Composite material, preparation method thereof and quantum dot light-emitting diode
A composite material and molar weight technology, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve problems such as titanium dioxide band gap and unsatisfactory electron transport effect, achieve strong affinity, reduce donor ionization energy, and increase free carrier concentration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
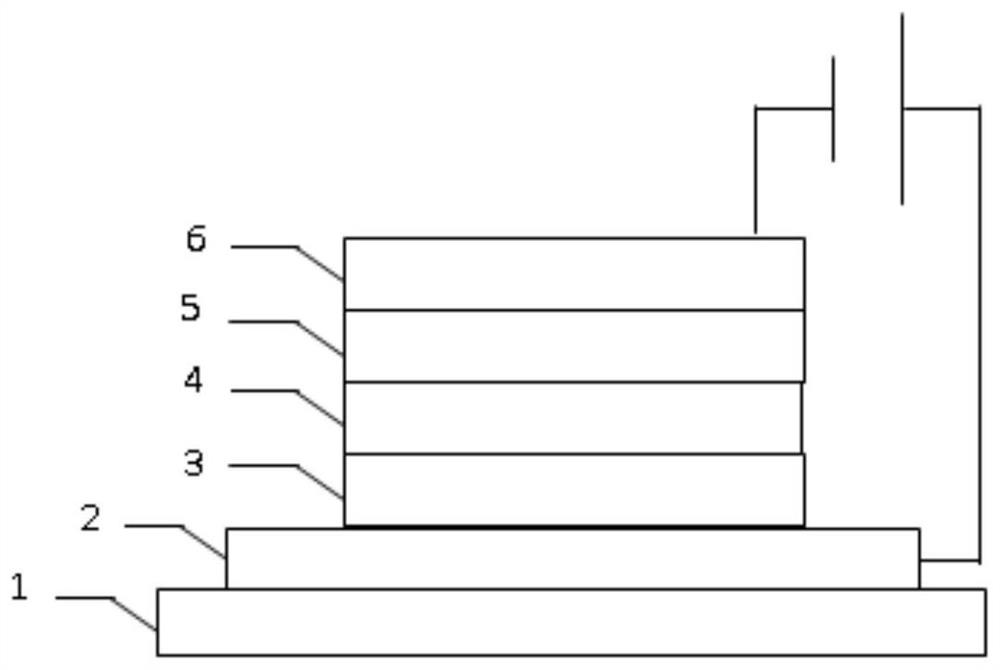
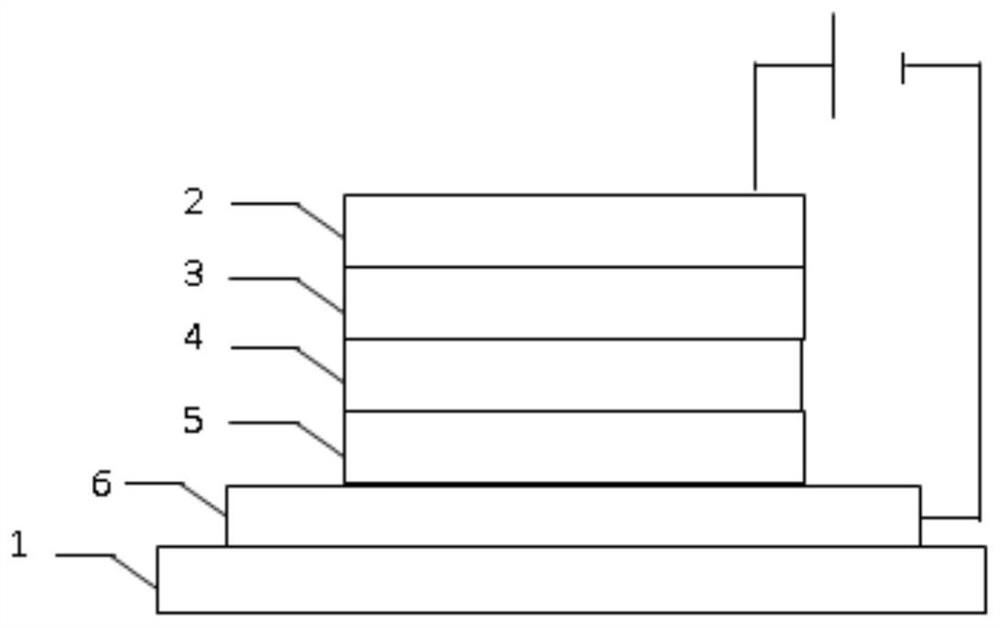
[0025] On the other hand, the embodiment of the present invention also provides a method for preparing a composite material, such as figure 1 Shown, this preparation method comprises the steps:
[0026] S01: Provide titanium salt, phosphate and vanadium salt;
[0027] S02: dissolving the titanium salt, phosphate and vanadium salt in an organic solvent to obtain a mixed solution;
[0028] S03: mixing the mixed solution with lye and heating to obtain a precursor solution;
[0029] S04: performing solid-liquid separation on the precursor solution to obtain a composite material.
[0030] In the preparation method of the composite material provided by the embodiment of the present invention, a P-V co-doped TiO is prepared by the sol-gel method. 2 Nano-materials, the preparation method is simple, low-cost, suitable for large-scale, large-scale preparation; the final composite material can make TiO 2 The electron Fermi level moves to the conduction band, making TiO 2 The forbidden...
Embodiment 1
[0051] Taking the use of titanium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, vanadium chloride, ethanol, and sodium hydroxide as examples, the preparation of composite thin films is introduced, including the following steps:
[0052] 1) Add an appropriate amount of titanium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium chloride to 50ml of ethanol, stir and dissolve at 70°C to form a salt solution with a total concentration of 0.5M, wherein the molar ratio of titanium: (phosphorus + vanadium) It is 1:0.05; the molar ratio of phosphorus: vanadium is 1:3.
[0053] 2) Take sodium hydroxide by weighing, dissolve in the solution of 10ml ethanol, prepare lye; According to OH - and M x+ (M=titanium+phosphorus+vanadium) molar ratio is 4.5:1. Add lye to the salt solution to form a mixed solution with a pH of 13, and then stir at 70°C for 4 hours to obtain a uniform solution.
[0054] 3) After the solution is cooled, spin-coat the treated ITO with a homogenizer and anneal at 250°C to ...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Taking the use of titanium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, vanadium chloride, ethanol, and sodium hydroxide as examples, the preparation of composite materials is introduced, including the following steps:
[0057] 1) Add an appropriate amount of titanium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate and vanadium chloride to 50ml of ethanol, stir and dissolve at 70°C to form a salt solution with a total concentration of 0.5M, wherein the molar ratio of titanium: (phosphorus + vanadium) It is 1:0.07; the molar ratio of phosphorus:vanadium is 1:2.5.
[0058] 2) Take sodium hydroxide by weighing, dissolve in the solution of 10ml ethanol, prepare lye; According to OH - and M x+ (M=titanium+phosphorus+vanadium) molar ratio is 4.5:1, add lye to the salt solution to form a mixed solution with pH=13, then stir at 70°C for 4 hours to obtain a homogeneous solution.
[0059] 3) After the solution is cooled, spin-coat the treated ITO with a homogenizer and anneal at 250°C to obtai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com