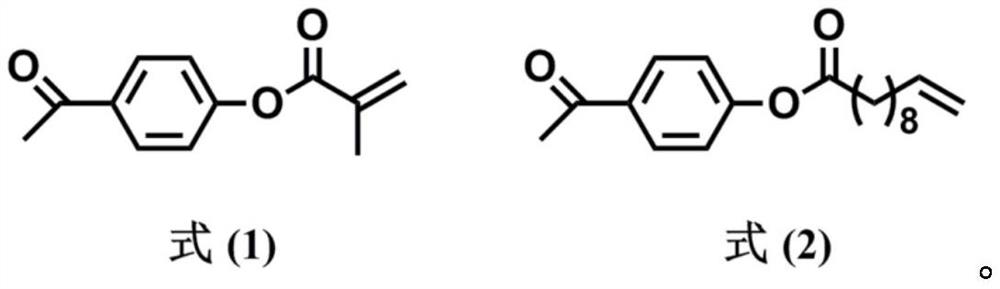
Patents
Literature
47results about How to "Lower ionization energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
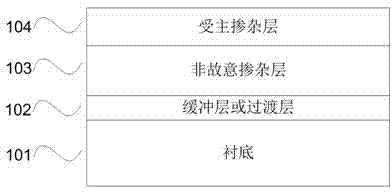
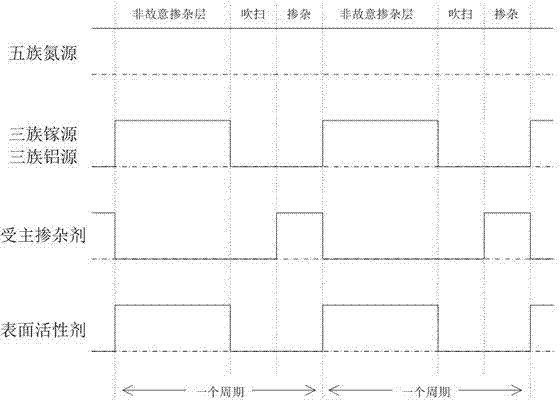
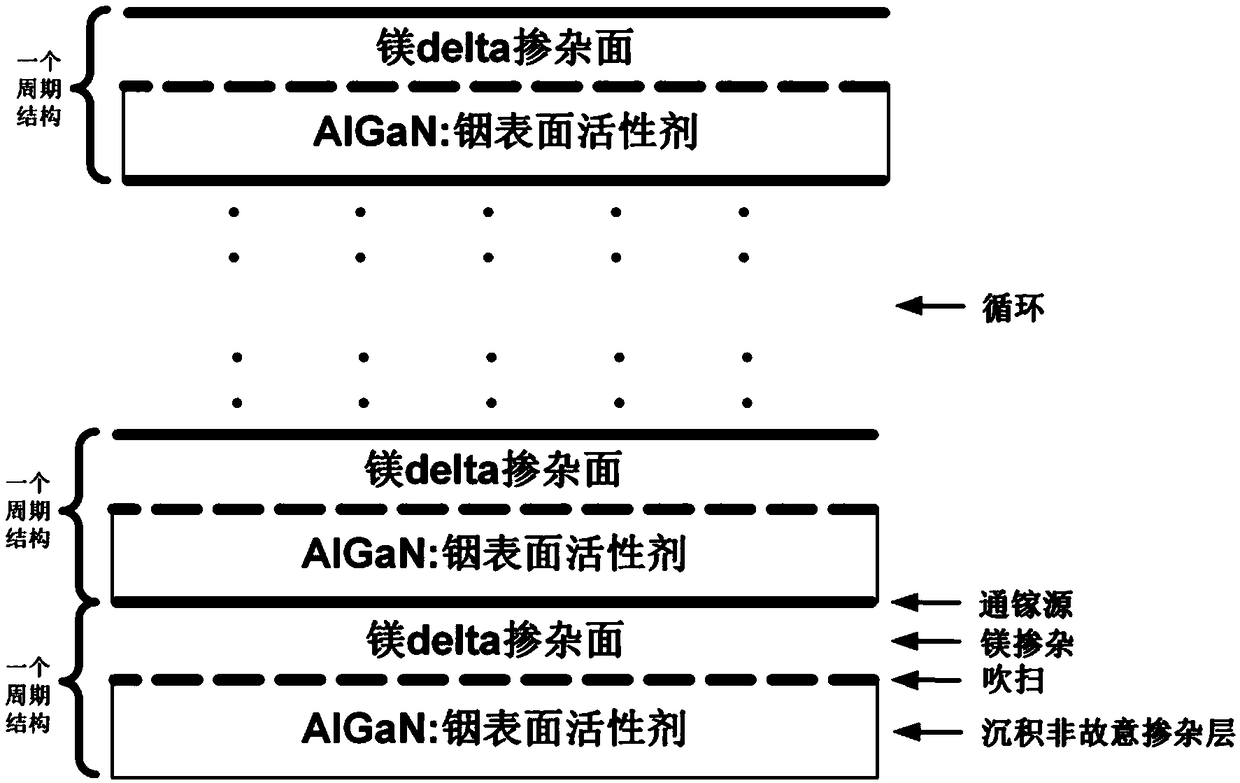
Preparation method of p type GaN and AlGaN semiconductor material
ActiveCN102903615AEasy to desorbImprove bindingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDimethylhydrazineSemiconductor materials
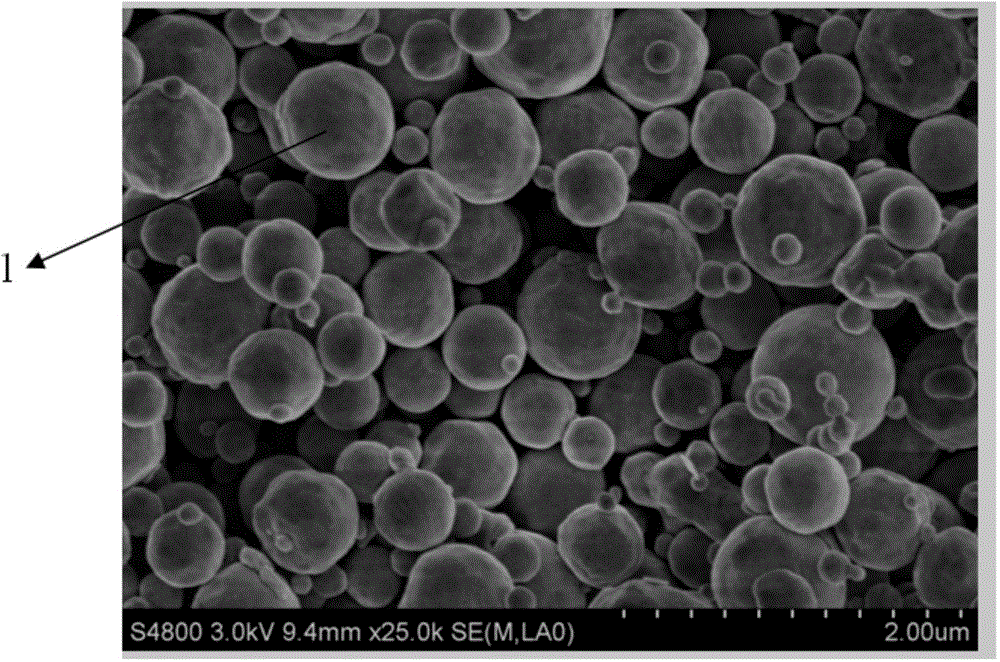
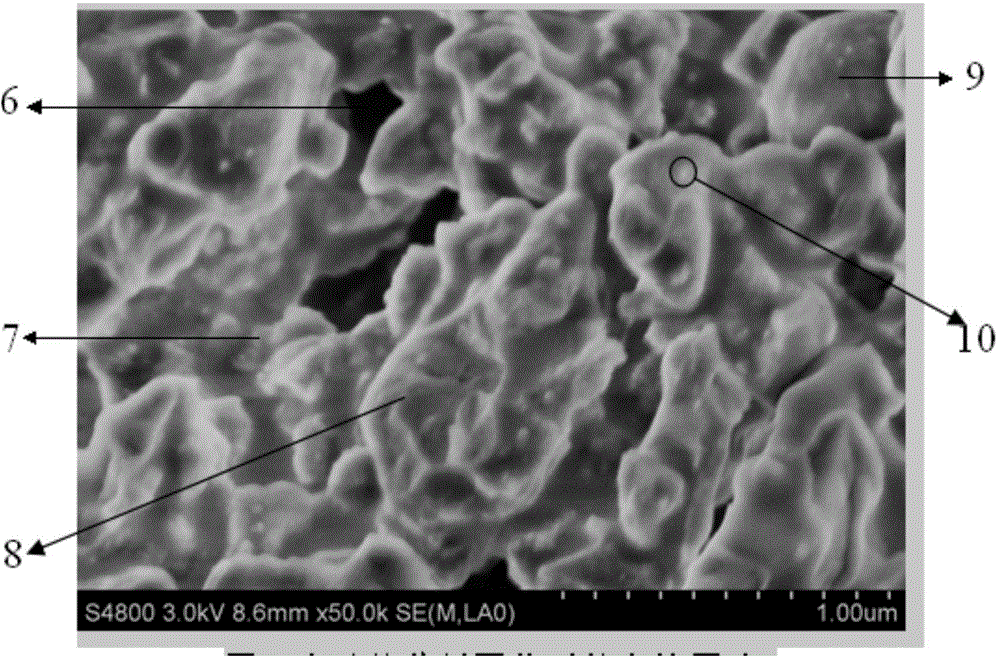
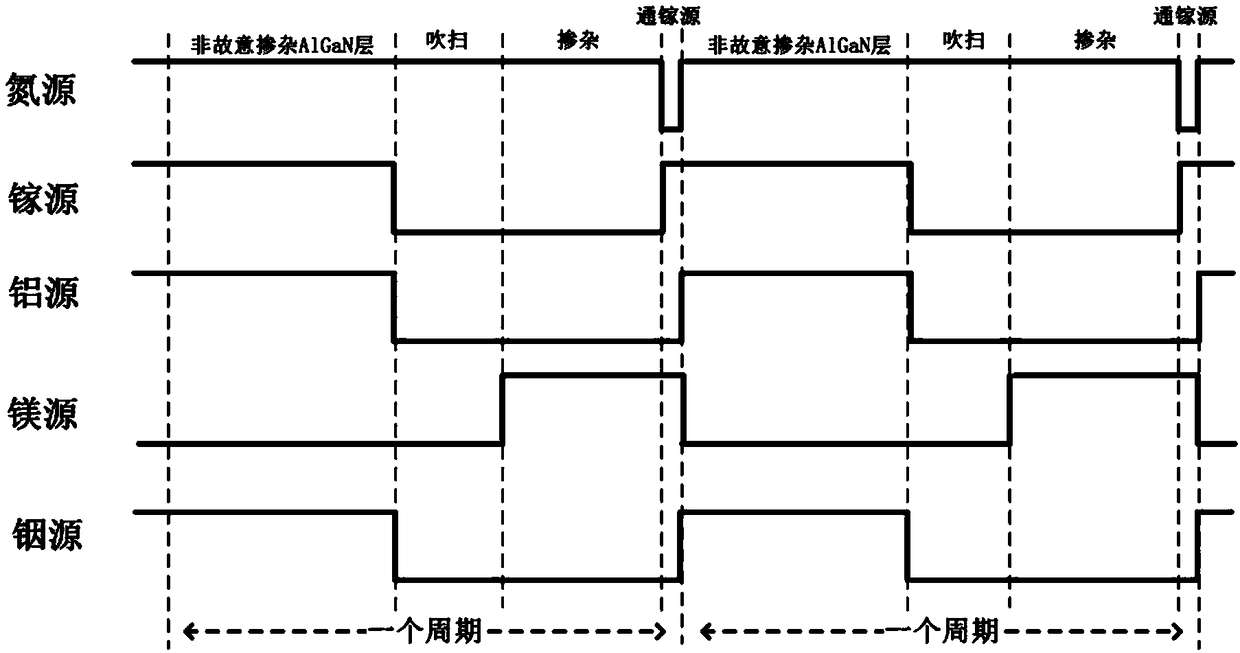
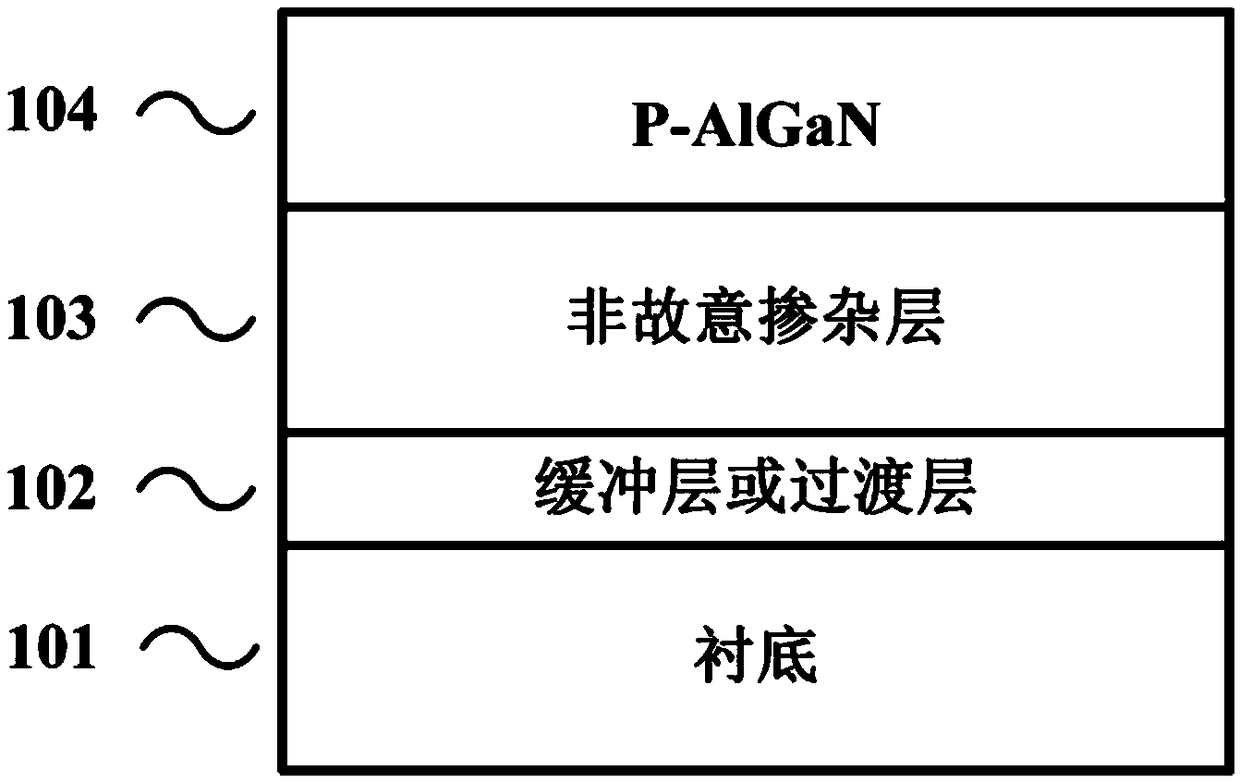
The invention discloses a preparation method of a p type GaN and AlGaN semiconductor material. A substrate, and a buffer layer or a transition layer, an unintended doped layer and an acceptor doped layer grown on the substrate from bottom to top are contained; in a growth process of the structure, ammonia or nitrogen dimethylhydrazine is used as a five-group nitrogen source; trimethyl gallium or TEGa used as a three-group gallium source, trimethylaluminium or triethyl aluminum used as a three-group aluminium source, and trimethylindium or TEIn used as a three-group indium source are collectively called three-group metal sources; and the trimethylindium or the TEIn is also used as a surface active agent and used in the acceptor doped layer. According to the method, the trimethylindium or the TEIn is used as the surface active