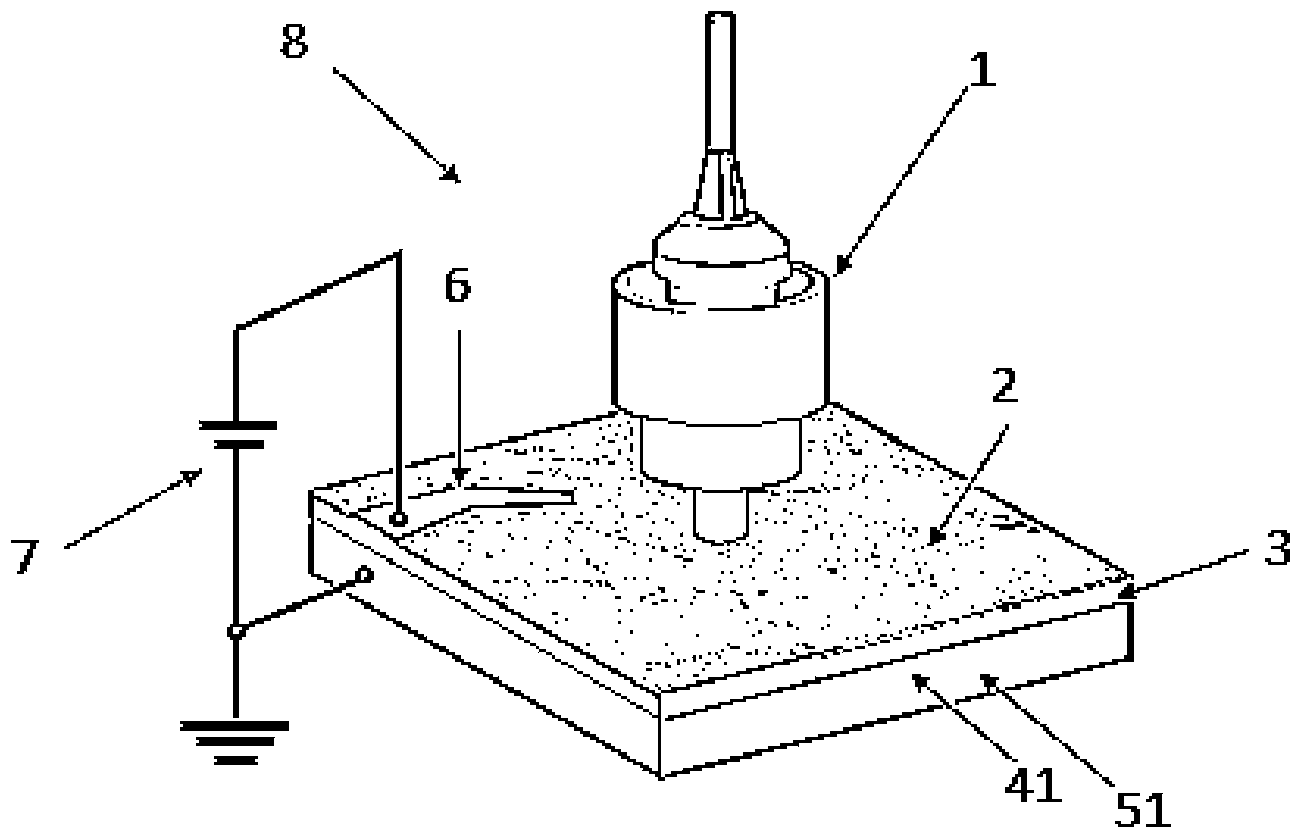
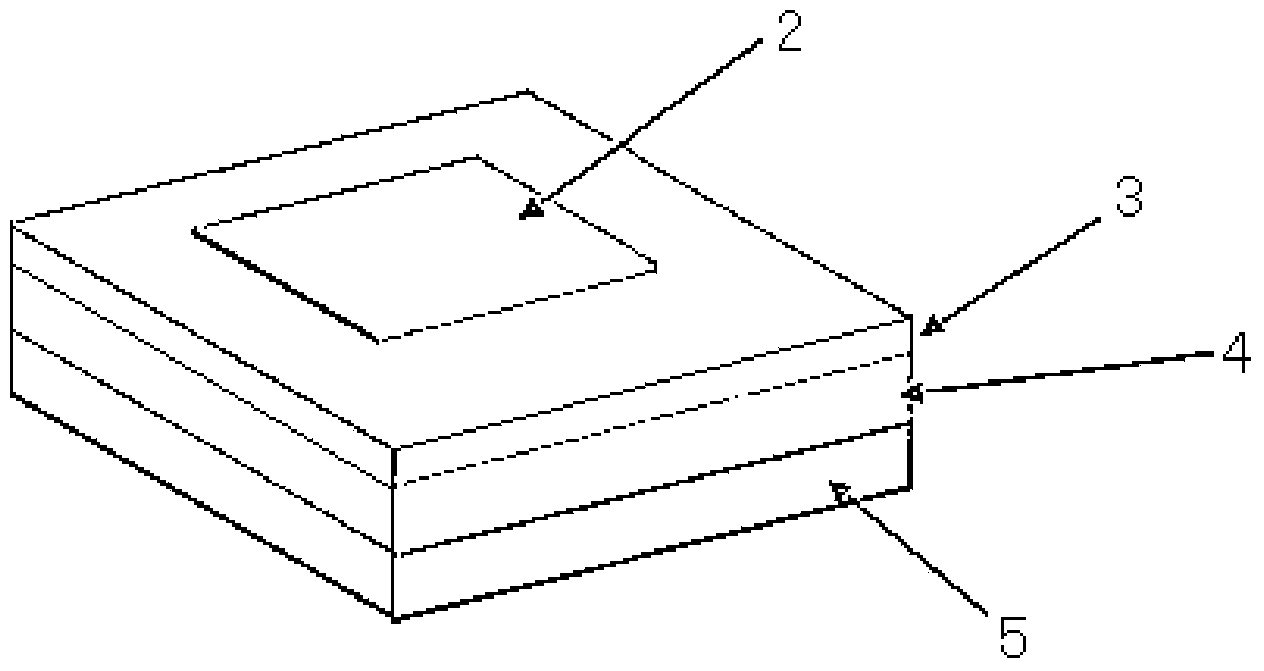
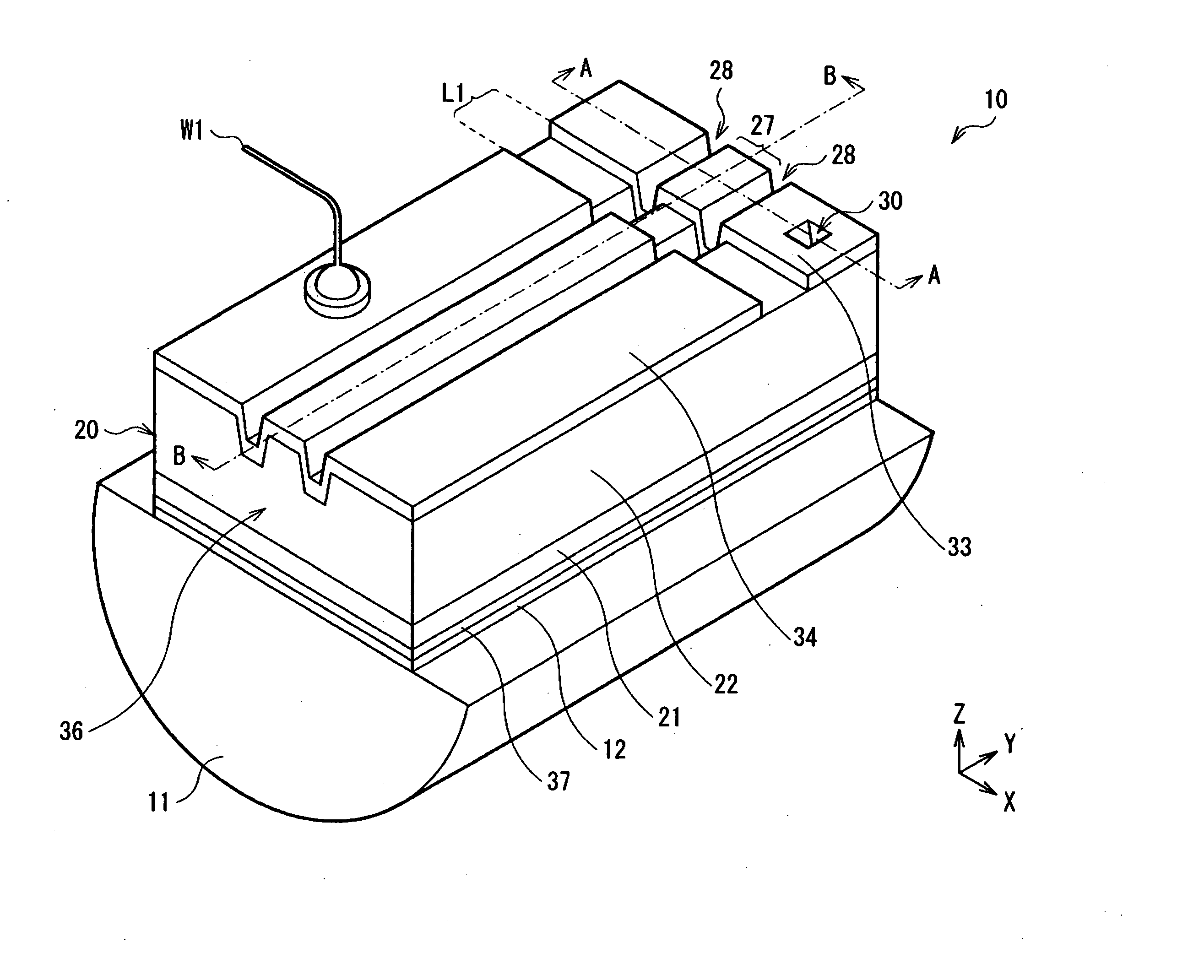
Patents
Literature
1054 results about "Saturable absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Saturable absorption is a property of materials where the absorption of light decreases with increasing light intensity. Most materials show some saturable absorption, but often only at very high optical intensities (close to the optical damage). At sufficiently high incident light intensity, atoms in the ground state of a saturable absorber material become excited into an upper energy state at such a rate that there is insufficient time for them to decay back to the ground state before the ground state becomes depleted, and the absorption subsequently saturates. Saturable absorbers are useful in laser cavities. The key parameters for a saturable absorber are its wavelength range (where it absorbs), its dynamic response (how fast it recovers), and its saturation intensity and fluence (at what intensity or pulse energy it saturates). They are commonly used for passive Q-switching.
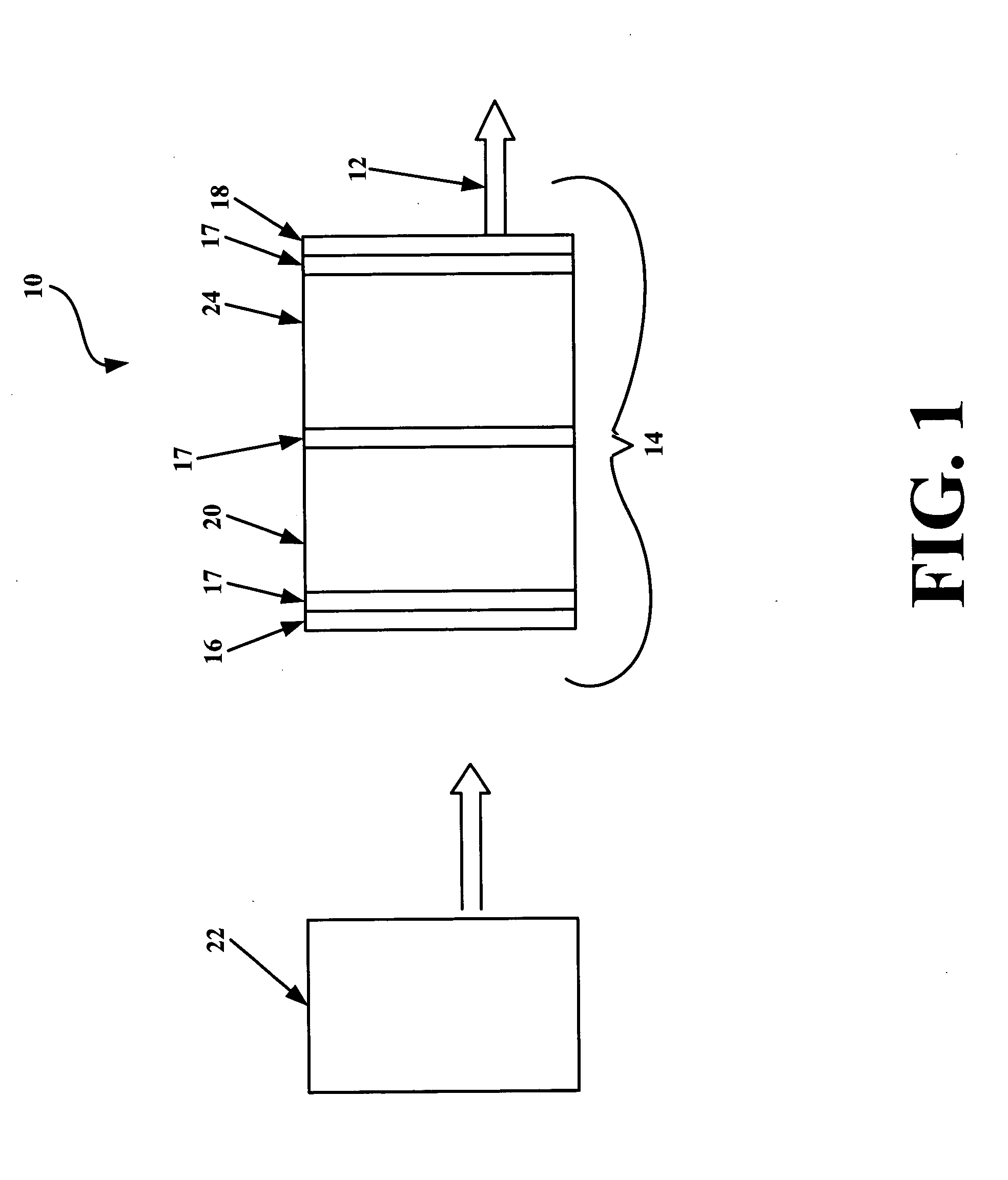
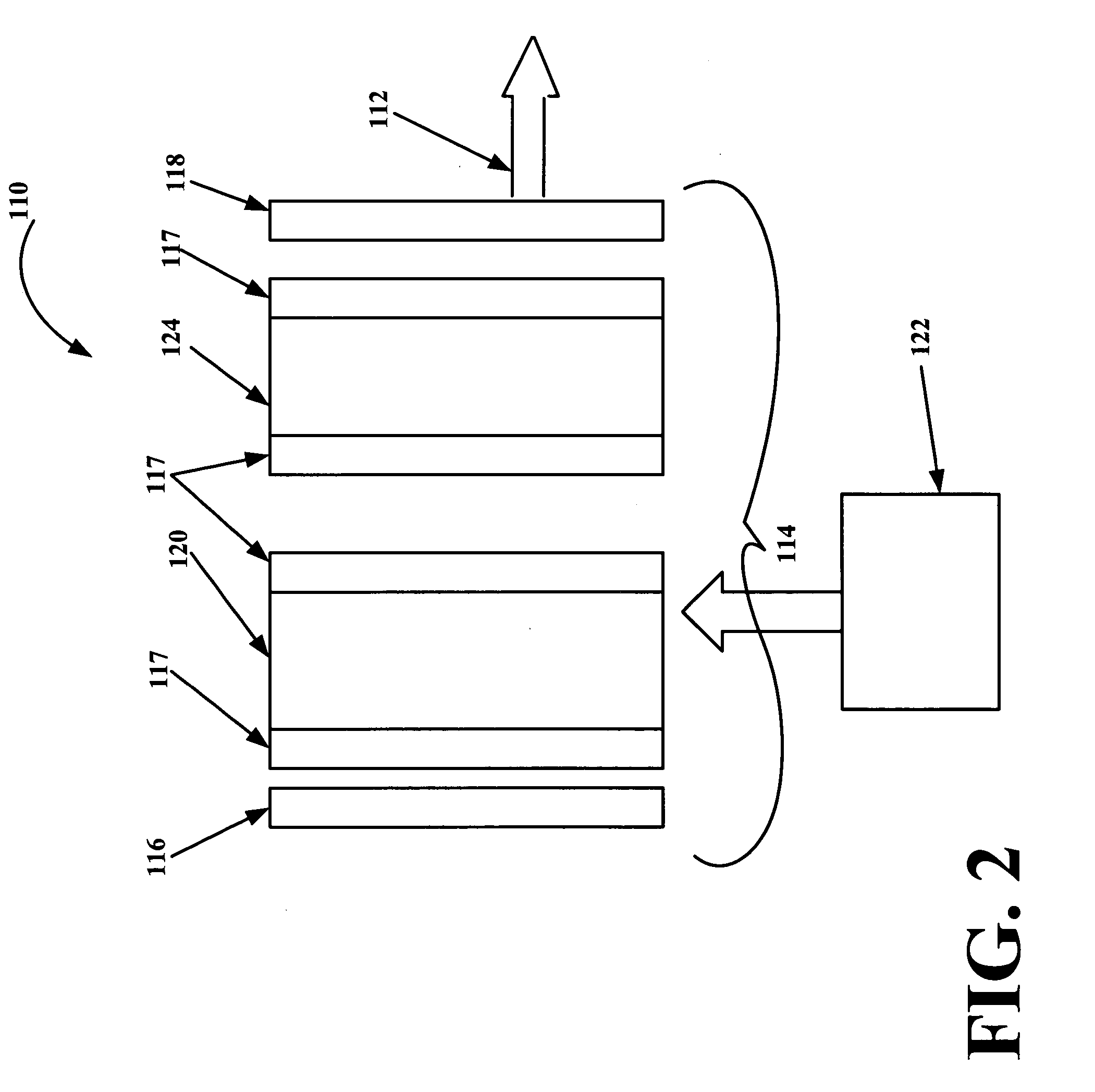
Q-switched microlaser apparatus and method for use
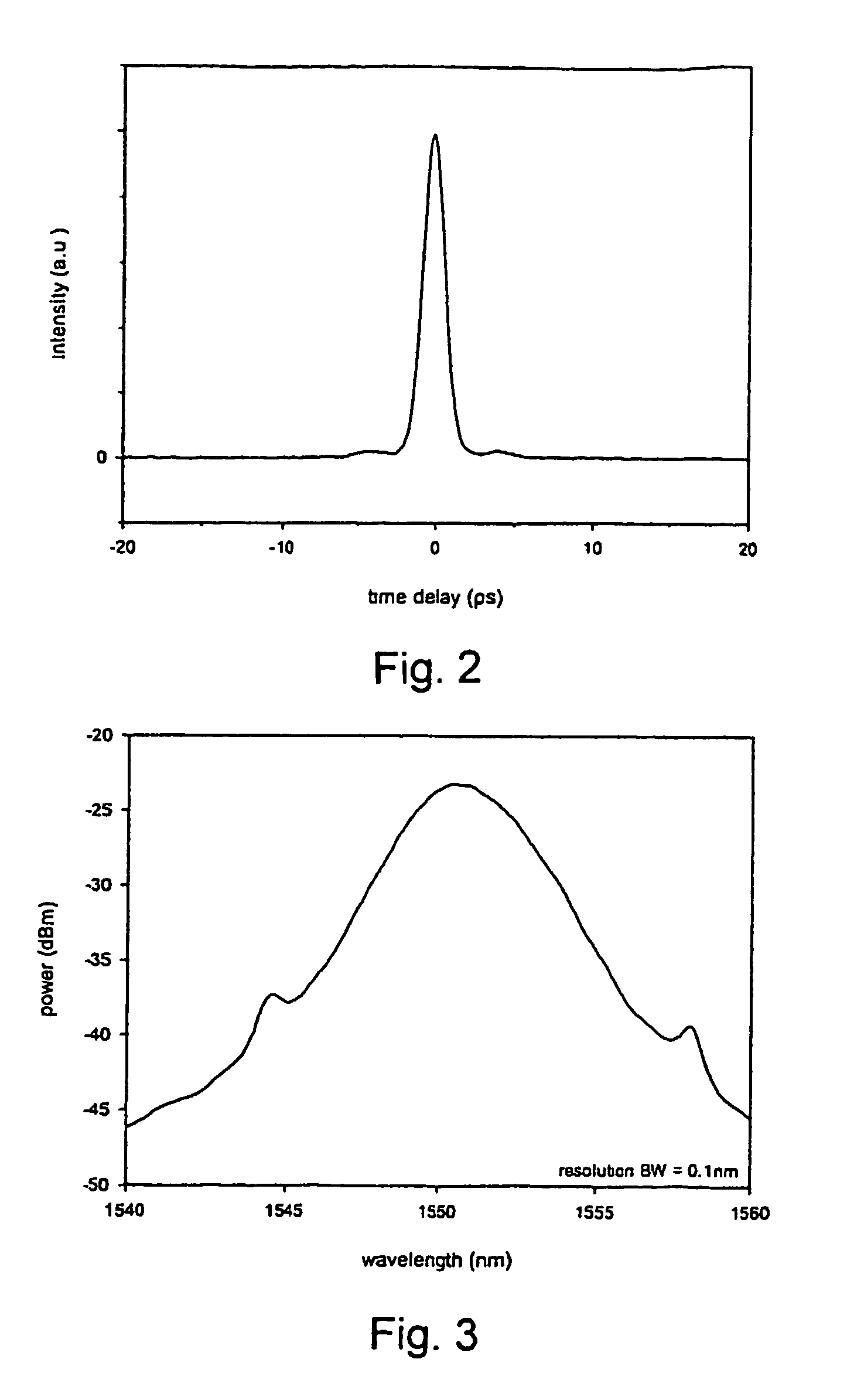
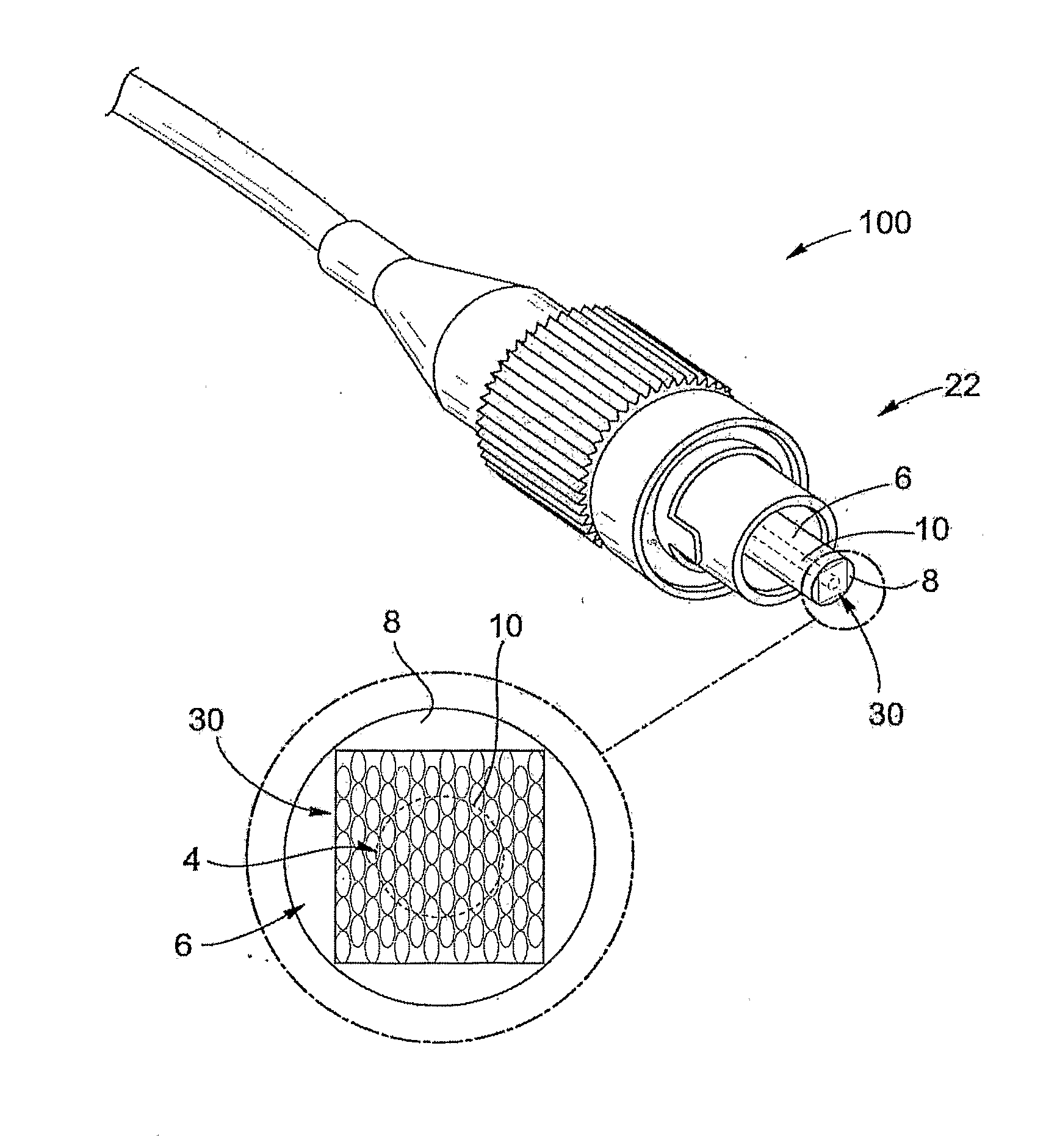
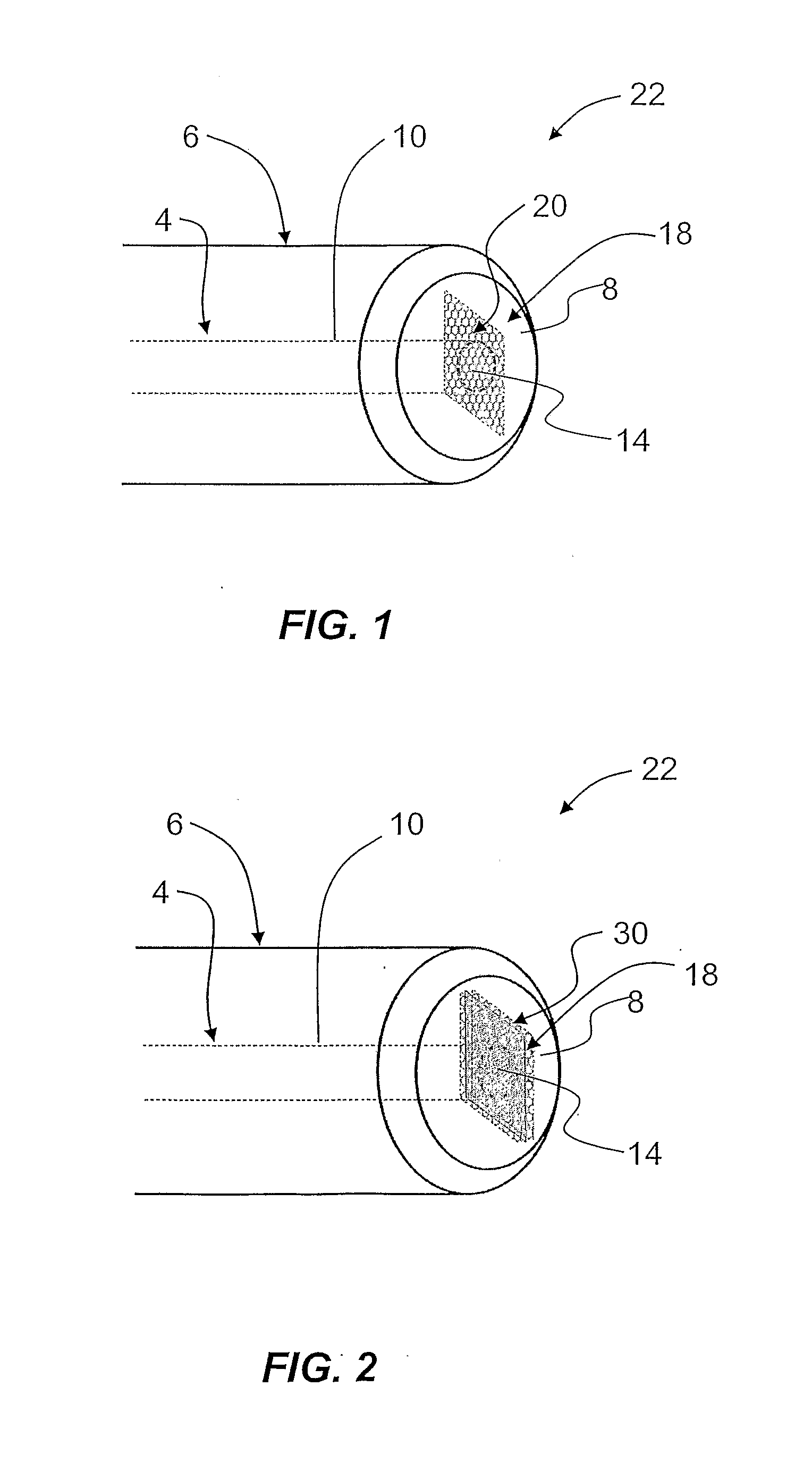
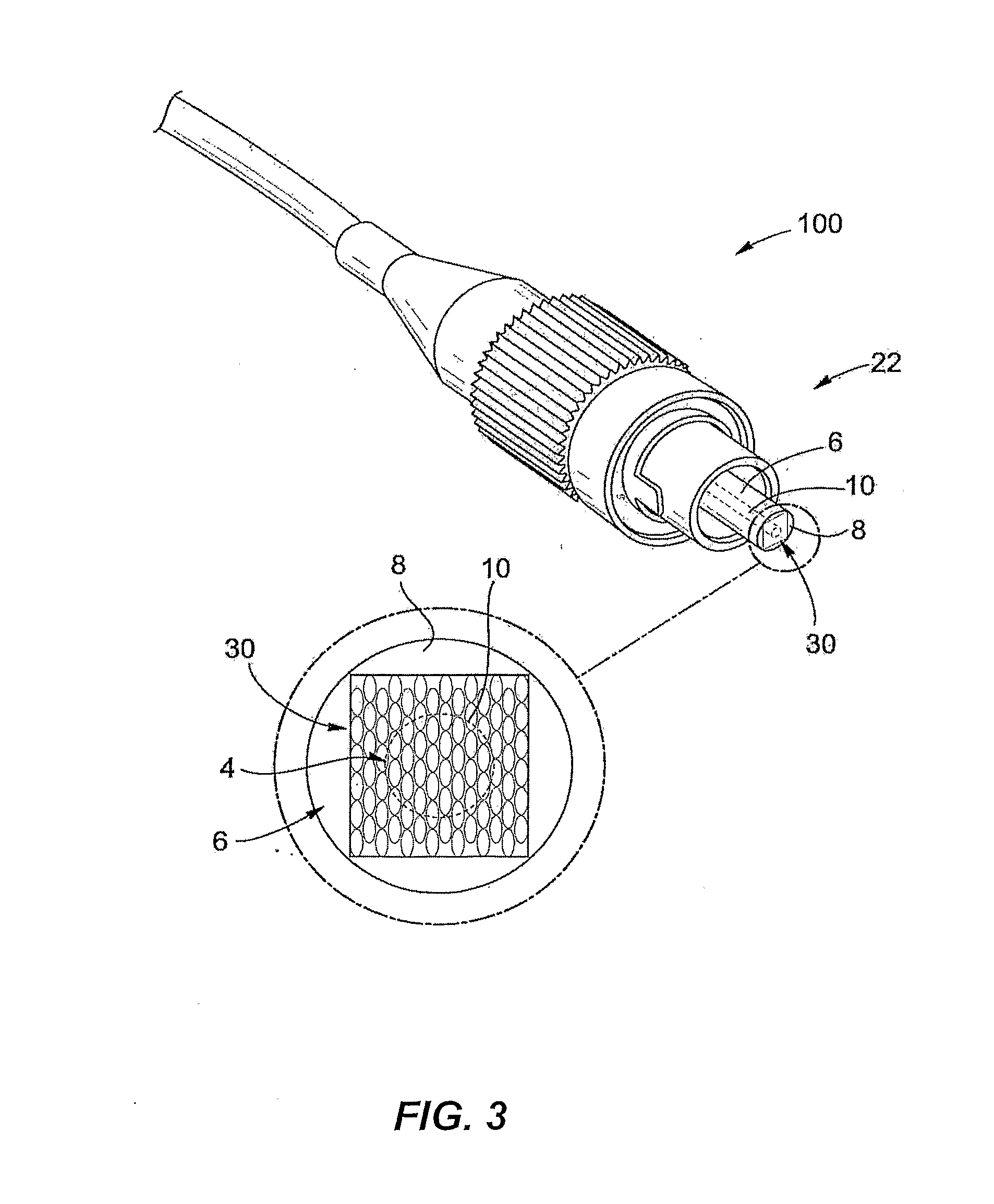
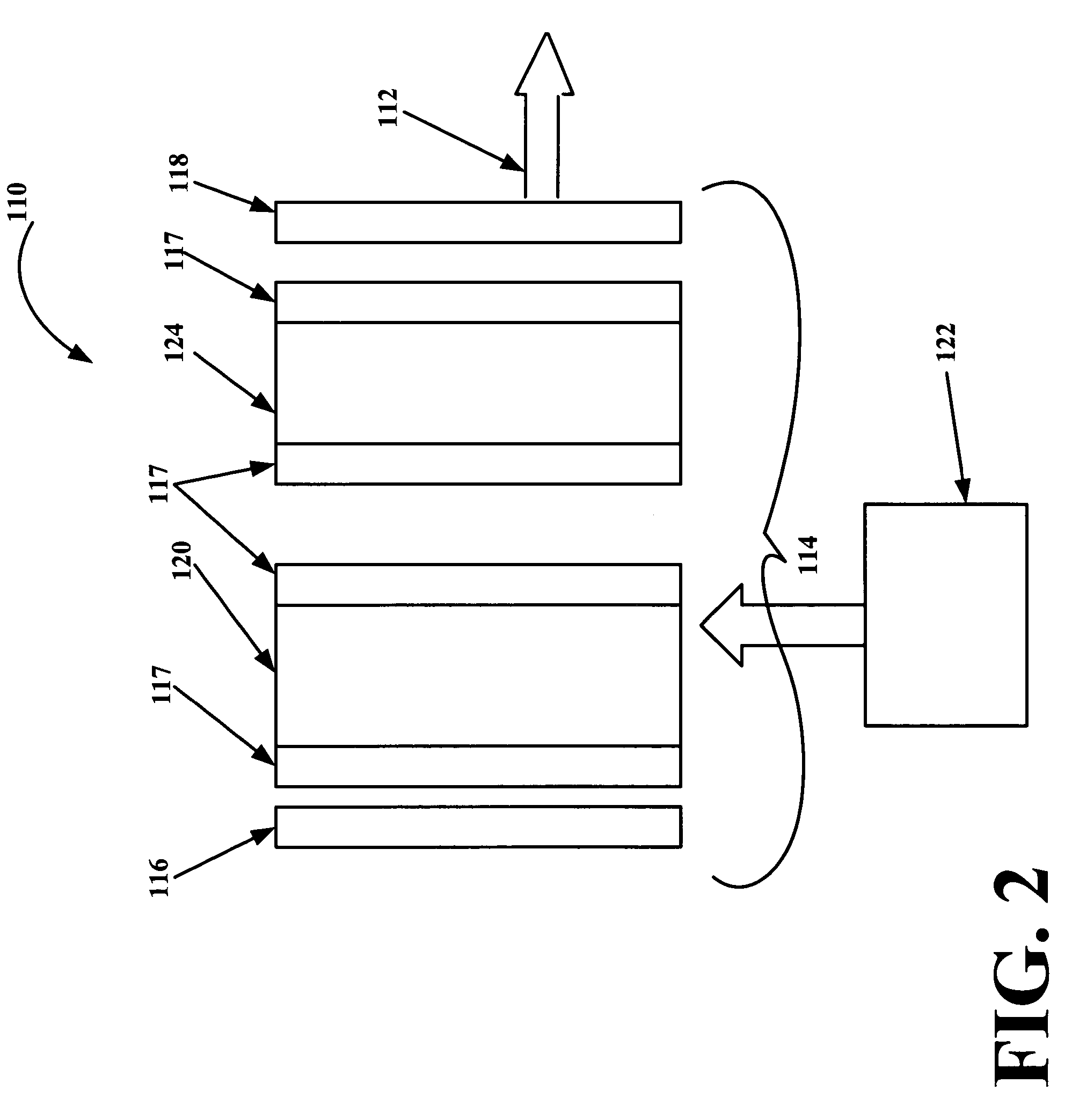
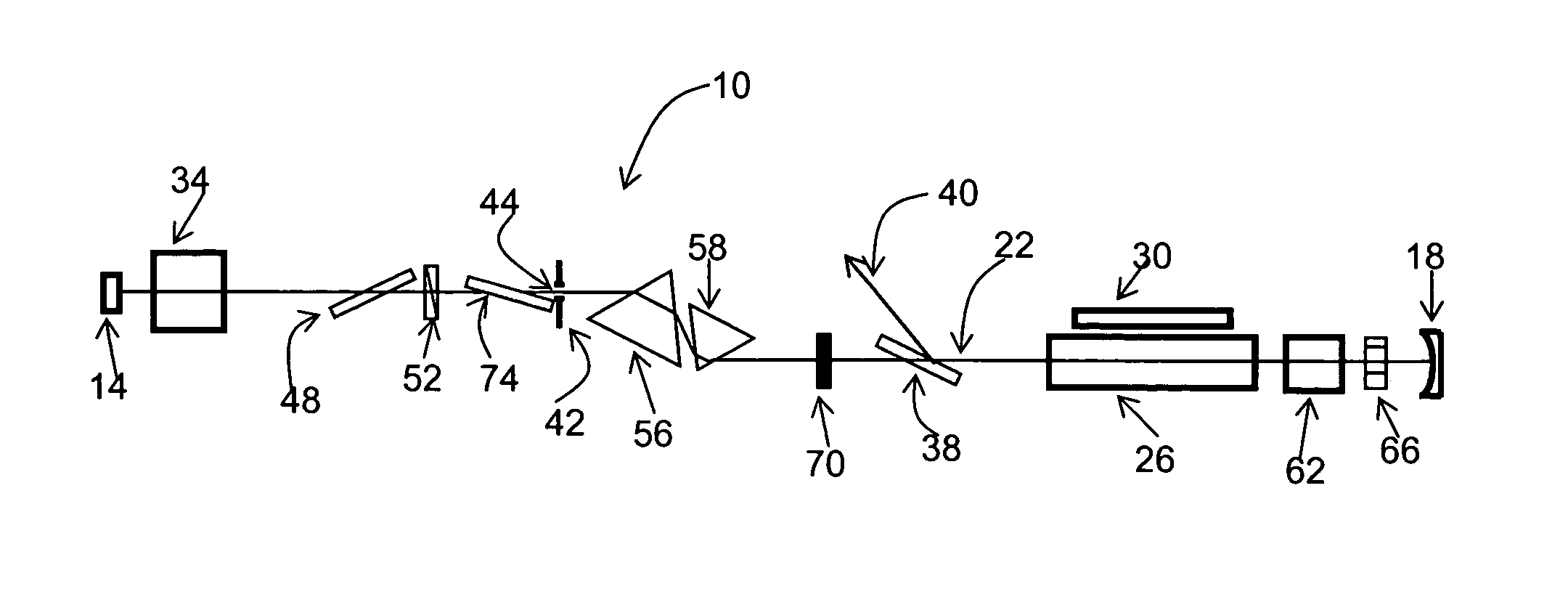
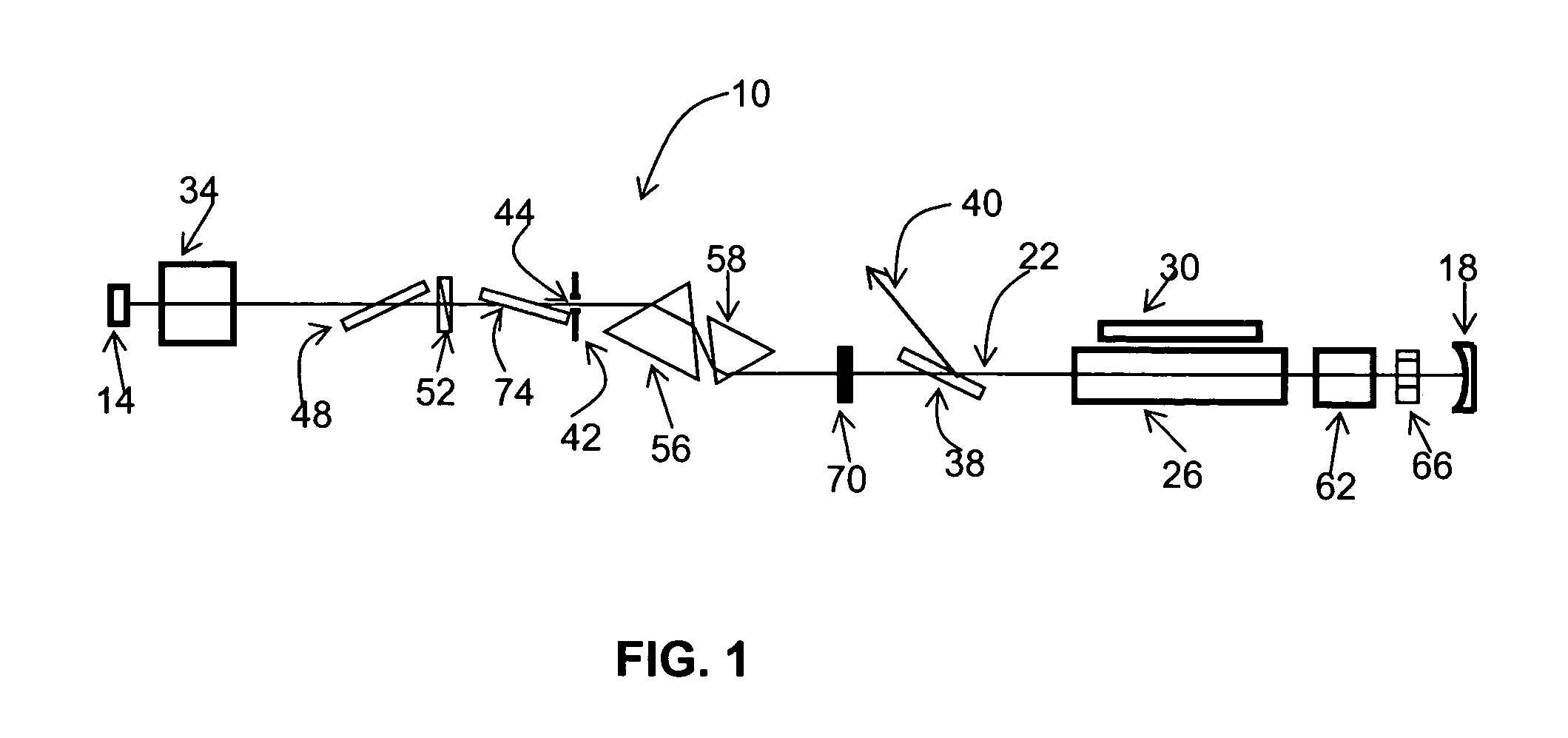
A monolithic passively Q switched microlaser includes an optically transparent heat conductive element bonded to a gain medium, which is in turn bonded to a saturable absorber, which may also be bonded to a second optically transparent heat conductive element. Only the gain medium and saturable absorber are disposed within the laser resonator.
Owner:KK TOPCON +1
Mode-locked multi-mode fiber laser pulse source
InactiveUS20050008044A1High energy storageIncrease the sectionCoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionHigh power lasersPeak value
