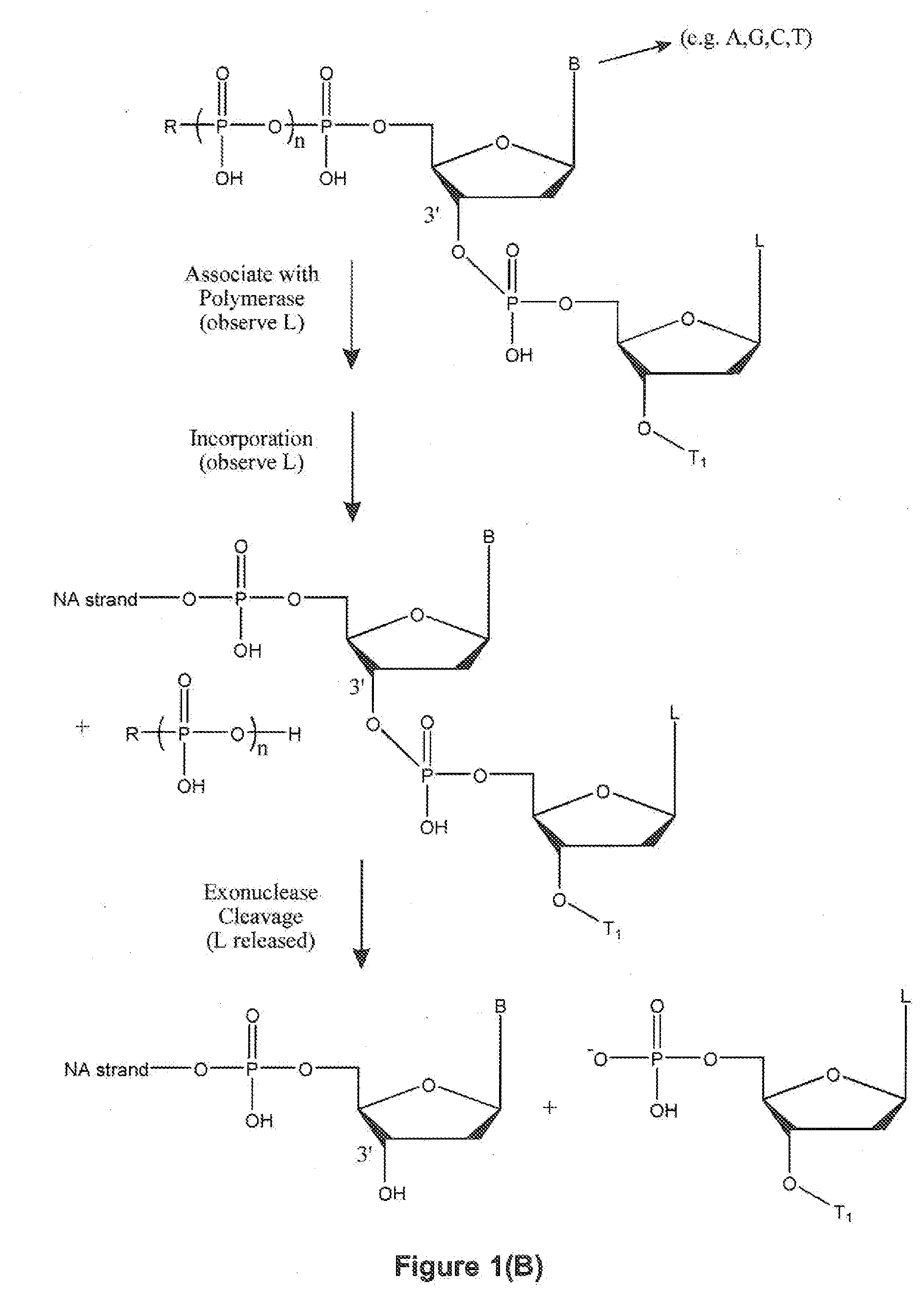
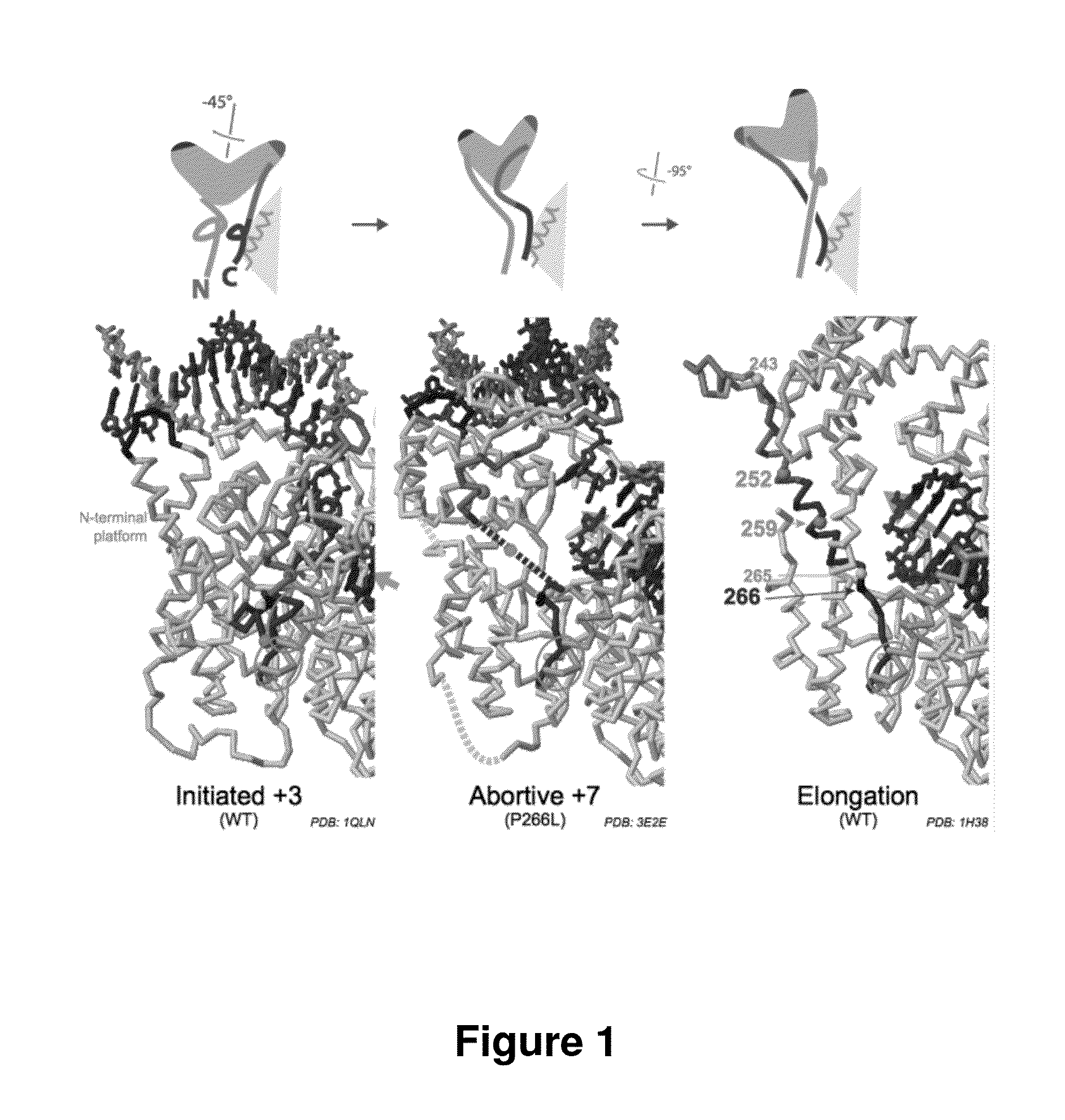
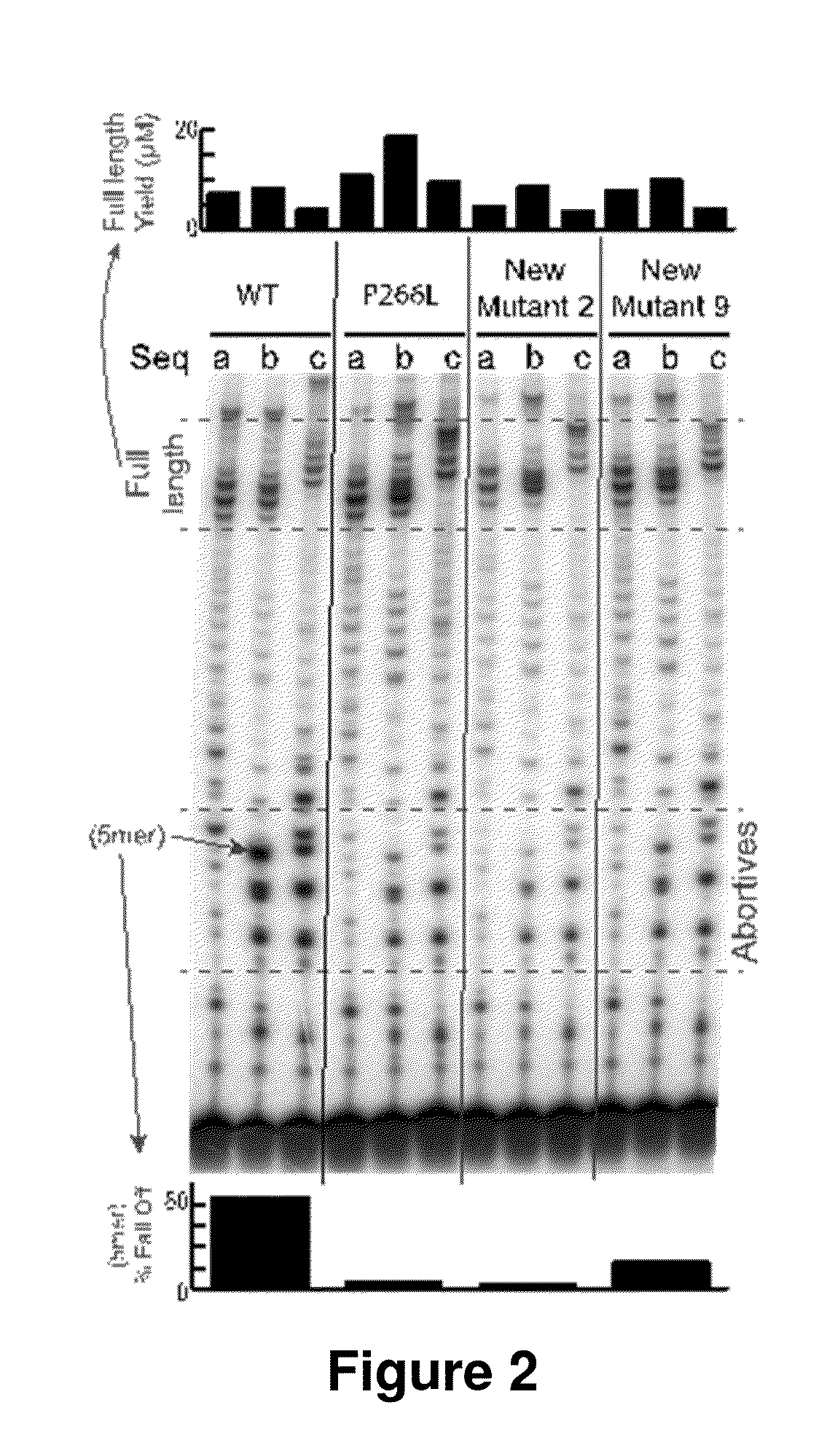
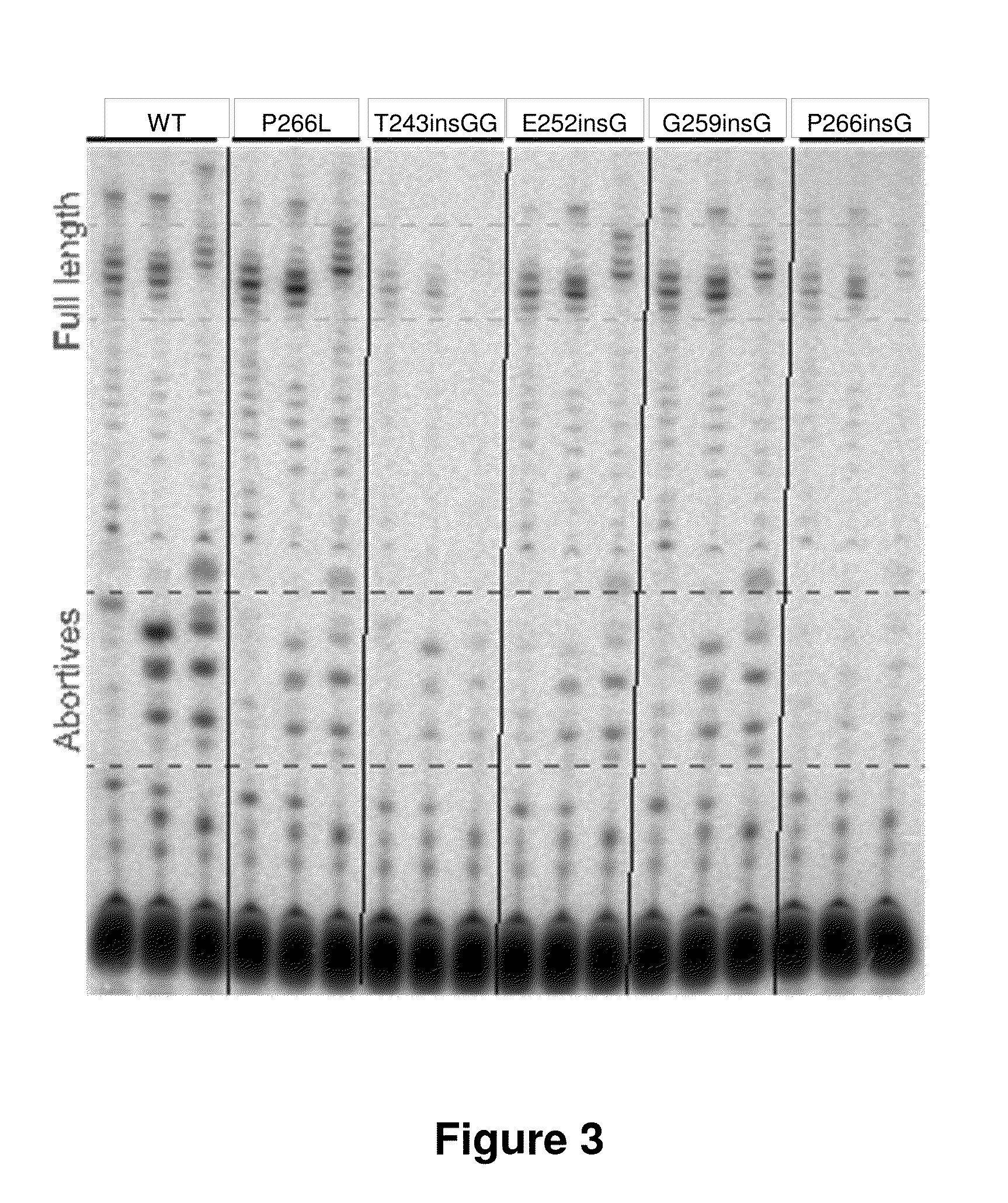
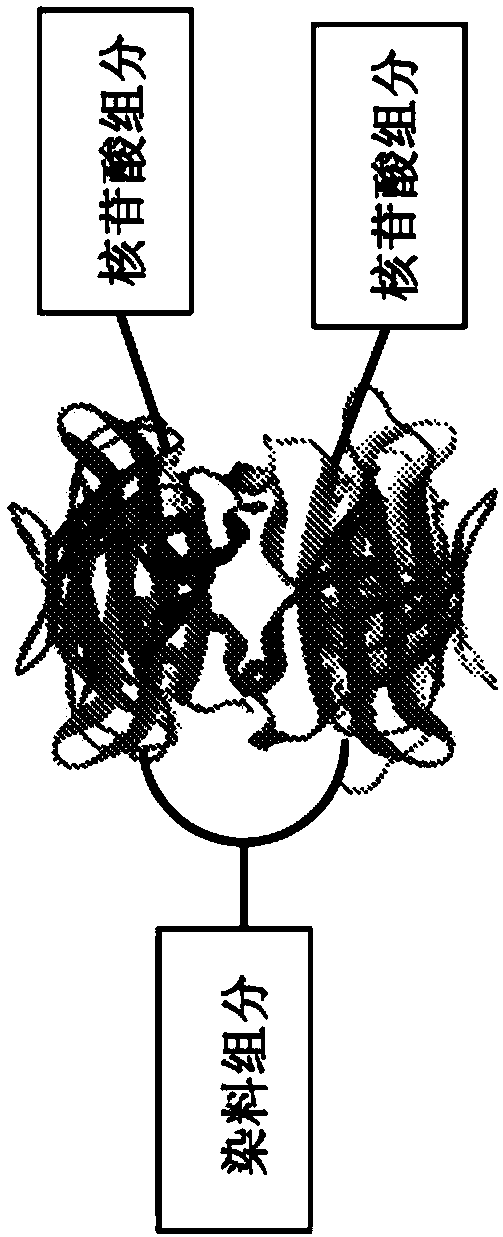Patents
Literature
32 results about "PHA polymerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
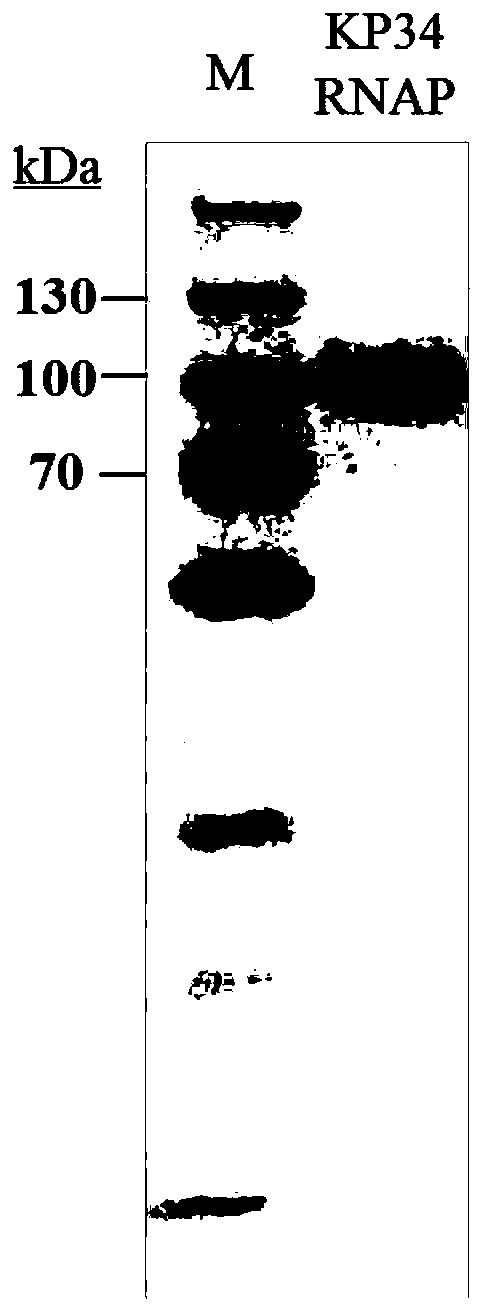
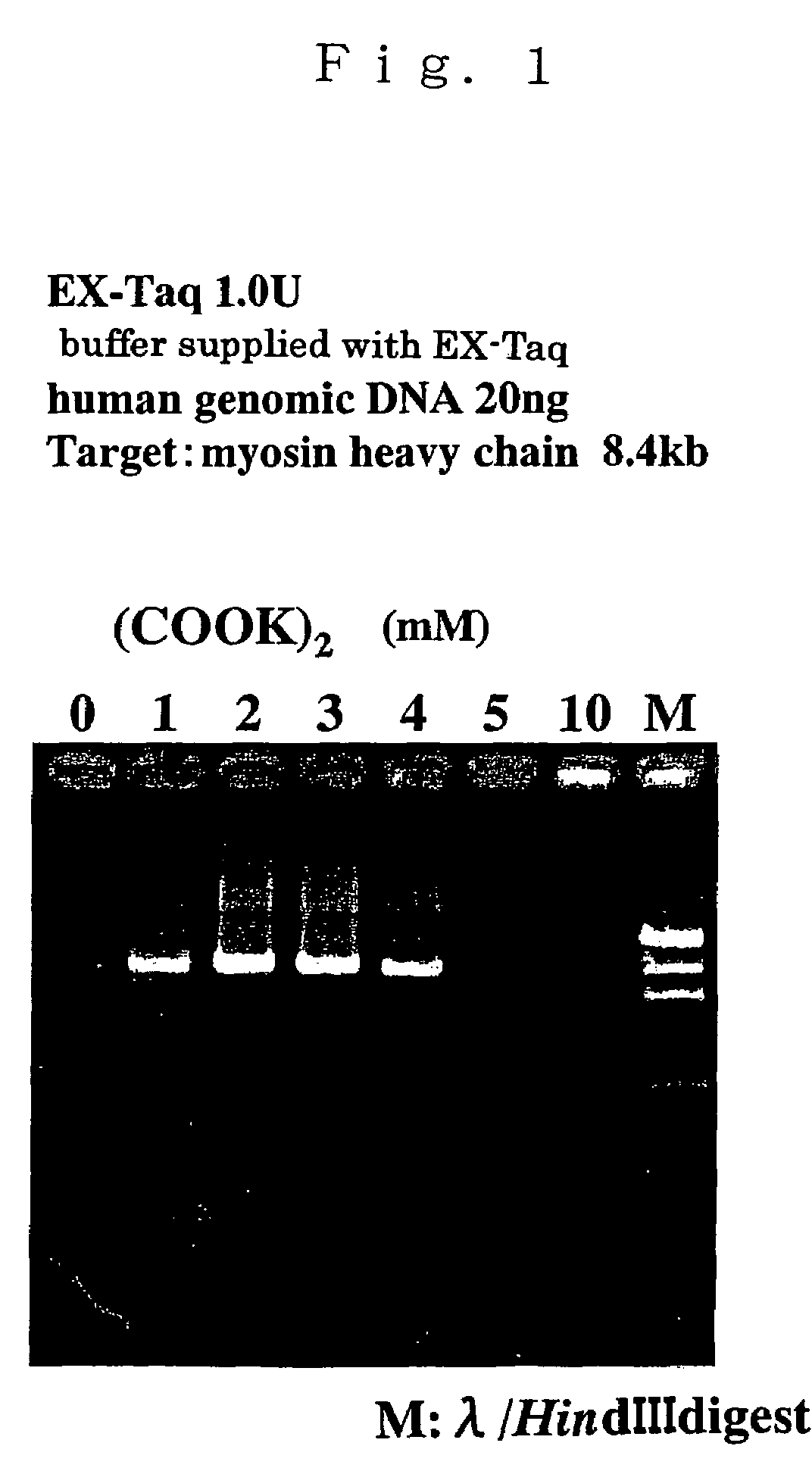
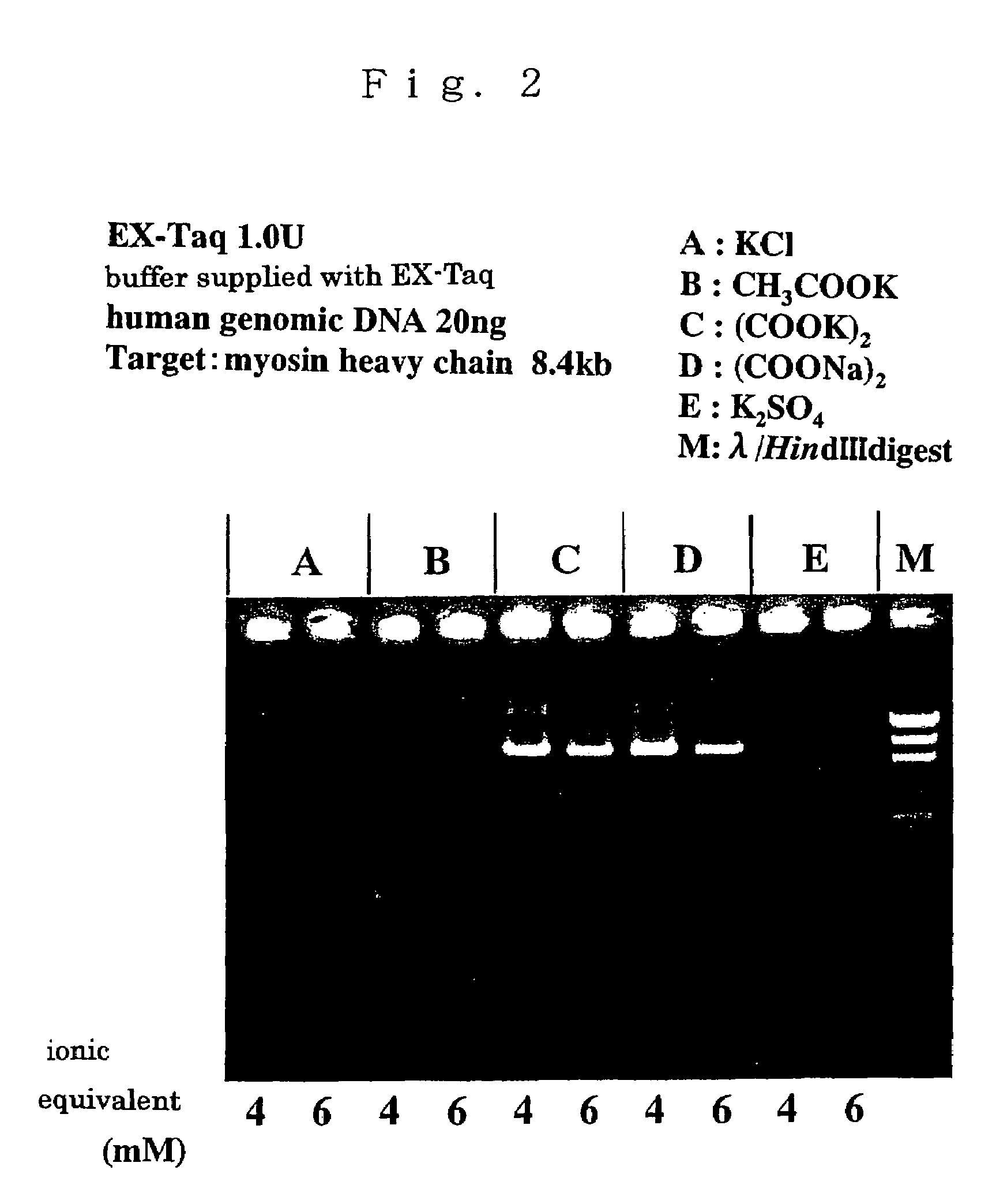
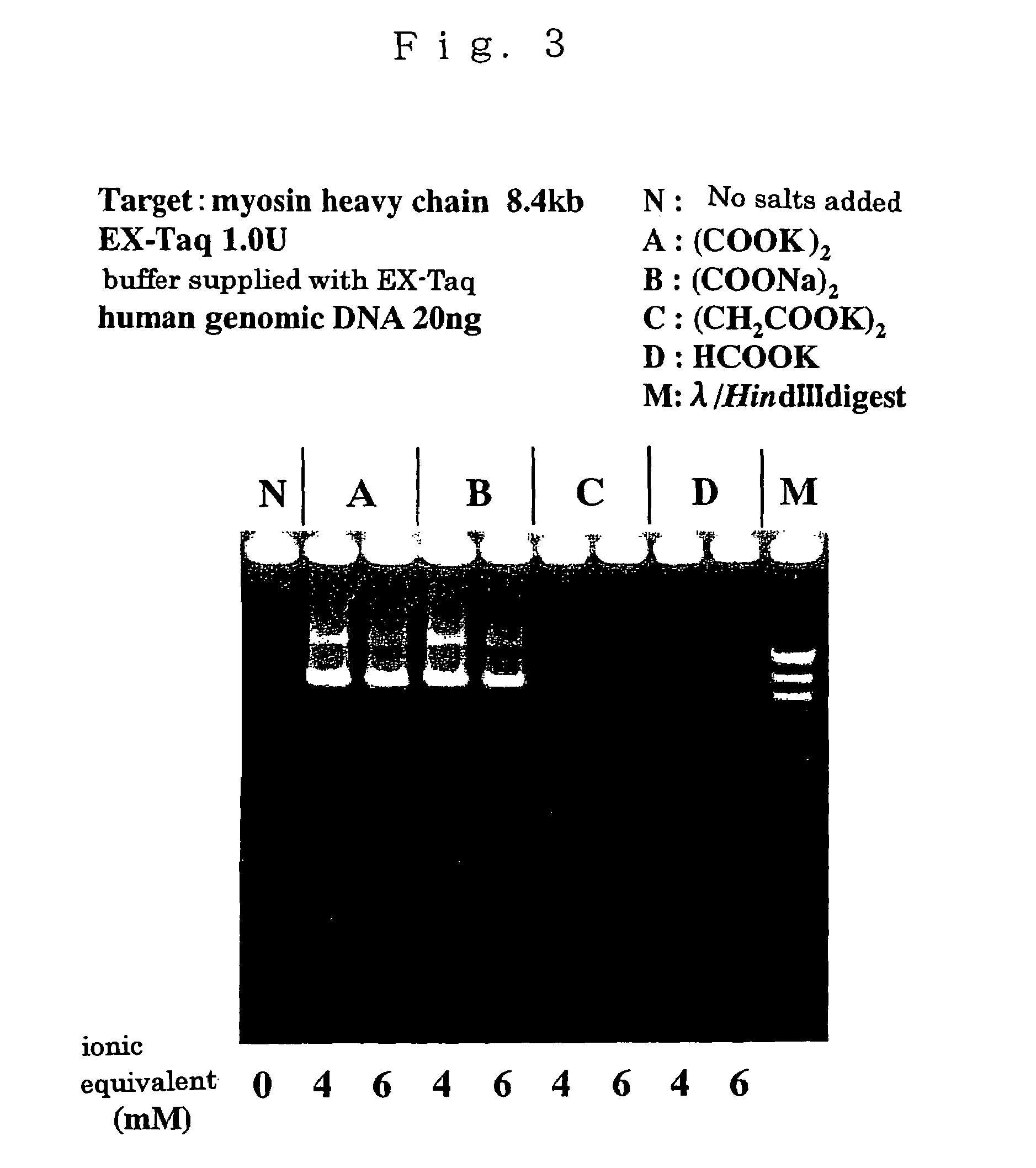
Compositions for enhancing DNA synthesis, DNA polymerase-related factors and utilization thereof
ActiveUS7384739B2High synthetic activityEnhancing PCR success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesEnzymatic synthesisPHA polymerase
The invention provides methods, kits, and compositions for enhancing synthesis of DNA involving a carboxylate ion-supplying substance that is effective in promoting DNA synthesis in enzymatic DNA synthesis reactions. The invention further provides a thermostable DNA polymerase-related factor derived from Thermococcus species, which has an activity to promote the DNA synthesis activity of DNA polymerase or which binds to DNA polymerase.