agent to assist growth, and simultaneously, the acceptor doped layer is prepared by adopting a delta doping method. According to the method, the doping efficiency of acceptor doped magnesium atoms is increased, and simultaneously, the self-compensation effect is suppressed, so that the p type GaN and AlGaN semiconductor material with favorable crystalline quality and high hole concentration is obtained.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
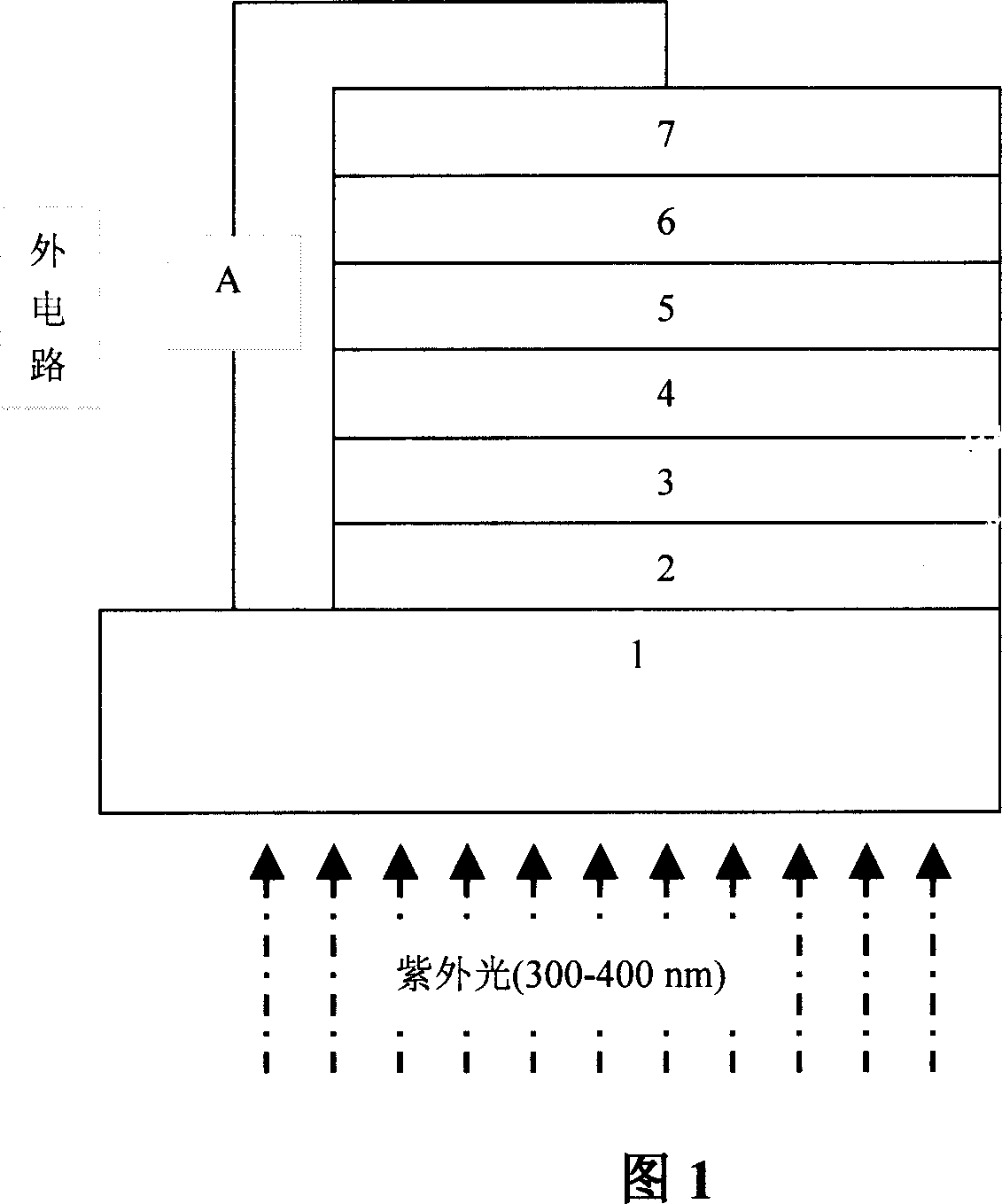
Organic ultraviolet detector
InactiveCN101055205AReduce volumeReduce weightPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsUltraviolet detectorsUltraviolet lights
The invention belongs to the material and component field of organic ultraviolet detector comprising a substrate, a transparent conductive film, an electronic donor layer, a mixing layer, an electronic receptor layer, and an electronic collection electrode layer, characterized in that: the thin mixing layer of electronic donor and electronic receptor is disposed between the electronic donor layer and the electronic receptor layer, and the absorption band of the used functional material is located in the ultraviolet region of 300-400nm, the UV light with center wavelength of 365nm are used as UV light source. The organic light detector is organic photovoltaic diode which is sensitive to ultraviolet light and not sensitive to the visual light, can be applicable in the science, industry and business field with simple fabricating process, cheap material and component, small volume, and convenience for carrying, therefore tending to be used widely.