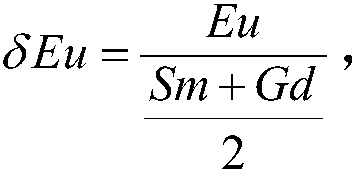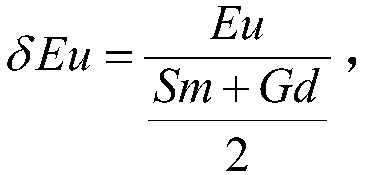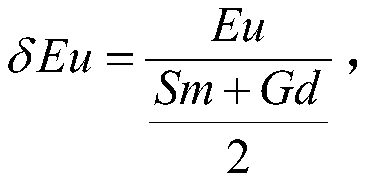Patents
Literature
69 results about "Cathodoluminescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cathodoluminescence is an optical and electromagnetic phenomenon in which electrons impacting on a luminescent material such as a phosphor, cause the emission of photons which may have wavelengths in the visible spectrum. A familiar example is the generation of light by an electron beam scanning the phosphor-coated inner surface of the screen of a television that uses a cathode ray tube. Cathodoluminescence is the inverse of the photoelectric effect, in which electron emission is induced by irradiation with photons.
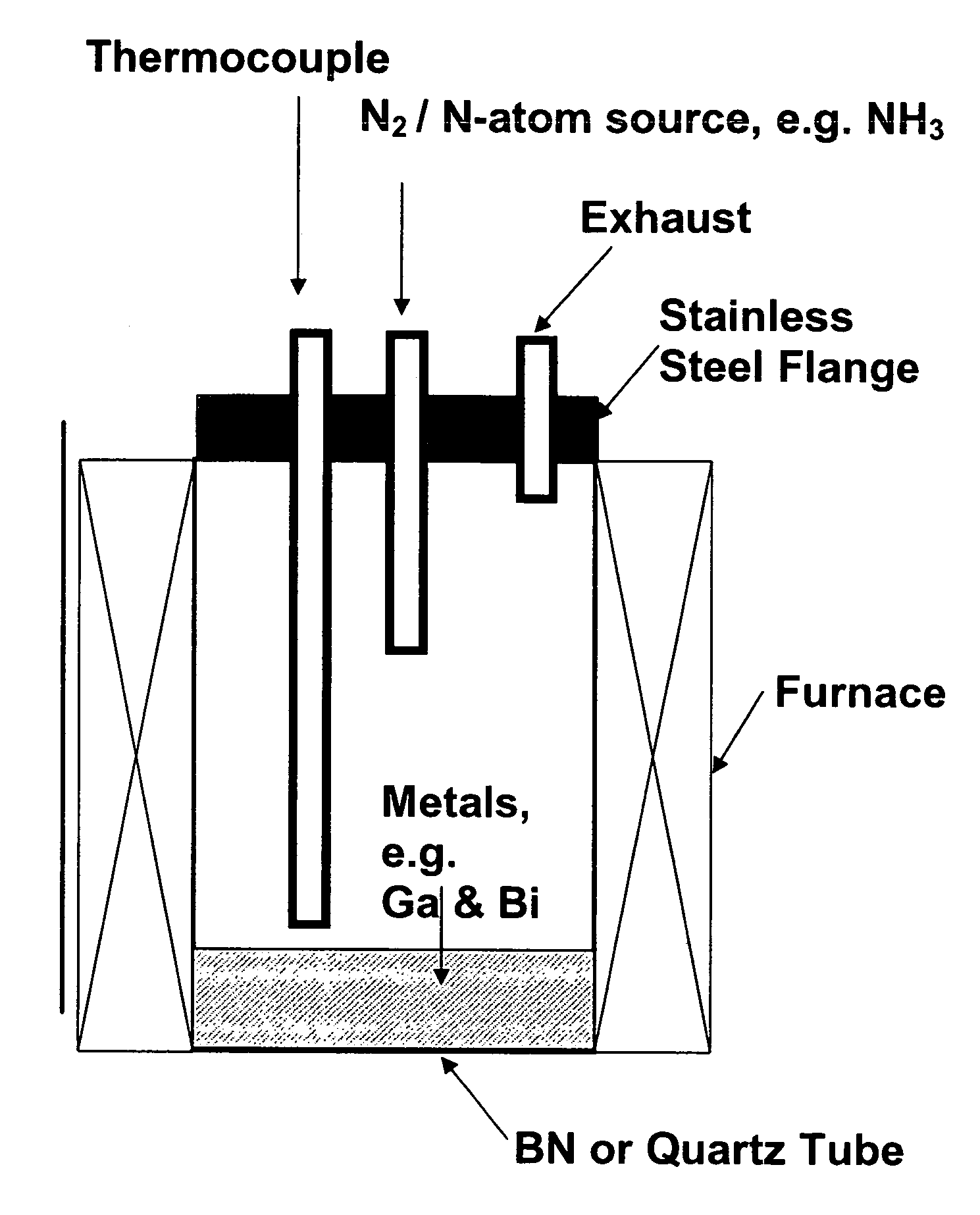
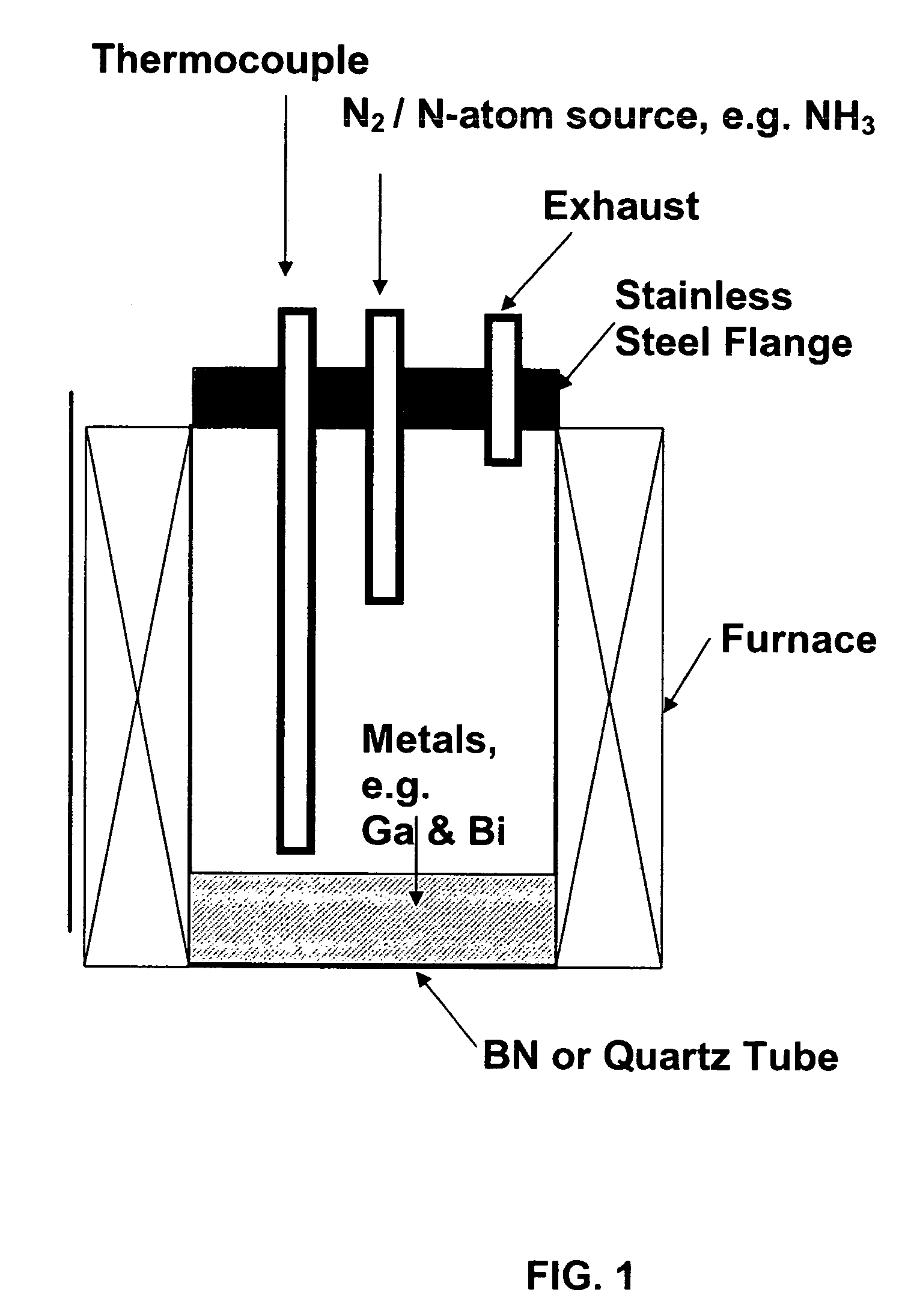
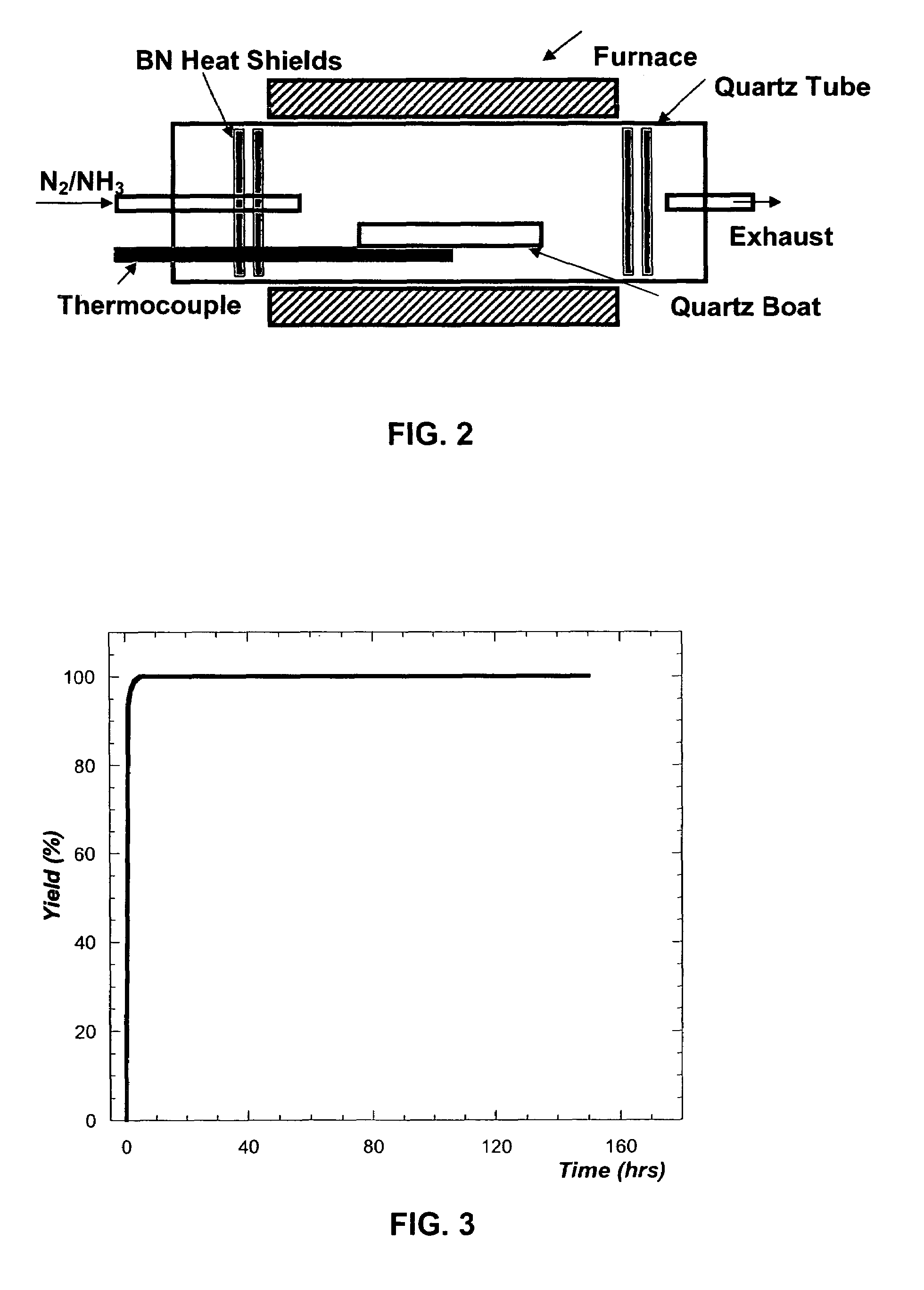
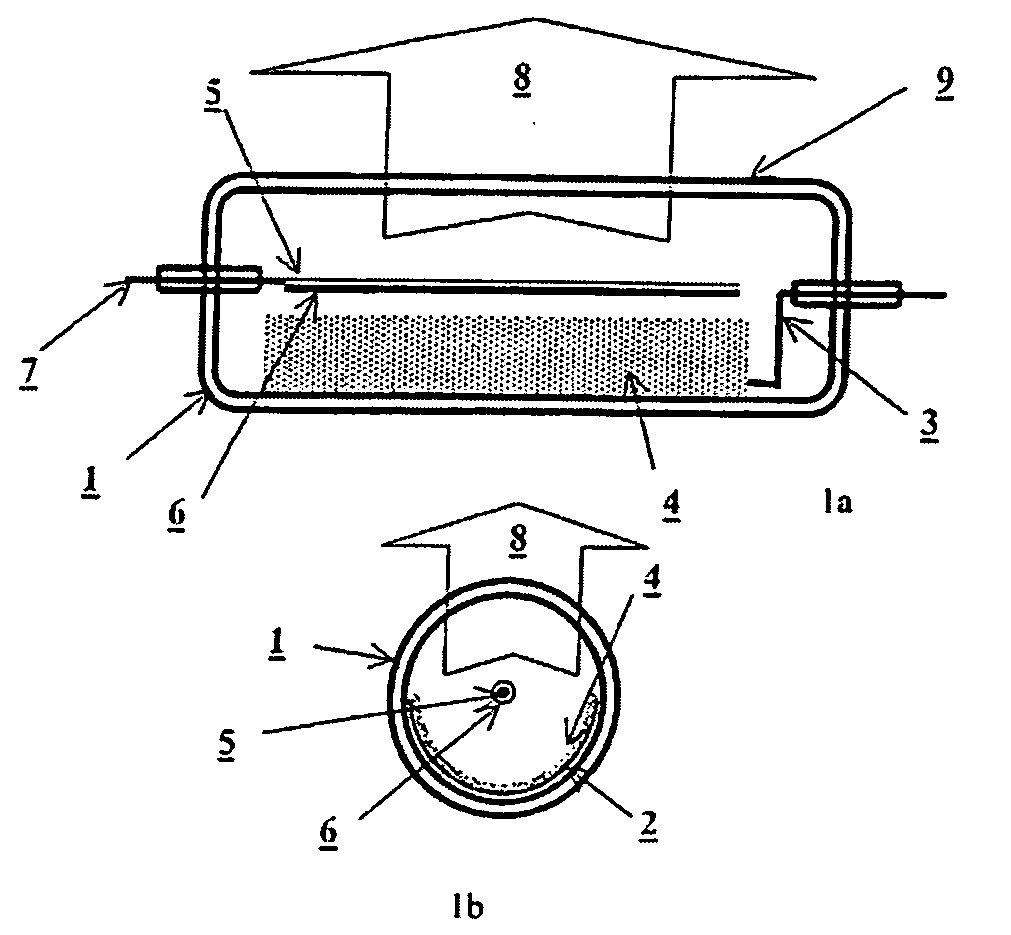
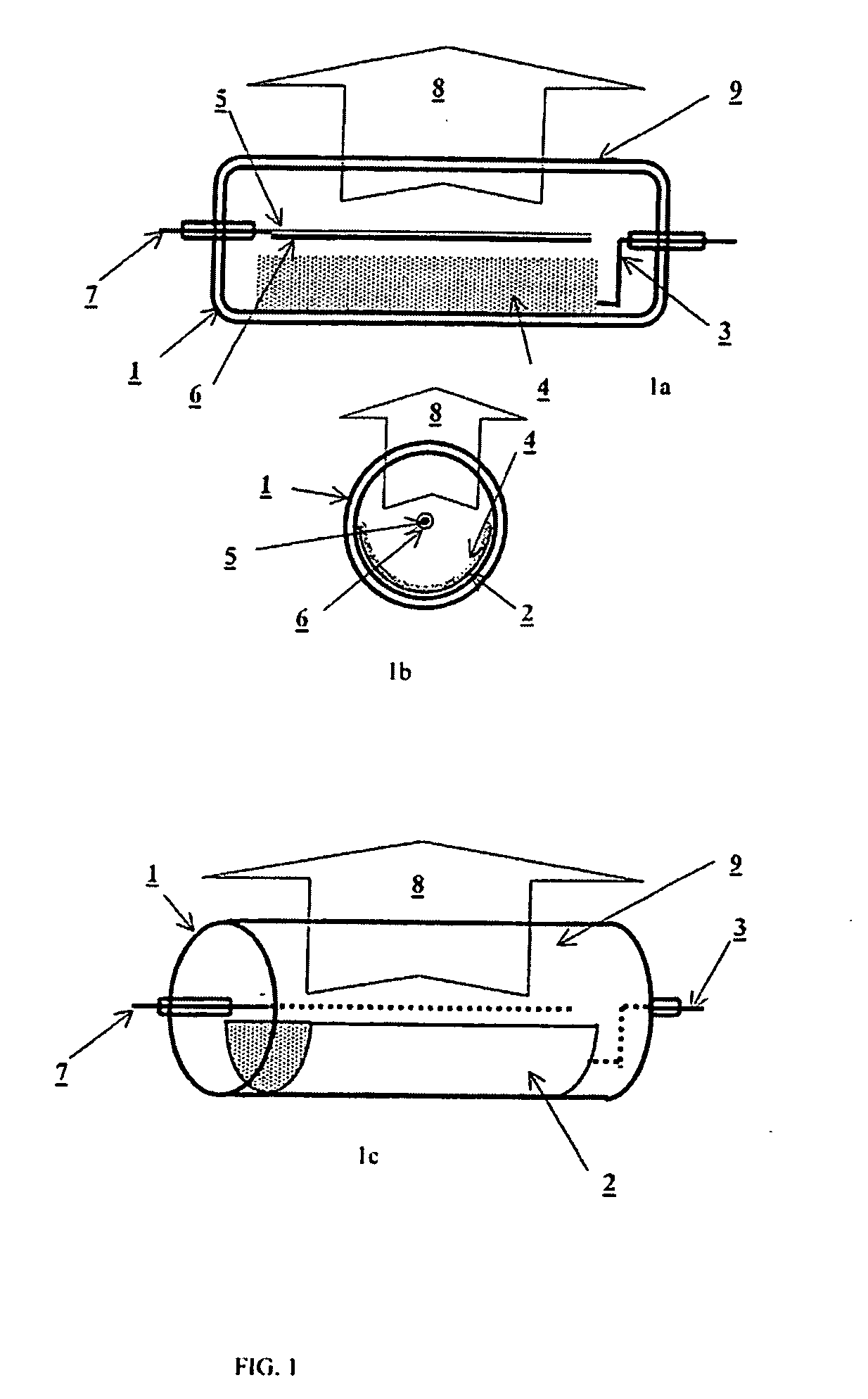
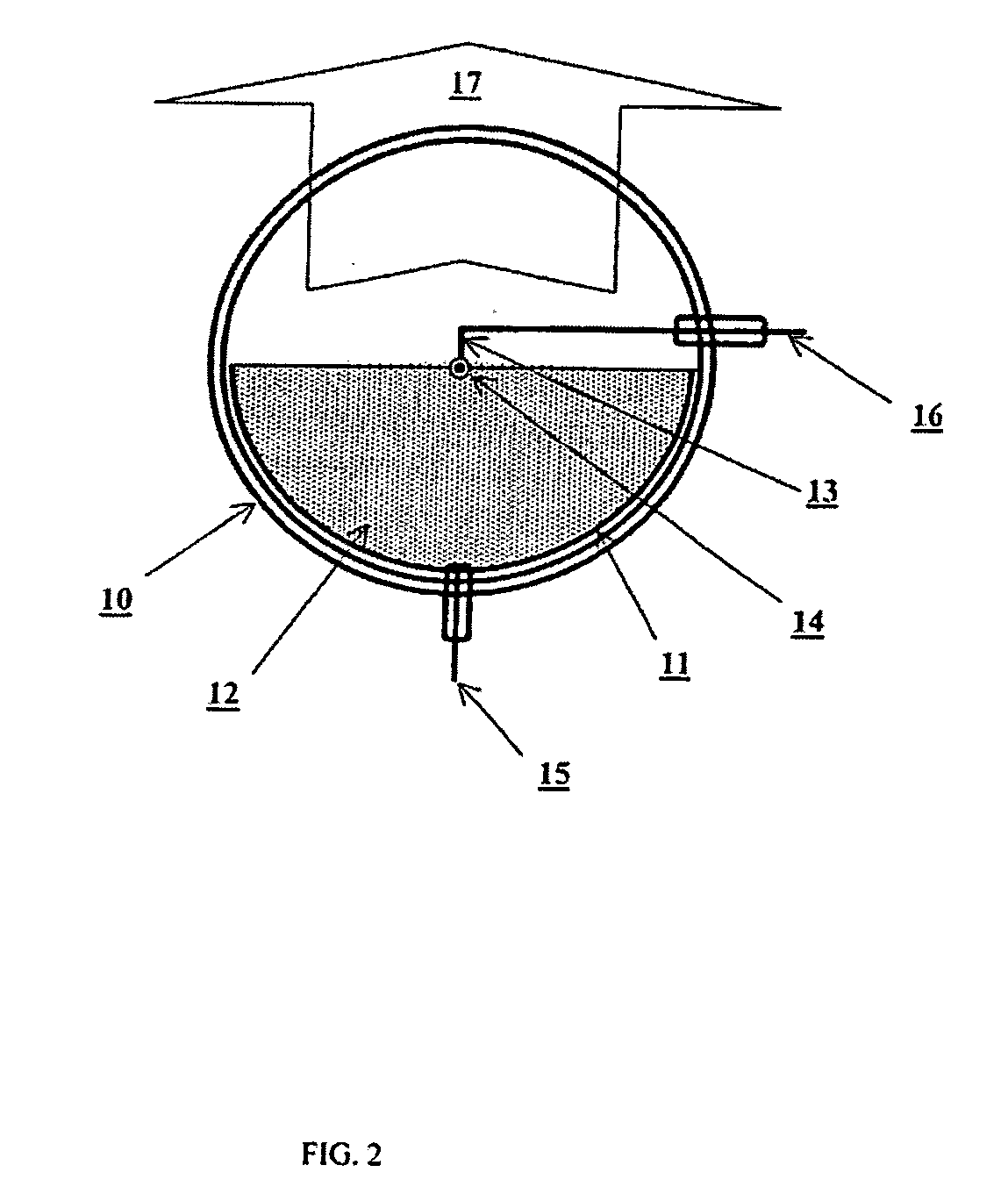
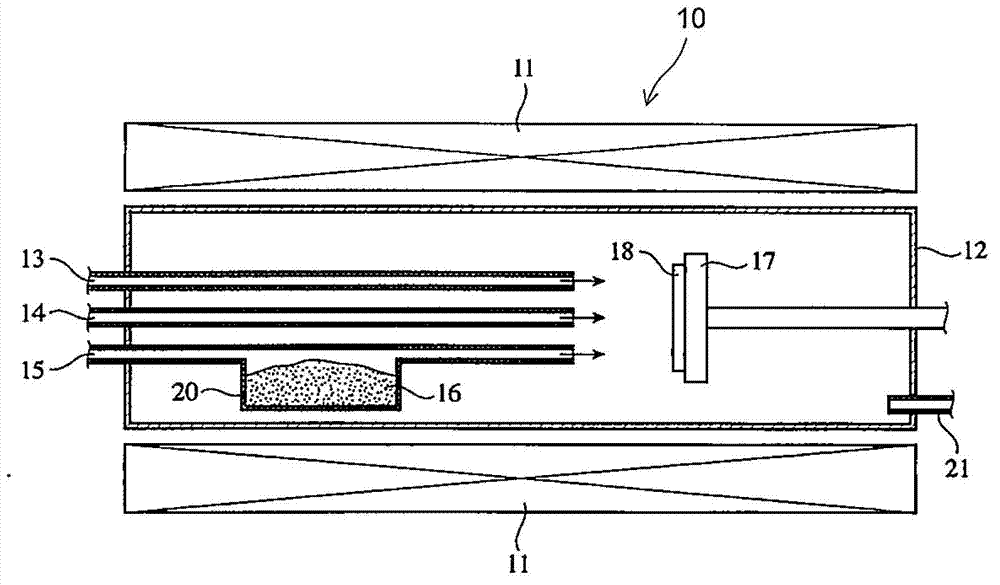
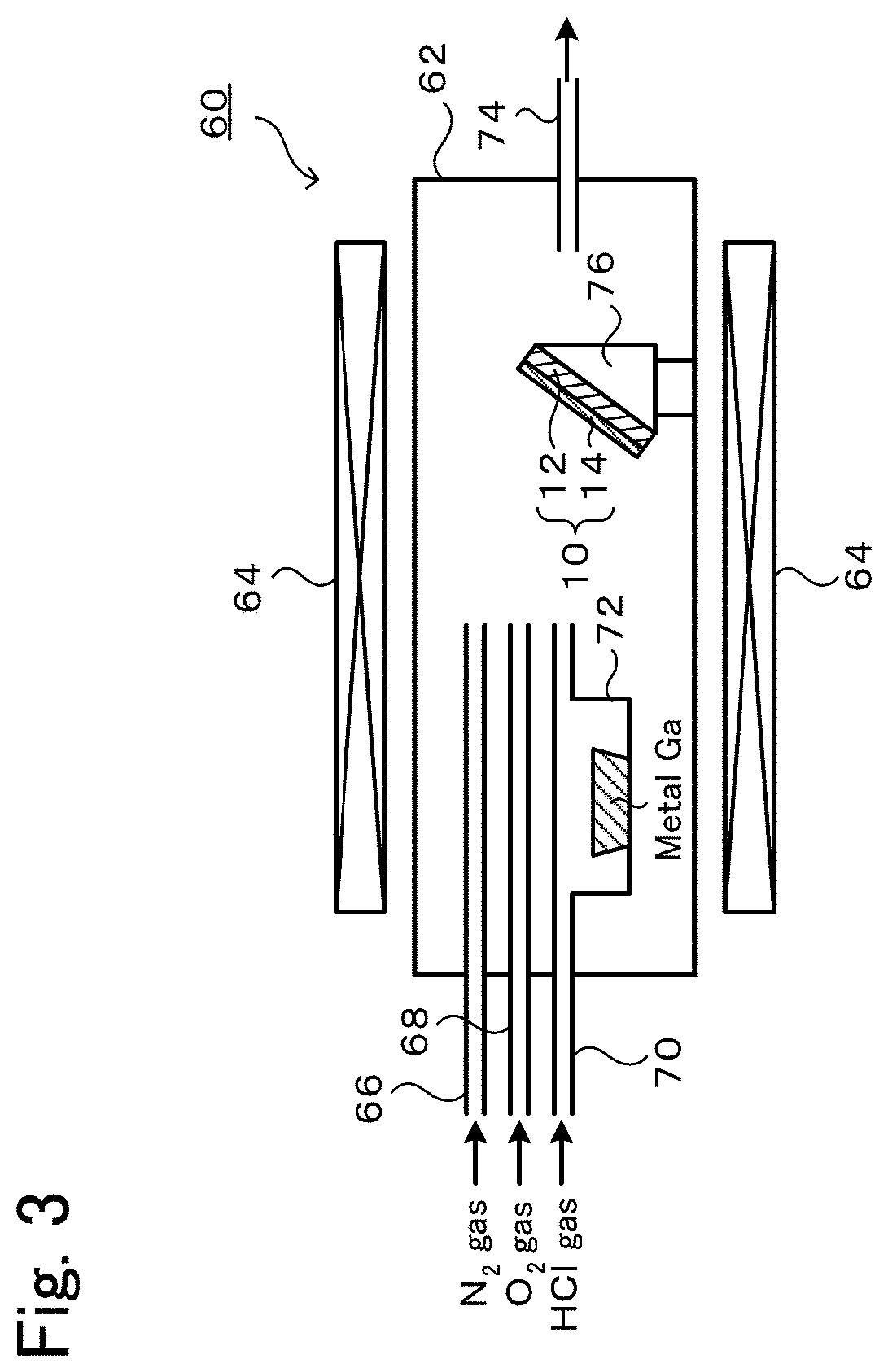
Method of making Group III nitrides
InactiveUS7381391B2High purityShort reaction timePolycrystalline material growthNitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsOptical propertyGlow Discharge Mass Spectrometry
The present invention provides compositions and a novel high-yielding process for preparing high purity Group III nitrides. The process involves heating a Group III metal and a catalytic amount of a metal wetting agent in the presence of a nitrogen source. Group III metals can be stoichiometrically converted into high purity Group III nitride powders in a short period of time. The process can provide multi-gram quantities of high purity Group III nitrides in relatively short reaction times. Detailed characterizations of GaN powder were preformed and are reported herein, including morphology and structure by SEM and XRD, optical properties by cathodoluminescence (CL), and Raman spectra to determine the quality of the GaN particles. The purity of GaN powder was found to be greater than 99.9% pure, as analyzed by Glow Discharge Mass Spectrometry (GDMS). Green, yellow, and red light emission can be obtained from doped GaN powders.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
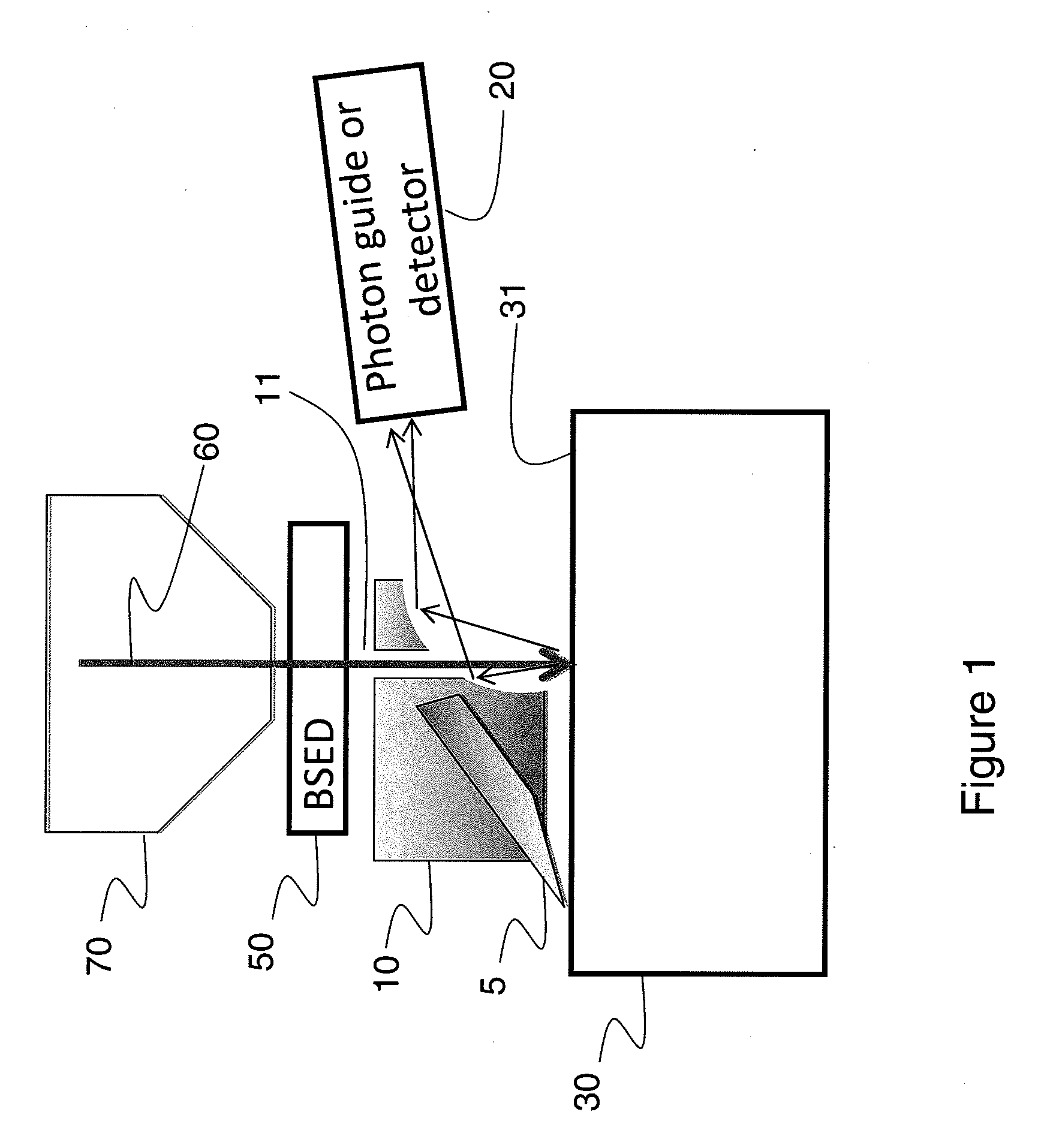
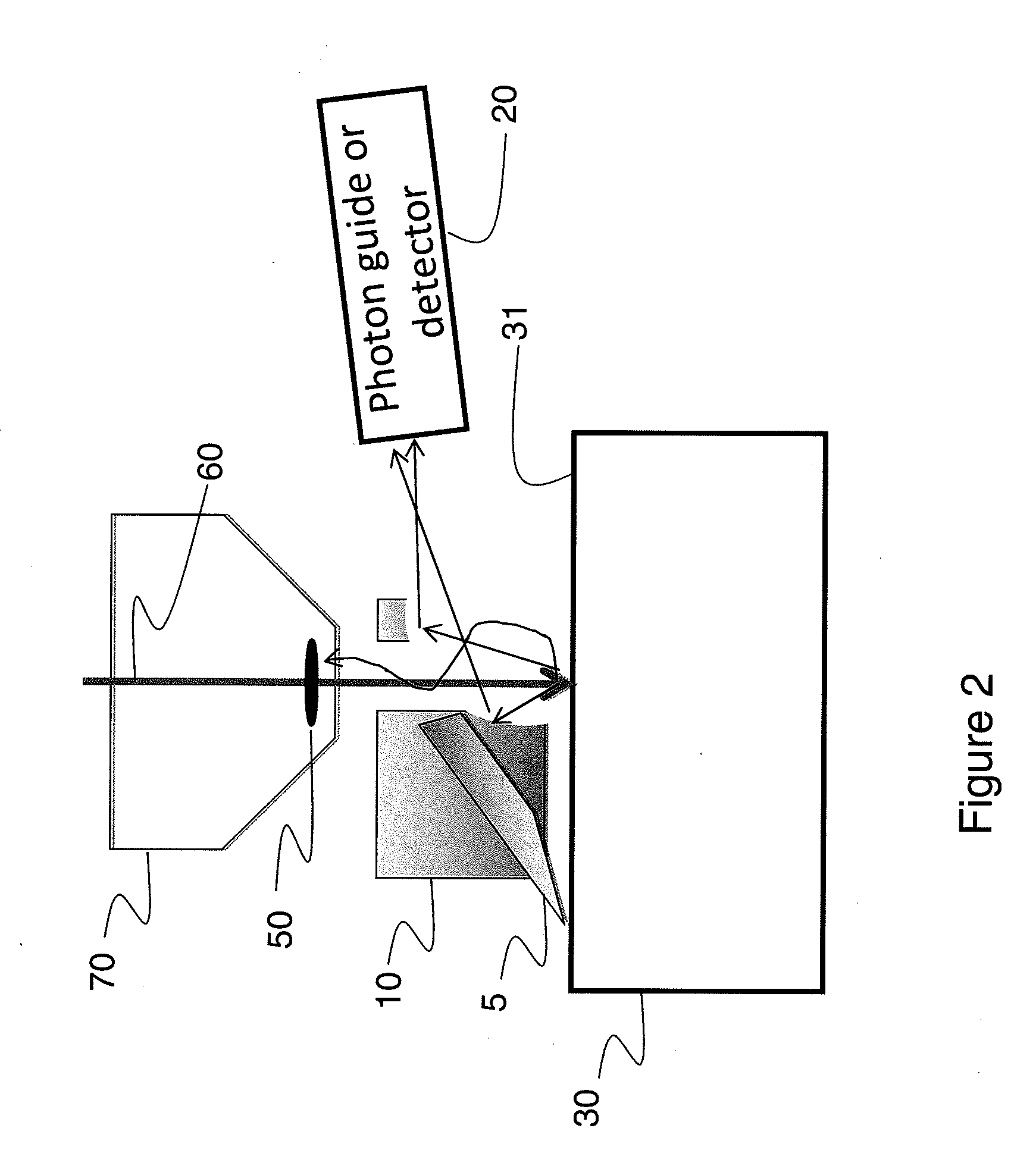
System and method for sample analysis by three dimensional cathodoluminescence
InactiveUS20130140459A1Increase the amount of lightMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesIon beamSecondary electrons