Owner:TOYOBO CO LTD
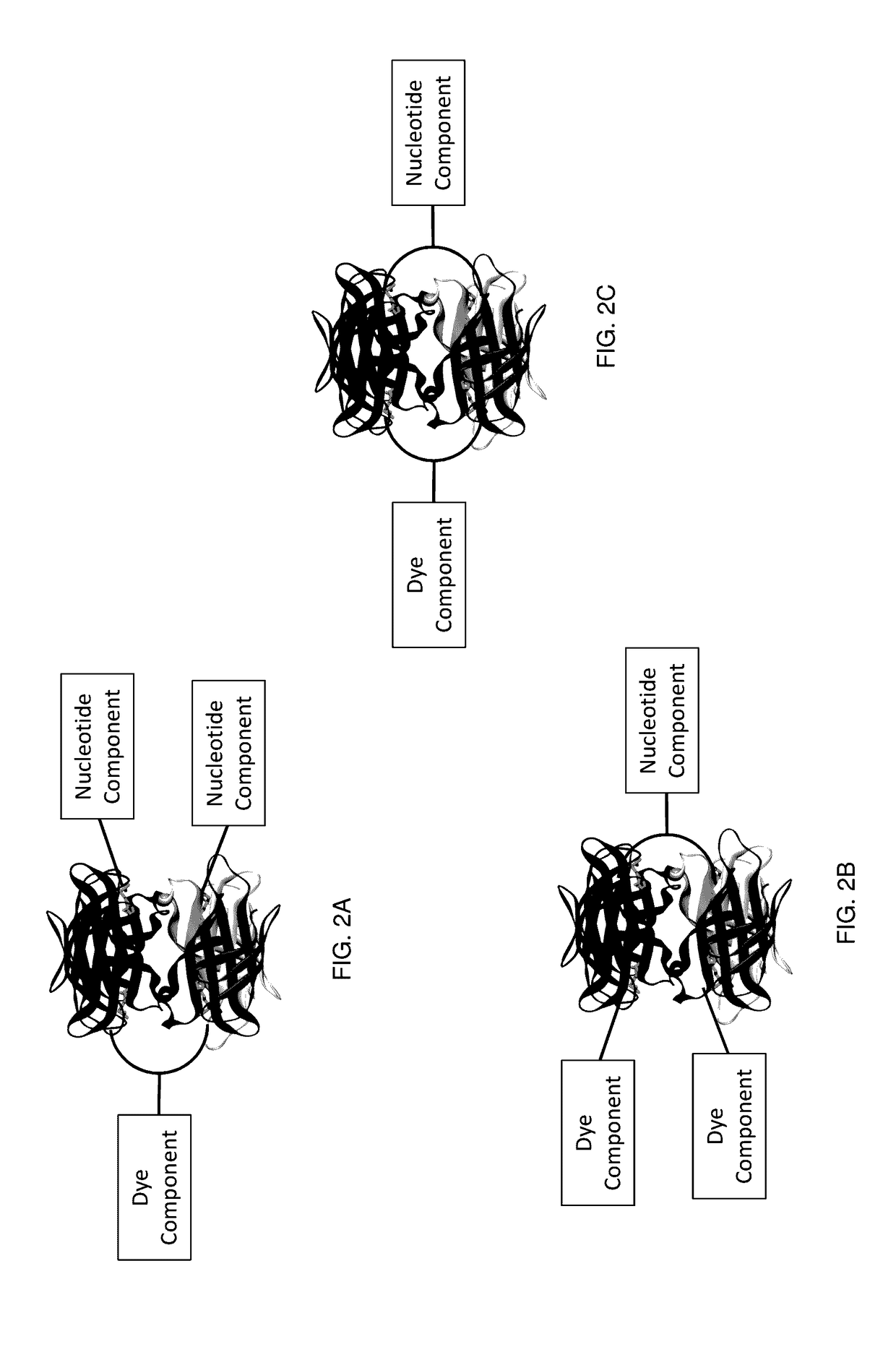
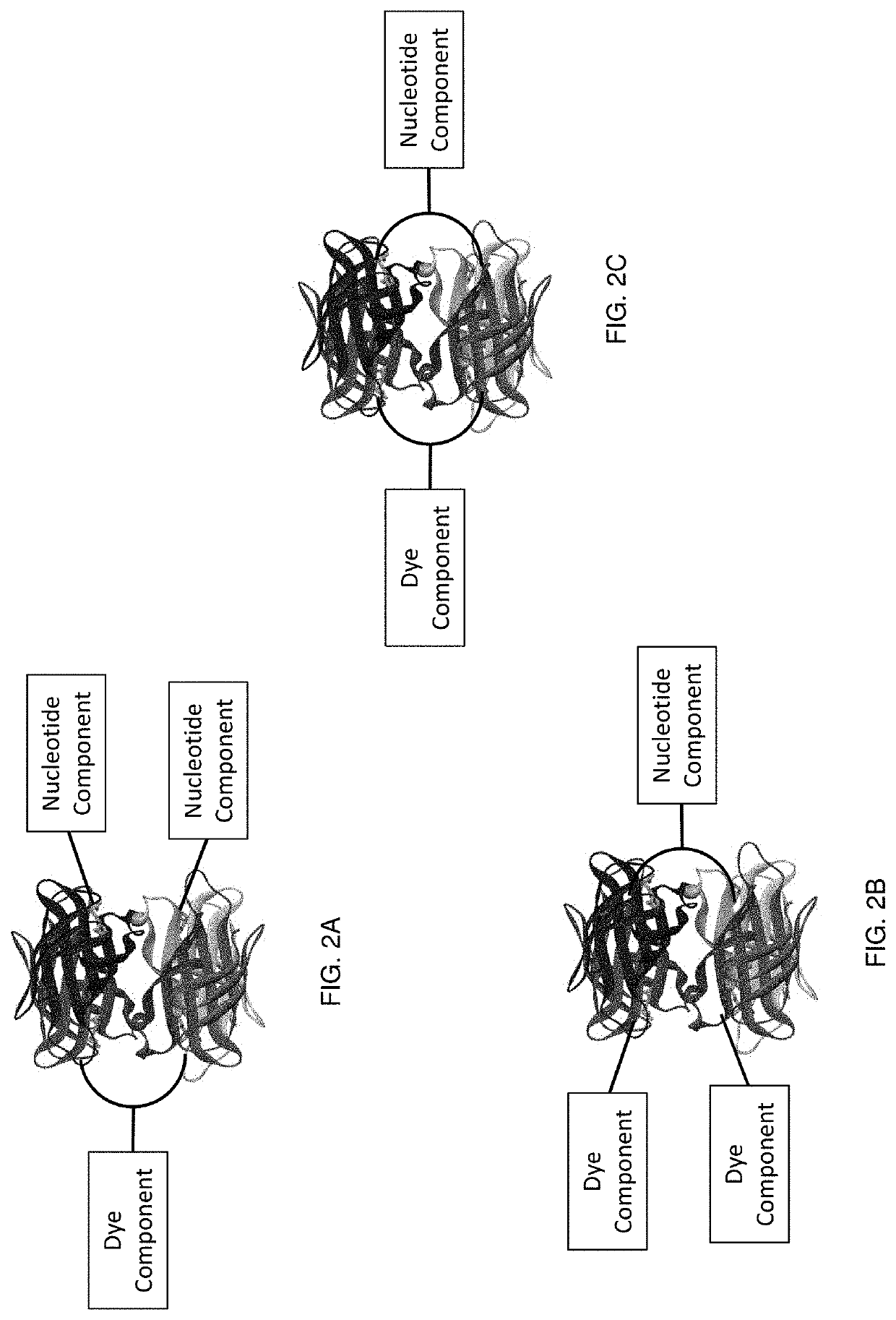
Protected dye-labeled reagents
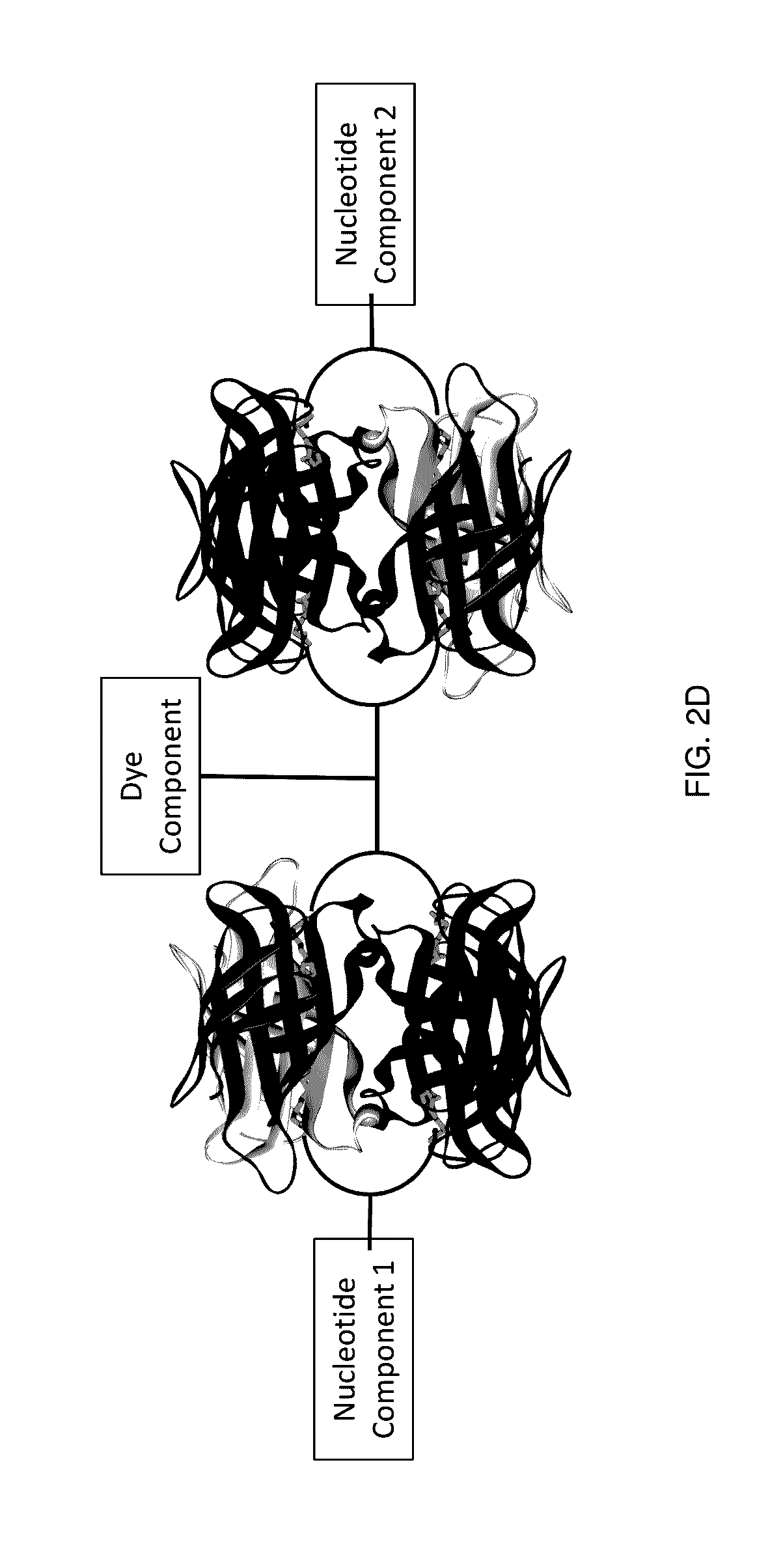
ActiveUS20170145495A1Reduce photodamageIncrease brightnessSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh densityNucleotide
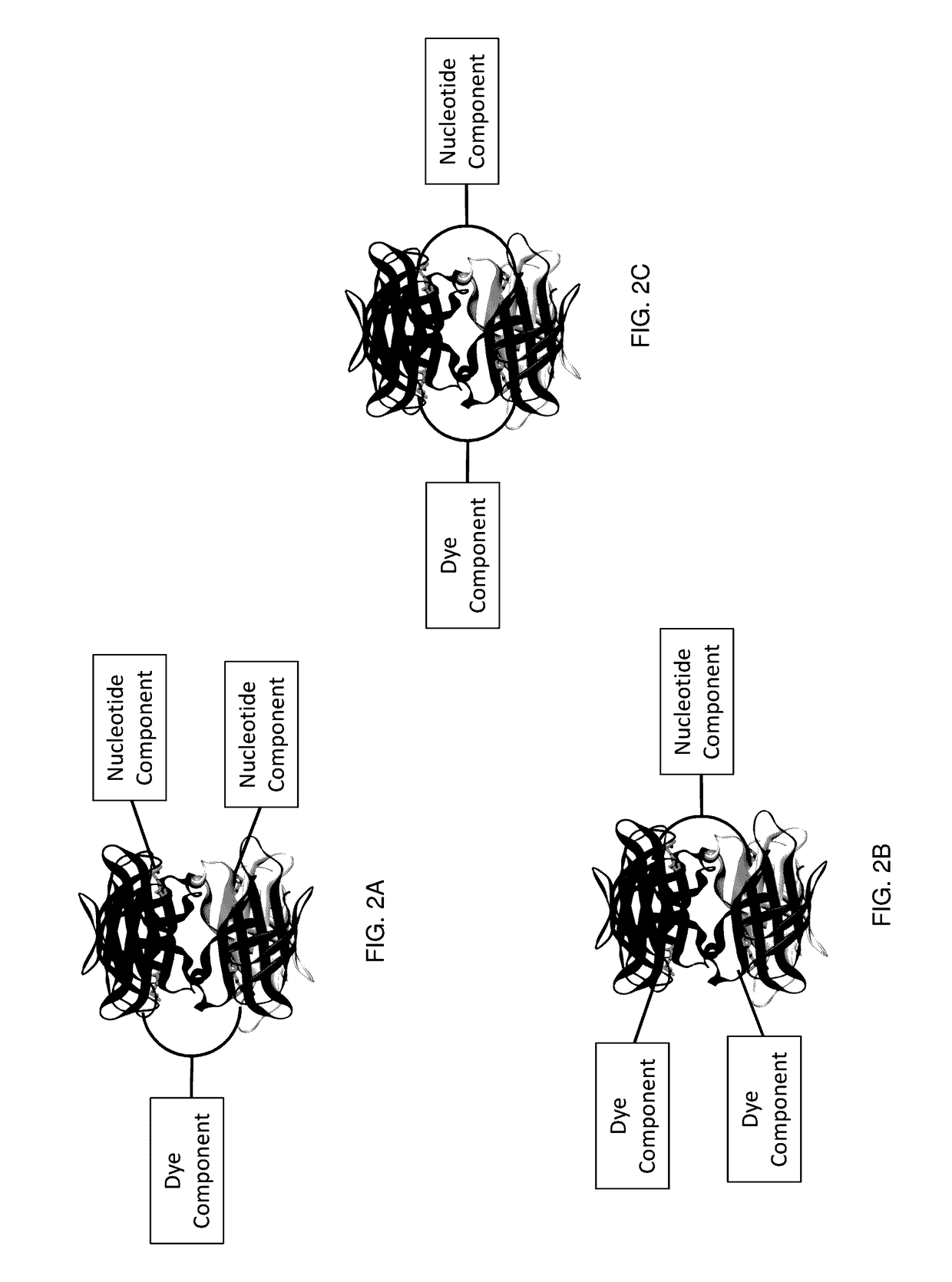
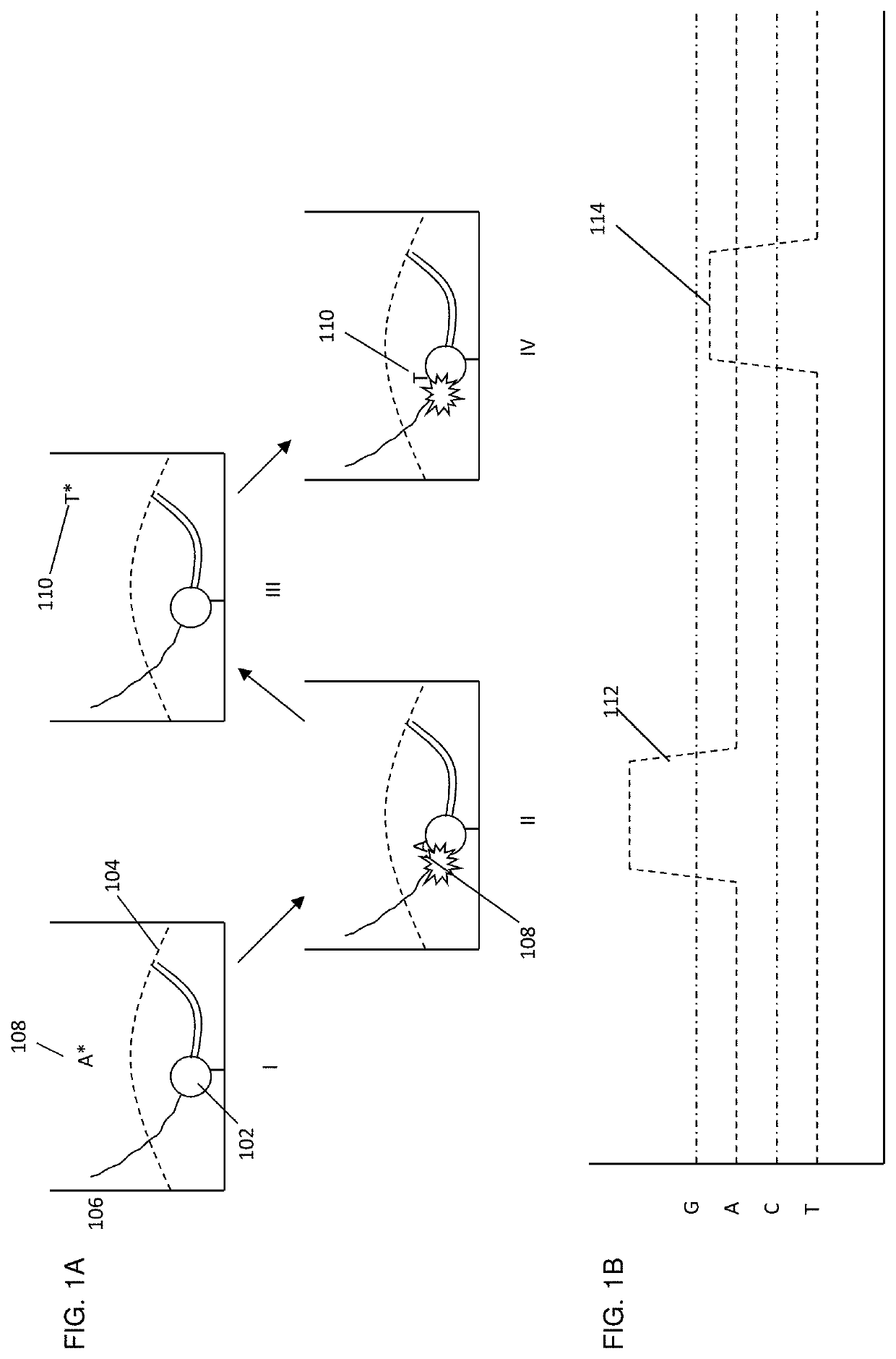
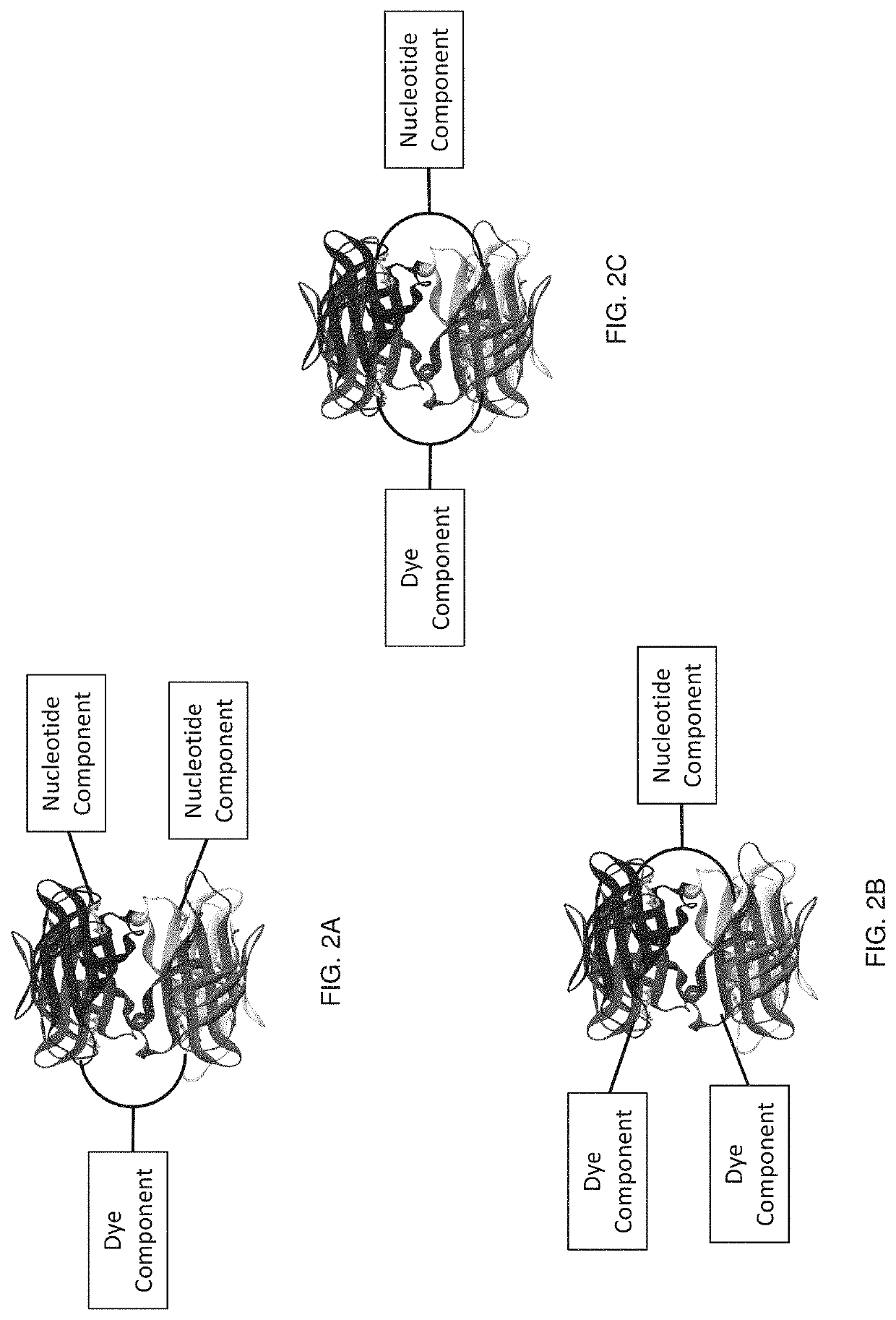
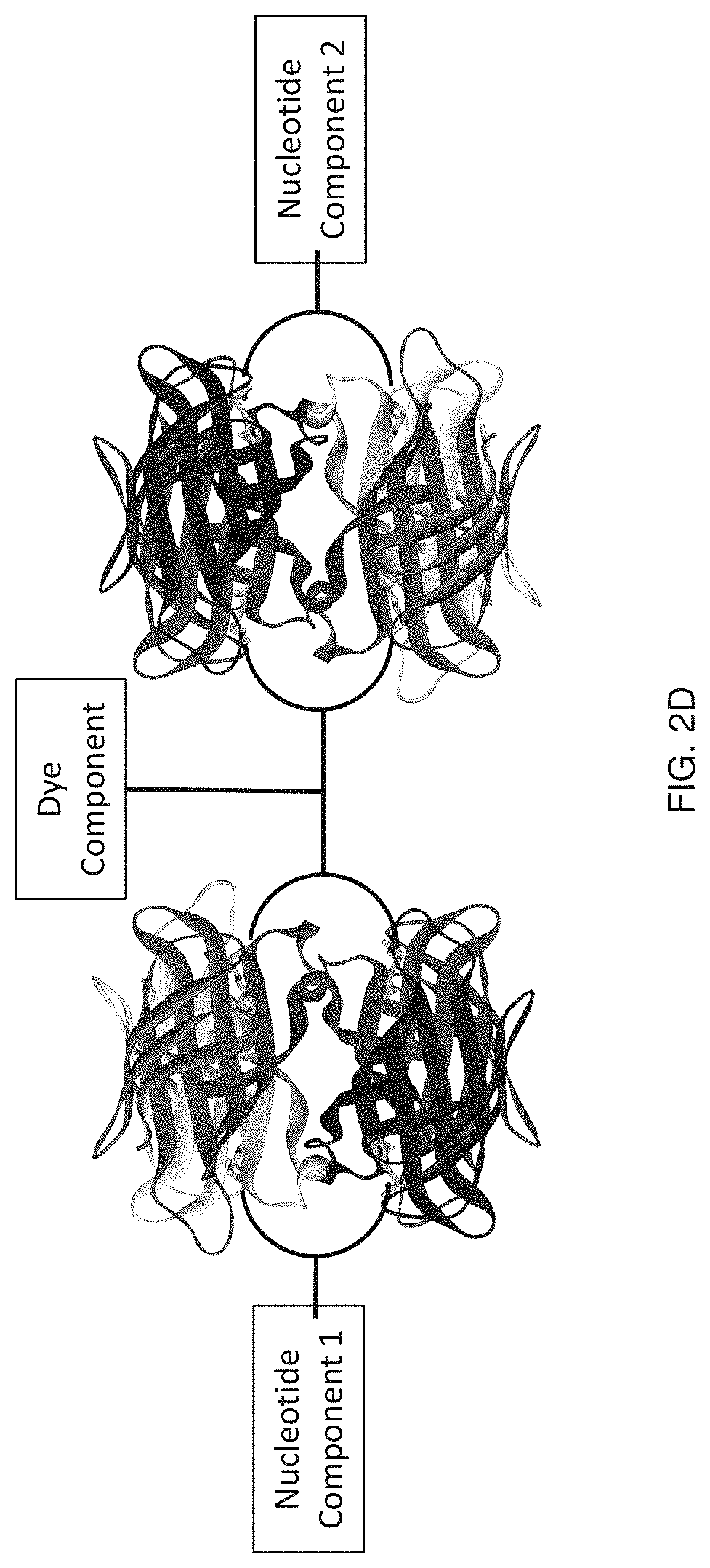
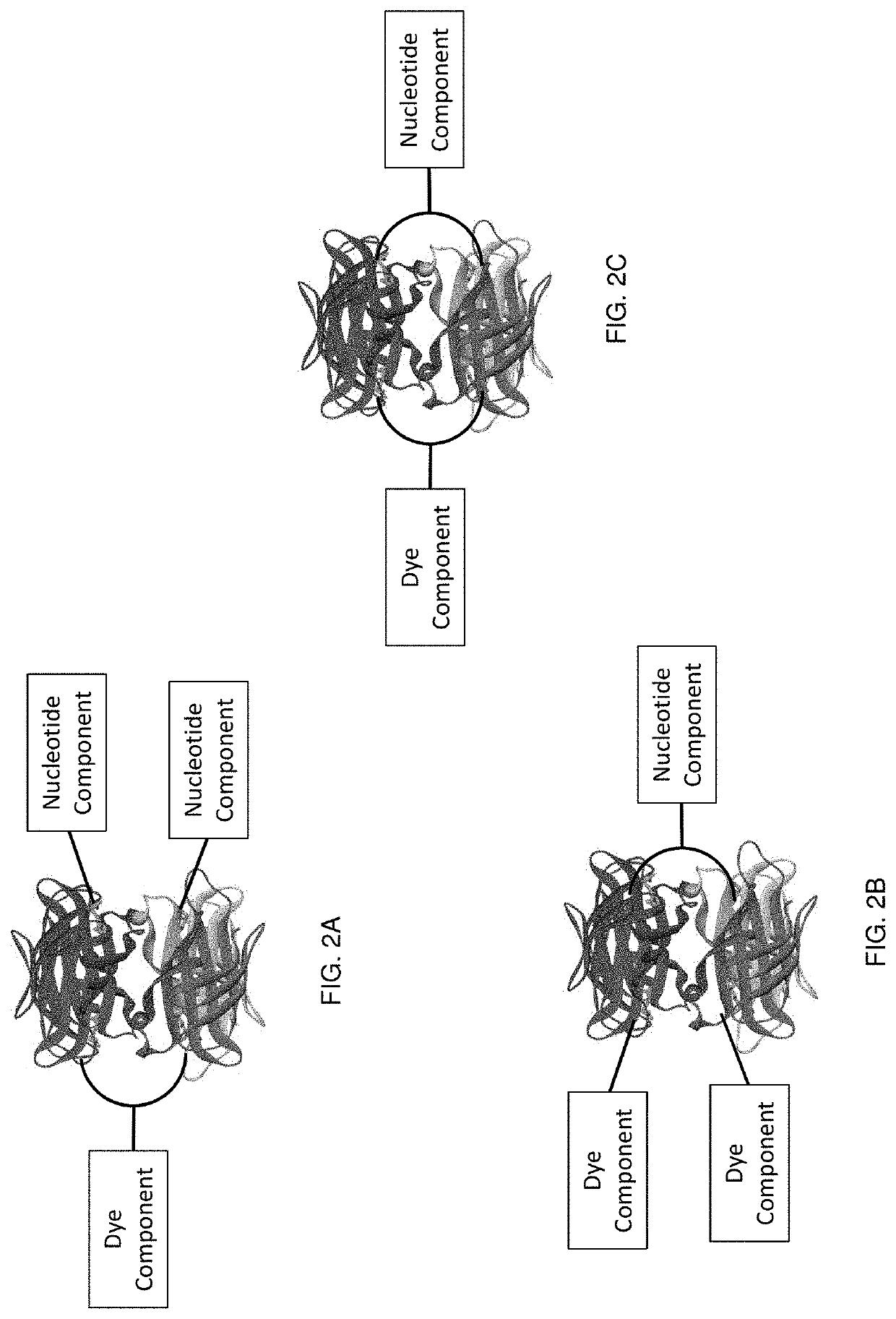
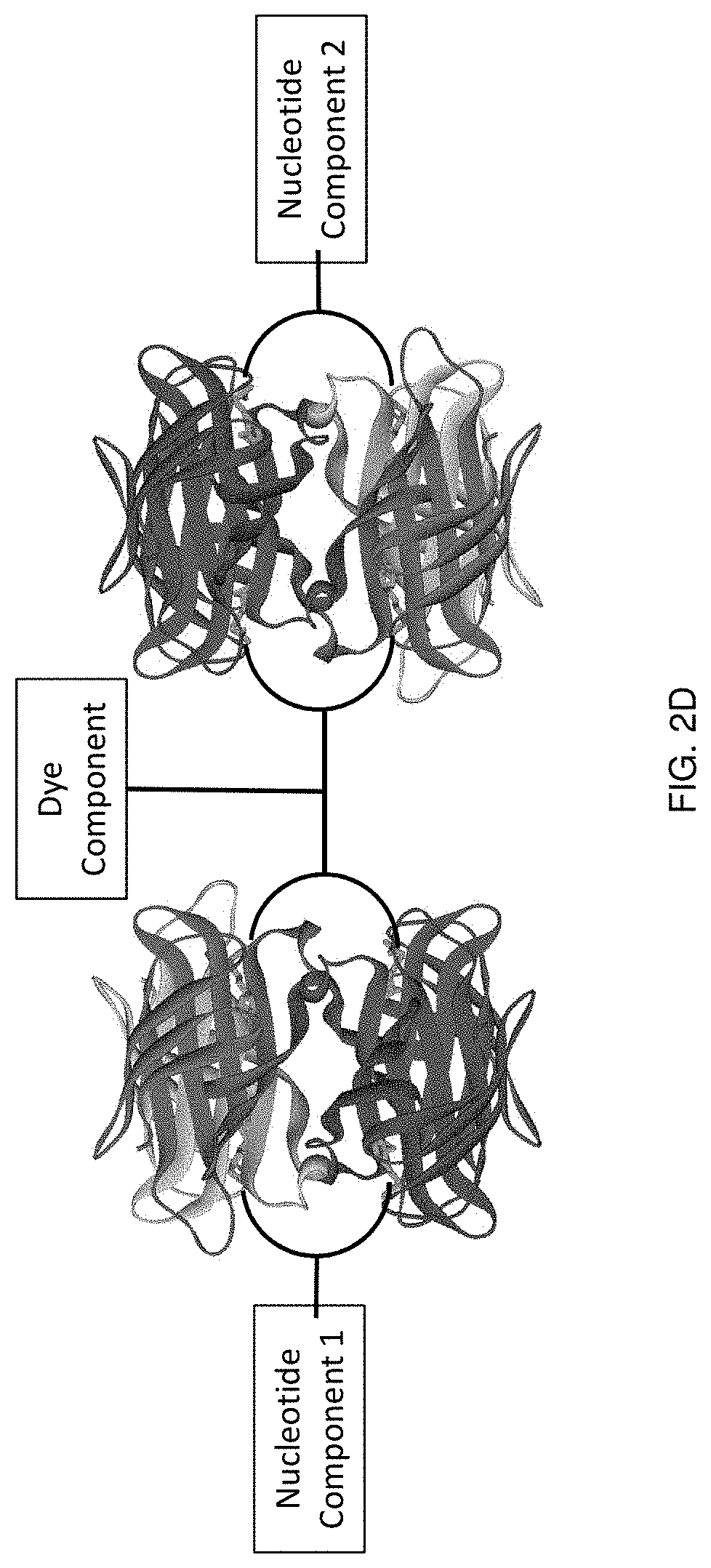
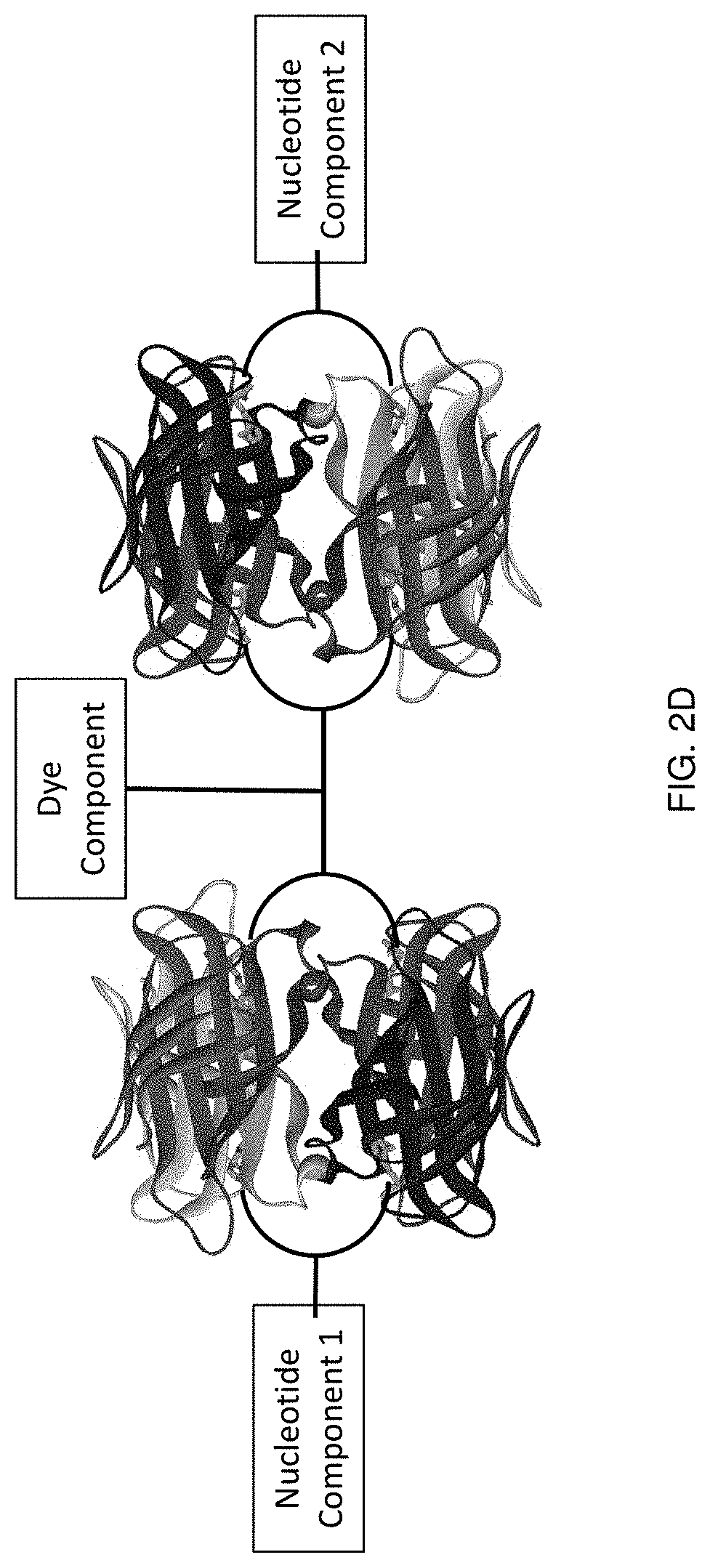
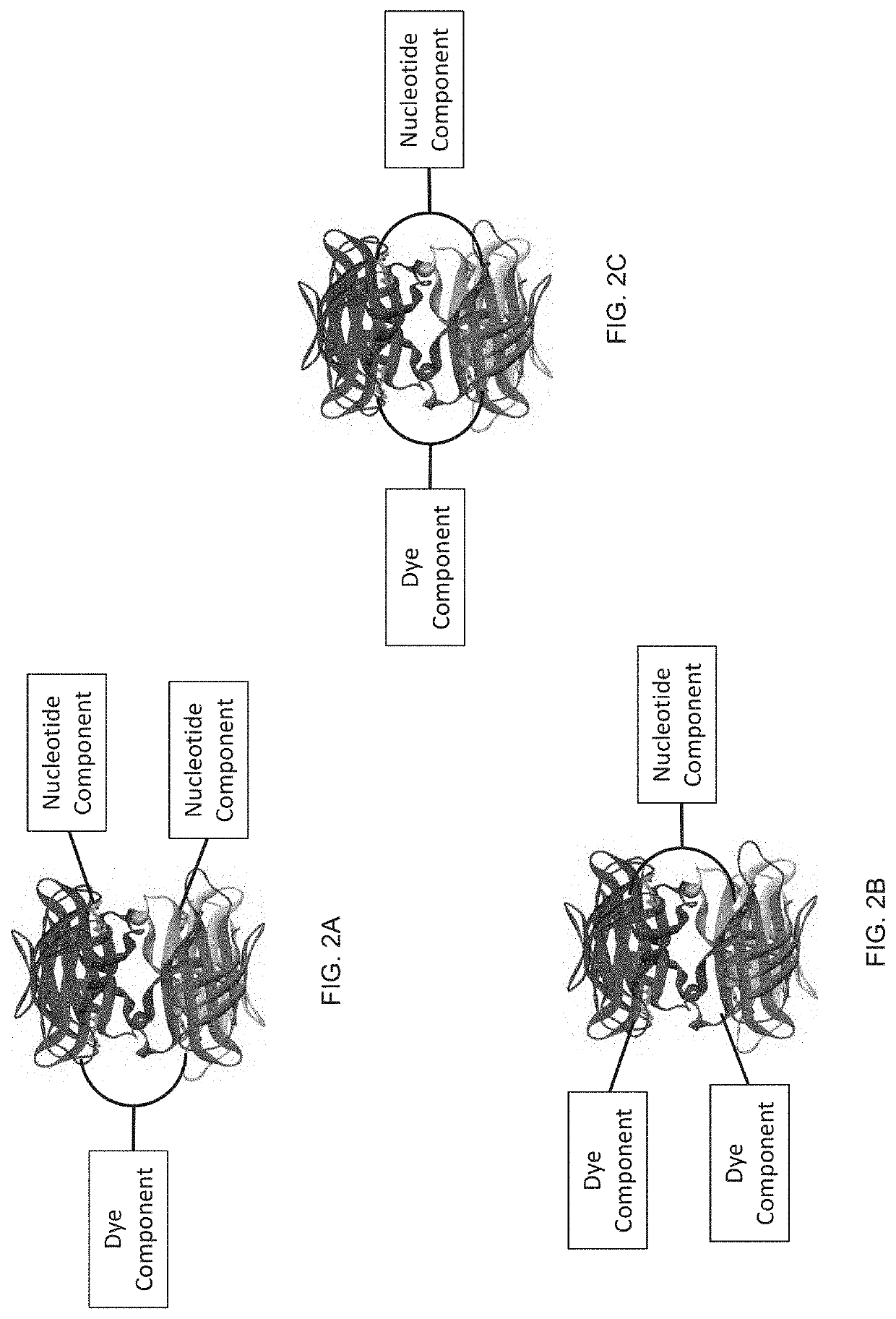
Labeled nucleotide analogs comprising at least one avidin protein, at least one dye-labeled compound, and at least one nucleotide compound are provided. The analogs are useful in various fluorescence-based analytical methods, including the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, such as single molecule real time nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The analogs are detectable with high sensitivity at desirable wavelengths. They contain structural components that modulate the interactions of the analogs with DNA polymerase, thus decreasing photodamage and improving the kinetic and other properties of the analogs in sequencing reactions. Also provided are nucleotide and dye-labeled compounds of the subject analogs, as well as intermediates useful in the preparation of the compounds and analogs. Compositions comprising the compounds, methods of synthesis of the intermediates, compounds, and analogs, and mutant DNA polymerases are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Single molecule sequencing with two distinct chemistry steps
ActiveUS20110212437A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePHA polymerase
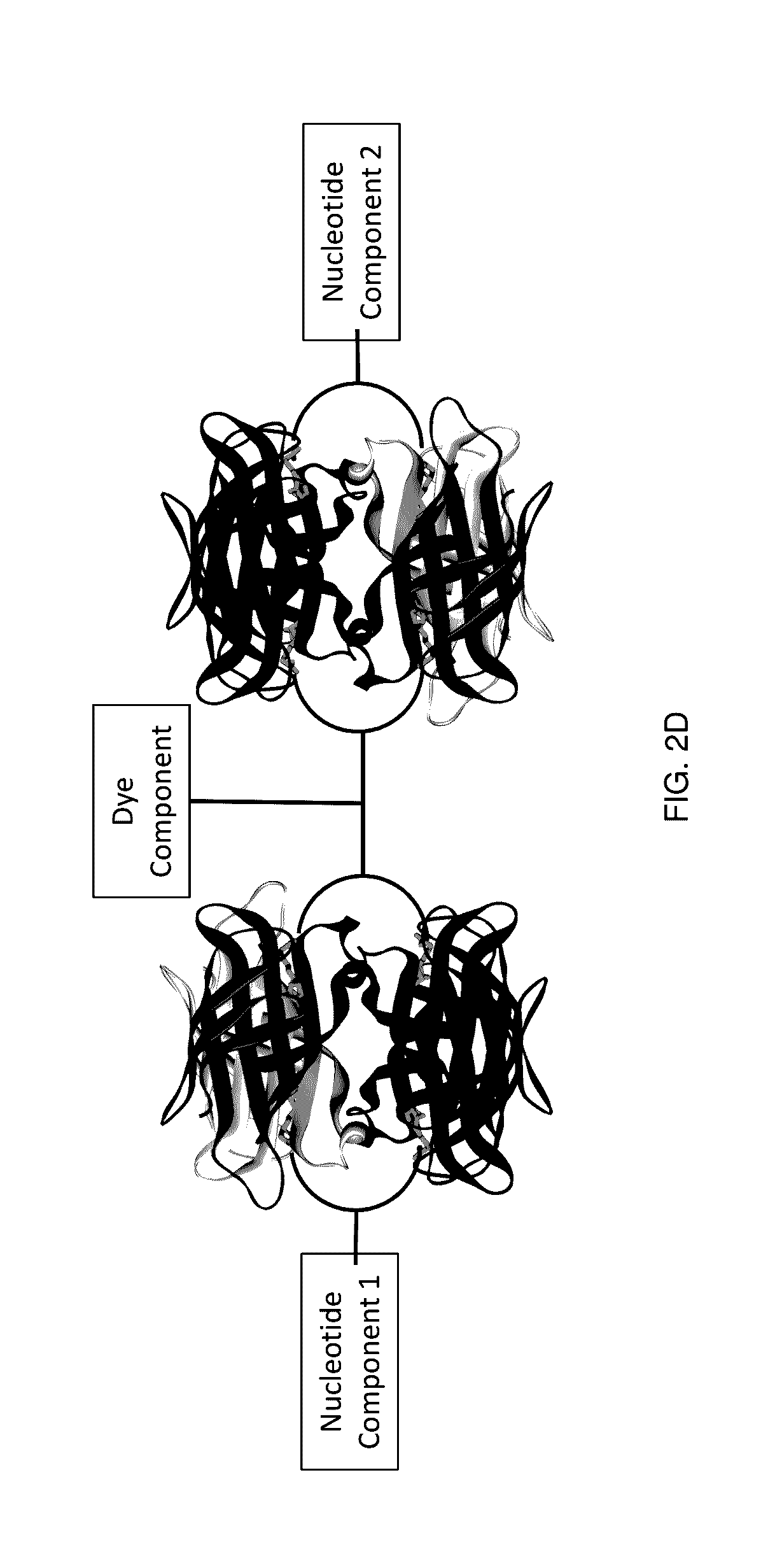
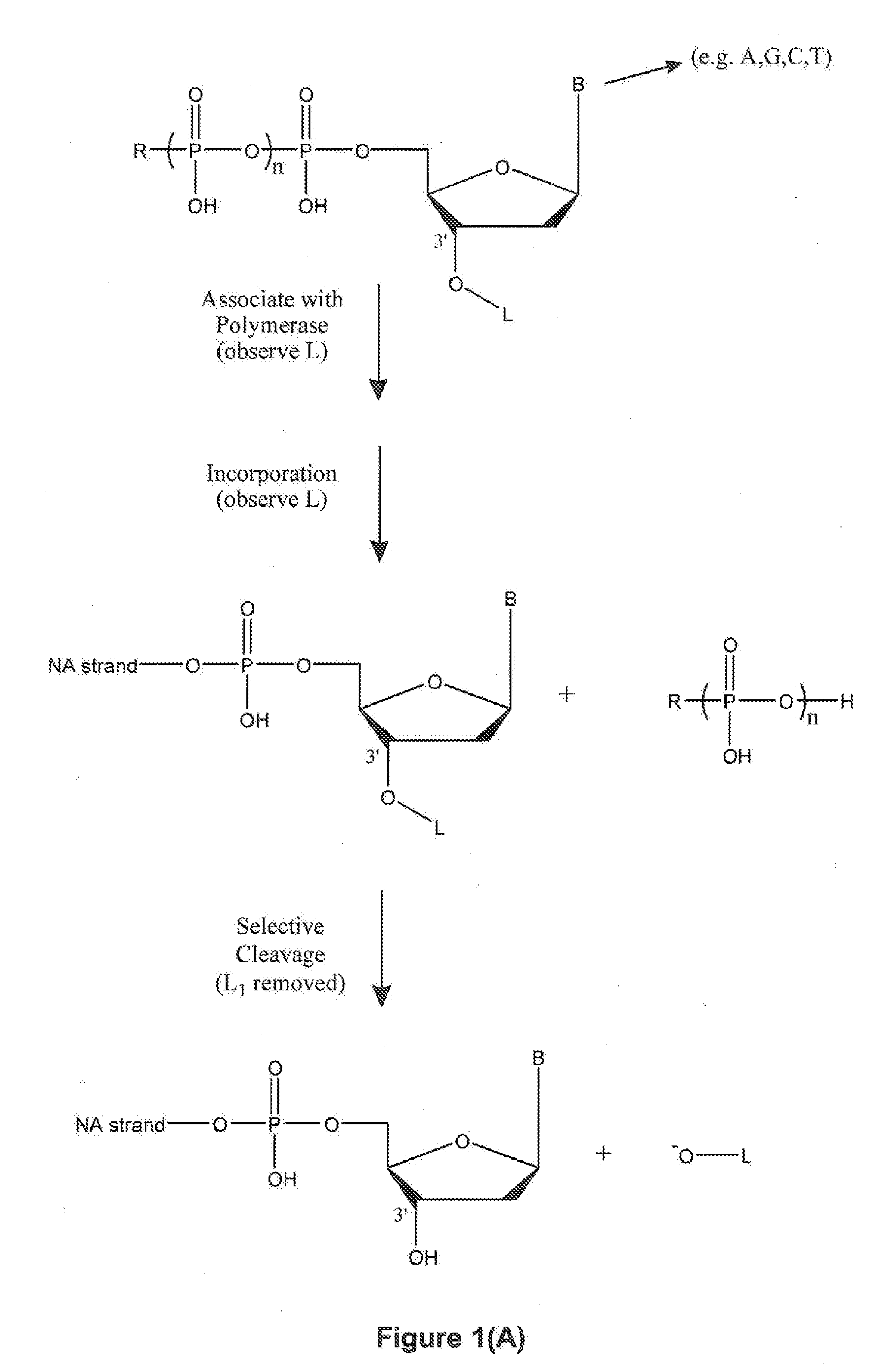
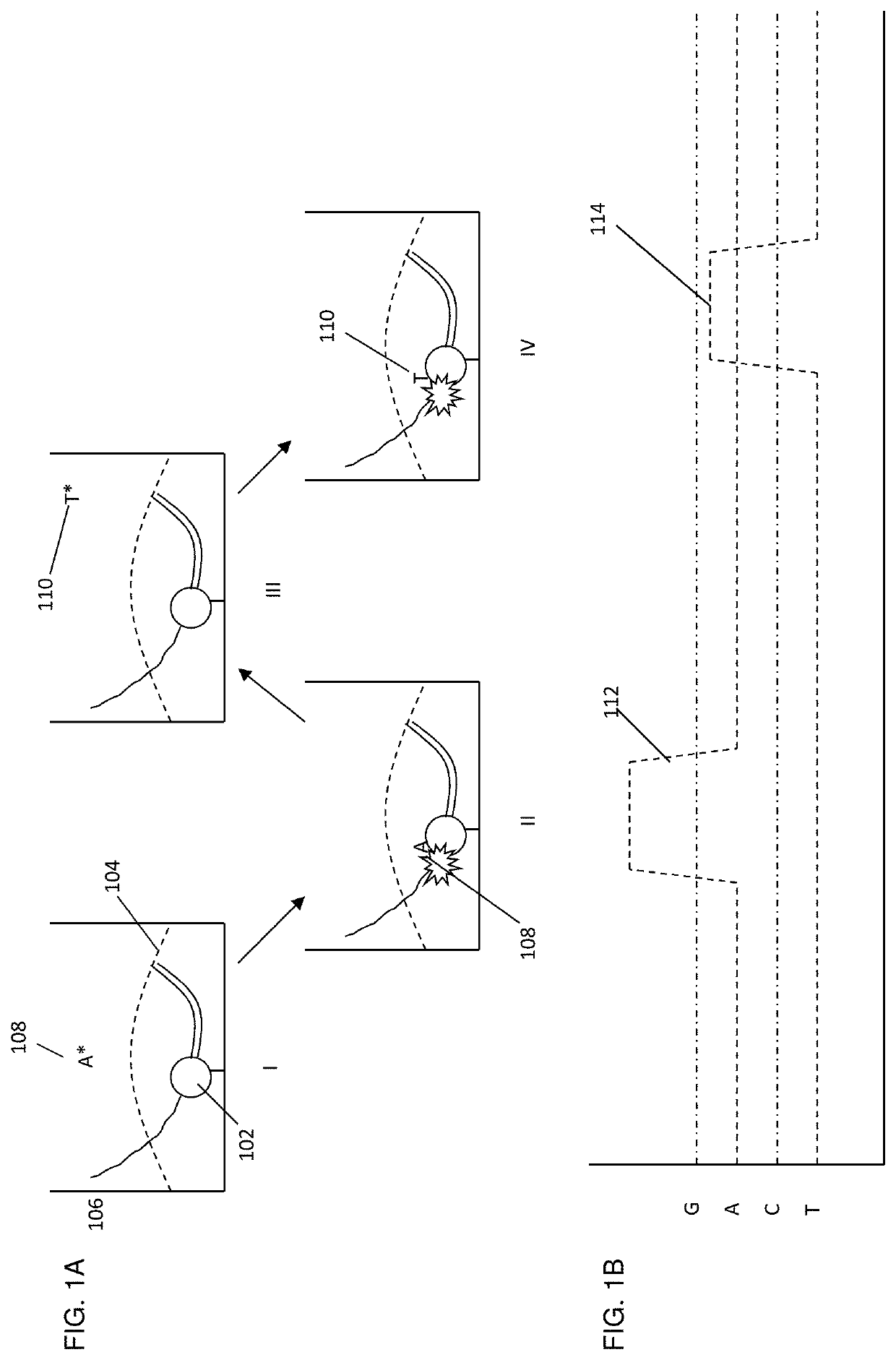
Methods, Compositions, and Systems are provided for nucleic acid sequencing where the sequential incorporation of nucleotides uses two distinct chemical steps. A plurality of nucleotide analogs, each having a labeled leaving group at its 3′ hydroxyl can be sequentially added to a growing strand in the presence of a selective cleaving activity that cleaves the 3′ hydroxyl leaving group preferentially after it has been incorporated. The selective cleaving agent can comprise an exonuclease activity, and the exonuclease activity can be a polymerase-associated exonuclease activity. Nucleotide analogs having labels on both a cleavable polyphosphate portion and on a 3′ hydroxyl leaving group can provide signals characteristic of nucleotide analog incorporation. Systems having illumination optics, collection optics, and substrates observe signals from the labels as they are being incorporated into a growing nucleic acid strand, allowing for the sequencing of template nucleic acids.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Modified t7-related RNA polymerases and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20130224793A1Lower Level RequirementsLower energy barrierBacteriaSugar derivativesGeneticsPHA polymerase
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Modified nucleotide reagents
ActiveUS10676788B2Increase ratingsMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesChemical compoundPHA polymerase
Labeled nucleotide analogs comprising at least one avidin protein, at least one dye-labeled compound, and at least one nucleotide compound are provided. The analogs are useful in various fluorescence-based analytical methods, including the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, such as single molecule real time nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The analogs are detectable with high sensitivity at desirable wavelengths. They contain structural components that modulate the interactions of the analogs with DNA polymerase, thus decreasing photodamage and improving the kinetic and other properties of the analogs in sequencing reactions. Also provided are nucleotide and dye-labeled compounds of the subject analogs, as well as intermediates useful in the preparation of the compounds and analogs. Compositions comprising the compounds, methods of synthesis of the intermediates, compounds, and analogs, and mutant DNA polymerases are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Mutant A type DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, and encoding gene and application of mutant A type DNA polymerase