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for epitaxial growth of ultraviolet LED with high luminous efficacy
The invention provides a new method for epitaxial growth of an ultraviolet LED. By the adoption of the method for epitaxial growth of the ultraviolet LED, the growth difficulty can be greatly lowered, and the radiant power of the ultraviolet LED is greatly increased. An AlGaN / AlxInyGa1-x-y layer is grown for a plurality of periods, wherein x, y, z and w meet the following requirements for x
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
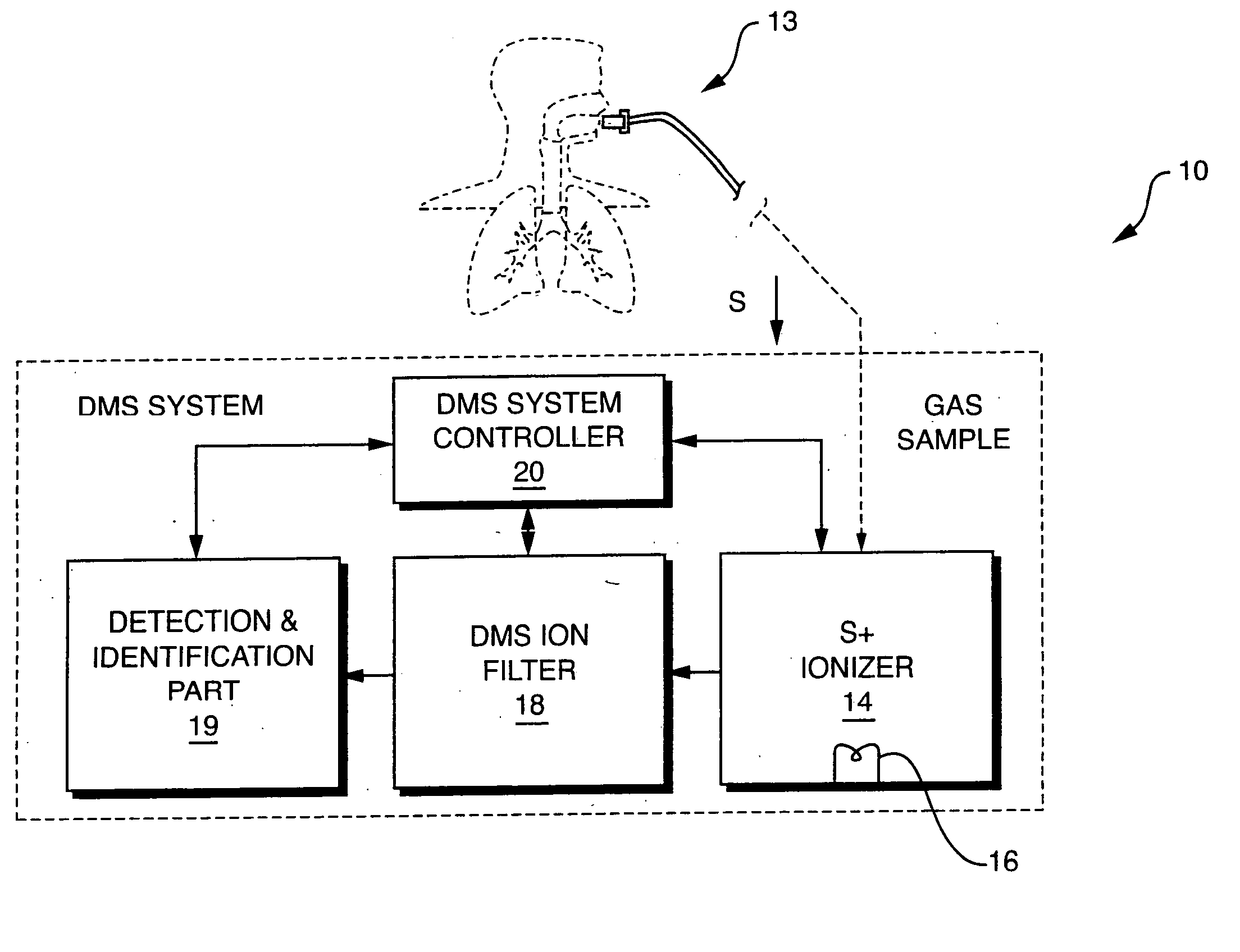
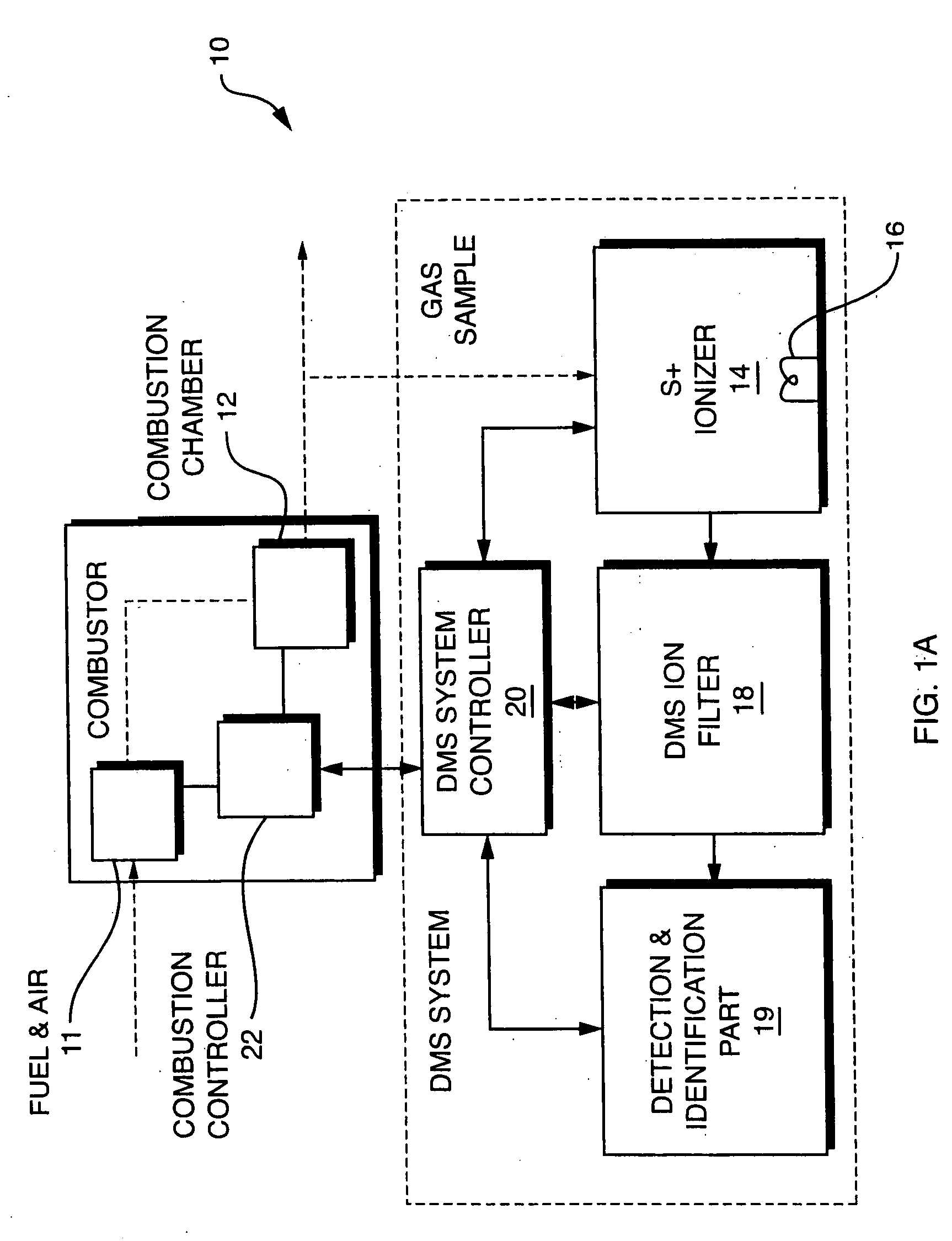
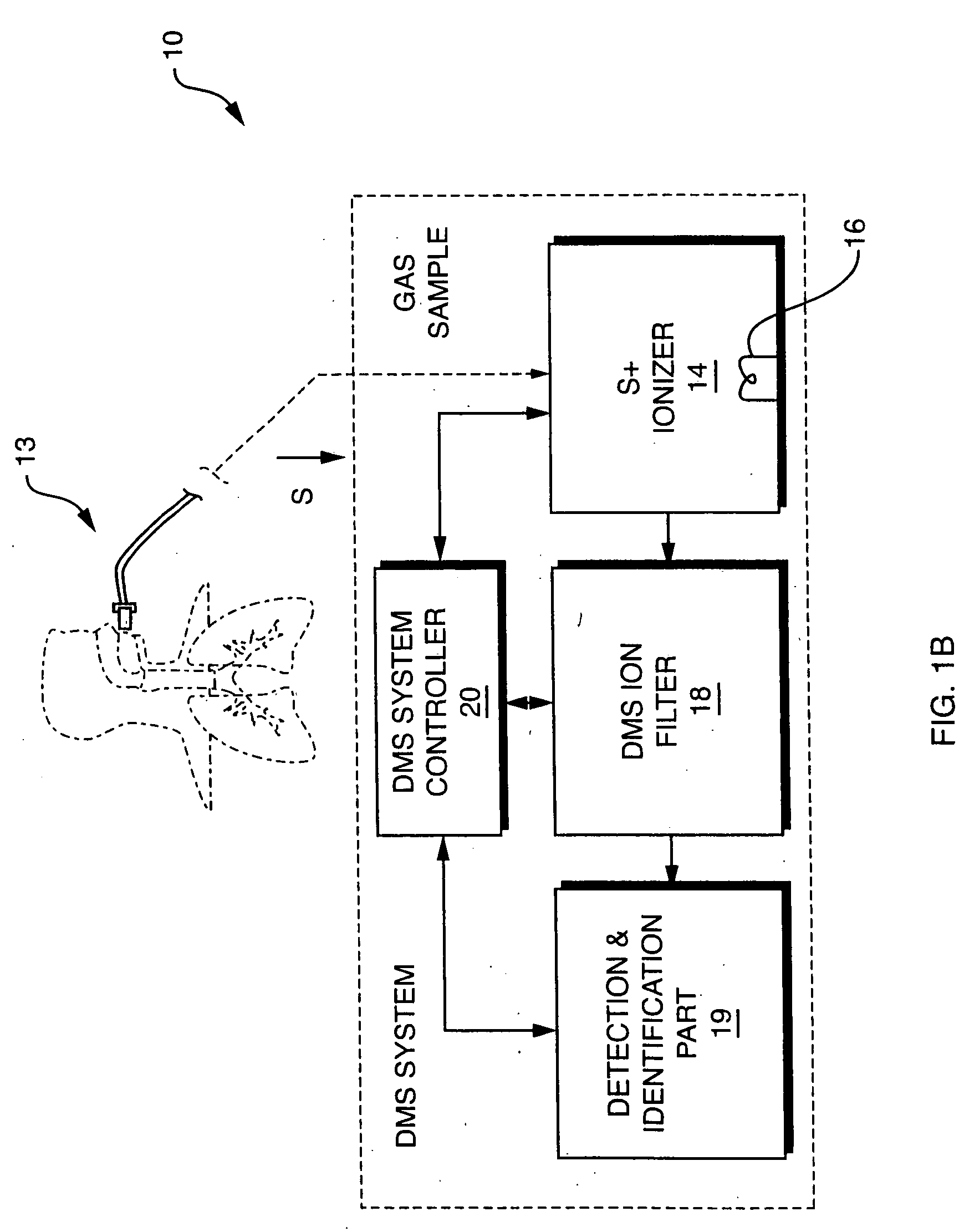
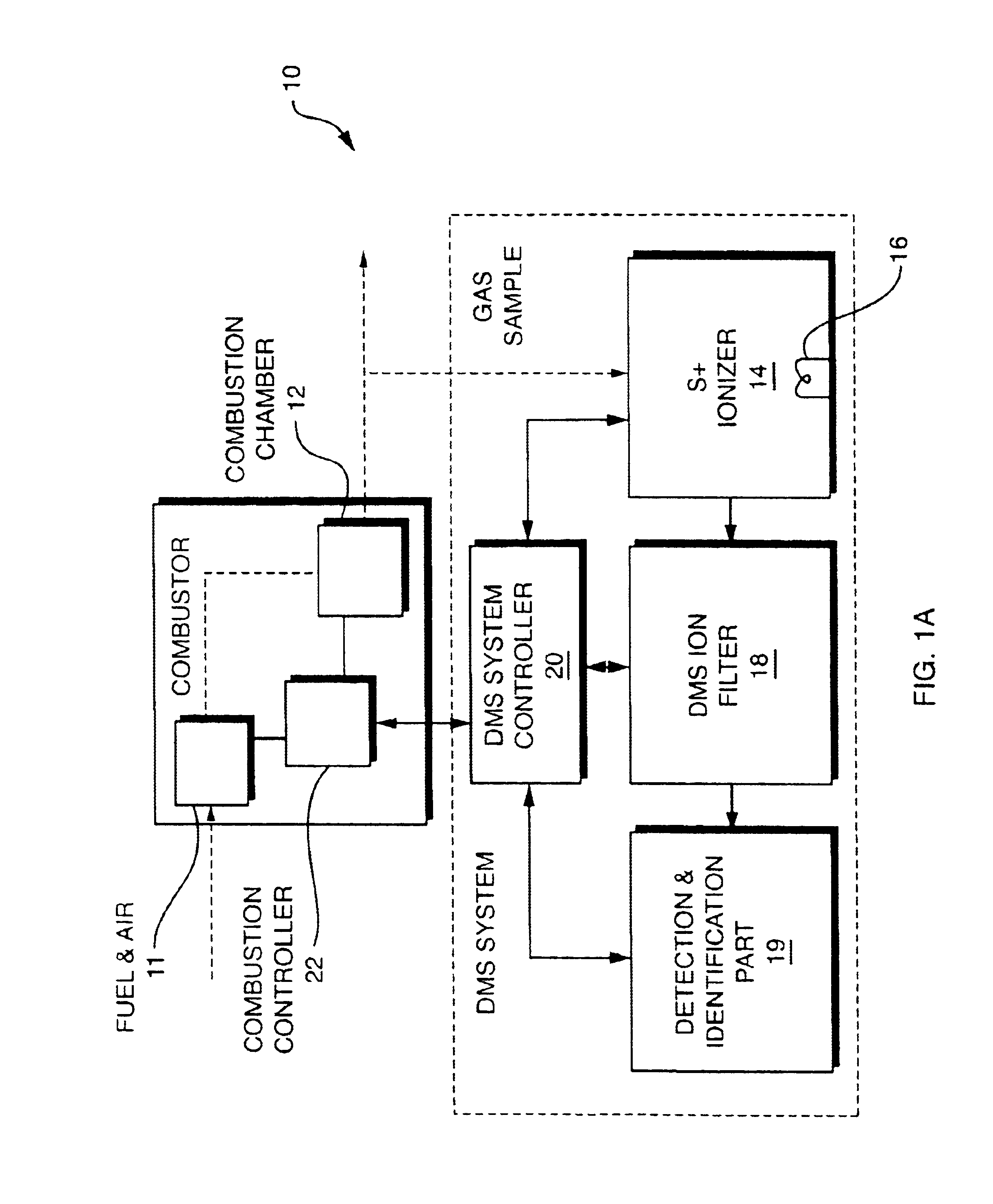
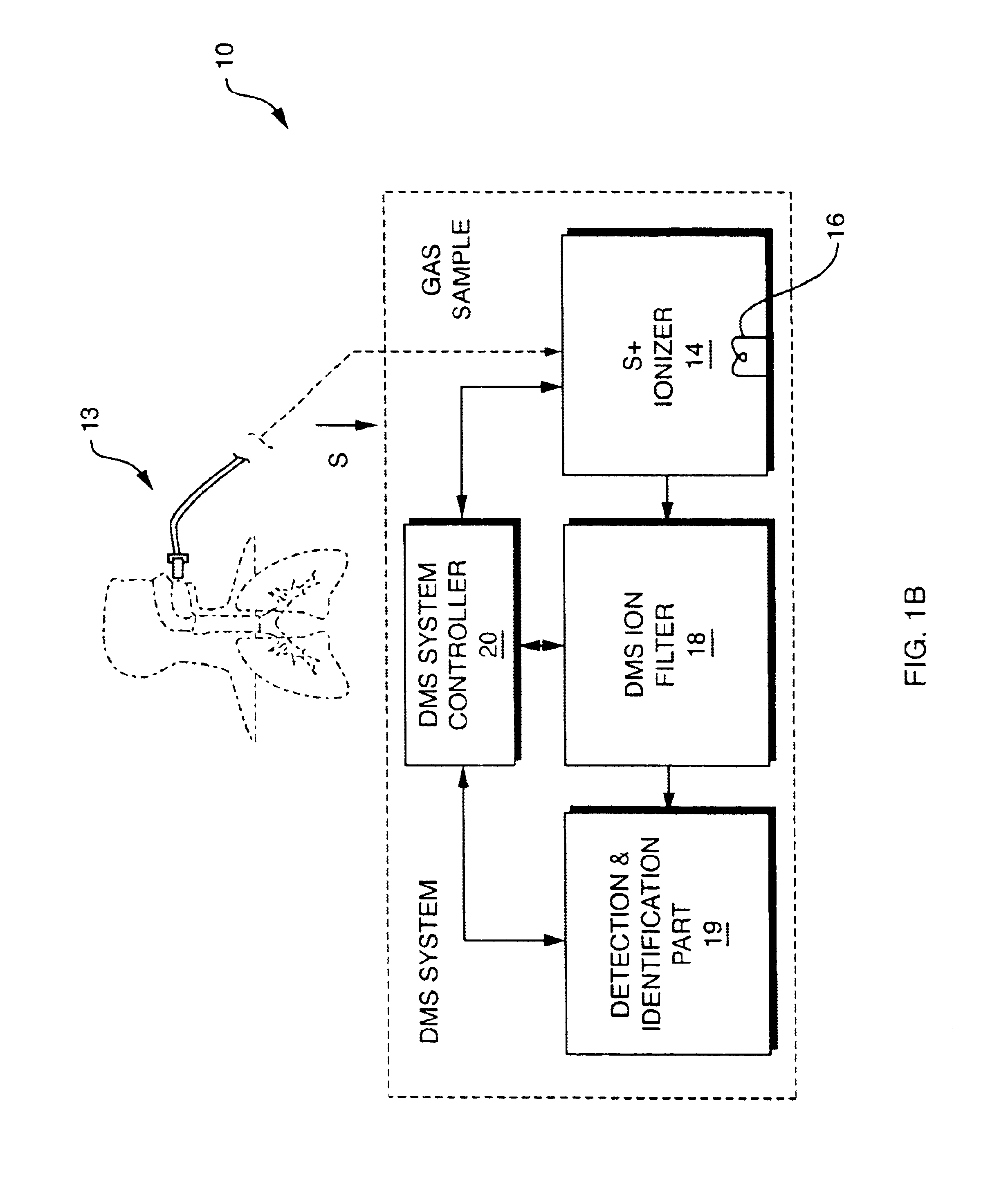
NOx monitor using differential mobility spectrometry
InactiveUS20050092914A1Fast response timeHigh sensitivityParticle separator tubesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSystem usageIon source
System for detection and analysis of gas samples in fieldable real-time Differential Mobility Spectrometry (DMS) chemical sensor system which uses non-radioactive ion source for monitoring and detecting NOx emissions; provides reliable methods for detecting and monitoring of anthropogenic sources of NOx; also detection of NO in exhaled breath for patient health diagnosis.
