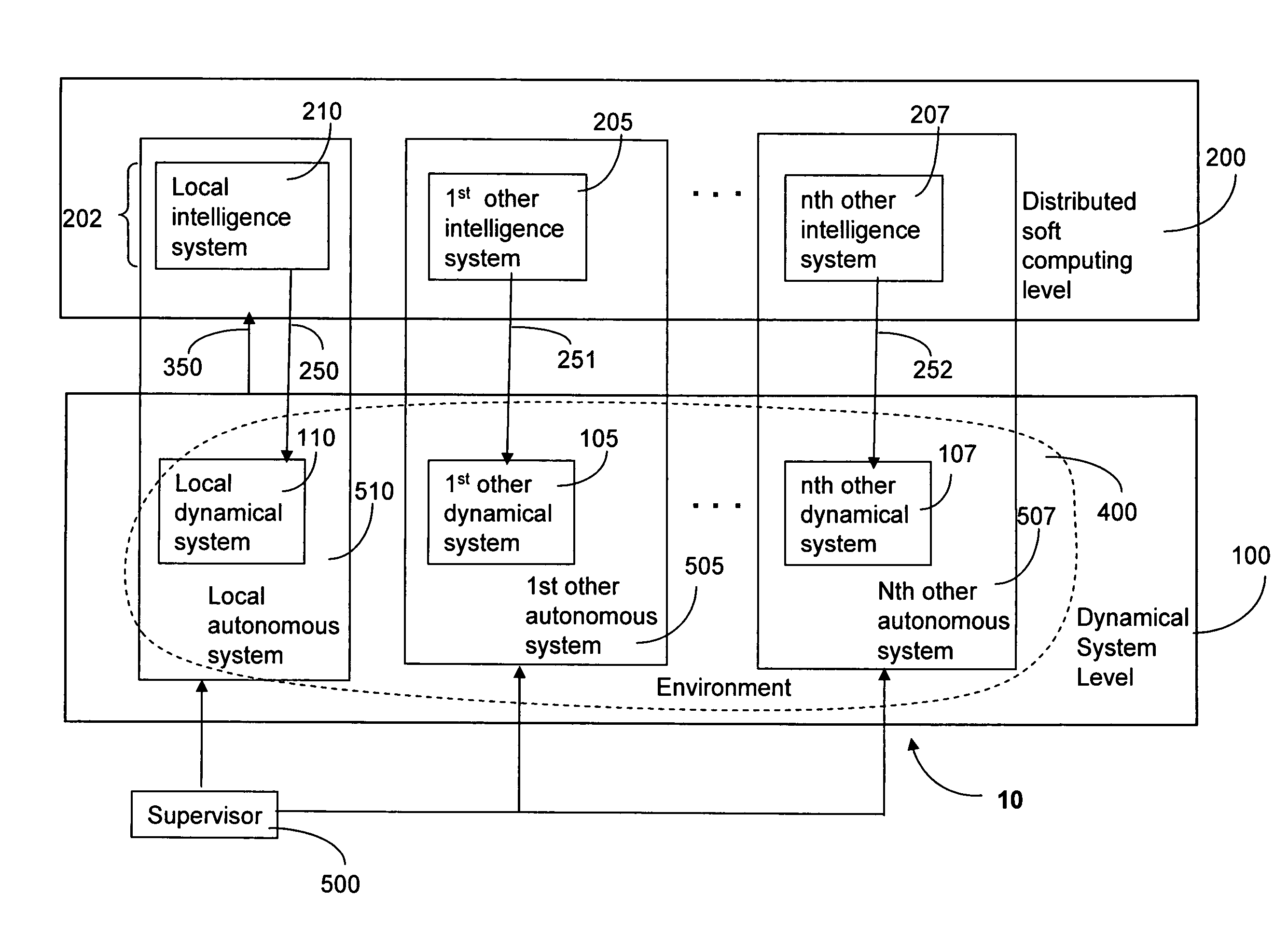
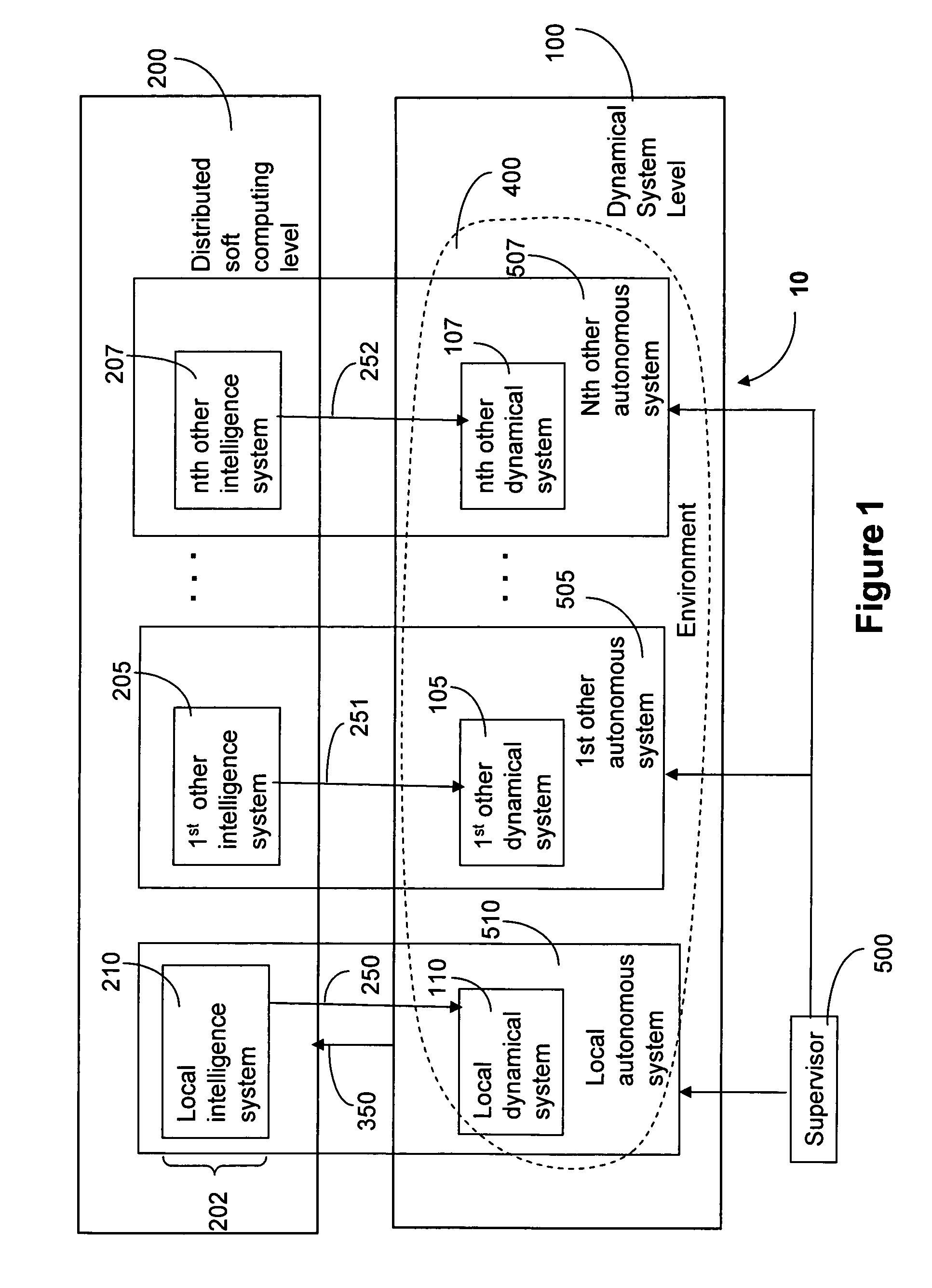
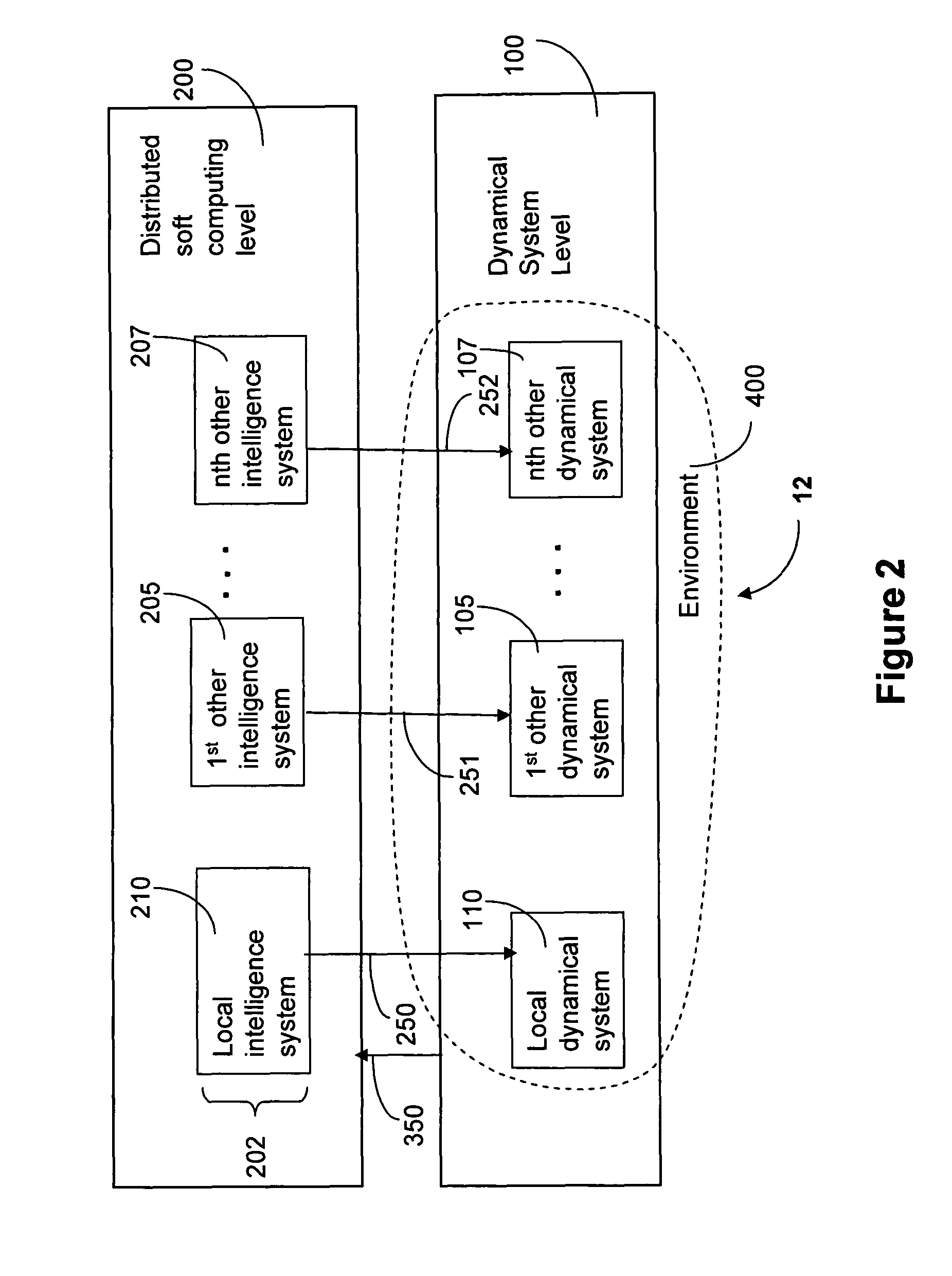
Method for soft-computing supervision of dynamical processes with multiple control objectives
ActiveUS7769474B2Reduce switchingVehicle testingWave amplification devicesControl objectiveSimulation
A method to supervise a local dynamical system having multiple preset control objectives and operating in conjunction with other dynamical systems. The method includes receiving state input from dynamical systems in an environment at a distributed soft computing level, generating weights and applying the weights to the preset control objectives using soft computing methods to form weighted control objectives. The weights are computed based on the received state input. The method also includes generating a command signal for the local dynamical system based on the weighted control objectives and transmitting the command signal to a controller in the local dynamical system.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Construction method of boundary forest model, multi-working-condition soft computing model updating method for complex industrial process and application thereof
ActiveCN110795846AStable and reliable outputReliable predictive valueDesign optimisation/simulationCAD numerical modellingAlgorithmData mining
The invention discloses a construction method of a boundary forest model, a multi-working-condition soft computing model updating method for a complex industrial process and an application thereof, belonging to the field of computer application. In order to solve the problem that prediction values are unreliable due to the fact that leaf nodes of a tree integration model easily generate blank areas in an output range, when a current training set under a certain working condition is known, the construction method comprises the steps: setting different leaf node minimum sample numbers, and establishing K tree integration models with different leaf node boundaries by using different leaf node minimum samples; predicting output values of all samples in the current training set by using a treeintegration model, and forming a prediction matrix by the predicted output values; according to the prediction output value of the prediction matrix, constructing a correlation matrix of the prediction output value and a real output value; and calculating a fusion weight vector, using the weight vector, and fusing the tree integration models with different boundaries into a boundary forest model,so that the leaf nodes of different tree models cover each other, and the blank area of a single tree on an output boundary is filled, and a reliable prediction value is generated.