ActiveCN107299091AIncorporation efficiency increasedNo loss of amplification efficiencyTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyPolymerase L
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and discloses mutant A type DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, and an encoding gene and an application of the mutant A type DNA polymerase. The mutant A type DNA polymerase is generated by amino acid site mutation of conservational motif of A type DNA polymerase in a dNTP (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate) bond zone. Compared with the A type DNA polymerase not modified or mutated, the mutant A type DNA polymerase has increased dUTP (deoxyuridine triphosphokinase) doping speed; a dUTP doping effect of the mutant A type DNA polymerase is obviously better than control A type DNA polymerase; therefore, the mutant A type DNA polymerase is more applicable to some nucleic acid amplification systems using dUTP to substitute dTTP (deoxy- thymidine triphosphate) and allows the system to avoid nucleic acid amplification product contamination and not to lose amplification efficiency of a target product at the same time; and the mutant A type DNA polymerase meets application requirements of multiple PCR (polymerase chain reaction) fields of food, animal quarantine, human disease screening and the like, a forensic medicine field and a scientific research.
Owner:SUZHOU NUHIGH BIOTECH
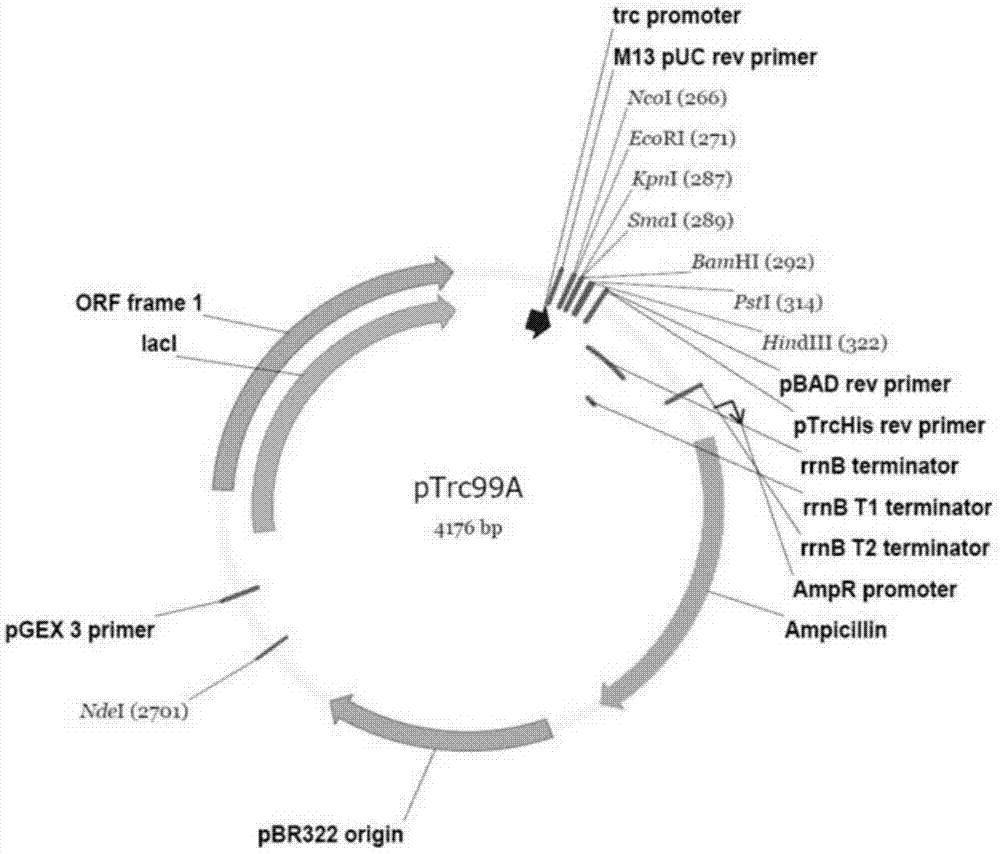
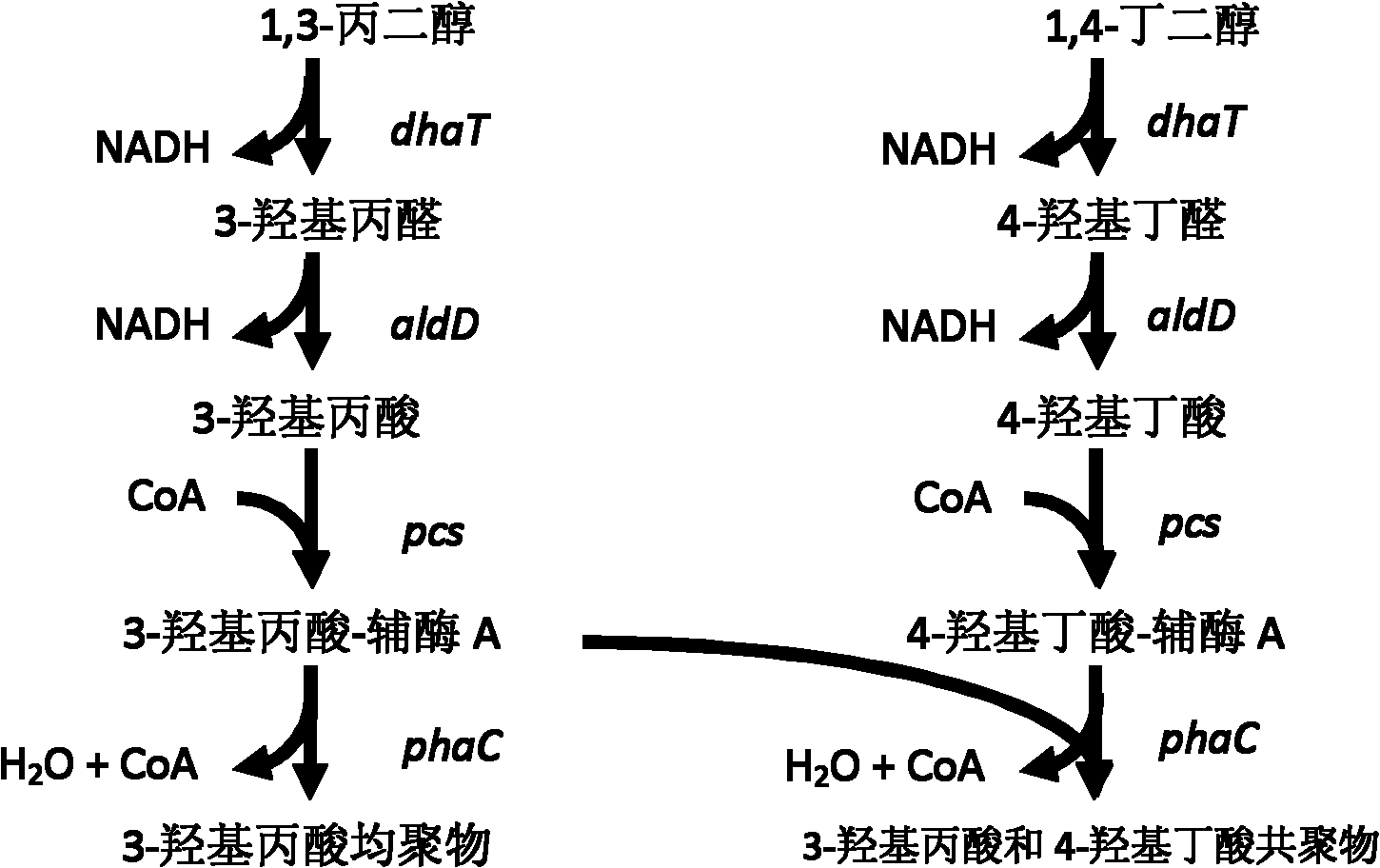
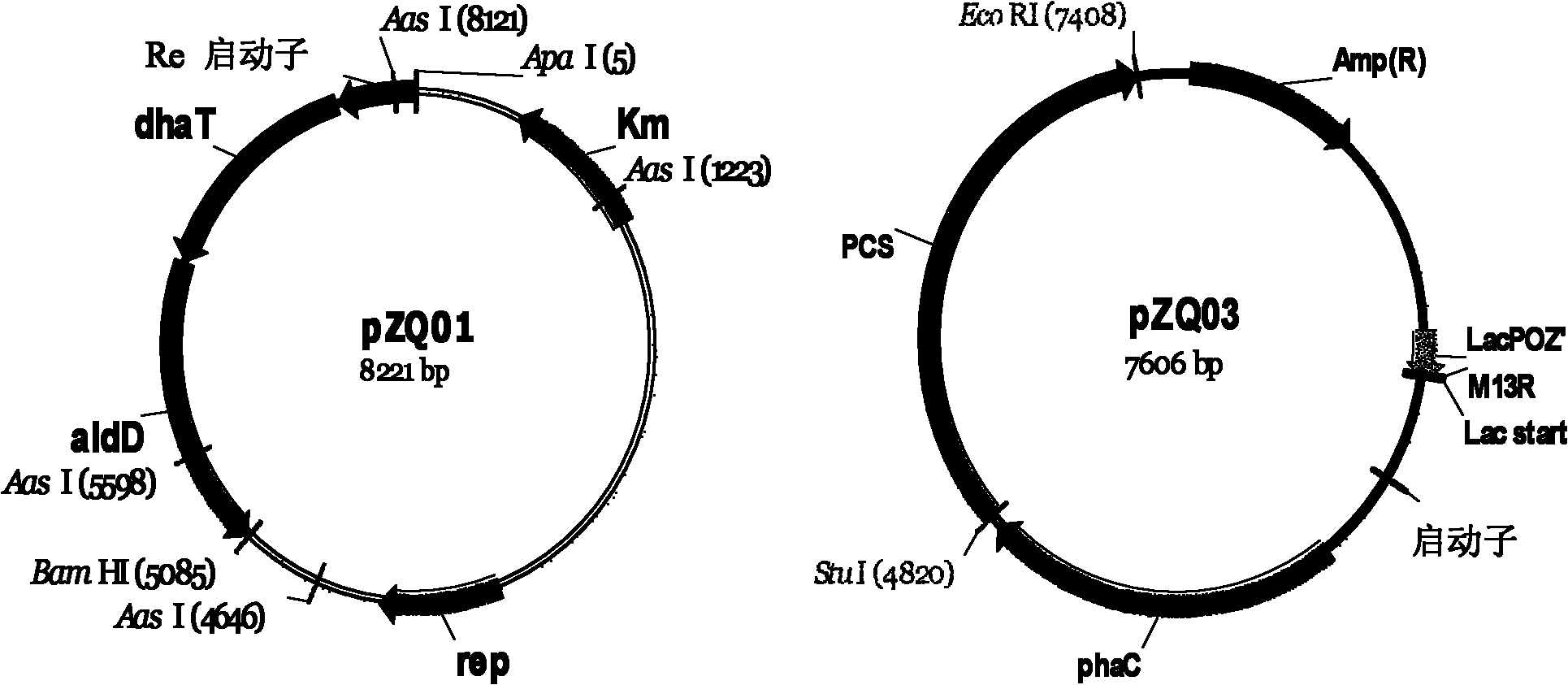
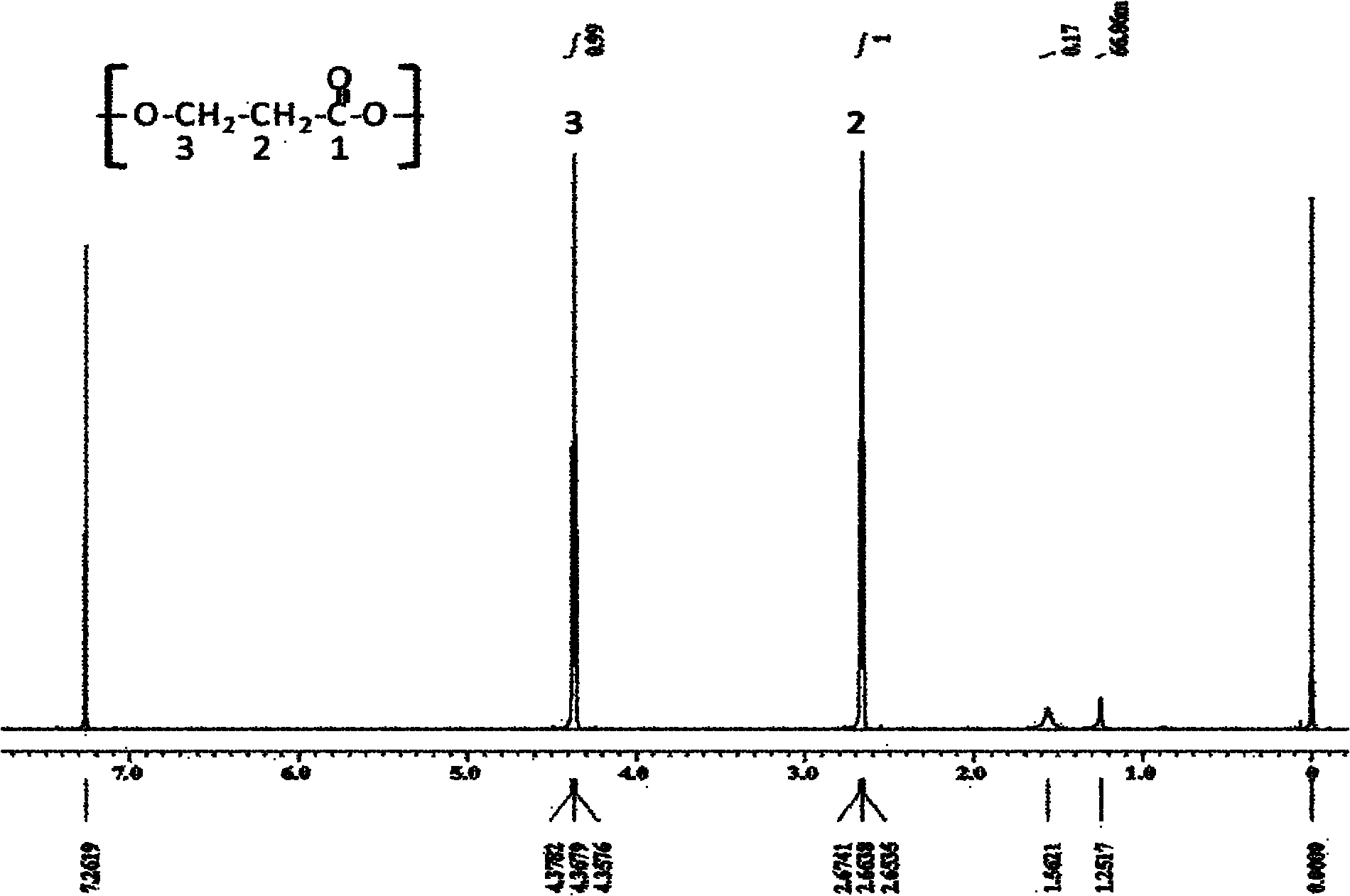
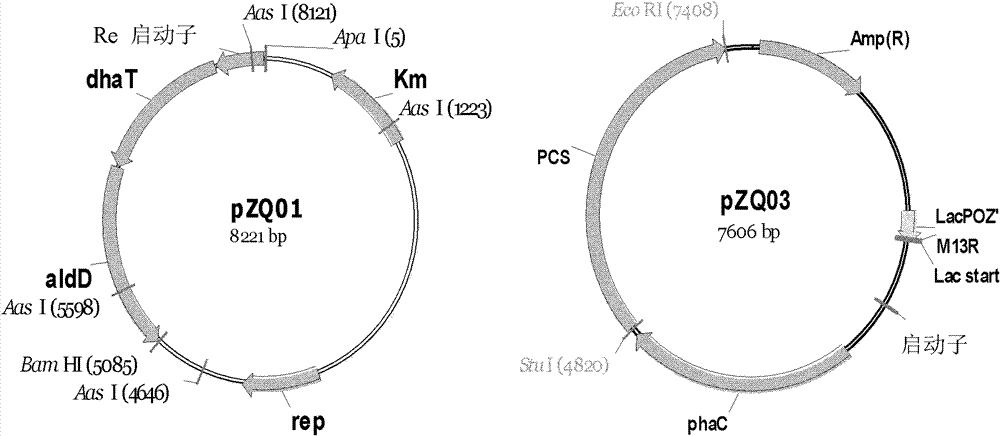
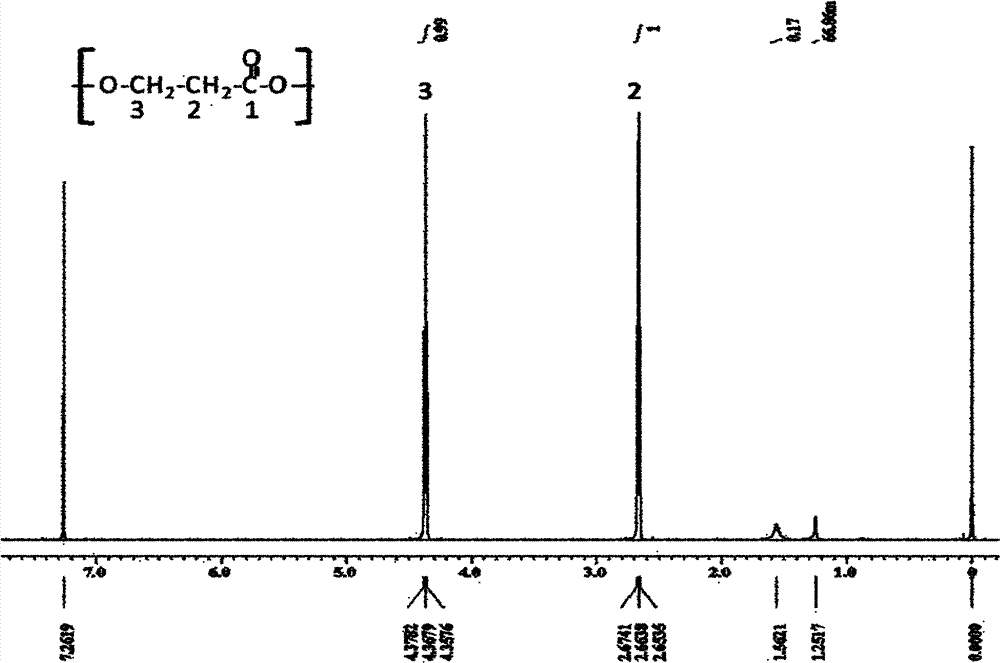
Recombinant strain for producing 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and/or 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and application thereof
ActiveCN102174542AImprove conversion efficiencySimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidPolymerase L
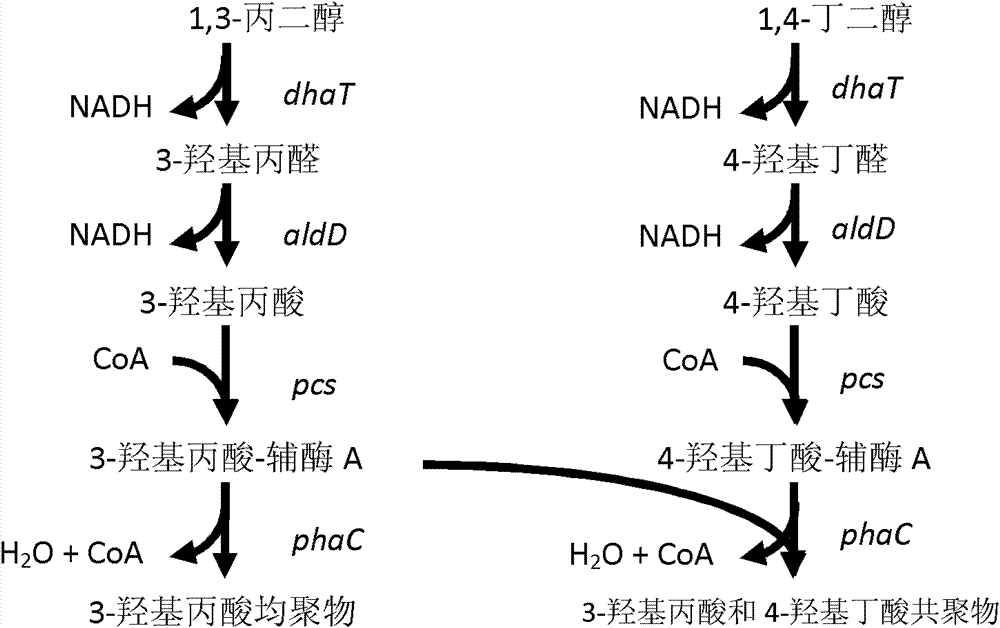
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for producing a 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and / or a 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and an application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant strain comprises the following steps: leading 1,3-Propanediol dehydrogenase coded genes, aldehyde dehydrogenase coded genes, 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) polymerase coded genes into a starting strain to obtain the recombinant strain. The experiments in the invention prove that the engineering bacteria can efficiently express 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA polymerase coded genes and enable the 3-hydracrylic acid to be finally polymerized into 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer (P(3HP)) from the 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A. Minitype fermentation tank experiments show that the engineering bacteria provided by the invention can have a maximum P (3HP) output of 8.9g / L after being fermented in a 6L fermentation tank and the P (3HP) can account for a maximum 91.5% of cell dry weight. In addition, the recombinant strain provided by the invention has the advantages of simple production process, low costs and broad application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
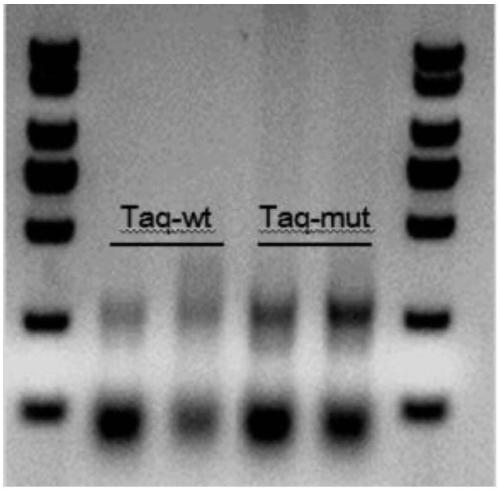
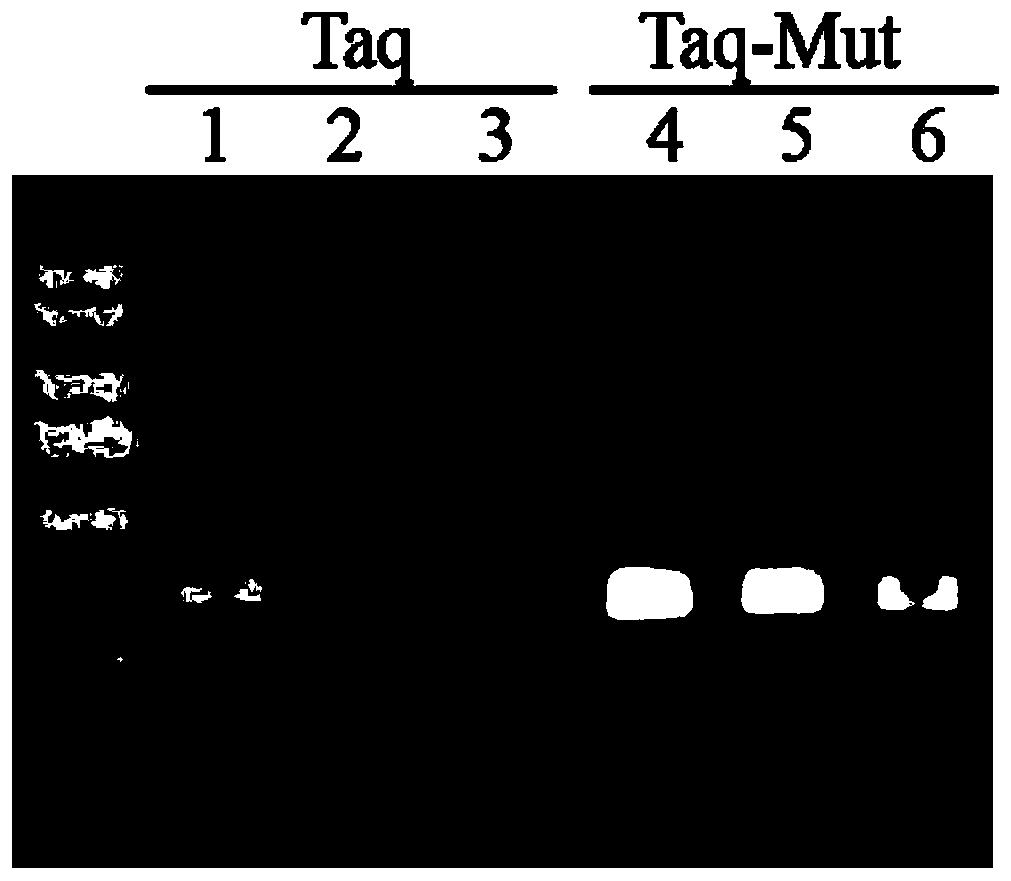
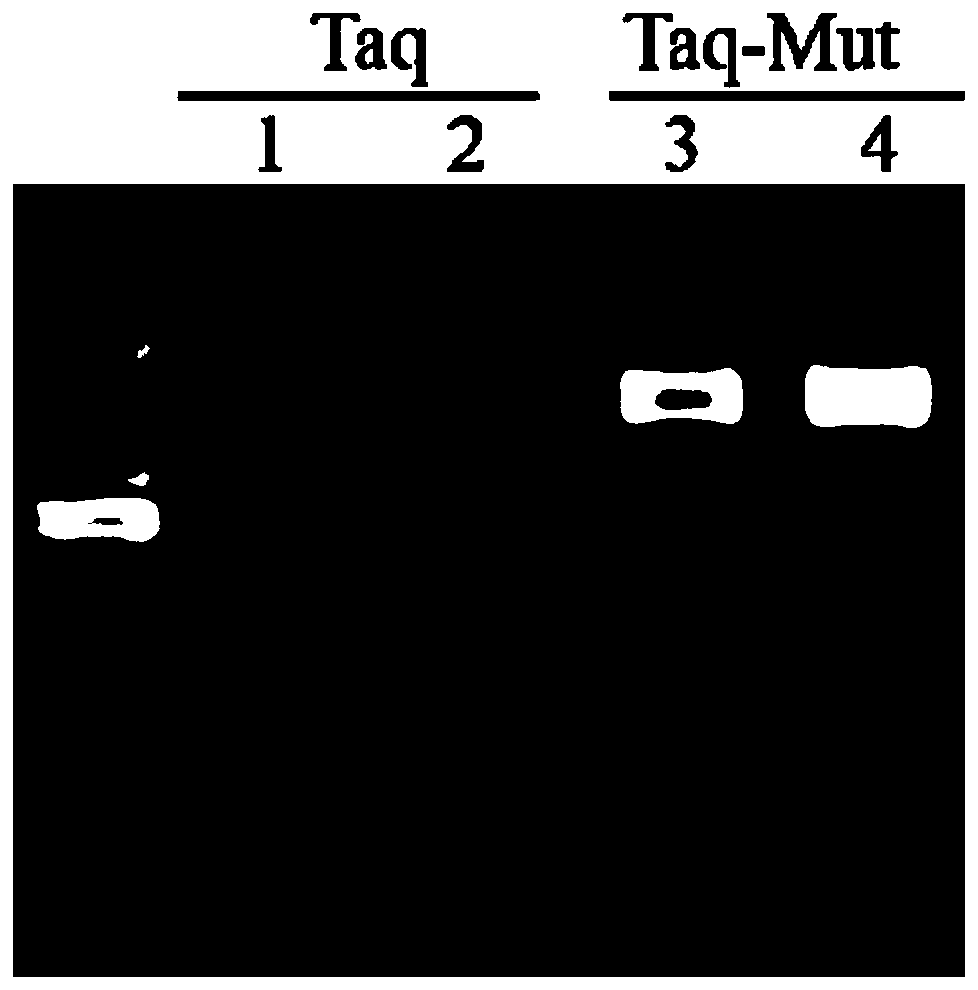
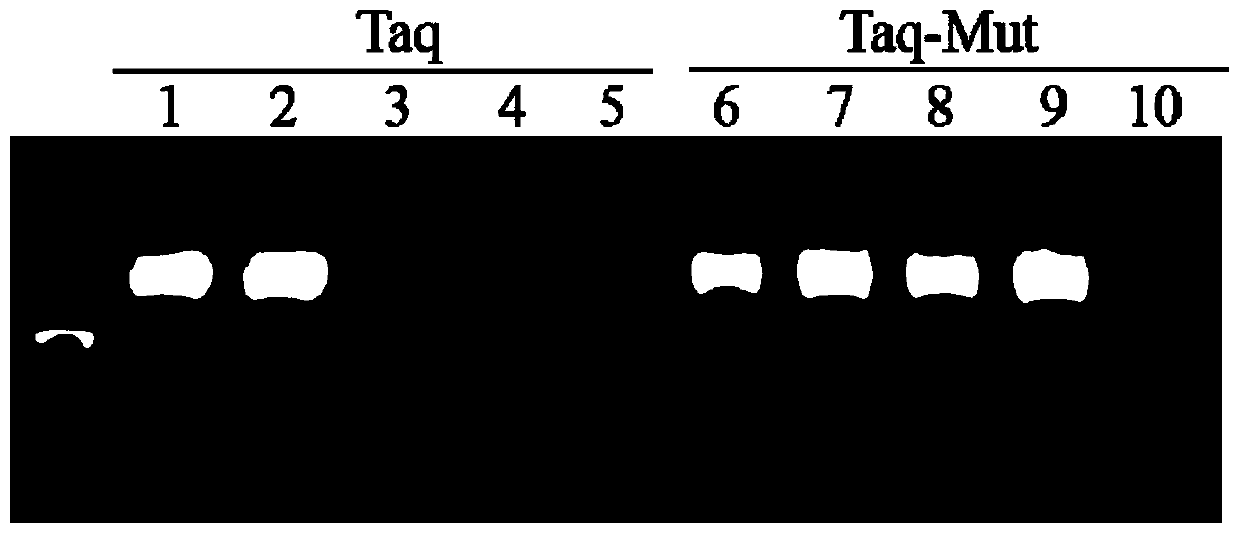
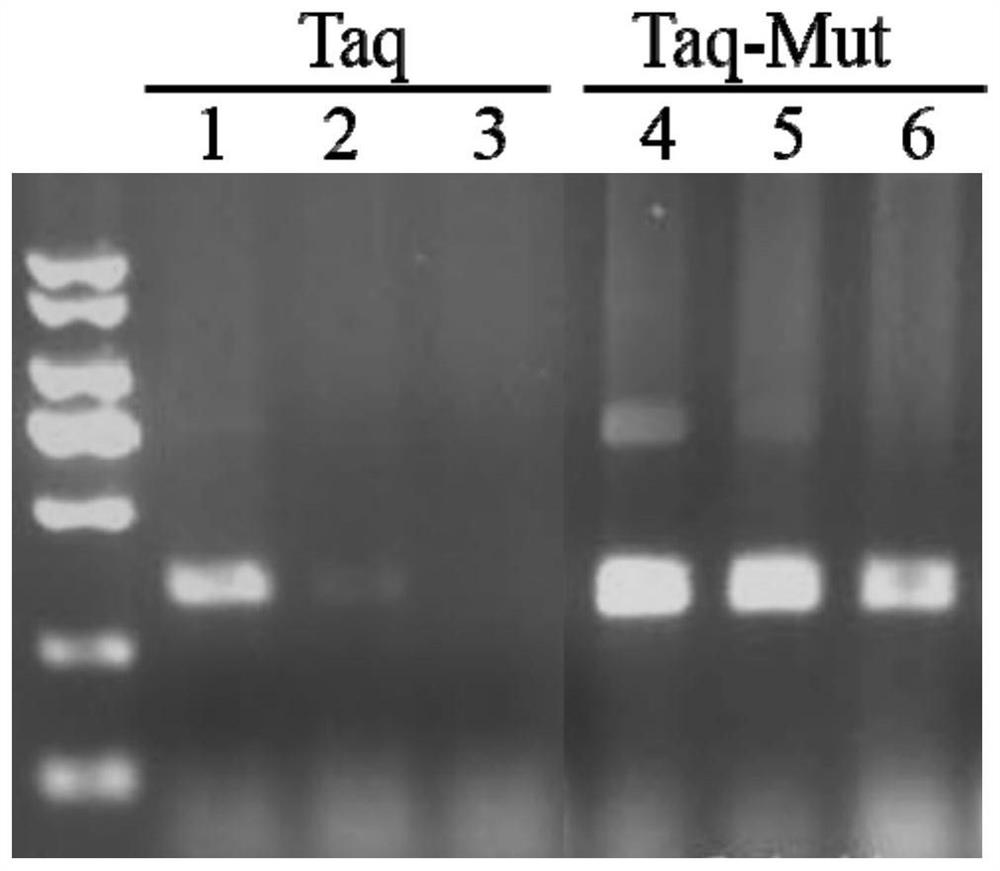
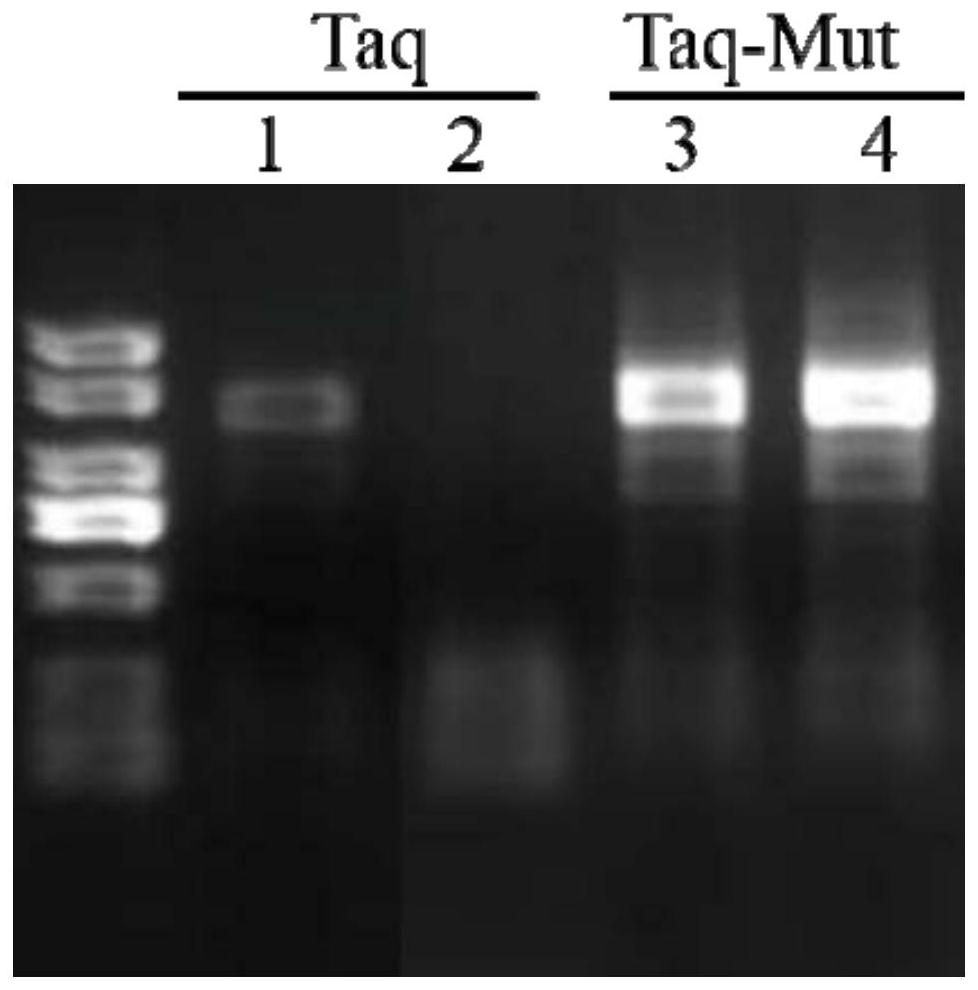
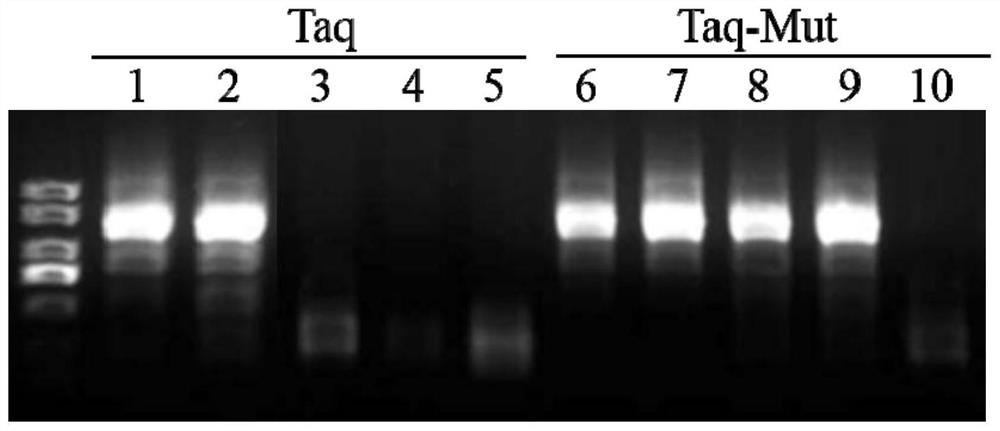
Taq DNA polymerase mutant and application thereof
InactiveCN109402082AIncrease productionHigh sensitivityTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyTaq polymerase
The invention provides a Taq DNA polymerase mutant and application thereof. The Taq DNA polymerase mutant is an amino acid sequence formed by insertion, substitution or depletion of one or more aminoacids in an amino acid sequence of Taq DNA polymerase shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, or by addition or deletion of one or more amino acids in the sequence of SEQ ID NO. 1. Compared with Taq DNA polymerase shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, the amino acid sequence has enhanced amplification sensitivity and increased yield. The Taq DNA polymerase mutant has higher sensitivity and yield than original Taq DNA polymeraseand is also suitable for multiple amplification of low-quality samples.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