Owner:SIONEX
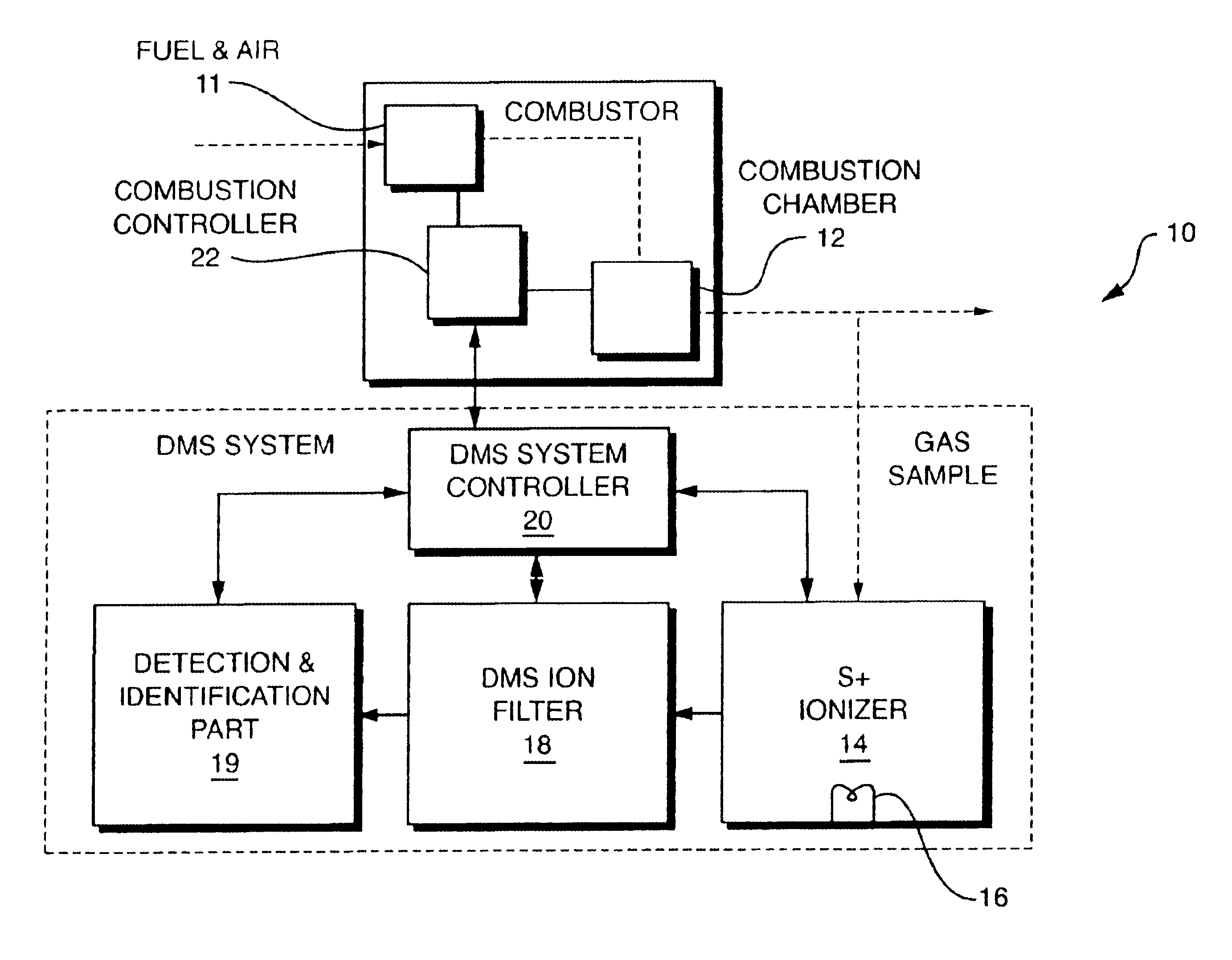
NOx monitor using differential mobility spectrometry
InactiveUS7019291B2Fast response timeHigh sensitivityParticle separator tubesSpectrum investigationNitrogen oxideIon source
System for detection and analysis of gas samples in fieldable real-time Differential Mobility Spectrometry (DMS) chemical sensor system which uses non-radioactive ion source for monitoring and detecting NOx emissions; provides reliable methods for detecting and monitoring of anthropogenic sources of NOx; also detection of NO in exhaled breath for patient health diagnosis.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Process for growing P-type ZnO crystal film by real-time doping nitrogen
InactiveCN1391259AReal-time dopingGood repeatabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSputteringNitrogen
A process for growing P-type ZnO crystal film by real-time doping of nitrogen includes washing substrate, putting it in reaction chamber of sputter equipment, vacuumizing heating, substrate to 200-600 deg.c, introducing the mixture of high-purity NH3 and O2, and sputter growing with high-purity Zn as target under 1-10 MPa.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Growth method of p-type AlGaN semiconductor material
ActiveCN108987256AReduced Displacement Formation EnergyImprove retentionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDimethylhydrazineIndium
The invention discloses a growth method of p-type AlGaN semiconductor material, the semiconductor material is grown by a technical method of adding a gallium source through step into a surfactant-assisted magnesium delta doping, Ammonia gas or dimethylhydrazine nitrogen is used as group V nitrogen source in the growth of p-type AlGaN semiconductor material, Trimethylgallium or triethylgallium is used as a Group III gallium source, trimethylaluminum or triethylaluminum is used as a Group III aluminum source, trimethylindium or triethylindium is used as a Group III indium source, collectively referred to as a Group III metal source, and trimethylindium or triethylindium is also used as a surfactant in the acceptor doping layer. The method of the invention can improve crystal quality, increase doping concentration of acceptor doped magnesium atoms, reduce acceptor ionization energy by enhancing valence band modulation, and further suppress self-compensation effect, thereby obtaining p-type AlGaN semiconductor material with high crystal quality and high hole concentration.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Dry etching method and apparatus
InactiveUS7371690B2Lower resistanceLower ionization energySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistNoble gas
A condition without using Ar as plasma gas is applied to processing of an organic anti-reflection-coating, which suppresses a spatter effect and decreases the cleavage of C—H and OC—O bonds in a resist. As a result, roughness of the resist after processing the anti-reflection-coating can be suppressed, and pitting and striations after processing a next film to be processed, that is an insulating film, can be prevented. For a rare gas to be used at the time of processing the insulating film, any one of Xe, Kr, a mixed gas of Ar and Xe, and a mixed gas of Ar and Kr is applied in place of Ar, giving rise to reduction in pitting and striations after etching. In addition, a dry etching method with less critical-dimension shift and excellence in both apparatus cost and throughput can be provided by performing resist modification and etching by turns.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
High-mobility high-hole concentration P-type AlGaN material and growth method thereof
ActiveCN109300980AHigh Mobility High Hole ConcentrationHigh mobility and high hole concentration achievedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge carrierLow mobility
The invention relates to a high-mobility high-hole concentration P-type AlGaN material and a growth method thereof and belongs to the technical field of semiconductors. With the high-mobility high-hole concentration P-type AlGaN material and the growth method thereof of the invention adopted, the problems of low mobility and low hole concentration of P-type AlGaN in the prior art can be solved. The P-type AlGaN material of the present invention comprises an aluminum nitride layer, a doped epitaxial layer and a graded epitaxial layer which are arranged sequentially from bottom to top; the aluminum nitride layer is an Al polarity surface; the doped epitaxial layer is made of a Mg doped P-type AlGaN material; the doped epitaxial layer is a metal polarity surface; the graded epitaxial layer isof a multilayer structure from bottom to top; each layer of the multilayer structure of the graded epitaxial layer is made of an unintentionally doped AlxGa1-xN material; and the Al components of theunintentionally doped AlxGa1-xN materials of the multilayer structure gradually decrease from bottom to top. According to the P-type AlGaN material of the invention, on the basis of polarization-induced charges and the separation of a carrier transport region from an impurity ionization region, high mobility and high hole concentration can be realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Iodine medium ground gas supply device for Hall thruster and using method
ActiveCN111140450ALower ionization energyLow priceMeasurement devicesMachines/enginesControl cellEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of aerospace Hall electric propulsion, in particular to an iodine medium ground gas supply device for a Hall thruster and a using method. The iodine mediumground gas supply device includes an iodine vapor generating unit and an iodine vapor flow control unit, wherein the iodine vapor generating unit includes a solid iodine storage tank and a first pressure sensor. The iodine vapor flow control unit includes a shut-off valve, a pressure relief valve, a second pressure sensor and a flow control valve. The iodine medium ground gas supply device for the Hall thruster adopts an iodine medium propellant to achieve good thrust parameter performance, and the thruster is more efficient. An iodine medium is heated and sublimated into iodine vapor for transportation, the condensation of the iodine vapor in the transportation process is prevented, the flow rate of the iodine vapor can be controlled in real time, and it is ensured that the iodine vaporcan be stably and accurately transported to the Hall thruster.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
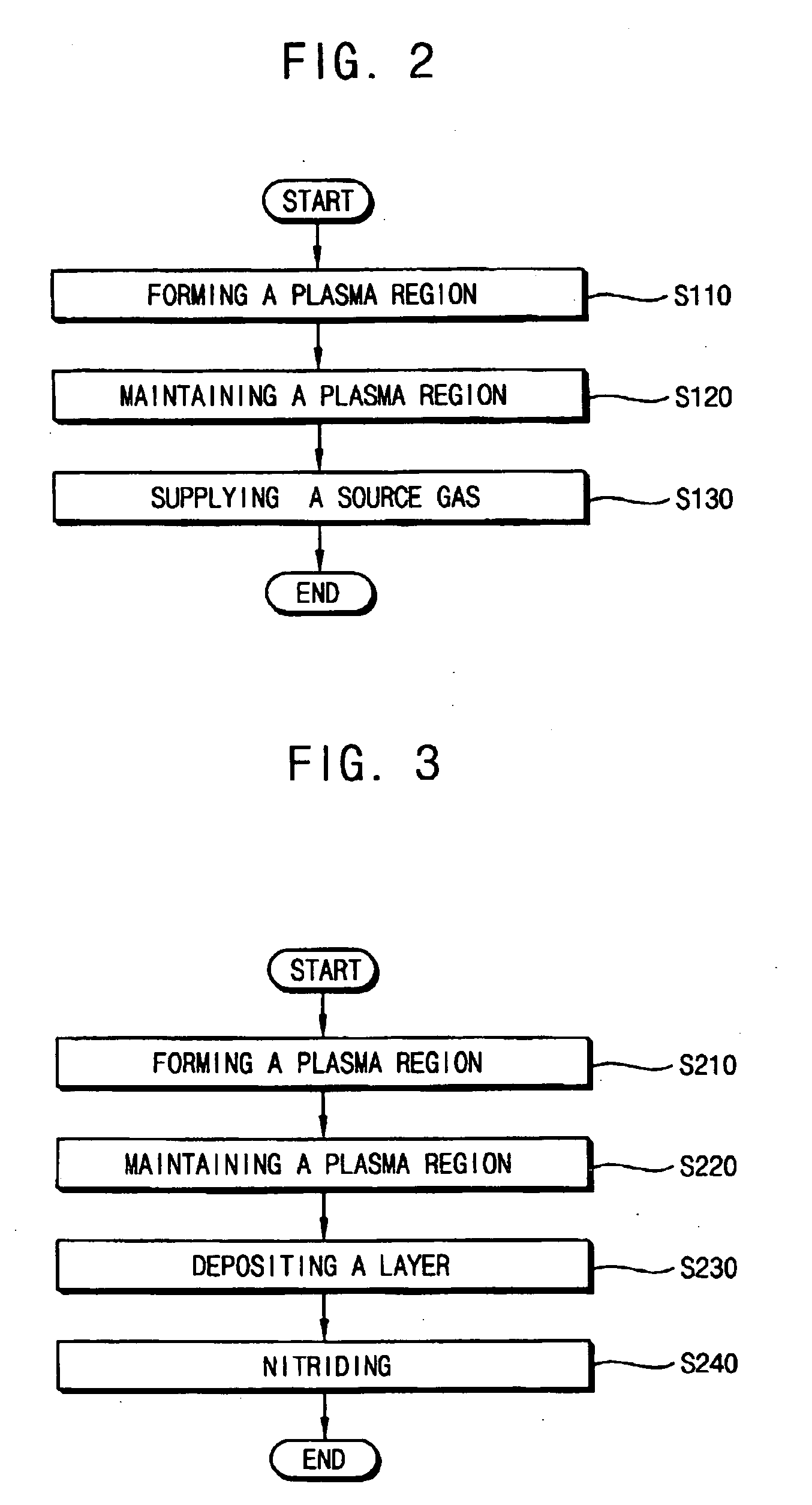
Method of forming plasma and method of forming a layer using the same
InactiveUS20070042132A1Lower ionization energyReduce harmDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
A method of forming plasma used in a process of manufacturing a semiconductor device and a method of forming a layer for a semiconductor device using the plasma are disclosed. The plasma forming method includes forming a plasma region in a sealed space by supplying a plasma source gas into the sealed space at a first flow rate and maintaining the plasma region by supplying a plasma maintenance gas into the sealed space at a second flow rate higher than the first flow rate. The plasma source gas includes a first gas having a first atomic weight, and the plasma maintenance gas includes a second gas having a second atomic weight lower than the first atomic weight. The plasma source gas includes argon and the plasma maintenance gas includes helium. The method may further include forming the layer on a wafer by supplying a source gas into the sealed space.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
N,N'-diphenyl-N,N'-di(9,9-dimethyl fluorene-2-yl)-N-hexyl-(4,4'-diamine phenyl) carbazole and synthetic method thereof
ActiveCN105384679ALower ionization energyLower glass transition temperatureOrganic chemistryLuminescent compositionsOrganic synthesisAniline
The invention discloses N,N'-diphenyl-N,N'-di(9,9-dimethyl fluorene-2-yl)-N-hexyl-(4,4'-diamine phenyl) carbazole and a synthetic method thereof and belongs to the field of organic synthesis. According to the synthetic method, 2,7-dibromo-carbazole is used as a raw material and subjected to N-alkylation and a Suzuki coupled reaction to synthesize 2,7-di(4-bromophenyl)-N-hexyl carbazole; 2-bromo-9,9-dimethyl fluorene and aniline are used as raw materials and subjected to a Buchwald-Hartwig coupled reaction to synthesize 9,9-dimethyl-N-phenyl fluorine-2-amine; lastly, 2,7-di(4-bromophenyl)-N-hexyl carbazole and the 9,9-dimethyl-N-phenyl fluorine-2-amine are used as raw materials and subjected to a Buchwald-Hartwig coupled reaction to synthesize a target compound. The target compound has good heat stability and glass transition temperature and is suitable for hole transport materials of organic light-emitting devices.
Owner:PUYANG HUICHENG ELECTRONICS MATERIAL
Ultraviolent LED epitaxial structure and growth method thereof
ActiveCN107689405ALower ionization energyIncrease concentrationSemiconductor devicesUltravioletScattering effect
The invention provides a growth method for an ultraviolet LED epitaxial structure, specially a special growth process for multiple quantum wells of an active area, and the special growth process comprises the following steps: growing LP and PAL as an integral superlattice, wherein a growth period is 5-20; adopting roof type gradual doping for doping of Mg, i.e., gradually reducing after doping ofMg firstly gradually increases to reach a peak value, wherein doping is in symmetrical distribution. Through the superlattice growth, ionization energy of Mg can be reduced, hole concentration is improved, the impurity scattering effect on the hole is reduced, and more holes are injected into a light-emitting area, so that light emitting efficiency is improved. The method is an effective method capable of improving efficiency of an ultraviolet LED; and meanwhile, an apparatus has very good light emitting efficiency, so that photoelectric property of the apparatus is improved.