A system is disclosed for obtaining layered cathodoluminescence images of a sample wherein the light collecting equipment is highly efficient and wherein the microtoming or Focused Ion Beam equipment does not interfere with the efficiency of the light collecting equipment and wherein the position of the sample with respect to the light collecting equipment is not disturbed in the microtoming or ion beam milling process. Embodiments are disclosed allowing simultaneous collection of cathodoluminescence images and collection of other electron based imaging signals such as backscattered and secondary electrons.
Owner:GATAN INC
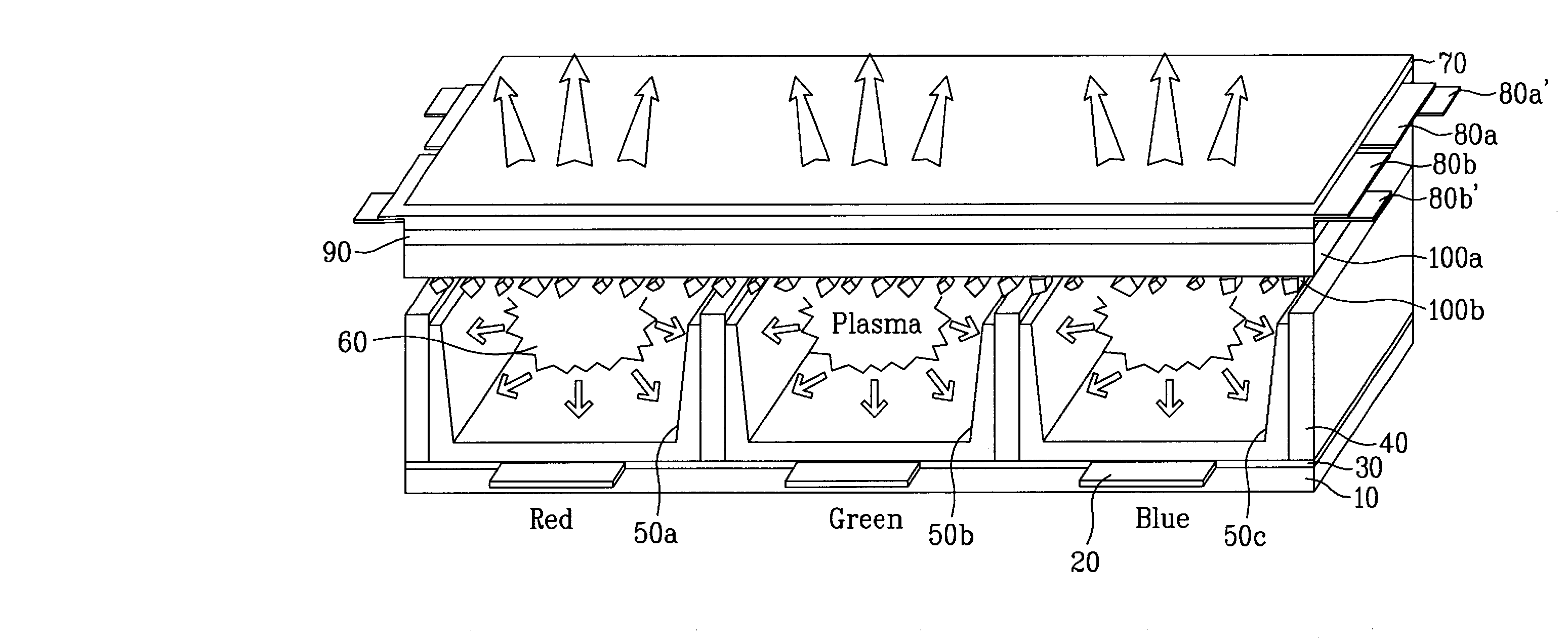
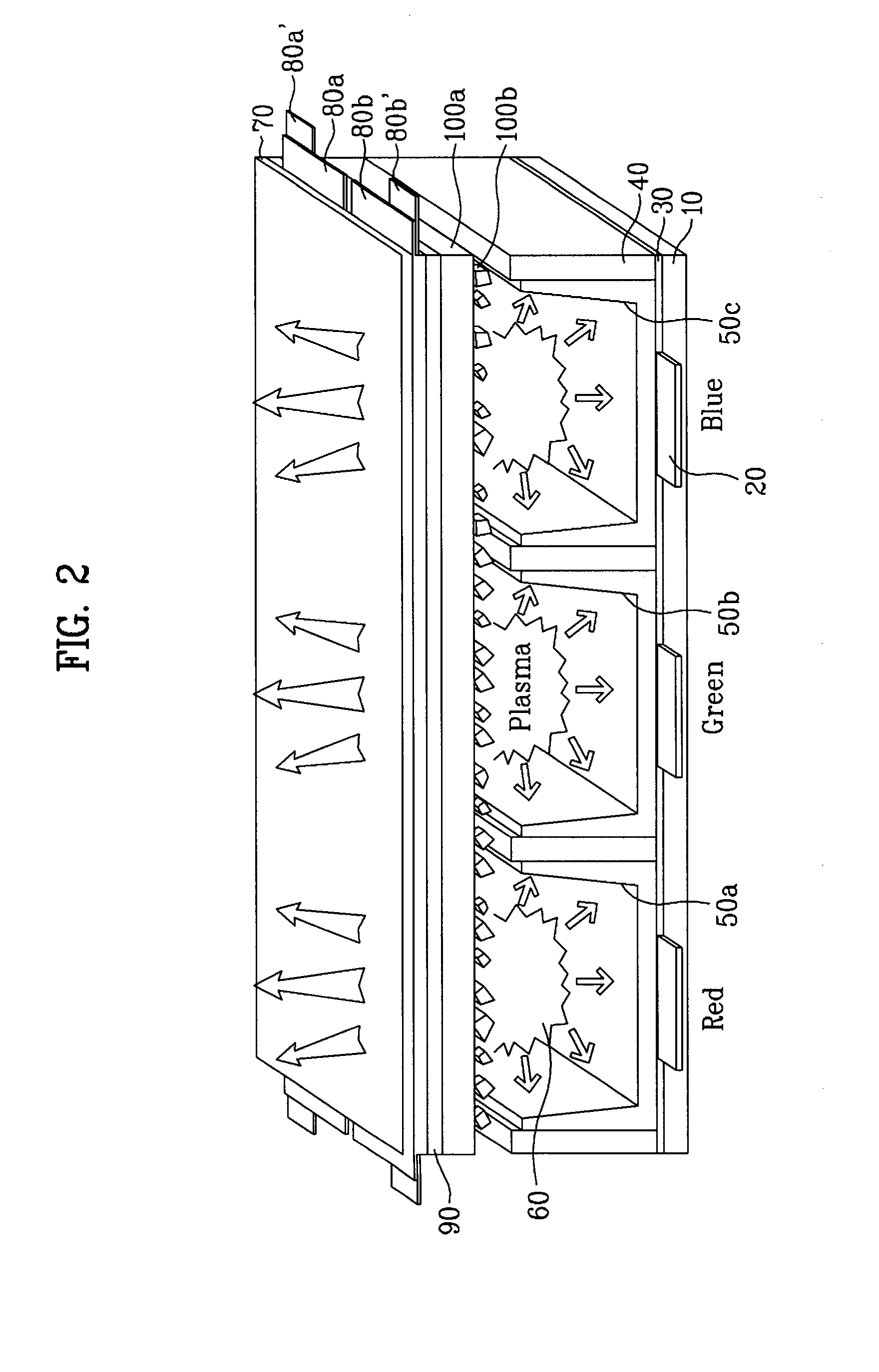
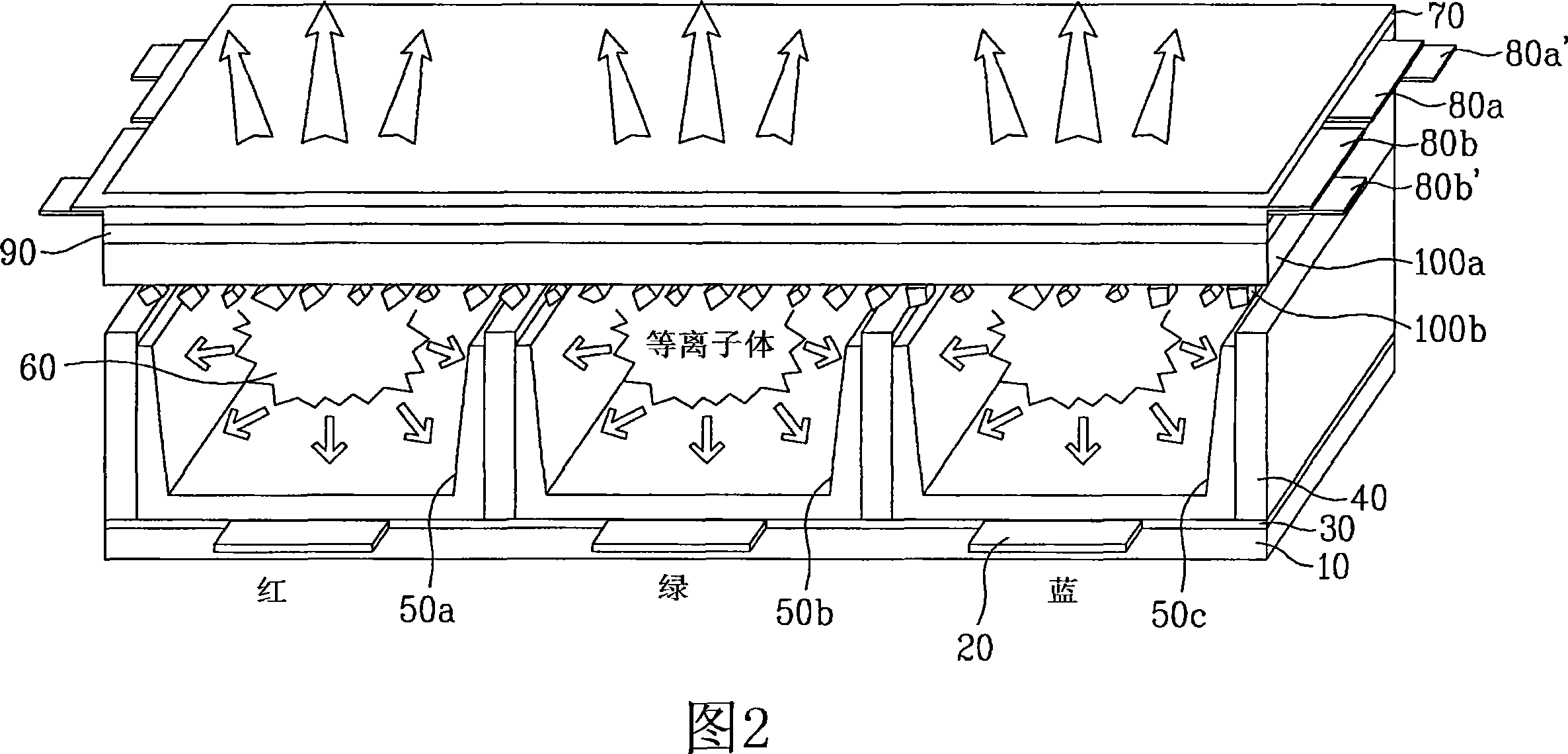
Plasma display panel and related technologies
A protective layer of a plasma display panel is disclosed. In the plasma display panel including a first panel and a second panel arranged to face each other while interposing barrier ribs therebetween, the plasma display panel further includes a first protective layer formed on a dielectric layer of the first panel, and a second protective layer formed on the first protective layer and containing a metallic oxide having a maximum cathode ray luminescence value within a wavelength region of 300 to 500 nanometers.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
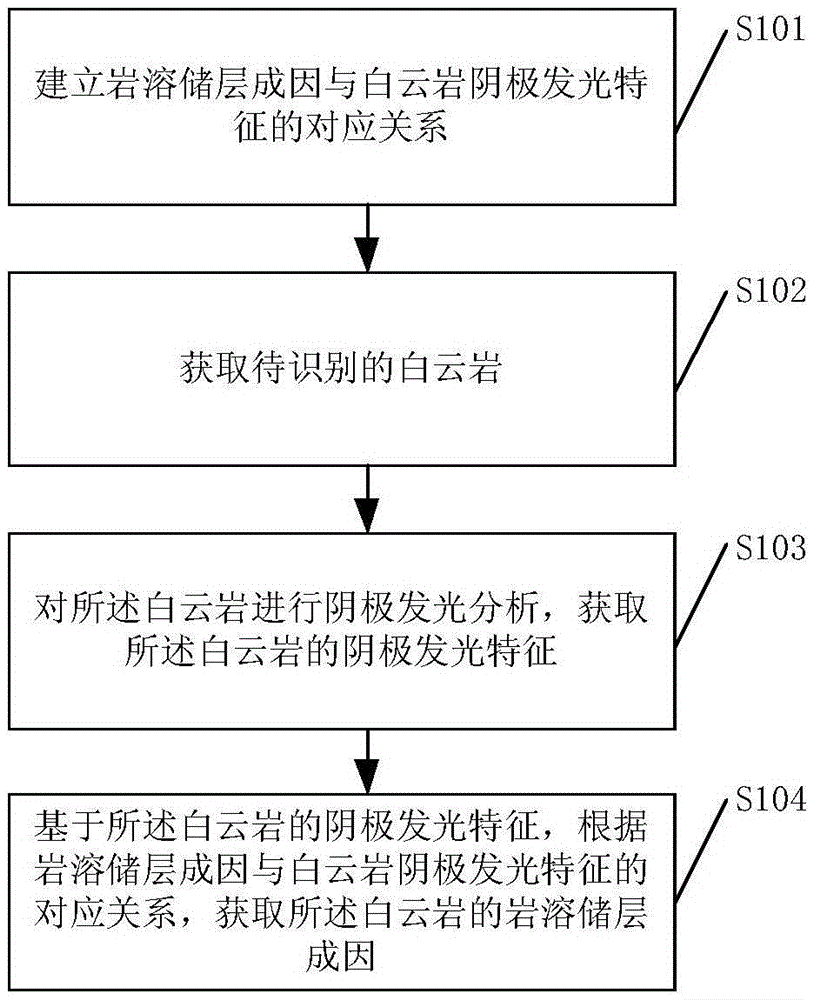
Dolomite karst reservoir genesis identification method and apparatus
InactiveCN105488513AQuick identificationShorten the timeCharacter and pattern recognitionGeomorphologyKarst
Embodiments of the invention disclose a dolomite karst reservoir genesis identification method and apparatus. The method comprises: establishing a correspondence relationship between a karst reservoir genesis and a dolomite cathodoluminescence feature; obtaining to-be-identified dolomite; performing cathodoluminescence analysis on the dolomite to obtain the dolomite cathodoluminescence feature; and based on the dolomite cathodoluminescence feature, obtaining the dolomite karst reservoir genesis according to the correspondence relationship between the karst reservoir genesis and the dolomite cathodoluminescence feature. According to the method and the apparatus provided by the embodiments of the invention, the type of the dolomite karst reservoir genesis can be quickly identified.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Cathodoluminescent light source
InactiveUS20050174059A1Improve energy conversionDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsPhosphorLuminous flux
A cathodoluminescent light source comprising a field-emission cathode serving as a source of electrons, an anode having a specular light-reflecting surface, and an electron-excited phosphor applied to the specular light-reflecting anode surface. The cathode and anode are enclosed in an evacuated housing having a transparent surface, so as to let the electron-excited phosphor on the anode surface, be irradiated with an electron beam, and let the luminous flux resulting from the process of cathodoluminescence, to emerge.