Tolerance-improved mutant Taq DNA polymerase as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110684752AImprove toleranceHigh polymerization amplification abilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPHA polymeraseMutant
The invention discloses tolerance-improved mutant Taq DNA polymerase as well as a preparation method and application thereof. According to the tolerance-improved mutant Taq DNA polymerase, one or moreamino acids are inserted, substituted or deleted in an amino acid sequence of Taq DNA polymerase shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and compared with the Taq DNA polymerase shown in SEQ ID NO.1, the amino acid sequence has significantly enhanced impurity tolerance. The recombinant Taq DNA polymerase mutant has remarkably enhanced tolerance to blood, fluorochrome and high ion strength, and can directly performPCR detection on blood samples, save time and avoid false negative.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
Modified nucleotide reagents
InactiveUS20170145502A1Decreased KmIncreases enzymatic rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh densityNucleotide
Labeled nucleotide analogs comprising at least one avidin protein, at least one dye-labeled compound, and at least one nucleotide compound are provided. The analogs are useful in various fluorescence-based analytical methods, including the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, such as single molecule real time nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The analogs are detectable with high sensitivity at desirable wavelengths. They contain structural components that modulate the interactions of the analogs with DNA polymerase, thus decreasing photodamage and improving the kinetic and other properties of the analogs in sequencing reactions. Also provided are nucleotide and dye-labeled compounds of the subject analogs, as well as intermediates useful in the preparation of the compounds and analogs. Compositions comprising the compounds, methods of synthesis of the intermediates, compounds, and analogs, and mutant DNA polymerases are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method for producing short-and-medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) and functional derivatives thereof
ActiveCN111235173AControllable ratioReduce energy consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLong chain fatty acidBinding site
The invention discloses a construction method of a recombinant bacterium for producing short-and-medium-chain-length PHA and functional derivatives thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing a coding gene of specific PHA polymerase, a coding gene of a key protein of a PHA synthesis pathway, a promoter or a mutated promoter, related genes capable of enhancing carbon source utilization capacity of medium-chain and long-chain fatty acids, the ribosome binding site RCJ and the ribosome binding site RD into a starting strain from which an endogenous PHA polymerase gene is knocked out; and adjusting the proportions of all monomers in the short-and-medium-chain-length PHA and the functional derivatives thereof in the recombinant bacteria so as to realize controllable production of the short-and-medium-chain-length PHA and the functional derivatives thereof.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Modified T7-related RNA polymerases and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9045740B2Lower Level RequirementsLower energy barrierBacteriaSugar derivativesGeneticsPHA polymerase
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Method for producing short, medium and long chain polyhydroxyfatty acid copolymers by microorganisms
