Preparation method of p type GaN and AlGaN semiconductor material
A semiconductor, p-type technology, used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve problems affecting the performance of optoelectronic devices, adverse production and commercial applications, narrow growth windows, etc., to reduce defect density, The effect of increasing hole concentration and improving crystal quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
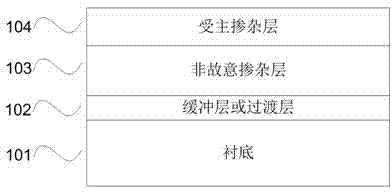
[0037] This implementation case will be described in detail figure 1 The growth structure of the p-type GaN semiconductor material is shown as image 3 shown. A buffer layer 302 , an unintentionally doped GaN layer 303 and an acceptor Mg-doped GaN layer 304 are sequentially grown on the sapphire substrate 301 by using a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) epitaxial growth method.
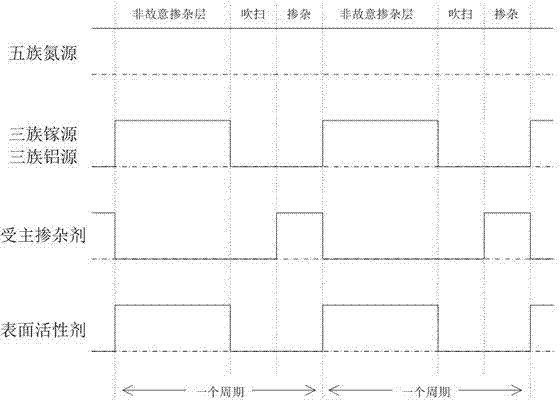
[0038] In the growth process of this embodiment, ammonia gas is used as the Group V nitrogen source; trimethyl gallium is used as the Group III gallium source; and trimethyl indium is used as the surfactant in the acceptor Mg-doped GaN layer 304 . The realization of this structure includes the following six steps:
[0039] (1) Place the c-plane sapphire substrate 301 in the reaction chamber, and use the metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) epitaxial growth method to grow on the sapphire substrate 301 image 3 The epitaxial structure shown.
[0040] (2) The buffer layer (30...
Embodiment 2
[0050] This implementation case will be described in detail figure 1 The growth structure of the p-type AlGaN semiconductor material shown, as Figure 5 shown. A buffer layer 502 , an unintentionally doped AlGaN layer 503 and an acceptor Mg-doped AlGaN layer 504 are sequentially grown on the sapphire substrate 501 by a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) epitaxial growth method.
[0051] In the growth process of this example, ammonia gas is used as the source of Group V nitrogen; trimethylgallium is used as the source of Group III gallium, and trimethylaluminum is used as the source of Group III aluminum; The acceptor Mg-doped AlGaN layer 304 is used. The realization of this structure includes the following six steps:
[0052] (1) Place the c-plane sapphire substrate 501 in the reaction chamber, and use the metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) epitaxial growth method to grow on the sapphire substrate 501 Figure 5 The epitaxial structure shown.
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com