Owner:OBRAZTSOV ALEXANDR NIKOLAEVICH
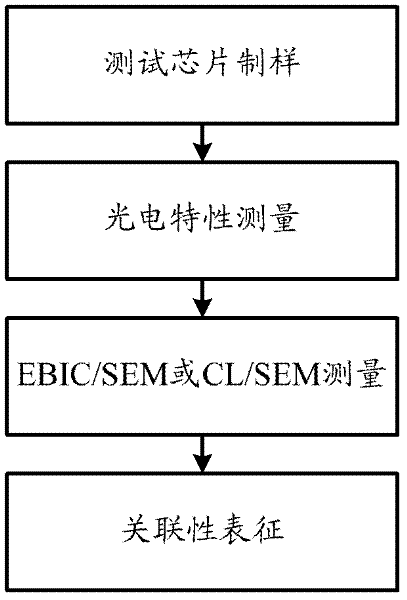
Systematic characterization method for relation between defects of photovoltaic detection materials and performance of devices
InactiveCN102645443AEasy to manufactureMeet performance testing requirementsMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionTest sampleStatistical analysis
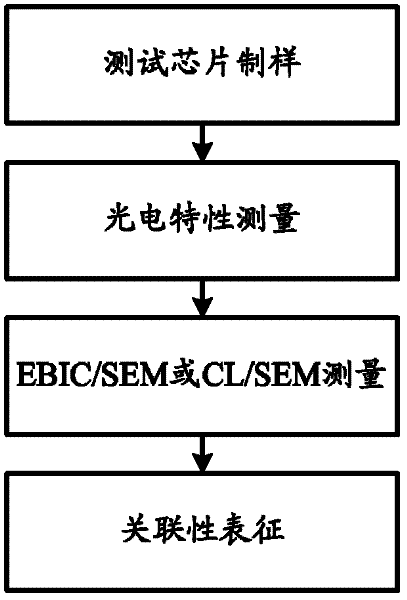
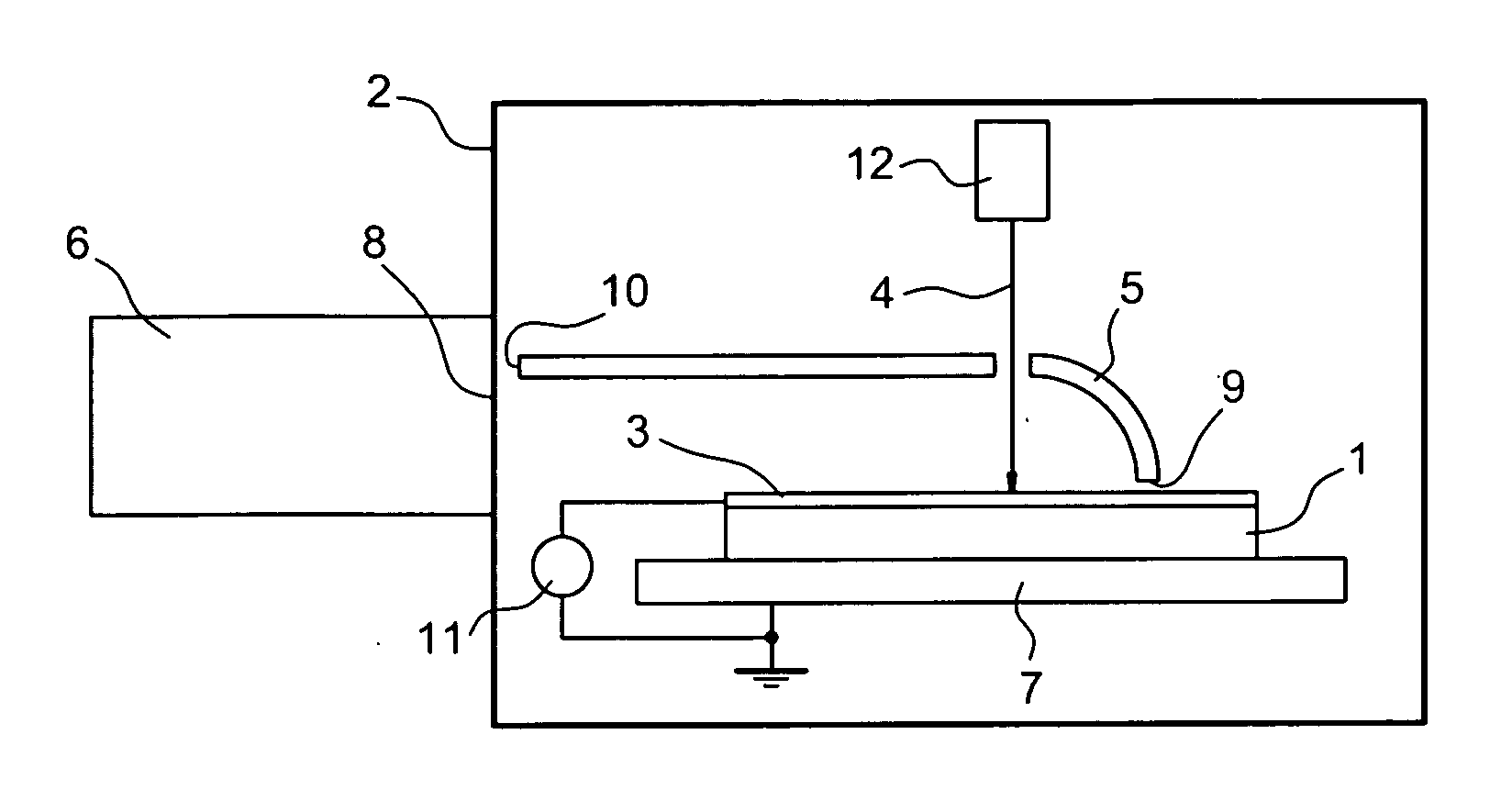
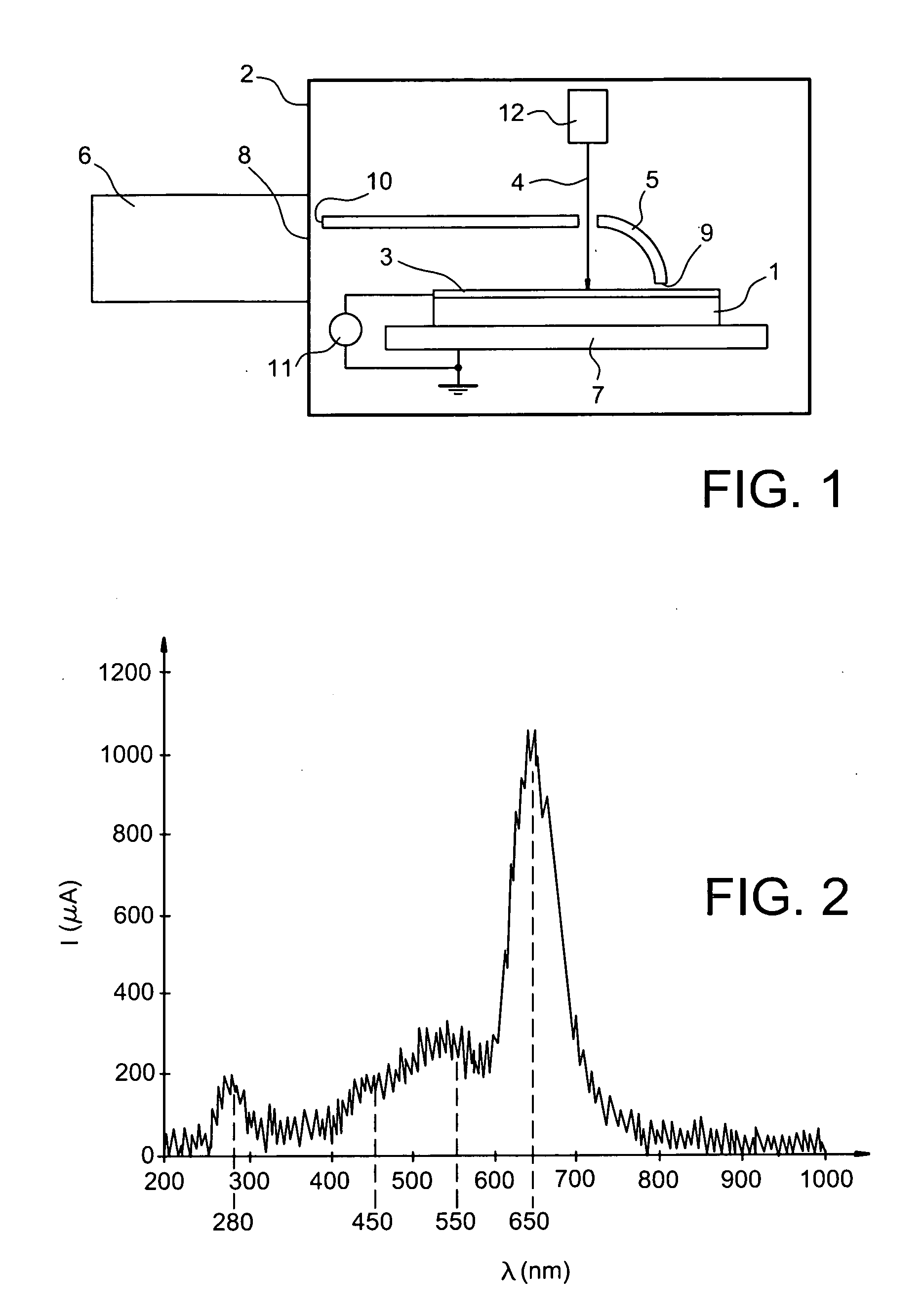
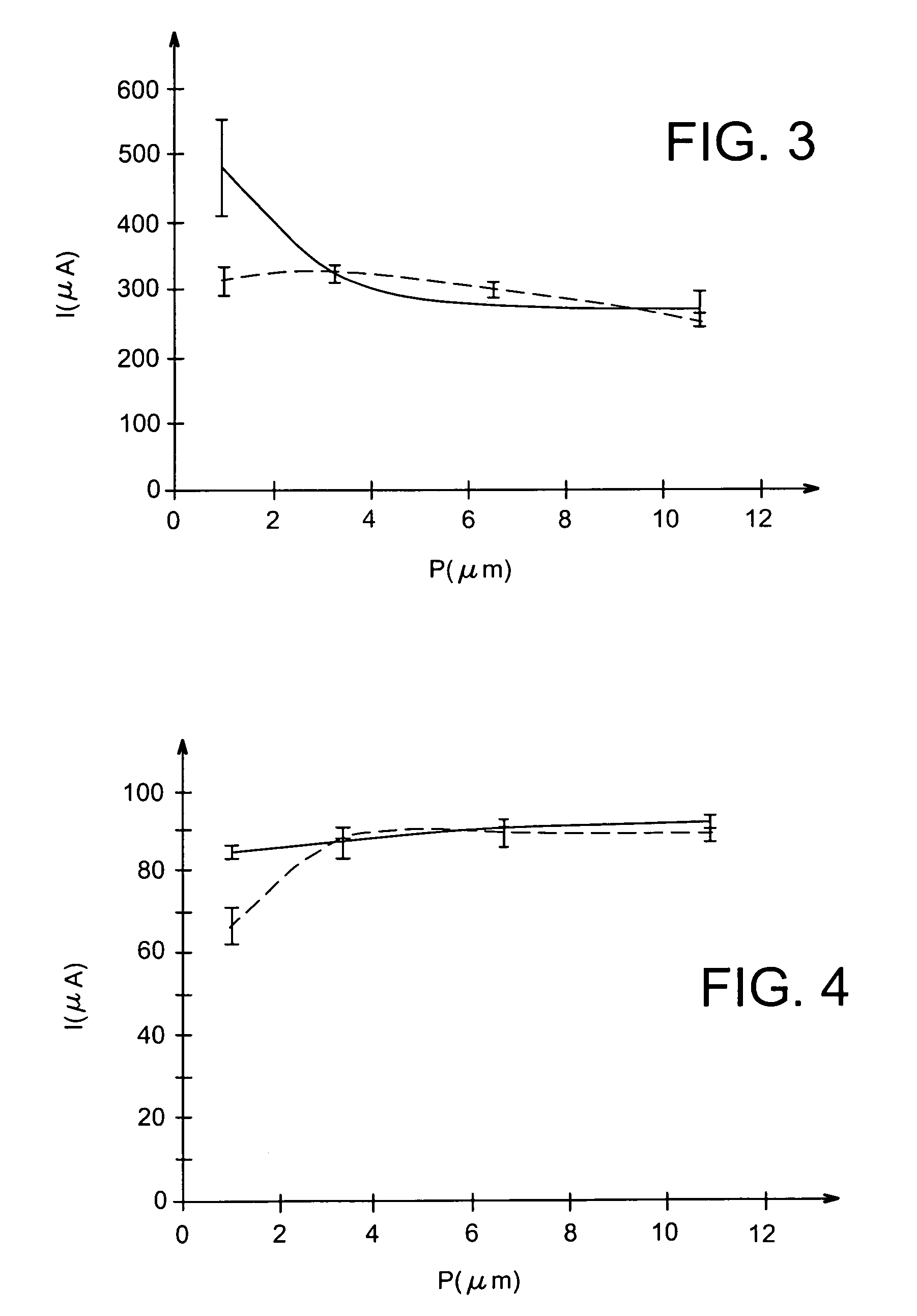
The invention relates to a systematic characterization method for the relation between the defects of photovoltaic detection materials and the performance of devices, which includes the following steps: according to the variety and characteristics of a photovoltaic detection material, a test chip is designed and packaged to form a test sample; the photoelectric characteristics of the test sample are measured and characterized; on the same test sample, an electron beam-induced current / scanning electron microscope or cathodoluminescence / scanning electron microscope combination-combined method is used for carrying out the measurement, characterization and statistical analysis of performance-related defects; and according to the directly related test characterization result obtained in the previous step, systematic characterization is carried out on the relation between the defects of the material and the performance of the device. The systematic characterization method can prevent the problems of uncertainty and randomness existing in the relation between the performance of the device made from the material and the measured defects of the material.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
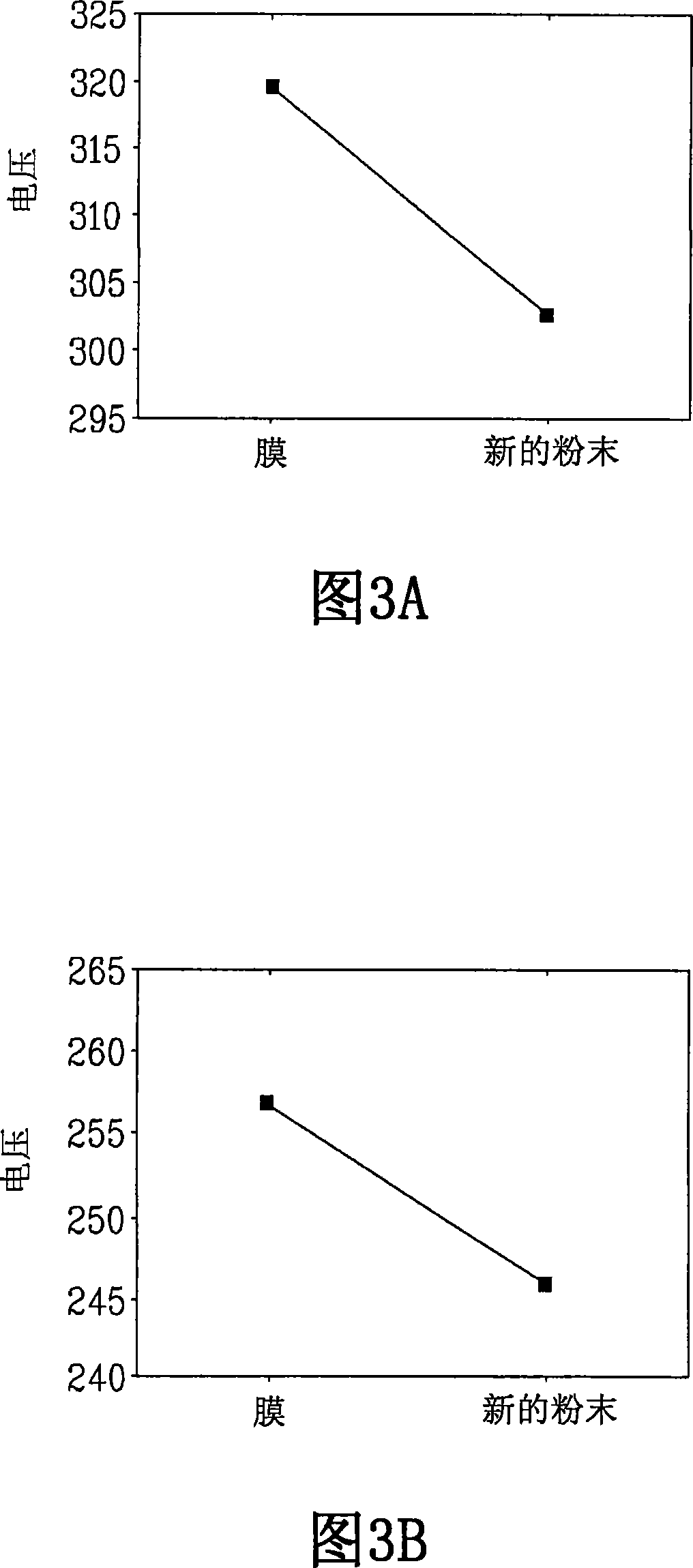
Method for non-distructive measurement or comparison of a laser radiation content in optical components
InactiveUS20070112529A1Quantitative measurementElectrical testingOptical apparatus testingNon destructiveManufacturing technology
A predictive choice process of a manufacturing process of an optical component intended to be subjected to laser fluxes, the choice being intended to select from among several possible manufacturing processes that which results in components having better laser flux behaviour than those obtained by the other possible processes characterised in that a) a number N of cathodoluminescence measurements are made on components obtained by a first of the possible manufacturing processes, while the component receives an electronic beam having a determined energy, a focus on the surface of the determined component and a determined intensity controlled by a value of a ground current measured on the component, while it is being subjected to said electronic beam, b) an average cathodoluminescence value on the N measurements is calculated, c) operations a) and b) on components obtained by each of the other possible manufacturing processes are repeated, d) the most advantageous manufacturing process is decided as the one for which the average cathodoluminescence value is the lowest.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
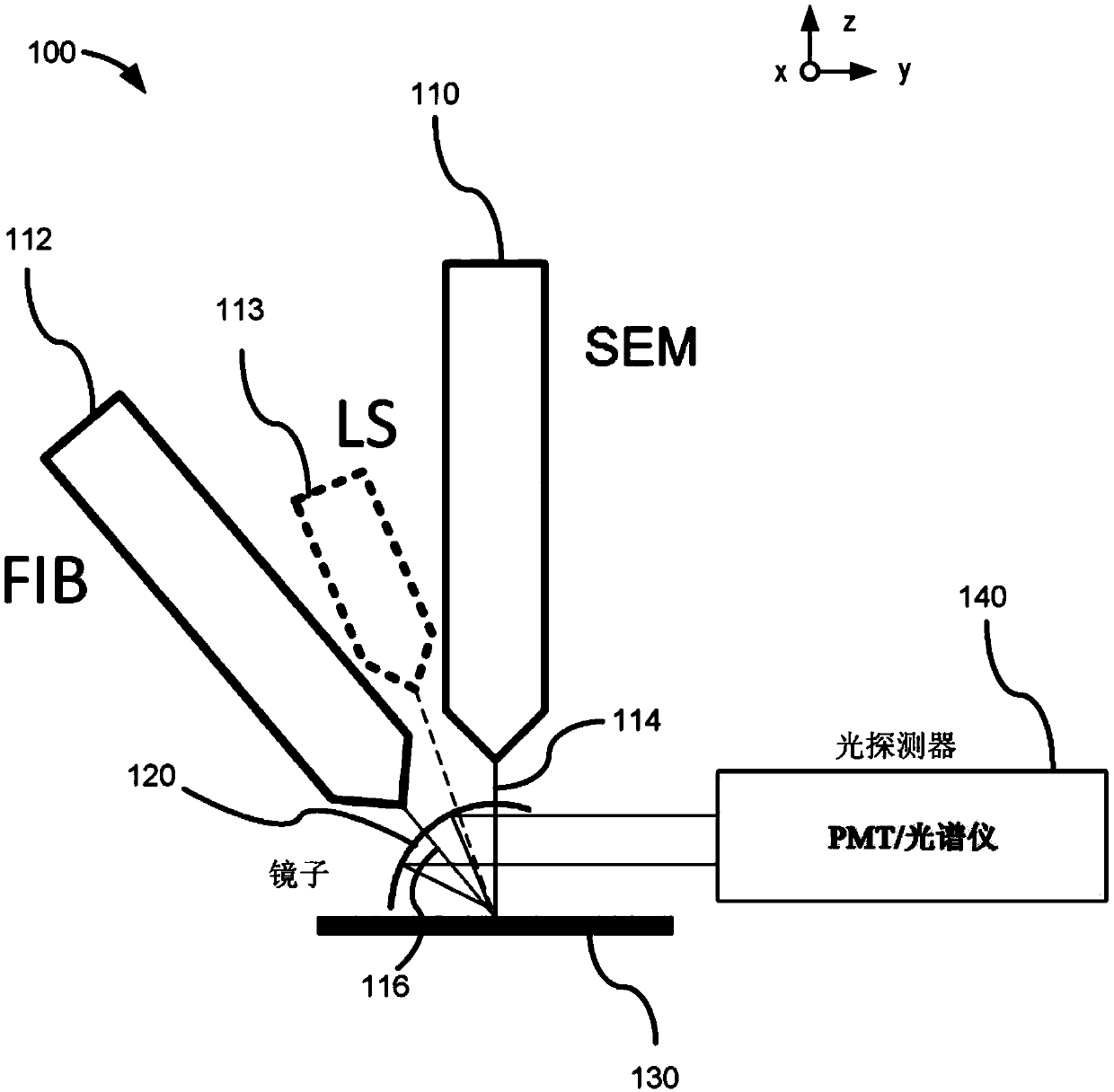
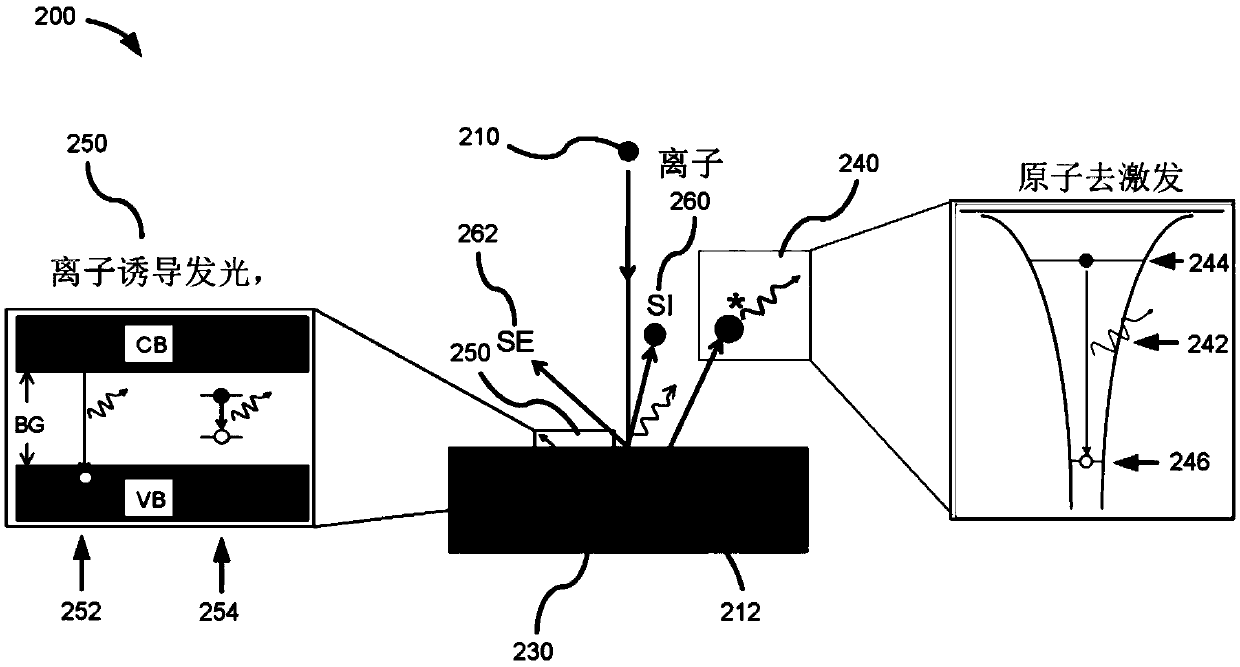
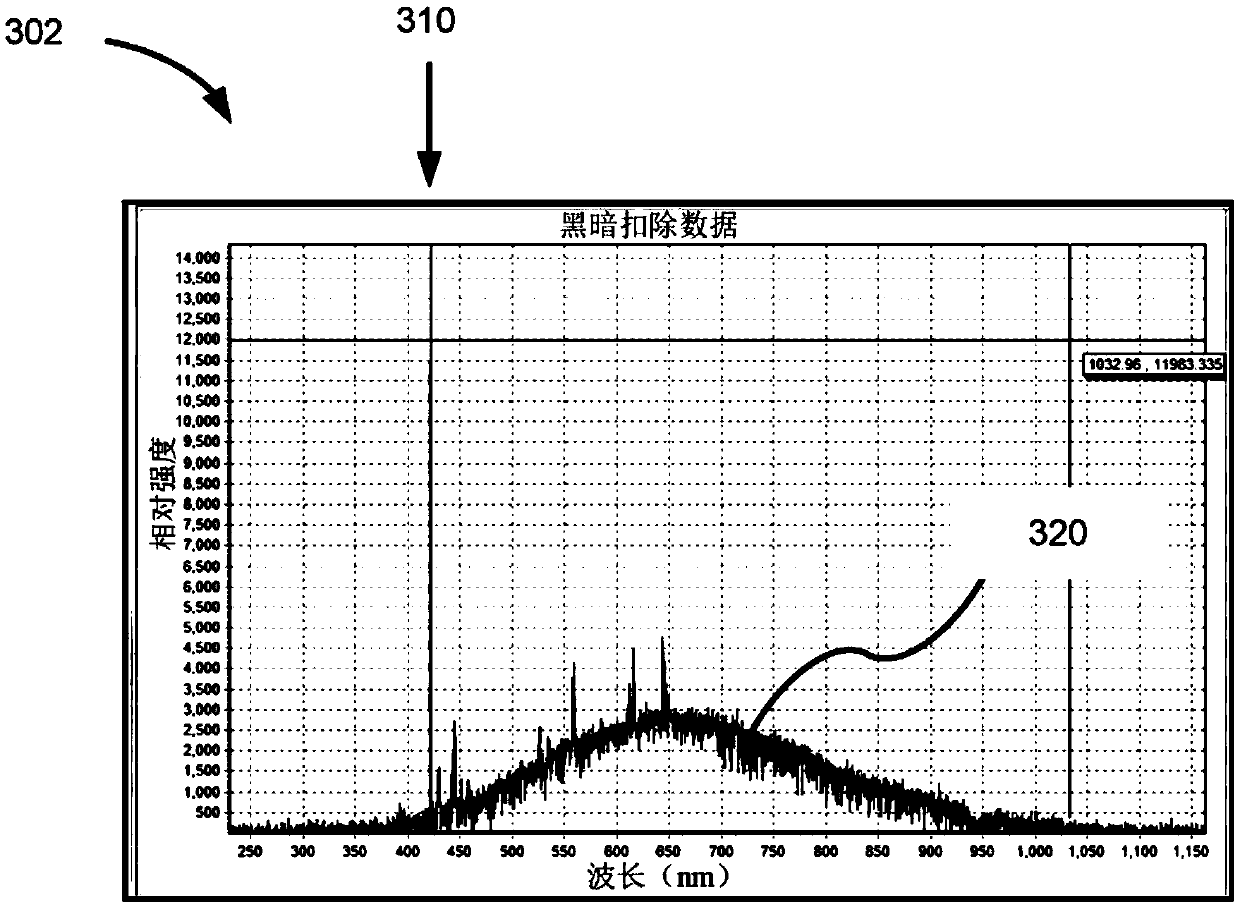
Combined sem-cl and fib-ioe microscopy
PendingCN109979793AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesPhoton emissionIon beam
The present invention provides example embodiments for performing microscopy using microscope systems that combine both scanning-electron-microscope-cathodoluminescence (SEM-CL) microscopy and focused-ion-beam ion-induced optical emission (FIB-IOE) microscopy. Certain embodiments comprise operating a microscopy system in a first microscopy mode in which an electron beam interacts with a sample ata sample location and causes first-mode photons and electrons to be emitted, the first-mode photons including photons generated through a cathodoluminescence process; and operating a microscopy systemin a second microscopy mode in which an ion beam interacts with a sample at the sample location and causes second-mode photons to be emitted, the second-mode photons including photons generated through an ion-induced luminescence process and photons generated through an atomic de-excitation process.
