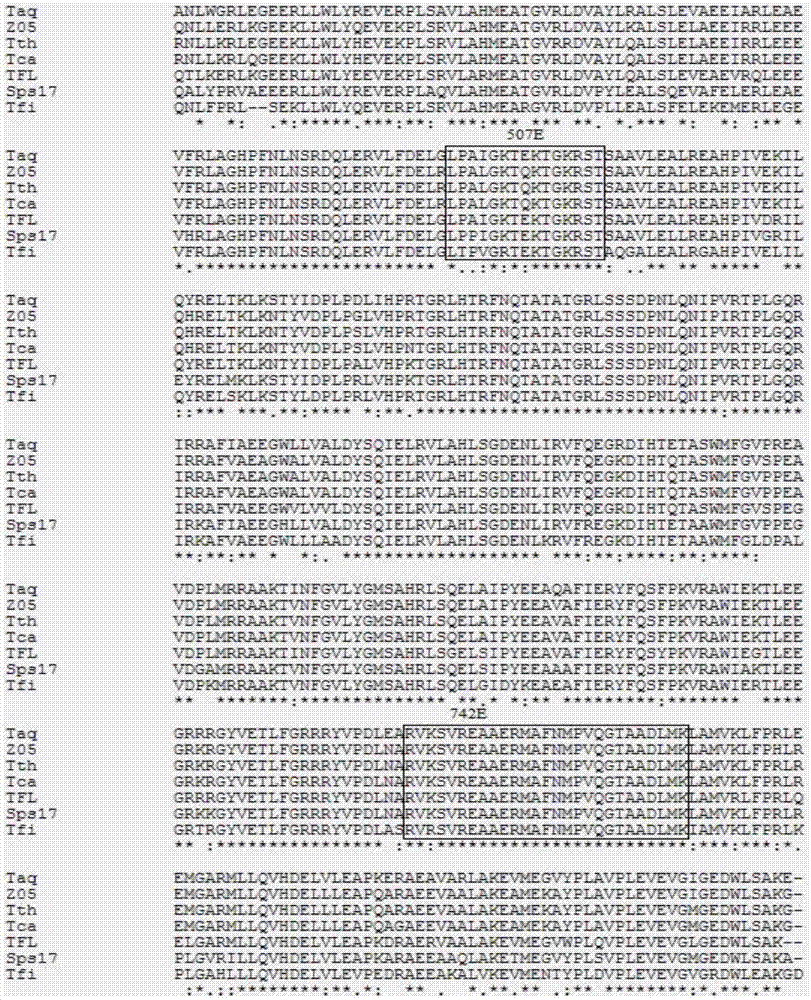
Mutant A type DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, and encoding gene and application of mutant A type DNA polymerase
A technology of polymerase and mutation, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of low incorporation rate, limitation of application fields, low amplification efficiency of target products, etc., and achieve the effect of improving incorporation efficiency and preventing pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Embodiment 1: the preparation of mutant Taq enzyme
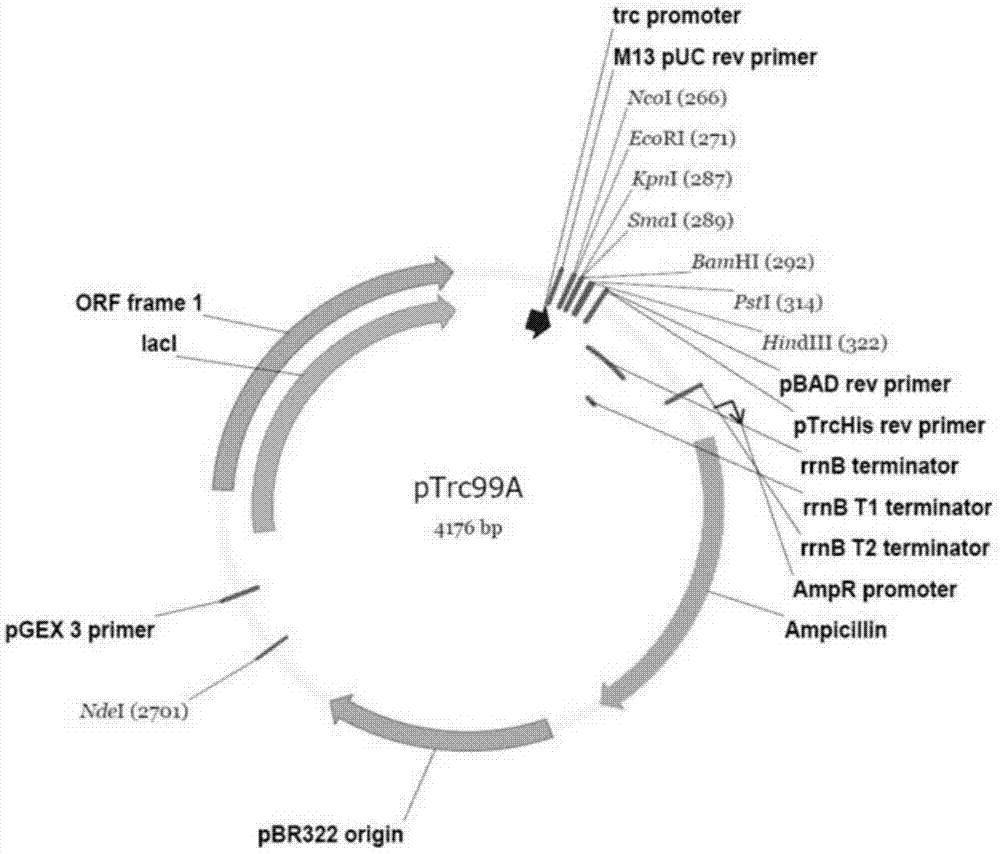
[0080] Using the commercialized pTrc99A plasmid (see the plasmid map image 3 ), the target fragment of Taq polymerase was constructed through ncoI and pstI two restriction sites, the mutant enzyme adopts the method of site-directed mutagenesis, and the 5' ends of the upstream and downstream primers are complementary and coincident with 10-15 bases for mutation, and the whole plasmid PCR is carried out.
[0081] Primer sequence (sequence as in SEQ ID NO: 12-39):
[0082] 664L upstream: GGCCAAGCTCATCAACTTCGGGGTCCTCTACGG
[0083] Downstream of 664L: GATGAGCTTGGCCGCCCGGCGCAT
[0084] 664I Upstream: GGCCAAGATCATCAACTTCGGGGTCCTCTACGG
[0085] Downstream of 664I: GATGATCTTGGCCGCCCGGCGCAT
[0086] 664M upstream: GGCCAAGATGATCAACTTCGGGGTCCTCTACGG
[0087] 664M Downstream: GATCATCTTGGCCGCCCGGCGCAT
[0088] 660Y upstream: CGCTATGCGGCCAAGACCATCAACTTCGG
[0089] Downstream of 660Y: TGGCCGCATAGCGCATCAGGGGGTC
[0090] 661T ...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Example 2: Comparison of the amplification efficiencies of the mutant 142N (T664v) and wild-type 142N using dUTP and dTTP as substrates for target products