A laser utilizes a cavity design which allows the stable generation of high peak power pulses from mode-locked multi-mode fiber lasers, greatly extending the peak power limits of conventional mode-locked single-mode fiber lasers. Mode-locking may be induced by insertion of a saturable absorber into the cavity and by inserting one or more mode-filters to ensure the oscillation of the fundamental mode in the multi-mode fiber. The probability of damage of the absorber may be minimized by the insertion of an additional semiconductor optical power limiter into the cavity. To amplify and compress optical pulses in a multi-mode (MM) optical fiber, a single-mode is launched into the MM fiber by matching the modal profile of the fundamental mode of the MM fiber with a diffraction-limited optical mode at the launch end, The fundamental mode is preserved in the MM fiber by minimizing mode-coupling by using relatively short lengths of step-index MM fibers with a few hundred modes and by minimizing fiber perturbations. Doping is confined to the center of the fiber core to preferentially amplify the fundamental mode, to reduce amplified spontaneous emission and to allow gain-guiding of the fundamental mode. Gain-guiding allows for the design of systems with length-dependent and power-dependent diameters of the fundamental mode. To allow pumping with high-power laser diodes, a double-clad amplifier structure is employed. For applications in nonlinear pulse-compression, self phase modulation and dispersion in the optical fibers can be exploited. High-power optical pulses may be linearly compressed using bulk optics dispersive delay lines or by chirped fiber Bragg gratings written directly into the SM or MM optical fiber. High-power cw lasers operating in a single near-diffraction-limited mode may be constructed from MM fibers by incorporating effective mode-filters into the laser cavity. Regenerative fiber amplifiers may be constructed from MM fibers by careful control of the recirculating mode. Higher-power Q-switched fiber lasers may be constructed by exploiting the large energy stored in MM fiber amplifiers.