Owner:FEI CO
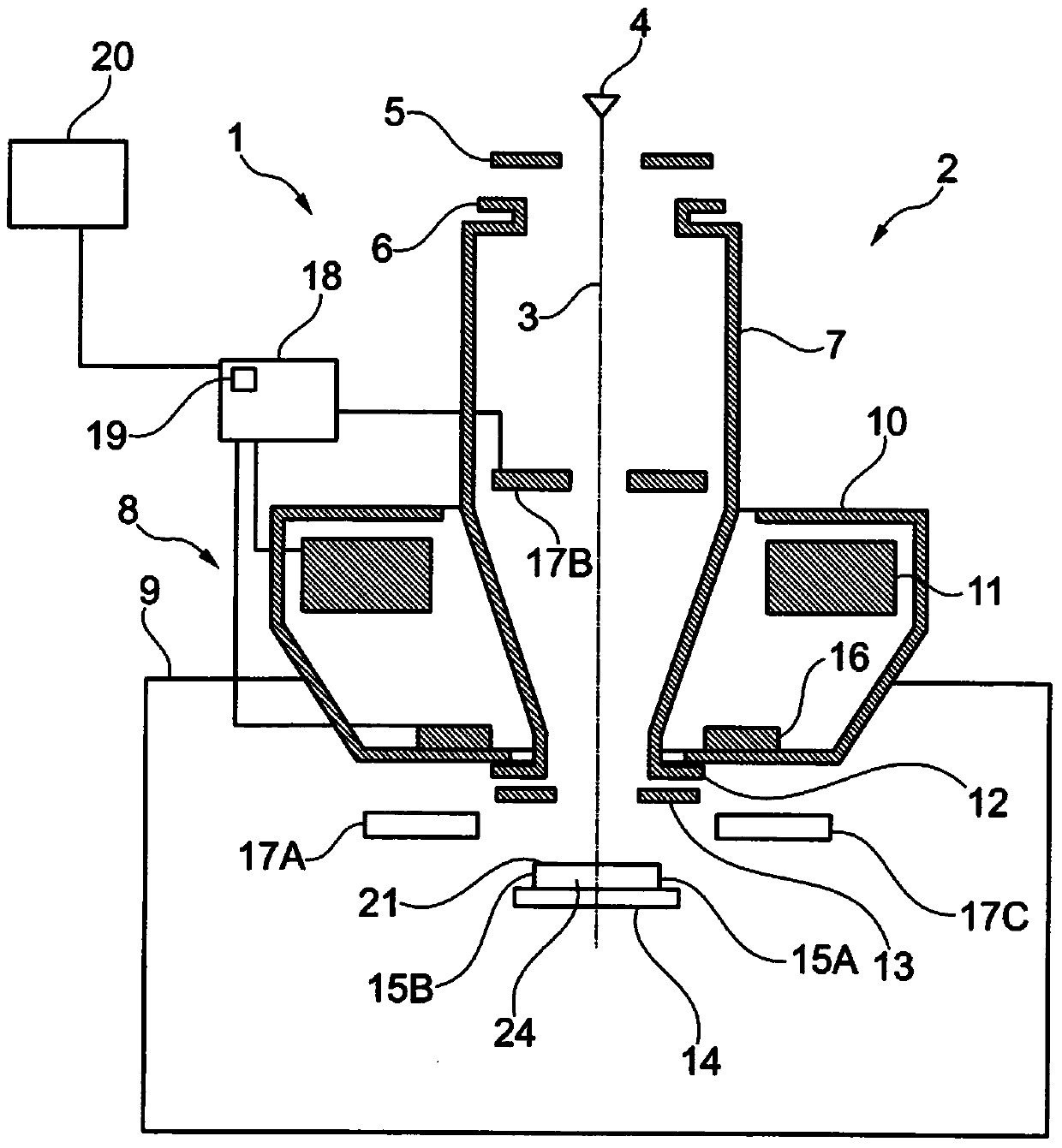
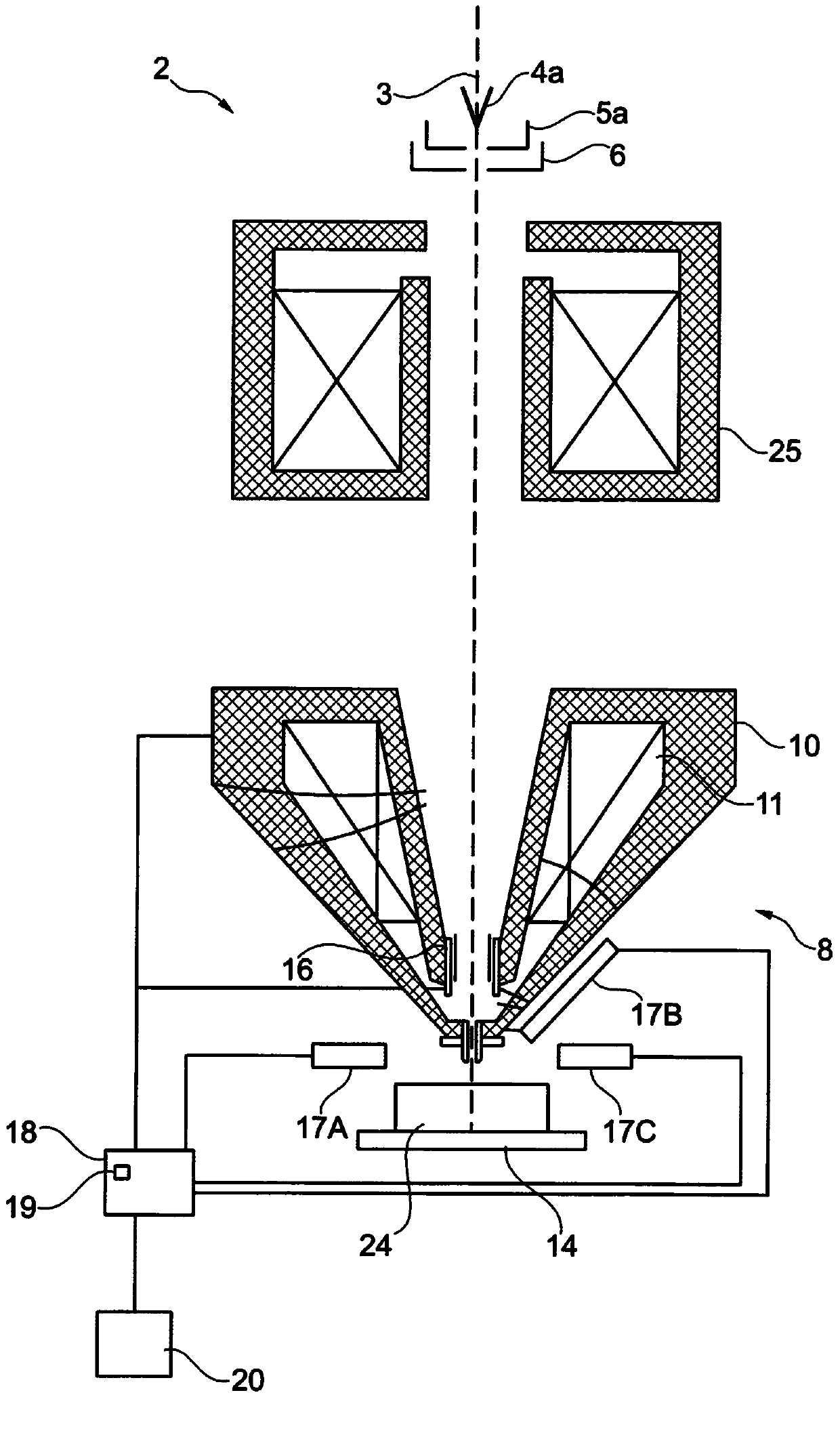
Method of analyzing sample and charged particle beam device for analyzing sample
ActiveCN104089966AElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionParticle physicsCathodoluminescence
The invention refers to a method and a charged particle beam device (1) for analyzing an object (24) using a charged particle beam interacting with the object (24). The object (24) comprises a sample (15A) embedded in a resin (15B). Interaction radiation in the form of cathodoluminescence light is detected for identifying areas in which the resin (15B) is arranged and in which the sample (15A) is arranged. Interaction particles are detected to identify particles within the resin (15B) and the sample (15A) for further analysis by using EDX analysis.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
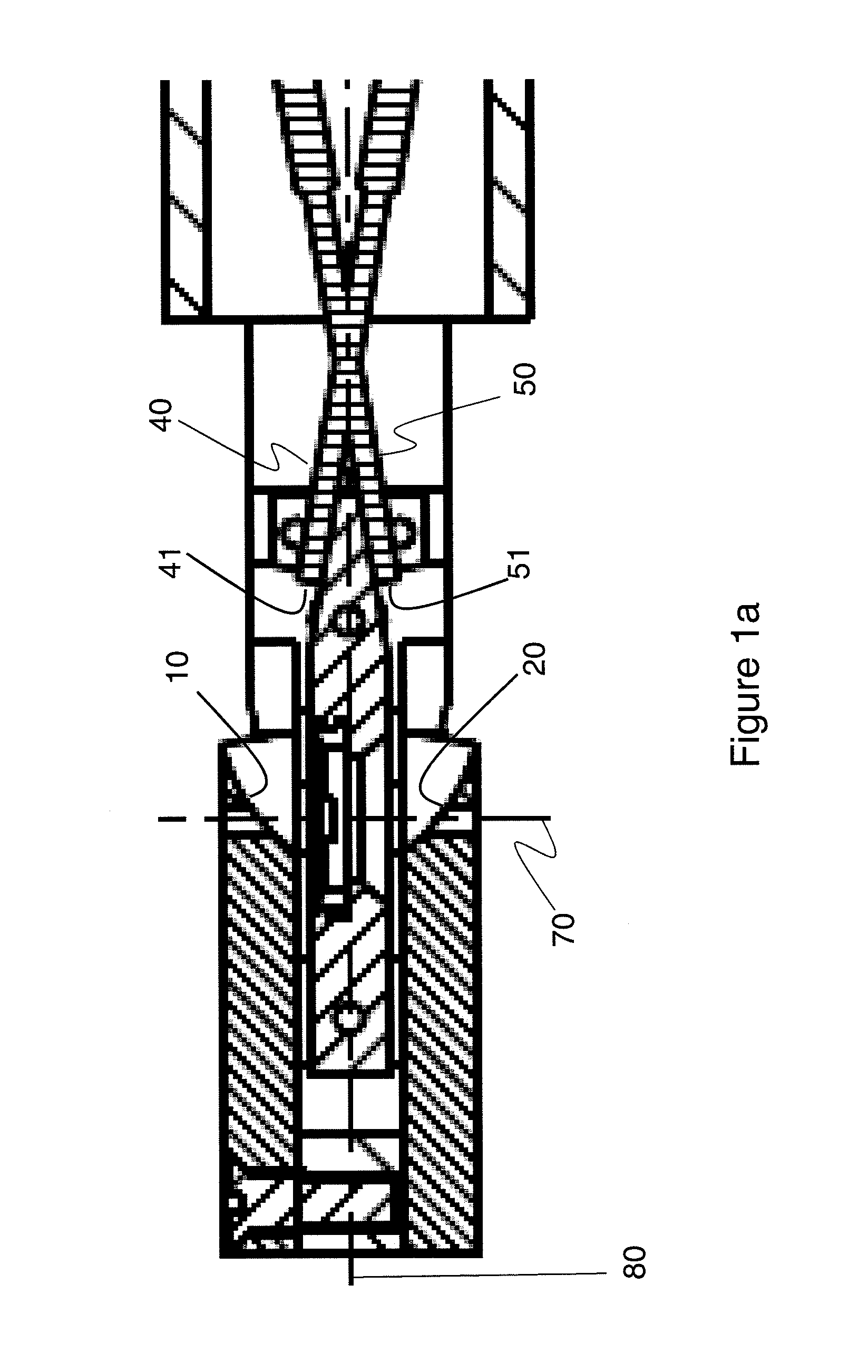
Apparatus for collection of cathodoluminescence signals
InactiveUS20130141803A1Improve collection efficiencyIncrease the number ofMirrorsElectric discharge tubesGoniometerConfined space
A side entry TEM holder incorporates a miniature tilted off axis elliptical mirror to collect cathodoluminescence from the specimen and couple it efficiently into a tilted fiber optic integrated into the holder. The design is compatible with the cryogenic operation of the holder. TEM specimens are partially transparent to the electron beam, and so light can be emitted above and below the specimen. The same principle of off-axis mirror and tilted fiber can be utilized to collect light from above and below the specimen yet fit into the very confined space required by insertion through the goniometer and for operation between narrow gap pole pieces. With a dual system, the emission of light from above the specimen can be compared to that from below thereby enhancing the versatility of the analytical technique.
Owner:GATAN INC
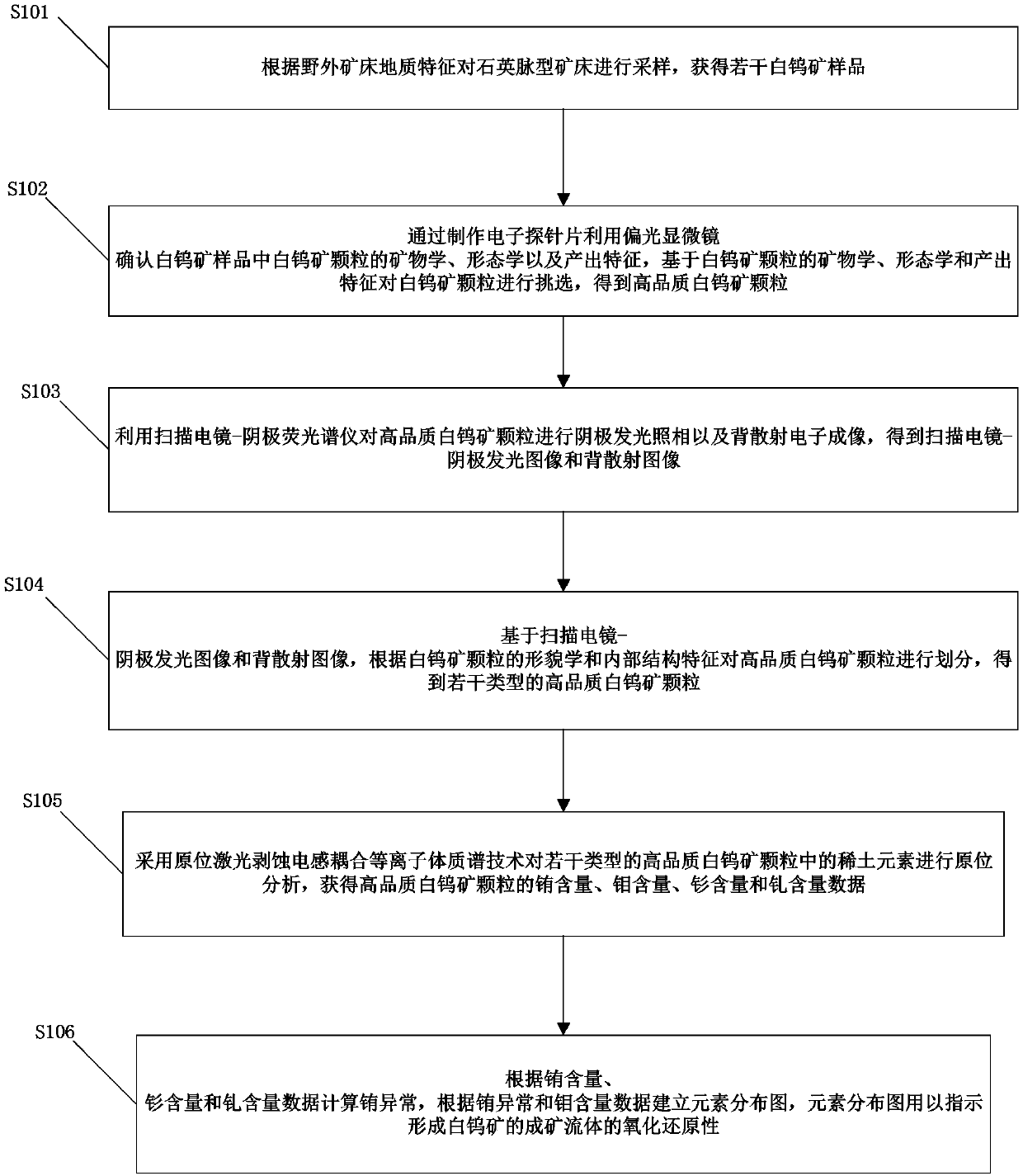
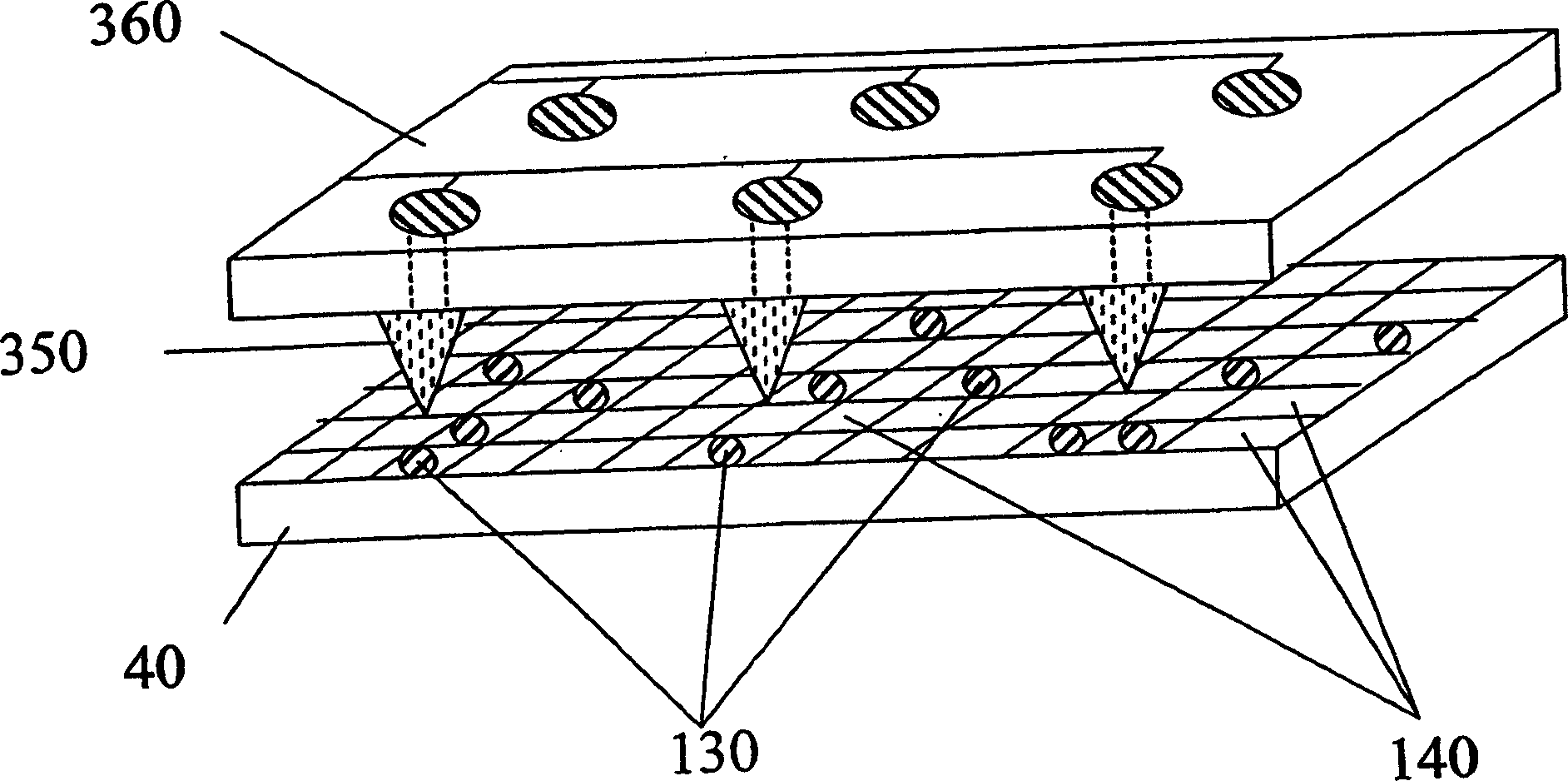
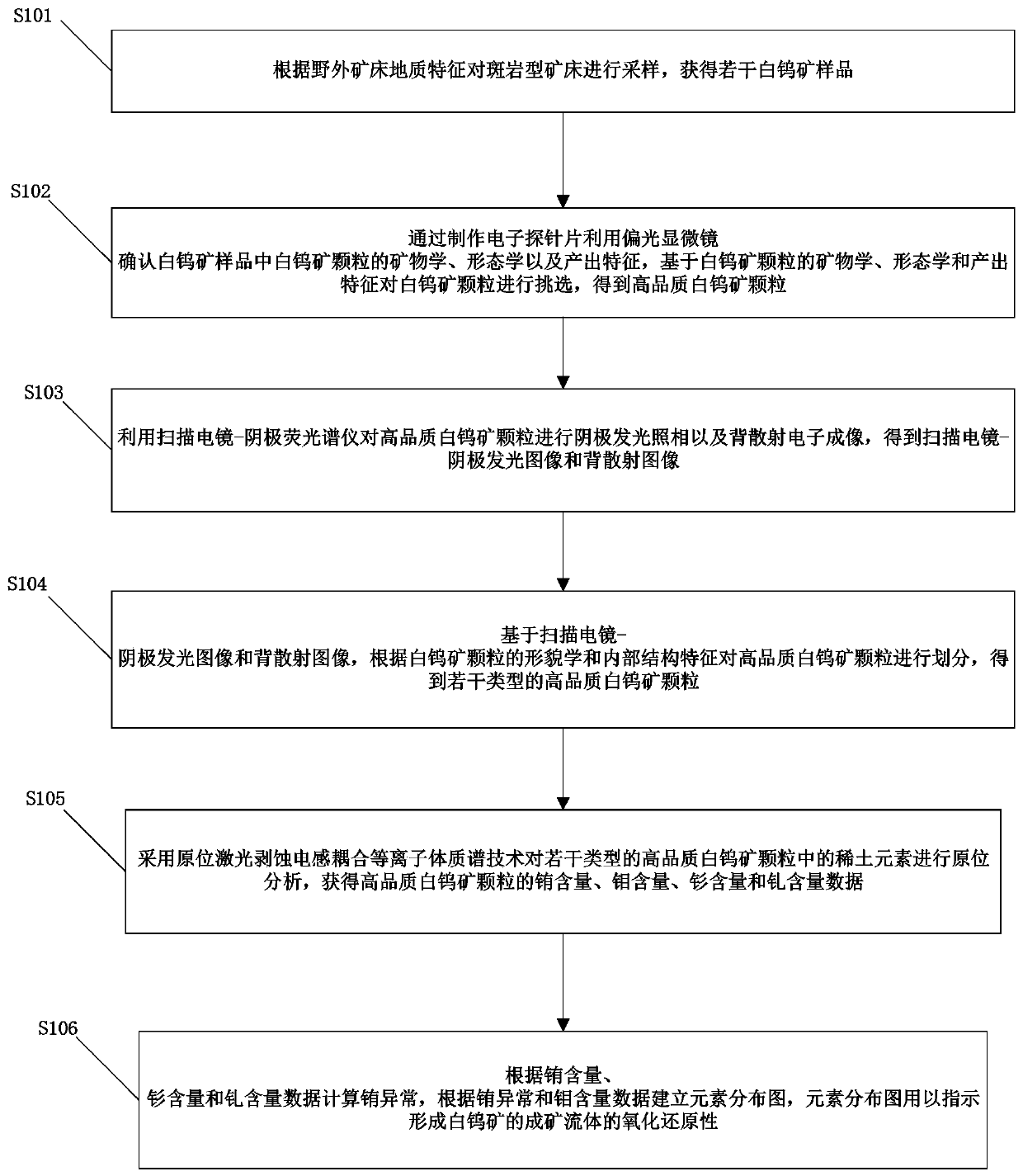
Method for discriminating redox property of ore-forming fluid based on cathodoluminescence characteristic of scheelite in quartz vein type deposit
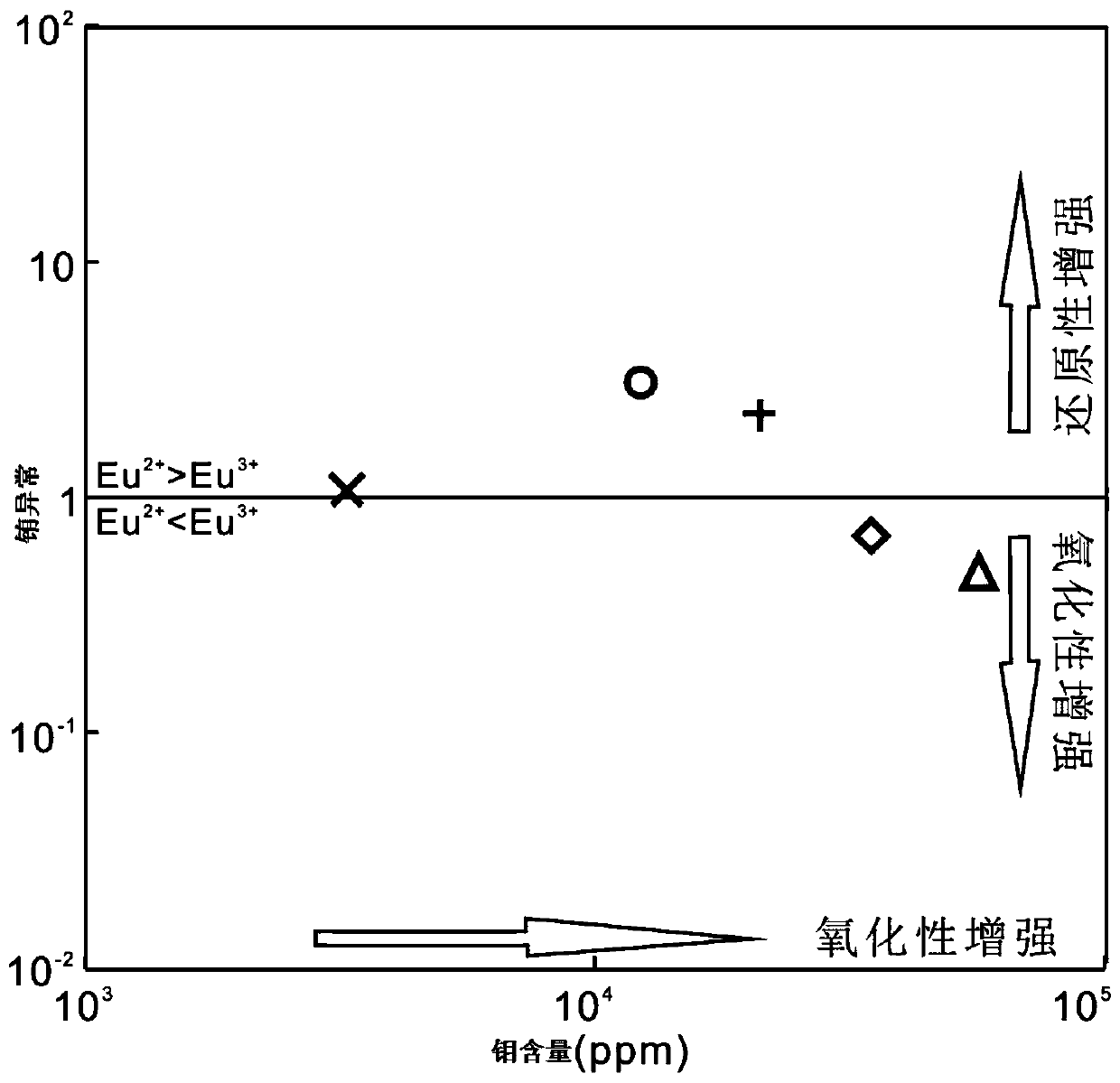
InactiveCN107632035AGuide the direction of prospectingIntuitiveMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRare-earth elementEuropium