The invention discloses a method for producing short, medium and long chain polyhydroxyfatty acid copolymer by microorganism. The recombinant bacterium of the invention is obtained by modifying the starting bacterium as follows (a1), (a2) and (a3): (a1) introducing a low-specific PHA polymerase gene; (a) introducing an encoding gene of a key protein of the PHB synthesis pathway; (a3) knocking outthat encoding gene of the key enzyme of the fatty acid de novo synthesis pathway. The invention also protects the recombinant bacteria mentioned above in preparing SCL-Co-MCL PHA. The invention can prepare SCL by adjusting the proportion of carbon source controllable SCL-Co-MCL PHA. Poly (3HB-Co-MCL 3HA) random copolymer or block copolymer can also be produced by controlling the addition time of the carbon source. The invention is applicable to SCL with controllable production ratio SCL-Co-MCL PHA is of great significance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
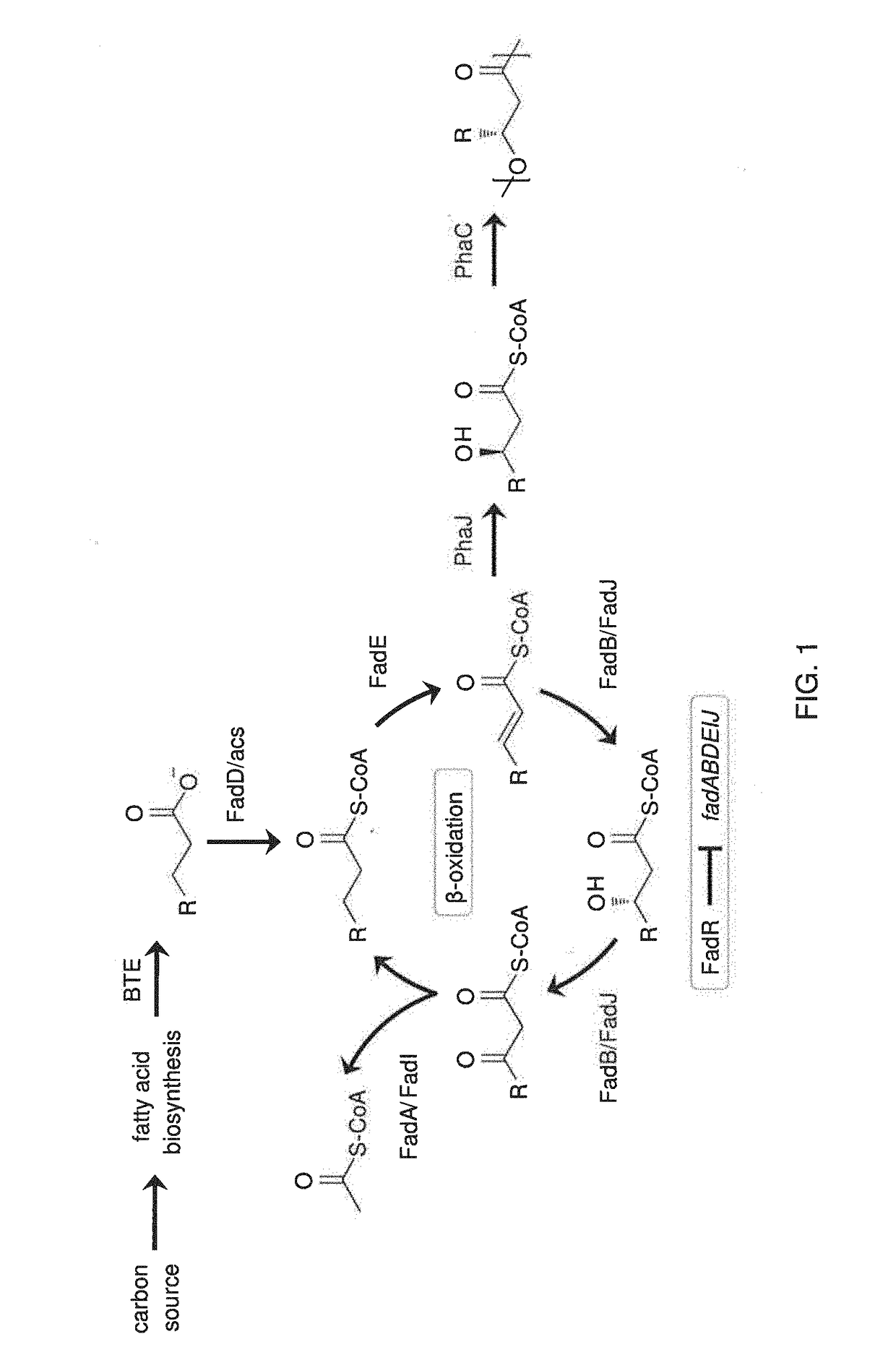
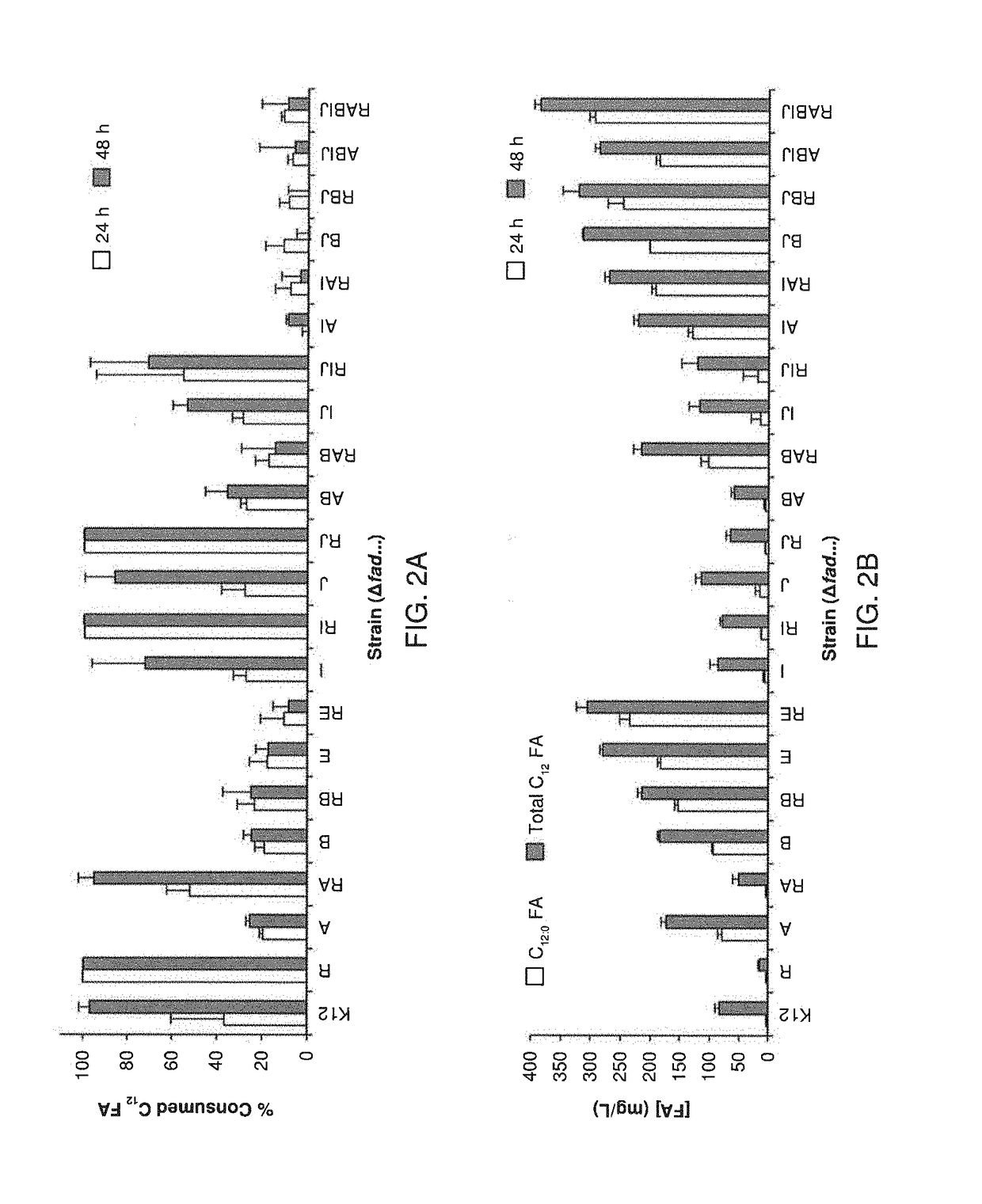
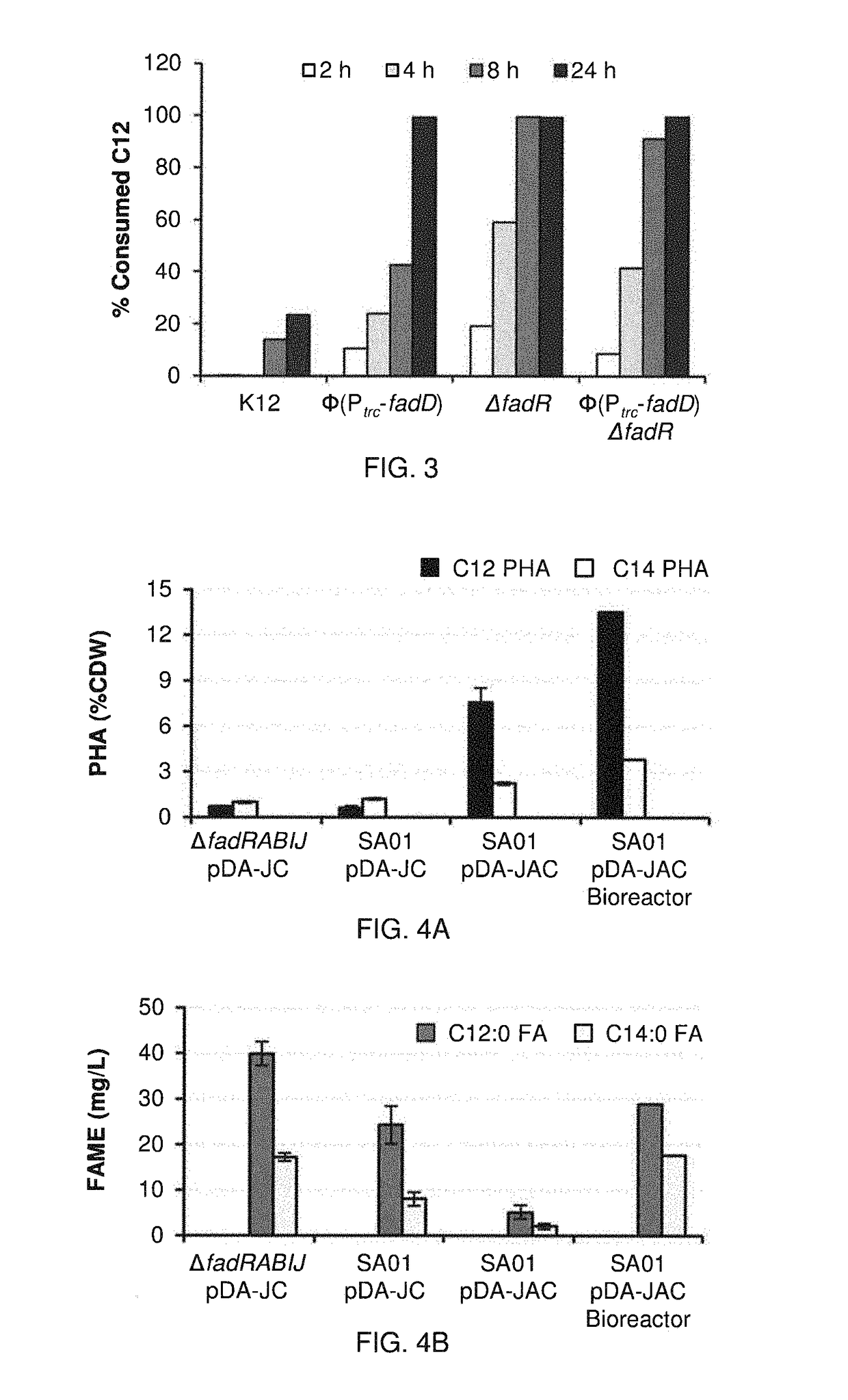
Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates with a defined composition from an unrelated carbon source
Cells and methods for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates. The cells comprise one or more recombinant genes selected from an R-specific enoyl-CoA hydratase gene, a PHA polymerase gene, a thioesterase gene, and an acyl-CoA-synthetase gene. The cells further have one or more genes functionally deleted. The functionally deleted genes include such genes as an enoyl-CoA hydratase gene, a 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, and a 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase gene. The recombinant cells are capable of using producing polyhydroxyalkanoates with a high proportion of monomers having the same carbon length from non-lipid substrates, such as carbohydrates.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Labeled nucleotide analogs, reaction mixtures, and methods and systems for sequencing
ActiveUS10781483B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical compoundPHA polymerase
Labeled nucleotide analogs comprising at least one avidin protein, at least one dye-labeled compound, and at least one nucleotide compound are provided. The analogs are useful in various fluorescence-based analytical methods, including the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, such as single molecule real time nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The analogs are detectable with high sensitivity at desirable wavelengths. They contain structural components that modulate the interactions of the analogs with DNA polymerase, thus decreasing photodamage and improving the kinetic and other properties of the analogs in sequencing reactions. Also provided are nucleotide and dye-labeled compounds of the subject analogs, as well as intermediates useful in the preparation of the compounds and analogs. Compositions comprising the compounds, methods of synthesis of the intermediates, compounds, and analogs, and mutant DNA polymerases are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Modified nucleotide reagents
ActiveUS20200087722A1Increase ratingsMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesChemical compoundPHA polymerase
Labeled nucleotide analogs comprising at least one avidin protein, at least one dye-labeled compound, and at least one nucleotide compound are provided. The analogs are useful in various fluorescence-based analytical methods, including the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, such as single molecule real time nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The analogs are detectable with high sensitivity at desirable wavelengths. They contain structural components that modulate the interactions of the analogs with DNA polymerase, thus decreasing photodamage and improving the kinetic and other properties of the analogs in sequencing reactions. Also provided are nucleotide and dye-labeled compounds of the subject analogs, as well as intermediates useful in the preparation of the compounds and analogs. Compositions comprising the compounds, methods of synthesis of the intermediates, compounds, and analogs, and mutant DNA polymerases are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Recombinant strain for producing 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and/or 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and application thereof
ActiveCN102174542BImprove conversion efficiencySimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCoenzyme A biosynthesisCoenzyme A Ligases