Owner:FERMANN MARTIN E +1
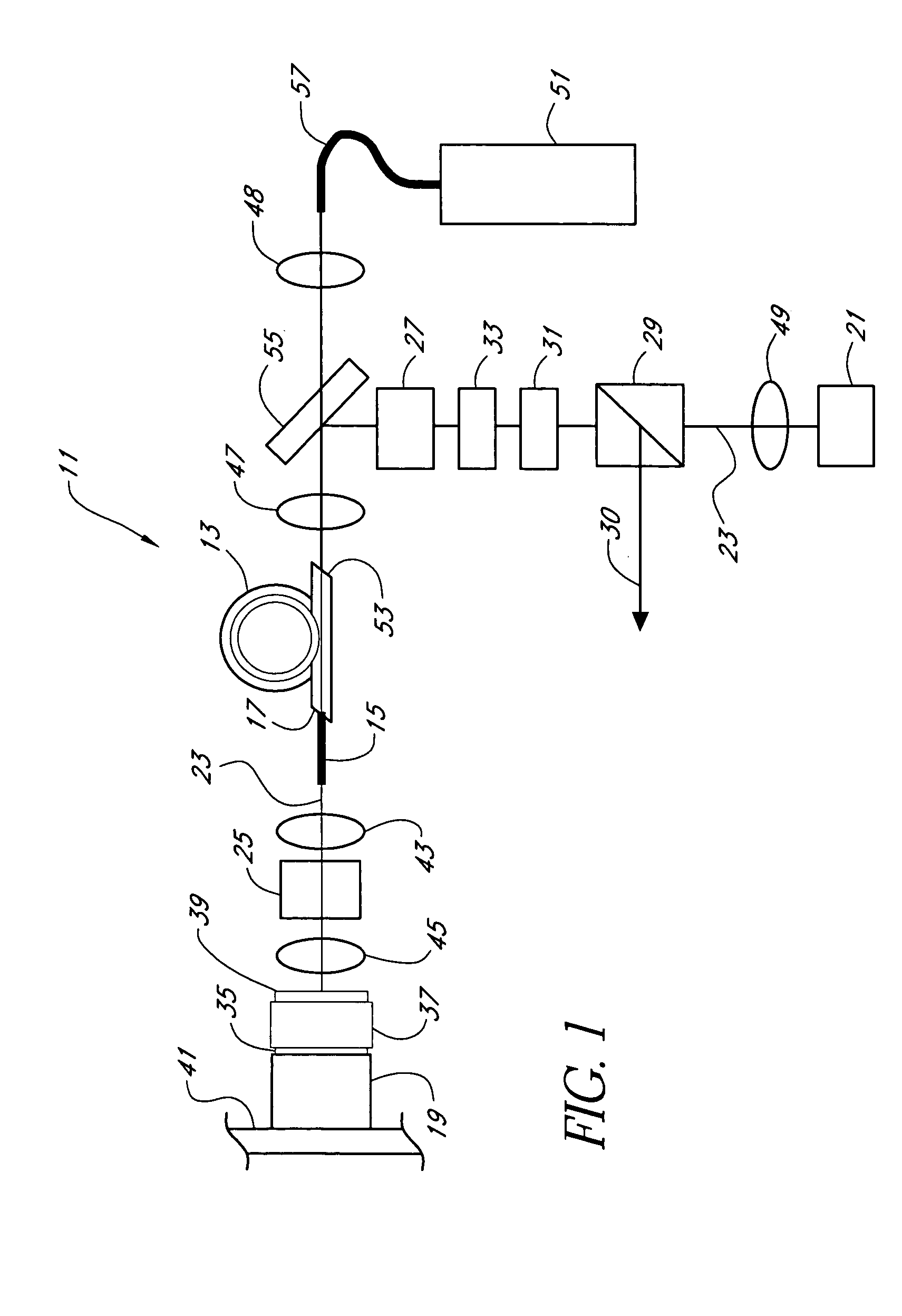
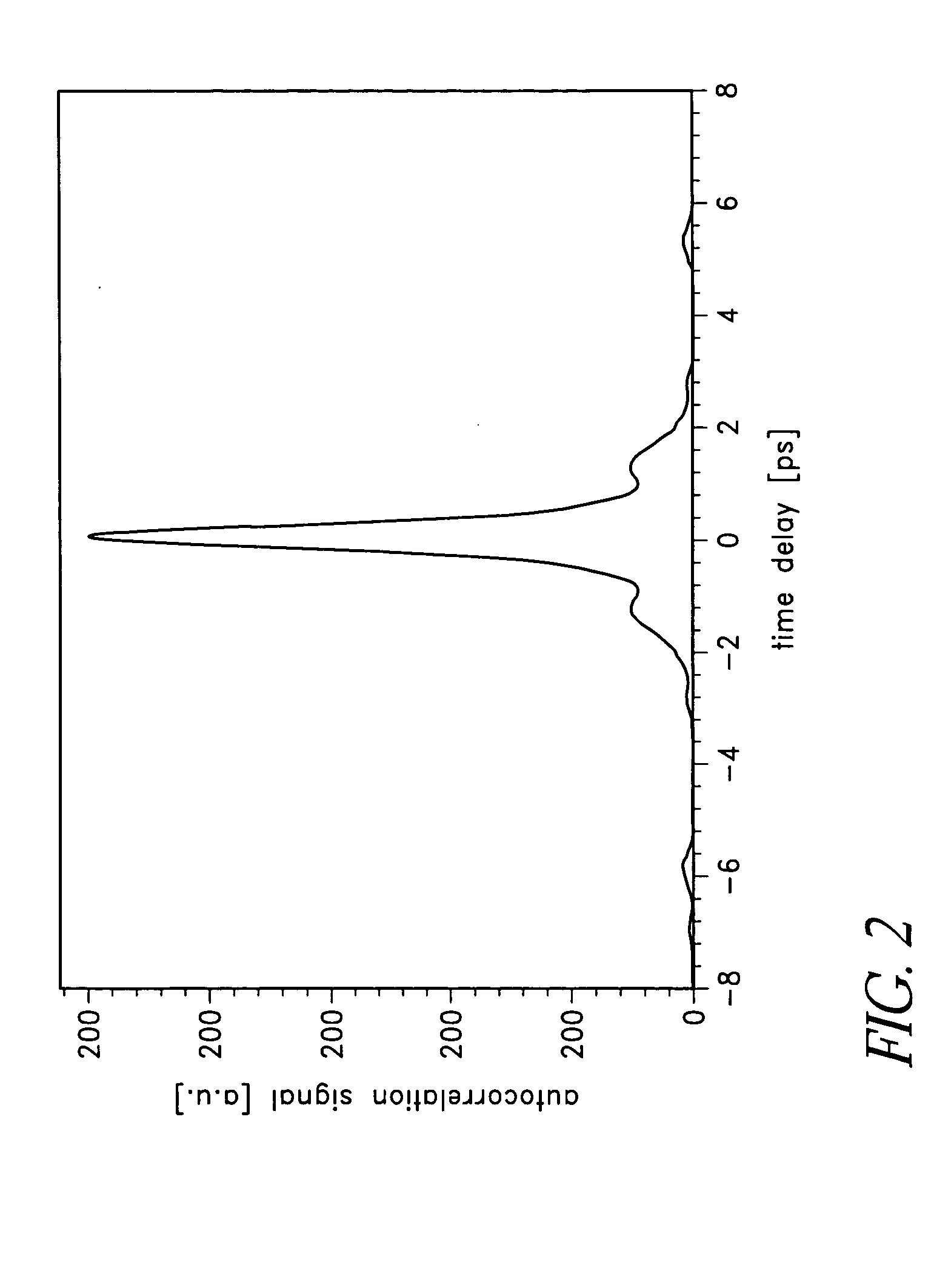
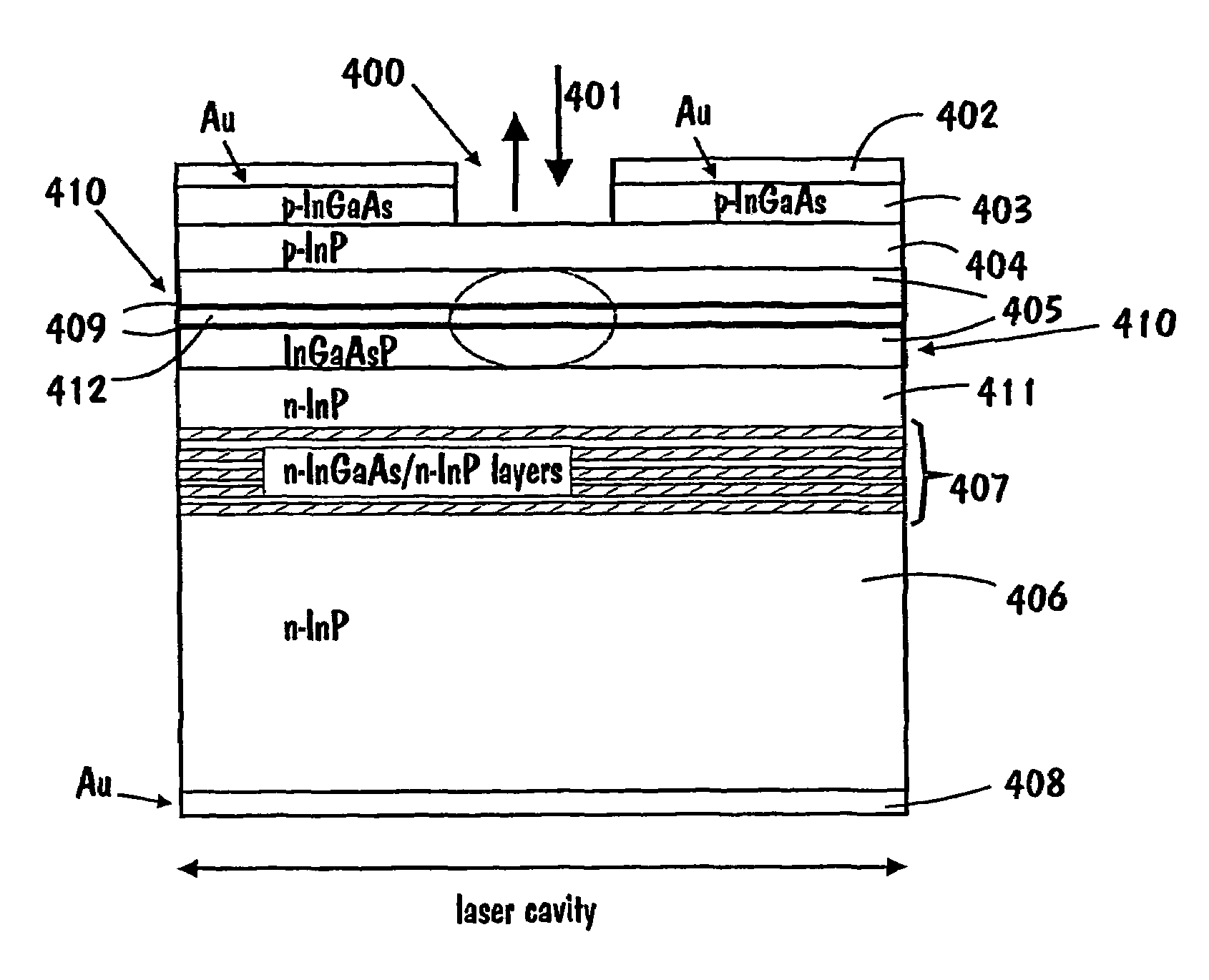
Optical modulator
InactiveUS7313291B2Laser active region structureLaser output parameters controlIn planeControl signal
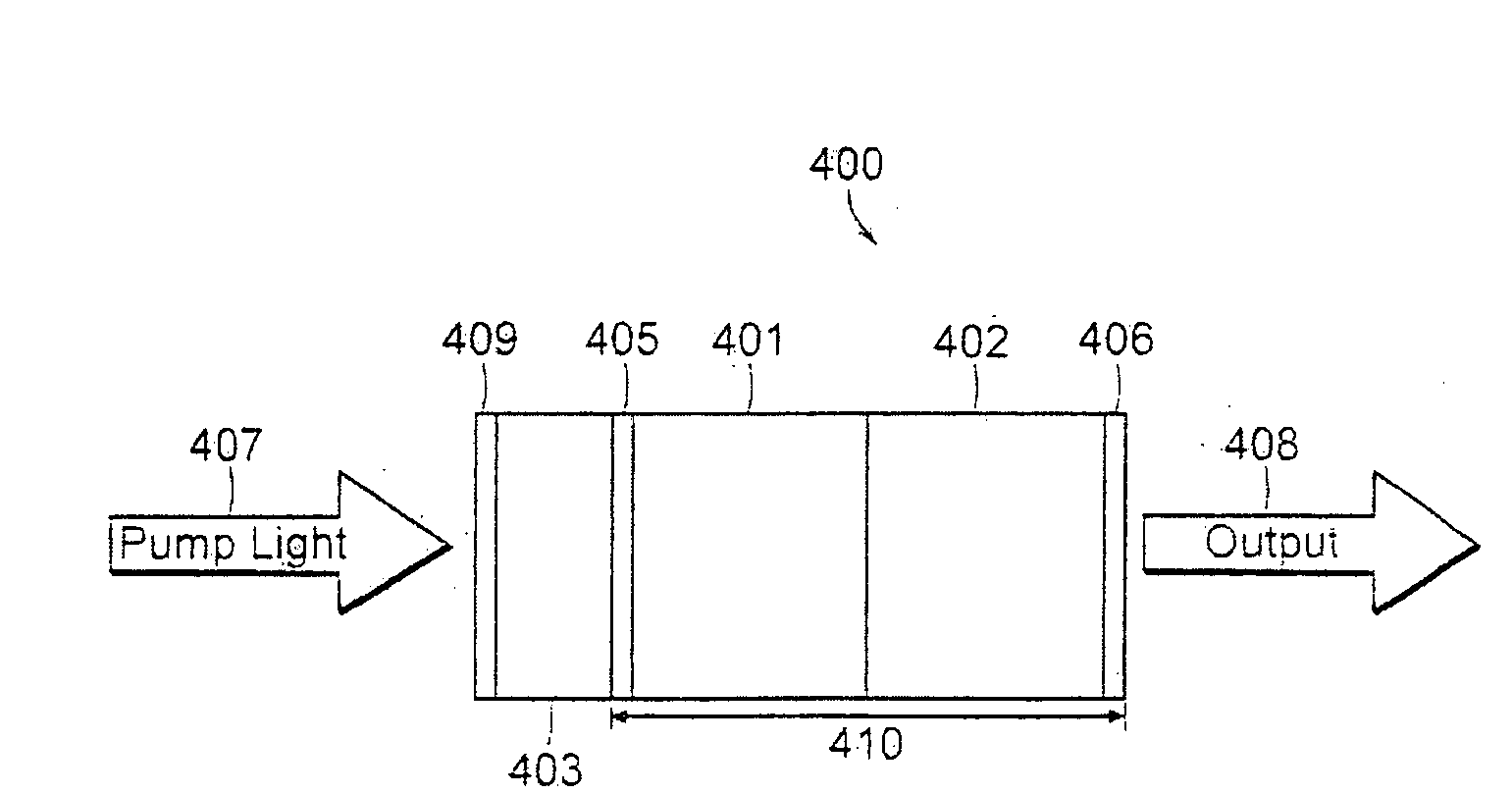
The invention relates to an optically pumped multilayered modulator having surface-normal geometry. The multilayer structure comprises an absorber section through which an optical signal (401) to be modulated is coupled from an input (401) to an output (400). The multilayer structure further comprises control means for supplying a control signal for controlling the transmission characteristics of the absorber section. The control signal is generated by an in-plane waveguide-type laser integrated monolithically with the saturable absorption region. The in-plane control laser includes waveguide regions (405) and multiple-quantum-well layers (409) used as a gain medium. The laser beam is adapted to travel through the absorber section in order to modulate the transmission characteristics of the absorber section.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY +1
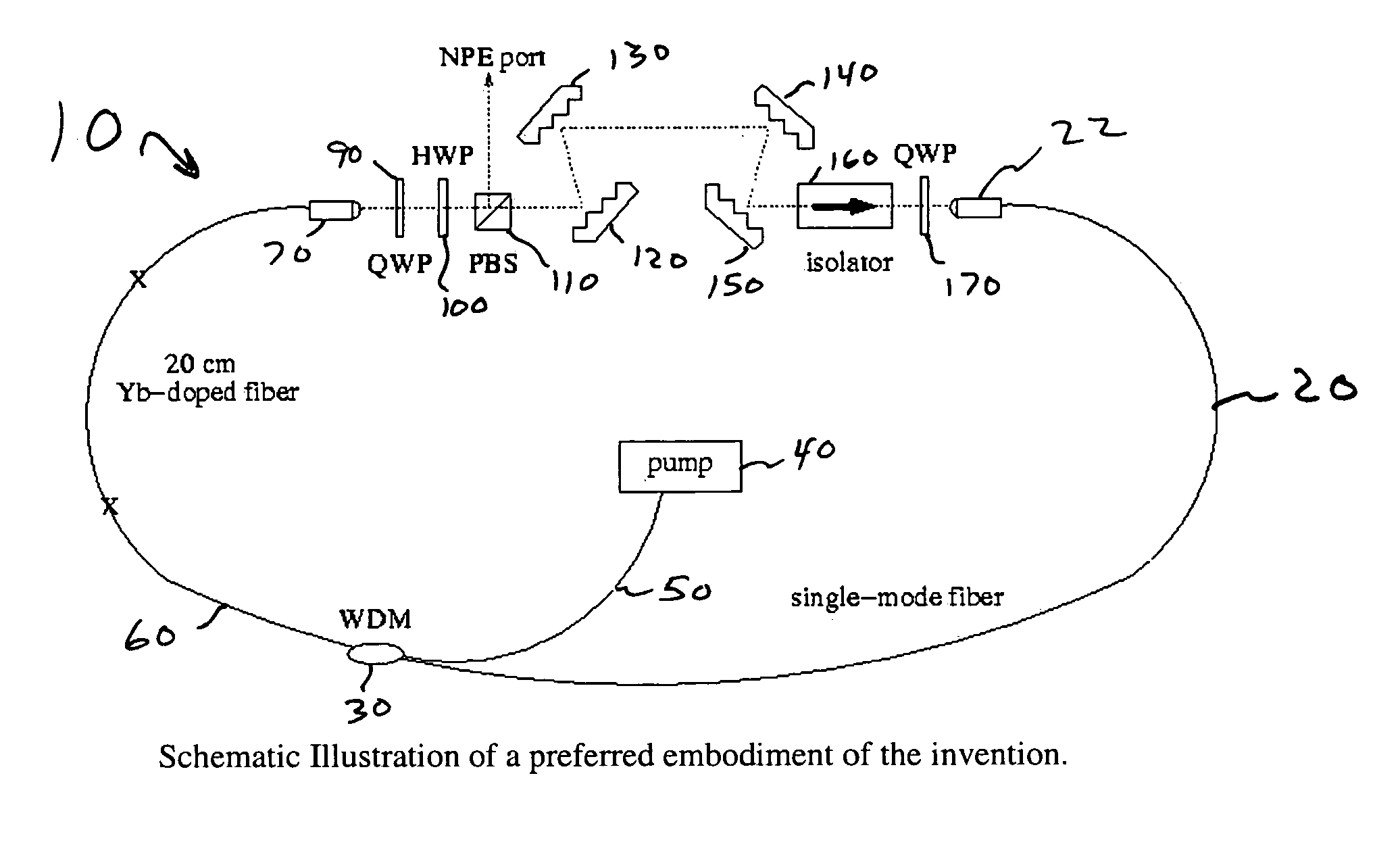
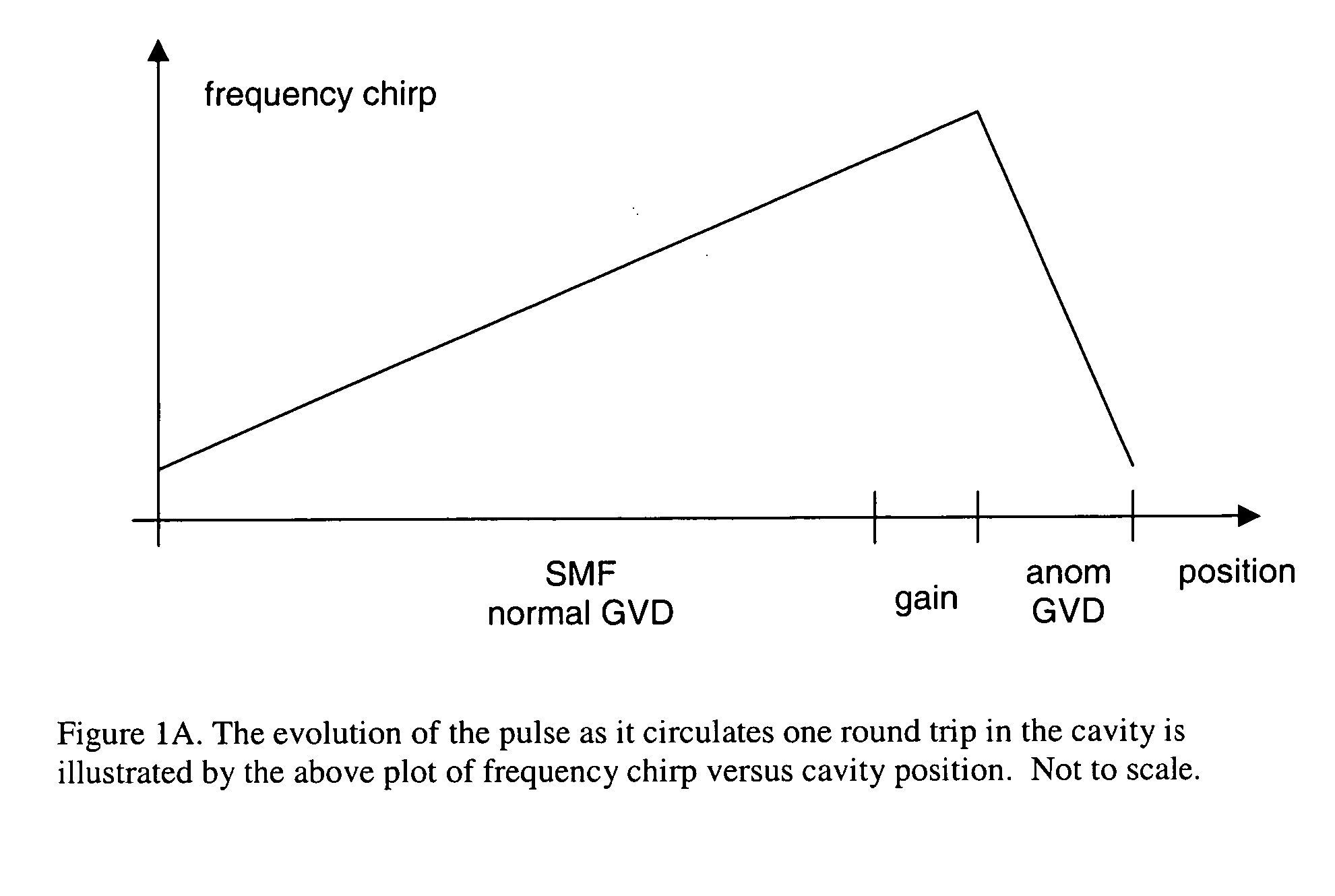
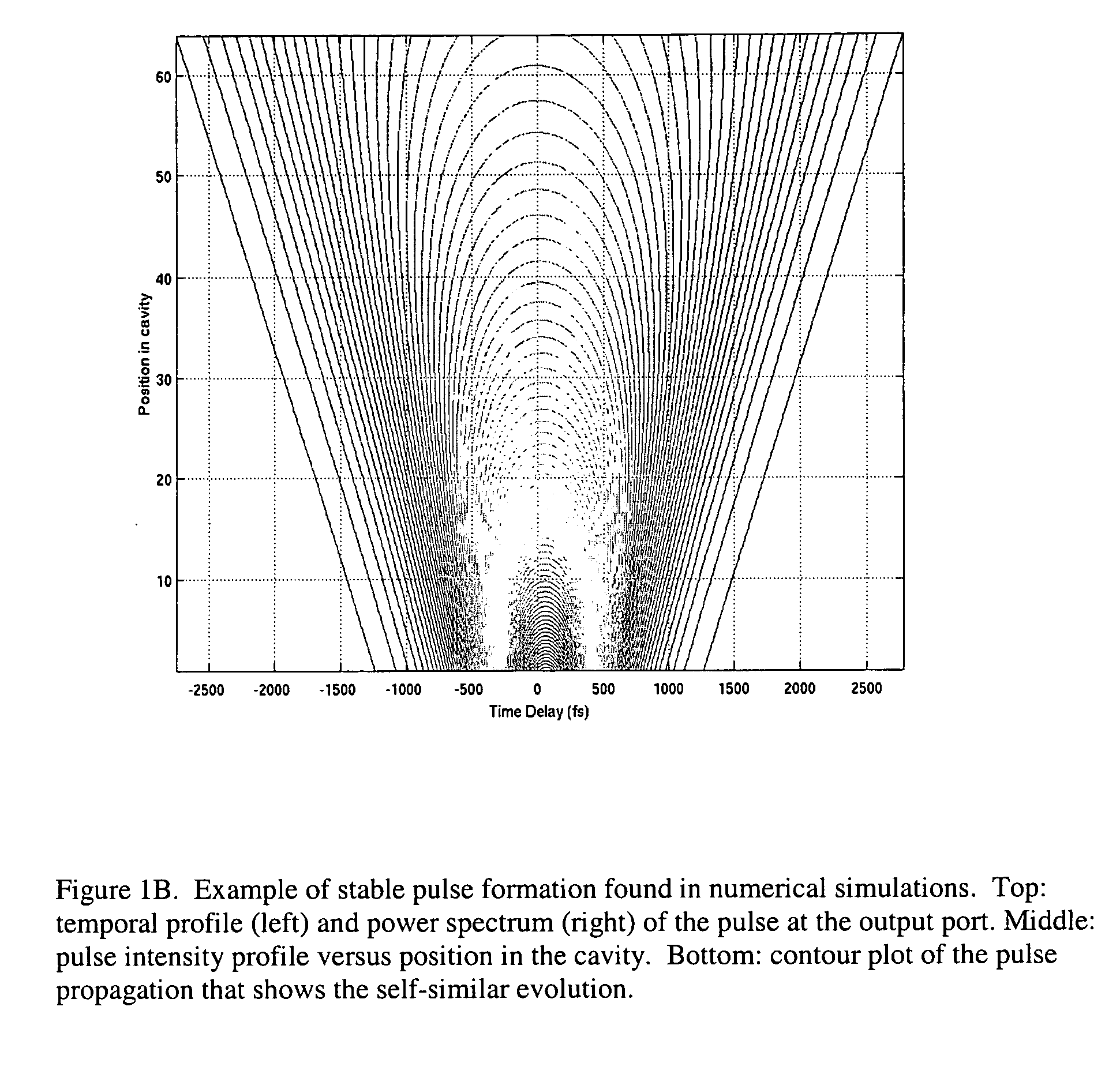
Self-similar laser oscillator
InactiveUS20050169324A1Stable operation of laserHigh bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialState of artHigh energy
A laser producing high energy ultrashort laser pulses comprises a normal dispersion segment, a gain segment, an anomalous dispersion segment with negligible nonlinearity and an effective saturable absorber arranged to form a laser cavity. Each segment is optically interconnected so that a laser pulse will propagate self-similarly therein. (A pulse that propagates in a self-similar manner is sometimes referred to as a “similariton.”) With this laser the limitations of prior art laser oscillators are avoided. Also provided are means for pumping the gain medium in the laser cavity, and means for extracting laser pulses from the laser cavity. The laser cavity is preferably a ring cavity. Preferably the laser is configured to achieve unidirectional circulation of laser pulses therein. This configuration is scalable to much higher pulse energy than lasers based on soliton-like pulse shaping.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Passive Q-switch modulated fiber laser
InactiveUS20060007965A1High average and peak power pulseLow costLaser using scattering effectsSurgical instrument detailsExcited stateOptoelectronics
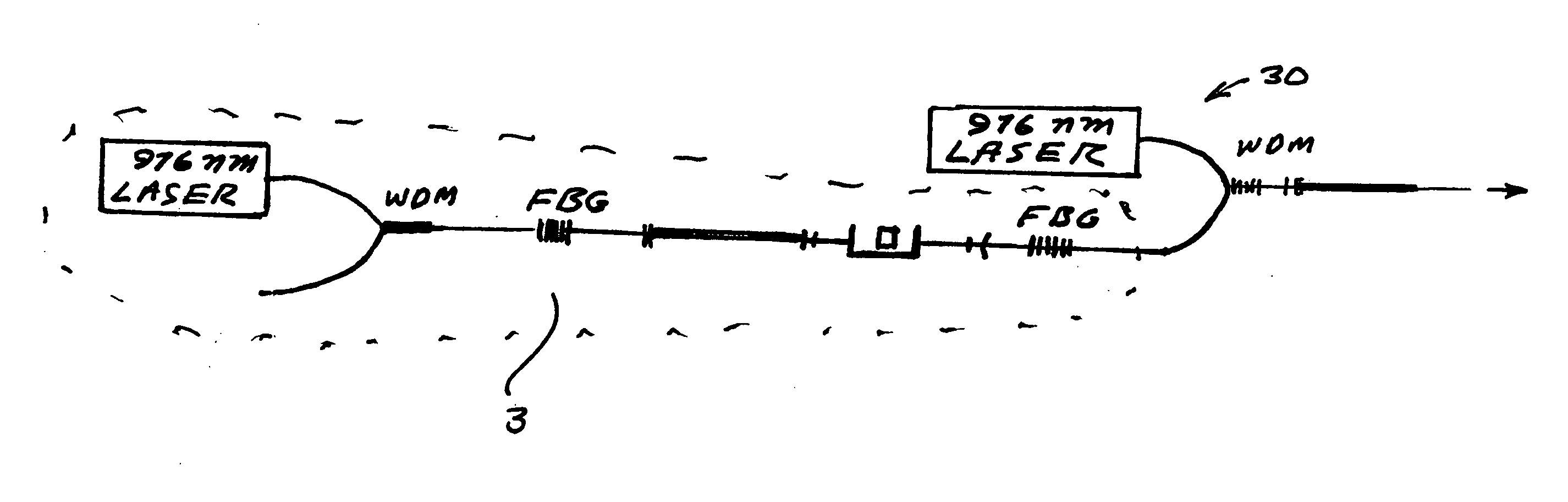
An all-fiber erbium laser oscillating in a passive Q switched mode. The laser includes a crystal saturable absorber that may be Co2+:ZnSe or Cr2+:ZnSe. In preferred embodiments continuous pumping or short pulse pumping may be utilized. The laser is characterized by low threshold high-power, short-pulse generation. In preferred embodiments the threshold is only about 20 mW. The crystals are bleached at extremely low intensity, of about 0.8 kW / cm2 and provide moderate relaxation time of the excited state (290 μs) within a spectral range of about 1400-1800 nm. The simplicity of the design and low cost of that laser 2000).