The invention provides a method for discriminating the redox property of an ore-forming fluid based on the cathodoluminescence characteristic of scheelite in a quartz vein type deposit. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining multiple scheelite samples; choosing scheelite particles based on the mineralogy, the morphology and the output characteristics of the scheelite particles in thescheelite samples in order to obtain high-quality scheelite particles; obtaining the scanning electron microscopy-cathodoluminescence images and the back scattering images of the high-quality scheelite particles; dividing the high-quality scheelite particles based on the scanning electron microscopy-cathodoluminescence images and the back scattering images according to the morphology and internalstructural characteristics of the scheelite particles in order to obtain multiple types of the high-quality scheelite particles; carrying out in-situ analysis on rare earth elements in the multiple types of the high-quality scheelite particles to obtain europium content and molybdenum content data; and establishing an element distribution map according to the europium content and molybdenum content data, wherein the element distribution map is used for indicating the redox property of the ore-forming fluid for forming the scheelite.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
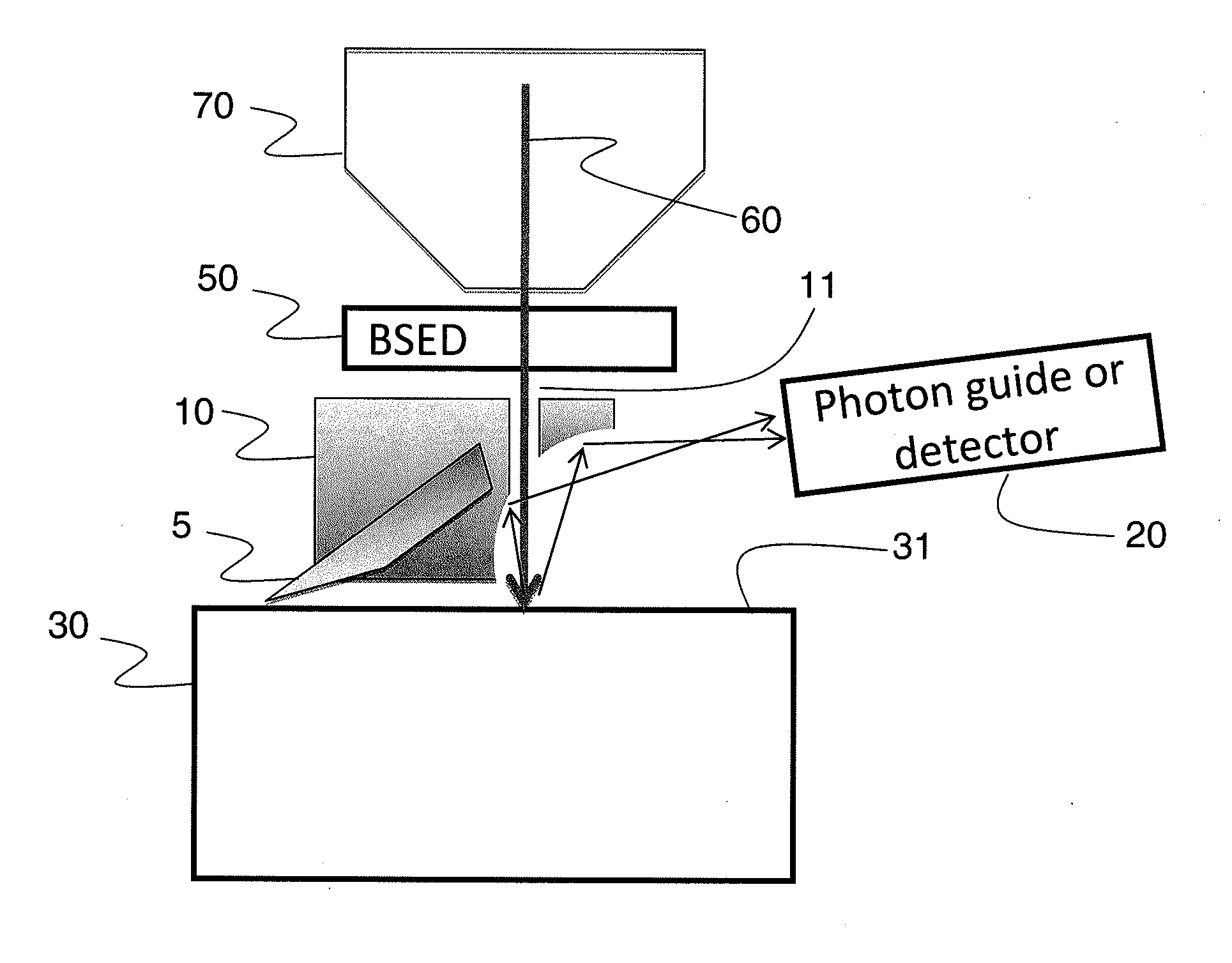
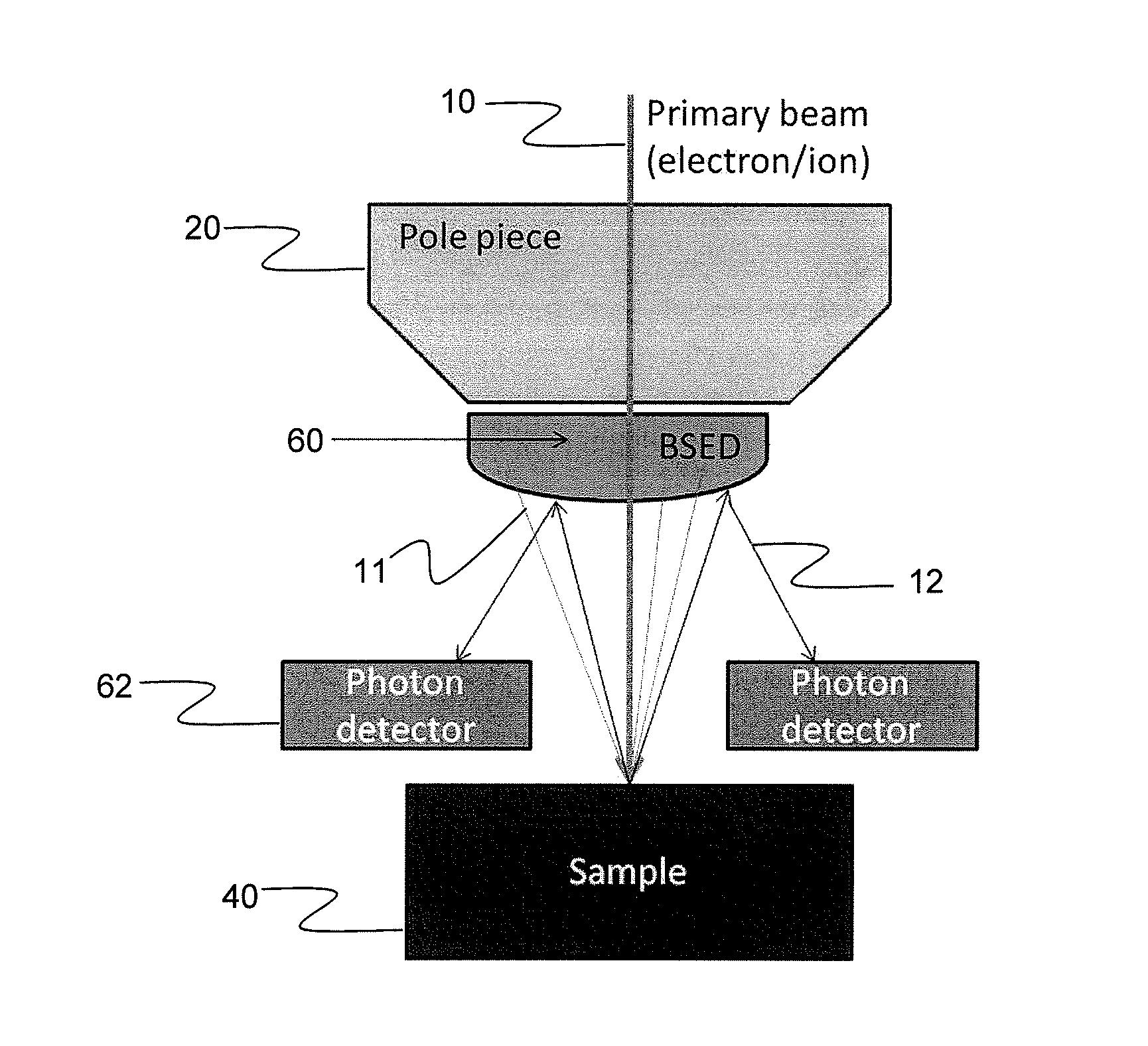
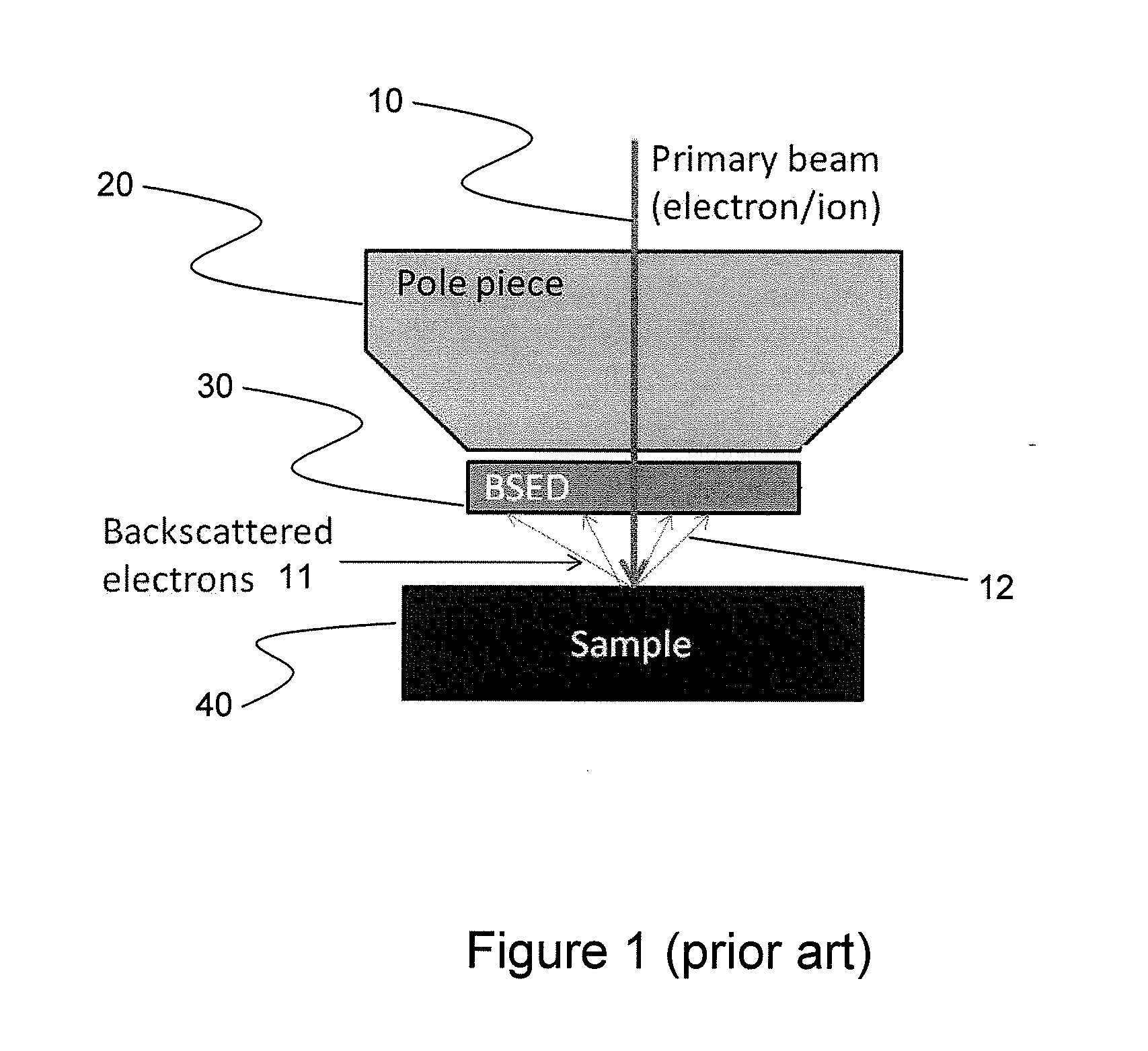
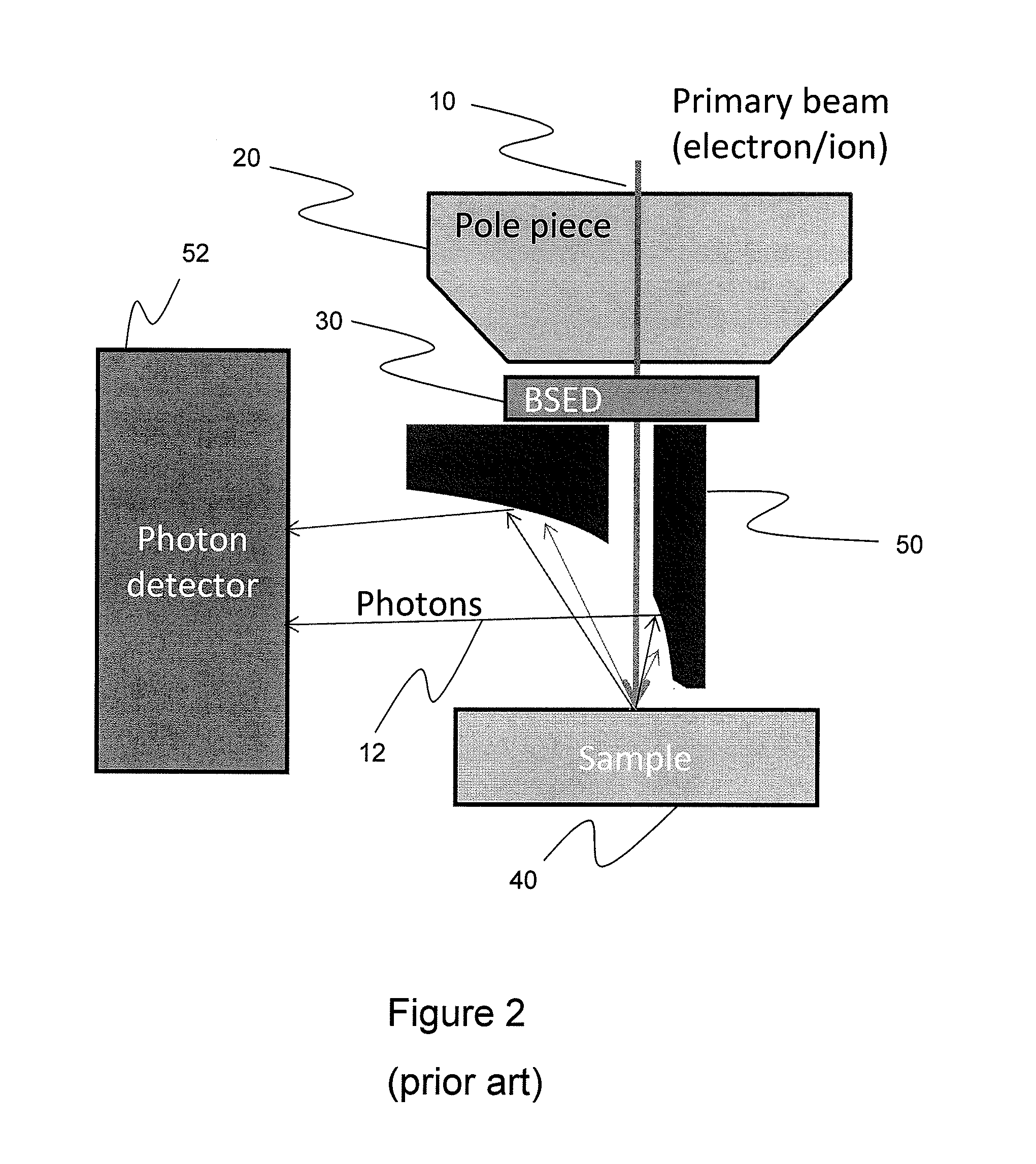
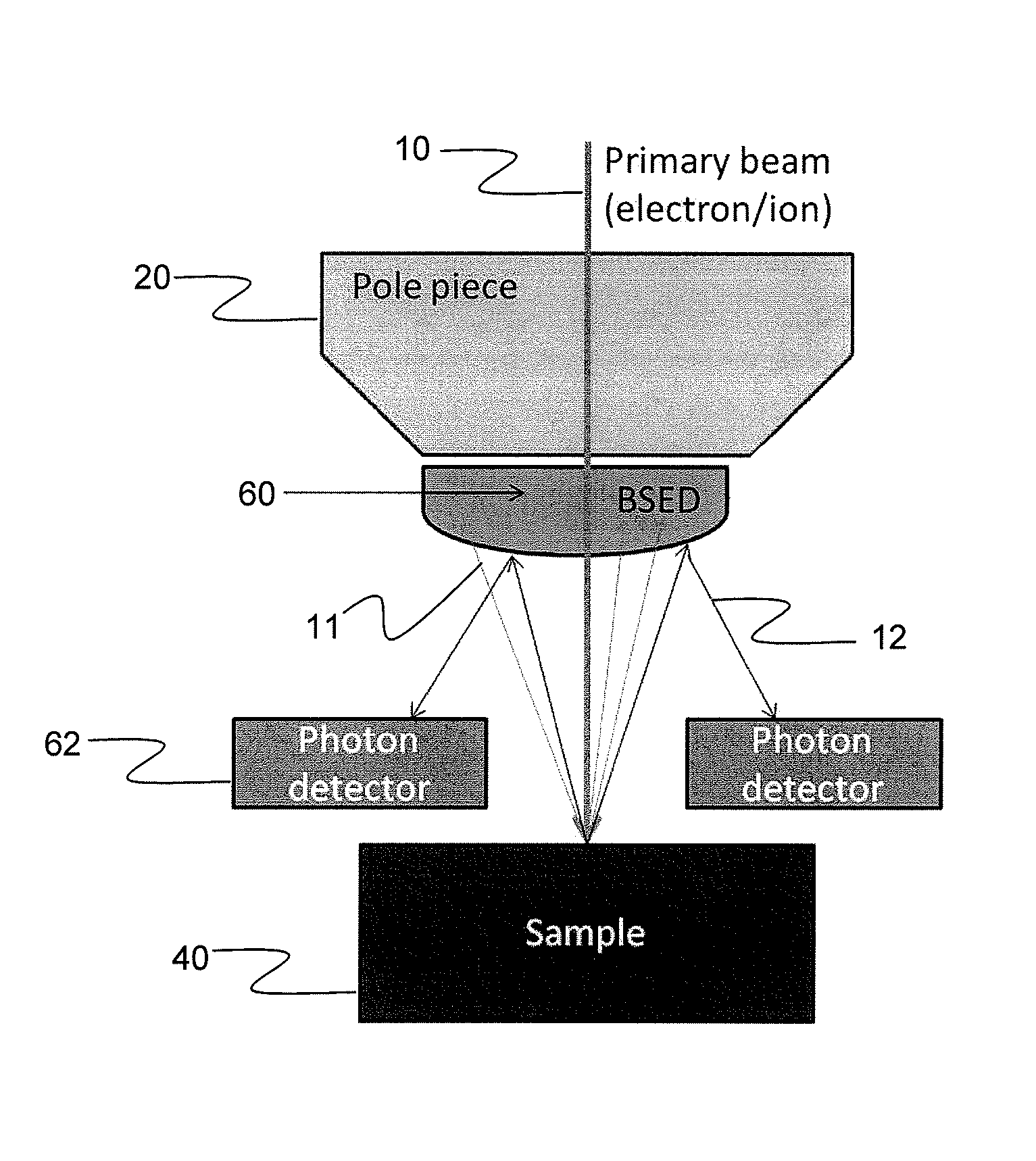
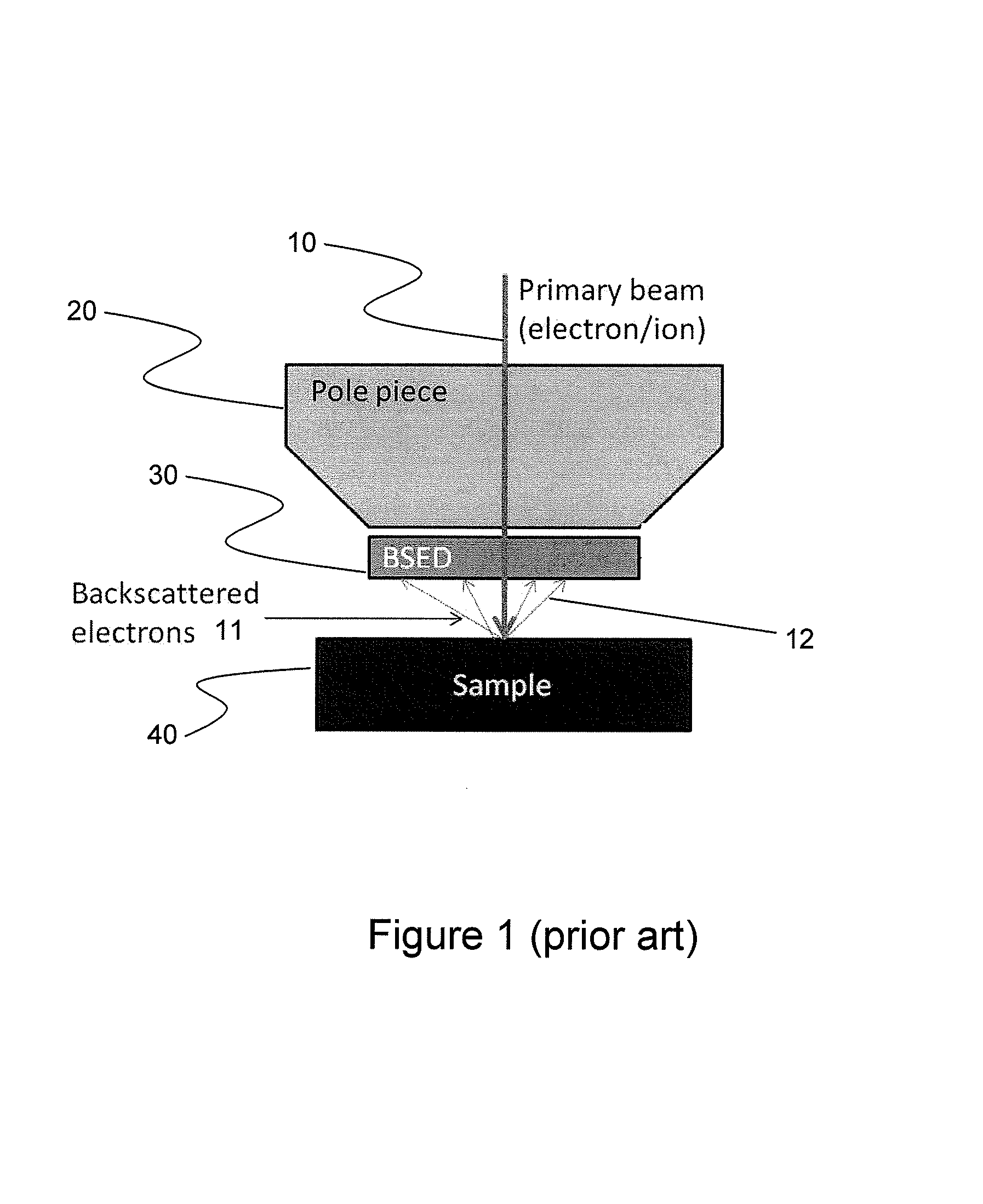
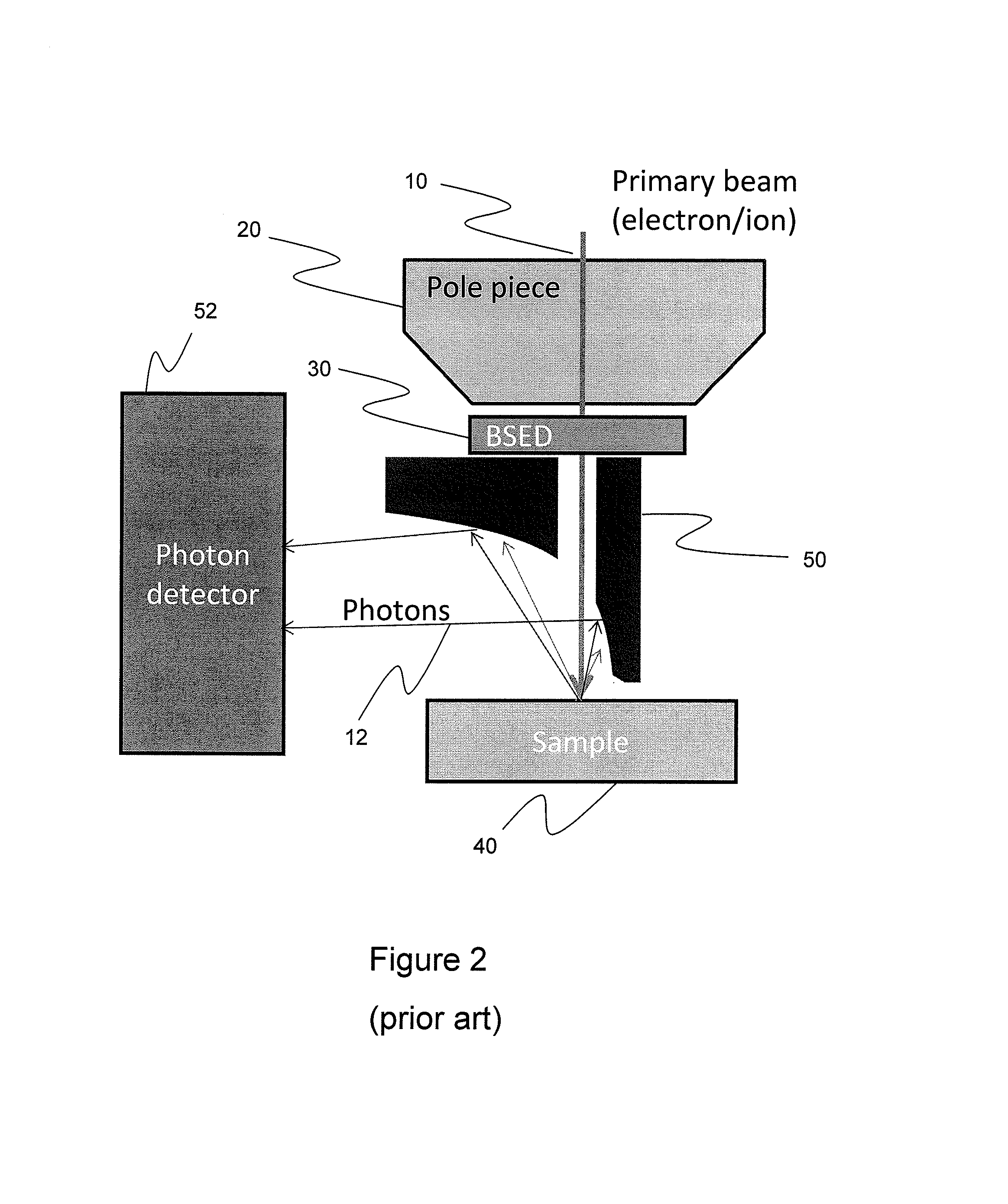
Integrated Backscattered Electron Detector with Cathodoluminescence Collection Optics
ActiveUS20130099116A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesPhoton detectionElectron
Owner:GATAN INC
Gallium nitride substrate and epitaxial wafer
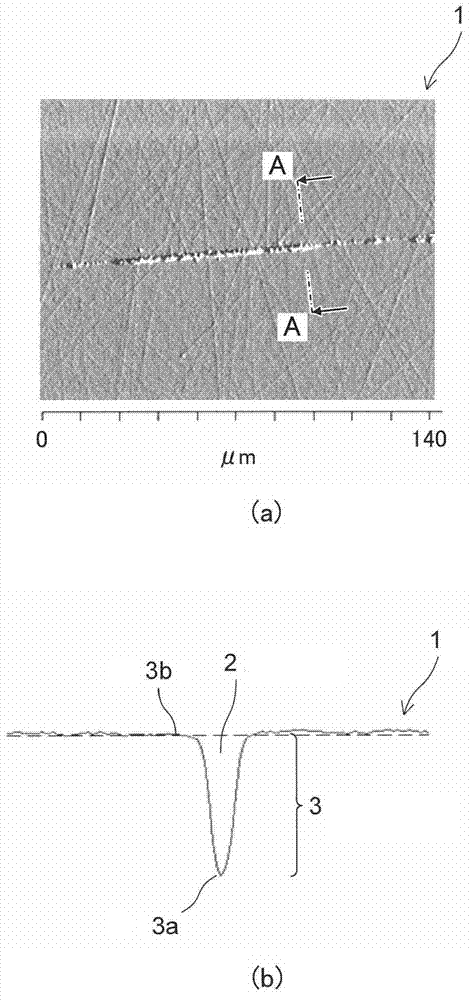
InactiveCN103367571AImprove qualityGood quality crystallinitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLuminous intensityGallium nitride
The invention provides a gallium nitride substrate that is capable of growing an epitaxial growth layer having a good crystalline quality even if the surface has physical level differences, and an epitaxial wafer that a surface thereof has good flatness by growing the epitaxial growth layer on the above-mentioned gallium nitride substrate. According to one embodiment of the invention, the gallium nitride substrate (1) comprises: a plurality of physical level differences (3) in a surface thereof. All the physical level differences (3) existing in the surface have a dimension of not more than 4 mum. A relationship of (H-L) / H100<=80 is satisfied in all the physical level differences (3), where H represents a higher value of cathodoluminescence emission intensities of a wavelength corresponding to a bandgap of the gallium nitride substrate, and L represents a lower value of the cathodoluminescence emission intensities, the cathodoluminescence emission intensities being measured in an upper step (3b) and a lower step (3a) of the physical level difference.