Owner:宁波安芯美半导体有限公司
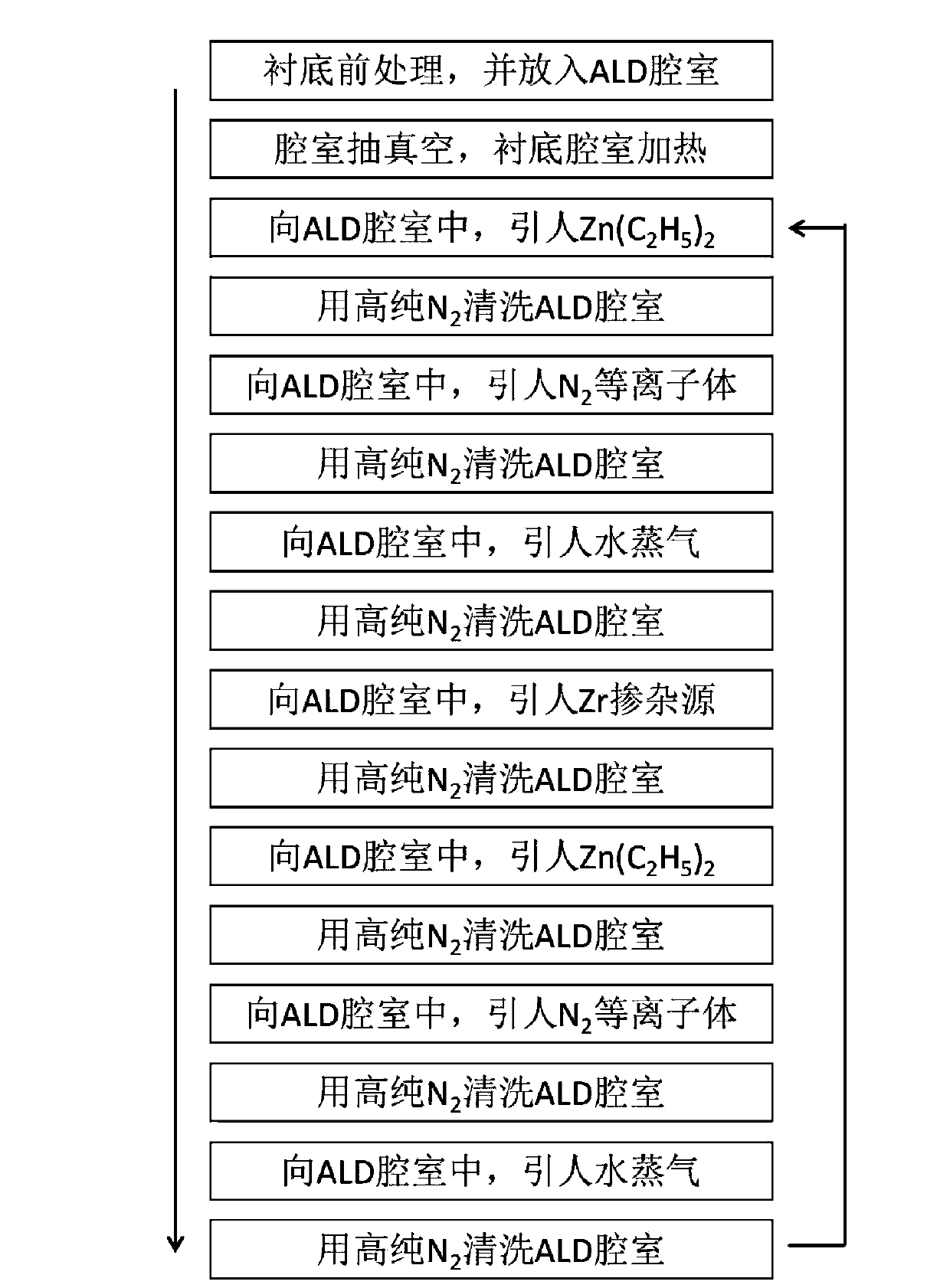
Preparation method for co-doped zinc oxide film through atomic layer deposition
ActiveCN103866275AImprove stabilityPromote formationChemical vapor deposition coatingOxygenAtomic layer deposition
The present invention discloses a preparation method for a co-doped zinc oxide film through atomic layer deposition. The preparation method comprises: placing a substrate in an ALD reaction chamber, heating the substrate and the chamber pipeline, and sequentially carrying out multi-component composite deposition, wherein the composite deposition comprises respectively introducing one doped deposition of a doped element Zr-containing doped source, second zinc source deposition, two nitrogen doped source depositions and two oxygen source depositions after first zinc source deposition to form N-Zr-N co-doping, wherein the deposition sequence of the nitrogen doped source deposition and the oxygen source deposition is that the oxygen source deposition and the nitrogen doped source deposition are sequentially performed, and the deposition sequence of the doped element Zr-containing doped source deposition and the second zinc source deposition is that the second zinc source deposition and the doped element Zr-containing doped source deposition are sequentially performed. With the method, the in situ donor-acceptor co-doping can be performed on the zinc oxide film so as to increase the doping amount of the acceptor element and promote the p type conversion of the zinc oxide film.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mercury-free discharge lamp
ActiveUS20150348771A1Lower ionization energyIncrease productionElectric discharge tubesDischarge tube main electrodesDevitrificationNoble gas
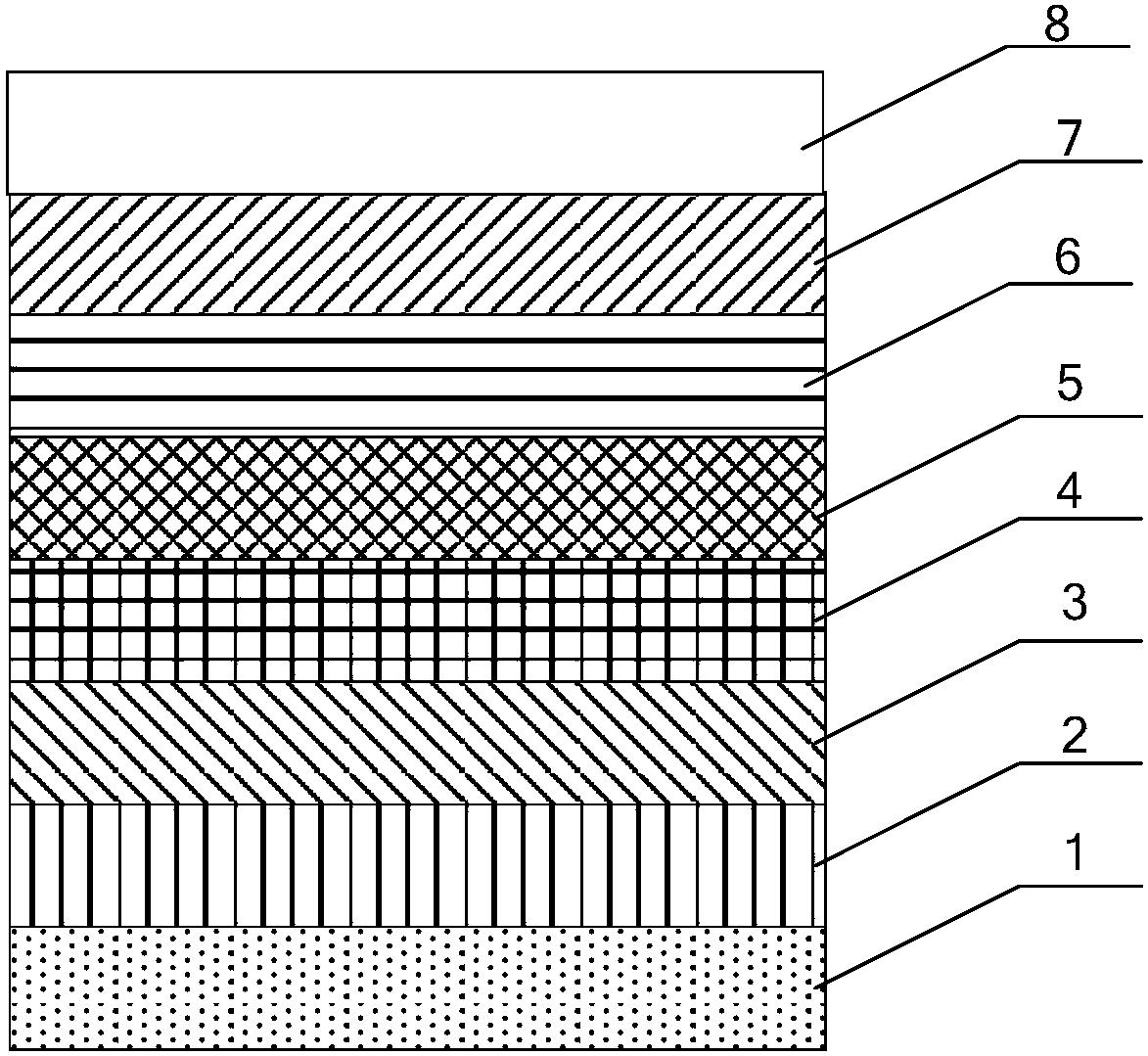
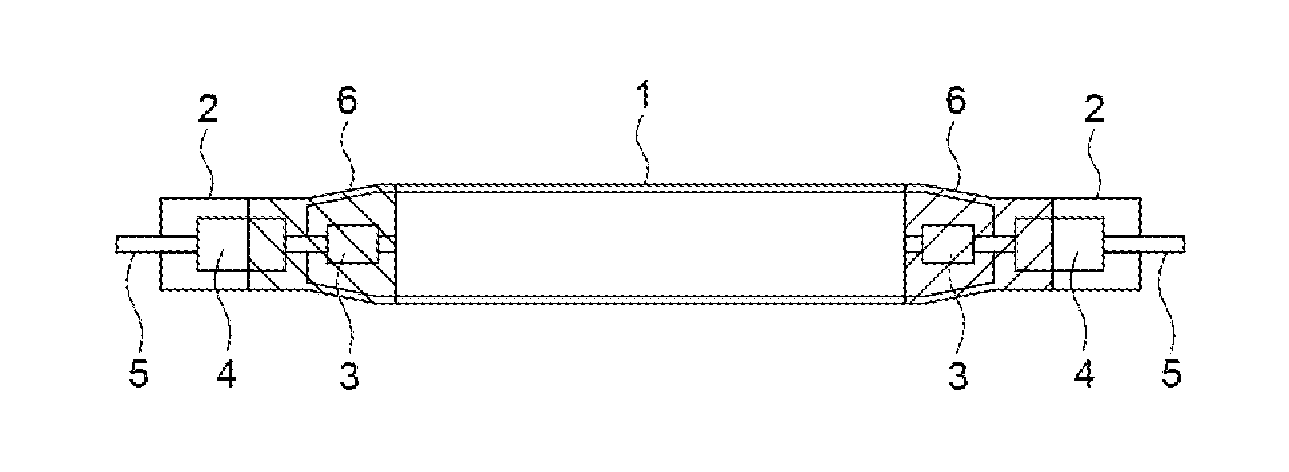
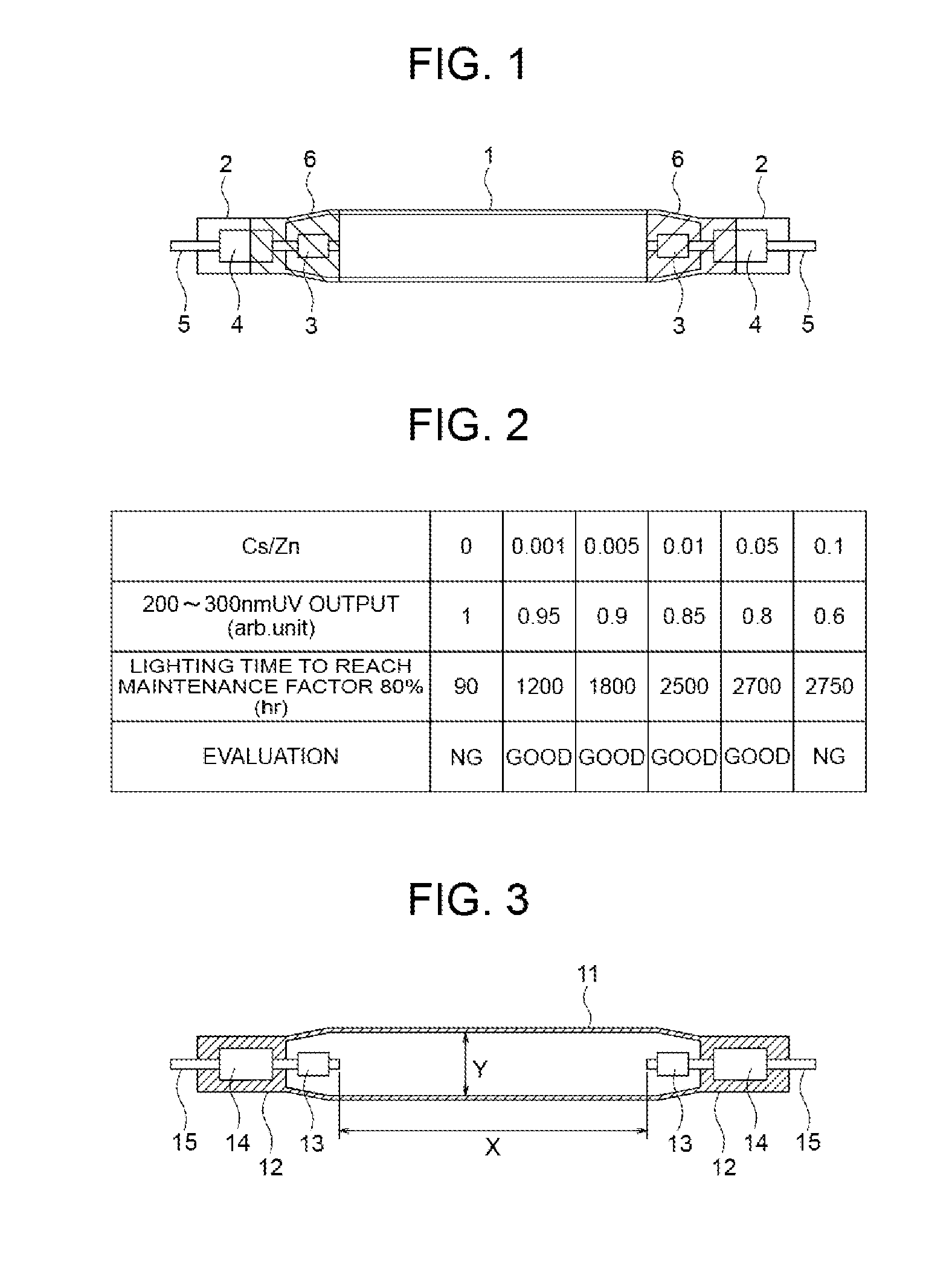
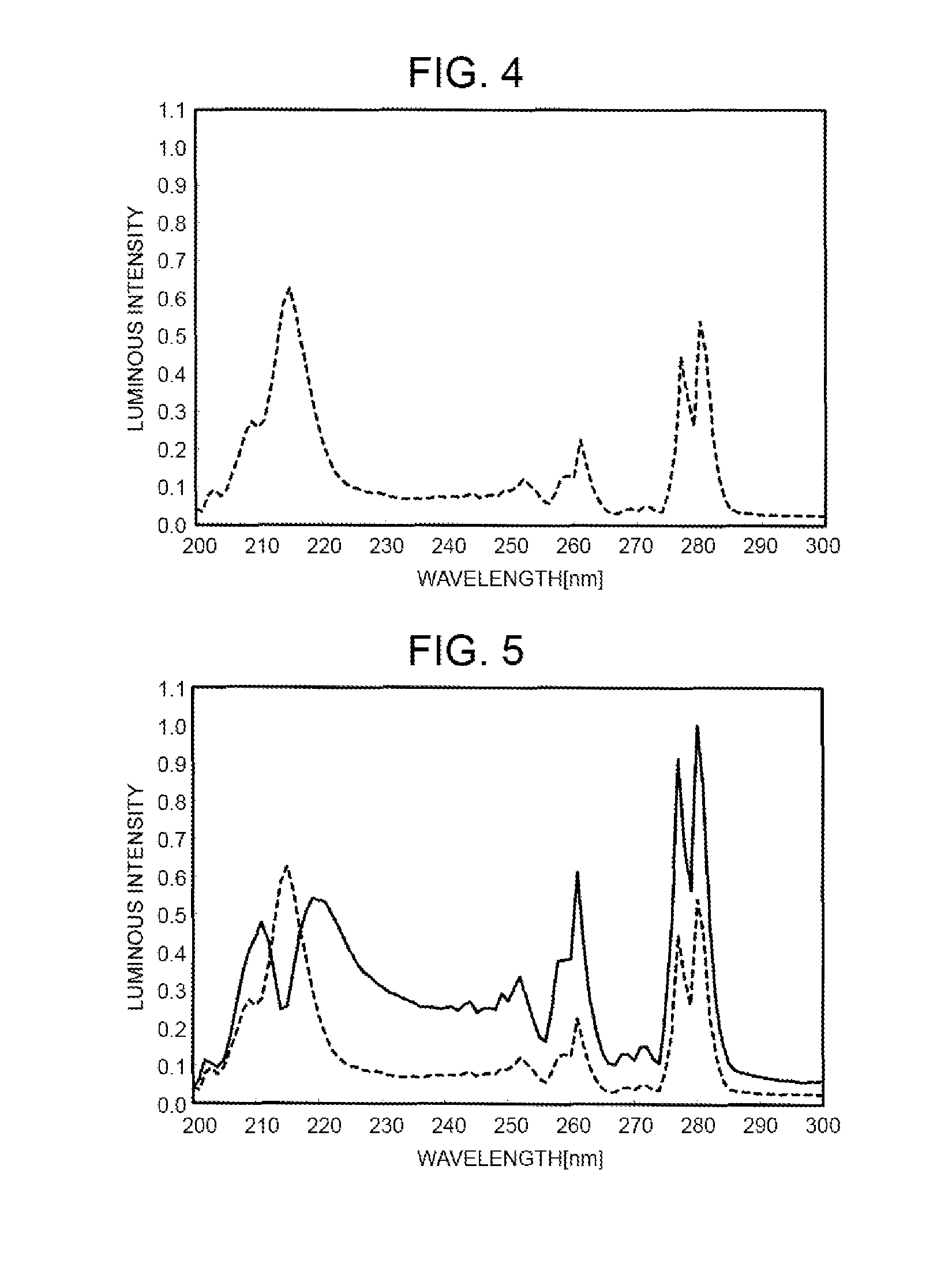
A mercury-free discharge lamp includes a luminous tube, and a pair of electrodes in the luminous tube such that the electrodes face each other in the luminous tube. The discharge lamp also includes a pair of thermal insulation films formed on an outer surface of the luminous tube around the electrodes, respectively. Zinc, halogen, and a noble gas are sealed in the luminous tube. A metal is also sealed in the luminous tube. The metal has a lower ionization energy than zinc. A ratio of a molar density of the metal to a molar density of zinc is 0.001 to 0.05. The mercury-free discharge lamp has a long life and can emit an ultraviolet beam in a short wavelength range (200-350 nm) at a high output and a high luminous efficacy without causing devitrification of the luminous tube.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Ultralow temperature preparation method of TMO film and TMO-TFT
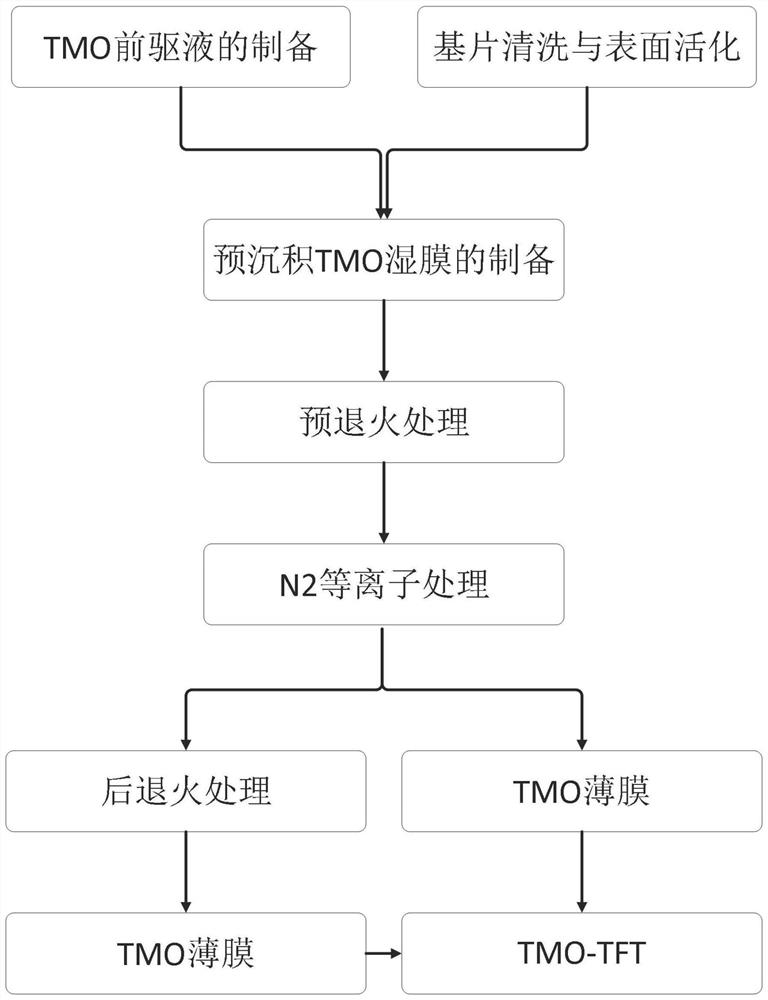
PendingCN114121661AReduce condensationReduce the temperatureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysical chemistryThin membrane