Owner:PHARMALASE
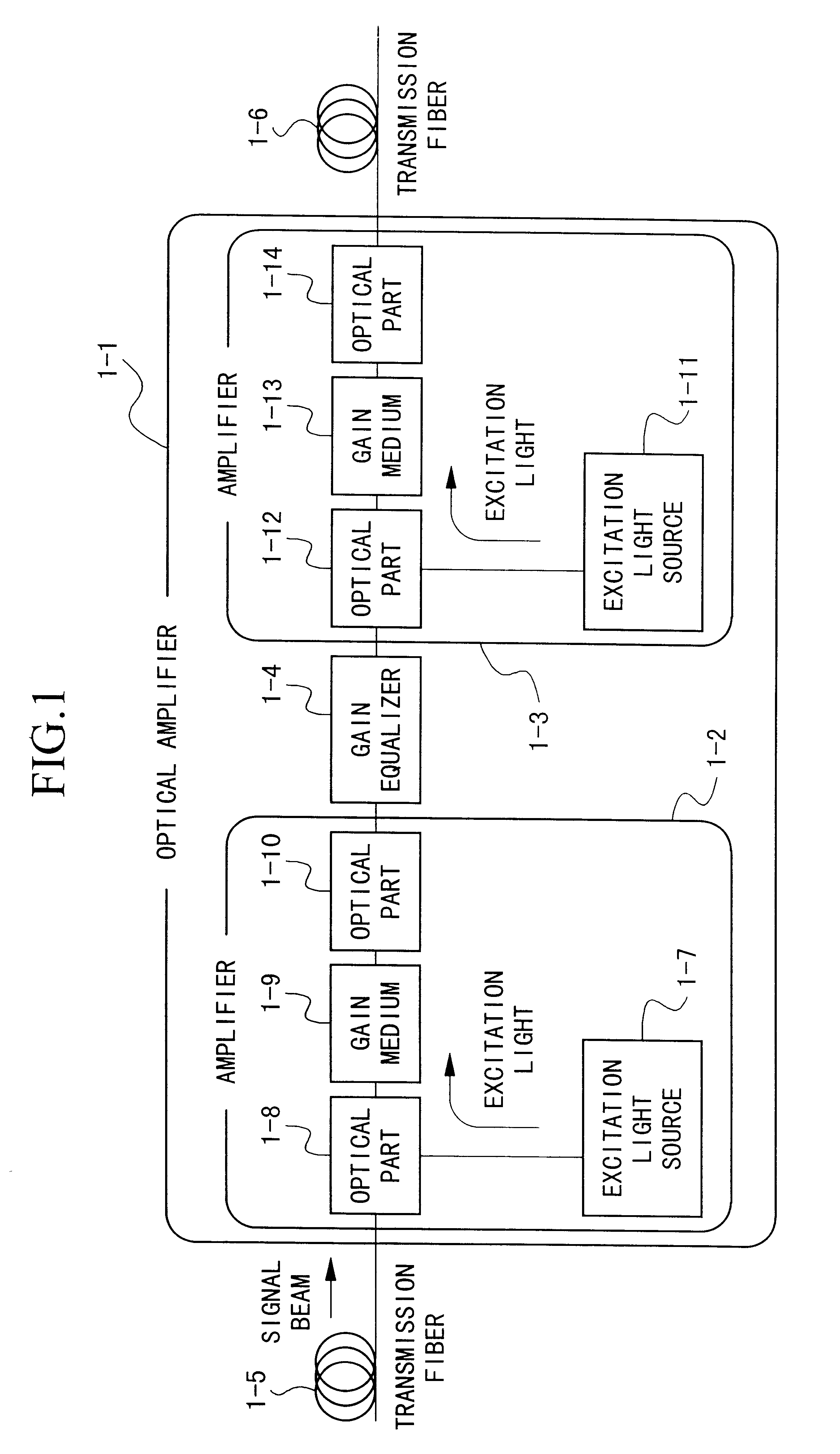
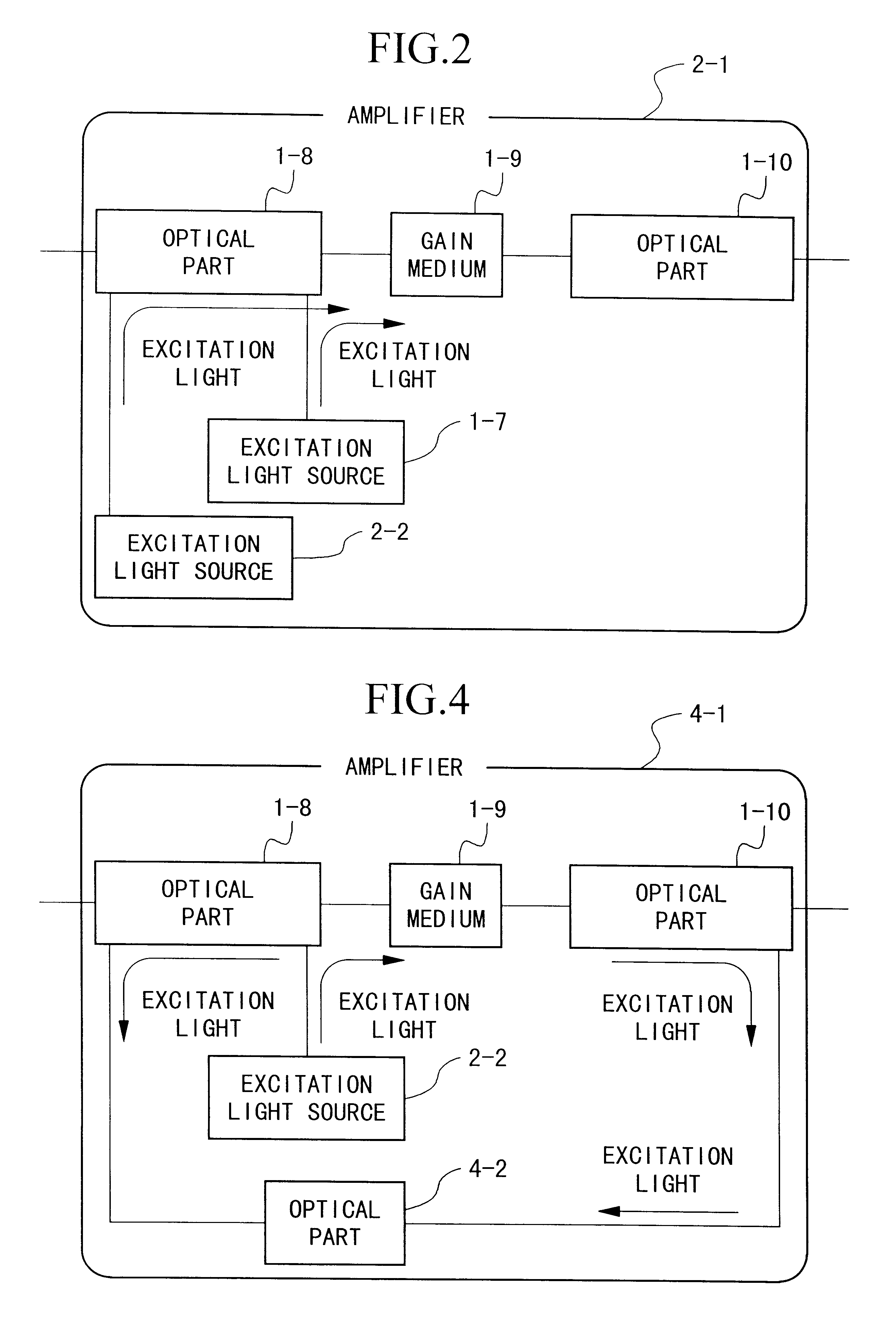
Optical amplifier and transmission system using the same
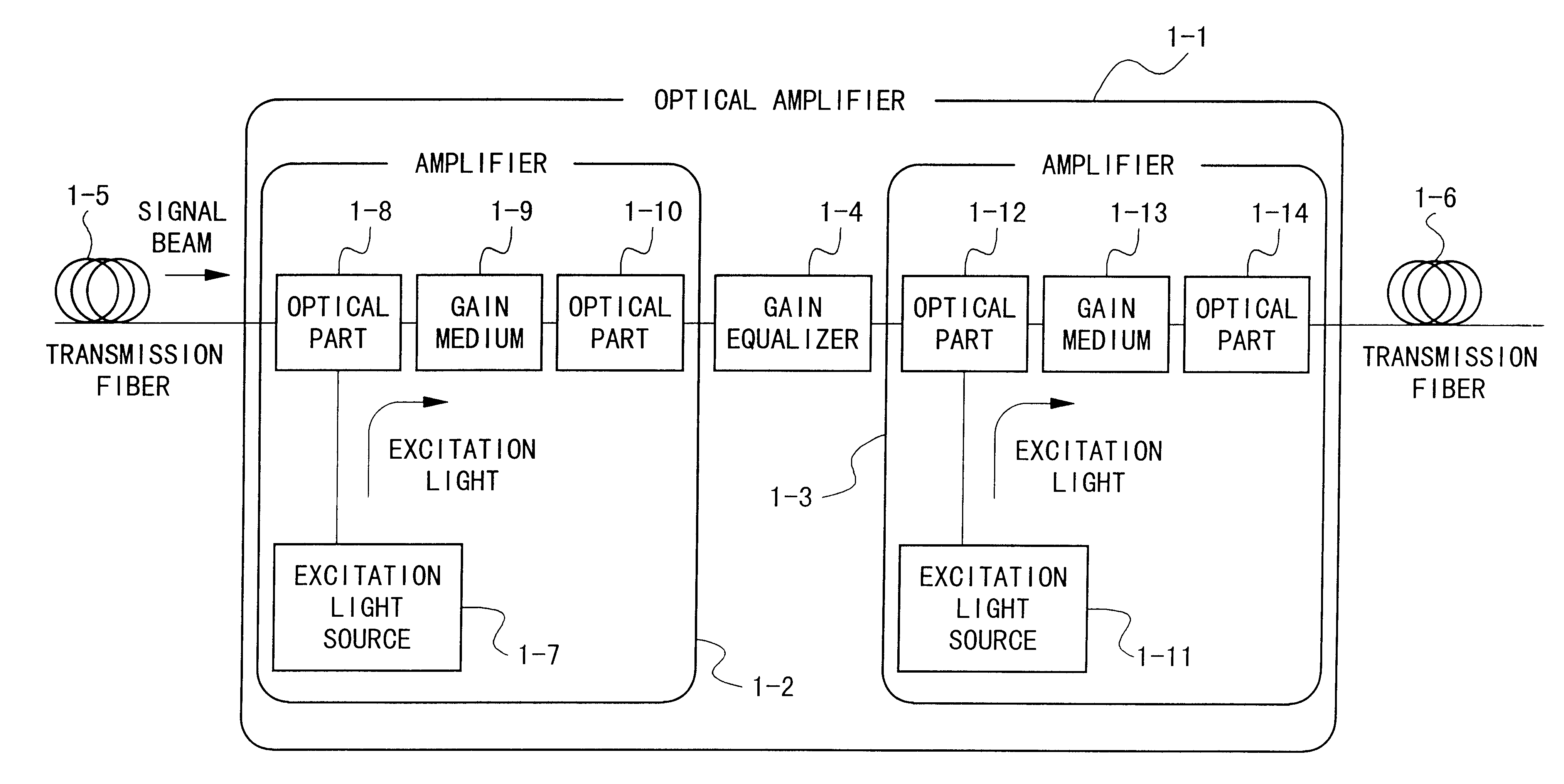
InactiveUS6172803B1Laser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesFiberErbium doping
An optical amplifier having a two-stage construction using an erbium doped fiber (EDF) as a gain medium. The erbium dopant concentration is 1000 ppm, and the unsaturated absorption coefficient of the signal beam at 1550 nm is 1 dB / m. The length of the EDF 14-8 is 10 m, and the length of the EDF 14-12 is 70 m. The excitation light sources 14-6 and 14-10 are semiconductor lasers of 1.53 mum, and the excitation light power is 100 mW. Multiplexers 14-7 and 14-11 are inductive multi-layer film filters, and the gain equalizer 14-4 is a Fourier filter. The peak loss of the Fourier filter is 17 dB. The gain of the EDF 14-8 is 25 dB, and the gain of the EDF 14-12 is 15 dB. Two optical isolators are installed on a pre-stage amplifier, and one on a post-stage amplifier in order to prevent laser oscillation.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Optical pulse lasers
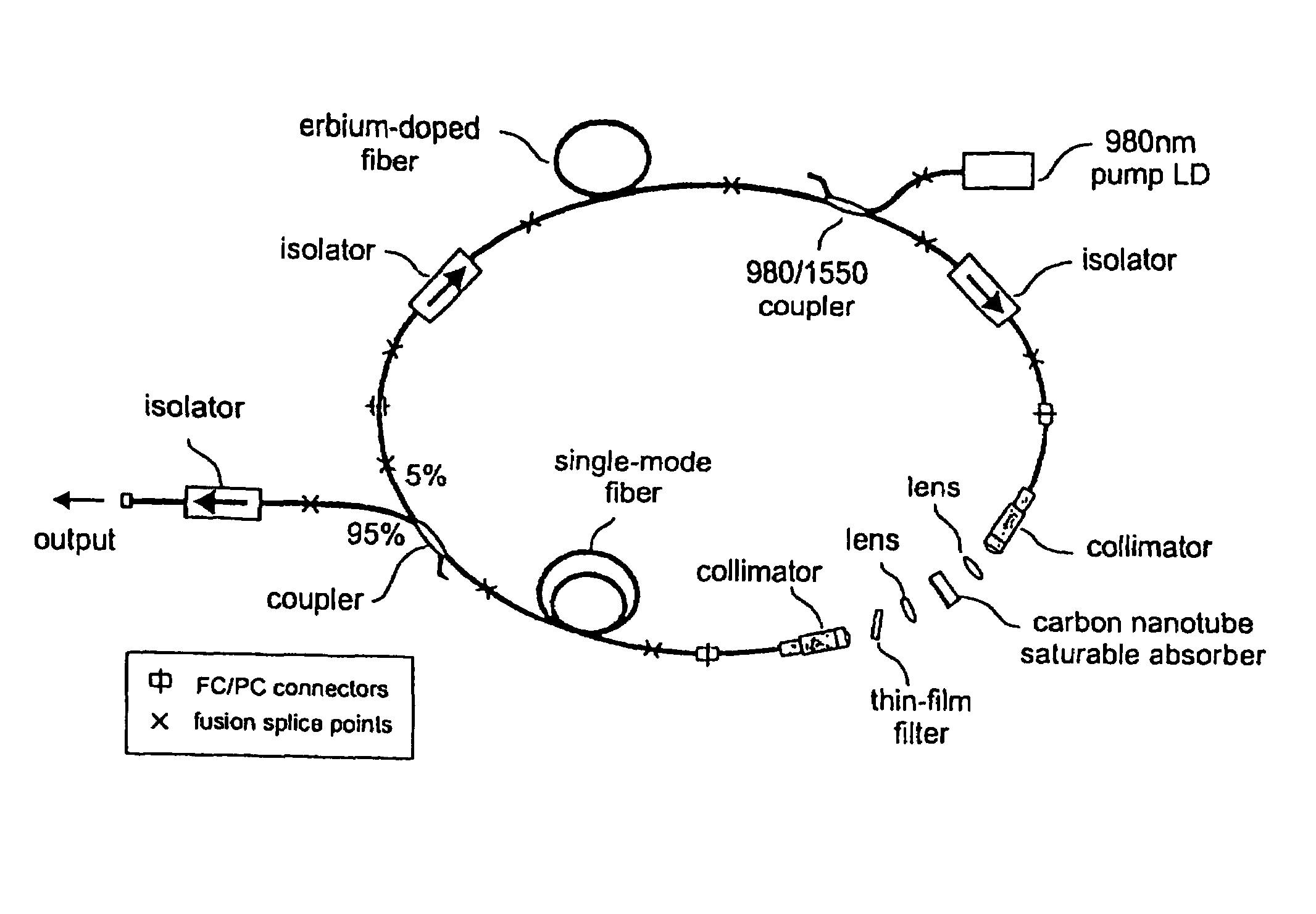
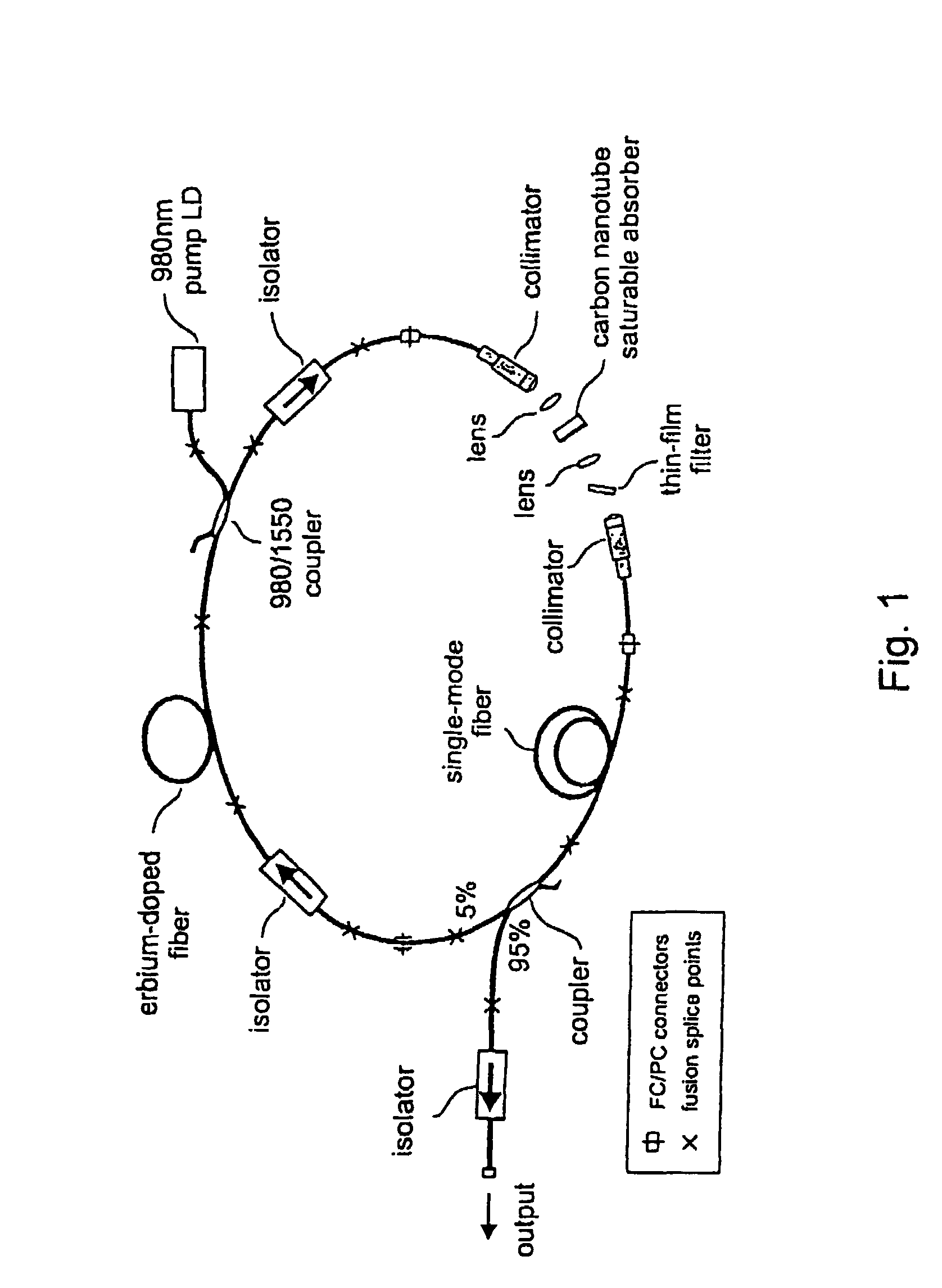
InactiveUS7372880B2Fast recovery timeHigh optical damage thresholdMirrorsNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeMode-locking
The present invention provides pulsed lasers which employ carbon nanotubes, particularly layers of carbon nanotubes, as saturable absorbers, mode lockers or for Q-switching elements. The present invention also provides methods and materials for mode-locking and Q-switching of lasers in which carbon nanotubes are employed as non-linear optical materials and / or saturable absorbers which facilitate mode-locking and / or Q-switching. The invention further provides mode locker and Q-switching elements or devices which comprise one or more layers containing carbon nanotubes which layer or layers function for mode locking and / or Q-switching.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Graphene-based saturable absorber devices and methods
InactiveUS20120039344A1Improve performanceInexpensive to fabricateLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionGraphene derivativesFacet