Owner:DONGBEI UNIVERSITY OF FINANCE AND ECONOMICS
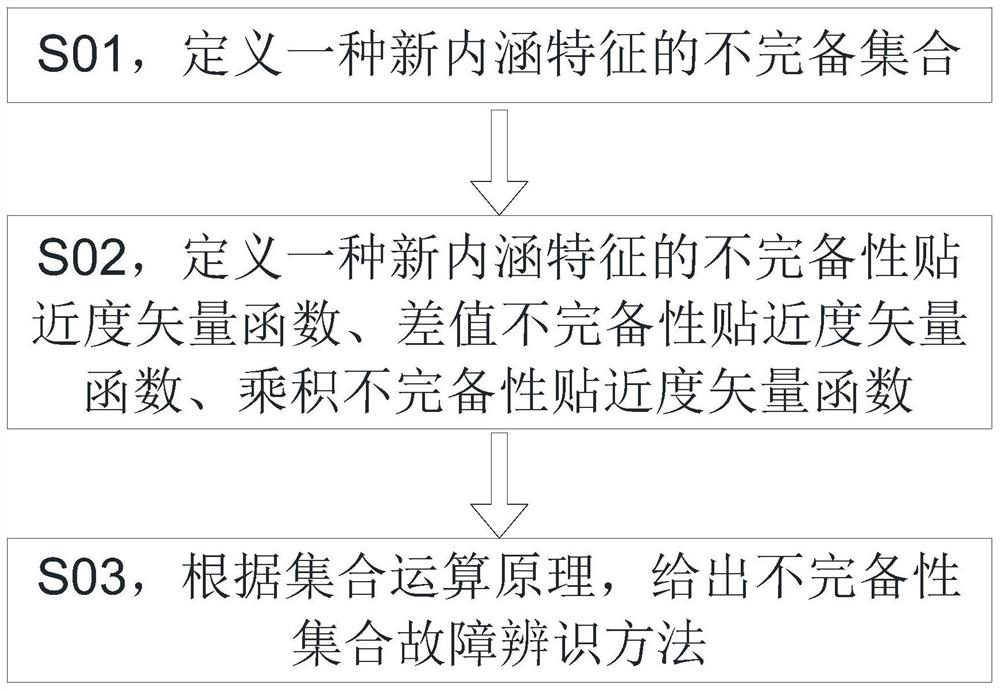
Fault identification method based on incomplete information
ActiveCN113537082ARealize processingRealize acquisitionCharacter and pattern recognitionManufacturing computing systemsInformation processingEngineering
The invention discloses a fault identification method based on incomplete information, and belongs to the technical field of fault identification. The invention discloses a fault identification method based on incomplete information. The method comprises the following steps: S01, defining an incomplete set of new connotation features; S02, defining an incomplete closeness vector function, a difference incomplete closeness vector function and a product incomplete closeness vector function of a new connotation feature; and S03, giving an incomplete set fault identification method according to a set operation principle. According to the method, incomplete information can be analyzed and processed, information acquisition, processing, fault identification and decision making can be effectively and rapidly realized, and a basis is provided for combination of a subsequent incomplete information processing mode and other soft science and soft computing methods.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Method for monitoring current sensor angular difference online based on kernel independent component analysis
InactiveCN101576611BHigh separation precisionImprove robustnessVoltage-current phase angleCurrent sensorIndependent component analysis
The invention relates to the technical field of current signal high-precision separation and angular difference measurement, and in particular discloses a method for monitoring current sensor angular difference online based on kernel independent component analysis. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a sine-wave current test signal and normal working current into a current sensor together, and sampling a mixed signal output by the current sensor to obtain a mixed sampled signal; inputting the mixed sampled signal into a signal separation module which removes mean values of andwhitens the mixed sampled signal, and applies the kernel independent component analysis to extract a test signal from the mixed sampled signal; and inputting the former sine-wave current test signal and the extracted test signal into an angular difference comparison module together, wherein the angular difference comparison module performs angular difference computation and calibrates the angulardifferences according to the result of the computation. The method uses a soft computing mode to achieve online calibration and check on the angular difference of the current sensor, and the algorithmhas the advantages of high separation precision, good robustness and the like.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com