The invention provides an ultralow temperature preparation method of a TMO thin film and a TMO-TFT. The ultralow-temperature preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a TMO precursor solution; s2, cleaning a substrate and activating the surface of the substrate; s3, preparation of a pre-deposited TMO wet film; s4, pre-annealing is conducted on the pre-deposited TMO wet film obtained in the S3, and a pre-annealed TMO thin film is obtained; s5, carrying out N2 plasma treatment or N2 plasma treatment and post-annealing on the pre-annealed TMO thin film obtained in S4 to obtain a TMO thin film; and S6, preparing a TFT by taking the TMO thin film obtained in the step S5 as an active layer, and obtaining the TMO-TFT. The TMO thin film and the TMO-TFT are prepared at the ultralow temperature while it is guaranteed that the TMO thin film has the good semiconductor characteristic and the TMO-TFT shows the excellent electrical characteristic, and therefore the compatibility of the TMO-TFT and the flexible substrate is enhanced.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Process for growing P-type ZnO crystal film by real-time doping nitrogen
InactiveCN1206703CReal-time dopingIncrease the doping concentrationVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringGrown film
The method for real-time nitrogen-doped growth of p-type ZnO crystal thin film of the present invention adopts magnetron sputtering method, puts into the reaction chamber of DC reactive magnetron sputtering device after the substrate surface is cleaned first, and the vacuum degree of reaction chamber is pumped to at least 10 -3 Pa, then heat the substrate so that the substrate temperature is 200-600°C, and use high-purity ammonia gas NH 3 and high-purity oxygen O 2 It is sputtering gas, the two kinds of gases are respectively controlled by the flowmeter and input into the buffer chamber of the device, and then introduced into the vacuum reaction chamber after being fully mixed in the buffer chamber, and under the pressure of 1-10Pa, high-purity Zn is used as the target material for sputtering growth , where the partial pressure ratio of ammonia to oxygen is adjusted according to the doping concentration. According to NH 3 with O 2 P-type ZnO crystal films with different doping concentrations can be prepared with different partial pressure ratios, and the growth time is determined by the required thickness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for operating an electric arc furnace, and electric arc furnace
InactiveUS20160273062A1Improve cooling effectCooling can be limitedElectric discharge heatingCrucible furnacesElectric arc furnaceChemical reaction
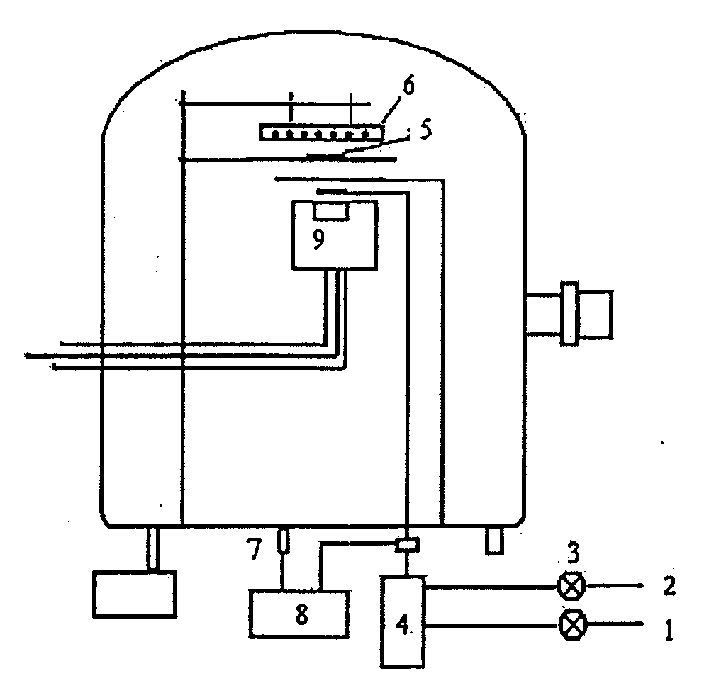
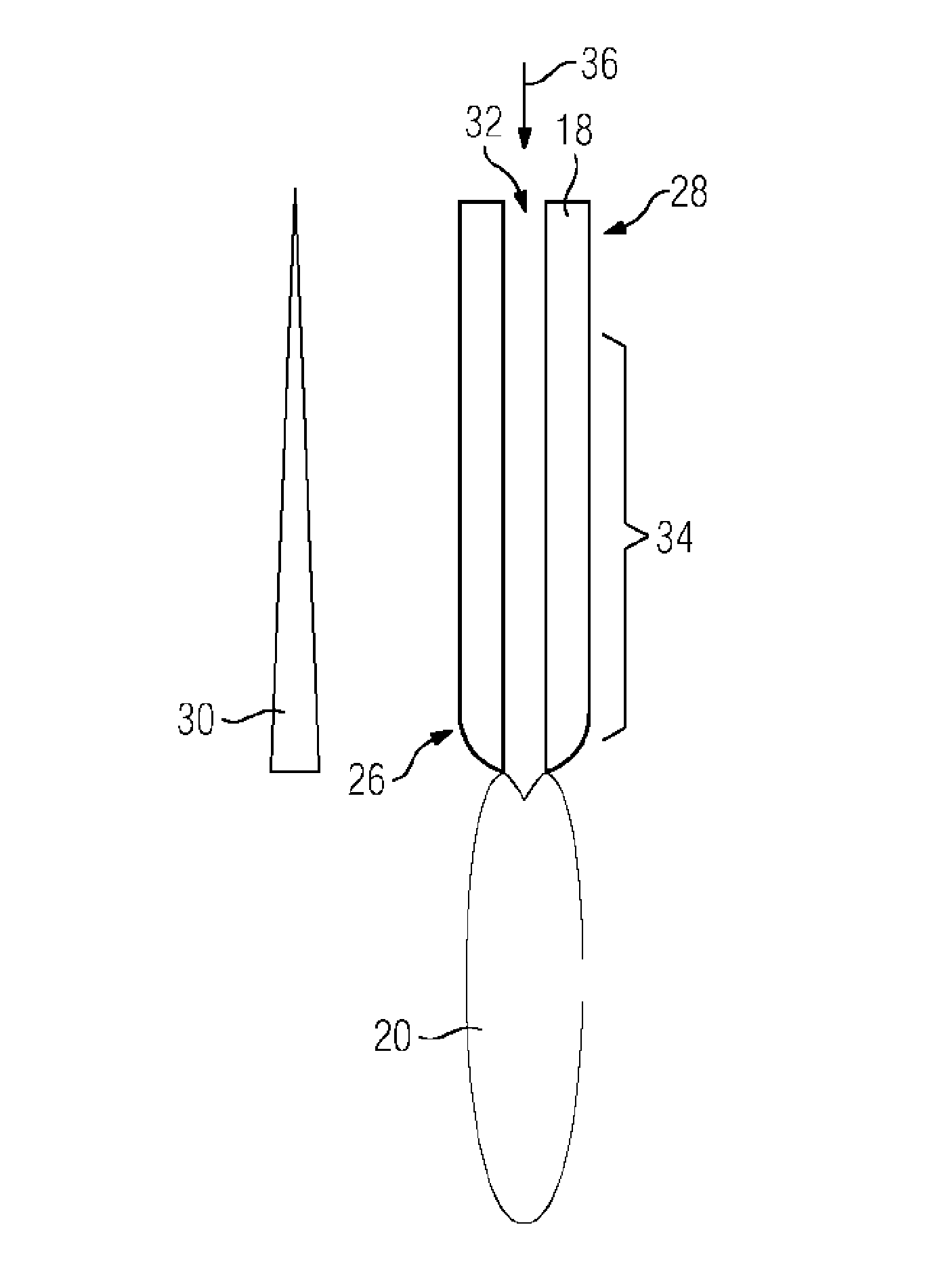
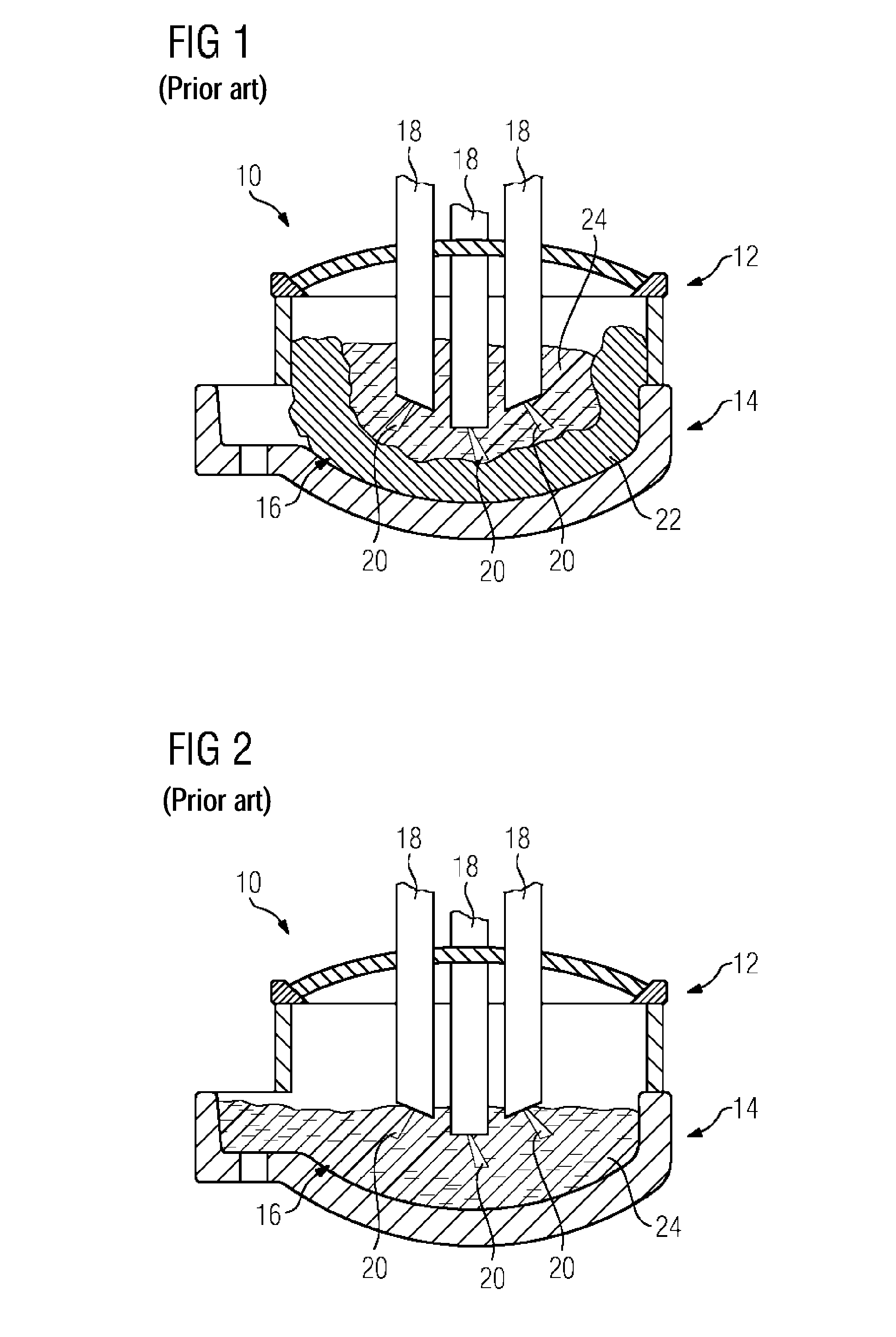
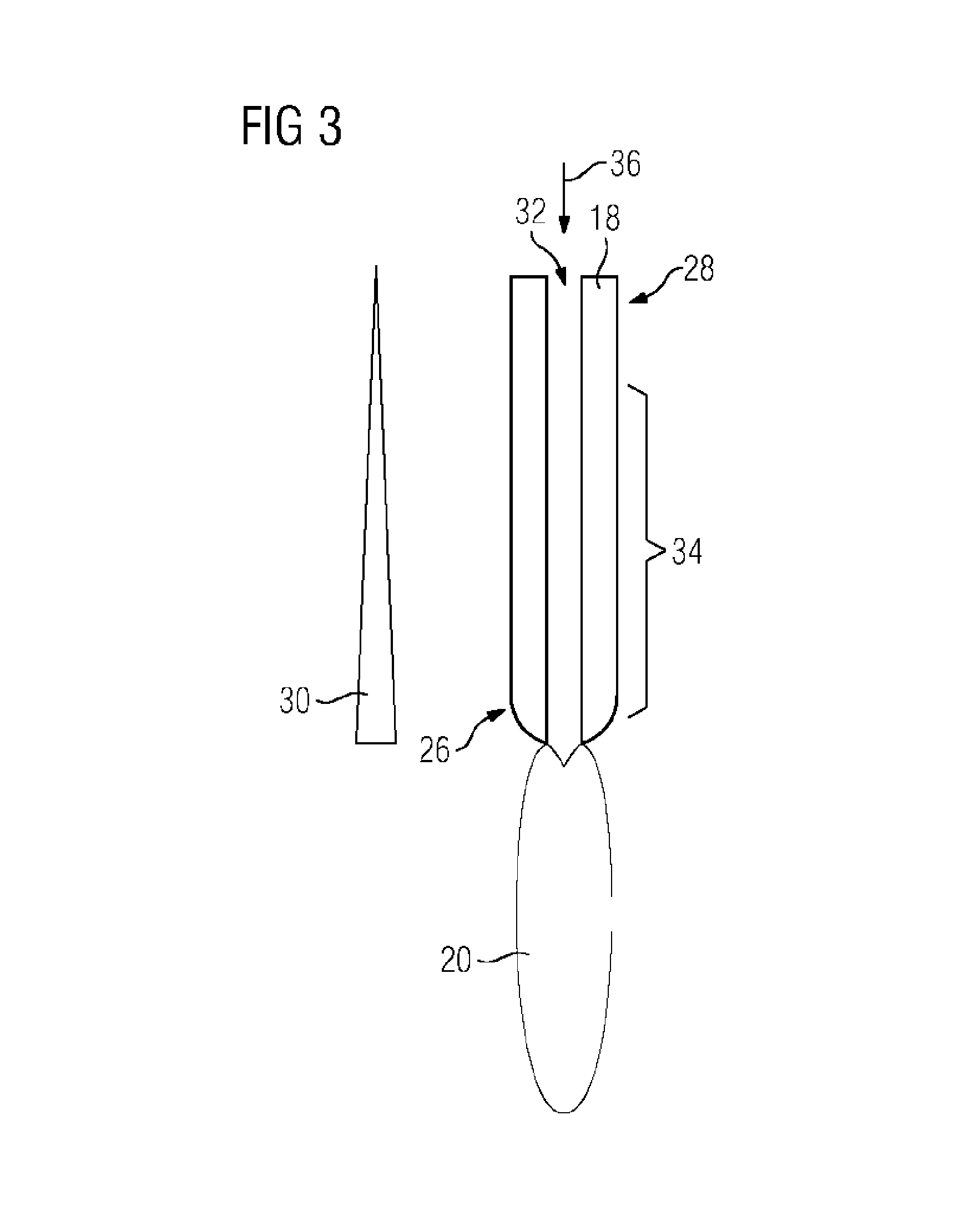
A method for operating an electric arc furnace (10) which has at least one electrode (18) having a through-opening (32). An electric arc (20) is generated between the at least one electrode (18) and a material to be melted (16). A first additive is introduced into the through-opening (32) of the electrode (18) for causing an endothermic chemical reaction which is controlled such that the chemical reaction is caused in a predetermined region (34) of the at least one electrode (18), wherein the region faces the material to be melted (16).