A graphene-based saturable absorber device suitable for use in a ring-cavity fiber laser or a linear-cavity fiber laser is disclosed. The saturable absorber device includes an optical element and a graphene-based saturable absorber material supported by the optical element and comprising at least one of graphene, a graphene derivative and functionalized graphene. An examplary optical element is an optical fiber having an end facet that supports the saturable absorber material. Various forms of the graphene-based saturable absorber materials and methods of forming same are also disclosed.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
Apparatus and methods for optical neural network
ActiveCN109477938AWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical neural networkOptical nonlinearity
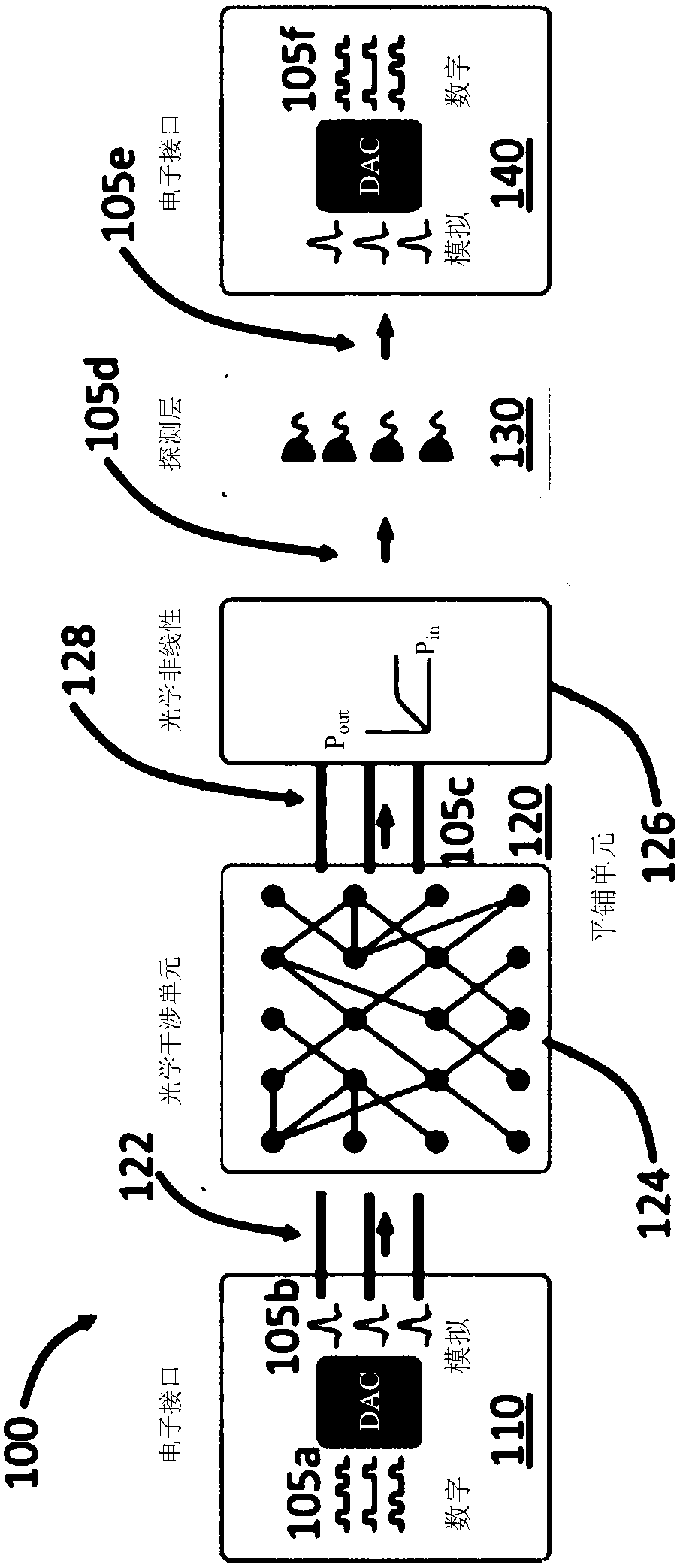
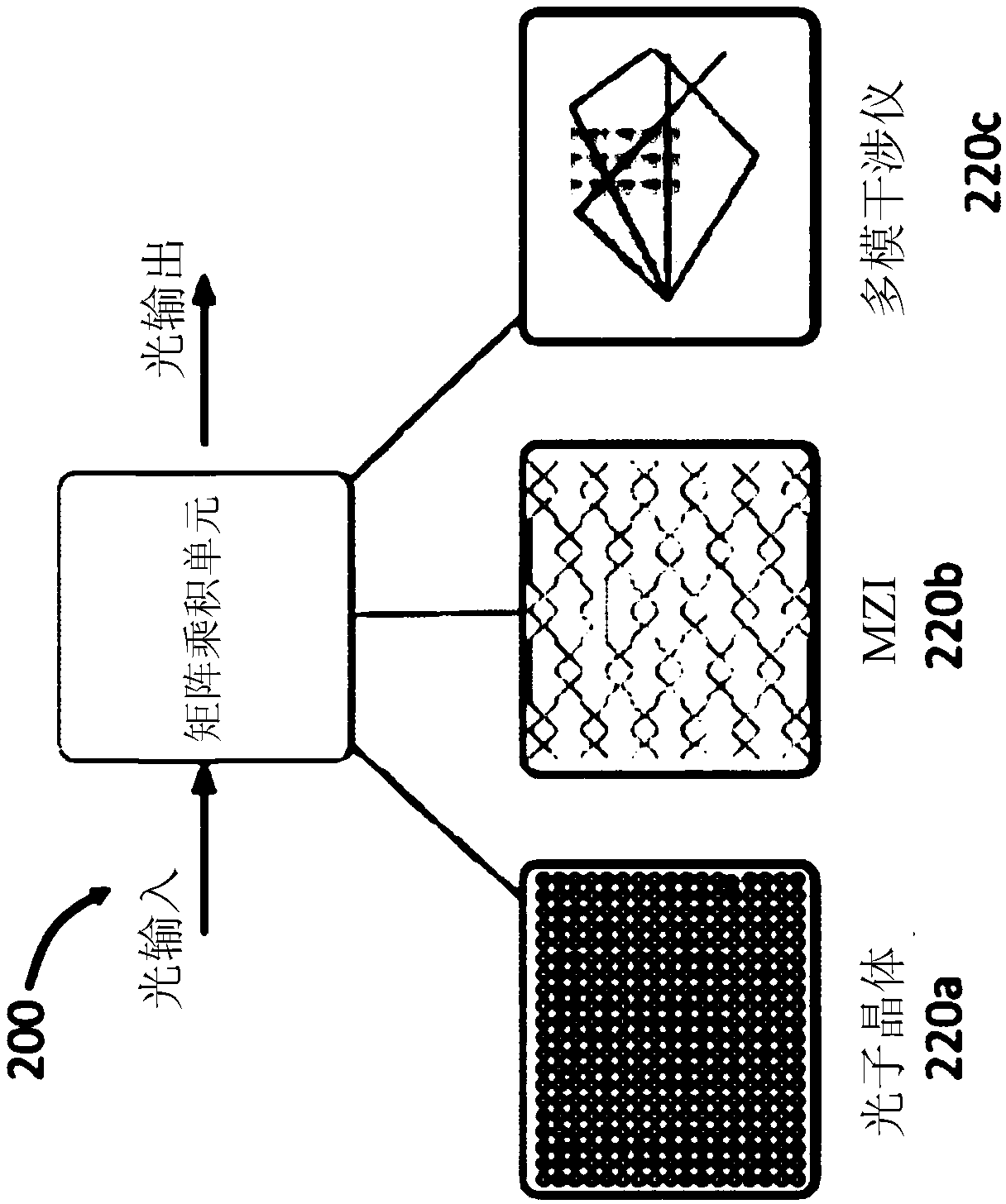
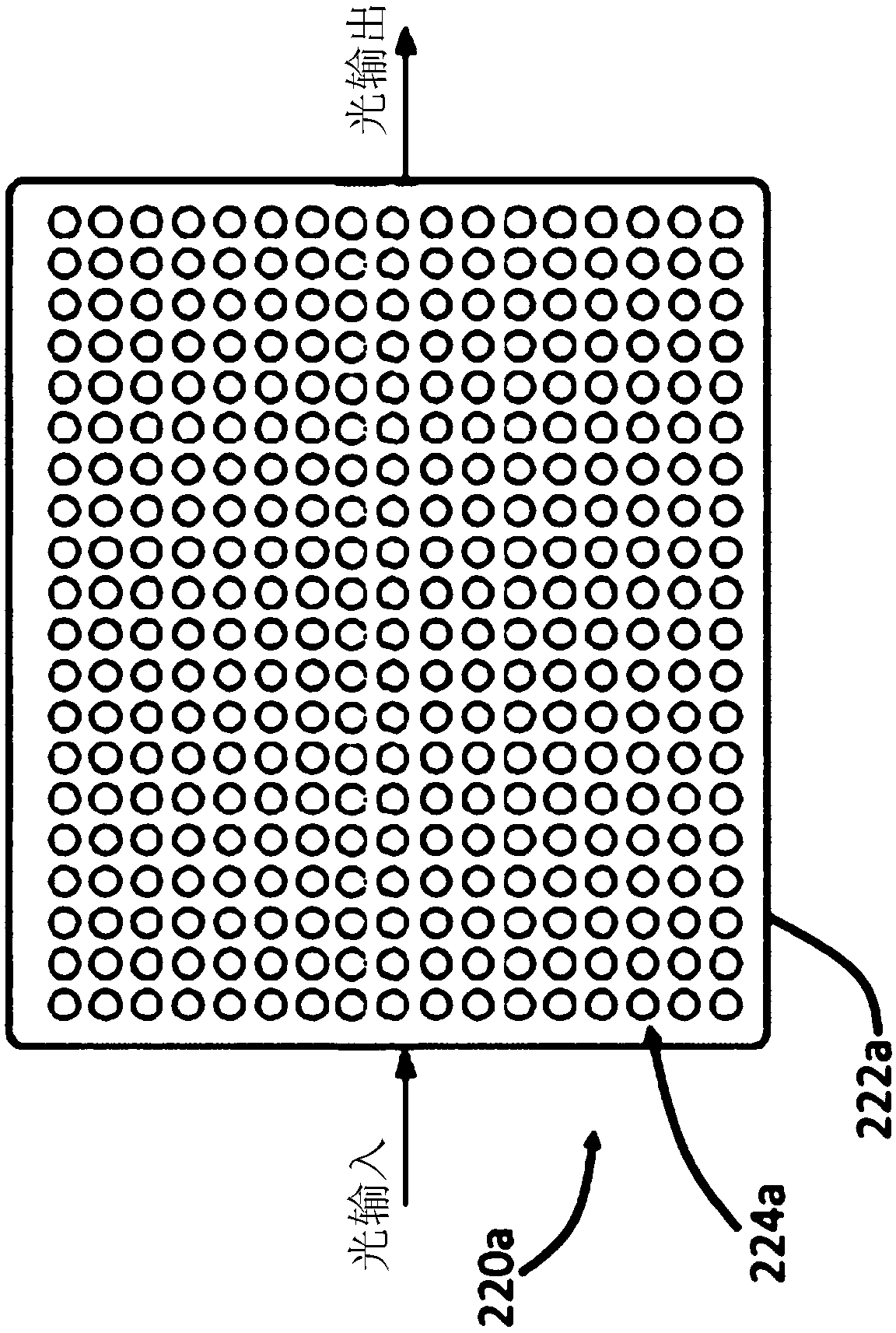
An optical neural network is constructed based on photonic integrated circuits to perform neuromorphic computing. In the optical neural network, matrix multiplication is implemented using one or moreoptical interference units, which can apply an arbitrary weighting matrix multiplication to an array of input optical signals. Nonlinear activation is realized by an optical nonlinearity unit, which can be based on nonlinear optical effects, such as saturable absorption. These calculations are implemented optically, thereby resulting in high calculation speeds and low power consumption in the optical neural network.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Q-switched microlaser apparatus and method for use
ActiveUS20080247425A1Improve cooling effectGuaranteed uptimeLaser cooling arrangementsResonatorLaser
A monolithic passively Q switched microlaser includes an optically transparent heat conductive element bonded to a gain medium, which is in turn bonded to a saturable absorber, which may also be bonded to a second optically transparent heat conductive element. Only the gain medium and saturable absorber are disposed within the laser resonator.
Owner:KK TOPCON +1
Optical pulse lasers
InactiveUS20060198399A1Easy to operateFast recovery timeMirrorsNanoinformaticsMode-lockingCarbon nanotube
The present invention provides pulsed lasers which employ carbon nanotubes, particularly layers of carbon nanotubes, as saturable absorbers, mode lockers or for Q-switching elements. The present invention also provides methods and materials for mode-locking and Q-switching of lasers in which carbon nanotubes are employed as non-linear optical materials and / or saturable absorbers which facilitate mode-locking and / or Q-switching. The invention further provides mode locker and Q-switching elements or devices which comprise one or more layers containing carbon nanotubes which layer or layers function for mode locking and / or Q-switching.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