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for producing a 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer and / or a 3-hydracrylic acid copolymer and an application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant strain comprises the following steps: leading 1,3-Propanediol dehydrogenase coded genes, aldehyde dehydrogenase coded genes, 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) polymerase coded genes into a starting strain to obtain the recombinant strain. The experiments in the invention prove that the engineering bacteria can efficiently express 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A ligase coded genes and PHA polymerase coded genes and enable the 3-hydracrylic acid to be finally polymerized into 3-hydracrylic acid homopolymer (P(3HP)) from the 3-hydracrylic acid coenzyme A. Minitype fermentation tank experiments show that the engineering bacteria provided by the invention can have a maximum P (3HP) output of 8.9g / L after being fermented in a 6L fermentation tank and the P (3HP) can account for a maximum 91.5% of cell dry weight. In addition, the recombinant strain provided by the invention has the advantages of simple production process, low costs and broad application prospects.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Protected dye-labeled reagents
ActiveUS10669299B2Reduce photodamageIncrease brightnessSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical compoundPHA polymerase
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Modified nucleotide reagents
ActiveCN108603219ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical compoundPHA polymerase
Labeled nucleotide analogs comprising at least one avidin protein, at least one dye-labeled compound, and at least one nucleotide compound are provided. The analogs are useful in various fluorescence-based analytical methods, including the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, such as single molecule real time nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The analogs are detectable with high sensitivity at desirable wavelengths. They contain structural components that modulate the interactions of the analogs with DNA polymerase, thus decreasing photodamage and improving the kinetic and other properties of the analogs in sequencing reactions. Also provided are nucleotide and dye-labeled compounds of the subject analogs, as well as intermediates useful inthe preparation of the compounds and analogs. Compositions comprising the compounds, methods of synthesis of the intermediates, compounds, and analogs, and mutant DNA polymerases are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates with a defined composition from an unrelated carbon source
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
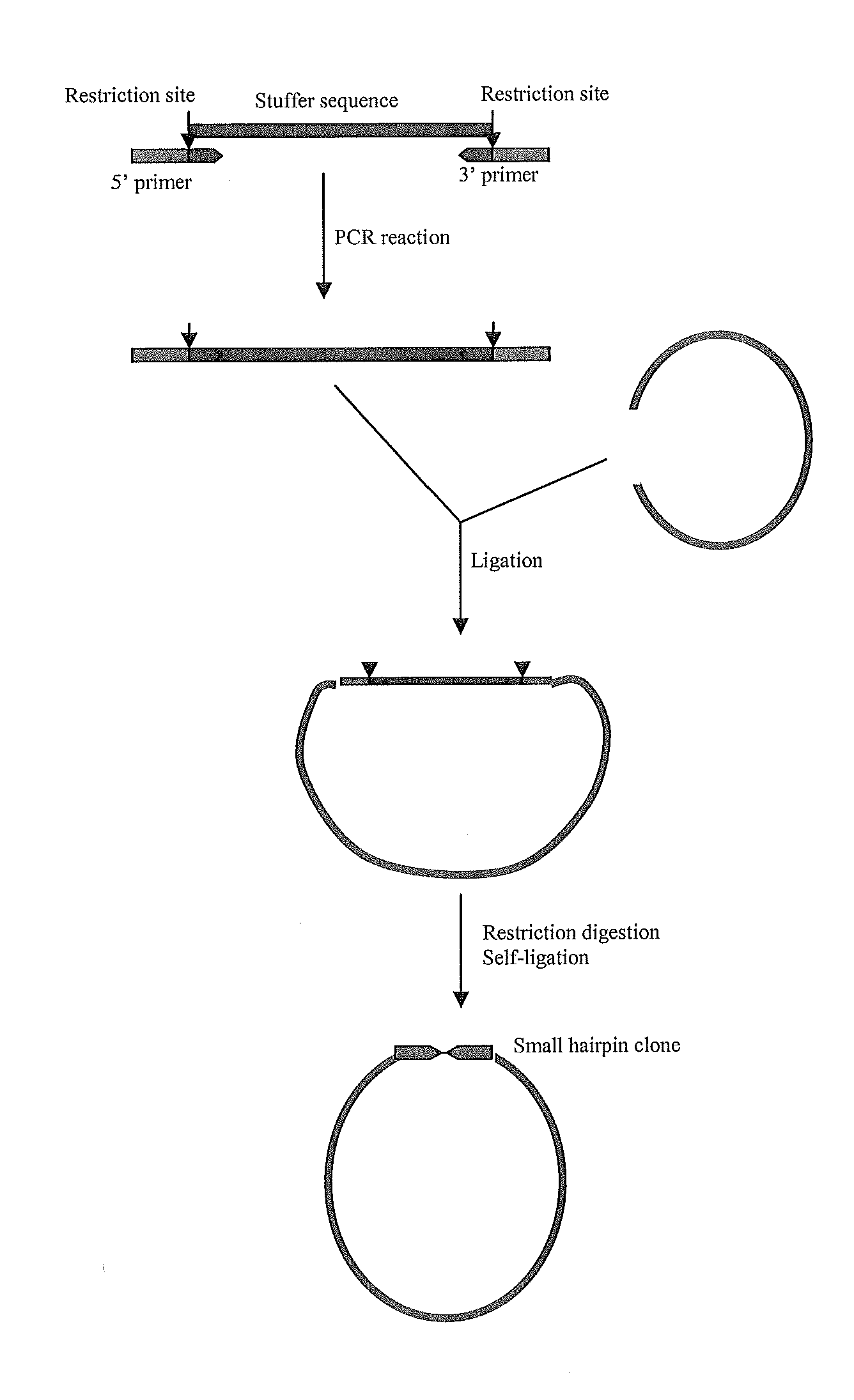
EFFICIENT GENE SILENCING IN PLANTS USING SHORT dsRNA SEQUENCES
InactiveUS20110231955A1Efficient expressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCis actingGene silencing
Methods and means are provided to increase the efficiency of gene silencing when using dsRNA sequences which have a stem length shorter than about 200 base pairs by providing chimeric genes encoding such dsRNA sequences with a promoter recognized by DNA dependent RNA polymerase III comprising all cis-acting promoter elements which interact with DNA dependent RNA polymerase III.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
A method for microbial production of short, medium and long chain polyhydroxy fatty acid copolymers
The invention discloses a method for microorganisms to produce short, medium and long chain polyhydroxy fatty acid copolymers. The recombinant bacterium of the present invention is obtained by carrying out the following (a1), (a2) and (a3) transformations on the starting bacterium: (a1) importing the low-specificity PHA polymerase gene; (a2) importing the key protein of the PHB synthesis pathway Coding gene; (a3) Knocking out the coding gene of the key enzyme of fatty acid de novo synthesis pathway. The present invention also protects the application of any one of the above recombinant bacteria in the preparation of SCL-co-MCL PHA. The present invention can controllably prepare SCL-co-MCL PHA by adjusting the ratio of carbon source, and can also produce Poly(3HB-co-MCL 3HA) random copolymer or block copolymer by controlling the addition time of carbon source. The present invention is of great significance for the production of SCL-co-MCL PHA with controllable ratio.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