Owner:SUMITOMO CHEM CO LTD
Indium surfide and gallium surfide for ultrahigh density data storage device and phase transformation meidum of indium-gallium surfide
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO
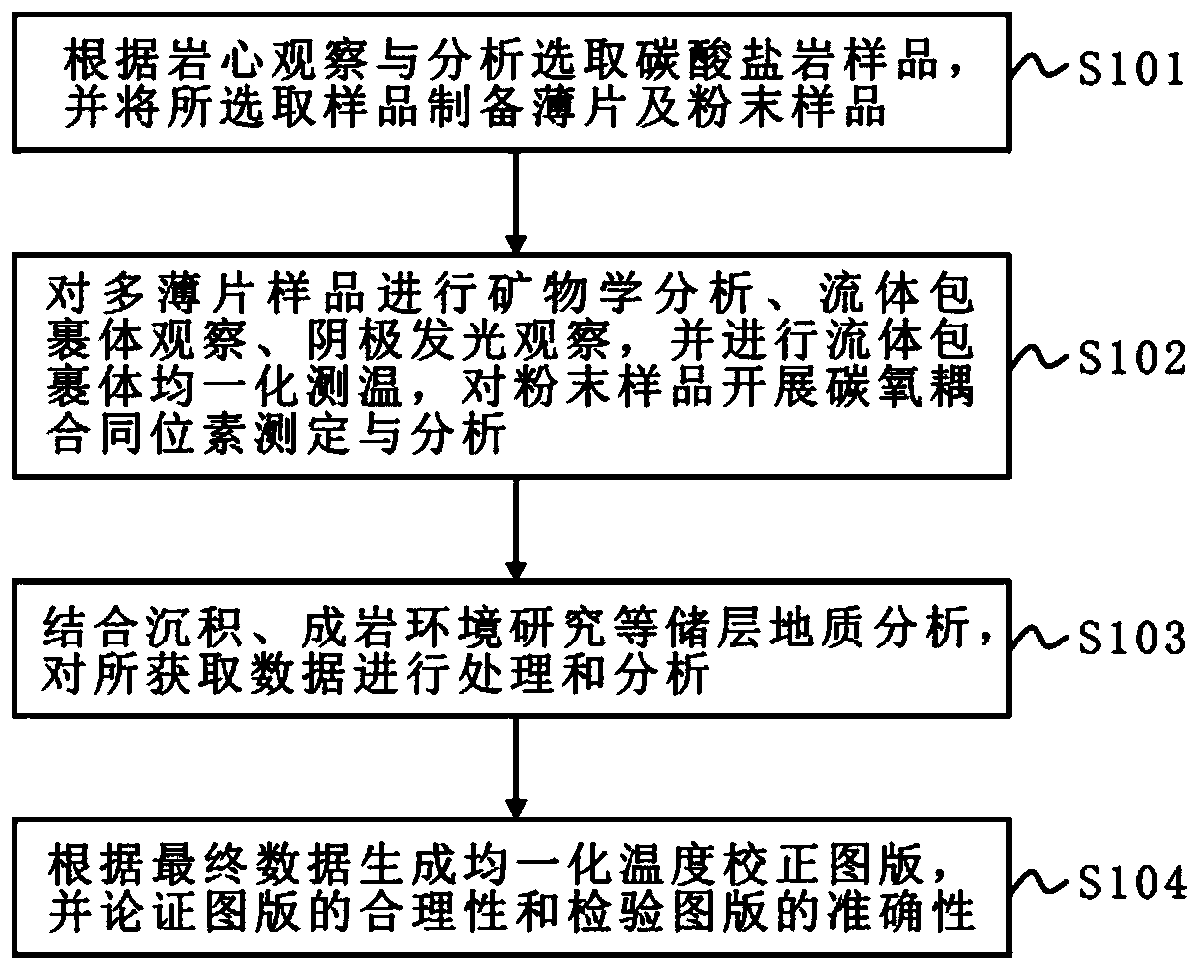
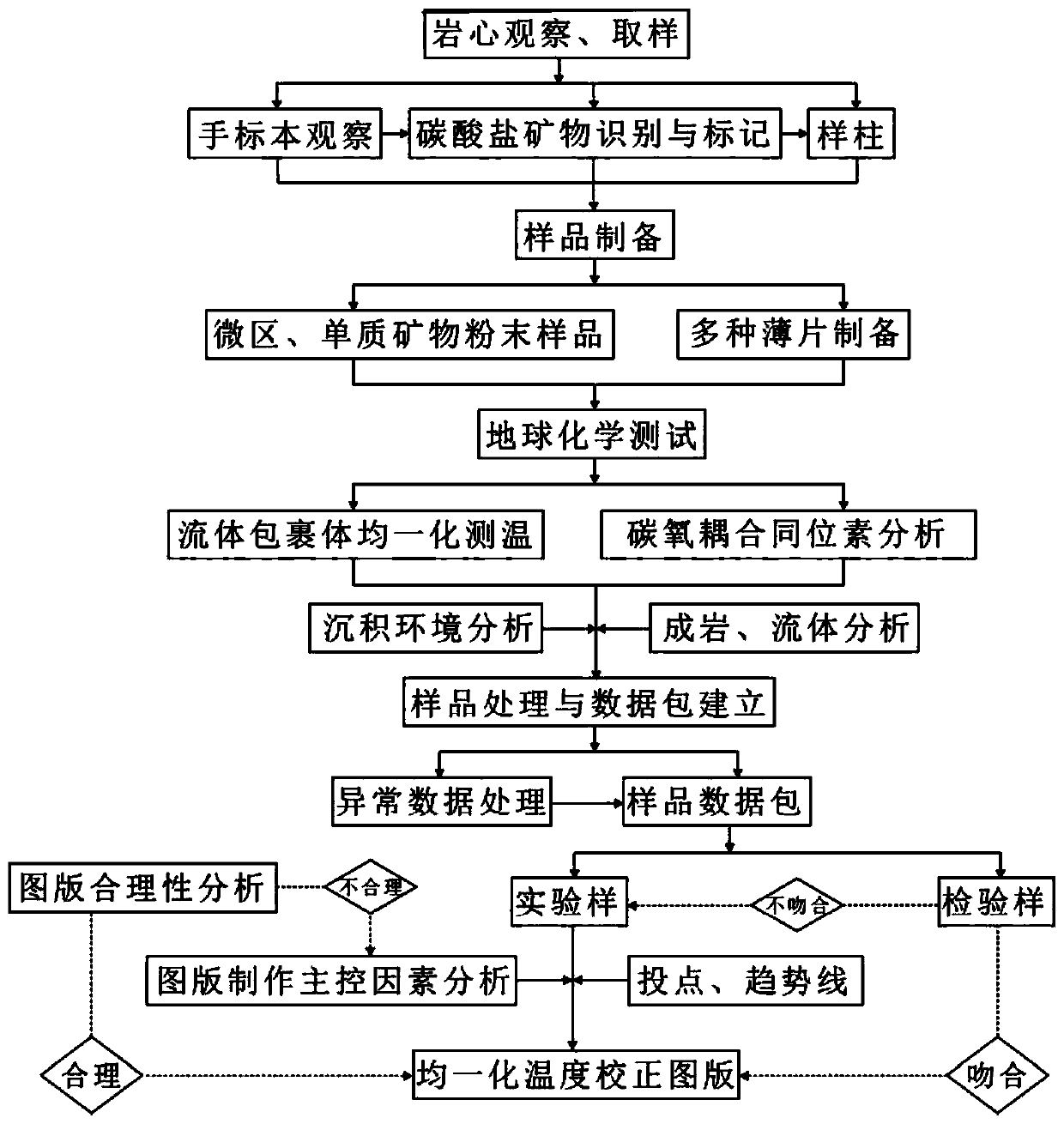
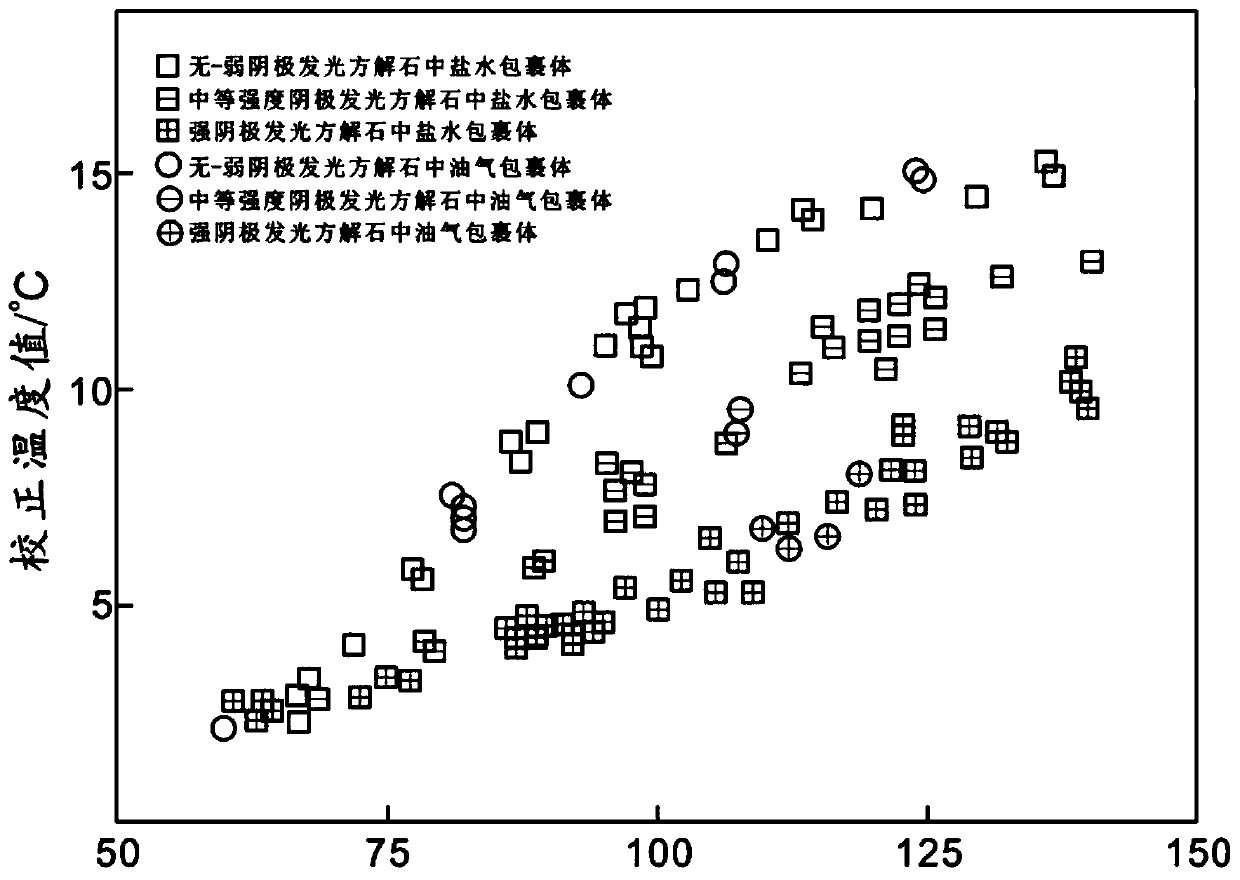
Method for establishing diagenetic paleo-fluid temperature correction map of marine carbonate rock reservoirs
InactiveCN109781966AGet accurate temperature quicklyOvercome the disadvantage of large error in uniform temperature measurementPreparing sample for investigationEarth material testingIsotopeOxygen
The invention discloses a method for establishing a diagenetic paleo-fluid temperature correction map of marine carbonate rock reservoirs. The method comprises: S1, selecting a plurality of carbonaterock samples according to core observation and analysis and processing the plurality of selected samples to obtain thin sheet and powder samples; S2, carrying out mineralogy analysis, fluid inclusionobservation, and cathodoluminescence observation on the thin sheet samples to obtain an analysis result, carrying out fluid inclusion homogenization temperature measurement on the thin sheet samples obtained in the S1, and carrying out carbon-oxygen coupled isotope determination on the powder samples; S3, processing and analyzing the homogenization temperature value and the carbon-oxygen coupled isotope temperature value by combining the analysis result in the S2; and S4, establishing a correction map of the fluid inclusion homogenization temperature and verifying the rationality and accuracyof the map. Therefore, the fluid inclusion homogenization temperature can be correct, thereby obtaining an accurate diagenetic paleo-fluid temperature.
Owner:XI'AN PETROLEUM UNIVERSITY
Plasma display panel and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveCN101114561AVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureSolid cathode detailsSecondary electronsOxygen
A protective layer, a protective layer manufacturing method of a plasma display panel, a plasma display panel, and a plasma display panel manufacturing method are provided to enhance emission characteristics of secondary electrons and to improve brightness and power consumption. A protective layer includes a first layer(280) and a second layer(280'). The first layer includes MgO. The second layer is formed on the first layer and includes a single crystalline metal oxide. The single crystalline metal oxide has a maximum value of cathode luminescence in a wavelength region of 300-500 nanometers. The single crystalline metal oxide is formed by supplying oxygen of 2-20sccm and argon of 0-18sccm in a gas state of a metal. The second layer is formed by coating irregularly particles including single crystalline metal powders on an entire surface of the first layer.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Cathode luminescence imaging method of monazite
InactiveCN107727677ASolve the overall black problem of cathode luminescenceReflect internal structural featuresMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationScanning electron microscopeMonazite
The invention discloses a cathode luminescence imaging method of monazite, which comprises: making a target for monazite mineral particles to obtain a resin target; polishing the resin target to expose the monazite to the resin target; Coating the monazite of the above-mentioned resin target, with the coated surface facing up, and fixing the coated resin target on the sample stage of the field emission scanning electron microscope with conductive glue, and vacuumizing the sample chamber of the field emission scanning electron microscope to make the resin target Under vacuum conditions; select the working distance of the cathodoluminescence probe; select the accelerating voltage of the electron beam; select the beam spot size of the electron beam; select the primary gain value; obtain the image of the single particle of monazite. The invention performs high-resolution cathodoluminescence luminescence imaging on monazite, solves the problem that monazite has always been black in cathodoluminescence, achieves a clear reflection of the internal structure characteristics of monazite, and achieves the purpose of accurate point selection for in-situ micro-region dating of monazite .
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of producing blue powder for cathode ray
InactiveCN101130688AReduce heat sensitivityIncreased passivationCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesLuminescent compositionsAluminium chlorideSlurry
The invention relates to a making method of blue powder for cathode beam, which comprises the following steps: washing after incandescing mixture of zinc blend, sodium chloride, aluminum sulfate, sulfur and aluminium chloride till conductivity of supernatant being 100mu S / cm-700mu S / cm; fetching powder solid and ball grinding after dewatering; adding colorant after re-atomizing-pulping till being latex and adjusting acidness of slurry with hydric sulphate; re-atomizing-pulping after washing, dewatering, drying the powder and screening; adjusting the acidness of the slurry with caustic soda after adding G / A glue, silicon dioxide and zinc sulfate; adding aluminum oxide and drying to produce cathode-ray luminescent material with reduced heat sensitivity. The invention achieves to reduce the heat sensitivity when coats display screen with the luminescent powder after adding the aluminum oxide after coloring dealing with the luminescent powder. The luminescent powder with adding the aluminum oxide is an effective blue light fluorophor because of uniform grain, purifying color purity and fine luminous property, which improves screening characteristics remarkably.