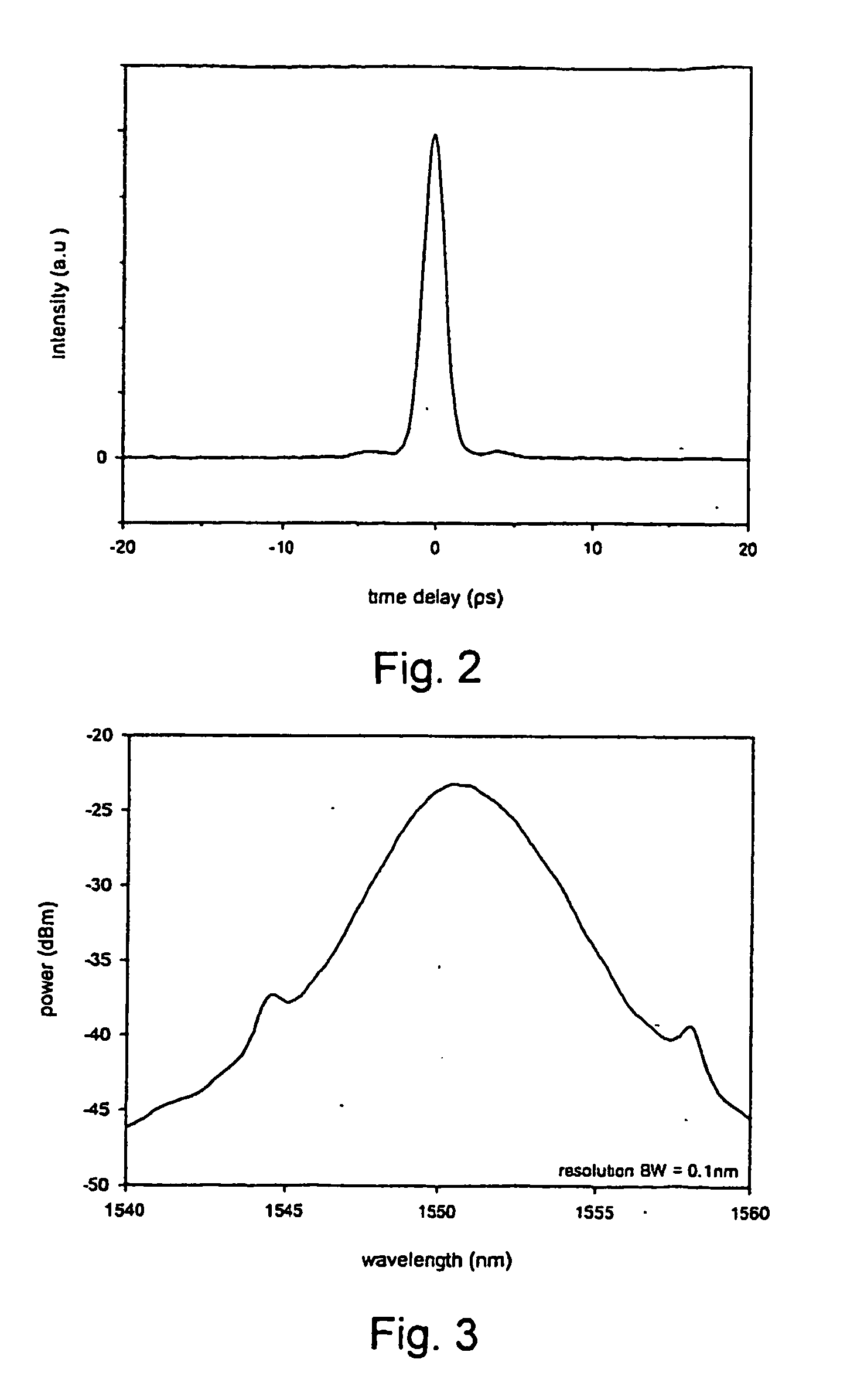
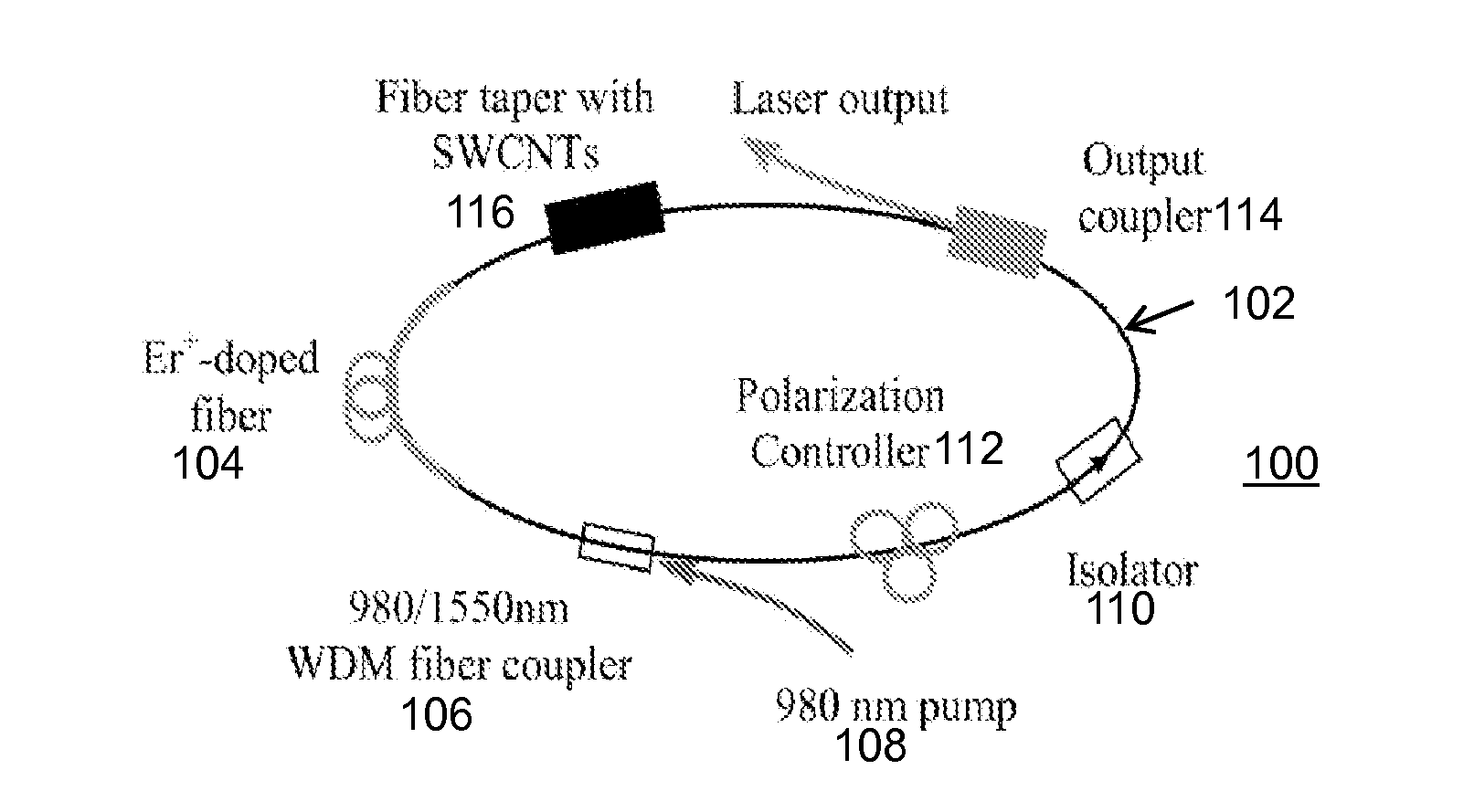
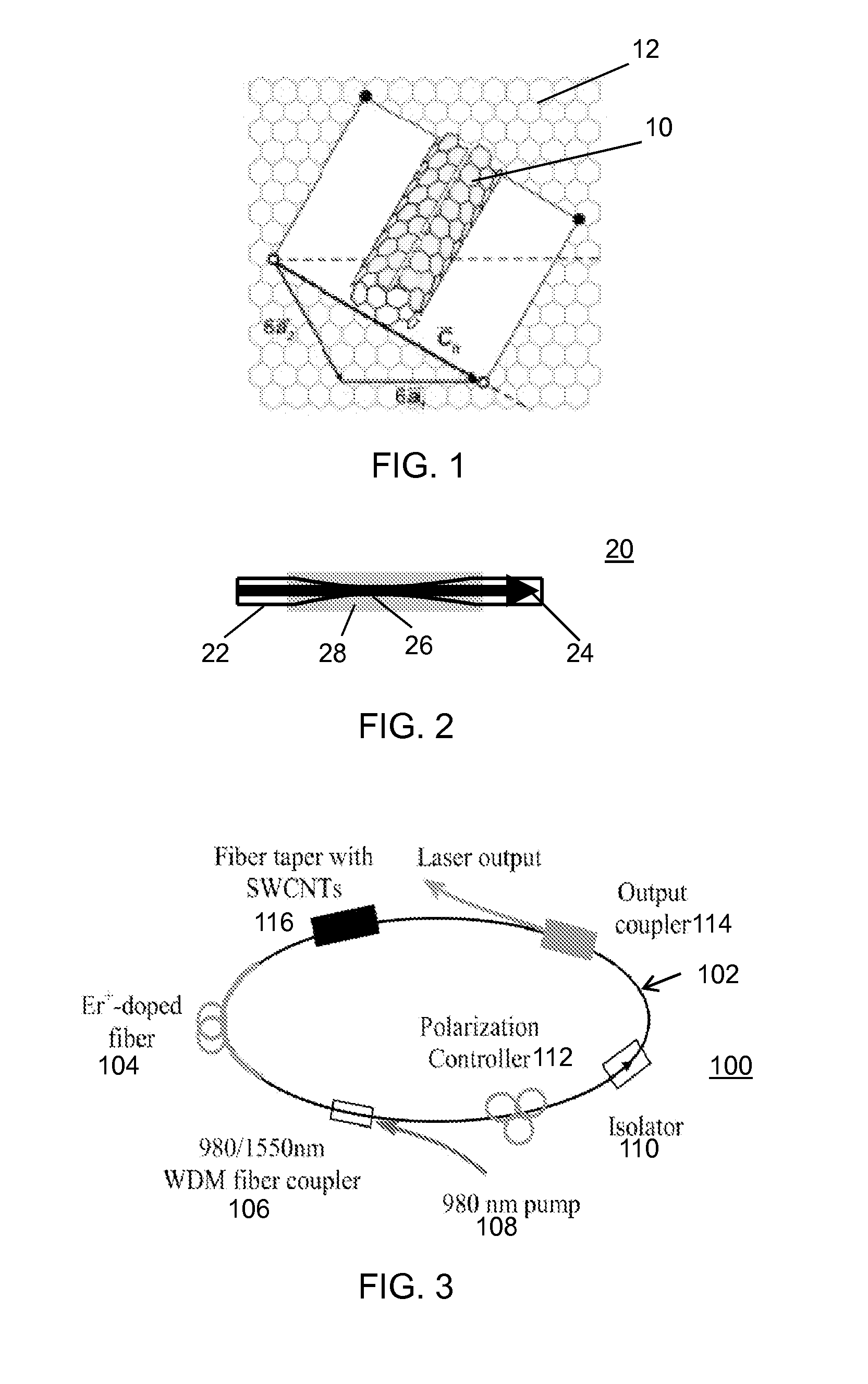
Saturable absorber using a fiber taper embedded in a nanostructure/polymer composite and lasers using the same
ActiveUS20110280263A1Wide working wavelength rangeSimplify the manufacturing processLaser using scattering effectsOptical articlesFiberAir interface
A saturable absorber (SA) is constructed using a fiber taper embedded in a carbon nanotube / polymer composite. A fiber taper is made by heating and pulling a small part of standard optical fiber. At the taper's waist light is guided by the glass-air interface, with an evanescent field protruding out of the taper. Carbon nanotubes mixed with an appropriate polymer host material are then wrapped around the fiber taper to interact with the evanescent field. Saturable absorption is possible due to the unique optical properties of the carbon nanotubes. The device can be used in mode-locked lasers where it initiates and stabilizes the pulses circulating around the laser cavity. The SA can be used in various laser cavities, and can enable different pulse evolutions such as solitons, self-similar pulses and dissipative solitons. Other applications include but are not limited to optical switching, pulse cleanup and pulse compression.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
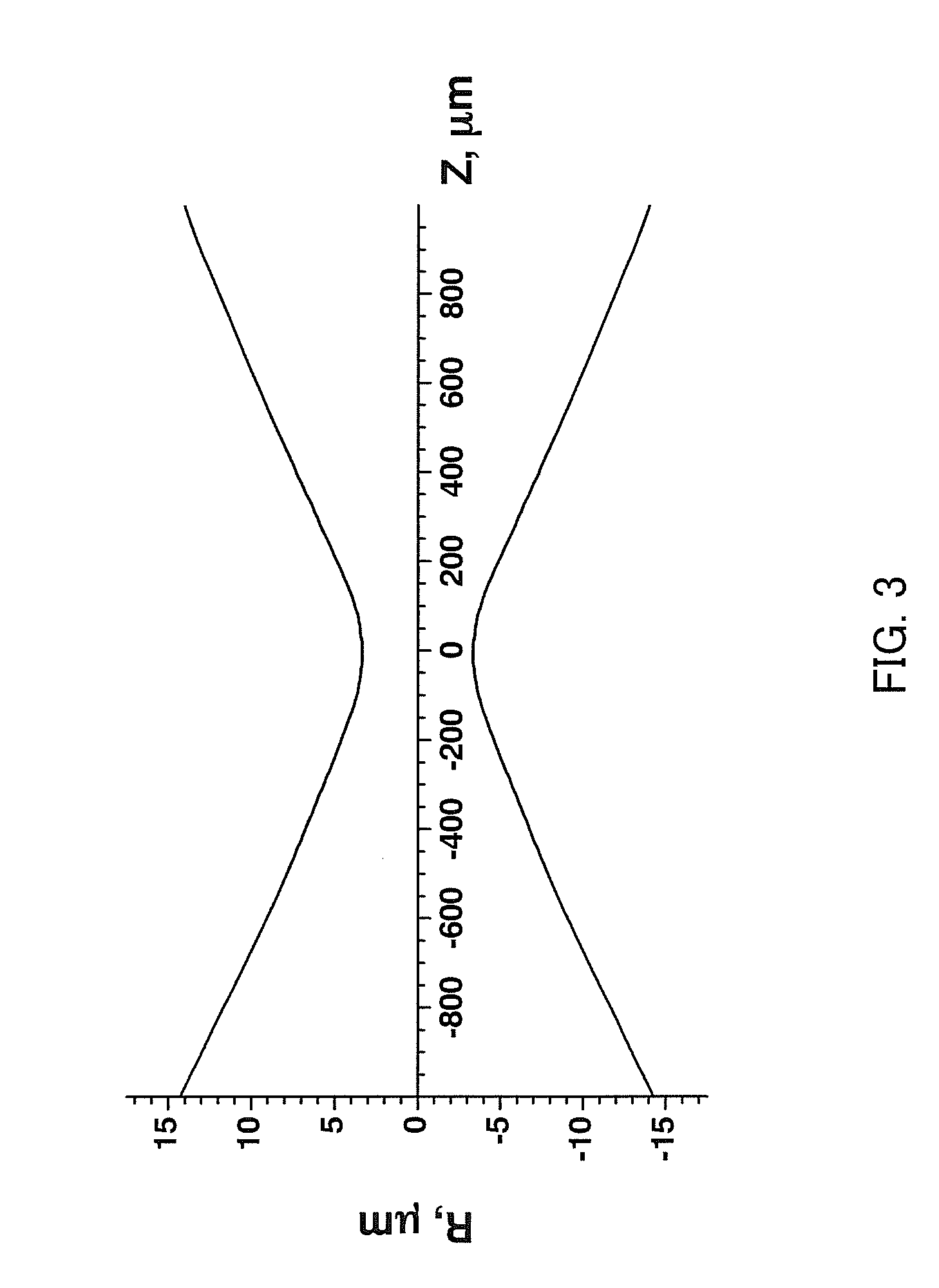
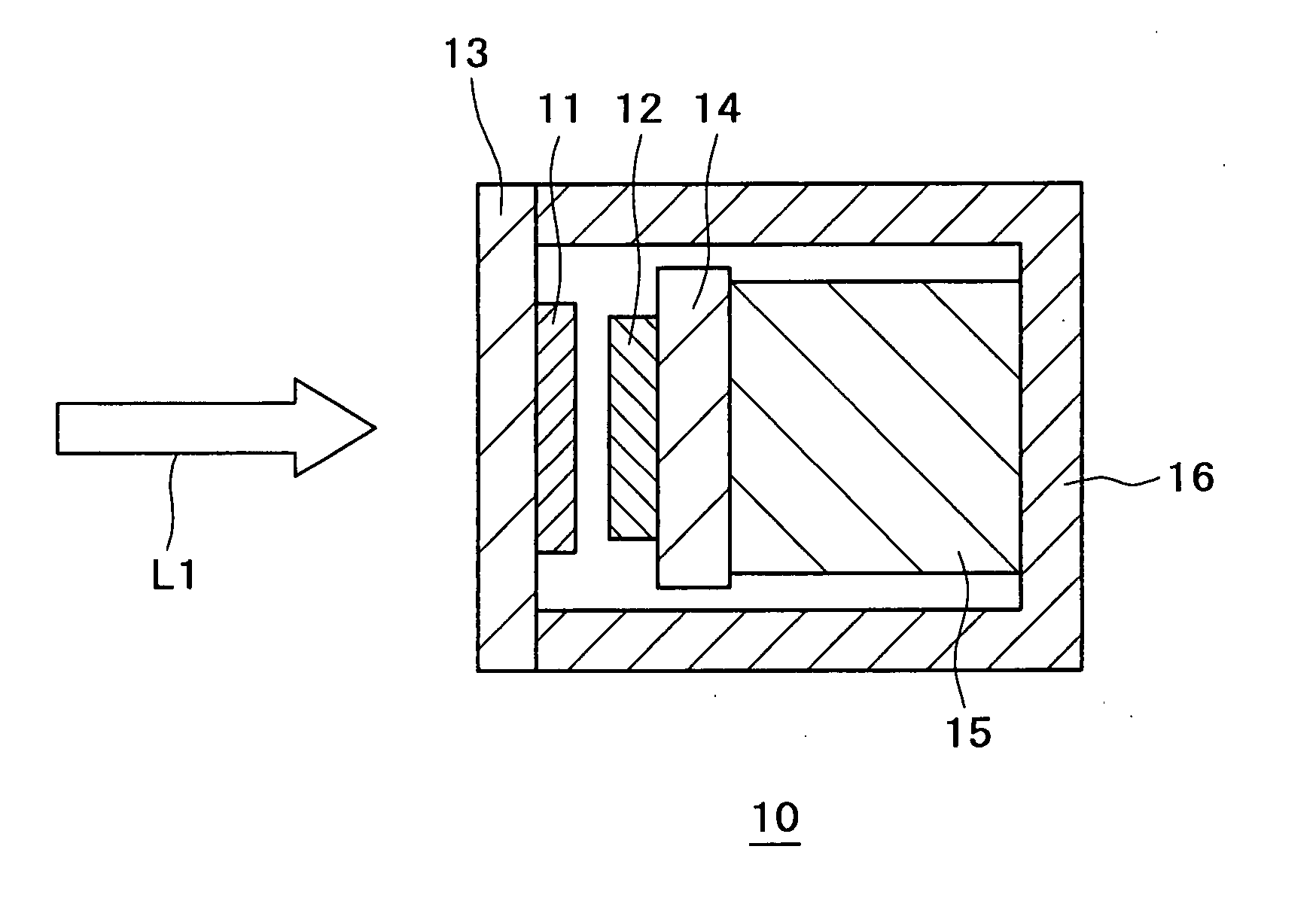
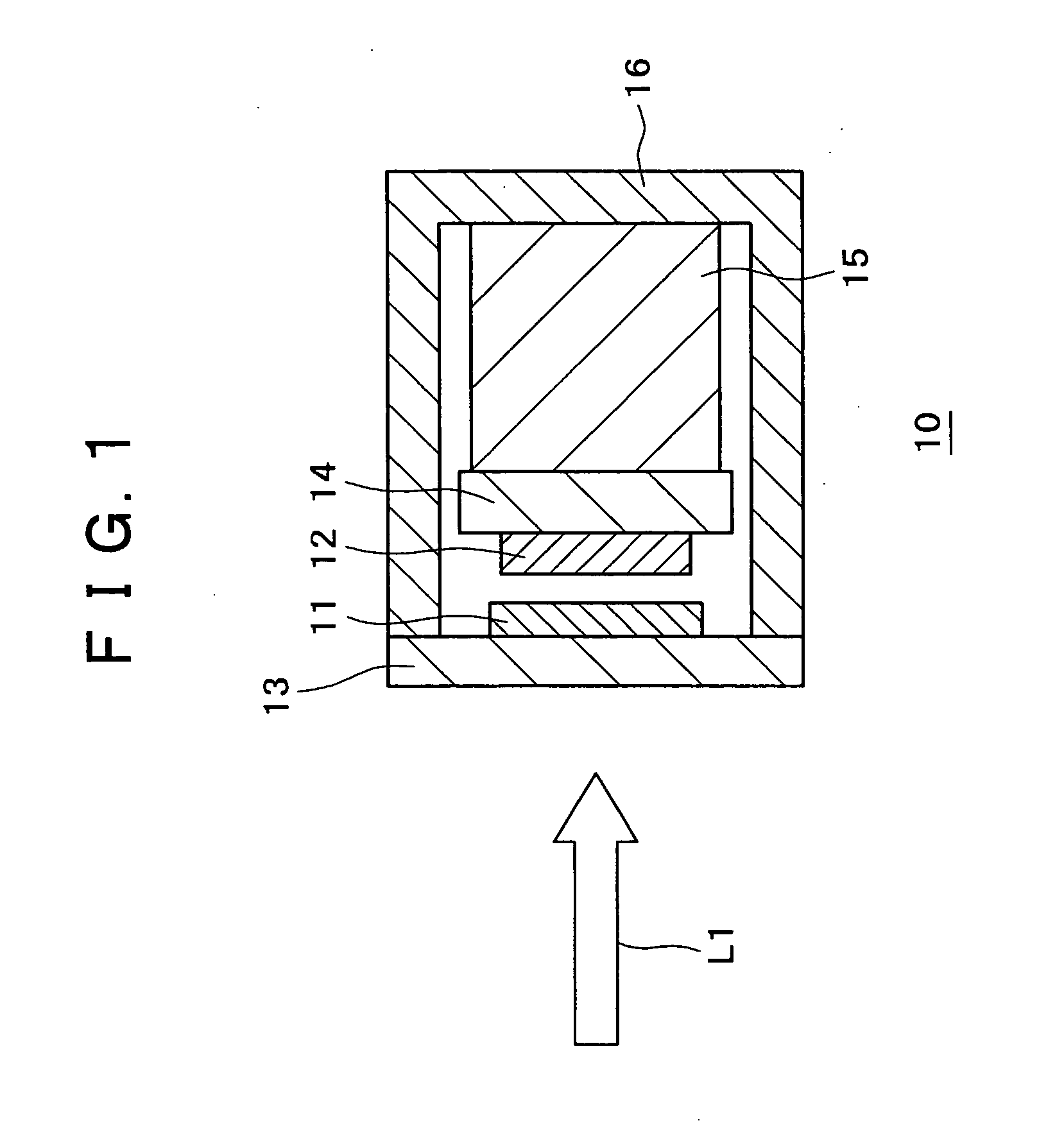
Solid microlaser passively switched by a saturable absorber and its production process
InactiveUS6023479AOptical rangefindersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsSaturable absorption
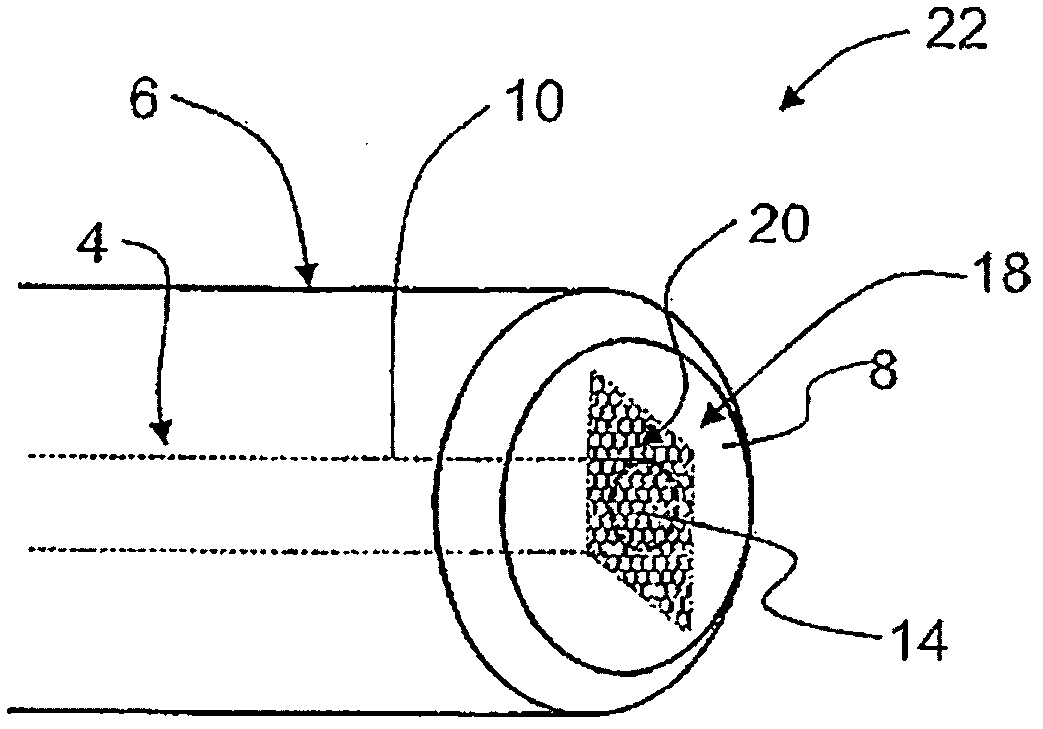
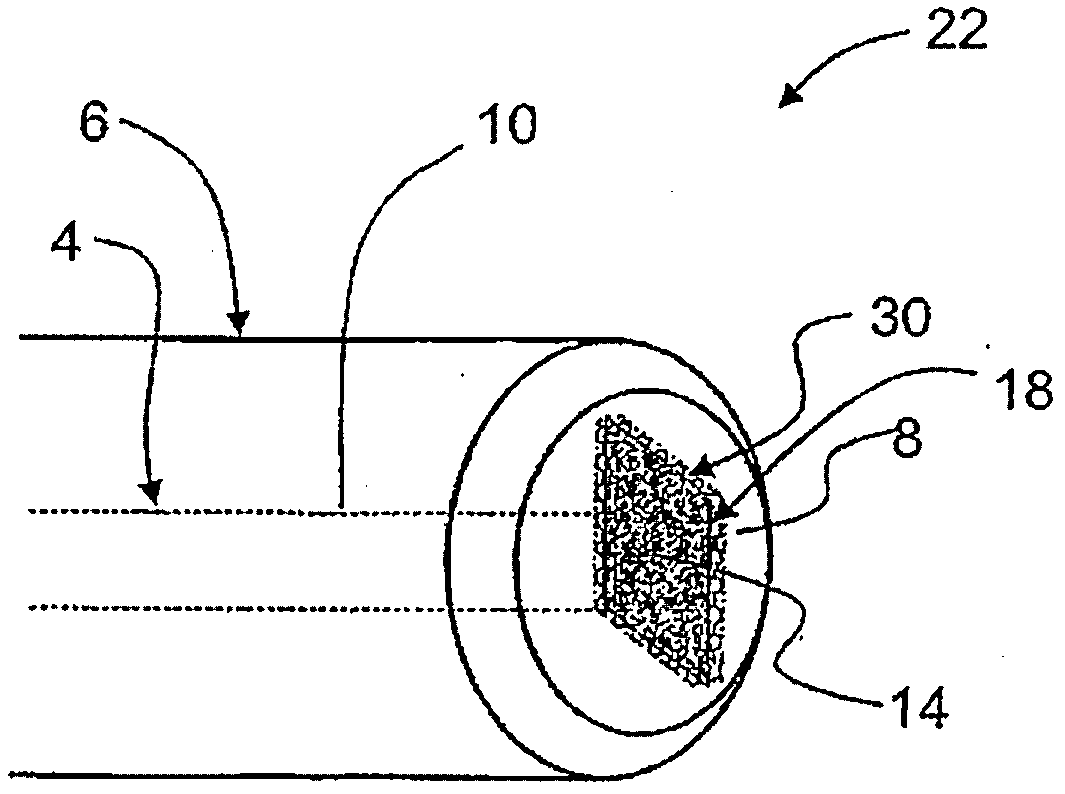
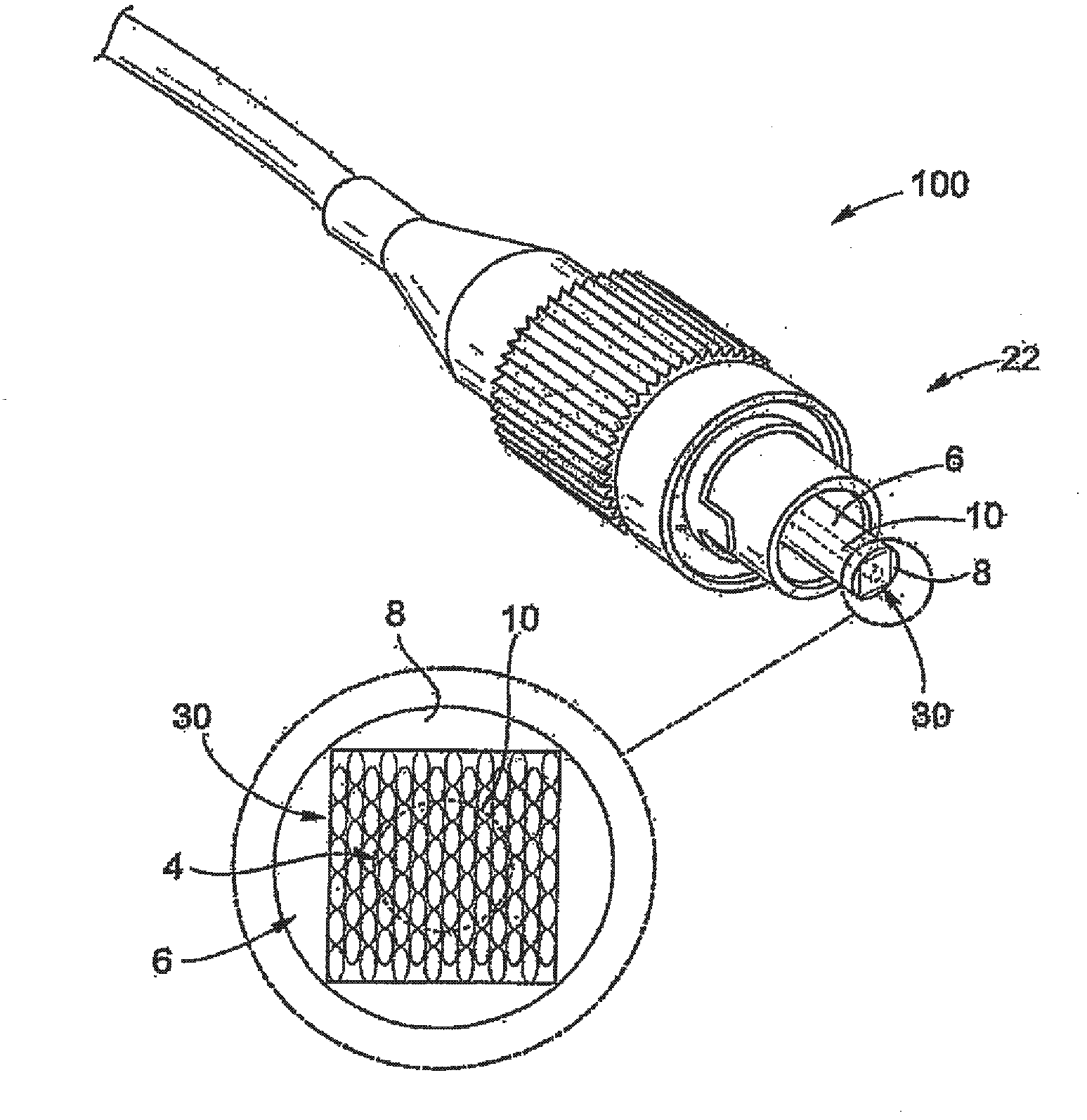
The invention relates to a microlaser cavity (10) having: a solid active medium (2) emitting at least in a wavelength range between 1.5 and 1.6 mu m, and a saturable absorber (4) of formula CaF2:Co2+ or MgF2:Co2+ or SrF2:Co2+ or BaF2:Co2+ or La0.9Mg0.5-xCoxAl11.433O19 or YAlO3:Co2+ (or YAl5-2xCoxSixO3) or Y3Al5-x-yGaxScyO12:Co2+ (or -3Al5-x-y2zGaxScyCozSizO12) or Y3-xLuxAl5O12Co2+ (or Y3-xLuxAl5-2yCoySiyO3) or Sr1-xMgxLayAl12-yO12:Co2+ (or Sr1-xMgx-yCoyLazAl12-zO12, with o<y<x).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
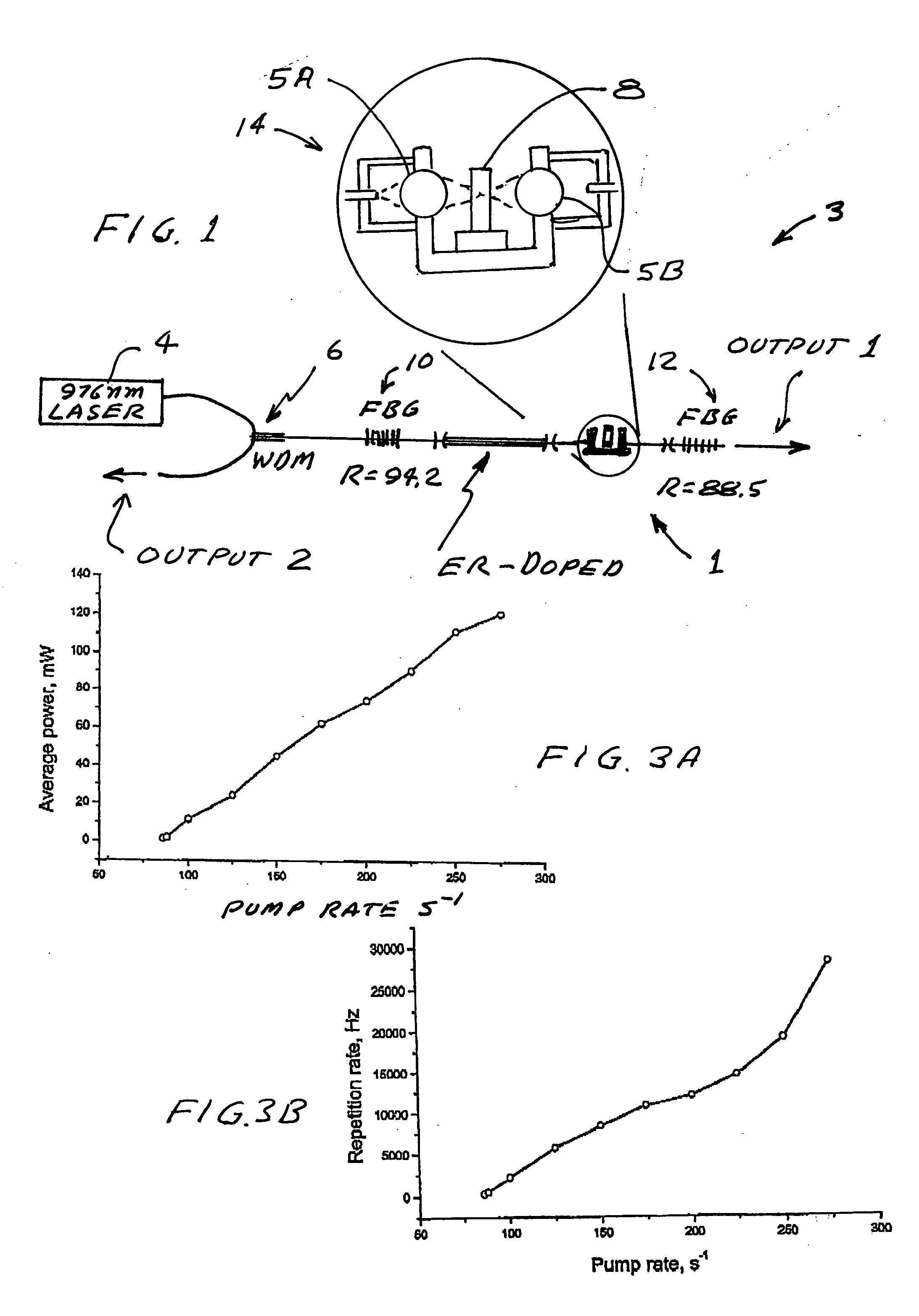
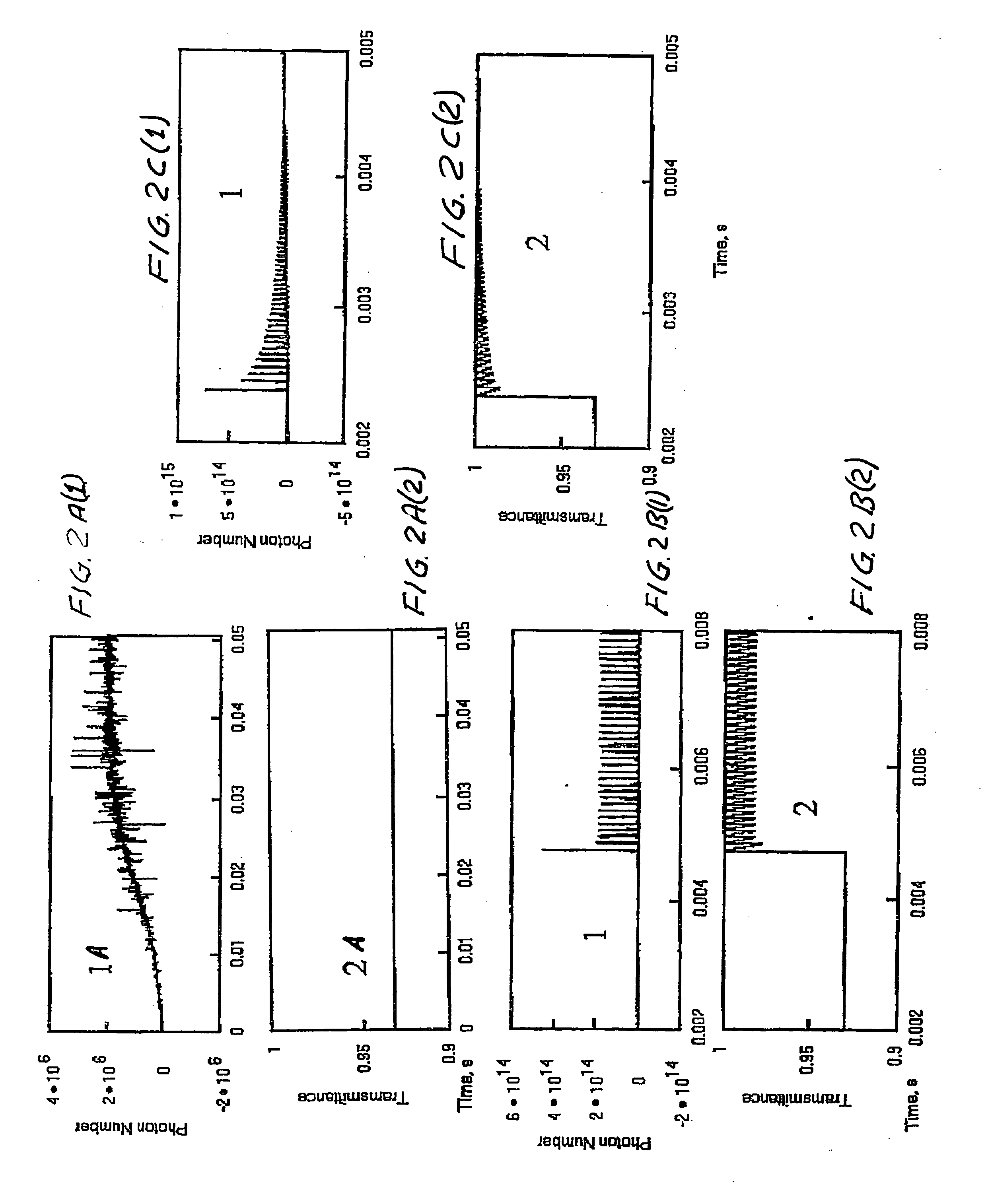
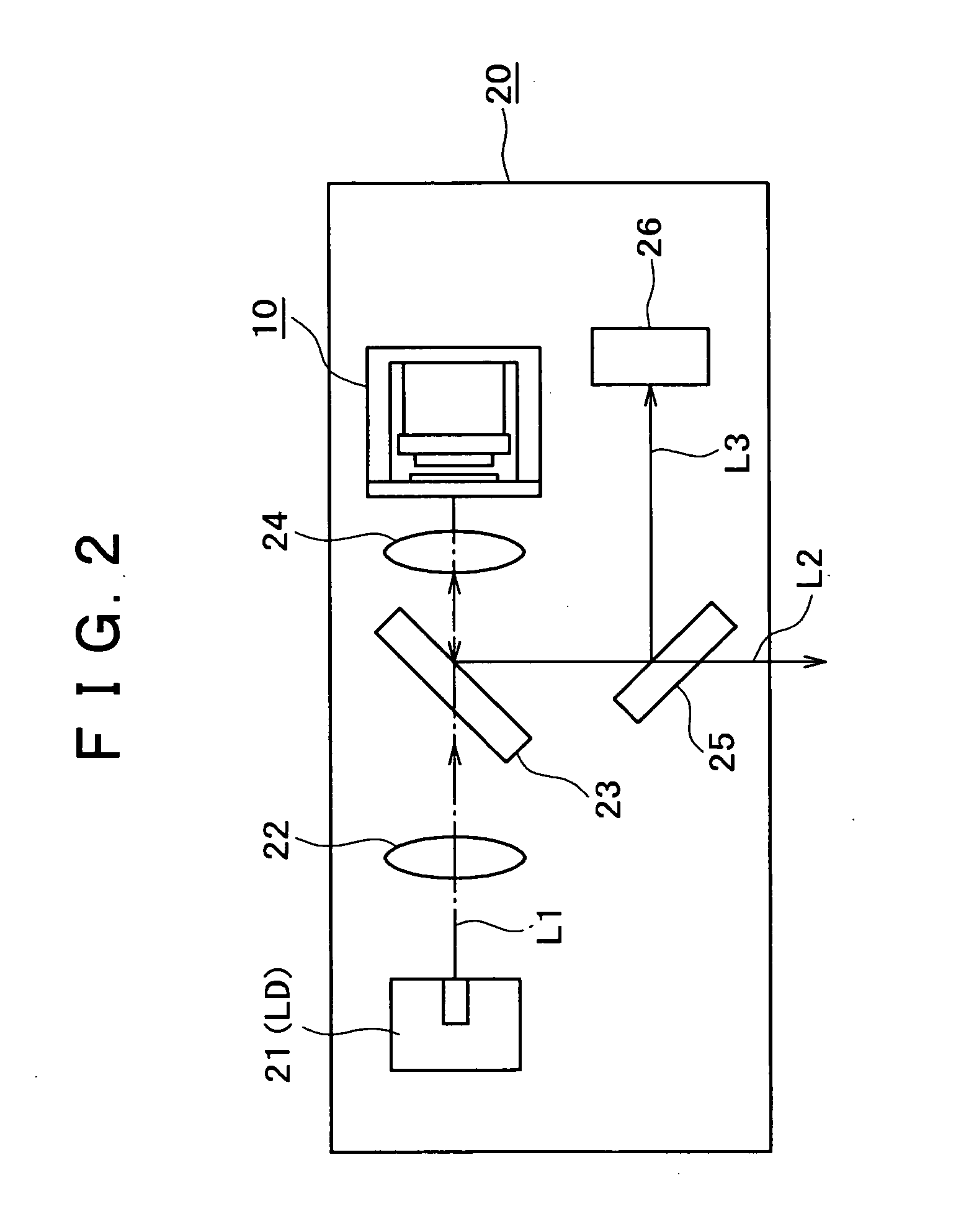