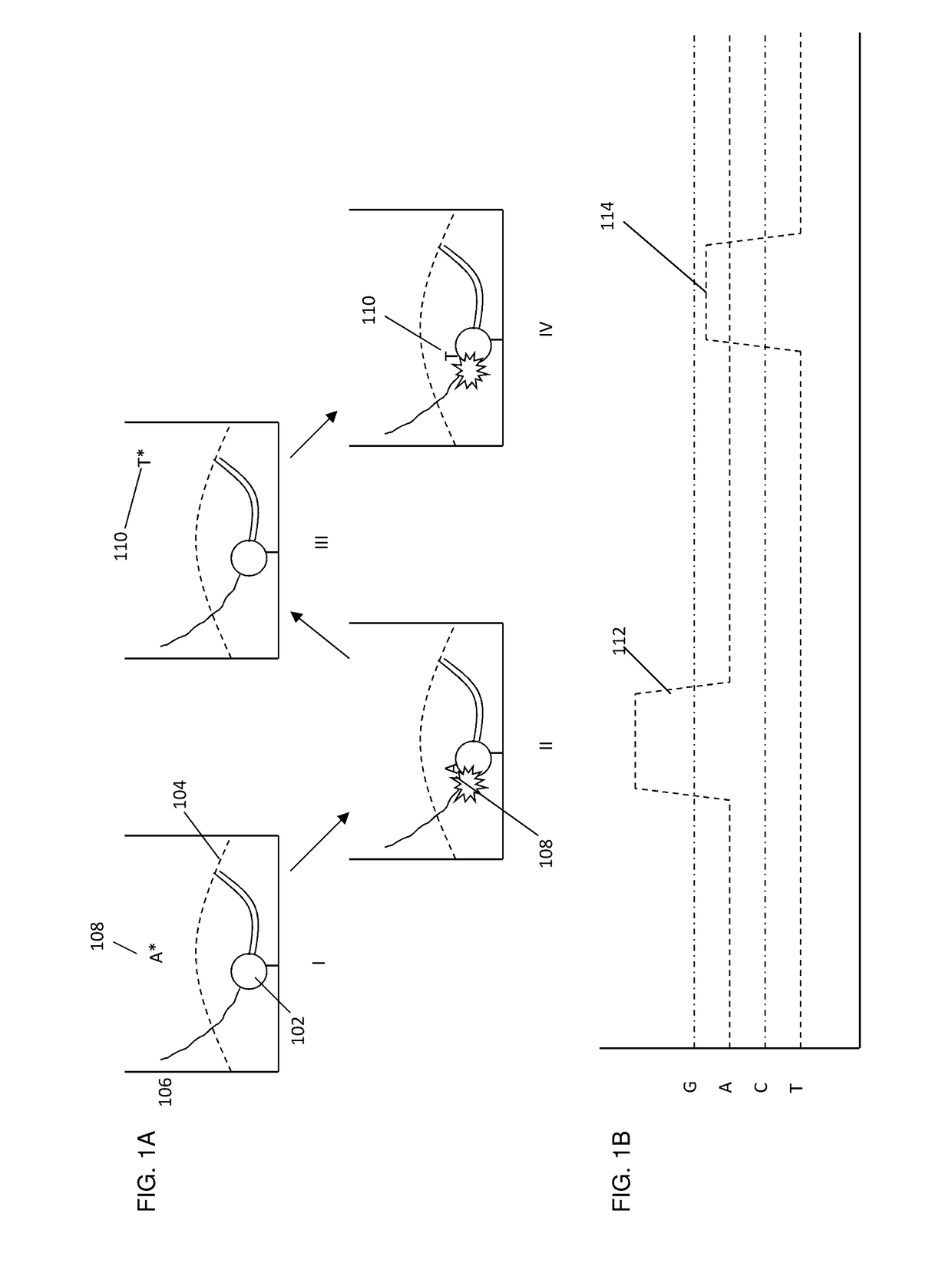
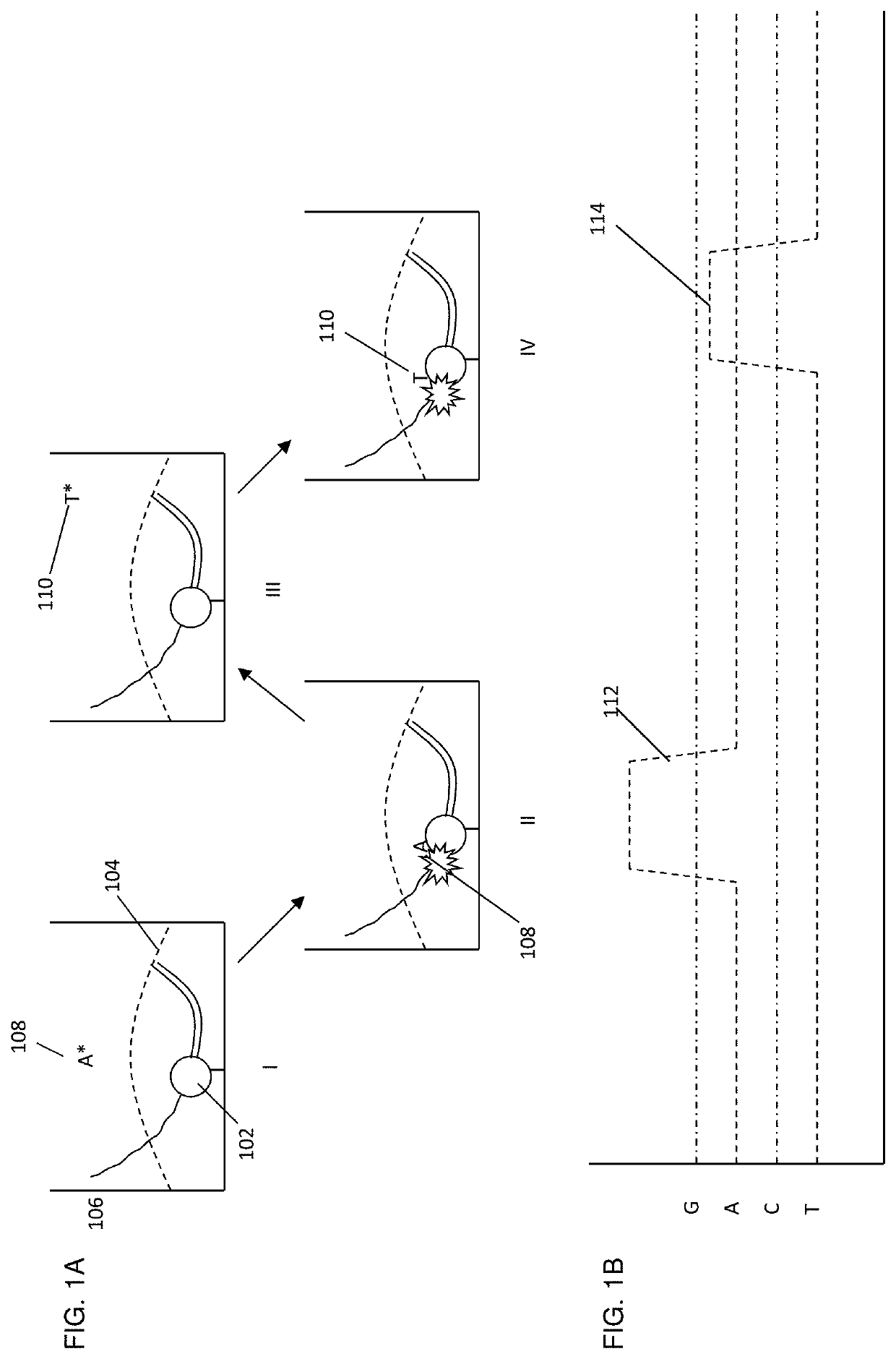
DNA polymerases having modified nucleotide binding site for DNA sequencing
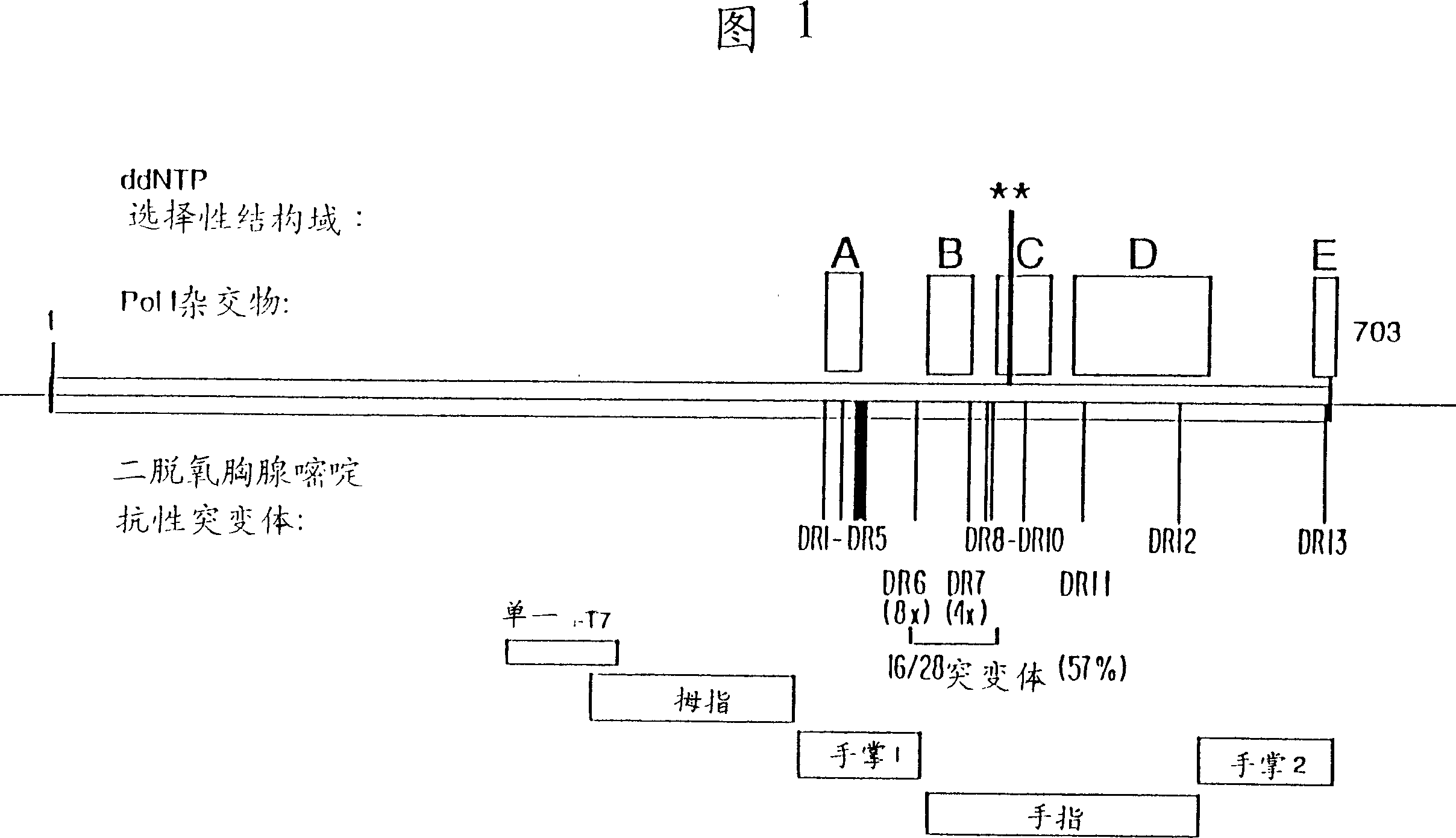
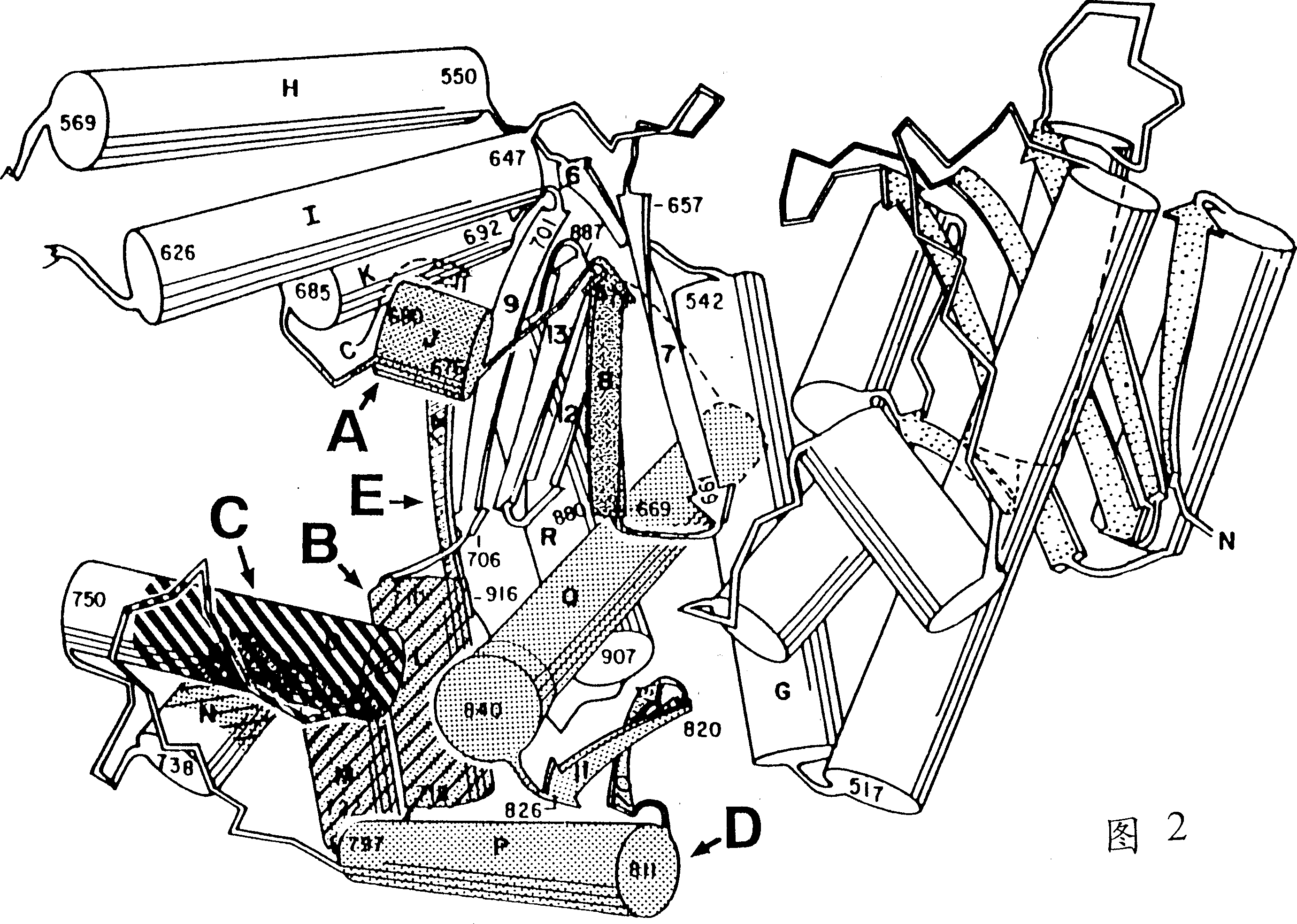
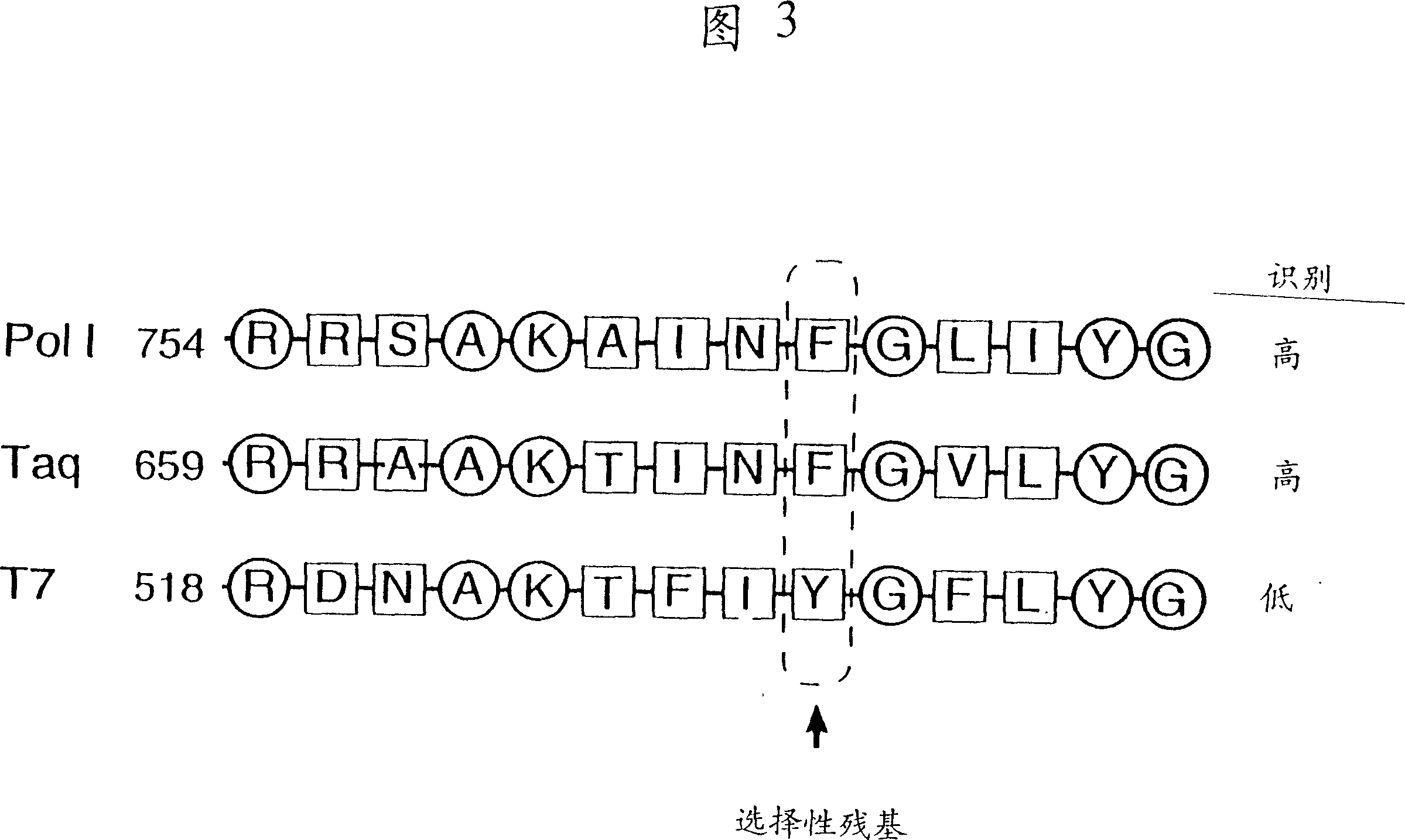
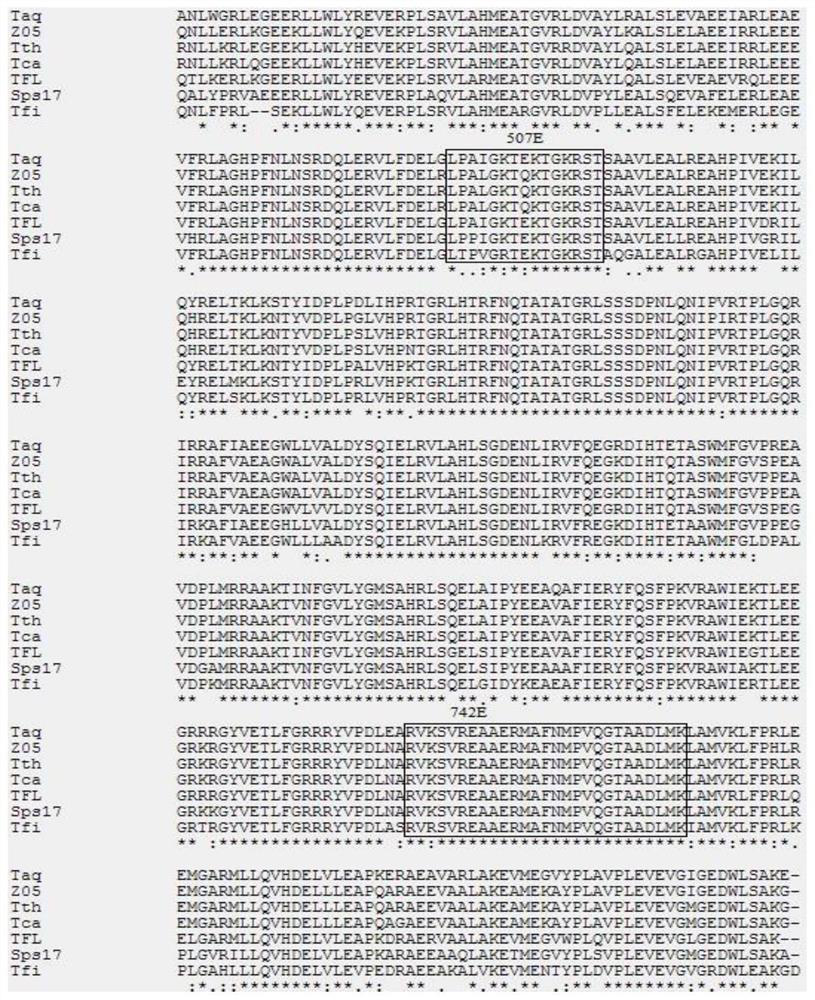
Modified gene encoding a modified DNA polymerase wherein the modified polymerase incorporates dideoxynucleotides at least 20-fold better compared to the corresponding deoxynucleotides as compared with the corresponding naturally-occurring DNA polymerase. <IMAGE>
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
A kind of mutant type a dna polymerase and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN107299091BIncorporation efficiency increasedNo loss of amplification efficiencyTransferasesFermentationMultiplexPHA polymerase
The present invention relates to the field of molecular biology, and discloses a mutant type A DNA polymerase and its coding gene and application. The mutant type A DNA polymerase generates amino acids from a conserved motif in the dNTP binding region of the type A DNA polymerase site mutations. The present invention provides a mutant type A DNA polymerase with enhanced dUTP incorporation speed compared with unmodified mutant type A DNA polymerase, and the dUTP incorporation effect is obviously better than that of the control type A DNA polymerase , so it is more suitable for some nucleic acid amplification systems that use dUTP instead of dTTP, so that the system can prevent the contamination of nucleic acid amplification products without losing the amplification efficiency of the target product, so as to meet the requirements of food, animal quarantine, and human disease screening. Such as multiplex PCR field, forensic field and scientific research application needs.
Owner:SUZHOU NUHIGH BIOTECH
Polymerase compositions and methods of making and using same
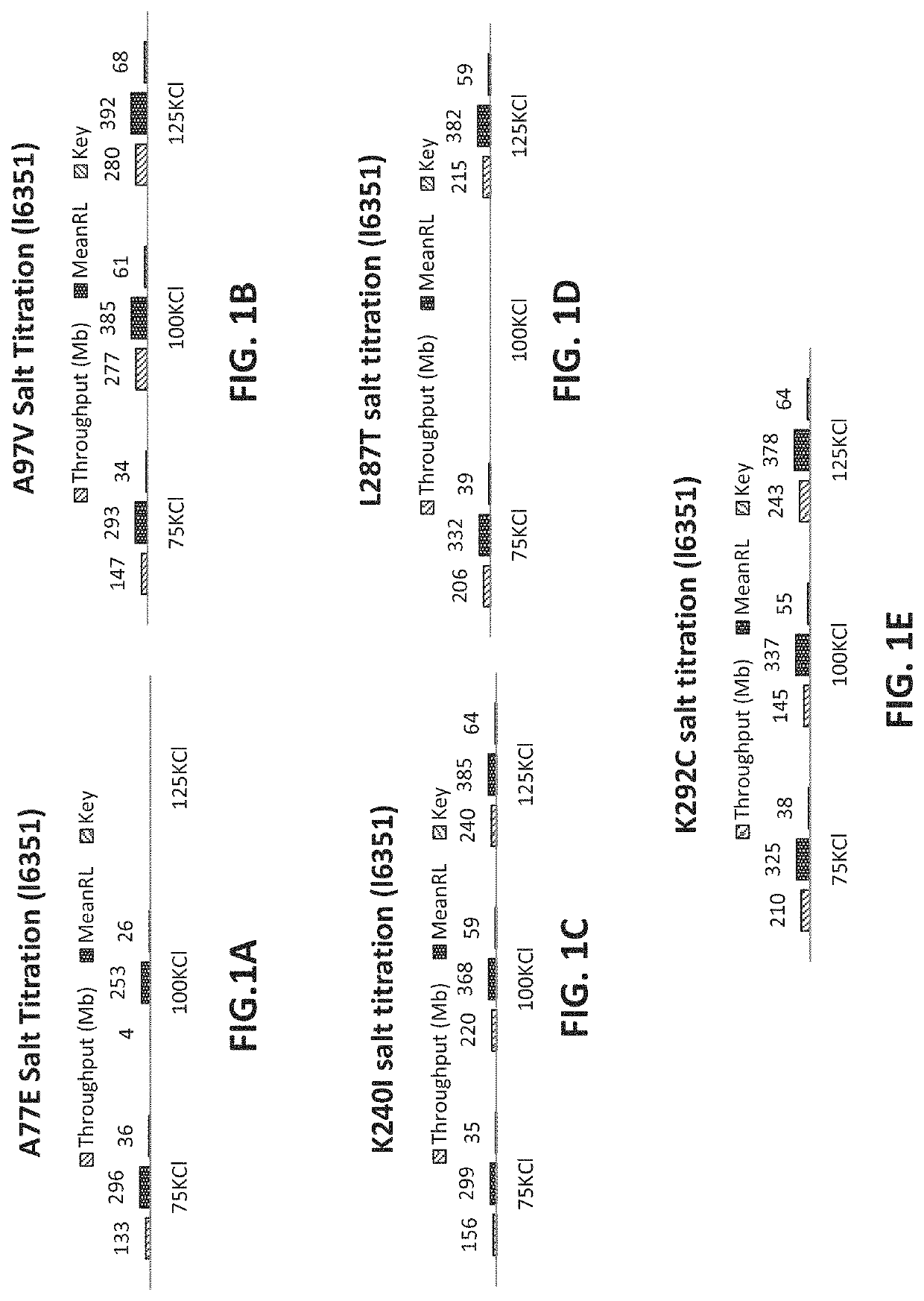
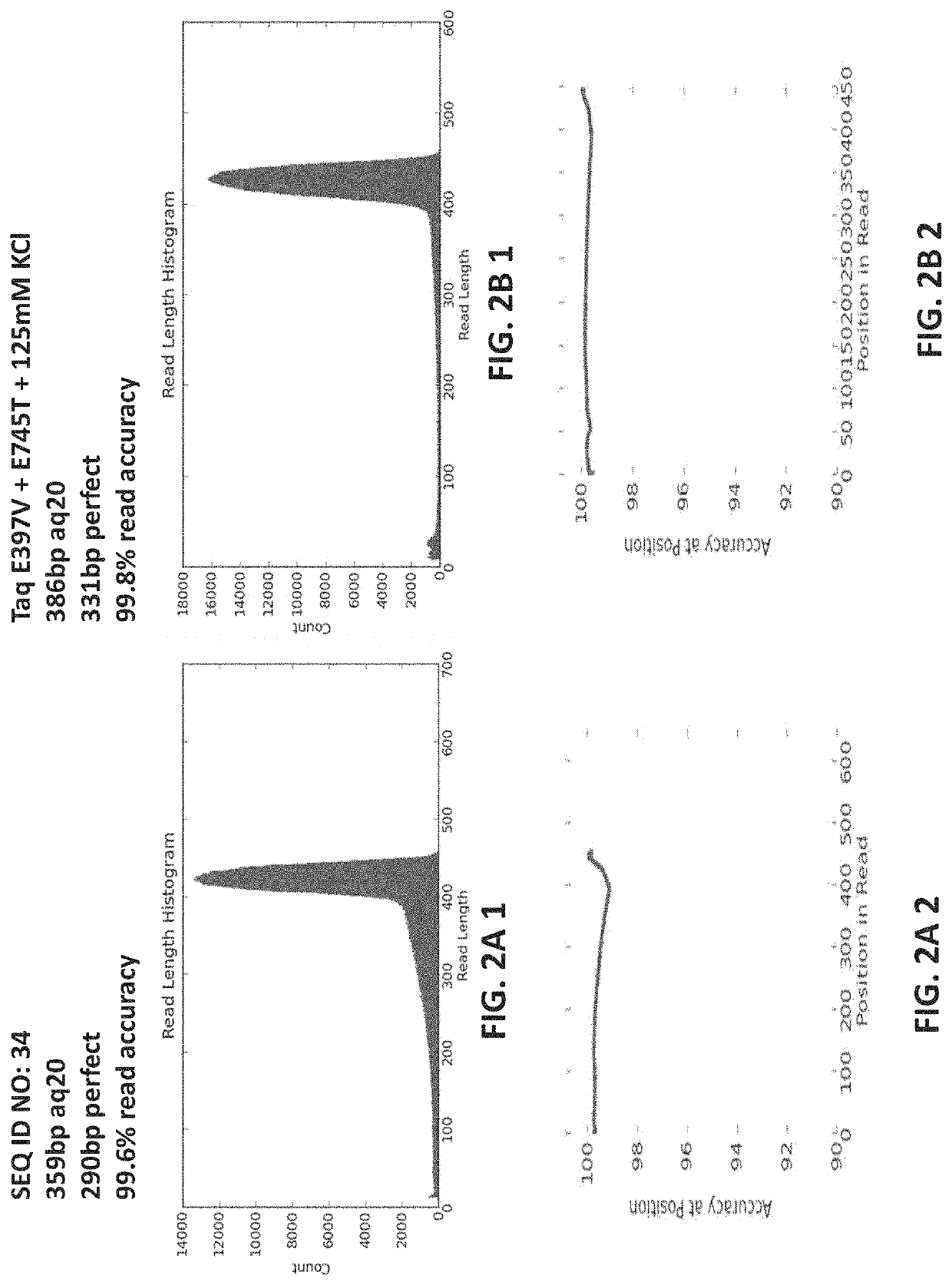
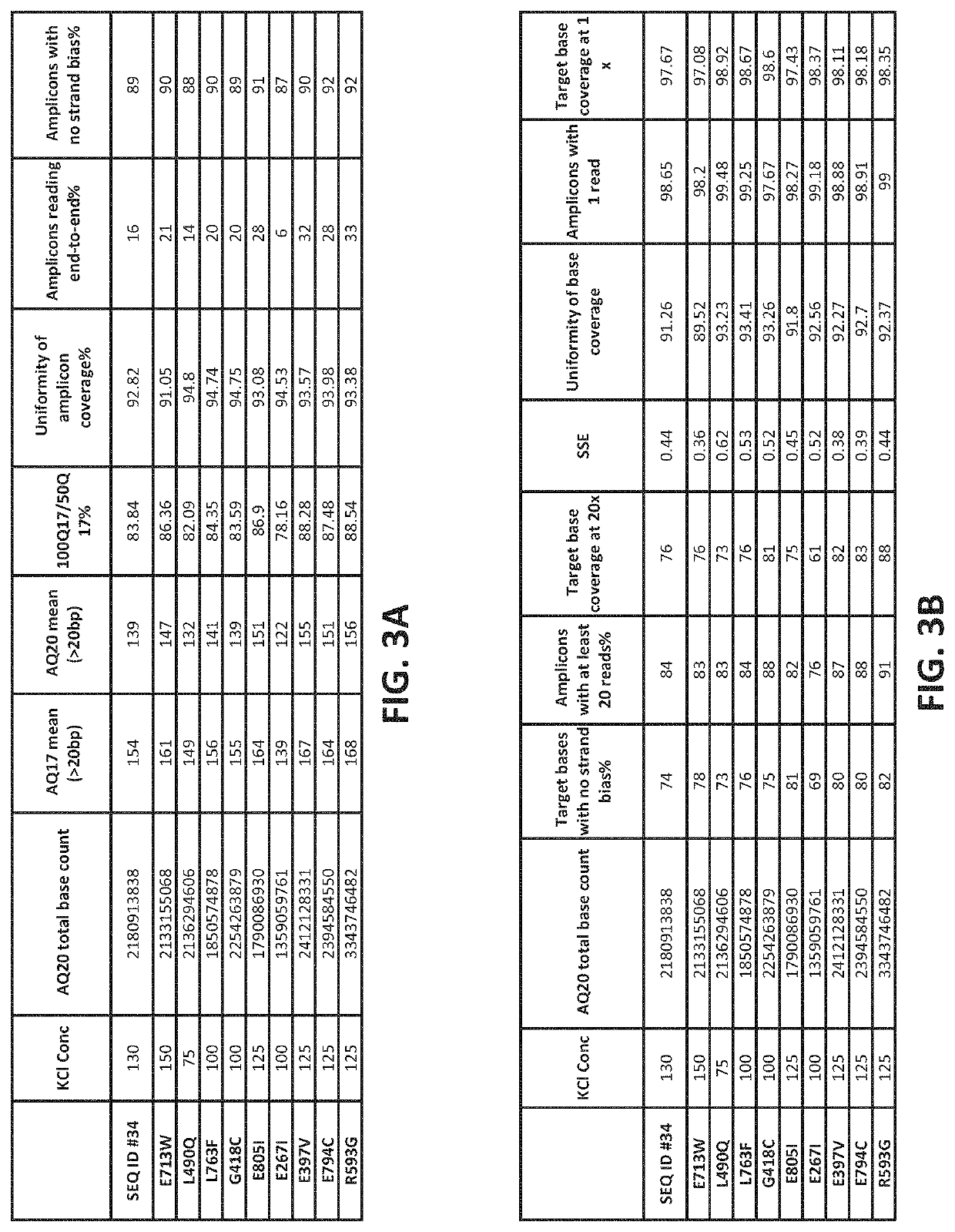
PendingUS20220307071A1Reduced strand biasExpand coverageMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPHA polymeraseTaq polymerase
The present disclosure provides compositions, methods, kits, systems and apparatus that are useful for nucleic acid polymerization. In particular, modified polymerases and biologically active fragments thereof, such as modified Taq polymerases, are provided that allow for improved nucleic acid amplification. In some aspects, the disclosure provides modified polymerases having improved thermostability, accuracy, processivity and / or read length as compared to a referenceTaq polymerase. In some aspects, the disclosure relates to modified polymerases or biologically active fragments thereof, useful for amplification methods, and in practically illustrative embodiments, emulsion PCR.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Single subunit RNA polymerase, its purification method and its application in RNA synthesis
ActiveCN108018271BImprove transcription efficiencyTransferasesFermentationT7 RNA polymeraseTotal amino acids
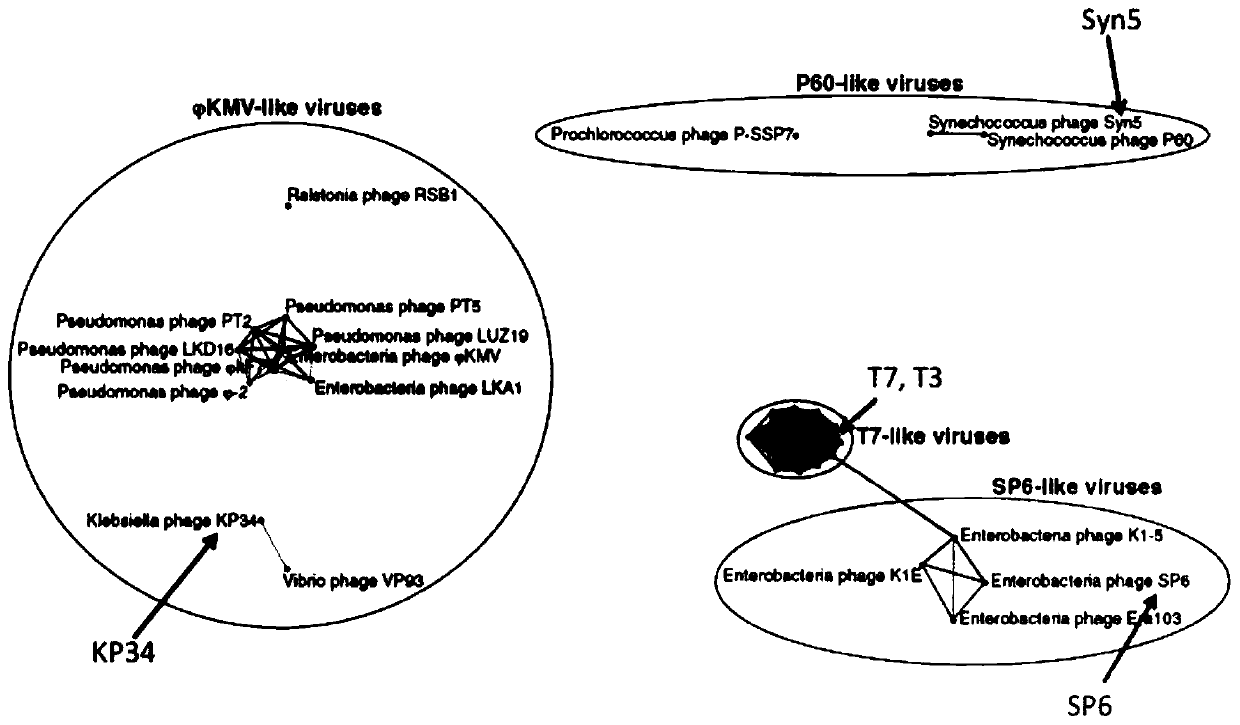
The invention discloses a single-subunit RNA polymerase and its purification method and application in RNA synthesis. The single-subunit RNA polymerase is a single-subunit RNA polymerase derived froma phi KMV phage or an other phage single-subunit RNA polymerase with a protein sequence which is 25% or more homologous to the single-subunit RNA polymerase derived from the phi KMV phage, contains acharacteristic amino acid sequence shown in the formula of SEQ ID NO. 1 in the sequence table and has the total amino acid sequence number of 800 and 830. The research result shows that the RNA polymerase has a long-distance relationship with the existing RNA tool enzyme and high transcription efficiency. Compared with the existing T7 RNA polymerase and Syn5 RNA polymerase, the single-subunit RNApolymerase solves the problem that the synthesis of RNA rich in a stable and high-level structure from the T7 RNA polymerase and Syn5 RNA polymerase produces complex products. The single-subunit RNA polymerase produces same transcription products.