Owner:CAIHONG GRP ELECTRONICS CO LTD
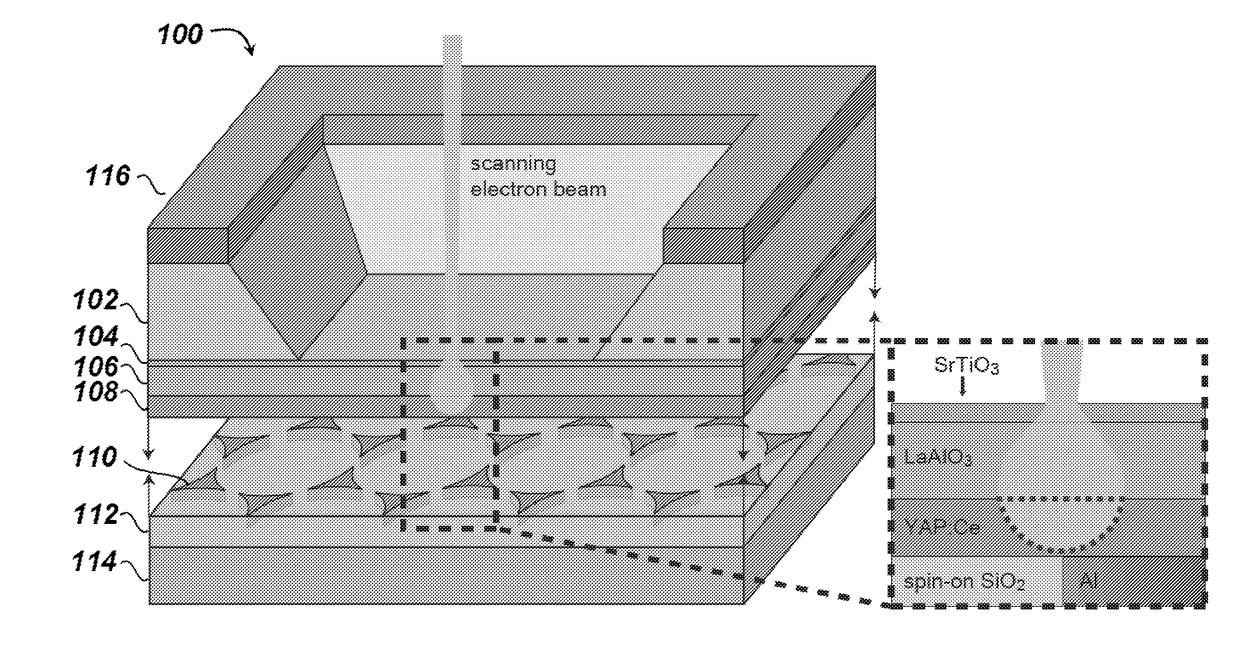
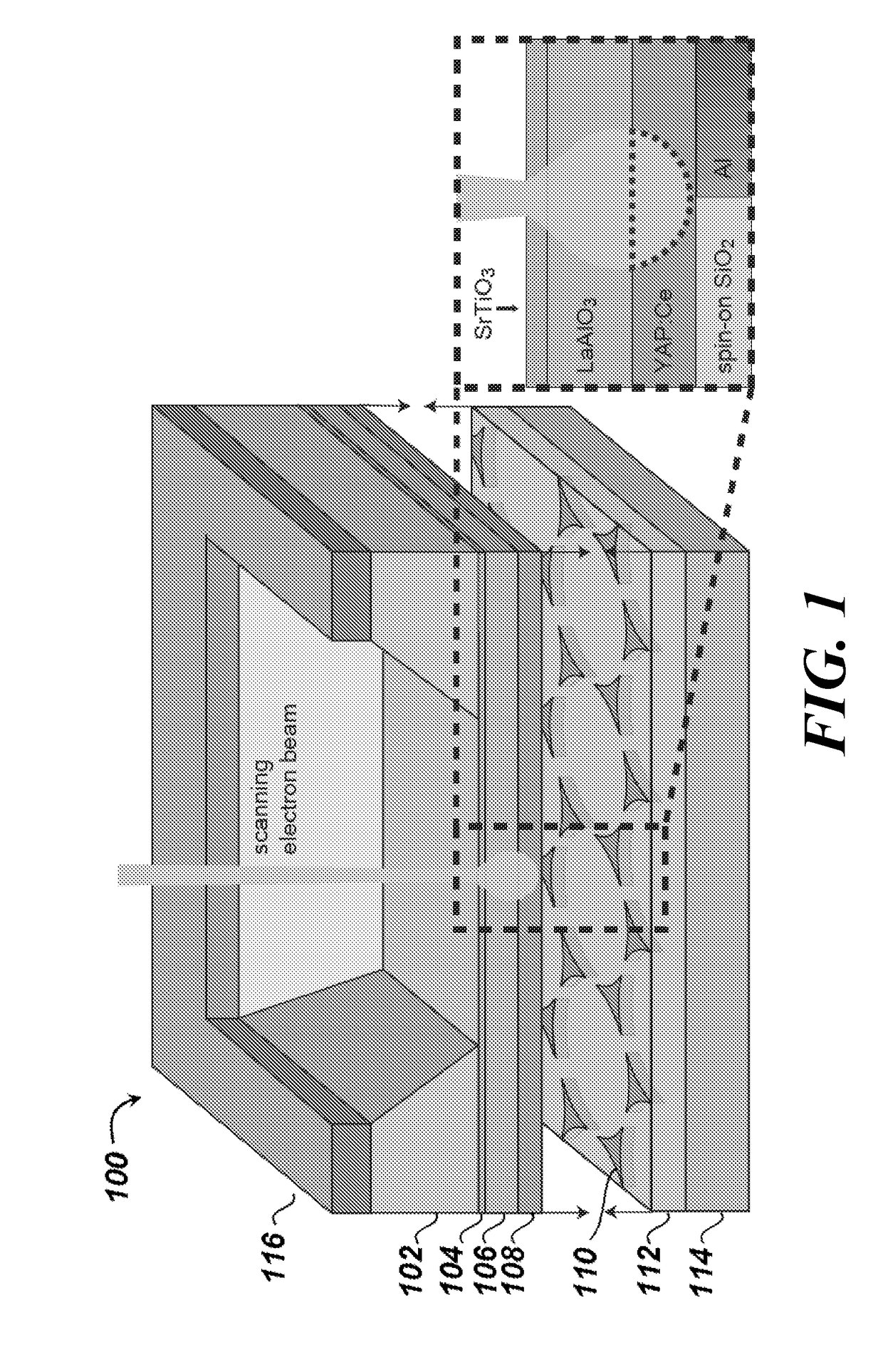
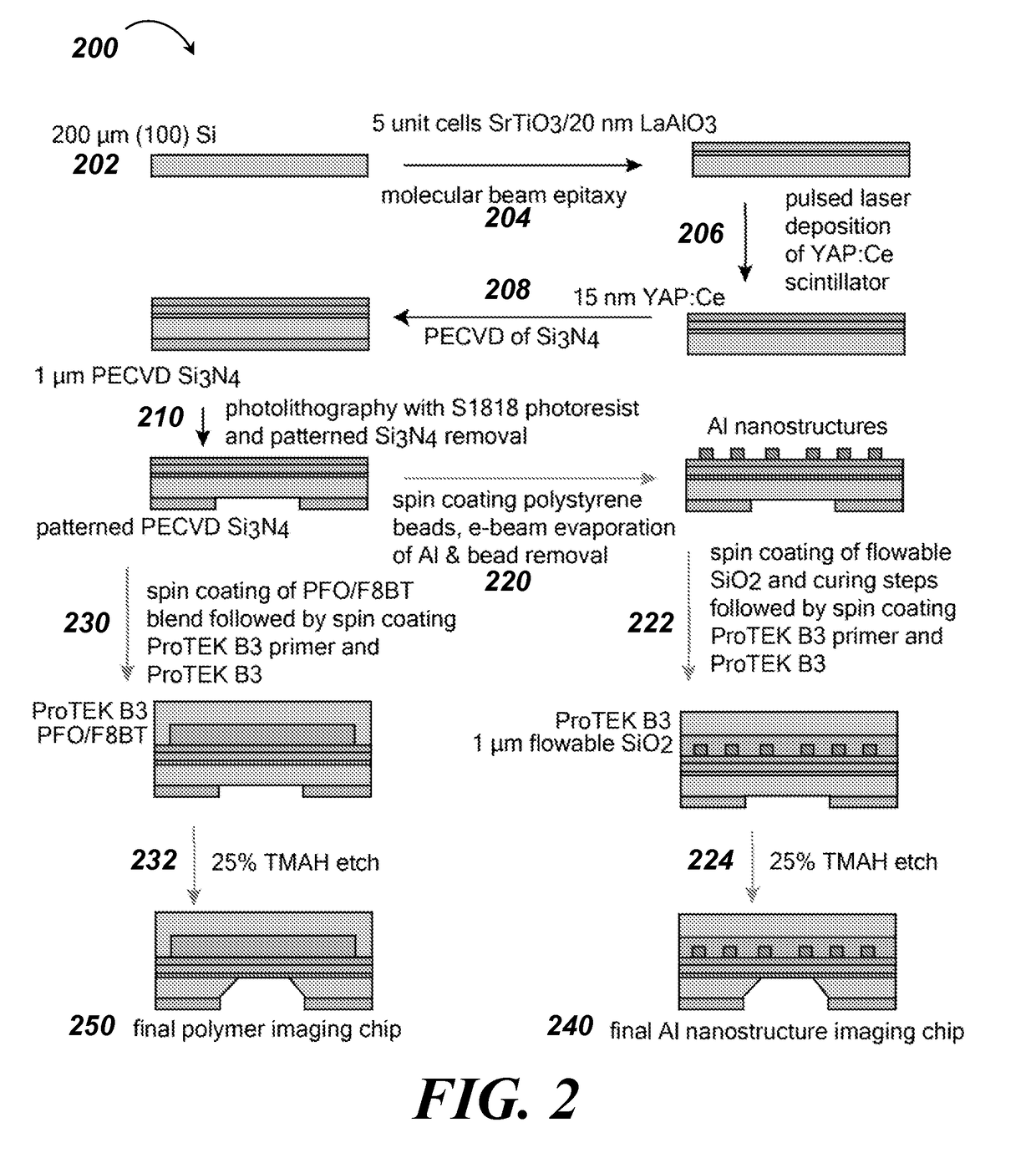
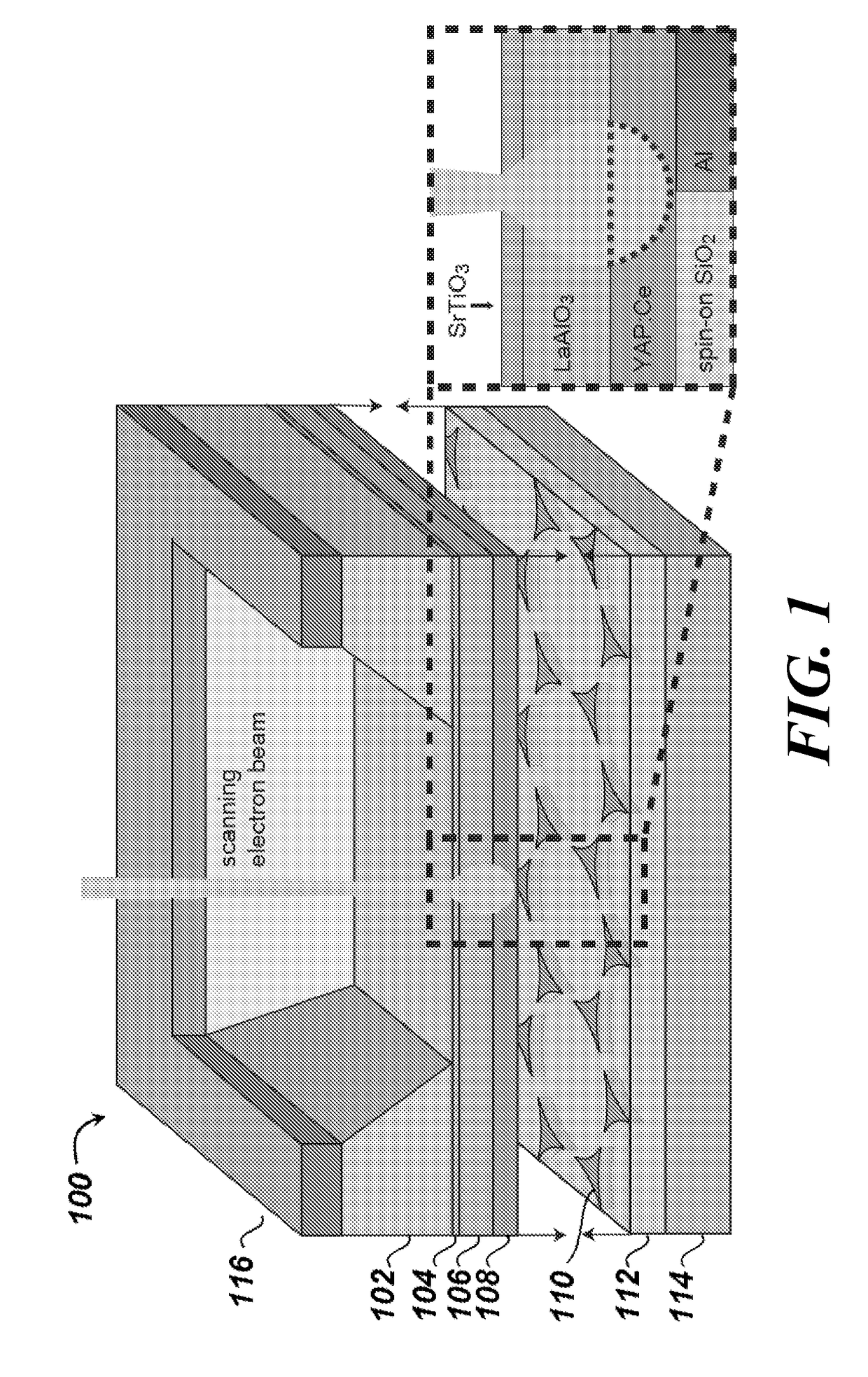
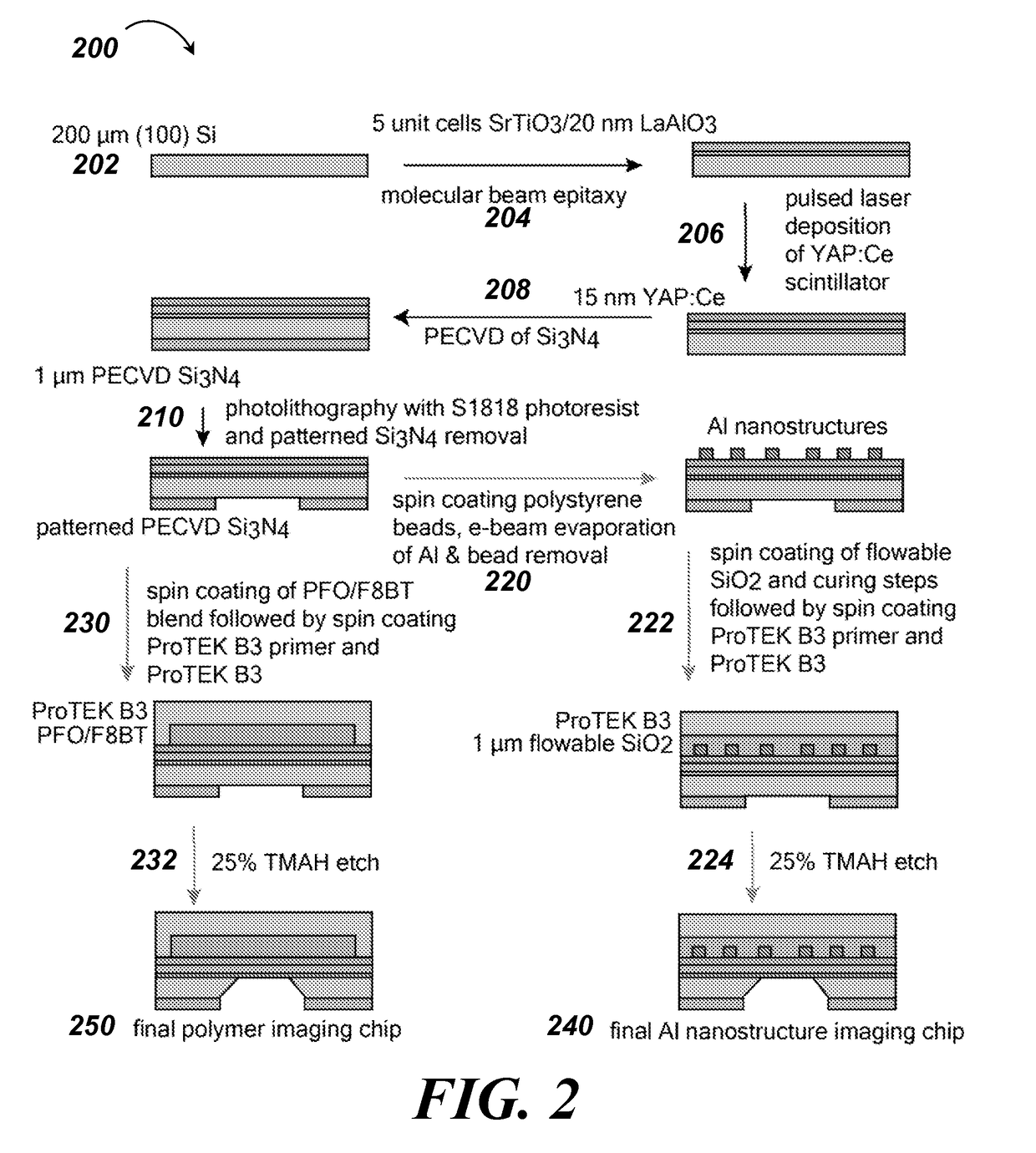
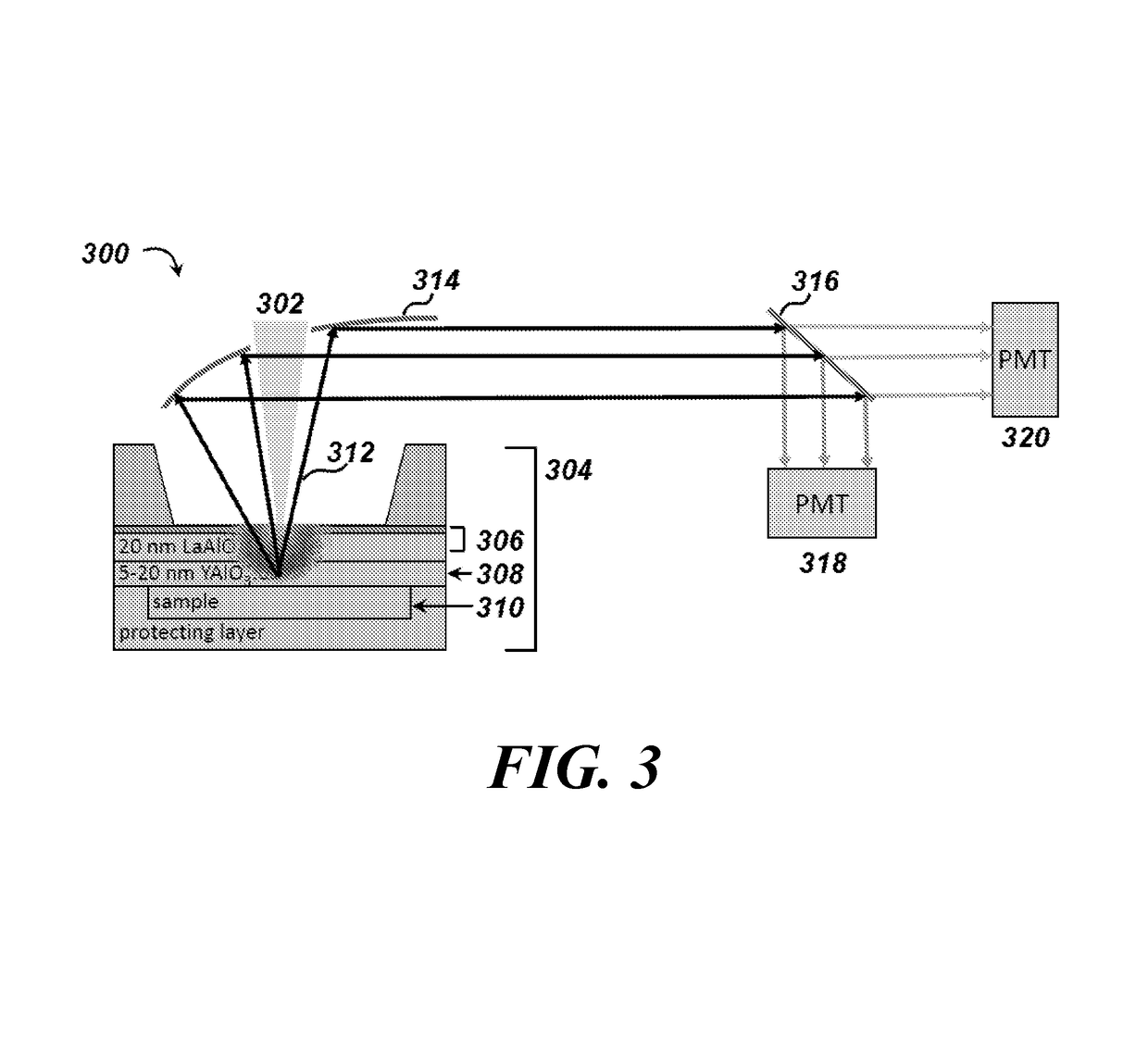
Cathodoluminescence-activated nanoscale imaging
ActiveUS20180080885A1High resolutionMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionNon invasiveElectron
Provided herein are non-invasive methods of nanoscale imaging of a sample using an illumination layer and an electron beam. For example, the electron may activate the illumination layer without activating the sample, and the illumination layer may emit cathodoluminescence to produce a nanoscale image of the sample.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
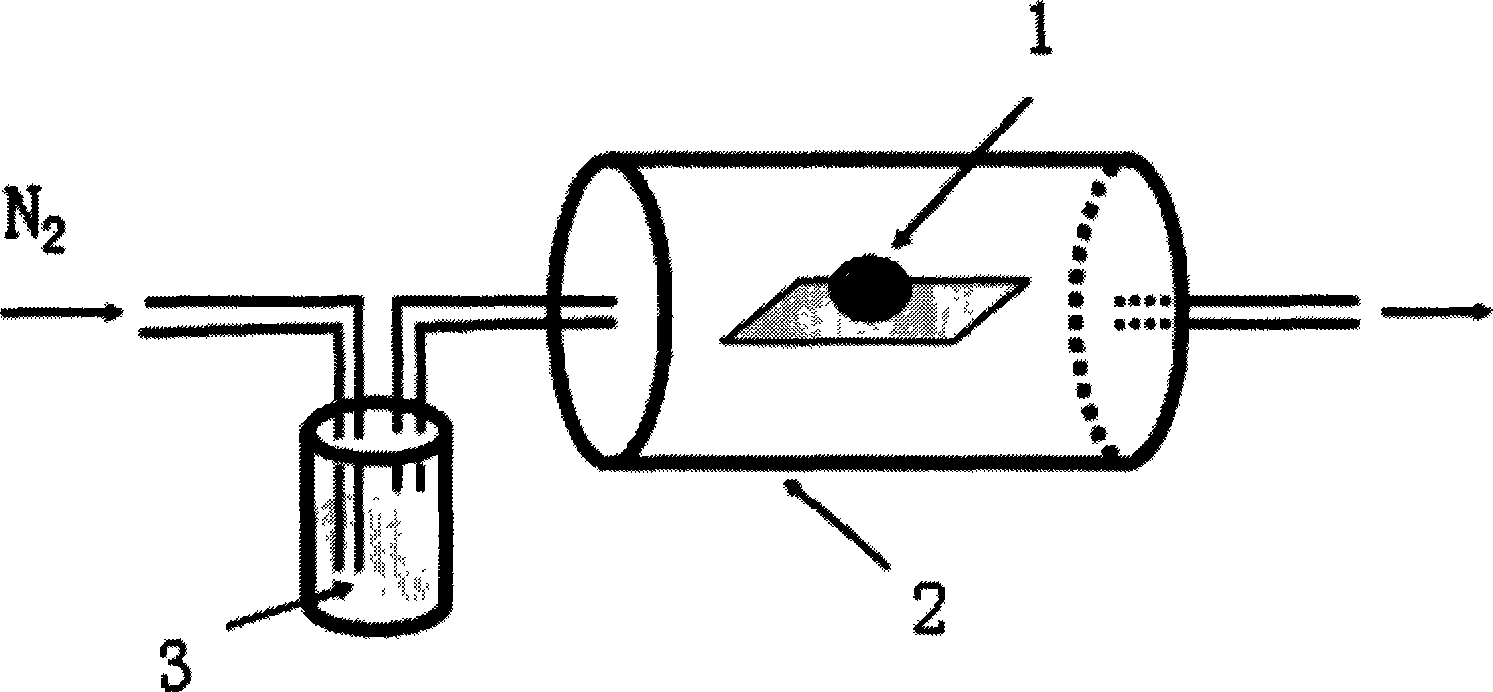
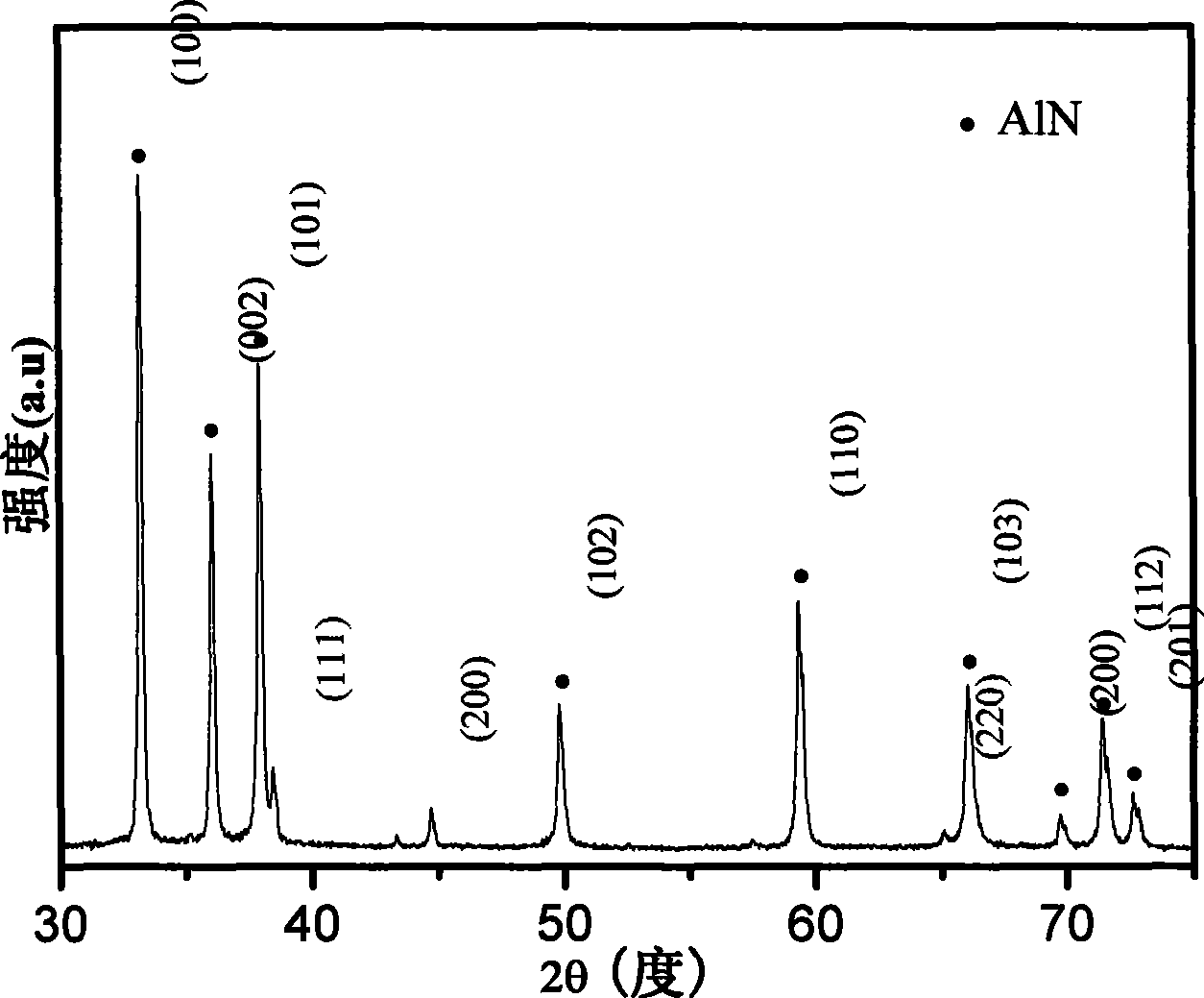
Method for preparing semi-conducting material nano structure aluminum nitride
InactiveCN101456543AEasy to collectNo pollution in the processNitrogen compoundsSemiconductor materialsNitrogen
The invention discloses a method for quickly preparing a semiconductor material nano-belt, which comprises: firstly, grinding aluminum powder until the particle diameter is between 50 and 1,000 nanometers, and placing the ground powder into a reaction tube; secondly, blowing dried nitrogen into the reaction tube; and thirdly, heating the reaction tube, making aluminum react with the nitrogen at a temperature of between 700 and 1,200 DEG C, and collecting products in situ to obtain a large quantity of aluminum nitride nano-belts. The method uses the nitrogen instead of ammonia as a source to generate an aluminum nitride nano structure for the first time, and has short reaction time, low temperature, low cost and no environmental pollution. The nano structure has wider application scope due to the special shape. Compared with commercial aluminum nitride, nanophase materials prepared by the method have strong ultraviolet cathodoluminescence. The invention is a method for preparing the nanophase materials with great economic value and use value, and has wide market prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Integrated backscattered electron detector with cathodoluminescence collection optics
An apparatus for simultaneous detection of backscattered electrons and photons from a sample. The device includes a direct detection backscattered electron detector and a photon detector. The backscattered electron detector has a reflective surface that reflects photons emitted by the sample onto the photon detector.