System and method for a passively Q-switched, resonantly pumped, erbium-doped crystalline laser
The laser includes a resonant cavity formed between a first mirror and a second mirror. An unsensitized Erbium-doped crystal gain medium for producing laser gain is disposed within the resonant cavity. A saturable absorber is disposed within the resonant cavity. A pump source is positioned to energize the gain medium. The saturable absorber, the laser gain, the resonator length, and the second mirror being selected so that output pulses having a duration of less than 75 nanoseconds are generated by the laser.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
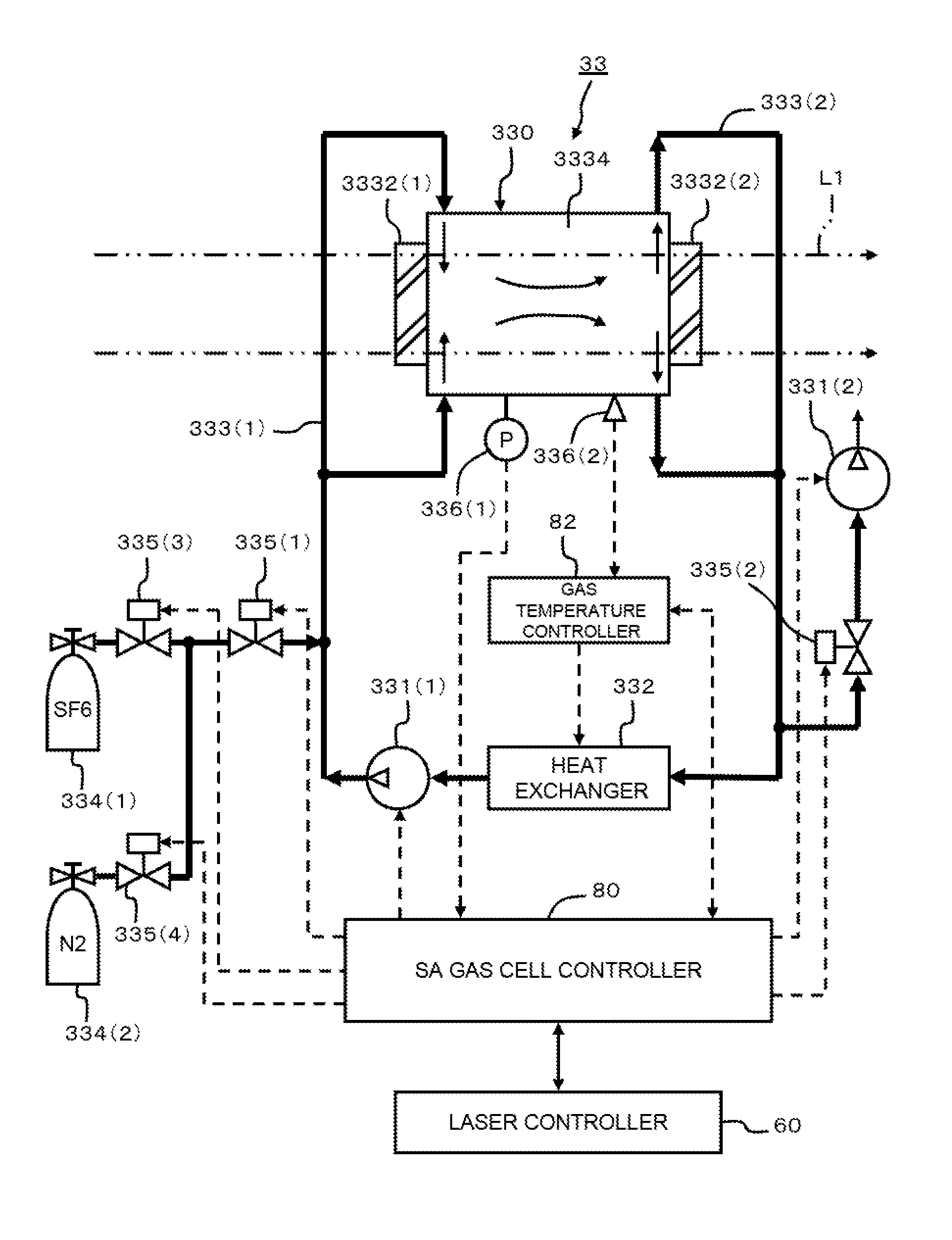
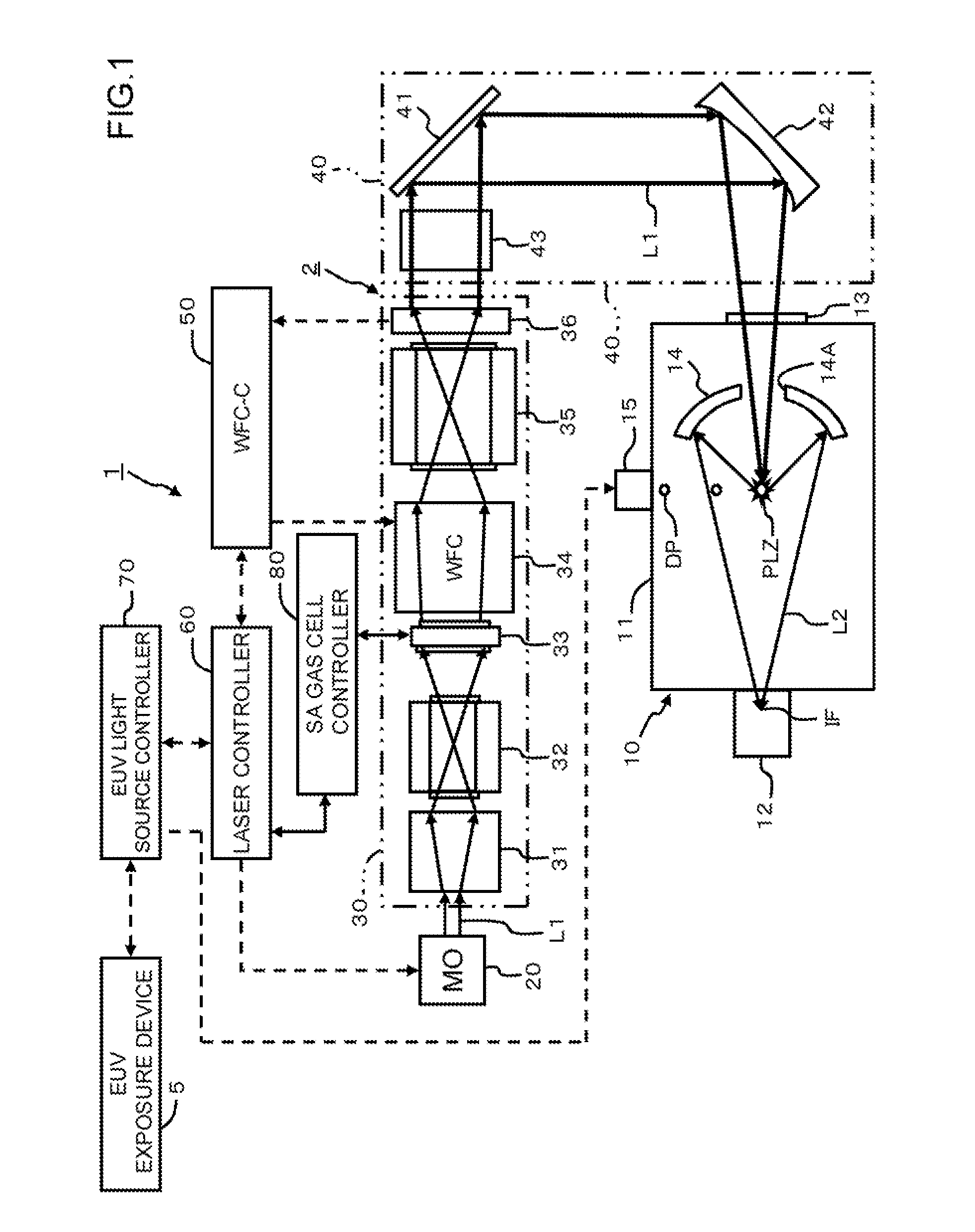
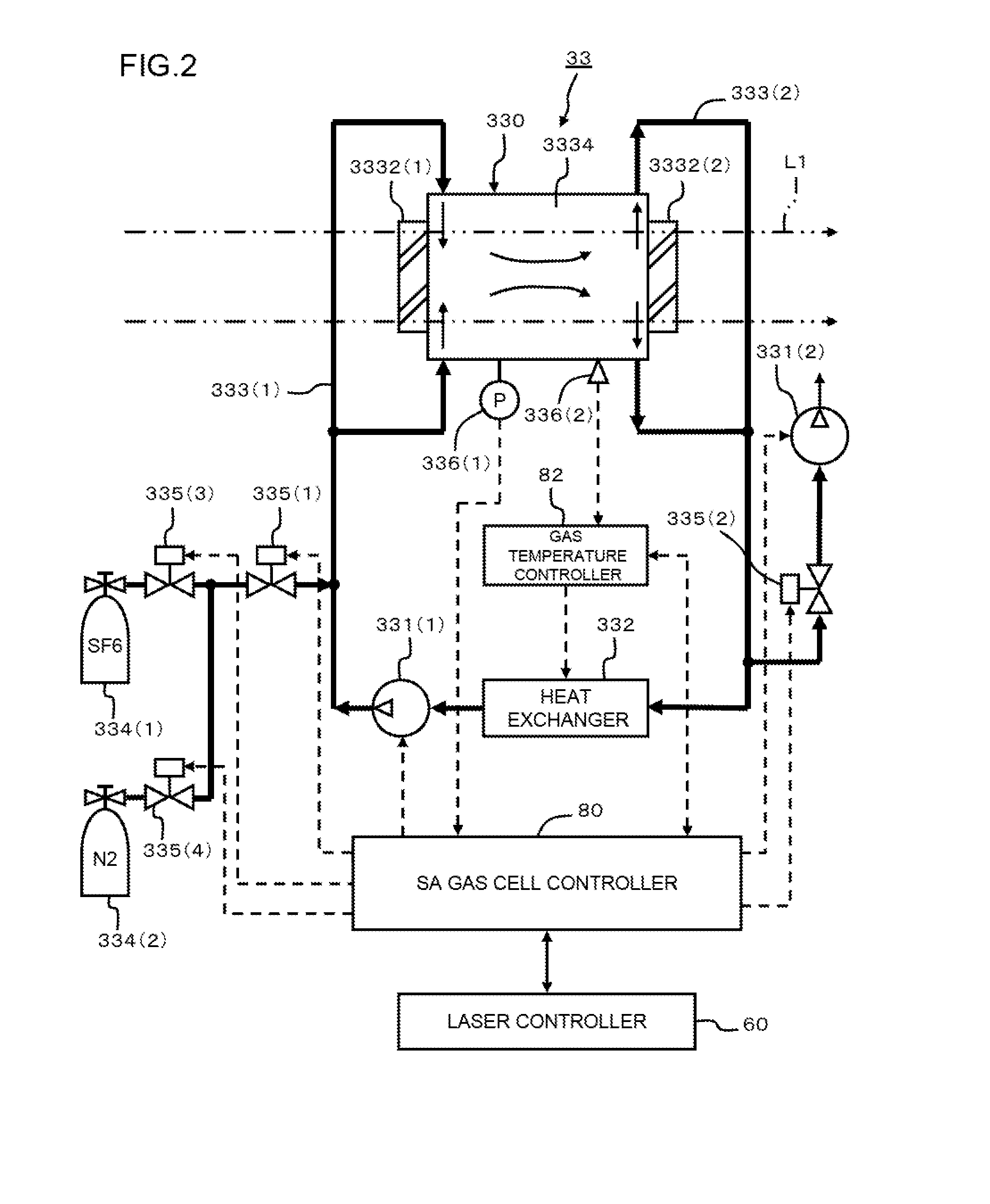
Extreme ultraviolet light source device, laser light source device for extreme ultraviolet light source device and method for controlling saturable absorber used in extreme ultraviolet light source device
ActiveUS20100078580A1Guaranteed uptimeGood compensationRadiation pyrometryRadiation/particle handlingGas cylinderLaser light
An EUV light source of the present invention is capable of using a saturable absorber stably and continuously in a high heat load state. A saturable absorber (SA) device is disposed on a laser beam line to absorb feeble light, such as self-excited oscillation light, parasitic oscillation light or return light. SA gas from an SA gas cylinder and buffer gas from a buffer gas cylinder are mixed to be a mixed gas. The mixed gas is supplied to an SA gas cell via a supply pipeline, and absorbs the feeble light included in the laser beam. The mixed gas is exhausted via an exhaust pipeline, and is sent to a heat exchanger. The mixed gas, cooled down by a heat exchanger, is sent back to the SA gas cell by a circulation pump.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
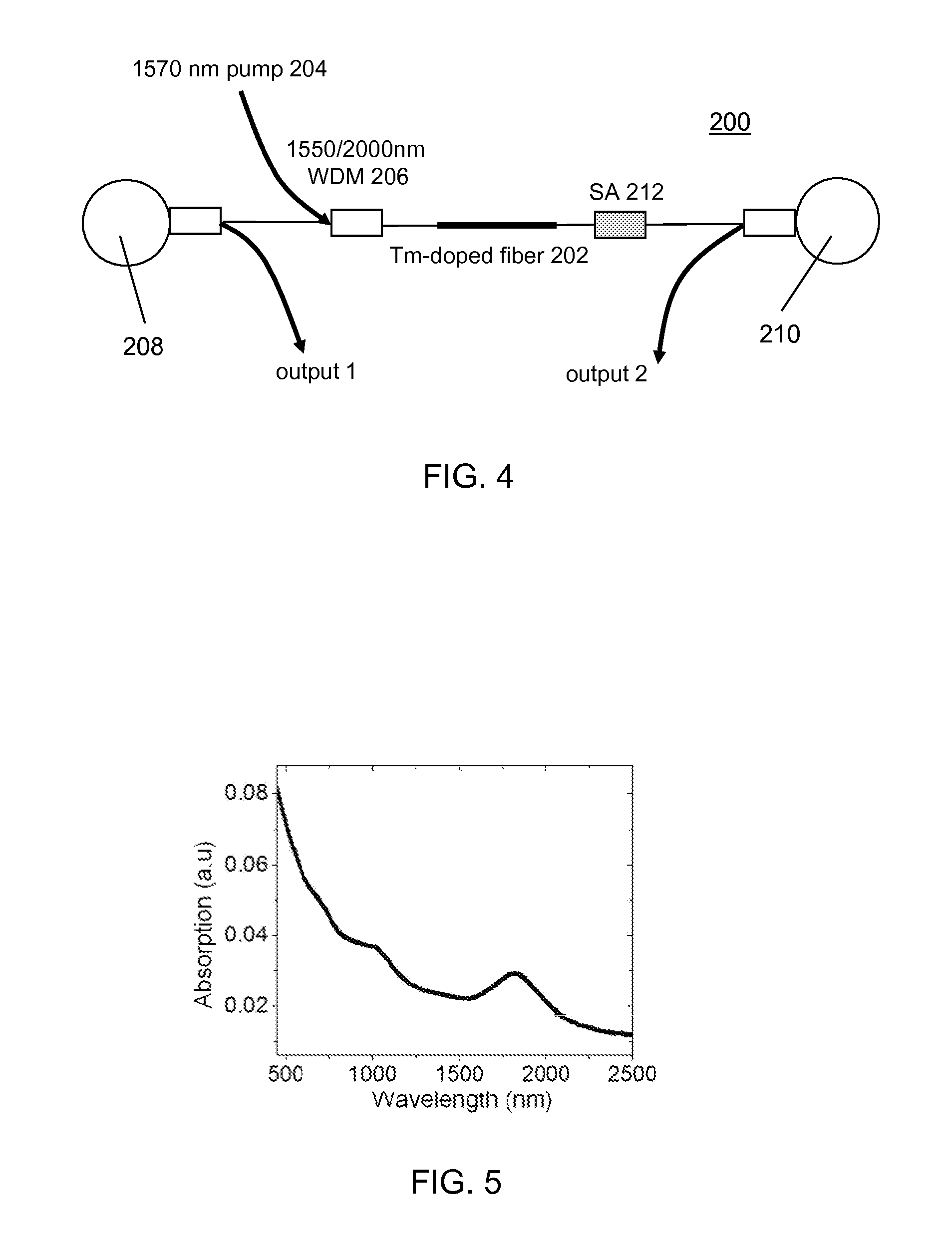
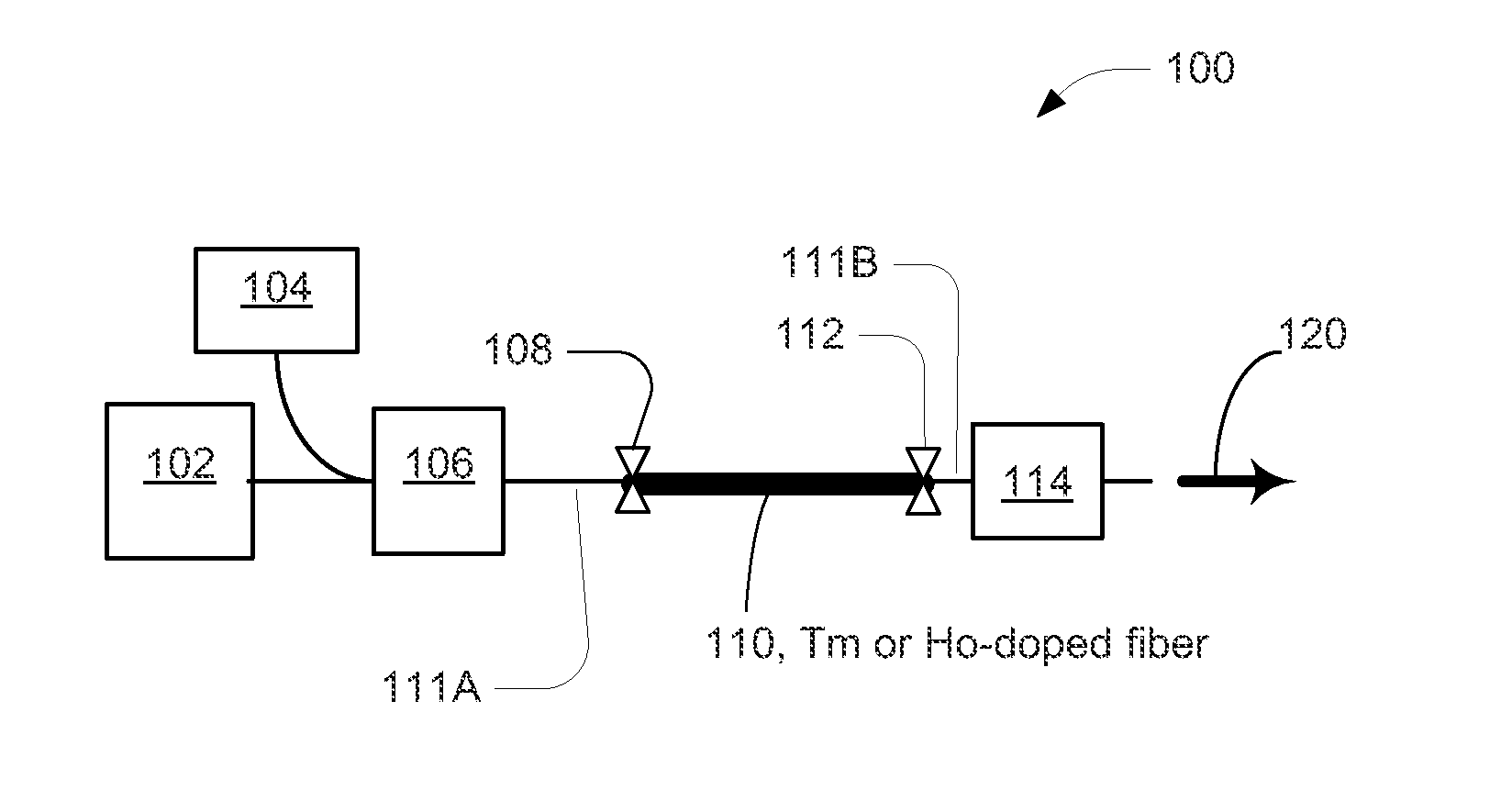
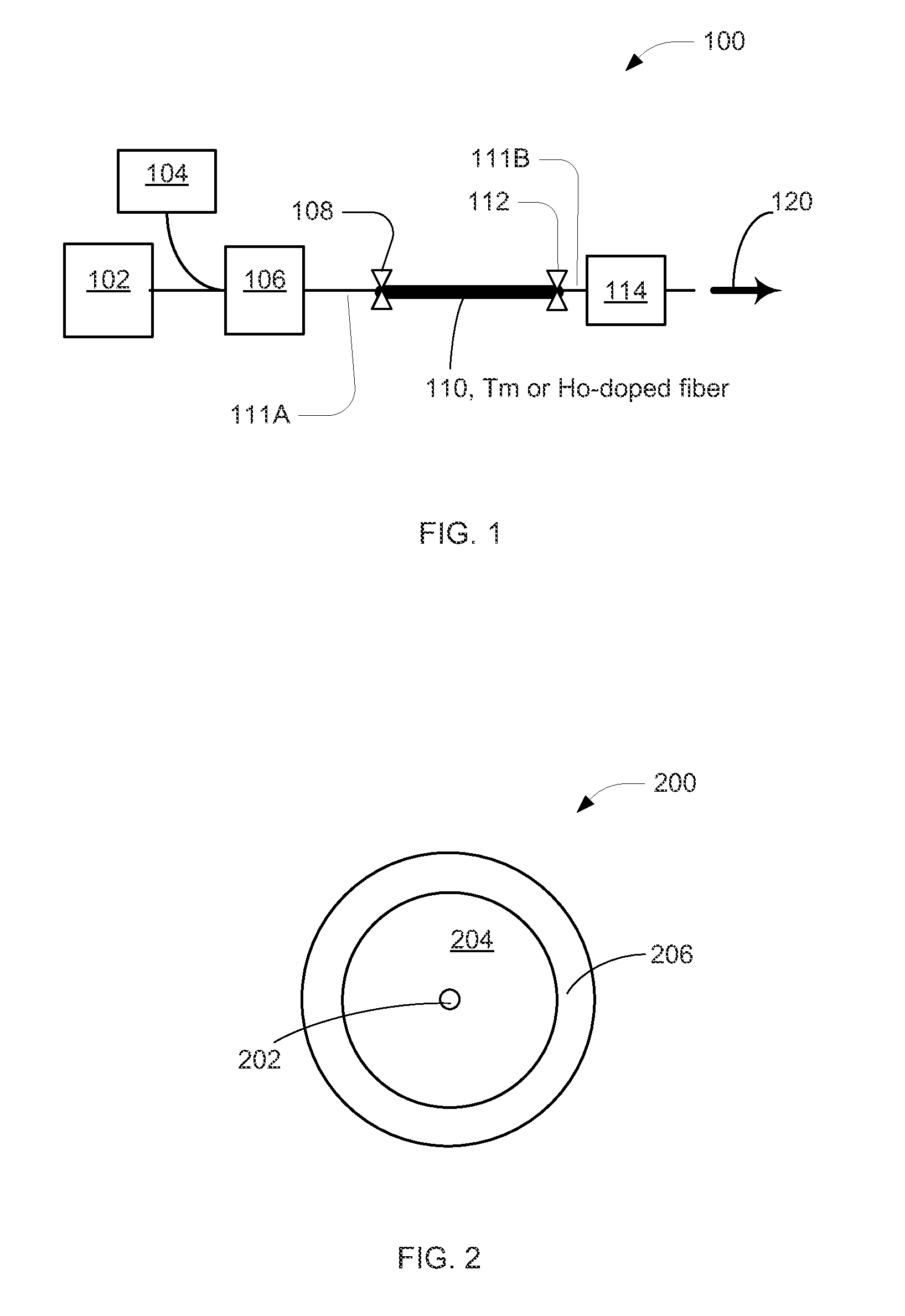
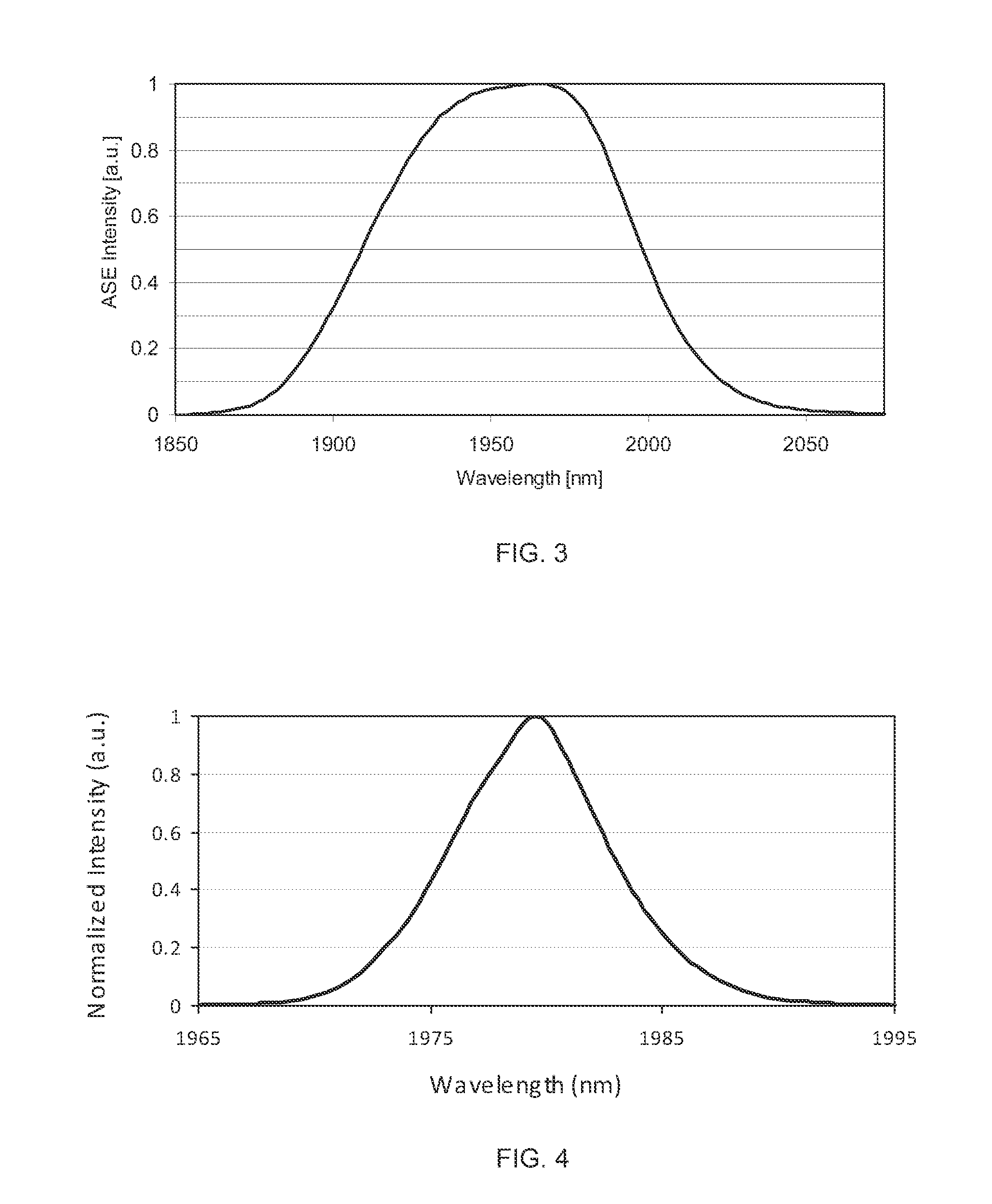
Mode-Locked Two-Micron Fiber Lasers
A mode-locked fiber laser comprising a multicomponent glass fiber doped with a trivalent rare-earth ion of thulium and / or holmium and including a fiber-optic based passive saturable absorber that contains an adhesive material mixed with a saturable absorbing components and is disposed along the length of an optical fiber such as to assure that a mode propagating within the fiber spatially overlaps with the volume occupied by the saturable absorbing components.