Owner:RNASYN BIOTECH CO LTD
Protected dye-labeled reagents
ActiveUS20200299319A1Reduce photodamageIncrease brightnessSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementChemical compoundPHA polymerase
Labeled nucleotide analogs comprising at least one avidin protein, at least one dye-labeled compound, and at least one nucleotide compound are provided. The analogs are useful in various fluorescence-based analytical methods, including the analysis of highly multiplexed optical reactions in large numbers at high densities, such as single molecule real time nucleic acid sequencing reactions. The analogs are detectable with high sensitivity at desirable wavelengths. They contain structural components that modulate the interactions of the analogs with DNA polymerase, thus decreasing photodamage and improving the kinetic and other properties of the analogs in sequencing reactions. Also provided are nucleotide and dye-labeled compounds of the subject analogs, as well as intermediates useful in the preparation of the compounds and analogs. Compositions comprising the compounds, methods of synthesis of the intermediates, compounds, and analogs, and mutant DNA polymerases are also provided.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
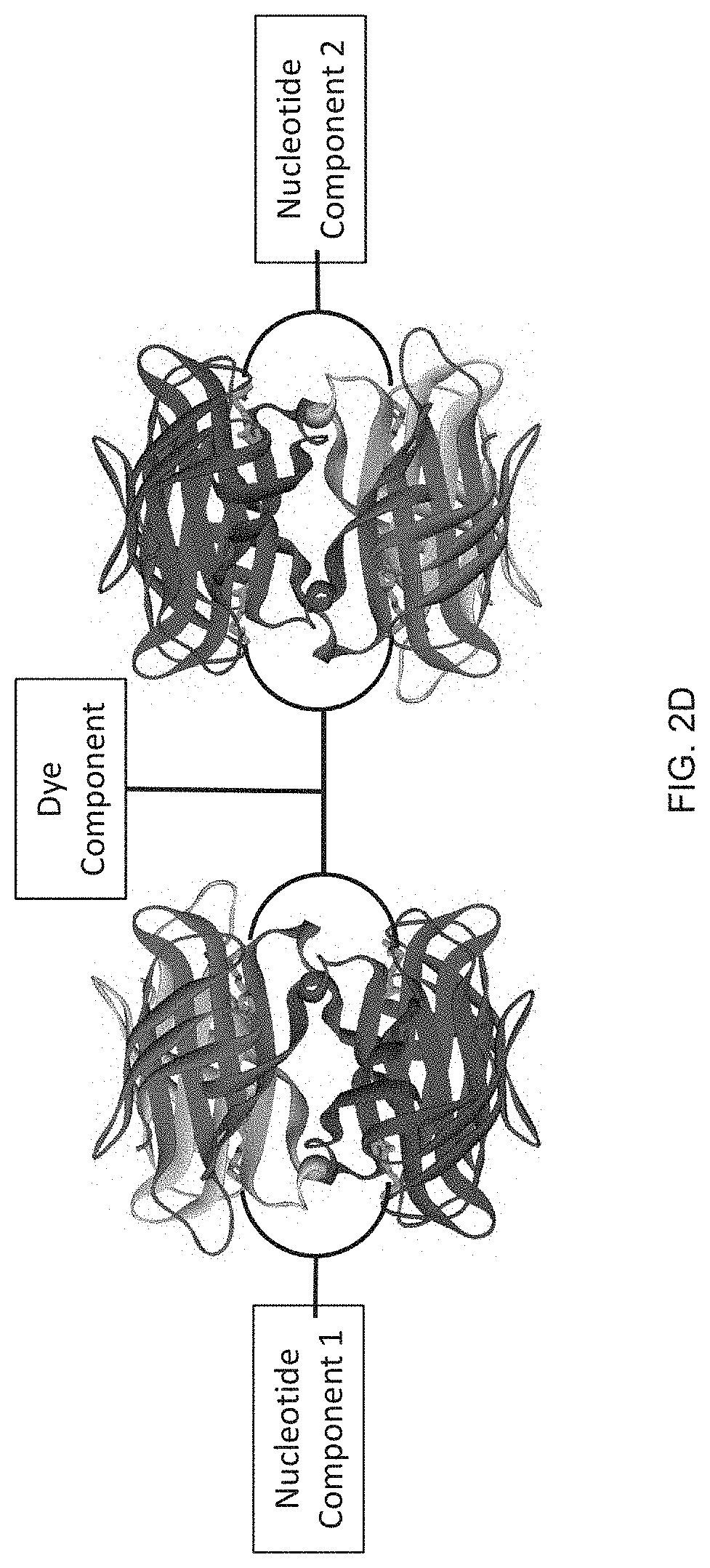
Poly(UG) polymerase, constructs, and methods of making and using the same
Methods, kits, and compositions of matter relating to poly(UG) polymerases are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method includes: contacting an RNA substrate with a poly(UG) polymerase; and allowing the poly(UG) polymerase to add a poly(UG) sequence to the end of the RNA substrate by retaining contact between the RNA substrate and the poly(UG) polymerase for a period of time from about 1 second to about 28 days. The poly(UG) polymerase can be Caenorhabditis elegans RDE-3.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
A mutant taq DNA polymerase with improved tolerance and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN110684752BImprove toleranceHigh polymerization amplification abilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPHA polymeraseMutant
Owner:NANJING VAZYME BIOTECH CO LTD
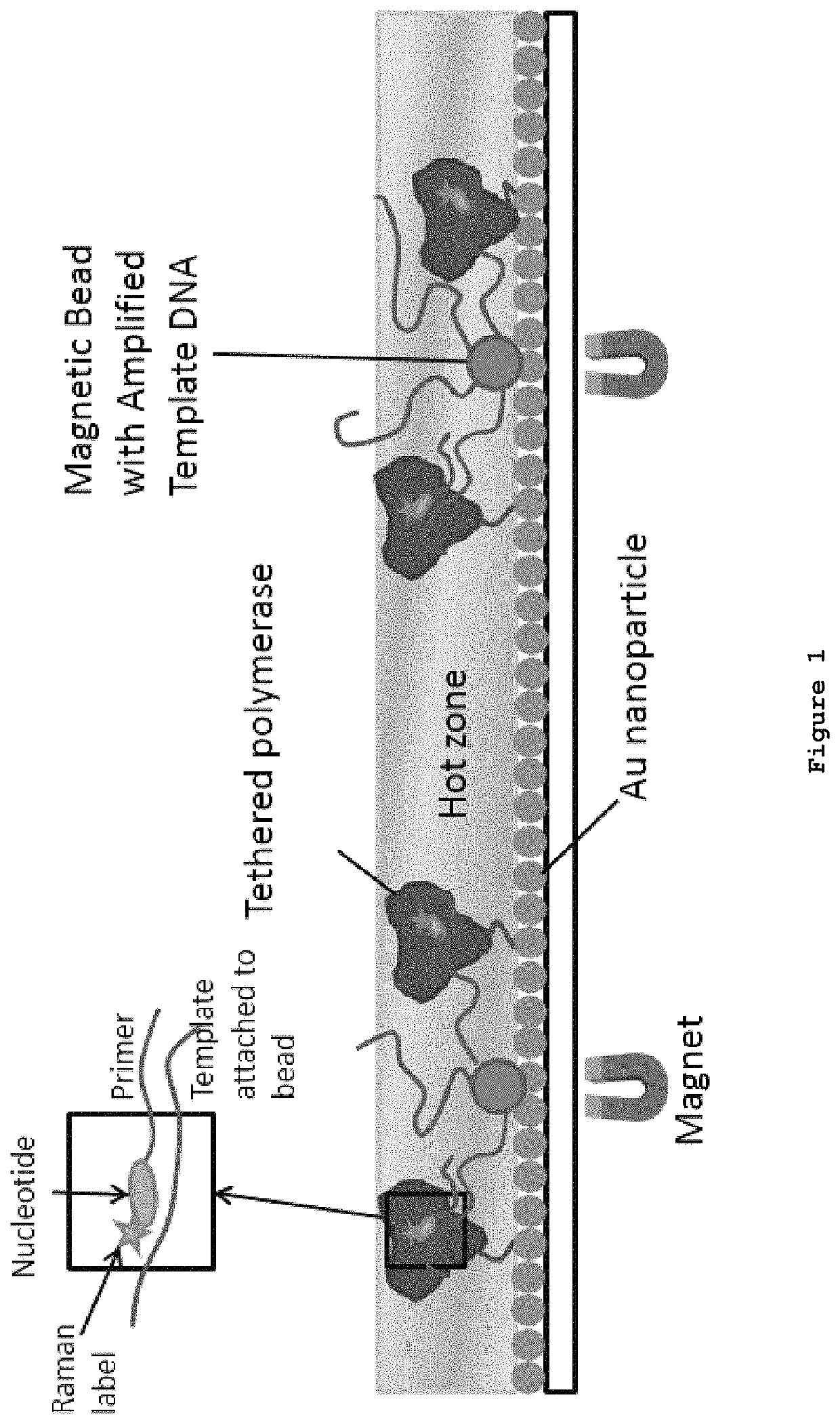
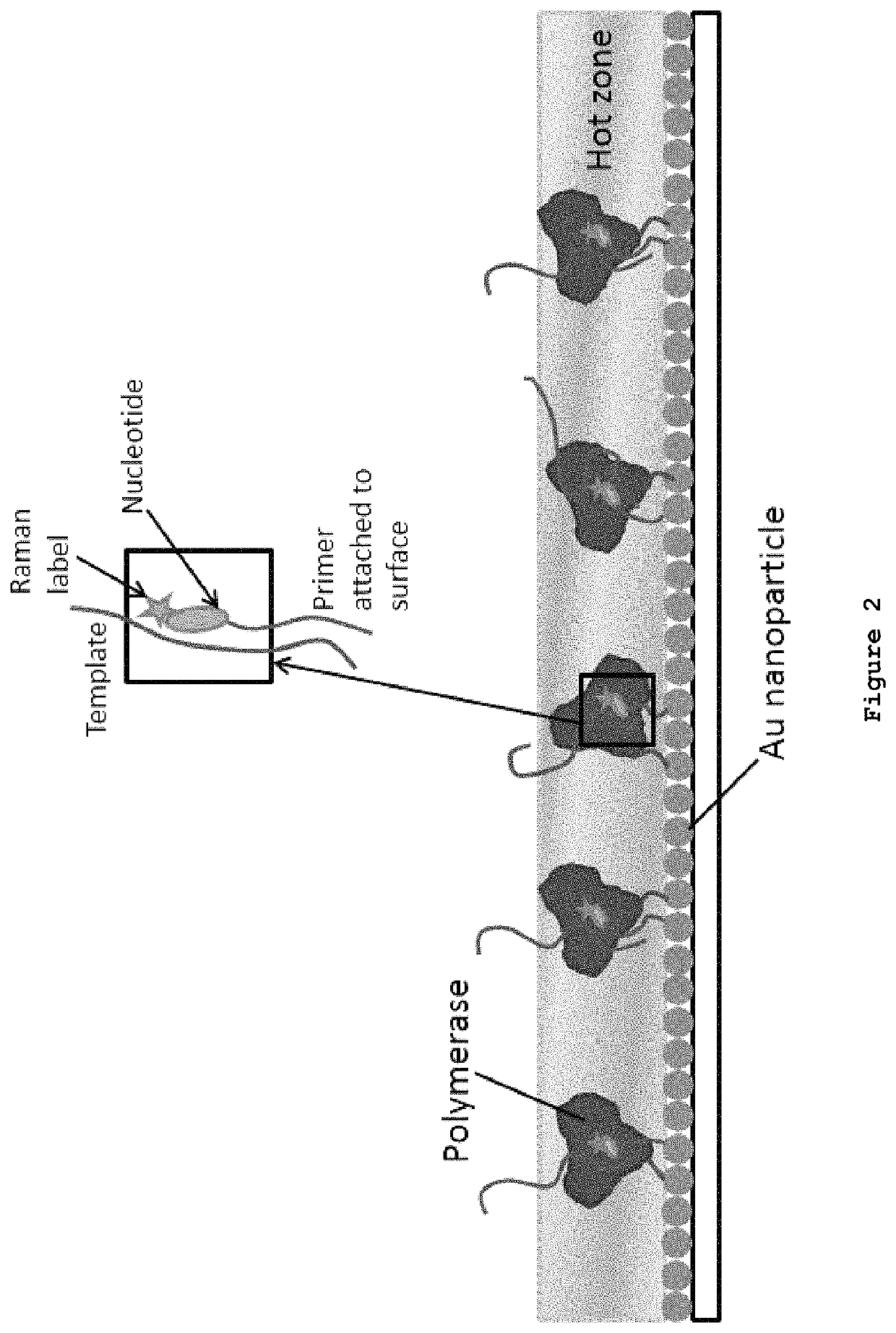
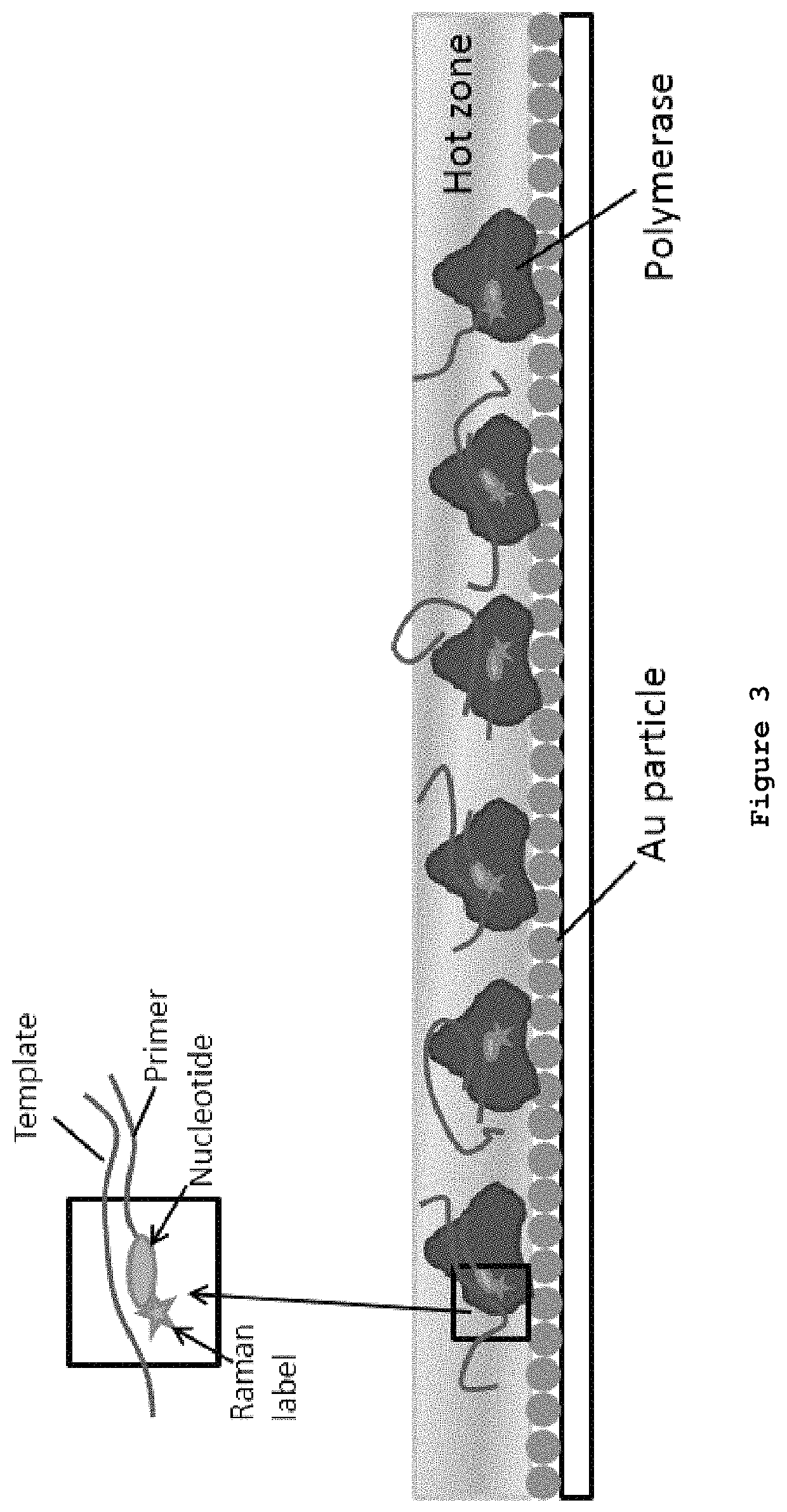
DNA sequencing by synthesis with nucleotide analogues and Raman detection
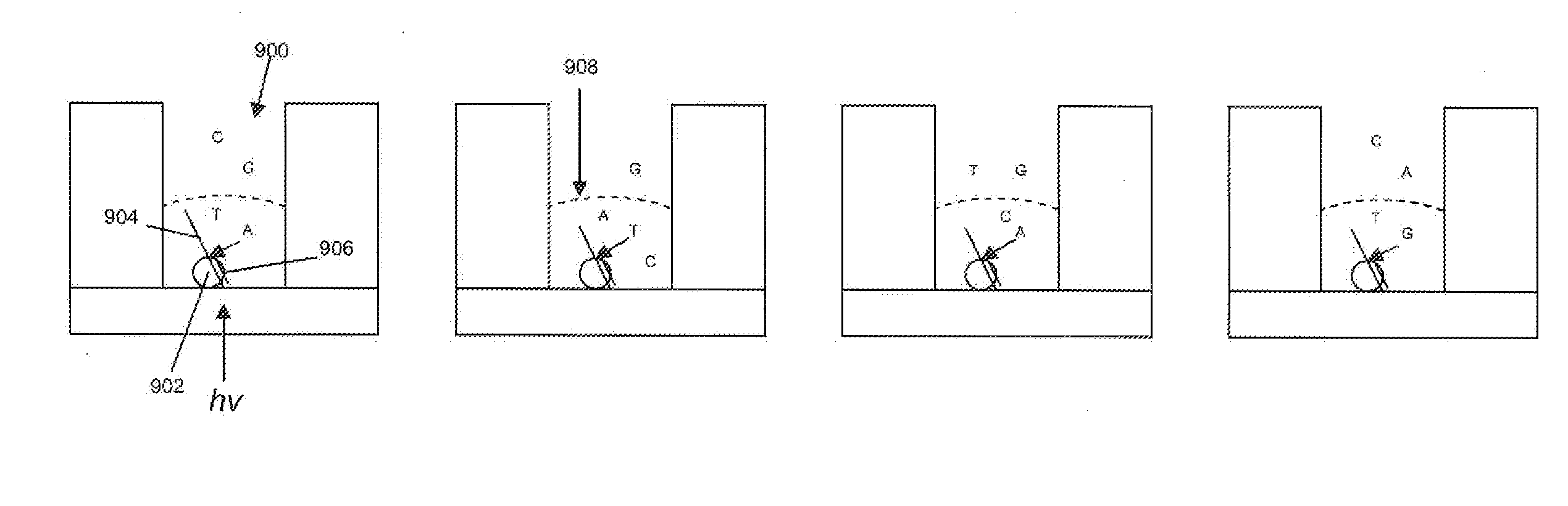
ActiveUS11225687B2High sensitivityMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopyNucleotide
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com