[0113] In this example, the amplification efficiencies of the mutant 142N (T664V) and wild-type 142N using dUTP and dTTP as substrates for the target product were compared. The template used was M13 phage DNA (SEQ ID NO: 40). 550ng / ul, the amplification products were 1000bp and 500bp in size.
[0114] The amplified product is the primer sequence of the 1000bp system
[0115] Upstream primer TACAGTCTGACGCTAAAGGCAAA (SEQ ID NO: 41)
[0116] Downstream primer GTACCGCACTCATCGAGAACAAG (SEQ ID NO: 42)
[0117] The primer sequence of the amplification product is 500bp system:
[0118] Upstream primer ATGGTAATGGTGCTACTGGTGATTT (SEQ ID NO: 43)
[0119] Downstream primer CAAAGTCAGAGGGTAATTGAGCG (SEQ ID NO: 44)
[0120] The PCR reaction system is 25ul, each of dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP or dUTP contains 200uM, the concentrat...
Embodiment 3
[0128] Example 3: Comparison of amplification efficiencies of target products when mutant Taq enzymes (T664N, A661V, R660Y, T664V, A661T) and wild-type Taq enzymes use different ratios of dATP:dGTP:dCTP:dUTP as substrates
[0129] In this example, referring to Example 2, the system was compared with different mutant Taq enzymes (T664N, A661V, R660Y, T664V, A661T) and wild-type Taq enzymes when dUTP and dTTP were used as substrates for the target product M13 phage DNA amplification efficiency. The primer sequence dATP:dGTP:dCTP:dUTP with an amplification product of 500bp is 1:1:1:2 and 1:1:1:3.
[0130] PCR thermocycling conditions were 95°C, 30s; 30cycles (95°C, 5s; 60°C, 10s, 72°C, 40s single).
[0131] See the experimental results Image 6 , the experimental results are reflected by the brightness of the electrophoretic bands of the amplified products.
[0132] Image 6 It can be seen that when the ratio of dATP:dGTP:dCTP:dUTP is 1:1:1:2 and 1:1:1:3, neither the mutant T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com