Owner:ADVALUE PHOTONICS
Optical element, and manufacturing method thereof
An optical element according to the present invention has a thin film, in which single-wall carbon nanotubes are laminated, and utilizes a saturable absorption function of the single-wall carbon nanotubes. Further, in a method for producing the optical element according to the present invention, the thin film is formed by spraying, to a body to be coated, a dispersion liquid prepared by dispersing the single-wall carbon nanotubes in a dispersion medium. Accordingly, a nonlinear optical element, which can operate in an optical communication wavelength region and which is extremely inexpensive and efficient, and a method for producing the optical element can be provided.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Low-repetition-rate ring-cavity passively mode-locked fiber laser
InactiveUS20090003391A1Laser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserFiber disk laser
A ring-cavity, passively mode locked fiber laser capable of producing short-pulse-width optical pulses at a relatively low repetition rate. The fiber laser uses a one-way ring-cavity geometry with a chirped fiber Bragg grating (CFBG) at its reflecting member. The CFBG is part of a dispersion compensator that includes an optical circulator that defines a one-way optical path through the ring cavity. A doped optical fiber section is arranged in the optical path and serves as the gain medium. A pump light source provides the pump light to excite the dopants and cause the gain medium to lase. A saturable absorber is operable to effectuate passive mode-locking of the multiple modes supported by the ring cavity. The ring cavity geometry allows to achieve mode locking with single pulse operation in a longer cavity length than conventional linear cavities. Furthermore, the longer cavity length reduces the constraints on the chirp rate of the CFBG. This, in turn, allows the CFBG to have a relatively high reflectivity, which provides the necessary dispersion compensation and cavity loss for generating short optical pulses at a low repetition rate.
Owner:CORNING INC
System and method for a passively Q-switched, resonantly pumped, erbium-doped crystalline laser
The laser includes a resonant cavity formed between a first mirror and a second mirror. An unsensitized Erbium-doped crystal gain medium for producing laser gain is disposed within the resonant cavity. A saturable absorber is disposed within the resonant cavity. A pump source is positioned to energize the gain medium. The saturable absorber, the laser gain, the resonator length, and the second mirror being selected so that output pulses having a duration of less than 75 nanoseconds are generated by the laser.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
Graphene-based saturable absorber devices and methods
InactiveCN102439802AActive medium shape and constructionAdhesivesGraphene derivativesFunctionalized graphene
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
Process for preparing glass fiber composite type silicon dioxide aerogel insulation quilt
The invention discloses a process for preparing a glass fiber composite type silicon dioxide aerogel insulation quilt. The process mainly comprises the following steps: absorbing a silicon dioxide aerogel liquid till being saturated by using a glass fiber quilt, gelling under specific conditions, and drying supercutical fluid CO2 to form a reinforced aerogel material. The glass fiber composite type silicon dioxide aerogel insulation quilt prepared by using the process is excellent in heat preservation property, mechanical property and fireproof and waterproof property, and is convenient to construct. By adopting the process, a solvent replacement step is avoided, the operation is simple and easy, the operation process is controllable, and continuous production can be achieved.
Owner:GUIZHOU AEROSPACE WUJIANG MACHINERY & ELECTRICITYEQUIP
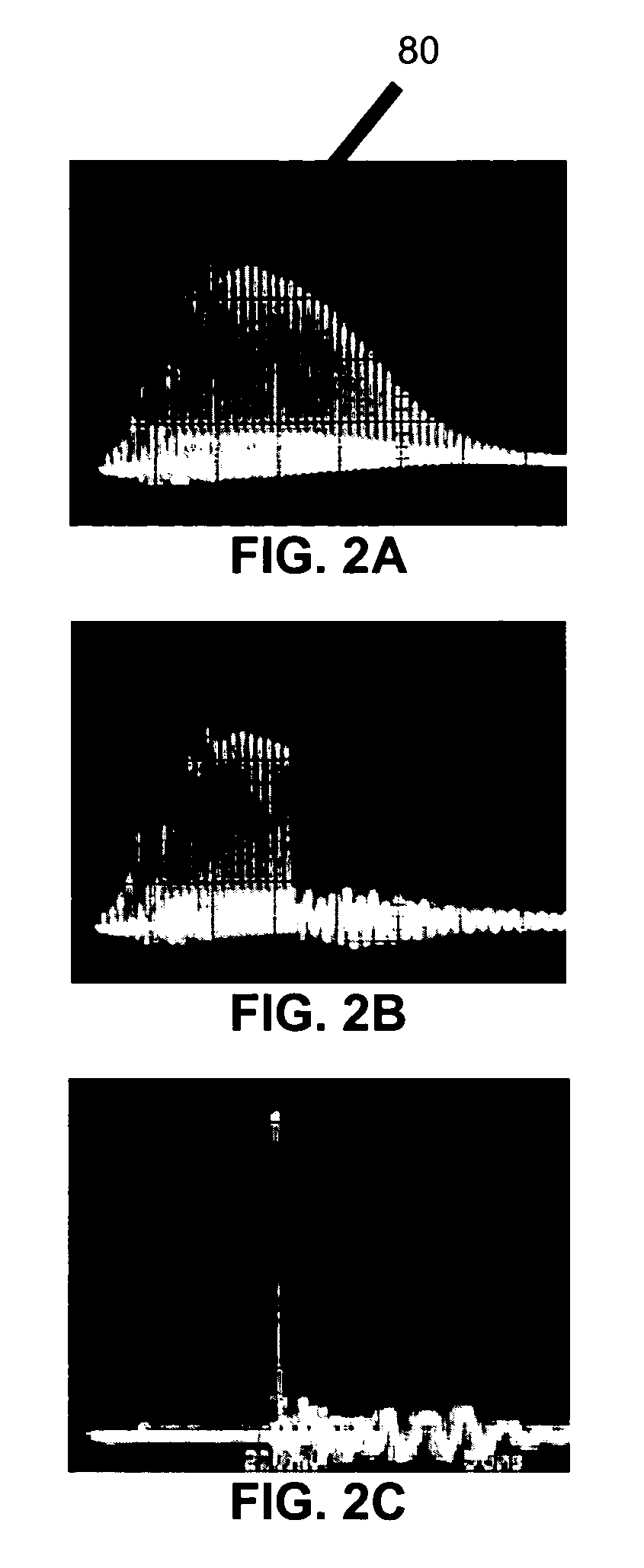
Mode-locked laser with variable pulse duration
ActiveUS20050074038A1Fine pulse duration variabilityCoarse pulse duration variabilityActive medium materialNegative feedbackPicosecond laser
A pulsed, mode-locked, picosecond laser having a solid-state laser medium, a saturable absorber (SA), and a passive negative feedback (PNF) element. The SA is “slow,” having an absorption recovery time which is longer than a desired duration of an output pulse. The SA and the PNF element together mode-lock the laser to produce an output pulse or pulses of a given duration. The position of the SA along the beam path and the orientation of the SA with respect to the beam path can be varied to vary the output pulse duration over a wide range.
Owner:CONTINUUM ELECTRO OPTICS
Two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber and production method thereof
InactiveCN104218443AWide wavelength rangeReduce absorption lossActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionMode-lockingWavelength
The invention relates to a two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber and a production method thereof, and belongs to the field of saturable absorbers of lasers. The two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber comprises a substrate, a high-reflection layer, a saturable absorption layer and a functional layer. One end face of the functional layer is connected with the saturable absorption layer, one end face of the saturable absorption layer is connected with the high-reflection layer, and one end face of the high-reflection layer is connected with the substrate. By the two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber and the production method thereof, application of the lasers, such as Q-switching, mode locking and optical signal processing, is realized. By the high-reflection layer formed by composite materials, absorption loss is reduced and reflection rate is increased, and optimal material combinations can be found in terms of different wave lengths.
Owner:鲍小志
Active and passive Q-adjusted single longitudinal mode laser
InactiveCN1645691AShort pulse widthHigh degree of polarizationOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialResonant cavityLongitudinal mode
The invention consists of pumping source, cavity, and a group of coupling device set between the pumping source and cavity, and connected with pumping source through optical fiber. The cavity consists of front cavity mirror and back cavity mirror coated with film. The double-doped crystals and active Q-switch are set between the front and back mirrors. A cooling device is set on the double-doped crystals. The invention features using active Q-switch to control the passive Q-switch for getting prelase pulse, and using saturable absorption crystals as longitudinal mode selector for making the solid single longitudinal mode laser work under higher pumping power.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
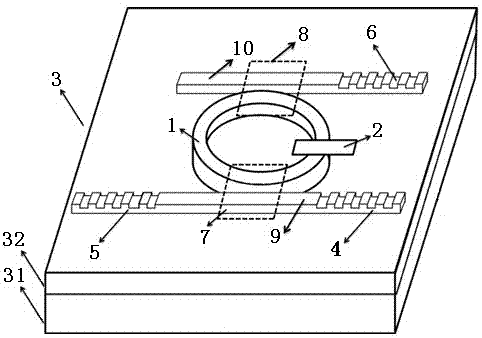
Two-dimensional stratified material saturable absorber device and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a two-dimensional stratified material saturable absorber device which comprises a substrate. The substrate is a high reflection mirror plated with a back electrode, a dielectric layer and a two-dimensional stratified saturable absorption material are arranged on the high reflection mirror in sequence, an electrode is arranged on the two-dimensional stratified saturable absorption material in an evaporation mode, a voltage source is arranged between the electrode and the back electrode, an optical fiber pigtail is arranged above the two-dimensional stratified saturable absorption material, and the saturable absorption device is attached to the optical fiber pigtail. According to a method, the advantages of a two-dimensional stratified saturable absorber are inherited, such as high performance, low manufacturing cost and easy combination, and CW light and Pulse light can be switched over fast by adjusting grid voltages and freely adjusting the starting threshold value of a laser locking mold.
Owner:南京科耐激光技术有限公司
Laser diode and laser diode device
InactiveUS20070064758A1Easy to installEasy to manufactureOptical wave guidanceSolid-state devicesGainSemiconductor
A laser diode capable of being easily mounted, and a laser diode device in which the laser diode is mounted are provided. A hole is disposed in a semiconductor layer, and a p-type electrode and an n-type semiconductor layer are electrically connected to each other by a bottom portion (a connecting portion) of the hole. Thereby, the p-type electrode has the same potential as the n-type semiconductor layer, and a saturable absorption region is formed in a region corresponding to a current path. Light generated in a gain region (not shown) is abosorbed in the saturable absorption region to be converted into a current. The current is discharged to a ground via the p-side electrode and the bottom portion, and an interaction between the saturable absorption region and the gain region is intitiated, thereby self-oscillation can be produced.
Owner:SONY CORP
Saturable Absorber of Polyimide Containing Dispersed Carbon Nanotubes
InactiveUS20080258117A1Increase resistanceImprove transmittanceMaterial nanotechnologyDiffusing elementsOrganic solventCarbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube-dispersed polyimide saturable absorber excellent in an optical quality, obtainable by mixing a carbon nanotube dispersion liquid comprising a carbon nanotube, an amide-based polar organic solvent, and a nonionic surfactant and / or a polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) with a mixture solution of a solvent soluble polyimide and an organic solvent. A method for producing the same, comprising the steps of dispersing a single-walled carbon nanotube in a mixture solution of an amide-based polar organic solvent and a nonionic surfactant under intensive stirring, mixing the resultant dispersion liquid with a polyimide mixed organic solvent, and removing the solvent.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Method of stabilizing laser beam, and laser beam generation system
InactiveUS20050018723A1Constant characteristicVariation in characteristicActive medium materialExcitation beamLight beam
A laser beam generation system comprises a solid state laser oscillator excited by an excitation beam, and a Q switch for pulsating laser oscillation by use of a saturable absorber, wherein the optical path length of a laser resonator is variable. The pulse of a laser beam generated from the laser beam generation system is detected, and variation of the optical path length of the laser resonator is controlled based on a characteristic of the detected pulse, to thereby stabilize the laser beam. The laser beam generation system may further comprise resonator length regulation element for varying the optical path length of the laser resonator, and detection element for detecting the pulse laser beam outputted, wherein the optical path length of the laser resonator is regulated by the resonator length regulation element based on a characteristic of the pulse detected by the detection element.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical soliton generation device based on passive mode-locked ytterbium-doped fiber laser
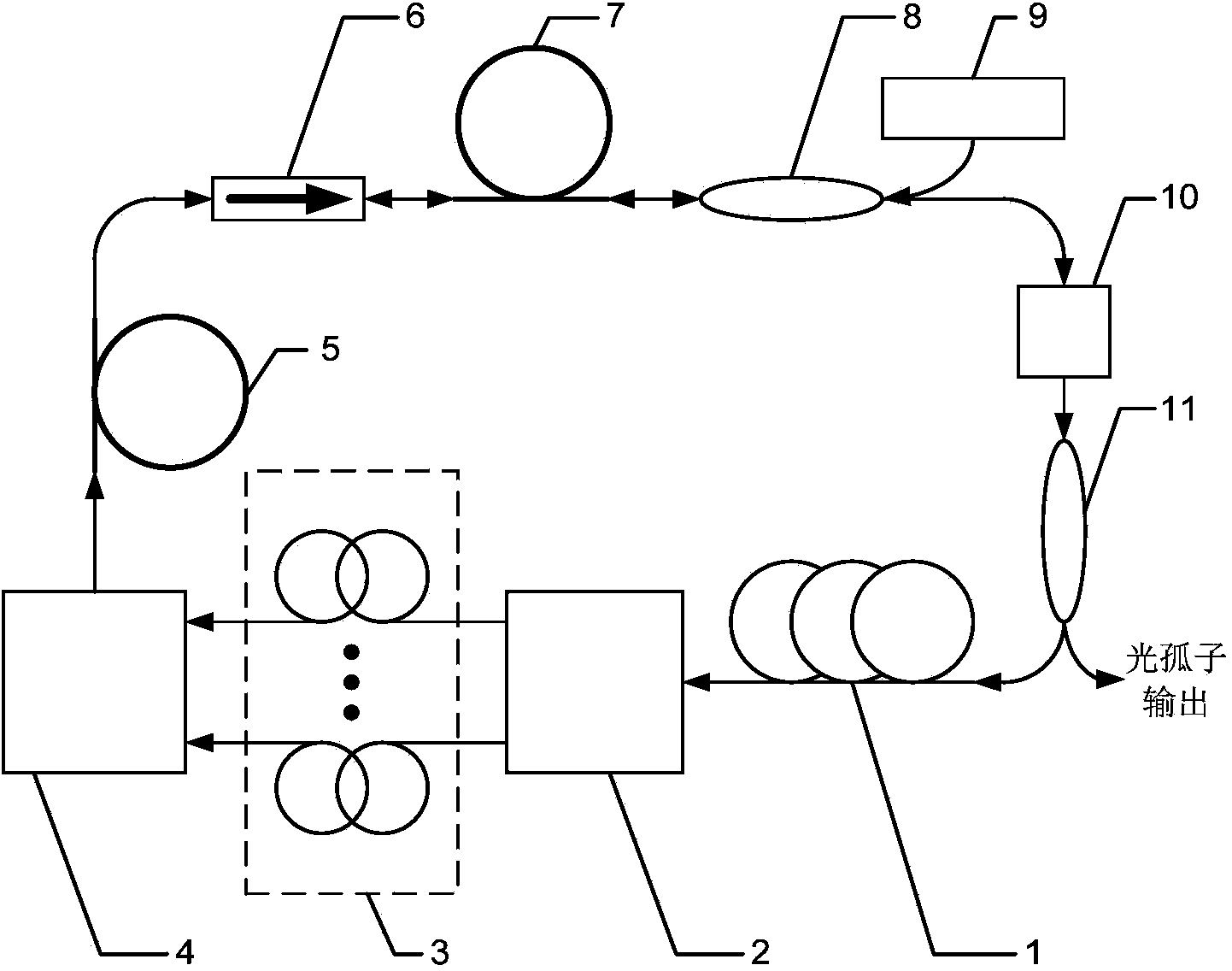
InactiveCN104037599AParameter unchangedInsertion loss constantActive medium shape and constructionFiber disk laserOptical coupler
The invention belongs to the technical field of photoelectric equipments, in particular to a device capable of generating various optical solitons. The optical soliton generation device based on a passive mode-locked ytterbium-doped fiber laser comprises a polarization controller (1), a 1*N optical switch (2), an optical fiber group (3), a 1*N optical coupler (4), a dispersion compensation fiber (5), an optical isolator (6), a ytterbium-doped fiber, a light wavelength division multiplexing (8), a pump light source (9), a saturable absorber (10) and a 1*2 optical coupler (1). In the same passive mode-locked ytterbium-doped fiber laser system, the optical soliton generation device based on the passive mode-locked ytterbium-doped fiber laser is capable of obtaining parabolic dissipative soliton single-pulse optical solitons, hyperbolic secant-shaped soliton single-pulse optical solitons, bounded multi-soliton optical solitons of the two optical pulses and other optical solitons; when switching between different types of solitons, a user does not need to change a light path structure, and the switching speed is very fast.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Two-dimensional stratified material based SOI (Semicon-on-insulator) base micro loop filter
The invention discloses a two-dimensional stratified material based SOI (Semicon-on-insulator) base micro loop filter. The two-dimensional stratified material based SOI base micro loop filter comprises an SOI substrate which is formed by a buried oxide layer and top silicon; an SOI micro loop resonant cavity, input straight waveguide and output straight waveguide are arranged on the top silicon and the input straight waveguide and output straight waveguide are arranged on the upper side and the lower side of the SOI micro loop resonant cavity, so that the SOI waveguide structure is formed; two-dimensional stratified materials cover the SOI waveguide structure; two ends of the input straight waveguide are provided with input end optical grating and direct connection optical grating; one end of the output straight waveguide is provided with output end optical grating; areas of the SOI micro loop resonant cavity, which are close to the input straight waveguide and the output straight waveguide, form into a first coupling area and a second coupling area. Compared with the traditional technology, the two-dimensional stratified material based SOI base micro loop filter has the advantages of being narrow in 3dB band width, high in extinction ratio, less in noise, compatible with CMOS technology and widely applied to the on-chip optical interconnection network in the future due to the fact that the SOI base filter is further filtered due to the saturated absorption effect of two-dimensional stratified materials.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com