Owner:PRIMETALS TECH GERMANY
Method for improving sintering property of manganese-cobalt-iron-base thermal sensitive ceramic
InactiveCN109485402AReduce mass transfer resistanceLower sintering temperatureNegative temperature coefficient thermistorsResistor manufactureCeramic sinteringSesquioxide
The invention provides a method for improving the sintering property of manganese-cobalt-iron-base thermal sensitive ceramic. The method comprises the steps of with transition metal oxides including cobalt sesquioxide, trimanganese tetroxide and iron sesquioxide as main raw materials, adding a trace sintering aid, namely bismuth trioxide, preparing a powder material by virtue of a solid-phase reaction method, and finally preparing the manganese-cobalt-iron-base thermal sensitive ceramic by virtue of forming and sintering processes. According to the manganese-cobalt-iron-base thermal sensitiveceramic prepared by virtue of the preparation method, the crystallinity of crystals can be greatly improved, and the sintering temperature can be greatly deceased. The material constant B25 / 50 of theceramic is 3695K-3730K, the room temperature specific resistance rho value is 656omaga.cm-894omaga.cm, and the ceramic has very good thermal sensitivity and consistency and can be widely applied to the temperature measurement and control of electronic parts and components such as high-precision instruments.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Slurry for anti-static device
ActiveCN104650808AAvoid shockGood dispersionOther chemical processesSemiconductor materialsMetallurgy
The invention discloses slurry for an anti-static device. The slurry is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 10-15% of an organic carrier, 10-15% of glass powder, 10-20% of a wrapped conductive material, 20-30% of a spherical semiconductor material ZnO, 10-20% of spherical aluminum oxide powder, 1-5% of spherical nano Pt powder or Pd powder, and 1-5% of a solid powder dispersant.
Owner:SEMITEL ELECTRONICS
Composite material and preparation method thereof and quantum dot light-emitting diode
ActiveCN110752301ALower resistanceLower ionization energyMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesElectronic conductivityElectron transmission
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano materials, and particularly relates to a composite material, a preparation method thereof and a quantum dot light-emitting diode. The composite material comprises ZnS nano-particles and Se and Ga elements doped in the ZnS nano-particles. The composite material is the Zns nanoparticles co-doped by the acceptor (Se)-donor (Ga), the doping of the Se-Ga in the composite material can improve the free carrier concentration of ZnS, so that the resistance of ZnS is reduced, the conductivity is increased, and the electron transmission capability of the composite material is finally improved; and the composite material can be used as a QLED electron transmission material, so that the effective compounding of electrons-holes in a quantum dot lightemitting layer can be promoted, the influence on the device performance by the exciton accumulation can be reduced, and the performance of the device and display performance are improved.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Long-acting high-voltage direct-current breakdown resistant polyethylene resin as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to long-acting high-voltage direct-current breakdown resistant polyethylene resin as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of polyethylene resin. The problems that the existing polyethylene insulating material has inherent low breakdown field strength, and a voltage-resistant monomer is easy to migrate and separate out are solved. The long-acting high-voltage direct-current breakdown resistant polyethylene resin is prepared from the following raw materials in 100 parts by weight: 88.0-92.9 parts by weight of pre-irradiated polyethylene resin, 5-10 parts by weight of polyethylene grafted styrene polymer resin and 0.1-2.0 parts by weight of voltage-resistant monomer. The polyethylene resin voltage-resistant monomer is bonded to a polyethylene resin molecular chain, so migration and precipitation are limited, and the polyethylene resin voltage-resistant monomer has long-acting breakdown resistance; through a high-voltage direct-current breakdown experiment, the direct-current breakdown field strength is 397.8-497.6 kV / mm, and the direct-current breakdown field strength is 392.1-460.5 kV / mm after accelerated migration is carried out for 288 h at the temperature of 75 DEG C.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A kind of epitaxial growth method of high-efficiency ultraviolet LED
The invention provides a new method for epitaxial growth of an ultraviolet LED. By the adoption of the method for epitaxial growth of the ultraviolet LED, the growth difficulty can be greatly lowered, and the radiant power of the ultraviolet LED is greatly increased. An AlGaN / AlxInyGa1-x-y layer is grown for a plurality of periods, wherein x, y, z and w meet the following requirements for x<z<1, w<y<1, 0<z+w<1 and 0<x+y<1. Through the component ratio relationship of Al, In and Ga, all components of an AlxInyGa1-x-yN layer can be well matched with lattices of the AlGaN layer, stress is reduced, the crystalline quality of AlGaN and AlxInyGa1-x-y materials is improved, and threading dislocation can also be avoided.
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
Ceramic halogen lamp
InactiveCN104183466AIncrease vapor pressureIncrease steam pressureGas discharge lamp detailsNoble gasSodium iodide
Provided is a ceramic halogen lamp which comprises a ceramic electric arc tube filled with a rare gas, first metal halides, second metal halides, and zinc. The first metal halides comprise sodium iodide, thallium iodide, dysprosium iodide, and thulium iodide. The second metal halides comprise zinc iodide and gallium iodide. The ceramic halogen lamp is environmentally friendly.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +2
Preparation method for N-Zr co-doping of zinc oxide thin film
ActiveCN103866267AImprove stabilityPromote formationChemical vapor deposition coatingOxygenZinc oxide thin films
The invention discloses a preparation method for N-Zr co-doping of a zinc oxide thin film. The method comprises the steps of placing a substrate in an ALD reaction chamber, heating the substrate and a chamber pipeline, and then carrying out multi-component composite deposition. The composite deposition comprises: after primary zinc source deposition, respectively introducing doping deposition of a doping source containing a doping element Zr for one time, secondary zinc source deposition, nitrogen doping source deposition for two times and oxygen source deposition for two times, and thus forming N-Zr-N co-doping; the sequence of the nitrogen doping source deposition and the oxygen source deposition is that firstly the nitrogen doping source deposition is carried out and then the oxygen source deposition is carried out; the sequence of the doping element Zr-containing doping source deposition and the secondary zinc source deposition is that firstly the doping element Zr-containing doping source deposition is carried out and then the secondary zinc source deposition is carried out. The method can be used for in-situ donor-acceptor co-doping on the zinc oxide thin film, so as to increase the doped amount of the acceptor element, and promote p-type conversion of the zinc oxide thin film.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Titanium monoxide electrolytic capacitor anode and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1889213AImprove performanceIncrease specific volumeElectrolytic capacitorsElectrolysisAlloy
The invention relates to the pole of the electrolyzing capacitor, especially the positive pole of the electrolyzing capacitor made of titanium oxide or adulterated titanium oxide, and its producing method. Its character is as follow. Oxygen index range of titanium oxide is more than 0.8 and less than 1.2. The adulterant includes valve metal, one or several kinds of low price oxide of valve metal or their alloy and mixture. The adulterant range is between 0 and 50 wt%. The invention decreases the producing cost, ionization energy and the content of low price titanium oxide in the TiO2 oxide film and increases oxidation rate. The positive pole of the electrolyzing capacitor made of it has high stabilization and high specific votume up to 40000 muF .V .g-1-240000 muF .V .g-1. The creepage current is weak and K is 0.1 muA . muF-1 . V-10.005 muA . muF-1 .V-1.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Compounds, electronic components and electronic devices
ActiveCN111018843BStable structureNot easy to decomposeOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesAlkoxy groupHigh electron
The application provides a compound, an electronic component and an electronic device, which relate to the technical field of organic materials. The compound is shown in formula I, wherein, X 1 、X 2 and X 3 The same or different, and each independently selected from: carbon or nitrogen, where X 1 、X 2 and X 3 Not simultaneously carbon; L is selected from: single bond, arylene, heteroarylene, aralkylene, heteroaralkylene; Ar 1 is selected from: alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, alkoxy, alkylamino, arylamino, aralkylamino; Ar 2 、Ar 3 The same or different, and each independently selected from: cycloalkyl, aryl, heteroaryl, alkoxy, alkylamino, arylamino, aralkylamino. The compound of the present application can reduce the working voltage of the electronic components, improve the luminous efficiency of the electronic components and prolong the service life of the devices.