Owner:GATAN INC
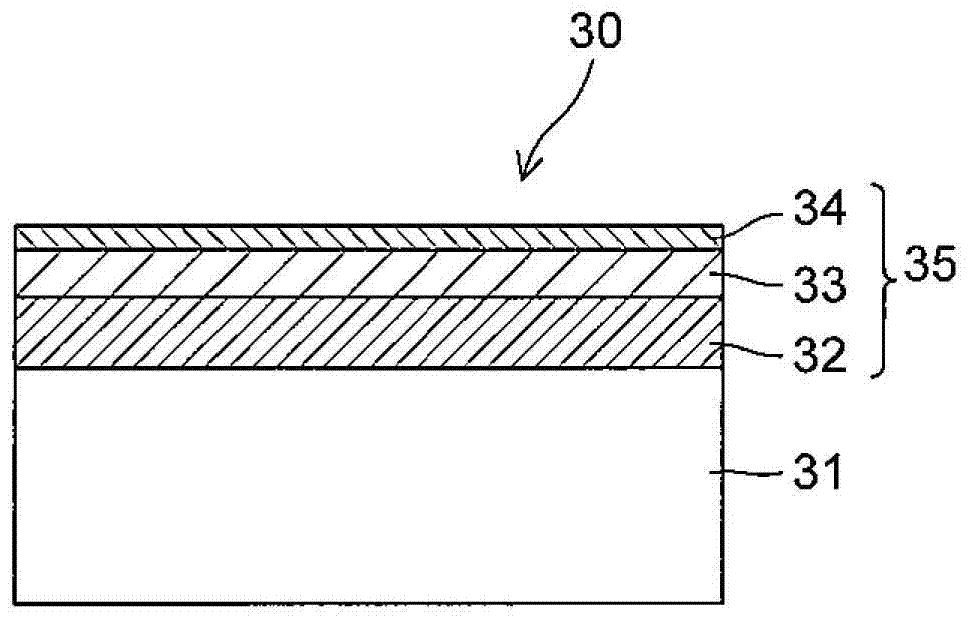
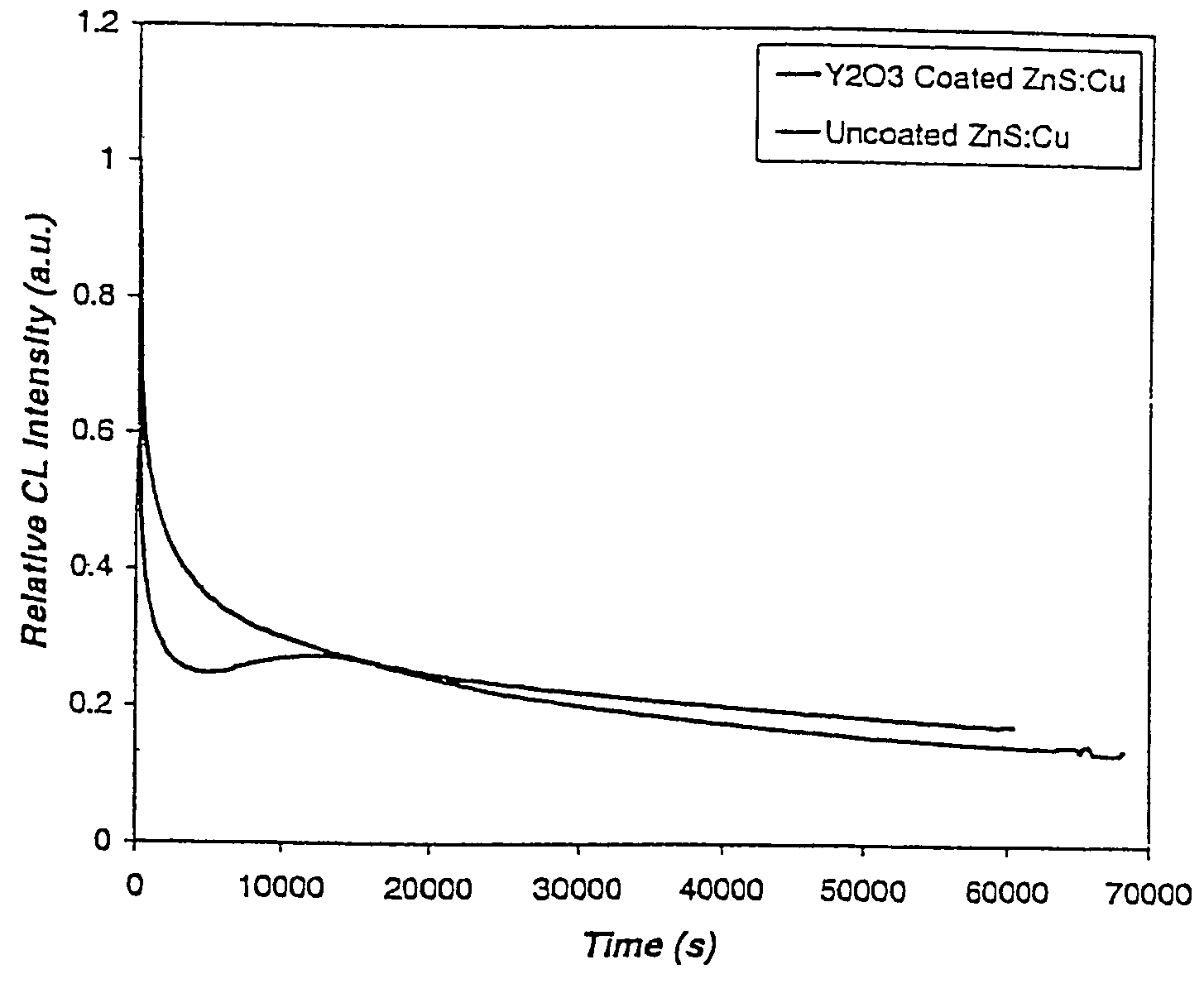
Rare earth oxide coated phosphors
InactiveUS7341779B2Synthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsFluorescenceRare earth
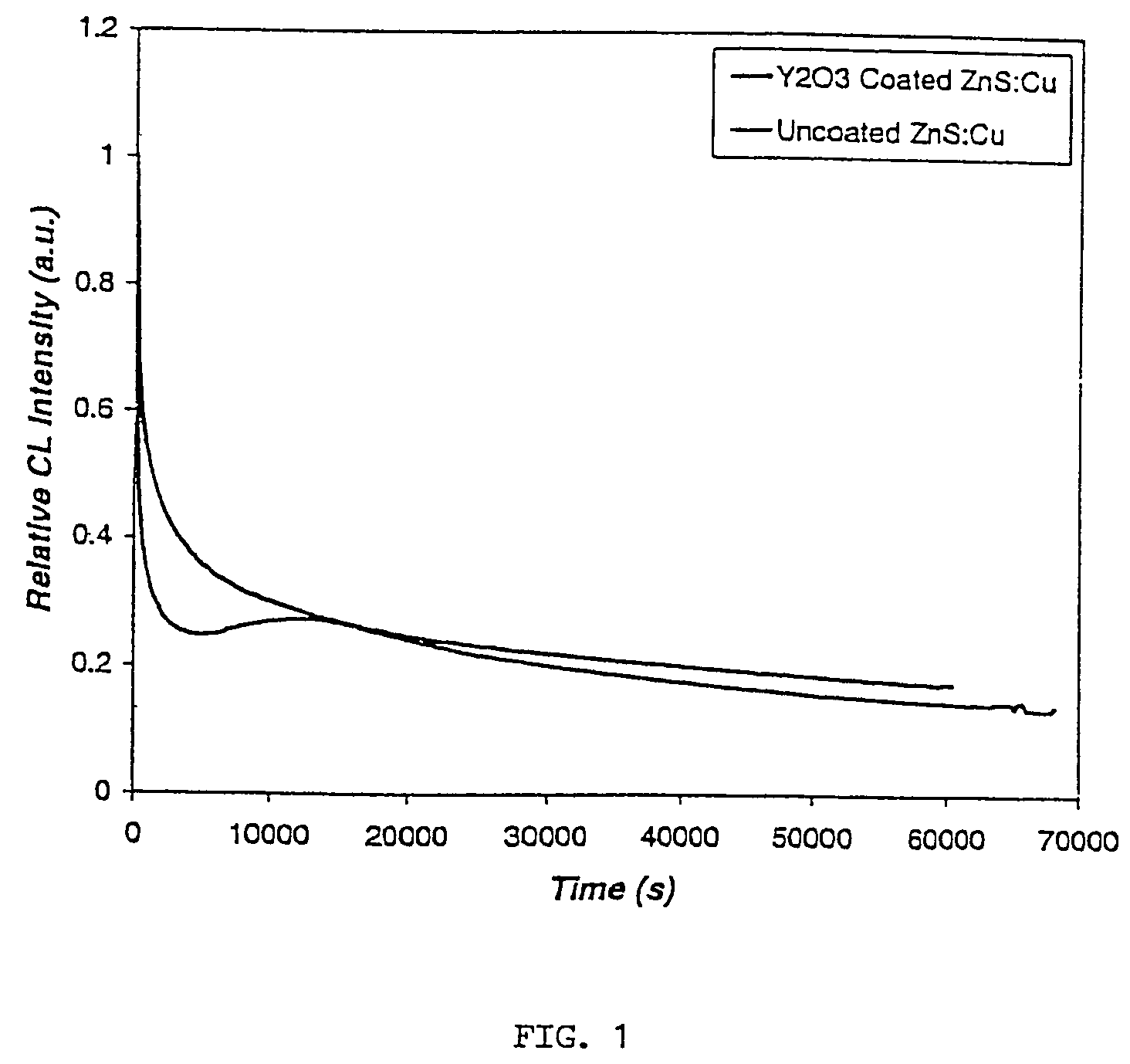
The present invention provides surface coated phosphors useful in field emission displays and vacuum fluorescent displays. The surface coated phosphor comprises a thin coating of rare earth oxide, e.g., yttrium oxide, disposed on an uncoated phosphor such as a sulfide phosphor. The present invention further provides a process for preparing a surface coated phosphor comprising contacting the uncoated phosphor with a rare earth hydroxide gel solution to obtain a rare earth hydroxide gel coated phosphor, drying the gel coated phosphor to remove solvent residues, and heat treating the dried rare earth hydroxide gel coated phosphor. The surface coated phosphors of the present invention have improved cathodoluminescence efficiency, coulombic aging resistance, chemical, and / or oxidative stability.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP +1
Electrode for photoelectric conversion elements, manufacturing method of the same, and dye-sensitized solar cell
InactiveUS20100243060A1Increased durabilityExtended product life-cycle of photoelectricElectrolytic capacitorsFinal product manufacturePhotoelectric conversionSolar cell
An electrode for photoelectric conversion elements having high initial characteristics and excellent durability, a manufacturing method of the electrode for photoelectric conversion elements, and a dye-sensitized solar cell are provided. An electrode for photoelectric conversion elements according to the present invention has a structure in which a metal oxide layer containing zinc oxide is provided on a base. The metal oxide layer has a plurality of bump-like protrusions formed so as to protrude radially from the base side, and also has an emission peak in a region of 350 to 400 nm in cathodoluminescence measurement. The metal oxide layer is preferably heat treated at 220 to 500° C.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
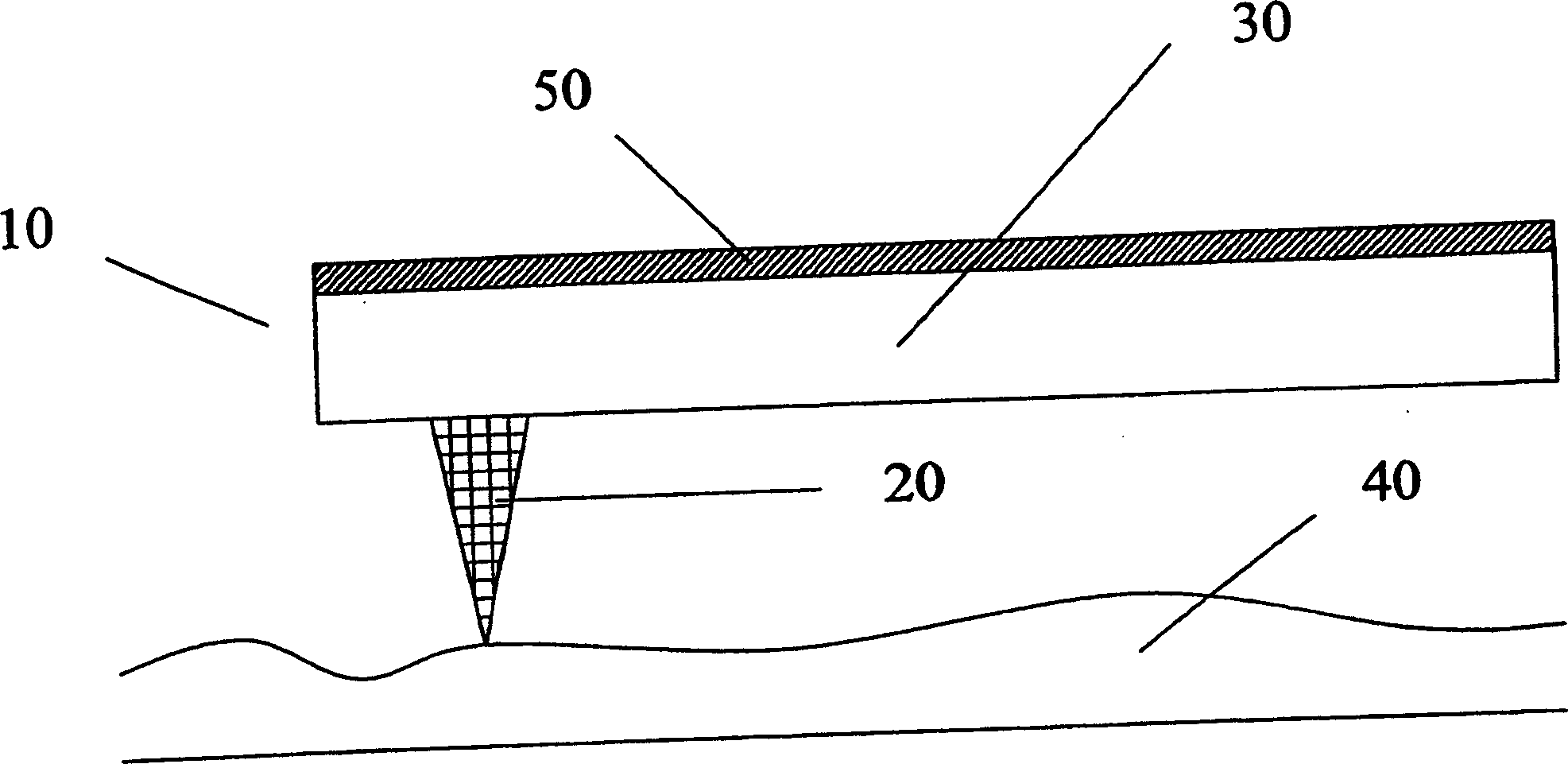
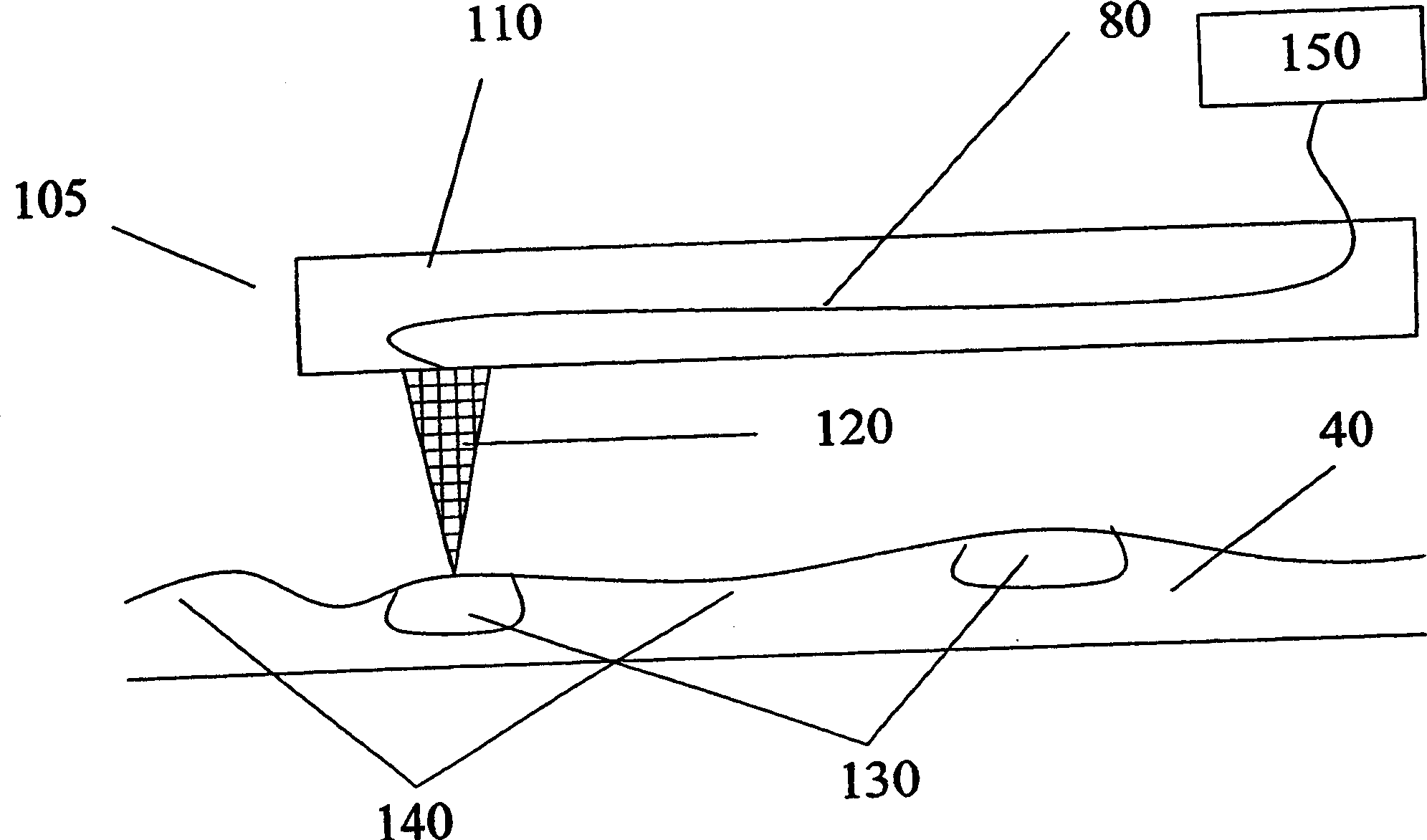
Data storage medium based on diode, cathodic conductivity and cathodic luminescence
InactiveCN1367534AElectron beam carrier recordingIndividual molecule manipulationThermal energyLight energy
The present invention provides data storage media based on diode and cathode conductivity and cathodoluminescence. An ultra-high density data storage device comprising at least one energy communication element (120) and a storage medium (40) generally comprising at least one rectifying junction. The energy communication element (120) is generally capable of emitting energy such as, but not limited to, thermal energy, light energy, and electronic energy. The energy communication element is generally located near or in contact with the storage medium. The storage medium generally includes nanoscale storage regions (130, 140).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Discrimination method of redox property of ore-forming fluid based on cathodoluminescence characteristics of scheelite in porphyry deposit
ActiveCN107655915BGuide the direction of prospectingMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRare-earth elementScanning electron microscope
The invention provides a method based on the cathode luminescence feature of scheelite in a porphyry deposit and used for distinguishing the redox properties of an ore-forming fluid. The method includes: acquiring a plurality of scheelite samples; selecting scheelite particles on the basis of the mineralogy, morphology and production features of the scheelite particles in the scheelite samples toobtain high-quality scheelite particles; acquiring the scanning electron microscope-cathode luminescence image and back scattering image of the high-quality scheelite particles; based on the scanningelectron microscope-cathode luminescence image and the back scattering image, dividing the high-quality scheelite particles according to the morphology and internal structural features of the scheelite particles to obtain a plurality types of high-quality scheelite particles; performing in-situ analysis on rare-earth elements in the plurality types of high-quality scheelite particles to obtain europium content and molybdenum content data; calculating europium anomaly according to the europium content data, and building an element distribution diagram according to the europium anomaly and the molybdenum content data, wherein the element distribution diagram is used for indicating the redox properties of the ore-forming fluid of the scheelite.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Electrode for photoelectric conversion elements, manufacturing method of the same, and dye-sensitized solar cell
InactiveCN101853737AHigh initial characteristicsIncreased durabilityLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufacturePhotoelectric conversionSolar cell
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
In-situ characterization method for nano wires
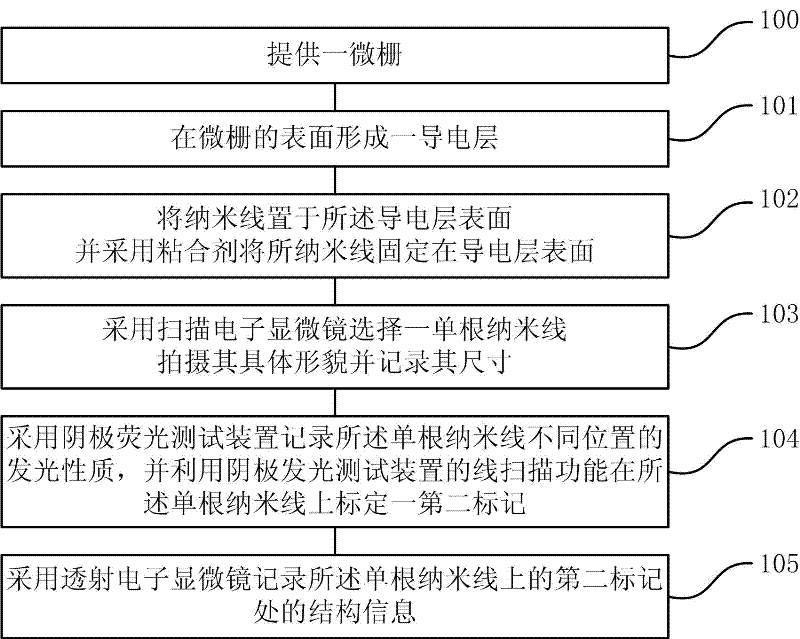
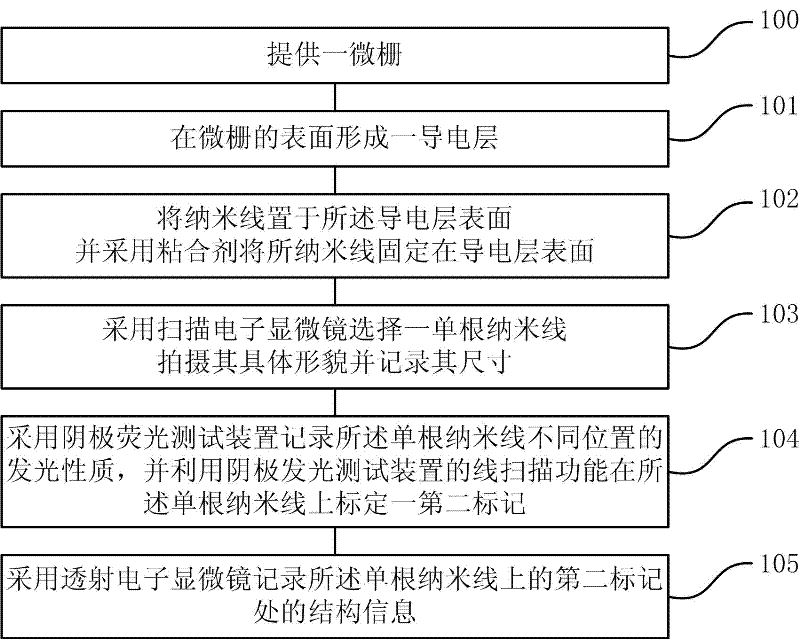
The invention provides an in-situ characterization method utilizing SEM-CL (Scanning Electron Microscopy-Cathodoluminescence) and a TEM (Transmission Electron Microscope). The method comprises the following steps: 1) providing a micro grid; 2) forming a conducting layer on the surface of the micro grid; 3) placing nano wires on the surface of the conducting layer and fixing the nano wires on the surface of the conducting layer by utilizing an adhesive; 4) utilizing a scanning electronic microscope to select a single nano wire, shooting the specific morphology of the single nano wire and recording the size of the single nano wire; 5) utilizing a cathode fluorescence testing device to record the luminance of different positions of the single nano wire, and utilizing the line scanning function of the cathode fluorescence testing device to calibrate a second mark on the single nano wire; and 6) utilizing a transmission electron microscope to record the structural information of the second mark on the single nano wire. According to the invention, a special fine sampling and testing method is utilized, the structural information obtained by the TEM is directly related with the luminescence obtained by the SEM-CL, and a bridge between a nano structure of a material and the luminescence of the material is constructed.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI +1
alpha-Ga2O3 SEMICONDUCTOR FILM
PendingUS20220238645A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingDark spotWavelength range
An α-Ga2O3 semiconductor film according to the present invention has a measurement point (dark spot) with a maximum emission intensity A of not more than 0.6 times the average value X of top 5% of the maximum emission intensities A at all measurement points in intensity mapping of plane cathodoluminescence, wherein the maximum emission intensity A at each measurement point is determined in the wavelength range of 250 to 365 nm.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Cathodoluminescence-activated nanoscale imaging
Provided herein are non-invasive methods of nanoscale imaging of a sample using an illumination layer and an electron beam. For example, the electron may activate the illumination layer without activating the sample, and the illumination layer may emit cathodoluminescence to produce a nanoscale image of the sample.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com