Owner:SHAANXI LIGHTE OPTOELECTRONICS MATERIAL CO LTD
Composite material, preparation method thereof and quantum dot light-emitting diode
ActiveCN112397625ALower resistanceLower ionization energyMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor devicesElectron holeOrganosolv
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano materials, and particularly relates to a composite material, a preparation method thereof and a quantum dot light-emitting diode. The composite material comprises titanium dioxide nanoparticles, and phosphorus elements and vanadium elements which are doped in the titanium dioxide nanoparticles. The preparation method of the composite material comprises the following steps: providing titanium salt, orthophosphate and vanadium salt; dissolving the titanium salt, orthophosphate and vanadium salt in an organic solvent to obtain a mixed solution;mixing the mixed solution with alkali liquor, and heating to obtain a precursor solution; and carrying out solid-liquid separation on the precursor solution to obtain the composite material. The composite material provided by the invention is used as a hole transport material of the quantum dot light-emitting diode, can promote effective recombination of electrons and holes in a quantum dot light-emitting layer, and reduces the influence of exciton accumulation on the device performance, thereby improving the display performance of the device.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
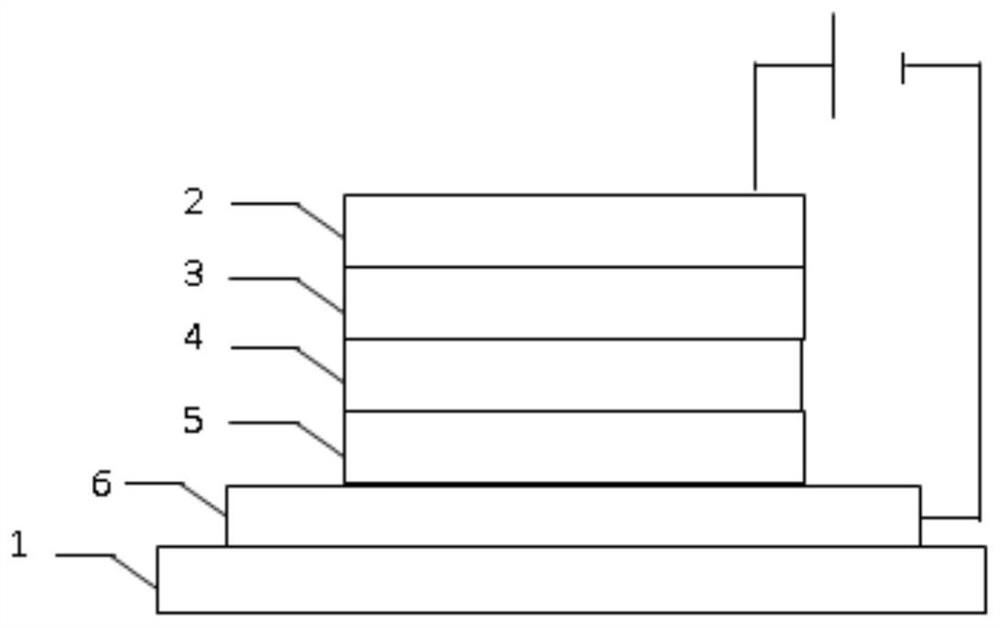
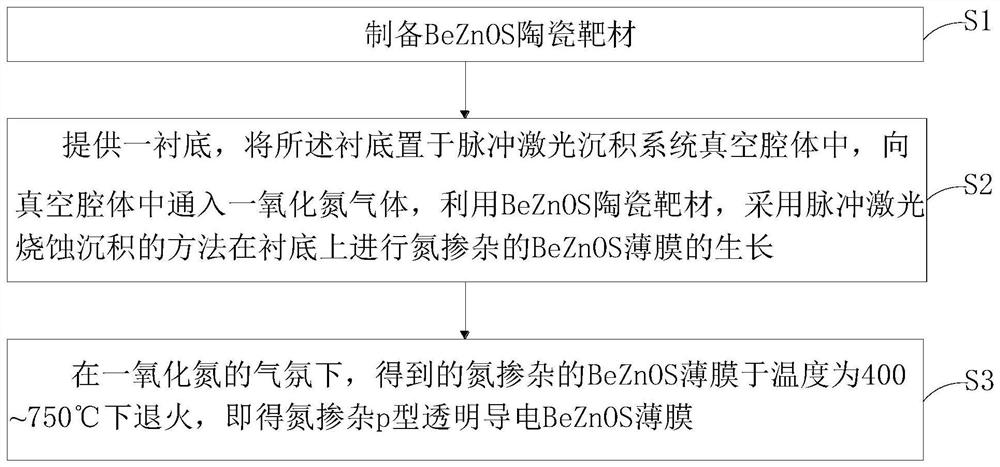
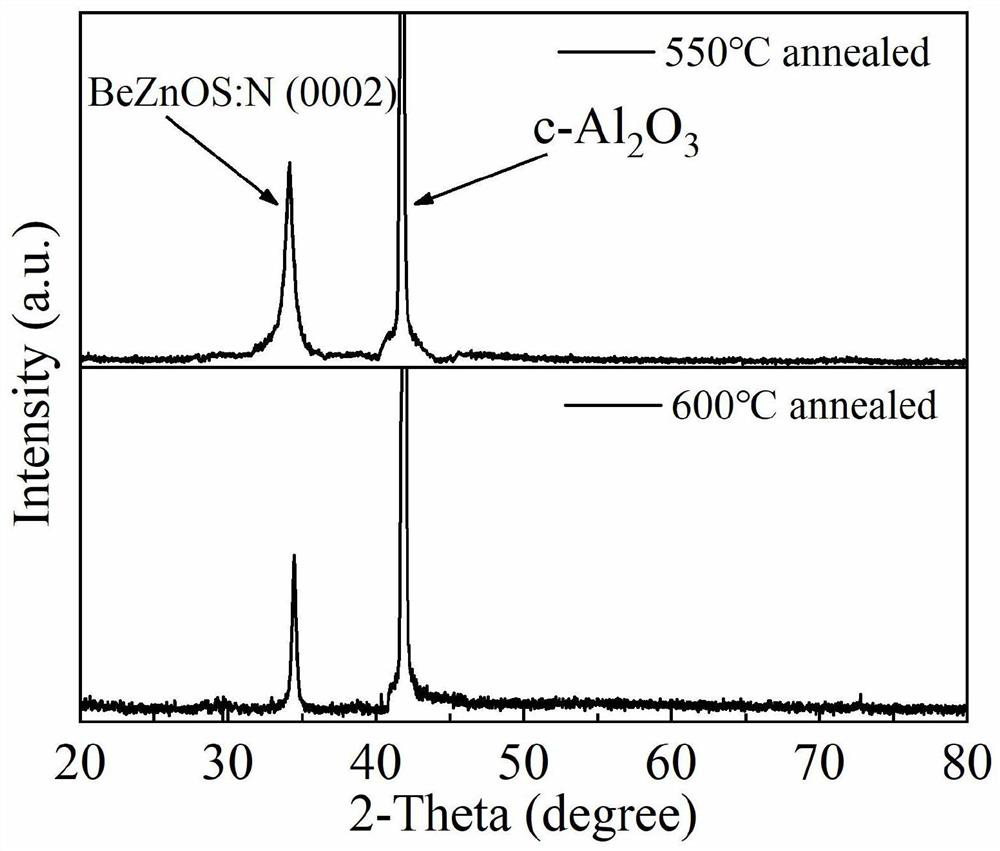
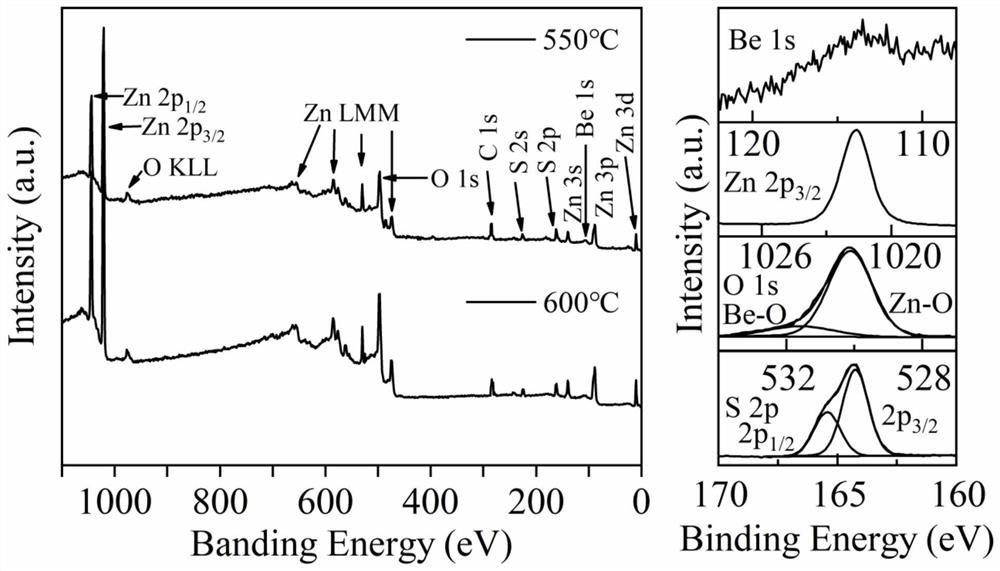
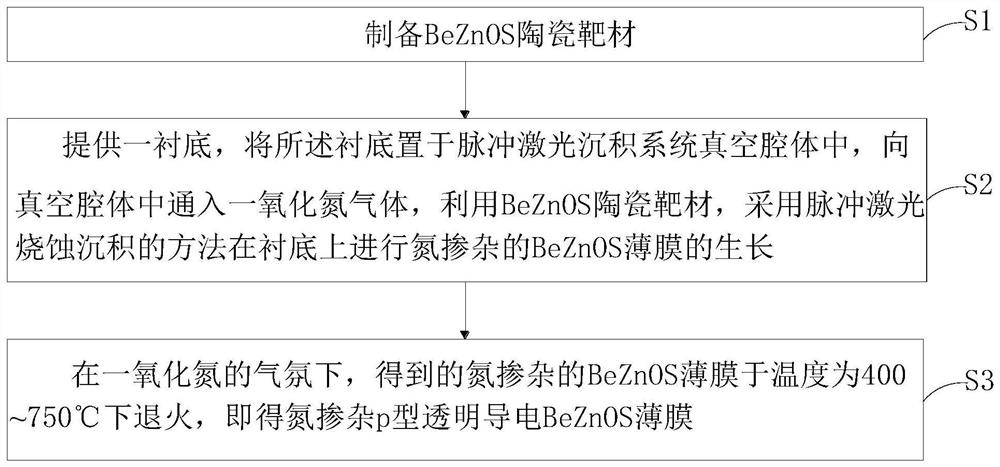
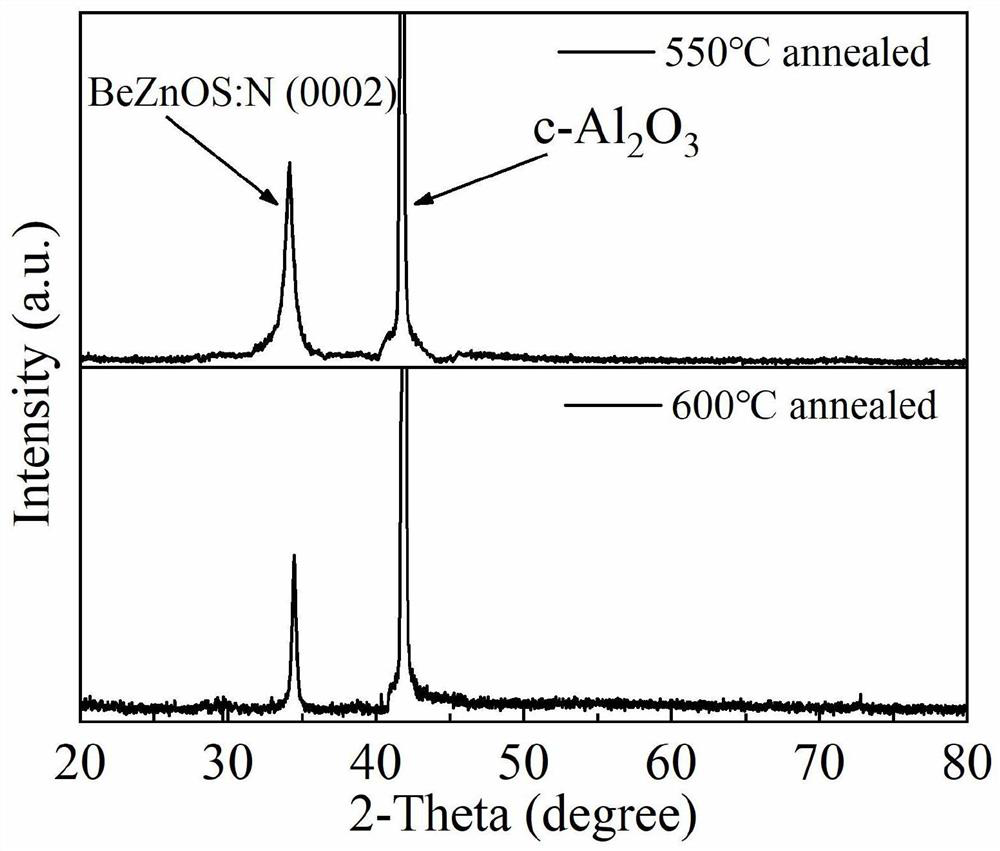
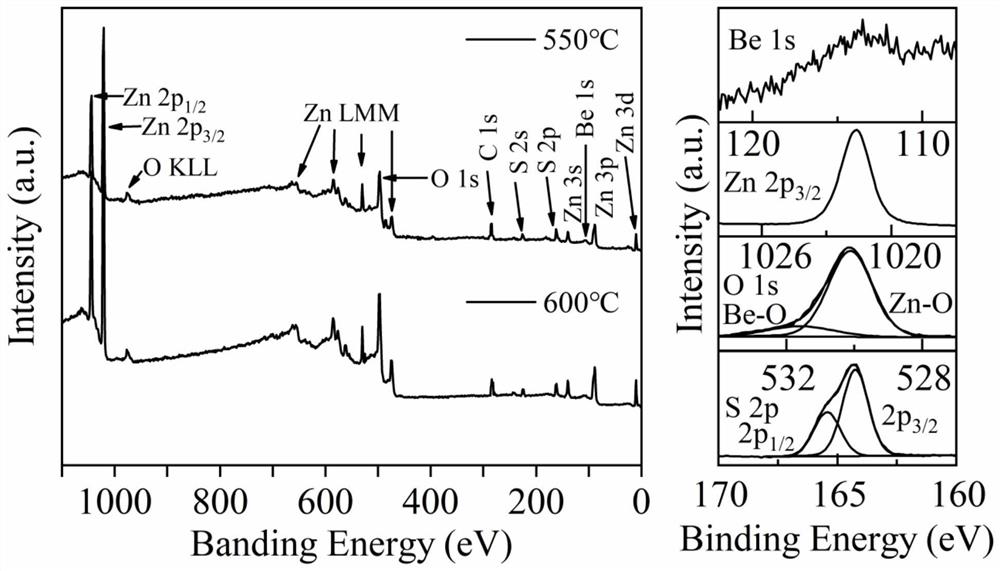
Nitrogen-doped p-type transparent conductive beznos thin film and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112195438BLower energy levelLower ionization energyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingValence bandElectronic structure
The invention provides a nitrogen-doped p-type transparent conductive BeZnOS film and its preparation method and application. The preparation method includes: preparing a BeZnOS ceramic target; providing a substrate, and placing the substrate in a vacuum chamber of a pulsed laser deposition system In the process, nitric oxide gas is introduced into the vacuum cavity, and the nitrogen-doped BeZnOS film is grown on the substrate by using the BeZnOS ceramic target material and the method of pulsed laser ablation deposition; the obtained nitrogen-doped BeZnOS The thin film is annealed at a temperature of 400-750° C. to obtain a nitrogen-doped p-type transparent conductive BeZnOS thin film. In the preparation method of the present invention, doping Be and S in ZnO to form a BeZnOS alloy can continuously adjust its energy band structure and electronic structure while maintaining the hexagonal structure of ZnO, more stable Be-N bonds and higher valence band tops Can reduce N o energy level, increasing N o stability.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV +1
Nitrogen-doped p-type transparent conductive BeZnOS film as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112195438ALower energy levelLower ionization energyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingValence bandElectronic structure
The invention provides a nitrogen-doped p-type transparent conductive BeZnOS film as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing a BeZnOS ceramic target material; providing a substrate, placing the substrate in a vacuum cavity of a pulse laser deposition system, introducing nitric oxide gas into the vacuum cavity, and growing a nitrogen-doped BeZnOS film on the substrate by using a BeZnOS ceramic target material and adopting a pulse laser ablation deposition method; and annealing the obtained nitrogen-doped BeZnOS filmat the temperature of 400-750 DEG C to obtain the nitrogen-doped p-type transparent conductive BeZnOS film. According to the preparation method, Be and S are doped into ZnO to form BeZnOS alloy, an energy band structure and an electronic structure of the BeZnOS alloy can be continuously adjusted, meanwhile, a hexagonal structure of ZnO can be kept, the more stable Be-N bond and the higher valenceband top can reduce the energy level of No, and the stability of No is improved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com